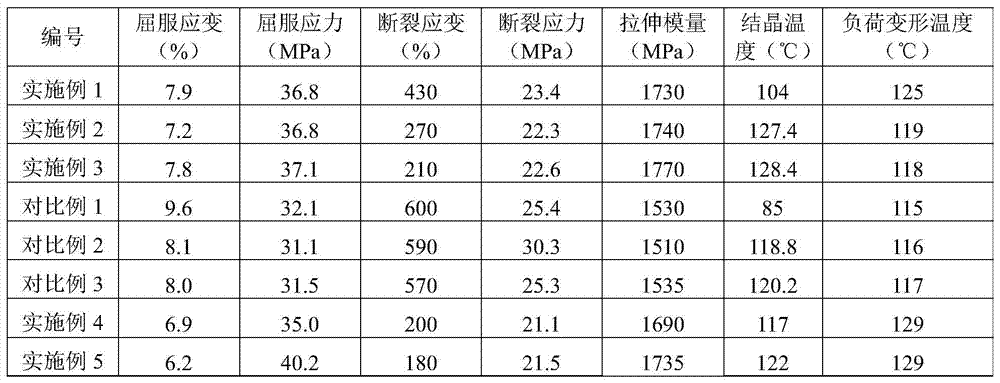
Patents
Literature
30results about How to "Reduce tensile strain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
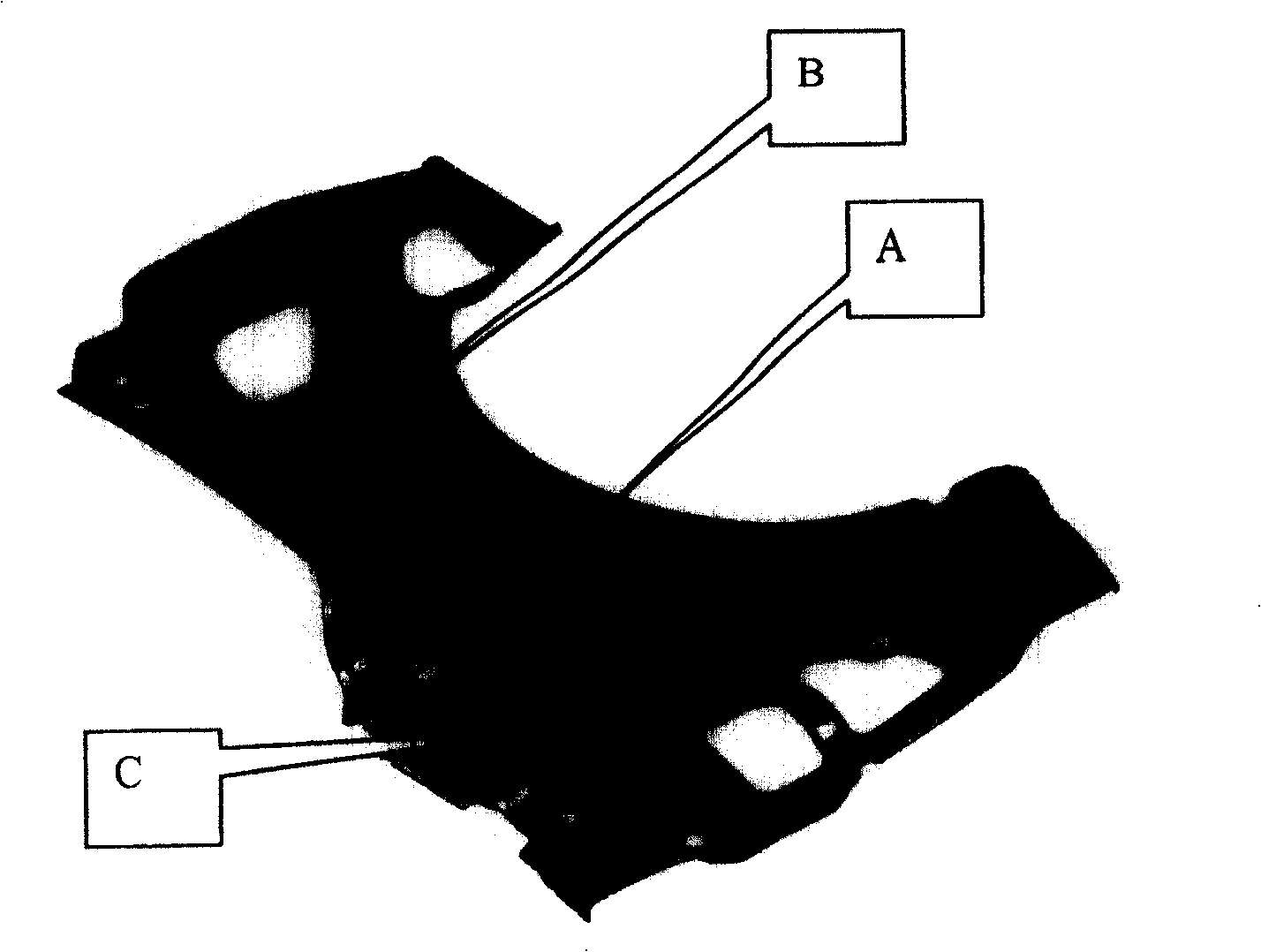
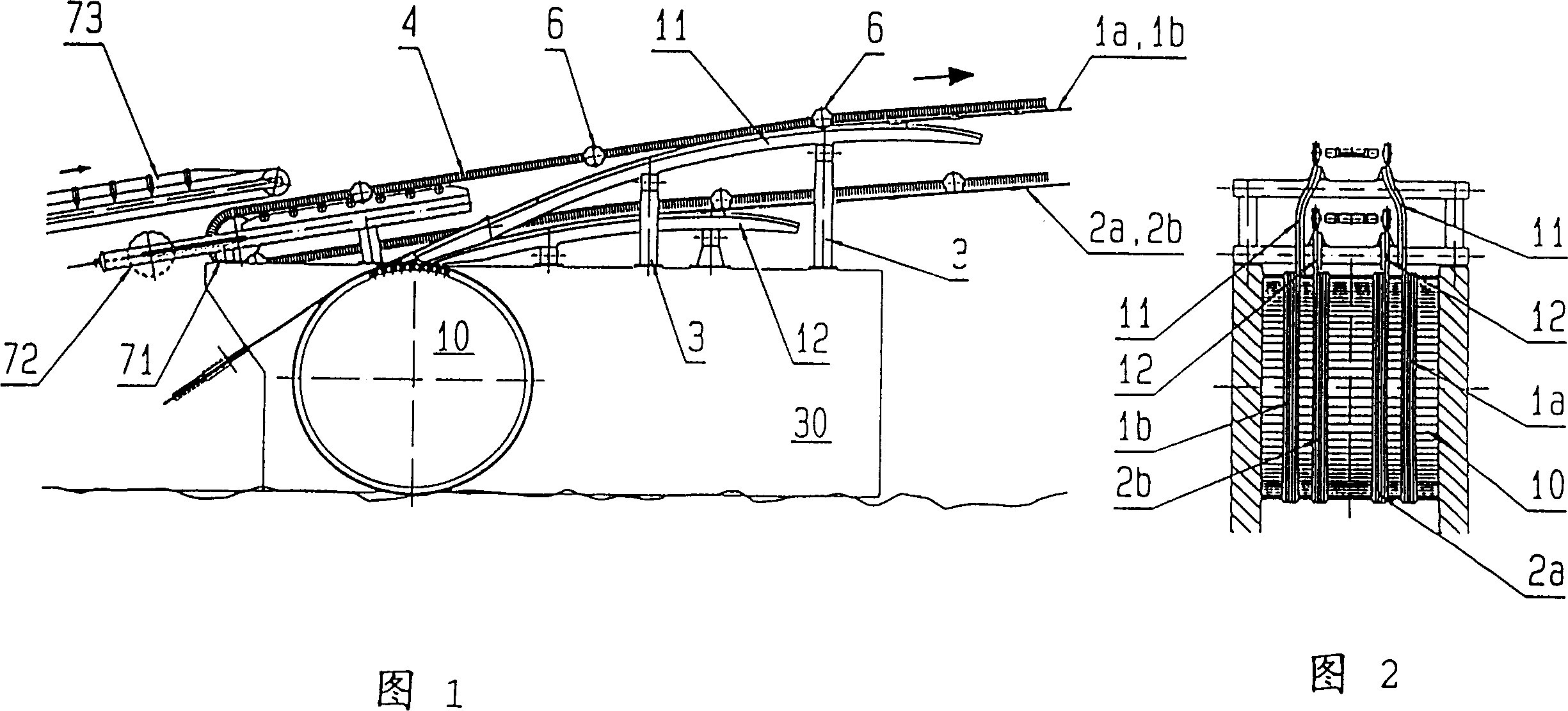
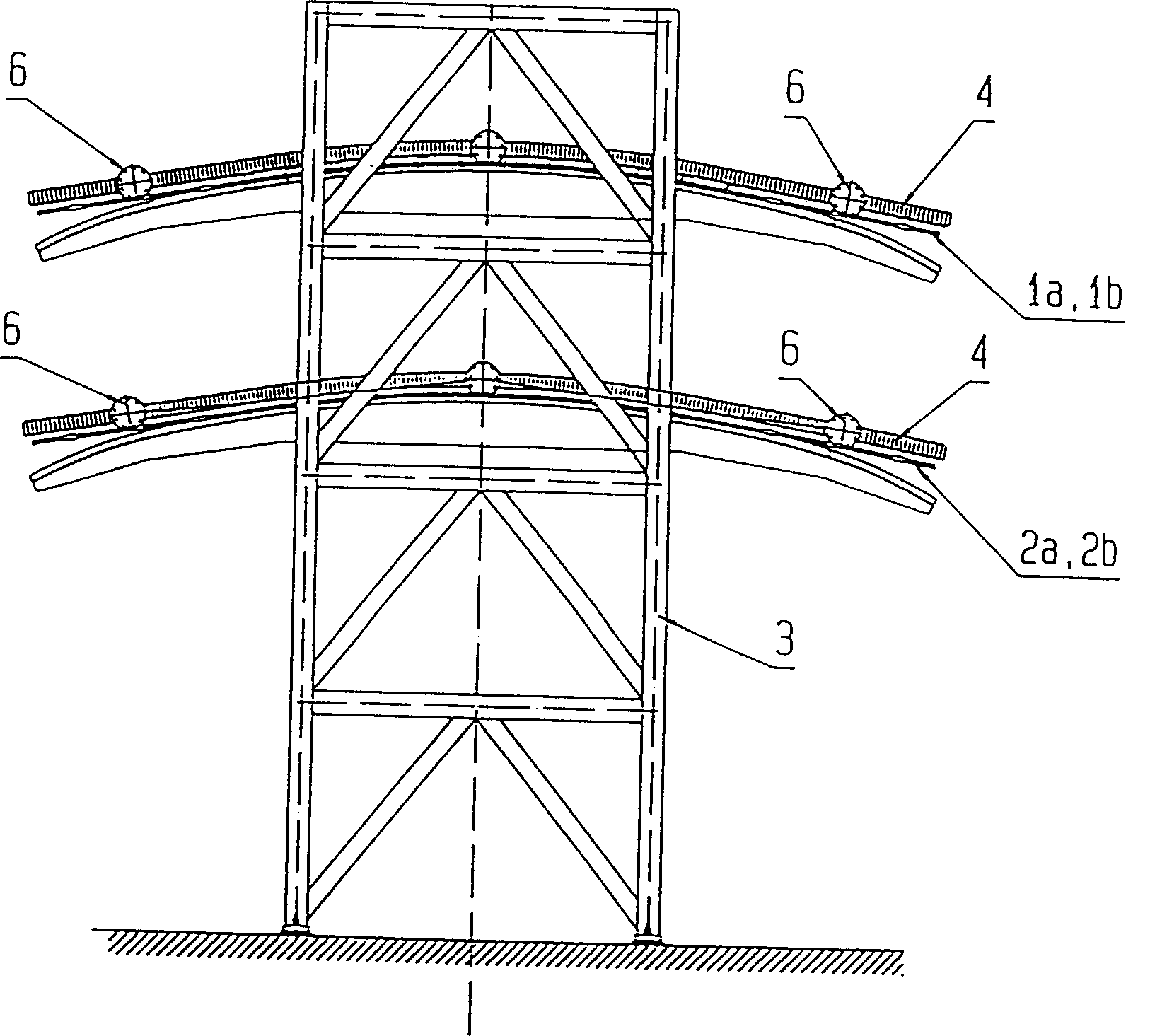
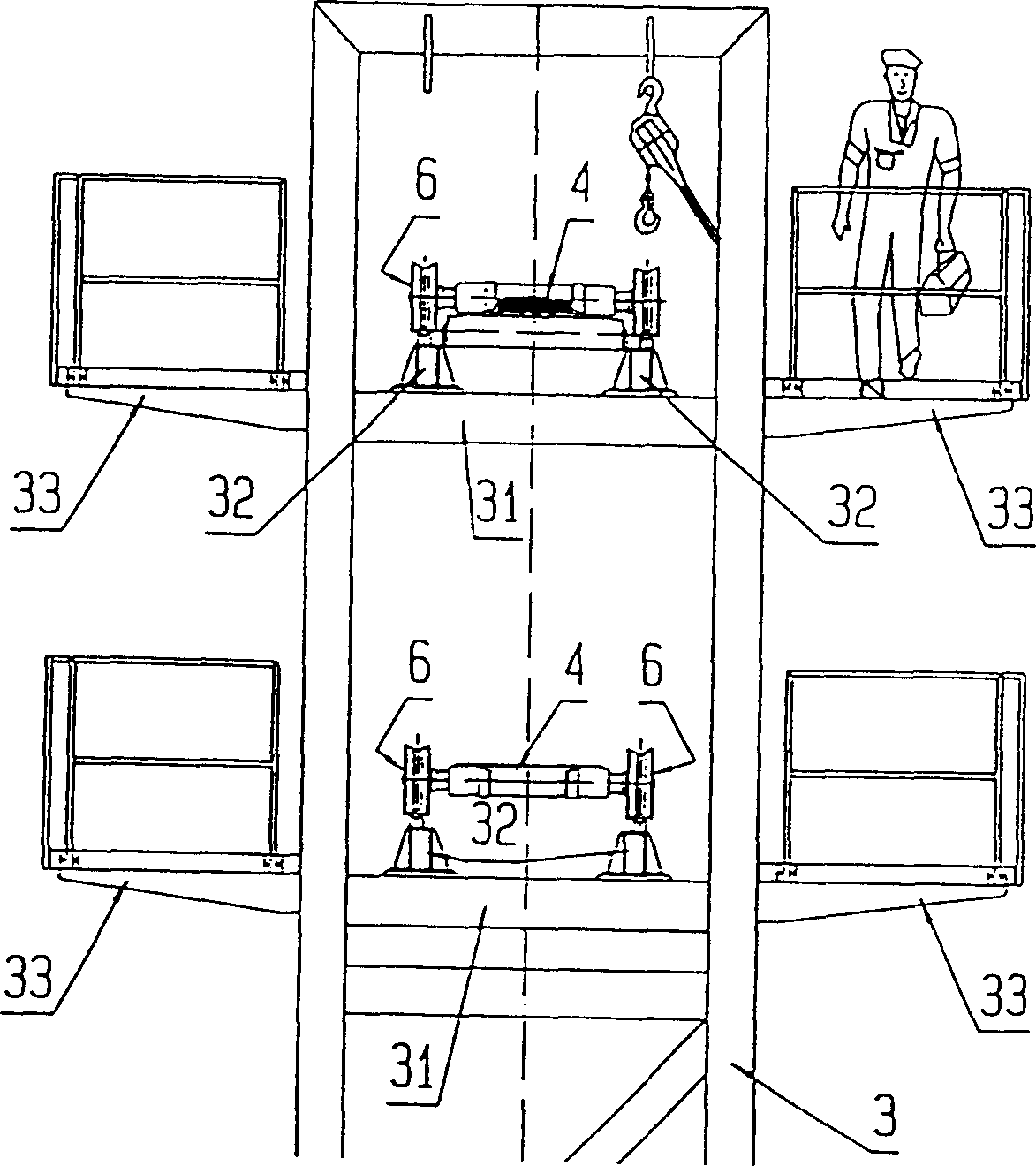
Cannula stent
ActiveUS7172623B2Optimize allocationIncreasing selected widthStentsBlood vesselsEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
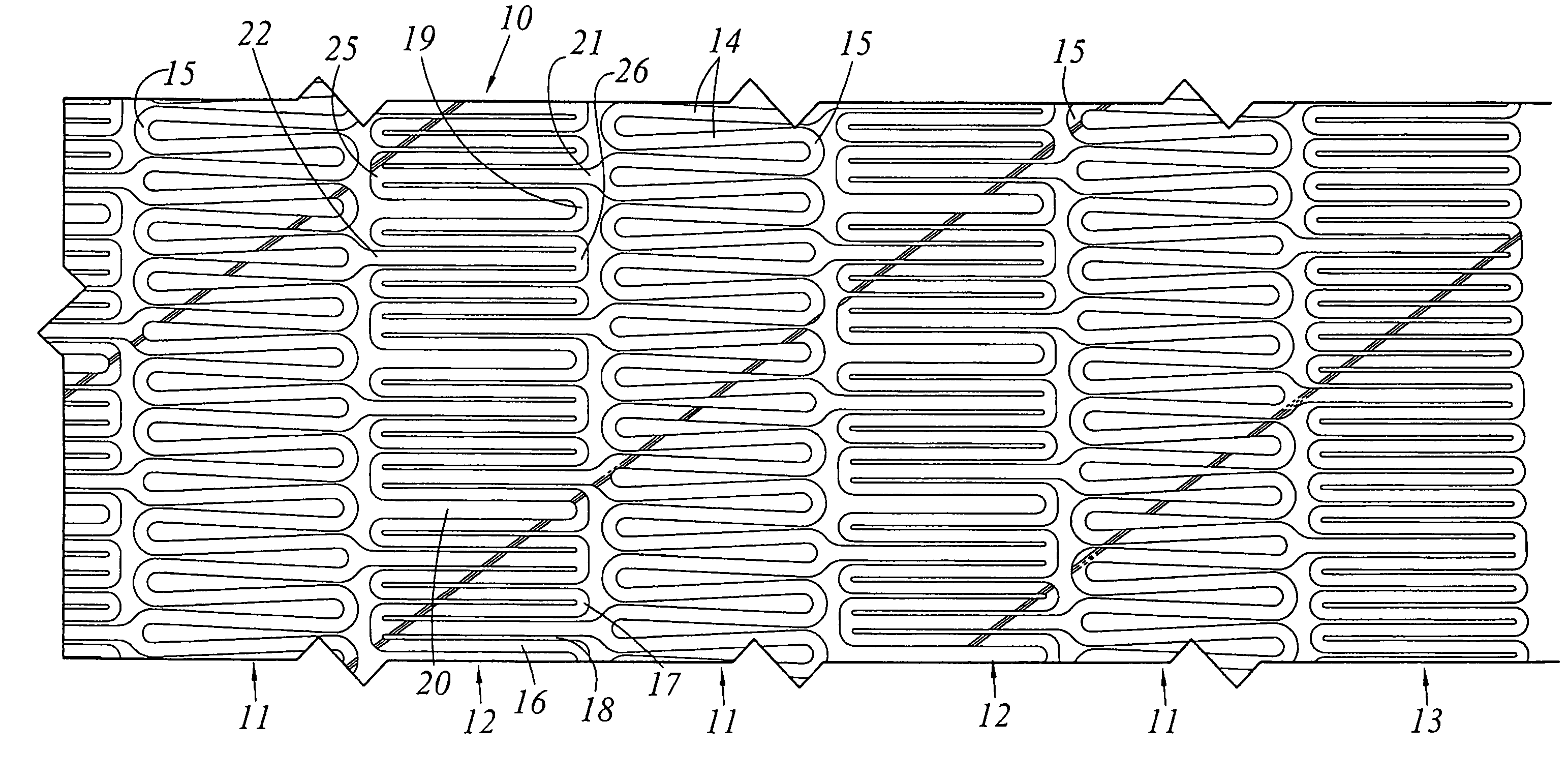
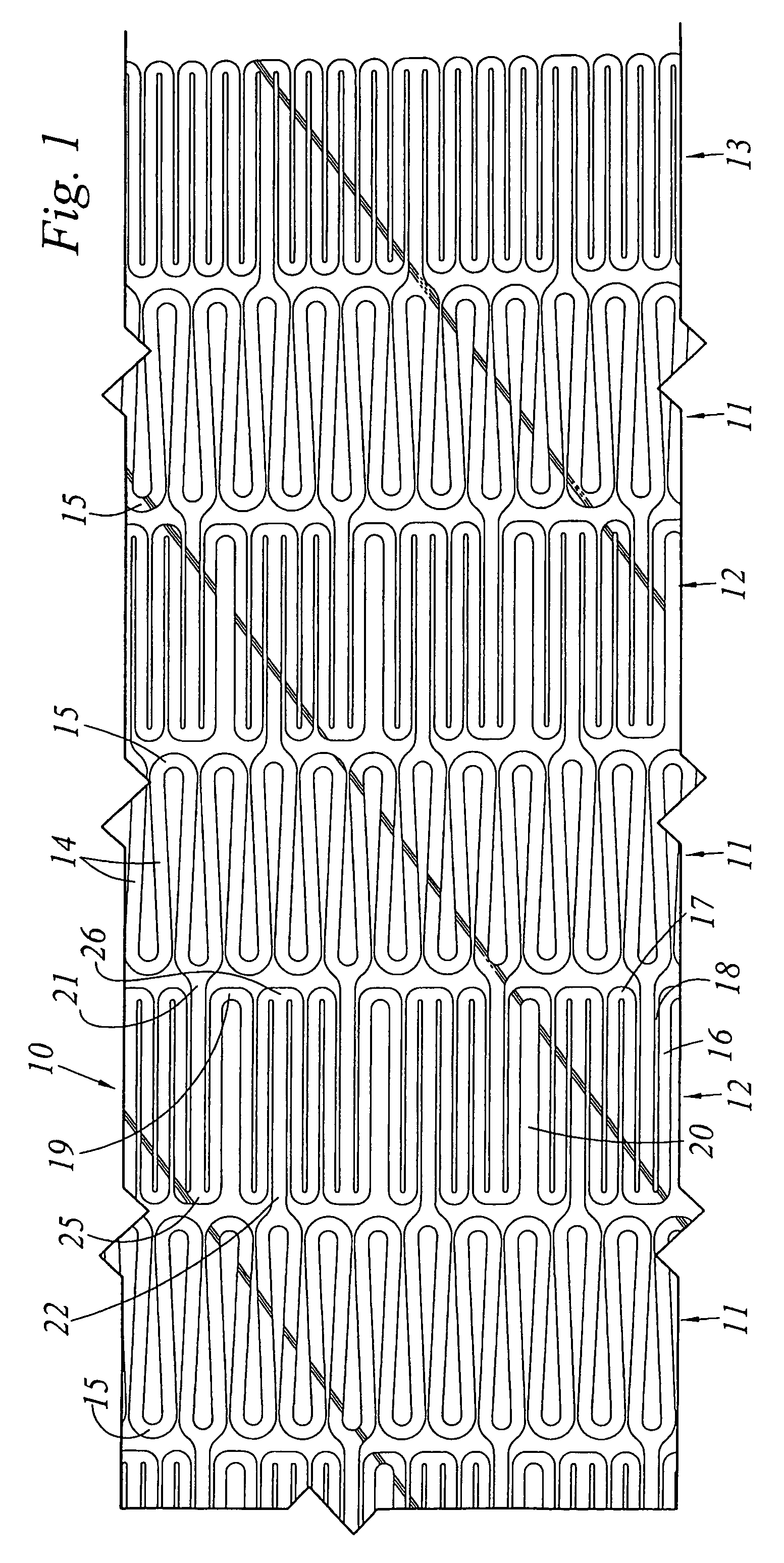
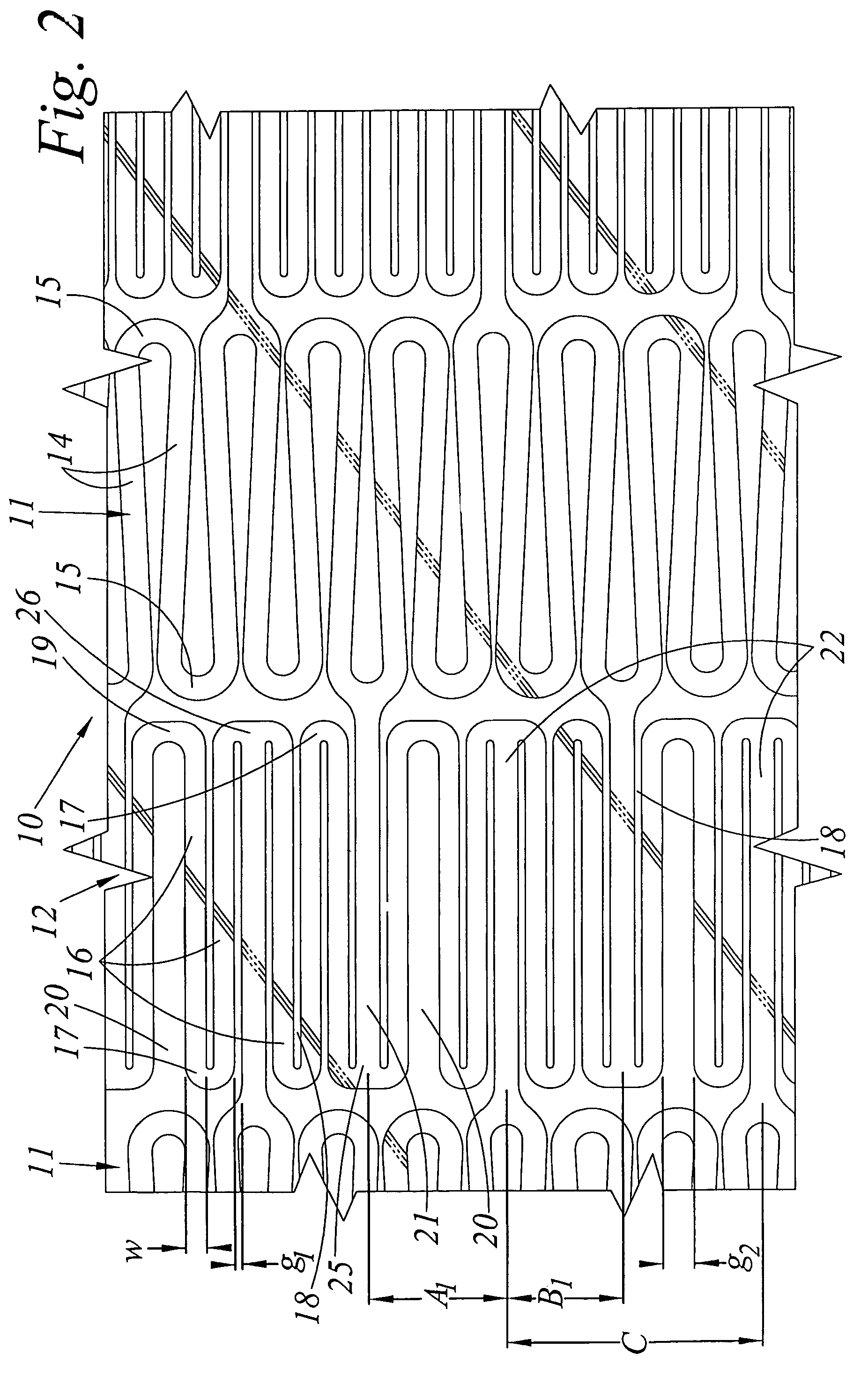
A stent (30) formed from cannula and having flexible segments (31) and high hoop strength segments (32) alternating therealong. Longitudinal struts or tie bars (41) interconnect the segments. Minimal length reduction of the strut occurs upon expansion. In the high hoop strength segment (32), struts (37) in a zig-zag configuration (Gianturco Z-stent) are initially parallel in the unexpanded strut condition. In the flexible segment (31), struts (58) extend from a respective C-shaped bend (59) to converge at the opposite ends thereof when unexpanded. In one embodiment, certain adjacent struts (39–41) of the hoop segment are spaced apart by elongated openings or gaps (46, 48) interposed therebetween and interconnected at their respective ends (42, 44) to form a T-shaped strut interconnection (45). The selected width (50, 51) of the first and third struts (54, 57) increases toward the ends (47, 48) of the elongated openings (46, 48) adjacent the strut interconnection (45). This strut width increase about one end of the strut significantly reduces the tensile strain exhibited about the opening end when the stent is radially expanded during manufacture. The tip length (52, 55) of the struts about the interconnection (45) is also adjusted (increased) along with the other C-shaped strut interconnections (59, 71) to further distribute the tensile strain developed during radial expansion.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
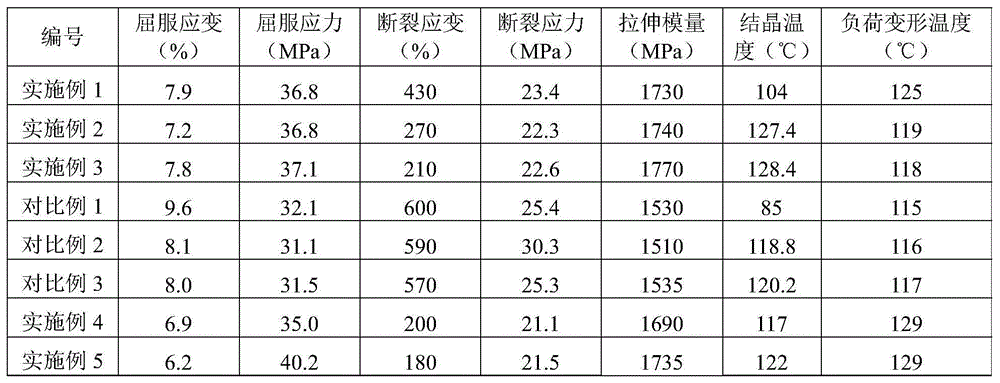
Polypropylene composition and polypropylene material as well as application thereof
ActiveCN104558821AReduce tensile strainHigh tensile strengthFixed capacitor dielectricSoil preservationTensile strainHeat resistance
The invention provides a polypropylene composition and a polypropylene material as well as an application thereof. The polypropylene composition comprises polypropylene, a nucleating agent and an antioxidant, wherein the nucleating agent comprises a crystal form alpha nucleating agent and a crystal form beta nucleating agent, the crystal form alpha nucleating agent is selected from one or more of an inorganic crystal form alpha nucleating agent, a sorbitol nucleating agent and an organic phosphate nucleating agent, and the crystal form beta nucleating agent is selected from one or more of a mixture of binary acid and an II Ath group of metal salts, a rare earth crystal form beta nucleating agent and an amide nucleating agent. The polypropylene material prepared from the polypropylene composition provided by the invention can be used for well integrating effects of relatively low tensile strain, relatively high tensile strength and relatively good heat resistance and long-term creeping strength, and has great industrial application prospects.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
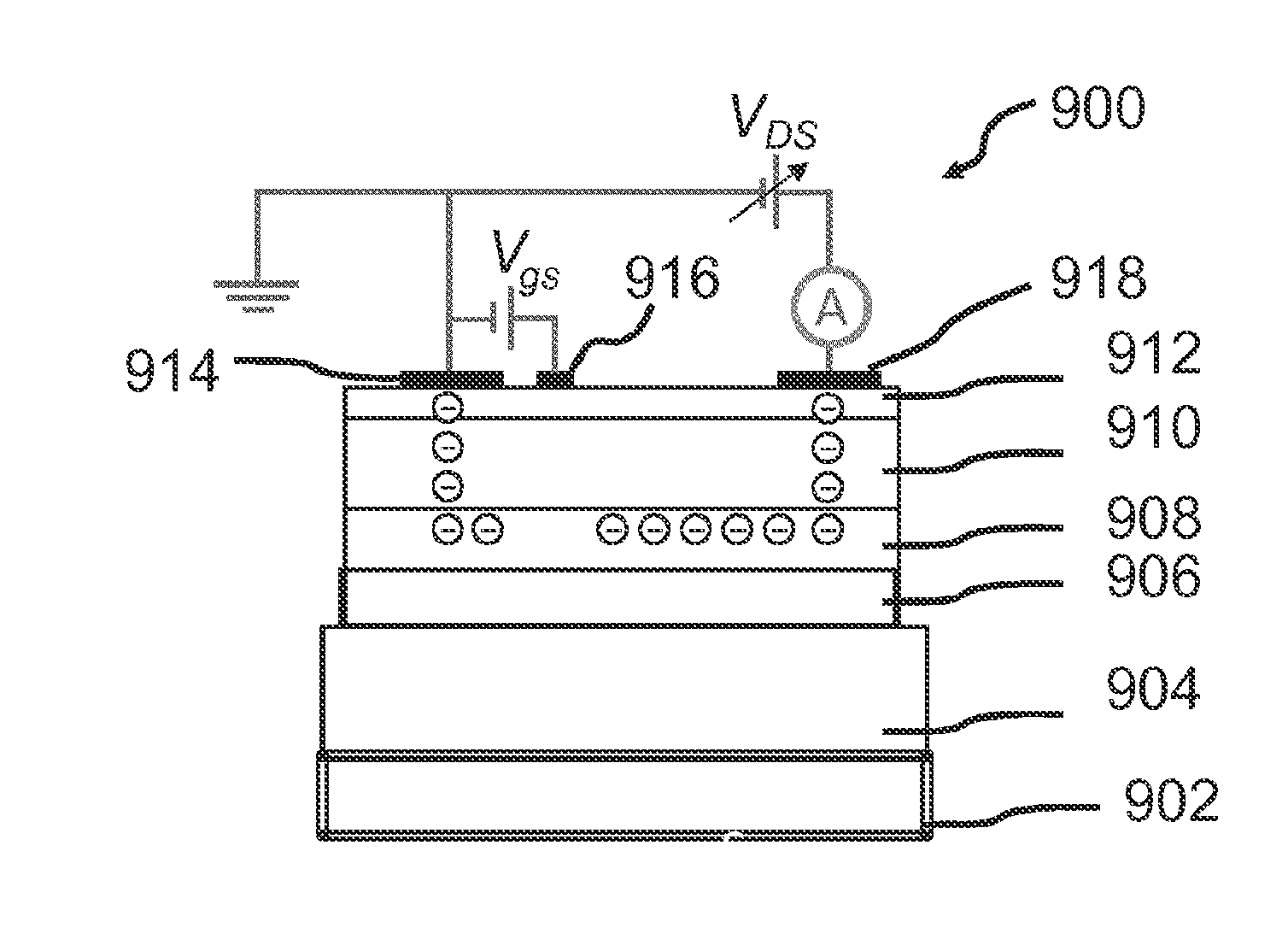
Layer structure for a group-iii-nitride normally-off transistor
A layer structure for a normally-off transistor has an electron-supply layer made of a group-III-nitride material, a back-barrier layer made of a group-III-nitride material, a channel layer between the electron-supply layer and the back-barrier layer, made of a group-III-nitride material having a band-gap energy that is lower than the band-gap energies of the other layer mentioned. The material of the back-barrier layer is of p-type conductivity, while the material of the electron-supply layer and the material of the channel layer are not of p-type conductivity, the band-gap energy of the electron-supply layer is smaller than the band-gap energy of the back-barrier layer. In absence of an external voltage a lower conduction-band-edge of the third group-III-nitride material in the channel layer is higher in energy than a Fermi level of the material in the channel layer.
Owner:AZUR SPACE SOLAR POWER
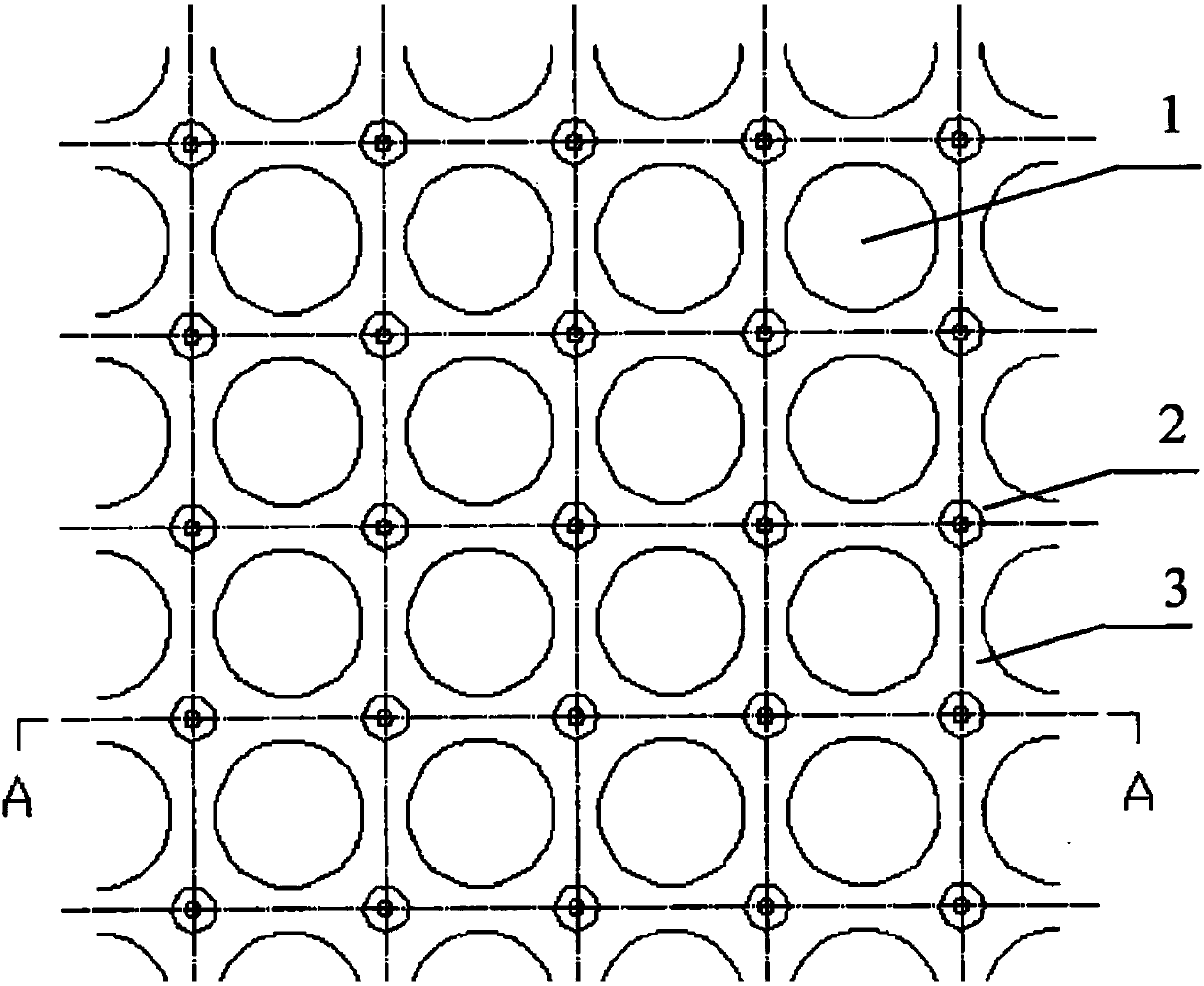
Earth work grille for reinforcing highway foundation and its use method
InactiveCN101413244AHigh strengthHigh-strength high-modulus polyvinyl chloride polymer material with high strengthExcavationsRoads maintainenceExtensibilityStress concentration
The invention provides a geotechnical grille for reinforcing highway subgrade, as well as an application method thereof. A grille net is formed by vertically and horizontally weaving high-strength and high-modulus polyvinyl chloride polymers, so as to increase the tensile strength of reinforced belts; an outer layer of the grille is coated with a modified rubber coating; rubber is mixed with anti-aging agent, antioxidant, light screener and other master batches, so as to increase the creep resistance and corrosion resistance of the reinforced belts; surface layers of the longitudinal and transverse reinforced belts of the grille are provided with coil-shaped embossed threads so as to increase friction force with soil; meshes of the grille are round so as to reduce stress concentration and increase the extensibility of the reinforced belts; and nodes of the reinforced belts of the grille are provided with bilateral strengthening columns, so as to stop the slippage between soil body and the grille, increase the shearing resistance of the subgrade, balance settlement and prevent the grille from being pulled out of the subgrade. The geotechnical grille has the advantages that the grille is high in the strength of polymer materials, little in creep because of the modified rubber smeared outside, high in tensile strength and low in tensile strain, and the round meshes, the threads of the reinforced belts and the strengthening columns fully occlude the soil body so as to form a space compound strengthening structure, thereby improving the entire shearing strength and settlement balancing performance of the subgrade.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
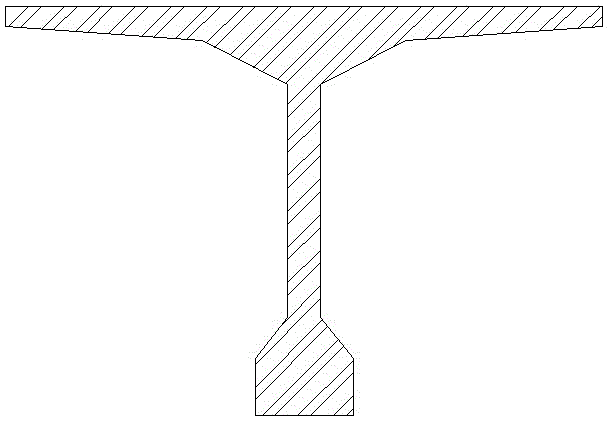
Prefabricated T-shaped beam and method of building continuous beam bridge by adopting prefabricated T-shaped beams
InactiveCN105019350AAvoid crackingReduces the possibility of crackingBridge structural detailsBridge erection/assemblyBridge engineeringTensile strain
The invention relates to a prefabricated T-shaped beam and a method of building a continuous beam bridge by adopting the prefabricated T-shaped beams, and belongs to the field of bridge engineering. The T-shaped beam is an improved form of the conventional prefabricated T-shaped beam, and bottom flanges are additionally arranged at the ends, so that the cross sections of the ends are I-shaped. Longitudinal prestressed ducts are formed in the bottom flanges, and the longitudinal prestressed ducts are also formed in top plates of the ends. The bridge is formed in a manner that the prefabricated T-shaped beams are spliced, simply supported and then connected. Longitudinal prestress is tensioned on the bottom flanges, and negative bending moment prestress is tensioned on the top plates. Certain prestress is exerted on compressed zones at the bottoms, so that cracks under the effects of temperature and the like can be avoided. The compression areas of the bottom flanges are increased, the compressive strain of the compressed zones is decreased under the effect of negative bending moment, correspondingly, the tensile strain at the tops is also decreased and thus the possibility of cracking of the bridge deck can be lowered. As the cross sections of the ends are changed to be I-shaped, transportation and installation are convenient, and the construction of the continuous beam bridge is also convenient. The method of building the continuous beam is convenient to construct, and cracks of the top plates at pier top areas are favorably decreased.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Long-service-life flexible base asphalt pavement structure
ActiveCN112376349AGuaranteed service lifeImproves rutting resistanceIn situ pavingsCrushed stoneStructural engineering
The invention discloses a long-service-life flexible base asphalt pavement structure, and belongs to the technical field of pavement structures. The pavement structure sequentially comprises, from topto bottom: an asphalt concrete upper surface layer with a thickness of 3-6 cm; a high-modulus anti-rutting asphalt concrete middle surface layer with a thickness of 6-12 cm; a high-modulus asphalt concrete lower surface layer with a thickness of 8-16 cm; an anti-fatigue asphalt concrete layer with a thickness of 4-6 cm; a graded broken stone base layer with a thickness of 10-16 cm; a reinforced graded broken stone subbase layer with a thickness of 12-18 cm; a roadbed improvement soil layer. According to the long-service-life flexible base asphalt pavement structure, the defect of inherent reflection cracks existing all the time is overcome, the consumption of non-renewable resource gravel aggregate is reduced from the perspectives of environment and resources, and the problem that the service life design and the service state evaluation of an asphalt pavement are not clear is solved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Drawing work supplement method and drawing mould
InactiveCN1970189AIncrease the degree of deformationIncrease deformation stiffnessShaping toolsWorkmanshipEdge region
It relates to a extension workmanship supplementary method, stretching plate material into low end and high end materials with at least one rib being extended on the circumference of the low end material. It also provides a extension mold, with convex and concave mold are of the same shape with high end and low end and at least one boss at the surrounding area of the low end. In this way, it can supplement extension for low end material, strengthening deformation rigidity of it, eliminating partial wrinkling of the parts, reducing flowing resistance, increasing material's flow into high end material of the supplement piece to reduce the stress deformation of the material to eliminate breach.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
A kind of prefabricated T-beam and its method of building continuous beam bridge
InactiveCN105019350BAvoid crackingReduces the possibility of crackingBridge structural detailsBridge erection/assemblyBridge engineeringTensile strain
The invention relates to a prefabricated T-shaped beam and a method of building a continuous beam bridge by adopting the prefabricated T-shaped beams, and belongs to the field of bridge engineering. The T-shaped beam is an improved form of the conventional prefabricated T-shaped beam, and bottom flanges are additionally arranged at the ends, so that the cross sections of the ends are I-shaped. Longitudinal prestressed ducts are formed in the bottom flanges, and the longitudinal prestressed ducts are also formed in top plates of the ends. The bridge is formed in a manner that the prefabricated T-shaped beams are spliced, simply supported and then connected. Longitudinal prestress is tensioned on the bottom flanges, and negative bending moment prestress is tensioned on the top plates. Certain prestress is exerted on compressed zones at the bottoms, so that cracks under the effects of temperature and the like can be avoided. The compression areas of the bottom flanges are increased, the compressive strain of the compressed zones is decreased under the effect of negative bending moment, correspondingly, the tensile strain at the tops is also decreased and thus the possibility of cracking of the bridge deck can be lowered. As the cross sections of the ends are changed to be I-shaped, transportation and installation are convenient, and the construction of the continuous beam bridge is also convenient. The method of building the continuous beam is convenient to construct, and cracks of the top plates at pier top areas are favorably decreased.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Construction method based on geonet reinforced subgrade
The invention relates to the technical field of highway roadbed construction, in particular to a construction method based on geonet reinforced roadbed, the geogrid network is made of high-strength and high-modulus polyvinyl chloride polymer vertically and horizontally, and the outer layer of the grid is covered with modified Rubber coating, the rubber is mixed with anti-aging agent, antioxidant and light shielding agent and other masterbatches, the mesh of the geogrid is circular, and there are double-sided reinforcement columns at the joints of the geogrid ribs, and the length of one side is about 3.5cm , There are ring-shaped embossed threads on the surface of the longitudinal and transverse ribs of the grille. In the present invention, the high-strength and high-modulus polyvinyl chloride polymer material has high strength, the outer layer is coated with modified rubber, the creep is small, and it has the properties of high tensile strength and low tensile strain.
Owner:合肥华福土工合成材料有限公司
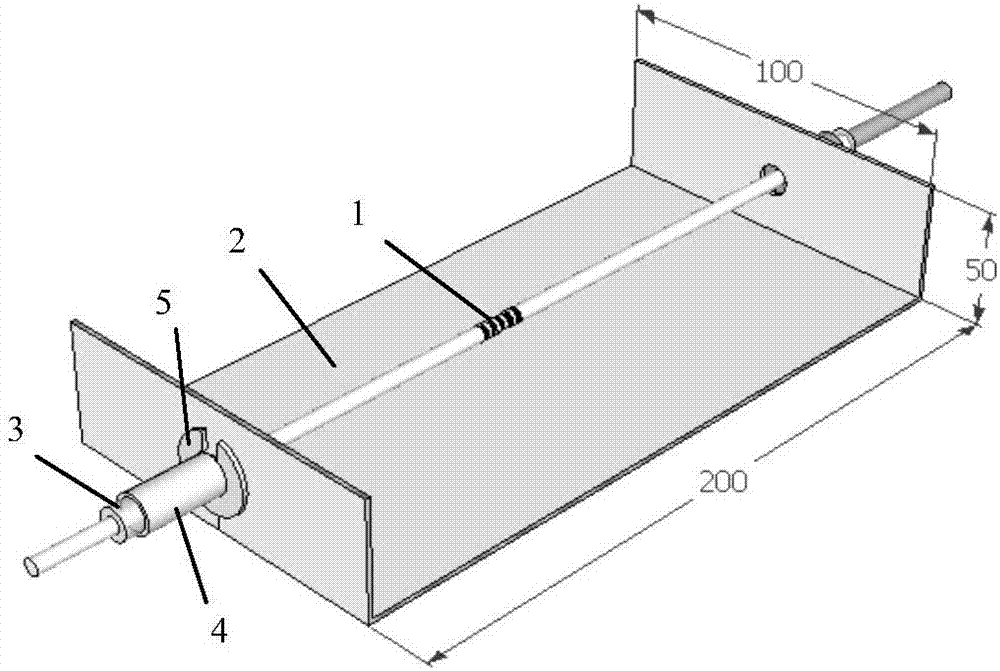
Optical fiber grating-based surrounding rock internal strain monitoring method
The present invention relates to an optical fiber grating-based surrounding rock internal strain monitoring method. According to the method, a bare optical fiber grating sensor, an U-type stainless steel test piece, a metal gasket and an encapsulation steel pipe are adopted to form an optical fiber grating pre-tensioning device; compression strain in surrounding rock measured by the optical fiber grating pre-tensioning device is the decreased tension strain of the optical fiber grating sensor; and the optical fiber grating sensor is always in a tensioned state in a whole monitoring process, and therefore, the accuracy of a measurement result can be ensured, and the survival rate of the fiber grating sensor can be improved.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
Novel integral bridge guide plate and construction method thereof
PendingCN110230255AAvoid crackingPrevent subsidenceBridge structural detailsBridge erection/assemblyAbutmentRoad surface
The invention relates to a novel integral bridge guide plate and a construction method thereof. The novel integral bridge guide plate comprises a novel guide plate; a groove is formed downwards in theupper surface of the novel guide plate; a sliding layer is paved on the upper surface of the groove; a plurality of prefabricated concrete blocks are paved on a surface of the sliding layer; steel pipes are reserved in the prefabricated concrete blocks, and tension steel bars are arranged in the steel pipes in a penetrating mode; the left end of the novel guide plate is connected with a main beamthrough the tension steel bars, the lower end of the main beam is supported through a flexible bridge abutment, the bottom of the flexible bridge abutment and a pile foundation are fixedly arranged into a whole, and the novel integral bridge guide plate is reasonable in structure and can effectively prevent a road surface from cracking.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
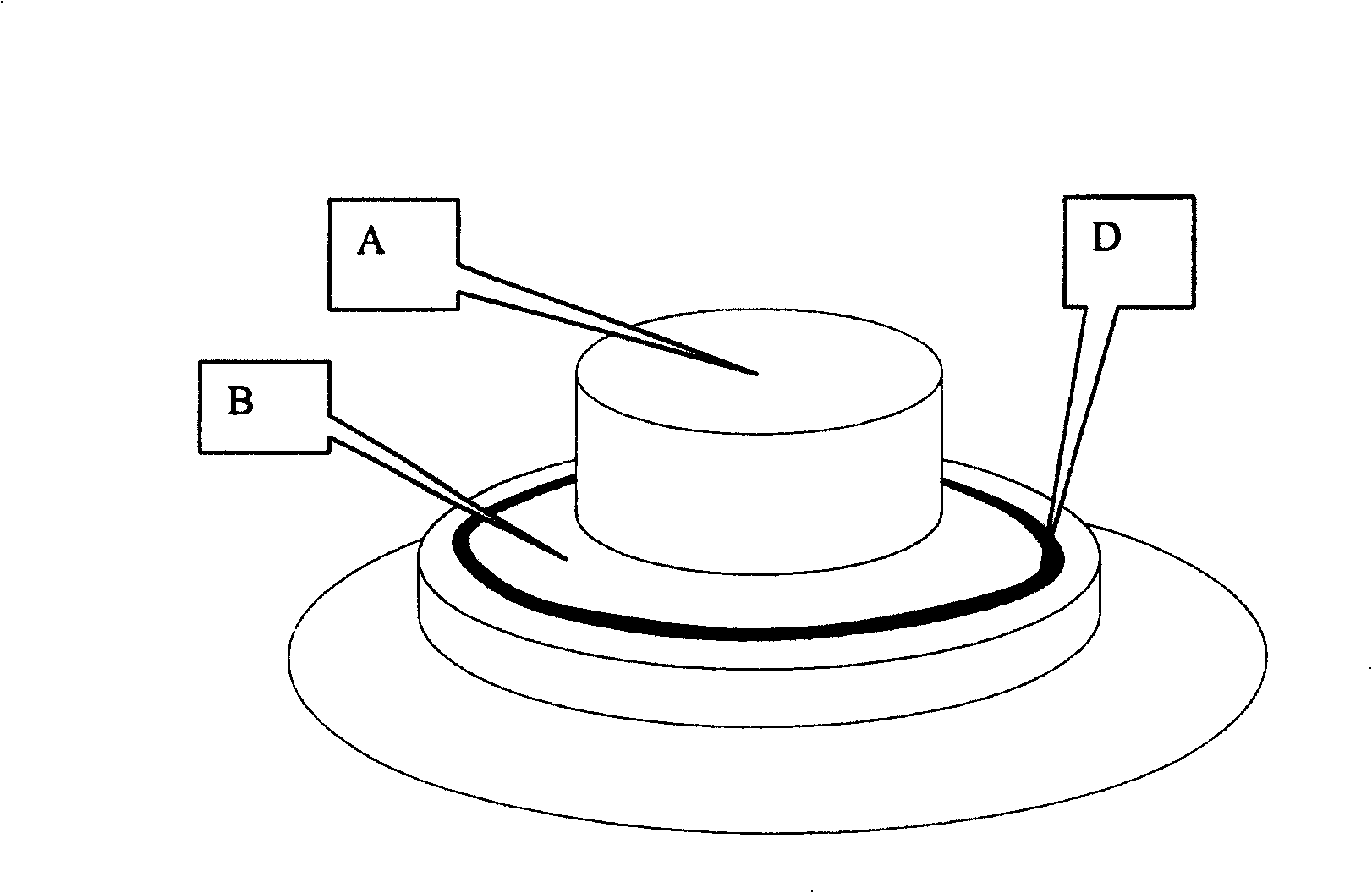
Buried semiconductor laser and method for manufacturing the same
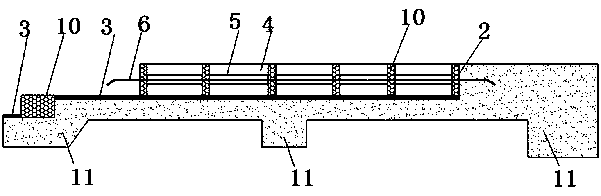
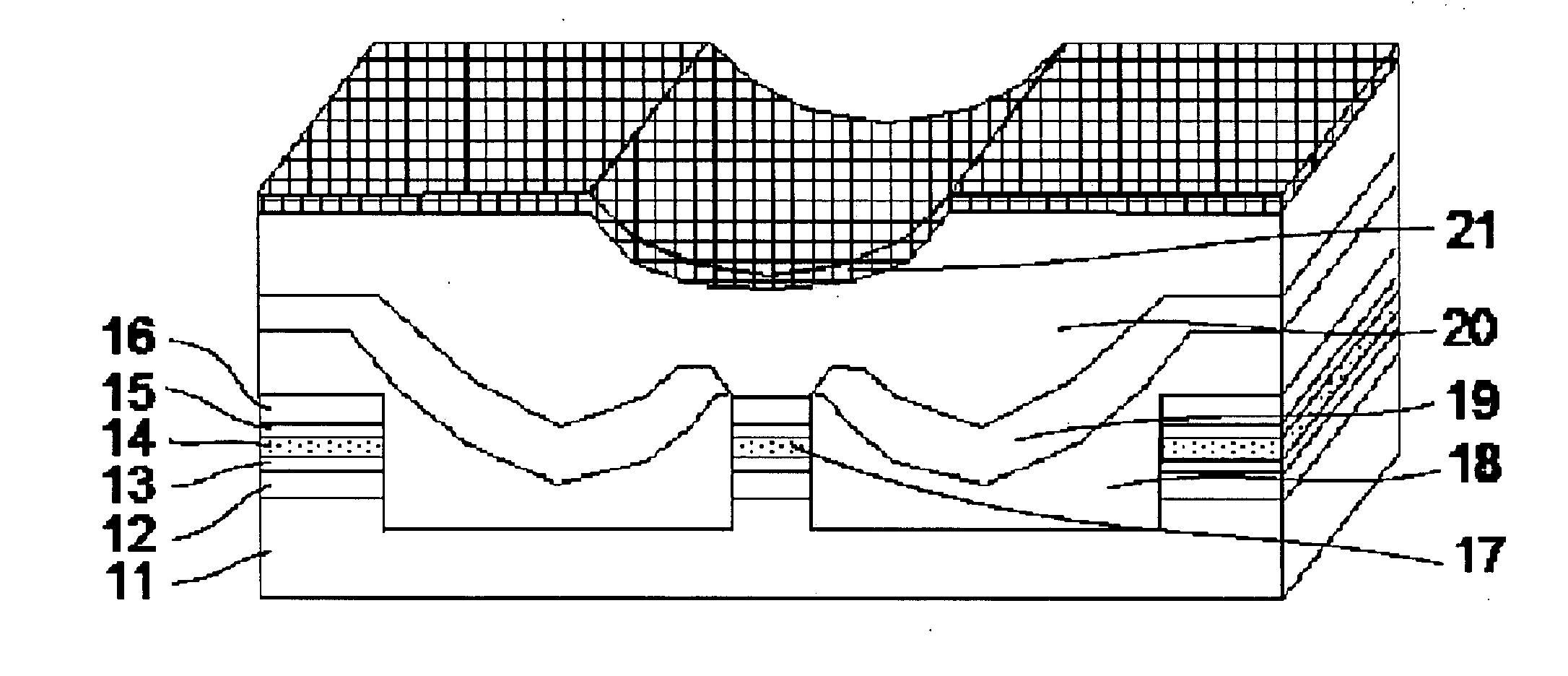
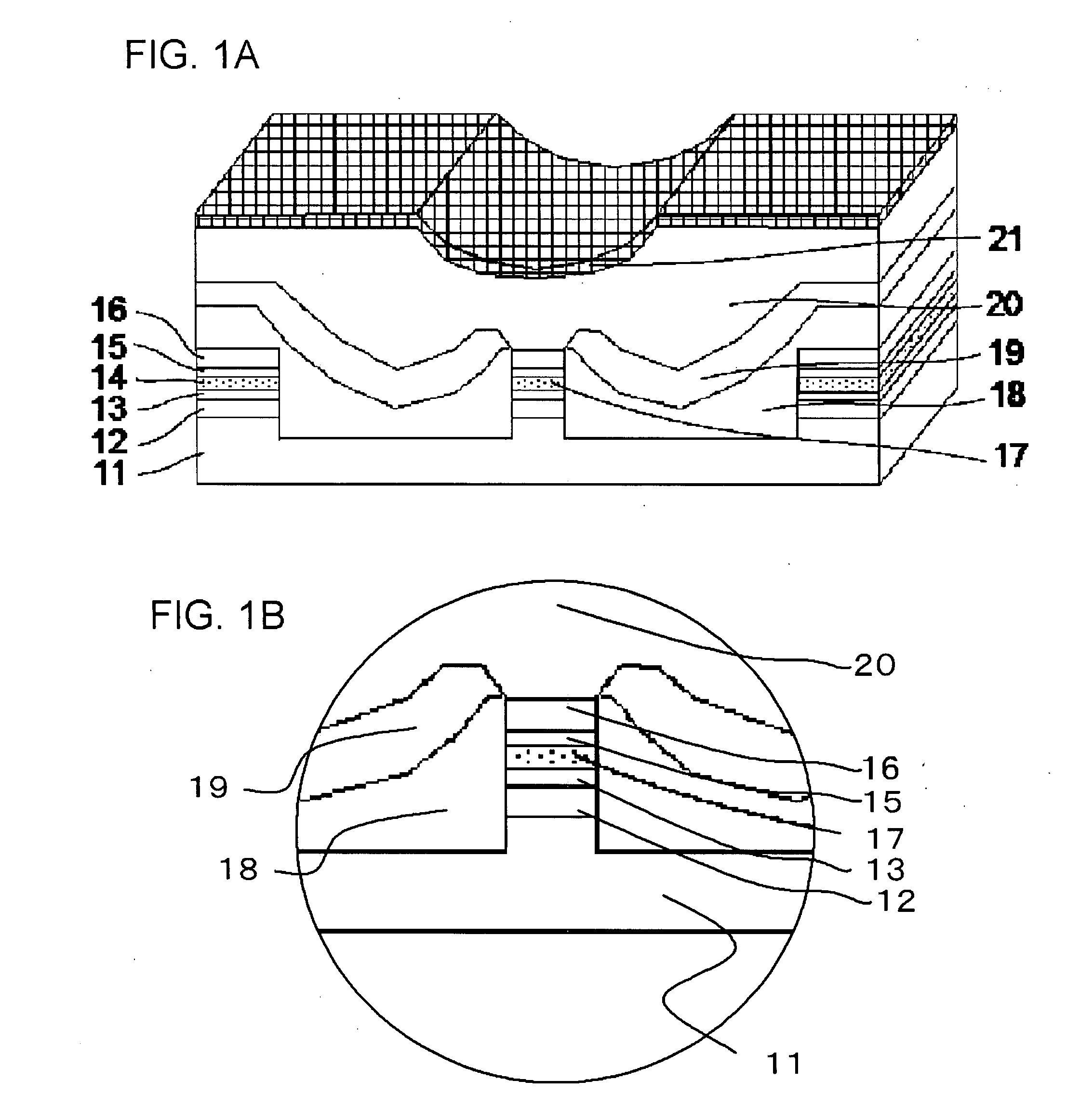
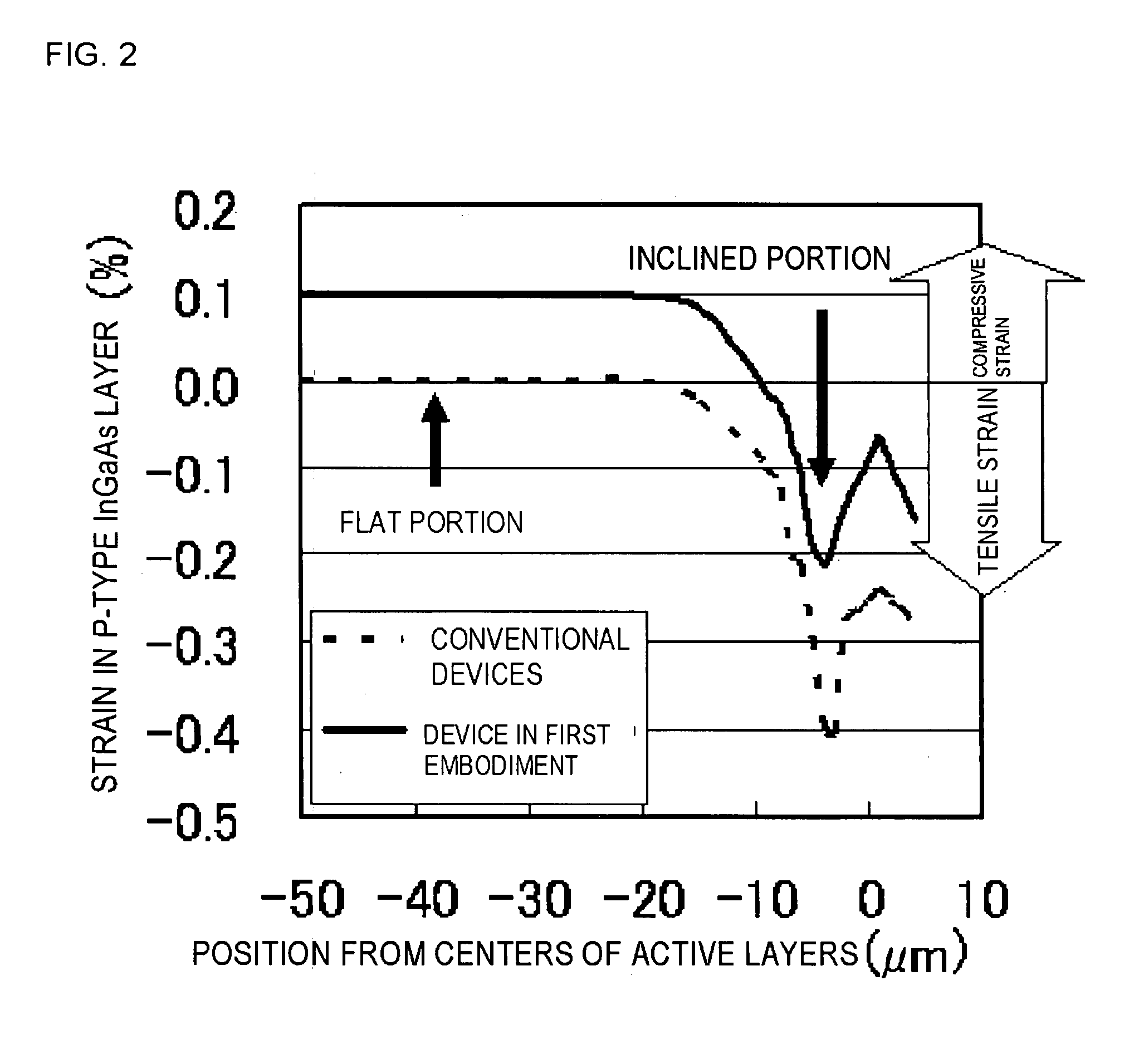
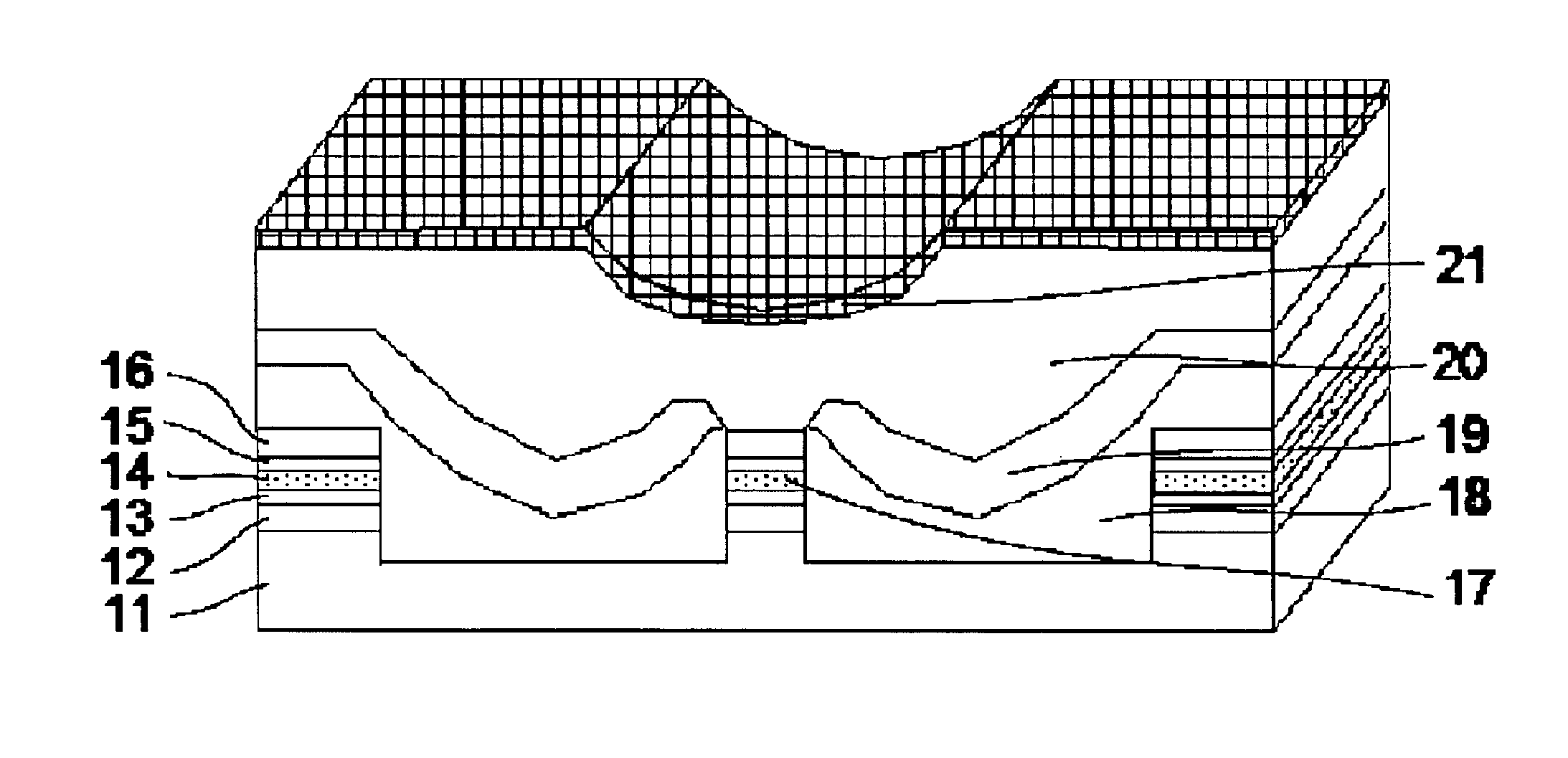
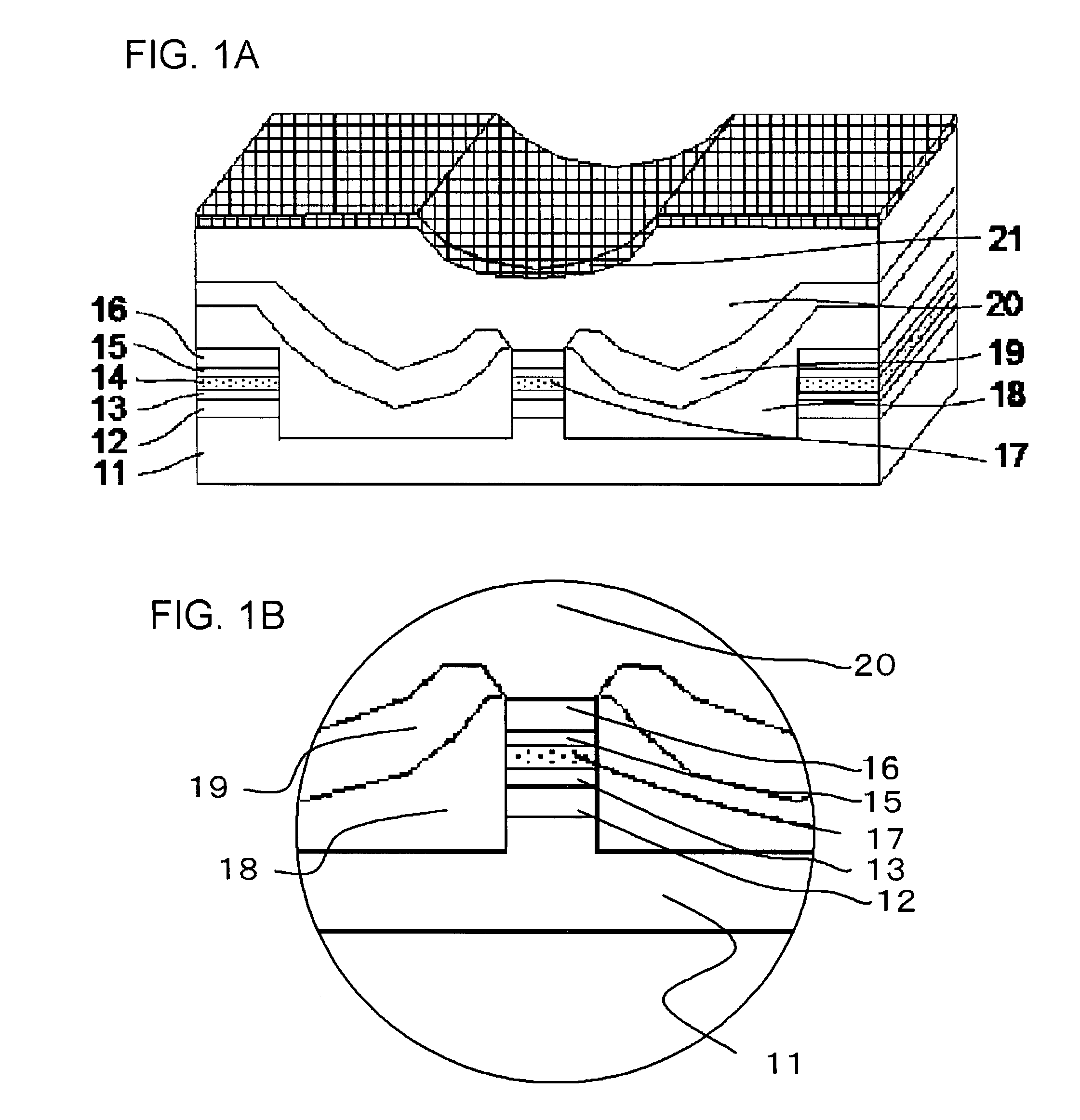
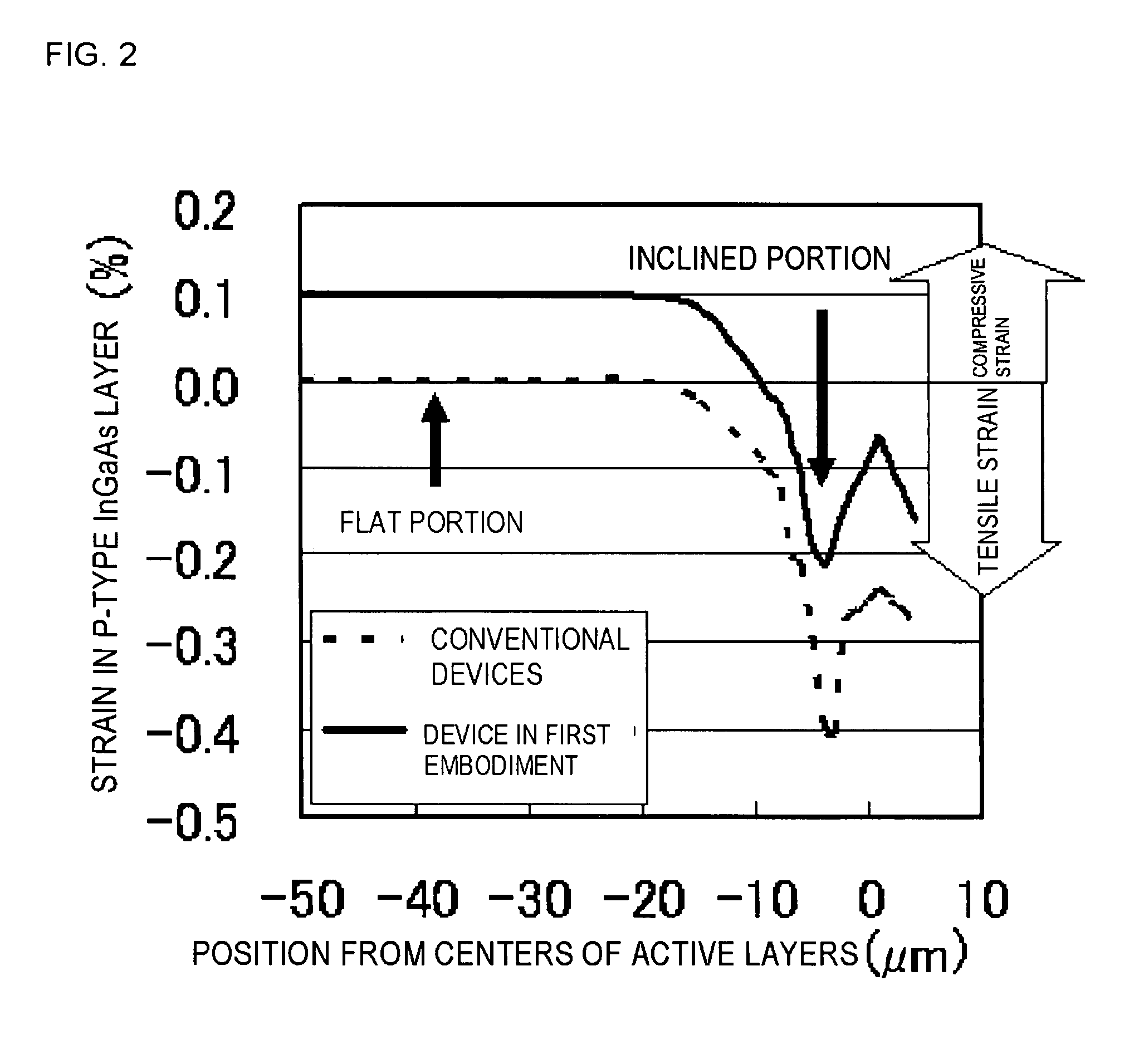
InactiveUS20080137702A1Reduce misalignmentReduce tensile strainLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndium arsenideSemiconductor package
A buried semiconductor laser exhibiting a reduced dislocation of a contact layer is achieved. A buried semiconductor laser, comprising: an n-type indium phosphide (InP) substrate; an active layer disposed on the n-type InP substrate; block layers provided so as to bilaterally disposed on both sides of the active layer; a clad layer provided so as to cover the active layer and the block layers; and a p-type gallium indium arsenide (InGaAs) contact layer provided on the clad layer, wherein the p-type InGaAs contact layer has a compressive strain.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Red light semiconductor laser based on GexSi<1-x> variable lattice constant matrix
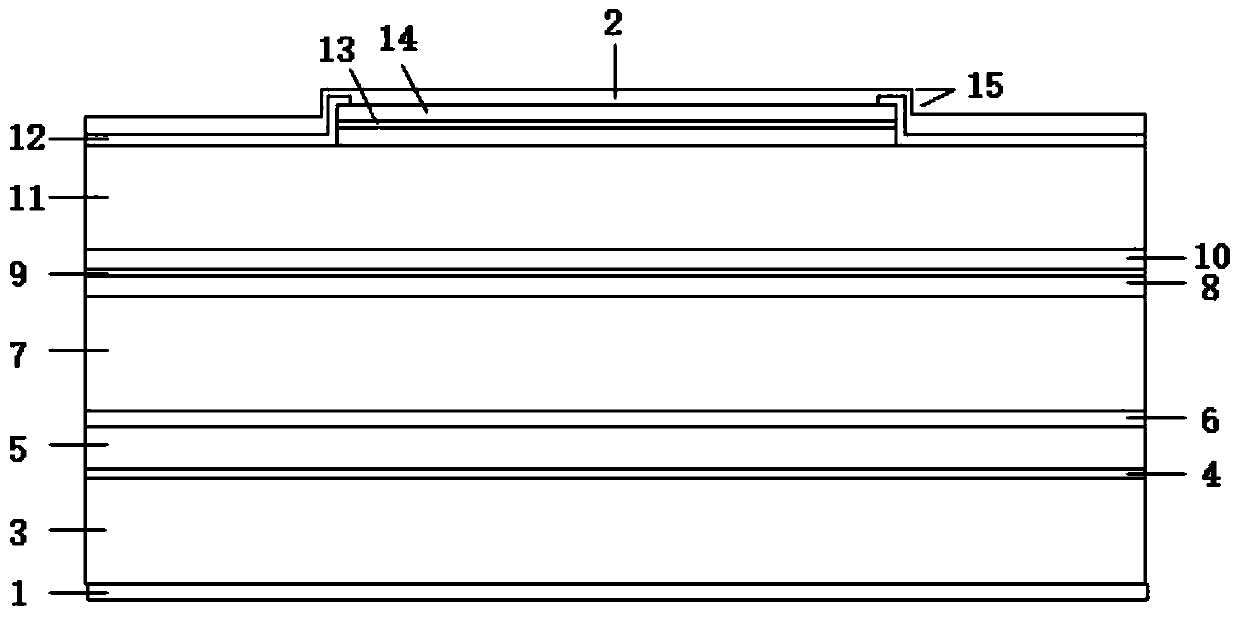
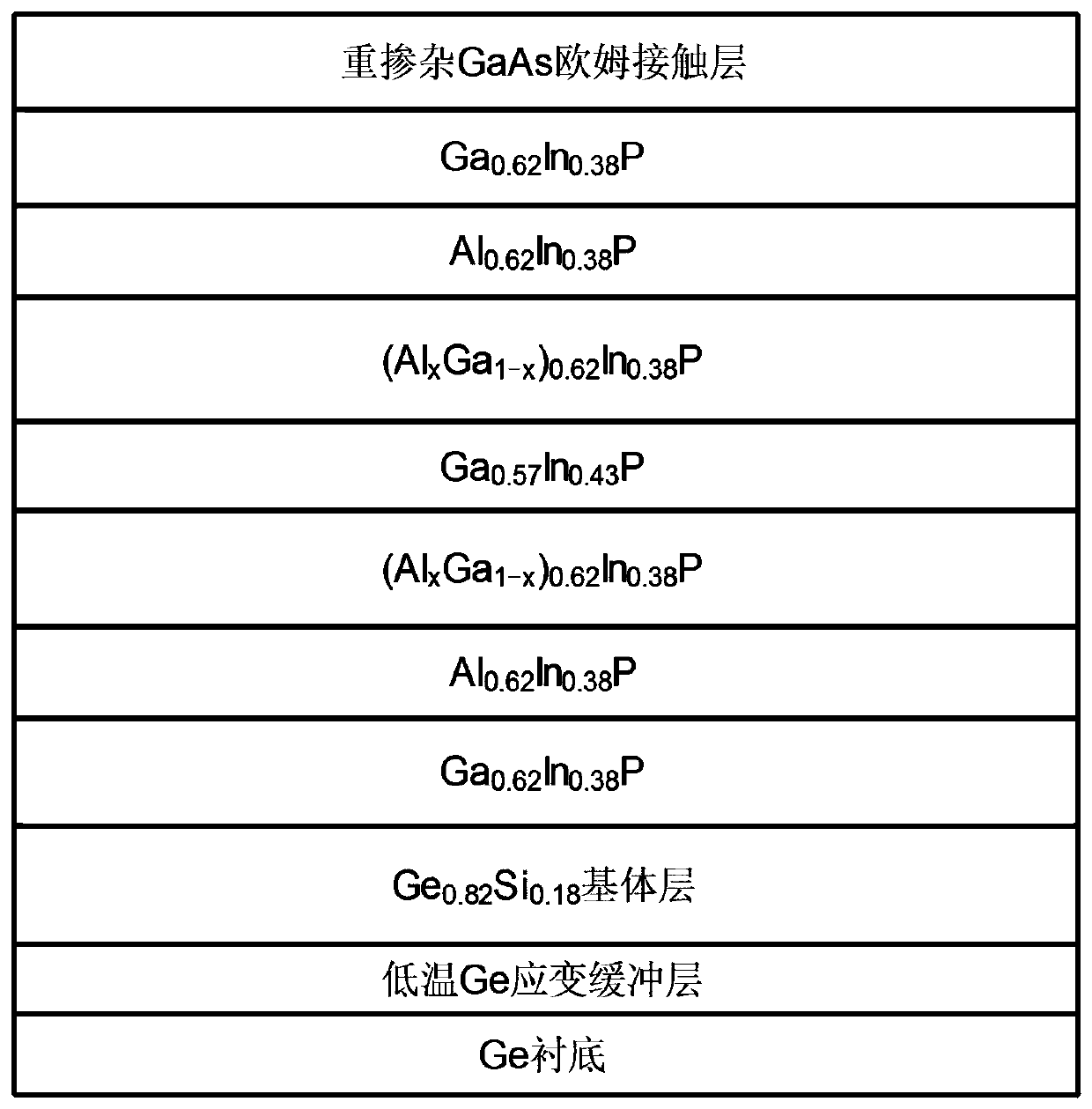
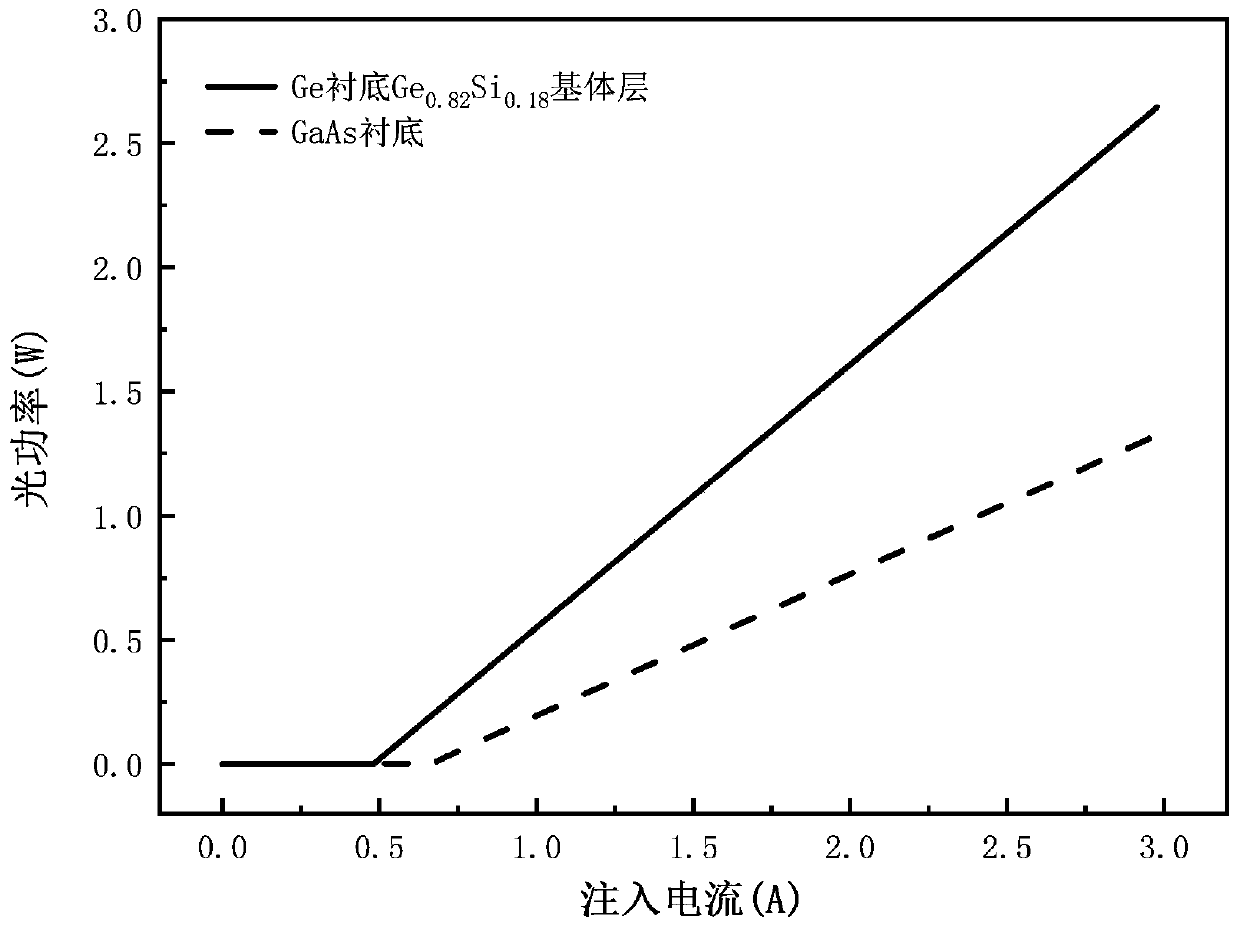
InactiveCN110165555AReduce tensile strainIncreased output power and photoelectric conversion efficiencyLaser detailsLaser active region structurePhysicsSurface electrode
The invention discloses a red light semiconductor laser based on a GexSi<1-x> variable lattice constant matrix. The laser structurally comprises an N-surface electrode, a germanium substrate, a strainbuffer layer, a germanium-silicon matrix layer, a buffer layer, a lower limiting layer, a lower waveguide layer, a quantum well, a quantum barrier, an upper waveguide layer, an upper limiting layer,a barrier layer, a dielectric film, an ohmic contact layer and a P-surface electrode in sequence from bottom to top. According to the red-light semiconductor laser, the tension strain of the quantum well is reduced while the active region lasing wavelength is shortened, the problem that the active region with large tension strain has many defects in an ultra-short wavelength red-light laser can besolved, and meanwhile, the output power and the photoelectric conversion efficiency of a band laser are also improved.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
A steel bridge deck pavement structure and pavement method
ActiveCN104452586BReduced shear stiffnessLow shear stiffnessBridge structural detailsBridge erection/assemblyTensile strainBridge deck
The invention discloses a steel bridge deck pavement structure. The steel bridge deck pavement structure is simple and reasonable in structure, a flexible connecting piece is low in shearing rigidity, good in anti-fatigue performance and constant in pull-out capacity and shearing strength, initial shearing rigidity is low, shearing force is kept around one third of the strength with continuous sliding deformation, shearing force value of local fittings can be effectively lowered, stress of bridge deck pavement layer close to rigid pillars is improved, crushing destruction of the bridge deck pavement layer is effectively avoided, the problem about local cracking of the surface of the pavement layer is solved, assumption of common design at present is met, and multiple pavement diseases and problems existing in the steel bridge deck pavement layer at present can be effectively solved. The pavement method is easy and convenient to operate, the pavement layer paved by a steel fiber reinforced concrete layer and an asphalt concrete layer form an integral, tensile capacity is increased, thickness is increased, tensile stress and tensile strain of the surface of the pavement layer can be effectively reduced, and the problem about cracking of the surface of the pavement layer can be effectively solved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIV OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC POWER
Fiber-reinforced polymer strip with improved durability and lattice geogrid using same
PendingCN113646486AImprove adhesionIncreased durabilityGeotextilesExcavationsPolymer sciencePolymer resin
The present invention relates to a fiber-reinforced polymer tape having improved durability, the fiber-reinforced polymer tape comprising: a plurality of fiber aggregates as a reinforcing material; a thermoplastic polymer resin as a coating material; and a binder using a powder binder on the surface of the reinforcing material, characterized in that when manufacturing the fiber-reinforced polymer tape, the powder binder is applied around the reinforcing fibers to reinforce the adhesive force with the polymer resin coated on the reinforcing fibers, thereby improving the durability of the fiber-reinforced polymer tape itself.
Owner:HUVIS CORP
Stretchable layered thermal camouflage material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN114701222AUnique structureEasy to stretchLamination ancillary operationsFibre typesFiberSpinning
The invention discloses a stretchable layered thermal camouflage material and a preparation method thereof.The layered thermal camouflage material comprises a carbon material electrode layer, an ionic conductive gel layer and an electrochromic functional layer which are sequentially arranged from bottom to top, and the preparation method comprises the steps that a porous thermoplastic polyurethane fiber membrane is prepared through electrostatic spinning; soaking in an aqueous dispersion of carbon black particles and carboxylated carbon nanotubes, drying to obtain a carbon material electrode layer, adding a waterborne polyurethane aqueous solution and an ionic liquid into water, mixing, coating the surface of the electrode layer with the mixture, and drying to obtain an ionic conductive gel layer; and soaking the porous thermoplastic polyurethane fiber membrane in a mixed solution containing conductive macromolecules, drying, attaching to the gel layer, and packaging to obtain the product. The stretchable layered thermal camouflage material is excellent in tensile property, the tensile strain can reach 460%, the thermal camouflage property of the stretchable layered thermal camouflage material still keeps stable after 5000 times of cyclic stretching recovery under the tensile strain of 60%, and the preparation method is low in cost and high in practicability.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
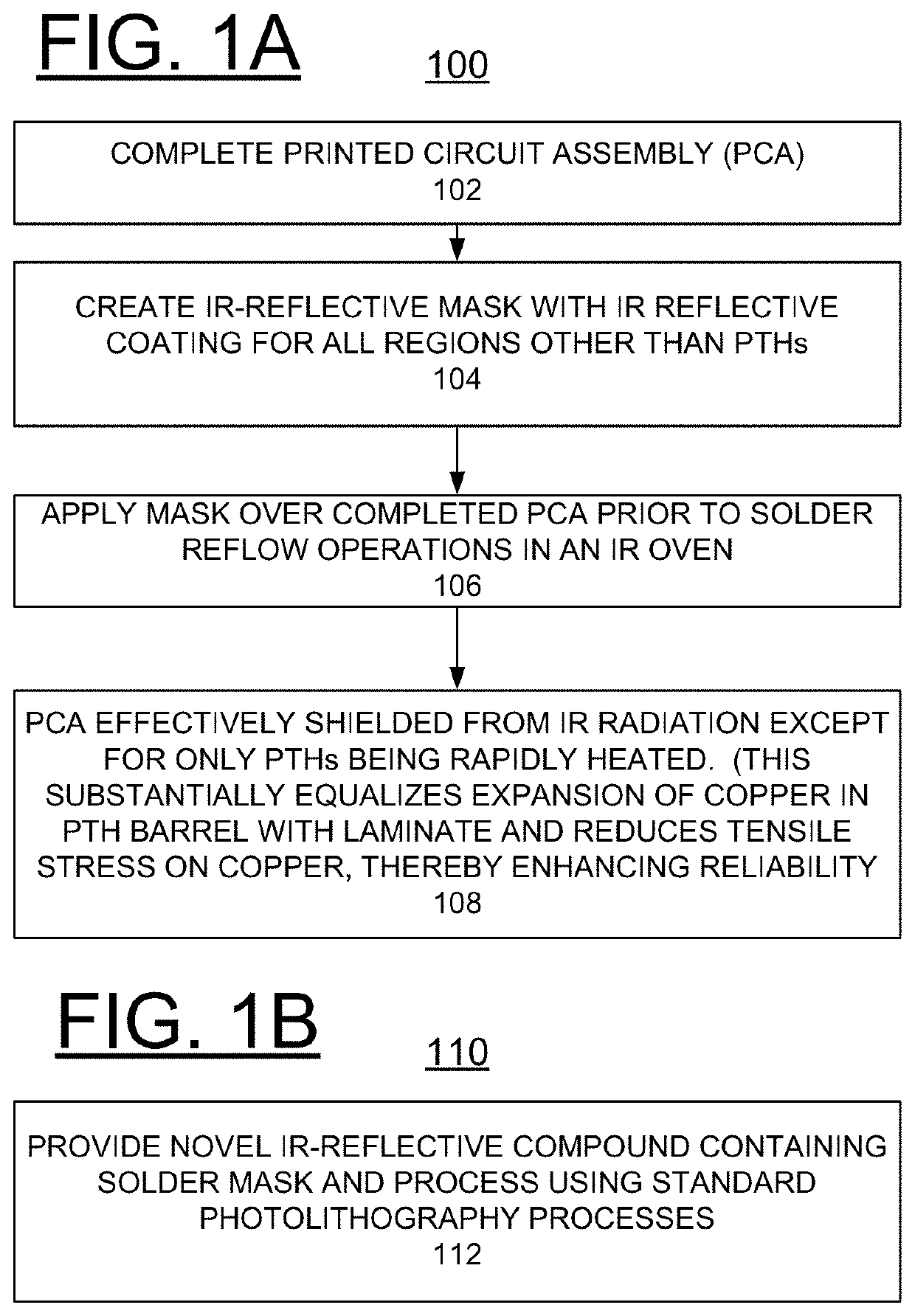
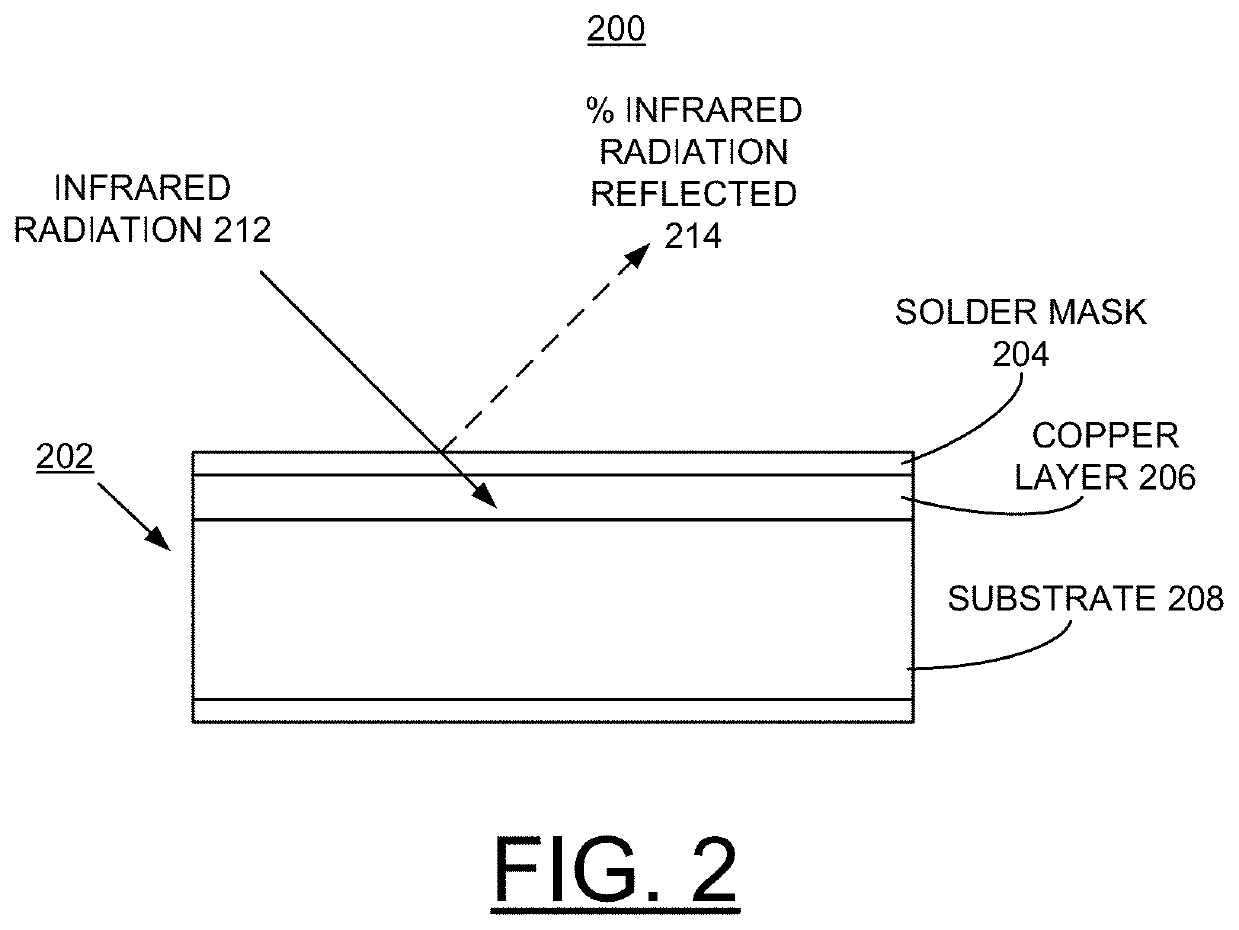
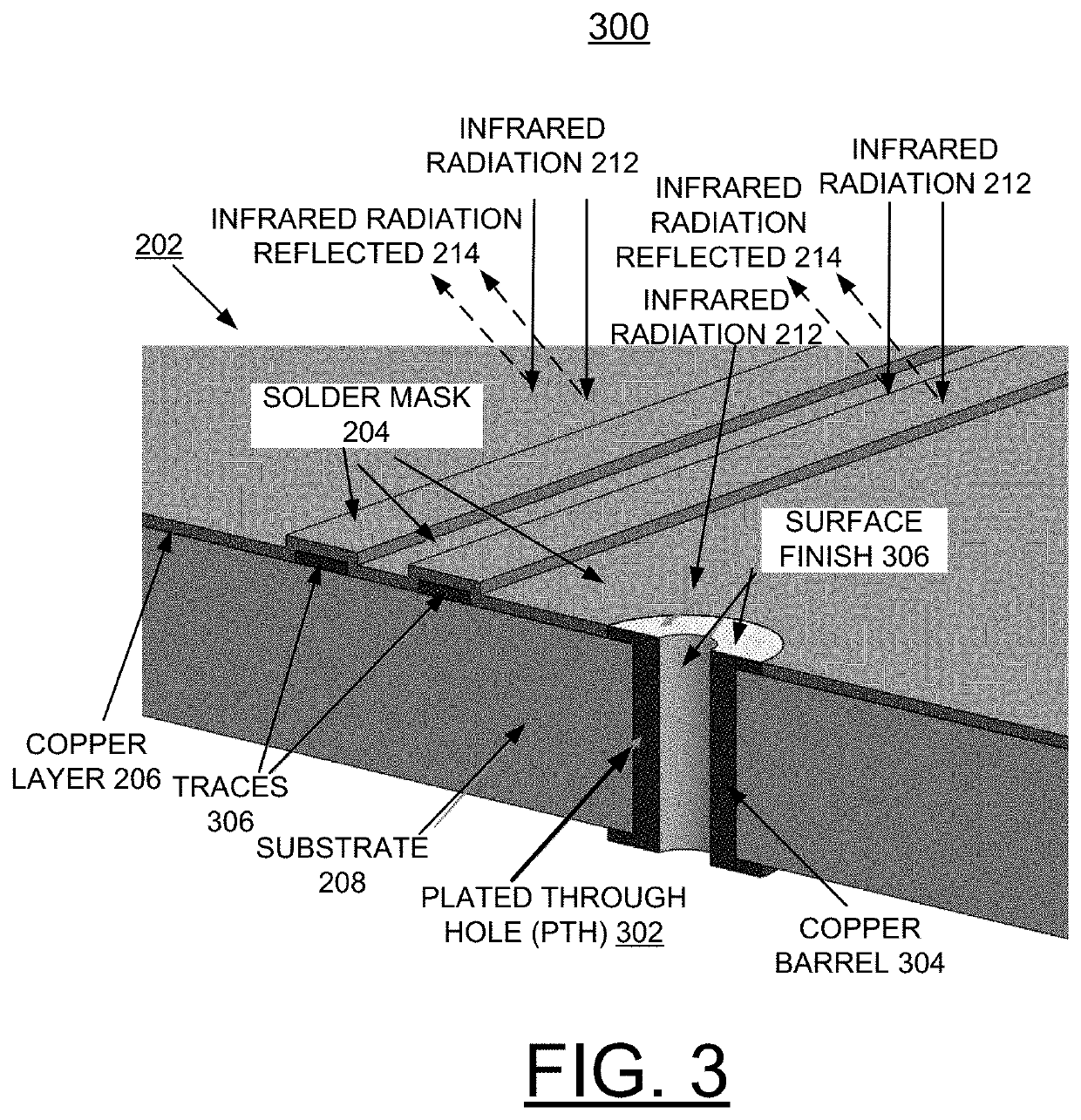
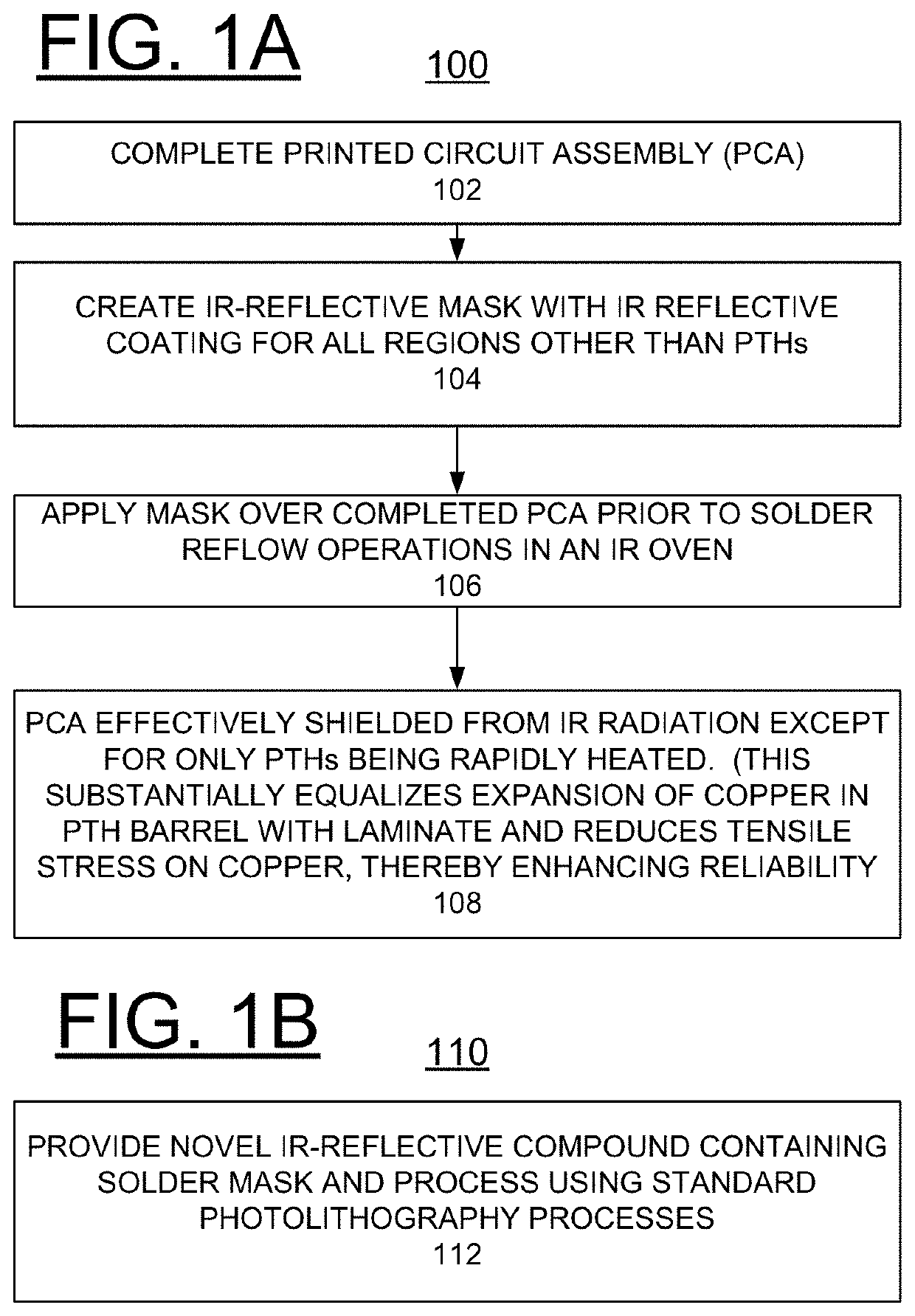
Implementing ir reflective mask to minimize cte mismatch between laminate and pth copper
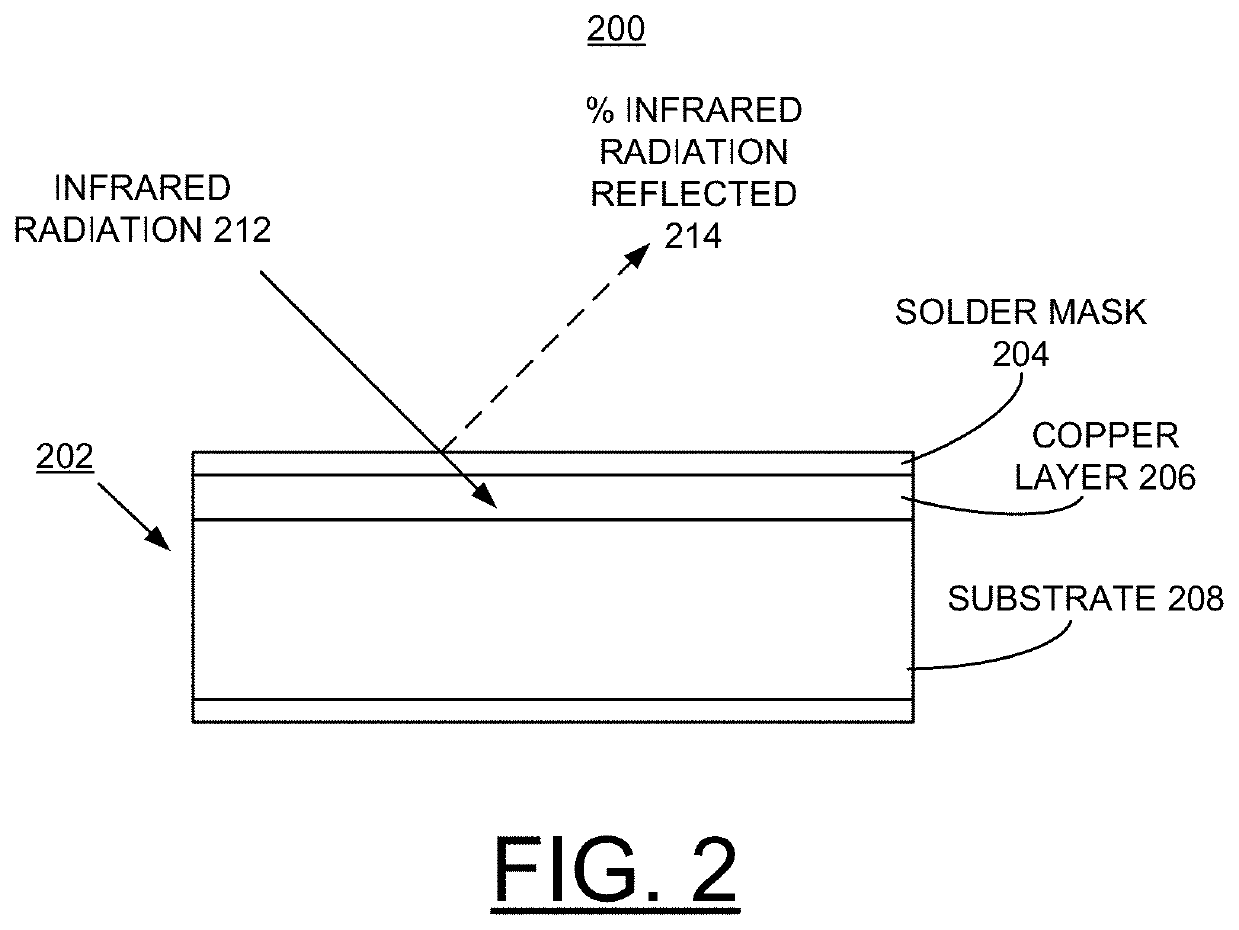
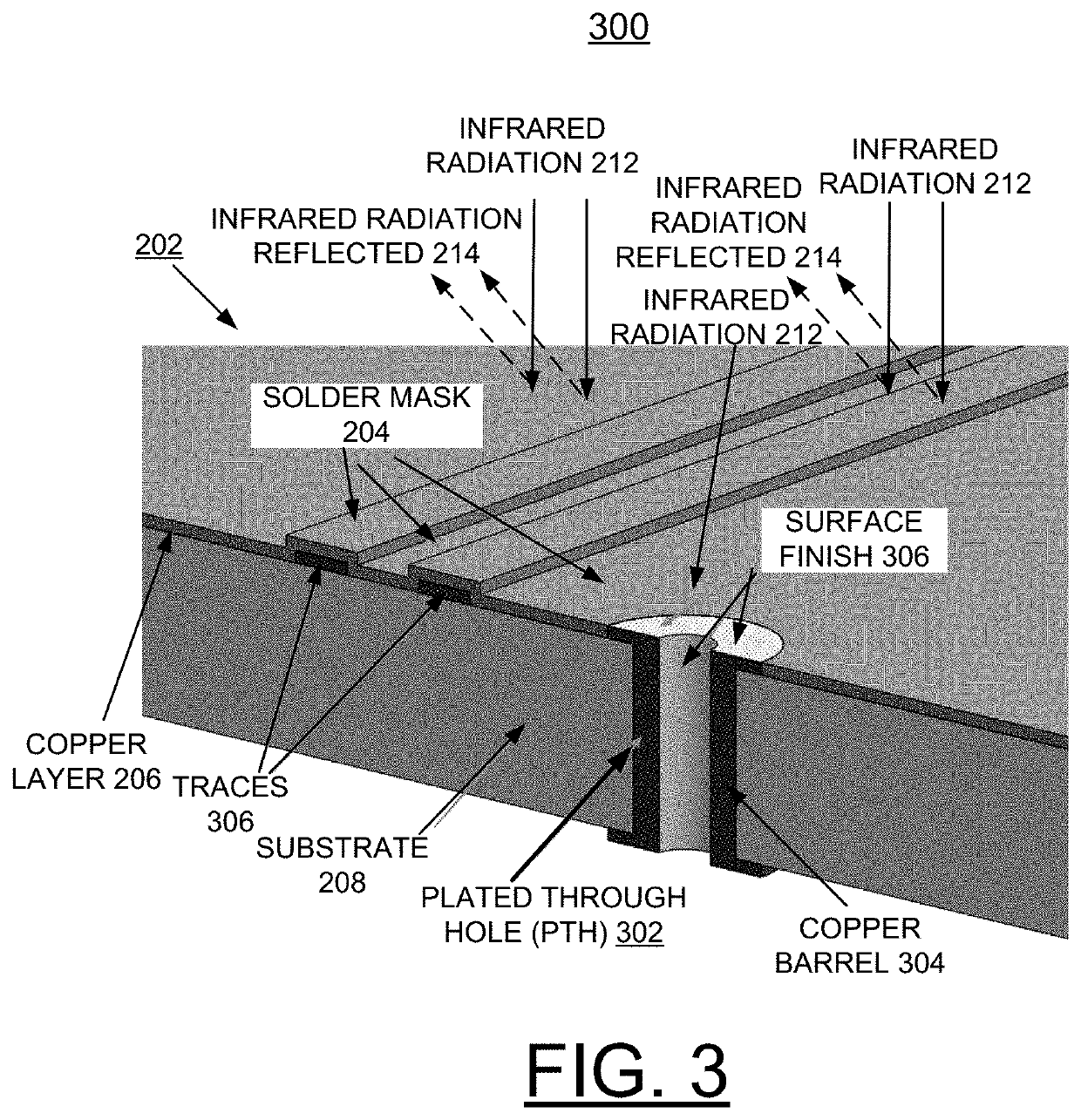
ActiveUS20190364670A1Increasing PTH reliabilityIncrease ratingsPrinted circuit assemblingMirrorsTensile strainSolder mask
A method and structure are provided for implementing manufacture of a printed circuit board (PCB) with one of an infrared (IR) reflective mask or a novel solder mask to minimize coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) mismatch between PCB laminate and plated through hole (PTH) copper. At least one of an IR-reflective mask and a solder mask composition for use in IR reflow processes is created such that radiant heat is reflected away from the major portion of the PCB yet permitted to impinge upon the PTHs. The copper within the PTH expands due to radiant heating while the bulk laminate expansion is significantly reduced due to the reflected IR radiation. Consequently, the CTE mismatch is minimized and tensile strain of the copper in the PTH is reduced, providing enhanced reliability.
Owner:IBM CORP
Sulfur-containing furandicarboxylic acid polyester and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses sulfur-containing furandicarboxylic acid polyester, and relates to the field of biomass-based high polymer materials, and the structural formula of the sulfur-containing furandicarboxylic acid polyester is shown in the specification, n is more than or equal to 5 and less than or equal to 3000, R on the main chain is a disulfide bond, and R is any one of structures shown in the specification. The invention also provides a preparation method of the polyester. The invention has the beneficial effects that the polyester has a unique chemical structure and excellent mechanical properties, and the mechanical property parameters after tabletting and film making are as follows: the breaking strength is 14.7 Mpa, and the elongation at break is 420%.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Manufacturing technique of cold-bending steel sheet pile
InactiveCN101130956BImprove machining accuracyReduce the probability of crackingBulkheads/pilesStrip steelEngineering
The present invention discloses production process of cold bent steel sheet pile with raised preliminary shaft machining precision. The technological scheme of the present invention is that the cold bent steel sheet pile is produced with strip steel blank and through stepped bending deformation including final closed pass bending to form preliminary shaft. The process has high preliminary shaft machining precision and less cracking of preliminary shaft during bending deformation. The production process of the present invention may be applied widely in producing different types of cold bent steel sheet pile, especially U-shaped cold bent steel sheet pile.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
A kind of polypropylene composition and polypropylene material and its application
ActiveCN104558821BReduce tensile strainHigh tensile strengthFixed capacitor dielectricSoil preservationTensile strainHeat resistance
The invention provides a polypropylene composition and a polypropylene material as well as an application thereof. The polypropylene composition comprises polypropylene, a nucleating agent and an antioxidant, wherein the nucleating agent comprises a crystal form alpha nucleating agent and a crystal form beta nucleating agent, the crystal form alpha nucleating agent is selected from one or more of an inorganic crystal form alpha nucleating agent, a sorbitol nucleating agent and an organic phosphate nucleating agent, and the crystal form beta nucleating agent is selected from one or more of a mixture of binary acid and an II Ath group of metal salts, a rare earth crystal form beta nucleating agent and an amide nucleating agent. The polypropylene material prepared from the polypropylene composition provided by the invention can be used for well integrating effects of relatively low tensile strain, relatively high tensile strength and relatively good heat resistance and long-term creeping strength, and has great industrial application prospects.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
Drawing work supplement method and drawing mould
InactiveCN100448562CIncrease the degree of deformationIncrease deformation stiffnessShaping toolsWorkmanshipMaterials science
It relates to a extension workmanship supplementary method, stretching plate material into low end and high end materials with at least one rib being extended on the circumference of the low end material. It also provides a extension mold, with convex and concave mold are of the same shape with high end and low end and at least one boss at the surrounding area of the low end. In this way, it can supplement extension for low end material, strengthening deformation rigidity of it, eliminating partial wrinkling of the parts, reducing flowing resistance, increasing material's flow into high end material of the supplement piece to reduce the stress deformation of the material to eliminate breach.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Novel road base structure
PendingCN111138143AReduce tensile stressReduce tensile strainIn situ pavingsChemistryReflective crack
The invention relates to a novel road base structure, which comprises an upper base layer (3) and a lower base layer (4) and is characterized in that the strength of the base layers is 6.0 to 9.0 MPa;the upper base layer (3) is waste rubber modified cement stabilized macadam; the lower base layer (4) is cement stabilized macadam; the upper base layer (3) is prepared from the following mineral aggregate (by weight): 15%-25% of 10-30 mm macadam, 20%-27% of 10-20 mm macadam, 15%-25% of 5-10 mm macadam, 17%-21% of stone nitrate and 2%-12% of waste rubber powder, wherein cement is added in an amount which is 5-10 percent of the total weight of the mineral aggregate, and the thickness of the upper base layer (3) is 15-25cm; and the lower base layer (4) is prepared from the following mineral aggregate (by weight): 15%-25% of 10-30 mm broken stone, 20%-27% of 10-20 mm broken stone, 15%-25% of 5-10 mm broken stone and 23%-33% of mirabilite, wherein cement is added according to the dosage of 5-7% of the total weight of the mineral aggregate, and the thickness of the lower base layer (4) is 15-25 cm. The structure can reduce the tensile stress and tensile strain of the bottom of the asphaltsurface layer, reduce the sensitivity to wheels, reduce reflection cracks caused by cracking of the lower base layer and reduce cracks of the asphalt surface layer.
Owner:SHANDONG JIAOTONG UNIV
Conveyor system for transporting goods via conveyor belt or the like
A conveyor system for transporting goods has an endless conveyor belt and two support tracks, disposed one above the other, for supporting the conveyor belt. The conveyor belt is formed with a plurality of transverse beams which are spaced apart from one another in a conveying direction of the conveyor belt. Carrying rollers are supported on the transverse beams. The support are formed with carrying cables on which the rollers are supported. The weight of the conveyor belt is transmitted onto the carrying cables.
Owner:INNOVA PATENT GMBH
Implementing IR reflective mask to minimize CTE mismatch between laminate and PTH copper
ActiveUS11153976B2Minimize coefficientOvercome disadvantagesPrinted circuit assemblingMirrorsIr reflectionThermal dilatation
A method and structure are provided for implementing manufacture of a printed circuit board (PCB) with one of an infrared (IR) reflective mask or a novel solder mask to minimize coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) mismatch between PCB laminate and plated through hole (PTH) copper. At least one of an IR-reflective mask and a solder mask composition for use in IR reflow processes is created such that radiant heat is reflected away from the major portion of the PCB yet permitted to impinge upon the PTHs. The copper within the PTH expands due to radiant heating while the bulk laminate expansion is significantly reduced due to the reflected IR radiation. Consequently, the CTE mismatch is minimized and tensile strain of the copper in the PTH is reduced, providing enhanced reliability.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
A large-core flexible optical fiber ribbon cable and its sheath processing device
ActiveCN113655581BAvoid crackingAchieve bend radiusFibre mechanical structuresFiber bundleRibbon cable
The invention discloses a flexible optical fiber ribbon optical cable with a large number of cores, which comprises a water blocking tape, a loose tube, an inner sheath, a middle sheath, and an outer sheath arranged from the inside to the outside, and the optical fiber ribbon matrix is arranged on the loose tube Inside, multiple Kevlar fiber bundles are evenly arranged between the inner and outer walls of the loose tube. The invention can solve the technical problem that the existing large-core optical fiber ribbon cable cannot achieve extreme bending radius, and the tensile performance is poor at the same time, and because the strengthening core has a large bending internal stress in an extremely bending application environment, it will affect the optical cable. Structural integrity, and technical issues that may damage the optical fiber. The invention also discloses a middle sheath processing device for large-core flexible optical fiber ribbon cable, which includes an inner sheath, a driving screw, an auxiliary screw, galvanized straight steel wires, and a pair of pressing driving wheels engaged with each other.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
A long-life flexible base asphalt pavement structure
ActiveCN112376349BGuaranteed service lifeImproves rutting resistanceIn situ pavingsCrushed stoneStructural engineering
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Full-thickness asphalt pavement structure with steel wire mesh reinforced asphalt concrete as base layer
ActiveCN114717901AImprove the forceHigh tensile strengthPaving reinforcementsIn situ pavingsStructural engineeringRoad surface
The invention relates to a full-thickness asphalt pavement structure taking steel wire mesh reinforced asphalt concrete as a base layer, and the pavement structure sequentially comprises a high-rut-resistance asphalt concrete surface layer, a high-rut-resistance asphalt concrete surface layer and a high-rut-resistance asphalt concrete surface layer from top to bottom, the thickness of the high-modulus asphalt concrete bonding layer is 6-15 cm; the thickness of the high-modulus asphalt concrete base layer is 13-22 cm; in the steel wire mesh layer, the diameter of steel wires of a steel wire mesh is 0.8-2.0 mm, and the hole size of the steel wire mesh is between 20 mm * 20 mm and 80 mm * 80 mm; the thickness of the slurry seal layer is 6-10 mm; and the steel wire mesh needs to be subjected to tackifying and roughness increasing treatment. The steel wire mesh is arranged on the slurry seal and located on the lower portion of the pavement structure, the direction of steel wires is consistent with the stress direction of the overlay, the advantage of high tensile strength of steel wire materials can be fully played, fine steel wires are selected, good bond stress can be formed between the asphalt mixture and the steel wires, interlayer defect gaps are reduced, and the strength of the pavement structure is improved.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Buried semiconductor laser and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7782919B2Reduce tensile strainReduced chance of generation of dislocationLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndium arsenideContact layer
A buried semiconductor laser exhibiting a reduced dislocation of a contact layer is achieved. A buried semiconductor laser, comprising: an n-type indium phosphide (InP) substrate; an active layer disposed on the n-type InP substrate; block layers provided so as to bilaterally disposed on both sides of the active layer; a clad layer provided so as to cover the active layer and the block layers; and a p-type gallium indium arsenide (InGaAs) contact layer provided on the clad layer, wherein the p-type InGaAs contact layer has a compressive strain.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
A horizontal sliding anti-seepage connection structure between geomembrane and asphalt concrete panel
ActiveCN112900365BGuaranteed connection reliabilityReduce tensile strainMarine site engineeringSoil scienceGeomembrane
The invention discloses a horizontal sliding anti-seepage connection structure between a geomembrane and an asphalt concrete panel, which belongs to the field of water conservancy and hydropower engineering. The geomembrane of the present invention and the asphalt concrete panel are overlapped through a reinforced concrete connecting plate, and a horizontal sliding plastic water-stop material is arranged between the asphalt concrete panel and the reinforced concrete connecting plate, so that the anti-seepage joint can slide horizontally, and at the same time The contact part between the geomembrane and the reinforced concrete connecting plate is provided with an overfilled bulge to reduce the "clamp effect" caused by the local stress concentration of the geomembrane and ensure the reliability of the seepage prevention of the lap joint of the geomembrane.
Owner:POWERCHINA HUADONG ENG COPORATION LTD
A Method of Strengthening Highway Subgrade Using Geogrid
InactiveCN101413244BHigh strengthHigh-strength high-modulus polyvinyl chloride polymer material with high strengthExcavationsRoads maintainenceTensile strainMasterbatch
The invention relates to a geotechnical grid used for highway subgrade reinforcement and its application method. The grid net is made of high-strength and high-modulus polyvinyl chloride polymer vertically and horizontally to enhance the tensile strength of the ribs; the outer layer of the grid is covered with Modified rubber coating, the rubber is mixed with anti-aging agent, antioxidant and light shielding agent and other masterbatches; the surface layer of the grid longitudinal and transverse ribs has circular embossed threads, and the grid mesh is circular to reduce stress concentration , to enhance the extensibility of the ribs; there are double-sided "strengthening columns" at the joints of the grid ribs to prevent the sliding between the soil and the grid, enhance the shear performance of the subgrade, balance the settlement, and prevent the grid from being pulled out of the subgrade. The invention has the advantages of high strength of polymer material, external coating of modified rubber, small creep, high tensile strength and low tensile strain; the circular mesh, tendon thread and "reinforcing column" are fully occluded with the soil, A space composite strengthening structure is formed, which improves the overall shear strength of the subgrade and the performance of balanced settlement.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com