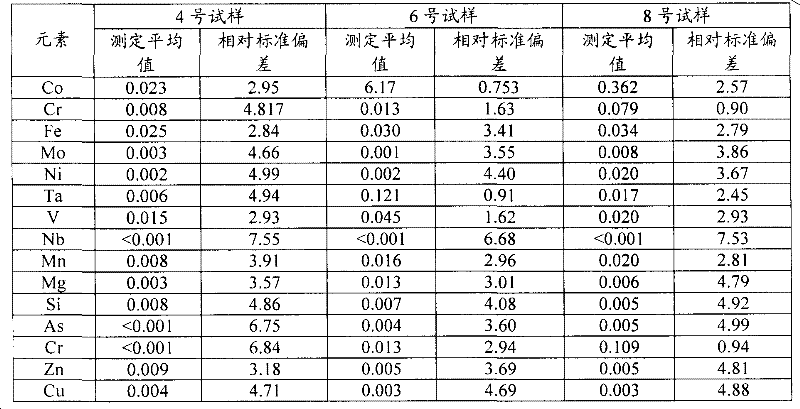
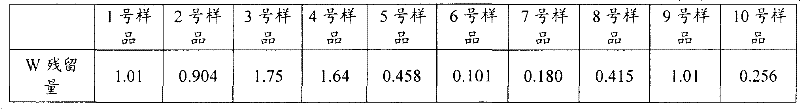
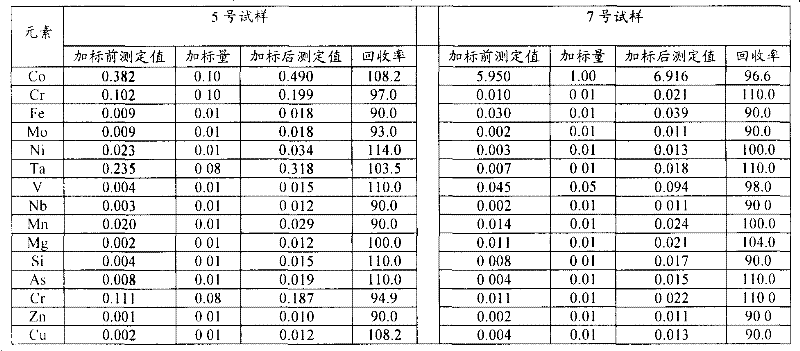
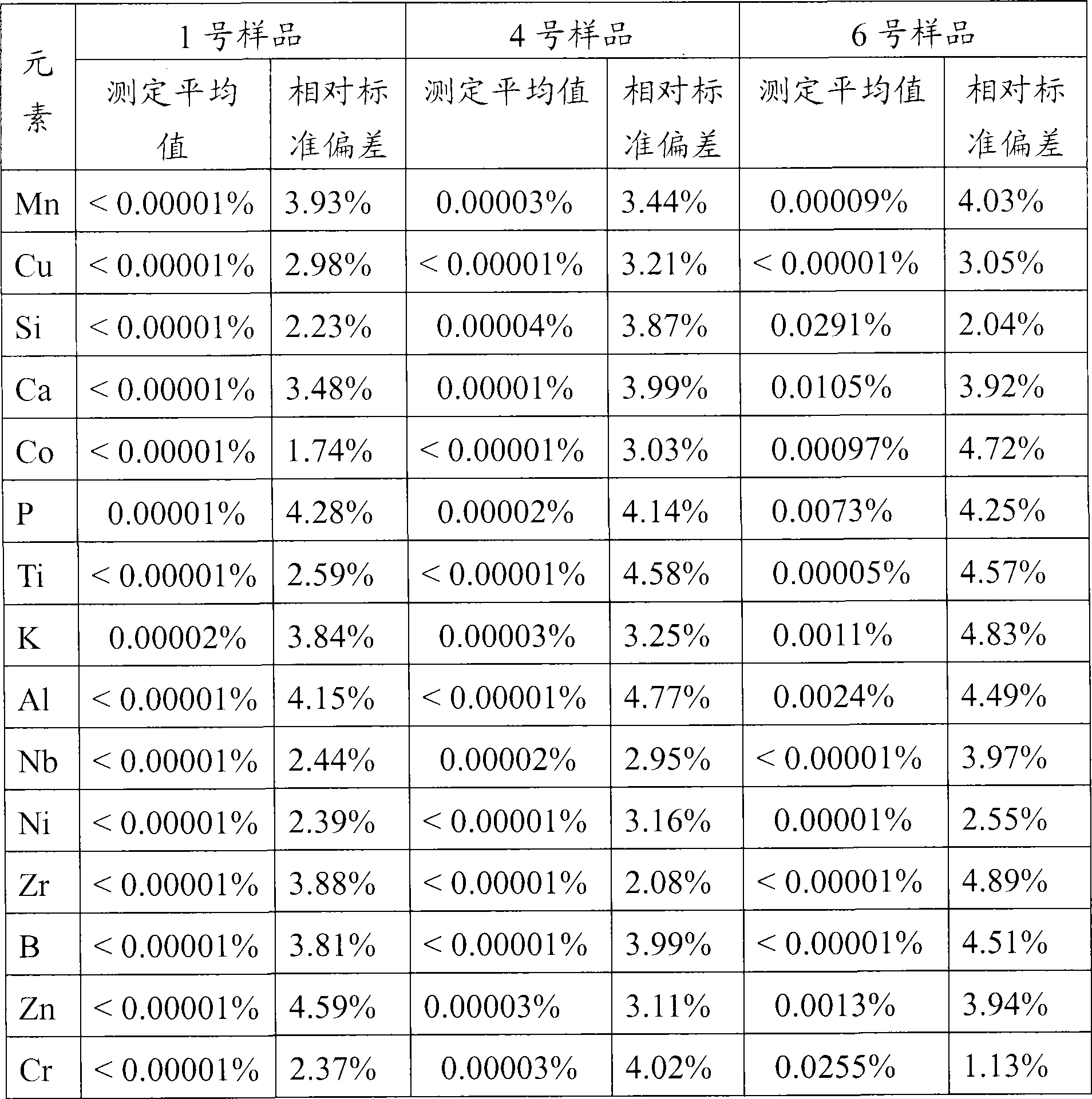
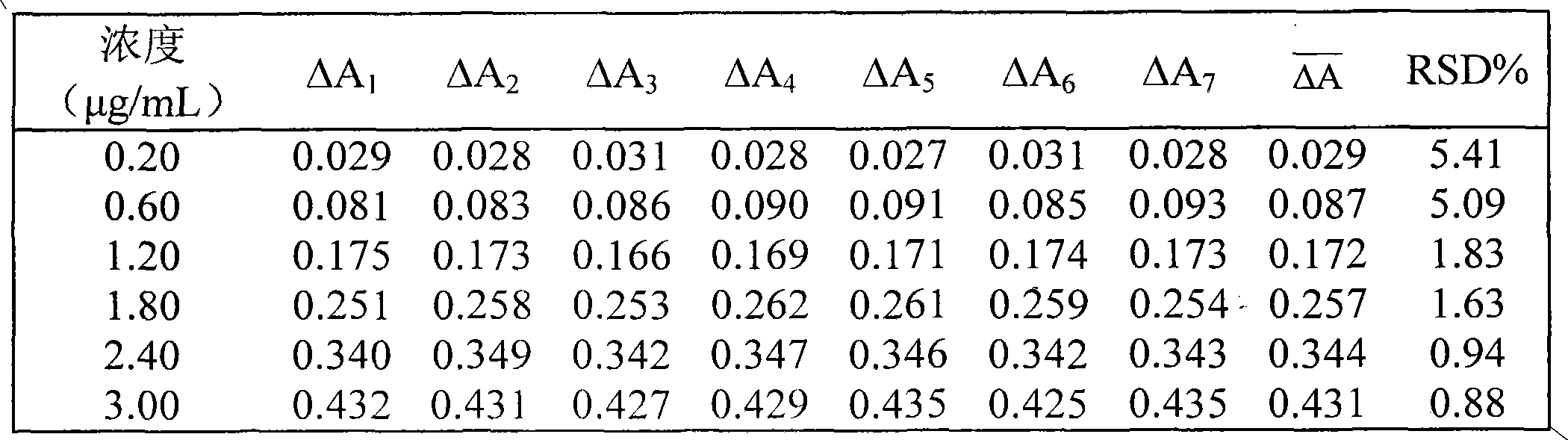
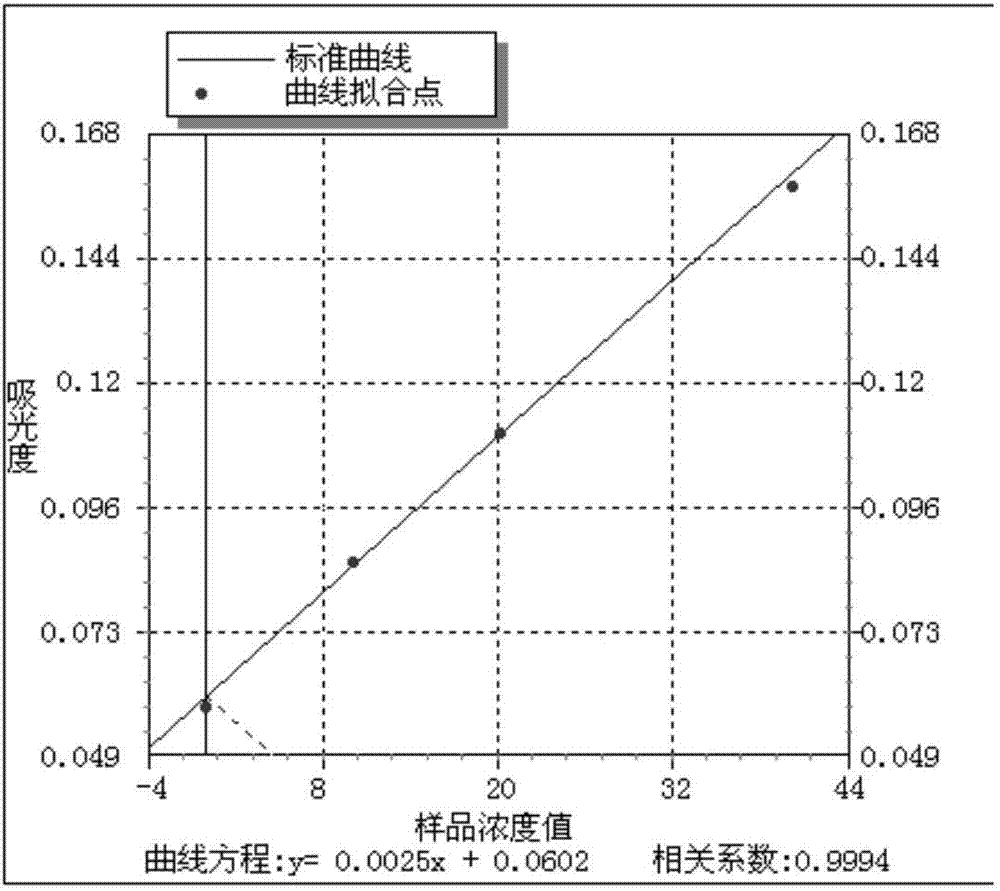
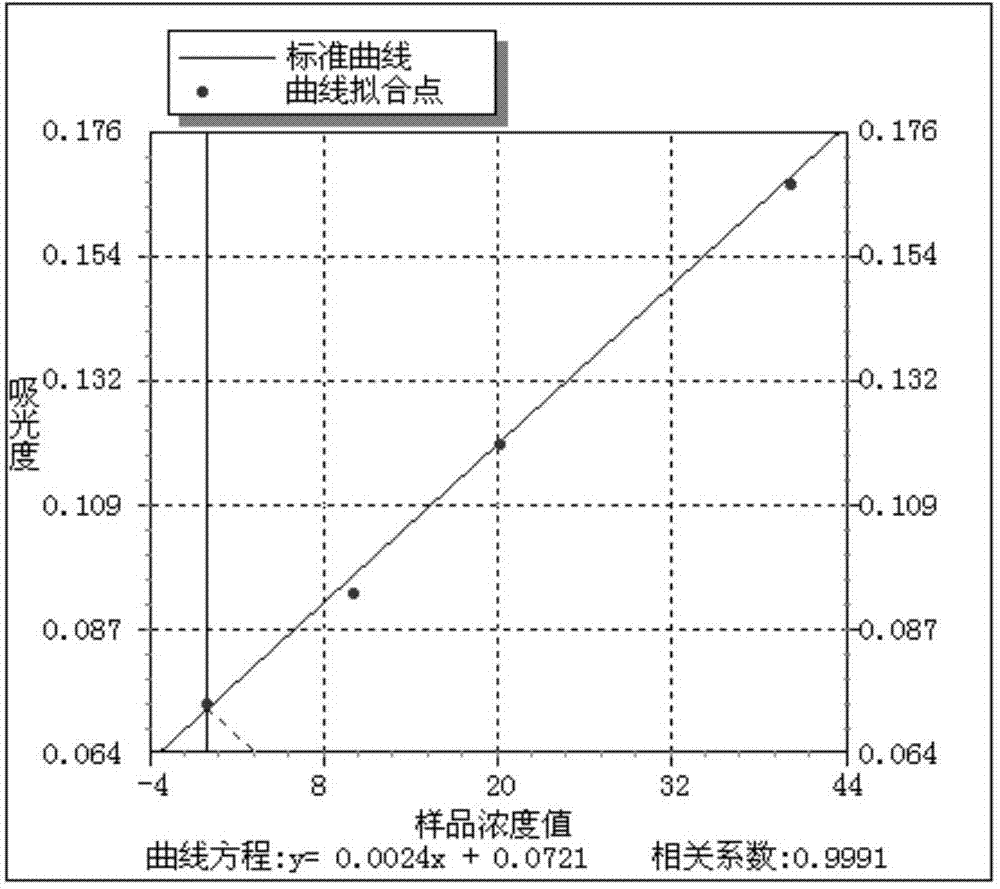
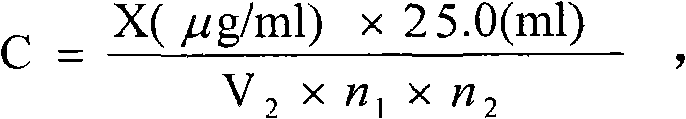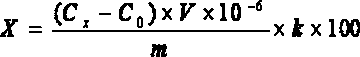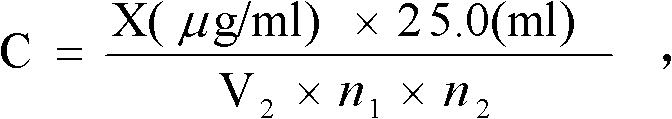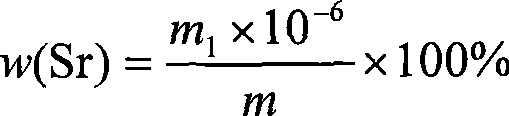Patents
Literature
99 results about "Flame atomic absorption spectrometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
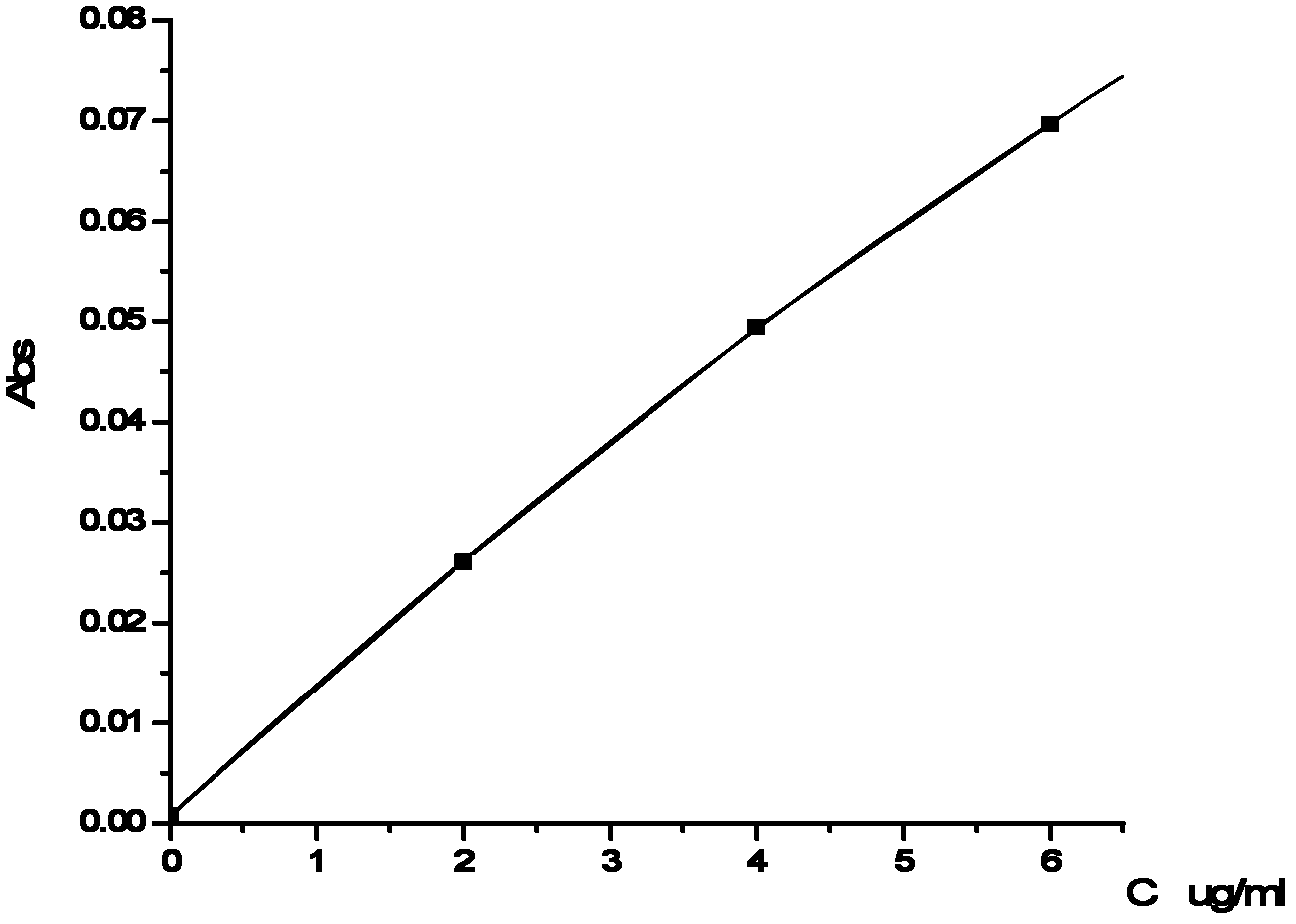
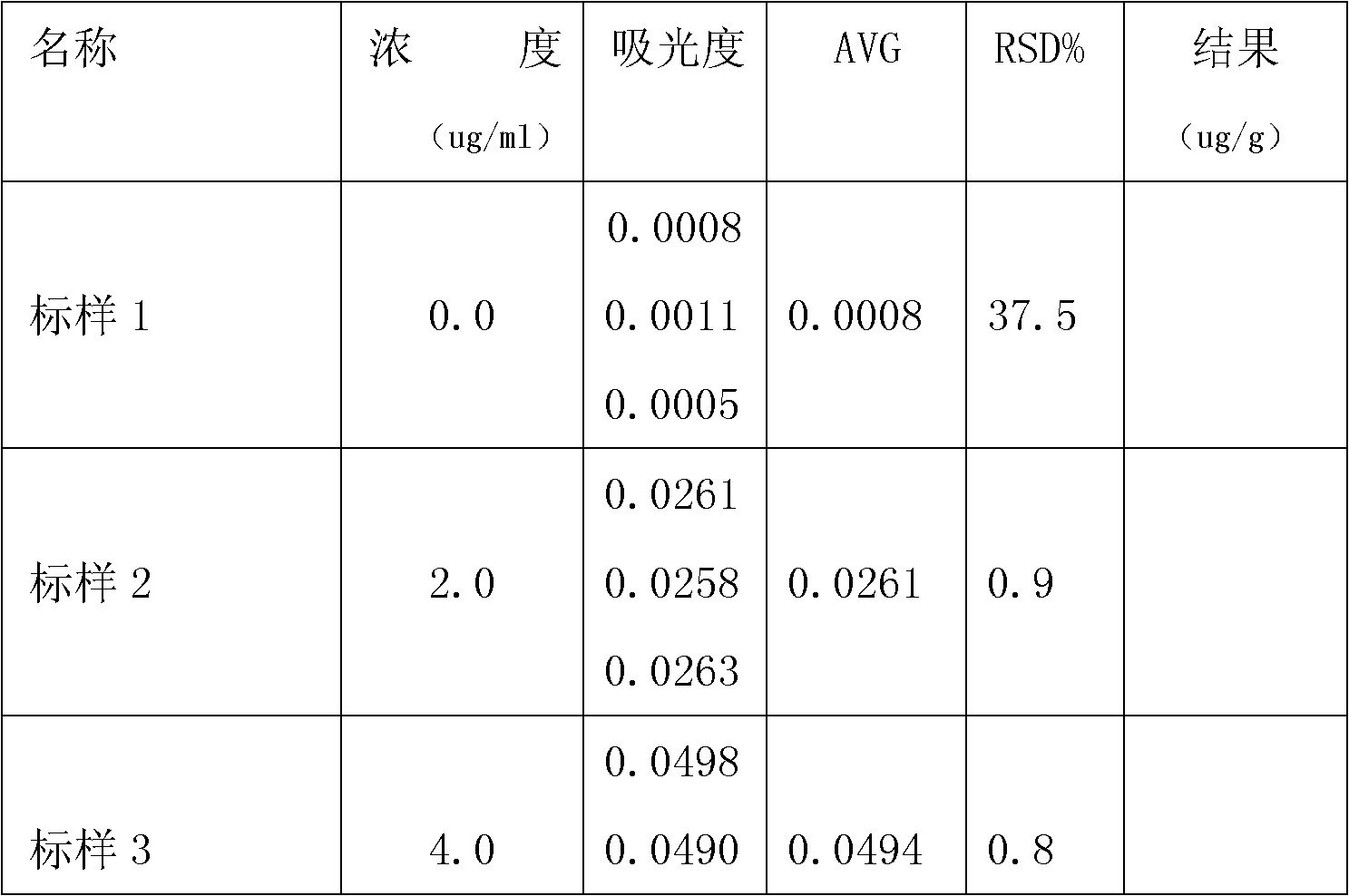
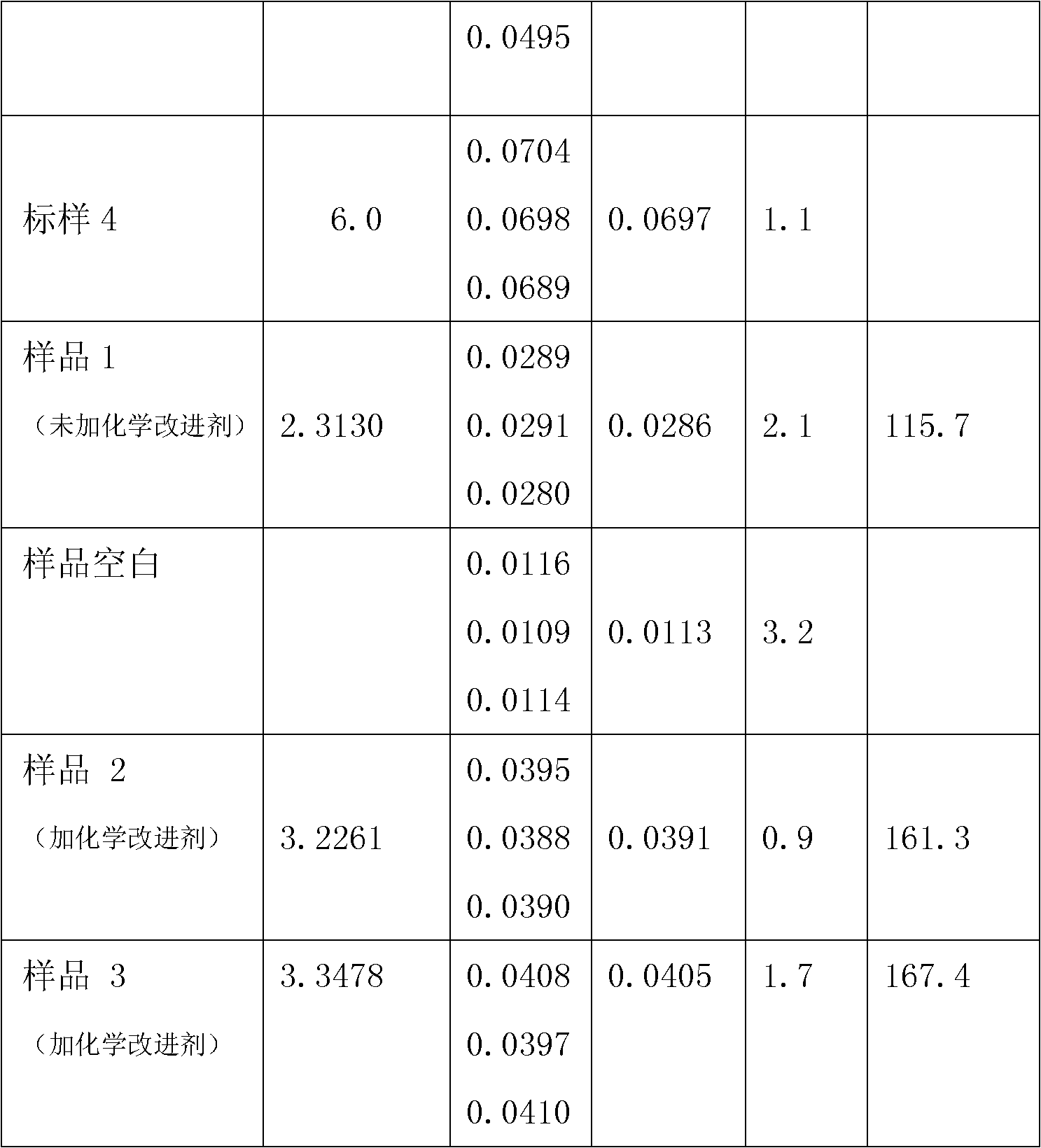
Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry Flame Atomic Absorption is a very common technique for detecting metals present in samples. The technique is based on the principle that ground state metals absorb light at a specific wavelength. Metal ions in a solution are converted to atomic state by means of a flame.
Method of digesting, settling and separating tungsten-based samples and detection method for tungsten-based samples
ActiveCN102230861APreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpectrophotometryInductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy
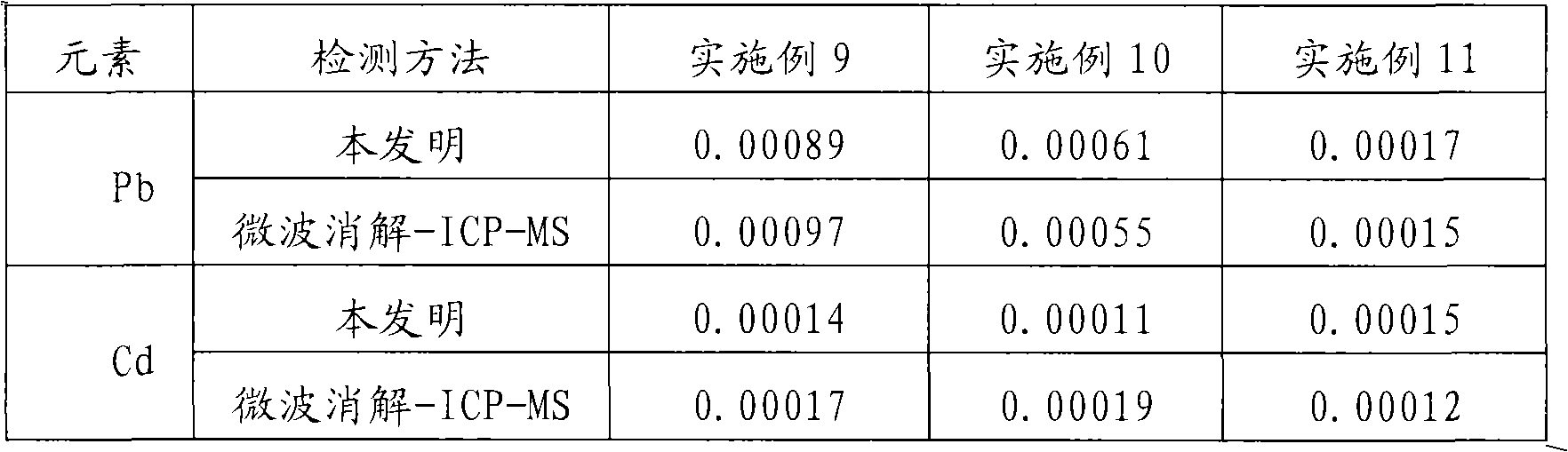
The invention discloses a method of digesting, settling and separating tungsten-based samples and a detection method for tungsten-based samples. The method of digesting, settling and separating tungsten-based samples comprises the following steps: putting a tungsten-based sample in a container, adding water and nitric acid into the container, keeping the container airtight, carrying out microwavedigestion and settlement-separation on the sample under gradient temperatures, and restarting microwave for rinsing and deposition after the temperature of the solution decreases and is close to the boiling point of water so as to obtain a sample solution for detection and precipitates of tungstic acid. The detection method for tungsten-based samples in the invention is to analyze the digested sample solution with at least one analytical method selected from the group consisting of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry, flame atomic absorption spectrometry, graphite oven atomic absorption spectrometry and spectrophotometry so as to obtain the content of elements in the tungsten-based sample.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON AND STEEL +1
Method for clearing and detecting vanadic oxide
InactiveCN101532929AAvoid volatile lossAvoid pollutionPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMulti methodPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for clearing and detecting vanadic oxide which includes steps as follows: taking vanadic oxide to a container, adding nitric acid to the container, processing pre-action under the normal temperature, then closing the container, processing microwave clearing. The detecting method includes steps as follows: using one or many methods of an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry, a flame atomic absorption spectrometry and a graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry for analyzing the cleared vanadic oxide, accordingly, obtaining elementary content of vanadic oxide sample.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP VANADIUM TITANIUM & RESOURCES +3
Digestion and determination method of heavy metals in waste dust-collecting bag
InactiveCN102313706APreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsDust controlNon-ferrous extractive metallurgy
The invention discloses a digestion and determination method of heavy metals in a waste dust-collecting bag, and relates to microwave digestion of the waste bags generated by iron and steel smelting and non-ferrous metal smelting (such as lead-zinc smelting and copper smelting). The method comprises the following steps: mixing the waste dust-collecting bag with a digestion acid system composed ofnitric acid, hydrogen peroxide and hydrofluoric acid in a polytetrafluoroethylene-sealed pressurized digestion tank at normal temperature, shaking up and keeping standing overnight; and performing the microwave digestion under certain conditions and then performing heavy metal determination. By adopting the method, the waste dust-collecting bag is made into a digestion solution, and flame atomic absorption spectroscopy (FAAS) is further adopted for determining the content of the heavy metals in the digestion solution.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Digestion method and detection method for vanadium-nitrogen-titanium-iron mixed alloy conductor
ActiveCN103808558APromotes fast digestionStable storagePreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationAlloyDigestion
The invention provides a digestion method and a detection method for a vanadium-nitrogen-titanium-iron mixed alloy cored wire. The digestion method comprises the following steps: putting a cored wire into a container, adding a concentrated nitric acid and a concentrated hydrochloric acid to the container; carrying out first time of pre-reaction under an open state; adding a concentrated sulfuric acid and carrying out second time of pre-treatment under the open state; carrying out digestion and complexation reaction by microwave in a closed state, so as to obtain a solution. The detection method comprises the following steps: cooling the solution, diluting and fixing volume to obtain a sample solution; determining the content of elementary compositions in one or more sample solutions by using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry, flame atomic absorption spectrometry, titration, spectrophotometry and an electrochemical process. The digestion method and the detection method have the advantages of being safe to operate, simple and rapid, efficient and complete, fewer in man-made factors, and easy to accurately control and repeatedly reappear, and technical indexes such as the accuracy, the precision and the like of an analysis result are improved.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Method for determining iron content in nori with flame atomic absorption spectrometry
InactiveCN103528879AFast and full digestionShorten digestion timePreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsMicrowave ovenPerchloric acid
The invention provides a method for determining iron content in nori with a flame atomic absorption spectrometry. The method comprises the following steps: dyeing a sample at a high temperature to remove water; immersing the sample into a digestion solvent for long time and then pre-treating under high-temperature, high-pressure and closed conditions, so as to rapidly transfer iron in the sample into the digestion solvent at maximum, wherein the digestion solvent is a mixed acid of nitric acid and perchloric acid at a volume ratio of 4:1; heating and digesting by using a microwave oven so as to achieve a high temperature instantly and shorten the digestion time. According to the method provided by the invention, the problems of a traditional method that the consumed time is long and the use amount of solvents is great when the flame atomic absorption spectrometry is used for determining microelements and the environmental pollution caused by the solvents is serious are solved; the method has the advantages of rapidness and convenience, good repeatability and good accuracy, and is applicable to determining the microelements of similar materials.
Owner:SUZHOU GUOHUAN ENVIRONMENT DETECTION
Method for determining nickel content in soil by microwave digestion-flame atomic absorption spectrometry
InactiveCN103558173AImprove atomization efficiencyHigh measurement sensitivityPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsPolyoxyethylene castor oilTrace element
The invention provides a method for determining a nickel content in soil by microwave digestion-flame atomic absorption spectrometry, wherein the method is characterized by: pretreating a soil sample by combining long-time immersion and stepedly heated microwave digestion, using polyoxyethylene castor oil glycerin ether as an activator, raising atomization efficiency of nickel atoms in flame, raising determination sensitivity, thereby raising sensitivity; based on linear relation of absorbance and nickel content determined by a flame atomic abserption spectrometer by a standard solution, measuring and calculating to obtain the content of nickel atoms in soil. The method provided by the invention solves problems that a method for determining trace elements by traditional atomic absorption spectrometry has disadvantages long time consumption, low sensitivity, large solvent consumption amount, and severe environment pollution caused by a solvent, and the method provided by the invention has advantages of good precision, high recovery rate, accuracy, reliability, rapidness and convenience.
Owner:SUZHOU GUOHUAN ENVIRONMENT DETECTION
Method for measuring ruthenium content using ethyne-air flame atomic absorption spectrometry
ActiveCN101109700ASmall physical hazardImprove analysis accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsPotassium hydroxideLamp current
The invention provides a method for determining ruthenium content by acetylene-air flame atom absorption spectrum method, the procedures for which are: a sample is dried under 100-120 centigrade, burned under 400-600 centigrade, residual ash is removed; potassium hydroxide is added in a reference pure ruthenium powder and sample, which is heated under 360-390 centigrade to dissolve; surplus chlorhydric acid is added, so that the solution is acid; some de-saline water is added in the solution to prepare standard mother solution and sample solution; standard solutions of different concentrations are prepared by taking sample blank liquid as thinner; the spectrometer wavelength is adjusted to 344.9 nm, the acetylene flow 65 l / h, lamp current 10 mA; the zero is calibrated by using sample blank liquid, the standard solution is determined, and a standard work curve is established, parameters of the sample are input, the concentration and content of the ruthenium are measured in the sample. The invention has a rapid measuring speed, high accuracy, low harm on the operator, and is applicable for determining the ruthenium content in various solid or liquid multi-component substances, especially the ruthenium content in ruthenium / carbon catalyzer.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for detecting content of iron in photovoltaic glass based on X-ray fluorescence energy spectrum
ActiveCN102980905ASolve the shortageRegulate the marketMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRelative standard deviationSpectroscopy
The invention discloses a method for detecting content of iron in photovoltaic glass based on X-ray fluorescence energy spectrum, belonging to the technical field of detection. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting a representative photovoltaic glass sample, and manufacturing a calibration sample after the value of the iron content achieves constant by using a flame atomic absorption spectrometry, so that a problem that a standard sample in photovoltaic glass iron content measurement is in shortage is solved; measuring the calibration sample with constant photovoltaic glass iron content on an X-ray fluorescence energy disperse spectroscopy; establishing a calibration curve of the content of the iron in the photovoltaic glass, which is measured by adopting the X-ray fluorescence energy spectrum method; measuring the content of the sample in the photovoltaic glass sample by adopting the established calibration curve and the X-ray fluorescence energy disperse spectroscopy under a working condition the same as that in measuring the calibration sample. According to the method provided by the invention, the relative standard deviation (n =11) of the iron content measurement is between 4.5% and 9.0%, and the method is precise and reliable. The method is applied to analyzing a photovoltaic glass practical sample, the measured result is consistent with the analyzed result of the soda-lime-silica glass chemical analysis method of the national standard method GB / T1347-2008, and the working efficiency is more than 50 times that of the national standard method GB / T1347-2008, so that the requirements of quickly analyzing large-scale samples can be satisfied.
Owner:WUXI INSPECTION TESTING & CERTIFICATION INST
Quantitative analysis method for measuring trace nickel in water by microwave digestion-flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS)
InactiveCN101968436AReduce dosageEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsSpectrographAbsorbance
The invention relates to a quantitative analysis method for measuring trace nickel in water by microwave digestion-flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS), which is characterized in that: pretreatment is performed on a water sample by combining low-temperature concentration and microwave digestion; nonylphenol polyoxyethylene-10-ether (NP-10) is used as activating agent; and the trace content is obtained from a regression equation or a working curve according to the linear relation between the absorbance difference between the water sample and the blank solution measured by a flame atomic absorption spectrograph and the nickel content. The invention has the advantages of simple microwave digestion pretreatment process, small reagent amount, environmental protection, time saving, high efficiency and the like and is a fast, accurate, flexible and widely-applicable analysis method for measuring trace nickel in water.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
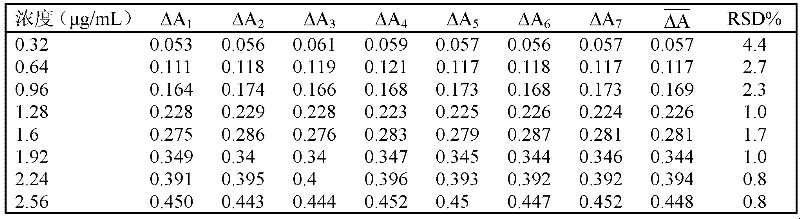
Method for measuring content of trace cadmium in rice by utilizing flame atomic absorption spectrometry
InactiveCN103499549AImprove atomization efficiencyHigh test sensitivityPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsRelative standard deviationPhysical chemistry
The invention provides a method for measuring the content of trace cadmium in rice by utilizing a flame atomic absorption spectrometry. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of preprocessing a rice sample by utilizing a microwave digestion manner in which a long-time soaking manner is combined with a step type heating manner, after the digestion, reacting cadmium ions with potassium iodide to generate CdI4<2->, reacting the CdI4<2-> with methyl green (MG) to generate a hydrophobic ionic association compound, extracting the hydrophobic ionic association compound into a micelle phase of a TritonX-114 nonionic surfactant, and measuring the cadmium content in the micelle phase by utilizing the flame atomic absorption spectrometry. The method solves the problems that the measurement of the trace cadmium by utilizing a traditional flame atomic absorption spectrometry is low in sensitivity and is easily interfered by matrixes and has the advantages of high precision and recovery rate, small relative standard deviation, accuracy, reliability, rapidness and convenience.
Owner:SUZHOU GUOHUAN ENVIRONMENT DETECTION
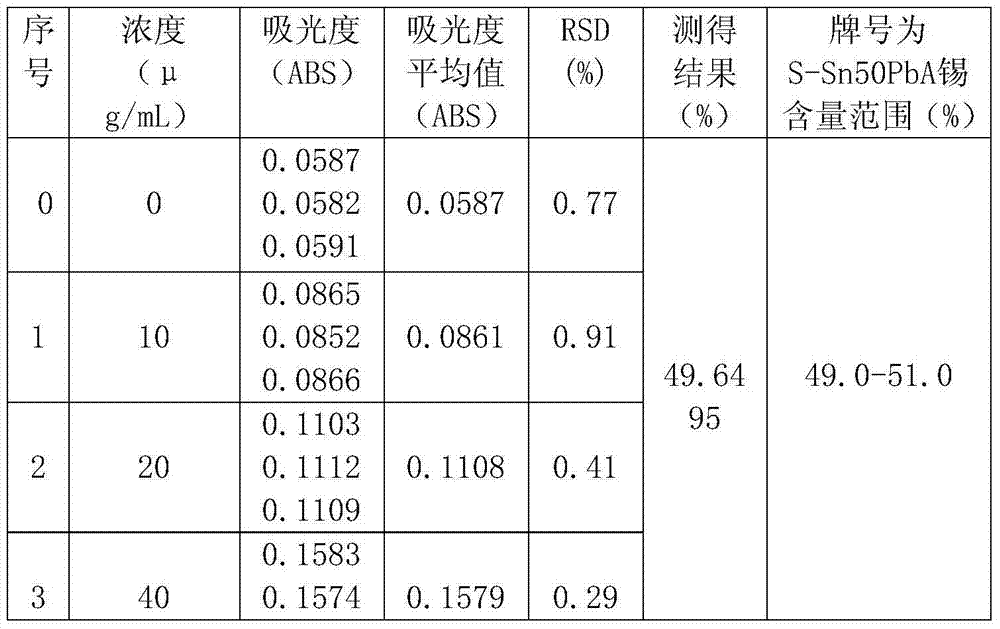
Method for testing tin content of tin-lead solder through flame atomic absorption spectroscopy method
InactiveCN103592239AEasy to operateImprove test accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsHydrofluoric acidDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for testing tin content of a tin-lead solder through a flame atomic absorption spectroscopy method. According to the method, nitric acid, hydrofluoric acid and hydrogen peroxide are used as solvents to rapidly decompose the tin-lead solder, the ratio of the nitric acid to the hydrofluoric acid to the hydrogen peroxide is 1:2:1, a sample is heated and dissolved by an electric heating plate at the low temperature, the absorbancy of the tin in a decomposition solution is measured by using the air-acetylene fuel-lean flame atomic absorption spectroscopy method, and the tin content in the decomposition solution is calculated by using a standard addition method. The method is high in testing accuracy and relatively small in error, the whole analysis test process is simple in operation, the amount of acid used is small, and the method is capable of rapidly analyzing the tin content of the tin-lead solder.
Owner:ANHUI WAYEE SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method for determining content of zinc in mung beans by using cloud point extraction-atomic spectrum method
InactiveCN103499537AHigh sensitivityImprove accuracyPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsRelative standard deviationAlkylphenol
The invention provides a method for determining the content of zinc in mung beans by using a cloud point extraction-atomic spectrum method. The method is characterized by being comprising the flowing steps: pretreating mung bean samples by cold digestion and heating digestion through long-time soaking, combining 1-(2-pyridine azo)-2 naphthol (PAN) ethanol solution as a complexing agent with zinc to form a stable hydrophobic ionic associate after digestion, adding alkylphenol and ethylene oxide condensation compound to obtain a non-ionic surface active agent, extracting to obtain the non-ionic surface active agent organic phase, and determining the content of the zinc in the non-ionic surface active agent organic phase by using a flame atomic absorption spectrometry after dissolving and diluting of nitric acid and ethanol. The method solves the problems that a traditional method has low sensitivity to microelements and can be easily interfered by co-existing ions by using the flame atomic absorption spectrometry, and has the advantages of accuracy, reliability, high recovery rate, low relative standard deviation, high enrichment coefficient, rapidness and convenience.
Owner:SUZHOU GUOHUAN ENVIRONMENT DETECTION
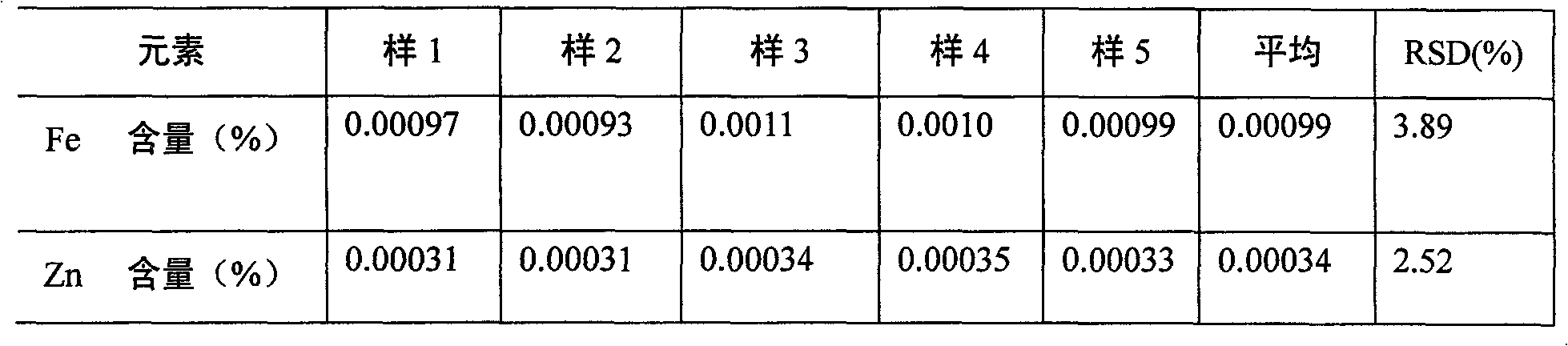
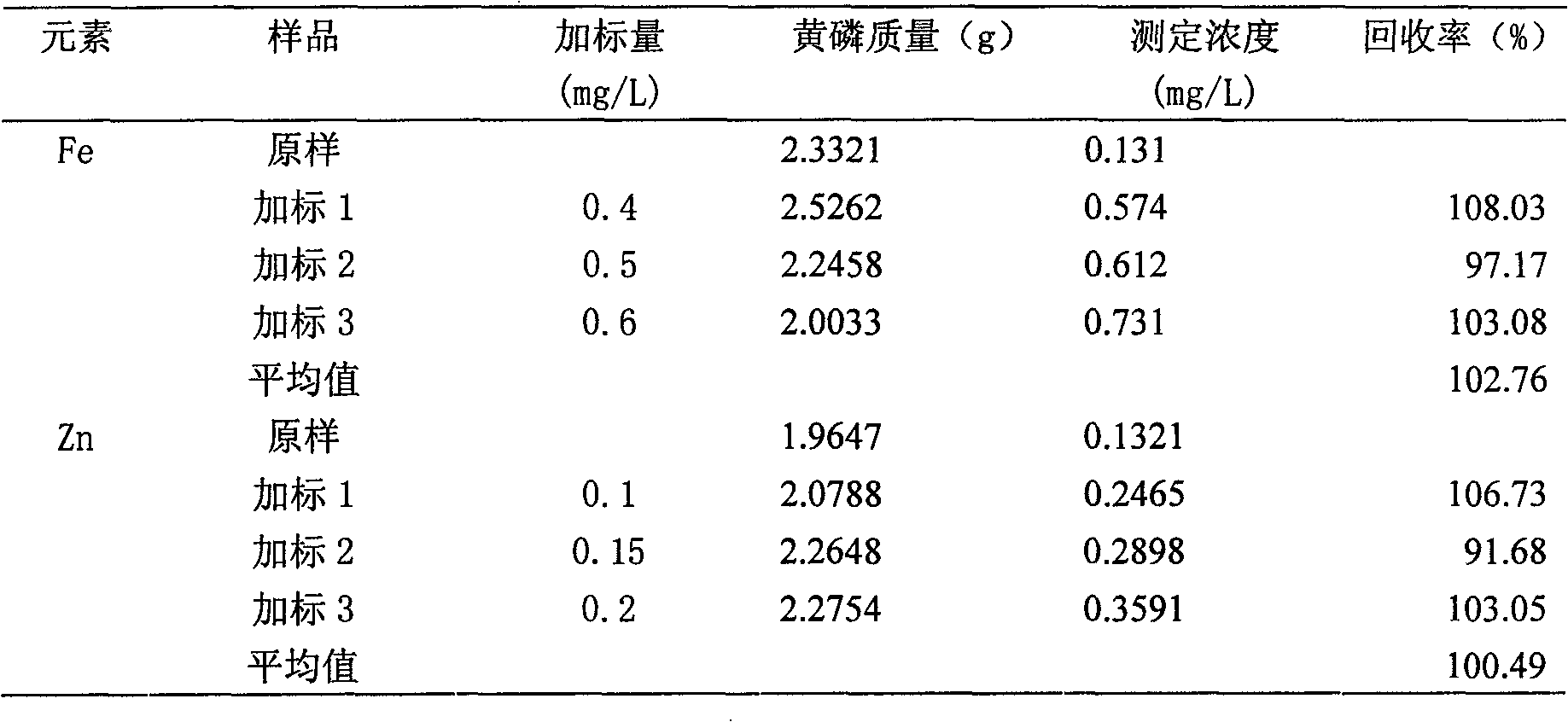
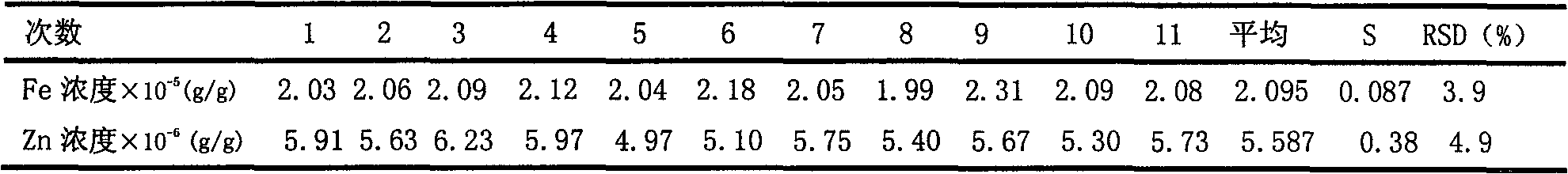
Atomic absorption spectrometry of content of Fe and Zn impurities in yellow phosphorus
InactiveCN101650301AImprove the measurement methodEnhanced inhibitory effectPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsPhosphateSample water
The invention discloses an atomic absorption spectrometry of the content of Fe and Zn impurities in yellow phosphorus. The atomic absorption spectrometry mainly comprises the following steps: (1) heating and digesting yellow phosphorus by nitric acid with a volume concentration no lower than 50 percent to prepare a sample solution with a phosphoric acid concentration of 0.5-0.8mol / l; (2) extracting and separating phosphoric acid in the sample solution prepared in the step (1) by tri-butyl-phosphate, discarding organic phases and reserving a sample aqueous solution; (3) preparing a standard solution with different set concentrations of Fe and Zn, extracting the standard solution according to the same extracting condition of the step (2), measuring Fe and Zn of the obtained standard water-phase solution by a flame atomic absorption spectrometry method and drawing a working curve; (4) measuring the Fe and Zn of the sample water-phase solution obtained in the step (2) by the flame atomicabsorption spectrometry method and comparing a measurement result with the standard working curve measured and drawn in the step (3) to solve the content of Fe and Zn impurities in the yellow phosphorus sample to be measured.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
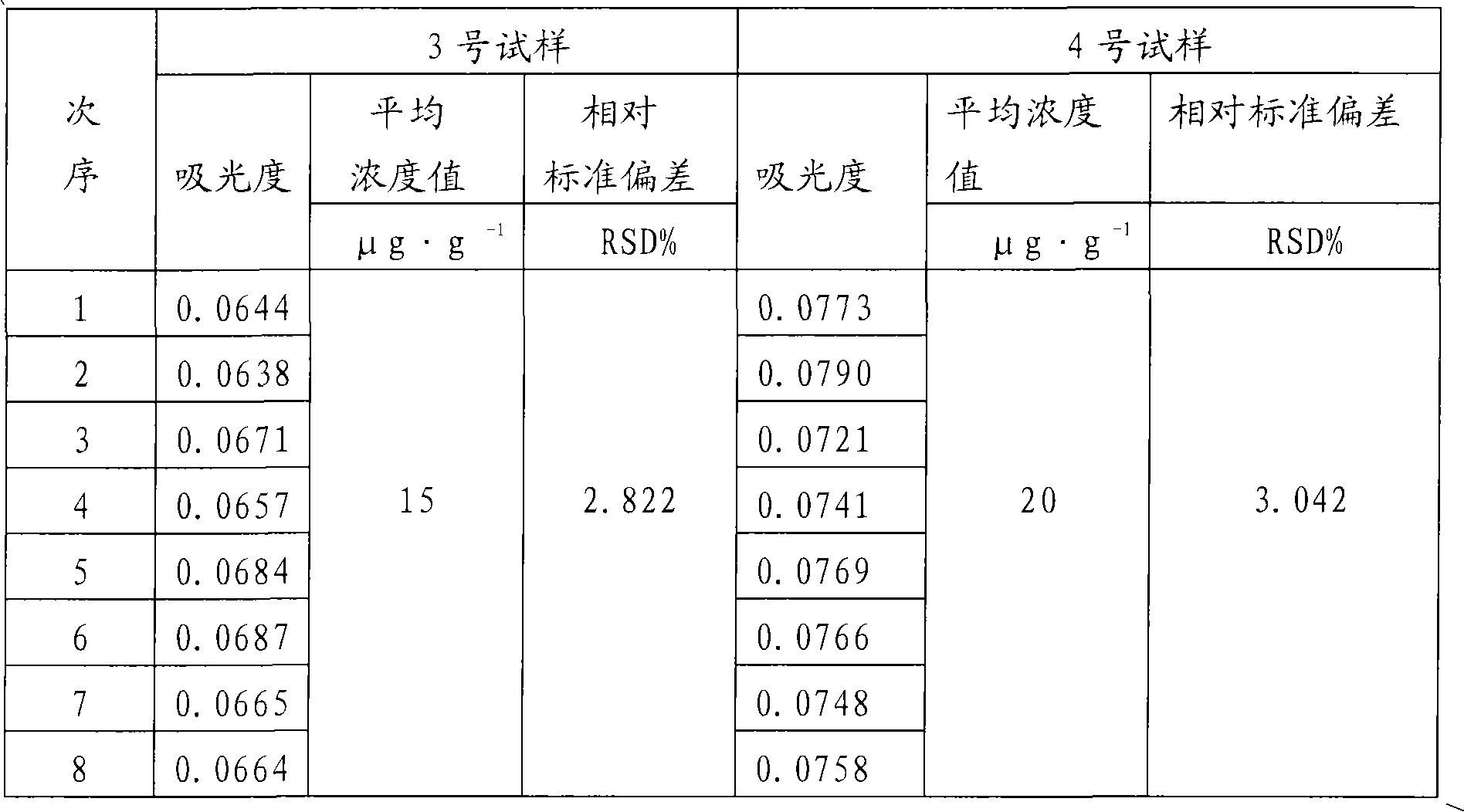
Sample preparation method and detecting method for detecting impurities in titanyl sulfate solution
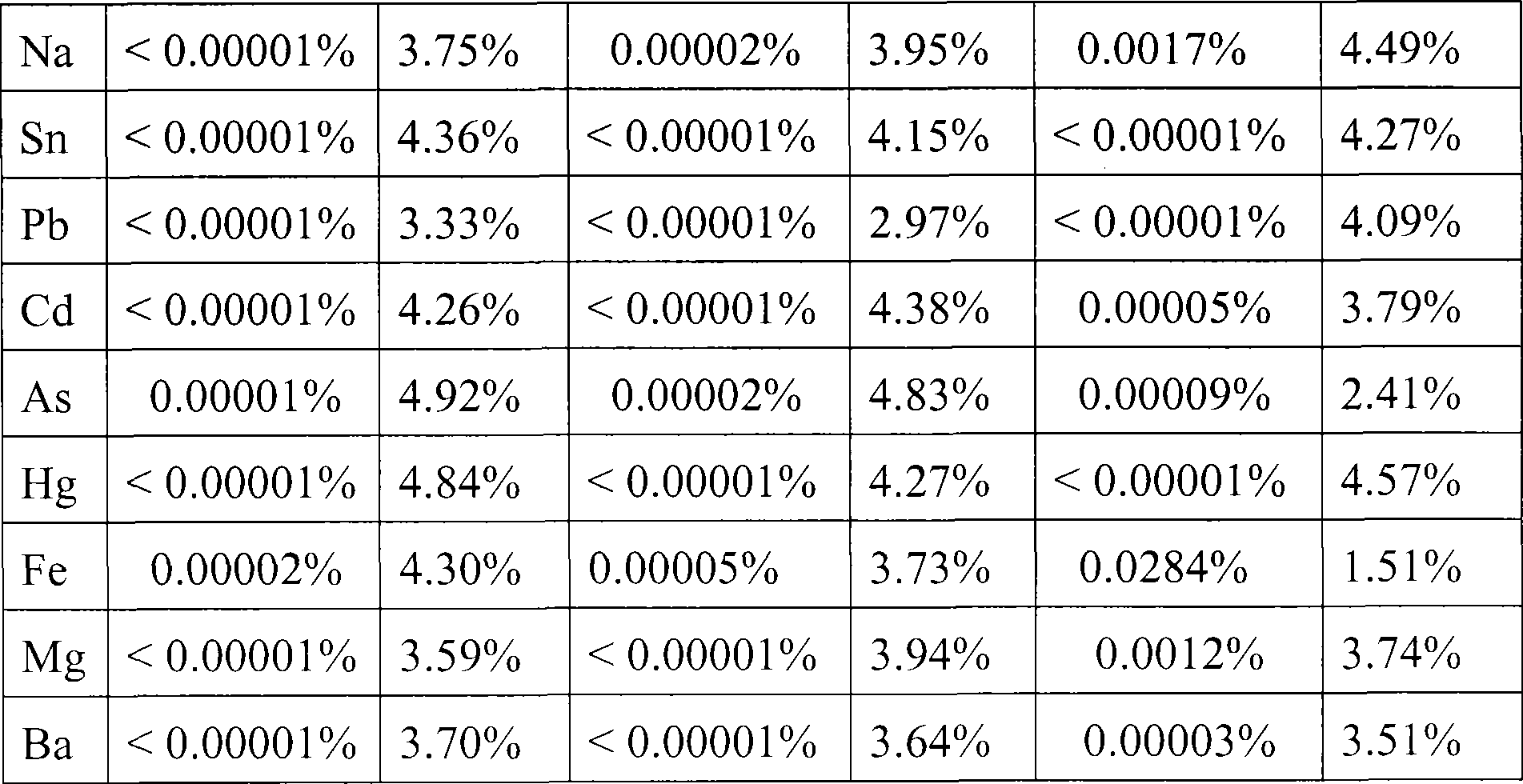
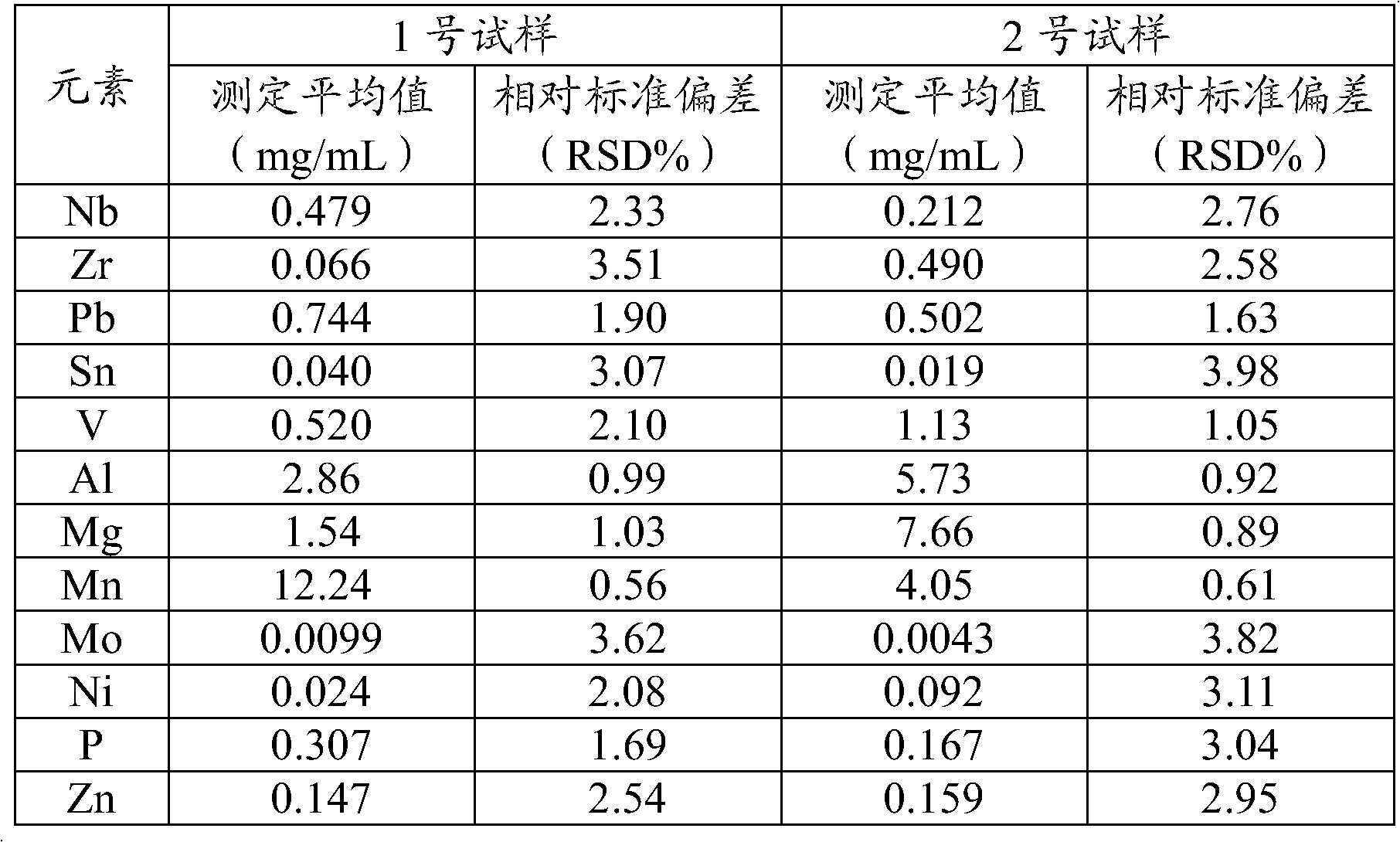
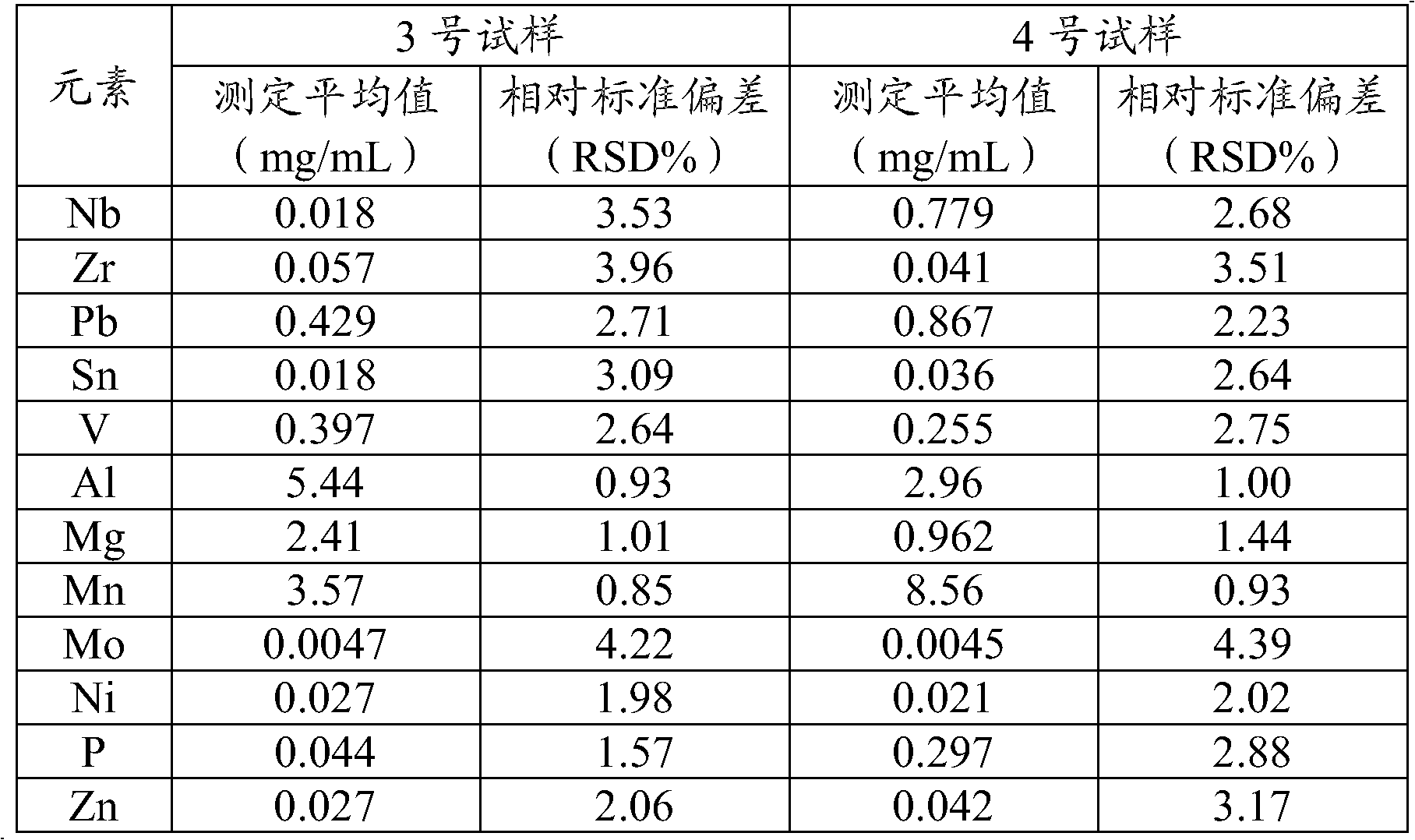
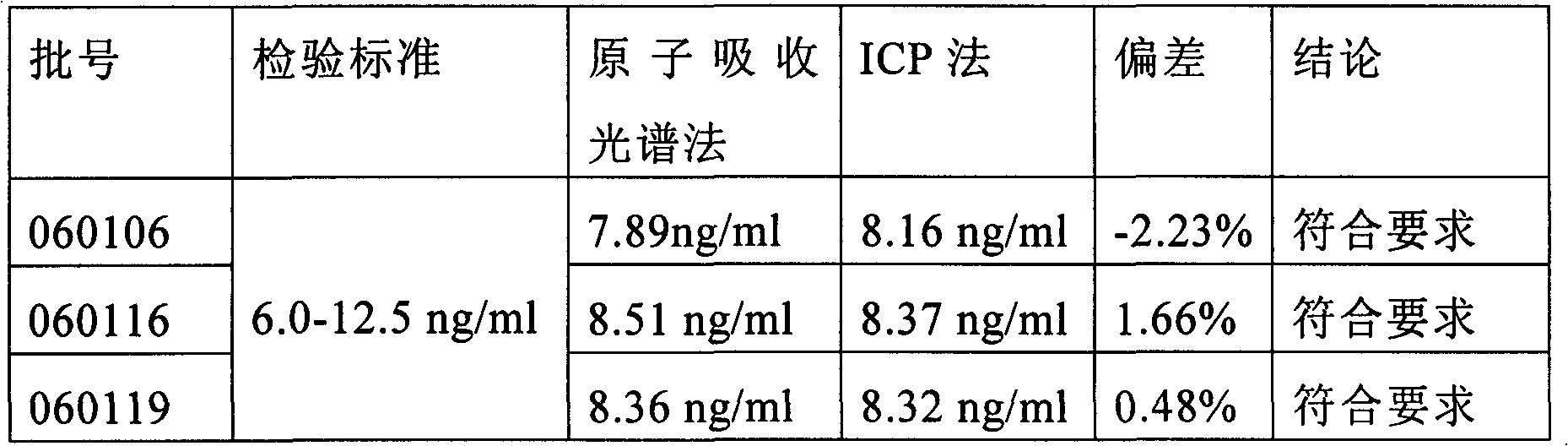
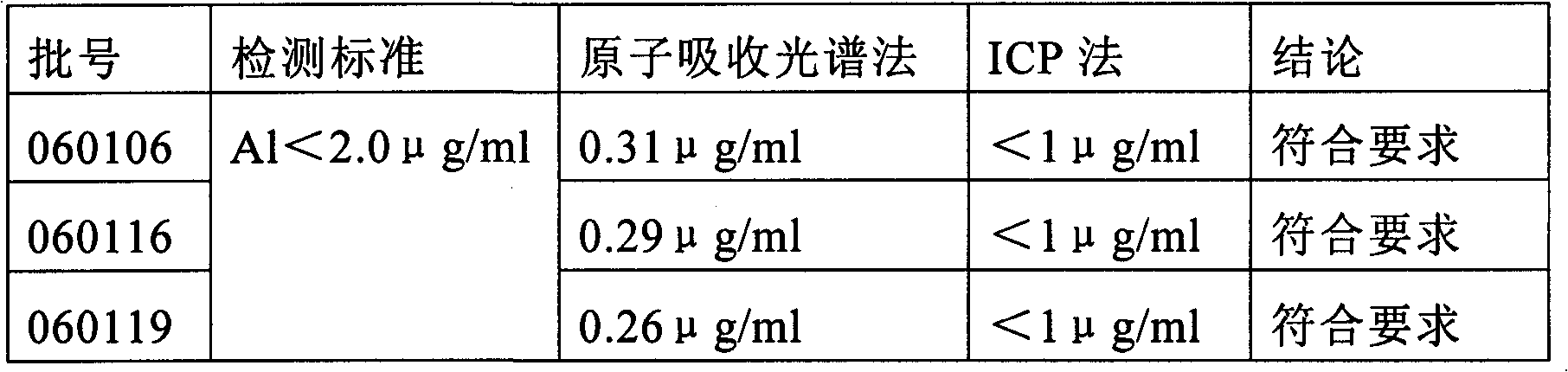
The invention discloses a sample preparation method and detecting method for detecting impurities in a titanyl sulfate solution. According to the invention, the sample preparation method for detecting impurities in the titanyl sulfate solution comprises the following steps: diluting the titanyl sulfate solution by using a mixed solution of ethanol and water so as obtain the sample used for detecting the impurities in the titanyl sulfate solution. According to the invention, the method for detecting the impurities in the titanyl sulfate solution comprises the following steps: preparing the sample by using the sample preparation method, and detecting the content of at least one element of Nb, Zr, Pb, Sn, V, Al, Mg, Mn, Mo, Ni, P and Zn in the sample by using at least one method of inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, flame atomic absorption spectrometry and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Method for measuring contents of strontium and aluminum in strontium chloride injection by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry
InactiveCN102914504ALow investment costLow running costPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsInductively coupled plasma mass spectrometryAnalysis method
The invention relates to a method for measuring the contents of strontium and aluminum in a strontium chloride injection by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. The method comprises the following steps of: precisely absorbing a standard solution and diluting; preparing the diluted solution to the standard solution; measuring the standard solution by using the atomic absorption spectrometry to obtain a standard curve; measuring the strontium chloride injection by using the atomic absorption spectrometry; and comparing the standard curve to obtain the contents of the strontium and the aluminum in the strontium chloride injection. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics that the input and operation cost is low and expenses consumed by an ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry) are 4 times of the expenses GFAAS (Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry); and the method has the advantages of simplicity in operation, low detection limit and the like, and is mature in the analysis method.
Owner:SHANGHAI ATOM KEXING PHARMA
Method for measuring contents of Fe, Mn, Cu, Tin and Mg in titanium sponge, titanium and titanium alloy
InactiveCN102735515AImprove accuracyEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsHydrofluoric acidTitanium
The invention provides a method for measuring contents of Fe, Mn, Cu, Tin and Mg in titanium sponge, titanium and titanium alloy, which comprises the steps of: adding hydrochloric acid, hydrofluoric acid and boric acid into the sample for dissolving the sample; and adding strontium chloride for eliminating interference to obtain a sample liquid to be measured. The conventional flame atomic absorption spectrometry is used for measuring the absorbance of the sample liquid to be measured, and the corresponding content values of Fe, Mn, Cu, Tin and Mg can be obtained in the standard working curve of Fe, Mn, Cu, Tin and Mg according to the absorbance. The method not only is simple in operation, but also is high in accuracy rate of contents of Fe, Mn, Cu, Tin and Mg; and the measurement result is good in stability, repeatability and accuracy, thus completely meeting the demand of measuring the contents of Fe, Mn, Cu, Tin and Mg in titanium sponge, titanium and titanium alloy in the daily life.
Owner:WUKUN STEEL
Sample treatment method for measuring antimony in polyester chip with flame atomic absorption spectrometry
InactiveCN102608044ARaise the ashing temperatureLow ion contentPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsPolyesterRoom temperature
The invention discloses a sample treatment method for measuring antimony in a polyester chip with flame atomic absorption spectrometry. The sample treatment method comprises the steps of: weighing and conducting low-temperature heating on an appropriate polyester chip sample, ashing the sample for approximately 1h after the sample is completely carburized, taking out and cooling the ashed sample to be at room temperature, adding approximately 2ml of 10% (approximately) magnesium nitrate and evaporating to dryness, putting a quartz beaker of the dried sample into a muffle furnace, setting the temperature of a furnace body to be approximately 500 DEG C, ashing for approximately 2h, taking out and cooling the beaker for placing the completely ashed sample to be at the room temperature, adding approximately 2ml of 68%-70% hydrochloric acid, moving the dissolved sample into a 50ml volumetric flask, adding deionized water to be a constant volume, and obtaining a product. In the sample treatment method, the sensitivity of the sample in the measurement by the flame atomic absorption method is improved, the precision is improved, the measuring speed is high, the interference is small, the accuracy is high, the measuring cost is low, and the sample treatment method is particularly applicable to the quality detection in polyester chip manufacturers.
Owner:ANHUI WAYEE SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method for analyzing gold in tin and tin alloy waste
InactiveCN103115886AIncrease dosageControl pHColor/spectral properties measurementsRelative standard deviationLead oxide
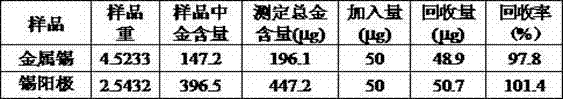
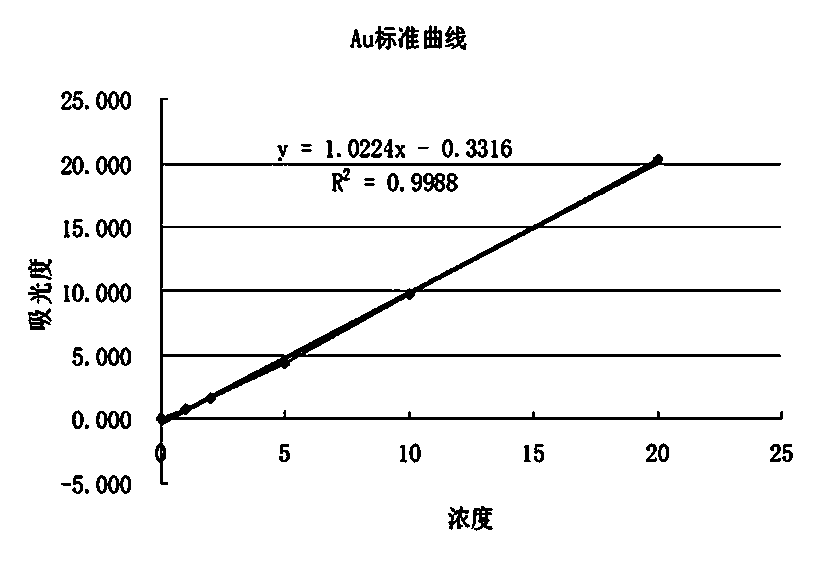
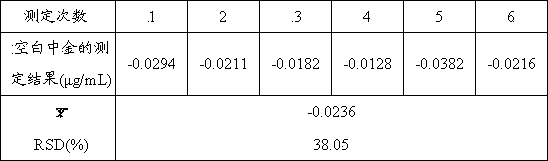
The invention relates to a method for analyzing gold in tin and tin alloy waste, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: heating a sample together with sodium carbonate, boron, silicon dioxide, lead oxide, flour and pure silver, cooling, and taking out a lead button; cupelling while keeping the temperature at 850 DEG C so that the gold and the added silver form a silver-gold alloy; dissolving the silver-gold alloy in aqua-regia; and in a 5% or so hydrochloric acid medium, measuring the gold in the tin and tin alloy waste by air-acetylene flame atomic absorption spectrometry. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of ideal separation and enrichment effects and accurate and stable analytic result, and is simple to operate; and the relative standard deviation is less than 1.0%, and the recovery rate is 97.8-101.4%.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RES INST OF NON FERROUS METALS
Method for rapidly measuring content of gold in gold-loaded resin material
InactiveCN103926205AEfficient enrichmentHigh recovery ratePreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsThioureaGold content
The invention discloses a method for rapidly measuring the content of gold in a gold-loaded resin material. A national standard fire assaying method is replaced by a gold-thiourea decomposition gold removal method with plastic foam for adsorption enrichment and separation of a sample, the gold content is directly measured by a flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS) instrument, a gravimetric method in the national standard is changed, the sample pretreatment and test process is simplified, the analysis time is shortened, and the test cost is saved. According to the technical means of plastic foam method pretreatment, the defects that the program is complicated, special equipment such as a fire assaying furnace and a cupellation furnace are needed, the cost is high and the like are overcome, the technical defects of element content loss, insufficient extraction and the like brought by direct use of the FAAS are also overcome, the method system for rapidly measuring the content of gold in the gold-loaded resin material is established, a rapid, convenient and accurate detection effect is achieved, and the method is high in practicality and value.
Owner:新疆出入境检验检疫局检验检疫技术中心
Method for determining content of methyl mercury in fish meat
InactiveCN105092561AReduce dosageFast microwave extractionAnalysis by thermal excitationColor/spectral properties measurementsAbsorbanceMeat sample
The invention discloses a method for determining the content of methyl mercury in fish meat. The method includes the steps: after a fish meat sample is pretreated, extracting methyl mercury in a microwave extraction apparatus by adopting a mixed solution of dichloromethane and hydrochloric acid, then carrying out reverse extraction of methyl mercury by a 2-mercaptoethanol solution, taking a supernatant through centrifugation, finally determining the absorbance by flame atomic absorption spectrometry, and thus obtaining the concentration of methyl mercury in the sample through a standard curve. With combination of the microwave assisted extraction and the flame atomic absorption spectrometry, the content of methyl mercury in the fish meat is determined, and the method has the advantages of being higher in accuracy, convenient to operate, and safe and simple.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Quantitative analytical method for determining trace cobalt in water by utilizing microwave digestion flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS) method
InactiveCN102519939AImprove atomization efficiencyEliminate the effects of background absorptionPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationDigestionLinearity
The invention relates to a quantitative analytical method for determining trace cobalt in water by utilizing a microwave digestion flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS) method, which is characterized by utilizing low-temperature heating concentration combined with microwave digestion to pretreat a water sample, utilizing polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG-400) to serve as an activating agent, and obtaining cobalt content according to linear relation between absorbency difference and the cobalt content and according to regression equation or a working curve, wherein the absorbency difference is measured by a flame atomic absorption spectrometer respectively through a water sample determining system and reagent blank solution. The quantitative analytical method for determining the trace cobalt in the water by utilizing the FAAS method has the advantages of being simple in digestion pretreatment process, less in reagent consumption, environment-friendly, saving in time, high in efficiency, analysis accuracy and sensitivity, low in analysis cost and low in maintenance cost of an instrument, and is an analysis method which is fast, accurate, insensitive and wide in application and used for determining the trace cobalt in the water.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
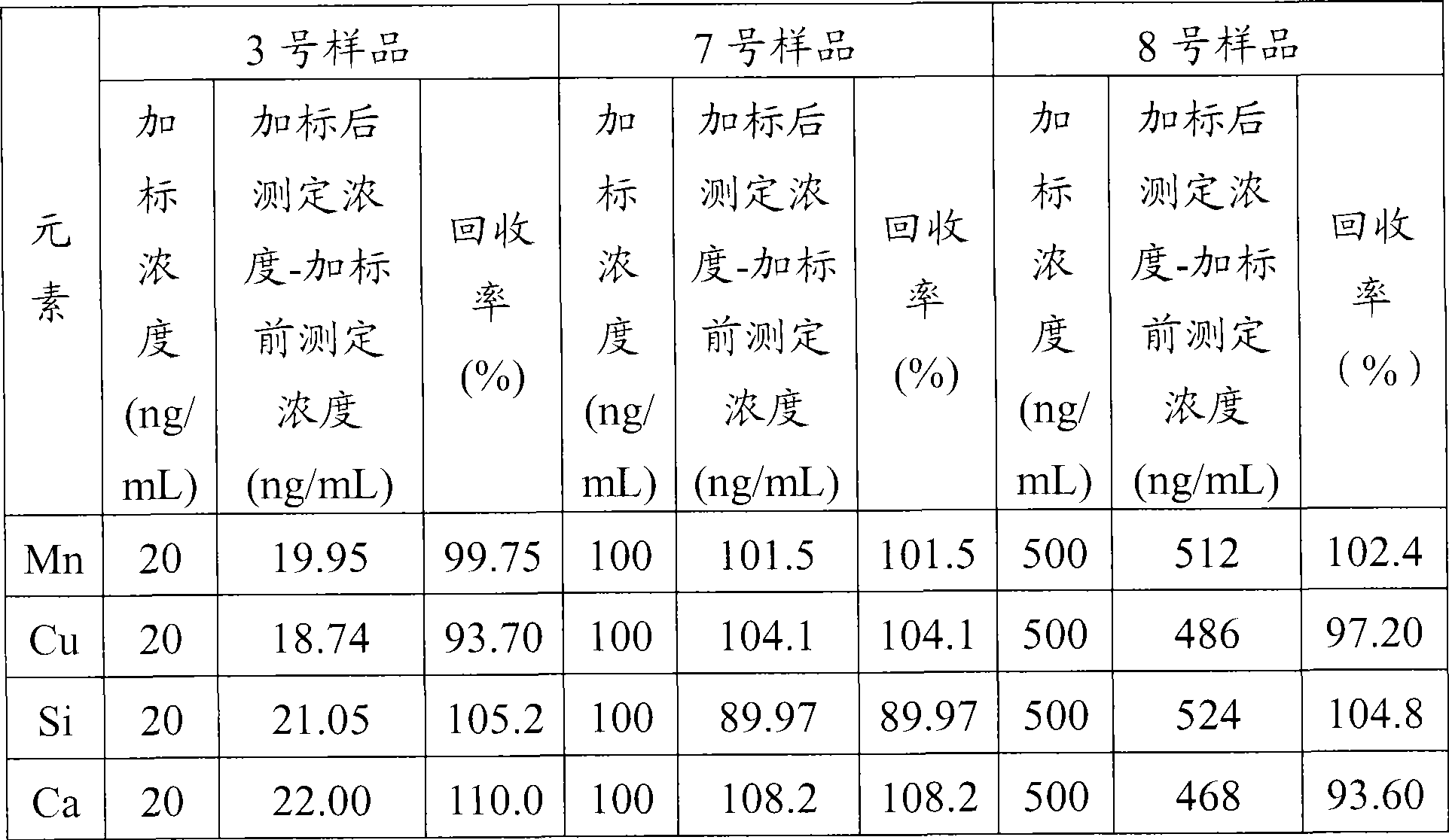
Method for measuring contents of manganese, copper and oxides in directly reduced iron
ActiveCN102243153AImprove accuracyEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationManganeseDissolution
The invention provides a method for measuring contents of calcium oxide, magnesium oxide, potassium oxide, sodium oxide, manganese and copper in directly reduced iron. An absorbance value of a sample solution is measured by using a conventional flame atomic absorption spectrometry method, and corresponding contents of calcium oxide, magnesium oxide, potassium oxide, sodium oxide, manganese and copper are obtained according to the absorbance value in a standard working curve of calcium oxide, magnesium oxide, potassium oxide, sodium oxide, manganese and copper. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of: adding hydrochloric acid in a sample, adding mixed acid of nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid, adding perchloric acid for dissolving, adding diluted hydrochloric acid for dissolving salts, and filtering a dissolution solution to prepare the sample solution. The method is convenient for operation, and has high accuracy rate of measured contents of calcium oxide, magnesium oxide, potassium oxide, sodium oxide, manganese and copper; and measurement results in the method have better stability, repeatability and accuracy. Experiments prove that the method is reliable and practical, and can meet demands of daily measuring the contents of calcium oxide, magnesium oxide, potassium oxide, sodium oxide, manganese and copper in the directly reduced iron.
Owner:WUKUN STEEL +1
Solid suspension dispersing agent for testing sample, preparation method and testing method thereof
InactiveCN101819107AFast preparationEfficient preparationPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationUltrasonic oscillationInductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy
The invention discloses a dispersing agent for solid suspension and a preparation method thereof in the testing technique of suspension solid sampling elements. The dispersing agent is mixed liquid formed by combining agar, ethanol and water proportionally. The preparation method for the dispersing agent comprises the following steps of: weighing a proper amount of the agar and placing the agar in a container; adding water to dissolve and clarify through ultrasonic oscillation at the room temperature or at the temperature of no higher than 40 DEG C; diluting and determining the volume by using the ethanol; and then oscillating for a plurality of minutes ultrasonically. The preparation method for the solid suspension comprises the following steps of: weighing titanium dioxide, vanadium pentoxide, iron oxide red or other samples to be tested and placing the titanium dioxide, the vanadium pentoxide, the iron oxide red or other samples into a container; adding the mixed dispersing agent of the agar and the ethanol; determining the volume by using water; and oscillating ultrasonically to obtain the solid suspension of the sample to be tested. The testing method comprises the following step of directly testing and analyzing the produced solid suspension by adopting instruments of graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry, flame atomic absorption spectrometry or inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry and the like so as to obtain the content of the elements in the sample.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP VANADIUM TITANIUM & RESOURCES +2
Method for separation, enrichment and detection of Cu and Zn in food
InactiveCN105241833ASimple processFast detection of precipitationPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsVector elementPhenanthroline
The invention discloses a method for separation, enrichment and detection of Cu and Zn in food. The method is as below: co-precipitating Cu and Zn in a food sample with 2,9 -dimethyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10- phenanthroline disodium sulfonic acid (BCP); and then determining the content of Cu and Zn by using a flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS). The method has the advantages of simple process, high detection and sedimentation speed and low cost; BCP is used as a co-precipitation agent, and no vector element is needed. Compared with the prior literature art, the method has the advantages of low detection limit and high degree of accuracy.
Owner:云南商测质量检验技术服务有限公司
Method for testing content of nickel in industrial sulfuric acid by flame atomic absorption spectroscopy method
InactiveCN104165856AEasy to operateAvoid lostColor/spectral properties measurementsMetal impuritiesDigestion
The invention relates to a method for testing the content of nickel in industrial sulfuric acid by a flame atomic absorption spectroscopy method. The method provided by the invention is mainly used for analyzing and detecting aiming at industrial sulfuric acid. A sample is not required to be subjected to digestion processing; the absorbance of a nickel element in a sample is determined by adopting an air-acetylene flame atomic absorption spectrometry, and the content of the nickel element is calculated by adopting a standard curve method. The method provided by the invention is accurate, rapid, and is good in trace amount and reproducibility, and is a method for rapidly analyzing and determining the content of the nickel element in the industrial sulfuric acid. In the preparation of industrial sulfuric acid, metal impurities of ferrum, copper, nickel and the like are inevitably brought into industrial sulfuric acid products for the reasons of mineral sources, pipelines, equipment and the like, the impurities not only affect the quality of the industrial sulfuric acid products, but also affect the use of the industrial sulfuric acid in the industries of electronics, reagents, pharmacy, textile and the like; in the quality standard of the domestic industrial sulfuric acid, the contents of ferrum, arsenic, lead and mercury are required correspondingly, but the content of metal nickel is not defined. According to the method provided by the invention, the metal nickel in the industrial sulfuric acid is detected by utilizing a flame atomic absorption spectrometer, an analytical method is established, and means and reference data are provided for completing relevant quality standard.
Owner:JILIN INST OF CHEM TECH
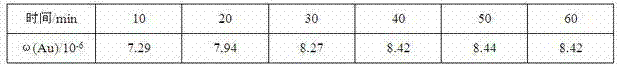
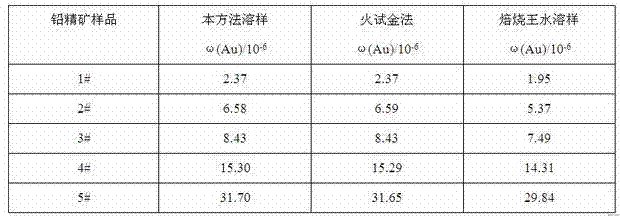
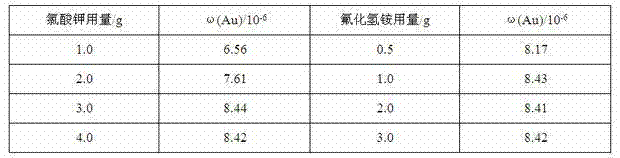
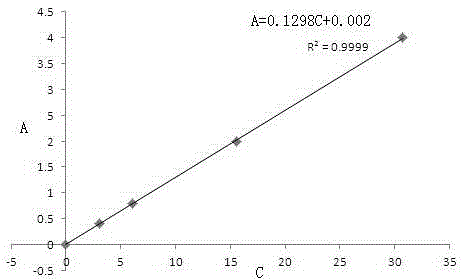
Rapid determination method for gold in lead concentrate by adopting flame atomic absorption spectrometry
InactiveCN103163092AStrong oxidation abilityAvoid the formation of precipitatesColor/spectral properties measurementsWater bathsDissolution reaction
The invention relates to the technical field of analytical test and in particular relates to a rapid determination method for gold in lead concentrate by adopting a flame atomic absorption spectrometry. The rapid determination method provided by the invention comprises the following concrete steps of: firstly adding concentrated nitric acid to oxidize an ore sample, so that massive sulphur is oxidized into sulphate ions to be removed, a lead nitrite solution is also generated, formation of massive lead chloride precipitate when chloroazotic acid dissolves the ore sample is avoided and encapsulated gold is exposed; then hermetically dissolving the ore sample by adopting potassium chlorate-ammonium hydrogen fluoride, so that chloric acid generated after potassium chlorate reaction has strong oxidability, ammonium hydrogen fluoride can decompose gold encapsulated in silification minerals such as quartz and the like, the ore sample can be thoroughly decomposed when chloric acid and ammonium hydrogen fluoride are combined under the hermetically sample dissolution condition and the gold in the ore sample can be completely dissolved; and carrying out an inverse dissolution reaction in a boiling water bath, separating and enriching with activated carbon, and then adopting an atomic absorption method. The rapid determination method provided by the invention has the advantages of less interference, low detection limit, no roasting on the ore sample, direct sample weighing and sample dissolving, easy and quick operation, high efficiency and low cost and is especially applicable to determination of samples in batches.
Owner:INST OF MULTIPURPOSE UTILIZATION OF MINERAL RESOURCES CHINESE ACAD OF GEOLOGICAL SCI
Detection method of trace methylmercury in alga
InactiveCN104406926AWide detection rangeHigh precisionPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsMethylmercuryStandard solution
The invention provides a detection method of trace methylmercury in alga. The detection method comprises the following steps: (1) ultrasonic extraction of methylmercury; (2) drawing of a standard curve; (3) measurement of the content of methylmercury in a standard solution and a sample solution by adopting the flame atomic absorption spectrometry. The content of trace methylmercury is measured by the combination of the ultrasonic extraction and the flame atomic absorption spectrometry, the detection range is wide, methylmercury with the concentration of 0-4 mg / L can be detected, and the detection method has relatively high accuracy, besides, is convenient, fast, simple and safe in operation, and is suitable for industrial application.
Owner:DONGCHEN LEADER TESTING
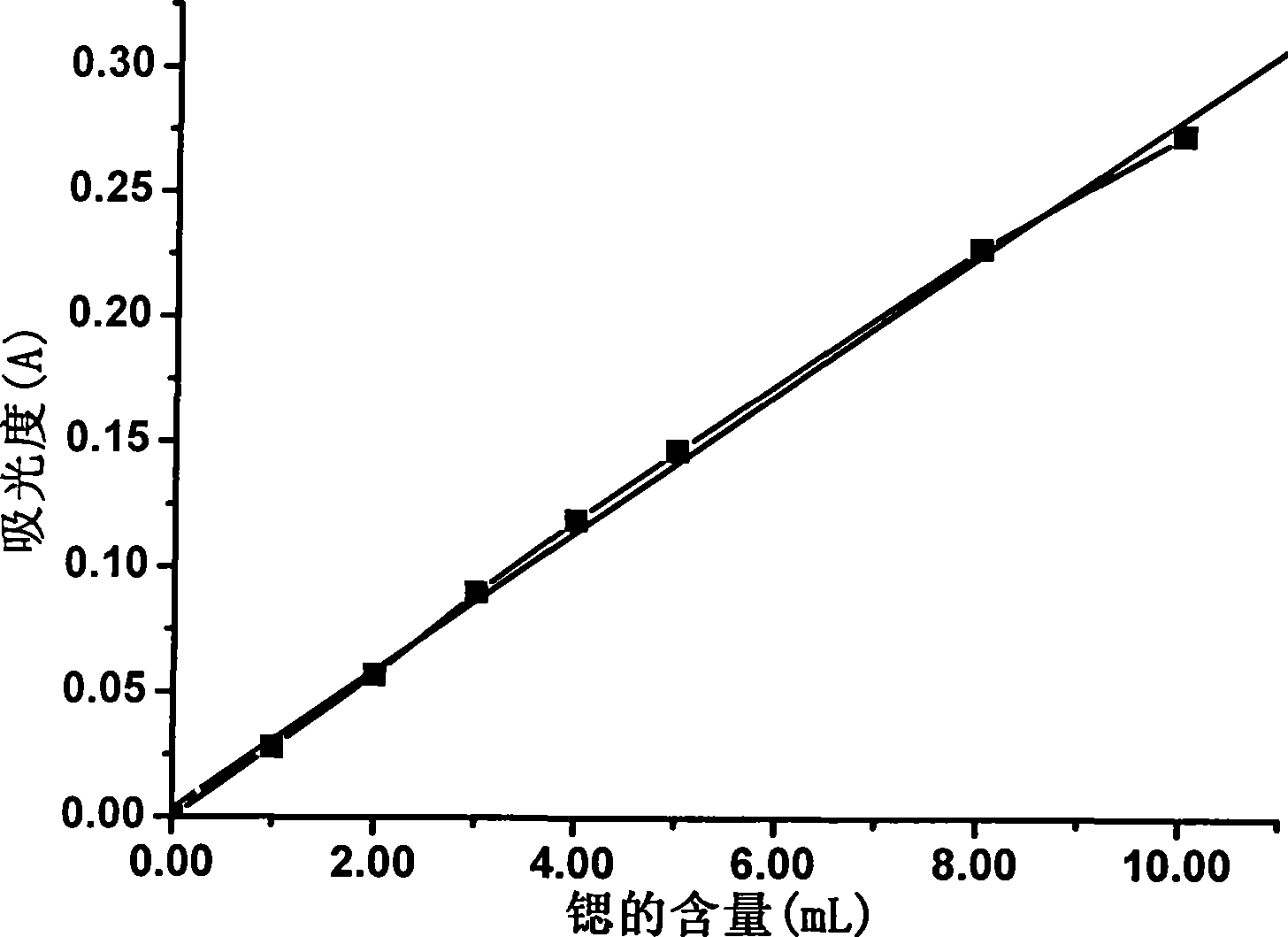
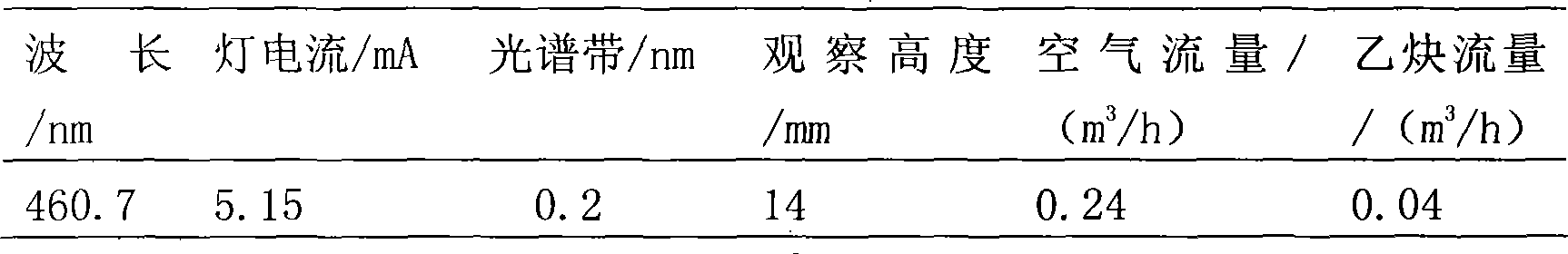
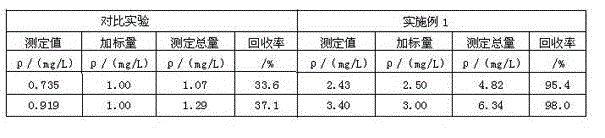
Method for detecting strontium content in magnesium-strontium intermediate alloy by flame atomic absorption spectrometry
InactiveCN101398376ASimple methodReliable test resultsColor/spectral properties measurementsDistilled waterStrontium
The invention provides a method used for measuring the content of strontium in Mg-Sr preliminary alloy by a flame atomic absorption spectrometry; the method adopts the flame atomic absorption spectrometry to measure the content of the strontium in the Mg-Sr preliminary alloy and comprises the steps as follows: a sample is placed in a conical bottle and distilled water is added in the conical bottle; subsequently, hydrochloric acid solution and hydrogen peroxide are added; after the sample is completely dissolved, the solution is cooled and transferred to a volumetric flask, diluted to a calibration and uniformly mixed; the sample is measured under the working condition of an atomic absorption spectrophotometer; the content of the strontium is queried on the working curve of the strontium; and simultaneously, a recovery test is carried out by a recovery rate testing method. The method can detect the content of the strontium in the Mg-Sr preliminary alloy and provide the judgment basis for exactly measuring the content of strontium in the Mg-Sr preliminary alloy.
Owner:CHANGAN AUTOMOBILE (GRP) CO LTD
Method for determining calcium and magnesium ions in wastewater
InactiveCN102749294AImprove responseAvoid reactionPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsPhosphoric acidWastewater
The invention relates to a method for determining calcium and magnesium ions in wastewater. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) adding a strontium salt into wastewater: first, sampling wastewater, and adding a hydrochloric acid solution into the wastewater, then adding strontium chloride with a concentration of 200g / L, with the wastewater, the strontium chloride and the hydrochloric acid solution in a volume ratio of 2-2.5:1-1.3:1; and (2) using flame atomic absorption spectrometry to determine the absorbance of calcium and magnesium ions in the sampled wastewater, and then making use of a standard curve of concentrations of calcium and magnesium ions to absorbance to calculate the concentrations calcium and magnesium ions. By adding the strontium salt into the wastewater in advance, the invention makes sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid in a wastewater matrix react with the strontium salt more easily, thereby effectively preventing the calcium and magnesium ions from reacting with sulfuric acid or phosphoric acid and releasing calcium and magnesium ions, which can be atomized well. Therefore, the accuracy of the measurement of calcium and magnesium ion content can be greatly improved.
Owner:SUZHOU GUOHUAN ENVIRONMENT DETECTION
Method for detecting trace amounts of copper in soil
InactiveCN104215593AEasy to operateHigh sensitivityColor/spectral properties measurementsRelative standard deviationMagnetic stirrer
The invention relates to a method for detecting trace amounts of copper in soil and belongs to the field of environmental sample detection methods. The method includes the steps of properly drying a soil sample, grinding the soil sample in a grinding mill for 8min, sieving appropriate amount of the sample with a sieve of 360 meshes, grinding for 16min, placing in a dryer for being used later, placing 0.5000g of the sample in a beaker of 100ml, adding 50ml of 1% nitric acid, injecting the sample at the center15mm from the liquid surface under the stirring of a magnetic stirrer, measuring the absorbance according to a set measuring condition of an atomic absorption spectrometer, and correspondingly calculating the concentration according to a standard operation curve. According to the method for detecting trace amounts of copper in soil, the trace amounts of copper in soil is detected through the suspended sample injection flame atomic absorption spectrometry, the obtained detection limit is 0.12 mu g / g, the relative standard deviation (RSD) is 4.6%, the recovery is 98-104%, the operation is simple and easy to do, the sensitivity is high, the recovery and accuracy are good, the speed is high and the costs are low.
Owner:SHAANXI HUALU CHEM ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com