Patents
Literature
47results about How to "Suitable for practical application" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bidirectional quantum time synchronization method based on frequency entangled light sources
ActiveCN108718218AHigh measurement accuracySimple structureTime-division multiplexPhotonic quantum communicationSignal lightLength wave
The invention provides a bidirectional quantum time synchronization method based on frequency entangled light sources. Two entangled light sources with same wavelength are placed at a place A and a place B respectively, and signal lights generated by the entangled light sources pass through an optical fiber circulator, are transmitted in opposite directions through a same optical fiber, and are detected by detectors at the opposite places; idle lights generated by the entangled light sources are detected by a detector at a uniform place of the entangled light sources; a clock a at the place arecords the time (tij} and time (t2j} for photons emitted by the entangled light source at the place a to reach the detectors at two places, and a clock b at the place b records time (t3j} and time (t4j} for photons emitted by the entangled light source at the place b to reach the detectors at two places, wherein j is representative of jth photon; the (tij} and (t2j} are subjected to cross-correlation operation to obtain t2-t1; the (t3j} and (t4j} are subjected to cross-correlation operation to obtain t4-t3; the clock difference t0 between the clock a and the clock b is equal to half of the difference of (t2-t1) and (t4-t3). The bidirectional quantum time synchronization method based on the frequency entangled light sources is high in measurement precision, and an applied device is simplein structure.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
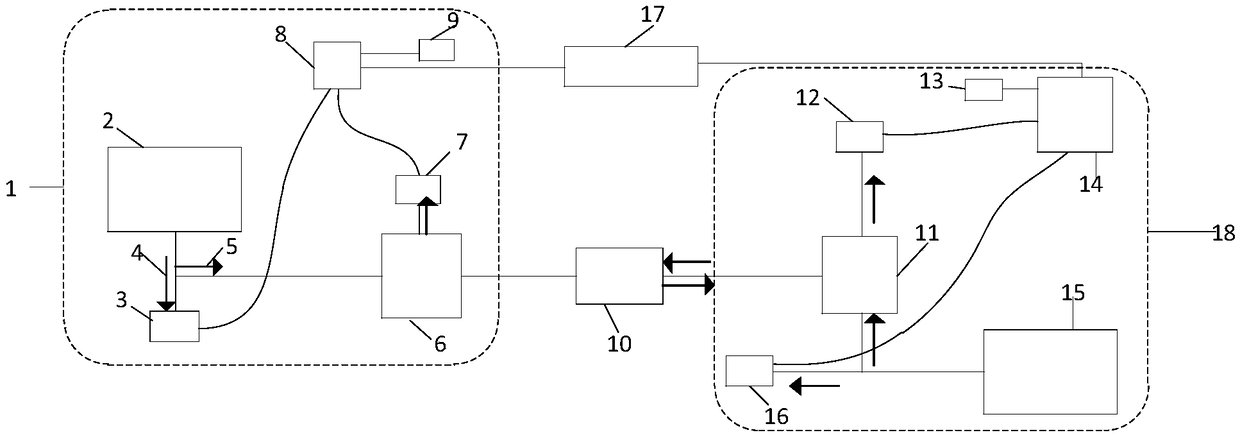
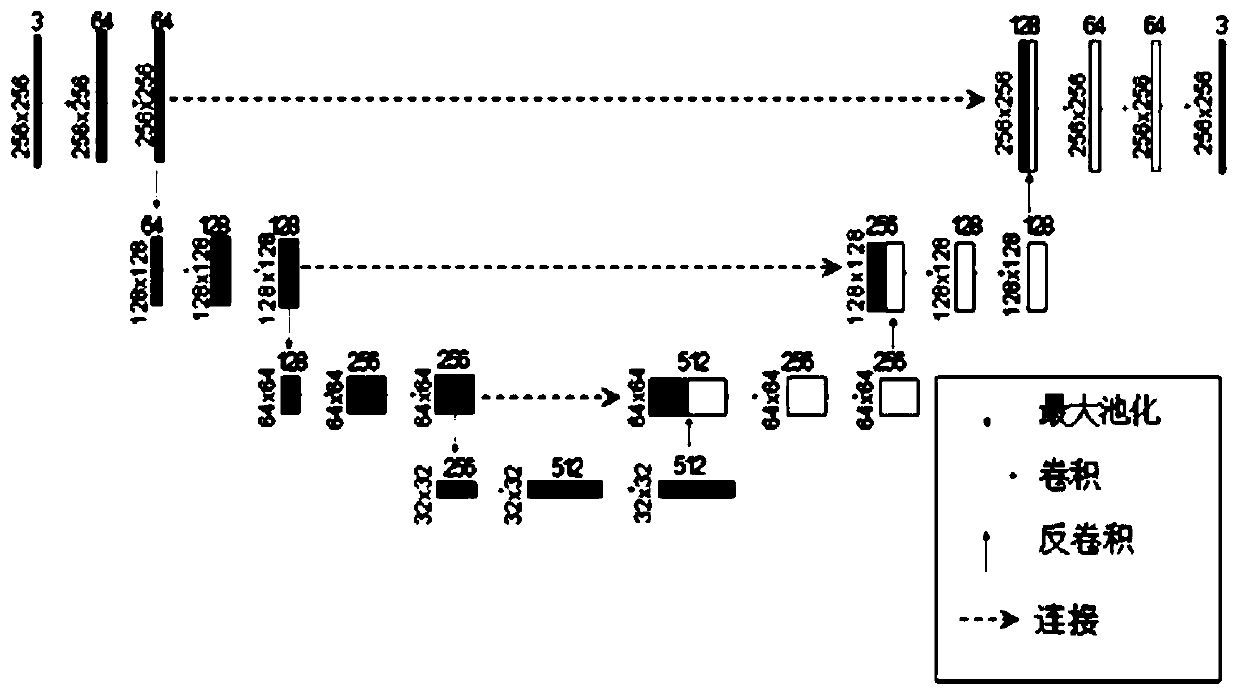
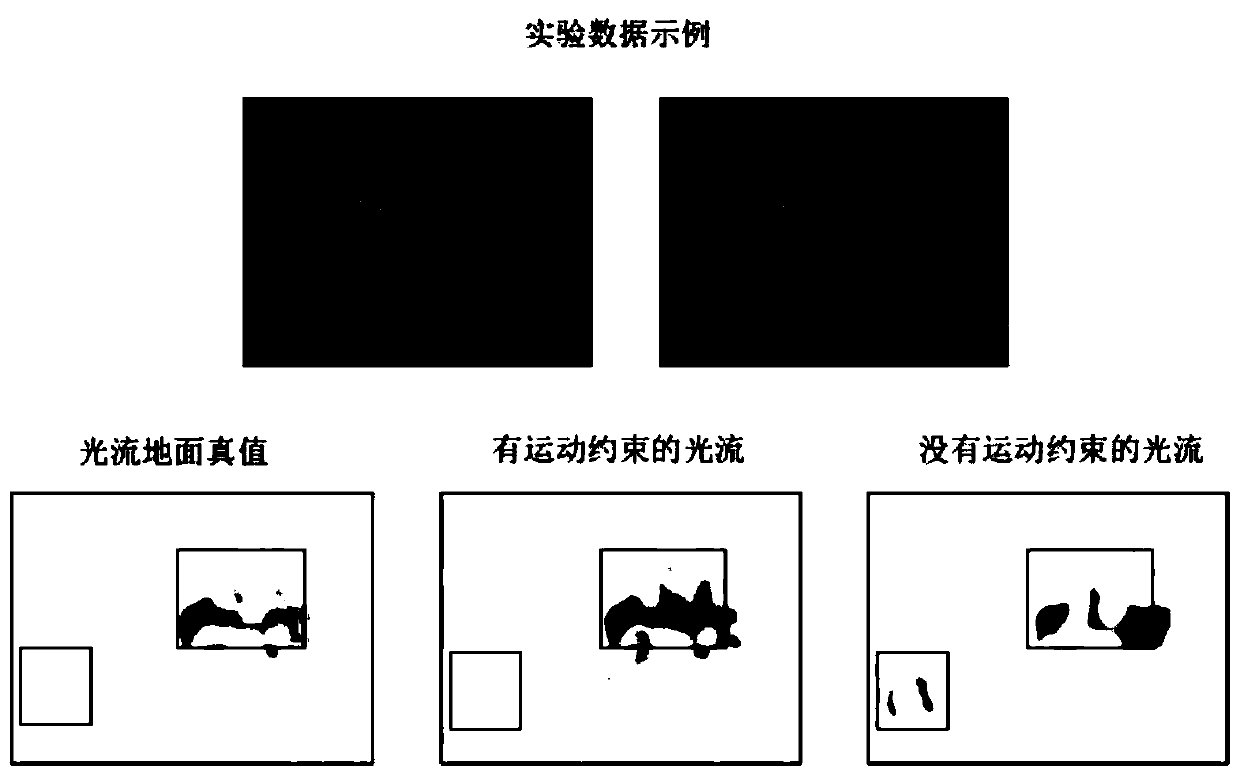
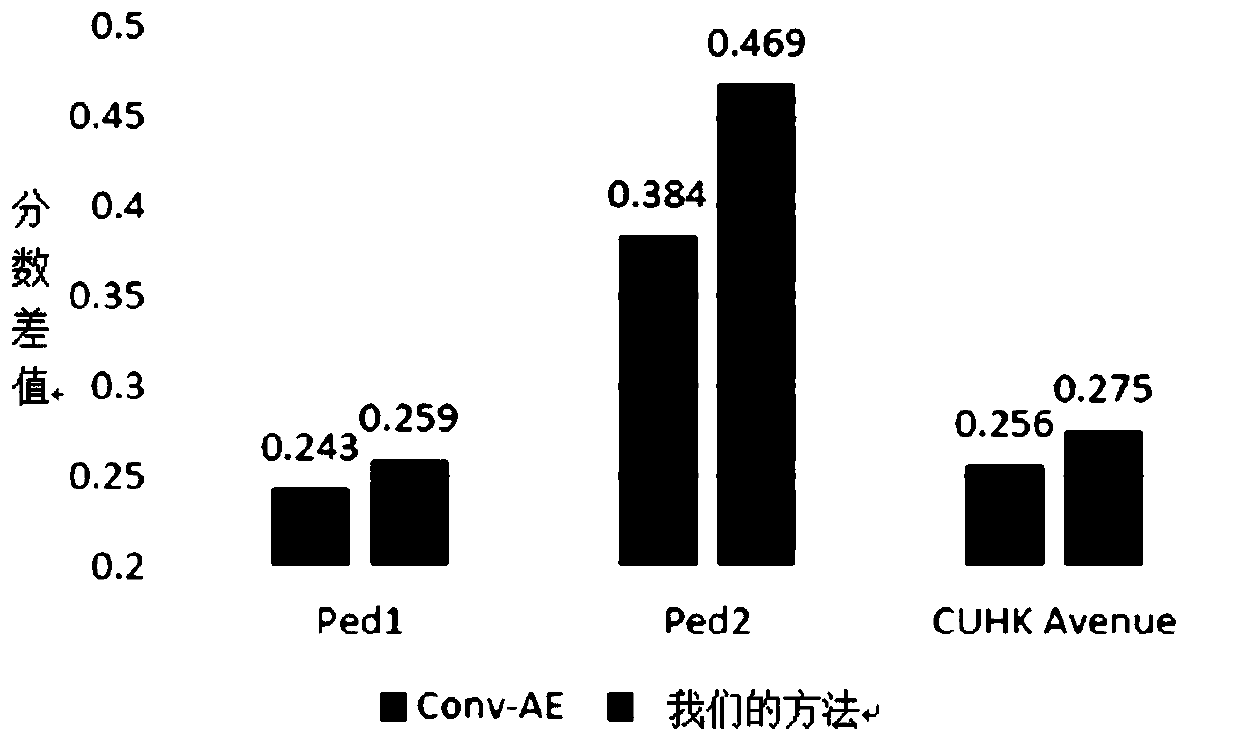
Abnormal behavior detection method based on generative adversarial network
InactiveCN110705376AImprove accuracySuitable for practical applicationCharacter and pattern recognitionData setAlgorithm
The invention discloses an abnormal behavior detection method based on a generative adversarial network (GAN). The method comprises the following steps that firstly, a U-Net network is built and serves as a generator module in a GAN, and not only is appearance (space) constraint used, but also motion (time) constraint is introduced; secondly, a patch discriminator (patch discriminator) is adoptedas a discriminator module in the GAN; and then, alternately performing adversarial training on the generator and the discriminator until the discriminator cannot distinguish the generated frame and the real frame. And finally, carrying out an abnormal behavior detection experiment through the trained GAN model. Experimental results on three public and available anomaly detection data sets show that the method provided by the invention effectively improves the accuracy of anomaly behavior detection.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
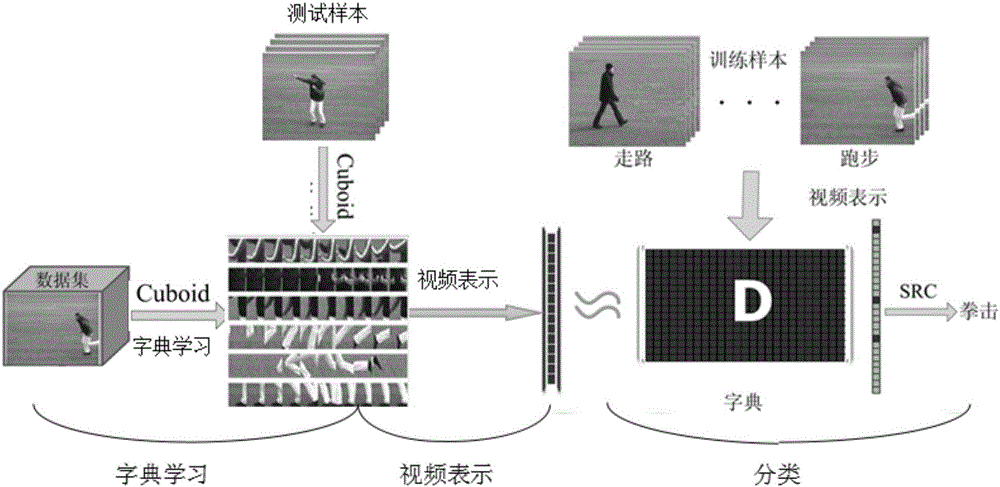
Similarity-weight-semi-supervised-dictionary-learning-based human behavior identification method
ActiveCN105095863ASuitable for practical applicationImprove discrimination abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionLearning basedDictionary learning
The invention discloses a similarity-weight-semi-supervised-dictionary-learning-based human behavior identification method. With the method, a problem of low human behavior identification rate of the existing supervision method in the prior art can be solved. The identification method comprises: (1), an inputted data set is divided into test samples and training samples; (2), local feature detection is carried out on all samples and local features with the labeled samples are selected randomly to obtain an initialized dictionary; (3), according to the initialized dictionary, dictionary learning is carried out by using a semi-supervised method; (4), group sparse coding is carried out on all samples by using the learned dictionary to obtain a coding matrix of each sample; (5), vectorization is carried out on the coding matrix of each sample to obtain a final expression; and (6), testing sample classification is carried out by using the final expression of each sample and a sparse representation classification method to complete human behavior identification in the testing samples. Therefore, discrimination of dictionary learning is enhanced; the human behavior identification rate is improved; and the method can be used for target detection in a video.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
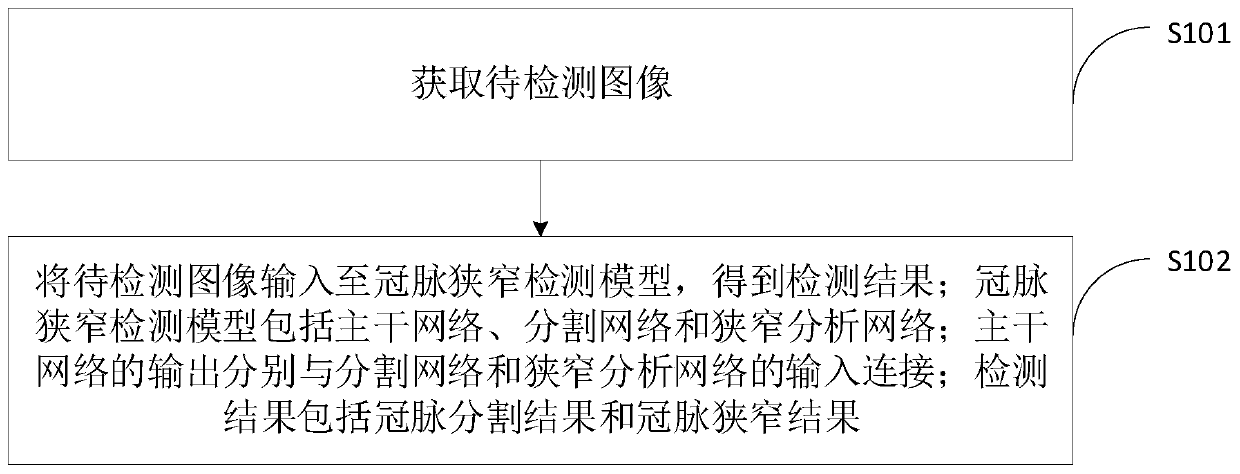
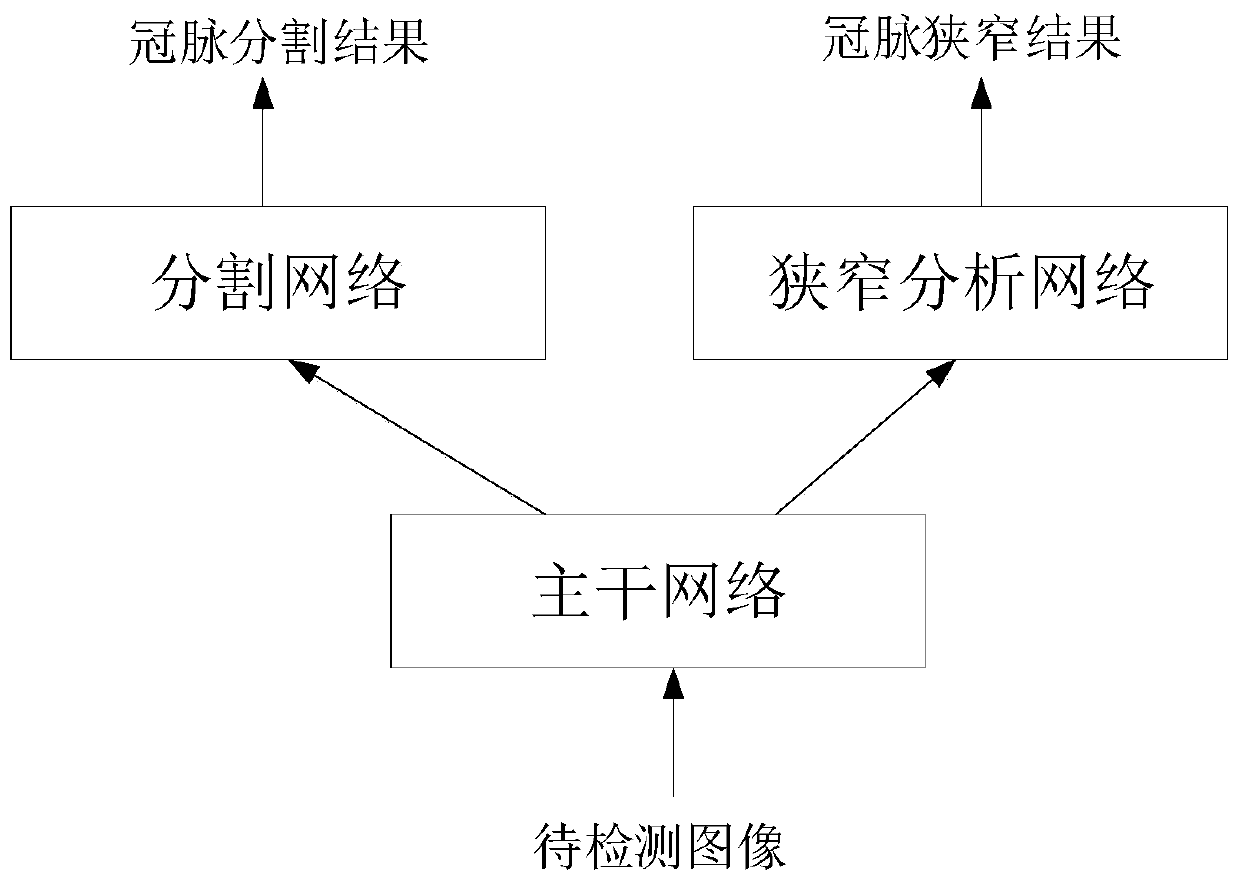
Crown artery stenosis detection method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
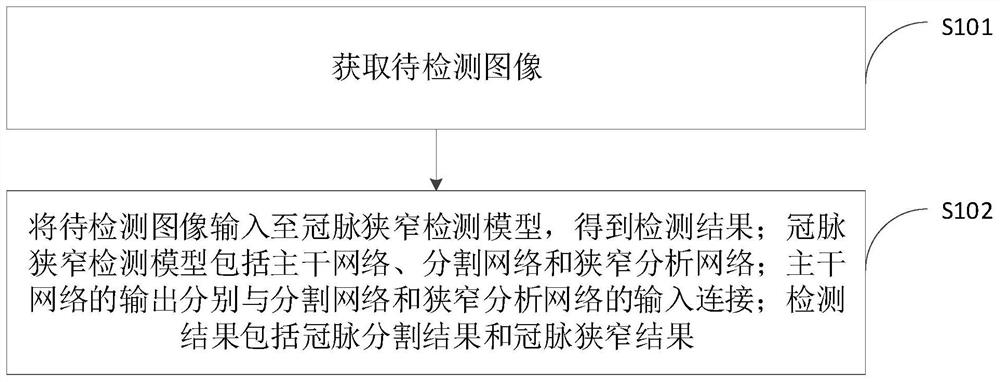
ActiveCN110310256AImprove learning performanceReduce the risk of overfittingImage enhancementImage analysisComputer equipmentStenosis
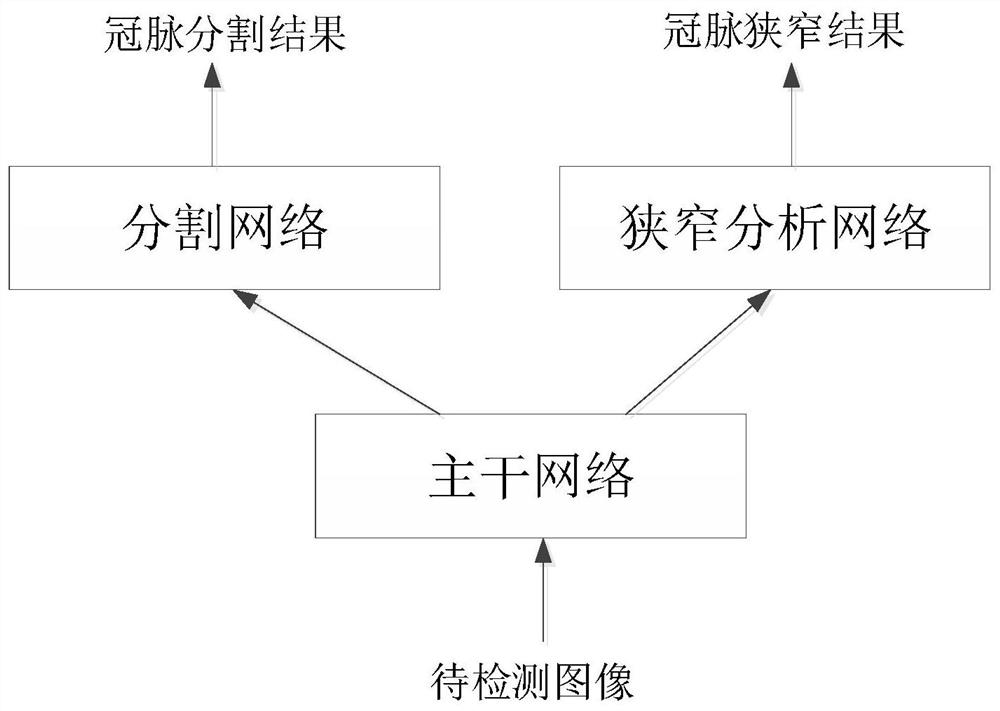
The invention provides a coronary artery stenosis detection method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium. The coronary artery stenosis detection method and device are characterized in that a detection result is obtained by inputting an obtained to-be-detected image into a coronary artery stenosis detection model; the coronary artery stenosis detection model comprises a trunk network,a segmentation network and a stenosis analysis network, and the output of the trunk network is connected with the input of the segmentation network and the input of the stenosis analysis network; thedetection result comprises a coronary artery segmentation result and a coronary artery stenosis result. Due to the structure of the coronary artery stenosis detection model, the coronary artery stenosis detection model comprises a segmentation network and a stenosis analysis network. Therefore, the coronary artery stenosis detection model is a multi-task model, can segment the input images to bedetected at the same time and conduct stenosis detection on the input image to be detected, so as to obtain detection results including at least two types, namely the coronary artery segmentation result and the coronary artery stenosis result.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING INTELLIGENT MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Highly effective phosphorus removal bacteria and its produced bacteria formulation
InactiveCN1807585AEasy to useReduce production and use costsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiological propertyPseudomonas putida
The bacterium agent in this invention is used to biologically strenghen dephosphor- ization process in urban sewage treatment plant. It has mainly two uses: quickly start the biodephosphorization ability of new sewage treatment plant; resume the strong biodephosphorization ability of exasperate dephosphorization system. It is made from high efficient ployphospher bacterial strain GM6, and it is odor Pseudomonas putida from appraising result. Its main biocharacteristic is G-. Its thalli is rhabditiform with the size of 0. 7í‡2. 5ª–m, and it is facultative anaero-bic; it is positive in indole reaction, oxidase and sulfate reduction reaction; while negative in methyl red test, V-P reaction, citrate test and hydrogen sulfide reaction; the number of the strain 16S rDNA is DQ133506. The strain can be used to sewage dephosphorization.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Abnormal behavior detection method based on improved pseudo three-dimensional residual neural network
ActiveCN110263728AImprove accuracySuitable for practical applicationCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesFeature vectorAnomalous behavior
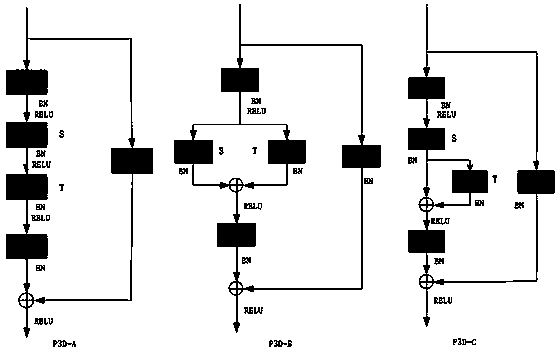
The invention discloses an abnormal behavior detection method based on an improved pseudo three-dimensional residual neural network, and the method comprises the following steps of firstly, dividing each video in a training set into a plurality of video clips; secondly, inputting all video clips of the video into the improved pseudo three-dimensional residual neural network to obtain the characteristics of the video clips; secondly, taking the average value of the feature vectors of all frames in each segment, and then performing L2 norm normalization on the feature average value to obtain the feature vector of the video segment; and finally, inputting the feature vector of the video clip into a three-layer full connection neural network, and outputting an abnormal score of the video clip. Experimental results show that compared with an existing method, the method provided by the invention further improves the accuracy of the abnormal behavior detection and is more suitable for the practical application.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for efficiently preparing beta-carboxyl phosphate
ActiveCN104497044AImprove compatibilityHigh yieldGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsIron saltsPhosphate
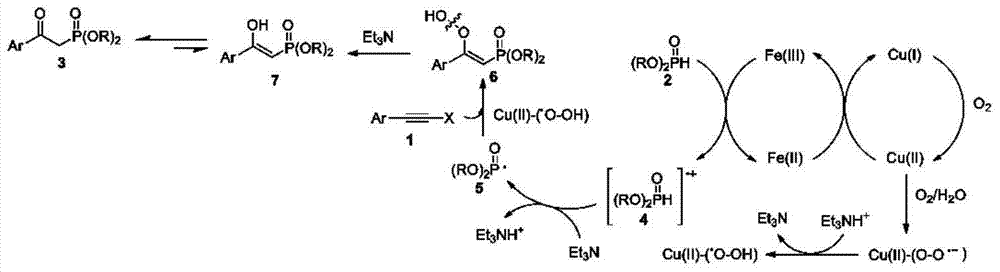
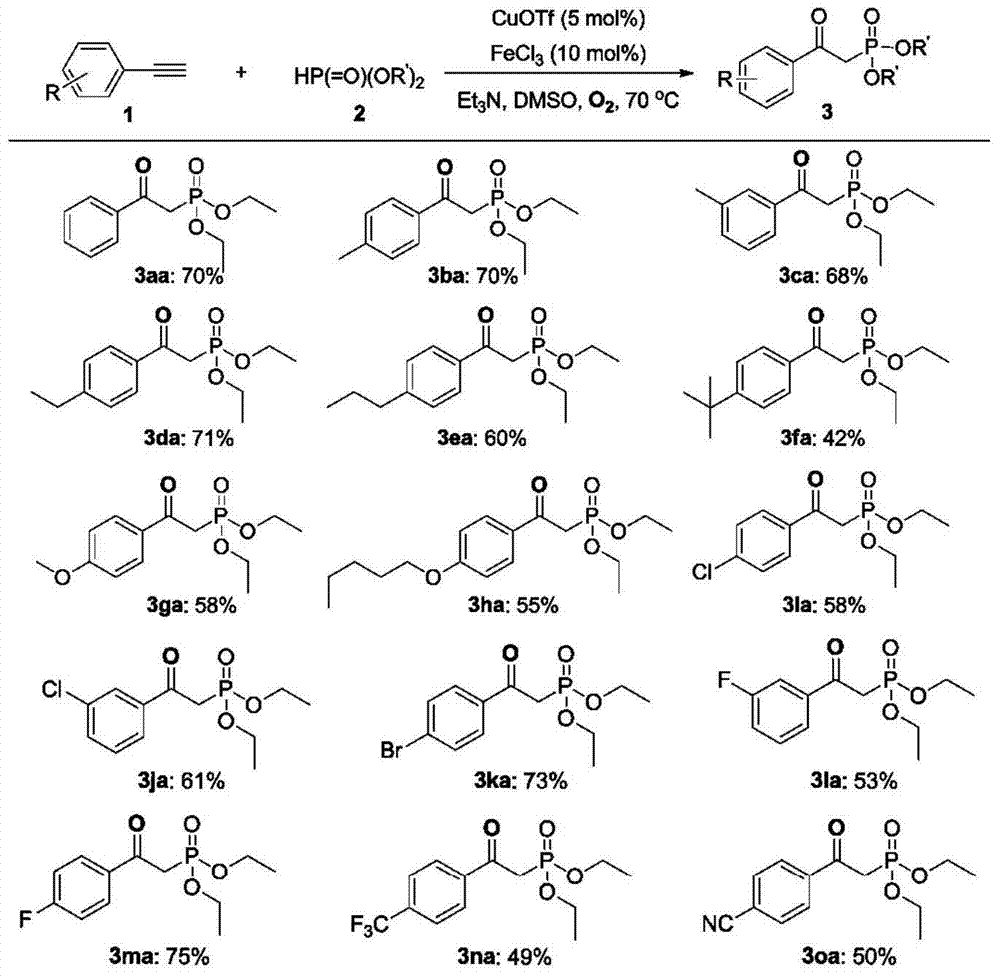
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing beta-carboxyl phosphate from alkyne or alkynyl carboxylic compounds and phosphite ester in the presence of copper / iron salt serving as catalysts and molecular oxygen serving as an oxidant. According to the method, multifunctional beta-carboxyl phosphate is obtained by virtue of a novel method having wide substrate range in the presence of the inexpensive catalysts (copper salts and iron salts) in oxygen, which is in a sharp contrast with previously reported view that alkyne cannot act in the presence of molecular oxygen. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, easily available raw materials, good compatibility with various reactants, strong practicality and high yield and can be widely applied to various functional reactions.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
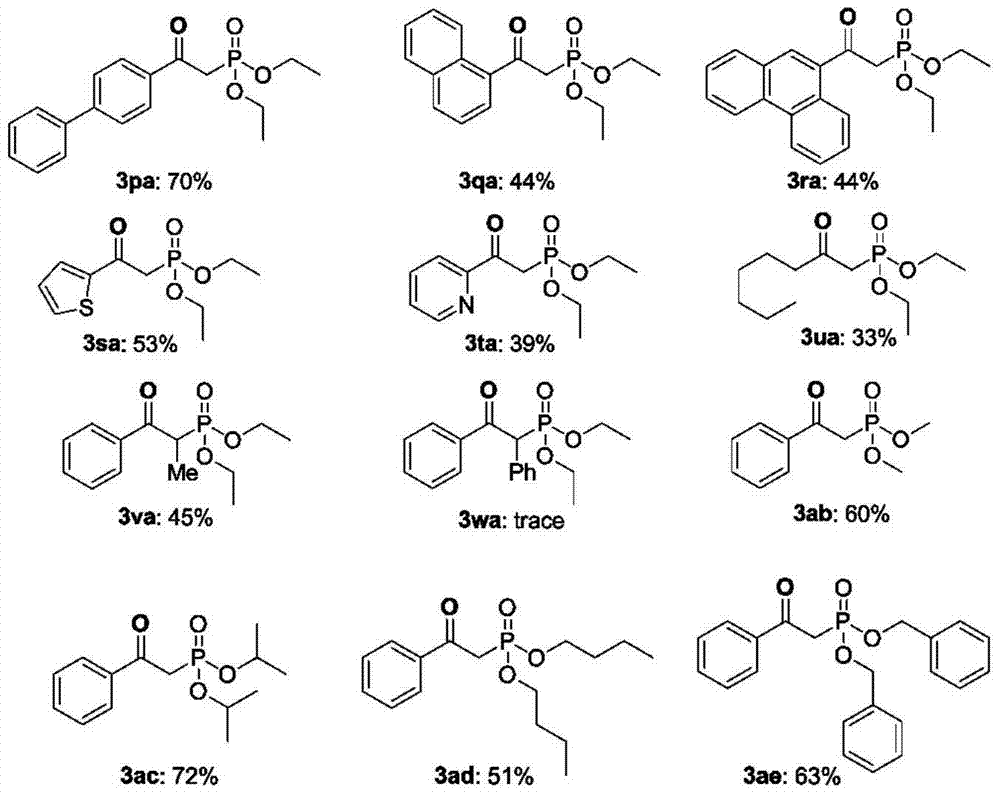
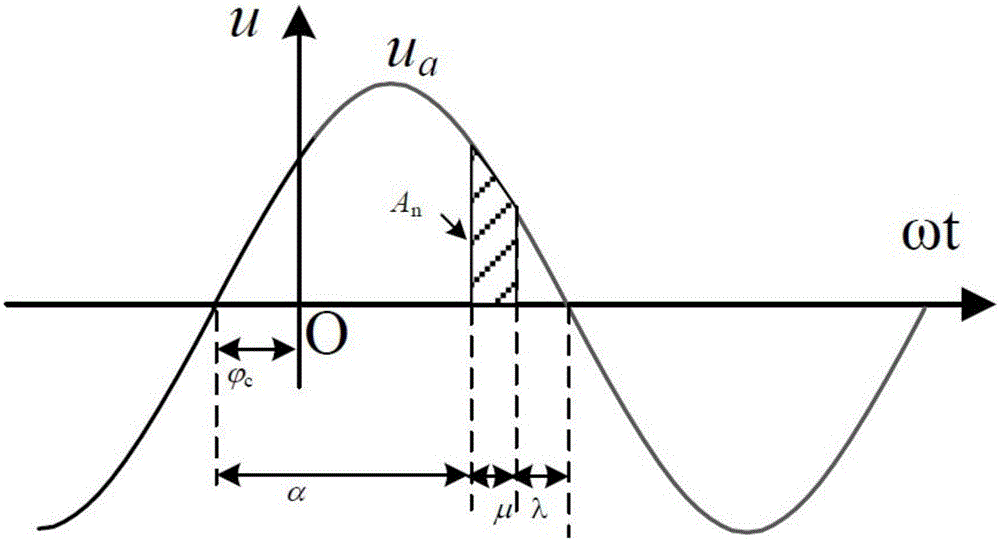
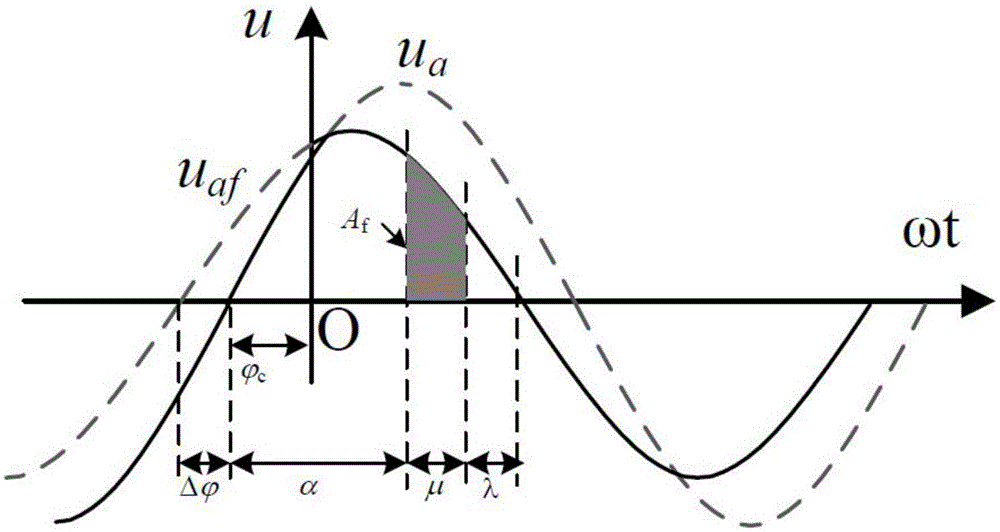
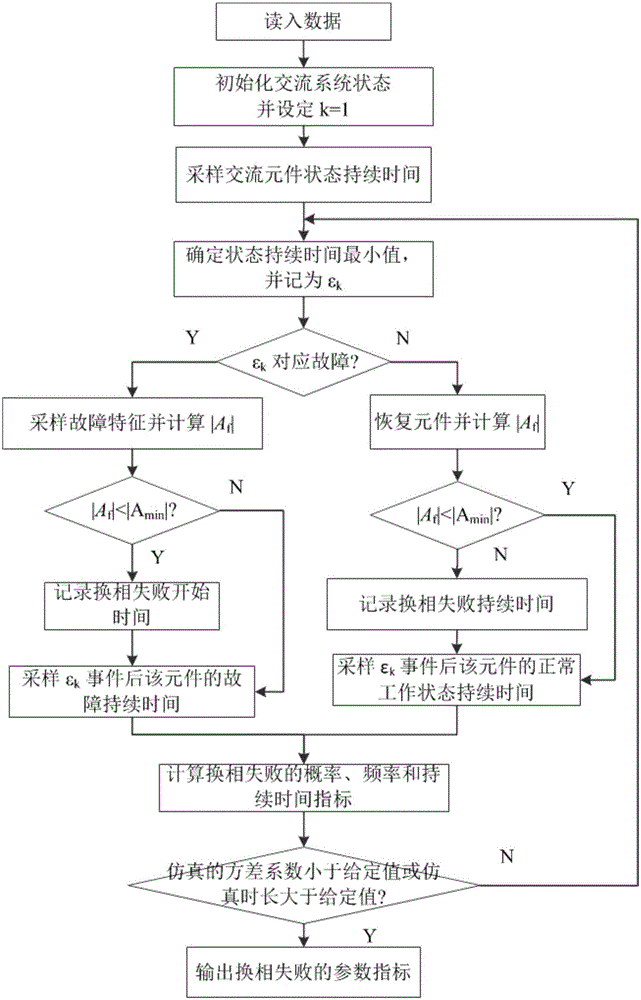
High-voltage direct-current power transmission system reliability assessment method considering alternating-current side fault
ActiveCN105140973ASuitable for practical applicationData processing applicationsElectrical apparatusHigh-voltage direct currentAlternating current
The invention provides a high-voltage direct-current power transmission system reliability assessment method considering an alternating-current side fault. A line commutated converter reliability modeling and probability index evaluation method is provided and is combined with an existing high-voltage direct-current power transmission system reliability assessment method, so that a problem that the influence on the high-voltage direct-current power transmission system reliability by the alternating-current side fault can not be taken into consideration by the traditional high-voltage direct-current power transmission system reliability assessment method can be solved. Therefore, precision and engineering practicability of the high-voltage direct-current power transmission system reliability assessment method can be improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
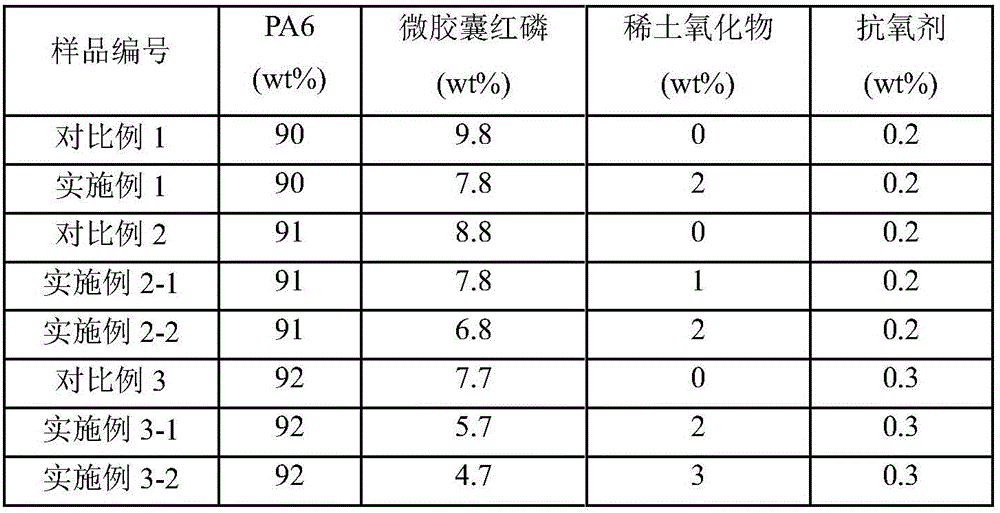
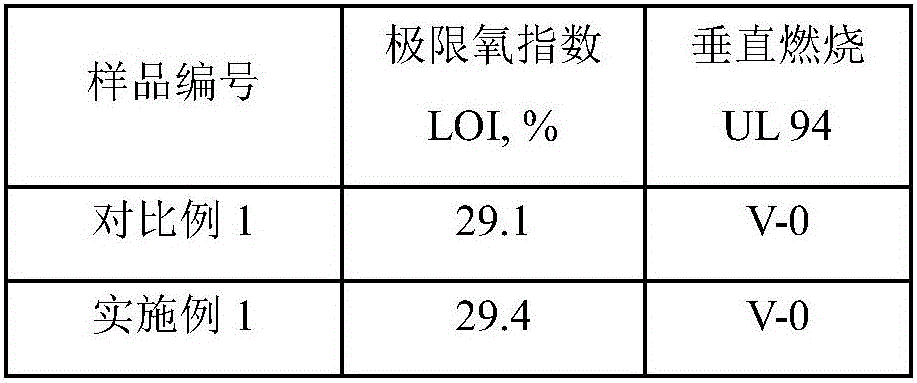
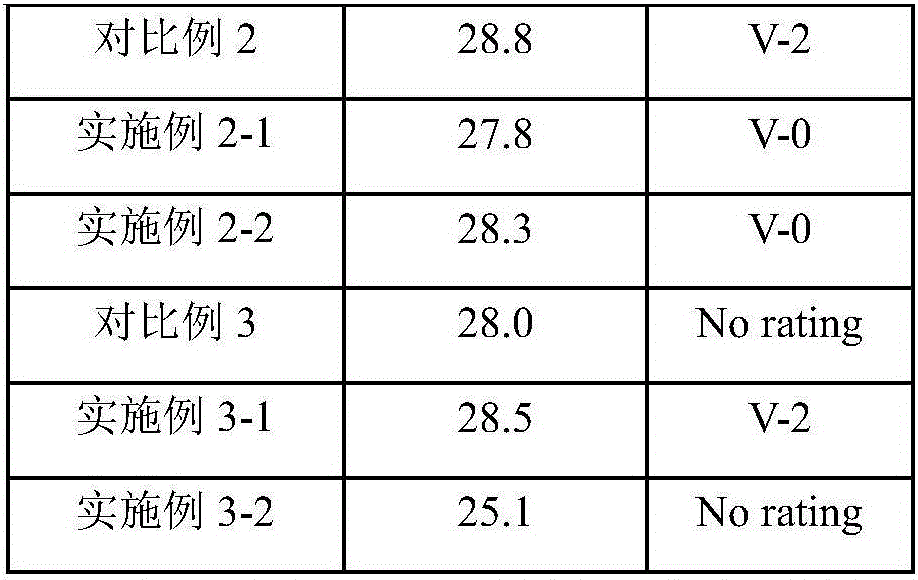
Rare-earth oxide and microencapsulated red phosphorus synergic flame retardance PA6 composite and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106751778AImproved Density and ContinuityCondensed phase flame retardant effect is goodChemistryMass transfer
The invention provides a rare-earth oxide and microencapsulated red phosphorus synergic flame retardance PA6 composite and a preparation method thereof. The rare-earth oxide and microencapsulated red phosphorus synergic flame retardance PA6 composite is characterized by being prepared from PA6, microencapsulated red phosphorus and rare-earth oxide. Rare-earth oxide is introduced into a red phosphorus flame-resistant polymer material system, rare-earth oxide can catalyze dehydrated carbonization of red phosphorus, a more compact and continuous charcoal layer structure can be formed, the mass transfer process of volatile products generated by polymer degradation to a gas phase is blocked, feedback of heat generated by gas phase combustion to a condensed phase is also blocked, and flames are prevented from propagating and spreading.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
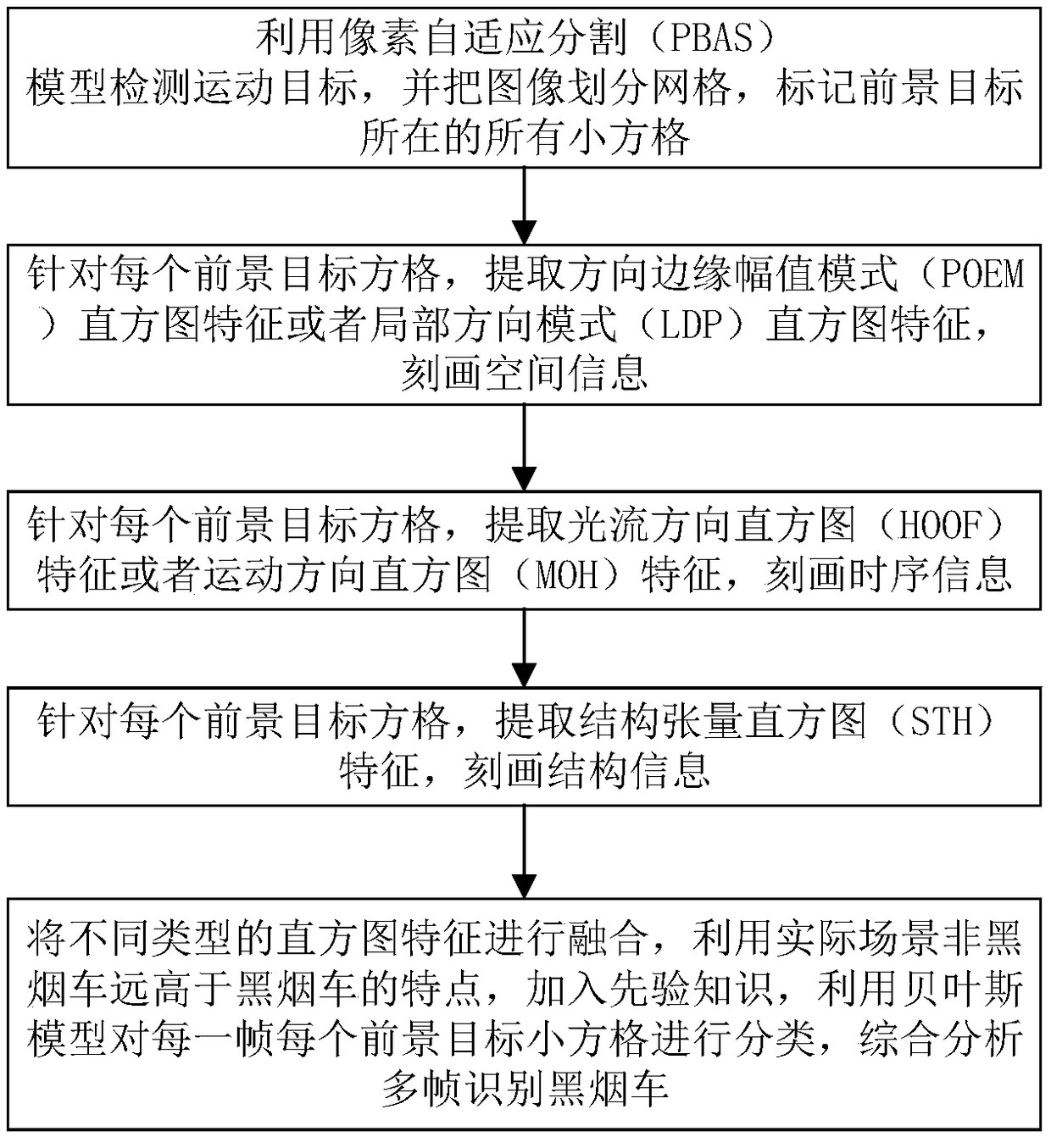
A smoky vehicle detection method based on pixel adaptive segmentation and Bayesian model
ActiveCN109271904AImprove performanceRobustImage enhancementImage analysisTemporal informationMultiple frame
The invention discloses a black smoke vehicle detection method based on pixel adaptive segmentation and Bayesian model. The black smoke vehicle detection method comprises the following steps: detecting a moving target by using a PBAS model, dividing an image into grids, and marking all small squares where a foreground target is located; for each foreground target grid, extracting POEM histogram orLDP histogram to characterize the spatial information, for each foreground target grid, extracting HOOF histogram or MOH histogram to characterize the temporal information, for each foreground targetgrid, extracting the STH feature and depicting the structure information, fusing different types of histogram features, using the characteristics of non-smoky vehicles being much higher than smoky vehicles in the actual scene to add a priori knowledge, classifying the small squares of each foreground target in each frame by Bayesian model, and comprehensively analyzing multi-frame recognition ofsmoky vehicles. The invention can automatically identify the black smoke vehicle from the traffic flow, improves the detection rate, reduces the false alarm rate, and has robustness to shadows.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Adjustable and controllable reflection type terahertz polarization converter based on vanadium dioxide
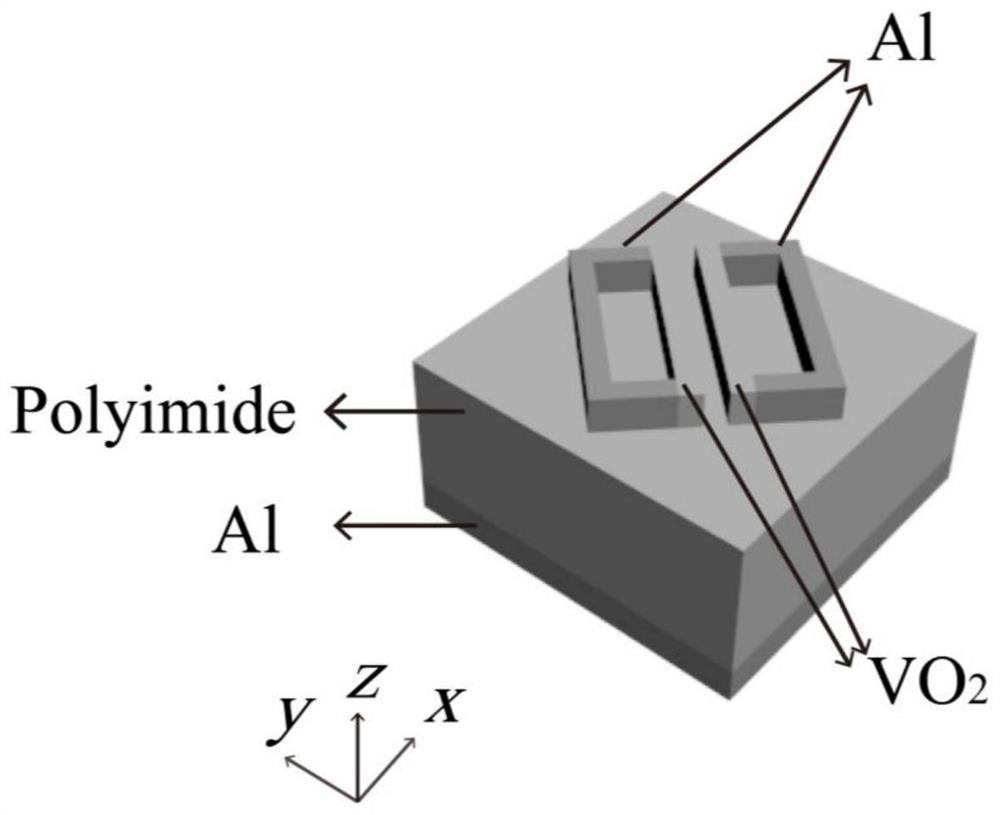
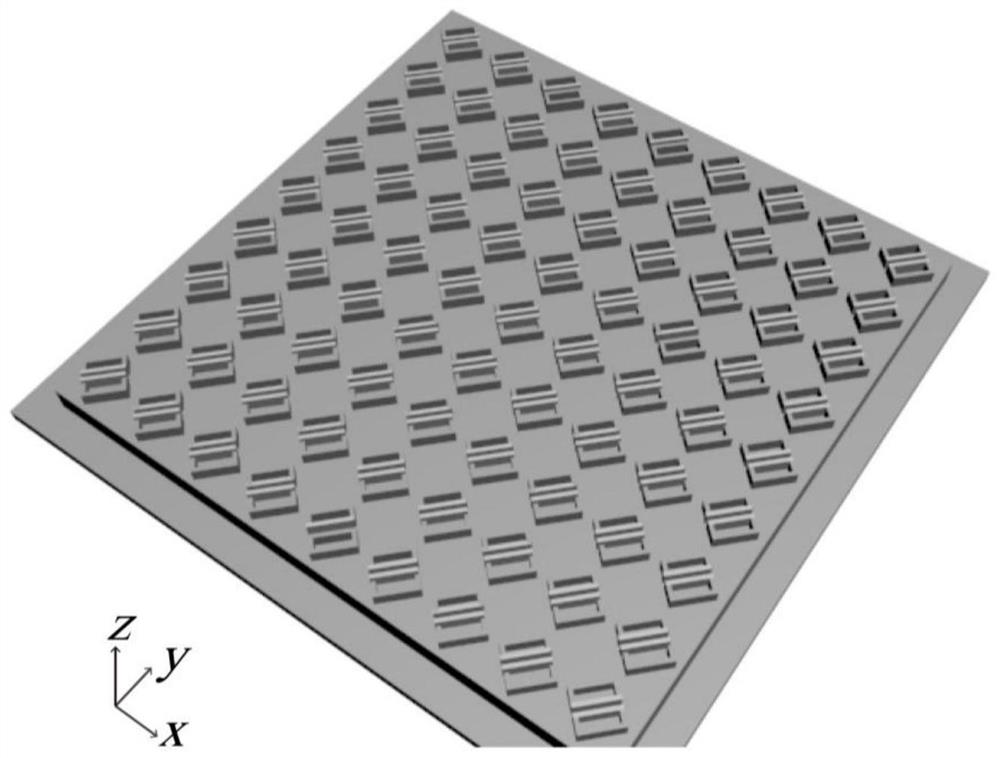
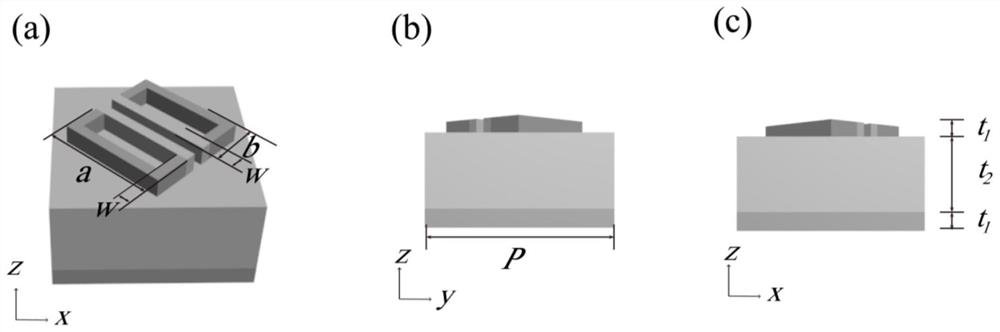
ActiveCN112882259APracticalActive modulation of reflection amplitudePolarising elementsNon-linear opticsVanadium dioxideConverters
The invention discloses an adjustable and controllable reflection type terahertz polarization converter based on vanadium dioxide, wherein an efficient and tunable reflection type polarization converter is realized based on a phase change process of vanadium dioxide from an insulation state to a metal state. The polarization converter has an active adjustment and control function on terahertz waves, wherein the unit structure of the polarization converter is composed of a three-layer structure, the bottom layer is an aluminum metal reflecting layer, the middle layer is a polyimide dielectric layer, the top layer is a double-skew symmetrical rectangular resonant ring composed of aluminum metal and phase-change material vanadium dioxide, and periodical arranging is performed in the x and y directions to form a metasurface microstructure. According to the invention, the polarization converter has an active regulation and control function on reflection amplitude under high polarization conversion efficiency, has very strong robustness on perturbation conditions such as structural defects of the polarization converter, external environment and the like, overcomes the defects of passive regulation and control in a traditional structural device, and can realize regulation and control on amplitude at different temperatures.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
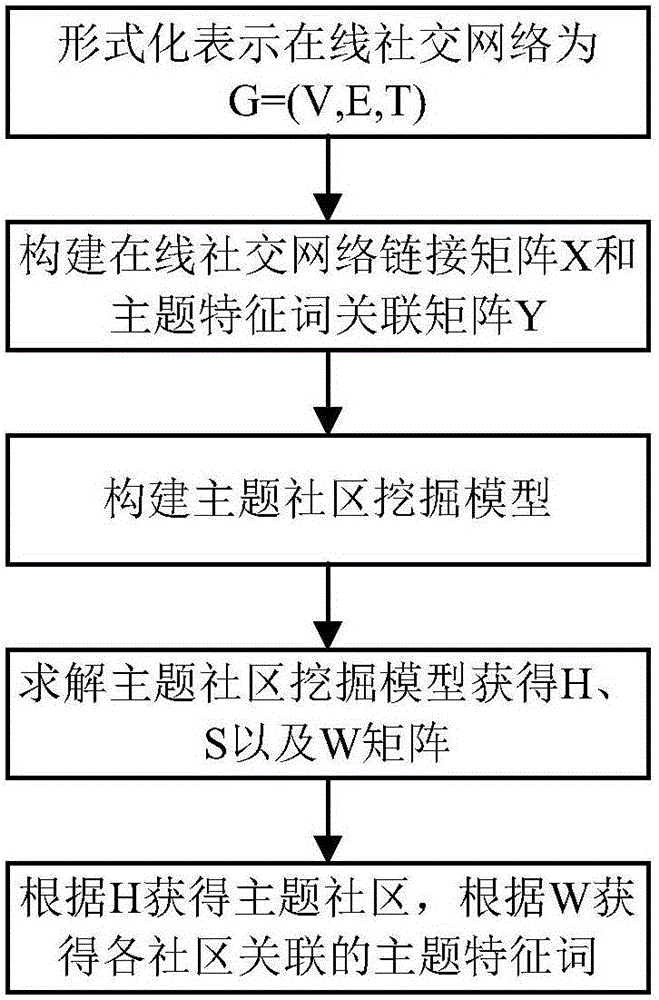
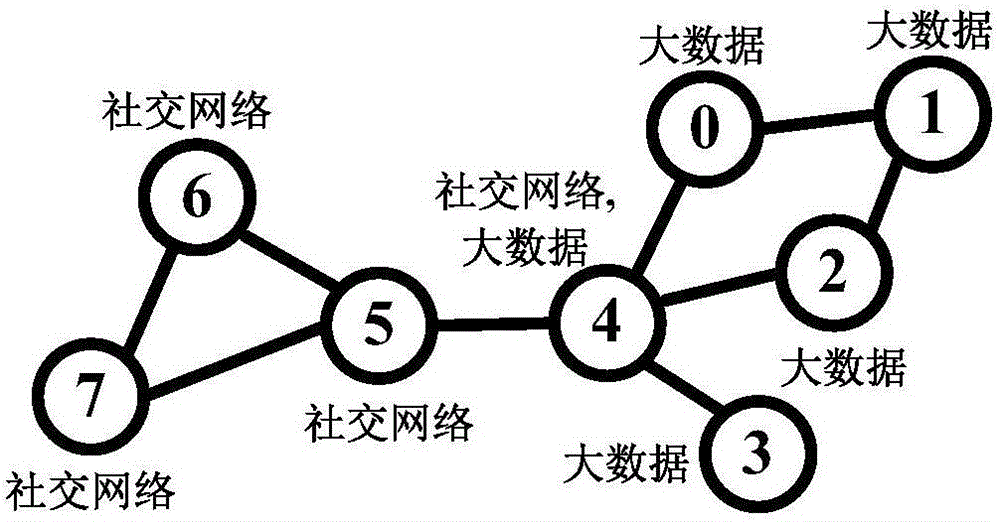
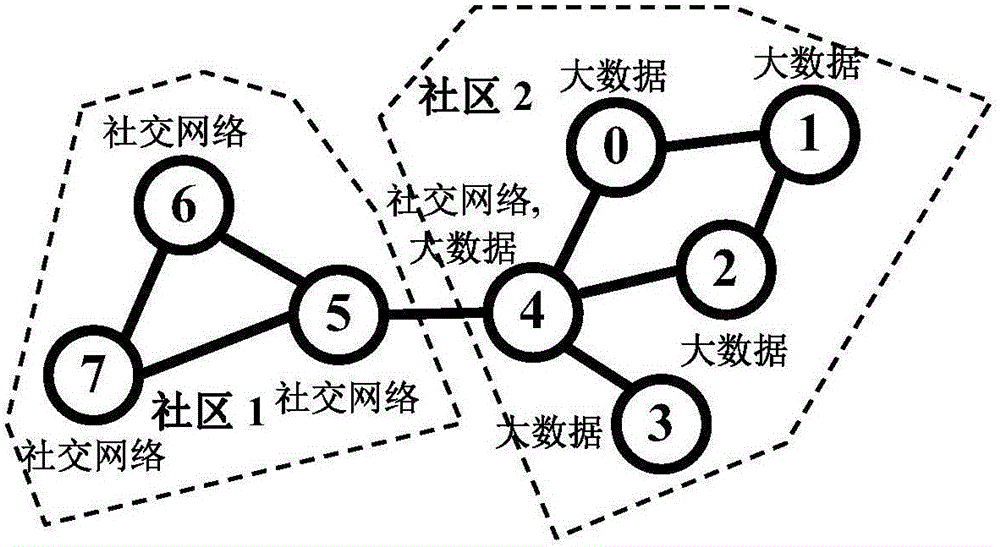
Subject community mining method for online social networking service
ActiveCN105760426AGuarantee the quality of excavationSuitable for practical applicationData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsMatrix decompositionCommunity mining
The invention provides a subject community mining method for an online social networking service.The subject community mining method is based on nonnegative matrix factorization (NMF).User node link information and content information can be integrated in a unified mode through an NMF model, an affiliation matrix between user nodes and communities and a correlation intension matrix between communities and subject feature words are obtained with the matrix approximative decomposition method, and then subject community mining can be directly conducted by means of matrix decomposition information.By the adoption of the method, user node link information and content information can be processed with a unified model, mining is easier and more efficient, mining quality is higher, and therefore the method is more suitable for being actually applied to mining of subject communities in the online social networking service.
Owner:ZHONGKAI UNIV OF AGRI & ENG +1
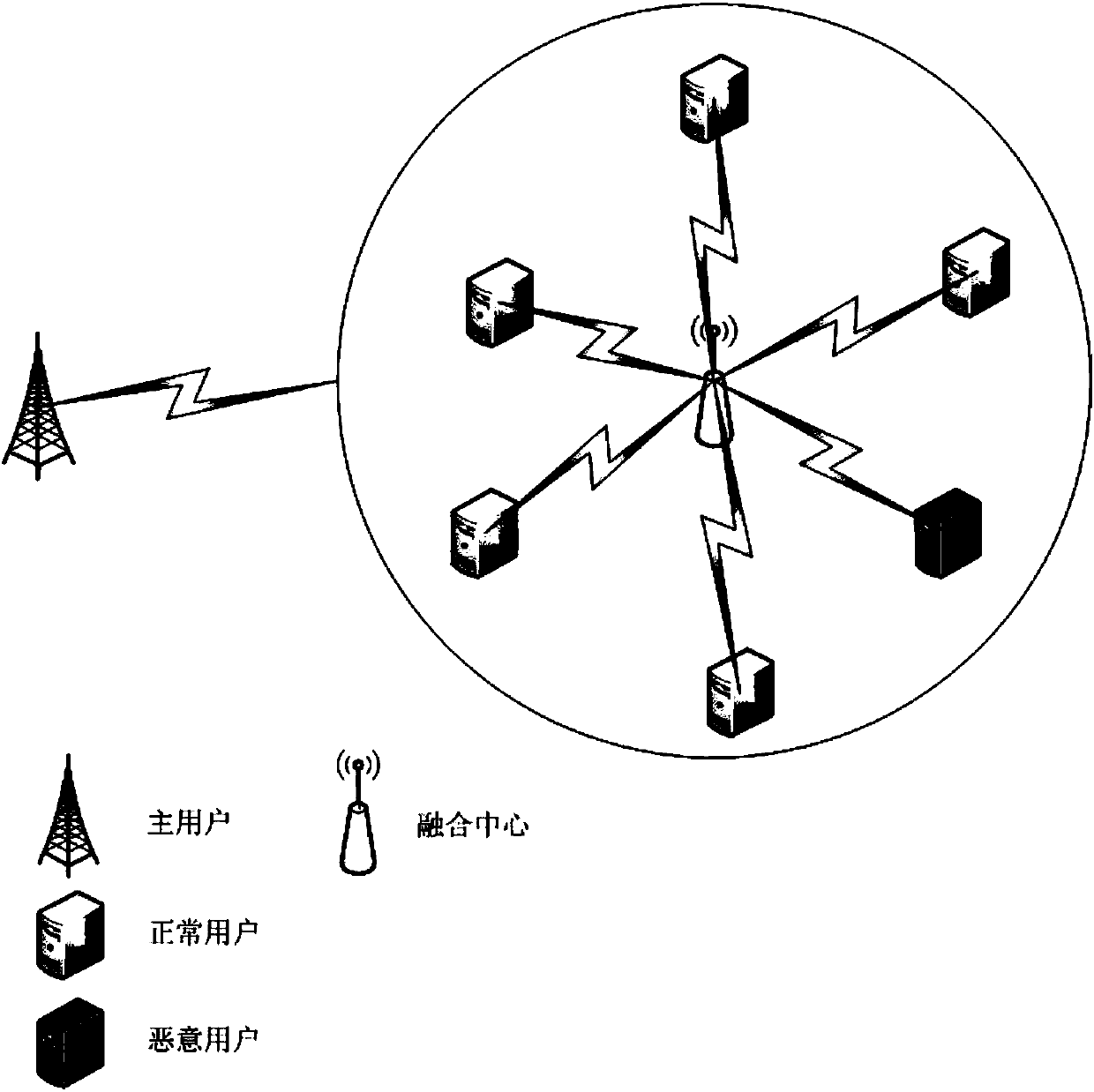
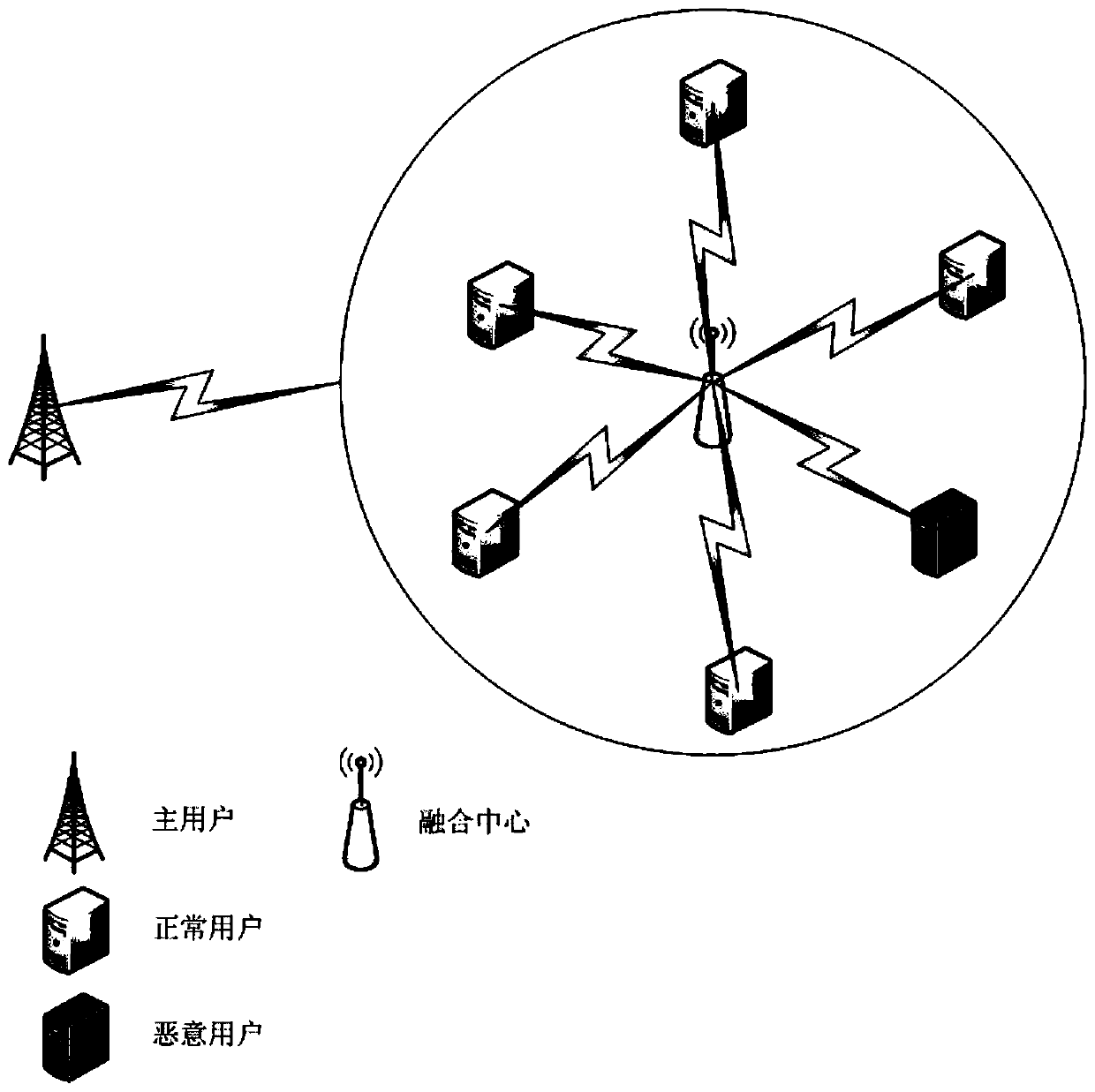
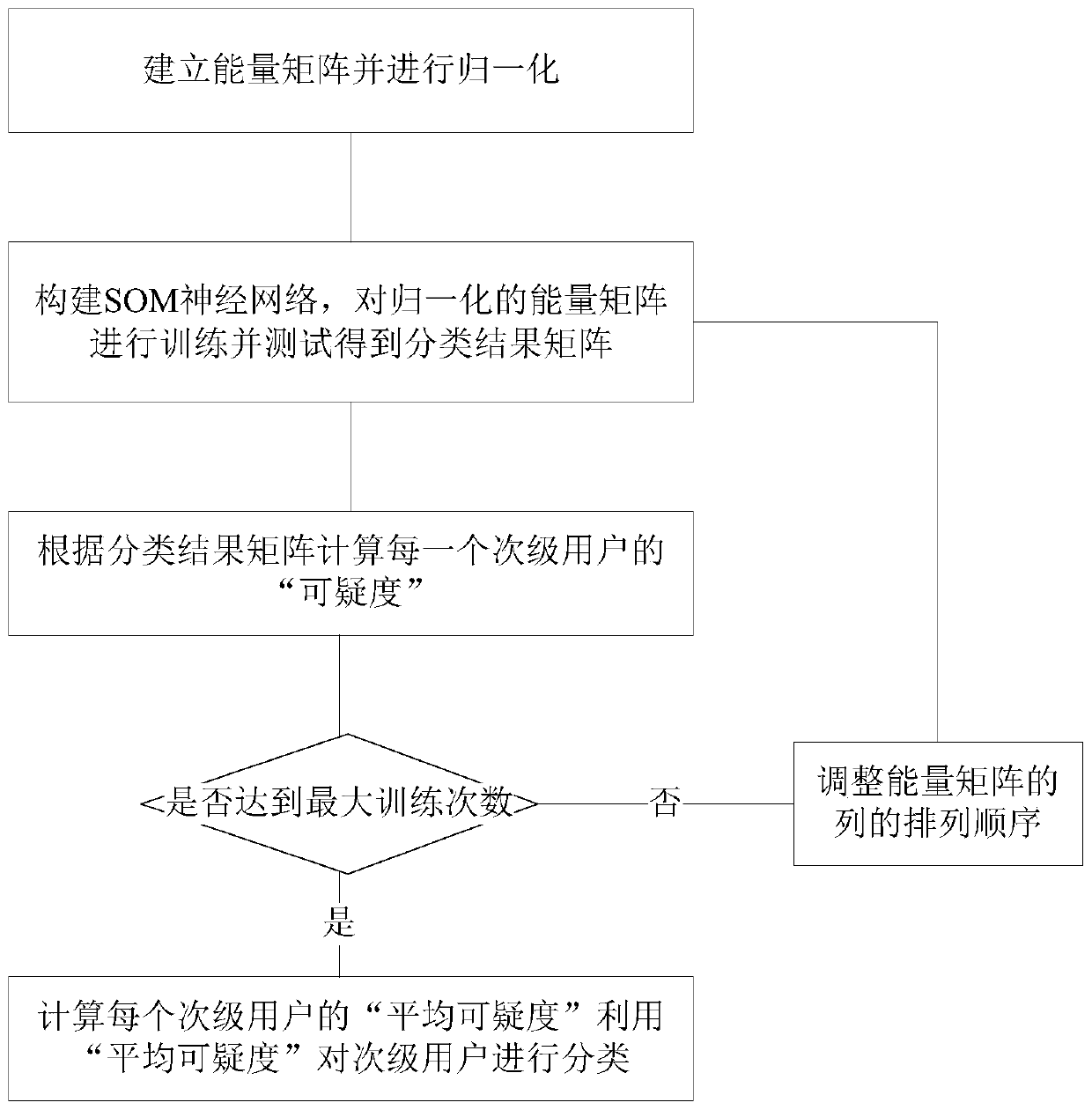
Self-organization mapping (SOM) neural network-based malicious user discrimination method in cognitive radio
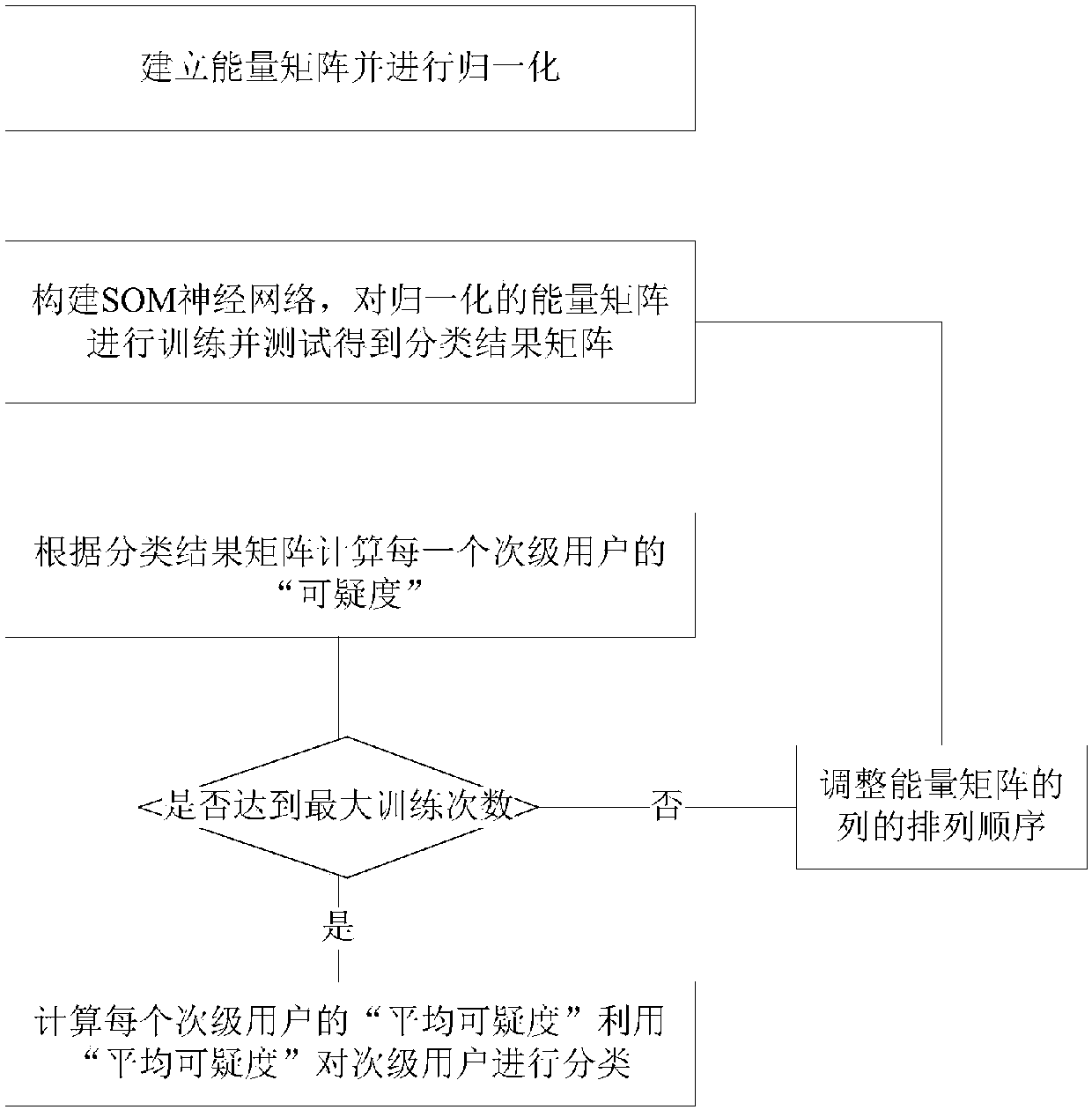
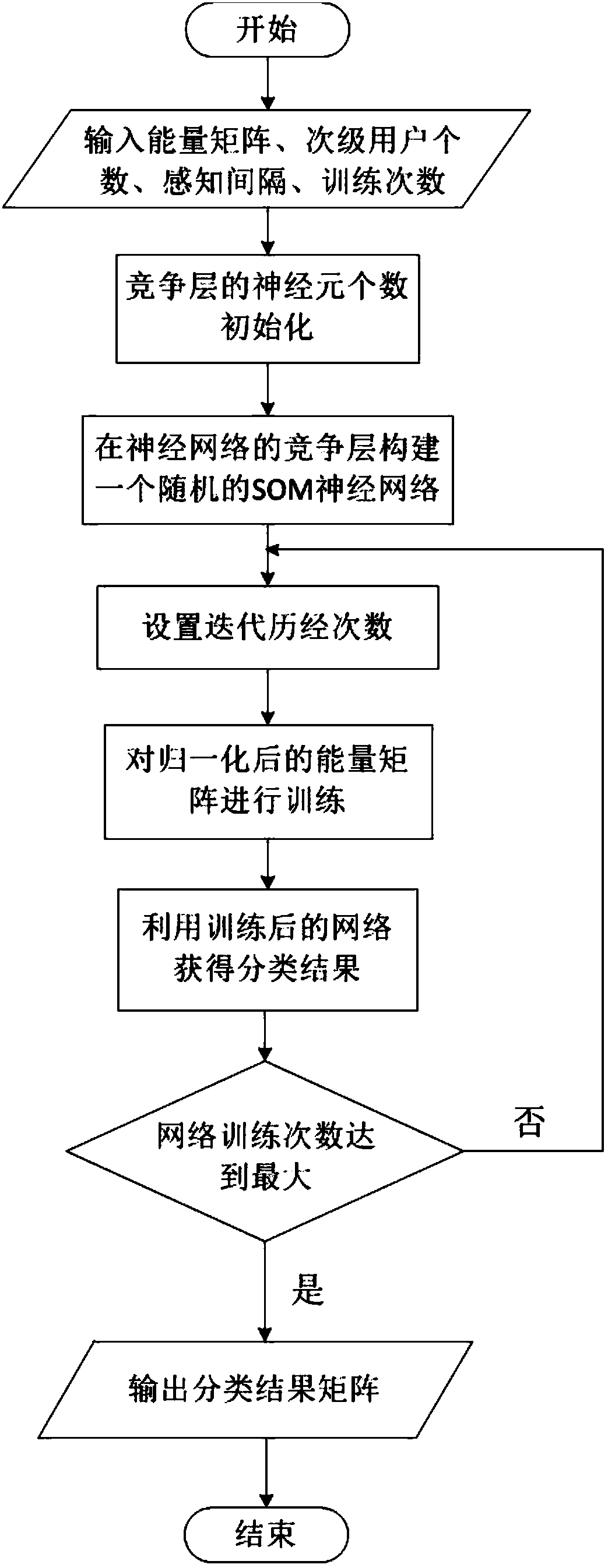
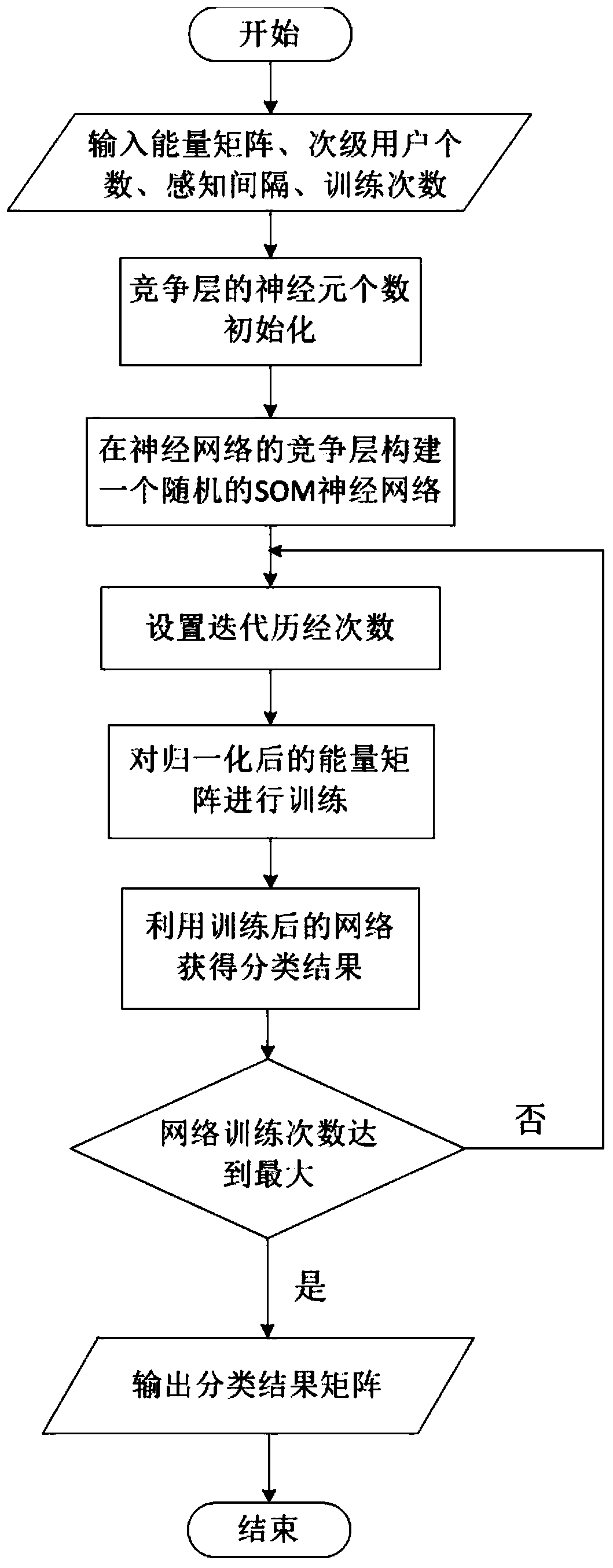
ActiveCN107592635ABroad room for developmentEliminate shortcomingsSecurity arrangementHigh level techniquesMachine learningCognitive radio
The present invention discloses an SOM neural network-based malicious user discrimination method in cognitive radio. The method of the present invention utilizes an SOM neural network to learn the distribution characteristics of an input energy matrix, effectively classifies the input according to the learning results, and comprises the step of firstly introducing a suspicious degree concept, wherein the suspicious degree is distributed according to the number of the secondary users of each type after every time training. In order to eliminate the defects of the conventional SOM neural network, the present invention further provides an average suspicious degree concept. The concrete steps comprise obtaining an energy matrix, utilizing an SOM neural network algorithm to train the energy matrix to obtain a classification matrix, calculating the suspicious degree of each secondary user, constructing an index matrix and repeating the training process, averaging the suspicious degrees obtained at each time, namely obtaining the average suspicious degree, utilizing the average suspicious degree to classify the secondary users, and identifying the malicious users or the normal users.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Composite soft form board liquid material plasma spray method for preparing gas-sensitive coating of hollow micro-nano structure
ActiveCN109182952ALarge specific surface areaImprove work efficiencyMolten spray coatingRoom temperaturePlasma sprayed
The invention discloses a composite soft form board liquid material plasma spray method for preparing a gas-sensitive coating of a hollow micro-nano structure and belongs to the technical fields of engineering and material science. The spray method comprises the specific steps that suspension liquid of a hollow spherical shell structure serves as a liquid material, wherein the suspension liquid issynthesized through a composite soft form board method; the gas-sensitive coating of the hollow micro-nano structure is prepared in a manner of liquid material plasma spray; and high response is madeto specific gas under the conditions of the low temperature even the room temperature, and the response / recovery time of the gas-sensitive coating is shorted, and long-time stability of the gas-sensitive coating is good. The gas-sensitive coating prepared through the method is controllable in structural appearance, high in specific surface area, good in gas-sensitive performance and low in cost.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
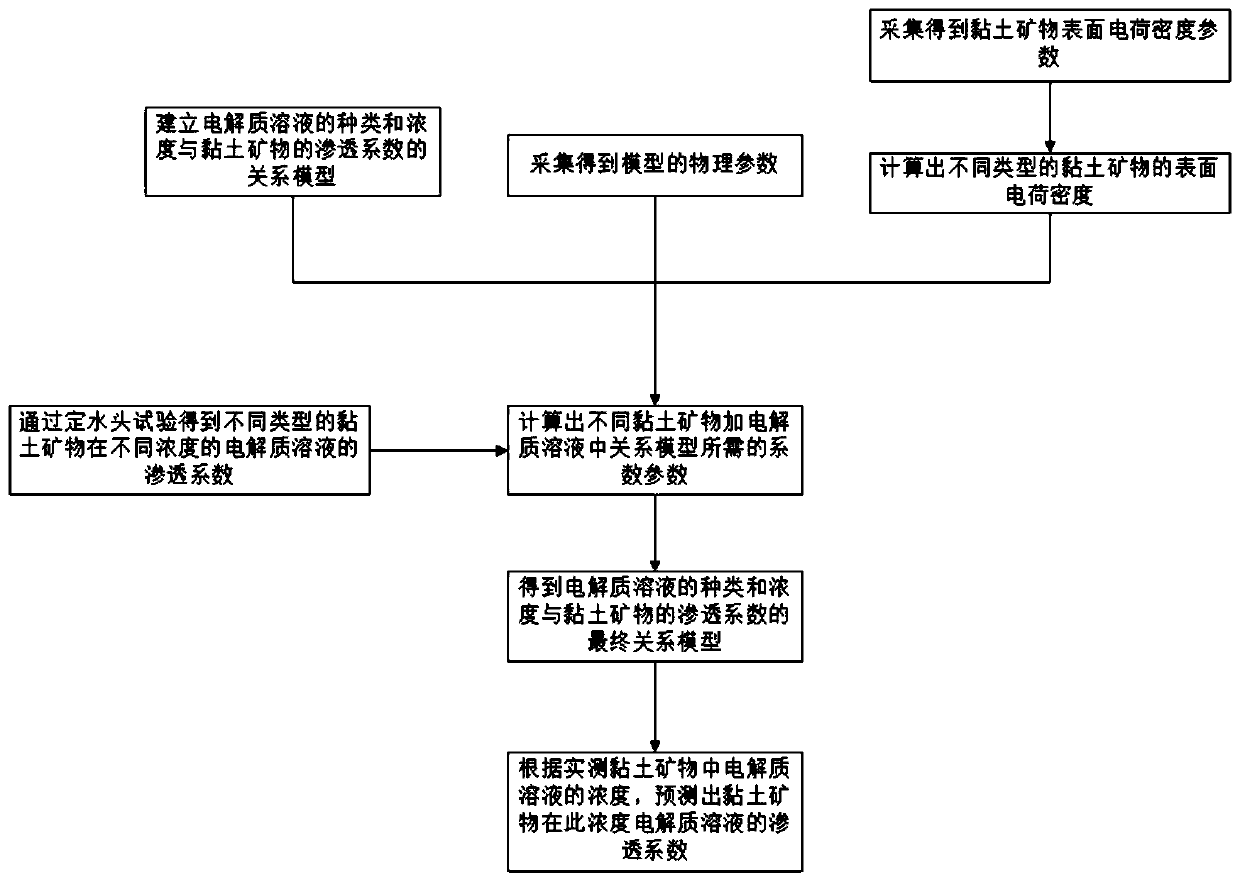
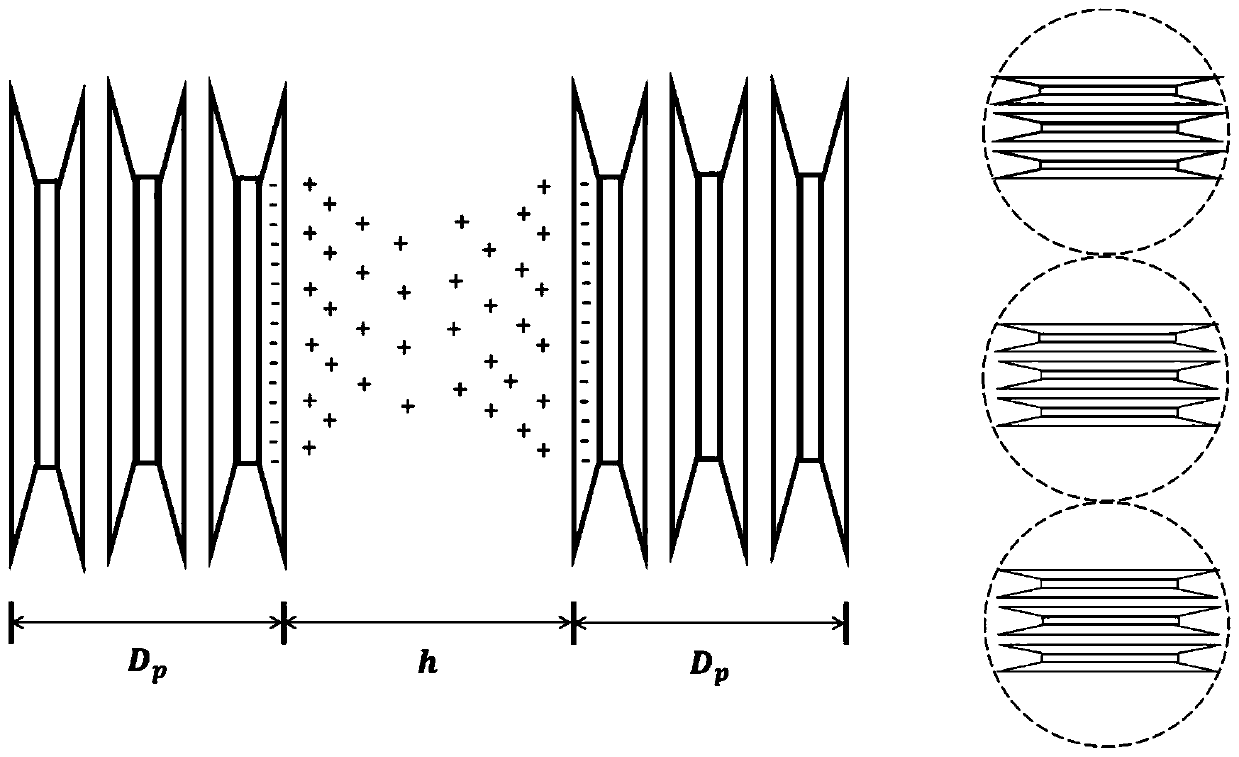
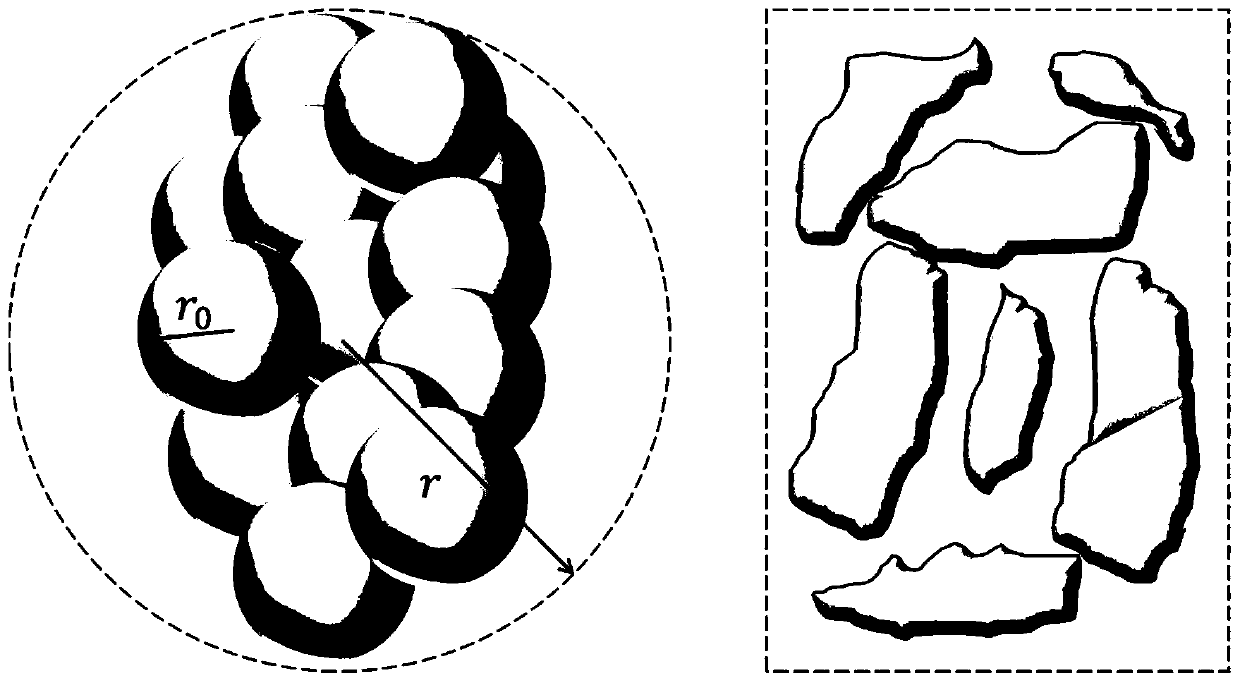
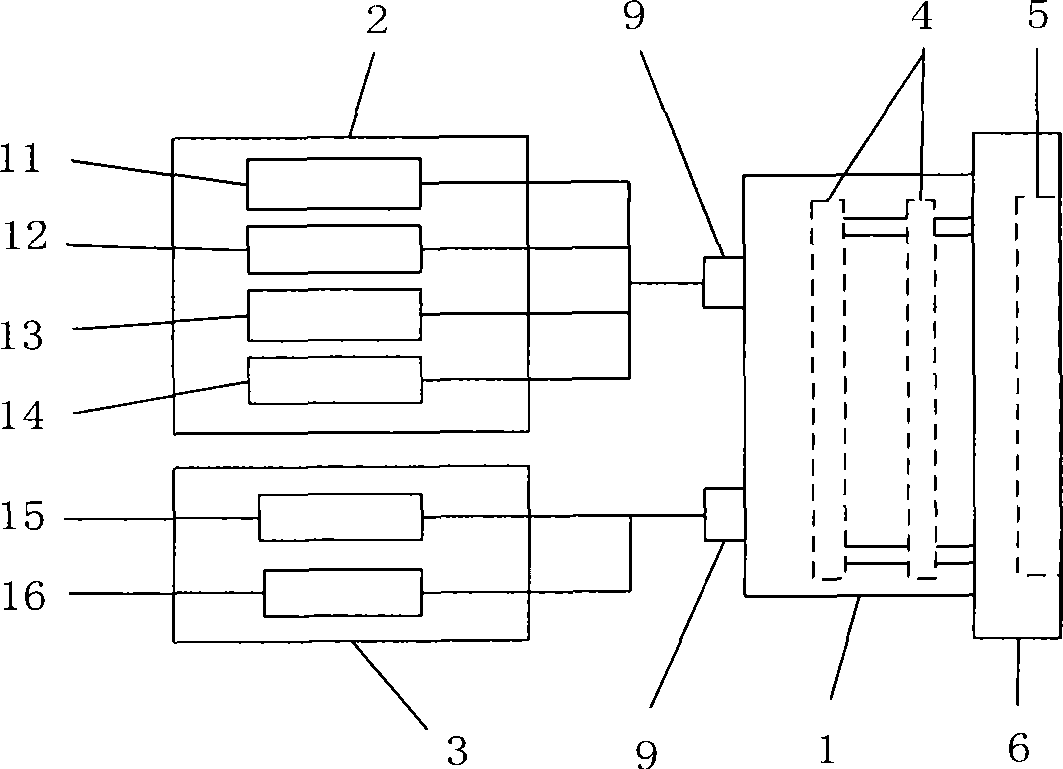
Method for predicting saturated permeability coefficient of clay mineral in electrolyte solution
ActiveCN109856028ASuitable for practical applicationGuaranteed unchangedPermeability/surface area analysisClay mineralsOsmotic coefficient
The invention provides a method for predicting a saturated permeability coefficient of a clay mineral in an electrolyte solution. The method comprises: step one, establishing a relationship model between types and concentrations of electrolyte solutions and permeability coefficients of the clay minerals; step two, carrying out collection to obtain a physical parameter of the model and a clay surface charge density parameter; step three, calculating surface charge densities of different types of clay minerals in a polar solution; step three, carrying out fixed-water-head testing to obtain permeability coefficients of different types of clay minerals certain designated electrolyte solutions with different concentrations and calculating relevant parameters needed by the model based on the relationship model and the surface charge densities of the clay mineral in the polar solution; and step four, on the basis of the relationship model with relevant parameters introduced and an actually measured electrolyte solution concentration, predicting a permeability coefficient of a clay mineral in the electrolyte solution with the concentration. Compared with the prior art, the invention provides a method capable of predicting the permeability coefficient of the clay mineral accurately theoretically.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
An automatic foam proportional mixing digital display controlling module
InactiveCN101543668AFlexible composition of closed-loop control loopsMeet the control precision requirementsControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsFire rescueBrushless motorsEngineering
The present invention pertains to the field of firefighting equipment, concretely relates to an automatic foam proportional mixing digital display controlling module and consists of microcomputer control unit, sensor unit and driver unit. The microcomputer control unit consists of circuit board component, electric signal connector, display and operating mechanism, and housing. They are overlapped in the housing. The circuit board component consists of microprocessor, electric signal input interface, electric signal output interface and digital communication interface. The electric signal connector and the display and operating mechanism are inside the housing; the sensor unit includes water flowmeter, foam flowmeter, and one or several types of level sensor or pressure sensor; the driver unit includes one or several types of DC brushless motor driver and electric valve driver; the electric signal input interface, electric signal output interface and digital communication interface of the electric circuit component are connected to the sensing component of the sensor unit and the driving component of the driver unit with electric signal connector. The present invention may greatly raise the automation degree of proportional foam mixing, and realize accurate control and adjustment of less than 1% mixing proportion.
Owner:SHANGHAI FIRE RES INST OF THE MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY +1
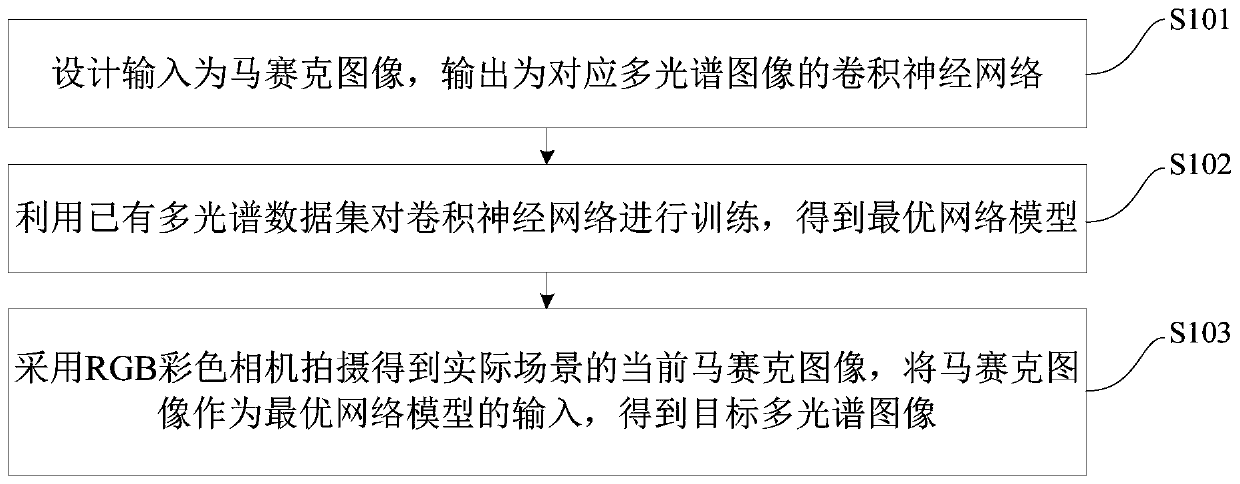
Multispectral imaging method and device based on RGB camera and deep neural network
ActiveCN110443865ASuitable for practical applicationAchieving federated acquisition2D-image generationNeural architecturesDeep neural networksNetwork model
The invention discloses a multispectral imaging method and device based on an RGB camera and a deep neural network, and the method comprises the following steps: designing a convolutional neural network which takes a mosaic image as an input and takes a corresponding multispectral image as an output; training the convolutional neural network by using the existing multispectral data set to obtain an optimal network model; and shooting by adopting an RGB color camera to obtain a current mosaic image of an actual scene, and taking the mosaic image as the input of the optimal network model to obtain a target multispectral image. According to the method, calculation imaging from mosaic images to multispectral images can be directly completed by utilizing the deep neural network, and the methodis more suitable for practical application and is simple and easy to implement.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
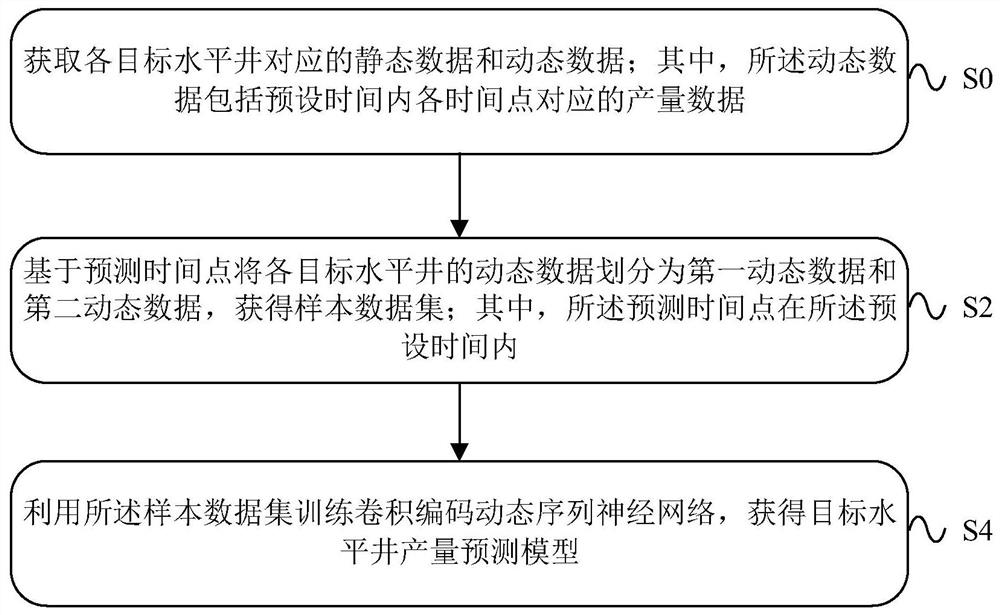
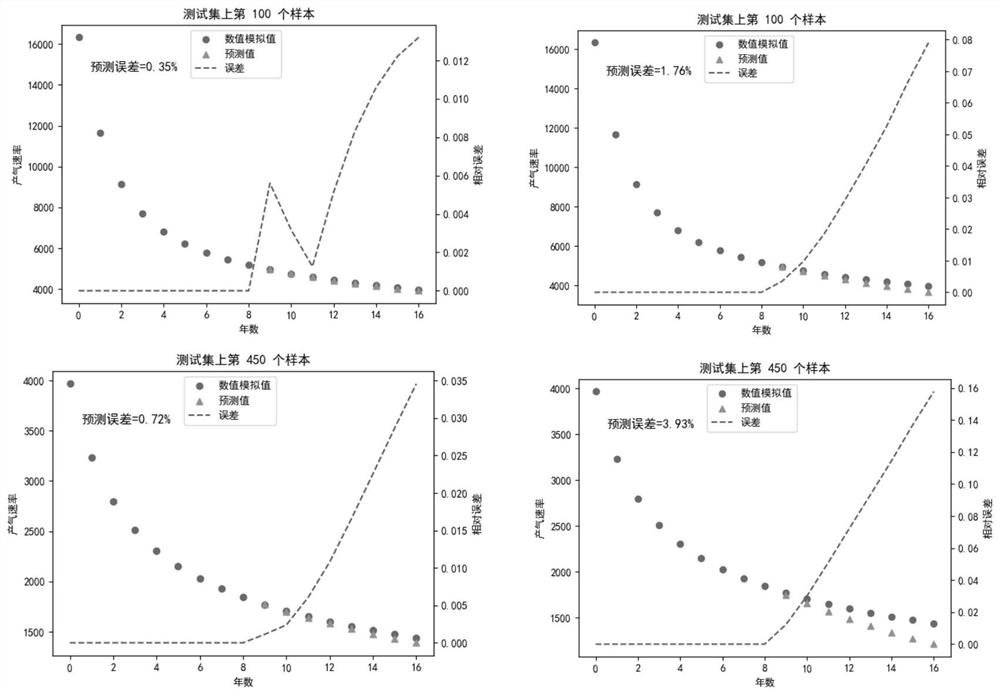
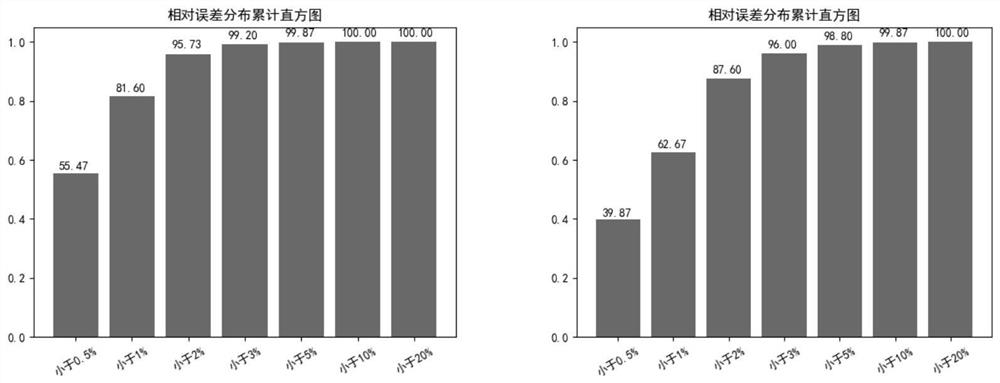
Yield prediction method, device and equipment based on convolutional coding dynamic sequence network
The embodiment of the invention provides a yield prediction method, device and equipment based on a convolutional coding dynamic sequence network. The yield prediction method comprises the steps of obtaining static data and dynamic data corresponding to each target horizontal well, wherein the dynamic data comprises yield data corresponding to each time point in the preset time; dividing the dynamic data of each target horizontal well into first dynamic data and second dynamic data based on the prediction time point to obtain a sample data set, wherein the prediction time point is within the preset time; and training the convolutional coding dynamic sequence neural network by using the sample data set to obtain a target horizontal well yield prediction model. According to the embodiment of the invention, the accuracy of productivity prediction of the fractured horizontal well can be improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
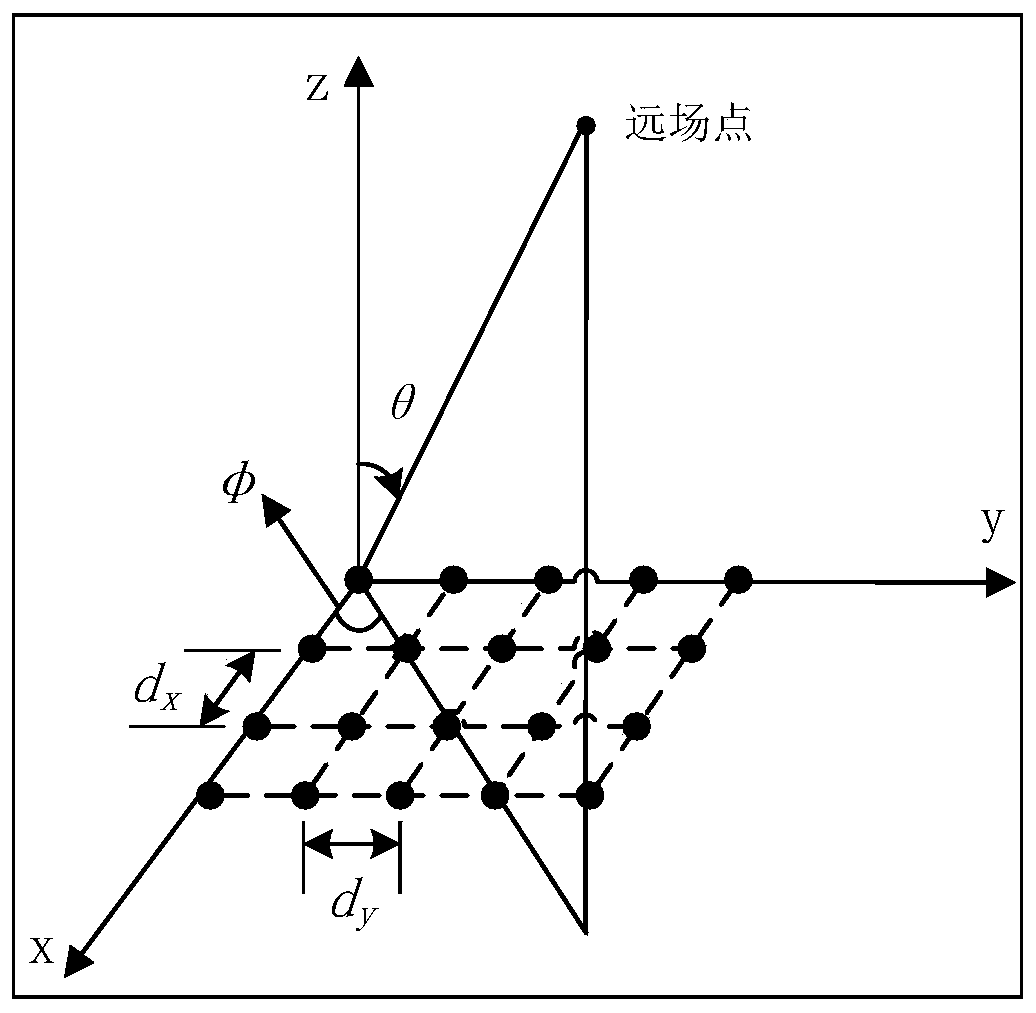
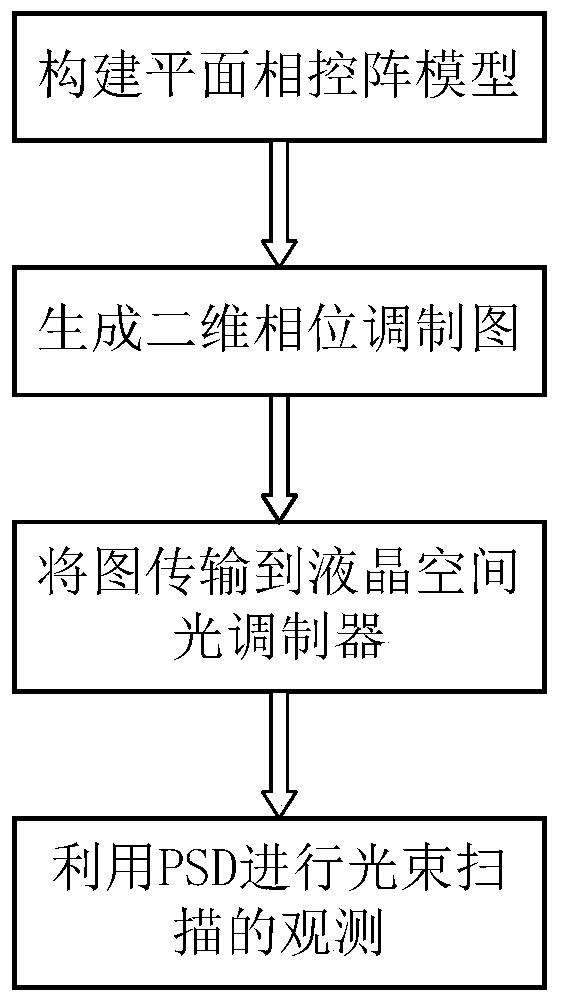
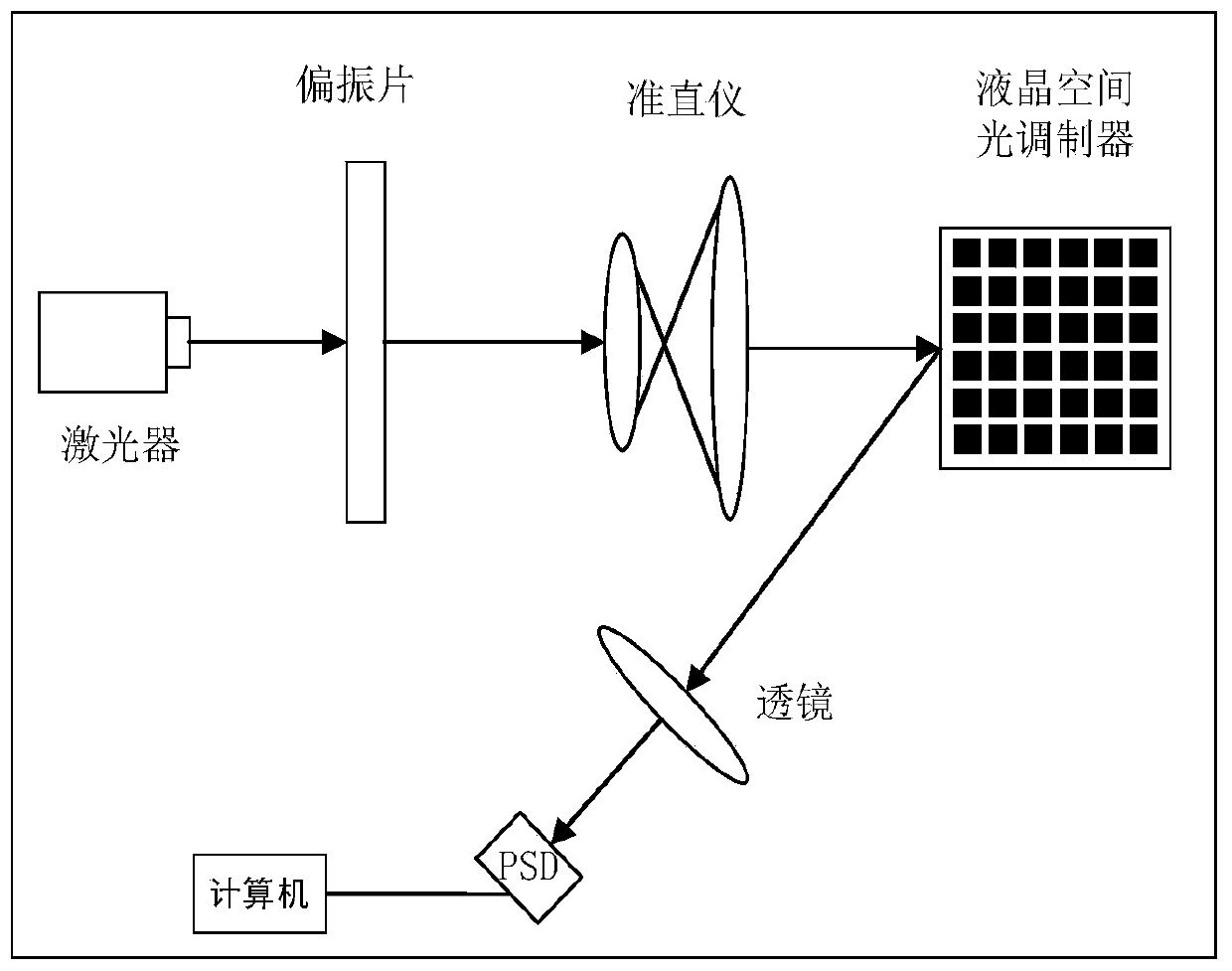
Planar phased array-based two-dimensional beam scanning method
InactiveCN109782433AContinuous scanHigh diffraction efficiencyStatic indicating devicesElectromagnetic transmissionComputational physicsPhysics
The invention discloses a planar phased array-based two-dimensional beam scanning method. According to the prior art, when a liquid crystal spatial light modulator is adopted to deflect a two-dimensional beam, only a limited deflection angle can be realized; a one-dimensional phase modulation diagram needs to be rotated; an entire scanning range is in sparse and uneven concentric circle distribution; and as a scanning angle increases, diffraction efficiency is seriously degraded, and as a result, problems such as a problem of failure to meet the practical requirements of capture, tracking andaiming (ATP) in spatial optical communication which require beam continuous scanning can be solved. With the method adopted, the problems of scanning range discreteness and uneven distribution can besolved, diffraction efficiency can be improved, and the requirements of practical application can be better met.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
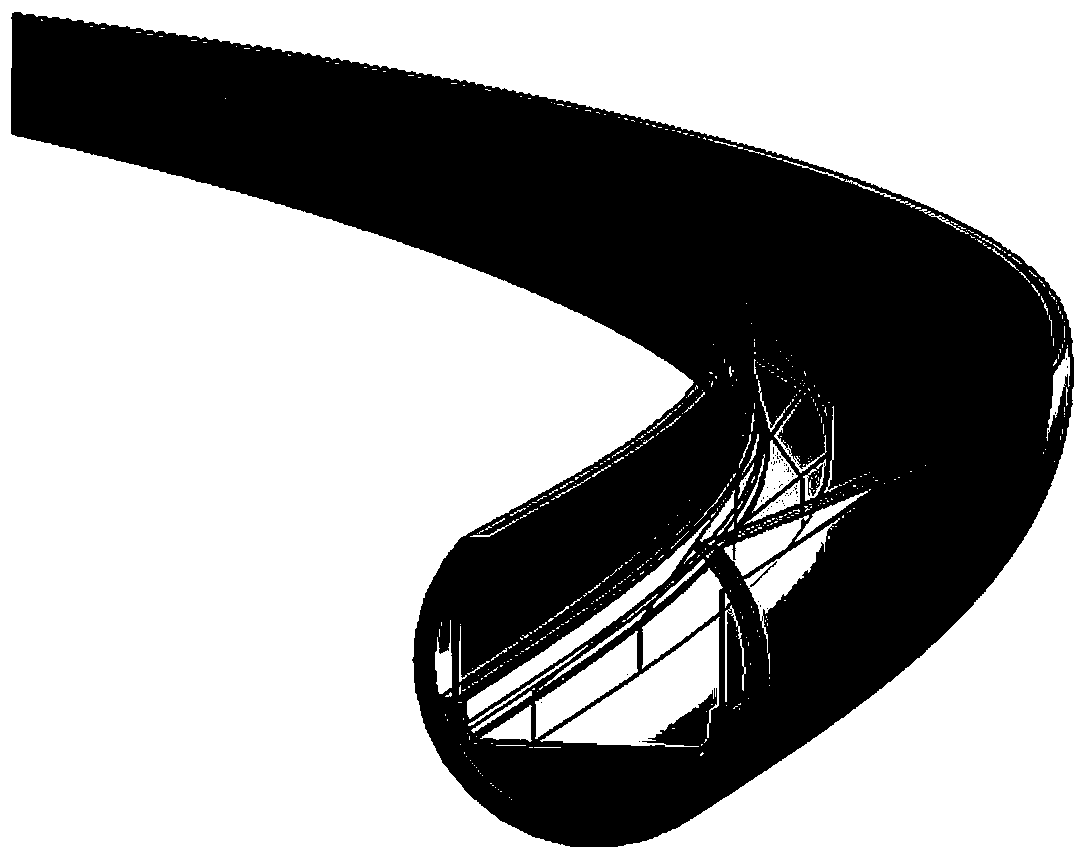
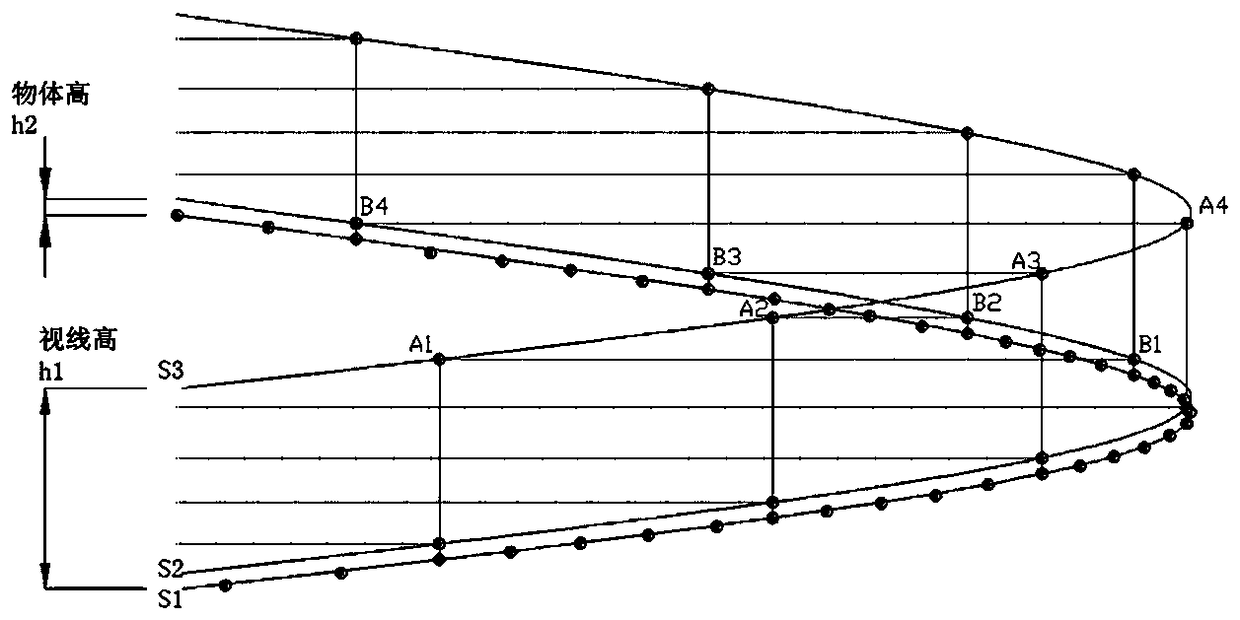
Method for calculating three-dimensional stopping sight distance of urban underground road
ActiveCN108959703AMeet the line of sight requirementsMeet the requirements of parking sight distanceDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsViewpointsSimulation
The invention in particular relates to a method for calculating the three-dimensional stopping sight distance of an urban underground road. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of determining a viewpoint and an object position, drawing a sight line and a section envelope line, generating a final sight distance envelope surface and judging whether a sight distance requirement is satisfied or not. The method in the invention has the advantages that: from the three-dimensional linear combination space angle of a road, it closes to the actual situation; whether the road satisfies the stopping sight distance requirement or not can be rapidly verified through a convenient method; therefore, the method has the important effect for verification and optimal design; and thus, the method is simple and feasible, and suitable for practical application.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ENG DESIGN INST GRP
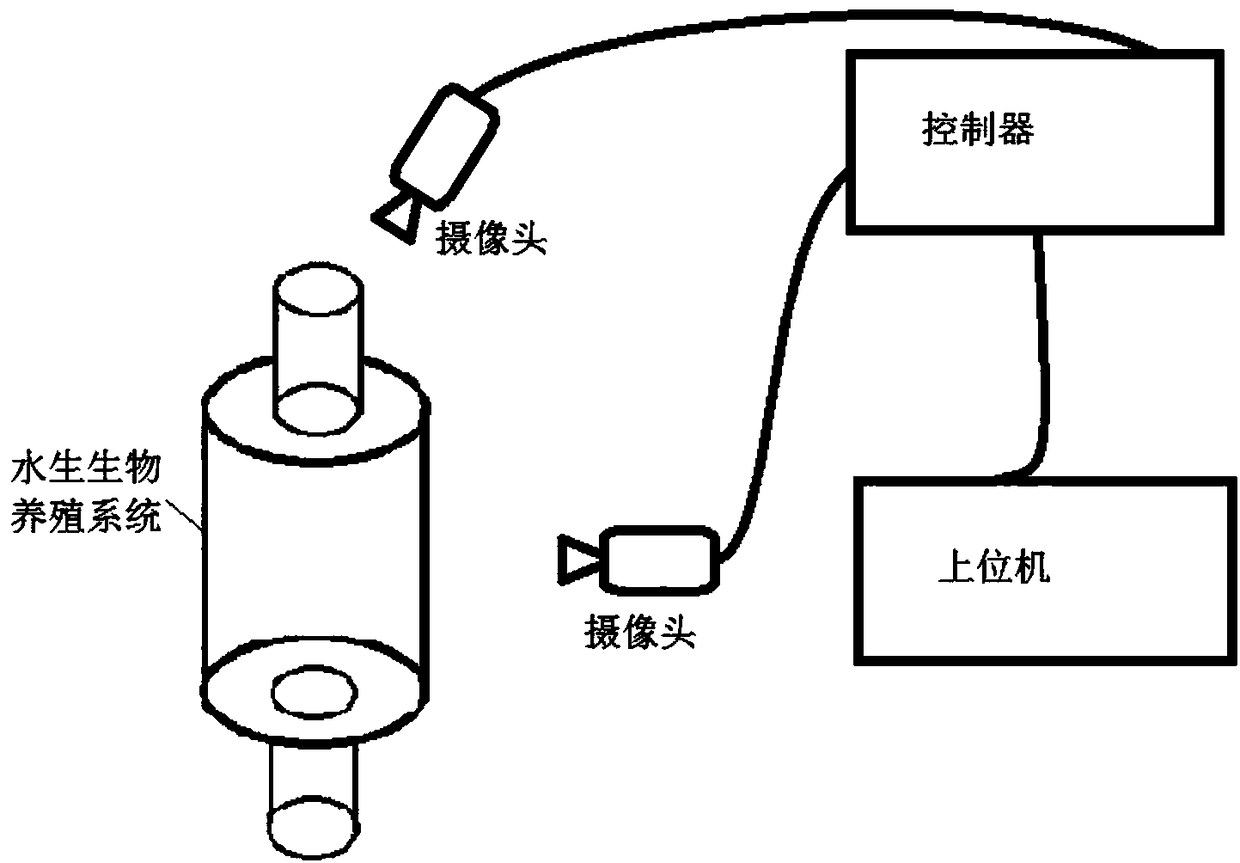
Multi-target unlabelled aquatic organism identification tracking method and system
ActiveCN108376238AIncrease credibilityReduce error rateCharacter and pattern recognitionVideo storageVideo transmission
The invention discloses a multi-target unlabelled aquatic organism identification tracking method and system; the method comprises the following steps: 1, using an aquatic organism culturing system toculture aquatic organisms; 2, using two cameras, arranged on the top and a side face of the aquatic organism culturing system, to respectively gather videos of the aquatic organisms, and sending thegathered videos to a controller; 3, data processing: using the controller to process the video images gathered by the two cameras, thus finally obtaining aquatic organism three dimensional tracks. Theproblems that in existing organism tracer technology the organism individual distinguish capability is low, and too much video storage space is taken are solved via the unlabelled identity identification technology and video three dimensional processing.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Infrared beacon underground parking space navigation system based on infrared technology and method thereof
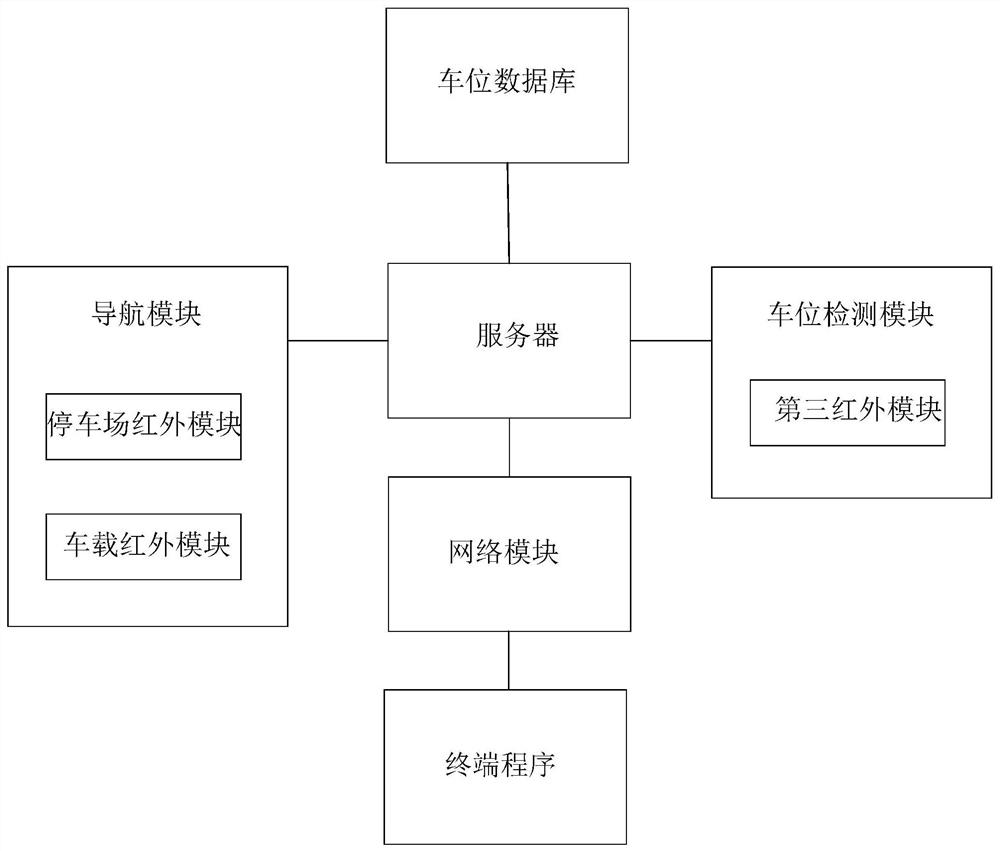
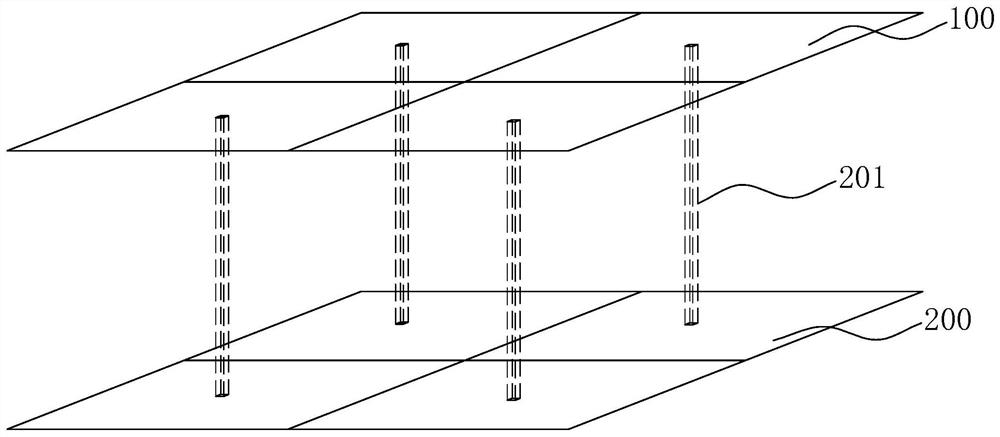
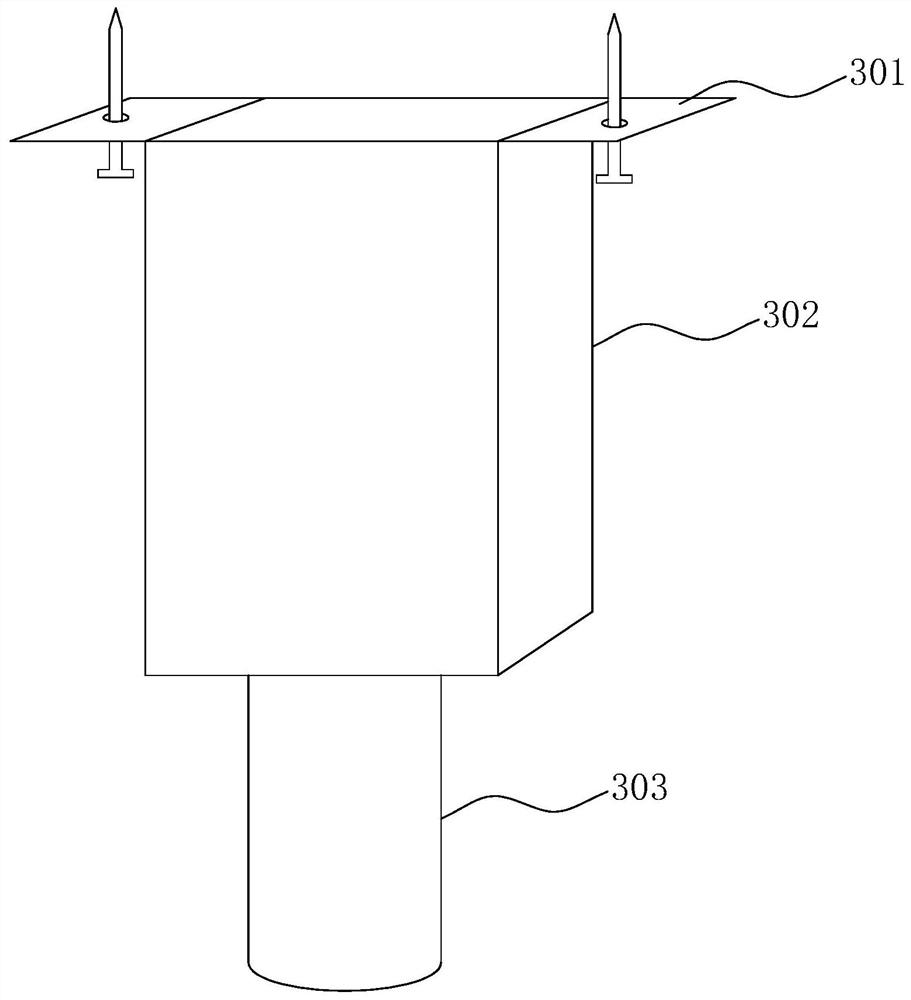
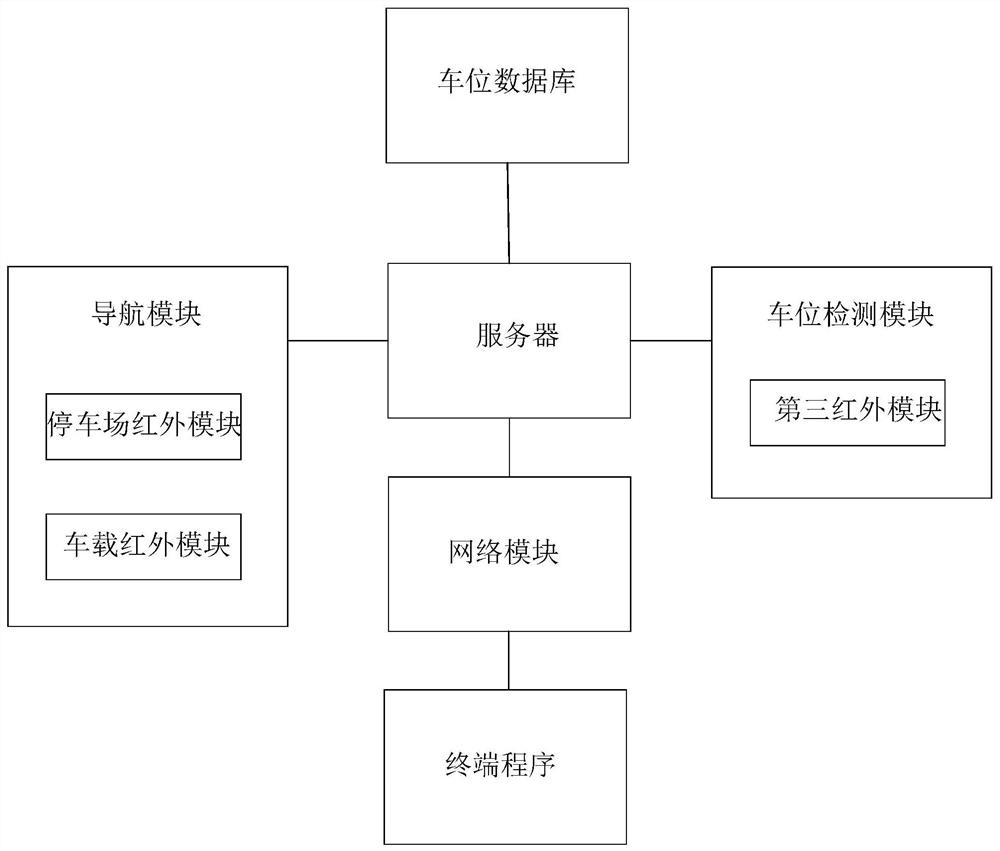
ActiveCN111986510AAccurate positioning accuracyReduce distractionsIndication of parksing free spacesIn vehicleParking space
The invention relates to an infrared beacon underground parking space navigation system based on an infrared technology. The infrared beacon underground parking space navigation system comprises a navigation module, a parking space detection module, a parking space database, a network module, a server and a terminal program, the navigation module comprises a parking lot infrared module and a vehicle-mounted infrared module; the parking lot infrared module comprises a plurality of first infrared modules, the first infrared modules are arranged at the top of the parking lot to form a positioningnetwork, and the first infrared modules are used for transmitting infrared signals with position information to the vehicle-mounted infrared modules; the parking lot infrared module further comprisesa second infrared module arranged at the entrance of the parking lot, and the second infrared module is used for transmitting an infrared signal with map downloading information to the vehicle-mounted infrared module. The method has the advantages that after the optimal parking space is distributed, the vehicle owner goes to the optimal parking space according to the route to park the vehicle, and the vehicle is not stopped in the optimal parking space and the optimal parking space is occupied, so that the method is more suitable for practical application.
Owner:绍兴创元电子科技有限公司
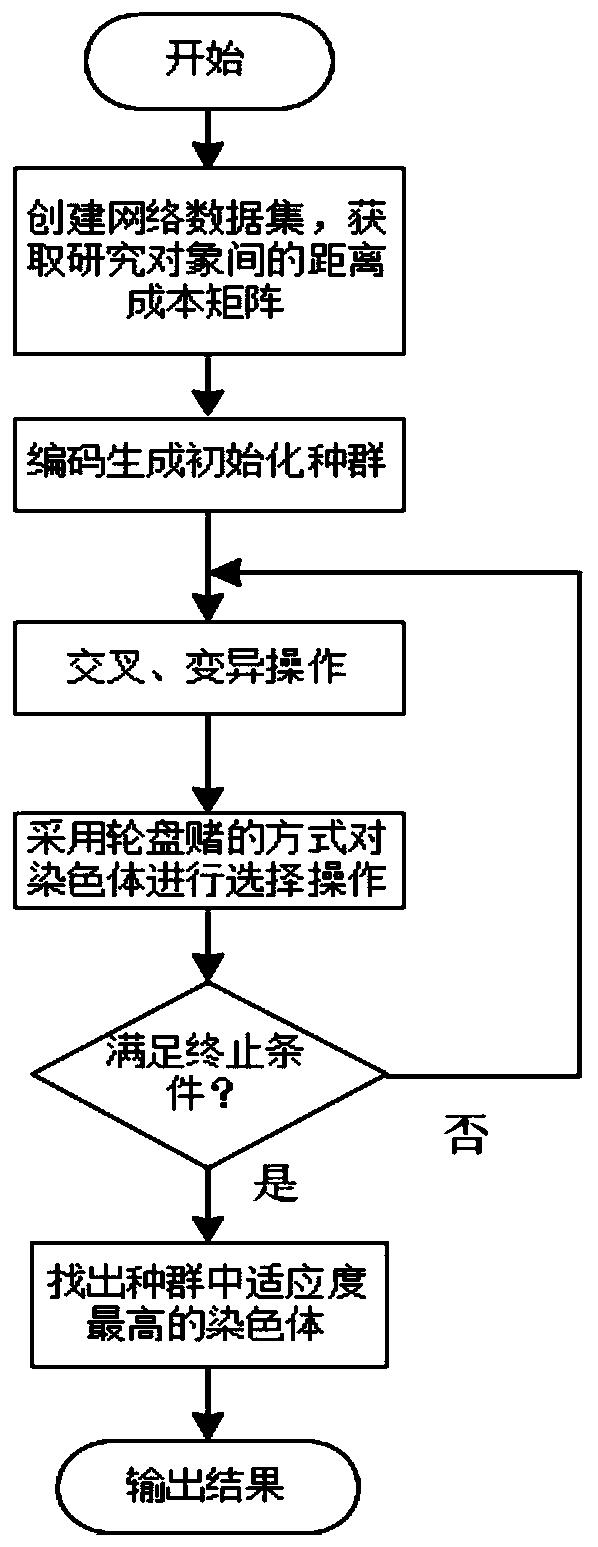
Vehicle path optimization method based on road network accessibility
InactiveCN110689165ASolving Path Planning ProblemsHave pursuasive powerForecastingGenetic algorithmsData setSimulation
The invention discloses a vehicle path optimization method based on road network accessibility, and the method comprises the steps: firstly building a network data set of a research region, and obtaining a real road distance between research object points; then, under the condition that vehicle load constraints are met, carrying out coding operation on the distribution center and the client pointsin a natural number coding mode, and completing population initialization; after crossover and mutation operations are carried out on the population, adopting a roulette mode to carry out selection operation on the current population, screening out chromosomes with relatively high fitness to form a new population, and repeating the crossover, mutation and selection operations until an iteration termination condition is met; and finally, outputting the chromosome with the highest fitness in the population, i.e., the optimal path scheme for vehicle distribution. The invention provides a vehiclepath optimization method based on road network accessibility, which is more suitable for practical application.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
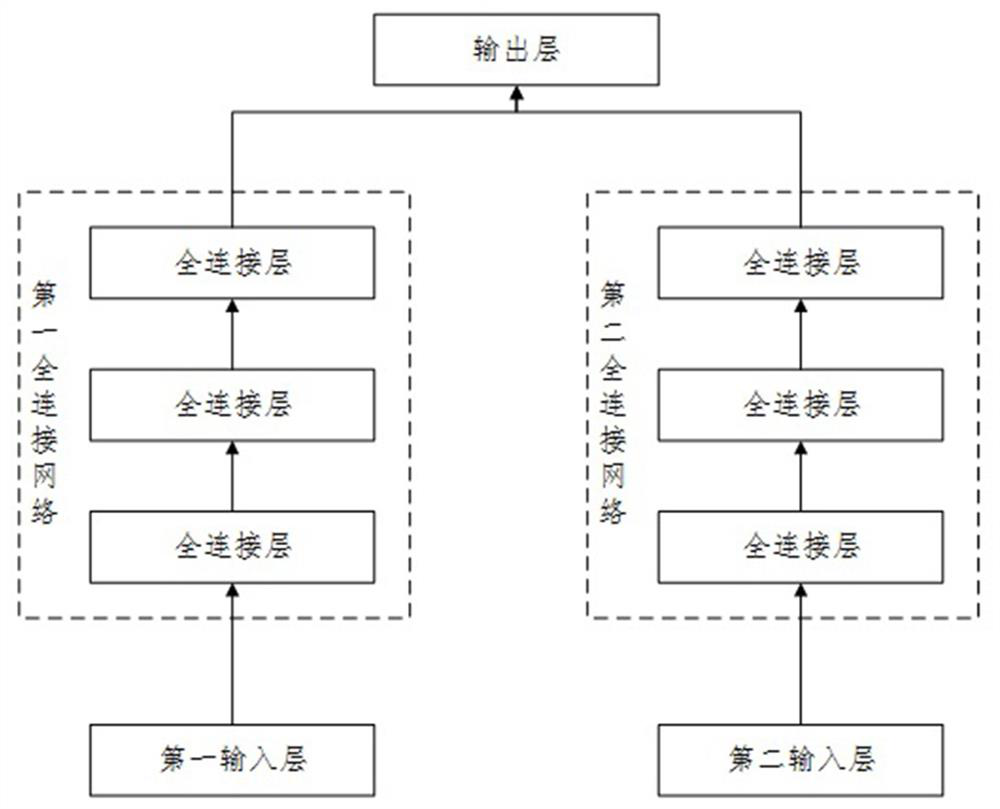
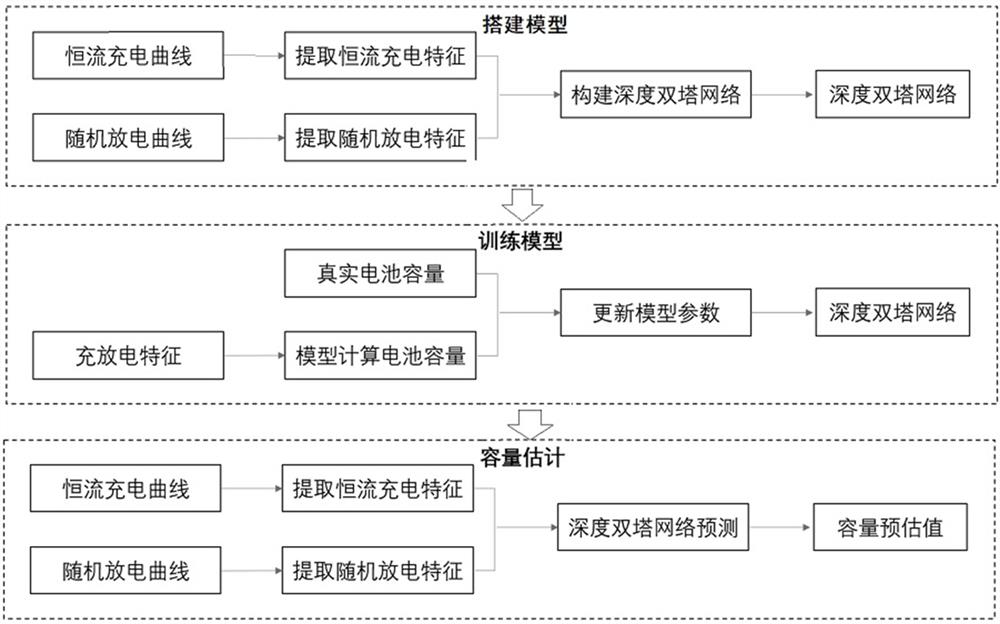
Battery capacity estimation model and method based on double-tower deep learning network
The invention relates to the technical field of battery capacity prediction, and in particular, relates to a battery capacity estimation model and method based on a double-tower deep learning network. The battery capacity estimation model comprises a first input layer used for inputting a constant current charging characteristic sequence, a first fully connected network for processing the constant current charging characteristic sequence and generating a first output, a second input layer used for inputting a random discharge characteristic sequence, a second fully connected network for processing the random discharge characteristic sequence and generating a second output, and an output layer used for combining the first output and the second output to generate an estimated battery capacity. The method is realized based on the model. The method has higher battery capacity estimation precision.
Owner:杭州宇谷科技股份有限公司
Novel nanometer flame-retardant composite material
InactiveCN104164062AWide range of applicationsReduce dosagePolyethylene terephthalate glycolFire retardant
The invention discloses a novel nanometer flame-retardant composite material. The composite material is characterized by comprises the following substances by weight: 35 to 70 parts of glass fiber reinforced polyethylene terephthalate ester, 15 to 23 parts of rare earth phenyl phosphonate, 10 to 20 parts of aluminum hydroxide, 3 to 8 parts of ethylene acrylate, 1 to 9 parts of high density polyethylene, 5 to 9 parts of diammonium phosphate, 3 to 11 parts of hexabromo water dispersion, 4 to 12 parts of superoxide dismutase, 10 to 18 parts of tetra(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxy)pentaerythritol phenylpropionate, 20 to 31 parts of methyl benzoate, 5 to 17 parts of polyvinyl alcohol and 10 to 24 parts of chlorobenzene. The novel nanometer flame-retardant composite material has a wide application scope, reduces the usage amount of a fire retardant, enables cost to be saved, accords with the trend of environmental protection and conservation, is simple and easy to prepare and process, exerts an obvious effect, accords with practical application conditions and is quite possible to be marketed.
Owner:QINGDAO HUA CHENG TIAN MACHINERY MFG
Meteorological field data conversion method suitable for HYSPLIT atmospheric diffusion model
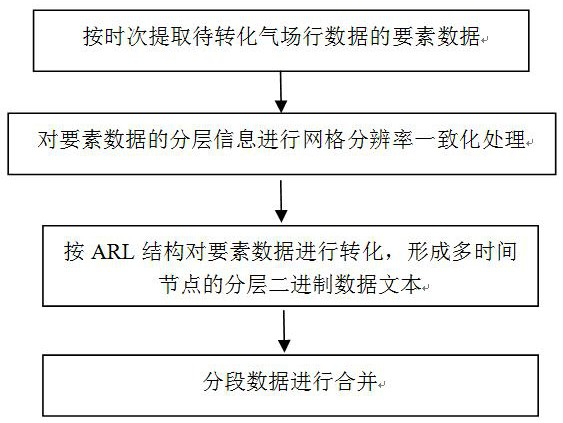
PendingCN112232026AFast merge processingAdd applicable meteorological field data sourcesNatural language data processingField dataPredictive analytics
The invention discloses a meteorological field data conversion method suitable for an HYSPLIT particle Lagrange atmospheric diffusion model, and the method enables the converted meteorological input field data information to be stored in a segmented manner, is high in readability, can achieve the quick combination of segmented data, and generates a meteorological field file needed by the HYSPLIT model; the method can achieve the cross-platform operation, supports LINUX, Windows 7 / 10 and Mac OX platforms, improves the meteorological field file making efficiency required by the HYSPLIT model, increases meteorological field data sources suitable for the model, and the HYSPLIT model is more suitable for practical application of prediction and analysis services.
Owner:南京智汇环境气象产业研究院有限公司 +3
Infrared Beacon Underground Parking Space Navigation System and Its Method Based on Infrared Technology
ActiveCN111986510BAccurate positioning accuracyReduce distractionsIndication of parksing free spacesIn vehicleParking space
This application relates to an infrared beacon underground parking space navigation system based on infrared technology, including: a navigation module, a parking space detection module, a parking space database, a network module, a server and a terminal program; the navigation module includes a parking lot infrared module and a vehicle-mounted infrared module; the parking lot infrared module The module includes several first infrared modules, which are arranged on the top of the parking lot to form a positioning network. The first infrared module is used to transmit infrared signals with location information to the vehicle-mounted infrared module; the parking lot infrared module also includes The second infrared module at the field entrance is used to transmit an infrared signal with map download information to the vehicle-mounted infrared module. The effect of this application: this application considers different situations such as car owners go to the best parking space to park according to the route, stop at the best parking space and the best parking space is occupied after the best parking space is allocated, which is more suitable for practical application.
Owner:绍兴创元电子科技有限公司
Two-way Quantum Time Synchronization Method Based on Frequency Entanglement Light Source
ActiveCN108718218BHigh measurement accuracySimple structureTime-division multiplexPhotonic quantum communicationSignal lightParticle physics
The invention provides a bidirectional quantum time synchronization method based on frequency entangled light sources. Two entangled light sources with same wavelength are placed at a place A and a place B respectively, and signal lights generated by the entangled light sources pass through an optical fiber circulator, are transmitted in opposite directions through a same optical fiber, and are detected by detectors at the opposite places; idle lights generated by the entangled light sources are detected by a detector at a uniform place of the entangled light sources; a clock a at the place arecords the time (tij} and time (t2j} for photons emitted by the entangled light source at the place a to reach the detectors at two places, and a clock b at the place b records time (t3j} and time (t4j} for photons emitted by the entangled light source at the place b to reach the detectors at two places, wherein j is representative of jth photon; the (tij} and (t2j} are subjected to cross-correlation operation to obtain t2-t1; the (t3j} and (t4j} are subjected to cross-correlation operation to obtain t4-t3; the clock difference t0 between the clock a and the clock b is equal to half of the difference of (t2-t1) and (t4-t3). The bidirectional quantum time synchronization method based on the frequency entangled light sources is high in measurement precision, and an applied device is simplein structure.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Malicious user identification method based on som neural network in cognitive radio
ActiveCN107592635BEliminate shortcomingsSuitable for practical applicationSecurity arrangementNetwork planningNeural network learningEngineering
The invention discloses a malicious user discrimination method based on a self-organizing map neural network in a cognitive radio. The invention uses a self-organizing map (referred to as SOM) neural network to learn the distribution characteristics of an input energy matrix, and calculates the input amount according to the learning result. effective classification. First, the concept of "suspiciousness" is introduced, and its size is allocated according to the number of secondary users contained in each category after each training. In order to eliminate the defects of the traditional SOM neural network, the present invention further proposes the concept of "average suspiciousness". The specific steps include: obtaining the energy matrix, using the SOM neural network algorithm to train the energy matrix to obtain the classification matrix, calculating the "suspiciousness" of each secondary user, constructing the index matrix and repeating the training process, and calculating the "suspicious degree" obtained each time degree", that is, the "average suspicious degree", and use the "average suspicious degree" to classify secondary users to identify malicious users or normal users.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Coronary stenosis detection method, device, computer equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN110310256BImprove detection accuracyImprove learning effectImage enhancementImage analysisCoronary arteriesComputer science
A coronary stenosis detection method, device, computer equipment, and storage medium provided by the application obtain detection results by inputting acquired images to be detected into a coronary stenosis detection model; wherein the coronary stenosis detection model includes a backbone network , a segmentation network and a stenosis analysis network, the outputs of the backbone network are respectively connected to the inputs of the segmentation network and the stenosis analysis network; the detection results include coronary artery segmentation results and coronary artery stenosis results. From the structure of the coronary stenosis detection model above, it can be seen that the coronary stenosis detection model includes a segmentation network and a stenosis analysis network. Therefore, the above coronary stenosis detection model is a multi-task model, which can simultaneously realize the detection of the input Segmenting the image, and performing stenosis detection on the input image to be detected, to obtain at least two types of detection results, namely coronary artery segmentation results and coronary artery stenosis results.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING INTELLIGENT MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com