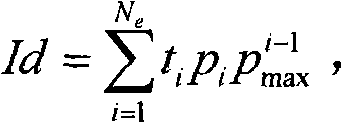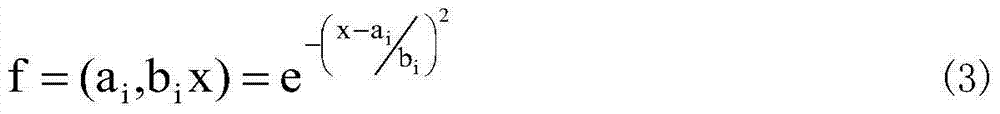Patents
Literature
51 results about "Species group" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A species group is an informal taxonomic rank into which an assemblage of species within a genus are grouped because of their morphological similarities. Different definitions exist. Some authors use the term for species that share a geographic range and cannot interbreed. Others use the term for a group of related species with separate geographic ranges that might interbreed if opportunity arises. Others use the term for a group that has not yet been sufficiently studied, which might or might not have a monophyletic origin.
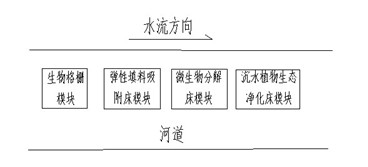
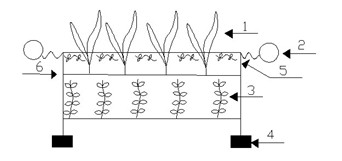
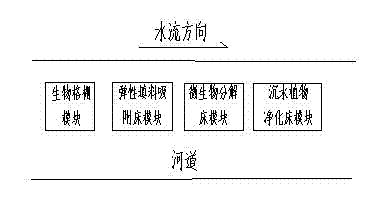
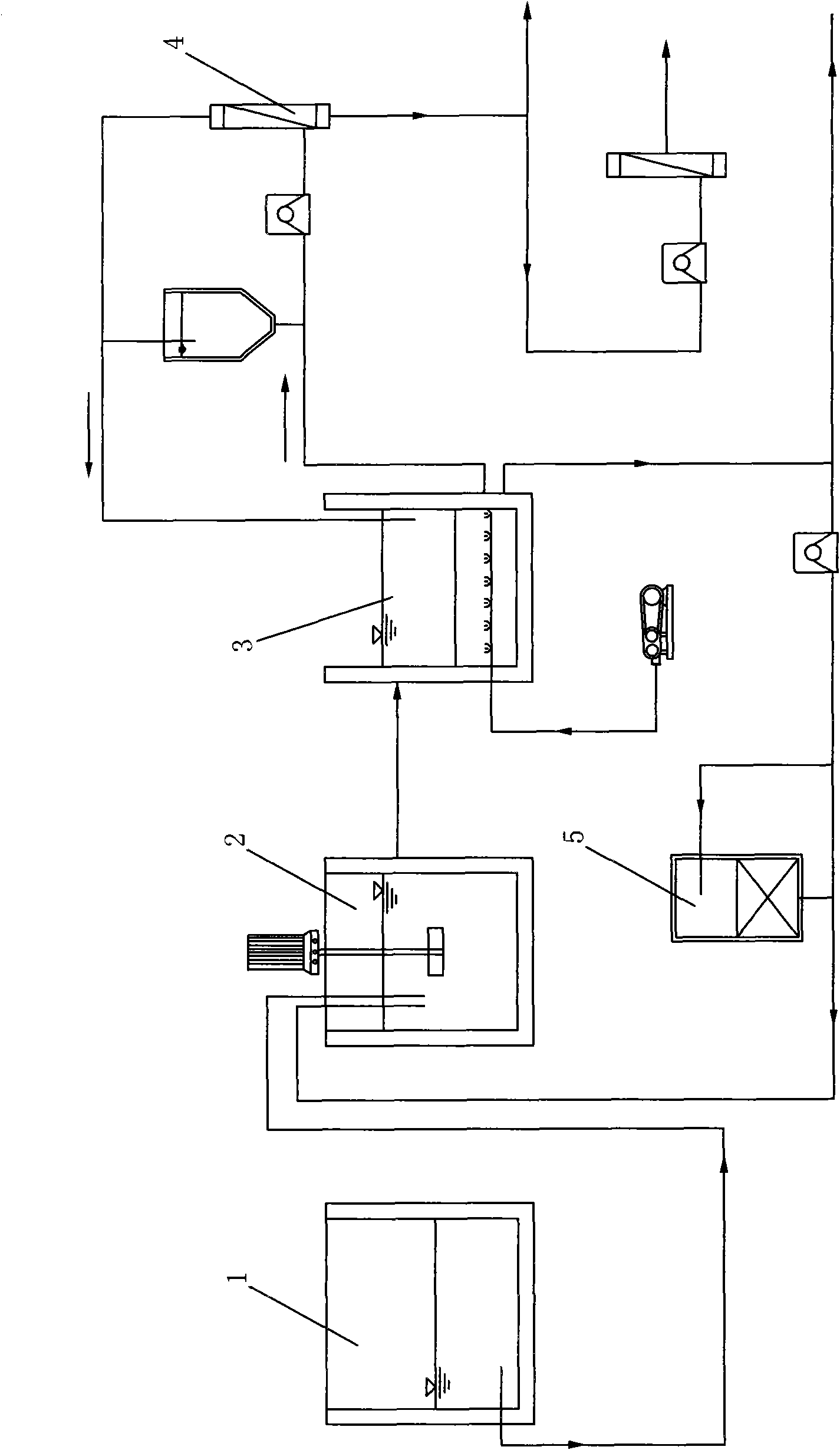
Modular system for purification of polluted river water body and application of the same
InactiveCN102219339AReduce pollution loadEffective interceptionMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by sorptionGratingDecomposition
The invention belongs to the technical field of treatment of environment pollution, and more specifically relates to a modular system for purification of a polluted river water body and application of the same. The modular system mainly comprises a biological grating module, an elastic filling material adsorption bed module, a microbial ecological decomposition suspending bed module and a sunken plant ecological purification suspending bed module. The biological grating module is composed of a framework, sunken plants, floating plants and emerged plants; the elastic filling material module consists of a framework structure, hydrophilic elastic filling materials and hydrophobic elastic filling materials; the microbial bed module comprises a framework structure, a micropore aeration mechanism and microbes; and the sunken plant purification bed module is composed of the species group of sunken plants and a bed body. According to the invention, the position of the polluted river water purification modules in a water body can be adjusted according to pollution degrees of the water body; the modular system can effectively purify water quality of a polluted river water body and a black and odorous river water body and reduce river pollution load; therefore, the invention is of significance for purification of river water bodies.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
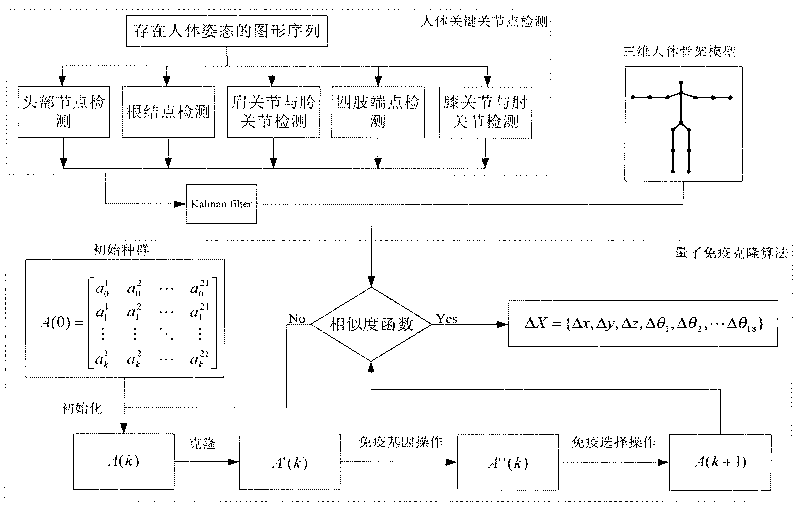
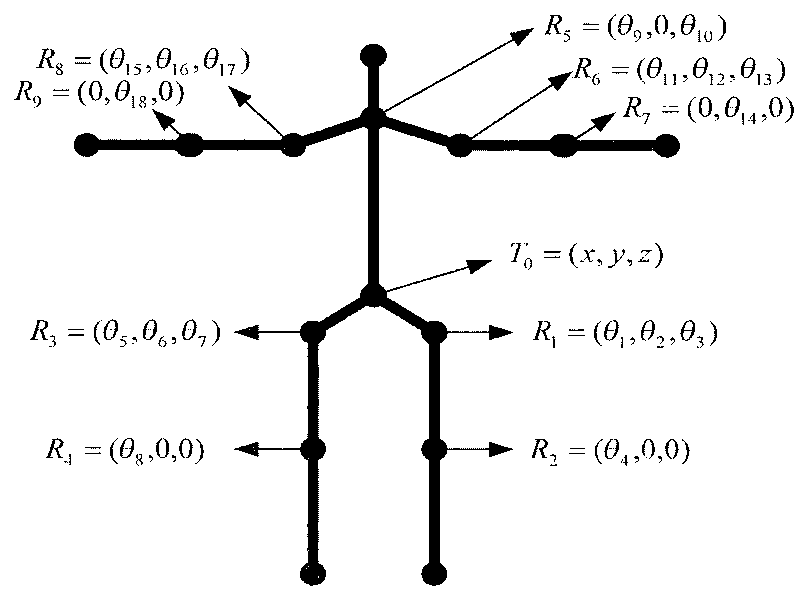
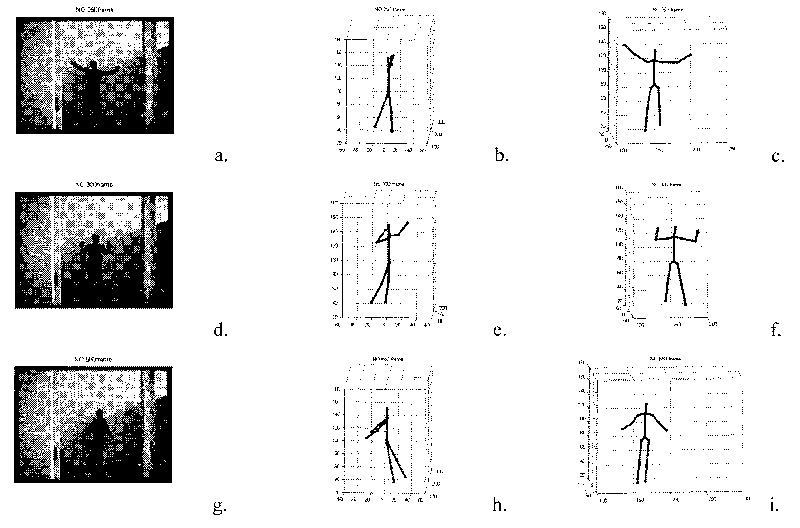
Three-dimensional human body motion tracking method based on quantum immune clone algorithm
InactiveCN101692284AReasonable and stable movementRealize dynamic posture adjustmentImage analysisGenetic modelsHuman bodyState parameter
The invention discloses a three-dimensional human body motion tracking method based on quantum immune clone algorithm. The tracking process comprises: detecting articulation points of the human body in a two dimension picture in a unary picture sequence with human body gesture existing, using a kalman filter to predict the articulation points not detected, and simultaneously establishing a three-dimensional human body model; applying quantum immune clone algorithm in human body tracking, initializing species group, setting initial parameters of human body motion, then carrying out clone operation, performing operation of immunizing genes and immunoselection to generate a new species group; substituting the state parameters of the new species group in the three-dimensional human body model, using likelihood function to calculate the distance affinity, retaining the optimal solution, performing multiple times of substitution and calculation to obtain the ideal human body motion parameters to restore the three-dimensional human body gesture. The invention has the advantages of lower calculation cost and capable of obtaining three-dimensional human body gesture quickly, and is applicable to tracking of human body motion gesture in scene monitoring, motion analysis and health assessment.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
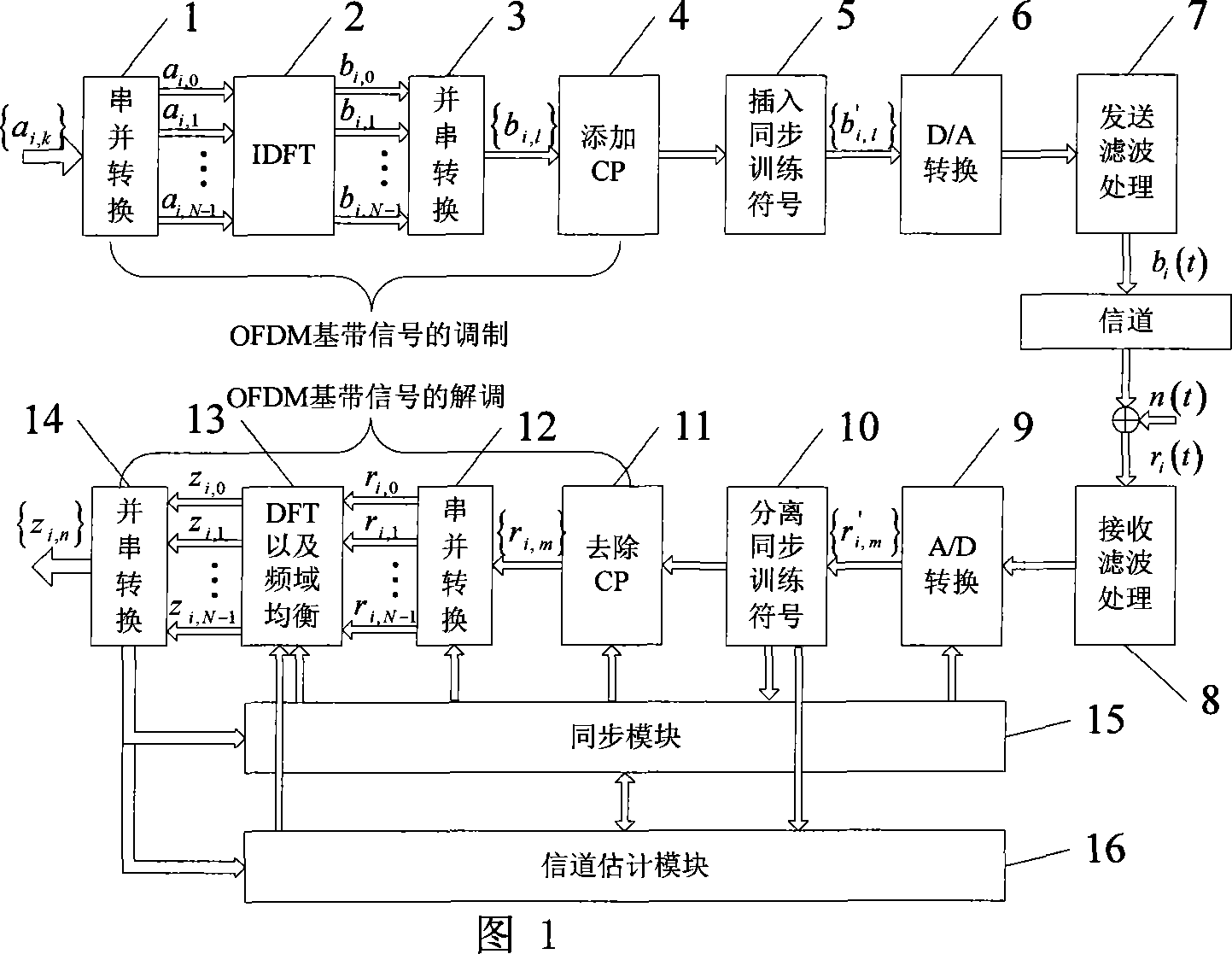
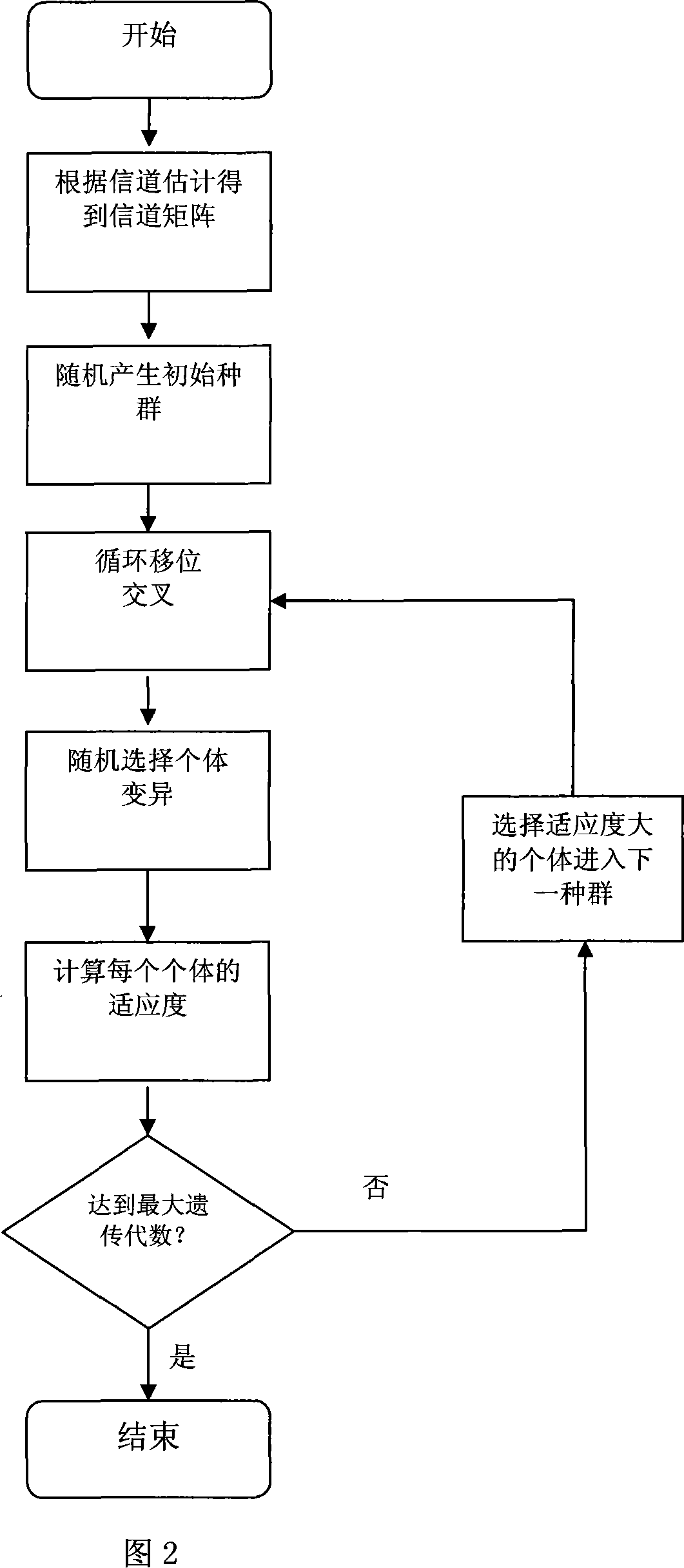
OFDM sub-carrier allocation method based on generic algorithm
InactiveCN101146079AImprove performanceIncrease the speed of genetic evolutionMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksWireless transmissionCarrier signal
The invention provides an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system subcarrier allocation method based on SGA in wireless transmission technology field. Firstly, the invention obtains channel status information of each user on different subcarriers, according to channel estimation; and then, transfers SGA for optimum subcarrier allocation; wherein the SGA adopts integer coding and cyclic shift scissor to improve search capability; after fitness function computation of species group with generic variation each time, continues to judge whether the algorithm should stop, according to the termination condition and obtains the subcarrier allocation proposal. Compared with prior art, the invention improves system performance greatly and the advanced SGA in the invention has faster velocity of convergence, compared with the traditional SGA.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Dynamic flight path planning method based on adaptive mutation genetic algorithm
The invention discloses a dynamic flight path planning method based on adaptive mutation genetic algorithm, comprising the steps of: generating an initial species group at random and calculating the degree of adaptability thereof; counting feasible solutions E(t) in the species group and performing elite preservation operation; performing intersection, mutation, insertion and deleting operations on non-feasible solutions S(t); calculating the degree of adaptability of a transitional species group composed of the operated E(t) and S(t); obtaining individuals and the feasible solutions generated at random in the individuals by E(t) single point random mutation in order to replace the non-feasible solutions in the transitional species group; judging whether the evolution reaches the extent that an algebra selected according to the complexity of problem or the species group is converged; and if so, taking the optimal invividual in the species group as the planned flight path. The method of the invention can improve the variety and convergence capacity of the species groups; a feasible solution path can be provided for the problem of time-varying dynamic optimization for the dynamic flight path planning.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Chemical procedure modelling approach possessing reconstructed operation RNA genetic algorithm
InactiveCN101339628AImprove the disadvantages of premature convergenceIncrease diversityGenetic modelsMathematical modelSpecies groups
The invention discloses a chemical engineering process modeling method of an RNA genetic algorithm with remodeling operation, which has the following steps: 1) actual input and output sampling data is obtained by on-site operation or experiment, and then the sum of the absolute value of the error between the estimated output and the actual output of a chemical engineering process model is used as the objective function of the RNA genetic algorithm for optimization research; 2) algorithm control parameters is set; 3) the RNA genetic algorithm with remodeling operation is operated to do estimation for the unknown parameters of the chemical engineering process model, then the estimated value of the unknown parameters of the chemical engineering process model is obtained by the minimized objective function, and the estimated value of the unknown parameters is substituted into the chemical engineering process model to form a mathematical model of the chemical engineering process. The excellent genes of original species group is preserved when the diversity of the species group is increased effectively, thereby avoiding the defects of the premature convergence of traditional genetic algorithm and the convergence of locally optimal solution better.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Metagenome data analysis method based on next-generation sequencing technology
PendingCN112071366ASolve incomplete problemsThe analysis process is reasonableCharacter and pattern recognitionHybridisationGenomicsContig
The invention discloses a metagenome data analysis method based on a next-generation sequencing technology, which comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out quality control on original sequencing data to obtain clean reads; (2) performing species annotation on the clean reads subjected to the quality control; (3) performing statistical analysis on the sample diversity based on a species abundance matrix; (4) performing statistical analysis on species with significant differences among sample groups based on the species abundance matrix; (5) splicing and assembling the clean reads to obtain a contigs sequence; (6) packaging the contigs obtained by splicing and assembling into boxes to obtain bins; (7) carrying out gene annotation on the bins subjected to boxing; (8) performing statistical analysis on the genes with significant differences among the sample groups based on the gene abundance matrix; and (9) based on the gene annotation result, performing function and species annotation on the sequence. A whole process from metagenome next-generation sequencing data processing to species composition analysis, gene composition analysis and function annotation is provided, an accurate analysis result is provided for researchers, and the metagenomics problem is comprehensively analyzed.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
A dynamic channel allocation method based on generic algorithm
InactiveCN101262701ADiversity/multi-antenna systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNonlinear methodsDynamic channel
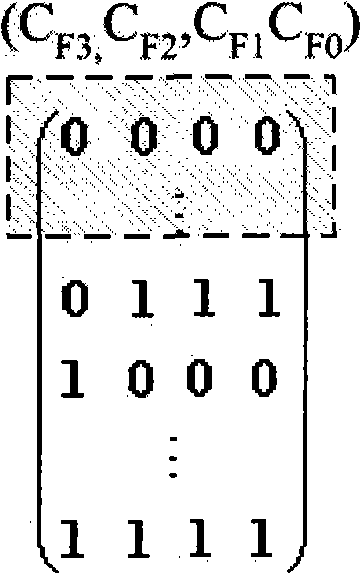
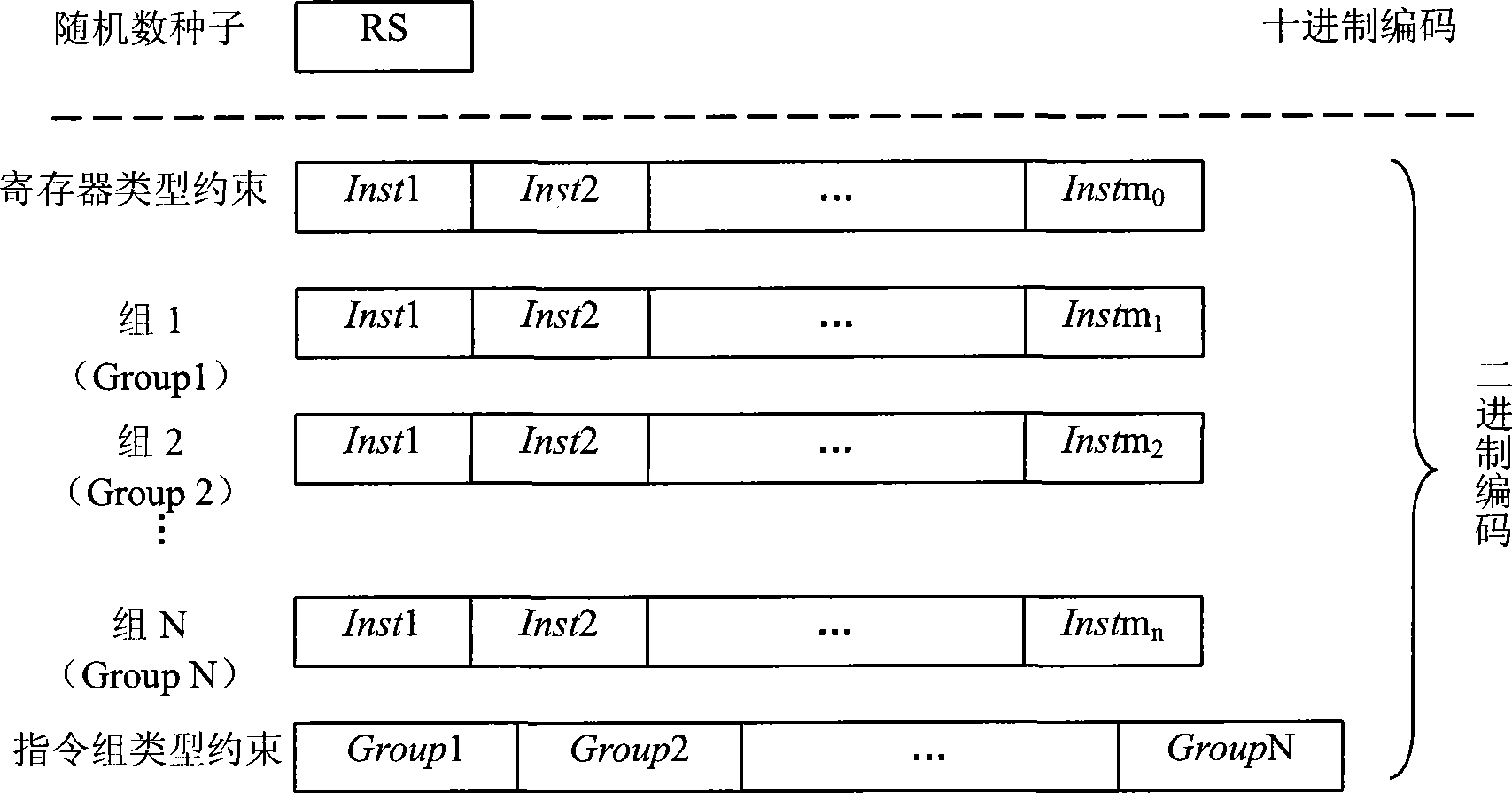
The invention uses genetic algorithms to realize dynamic channel allocation (DMA). By contrast, a nonlinear method is more suitable for nonlinear characteristics of the reality and for parallel arithmetic, can be flexibly transferred to fit various wireless channel allocation technologies; the invention is additionally characterized that channel performance is collectively estimated and channel resources are equally distributed so as to comparatively improve the comprehensive utilization ratio of the channel resource. The invention adopts carrier frequency, time slot, spread spectrum codes and the angle of wave beam as genomes to realize chromosome coding; the operating procedure is that a sliding window is used for filtering a species group to form a vector X which equals (CF3, C, F2, CF1, CF0, TS2, TS1, TS0, SF3 ,SF2, SF1, SF0, BS2, BS1, BS0), and then the genetic algorithms, such as hybridization, variation, etc., are selected to realize the dynamic allocation and optimization of the channel.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method and system for driving accidental validation integrated circuit by coverage rate
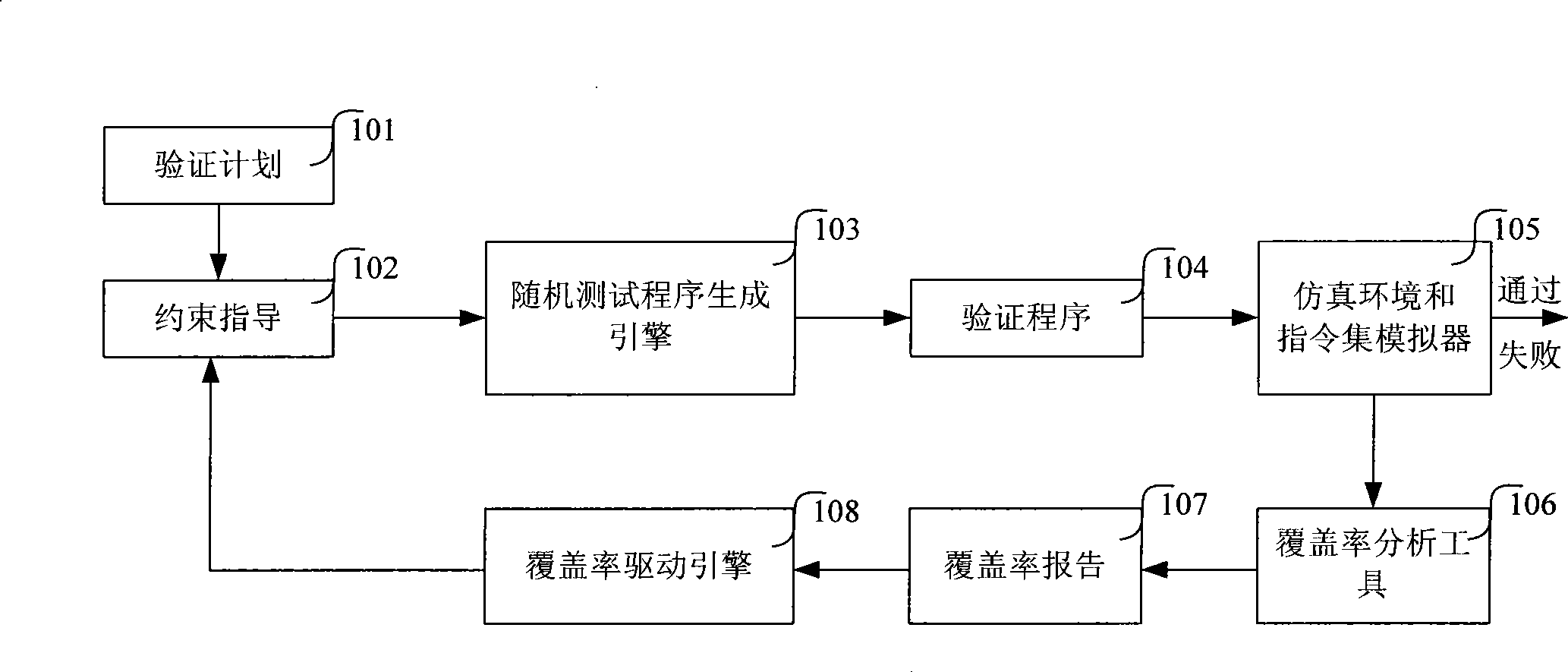
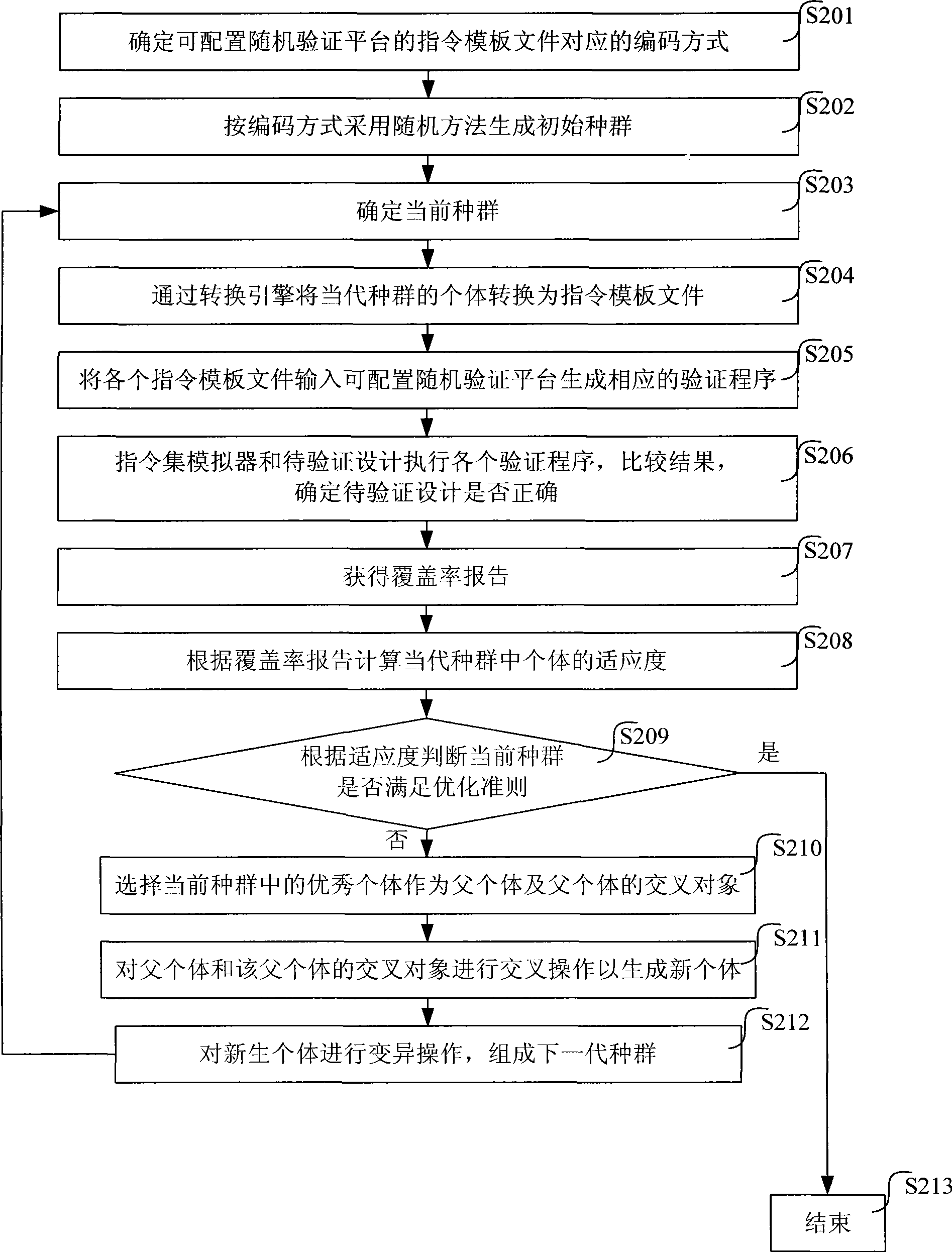
ActiveCN101488160AFast searchIncrease coverageGenetic modelsSpecial data processing applicationsRelationship - FatherSpecies groups
The invention relates to a method and a system of a coverage-driven random verification of an integrated circuit; the method comprises the following steps: step 1, an initial species group is generated, and the current species group is initialized as the initial species group; step 2, a verifying procedure is generated according to the current species group, and the verifying procedure is executed by an instruction set simulator and a to-be-verified design, whether the to-be-verified design is accurate is determined by comparing two executing results, and a coverage rate report is obtained at the same time; step 3, individual adaptability of the current species group is calculated according to the coverage rate report, and whether the current species group meets optimization criteria is judged according to the adaptability, if yes, the verification is finished, if not, the step four is executed; step 4, an excellent individual in the current species group is chose as a father individual according to the adaptability, and an intersect object of the father individual is chose for carrying out intersection operation to generate a new individual which is composed of a next species group, and the current species group is updated into the next species group, and the step 2 is carried out. The method and the system can automatically optimize the verifying procedure.
Owner:LOONGSON TECH CORP
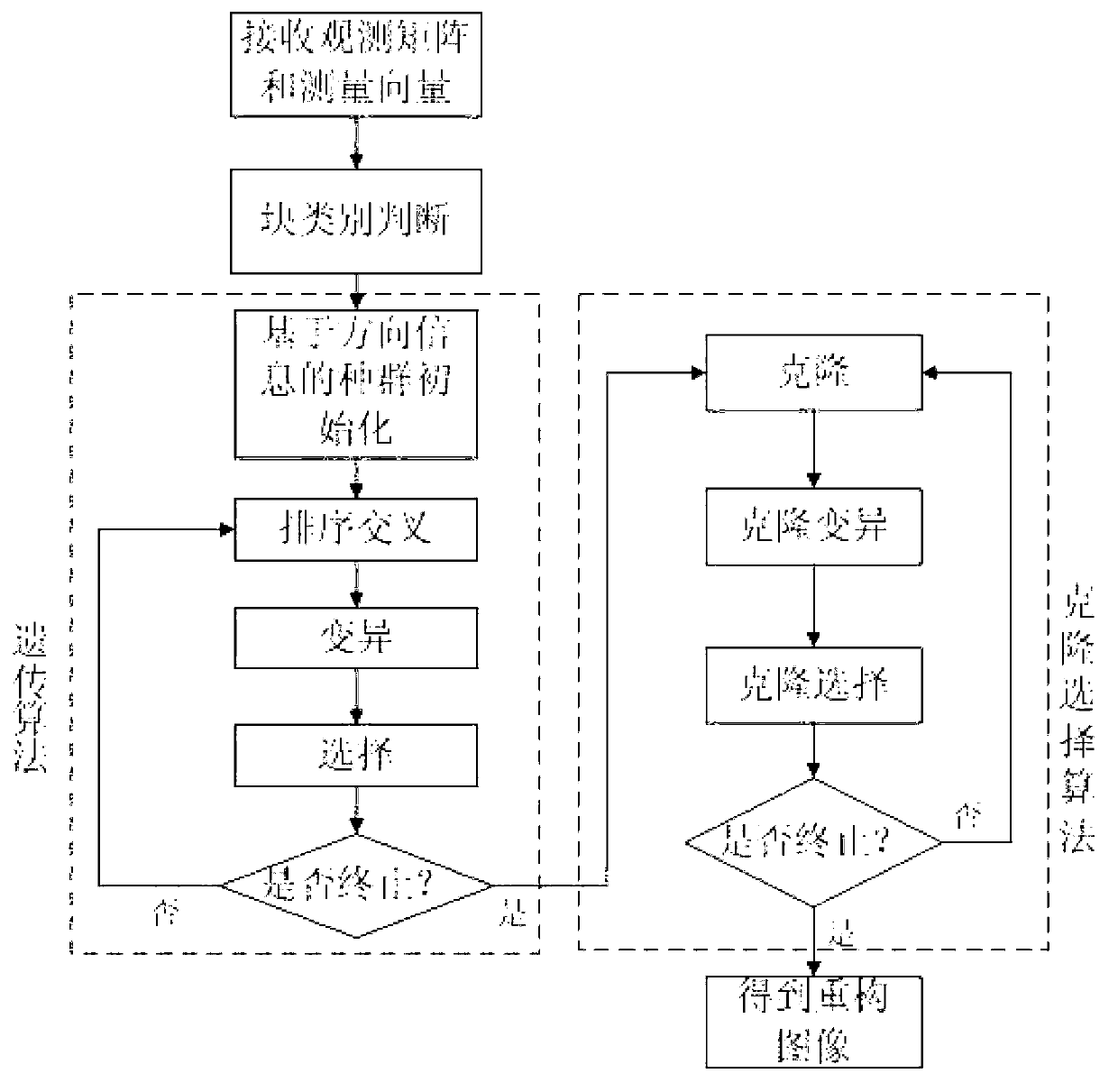
Compressed sensing image reconstruction method based on principal component analysis (PCA) redundant dictionary and direction information
ActiveCN103198500AQuality improvementGood image reconstructionImage enhancement2D-image generationPrincipal component analysisReconstruction method
The invention discloses a compressed sensing image reconstruction method based on a principal component analysis (PCA) redundant dictionary and direction information. The compressed sensing image reconstruction method based on the PCA redundant dictionary and the direction information mainly solves the problem that in an existing compressed sensing reconstruction method OMP, a reconstructed image under a blocking compressed sensing framework has blocking effect and fuzzy texture. The compressed sensing image reconstruction method based on the PCA redundant dictionary and the direction information comprises the following steps: constructing the PCA redundant dictionary; receiving measurement matrixes and blocking measurement vector quantities, and judging category of an image block to be reconstructed according to each blocking measurement vector quantity; designing a species group initialization scheme and a sequencing cross operator based on the direction information on each image block to be reconstructed, and using a genetic algorithm and a clone selection algorithm to achieve reconstruction of each image block under the PCA redundant dictionary. Compared with an OMP method, the compressed sensing image reconstruction method based on the PCA redundant dictionary and the direction information has the advantages of being capable of seeking an optimum sparse representation of each image block from the overall situation under the PCA redundant dictionary, clear in texture and edge of the reconstructed image, and capable of being used for acquiring a high quality image in the process of reconstructing images under the blocking compressed sensing framework.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
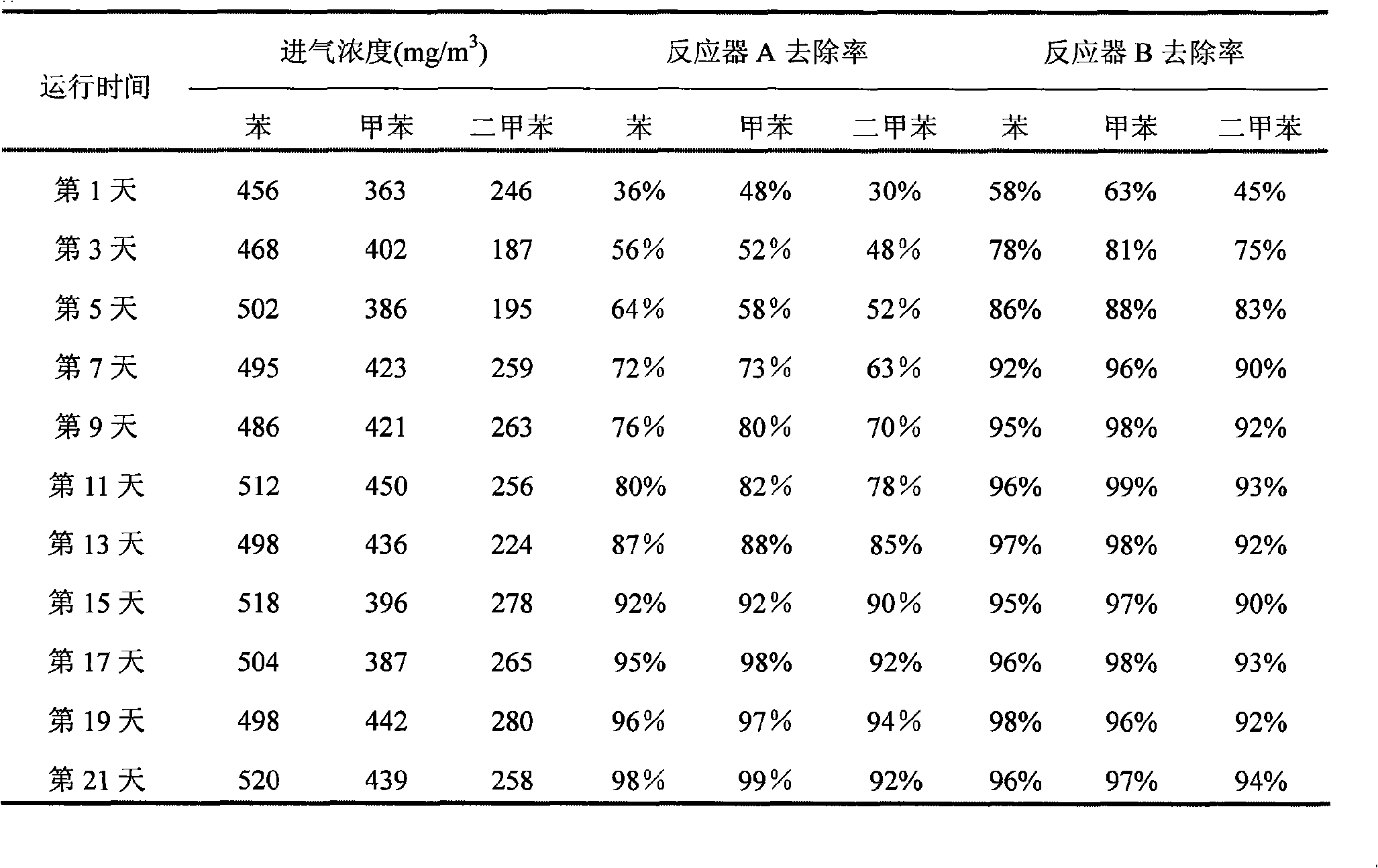
Method for preparing compound microbial preparation for degrading í«three-benzeneí» VOCs exhaust air
InactiveCN101327405ARich populationReasonable community structureMicroorganismsDispersed particle separationSludgeEngineering
The present invention discloses a method for producing the compound micro-organism microbial inoculum that is used for degrading the waste gas of VOCs. Firstly, culture medium containing the triphenyl substance is adopted to naturalize the active mud that is taken from a sewage treatment plant; the active dirt that is obtained in the domestication way and has high degrading performance is used as the mixed strain to be inoculated to the microbial inoculum carrying material, and the compound micro-organism microbial inoculum can be obtained after the solid fermentation culture. The preparing method comprises the steps of domestication of the active mud, mixing of the microbial inoculum carrying material at a giving ratio and the solid fermentation culture, so that the preparing method is simple, and the cost is low, and the advantages that the species group of the active mud mixture micro-organism is rich, the bacteria group structure is reasonable, and the microbial inoculum favors the long-term storage are effectively combined. Since the preparing method is used for preparing the target pollutant, the domestication time in the actual application of the waste-gas organism treatment can be shortened, and the rapid startup of the reaction device can be accelerated. The active mud rapid-startup waste-gas organism purification reactor can be substituted, so as to realize the high-efficient degrading of the target pollutant.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
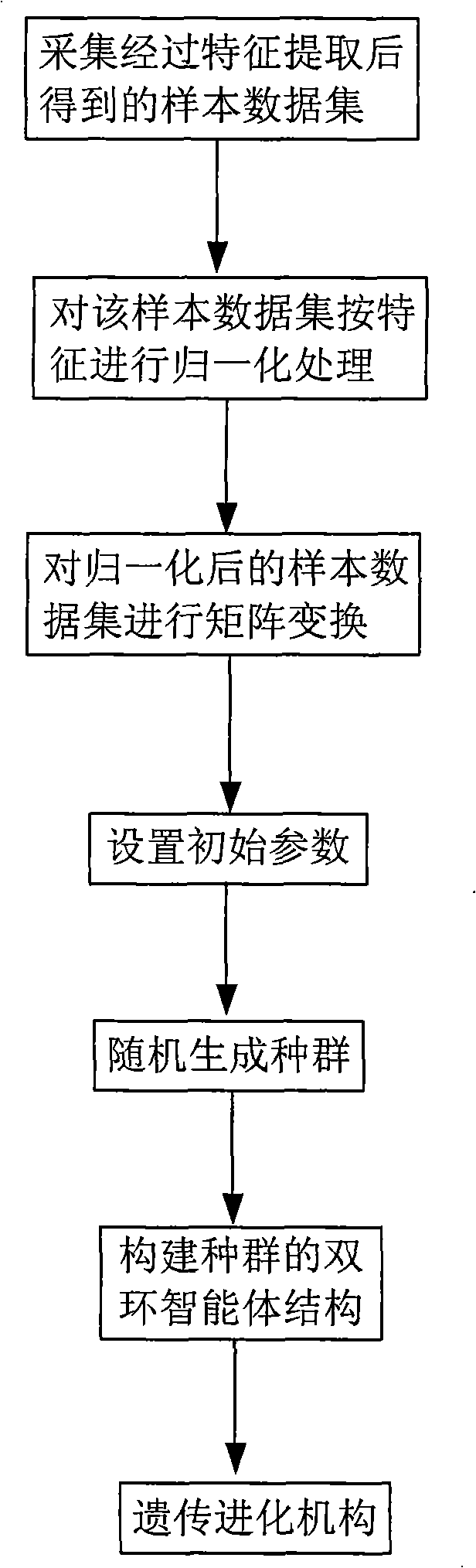
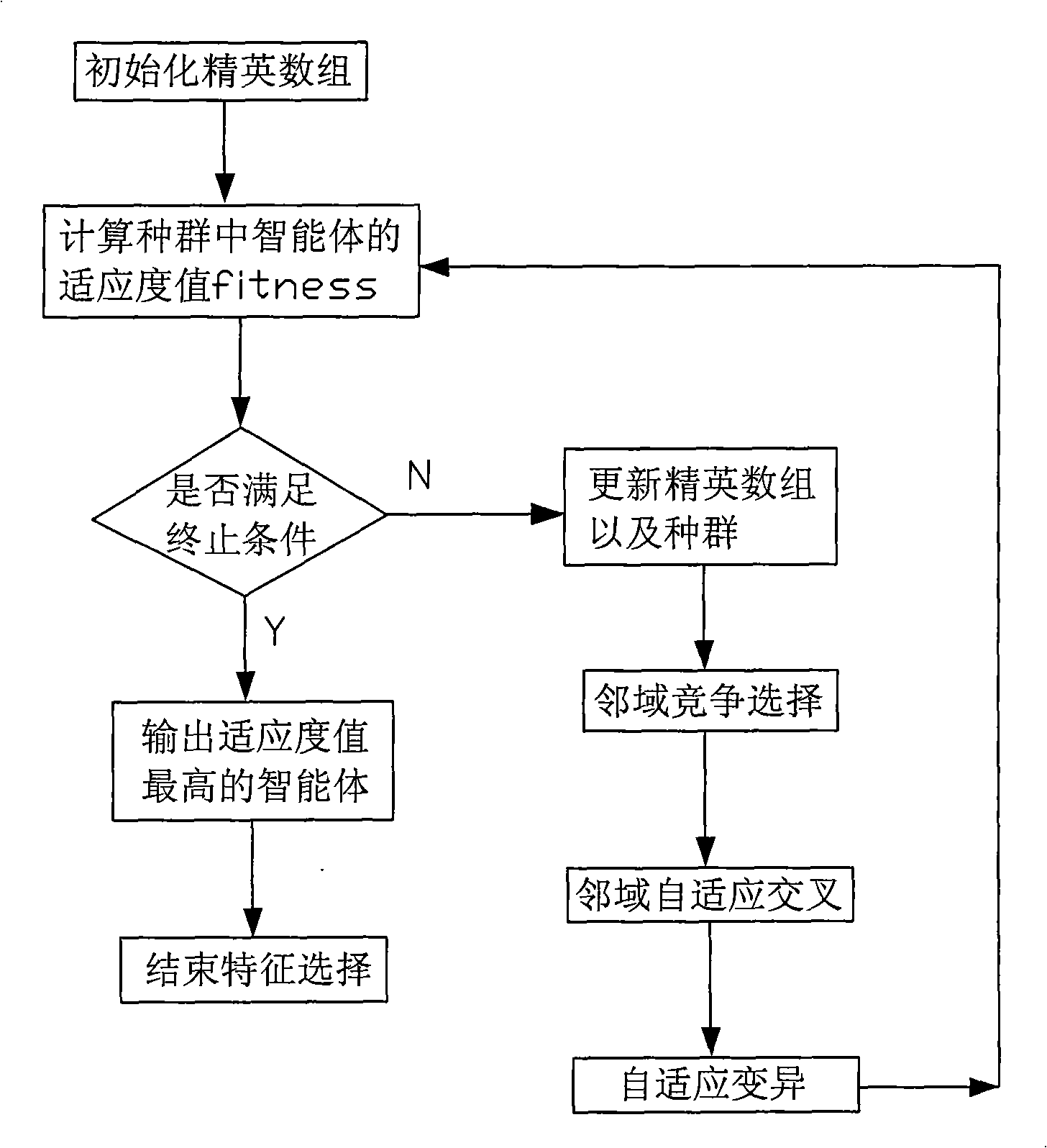
Method for selecting characteristic facing to complicated mode classification
InactiveCN101324926AFast convergenceImprove search efficiencyGenetic modelsCharacter and pattern recognitionCharacteristic spaceSpecies groups
The invention provides a feature selection method for complex pattern classification. On the basis of the traditional genetic method, the method allows a species group to be divided into a plurality of sub-species groups by improving the structure of the species group into a dicyclic intelligent agent network configuration. Information is passed among the sub-species groups through the sharing intelligent agent. The genetic evolution of all sub-species groups is conducted simultaneously. The improved dynamic neighborhood competitive operation and the neighborhood adaptive crossover operating method improve the efficiency of the genetic evolution. At the same time, binary coding mode is introduced to express whether a certain feature is selected or not, thereby facilitating coding and decoding, and achieving the high efficient feature selection. Compared with the traditional feature selection, the feature selection method has the advantages of higher adaptability, and quick search in feature space with high dimension and multimodal, thereby effectively avoiding being trapped in local extremum and acquiring relatively satisfied feature selection results.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
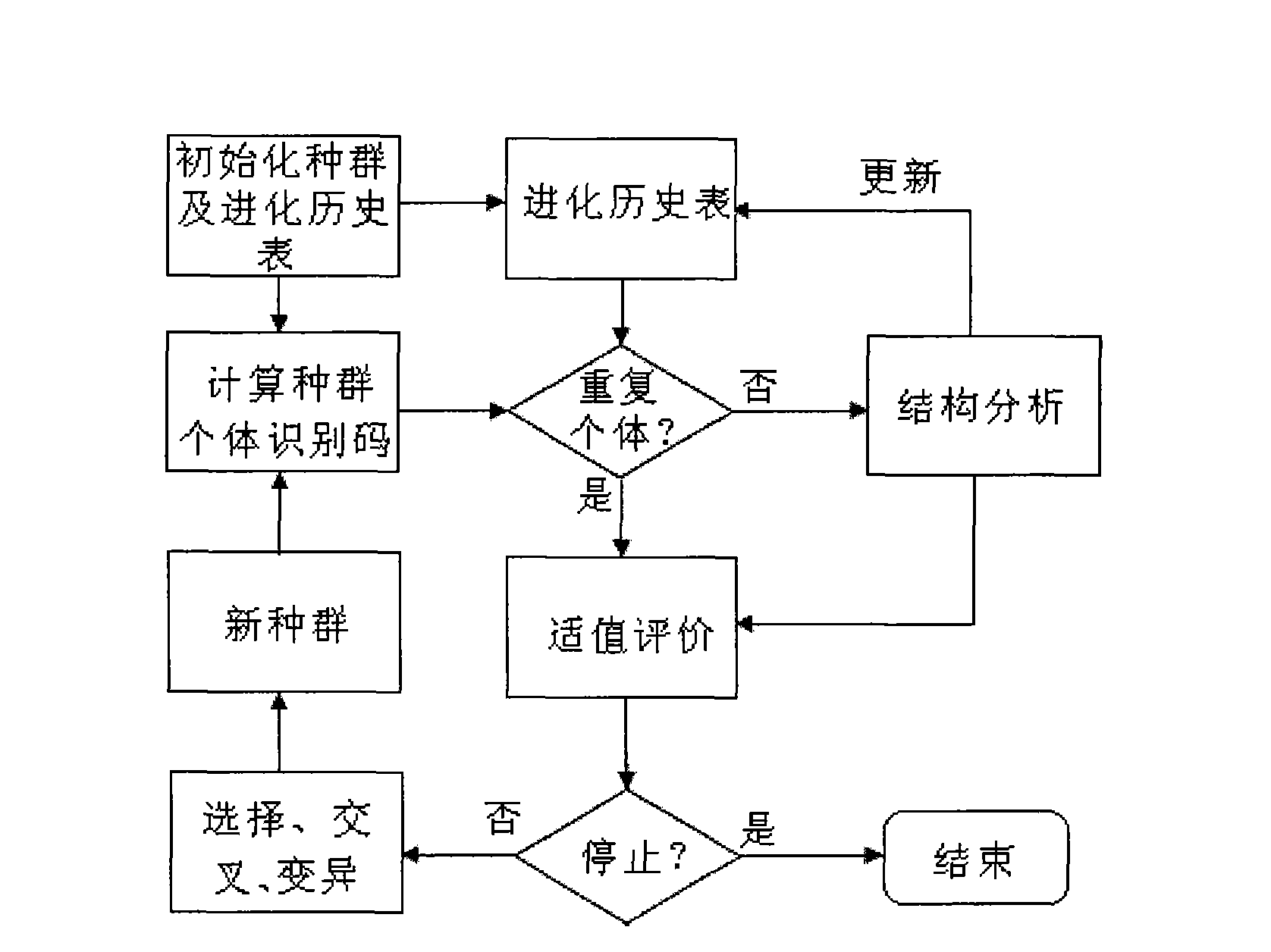
Method for improving genetic algorithm structural optimization efficiency
InactiveCN101582130AImprove computing efficiencySmall amount of calculationGenetic modelsGenetic algorithmFinite element method
The invention relates to a method for improving genetic algorithm structural optimization efficiency, namely a method introducing individual identification codes, comprising the following steps: initializing a species group and an evolutionary history list; calculating the individual identification codes of the current species group; judging whether the individual is an overlapping individual according to the individual identification code; analyzing the structure of the new individual by means of finite element method; updating the evolutionary history list; evaluating the fitness of the overlapping individuals and the new individuals undergoing structural analysis and obtaining corresponding fitness; judging whether the algorithm is finished, if no, obtaining a new species group by carrying out selection, intersection and variation on the species group, and turning to the start step to operate circularly. The invention adopts the individual identification method to solely mark a chromosome with an identification code, thus avoiding the structural analysis of overlapping individuals, decreasing the amount of calculation effectively, improving the calculating efficiency of genetic algorithm structural optimization. The invention can be widely applied to optimization problems in various fields of discrete structures based on genetic algorithm.
Owner:WUXI RES INST OF APPLIED TECH TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Industrial process modeling forecasting method oriented at flow object
InactiveCN104732067AImplement automatic filteringReduce restrictionsSpecial data processing applicationsData warehouseData set
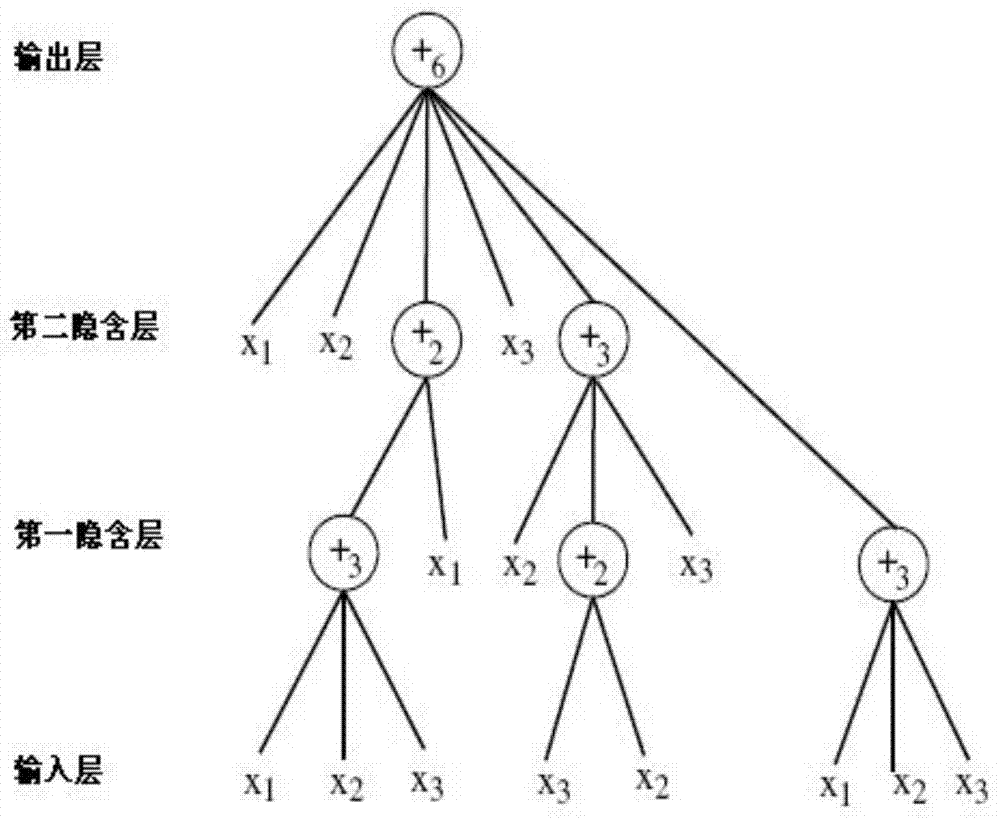
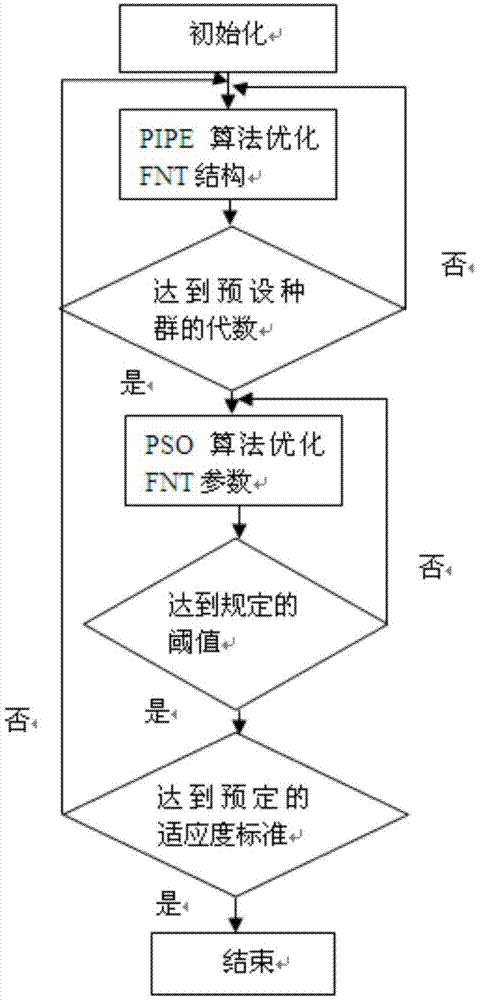
The invention discloses an industrial process modeling forecasting method oriented at a flow object. The method comprises the following steps: building FNT models, extracting an industrial flow object original data set S from a data warehouse which has already been generated by the flow object, creating an initial species group of the FNT models, and customizing the individual numbers of the species group as required, wherein each individual represents an FNT model; utilizing the PIPE algorithm for optimizing FNT model structures, and adopting mean square errors or root-mean-square errors for fitness functions; utilizing the particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm for optimizing FNT model parameters; utilizing the FNT models for conducting modeling forecast for a flow object production process. According to the method, based on the flexible neural tree, an equation of variation tendency among measuring point data of the flow object is obtained, the industrial production process is simulated, based on relevant parameters of a current production state, production states in a period of time in the future are forecast, so that an enterprise is assisted and instructed for adjusting the production process parameters, and the production is guided for drawing on advantages and avoiding disadvantages in a microcosmic sense.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Screening method for species group with heterosis of germany mirror carp
InactiveCN101403006AScreening results are accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrosatelliteCyprinus
The invention relates to a screening method of dominant hybridization species of German mirror carps and discloses a screening method of the dominant hybridization species of carps. The invention provides an effective screening method of the dominant hybridization species of the German mirror carps so as to ensure the genetic diversity of hybrids thereof, thus reducing the workloads, shortening the breeding period, decreasing the breeding cost and improving the success rate of selective breeding. The screening method includes the following steps: 1. morphological marker; 2. microsatellite molecular maker; and 3. data analysis. The method screens the dominant hybridization species of the German mirror carps by combining the morphological marker and the microsatellite molecular marker. The genetic differences between the species are dually tested and the screening results are more accurate.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG RIVER FISHERY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF FISHERIES SCI
Polymorphism micro-satellite DNA molecular marker for deer and application of polymorphism micro-satellite DNA molecular marker
ActiveCN107164468AClear bandHigh polymorphismMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic diversityGenetics
The invention relates to a micro-satellite DNA molecular marker for cervine animals. The molecular markers can be used for identifying allelic polymorphism, identify same or related cervine animals, distinguish the cervine animals and research the genetic diversity of the species group. The molecular marker can also be used for the genetic and phenotype research utilizing a statistics method such as linkage analysis, association mapping, linkage imbalance. The information can be used for breeding and / or selecting plants.
Owner:INST OF SPECIAL ANIMAL & PLANT SCI OF CAAS
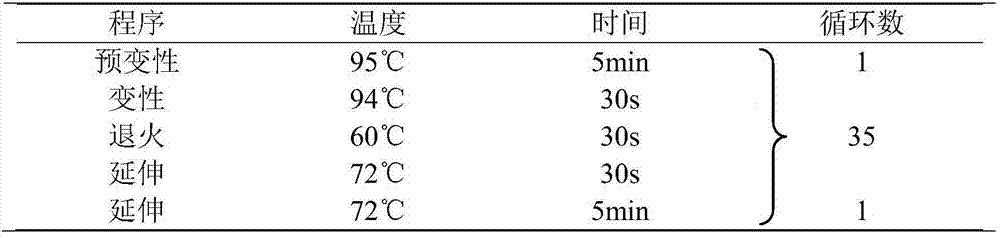
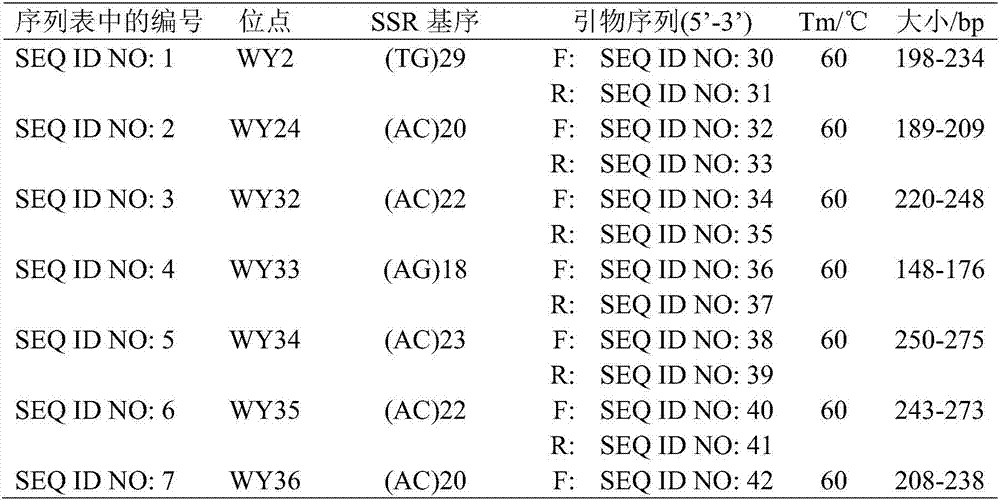
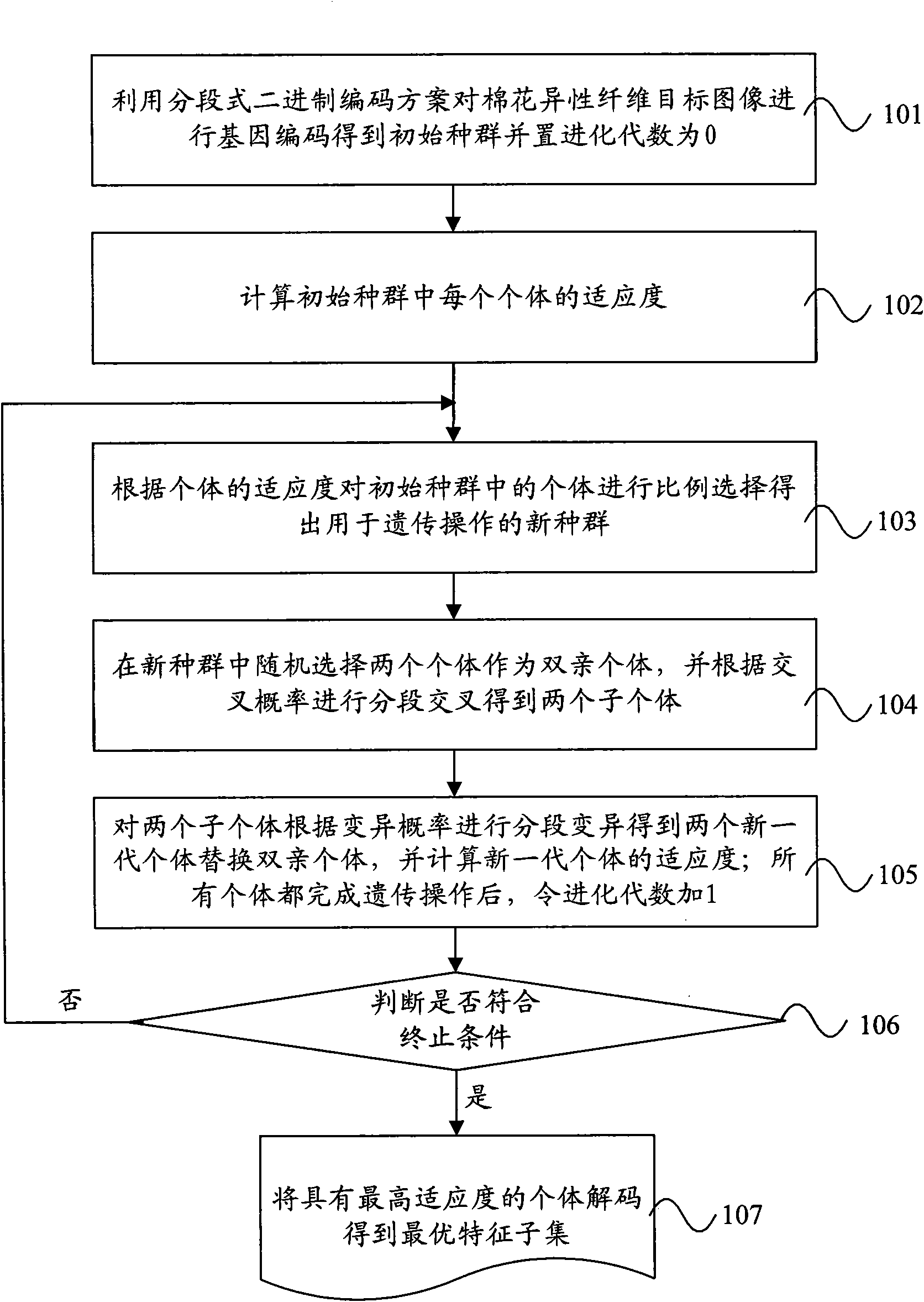
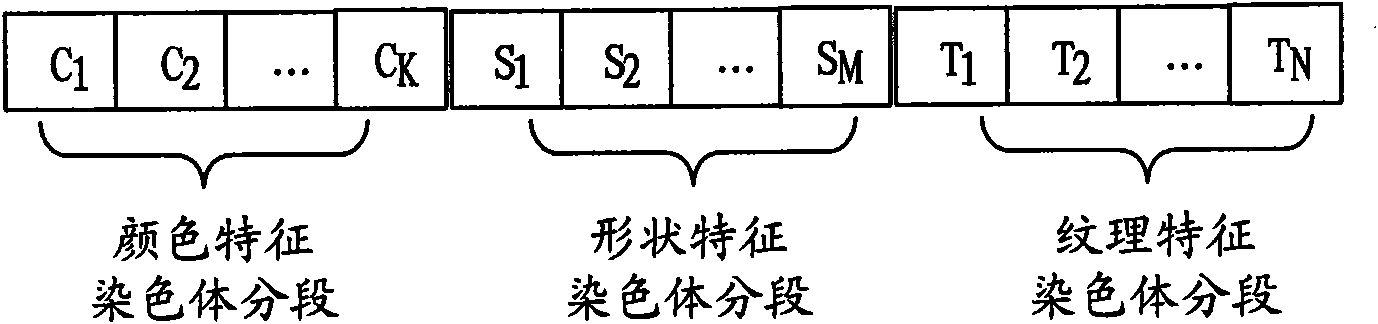
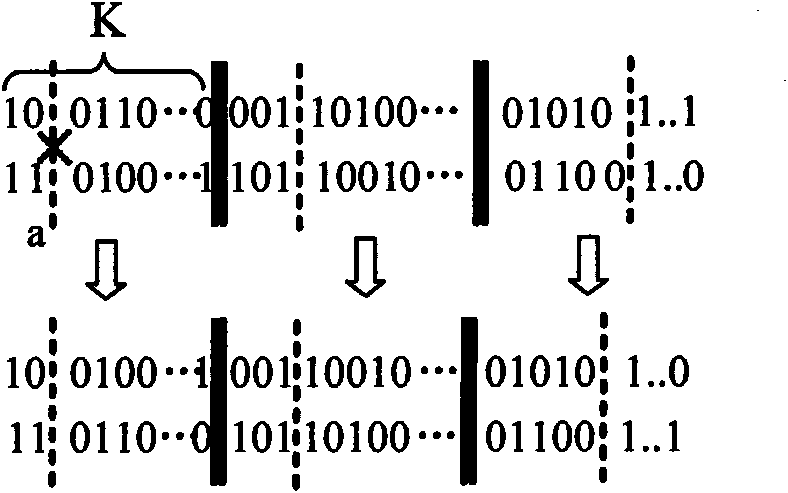
Method and system for selecting feature of cotton heterosexual fiber target image
The invention discloses a method and system for selecting the feature of cotton heterosexual fiber target image. The method includes: conducting the gene encode for the to-be-selected color feature, shape feature and texture characteristic of the cotton heterosexual fiber target image by using the sectional type binary encoding project and generating the initial species group randomly; calculating the sufficiency of the individual in the initial species group; selecting the initial species group according to the sufficiency to obtain new species group; conducting the sectional intersect and variation for the individual in the new species group to produce new individual and substitute original individual, calculating the sufficiency of the new individual; judging whether the sufficiency conforms to the stopping condition; if the sufficiency conforms to the stopping condition, encoding the individual with highest sufficiency to obtain the optimum feature subclass of the cotton heterosexual fiber target image. In the invention, the overlay of different feature in the cotton heterosexual fiber target image is realized, the optimum feature subclass with the optimum classifying capability is selected, thus being beneficial for the subsequent realization of the quick right classification of the heterosexual fiber.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
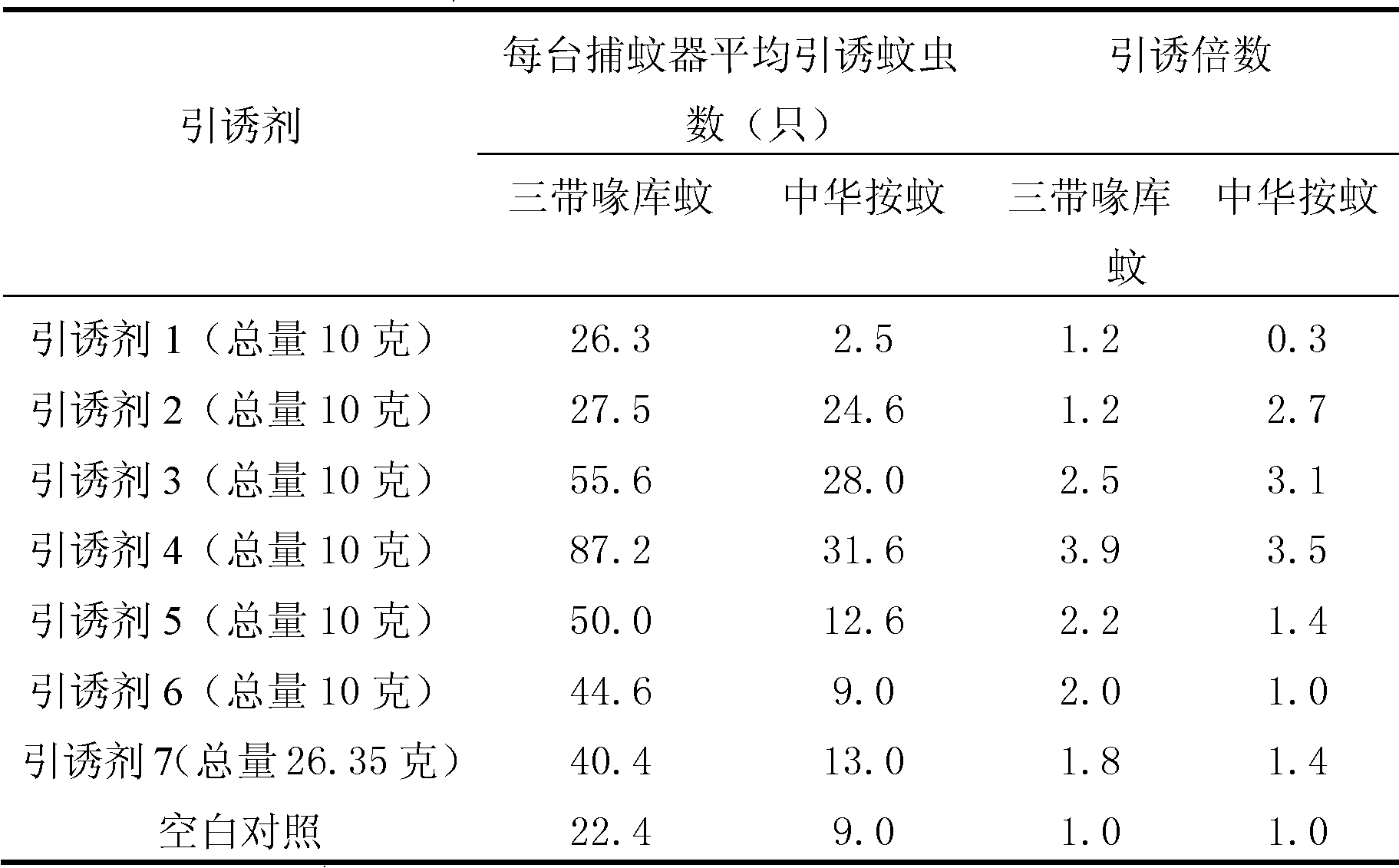
Mosquito attractant and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses mosquito attractant and a preparation method thereof. The mosquito attractant consists of 1-octene-3-alcohol and beta-cyclodextrin; and the weight ratio of the 1-octene-3-alcohol to the beta-cyclodextrin is: (0.5 to 2.5):(7.5 to 24.69). The weight ratio of the 1-octene-3-alcohol to the beta-cyclodextrin is: (0.5:9.5), (0.63:9.37), (1:9), (1.5:8.5), (2:8), (2.5:7.5) or (1.66:24.69). Approved by experiment, the mosquito attractant has attractive activities for culex tritaeniorhynchus and anopheles sinensis, mosquitoes can be attracted by smell substances which are volatilized by the attractant, and the mosquito attractant can be used for the species group monitoring and attraction and prevention of the culex tritaeniorhynchus and the anopheles sinensis.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Bactrocera dorsalis hendel attractant
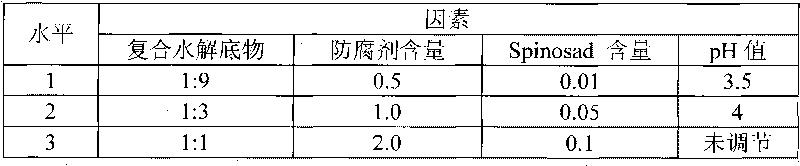
ActiveCN101697739AImprove securitySecurity is not threatenedBiocidePest attractantsYeastEcological environment
The invention discloses a bactrocera dorsalis hendel attractant, wherein the prescription of the attractant is a hydrolysate obtained by enzyme hydrolyzing soy protein and saccharomyces verevisiae protein according a certain ratio under some condition. The attractant not only is good for the environmental protection and the fruit safety, but also can prevent from environment pollution, and can not threaten human health and natural enemy of the bactrocera dorsalis hendel. The attractant has simple preparation method and low preparation cost, and can lead the hydrolysate to stably keep higher attractive force. The attractant has good attractive function to the female and fame bactrocera dorsalis hendel, thereby being capable of controlling the amount of species group of the bactrocera dorsalis hendel, reducing damage rate, and having good popularization meaning.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Unmanned aerial vehicle group photo shooting method
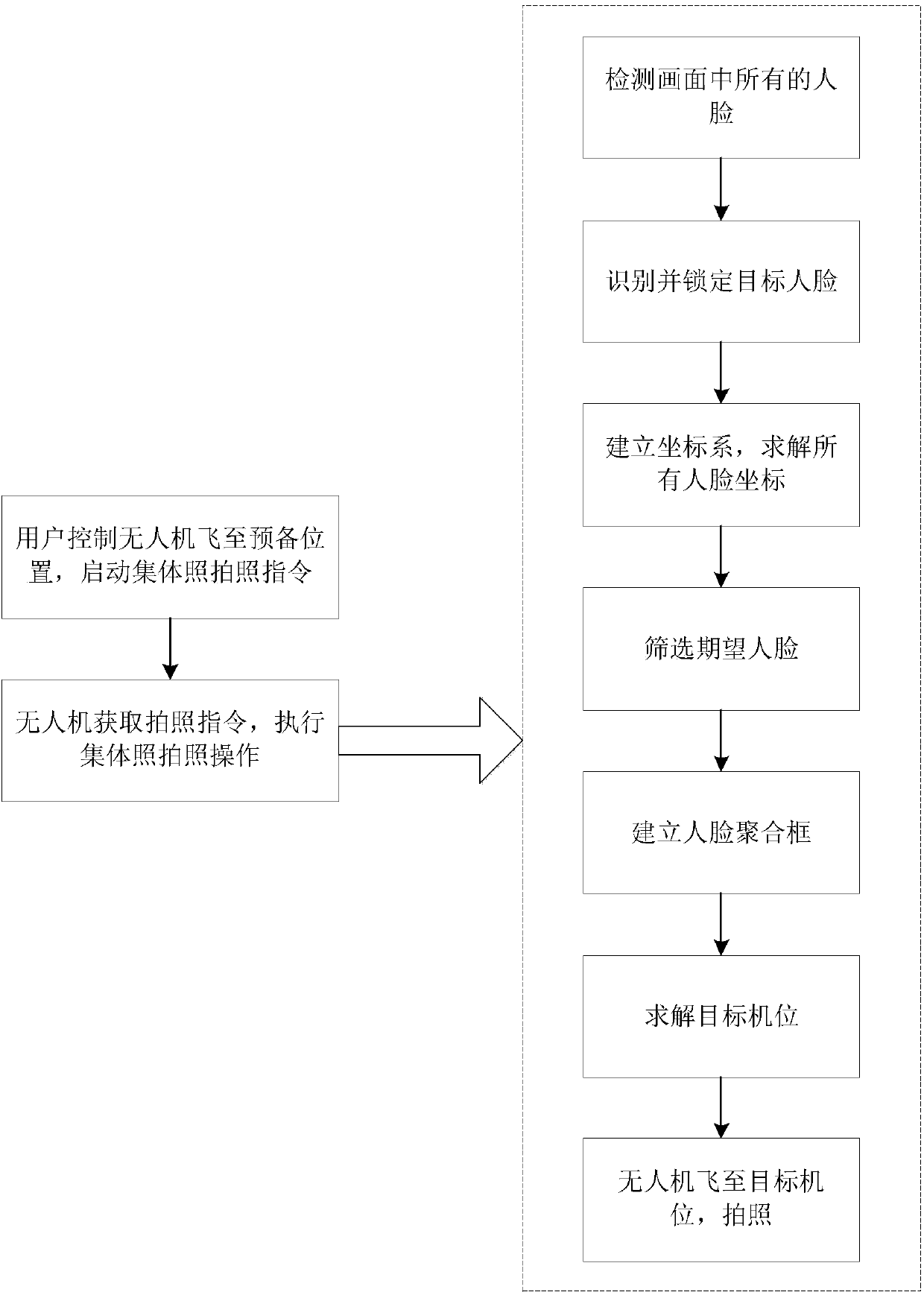
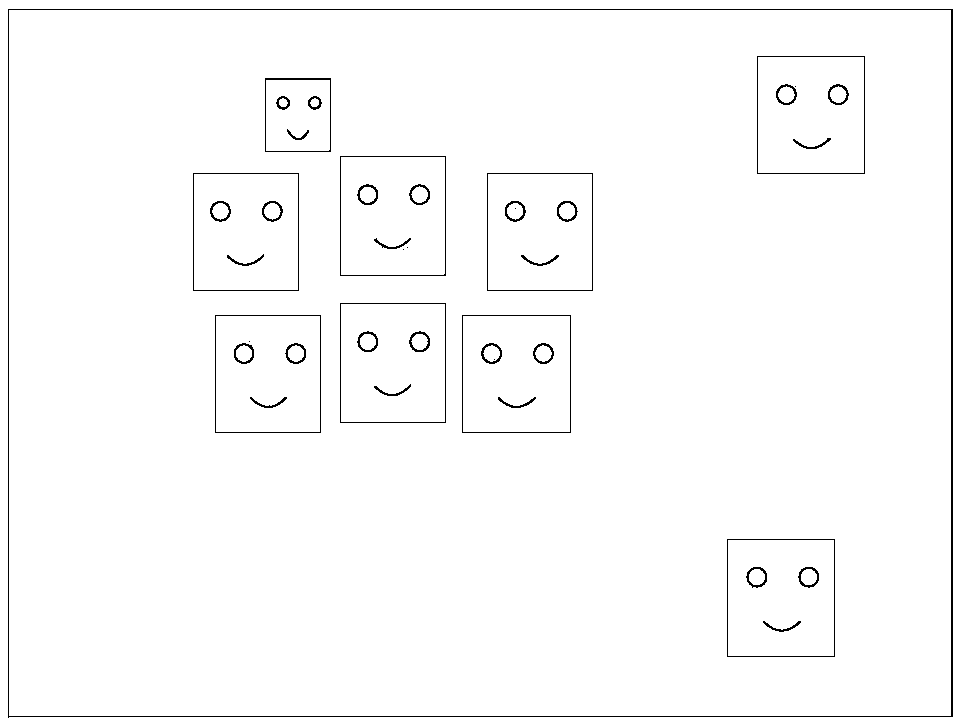
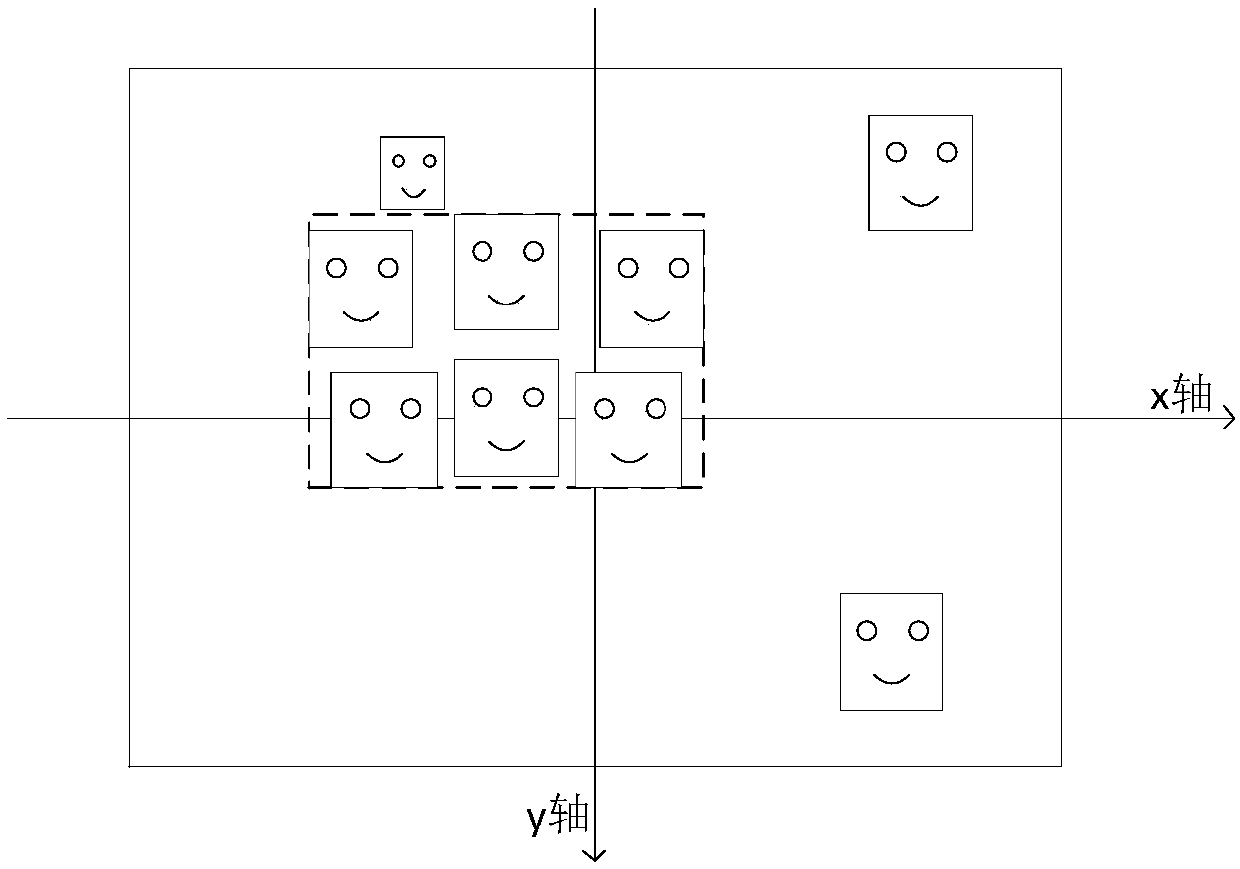
InactiveCN107703962AQuality improvementGood effectPosition/course control in three dimensionsFace detectionShooting method
A method for shooting a group photo of an unmanned aerial vehicle, which relates to the field of unmanned aerial vehicles, solves the problem that the existing unmanned aerial vehicle must manually control the unmanned aerial vehicle to fly to the target position when taking pictures, and completes the technical deficiencies of the target composition, including the following steps: (1) ) Use face detection to frame all the faces in the picture; (2) Through face recognition, lock the target face in the picture; (3) Establish a coordinate system to solve the position of all faces in the picture (x, y, z ) (4) Screen out the expected face (5) Determine the key face frame according to the screened out expected face; (6) Solve the UAV target according to the position of the key face frame and the face aggregation frame in the target composition target plane. The present invention can realize that the UAV automatically completes the group photo person selection and composition, simplifies the UAV photo-taking process, makes the photo-taking process more intelligent, and improves the user's photo-taking experience.
Owner:上海瞬动科技有限公司合肥分公司
Breed conservation method for Sansui ducks
The invention discloses a breed conservation method for Sansui ducks. The breed conservation method for the Sansui ducks is characterized by including the first step of establishing Sansui duck original species groups, collecting hatching eggs from more than five villages and towns in a Sansui duck main aquiculture area, carrying out disinfection and hatching on the hatching eggs after egg selection, duckling selection and mature duck selection, preserving the Sansui ducks with obvious varietal characteristics, wherein families are set up among the 120-day-old Sansui ducks according to the proportion of one male duck to ten female ducks, and each family includes twenty female ducks and two male ducks to form a zero-generation species group, the second step of carrying out family-tree hatching, that is, labeling family numbers, male duck poultry rings and female duck poultry rings, arranging egg laying boxes, collecting the hatching eggs at a set time, carrying out hatching with the individual families as the unit and labeling the family numbers and female duck numbers on ducklings, and the third step of reserving breeding ducks in a random equivalent mode, wherein according to the requirements of 'reserving the ducklings equivalently in all the families and carrying out random apolegamy', every two years is regarded as one generation, the breeding ducks are selected and reserved according to the proportion of twelve female ducks to one male duck when the ducklings grow to 120 days, and new families are merged totally and randomly reestablished according to species groups of the selected and reserved breeding ducks.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
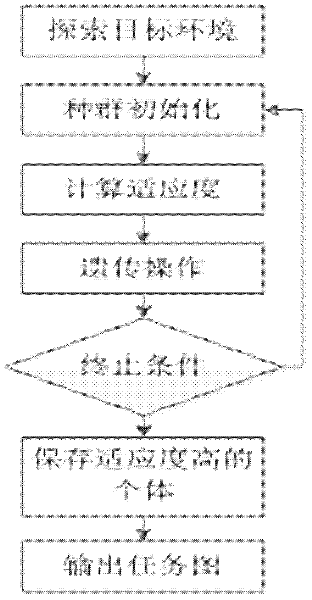
Hierarchical reinforcement learning task graph evolution method based on cause-and-effect diagram
InactiveCN102521203AImprove adaptabilitySpeed up searchGenetic modelsDigital computer detailsAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
The invention provides a hierarchical reinforcement learning task graph evolution method based on a cause-and-effect diagram. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out parameter setting; (2) exploring a cause-and-effect diagram in a target environment; (3) carrying out initialization on a species group N; (4) calculating a fitness value; (5) carrying out genetic operation, wherein the genetic operation comprises selection, intersection and variation; and maintaining the cause-and-effect relationship between nodes in the operation; (6) judging whether to stop; (7) saving K task graphs G1, G2,..., Gk with the highest fitness corresponding to the cause-and-effect diagram; and (8) outputting the task graph G1 with the highest fitness. Compared with the prior art, the automatization and high efficiency of the task graphs constructed by the method of the invention can be suitable for large-scale complex systems and can be applied to the dynamic change situations of the system environment. The method provided by the invention only depends on the changes of the cause-and-effect diagram of the target environment, predicts the task level changes of the target environment when the cause-and-effect diagram of the target environment is changed regularly, and rapidly and efficiently generates an MAXQ task graph.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Mononucleotide polymorphism of milk goat MFG-E8 genes and detection method thereof
InactiveCN101705288AAccurate detectionQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyEnzyme digestion
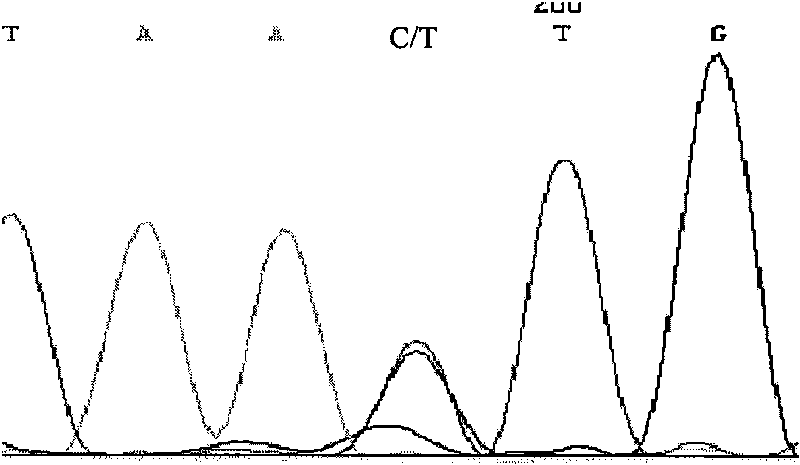
The invention discloses a mononucleotide polymorphism of milk goat MFG-E8 genes and a detection method thereof. The invention takes the whole genome DNA of the milk goat to be detected containing the MFG-E8 genes as the template, takes the primer coupled P (comprising P1, R1 and newP) as the primer, and takes the PCR amplified milk goat MFG-E8 as the genes; the restriction enzyme EcoRV is utilized to digest PCR amplifying products, and then polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is carried out on the amplified segments after enzyme digestion; the mononucleotide polymorphism of the 12892nt of the milk goat MFG-E8 genes is identified according to the results of polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. As the MFG-E8 gene function relates to development of breast, butter fat, total solids and other milk elements, the detection method provided by the invention lays a foundation for the establishment of the relation between the SNP and the milk component of the MFG-E8 genes, so as to be used for the marker-assisted selection of the properties of Chinese milk goat and the rapid establishment of milk goat species group with excellent genetic resources.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
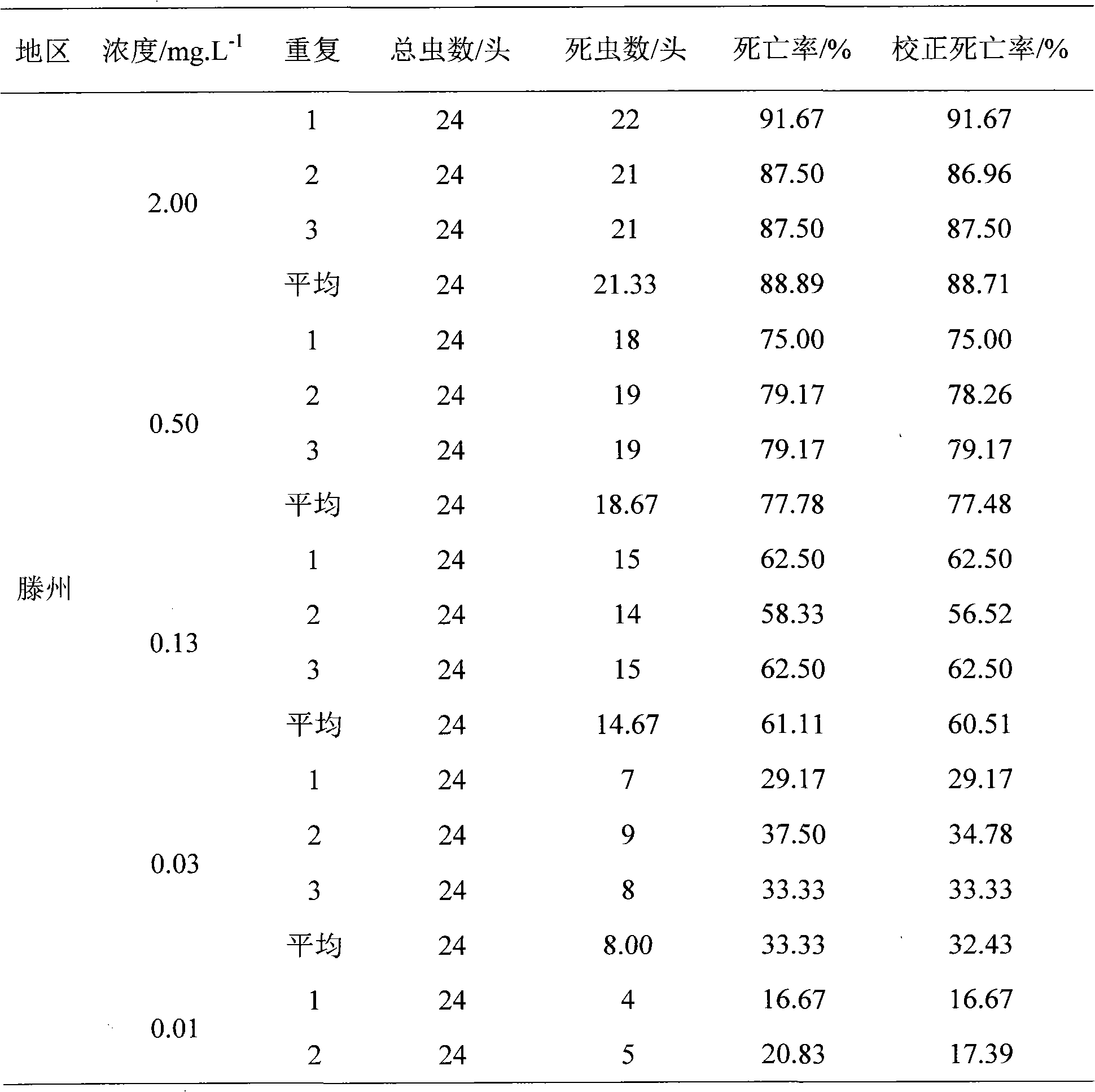
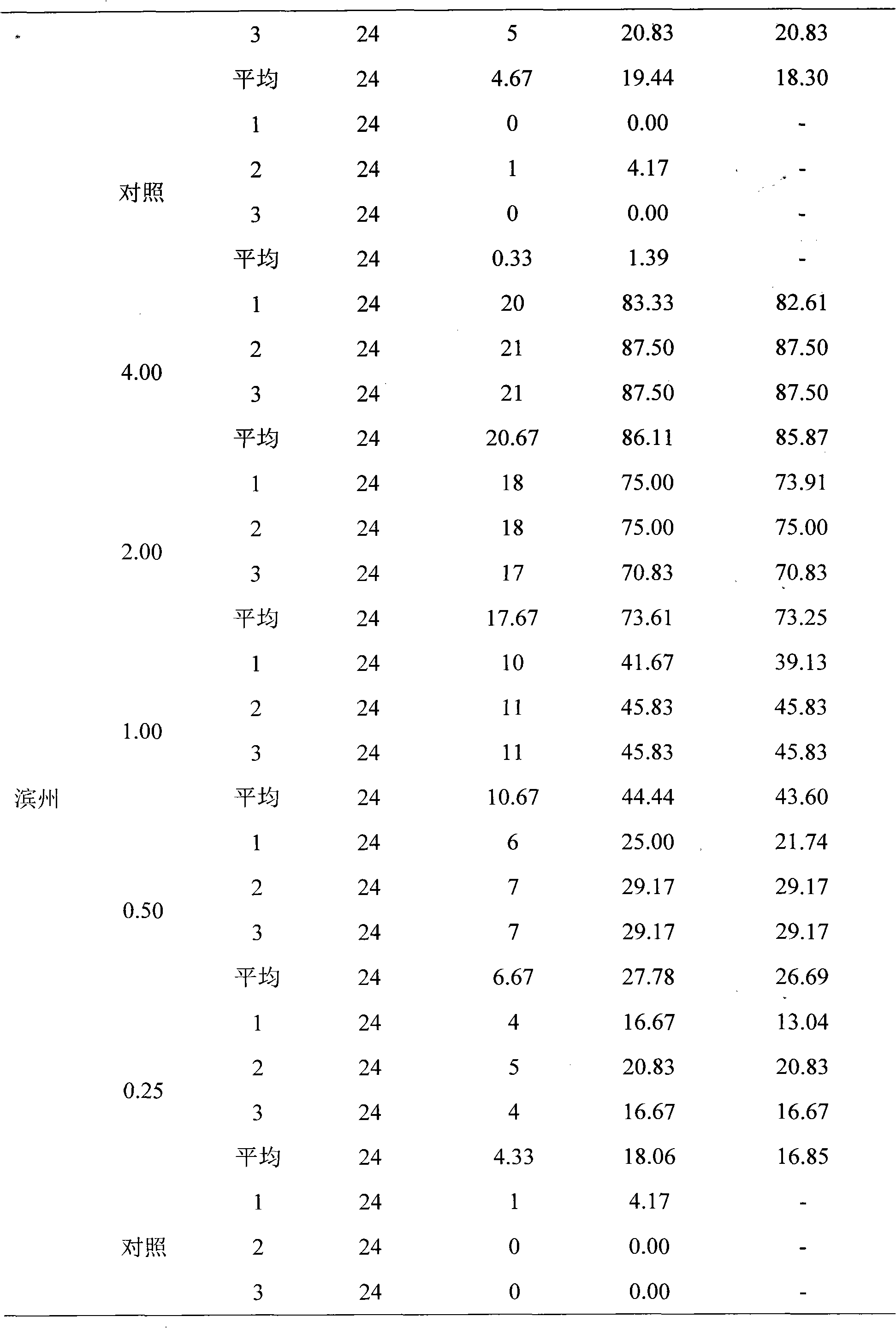
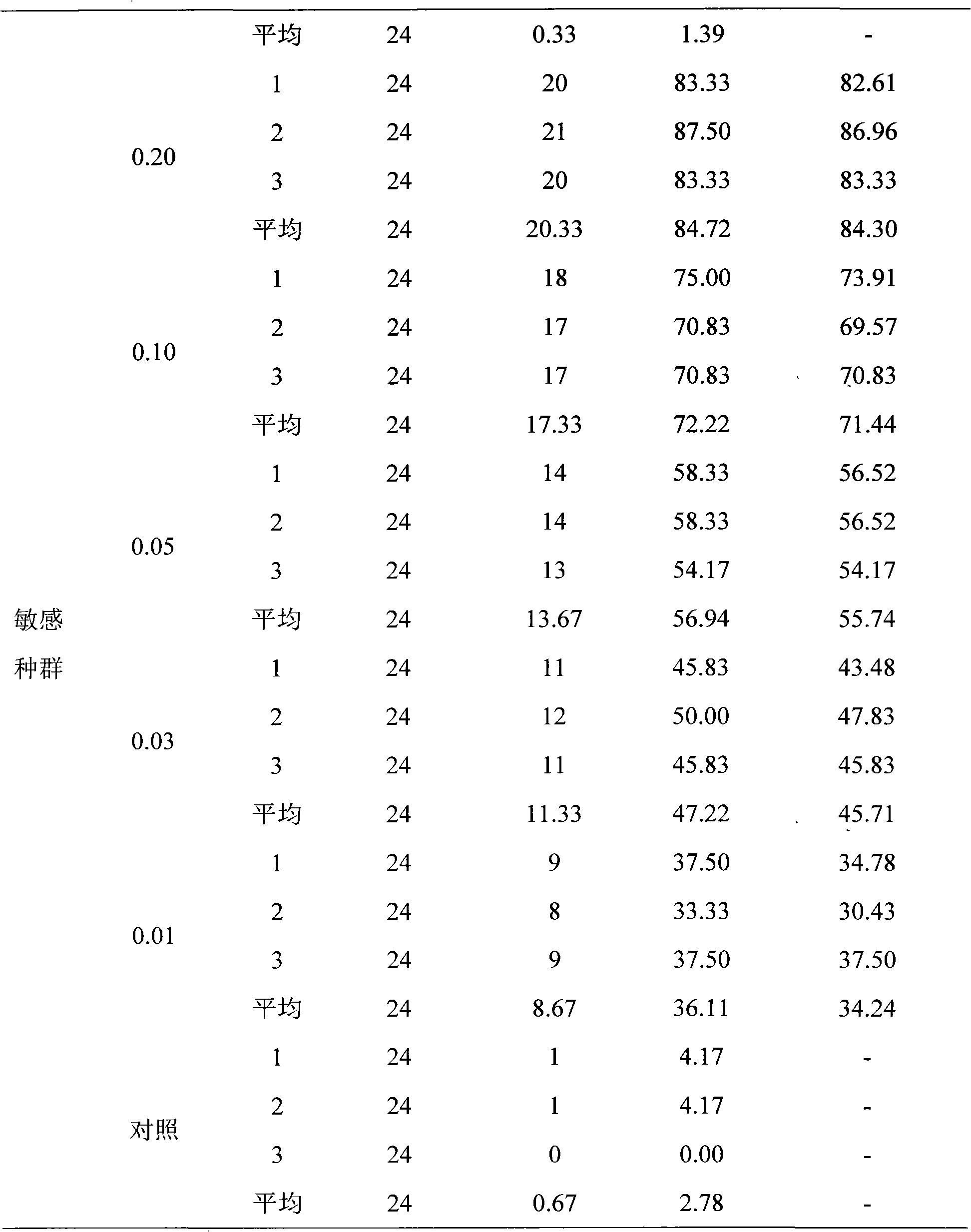
Method for monitoring drug resistance of spodostera exigua hubner to insecticides
InactiveCN102175845AImprove wetting and spreading effectImprove accuracyBiological testingMortality rateSpecies groups
The invention relates to a method for monitoring drug resistance of insecticides. The method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining a species group of spodostera exigua hubner in at least one geographical region via field collection; (2) transferring the species group of spodostera exigua hubner collected in fields into indoor for propagating one generation; (3) hungering the propagated one generation three-age spodostera exigua hubner for 2 hours, and performing the drug resistance measurement; (4) diluting at least one insecticide crude drug into five concentrations that the death rate is 10%-90%, and dipping cabbage round leaves to obtain poisonous leaves which are used for feeding the spodostera exigua hubner; and (5) checking the result after a certain time to obtain the drug resistance level of the spodostera exigua hubner in a region to a certain insecticide. The method determines the resistance condition of the spodostera exigua hubner in fields to insecticides via monitoring the drug resistance of the species group of spodostera exigua hubner to insecticides, so that effective guidance can be supplied for the resistance management and integrated control of spodostera exigua hubner.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Analogue circuit fault diagnosis method based on improved type clone selection algorithm
ActiveCN103714385AEliminate rejectionReduce misclassificationGenetic modelsClonal selection algorithmDiagnosis methods
The invention discloses an analogue circuit fault diagnosis method based on an improved type clone selection algorithm. The method includes the first step of canceling the decision rules that an original decision algorithm determines which diagnosis radiuses faults belong to based on experience, and adopting the minimum Euclidean distance as a diagnosis decision condition, the second step of modifying an affinity calculation formula and utilizing a formula f=1 / (1+d) to replace an original formula f=1 / d so as to prevent overflowing in calculation and standardize the affinity within a fixed range of (0,1], and the third step of modifying an overall affinity calculation mode and utilizing an average value expression method of the affinity of all individuals in a species group to replace a sum expression method of the affinity of all the individuals in the species group. Through the first step, failure switch-off can be eliminated, false switch-off and excessive switch-off can be reduced and the fault diagnosis rate can be improved. Through the second step, calculation is convenient and the comparability of the affinity is higher. The improved type clone selection algorithm is applied to analogue circuit fault diagnosis and has superior performance.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE MEASUREMENT & CONTROL TECH
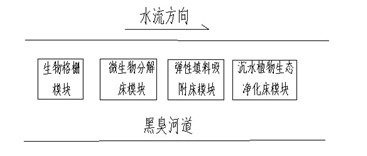
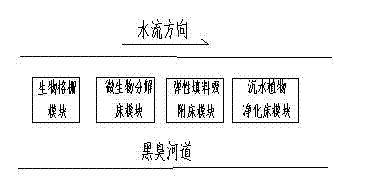
Modular system for purification of polluted river water body and application of the same
InactiveCN102219339BReduce pollution loadEffective interceptionMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by sorptionGratingDecomposition
The invention belongs to the technical field of treatment of environment pollution, and more specifically relates to a modular system for purification of a polluted river water body and application of the same. The modular system mainly comprises a biological grating module, an elastic filling material adsorption bed module, a microbial ecological decomposition suspending bed module and a sunken plant ecological purification suspending bed module. The biological grating module is composed of a framework, sunken plants, floating plants and emerged plants; the elastic filling material module consists of a framework structure, hydrophilic elastic filling materials and hydrophobic elastic filling materials; the microbial bed module comprises a framework structure, a micropore aeration mechanism and microbes; and the sunken plant purification bed module is composed of the species group of sunken plants and a bed body. According to the invention, the position of the polluted river water purification modules in a water body can be adjusted according to pollution degrees of the water body; the modular system can effectively purify water quality of a polluted river water body and a black and odorous river water body and reduce river pollution load; therefore, the invention is of significance for purification of river water bodies.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Traditional Chinese medicine composition capable of keeping whole antibody level of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome and introduction method
ActiveCN104798727AConsistent levelPersistent contact infectionAntiviralsFungi medical ingredientsGynecologySpecies groups
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine composition capable of keeping a whole antibody level of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome. The traditional Chinese medicine composition comprises radix bupleuri, Indian strawberries, scutellaria baicalensis, ephedra herbs, kudzuvine roots, coptis chinensis, nightshade powder, fomes japonica, secotium agaricoides (czern.) hollos, lemon slices, caulis clematidis armandii, rhizoma anemarrhenae, gypsum and water. The invention further provides an introduction method for keeping the whole antibody level of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome. A reserve with a higher antibody value and pluriparous pigs with gradually reduced antibodies are mutually and naturally infected, and the whole antibody level keeps consistent; the whole reproductive and respiratory syndrome antibody in species groups is not reduced; the periodic fluctuation caused by yin and yang match of pig groups in different regions is avoided, so that the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome is not burst in the pig groups in a large scale, and the loss of cultivation fields, caused by the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome, is reduced.
Owner:河南民正农牧股份有限公司
Method for advanced treatment and recycling of petroleum and petrochemical wastewater
InactiveCN101597122AImprove impact resistanceShort training periodWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesUltrafiltrationWater quality
The invention provides a method for the advanced treatment and recycling of petroleum and petrochemical wastewater and relates to the technical field of water treatment, in particular to the technical field of the advanced treatment and recycling of oil refining wastewater and oilfield produced wastewater. With an agitator adopted, anaerobic biological reaction, aerobic treatment are carried out on the petroleum and petrochemical wastewater in sequence, finally the wastewater with mud going through the aerobic treatment is filtered by an ultrafiltration membrane, the filtered water is recycle water. The method of the invention can shorten cultivation cycle at the initial stage of wastewater biochemistry, improve impact resistance capacity of the biochemical system in the process of operation, and adapt to wastewater which is biochemically difficult to degrade and suffers lack of nutrients; in addition, the method can strengthen activity of microorganism by biological modifier, sustain species group stability of micro-ecological flora and ensure long term, valid and stable operation of the whole system; and the treated recycle water features little change of water quality and low retention level of organism.
Owner:JIANGDU COUNTY ENVIRONMNT PROTECTION EQUIPS FACTORY
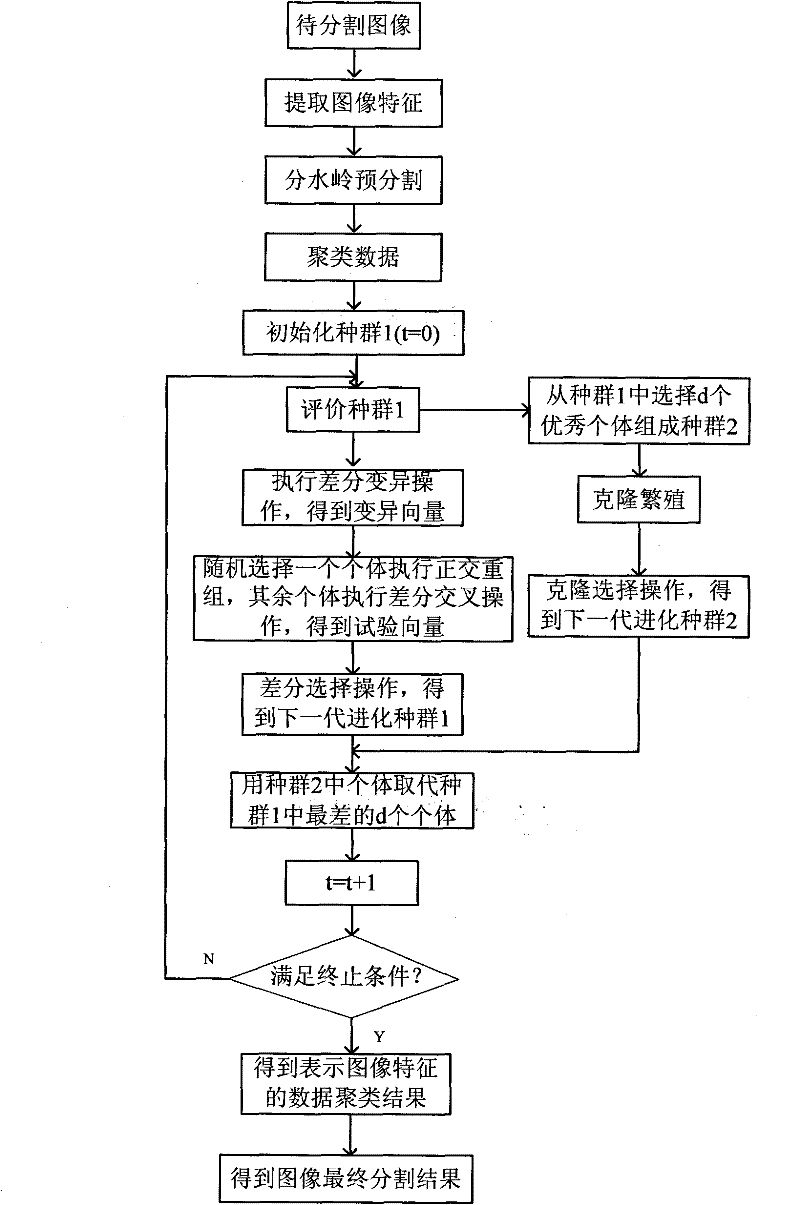
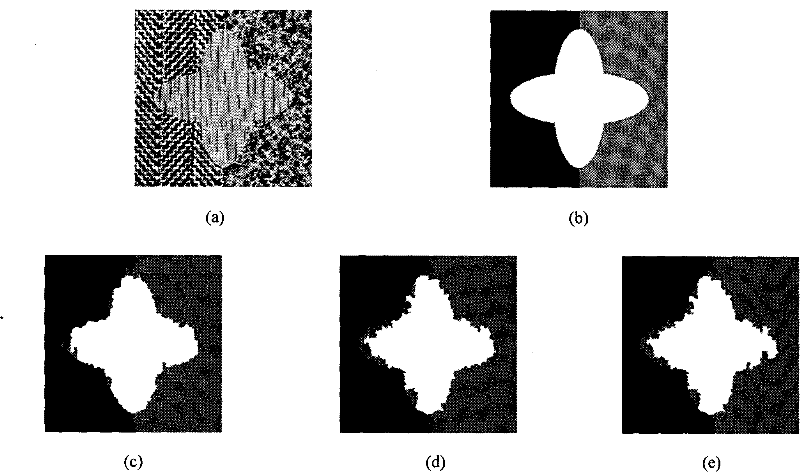
Image segmentation method based on differential immune clone clustering
ActiveCN101866490BDiversity guaranteedAvoid falling intoImage analysisGenetic modelsClustered dataPattern recognition
The invention discloses an image segmentation method based on differential immune clone clustering, belonging to the field of image processing and aiming at solving the problems that the existing clustering technology has slow convergence rate, poor stability and is easy to sink in local extreme values. The realization steps thereof are as follows: 1) extracting gray-level co-occurrence matrix and wavelet transform characteristics from an image to be segmented; 2) carrying out watershed pre-segmentation on the image to be segmented, getting the mean value of pixel characteristics belonging tothe same block to obtain clustering data; 3) carrying out initialization and individual encoding on species group 1; 4) calculating the fitness value of individuals in species group 1 to obtain the antibody in species group 2 to update an elite species group; 5) respectively designing different manipulators for the species group 1 and the species group 2, carrying out differential variation, orthogonal recombination, binominal intersection and selection operation in sequence on the species group 1, and carrying out proportional cloning, hyper-mutation and cloning selection operation on the species group 2 in sequence; and 6) outputting image segmentation results. The invention has the advantages of high convergence speed, high stability, good consistency of segmentation results regions and complete reserved information, can effectively segment texture images and SAR images, and can be applied to target recognition of SAR images.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Eco-animal husbandry production control method
InactiveCN101290667APromote conversionReasonable layoutData processing applicationsAgricultural scienceResource utilization
The invention discloses a method for regulating and controlling production in livestock husbandry, belonging to the livestock husbandry field. The method solves the problems that in the prior livestock husbandry, production design, regulation and control are inadequate in overall coordination and local imbalance and error are found. According to the ecology principle and the production characteristics of a livestock husbandry system, the method regulates and controls the design and management by applying a mathematical method from the following four steps of: 1) the balance between a community and social resource and environment conditions, 2) the balance between a species group and a natural resource condition, 3) the balance between a breed and a regional environment condition and 4) the optimization of individual development. The method for regulating and controlling production in livestock husbandry provided by the invention creates coordinated development between an animal production colony structure and resources and achieves the aims of having reasonable layout, optimized structure and normative management, improving the resource utilization rate, promoting resource transformation and improving economic benefit.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
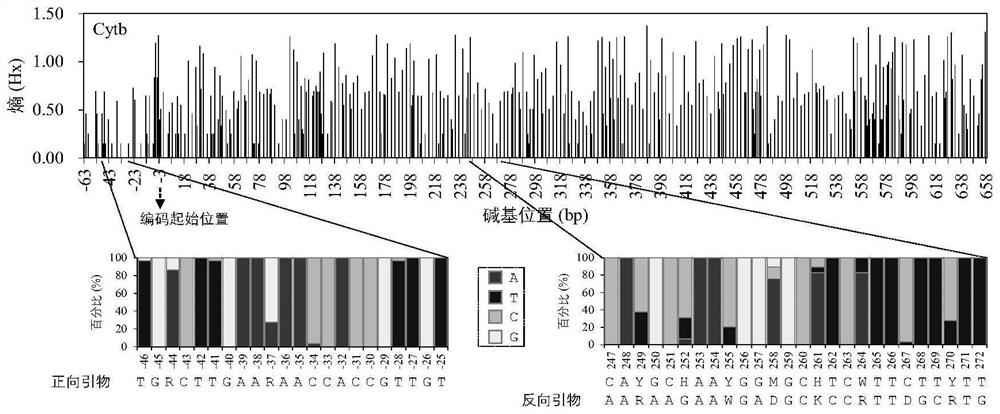
Primer for monitoring DNA of fish environment at middle and upper reaches of Yarlung Zangbo River
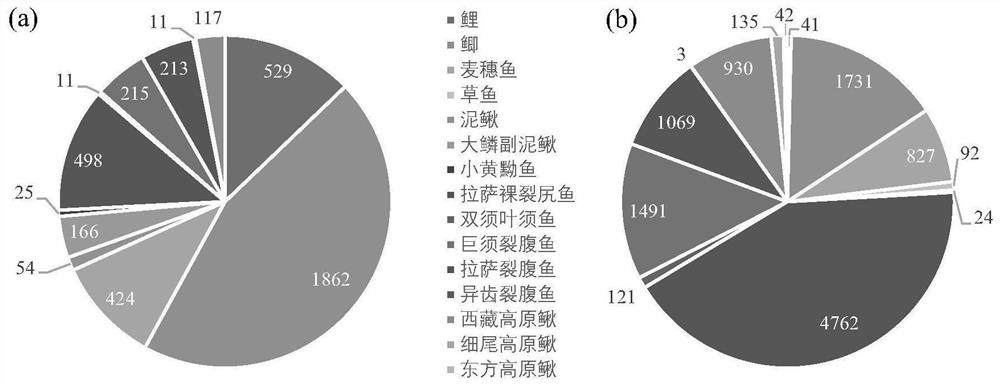
PendingCN113881781AAccurate and comprehensive detection effectAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHigh throughput sequenceZoology
The invention relates to a primer for monitoring DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) of a fish environment in the middle and upper reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River and an application method thereof, and belongs to the field of molecular ecology. The primers comprise the following components of YZR-Cytb-F:TGRCTTGAARAACCACCGTTGT and YZR-Cytb-R: AARAAGAAWGADGCKCCRTTDGCRTG. The method comprises the following steps of (1) collecting a water sample and extracting eDNA; (2) slightly transforming the primer and then carrying out primary PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) on eDNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid); (3) carrying out secondary PCR on the purified product of the primary PCR by using an Illumina library building primer; (4) performing high-throughput sequencing on the purified product of the second PCR; and (5) analyzing the fish species composition in the water sample according to the sequencing data. The primer has an identification effect on the species level of all fishes in the middle and upper reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River, and the method can be used for accurately and completely monitoring the species diversity of the fishes in the middle and upper reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River on the premise of not damaging the environment and fish populations.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com