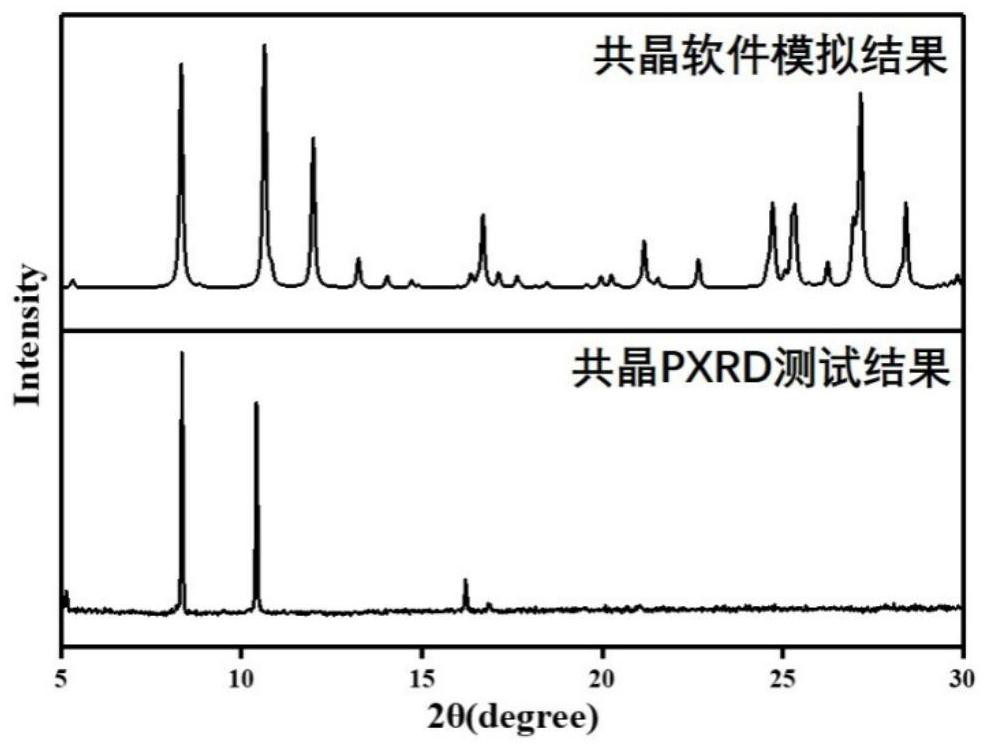
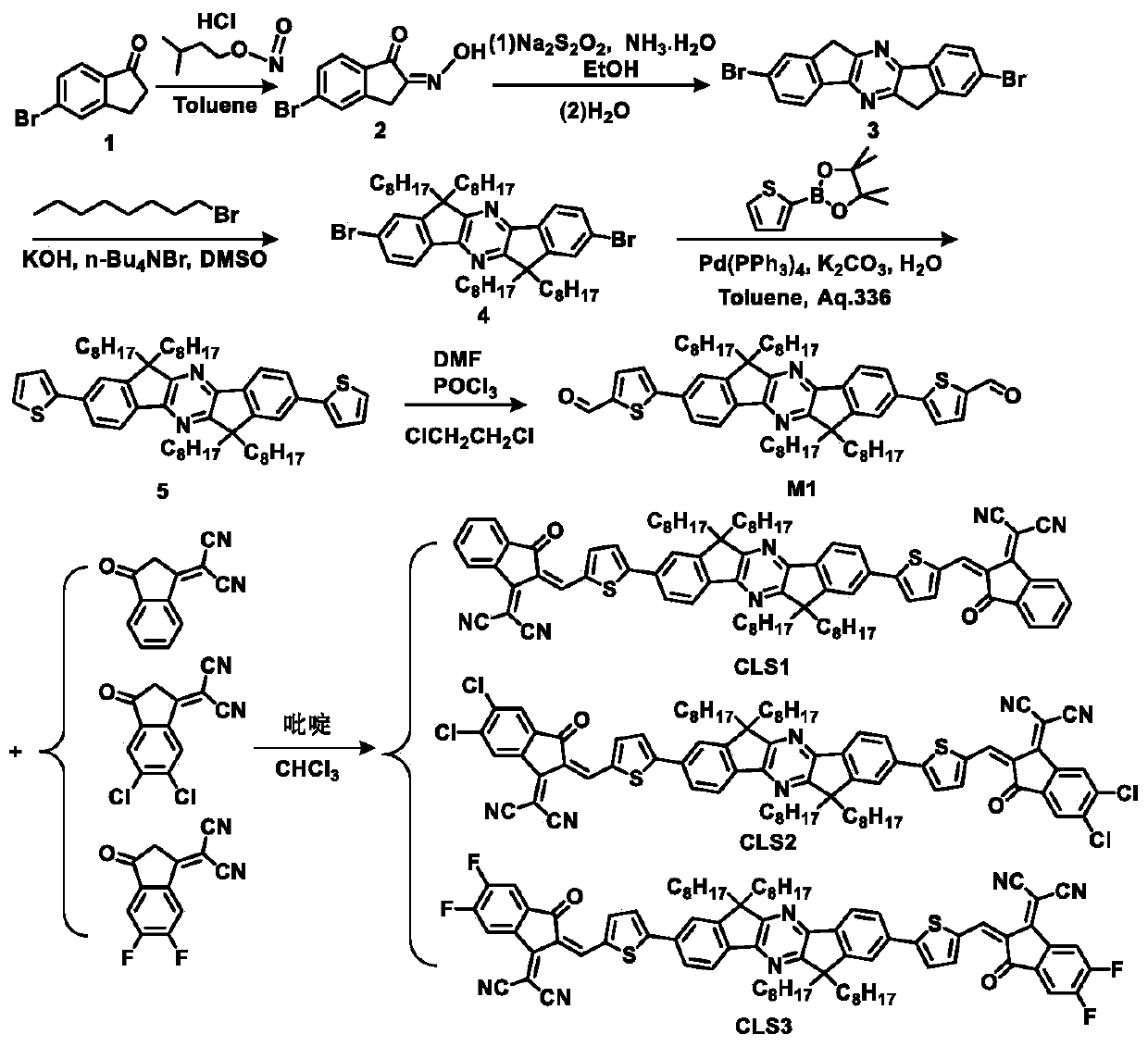
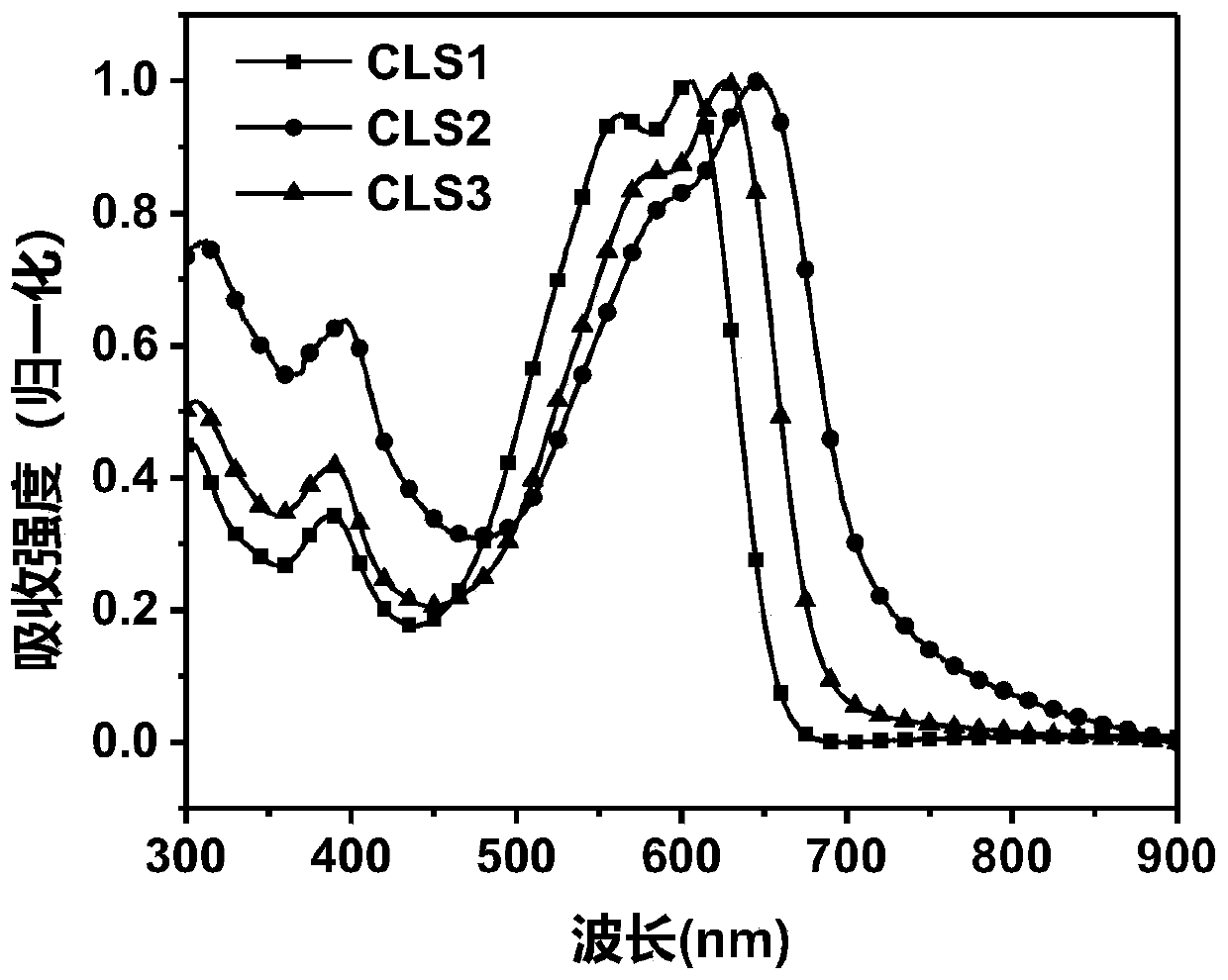
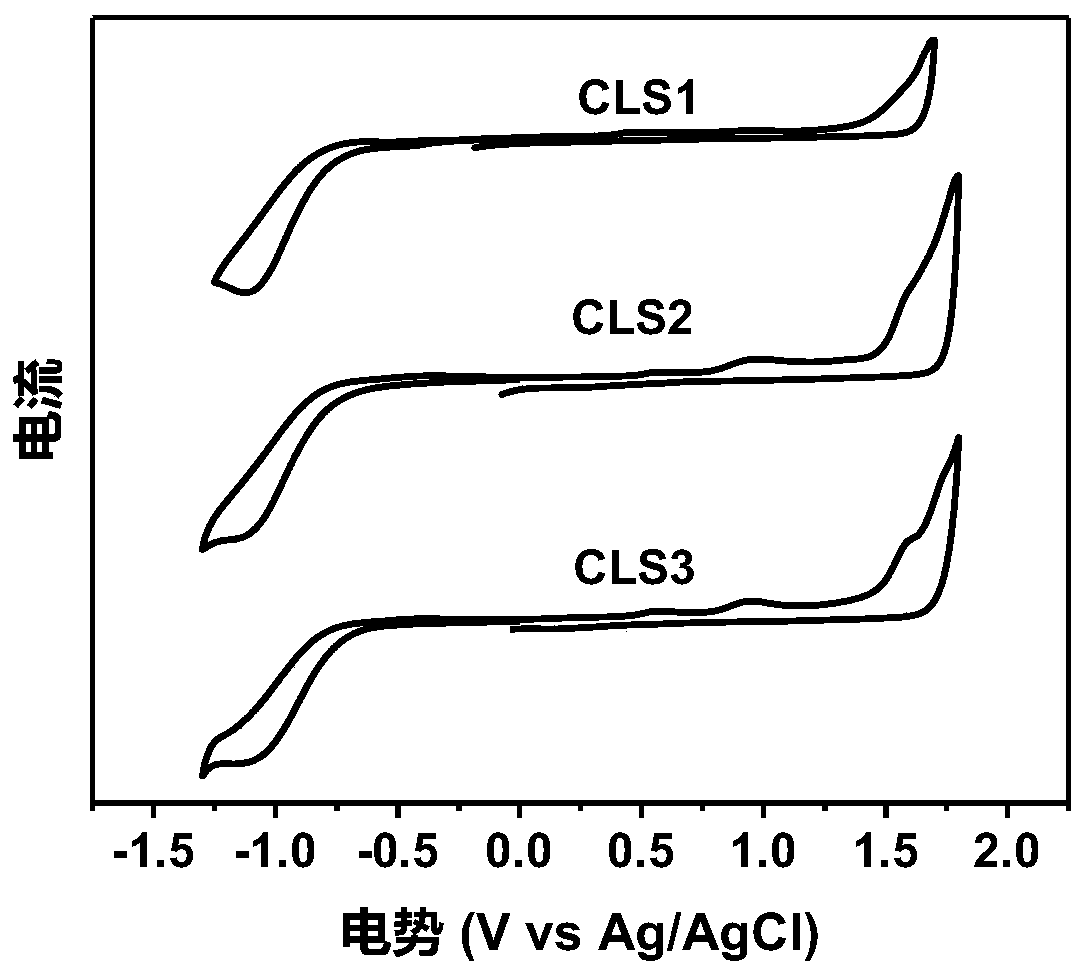
Patents
Literature
45 results about "Cyanomethylidyne" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cyanomethylidyne; dicyanomethylene; from MeSH. Depositor-Supplied Synonyms. Chemical names and identifiers provided by individual data contributors and associated to PubChem Substance records. Synonyms of Substances corresponding to a PubChem Compound record are combined.
Imaging members
InactiveUS6756169B2Few stepsLow costElectrographic process apparatusElectrographic processes using charge patternQuinoneThiopyran
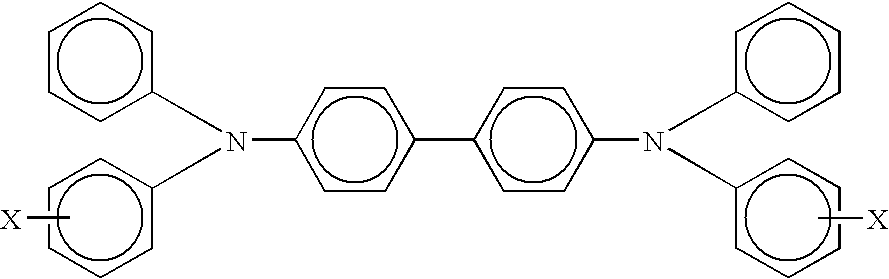
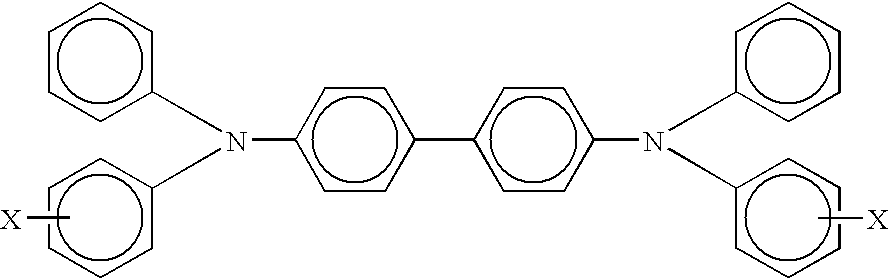
A member including for example, a supporting layer and a single photogenerating layer, the photogenerating layer comprising particles including hydroxygallium phthalocyanine phthalocyanine Type V, x polymorph metal free phthalocyanine, or chlorogallium phthalocyanine dispersed in a matrix comprising an arylamine hole transporter and an electron transporter selected from the group consisting of N,N'bis(1,2-dimethylpropyl)-1,4,5,8-naphthalenetetracarboxylic diimide, 1,1'-dioxo-2-(4-methylphenyl)-6-phenyl-4-(dicyanomethylidene)thiopyran, and a quinone selected from the group consisting of carboxybenzylhaphthaquinone, and tetra (t-butyl) diphenoquinone, and mixtures thereof, and a film forming binder.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Imaging members
InactiveUS20040018440A1High trafficFew stepsElectrographic process apparatusElectrographic processes using charge patternQuinoneThiopyran
A member including for example, a supporting layer and a single photogenerating layer, the photogenerating layer comprising particles including hydroxygallium phthalocyanine phthalocyanine Type V, x polymorph metal free phthalocyanine, or chlorogallium phthalocyanine dispersed in a matrix comprising an arylamine hole transporter and an electron transporter selected from the group consisting of N,N'bis(1,2-dimethylpropyl)-1,4,5,8-naphthalenetetracarboxylic diimide, 1,1'-dioxo-2-(4-methylphenyl)-6-phenyl-4-(dicyanomethylidene)thiopyran, and a quinone selected from the group consisting of carboxybenzylhaphthaquinone, and tetra (t-butyl) diphenoquinone, and mixtures thereof, and a film forming binder.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Imaging members
InactiveUS6656650B1Eliminate needFew stepsRadiation applicationsElectrographic process apparatusQuinoneThiopyran
A member including, for example, a supporting layer and a single photogenerating layer, the photogenerating layer comprising particles including hydroxygallium phthalocyanine phthalocyanine Type V, x polymorph metal free phthalocyanine, or chlorogallium phthalocyanine dispersed in a matrix comprising an arylamine hole transporter and an electron transporter selected from the group consisting of N,N'bis(1,2-dimethylpropyl)-1,4,5,8-naphthalenetetracarboxylic diimide, 1,1'-dioxo-2-(4-methylphenyl)-6-phenyl-4-(dicyanomethylidene)thiopyran, and a quinone selected from the group consisting of carboxybenzylhaphthaquinone, and tetra (t-butyl) diphenoquinone, and mixtures thereof, and submicrometer size polytetrafluroethylene particles, and a film forming binder.
Owner:XEROX CORP
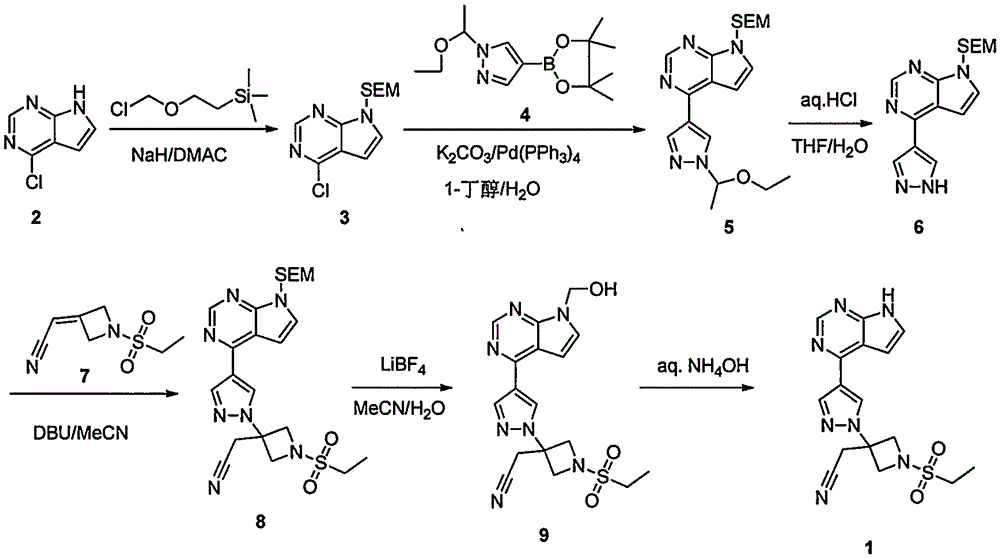
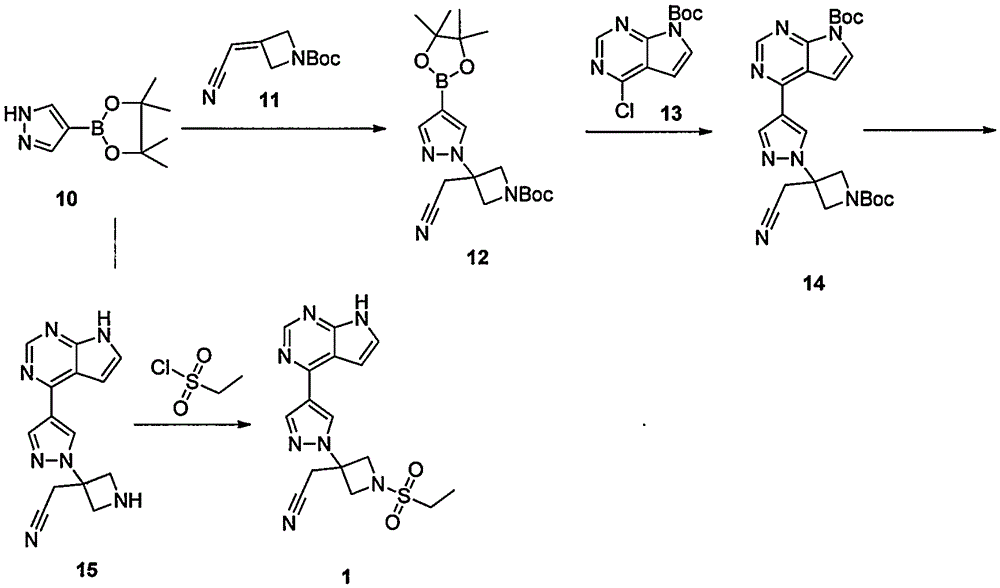
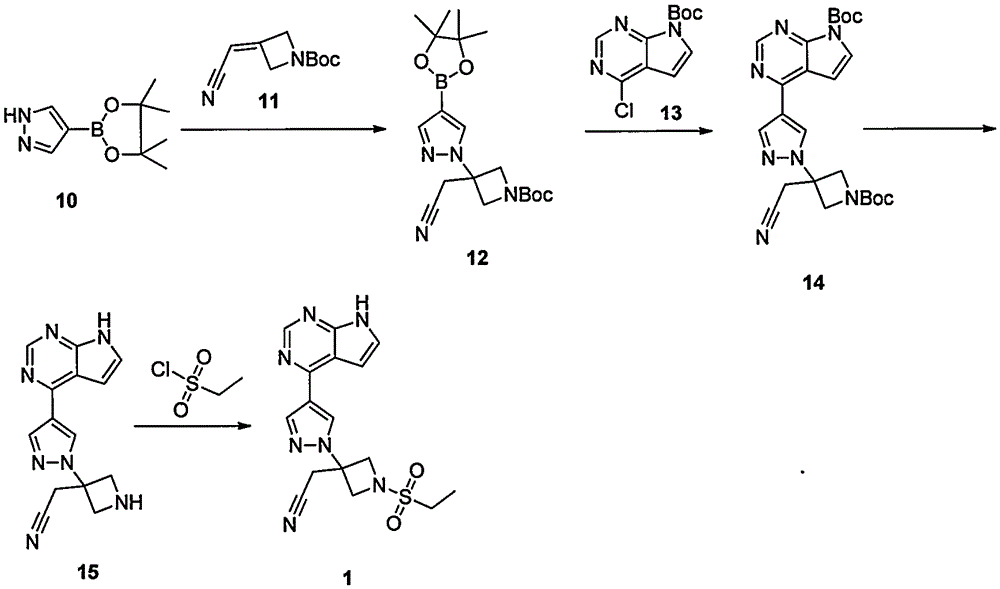
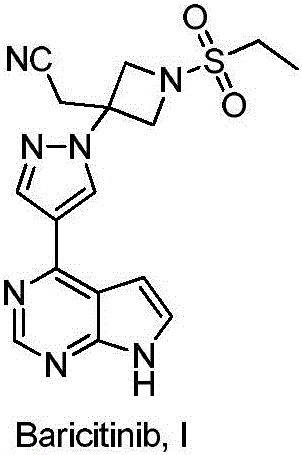
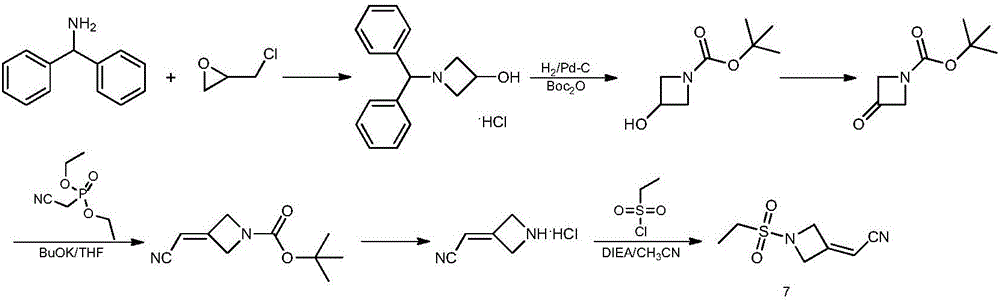
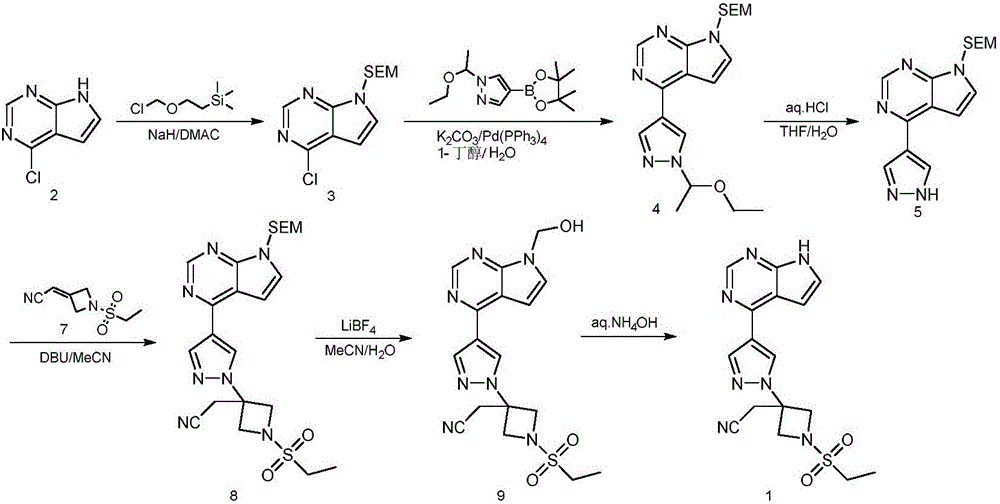
Method for preparing baricitinib
ActiveCN105294699ARaw materials are easy to getSimple processOrganic chemistryCyclobutaneCyanomethylidyne
The invention provides a method for preparing baricitinib. The method comprises the following steps: by taking 4-pyrazol boric acid pinacol ester (10) as an initial raw material, performing Michael addition reaction on the initial raw material and 3-(icyanomethylene) azacyclo-cyclobutane-1-tert-butyl formate (11) so as to prepare an intermediate 12, and performing catalytic coupling reaction on 12 and 13, thereby preparing an intermediate 14; removing two-molecule tert-butyl formate of the intermediate 14, thereby preparing an intermediate 15; performing sulfamide reaction on the intermediate 15 and ethanesulfonyl chloride in an organic solvent, thereby obtaining a final product baricitinib (1). The method for preparing baricitinib has the advantages that the raw materials are easy to obtain, the process is simple, the operation is convenient, the reaction yield is high when being compared with that of document records, the atom utilization rate is high, industrial production can be easily achieved, and the like. The reaction general formula is as shown in the specification.
Owner:SHANGHAI XUNHE PHARMA TECH CO LTD
Pyran derivatives
InactiveUS6455579B1Efficient use ofImprove efficiencyBiocidePhotosensitive materialsDye laserMethyl group
Disclosed are pyran derivatives, which have distinctive sensitivity to visible light and distinctive luminous ability. The derivatives are useful in photopolymerization, electroluminescence, and dye lasers, and are obtainable through a step of reacting a compound having a 4-cyanomethylene-2-methyl-4H-pyran skeleton with a compound having a 3-formylcoumarin skeleton.
Owner:HAYASHIBARA BIOCHEMICAL LAB INC
Binaphthol-based aggregation-induced light-emitting chiral fluorescent material
InactiveCN105154068AImprove solubilityAberrant aggregation-induced quenching of CD signalsCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationSolubilityOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a binaphthol-based aggregation-induced light-emitting chiral fluorescent material. The fluorescent material is prepared through simple condensation reaction carried out by taking chiral binaphthol with any structure as a framework and dicyanomethylidene as an electron acceptor. The fluorescent material disclosed by the invention has favorable solubility in a common organic solvent, is hardly dissolved into water, not only has aggregation-induced light-emitting property, but also shows an abnormal aggregation-induced CD signal quenching phenomenon so as to provide a new approach for constructing a binaphthol-based chiral sensor.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Lysosome-targeted Cys near-infrared fluorescent probe and preparation method and application thereof
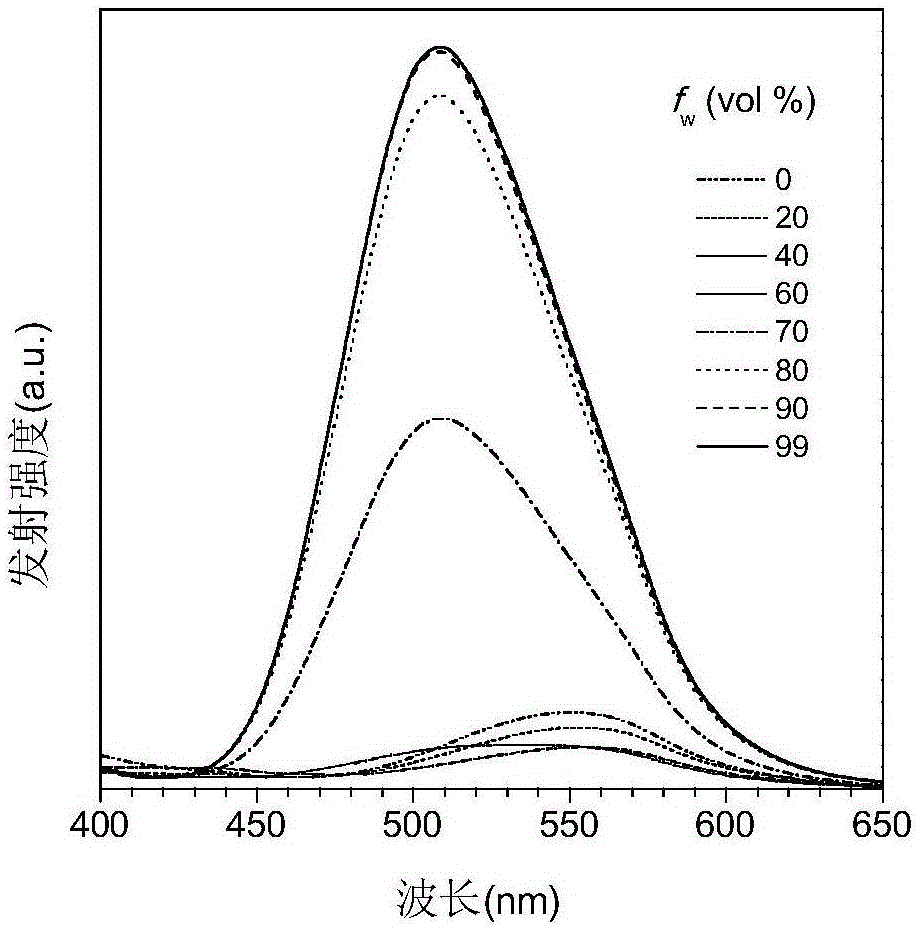
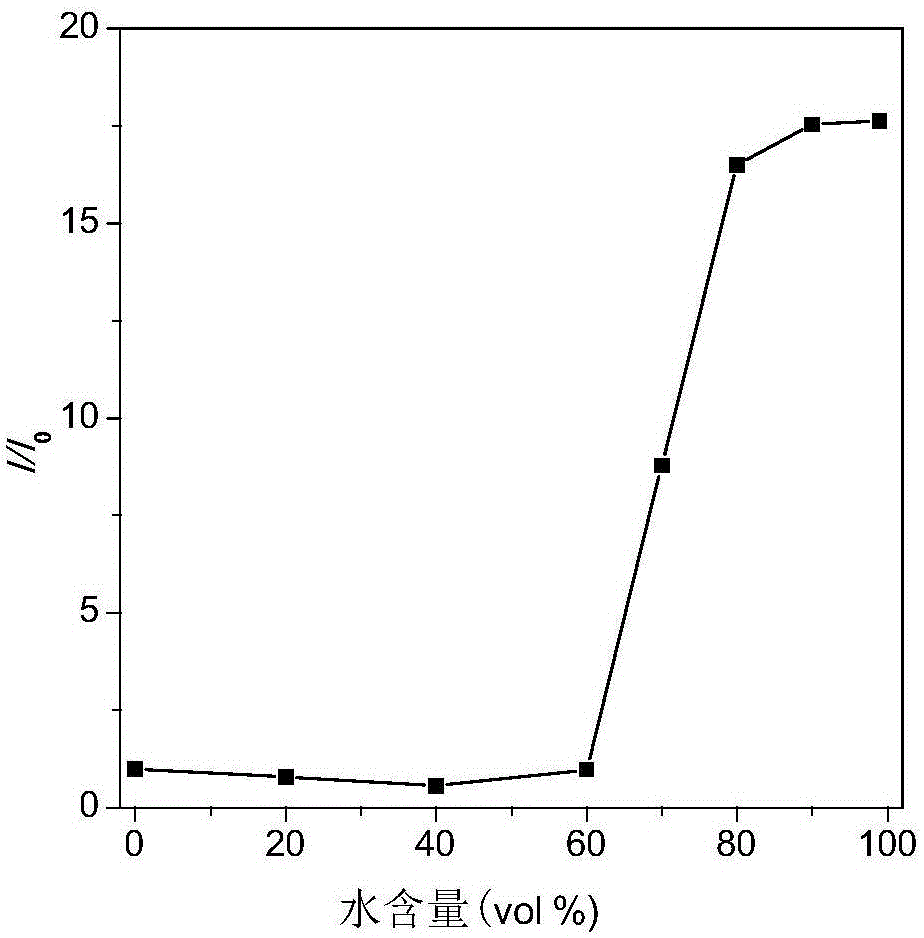
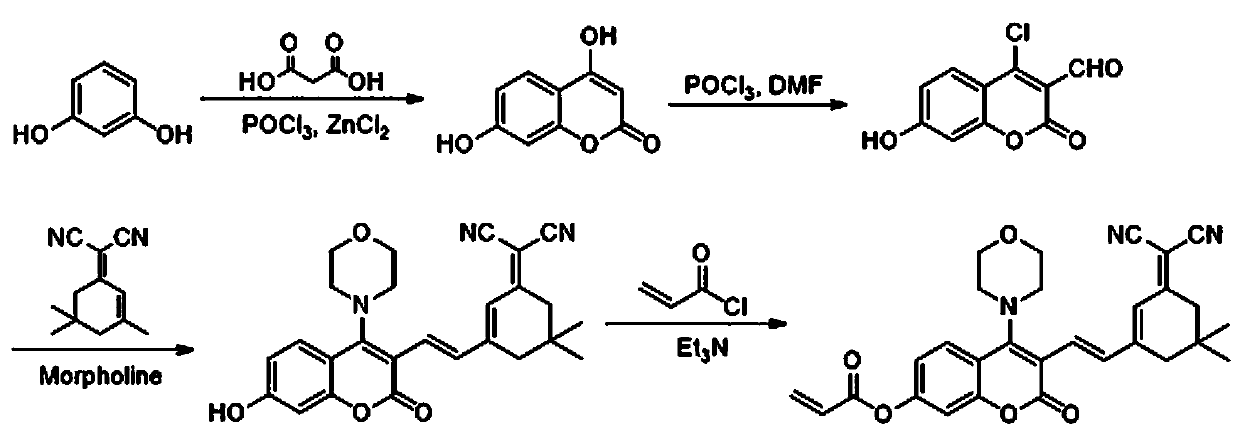
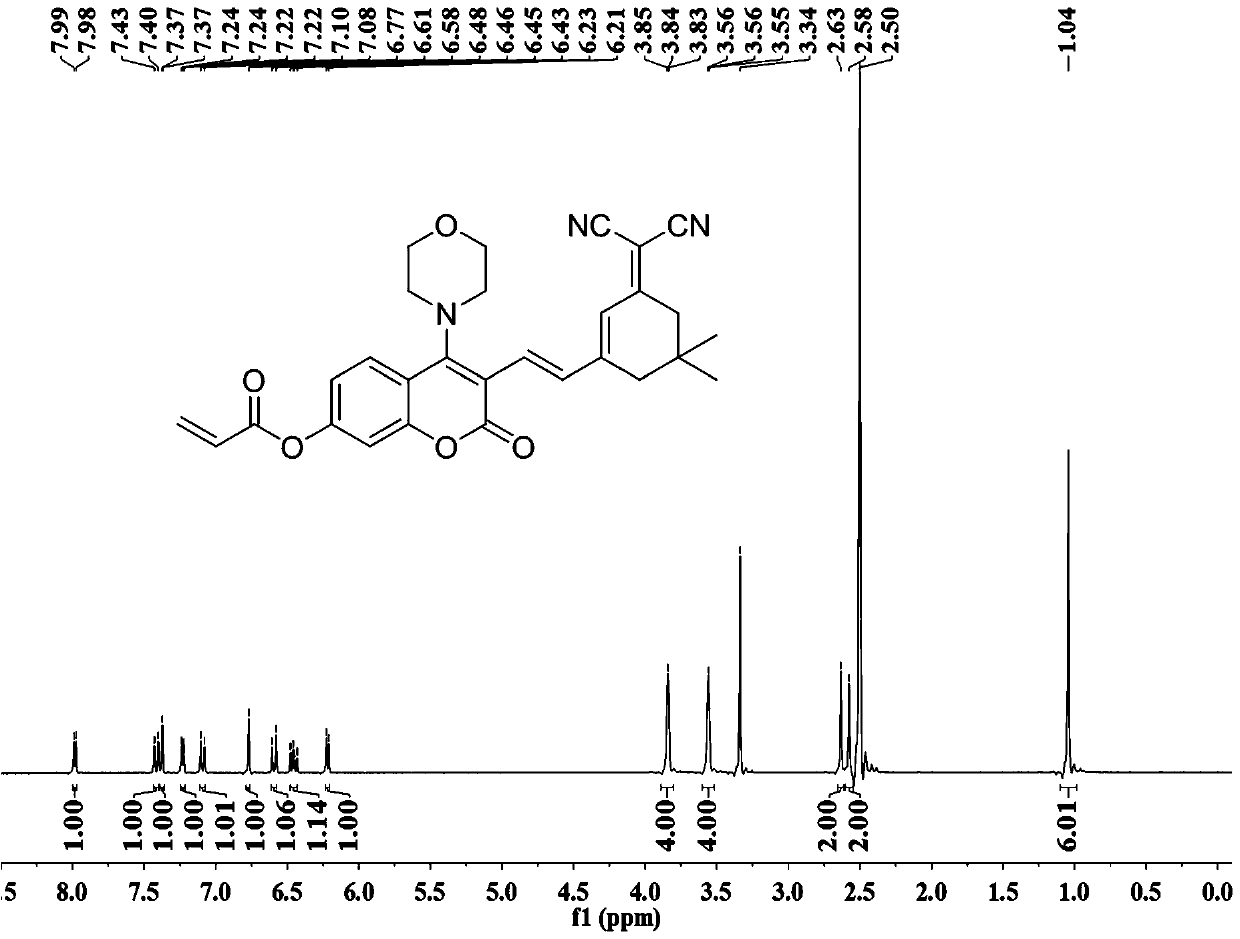
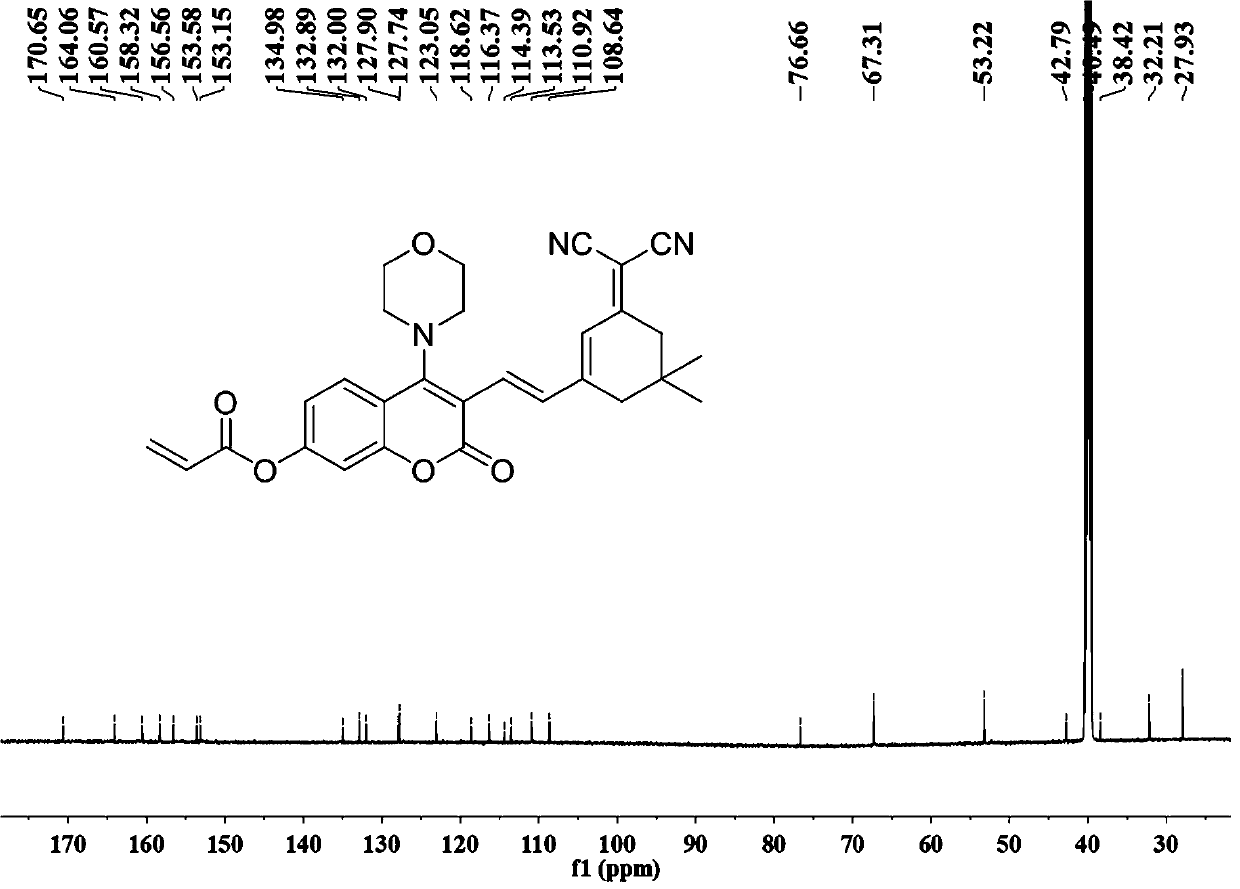
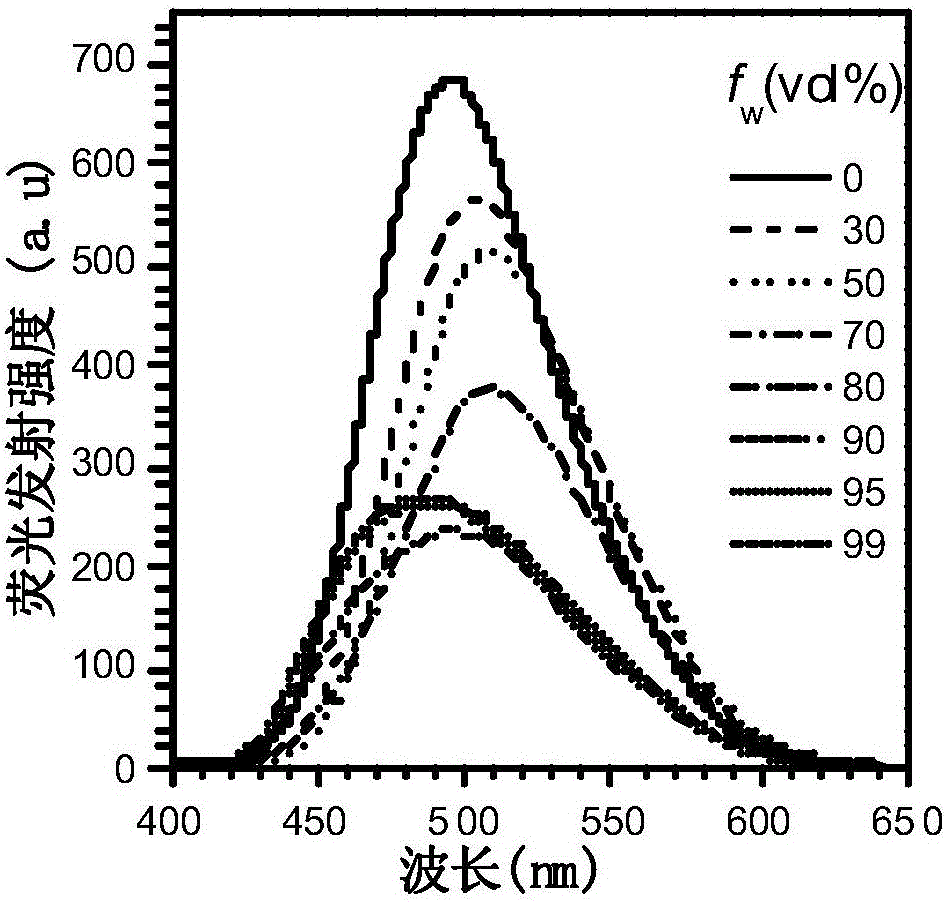
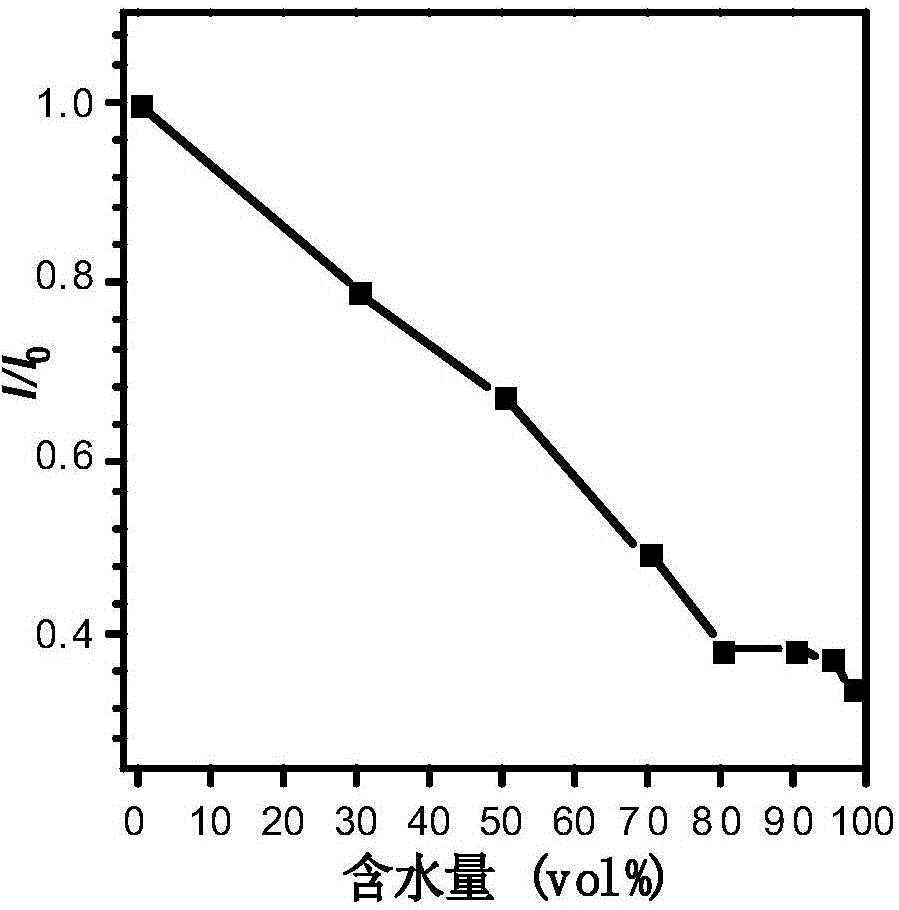
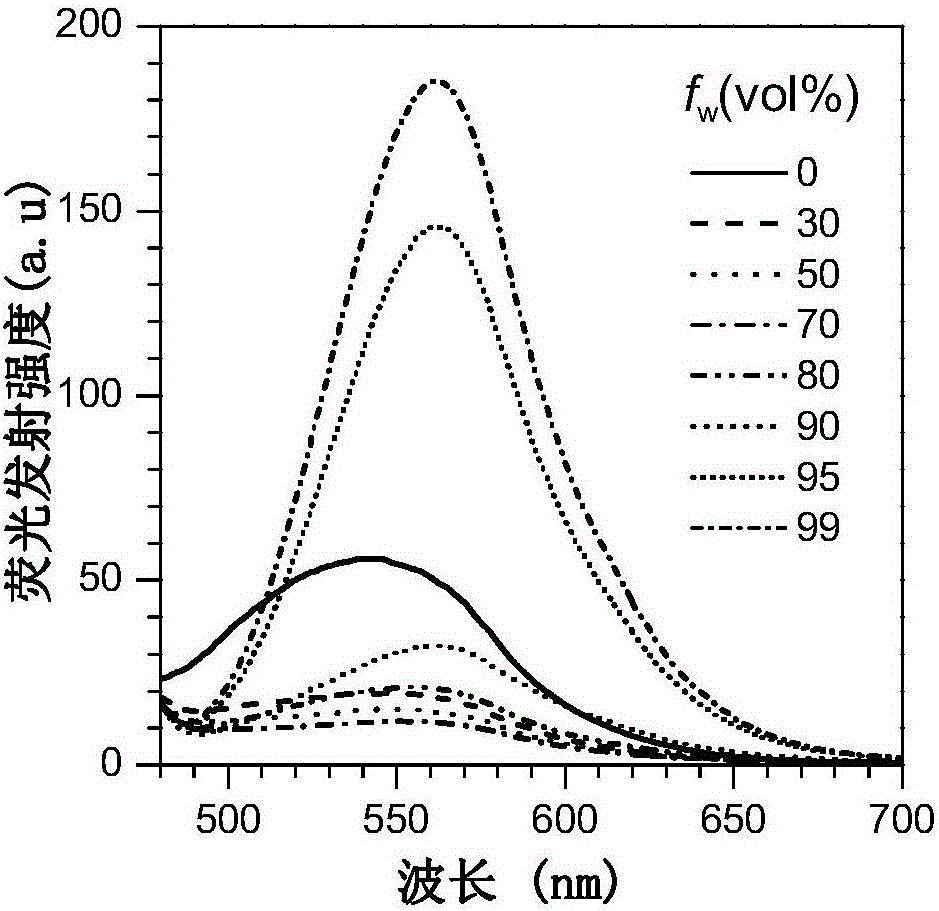
ActiveCN111499604AUndisturbedNovel structureOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceMeth-Lysosomal targeting
The invention belongs to the technical field of analysis and detection, and provides a lysosome-targeted Cys near-infrared fluorescent probe and a preparation method and application thereof. The near-infrared fluorescent probe is 3-(2-(3-(dicyanomethylene)-5,5-dimethylcyclohexen-1-yl)vinyl)-4-morpholinyl coumarin-7-acrylate which is abbreviated as DCICA. The prepared lysosome-targeted Cys near-infrared fluorescent probe has the characteristics of novel structure, lysosome targeting performance and near-infrared fluorescence emission (wherein an emission wavelength is 680 nm), can realize high-selectivity high-sensitivity detection of a Cys content of a solution, conducts specific detection of Cys in cell lysosome by using a laser confocal imaging technology, is of important guiding significance to research on the molecular mechanism of participation of the Cys in the life activity of the lysosome, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
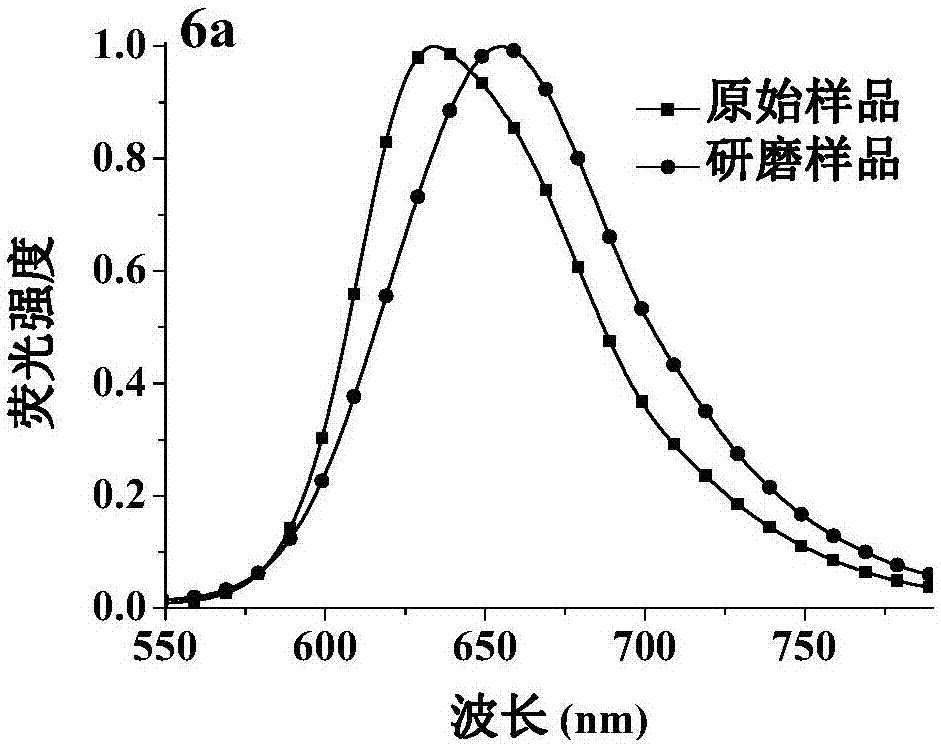
Fluorescent material with properties of aggregation-induced emission and piezochromism
InactiveCN106187817AGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsLuminescent compositionsSolubilityAggregation-induced emission
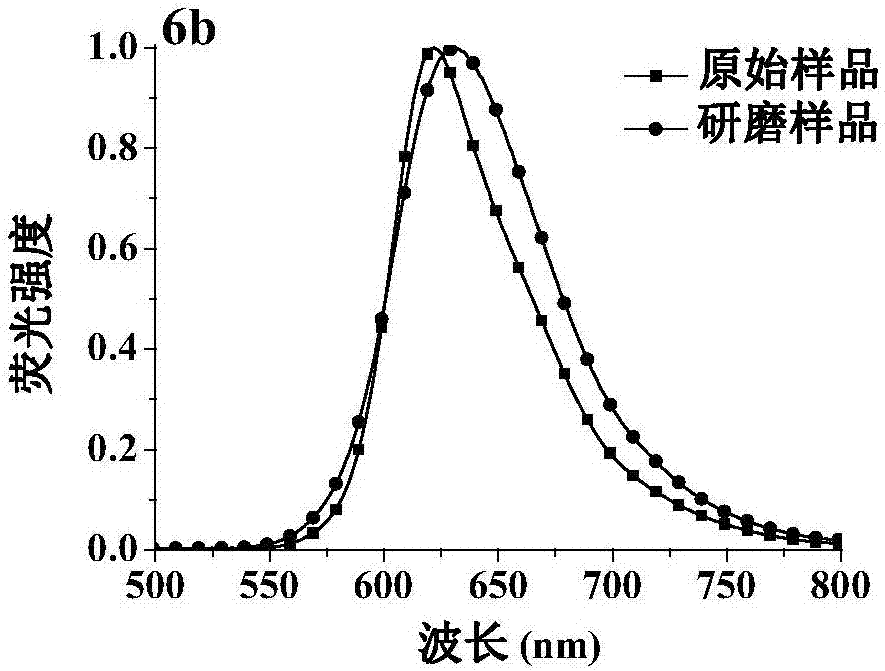
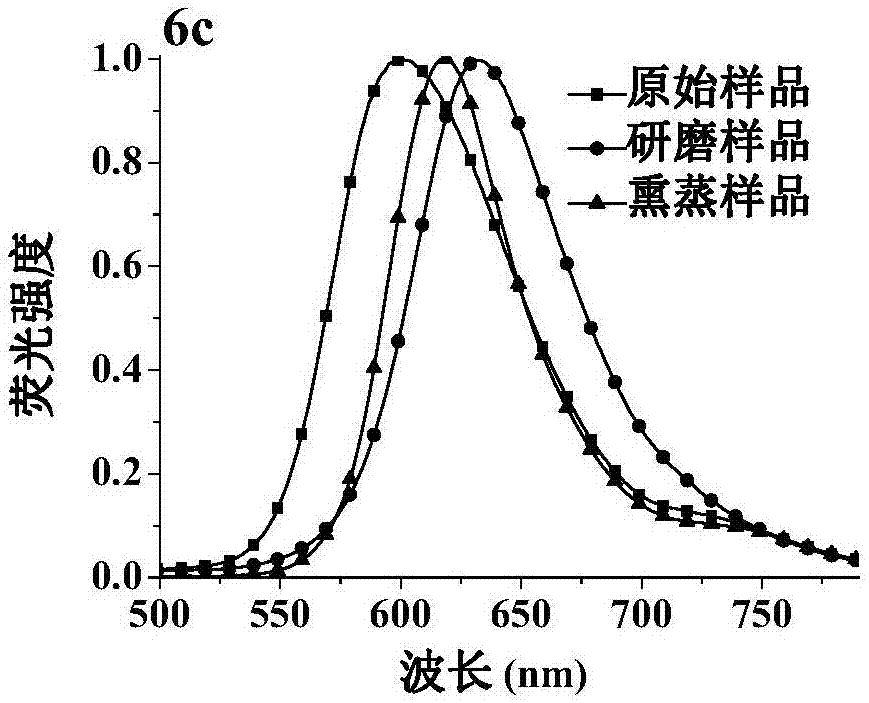
The invention discloses a fluorescent material with properties of aggregation-induced emission and piezochromism. A structural formula of the fluorescent material is as shown in the specification. The fluorescent material is prepared through a simple condensation reaction by taking dicyanomethylene as an electron acceptor. The fluorescent material is high in solubility in common organic solvents but hardly dissolved in water and forms nano aggregates, so that the characteristic of aggregation-induced emission is achieved. By grinding, fluorescence emission wavelength of the fluorescent material moves towards a long wave direction and recovers after fumigation with dichloromethane, so that the property of piezochromism is achieved.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Preparation method of baricitinib
ActiveCN107176955ARaw materials are easy to getSimple processOrganic chemistrySulfonyl chlorideBoronic acid
The invention discloses a preparation method of baricitinib. The method comprises the following steps: performing a substitution reaction on 4-chloro-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine (II) serving as a raw material and benzene sulfonyl chloride in the presence of an alkali to obtain an intermediate III; then, performing a Suzuki coupling reaction on the intermediate III and 4-pyrazole-4-boronic acid pinacol ester in the presence of a palladium catalytic system and an alkali to obtain an intermediate V; then performing a Michael addition reaction on the intermediate V and 3-(cyanomethylene)azetidine-1-tert-butyl formate in the presence of a catalyst to obtain an intermediate VII; then removing Boc protection from the intermediate VII under the action of hydrochloric acid to obtain an intermediate VIII; then performing a sulfoamidate reaction on the intermediate VIII and ethyl sulfonyl chloride in an organic solvent in the presence of an alkali to obtain an intermediate IX; lastly, removing benzenesulfonyl protection from the intermediate IX under the action of tetramethylammonium fluoride or tetrabutylammonium fluoride or a trihydrate of the tetramethylammonium fluoride or the tetrabutylammonium fluoride to obtain baricitinib (I). Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of adoption of readily-available raw materials, low cost, high product yield and easiness for industrial production.
Owner:NANJING YOKO PHARMA +2
Dicyanomethylene-4H-pyran derivatives as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107382982AThe synthesis process is simpleEasy to purifyOrganic chemistryTenebresent compositionsColor changesStructural unit
The invention particularly relates to dicyanomethylene-4H-pyran derivatives as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method of the dicyanomethylene-4H-pyran derivatives comprises the following steps: (1) 2,6-dimethyl-4H-pyran-4-one 1 as a starting material is subjected to an addition-elimination reaction with malononitrile, and an intermediate 2 is obtained; (2) the intermediate 2 is subjected to an addition-elimination reaction with indolal with different alkyl chains, and the dicyanomethylene-4H-pyran derivatives are obtained. Indole structural units with different alkyl groups and dicyanomethylene-4H-pyran structural units are introduced into the field of organic solid luminescent materials, novel piezoluminescence color change materials are developed, and the derivatives play an important role in the field of photoelectricity. The provided method adopts a simple synthesis process, purification is easy, and the synthesized piezoluminescence materials are quite applicable to various fields of preparation of pressure sensors, anti-counterfeiting trademarks and the like and have good scientific research value and industrialized application potential.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
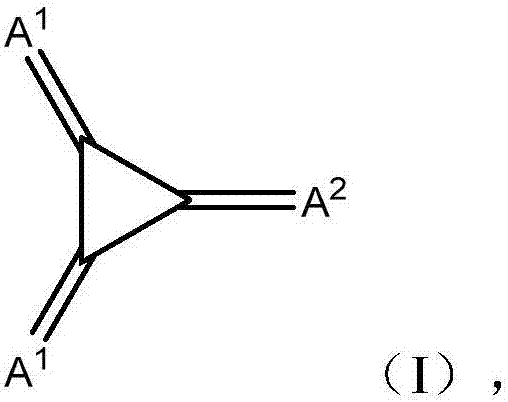
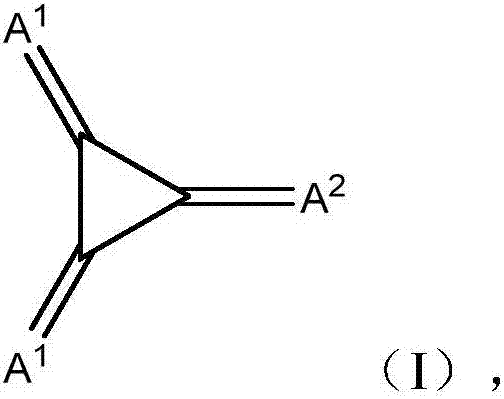
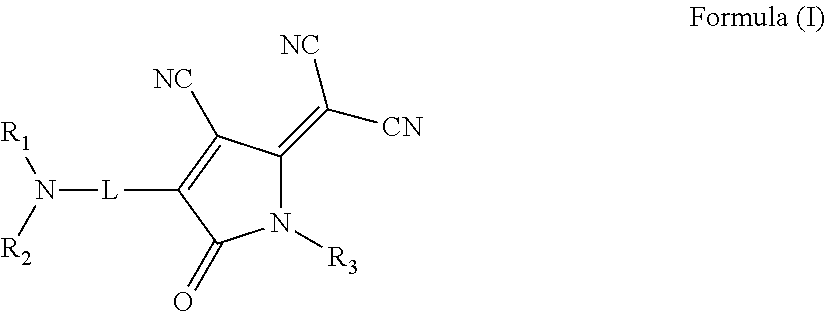
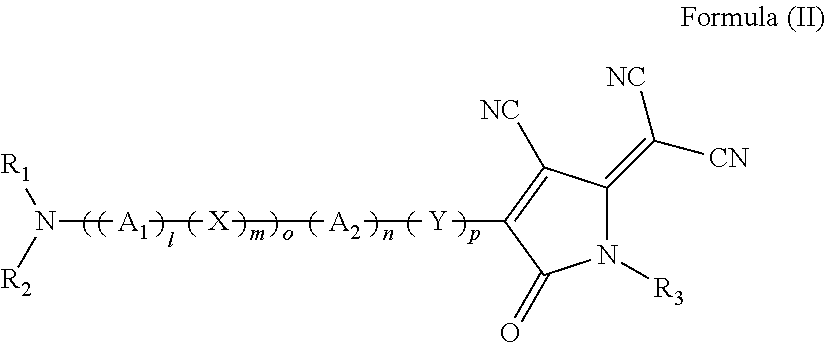
Substituted 1,2,3-triylidenetris(cyanomethanylylidene)) cyclopropanes for vte, electronic devices and semiconducting materials using them
The present invention relates to a process for preparation of an electrically doped semiconducting material comprising a [3]-radialene p-dopant or for preparation of an electronic device containing a layer comprising a [3]-radialene p-dopant, the process comprising the steps : (i) loading an evaporation source with the [3]-radialene p-dopant; and (ii) evaporating the [3]-radialene p-dopant at an elevated temperature and at a reduced pressure, wherein the [3]-radialene p-dopant is selected from compounds having a structure according to formula (I) wherein A1 and A2 are independently aryl- or heteroaryl- substituted cyanomethylidene groups, the aryl and / or heteroaryl is selected independently in A1 and A2 from 4-cyano-2,3,5,6-tetrafluorphenyl,2,3,5,6-tetrafluorpyridine-4-yl, 4-trifluormethyl-2,3,5,6-tetrafluorphenyl, 2,4-bis(trifluormethyl)-3,5,6-trifluorphenyl, 2,5-bis(trifluormethyl)-3,4,6-trifluorphenyl, 2,4,6-tris(trifluormethyl)-1,3-diazine-5-yl, 3,4-dicyano-2,5,6-trifluorphenyl, 2-cyano-3,5,6-trifluorpyridine-4-yl, 2-trifluormethyl-3,5,6-trifluorpyridine-4-yl, 2,5,6-trifluor-1,3-diazine-4-yl and 3-trifluormethyl-4-cyano-2,5,6-trifluophenyl), and at least one aryl or heteroaryl is 2,3,5,6-tetrafluorpirydine-4-yl, 2,4-bis(trifluormethyl)-3,5,6-trifluorphenyI, 2,5-bis(trifluormethyl)-3,4,6-trifluorphenyl, 2,4,6-tris(trifluormethyl)-1,3-diazine-5-yl, 3,4-dicyano-2,5,6-trifluorphenyl, 2-cyano-3,5,6-trifluorpyridine-4-yl, 2-trifluormethyl-3,5,6-trifluorphenyl, provided that the heteroaryl in both A1 and A2 cannot be 2,3,5,6-tetrafluorpyridine-4-yl at the same time, respective [3]-radialene compounds, and semiconducting materials and layer, and electronic devices comprising said compounds.
Owner:NOVALED GMBH
Substituted 1,2,3-Triylidenetris(cyanomethanylylidene) Cyclopropanes for VTE, Electronic Devices and Semiconducting Materials Using Them
ActiveUS20170373251A1High yieldHigh purityOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesTetrafluoroethyleneDopant
The present invention relates to a process for preparation of an electrically doped semiconducting material comprising a [3]-radialene p-dopant or for preparation of an electronic device containing a layer comprising a [3]-radialene p-dopant, the process comprising the steps: (i) loading an evaporation source with the [3]-radialene p-dopant; and (ii) evaporating the [3]-radialene p-dopant at an elevated temperature and at a reduced pressure, wherein the [3]-radialene p-dopant is selected from compounds having a structure according to formula (I) wherein A1 and A2 are independently aryl- or heteroaryl-substituted cyanomethylidene groups, the aryl and / or heteroaryl is selected independently in A1 and A2 from 4-cyano-2,3,5,6-tetrafluorphenyl,2,3,5,6-tetrafluorpyridine-4-yl, 4-trifluormethyl-2,3,5,6-tetrafluorphenyl, 2,4-bis(trifluormethyl)-3,5,6-trifluorphenyl, 2,5-bis(trifluormethyl)-3,4,6-trifluorphenyl, 2,4,6-tris(trifluormethyl)-1,3-diazine-5-yl, 3,4-dicyano-2,5,6-trifluorphenyl, 2-cyano-3,5,6-trifluorpyridine-4-yl, 2-trifluormethyl-3,5,6-trifluorpyridine-4-yl, 2,5,6-trifluor-1,3-diazine-4-yl and 3-trifluormethyl-4-cyano-2,5,6-trifluophenyl), and at least one aryl or heteroaryl is 2,3,5,6-tetrafluorpirydine-4-yl, 2,4-bis(trifluormethyl)-3,5,6-trifluorphenyl, 2,5-bis(trifluormethyl)-3,4,6-trifluorphenyl, 2,4,6-tris(trifluormethyl)-1,3-diazine-5-yl, 3,4-dicyano-2,5,6-trifluorphenyl, 2-cyano-3,5,6-trifluorpyridine-4-yl, 2-trifluormethyl-3,5,6-trifluorphenyl, provided that the heteroaryl in both A1 and A2 cannot be 2,3,5,6-tetrafluorpyridine-4-yl at the same time, respective [3]-radialene compounds, and semiconducting materials and layer, and electronic devices comprising said compounds.
Owner:NOVALED GMBH
Colorimetric-fluorescent probe for detecting hypochlorite radical, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110627756ARealize visual detectionRealize detectionOrganic chemistryColor/spectral properties measurementsHypochloriteFluorescence
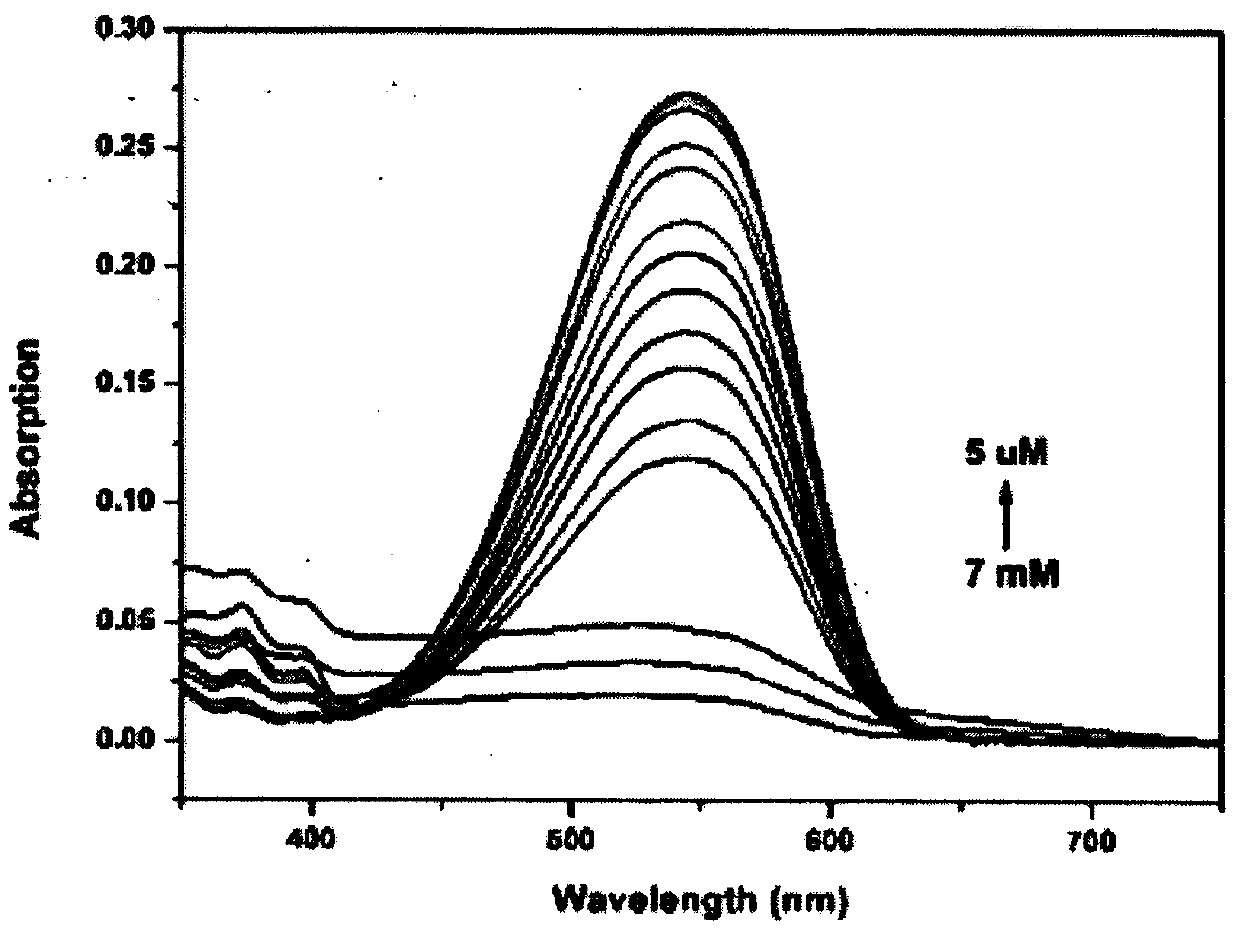
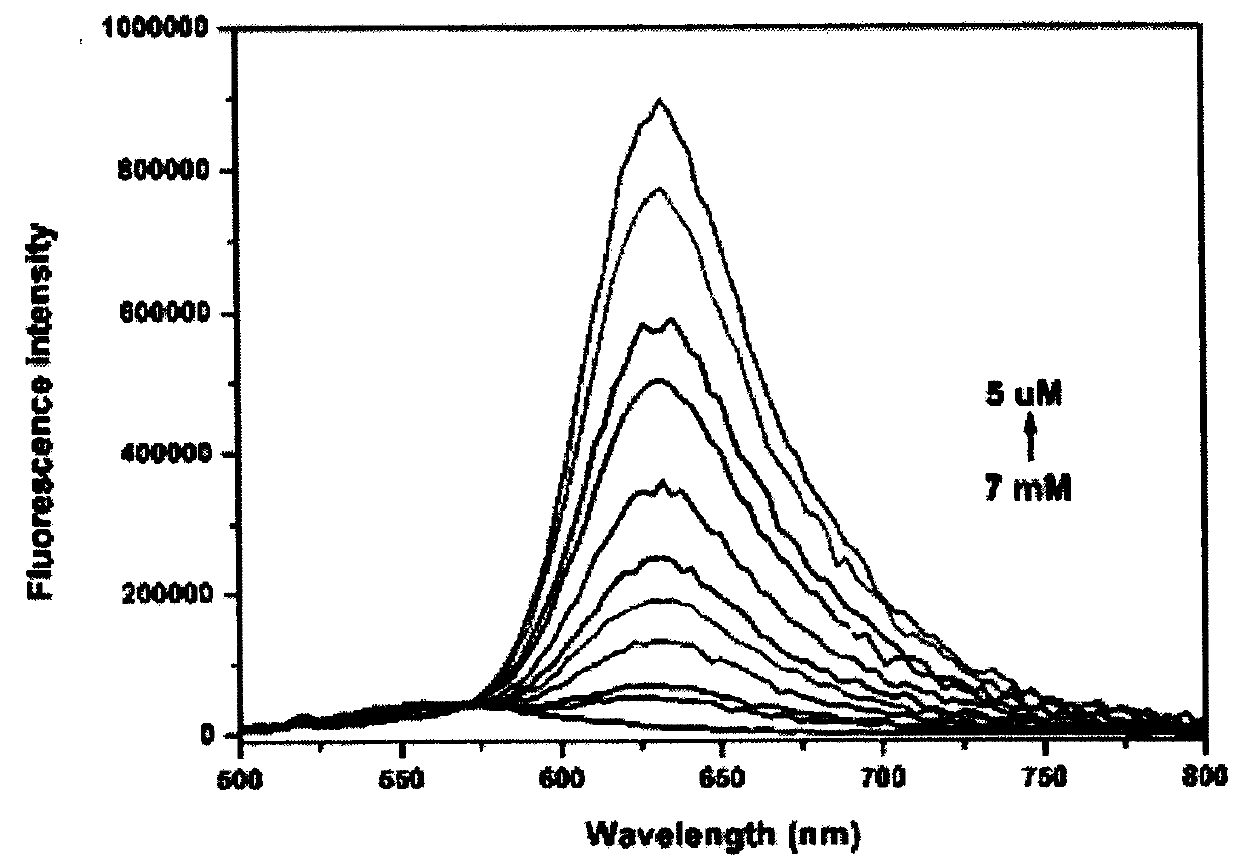
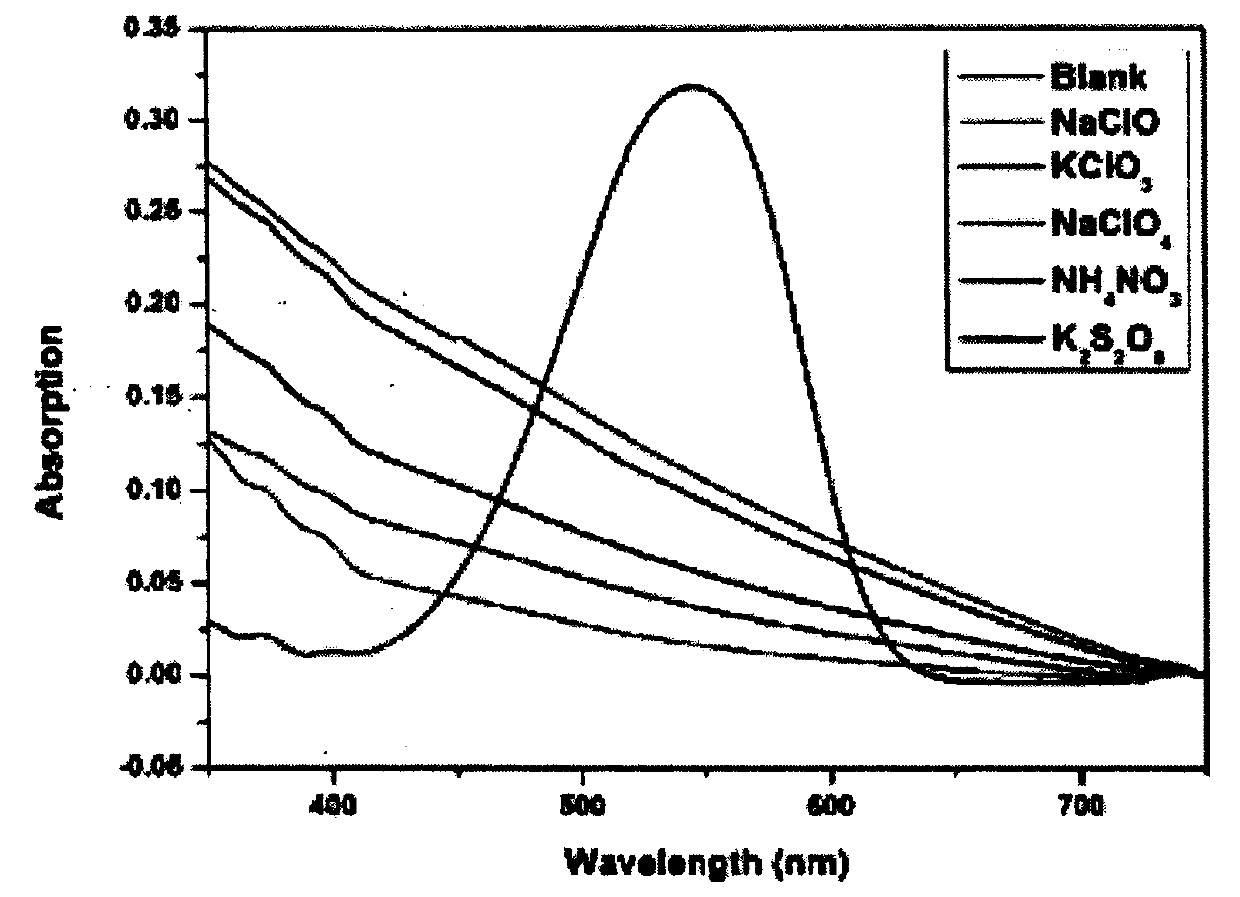
The invention provides a colorimetric-fluorescent probe for detecting hypochlorite radical, a preparation method and application thereof. Aldehyde aniline and a 2-(3-cyano-4, 5, 5-trimethylfuran-2(5H)-acyl)acrylonitrile electron-withdrawing group are subjected to Knoevenagel condensation, thus obtaining the colorimetric-fluorescent probe (E)-((4-(2-(4-cyano-5-(dicyanomethylene)-2, 2-dimethyl-2, 5-dihydrofuran-3-yl)vinyl)phenyl)azanediyl)bis(ethane-2, 1-diyl)diacrylate. The response group of the probe to hypochlorite radical is C=C double bond, in a mixed solution of an organic solvent and water, the single probe has a fluorescence emission peak position at 632nm and an ultraviolet absorption peak position at 544nm, and when used for detecting hypochlorite radical, the probe shows obvious fluorescence quenching and fading response, the response speed is high, and real-time detection of hypochlorite radical can be realized; the detection sensitivity is high, and the detection limit is aslow as 0.19microM; and the probe can accurately determine the content of hypochlorite radical in a water sample and non-standard explosive raw material in the environment.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
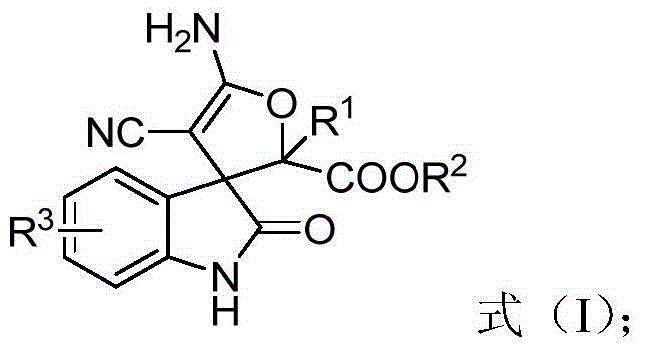
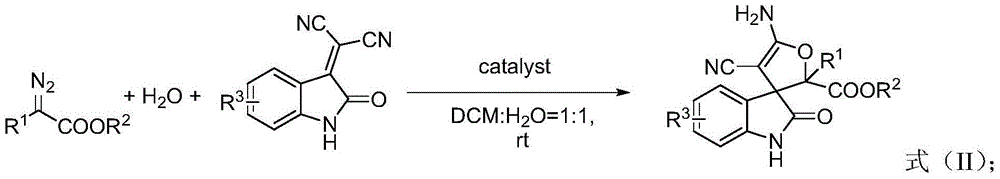
3,3'-dihydrofuran spiro-oxoindole derivative and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105713001AToxicAtom utilization is highOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsDrug biological activityCyanomethylidyne
The invention discloses a 3,3'-dihydrofuran spiro-oxoindole derivative and a preparation method thereof. Cyano methylene oxoindole, water and diazonium are used as raw materials, a transition metal salt is used as a catalyst, dichloromethane and water are used as a mixed solvent, and the compound represented by the formula (I) is prepared by a one-step reaction. The invention also provides an application of the 3,3'-dihydrofuran spiro-oxoindole derivative in preparation of tumor suppressing drugs, and the 3,3'-dihydrofuran spiro-oxoindole derivative can be used as a potential bioactive skeleton. The high atom economic reaction is applied, the target product is prepared with high yield, and the method has the advantages of short synthetic route, green and environmental protection, simple operation and the like.
Owner:广东和博制药有限公司
Organic photovoltaic material and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110218216AEasy to makeHigh yieldOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesHigh electronThermal stability
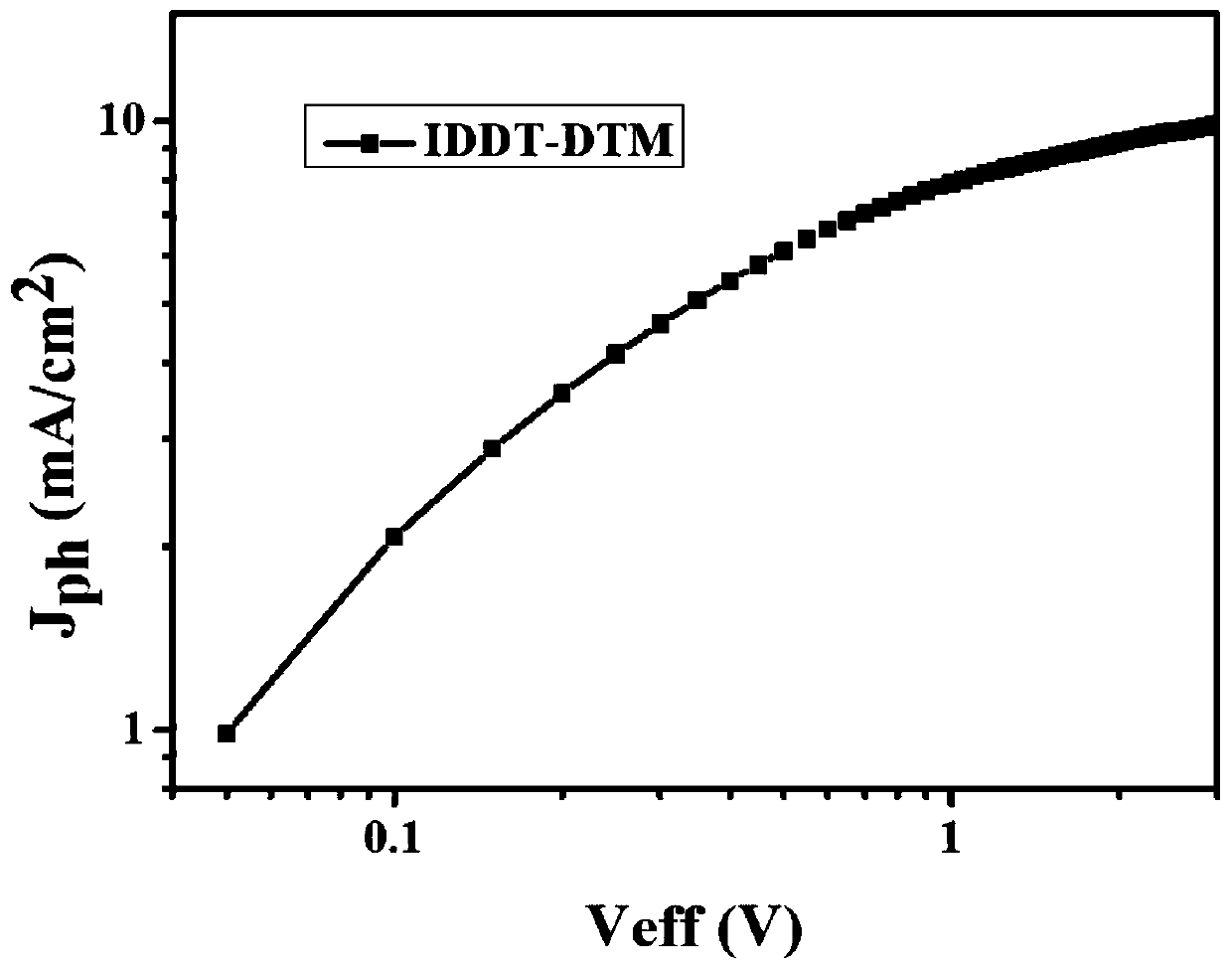
The invention discloses an organic photovoltaic material, a preparation method and application thereof. The material takes 3-(dicyanomethylene)-2, 3-dihydrobenzothiophene-1, 1-Dioxide (DTM) as an endgroup and one or more donor units as a bridging framework, and has a structural general formula shown in a formula I, wherein D and D1 are conjugated structural system bridging units. The organic photovoltaic material of the invention has the characteristics of simple preparation, easy control of reaction process, easy separation and purification, easy adjustment of energy level and spectrum and the like. The material also has good thermal stability, film forming stability and high electron and hole mobility, and a photovoltaic device prepared by the material has high photoelectric conversionefficiency and has potential application value in the technical field of photovoltaic.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
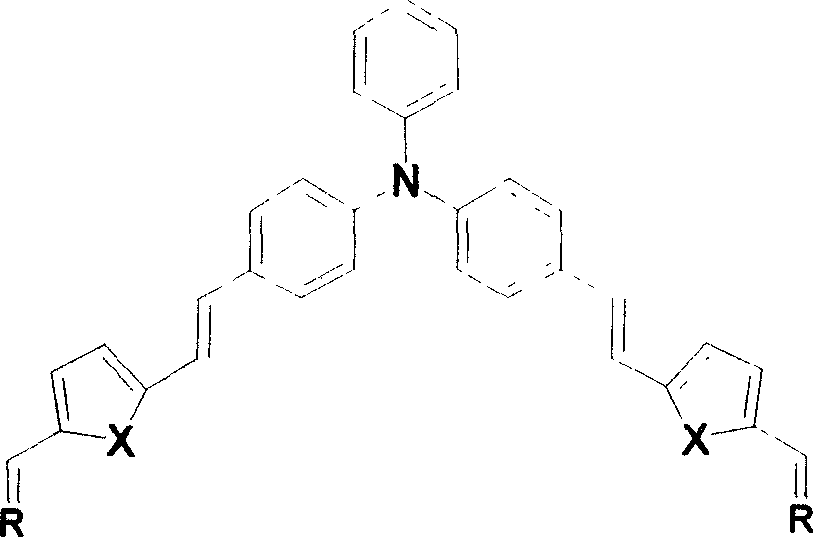
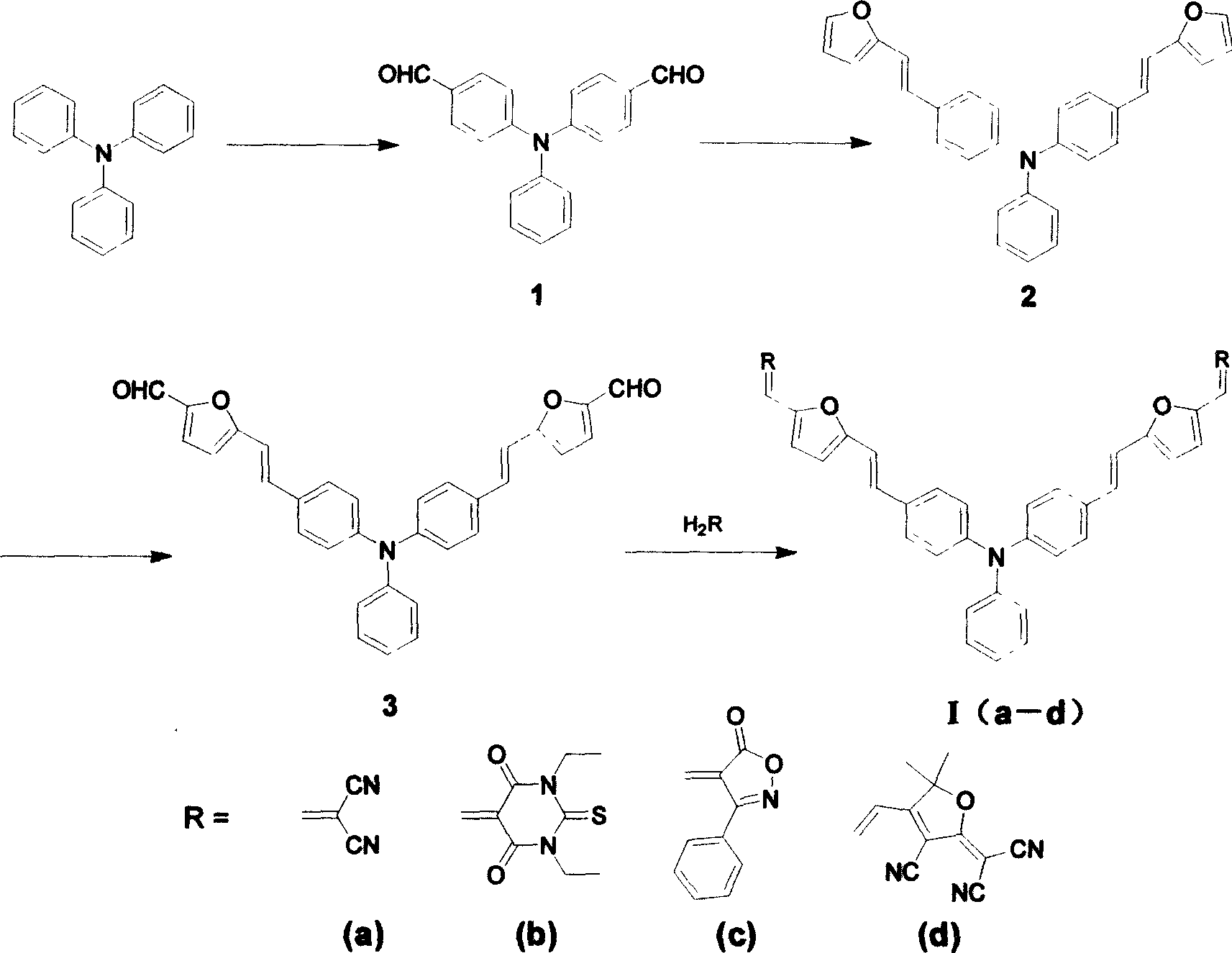
Y-type second-order non-linear optical luminophor contg. triphenylamine, prepn. method and use thereof
InactiveCN1830972AGood optical clarityHigh second-order nonlinear optical performanceOrganic chemistryLuminescent compositionsThiobarbituric acidAniline
A Y-type two-order non-linear optical chromogen containing triphenylamine group and its preparing process are disclosed. It can be used as two-order non-linear optical material used in remote communication, data storage, phase conjugation, etc.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Non-fullerene electron acceptor material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113336777AThe synthesis process is mature and easy to controlHigh synthetic yieldSilicon organic compoundsFinal product manufactureSolar batteryPolymer chemistry
The invention discloses a non-fullerene electron acceptor material and a preparation method and application thereof. The star-shaped non-fullerene electron acceptor material is obtained by taking an electron donating structure as a central core unit and a five-membered fused ring as an arm unit, and blocking a terminal group by using electron withdrawing groups such as 3-(dicyanomethylene) indanone and derivatives thereof. The material not only maintains the advantages of a linear non-fullerene electron acceptor material, but also has high electron mobility and isotropic charge transfer characteristics of a fullerene electron acceptor material, and the multidimensional geometric structure of the material is beneficial to intramolecular charge transfer, so that the energy gap is reduced and the absorption range is expanded, and the star-shaped multi-dimensional structure can effectively inhibit excessive aggregation and is beneficial to exciton dissociation. The material can be used as an electron acceptor material of an active layer to be widely applied to preparation of organic solar cells, and excellent material film stability and excellent photoelectric conversion characteristics can be obtained.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Nonlinear optical materials and nonlinear optical device using the same
InactiveUS20150014607A1Improve photostabilityGood optical performanceOrganic chemistryPolarising elementsArylPolymer science
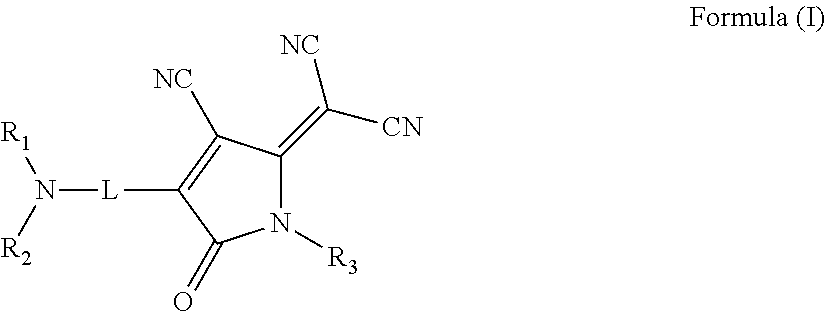
There is provided an organic nonlinear optical material including a polymer binder and a compound represented by the following Formula (I):wherein, in Formula (I),R1 and R2 each independently represent a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group or a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group;R3 represents a hydrogen atom, a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, or a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group; andL represents a divalent linking group connecting a nitrogen atom and an oxopyrroline ring having a dicyanomethylidene group in a π-conjugated system containing an azo group (—N═N—).
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Fluorophore compounds and their use in biological systems
Fluorophore compounds and methods for their use are disclosed. The fluorophores contain a 2-dicyanomethylen-3-cyano-2,5-dihydrofuran (DCDHF) moiety and one or more donor groups conjugated to the 2-dicyanomethylen-3-cyano-2,5-dihydrofuran group. The donor groups can contain atoms with free electron pairs such as oxygen, sulfur, nitrogen, or phosphorous. The fluorophore compounds can be used to label and detect biological molecules and biological structures either in vivo or in vitro.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
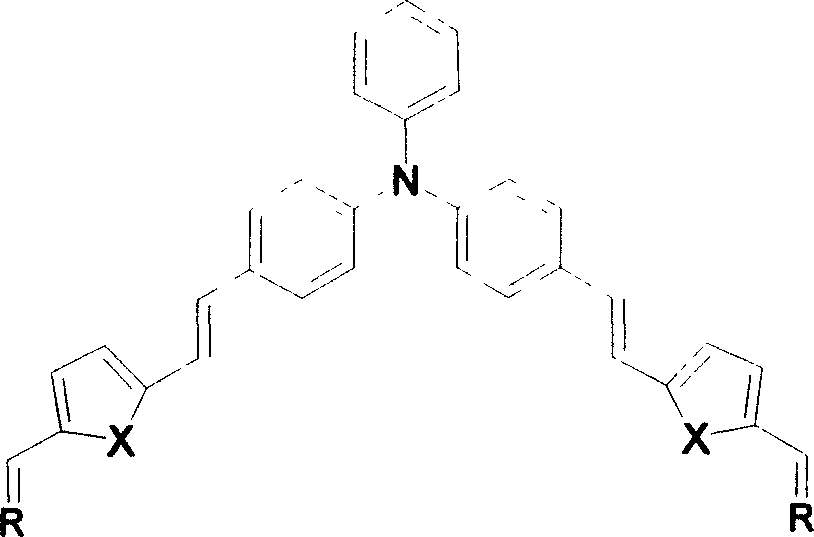
Y-type second-order non-linear optical luminophor contg. triphenylamine, prepn. method and use thereof
InactiveCN100386321CGood optical clarityHigh second-order nonlinear optical performanceOrganic chemistryLuminescent compositionsThiobarbituric acidAniline
A Y-type two-order non-linear optical chromogen containing triphenylamine group and its preparing process are disclosed. It can be used as two-order non-linear optical material used in remote communication, data storage, phase conjugation, etc.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
N-type organic small molecule semiconductor based on indenothiophene as core as well as preparation method and application of n-type organic small molecule semiconductor
InactiveCN108822076AImprove efficiencyStrong light absorptionOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOrganic solar cellHigh absorption
The invention discloses an n-type organic small molecule semiconductor based on indenothiophene as a core as well as a preparation method and an application of the n-type organic small molecule semiconductor, and particularly provides the n-type organic small molecule semiconductor based on indenothiophene as the core, thiophene as a bridge and 1,3-indanedione, malononitrile or 2-(5,6-difluoro-3-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-ylidene)malononitrile as an end group, the preparation method of the n-type organic small molecule semiconductor and the application of molecules as a receptor material in organic non-fullerene solar cells. The n-type organic small molecule semiconductor based on indenothiophene as the core has the advantages of capacity of processing in a solution form, wide absorptionspectrum, high absorption coefficient, excellent thermal stability and appropriate energy level, and is an ideal non-fullerene receptor material for organic solar cells.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Colorimetric-fluorescent fiber membrane for detecting hypochlorite ions, and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a colorimetric-fluorescent fiber membrane for detecting hypochlorite ions, and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the fluorescent fiber membrane comprises the following steps: carrying out free radical polymerization on a double bond-containing colorimetric-fluorescent probe molecule ((E)-((4-(2-(4-cyano-5-(dicyanomethylene)-2,2-dimethyl-2,5-dihydrofuran-3-yl)vinyl)phenyl)azanediyl)bis(ethane-2,1-diyl)diacrylate) and hydroxyethyl methacrylate to obtain modified poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate), and grinding the modified poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate)and polystyrene to obtain the colorimetric-fluorescent fiber membrane. The colorimetric-fluorescent fiber membrane for detecting hypochlorite ions has a fluorescence emission peak at 632 nm and an ultraviolet absorption peak at 544 nm, has obvious fluorescence quenching and fading response and a high response speed when used to detect the hypochlorite ions, and achieves onsite, rapid, convenientand visual detection of hypochlorite ions in a water sample in the environment and a non-standard explosive raw material.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
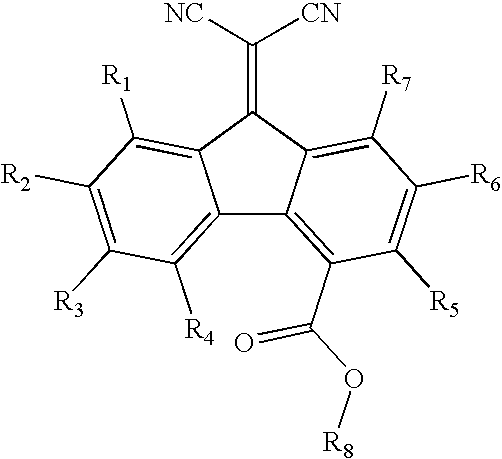
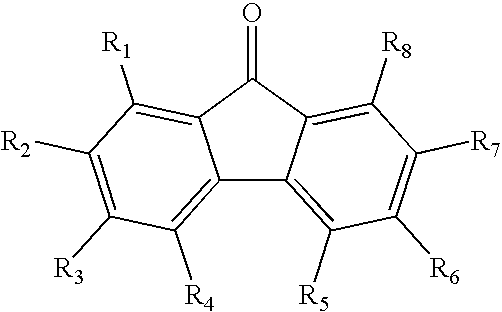
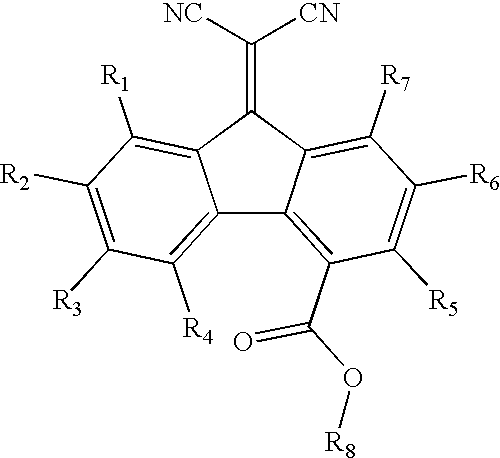
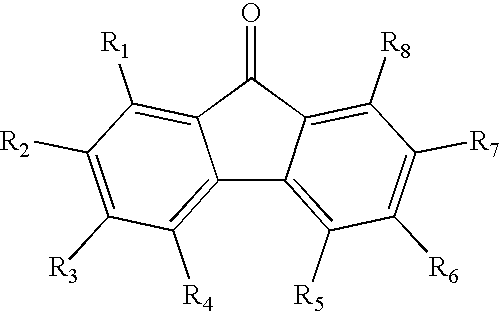
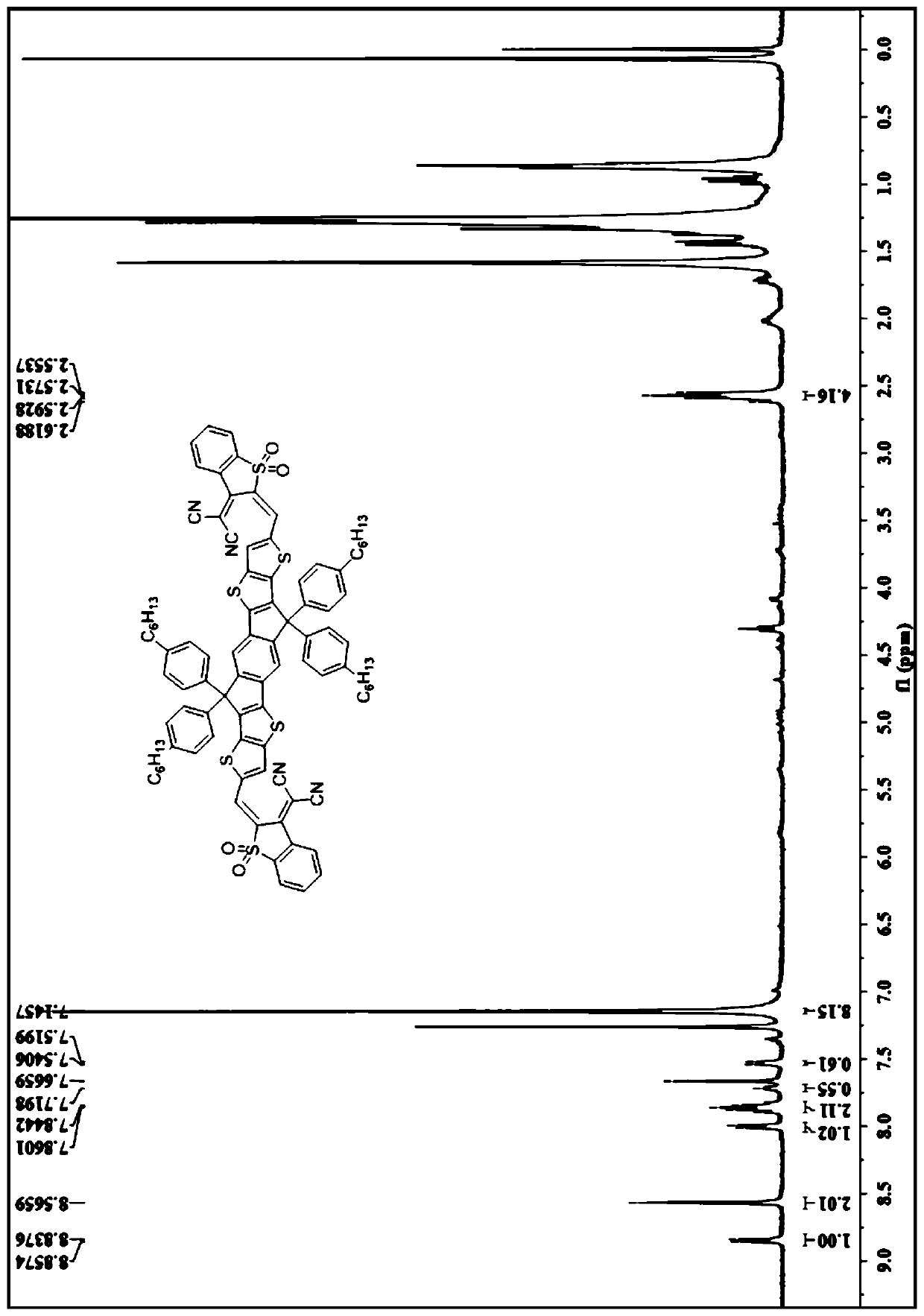
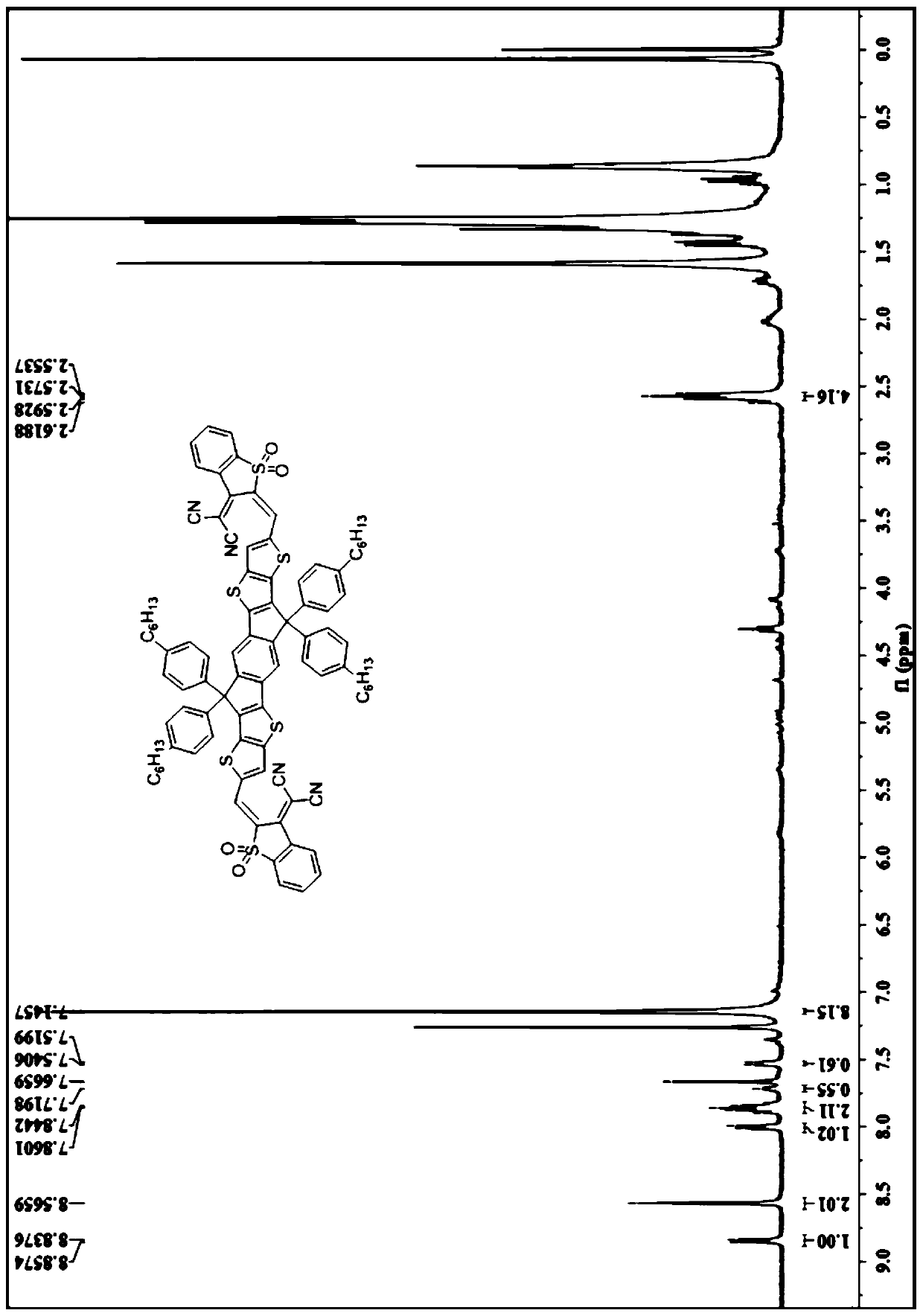
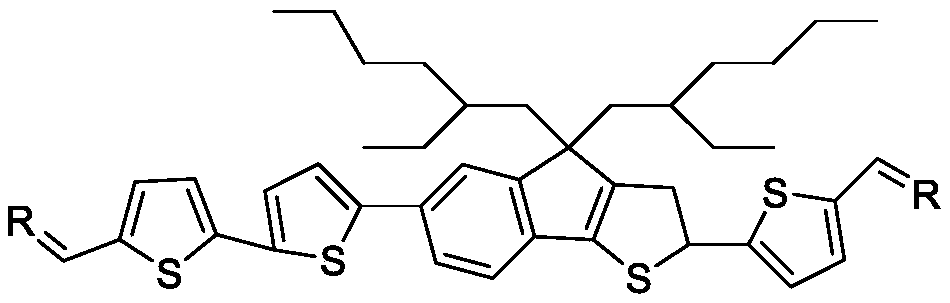
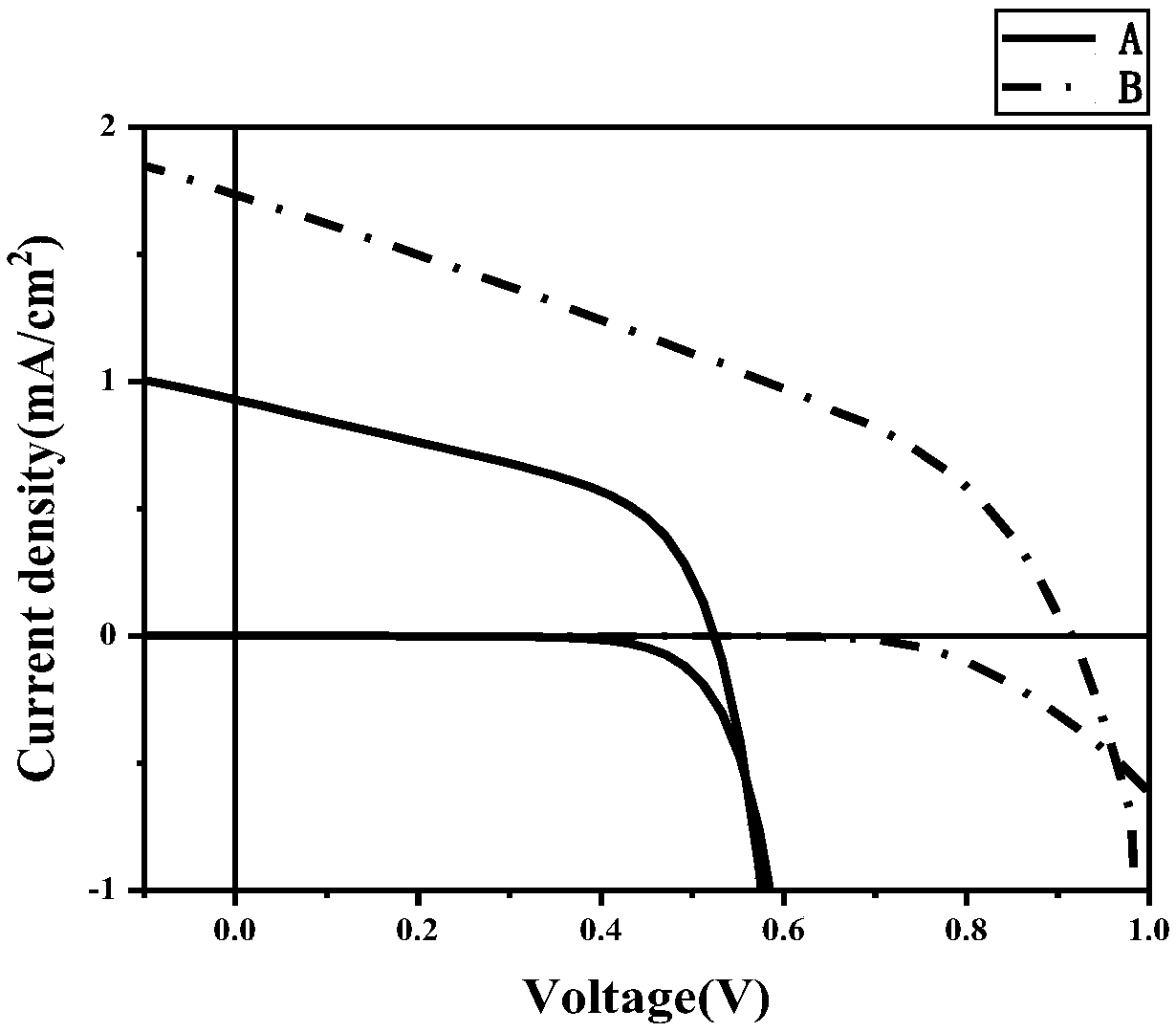
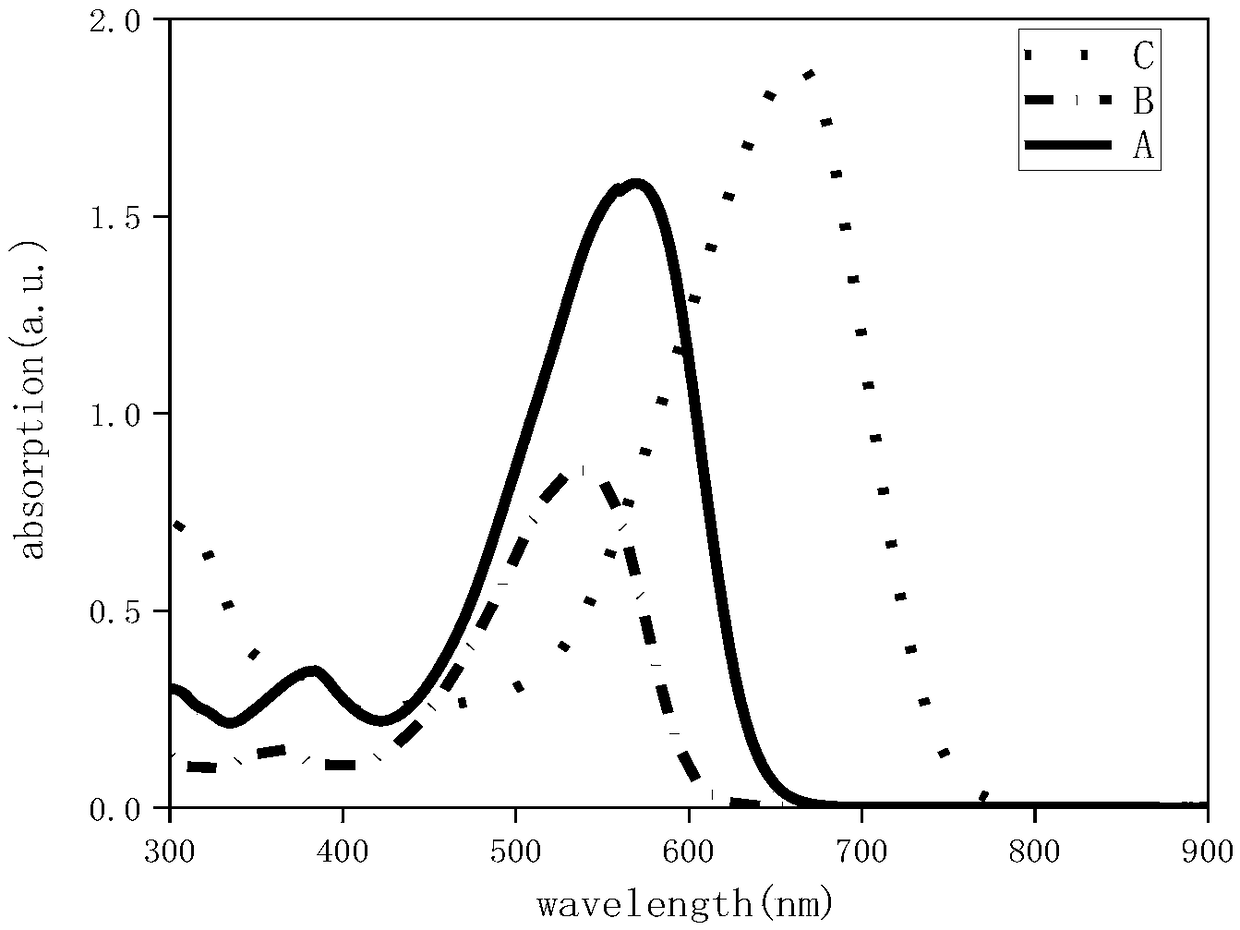
A-D-A type photovoltaic small molecule receptor taking indeno[1,2-b]fluorine as core, as well as preparation method and application of A-D-A type photovoltaic small molecule receptor
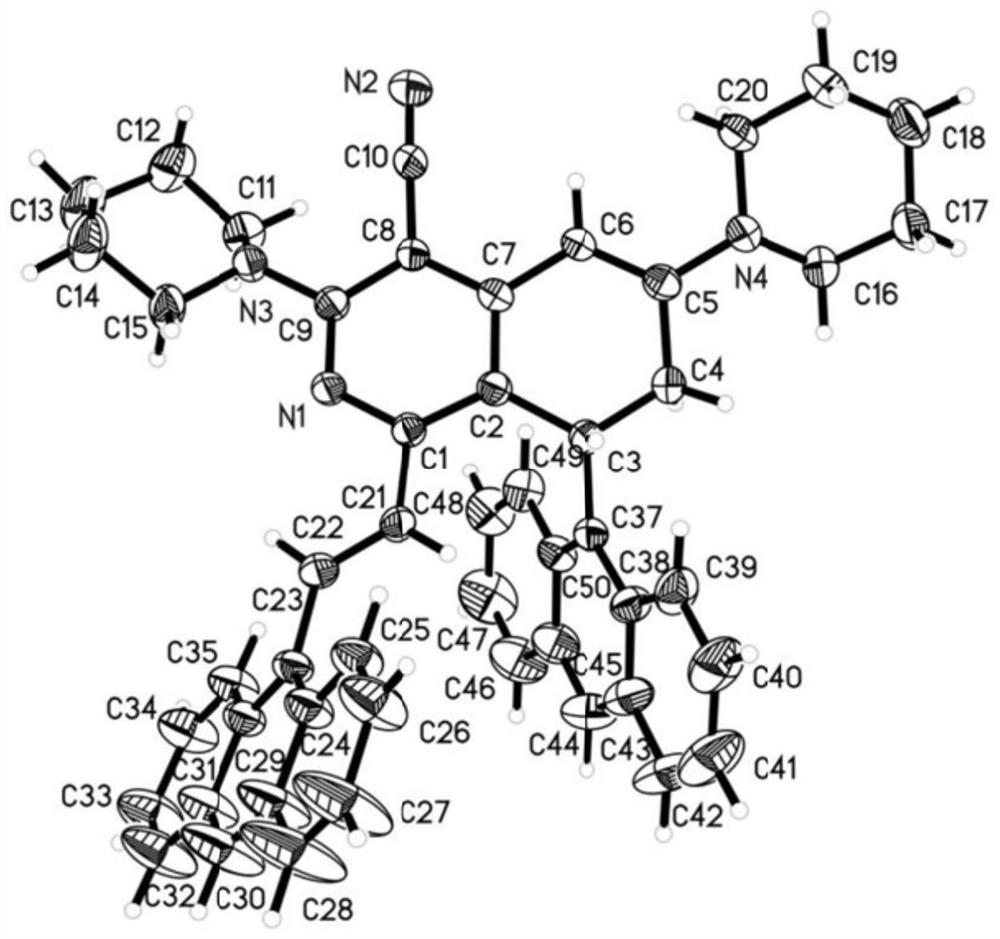
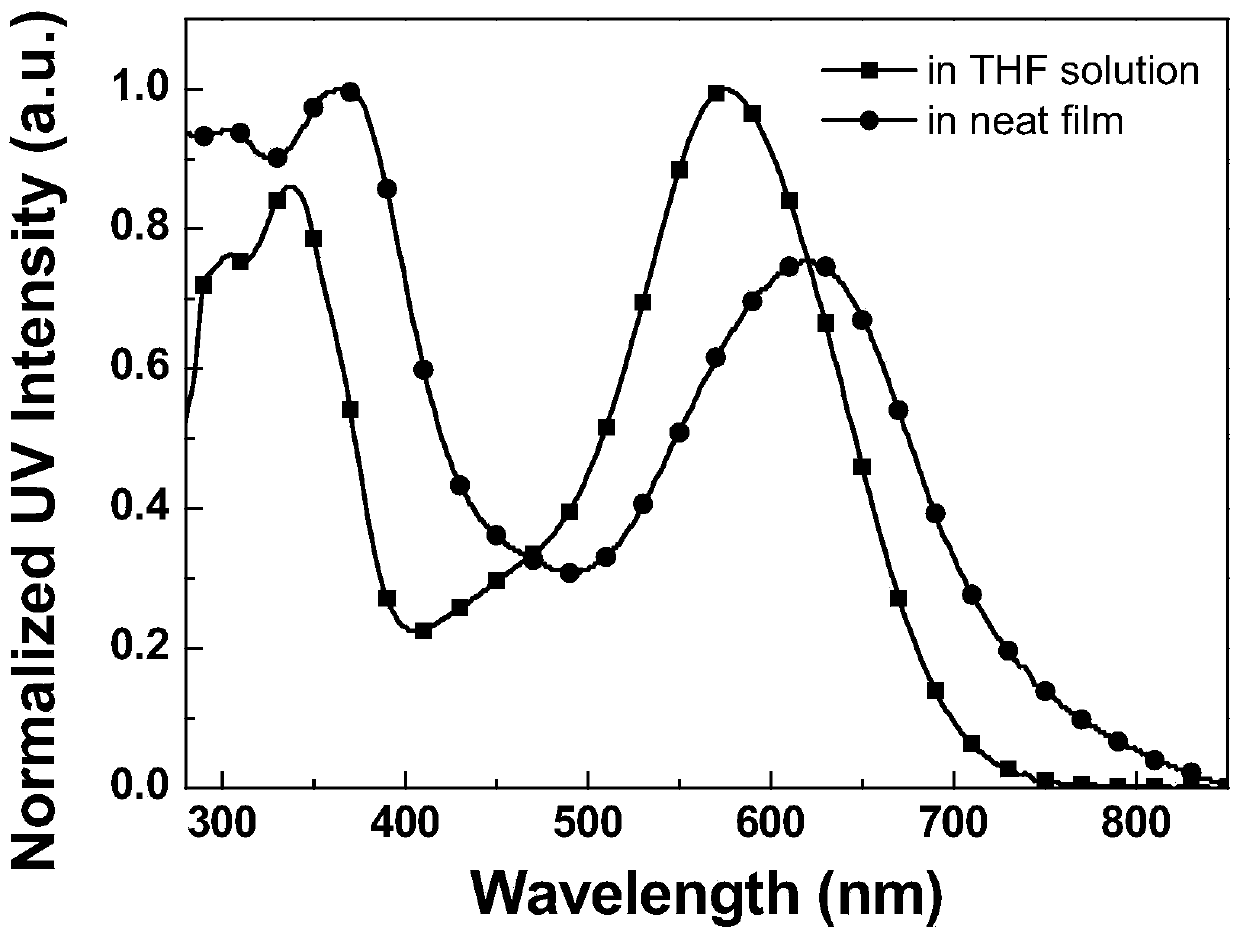
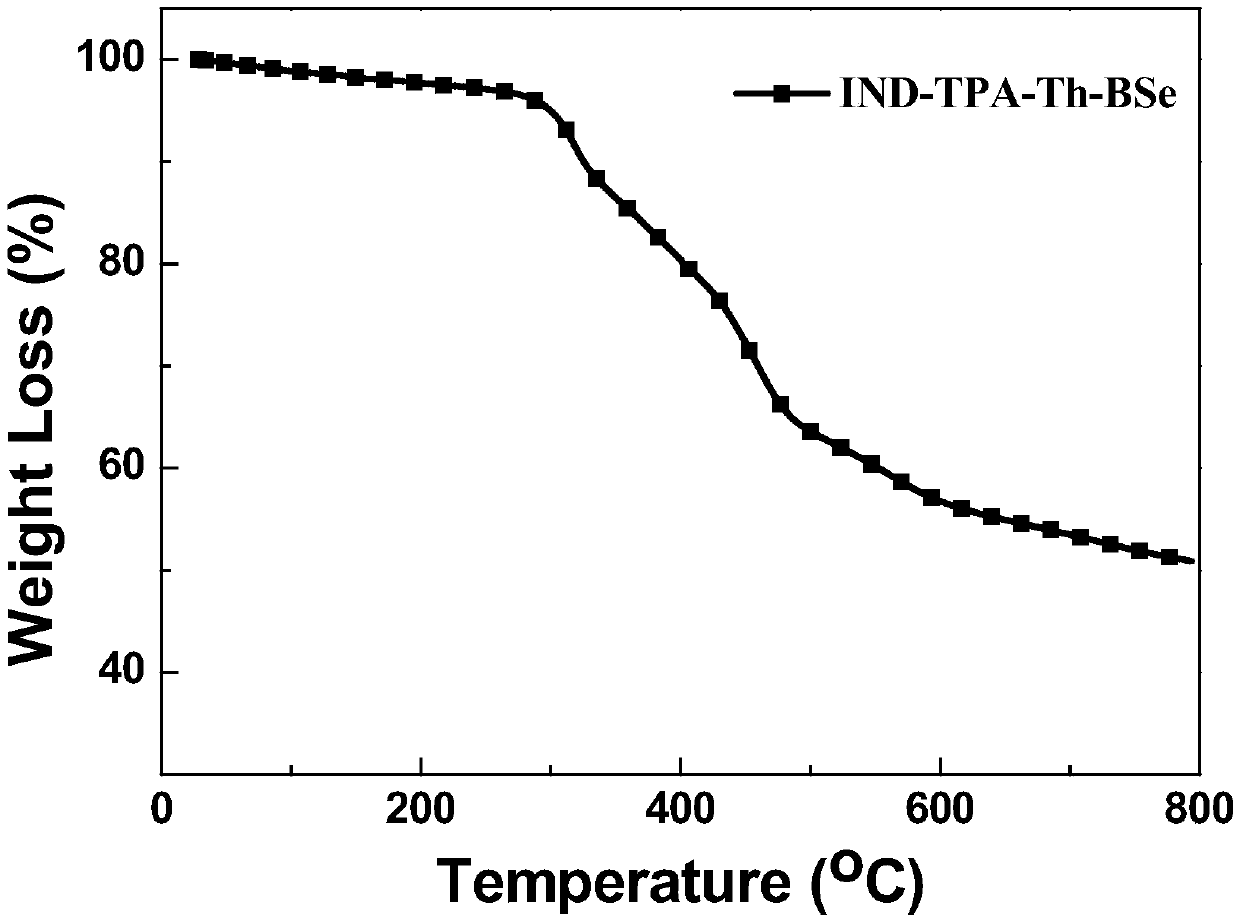
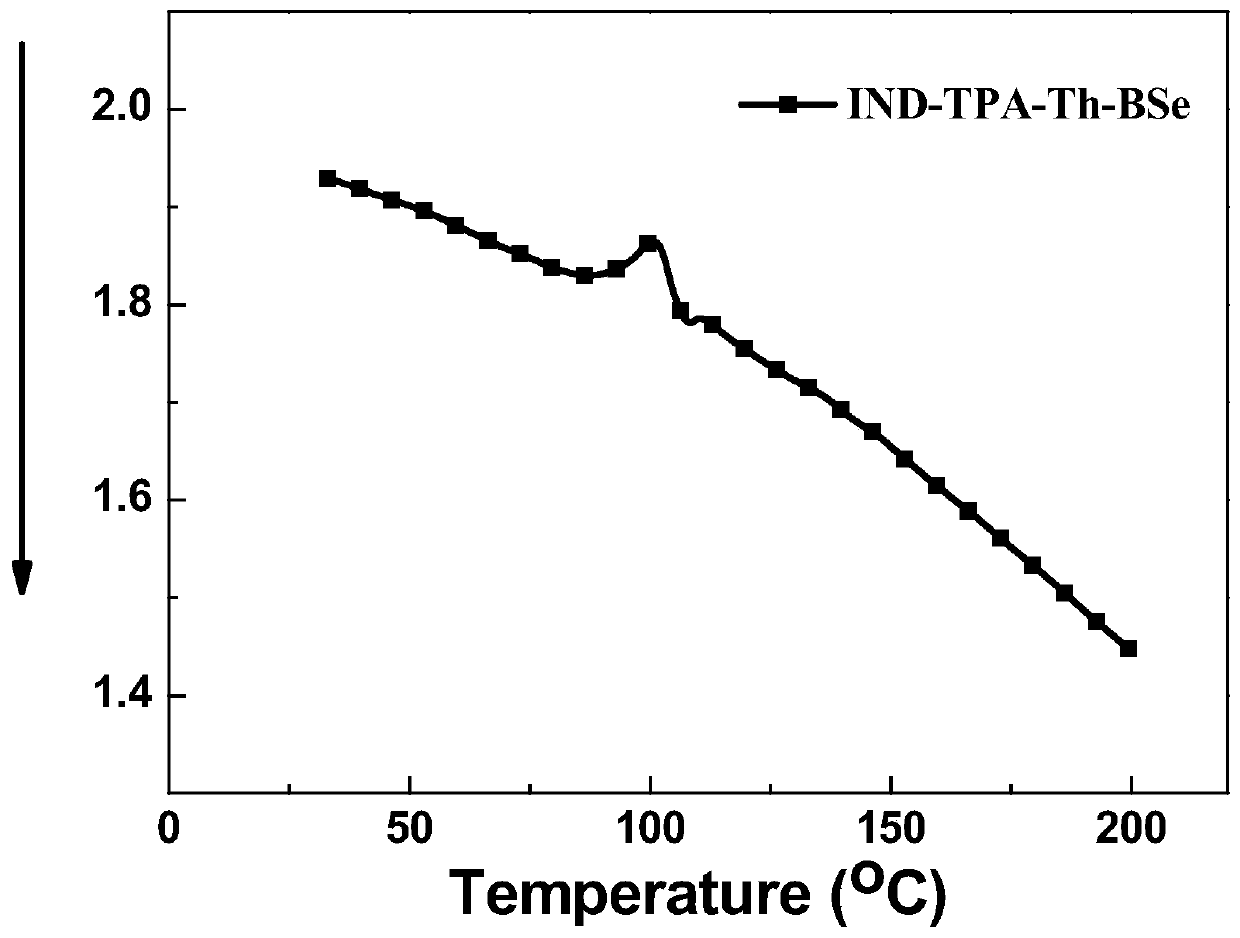
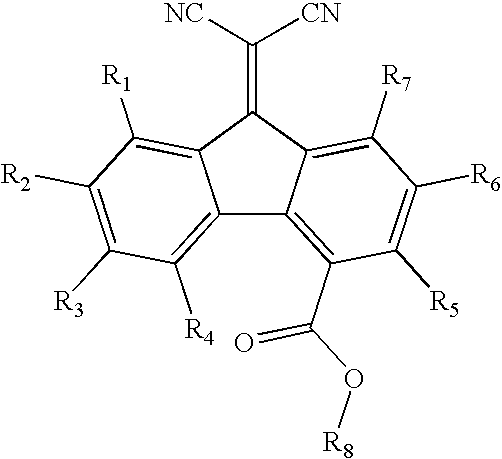
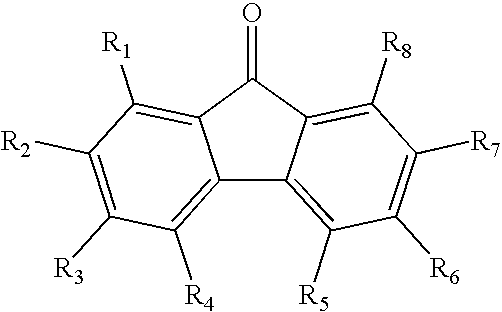
InactiveCN110028488AGood opticsExcellent ElectrochemistryOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesKetoneCyanomethylidyne
The invention discloses an A-D-A type photovoltaic small molecule receptor taking indeno[1,2-b]fluorine as a core. Indeno[1,2-b]fluorine is taken as a central receptor unit, fluoro-substituted 3-(dicyano methylene)indigo ketone as a blocking receptor unit, and mono selenophen or vinyl selenophen as a phi bridge solution treated small molecule receptor material, wherein the A-D-A type photovoltaicsmall molecule receptor taking mono selenophen or vinyl selenophen as phi bridges are called as FICBF-Se and FICBF-SeVi respectively. The invention also provides a preparation method of the A-D-A typephotovoltaic small molecule receptor taking indeno[1,2-b]fluorine as the core. The A-D-A type photovoltaic small molecule receptor taking indeno[1,2-b]fluorine as the core, provided by the invention,applied to solar devices has excellent optical, electrochemical and photovoltaic performances.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
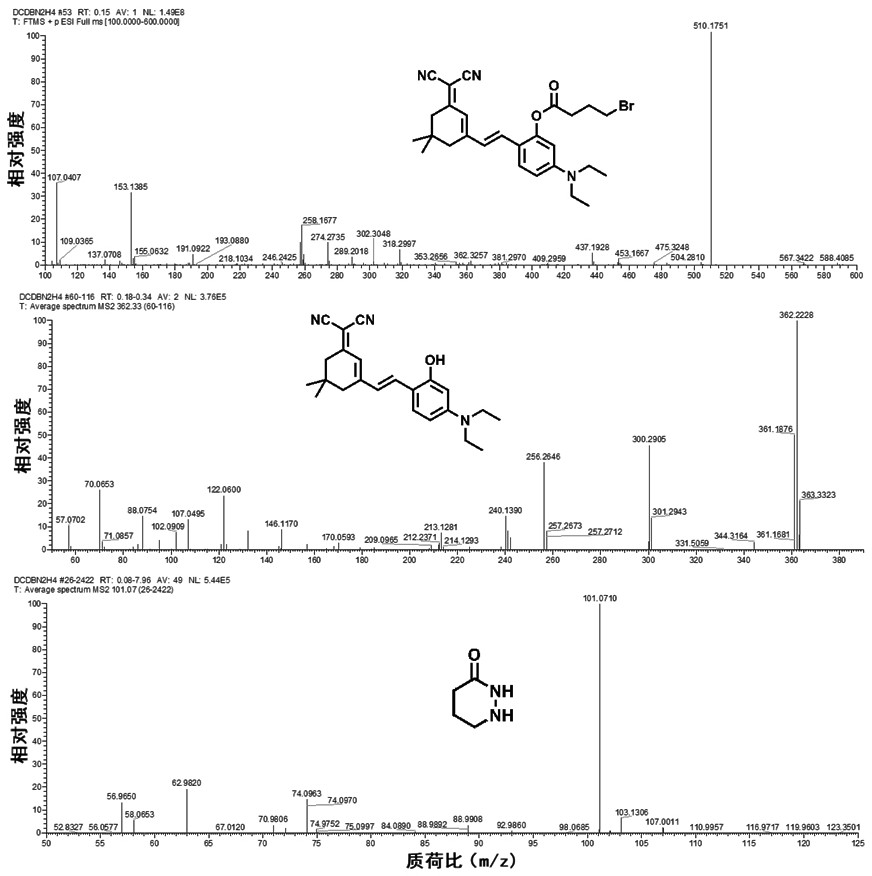
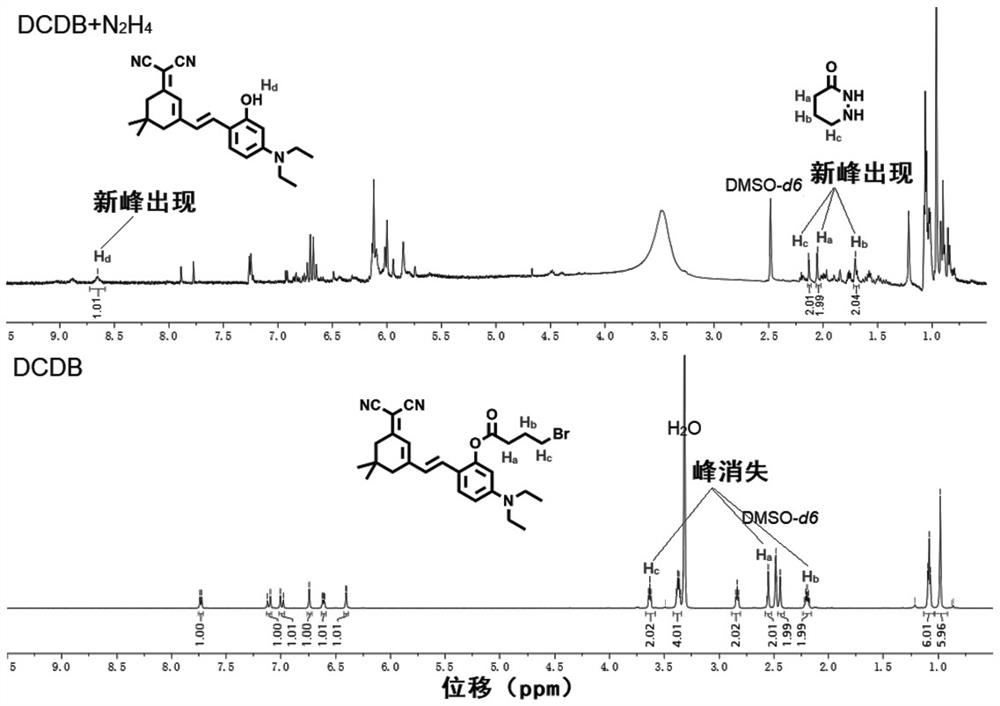
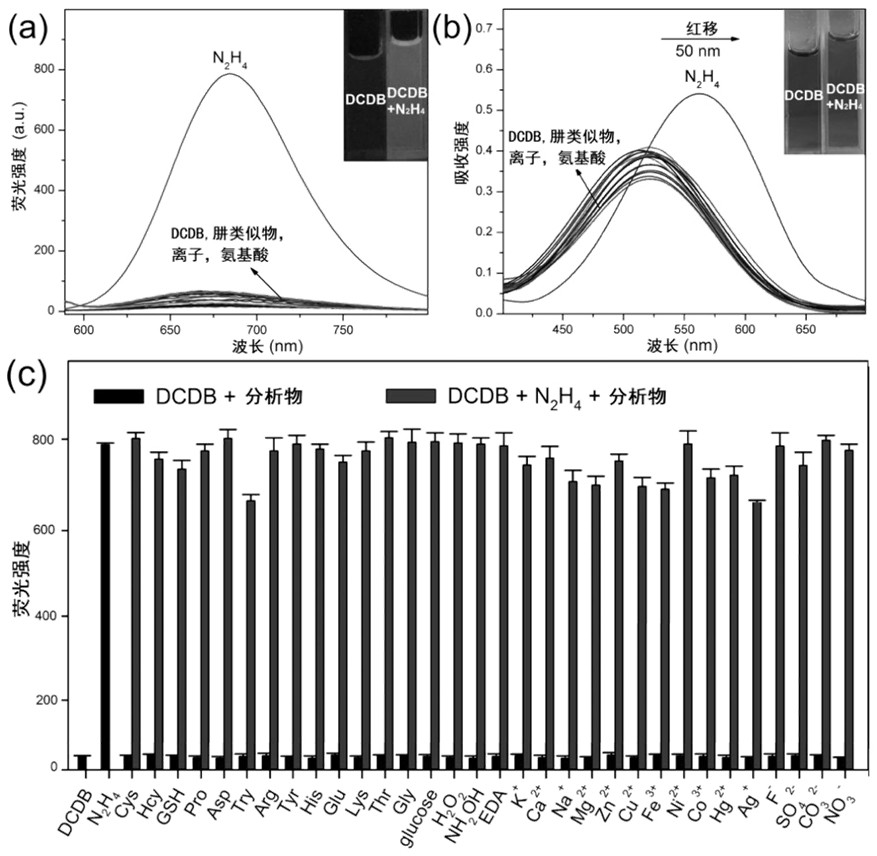
Near-infrared fluorescent compound for specific detection of hydrazine and preparation method of near-infrared fluorescent compound
PendingCN111807993ASimple preparation stepsRaw materials are easy to getCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationCell membraneCytotoxicity
The invention discloses a novel near-infrared fluorescent compound for specific detection of hydrazine, wherein the near-infrared fluorescent compound is (E)-2-(2-(3-(dicyanomethylene)-5,5-dimethylcyclohexyl-1-ene-1-yl)vinyl)-5-(diethylamino)phenyl 4-bromobutyric acid and is capable of specifically detecting hydrazine in an organism. The near-infrared fluorescent compound is simple in preparationprocess, readily available in raw materials, low in cost and stable in structure, has relatively good cell membrane permeability and relatively low cytotoxicity, can enter living cells and animal tissues and react with exogenous hydrazine to generate strong red fluorescence which can be distinguished by naked eyes; ultraviolet absorption and fluorescence spectrophotometry analysis shows that the near-infrared fluorescent compound has excellent selectivity to hydrazine under various interferents and has quite strong anti-interference capability to common biomolecules; the novel near-infrared fluorescent compound not only can selectively recognize exogenous hydrazine, but also can quantitatively detect hydrazine with high sensitivity in the growth environment of various living cells, and issuccessfully applied to imaging of living cells and zebra fishes.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Lipid droplet targeted fluorescent dye as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113045908AHigh purityImprove efficiencyStyryl dyesMethine/polymethine dyesBenzaldehydePhenyl group
The invention discloses a lipid droplet targeting fluorescent dye as well as a preparation method and an application thereof, and the preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out a simple reaction on 1,3-bis (dicyanomethylene)indan and 4-[bis(4-methylphenyl)amino]benzaldehyde, and carrying out recrystallization purification to obtain pure 2, 2'-(2-(4-(di-p-methylphenyl amino) benzylidene)-1H-indene-1, 3(2H)-dialkylene) dimethyl nitrile in the formula (I). The preparation method is simple, the fluorescent dye can be obtained in one step, almost no by-product exists, the efficiency is high, the cost is low, and the fluorescent dye has the potential of large-scale preparation, and the prepared lipid droplet targeted fluorescent dye can be used for monitoring the dynamic change of lipid droplets in cells and can be used for distinguishing immune cells from tumor cells.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
4-cyano-7, 8-dihydroisoquinoline derivative as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112745299AFull Color Tunable Solid State EmitterRaw materials are easy to getOrganic chemistryLuminescent compositionsPtru catalystOrganic synthesis
The invention relates to the technical field of organic synthesis, in particular to a 4-cyano-7, 8-dihydroisoquinoline derivative as well as a preparation method and application thereof. According to the invention, symmetric and asymmetric dicyanomethylene-4H-pyran derivatives and secondary amine are used as raw materials, and a series of 4-cyano-7, 8-dihydroisoquinoline derivatives are prepared through ring opening and continuous ring closing reactions; and the reaction has the advantages of easily available raw materials, mild reaction conditions, wide substrate range, high yield and the like, is simple to operate, and avoids the defects of tedious steps, harsh reaction conditions, use of toxic and expensive metal catalysts and the like in conventional isoquinoline compound construction. The preparation method provides new possibilities for design and synthesis of isoquinoline molecules and application of the isoquinoline molecules in solid-state fluorescent materials.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
A-D-A-D-A type organic micromolecular solar cell donor materials, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110229148ABroaden the absorption bandImprove device performanceOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOrganic solar cellElectron donor
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Narrow-band gap non-condensed ring small molecule receptor and preparation method and application thereof
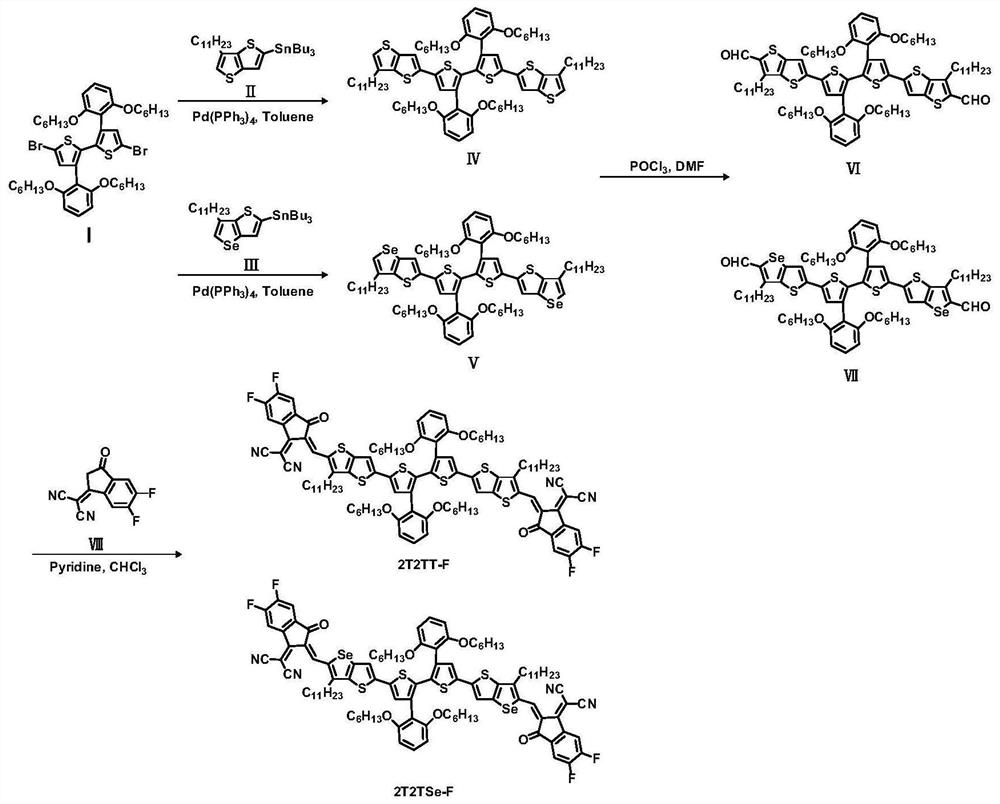
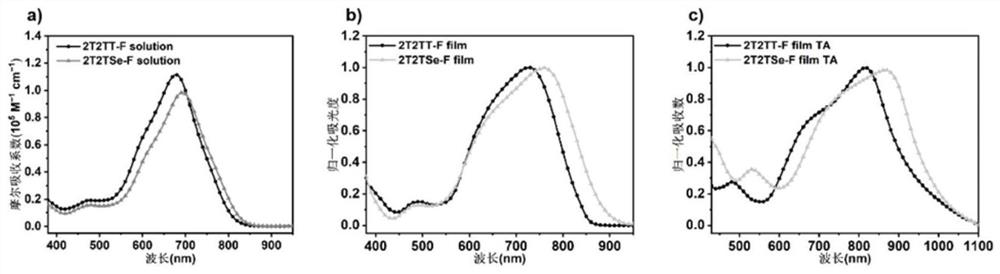
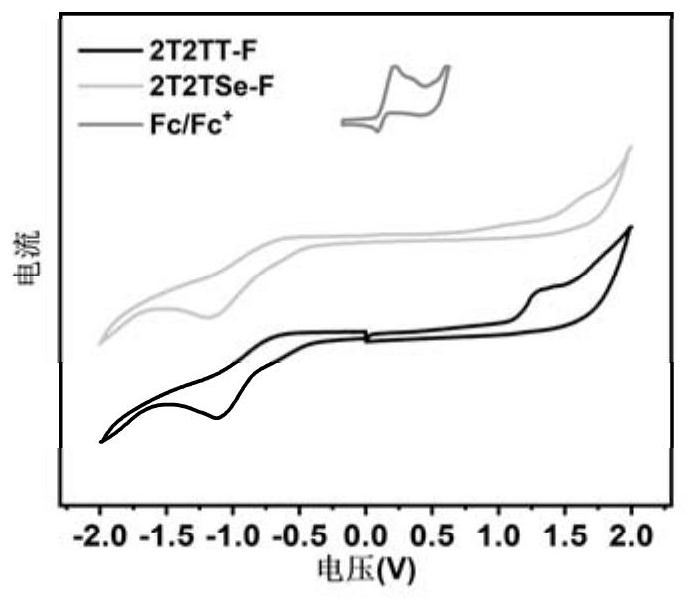
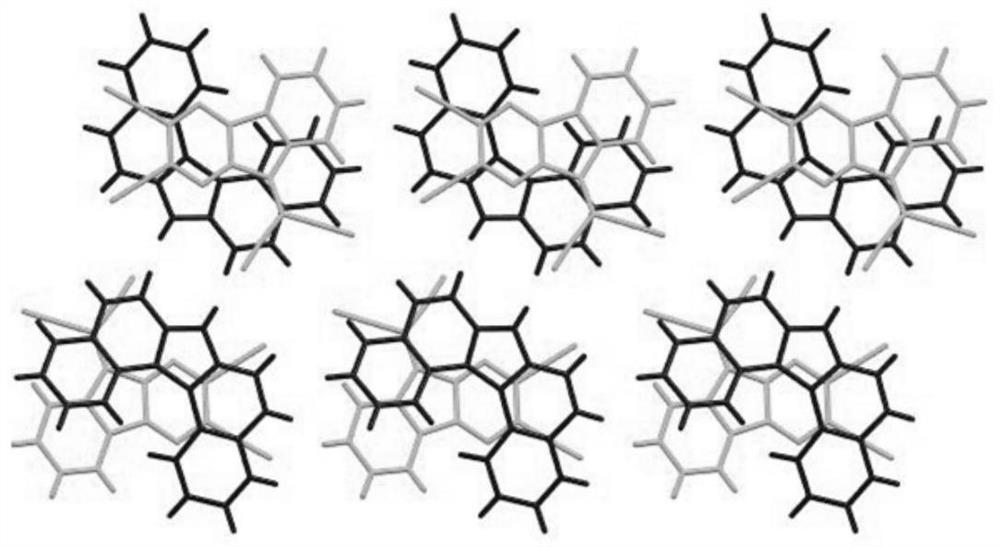
The invention discloses a narrow-band gap non-condensed ring small molecule receptor which is characterized in that bithiophene or thieno-selenophen is used as a pi bridge, bithiophene with a benzene ring side chain is used as a core, and difluoro-substituted 3-(dicyanomethylene) indanone (FINCN) is used as a terminal receptor unit, namely 2T2TT-F and 2T2TSe respectively. The structural formula is as the following. The invention also discloses a preparation method and application of the narrow-band gap non-condensed ring small molecule receptor. And when the material is applied to organic solar cell devices, the material has good optical and electrochemical properties and photovoltaic performance.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Organic piezoelectric composite material and preparation and application thereof
PendingCN114349680AGood voltage output performanceEfficient conversionOrganic chemistryPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionMeth-Electron donor
The invention discloses an organic piezoelectric composite material as well as preparation and application thereof, and the material is prepared by mixing an electron-deficient acceptor azafluorene derivative a: 9-(dicyanomethylene)-9H-indeno [1, 2-b] pyrazine-2, 3-dicarbonitrile and an electron-rich donor derivative b: 7H-dibenzo [c, g] carbazole. The whole preparation process is simple, and quantitative production is easy to realize. According to the horizontal electrode piezoelectric device prepared on the basis of the organic piezoelectric composite material, the piezoelectric output voltage reaches about 200mV, and the short-circuit current reaches about 5nA; the self-powered piezoelectric-triboelectricity composite device obtained by compounding with PDMS can effectively sense external pressure and effectively convert mechanical energy into electric energy, the triboelectricity output voltage reaches about 60 V, and the short-circuit current is about 1.5 microamperes.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
A-pi-D-pi-A type organic small molecule based on diindenopyrazine as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110818698AAdjustable Absorption SpectrumImprove thermal stabilityOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOrganic solar cellMolecular orbital energy
The invention discloses an A-pi-D-pi-A type organic small molecule based on diindenopyrazine as well as a preparation method and application of the A-pi-D-pi-A type organic small molecule. In the A-pi-D-pi-A type organic small molecule, an IPY unit for electron donating is used as a central core D, thiophene is used as a pi conjugate bridge, and 3-(dicyanomethylene) indene-1-one or 5, 6-dichloro-3-(dicyanomethylene) indene-1-one or 5, 6-difluoro-3-(dicyanomethylene) indene-1-one is used as an electron withdrawing terminal A. The preparation method comprises the step of carrying out Knoevenagelcondensation reaction on intermediate M1 and A under the action of a solvent and a catalyst. By changing the different electron withdrawing terminal A, regulation and control of the A-pi-D-pi-A typeorganic small molecule on photoelectric properties such as a small molecular structure, an absorption spectrum, a band gap and a proline molecular orbital energy level can be realized, a small molecular photoelectric functional material with excellent photoelectric properties is prepared, and the small molecular photoelectric functional material can be applied to preparation of organic solar cells.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
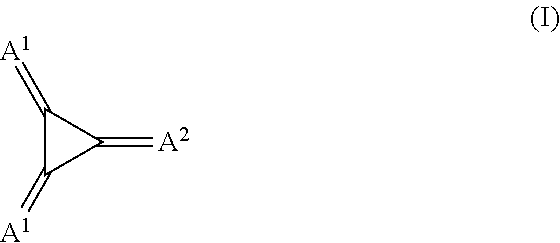
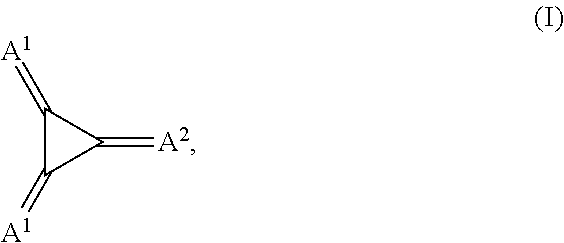
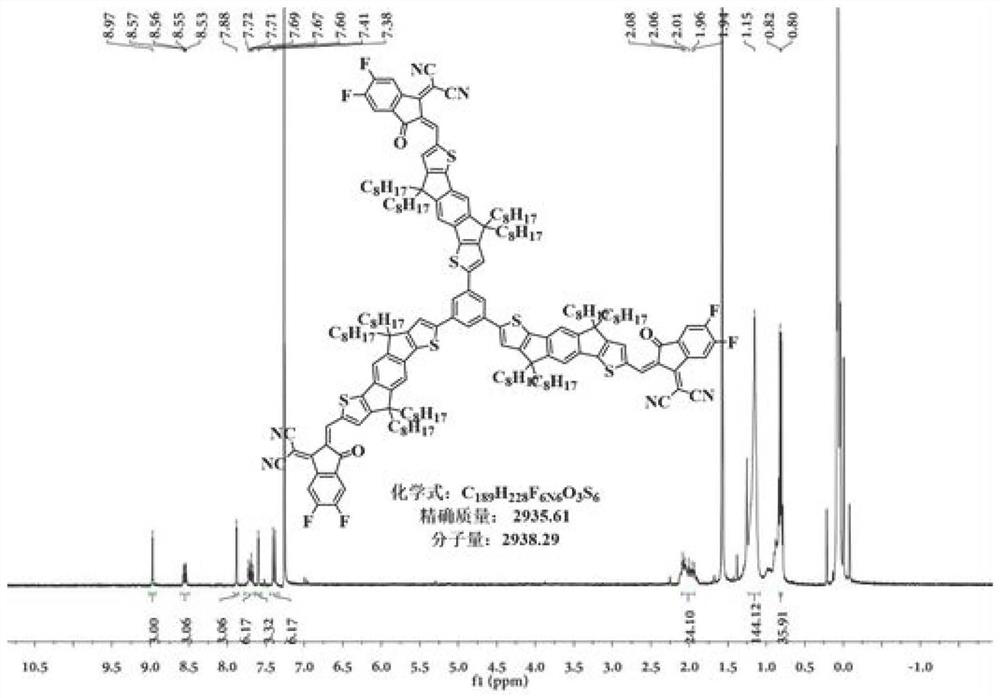
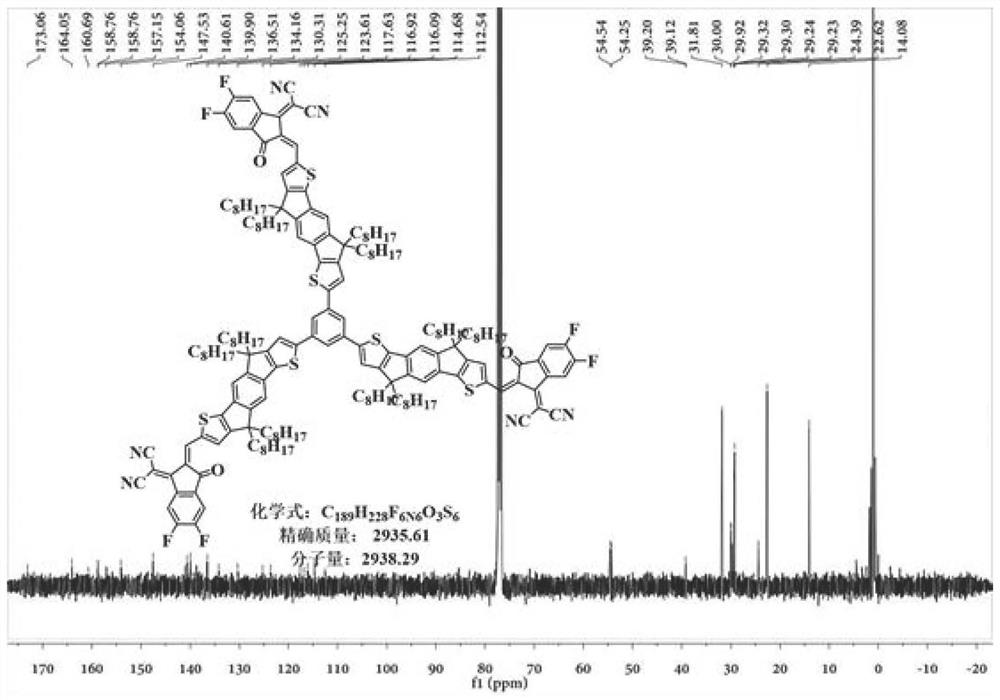
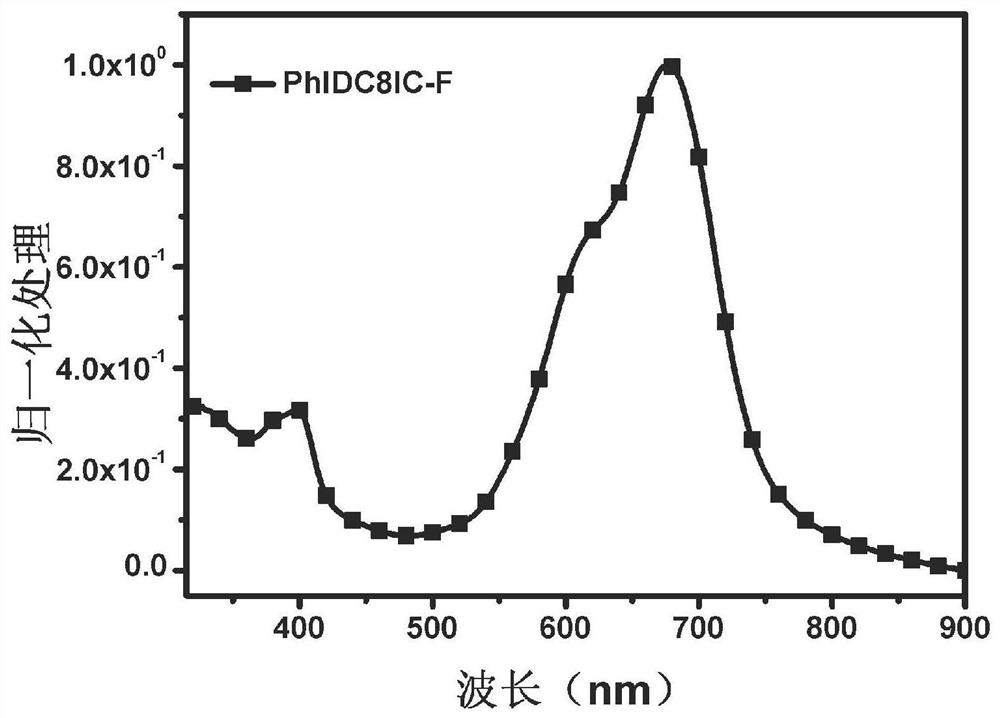
![A-D-A type photovoltaic small molecule receptor taking indeno[1,2-b]fluorine as core, as well as preparation method and application of A-D-A type photovoltaic small molecule receptor A-D-A type photovoltaic small molecule receptor taking indeno[1,2-b]fluorine as core, as well as preparation method and application of A-D-A type photovoltaic small molecule receptor](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/856ca5a2-3e6b-469d-a2e4-7b04560e8a4a/HDA0002061762160000011.png)
![A-D-A type photovoltaic small molecule receptor taking indeno[1,2-b]fluorine as core, as well as preparation method and application of A-D-A type photovoltaic small molecule receptor A-D-A type photovoltaic small molecule receptor taking indeno[1,2-b]fluorine as core, as well as preparation method and application of A-D-A type photovoltaic small molecule receptor](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/856ca5a2-3e6b-469d-a2e4-7b04560e8a4a/HDA0002061762160000012.png)
![A-D-A type photovoltaic small molecule receptor taking indeno[1,2-b]fluorine as core, as well as preparation method and application of A-D-A type photovoltaic small molecule receptor A-D-A type photovoltaic small molecule receptor taking indeno[1,2-b]fluorine as core, as well as preparation method and application of A-D-A type photovoltaic small molecule receptor](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/856ca5a2-3e6b-469d-a2e4-7b04560e8a4a/HDA0002061762160000013.png)