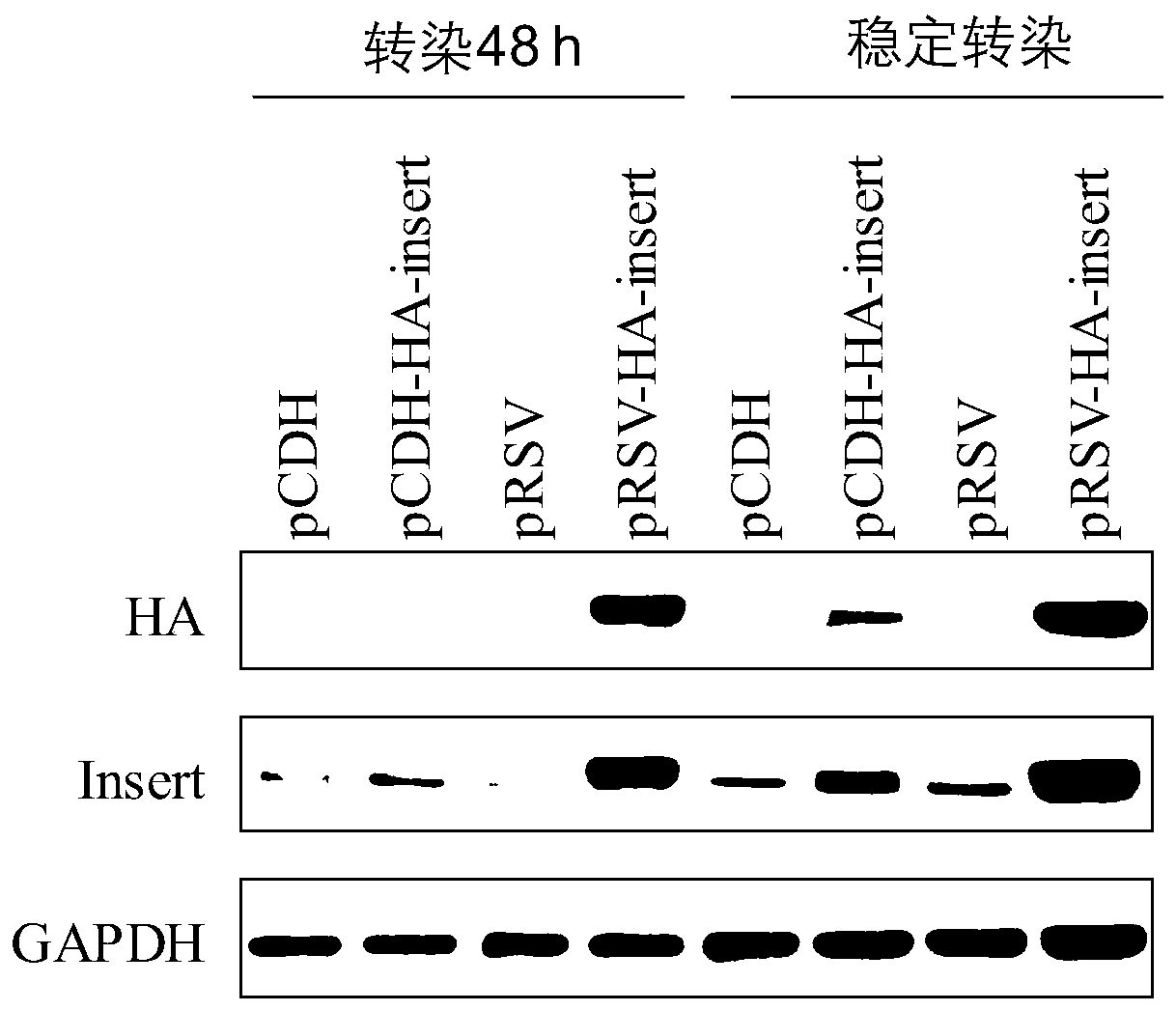
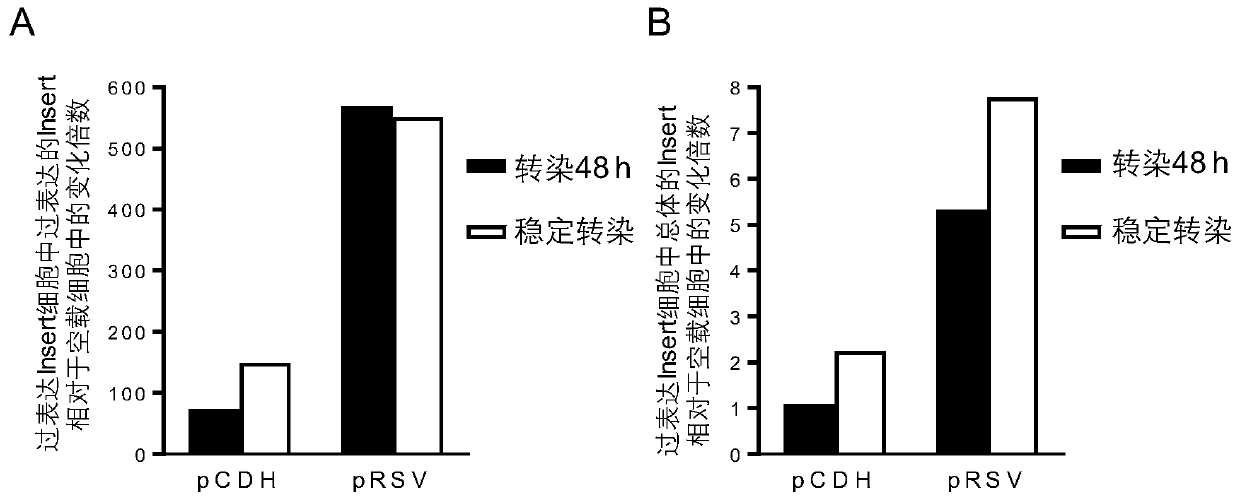
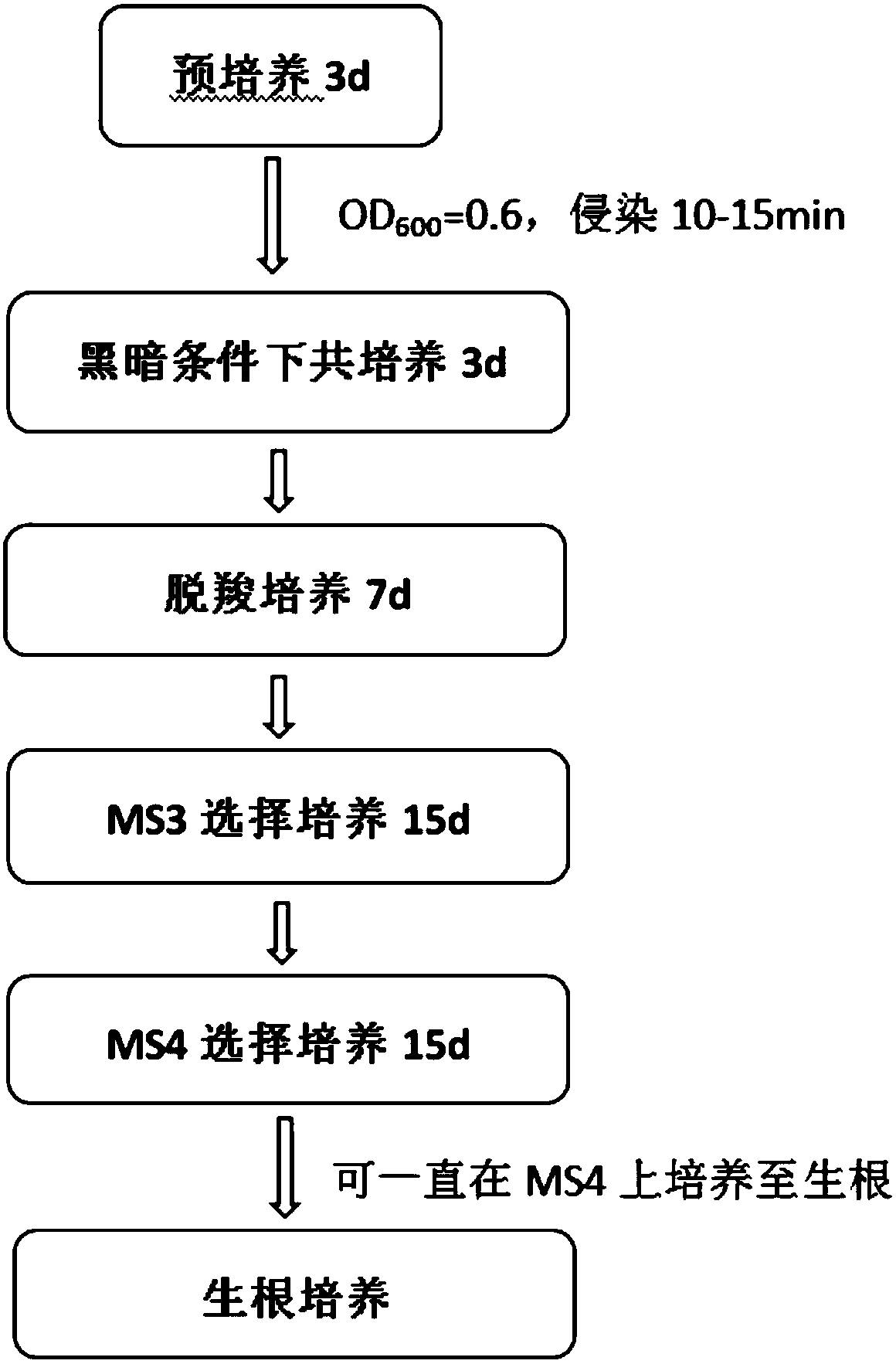
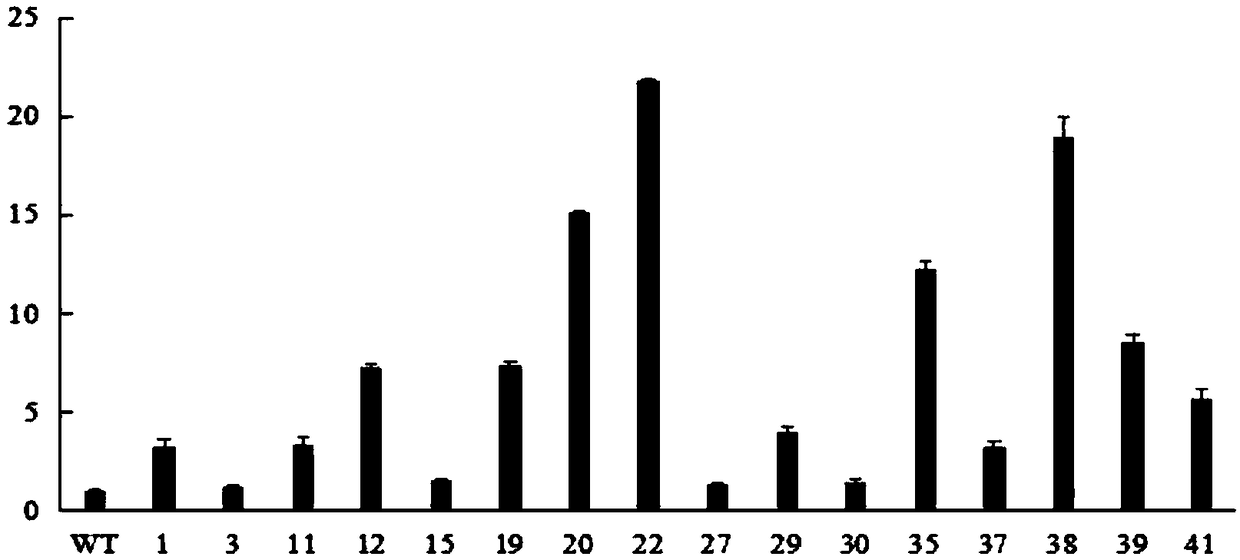
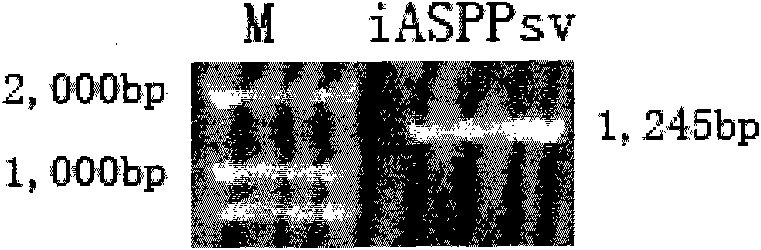Patents
Literature
191 results about "Vector (molecular biology)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In molecular cloning, a vector is a DNA molecule used as a vehicle to artificially carry foreign genetic material into another cell, where it can be replicated and/or expressed (e.g., plasmid, cosmid, Lambda phages). A vector containing foreign DNA is termed recombinant DNA. The four major types of vectors are plasmids, viral vectors, cosmids, and artificial chromosomes. Of these, the most commonly used vectors are plasmids. Common to all engineered vectors are an origin of replication, a multicloning site, and a selectable marker.
Cell model obtained after targeted knockout of rabbit bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP2) gene based on CRISPR/Cas9 and application thereof
InactiveCN106047803AEasy to prepareLow costBone-inducing factorOsteogenic factorMorphogenesisMesenchymal stem cell
The invention relates to a cell model obtained after targeted knockout of a rabbit BMP2 gene based on CRISPR / Cas9 and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of molecular biology and biomedicine. According to the invention corresponding oligos are synthesized for three targeting sites of the rabbit BMP2 gene on the design principles of CRISPR / Cas9 and are constructed on px458 vectors; and a CRISPR / Cas9 system is constructed directed at the three targeting sites in rabbit mesenchymal stem cells, and the CRISPR / Cas9 system can effectively knock out the rabbit BMP2 gene, is easy to operate and has high rabbit BMP2 gene knockout efficiency. The cell model disclosed in the invention can greatly promote research related to the functions and signaling pathways of the BMP2 gene.
Owner:QINGDAO JIAOZHOU CENT HOSPITAL
Lactococcus promoters and uses thereof
ActiveUS8759088B2Increase the number ofHigh expressionBiocideBacteriaHeterologousFusion Protein Expression
The invention is in the field of molecular biology, and relates to recombinant engineering and protein expression. More in particular, the invention relates to nucleic acids for recombinant expression of proteins comprising sequences derived from Lactococcus and useful as promoters. The invention further relates to vectors comprising the nucleic acids and host cells transformed therewith. The invention also covers the use of host cells comprising the nucleic acids or vectors for expressing heterologous or homologous proteins; and also for delivery, especially therapeutic delivery, of the said proteins to subjects.
Owner:INTREXON ACTOBIOTICS NV
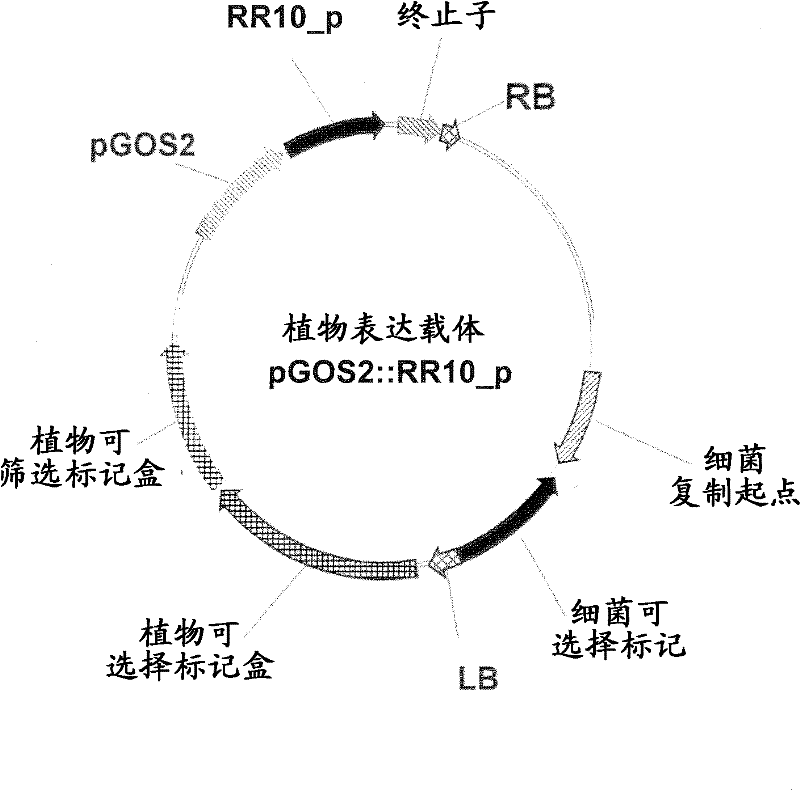
Plants having enhanced yield-related traits and a method for making the same
The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing various economically important yield-related traits in plants. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for enhancing yield-related traits in plants by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding an ASPAT (Asparatate AminoTransferase) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding an ASPAT polypeptide, which plants have enhanced yield-related traits relative to control plants. The invention also provides hitherto unknown ASPAT-encoding nucleic acids and constructs comprising the same, useful in performing the methods of the invention. Furthermore, the present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for increasing various plant yield-related traits by increasing expression in a plant of a nucleic acid sequence encoding a MYB91 like transcription factor (MYB91 ) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having increased expression of a nucleic acid sequence encoding an MYB91 polypeptide, which plants have increased yield- related traits relative to control plants. The invention additionally relates to nucleic acid sequences, nucleic acid constructs, vectors and plants containing said nucleic acid sequences. Even furthermore, the present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for improving various plant growth characteristics by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a GASA (Gibberellic Acid-Stimulated Arabidopsis). The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a GASA, which plants have improved growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants or other control plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention. Yet furthermore, the present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing various economically important yield-related traits in plants. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for enhancing yield-related traits in plants by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding an AUX / IAA (auxin / indoleacetic acid) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding IAA polypeptide, which plants have enhanced yield-related traits relative to control plants. The invention also provides constructs comprising AUX / IAA-encoding nucleic acids, useful in performing the methods of the invention.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Codon optimized porcine circovirus type 2 Cap protein coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN103451196AStructuredImproving immunogenicityBacteriaViral antigen ingredientsPorcine CircovirusesImmunogenicity
The invention provides a codon optimized porcine circovirus type 2 Cap protein coding gene and application thereof, and belongs to the field of the molecular biology. The Cap protein coding gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also provides a recombinant vector containing the gene and recombinant bacteria containing the gene. A method for preparing porcine circovirus type 2 virus-like particles comprises the steps of inducing the recombinant bacteria to express a porcine circovirus type 2 Cap protein, lysing the recombinant bacteria, and taking the lysate for purification to obtain the porcine circovirus type 2 virus-like particles. The invention also provides a gene engineering subunit vaccine with the virus-like particles as an active ingredient. The codon optimized porcine circovirus type 2 Cap is capable of realizing abundant soluble expression. The virus-like particles (VLP) are assembled from the Cap proteins and have excellent immunogenicity. A vaccine prepared from the virus-like particles provided by the invention is capable of preventing porcine circovirus type 2 infection and has the advantages of good immunogenicity, high antibody level and effective protection after challenge.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Classical swine fever virus recombinant E2 protein and IgM (immune globulin M) antibody ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) test kit thereof
ActiveCN102532281AGood antigenicityGood repeatabilityBacteriaVirus peptidesEscherichia coliClassical swine fever virus CSFV
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and relates to a classical swine fever virus recombinant E2 protein and an IgM (immune globulin M) antibody ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) test kit thereof. The classical swine fever virus E2 protein expressed by recombinant Escherichia coli is obtained by cloning the main antigen region of E2 protein into a pronucleus expression vector to obtain a recombinant expression vector, transforming the recombinant expression vector to Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) and expressing and purifying with the recombinant Escherichia coli. A Westernblot test indicates that the protein has good antigenicity. According to the invention, an elisa plate is coated the protein; an ELISA method is established through optimization of antigen coating concentration, serum dilution and action time, secondary antibody concentration and action time as well as developing time for the purpose of detecting negative serum so as to determine a critical value and a judgment standard. According to the invention, the expression of a recombinant strain constructed by the recombinant E2 protein on a heterologous protein is stable, and the recombinant strain is good in antigenicity; and on the basis, the recombinant E2 protein disclosed by the invention is used for establishing a CSFV (classical swine fever virus) IgM antibody ELISA test kit for the first time.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Recombined chicken alpha interferon gene and recombinant vector thereof
InactiveCN101338314AStrong antiviral activityEase of mass productionFungiMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationAnti virus
The invention relates to a novel gene sequence of a recombinant chicken Alpha interferon, constructs a recombinant expression vector thereof and belongs to a gene engineering biological product obtained by a molecular biology method. The gene sequence of a newly designed chicken Alpha interferon is recombined into a pPICZ Alpha-A vector and then is confirmed on the special position of a microzyme by an electric conversion mode. Besides, a pichia expression system is adopted to express a foreign gene, thus being beneficial to the commercial production of the chicken interferon. The protein expressed by a gene group after being diluted by 4365158.3 times can completely restrain the attraction of vesicular stomatitis virus of 100-1000TCID50. Compared with a natural chicken Alpha interferon, the novel gene sequence of a recombinant chicken Alpha interferon has a higher anti-virus effect; the anti-virus effect thereof is improved by 8 times. Test also detects that the protein expressed by the gene can restrain the proliferation of a newcastle disease virus and an avian influenza virus; besides, the effect of the interferon with high concentration is more remarkable.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
NDV (Newcastle disease virus) recombinant virus expressing DHAV-1 and DHAV-3 VP1 genes and application thereof
ActiveCN105754959AReduce manufacturing costAvoid interferenceSsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseDuck hepatitis A virusHepatitis A viruses
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology and particularly relates to NDV (Newcastle disease virus) recombinant virus expressing DHAV-1 and DHAV-3 VP1 genes.The recombinant virus is recorded as rLS-1VP1-2A-3VP1 and is obtained inserting serially connected DHAV-1 and DHAV-3 VP1 genes into an NDV vector and carrying out saving.The NDV (Lasota strain) is used as the vector for the recombinant virus, the serially connected DHAV-1 and DHAV-3 VP1 genes are inserted into the NDV (Lasota strain) to obtain a vector, and the DNV recombinant virus co-expressing DHAV-1 and DHAV-3 VP1 genes is obtained by determining an optimal insertion site to insert the DHAV VIP1 gene; the recombinant virus is useful in preventing duck hepatitis A viruses (type 1 and type 3) and duck Newcastle disease and filling the current blank of DHAV-3 vaccines.
Owner:POULTRY INST SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI SHANDONG SPECIFIC PATHOGEN FREEN CHICKS RES CENT
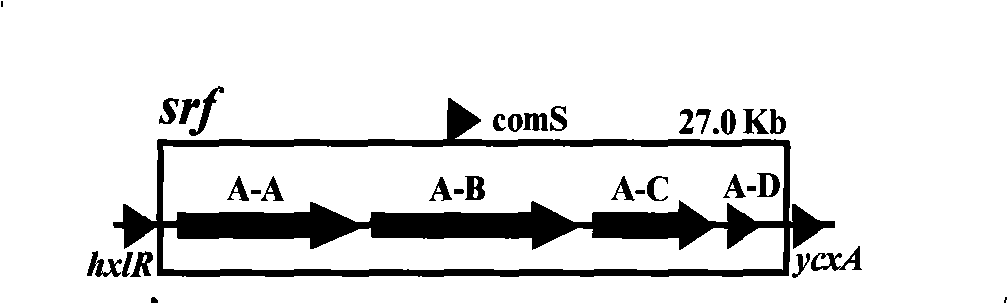
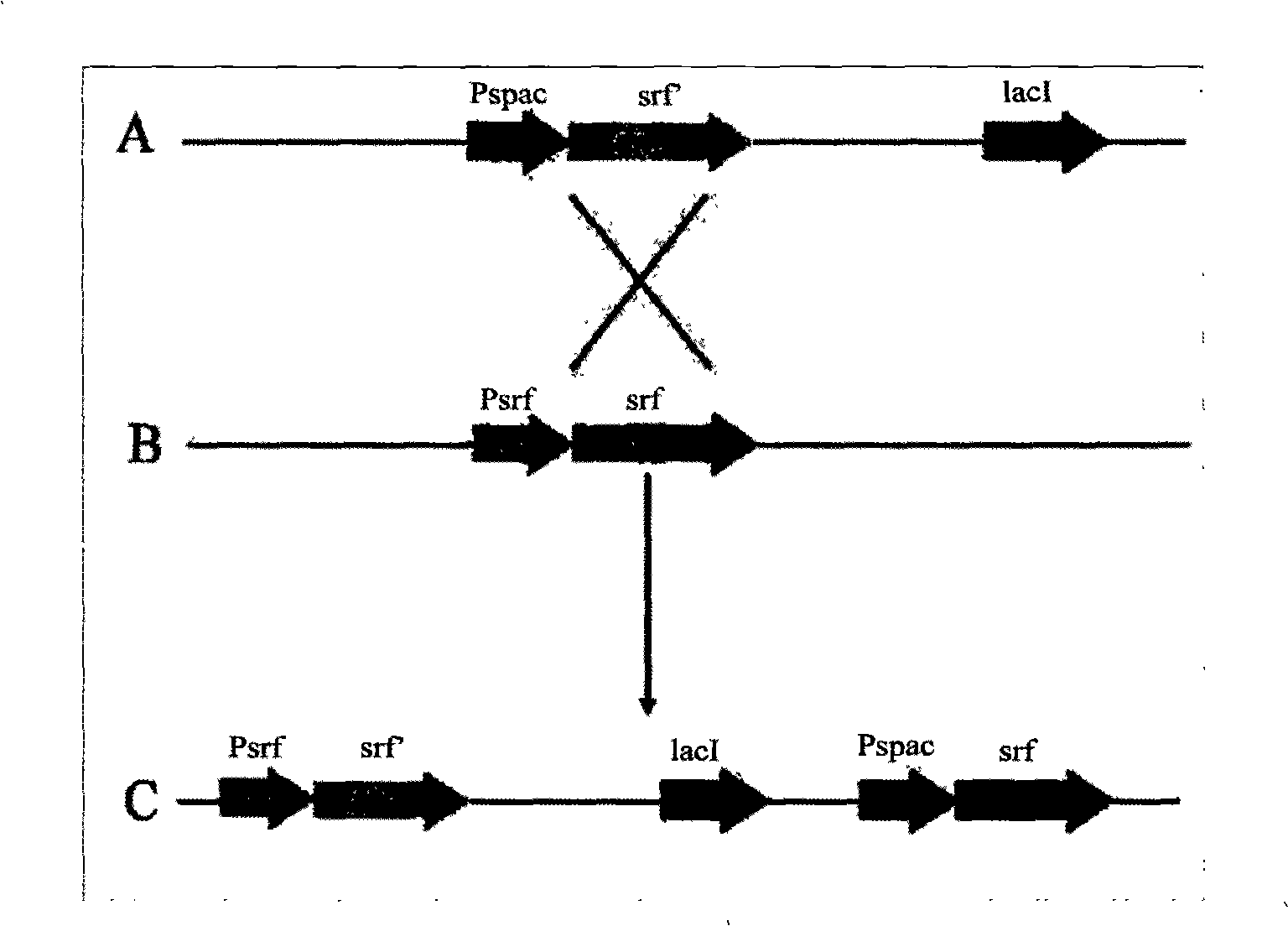
Promotor replacement method for improving volume of production of bacillus subtilis surfactin
InactiveCN101402959AIncrease productionEasy to produceBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyAntimikrobielle peptide
The invention relates to a promoter replacement method for improving the yield of Bacillus subtilis surfactin, belonging to the biotechnology field. The DNA homologous integration technology is adopted for allowing a promoter Pspac to replace the promoter of a Bacillus subtilis fmbR surfactin synthase gene. The homologous sequence of 1081bp is obtained by amplification from an fmbR strain genome through the PCR method and connected to HindIII and BamH I restriction enzyme cutting sites of a plasmid pMUTIN4, a well constructed vector is converted into wild Bacillus subtilis fmbR, thereby realizing the replacement through the screening by an antibiotic culture medium and the molecular biology method. The method can directly improve an antimicrobial peptide production strain on genetics, thereby having potential application value in industry. The yield of the strain surfactin is improved by about 4.85 times, and the yield of the surfactin can be improved by about 10 times under the IPTG induction.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
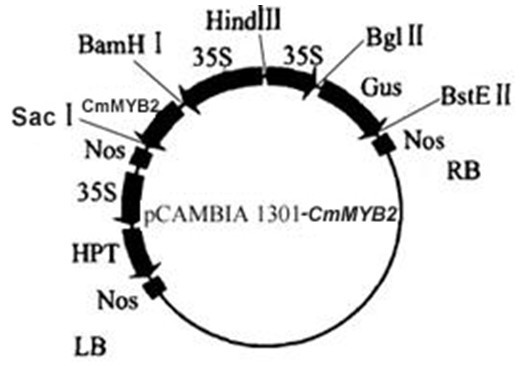
Chrysanthemum stress-resistance transcription factor CmMYB2 as well as plant expression vector, construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN102161697AImprove stress resistanceImprove salt tolerancePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a chrysanthemum stress-resistance transcription factor CmMYB2 as well as a plant expression vector, a construction method and an application thereof, belonging to the field of molecular biology. The expression vector pCAMBIA1301-CmMYB2 is constructed with the construction method which comprises the following steps: inserting the CmMYB2 gene into a colon vector pMD19-Tsimplevector (Takara); and after carrying out enzyme digestion on the CmMYB2 gene by BamHI (Takara) and SacI (Takara), connecting to the BamHI locus and SacI locus of an expression vector pCAMBIA1301. The plant expression vector is used for the genetic transformation of plants, the CmMYB2 gene is subjected to over expression under the starting of CaMV35S to synthesize a great quantity of MYB2 proteins, regulate the expression of a downstream target gene and improve plant stress resistance.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
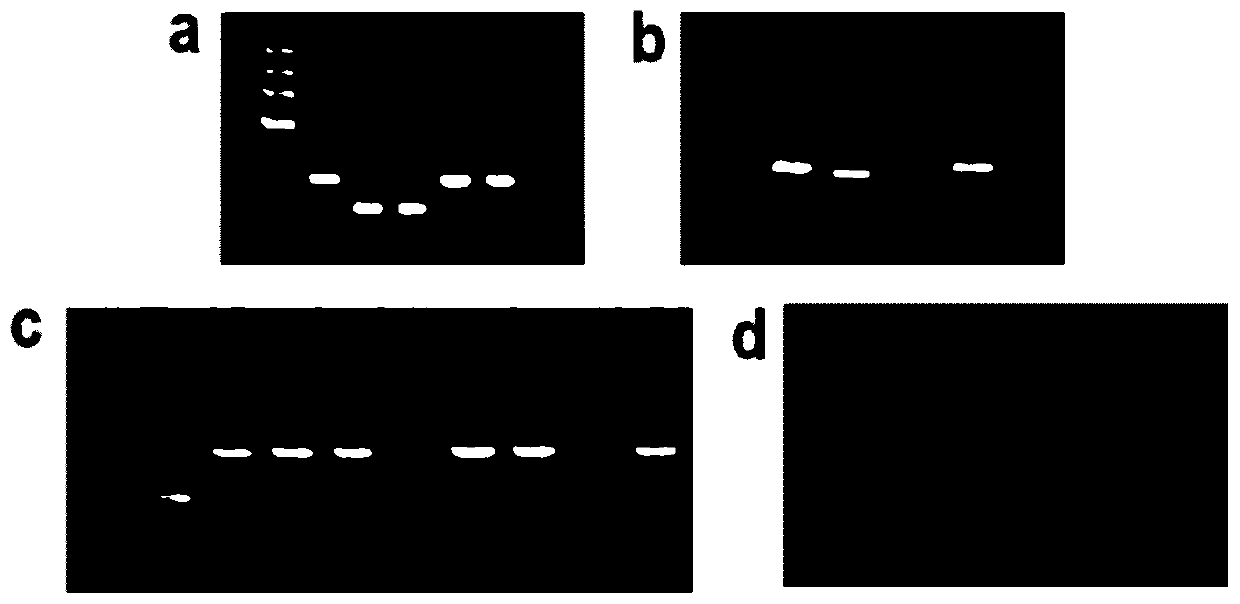
lncRNA lnc12 and application thereof in regulation of development of adventitious roots of poplar
ActiveCN110760515ARooting time delayReduced rooting rateBacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyOpen reading frame
The invention discloses lncRNA lnc12 and application thereof in regulation of development of adventitious roots of poplar, and relates to the technical field of plant molecular biology. The lncRNA lnc12 is obtained through cloning by an RACE technology, a cDNA total-length sequence of the lncRNA lnc12 is shown in SEQ ID NO:1, and one small open reading frame with length of 159 bp exists. Construction of 35S::lnc12 sORF-GFP and 35S::lnc12 5'UTR+sORF-GFP vectors and transient expression verification in protoplasts of poplar find that the lnc12 has no encoding capacity. Through lnc12 overexpression vector constructon, stable inheritance conversion of poplar and positive plant screening, lnc12 overexpression transgenic poplar is obtained, the micro-cutting rooting time of the poplar is obviously delayed, the rooting rate is significantly reduced, and the number of adventitious roots and root hair thereof is smaller than that of control plants.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
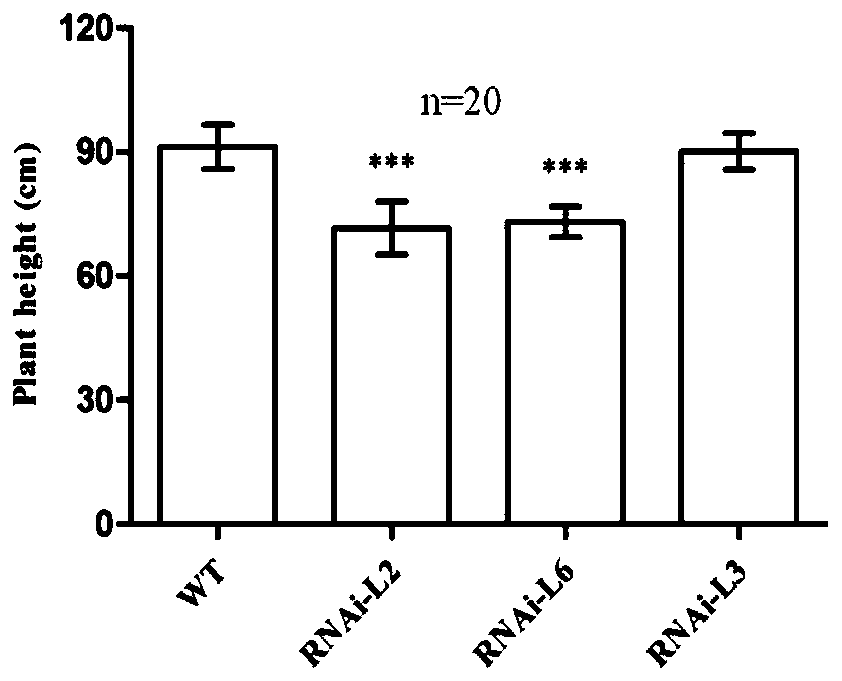
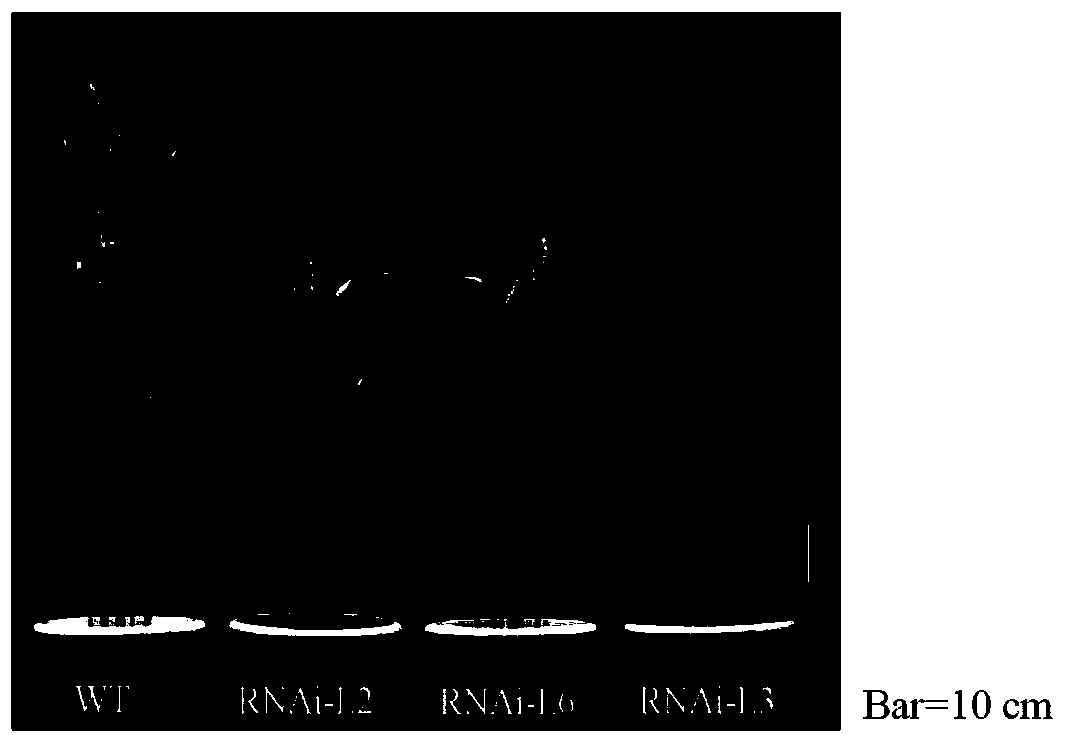
Wheat TaARF12 gene and application thereof
ActiveCN110846323AReduce plant heightGermplasm improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyWild type
The invention provides a wheat TaARF12 gene and application thereof, and belongs to the field of molecular biology of crops. A designed primer clones a coding region sequence of TaARF12 from cDNA of Chinese spring young ears, and the coding region sequence of the TaARF12 gene in homologous chromosomes A, B and D is represented as SEQ ID NO. 1-3 respectively. A TaARF12-specific RNAi fragment is selected, an RNAi vector is created, and Fierder is transformed. A CRISPR / Cas9 vector is used to create a gene editing vector containing two target sites and transform wild-type Fierder. Obtained RANi transgenic lines and gene editing lines have similar phenotypes, with plants becoming shorter and ears becoming longer. It is indicated that the wheat TaARF12 gene can regulate the plant height and theear length, and the plants become shorter and the ears become longer after the gene is interfered and expressed.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
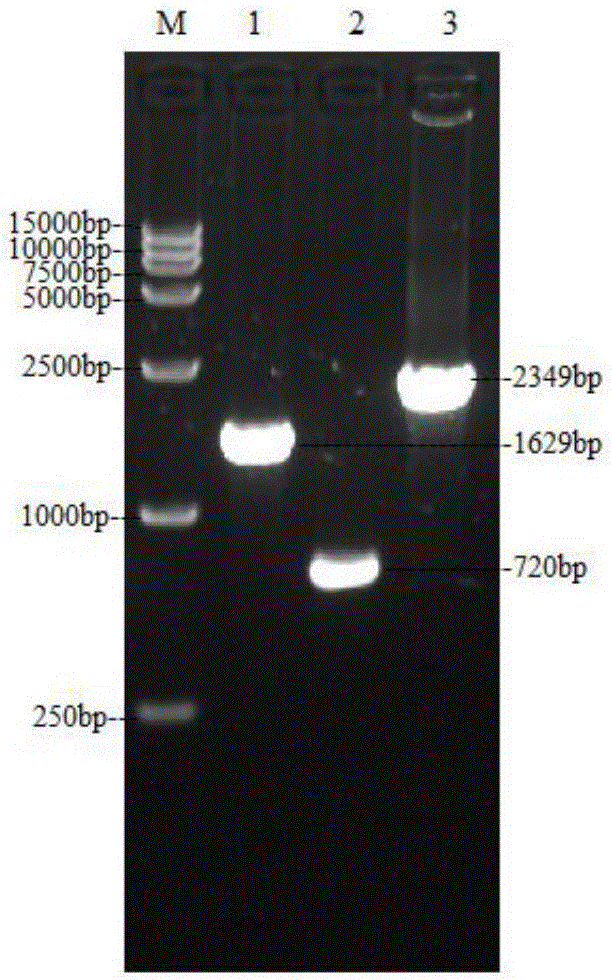
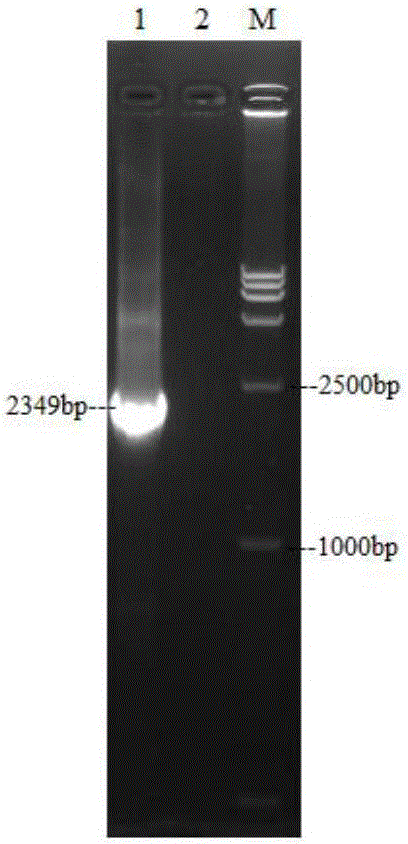
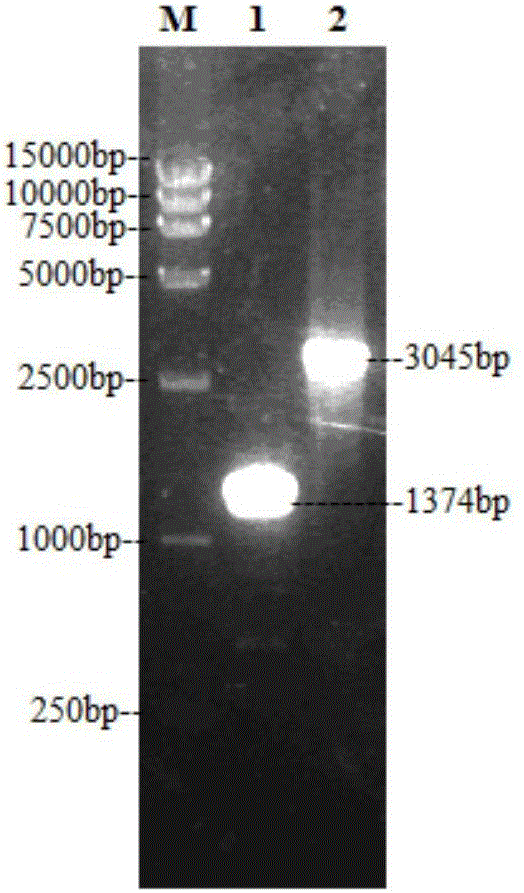
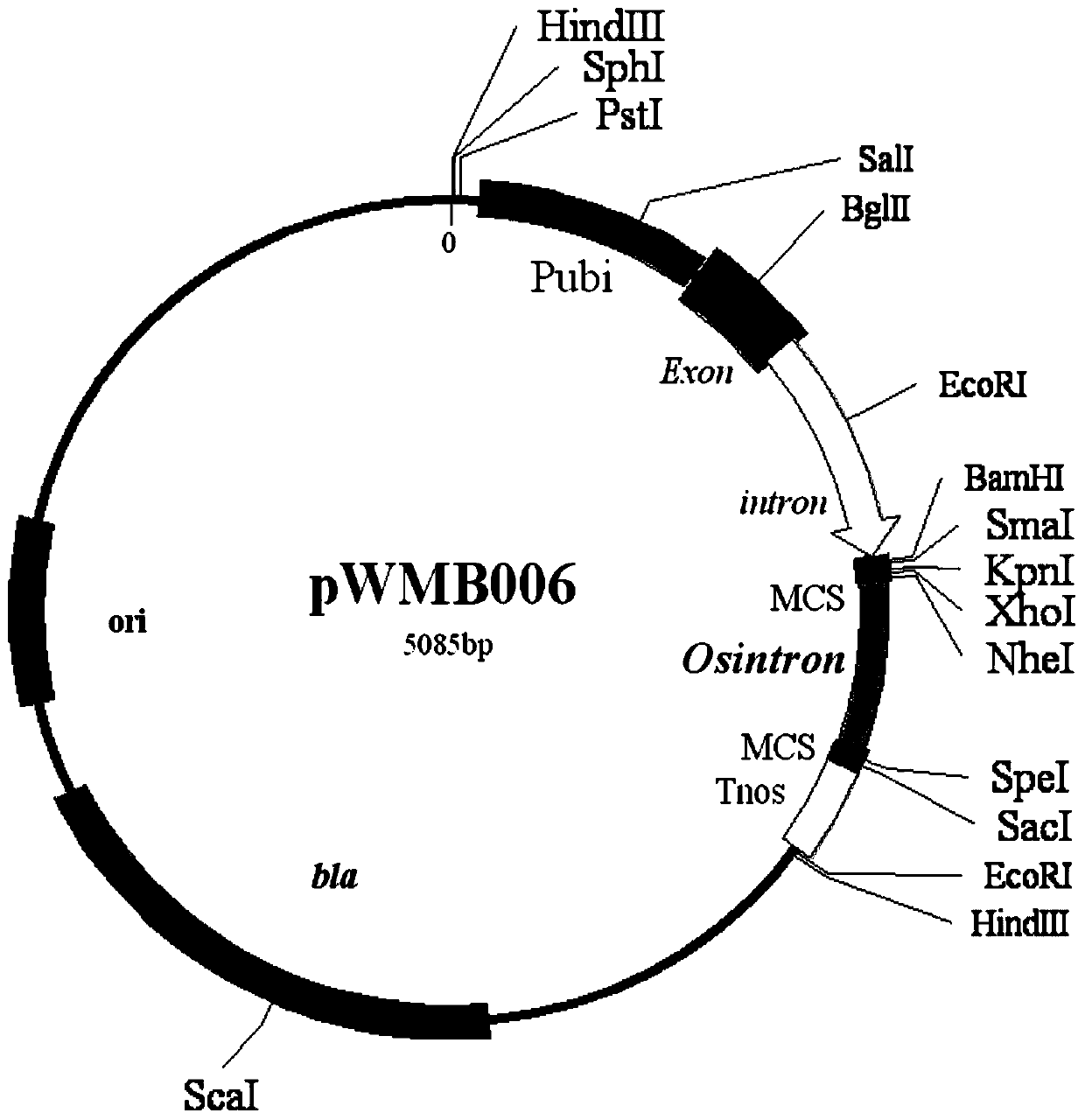
Method for constructing full-length infectious cDNA [complementary DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)] of PEDV JS2008 (porcine epidemic diarrhea virus JS2008) strains and application of full-length infectious cDNA
ActiveCN107267532AImprove efficiencySsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesSilent mutationEnzyme digestion
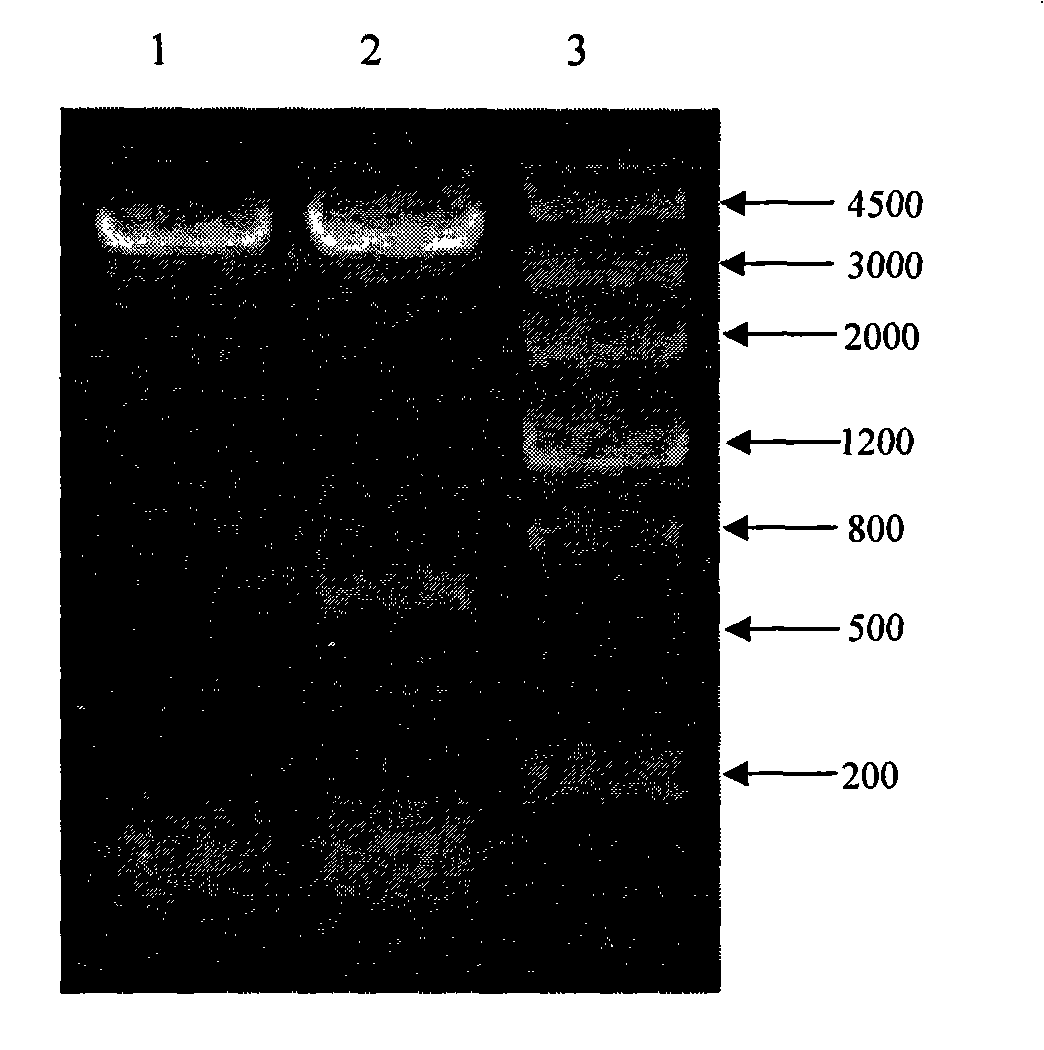
The invention provides a method for constructing full-length infectious cDNA [complementary DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)] of PEDV JS2008 (porcine epidemic diarrhea virus JS2008) strains and application of the full-length infectious cDNA, and belongs to the field of molecular biology and virology. The method for constructing the full-length infectious cDNA of the PEDV JS2008 strains includes steps of amplifying 6 fragments from reverse transcription products of total virus RNA (ribonucleic acid) of the PEDV JS2008 strains, inserting the fragments into vectors pSMART and carrying out silent mutation on enzyme digestion sites of incision enzymes PflmI at inappropriate locations; carrying out enzyme digestion on various recombinant vectors, recycling target cDNA fragments and connecting the target cDNA fragments with one another to obtain the full-length infectious cDNA of the PEDV JS2008 strains. The reverse transcription products are used as templates. The method for constructing the full-length infectious cDNA of the PEDV JS2008 strains and the application have the advantages that the method is ingenious, is high in efficiency and can be applied to rescuing porcine epidemic diarrhea viruses, and accordingly research on PEDV pathogenic mechanisms and novel vaccine can be carried out.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
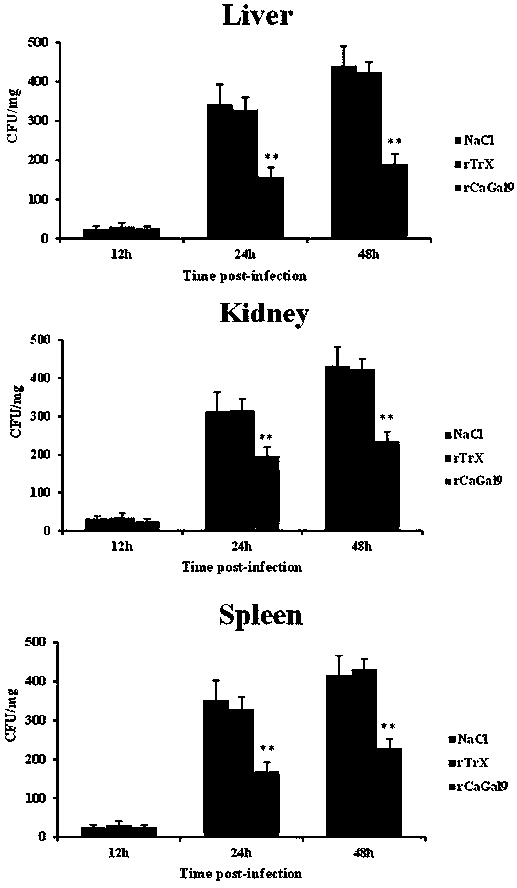
Preparation method and application of fish-derived galactose lectin CaGal recombinant protein
InactiveCN108409850AMaintain natural biological activityEasy to prepareAntibacterial agentsBacteriaEscherichia coliAquatic animal
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a fish-derived galactose lectin CaGal recombinant protein, and belongs to the field of aquatic animal molecular biology. According to the technical scheme, the cDNA of Qihe crucian carp Carassius auratus is took as a template, F / R is used as the primer for carrying out PCR amplification, the PCR product CaGal is connected with a carrier pET-32a to construct pET-32a-CaGal recombinant expression vector; the vector is transformed into escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) to obtain the escherichia coli expression strain pET-32a-CaGal-BL21 which can express the galactose lectin CaGal recombinant protein, and the galactose lectin CaGal recombinant protein can be obtained through separation and purification. The galactose lectin CaGal recombinant protein can keep the natural biological activity, so that pathogenic bacteria such as aeromonas hydrophila can be effectively inhibited, the antibacterial effect is obvious, and the preparation method is simple and can be used as a novel fish immune additive or an antibacterial drug.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
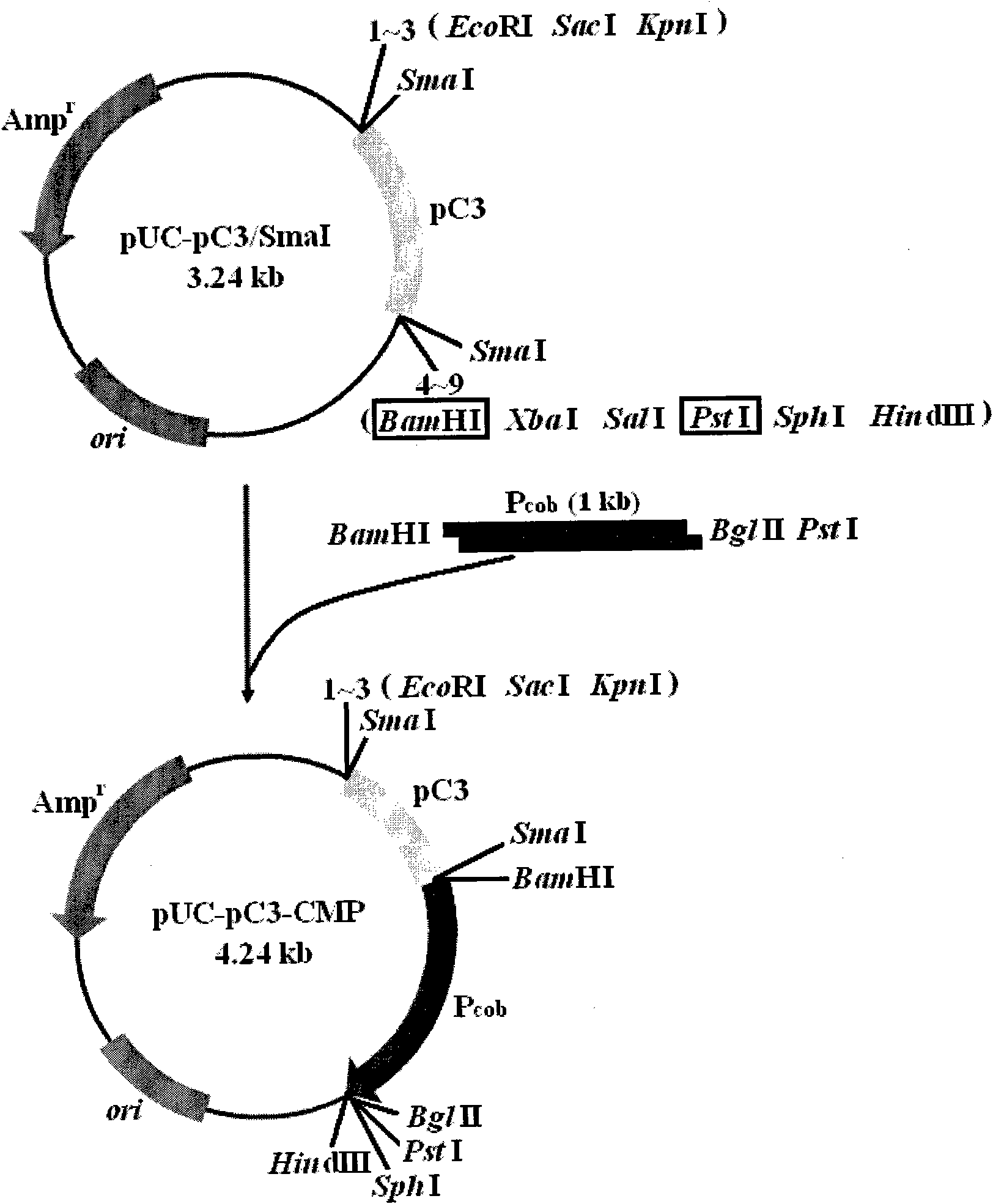
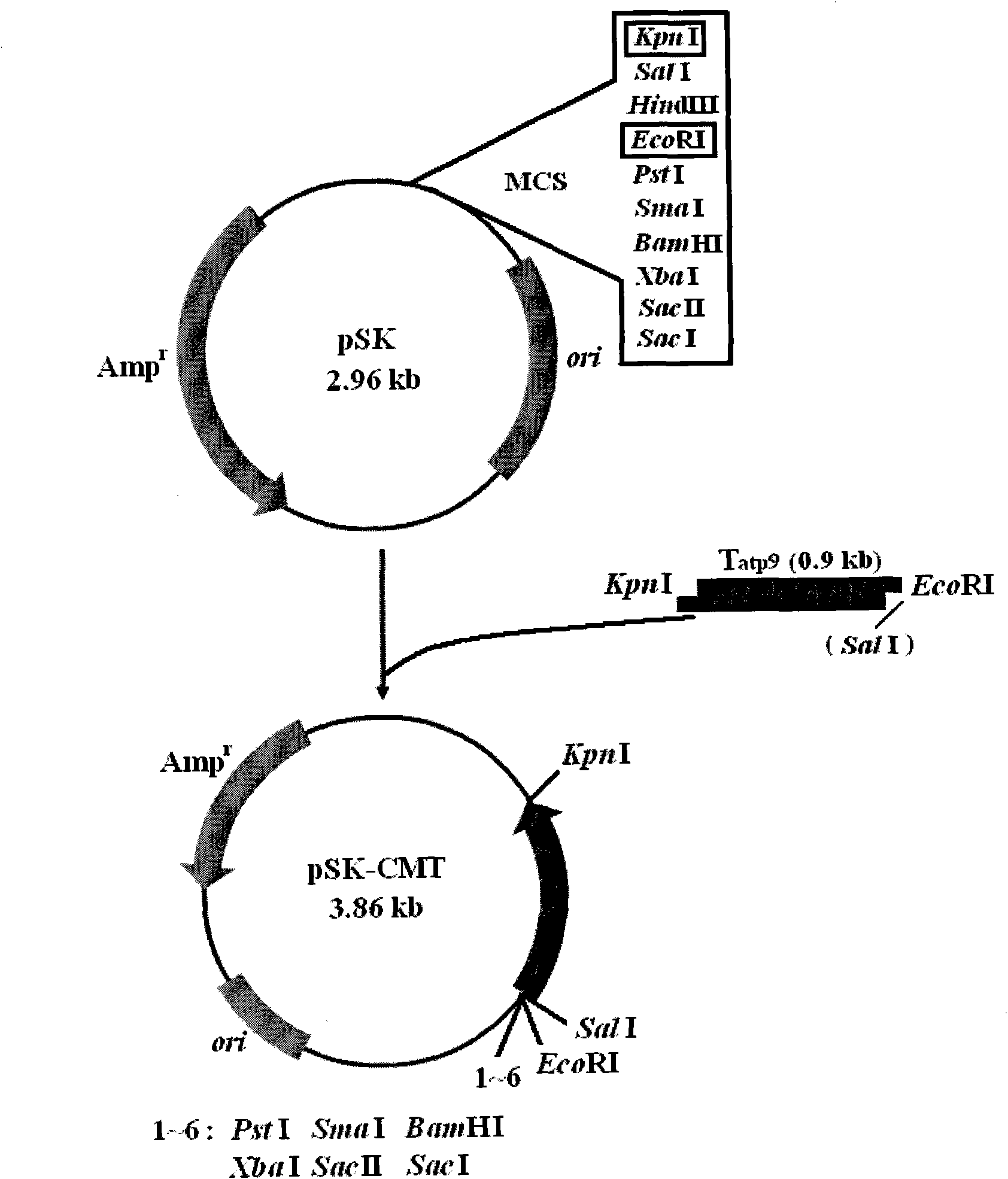
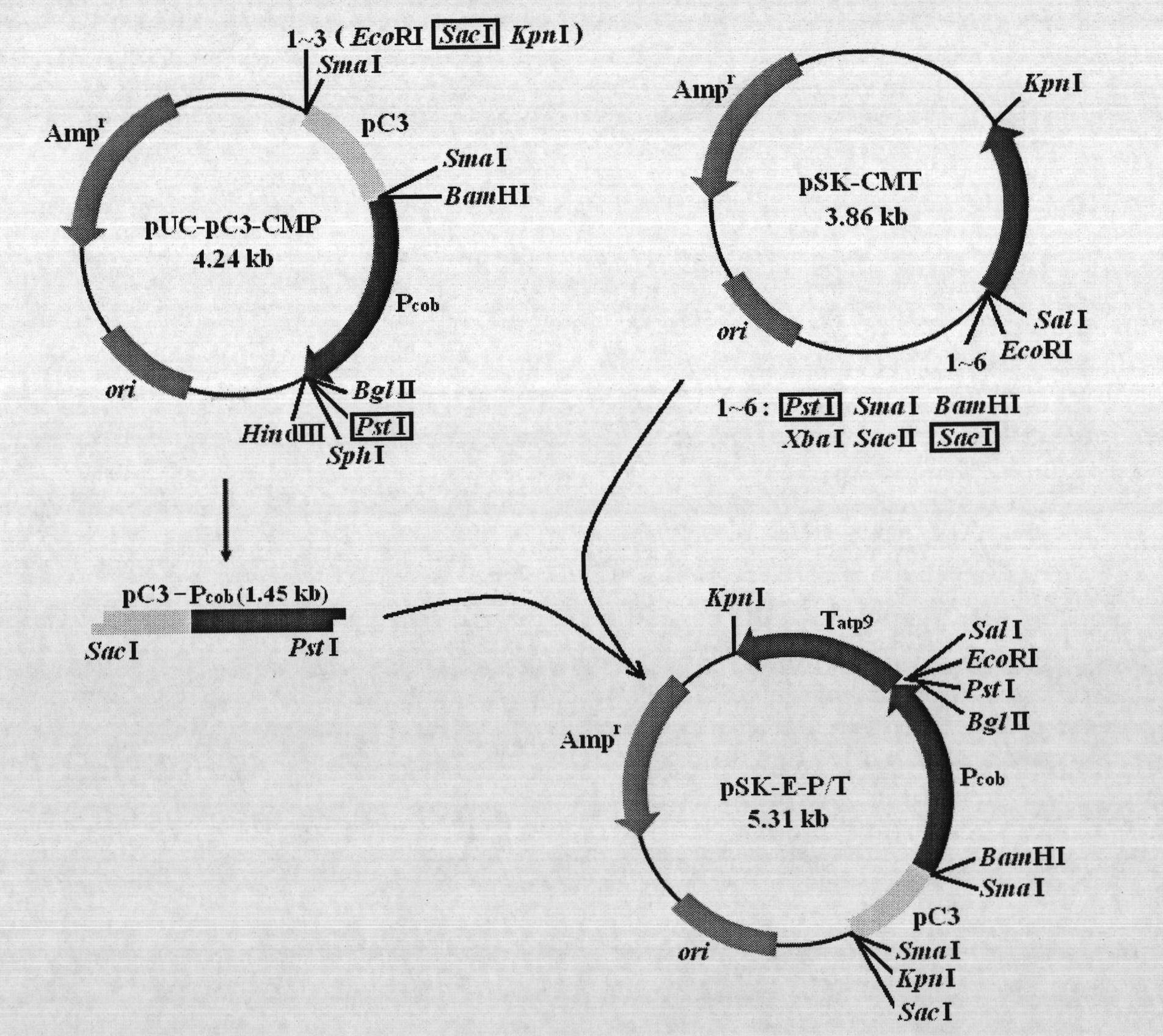
General expression vector pSK-E-P/T construction for plant mitochondria and promoter activity identification
InactiveCN101974560APromote cloningEasy to filterBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPromoter activity
The invention relates to general expression vector pSK-E-P / T construction for plant mitochondria and promoter activity identification. Cucumber mitochondria plasmids pC3 (sequence 1) are discovered for the first time, a gene cob upstream promoter sequence (sequence 2) and a gene atp9 downstream terminator sequence (sequence 3) of the cucumber mitochondria obtained through PCR (polymerase chain reaction) are constructed into a general expression vector pSK-E-P / T (sequence 4) of the plant mitochondria, and the vector also carries replicons copied in escherichia coli and Ampr resistance genes so as to facilitate cloning of exogenous genes and recon screening. Measurement of enzyme activity of promoter -1acZ report gene fusion plasmids in the escherichia coli and fluorescence microscope observation of psk-E-GFP for transforming the green fluorescence of the escherichia coli prove that the promoter on the expression vector has transcriptional activity. The invention provides a novel molecular biology technology tool for researching important life science hotspot problems such as cell apoptosis and the like related with the mitochondria by a mitochondria transformation path.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
E.tenella TERT associated protein gene and medical uses thereof
InactiveCN104946667AEasy to findEasy to operateAntiparasitic agentsAntibody medical ingredientsTelomeraseActivity regulation
The present invention provides an E.tenella TERT associated protein gene, and particularly relates to applications of the protein in telomerase activity regulation, wherein the protein has a negative regulation effect on the E.tenella telomerase activity, and develops the new research field for deep research on cell and molecular biology characteristics of coccidian and finding of new chicken coccidian preventing and treating drugs, vaccine acting target sites and the like. According to the present invention, the advantages of high efficiency and practicality are provided, a plurality of positive interaction proteins can be obtained through the yeast two-hybrid screening and verification so as to easily find the new function protein, and the method of the present invention is mature and is easy to operate compared with the comparative analysis, the proteomics, the transcriptomics, and other technologies; and the E.tenella virus transforming vector-mediated ribozyme provides the simple and easy-performing method for the research on the functions of the gene in the insect body.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Identification method and application of coding protein Pm_MF
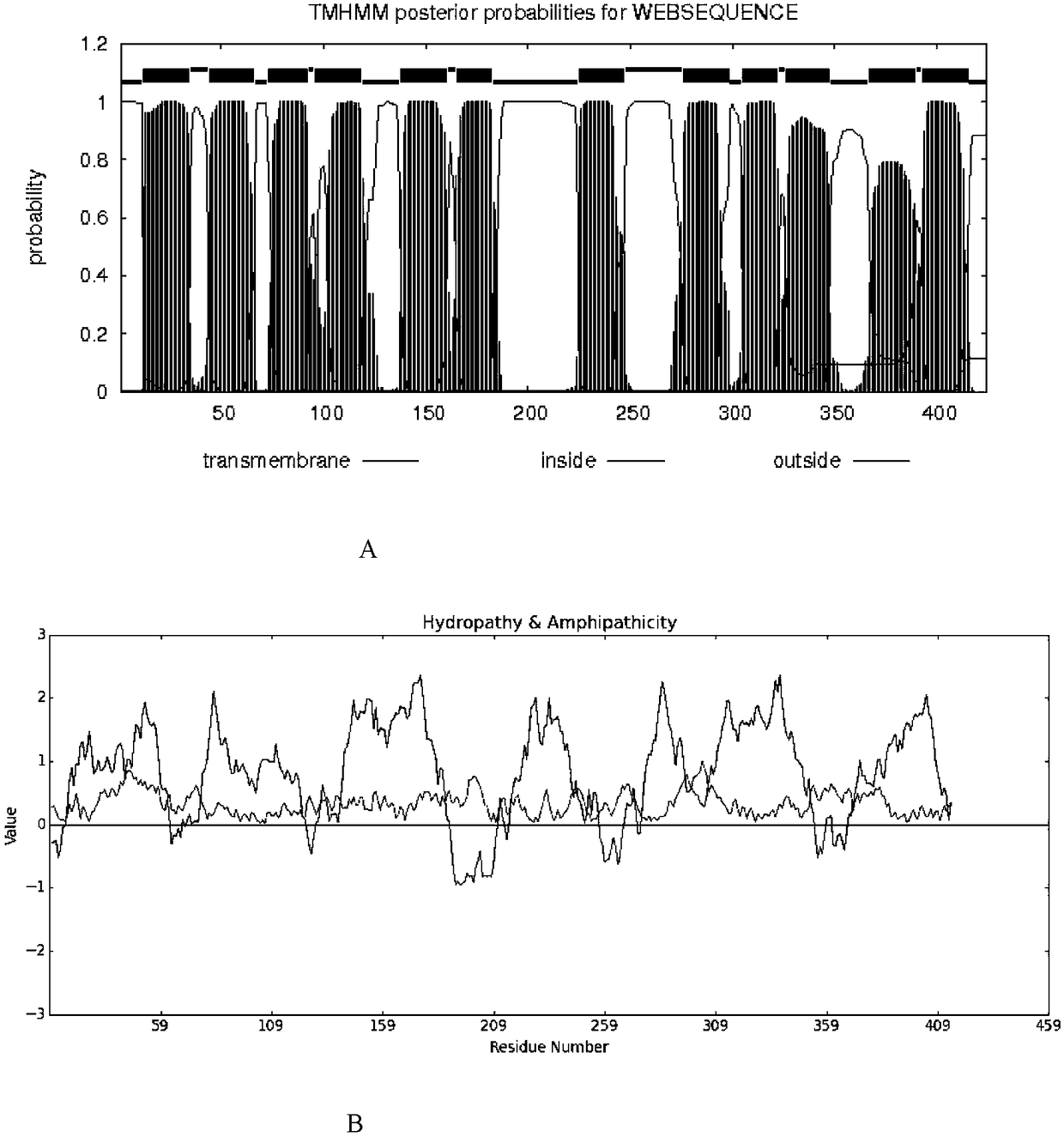
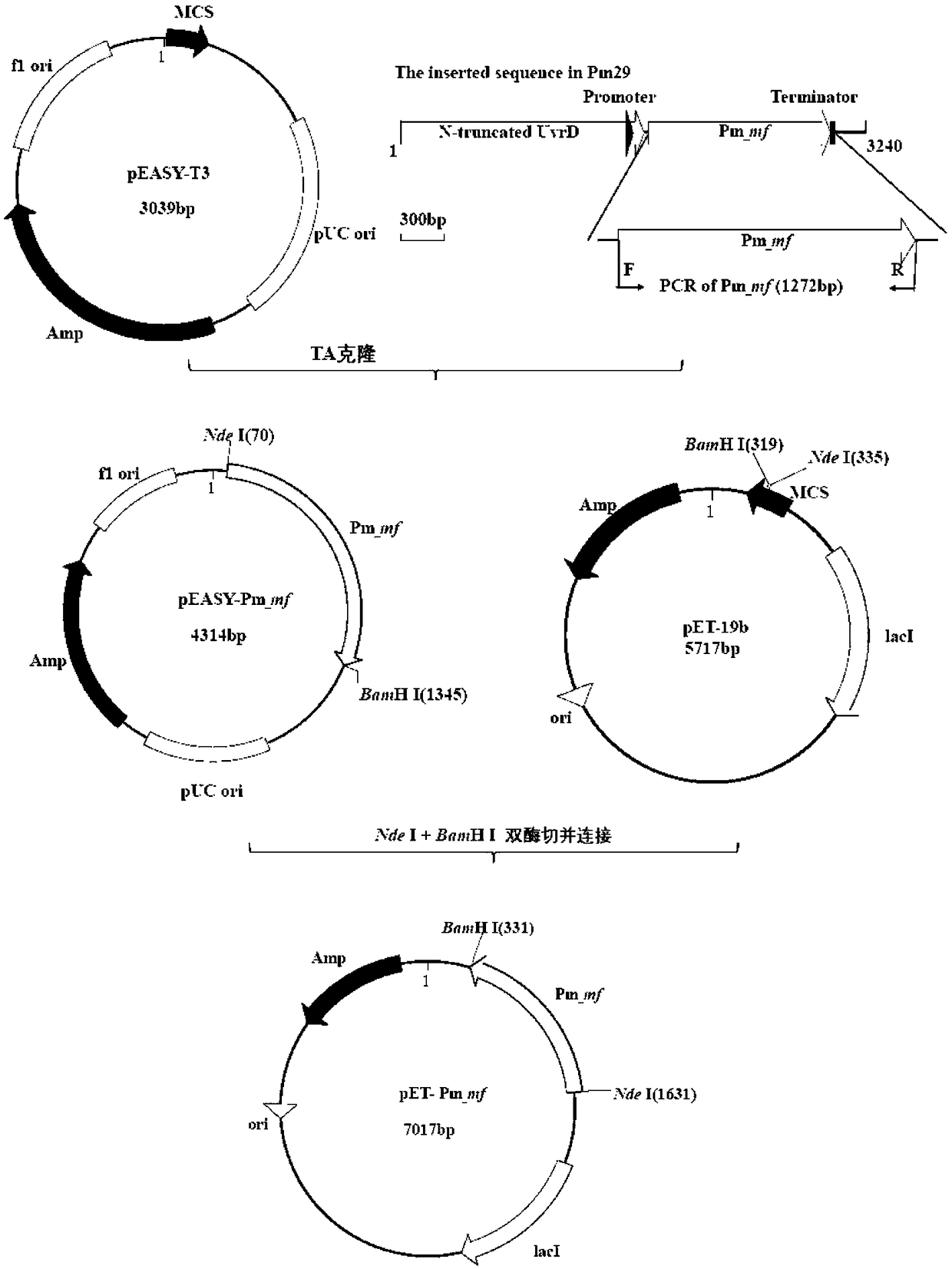
PendingCN108330141AImprove salt-alkali toleranceRich microbial salt-alkali tolerance gene resourcesBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringOpen reading frame
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology and genetic engineering, and discloses an identification method and application of coding protein Pm_MF. The amino acid sequence of the protein Pm_MF is SEQ ID NO.2; the protein gene Pm_mf is a 1272bp complete open reading frame ORF; the nucleotide sequence of the ORF is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The identification method comprises thefollowing steps of screening out a fragment containing a saline-alkaline tolerance gene, building a prokaryotic expression vector containing the Pm_mf gene, and the like. The protein provided by the invention can be used for building the efficient saline-alkaline tolerance engineering bacteria or stress resistance crops and the like; various medicine resistance protein functions can be used for gene engineering carrier screening marking; particularly, great values are realized by the duplex functions of saline-alkaline tolerance capability and the medicine resistance screening marking in aspects of saline-alkaline stress resistance gene engineering strains and plants.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Novel lipase as well as gene, engineering bacteria and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107365755AImprove heat resistanceEfficient expressionFungiBacteriaPichia pastorisWild type
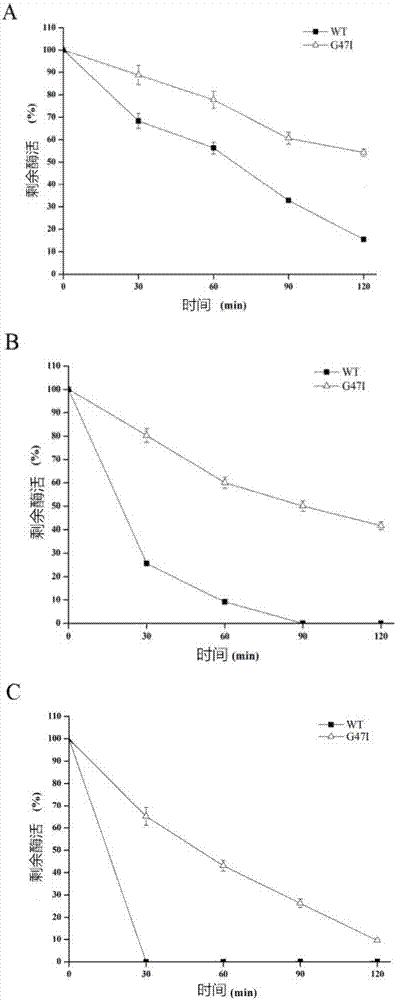
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering of enzyme, and particularly relates to novel lipase as well as a gene, engineering bacteria and a preparation method thereof. A wild-type lipase gene is obtained by virtue of a molecular biology technical means, after a recombinant vector is established by virtue of digestion, connection and the like, an error-prone PCR technique is used for randomly mutating the wild-type lipase gene to obtain a lipase mutant G47I and a coded gene mpcl3 thereof, the recombinant vector is re-established, so that the high-efficient expression in bacillus subtilis WB600 and pichia pastoris GS115 can be realized, and heat-resistant lipase can be obtained by virtue of techniques such as fermentation and extraction.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus as well as cloning vector and gene insertion method thereof
InactiveCN111996174AGenetic stabilityMaintain growth characteristicsSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsCdna cloningGenetic engineering
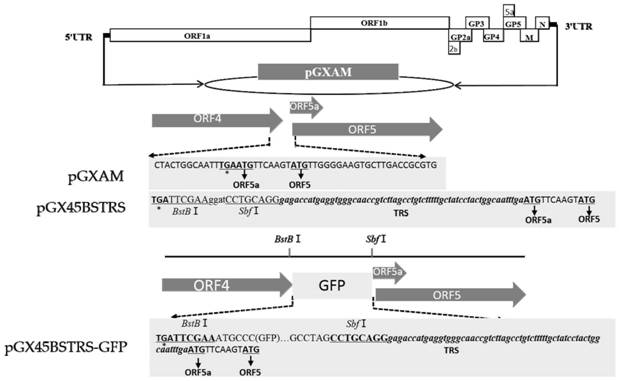
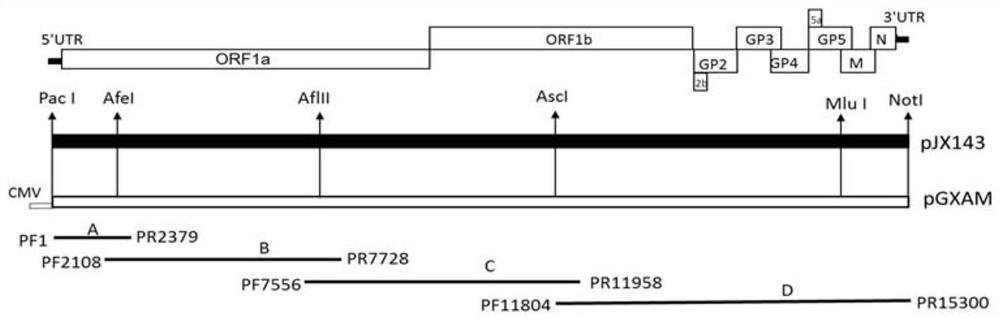
The invention discloses a porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus with a preservation number of CCTCC NO:V 202020. Accordingly, the inventor constructs virus genome full-length infectiousclone pGXAM and establishes a corresponding construction method and a gene insertion method. According to a vector, Gxnn1396-P96 is used as a female parent, and Gxnn1396-P96 is used as a male parent,a PRRSV full-length infectious clone vector is constructed by means of molecular biology, an independent transcription regulating sequence (TRS) is inserted into ORF4 and ORF5a on the basis of cDNA cloning, and the PRRSV recombinant virus for expressing a green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene is constructed. The successful construction of the fluorescence labeled virus lays a foundation for the development of recombinant porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus genetic engineering vaccines.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
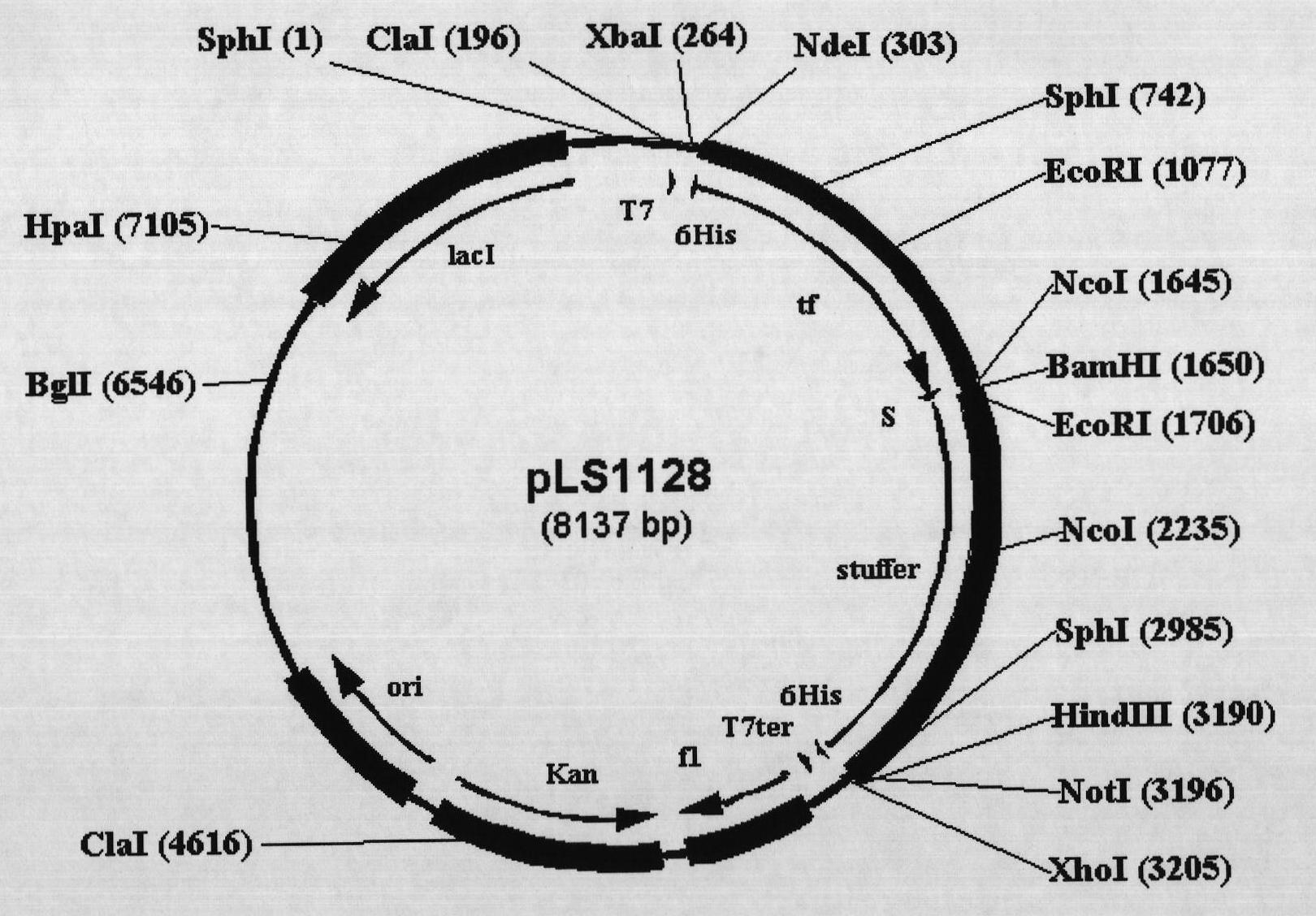
Escherichia coli protein expression vector using trigger factor as fusion tag and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN101921800AConvenient inductionGuaranteed dose effectHybrid peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionNicotiana tabacumProtein target
The invention relates to an Escherichia coli protein expression vector pLS1128 using a trigger factor originated from Escherichia coli as a fusion tag. The vector is obtained by cloning nucleotide sequences of six coded histidines, a trigger factor gene, a base sequence of a cleavage site of coded tobacco etch virus protease and a filling segment for cloning to an Escherichia coli expression vector pET30a. After a target gene is cloned to the downstream of the trigger factor gene by a gene cloning means, the target gene and the trigger factor gene are inducted to express fusion protein; the trigger factor functions as chaperone; and the target protein is promoted to be folded correctly so as to show a dissoluble state. The vector of the invention can be widely applied to expression on and the dissolubility of the target protein, research of genetics, molecular biology, biochemistry and the like and industrial production of the target protein.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Recombinant polymerase, encoding gene, preparation method, vector, kit and application
PendingCN112661861AImprove continuous synthesis abilityImprove scalabilityFermentationHybrid peptidesEscherichia coliProtein target
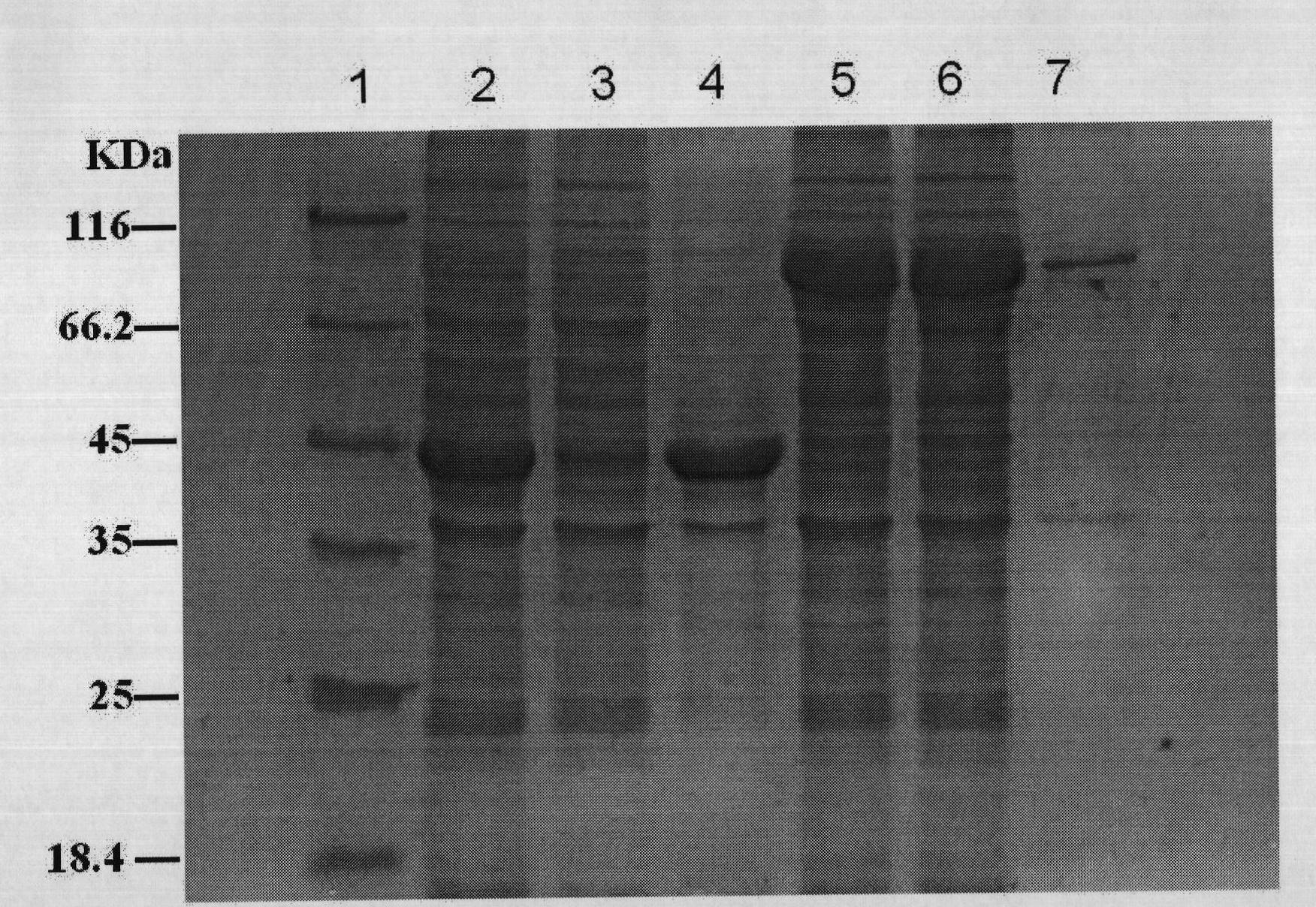
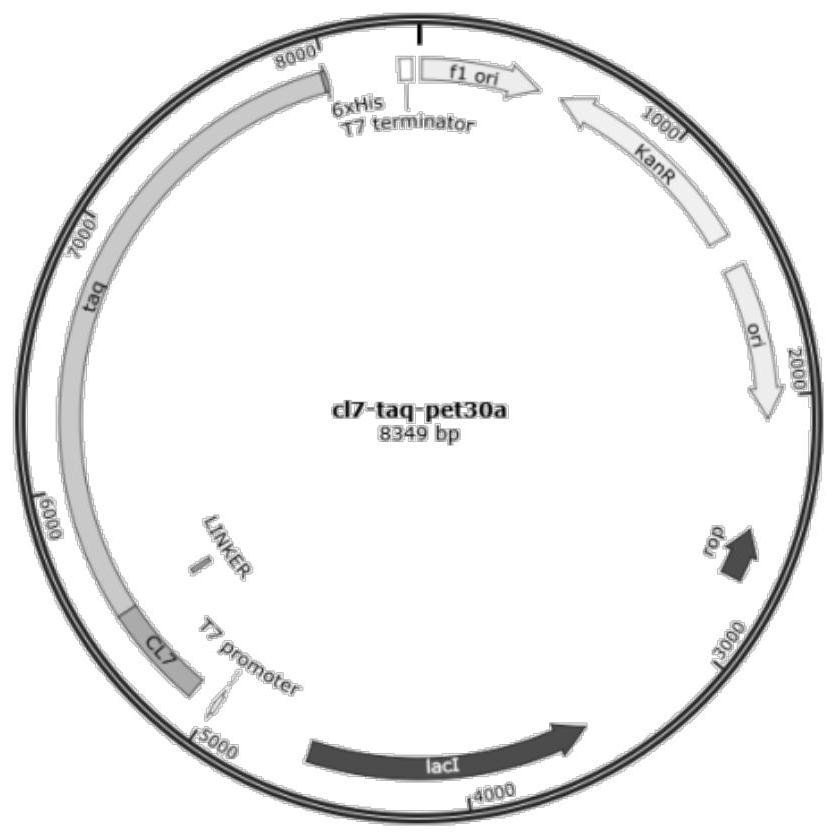
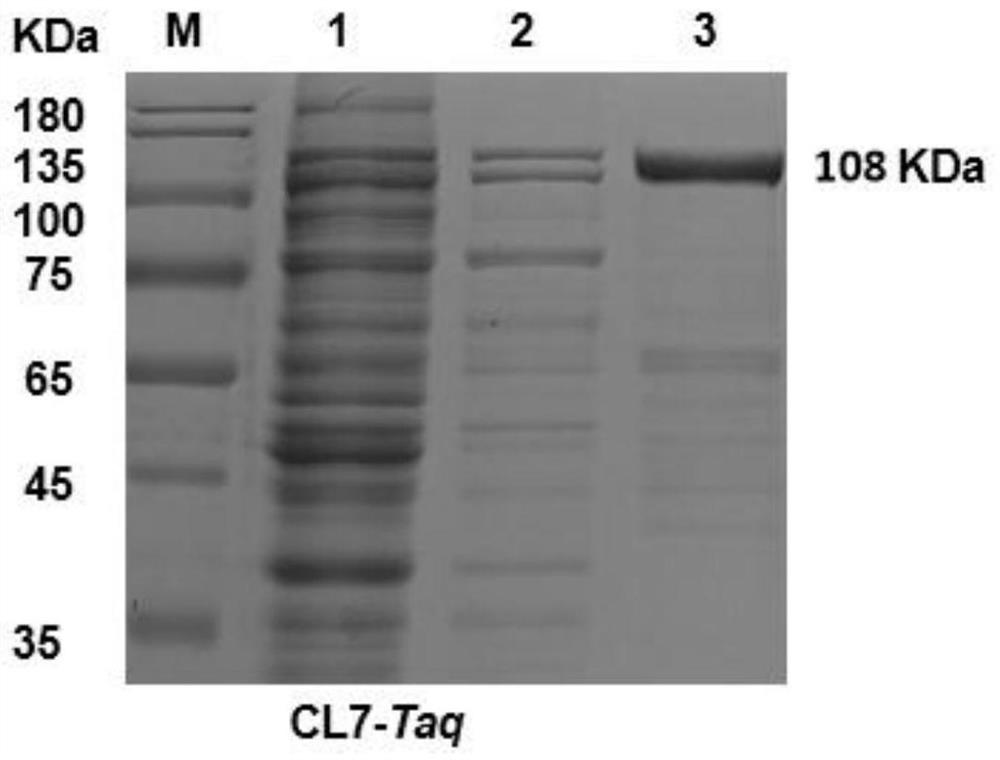
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology and protein engineering, and discloses a recombinant polymerase, an encoding gene, a preparation method, a carrier, a kit and application; wherein the recombinant polymerase is derived from a hybrid DNA polymerase obtained by covalently connecting a protein Cl7 to the N end of a Taq DNA polymerase protein sequence in a Thermous aqueatus YT1 strain through a flexible connection sequence, and the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID No.4; or the sequence is an amino acid sequence which is formed by replacing, deleting or adding one or more amino acids and has the same function. The expression vector pET30a-Cl7-Taq disclosed by the invention is used for converting escherichia coli and inducing expression to obtain a target protein Cl7-Taq. The continuous synthesis capability of TaqDNA polymerase in PCR nucleic acid amplification is greatly improved, and the TaqDNA polymerase has a wide application prospect.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Specificity overexpression mouse model of transduction iASPPsv cancer gene in hemopoietic system and preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN101899445AReduce in quantityImprove proliferative abilityFermentationIn-vivo testing preparationsProgenitorEnzyme digestion
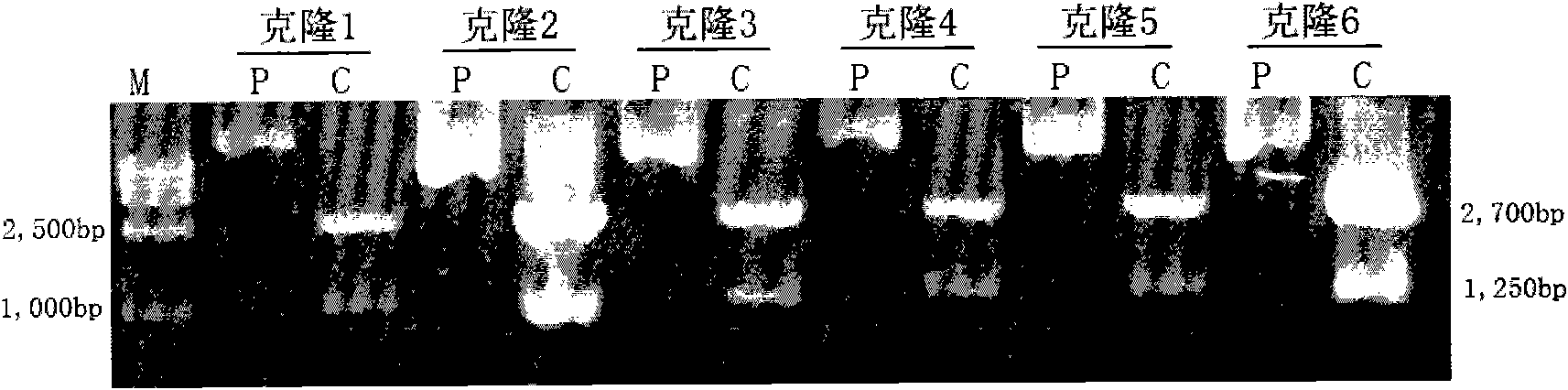
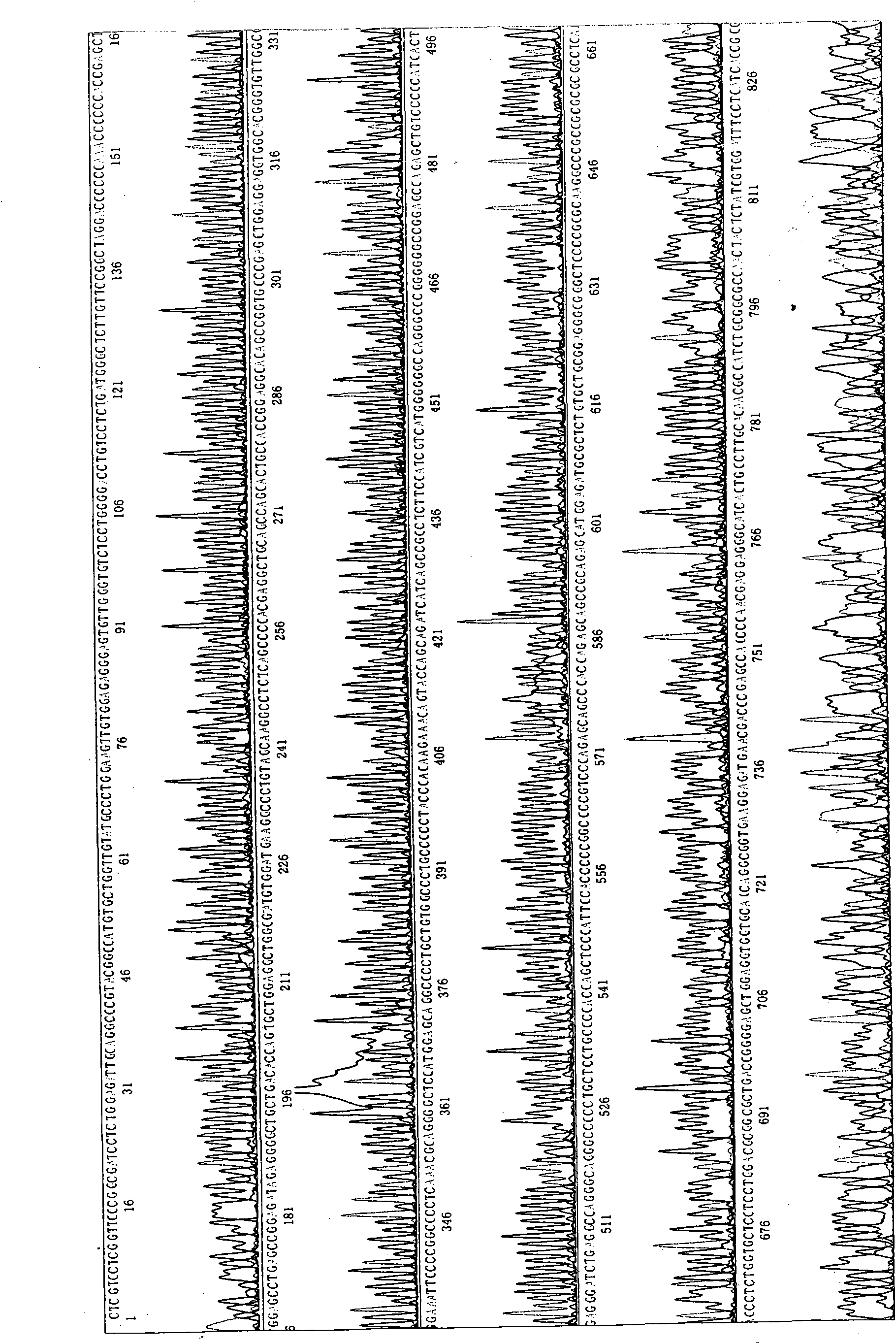
The invention discloses a specificity overexpression mouse model of a transduction iASPPsv cancer gene in a hemopoietic system and a preparation method and the use thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing an hM HS21 / 45vav-iASPPsv plasmid, removing a prokaryotic expression vector part after the plasmid is subjected to the Hind III enzyme digestion, and standing the product for low-voltage electrophoresis over night after the linearization followed by glue cutting, recovery, purification and nucleic acid concentration regulation. By the method of microinjection, the transgenic vector, hM HS21 / 45vav-iASPPsv, is injected to a zygote of a C57 mouse, and the zygote is implanted in a uterus of a pseudopregnancy mouse. 19 to 21 days after the operation, a new mouse is born and subjected to ear cutting, numbering and tail cutting after 3 weeks. DNA is extracted from the tail to detect the integration of the target gene, iASPPsv, by using PCR. The specificity overexpression mouse model of the transduction iASPPsv cancer gene in hemopoietic system is obtained by using molecular biology, experimental zoology and the like to successfully establish an experimental method for detecting the amplification, oriented differentiation, migration, apoptosis and the like of hematopoietic stem / progenitor cells and lay a foundation for the mechanism research and targeted therapy for further explaining the transformation of normal hematopoietic stem / progenitor cells to tumor cells.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
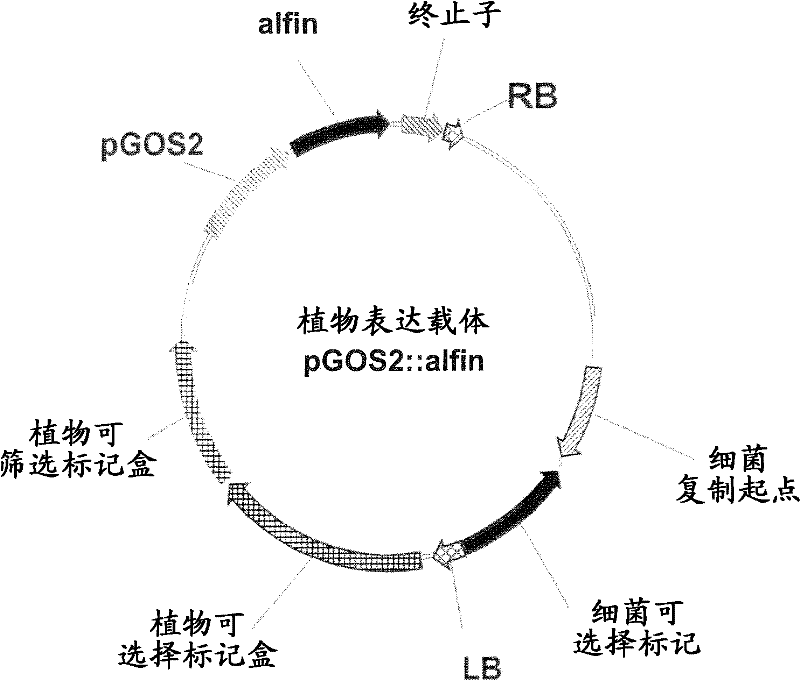
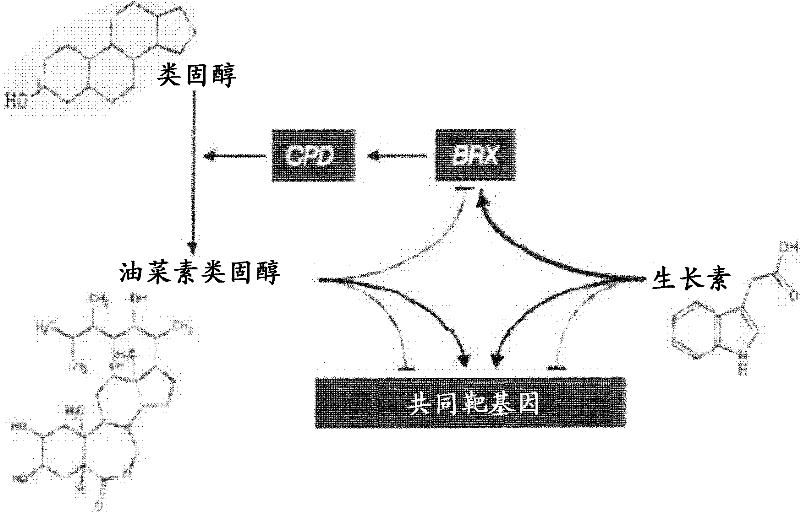
Plants with enhanced abiotic stress tolerance and/or enhanced yield-related traits and methods for their preparation
InactiveCN102300991AClimate change adaptationVector-based foreign material introductionGrowth plantWild type
The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and relates to methods for enhancing various plant yield-related traits by increasing expression in plants of nucleic acid sequences encoding Brevis Radix-like (BRXL) polypeptides. The present invention also relates to plants having increased expression of a nucleic acid sequence encoding a BRXL polypeptide, said plants having enhanced yield-related traits relative to control plants. The invention also relates to nucleic acid sequences, nucleic acid constructs, vectors and plants comprising said nucleic acid sequences.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
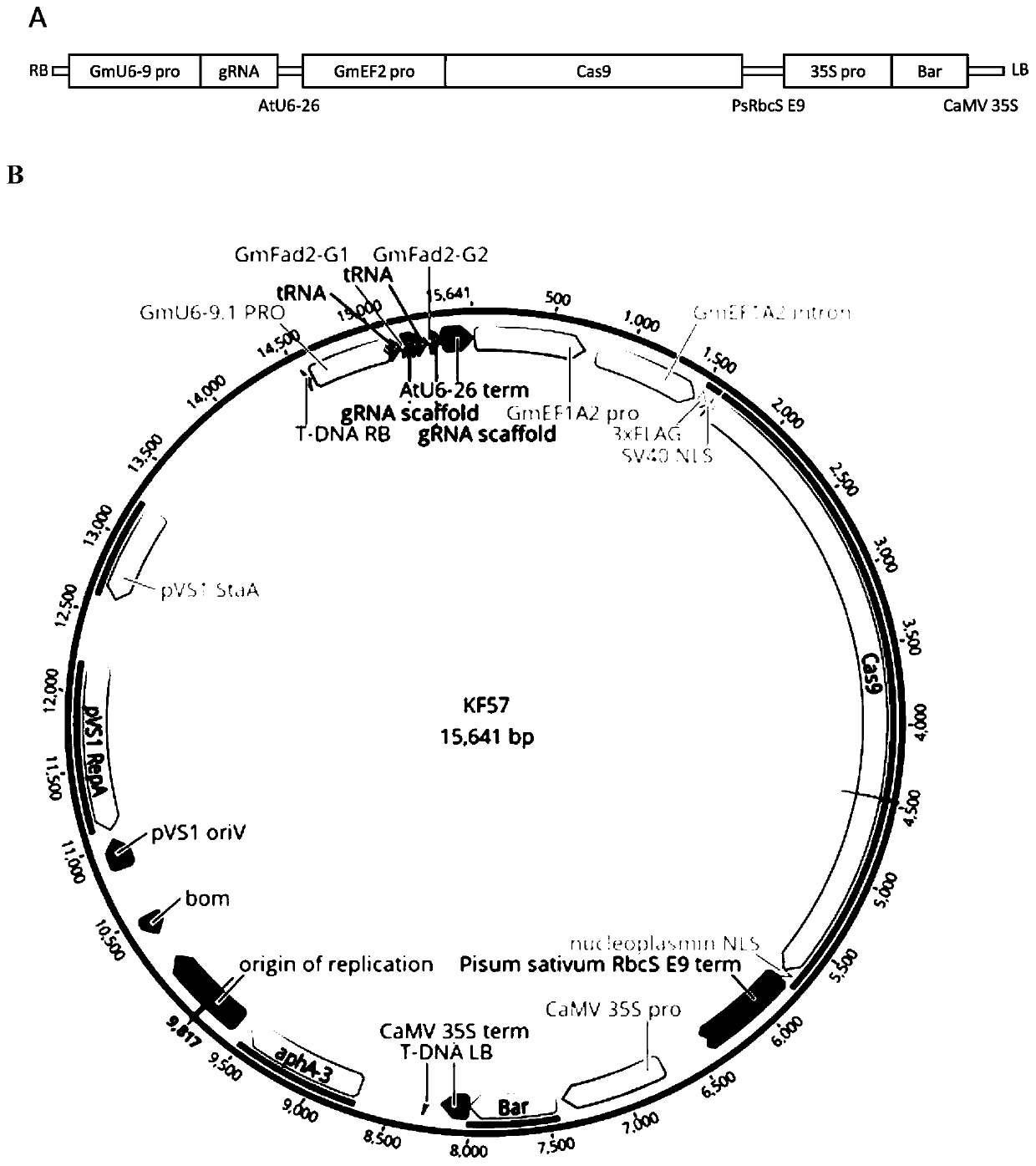
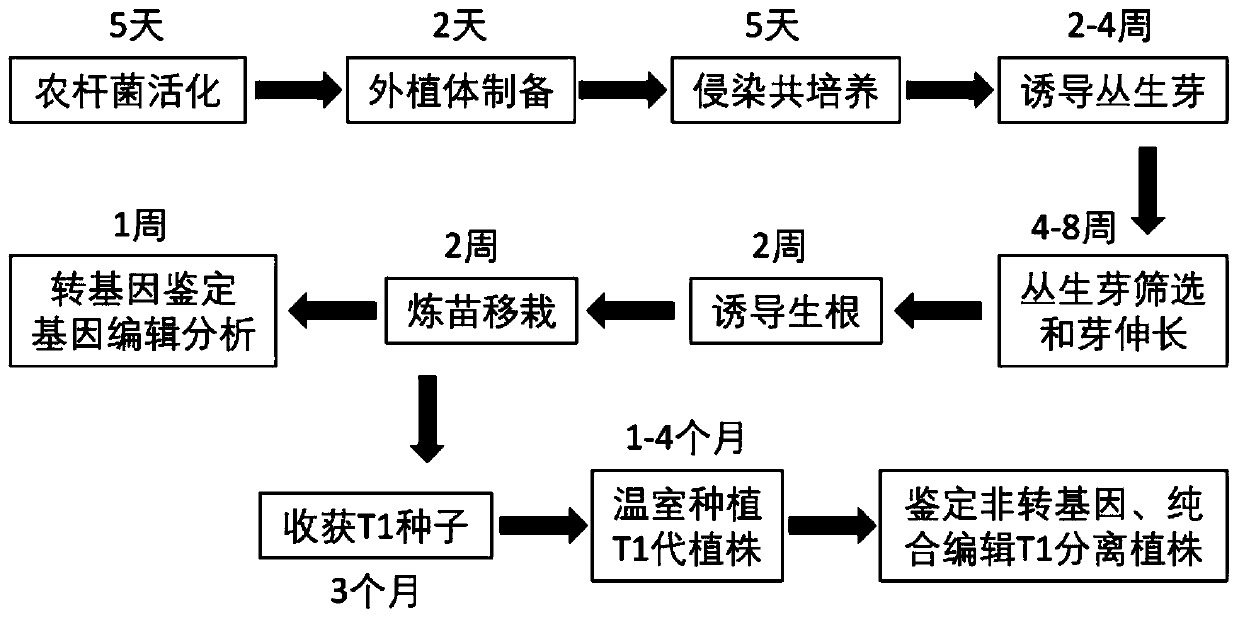
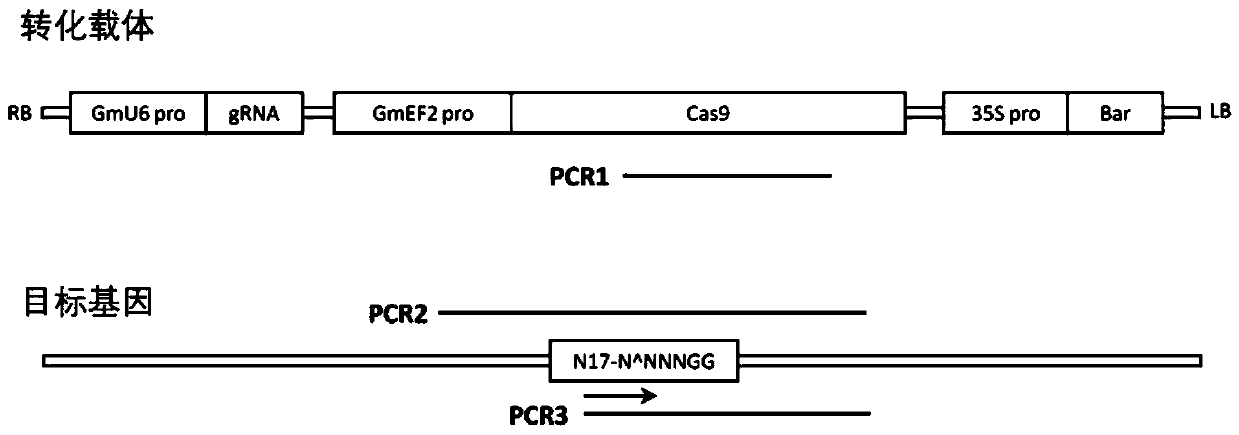
Genetic transformation, gene editing and analysis methods of main soybean varieties
PendingCN111073904ARapid genetic transformationEfficient genetic transformationPlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionVector (molecular biology)Promoter
The invention belongs to the field of crops, and particularly relates to genetic transformation, gene editing and analysis methods of main soybean varieties. The invention discloses a gene editing andtransforming vector which is based on a CRISPR / Cas9 system and takes an agrobacterium transforming vector pCambia3301 as a skeleton, and a promoter is designed for improving expression of Cas9 and gRNA. According to the invention, rapid and effective genetic transformation of the main soybean varieties is realized for the first time, and a simple and rapid PCR amplification sequencing analysis method for identifying the gene editing effect is developed. Through genetic separation and screening by molecular biology analysis technology, gene editing offspring plants which do not carry exogenousgenes of the soybean varieties for production are successfully obtained, and editing sites are stably inherited.
Owner:北大荒垦丰种业股份有限公司
Method for exogenous gene expression optimization in salmonella
InactiveCN103074357AHigh expressionVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliNucleotide
The present invention provides a method for exogenous gene expression optimization in salmonella. The method comprises the following specific steps: carrying out statistics from a NCBI database to obtain a salmonella codon usage frequency table; analyzing usage frequency of every codon; cloning or synthesizing a target gene, determining a nucleotide sequence of the target gene, adopting a molecular mutation manner or a gene synthesis manner to carry out mutation of the codon having a lowest salmonella codon usage frequency and the codon having a higher salmonella codon usage frequency in the target gene into the codon having a highest usage frequency under a condition of no change of amino acids according to the salmonella codon usage frequency table and an amino acid codon corresponding table to obtain a new nucleotide segment encoding the target gene; adopting a molecular biology method to insert the new nucleotide segment encoding the target gene into an expression vector, transforming the obtained vector to gene engineering escherichia coli, and identifying the obtained clones; and transforming the target gene-containing expression vector into salmonella, wherein the target gene-containing expression vector is identified, and a correct result is obtained.
Owner:GUANGDONG DAHUANONG ANIMAL HEALTH PRODS +1
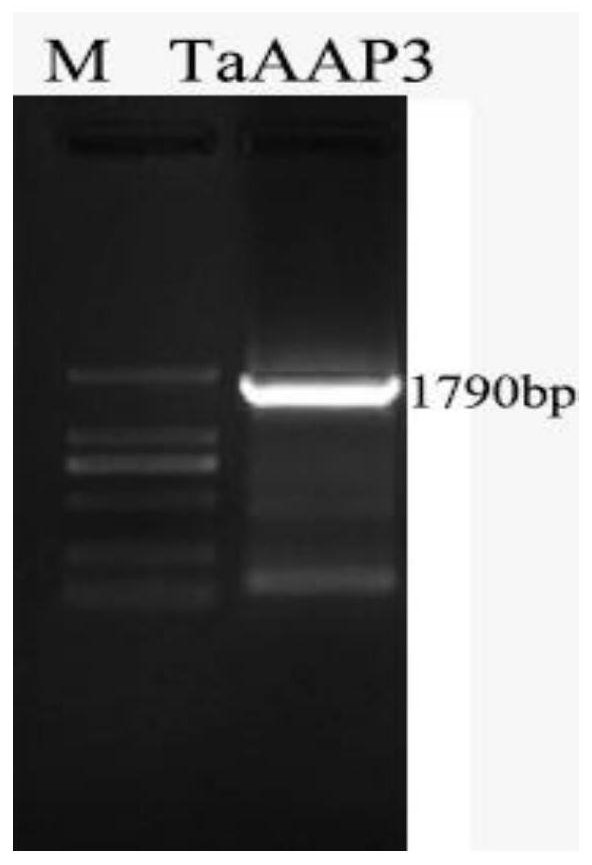
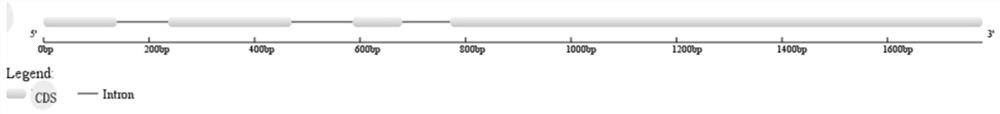
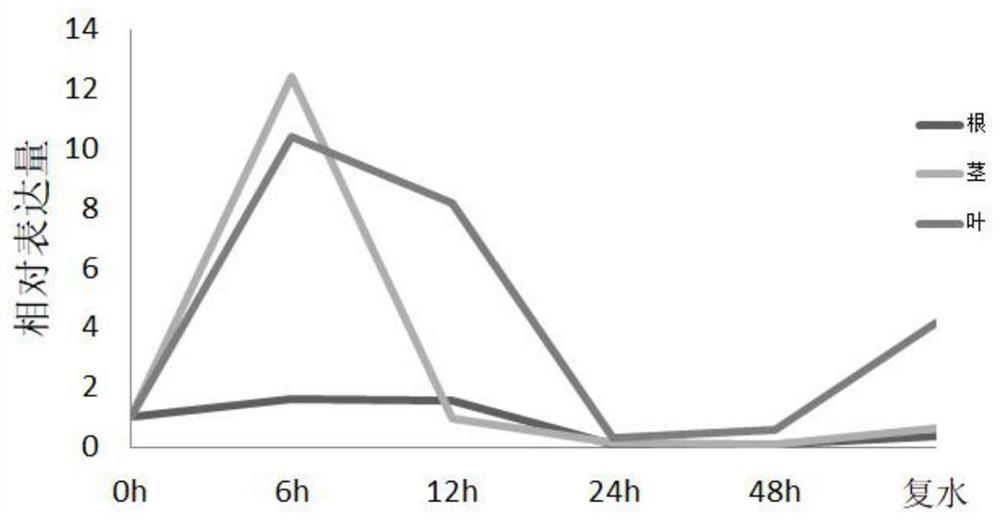
Wheat salt-tolerant gene TaAAP3 and application thereof
InactiveCN112342222AIncreased milk salt abilityEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyGenetically modified wheat
The invention relates to the technical fields of gene engineering, molecular biology and genetic breeding science, and particularly relates to a wheat salt-tolerant gene AAP3 and application thereof.The invention discloses a genome sequence of an amino acid permease gene TaAAP3 and an expression mode of the gene under the salt stress. An overexpression vector containing the gene TaAAP3 and a wheat transgenic plant for overexpression of the gene are obtained. Experiments prove that according to the invention, the salt tolerance of transgenic wheat is remarkably higher than that of a control (non-transgenic wheat), and the wheat salt-tolerant gene AAP3 can be used for salt-tolerant breeding of wheat and has huge application value.
Owner:CROP RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
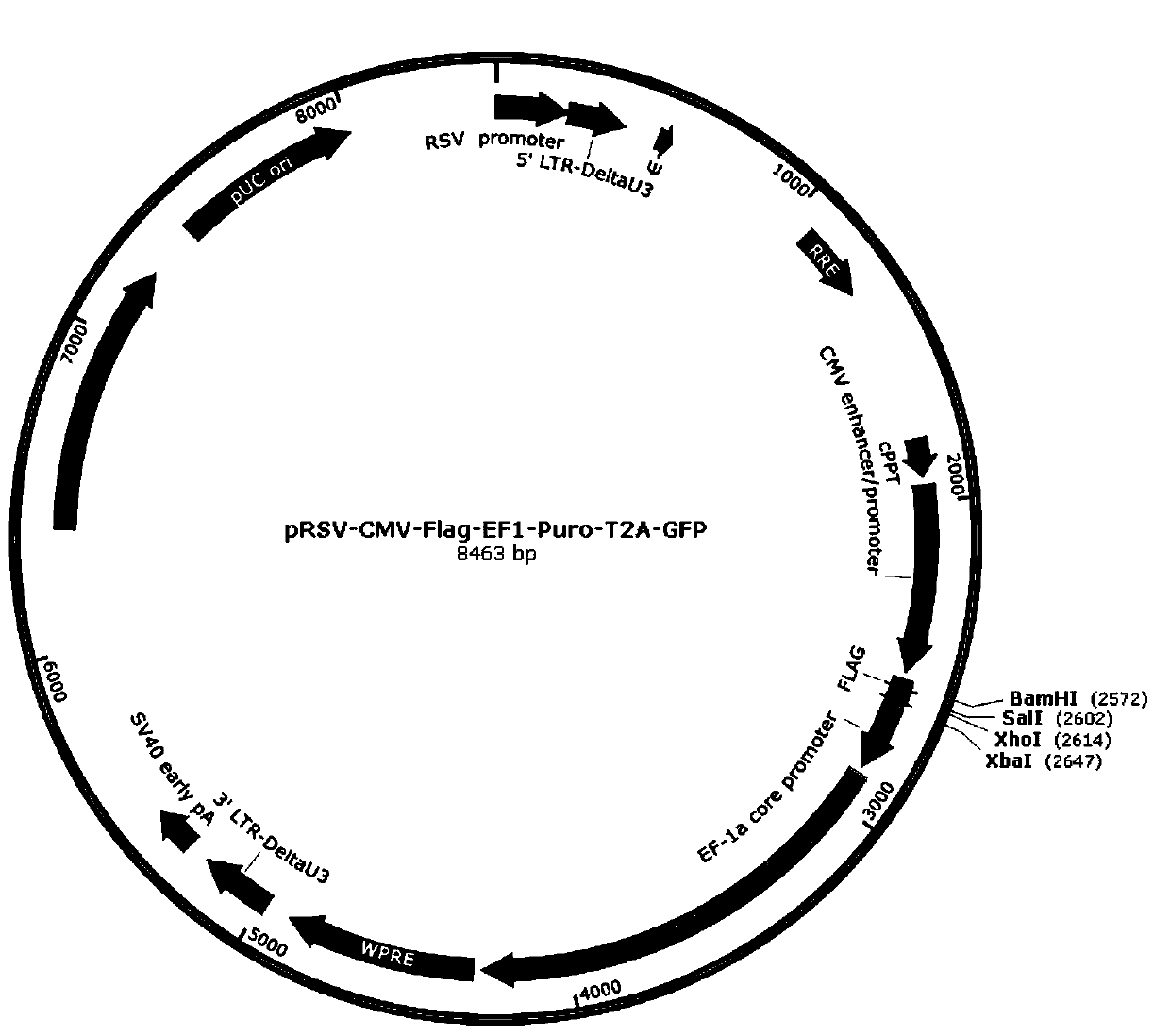
Design and application for lentiviral expression vector
ActiveCN110982842AEfficient gene insertionMonitor transfection efficiency over timeBiological material analysisBiological testingTranscription startInsertion
The invention belongs to the fields of molecular biology and cytobiology, and specifically relates to a design and an application for a lentiviral expression vector. According to the vector designed by the invention, a CMV enhancer and a CMV promoter are used as transcription starting elements of an insertion gene; an EF1a-core promoter is adopted as a transcription starting element for screeningand marking puromycin and green fluorescent protein (GFP), and a puromycin resistance gene and a GFP sequence are connected and expressed in series through T2A; a lentiviral vector is adopted as a vector skeleton, and two above-mentioned elements are inserted into the skeleton vector; thus, the lentiviral expression vector is obtained by reasonable design and optimization. By adoption of the lentiviral vector designed by the invention, the inserted gene can be efficiently expressed, and the expression efficiency of the lentiviral expression vector is superior to the expression efficiency of conventional vectors with the same type of characteristics.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Efficiency and rapid transgenic method for chrysanthemum
InactiveCN108118068AVector-based foreign material introductionTransformation efficiencyDecarboxylation
The invention discloses an efficiency and rapid transgenic method for chrysanthemum, belonging to the fields of genetic breeding of the chrysanthemum and molecular biology. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting a chrysanthemum stem as an explant, and carrying out pre-culturing on a pre-culturing medium; (2) activating and culturing recombinant expression vector transformed agrobacterium liquid, enriching thalli, and carrying out resuspension by virtue of an MS liquid culture medium, so as to obtain infection liquid; (3) soaking the explant pre-cultured in the step (1) into the infection liquid, and carrying out infection by virtue of a vacuum negative pressure method; and (4) putting the infected explant onto the pre-culturing medium, carrying out co-culturing in a dark condition, carrying out decarboxylation culture on a decarboxylation culture medium, finally, sequentially carrying out selective culture by virtue of a selective culture medium 1 and a selective culture medium 2, when determining that agrobacterium does not outbreak, carrying out subculture on a root culture medium, and carrying out further rooting screening, so as to obtain genetic chrysanthemumplants. Compared with a traditional leaf-disc-method transgenic method for the chrysanthemum, the method has the advantages that the transgenosis time is remarkably shortened, the conversion efficiency of transgenosis of the chrysanthemum is increaed, the workload of science researchers is reduced, a new way is provided for the efficient conversion and gene function analysis of the chrysanthemum,and a new thought is provided for the transgenosis of other plants.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
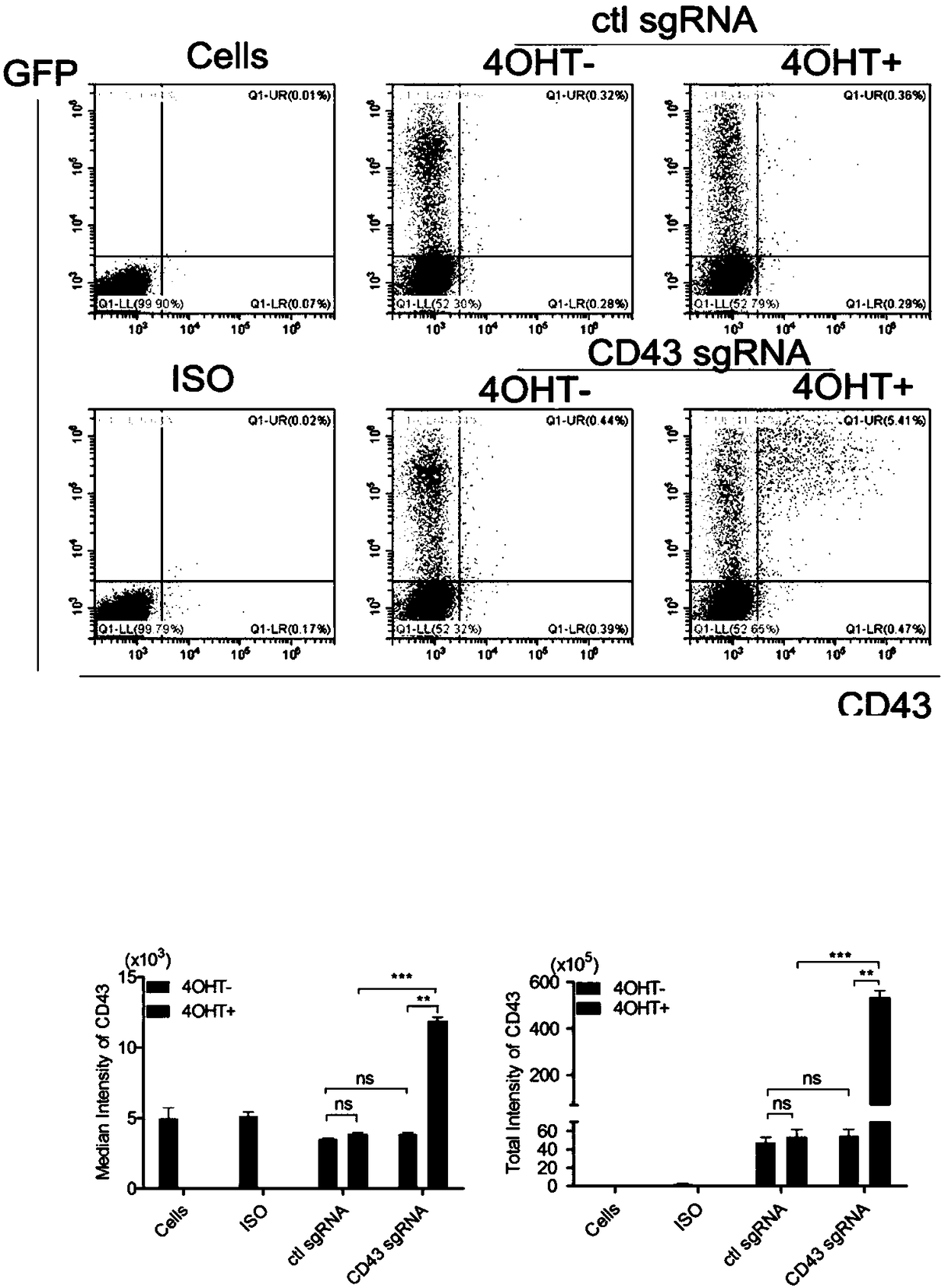
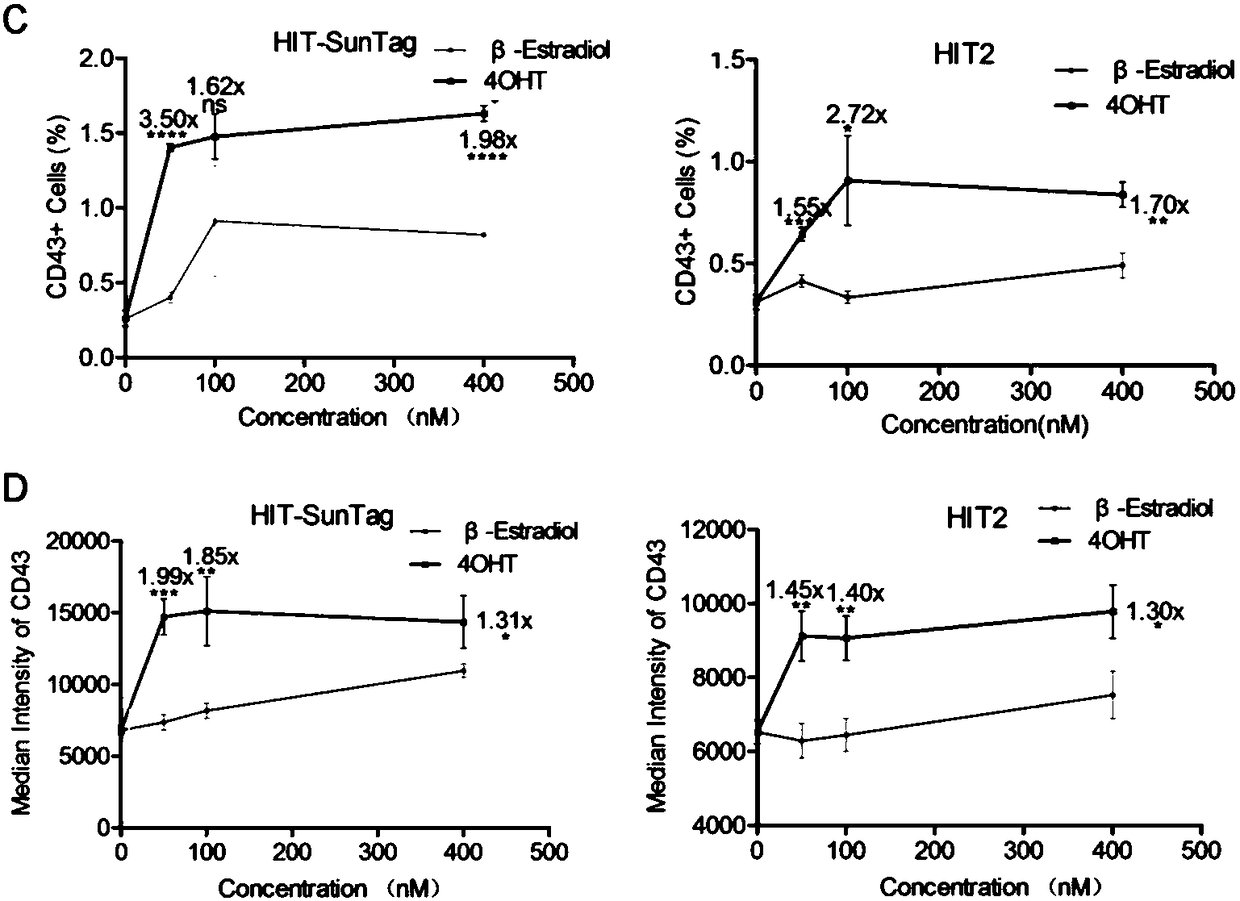
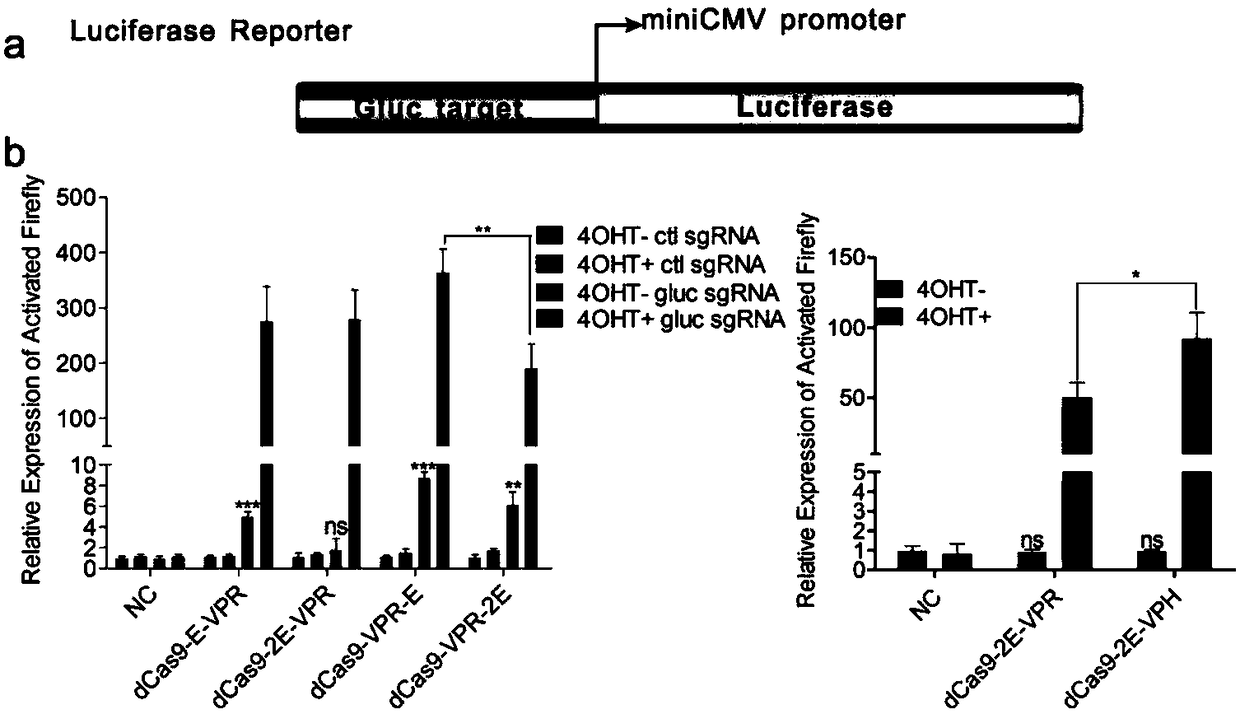
Drug-inducible CRISPR/Cas9 system for gene transcription activation
ActiveCN109207518ADecreased transcriptional activityIncrease transcriptional activityVectorsHydrolasesBioinformaticsTranscription Activation
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology, in particular to a drug inducible CRISPR / Cas9 system for gene transcription activation. The drug inducible CRISPR / Cas9 system comprises 16-22ntsgRNA targeting a specific gene site and any one of vector / vector combination as (1)-(3) below: (1) a vector expressing fusion protein dCas9-(ERT2)n-ADs or dCas9-ADs-(ERT2)n; (2) a vector combinationexpressing fusion protein dCas9-(NLS) m or dCas9-(ERT2)n and MCP-(ERT2)n-ADs; (iii) a vector combination expressing fusion protein dCas9-(NLS)m-(GCN4)p and scFv-(ERT2)n-ADs. Compared with the prior art, the system of the invention can more effectively realize the regulation of drug-induced gene transcription activation, and has more flexible and convenient operation and lower background activity.It is helpful to control the dynamic biological process effectively and precisely, and has great value for the research and development of biomedicine.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
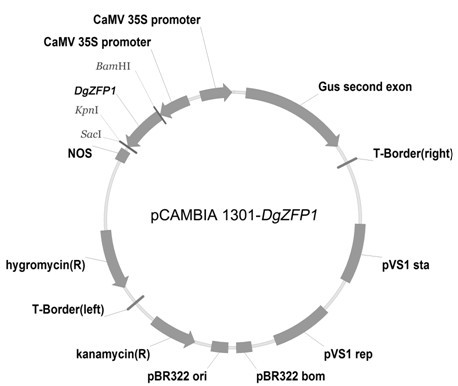
Chrysanthemum anti-retroelement DgZFP1, plant expression vector thereof, construction method thereof and application thereof
InactiveCN102154320AImprove salt tolerancePlant variety improvementFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyLotus japonicus
The invention provides a chrysanthemum anti-retroelement DgZFP1, a plant expression vector thereof, a construction method thereof and application thereof, belonging to the field of molecular biology. The expression vector pCAMBIA1301-DgZFP1 constructed by the invention is a recombinant plasmid which is obtained by the means that a DgZFP1 gene is inserted into a cloning vector pMD19-T simple vector (Takara), is performed by means of double digestion through BamH1 (Takara) and KpnI (Takara), and is connected with the BamH1 site and the KpnI site of the vector pCAMBIA1301 (Invitrogen). The plant expression vector is used for the genetic transformation of the plant, and the DgZFP1 gene is excessively expressed under the promotion of a CaMV35S promoter, so that a large number of the DgZFP1 protein is synthesized, the expression of the downstream gene is regulated and controlled, and the plant salt tolerance of the plant is improved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
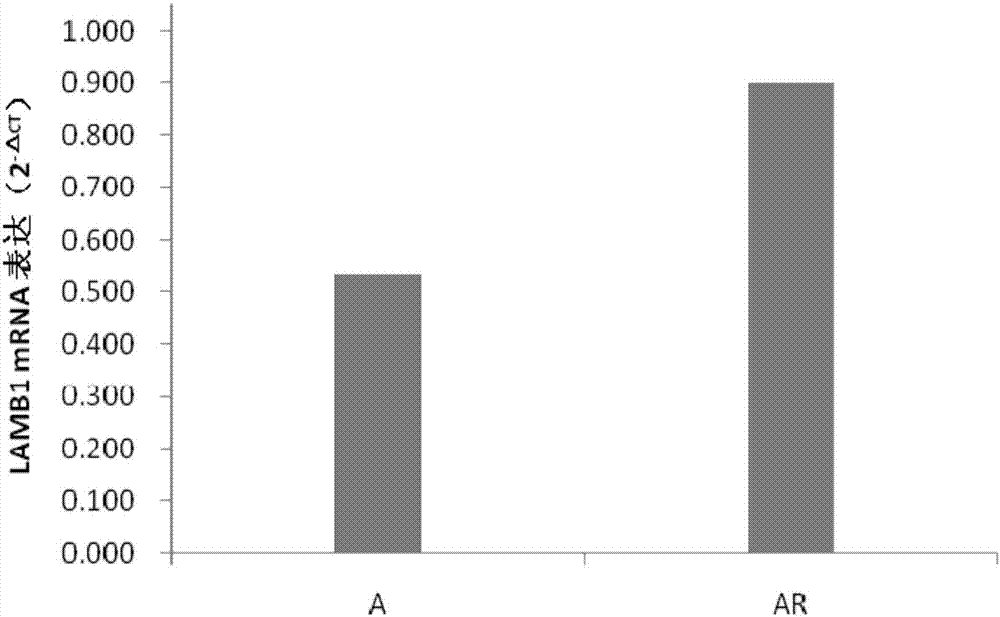
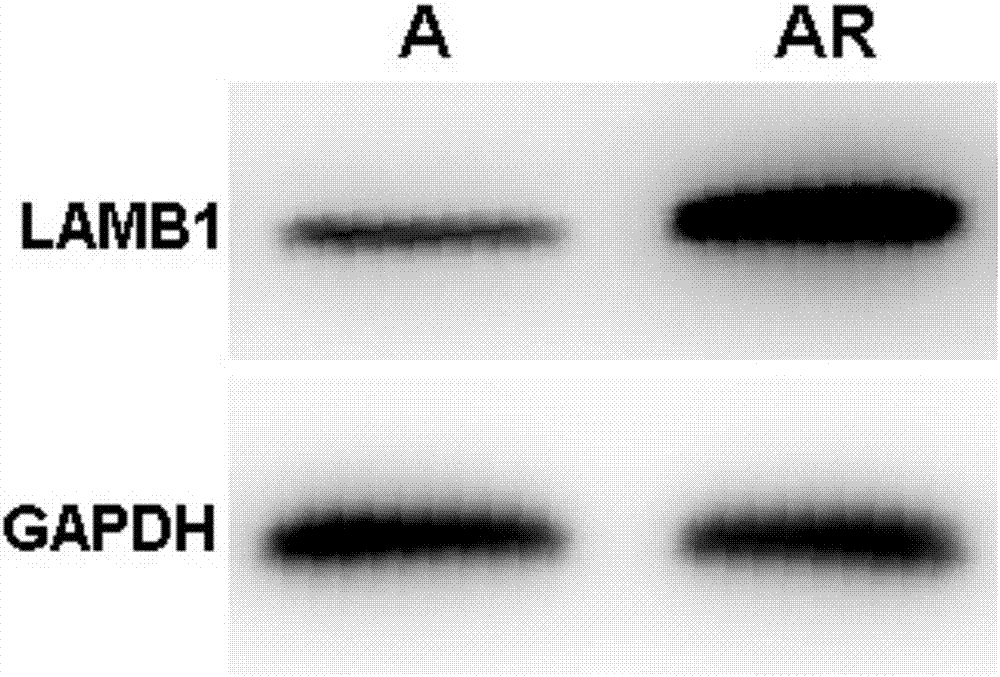
siRNA capable of specially inhibiting expression of LAMB1 gene and recombinant vector and application of siRNA
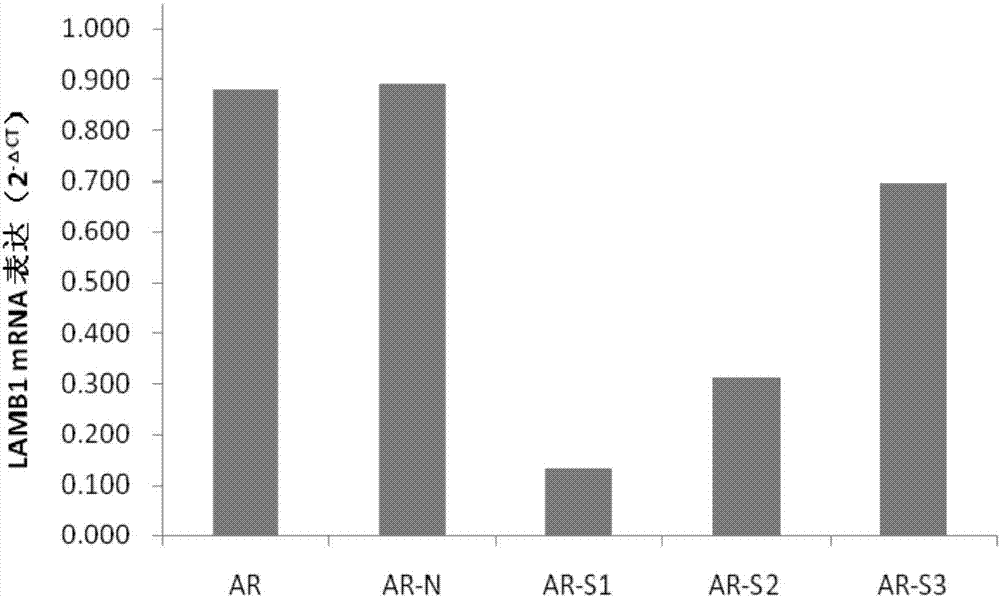
InactiveCN107354157AReduce proliferationPromote apoptosisOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCancer cellHepatocellular carcinoma
The invention discloses siRNA capable of specially inhibiting expression of an LAMB1 gene, a recombinant vector of the siRNA and application of the siRNA in reversing ovarian cancer taxol resistance, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology and biological medicine. The siRNA comprises a sense strand and an antisense strand, the sense strand is 5'-UGUUUGAAAGCCGAAUCUGCG-3', and the antisense strand is 5'-CAGAUUCGGCUUUCAAACAAA-3'. According to the siRNA, mRNA and protein expression of the LAMB1 gene in a cancer cell can be inhibited specially and efficiently, proliferation of the cancer cell is reduced, cell apoptosis is increased, the invasiveness and migration capability of the cancer cell is reduced, and moreover, the resistance of an ovarian cancer cell to taxol can be reversed effectively. The invention further provides the application of the siRNA and the recombinant vector thereof in preparing medicines treating an ovarian cancer, a hepatocellular cancer, a colorectal cancer, a malignant glioma, a prostatic cancer or a gastric cancer and medicines reversing the ovarian cancer taxol resistance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com












![Method for constructing full-length infectious cDNA [complementary DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)] of PEDV JS2008 (porcine epidemic diarrhea virus JS2008) strains and application of full-length infectious cDNA Method for constructing full-length infectious cDNA [complementary DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)] of PEDV JS2008 (porcine epidemic diarrhea virus JS2008) strains and application of full-length infectious cDNA](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/57c6167a-9839-4561-aaaf-e44fa84810a4/HDA0001373833190000011.png)
![Method for constructing full-length infectious cDNA [complementary DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)] of PEDV JS2008 (porcine epidemic diarrhea virus JS2008) strains and application of full-length infectious cDNA Method for constructing full-length infectious cDNA [complementary DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)] of PEDV JS2008 (porcine epidemic diarrhea virus JS2008) strains and application of full-length infectious cDNA](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/57c6167a-9839-4561-aaaf-e44fa84810a4/HDA0001373833190000012.png)
![Method for constructing full-length infectious cDNA [complementary DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)] of PEDV JS2008 (porcine epidemic diarrhea virus JS2008) strains and application of full-length infectious cDNA Method for constructing full-length infectious cDNA [complementary DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)] of PEDV JS2008 (porcine epidemic diarrhea virus JS2008) strains and application of full-length infectious cDNA](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/57c6167a-9839-4561-aaaf-e44fa84810a4/HDA0001373833190000021.png)