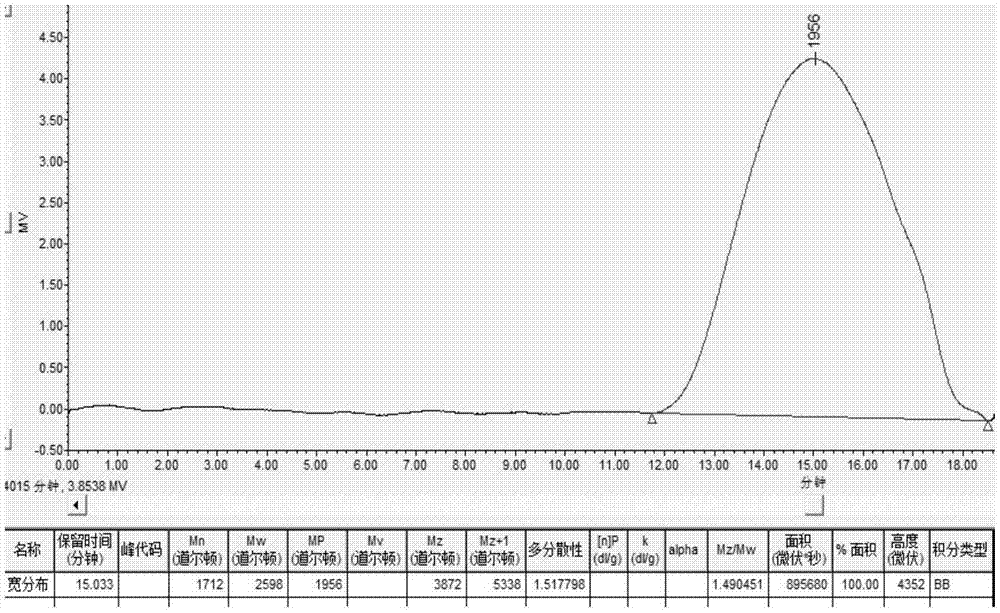
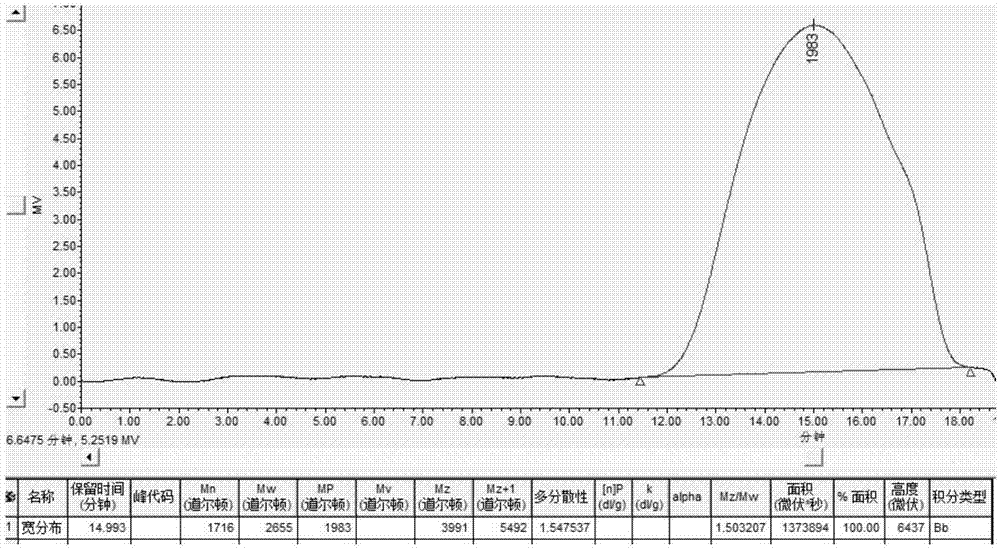
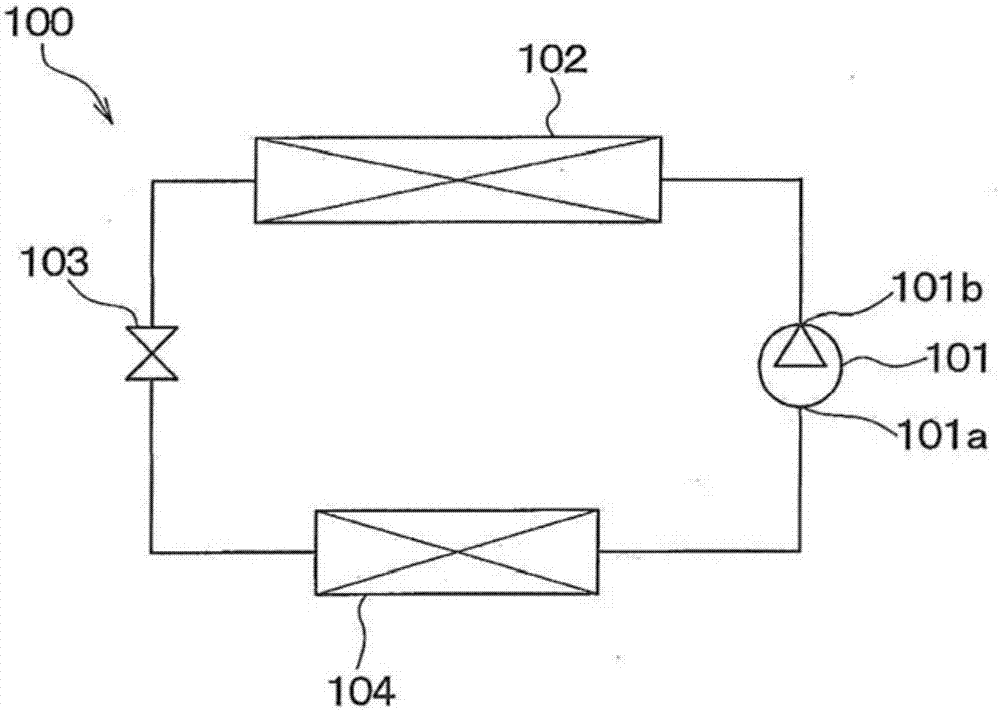
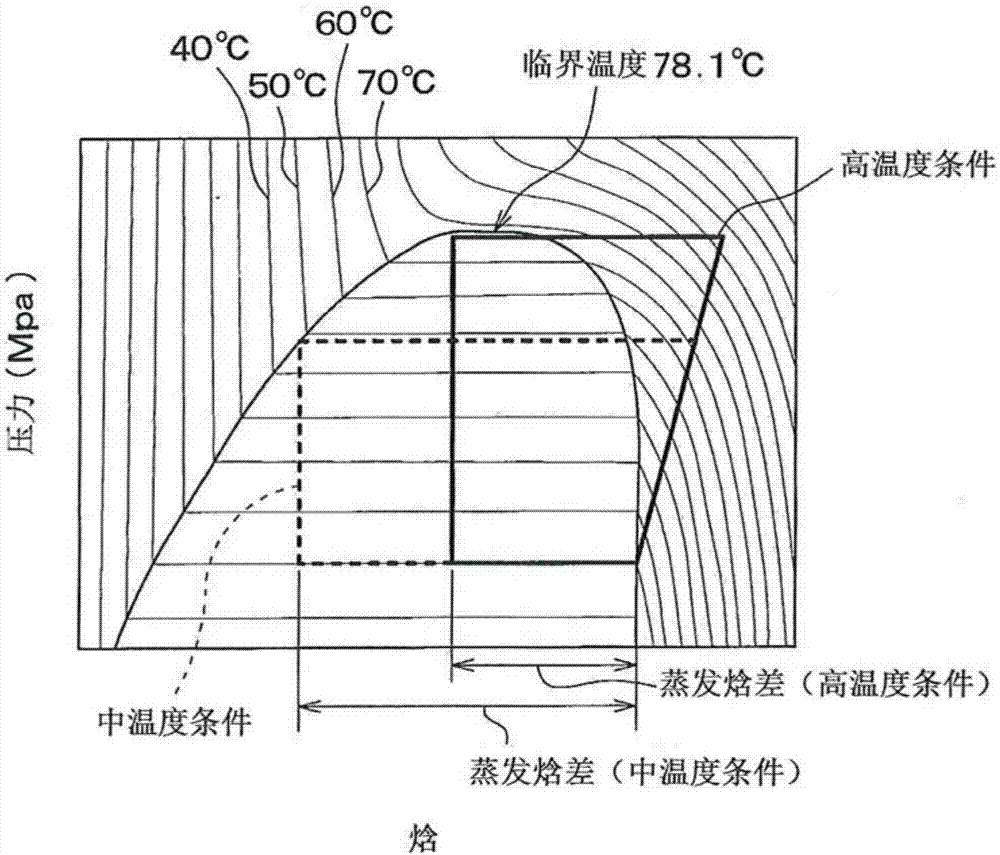
Patents
Literature
67results about How to "High critical temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Optical article having a temperature-resistant anti-reflection coating with optimized thickness ratio of low index and high index layers
ActiveUS7692855B2Improve the immunityHigh critical temperatureMirrorsOptical filtersAnti-reflective coatingHeat resistance
The present invention relates to an optical article having anti-reflection properties and high thermal resistance, comprising a substrate having at least one main face coated with a multi-layer anti-reflection coating comprising a stack of at least one high refractive index layer and at least one low refractive index layer, wherein the ratio:RT=sumofthephysicalthicknessesofthelowrefractiveindexlayersoftheanti-reflectioncoatingsumofthephysicalthicknessesofthehighrefractiveindexlayersoftheanti-reflectioncoatingis higher than 2.1. If the anti-reflection stack comprises at least one low refractive index layer having a physical thickness ≧100 nm which is not the outermost layer of the anti-reflection coating, said relatively thick layer and the underlying layers are not taken into account in RT calculation.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
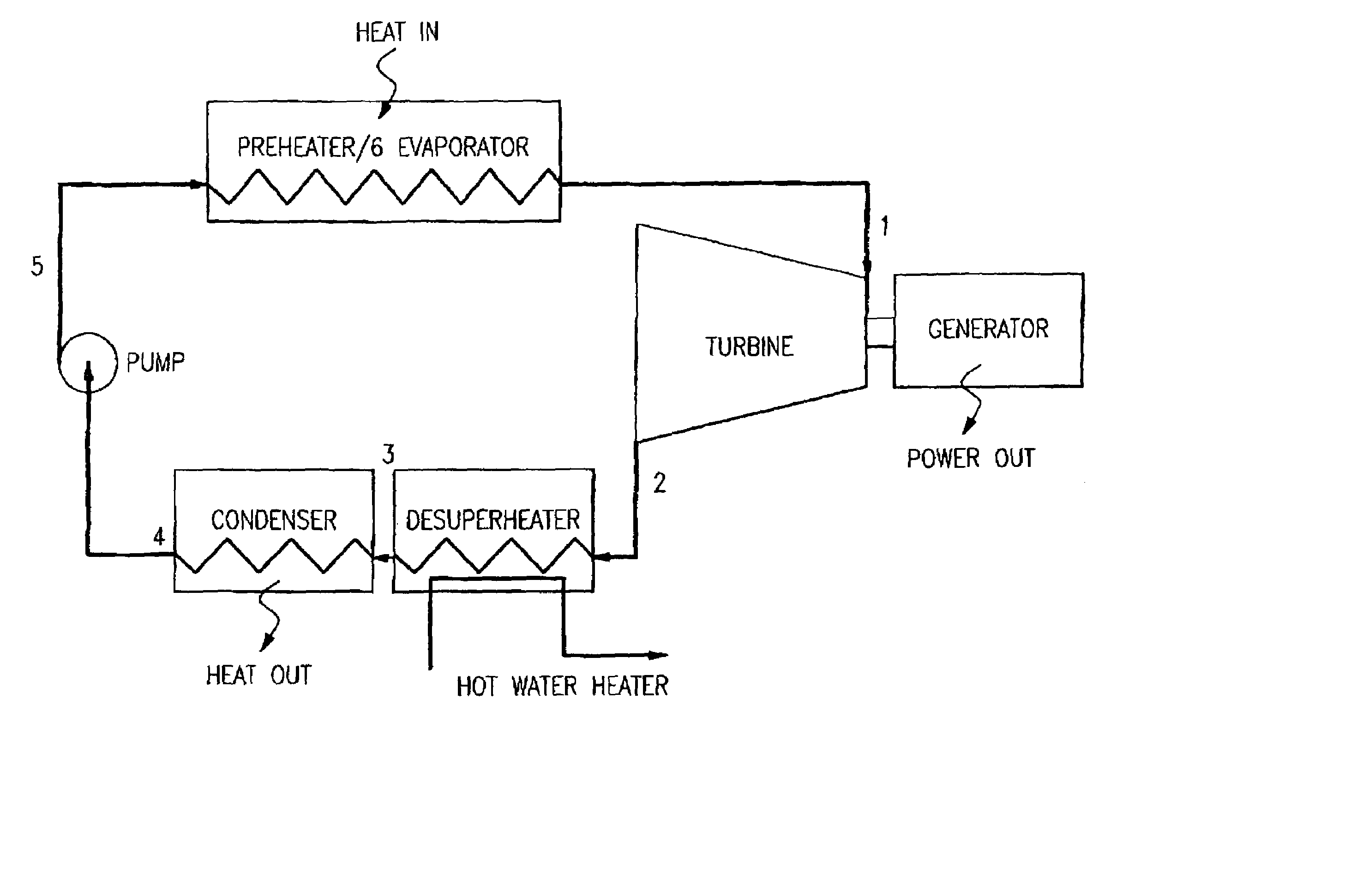
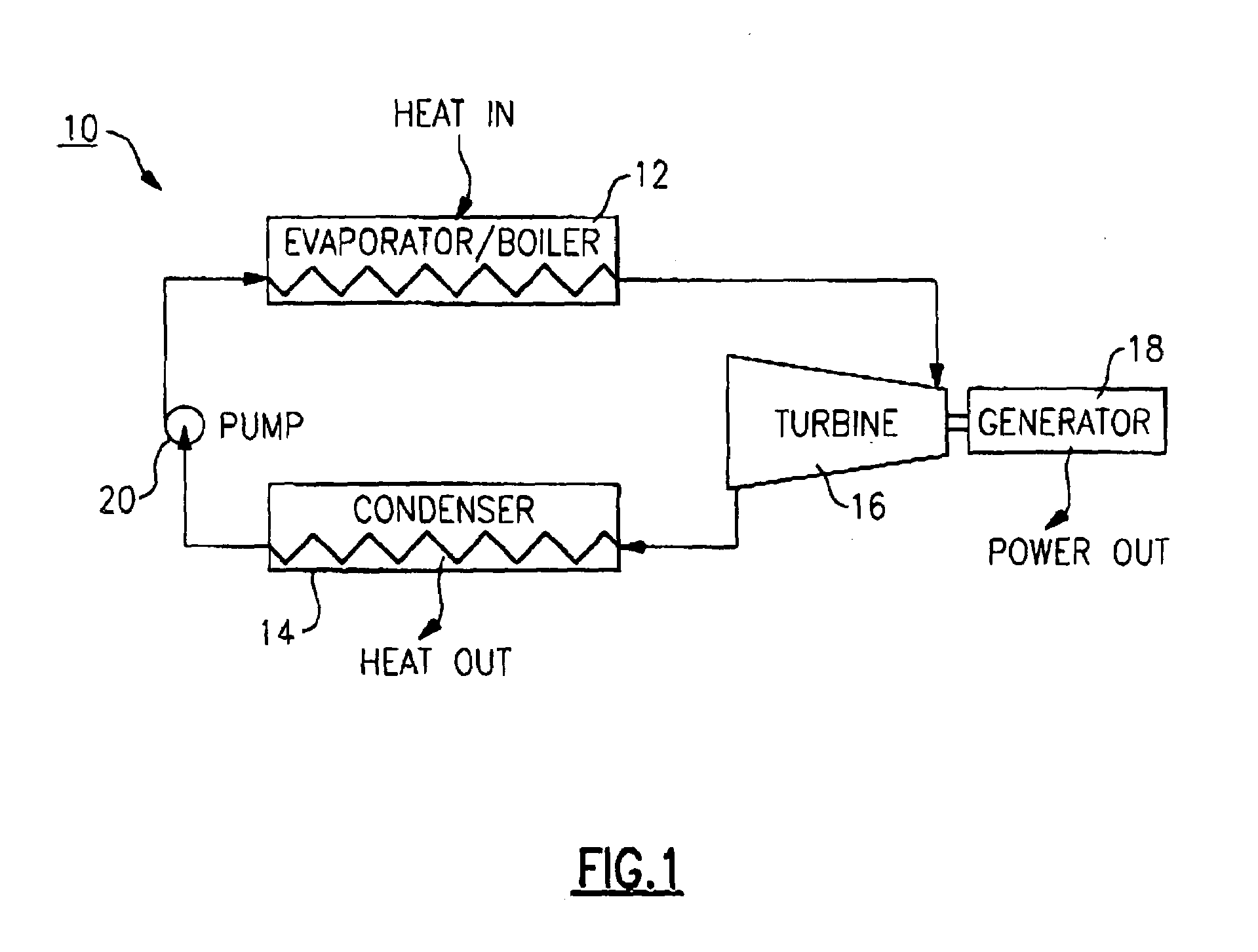
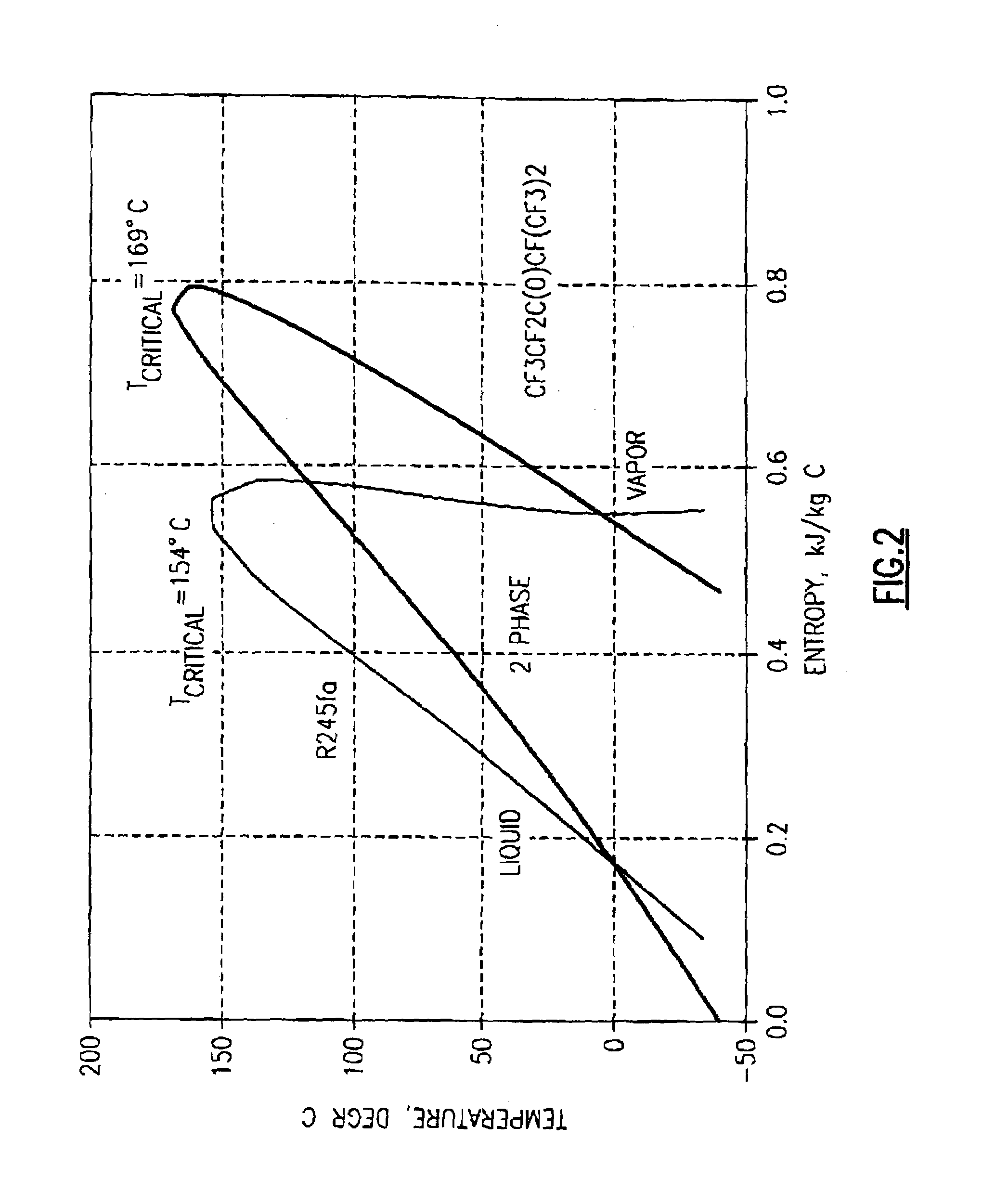
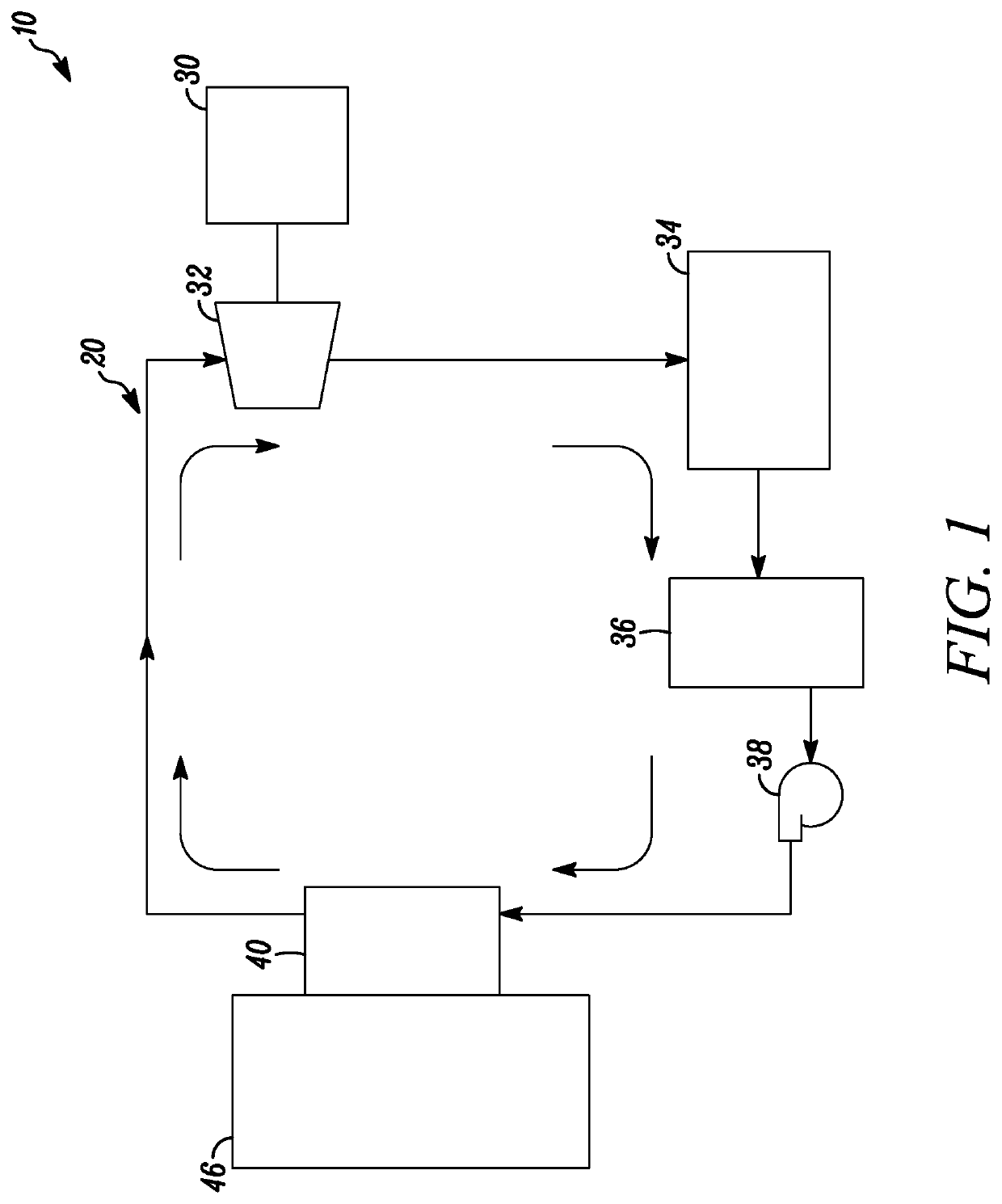
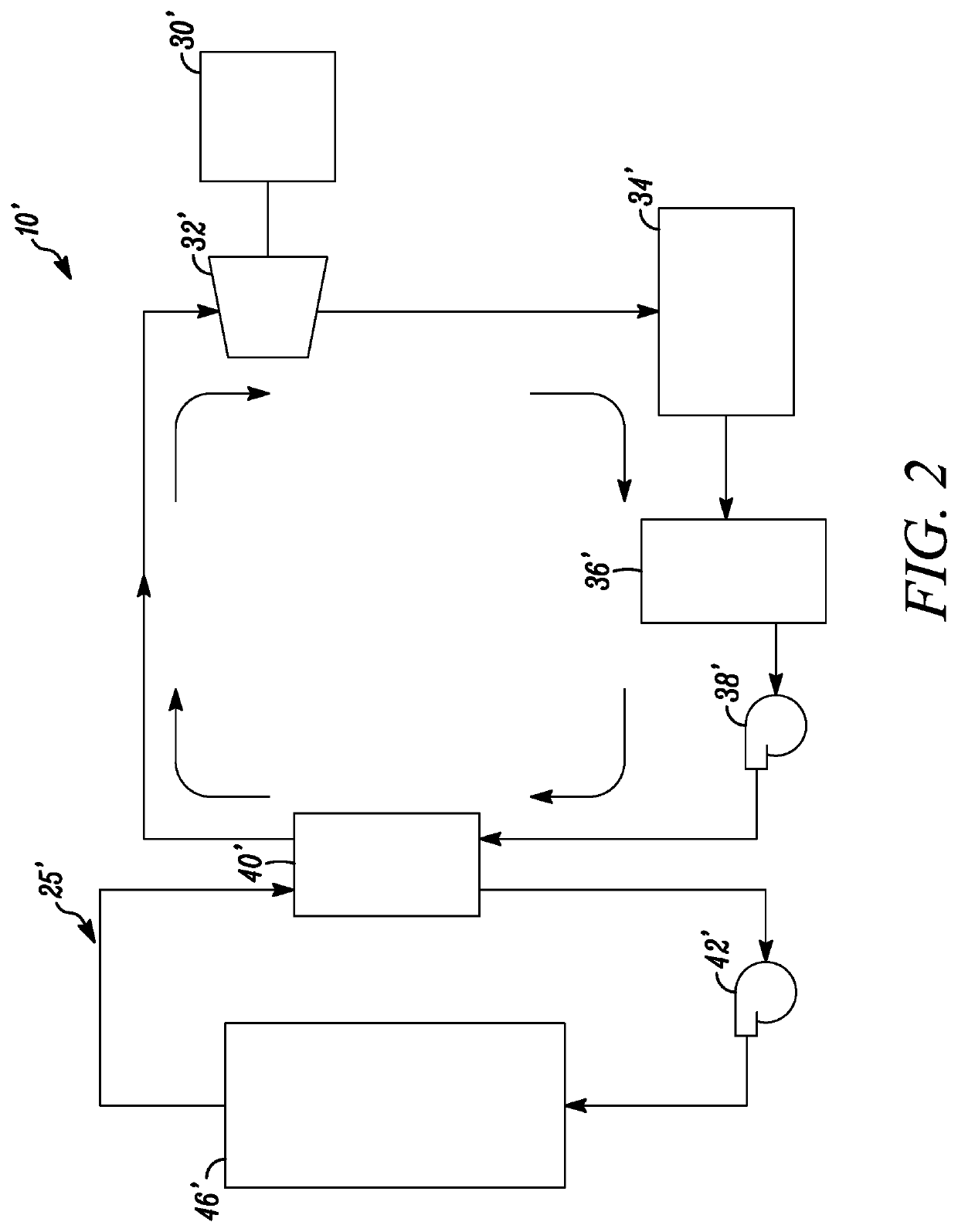
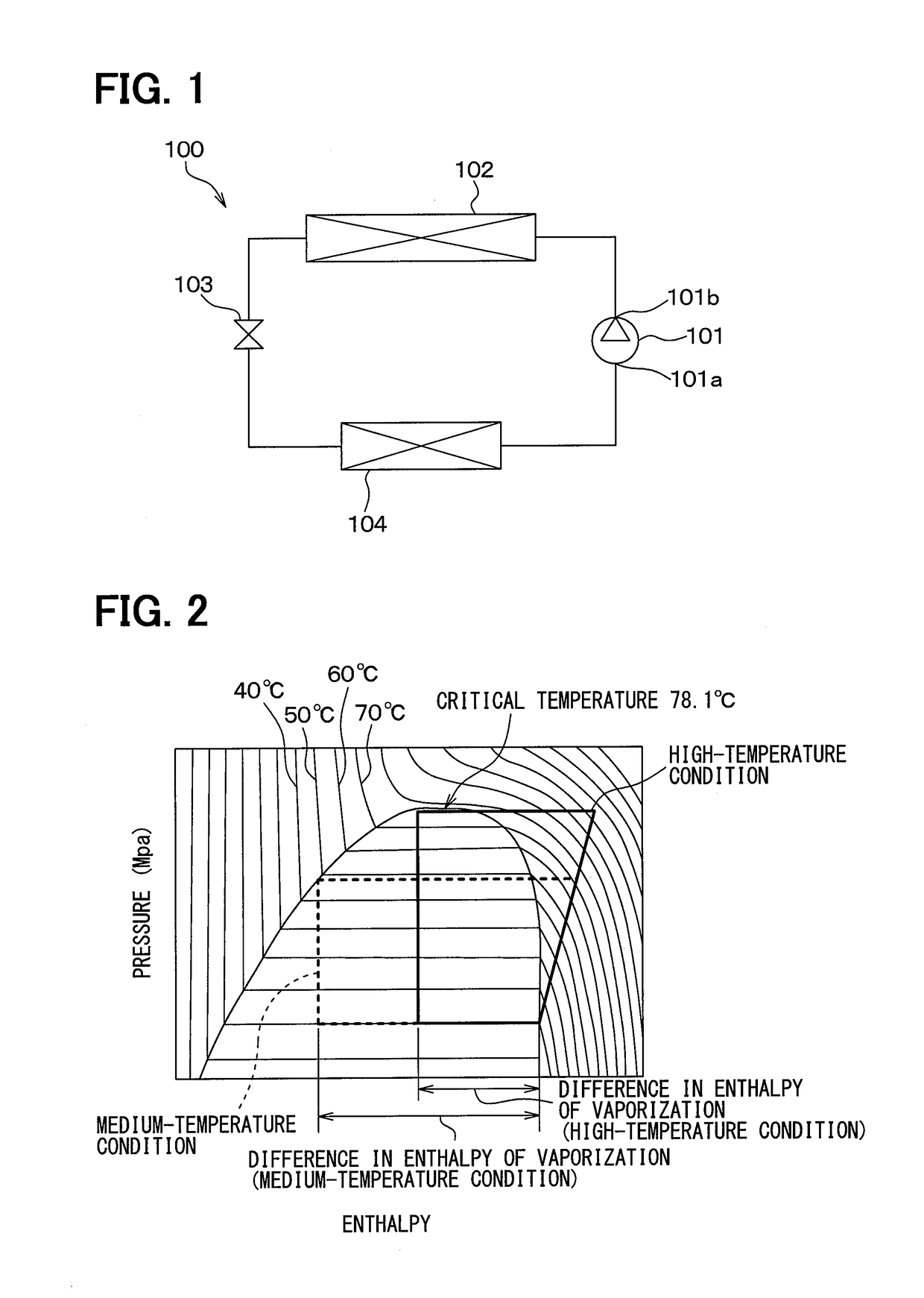
Organic rankine cycle fluid
ActiveUS7100380B2Reduce stressReduce speedCompression machines with non-reversible cycleHeat-exchange elementsOrganic Rankine cycleProcess engineering
A method of operating an organic rankine cycle system wherein a liquid refrigerant is circulated to an evaporator where heat is introduced to the refrigerant to convert it to vapor. The vapor is then passed through a turbine, with the resulting cooled vapor then passing through a condenser for condensing the vapor to a liquid. The refrigerant is one of CF3CF2C(O)CF(CF3)2, (CF3)2 CFC(O)CF(CF3)2, CF3(CF2)2C(O)CF(CF3)2, CF3(CF2)3C(O)CF(CG3)2, CF3(CF2)5C(O)CF3, CF3CF2C(O)CF2CF2CF3, CF3C(O)CF(CF3)2.
Owner:NANJING TICA AIR CONDITIONING CO LTD
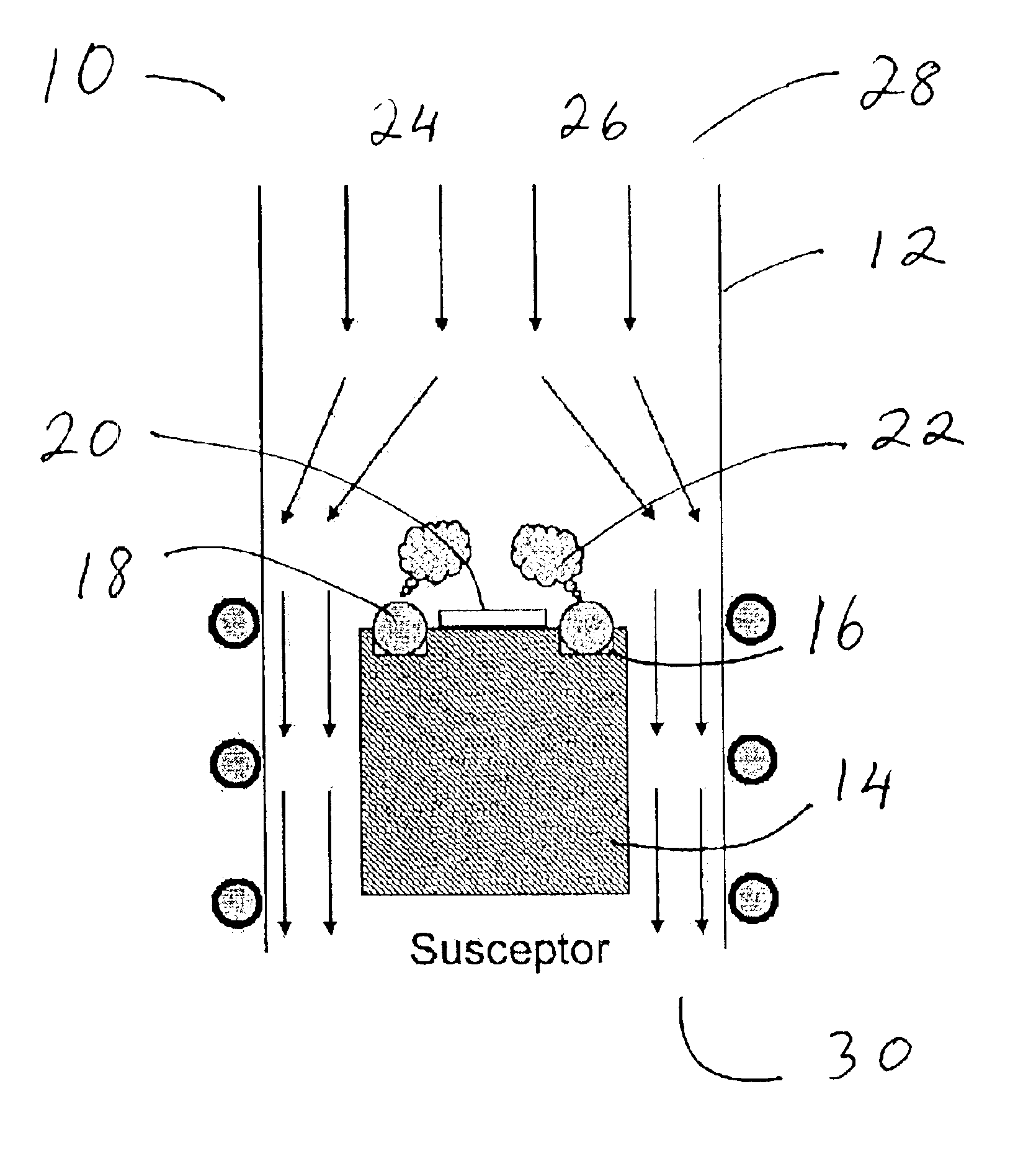
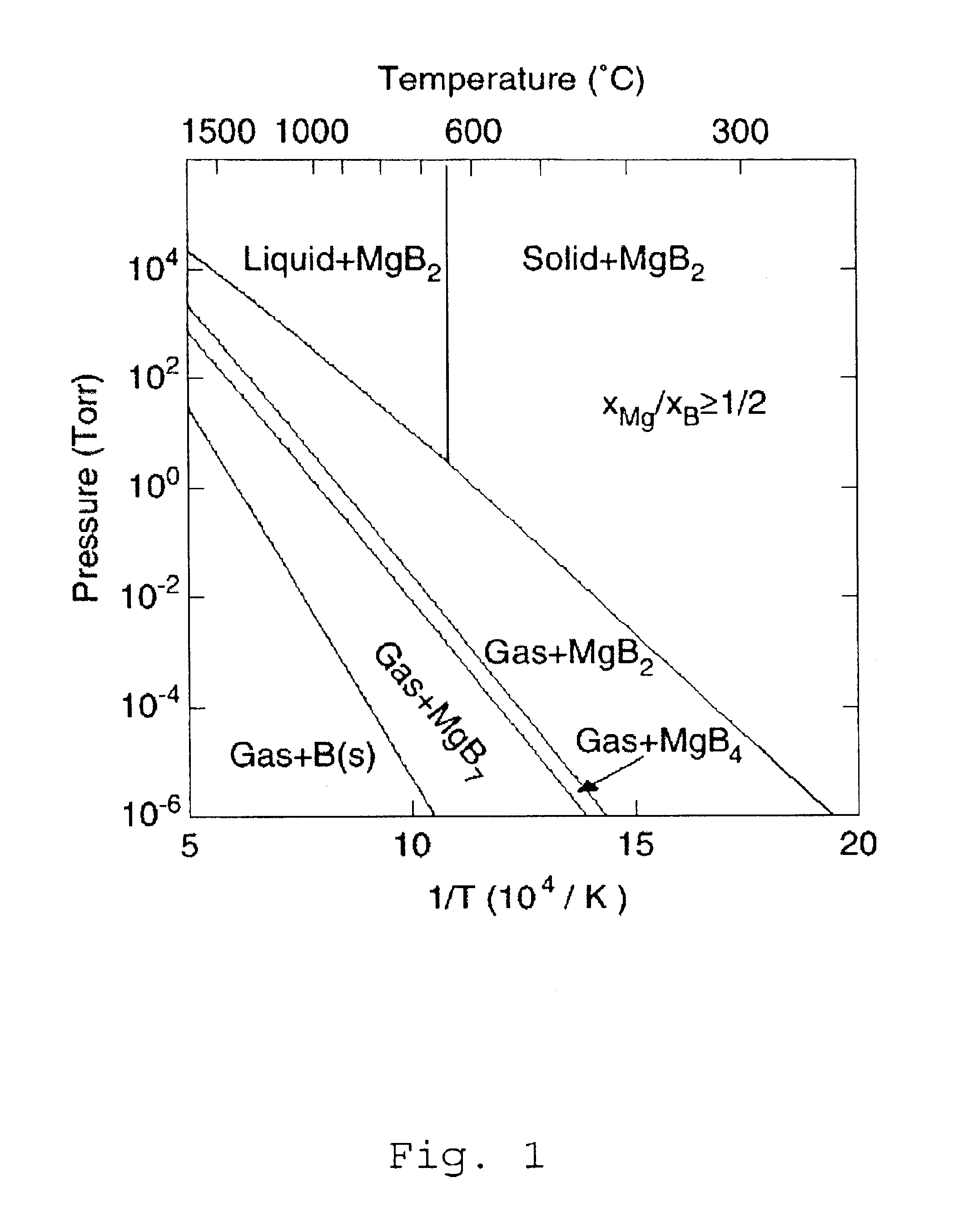
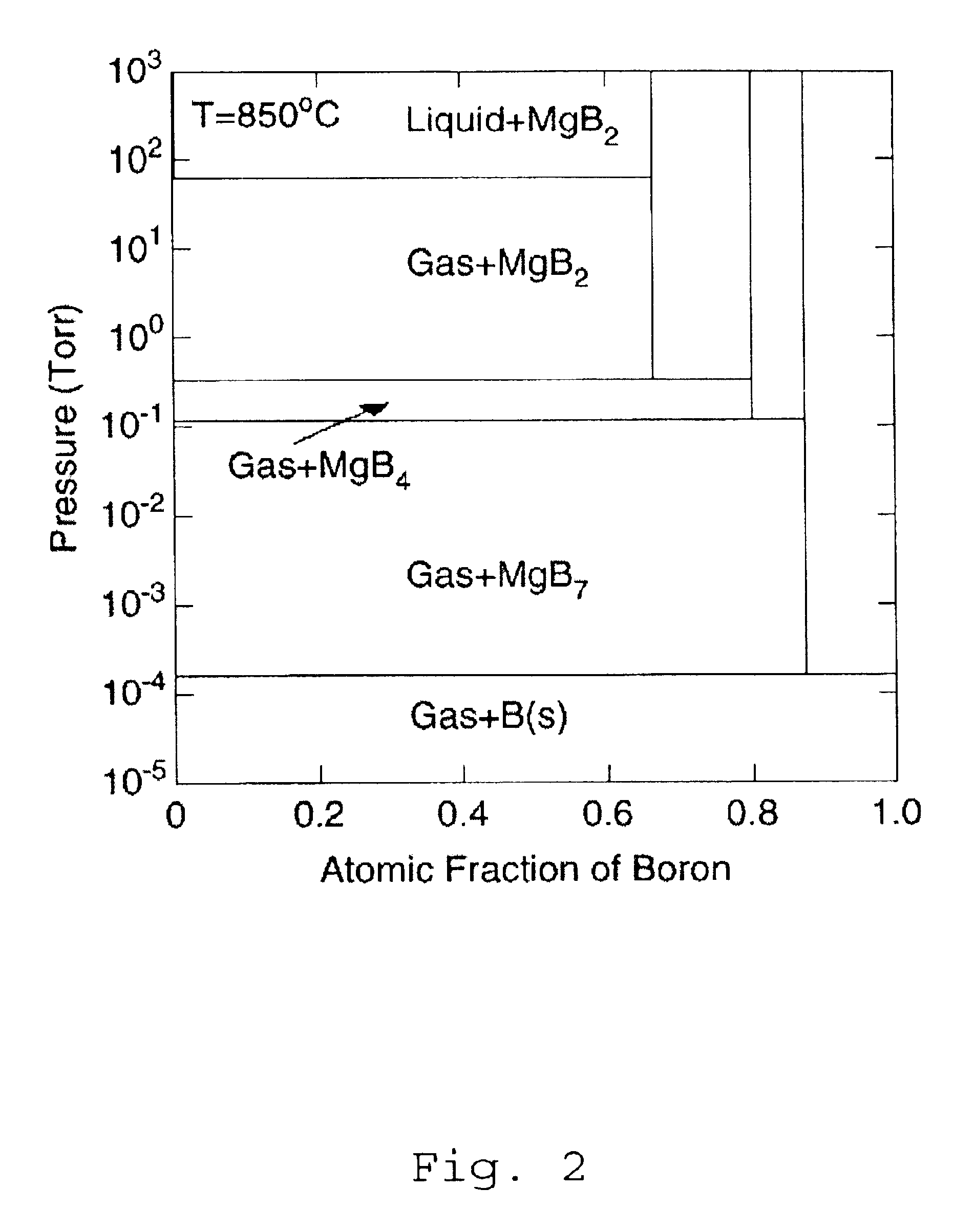
Method for producing boride thin films
InactiveUS6797341B2High purityReduce roughnessElectric discharge heatingVacuum evaporation coatingGas phaseBoron containing
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Use of perfluoroheptenes in power cycle systems
ActiveUS11220932B2High critical temperatureLow vapor pressureSteam engine plantsWorking fluidPower cycle
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Large-size corrosion resisting neodymium iron boron permanent magnetic material and manufacturing process thereof
ActiveCN101364464AHigh critical temperatureHigh densityInorganic material magnetismCorrosion resistantNeodymium iron boron
The invention discloses a large-size corrosion-resistant neodymium-ferrum-boron (Nd-Fe-B) permanent magnetic material and a preparation method thereof. The permanent magnetic material is characterized by the following metal elements (by weight percentage): Nd: x1%, Dy: x2%, Tb: x3%, Pr: x4%, Fe: y1%, Co: y2%, B: 0.9-1.1%, Cu: z1%, Al: z2%, and Ga: z3%; wherein x2 is higher than or equal to 0 and lower than or equal to 10, x3 is higher than or equal to 0 and lower than or equal to 5, x4 is higher than or equal to 0 and lower than or equal to 5, the sum of x1, x2, x3 and x4 is higher than or equal to 29 and lower than or equal to 33, y2 is higher than or equal to 0 and lower than or equal to 10, the sum of y1 and y2 is higher than or equal to 65 and lower than or equal to 69, z1 is higher than or equal to 0 and lower than or equal to 0.5, z2 is higher than or equal to 0 and lower than or equal to 1, and z3 is higher than or equal to 0 and lower than or equal to 1. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing the above elements and making into thin sheet alloy by using the rapid strip casing process, breaking, pulverizing to powder, press-forming under a parallel magnetic field and a vertical magnetic field, isostatic-pressing, and sintering to obtain the large-size corrosion-resistant Nd-Fe-B permanent magnetic material.
Owner:YANTAI DONGXING MAGNETIC MATERIALS INC
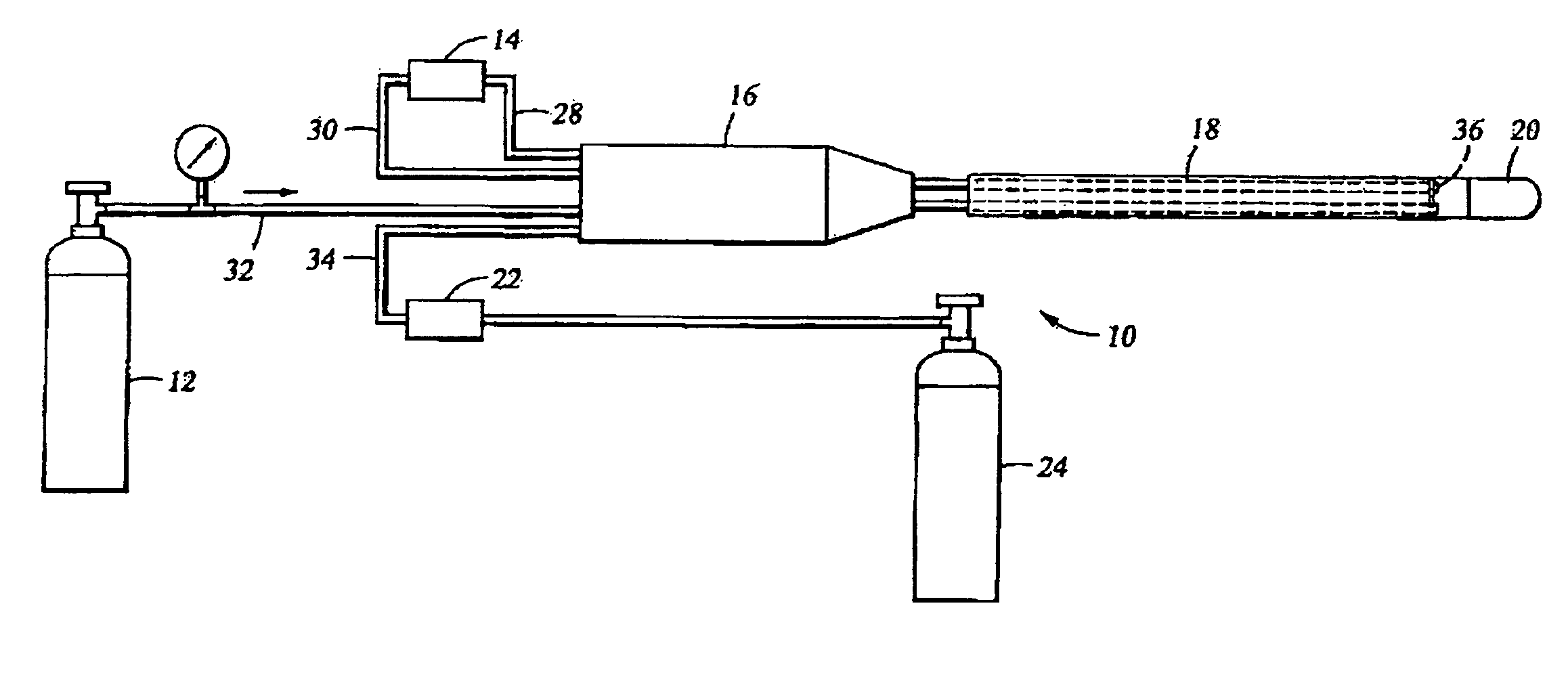
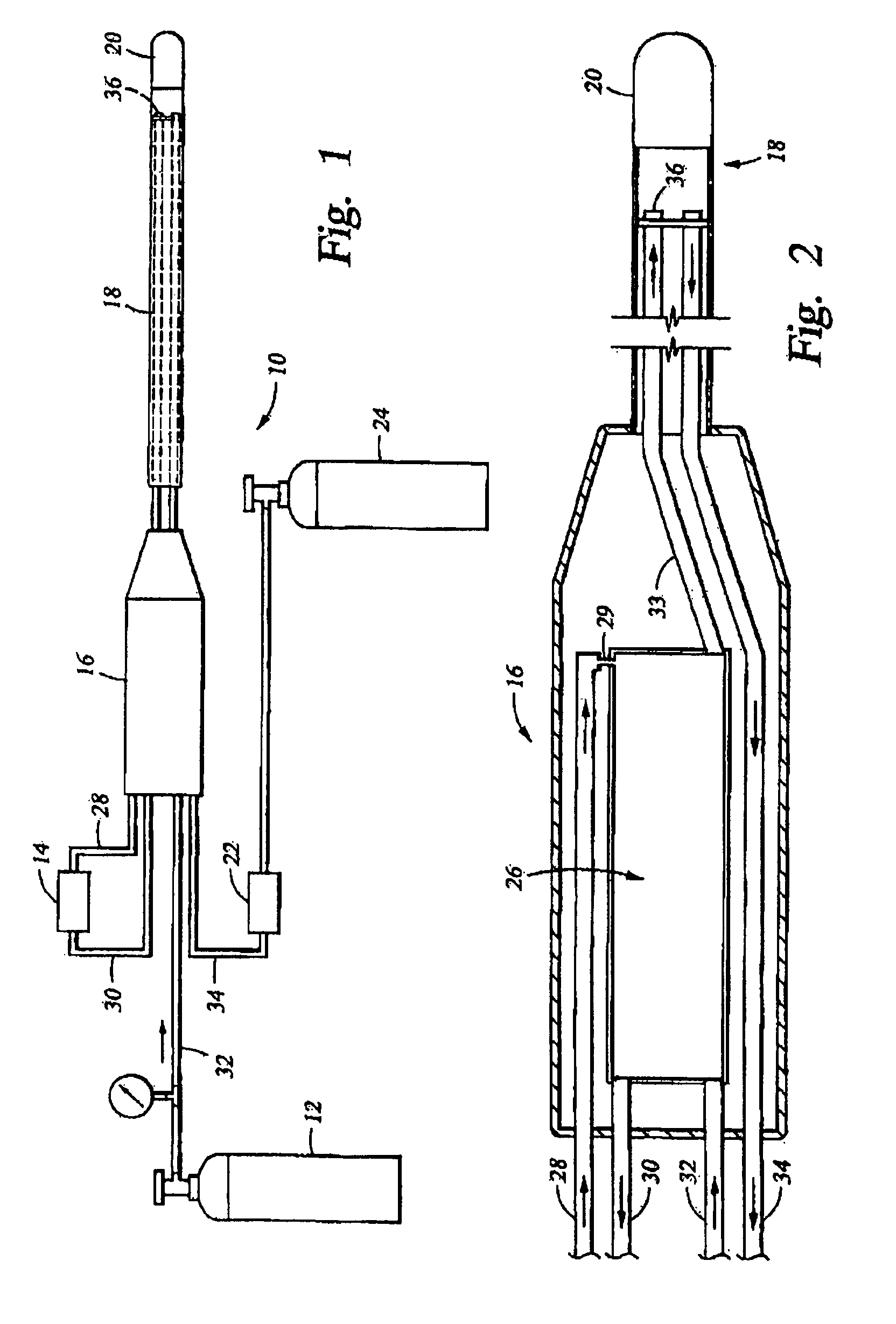
Precooled cryogenic ablation system
InactiveUSRE40049E1Available cooling powerReduce the temperatureDomestic cooling apparatusCatheterEngineeringCardiac blood vessel
A method and apparatus for using a secondary refrigerant to precool and liquefy a primary refrigerant, then vaporizing and expanding the primary refrigerant to cool a cold tip of a cryosurgical instrument for ablation of biological tissue, such as cardiovascular tissue, in particular endocardiac tissue and tissue inside a cardiac blood vessel. The secondary refrigerant has a critical temperature above the critical temperature of the primary refrigerant, and a cooling temperature below the critical temperature of the primary refrigerant, thereby facilitating the use of the precooling step to provide liquid primary refrigerant in an operating room environment in which the primary refrigerant could not otherwise be provided in the liquid phase.
Owner:COOPERSURGICAL INC
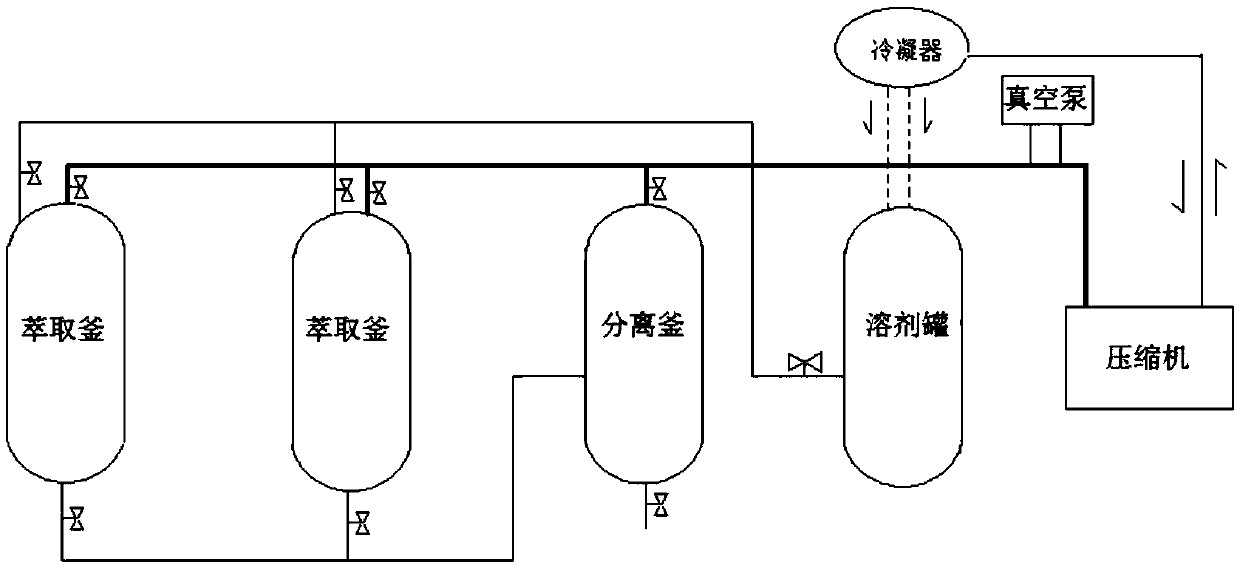
A method of extracting bay leaf oil from bay leaves with subcritical n-butane fluid
The invention relates to a method of extracting bay leaf oil from bay leaves with subcritical n-butane fluid. The method includes smashing, adding into a tank, dipping with an n-butane solvent, extracting, distilling, and the like. Extraction temperature and pressure can be accurately controlled by utilization of a subcritical extraction device. The method is high in extraction efficiency, low in device manufacturing cost, high in raw material treating amount, simple in process, low in production cost and free of solvent residue. A whole process of the method is performed at low temperature under an oxygen-free state. Extraction and separation are performed at the same time. The extraction speed is high. Recovery and reutilization of the solvent can be achieved.
Owner:郑州雪麦龙食品香料有限公司
On-board battery fire extinguishing structure using hybrid fire extinguishing agent
The invention discloses an on-board battery fire extinguishing structure using a hybrid fire extinguishing agent. The on-board battery fire extinguishing structure comprises a first fire extinguishing tank mounted outside a battery case, on-board batteries are fixed in the battery case, a spraying pipe of the first fire extinguishing tank is connected into the battery case, and the first fire extinguishing tank is filled with the fire extinguishing agent which is prepared from, by volume, 3%-40% of liquid-state hexafluoropropane, 3%-40% of liquid-state heptafluoropropane and the balance of liquid-state carbon dioxide through mixing. The on-board battery fire extinguishing structure has the advantages of physical fire extinguishing and chemical fire extinguishing.
Owner:ZEPHYR INTELLIGENT SYST SHANGHAI CO LTD
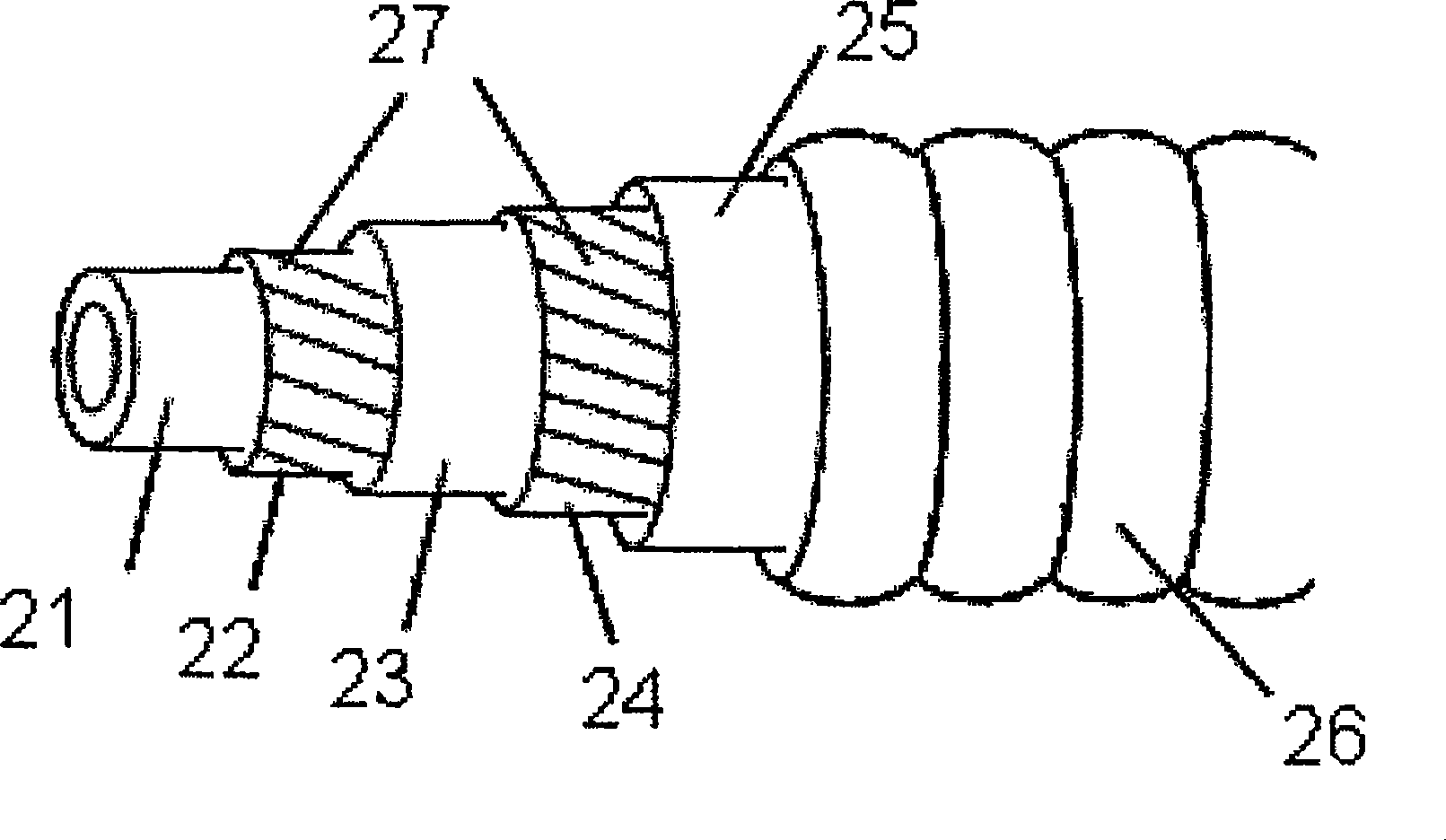
SUPERCONDUCTIVE ELEMENT CONTAINING Nb3Sn
InactiveUS20070238620A1Improve superconductivityHigh critical temperatureSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentHigh critical temperatureMetallic materials
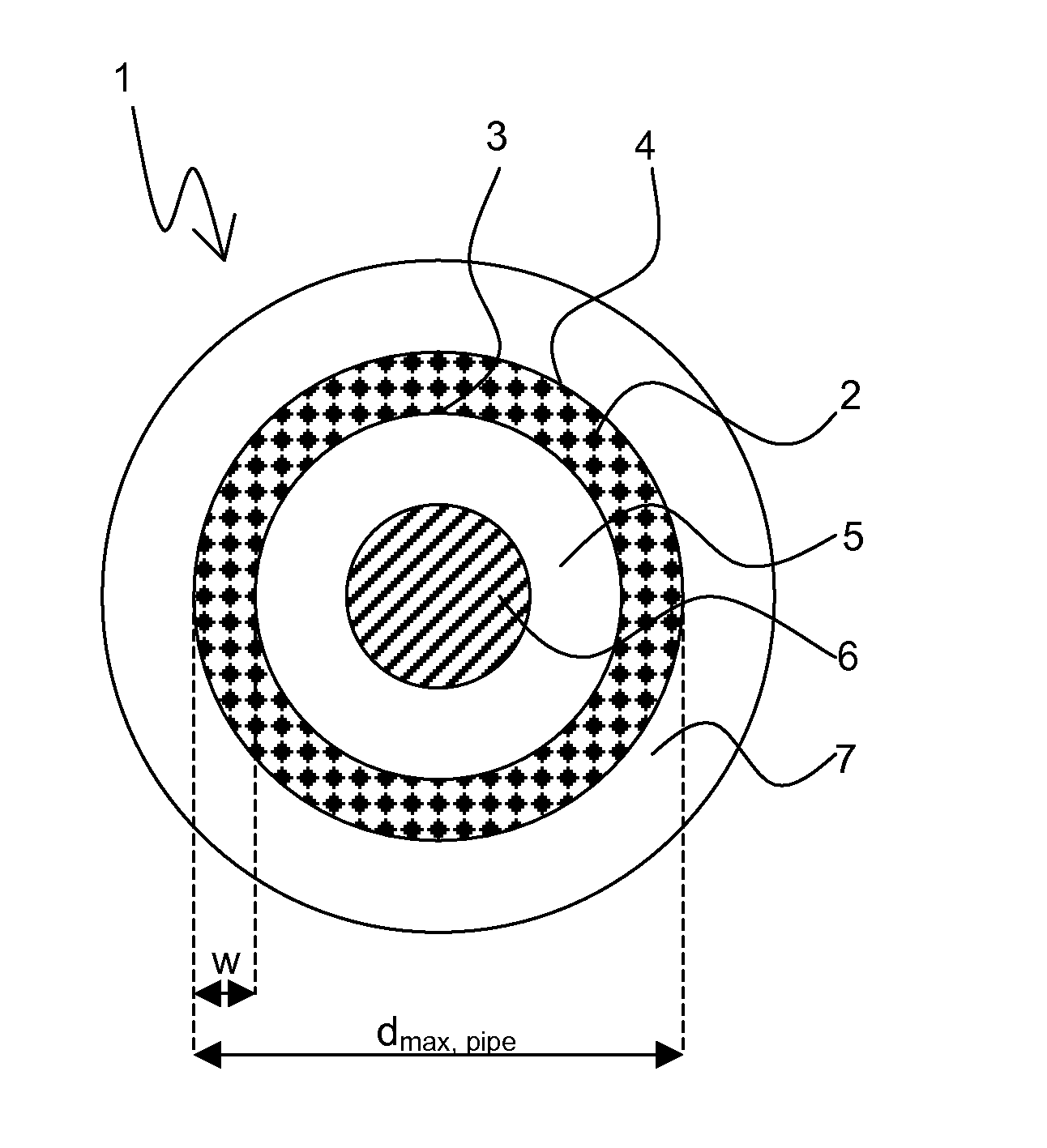
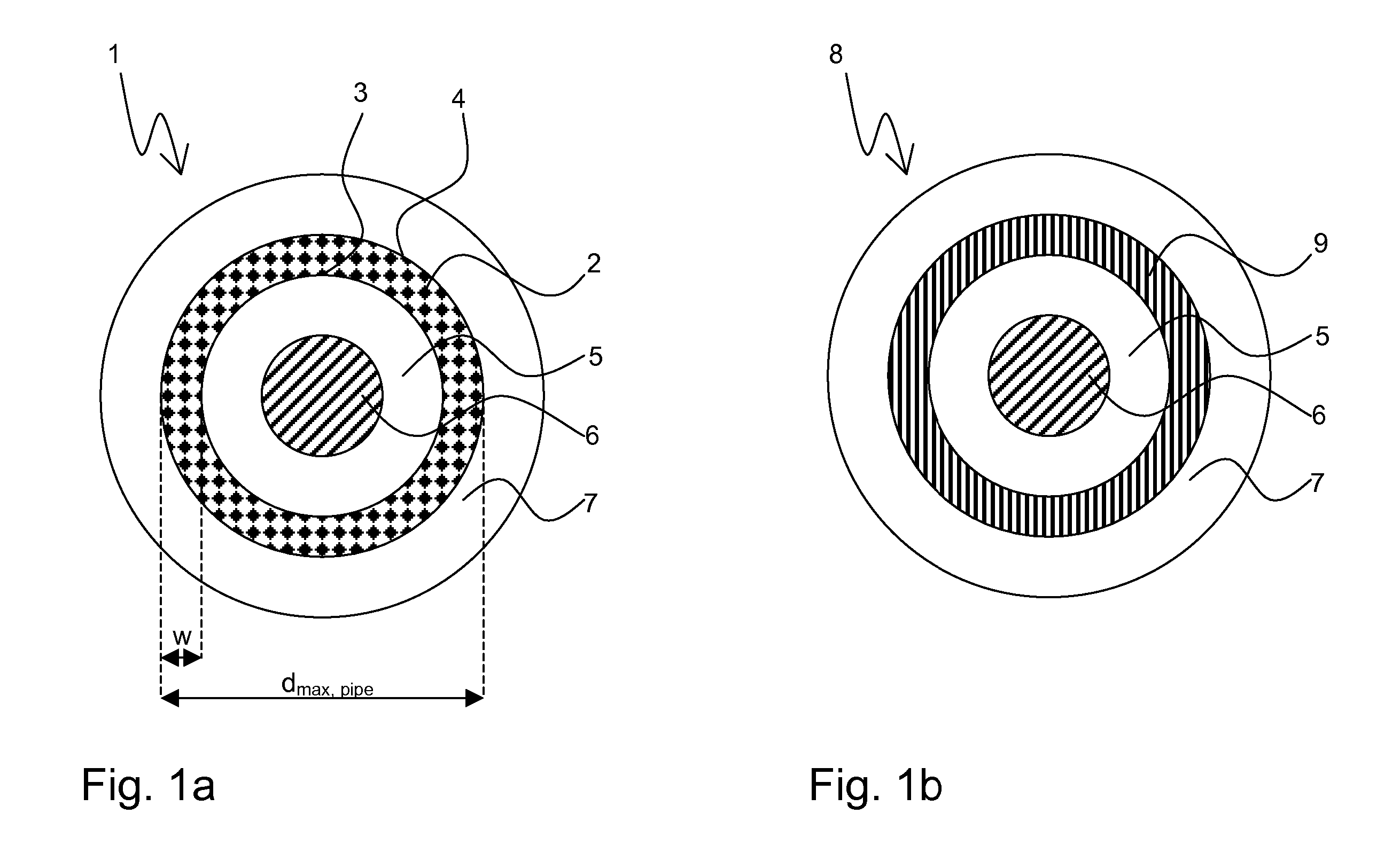
A superconductive element containing Nb3Sn, in particular a multifilament wire, comprising at least one superconductive filament (8) which is obtained by a solid state diffusion reaction from a preliminary filament structure (1), said preliminary filament structure (1) containing an elongated hollow pipe (2) having an inner surface (3) and an outer surface (4), wherein said hollow pipe (2) consists of Nb or an Nb alloy, in particular NbTa, wherein the outer surface (4) is in close contact with a surrounding bronze matrix (5) containing Cu and Sn, and wherein the inner surface (3) is in close contact with an inner bronze matrix (5) also containing Cu and Sn, is characterized in that the inner bronze matrix (5) of the preliminary filament structure (1) encloses in its central region an elongated core (6) consisting of a metallic material, said metallic material having at room temperature (=RT) a thermal expansion coefficient αcore<17*10−6K−1, preferably αcore≦8*10−6 K−1, said metallic material having at RT a yield strength Rp0.2>300 MPa, said metallic material having at RT an elongation at rupture A>20%, and wherein the metallic material of the core (6) is chemically inert with respect to the material of the inner bronze matrix (5) up to a reaction temperature T of the solid state diffusion reaction. This element has improved superconductive properties in a large volume fraction of its superconductive filaments, in particular a high critical temperature Tc and a high critical magnetic filed strength Bc2, and is mechanically stable enough for commercial applications such as magnet coils.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
Josephson device, method of forming Josephson device and superconductor circuit
InactiveUS8032196B2Improve IcRn productSuppress inconsistencySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsOxygenMaterials science
A Josephson device includes a first superconducting electrode layer, a barrier layer and a second superconducting electrode layer that are successively stacked. The first and second superconducting electrode layers are made of an oxide superconductor material having (RE)1(AE)2Cu3Oy as a main component, where an element RE is at least one element selected from a group consisting of Y, La, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb and Lu, and an element AE is at least one element selected from a group consisting of Ba, Sr and Ca. The barrier layer is made of a material that includes the element RE, the element AE, Cu and oxygen, where in cations within the material forming the barrier layer, a Cu content is in a range of 35 At. % to 55 At. % and an RE content is in a range of 12 At. % to 30 At. %, and the barrier layer has a composition different from compositions of the first and second superconducting electrode layers.
Owner:THE CHUGOKU ELECTRIC POWER CO INC +1
Gas turbine engine with cooling system
ActiveUS9759130B2Preventing pyrolysis and cokingPrevent degradationTurbine/propulsion engine coolingEngine fuctionsThermal contactGas turbines
A cooling system for a gas turbine engine. The system includes a fuel air heat exchanger with a fuel passage that is in thermal contact with an engine cooling air passage. The system further includes a fuel deoxygenator located upstream of the fuel air heat exchanger and configured to deliver deoxygenated fuel to the fuel air heat exchanger fuel passage. The system also includes a valve configured to moderate engine cooling air flow to the engine cooling air passage.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Household appliance containing a heat transfer fluid
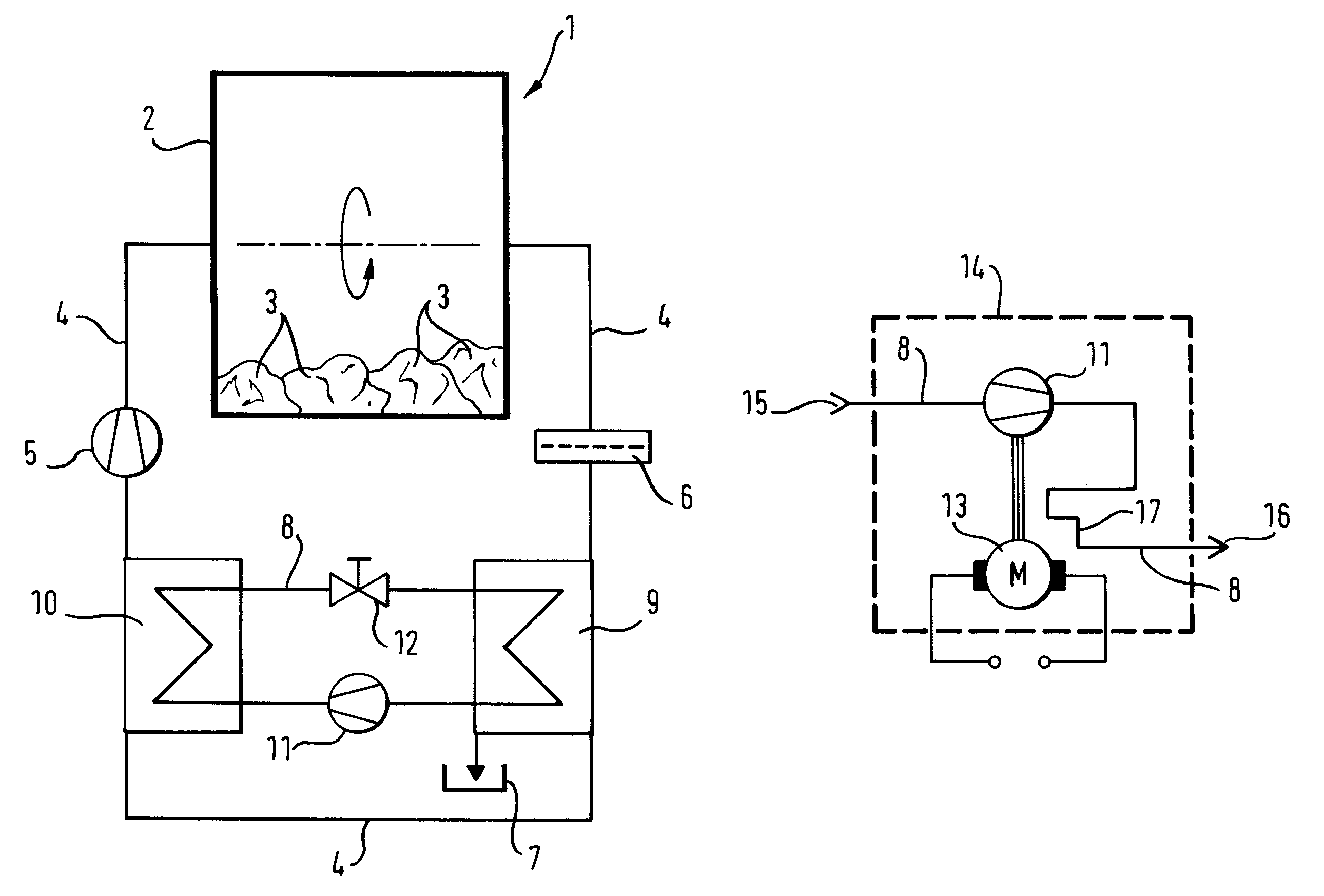
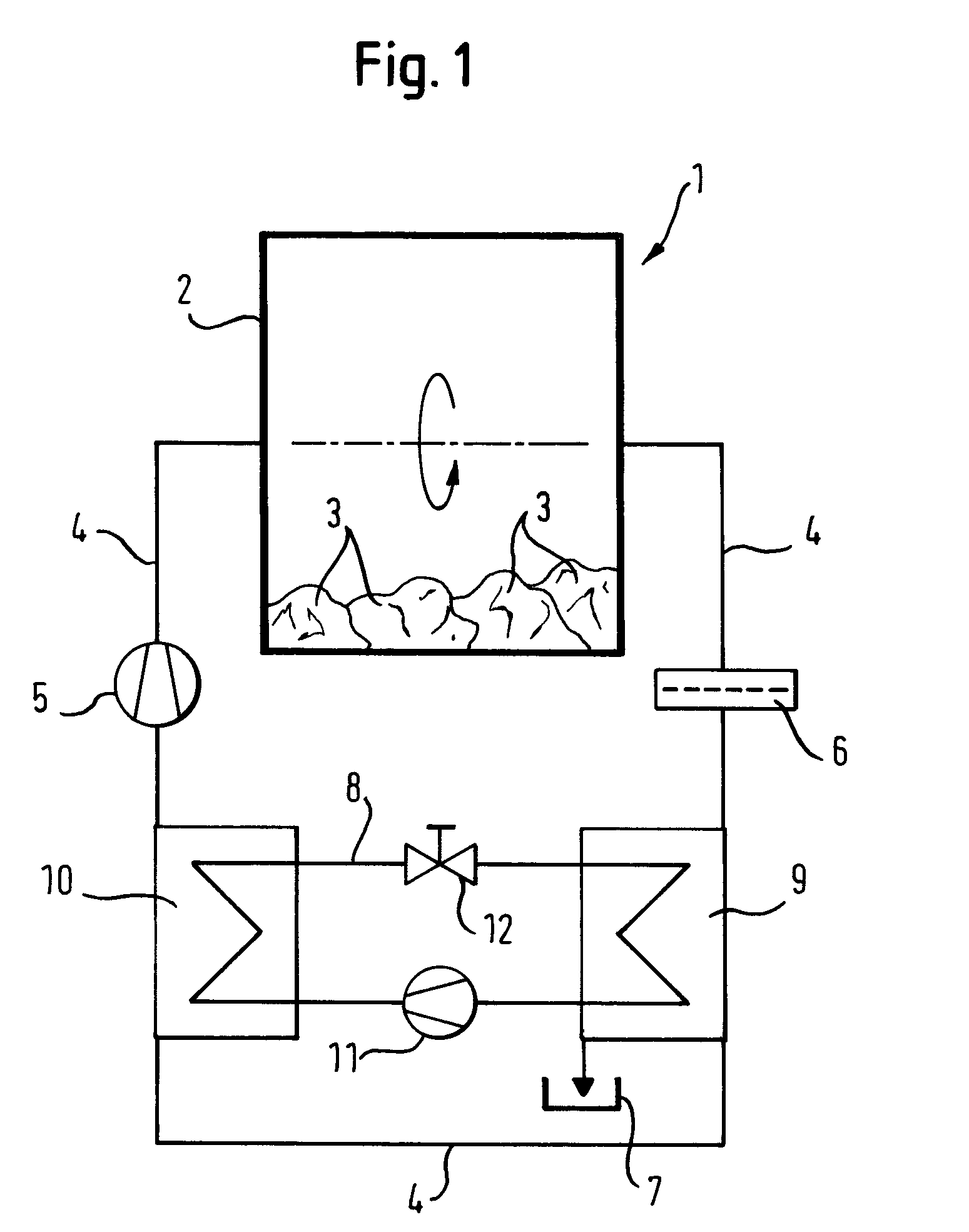
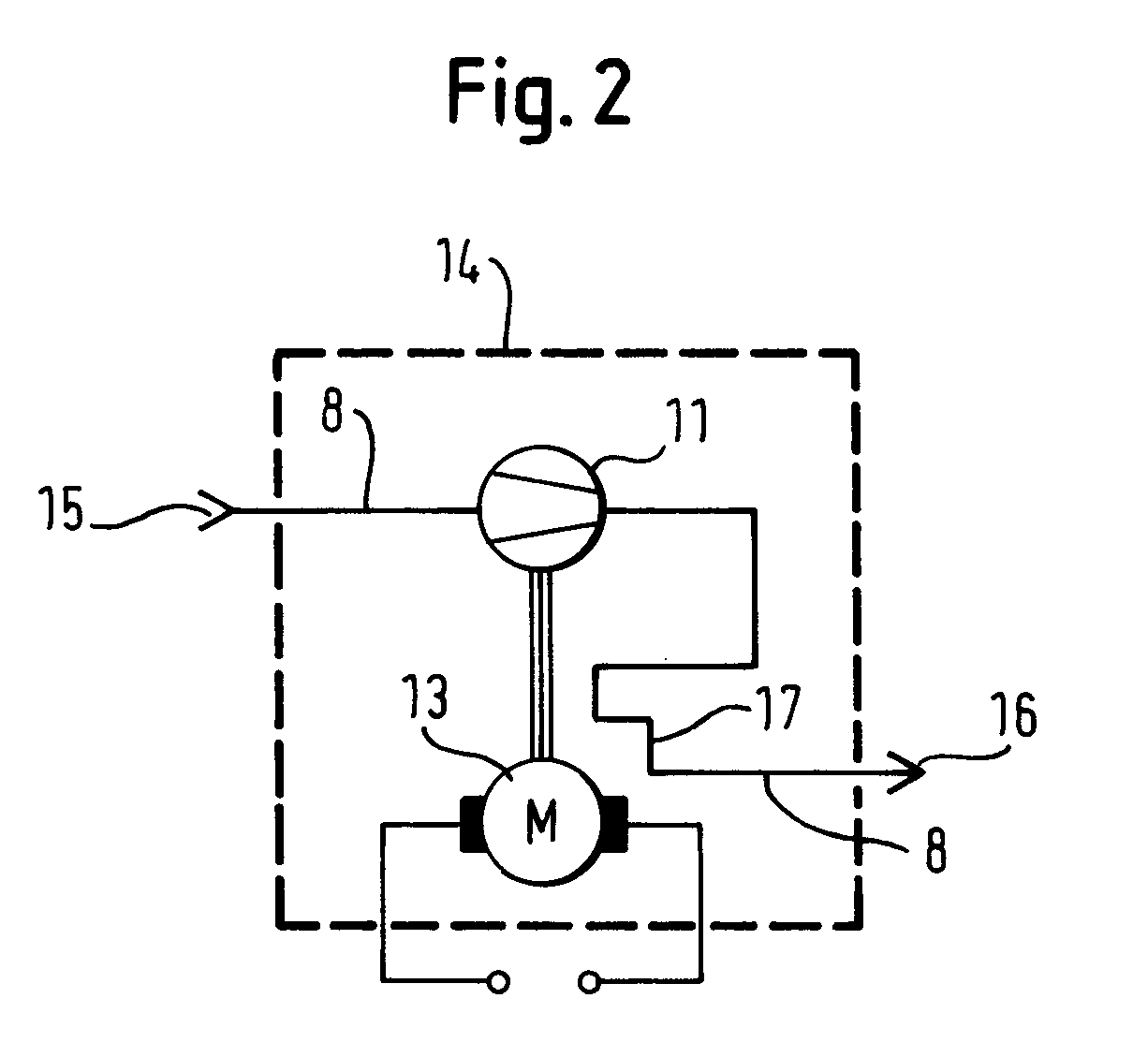
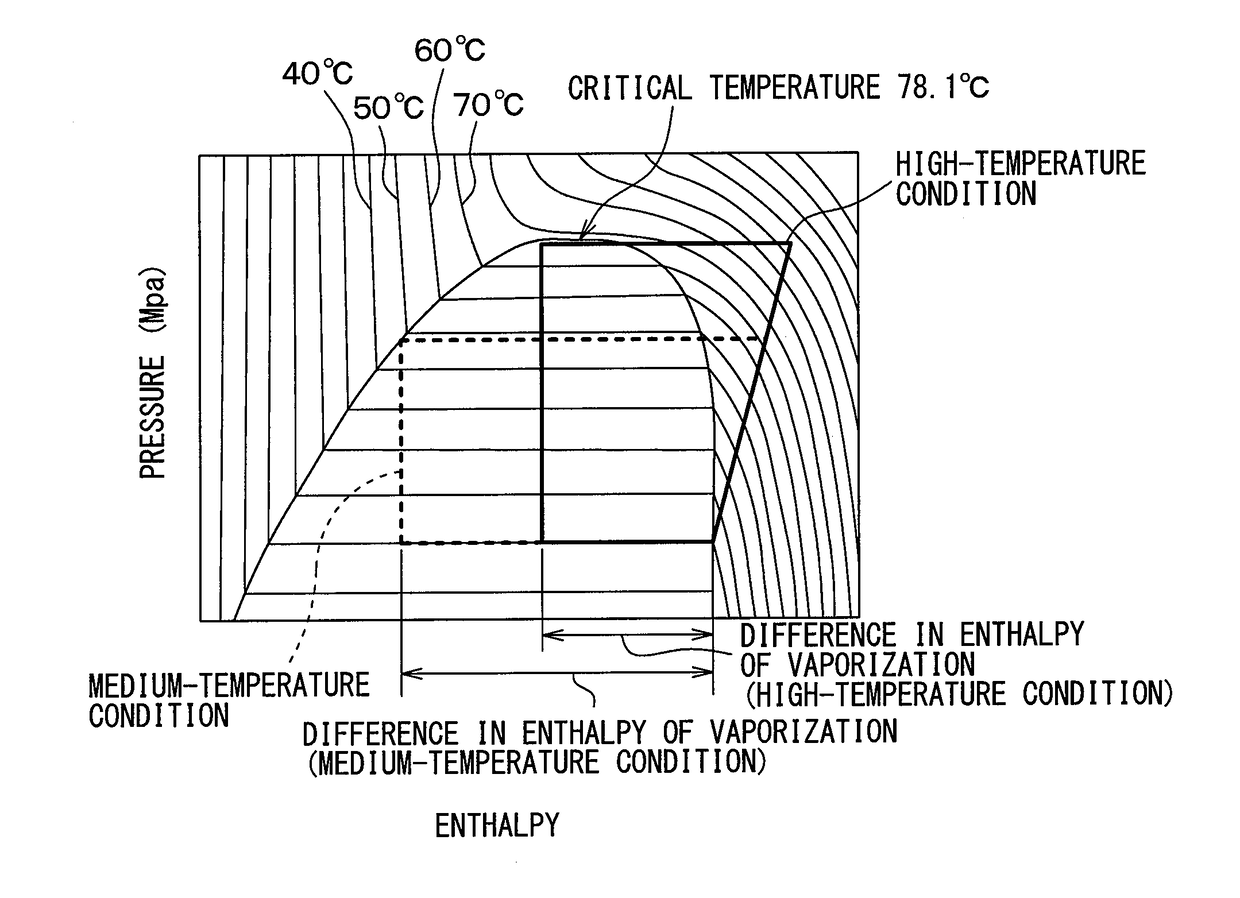
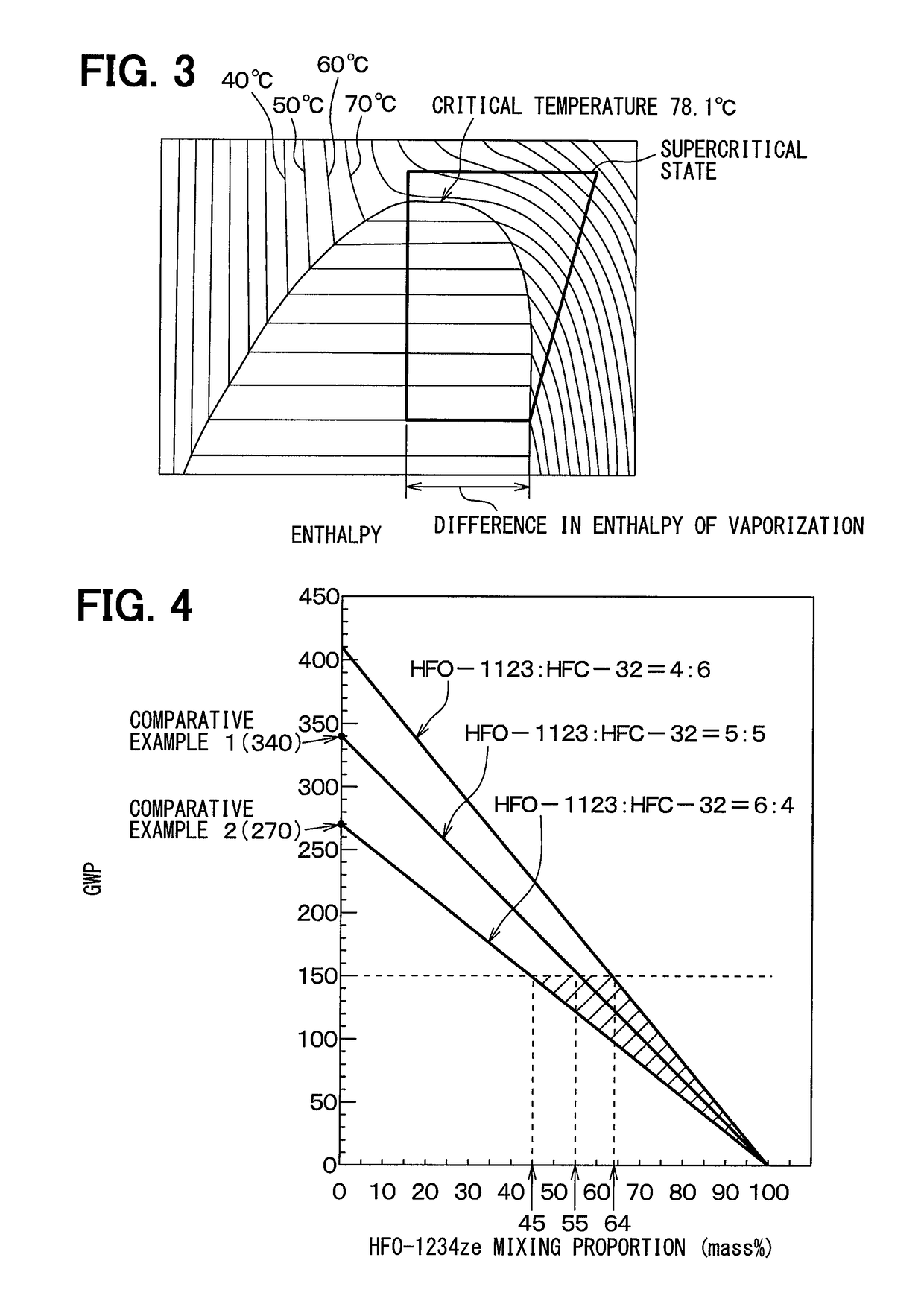
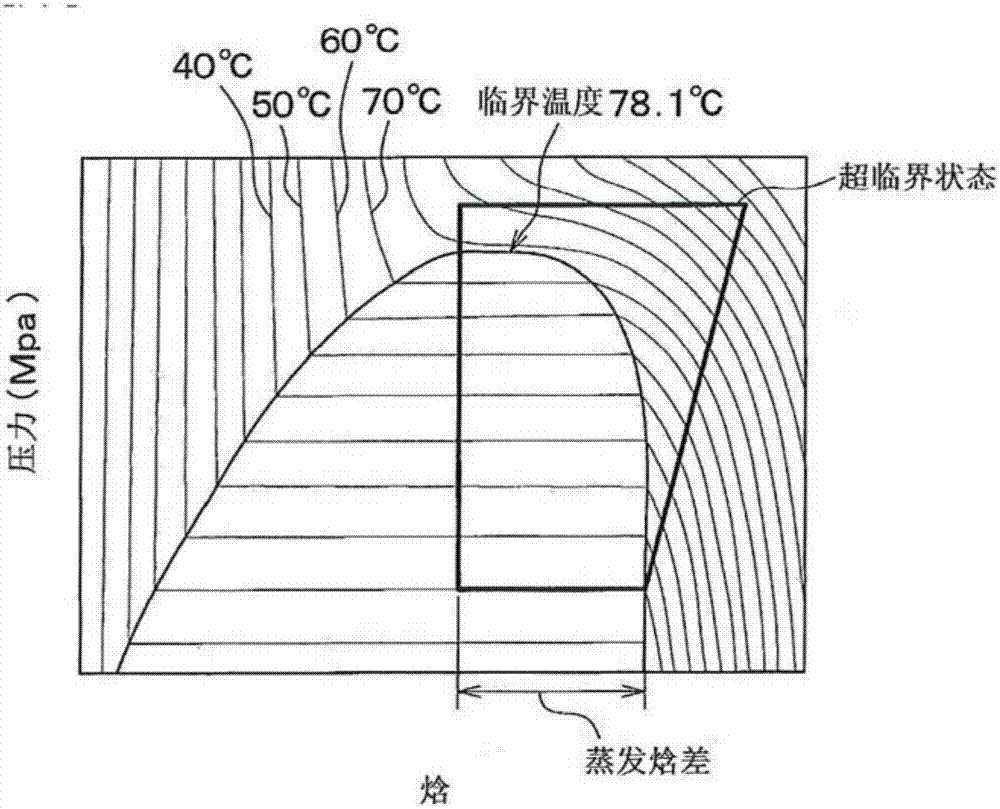
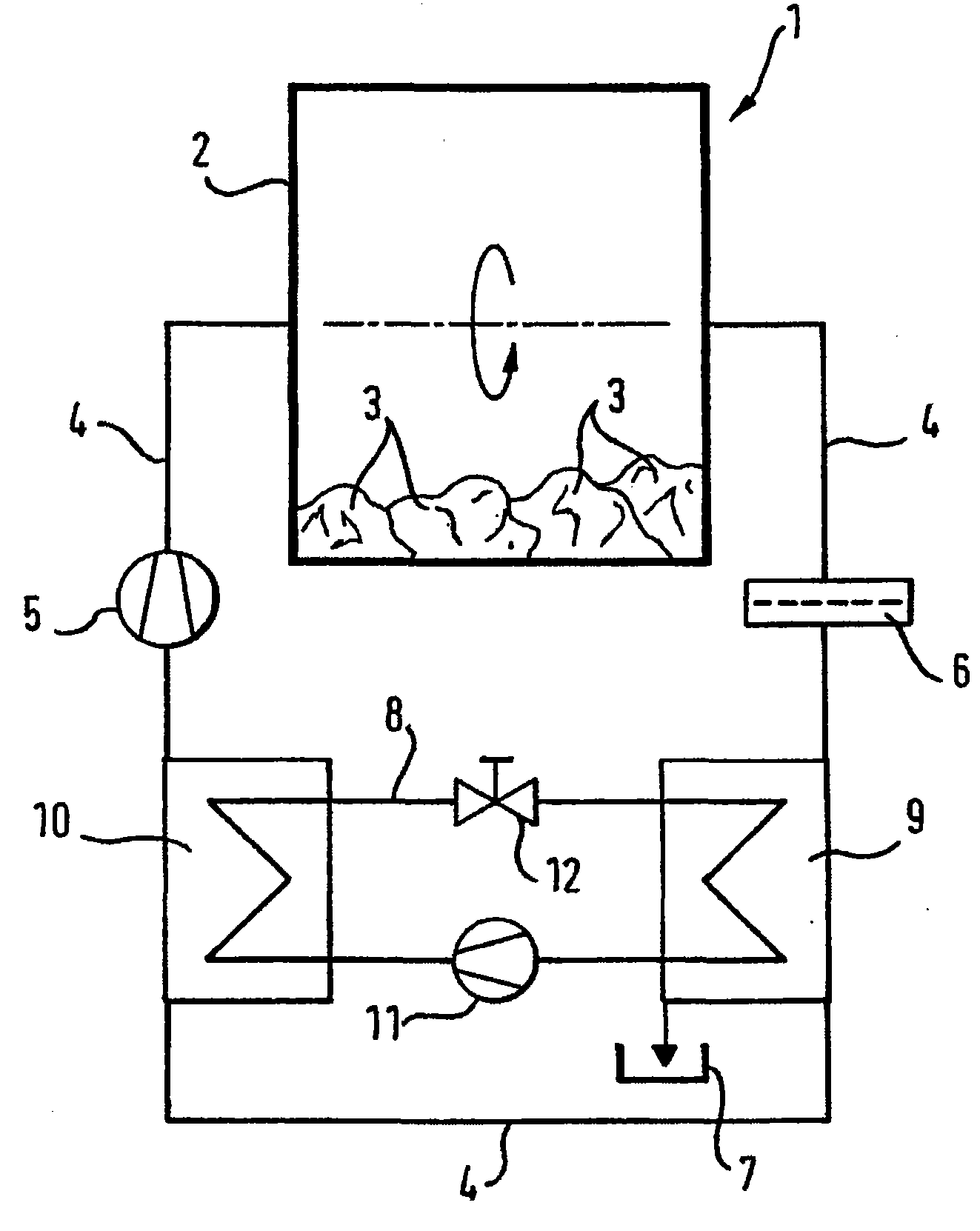
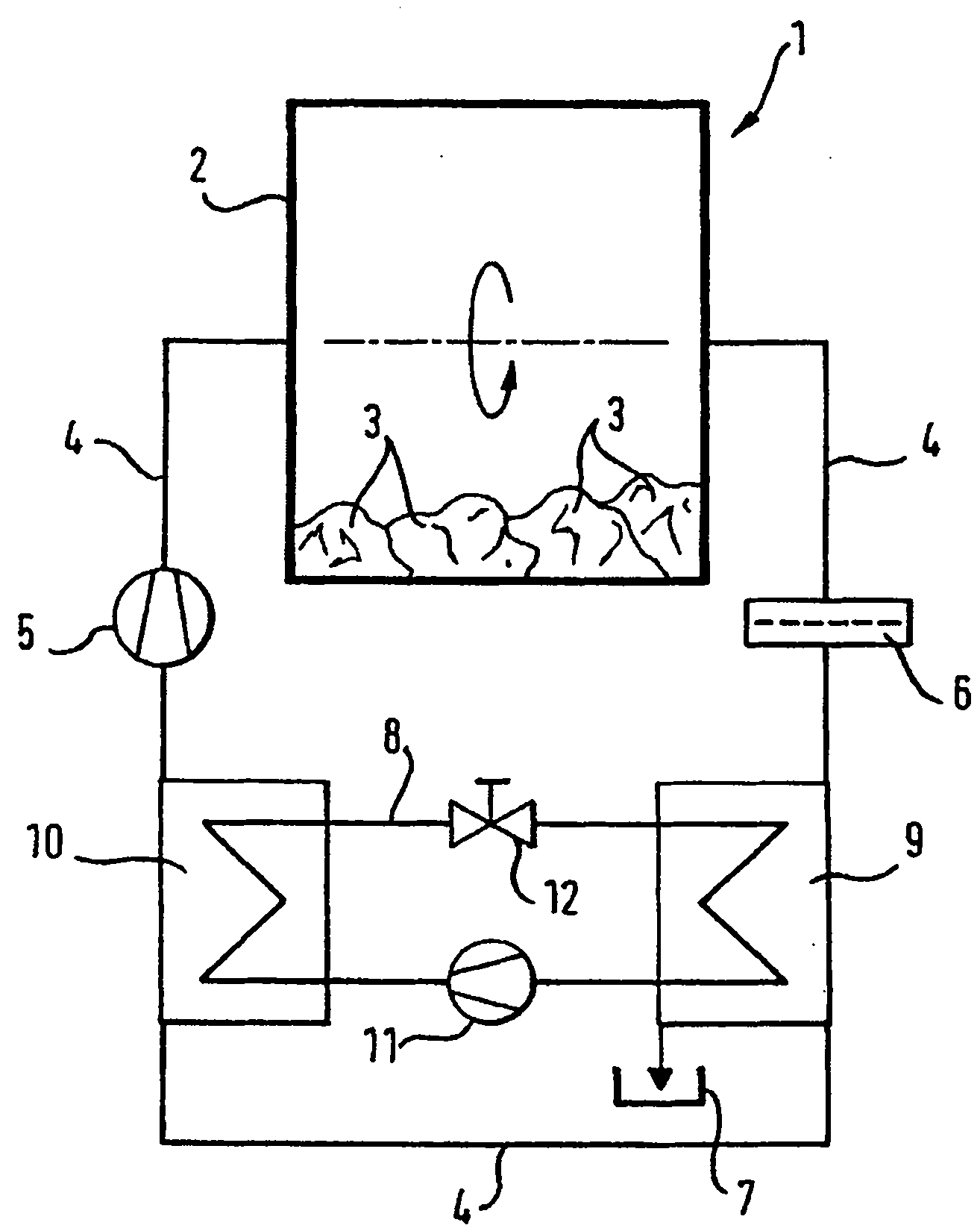
InactiveUS8356423B2High degree of temperature controlEasy temperature controlAir-treating devicesHeat pumpsBoiling pointVaporization
A household appliance includes a drying chamber, a process air loop and a heat pump. The heat pump includes a heat transfer loop containing a heat transfer fluid, an evaporator heat exchanger, a liquefier heat exchanger, a compressor, and a nozzle. The heat transfer fluid has a critical temperature above 60° C., a nominal heat of vaporization at boiling point of at least 220 kJ / kg, a GWP index of less than 150 and a lower flammability level of at least 0.1 kg / m3. Preferably, the household appliance is a dryer for drying wet laundry.
Owner:BSH BOSCH & SIEMENS HAUSGERAETE GMBH
Josephson device, method of forming Josephson device and superconductor circuit
ActiveUS20080051292A1Improve IcRn productSuppress inconsistencySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsOxygenMaterials science
A Josephson device includes a first superconducting electrode layer, a barrier layer and a second superconducting electrode layer that are successively stacked. The first and second superconducting electrode layers are made of an oxide superconductor material having (RE)1(AE)2Cu3Oy as a main component, where an element RE is at least one element selected from a group consisting of Y, La, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb and Lu, and an element AE is at least one element selected from a group consisting of Ba, Sr and Ca. The barrier layer is made of a material that includes the element RE, the element AE, Cu and oxygen, where in cations within the material forming the barrier layer, a Cu content is in a range of 35 At. % to 55 At. % and an RE content is in a range of 12 At. % to 30 At. %, and the barrier layer has a composition different from compositions of the first and second superconducting electrode layers.
Owner:THE CHUGOKU ELECTRIC POWER CO INC +1
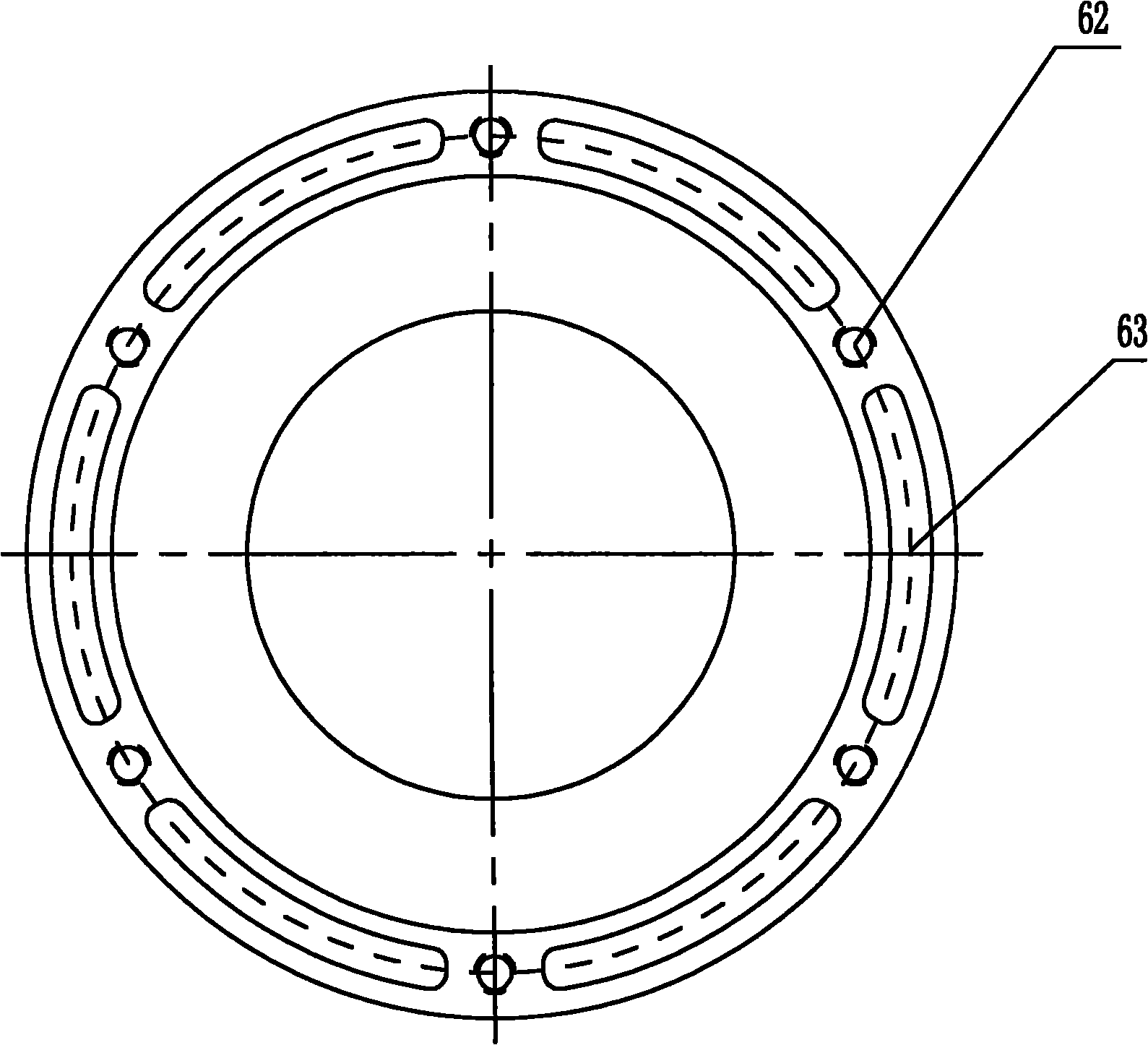
High-temperature resistant pump
The invention discloses a high-temperature resistant pump comprising a pump body, an impeller, a shaft sleeve, a pump shaft and a pump cover, wherein the pump body is U shaped and is installed on the shaft sleeve; the shaft sleeve and the impeller are arranged on the pump shaft; the impeller is positioned in the groove of the pump body; the pump cover is connected to the front end of the pump body; the pump shaft is connected with the main shaft of a motor; a shaft cooling sleeve and a fan are arranged between the pump body and the motor in sequence; the shaft cooling sleeve is connected with the pump body; the middle part of the shaft cooling sleeve is fully cylindrical, and round cooling fins are evenly distributed at the periphery of the shaft cooling sleeve; a shell is arranged outside the shaft cooling sleeve; two ends of the shell are respectively connected with the motor and the pump body; and a mechanical sealing element is arranged between the shaft cooling sleeve and the fan and on the shaft cooling sleeve. The high temperature-resistant pump has simple structure, low cost and long service life and is simple to manufacture and maintain.
Owner:福建省福安市力德泵业有限公司
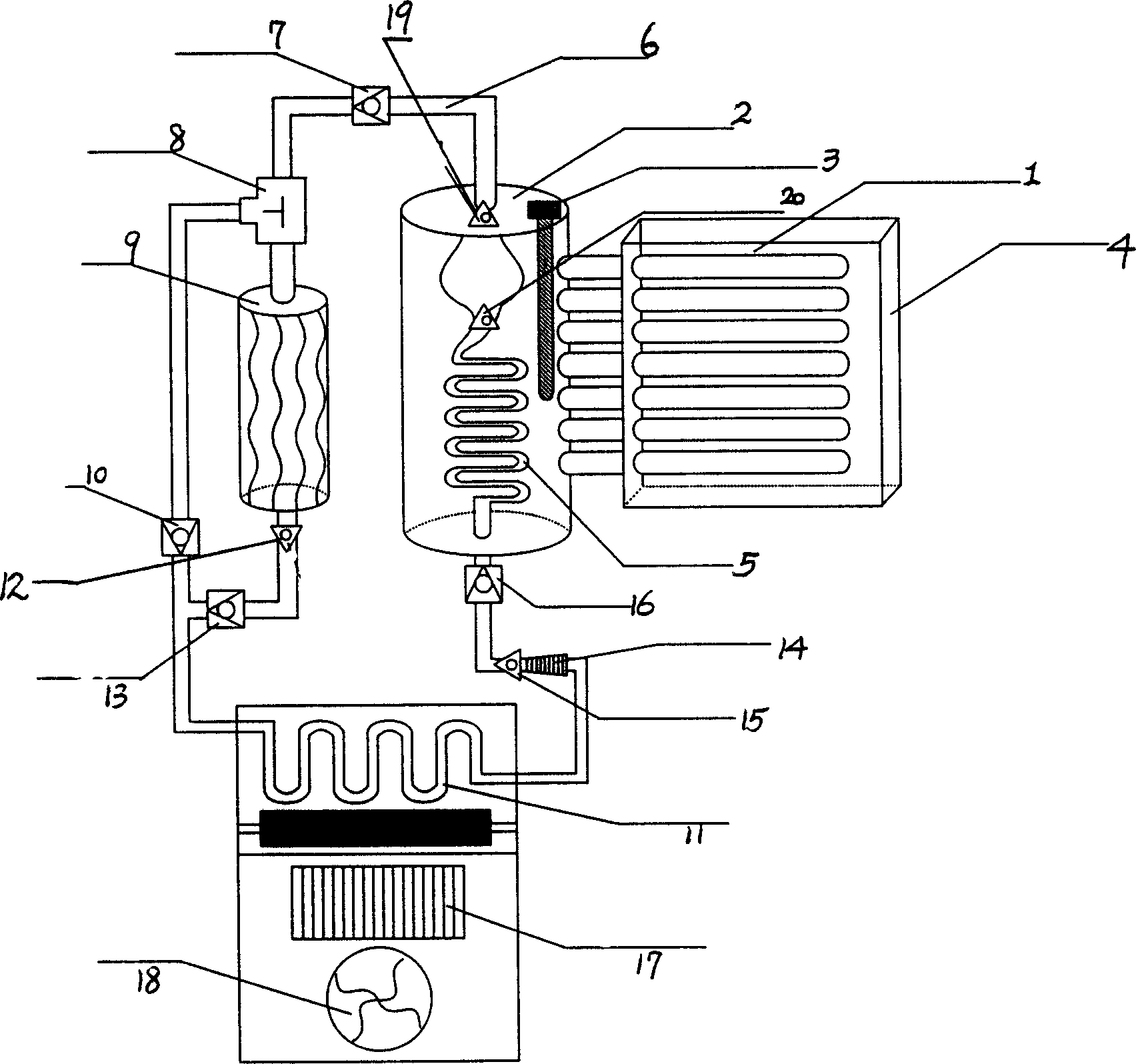
Solar cooling-heating air-conditioner
InactiveCN1584430ALow critical pressureHigh critical temperatureSolar heat devicesAir conditioning systemsClosed loopEngineering
A solar air conditioner consists of tubular energy collectors, an energy-storing part, an automatic light-electric inter-compensator, an exchanger, one-way valves, solenoid three-way valves, a condenser, a distiller, a pressure-reducing throttle valve, an enhancer, pressure-regulating valves, a relay console, a blower, and conveying and conducting pipes. Its outdoor unit consists of the tubular energy collectors and energy storing part with the exchanger and the automatic light-electric inter-compensator inside. The exchanger is connected with the condenser and then enhancer via one-way valves and solenoid three-way valves and pressure-regulating valves. The distiller with the relay console and blower is connected with the condenser and enhancer at both ends of the distiller respectively. The said inter-compensator is connected with relay console via electric wires. The conveying and conducting pipes make connection of all parts. It has a simple structure, saves energy, runs in a closed loop at low cost stably and durably, without media loss and noise, and is easy to be used widely.
Owner:张勇
Superconducting oxide material, process for producing the same, and superconducting wire and superconduction apparatus both employing the superconducting material
InactiveCN101401171AHigh critical temperatureImprove performanceSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesHigh critical temperatureStrontium
A process for producing a (Bi,Pb)2Sr2Ca2Cu3Oz superconducting oxide material which comprises a step in which raw materials are mixed and two or more heat treatment steps in which the mixed materials are heat-treated. The heat treatment steps comprise a first heat treatment step in which (Bi,Pb)-2223 crystals are formed and a second heat treatment step in which after the formation of the (Bi,Pb)-2223 crystals, the strontium content in the (Bi,Pb)-2223 crystals is heightened. The second heat treatment step is conducted at a lower temperature than the first heat treatment step. Thus, a (Bi,Pb)-2223 type superconducting oxide material having a high critical temperature is obtained.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Working medium for heat cycle
InactiveUS20170369754A1Low GWPsHigh critical temperatureCompression machines with non-reversible cycleHeat-exchange elementsProcess engineeringEngineering
Owner:DENSO CORP
Novel power cycle mixed working medium taking CO2 as main component, as well as system and method thereof
ActiveCN103937459AHigh critical temperatureLow critical pressureHeat-exchange elementsButenePower cycle
The invention relates to the technical field of power machinery, and discloses a novel power cycle mixed working medium taking CO2 as a main component, as well as a system and a method thereof. The mixed working medium is prepared by physically mixing CO2 with one of propane, cyclopropane, propyne, butane, iso-butane, cis-butene, trans-butene and cyclopentane at certain proportion. The mixed working medium takes CO2 as a main component and one of propane, cyclopropane, propyne, butane, iso-butane, cis-butene, trans-butene and cyclopentane as a second component, so that the mixed working medium can be condensed by the conventional cooling water, and the working medium also has lower flammability. When being used for exchanging heat with a heat source fluid, the mixed working medium has better temperature matching, and the cycling has higher efficiency.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Superconductive element containing Nb3Sn
InactiveUS7505800B2Improve superconductivityIncrease in sizeSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentThermal dilatationMetallic materials
A superconductive element containing Nb3Sn, in particular a multifilament wire, comprising at least one superconductive filament (8) which is obtained by a solid state diffusion reaction from a preliminary filament structure (1), said preliminary filament structure (1) containing an elongated hollow pipe (2) having an inner surface (3) and an outer surface (4), wherein said hollow pipe (2) consists of Nb or an Nb alloy, in particular NbTa, wherein the outer surface (4) is in close contact with a surrounding bronze matrix (5) containing Cu and Sn, and wherein the inner surface (3) is in close contact with an inner bronze matrix (5) also containing Cu and Sn, is characterized in that the inner bronze matrix (5) of the preliminary filament structure (1) encloses in its central region an elongated core (6) consisting of a metallic material, said metallic material having at room temperature (=RT) a thermal expansion coefficient alphacore<17*10-6K-1, preferably alphacore<=8*10-6 K-1, said metallic material having at RT a yield strength Rp0,2>300 MPa, said metallic material having at RT an elongation at rupture A>20%, and wherein the metallic material of the core (6) is chemically inert with respect to the material of the inner bronze matrix (5) up to a reaction temperature T of the solid state diffusion reaction. This element has improved superconductive properties in a large volume fraction of its superconductive filaments, in particular a high critical temperature Tc and a high critical magnetic filed strength Bc2, and is mechanically stable enough for commercial applications such as magnet coils.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
Graphene / doped two-dimensional layered material Van der Waals heterojunction superconducting composite structure, superconducting device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN110429174AIncrease concentrationIncrease contactSuperconductor detailsDissimilar materials junction devicesHeterojunctionHigh critical temperature
The invention provides a graphene / doped two-dimensional layered material Van der Waals heterojunction superconducting composite structure, a superconducting device and a manufacturing method thereofand relates to the superconducting material technology field. A graphene layer and a layered structure of 2n + 1 layers formed by alternative doped two-dimensional layered materials are included. Anouter layer of the layered structure is the graphene layer, and the n is an integer of 1 to 50. A region where graphene and the doped two-dimensional layered material are completely overlapped vertically forms a superconducting region. The graphene layer and the doped two-dimensional layered material are self-assembled into one body by a Van der Waals force. A defect that an existing Van der Waalsheterojunction superconducting material can only work at an extremely low temperature is solved. The graphene / doped two-dimensional layered material heterojunction superconducting material has a simple structure, excellent performance, a high critical temperature and a high critical magnetic field, low material cost, and good mechanical and machining performance.
Owner:孙旭阳
Beryllium-containing ceramic precursor preparation method
The present invention provides a beryllium-containing ceramic precursor preparation method, which comprises: dissolving polycarbosilane and beryllium 2,4-pentanedionate in a solvent, uniformly mixing, and distilling to remove the solvent to obtain a mixture; and under a protection atmosphere, heating the mixture, and carrying out a coupling reaction to obtain the beryllium-containing ceramic precursor. According to the present invention, the prepared beryllium-containing ceramic precursor has characteristics of high thermal decomposition stability, simple preparation method and low cost, and meets the industrial production requirements.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Delayed breaker for viscoelastic surfactant-based fluids
ActiveCN107109198AHigh critical temperatureCompression machines with non-reversible cycleHeat-exchange elementsBetaineFluid composition
Compositions and methods are provided for delayed breaking of viscoelastic surfactant gels inside subterranean formations. Breaking is accomplished without mechanical intervention or use of a second fluid. The delayed breaking agent is selected from alkyl ether phosphates and salts thereof, alkylaryl ether phosphates and salts thereof, alkyl sulfates and salts thereof, alkylaryl sulfates and salts thereof, alkyl ether sulfates and salts thereof, alkylaryl ether sulfates and salts thereof, and mixtures of any of the foregoing. The viscoelastic surfactant can be a zwitterionic surfactant, and can be selected from the group consisting of sultaines, betaines, and amidoamine oxides.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Hunger-type indirect solar air conditioner
InactiveCN1710346ALow critical pressureHigh critical temperatureLighting and heating apparatusAir conditioning systemsLight pipeSolenoid valve
An air conditioner of indirect solar energy is composed of light pipe receiver , energy accumulator , exchanger , four - way solenoid valve , condenser , evaporator , booster , pressure release gate valve , pressure release and charging valve , fan , relay control panel and transfusion pipe . It features connecting light pipe receiver to energy accumulator in parallel for forming energy receiver outdoor, setting exchanger connected respectively with condenser and four - way solenoid valve at top and bottom in energy accumulator and connecting evaporator to condenser and four - way solenoid valve separately through transfusion pipe.
Owner:张勇
Preparation method of Bi-2212 high-temperature superconductive thick film
InactiveCN102509762AEasy to prepareGood process repeatabilitySuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentOrganic solventMicrometer
The invention discloses a preparation method of a Bi-2212 high-temperature superconductive thick film, which includes the following steps: firstly, dissolving binder into organic solvent and then adding Bi-2212 powder to obtain turbid liquid; secondly, coating the turbid liquid on a scrubbed metal base band through a dip-coating method, and then drying the base band; thirdly, cold pressing the metal base band which is dried through a cold press under the pressure of 15MPa-20MPa for 10-20min; and fourthly, sintering the cold-pressed metal base band in pure oxygen to obtain a Bi-2212 superconductive thick film with the thickness of 10-80 micrometers. The cold press is adopted to cold press the Bi-2212 thick film prepared through the dip-coating method, the density of the Bi-2212 superconductive layer of the film is increased under the premise of not damaging the superconductive layer, thereby the effective current carrying area of the superconductive layer is increased and the engineering current density of the Bi-2212 thick film is increased.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
Anti-oxidation and anti-thermal fatigue hot working die steel and manufacturing method thereof
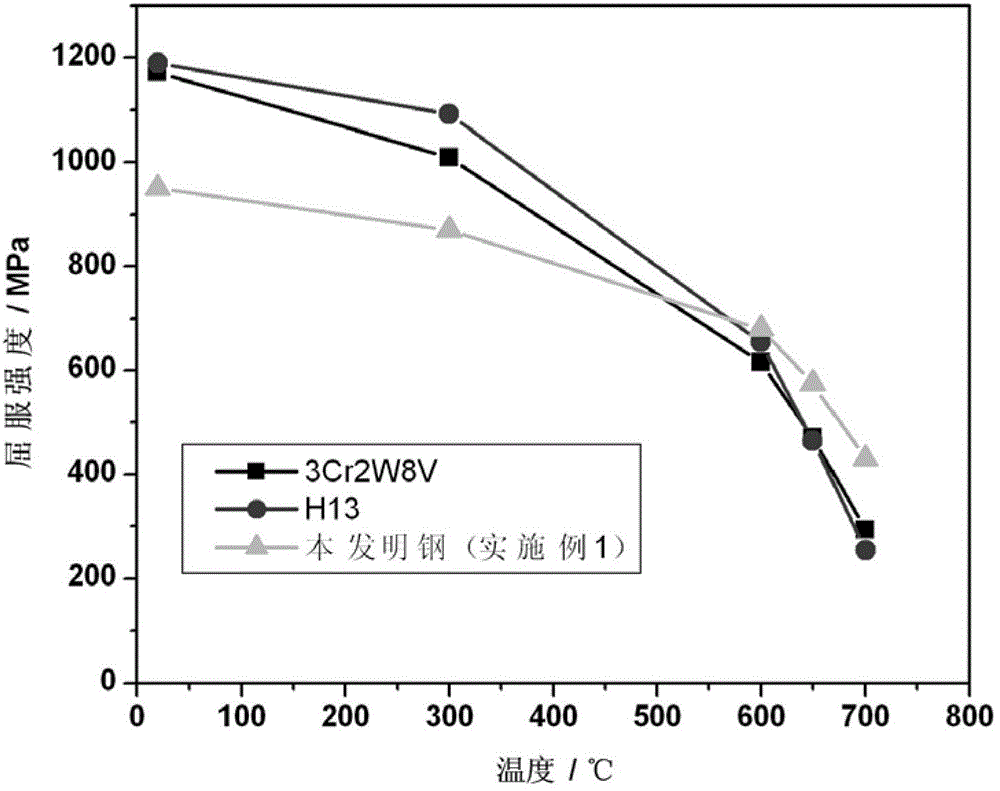
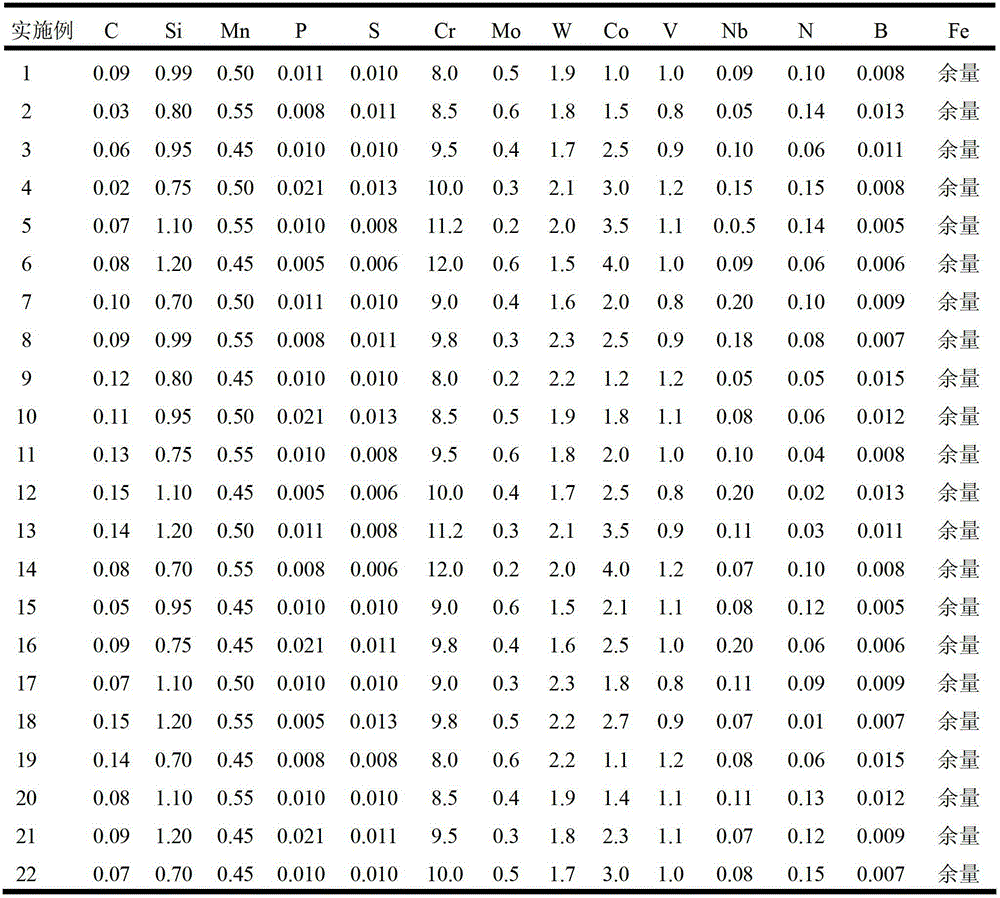
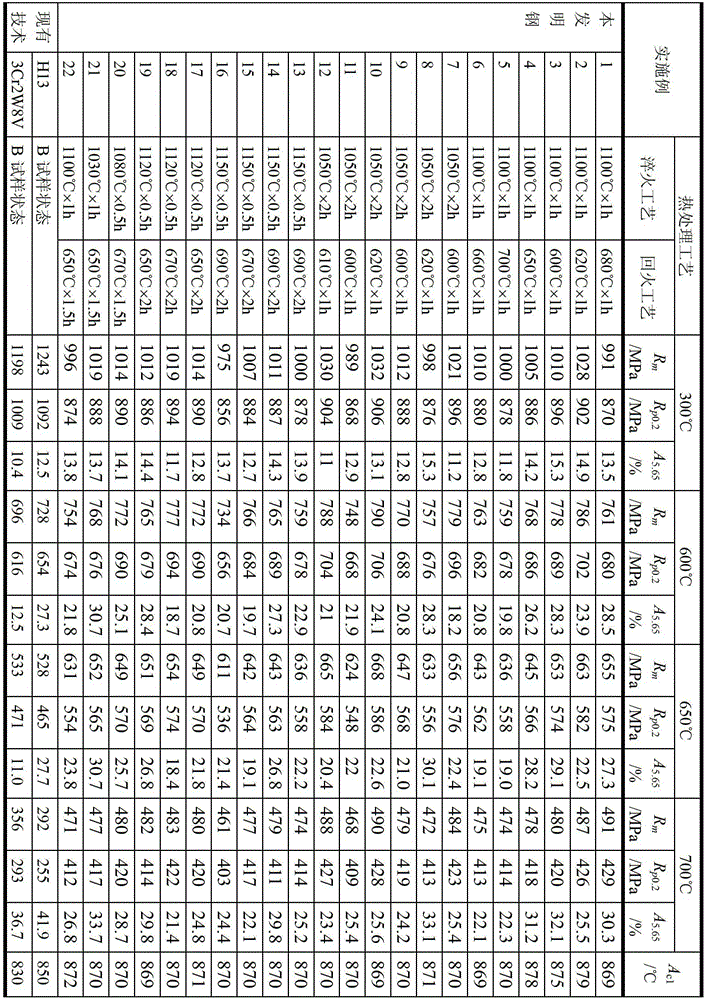
The invention discloses anti-oxidation and anti-thermal fatigue hot working die steel which is characterized by including, by mass percent, 0.02 to 0.15 of carbon, 0 to 1.2 of silicon, 0 to 0.6 of manganese, 0 to 0.030 of phosphorus, 0 to 0.015 of sulfur, 8.0 to 12.0 of chromium, 0.2 to 0.6 of molybdenum, 1.5 to 2.3 of tungsten, 0.8 to 1.2 of vanadium, 0.01 to 0.1 of nitrogen, 0.05 to 0.20 of niobium, 1.0 to 4.0 of cobalt, 0.005 to 0.015 of boron, and the balance iron and inevitable impurities. The manufacturing method includes subjecting raw material compositions forming elements to smelting and casting to obtain die steel ingots; forging or rolling the die steel ingots; annealing the forged or rolled die steel ingots; and subjecting the annealed die steel ingots to final thermal treatment. The manufacturing method is characterized in that the annealing process includes that air cooling is kept at a temperature of 800 DEG C to 850 DEG C for 1-2h; and the final thermal treatment process includes that oil cooling is kept at a temperature of 1030 DEG C to 1150 DEG C for 0.5-2h, and air cooling is kept at a temperature of 600 DEG C to 700 DEG C for 1-2h. Compared with the prior art, the anti-oxidation and anti-thermal fatigue hot working die steel and the manufacturing method thereof have the advantages that the hot working die steel manufactured at a temperature above 600 DEG C has a high high-temperature strength and a stagnation temperature compared with the existing hot working die steel such H13 steel and 3Cr2W8V steel, accordingly, high anti-oxidation and anti-thermal fatigue performances are provided, and anticorrosion and anti-oxidation performances are improved greatly compared with the existing hot working die steel because many chromium elements are contained.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
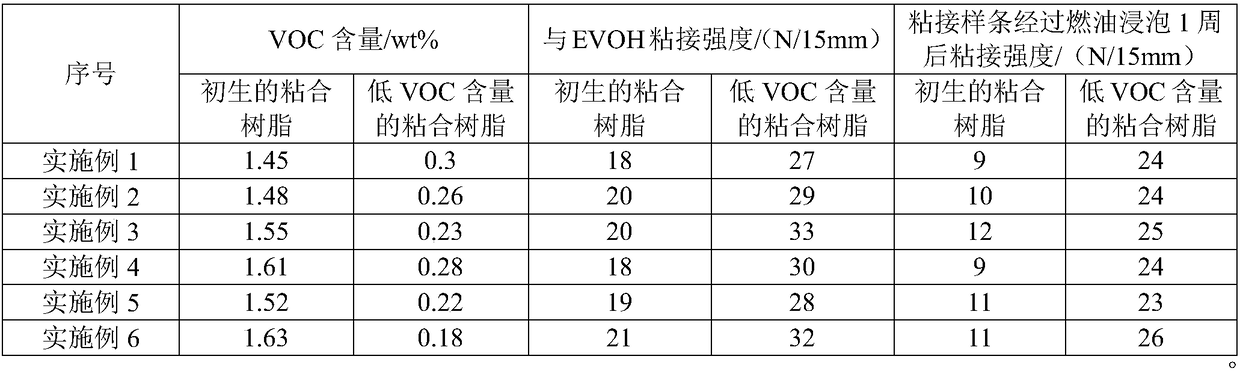
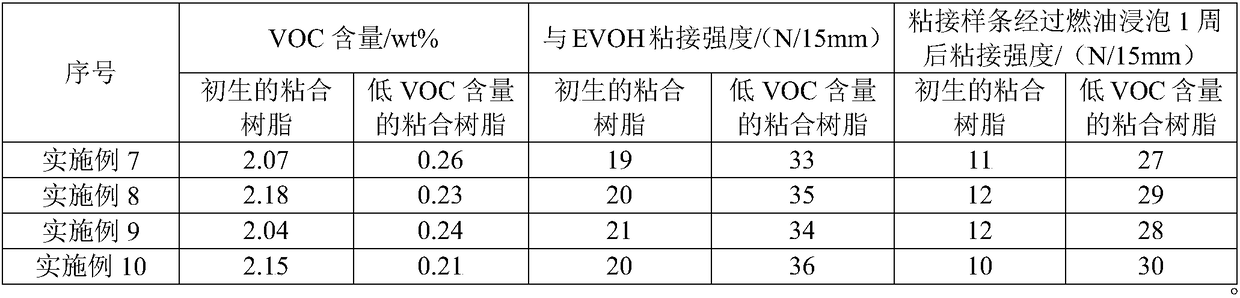
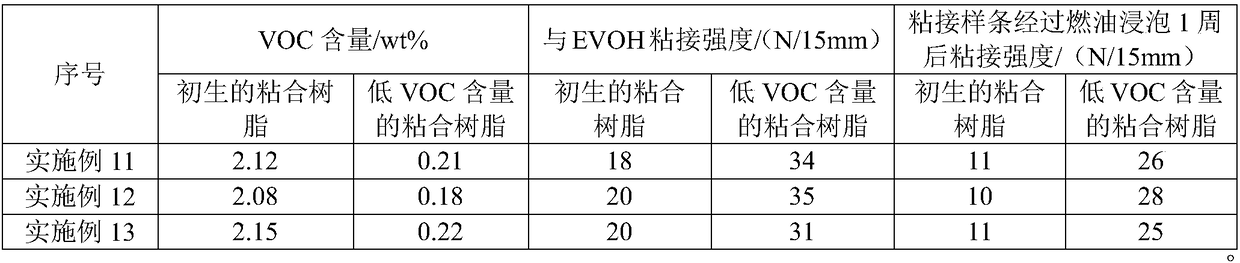
Preparation method of low-VOC bonding resin
ActiveCN108546531ALow VOC contentImprove performanceMacromolecular adhesive additivesBulk chemical productionAging resistanceTetrachloroethane
The invention relates to the technical field of bonding resins, and concretely relates to a preparation method of a low-VOC bonding resin. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a primary bonding resin from a matrix resin, a graft monomer, an initiator, a tackifying resin and a functional assistant through a double screw extruder, feeding the primary bonding resin into a supercritical device, and removing VOCs from the primary bonding resin by a purifying solvent to obtain the low-VOC bonding resin, wherein the purifying solvent is one or more of carbon dioxide, 1,1,1,2-tetrachloroethane, methane, ethane, propane, ethylene and propylene. The supercritical fluid purification of the primary bonding resin in the method greatly reduces the content of the VOCs in orderto effectively improve the use performance and the safety performance of an automobile plastic fuel tank; and the preparation method has the advantages of environmentally-friendly and efficient preparation process, and simple process route, and the tackifying resin and the functional assistant can improve the flowability, the adhesion and the aging resistance of the bonding resin.
Owner:NINGBO NENGZHIGUANG NEW MATERIALS TECH
Household appliance containing a heat transfer fluid
InactiveCN101835933AEffective absorptionReduce absorptionHeat pumpsTextiles and paperBoiling pointVaporization
The invention relates to a household appliance (1) comprising a drying chamber (2) for drying wet articles (3) therein, a process air loop (4) for circulating process air to dry the articles (3) and a heat pump (8, 9, 10, 11, 12). Said heat pump (8, 9, 10, 11, 12) comprises a heat transfer loop (8) containing a heat transfer fluid to be circulated through said heat transfer loop (8), an evaporator heat exchanger (9) for transferring heat from the process air into said heat transfer fluid by evaporating said heat transfer fluid, a liquefier heat exchanger (10) for transferring heat from said heat transfer fluid to the process air by liquefying said heat transfer fluid, a compressor (11) for compressing the heat transfer fluid and driving the heat transfer fluid through said heat transfer loop (8), and a nozzle (12) for decompressing said heat transfer fluid. Further, said heat transfer fluid has a critical temperature above 60 DEG C, a nominal heat of vaporization at boiling point of at least 220 kJ / kg, a GWP index of less than 150 and a lower flammability level of at least 0,1 kg / m3.
Owner:BOSCH SIEMENS HAUSGERATE GMBH
Superconductor probe coil for NMR apparatus
InactiveUS20060006868A1Improve stress conditionHigh critical temperatureSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentSuperconducting magnets/coilsBorideOrganic polymer
An NMR apparatus which includes an NMR probe coil of a superconductor made of magnesium 2-boride formed on the surface of a substrate made of a flexible organic polymer material.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Battery fire extinguisher achieving fire extinguishment with hexafluoropropane and carbon dioxide
The invention discloses a battery fire extinguisher achieving fire extinguishment with hexafluoropropane and carbon dioxide. The battery fire extinguisher comprises a fire extinguishment bottle installed outside a battery box, wherein a vehicle-mounted battery is fixedly arranged in the battery box, a spray pipe of the fire extinguishment bottle is arranged in the battery box, the fire extinguishment bottle is filled with fire extinguishment materials which are intermixtures formed by the hexafluoropropane and the carbon dioxide, both the hexafluoropropane and the carbon dioxide are of a liquid state, the hexafluoropropane accounts for 15%-18% of the intermixtures (by volume), and the balance is the carbon dioxide. The battery fire extinguisher has the advantages of being capable of conducting physical fire extinguishment and chemical fire extinguishment simultaneously.
Owner:ZEPHYR INTELLIGENT SYST SHANGHAI CO LTD
High temperature superconducting material and method for preparing high temperature superconducting material
InactiveCN105845269ASolve the disadvantages of low critical temperatureHas superconducting propertiesSuperconductors/hyperconductorsApparatus for heat treatmentHigh critical temperatureYttrium
The invention discloses high temperature superconducting material and a method for preparing the high temperature superconducting material. The high temperature superconducting material is composed of yttrium, aluminum, nickel, lithium, zinc, barium and boron of which the molar ratio is 1:6-9:1-3:2-6:3-6:1.5:1-2. The preparation method comprises the steps that 1) a nitrate mixed solution is prepared; 2) citric acid is added in the nitrate mixed solution; 3) heating concentration is performed on the mixed solution obtained in the step 2) until gel is completely combusted so that powder material is formed; 4) powder is evenly ground; and 5) the ground powder is put in a high temperature furnace for calcining and then taken out after cooling to room temperature so that superconducting material is obtained. A sol-gel method and a high temperature calcining method are adopted for preparation so that the homogeneous superconducting material is formed, the defect of low critical temperature of the existing superconducting material can be solved, the superconducting material having higher critical temperature is prepared, and the superconducting material has the superconductivity under the condition of high temperature.
Owner:CHENGDU JUNHE TIANCHENG TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com