Patents
Literature
52 results about "Renal inflammation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
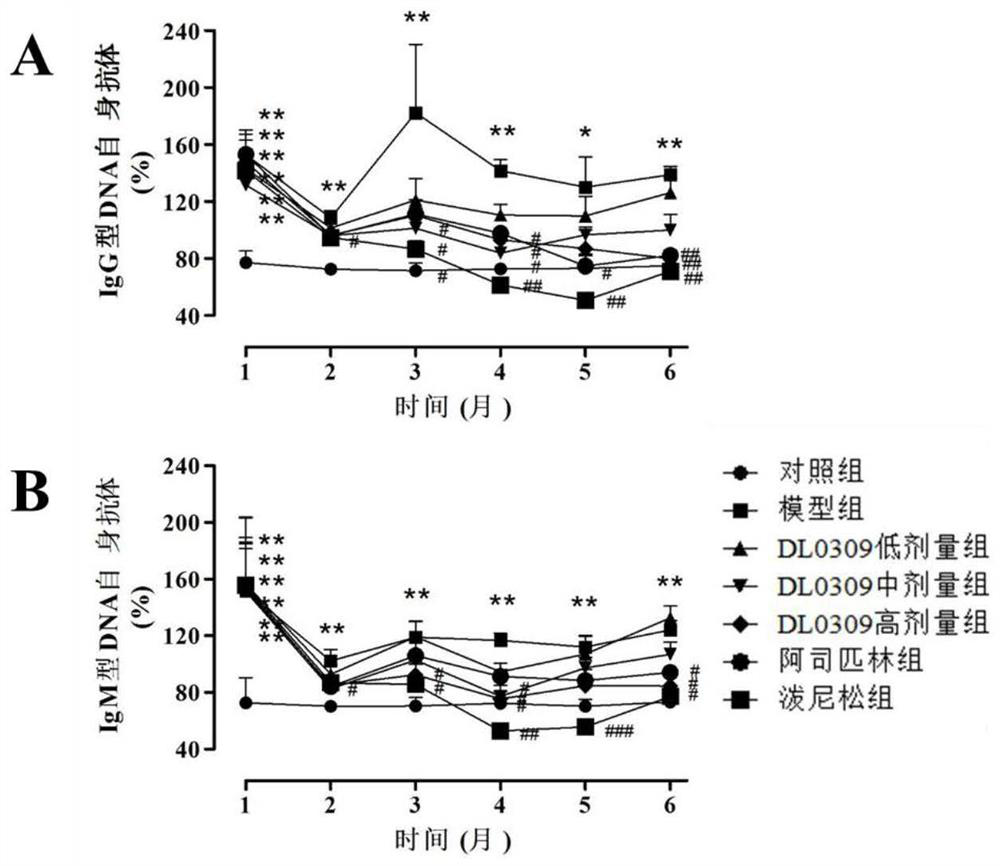
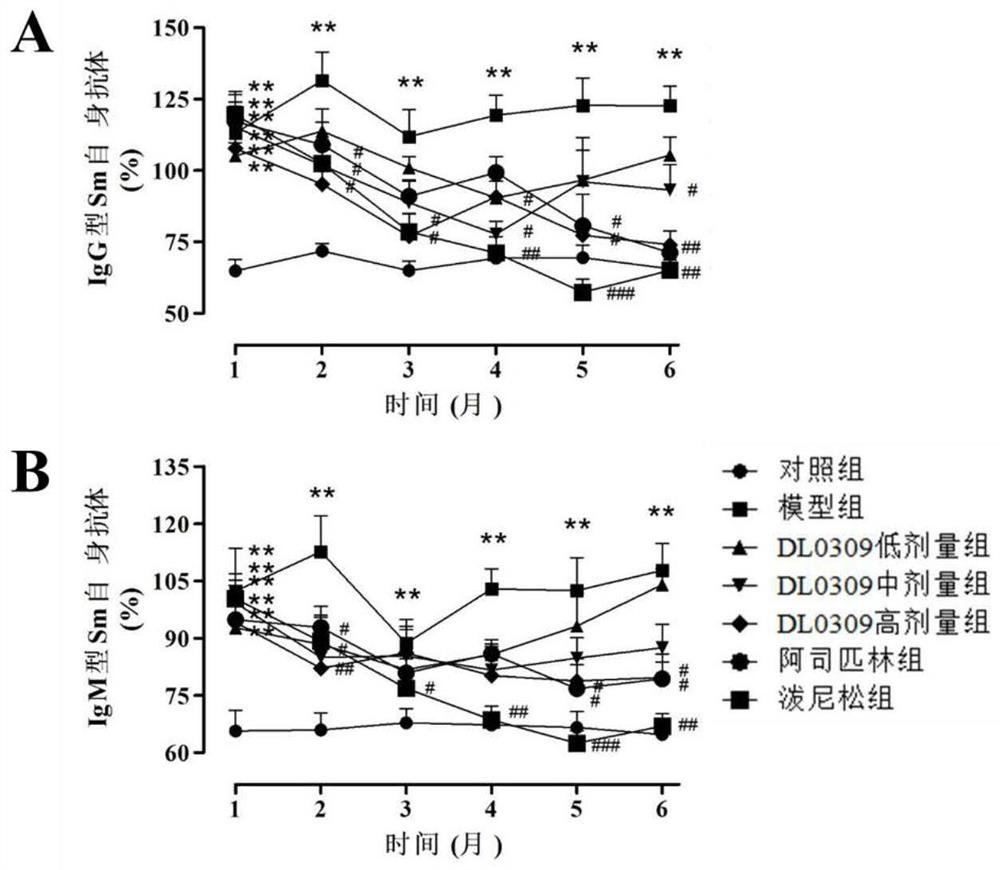
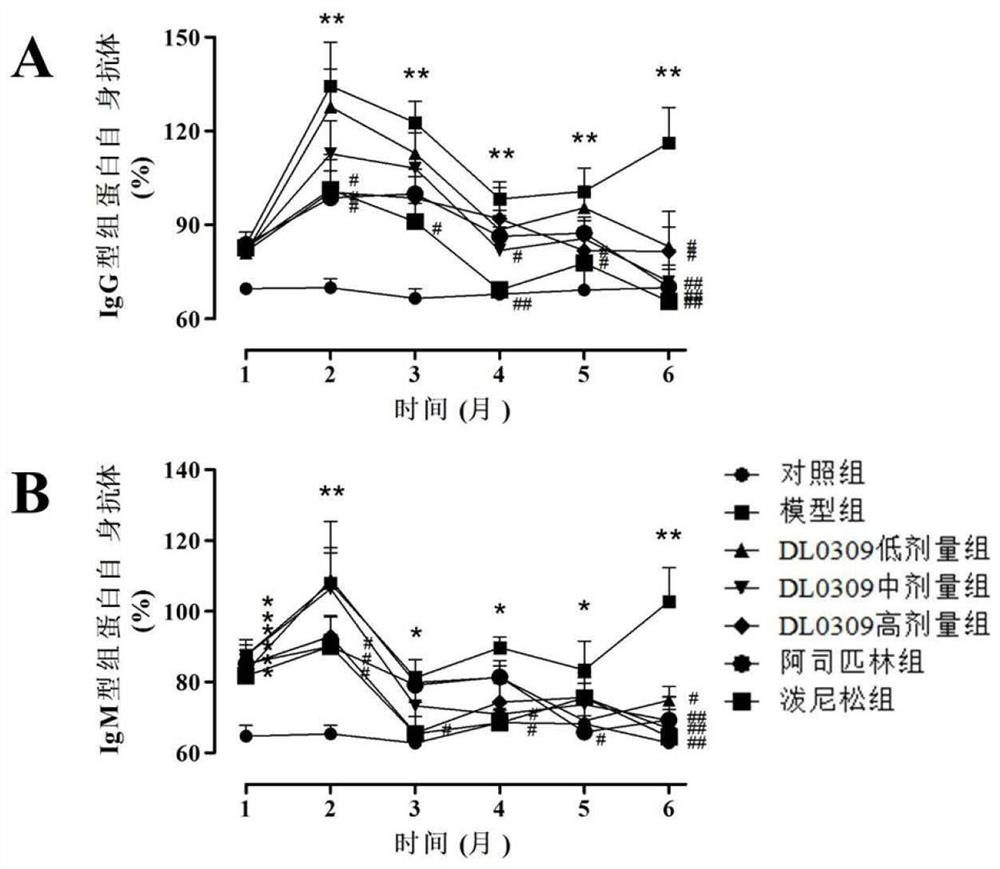
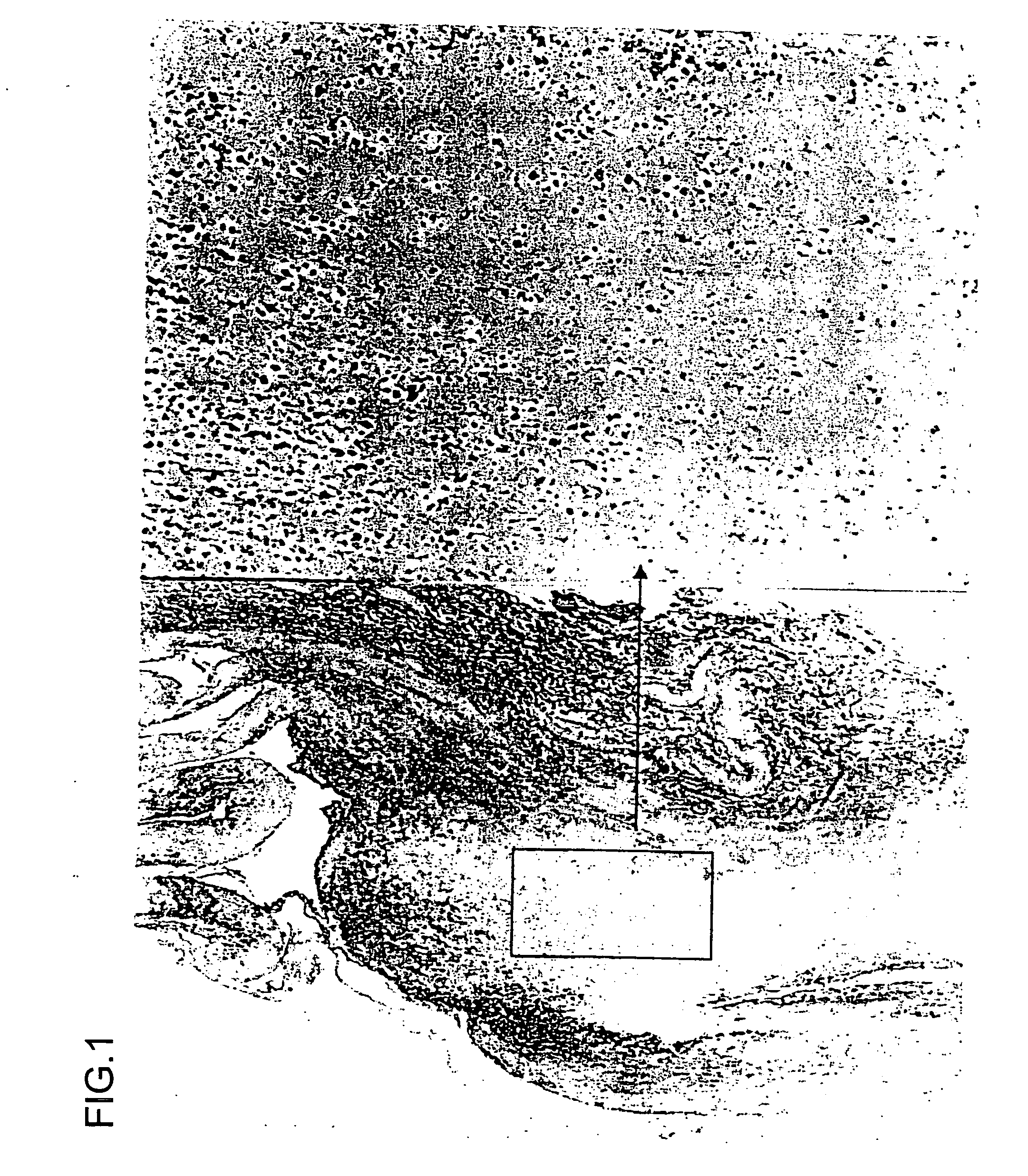
Pyelonephritis is inflammation that results from a urinary tract infection that reaches the renal pelvis of the kidney. Lupus nephritis is inflammation of the kidney caused by systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), a disease of the immune system.
Remedy for chronic disease
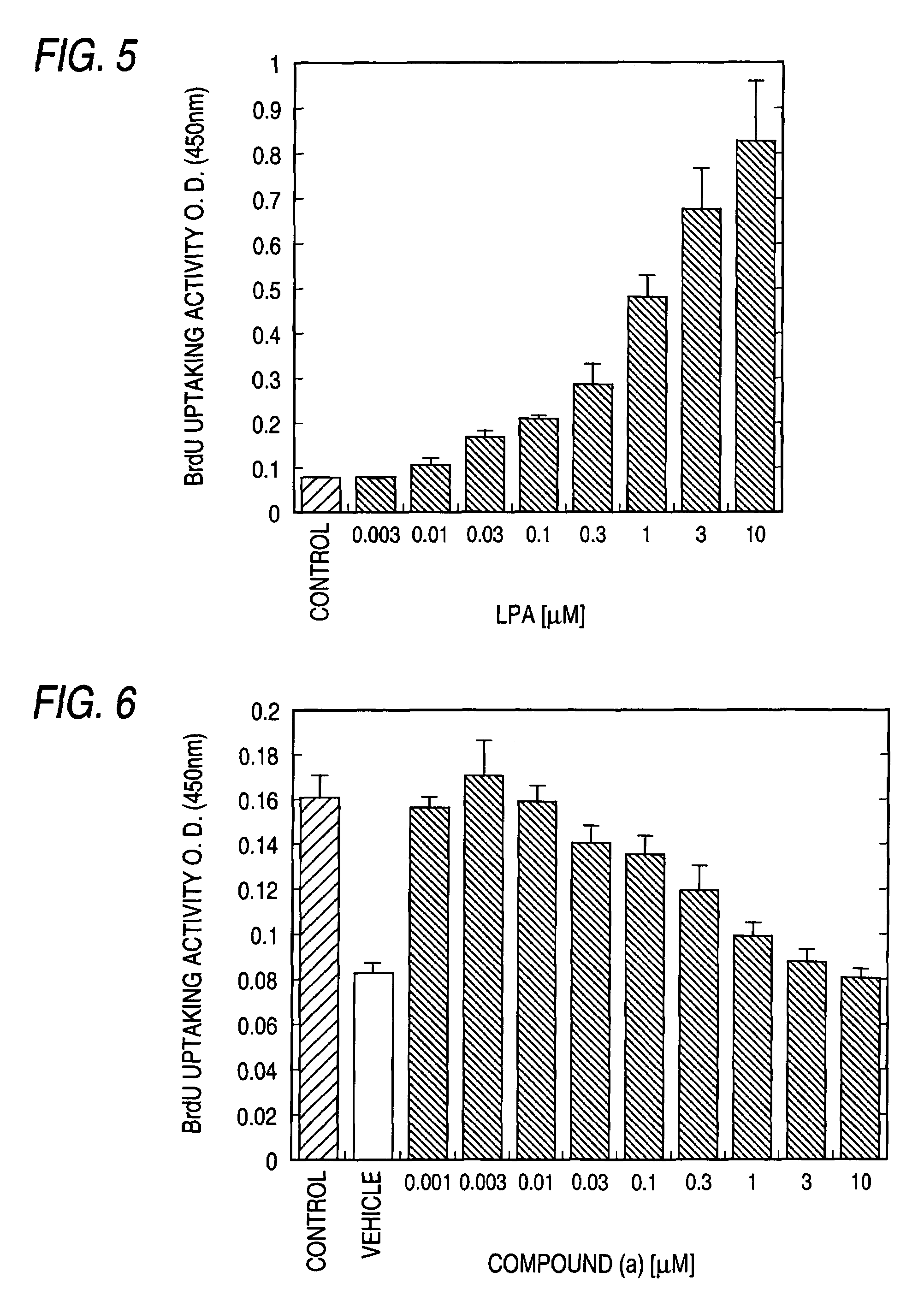
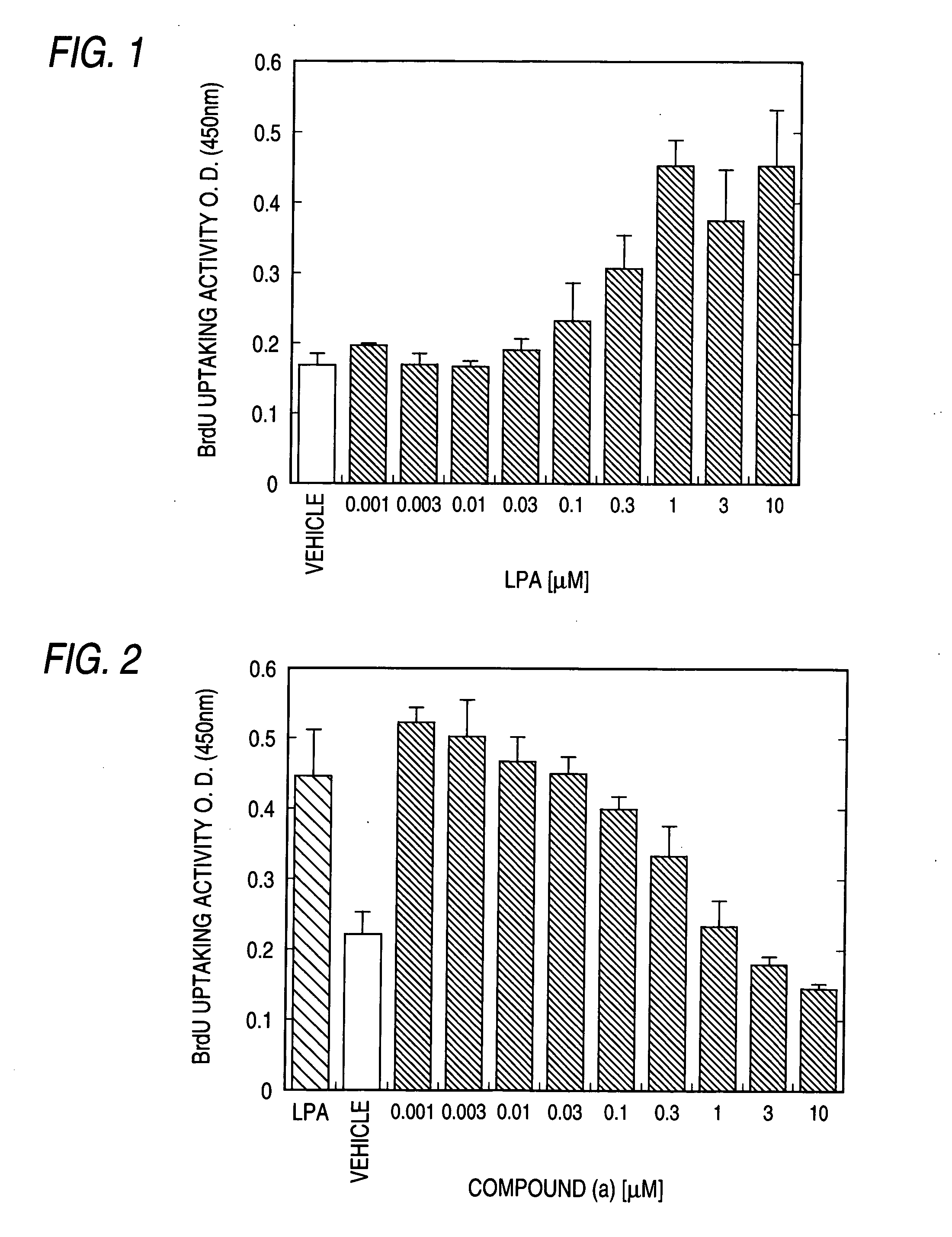
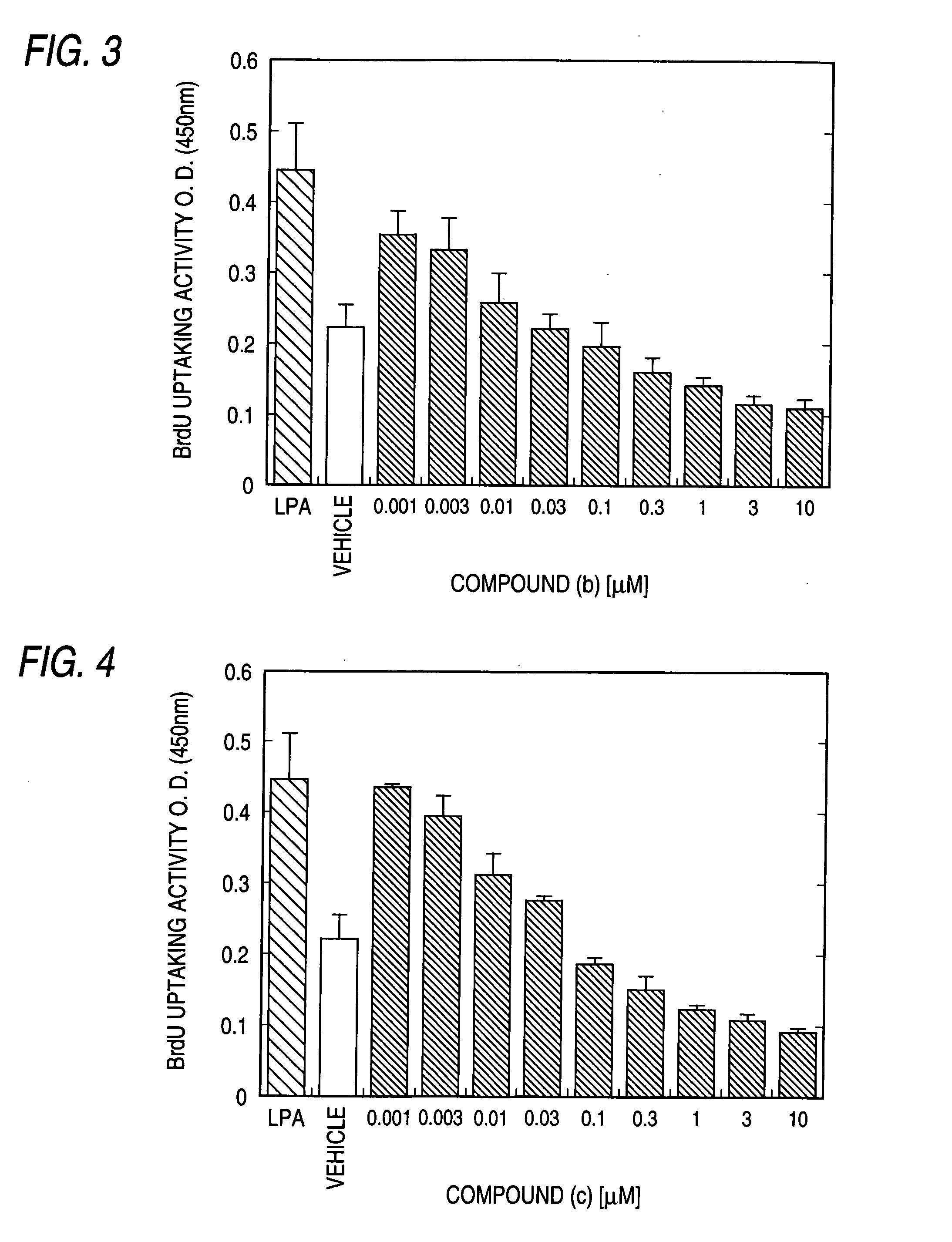
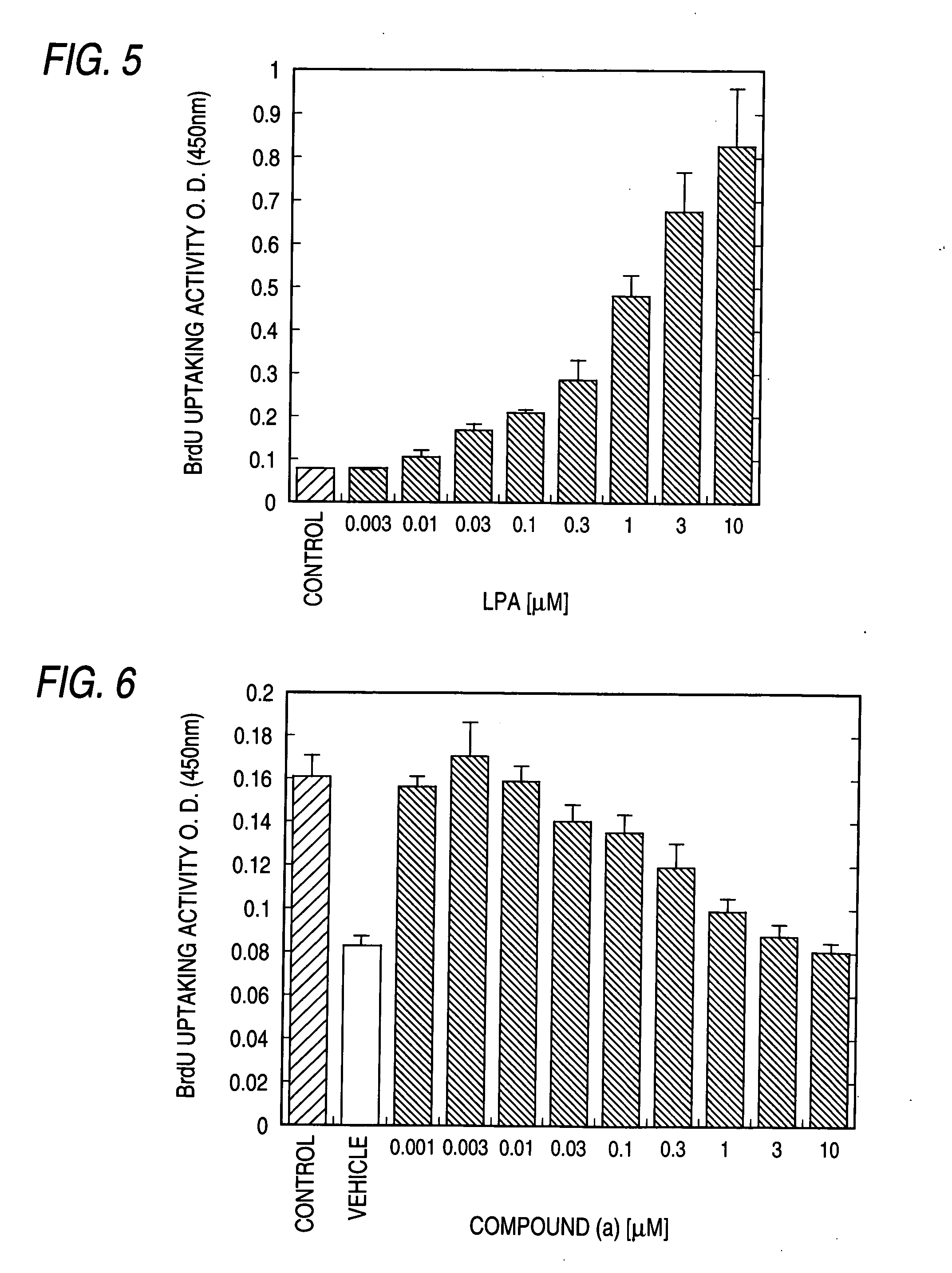
InactiveUS7300917B2Easy to prepareLow toxicityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsLPA ReceptorsDisease cause
A remedy and / or a preventive for a chronic disease which contains an EDG-2 antagonist. Because of binding to a subtype EDG-2 of LPA receptor, an EDG-2 antagonist is useful in treating and / or preventing chronic diseases (for example, diseases caused by the progress of chronic asthma, glomerular nephritis, obesity, arteriosclerosis, rheumatoid and atopic diseases) induced and made chronic by tissue cells whose proliferation is accelerated by LPA mediated by EDG-2.
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
Remedy for chronic disease
InactiveUS20060135577A1Effective preventionEffective treatmentBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsLPA ReceptorsAntagonist
A remedy and / or a preventive for a chronic disease which contains an EDG-2 antagonist. Because of binding to a subtype EDG-2 of LPA receptor, an EDG-2 antagonist is useful in treating and / or preventing chronic diseases (for example, diseases caused by the progress of chronic asthma, glomerular nephritis, obesity, arteriosclerosis, rheumatoid and atopic diseases) induced and made chronic by tissue cells whose proliferation is accelerated by LPA mediated by EDG-2.
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
Kidney-targeted medicine vector and the formed prodrug, preparation method and uses
InactiveCN1879889ASmall toxicityGood curative effectPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseGlucocorticoid
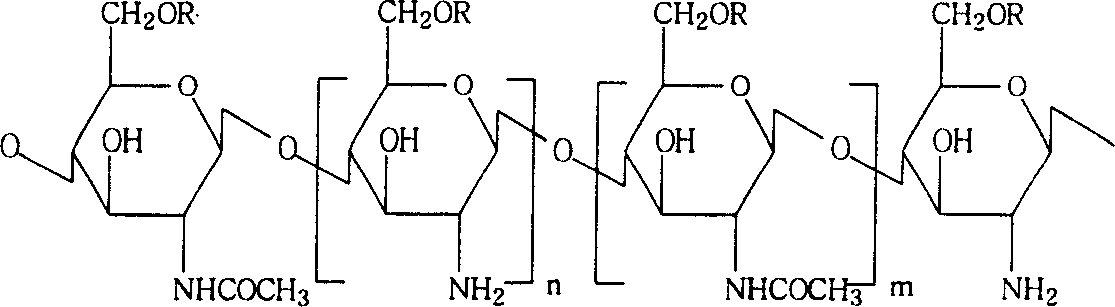
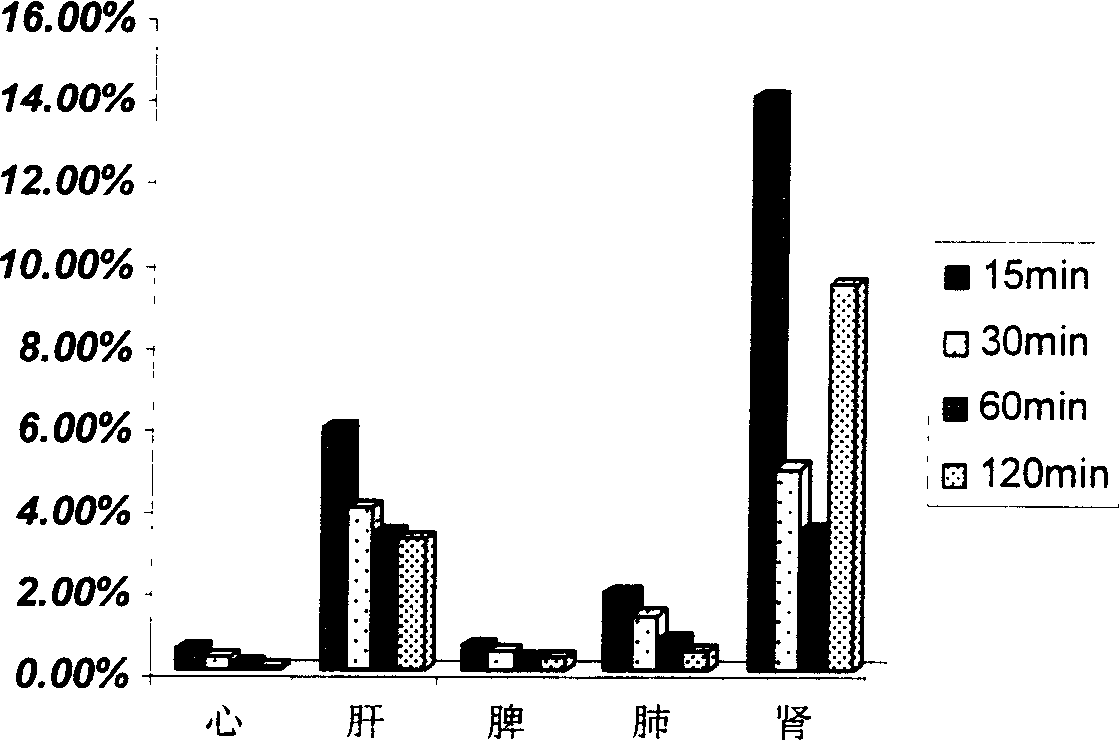
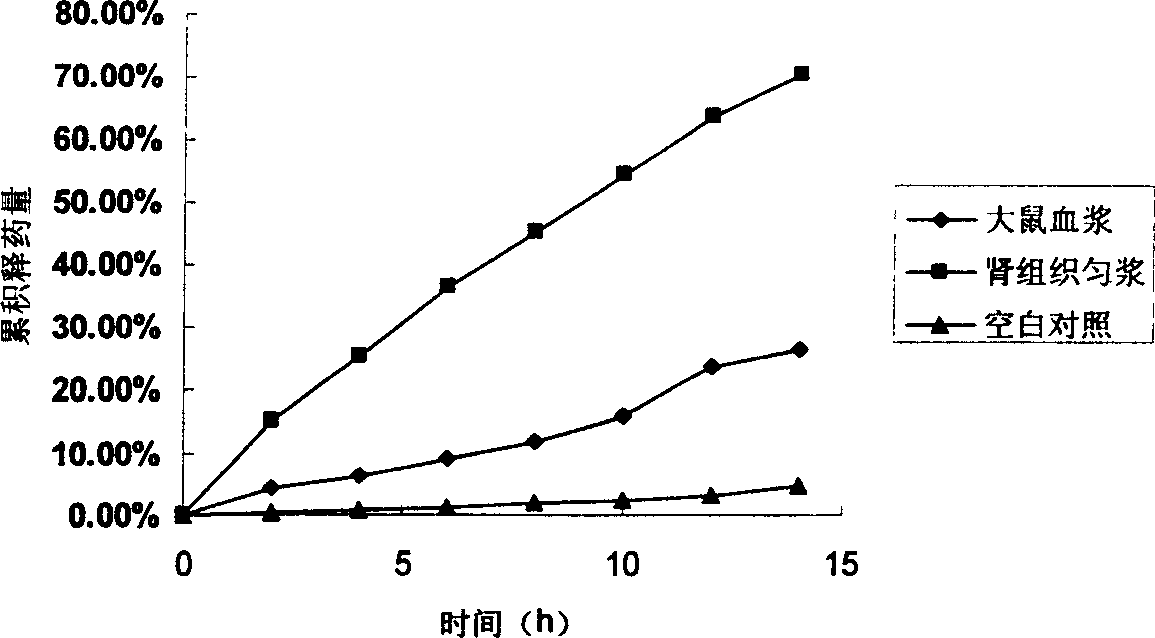
The invention relates to a new kidney target medicine carrier and relative precursor medicine, relative preparation method and application, wherein it comprises: degrading and deriving the natural chitose to obtain the chitose or its derivant with low molecule weight, with better kidney target proerpty; said medicine carier via chemical bond is linked to the anti-cancer medicine or glucocorticoids, or immunosuppressant, to obtain the precursor medicine; the medicine molecule is connected to the carrier via chemical bond. The experiments have proved that: said medicine can release the active component at kidney. And the invention has simple process, stable property and the application for batch production.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Staple type oligonucleotide and drug comprising the same
ActiveUS20060276421A1Improve in instabilityReduce doOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderPsoriasisArthritis
Conventional oligonucleotides are opened at both ends and thereby unstable. The stability of them against catabolic enzymes is increased by phosphorothioate modification, but such phosphorothioate causes toxicity. The present invention provides oligonucleotides and medicaments in which these problems are improved. That is, it provides a staple oligonucleotides and medicaments containing the same as the active ingredient. Specifically, it provides transcription factor inhibitors, antisense oligonucleotides and siRNAs. More specifically, it provides agents for preventing, treating or improving inflammation, autoimmune diseases, central diseases, reperfusion injury in ischaemic diseases, worsened prognosis after organ transplantation or organ surgery, or restenosis after PTCA. Further specifically, it provides agents for preventing, treating or improving arthritis, dermatitis, nephritis, hepatitis, renal failure, cystitis, prostatitis, urethritis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn disease, chronic rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, psoriasis, cutaneous ulcer or decubitus.
Owner:ANGES MG INC
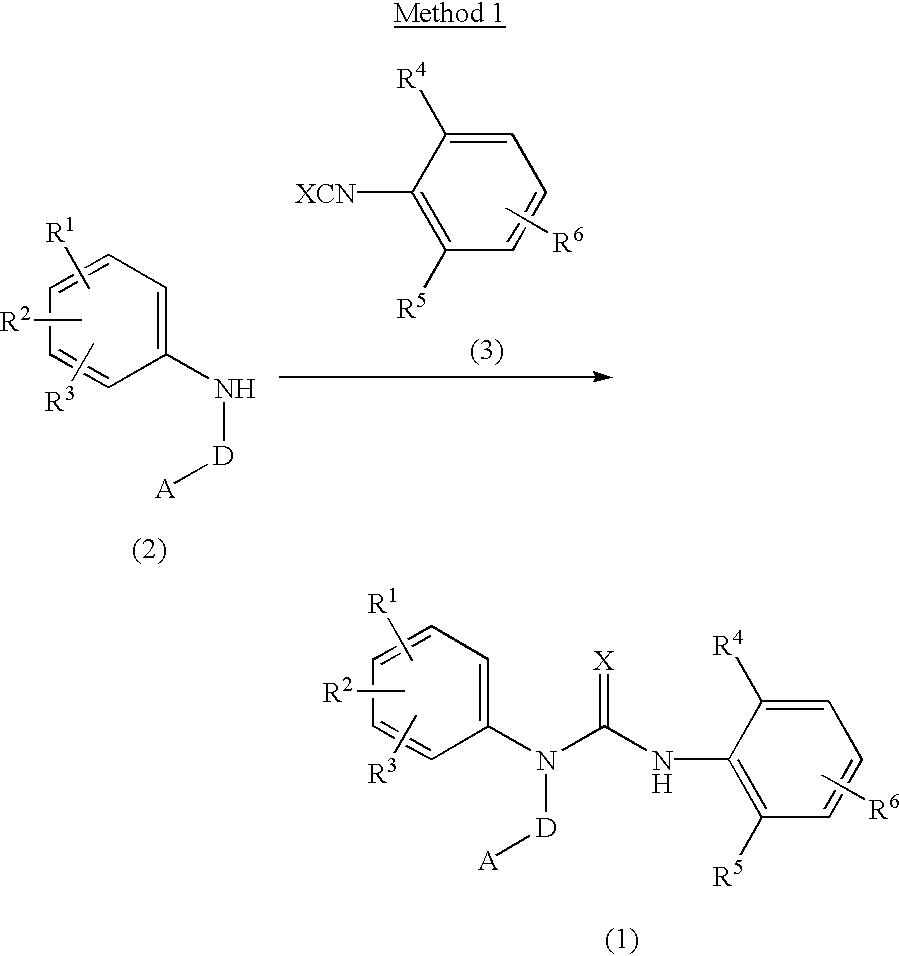
3-substituted urea derivatives and medicinal use thereof
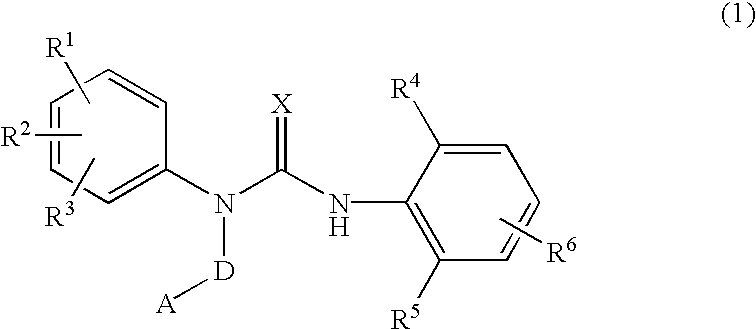
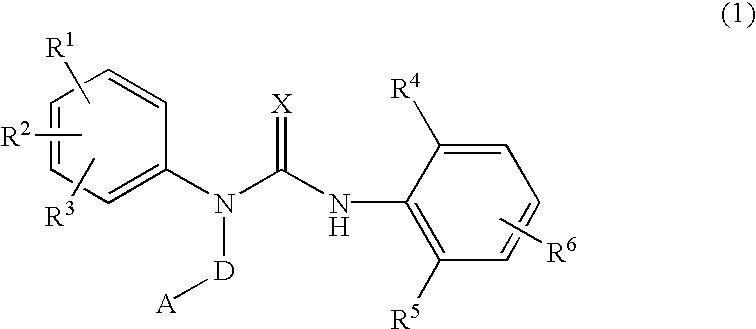
InactiveUS7105567B2Antibacterial agentsUrea derivatives preparationRESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME ADULTWhite blood cell
The present invention relates to a urea derivative of the formula (1)wherein each symbol is as described in the specification, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and pharmaceutical use thereof. The compound of the present invention has a C5a receptor antagonistic action and is useful as an agent for the prophylaxis or treatment of diseases or syndromes due to inflammation caused by C5a [e.g., autoimmune diseases such as rheumatism, systemic lupus erythematosus and the like, sepsis, adult respiratory distress syndrome, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, allergic diseases such as asthma and the like, atherosclerosis, cardiac infarction, brain infarction, psoriasis, Alzheimer's disease and serious organ injury (e.g., pneumonia, nephritis, hepatitis, pancreatitis and the like) due to activation of leukocytes caused by ischemia, trauma, burn, surgical invasion and the like]. In addition, it is useful as an agent for the prophylaxis or treatment of infectious diseases caused by bacteria or virus that invades via a C5a receptor.
Owner:MITSUBISHI TANABE PHARMA CORP
Heterocyclic compound containing nitrogen atom and use thereof
InactiveUS20070043079A1Promote oral absorptionAvoid problemsAntibacterial agentsBiocideAcquired immunodeficiencyAutoimmune condition
The present invention relates to a medicament comprising the compound of formula (I) wherein all symbols have the same meanings as defined in the specification, a salt thereof or a prodrug thereof. The compound of the present invention is useful for the prevention and / or treatment of immune diseases such as various types of inflammation, autoimmune disease, allergic diseases, etc.; infection concerning inflammation or HIV infections (e.g. asthma, nephritis, nephropathy, hepatitis, arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, rhinitis, conjunctivitis, ulcerative colitis, etc.), organ transplantation rejection, immunosuppression, psoriasis, multiple sclerosis, optic neuritis, polymyalgia rheumatica syndrome, uveitis, vasculitis, human immunodeficiency virus infection (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome etc.), atopic dermatitis, urticaria, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, allergic eosinophilic gastroenteritis, osteoarthritis, ischemic reperfusion injury, acute respiratory distress syndrome, shock accompanying bacteria infection, diabetes, cancer metastasis, atherosclerosis, etc.).
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
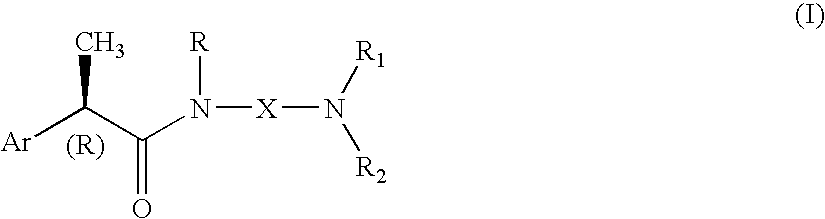
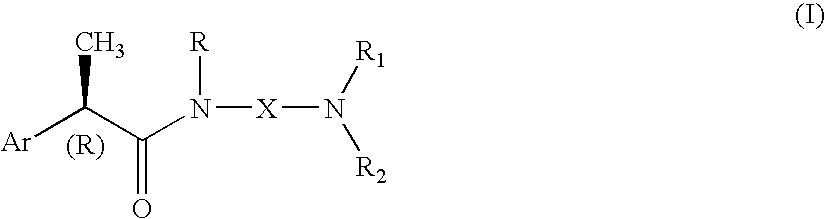
Omega aminoalkylamides of R-2 aryl propionic acids as inhibitors of the chemotaxis of polymorphonucleate and mononucleate cells
InactiveUS20050080067A1Suppression problemBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPropanoic acidEnantiomer
(R)-2-Arylpropionamide compounds of formula (I) are described. The process for their preparation and pharmaceutical preparations thereof are also described. The 2-Arylpropionamides of the invention are useful in the prevention and treatment of tissue damage due to the exacerbate recruitment of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (leukocytes PMN) and of monocytes at the inflammatory sites. In particular, the invention relates to the R enantiomers of omega-aminoalkylamides of 2-aryl propionic acids, of formula (I), for use in the inhibition of the chemotaxis of neutrophils and monocytes induced by the C5a fraction of the complement and by other chemotactic proteins whose biological activity is associated with activation of a 7-TD receptor. Selected compounds of formula (I) are dual inhibitors of both the C5a-induced chemotaxis of neutrophils and monocytes and the IL-8-induced chemotaxis of PMN leukocytes. The compounds of the invention are used in the treatment of psoriasis, ulcerative cholitis, glomerular nephritis, acute respiratory insufficiency, idiopathic fibrosis, rheumatoid arthritis and in the prevention and the treatment of injury caused by ischemia and reperfusion.
Owner:DOMPE FARM SPA
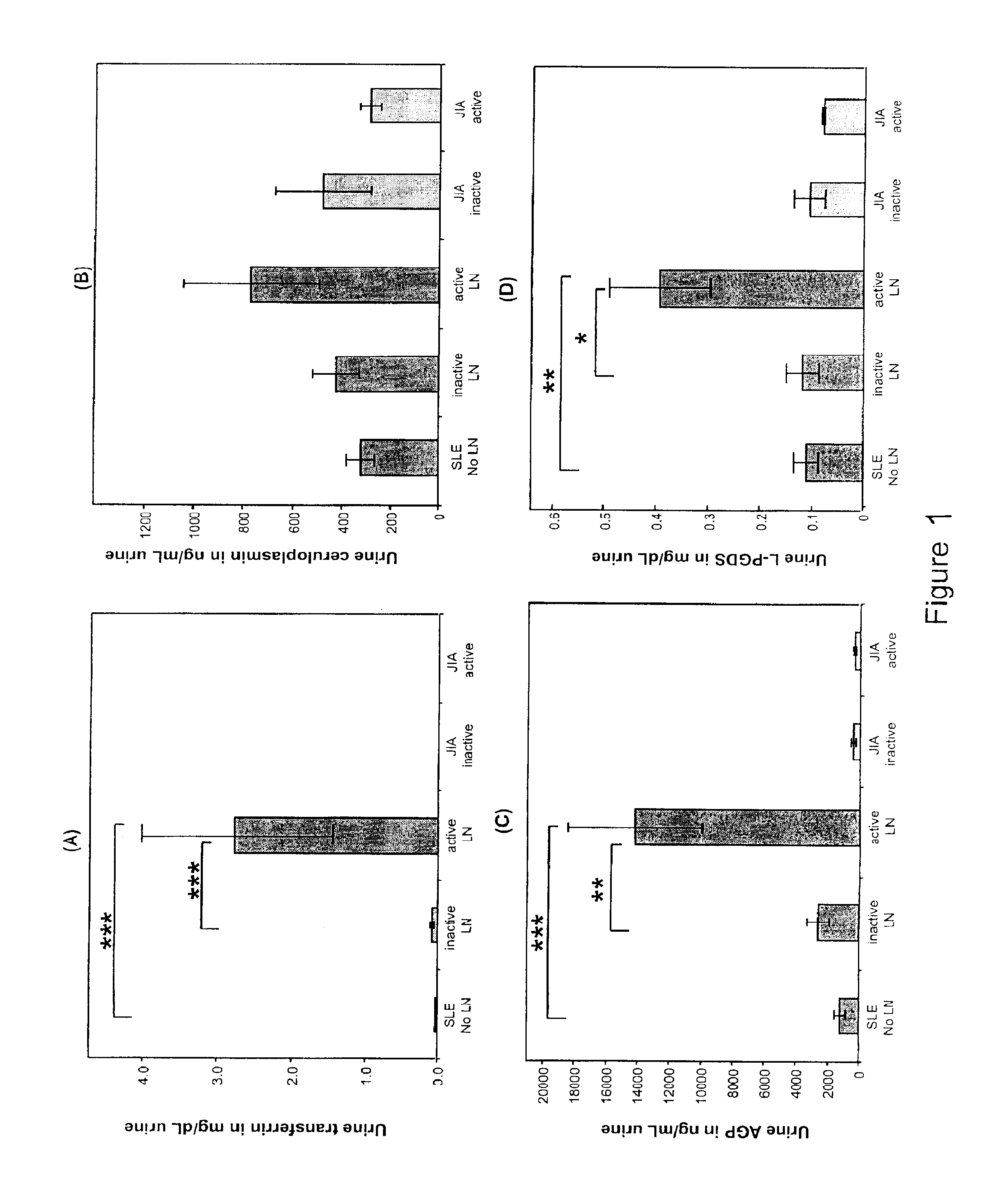
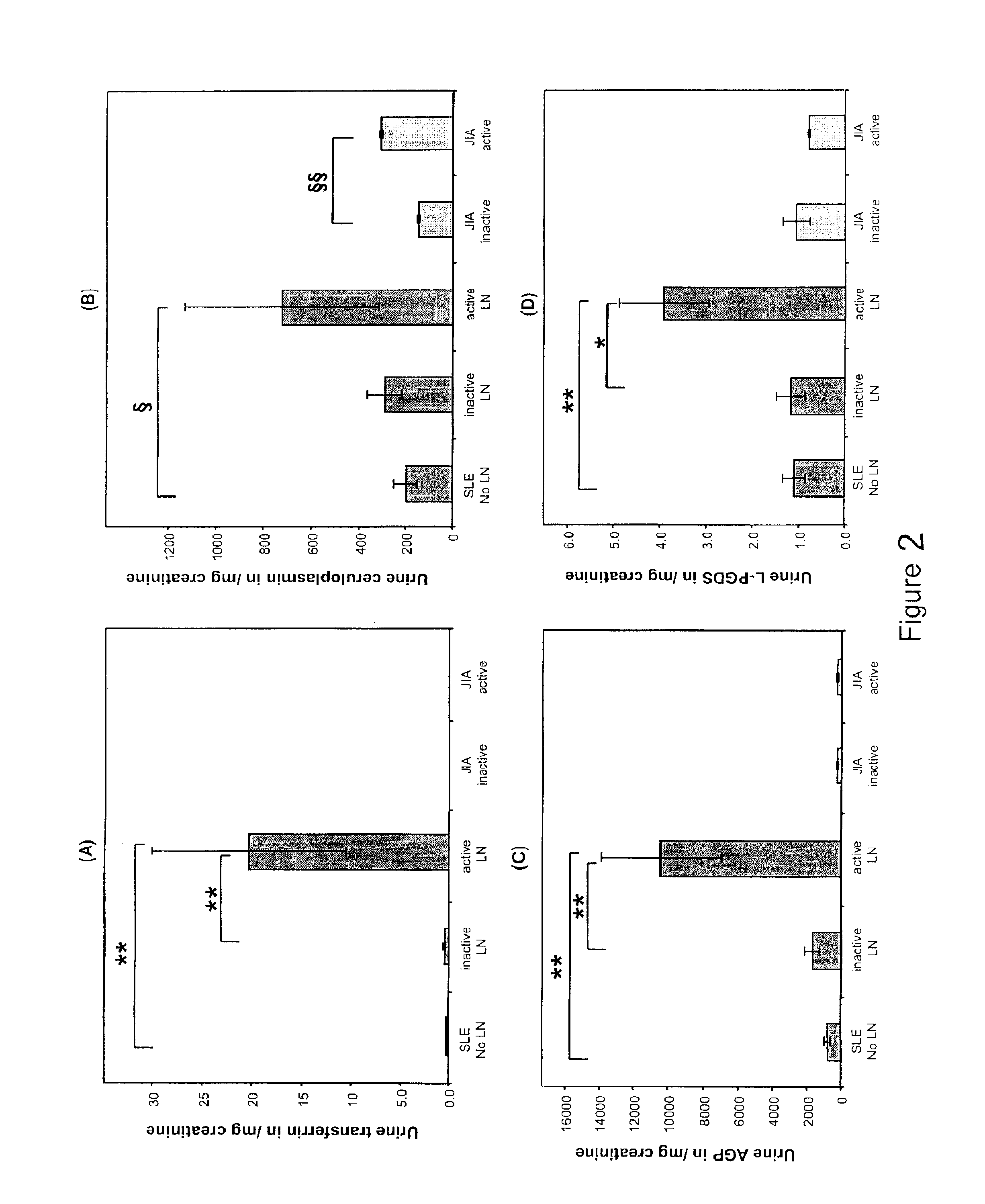
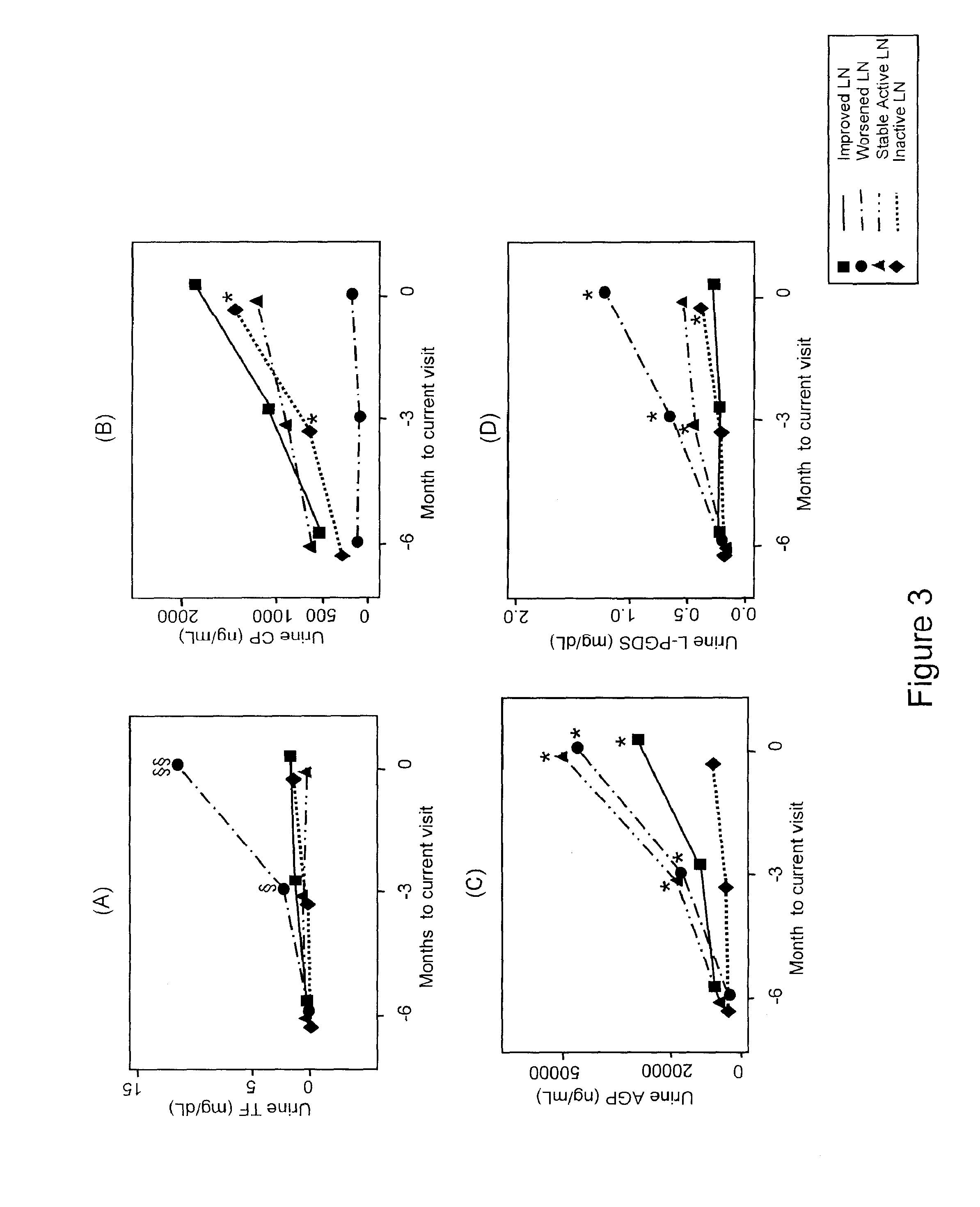
Detection of worsening renal disease in subjects with systemic lupus erythematosus
ActiveUS20100323911A1Worsening renal disease activityAccurate determinationLibrary screeningDisease diagnosisProstaglandins DDisease activity
Methods for the detection of active lupus nephritis (LN) and worsening renal disease activity and / or active LN in patients diagnosed with systemic lupus erythematosus, using a panel of biomarkers including transferrin (Tf), ceruloplasmin (Cp), alpha-1-acid glycoprotein (AGP1), lipocalin-like prostaglandin D synthetase (L-PGDS), and urinary neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (UNGAL).
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
8-azaprostaglandin derivatives and medical use thereof
The pharmaceutical composition comprising the compound of the invention having 8-azaprostaglandin skeleton represented by formula (I)(wherein, all the symbols have the same meanings as that of the specification) a salt thereof, a solvate thereof or a cyclodextrin clathrate thereof, or a prodrug thereof and them as active ingredient have EP4 agonistic action and thus are considered useful for the prevention and / or treatment of immunological diseases, asthma, neuronal cell death, arthritis, lung failure, pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary emphysema, bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, liver damage, acute hepatitis, nephritis, renal insufficiency, hypertension, myocardial ischemia, systemic inflammatory response syndrome, sepsis, hemophagous syndrome, macrophage activation syndrome, Still's disease, Kawasaki disease, burn, systemic granulomatosis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, hypercytokinemia at dialysis, multiple organ failure, shock and glaucoma, etc. Furthermore, the compounds also have an action of accelerating bone formation, so it is expected to be useful for the prevention and / or treatment of diseases associated with loss in bone mass, for example, primary osteoporosis, secondary osteoporosis, bone metastasis of cancer, hypercalcemia, Paget's disease, bone loss, osteonecrosis, bone formation after bone operation, alternative treatment for bone grafting.
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
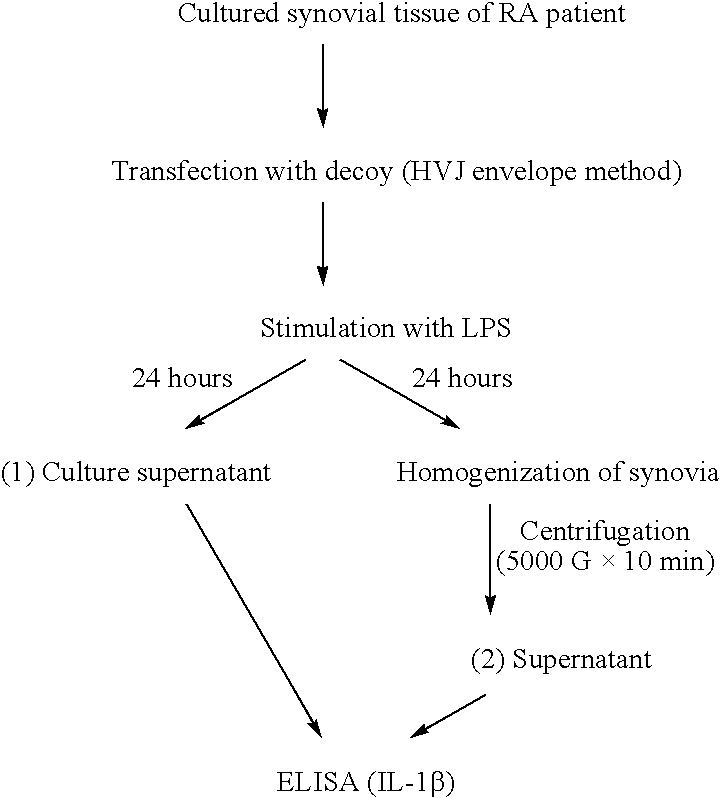
Pharmaceutical composition containing decoy and use of the same
InactiveUS20060263422A1Apparent advantageOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderPercent Diameter StenosisLiposome
A pharmaceutical composition is provided for treatment and / or prevention of a disease, a disorder and / or a condition caused by expression of a gene controlled by NF-κB or ets. The composition comprises at least one decoy and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The decoy is an NF-κB decoy, an ets decoy, or a chimera decoy of NF-κB and ets. The disease is cerebral aneurysm, cancer, Marfan's syndrome, aortic detachment, post-angioplasty restenosis, chronic articular rheumatism, asthma, atopic dermatitis, nephritis, renal failure, or plaque rupture. Alternatively, the disease is a disease associated with eosinophilic abnormality (e.g., asthma, vascular diseases, allergic diseases, parasite diseases). The pharmaceutically acceptable carrier may be a hydrophilic polymer, a liposome, or the like.
Owner:ANGES MG INC
Kidney essence pill formula for treating chronic pyelonephritis and preparation method of kidney essence pill
InactiveCN103550641AGood curative effectPromote absorptionMammal material medical ingredientsUrinary disorderSalvia miltiorrhizaSide effect
The invention discloses a kidney essence pill formula for treating chronic pyelonephritis and a preparation method of the kidney essence pill, belonging to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicine formula. The kidney essence pill comprises the following raw materials of effective ingredients in parts by weight: 20-38g of rhizoma smilacis glabrae, 15-30g of Chinese yam, 15-30g of phymatopsis hastata, 10-30g of red bean, 10-30g of semen coicis, 12-28g of oyster, 9-24g of tortoise shell, 6-15g of morinda officinalis, 9-15g of lophatherum gracile, 7-15g of cortex lycii radicis, 5-12g of rhizoma alismatis, 4-12g of sparganii rhizoma, 4-10g of earthworm, 3-11g of myrrh, 3-9g of salvia miltiorrhiza, 3-9g of golden cypress, 3-8g of tangerine seed, and 1-3g of endothelium corneum gigeriae galli. The kidney essence pill formula is perfect in selecting raw materials and unique in compatibility of medicines, aims at pathogeny of nephritis such as spleen-kidney-yang deficiency, urination disorder, and retention of damp-heat in the interior, has effects on clearing heat and promoting diuresis, detoxifying and treating stranguria, inducing diuresis to alleviate edema, tonifying kidney and nourishing blood. The kidney essence pill is prepared through reasonable combination of raw materials. Clinical verification shows that the kidney essence pill has good absorption effect, obvious curative effect, no toxic and side effects, and no clinical adverse reaction, meets clinical requirements, is an ideal pill for curing kidney.
Owner:杨玉贵
Toxin peptides with extended blood halflife
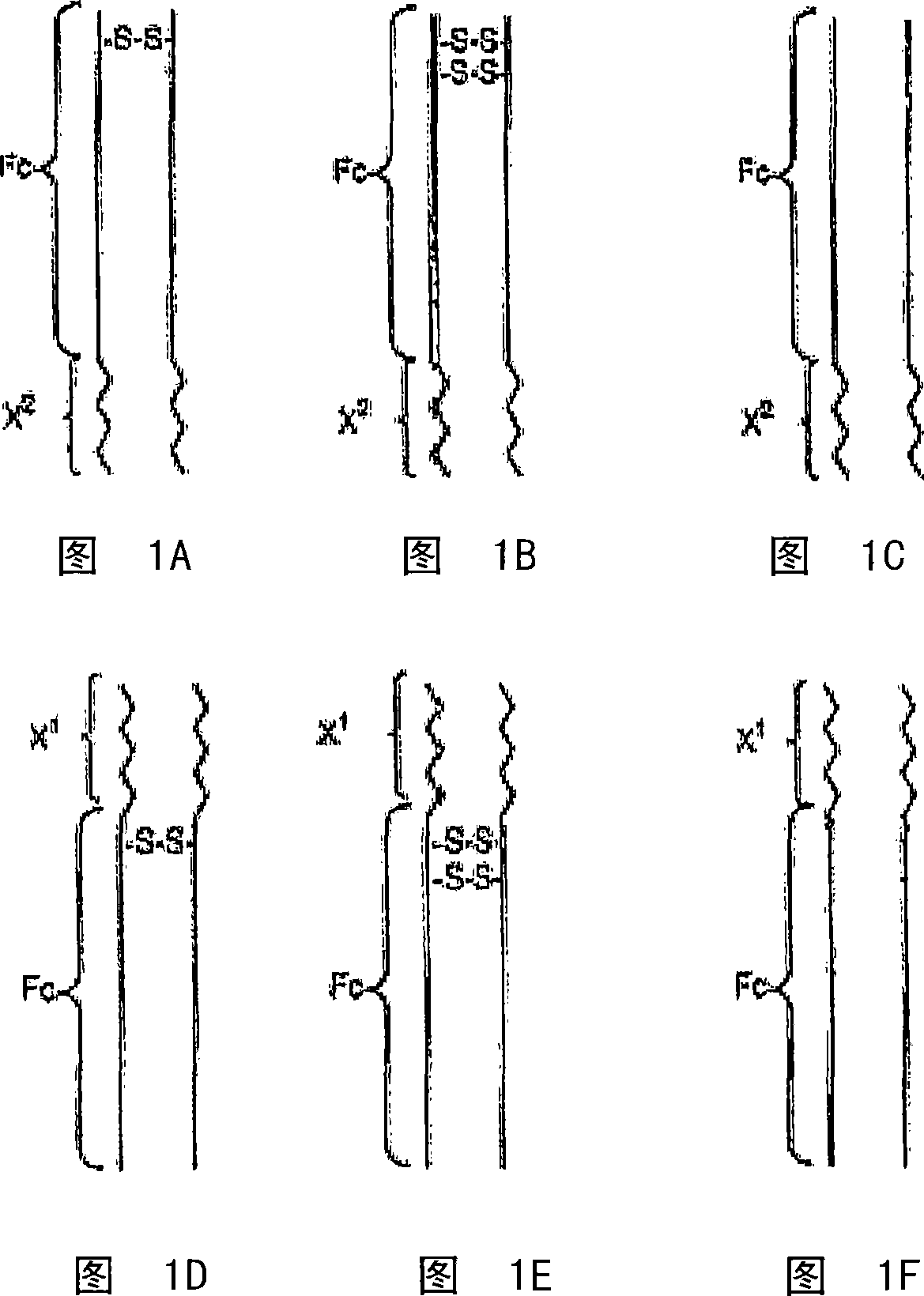
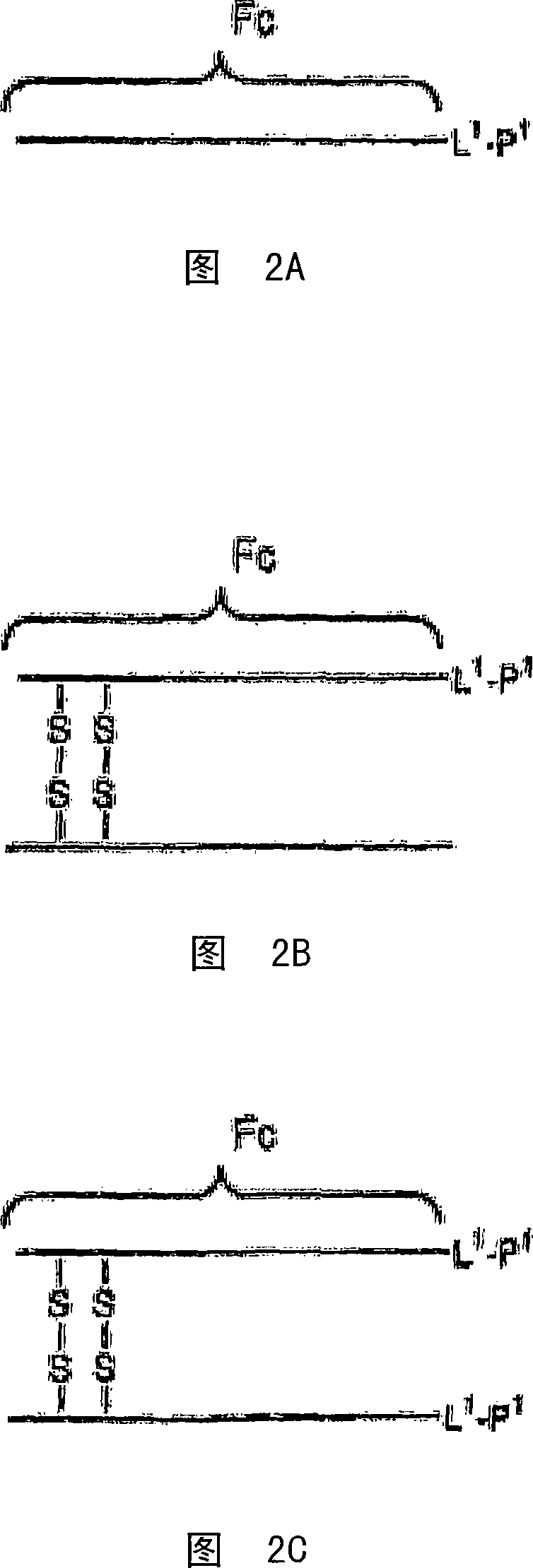
InactiveCN101232903APeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsInflammatory Bowel DiseasesHalf-life
Disclosed is a composition of matter of the formula (X<1>)a-(F<1>)d-(X<2>)b-(F<2>)e-(X<3>)c and multimers thereof, in which F<1> and F<2> are half-life extending moieties, and d and e are each independently 0 or 1, provided that at least one of d and e is 1; X<1>, X<2>, and X<3> are each independently -(L)f-P-(L)g-, and f and g are each independently 0 or 1; P is a toxin peptide of no more than about 80 amino acid residues in length, comprising at least two intrapeptide disulfide bonds; L is an optional linker; and a, b, and c are each independently 0 or 1, provided that at least one of a, b and c is 1. Linkage to the half-life extending moiety or moieties increases the in vivo half-life of the toxin peptide, which otherwise would be quickly degraded. A pharmaceutical composition comprises the composition and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. Also disclosed are a DNA encoding the inventive composition of matter, an expression vector comprising the DNA, and a host cell comprising the expression vector. Methods of treating an autoimmune disorder, such as, but not limited to, multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetes, psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, contact-mediated dermatitis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, asthma, allergy, restinosis, systemic sclerosis, fibrosis, scleroderma, glomerulonephritis, Sjogren syndrome, inflammatory bone resorption, transplant rejection, graft-versus-host disease, and lupus and of preventing or mitigating a relapse of a symptom of multiple sclerosis are also disclosed.
Owner:AMGEN INC
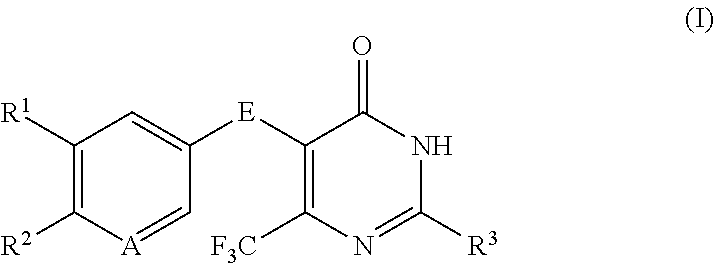
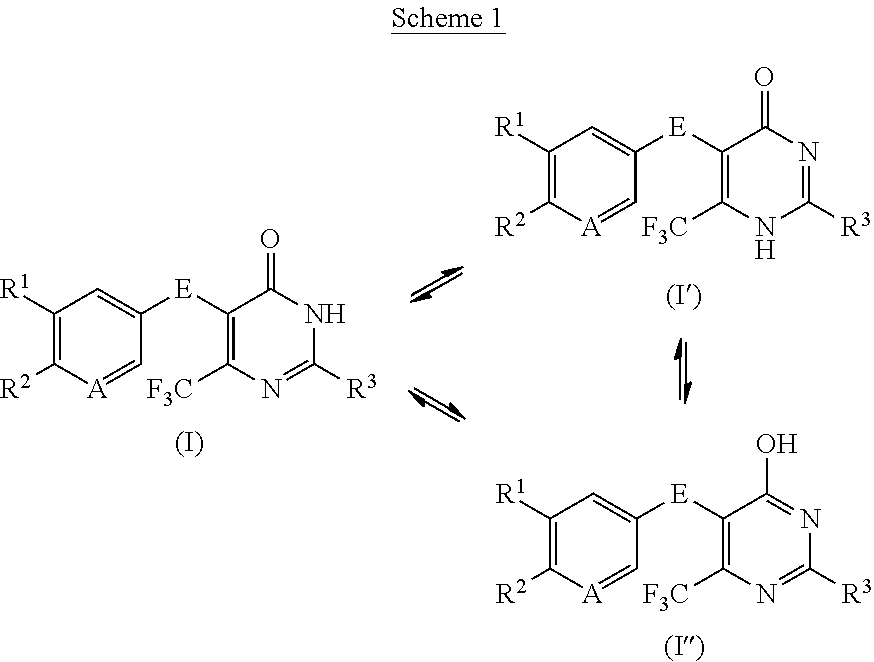
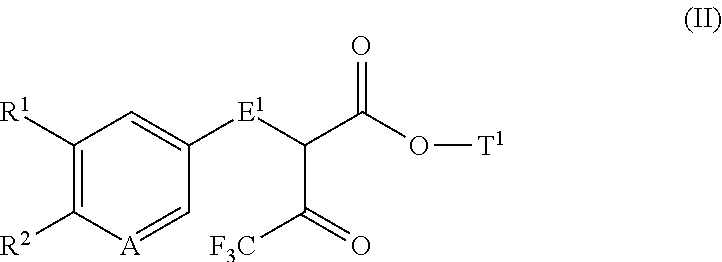
Disubstituted trifluoromethyl pyrimidinones and their use
The present application relates to novel 2,5-disubstituted 6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-4(3H)-one derivatives, to processes for their preparation, to their use alone or in combinations for the treatment and / or prevention of diseases, and to their use for preparing medicaments for the treatment and / or prevention of diseases, in particular for treatment and / or prevention of cardiovascular, renal, inflammatory and fibrotic diseases.
Owner:BAYER PHARMA AG
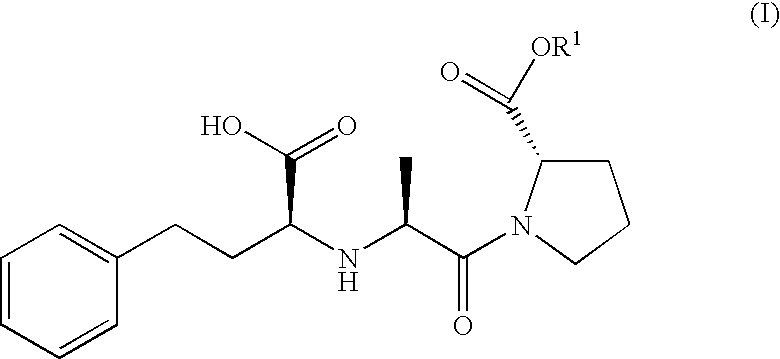
Proline ester and preparation containing the same for percutaneous administration
InactiveUS20050288232A1Valid conversionGood physical and chemical stabilityBiocideAngiotensinsDisease causeChemistry
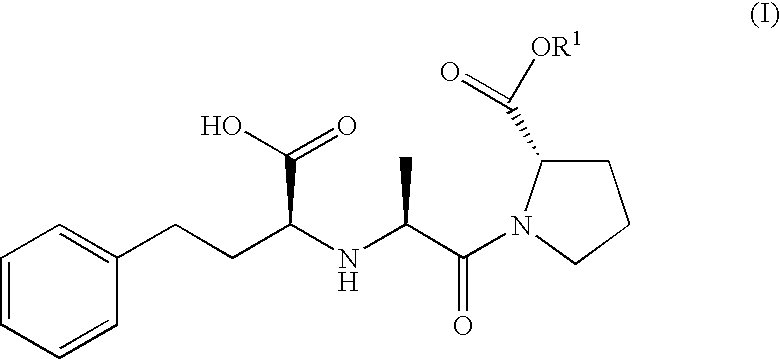
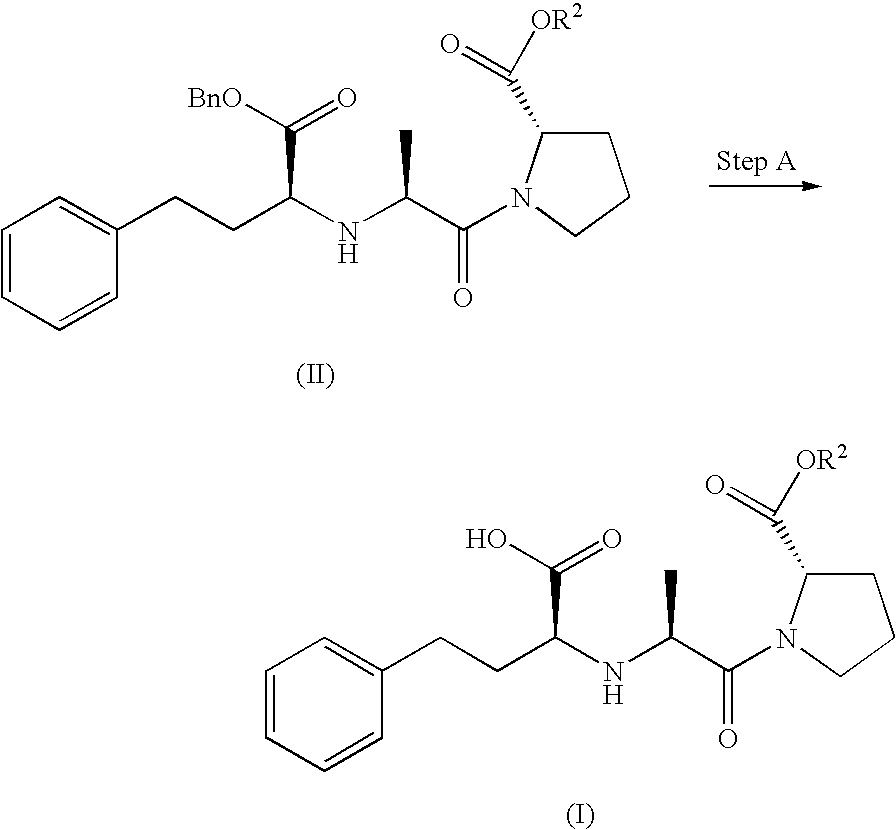
A proline ester represented by the following formula (I): wherein R1 represents a hydroxy-lower alkyl group, a lower alkoxy-lower alkyl group, or a lower alkoxy-lower alkoxy-lower alkyl group or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The proline ester (I) of the present invention and a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof are useful as a prodrug of enalaprilat, which is a medicine useful for preventing or treating circulatory diseases such as hypertension, cardiac diseases (e.g., cardiac hypertrophy, cardiac failure, and myocardial infarct), nephritis, and apoplexy. Thus, a drug containing the ester or a salt thereof is preferably formulated to a percutaneous preparation, particularly a patch, from the viewpoint of medicinal activity and use.
Owner:TOAEIYO
Anti-inflammatory hexapeptide
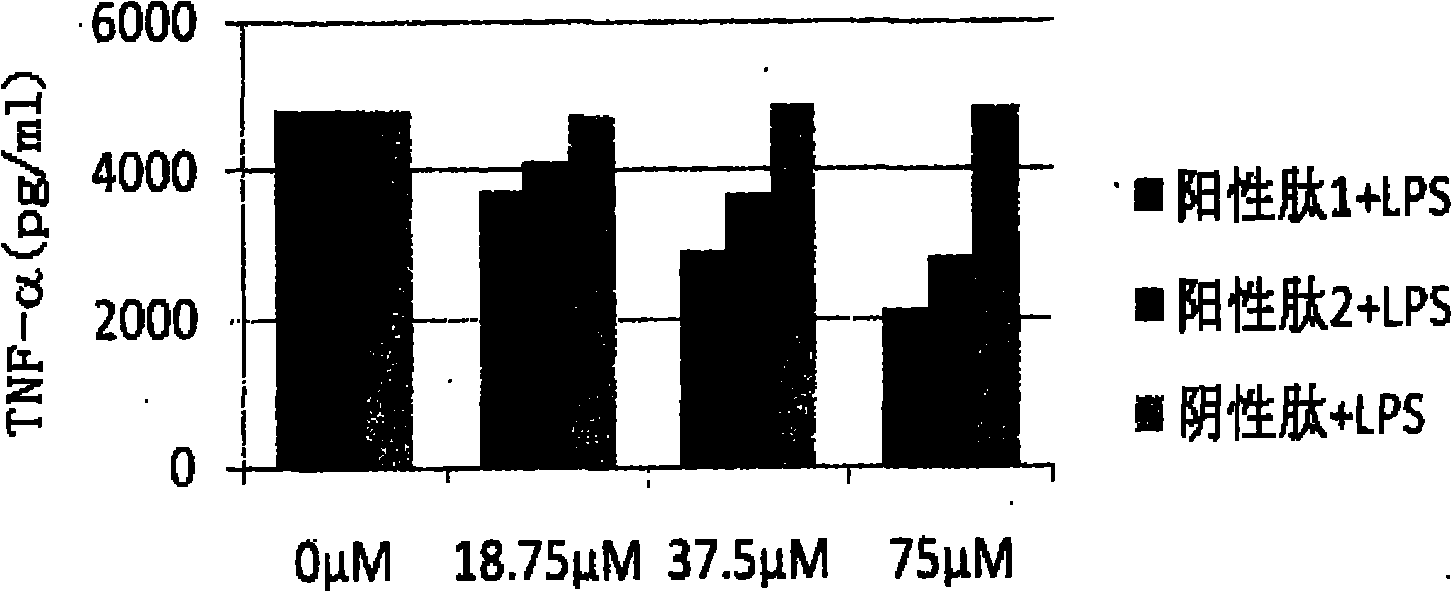
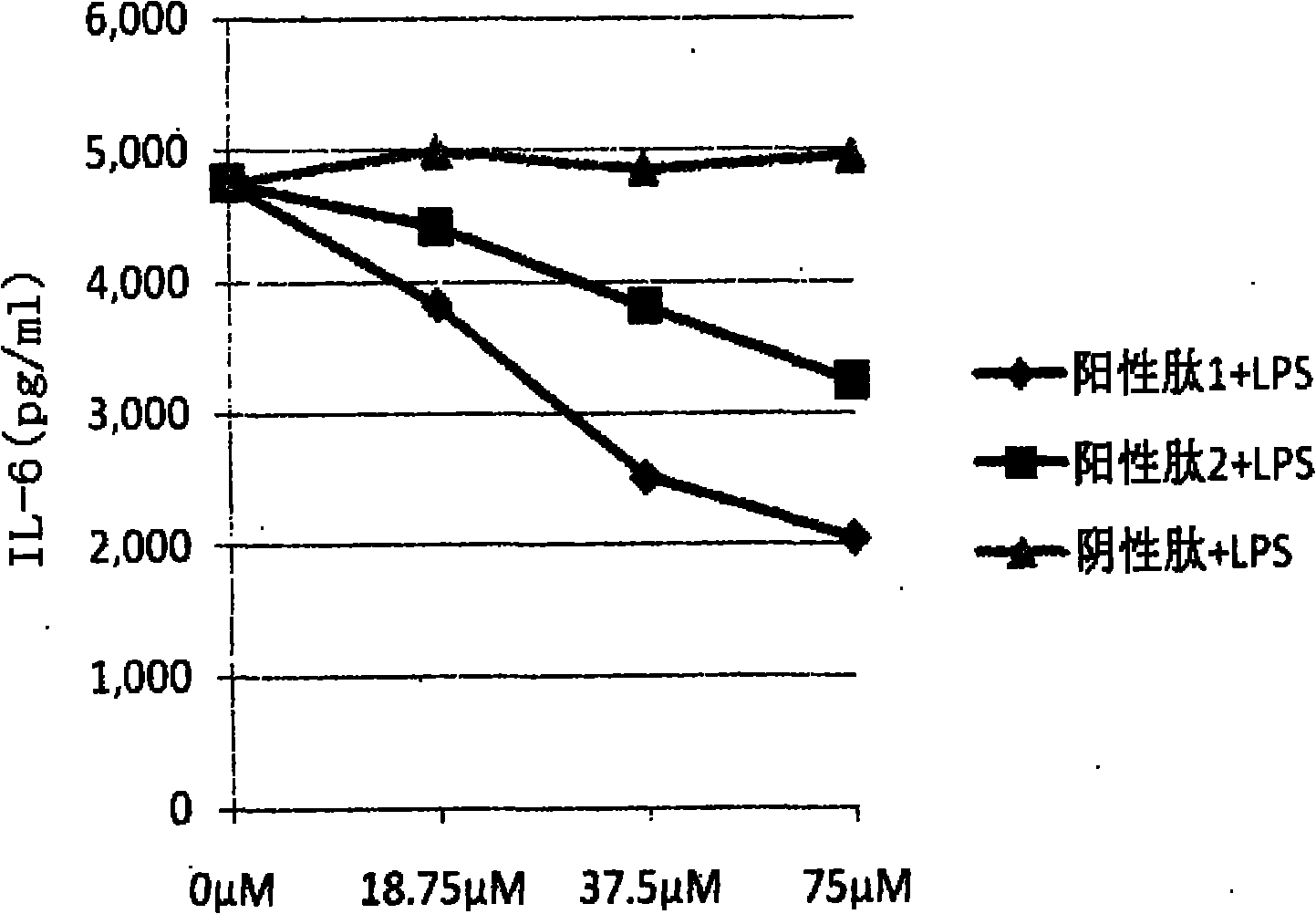
The invention relates to anti-inflammatory hexapeptide Lys, Val, Cit Lys Pro Val as well as preparation and application thereof. The invention also comprises a method for preparing the polypeptide. The method is selected from the conventional solid phase synthesis method, a synthesis method in a solution, a gene recombination method or a chemical synthesis method. The medicament is used for treating inflammatory immune relevant diseases, wherein the inflammatory relevant diseases comprise sepsis, septic shock, rheumatoid (rheumatoid) arthritis, asthma, acute and chronic glomerulonephritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and the like.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Decoy-containing pharmaceutical compositions and method of using the same
InactiveUS20070142314A1Effective treatmentOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderPercent Diameter StenosisGene control
A pharmaceutical composition is provided for treatment and prevention of a disease caused by expression of a gene controlled by NF-κB or ets. The composition comprises at least one decoy and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The decoy is an NF-κB decoy, an ets decoy, or a chimera decoy of NF-κB and ets. The disease is cerebral aneurysm, cancer, Marfan's syndrome, aortic detachment, post-angioplasty restenosis, chronic articular rheumatism, asthma, atopic dermatitis, nephritis, renal failure, or plaque rupture. The pharmaceutically acceptable carrier may be a hydrophilic polymer.
Owner:ANGES MG INC
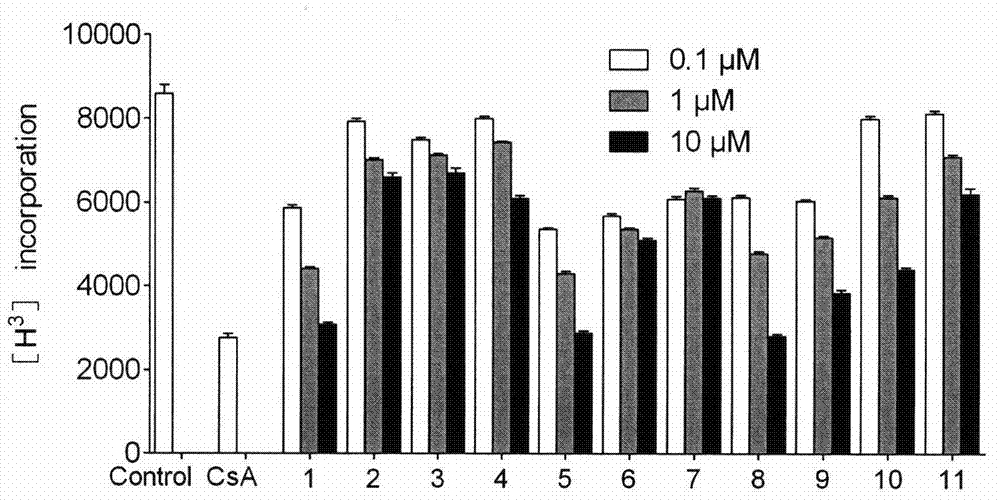
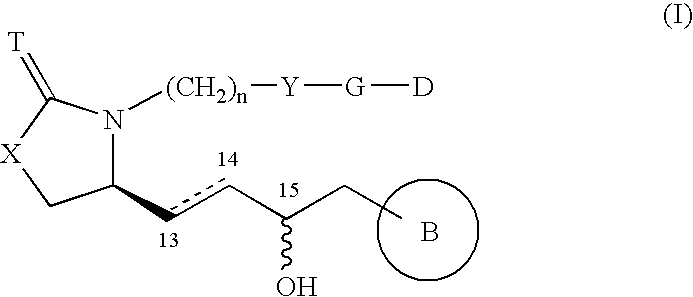
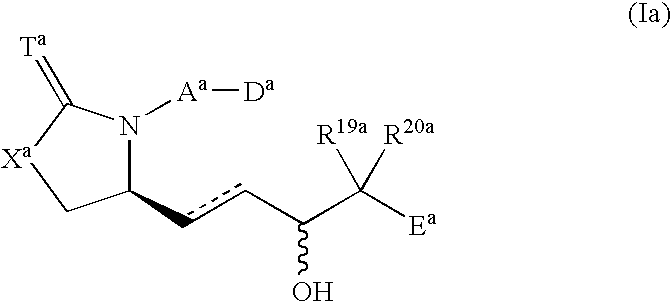
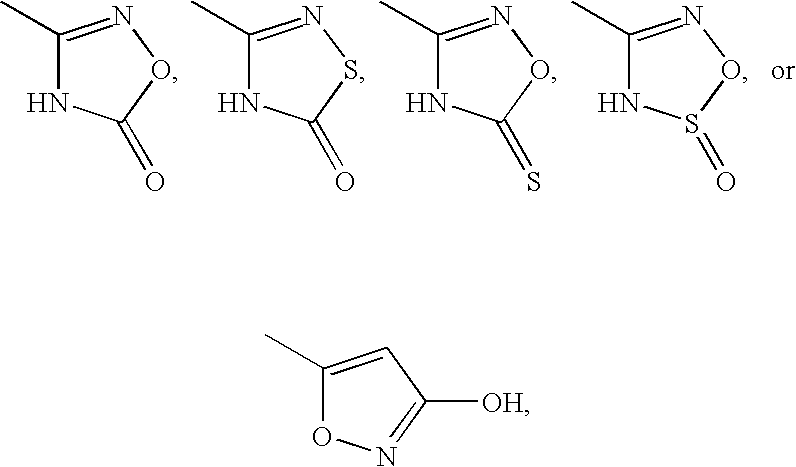
5-[6-[[3-(4,5,6,7-tetrahydropyrazolo[4,3-c]pyridin-1-yl)azetidin-1-yl]methyl]morpholin-4-yl]quinoline-8-carbonitrile derivatives and similar compounds as tlr7-9 antagonists for treating systemic lupus erythematosus
PendingUS20210300924A1High activityLow CYP inhibitionOrganic chemistryImmunological disordersTLR8Autoimmune condition
The present invention relates to a compound of formula (I) wherein R4 is C1-6alkyl, halogen or cyano; R5 is halogen; R2 is 4,5,6,7-tetrahydropyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridinyl which is unsubstituted or substituted by C1-6alkyl or haloC1-6alkyl; 4,5,6,7-tetrahydropyrazolo[4,3-c]pyridinyl which is unsubstituted or substituted one or two times by C1-6alkyl; or 5,6-dihydro-4H-pyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrazolyl; R3 is C1-6alkyl; L is azetidinyl or piperidinyl; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, for use as a TLR7, TLR8 and / or TLR9 antagonist for the treatment or prophylaxis of autoimmune diseases, such as e.g. systemic lupus erythematosus or lupus nephritis.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
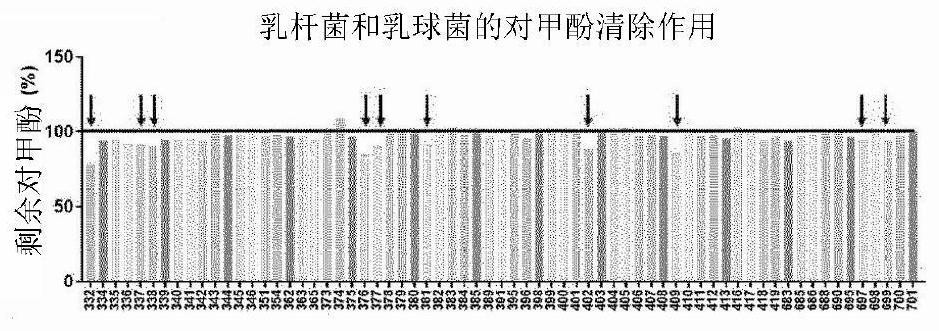
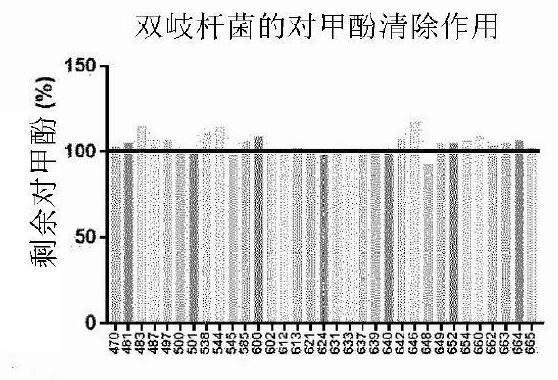
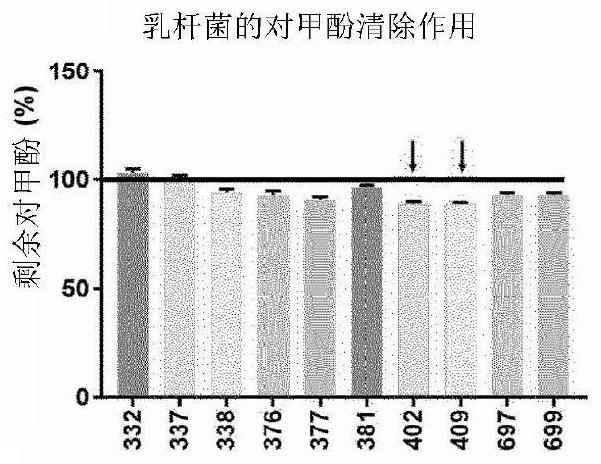
Lactobacillus acidophilus KBL409 strain and application thereof
The invention relates to a lactobacillus acidophilus KBL409 strain and an application of the lactobacillus acidophilus KBL409 strain. The Lactobacillus acidophilus KBL409 strain (registration number KCTC 13518BP) according to the present invention alleviates renal inflammation and the concentration of uremic substances (such as blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, p-cresol and the like) in blood to protect the kidney, and exhibits the effects of proteinuria alleviation, renal mitochondrial function recovery and renal fibrosis inhibition. And therefore, the compound can be effectively applied to improvement of renal function and prevention and treatment of nephropathy (including chronic nephropathy).
Owner:KO BIOLABS INC
Application of traditional Chinese medicine composition in preparation of medicine for treating kidney disease
InactiveCN104644768AGood treatment effectReduced responseAnthropod material medical ingredientsUrinary disorderPharmacologyDiabetic nephropathy
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine and particularly relates to an application of a traditional Chinese medicine composition in preparation of medicine for treating kidney disease. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is obtained by performing ethanol extracting on the following raw materials: 6-10 parts of giant knot weed, 5-8 parts of plantain herb, 5-8 parts of glossy privet fruit and 1-4 parts of beehive. The traditional Chinese medicine composition can be used for treating the kidney diseases such as diabetic nephropathy, renal edema and renal edema, and is quick in effect, short in course of treatment, high in cure rate and low in toxic side effect, and also is simple in operation process, stable in medical effect and easy to popularize.
Owner:GUANGDONG ROC MEDICINAL TECH CO LTD
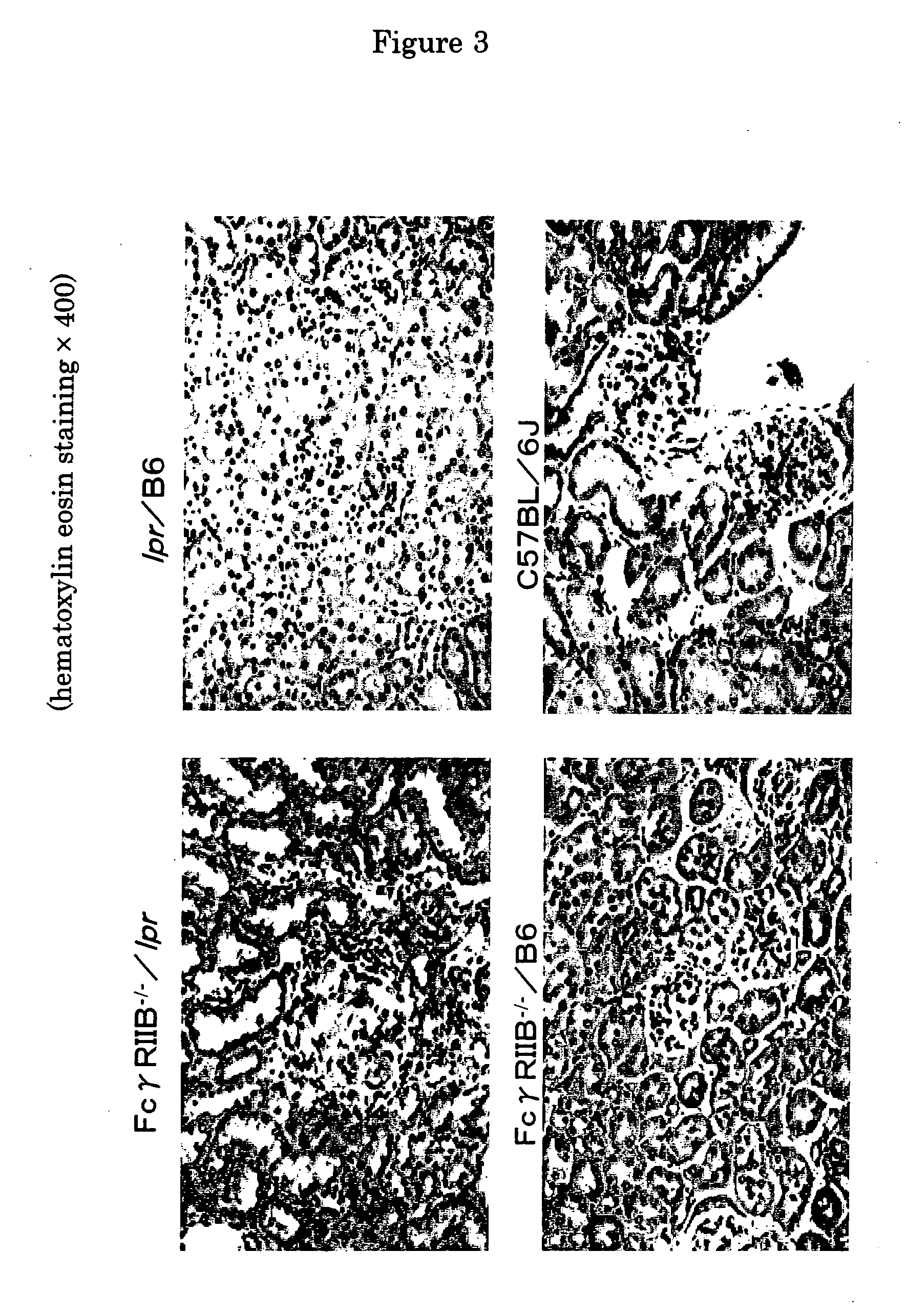
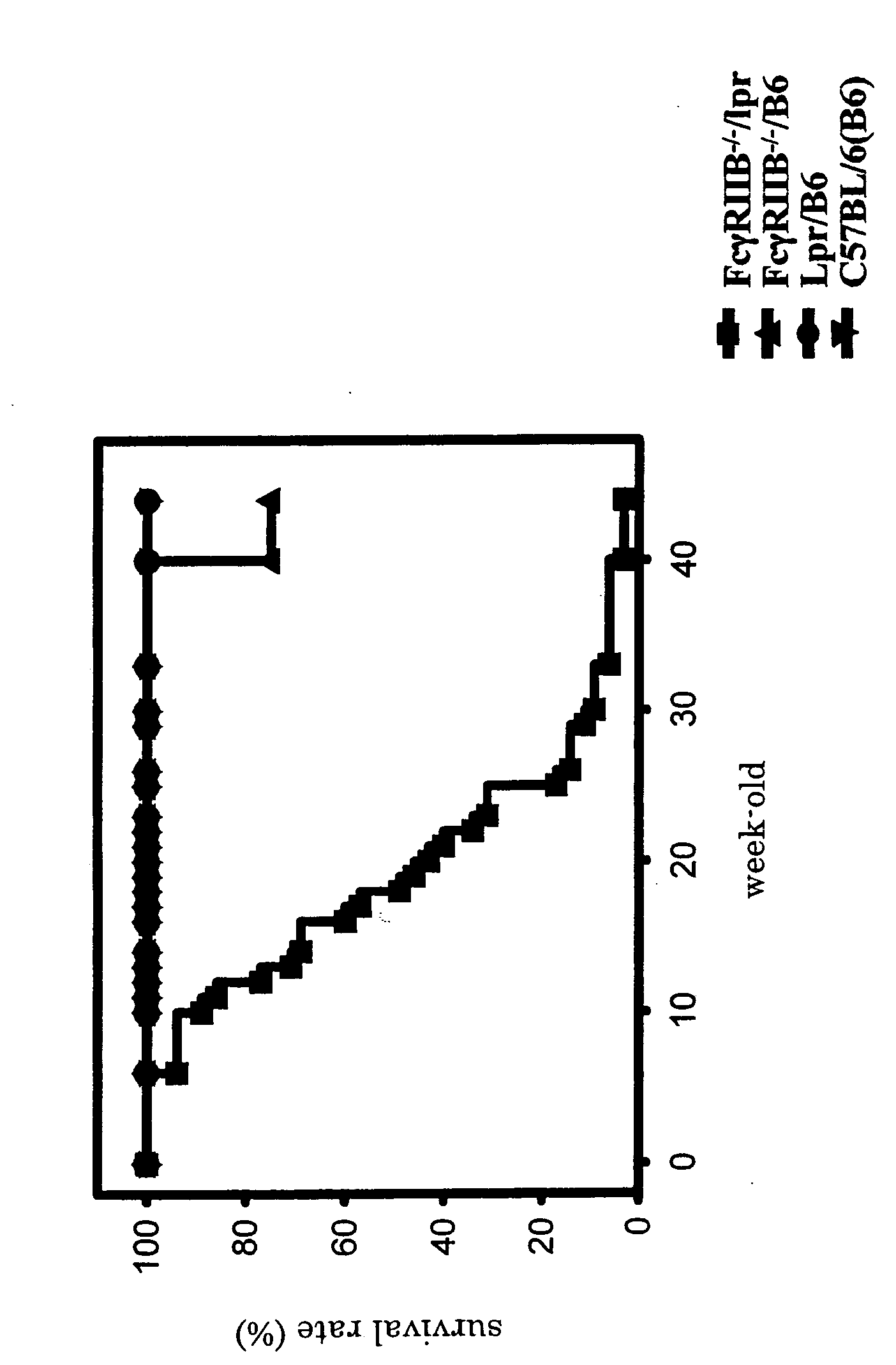
Nonhuman Model animal of syntemic lupus erythematosus
InactiveUS20050066378A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansScreening methodSingle strand
The present invention is to provide a non-human animal model of systemic lupus erythematosus wherein generation of anti-double stranded DNA antibody and anti-single stranded antibody is induced, and that is made to spontaneously develop glomerulonephritis and arthritis, and a screening method for a therapeutic agent for systemic lupus erythematosus wherein the non-human animal model is used. FcγRIIB deficient mouse that is not made to spontaneously develop autoimmune pathology although its autoantibody response is enhanced is backcrossed into C57BL / 6J (B6) mouse for 12 generations to generate FcγRIIB deficient B6 mouse, the FcγRIIB deficient B6 male mouse is intercrossed with lpr / B6 female mouse, and thus obtained FcγRIIB+ / − / lpr+ / − mice were further crossed to generate a mouse model of systemic lupus erythematosus.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
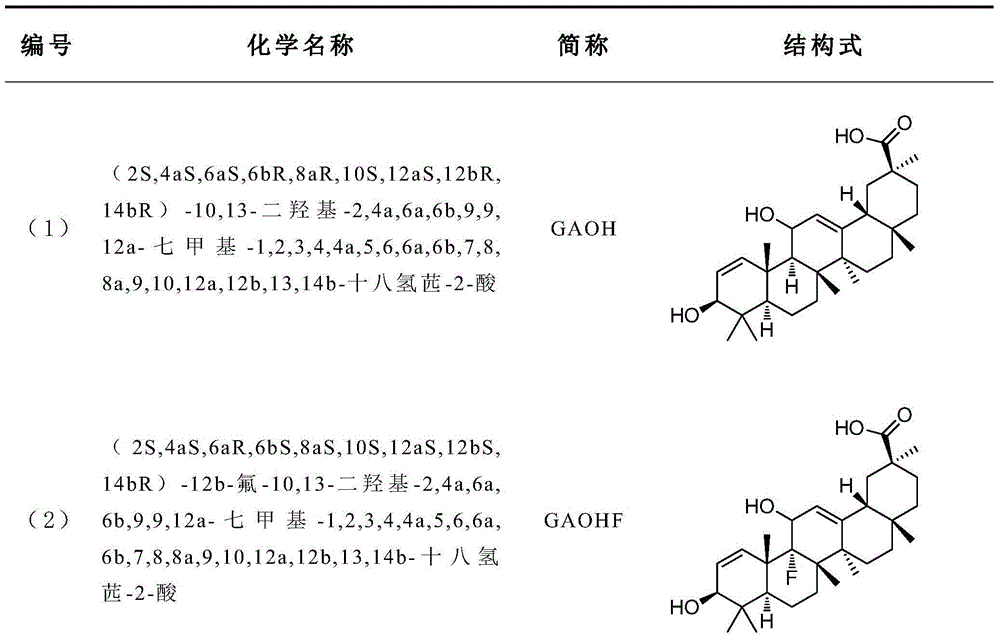
GAOH derivative and medical application thereof
ActiveCN104530176AGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderImmunologic disordersAutoimmune disease
The invention provides a GAOH derivative of a new structure. The compounds have great curative effects on inflammatory bowel diseases, hepatitis viruses, foot swelling, ear swelling, arthritis, pneumonia, nephritis, rhinitis, cerebral apoplexy, myocardial ischemia, atherosclerosis, arrhythmia, autoimmune disease, senile dementia, depression, schizophrenia, malignancy and tumor adjuvant therapy, virus infectious diseases, peptic ulcer, analgesia, antianaphylaxis, antiendotoxin, antishock and diabetes or diabetic complication.
Owner:WUHAN WORLDNER UNITED PHARMA
Pharmaceutical composition containing sirt2 inhibitor
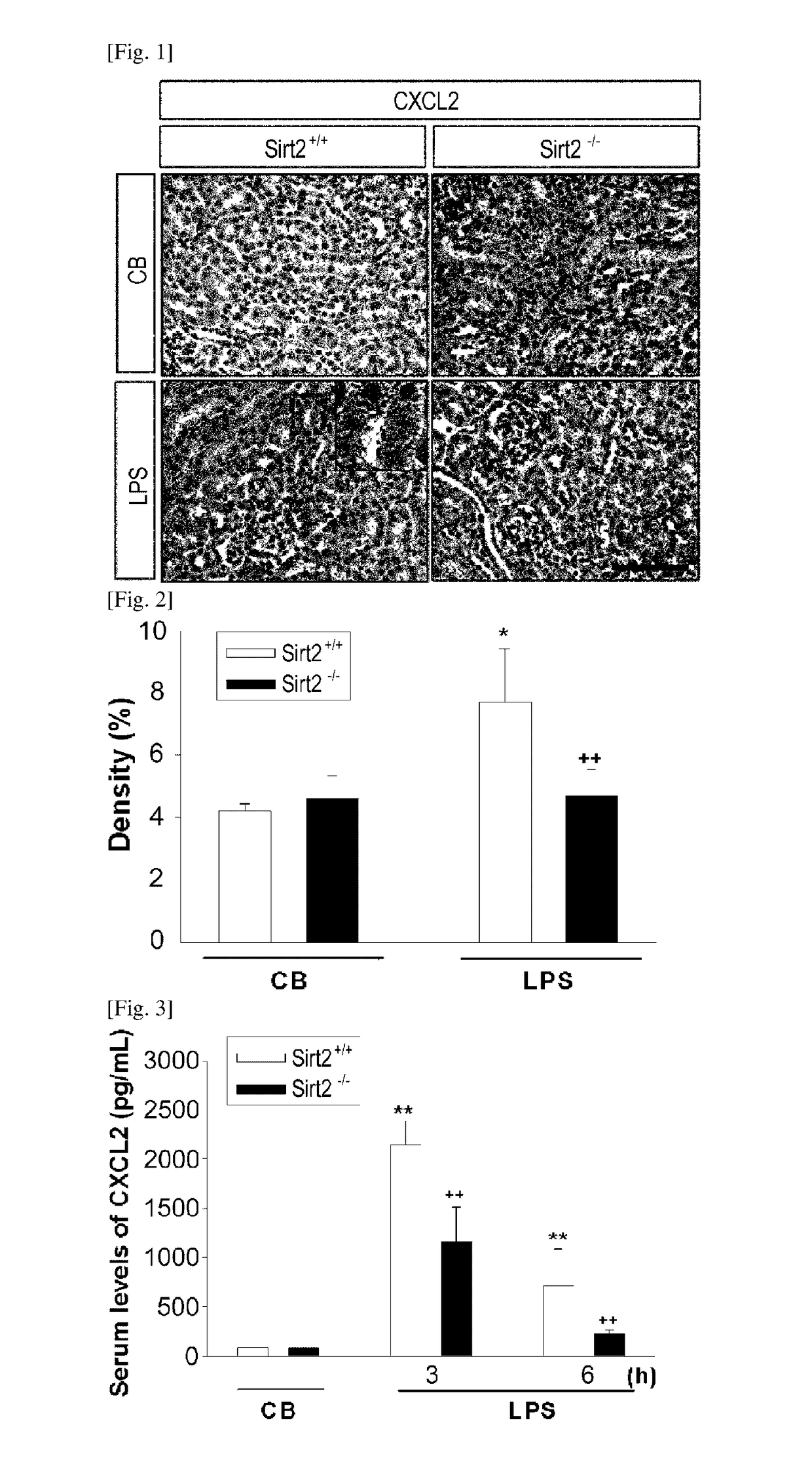
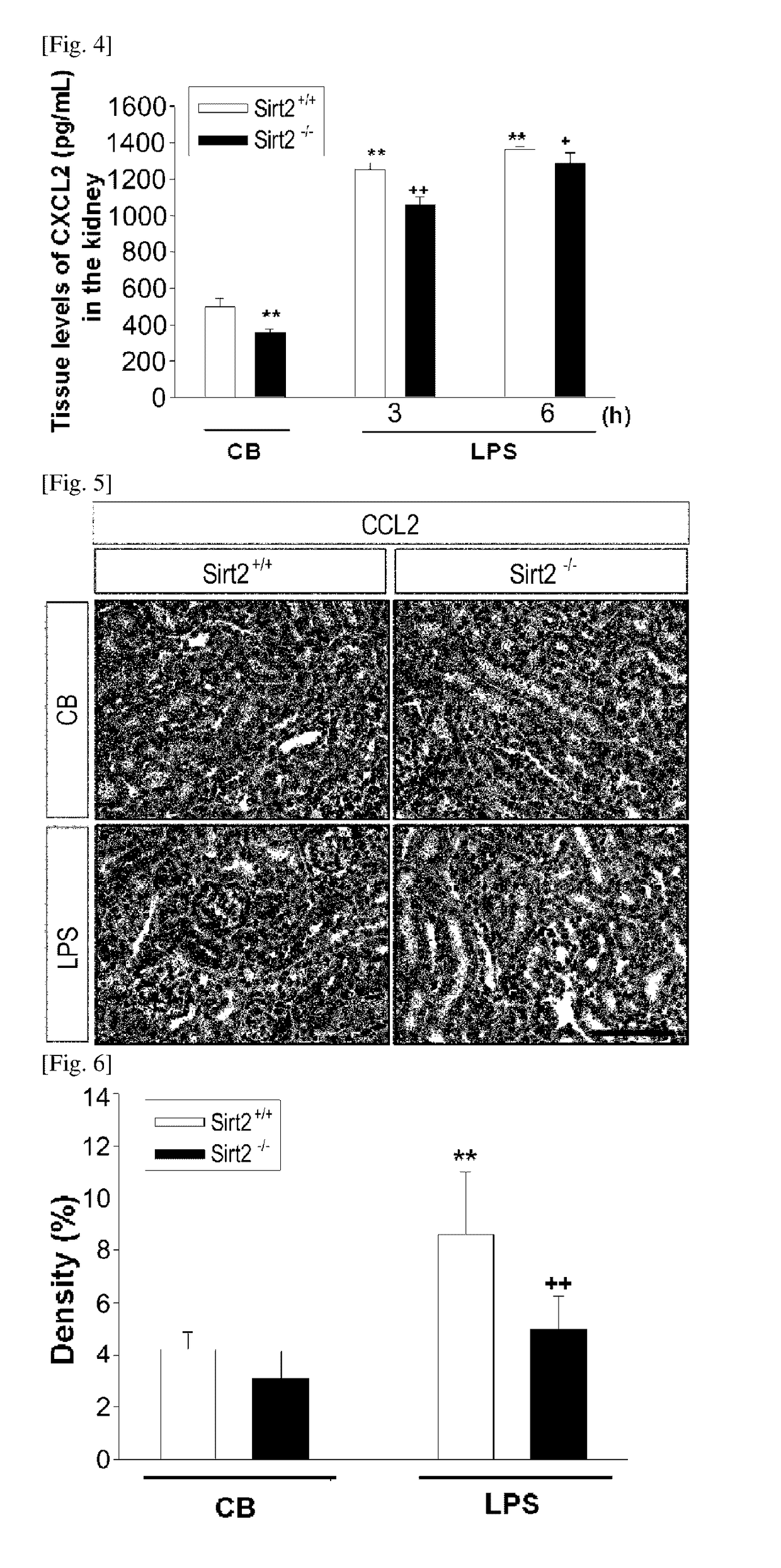
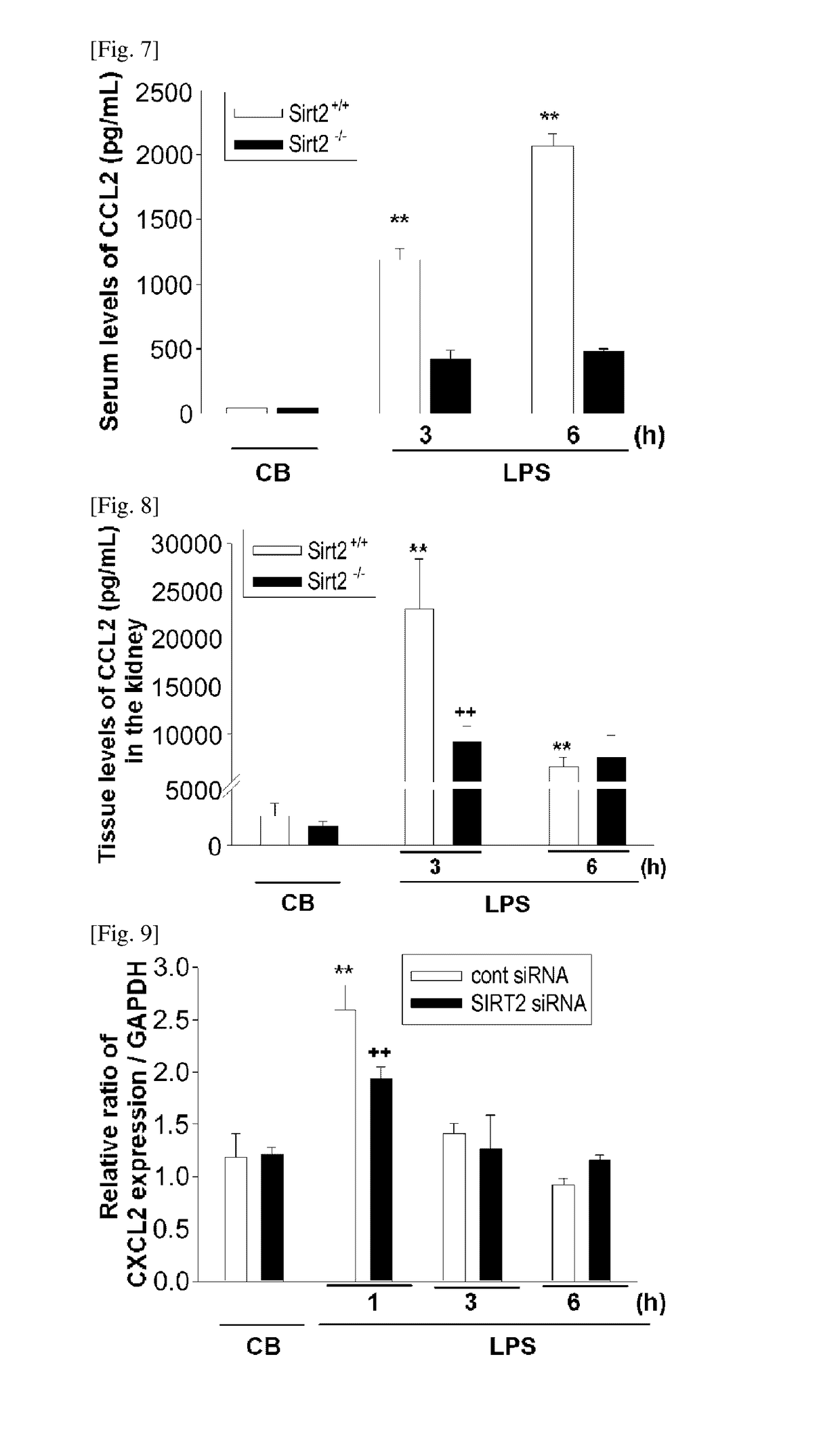
InactiveUS20170128459A1Reducing renal inflammationAvoid injuryAntineoplastic agentsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsDiseaseSide effect
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition containing a SIRT2 inhibitor and, more specifically, to: a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating renal inflammatory diseases, which are caused by sepsis, by controlling inflammation-inducing factors by sepsis through the regulation of SIRT2 gene expression so as to reduce renal inflammation, thereby preventing a kidney injury; and a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating cancer, having an effect of increasing anticancer efficacy while reducing nephrotoxicity, which is a side effect of cisplatin, when administered together with cisplatin.
Owner:IND COOP FOUND CHONBUK NAT UNIV +1
Traditional Chinese medicine for treating wind-heat common cold type renal corpuscle nephritis hematuria
InactiveCN104127752AAdjustable serum copper/zinc ratioImprove immunityUnknown materialsUrinary disorderWolfiporia extensaAstragalus mongholicus
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine for treating wind-heat common cold type renal corpuscle nephritis hematuria. The specific formula of the traditional Chinese medicine comprises the following raw materials by weight: 6-15g of flos lonicerae, 6-15 of fructus forsythiae, 6-12g of fructus arctii. 9-15g of radix isatidis, 5-10g of rhizoma dryopteris crassirhizomatis, 9-15g of radix scrophulariae, 9-30g of radix astragali seu hedysari, 9-30g of radix pseudostellariae, 5-10g of radix saposhnikoviae, 6-12g of rhizoma atractylodis macrocephalae, 6-12g of radix angelicae sinensis, 10-15g of poria cocos, 9-30g of semen coicis, 6-10g of rhizoma alismatis, 9-30g of herba plantaginis,15-60g of Oldenlandia diffusa, 9-30g of rhizoma imperatae, 5-12g of herba cirsii, 6-10g of charred madder roots, 6-12g of radix paeoniae rubra, 2-3g of powdered notoginseng roots, and 1-2g of ground squama manis. The traditional Chinese medicine for treating wind-heat common cold type renal corpuscle nephritis hematuria can achieve the purpose of not only invigorating the blood circulation, but also enhancing immunity and regulating the ratio of copper / zinc in serum of a patient with renal corpuscle nephritis, which cannot be achieved by common medicines and is easily neglected.
Owner:王祥生
Drug for treating systemic lupus erythematosus
PendingCN111514296ADelay deathDelay progressImmunological disordersSulfur/selenium/tellurium inorganic active ingredientsInflammatory factorsImmune complex deposition
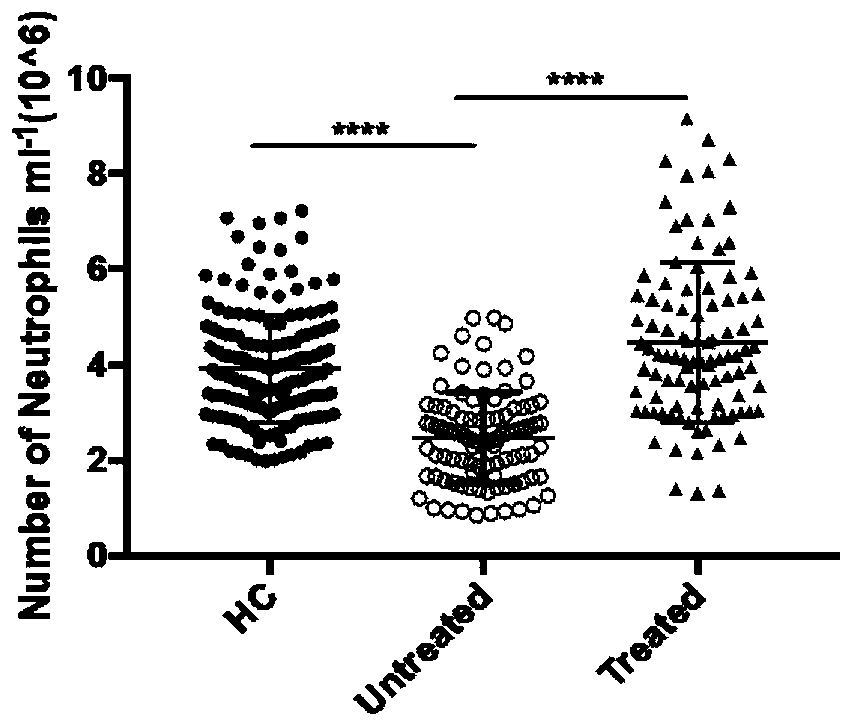
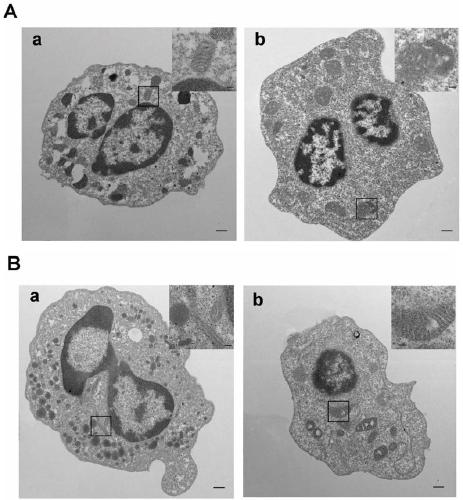
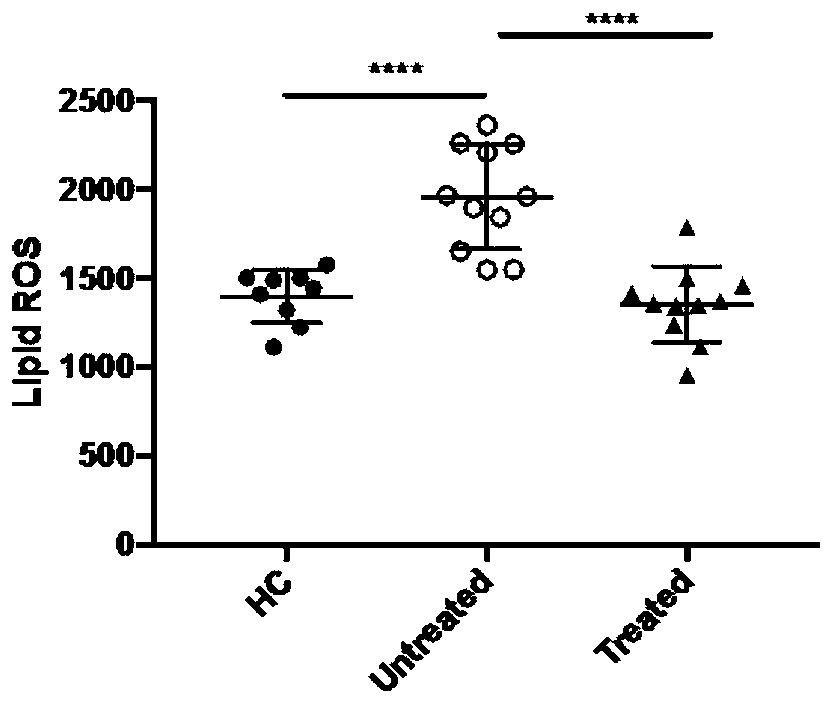
The invention discloses application of an ferroptosis inhibitor as an active ingredient in preparation of a drug for treating systemic lupus erythematosus. Researches find that neutrophils of an SLE patient spontaneously generate ferroptosis, and the neutrophils return to normal after effective systemic treatment. The ferroptosis inhibitor liproxstatin-1 (LPX-1) can be used for delaying the deathrate of neutrophils and inhibiting ferroptosis. The Crispr / cas9 technology demonstrates that increased ferroptosis can enable C57 / B6 mice to spontaneously develop lupus phenotype. In an MRL / lpr mice model, the LPX-1 treatment can slow down the progress of lupus diseases, and the spleen, lymph node size, nephritis and proteinuria levels, deposition of renal immune complexes, and levels of inflammatory factors in the treated mice are similar to those in the cyclophosphamide-treated group, indicating that the treatment effect of LPX-1 is similar to that of cyclophosphamide. Due to different action mechanisms, the LPX-1 does not have cytotoxicity similar to cyclophosphamide, so that the LPX-1 can be a better lupus treatment drug.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
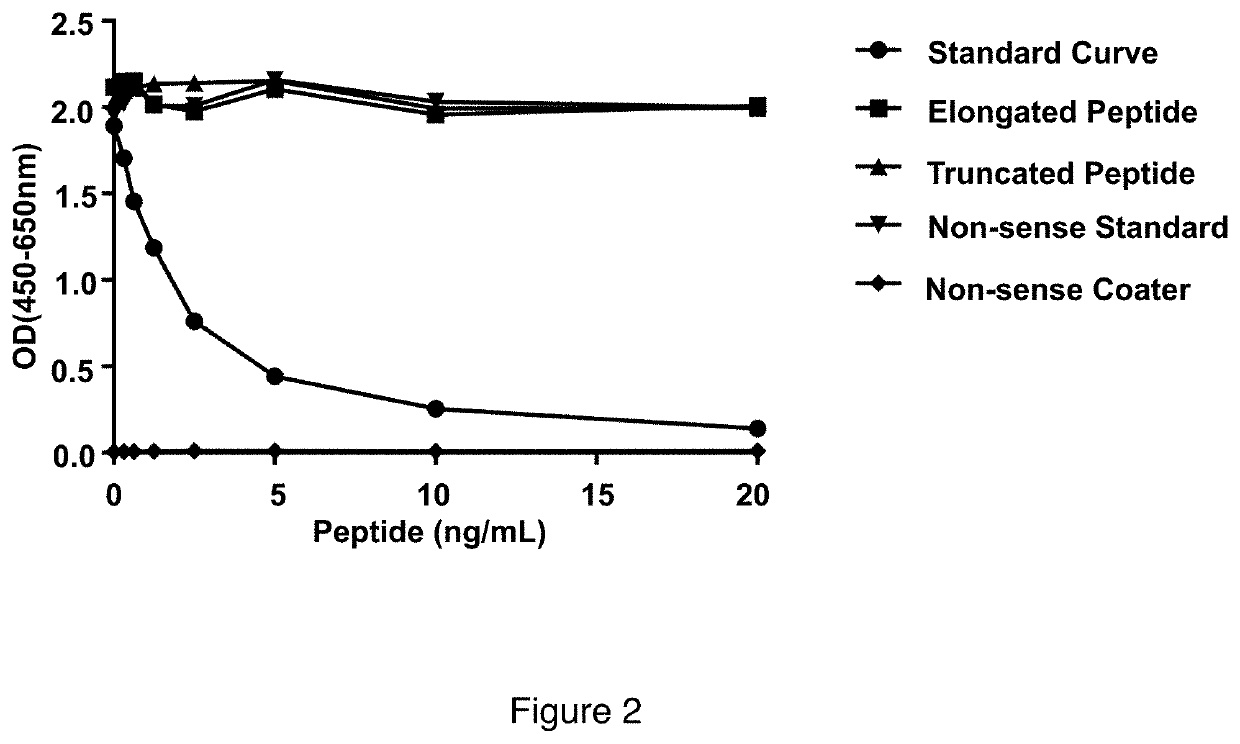
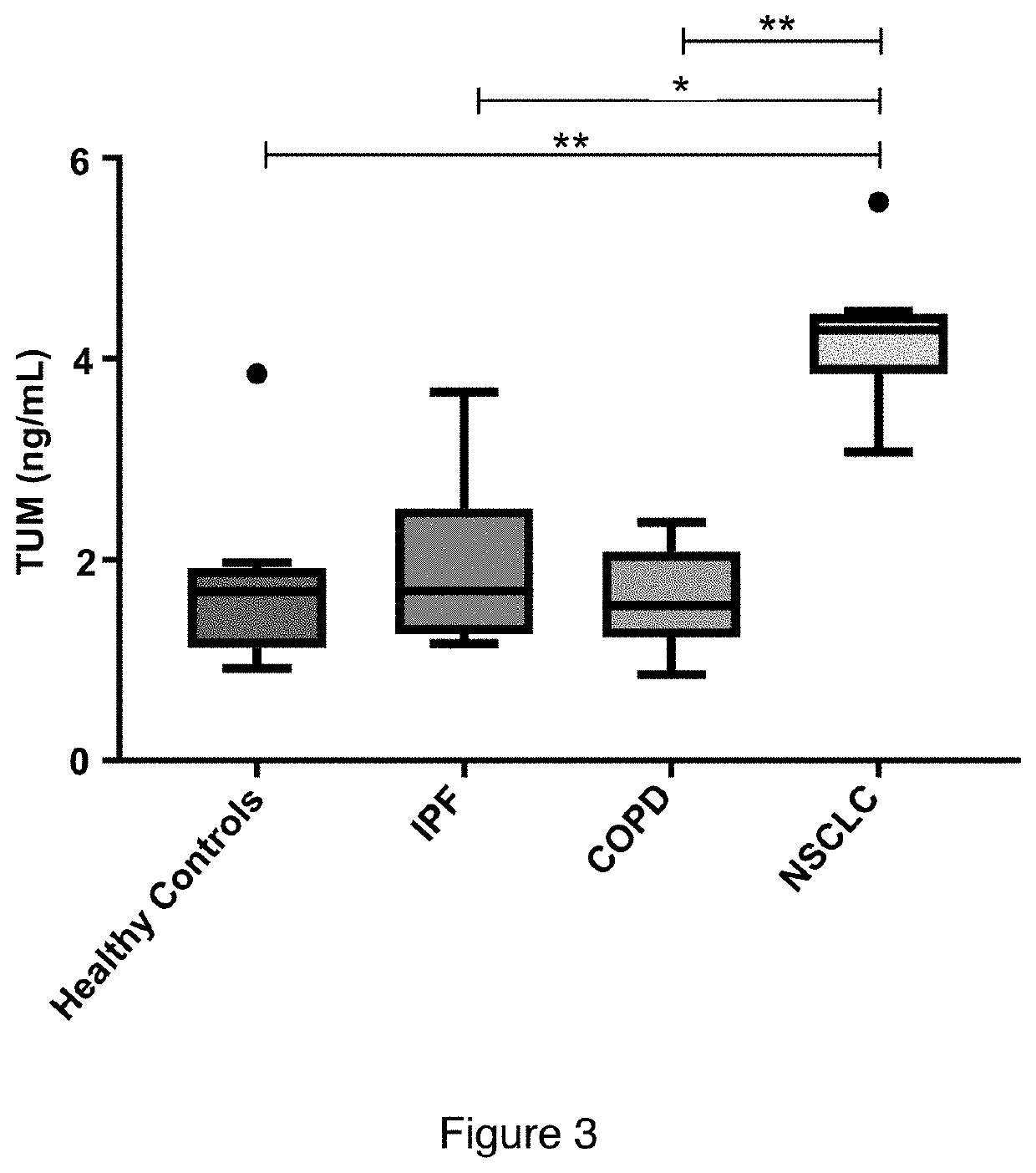
Tumstatin Assay
InactiveUS20200340994A1Excellent diagnostic utilityImprove overall utilizationImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDisease diagnosisNephrosisDiabetes mellitus
The present invention relates to an assay for detecting Tumstatin, and its use in evaluating lung cancers, such as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), chronic kidney disease (CKD), such as CKD resulting from diabetes, lupus nephritis (LN) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Owner:NORDIC BIOSCI
Application of salvianolic acid A in pharmacy
InactiveCN102614164AInhibition of activationOrganic active ingredientsUrinary disorderMesangiumBiological activation
The invention discloses application of salvianolic acid A in pharmacy, and relates to application of salvianolic acid A in terms of preparation of medicines for suppressing activation of renal fibroblasts and intercapillary cells, preparation of medicines for reducing renal fibrosis, preparation of medicines for improving urine protein, preparation of medicines for improving renal functions, preparation of medicines for relieving renal inflammation and collagen deposition and preparation of medicines for relieving related genes and protein of renal fibrosis indexes. A screening platform for activation of renal fibroblasts and intercapillary cells of mice induced by TGF (transforming growth factor)-beta 1 is designed, and experiments show that from 4.94X10-5g / ml to 4.94X10-5g / ml of salvianolic acid A can suppress activation of the renal fibroblasts and intercapillary cells of the mice induced by the TGF-beta 1. A vitro experiment of the salvianolic acid A functioning to the mice in a UUO (unilateral ureteral obstruction) model and a Platt model is further designed and shows that medium-dosage salvianolic acid A (10mg / kg / d) and high-dosage salvianolic acid A (17.1mg / kg / d) can reduce urine protein, renal functions and related genes and protein of renal fibrosis of the mice in the UUO model and the Platt model.
Owner:SHUGUANG HOSPITAL AFFILIATED WITH SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
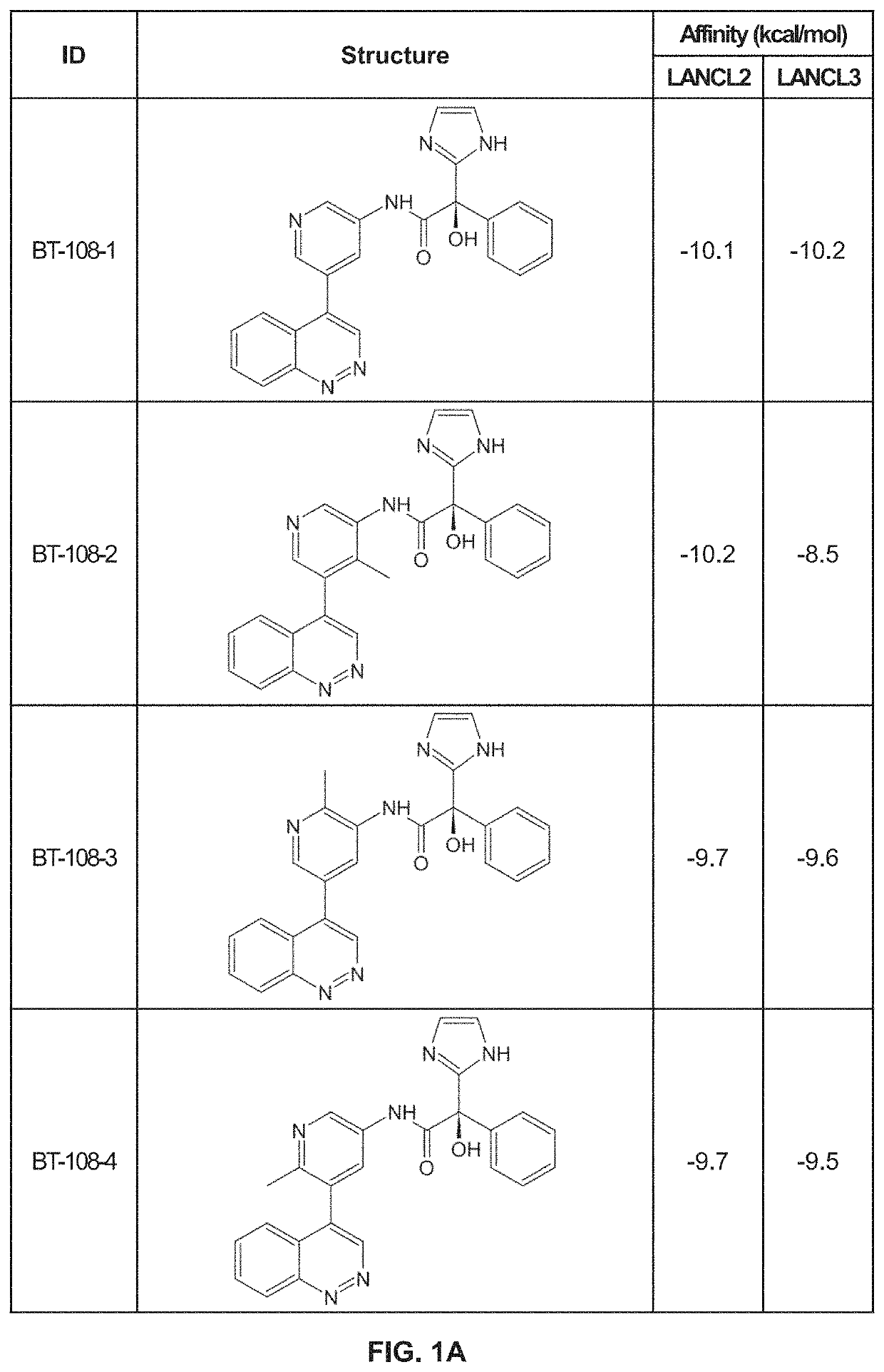
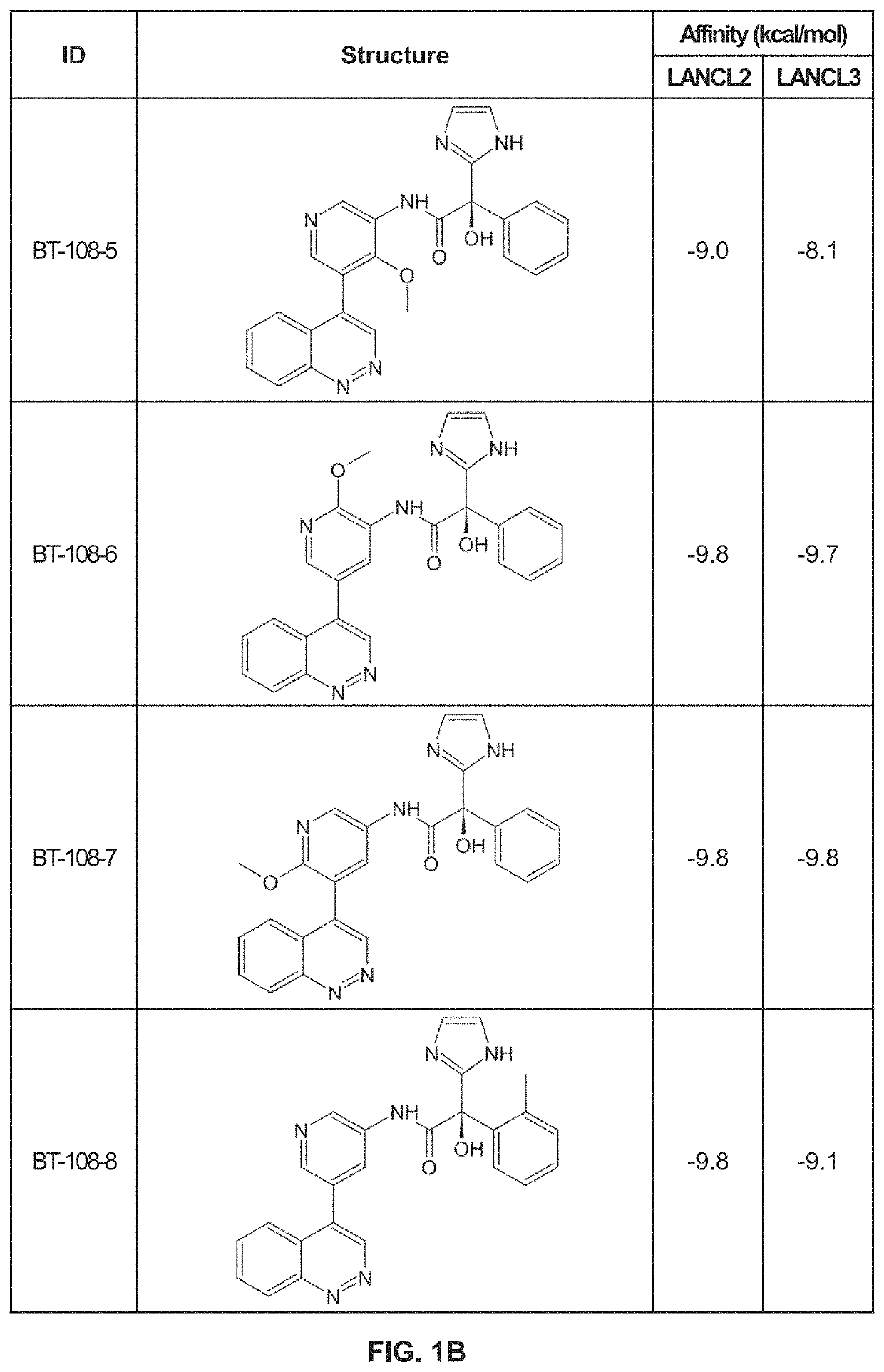
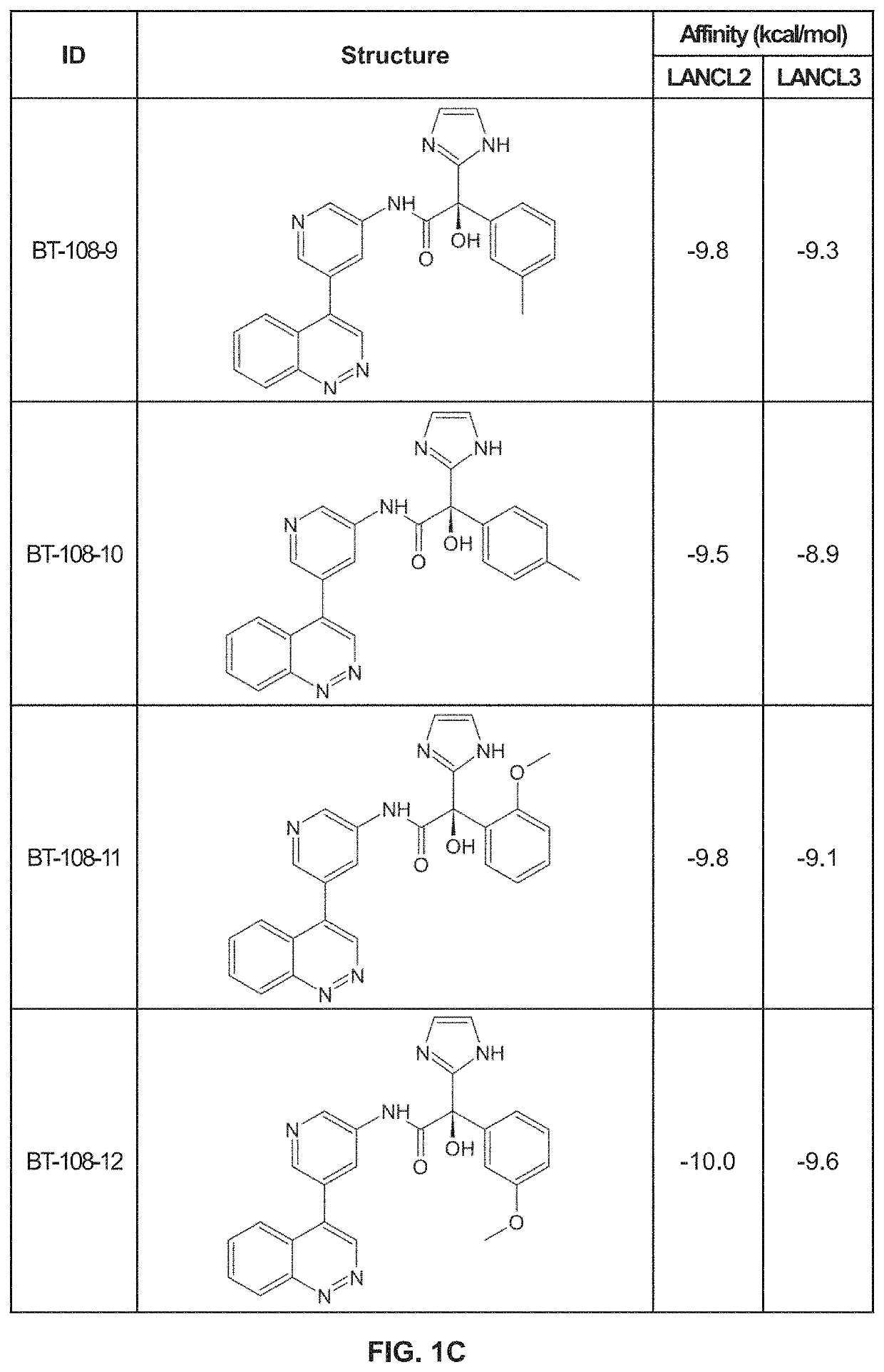
LANCL ligands
Provided are compounds of Formula (I):The compounds target the lanthionine synthetase C-like (LANCL) family of proteins, including LANCL2 and LANCL3. The compounds can be used to treat conditions such as inflammatory diseases, metabolic diseases, autoimmune diseases, cancers, and infectious diseases. Exemplary conditions include inflammatory conditions of the liver, such as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, and cirrhosis; inflammatory conditions of the bile duct, such as primary biliary cholangitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis; inflammatory bowel disease, such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis; lupus, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, lupus nephritis, and cutaneous lupus; arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis; hyperglycemia, such as type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and prediabetes and associated conditions such as atherosclerosis and diabetic kidney disease; psoriasis; and multiple sclerosis.
Owner:NIMMUNE BIOPHARMA INC
Psmp antagonists for use in treatment of fibrotic disease of the lung, kidney or liver
PendingCN113348178AEliminate or reduce riskSmall doseDigestive systemImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsAntiendomysial antibodiesBile Juice
Disclosed are antagonists of PC3-secreted microprotein (PSMP) and use of the antagonists for treatment of liver, lung, or kidney fibrosis, including various diseases or disorders associated with liver, lung, or kidney fibrosis such as, e.g., non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), alcoholic liver disease (ALD), primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), drug-induced lung injury, acute kidney injury (AKI), chronic kidney disease (CKD), lupus nephritis, IgA nephropathy, and membranous glomerulonephritis. Also disclosed are PSMP antagonists and their use for treatment of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Suitable PSMP antagonists for use in disease treatment include PSMP-binding proteins such as, for example, neutralizing anti-PSMP antibodies.
Owner:MAPLE BIOTECH LLC
Use of methyl salicylate glycoside in the preparation of medicines for preventing and/or treating systemic lupus erythematosus and its complications
ActiveCN106924272BReduce depositionEnhance immune functionOrganic active ingredientsSugar food ingredientsInflammatory factorsAutoantibody
The invention discloses the use of a class of methyl salicylate glycoside compounds represented by the general formula (1) and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof in the preparation of medicines for preventing and / or treating systemic lupus erythematosus and its complications. In the present invention, methyl salicylate glycoside has the pharmacological effect of reducing the expression levels of autoantibodies and inflammatory factors in lupus mice and improving immune function; it has the effect of slowing down the pathological process of lupus arthritis; The pharmacological effect of immune complex deposition and improving renal function in lupus mice; it has the effect of protecting spleen function in lupus mice. Methyl salicylate glycosides are monomeric compounds extracted and separated from the traditional Chinese herbal medicine Dianbaizhu, which has the advantages of low toxicity, simple extraction process, and mature synthetic route; its raw material resources are vast, and it is easy to prepare in large quantities. With good application and development prospects, it is an ideal new type of traditional Chinese medicine monomer for the treatment of complications such as systemic lupus erythematosus and its immune dysfunction, lupus arthritis, lupus nephritis, and lupus spleen injury.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Benzimidazole compound and application thereof
InactiveCN103113307AGood effectNovel mechanismNervous disorderOrganic chemistrySide effectAutoimmune disease
The invention belongs to the technical field of bio-pharmaceuticals, and provides application of a benzimidazole compound serving as an immunosuppressor in preparation of medicines for treating autoimmune diseases in the presence of T cells, such as inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus and autoimmunenephritis. A series of novel compounds synthesized by the benzimidazole compound have the advantages of being remarkable in efficacy, novel in mechanism, effective in oral taking, and less in toxic and side effects; and compared with a conventional medicine, the benzimidazole compound is remarkably advantaged in simple synthesis route and environment-friendly.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
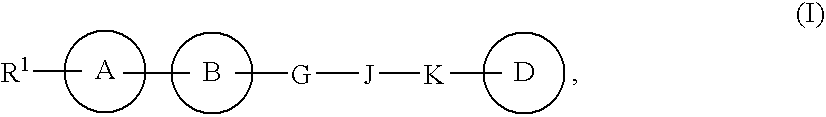
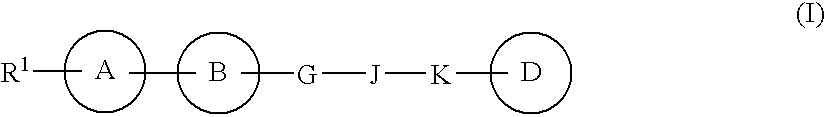






![5-[6-[[3-(4,5,6,7-tetrahydropyrazolo[4,3-c]pyridin-1-yl)azetidin-1-yl]methyl]morpholin-4-yl]quinoline-8-carbonitrile derivatives and similar compounds as tlr7-9 antagonists for treating systemic lupus erythematosus 5-[6-[[3-(4,5,6,7-tetrahydropyrazolo[4,3-c]pyridin-1-yl)azetidin-1-yl]methyl]morpholin-4-yl]quinoline-8-carbonitrile derivatives and similar compounds as tlr7-9 antagonists for treating systemic lupus erythematosus](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/fa223728-1abb-4f68-8b4d-817cd7a5a72d/US20210300924A1-C00001.png)
![5-[6-[[3-(4,5,6,7-tetrahydropyrazolo[4,3-c]pyridin-1-yl)azetidin-1-yl]methyl]morpholin-4-yl]quinoline-8-carbonitrile derivatives and similar compounds as tlr7-9 antagonists for treating systemic lupus erythematosus 5-[6-[[3-(4,5,6,7-tetrahydropyrazolo[4,3-c]pyridin-1-yl)azetidin-1-yl]methyl]morpholin-4-yl]quinoline-8-carbonitrile derivatives and similar compounds as tlr7-9 antagonists for treating systemic lupus erythematosus](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/fa223728-1abb-4f68-8b4d-817cd7a5a72d/US20210300924A1-C00002.png)
![5-[6-[[3-(4,5,6,7-tetrahydropyrazolo[4,3-c]pyridin-1-yl)azetidin-1-yl]methyl]morpholin-4-yl]quinoline-8-carbonitrile derivatives and similar compounds as tlr7-9 antagonists for treating systemic lupus erythematosus 5-[6-[[3-(4,5,6,7-tetrahydropyrazolo[4,3-c]pyridin-1-yl)azetidin-1-yl]methyl]morpholin-4-yl]quinoline-8-carbonitrile derivatives and similar compounds as tlr7-9 antagonists for treating systemic lupus erythematosus](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/fa223728-1abb-4f68-8b4d-817cd7a5a72d/US20210300924A1-C00003.png)