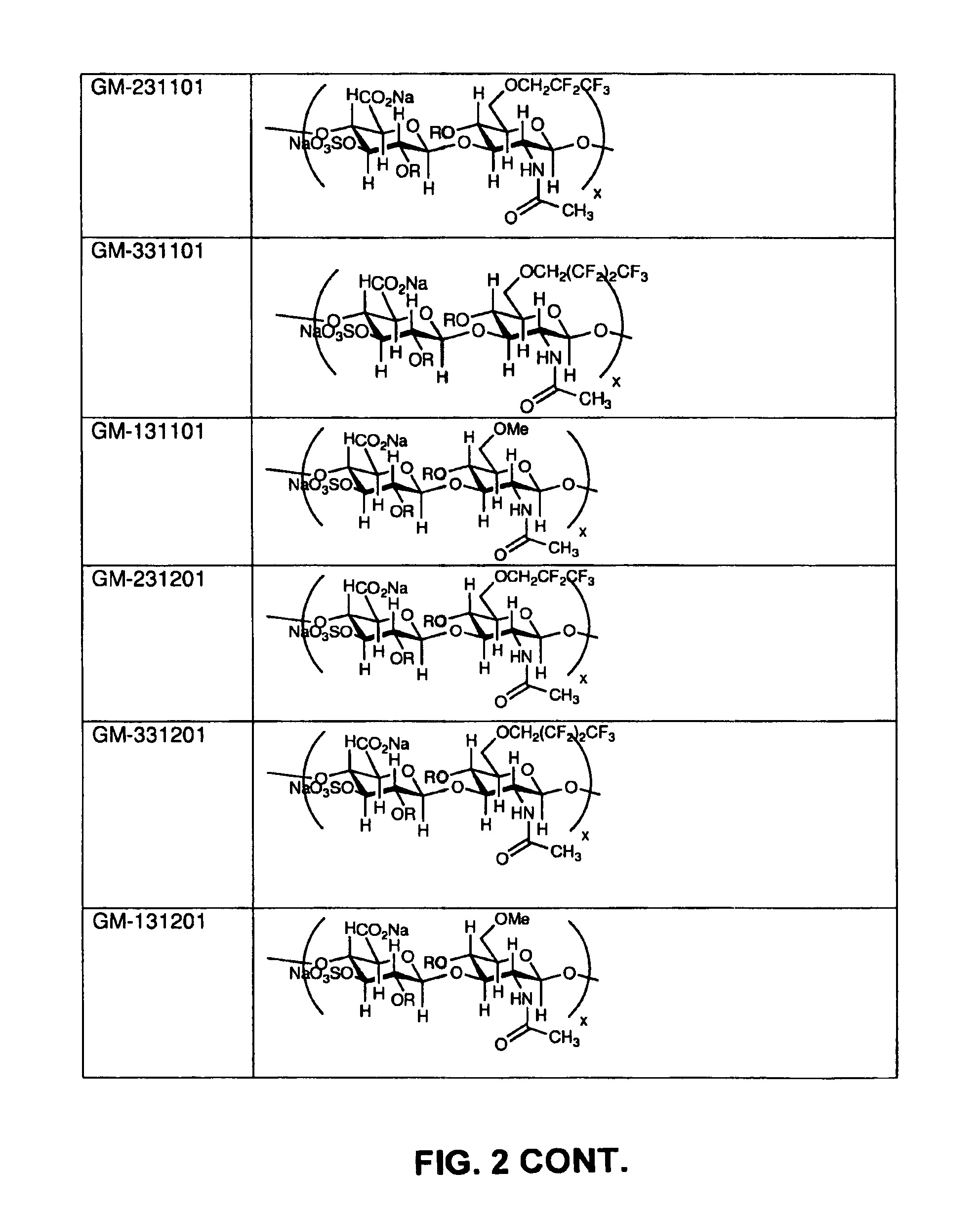
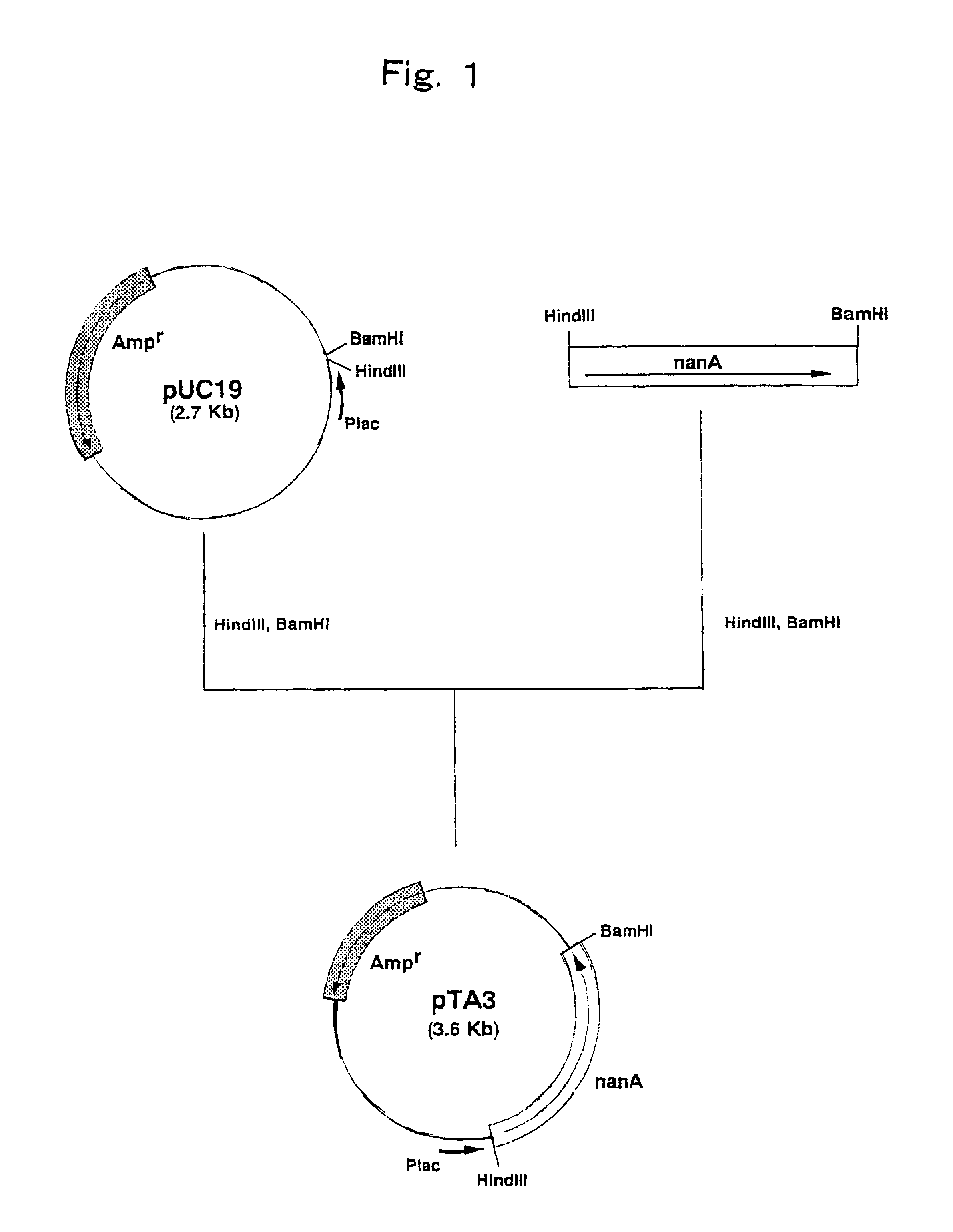
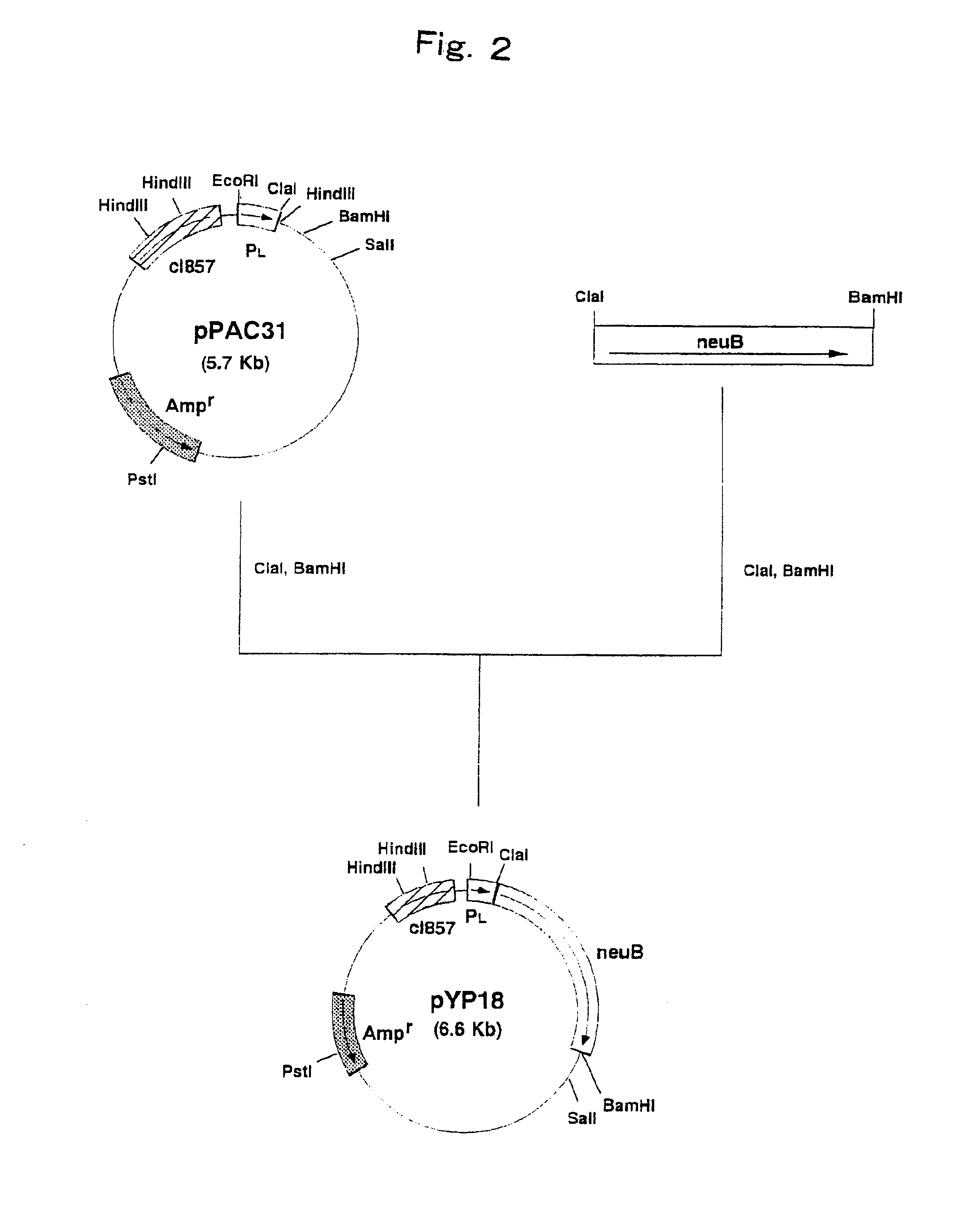
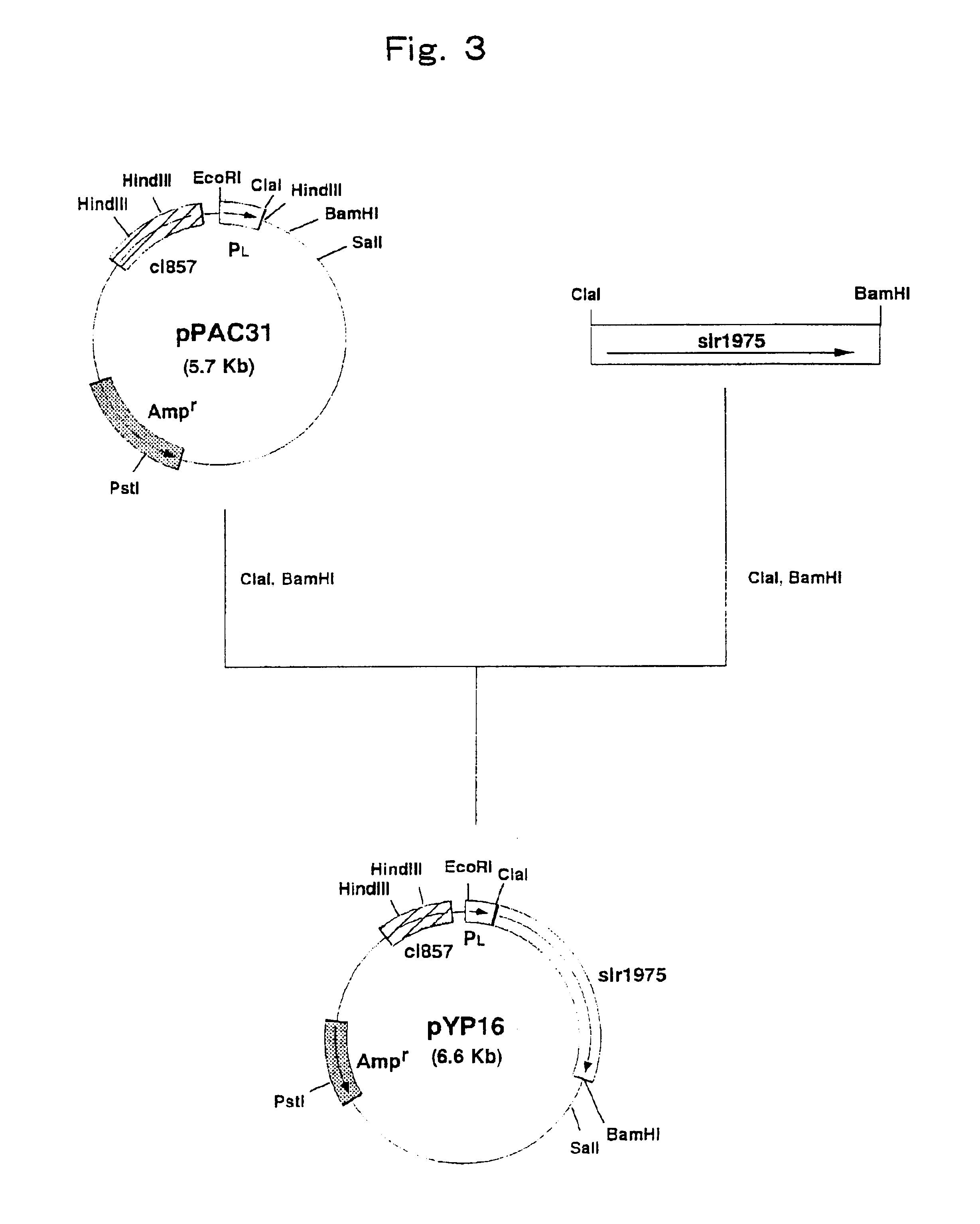
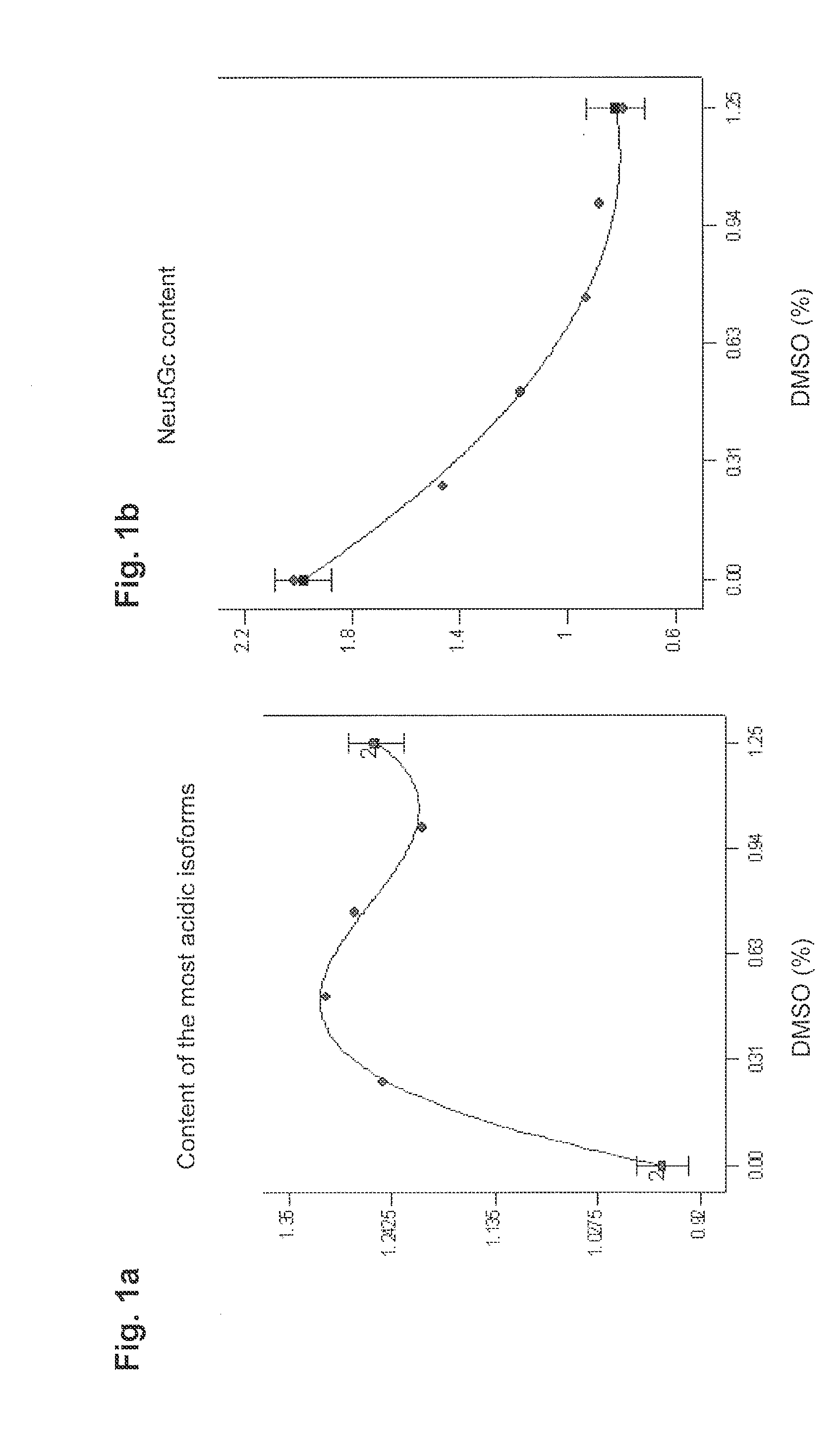
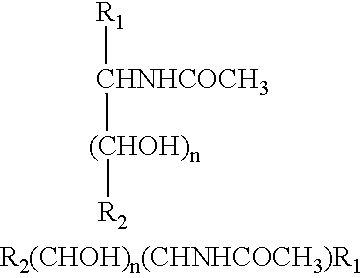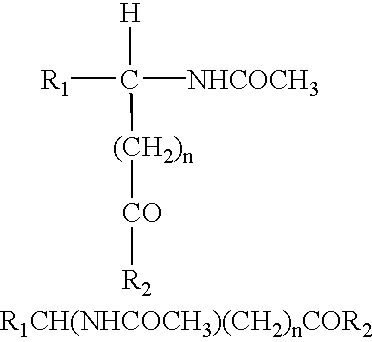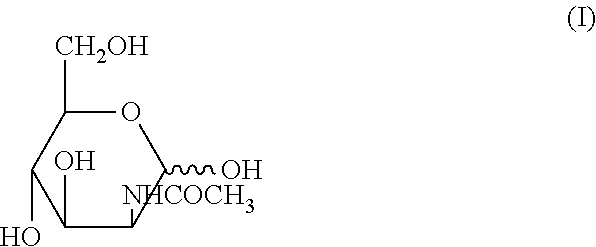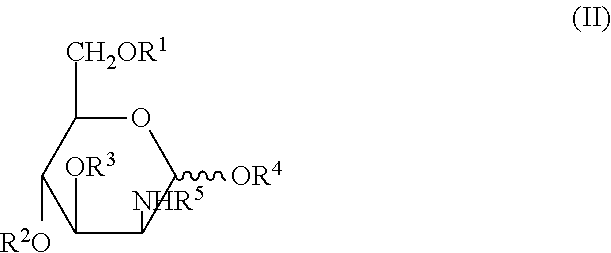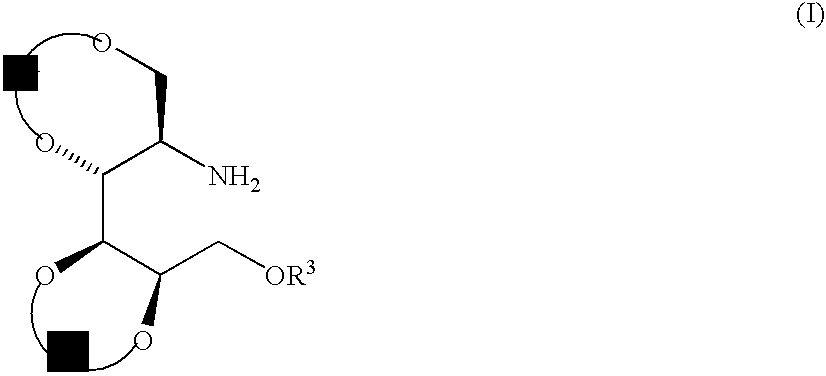Patents
Literature
94 results about "Glycosylamine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
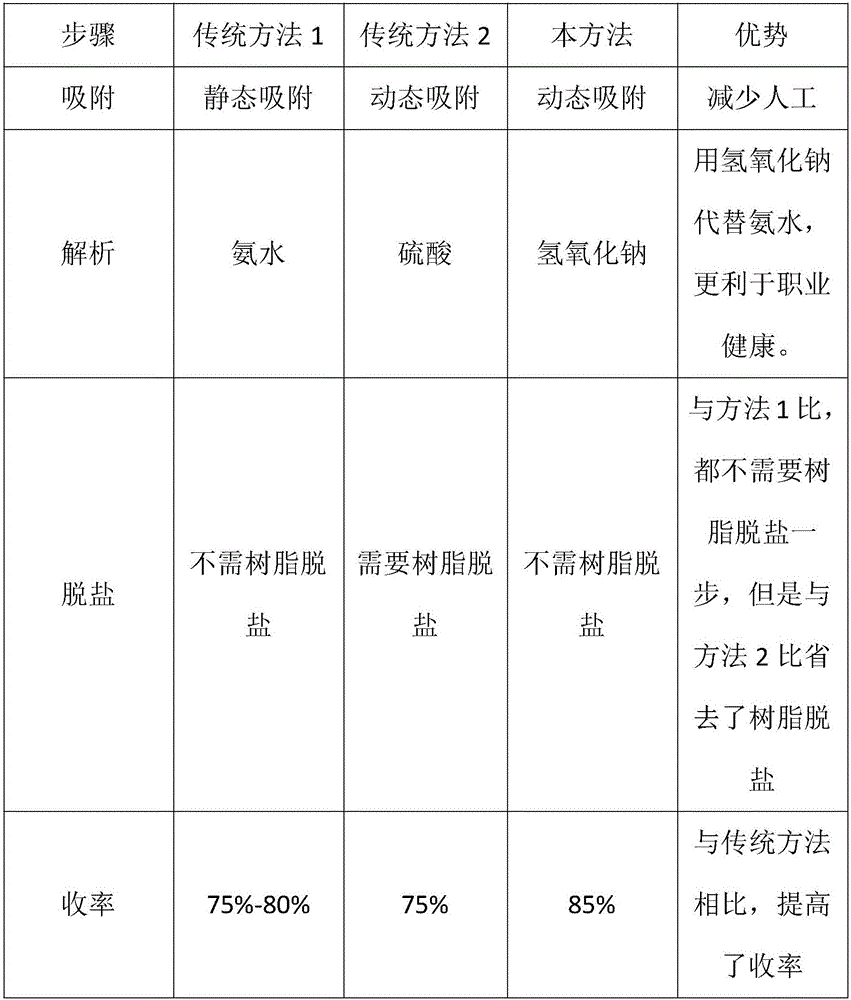
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
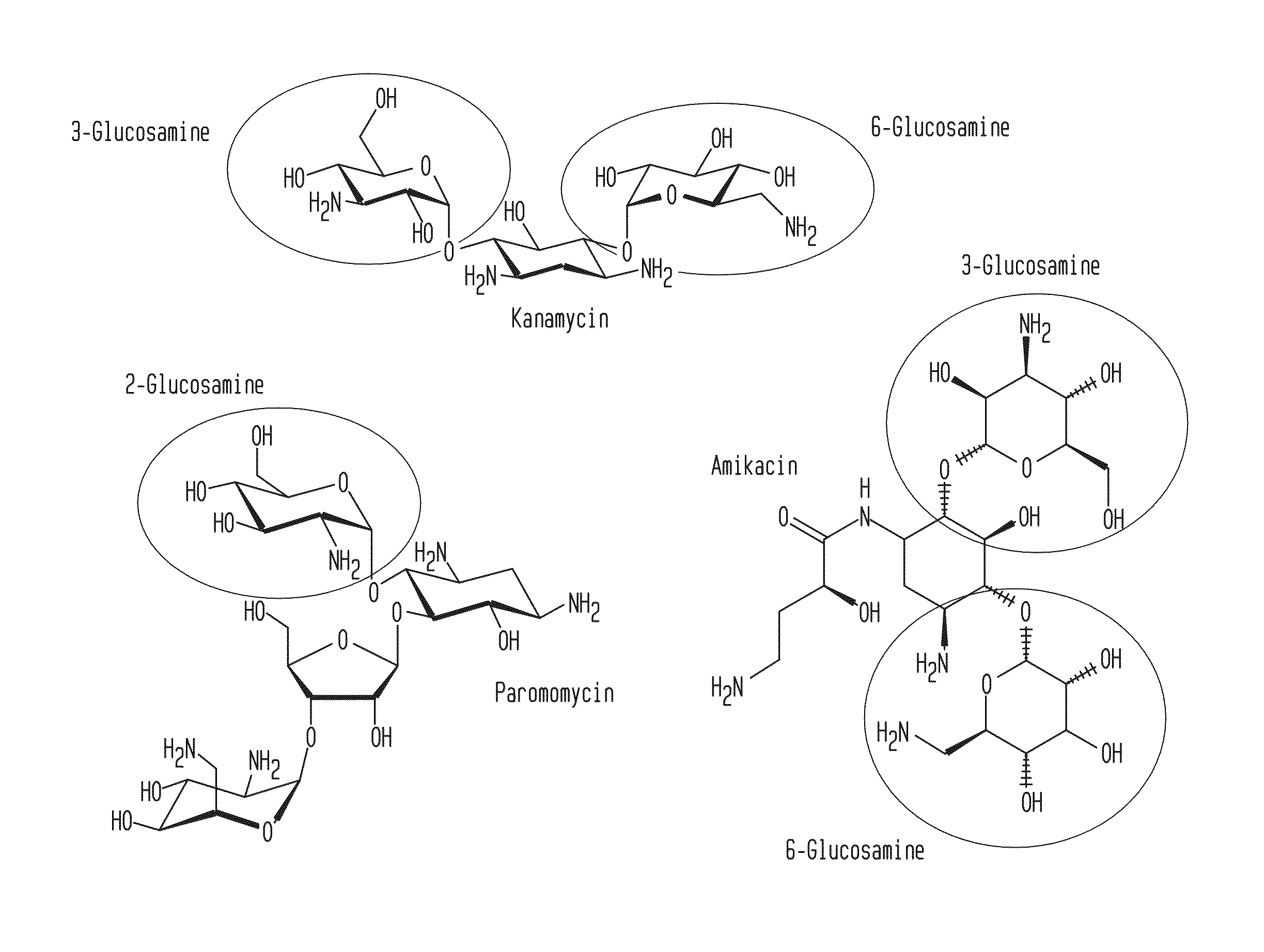
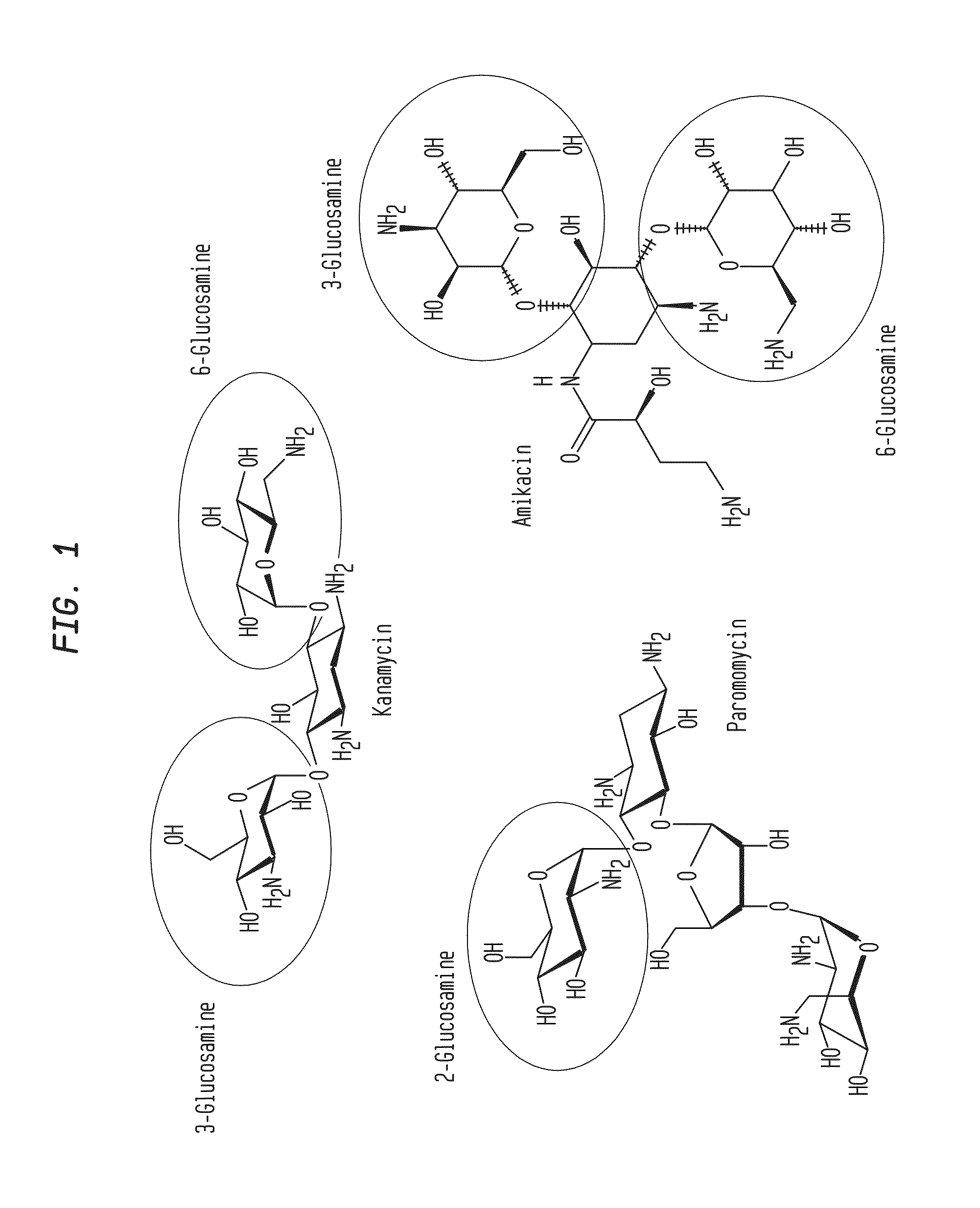
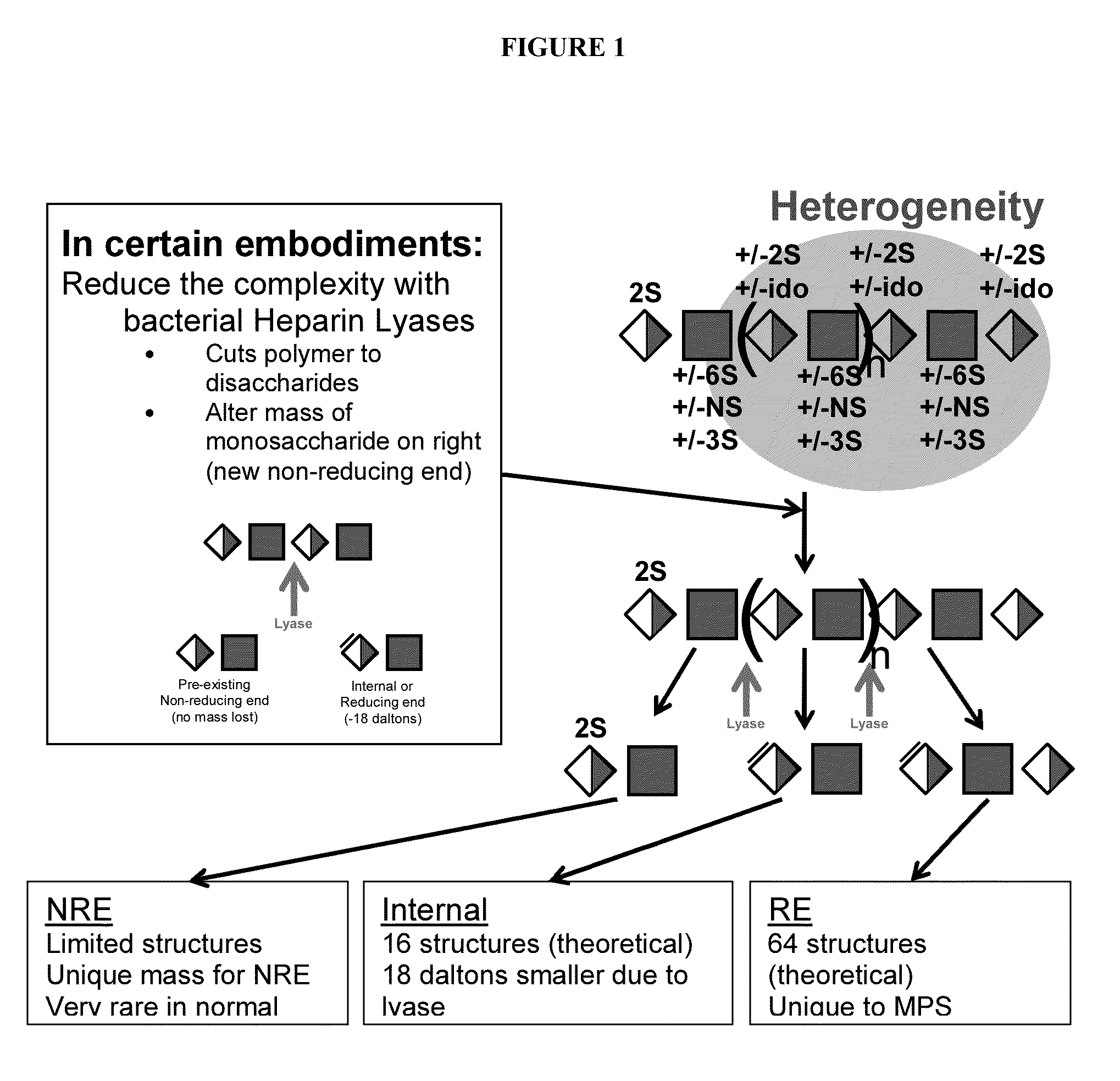
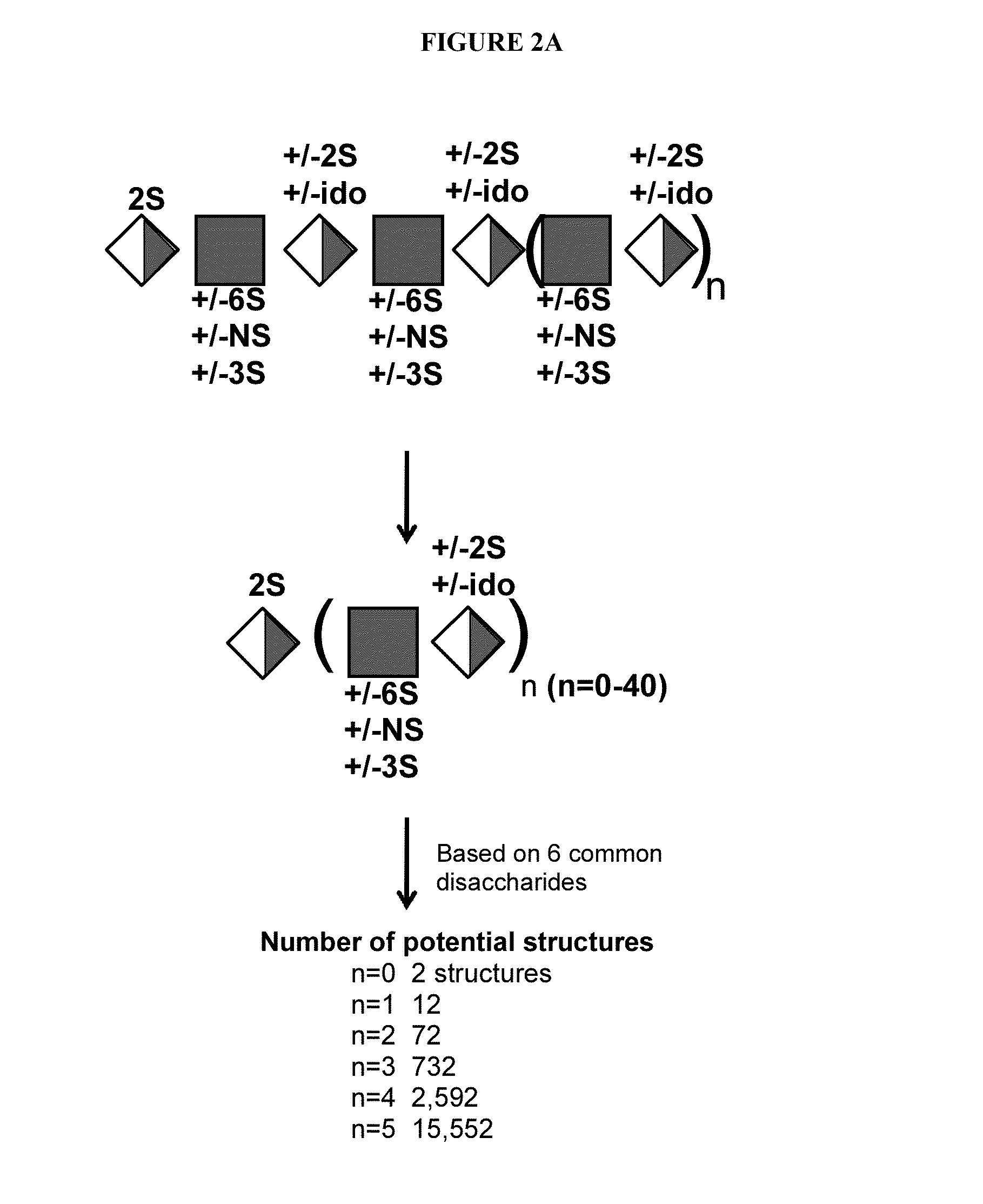
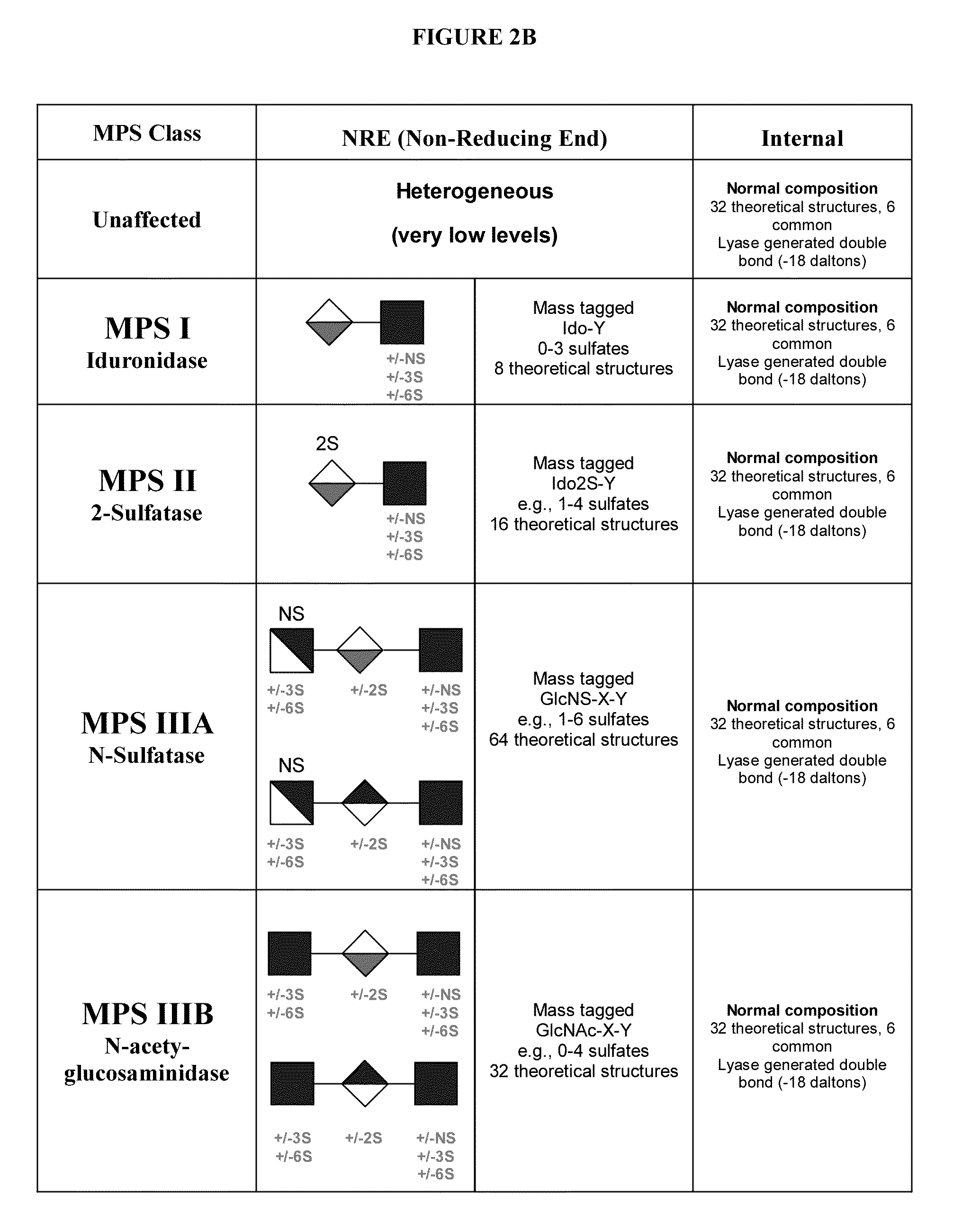
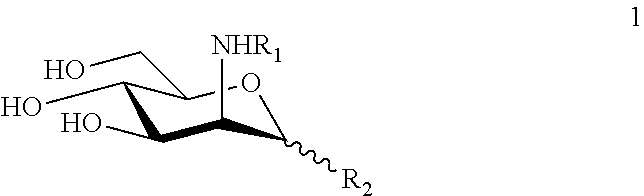
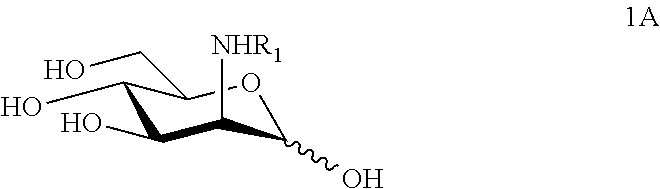
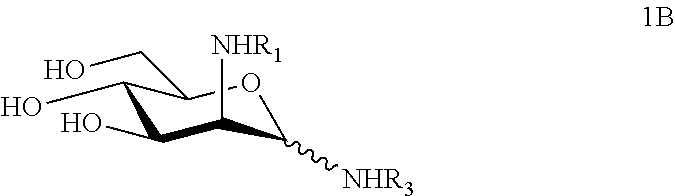
Glycosylamines are a class of biochemical compounds consisting of a glycosyl group attached to an amino group, -NR₂. They are also known as N-glycosides, as they are a type of glycoside. Glycosyl groups can be derived from carbohydrates. The glycosyl group and amino group are connected with a β-N-glycosidic bond, forming a cyclic hemiaminal ether bond (α-aminoether).
Staphylococcus antigen and vaccine
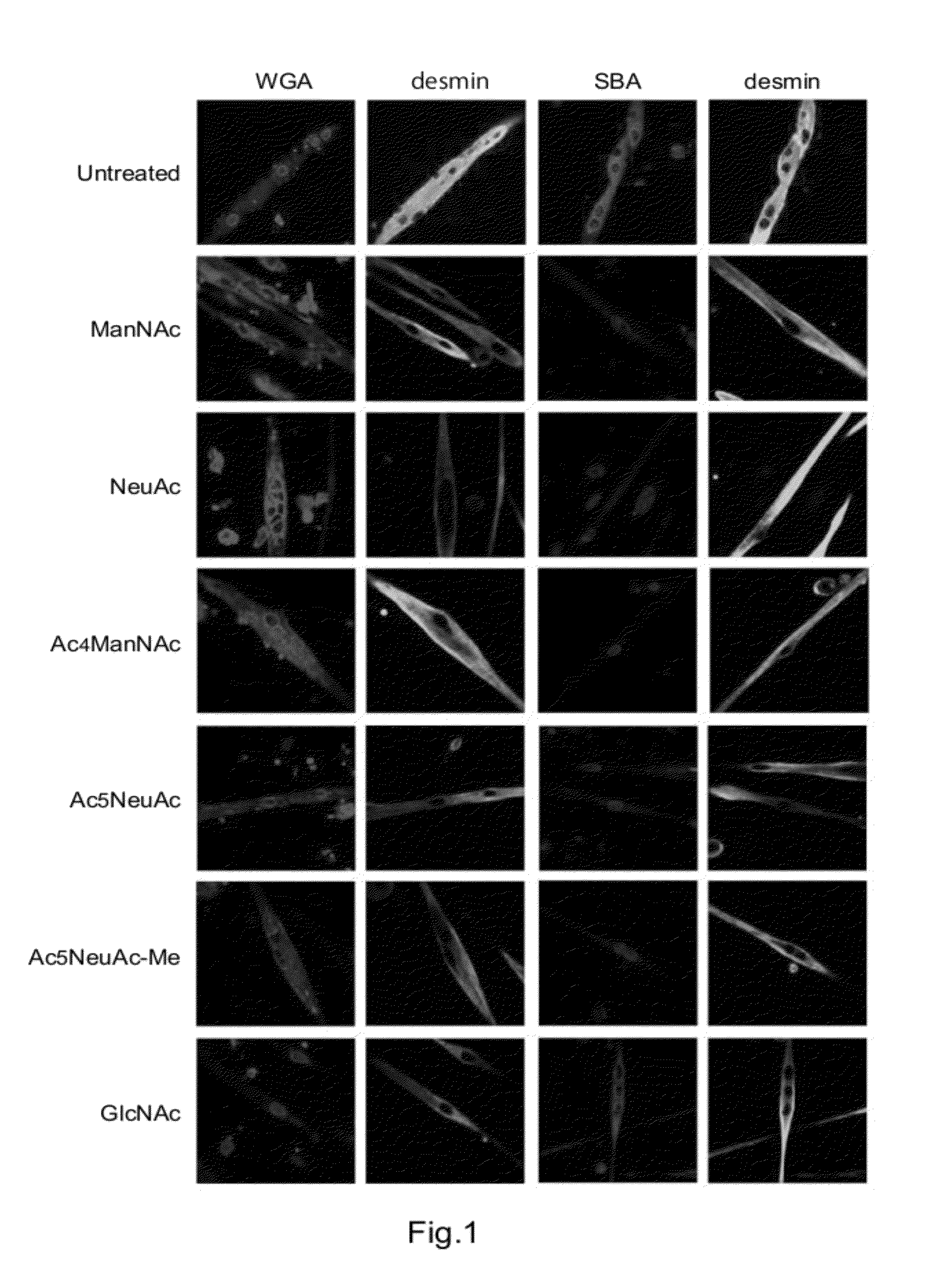
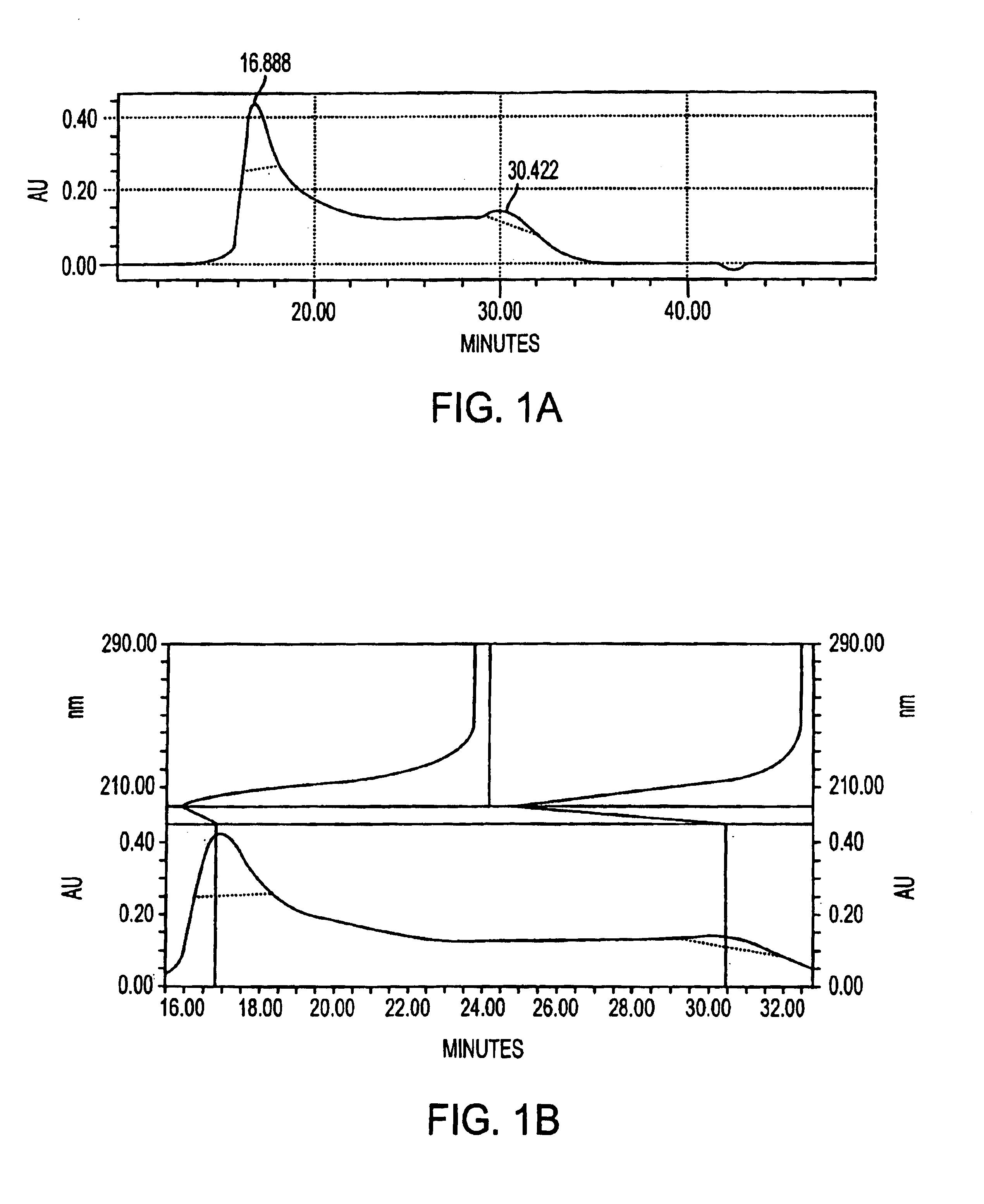
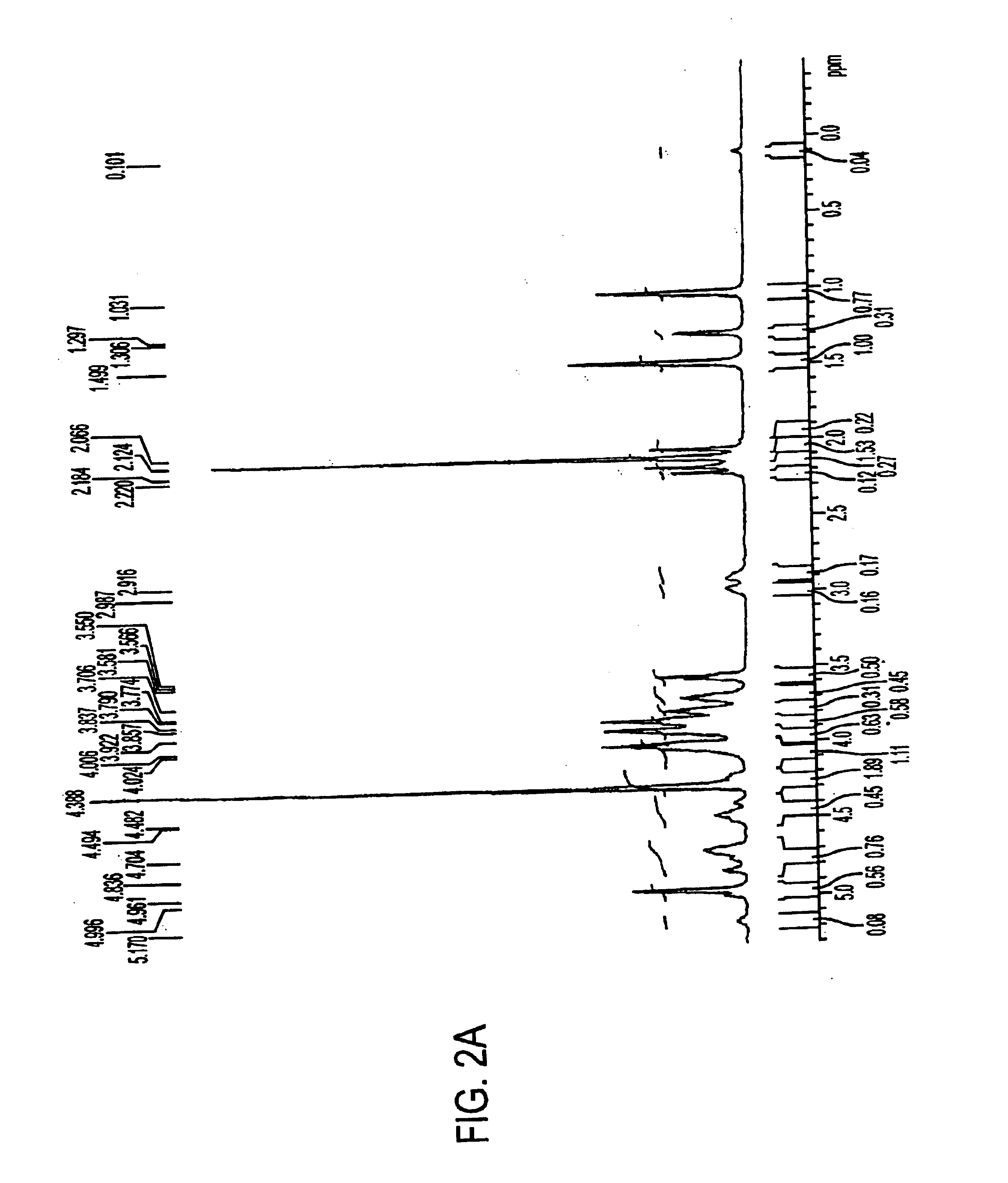
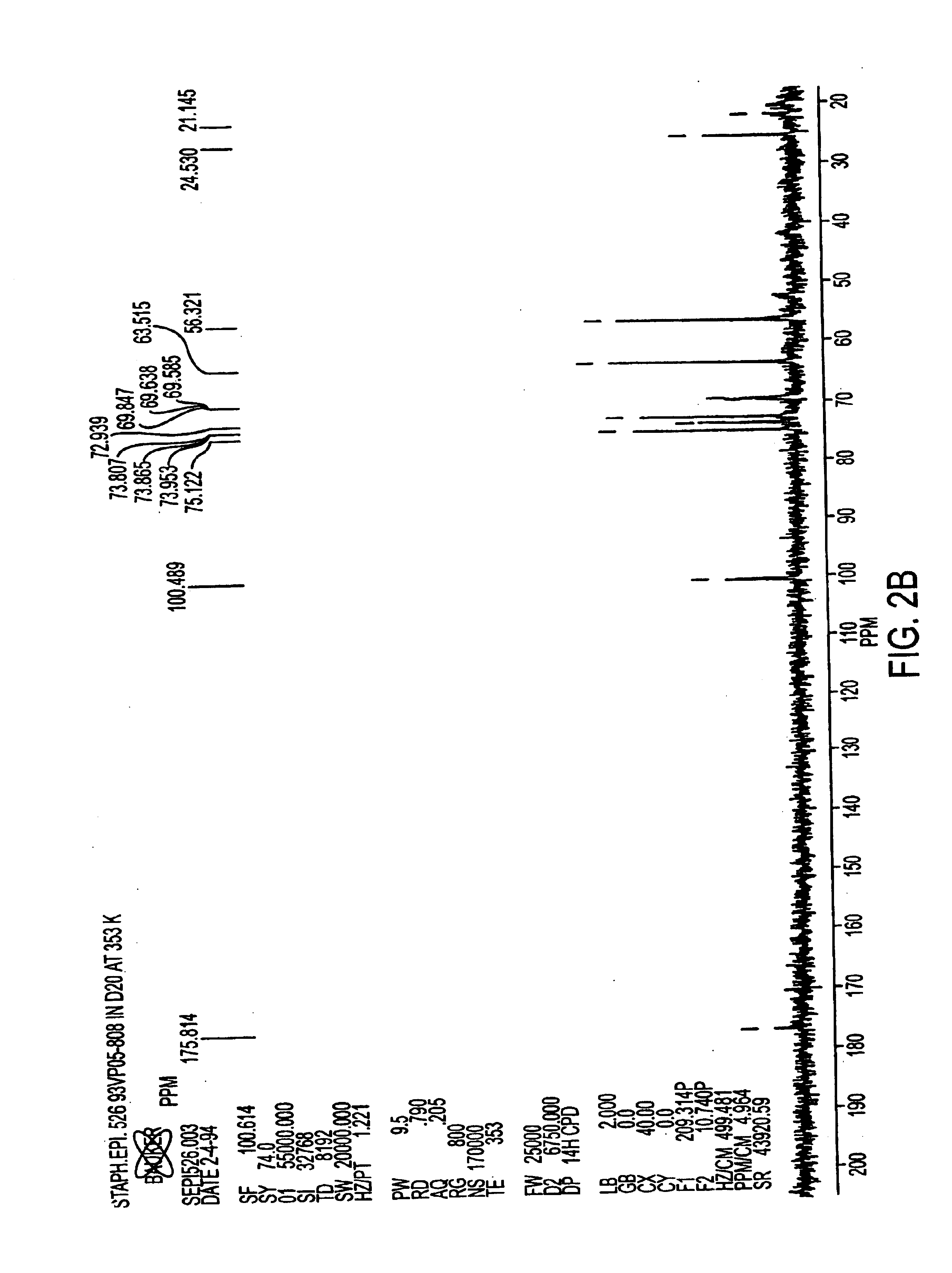
A negatively-charged Staphylococcus antigen contains amino acids and a N-acetylated hexosamine as a major carbohydrate component. The antigen is common to many coagulase-negative strains of Staphylococcus, including S. epidermidis, S. haemolyticus, and S. hominis. Staphylococcus strains that carry the antigen include many clinically significant strains of Staphylococcus. The antigen and antibodies to the antigen are useful in kits and assays for diagnosing Staphylococcus infection. Vaccines of the antigen and of whole cells that carry the antigen also are disclosed.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
N-acetyl aldosamines and related N-acetyl compounds, and their topical use
Compositions comprising N-acetyl-aldosamines, N-acetylamino acids, and related N-acetyl compounds are useful to alleviate or improve various cosmetic conditions and dermatological disorders, including changes or damage to skin, nail and hair associated with intrinsic aging and / or extrinsic aging, as well as changes or damage caused by extrinsic factors. N-acetyl-aldosamines, N-acetylamino acids, and related N-acetyl composition may further comprise a cosmetic, pharmaceutical or other topical agent to enhance or create synergetic effects.
Owner:TRISTRATA TECH
Glycomimetic antagonists for both E-and P-selectins
Compounds and methods are provided for modulating in vitro and in vivo processes mediated by selectin binding. More specifically, selectin modulators and their use are described, wherein the selectin modulators that modulate (e.g., inhibit or enhance) a selectin-mediated function comprise particular glycomimetics linked to a member of a class of compounds termed BASAs (Benzyl Amino Sulfonic Acids).
Owner:GLYCOMIMETICS
Detection of oligosaccharides
Provided herein are processes for detecting oligosaccharides in a biological sample. In specific instances, the biological sample is provided from an individual suffering from a disorder associated with abnormal glycosaminoglycan accumulation.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Derivatives of partially desulphated glycosaminologycans endowed with antiangiogenic activity and devoid of anticogulating effect
InactiveUS20030013682A1Increased systemic levelShorten the lengthEsterified saccharide compoundsOrganic active ingredientsChemical compoundAnticoagulant effect
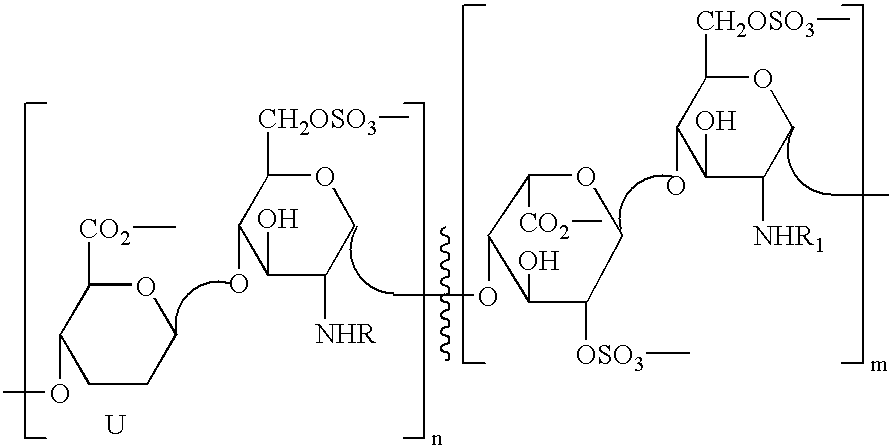
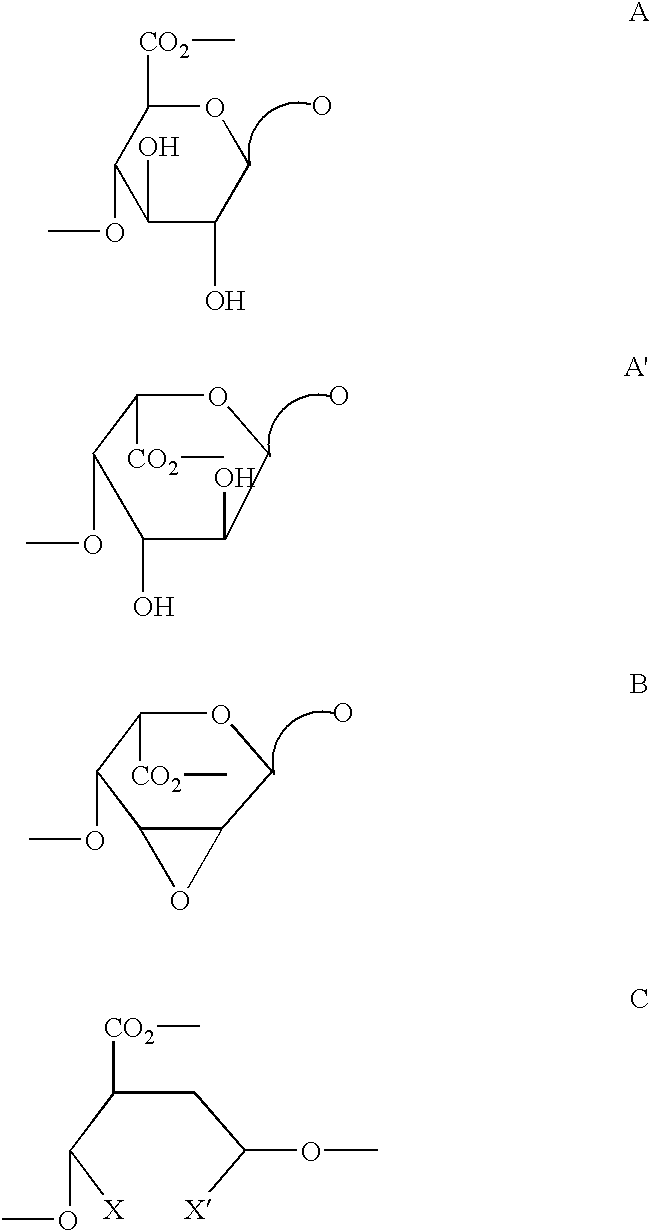
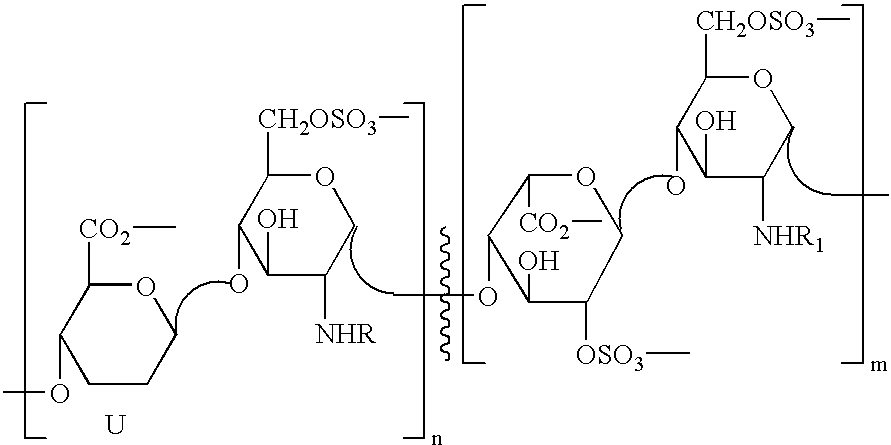
Partially desulphated glycosaminoglycan derivatives are described, particularly heparin, and more particularly formula (I) compounds, where the U, R and R1 groups have the meanings indicated in the description. Said glycosaminoglycan derivatives are endowed with antiangiogenic activity and are devoid of anticoagulant activity.
Owner:SIGMA TAU IND FARMACEUTICHE RIUNITE SPA
Therapeutic pharmaceutical agent for diseases associated with decrease in function of gne protein, food composition, and food additive
InactiveUS20120264928A1Easily embodiedEsterified saccharide compoundsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseFood additive
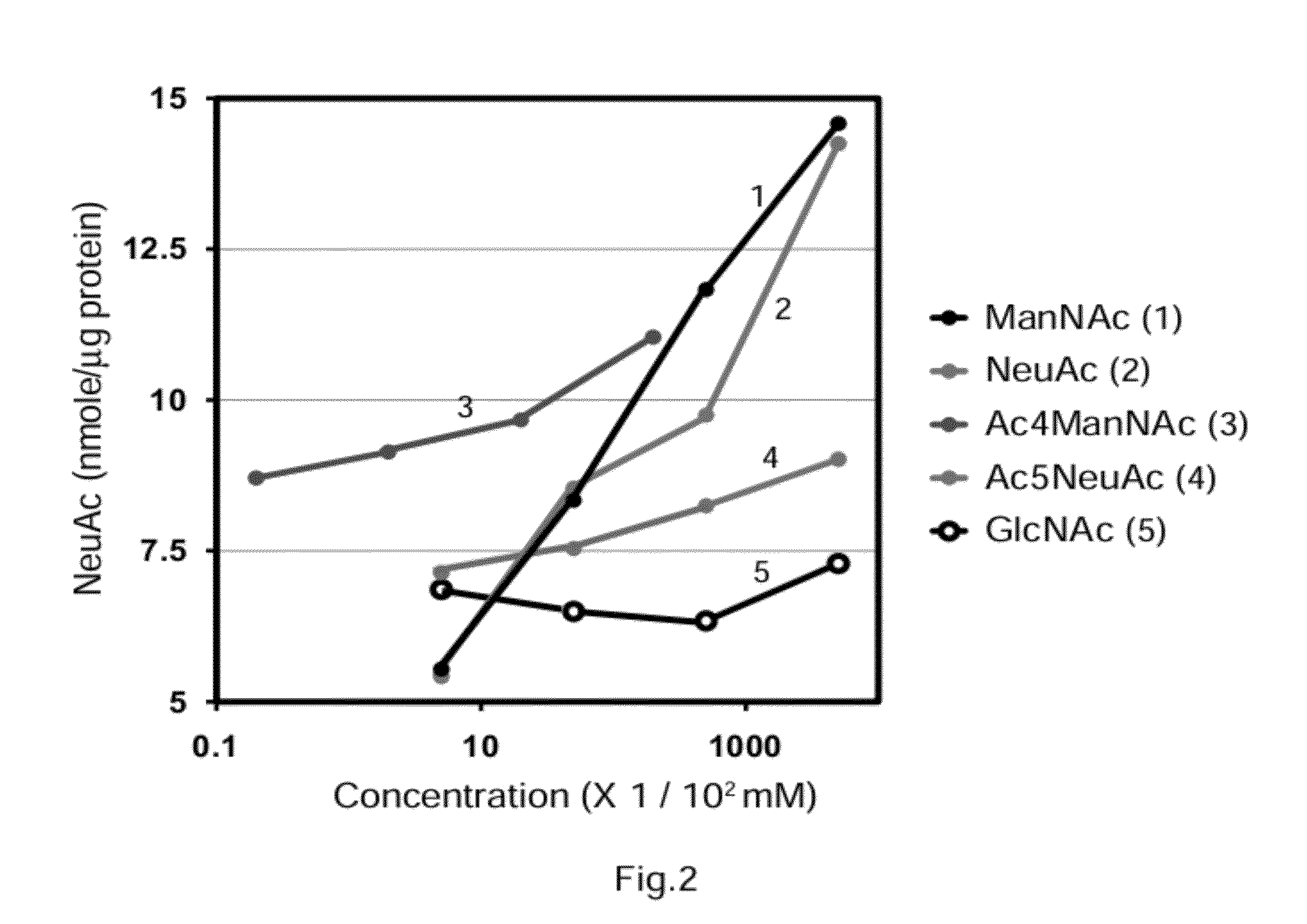
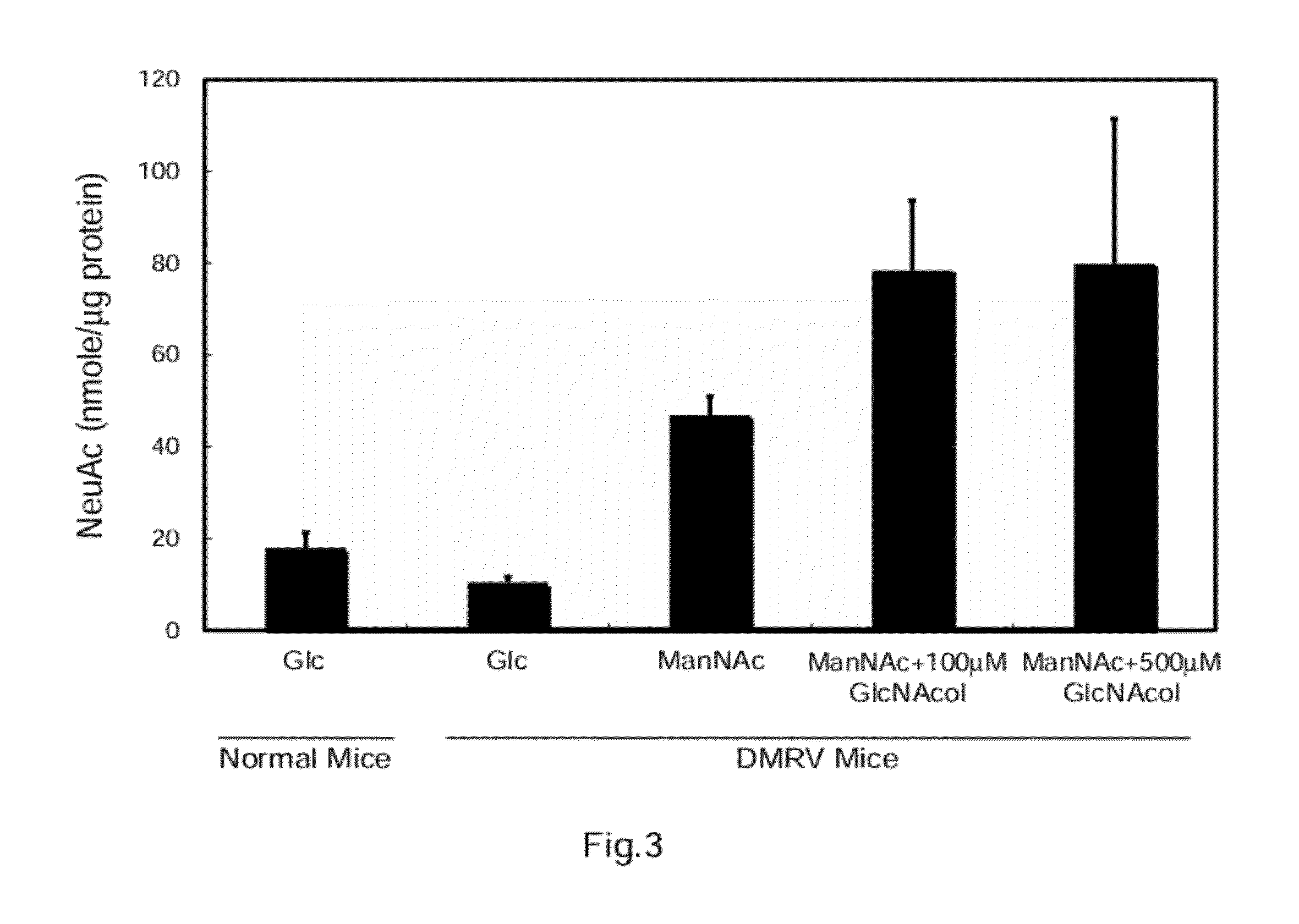
Disclosed are a therapeutic pharmaceutical agent for diseases associated with the decrease in the function of GNE protein, a food composition, and a food additive. The therapeutic pharmaceutical agent is characterized by comprising a compound capable of increasing the quantity of N-acetylneuraminic acid in cells. Examples of the compound to be contained in the therapeutic pharmaceutical agent include N-acetylneuraminic acid, an intermediate produced downstream from N-acetylmannosamine in an N-acetylneuraminic acid biosynthesis pathway, an N-acetylneuraminic acid derivative, an N-acetylmannosamine derivative, an N-acetylneuraminic acid-containing compound, an N-acetylneuraminic acid derivative-containing compound, an N-acetylmannosamine-containing compound, an N-acetylmannosamine derivative-containing compound, an inhibitor of a degrading enzyme for N-acetylneuraminic acid, an inhibitor of a degrading enzyme for N-acetylmannosamine, an inhibitor of a degrading enzyme for the intermediate, and others.
Owner:HEALTH SCI TECH TRANSFER CENT JAPAN HEALTH SCI FOUND
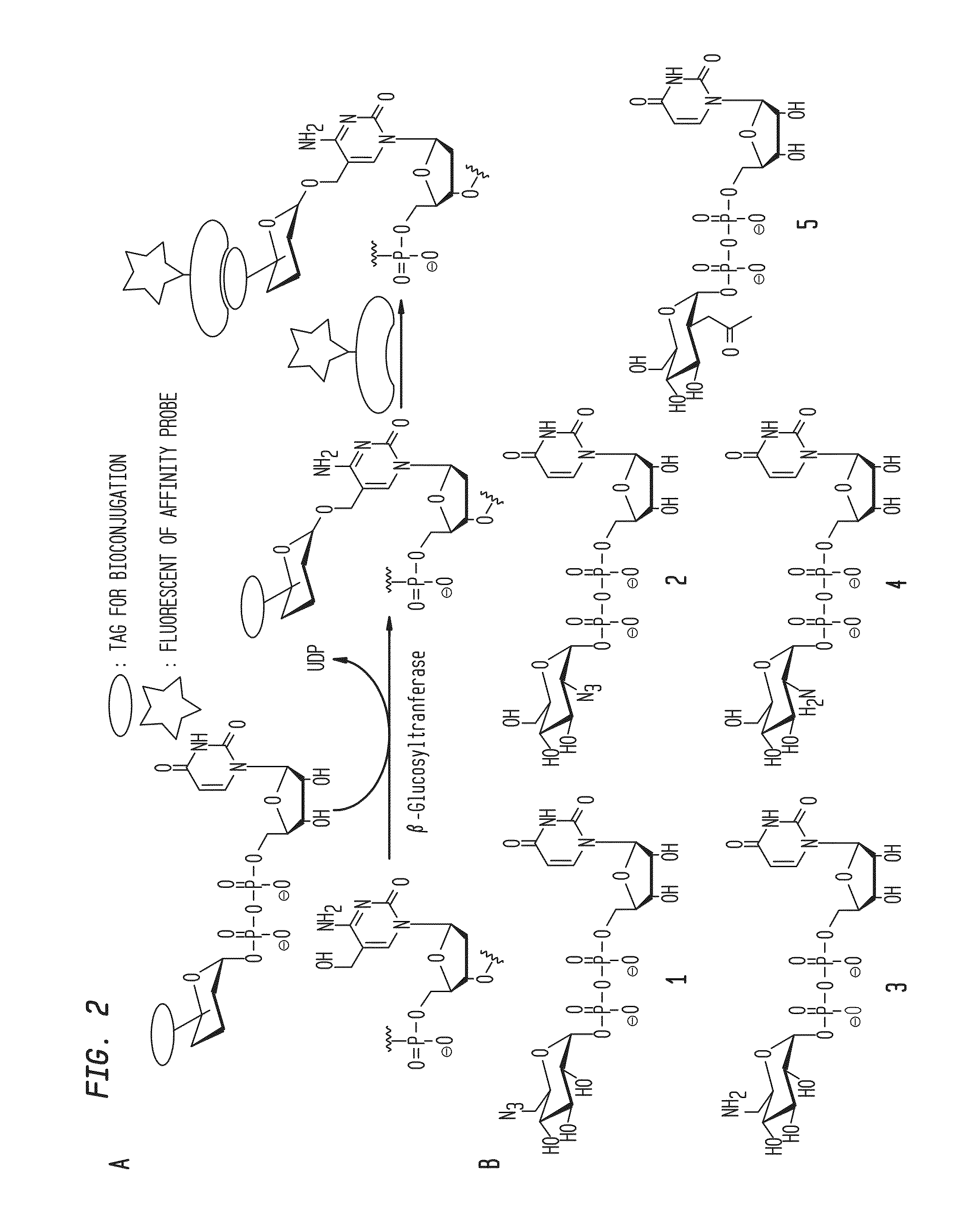
Compositions and methods for the transfer of a hexosamine to a modified nucleotide in a nucleic acid
ActiveUS9200260B2Selective control over cleavage of the nucleic acidFusion with DNA-binding domainSugar derivativesNucleotideHexosamines
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Sulfated heparin oligosaccharide as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105504097AShort sugar chainSmall molecular weightOrganic active ingredientsFermentationSulfationLymphatic Spread
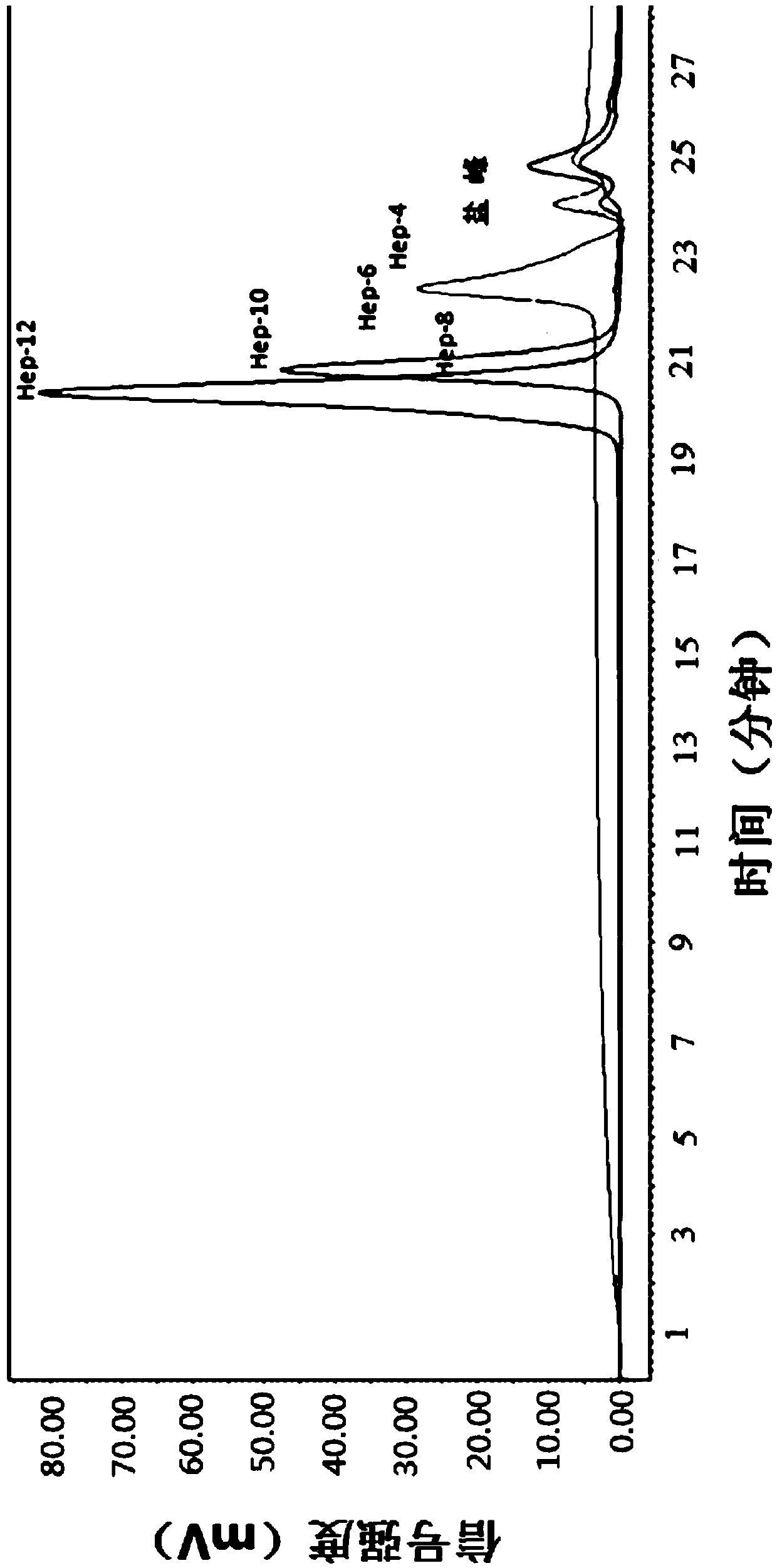
The invention provides sulfated heparin oligosaccharide as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The sulfated heparin oligosaccharide is characterized in that a non-reducing end of a sulfated heparin oligosaccharide molecule contains an unsaturated double bond produced through enzymolysis of heparinase as well as uronic acid derivatives and glycosylamine derivatives; the sulfated heparin oligosaccharide has a structure represented by a formula I, wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, R9, Ra, Rb, Rc and Rd are independently SO3<-> or H; Rx', Ry' and Rz' are independently COCH3 or SO3<->, and n is 1-3. The sulfated heparin oligosaccharide with controllable sulfating degree prepared by virtue of the preparation method has very high activity for inhibiting heparanase in vitro, the activity of the sulfated heparin oligosaccharide for inhibiting cell adhesion and migration is 4-5 times higher than that of heparin, and the activity for inhibiting tumor metastasis in mice is 2-3 times higher than that of the heparin; the sulfated heparin oligosaccharide has relatively good tumor metastasis resistance and relatively high specificity.
Owner:SHENZHEN HEPALINK PHARMA GRP CO LTD
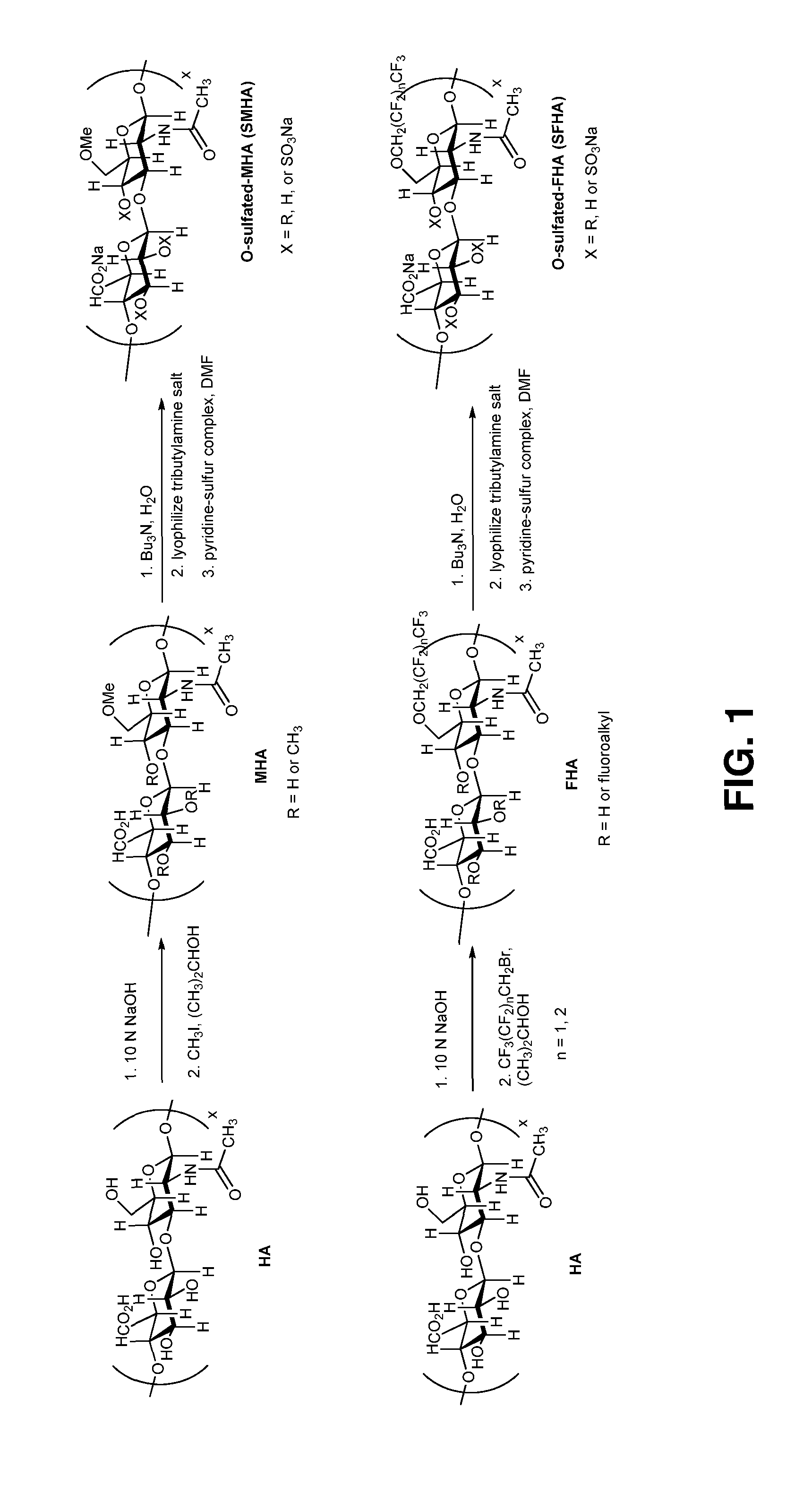
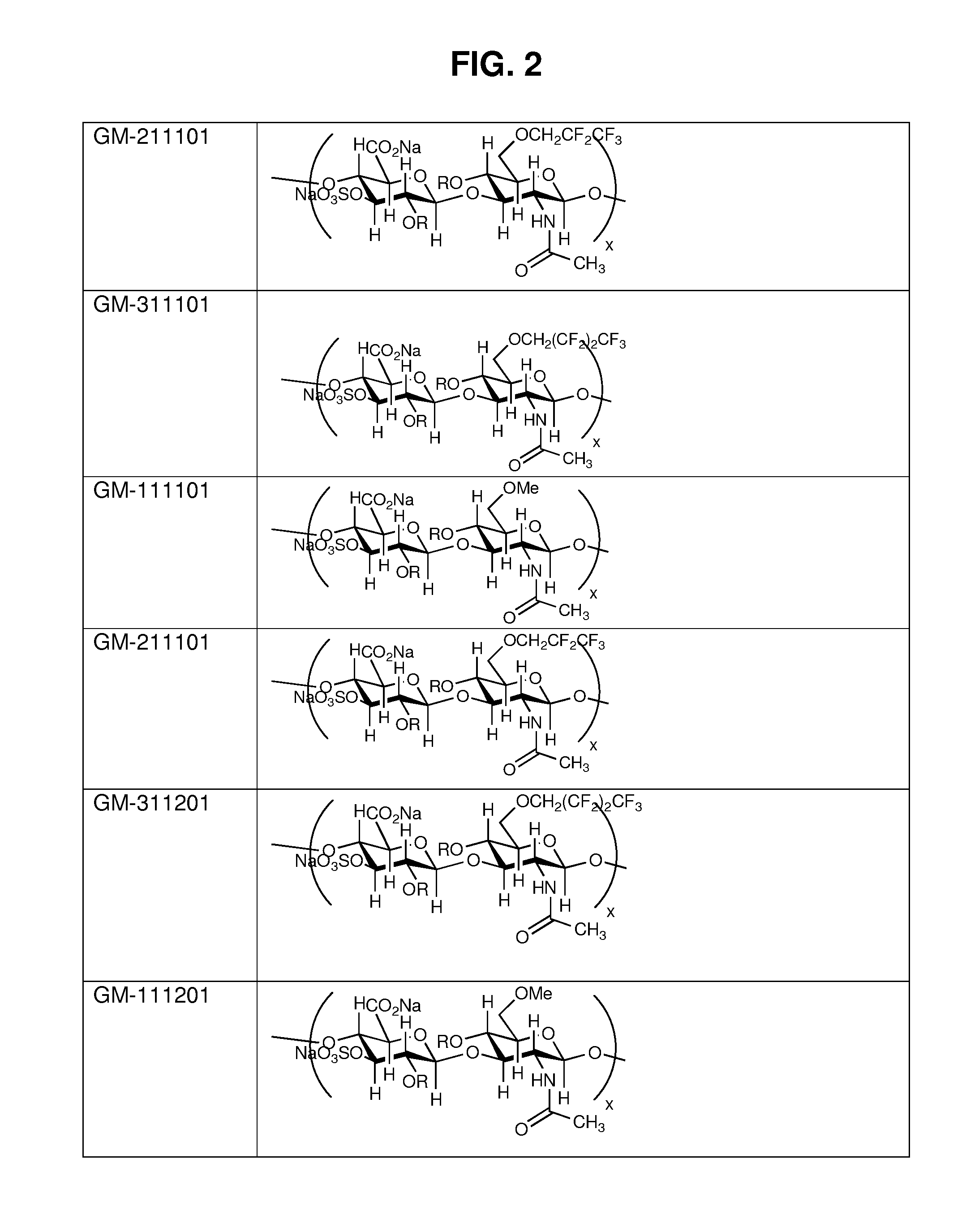
Alkylated semi-synthetic glycosaminoglycosan ethers, and methods of making and using thereof
Described herein is the synthesis of alkylated and semi-synthetic glycosaminoglycosan ethers, referred to herein as “SAGEs.” The synthesis of sulfated alkylated SAGEs is also described. The compounds described herein are useful in a number of applications including wound healing, drug delivery, and the treatment of a number of inflammatory diseases and skin disorders.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Staphylococcus antigen and vaccine
InactiveUS20050118190A1Antibacterial agentsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaHexosaminesCoagulase test
A negatively-charged Staphylococcus antigen contains amino acids and a N-acetylated hexosamine as a major carbohydrate component. The antigen is common to many coagulase-negative strains of Staphylococcus, including S. epidermidis, S. haemolyticus, and S. hominis. Staphylococcus strains that carry the antigen include many clinically significant strains of Staphylococcus. The antigen and antibodies to the antigen are useful in kits and assays for diagnosing Staphylococcus infection. Vaccines of the antigen and of whole cells that carry the antigen also are disclosed.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Methods for inducing orexin neurons and agent for treating narcolepsy or eating disorder
ActiveUS20140349964A1Improve securityBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementPluripotential stem cellSirtuin 1
The invention provides a method for producing an orexin neuron by culturing a pluripotent stem cell or a neural progenitor cell in the presence of N-acetyl-D-mannosamine and optionally in the presence of at least one inhibitor selected from the group consisting of a Sirtuin 1 inhibitor and an O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine transferase inhibitor. The invention also provides a therapeutic agent for narcolepsy or eating disorders, such as anorexia, containing N-acetyl-D-mannosamine, which is based on the induction of orexin neuron in vivo.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Formula of Amadori reactive flavor, preparation method of Amadori reactive flavor and use of Amadori reactive flavor
ActiveCN106520368AGreat tasteImprove fullnessTobacco preparationEssential-oils/perfumesSolventSide reaction
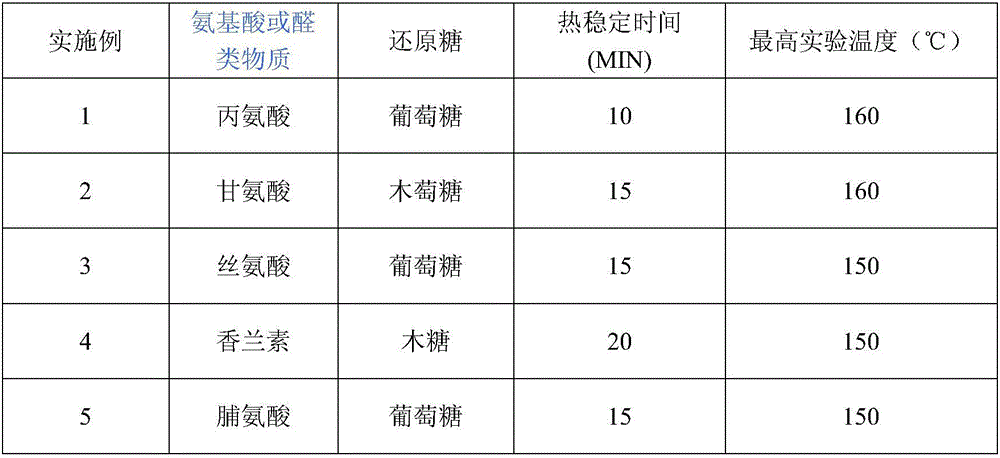
The invention provides a formula of an Amadori reactive flavor, a preparation method of the Amadori reactive flavor and a use of the Amadori reactive flavor. The preparation method comprises that reducing sugar, amino acids or an aldehyde substance as a raw material undergo a reflux reaction in a solvent with a drying agent in a basic environment to produce Schiff bases of the amino acid and reducing sugar, after the reaction, N-substituted glycosylamine is subjected to Amadori rearrangement to form an Amiadori reactant in the presence of a catalyst, the reactant is subjected to vacuum concentration to form a crude product, the crude product is subjected to recrystallization, and the crystals are dried to form an Amadori reactive mixture. The preparation method has the advantages of simple operation, low cost and high yield, prevents the dark brown viscous material which is produced from the reducing sugar and amino acid and is difficult to treat, and has les side reaction. The reaction product can be used in cut tobacco, cut stems, tobacco sheets and cigarette papers, improve the taste of cigarettes, increase the aroma of tobacco sheet cigarettes and improve the smoking effects.
Owner:HUBEI CHINA TOBACCO IND
Detection of oligosaccharides
Provided herein are processes for detecting oligosaccharides in a biological sample. In specific instances, the biological sample is provided from an individual suffering from a disorder associated with abnormal glycosaminoglycan accumulation.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
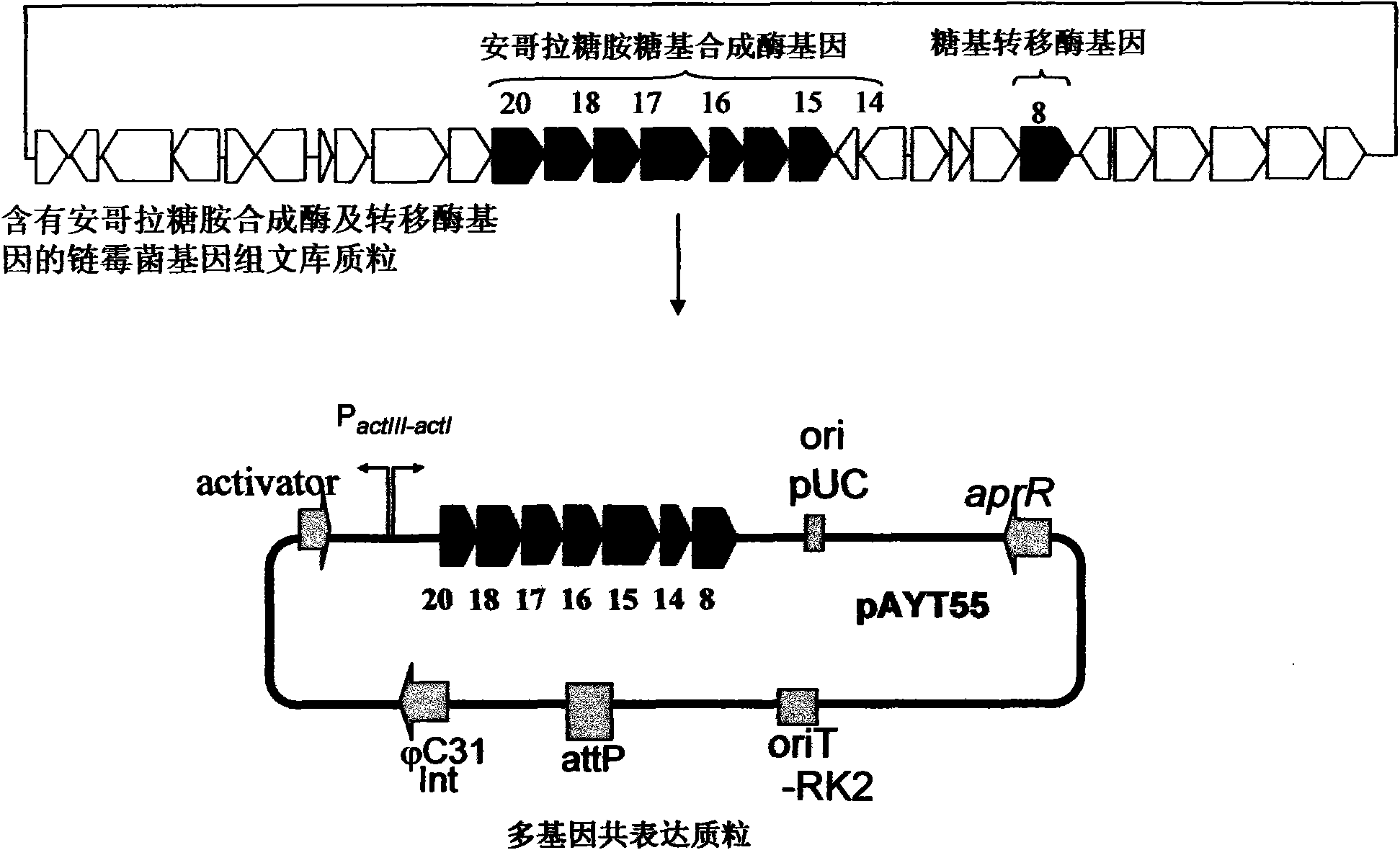
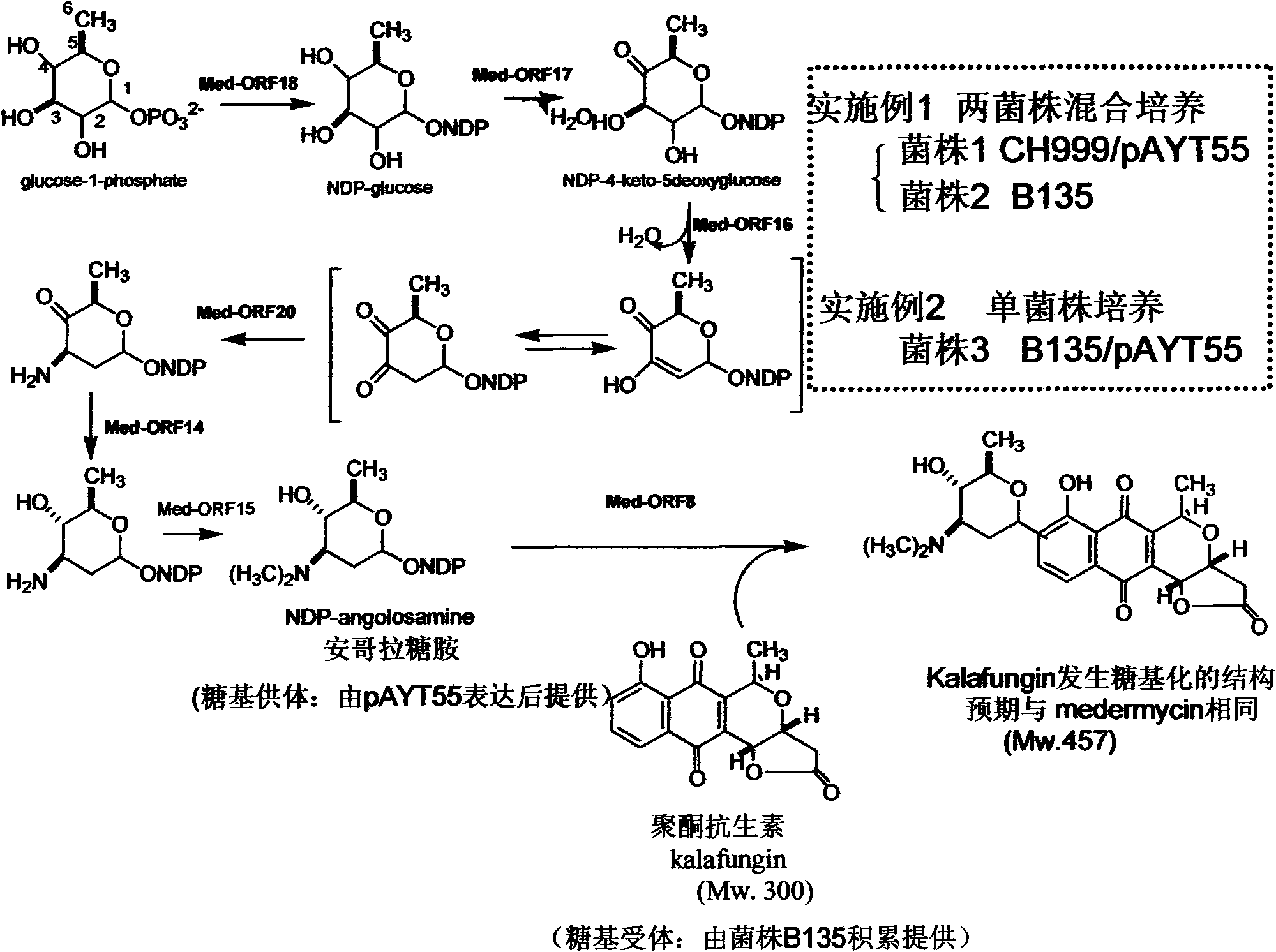
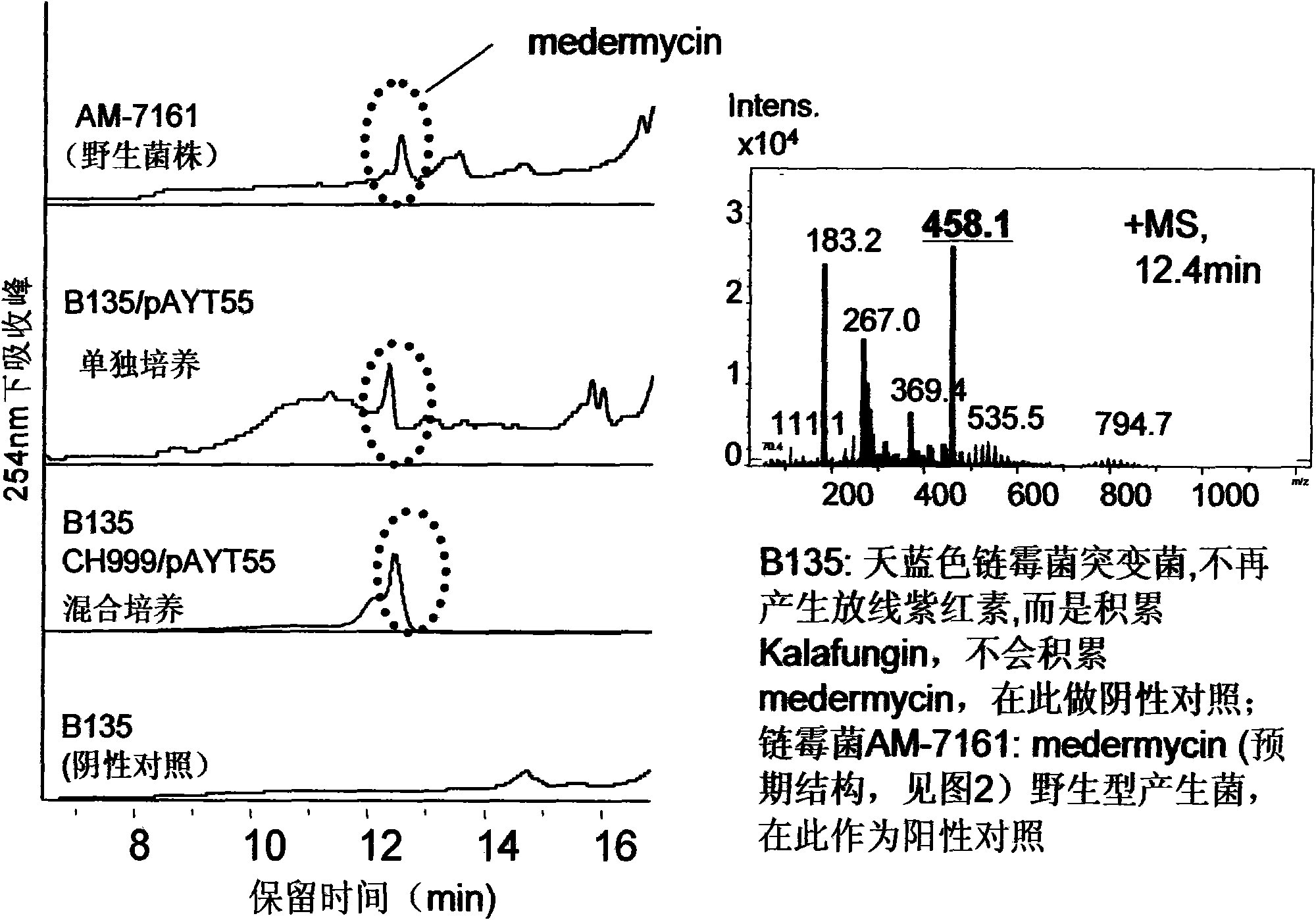
Construction and application of multiple gene coexpression system containing angolosamine glycosylsynthetase and glycosyltransferase
InactiveCN101613711ASimplify the screening processGuaranteed normal expressionMicroorganism based processesFermentationPolyketideGene coexpression
The invention provides construction and application of a multiple gene co-expression system containing angolosamine glycosylsynthetase and glycosyltransferase. The invention is characterized by taking a streptomyces genome bank plasmid as a template; amplifying six angolosamine synthetase genes and a glycosyltransferase gene through PCR and connecting the genes in sequence and placing the genes in the lower reaches of a streptomyces promoter PactIII-actI to form a transcription unit; transferring the transcription unit to a streptomyces plasmid carrier pSET152, thus constructing a streptomyces expression plasmid pAYT55 co-expressed by multiple genes; leading the pAYT55 into a host cell streptomyces coelicolor CH999, mixedly culturing obtained engineering bacteria and streptomyces B135 of accumulated polyketide kalafungin, thus realizing bioconversion of kalafungin into a novel antibiotic with angolosamine; or directly leading pAYT55 into the streptomyces B135 and carrying out single culture to realize glycosylation of kalafungin. Therefore, by adopting the system, rare angolosamine can be synthesized in the cell and angolosamine modification can be carried out on polyketide by adopting the low substrate recognition specificity of antibiotic glycosyltransferases.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Preparation and preservation method of biovalve material treated by combination of double-bond polymerization and enzyme inhibitor
InactiveCN110772666AImprove stabilityImprove anti-calcification propertiesTissue regenerationProsthesisPolymer scienceGlycidyl methacrylate
The invention discloses a preparation and preservation method of a biovalve material treated by combination of double-bond polymerization and an enzyme inhibitor. The preparation method comprises thefollowing steps that a, a swim bladder is cut and decellularized; b, the decellularized swim bladder is soaked in a glycidyl methacrylate solution and an initiator for double-bond polymerization and crosslinking; c, a glycosaminoglycase inhibitor is adopted for soaking; d, a mixed solution of carbodiimide and N-hydroxysuccinimide is adopted for crosslinking and fixation; and e, a bacteriostatic solvent is adopted for preservation after rinsing, or preservation is conducted after an alcoholic solution is adopted for dehydrating and drying. According to the prepared biovalve material, the stability and anti-calcification performance of glycosaminoglycan are improved, and a novel biovalve material with application prospect is achieved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for extracting gentamycin sulfate from gentamicin fermentation broth
InactiveCN106083952AAutomate operationLow costSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationFiltrationIon-exchange resin
The invention aims to provide an improved method for extracting gentamycin sulfate from gentamicin fermentation broth. The method comprises the steps of fermentation broth filtration, adsorption through weakly acidic cation exchange resin, resolving, concentration, salt conversion and spray drying and the like. Gentamicin is one of main antibacterial drugs used for treating various gram-negative bacteria infections clinically at present and is a multicomponent mixture composed of 2-deoxystreptamine, magenta glycosylamine and garosamine and the like. According to the extraction method, the adsorption is performed through the cation exchange resin, resolving is performed through sodium hydroxide solution, decoloration is performed through anion exchange resin, nanofiltration concentration desalting is performed, finally salt conversion is performed, active carbon decoloration is performed, and the finished product is obtained through spray drying. The method has the advantages of being high in production efficiency, less in environmental pollution and good in finished product quality.
Owner:HEBEI SHENGXUE DACHENG PHARMA
Preparation method of swimming bladder bioprosthetic valve material and preservation method thereof
InactiveCN110755688AImprove stabilityImprove anti-calcification propertiesTissue regenerationProsthesisSwim bladderBiology
The invention discloses a preparation method of a swimming bladder bioprosthetic valve material and a preservation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a, cutting anddecellularizing swimming bladders; b, carrying out cross-linking immobilization on the decellularized swimming bladders by adopting glutaraldehyde; c, carrying out cross-linking post-treatment by adopting a polyphenol glycosaminoglycan enzyme inhibitor or carrying out cross-linking post-treatment by adopting a polyphenol compound and ferric chloride; and d, after rinsing, preserving by adopting anantibacterial solvent or preserving after dehydrating and drying by adopting an alcoholic solution. According to the swimming bladder bioprosthetic valve material prepared by the invention, the stability and the anti-calcification performance of glycosaminoglycan are improved, and the swimming bladder bioprosthetic valve material is the novel bioprosthetic valve material with an application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
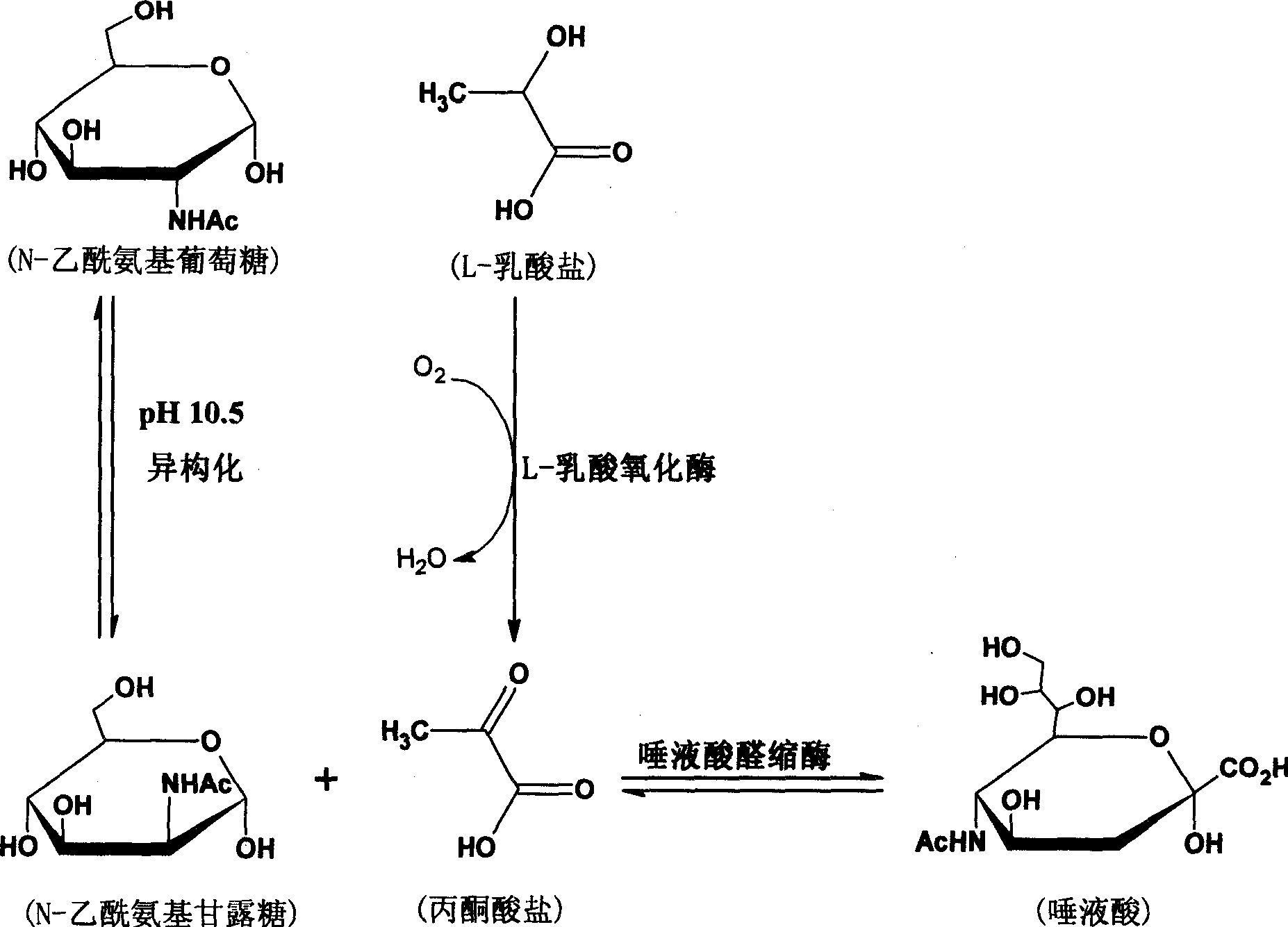
Preparation of valuable sialinic acid from cheap sodium lactate by multi-step coupling bio-conversion
InactiveCN1584015AReduce accumulationElimination of substrate inhibitionBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliSodium lactate
A method for preparing valuable sialic acid by cheap sodium lactate through multi-step coupling biotransformation is disclosed. It includes culture containing lactic oxidase strain, construction and culture of E.coli HB101(pBV220-ALD), preparation of N-acetylmannosamine, sialic acid converting synthesis by complete cell containing lactic oxidase and sialic aldolase with cheap sodium lactate as precursor, and separation and purification of sialic acid by ion exchange. It achieves low cost, simple operation and extensive converting conditions.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
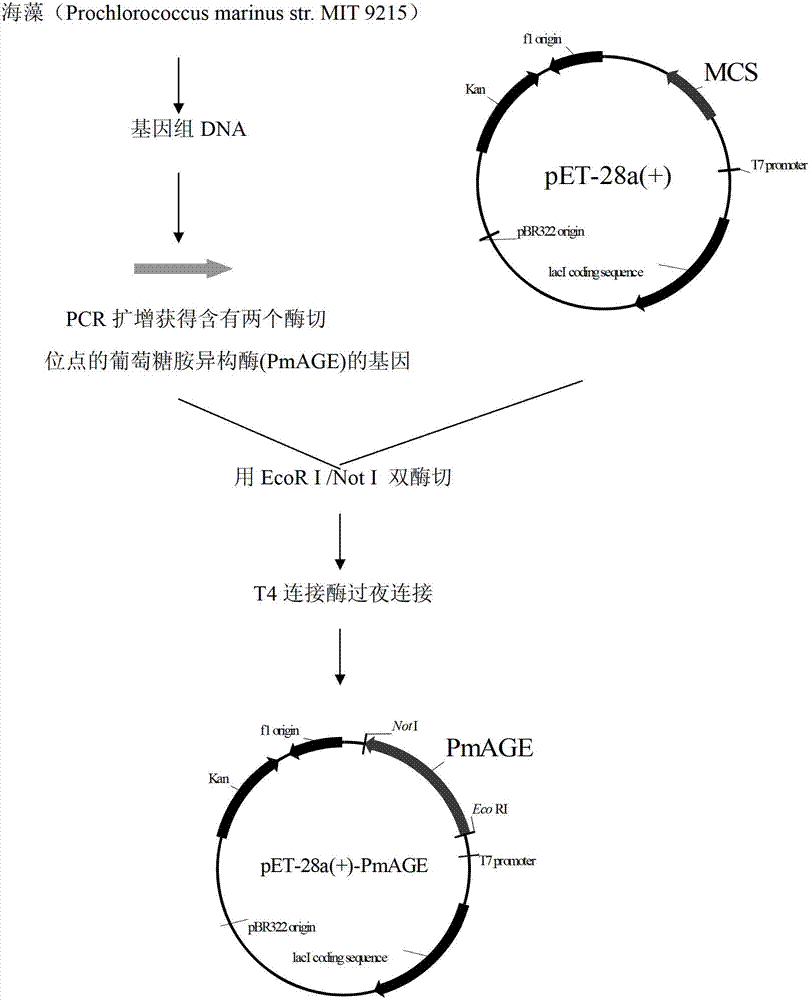
Application of N-acetylglucosamine isomerase in production of N-acetylmannosamine
ActiveCN103088090AGood effectIncrease enzyme activityMicroorganism based processesFermentationIsomeraseN-Acetylglucosamine
The invention discloses application of N-acetylglucosamine isomerase of which the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO:2 in catalytic synthesis of N-acetylmannosamine. The N-acetylmannosamine is prepared by taking the N-acetylglucosamine isomerase of which the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO:2 as a catalyst and taking N-acetylglucosamine as a substrate. According to the invention, the N-acetylglucosamine isomerase of which the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO:2 is used in the preparation of the N-acetylmannosamine for the first time, and favorable effect is achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Compositions for enhancing biological functions in organisms
The present invention provides a composition which includes elicitor compounds selected from the group consisting of: (N,N′diacetylhexobiose)n; (N,N′diacetylhexobiose)n having one or more associated amino acid residues, wherein the amino acid residues are valine or ornthine; (N,N′diacetylhexosamine)n having an associated (dihexobiose)n; (N,N′diacetylhexosamine)n having an associated (dihexobiose)n and one or more associated amino acid residues, wherein the amino acid residues are valine or ornithine; or combinations thereof. The (N,N′diacetylhexobiose)n and (N,N′diacetylhexosamine)n comprise N-acetylglucosamine or other amino hexosamines, while the (N,N′diacetylhexobiose)n and (dihexobiose)n are any D-hexoaldose or N-acetylamino derivative of D-hexoaldoses. In this aspect of the present invention, n=1 to 5 and the compounds are all 3 kDa or less. Also provided are a method for increasing the rate of fungal growth, a method for increasing extracellular fungal enzyme production, a method for increasing biological control of plant and animal diseases, a method for increasing a method for increasing resistance of plants to diseases, and a method of alleviating pain and increasing resistance to, or recovery from, diseases in animals, using the composition of the present invention.
Owner:LORITO MATTEO +3
Process for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid
The present invention provides a process for economically producing N-acetylneuraminic acid without using expensive materials such as pyruvic acid and phosphoenolpyruvic acid. The process comprises: allowing (i) a culture of a microorganism having N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase activity or N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase activity, or a treated matter of the culture, (ii) a culture of a microorganism capable of producing pyruvic acid or a treated matter of the culture, or a culture of a microorganism capable of producing phosphoenolpyruvic acid or a treated matter of the culture, (iii) N-acetylmannosamine, and (iv) an energy source which is necessary for the formation of pyruvic acid or phosphoenolpyruvic acid to be present in an aqueous medium to form and accumulate N-acetylneuraminic acid in the aqueous medium; and recovering N-acetylneuraminic acid from the aqueous medium.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KOGYO CO LTD
Prebiotic oral care methods using a saccharide
The disclosure relates to methods of enhancing beneficial oral bacteria and decreasing harmful oral bacteria comprising administering oral care compositions comprising a saccharide prebiotic, e.g., selected from D-turanose, D-melezitose, D-lactitol, myoinositol, and N-acetyl-D-mannosamine; and oral care compositions for use in such methods. The disclosure also relates to methods of using prebiotic oral care compositions, methods of screening, and methods of manufacture.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
Production of glycoproteins with low n-glycolylneuraminic acid (neu5gc) content
ActiveUS20140288281A1Unlimited applicability to achieveDegree of improvementCulture processCell culture mediaN-AcetylglucosamineMicrobiology
Owner:LEK PHARMA D D
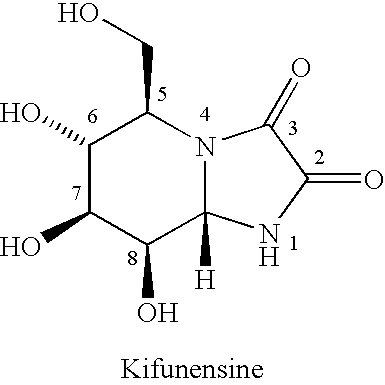
Process for preparing kifunensine intermediate and kifunensine therefrom
InactiveUS20040063973A1Easy to processSimpler chromatographic operationOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionCombinatorial chemistryMannitol
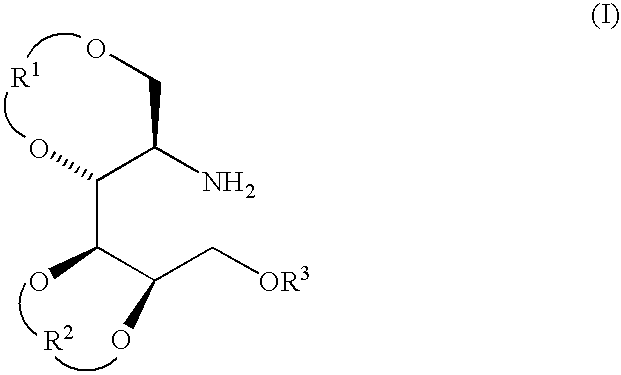
A novel method for the preparation of a compound of formula (I) from an N-protected-D-mannosamine. A compound of formula (I) is a useful intermediate for the preparation of kiftnensine, a potent and selective mannosidase inhibitor. The method includes protecting the hydroxyl group at the C-6 position of an N-protected-D-mannosamine, to give a 6-O-protected-N-protected-D-mannosamine; reducing the C-1 anomeric carbon atom of the 6-O-protected-N-protected-D-mannosamine to give a 6-O-protected-N-protected-D-mannitol; protecting the four hydroxyl groups of the 6-O-protected-N-protected-D-mannitol; and removing the nitrogen atom protecting group and optionally removing the C-6 oxygen atom protecting group to give the compound of formula (I): where R<1 >and R<2 >are each independently protecting groups which, together with the oxygen atoms to which they are attached, form a 5-, 6-, 7- or 8-membered ring; and R<3 >is hydrogen or a protecting group.
Owner:CALLAGHAN INNOVATION
Cubilose acid aldolase mutant as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103881997AHigh catalytic activityReduce manufacturing costGenetic engineeringFermentationSialic acidSodium pyruvate
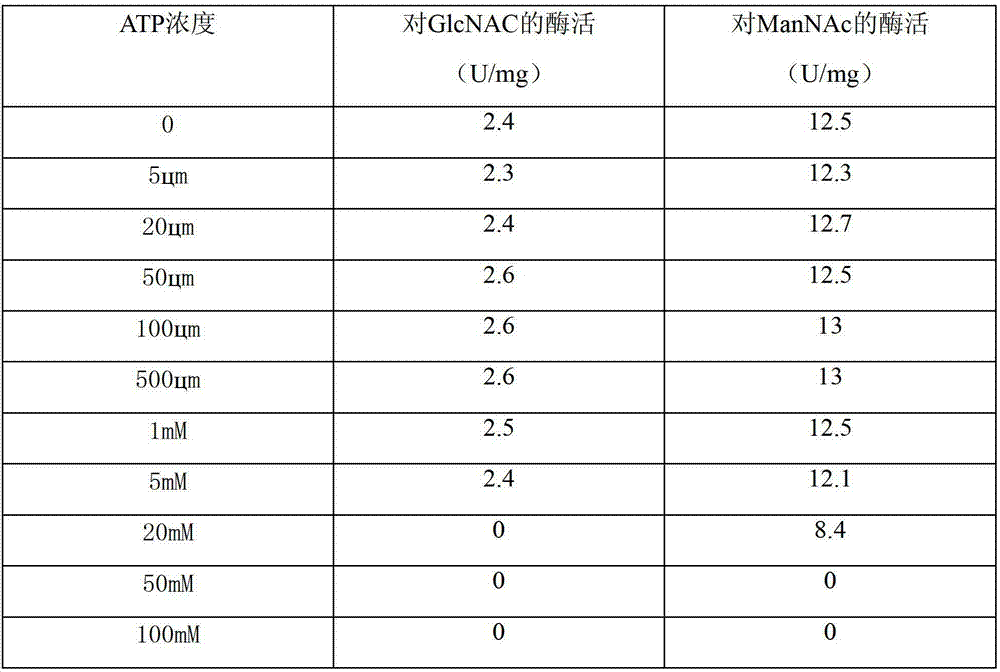
The invention discloses a cubilose acid aldolase mutant as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The cubilose acid aldolase mutant is obtained from sequence 2 in a sequence list through point mutation, and the point mutation is at least one mutation at the 25th site and 275th site of the sequence. Through site directed mutation on the cubilose acid aldolase, cubilose acid aldolase mutant with high catalytic activity is finally obtained. Besides, the mutant uses N-acetylmannosamine, sodium pyruvate and trinosin (ATP) as the substrate and has the cubilose acid aldolase catalytic activity which is at least 50% higher than that of the parent. Thus, the cubilose acid aldolase mutant can be used for producing cubilose acid (sialic acid), the production cost is lowered, and the market competitiveness of the corresponding product is enhanced.
Owner:BONTAC BIO ENG SHENZHEN
In vivo synthesis of sialylated compounds
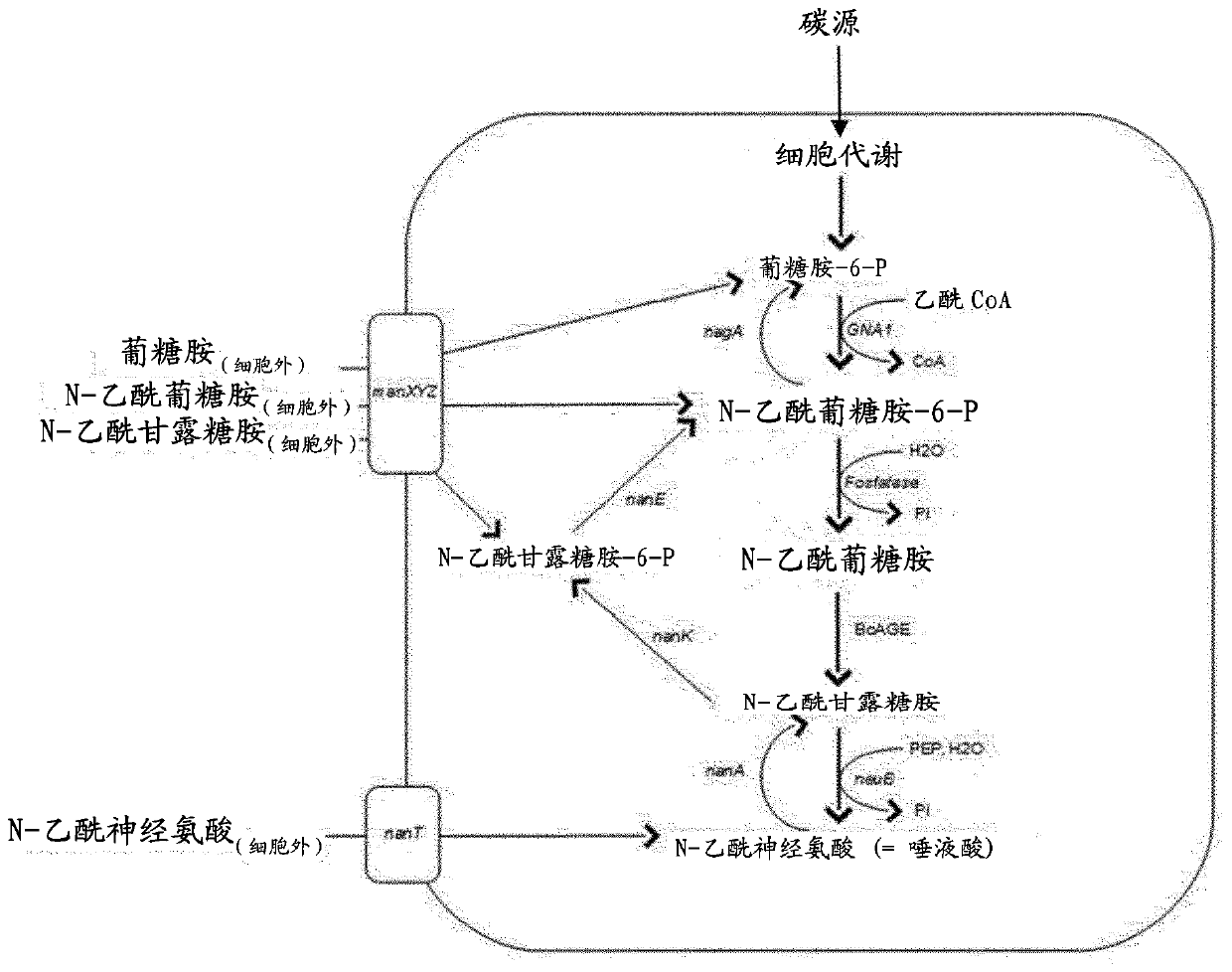
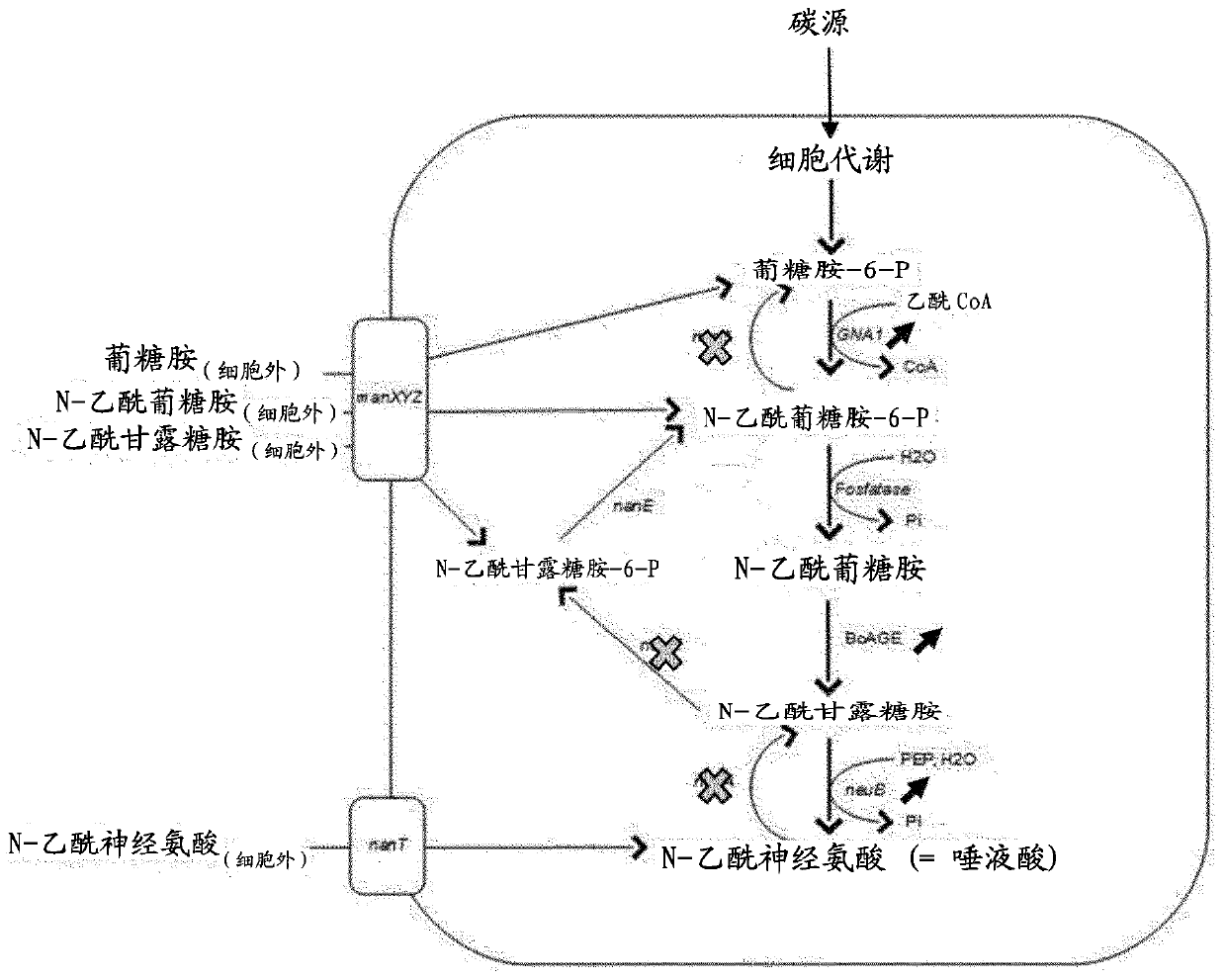
The present invention is in the technical field of synthetic biology and metabolic engineering. More particularly, the present invention is in the technical field of fermentation of metabolically engineered microorganisms. The present invention describes engineered microorganisms able to synthesize sialylated compounds via an intracellular biosynthesis route. These microorganisms can dephosphorylate N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate to N-acetylglucosamine and convert the N-acetylglucosamine to N-acetylmannosamine. These microorganisms also have the ability to convert N-acetylmannosamine to N-acetyl-neuraminate. Furthermore, the present invention provides a method for the large scale in vivo synthesis of sialylated compounds, by culturing a microorganism in a culture medium, optionally comprising an exogenous precursor such as, but not limited to lactose, lactoNbiose, N-acetyllactosamine and / or an aglycon, wherein said microorganism intracellularly dephosphorylates N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate to N-acetylglucosamine, converts N-acetylglucosamine to N- acetylmannosamine and convert the latter further to N-acetyl- neuraminate.
Owner:因比奥斯公司
Moisturizing cosmetic composition as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105662986AAvoid churnNo greasy feelingCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsPolyethylene glycolAdemetionine
The invention discloses a moisturizing cosmetic composition which is prepared from rosa canina fruit extract, acai berry fruit extract, sage extract, beta-sitosterol, olivoyl hydrolyzed wheat protein, cranberry seed oil, grape seed oil, bamboo juice, rice bran oil, glycosylamine peptide, dipotassium glycyrrhizinate, squalene, chestnut polysaccharide, vitamin E, lecithin, caprylic / capric polyethylene glycol glyceride, 1,2-propylene glycol, isopropyl myristate and the balance of deionized water. The moisturizing cosmetic composition disclosed by the invention has good using safety and stability and good appearance impression and avoids stimulation to skin and oily feel after use; and the active ingredients are reasonably collocated and cooperate together to realize a synergistic effect, and the cosmetic composition can quickly permeate into skin to supplement moisture to the skin and help keeping the skin moist. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the moisturizing cosmetic composition, which has the advantages of simple processing steps, no special requirements on equipment, high operability, low production cost and good stability and appearance impression of the product.
Owner:余云丰
N-substituted mannosamine derivatives, process for their preparation and their use
InactiveUS20140046051A1Esterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesMannosamineViral neuraminidase
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is a group removable by hydrogenolysis, and wherein R2 is OH or R2 is —NHR3 wherein R3 is a group removable by hydrogenolysis. The compound can be made from fructose by a Heyns-rearrangement. The compound can be used then to make free D-mannosamine or its salts, D-mannosamine building blocks and mannosamine containing oligo- or polysaccharides, N-acetyl-D-mannosamine and its hydrates and solvates, neuraminic acid derivatives, and viral neuraminidase inhibitors.
Owner:GLYCOM AS
Chemical synthesis method of Bacillus pyocyaneus 011 serotype O antigen oligosaccharide
ActiveCN109627270AThe method is simple and efficientAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntigenChemical synthesis
The invention discloses a chemical synthesis method of Bacillus pyocyaneus 011 serotype O antigen oligosaccharide, and belongs to the field of chemistry. The method comprises the steps that a D-glucose block, an L-fucosamine block and a D-fucosimide block are utilized to construct O antigen trisaccharide, wherein the D-glucose block or the L-fucosamine block is connected with the D-fucosimide block through a 1,2-alpha-cis-glycosidic bond, the D-glucose block is connected with the L-fucososamine block through a 1,2-alpha-trans-glycosidic bond, and the 1,2-alpha-cis-glycosidic bond is constructed in a mixed solvent; the mixed solvent comprises two or more of dichloromethane, diethyl ether and thiophene. The method has the advantages that D-mannose is utilized as a raw material to obtain D-fucose simply, conveniently and efficiently; the uniform construction of the cis-glycosidic bond is achieved by relying on the appropriate mixed solvent; the stereoselectivity can reach 100%; and the method has a good application prospect in the development of novel drugs and vaccines for resisting Bacillus pyocyaneus and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Bioactive green-lipped mussel extracts and uses thereof
PendingUS20210077540A1Improve the level ofHigh nutritional valueAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntiparasiticMetabolite
A biologically active non-lipid extract comprising of an isolated molecular weight fraction of <10 kDa or <1 kDa derived from New Zealand green-lipped mussels (Perna canaliculus). The extract exhibits biological activity selected from one or more of antihypertensive activity, antioxidant activity, antimicrobial activity, antiviral activity, and antiparasitic activity. The extract includes a plurality of biologically active substances selected from the group having free amino acids; peptides; cryptides; sugars and / or sugar-containing compounds including nucleosides and their derivatives; carbohydrates including glycoconjugates such as glycosides, glycosylamines, glycoproteins, glycopeptides, peptidoglycans; nitrogen-containing compounds including purines; phenolic compounds; minerals; metabolites.
Owner:SANFORD LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com