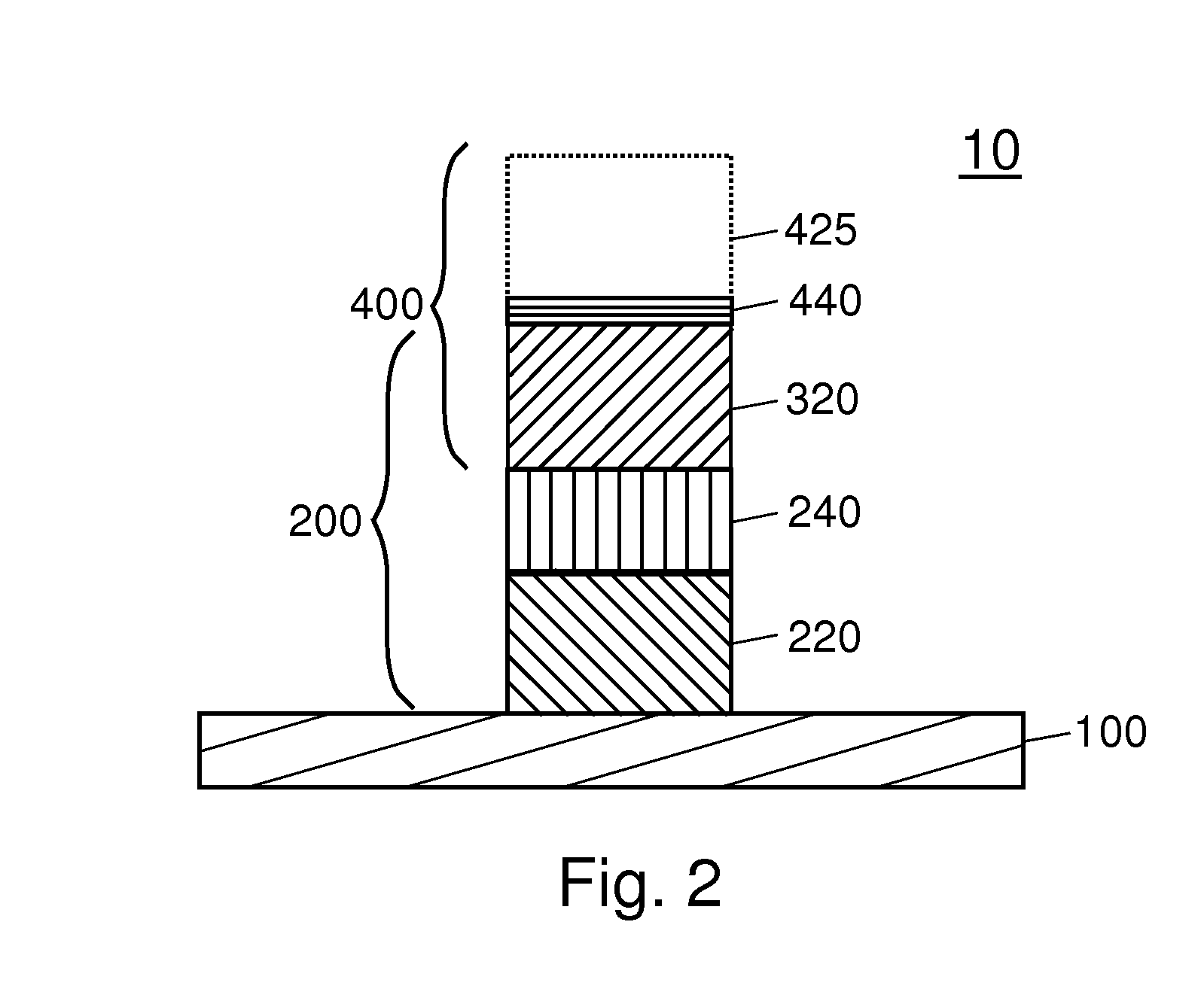
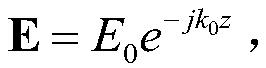Patents
Literature
89 results about "Plasmon waveguide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sensors
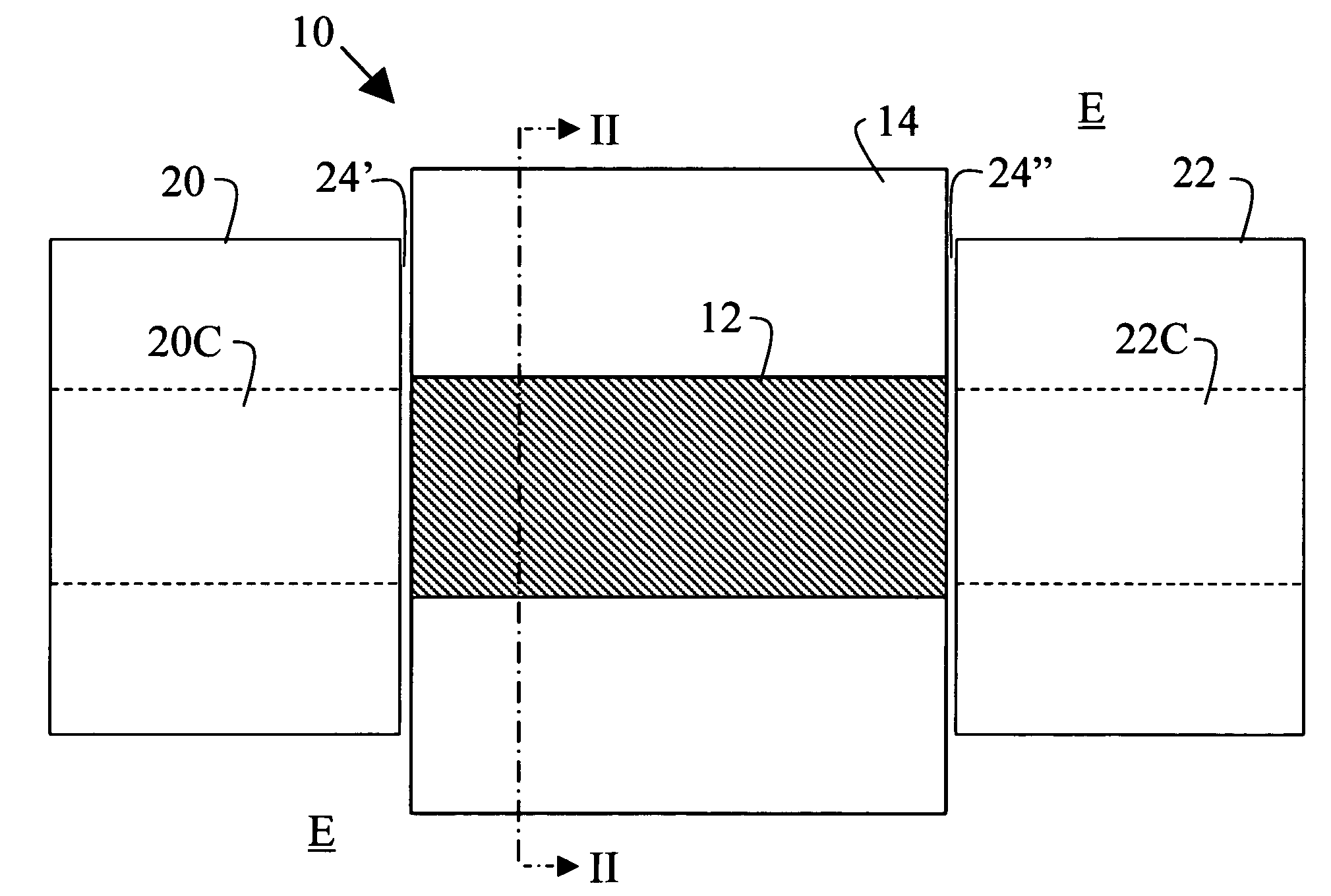
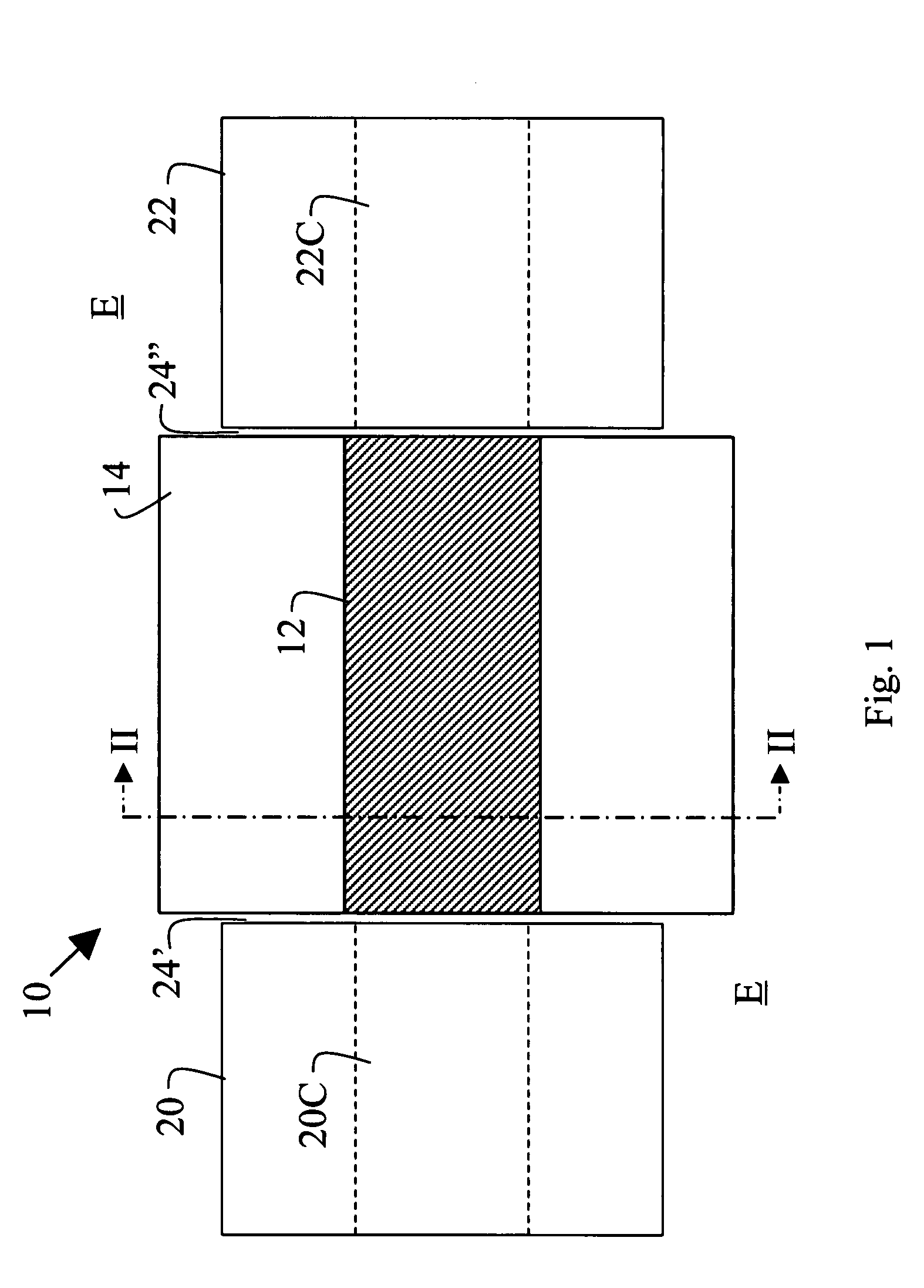
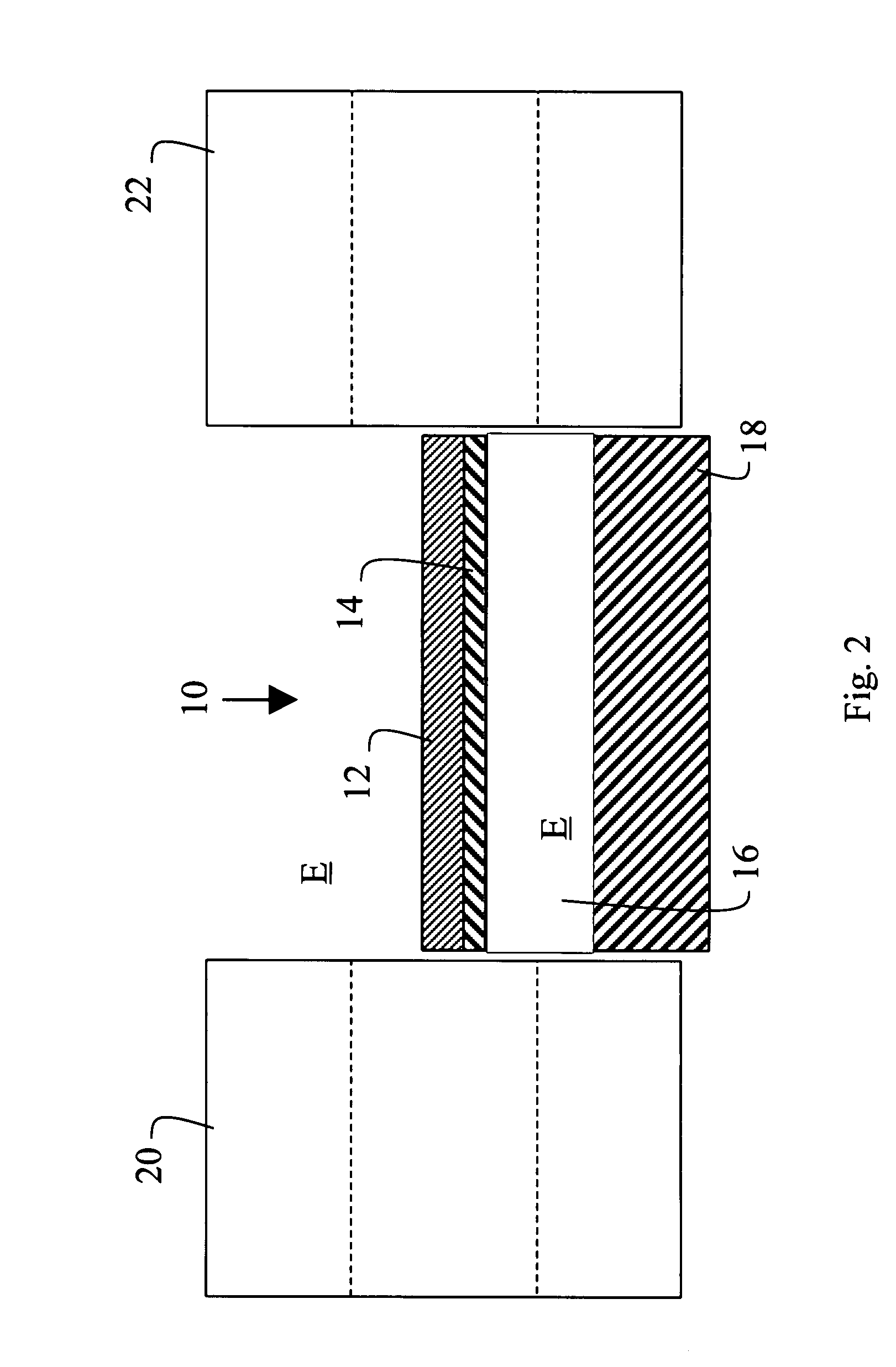
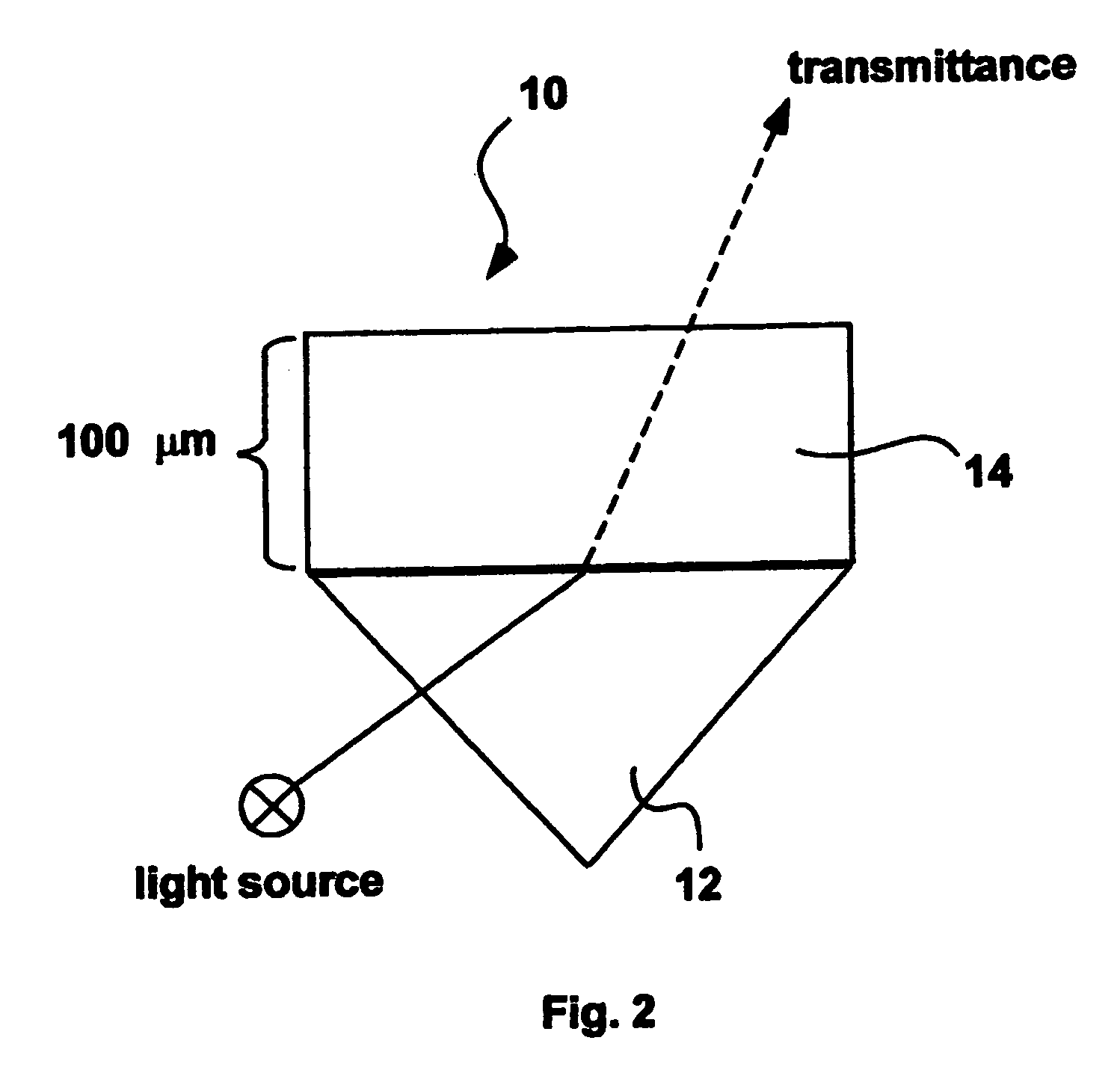
A gas sensor for hydrogen or other gases, especially flammable or explosive gases, has a plasmon-polariton waveguide comprising a metal strip on a membrane supported by a substrate in an environment in which the gas is to be introduced, and coupling means for coupling optical radiation into and out of the plasmon-polariton waveguide such that the optical radiation propagates therealong as a plasmon-polariton wave. The metal strip comprises by a chemical transducer (e.g. Pd or PdNi), the arrangement being such that exposure of the metal strip or coating to the gas to be monitored causes a change in the propagation characteristics of the plasmon-polariton wave and hence the optical radiation coupled out of the plasmon-polariton waveguide.
Owner:SPECTALIS
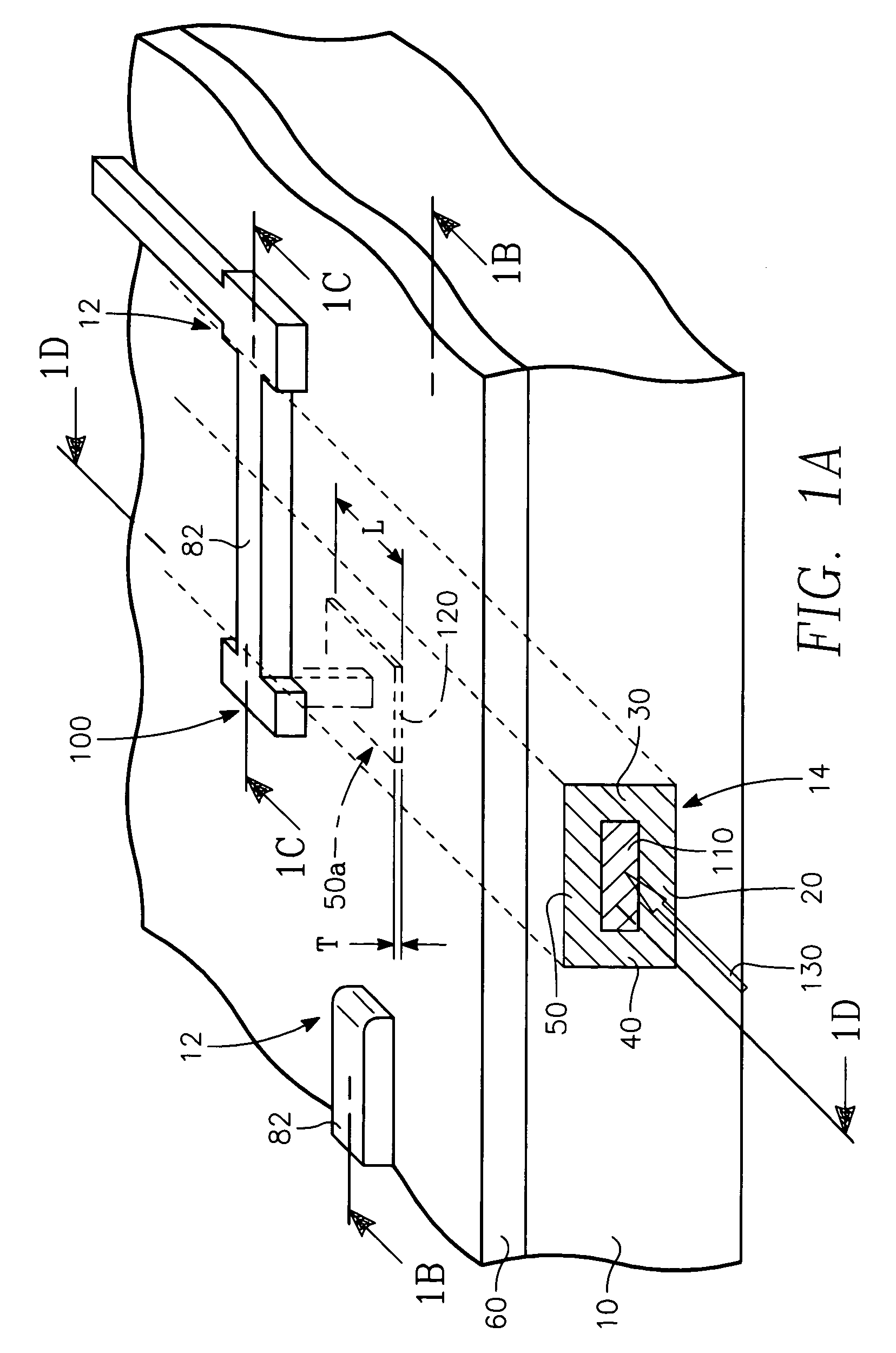
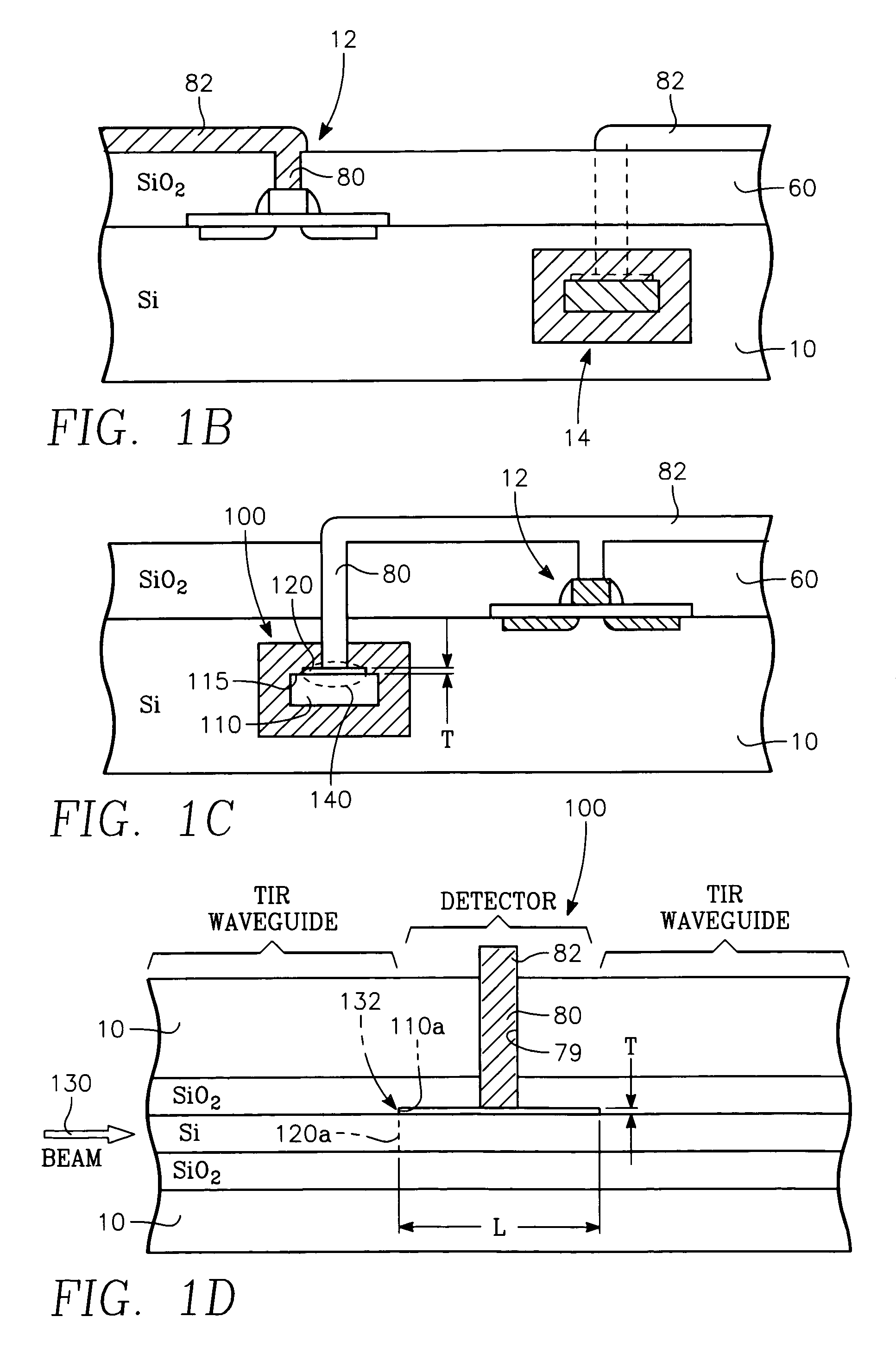
Planar integrated circuit including a plasmon waveguide-fed Schottky barrier detector and transistors connected therewith
InactiveUS7170142B2Easy to controlHigh precisionNanoopticsCoupling light guidesPlasmonic waveguideSchottky barrier
A planar integrated circuit includes a semiconductor substrate having a substrate surface and a trench in the substrate, a waveguide medium in the trench having a top surface and a light propagation axis, the trench having a sufficient depth for the waveguide medium to be at or below said substrate surface, and at least one Schottky barrier electrode formed on the top surface of said waveguide medium and defining a Schottky barrier detector consisting of the electrode and the portion of the waveguide medium underlying the Schottky barrier electrode, at least the underlying portion of the waveguide medium being a semiconductor and defining an electrode-semiconductor interface parallel to the light propagation axis so that light of a predetermined wavelength from said waveguide medium propagates along the interface as a plasmon-polariton wave.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Surface Plasmon Enhanced Optical Devices for Integrated Photonics
An optical device for integrated photonic applications includes a substrate, a dielectric waveguide and a surface plasmon waveguide. The dielectric waveguide includes a dielectric waveguide core disposed relative to a dielectric waveguide cladding and a common cladding. The surface plasmon waveguide includes a surface plasmon waveguide core disposed relative to the common cladding and a surface plasmon waveguide cladding. The common cladding couples the dielectric waveguide and the surface plasmon waveguide.
Owner:PHYSICAL SCI
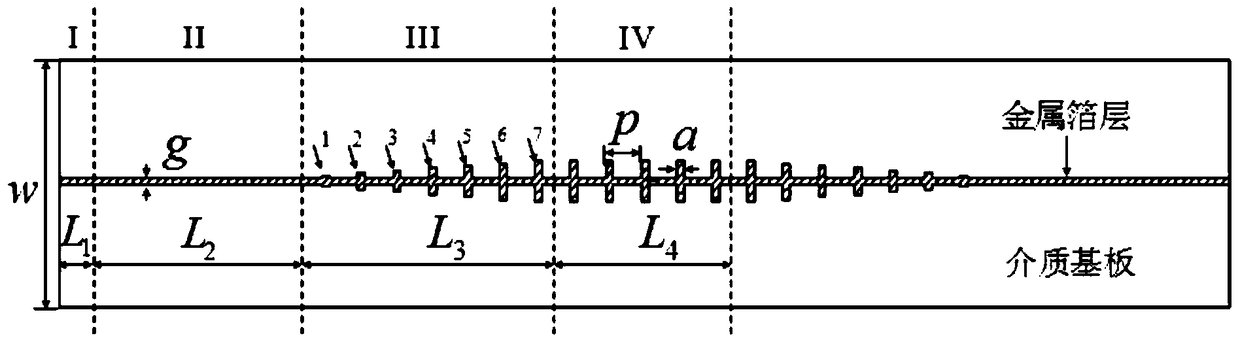
Ultra-wideband artificial surface Plasmon low-pass filter
InactiveCN105119030ARealize mutual conversionRealize ultra-wideband filtering functionWaveguide type devicesMetallic foilUltra-wideband
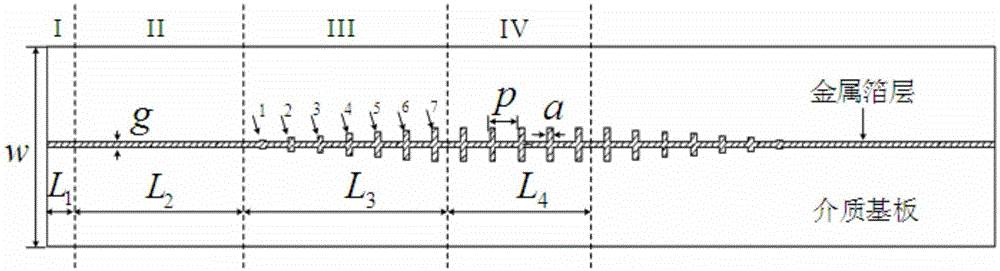
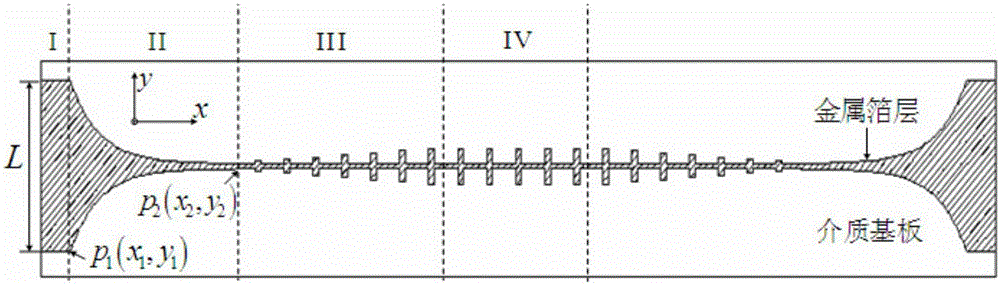
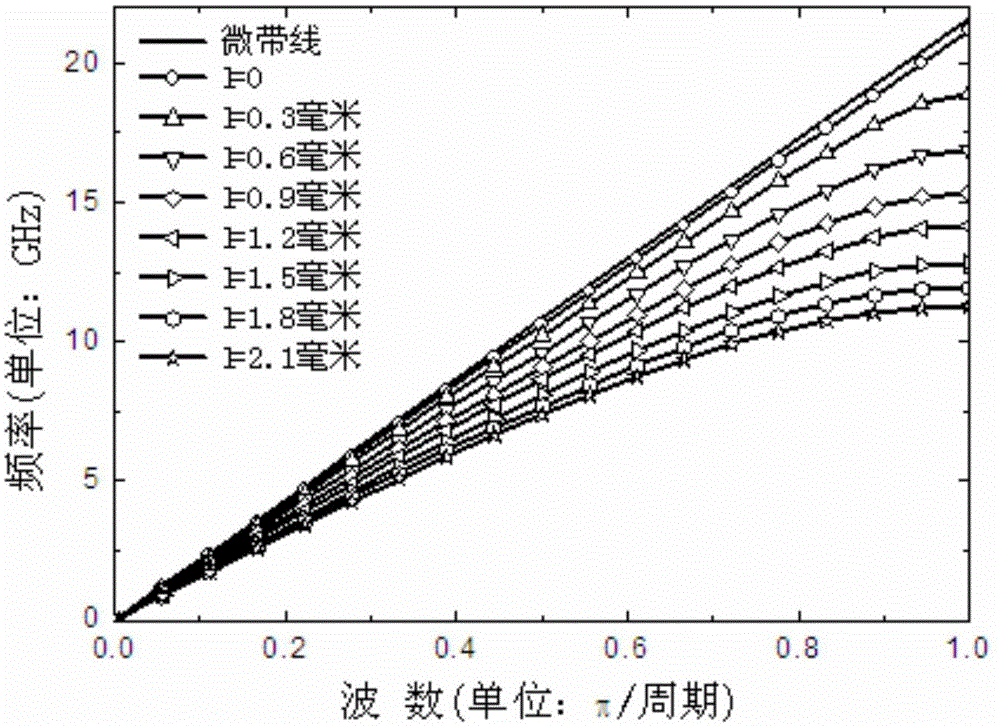
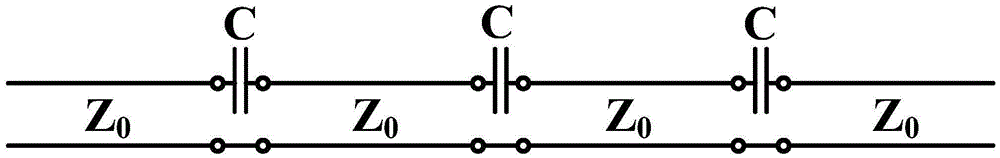
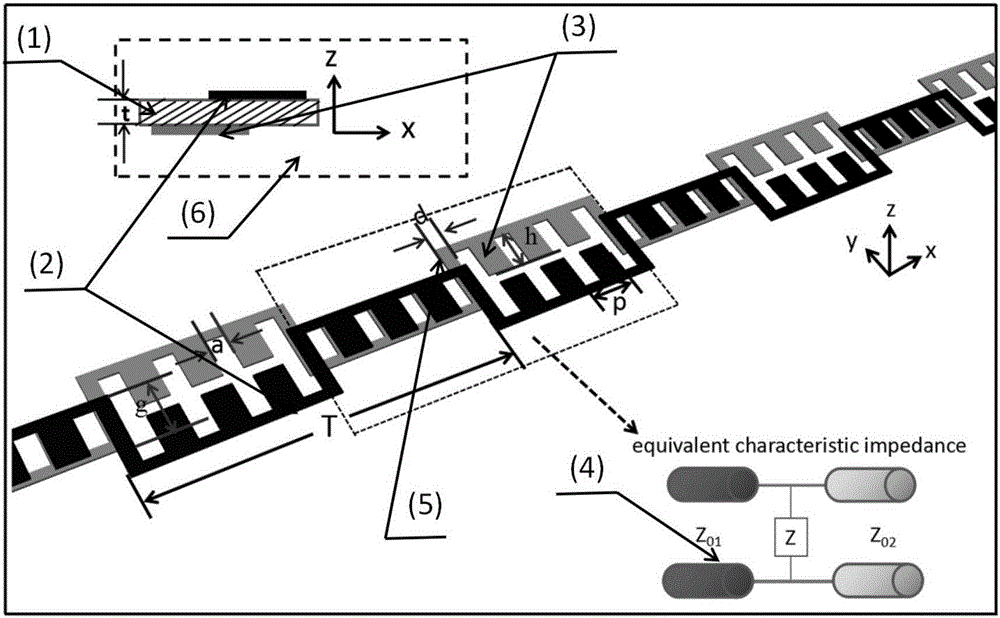
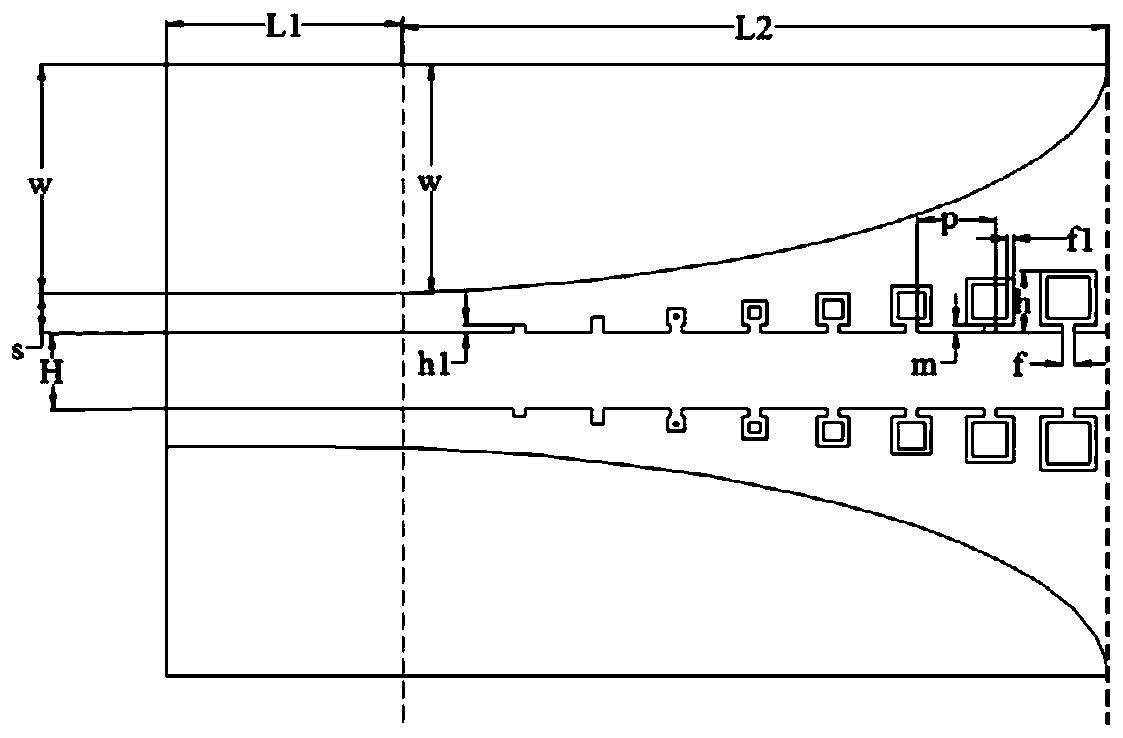
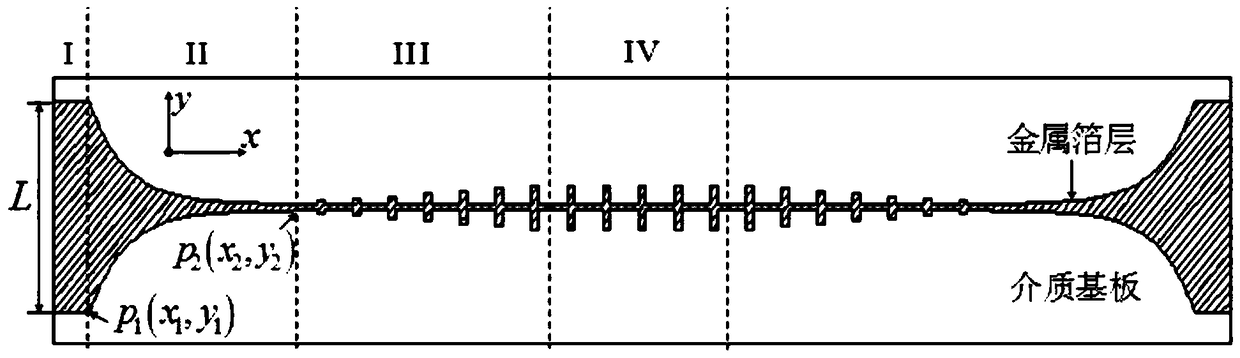
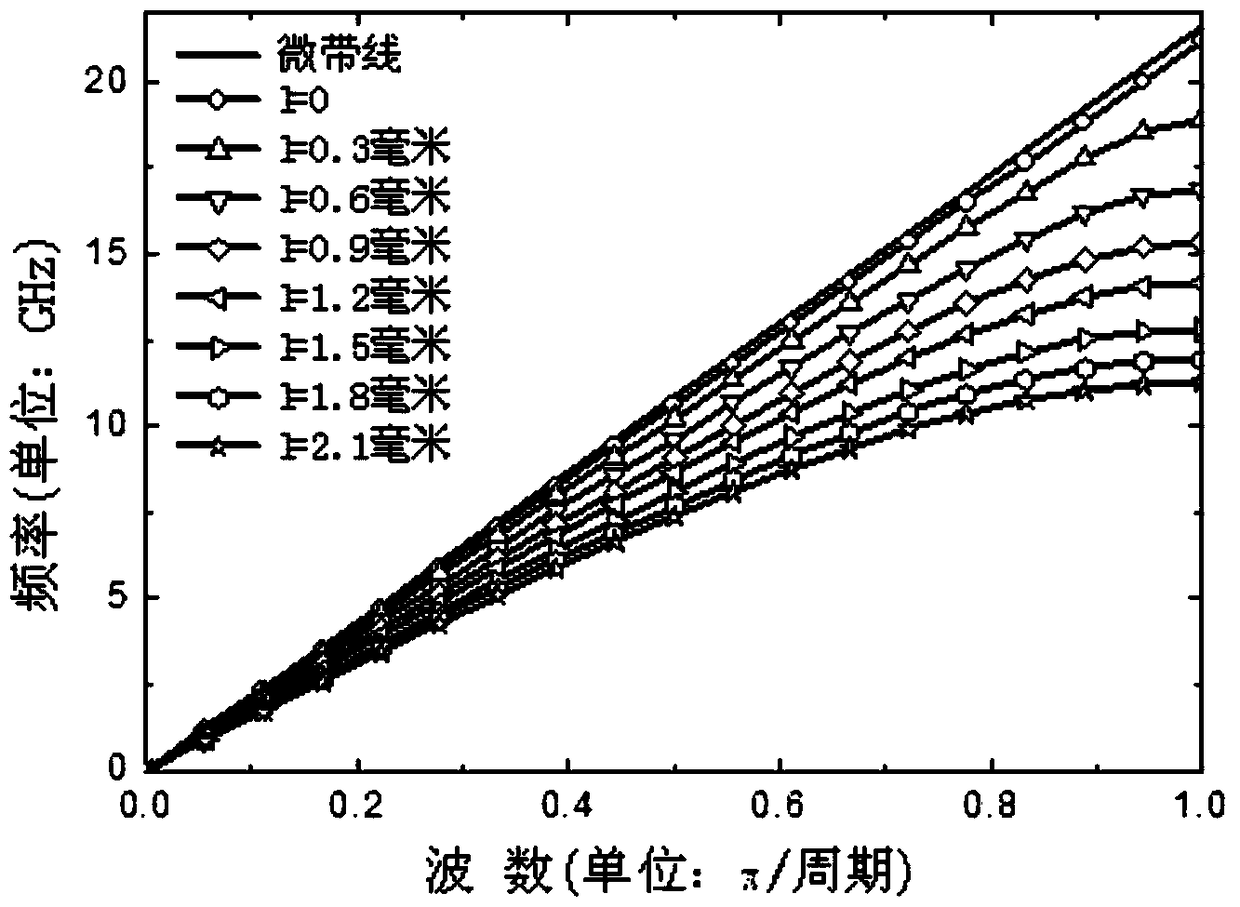
The invention discloses an ultra-wideband artificial surface Plasmon low-pass filter which is mainly formed by a dielectric substrate layer and metallic foil layers printed on the both side surfaces of the dielectric substrate layer. Waveguide structures are engraved on the metallic foil layers. Each waveguide structure is formed by a middle surface Plasmon waveguide portion, symmetric microstrip line portions at both ends, and two transition portions. The ultra-wideband artificial surface Plasmon low-pass filter may achieve effective transmission of artificial surface Plasmon waveguide, and has symmetric structure, easy processing, compact size, a ultra-wide band and high filtering performance, and is especially suitable for being used in cooperation with a conventional microwave or terahertz transmission line.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Long-range plasmon waveguide array synergy unit for solar cell
ActiveCN102184995AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyIncrease light field intensityLight-sensitive devicesCapacitor electrodesWaveguideWaveguide array
The invention belongs to the technical field of solar cells, in particular to a long-range plasmon waveguide array synergy unit for a solar cell. The specific structure of the long-range plasmon waveguide array synergy unit consists of a long-range plasmon waveguide array, a diffraction grating, a transparent conducting thin film, a glass substrate and a photovoltaic material. The long-range plasma laser waveguide array synergy unit is characterized in that: surface plasmons generated by the waveguide array synergy unit are used for localization to enhance the light field strength on the metal waveguide surface and improve the absorptivity of the solar cell to incident sunlight. Through the technology, the absorptivity of the solar cell to incident sunlight is increased under the condition of not affecting the normal absorption of a photovoltaic material on the top layer to the incident light of a light-facing face, and then the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the solar cell isimproved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Surface plasmon enhanced optical devices for integrated photonics
Owner:PHYSICAL SCI
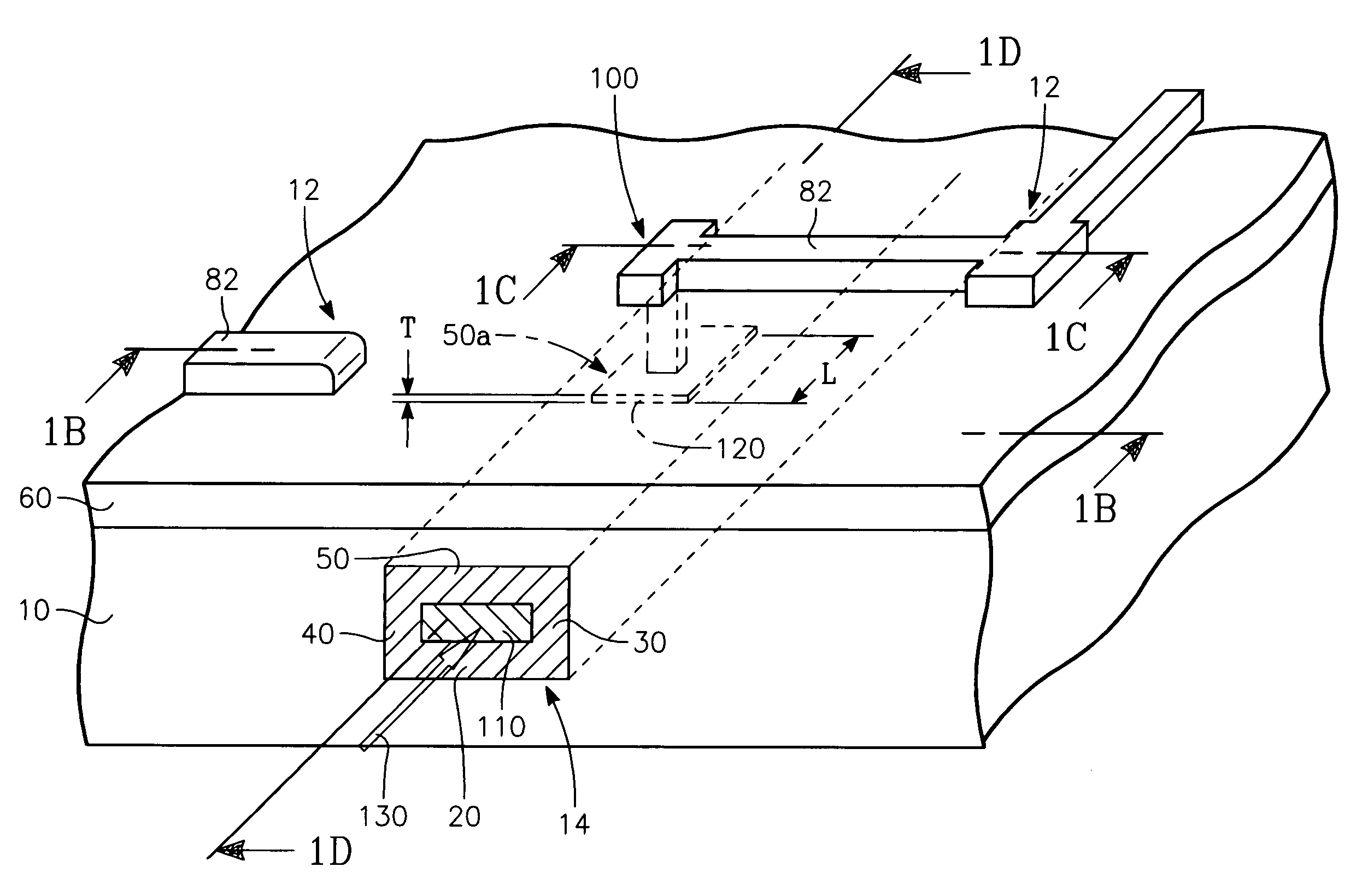
Sensor device for interference and plasmon-waveguide/interference spectroscopy
InactiveUS20070030489A1Improve observabilityAvoid damageRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryDielectricPlasmonic waveguide
Methods for measuring a property of a sample material present at an interface of an emerging medium in a spectroscopic device include a sensor (10) featuring at least one dielectric member (14) disposed upon a entrant medium (12), with the dielectric member being of an optical thickness selected to produce an observable interference effect for an incident angle of light below the critical angle of total internal reflection at the interface with the dielectric member (14). The dielectric member (14) of the sensor device (10) may be modified and functionalized for binding of a sample analyte by disposing a sensing surface area (38, 40, 42) upon it. Moreover, an metal layer (18) may be added to an entrant medium (20) to produce a sensor (16) that generates observable optical phenomena both above (resonance) and below (interference) a given critical angle.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
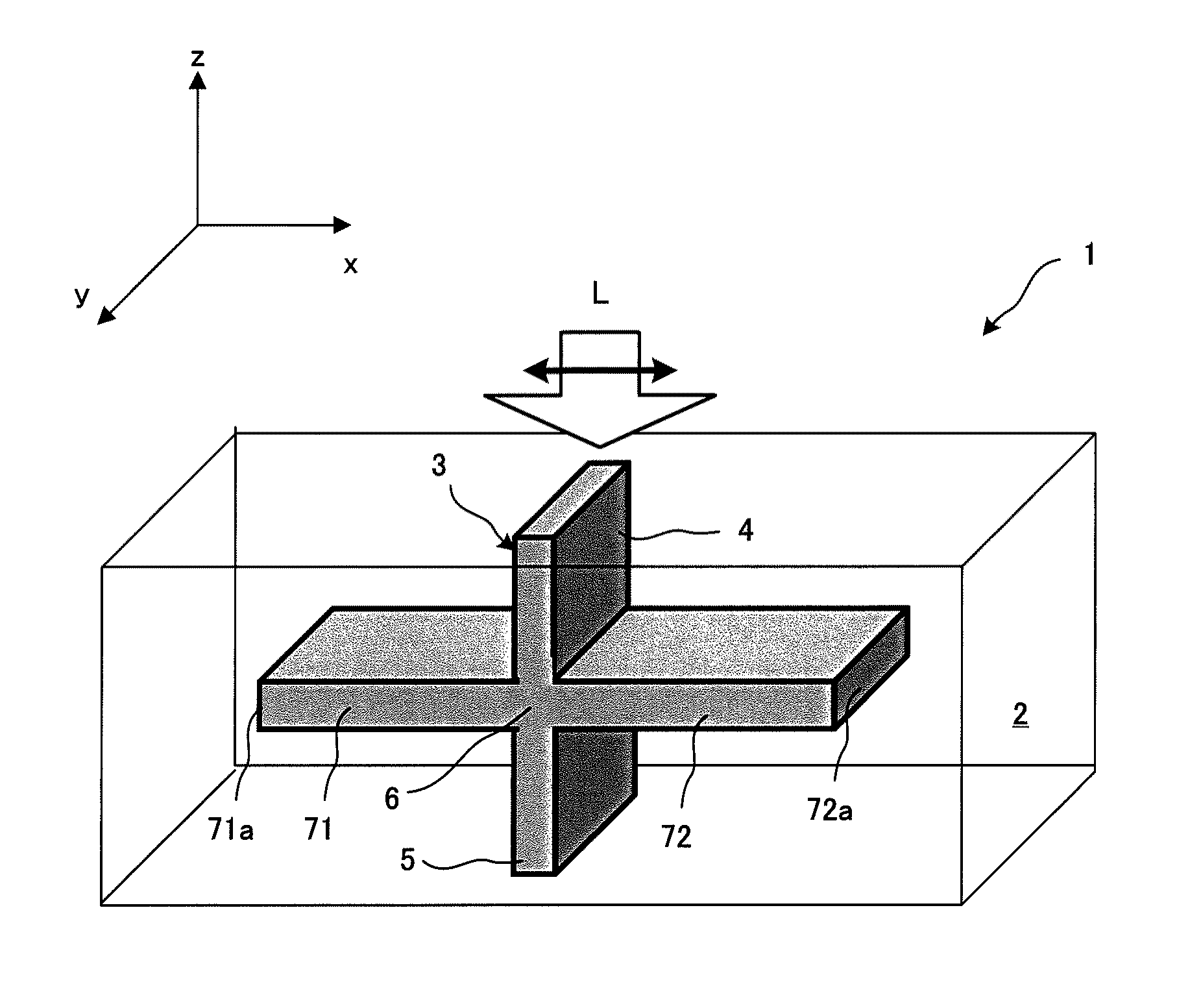
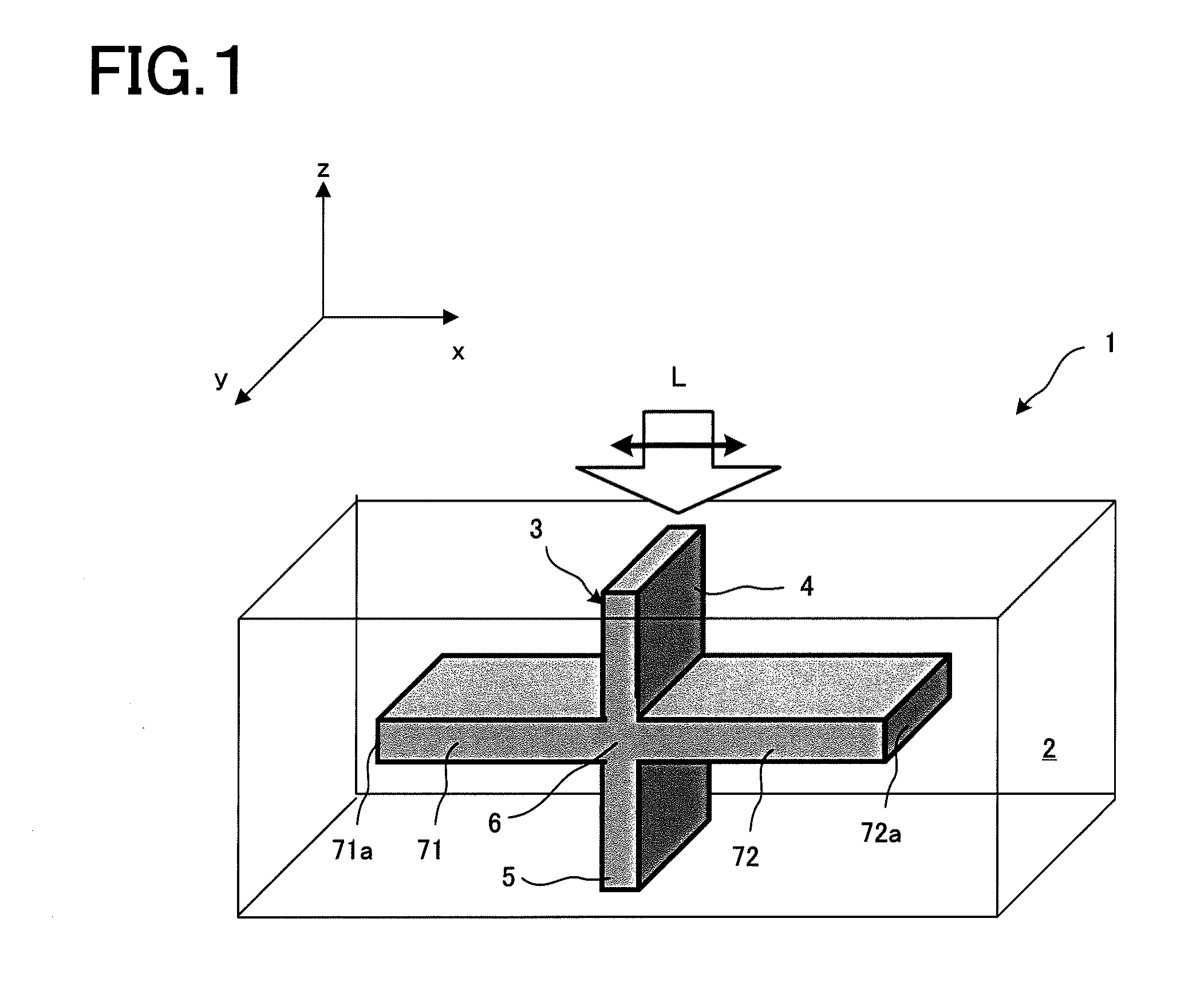
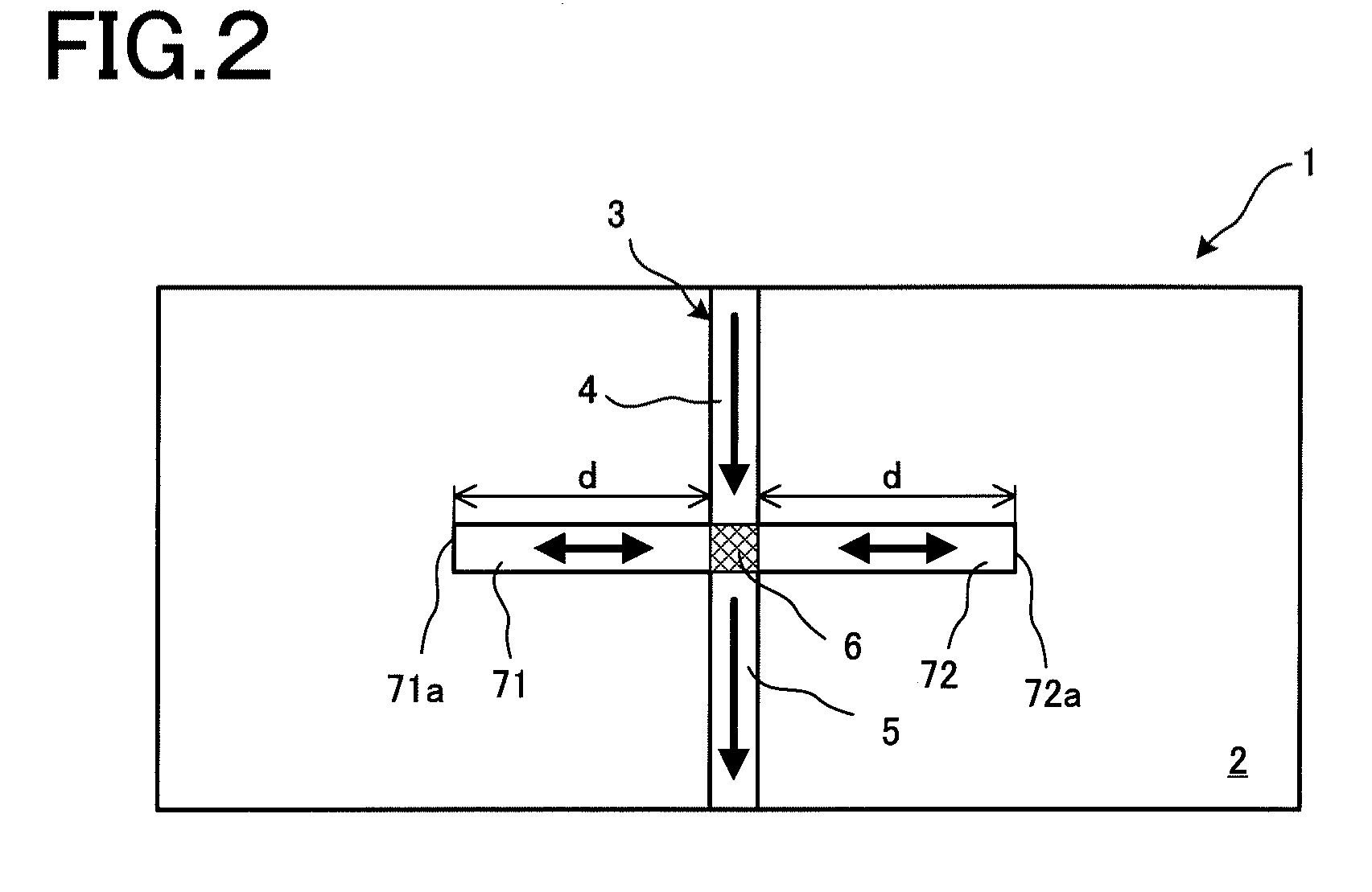
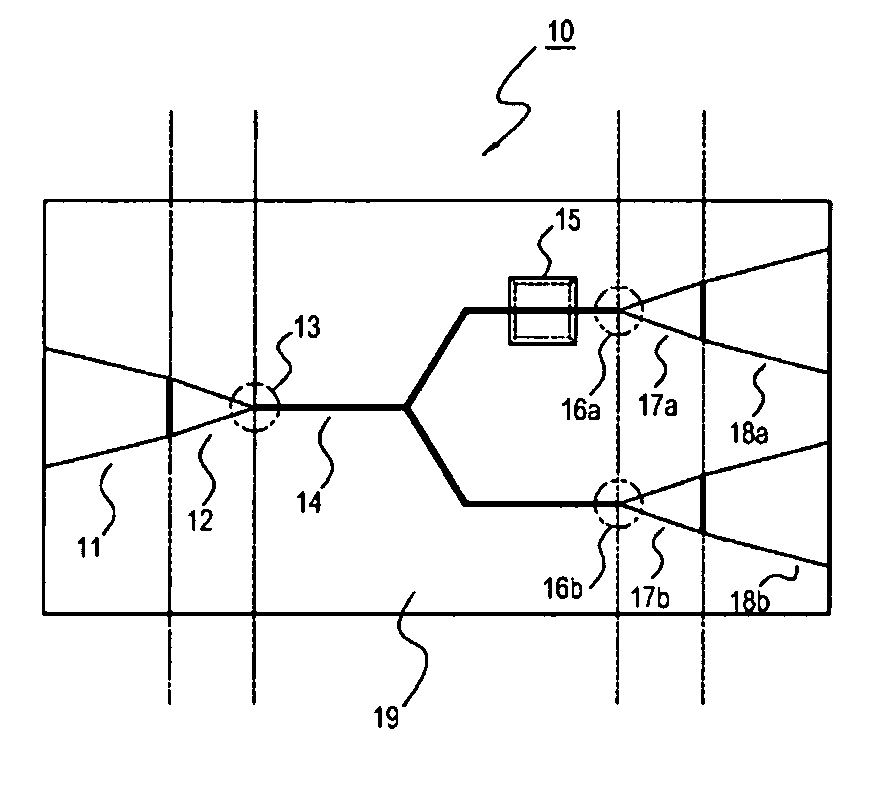
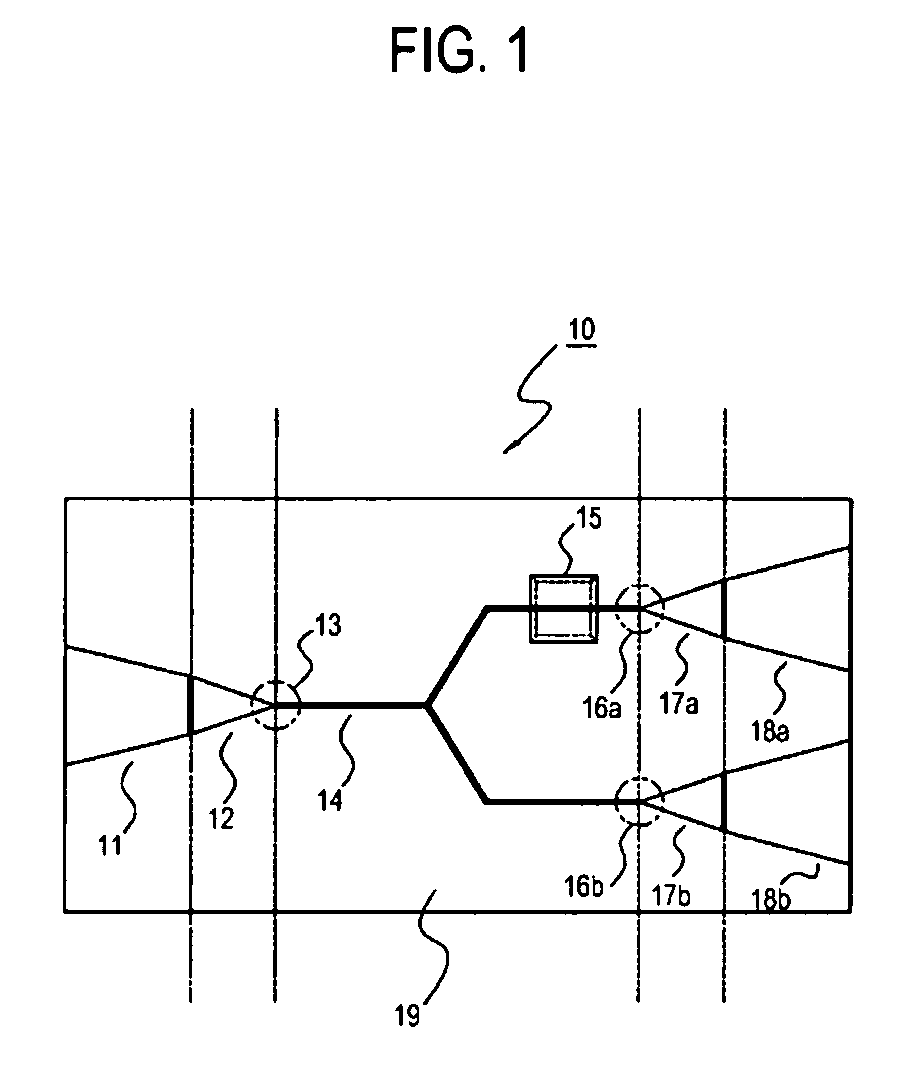
Plasmon waveguide and optical element using the same
InactiveUS20110103742A1Simple structureGood wavelength selectivityCladded optical fibreNanoopticsPlasmonic waveguideLength wave
Disclosed is a plasmon waveguide including cladding (2) consisted of metal, and a dielectric core (3) which is formed of a transparent material, surrounded by or sandwiched by the cladding (2), and has at least one cross-section having a thickness no more than the wavelength of the incident light. The plasmon waveguide is provided with: a incident-side plasmon waveguide (4) into which light (L) is incident; an emission-side plasmon waveguide (5) from which light (L) is emitted; a connection portion (6) connecting the incident-side plasmon waveguide (4) and emission-side plasmon waveguide (5); and a plasmon interference structure (7) which extends from the connection portion (6) in the direction intersecting the incident-side plasmon waveguide (4) or the emission-side plasmon waveguide (5), and has a terminal (7a) at which light (L) is reflected.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
Microwave vortex wave generator based on artificial surface plasmon and implement method thereof
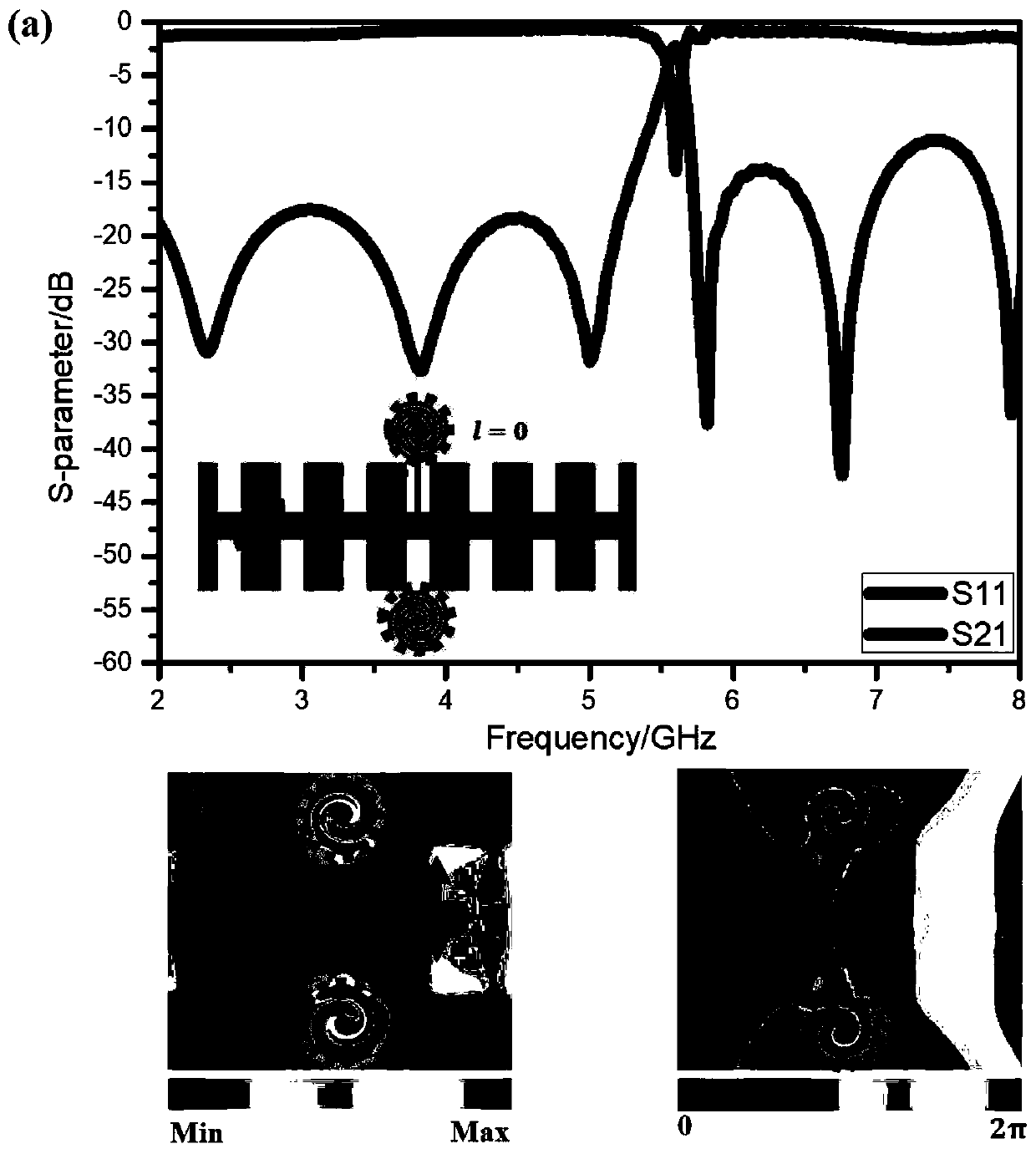
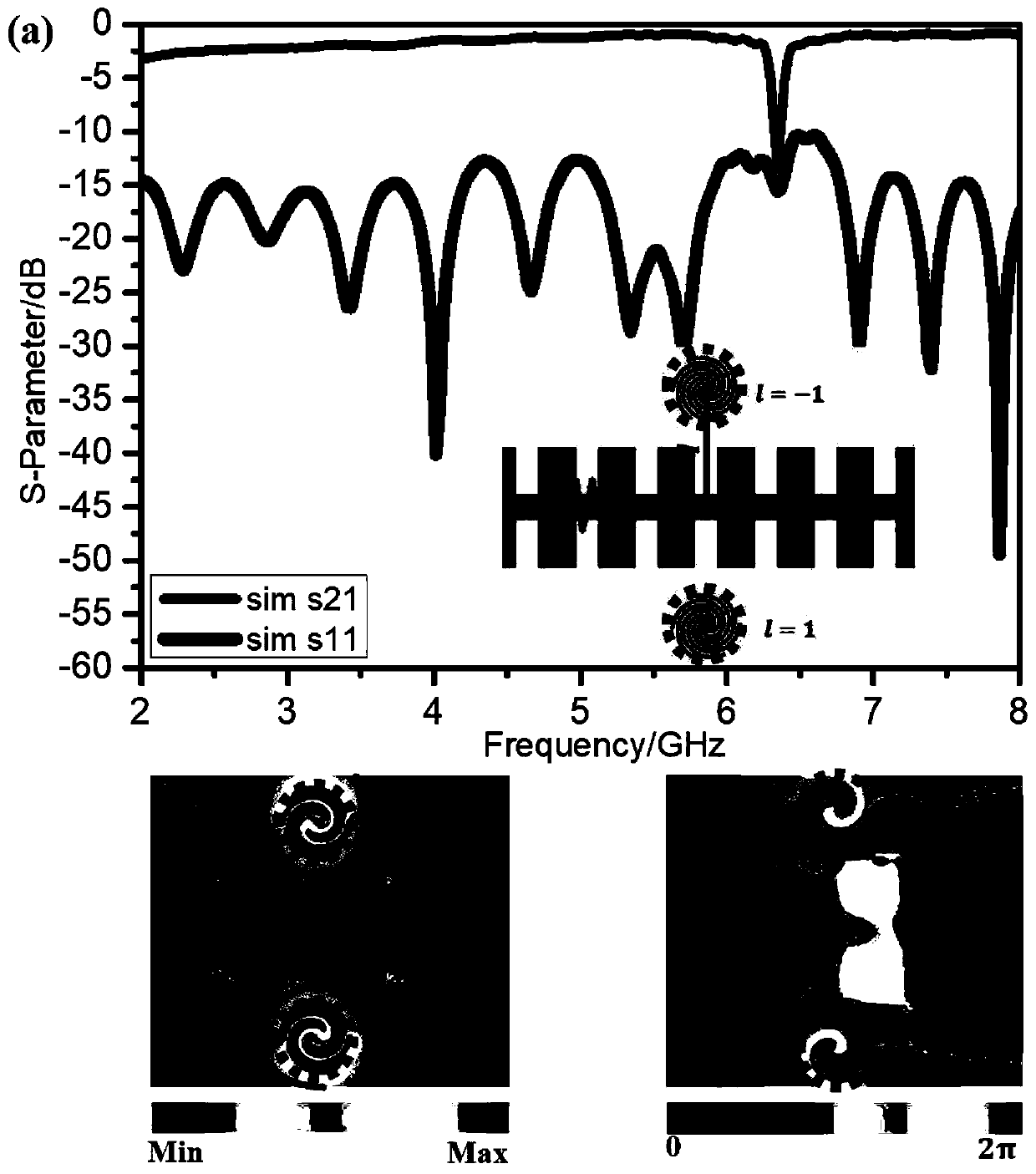
ActiveCN106848557ATransmission phase satisfiesReduce confusionRadiating elements structural formsIndividually energised antenna arraysAngular momentumWaveguide
The invention discloses a microwave vortex wave generator based on artificial surface plasmon. The microwave vortex wave generator works in a microwave frequency band, double layers of artificial surface plasmon waveguides achieve transmission of electromagnetic waves, and the waveguides on the upper layer are connected to the waveguides on the lower layer through a metal through hole. The radiation part of the microwave vortex wave generator is mainly achieved through a series of circular patches which are placed beside the artificial surface plasmon waveguides, and meanwhile the circular patches also provide phases needed for generating different vortex waves as resonators. The microwave vortex wave generator can have different vortex waves with different orbit angular momentum modes at different frequency positions without making any changes in structure.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
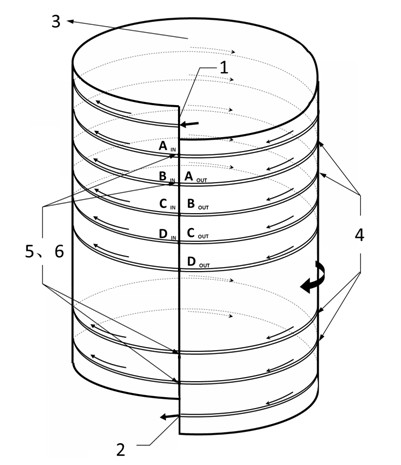
Optical gyro based on flexible surface plasmon polariton waveguide
ActiveCN102419175AAchieve polarizationHigh Optical GyroSagnac effect gyrometersLight signalWaveguide
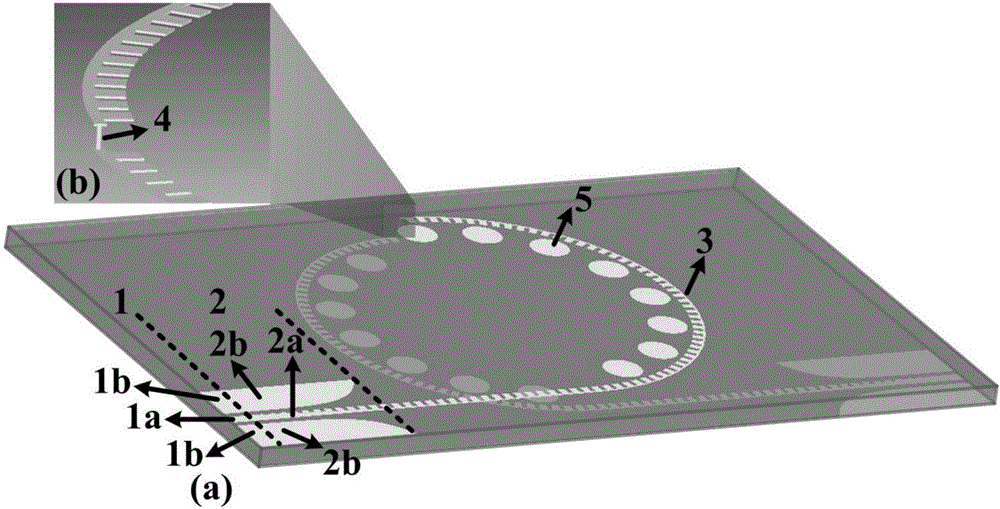
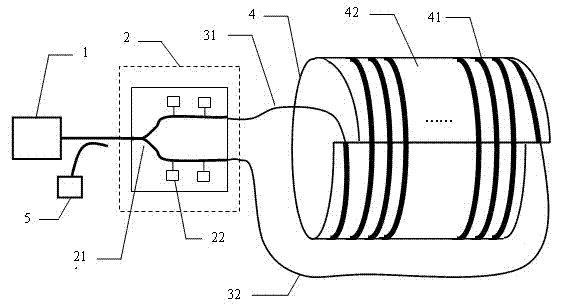
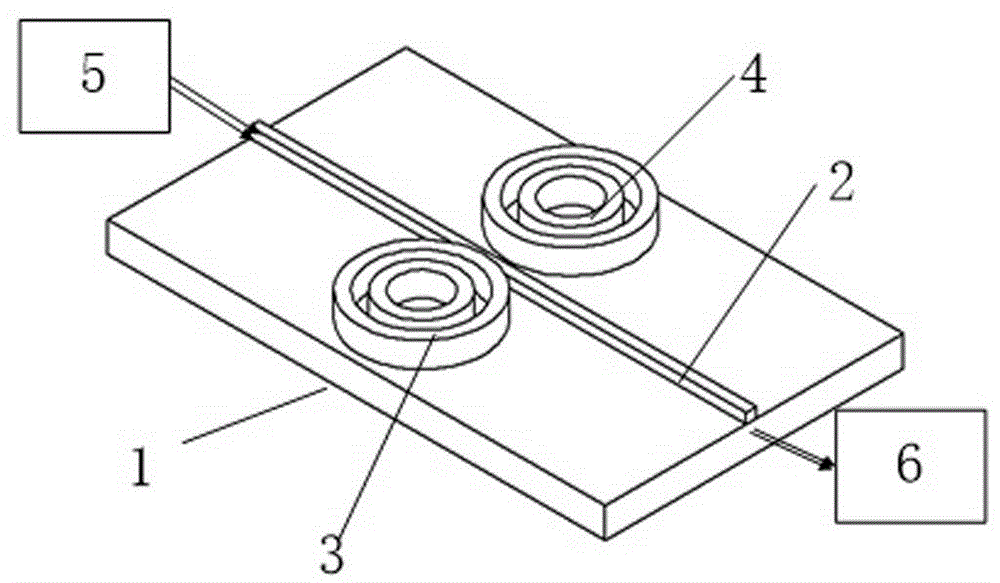
The invention relates to an optical gyro based on a flexible surface plasmon polariton waveguide. The optical gyro comprises a light source (1), a Y branched modulator (2), an input optic fiber (31), an output optic fiber (32), a flexible surface plasmon polariton waveguide cylindrical surface (4) and an optical detector (5), wherein the flexible surface plasmon polariton waveguide cylindrical surface (4) comprises a flexible surface plasmon polariton waveguide (41) and a flexible substrate (42); a light signal is output from the light source (1) to the Y branched modulator (2), subjected to modulation, and input from the input optic fiber (31) to the flexible surface plasmon polariton waveguide cylindrical surface (4); light is interfered in the flexible surface plasmon polariton waveguide (41) and transmitted from the output optic fiber (32) to the optical detector (5); and the rotational angular velocity is detected by the optical detector (5). The integration degree and the shock resistance of the optical gyro system are improved; and the structure of the optical gyro is simplified.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Band-stop filter based on artificial surface plasmons and stop band introducing method thereof
ActiveCN105655672AFacilitates maximum power transferSimple designWaveguide type devicesCapacitanceCoplanar waveguide
The invention discloses a band-stop filter based on artificial surface plasmons. The structure works in a microwave frequency range, and a metal structure is only adhered to the upper layer of a medium. The band-stop filter is fed by conventional coplanar waveguides, and transition structures between the coplanar waveguides and artificial surface plasmon waveguides are utilized to realize impedance matching and wave number matching between the two kinds of waveguides. According to the invention, two unit structures of double-edge wrinkling strip line artificial surface plasmon waveguides are used to form a new unit structure, a certain distance interval of periodic arrangement is formed between every two new unit structures, and a new artificial surface plasmon transmission line is formed. The transmission line is characterized in that, capacitance structures are introduced into the conventional double-edge wrinkling strip line transmission line, and a stop band can be introduced into the frequency band of the artificial surface plasmons, so that the function of the band-stop filter is realized.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
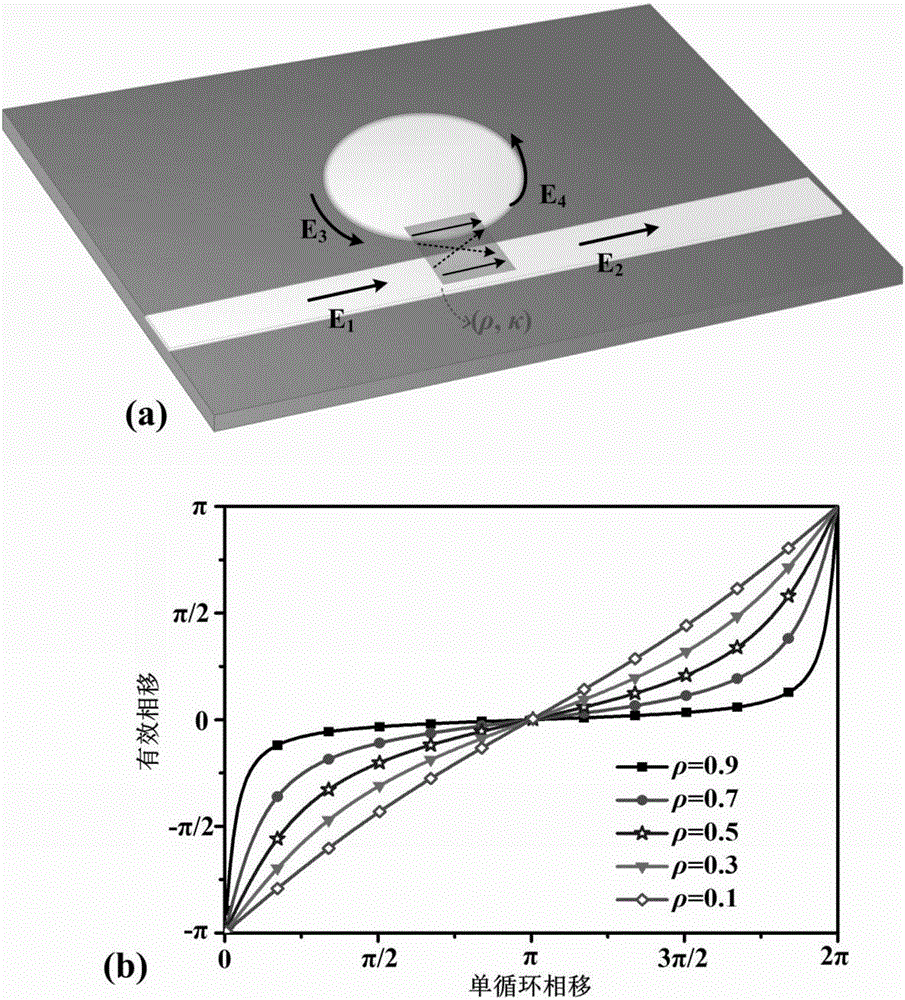
Adjustable resonant cavity based on flexible surface plasmon coupler, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109613632AHigh Q valueAchieving Coupling Ratio TuningOptical light guidesResonant cavityEngineering
The invention discloses an adjustable resonant cavity based on a flexible surface plasmon coupler, and a preparation method thereof. The adjustable resonant cavity comprises a tunable flexible surfaceplasmon coupler formed by an upper branch flexible waveguide and a lower branch flexible waveguide, a flexible surface plasmon directional coupler, a first flexible plasmon waveguide and a second flexible plasmon waveguide located on the lower branch flexible waveguide and used for conducting an optical signal, and a flexible surface plasmon resonant ring formed by coupling and docking two ends of the upper branch flexible waveguide; and the annular surface of the resonant ring is perpendicular to a plane on which the lower branch flexible waveguide is located. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing the tunable flexible surface plasmon coupler; separating the two left and right ends of the upper branch flexible waveguide and the lower branch flexible waveguide to the flexible surface plasmon directional coupler; and crimping and docking the two ends of the upper branch flexible waveguide so as to form the three-dimensional flexible surface plasmon resonant ring, and obtaining the adjustable resonant cavity. According to the resonant cavity, the bending loss can be reduced, and a Q value is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Dual-cylindrical MIM surface plasmon waveguide structured acceleration sensing device
InactiveCN104977427ASimple structureAcceleration measurement using interia forcesMems sensorsWaveguide
The invention discloses a dual-cylindrical MIM surface plasmon waveguide structured acceleration sensing device. The acceleration sensing device comprises a Si substrate. The acceleration sensing device is characterized in that the acceleration sensing device further comprises a first MIM waveguide structure and a second MIM waveguide structure which are in the same size, as well as an optical fiber straight waveguide; the MIM waveguide structures are cylindrical MIM waveguide structures; the first MIM waveguide structure and the second MIM waveguide structure are arranged on the Si substrate; the optical fiber straight waveguide is arranged on the Si substrate; the first MIM waveguide structure and the second MIM waveguide structure are symmetrically arranged at two sides of the optical fiber straight waveguide, and abut against the optical fiber straight waveguide; and the cylindrical MIM waveguide structures are symmetric gold-silicon dioxide-gold surface plasmon waveguides. With the device of the invention adopted, a defect that an MEMS sensor is limited by external environment and attributes of the MEMS sensor itself can be eliminated, and problems such as long response time and low sensitivity of a traditional micro ring sensor can be solved. The device of the invention has the advantages of simple structure and easiness in implementation.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Plasmon waveguide, biosensor chip and system
InactiveCN107271398AIncrease signal strengthHigh detection sensitivityScattering properties measurementsBiological testingSplit ringMicrofluidic channel
The embodiment of the invention provides a plasmon waveguide, a biosensor chip and a system. Specifically, the plasmon waveguide is applied in the biosensor chip, and comprises a substrate and a plasmon structure disposed on the upper surface of the substrate, the plasmon structure includes a plurality of plasmons in periodic arrangement, the plasmons are metal split rings, and the annular openings of the plasmons are used for fixation of antibody probes. According to the embodiment of the invention, the plasmon waveguide is disposed in the biosensor chip, and the antibody probes can be used for capture of target biomolecules in detection liquid flowing into a microfluidic channel, and the plasmon waveguide is employed to enhance the signal strength of THz wave emitted to the biosensor chip, thus enhancing the signal strength of reflection THz wave detected by a terahertz analyzer, and improving the detection sensitivity, signal-to-noise ratio and reliability.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF TERAHERTZ TECH & INNOVATION +1
Artificial surface plasmon field strength enhancer
InactiveCN104253294AAchieve heightAchieve efficient transmissionWaveguidesCoupling devicesElectrical conductorPhysics
The invention provides an artificial surface plasmon field strength enhancer, which comprises a traditional coaxial waveguide, a transition waveguide from the coaxial waveguide to an artificial surface plasmon waveguide, and a conical plasmon waveguide, wherein the transition waveguide comprises inner conductor and outer conductor transition, and the inner conductor transition is realized by a depth-increasing periodic annular groove array; the outer conductor transition is realized by a horn antenna with a gradually increased opening, and the conical plasmon waveguide consists of an annular groove array with constant depth and width, decreasing radius, and changeable period. The artificial surface plasmon field strength enhancer provided by the invention has the advantages of simple structure, compact size, efficient wideband, and high field strength enhancement multiples, is suitable for being matched with the traditional microwave or terahertz transmission circuit for use, and can be widely applied to the fields of microwave or terahertz imaging, high-resolution medicine endoscope technology, bio-detection, national security, food and agricultural product quality control, global environmental monitoring and information and radar communication technology and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Mode-controllable vector vortex light beam generation device and mode-controllable vector vortex light beam generation method
ActiveCN110635206ASmall structureEasy to manufactureRadiating elements structural formsAntennas earthing switches associationDielectric substrateLight beam
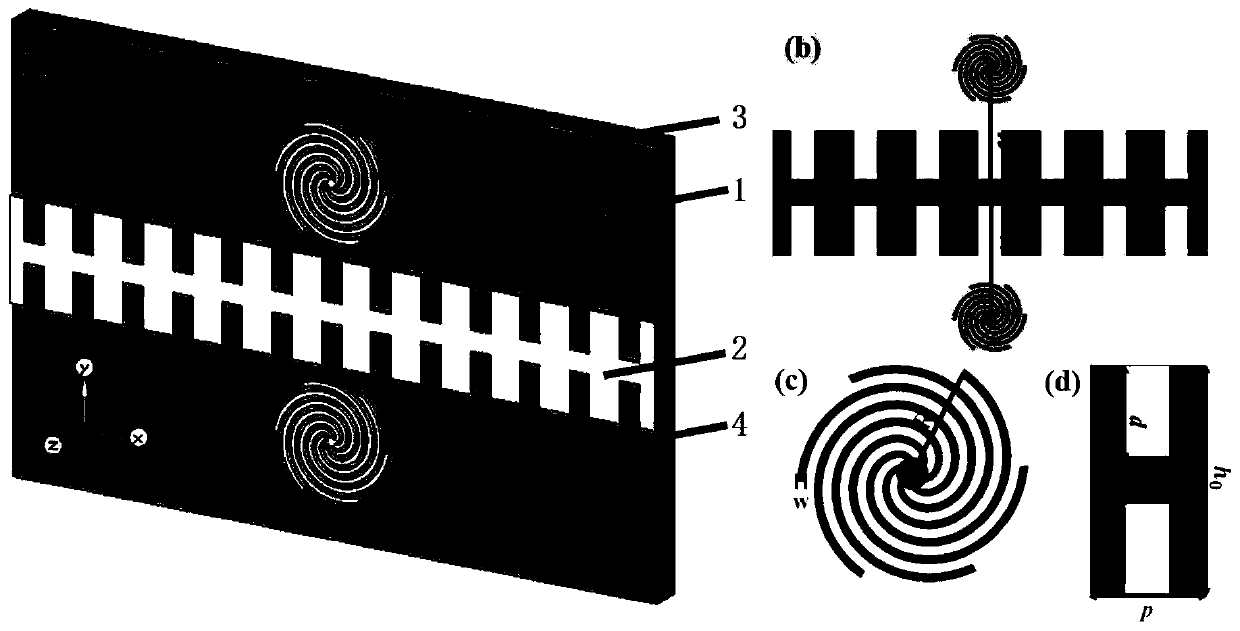
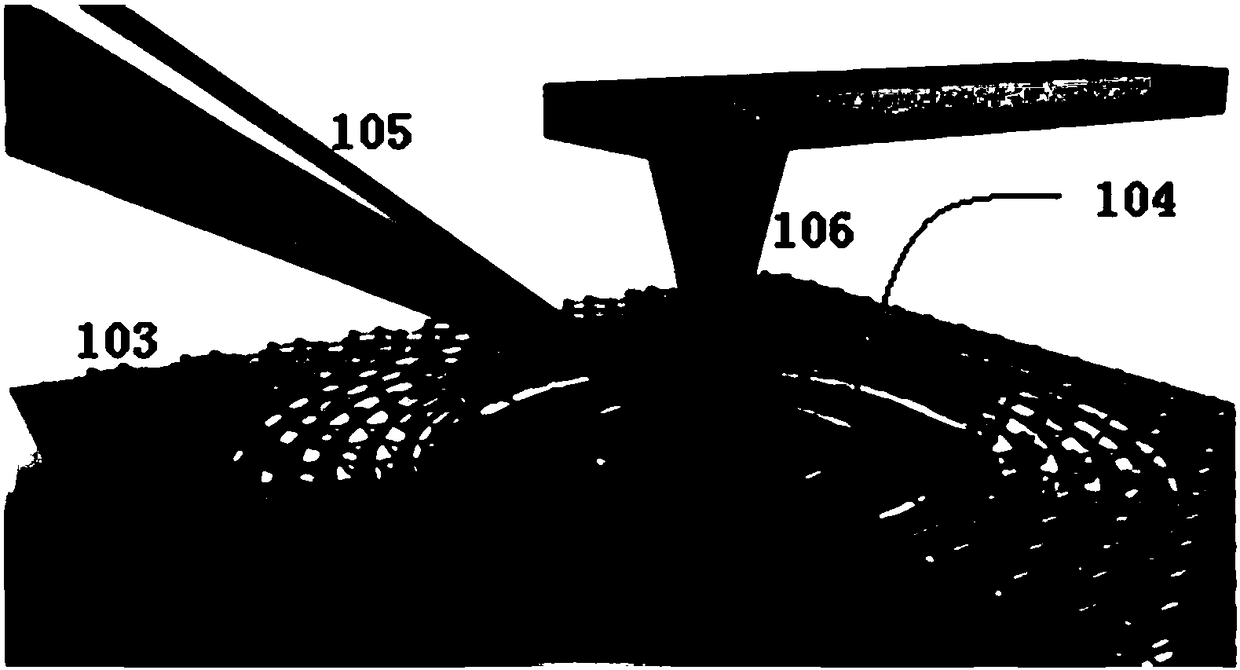
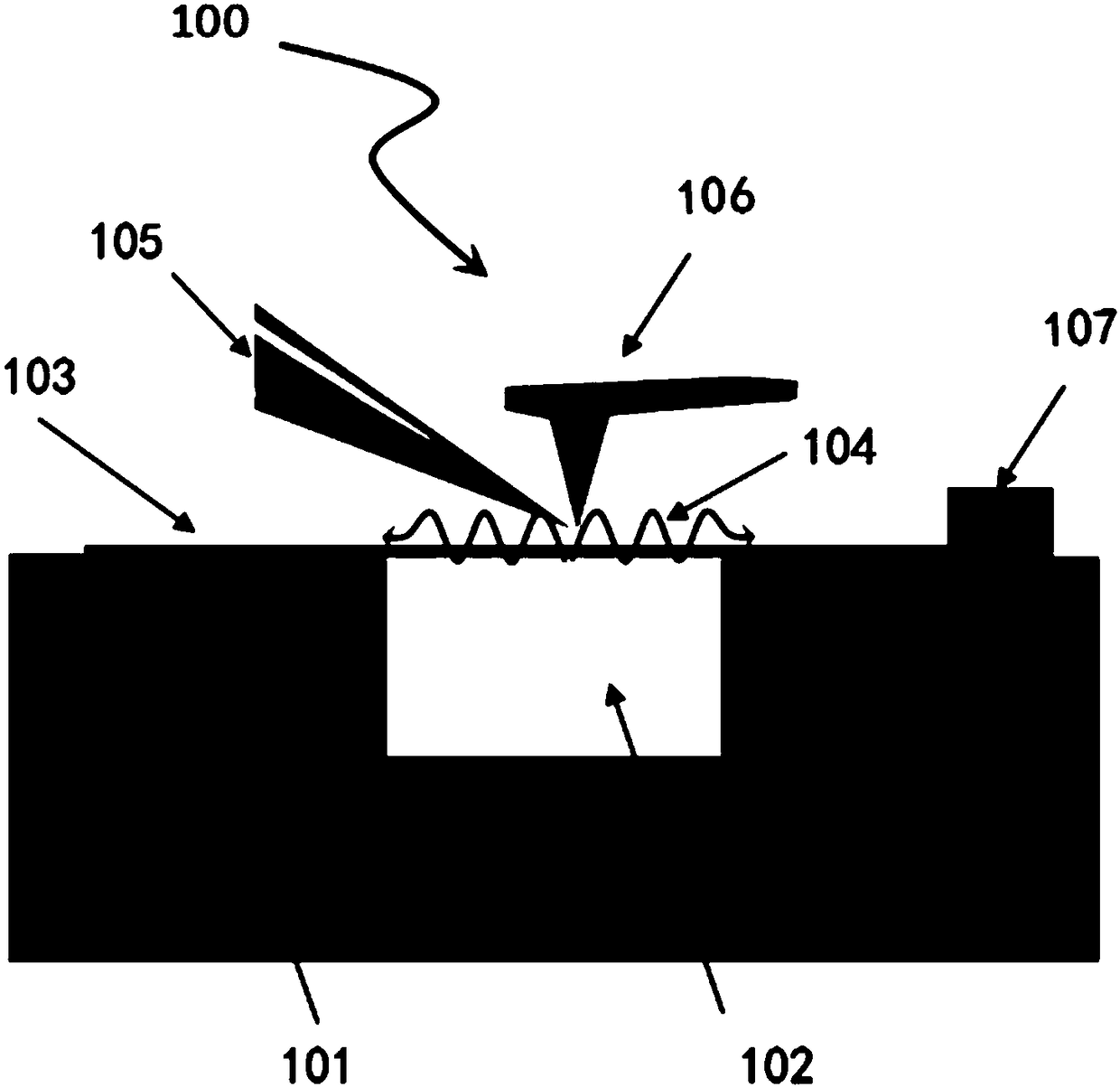
The invention relates to a mode-controllable vector vortex light beam generation device and a mode-controllable vector vortex light beam generation method, belongs to the technical field of vortex light beam generation and solves a problem that vector vortex light beams in different modes cannot be accurately generated in the prior art. The device comprises an electromagnetic wave transmitting device, an electromagnetic wave receiving device, a controller, adjustable Archimedes spiral metal particles, an artificial surface plasmon waveguide and a dielectric substrate, wherein the artificial surface plasmon waveguide is arranged above the dielectric substrate, an input end of the artificial surface plasmon waveguide is connected with an output end of the electromagnetic wave transmitting device, and the output end is connected with an input end of the electromagnetic wave receiving device, the controller is used for adjusting the shape and the position of the Archimedes spiral metal particles, and the adjustable Archimedes spiral metal particles are symmetrically arranged on two sides of the artificial surface plasmon waveguide. The device is advantaged in that the vector vortex light beams with the topological charge to be debugged can be generated, and the device is simple, easy to implement and low in cost and has outstanding technical advantages.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Suspended graphene propagation plasmon waveguide device and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108428986ALow decay rateEliminate dielectric lossWaveguidesUltrasound attenuationDielectric loss
The present invention provides a suspended graphene propagation plasmon waveguide device. The suspended graphene propagation plasmon waveguide device comprises a substrate, a graphene layer and an electrode which are disposed sequentially from bottom to top; the substrate comprises at least one hole structure and is used for supporting a graphene layer and an electrode; the graphene layer covers the hole structure of the substrate, so that a suspended graphene structure can be formed; and the electrode is used for electrical measurement and electrostatic regulation of graphene carrier concentration and is arranged on the graphene layer. According to the structure of the suspended graphene propagation plasmon waveguide device of the invention, propagation plasmons are supported on the suspended graphene structure; with such kind of structure adopted, the dielectric loss of the graphene plasmons can be effectively eliminated, and the decay rate of the plasmons can be reduced; and since the dielectric constant of the air is small, the wavelength of the plasmons on the suspended graphene is very long, and a long-wavelength propagation distance can be achieved with the low attenuation characteristic of the plasmons utilized.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Ultra wide band terahertz class surface plasmon coupler and coupling method
The invention discloses an ultra wide band terahertz class surface plasmon coupler and a coupling method. In the invention, a TEM mode compressor, a mode matcher and a surface mode radiator are adopted. Parameters of the above three portions are reasonably selected. Conversion efficiency from a TEM mode to a class surface plasmon mode is greatly increased and simultaneously an excitation band width of the class surface plasmon mode is widened. The coupler and the coupling method play a powerful role in promoting practical application of a class surface plasmon waveguide which is a novel waveguide in a terahertz wave band. The coupler of the invention is a whole metal structure so that electromagnetic energy losses introduced by the coupler are reduced. Simultaneously, processing of the coupler is convenient and integration is easy to achieve.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Metal waveguide device and NANO plasmonic integrated circuits and optical integrated circuit module using the same
ActiveUS20090214159A1Increase heightReduce power consumptionNanoopticsCoupling light guidesMicro structurePhotonics
Disclosed is a metal waveguide device, and nano plasmonic integrated circuits and an optical integrated circuit module using the same. The nano plasmonic integrated circuit module includes an input coupling unit, an input focusing unit, a surface plasmon polariton waveguide for guiding surface plasmon polaritons, a signal sensing / processing unit, an output defocusing unit, and an output coupling unit for converting surface plasmon polariton signals into optical signals. The optical integrated circuit module includes the nano plasmonic integrated circuit module, thus realizing highly integrated photonic circuits having a micro structure, low power consumption and low price.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
Flexible ultra-long surface plasmon polariton waveguide
InactiveCN102436029ALarge bending lossLong transmission distanceOptical light guidesFrequency waveMetallic materials
The invention relates to a flexible ultra-long surface plasmon polariton waveguide which comprises a photoelectric input end, a photoelectric output end, a flexible substrate and a flexible surface plasmon polariton waveguide line array, wherein the flexible surface plasmon polariton waveguide is manufactured on the flexible waveguide substrate, then a planar waveguide structure is bent, edges are further aligned for welding, and an ultra-long surface plasmon polariton waveguide structure with the independent photoelectric input end and the photoelectric output end is finally formed. The flexible surface plasmon polariton waveguide array comprises a flexible organic polymer cladding layer and a waveguide metal core layer, a selected metal material is gold, silver, copper, aluminum and other precious metal materials with surface plasmon resonance property in a light frequency wave band, and all light waveguide structures are made of an organic flexible polymer material, so that the flexible ultra-long surface plasmon polariton waveguide has great flexibility, can be bent arbitrarily and even folded, is small in volume and can further improve portability; and the surface plasmon polariton waveguide capable of simultaneously conducting photoelectric signals is adopted as a core layer, so that the obstacle that the photoelectric signals are not compatible is broken.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Mixed Plasmon waveguide Bragg grating with double-forbidden band
The invention discloses a mixed Plasmon waveguide Bragg grating with double-forbidden band; the mixed Plasmon waveguide Bragg grating comprises two mixed Plasmon waveguide Bragg grating sets with different period structures and coupled with admittance coupling waveguides on an incident terminal and emission terminal; the first set of mixed Plasmon waveguide Bragg grating is formed by alternativelyarranging two waveguides; the second set of mixed Plasmon waveguide Bragg grating is formed by alternatively arranging two waveguides; the two mixed Plasmon waveguide Bragg grating sets are respectively formed by periodically and alternatively filling two low refractive index materials A and B between a metal Ag bar and a high refractive index material Si. The mixed Plasmon waveguide Bragg grating is simple in structure, and can stop a TM mode on two assigned broadband positions; the waveguide length and grating period in a coupling zone can be changed so as to dynamically select transmissionbands in an assigned wave band, thus adjusting and optimizing the passband and forbidden band positions and performances.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
90-degree optical mixer based on hybrid plasmon waveguide structure
ActiveCN108345064AShorten the propagation distanceReduce transmission lossOptical light guidesDielectricMultimode interference
The invention discloses a 90-degree optical mixer based on a hybrid plasmon waveguide structure. The 90-degree optical mixer is composed of a single 4*4 multimode interference coupler (MMI). The hybrid plasmon waveguide structure consists of a dielectric waveguide layer, a slit dielectric interlayer on the dielectric waveguide layer, and a metal layer on the slit dielectric interlayer. When lightenters the hybrid plasmon waveguide, the special structure of the hybrid plasmon waveguide can excite a hybrid plasmon mode and confines the mode in the slit dielectric interlayer so that the propagation distance under the same optical path can be greatly reduced and thus the size of the device is greatly reduced. Thus, compared with a conventional dielectric waveguide mixer, the 90-degree opticalmixer is reduced in size from millimeters to micrometers, provides a new structural solution for highly integrated photonic devices and has far-reaching effects on the further integration of photonicdevices.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Cherenkov radiation device based on artificial surface plasmon
ActiveCN106486754AEasy to makeEasy to integrateRadiating elements structural formsAntennas earthing switches associationWaveguideStructure based
The invention discloses a Cherenkov radiation device design based on an artificial surface plasmon. The Cherenkov radiation device comprises a dielectric layer and two layers of metal sheets, wherein the two layers of metal sheets are fixedly connected with two sides of the dielectric layer and are in mirror symmetry along an extension direction of the metal sheets, the radiation device is of a structure based on dual layers of artificial surface plasmon waveguides, a periodic phase reverse structure is introduced into the waveguides, and thus, structural mutation with discontinuous impedance is generated in the structure. On the basis of the artificial surface plasmon waveguides, mode conversion and high-efficiency radiation of artificial surface plasmon are achieved, and moreover, the radiation and the beam direction of the artificial surface plasmon are effectively controlled by changing dispersion characteristics; by the Cherenkov radiation device, high-efficiency conversion between a conduction mode and a space radiation mode can be achieved, the development of a device and a functional device of a novel waveguide structure can be promoted to a great extent, and the Cherenkov radiation device has important application prospect in aspects of circuits, signal transmission, processing and the like in future.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Artificial surface plasmon waveguide based on symmetrical period of loop-shaped branch structure
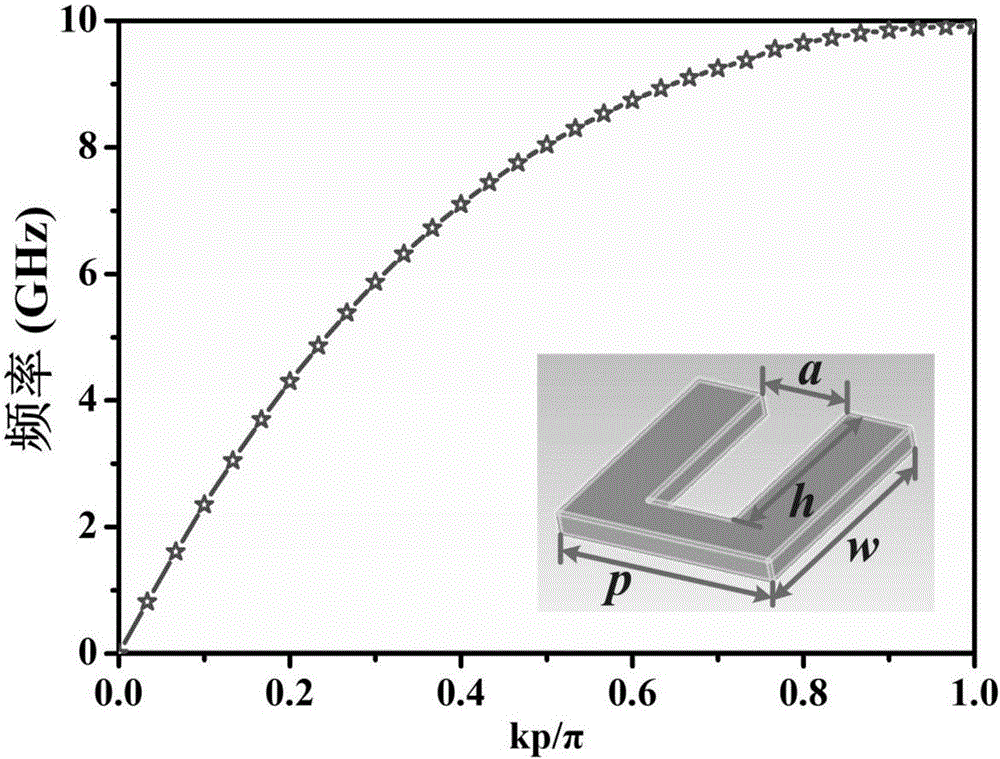
ActiveCN109802210AImproves bondageReduced waveguide sizeWaveguidesCoplanar waveguideDielectric substrate
The invention discloses an artificial surface plasmon waveguide based on a symmetrical period of a loop-shaped branch structure, and relates to an artificial surface plasmon waveguide. The waveguide comprises a dielectric substrate. A metal structure is arranged on one side of the dielectric substrate. The metal structure is provided with a coplanar waveguide feed structure, an intermediate artificial surface plasmon waveguide transmission structure and an artificial surface plasmon transition structure. The artificial surface plasmon transition structure is arranged between the coplanar waveguide feed structure and the intermediate artificial surface plasmon waveguide transmission structure. The coplanar waveguide feed structure is located at the two ends of the dielectric substrate. Theprogressive frequency is reduced, and the binding property of electromagnetic waves is enhanced. The method has important significance for reducing the size of the planar SSPP waveguide. The passbandrange can be changed by adjusting the size of the side length of a homocentric-squares-shaped branch knot. The advantages of small size, easy machining, high transmission rate and the like are achieved.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Filter synthesizing artificial surface plasmon device waveguide and substrate integrated waveguide
ActiveCN104767009AEasy to makeEasy to processWaveguide type devicesUltra-widebandDielectric substrate
The invention discloses a filter synthesizing an artificial surface plasmon device waveguide and a substrate integrated waveguide. The filter comprises the artificial surface plasmon waveguide and the substrate integrated waveguide. The substrate integrated waveguide comprises a first dielectric substrate and first metallization layers, and two rows of metallization through holes are formed in the first dielectric substrate. The artificial surface plasmon waveguide comprises a second dielectric substrate and second metallization layers, one or more metal grooves are formed in each second metallization layer, the depths of the metal grooves are sequentially increased from the two sides to the middle, the depths of the metal grooves are gradually increased till the depths are the same as the thicknesses of the corresponding second metallization layers, and the opening directions of the metal grooves in the second metallization layers on the upper surface and the lower surface are opposite. The filter has the advantages of being easy to machine, low in cost, small in thickness, low in weight and the like, a common circuit is conveniently manufactured, and high practical value is achieved; meanwhile an ultra-wideband filter and a narrowband filter are provided, and good filtering performance is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Terahertz photon on chip control system and control method thereof
ActiveCN102176463AGood lookingCompact structureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsHeterojunctionControl system
The invention relates to a terahertz photon on chip control system and a control method thereof. The system comprises a semiconductor heterojunction, a plasmon waveguide, a first source electrode, a first drain electrode, a first gate electrode, a second source electrode, a second drain electrode and a second gate electrode, wherein two-dimensional electron gases are formed on the surface of the semiconductor heterojunction; the first source electrode, the first drain electrode and the first gate electrode are formed on the surface of the semiconductor heterojunction and used for forming terahertz source quantum dots; and the second source electrode, the second drain electrode and the second gate electrode are formed on the surface of the semiconductor heterojunction and used for forming the terahertz source quantum dots. The terahertz photon on chip control system uses surface plasmon to integrate terahertz sources, detection, spread and modulation elements into a chip, thus realizing the terahertz photon on chip control.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Waveguide structure based on low frequency surface plasmon polaritons
InactiveUS9140855B2Improve behaviorIncrease valueWireless commuication servicesOptical light guidesTransfer modeElectromagnetic field
A structure of a low frequency surface plasmon polariton waveguide includes multiple unit cell blocks arranged at a sub-wavelength period to line up in a one-dimensional line-up direction to form a hollow metallic block periodic structure. Each unit cell blocs includes a body, a penetration section, and an open slot. The penetration section is formed in the unit cell block by extending in a direction perpendicular to the one-dimensional line-up direction so as to define a channel space in the unit cell block. In a low frequency spoof surface plasmon polariton transmission mode, in case of serving as a structure of an antenna, each unit cell block has an electromagnetic field distribution mostly confined in a channel space of the unit cell block; and in case of serving as a waveguide, the electromagnetic field is mostly distributed between two adjacent unit cell blocks with minority distributed in the channel space.
Owner:CHUNG HUA UNIVERSITY
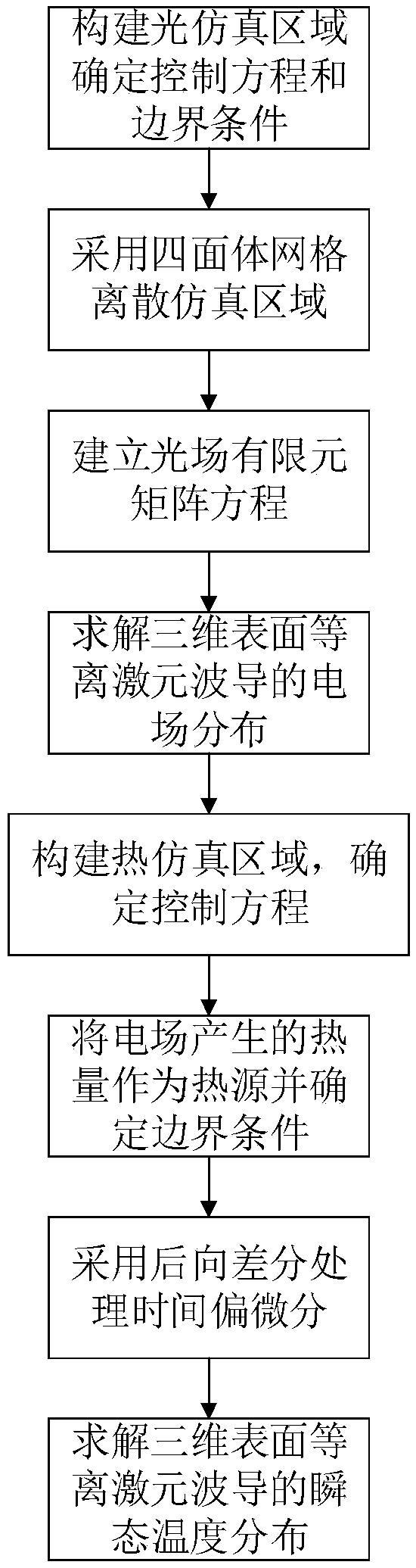
Photo-thermal effect simulation method for a surface plasmon waveguide
ActiveCN109492341AImprove simulation accuracyImprove Simulation EfficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsWave equationField analysis
The invention discloses a photo-thermal effect simulation method for a surface plasmon waveguide. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, determining an edge value problem of a light fieldpart based on an electric field vector wave equation and an electromagnetic boundary condition, discretizing a light field analysis area by adopting tetrahedral vector edge elements, establishing a light field finite element matrix equation according to a Galerkin method, and solving to obtain electric field distribution of a three-dimensional surface plasmon waveguide; then, heat generated by anelectric field is used as a heat source; determining an edge value problem of a thermal field part based on a transient heat conduction equation and a thermal boundary condition; a tetrahedral scalarnode element is adopted to discretize a thermal field analysis area, an unconditionally stable backward difference format is adopted to discretize a time domain, a thermal field finite element matrixequation of each time step is established according to a Galerkin method, and transient temperature distribution of the three-dimensional surface plasmon waveguide is obtained through solving. The method has the advantages of being high in simulation precision, wide in application range and high in solving efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
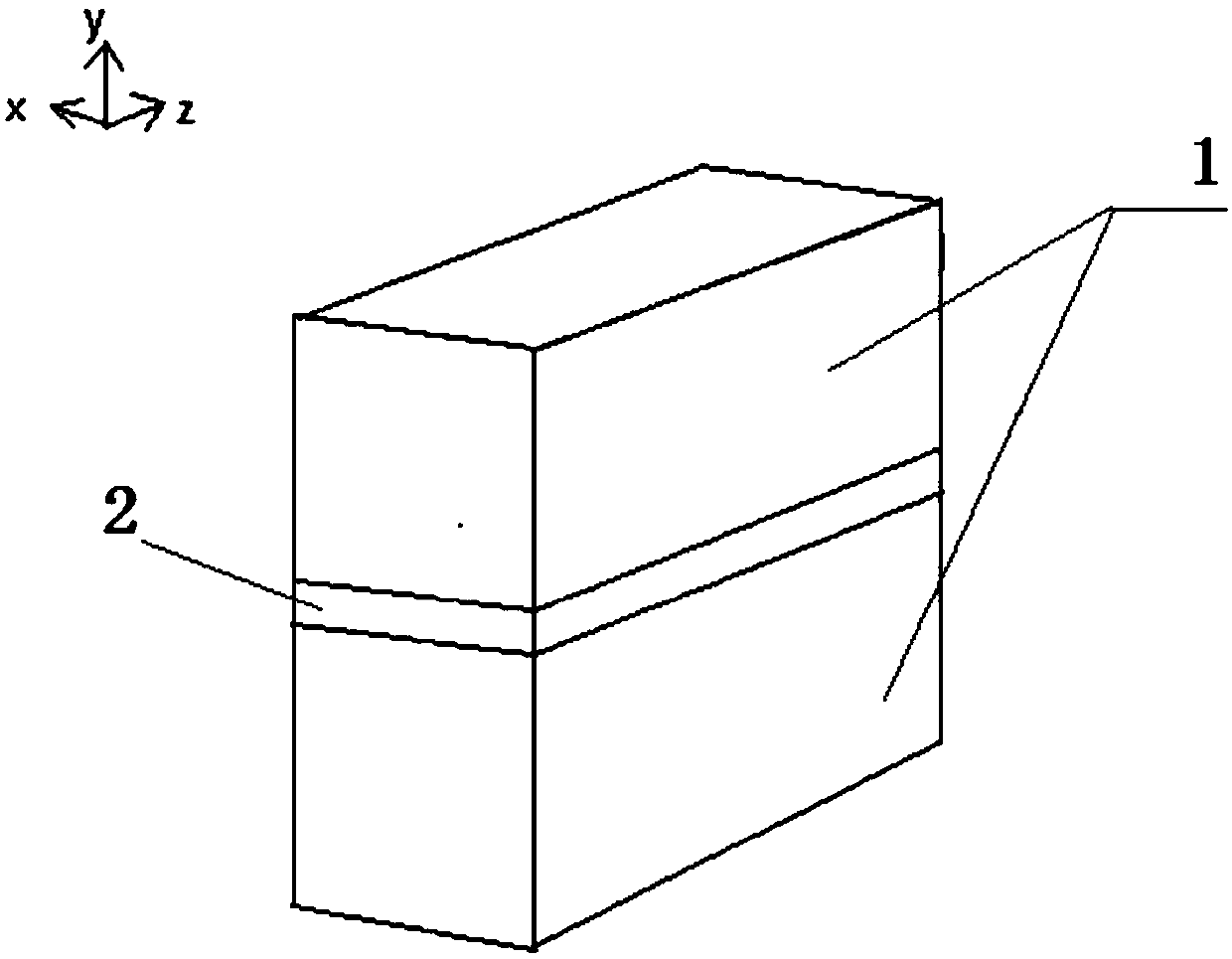
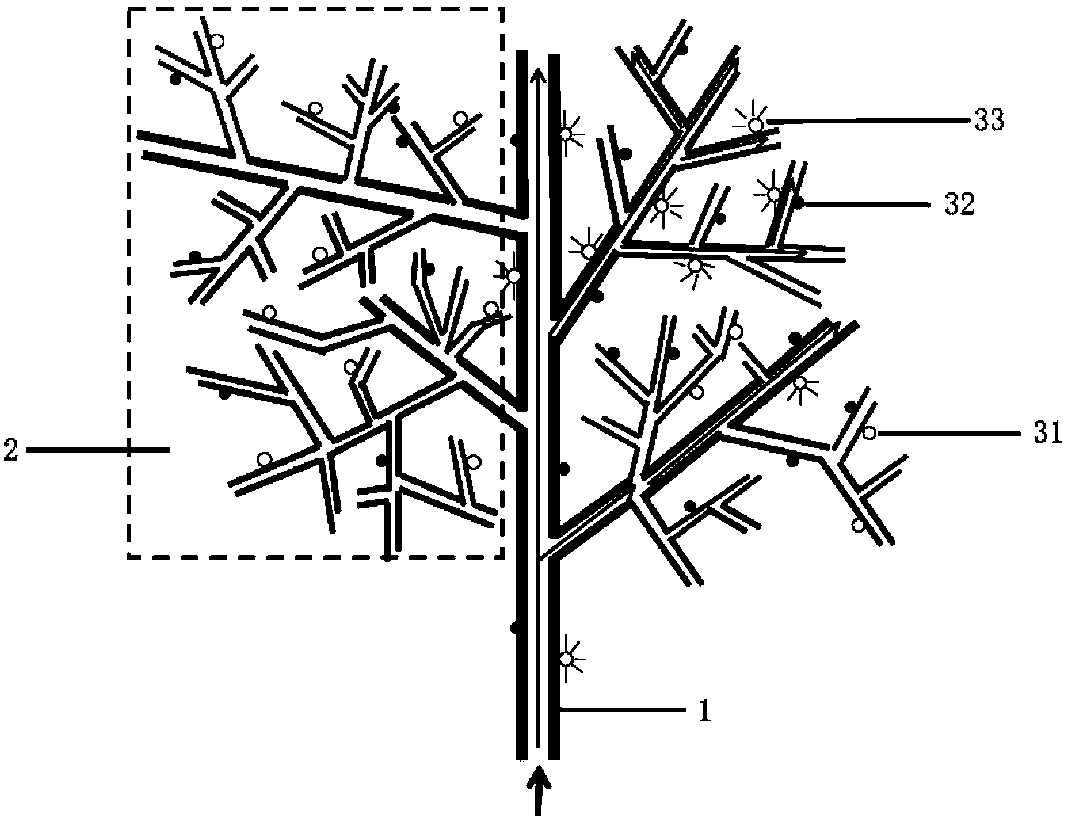
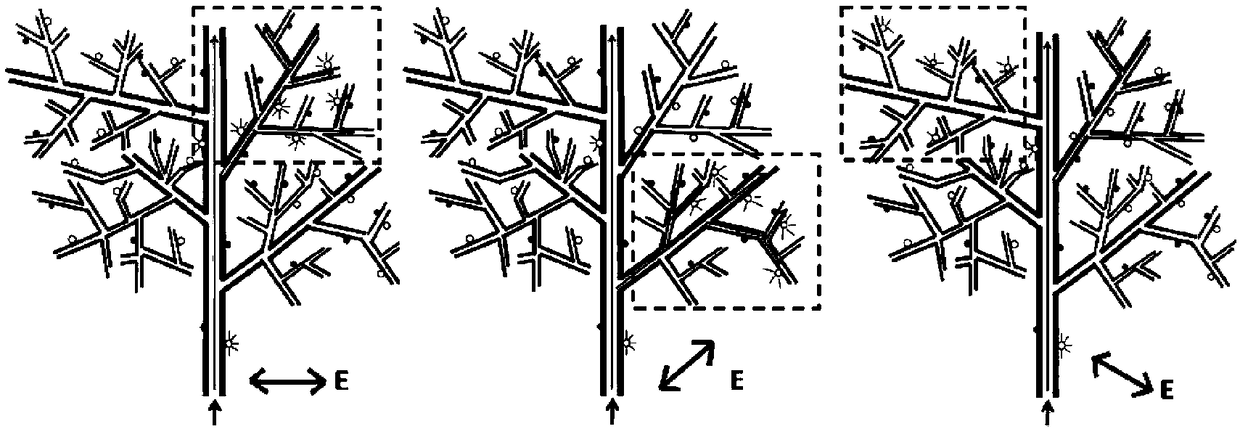
Branchy tree-shaped plasmon waveguide composite nano-structure synthesis method and optical manipulation method thereof
ActiveCN108303765AOriginalImprove localityMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingDiffraction effectNanowire
The invention provides a branchy tree-shaped plasmon waveguide composite nano-structure synthesis method and an optical manipulation method thereof. The branchy tree-shaped plasmon waveguide compositenano-structure synthesis method includes a plurality of steps, and each step can be accurately controlled. Thickness of a trunk of a tree-shaped nano-structure and thickness of a branch-shaped nano-structure growing on the trunk can be accurately controlled. quantum dots with / without housings are overlaid on the surface of the tree-shaped nano-structure to form a quantum dot composite tree-shapednano-structure, and the quantum dots without housings can be applied to chemocatalysis, environment monitoring, biosensing and other fields. When incidence of light occurs from one end of a nano wire, through the nano wire and the branch-shaped structure, the quantum dots with housings are excited to emit light, so that the branchy tree-shaped plasmon waveguide composite nano-structure synthesismethod and the optical manipulation method thereof can be applied to remote sensing Raman, novel lasers and other fields. Besides, through optical manipulation, the intensity and the polarization of the incident light can be changed, and then the quantum dots in a specific region can be controlled to emit light, so that the crosstalk effect, between scattering centers, interfering generation of diffraction effect, can be eliminated. Therefore, the branchy tree-shaped plasmon waveguide composite nano-structure synthesis method and the optical manipulation method thereof can be used for high resolution detection of sub-wavelength.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
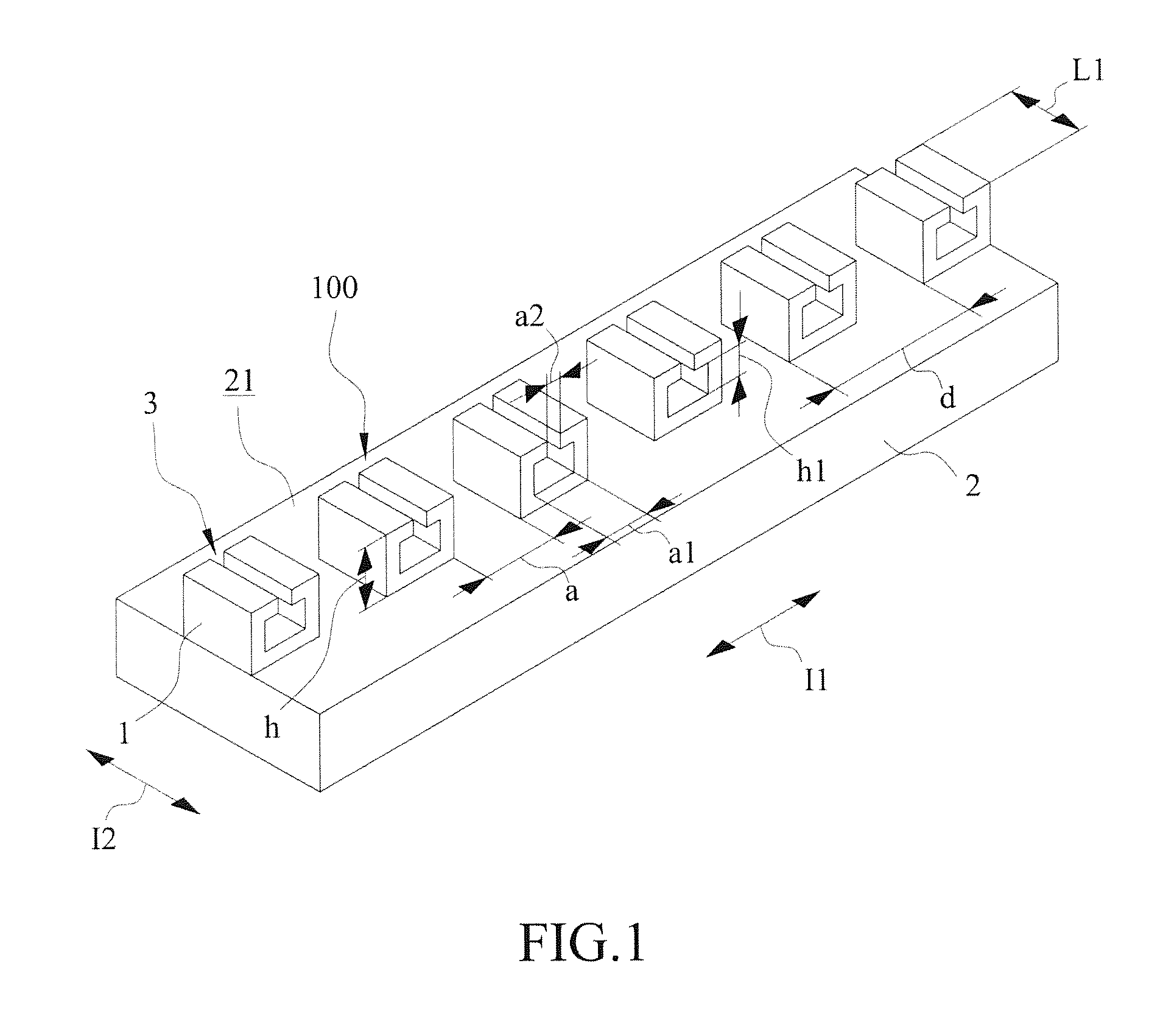
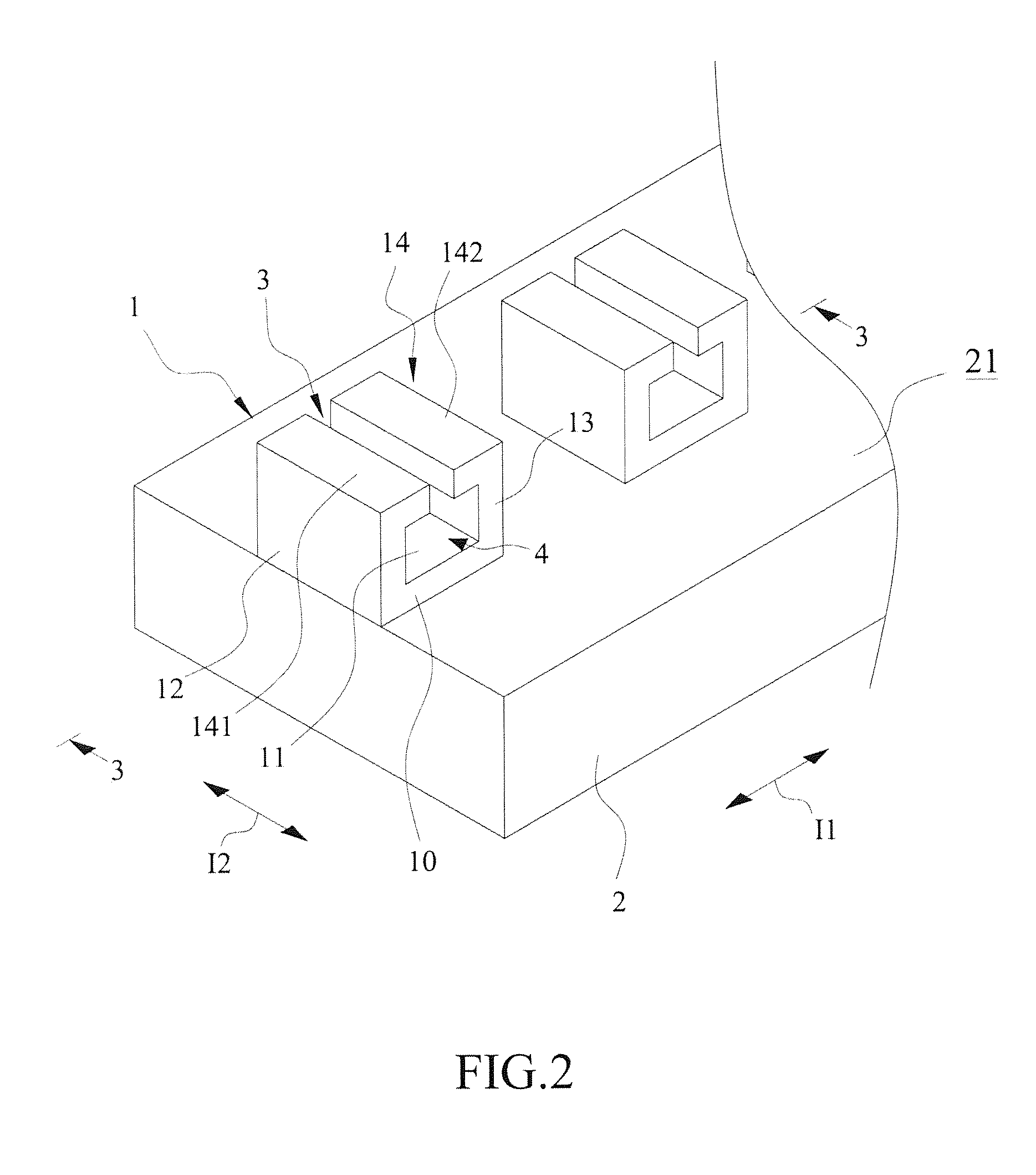
An Ultra-Wideband Artificial Surface Plasmon Low-Pass Filter
InactiveCN105119030BAchieve Impedance MatchingImprove localityWaveguide type devicesUltra-widebandMetallic foil
The invention discloses an ultra-wideband artificial surface Plasmon low-pass filter which is mainly formed by a dielectric substrate layer and metallic foil layers printed on the both side surfaces of the dielectric substrate layer. Waveguide structures are engraved on the metallic foil layers. Each waveguide structure is formed by a middle surface Plasmon waveguide portion, symmetric microstrip line portions at both ends, and two transition portions. The ultra-wideband artificial surface Plasmon low-pass filter may achieve effective transmission of artificial surface Plasmon waveguide, and has symmetric structure, easy processing, compact size, a ultra-wide band and high filtering performance, and is especially suitable for being used in cooperation with a conventional microwave or terahertz transmission line.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com