Patents
Literature
145 results about "Meso scale" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
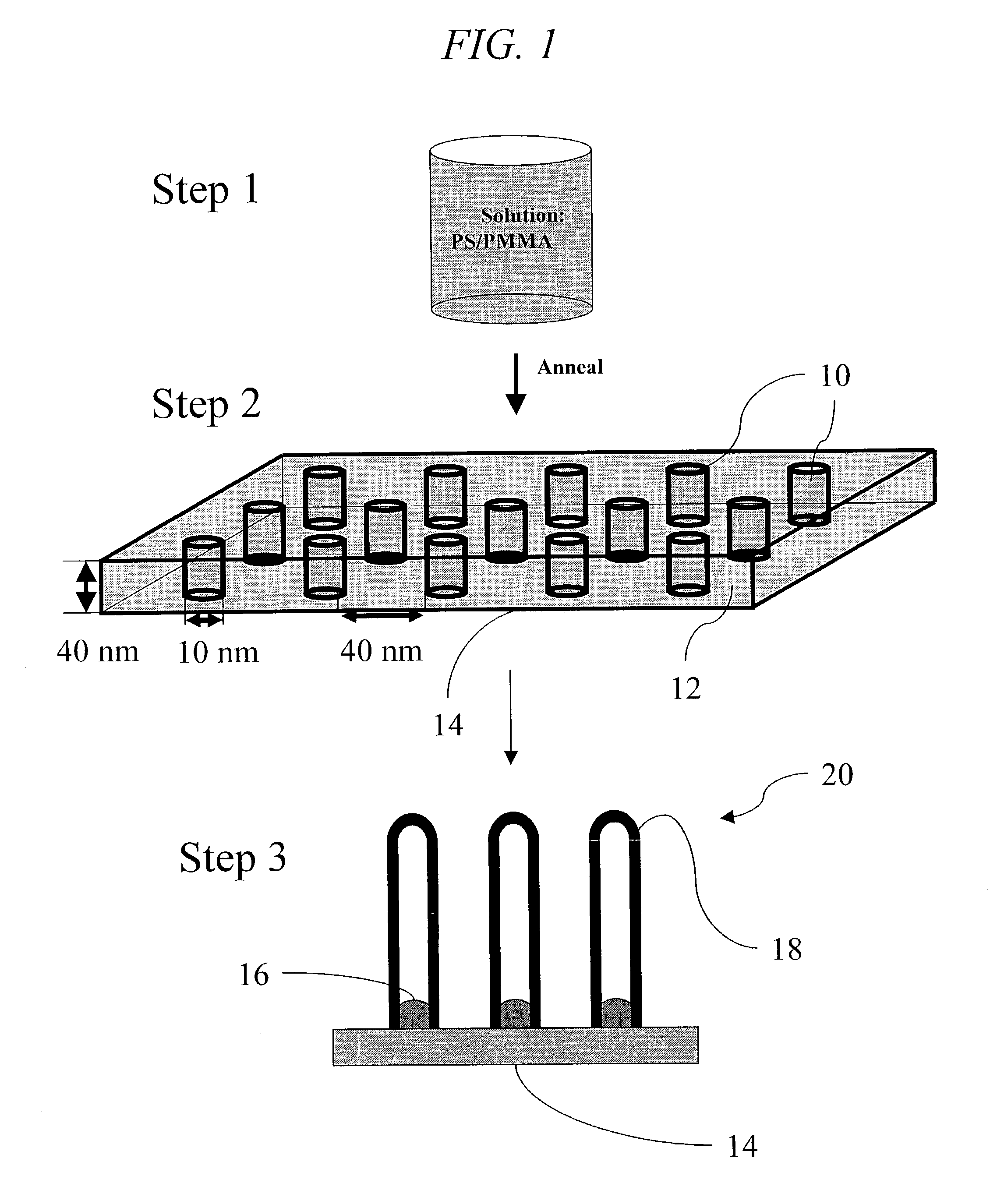
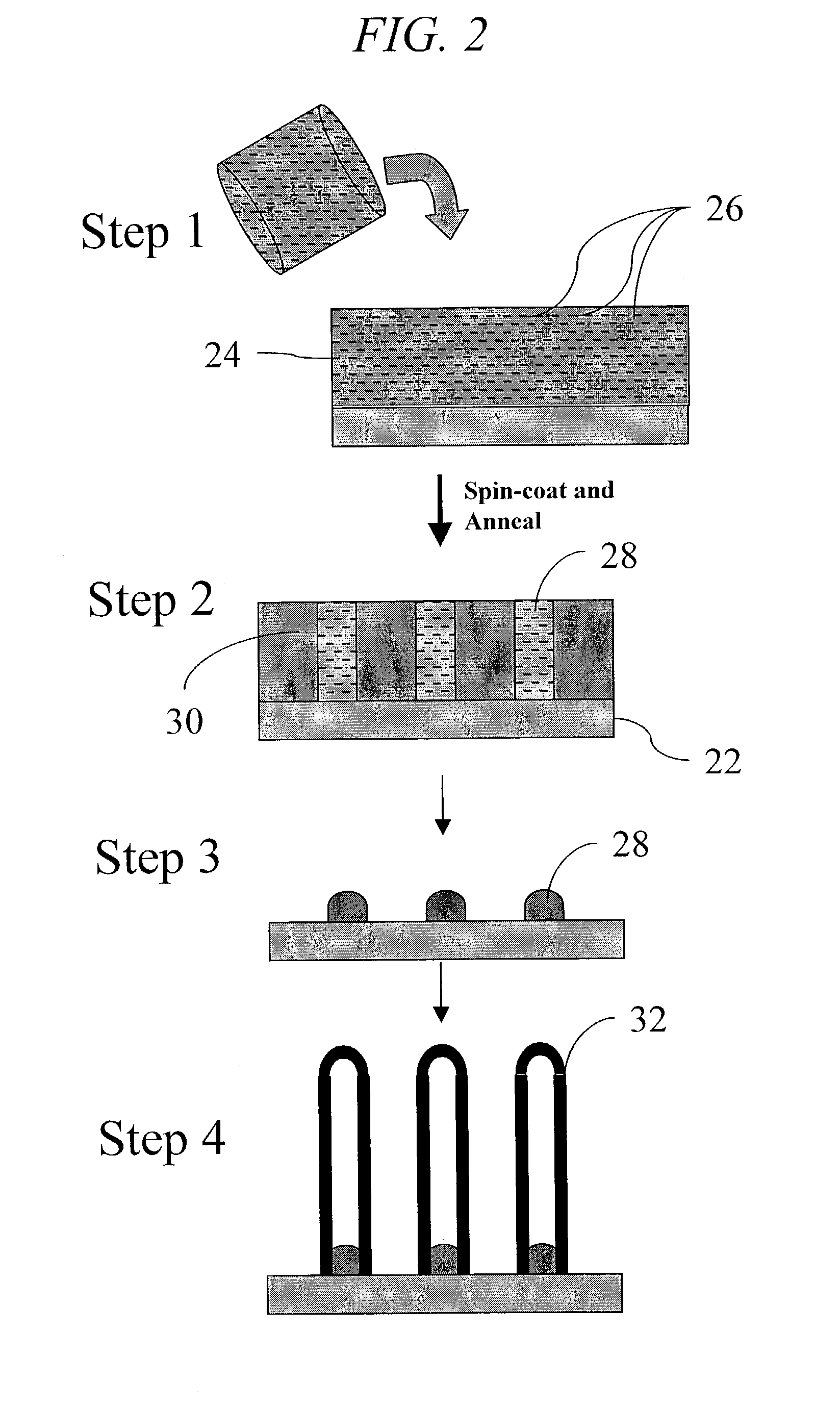
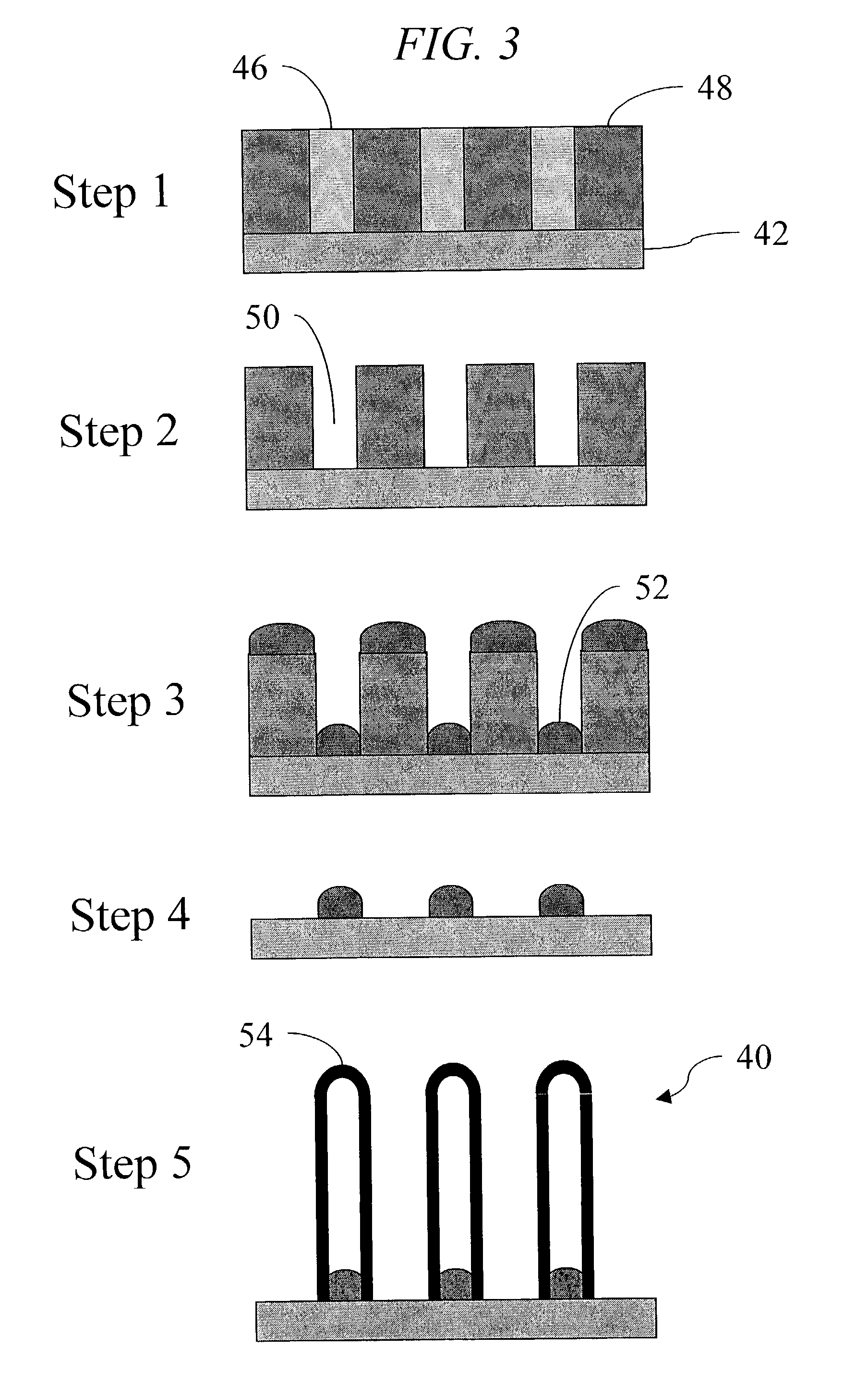
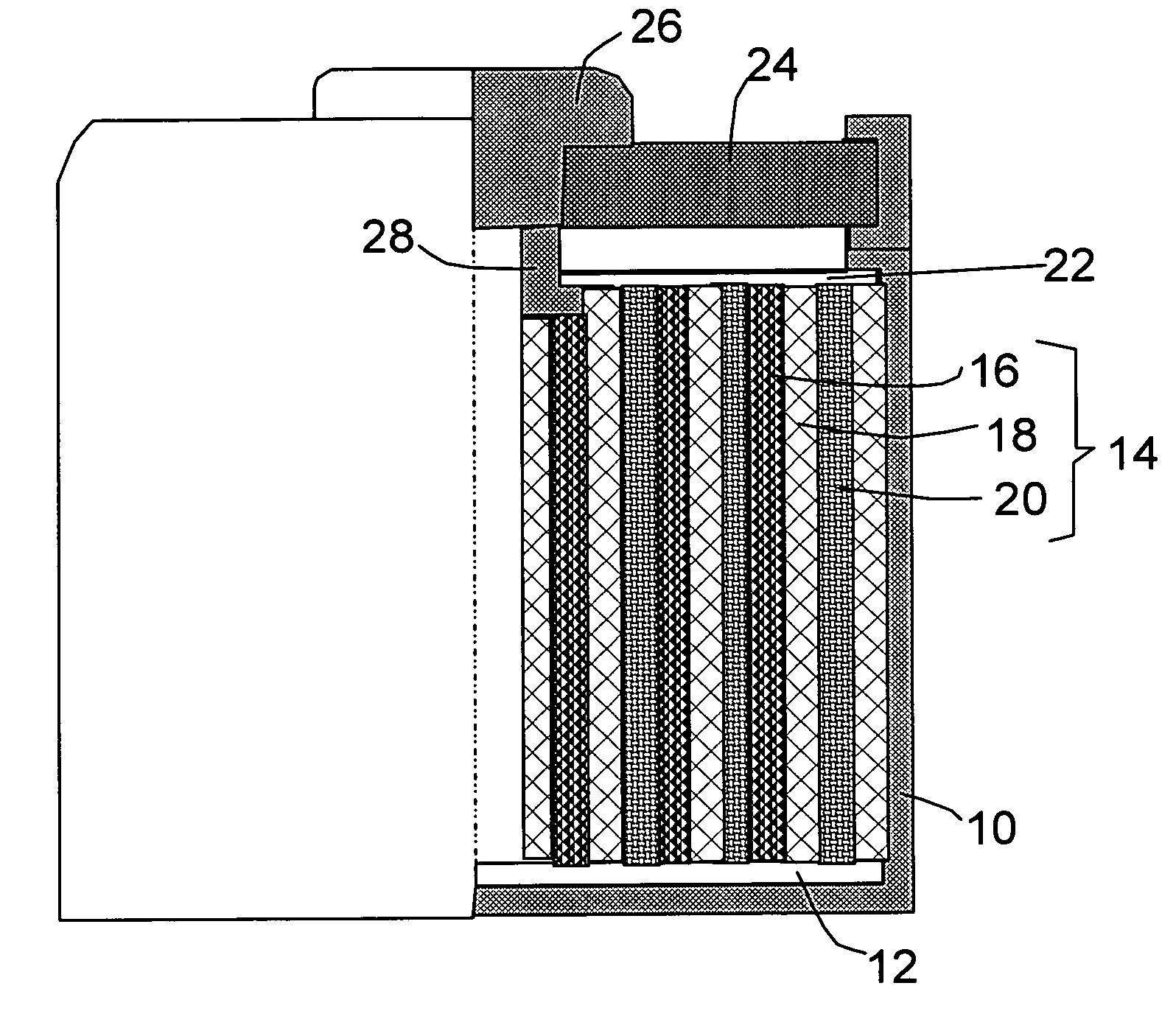
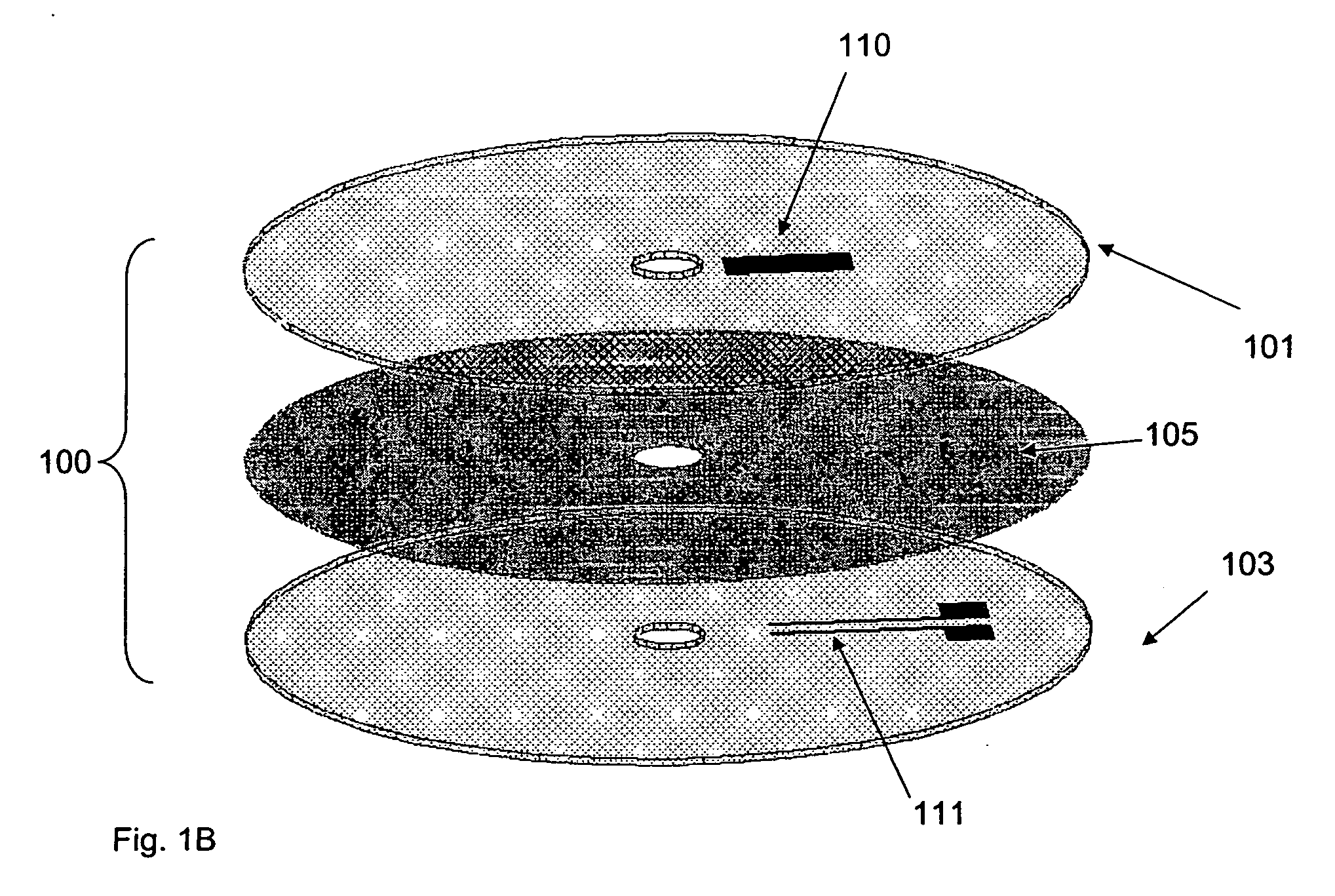
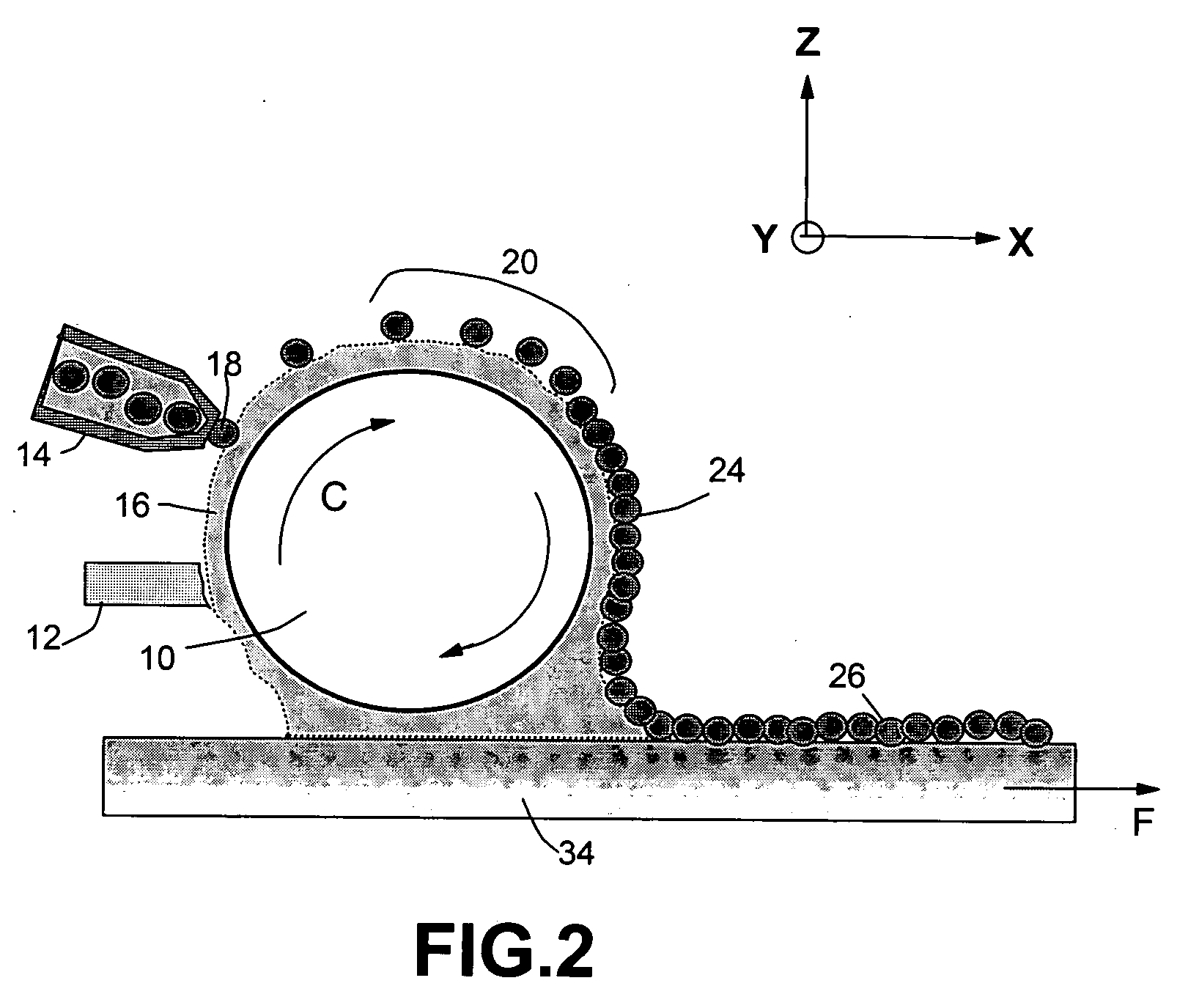
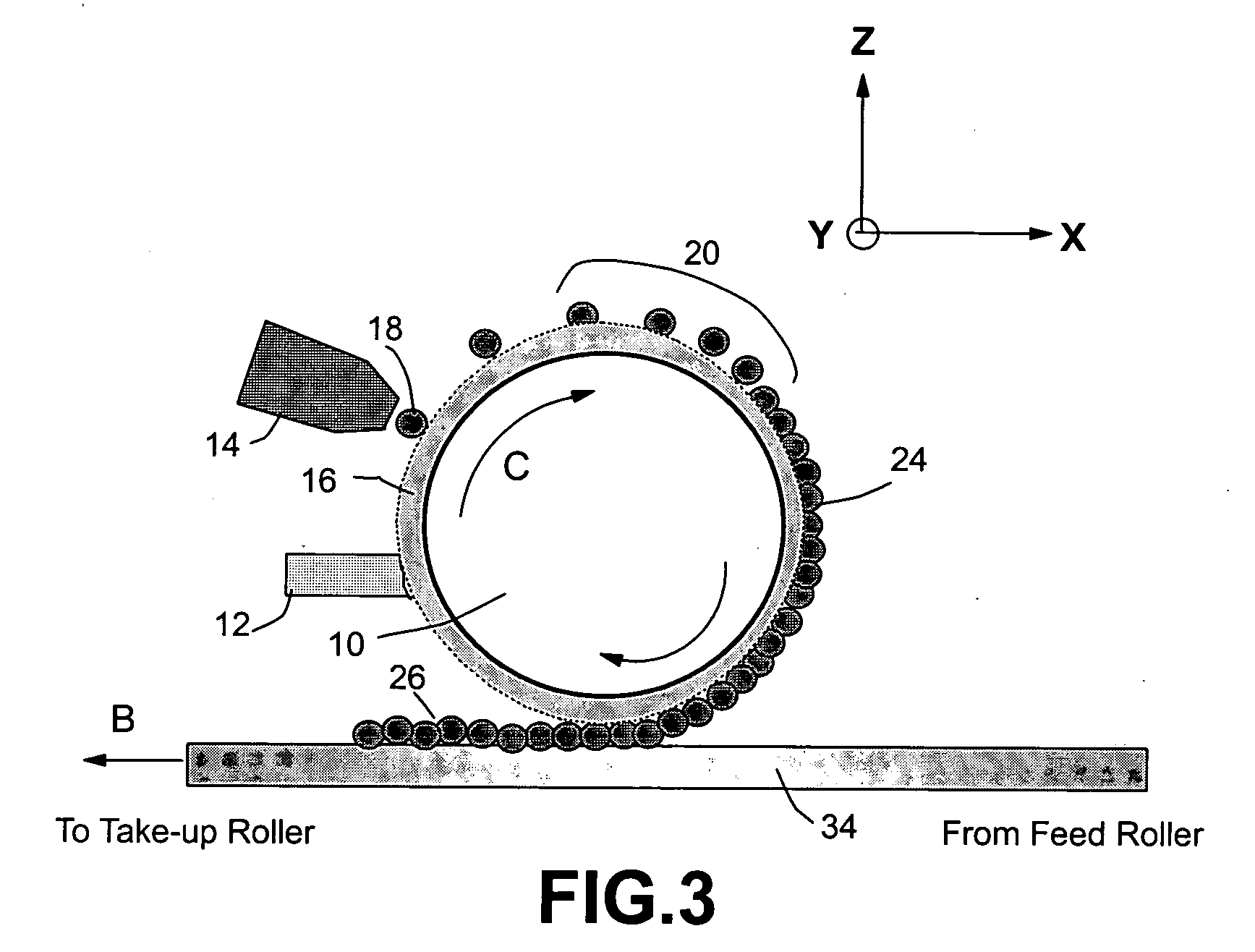
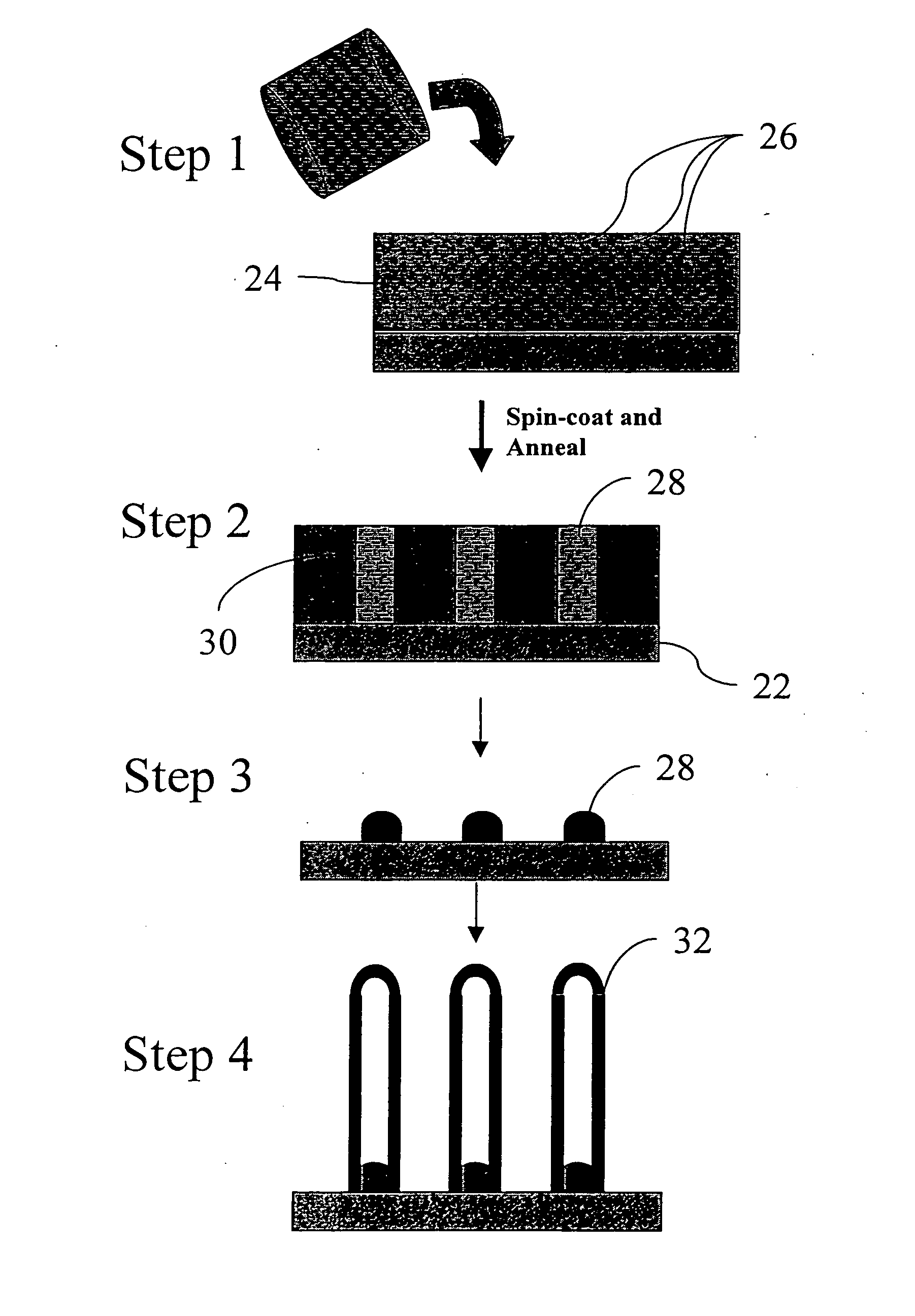
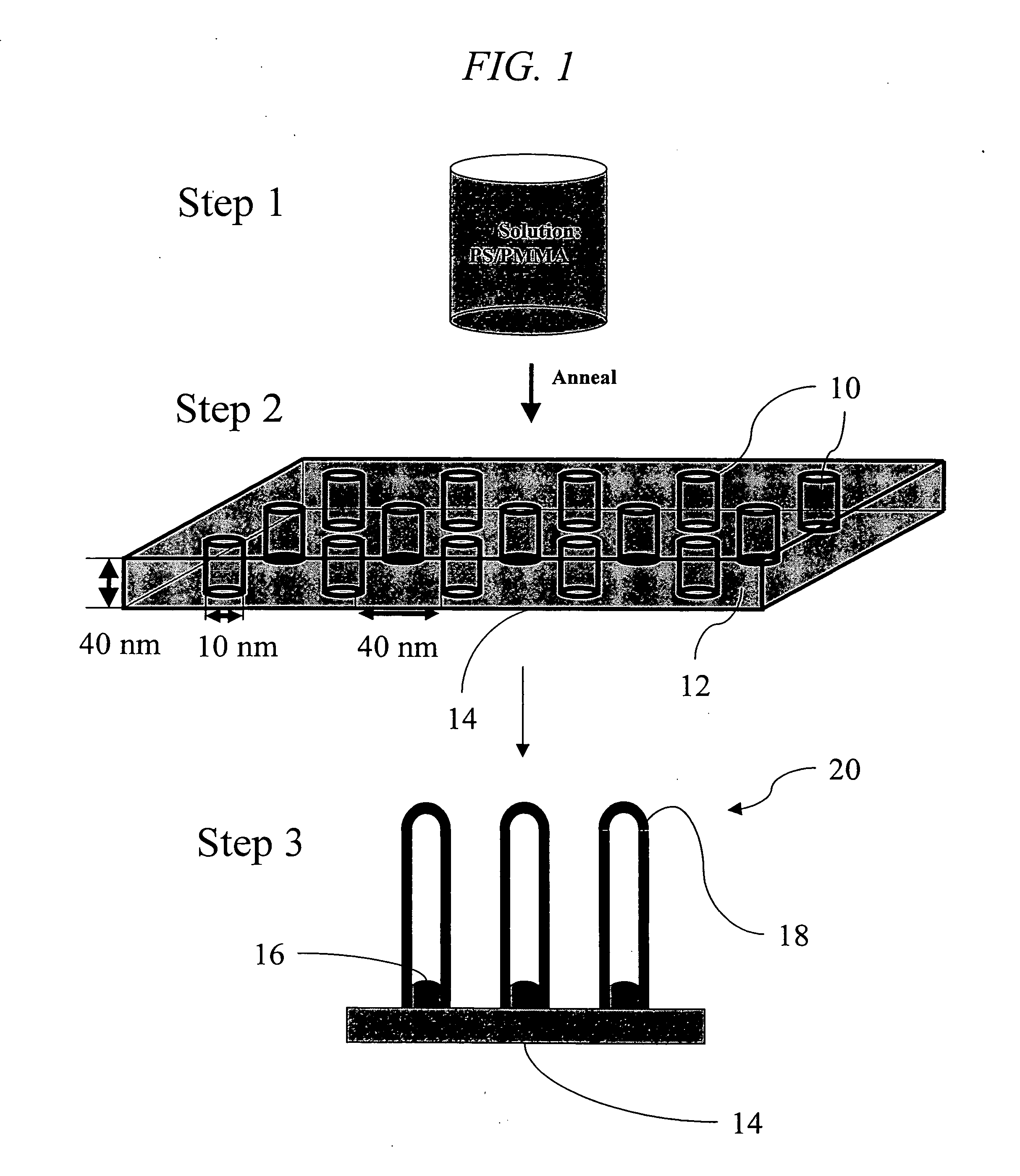
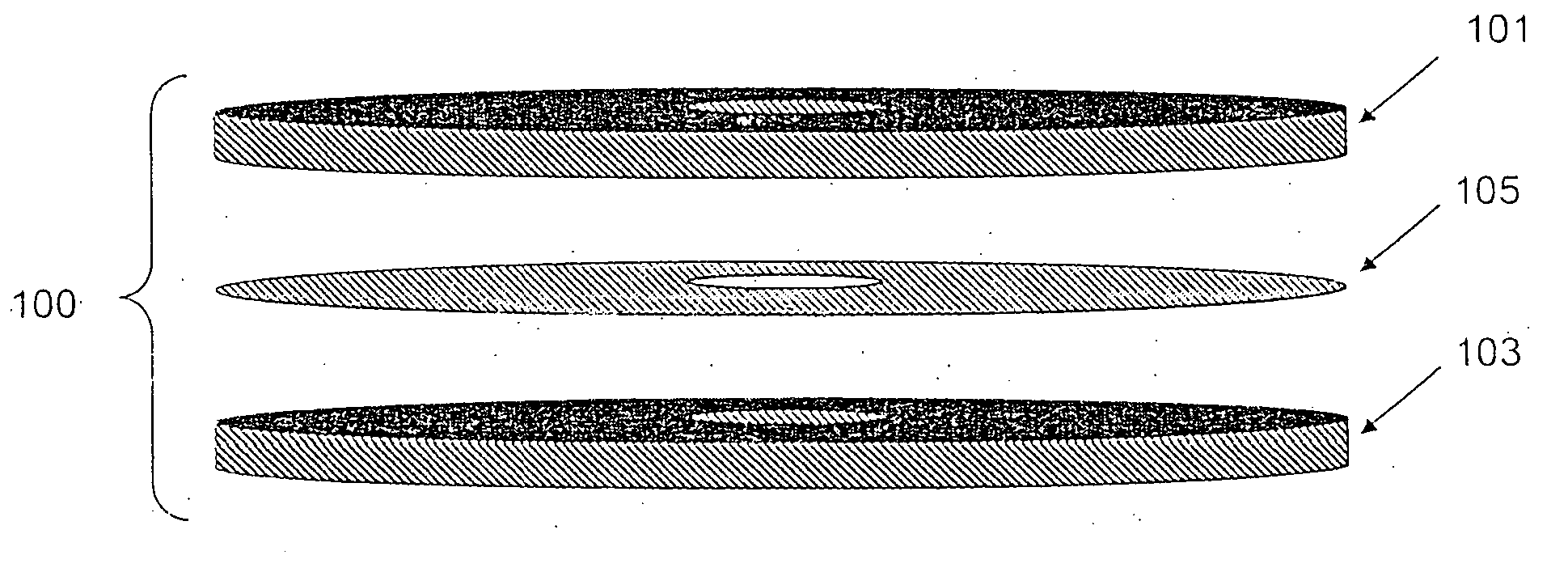
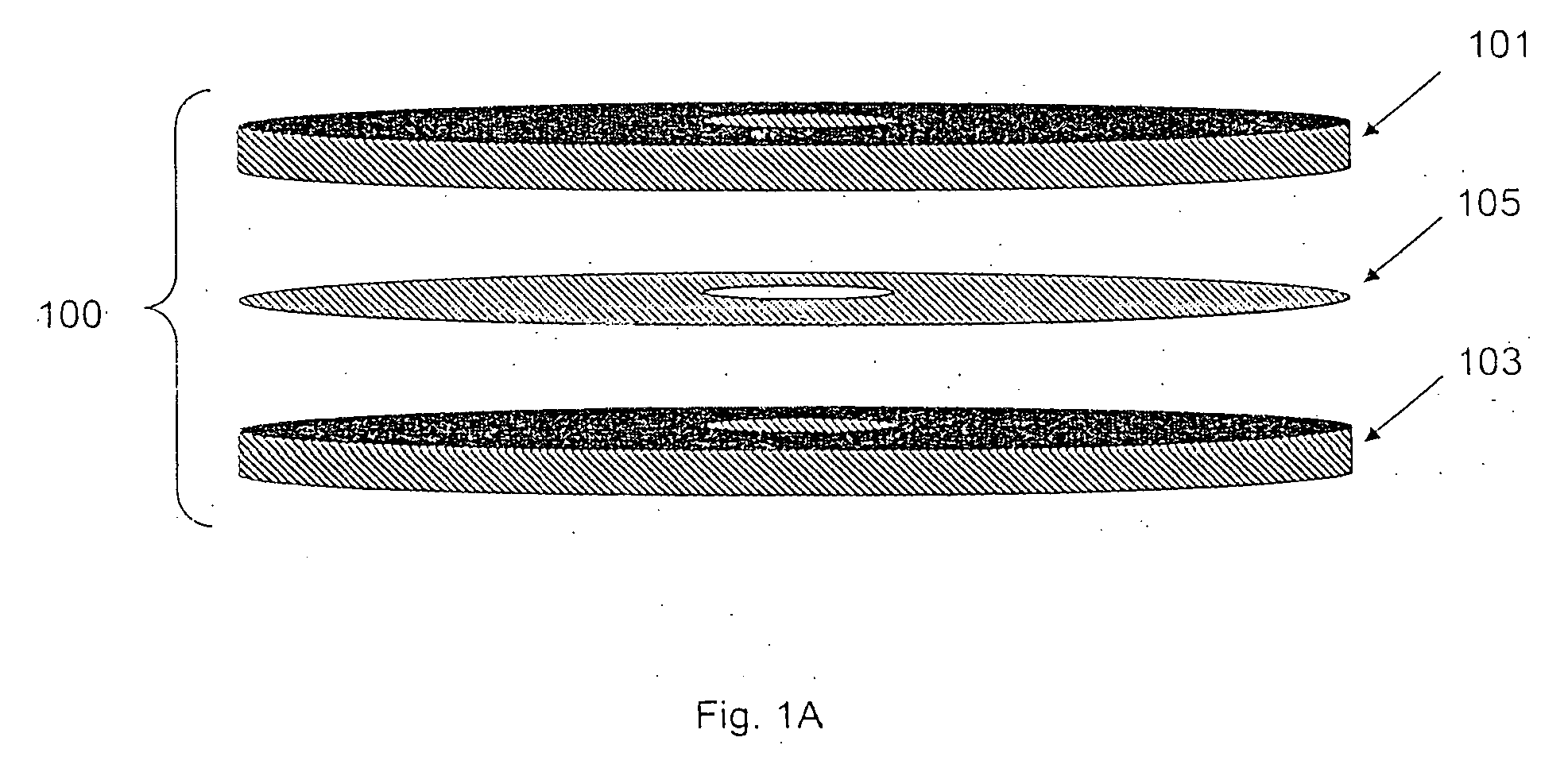
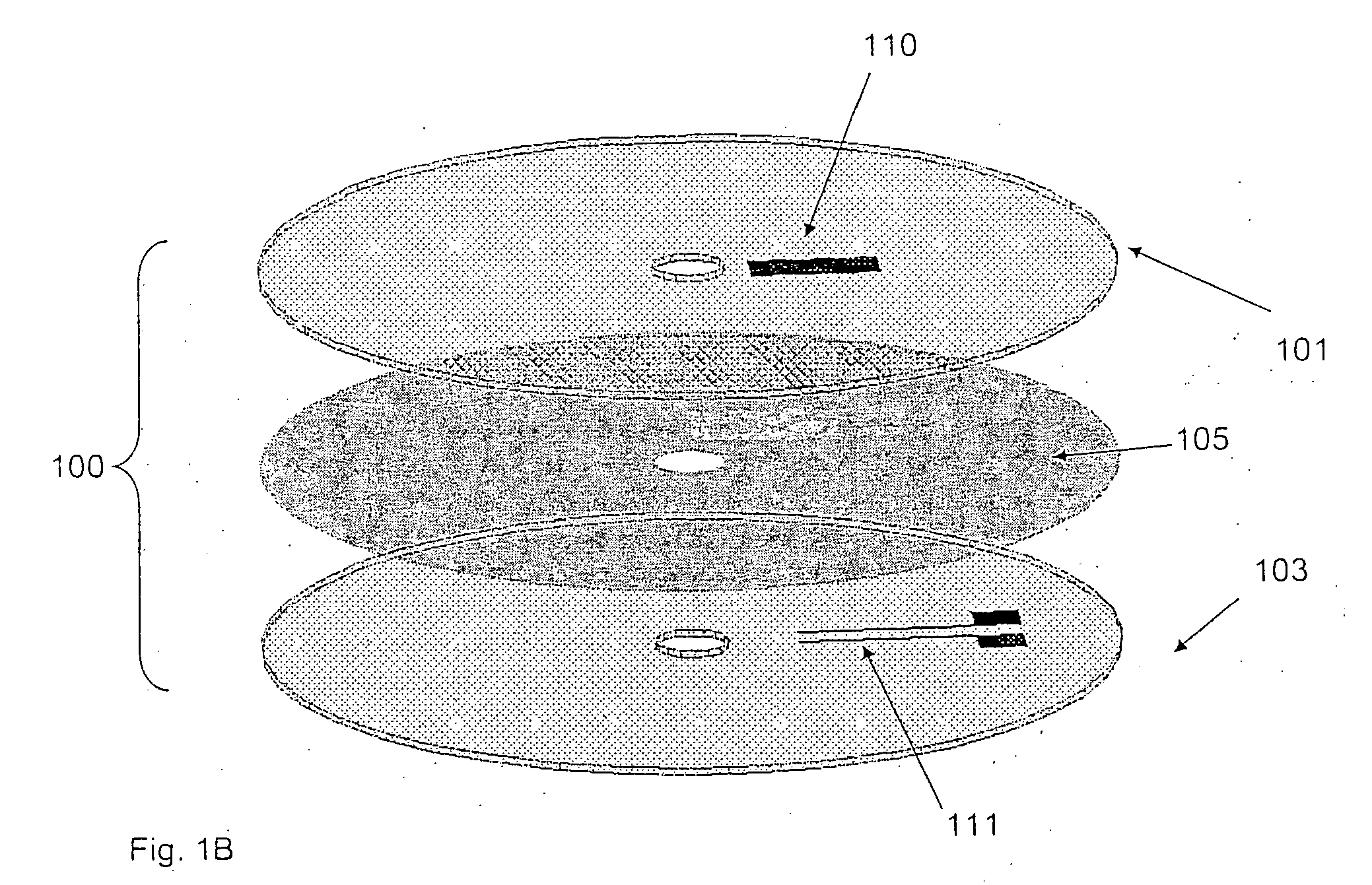
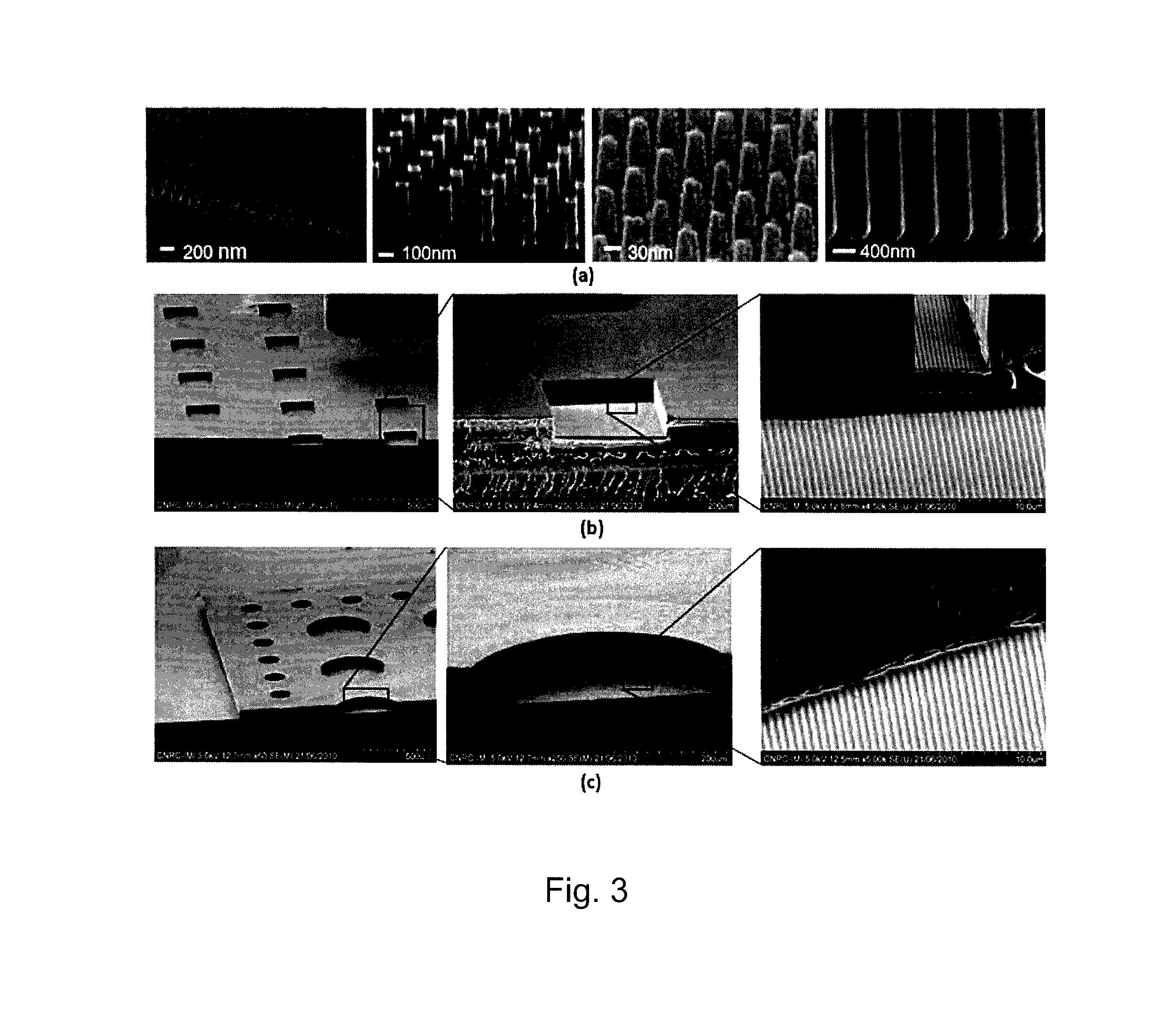
Method of producing regular arrays of nano-scale objects using nano-structured block-copolymeric materials
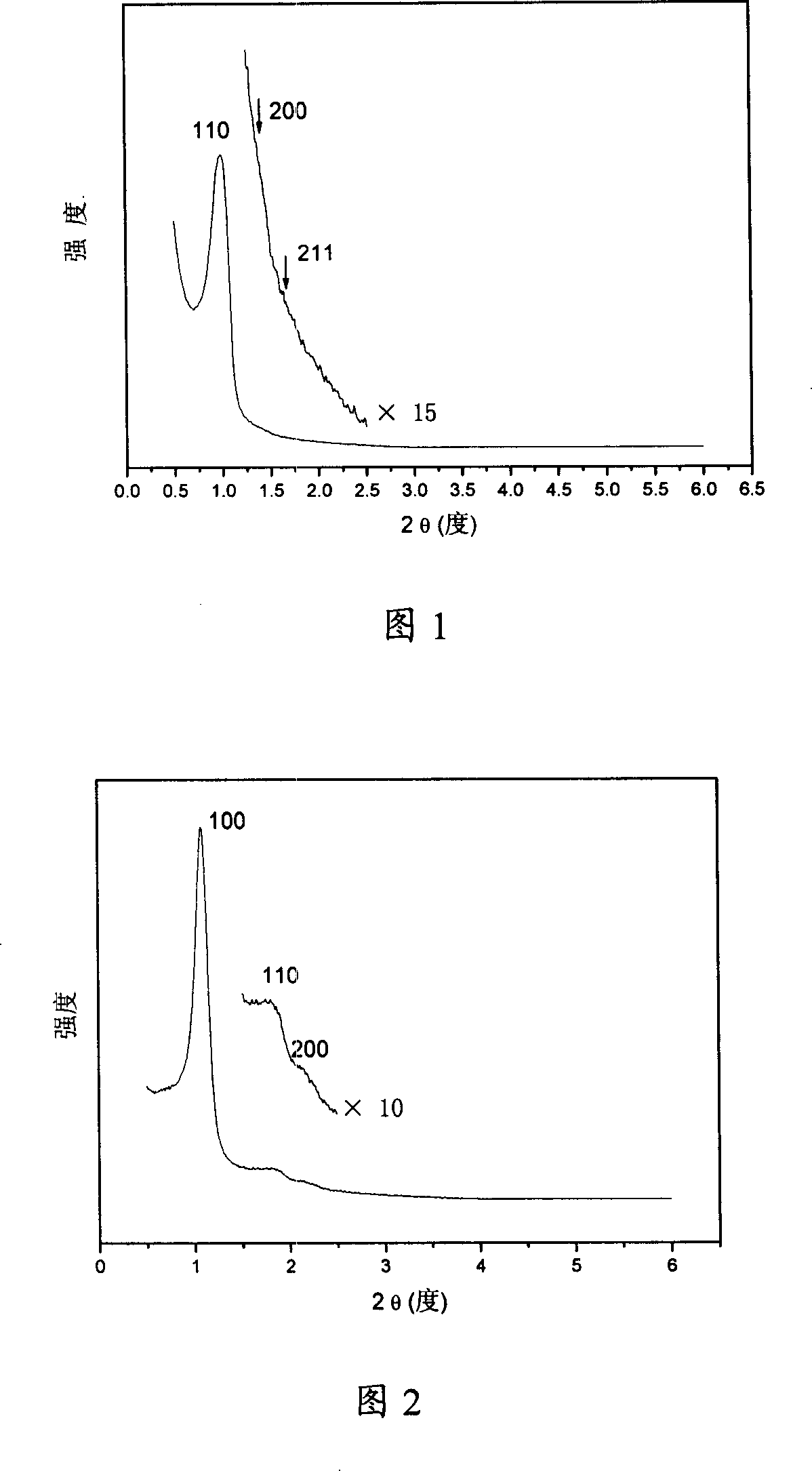
A method of forming a periodic array of nano-scale objects using a block copolymer, and nano-scale object arrays formed from the method are provided. The method for forming the arrays generally includes the steps of depositing a block copolymer of at least two blocks on a substrate to form an ordered meso-scale structured array of the polymer materials, forming catalytic metal dots based on the meso-scale structure, and growing nano-scale objects on the catalytic dots to form an ordered array of nano-scale objects.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
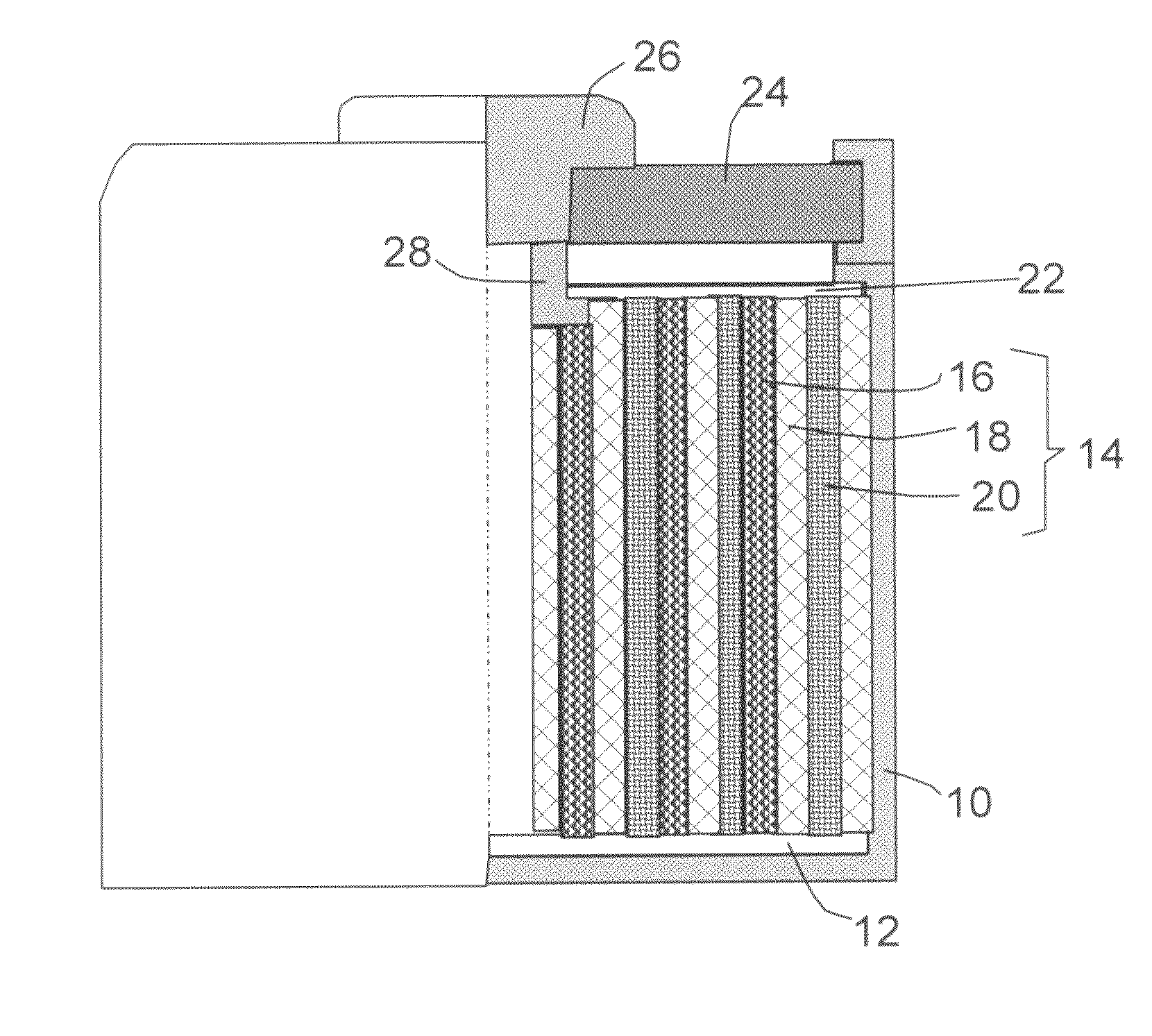
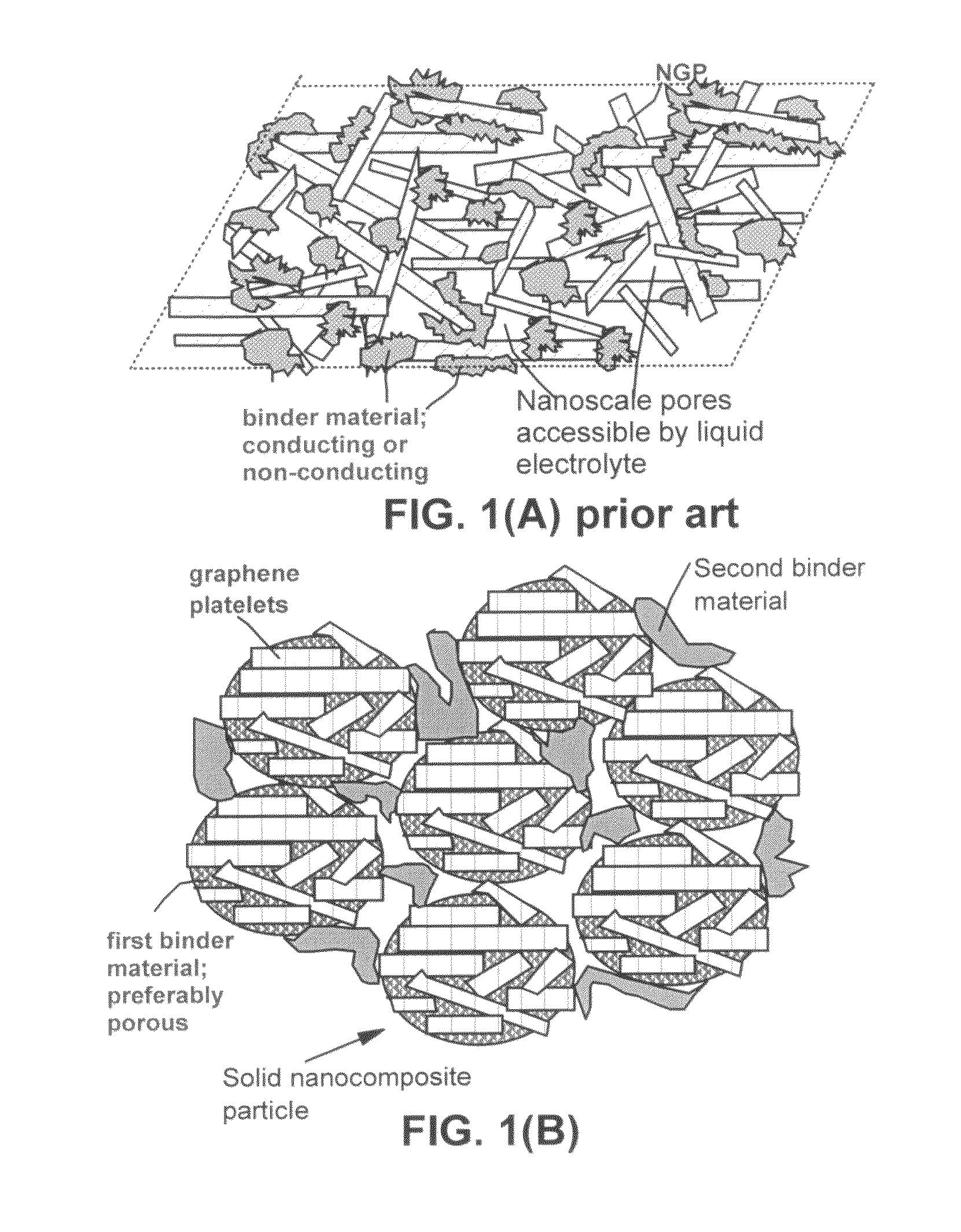
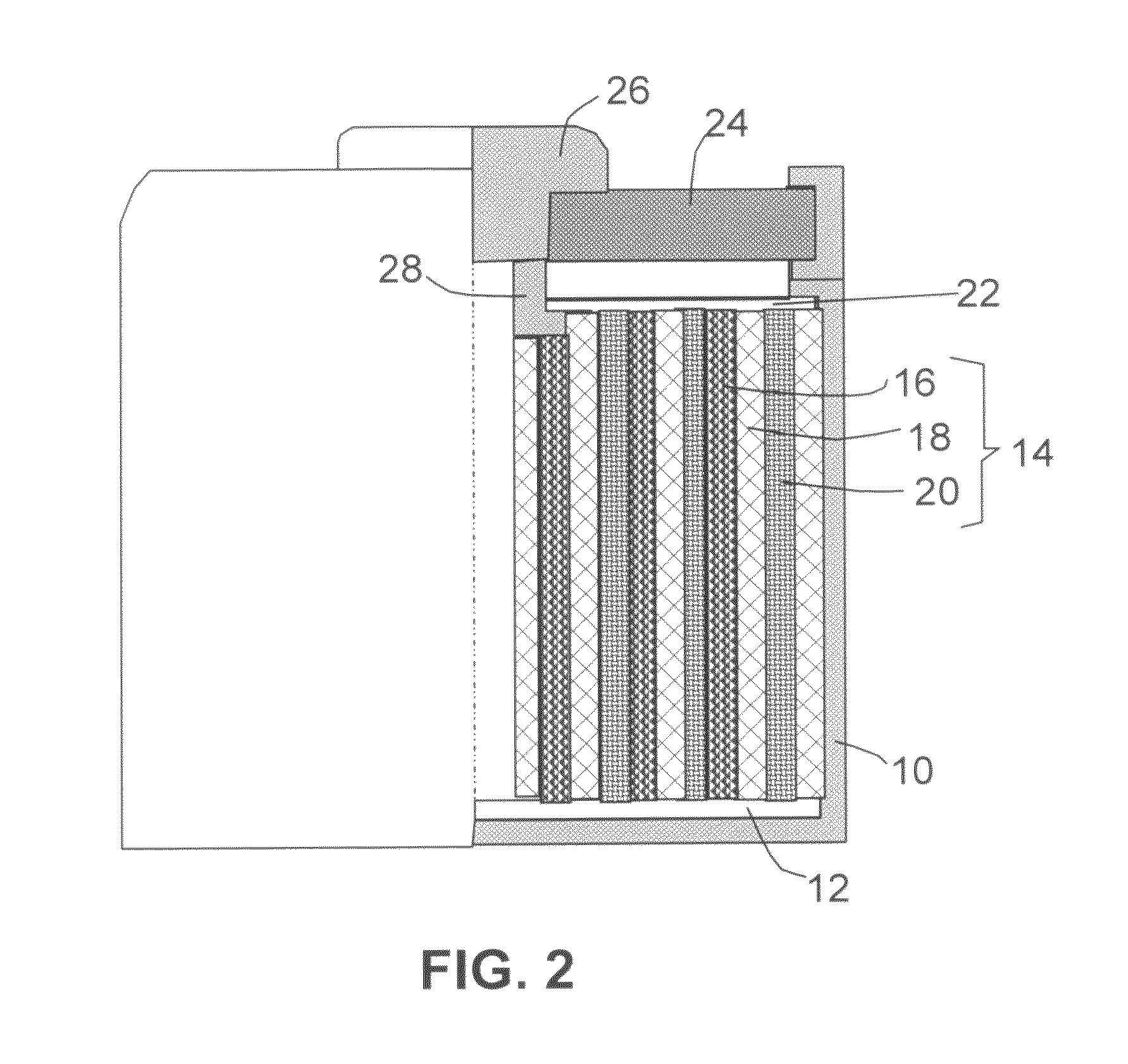
Graphene nanocomposites for electrochemical cell electrodes
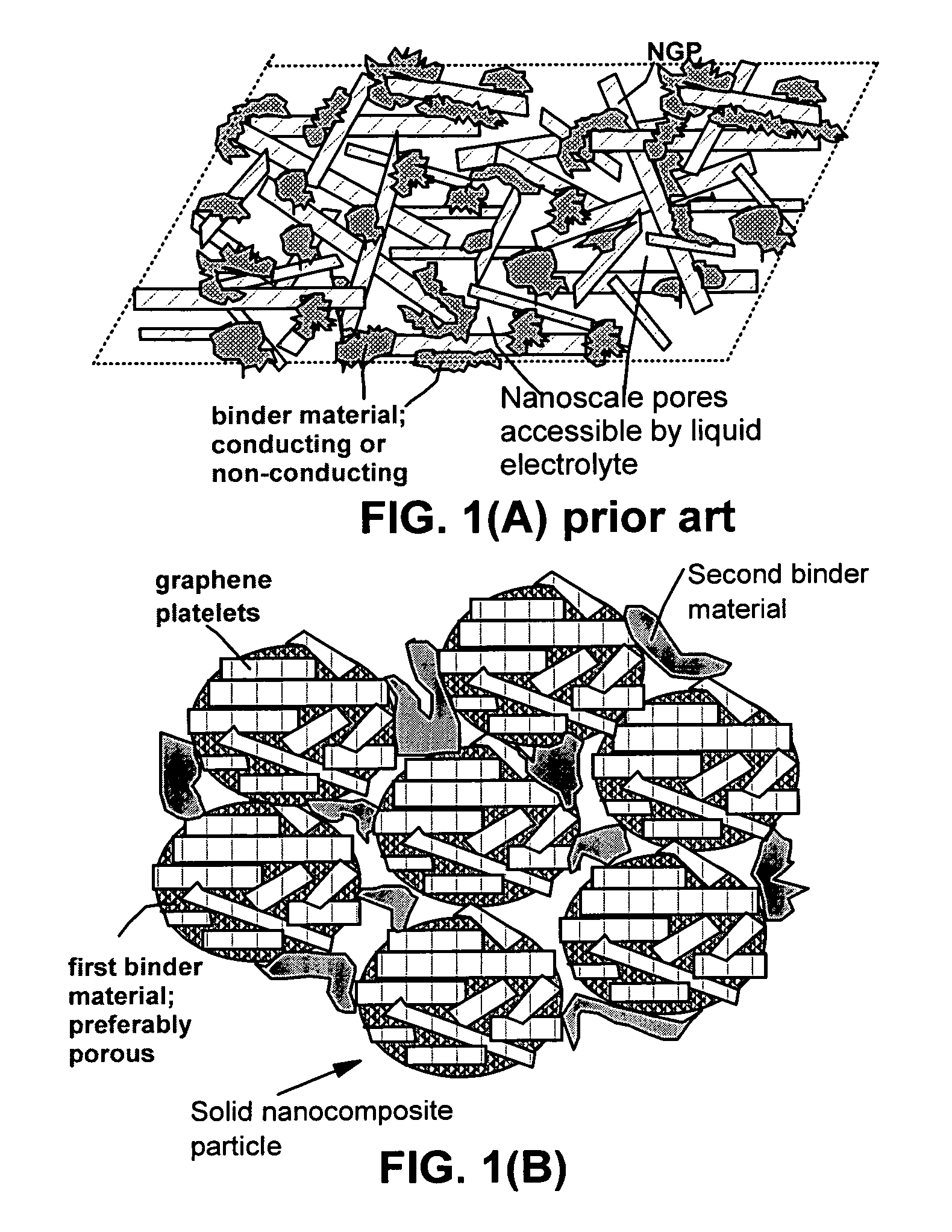
ActiveUS20100021819A1High and reversible anode capacityTedious and energy-intensiveMicroscopic fiber electrodesHybrid capacitor electrodesGraphene nanocompositesSolid particle
A composite composition for electrochemical cell electrode applications, the composition comprising multiple solid particles, wherein (a) a solid particle is composed of graphene platelets dispersed in or bonded by a first matrix or binder material, wherein the graphene platelets are not obtained from graphitization of the first binder or matrix material; (b) the graphene platelets have a length or width in the range of 10 nm to 10 μm; (c) the multiple solid particles are bonded by a second binder material; and (d) the first or second binder material is selected from a polymer, polymeric carbon, amorphous carbon, metal, glass, ceramic, oxide, organic material, or a combination thereof. For a lithium ion battery anode application, the first binder or matrix material is preferably amorphous carbon or polymeric carbon. Such a composite composition provides a high anode capacity and good cycling response. For a supercapacitor electrode application, the solid particles preferably have meso-scale pores therein to accommodate electrolyte.
Owner:NANOTEK INSTR GRP LLC
Devices and methods for programmable microscale manipulation of fluids
InactiveUS20050109396A1Shaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersSamplingEngineeringElectromagnetic radiation
The present invention is directed generally to devices and methods for controlling fluid flow in meso-scale fluidic components in a programmable manner. Specifically, the present invention is directed to an apparatus and method for placing two microfluidic components in fluid communication at an arbitrary position and time, both of which are externally defined. The inventive apparatus uses electromagnetic radiation to perforate a material layer having selected adsorptive properties. The perforation of the material layer allows the fluid communication between microfluidic components. Other aspects of this invention include an apparatus and method to perform volumetric quantitation of fluids, an apparatus to program arbitrary connections between a set of input capillaries and a set of output capillaries, and a method to transport fluid in centripetal device from a larger to a smaller radius. In addition, the present invention also is directed to a method to determine the radial and polar position of a pickup in the reference frame of a rotating device.
Owner:NOBLE VENTURE FINANCE II
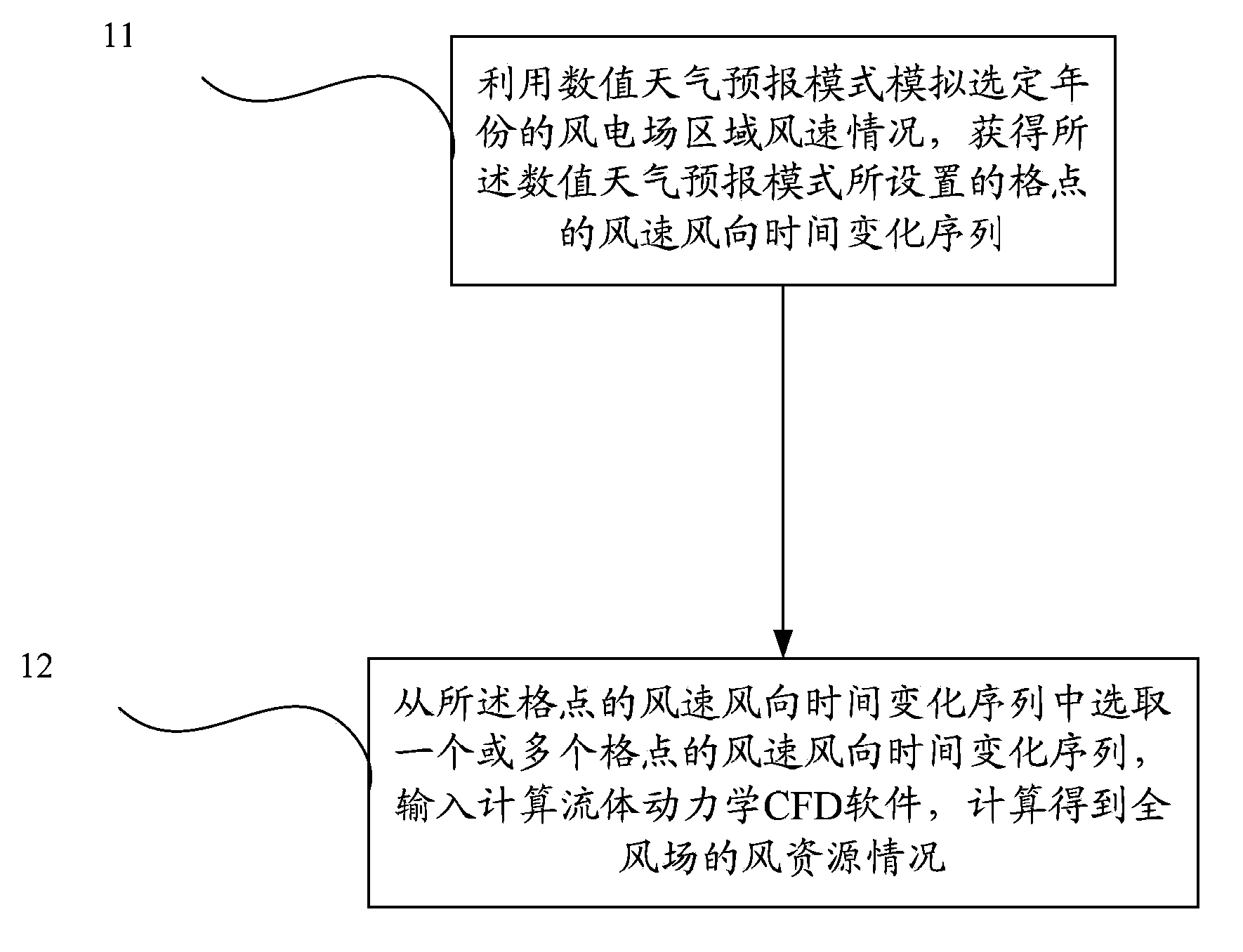
Wind resource assessment method based on numerical weather prediction and computational fluid dynamics
InactiveCN103514341AImprove accuracyImprove the rational arrangementSpecial data processing applicationsTerrainNumerical weather prediction
The invention discloses a wind resource assessment method based on numerical weather prediction and the computational fluid dynamics. According to the method, area wind speed situations of a wind power plant in a selected year are simulated in a numerical weather prediction model, so that numerical weather prediction results comprising wind speed and wind direction time variation sequences of the wind power plant are obtained; one or more wind speed and wind direction time variation sequences are selected from the numerical weather prediction results and input in CFD software of the computational fluid dynamics, and wind resource situations of the whole wind power plant can calculated and obtained. Compared with a method of combining a meso-scale numerical model and a micro-scale numerical model, the wind resource assessment method achieves more accurate physical solution and calculation of the wind power plant on a micro level, and meanwhile the effects on wind speed attenuation or turbulence from complex terrain and wake effects are considered. Compared with wind resource assessment conducted through the CFD software only, the method can provide input of more result points of the CFD software by being combined with results of the numerical weather prediction model.
Owner:SINOVEL WIND GRP
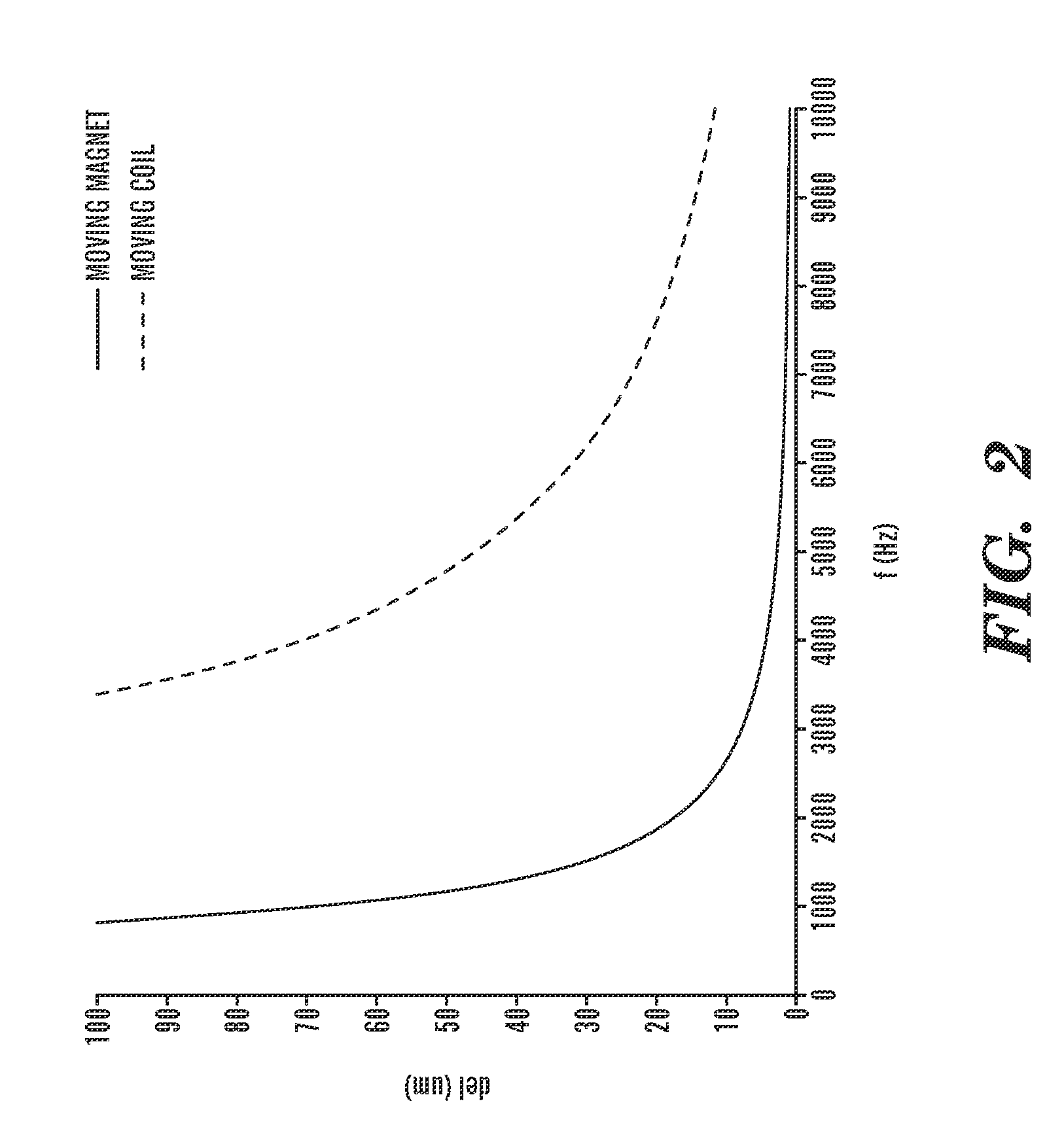
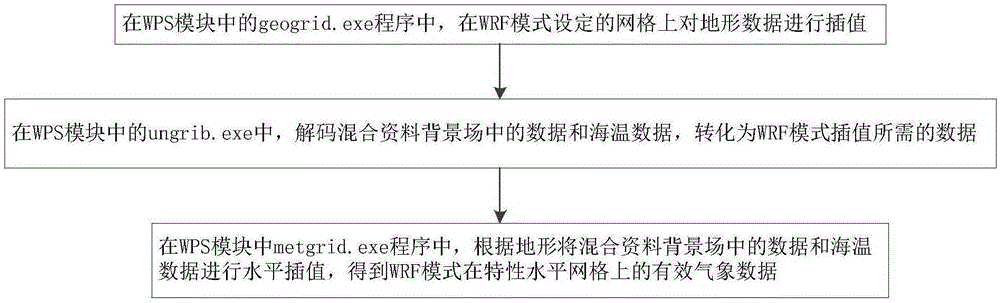
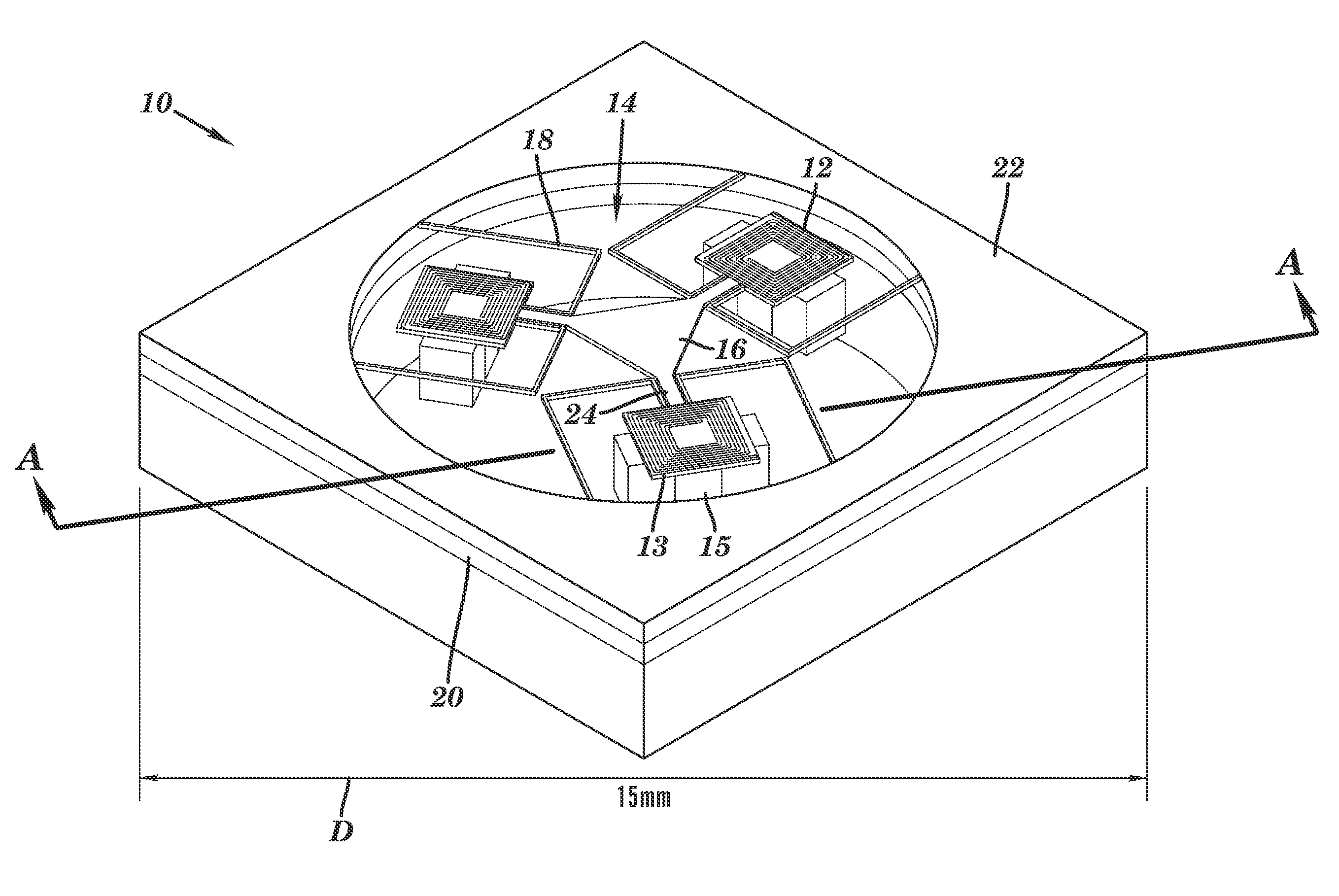
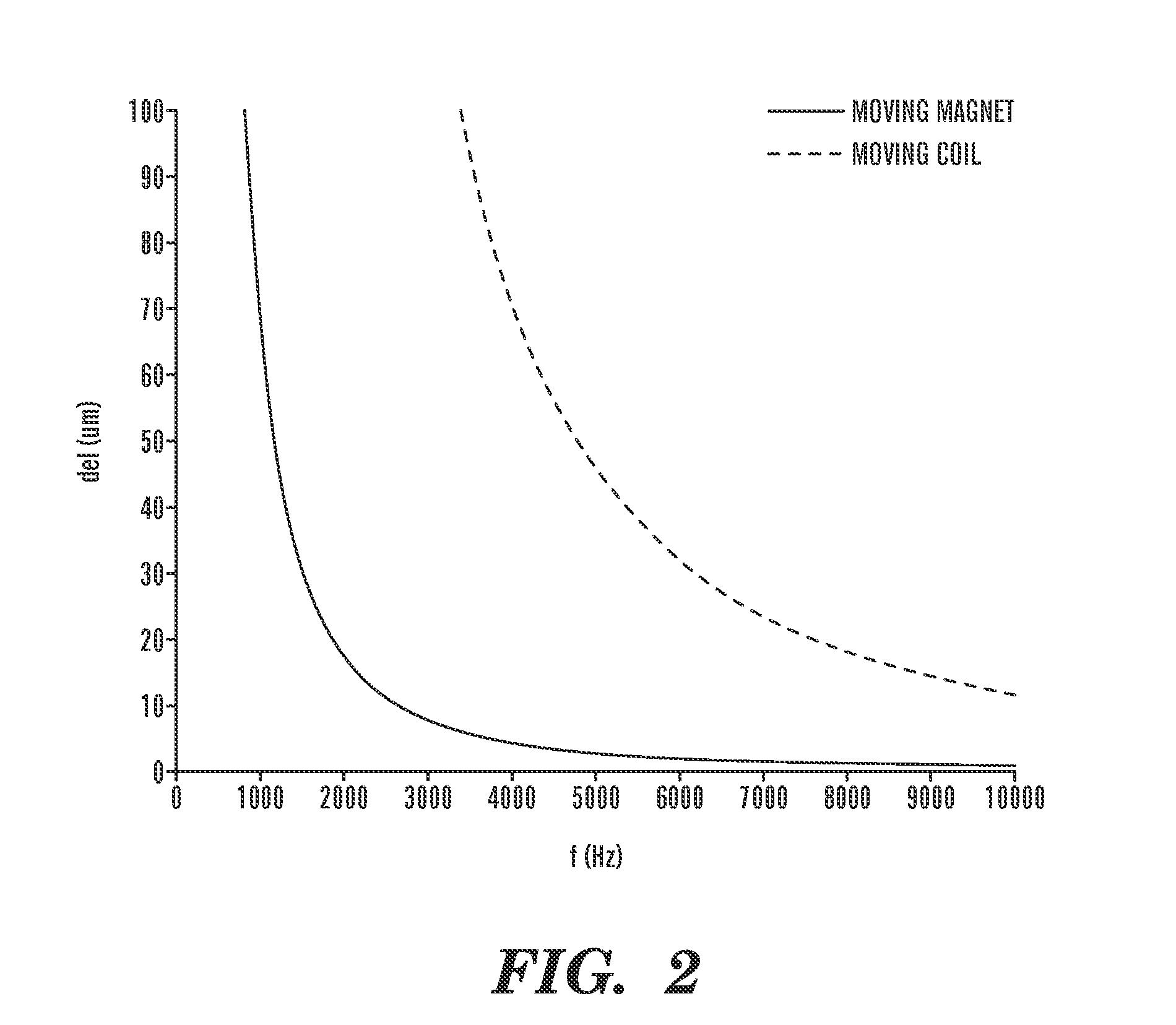
6-axis electromagnetically-actuated meso-scale nanopositioner
InactiveUS7557470B2Propulsion systemsClosed-cycle gas positive displacement engine plantCompliant mechanismIn plane
A MEMS actuator includes a coil stack in the form of microfabricated, electrically conductive first and second superposed layers. A magnet array is superposed in magnetic communication with the coil stack, with first and second coils being selectively, electrically actuatable to generate relative movement between the coil stack and the magnet array both in-plane and out-of-plane. In various embodiments, a plurality of the actuators are integrally coupled to a microfabricated compliant mechanism to provide a high bandwidth, six degree of freedom nanopositioner.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
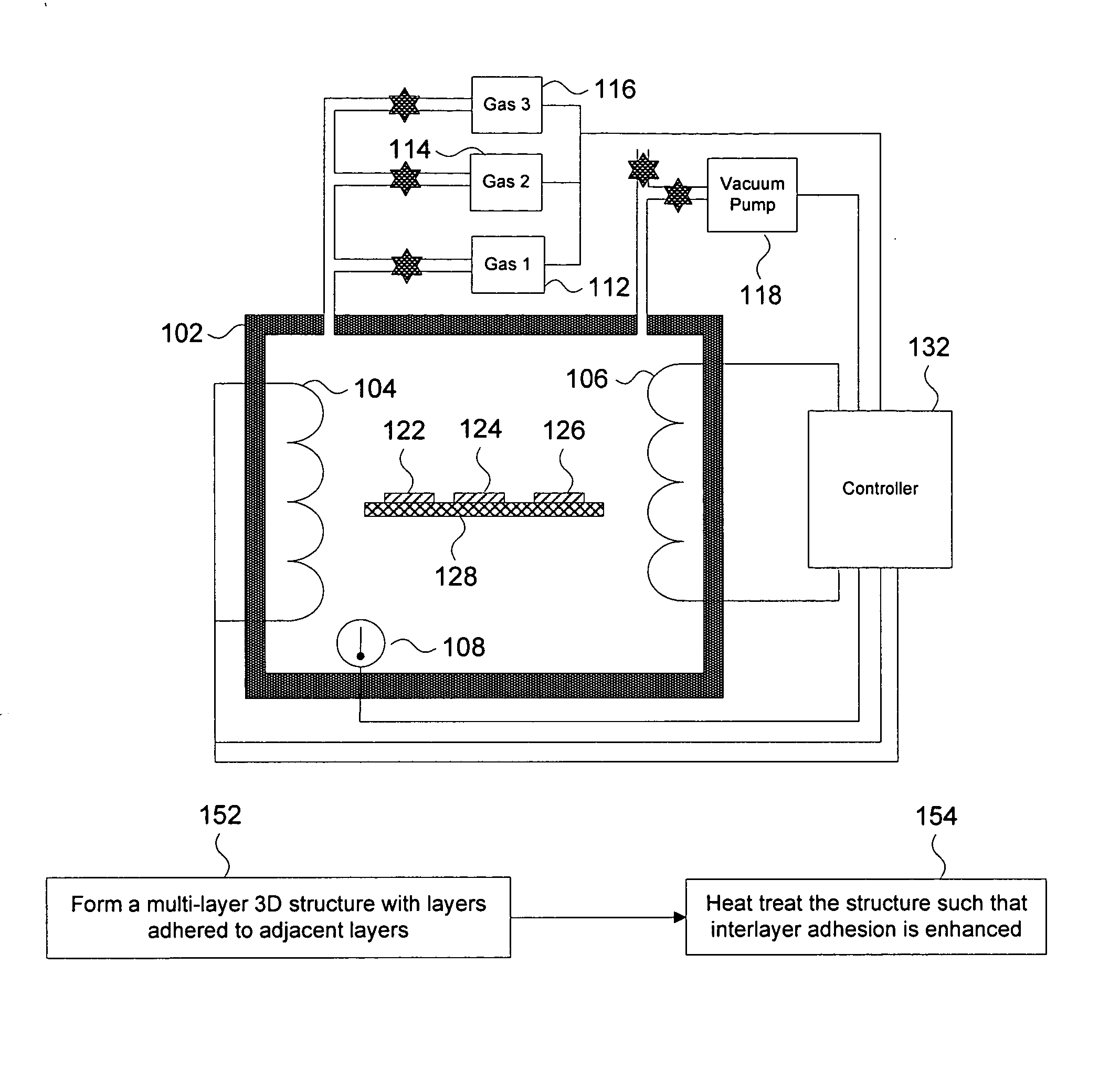
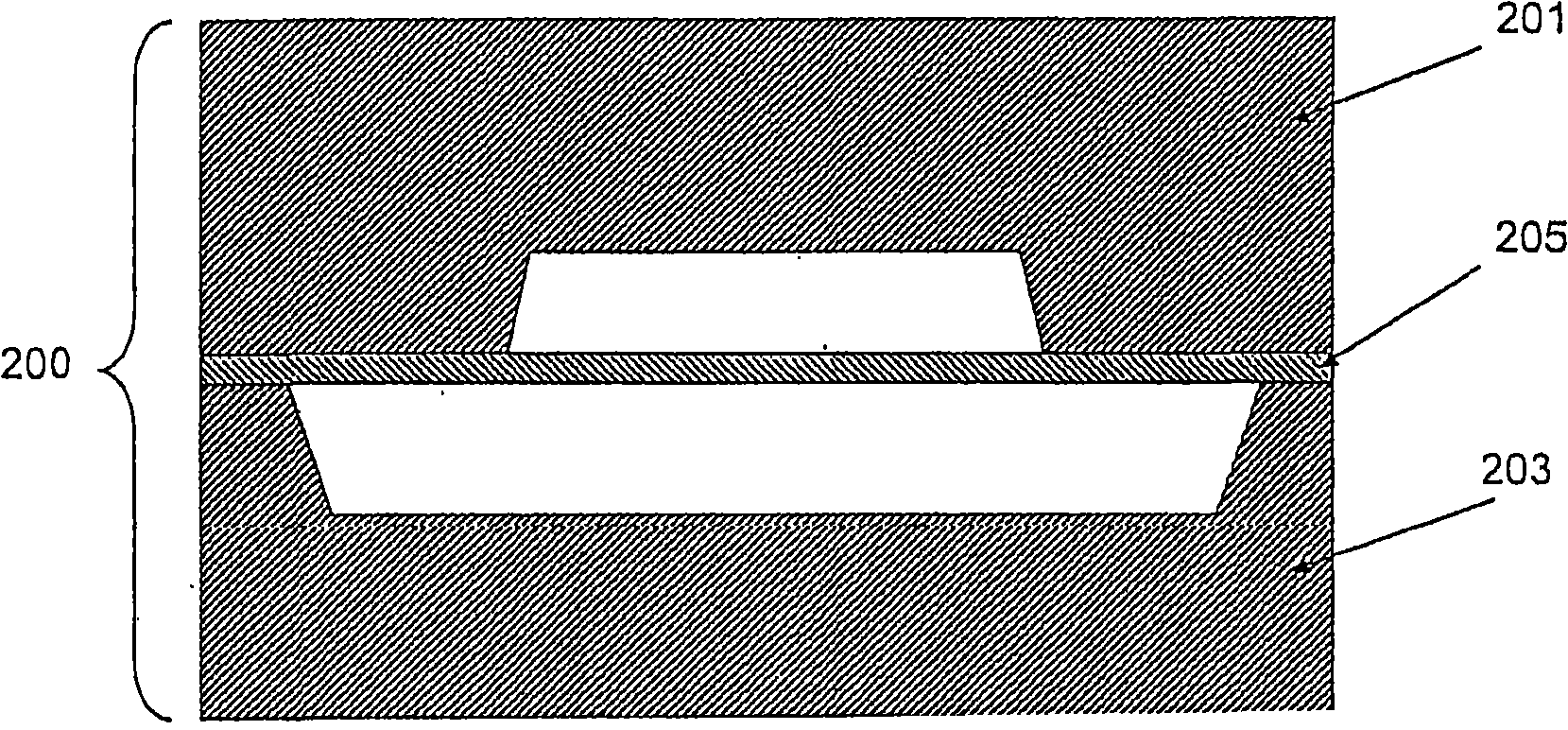
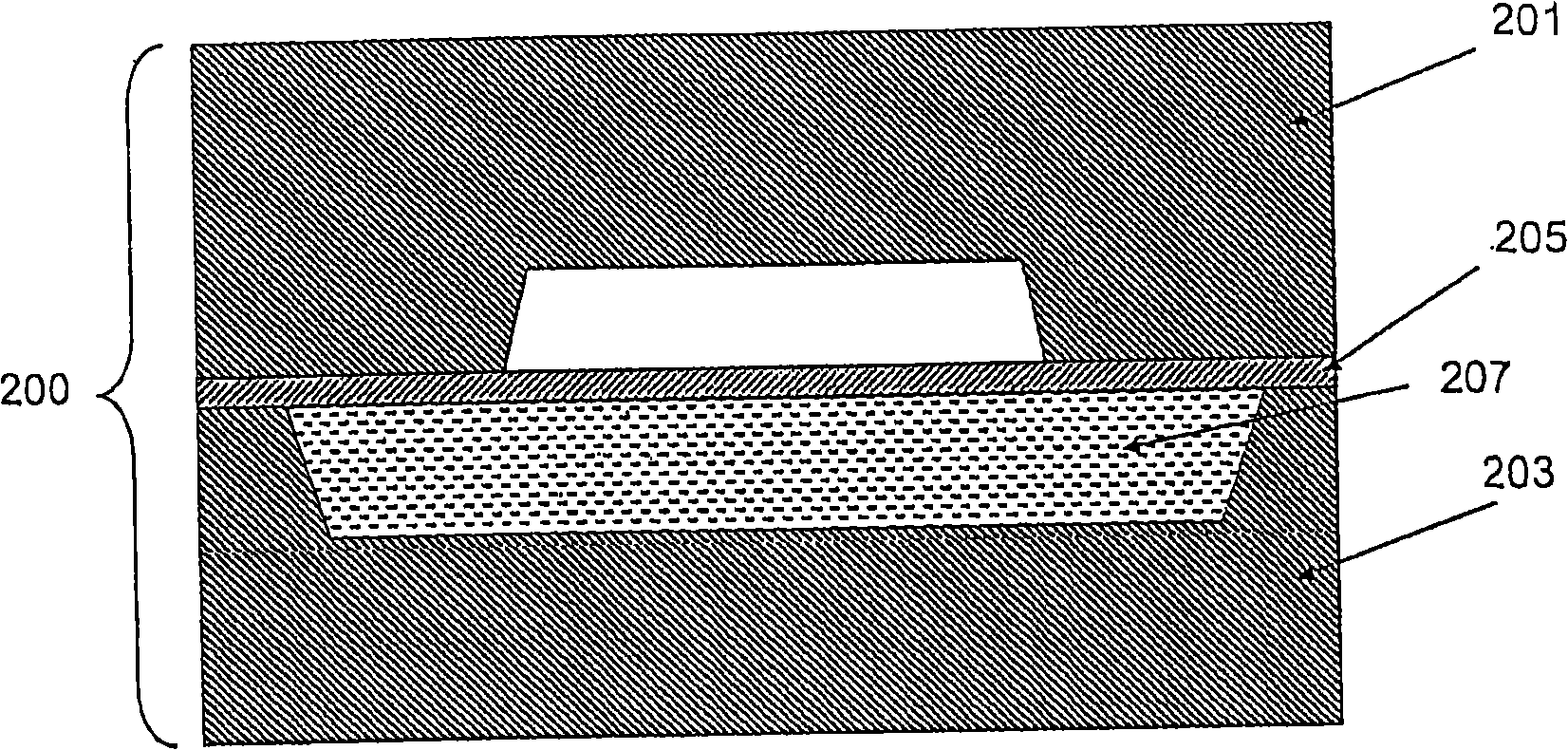
Method of electrochemically fabricating multilayer structures having improved interlayer adhesion
InactiveUS20050045585A1Improve propertiesImprove interlayer adhesionDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReducing atmosphereHeat treating
Multi-layer microscale or mesoscale structures are fabricated with adhered layers (e.g. layers that are bonded together upon deposition of successive layers to previous layers) and are then subjected to a heat treatment operation that enhances the interlayer adhesion significantly. The heat treatment operation is believed to result in diffusion of material across the layer boundaries and associated enhancement in adhesion (i.e. diffusion bonding). Interlayer adhesion and maybe intra-layer cohesion may be enhanced by heat treating in the presence of a reducing atmosphere that may help remove weaker oxides from surfaces or even from internal portions of layers.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Devices and methods for programmable microscale manipulation of fluids
InactiveUS7152616B2Shaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringElectromagnetic radiation
The present invention is directed generally to devices and methods for controlling fluid flow in meso-scale fluidic components in a programmable manner. Specifically, the present invention is directed to an apparatus and method for placing two microfluidic components in fluid communication at an arbitrary position and time, both of which are externally defined. The inventive apparatus uses electromagnetic radiation to perforate a material layer having selected adsorptive properties. The perforation of the material layer allows the fluid communication between microfluidic components. Other aspects of this invention include an apparatus and method to perform volumetric quantitation of fluids, an apparatus to program arbitrary connections between a set of input capillaries and a set of output capillaries, and a method to transport fluid in centripetal device from a larger to a smaller radius. In addition, the present invention also is directed to a method to determine the radial and polar position of a pickup in the reference frame of a rotating device.
Owner:NOBLE VENTURE FINANCE II
Fluid-assisted self-assembly of meso-scale particles
InactiveUS20050281944A1Reduce the amount requiredFacilitate intimate contactMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsFuel cellsProton
A method for the preparation of a monolayer of meso-scaled particles within a size range of one nanometer to several hundreds of microns. The method includes the steps of (A) providing a thin liquid film onto an external surface of a rotary member; (B) dispensing meso-scaled particles at a desired rate onto an external surface of the thin liquid film so as to position the particles at a gas-liquid interface; (C) forming a uniform monolayer of the particles on the gas-liquid interface; and (D) transferring the monolayer from the gas-liquid interface to a solid substrate. Monolayers of meso-scaled particles on solid surfaces are useful in many areas of science and technology, including functional coatings that modify the physical and chemical properties of the underlying surfaces. The method is particularly useful for the preparation of catalyzed proton exchange membranes for fuel cell applications.
Owner:JANG BOR Z
Method for screening crystallization conditions in solution crystal growth
InactiveUS7214540B2Peptide librariesSequential/parallel process reactionsProtein solutionCrystal growth
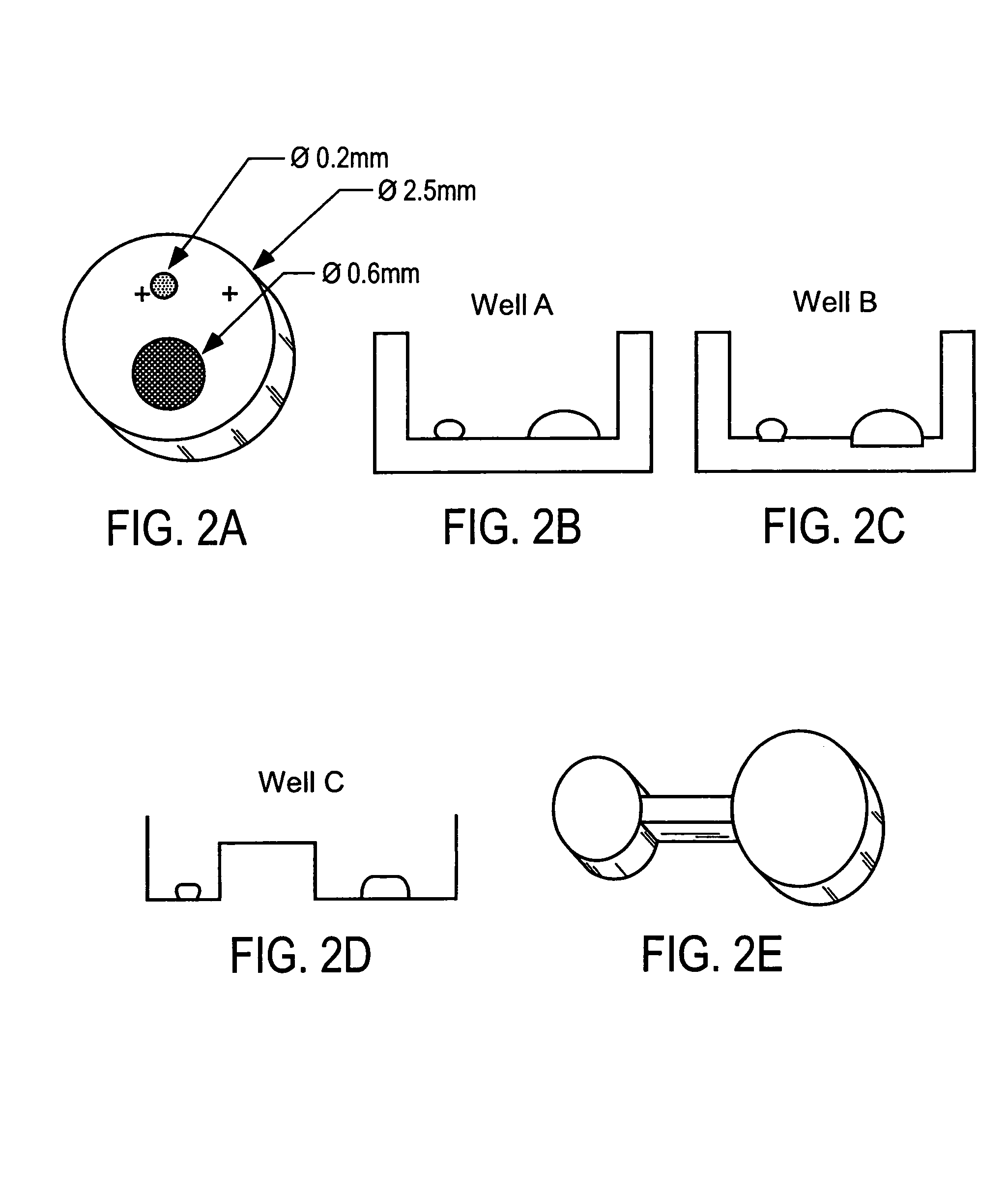
A method of screening protein crystal growth conditions on a nano or meso scale comprises providing a micro-electromechanical chip with a plurality of micro-chambers in the micro-electromechanical chip. A protein solution is placed into the micro-chambers by an automated jet type dispensing means with nano or meso scale precision. The protein crystal growth conditions of each of the micro-chambers is adjusted so that the protein crystal growth conditions of each of the micro-chambers differs. Crystallization of the protein solution in the micro-chambers is effected. Protein crystal growth in the micro-chambers is then observed.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
New algorithm for atmospheric environment capacity by using region air quality model
ActiveCN102819661AReflect the characteristics of regional transportationTheoretically reasonableSpecial data processing applicationsEnvironmental impact assessmentMeteorological models
The invention provides a new algorithm for an atmospheric environment capacity by using a region air quality model (RAQM). The new algorithm comprises the following computation steps: utilizing a meso-scale meteorological model to perform analog computation on an average value of year-round meteorological elements per hour in an estimation region to obtain uout and uin; utilizing the RAQM to perform analog computation on an average value of pollutant concentration per hour in an estimation year in the estimation region to obtain c; using a process analysis module to output transportation volumes Fout and Fin, dry deposition volume Ddry, wet deposition volume Dwet and chemical conversion volume T of pollutants per hour; performing the computation to obtain V and Asection; using cstandard to obtain a static volume of each atmospheric pollutant in the estimation region; and according to an expression of atmospheric environment capacity Q, performing the calculation to obtain a total environmental volume of atmospheric pollutants in the estimation region. With the adoption of the new algorithm provided by the invention, not only is the maximal capacity of atmospheres to contain the pollutants, regional transportation features of the atmospheric pollutants are reflected, but also key factors of influencing the pollutants in the estimation region are obtained, and assessment judgment basis such as more reasonable theories, more reliable data and more credible result can be provided for atmospheric environmental impact assessment.
Owner:INST OF ATMOSPHERIC PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY SCI
Synthesis of high mechanical stability non-metal element doped ordered mosopore carbon material
InactiveCN100999316ALarge specific surface areaUniform pore size distributionBond energyMolecular adsorption
This invention discloses a preparation method of functional order mesoporous carbon without metal. Make water-soluble phenol formaldehyde and response type of acid for polymerization, utilize predecessor and nonionic wetting agent to carry out organism-organism self assembly, get resin-nonionic wetting agent composite containing boron and phosphonium, remove surface acting agent by calcinating in inert atmosphere, carbonize with high temperature, get non-metal element functional ordered mesoporous polymer, and make order mesoporous carbon with boron or phosphonium. Its ordered meso-scale structure is divided into two kinds. It has characteristics of uniform large specific surface, pore diameter, bore, and path. Because boron oxygen bond of high bond energy is leaded in molecular constitution, it makes order mesoporous carbon with boron have strong mechanical stability. It can be used as wear-resisting stuff. It has lubricating, abrasion improving, service life of friction materials extending effects. It has extensive application prospect in catalytic action, heavy metal ion, and colorant molecular adsorption and electrode materials.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Graphene nanocomposites for electrochemical cell electrodes
ActiveUS9190667B2Reduce the amount of solutionIncreased rate capacityMicroscopic fiber electrodesHybrid capacitor electrodesGraphene nanocompositesSolid particle
Owner:NANOTEK INSTR GRP LLC
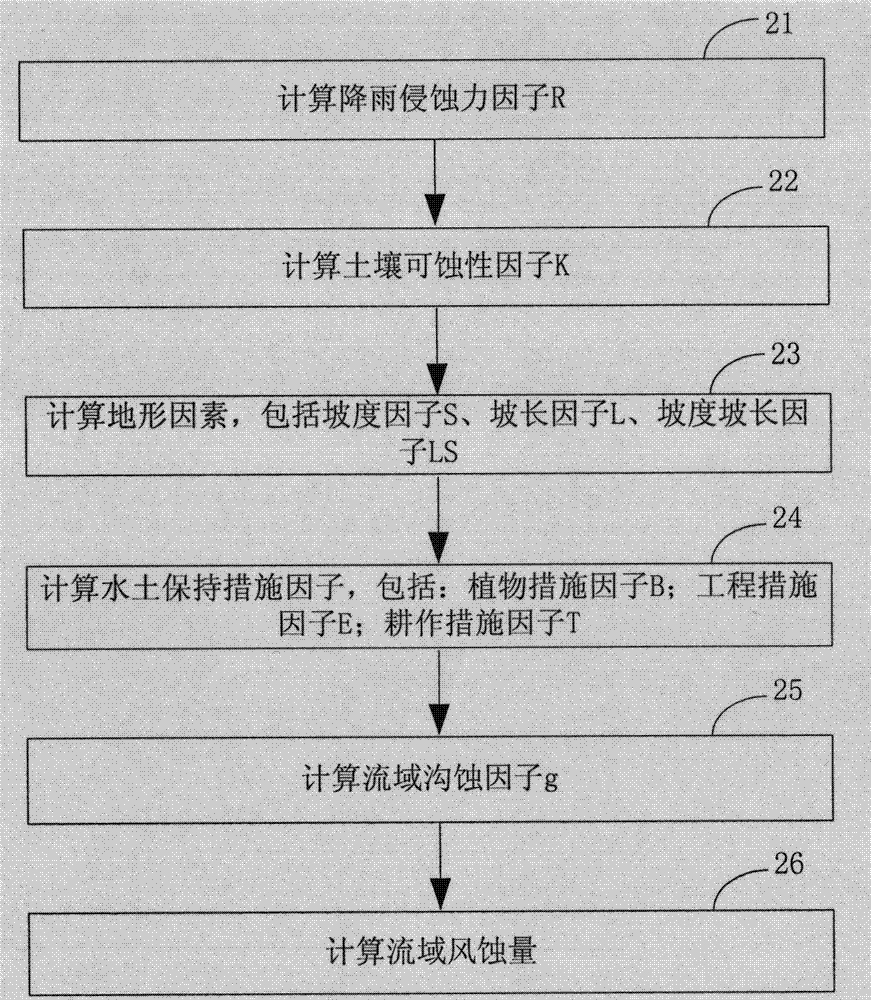
Spatio-temporal dynamic analysis method of soil erosion in meso-scale watershed based on GIS
InactiveCN103940974AMeet the design requirementsPromote absorptionEarth material testingObservation dataAnalysis method
The invention relates to a spatio-temporal dynamic analysis method of soil erosion in meso-scale watershed based on GIS. The spatio-temporal dynamic analysis method comprises following specific steps: the meso-scale watershed is divided into a plurality of grid cells as calculation units; soil erosion experiments are used for measuring research results and knowledge, and a plurality of factors related to soil erosion are extracted based on soil erosion experiment observation data; the plurality of factors are subjected to analysis and summary, an erosion factor collective drawing is established, and estimation on soil erosion amount of each grid cell is finished; and evaluation and analysis on watershed soil erosion states are finished based on soil erosion space variation analysis. According to the spatio-temporal dynamic analysis method, space nonuniformity of soil erosion and the factors of soil erosion is taken into consideration, so that a slope surface model is combined with GIS, and calculation on each unit is finished; and substance transmission and migration are taken into consideration appropriately, distribution calculation on soil loss is finished, and a soil erosion figure is obtained.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Devices and methods for programmable microscale manipulation of fluids
InactiveCN1745264AIncrease surface areaReduced diffraction limitShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersSamplingMicrofluidicsEngineering
The present invention is directed generally to devices and methods for controlling fluid flow in meso-scale fluidic components in a programmable manner. Specifically, the present invention is directed to an apparatus and method for placing two microfluidic components in fluid communication at an arbitrary position and time, both of which are externally defined. The inventive apparatus uses electromagnetic radiation to perforate a material layer having selected adsorptive properties. The perforation of the material layer allows the fluid communication between microfluidic components. Other aspects of this invention include an apparatus and method to perform volumetric quantitation of fluids, an apparatus to program arbitrary connections between a set of input capillaries and a set of output capillaries, and a method to transport fluid in centripetal device from a larger to a smaller radius. In addition, the present invention also is directed to a method to determine the radial and polar position of a pickup in the reference frame of a rotating device.
Owner:SPINX INC
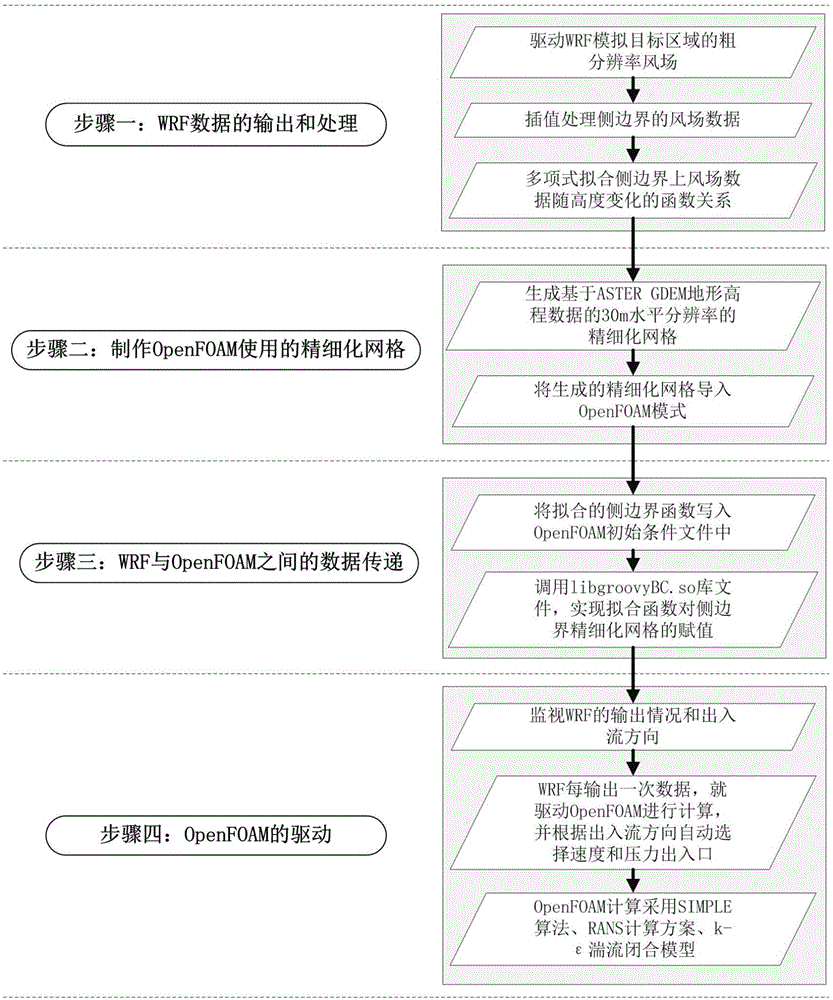
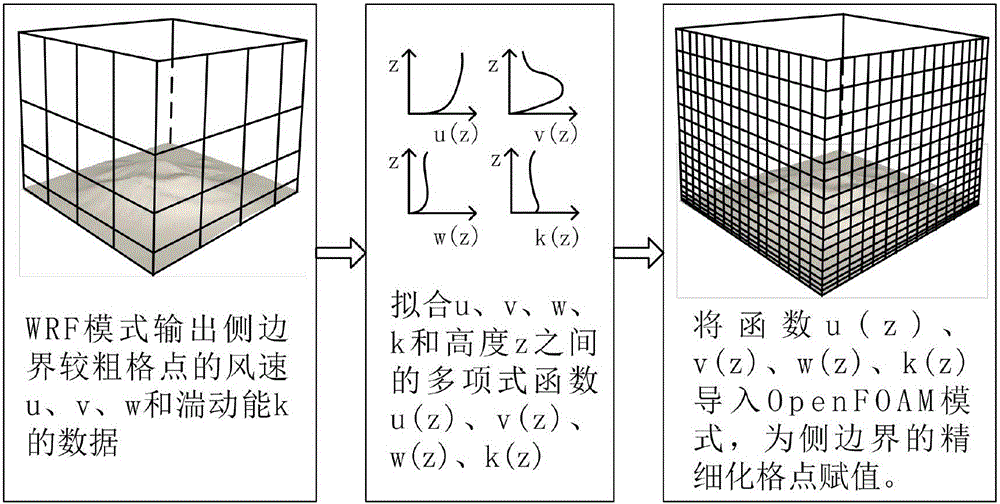
Method for simulating wind field by coupling WRF (weather research and forecasting) and OpenFOAM modes
ActiveCN106326625AGood effectImprove wind field simulationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSpecial data processing applicationsTerrainImage resolution
The invention relates to a method for simulating a wind field by coupling WRF (weather research and forecasting) and OpenFOAM modes. The method comprises the following steps of outputting and processing WRF data in a meso-scale weather mode; manufacturing a small-scale open-source OpenFOAM refined network in a CFD mode for calculating hydromechanics; transferring data between the WRF and OpenFOAM modes; driving the OpenFOAM mode to calculate. The method has the advantages that by adopting the technical scheme, the coupling calculation of the WRF and OpenFOAM modes is realized, the data with several-mile horizontal resolution in the WRF mode is downscaled into the data with 30m resolution in the OpenFOAM mode, the wind field simulating effect in the WRF mode under the complicated terrain is improved, the business levels of wind resource evaluation and wind power prediction are improved, and the predicting accuracy is improved.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +4
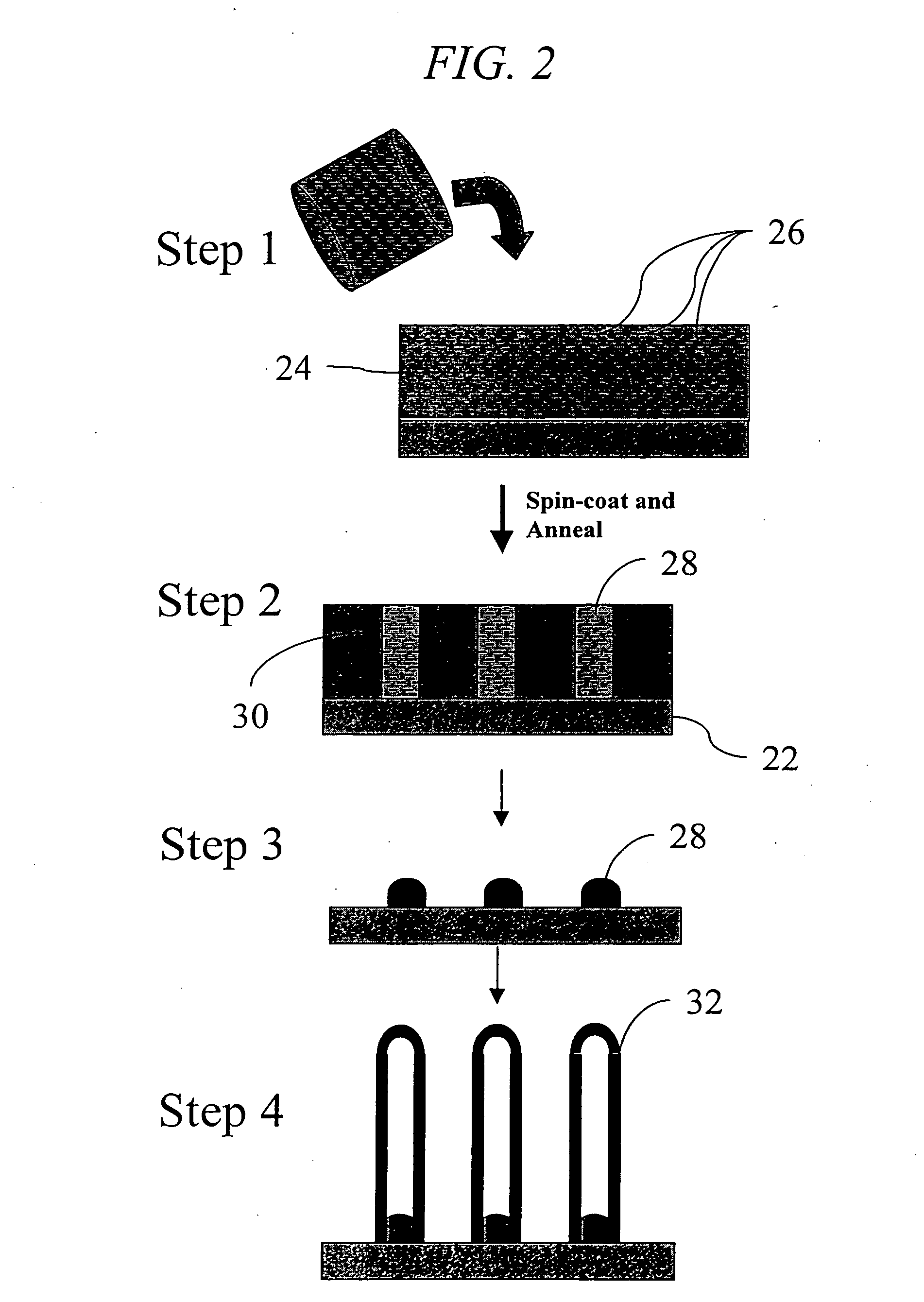
Method of producing regular arrays of nano-scale objects using nano-structured block-copolymeric materials
A method of forming a periodic array of nano-scale objects using a block copolymer, and nano-scale object arrays formed from the method are provided. The method for forming the arrays generally includes the steps of depositing a block copolymer of at least two blocks on a substrate to form an ordered meso-scale structured array of the polymer materials, forming catalytic metal dots based on the meso-scale structure, and growing nano-scale objects on the catalytic dots to form an ordered array of nano-scale objects.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Big data combined complex terrain wind electric field design platform and method
PendingCN106250656AHigh precisionConvenient guidanceData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsTerrainFatigue loading
The invention discloses a big data combined complex terrain wind electric field design platform and method. The big data combined complex terrain wind electric field design platform comprises a simulation platform, a big data workstation and an optimization layout platform; the simulation platform comprises a meso-scale numerical simulation module, a down-scale wind resource model module, a terrain considered wind field flowing model module and a wake stream model module which are connected successively; the data workstation comprises a wind electric field big data platform and a data analysis model module; and the optimization layout platform comprises a wind electric field generating capacity calculation model module, and a wind electric field optimization layout calculation model module. According to the big data combined complex terrain wind electric field design platform and method disclosed by the invention, a generating capacity model is corrected based on the big data workstation; operation modes and geographical factors which affect fan equipment are embodied in generating capacity calculation to reduce a fatigue loading rate of a fan; and thus, the maintenance cost is reduced, and the fan arrangement is optimized reasonably.
Owner:HUANENG CLEAN ENERGY RES INST +1
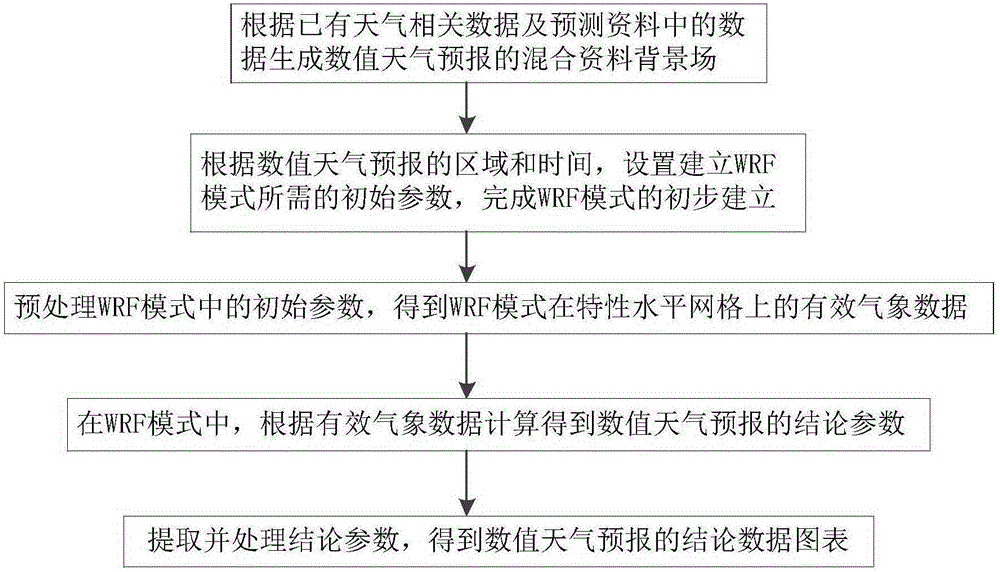
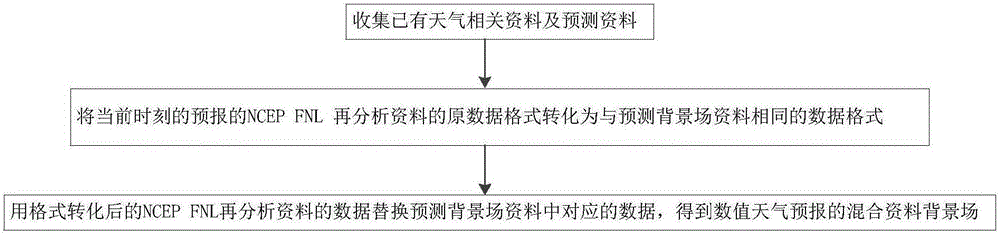
Numerical weather prediction method based on mixed ambient field
ActiveCN106339568AHigh precisionSave computing resourcesForecastingSpecial data processing applicationsNumerical weather predictionObservation data
The invention provides a numerical weather prediction method based on a mixed ambient field. According to the method, a mixed data ambient field of numerical weather prediction is generated based on the existing data of the relevant weather data and forecast data; initial parameters required in establishing a WRF mode are set to complete initial establishment of the WRF mode; effective meteorological data on feature level grid of the WRF mode is obtained; in the WRF mode, conclusion parameters of the numerical weather prediction is obtained by calculation according to the effective meteorological data; the conclusion parameters are extracted and processed to obtain conclusion data diagram of the numerical weather prediction. The present invention provides the mixed data using the reanalyzed data and the predicted background field as the background data for driving the meso-scale numerical weather prediction for numerical weather prediction; as the reanalyzed data itself assimilates a large number of observation data and the accuracy is high, which can significantly improve the accuracy of numerical weather prediction and save a lot of computing resources.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +4
6-Axis electromagnetically-actuated meso-scale nanopositioner
A MEMS actuator includes a coil stack in the form of microfabricated, electrically conductive first and second superposed layers. A magnet array is superposed in magnetic communication with the coil stack, with first and second coils being selectively, electrically actuatable to generate relative movement between the coil stack and the magnet array both in-plane and out-of-plane. In various embodiments, a plurality of the actuators are integrally coupled to a microfabricated compliant mechanism to provide a high bandwidth, six degree of freedom nanopositioner.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Devices and methods for programmable microscale manipulation of fluids
InactiveUS20070095393A1Heating or cooling apparatusLaboratory glasswaresEngineeringElectromagnetic radiation
The present invention is directed generally to devices and methods for controlling fluid flow in meso-scale fluidic components in a programmable manner. Specifically, the present invention is directed to an apparatus and method for placing two microfluidic components in fluid communication at an arbitrary position and time, both of which are externally defined. The inventive apparatus uses electromagnetic radiation to perforate a material layer having selected adsorptive properties. The perforation of the material layer allows the fluid communication between microfluidic components. Other aspects of this invention include an apparatus and method to perform volumetric quantitation of fluids, an apparatus to program arbitrary connections between a set of input capillaries and a set of output capillaries, and a method to transport fluid in centripetal device from a larger to a smaller radius. In addition, the present invention also is directed to a method to determine the radial and polar position of a pickup in the reference frame of a rotating device.
Owner:NOBLE VENTURE FINANCE II
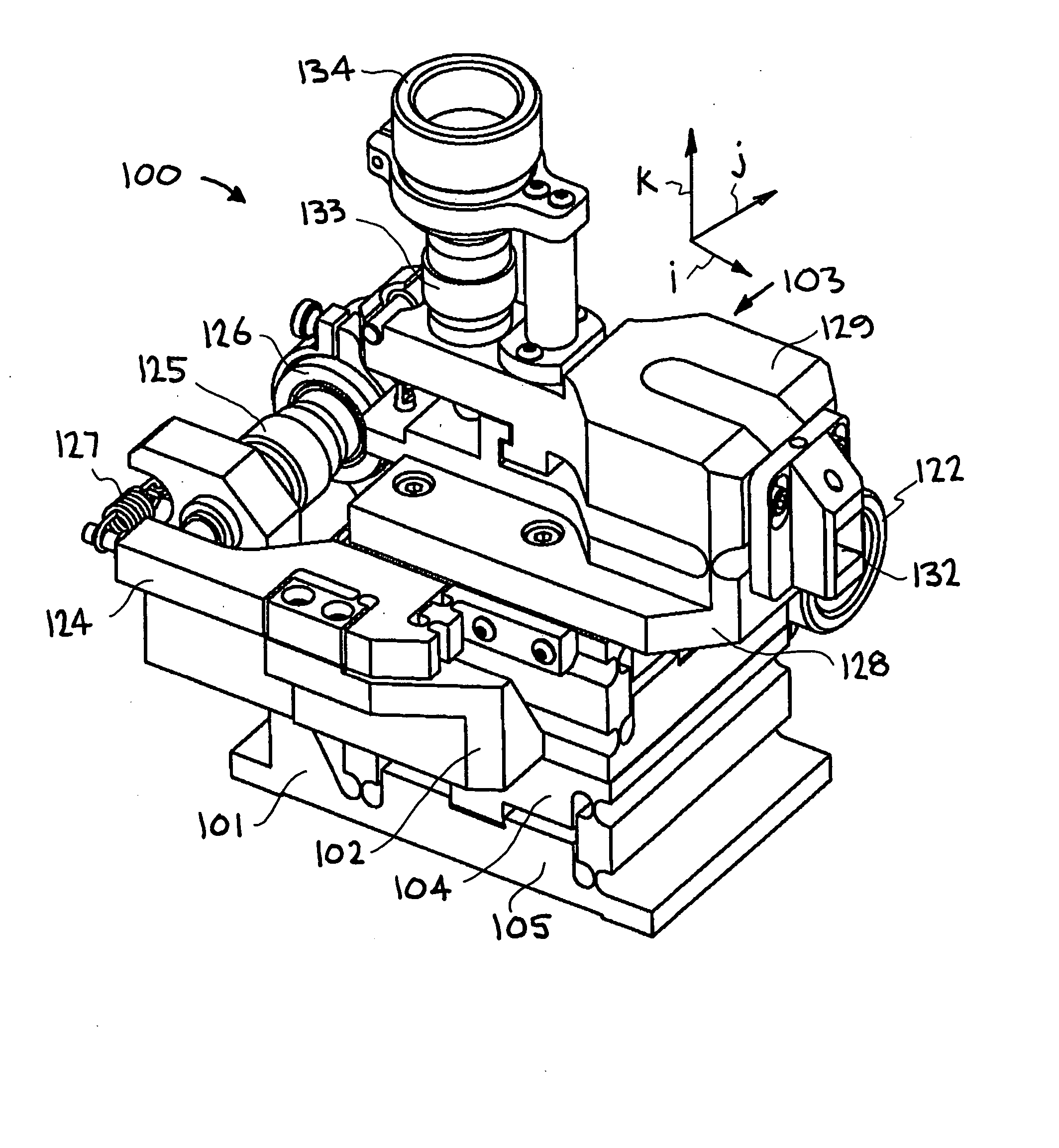
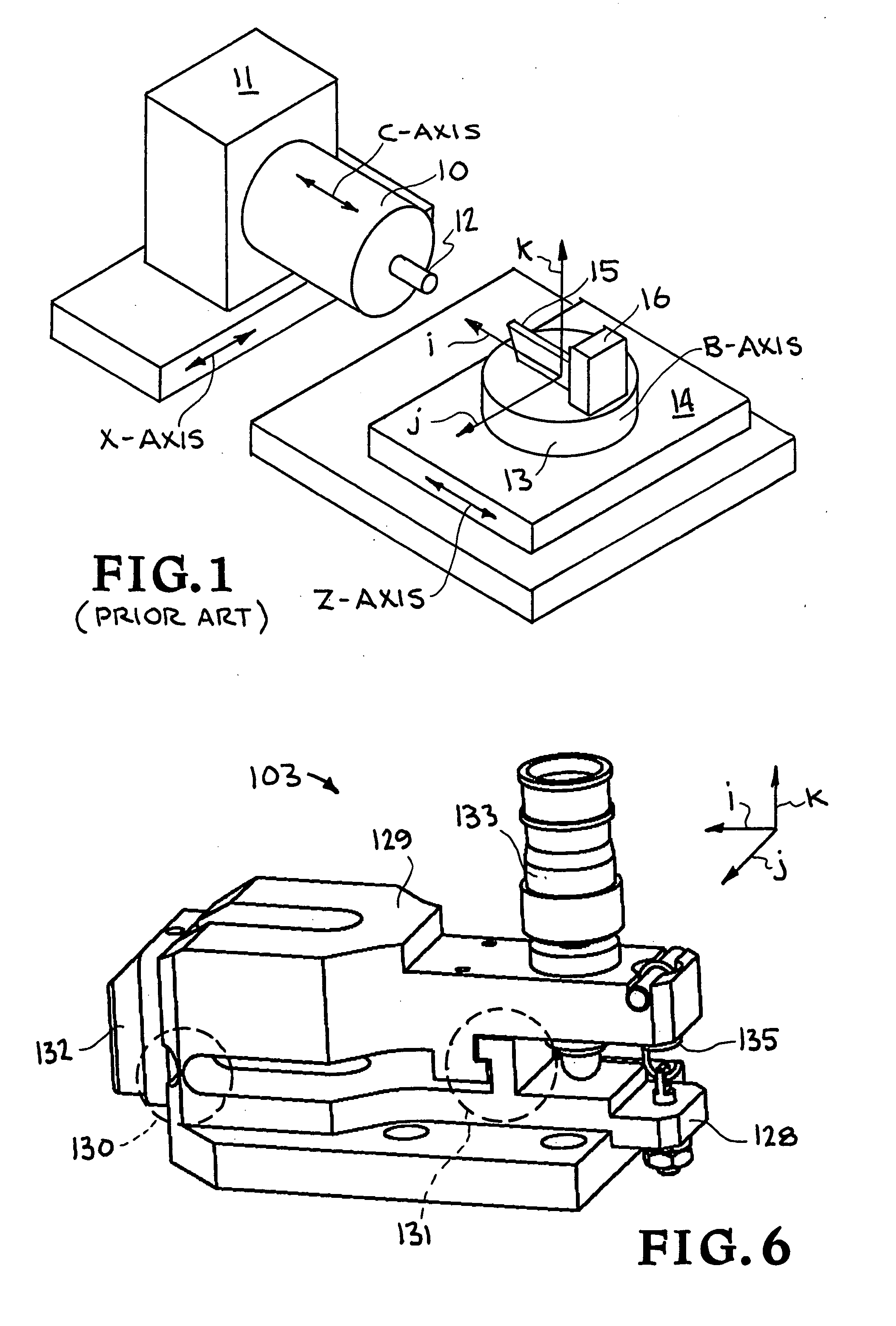
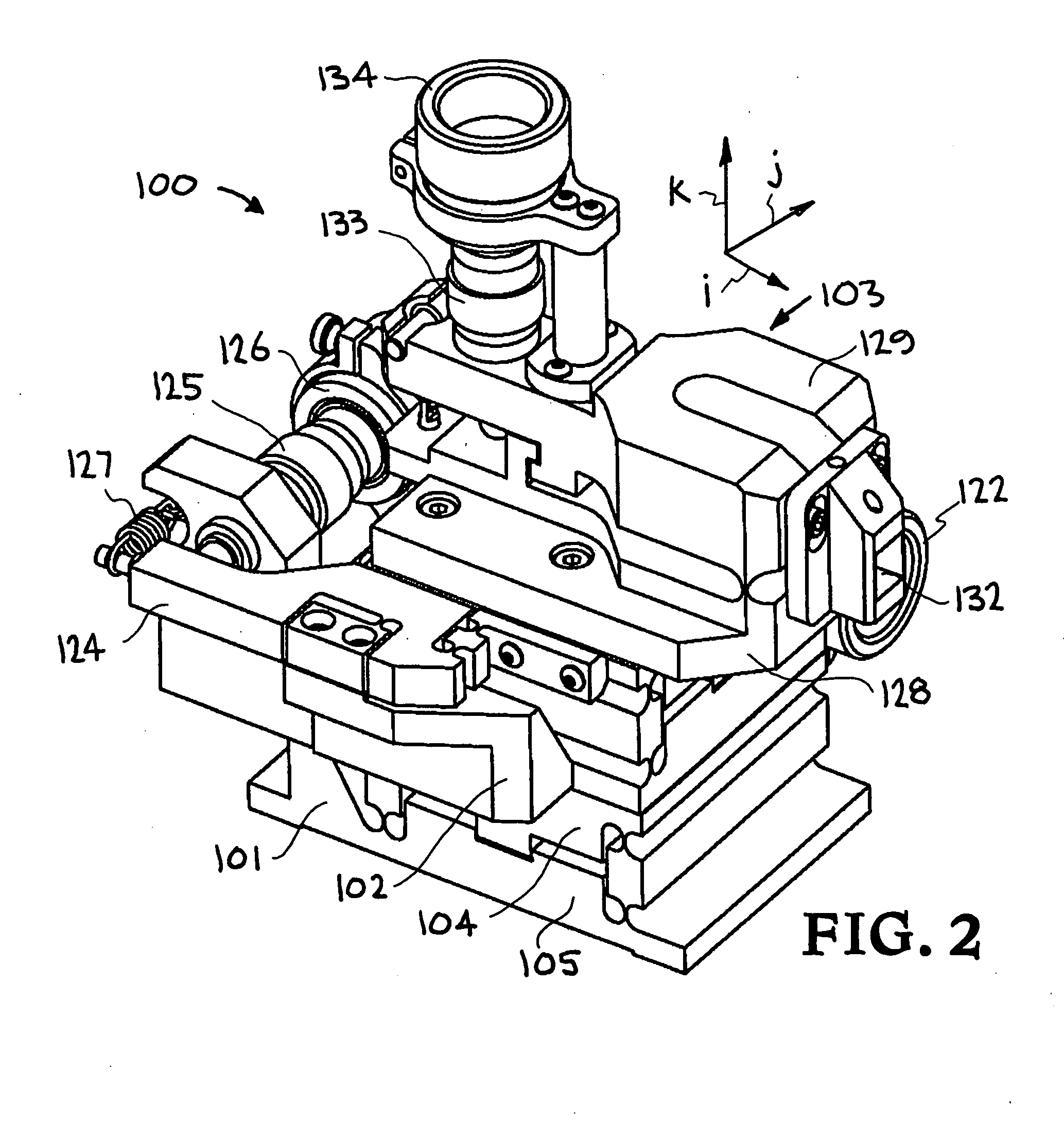
Precision tool holder with flexure-adjusted, three degrees of freedom for a four-axis lathe
InactiveUS20070261522A1Precise positioningMinimum errorLathesAutomatic/semiautomatic turning machinesDiamond turningThree degrees of freedom
A precision tool holder for precisely positioning a single point cutting tool on 4-axis lathe, such that the center of the radius of the tool nose is aligned with the B-axis of the machine tool, so as to facilitate the machining of precision meso-scale components with complex three-dimensional shapes with sub-μm accuracy on a four-axis lathe. The device is designed to fit on a commercial diamond turning machine and can adjust the cutting tool position in three orthogonal directions with sub-micrometer resolution. In particular, the tool holder adjusts the tool position using three flexure-based mechanisms, with two flexure mechanisms adjusting the lateral position of the tool to align the tool with the B-axis, and a third flexure mechanism adjusting the height of the tool. Preferably, the flexures are driven by manual micrometer adjusters. In this manner, this tool holder simplifies the process of setting a tool with sub-μm accuracy, to substantially reduce the time required to set the tool.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
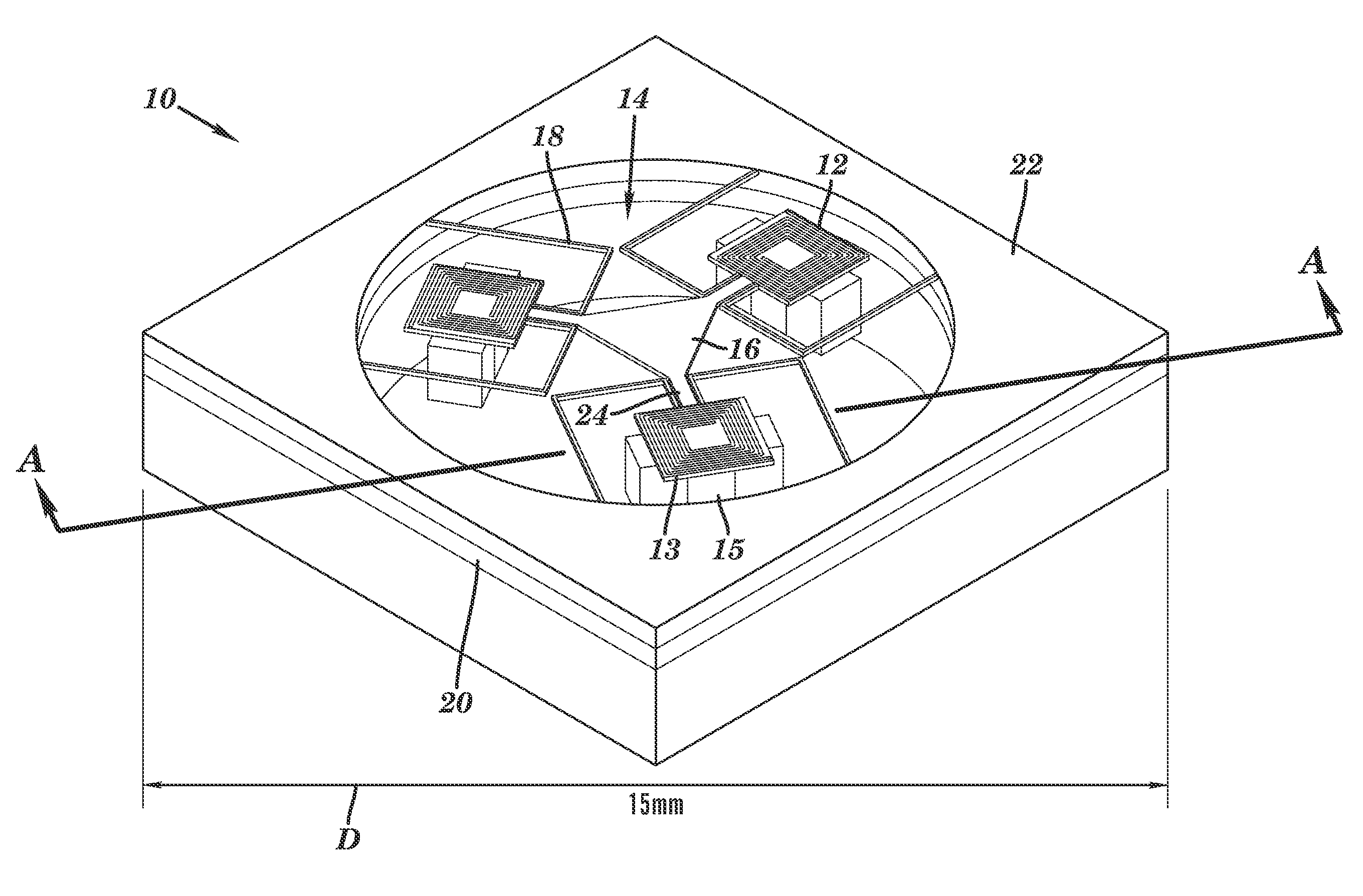
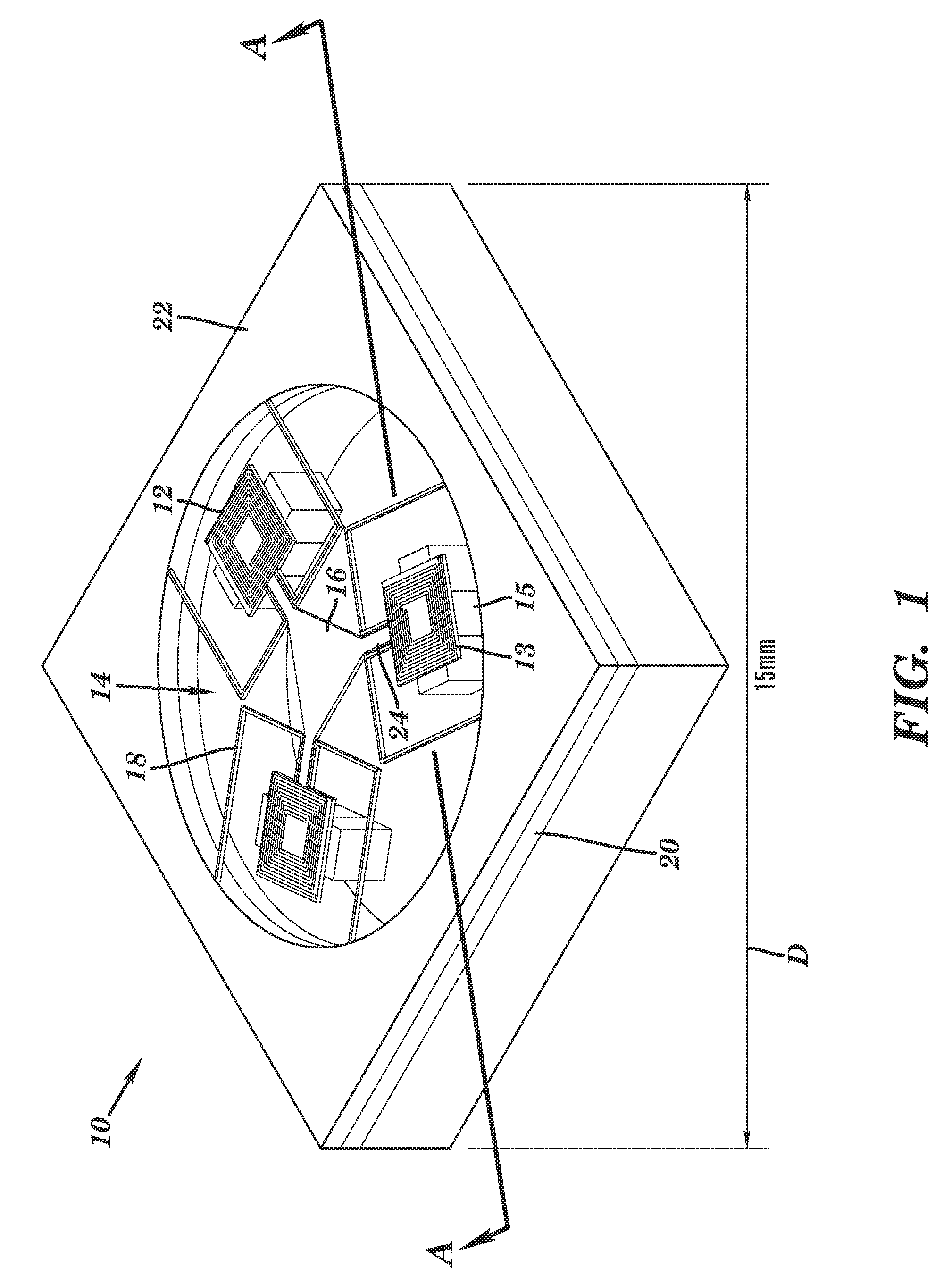
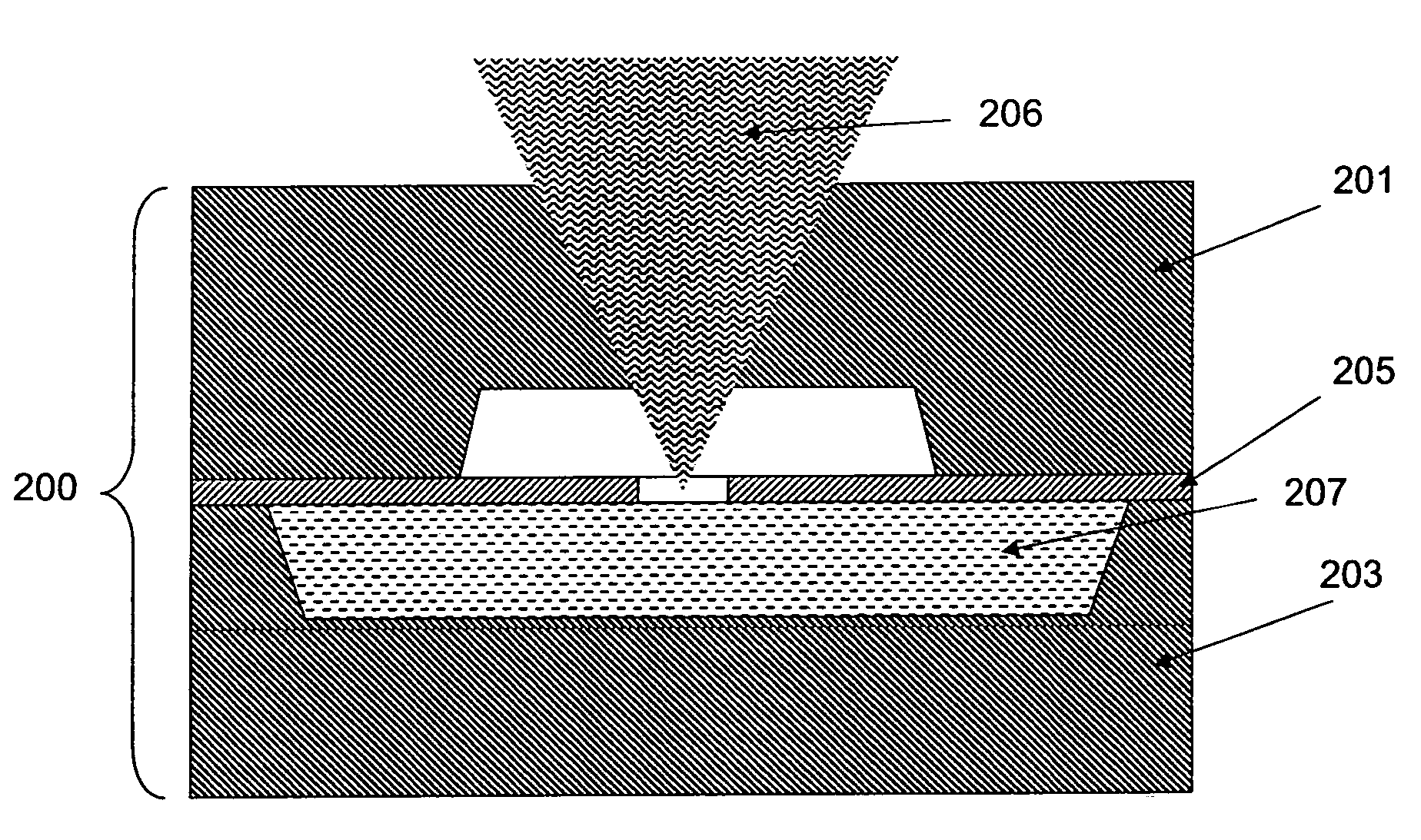
Microfluidic System Having Monolithic Nanoplasmonic Structures
ActiveUS20140004507A1Simple and robust and cost-effectiveLow costMaterial nanotechnologyServomotor componentsPolymer substrateEngineering
A microfluidic system, particularly suited as a cell culture system, is provided having a single monolithic biocompatible substrate with both a surface having an ordered array of nano-scale elements required for plasmonic response monitoring and a network of microchannels for precisely controlling cellular environment. The system has the additional advantages of low-volume consumption, rapid low-cost fabrication of molds with easily interchangeable microfluidic channel layouts, amenability to mass production, and in situ label-free real-time detection of cellular response, viability, behavior and biomolecular binding using plasmonic techniques. A ratio of greater than 0.2 between the cross-sectional dimension and the spacing distance of the nano-scale elements is useful for plasmonic response monitoring. A process for producing such a system involves fabrication of a master mold containing the nano-scale elements etched into a hard substrate, and the micro-scale and meso-scale features, such as channels and chambers, provided in a soft membrane bonded to the hard substrate. A stamp may be created by setting a settable liquid polymer or metal placed in the master mold and then the features of the intended device transferred to a polymeric substrate using the stamp.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
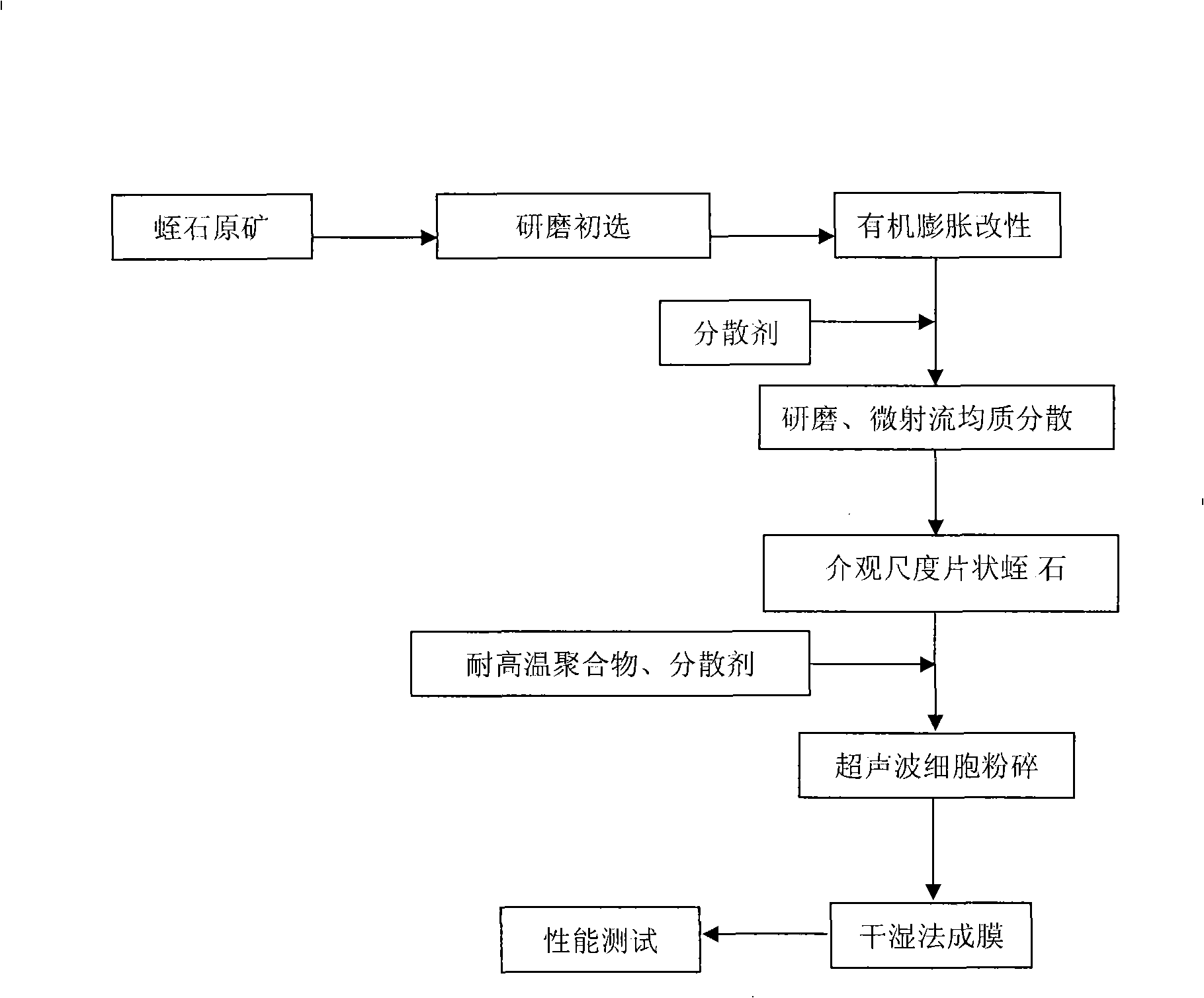
Method for preparing meso-scale flaky vermiculite and heat-resistant polymer heat insulation composite membrane
The invention provides a method for preparing mesoscale flaky vermiculite and high temperature polymer thermal insulation composite membrane. The invention adopts a technical proposal that primary mineral of vermiculite are ground to choose the part of vermiculite with a grain diameter less than 10 mu m; quaternary alkylammonium salt compound with a carbon chain of between 12 and 36 is used to modify the chosen vermiculite by organic expansion; a dispersing agent, grinding and a high-pressure homogenizer are adopted to treat the mesoscale flaky vermiculite; inorganic flaky vermiculite microcrystals are dispersed in organic high molecular polymer materials by using high temperature resistance polymer materials of poly(aryl ether sulfone) and poly(phthalazinone ether sulfone ketone) as continuous phrases and by methods of ultrasonic cell disruption, etc., and are formed into membranes by dry and wet methods. The products made by the method have extremely low heat conductivity, and excellent thermal insulation performance. Meanwhile, the composite membrane can be tightly covered on the surfaces of polysulfonamide and other fiber fabrics to improve the fireproof and thermal insulation properties, particularly the thermal insulation property of the fiber fabrics, can be used to make fire-protection clothing for safe access to fire ground or used as surface material for combat uniform.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
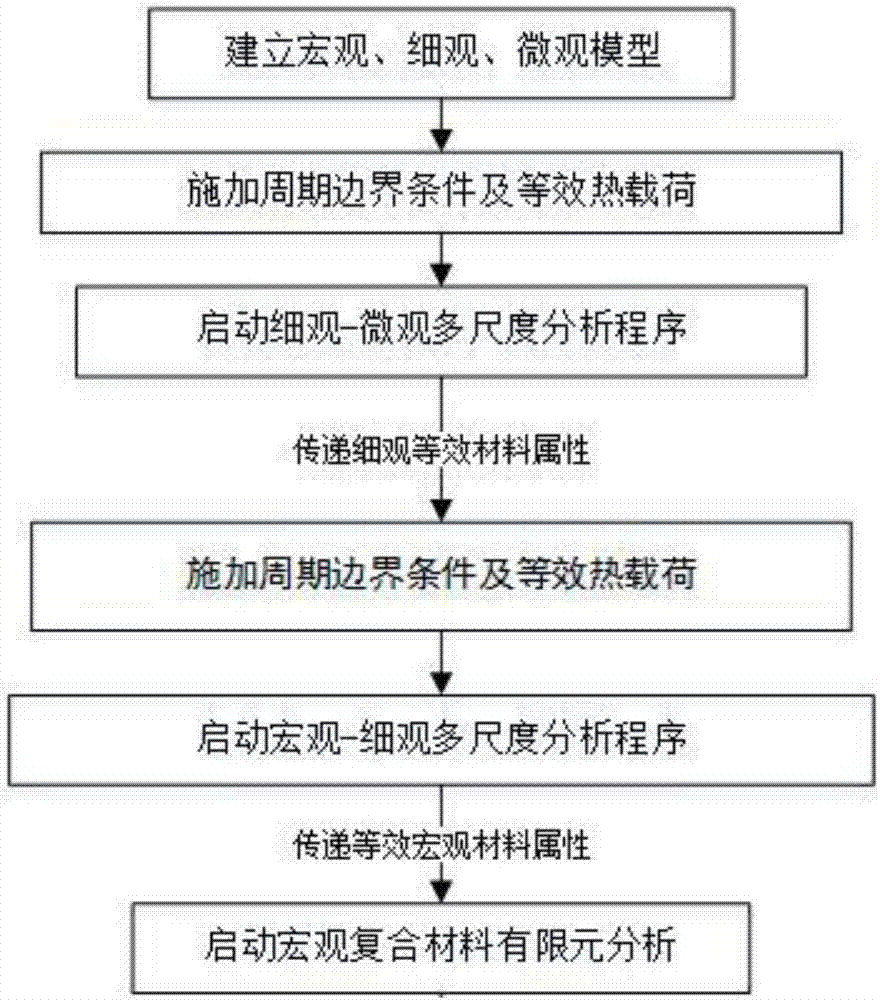
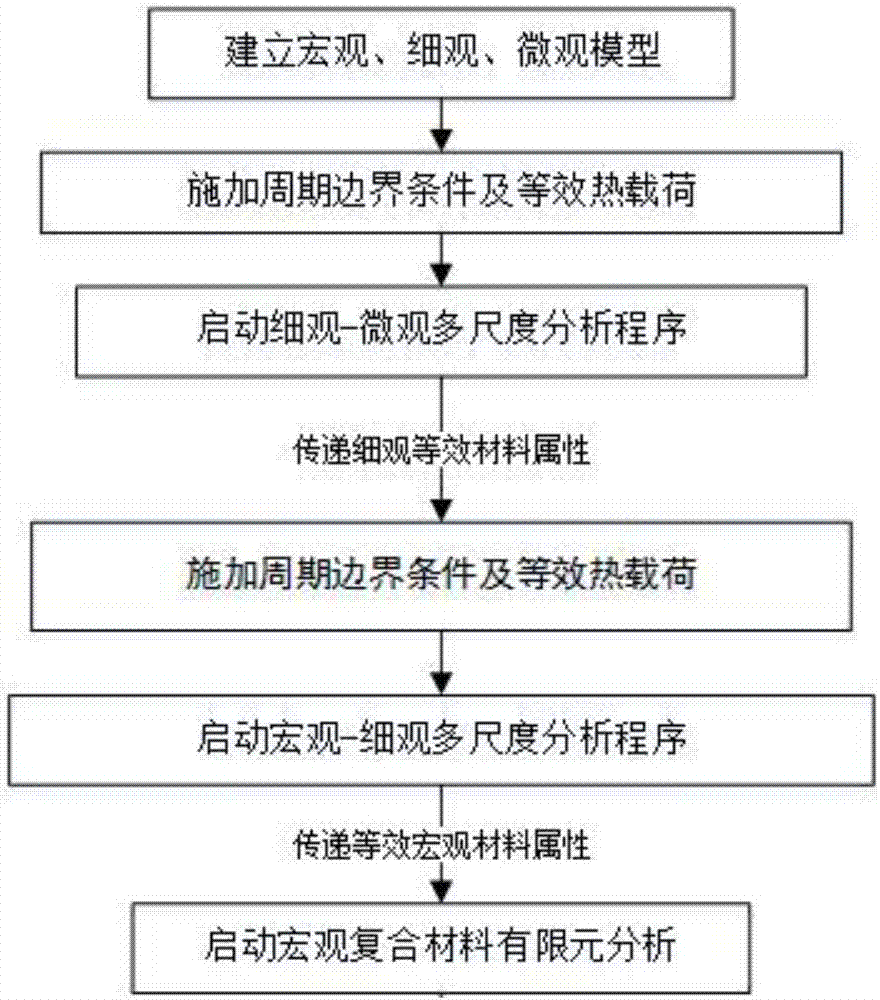
Multi-scale calculation method for equivalent heat conduction coefficient of complicated composite material structure
InactiveCN107451308AGood precisionIdentify the damage mechanismDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsScale modelStructure analysis
The invention provides a multi-scale calculation method for an equivalent heat conduction coefficient of a complicated composite material structure. According to the method, a scale separation method is adopted to separate a macro-scale structure, a meso-scale structure and a micro-scale structure, and all scale analysis models are established according to geometric characteristics of different scale models; a three-scale problem is converted into two multi-scale problems; a macro-meso multi-scale problem and a meso-micro multi-scale problem are analyzed in sequence, and an equivalent modulus obtained from a micro multi-scale problem is finally returned to a macro multi-scale problem. Through the method, the defects of low calculation efficiency and poor precision of traditional structure analysis methods are overcome, the efficiency and precision of structure performance prediction of a composite material are effectively improved, and the method can be used for guiding production, research and development and other work of the composite material. The method can be applied to complicated composite material structure design and analysis in the aerospace field and structural design thermal and mechanical analysis in other composite material engineering fields.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Value weather forecast and artificial intelligence (AI) coupling predication method for wind speed extremum of costal typhoon
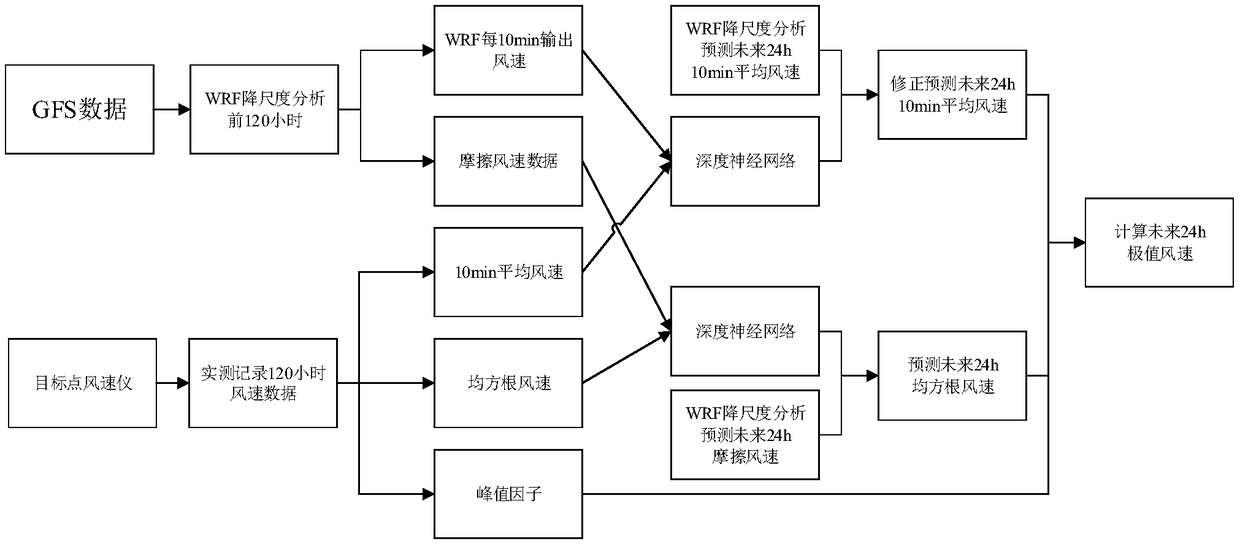
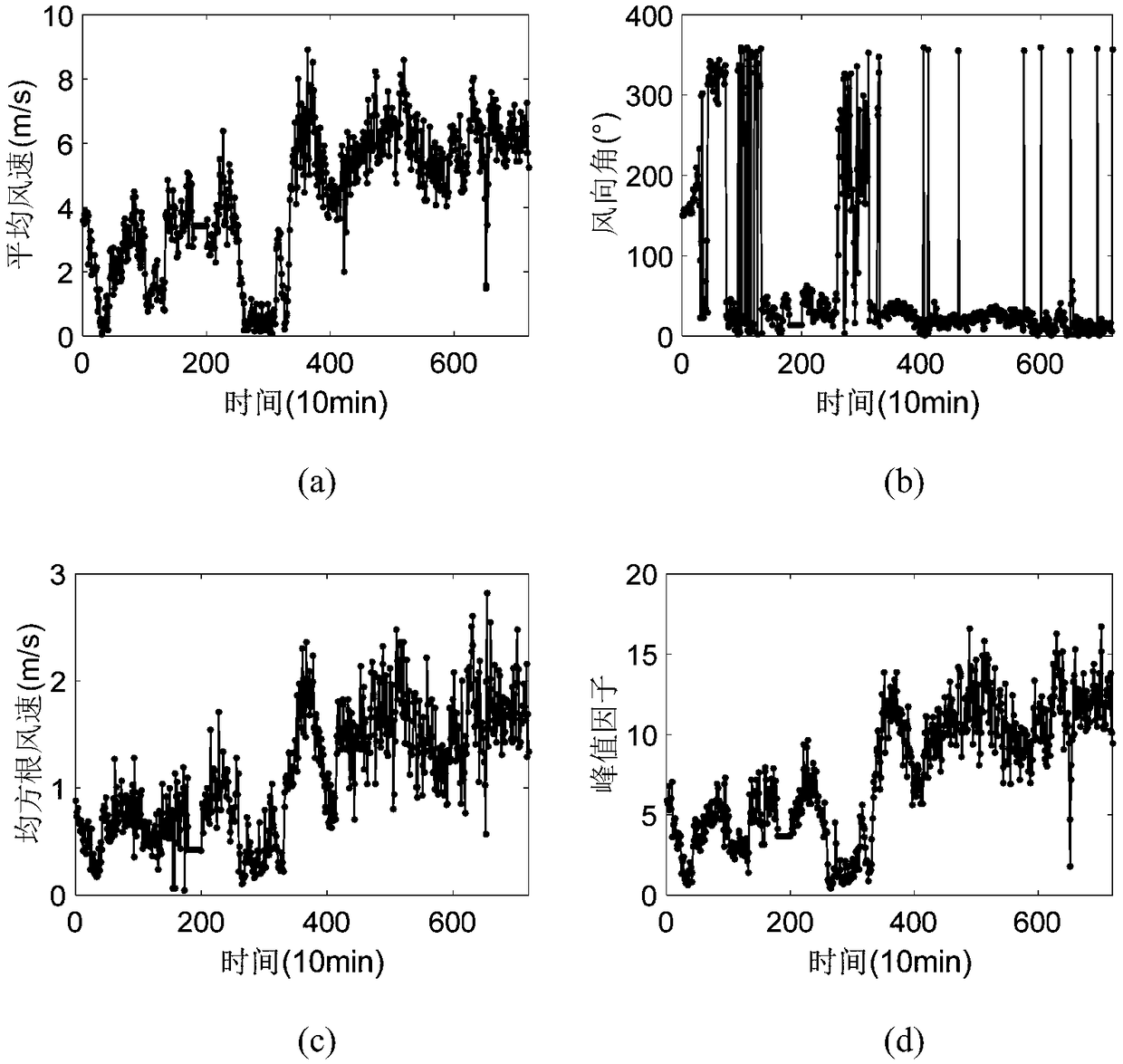
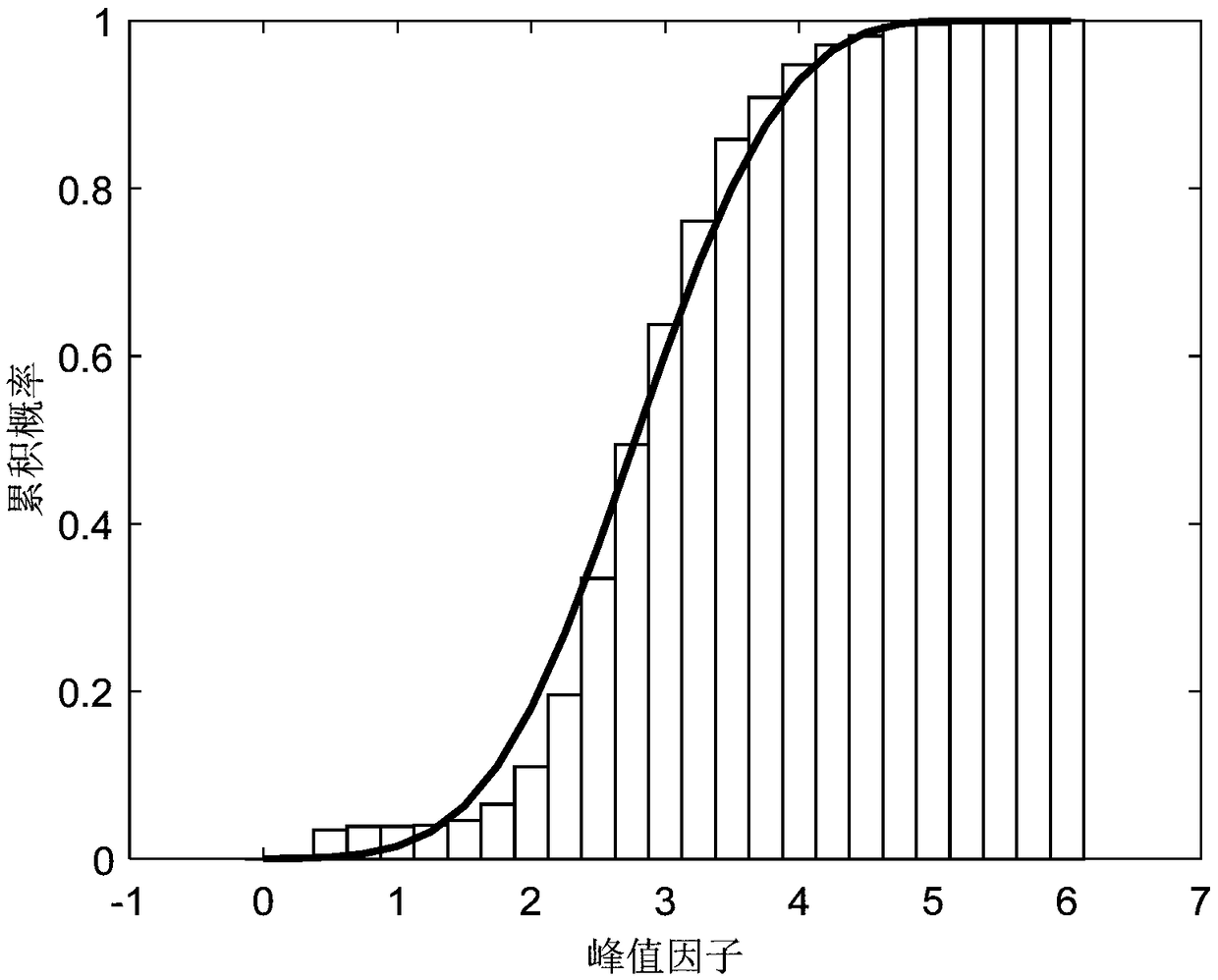
ActiveCN108983320AOvercoming the limitations of temporal and spatial precisionOvercome limitationsWeather condition predictionFluid speed measurementAnalysis dataAtmospheric sciences
The invention discloses a value weather forecast and AI coupling predication method for wind speed extremum of a costal typhoon. According to the prediction method, a value weather forecast based model is established, a deep neural network is trained according to practically measured data as well as the value weather forecast based model to obtain a deep neural network model after training, a meso-scale meteorological value mode simulation method is used to carry out dowscaling calculation again, wind speed and friction wind speed in further 24h are predicted, and an optimal peak factor is combined to obtain the wind speed extremum in the further 24h. Analysis data in the meso-scale value mode and subjective geographical information serve as input, the complex physical process of taking regard of is taken into integrated consideration, the average wind speed , the root mean square wind speed and the like of a specific target position with the practical physical meanings are predicted in a simulated way by solving an atmospheric movement equation, and the disadvantage that statistical prediction and AR predication methods rely on mathematical statistical methods completely is overcome.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
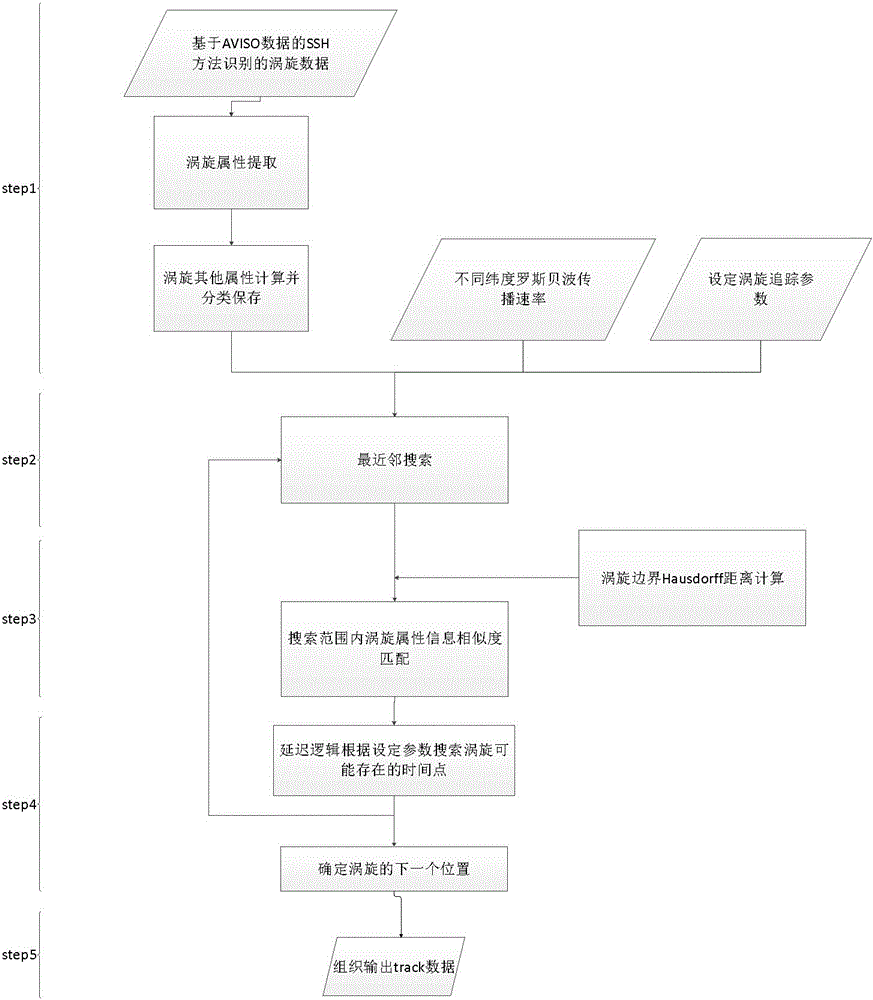
Long-time-series mesoscale eddy tracing method based on hybrid algorithm
InactiveCN105787284AUnderstanding Migration EvolutionTrusted Tracking PathSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsAlgorithmSea-surface height
The invention belongs to the crossing field of physical oceanography and computer graphics and image processing, and particularly relates to a mesoscale eddy tracing method based on a hybrid algorithm. The hybrid algorithm mainly comprises nearest neighbor search, deformation control based similarity match and delay logic. The method comprises the following steps: step one, for the nearest neighbor search, eddies in a search range are delineated according to global mesoscale eddy data recognized with an SSH (sea surface height) method; step two, for a deformation control based similarity match method, the eddies in the range and attributes of the eddies are subjected to similarity calculation of area, amplitude, kinetic energy, relative vorticity and Hausdorff distance, the eddy with the maximum similarity is selected as the position of the next eddy, and jump of an eddy path is avoided through combination of physical attributes and geometric attributes of the eddies; step three, the delay logic is adopted, search at multiple time points is considered, the eddies temporarily disappearing at certain time points are processed, and discontinuity of the eddy path is avoided, so that the purpose of multi-year long-term efficient tracing on the eddies is achieved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
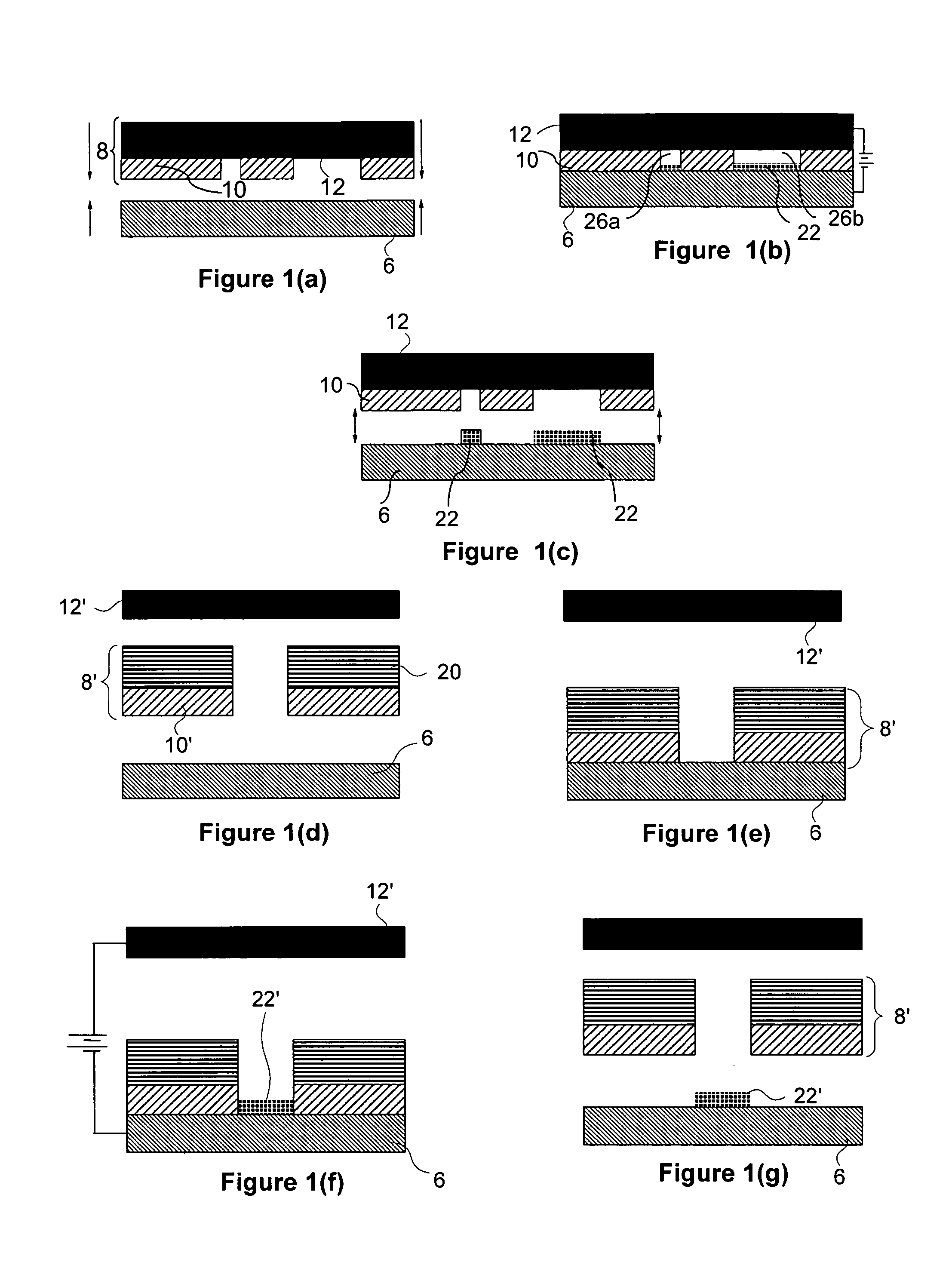
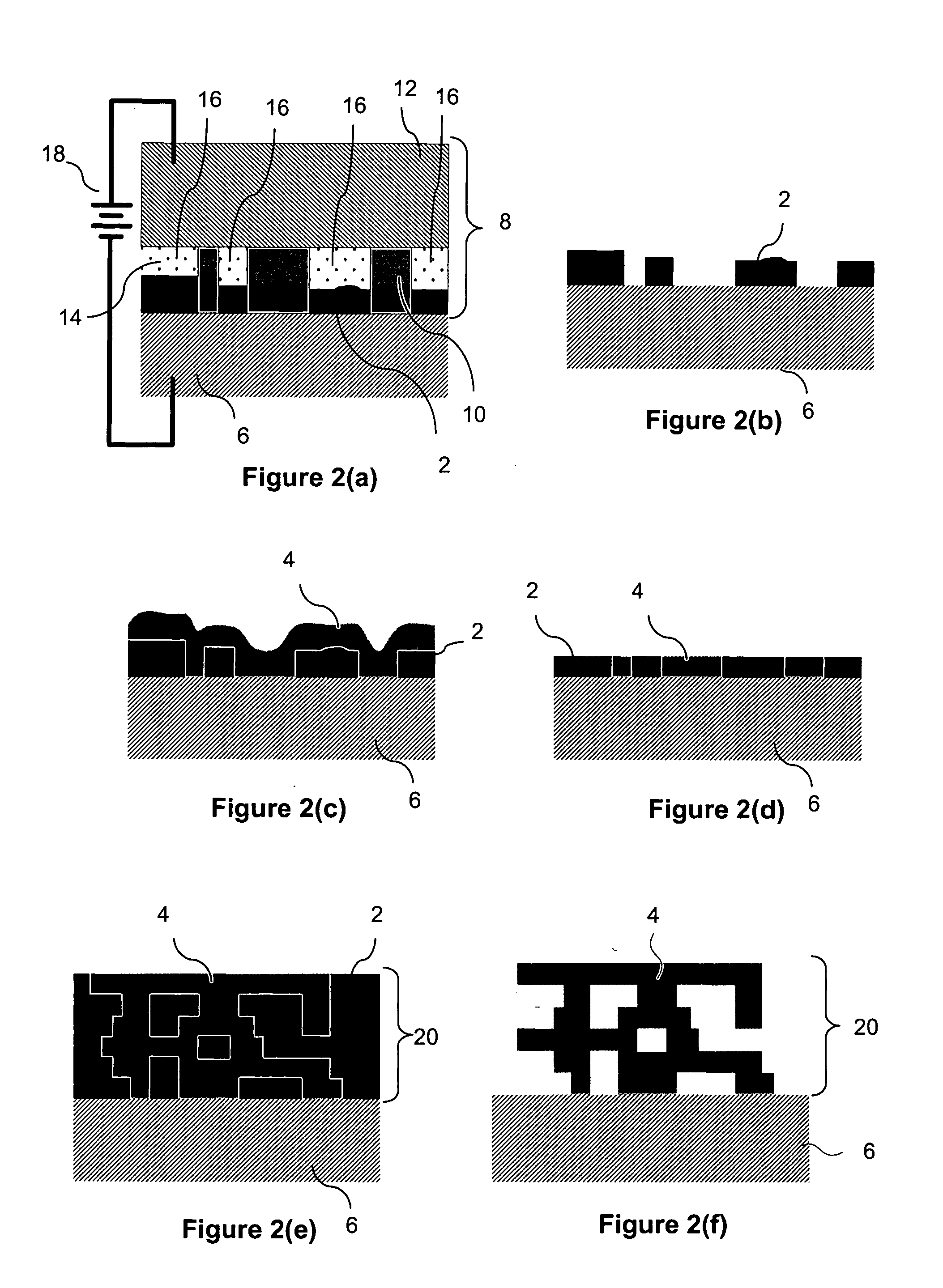
Methods for electrochemically fabricating structures using adhered masks, incorporating dielectric sheets, and/or seed layers that are partially removed via planarization
ActiveUS20060011486A1Simple methodAdditive manufacturing apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMaterial transferMaterials science
Embodiments of the present invention provide mesoscale or microscale three-dimensional structures (e.g. components, device, and the like). Embodiments relate to one or more of (1) the formation of such structures which incorporate sheets of dielectric material and / or wherein seed layer material used to allow electrodeposition over dielectric material is removed via planarization operations; (2) the formation of such structures wherein masks used for at least some selective patterning operations are obtained through transfer plating of masking material to a surface of a substrate or previously formed layer, and / or (3) the formation of such structures wherein masks used for forming at least portions of some layers are patterned on the build surface directly from data representing the mask configuration, e.g. in some embodiments mask patterning is achieved by selectively dispensing material via a computer controlled inkjet nozzle or array or via a computer controlled extrusion device.
Owner:MICROFAB
Dosimeter for programmable microscale manipulation of fluids
InactiveCN101291736ALow costEasy to openShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersLaboratory glasswaresMultiplexingDosimeter
The present invention is directed generally to devices and methods for controlling fluid flow in meso-scale fluidic components in a programmable manner. Specifically, the present invention is directed to an apparatus and method for placing two microfluidic components in fluid communication at an arbitrary position and time, both of which are externally defined. The inventive apparatus uses electromagnetic radiation to perforate a material layer having selected adsorptive properties. The perforation of the material layer allows the fluid communication between microfluidic components allowing volumetric quantitation of fluids. Using the perforation of the material functionality such as metering and multiplexing are achieved on a microscale. This functionality is achieved through basic operations, like dosimeters filling, dosimeters purging, dosimeters extraction, dosimeters ventilation and channels routing. Accordingly, these operations are performed in microfluidic platforms and are characterized extensively, allowing the realization of complex assays in a miniaturized format, where dilutions of proteins and assay readout can be performed in an extremely small footprint.
Owner:SPINKS CORP
Multi-scale calculation method for equivalent thermal expansion coefficient of complicated composite material structure
InactiveCN107451309AGood precisionIdentify the damage mechanismDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsScale modelStructure analysis
The invention provides a multi-scale calculation method for an equivalent thermal expansion coefficient of a complicated composite material structure. According to the method, a scale separation method is adopted to separate a macro-scale structure, a meso-scale structure and a micro-scale structure, and all scale analysis models are established according to geometric characteristics of different scale models; a three-scale problem is converted into two multi-scale problems; a macro-meso multi-scale problem and a meso-micro multi-scale problem are analyzed in sequence, and an equivalent modulus obtained from a micro multi-scale problem is finally returned to a macro multi-scale problem. Through the method, the defects of low calculation efficiency and poor precision of traditional structure analysis methods are overcome, the efficiency and precision of structure performance prediction of a composite material are effectively improved, and the method can be used for guiding production, research and development and other work of the composite material. The method can be applied to complicated composite material structure design and analysis in the aerospace field and structural design thermal and mechanical analysis in other composite material engineering fields.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Elastoplastic constitutive model of steel fiber reinforced concrete considering fiber slippage and construction method thereof
ActiveCN107153745AWide applicabilityGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsAxial compressionInequation
The invention provides an elastoplastic constitutive model of steel fiber reinforced concrete considering fiber slippage. The elastoplastic constitutive model of the steel fiber reinforced concrete is characterized in that the model is as shown in the following formula. According to the elastoplastic constitutive model of the steel fiber reinforced concrete considering fiber slippage disclosed by the invention, composite material mixing theories are used, and steel fiber and matrix concrete constitutive equations are respectively obtained based on a thermodynamic dissipation inequation. Matrix concrete is the elastoplastic constitutive model, and steel fibers are one-dimensional elastic constitutive models considering fiber interface slippage. The plasticity of the matrix concrete adopts Hsieh-Ting-Chen four-parameter yield criteria and Drucker-Prager classic plastic flow rules, and plastic hardening / softening criteria adopt a modified Guo Zhenhai model. The parameters of the steel fiber one-dimensional elastic constitutive model considering an interface are determined through a steel fiber pullout test. The parameters of the concrete elastoplastic constitutive model can be calibrated by uniaxial and true three-axial compression tests. The model considers a steel fiber slip mechanism in the meso-scale, and combines elastic constitutive structures of the ordinary concrete and the steel fibers to construct the elastoplastic constitutive model of the steel fiber reinforced concrete, thereby being simple and feasible, and having important promoting significance to basic theoretical research of the fiber reinforced concrete.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com