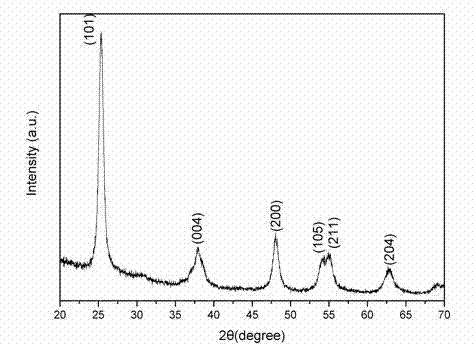
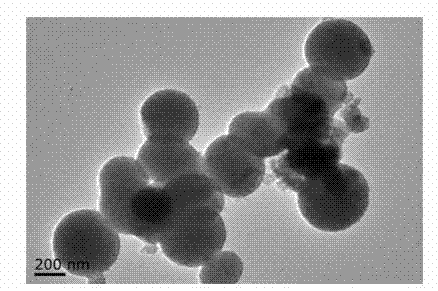
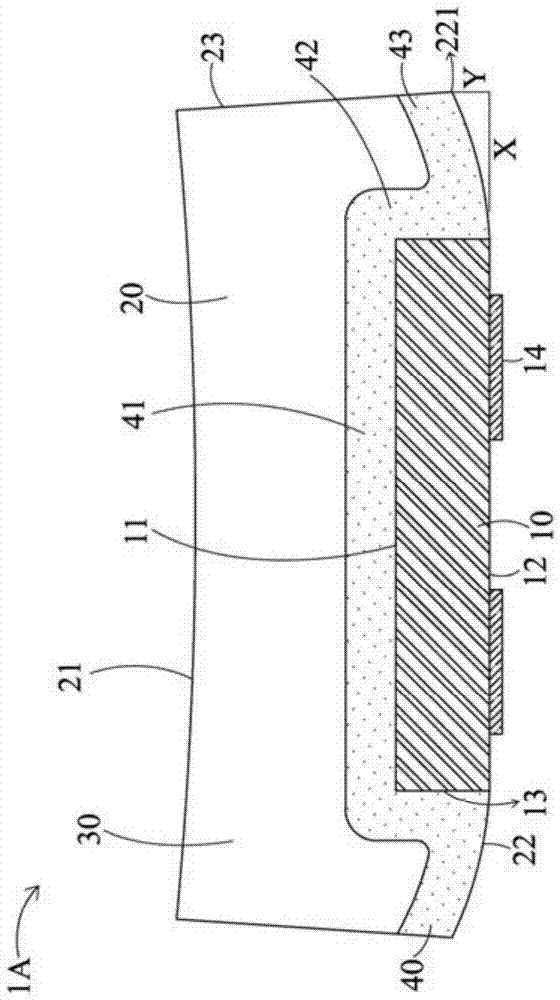
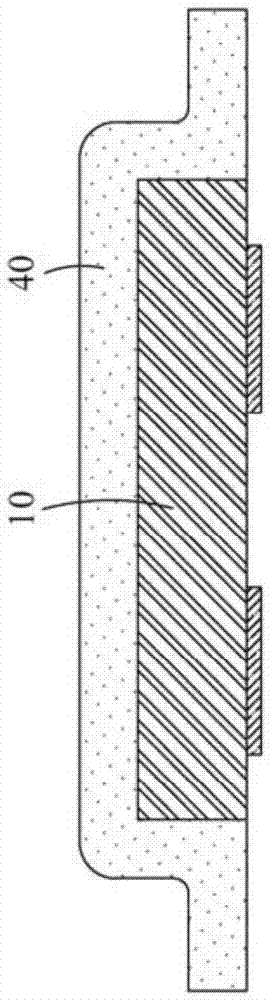
Patents
Literature
46results about How to "Improve quantum conversion efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
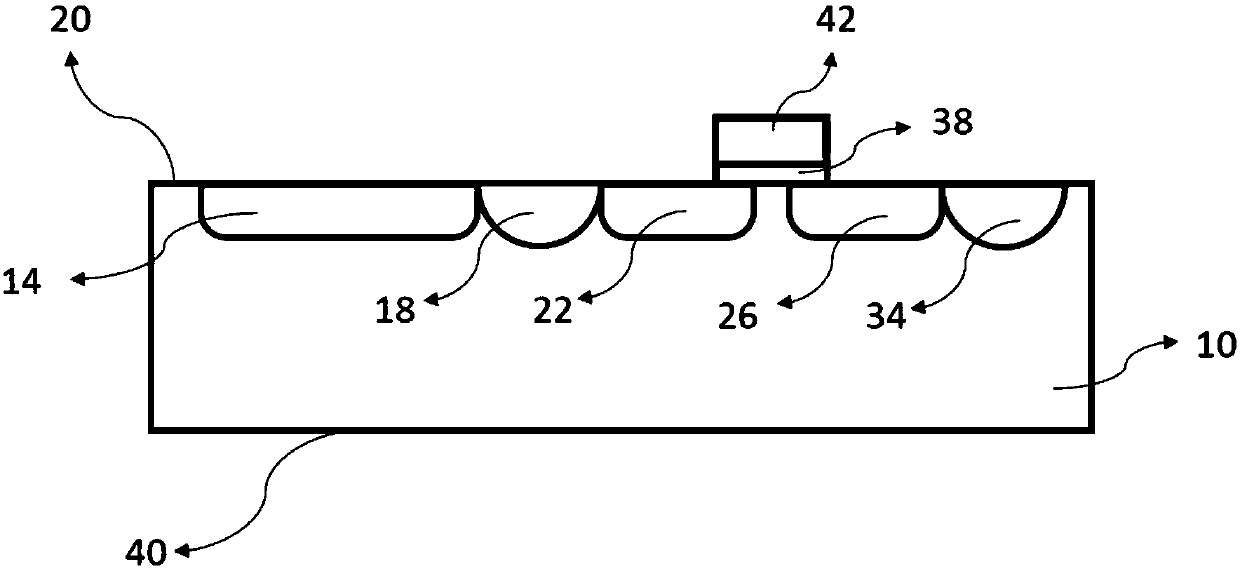
BiVO4 nano photoelectrode and application thereof in hydrogen production from water splitting
InactiveCN101775615AImprove quantum conversion efficiencyBroaden the photoresponse rangeElectrodesPhotocurrentWavelength range
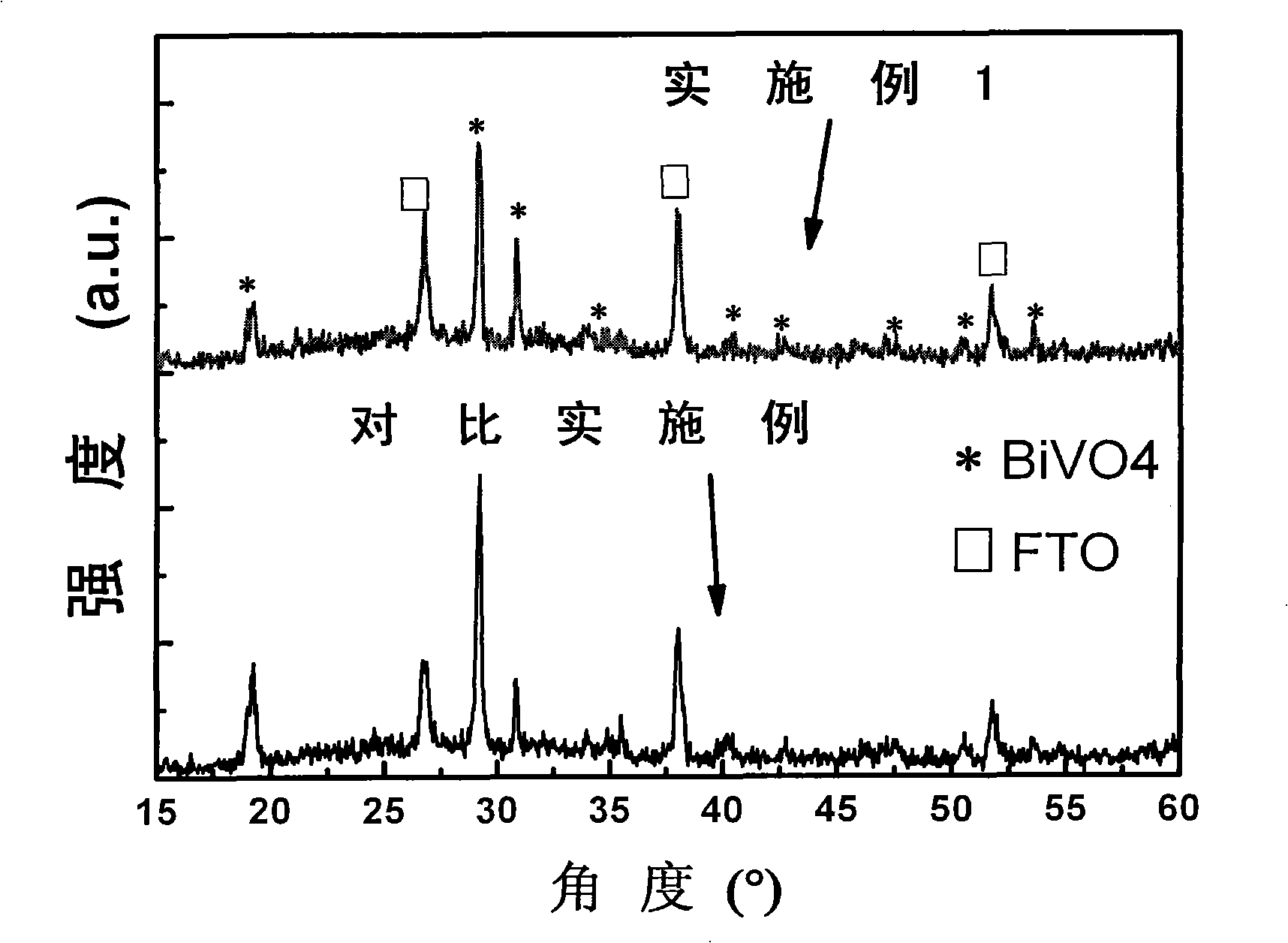
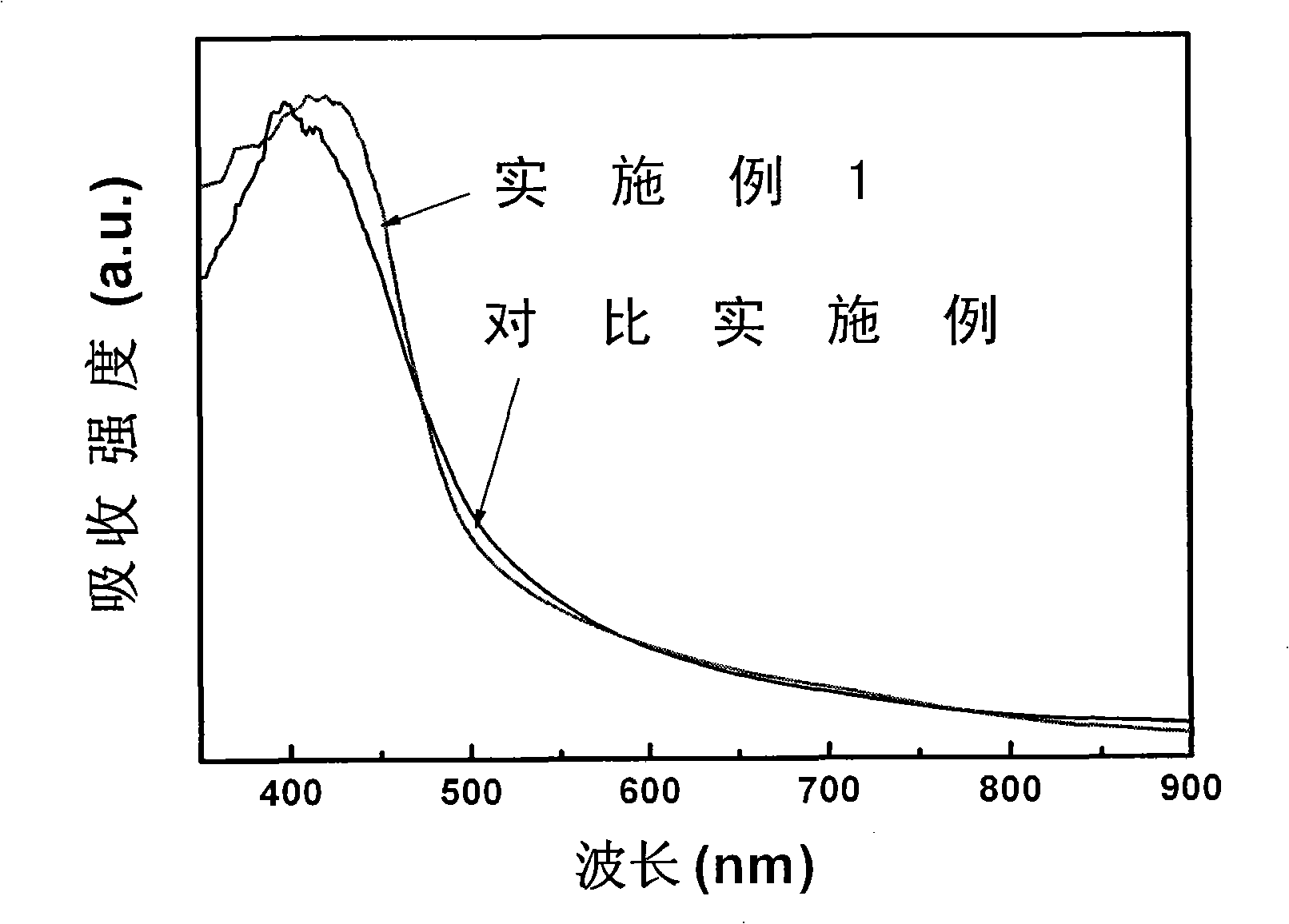
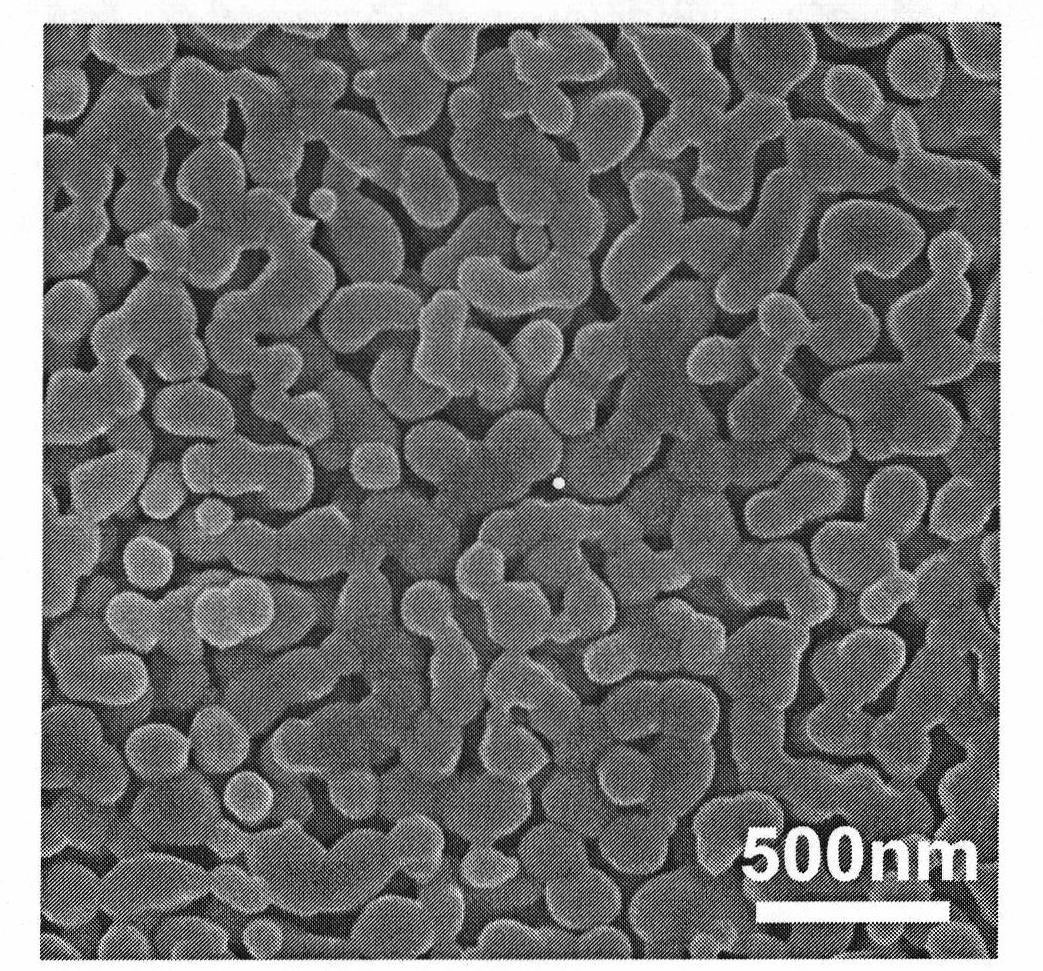
The invention relates to a BiVO4 nano photoelectrode and application thereof in the aspect of hydrogen production from water splitting, which can increase photocurrent and greatly improve the efficiency of quantum conversion. The BiVO4 nano photoelectrode comprises a BiVO4 nano-pore thin film, and BiVO4 is doped with metal cation, wherein the metal cation is one or a mixture with an arbitrary proportion of more than two of Sr<2+>, Ba<2+>, Cr<6+> and W<6+> by arbitrary proportion. As an improvement of the invention, the surface of the BiVO4 nano-pore thin film is also modified with a catalyst, wherein the catalyst is one or a mixture with an arbitrary proportion of more than two of the oxides of the hydroxides of Rh, W, Mo, Co, Fe, Mn and Ni. Compared with a pure BiVO4 electrode, the quantum conversion efficiency of the invention is greatly increased and reaches 70 percent within a wavelength range of 360-450nm, and a photoresponse range is broadened to 510nm.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
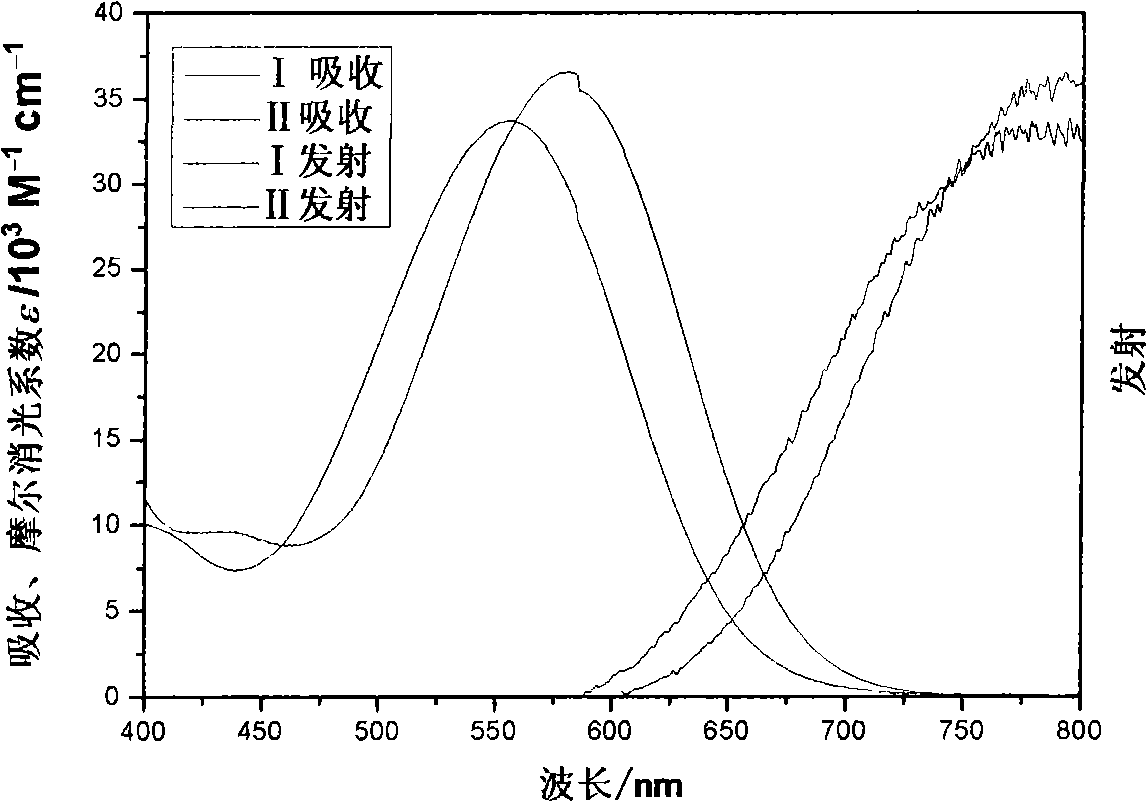
Organic dye with five-element heterocycle and derivative thereof as conjugate unit, and dye sensitization solar cell prepared thereby
ActiveCN101407639APromote absorptionSimple structure and easy accessLight-sensitive devicesMethine/polymethine dyesOrganic dyeCyanoacetic acid
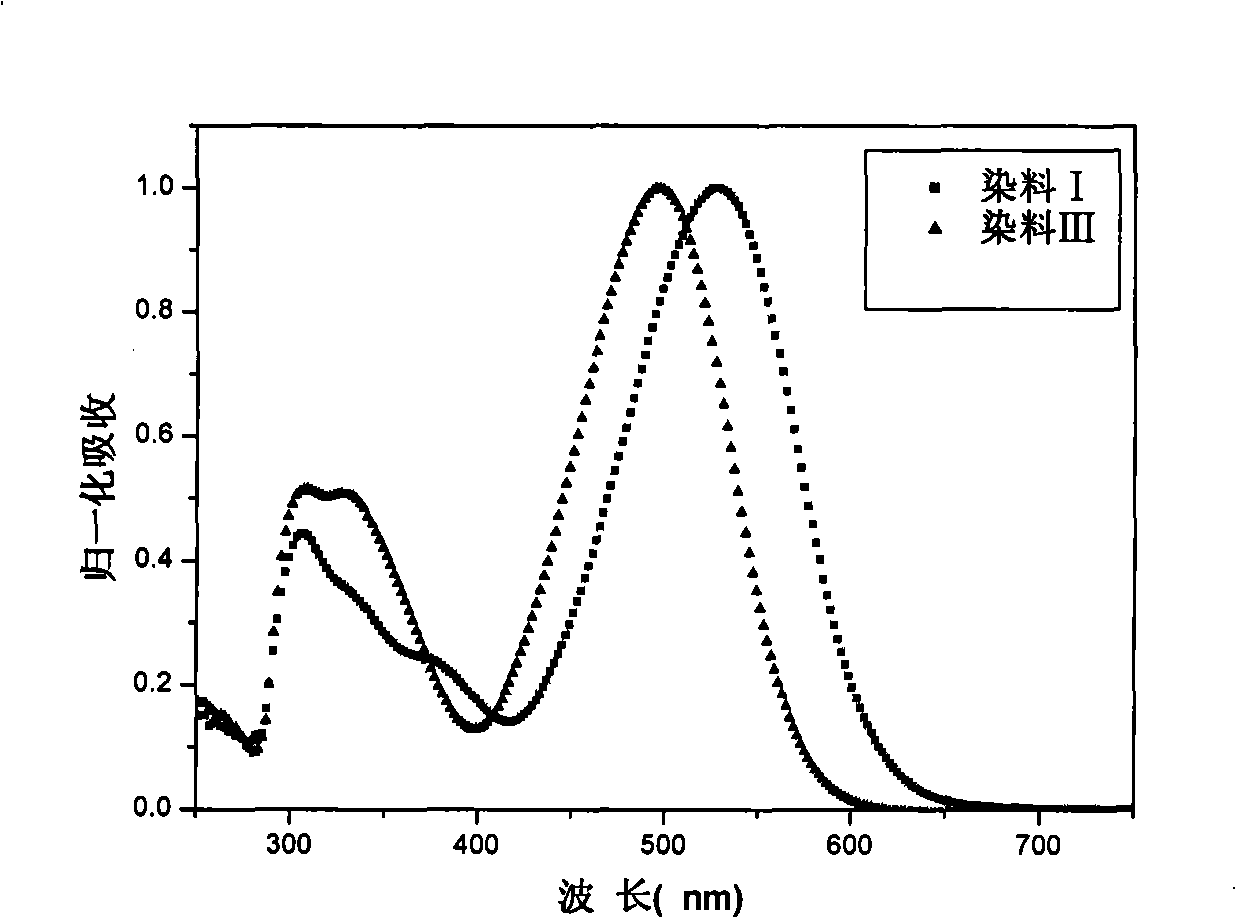
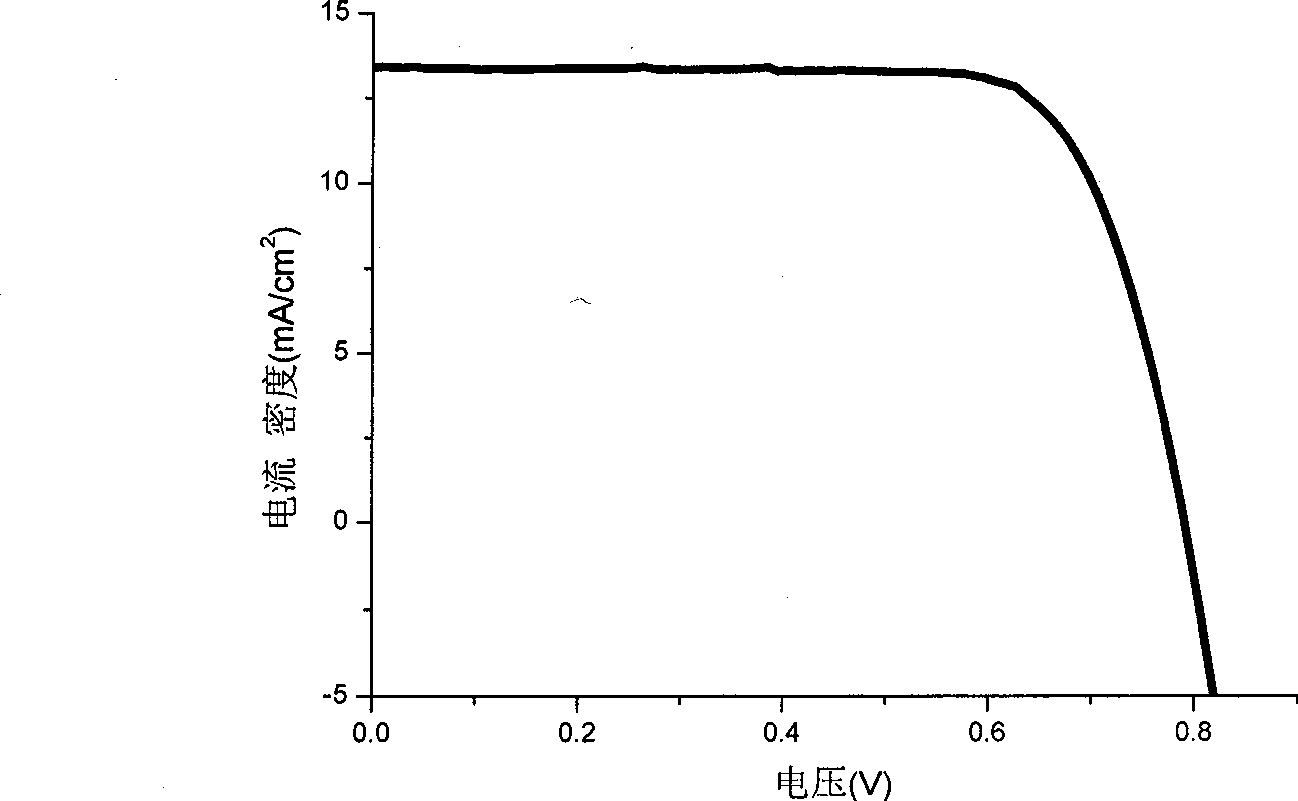
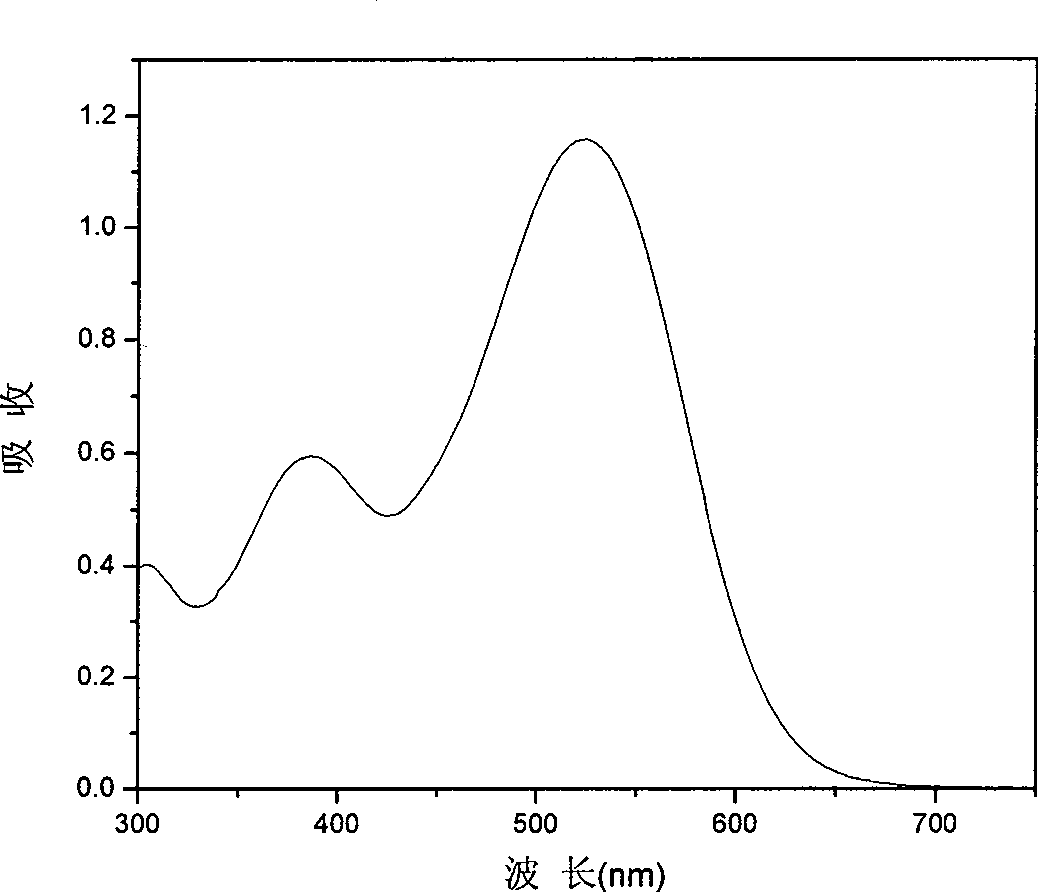
The invention provides an organic dye which uses five-membered heterocyclic ring, derivatives thereof and a dye-sensitized solar cell prepared by the organic dye. The dye uses the five-membered heterocyclic ring or the derivatives thereof as a Pi unit, uses substituted triarylamine as an electron donor, uses cyanoacetic acid structure as an electron acceptor, and belongs to molecule of D-Pi-A structure. The dye molecule belongs to pure organic compounds, the structure of the materials is simple and is easy to be obtained; expensive materials of metal of Ru and purifying agent of polydextrose do not need to use, the compound yield is higher, so the total yield is between 40 percent and 70 percent; besides, the performance of spectral absorption and molar extinction coefficient and the like of the dye are excellent; and the peak value of the spectral absorption is over 550nm at the most, the molar extinction coefficient is over 48000M<-1>cm<-1>, the peak value and the coefficient are more than the Ru dye, therefore, the dye has wider absorption range to the sunlight. The dye-sensitized solar cell prepared by the organic dye has the maximum of quantum conversion efficiency of 97 percent and the highest photoelectric conversion efficiency of more than 8.0 percent.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
Method and device for producing optical material, and an optical waveguide
InactiveUS20060001952A1Improve abilitiesImprove homogeneityLaser detailsMolten spray coatingReaction rateErbium doping
The invention relates to the production of light-amplifying optical material. Liquid reactant is atomized into droplets using a high velocity gas. The droplets are subsequently introduced into a flame. Reactants are oxidized in the flame and condensed by forming small particles. At least a fraction of said particles is collected and fused to form optical waveguide material, which is subsequently drawn to form an optical waveguide. According to the invention, the velocity of the atomizing gas stream is in the order of the velocity of sound. The high velocity enhances atomization and increases reaction rates in the flame. The residence times are reduced to such a degree that unwanted phase transformations in the produced particles are substantially minimized. Consequently, very homogeneous material is produced. Especially, in the production of erbium-doped silica, low percentage of clustered erbium ions is achieved.
Owner:LIEKKI OY
All solid state mid-infrared optical parametric oscillator
InactiveCN105449510AReduce thermal effectsImprove quantum conversion efficiencyLaser detailsPlane mirrorPigtail
An all solid state mid-infrared optical parametric oscillator comprises a 1.5 mum narrow linewidth laser diode (hereinafter referred to as LD) with pigtail output, a focusing coupling system, a first plane mirror, Er:YAG laser crystal, a saturable absorber Cr:ZnSe, a polarizer, a quartz plate etalon, a second plane mirror, MgO:PPLN nonlinear periodically poled crystal and a third plane mirror which are successively arranged along the laser output direction of the laser diode; a calcium fluoride etalon and a flat-concave cavity mirror are successively arranged along the reflected light direction of the second plane mirror. The pumping source of the invention is passively Q adjusted 1.6 mum pulse laser, the structure of the whole system is simpler and more compact, the power density of 1.6 mum laser in the cavity can be used, the converting efficiency and the output power of the whole QPM-OPO system is improved, the working wavelength of the whole system is controlled at the wave band safe to human eyes, the tunable output of the all solid state mid-infrared optical parametric oscillator is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Organic dye-stuff with multi-heterocycle derivant as conjugation unit and dye sensitized solar battery produced with the same
ActiveCN101429346AWide absorption rangeHigh synthetic yieldMethine/polymethine dyesLight-sensitive devicesOrganic dyeOrganic compound
The invention belongs to the technical field of solar cell and relates to an organic dye using a multi-heterocyclic derivant as a conjugate unit and a dye-sensitized solar cell made from the dye. The dye uses a plurality of heterocyclic derivants as a pi unit and belongs to a molecule with a D-pi-A structure. The dye has wide absorption spectrum and high photoelectric conversion efficiency and has application prospect in the solar cell through substituting for a noble metal dye. The dye molecule belongs to a pure organic compound; compared with the prior ruthenium dye, the organic dye does not need to use expensive metal ruthenium as a raw material and glucan as a purifying agent; additionally, the synthesis yield is high (the total yield is more than 40 percent); therefore, the organic dye has the advantages of low cost and simple production; in addition, the absorption spectrum of the dye exceeds 550 nm and the molar extinction coefficient exceeds 45000 M-1cm-1, which are far larger than the absorption spectrum and the molar extinction coefficient of the ruthenium dye; therefore, the organic has wider absorption range to solar ray. The dye-sensitized solar cell prepared from the dye has high quanta conversion efficiency (IPCE); the maximum of the quanta conversion efficiency exceeds 95 percent (nm); and the photoelectric conversion efficiency is more than 8.0 percent and exceeds that of other most pure organic dye-sensitized solar cells.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
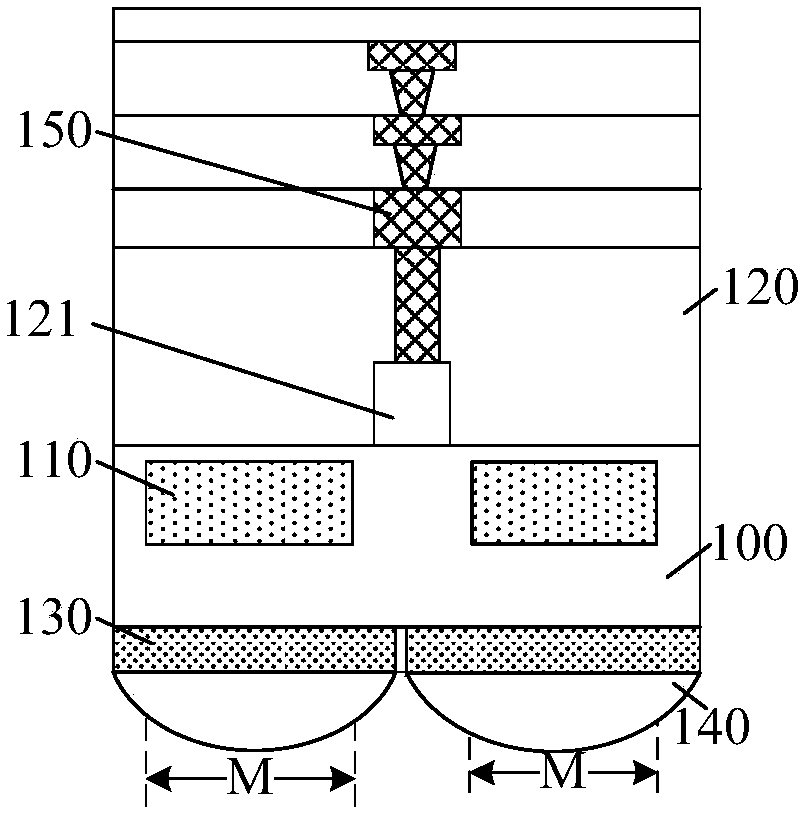
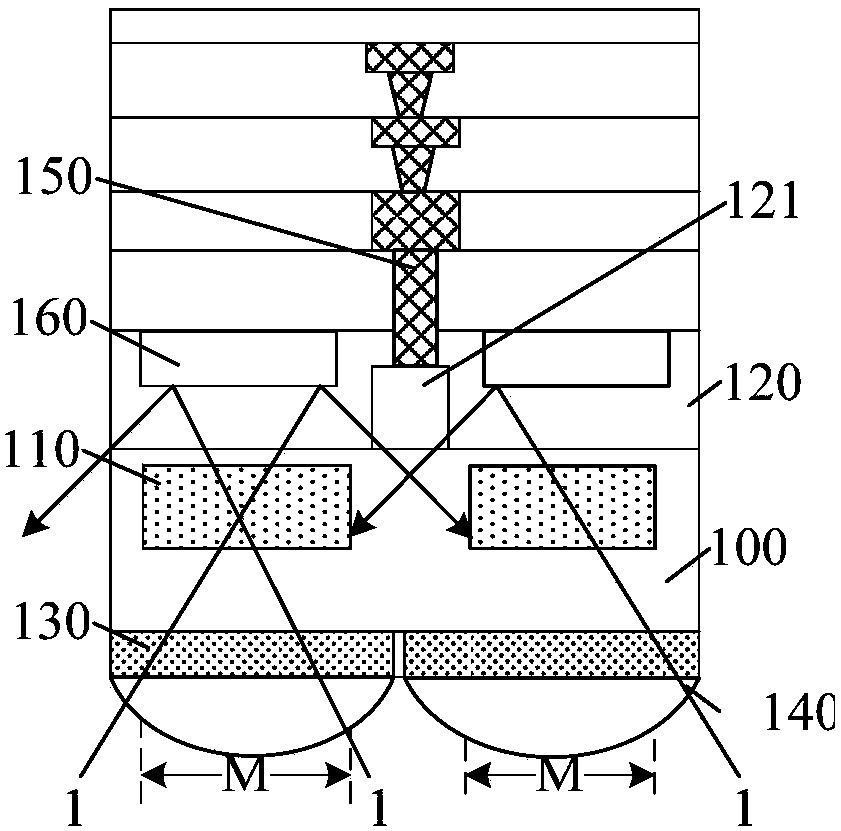
Mono-crystalline silicon double-sided solar cell and preparation method thereof
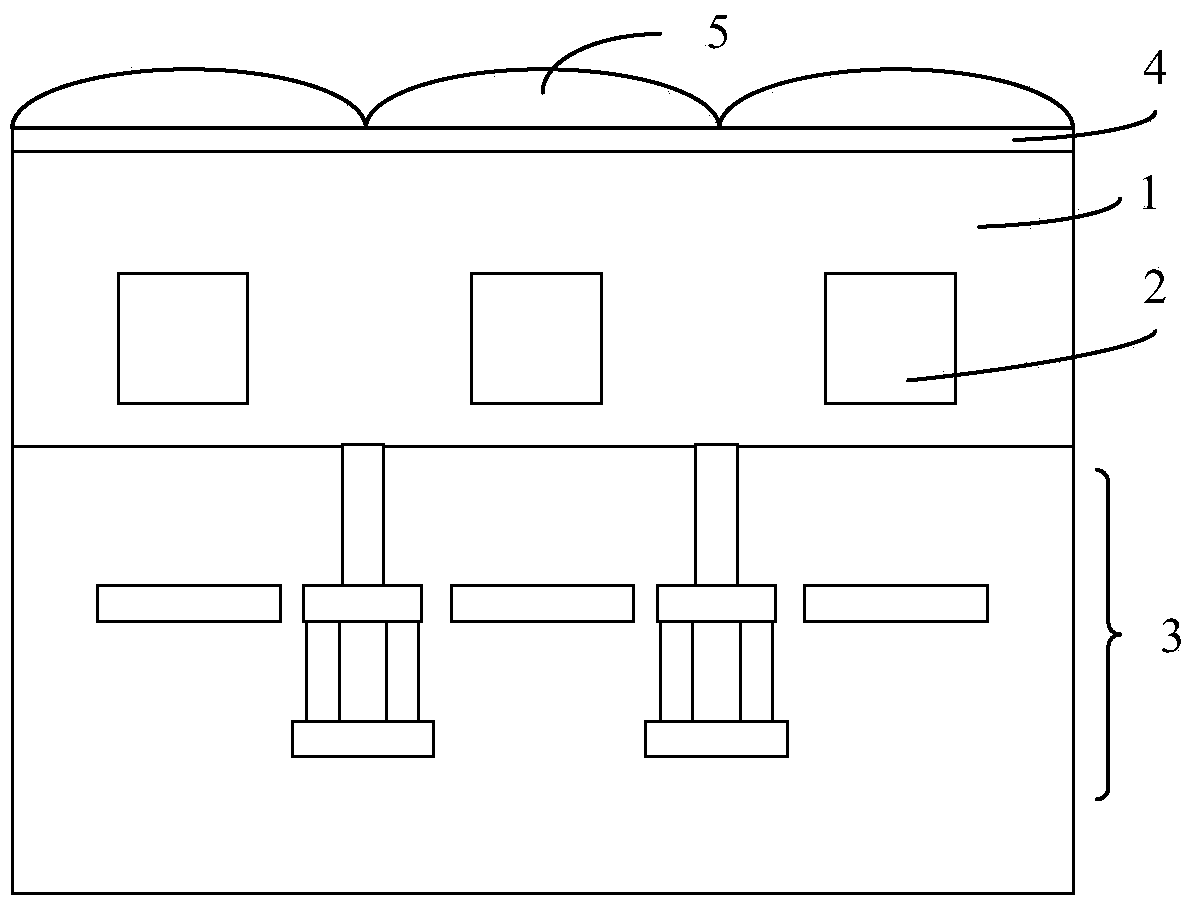
ActiveCN105826411ASmall surface areaIncrease reflectionFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationBack surface fieldCrystalline silicon
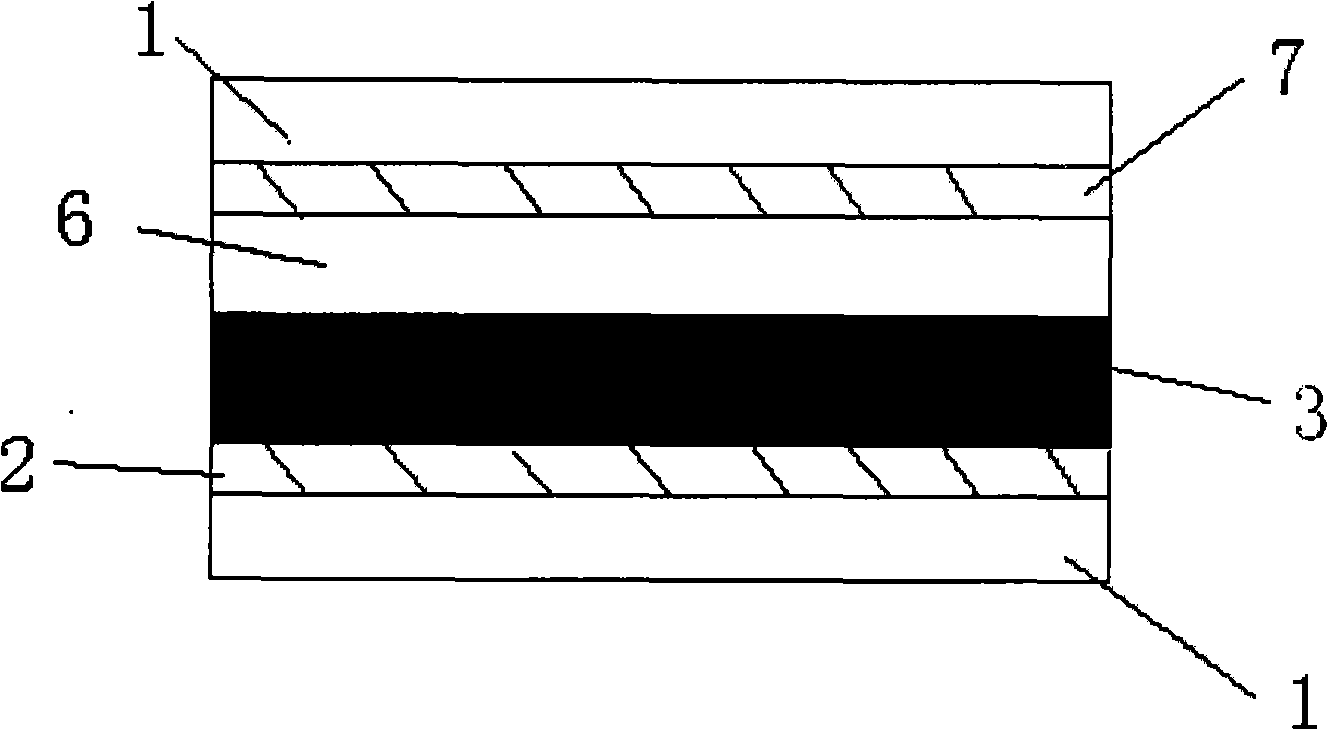
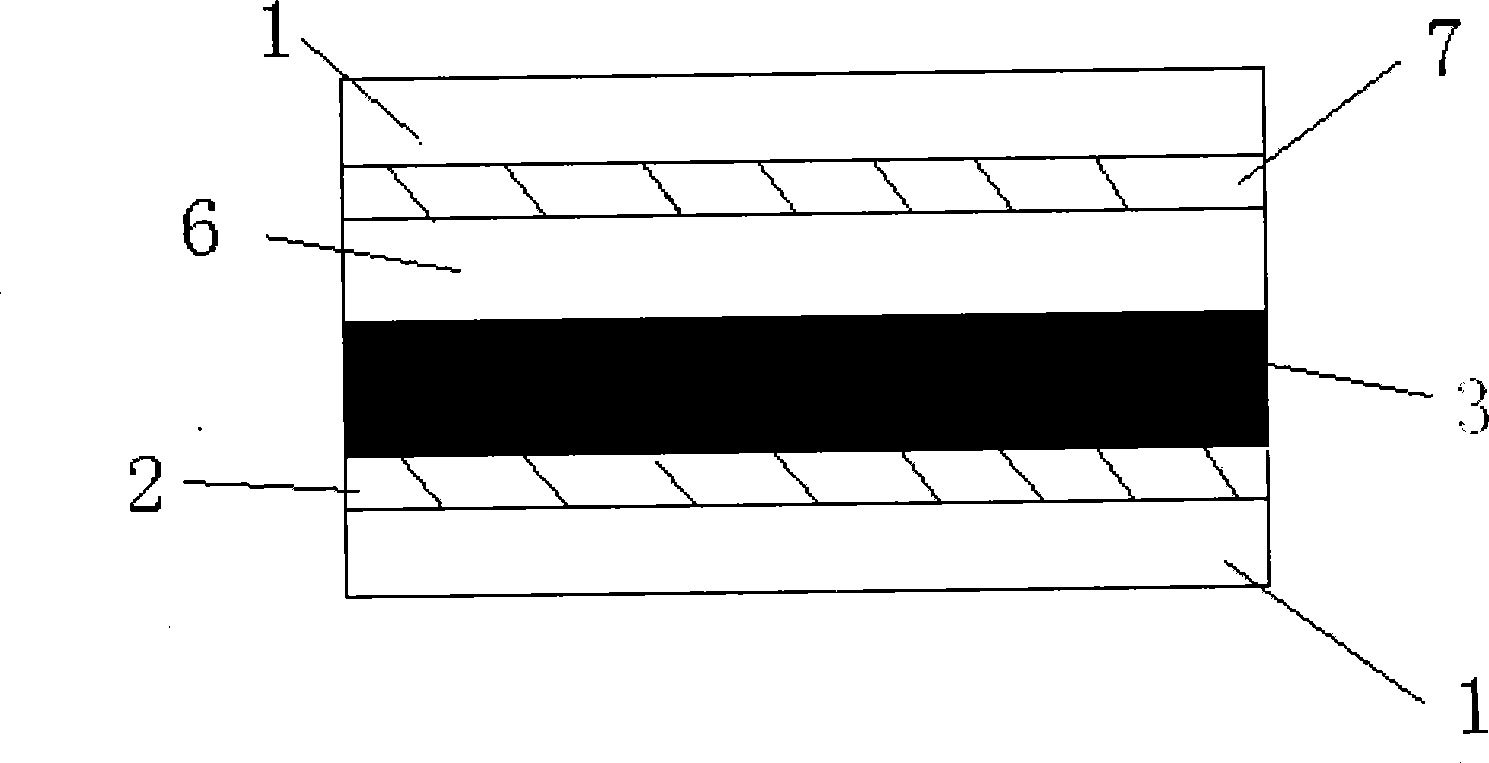
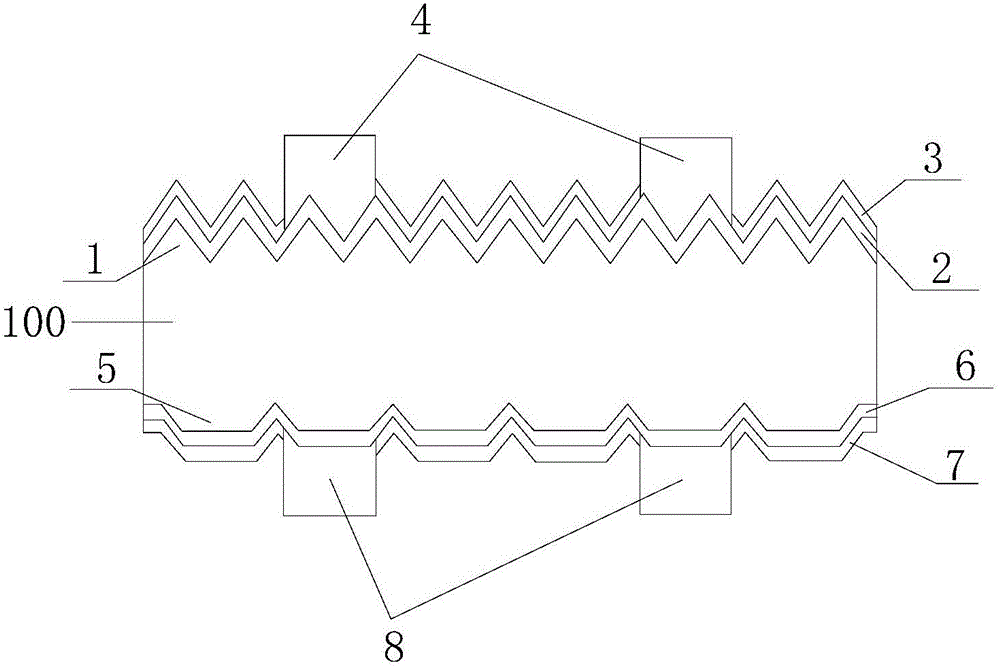
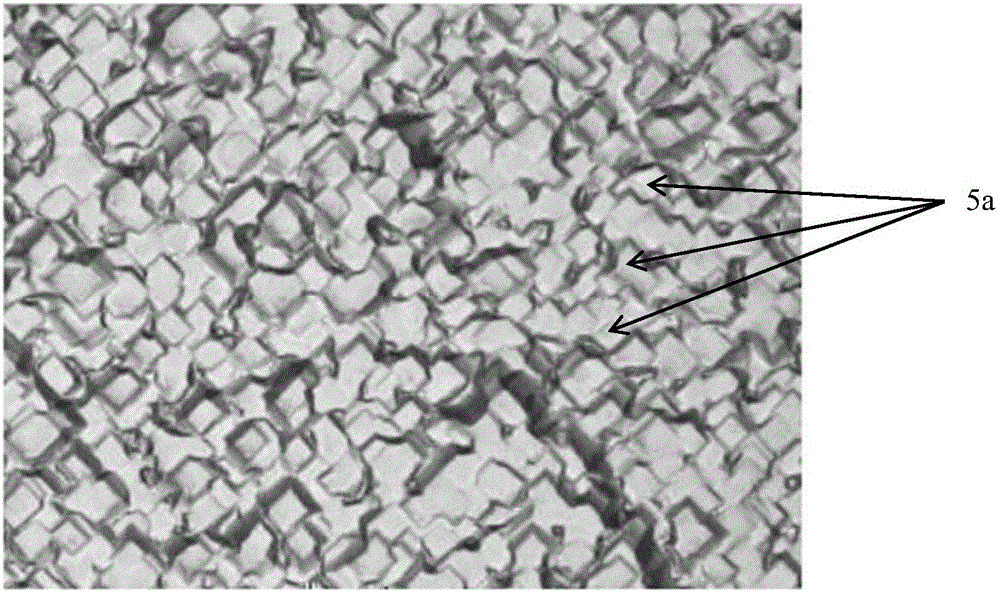
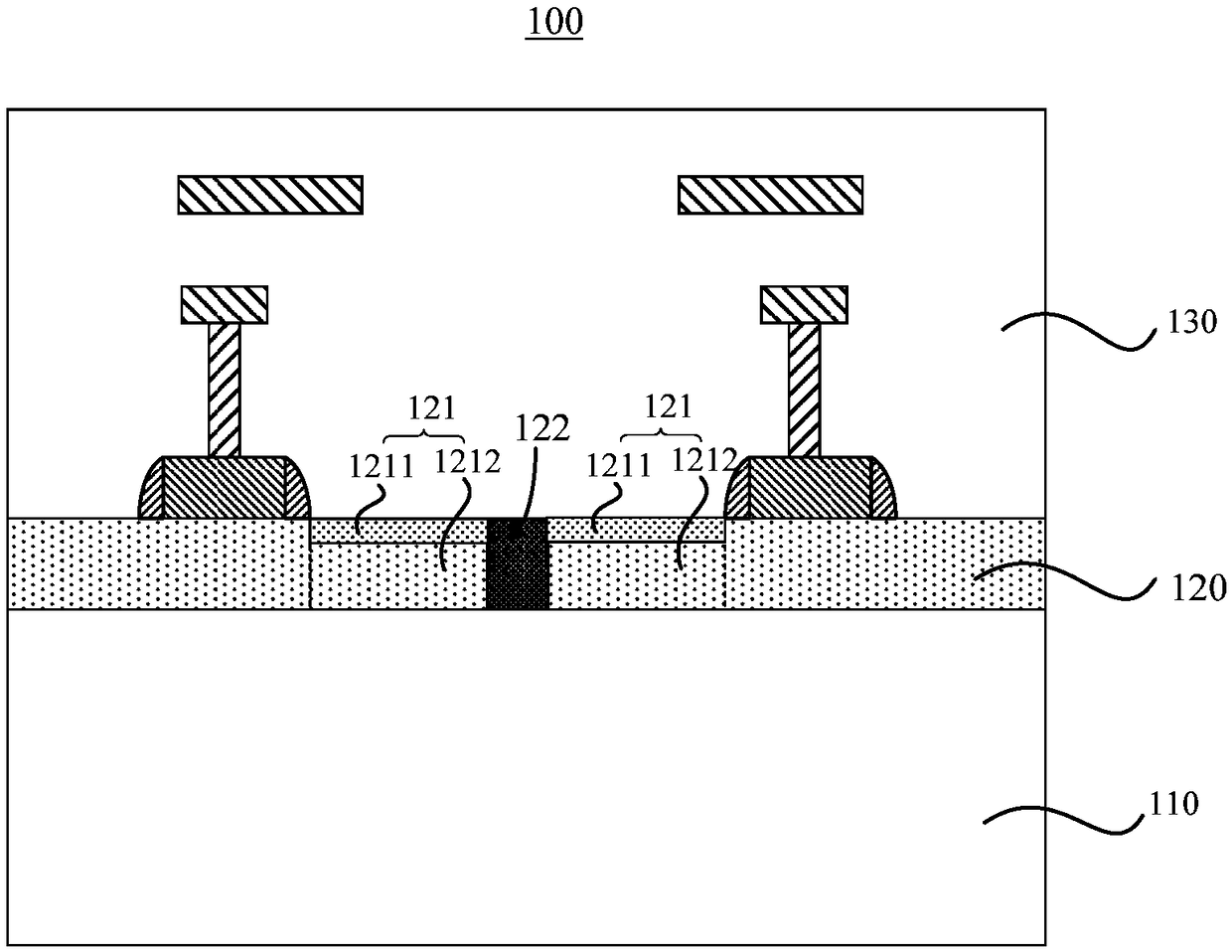
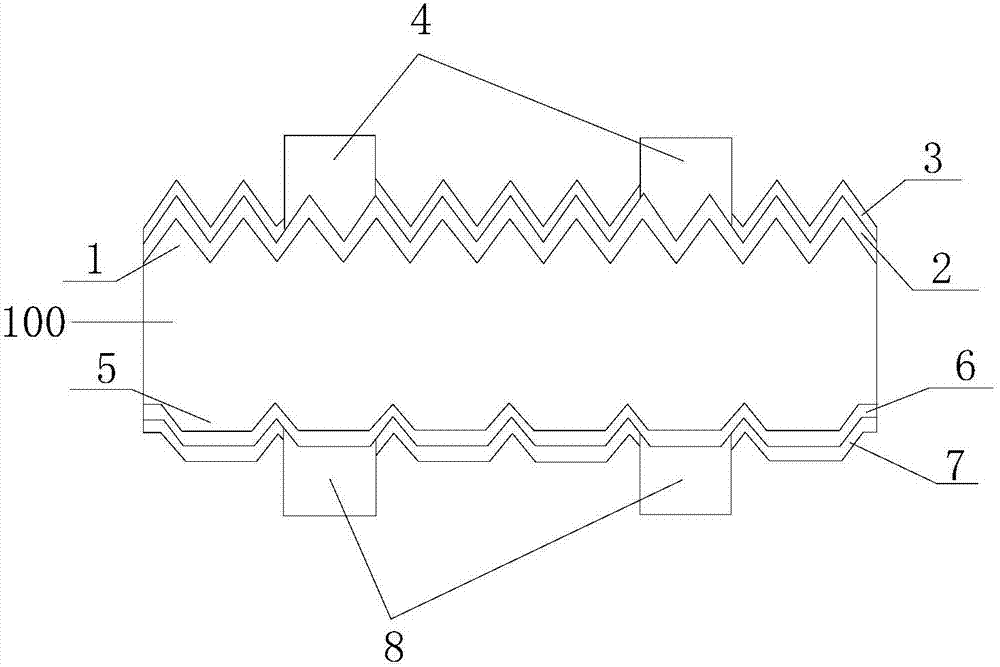
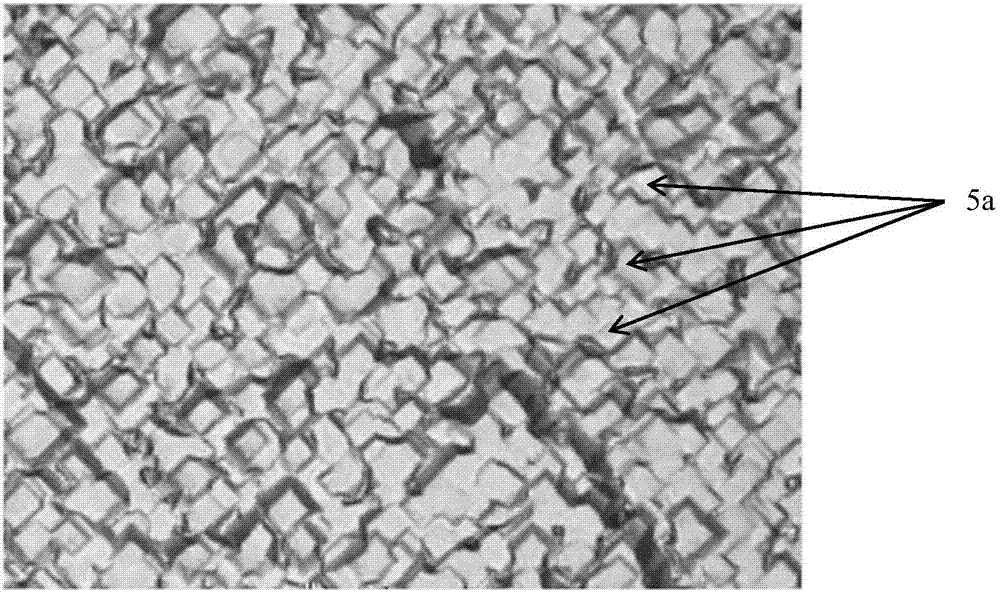
The invention discloses a mono-crystalline silicon double-sided solar cell. A front texturing morphology structure (1), a front PN emitter junction (2), a front passivated anti-reflection medium layer (3) and a front electrode (4) are sequentially formed on the front of a mono-crystalline silicon substrate (100). A back texturing morphology structure (5), a back surface field (6), a back passivated anti-reflection medium layer (7) and a back electrode (8) are sequentially formed on the back of the mono-crystalline silicon substrate. The solar cell is characterized in that the back texturing morphology structure (5) is a platform type texture surface, and platform structures (5a) are distributed on the mono-crystalline silicon substrate in a scattered, or tiled, or partially scattered, partially tiled, partially connected and partially overlapped way. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the mono-crystalline silicon double-sided solar cell. The minority carrier surface recombination and optical absorption characteristics of the double-sided solar cell are optimized, and the efficiency of quantum conversion is improved.
Owner:TRINA SOLAR CO LTD
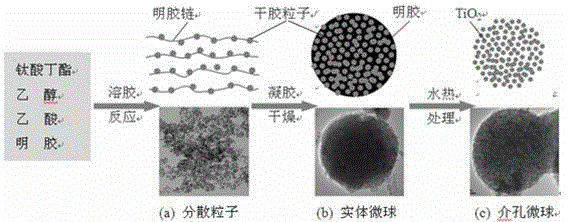
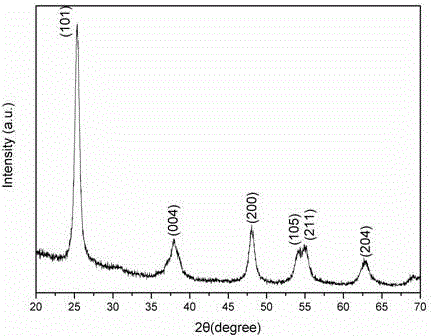
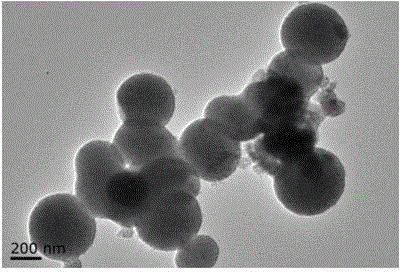
Preparation method for anatase titanium dioxide nanocrystalline mesoporous microsphere
InactiveCN103663548ASimple processReduce energy consumptionMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsAcetic acidAlcohol
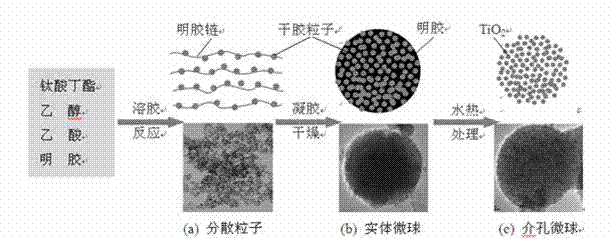
The invention discloses a preparation method for an anatase titanium dioxide nanocrystalline mesoporous microsphere. A butyl titanate alcoholic solution is prepared from butyl titanate and alcohol; a gelatin solution is prepared by gelatin and acetic acid; the gelatin solution is slowly dropped into the butyl titanate alcoholic solution to obtain a sol solution; then the sol solution is aged and dried to obtain dry gel; the dry gel is put into distilled water for boiling; after filtration cleaning is executed, the product is cleaned through the alcohol and then is dried to obtain the anatase TiO2 nanocrystalline mesoporous microsphere. The preparation technology disclosed by the invention is simple and favorable for large-scale popularization and application, and a used solvent is safe and environment-friendly.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
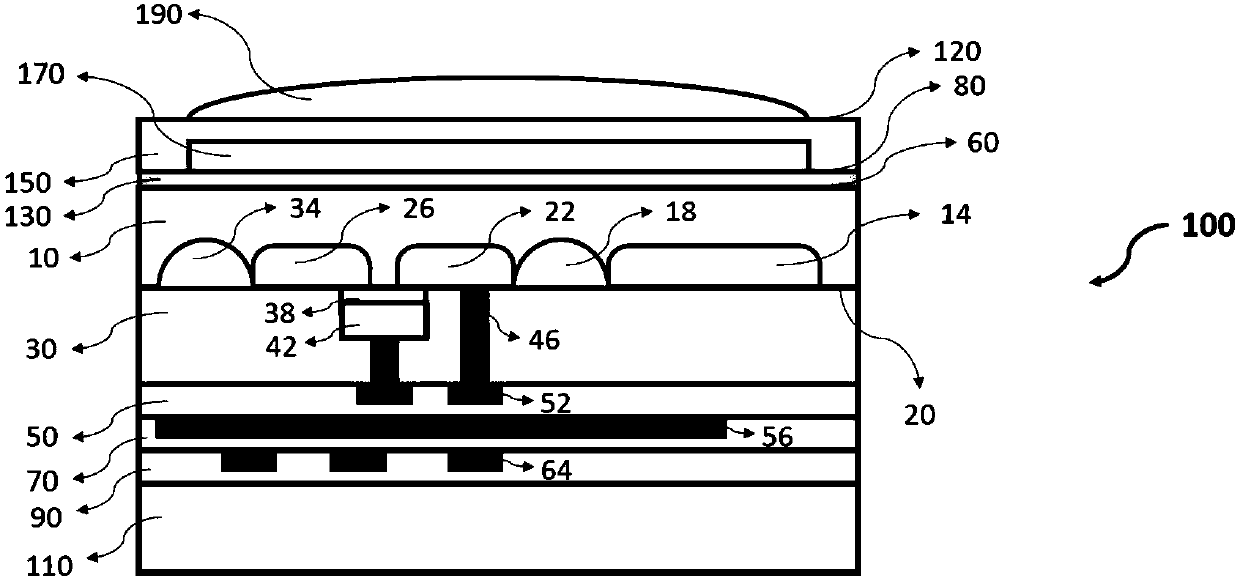
Chip scale package light-emitting apparatus having recessed design and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN106981554AAvoid Electrical Connection FailureImprove welding failure or poor welding qualitySemiconductor devicesEutectic bondingReflow soldering
The invention provides a chip scale package light-emitting apparatus having recessed design and a manufacturing method thereof. The chip scale package light-emitting apparatus includes a flip chip type LED chip and a cladding structure. The cladding structure covers the LED chip, and has a bottom surface warps upwardly to for a recessed shape. The invention also provides a manufacturing method for manufacturing the light-emitting apparatus. The apparatus and the method can avoid or improve poor quality of welding points between the light-emitting apparatus and a substrate which is often caused by greater gap between an electrode group of the LED chip and a welding pad of the substrate due to expansion of the cladding structure upon being heated in reflow soldering or eutectic bonding. Therefore, the apparatus and the method can secure the electrode group to the substrate. With excellent welding quality, failure of electrical connection of the light-emitting apparatus can be avoided, the thermal resistance between the light-emitting apparatus and the substrate can be lowered, temperature at the binding point can be lowered when the light-emitting apparatus operates, and light-emitting efficiency and reliability can be improved.
Owner:MAVEN OPTRONICS CO LTD
Phase focusing image sensor and forming method thereof
InactiveCN109449174AImprove performanceIncrease the amount of incoming lightSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesSemiconductorAbsorption layer
The invention discloses a phase focusing image sensor and a forming method thereof. According to the method, a semiconductor substrate, a first photosensitive structure and a first filter layer are provided, wherein the semiconductor substrate comprises a phase focusing area and has a first surface and a second surface opposite to the first surface; the first photosensitive structure is located inthe phase focusing area of the semiconductor substrate; the first photosensitive structure comprises a first surface and a second surface opposite to the first surface; the first photosensitive structure comprises an absorption layer which is used for absorbing near infrared light; the first surface of the first photosensitive layer is exposed from the absorption layer; the first filter layer islocated on the second surface of the phase focusing area of the semiconductor substrate; and natural light passes through the first filter layer. The performance of the phase focusing image sensor isimproved.
Owner:HUAIAN IMAGING DEVICE MFGR CORP
Organic light emitting display panel and organic light emitting display device
ActiveCN107331782AHigh display accuracyExtended service lifeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceLength wave
The invention discloses an organic light emitting display panel and an organic light emitting display device. The organic light emitting display panel comprises a substrate, and a first electrode, a first transmission layer, an organic light emitting layer, a second transmission layer and a second electrode sequentially arranged on the substrate, wherein the organic light emitting layer comprises a blue light-emitting layer and a sapphire light-emitting layer. The wavelength scope of the blue light emitted by the blue light-emitting layer is 460nm-490nm, and the wavelength scope of the sapphire light emitted by the sapphire light-emitting layer is 425nm-455nm. The organic light emitting display panel further comprises a chroma adjustment layer which is arranged on one side of the second electrode away from the substrate, and the chroma adjustment layer is used for adjusting the light emitted from the second electrode. A blue light-emitting layer and a sapphire light-emitting layer improve the light extracting rate of the organic light emitting display panel and prolong the service lifetime of the organic light emitting layer. The display effect of the organic light emitting display panel is improved.
Owner:WUHAN TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical waveguide material as well as method and device for producing it
InactiveCN1984851AEasy to controlWell mixedCladded optical fibreMolten spray coatingReaction rateErbium doping
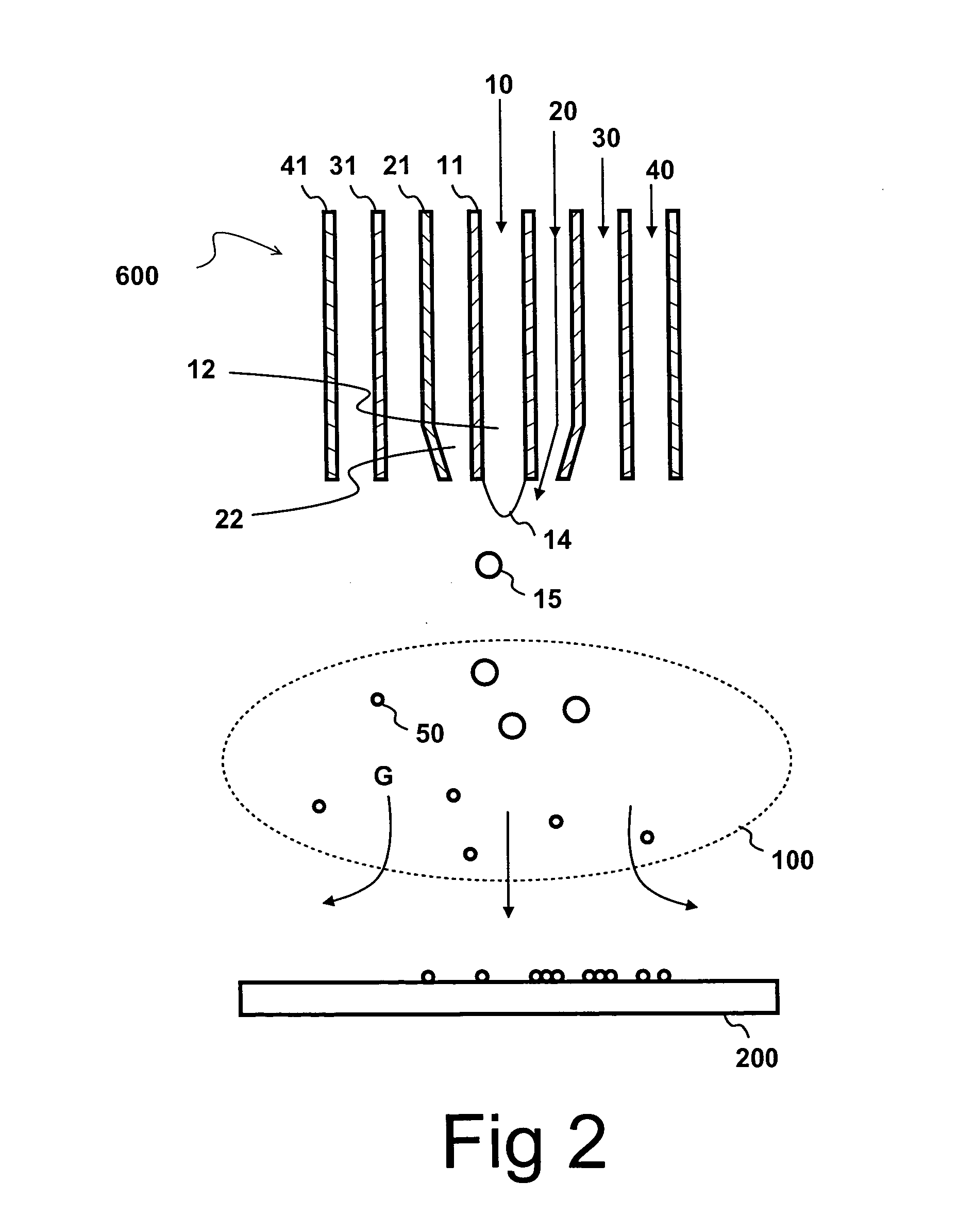
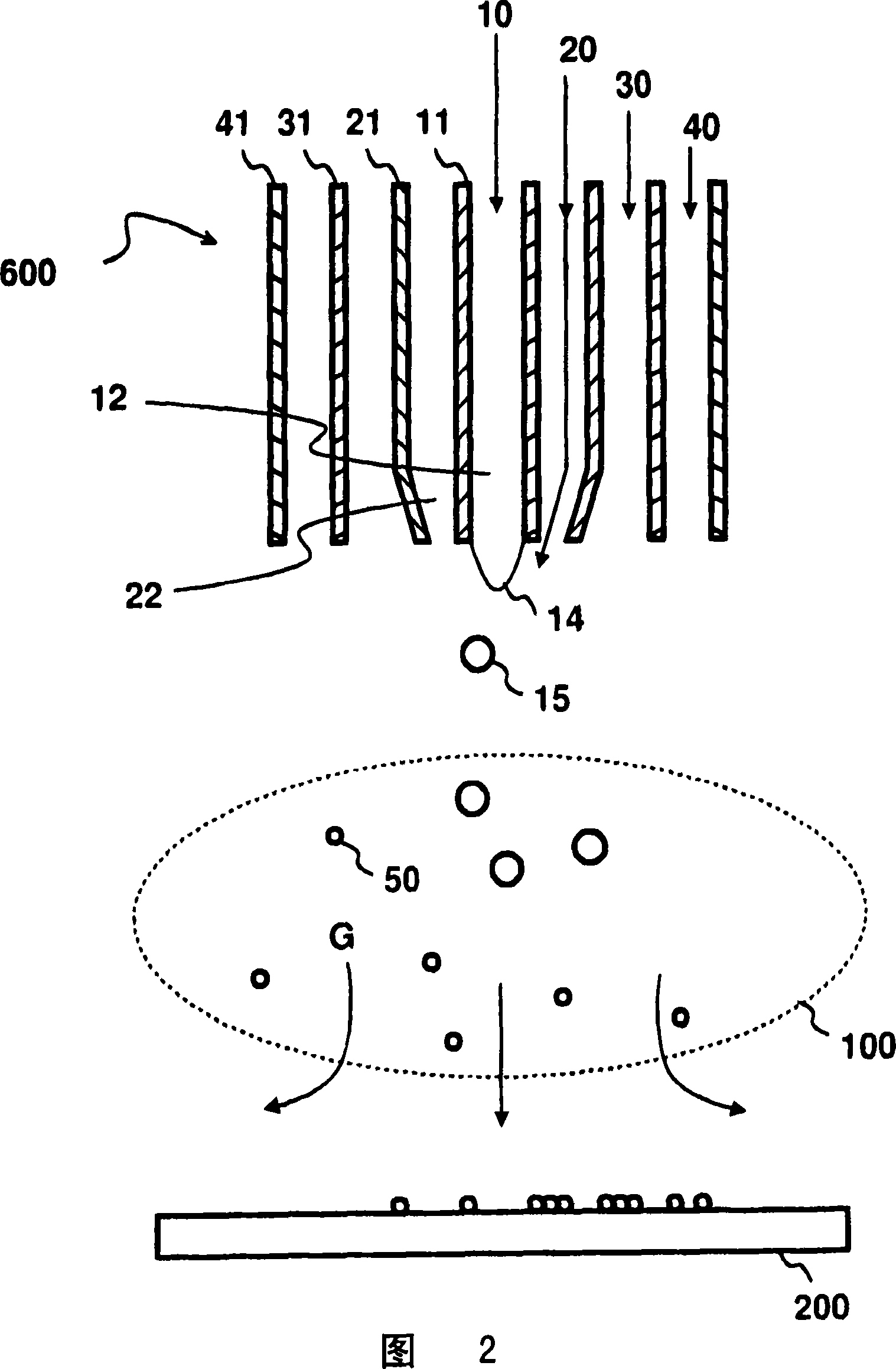
The invention relates to the production of light-amplifying optical material. Liquid reactant (10) is atomized into droplets (15) using a high velocity gas (20) . The droplets (15) are subsequently introduced into a flame (100) . Reactants (10, 30) are oxidized in the flame (100) and condensed by forming small particles (50) . At least a fraction of said particles (50) is collected and fused to form optical waveguide material, which is subsequently drawn to form an optical waveguide (750) . According to the invention, the velocity of the atomizing gas (20) stream is in the range of 0.3 to 1.5 times the velocity of sound. The high velocity enhances atomization and increases reaction rates in the flame (100) . The residence times are reduced to such a degree that unwanted phase transformations in the produced particles (50) are substantially minimized. Consequently, very homogeneous material is produced. Especially, in the production of erbium-doped silica, low percentage of clustered erbium ions is achieved.
Owner:LIEKKI OY
Direct growth method of flexible X-ray sensor scintillator layer
InactiveCN108010928AImprove reliabilityStable performanceX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentRadiation controlled devicesPhysicsPixel array
The invention provides a direct growth method of a flexible X-ray sensor scintillator layer. The growth method at least comprises the steps that firstly a flexible substrate layer of which the surfacehas preparation of a pixel array layer is provided; then the flexible substrate layer of which the surface has preparation of the pixel array layer is fixed on the plane support or the curved supportof the top part of a cavity, and a CsI scintillator layer is deposited on the surface of the pixel array layer by heating the CsI source of the bottom part of the cavity, wherein the CsI scintillatorlayer includes a CsI broken crystal layer and a CsI columnar crystal layer; and finally a sealed damp-proof layer is formed on the surface and the sidewall of the CsI scintillator layer. With application of the direct growth method, the CsI scintillator layer can be directly grown on the flexible substrate layer and the CsI layer can remain intact without crack when the sensor is bent, and the CsI can maintain performance without degradation even under the condition of multiple times of large-angle bending so as to have great reliability.
Owner:SHANGHAI IRAY TECH
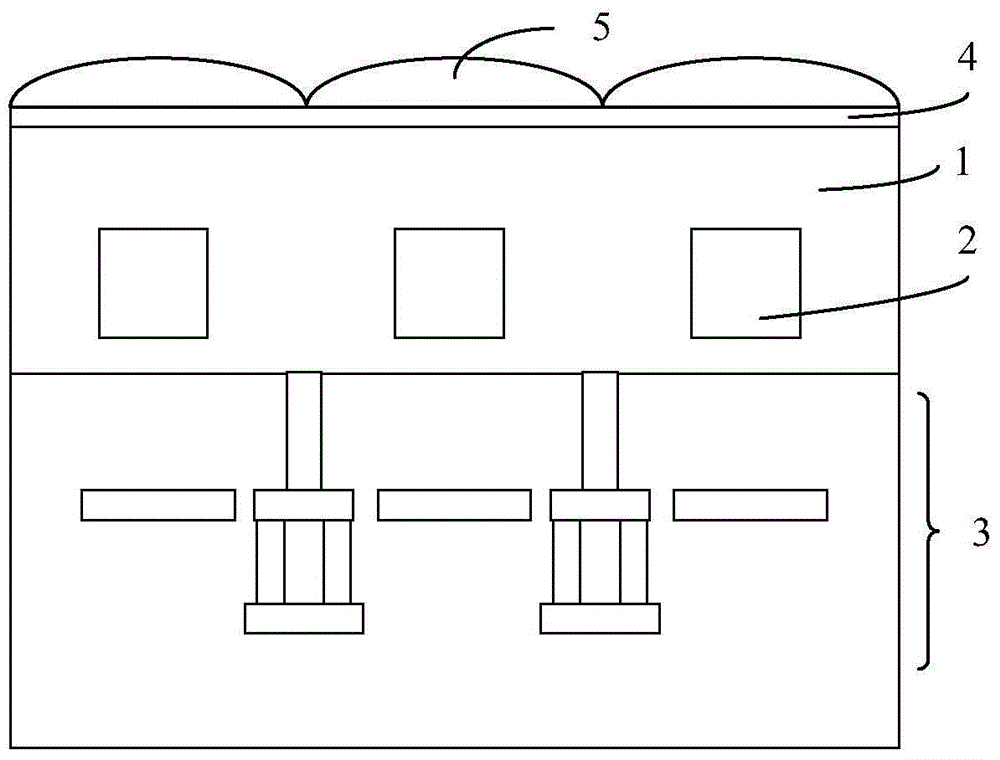
Image sensor and formation method thereof
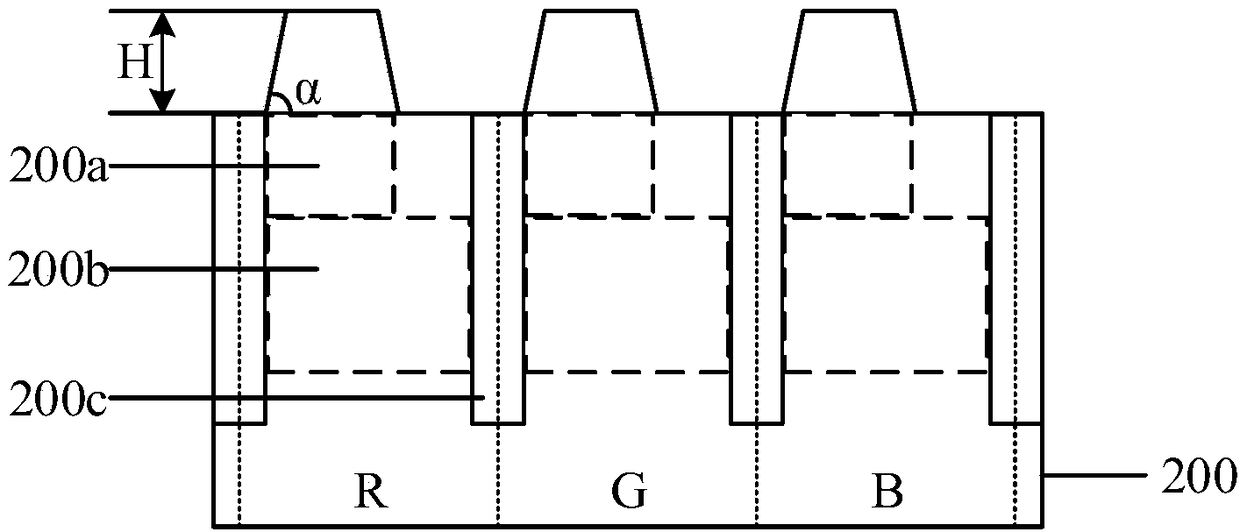
InactiveCN108428711AImprove quantum conversion efficiencyPromote conversionRadiation controlled devicesComputer graphics (images)Acute angle
The invention provides an image sensor and a formation method thereof. The formation method comprises the steps that a substrate is provided, the substrate comprises a plurality of pixel areas separate from one another; a block structure is formed on the surface of the substrate between each pair of adjacent pixel areas, the size of the bottom of each block structure is larger than that of the topof the corresponding block structure, and the side wall and bottom of each block structure have an acute angle; a color filter is formed on the surface of the substrate in each pixel area, and the color filters cover the side walls of the block structures. The image sensor formed by using the method has better performance.
Owner:HUAIAN IMAGING DEVICE MFGR CORP
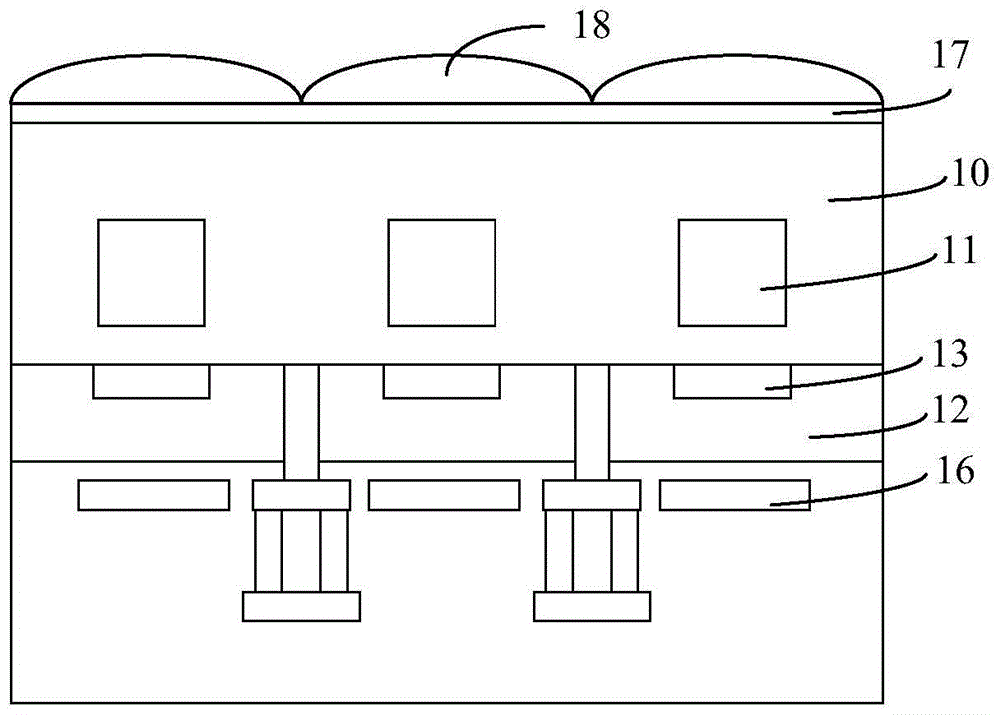
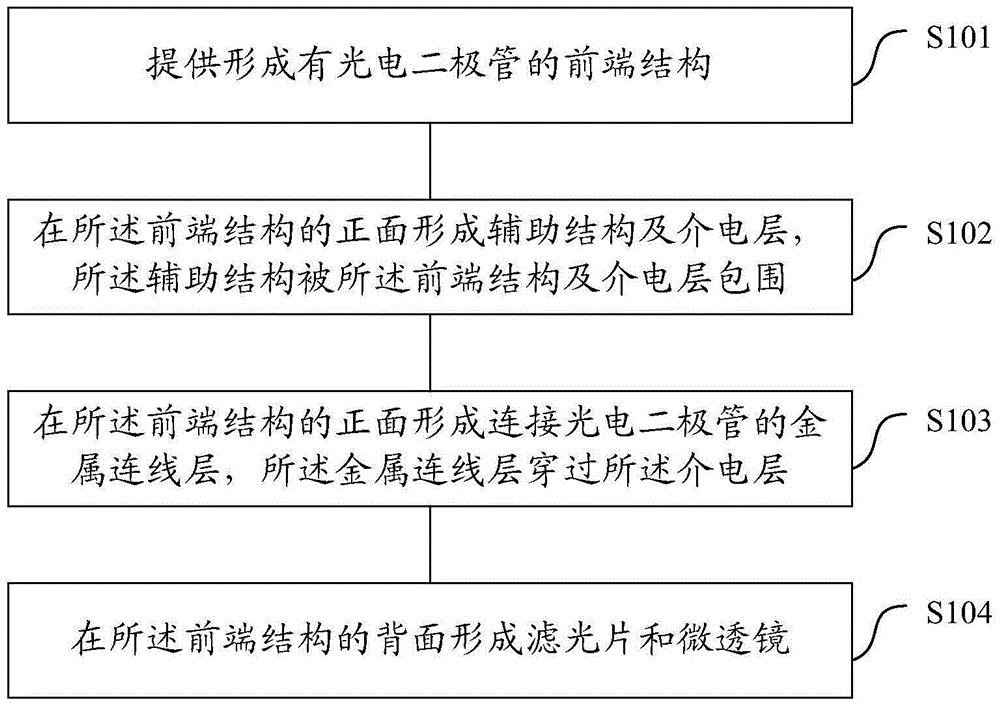
Back-illuminated CMOS image sensor and formation method thereof
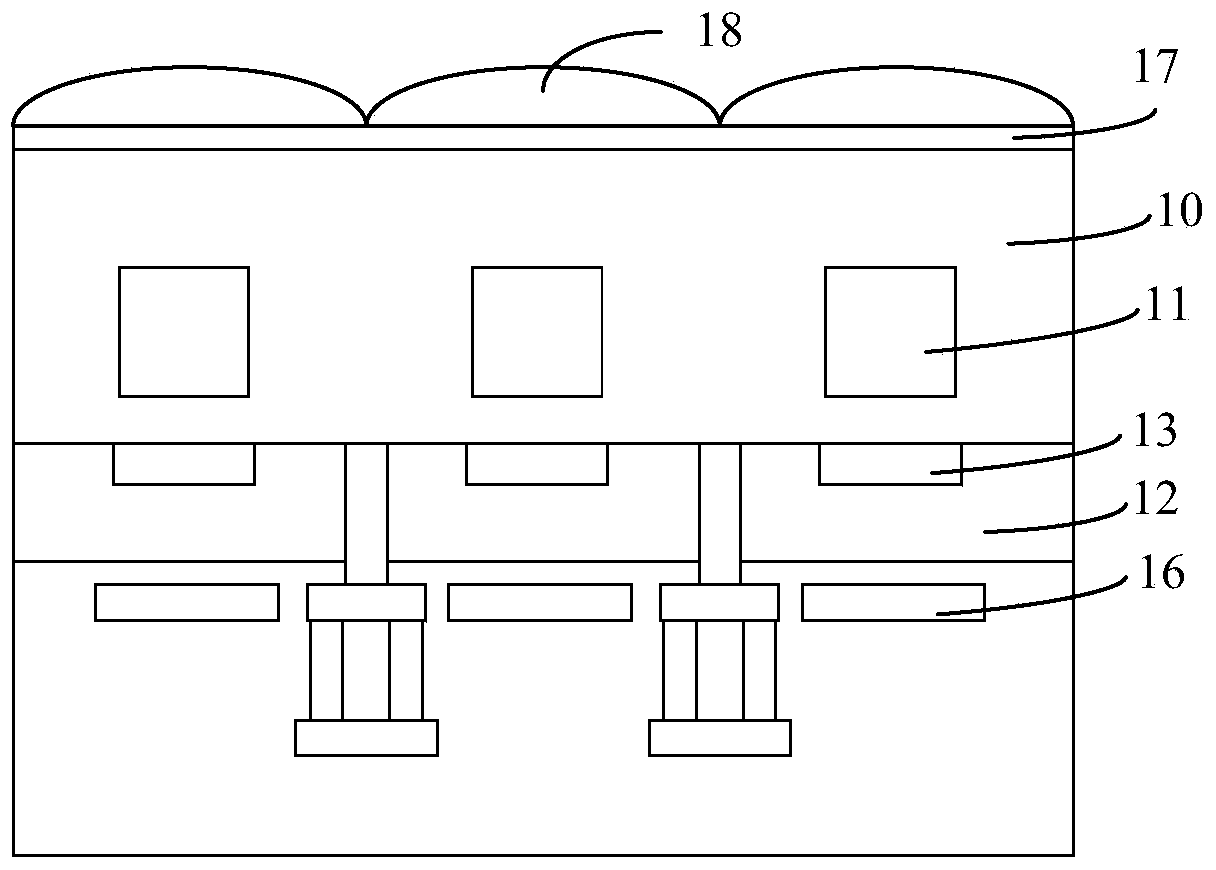
ActiveCN105206638APromote absorptionLow refractive indexRadiation controlled devicesCMOSRefractive index
The invention provides a back-illuminated CMOS image sensor and a formation method thereof. The back-illuminated CMOS image sensor includes a front-end structure with a photodiode as well as an auxiliary structure and a dielectric layer which are located at the front surface of the front-end structure, wherein the auxiliary structure is surrounded by the front-end structure and the dielectric layer, and the refraction rate of the auxiliary structure is lower than the refraction rates of the front-end structure and the dielectric layer. With the back-illuminated CMOS image sensor of the invention adopted, after incident light passes through the photodiode, parts of the incident light, which are subjected to total reflection, are increased, and can enter the photodiode again, and therefore, photons absorbed by the photodiode can be effectively increased, and quantum conversion efficiency can be improved.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
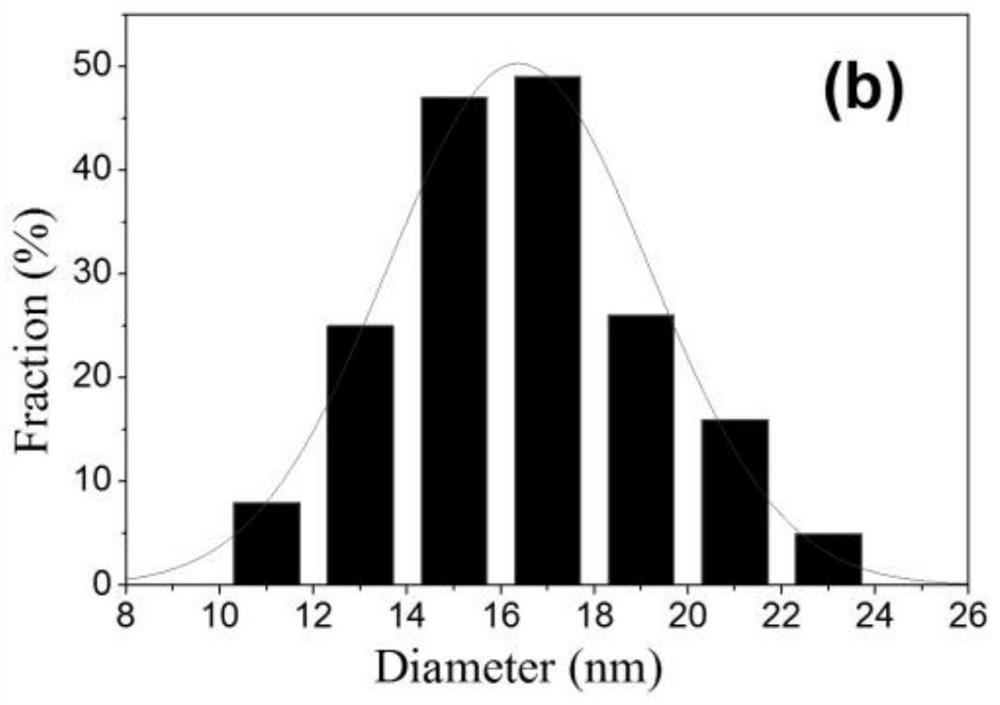
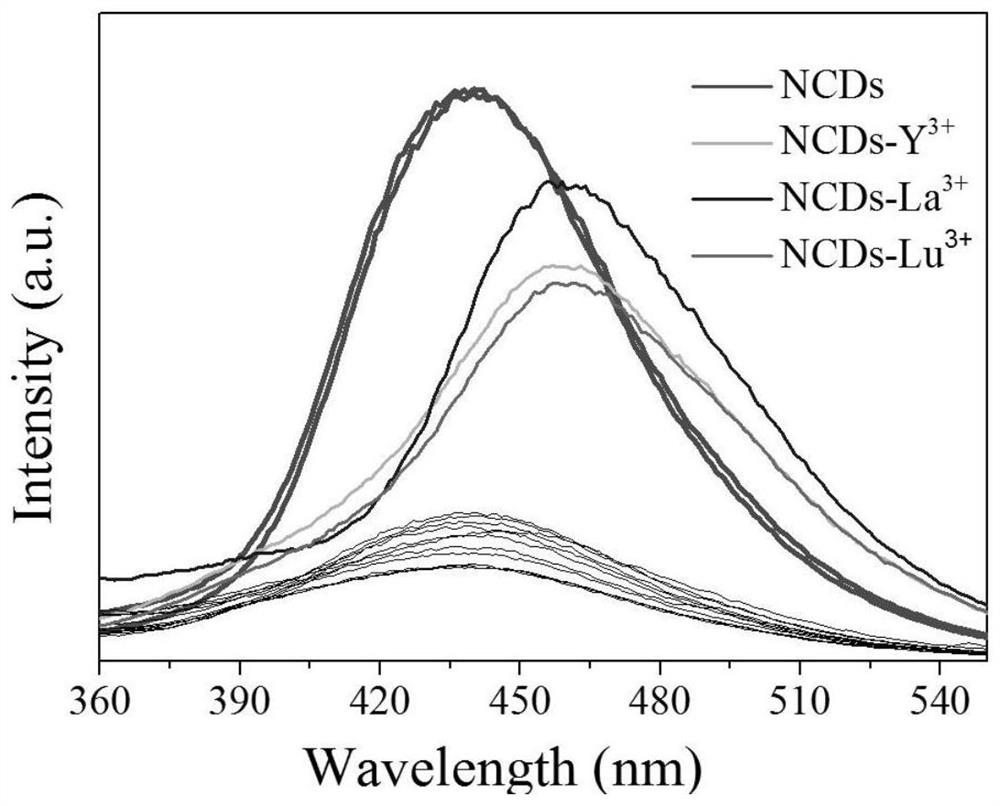
Rare earth element qualitative and quantitative detection method based on carbon quantum dot fluorescence mechanism
PendingCN111650172AQualitatively accurateQuantitative detectionMaterial nanotechnologyNano-carbonRare-earth elementFolic acid
The invention discloses a rare earth element qualitative and quantitative detection method based on a carbon quantum dot fluorescence mechanism and belongs to the field of rare earth element detection. Folic acid for example, a nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dot is synthesized by adopting a one-step hydrothermal method; the synthesized nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dot has an energy band structurewhich has high quantum conversion efficiency and emits blue light; due to the surface electronegativity, the synthesized nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dot can be well combined with positively chargedrare earth ions; a prepared nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dot solution can be combined with different types of rare earth; fluorescence spectral lines emitted by the synthesized nitrogen-doped carbonquantum dots are subjected to red shift and quenching; the content of the rare earth can be quantitatively analyzed through the change of fluorescence quenching; the red shift phenomenon can be applied to qualitative distinguishing of the rare earths; therefore, the rare earths can be divided into two types, the first group of rare earth ions Y < 3 + >, La < 3 + >, Lu < 3 + > and NCDs are combinedto enable the fluorescence emission peak of the NCDs to have obvious red shift, and the second type of rare earth ions Pr < 3 + >, Nd < 3 + >, Sm < 3 + >, Eu < 3 + >, Gd < 3 + >, Tb < 3 + > and Dy <3 + > have no similar phenomenon.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Image sensor and method of forming same
InactiveCN107845651AImprove quantum conversion efficiencyReduce Optical CrosstalkSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesOptoelectronicsReflective layer
The invention provides an image sensor and a method of forming the same. The image sensor includes a substrate having first and second surfaces opposite to each other; and a dielectric structure on the first side of the substrate. The substrate includes a plurality of discrete photosensitive regions and isolation regions surrounding the respective photosensitive regions, and each photosensitive region including a central region and a peripheral region surrounding the central region. The dielectric structure has reflective structures therein. The reflective structures are not in contact with the substrate. The reflective structures include reflective layers in the dielectric structure at the central regions and reflective frames located in the dielectric structure. The distance between eachreflective layer and the first surface is a first interval. The reflective frames are located in the isolation regions and the peripheral regions, or extend from the isolation regions to the peripheral regions. The distance between each reflective frame and the first surface is a second interval, and the second interval is smaller than the second interval. The image sensor can improve the quantumconversion efficiency and reduce the optical crosstalk.
Owner:HUAIAN IMAGING DEVICE MFGR CORP
Backside illuminated CMOS sensor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104576660AImprove quantum conversion efficiencyRadiation controlled devicesCMOS sensorPhotodiode
The invention discloses a backside illuminated CMOS sensor and a preparation method thereof. The backside illuminated CMOS sensor comprises a wafer, a dielectric layer arranged on the front surface of the wafer, a groove arranged in the dielectric layer and close to the wafer, and a through hole and a metal interconnecting wire which are arranged in the dielectric layer, wherein a plurality of photodiodes are formed in the wafer; the groove is positioned below the photodiodes; light reflecting substance is arranged in the groove; one end of the through hole is connected with the electrode of the wafer; the other end of the through hole is connected with the metal interconnecting wire; metal is arranged in the through hole. The backside illuminated CMOS sensor improves the quantum conversion efficiency, further improves the product image quality, is higher in compatibility than that of the traditional processing equipment, and is simple and practicable in technology.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
BSI image sensor and manufacture thereof
PendingCN110098203AReduce compoundingImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionEngineering
Owner:VISIONARY SEMICON INC
Organic dye and dye sensitization solar cell prepared thereby
ActiveCN101497745APromote absorptionImprove quantum conversion efficiencyLight-sensitive devicesSolid-state devicesOrganic dyeSolar cell
The invention relates to an organic dye and a dye-sensitized solar cell produced from the organic dye, in particular to an organic dye taking thiophene and 3,4-ethyl disulfide thiophene or the derivatives of the thiophene and the 3,4-ethyl disulfide thiophene as conjugated units and a dye-sensitized solar cell produced from the organic dye. The organic dye does not need expensive raw materials including metal such as ruthenium and decontaminant such as dextran glucan and has high synthetic yield of 60-70 percent in total; in addition, the organic dye has the maximum spectral absorption peak of over 580 nm, the molar extinction coefficient of over 36*10Mcm, wider sunlight absorption range and other excellent performance superior to the performance of ruthenium dye and most organic dye. The dye-sensitized solar cell produced from the organic dye has the maximum quantum conversion efficiency of 94 percent and the maximum monochromatic incident photon-to-electron conversion efficiency (IPCE) of over 7.0 percent.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
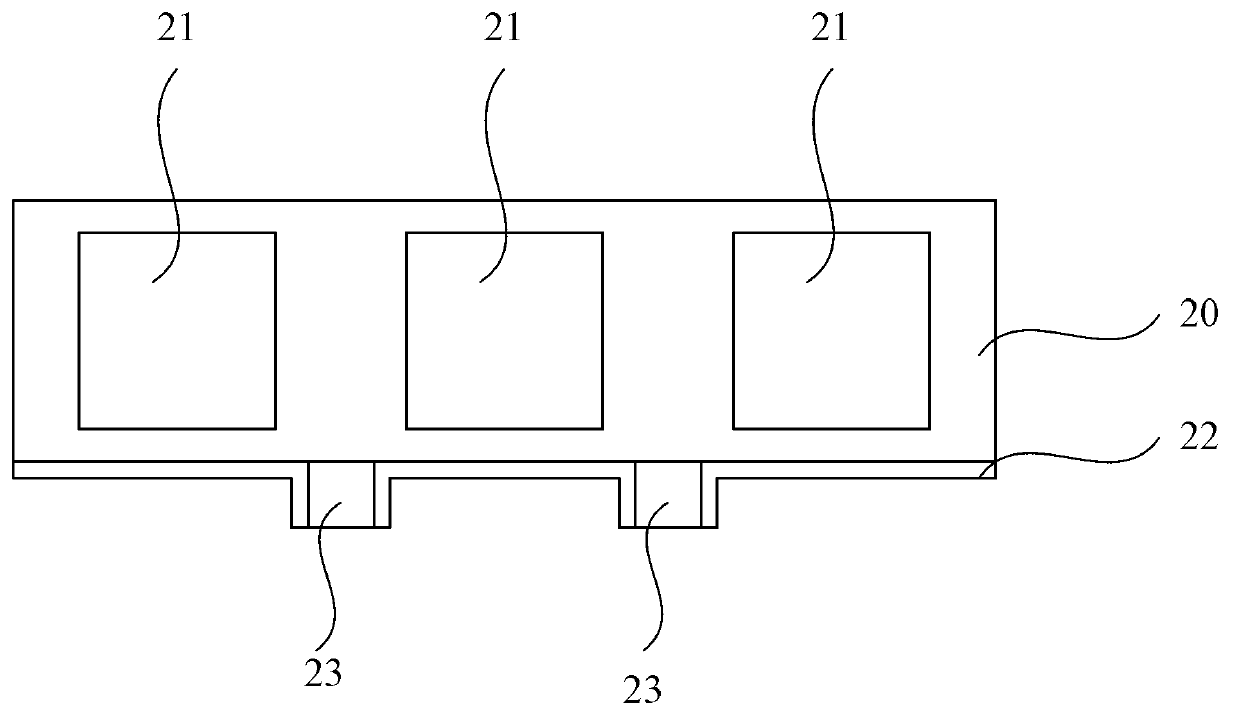
Image sensor and formation method thereof
ActiveCN108878464AIncrease the transmission pathIncrease profitSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
The technical scheme of the invention discloses an image sensor and a formation method thereof. The image sensor comprises a semiconductor substrate, a shallow groove isolation structure, a device structure and a reflecting layer, wherein the semiconductor substrate is divided into a plurality of regions, a photoelectric device is formed in the semiconductor substrate at each region, each region of the semiconductor substrate is provided with a protruding surface, the width of the protruding surface is adaptive to the size of the photoelectric device, the shallow groove isolation structure isformed in the semiconductor substrate and is arranged among the photoelectric devices, the device structure is arranged on the semiconductor substrate and in the semiconductor substrate, the reflecting layer is formed on the semiconductor substrate with the protruding surfaces, and the shallow groove isolation structure and the device structure are exposed. With the image sensor disclosed by the technical scheme, the quantum conversion efficiency of the image sensor is improved.
Owner:淮安西德工业设计有限公司
Backside illuminated CMOS image sensor and method for manufacturing same
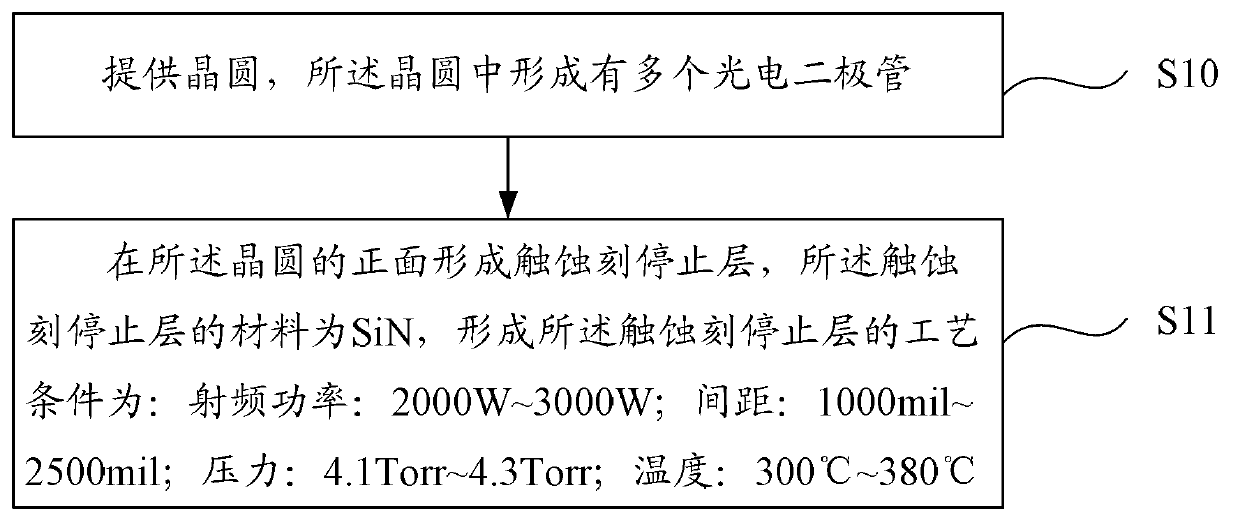
ActiveCN103346162AImprove reflectivityImprove quantum conversion efficiencyRadiation controlled devicesCMOSEngineering
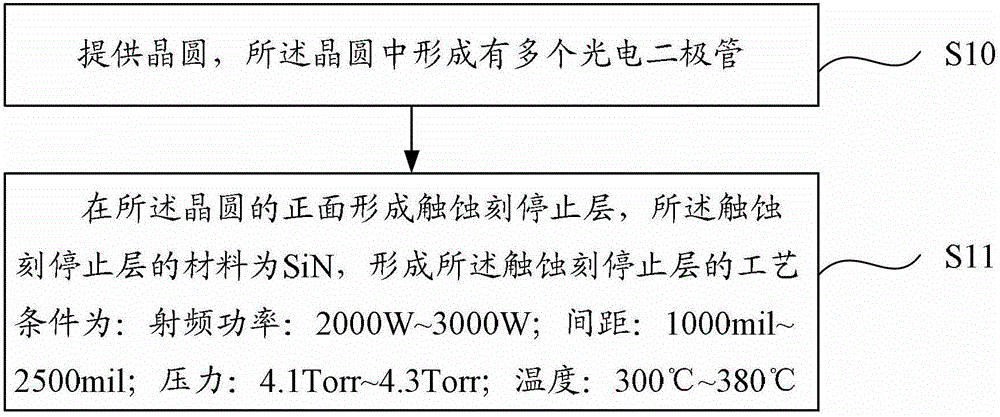
The invention provides a backside illuminated CMOS image sensor and a method for manufacturing the backside illuminated CMOS image sensor. The method comprises the steps that a wafer is provided, and a plurality of photodiodes are formed in the wafer; a touch etching stop layer is formed in the front of the wafer; the materials of the touch etching stop layer is SiN, and technological conditions for forming of the touch etching stop layer comprise 2000W-3000W radio-frequency power, a 1000mil-2500mil gap, 4.1Torr-4.3Torr pressure and a 300 DEG C-380 DEG C temperature. Due to the mode, the touch etching stop layer in the backside illuminated CMOS image sensor has high reflectivity, light irradiating on the backside illuminated CMOS image sensor can be well reflected in the photodiodes, and quantum converting efficiency is improved.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Preparation method for anatase titanium dioxide nanocrystalline mesoporous microsphere
InactiveCN103663548BSimple processReduce energy consumptionMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsAcetic acidAlcohol
The invention discloses a preparation method for an anatase titanium dioxide nanocrystalline mesoporous microsphere. A butyl titanate alcoholic solution is prepared from butyl titanate and alcohol; a gelatin solution is prepared by gelatin and acetic acid; the gelatin solution is slowly dropped into the butyl titanate alcoholic solution to obtain a sol solution; then the sol solution is aged and dried to obtain dry gel; the dry gel is put into distilled water for boiling; after filtration cleaning is executed, the product is cleaned through the alcohol and then is dried to obtain the anatase TiO2 nanocrystalline mesoporous microsphere. The preparation technology disclosed by the invention is simple and favorable for large-scale popularization and application, and a used solvent is safe and environment-friendly.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
A kind of back-illuminated cmos image sensor and its forming method
ActiveCN105206638BPromote absorptionLow refractive indexRadiation controlled devicesCMOSRefractive index
The invention provides a back-illuminated CMOS image sensor and a formation method thereof. The back-illuminated CMOS image sensor includes a front-end structure with a photodiode as well as an auxiliary structure and a dielectric layer which are located at the front surface of the front-end structure, wherein the auxiliary structure is surrounded by the front-end structure and the dielectric layer, and the refraction rate of the auxiliary structure is lower than the refraction rates of the front-end structure and the dielectric layer. With the back-illuminated CMOS image sensor of the invention adopted, after incident light passes through the photodiode, parts of the incident light, which are subjected to total reflection, are increased, and can enter the photodiode again, and therefore, photons absorbed by the photodiode can be effectively increased, and quantum conversion efficiency can be improved.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Solar battery
InactiveUS9391224B2Improve efficiencyImprove conductivityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingEngineeringSolar battery
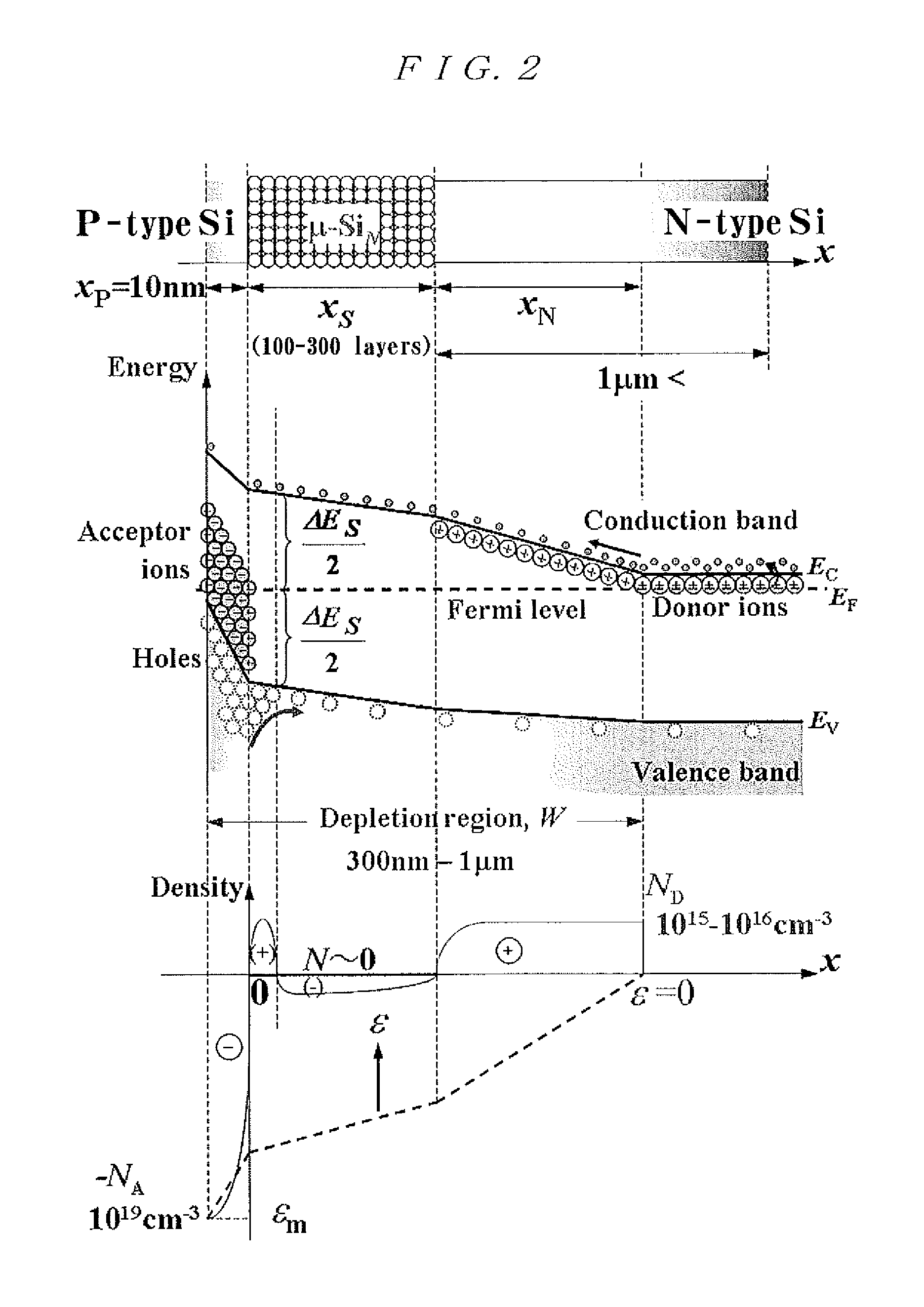
Disclosed is a solar battery which: is made from a silicon semiconductor; has a high quantum-conversion efficiency; requires a small number of production steps during manufacturing; and is capable of being recycled in view of environmental load and material recycling. Specifically, a solar battery according to an embodiment of the present invention has a basic structure of a P—SiN—N junction in which minute silicon clusters are inserted in a P—N junction, and includes a quantum dot layer having a multiple energy level structure consisting of an energy level of a valence band and an energy level of a conduction band, and intermediate energy levels located between both the bands. The quantum dot layer is composed by periodically arranging silicon quantum dots consisting of silicon clusters with an average particle diameter of 2.5 nm or less and an inter-quantum-dot distance of 1 nm or less.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Back-illuminated cmos image sensor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103346162BImprove reflectivityImprove quantum conversion efficiencyRadiation controlled devicesCMOSEngineering
The invention provides a backside illuminated CMOS image sensor and a method for manufacturing the backside illuminated CMOS image sensor. The method comprises the steps that a wafer is provided, and a plurality of photodiodes are formed in the wafer; a touch etching stop layer is formed in the front of the wafer; the materials of the touch etching stop layer is SiN, and technological conditions for forming of the touch etching stop layer comprise 2000W-3000W radio-frequency power, a 1000mil-2500mil gap, 4.1Torr-4.3Torr pressure and a 300 DEG C-380 DEG C temperature. Due to the mode, the touch etching stop layer in the backside illuminated CMOS image sensor has high reflectivity, light irradiating on the backside illuminated CMOS image sensor can be well reflected in the photodiodes, and quantum converting efficiency is improved.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Nickel-doped zinc oxide hierarchical structure photocatalytic nanomaterial and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103657662BImprove visible light absorptionVisible light catalytic activity is highMaterial nanotechnologyWater/sewage treatment by irradiationNickel saltOrganic dye
The invention discloses a nickel-doped zinc oxide hierarchical structure photocatalytic nano-material having a visible-light photocatalytic activity and a preparation method thereof. The component of the material is Zn1-xNixO, wherein x=0.5-10 mol%. The method comprises the steps: dissolving a zinc salt, a nickel salt and an alkali in an alcohol solvent or an alcohol / water mixed solvent to obtain a precursor solution with the total concentration of the metal ions of 0.0625-0.25 mol / L and the molar concentration of the alkali of 0.0625-2.5 mol / L; placing the precursor solution in a high-pressure reaction kettle for sealing reaction; after cooling, washing with ethanol, drying in air, and thus obtaining the photocatalytic nano-material having a nano-granular structure, a hollow sphere structure, an icosahedron structure, a hexagonal prism structure or a ball-like structure and other hierarchical structures. The material both has relatively strong photoabsorption and photoresponse in the visible light range of 400-700 nm, significantly improves the activity of visible-light photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes, and can be widely used for photocatalytic degradation treatment of dye industry wastewater.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
2-micron thulium-doped solid laser pumped in 1.6-micron erbium-doped laser cavity
PendingCN113991417AIncrease powerReduce thermal effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialErbium lasersHigh reflectivity
The invention discloses a 2-micron thulium-doped solid laser pumped in a 1.6-micron erbium-doped laser cavity. An input mirror has high transmissivity for 1.5-micron laser and has high reflectivity for 1.6-micron laser; the middle mirror has high transmittance for 1.6-micron laser and has high reflectivity for 2-micron laser; the output mirror has high reflectivity for 1.6-micron laser and has partial reflectivity for 2-micron laser; the input mirror, the middle mirror and the output mirror are arranged along the output direction of the 1.5-micron pumping source; the input mirror and the output mirror form a 1.6-micron laser resonant cavity; the middle mirror and the output mirror form a 2-micron laser resonant cavity; the erbium-doped solid laser medium generates 1.6-micron laser after receiving the 1.5-micron laser and is arranged between the input mirror and the middle mirror; and the thulium-doped solid laser medium generates 2-micron laser after receiving the 1.6-micron laser, and is arranged between the middle mirror and the output mirror. The laser is beneficial for improving laser efficiency and light beam quality.
Owner:中红外激光研究院(江苏)有限公司
Image sensor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN106298825BPromote absorptionImprove quantum conversion efficiencySolid-state devicesDiodeCMOSSemiconductor package
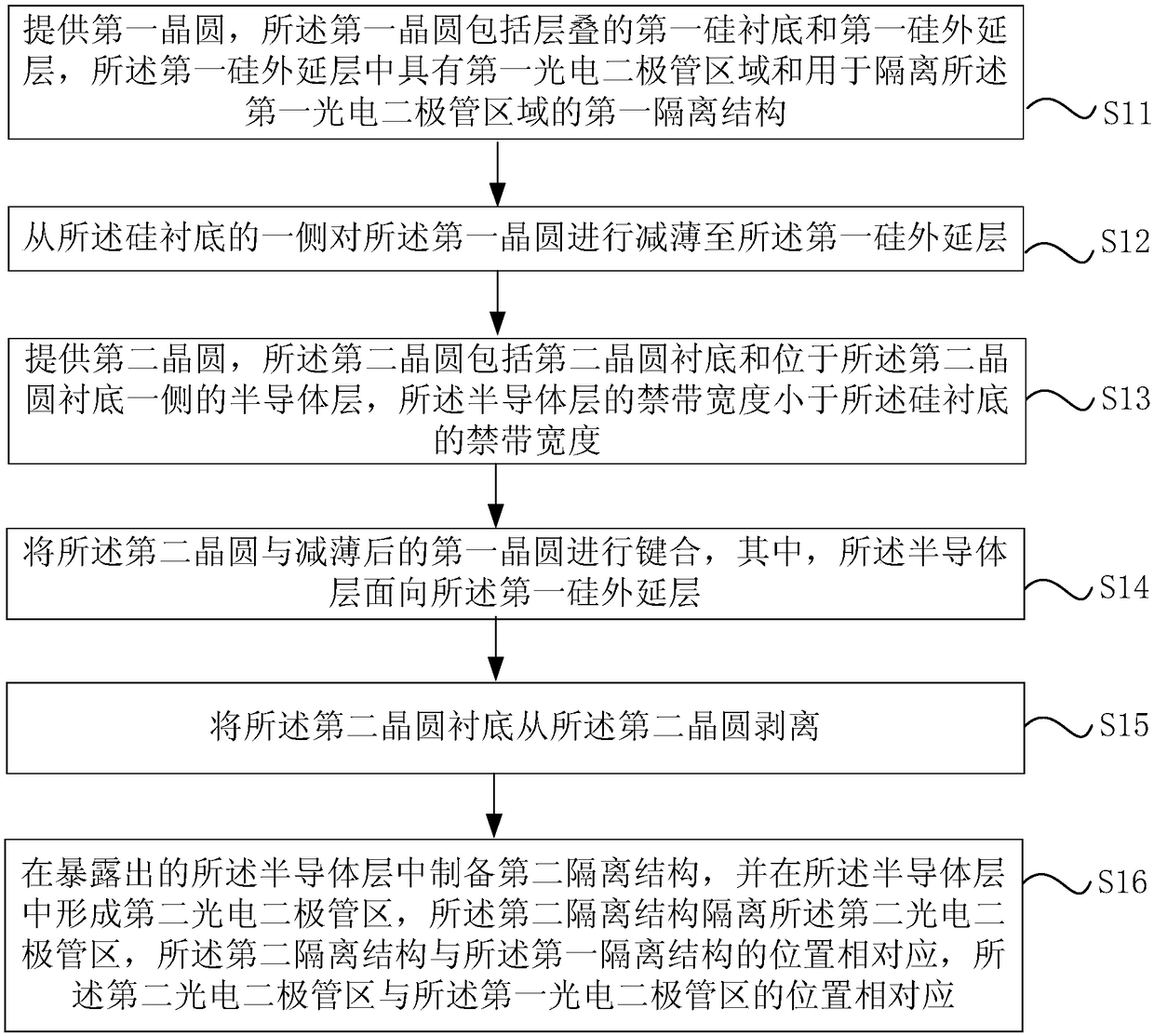
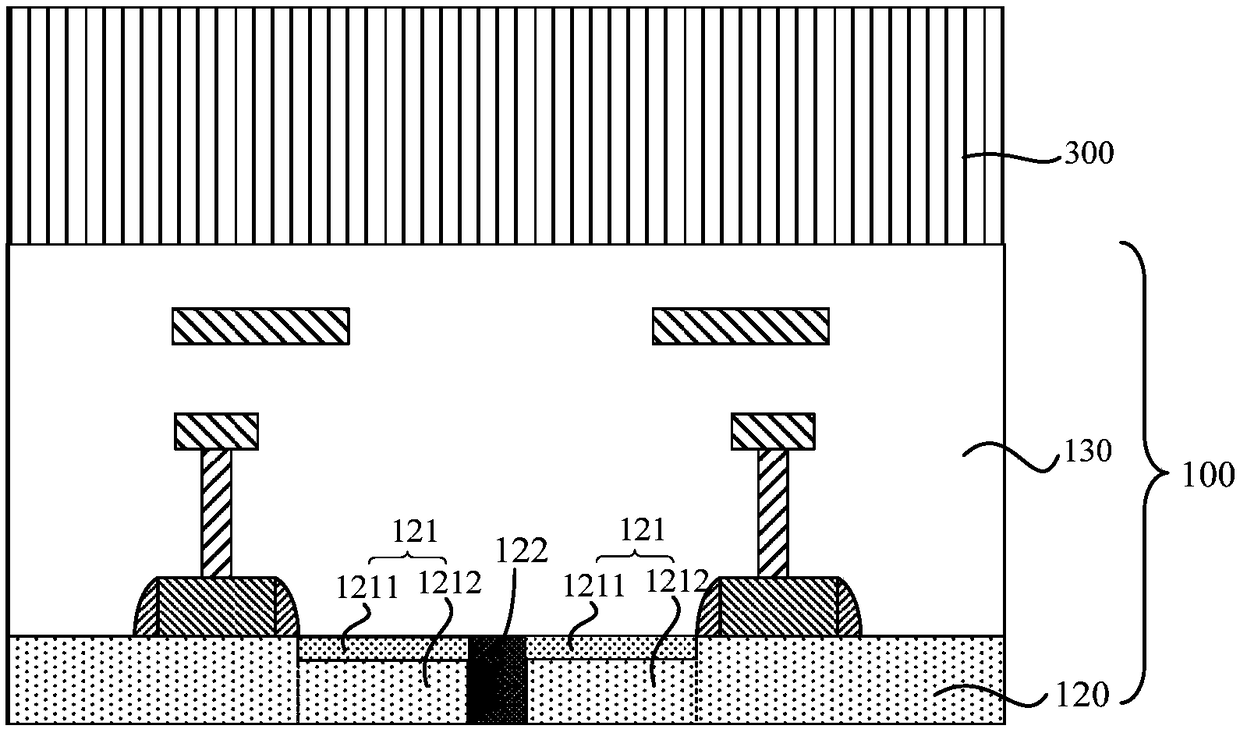
The invention discloses an image sensor and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: providing a first wafer which includes a first silicon substrate, a first silicon epitaxial layer and an interconnection layer which are successively laminated; thinning the first wafer from one side of the silicon substrate till the first silicon epitaxial layer; providing a second wafer which includes a second wafer substrate and a semiconductor layer which is arranged on one side of the second wafer substrate; bonding the second wafer and the thinned first wafer, the semiconductor layer facing towards the first silicon epitaxial layer; peeling the second wafer substrate from the second wafer; preparing a second isolation structure in the exposed semiconductor layer, and forming a second photoelectric diode region in the semiconductor layer. The semiconductor layer has a forbidden band with a width smaller than that of silicon. The image sensor can better absorb infrared lights, and effectively increase quantum conversion efficiency of a CMOS image sensor.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Monocrystalline silicon double-sided solar cell and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105826411BSmall surface areaIncrease reflectionFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationBack surface fieldCrystalline silicon
The invention discloses a mono-crystalline silicon double-sided solar cell. A front texturing morphology structure (1), a front PN emitter junction (2), a front passivated anti-reflection medium layer (3) and a front electrode (4) are sequentially formed on the front of a mono-crystalline silicon substrate (100). A back texturing morphology structure (5), a back surface field (6), a back passivated anti-reflection medium layer (7) and a back electrode (8) are sequentially formed on the back of the mono-crystalline silicon substrate. The solar cell is characterized in that the back texturing morphology structure (5) is a platform type texture surface, and platform structures (5a) are distributed on the mono-crystalline silicon substrate in a scattered, or tiled, or partially scattered, partially tiled, partially connected and partially overlapped way. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the mono-crystalline silicon double-sided solar cell. The minority carrier surface recombination and optical absorption characteristics of the double-sided solar cell are optimized, and the efficiency of quantum conversion is improved.
Owner:TRINA SOLAR CO LTD
A stacked spectral spectroscopic solar photocatalytic reaction system
ActiveCN109126661BIncrease profitAchieve Broad Spectrum ResponsePhysical/chemical process catalystsEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesPhotocatalytic reactionSpectral response
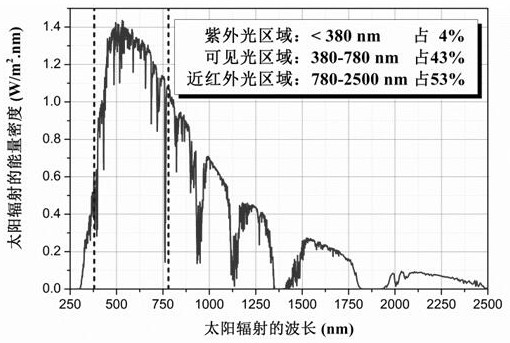
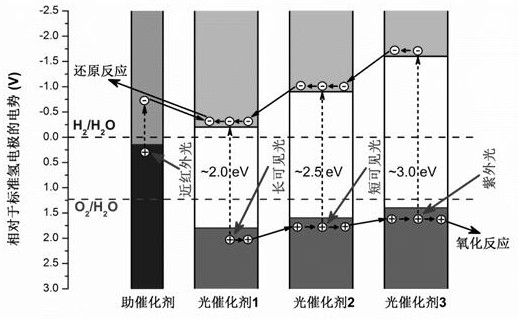
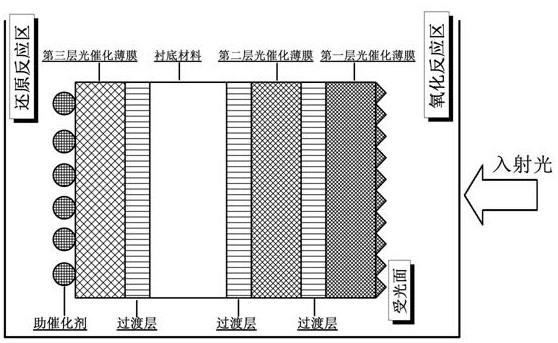
The invention discloses a laminated spectrum spectroscopic solar photocatalytic reaction system, which belongs to the technical field of solar energy utilization. The system is obtained by depositing N layers of photocatalytic thin film materials with gradually decreasing optical bandgap values and continuously changing band edge positions layer by layer on the substrate material, where N≥3; between two adjacent photocatalytic thin film materials There is a transition layer connection between them, and a co-catalyst with surface plasmon resonance effect is deposited on the Nth layer. The end face near the light-receiving surface is an anti-reflection and anti-reflection film with a porous-pyramid composite structure with a suede light-trapping effect. Its material composition The same material as the first layer of photocatalytic film. The significant advantages of the photocatalytic reaction system of the present invention are wide spectral response and high quantum conversion efficiency, which can greatly improve the utilization rate of solar energy.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com