Patents
Literature
44results about How to "Improve the conversion rate of hydrolysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
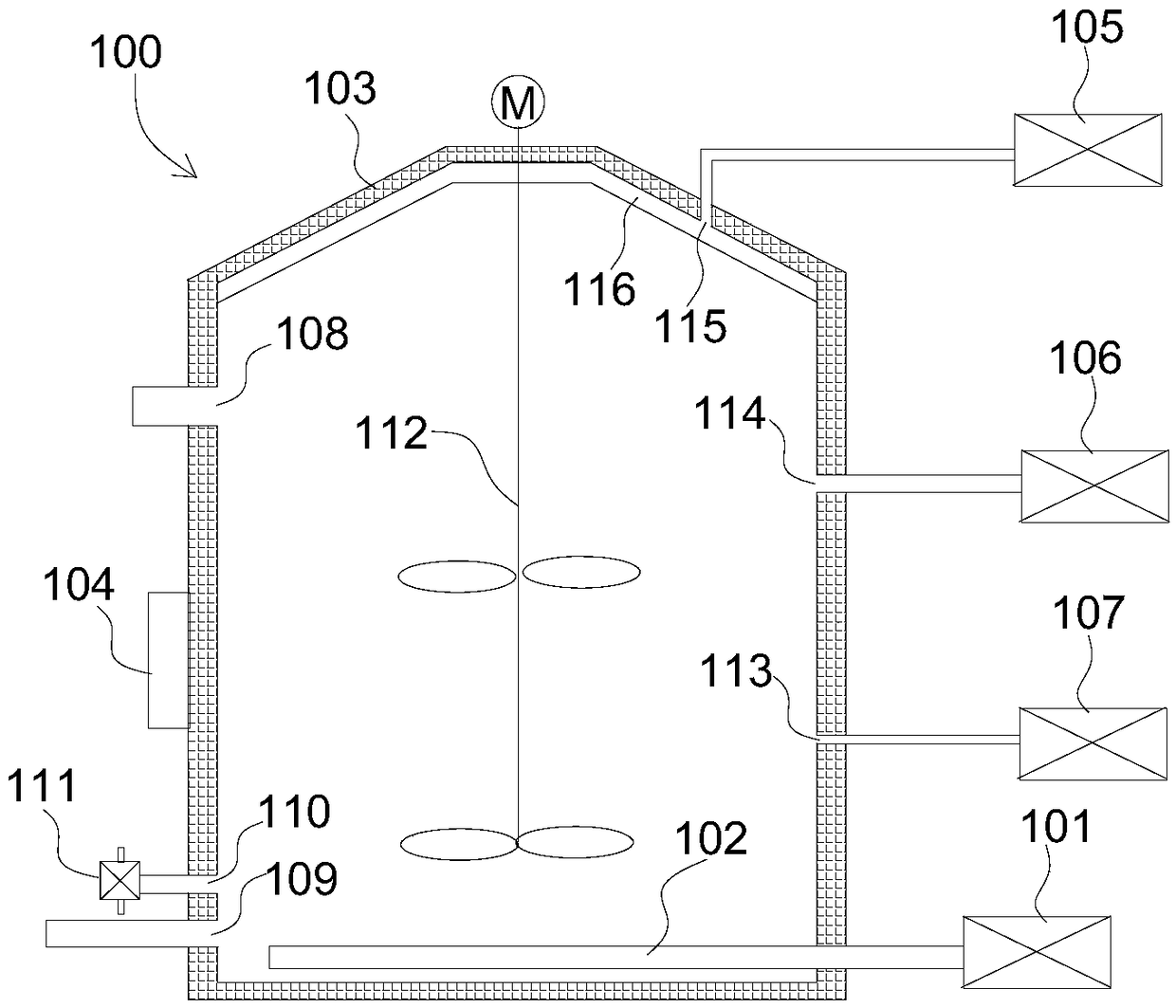
Carbonyl sulfur hydrolyzing catalyst
ActiveCN101239319AHigh catalytic activityImprove antioxidant propertiesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsDesorptionSulphur compound
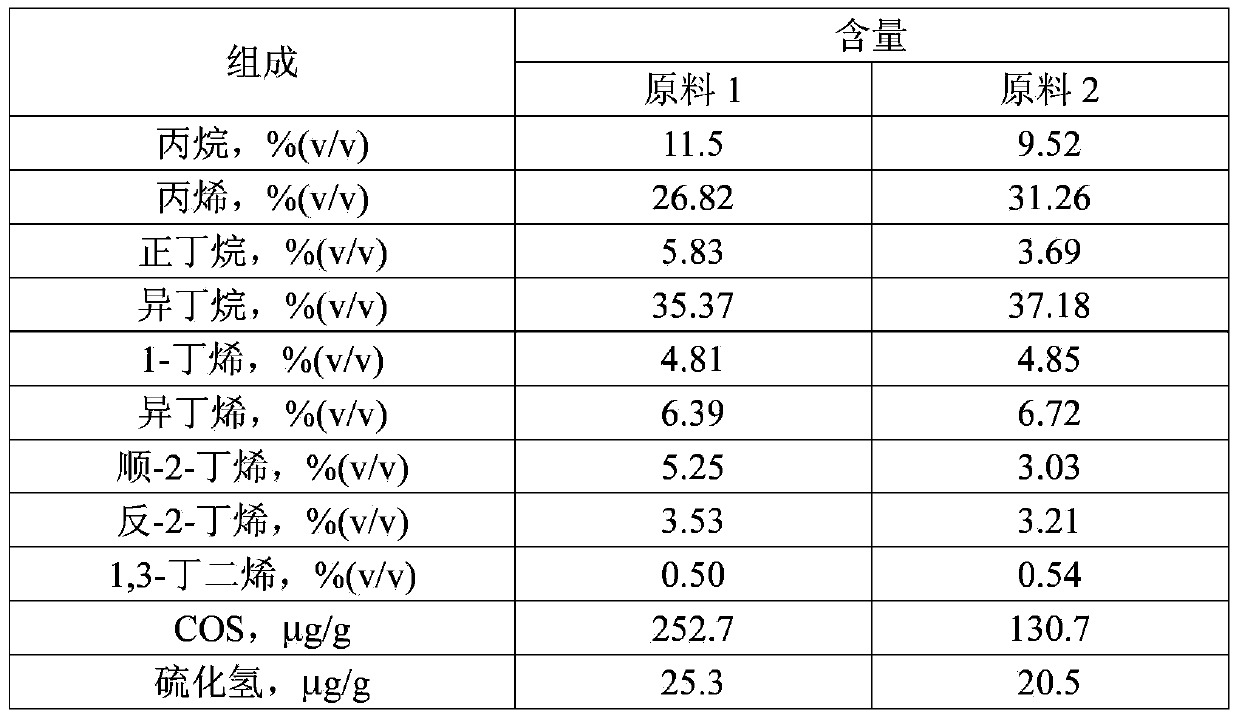
The present invention provides a carbonyl sulfur hydrolyst, including a carrier and an active component, characterized in that the active component of the catalyst includes an active component I and an active component II, the active component I is selected from sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate or their mixtures, the active component II is selected from following metal oxide: Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, or mixtures of their metal oxides, the catalyst carrier is selected from Al2O3 or mixture of Al2O3 and TiO2 or ZrO2, the percentage by weight in the catalyst: the active component I is 2wt%-15wt%, the active component II is 2wt%-15wt%, the carrier is 70wt%-96wt%. The catalyst is used for carboxide sulphur compound in desorption LPG, natural gas, refinery gas, catalytic cracking process gas, propylene and ethylene, the percent conversion is more than 95%.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Hydrolysis method of esters
InactiveCN1541991AImprove the conversion rate of hydrolysisEasy to separateOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationPhosphomolybdic acidHeteropoly acid
The ester hydrolyzing method includes hydrolyzing ester in water to produce C1-C10 fatty acid or aromatic acid and C1-C4 fatty alcohol under the presence of ammonium salt of heteropoly acid as catalyst. The ammonium salt of heteropoly acid is obtained through the reaction between heteropoly acid in Keggin structure and inorganic ammonium salt or organic amine, the heteropoly acid is selected from phosphotungstic acid, silicotungstic acid, silicomolybdic acid and phosphomolybdic acid; the inorganic ammonium salt is selected from ammonium carbonate, ammonium nitrate, ammonium sulfate, ammonium phosphate and diammonium hydrochloride; and the organic amine is selected from fatty amine, alicyclic amine and arylamine. The said ester hydrolyzing method can obtain high conversion rate in relatively lower water / ester ratio and relatively short time, and the catalyst is cheap and easy to separate from the product.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Low-temperature hydrolysis method for removing carbonyl sulfide in liquefied petroleum gas
ActiveCN103992831AHigh catalytic activityImprove the conversion rate of hydrolysisGaseous fuelsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsChemistryHydrogen sulfide
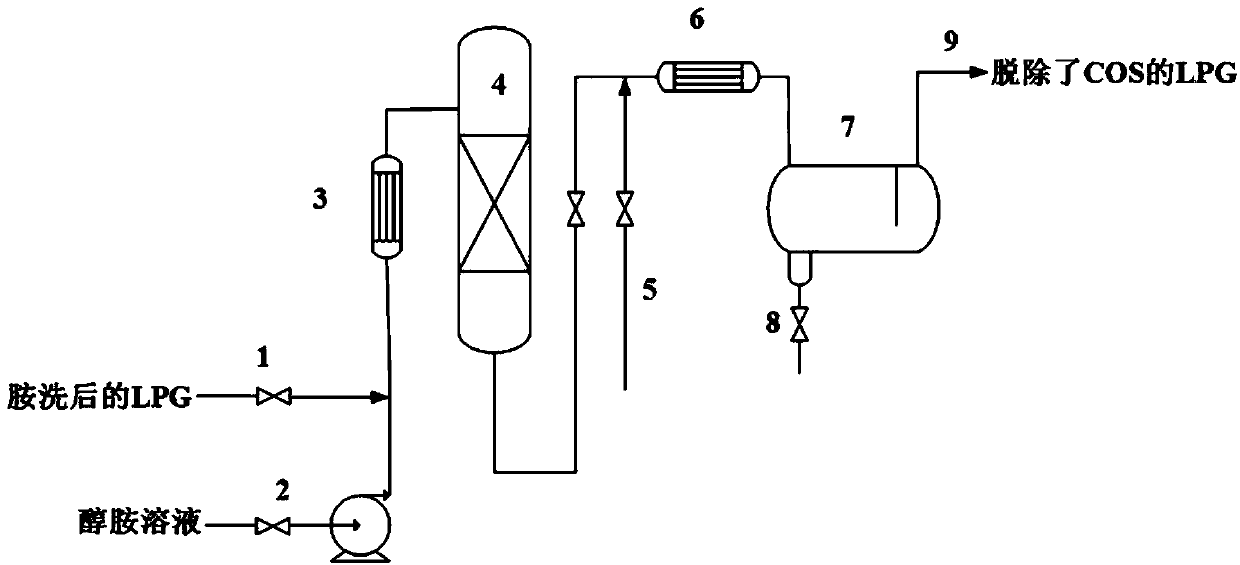
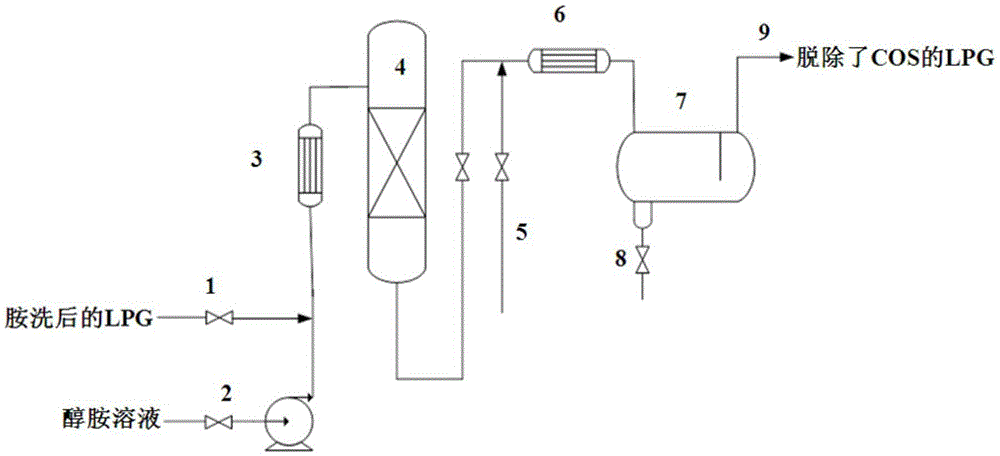
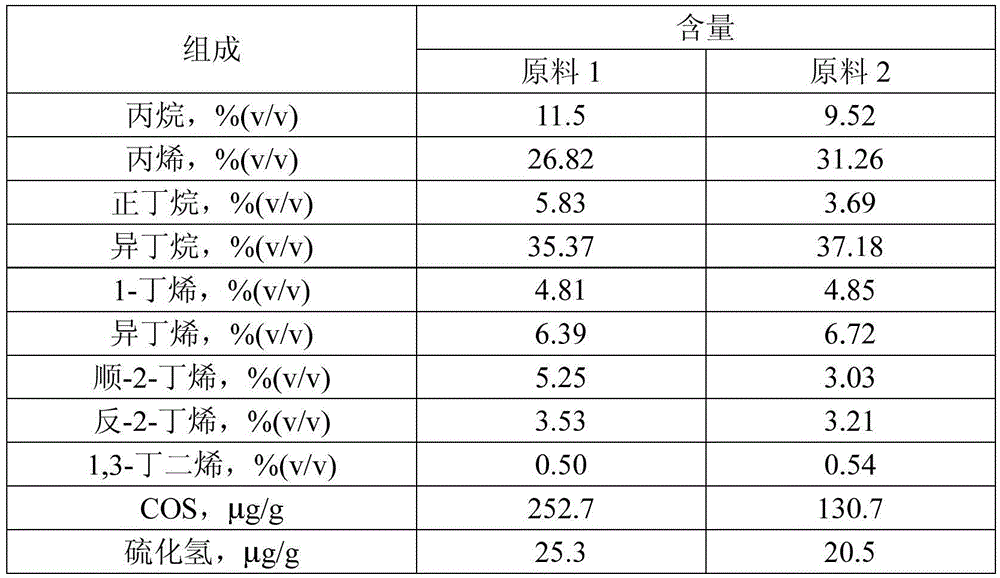
The invention provides a low-temperature hydrolysis method for removing carbonyl sulfide in liquefied petroleum gas. The method comprises the following steps: mixing the liquefied petroleum gas after amine washing with an alcohol amine solution, and performing hydrolysis reaction under the action of a carbonyl sulfide hydrolysis catalyst to remove carbonyl sulfide and hydrogen sulfide in the liquefied petroleum gas and hydrogen sulfide generated by hydrolysis; separating the liquefied petroleum gas from the alcohol amine solution, then washing with water to obtain the refined liquefied petroleum gas and recycling the alcohol amine solution, wherein the adding amount of the alcohol amine solution is 0.1%-20% of the weight of the liquefied petroleum gas. By adopting the low-temperature hydrolysis method for removing carbonyl sulfide in the liquefied petroleum gas provided by the invention, carbonyl sulfide and hydrogen sulfide in the liquefied gas can be removed in one step under the condition of 10-60 DEG C, the step of removing hydrogen sulfide in a conventional process is eliminated, the process is simple, the activity of the catalyst is high, the service life is long and the conversion rate of carbonyl sulfide is above 97%.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +3
Hydrolytic method of Chinese potato saponin
The invention relates to a hydrolysis method of dioscin. A solid acid catalyst is added to the reaction solution containing the dioscin according to the proportion of 0.1g to 100g / 100ml of extract and then the reaction solution is placed in water bath of 50 DEG C to 90 DEG C for reaction for 2h to 16h; after the hydrolysis, the reactant obtained is cooled to the room temperature and filtered in vacuum and the filter residue is dried at the temperature of 20 DEG C to 80 DEG C; the filter residue is extracted in organic solution for 4h to 12h continuously, the extract is separated and the organic solution thereof is recycled; finally the dioscin solid is obtained. The solid acid catalyst system adopted by the invention is a multiphase reaction; hydrogen ions are restrained on the surface of the catalyst rather than going into the body of the reaction solution, therefore, the acidification of the reaction solution is avoided and the loss of the hydrogen ions is rather small. The experimental result shows that the pH value of the solution phase after hydrolysis is 4 to 5 and the concentration of the hydrogen ions in the solution is 10,000 times lower than that of the solution which is hydrolyzed by hydrochloric acid, thus greatly reducing the pollution to the environment. The hydrolysis method has simple technology, moderate hydrolysis conditions and high hydrolysis conversion rate of the dioscin which is as high as 98 percent, thus fundamentally solving the problems of serious environmental pollution and equipment corrosion occurring in the inorganic acid catalysis hydrolysis process.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Reaction-extraction coupling method for preparation of hydroxylamine salt / hydroxylamine
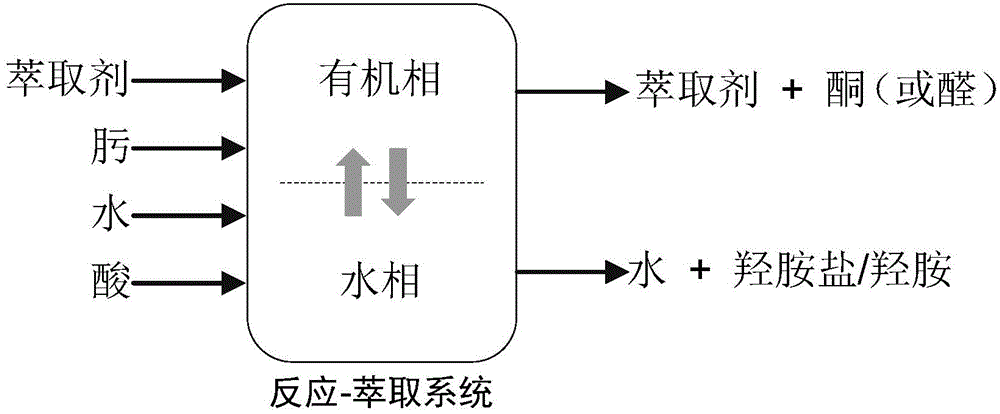
A oxime hydrolysis and solvent extraction coupling method for one step preparation of hydroxylamine salt / hydroxylamine. The invention is characterized in that oxime (ketoxime or aldoxime) is used as a raw material, and the hydrolysis reaction of oxime in an acidic solution and organic solvent extraction and separation are coupled, so that an extraction agent extracts the correspondingly generated ketone or aldehyde into an organic phase while the hydrolysis reaction is carried out, thus breaking the restrictions of oxime hydrolysis reaction chemical equilibrium under mild conditions, introducing the reaction to the direction for generation of hydroxylamine salt / hydroxylamine, and improving the reaction conversion rate and yield of hydroxylamine salt / hydroxylamine. The hydroxylamine salt preparation method provided by the invention has the characteristics of simple process and operation, mild reaction conditions, high conversion rate and selectivity, and low energy consumption, etc.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
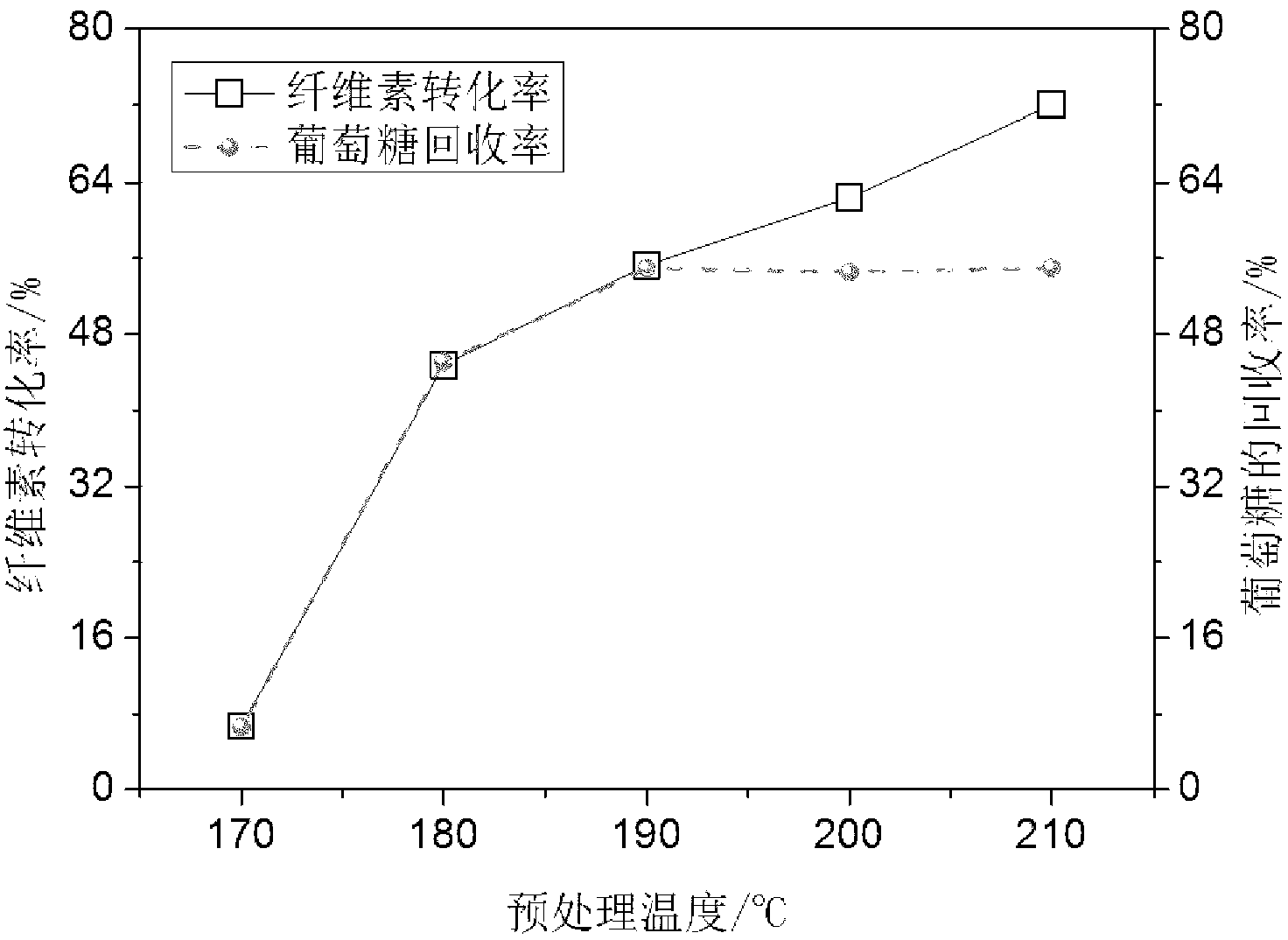
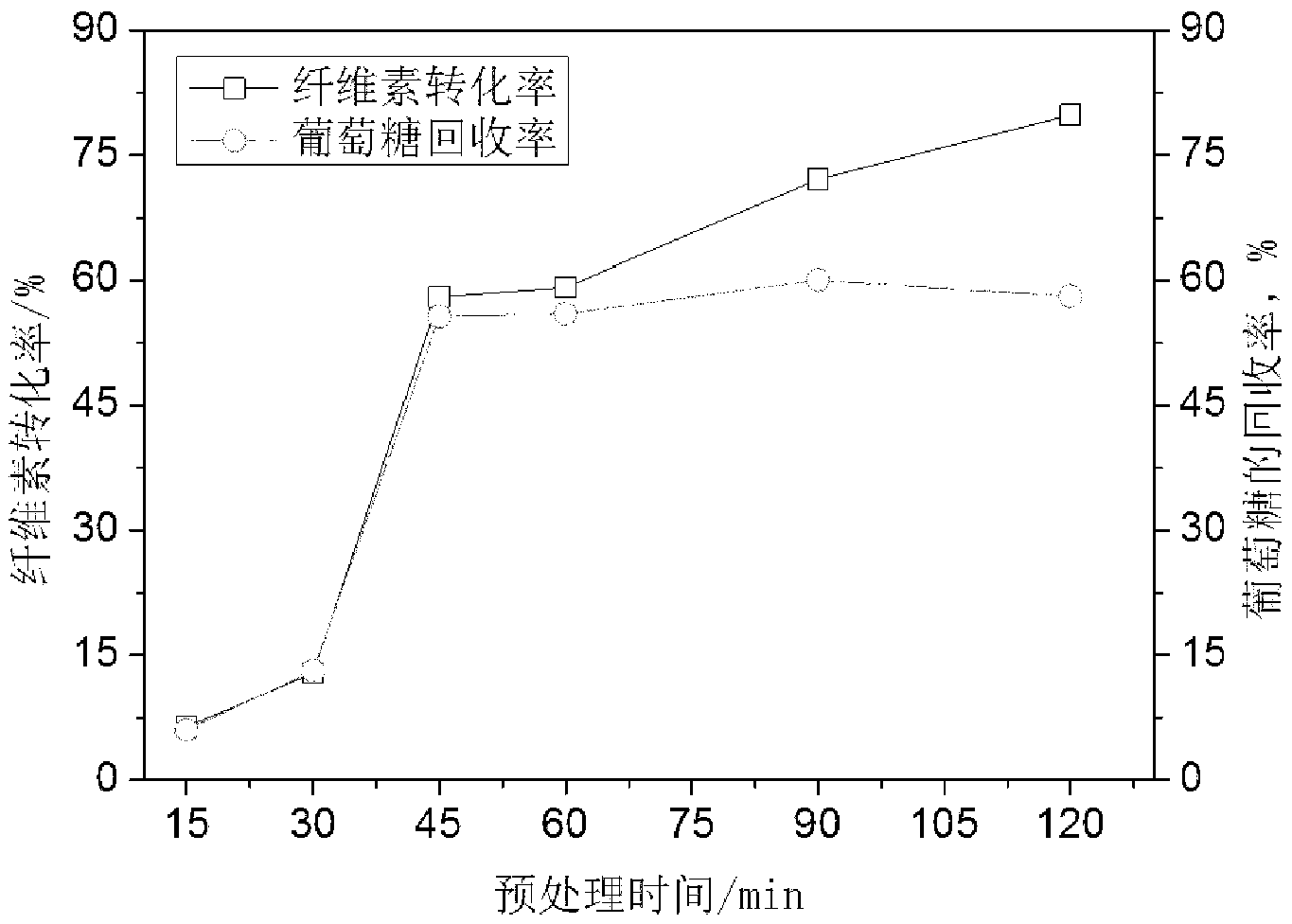
Preprocessing method capable of effectively improving efficiency of generating fermentable sugar by bamboo cellulose enzyme hydrolysis
InactiveCN103266148AImprove accessibilityImprove the conversion rate of hydrolysisFermentationFiberPretreatment method
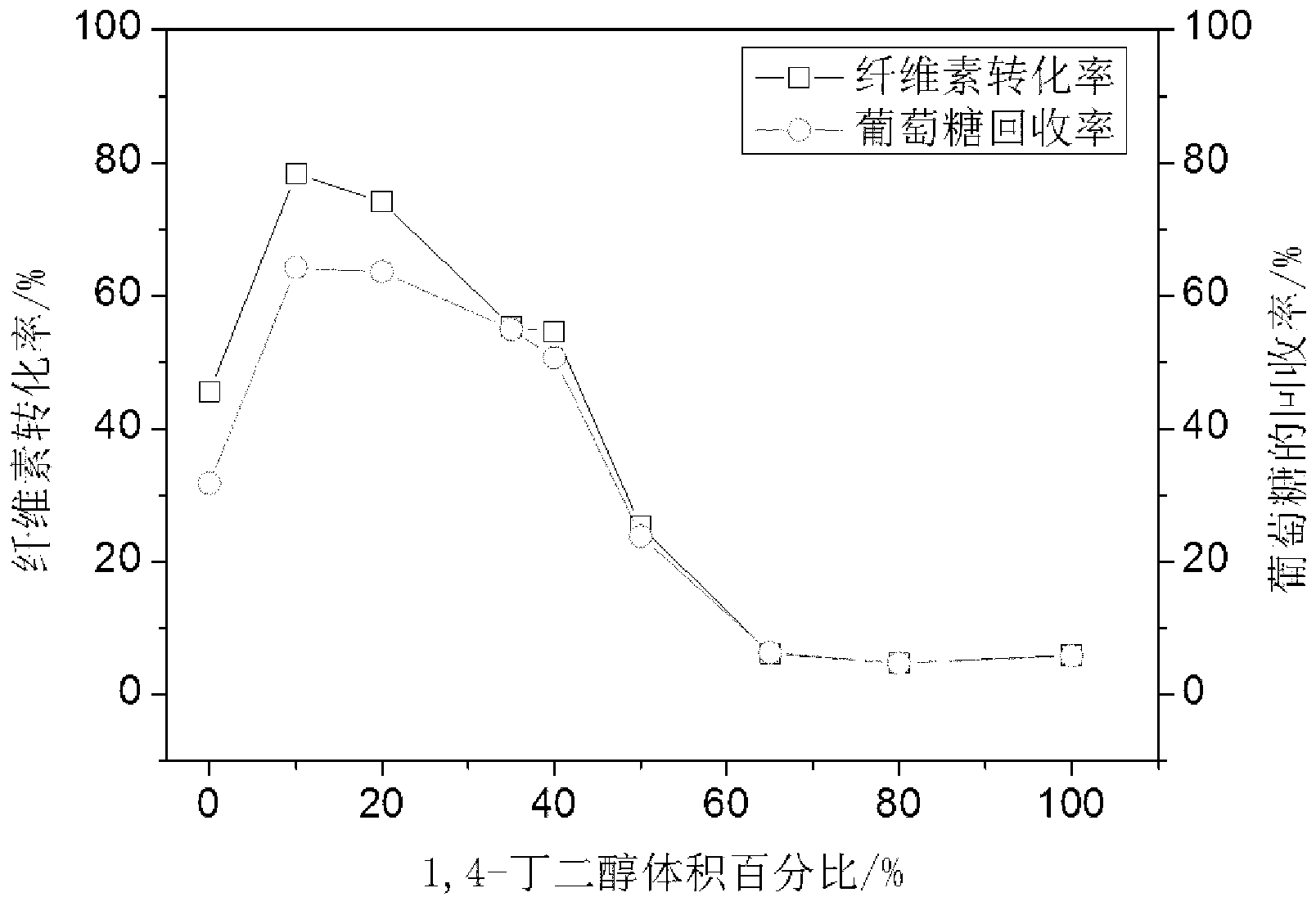
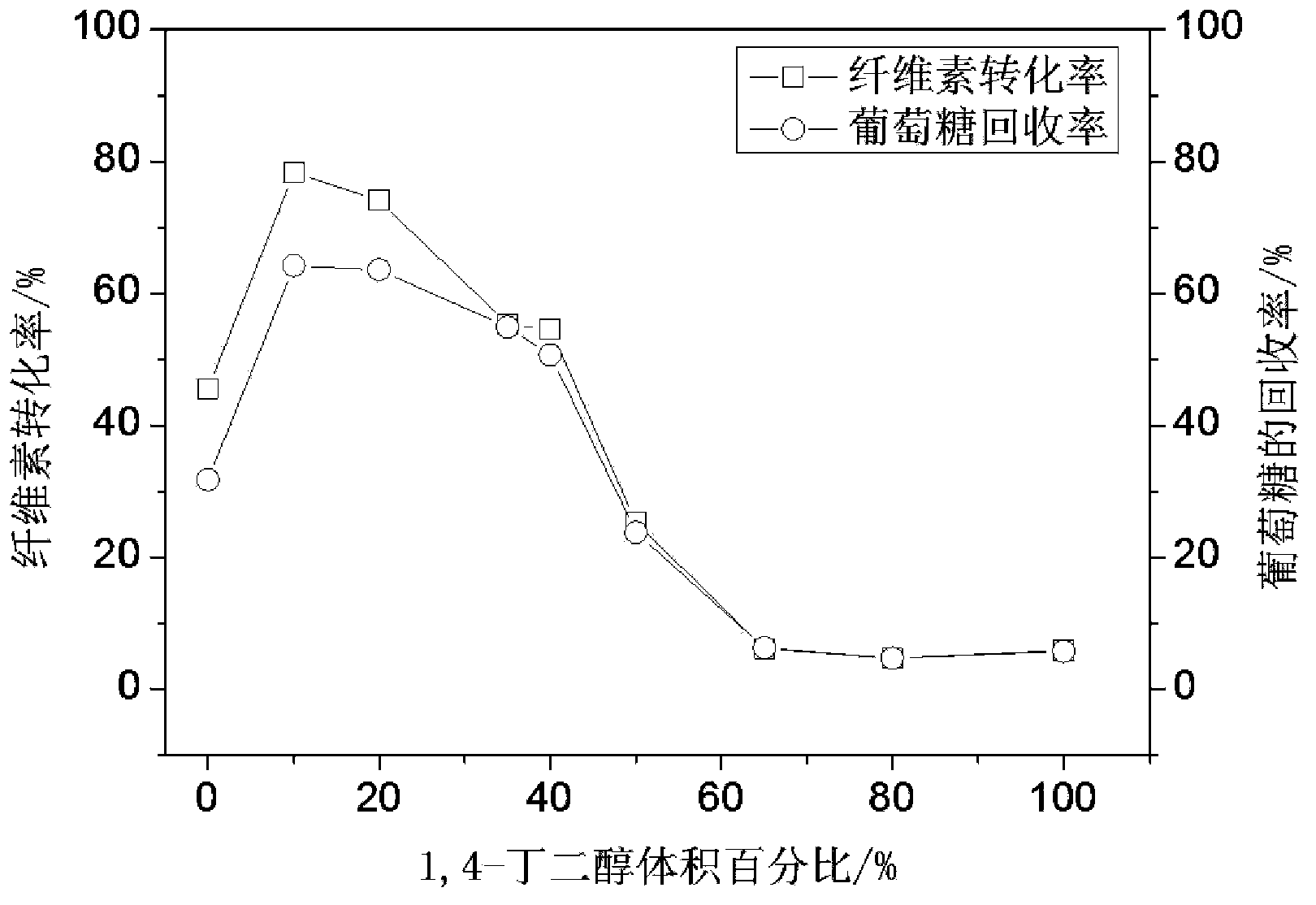
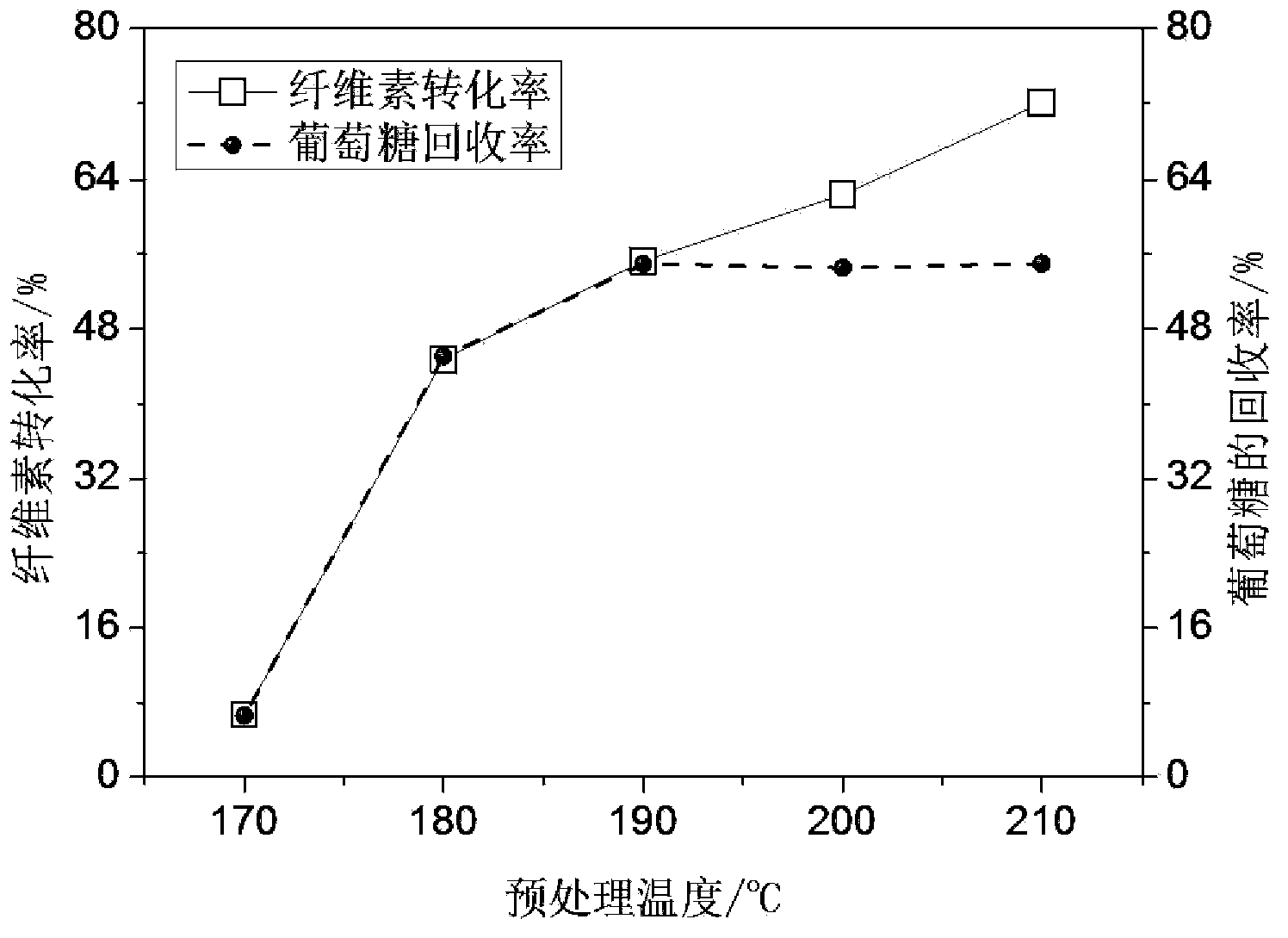
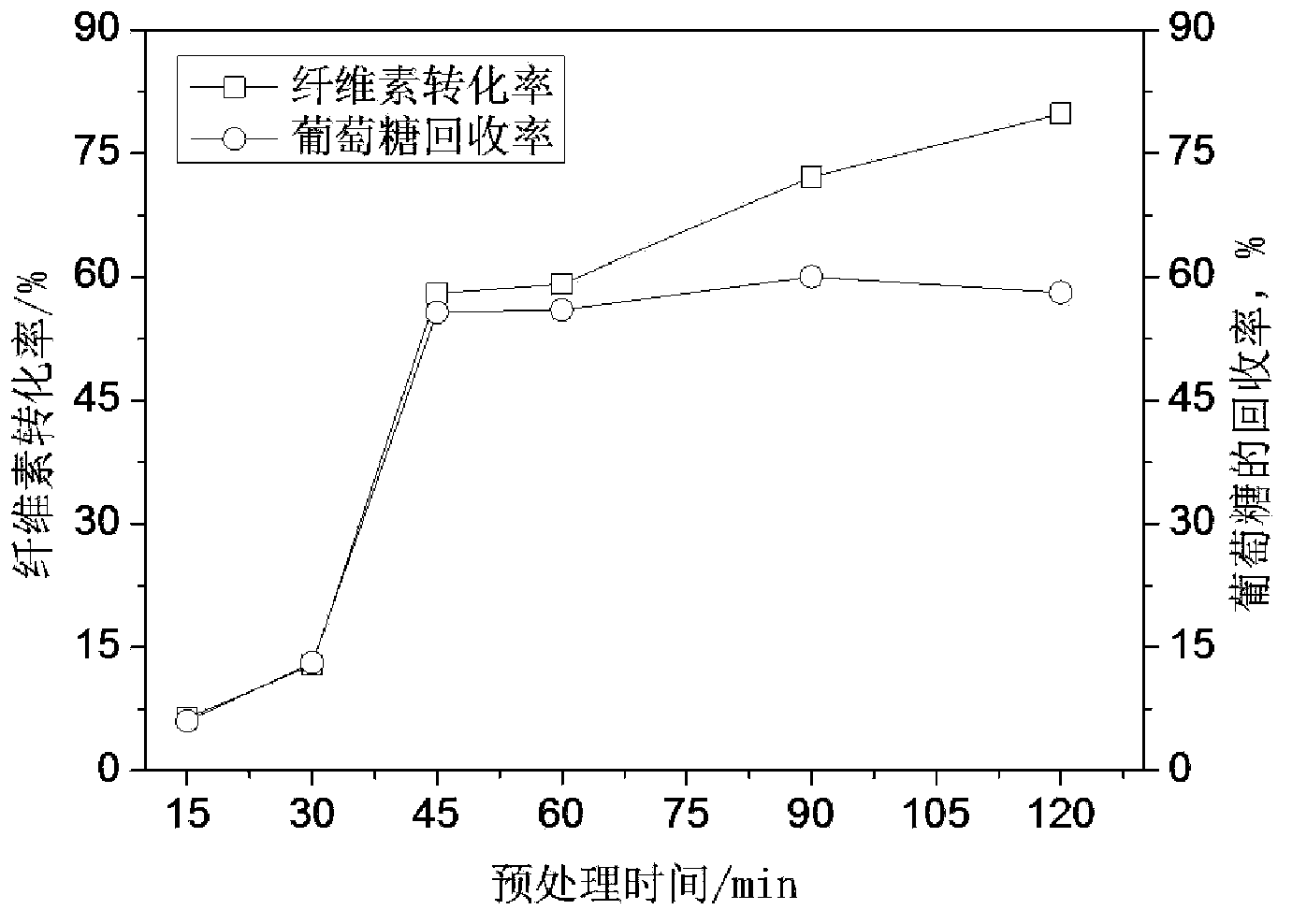
The invention discloses a preprocessing method capable of effectively improving the efficiency of generating fermentable sugars by bamboo cellulose enzyme hydrolysis. The preprocessing method comprises the following steps of: preparing materials; preprocessing acid catalyzed high-boiling alcohol; washing solid substrates obtained by preprocessing; milling the solid substrates by a millstone; and performing enzyme hydrolysis. By preprocessing the acid catalyzed high-boiling alcohol in the preprocessing method disclosed by the invention, hemicellulose and lignin can be synchronously and efficiently removed from bamboo fiber raw materials, and additionally, extractives and waxiness on the surfaces of the extractives can be effectively removed from the bamboo outer skin of the outer wall of bamboos. Compared with the existing acidic chemical preprocessing method, the recovery rate of fermentable glucose obtained by enzyme hydrolysis of cellulose in the bamboos after the high-boiling alcohol preprocessing is increased by 36 to 50%, and compared with the preprocessing method by using a low-boiling organic solvent, the recovery rate is increased by 10 to 15%. By using the preprocessing method in which a high-boiling alcohol / hydrosolvent system with acid catalysis and low alcohol content is utilized and the bamboos are preprocessed before enzyme hydrolysis within short time, the conversion efficiency of the cellulose in the bamboos to the fermentable sugars through enzyme hydrolysis can be improved, and the defect that the environmental pollution is caused by waste liquor can be overcome.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
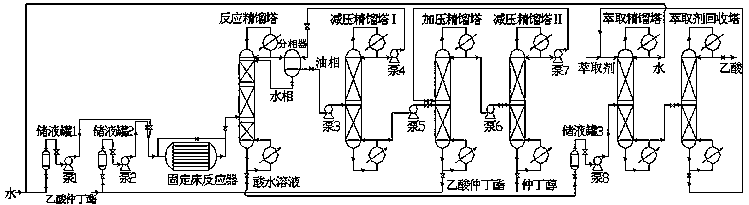
Method for producing high-purity sec-butyl alcohol through joint of fixed bed and reaction rectification
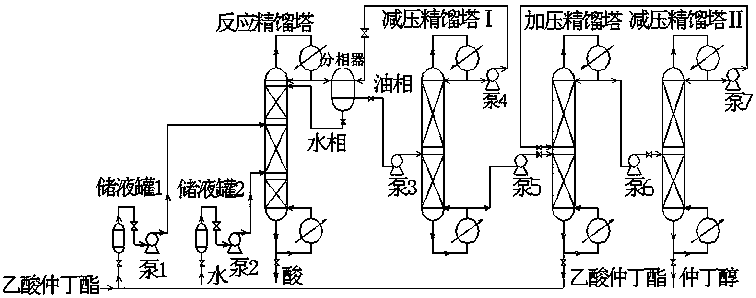
InactiveCN108017507AImprove the conversion rate of hydrolysisHigh purityOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationFixed bedReactive distillation
The invention discloses a method for producing high-purity sec-butyl alcohol through joint of a fixed bed and reaction rectification. Water and sec-butyl acetate are adopted as raw materials, preliminary catalytic hydrolysis is performed in a fixed bed reactor, further catalytic hydrolysis is performed in a reactive distillation column, a sec-butyl alcohol is generated, then, oil-water separationand three-step transformation rectification of decompression, pressurization and decompression are performed, and the high-purity sec-butyl alcohol is obtained. The reaction conditions are mild, the sec-butyl acetate hydrolysis conversion rate is high, and the byproduct acetic acid can be recycled for sec-butyl production.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
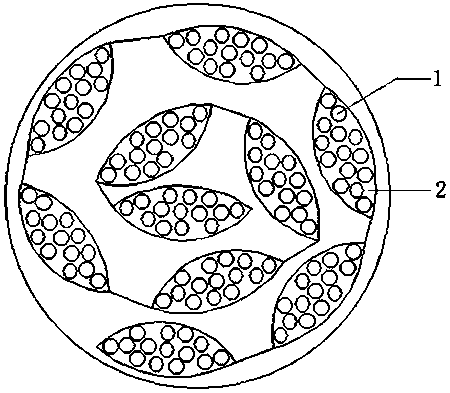
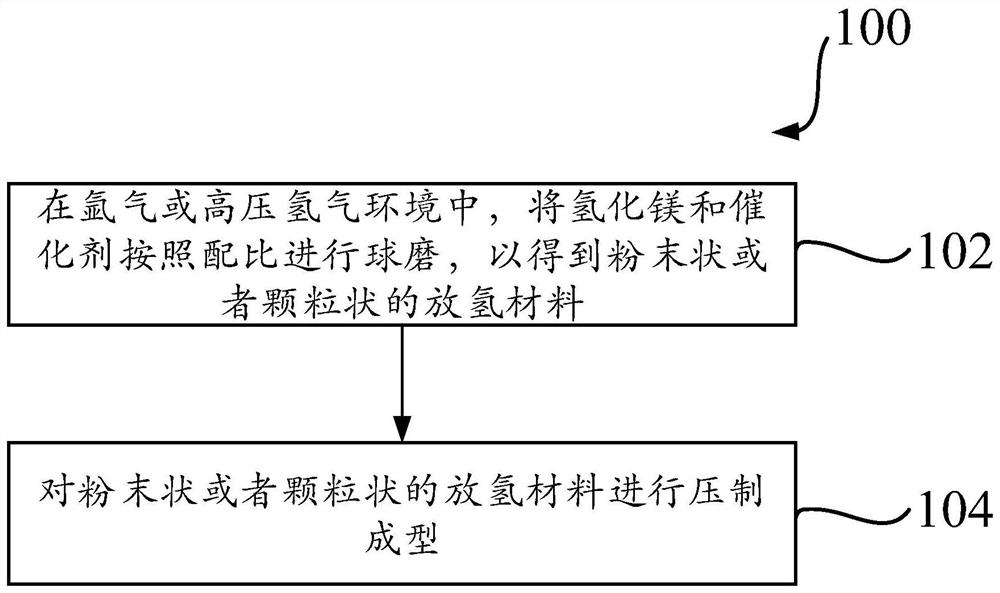
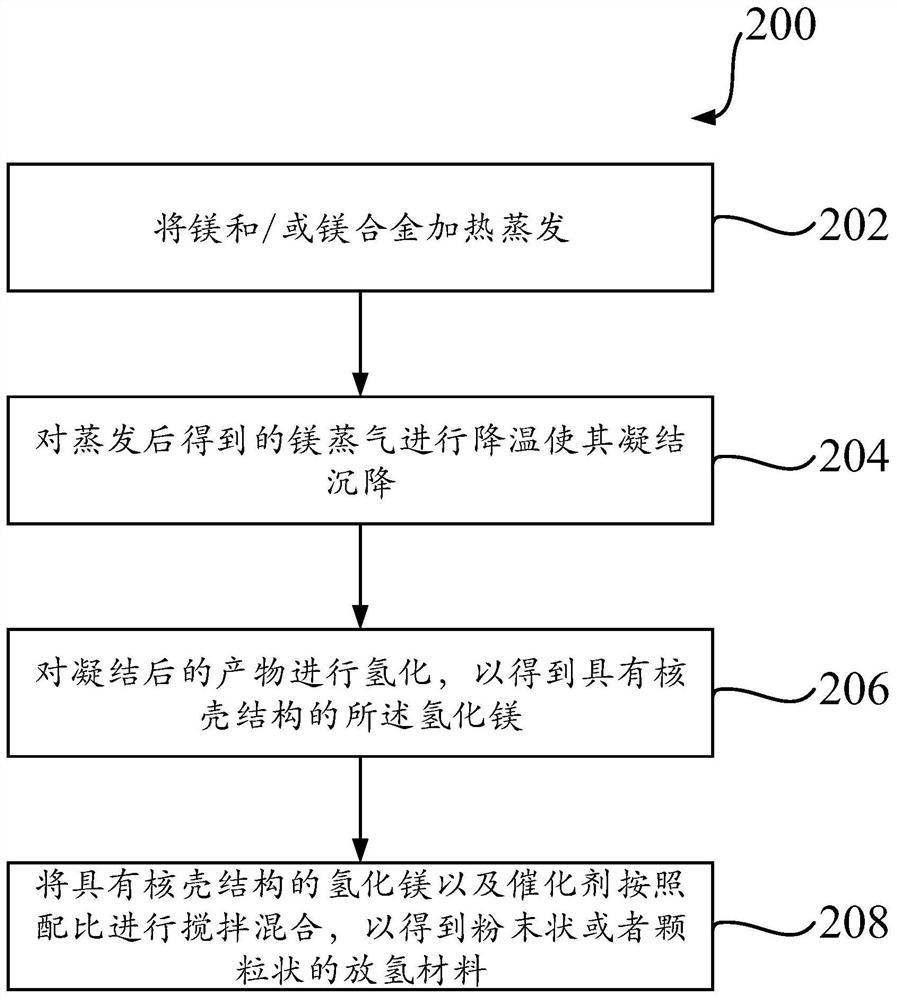
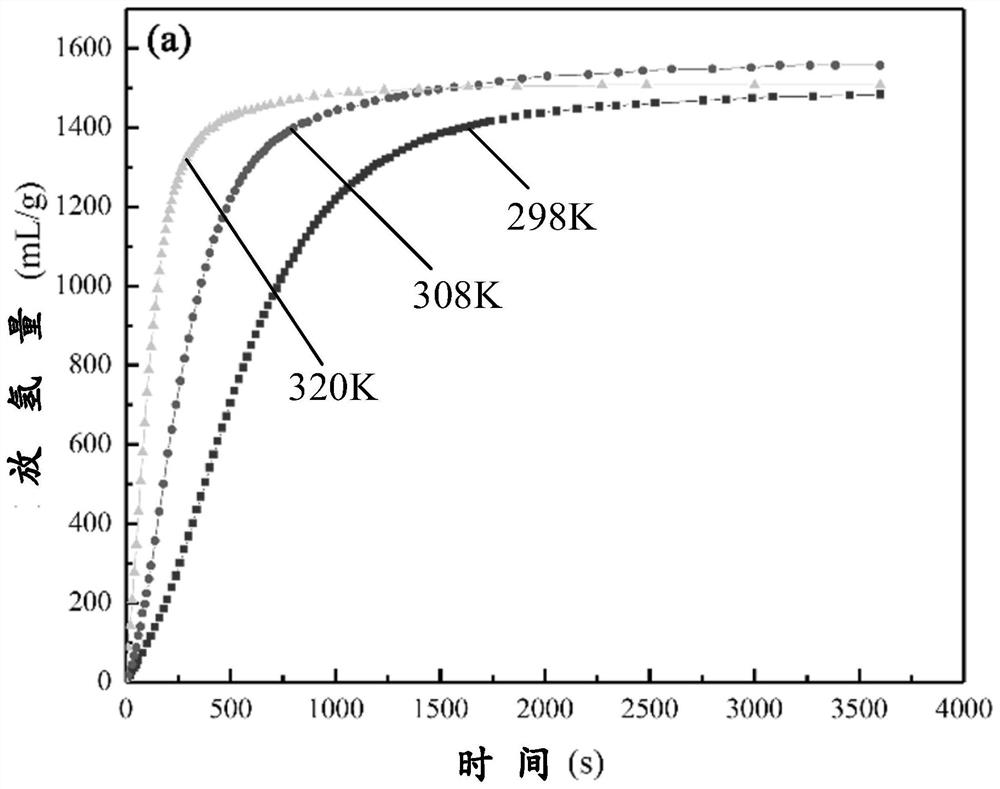
Magnesium-based hydrogen desorption material, preparation method thereof and hydrolysis hydrogen production method
ActiveCN111646429AConducive to achieving sustainable hydrogen depletionSustainable hydrogen depletion hasAlkali/alkaline-earth/beryllium/magnesium hydridesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrogen desorptionChloride
The invention discloses a magnesium-based hydrogen desorption material, a preparation method thereof and a hydrolysis hydrogen production method. The hydrogen desorption material comprises magnesium hydride and a catalyst, wherein the catalyst comprises at least one of oxide, chloride and hydride; and the mass ratio of the magnesium hydride to the catalyst is as follows: 1-50 parts of the magnesium hydride and 1-30 parts of the catalyst. The hydrogen desorption material disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of sustainable hydrogen desorption, high hydrogen production capacity, high hydrolysis conversion rate and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI MG POWER TECH CO LTD
Kitchen waste treatment method capable of improving capacity of treatment system and hydrolysis tank
The invention relates to the technical field of kitchen waste treatment, in particular to a method for improving the capacity of a kitchen waste anaerobic treatment system and a hydrolysis tank. According to the kitchen waste treatment method capable of improving the capacity of the treatment system and the hydrolysis tank, kitchen waste slurry is fed from 1 / 2 or above height of the tank wall of the hydrolysis tank and is synchronously stirred, so that the kitchen waste slurry can be fully mixed with original kitchen waste slurry in the hydrolysis tank from top to bottom; the temperature of the kitchen waste slurry in the hydrolysis tank is kept at 35+ / -3 DEG C by monitoring and interfering the environment in the hydrolysis tank, the average concentration of dissolved oxygen is kept at 0.5-1.0 mL / L, the pH value is kept at 3-5, the hydrolysis conversion rate can be remarkably increased, and therefore the treatment load of the treatment system is improved, by means of the method, the treatment load of the treatment system can be improved to be 4.5-6.5 kgVS / m<3>*d, the treatment residence time can be saved by about 40%, and the occupied space of an anaerobic tank can be saved by 25%or above; and the method has great application significance in increasing the treatment amount of the kitchen waste under the condition that an original kitchen waste treatment plant is not expanded.
Owner:广州市朗坤环境科技有限公司
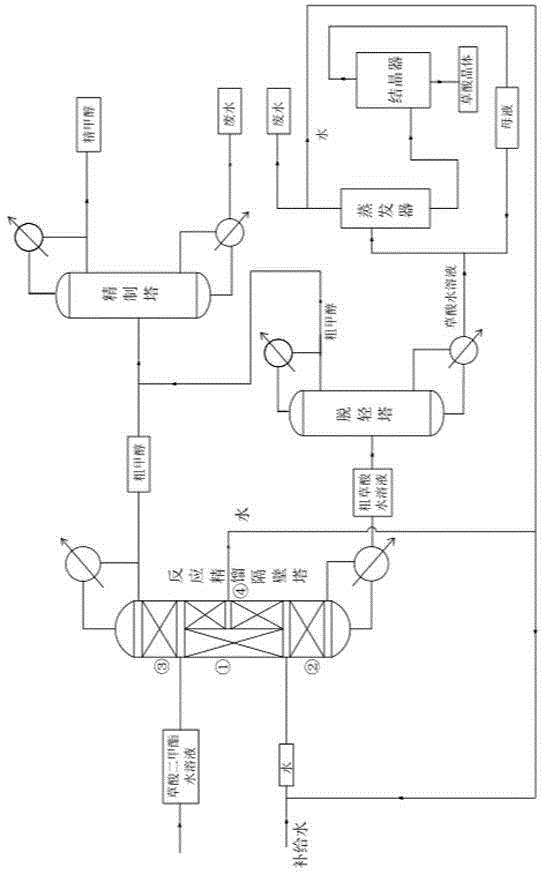
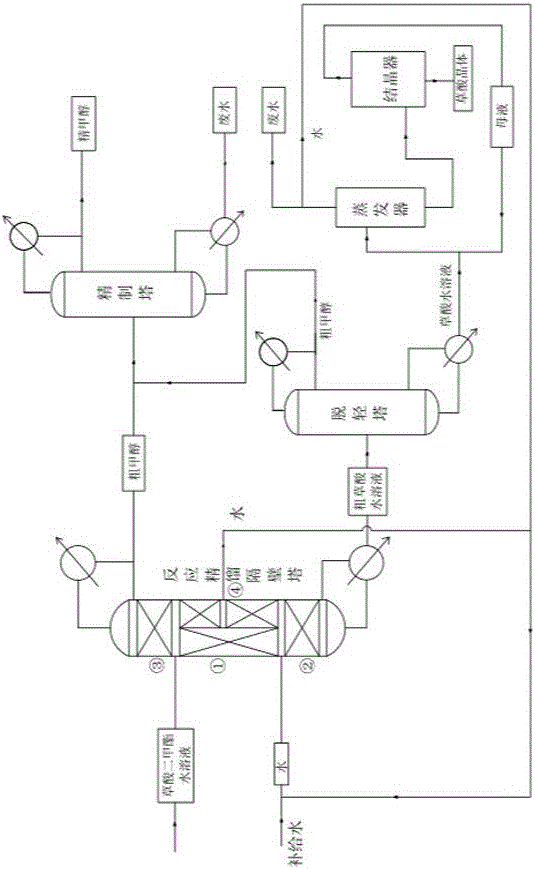
Technique for preparing oxalic acid by performing continuous reaction rectification hydrolysis on dimethyl oxalate
ActiveCN104892389AShort reaction timeLess investmentChemical industryPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEDimethyl oxalate
The invention discloses a technique for preparing oxalic acid by performing continuous reaction rectification hydrolysis on dimethyl oxalate. The raw material dimethyl oxalate is subjected to autocatalytic hydrolysis in a continuous reaction rectification dividing wall column to prepare the oxalic acid. The technique has the characteristics of high reaction speed, high reaction conversion rate, simple equipment, low energy consumption and no environmental pollution in the preparation process, and the hydrolysis conversion rate of the dimethyl oxalate is up to 99% above. The technique completely solves the problem that the dimethyl oxalate solid can not be subjected to continuous reaction rectification and can easily block the column.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
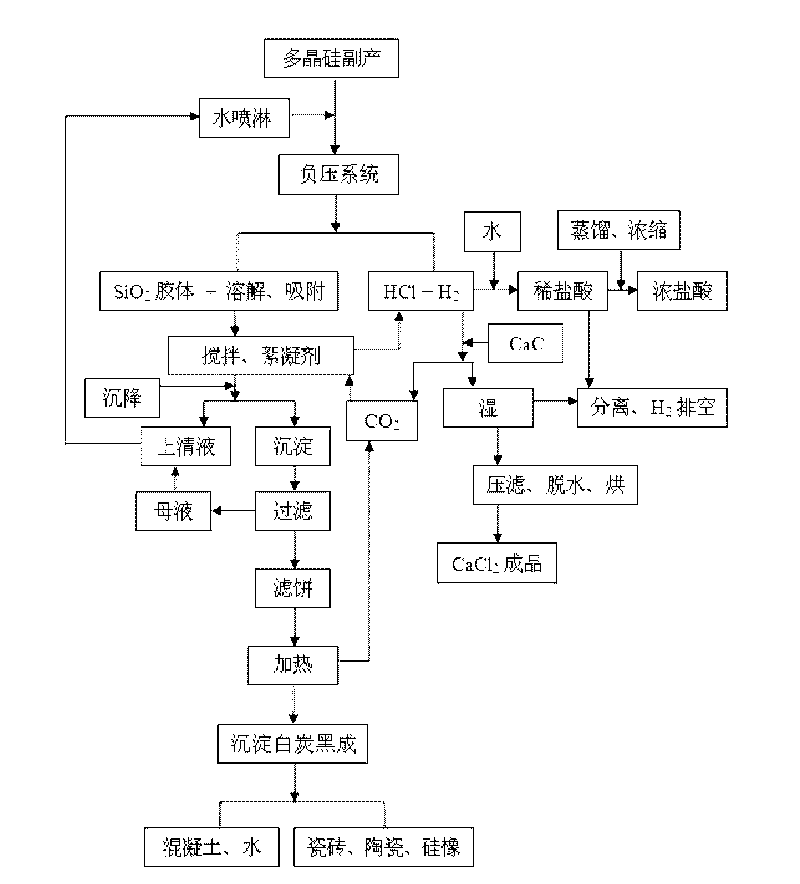
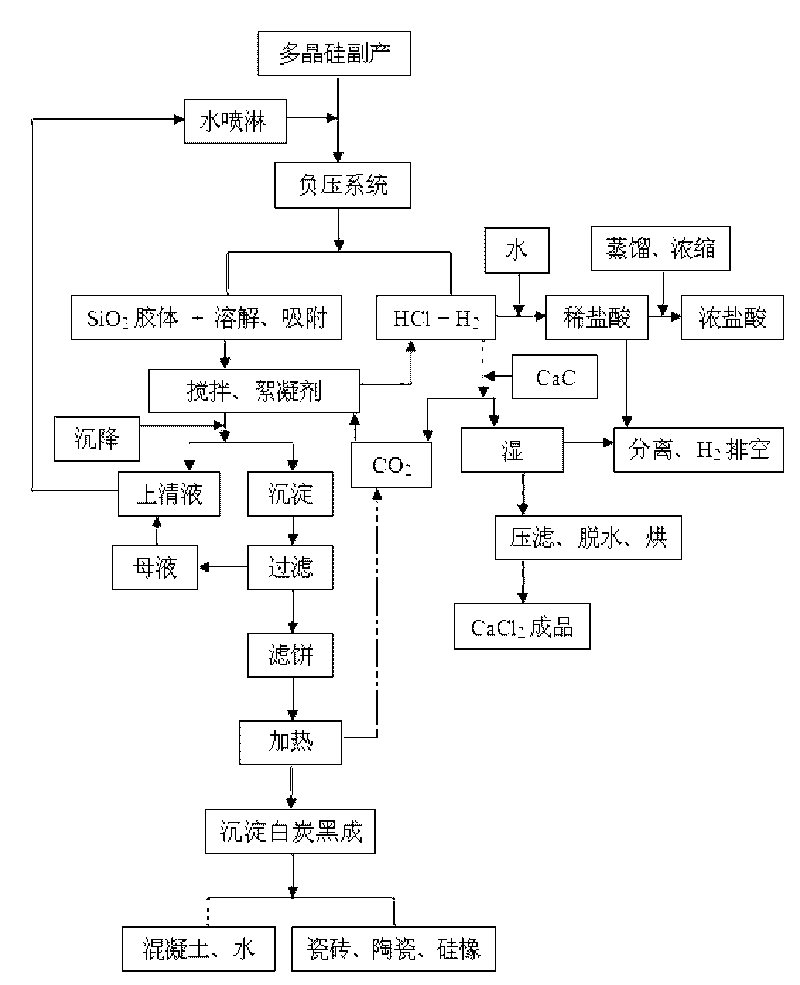
Method for comprehensively utilizing polysilicon by-product with low cost
InactiveCN101691226AResolve separabilitySolve the Cl in the silica product <sup>-<</sup> SilicaPreparation from chloridesHydrolysateReaction temperature
The invention relates to a method for comprehensively utilizing a polysilicon by-product with low cost, which belongs to the technical field of polysilicon production. The technical problem to be solved by the invention is to effectively separate a hydrolysate of the polysilicon by-product to obtain precipitated silica and HCl and comprehensively utilize the polysilicon by-product with low cost. The technical scheme of the invention comprises the steps of: performing a hydrolysis reaction on the polysilicon by-product and water in a mol ratio of 1: 3-6; separating gas HCl and a small quantity of H2 from the hydrolysate in a decompression separation mode; and adding a flocculating agent into a liquid from which the gas is separated to form a precipitate, and roasting the precipitate obtained after solid-liquid separation to remove the flocculating agent to obtain the precipitated silica. The method has low reaction temperature, does not need heating and cooling, has high hydrolysis conversion rate and good separation effect, can make full use of Si and Cl in the by-product, has low requirement on equipment, has high utilization value of the hydrolysate, and can realize consumption reduction, energy conservation and comprehensive utilization of resources.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for preparing bambusa chungii liquid
ActiveCN104041904AImprove color and stabilityImprove the conversion rate of hydrolysisFood preparationFood ingredient as mouthfeel improving agentFlavorHigh pressure
The invention discloses a method for preparing bambusa chungii liquid. The method comprises the following steps of pulping bambusa chungii, carrying out high-pressure treatment, carrying out enzymolysis, then, carrying out microfiltration, and sterilizing. According to the method, no food additive is added, and ultrahigh temperature is adopted to instantly sterilize bacteria, so that the nutrition and flavor of the bambusa chungii are preserved, and the bambusa chungii liquid is faint scent and slightly sweet; cane sugar is not artificially added, so that health problems resulting from the addition of white granulated sugar are avoided, and the bambusa chungii liquid is natural and healthy and meets the increasing demands of people on the safety, nutrition, flavor and taste of beverages.
Owner:GUANGXI JIANMEILE FOOD
Preparation method for red bamboo liquid
ActiveCN104013065AReduce recycling costsImprove the conversion rate of hydrolysisFood scienceFood additiveFlavor
The invention discloses a preparation method for red bamboo liquid. The preparation method comprises the following steps: beating, aqueous extraction, enzymolysis, microfiltration and sterilization. The preparation method is free of any kind of food additives and adopts a super high temperature instantaneous sterilization method, and the nutrition and flavor of the red bamboo are retained. The red bamboo liquid is pleasant and sweet in smell, is free of artificial sugar, and avoids the health problem caused by adding sugar. The red bamboo liquid has the characteristics of being natural and healthy and meets the higher and higher demand of people on safety, nutrition and flavor of beverage.
Owner:GUANGXI JIANMEILE FOOD
Process for preparing oxalic acid by continuous reaction distillation and hydrolysis of dimethyl oxalate
ActiveCN104892389BShort reaction timeLess investmentChemical industryPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEDistillation
The invention discloses a technique for preparing oxalic acid by performing continuous reaction rectification hydrolysis on dimethyl oxalate. The raw material dimethyl oxalate is subjected to autocatalytic hydrolysis in a continuous reaction rectification dividing wall column to prepare the oxalic acid. The technique has the characteristics of high reaction speed, high reaction conversion rate, simple equipment, low energy consumption and no environmental pollution in the preparation process, and the hydrolysis conversion rate of the dimethyl oxalate is up to 99% above. The technique completely solves the problem that the dimethyl oxalate solid can not be subjected to continuous reaction rectification and can easily block the column.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for catalyzing hydrolysis and decarboxylation of grease by using cell-like multiphase emulsion photoenzyme system
ActiveCN113621657AHigh catalytic efficiencyGood light transmissionFermentationChemical synthesisEthyl acetate
The invention belongs to the field of chemical production and chemical synthesis, and discloses a method for catalyzing hydrolysis and decarboxylation of grease by a cell-like multiphase emulsion photoenzyme system. The method comprises the following steps of: adding soluble salt, a polymer and / or hydrophilic alcohol, fatty acid light decarboxylase and grease into lipase liquid to prepare a cell-like multiphase emulsion system; or uniformly mixing the soluble salt, the polymer and / or the hydrophilic alcohol, the fatty acid light decarboxylase and the fatty acid to prepare the cell-like multiphase emulsion system; carrying out an enzyme catalysis reaction on the cell-like multiphase emulsion system under the condition of stirring and blue light irradiation; after the reaction is finished, adding ethyl acetate for carrying out extraction; standing or centrifuging until the product is divided into three layers; and collecting a supernatant product which is a hydrolyzed and decarboxylated product. The lipase can catalyze deep hydrolysis of glyceride, the fatty acid light decarboxylase can catalyze decarboxylation of free fatty acid, while rapid reaction and intelligent control are achieved, substrate inhibition can be relieved, and a novel multi-enzyme combined catalytic system which is efficient, controllable, easy in enzyme recovery and capable of synchronously separating products is established.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A low-temperature hydrolysis method for removing carbonyl sulfide in liquefied petroleum gas
ActiveCN103992831BHigh catalytic activityImprove the conversion rate of hydrolysisGaseous fuelsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsAlcoholCarbonyl sulfide
The invention provides a low-temperature hydrolysis method for removing carbonyl sulfide in liquefied petroleum gas. The method comprises the following steps: mixing the liquefied petroleum gas after amine washing with an alcohol amine solution, and performing hydrolysis reaction under the action of a carbonyl sulfide hydrolysis catalyst to remove carbonyl sulfide and hydrogen sulfide in the liquefied petroleum gas and hydrogen sulfide generated by hydrolysis; separating the liquefied petroleum gas from the alcohol amine solution, then washing with water to obtain the refined liquefied petroleum gas and recycling the alcohol amine solution, wherein the adding amount of the alcohol amine solution is 0.1%-20% of the weight of the liquefied petroleum gas. By adopting the low-temperature hydrolysis method for removing carbonyl sulfide in the liquefied petroleum gas provided by the invention, carbonyl sulfide and hydrogen sulfide in the liquefied gas can be removed in one step under the condition of 10-60 DEG C, the step of removing hydrogen sulfide in a conventional process is eliminated, the process is simple, the activity of the catalyst is high, the service life is long and the conversion rate of carbonyl sulfide is above 97%.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +3
Pre-processing method for strengthening corncob and corncob residue efficient enzymatic hydrolysis
InactiveCN107893093AImprove the conversion rate of hydrolysisReduce loadBiofuelsFermentationPretreatment methodEnzymatic hydrolysis
The invention discloses a pre-processing method for strengthening corncob and corncob residue efficient enzymatic hydrolysis. The pre-processing method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing slurry; (2) conducting mechanical pre-processing; and (3) conducting enzymatic hydrolysis, so as to obtain a hydrolysate, so that the corncob and corncob residue efficient enzymatic hydrolysis is strengthened. The pre-processing method provided by the invention, by processing corncobs and corncob residues by virtue of a mechanical pre-processing way, can reduce physical dimensions of raw materials, reduce a degree of crystallinity and improve the specific surface area and swelling performance of the raw materials, and subsequently, the efficiency of enzymatic hydrolysis is improved, and a relatively high glucose concentration and relatively high glucose conversion rate are finally guaranteed; with the application of the method, high-value utilization of the corncobs and the corncob residues can be achieved, and meanwhile, input cost of the enzymatic hydrolysis is reduced, the efficiency of the enzymatic hydrolysis is improved and a raw material foundation is provided for subsequent processing and utilization or for production of high-value-added products; therefore, the application field and scope of the corncobs and the corncob residues are expanded.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing granulose by resin catalysis
InactiveCN101200771AAvoid acid and alkaliAvoid process problemsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsOligosaccharidesPapermakingCorrosion
The invention discloses a resin catalysis method of preparing starch glucose which is characterized in that water is added in starch to prepare starch solution with the concentration of 10-40wt. percent; and then catalyst is added to change the solid-liquid ratio or the volume ratio of the catalyst and the starch solution to be 1 to 1-1 to 5; the mixture will react for 10-15h in an enclosed reactor at the temperature of 110-130 DEG C after being evenly stirred; the mixture is hydrolyzed to obtain the starch glucose. The invention can not only overcome the corrosion of the acid method on equipment and reduce the acid-base neutralization and the desalting process, but also overcome the problems of the acid method of high requirements for enzyme purity and activity, hard operating control, hart filtering and long production cycle. The method has the advantages of simple production procedures, less energy consumption and low production cost. The output starch glucose can be widely applied to industries and fields of food, medicine, chemical, papermaking, textile, etc.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing steroide compound 17-alpha ester
ActiveCN101891797BMake up for the impactPromote hydrolysisSteroids preparationCompound 17Prednisolone
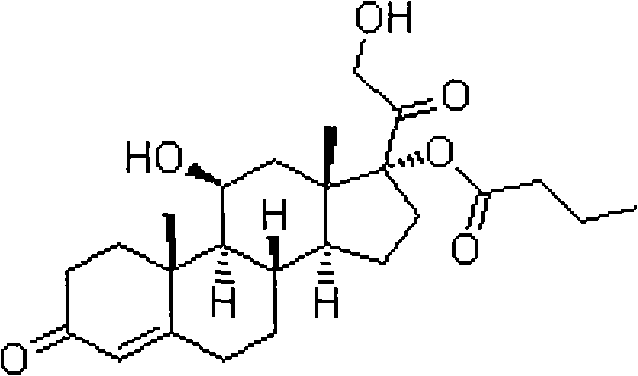
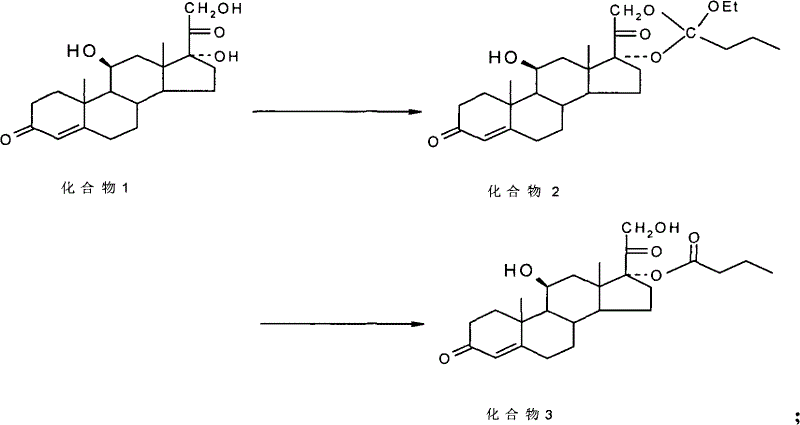
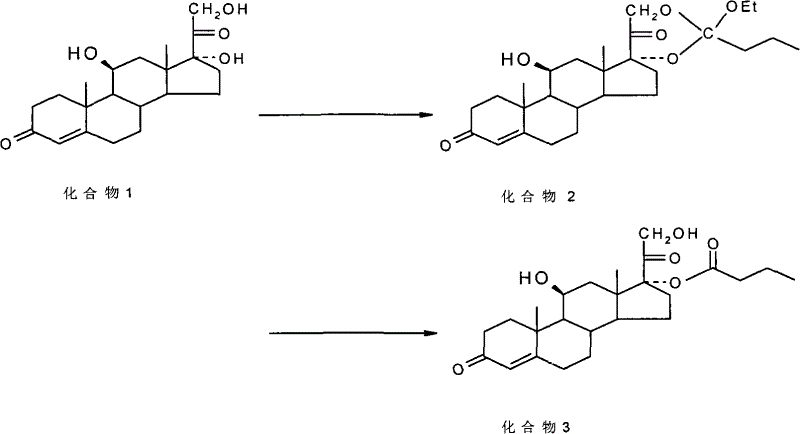
The invention discloses a method for preparing a sterides compound 17-alpha ester. The method comprises the following steps of: dissolving 17 alpha, 21-dihydroxyl sterides compound serving as a raw material in a cyclic ester solvent; adding an ester and a catalyst into the mixture and reacting the mixture to prepare a cyclic ester; and dissolving the prepared cyclic ester in a hydrolysis solvent,adding an orientation reagent and a hydrolysis reagent into the mixed solution and hydrolyzing the cyclic ester into the 17-alpha ester. The sterides compound is hydrocortisone, prednisolone, prednisone, hexadecadrol or betamethasone. The method has selective hydrolysis effect,, and can effectively enhance the conversion rate of a product, greatly increase product yield and greatly promote the preparation capability of a sterides medicament.
Owner:ZHEJIANG XIANJU PHARMA
Method for producing sec-butyl alcohol through continuous hydrolysis
ActiveCN107903150AImprove the conversion rate of hydrolysisHigh purityOrganic compound preparationChemical industryChemical reactionReactive distillation
The invention discloses a method for producing sec-butyl alcohol through continuous hydrolysis, and belongs to the field of chemical reactions and separation. The method takes the sec-butyl acetate asa main material, the sec-butyl acetate is subjected to catalytic hydrolysis in a reaction section of a reactive distillation column through a catalyst, and the high-purity sec-butyl alcohol is obtained through the oil water separation and the three-step pressure swing distillation comprising pressure reduction, pressurization and pressure reduction. The reaction rectification-pressure swing distillation coupling process is adopted to hydrolyze the sec-butyl acetate, the conversion rate of hydrolysis is high, the purity of the sec-butyl alcohol is high, and the operation condition of the reaction is mild.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for preparing bambusa chungii liquid
ActiveCN104041905AReduce recycling costsImprove the conversion rate of hydrolysisFood preparationFlavorFood additive
The invention discloses a method for preparing bambusa chungii liquid. The method comprises the following steps of pulping bambusa chungii, carrying out water extraction, carrying out enzymolysis, then, carrying out ultrafiltration and sterilizing. According to the method, no food additive is added, and ultrahigh temperature is adopted to instantly sterilize bacteria, so that the nutrition and flavor of the bambusa chungii are preserved, and the bambusa chungii liquid is faint scent and slightly sweet; cane sugar is not artificially added, so that health problems resulting from the addition of white granulated sugar are avoided, and the bambusa chungii liquid is natural and healthy and meets the increasing demands of people on the safety, nutrition, flavor and taste of beverages.
Owner:GUANGXI JIANMEILE FOOD
Method capable of producing fermentable sugars from corncob residues by efficient enzymatic hydrolysis
InactiveCN108179159ABroaden the field of applicationExpand scopeFermentationFiberEnzymatic hydrolysis
The invention discloses a method capable of producing fermentable sugars from corncob residues by efficient enzymatic hydrolysis. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing raw materials;(2) performing pretreatment with a chemical method; (3) collecting reacted corncob residues, repeatedly washing the corncob residues multiple times until the corncob residues are neutral to obtain washed corncob residues; (4) performing enzymatic hydrolysis to obtain a hydrolysate for completion of production of the fermentable sugars from the corncob residues by efficient enzymatic hydrolysis. According to the method, the corncob residues are treated with a chemical pretreatment technique, hydrophilic performance of lignin in fiber raw materials is improved, the lignin is dissolved out easily, and accordingly, enzymatic hydrolysis yield of the corncob residues is increased; the corncob residues can be used in a higher-value manner with the method, investing cost for enzymatic hydrolysisis reduced, enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency is increased, raw material basis is provided for follow-up processing and utilization or production of products with high added value, so that application field and range of the corncob residues are expanded, and use quantity of wood fiber raw materials can be reduced effectively.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
A kind of preparation method of Danzhu liquid
ActiveCN104013065BReduce recycling costsImprove the conversion rate of hydrolysisFood scienceFlavorFood additive
The invention discloses a preparation method for red bamboo liquid. The preparation method comprises the following steps: beating, aqueous extraction, enzymolysis, microfiltration and sterilization. The preparation method is free of any kind of food additives and adopts a super high temperature instantaneous sterilization method, and the nutrition and flavor of the red bamboo are retained. The red bamboo liquid is pleasant and sweet in smell, is free of artificial sugar, and avoids the health problem caused by adding sugar. The red bamboo liquid has the characteristics of being natural and healthy and meets the higher and higher demand of people on safety, nutrition and flavor of beverage.
Owner:GUANGXI JIANMEILE FOOD
Hydrolysis method of esters
InactiveCN1224596CImprove the conversion rate of hydrolysisEasy to separateOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationPhosphomolybdic acidHeteropoly acid
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Preprocessing method capable of effectively improving efficiency of generating fermentable sugar by bamboo cellulose enzyme hydrolysis
InactiveCN103266148BImprove accessibilityImprove the conversion rate of hydrolysisFermentationFiberPretreatment method
The invention discloses a preprocessing method capable of effectively improving the efficiency of generating fermentable sugars by bamboo cellulose enzyme hydrolysis. The preprocessing method comprises the following steps of: preparing materials; preprocessing acid catalyzed high-boiling alcohol; washing solid substrates obtained by preprocessing; milling the solid substrates by a millstone; and performing enzyme hydrolysis. By preprocessing the acid catalyzed high-boiling alcohol in the preprocessing method disclosed by the invention, hemicellulose and lignin can be synchronously and efficiently removed from bamboo fiber raw materials, and additionally, extractives and waxiness on the surfaces of the extractives can be effectively removed from the bamboo outer skin of the outer wall of bamboos. Compared with the existing acidic chemical preprocessing method, the recovery rate of fermentable glucose obtained by enzyme hydrolysis of cellulose in the bamboos after the high-boiling alcohol preprocessing is increased by 36 to 50%, and compared with the preprocessing method by using a low-boiling organic solvent, the recovery rate is increased by 10 to 15%. By using the preprocessing method in which a high-boiling alcohol / hydrosolvent system with acid catalysis and low alcohol content is utilized and the bamboos are preprocessed before enzyme hydrolysis within short time, the conversion efficiency of the cellulose in the bamboos to the fermentable sugars through enzyme hydrolysis can be improved, and the defect that the environmental pollution is caused by waste liquor can be overcome.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
A dry desulfurization purification process for ethylene-rich gas
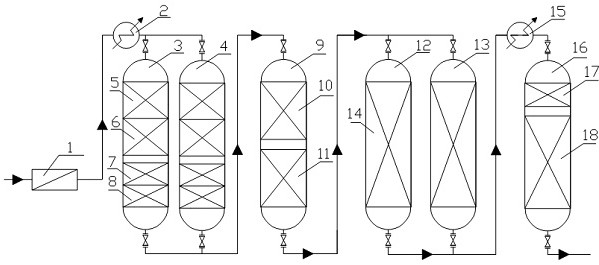
ActiveCN113332845BAvoid capillary condensationReduce the burden onGas treatmentDispersed particle separationDeoxygenationHydrolysis
The invention discloses a dry desulfurization and purification process for ethylene-rich gas. Ethylene-rich gas can be desulfurized by hydrolysis, fine deoxidation, dehydration and mercaptan removal, arsenic removal, mercury removal and other processes in sequence, and the COS in the raw material can be removed to less than 0.1ppm, O 2 Content less than 1ppm, H 2 O content is reduced to not more than 10ppm, As content is not more than 5ppb, Hg content is not more than 5ppb, NO X It is reduced to less than 10ppb, which meets the needs of subsequent ethylene cold box separation, and the pressure drop of the entire process bed is not greater than 50KPa. The process has the characteristics of simple process, less ethylene loss, high purification precision and low operating cost.
Owner:WUHAN KELIN FINE CHEM
A kind of preparation method of Danzhu liquid
ActiveCN104041904BImprove the conversion rate of hydrolysisConducive to the subsequent enzymatic hydrolysis processFood preparationFood ingredient as mouthfeel improving agentFood additiveFlavor
Owner:GUANGXI JIANMEILE FOOD
Hydrolytic method of Chinese potato saponin
The invention relates to a hydrolysis method of dioscin. A solid acid catalyst is added into the reaction solution containing the dioscin according to the proportion of 0.1g to 100g / 100ml of extract and then the reaction solution is placed in water bath of 50 DEG C to 90 DEG C for reaction for 2h to 16h; after the hydrolysis, the reactant obtained is cooled to the room temperature and filtered invacuum and the filter residue is dried at the temperature of 20 DEG C to 80 DEG C; the filter residue is extracted in organic solution for 4h to 12h continuously, the extract is separated and the organic solution thereof is recycled; finally the dioscin solid is obtained. The solid acid catalyst system adopted by the invention is a multiphase reaction; hydrogen ions are restrained on the surface of the catalyst rather than going into the body of the reaction solution, therefore, the acidification of the reaction solution is avoided and the loss of the hydrogen ions is rather small. The experimental result shows that the pH value of the solution phase after hydrolysis is 4 to 5 and the concentration of the hydrogen ions in the solution is 10,000 times lower than that of the solution which is hydrolyzed by hydrochloric acid, thus greatly reducing the pollution to the environment. The hydrolysis method has simple technology, moderate hydrolysis conditions and high hydrolysis conversion rate of the dioscin which is as high as 98 percent, thus fundamentally solving the problems of serious environmental pollution and equipment corrosion occurring in the inorganic acid catalysis hydrolysis process.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing glucose from bamboo cellulose
The invention relates to a method for preparing glucose from bamboo cellulose, belongs to the technical field of utiliztion of lignocellulose. Bamboo used as the raw material is subjected to hydrothermal treatment by a batch reactor, wherein the heating rate, maximum reaction temperature (250-240 DEG C) and cooling rate of the reaction are controlled to implement pretreatment on the bamboo cellulose; and the pretreated sample is subjected to enzyme hydrolysis to obtain the glucose. The method is simple and environment-friendly in the process and easy to control, and has favorable application prospects. After the bamboo cellulose is pretreated, the conversion rate of enzyme hydrolysis for generating glucose can be enhanced by 3.7 times, thereby implementing high-efficiency utilization of bamboo resources.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
A kind of preparation method of Danzhu liquid
ActiveCN104041905BReduce recycling costsImprove the conversion rate of hydrolysisFood preparationBiotechnologyFood additive
Owner:GUANGXI JIANMEILE FOOD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com