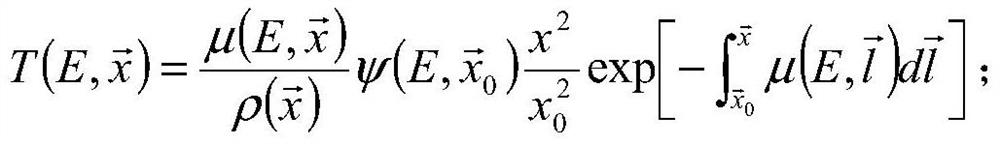Patents
Literature
60 results about "Electron density distribution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electron-density distribution. The electron-density distribution is the three-dimensional realspace arrangement of the electrons in the material. Because electrons are quantum mechanically delocalized, each electron occupies a 'fuzzy' region of space (electron cloud).
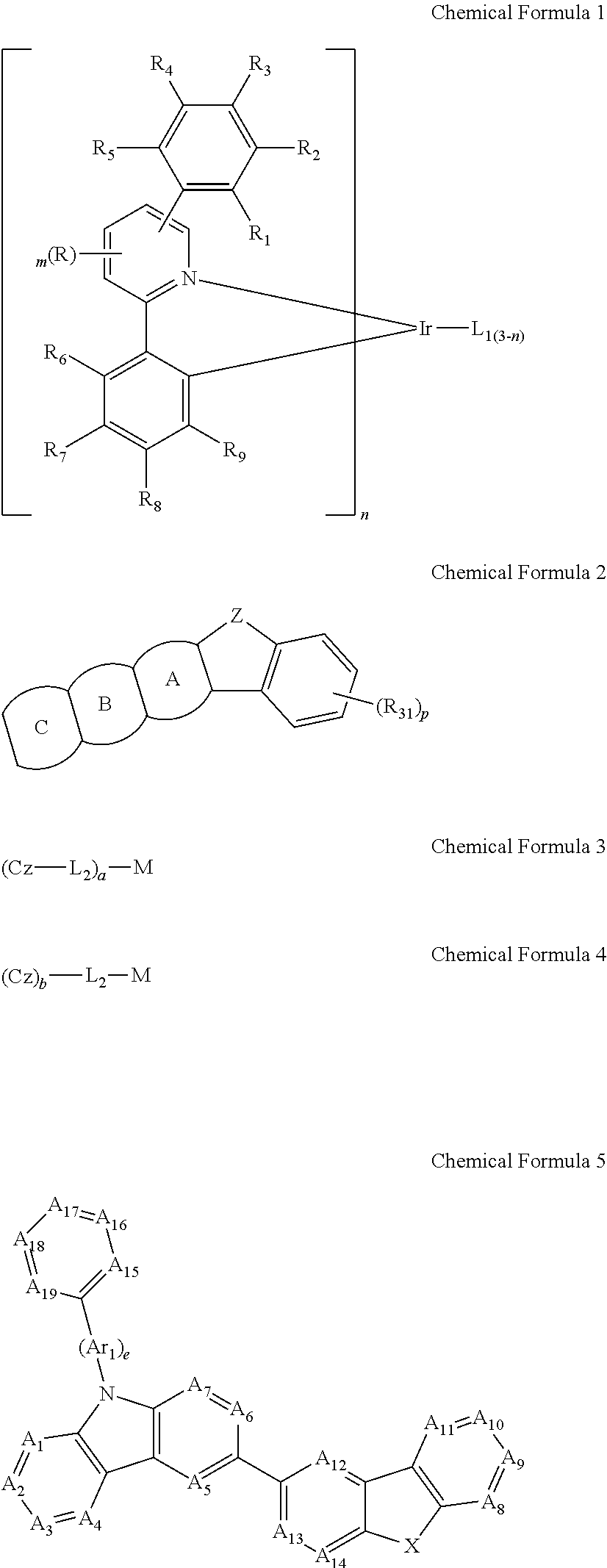
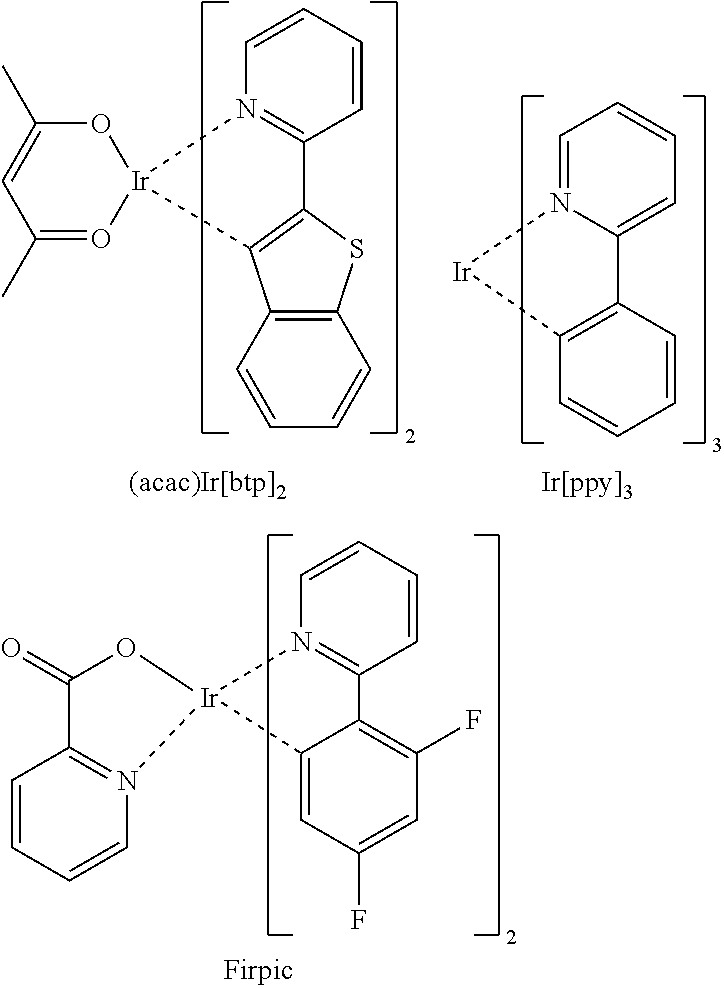
Electroluminescent device using electroluminescent compound as luminescent material
InactiveUS20140054564A1Improve luminous efficiencyIncreased operating lifeIndium organic compoundsElectroluminescent light sourcesEnergy transferOrganic electroluminescence
Provided is an organic electroluminescent device that exhibits an efficient host-dopant energy transfer mechanism, and thus, expresses a certain high-efficiency electroluminescent performance, based on improved electron density distribution. The organic electroluminescent device also overcomes low initial efficiency and short operation life property, and secures high-performance electroluminescent performance with high efficiency and long life property for each color.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS LLC
Method for preparing high depth-diameter-ratio three-dimensional micro-channel through electronic dynamic control
InactiveCN103706955AIncrease depthAspect ratioWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusTime domainFree electron density
The invention relates to a method for preparing a high depth-diameter-ratio three-dimensional micro-channel through electronic dynamic control, and belongs to the technical field of femtosecond laser applying. The time domain shaping is carried out on a femtosecond laser, the partial instant electronic dynamic condition ( especially the freedom electron density distribution), of a modified area is regulated and controlled, the appearance of a periodicity nanometer structure of the modified area is affected, the high depth-diameter-ratio three-dimensional micro-channel irrelative to polarization can be achieved, and compared with a traditional femtosecond laser machining method, the method has the advantage that the depth-diameter-ratio can be multiply increased during the three-dimensional micro-channel machining.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Soft x-ray laser based on Z-pinch compression of rotating plasma
InactiveUS20060232215A1Reduce light lossIncrease currentBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsBeam/ray deflecting arrangementsMagnetic tension forceVolumetric Mass Density
A method and apparatus for producing soft x-ray laser radiation based on z-pinch compression of a rotating low pressure plasma column are disclosed. A rotating, low pressure plasma column is created by electric discharge or by laser excitation inside a containment tube. Rotation of the plasma may be induced by viscous drag caused by rotation of the tube, or by magnetically driven rotation of the plasma as it is created in a plasma gun in the presence of an axial magnetic field, or both. A high power electrical discharge is then passed axially through the rotating plasma column to produce a rapidly rising axial current, resulting in z-pinch compression of the rotating plasma column radially inwardly with resultant stimulated emission of soft x-ray radiation in the axial direction. A rotating containment tube used in combination with magnetically driven rotation of the plasma column results in a concave electron density profile that in turn results in reduced wall ablation and also reduced refraction losses of the resultant soft x-rays.
Owner:FARTECH
Plasma treatment method and system
InactiveUS6066568AImprove in-plane uniformityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPeak valueLength wave
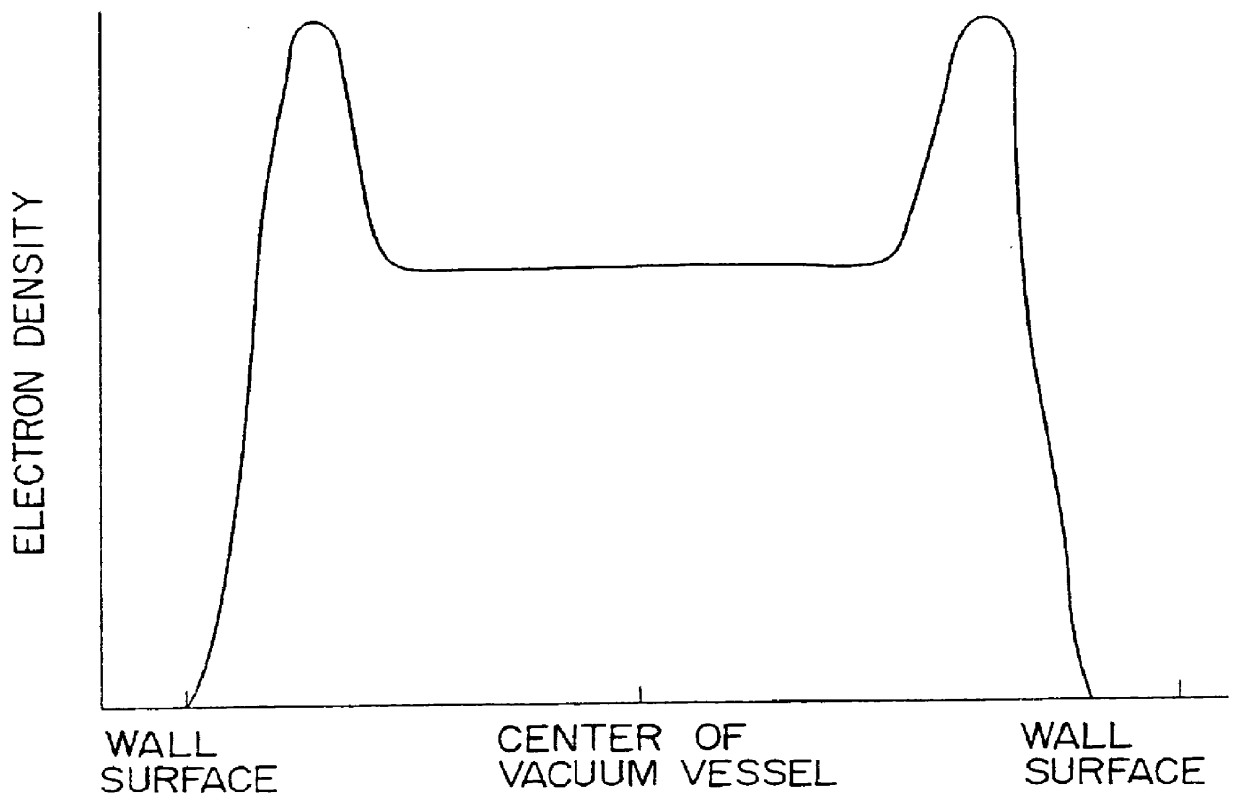
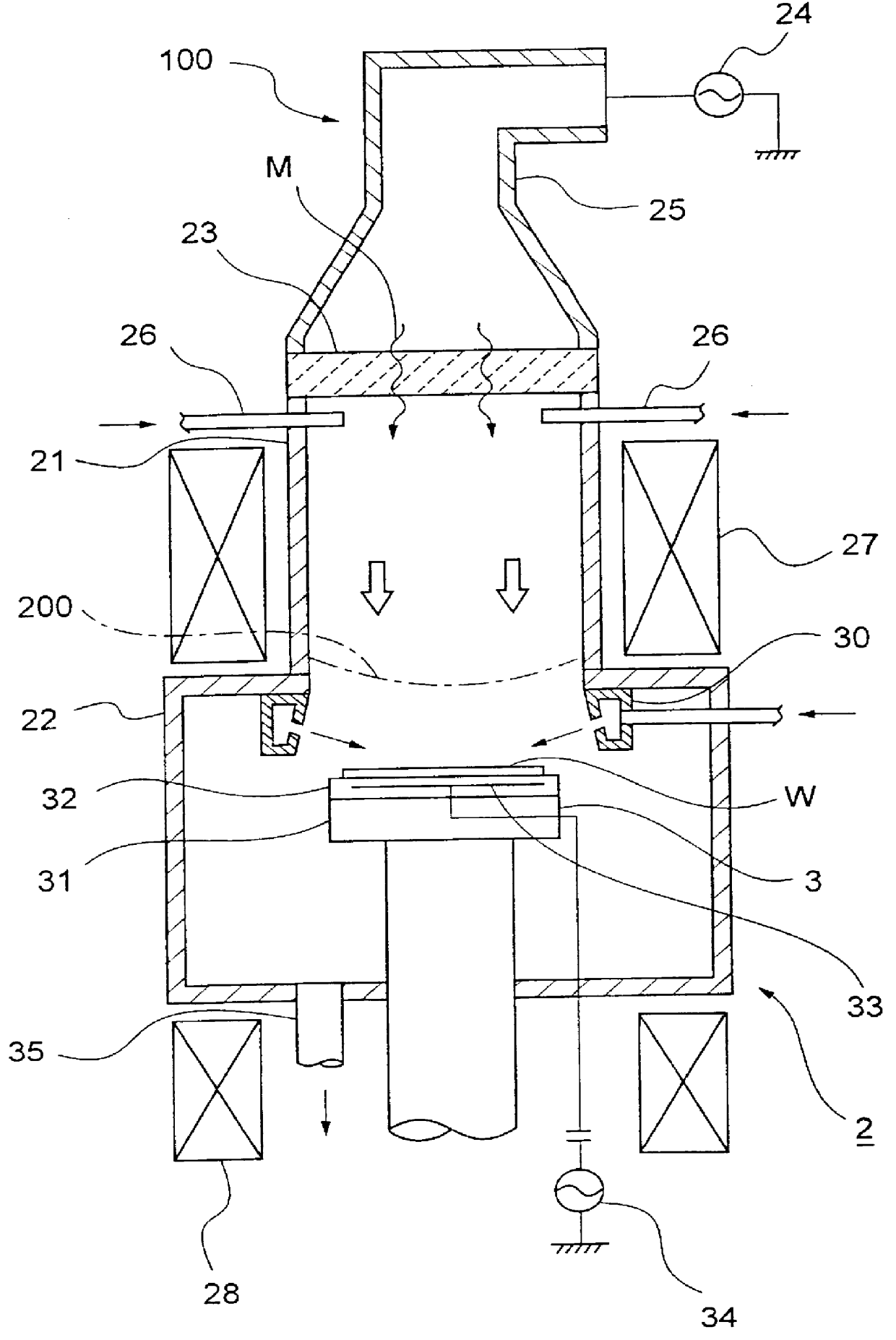
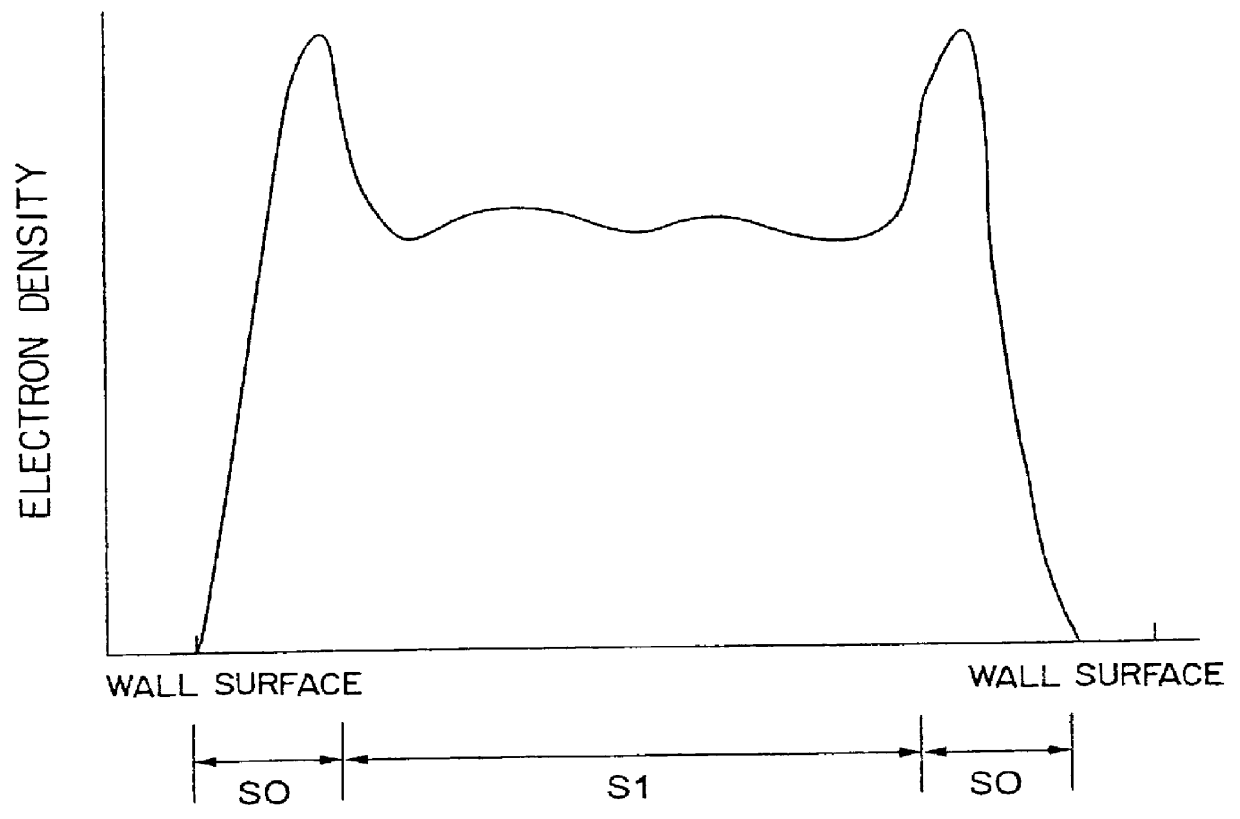
An electron density at an ECR point, which is spaced from a substrate to be treated and which faces the substrate, is set to be higher than or equal to 0.46 nc (nc: an upper limit side cut-off density of an X wave) and lower than nc. Thus, a high chevron distribution of electron density is formed in end portions of a magnetic field forming region, and a distribution of electron density having a lower peak value than those in the end portions is formed in a central portion of the magnetic field forming region. In this case, the periphery of a magnetic field crosses the inner wall of a vacuum chamber once between the ECR point and the substrate, and a space of one fourth or more of the wavelength of the X wave is formed between the periphery of the magnetic field and the inner wall of the vacuum chamber as the magnetic field runs downstream. Thus, it is possible to achieve an inplane uniform treatment when carrying out a treatment, such as a thin film deposition or etching, with ECR plasmas for a wafer.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Ionized layer chromatography technology and ionized layer delay correction method based on multi-scale subdivision
InactiveCN104007479AImprove delay calculation accuracyImprove computing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsDetection using electromagnetic wavesThree-dimensional spaceIonosphere
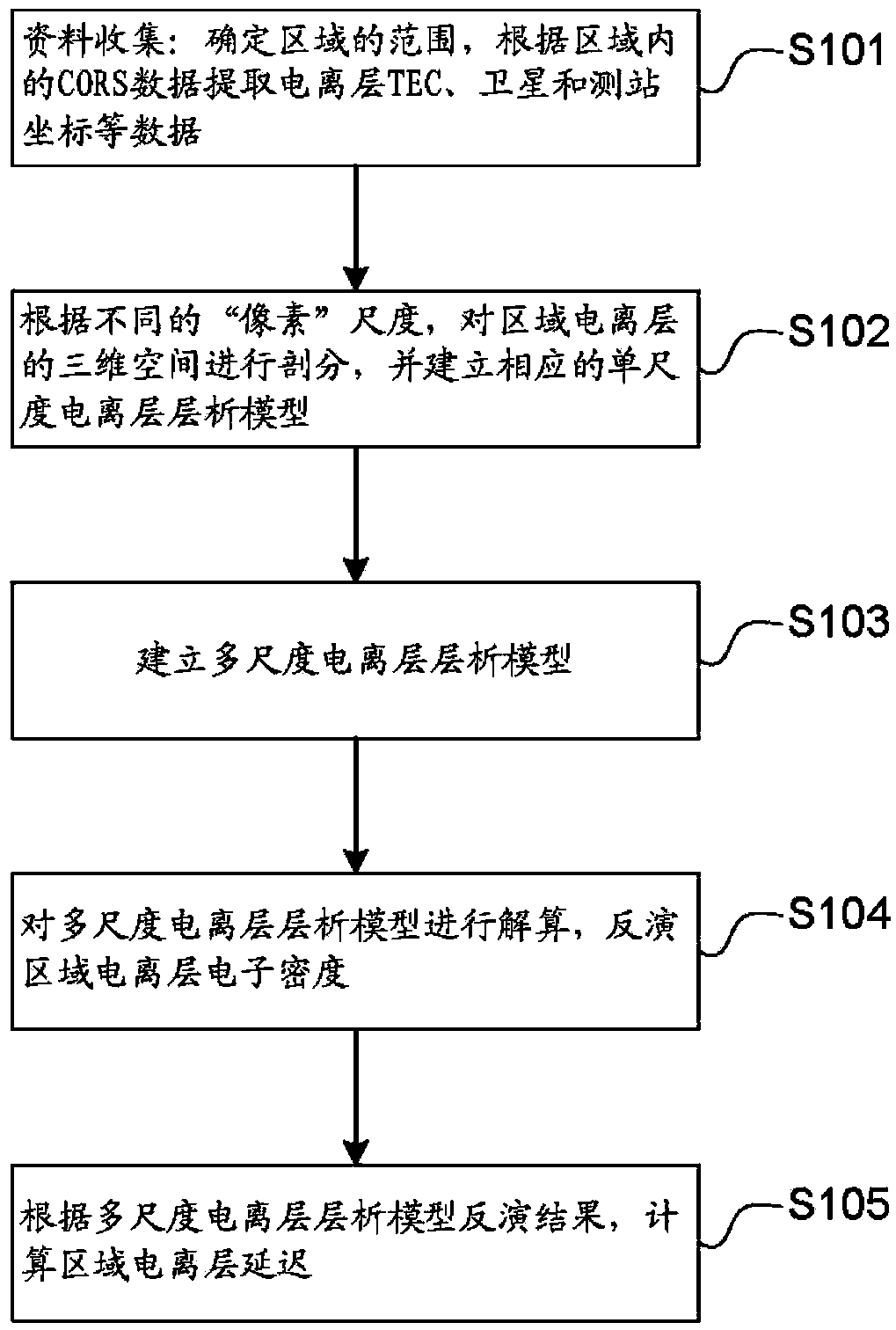
The invention discloses an ionized layer chromatography technology and an ionized layer delay correction method based on multi-scale subdivision. A three-dimensional space of an area ionized layer is subdivided according to different 'pixel' scales to obtain a plurality of different single-scale ionized layer chromatography models, unknown variables of the models are uniformly solved and weighted according to different weight factors to obtain solutions of a multi-scale chromatography model, and electron density distribution of the area ionized layer is reconstructed to obtain delay of the area ionized layer. The space activity rule of the reconstructed ionized layer is high in fitting degree, high in timeliness and convenient to use. According to the obtained area ionized layer, the delay quantity solution result is high in accuracy, so that the application range of CORS measurement results is enlarged. It is proved through a lot of project case application result analysis that the electron density distribution of the area ionized layer reconstructed through the method is more smooth and reasonable compared with a traditional single-scale ionized layer chromatography model, and ionized layer delay correction accuracy is improved by 30% on average.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Soft x-ray laser based on z-pinch compression of rotating plasma
InactiveUS7679027B2Increase currentImprove uniformityBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsBeam/ray deflecting arrangementsElectric dischargeStimulated emission
A method and apparatus for producing soft x-ray laser radiation. A low pressure plasma column is created by electric discharge or by laser excitation inside a rotating containment tube. Rotation of the plasma is induced by viscous drag caused by rotation of the tube, or by magnetically driven rotation of the plasma as it is created in a plasma gun in the presence of an axial magnetic field, or both. A high power electrical discharge is then passed axially through the rotating plasma column to produce a rapidly rising axial current, resulting in z-pinch compression of the rotating plasma column, with resultant stimulated emission of soft x-ray radiation in the axial direction. A rotating containment tube used in combination with magnetically driven rotation of the plasma column results in a concave electron density profile that results in reduced wall ablation and also reduced refraction losses of the soft x-rays.
Owner:FARTECH
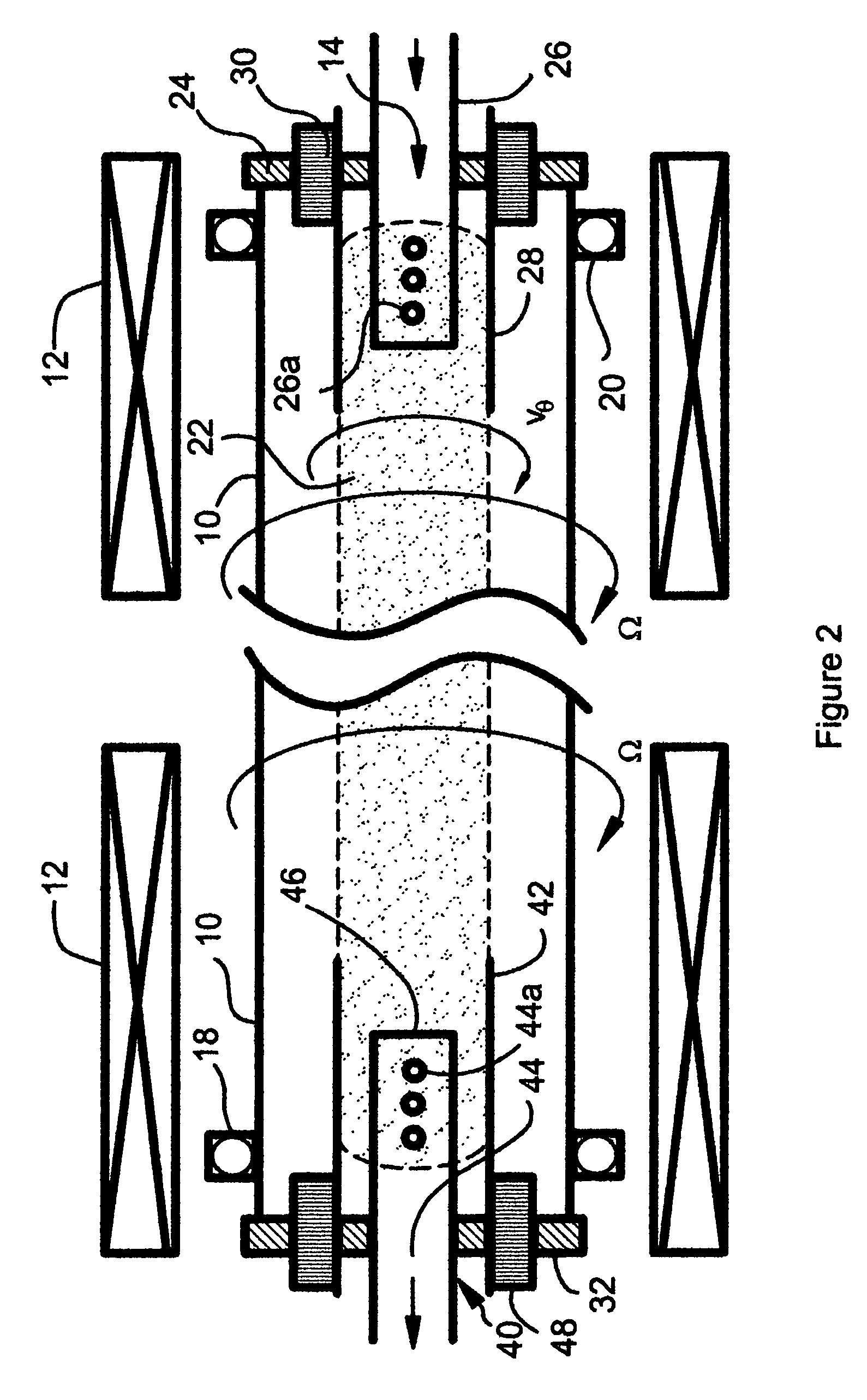
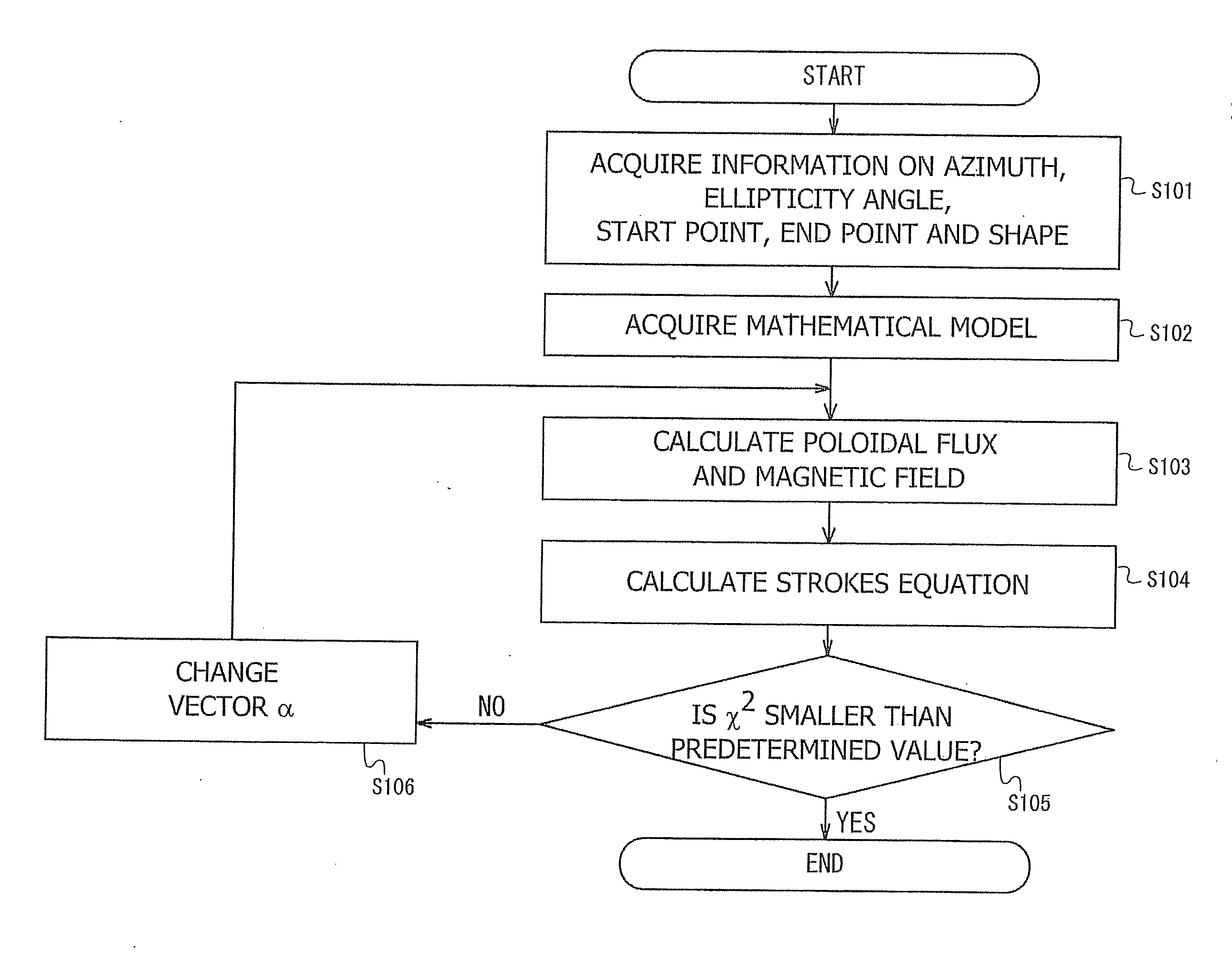
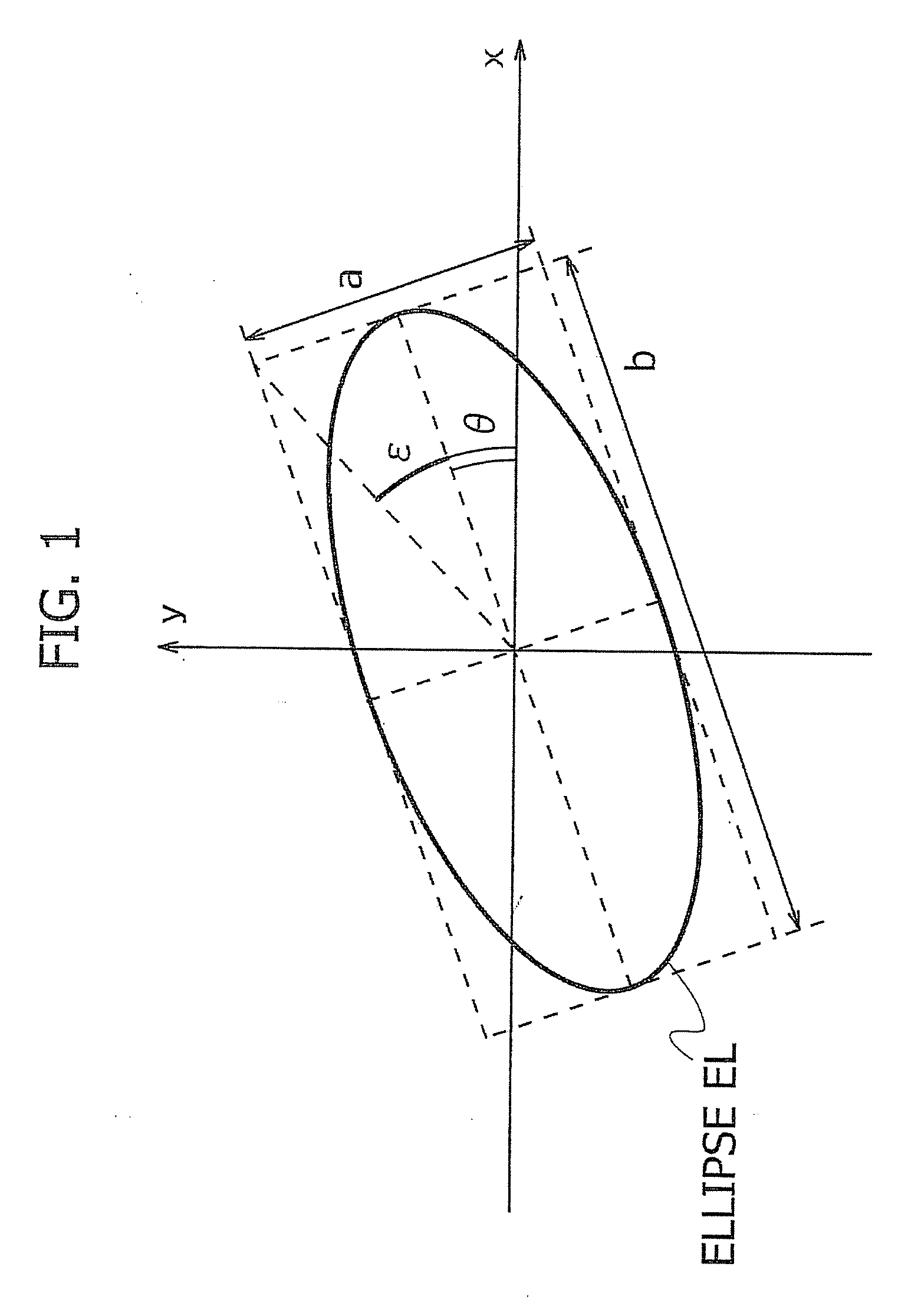
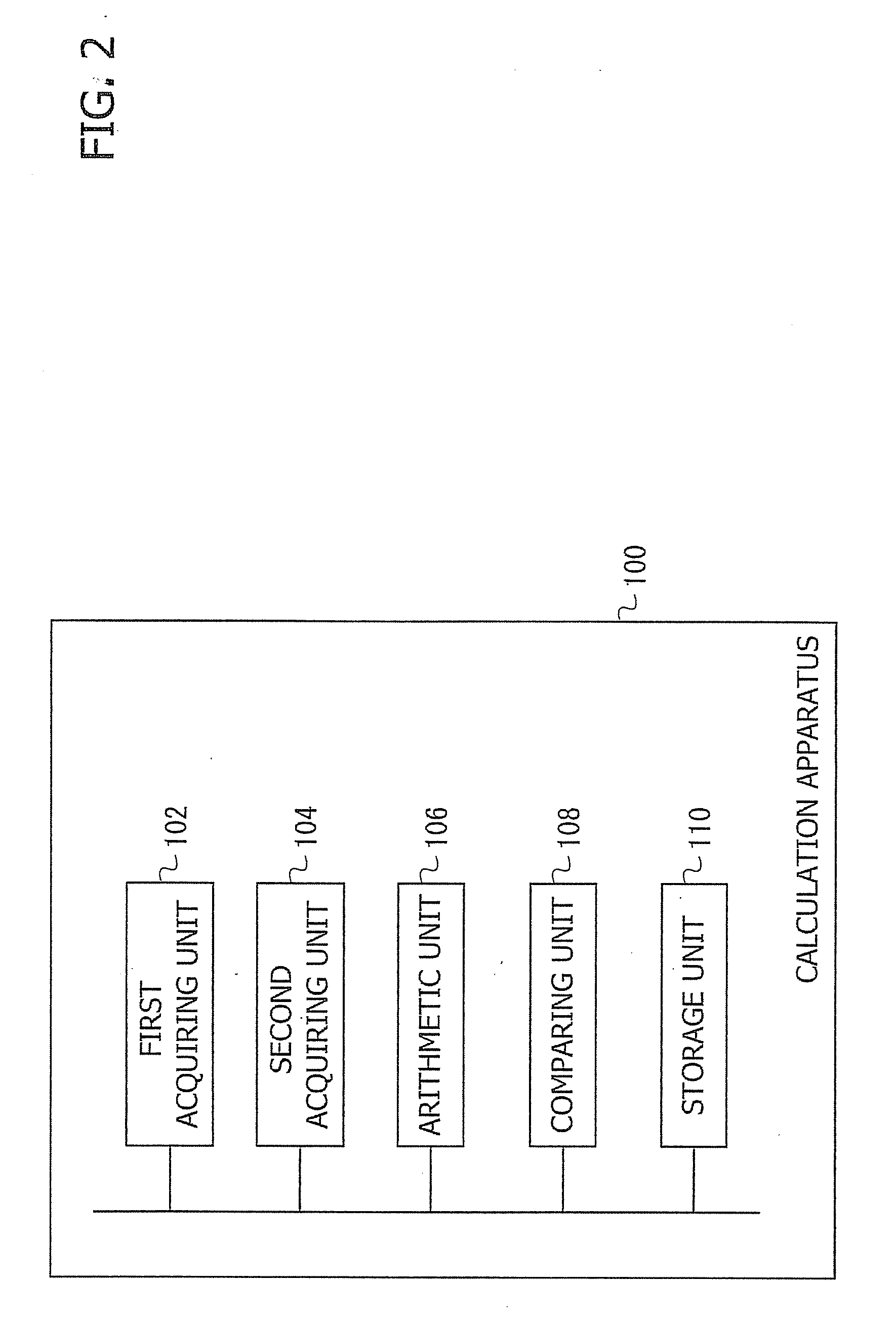
Calculation apparatus and calculation method of magnetic field, electron density and electron temperature
InactiveUS20130158961A1Difficult to obtainCurrent/voltage measurementMagnetisation measurementsElectron temperatureLaser beams
A calculation apparatus comprising: an acquiring unit to acquire an azimuth and an ellipticity angle of a polarization plane of a laser beam passing through a plasma; and a calculation unit to calculate at least one of a magnetic field profile, an electron density profile and an electron temperature profile in the plasma on the basis of the azimuth and the ellipticity angle.
Owner:JAPAN ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY INDEPENDANT ADMINISTRATIVE CORP
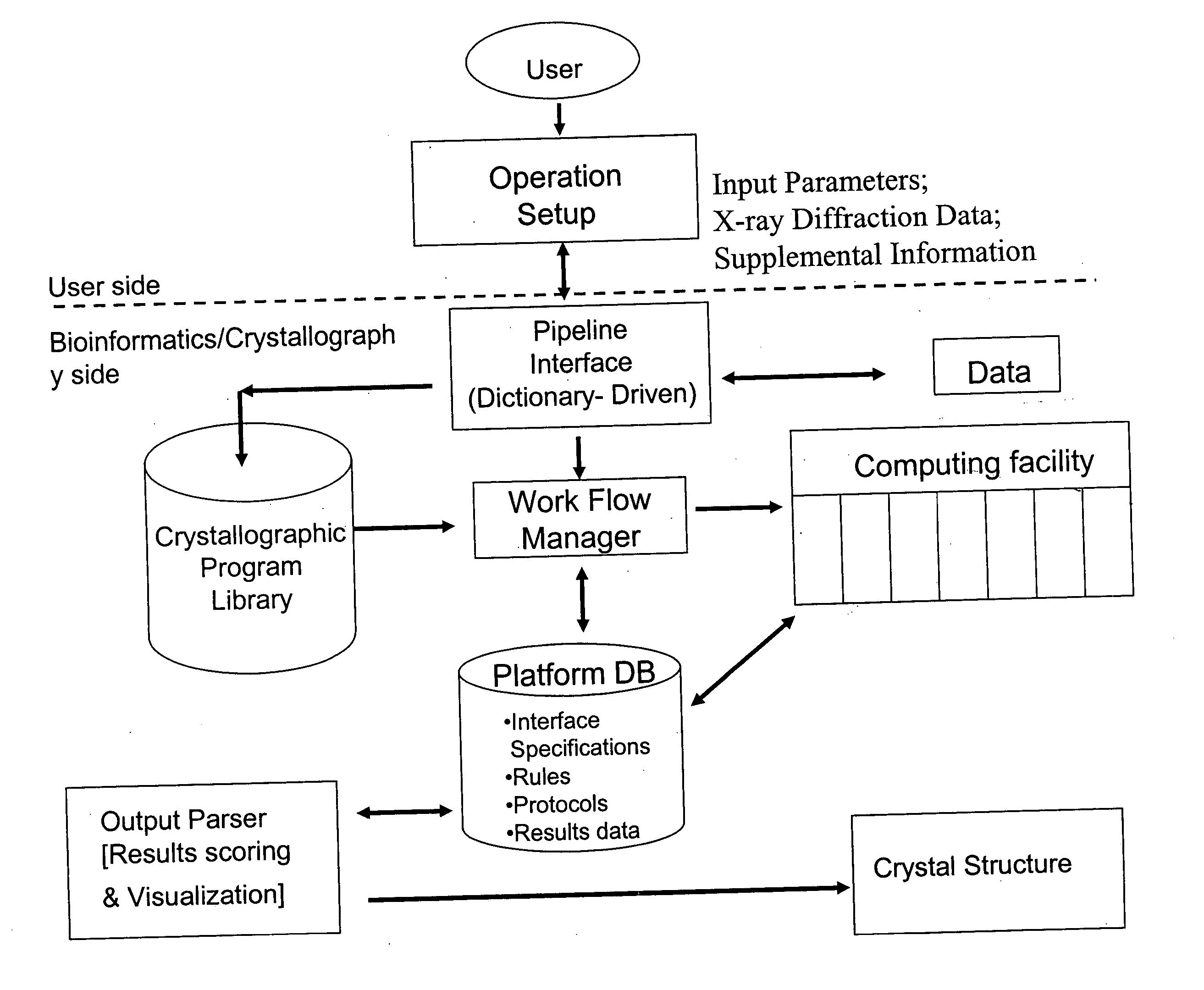
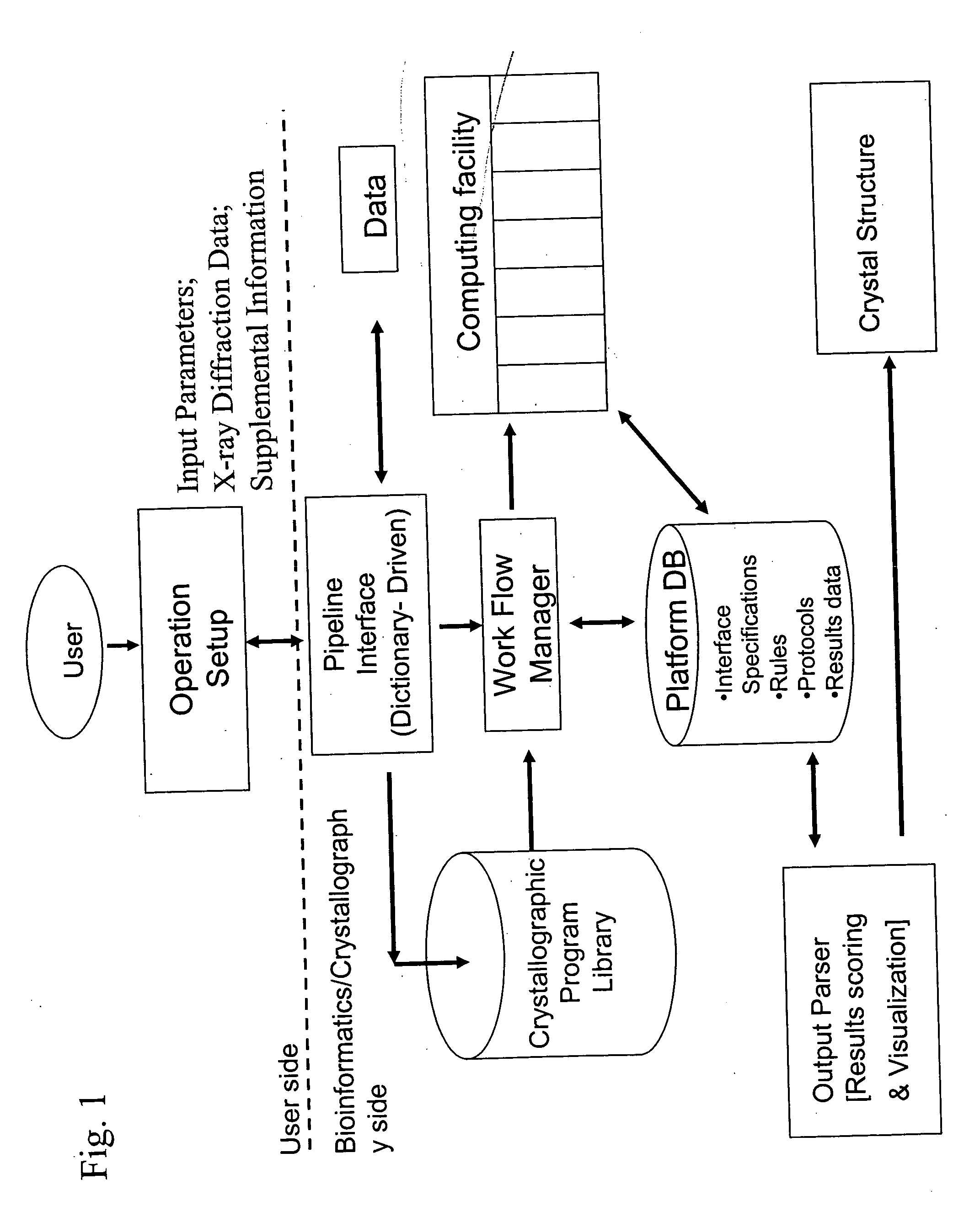
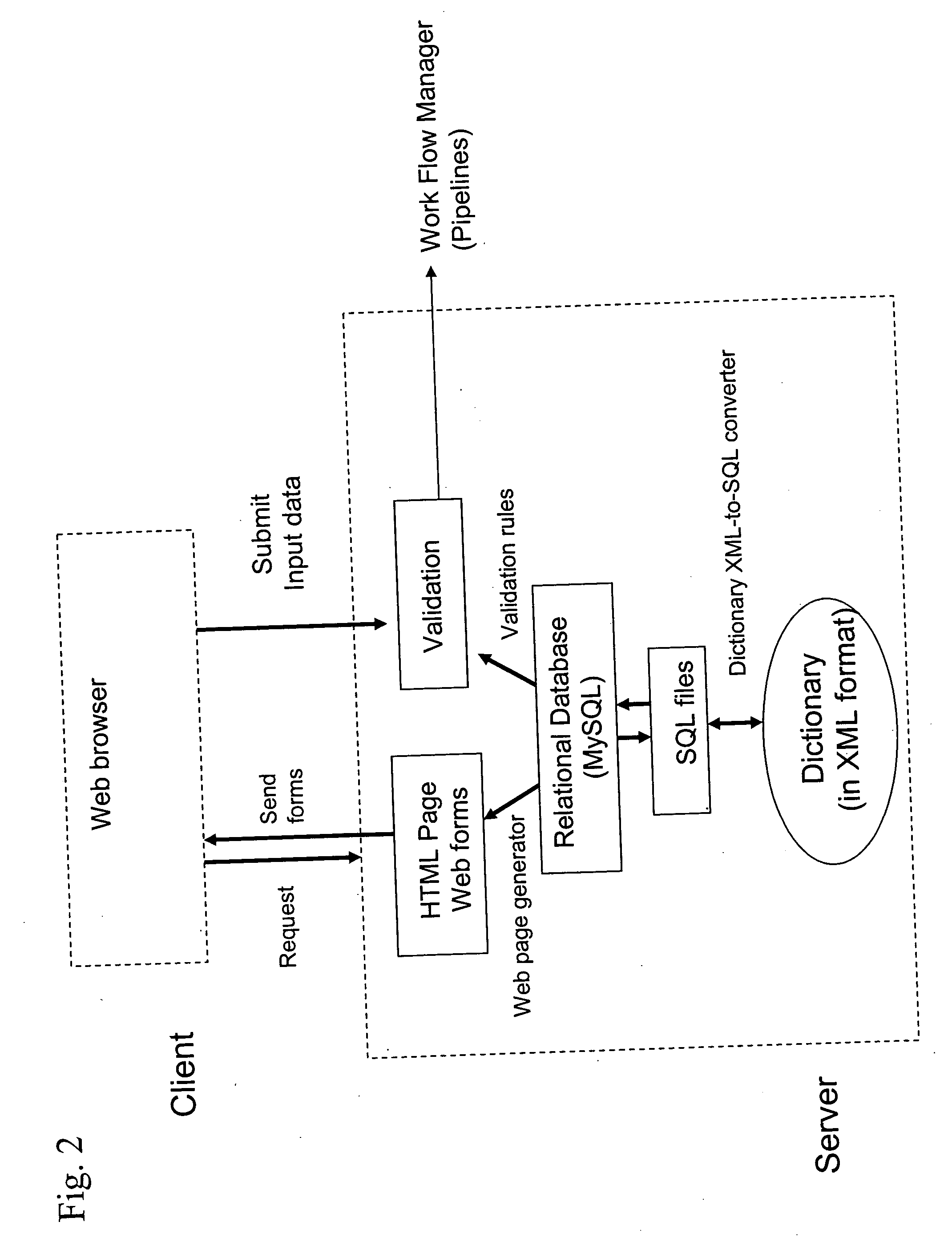
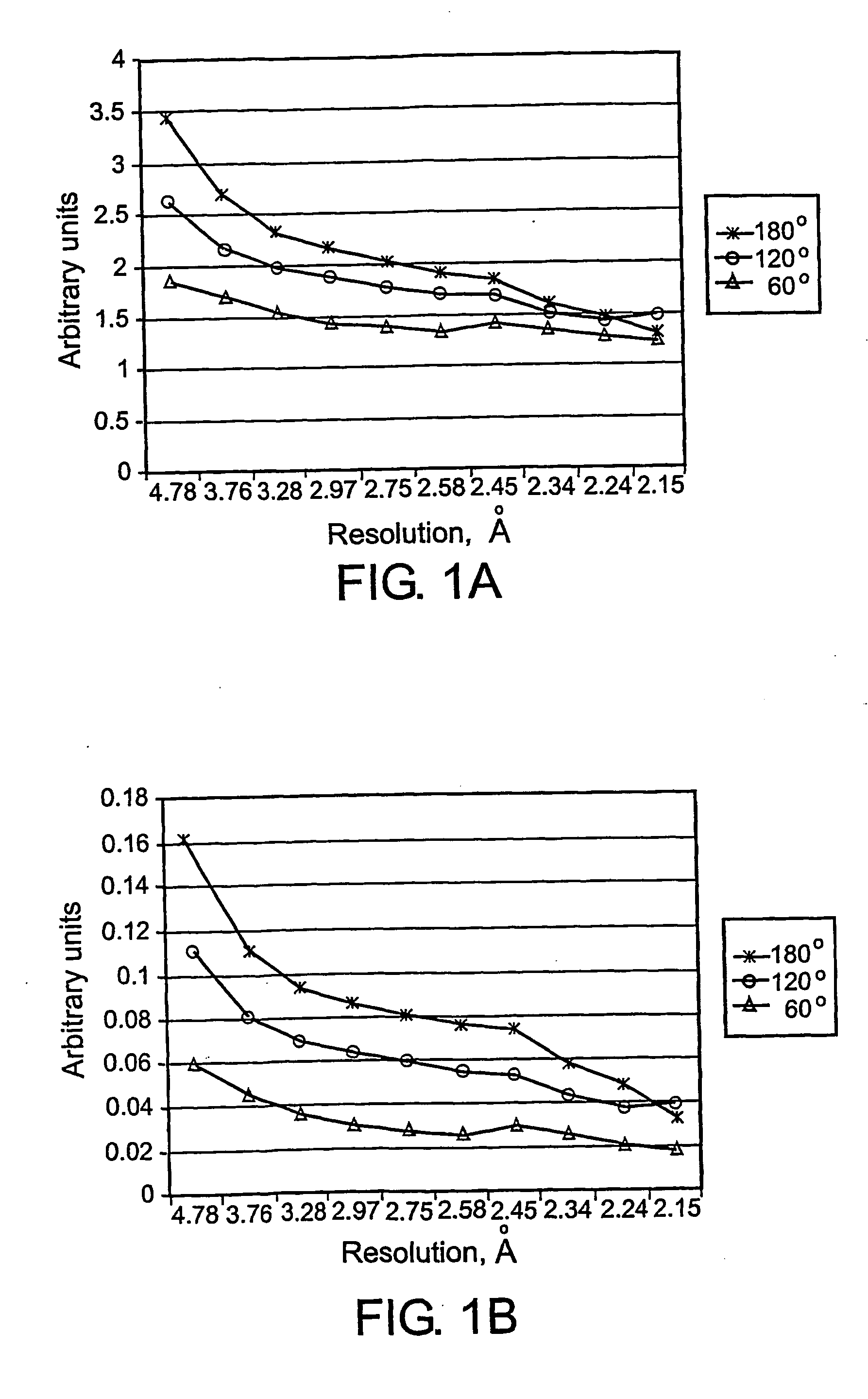
High-throughput methods for determining electron density distributions and structures of crystals
InactiveUS20060029184A1Efficient constructionLarge parameter spaceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMolecular entity identificationData setHigh flux
Disclosed are high-throughput methods for determining crystal structures from X-ray diffraction data, for example high-throughput crystal structure determination methods employing flexible, high-throughput modular computational pipelines, such as Bioperl computational pipelines. High-throughput methods for determining crystal structures can be fully or partially automated, and can be fully or partially computer executed. Crystal structure determination methods employing a pipeline interface, work flow manager and / or output parsers can be used to optimize the amount of structural information derived from an X-ray diffraction data set and increase the efficiency of calculating crystal structures from X-ray diffraction data.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
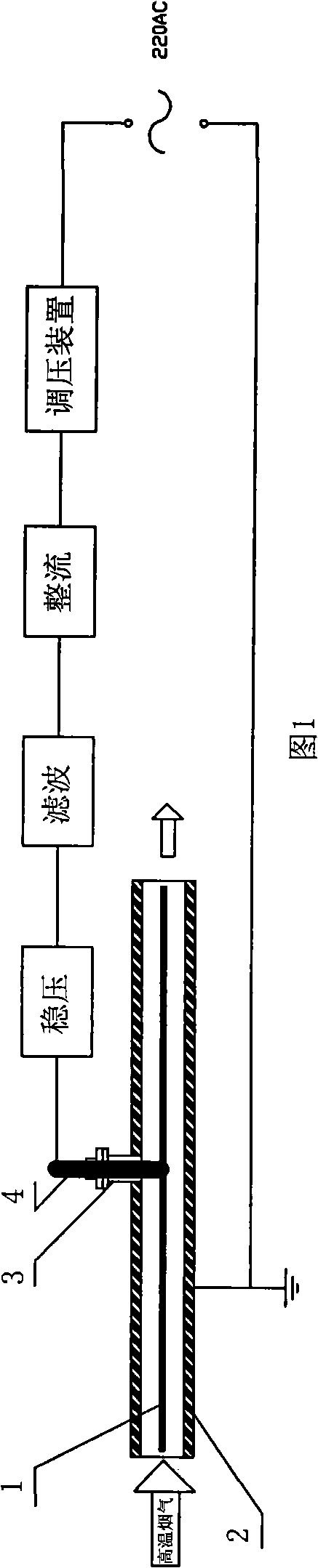
High-temperature flue gas thermal electron emission type particulate matter charge device
InactiveCN101322957AImprove uniformityImprove high temperature resistanceParticle charging/ionising stationsElectron density distributionCorona discharge
The invention discloses a particulate charged device with high temperature flue gas thermal electron-emission type, which consists of an emission electrode bar (1) and a conductive cylinder body (2); the composite functional material of rare-earth tungsten is adopted by the emission electrode bar as a thermal electron-emission cathode; the conductive cylinder body is grounded as a thermal electron-emission anode; an insulated sleeve (3) is arranged at the middle part of the conductive cylinder body; a conductive suspended bar (4) penetrates the insulated sleeve and the emission electrode bar is suspended into the conductive cylinder body. By adopting the composite functional material of rare-earth tungsten to produce thermal electronic-emission electrode, the performance of high-temperature resistance of the device of the invention is improved, thus causing the working temperature of device to be capable of reaching 1,200 DEG C; since the charged area adopts a ring structure, the characteristics of thermal electron-emission can be embodied fully, thus improving the uniformity of the density of the electron distribution; since the thermal electron emission technology is adopted, the current density in the charged area is 3 to 4 orders of magnitude higher than that of traditional charged technology with corona discharging type.
Owner:CHANGSHU NANJING NORMAL UNIV DEV RES INST
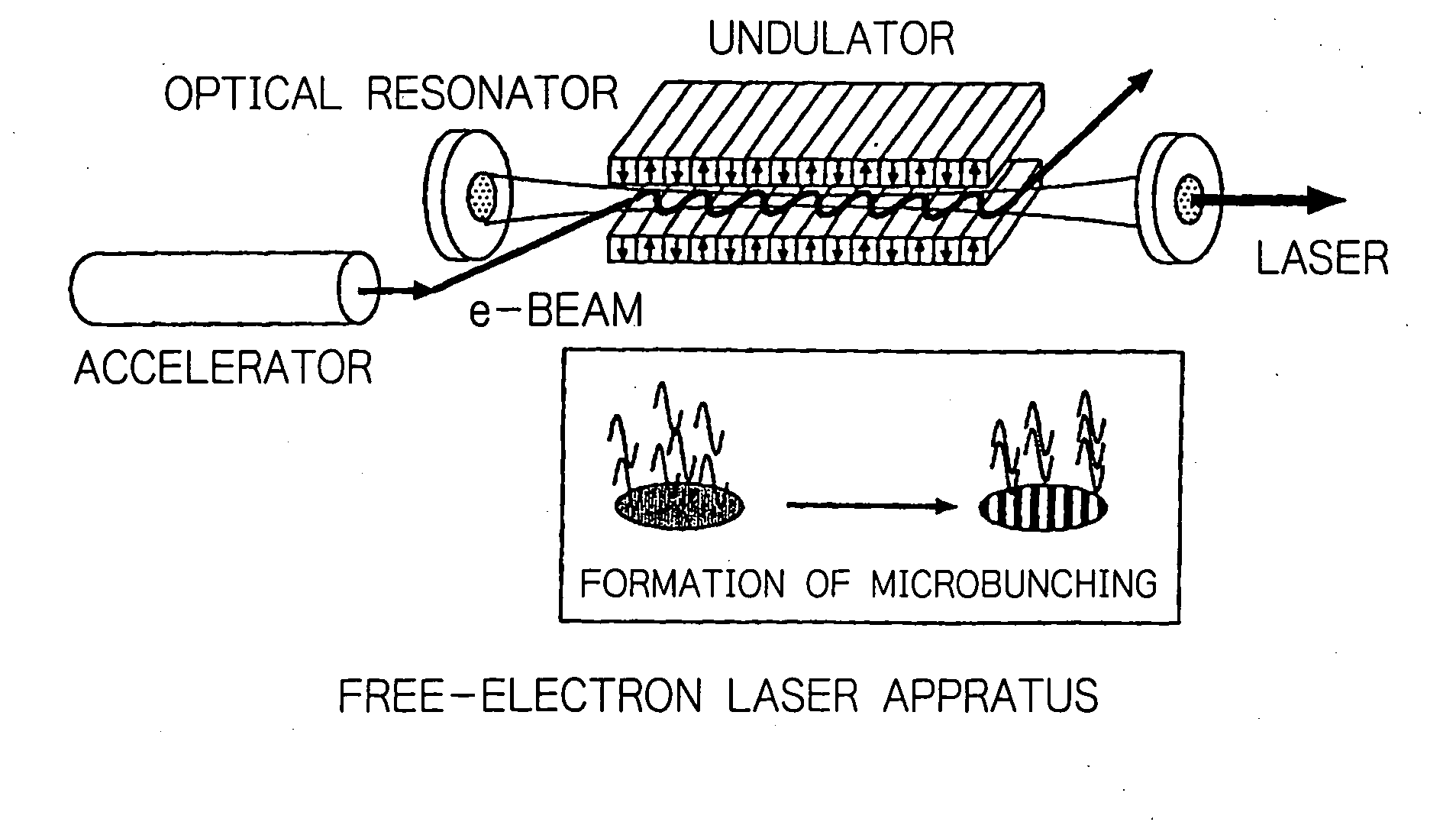
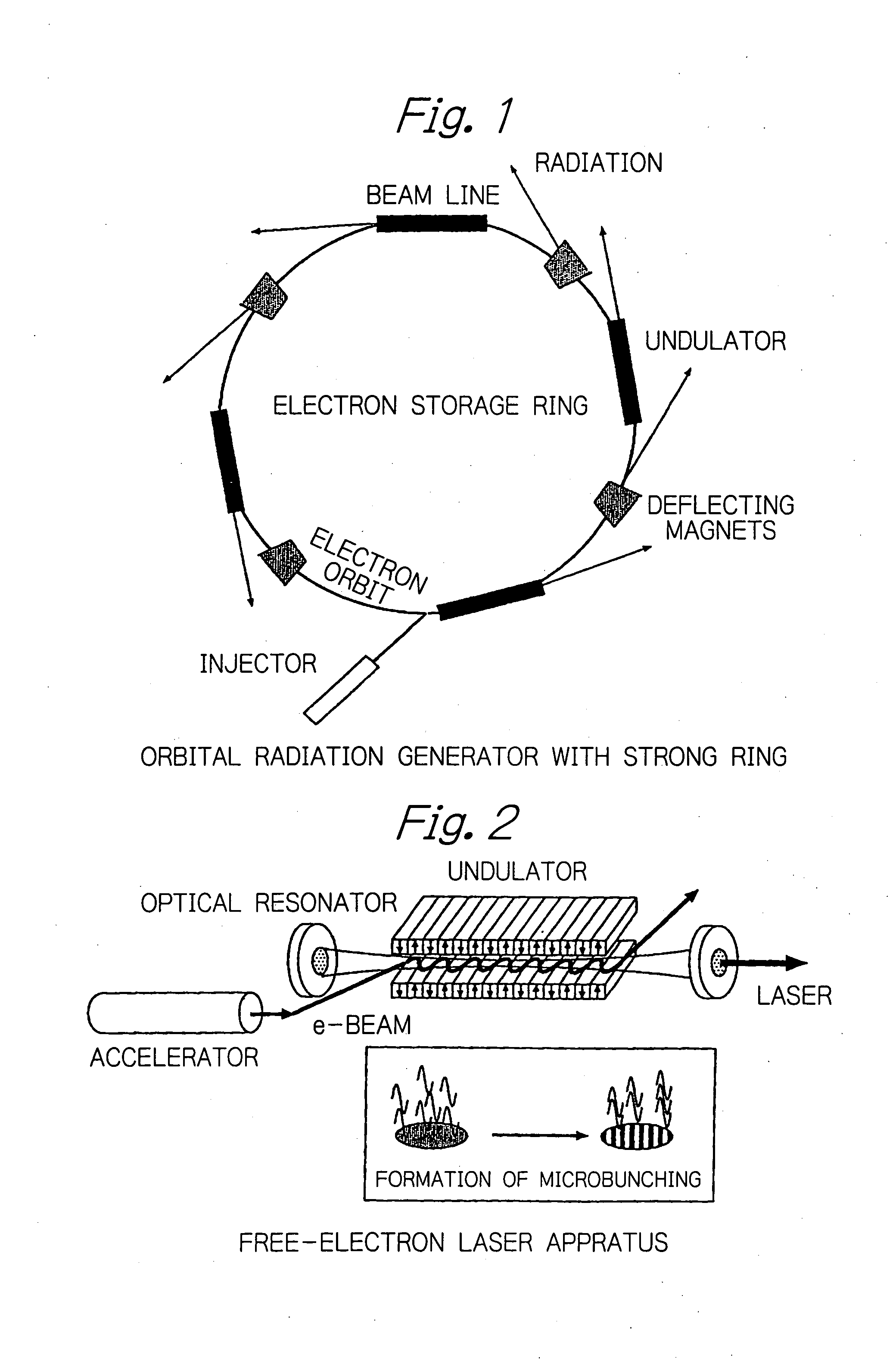
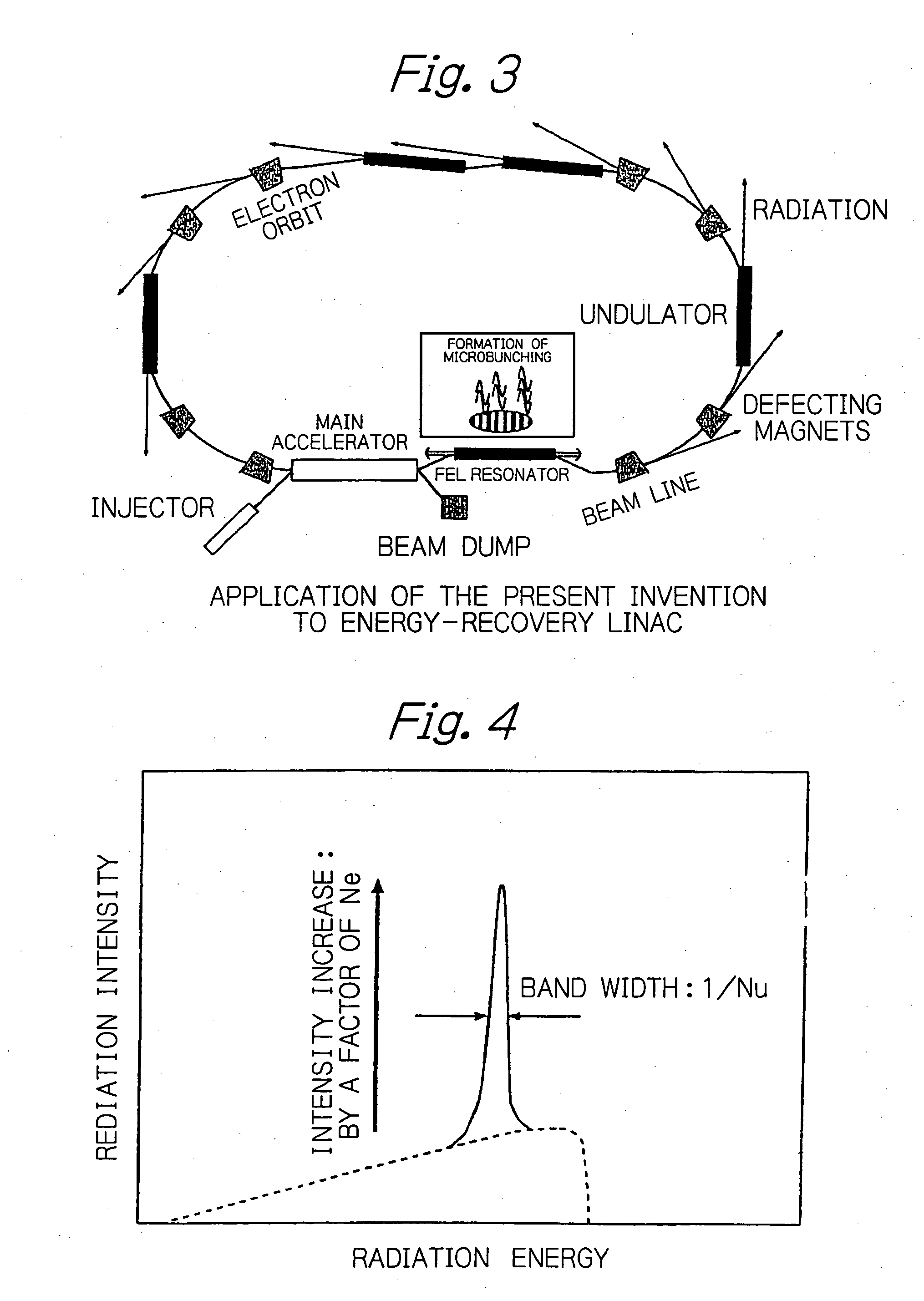
Method for enabling high-brightness, narrow-band orbital radiation to be utilized simultaneously on a plurality of beam lines
InactiveUS20050175042A1Radiation/particle handlingExcitation process/apparatusEnergy recovery linacElectron bunches
In an electron accelerator such as an electron storage ring, a linac or an energy-recovery linac, accelerated electron bunches are subjected to light-electron interaction to have a varying profile of electron density and the thus modulated electron bunches are passed between deflecting magnets or injected into an undulator to generate high-brightness, narrow-band orbital radiation, thereby enabling high-brightness, narrow-band orbital radiation to be utilized simultaneously on a plurality of beam lines.
Owner:JAPAN ATOM ENERGY RES INST
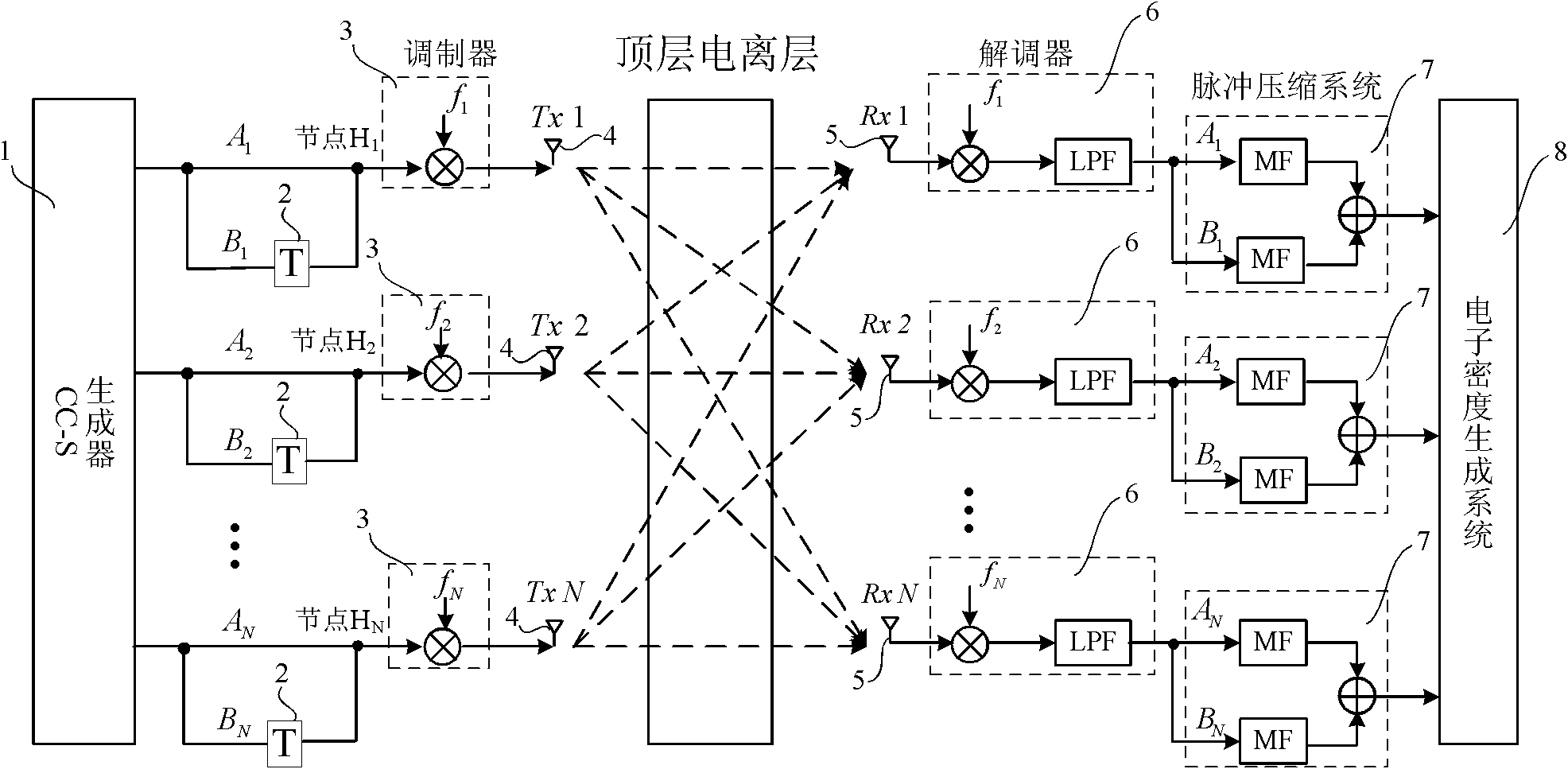
Top ionosphere detection space-borne MIMO radar system
InactiveCN102073041AHigh azimuth resolutionImprove work efficiencyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionIonospheric soundingIonogram
The invention discloses a top ionosphere detection space-borne MIMO radar system which belongs to the field of radar technology and compromises a complete complementary sequence generator, a pulse period delayer, a modulator, emission antennae, reception antennae, a demodulator, a pulse compression system and an electron density distribution generation system. The complete complementary sequence generator simultaneously generates N pairs of complementary sequences. The pulse period delayer alternatively inputs two complementary sequences to the modulator. N pairs of signals are modulated at N carrier frequencies respectively and sent out by the N emission antennae, and the echo signals are received by the N reception antennae. The demodulator demodulates signals on the N carrier frequencies. The signals are sent to the electron density distribution generation system after pulse compression to generate a two dimensional ionogram. The space-borne MIMO radar system is used for the top ionosphere detection. Compared with the prior ionosphere detector, the space-borne MIMO radar system of the invention can generate two dimensional ionograms and has very high orientation resolution and high work efficiency.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Ionized layer chromatography method and system based on high-orbit satellite-borne SAR system
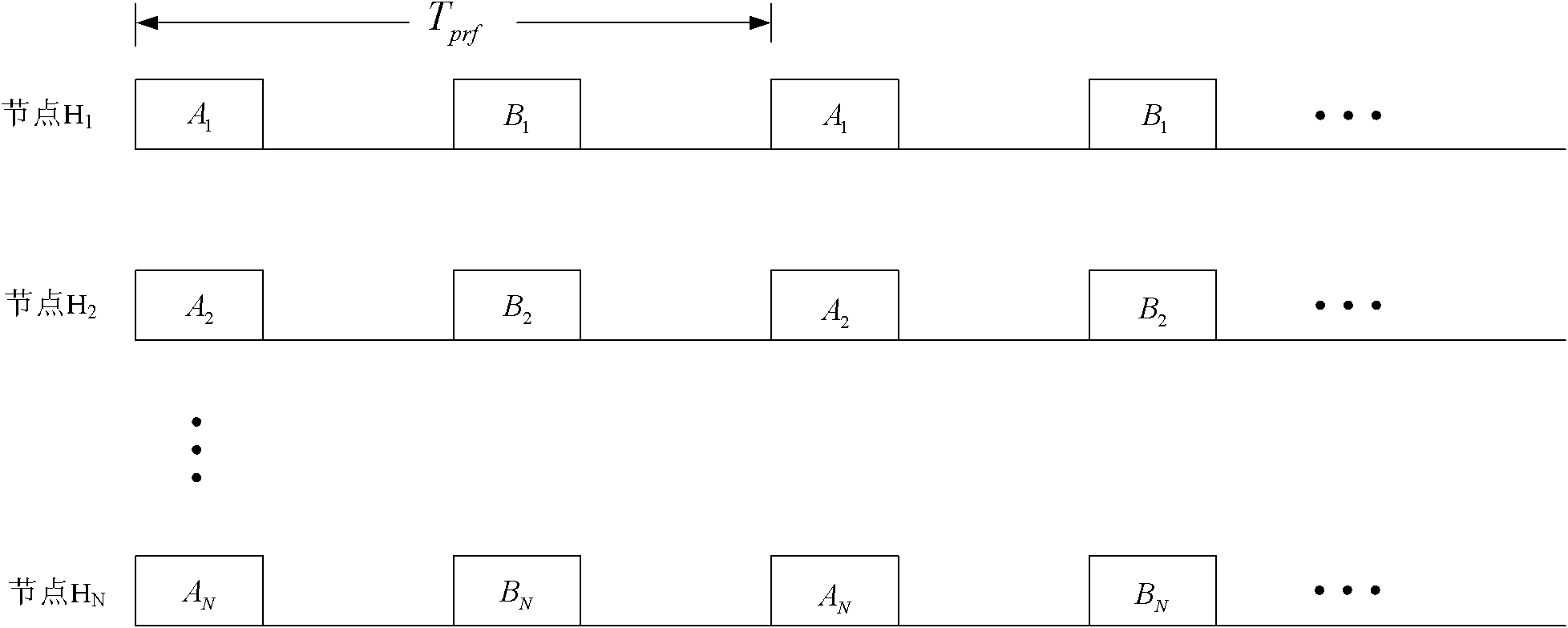
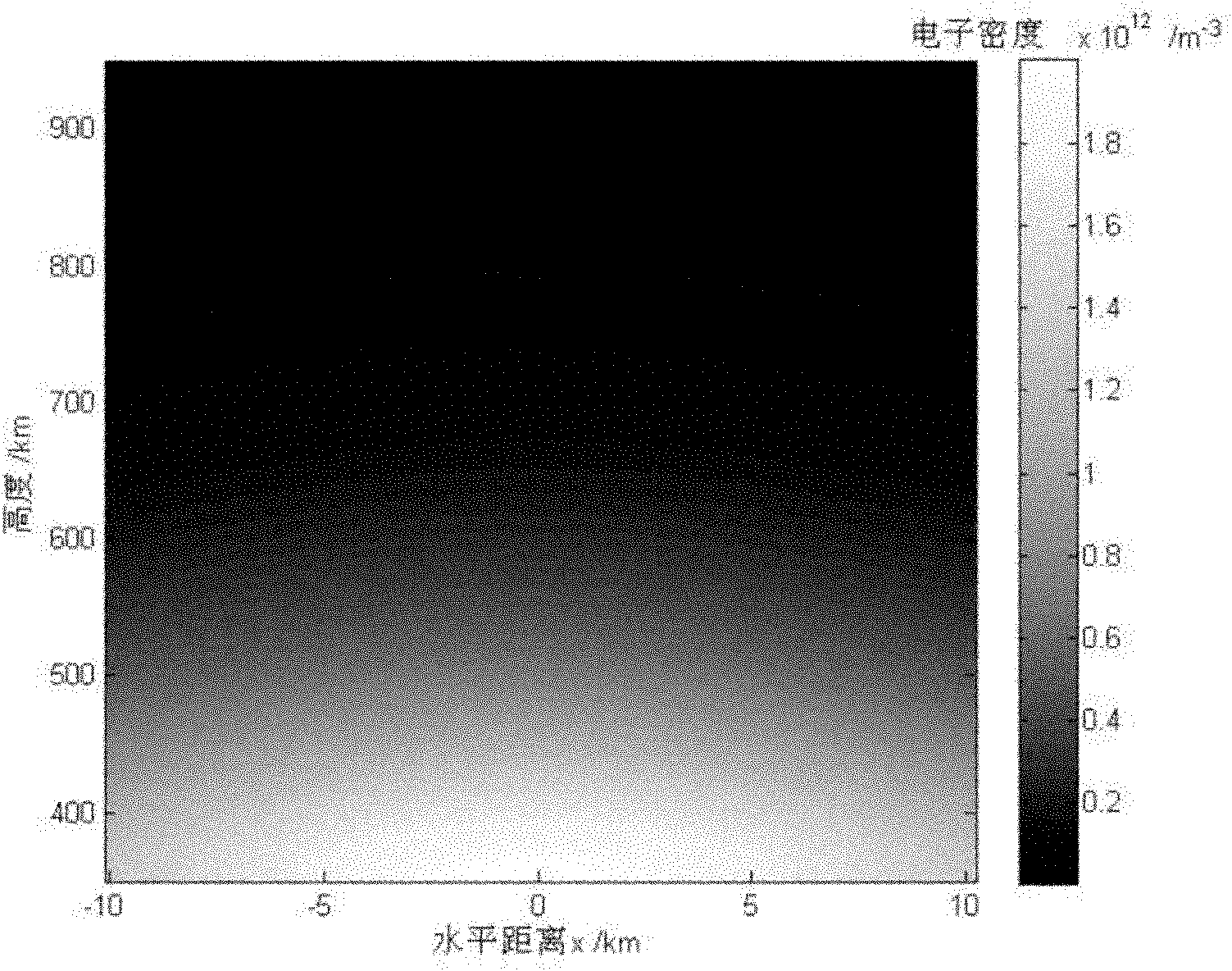
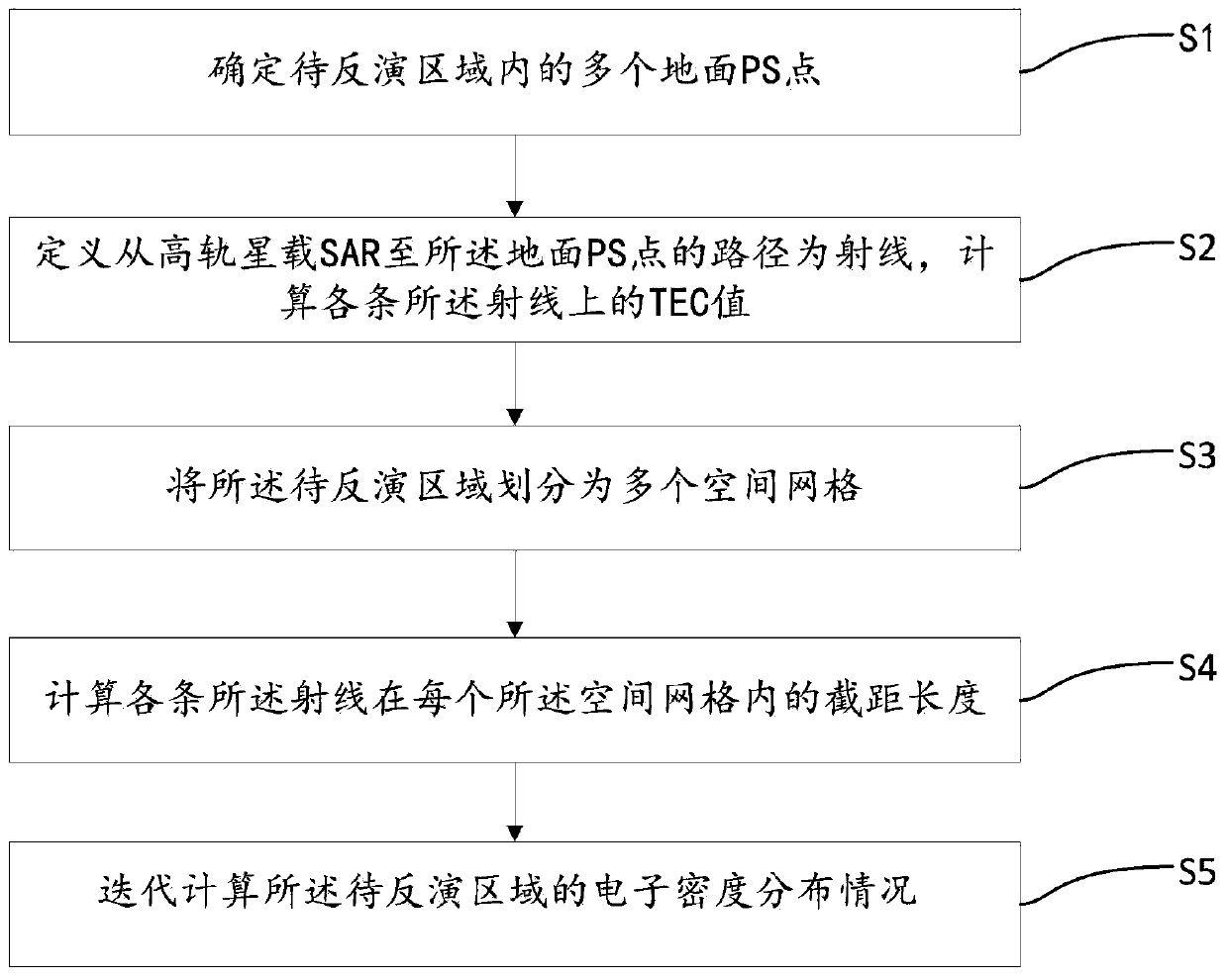
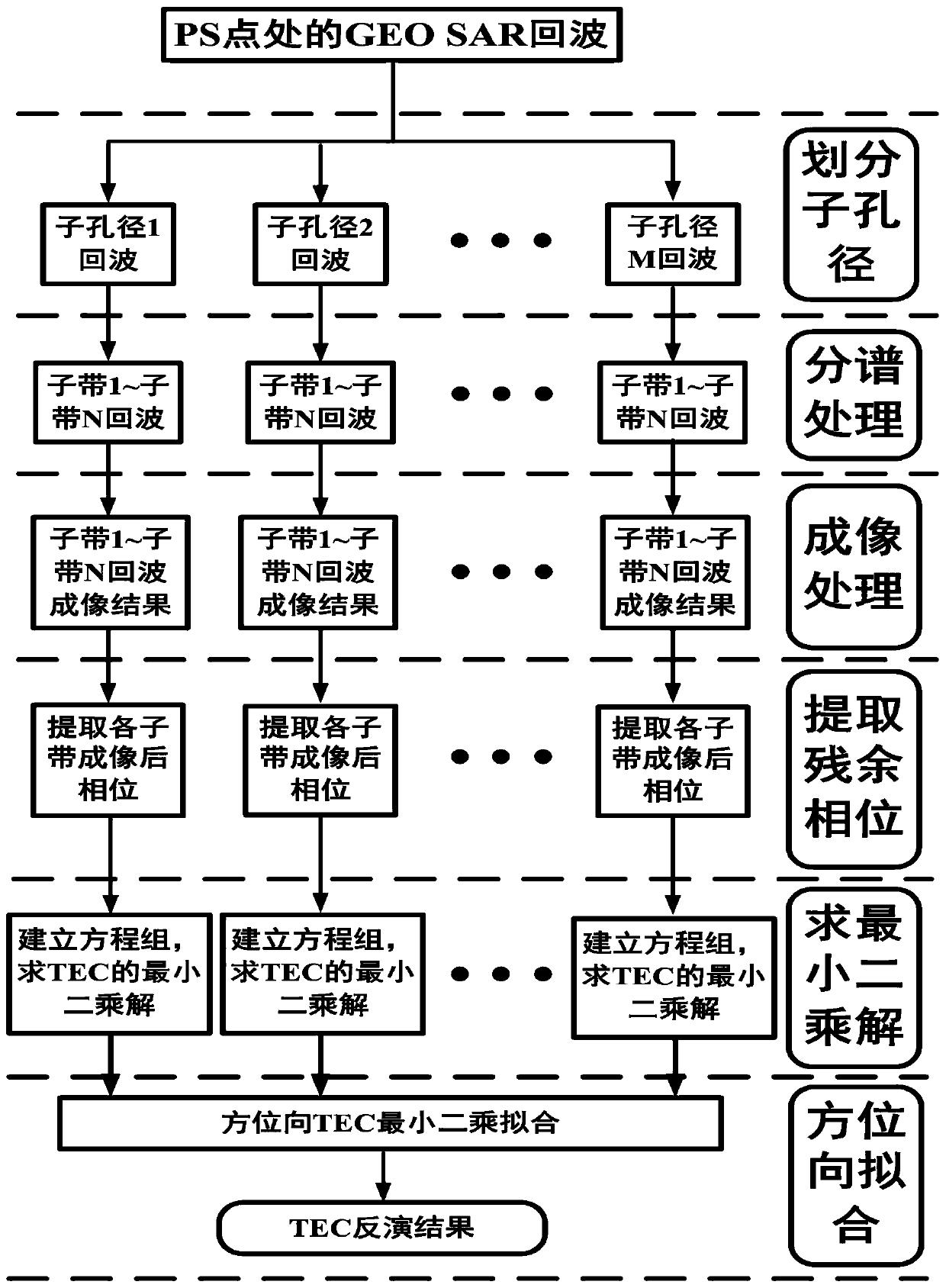
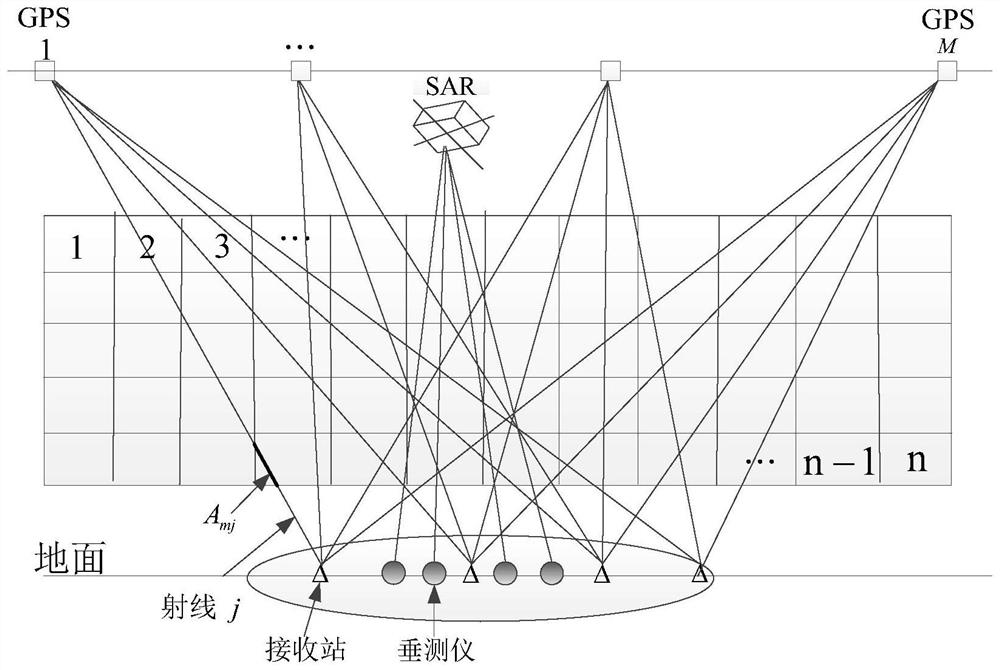
The invention discloses an ionized layer chromatography method and system based on a high-orbit satellite-borne SAR system. The ionized layer chromatography method based on the high-orbit satellite-borne SAR system comprises the following steps: determining a plurality of ground PS points in an area to be inverted; defining a path from a high-orbit satellite-borne SAR to a ground PS point as a ray, and calculating a TEC value on each ray; dividing the to-be-inverted area into a plurality of space grids; calculating an intercept length of each ray in each space grid; and iteratively calculatingan electron density distribution condition of the to-be-inverted area according to a formula, wherein Nejk+1 is an electron density value of a jth space grid after (k+1)th iteration, TECi is a TEC value of an ith ray, Ai is a length of the ith ray, Aij is the intercept length of the ith ray in a jth space grid, lambda k is a relaxation factor, and a value range is 0-1. In the invention, a capability of accurately inverting TEC of an ionized layer in real time in a complex environment can be achieved, and meanwhile accurate inversion of an electron density in a real-time large-range space canbe achieved.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF ELECTRONICS & INFORMATION TECH OF CETC
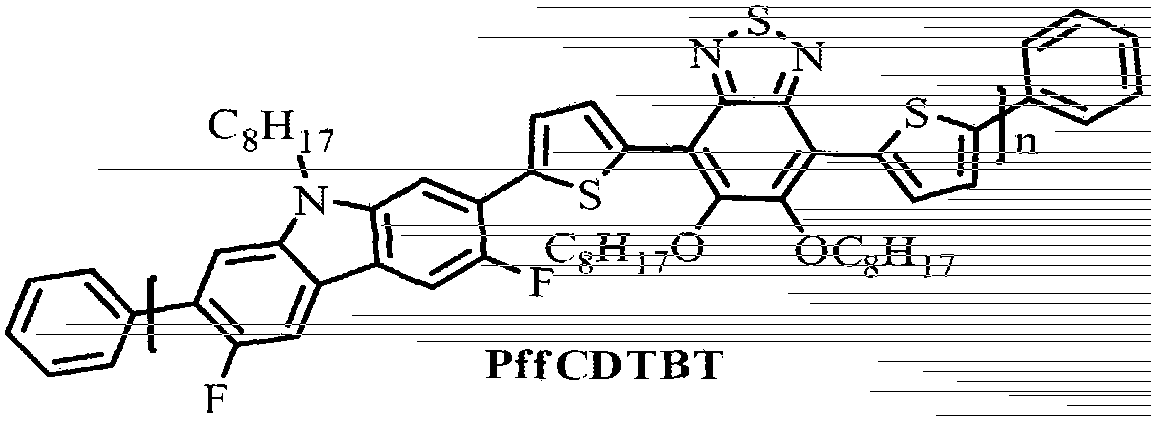
Preparation of novel fluorine-containing narrow band gap conjugated polymer material
InactiveCN103421166ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolymer scienceOrganic field-effect transistor
The invention discloses a preparation method for a novel fluorine-containing narrow band gap conjugated polymer material and applications. The structure of the fluorine-containing narrow band gap conjugated polymer is shown in the formula I, wherein n is an integer which is more than or equal to 4. At present, conjugated polymers with main chains with structures of alternate donors and acceptors are the focus of present research. Fluorine-containing organic conjugated polymers often have excellent thermostability, oxidation stability, corrosion resistance, hydrophobicity and lipophobicity fluoride substrates and electron density distribution overturn of fluorate aromatic rings. Some research on applications of fluorine substituted conjugated polymers in organic field effect transistors and organic luminescence diodes have been studied. But fluorine substituted materials are rare, especially as P type semiconductors, in applications of photovoltaic materials.
Owner:李翠红 +2
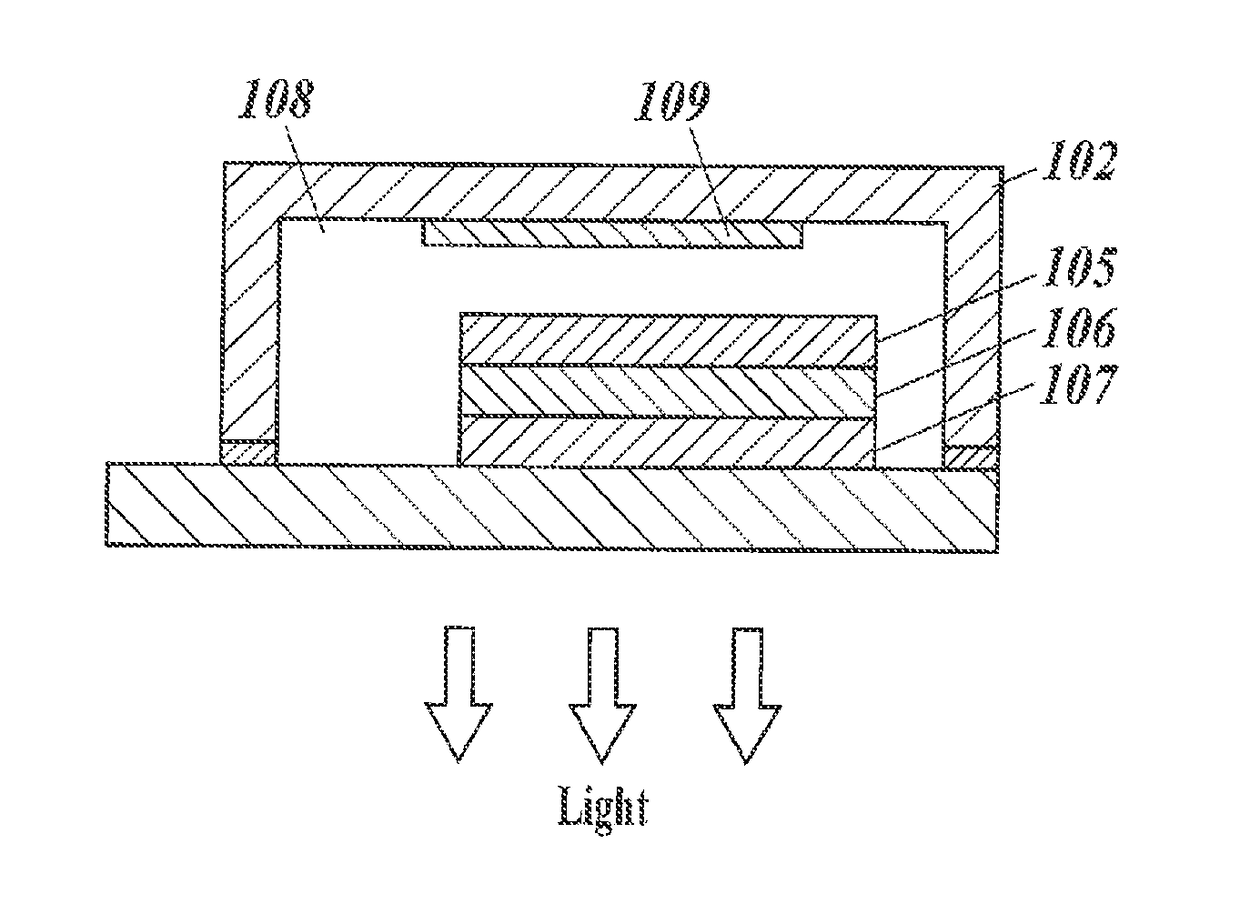
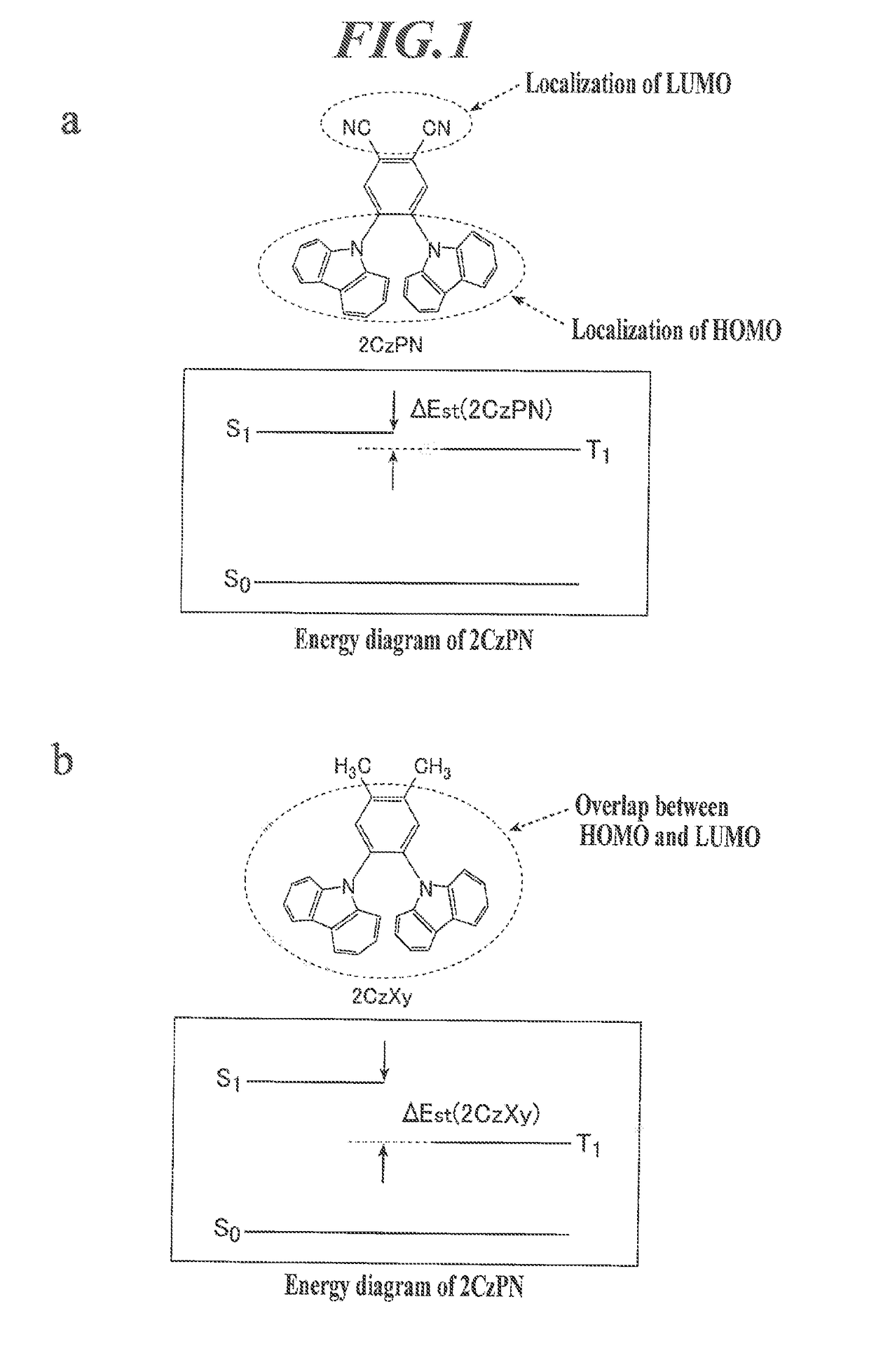
Organic electroluminescent device, thin luminous film, display apparatus, and lighting apparatus
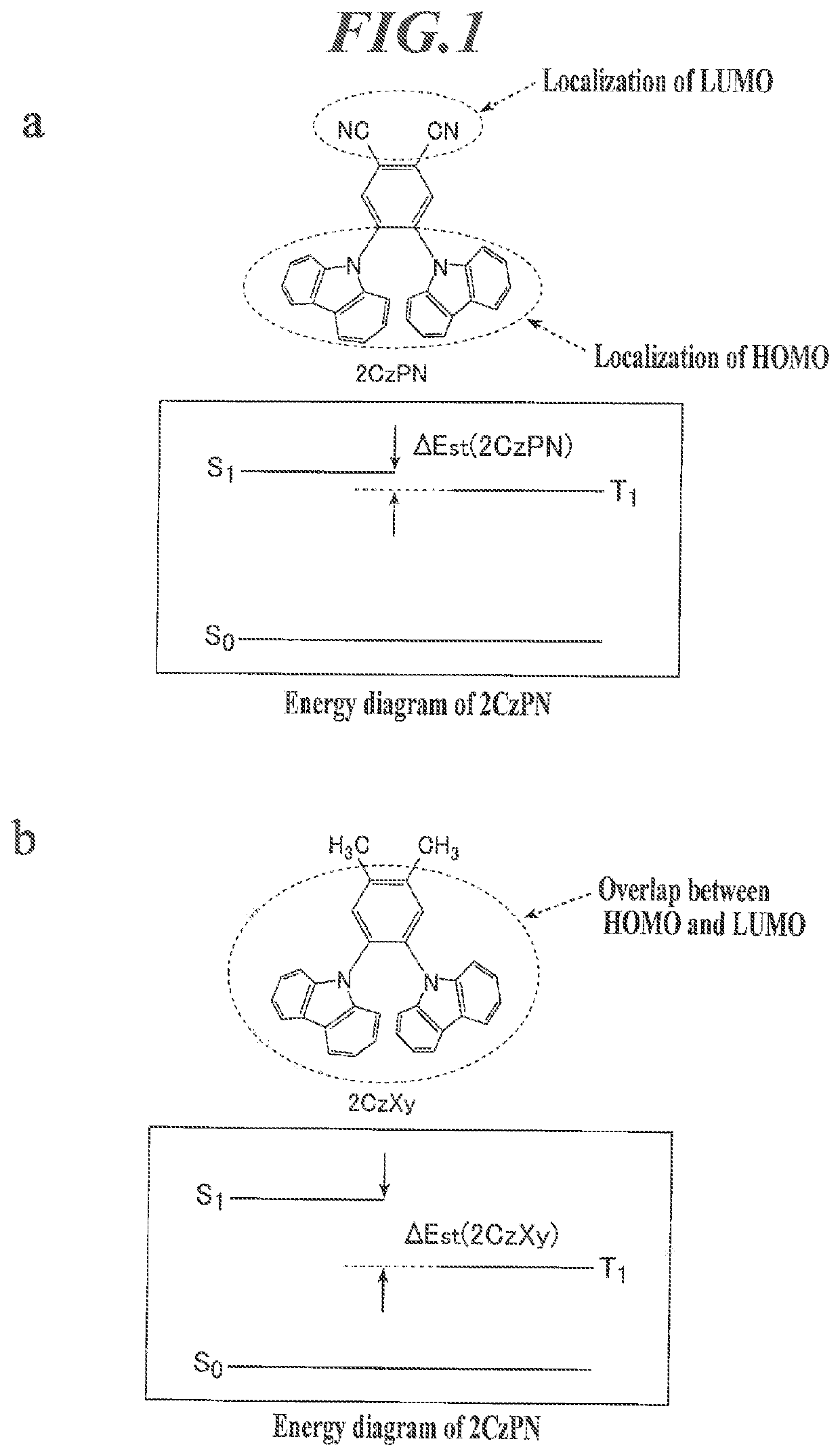
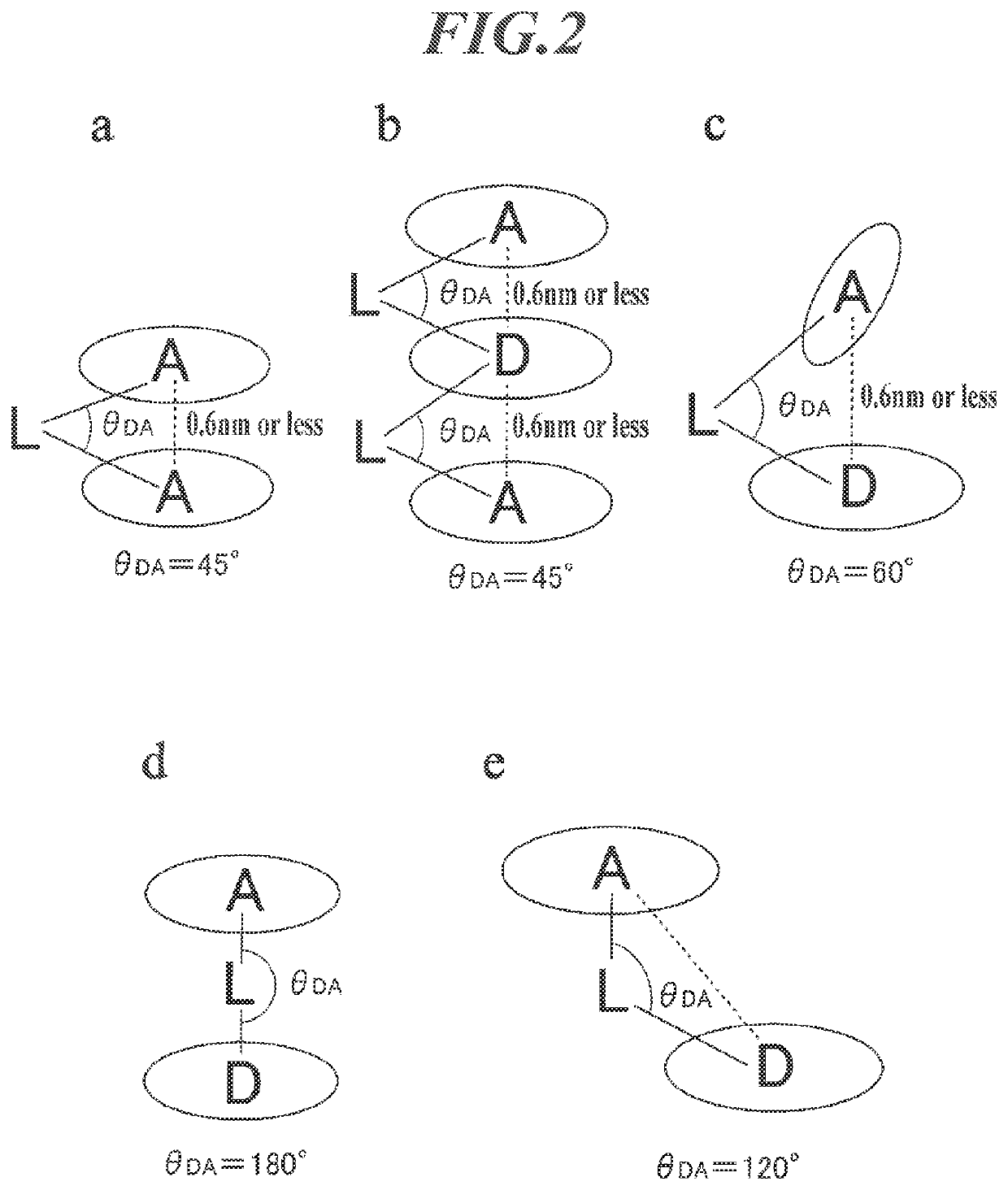
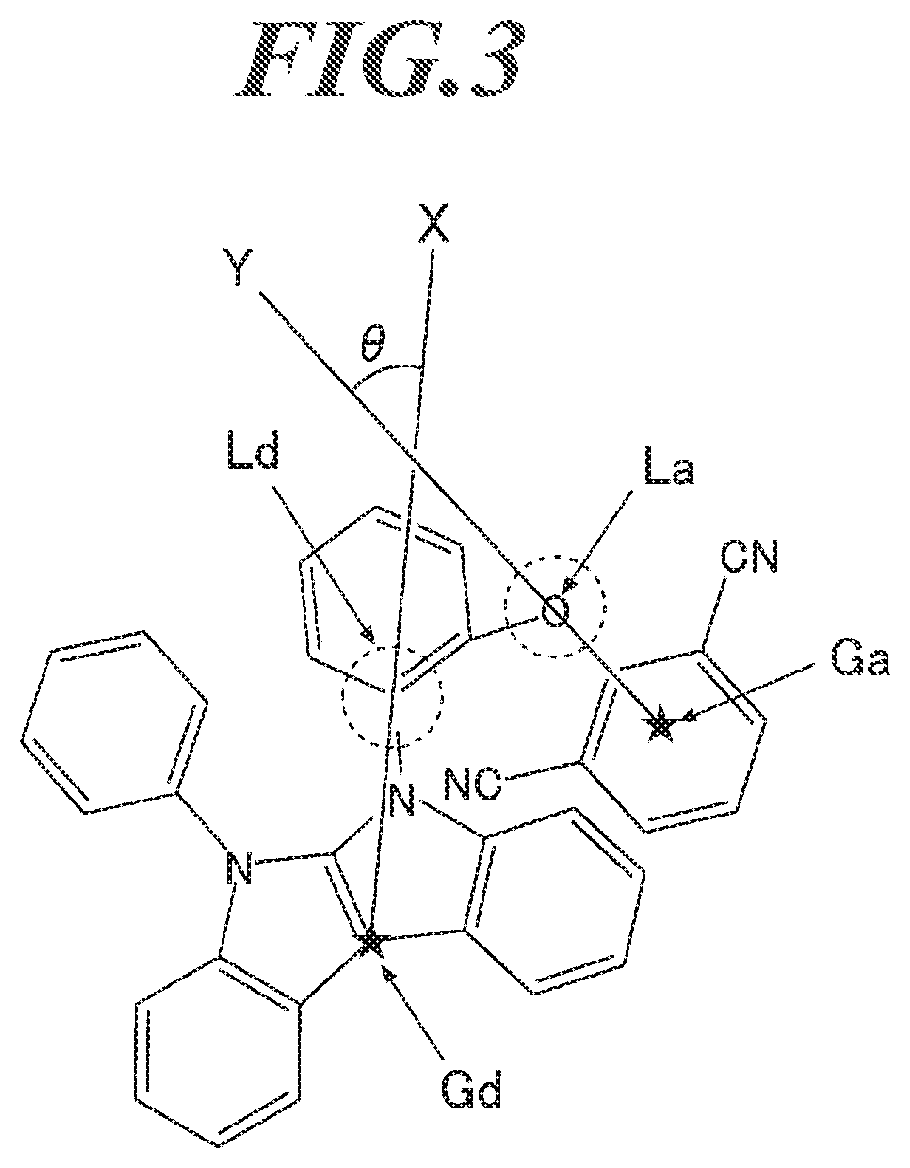
ActiveUS20180212157A1Improve efficiencyImprove stabilitySilicon organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsOrganic layerSpatial interaction
An organic electroluminescent device contains an anode, a cathode, and an organic layer containing at least one luminous layer. The organic layer is disposed between the anode and the cathode. At least one luminous layer contains a π-conjugated compound exhibiting no overlap between the electron density distributions of the HOMO and the LUMO in the molecule, such that electron transition between the HOMO and the LUMO occurs by a through-space interaction in the molecule. The π-conjugated compound has a π-conjugated aromatic ring at a moiety on which at least one of the HOMO and the LUMO is localized.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
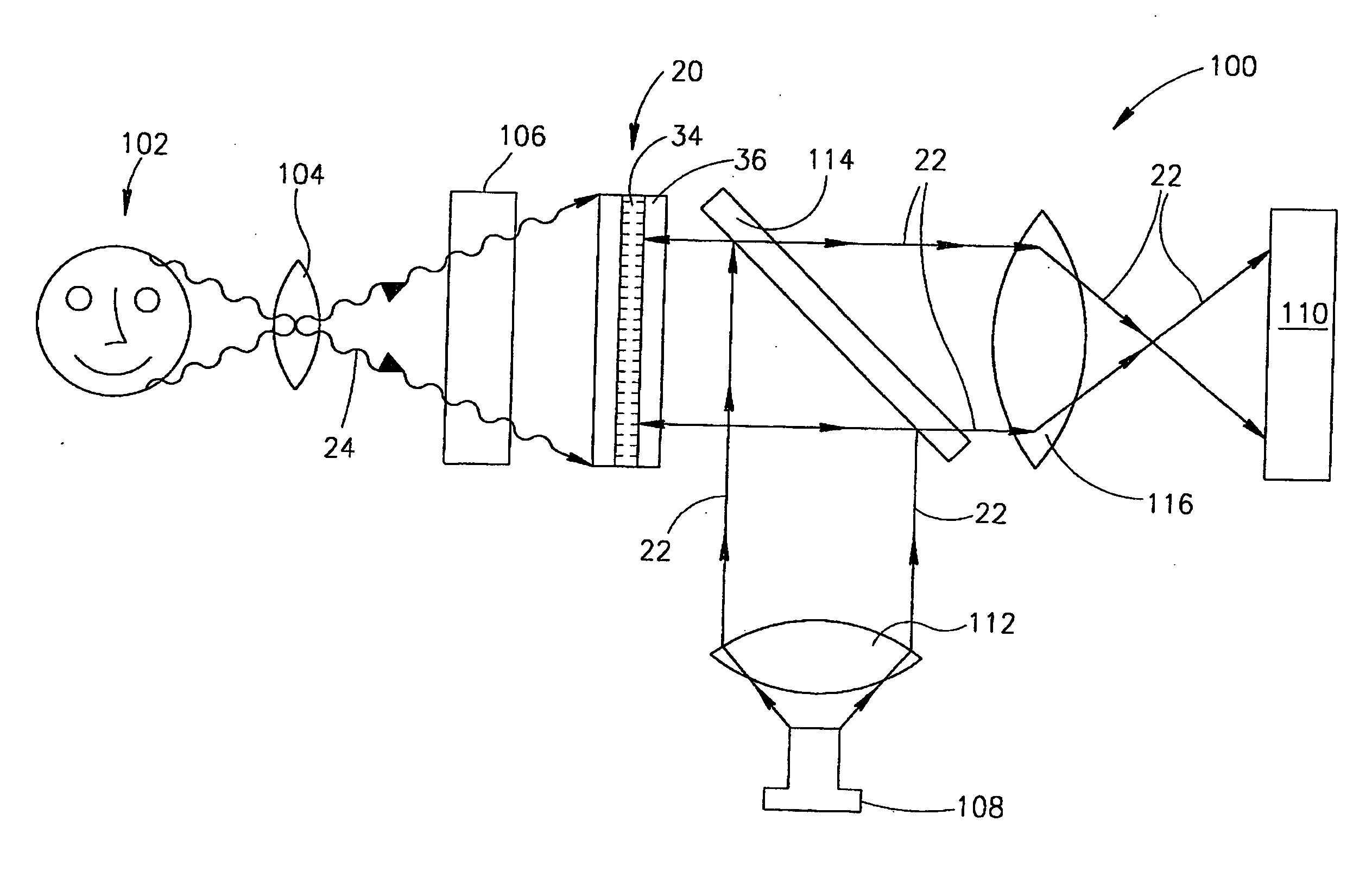
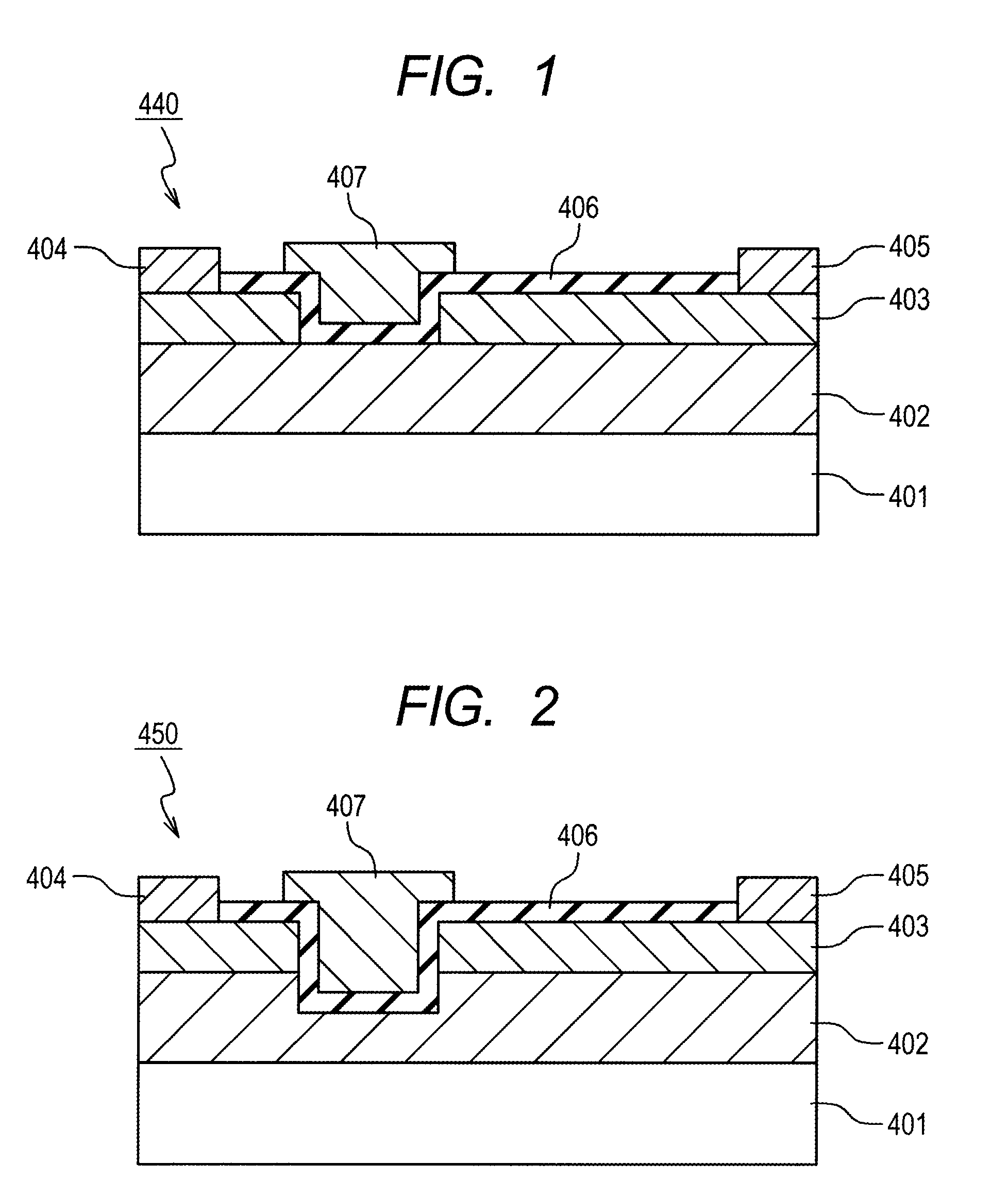
Solid state image wavelength converter
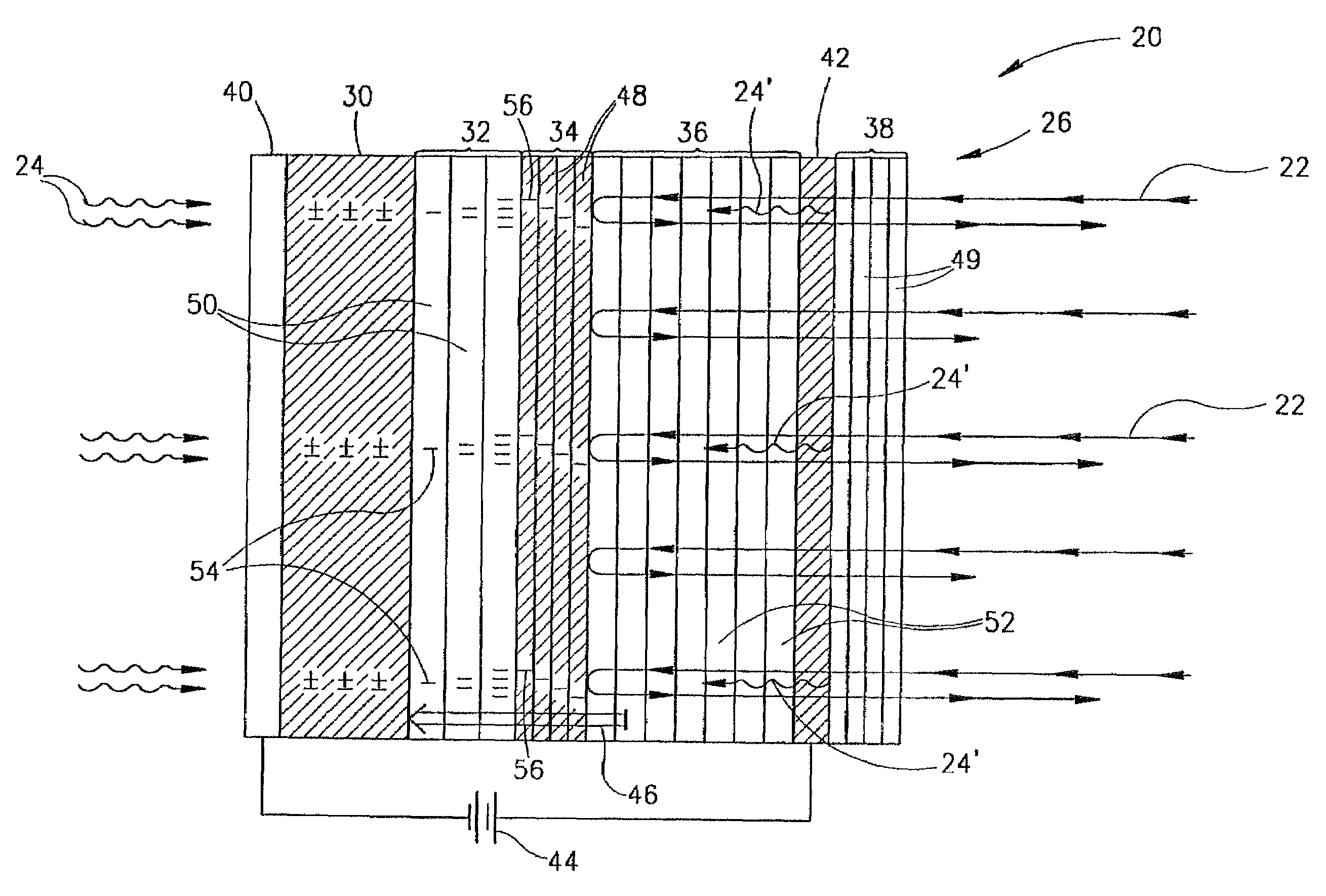
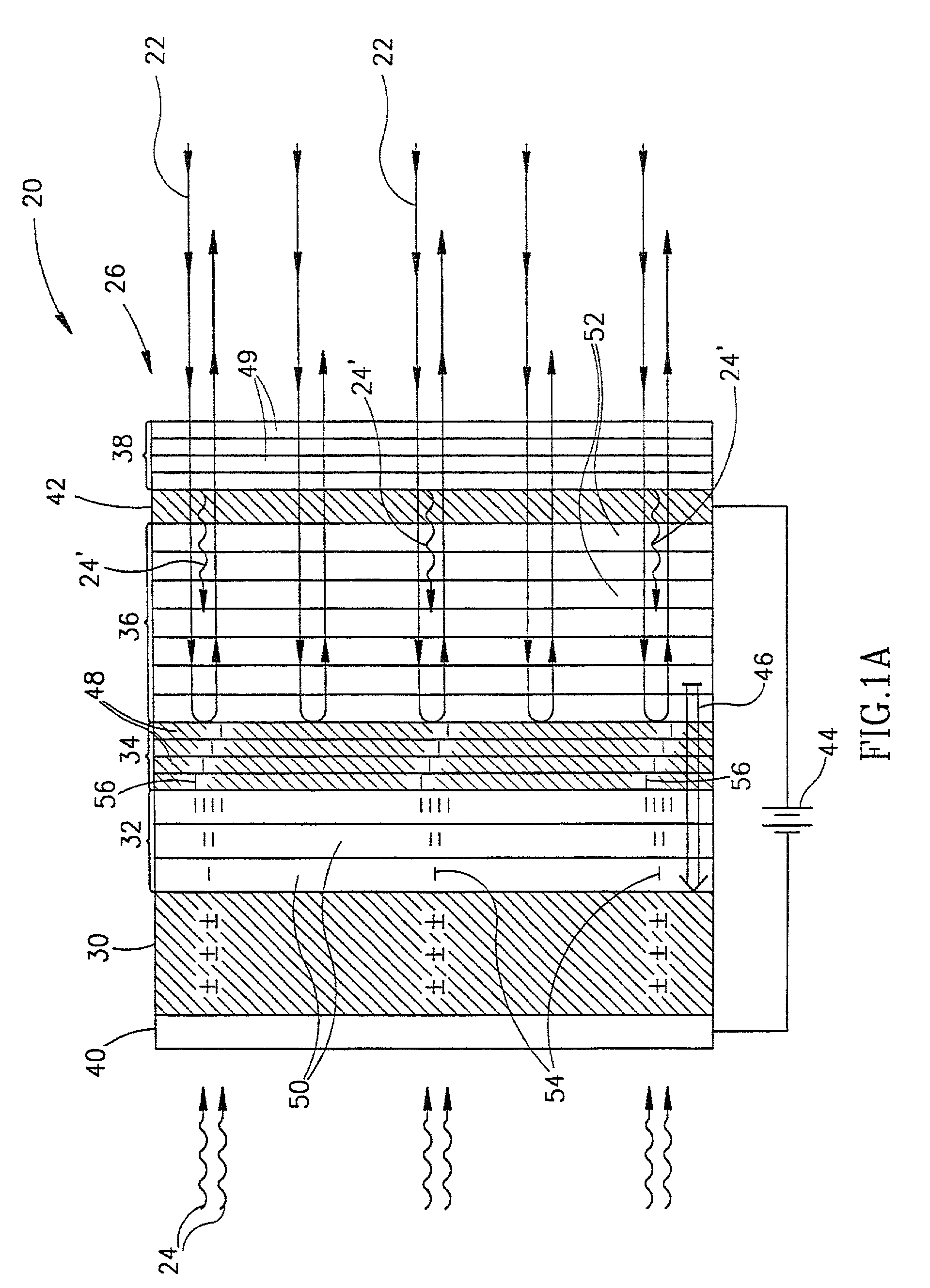
InactiveUS20070273770A1High sensitivityHigh-resolution imageTelevision system detailsNanoopticsElectric field modulationVolumetric Mass Density
A method for encoding information that is encoded in spatial variations of the intensity of light characterized by a first wavelength in light characterized by a second wavelength, the method comprising: transmitting the first wavelength light through a photo-conducting material in which electron-hole pairs are generated by absorbing photons from the first wavelength light to generate a first density distribution of electrons homologous with the spatial variations in intensity of the first wavelength light; trapping electrons from the first electron density distributions in a trapping region to generate an electric field homologous with the density distribution in a material that modulates a characteristic of light that passes therethrough responsive to an electric field therein; transmitting a pulse of light having sufficient energy to generate electron-hole pairs in the photo-conducting material through the modulating material and thereafter through the photo-conducting layer to generate a second additional electron density homologous with the first electron density distribution; trapping electrons from the second electron density distribution in the trapping region; and transmitting the second wavelength light through the modulating material thereby modulating the second wavelength light in response to the electric field and encoding it with the information.
Owner:MICROSOFT INT HLDG BV
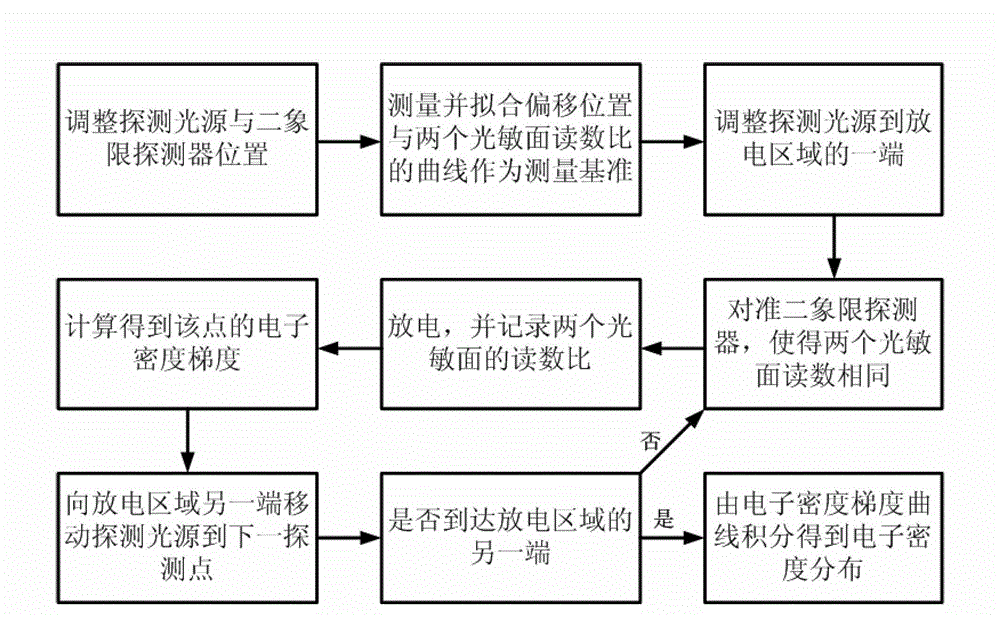
Discharge plasma electron density measuring device and method based on two-quadrant detector
InactiveCN103068136AOvercoming structural complexityOvercome the disadvantage of expensive equipmentPlasma techniqueMeasurement devicePlasma electron
The invention discloses a discharge plasma electron density measuring device and a method. The device comprises a detecting light source, a two-quadrant detector and a signal processor. The detecting light source and the two-quadrant detector are respectively placed on two rotating translation stages and respectively arranged at two ends of a discharge device, and a laser of the detecting light source aims at the center of the two-quadrant detector. The fact that the detecting light source and the two-quadrant detector move the same distance in the same dimension is repeated for times, and the response amplitude ratio of two photosensitive surfaces of the two-quadrant detector at different positions is recorded when power is discharged. Then, the discharge plasma electron density distribution on the dimension is calculated according to the response amplitude ratio of the two photosensitive surfaces by the signal processor. The discharge plasma electron density measuring device and the method overcome the defects of the complex system structure and expansive equipment of a traditional measuring device, and meanwhile can effectively improve measuring precision, do not interfere with discharge plasmas, and obtain the space distribution of the discharge plasma electron density.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Solid state image wavelength converter
InactiveUS7196390B1High sensitivityHigh-resolution imageTelevision system detailsNanoopticsDensity distributionTrapping region
A method for encoding information that is encoded in spatial variations of the intensity of light (24) of a first wave-length into light of a second wavelength, the method comprising: generating a first density distribution of electrons homologous with the spatial variations in intensity of the first wavelength light; generating a second additional electron density homologous with the first electron density distribution; trapping electrons from the first and second electron density distributions in a trapping region (34) to generate an electric field homologous with the density distributions in a material (36) that modulates a characteristic of light (22) that passes therethrough responsive to an electric field (46) therein; and transmitting the second wavelength light (22) through the modulating material (36) thereby modulating the second wavelength light in response to the electric field and encoding it with the information.
Owner:MICROSOFT INT HLDG BV
Femtosecond laser plasma channel interferogram phase and electron density extraction method
InactiveCN101776489AAccurate extractionQuick extractionOptical measurementsPhase differenceComputational physics
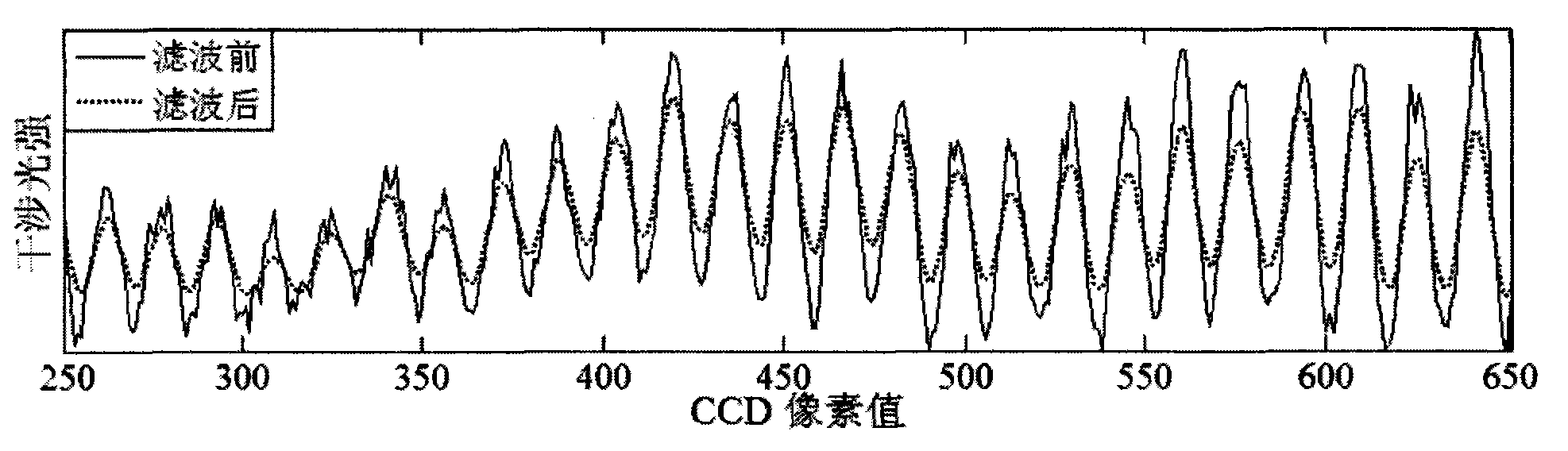
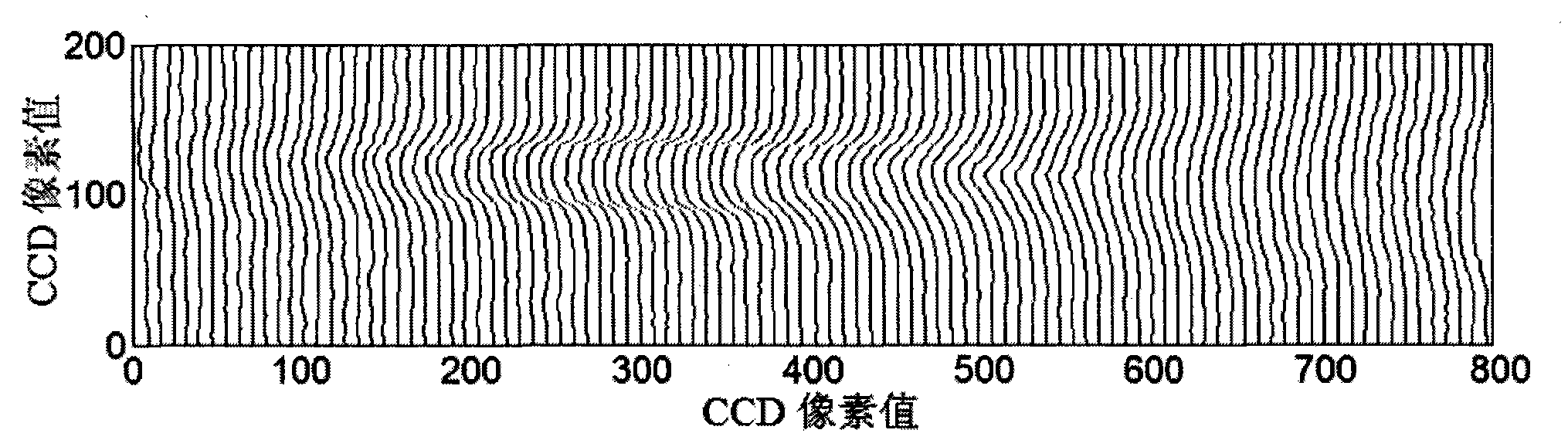
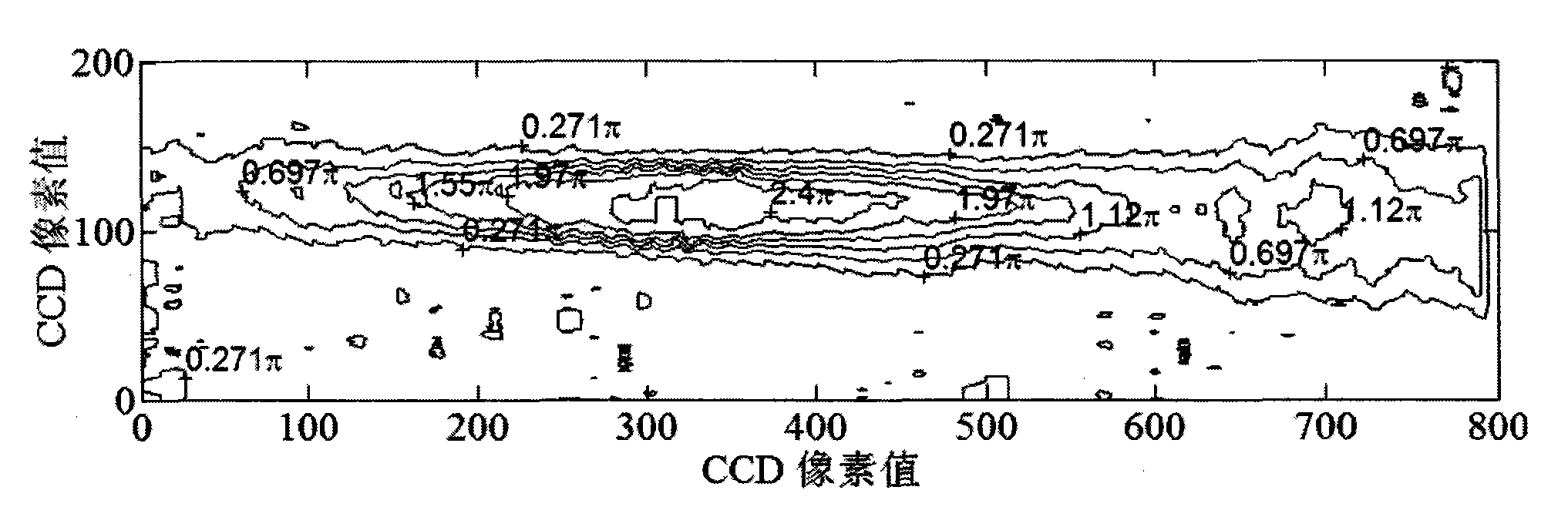
The invention discloses a femtosecond laser plasma channel interferogram phase and electron density extraction method, which comprises the following steps of: shooting a background interference light intensity diagram of probe light when no plasma exists and a plasma channel interference light intensity diagram when the plasma exists by a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera; filtering and denoising the diagrams; searching light and dark stripe positions; obtaining the plasma channel phase difference space distribution P(i, j) and the background phase difference space distribution Pbg(i, j) by calculating; obtaining a phase difference space distribution diagram P0(i, j) after deducting the background; denoising the phase difference space distribution diagram P0(i, j) after deducting the background; obtaining symmetrical phase distribution diagrams Ps(i, j) by symmetrizing the phase difference distribution of a smooth phase difference space distribution diagram; and obtaining a plasma channel electron density distribution diagram by treating the symmetrical phase distribution diagrams Ps(i, j) through an abel transformation method.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Monitoring signal-to-noise ratio in x-ray diffraction data
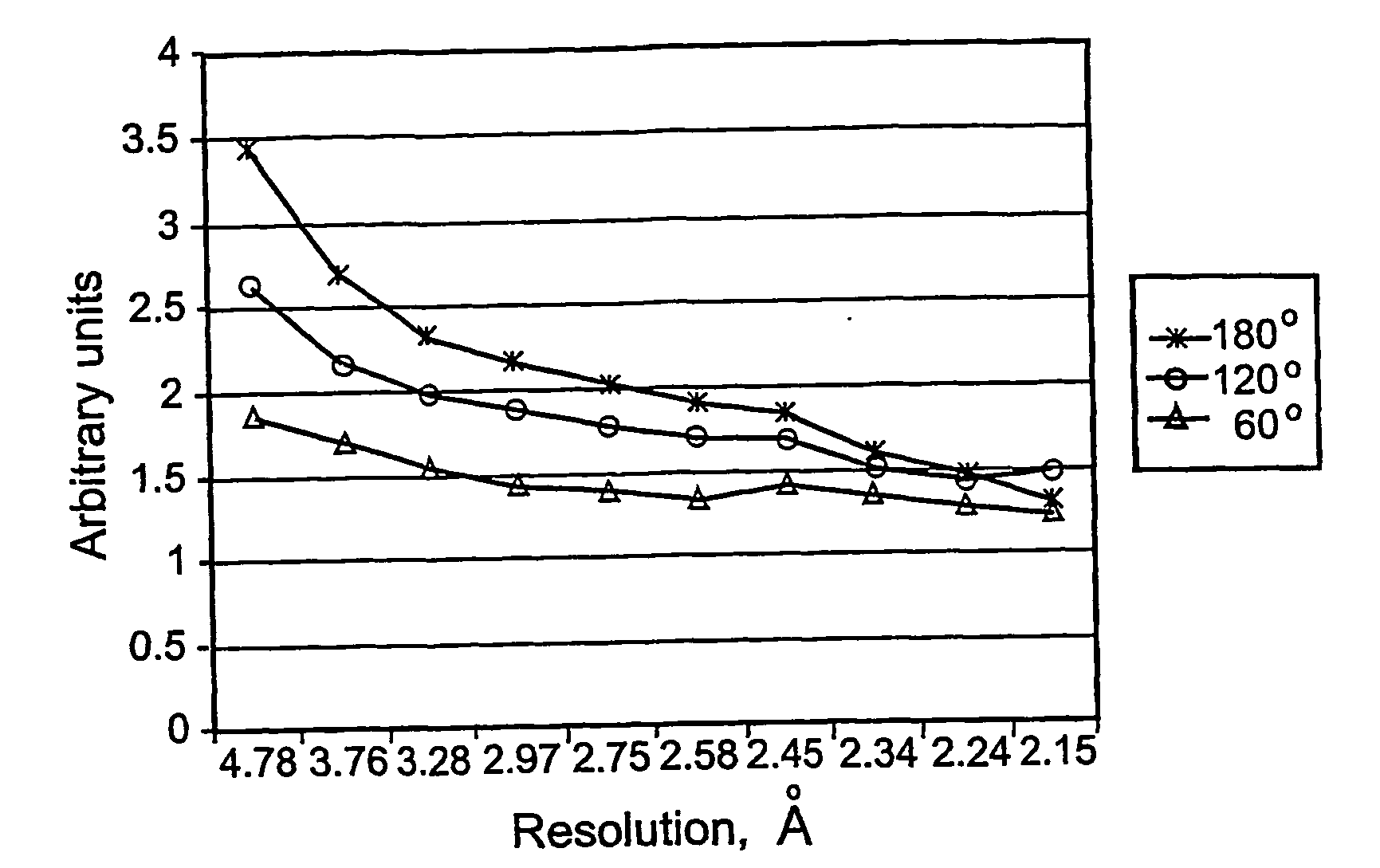
InactiveUS20060067470A1Error analysisRatio errorMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPresent methodSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The present invention relates to methods of diffractometrically determining the structures of materials by characterizing their electron density distributions. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods of collecting, processing and interpreting X-ray diffraction data, which allow real time evaluation of the signal-to-noise ratio in crystal diffraction experiments. The present methods related to the derivation of statistical indices for monitoring and evaluating signal-to-noise ratios in diffraction experiments. In addition, the present invention provides methods of determining the electron density distributions of crystals using anomalous scattering signals corrected for noise. Further, the present invention provides methods of increasing the signal-to-noise ratios in X-ray diffraction data.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC +1
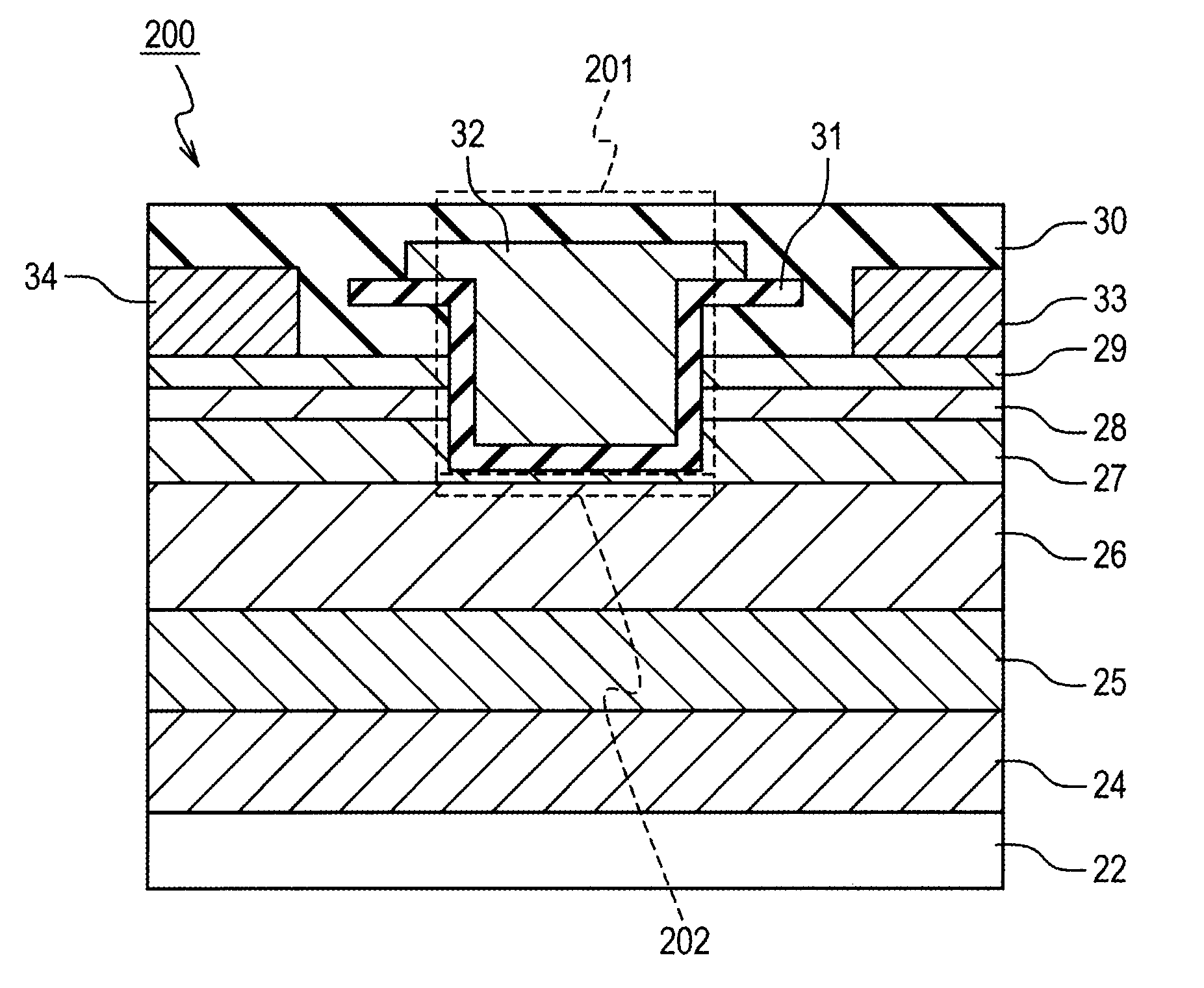
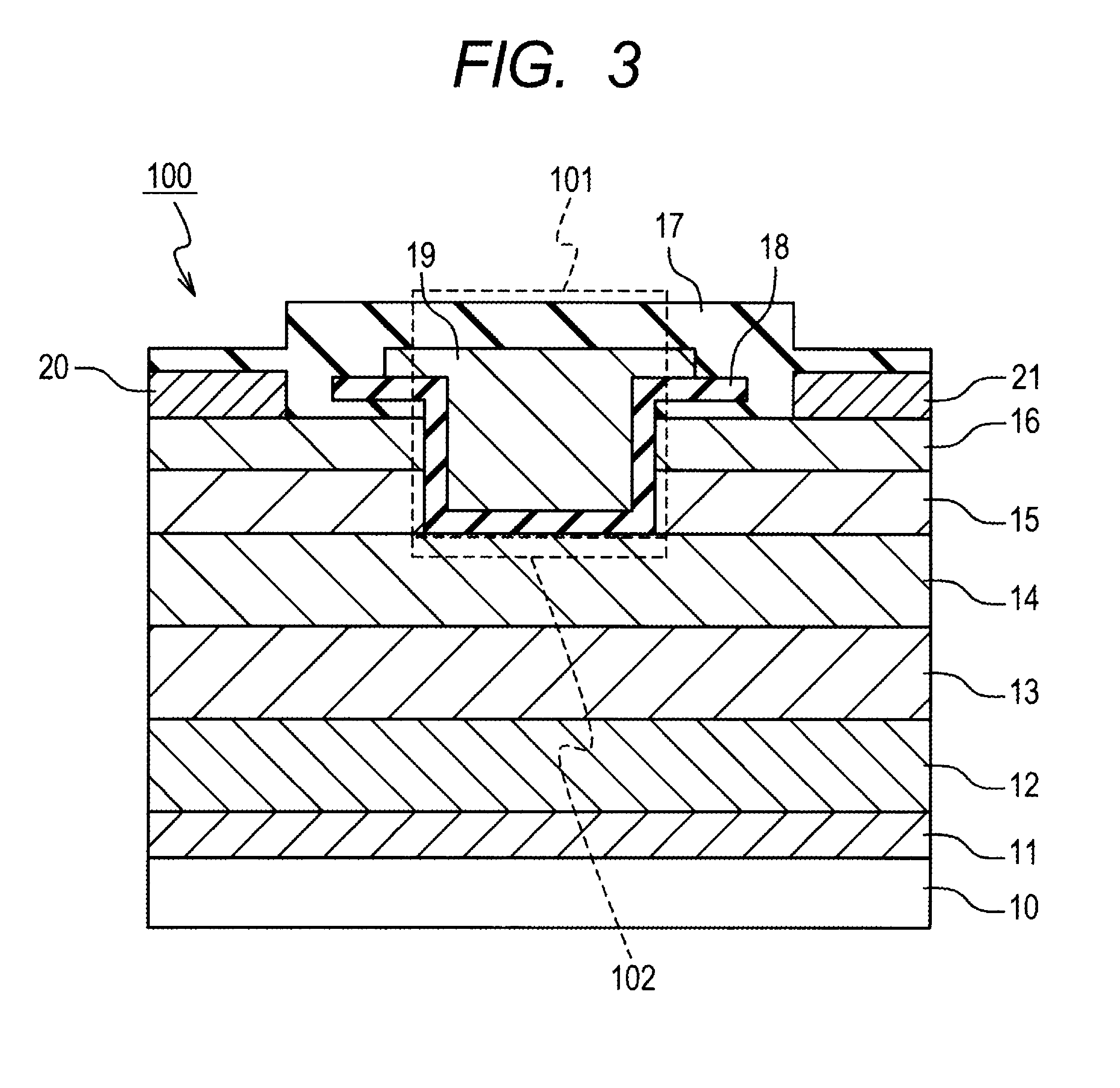
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS8643025B2Reduce yieldMany timesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDepth directionGate voltage
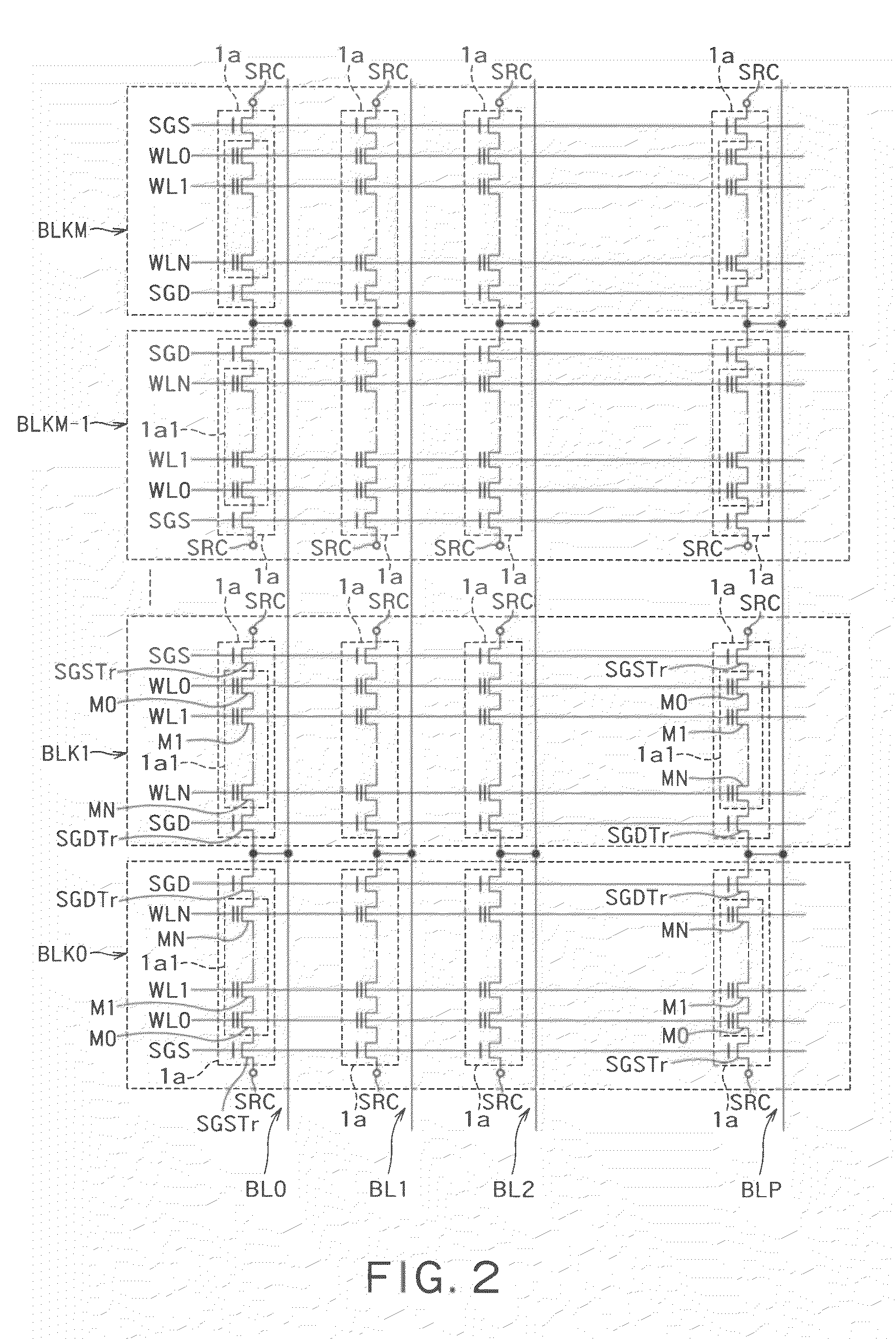
Object of the invention is to reduce the on resistance between source and drain of a nitride semiconductor device. Between a nitride semiconductor layer lying between source and drain regions and a nitride semiconductor layer serving as an underlying layer, formed is a material having an electron affinity greater than that of these nitride semiconductor layers and having a lattice constant greater than that of the nitride semiconductor layer serving as an underlying layer. As a result, an electron density distribution of a channel formed below a gate insulating film and that of a two-dimensional electron gas formed in a region other than the gate portion, when a gate voltage is applied, can be made closer in the depth direction, leading to reduction in on resistance.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Oxide cathode
ActiveCN105244244AImprove job stabilityExtend working lifeDischarge tube solid thermionic cathodesCold cathode manufactureHydrogenDecomposition
The invention provides an oxide cathode, which particularly comprises the following steps: preparing a cathode-based metal, and reserving a geometric margin on the peripheral surface of an emission layer; pouring nickel powder onto the cathode-based metal by a molding method and putting the entire cathode-based metal together with a mold into a hydrogen furnace for sintering into a nickel sponge layer, reserving a certain geometric margin on the prepared nickel sponge layer, filling the nickel sponge layer with alkali earth metal carbonate, mechanically compacting an emission surface of a cathode emission layer, and removing the residual geometric margin; carrying out pre-decomposition on the oxide cathode before pipe filling; and clamping the oxide cathode on a chuck of a lathe, turning the emission layer and the peripheral surface, removing the residual geometric margin, and then wiping away all particles attached to the cathode surface. The cathode surface provided by the invention becomes smooth, regular, bright and clean; a hot particle emission angle is reduced; deformation of emission electron density distribution is limited; the particle bombardment resistance of the cathode is improved; the sparking probability of the cathode emission surface is reduced; the work stability of the cathode is improved; and the lifetime of the cathode is prolonged.
Owner:甘肃虹光电子有限责任公司
Terahertz pulse intensity device
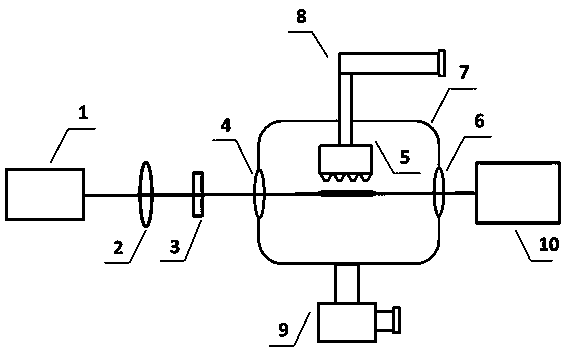
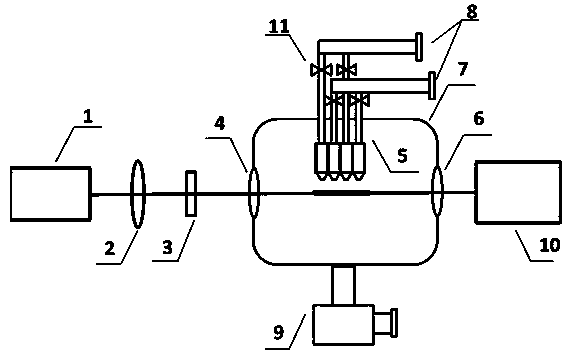
The invention relates to a terahertz pulse intensity device. Pumping laser which exits from a femtosecond laser sequentially passes through a focusing lens and frequency doubling crystal and then forms a two-color field light source, the two-color field light source passes through a vacuum chamber entrance window and then enters a vacuum pump, a gas spray nozzle group continuously and stably feeds gas to generate unevenly distributed gas targets at a position that the two-color field light source is focused for plasma drawing after the vacuum pump is vacuumized, and the density distribution of the gas targets can be controlled by adjusting gas type and the structure and the parameters of the gas spray nozzles, so that the electron density distribution of the plasma can be changed, the phase matching situation of the two-color light source during the plasma drawing is adjusted and the intensity maximization of generated terahertz pulses is realized. Besides, the gas which is fed by the gas spray nozzle group can be any gas or combination of various gases which enter from different pipes, adjustment can be made anytime according to the parameters of a laser light source used in experiments and the drawing state of generated plasmas, the structure of the device is simple and the application scope is wide.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH +1
Method and x-ray system for generating a phase contrast image
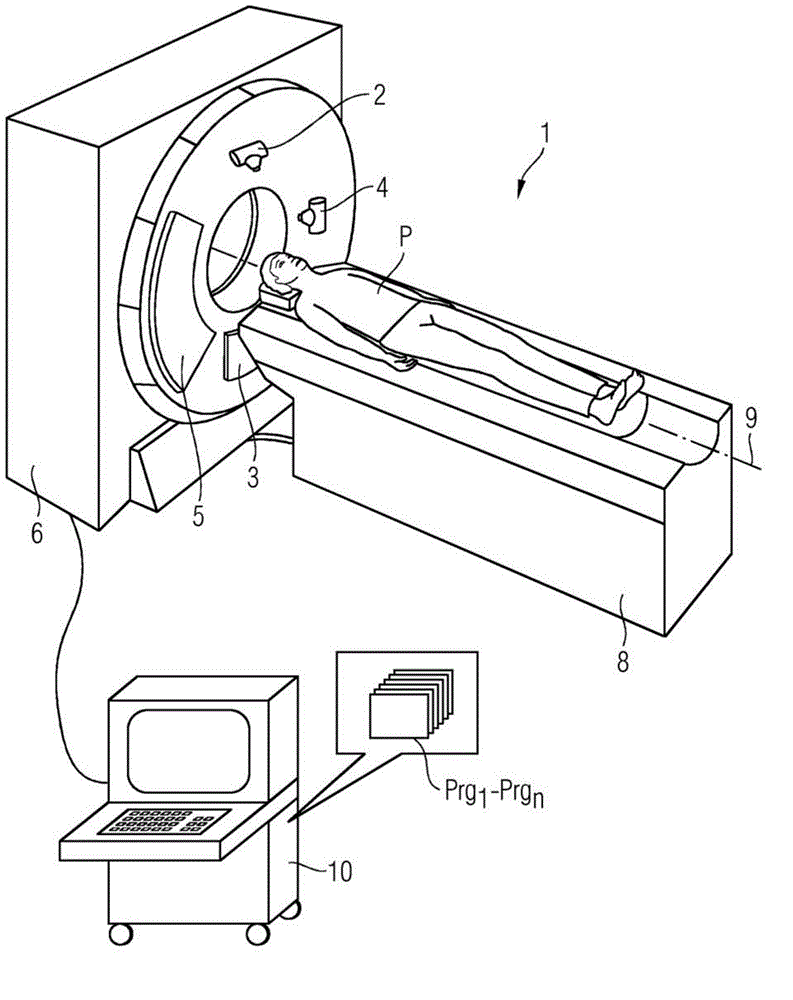
InactiveCN104427938ADetermine Absorption BehaviorMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHealth-index calculationSoft x rayUltrasound attenuation
A method and an X-ray system are disclosed for generating a phase contrast image of an examination object. In an embodiment, the distribution of an electron density in the examination object is determined by defining energy-dependent attenuation values for X-radiation with at least two different X-ray energy spectra, phase-shift values are obtained from the previously determined electron density distribution, and a phase contrast image is generated from the calculated phase-shift values.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
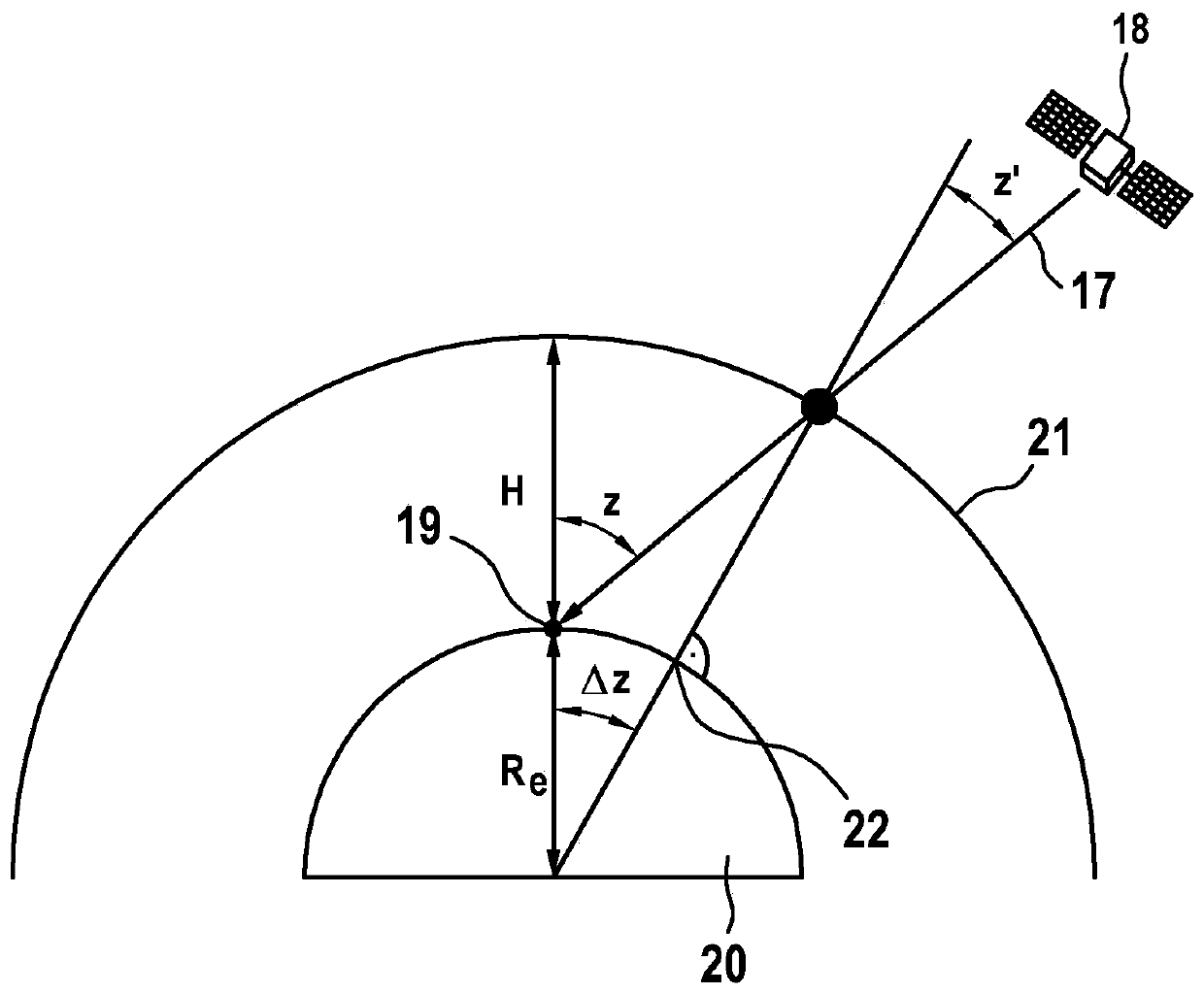
Method for determining an adaptive model of an electron density distribution
The invention relates to a method for determining a model of an electron distribution in the Earth's atmosphere, which is used to correct propagation time measurements of signals emitted by earth satellites for position determination operations using signal receivers, having at least the following steps of: a) determining local electron density data relating to provision locations (2), b) determining a local resolution accuracy on the basis of a local density of provision locations, c) determining functions for interpolating the electron density distribution determined in step a) on the basis of the resolution accuracy determined in step b), d) creating the model of the electron density distribution using the data determined in step a) and the functions determined in step c).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
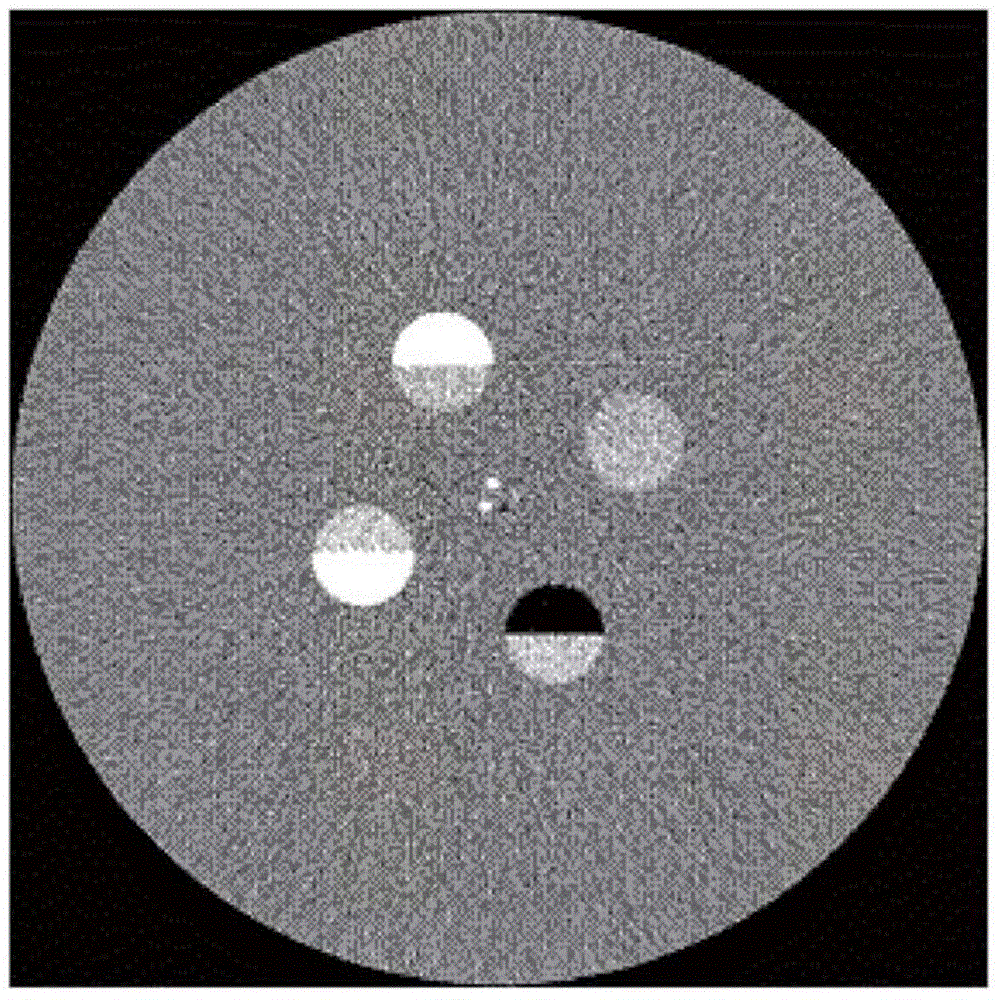
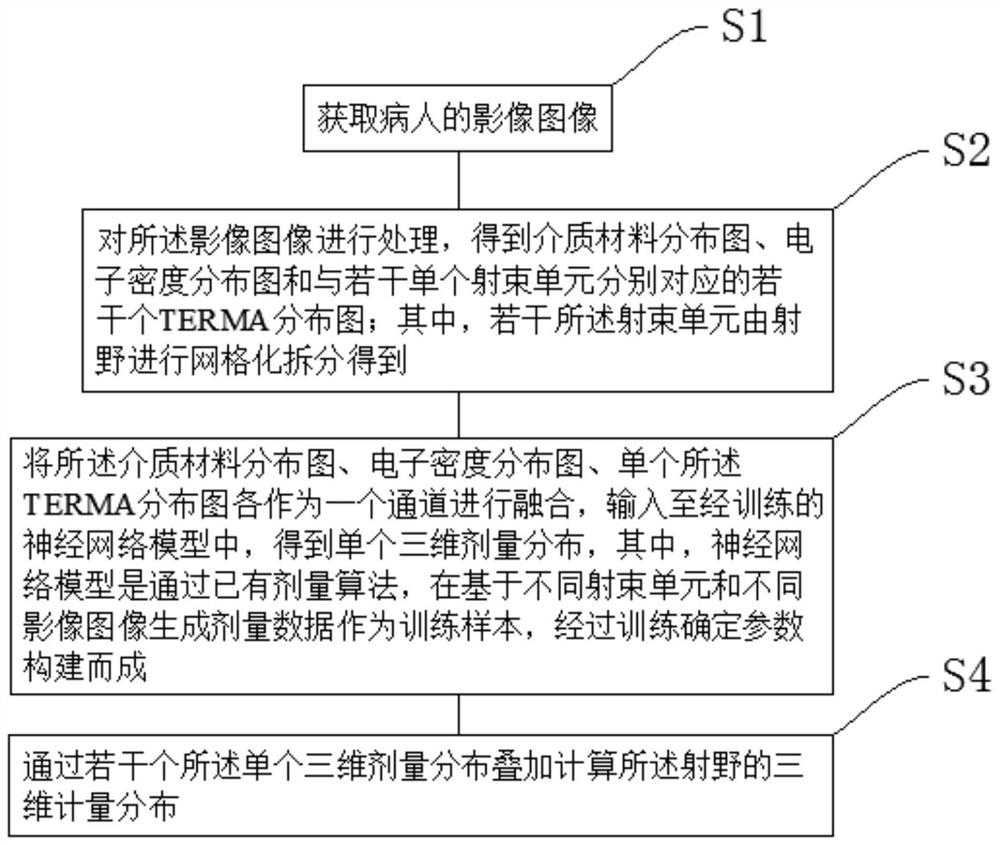
Three-dimensional dose calculation method, computer equipment and readable medium
PendingCN112086172AAvoiding the Dilemma of Sacrificing Computational EfficiencyImprove calculation accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisNerve networkAlgorithm
The invention discloses a three-dimensional dose calculation method, computer equipment and a readable medium. The three-dimensional dose calculation method comprises the steps of acquiring an image of a patient; processing the image to obtain a dielectric material distribution diagram, an electron density distribution diagram and a plurality of TERMA distribution diagrams corresponding to a plurality of single beam units respectively, wherein the plurality of beam units are obtained by performing gridding splitting on a radiation field; fusing the dielectric material distribution diagram, theelectron density distribution diagram and the single TERMA distribution diagram as a channel respectively, inputting into a trained neural network model to obtain single three-dimensional dose distribution, and calculating three-dimensional measurement distribution of the radiation field by superposing a plurality of single three-dimensional dose distribution. According to the method, the calculation efficiency is improved while the calculation accuracy is not reduced.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RAYDOSE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
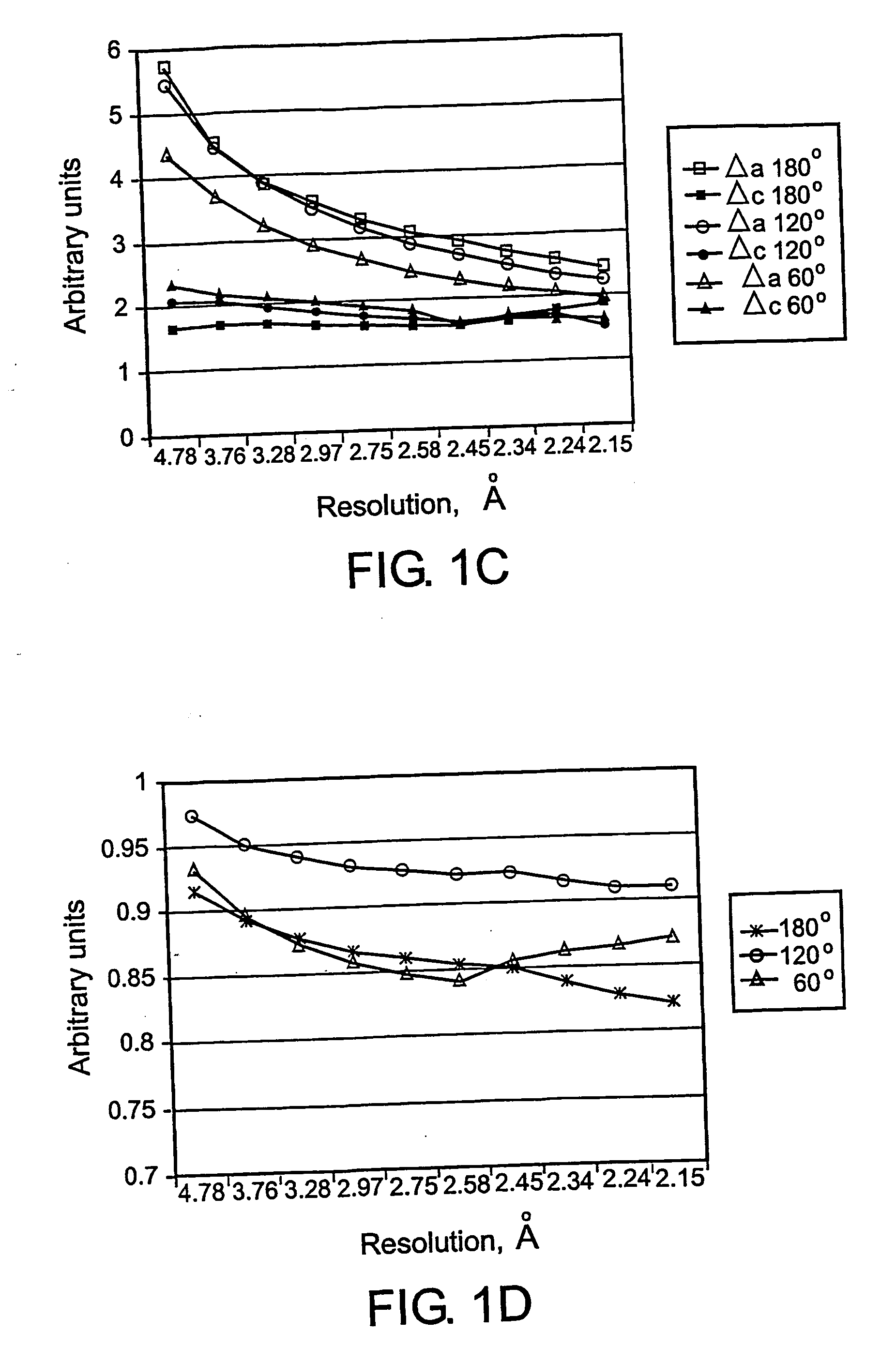
Method for evaluating crystal electron density distribution model and application thereof
The invention provides a method for evaluating a crystal electron density distribution model and application thereof. The evaluation method comprises the following steps: S1, calculating a structure amplitude value of an accurate electron density distribution model of a to-be-detected crystal subjected to first perturbation, and enabling the sum of accurate electron density distribution models of the various atoms in the to-be-detected crystal in a structure cell after perturbation to be the same as the extranuclear electron number of corresponding atoms by virtue of the first perturbation; S2, calculating a structure amplitude value of a current electron density distribution model of the to-be-detected crystal subjected to perturbation, and enabling a low-density area in the current electron density distribution model to be changed by virtue of perturbation; and S3, comparing the structure amplitude value in S2 with the structure amplitude value in S1 so as to evaluate the current electron density distribution model. The evaluation method disclosed by the invention can be used for crystal structure analysis. The traditional evaluation method is failed under the low data resolution condition, while the evaluation method provided by the invention is still effective.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Method for determining an electron density distribution in the earth's atmosphere
The invention relates to a method for determining a four-dimensional ionosphere model of an electron distribution in the Earth's atmosphere, which is used to correct runtime measurements of signals emitted by satellites, for position determinations by means of signal receivers, comprising at least the following steps: a) defining at least one distribution function based on at least one function parameter which is suitable to describe a distribution of electrons over the height of the Earth's atmosphere, b) receiving data from a plurality of runtime measurements by means of a plurality of movable dual-frequency signal receivers, in order to determine parameters that are representative for a total quantity of electrons along a signal transmission path from a satellite to a dual-frequency signal receiver, c) determining location-dependent and time-dependent function parameters for the distribution function at least by means of the parameters, d) providing the function parameters determined in step c) as a four-dimensional ionosphere model.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Ionized layer tomography method for improving iteration initial value precision
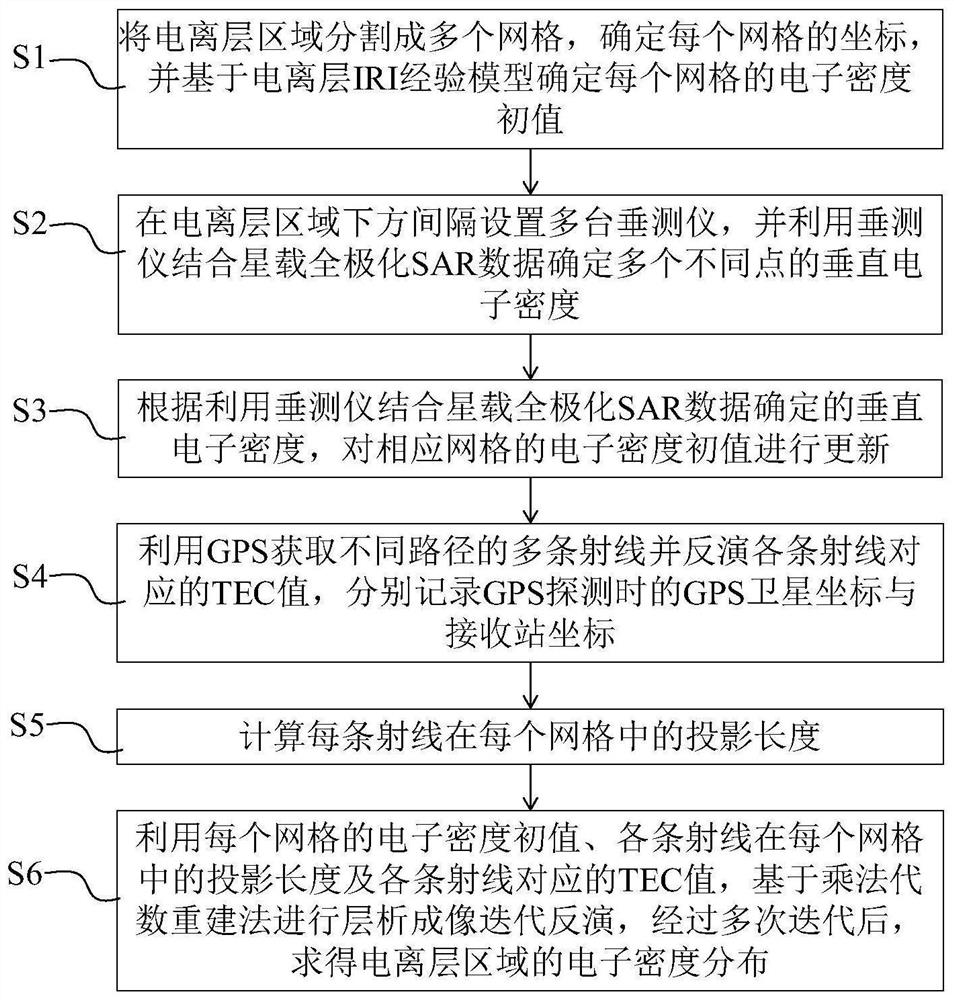
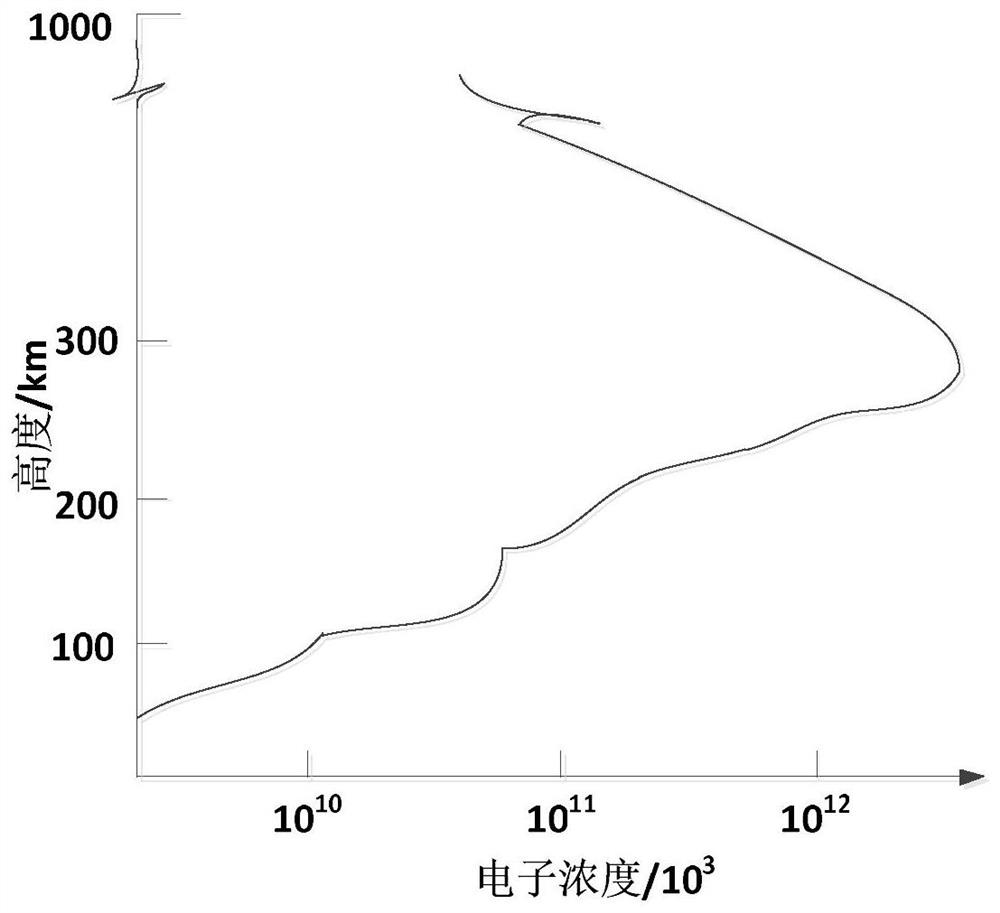
ActiveCN113093189AHigh precisionIncrease authenticitySatellite radio beaconingX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentMeasuring instrumentReconstruction method
The invention relates to an ionosphere tomography method for improving the precision of an iteration initial value, computer equipment and a computer readable storage medium. The method comprises steps of segmenting an ionosphere region into a plurality of grids, and determining the coordinate and the electron density initial value of each grid; a plurality of vertical measuring instruments being arranged below the ionosphere area at intervals, and the vertical measuring instruments being combined with satellite-borne full-polarization SAR data to determine the vertical electron density of a plurality of different points; updating an electron density initial value of the corresponding grid; acquiring a plurality of rays of different paths by using a GPS (Global Positioning System) and inverting a TEC value corresponding to each ray; calculating the projection length of each ray in each grid; and performing tomography iteration inversion based on a multiplication algebraic reconstruction method, and obtaining the electron density distribution of the ionized layer region after multiple iterations. According to the method, ionosphere IRI empirical model data is corrected by using the vertical measuring instrument and the satellite-borne full-polarization SAR data, so authenticity of an iteration initial value is improved, and ionosphere tomography precision can be improved.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
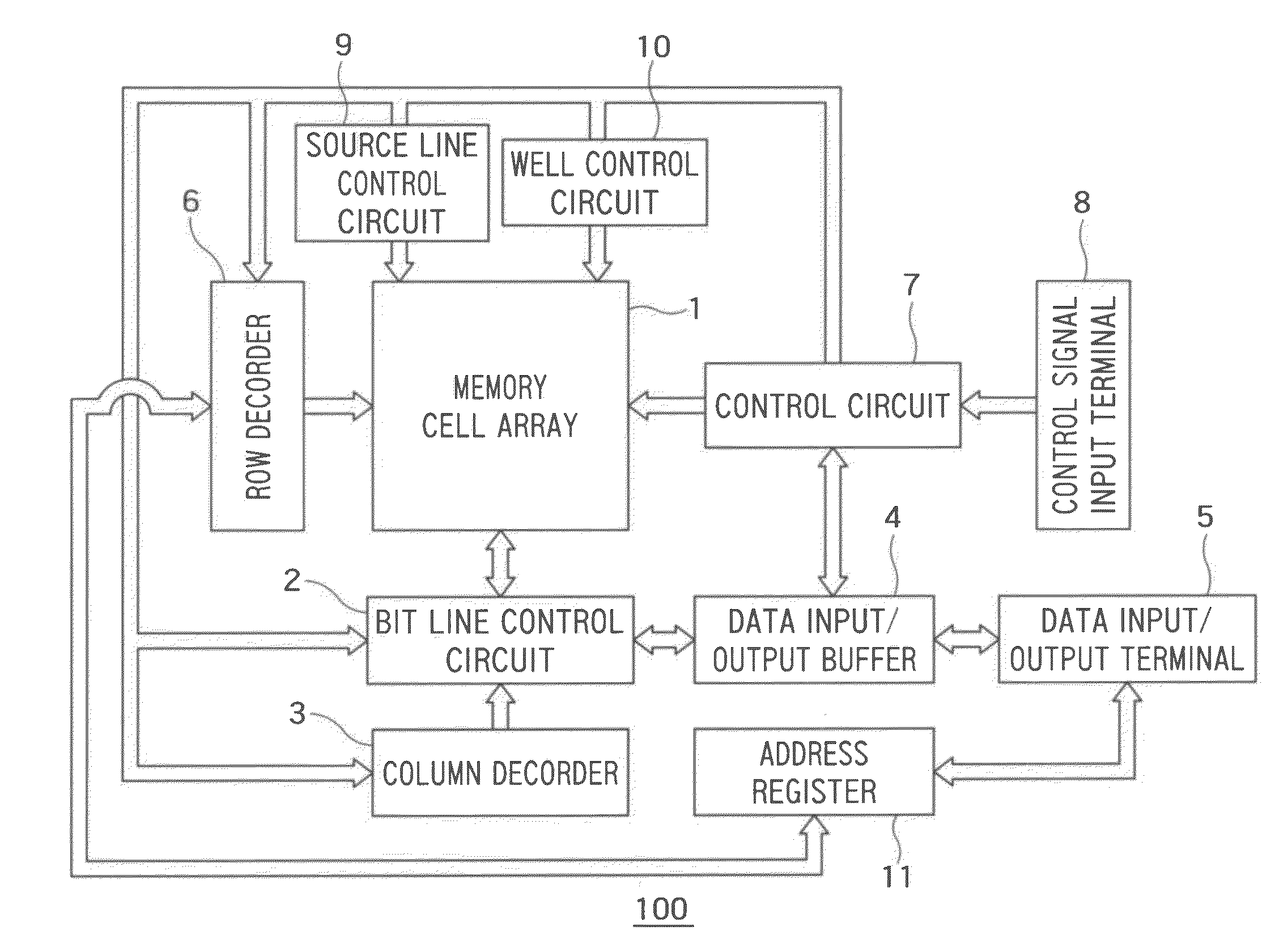
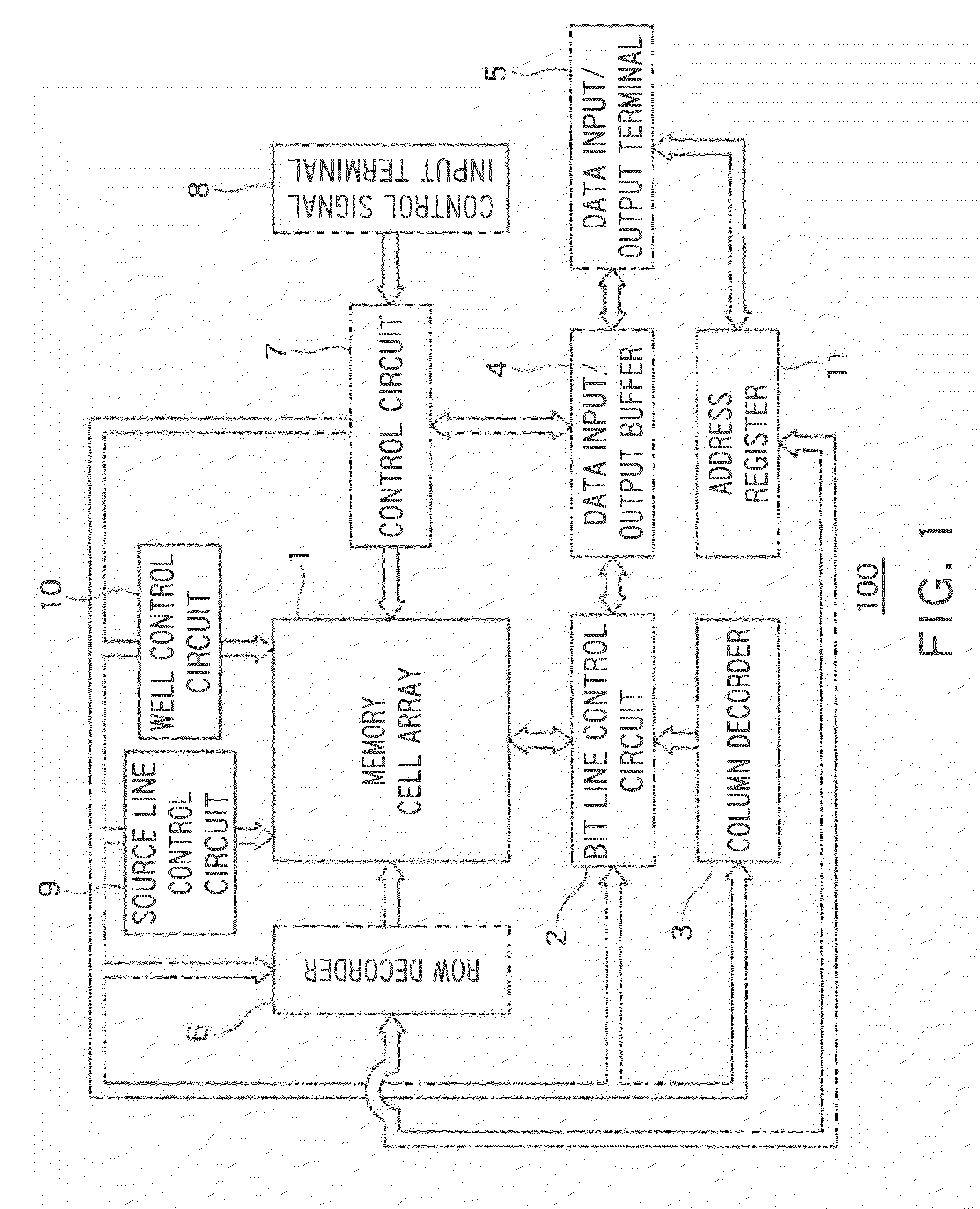
Method of evaluating a semiconductor storage device
A method of evaluating a semiconductor storage device of a floating gate type has calculating an electron density distribution of a tunnel insulating film of a memory cell by multiplying a change rate of a threshold voltage Vt of the memory cell of the semiconductor storage device with respect to the change of the logarithm of a time with ε*Cr*2k / Tox / q (where ε is the permittivity of the tunnel insulating film of the memory cell, Cr indicates a coupling ratio of the memory cell, Tox indicates the thickness of the tunnel insulating film, k indicates an attenuation rate of the existence probability when the charges are detrapped and is represented as k=(2mE / (h / 2π)2)0.5, m indicates the mass of the electron, E indicates an energy level of the trap of the tunnel insulating film, h indicates a Planck's constant, and π indicates a circumference ratio).
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Organic electroluminescent device, thin luminous film, display apparatus, and lighting apparatus
ActiveUS10862048B2Improve efficiencyImprove stabilitySilicon organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsOrganic electroluminescenceOrganic chemistry
An organic electroluminescent device contains an anode, a cathode, and an organic layer containing at least one luminous layer. The organic layer is disposed between the anode and the cathode. At least one luminous layer contains a π-conjugated compound exhibiting no overlap between the electron density distributions of the HOMO and the LUMO in the molecule, such that electron transition between the HOMO and the LUMO occurs by a through-space interaction in the molecule. The π-conjugated compound has a π-conjugated aromatic ring at a moiety on which at least one of the HOMO and the LUMO is localized.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com