Patents
Literature
166 results about "Bacterium coli" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods of genetic analysis of E. coli
InactiveUS20060051769A1Monitor gene expression levelBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical biologyNucleic acid sequencing
The invention provides nucleic acid sequences which are complementary, in one embodiment, to a wide variety of E. coli genes. The invention provides the sequences in such a way as to make them available for a variety of analyses. In one embodiment the nucleic acid sequences provided are present as an array of probes that may be used to measure gene expression of at least 20,000 E. coli genes and at least 500 intragenic regions. As such, the invention relates to diverse fields impacted by the nature of molecular interaction, including chemistry, biology, medicine, and medical diagnostics.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Immunization and/or treatment of parasites and infectious agents by live bacteria
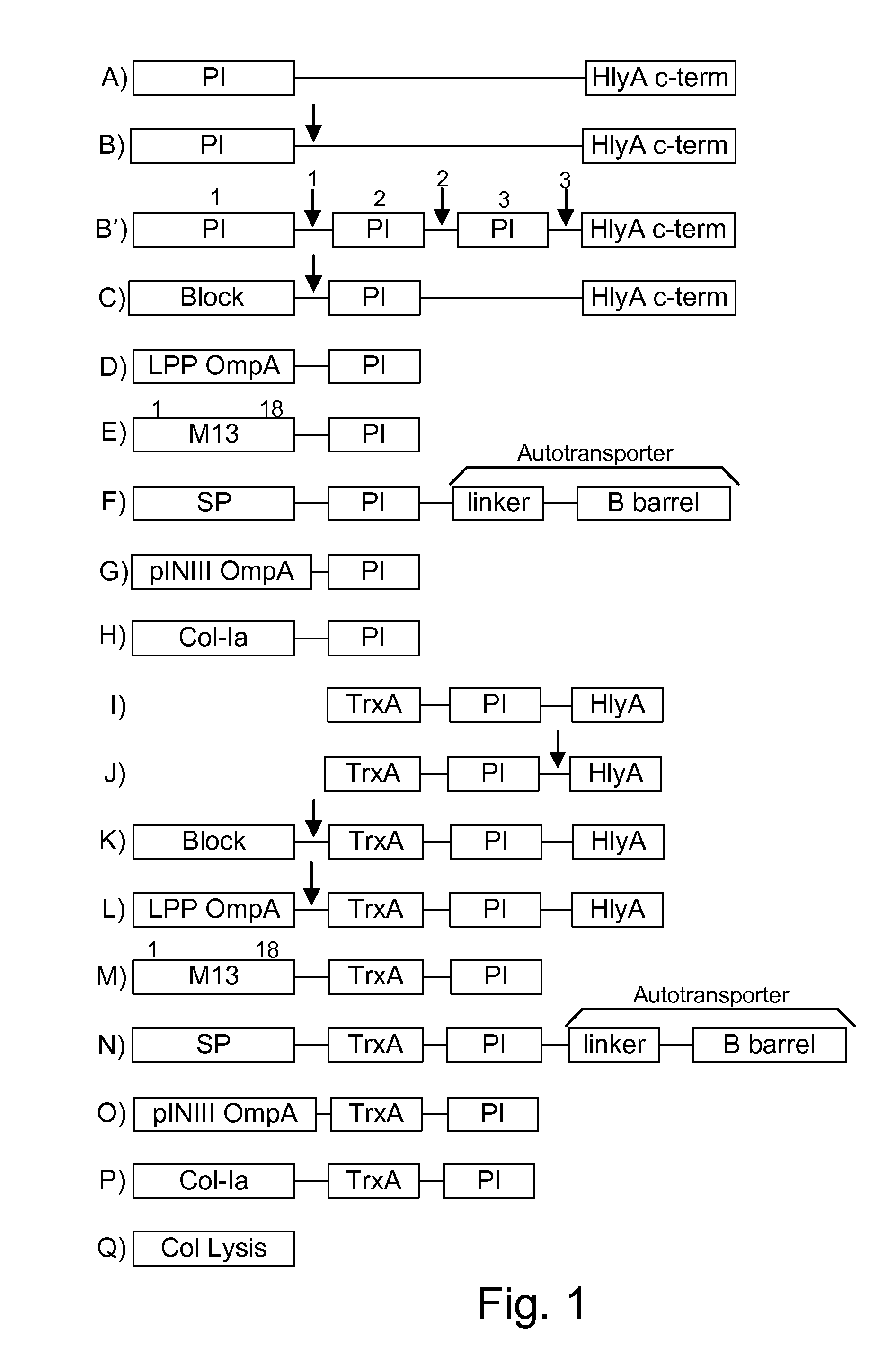
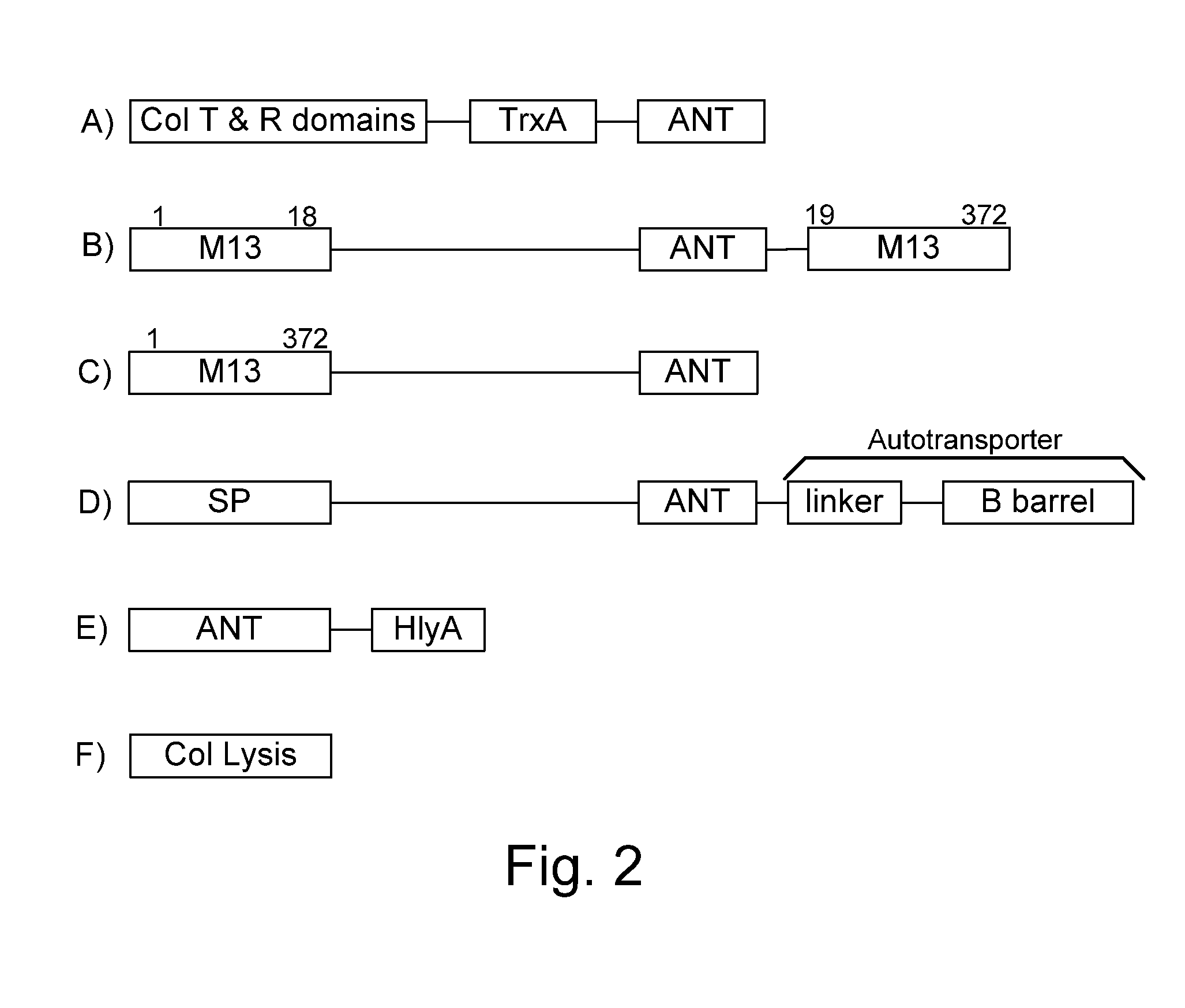
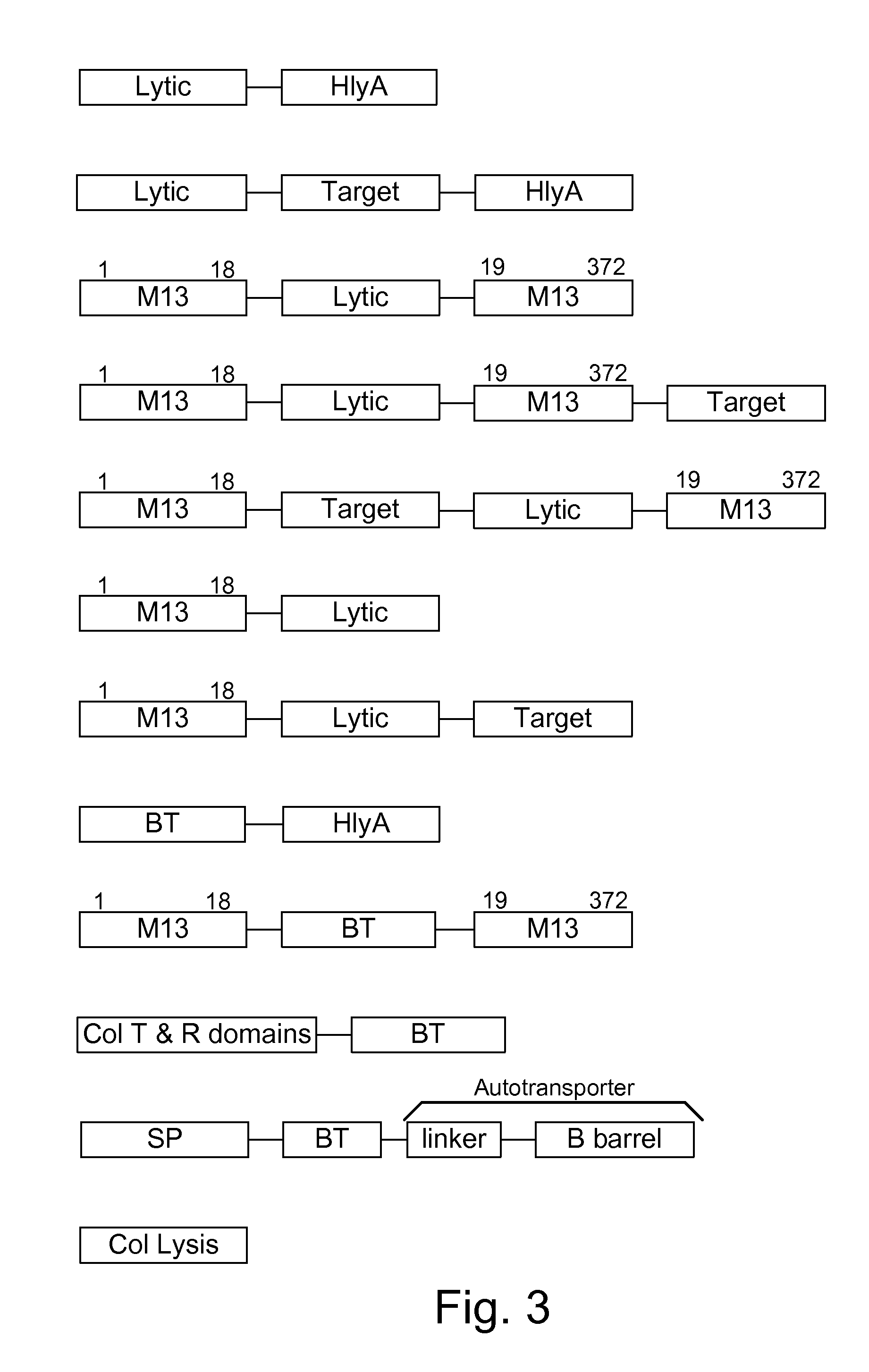
ActiveUS8771669B1Reducing eliminatingReducing or eliminating the targeted parasite, infectious diseaseVirusesBacteriaLytic peptideHuntingtons chorea
Chimeric proteins are expressed, secreted or released by a bacterium to immunize against or treat a parasite, infectious disease or malignancy. The delivery vector may also be attenuated, non-pathogenic, low pathogenic, or a probiotic bacterium. The chimeric proteins include chimeras of, e.g., phage coat and / or colicin proteins, bacterial toxins and / or enzymes, autotransporter peptides, lytic peptides, multimerization domains, and / or membrane transducing (ferry) peptides. The active portion of the immunogenic chimeric proteins can include antigens against a wide range of parasites and infectious agents, cancers, Alzheimer's and Huntington's diseases, and have enhanced activity when secreted or released by the bacteria, and / or have direct anti-parasite or infectious agent activity. The activity of the secreted proteins is further increased by co-expression of a protease inhibitor that prevents degradation of the effector peptides. Addition of an antibody binding or antibody-degrading protein further prevents the premature elimination of the vector and enhances the immune response.
Owner:BERMUDES DAVID G DR
Comparative phenotype analysis of two or more microorganisms using a plurality of substrates within a multiwell device
InactiveUS6387651B1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEscherichia coliPlant cell
The present invention relates to growing and testing microorganisms in a multitest format which utilizes a gel forming matrix for the rapid screening of clinical and environmental cultures. The present invention is suited for the characterization of commonly encountered microorganisms (e.g., E. coli, S. aureus, etc.), as well as commercially and industrially important organisms from various and diverse environments (e.g., the present invention is particularly suited for the growth and characterization of the actinomycetes and fungi). The present invention is also particularly suited for comparative analysis of phenotypic differences between cell types, including strains of microorganisms that have been designated as the same genus and species, as well as other cell types (e.g., mammalian, insect, and plant cells).
Owner:BIOLOG
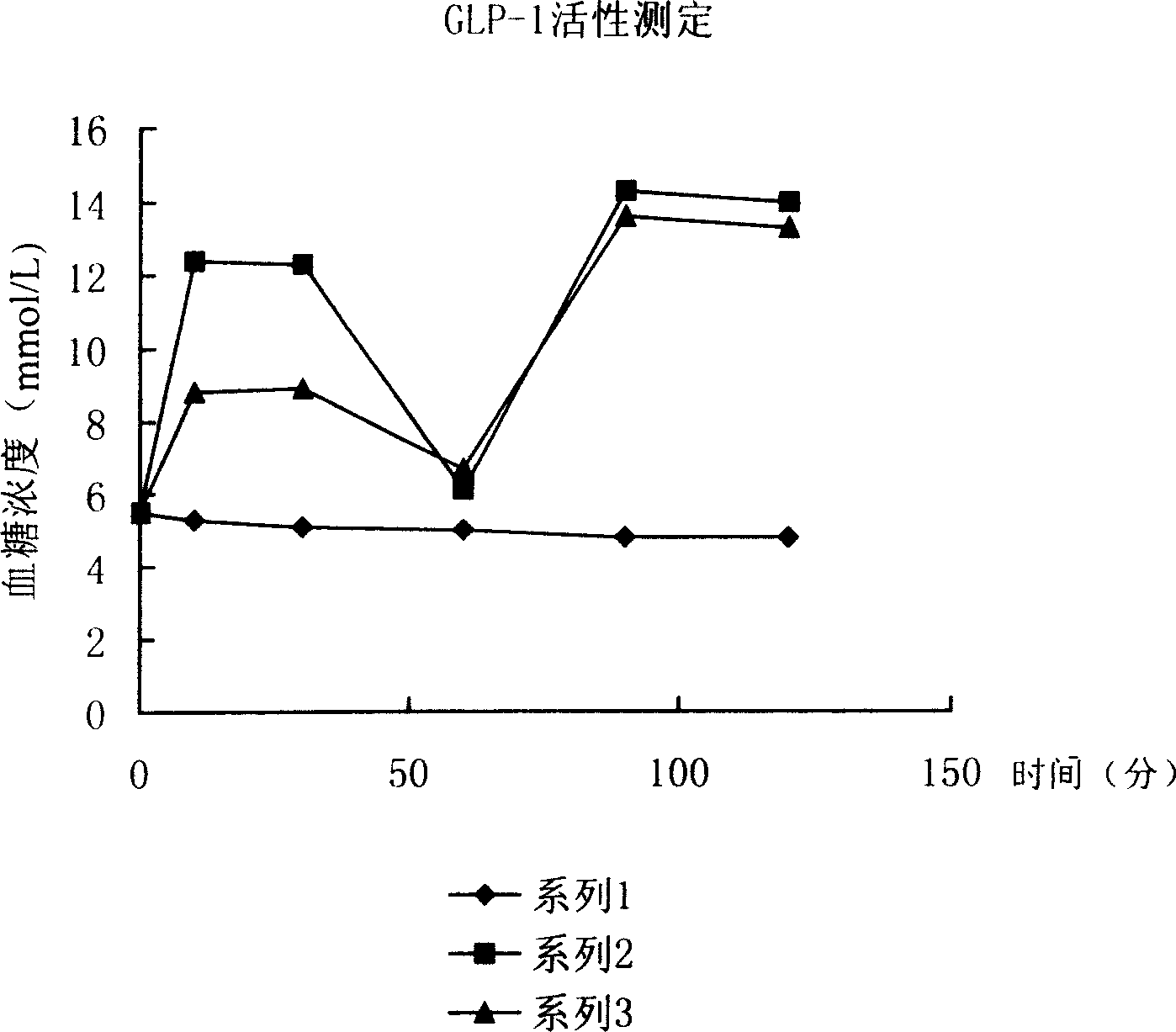
High efficiency experssino human glicentin-1 gene engineering bacteria and its construction method and use
The present invention belongs to the field of biological engineering technology. The gene engineering bacteria is colibacillus DH5-alpha, BL21(DE3) or BLR(DE3) carrying the recombinant plasmid of human glicentin-1 gene, i. e., GLP-1 gene. The construction process of the gene engineering bacteria includes connecting serially DNA sequence containing human glicentin-1 gene to form polymer, constituting expression vector and converting to colibacillus to obtain efficiently expressing human glicentin-1 gene engineering bacteria. With the gene engineering bacteria and through a three-step process of liquid culture, purification to produce human glicentin-1 fusion protein and preparation of human glicentin-1, human glicentin-1 product may be produced. The present invention has the advantages of high expression amount, less purification steps, high yield and low production cost.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
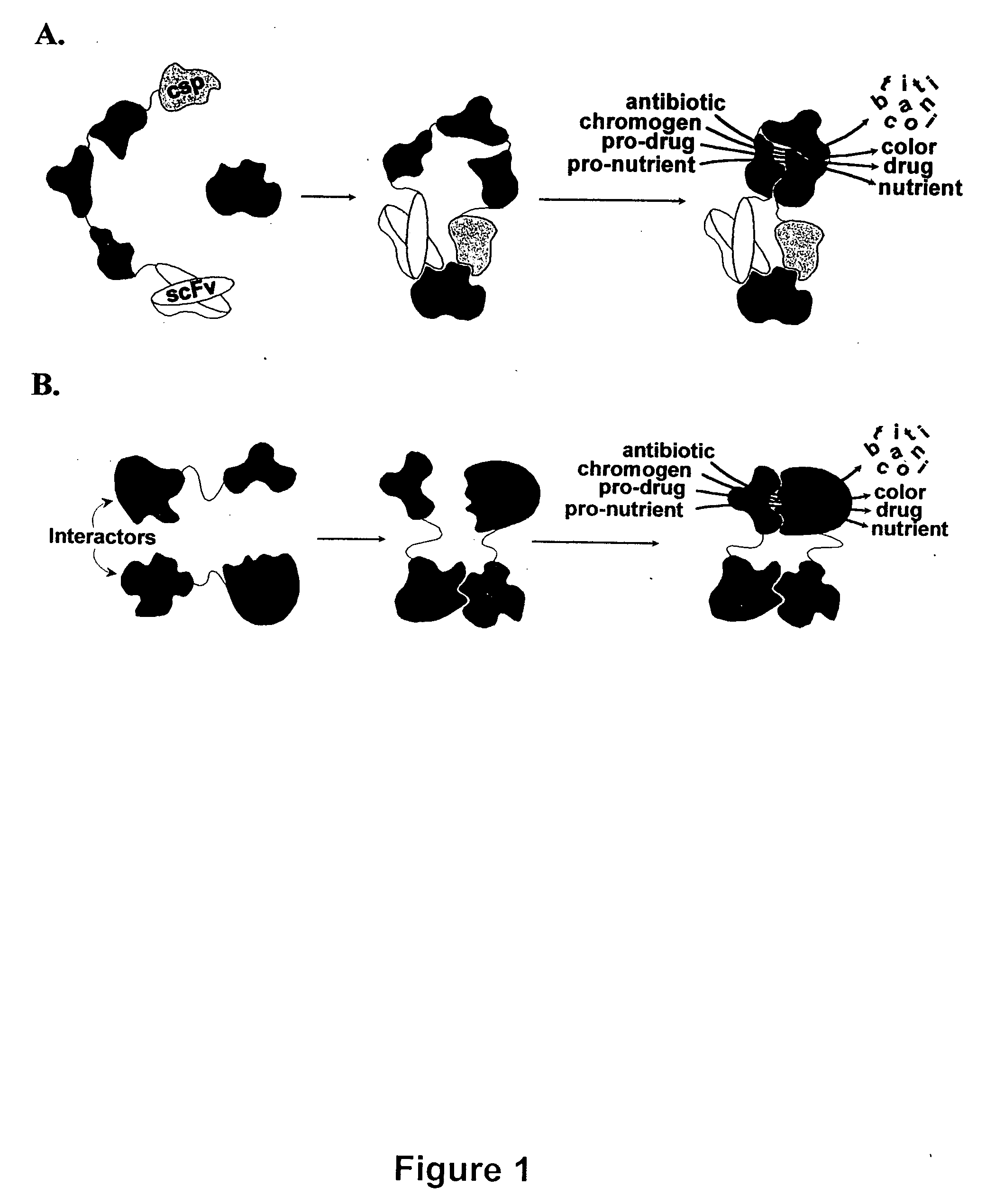
Breakpoint fusion fragment complementation system
InactiveUS20040038317A1Peptide librariesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologousRNA-Protein Interaction
Fragment pairs of a Class A beta-lactamase (TEM-1 of E. coli) are disclosed that depend for their functional reassembly into the parent protein on the interaction of heterologous polypeptides or other molecules which have been genetically or chemically conjugated to the break-point termini of the fragment pairs. In addition, methods are provided for identifying fragment pairs that will optimally reassemble into a functional parent protein. Fragment pairs that comprise molecular interaction-dependent enzymes find use in (1) homogeneous assays and biosensors for any analyte having two or more independent binding sites, (2) tissue-localized activation of therapeutic and imaging reagents in vivo for early detection and treatment of cancer, chronic inflammation, atherosclerosis, amyloidosis, infection, transplant rejection, and other pathologies, (3 cell-based sensors for activation or inhibition of metabolic or signal transduction pathways for high-efficiency, high-throughput screening for agonists / antagonists of the target pathway, (4) high-throughput mapping of pair-wise protein-protein interactions within and between the proteomes of cells, tissues, and pathogenic organisms, (5) rapid selection of antibody fragments or other binding proteins which bind specifically to polypeptides of interest, (6) rapid antigen identification for anti-cell and anti-tissue antibodies, (7) rapid epitope identification for antibodies, (10) cell-based screens for high-throughput selection of inhibitors of any protein-protein interaction.
Owner:KALOBIOS PHARMA
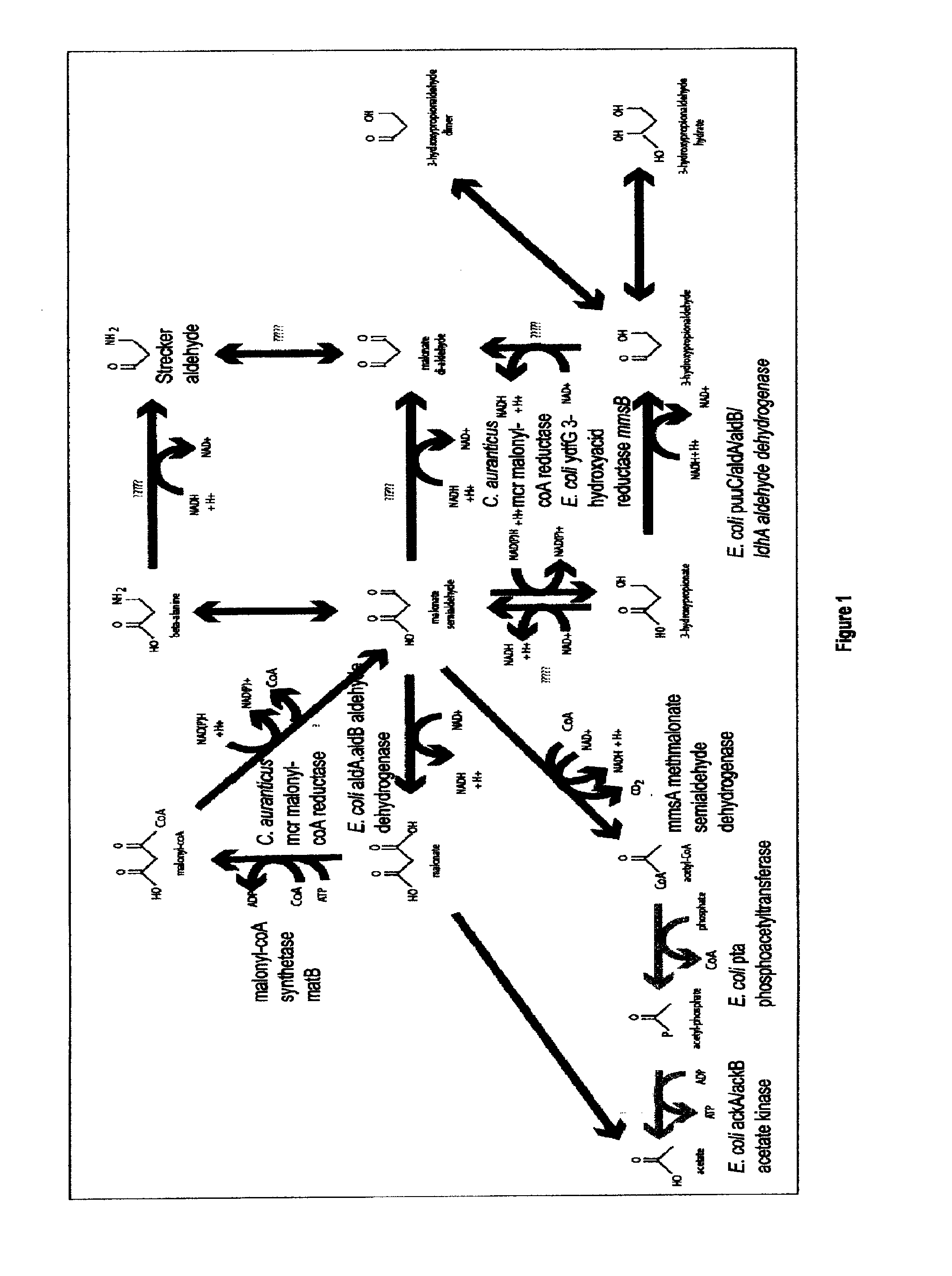
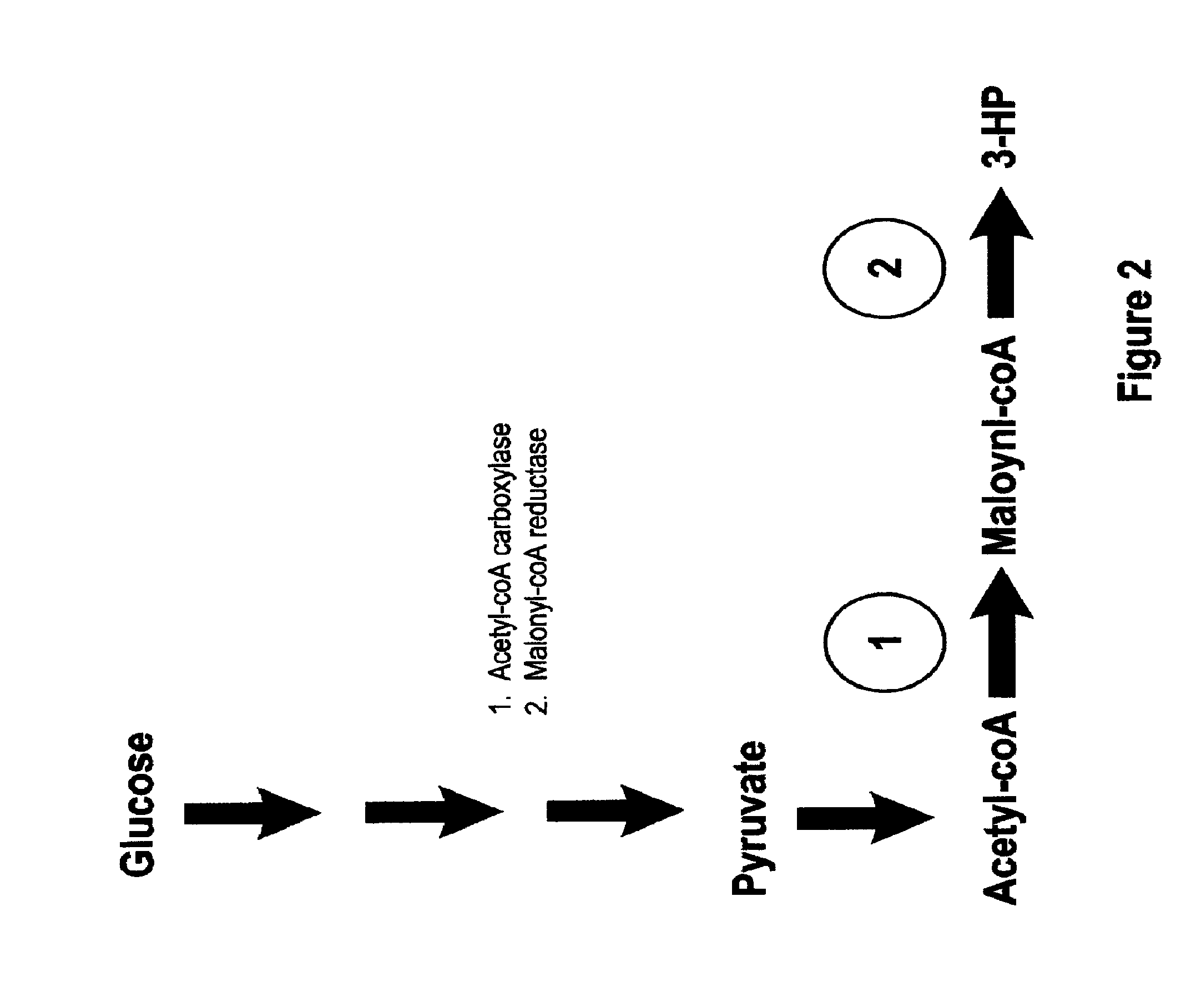
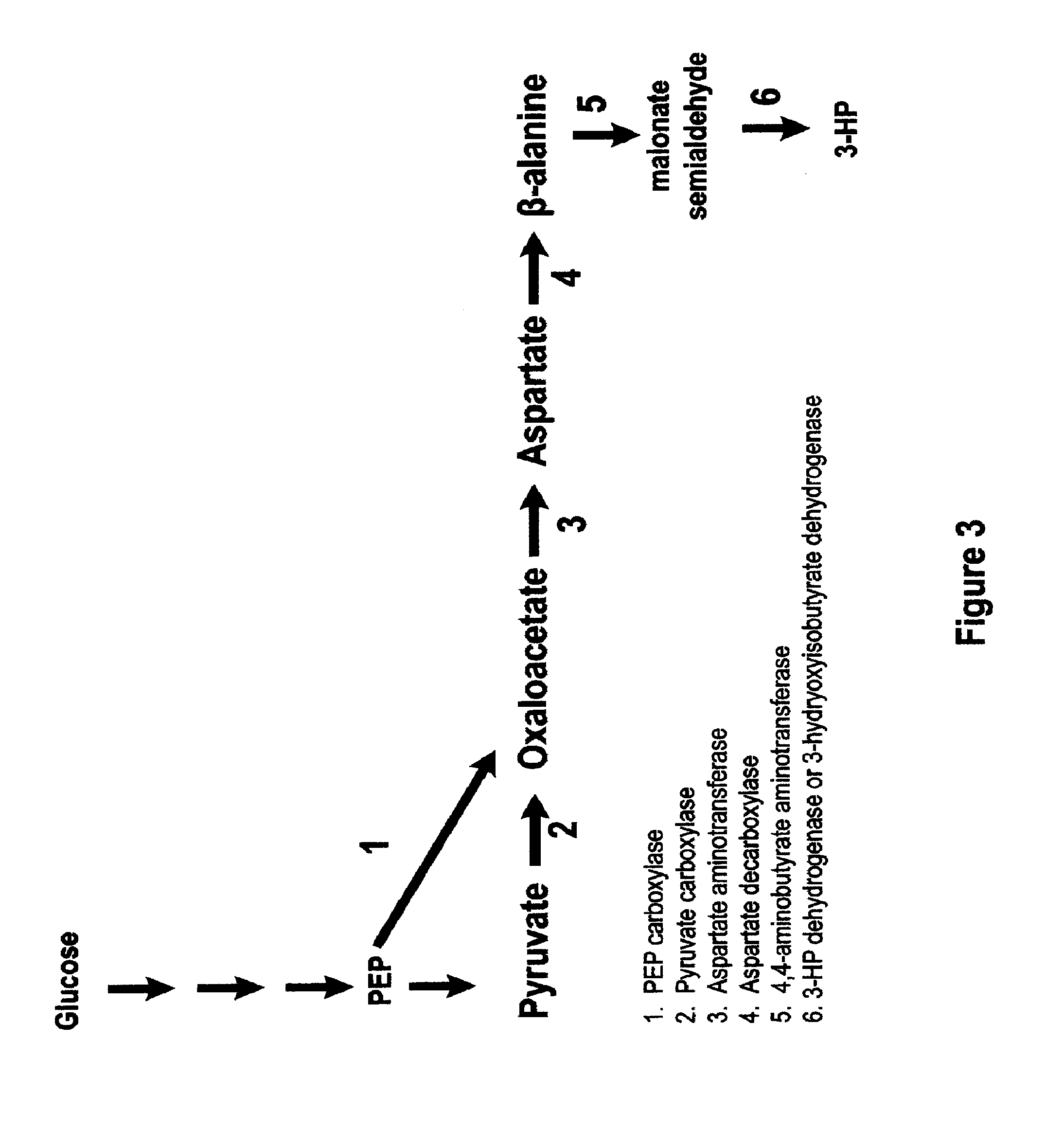
Methods, Systems And Compositions Related To Reduction Of Conversions Of Microbially Produced 3-Hydroxypropionic Acid (3-HP) To Aldehyde Metabolites
Owner:CARGILL INC
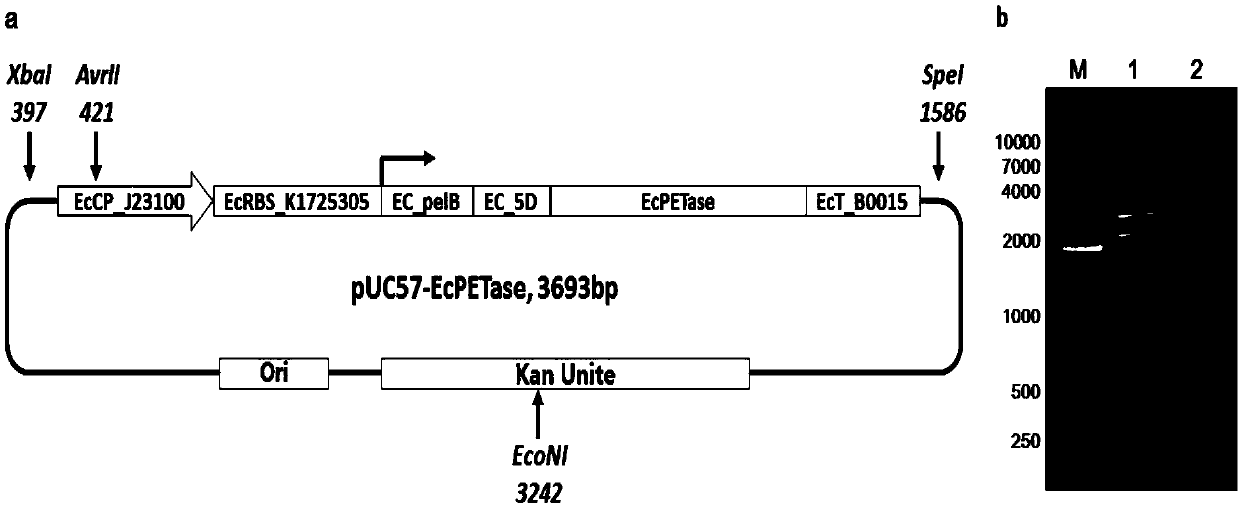
Genetic engineering strain for degrading PET (polyethylene terephthalate) plastics
ActiveCN107794252APossess lipolytic activityPromote efficient degradationPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
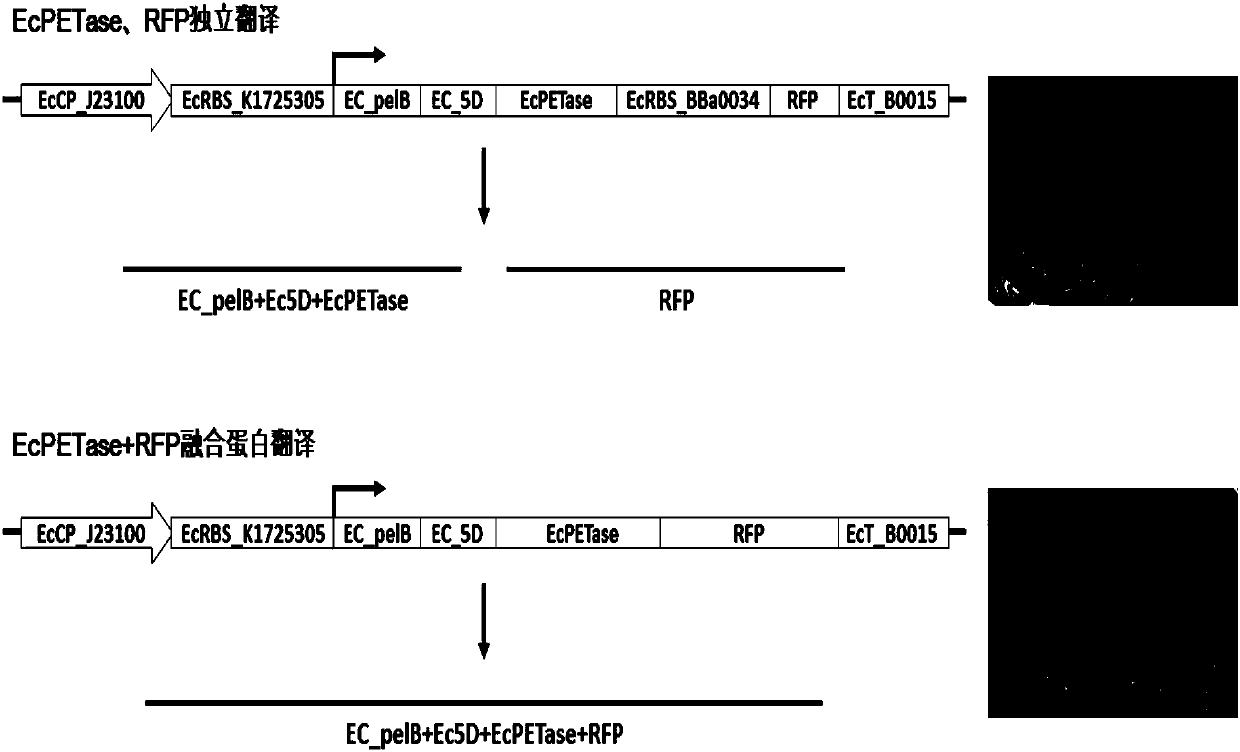
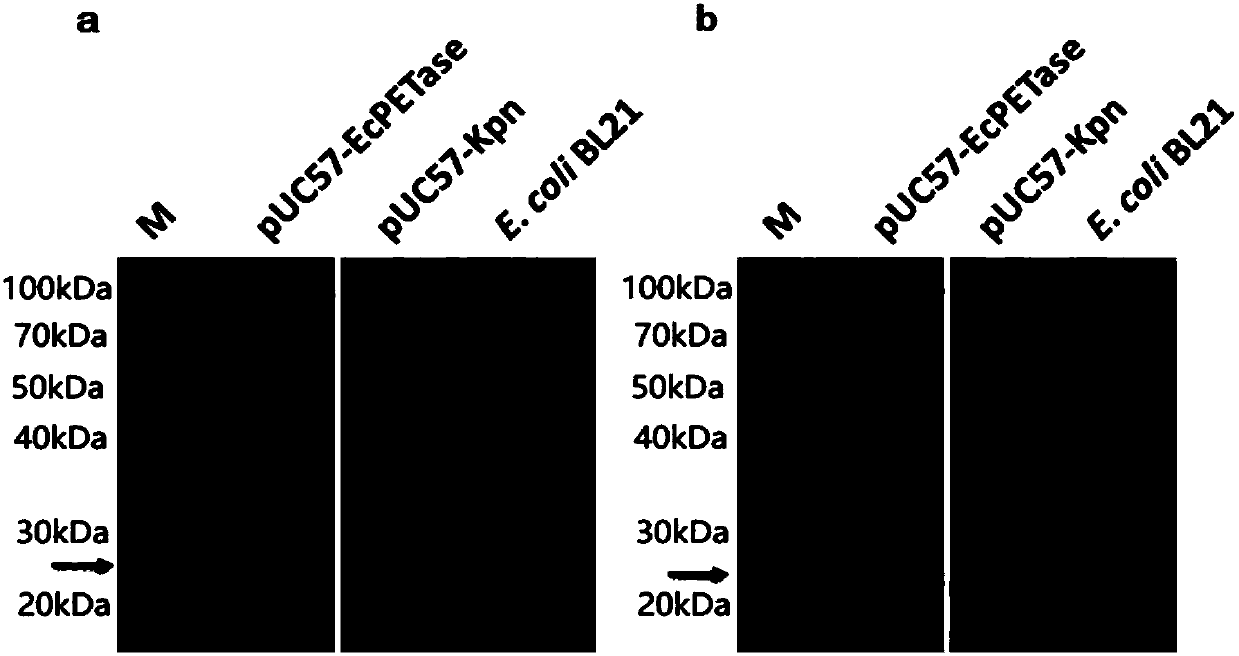
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial gene engineering, aims to solve the problem of difficult degradation of the PET (polyethylene terephthalate) plastics, and provides a PET hydrolytic enzyme expression unit, a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) recombined vector built based on the unit and an application of the vector, wherein the vector can effectively secrete colibacillus expressing PET hydrolase (PETase). The DNA recombined vector can effectively achieve secreting type constant expression of the PET hydrolytic enzyme in colibacillus host bacteria, nutrient solution of the vector has remarkable lipase biological activity, PET plastic films can be degraded in continuous culture process, a genetic engineering approach is provided for biodegradation of the PET plastics, andthe vector has a good application prospect.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Expression of mammalian proteins in Pseudomonas fluorescens
The invention is a process for improved production of a recombinant mammalian protein by expression in a Pseudomonad, particularly in a Pseudomonas fluorescens organism. The process improves production of mammalian proteins, particularly human or human-derived proteins, over known expression systems such as E. coli in comparable circumstances Processes for improved production of isolated mammalian, particularly human, proteins are provided.
Owner:PELICAN TECH HLDG INC
Novel polysaccharide and uses thereof
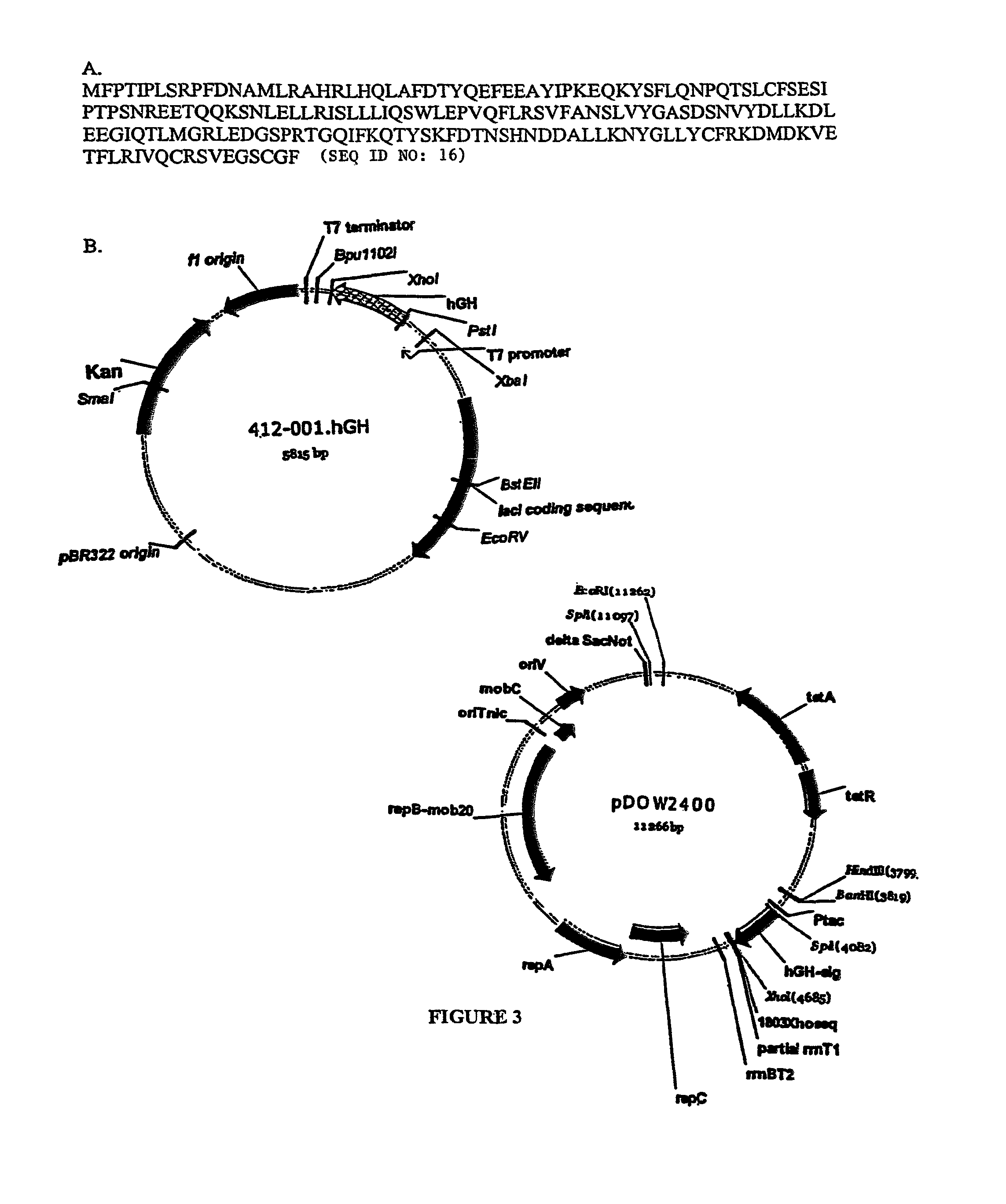
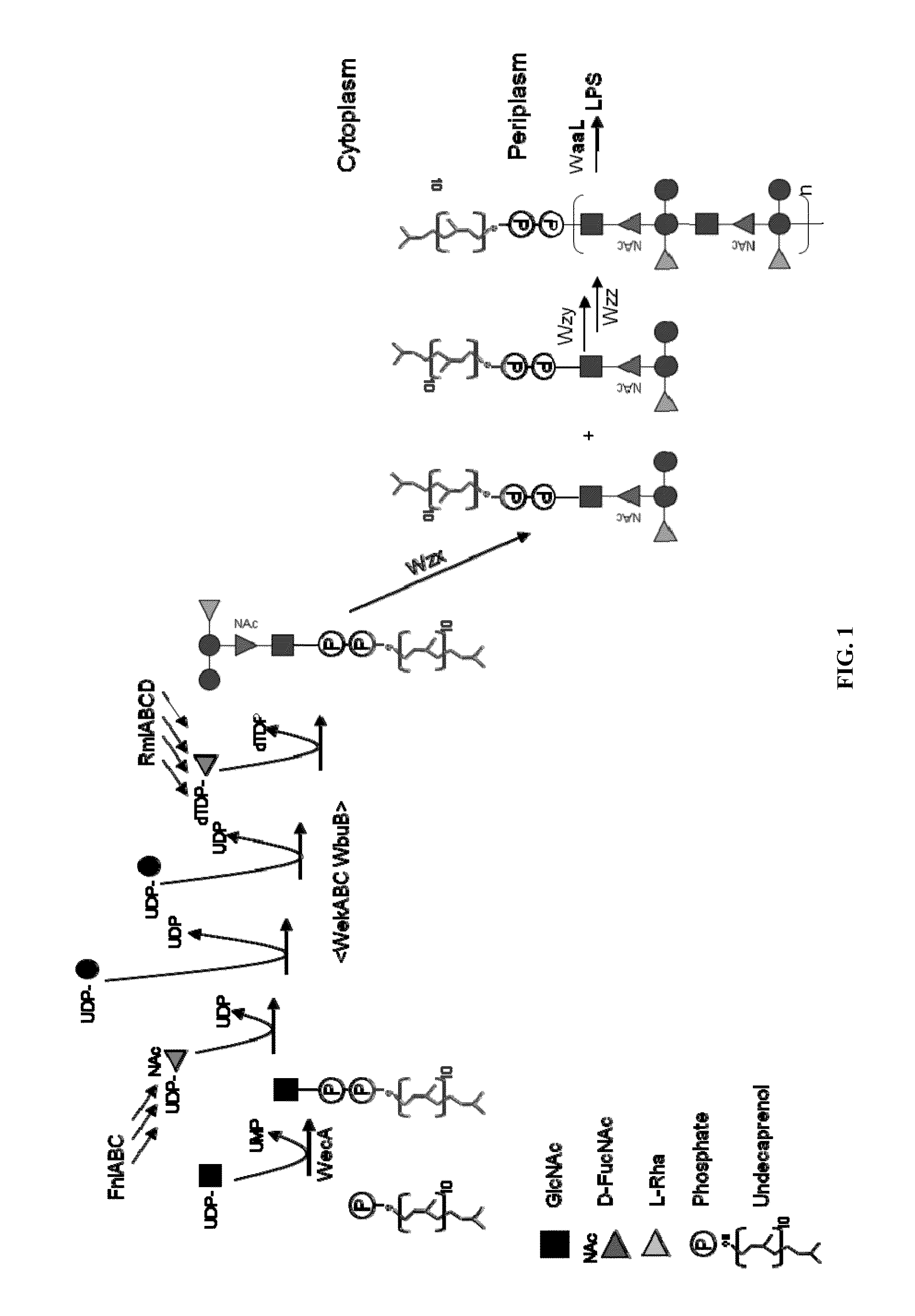
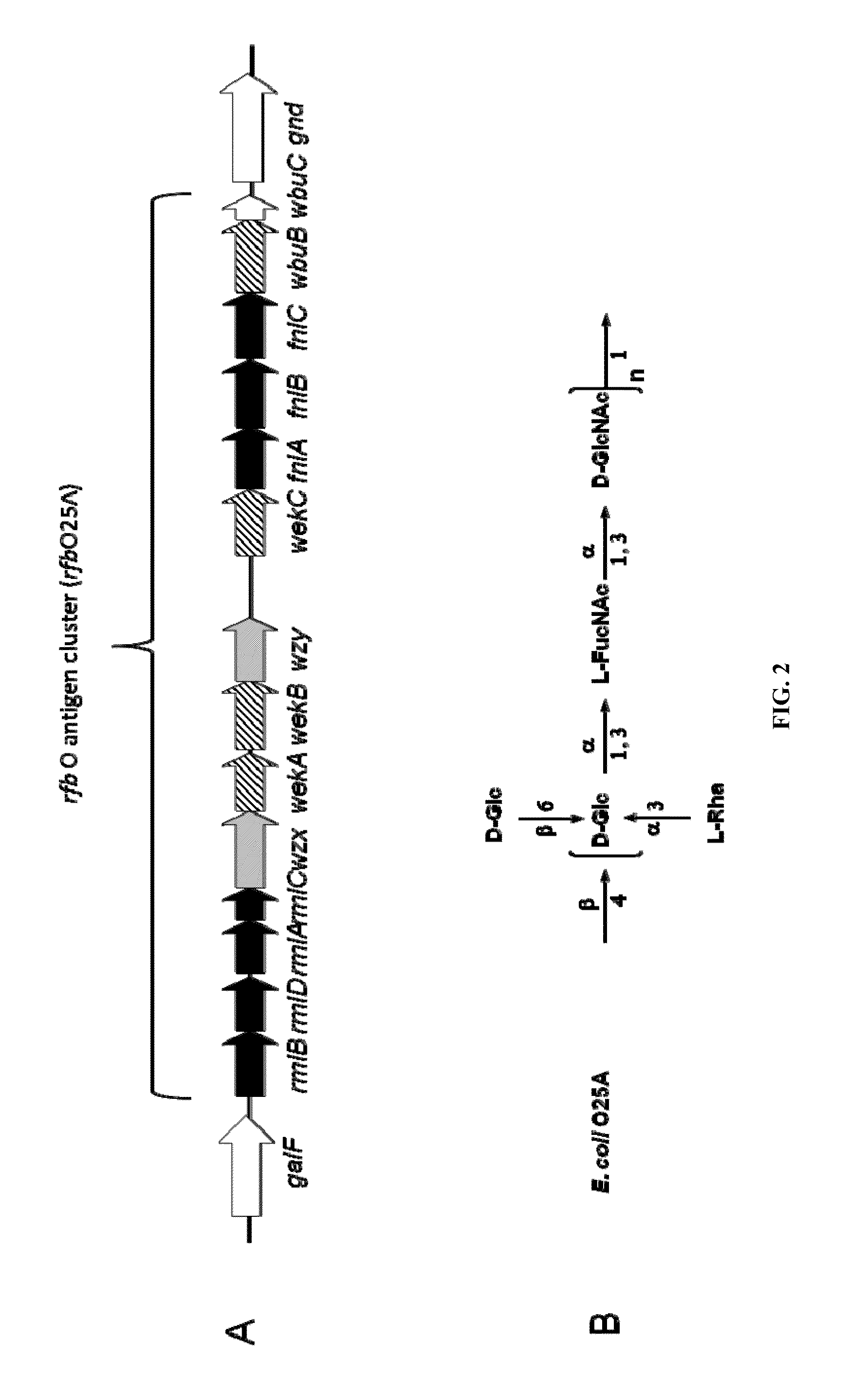
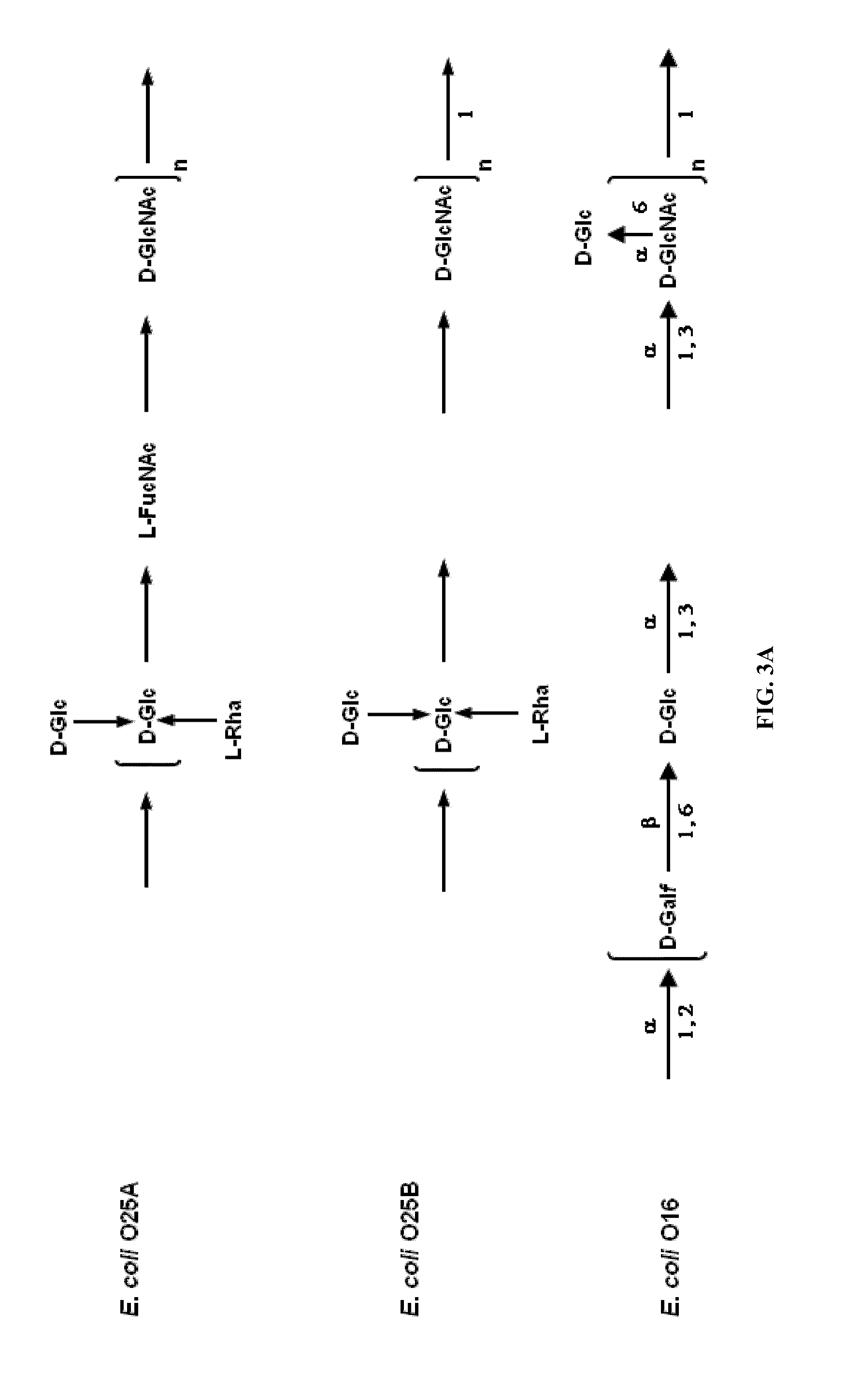
ActiveUS20150238588A1Reduce severityInhibit progressAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsPharmaceutical drugCarrier protein
Provided herein is a novel E. coli O polysaccharide, O25B. Also provided herein are prokaryotic host cells comprising enzymes (e.g., glycosyltransferases) used in O25B production. The host cells provided herein produce O25B bioconjugates, wherein said bioconjugates comprise O25B linked to a carrier protein. Further provided herein are compositions, e.g., pharmaceutical compositions, comprising O25B and / or bioconjugates comprising O25B. Such compositions can be used as vaccines against infection with ExPEC, and may further comprise one or more additional bioconjugates.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
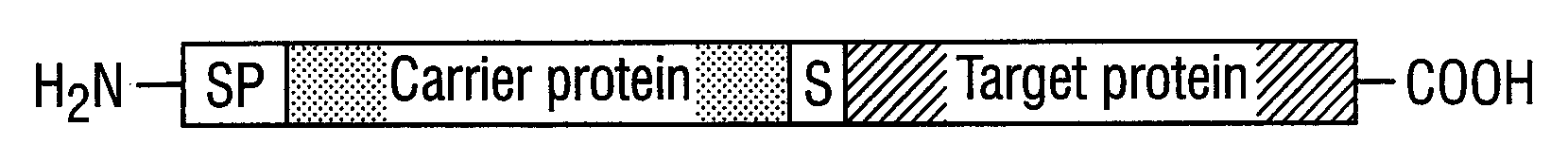
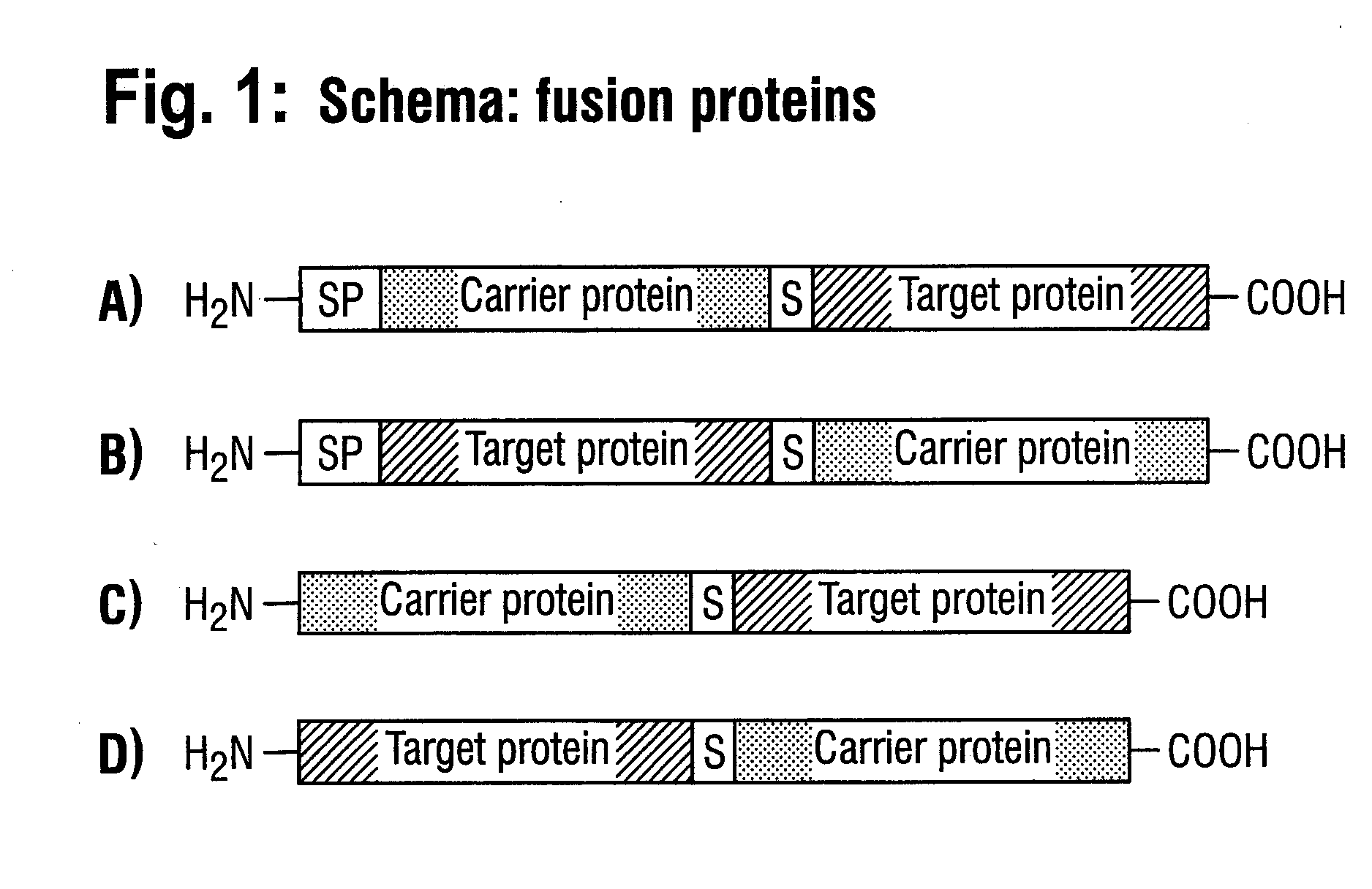
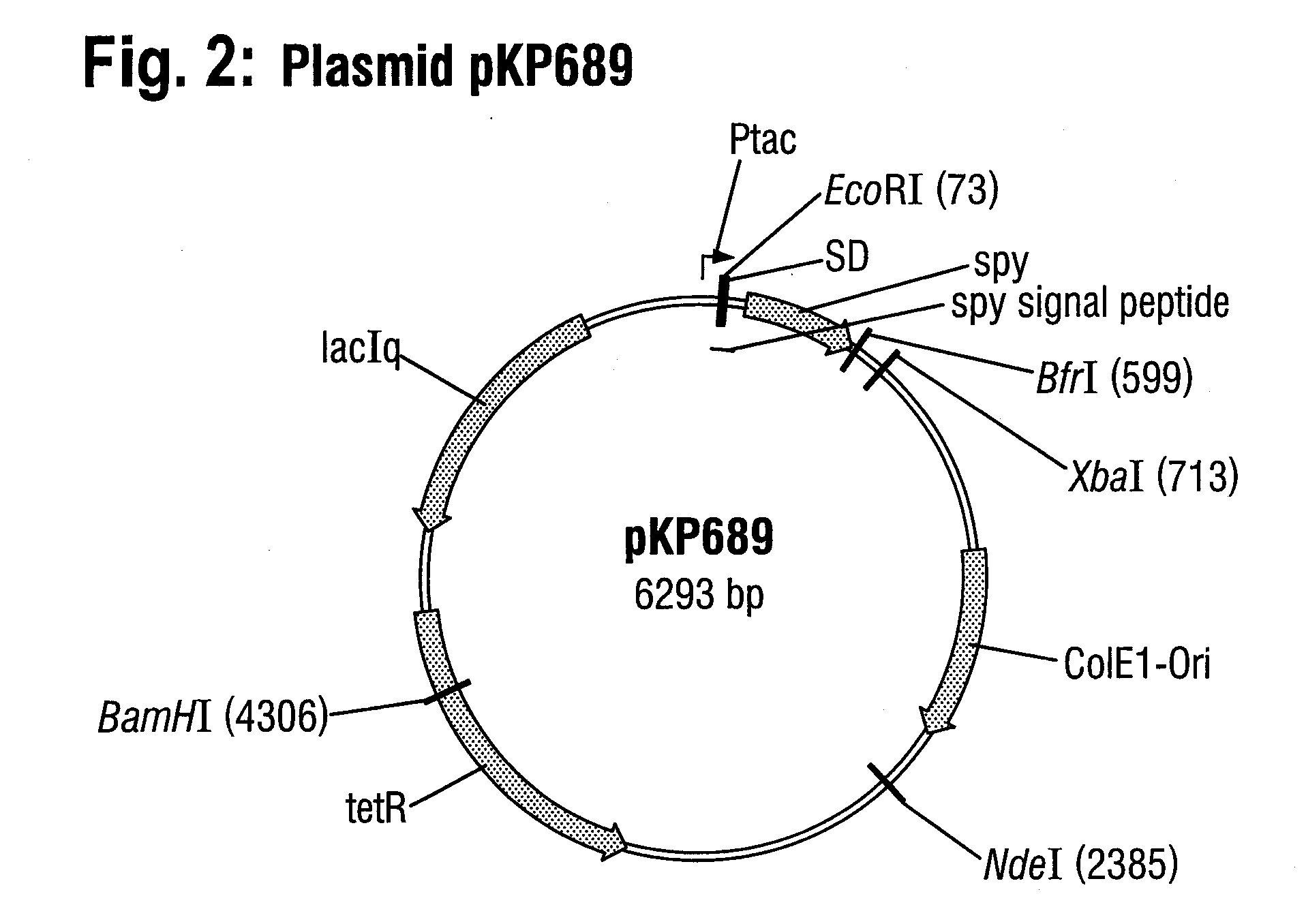
DNA construct and process for the fermentative production of fusion proteins
A DNA construct that allows the inexpensive production of a target protein in E. coli, consisting of a nucleic acid sequence encoding a signal peptide which is operably linked with a gene coding for a carrier protein which is linked with a gene coding for the target protein via a gene coding for a cleavable sequence S, wherein the gene coding for a carrier protein is the spy gene from E. coli.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Phosphorylated fusion proteins
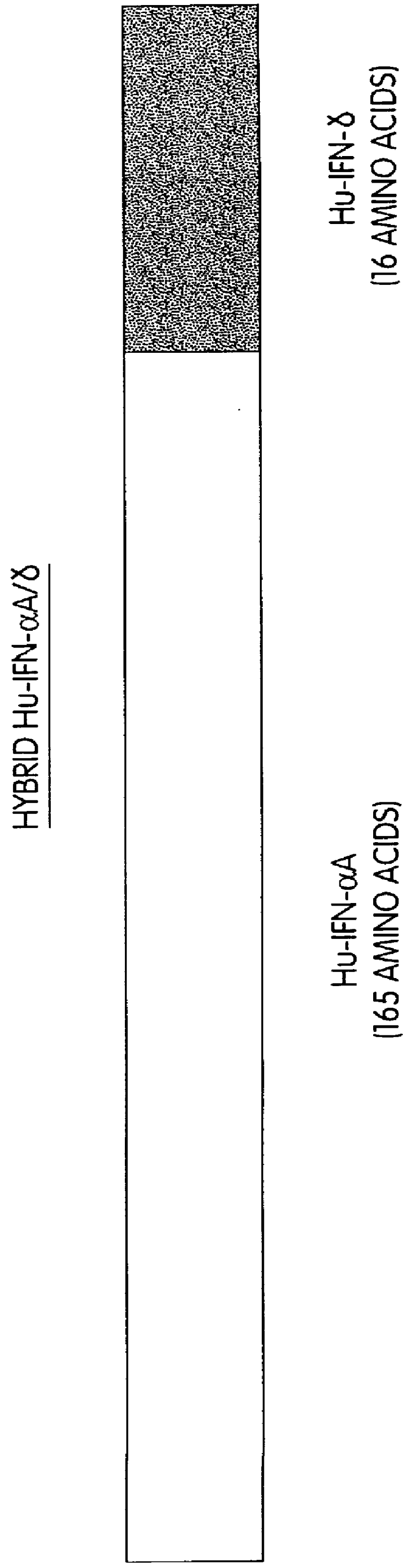
InactiveUS6150503AEnhanced radiationPhosphorylation reaction isBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsInterferonPhosphorylation site
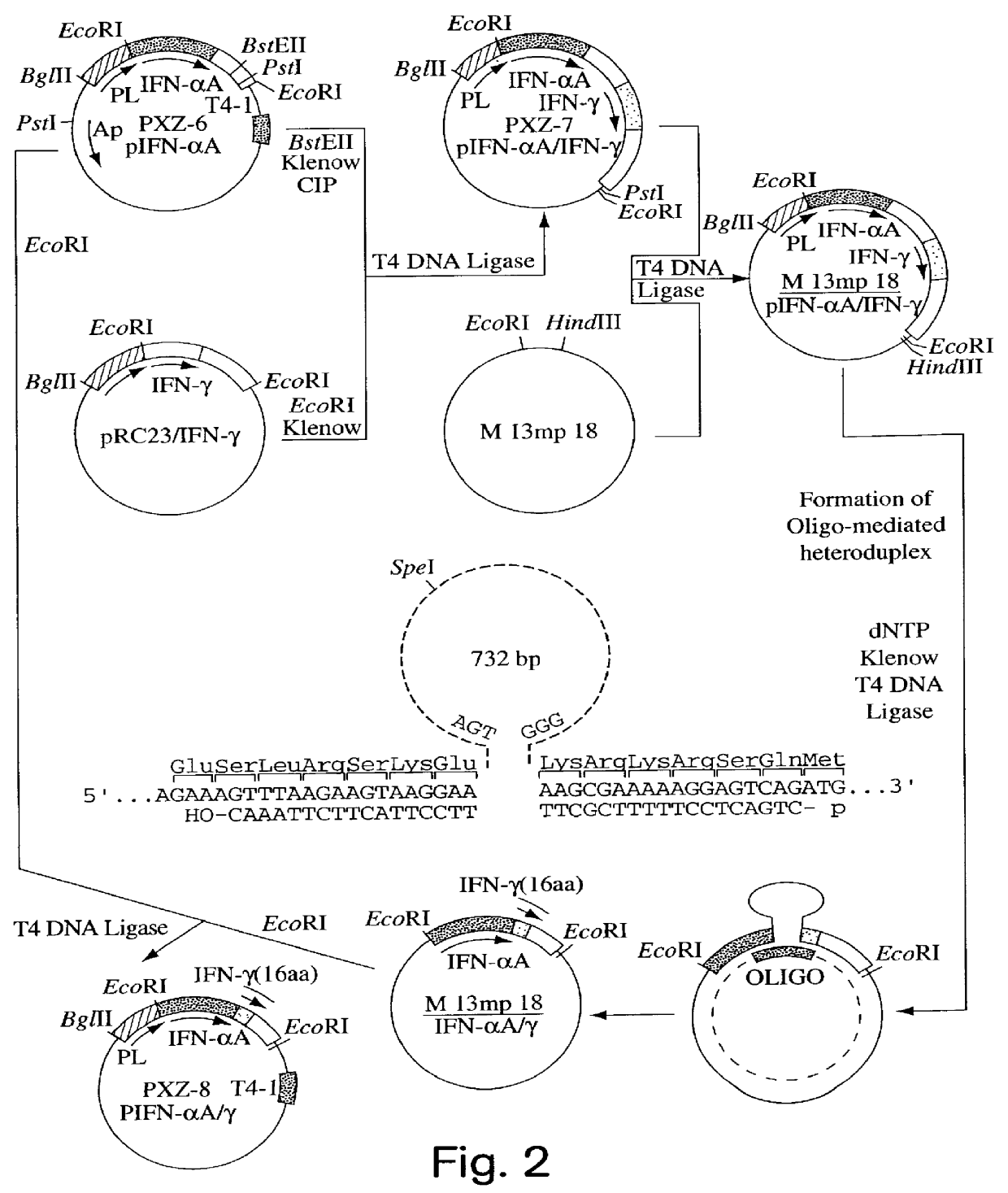
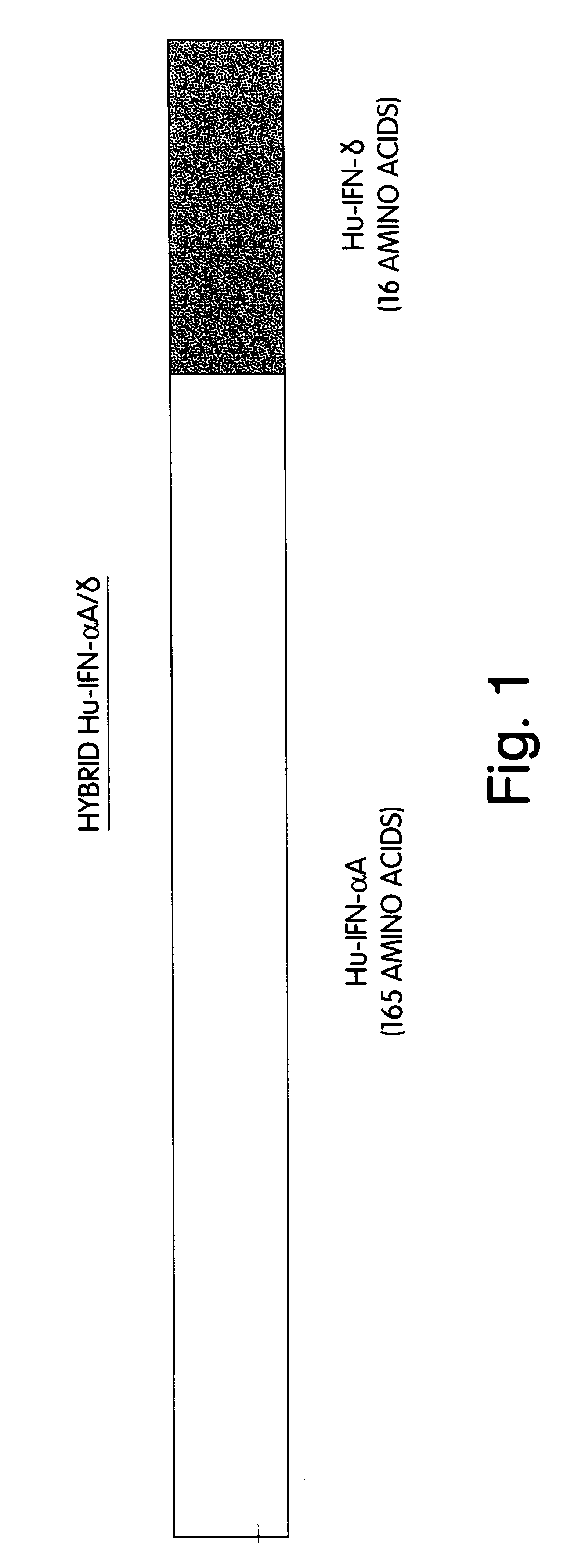
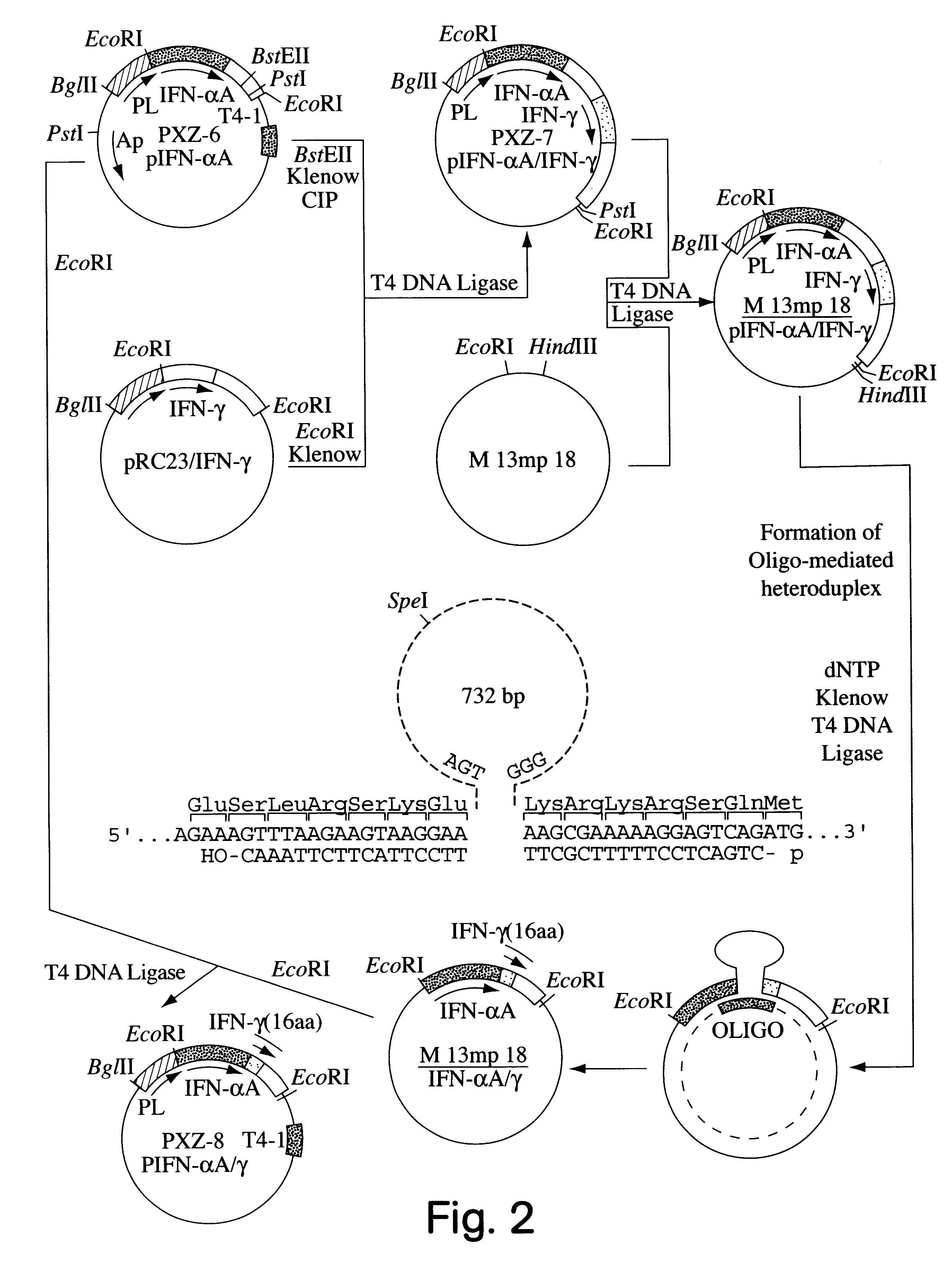
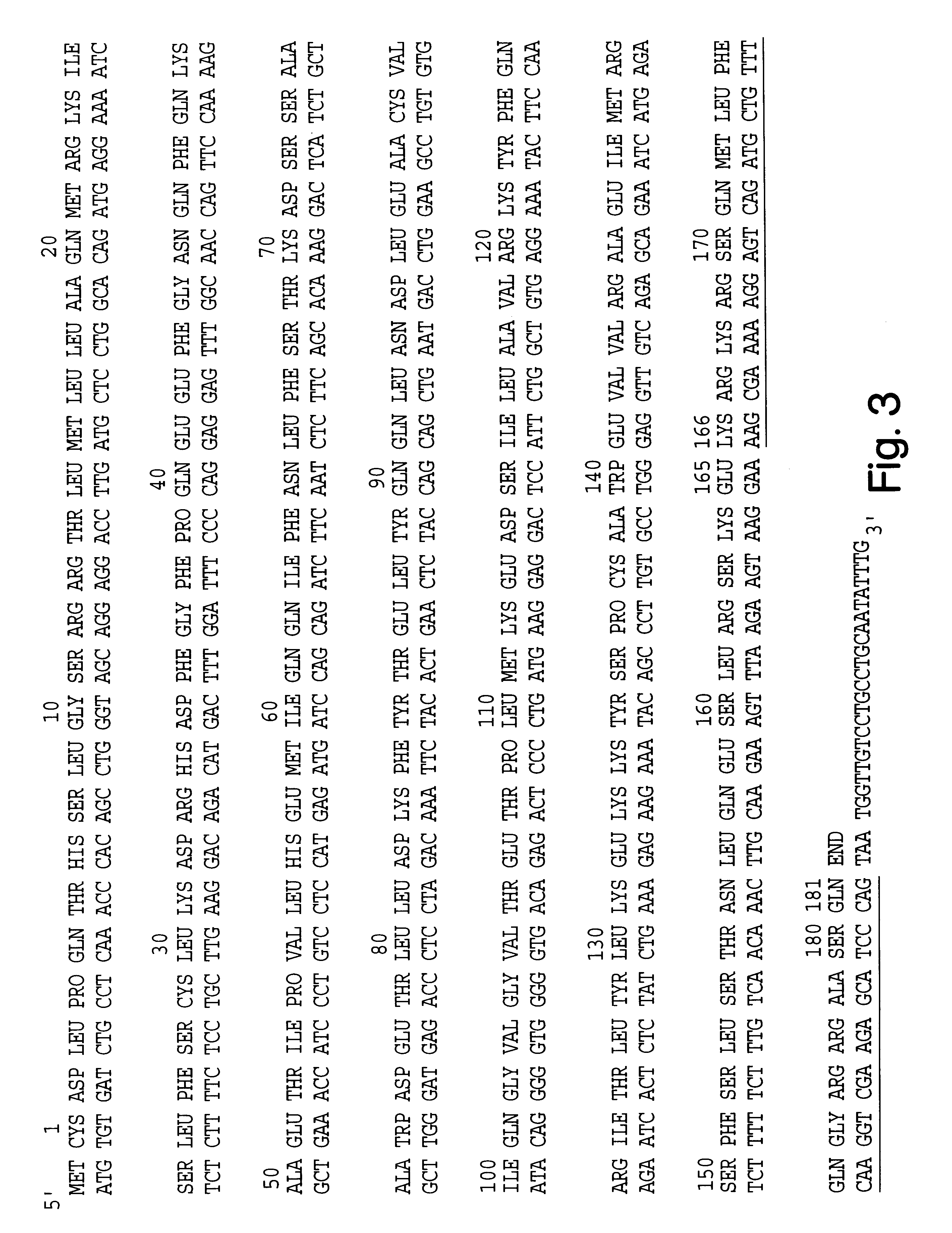
Modified proteins, modified interferons alpha 's and beta 's, phosphorylated modified proteins and DNA sequences encoding the above, applications and uses thereof. Modified phosphorylated Hu-IFN- alpha -like proteins are provided which carry an identifiable label such as a radio-label. Corresponding phosphorylatable Hu-IFN- alpha -like proteins which contain a putative phosphorylation site. DNA sequences which encode a Hu-IFN- alpha -like protein and contain a sequence encoding a putative phosphorylatable site. Appropriate expression vectors are used to transform compatible host cells of various microorganisms, such as E. coli. Numerous uses for the phosphorylated proteins are disclosed.
Owner:PESTKA BIOMEDICAL LAB
Method for producing extracellular pullulanase by applying auto-induction culture medium and dual-temperature control strategy
ActiveCN102676480AImprove abilitiesIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliMicroorganism
The invention provides a method for producing extracellular pullulanase by applying an auto-induction culture medium and a dual-temperature control strategy, belonging to the technical field of pullulanase production through microbial fermentation. The method has the following beneficial effects: pullulanase coding genes from Klebsiella variicola CCTCC M2012108 are inserted into an expression vector pET28a(+) to construct recombinant plasmids and E.coli is converted to obtain a recombination strain E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28a(+)-pulA containing the target pullulanase gene; the auto-induction culture medium is utilized to culture the recombinant E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28a(+)-pulA and ferment the recombinant E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28a(+)-pulA to generate enzyme by adopting the dual-temperature control mode of firstly culturing at 37 DEG C for 2-4 hours and then continuing culture at 25 DEG C for 48-72 hours; and after adopting the optimized fermentation conditions of the auto-induction culturemedium and dual-temperature, the extracellular pullulanase activity can reach 60-70U / mL. The method provides an effective strategy for producing extracellular pullulanase with recombinant E.coli and has great significance in the production process for developing novel recombinant pullulanase in future and application value of pullulanase.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Adenylate cyclase, and coding gene, vector, bacterial strain and application thereof
ActiveCN102212538ASimple processMild conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGenetic engineeringShort cycle
The invention provides adenylate cyclase, and a coding gene, a vector, a bacterial strain and application thereof. A DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequence for coding the adenylate cyclase provided by the invention has a base sequence represented by SEQ ID NO.:1. Furthermore, the invention further provides the adenylate cyclase coded by the DAN sequence, a recombinant vector including the DAN sequence, a host cell including the recombinant vector, and applications of all in production of the adenylate cyclase. The genetic engineering strain of colibacillus, disclosed by the invention, can beused for expressing the adenylate cyclase with high efficiency. The inducible enzyme activation thereof can achieve 7 U / mg or 10 U / mg. The bacterial strain is used for producing cyclic adenosine monophosphate and has the advantages of simple process, moderate condition, short cycle, few by-products and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Tuberculosis antigen specific whole blood IFN-gamma diagnosis kit, method for producing the same and method for using same
InactiveCN101493454ADiagnostic advantageShorten the timeBiological testingEscherichia coliEnzyme linked immunoassay
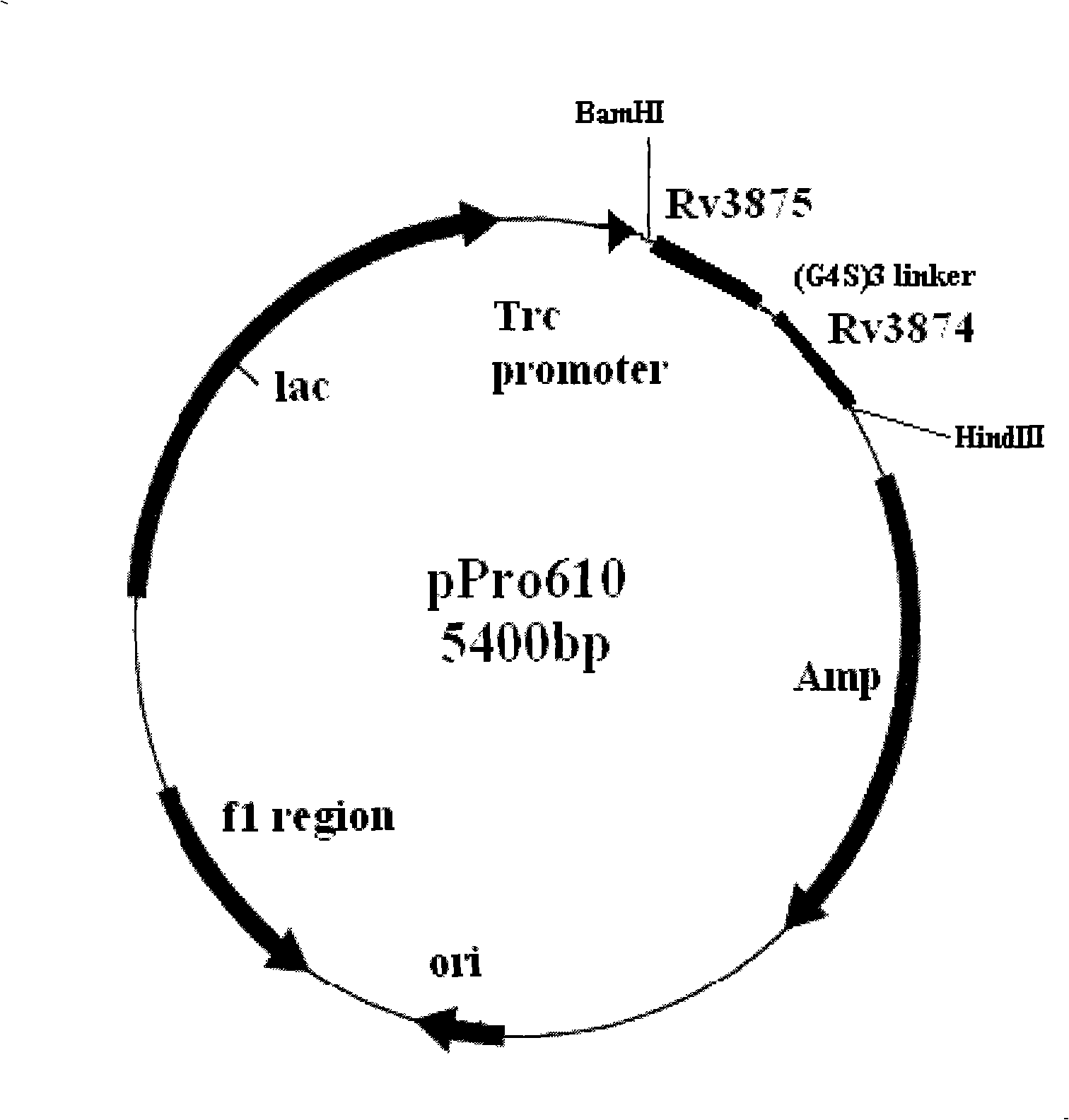
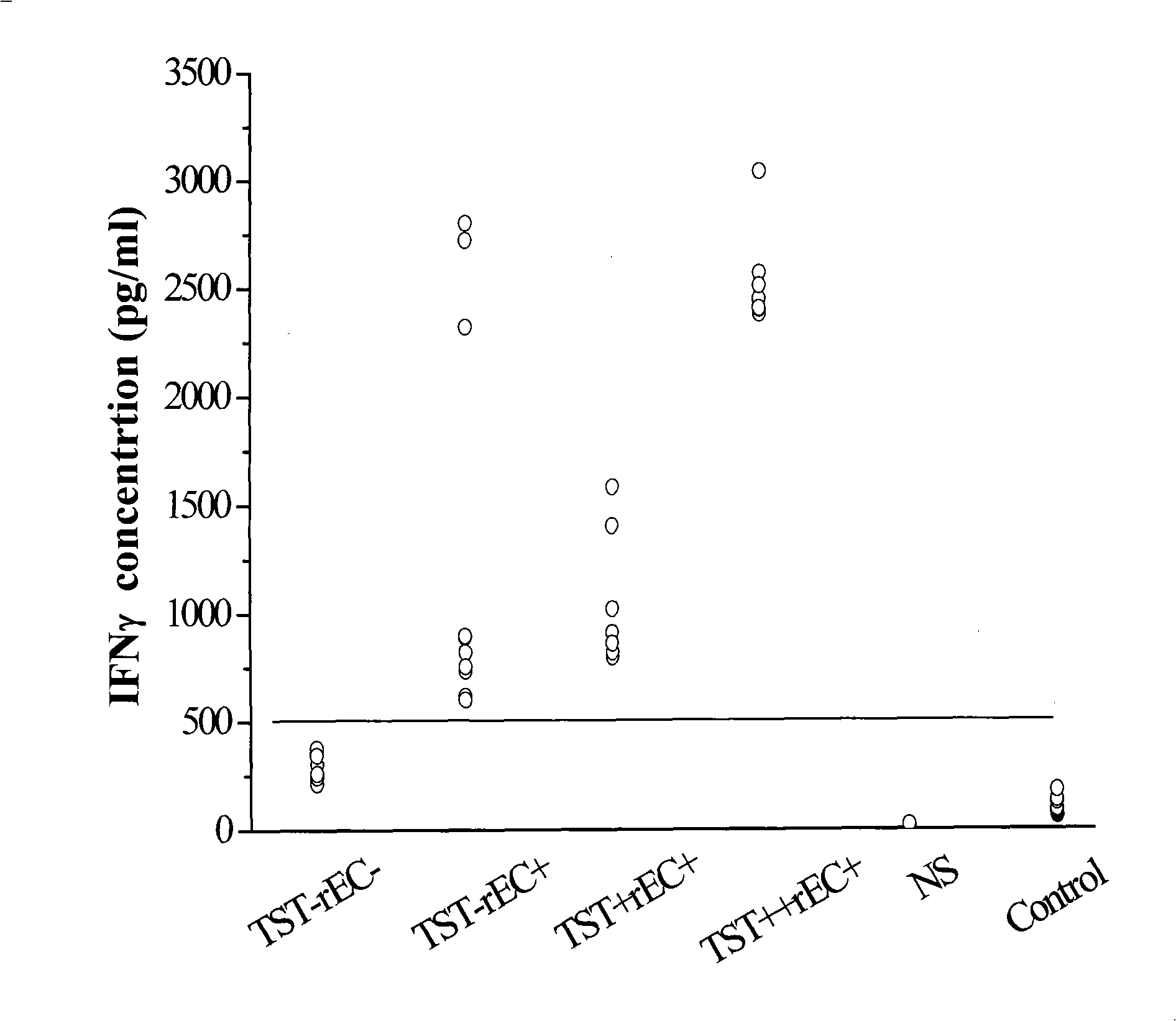
The invention relates to a diagnostic kit for tuberculosis and mycobacterium tuberculosis infectors, a preparation method and an application method thereof. By using the linker for encoding 15 amino acid (G4S1) 3, the encoding genes (SEQ.ID.NO.6) of a mycobacterium tuberculosis specific antigen Rv3875 and Rv3874 are connected in series, and then inserted into an E. coli expression vector, and the high-efficiency expression and purification for the fusion protein of Rv3875 and Rv3874 in the E. coli are achieved. The recombinant protein at least comprises 8 T cell epipositions which can be used for cell immunity diagnosis, and a diagnostic kit and diagnostic method for a whole blood IFN-Gamma release analysis method are established by taking the protein as the basis and combining the human IFN-Gamma enzyme-linked immunoassay technology, and can be used for the early, specific diagnosis and screening of tuberculosis and mycobacterium tuberculosis infectors.
Owner:范雄林
Toxophasma gondii detecting kit based on recombined antigen
InactiveCN1861633AImprove immune activityExcellent repeatabilityBiological testingAnimals/human peptidesSephadexEscherichia coli
A reagent kit based on recombinant antigen for detecting Toxoplasma is prepared through taking 542-1218 fragment (t SAG1) from the primary surface antigen gene SAG1 of Toxoplasma, subcloning it to soluble expression carrier pET32a(+), transferring it to colibacillus, configuring engineering bacterium pET32a-tSAG1 / BL21, IPTG induced efficient expression, ultrasonic splitting to obtain supernatant, purifying by Ni-NTA and Sephadex-G75, and coating the microholes on ELISA plate. Its test paper can also be prepared by same way.
Owner:深圳市绿诗源生物技术有限公司
Performance improved recombination staphylococcus aureus protein A affinity ligand and construction method thereof
ActiveCN103214563AImprove bindingImprove elutionMicroorganism based processesDepsipeptidesHigh concentrationEscherichia coli
The present invention discloses a performance improved recombination staphylococcus aureus protein A affinity ligand and a construction method thereof. The present invention adopts a molecular biology method. A sequence B of a nature protein A is selected for molecular transformation. A C-terminal of the sequence B is added with two cysteines, so that the protein A can pass through double-locus coupled chromatography matrix to stabilize the connection. Six glycines are added to the end of a second Loop of the sequence B to increase the length and reduce the binding force with an antibody, so that elution conditions are mild. On this basis, resistance performance to high concentration base of the protein A is transformed. Asparagines and phenylalanine at 23rd and 30th positions of the sequence B are respectively replaced by threonine and alanine to obtain a sequence Z with higher alkaline resistance properties. Then, isocaudarner is used for connecting sequence Zs of different numbers head-to-tail in series. The efficient expression system of e. coli is used for overexpression. The expressed recombination protein A is coupled to agarose matrix preparation affinity chromatography fillers and is used for purifying antibodies. Results show that the recombination protein A affinity ligand prepared by the present invention is good in elution performance and alkali resistance.
Owner:嘉兴千纯生物科技有限公司
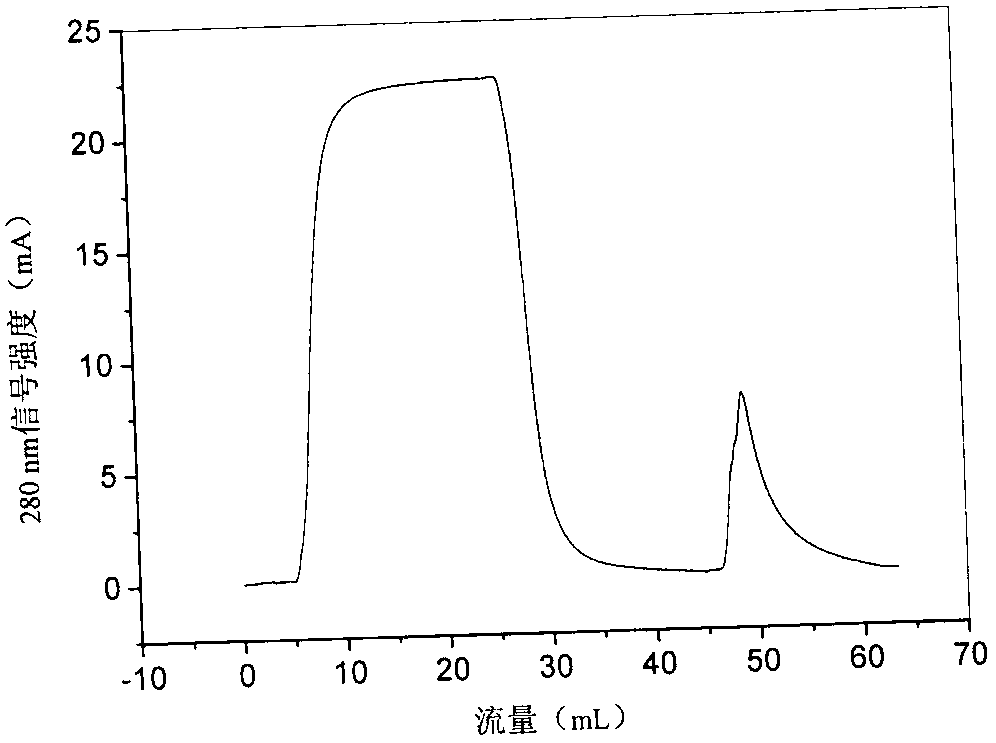
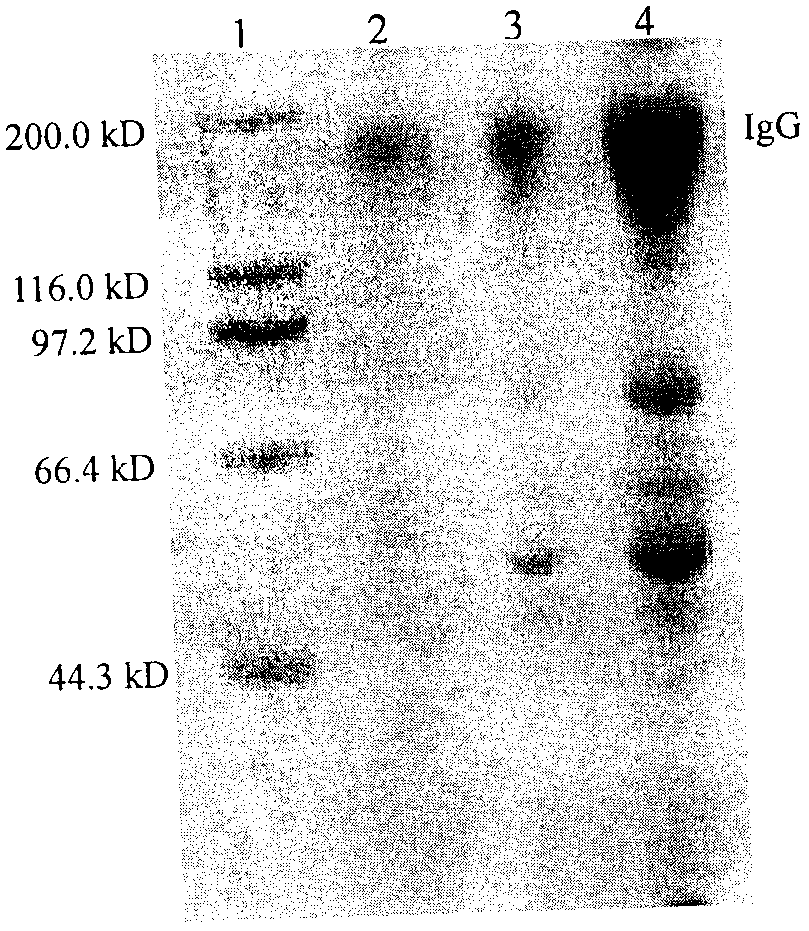
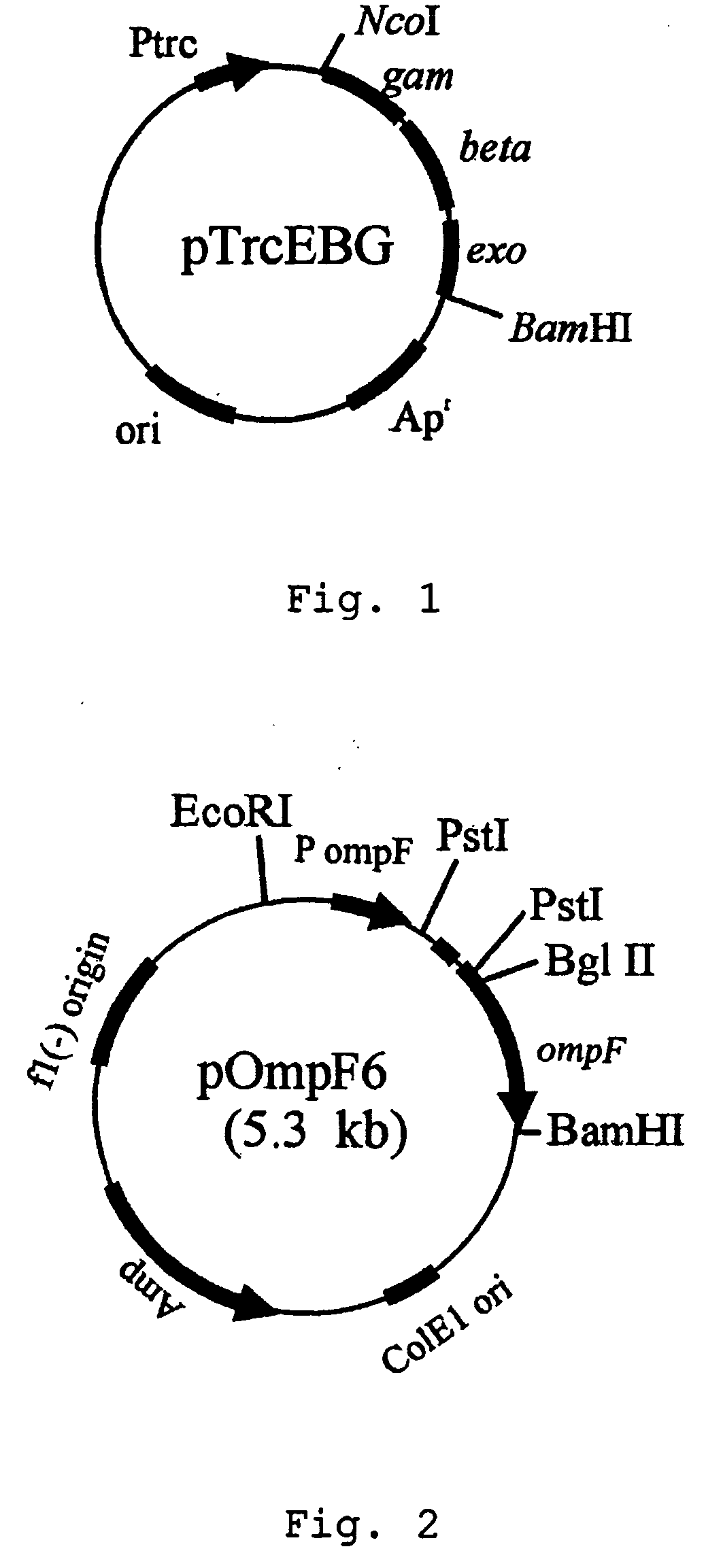
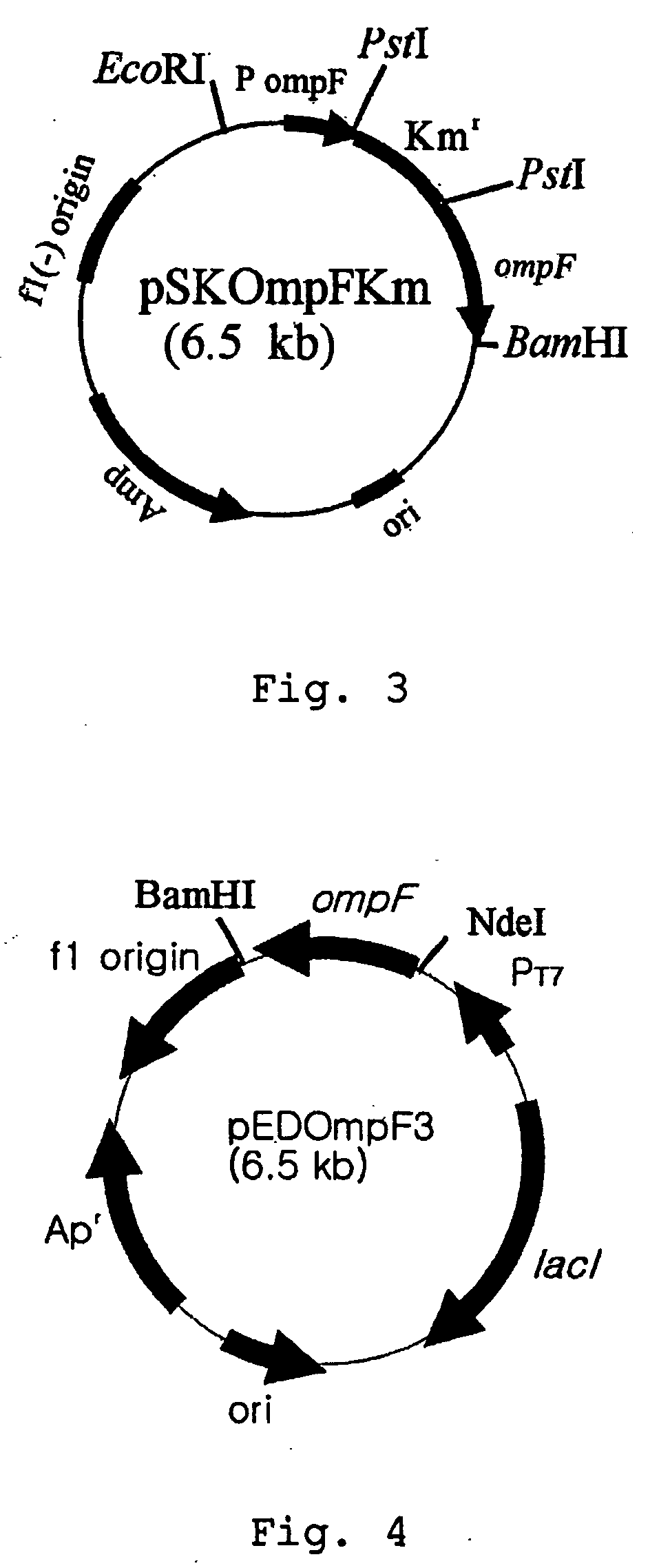
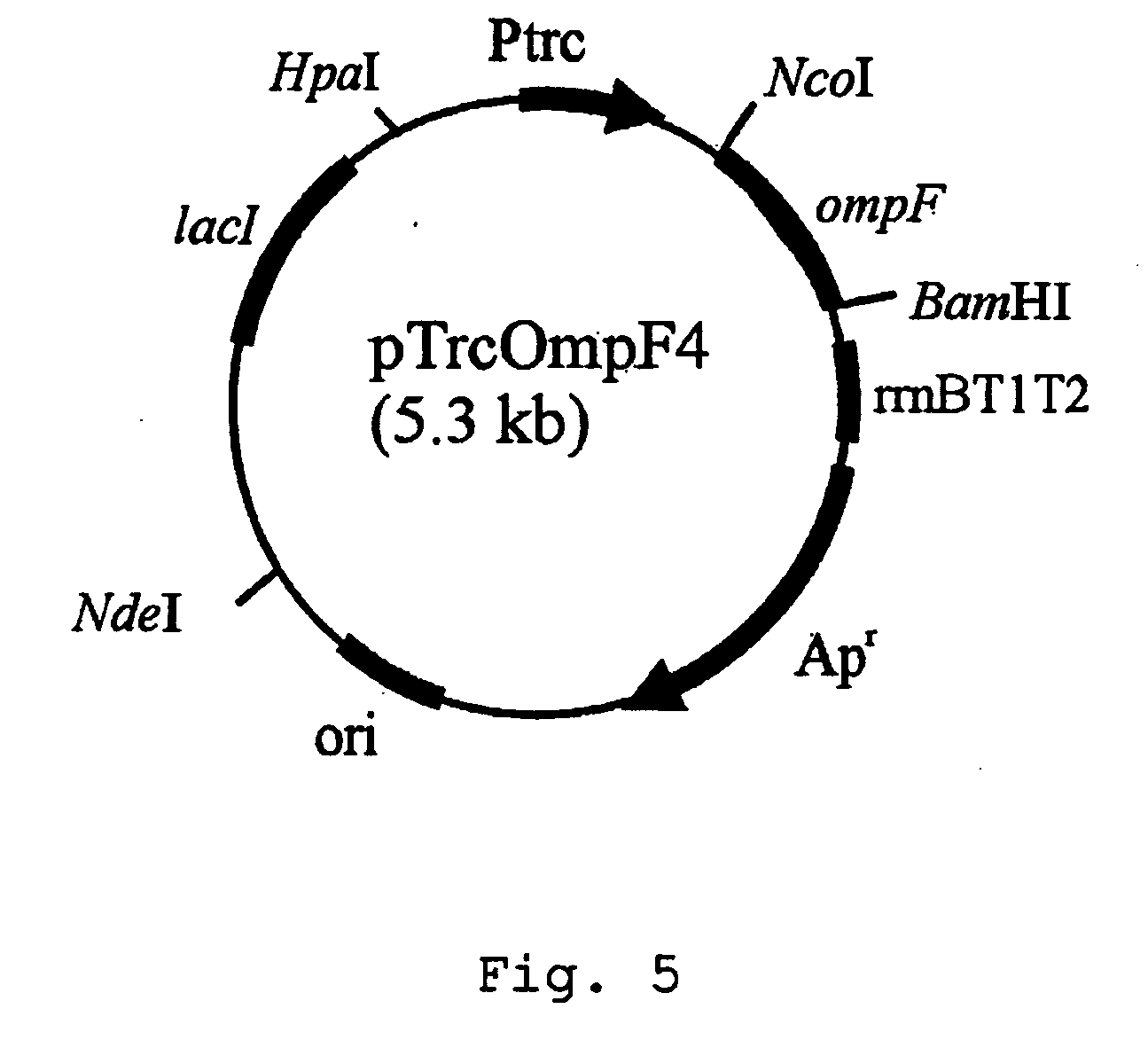
Method for extracellular production of target proteins employing OmpF in E.coli
The present invention provides an expression vector comprising genes encoding OmpF of E. coli and a desired protein, E.coli transformed with the expression vector, and a method for extracellular production of desired proteins by employing the same. The recombinant expression vector of the invention comprises an ampicillin-resistance gene, the OmpF promoter and the OmpF gene. In accordance with the invention, a desired protein can be produced extracellularly by a simpler method than conventional methods such that: secretory production of OmpF fusion protein begins simultaneously with growth of the cells through constitutive expression employing an OmpF promoter, and as the concentration of cells increases, the amount of secretory production of the protein also increases continuously. Therefore, desired proteins can be produced in large quantities by a high concentration culture of cells.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
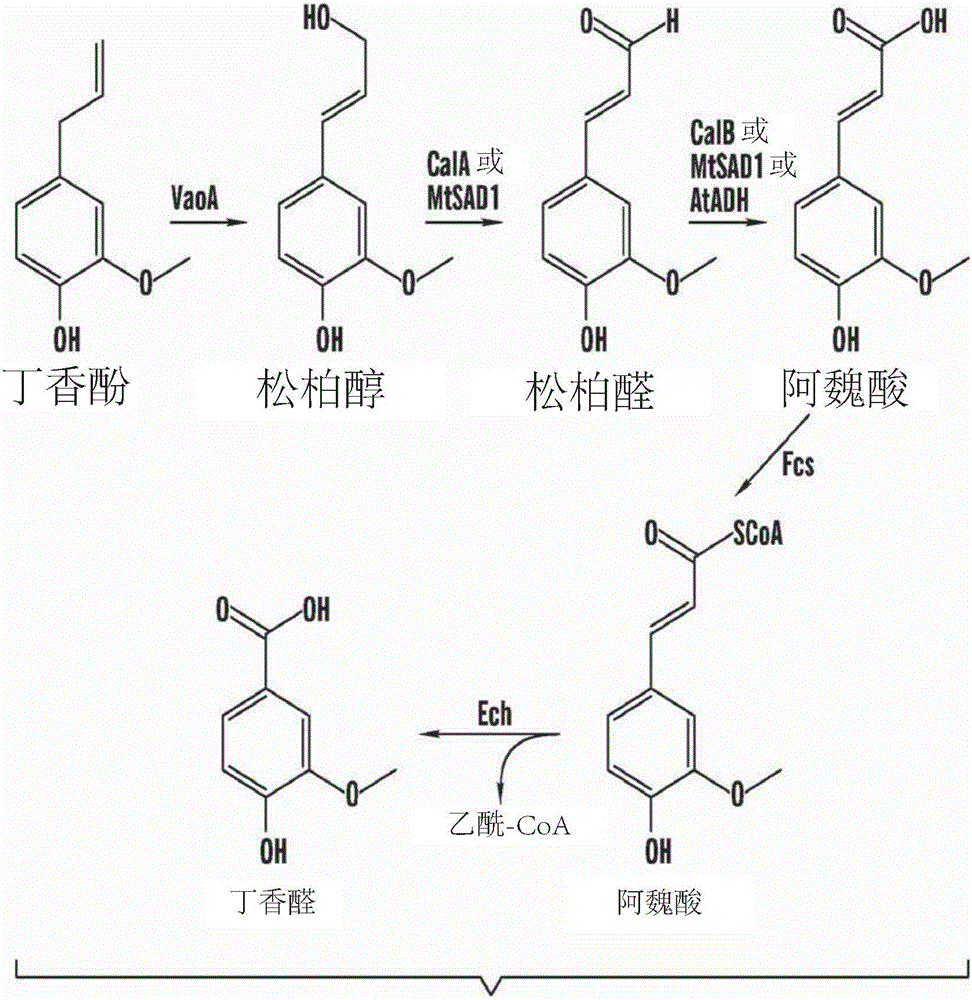
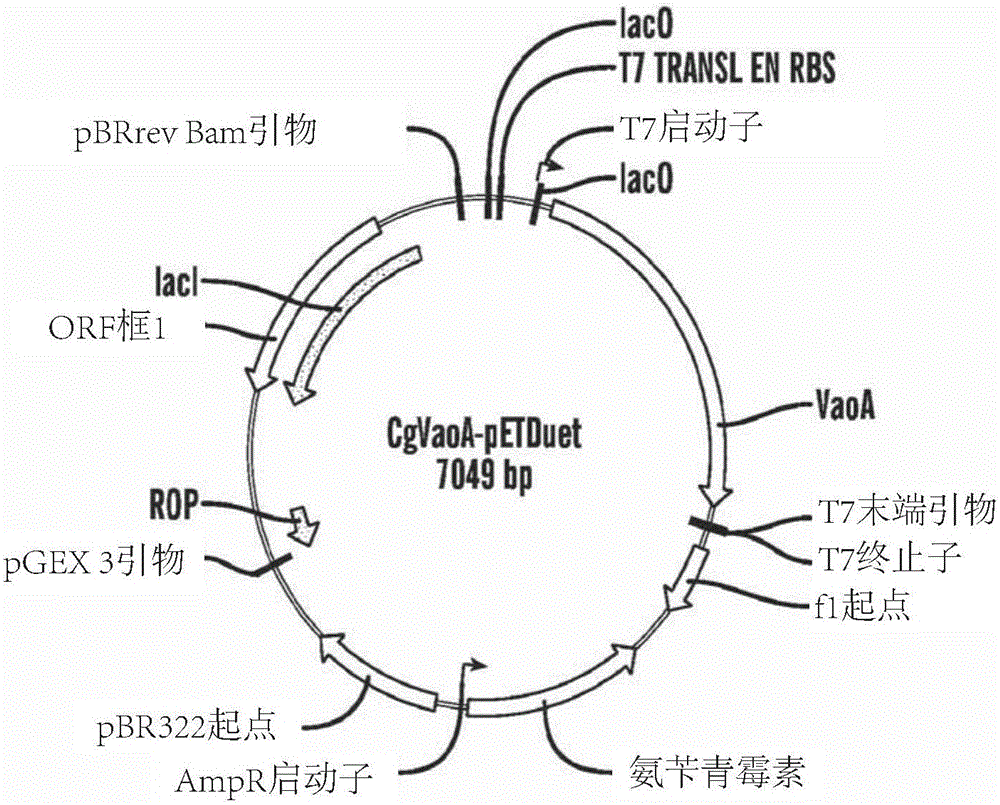
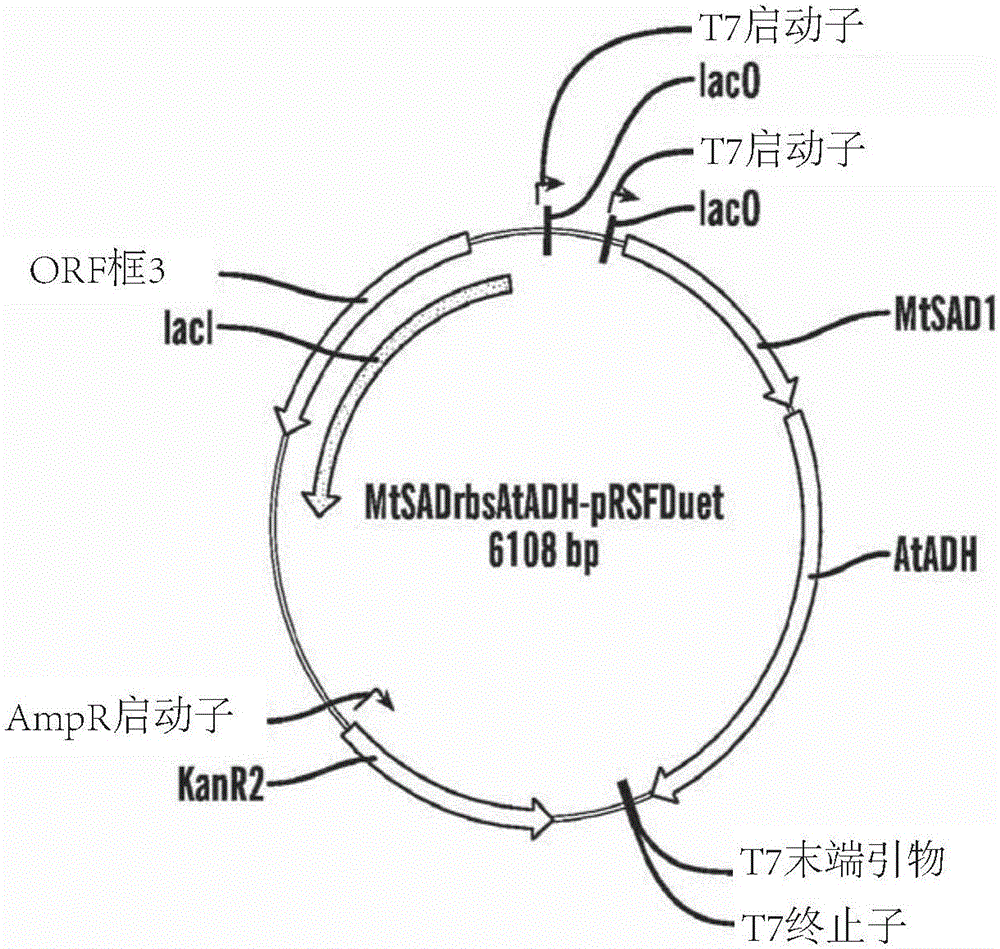
Methods of making vanillin via the microbial fermentation of ferulic acid from eugenol using a plant dehydrogenase.
A bioconversion method of making vanillin including expressing VaoA gene in a mixture, expressing MtSAD1 gene in the mixture, feeding eugenol to the mixture, and converting ferulic acid to vanillin by incubating with a microbial Amycolalopsis sp. strain (Zhp06) and / or a recombinant E.coli strain.
Owner:BGN TECH
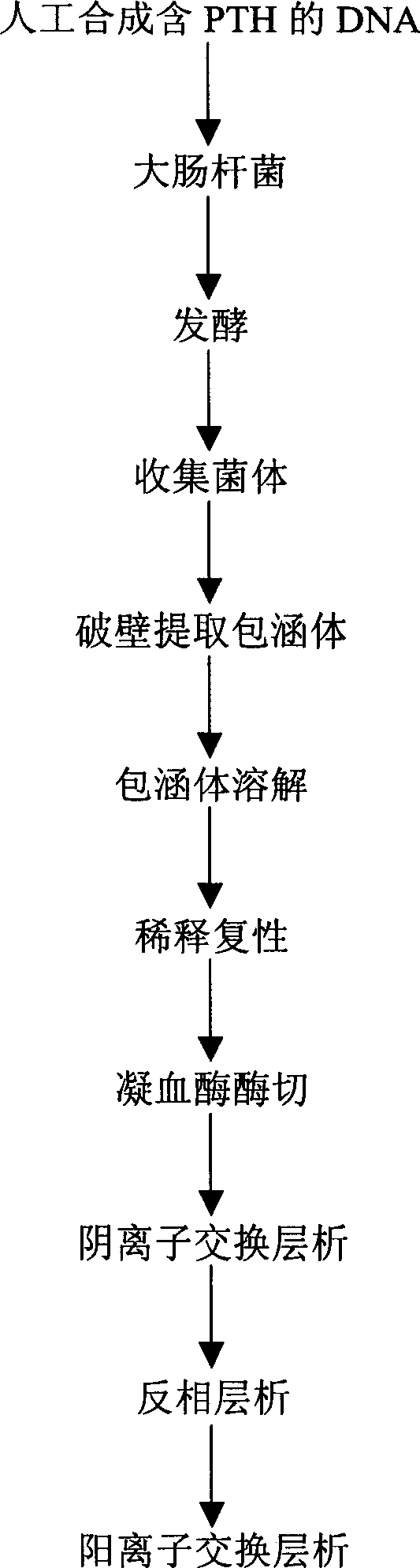
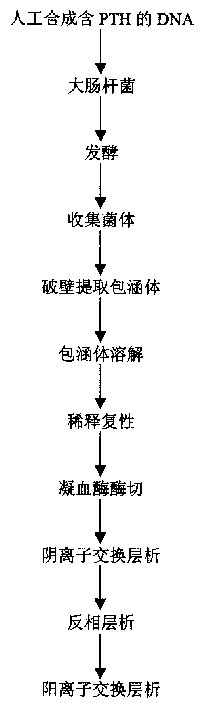
Prepn of recombinant human parathyroid hormone PTH (1-34)
The present invention relates to a preparation process of recombinant human parathyroid hormone PTH(1-34). The process constitutes a new engineering strain to result in high expression amount, simplepurifying course and low cost.The present invention adopts colibacillus degenerate codon modifying sequence corresponding cDNA, the basic sequence is L-V-P-R-PTH(1-34), where L-V-P-R is the enzyme incision site of thrombin. To the end of the nucleotides sequence, colibacillus terminator codon TAA is added; and in order to clone easily to the 5'-terminal enzyme incision site of EcoR I is added, and to the 3'-terminal, enzyme incision site of Sal I is added. High-purity recombinant huamn parathyroid hormone PTH(1-34) is obtained through fermentation of the engineering bacteria, occlusion body extraction, diluting renaturation, thrombase incision, anionic exchange chromatography and other steps.
Owner:西南生物工程产业化中试基地有限公司
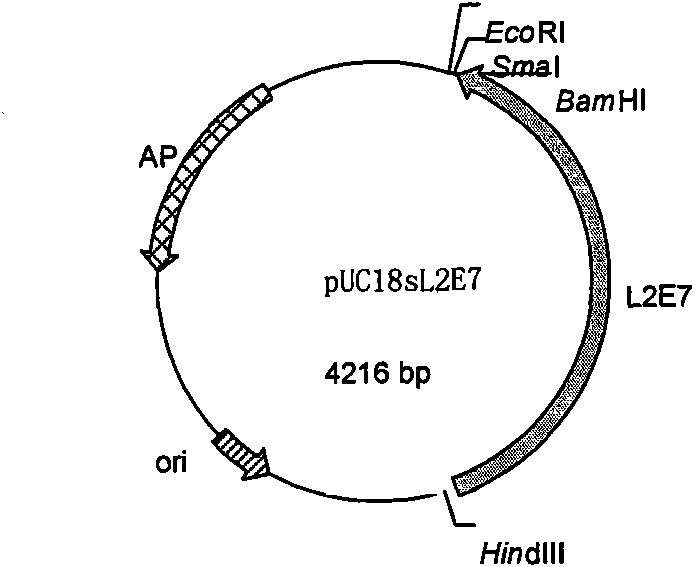
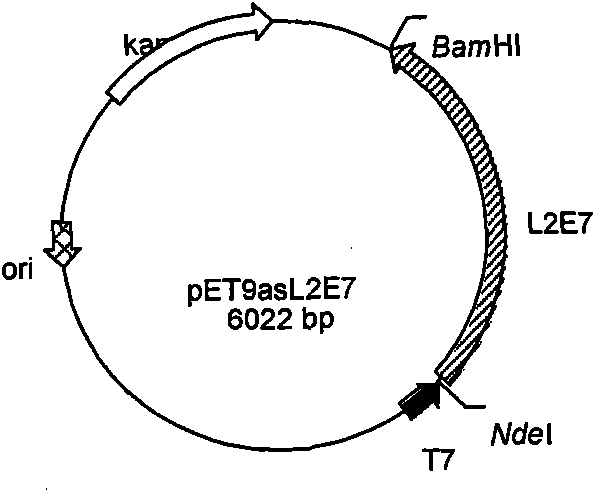
Human papilloma virus (HPV) fusion protein, gene, carrier, strain, preparation method and application
The invention relates to a codon-optimized gene of a 16-type L2E7 recombinant protein of human papilloma virus (HPV), which can be expressed efficiently in colibacillus. The optimized gene can be expressed efficiently by being inserted in a prokaryotic expression vector pET9a, and the expression level accounts for 50% of all viruses; an expression protein is immune to mice after being purified. Proved by experiment results, the protein has the same immunogenicity with a protein which is not expressed by the optimized gene and can induce the release of specific gamma-1NF; proved by tumor growth inhibition animal experiments, protein immunity has evident inhibition effect on tumor growth and the growth of 90% of mouse tumor cells can be inhibited completely. The prokaryotic high-efficiency expression system of L2E7 recombinant protein, which is established by the optimized gene, can be used in the pilot scale production and drug discovery of preventive and curative vaccines of HPV16 infection and relevant cervical carcinoma.
Owner:中国疾病预防控制中心病毒病预防控制所
Antimicrobial composition and method for use
InactiveUS20050266050A1Improved antimicrobial compositionImprove methodAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyTear lysozyme
An antimicrobial composition and a method for administering the antimicrobial composition through the water or feed of livestock, wherein the antimicrobial composition is made up of lysozyme and various other agents that act synergistically with lysozyme, such as, dried egg powder, albumen, a sequestering agent and / or a lantibiotic. The composition is used to inhibit the growth of, and diseases and epidemiological significant effects caused by, Clostridium perfinigens, E, coli and Salmonella, in the gut of livestock. More particularly, the antimicrobial composition and method relate to a feed additive that can be administered to poultry and / or swine through their feed. The use of such a feed additive may also inhibit other enteric pathogens that may be present in the gut of livestock.
Owner:NEOVA TECH
Expression vectors for producing modified proteins
InactiveUS6514753B1Phosphorylation reaction isExtended shelf lifeBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliMicroorganism
Modified proteins, modified interferons alpha's and beta's, phosphorylated modified proteins and DNA sequences encoding the above, applications and uses thereof. Modified phosphorylated Hu-IFN-alpha-like proteins are provided which carry an identifiable label such as a radio-label. Corresponding phosphorylatable Hu-IFN-alpha-like proteins which contain a putative phosphorylation site. DNA sequences which encode a Hu-IFN-alpha-like protein and contain a sequence encoding a putative phosphorylatable site. Appropriate expression vectors are used to transform compatible host cells of various microorganisms, such as E. coli. Numerous uses for the phosphorylated proteins are disclosed.
Owner:PESTKA BIOMEDICAL LAB
Method for preparing N-end acetylation modified thymosin alpha with recombined E. coli
The present invention discloses the preparation process of thynosin-alpha with acetylation modified N-end by using recombinant colibacillus. The preparation process includes obtaining thynosin-alpha gene, constructing recombinant expression vector containing thynosin-alpha, transforming prokaryotic cell, culturing prokaryotic cell and expressing thynosin-alpha, and separating and purifying thynosin-alpha with acetylation modified N-end. The present invention also discloses the process of utilizing recombinant colibacillus in preparing thynosin-alpha antigen with acetylation modified N-end and then cutting and separating to prepare thynosin-alpha-1 antigen with acetylation modified N-end, thynosin-alpha-2 antigen with acetylation modified N-end and similar matter. The thynosin-alpha with acetylation modified N-end has the functions of regulating immunity, cell proliferation, etc. and has wide application foreground in antivirus and antitumor.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
Spirulina culture method
PendingCN106635919AReduce contentReduce precipitationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnergy expenditureFully automatic
The invention discloses a spirulina culture method, which comprises the following steps of (1) putting a solid culture medium into a sterilization pot to be steamed and boiled; (2) performing inoculation: spreading algae species of spirulina into the culture medium in a fully automatic pollution-free room; after the inoculation is completed, automatically and uniformly stirring the materials; (3) performing three-dimensional culture on the spirulina to obtain spirulina liquid; (4) performing harvesting, washing and concentrated dewatering; performing spray drying; completing the culture; (5) sieving the cultured materials to prepare the scaled culture spirulina. The spirulina culture method has the advantages that the germ content is low; the culture efficiency is high; high efficiency and health are realized; the energy consumption is low; the precipitation and the wall attachment of the spirulina are reduced; the collecting rate of the spirulina is improved; the scaled culture of the spirulina can be realized.
Owner:JIANGXI ZHONGZAO BIOTECH
Protein complex system for increased immunogenicity and functionality, and methods making and use
ActiveUS20140017269A1Improving immunogenicityImprove functionalitySsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseEscherichia coliRotavirus RNA
Genes for proteins which spontaneously form dimers and / or oligomers can be recombinantly linked together, which upon expression in E. coli produces stable dimeric fusion proteins that spontaneously self-assemble into enormous, polyvalent complexes having increased immunogenicity and functionality. Linear, network and agglomerate complexes with enormous sizes and polyvalences are constructed using glutathione S-transferase, Norovirus P domains (NoV P− and NoV+), the protruding (P) domain of hepatitis E virus (HEV P), the astrovirus P domain (AstV), a monomeric peptide epitope (M2e of influenza virus), and / or a protein antigen (VP8* of rotavirus) fused in different combinations. The resulting complexes can contain hundreds to thousands NoV P-protein, HEV, AstV, M2e and / or VP8* copies and exhibit higher immunogenicity than the individual proteins alone. The large size and multivalent nature of the complexes are candidates as a bivalent or multivalent vaccines against Norovirus and other pathogens, and for generation of antibodies for diagnosis and research purposes.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Staphylococcus lyase and application thereof
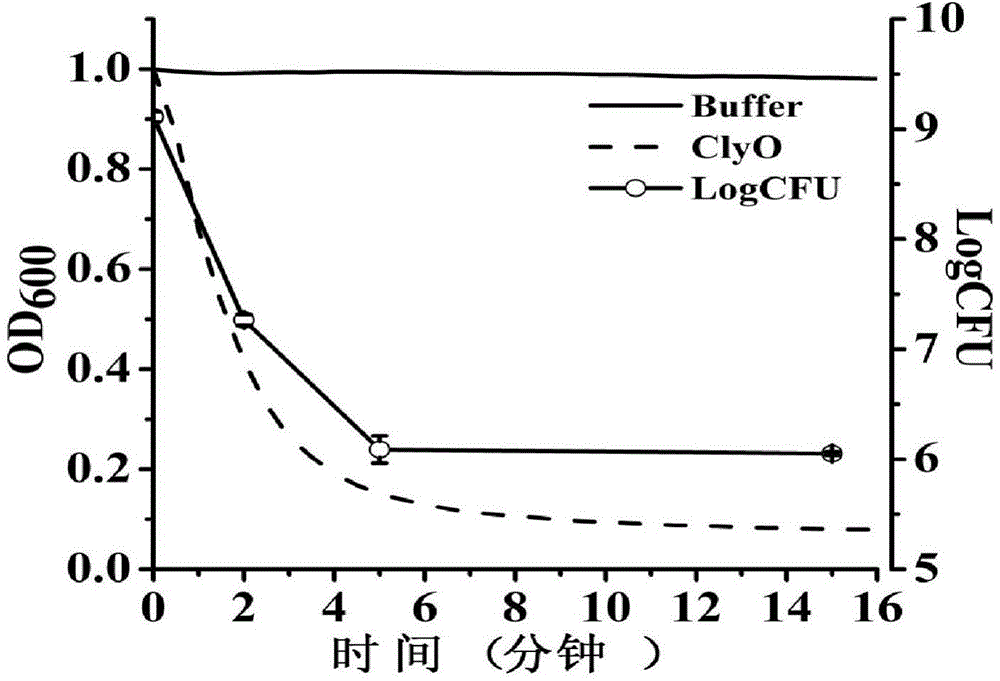
ActiveCN104805066AIncrease enzyme activityHigh activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsMethicillin sensitiveMethicillin resistance
The invention discloses lyase capable of killing staphylococci and an application of the lyase, which belong to the field of biological agents. The invention discloses an amino acid sequence and a coding gene sequence of the lyase. A pH range of the lyase which plays a role is wide, the activity of cracking the staphylococci is kept within the pH range of 4 to 11, and recombinant protease constructed by adopting coding genes can be solubly expressed in colibacillus BL21(DE3). The lyase can be used for efficiently killing various staphylococci in vitro, including methicillin sensitive staphylococcus aureus and methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus which are clinically separated, and the lyase can be used as antibiotics for treating staphylococcal infection in vivo. The disclosed lyase can be used for quickly cracking staphylococcal cell walls and releasing substances in cells, such as triphosadenine, DNA and the like, and the staphylococci can be detected by utilizing the released substances.
Owner:TARGET ANTI-BIOPHARMACEUTICAL TECH CO LTD
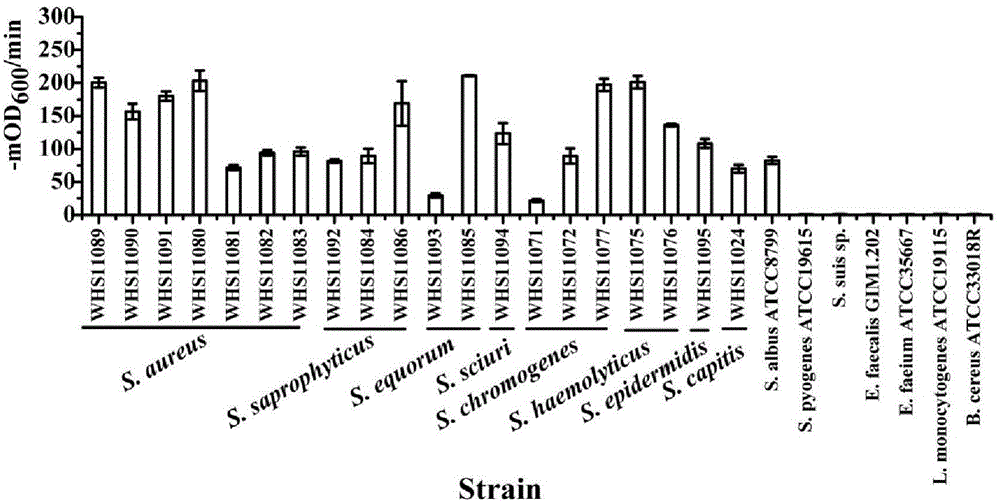
Methods of killing cells and use of same in prevention and treatment of cancer
ActiveUS20110076282A1Microbiological testing/measurementAntibody ingredientsAdenomatous polyposis coliCancer
A method of killing a cell having a mutation in an Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene is disclosed. The method comprises contacting the cell with an inhibitor of Casein kinase I (CKI), the CKI being selected from the group consisting of CKI-alpha and CKI-delta and CKI-epsilon, thereby killing the cell. The method may be used for treating cancers. Pharmaceutical compositions for treatment of cancers are also disclosed.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Recombinant scorpion toxin, its soluble expression and purification
InactiveCN1817902AStable purificationEasy to purifyPeptide preparation methodsFermentationChemistryToxin
Recombinant-scorpion entomotoxin rBmKIT, its soluble expression and purification are disclosed. The procedure is carried out by solvation expressing for BmK ITcDNA and a protein self-shearing element, fusing nucleotide sequence with 6 histidine coded on 3'end of BmK IT cDNA, breaking fermented broth of engineering bacterium by bacterium, protein extracting, self-shearing by fused protein, affinity chromatographing, concentrating sampler, high-temperature treating, gel filter chromatographing and purifying to obtain final product. It is soluble and simple.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Bt protein in-vitro insect resistance identification method
InactiveCN102086452AEfficient expressionMaintain integrityMicroorganism based processesAnimal feeding stuffEscherichia coliMortality rate
The invention relates to a Bt protein in-vitro insect resistance identification method which comprises the following steps: connecting a Bt gene to a protocaryon expression vector pET-28B; transferring the protocaryon expression vector containing the Bt gene into colibacillus BL21; inducing to express the Bt protein; extracting the induction-expressed Bt protein; mixing the Bt protein into an Ostrinia nubilalis larva artificial feed, and feeding Ostrinia nubilalis larvae; and after several days, making statistics on the mortality and growth conditions of the Ostrinia nubilalis larvae. The method is simple and quick to operate, is not restricted by time and seasons, has the advantage of low economic cost, and can be used for quickly carrying out Bt protein insect resistance identification.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
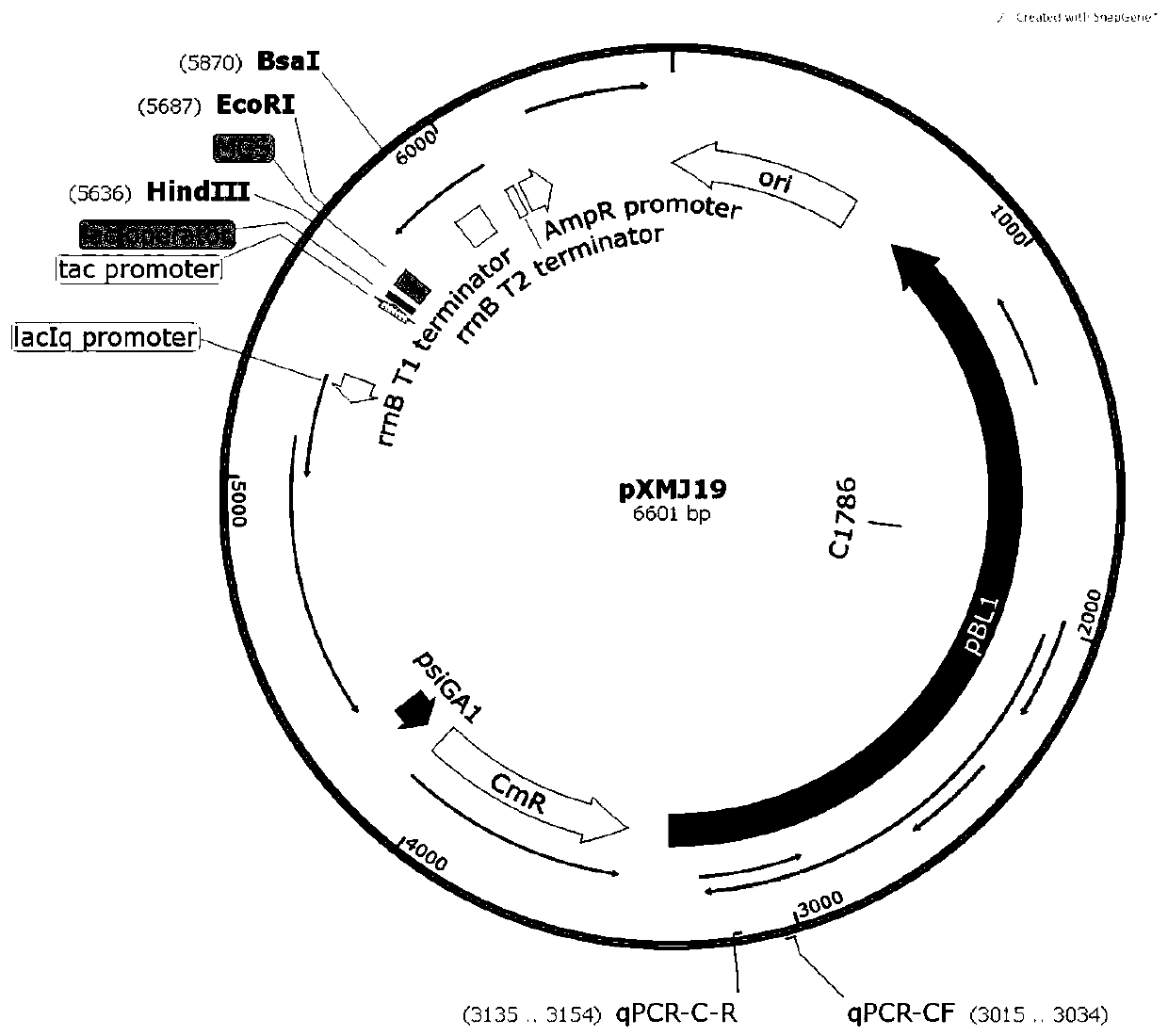
Corynebacterium and colibacillus double expression vector with high copy capability and building method thereof
ActiveCN110951767AImprove stabilityHigh expression yieldVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotideGenetics
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to a corynebacterium and colibacillus double expression vector with high copy capability. The nucleotide sequence of an expression plasmid is shown as SEQ ID NO:9. Through artificial mutagenesis on a nucleotide C in a 1786-th site in a corynebacterium replicon regulation position of a pXMJ19 carrier, a corynebacterium / colibacillus dual-purpose vector pXMJ19C1786T plasmid with the copy capability being about 12.5 times higher than that of a pXMJ19 plasmid is successfully obtained. The copy number of the pXMJ19 plasmid in the corynebacterium is about 20; and the copy number of the pXMJ19C1786T plasmid in the corynebacterium is 251. Meanwhile, the invention also discloses a building method of the expression plasmid.
Owner:ZHAOQING INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com