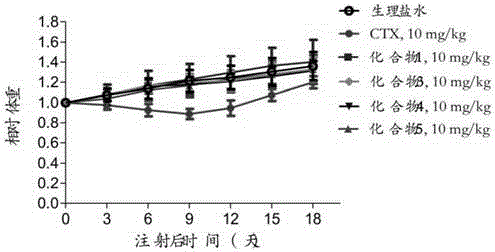
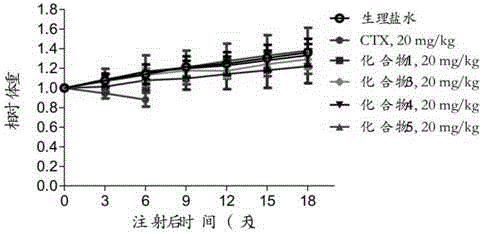
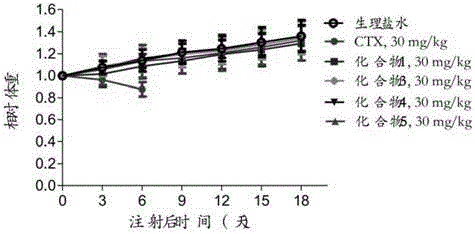
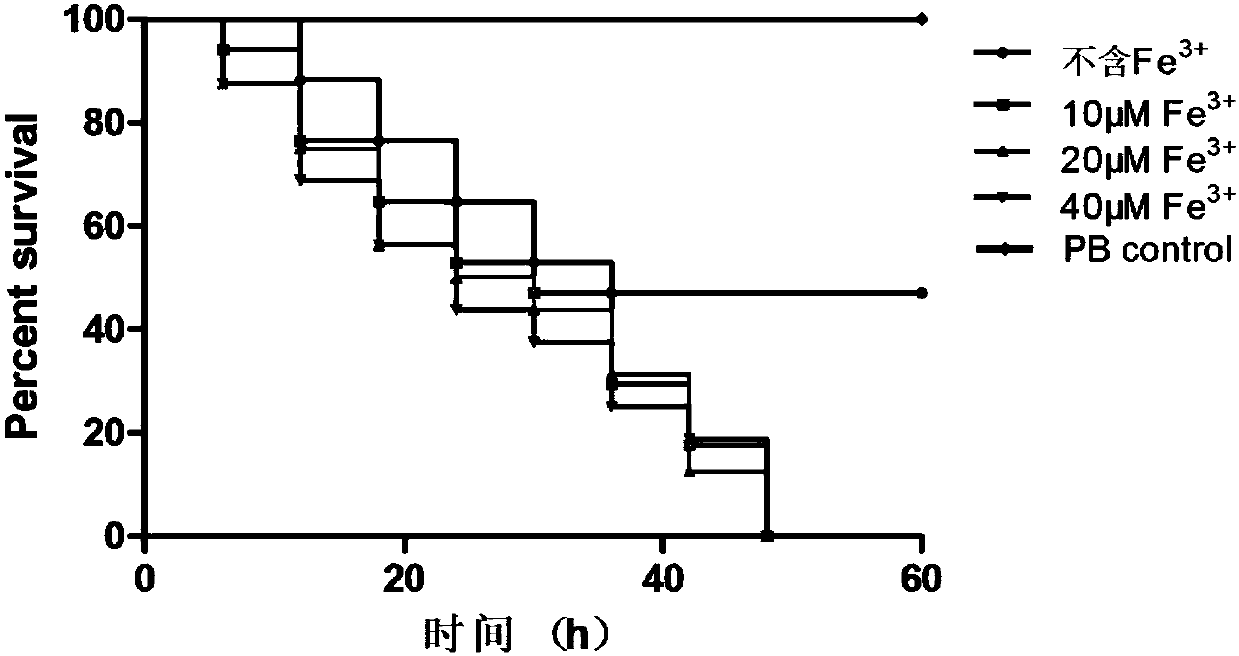
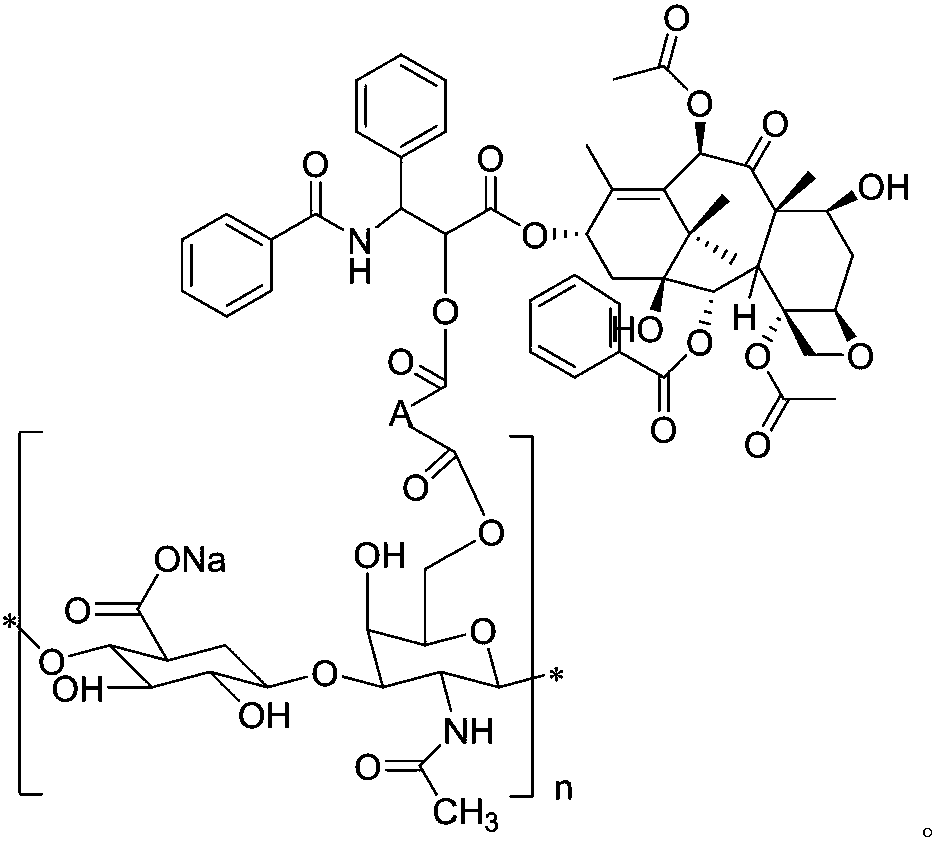
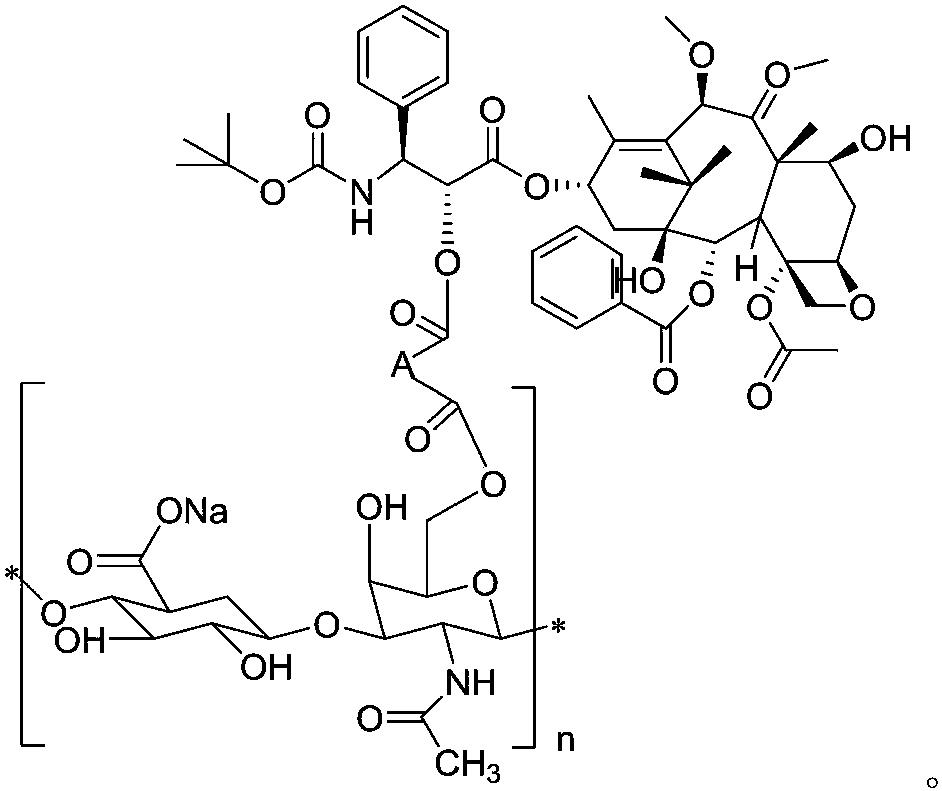
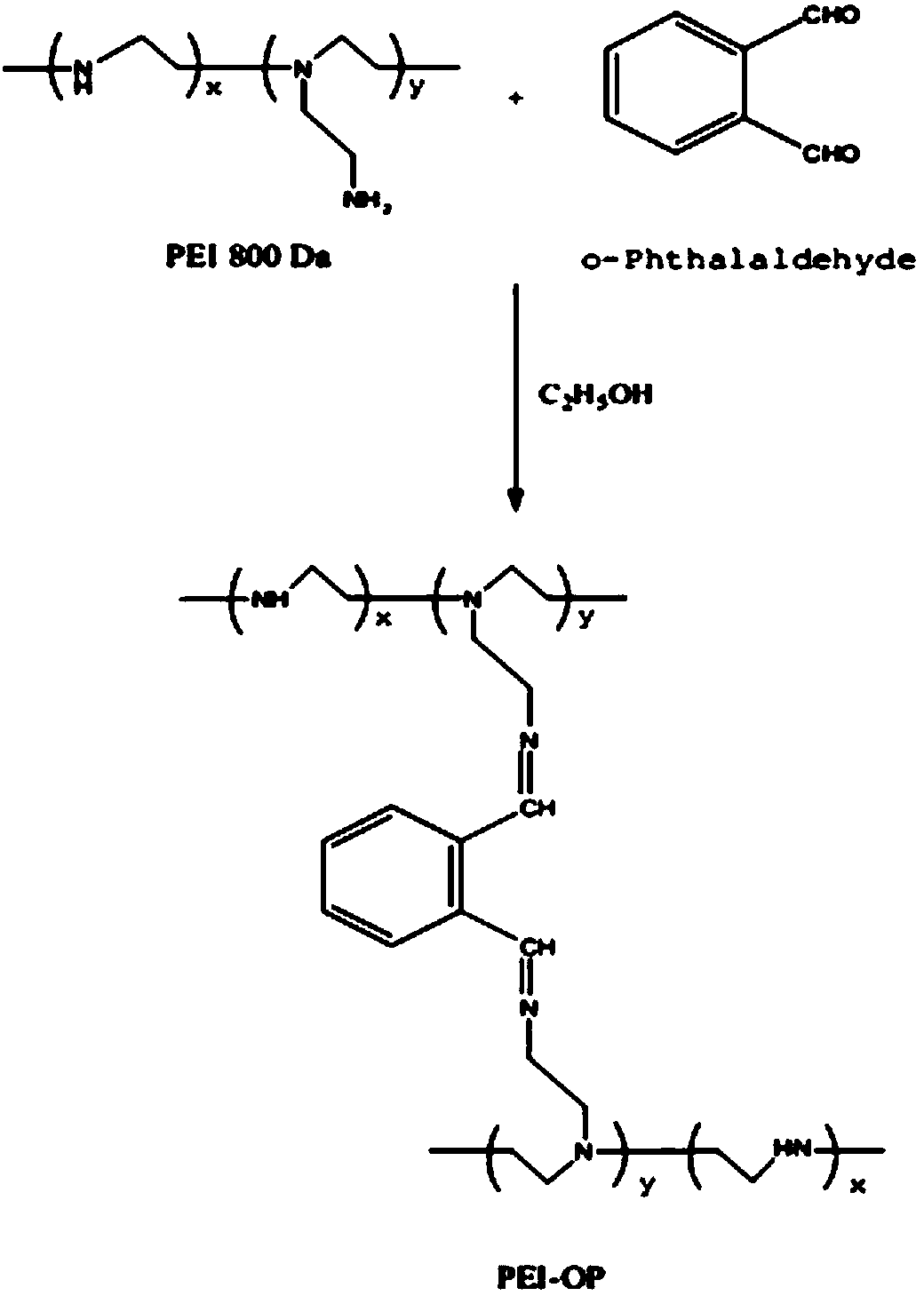
Patents
Literature
55 results about "In vivo toxicity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Preclinical in vivo toxicology is the study of toxic effects of chemical substances based on statistical and quantitative analysis. At Altogen Labs, toxicology studies can include acute, subchronic and chronic toxicity tests. Acute toxicology studies focus on the toxicological effects following a single large dose of the substance of interest.
IL-2 selective agonists and antagonists
InactiveUS6955807B1Great therapeutic useToxic reductionBacteriaSugar derivativesNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory ReceptorsNucleotide
The invention is directed to a polypeptide comprising a human IL-2 mutein numbered in accordance with wild-type IL-2 wherein said human IL-2 is substituted at at least one of positions 20, 88 or 126, whereby said mutein preferentially activates T cells over NK cells. D20H and I, N88G, I, and R, in particular have a relative T cell-differential activity much greater than native IL-2, with predicted associated reduced in vivo toxicity. The invention also includes polynucleotides coding for the muteins of the invention, vectors containing the polynucleotides, transformed host cells, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the muteins, and therapeutic methods of treatment.
Owner:AICURIS GMBH & CO KG
IL-2 selective agonists and antagonists
The invention is directed to a polypeptide comprising a human IL-2 mutein numbered in accordance with wild-type IL-2 wherein said human IL-2 is substituted at at least one of positions 20, 88 or 126, whereby said mutein preferentially activates T cells over NK cells. D20H and I, N88G, I, and R, in particular have a relative T cell-differential activity much greater than native IL-2, with predicted associated reduced in vivo toxicity. The invention also includes polynucleotides coding for the muteins of the invention, vectors containing the polynucleotides, transformed host cells, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the muteins, and therapeutic methods of treatment.
Owner:AICURIS GMBH & CO KG
Preparation method and application of a drug-loaded magnetic composite nanomaterial
InactiveCN102274519AImprove magnetic propertiesGood monodispersityOrganic active ingredientsInorganic non-active ingredientsApoptosisMagnetite Nanoparticles
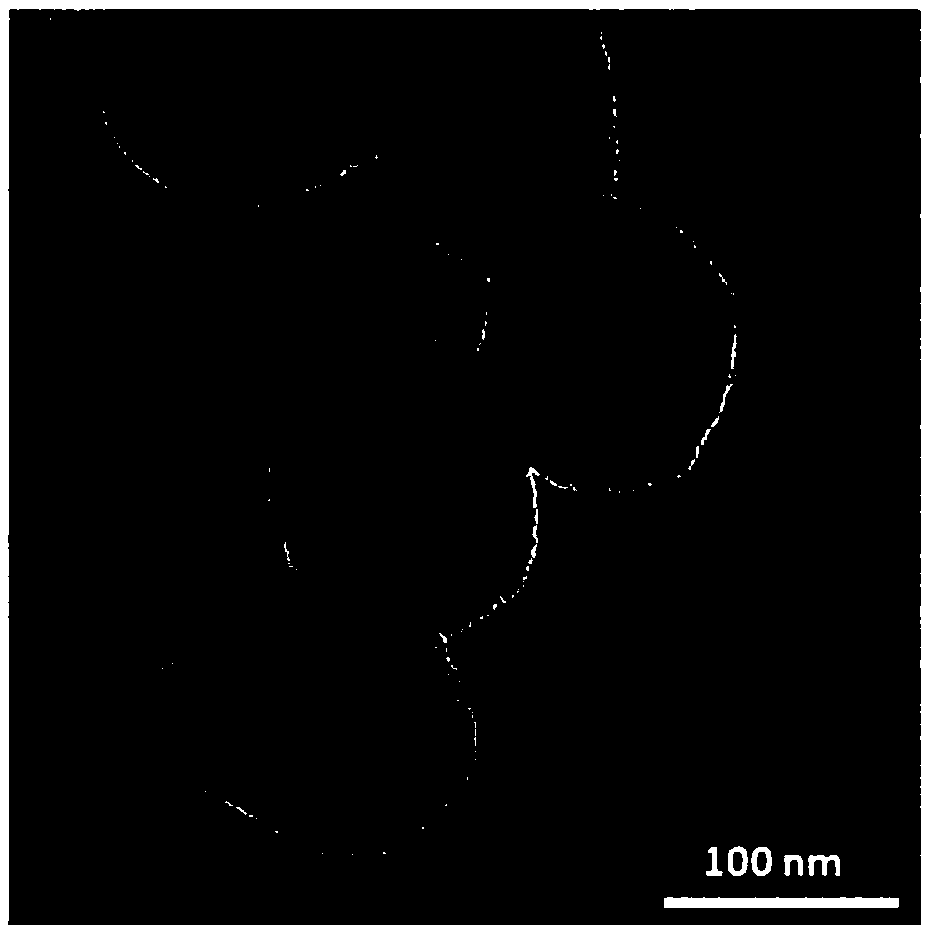
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a drug-loaded magnetic composite nanometer material. The fat-soluble solution (or emulsion) of the surface lipophilic magnetic nanoparticles and the drug is added to the dichloromethane solution of polylactic acid / glycolic acid copolymer (PLGA), and the three are mixed with each other to form an oil phase system. The oil phase system is added dropwise to the aqueous solution in which the surfactant Pluronic F127 is dissolved to form an oil-in-water system, and then the drug-loaded magnetic composite nanomaterial is obtained under the action of ultrasound. The drug-loaded magnetic composite nanomaterial can concentrate the drug in the tumor area under the action of an in vitro magnetic field to achieve targeting; the coating of PLGA solves the problem of mutual self-aggregation of magnetic particles, and the slow release control of the drug solves the problem It has great toxicity and side effects in the body and can be quickly taken up by tumor cells, leading to apoptosis of tumor cells and reversing the multidrug resistance of tumor cells.
Owner:卢世璧
Modified CpG oligodeoxynucleotide with improved immunoregulatory function
InactiveUS7408050B2Enhance immune regulation functionOrganic active ingredientsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsAnticarcinogenMedicine
The present invention relates to a modified CpG oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN) which is prepared by coupling a consecutive sequence of deoxyribothymine (dT) to the 3′-terminus of CpG ODN having immunoregularory function, thereby improving immunoactivity of splenocytes, macrophages and peripheral mononuclear cells, and therefore, can be effectively used as a vaccine adjuvant for preventing and treating hepatitis B or an anti-cancer agent. Since the phosphorothioate CpG ODN having the consecutive sequence of dT at its 3′-terminus shows high activity inducing Th-1 immune response and does not elicit in vivo toxicity with guaranteeing its safety, it can be effectively used as a vaccine adjuvant.
Owner:YONSEI UNIVERSITY
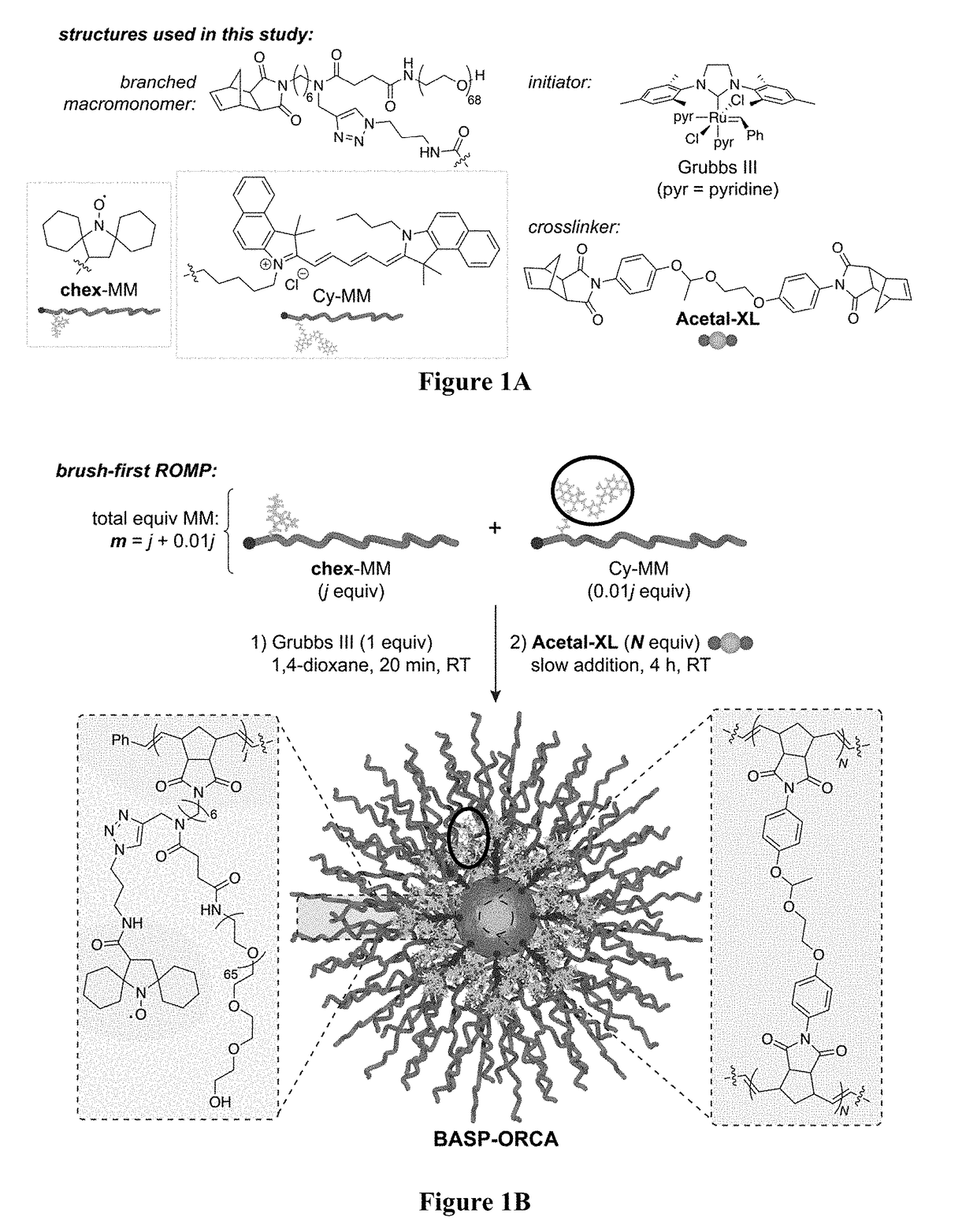
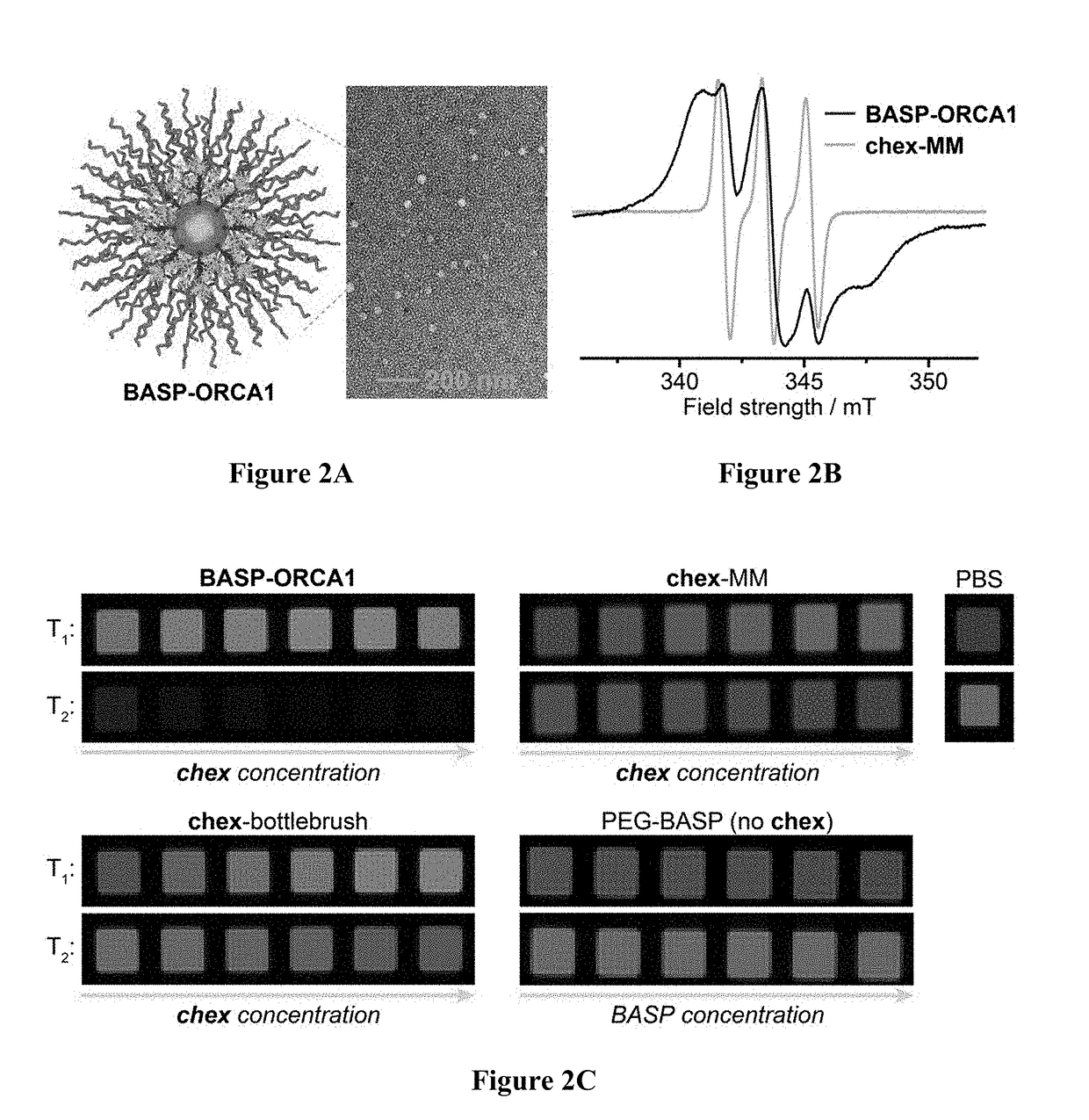
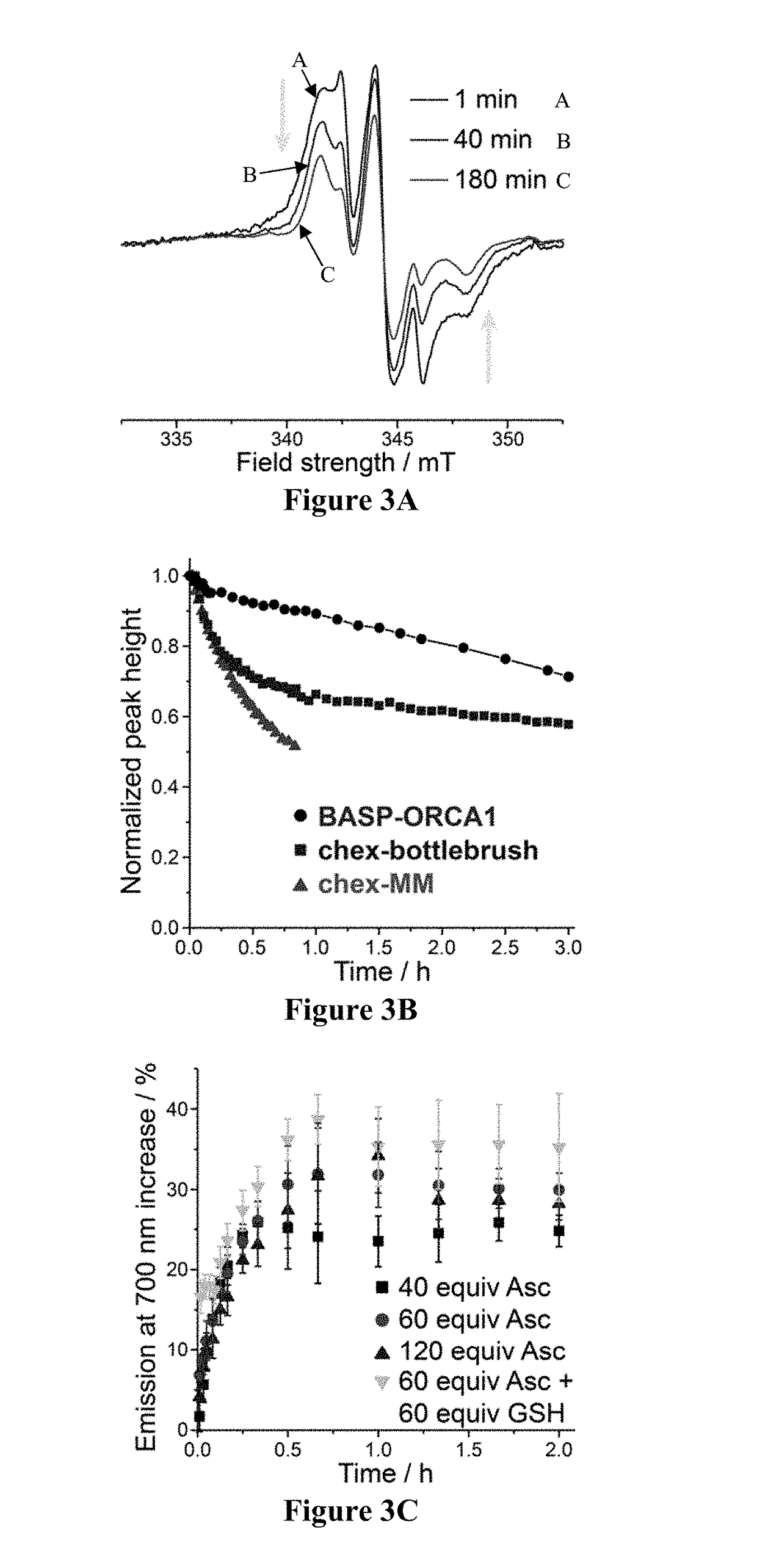
Brush-arm star polymer imaging agents and uses thereof
ActiveUS20190038782A1Improve the level ofHigh relaxivitiesPowder deliveryNanomedicineSolubilityNitrate
Disclosed are methods, compositions, reagents, systems, and kits to prepare nitroxide-functionalized brush-arm star polymer organic radical contrast agent (BASP-ORCA) as well as compositions and uses thereof. Various embodiments show that BASP-ORCA display unprecedented per-nitroxide and per-molecule transverse relaxivities for organic radical contrast agents, exceptional stability, high water solubility, low in vitro and in vivo toxicity, and long blood compartment half-life. These materials have the potential to be adopted for tumor imaging using clinical high-field 1H MRI techniques.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Indole alkaloid adduct, and preparation method and application thereof in preparing anti-tumor drug
ActiveCN103275106ALow toxicityReduce toxicity in the bodyOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsNormal cellIn vitro proliferation
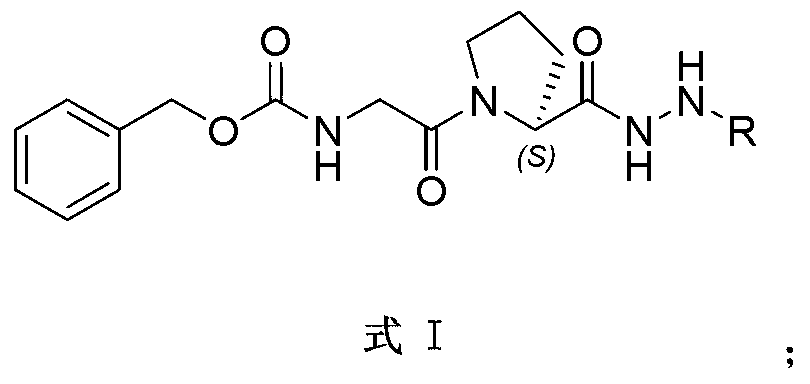
The invention relates to the field of anti-tumor drugs, and specifically discloses an indole alkaloid adduct, and a preparation method and an application thereof in preparing an anti-tumor drug. The indole alkaloid adduct has a structure shown as a formula I, wherein R is formed in the way that an indole alkaloid is subjected to hydrazinolysis and the hydrazinolysis product is bonded with hydrazine group. The indole alkaloid adduct can significantly reduce toxicity to normal cells and in-vivo toxicity and inhibit in-vitro proliferation of various tumor cell lines and the growth of tumor in the nude mouse bearing the tumor.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Water-soluble polyglutamic acid-cisplatin compound and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104815335AIncrease access rateReduce manufacturing costHeavy metal active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSolubilitySide chain
The invention is a continuation of the patent CN102499986A ''a macromolecule-cisplatin compound and its preparation method and application'', the content and claim of which are both suitable for the invention. The invention relates to a water-soluble polyglutamic acid-cisplatin compound and provides a preparation method and an application of the compound. The invention belongs to the field of a bio-medical technology. According to the invention, gamma-polyglutamic acid prepared by biological fermentation is used as a raw material, and a small molecular modifier and an active group at the side chain of the gamma-polyglutamic acid react to prepare a gamma-polyglutamic acid derivative; and then, cisplatin reacts with a modified carrier to prepare a drug-loaded compound containing free cisplatin as well as combined cisplatin. Water solubility of the water-soluble polyglutamic acid-cisplatin compound is remarkably enhanced than water solubility of existing cisplatin compounds, and utilization rate of cisplatin is raised. The water-soluble polyglutamic acid-cisplatin compound has a more excellent anti-tumor effect than cisplatin, and toxicity in vivo of the water-soluble polyglutamic acid-cisplatin compound is obviously reduced.
Owner:FANTAI INST OF CHEM MEDICINES NANJING
Aziridinyl quinone antitumor agents based on indoles and cyclopent[b]indoles
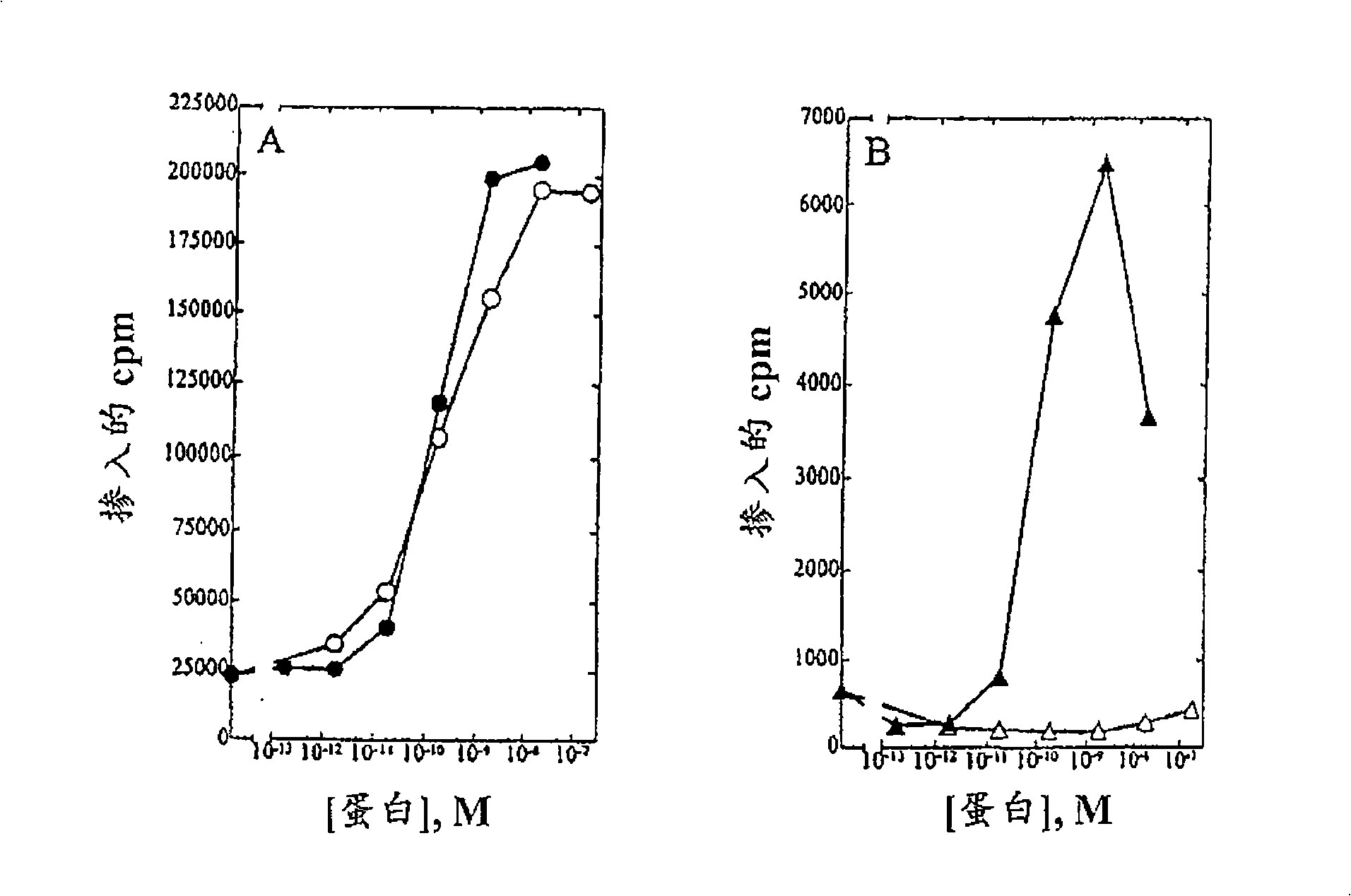
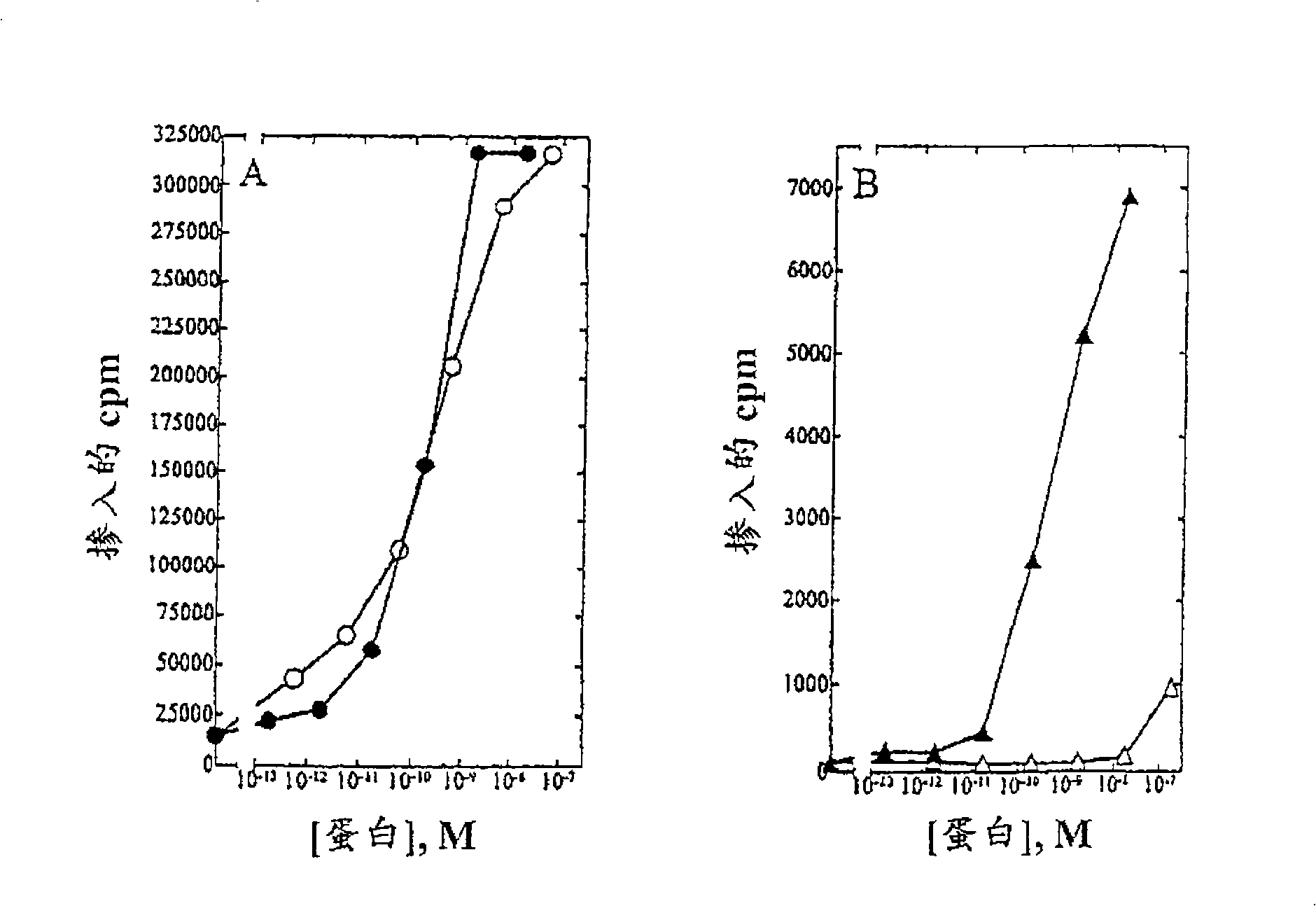
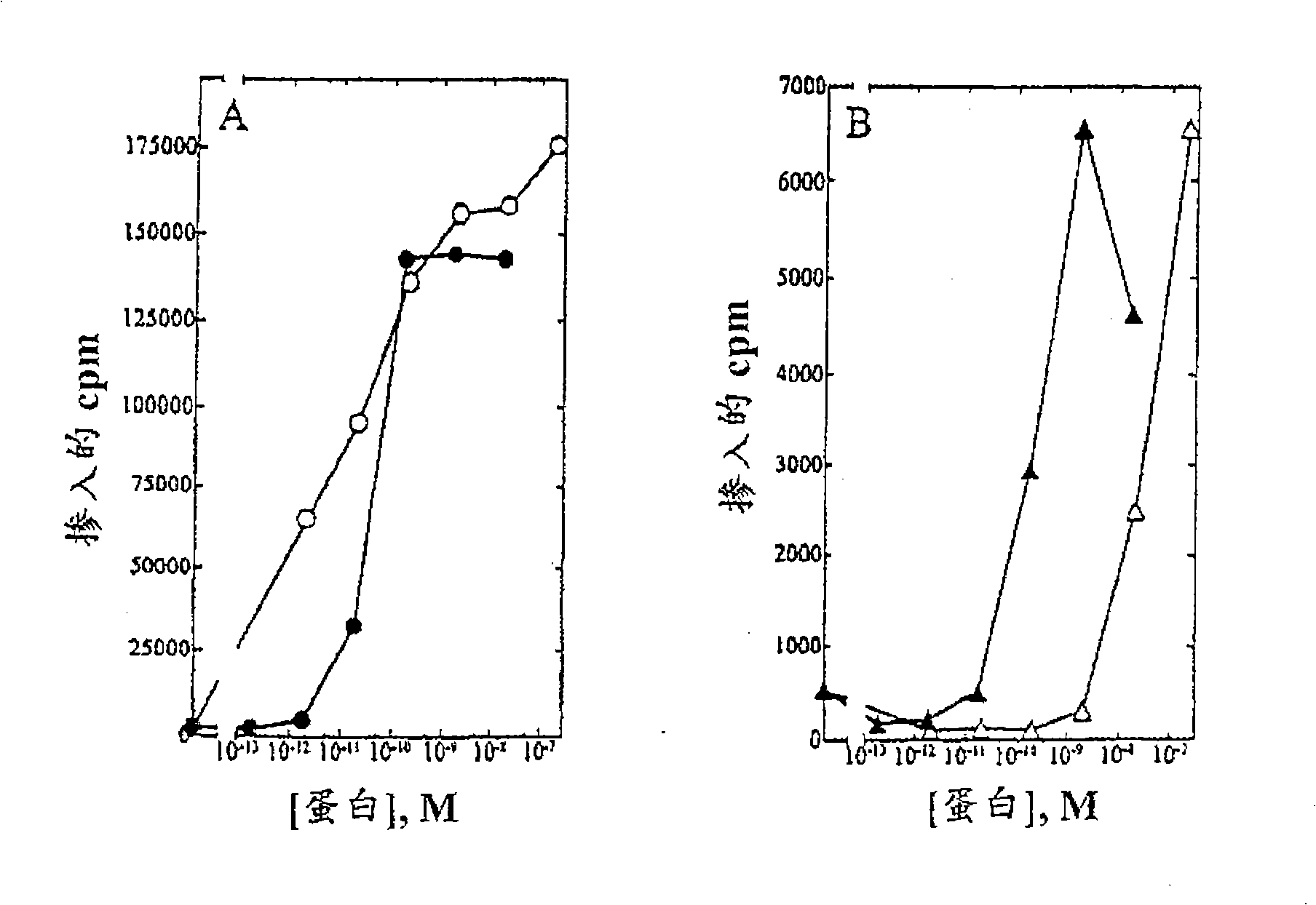
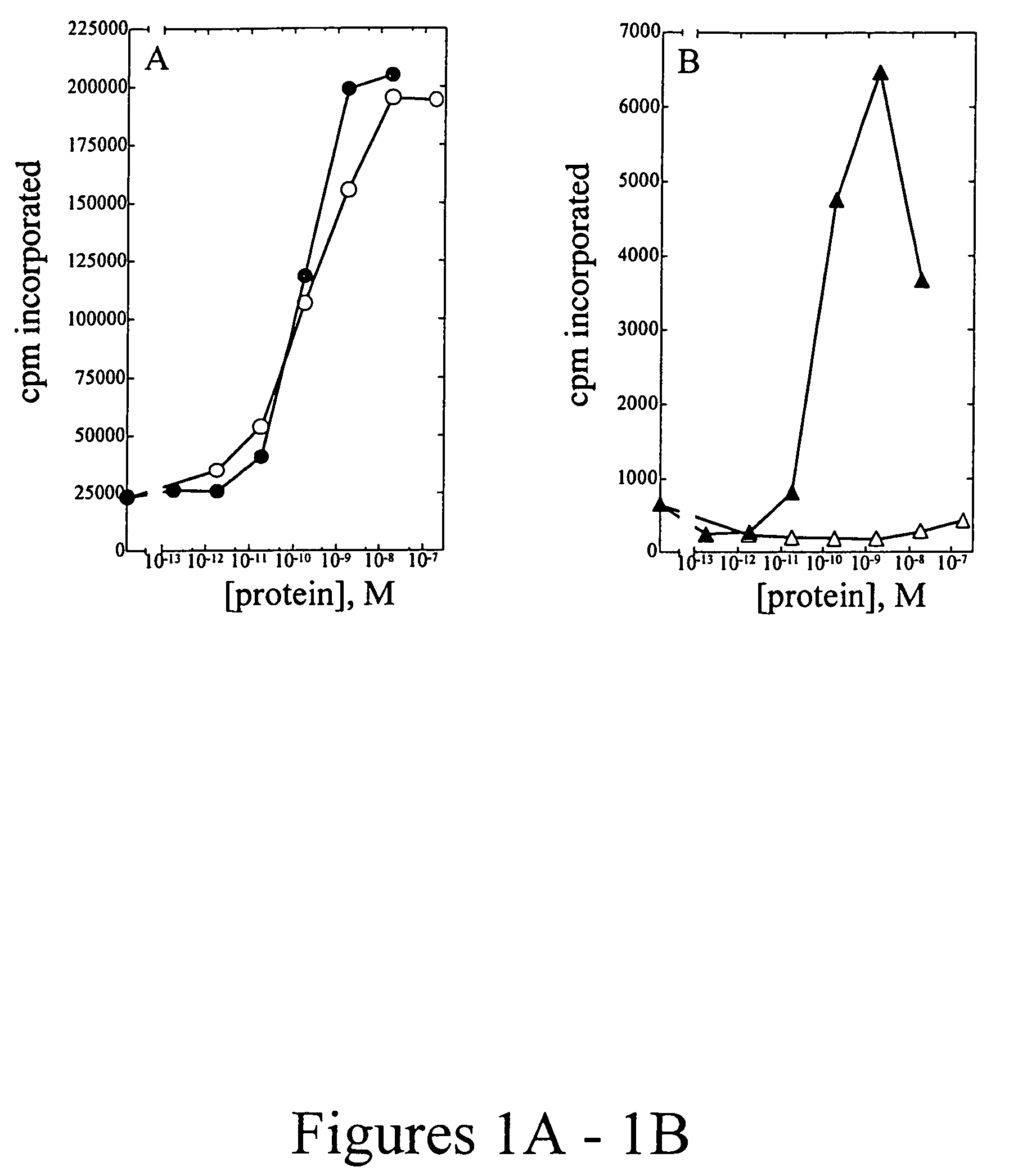
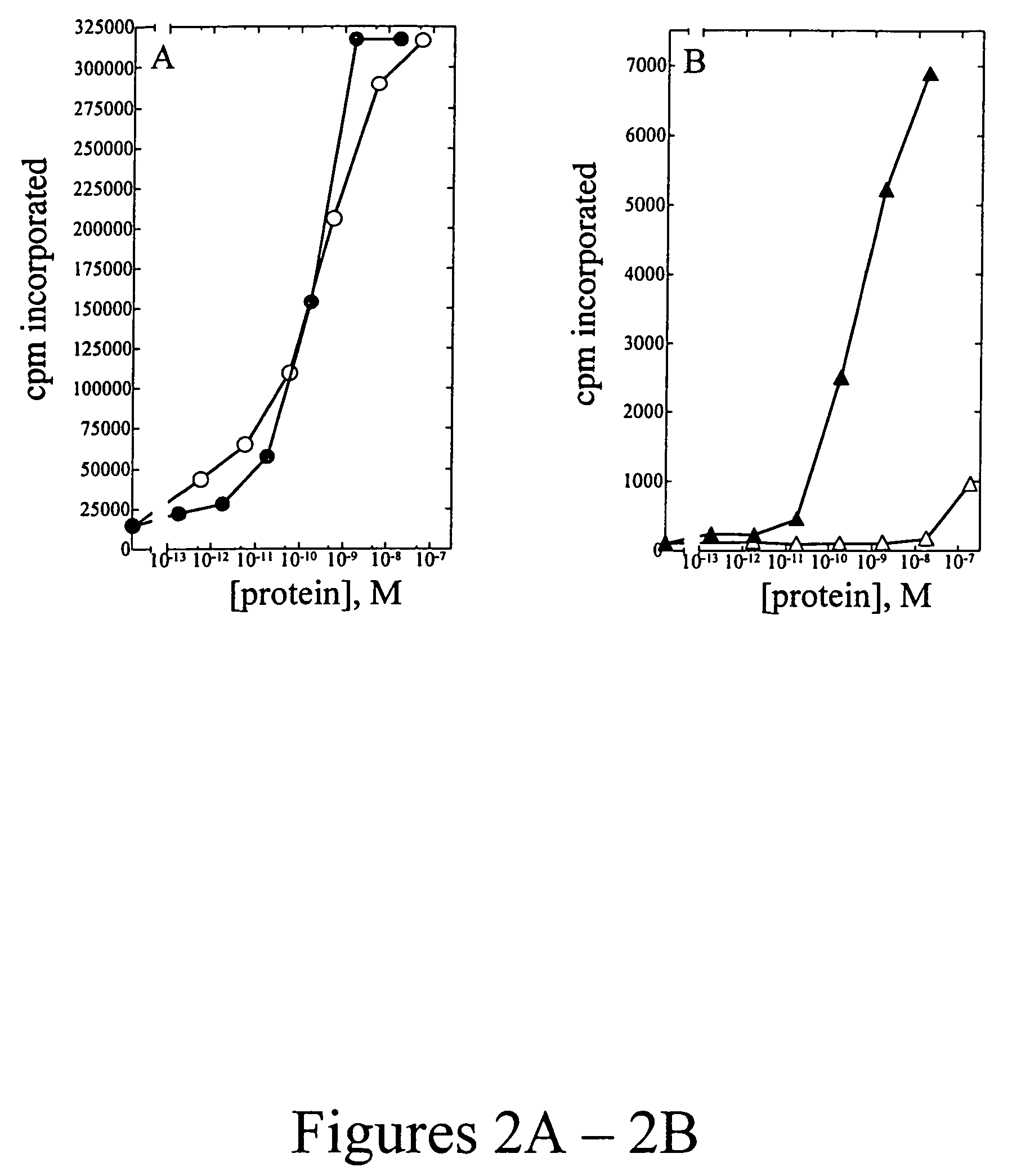
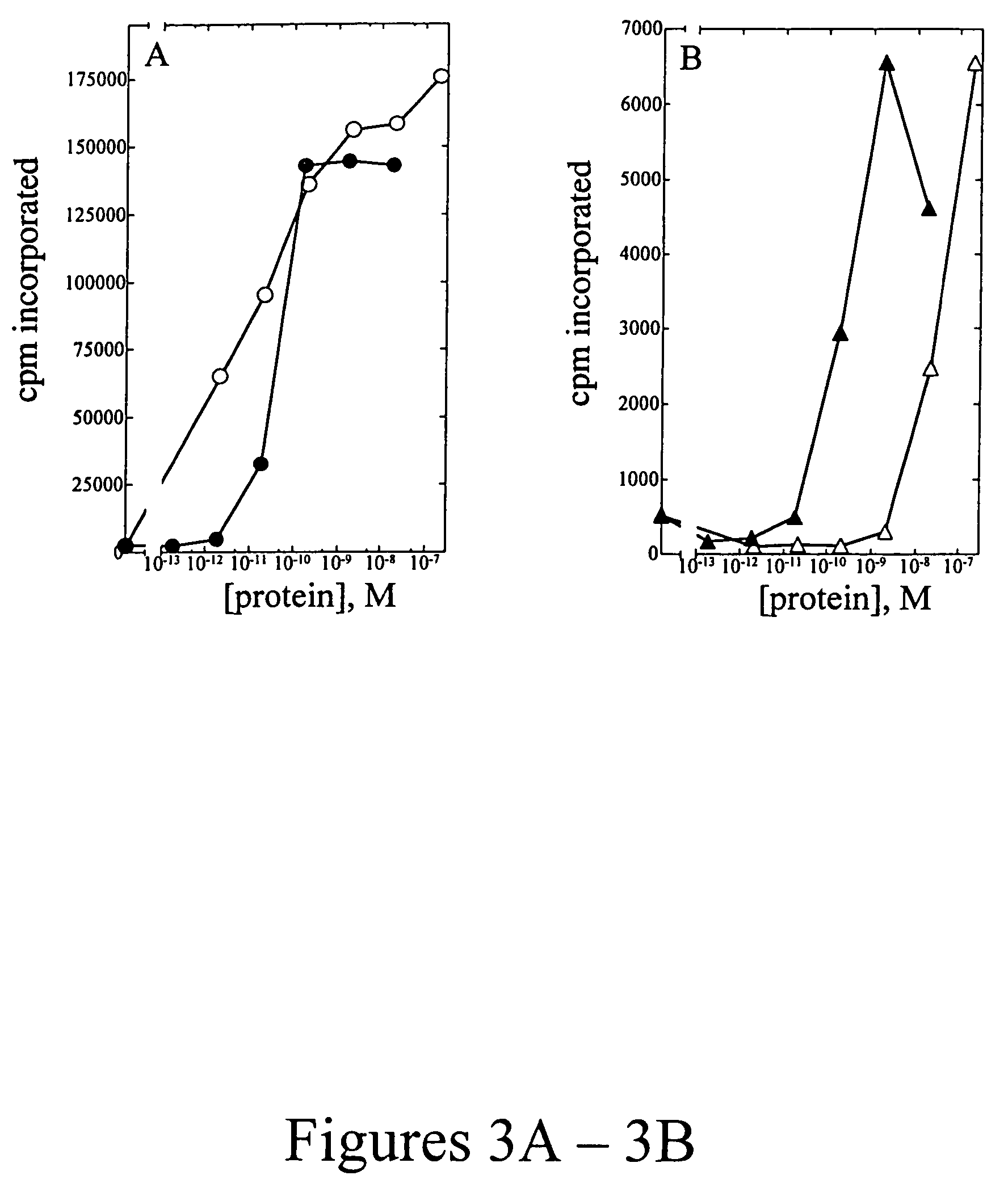
A large number of aziridinyl quinones represented by Series 1-9 were studied with respect to their DT-diaphorase substrate activity, DNA reductive alkylation, cytostatic / cytotoxic activity, and in vivo activity. As a result generalizations have been made with respect with respect to the following: DT-diaphorase substrate design, DT-diaphorase-cytotoxicity QSAR, and DNA reductive alkylating agent design. A saturating relationship exists between the substrate specificity for human recombinant DT-diaphorase and the cytotoxicity in the human H460 non-small-cell lung cancer cell line. The interpretation of this relationship is that reductive activation is no longer rate limiting for substrates with high DT-diaphorase substrate specificities. High DT-diaphorase substrate specificity is not desirable in the indole and cylopent[b]indole systems because of the result is the loss of cancer selectivity along with increased toxicity. We conclude that aziridinyl quinones of this type should possess a substrate specificity (VMAX / KM )<10x10-4 s-1 for DT-diaphorase in order not to be too toxic or nonselective. While some DNA alkylation was required for cytostatic and cytotoxic activity by Series 1-9, too much alkylation results in loss of cancer selectivity as well as increased in vivo toxicity. Indeed, the most lethal compounds are the indole systems with a leaving group in the 3a-position (like the antitumor agent EO-9). We conclude that relatively poor DNA alkylating agents (according to our assay) show the lowest toxicity with the highest antitumor activity.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Preparation method and application of cabazitaxel prodrug
ActiveCN106432141AIncreased Tolerated DoseReduce toxicity in vivoOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsSolubilityCabazitaxel
The invention discloses a cabazitaxel prodrug as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. A structural formula of the prodrug is represented as a formula (I) and the prodrug is prepared from cabazitaxel and hydrophobic molecules through an esterification reaction. The prodrug has better antitumor activity, can directly release active components in a hydrolytic manner in vivo, and can prevent in-vivo toxicity caused by direct injection of cabazitaxel. The prodrug has better solubility in water and can form nanoparticles in water through self-emulsification; the prodrug can be obtained with a single-step esterification method, is high in yield, low in preparation cost, high in stability and good in safety, meets requirements of clinical medication and large-scale industrial production, and has good market prospect and clinical application value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for screening drug which is resistant to pan-drug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii by using caenorhabditis elegans
ActiveCN107751089AReduce manufacturing costShort cycleCompounds screening/testingAnimal husbandryNalidixic acidPan drug resistant
The invention discloses a method for screening a drug which is resistant to pan-drug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii by using caenorhabditis elegans. First, a caenorhabditis elegans-pan-drug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii infection model used for screening the efficacy of a composition is constructed, wherein caenorhabditis elegans has double gene mutation of glp-4 and sek-1, the culture medium of the caenorhabditis elegans-pan-drug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii co-culture consists of 20% of BHI, 5-20[mu]m of nalidixic acid and 5-20[mu]g / ml of FeCl3; the concentration of the pan-drug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii is 1*10<6>-1*10<9>CFU / mL; the duration time of the bacterial infection on the caenorhabditis elegans is 6-12 hours; and the time of the treatment on an infected modelby a drug is 24-48 hours. The model can be used for fast and high-throughput screening of in-vivo antibacterial activity of various compounds or drugs or compositions, and compared with an in-vivo animal infection model, the model has the huge advantages of low preparation cost, short period and easy operation. Compared with an in vitro model, the model can be used to screen out compounds which have large in-vivo toxicity, poor metabolism and low in vitro-in vivo correlation.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GENERAL HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MILITARY COMMAND
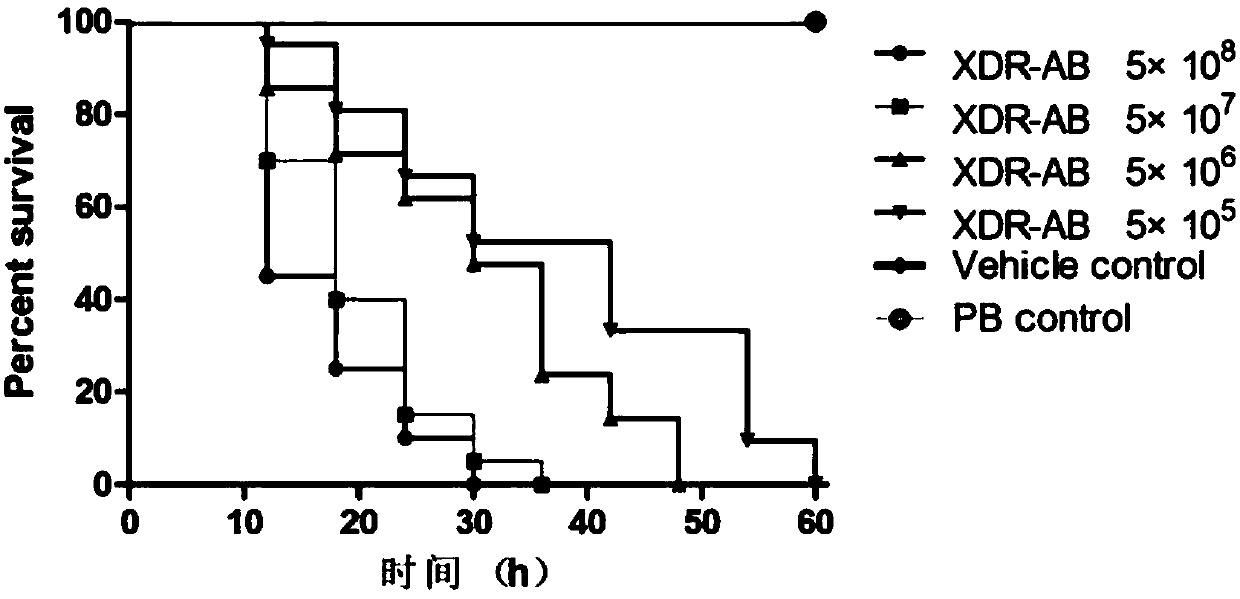
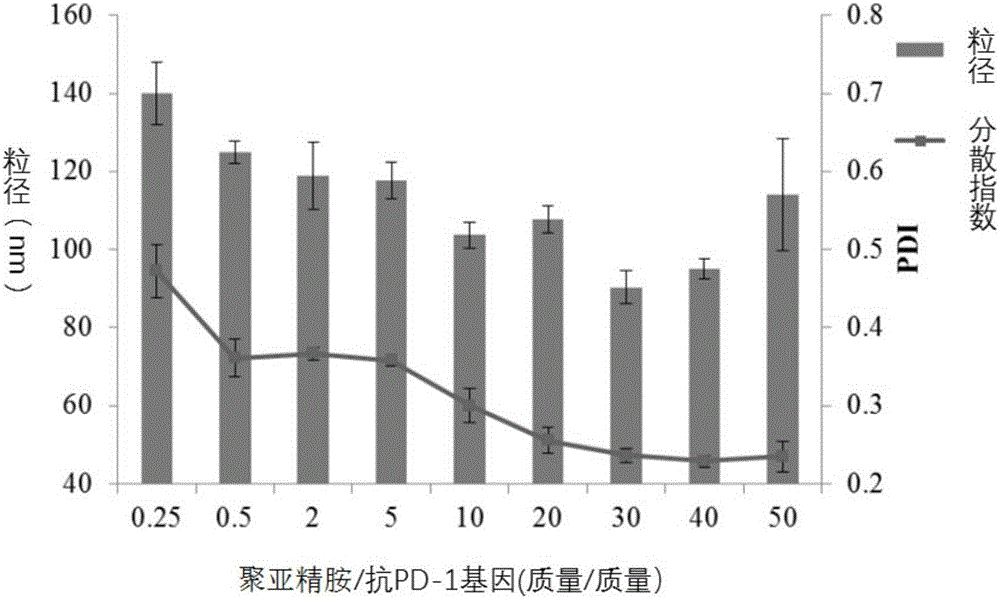
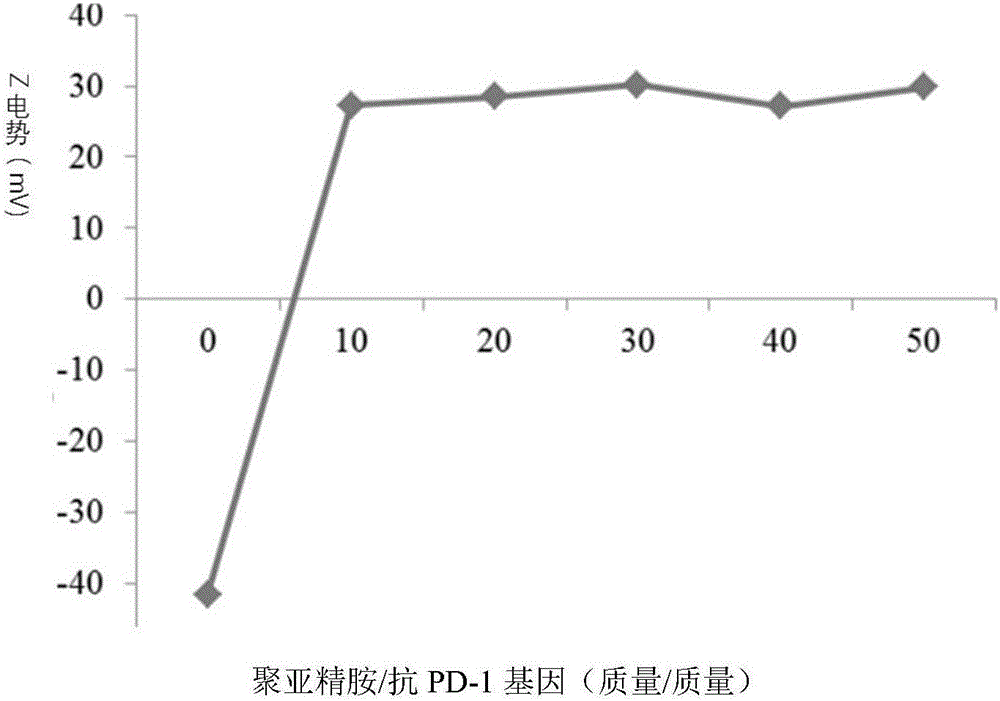
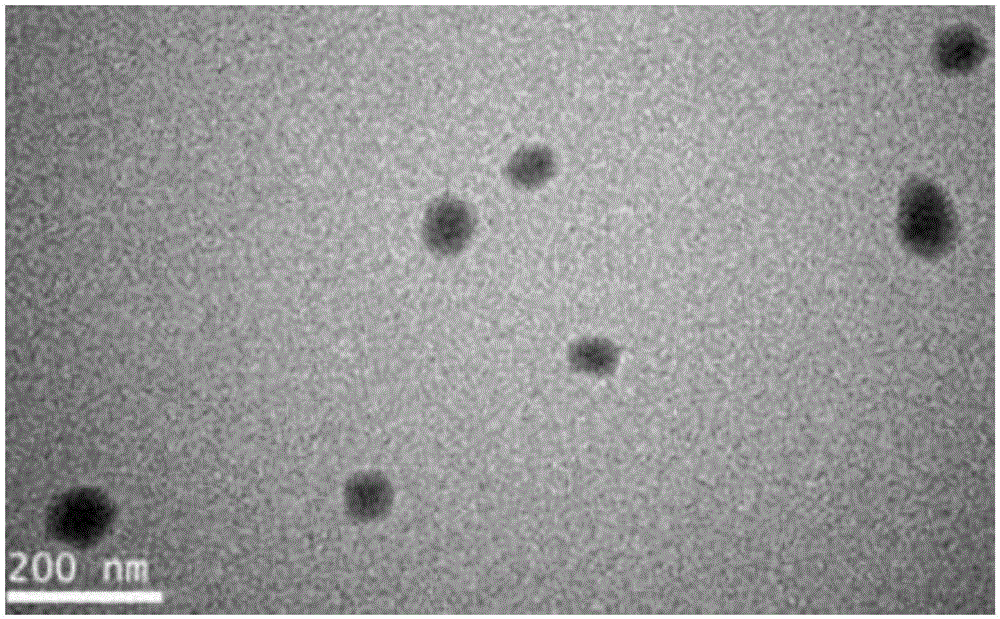
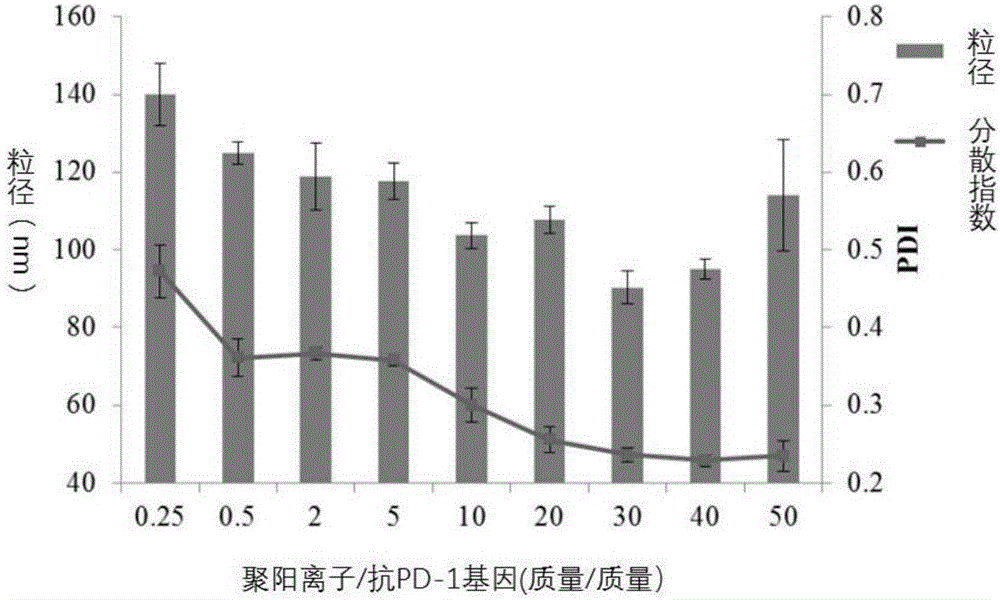
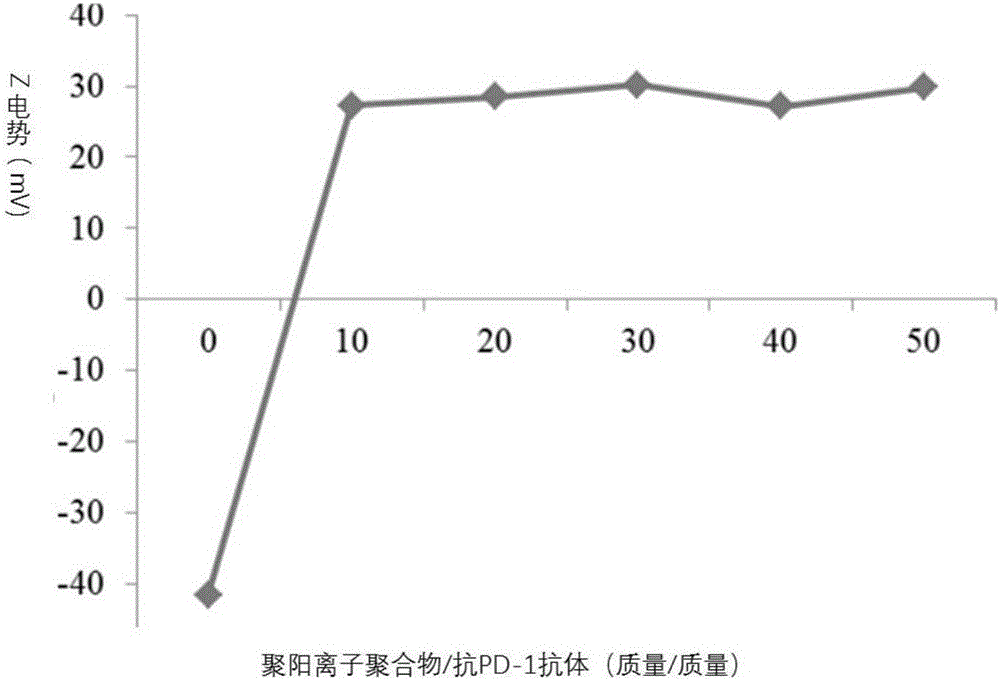
Compound containing anti-PD (Program Death)-1 gene and poly-spermidine and application of compound to treatment of tumors
InactiveCN106399380AEffective treatmentAchieving ImmunotherapyMammal material medical ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesAbnormal tissue growthMass ratio
The invention relates to the technical field of T cell tumor treatment and in particular relates to a compound containing an anti-PD (Program Death)-1 gene and poly-spermidine and application of the compound to treatment of tumors. The compound contains a polyspermidine polymer and the anti-PD-1 gene at the mass ratio of (1 to 100) : 1. The compound is transfected to a T cell in vitro to prepare a self-secretion anti-PD-1 antibody-T cell and can generate a PD-1 antibody, so as to help to block a PD-1 signal and effectively help a depleted T cell, and promote the T cell capable of resisting tumor immune response to treat the tumors. Compared with the prior art, the secretion anti-PD-1 antibody-T cell provided by the invention can be used for effectively treating the tumors, and immune treatment of the tumors can be realized; an in-vivo toxicity problem does not exist.
Owner:SHANGHAI YUNSHUN BIOTECH
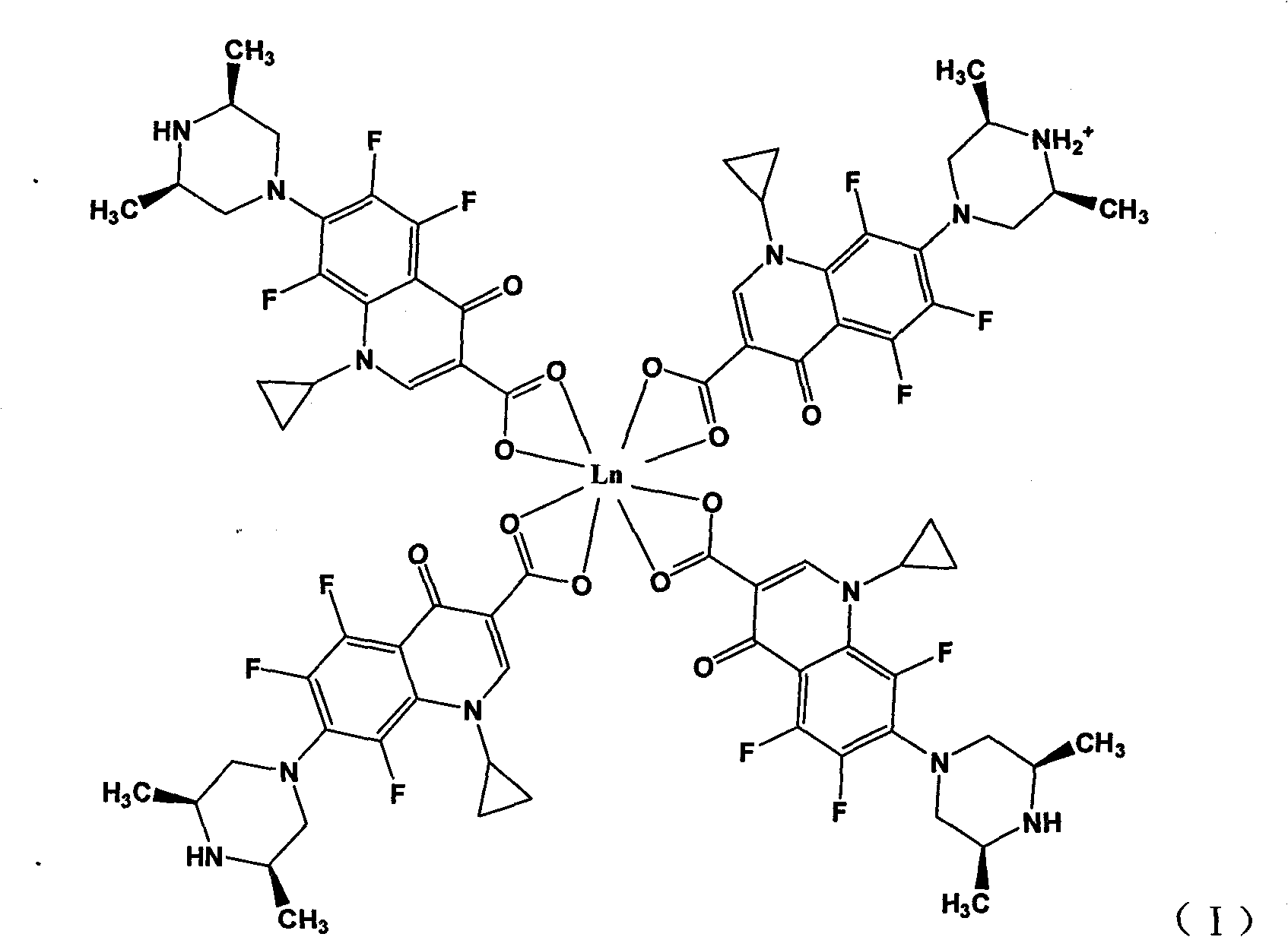
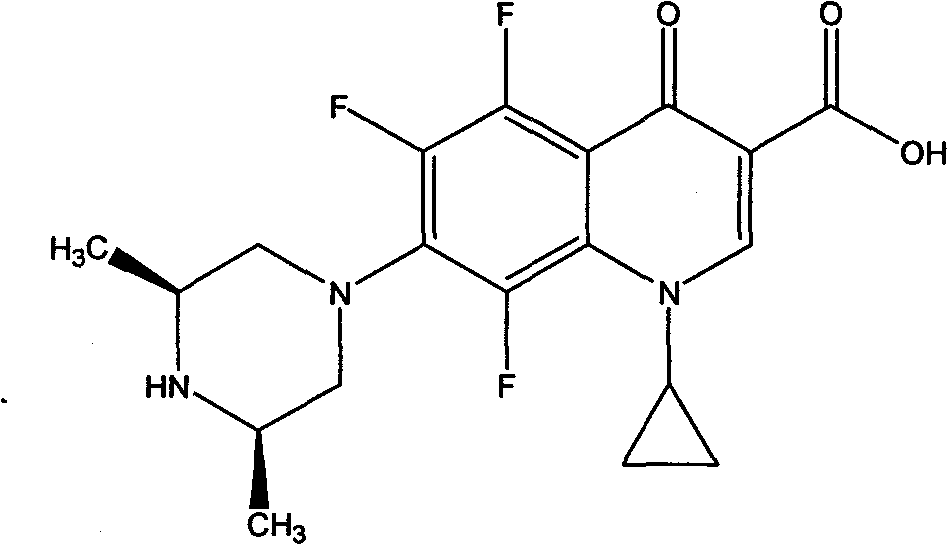
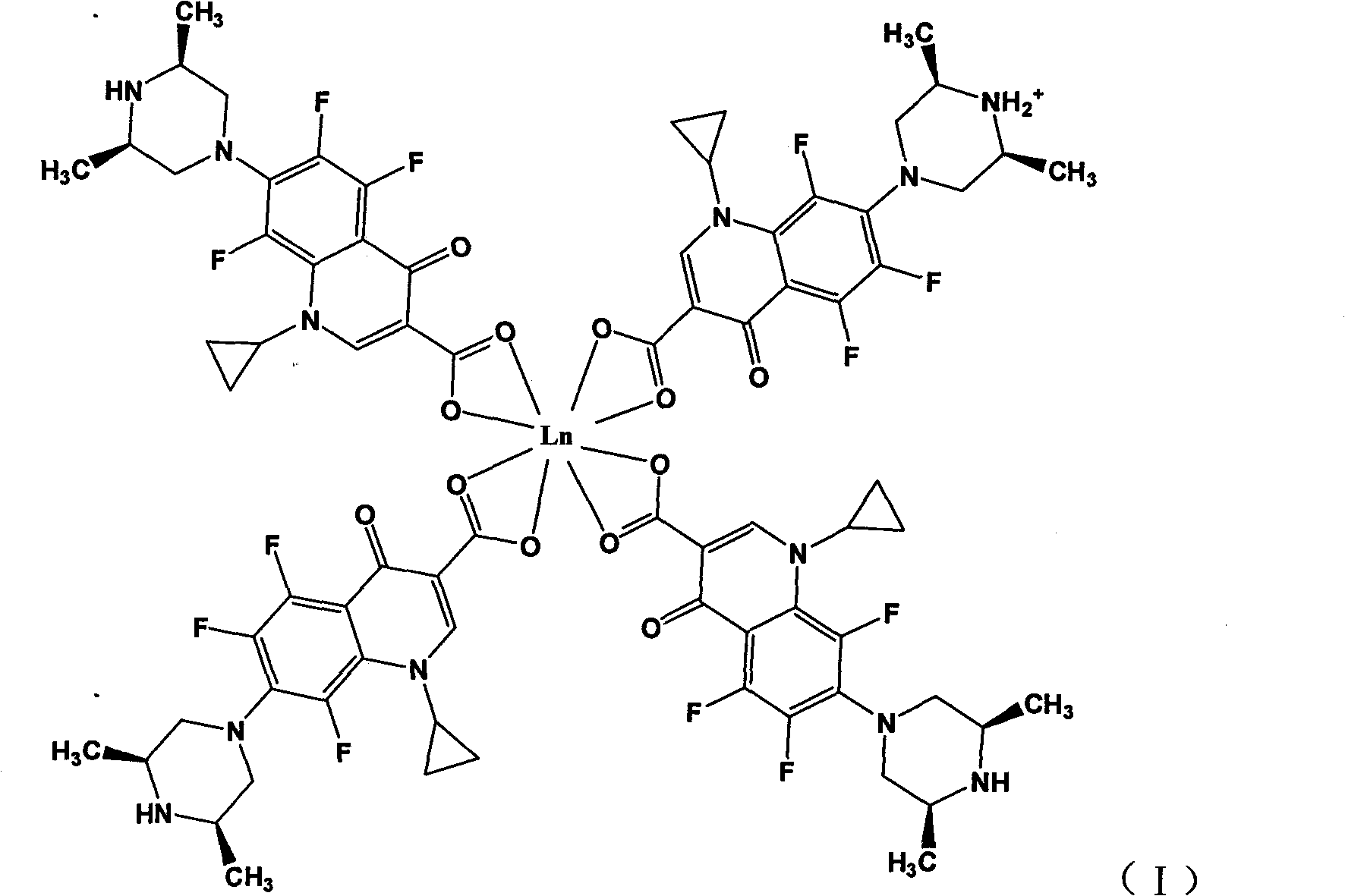
Rare earth metal complexes using orbifloxacin as ligand, method for synthesizing same and application thereof
InactiveCN101817817AHigh antibacterial activityIncrease toleranceAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAcute toxicity testingOrbifloxacin
The invention discloses rare earth metal complexes using orbifloxacin as a ligand, a method for synthesizing the same and application thereof. In the tests of the inhibiting effect of the complexes on bacteria such as salmonella pullorum, swine streptococcosis and bovine streptococcus uberis, the results show that the complexes have quite high bacteriostatic activity, wherein all of Er(III), Sm(III) and Eu(III) complexes of the orbifloxacin have certain bacteriostatic activity on the swine streptococcosis which cannot be inhibited by orbifloxacin and doxycycline. Mouse acute toxicity tests show that the complexes have low in-vivo toxicity to mice and are highly tolerable to mice. The toxicity of various complexes meets the acute oral toxicity ungraded standards of European Community and the PRC food security assessment grade-two (actually non-toxic) standard, wherein the neodymium complex of the orbifloxacin has the lowest toxicity.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
IL-2 selective agonists and antagonists
InactiveCN101319247AActivating activityReduce activationPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory ReceptorsAgonist
The invention is directed to a polypeptide comprising a human IL-2 mutein numbered in accordance with wild-type IL-2 wherein said human IL-2 is substituted at at least one of positions 20, 88 or 126, whereby said mutein preferentially activates T cells over NK cells. D20H and I, N88G, I, and R, in particular have a relative T cell-differential activity much greater than native IL-2, with predicted associated reduced in vivo toxicity. The invention also includes polynucleotides coding for the muteins of the invention, vectors containing the polynucleotides, transformed host cells, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the muteins, and therapeutic methods of treatment.
Owner:AICURIS GMBH & CO KG
Modified polyethyleneimine derivative as well as synthesis method and application thereof
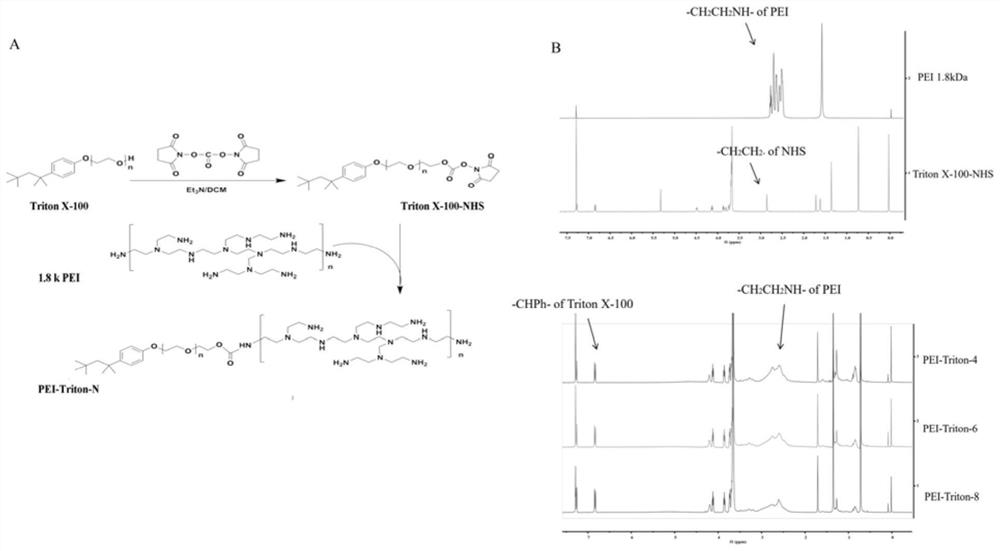
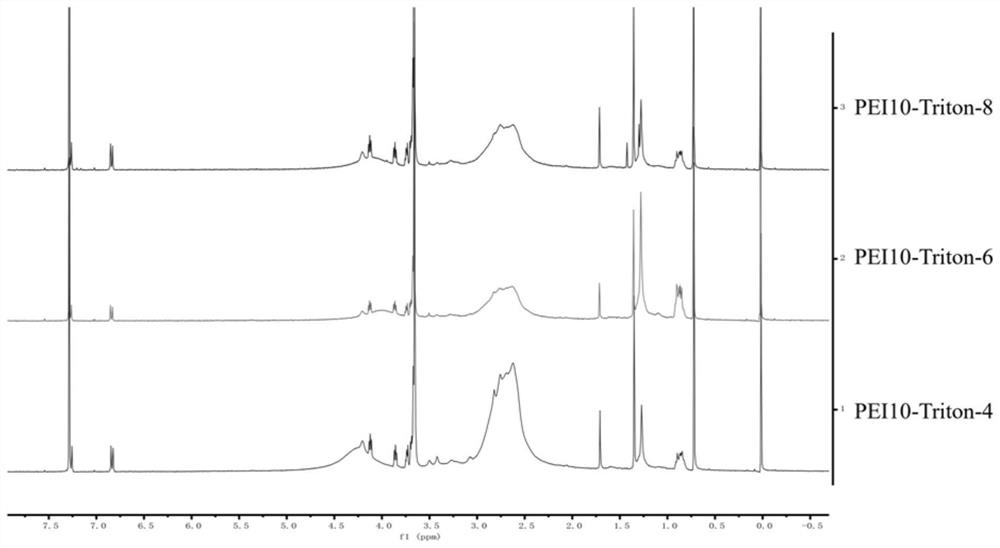
InactiveCN112142972AImprove transfection efficiencyGood gene delivery capability for local administrationPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsGene therapyCell EvaluationPerylene derivatives
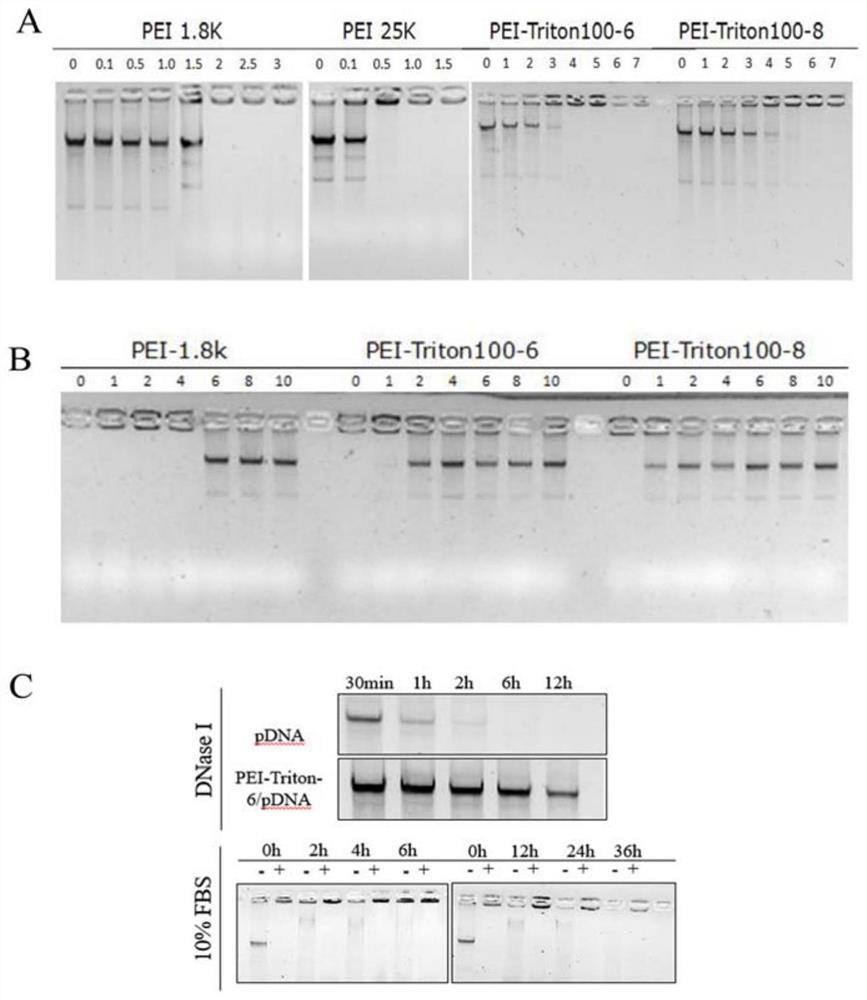
The invention discloses a modified polyethyleneimine derivative as well as a synthesis method and application thereof. According to the invention, Triton X-100 is conjugated to polyethyleneimine, suchthat a PEI-Triton-N carrier is obtained. In-vitro cell evaluation shows that the carrier shows good safety and stability; cell transfection effect experiments show that the carrier shows efficient and low-toxicity gene delivery capacity, can significantly improve the gene transfection efficiency of various cells including skin immortalized cells HaCaT difficult to transfect, and is an excellent in-vitro transfection reagent; an in-vivo toxicity experiment shows that the carrier has no obvious systemic toxicity; and a gene delivery experiment result of mouse skin local administration shows that the carrier has good local administration gene delivery capability and is a good local administration gene delivery vector.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Modified CpG oligodeoxynucleotide with improved immunoregulatory function
InactiveUS20050152921A1Improve survival rateSurvival rateOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAnticarcinogenCpG Oligodeoxynucleotide
The present invention relates to a modified CpG oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN) which is prepared by coupling a consecutive sequence of deoxyribothymine (dT) to the 3′-terminus of CpG ODN having immunoregularory function, thereby improving immunoactivity of splenocytes, macrophages and peripheral mononuclear cells, and therefore, can be effectively used as a vaccine adjuvant for preventing and treating hepatitis B or an anti-cancer agent. Since the phosphorothioate CpG ODN having the consecutive sequence of dT at its 3′-terminus shows high activity inducing Th-1 immune response and does not elicit in vivo toxicity with guaranteeing its safety, it can be effectively used as a vaccine adjuvant.
Owner:YONSEI UNIVERSITY
Method for screening probiotics
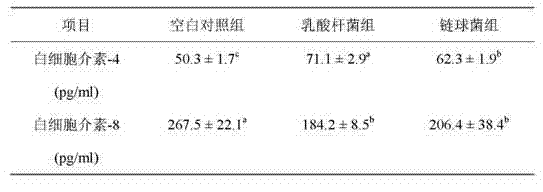
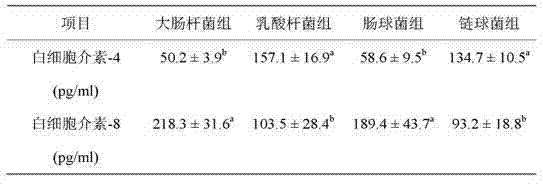
The invention discloses a method for screening probiotics. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out a primary culture on spleen tissues of a pig or a domestic animal; (2) attacking toxicity of the tissues through colon bacillus K88, and testing variations of levels of an interleukin 8 and an interleukin 4; (3) respectively processing the tissues through candidate probiotic strains, and testing variations of levels of two interleukins; (4) comparing the variations to select probiotic strains which are similar in variation degrees of the two interleukins but opposite in effect due to treatment of the colon bacillus K88; and (5) through the colon bacillus K88 animal toxicity attacking test, observing protecting effects of primarily selected probiotic strains, and finally determining an efficient probiotic strain. The method for screening the probiotic disclosed by the invention has the remarkable advantages that: the method combining in vitro immunology experiment and in vivo toxicity attacking experiment is high in accuracy, strong in pertinency and time-saving; and the screened probiotics can effectively replace antibiotic, and greatly reduce diseases caused by colon bacillus so as to promote the health of the animal.
Owner:江西华农恒青农牧有限公司
Taxane prodrug, preparation method and application thereof
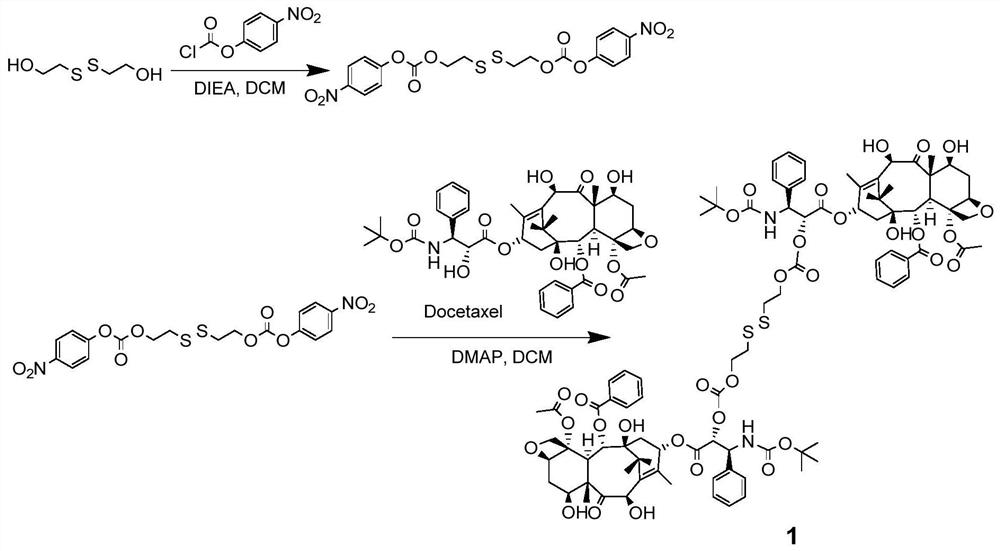
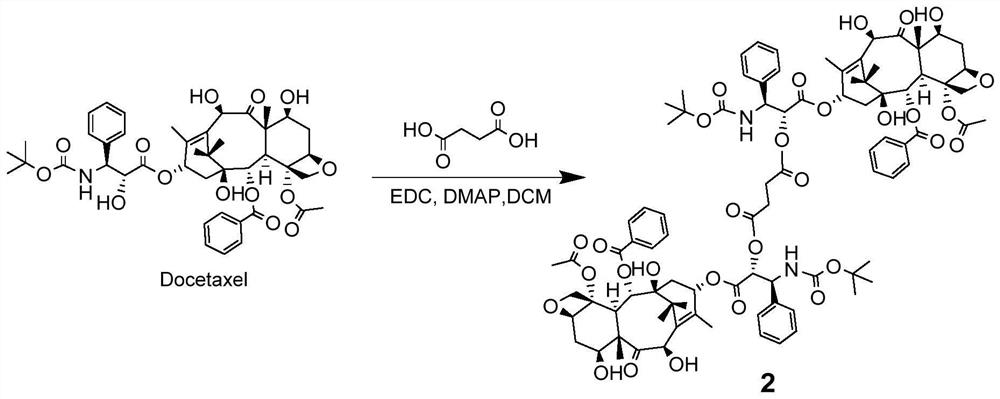
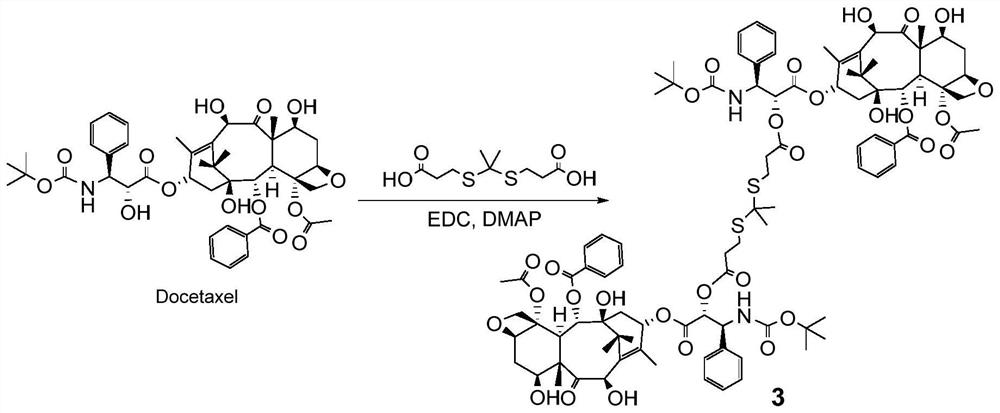
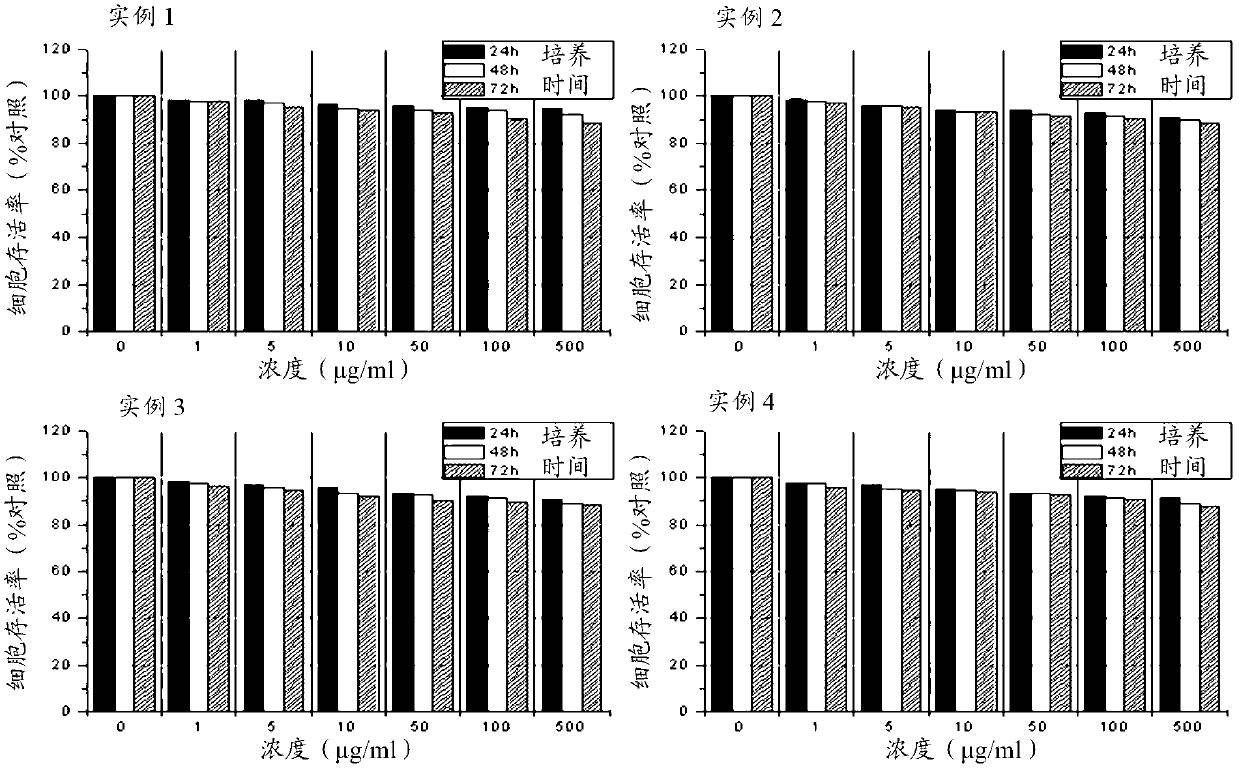
PendingCN112250647AIncreased Tolerated DoseReduce toxicity in vivoOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCabazitaxelDocetaxel
The invention discloses a taxane prodrug, which has a structure of Y1-R-Y2, wherein the Y1 and the Y2 are docetaxel or cabazitaxel, R comprises a specific connecting bond for environmental response intumor cells, and the taxane prodrug is generated by carrying out substitution or condensation reaction on a taxane drug and a tumor microenvironment-responsive connecting bond. According to the invention, the prodrug has good anti-tumor activity, can directly release active ingredients in vivo in a hydrolysis or oxidation mode, and can avoid in vivo toxicity caused by direct injection of taxane drugs; the prodrug disclosed by the invention not only has good solubility in water, but also can be self-emulsified in water to form nanoparticles; and the prodrug can be obtained through a single-step reaction method, the yield is high, the preparation cost is low, the stability is high, the safety is good, the requirements of clinical medication are met, the requirements of large-scale industrial production are met, and the prodrug has good market prospects and clinical application value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Radial shape of polymer compound containing iodine, preparation method thereof, and ct contrast medium composition containing same
InactiveCN103282056AEnsure Structural IntegrityIncrease productionOrganic active ingredientsRadioactive preparation carriersPurification methodsRetention time
The present invention relates to a radial shape of a polymer compound containing iodine capable of being used as an active ingredient of a CT contrast medium, a preparation method thereof, and a contrast medium composition containing the same. According to the present invention, the radial shape of the polymer compound containing iodine has a remarkably enhanced contrast effect retention time compared with a conventional low molecular weight contrast medium compound containing iodine. In addition, the polymer compound containing iodine forms a protective film by encompassing a compound containing iodine substituted near the surface of a central nucleus, which leaves room for causing various kinds of abnormal reactions with toxicity, with a relatively long biocompatible polymer chain layer, thereby preventing the exposure thereof to external environments to reduce in vivo toxicity, preventing the rapid absorption due to a macrophage to extend in vivo circulation time, and allowing the polymer compound containing iodine to be discharged from the body after an adequate time has passed since an in vivo injection. Further, the preparation method and the purification method of the polymer compound containing iodine are very simple, thereby enabling mass production in a high yield and at low costs, the polydispersity is very low, thereby providing high reproducibility in the preparation and effects, and all of the structures of the prepared radial shape of the polymer compound containing iodine comprise a covalent bond, thereby being structurally very stable, and thus the polymer compound containing iodine can be useful for the preparation of a CT contrast medium.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCIENCE & BIOTECHNOLOGY
Composite containing anti-PD-1 gene and polycation and its application in treating cancer
InactiveCN106434754AEffective treatmentAchieving ImmunotherapyOther foreign material introduction processesGene therapyAntitumor immunityT cell
The invention relates to the technical field of cancer treatment by T cell, and particularly relates to a composite containing anti-PD-1 gene and polycation and its application in treating tumor; the composite includes poly-cationic polymer and anti PD-1 gene in the mass ratio of 1-100: 1. The composite is transfected to the T cell externally, and the secretion anti OD-1 antibody-T cell is prepared, and PD-1 antibody can be generated, thus helping to stop the PD-1 signal, effectively helping the exhausted T cell, and promoting the T cell treatment cancer of antitumor immunity response. Compared with the prior art, the secretion anti OD-1 antibody-T cell can effectively treat tumor and realize the tumor immunological therapy; besides, the composite is free from in-vivo toxicity.
Owner:SHANGHAI YUNSHUN BIOTECH
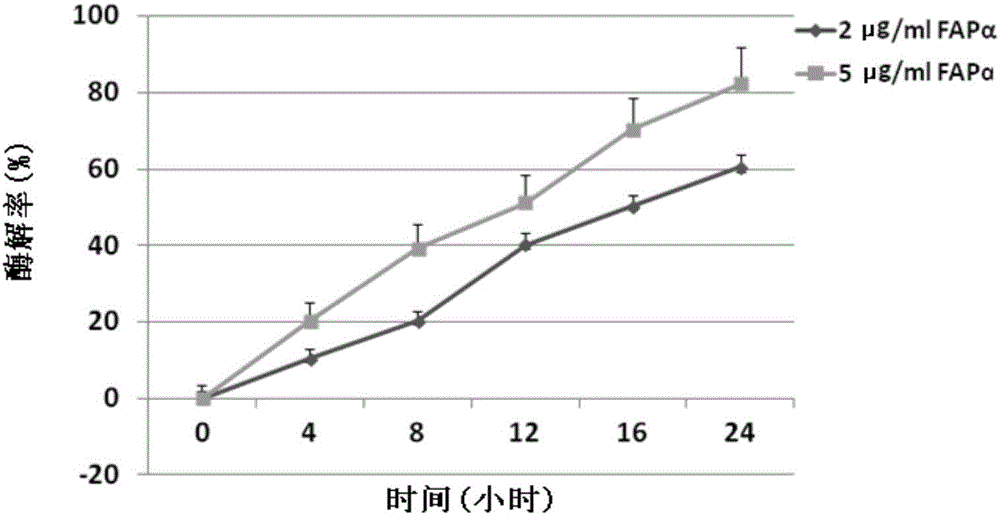
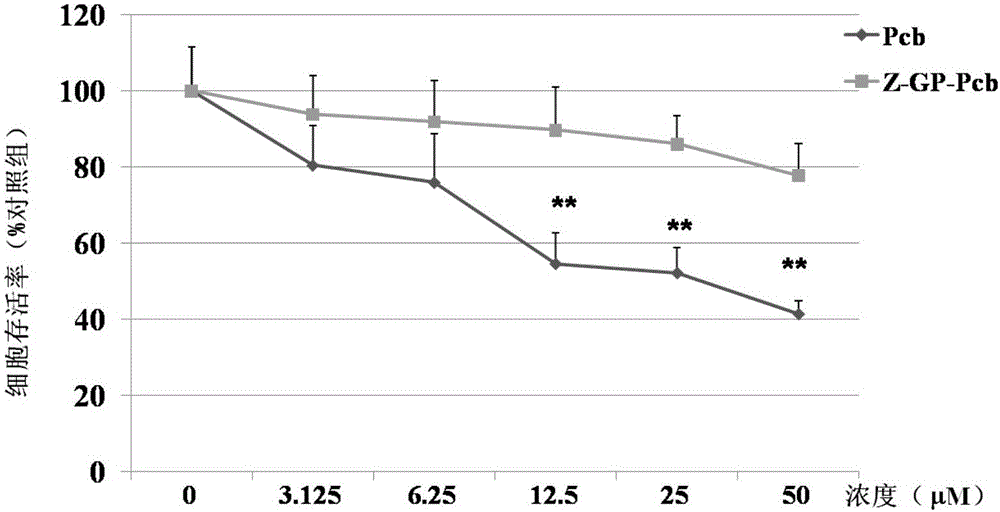
Antitumor compound targeting FAP-alpha enzyme and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106631957AMild reaction conditionsHigh purityOrganic chemistry methodsAntineoplastic agentsTumor targetSide effect
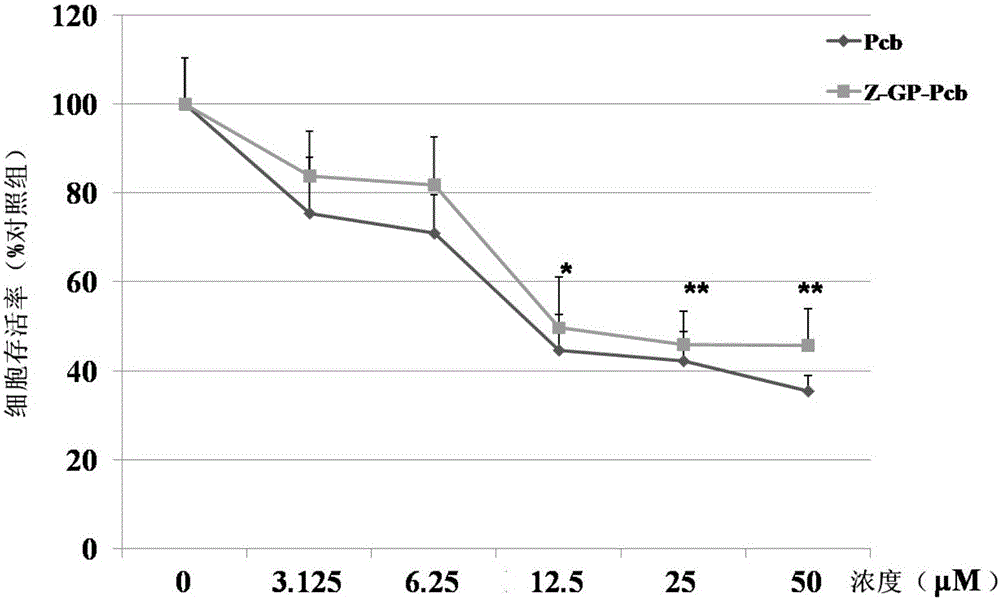
The invention discloses an antitumor compound targeting an FAP-alpha enzyme. The antitumor compound is named Z-GP-procarbazine; a dipeptide part (Z-GP) in the compound can be removed by specific hydrolysis of the FAP-alpha enzyme to release procarbazine. The Z-GP-procarbazine can significantly lower the toxicity and in-vivo toxicity of normal cells, can be free from the dipeptide part (Z-GP) in vivo and in vitro through specific hydrolysis of the FAP-alpha enzyme to release an enzymolysis product, and can significantly inhibit the growth of tumors in nude mice bearing tumors and lower the toxicity to non-target organs, thus reducing the deficiency of severe toxic and side effects of procarbazine as an anticancer drug. The invention provides a tumor targeting drug based on FAP-alpha. In addition, the invention discloses a preparation method of the Z-GP-procarbazine. The method has the characteristics of mild reaction conditions, simple experiment steps, high yield, high purity of a product, economical efficiency, practicability and the like. In addition, the invention discloses use of the Z-GP-procarbazine, a derivative of the Z-GP-procarbazine and a physiologically-acceptable salt of the Z-GP-procarbazine in preparation of antitumor drugs.
Owner:广州药本君安医药科技股份有限公司
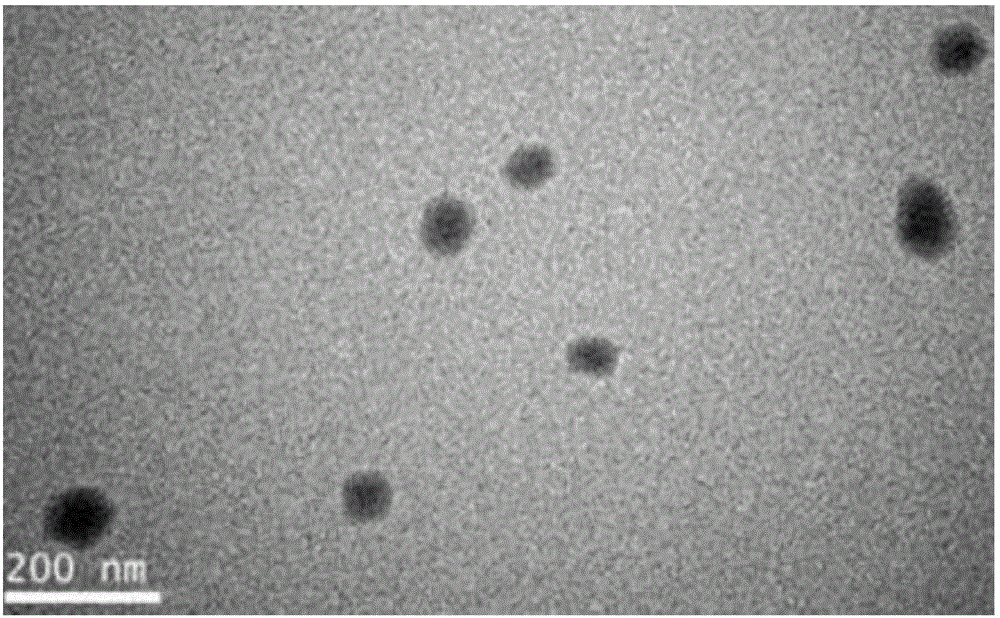
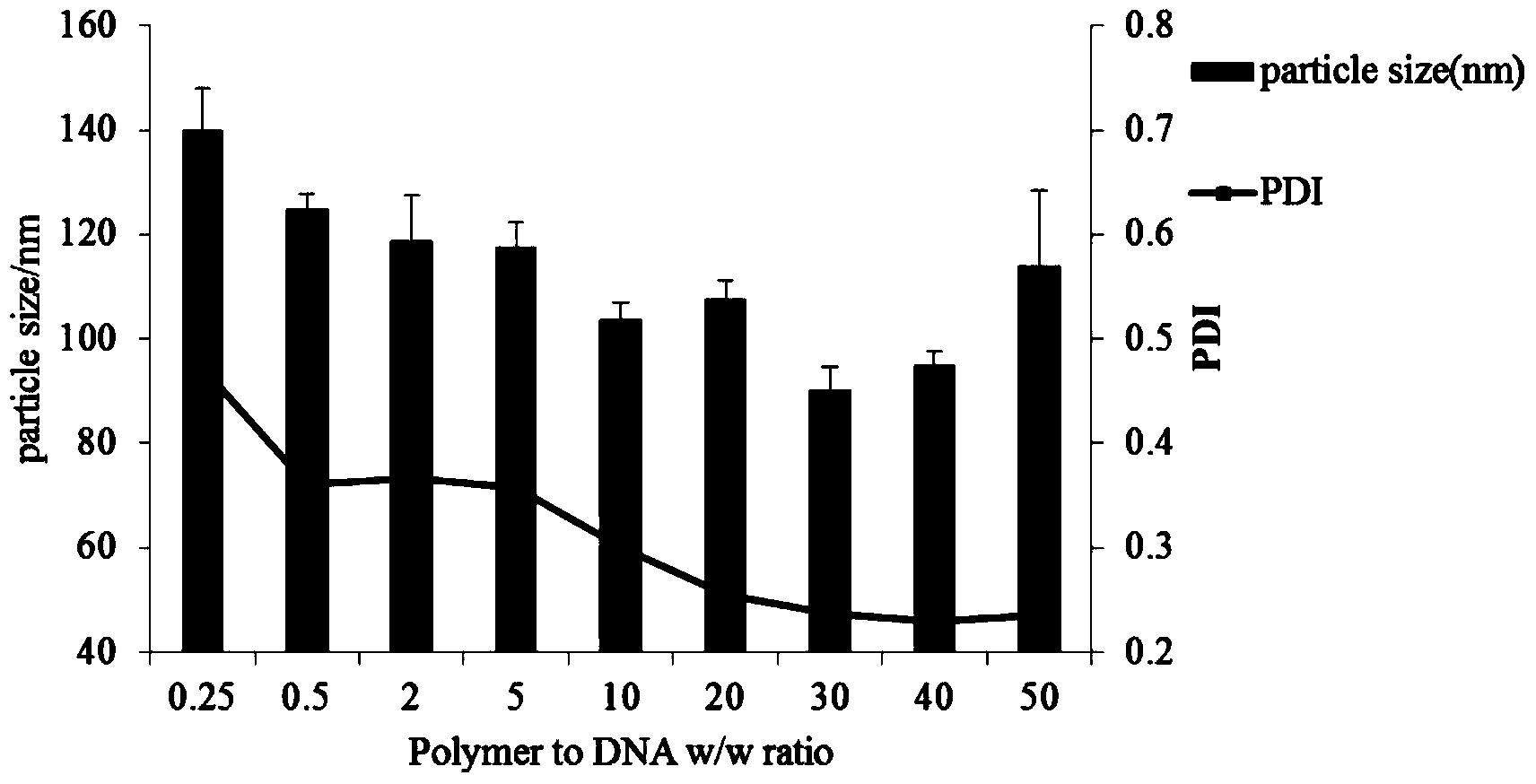
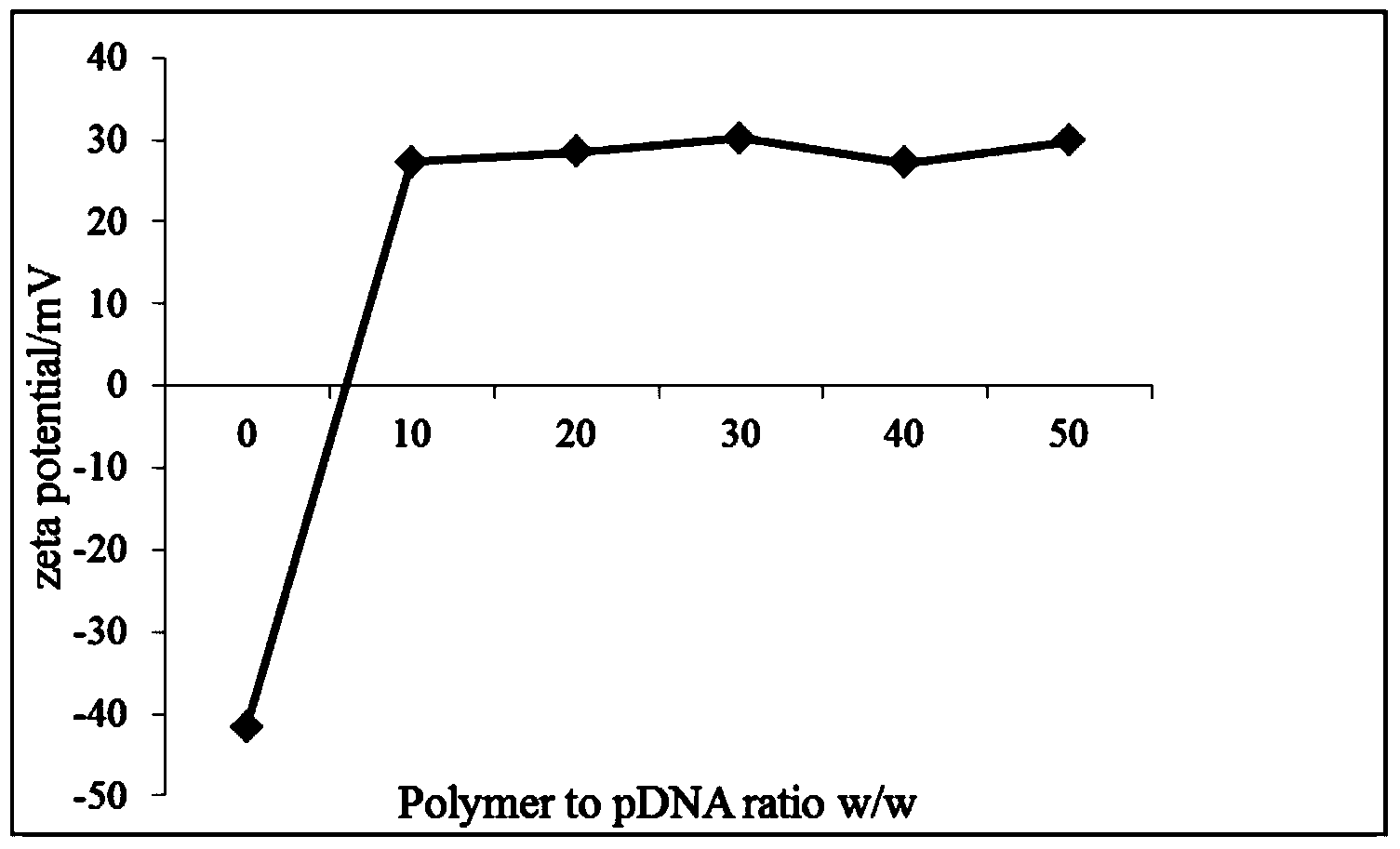
Poly spermine polymer-contained nano-particle, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104353085APrevent proliferationRealize deliveryPowder deliveryGenetic material ingredientsImmunogenicityNon targeted
The invention relates to the technical field of drugs for treating angiogenesis, in particular to a poly spermine polymer-contained nano-particle for treating angiogenesis, and a preparation method and application of the nano-particle. The poly spermine polymer-contained nano-particle comprises a poly spermine polymer and a genetic material, wherein the mass ratio of the poly spermine polymer to the genetic material is (1-100): 1. Compared with the prior art, the nano-particle provided by the invention can effectively inhibit angiogenesis, can realize the delivery of genetic material, can avoid problems of in vivo toxicity and in vivo immunogenicity, can avoid adhesion of in vivo non-target tissues as the nano-particle is uncharged, can realize targeting of in vivo diseased cells so as to effectively improve the targeting effect, and does not affect the endocytosis of the in vivo diseased cells.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
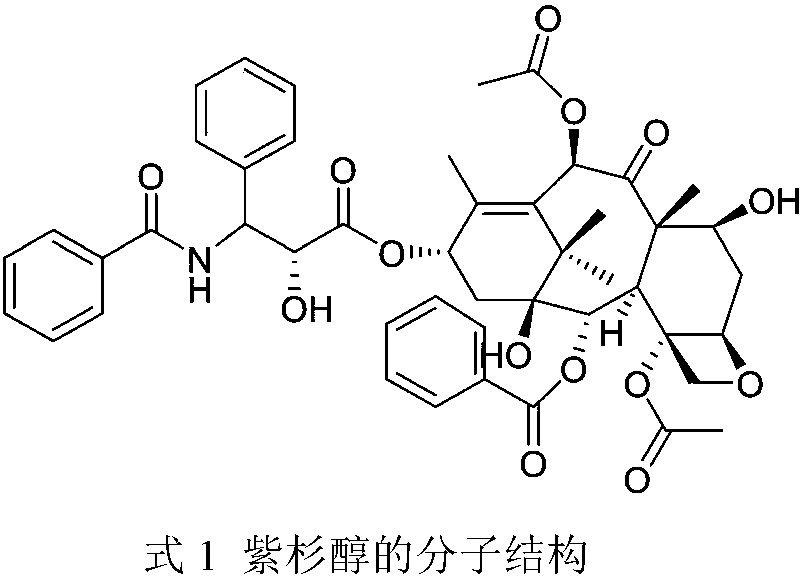
Preparation method of water-soluble paclitaxel anticancer drug
InactiveCN108467439AHigh anticancer activityLow toxicityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSolubilityDrug precursors
The invention discloses a preparation method of a water-soluble paclitaxel anticancer drug, and belongs to the field of medicine. A PTX drug precursor has similar antitumor activity to a clinical drugPTX, can be hydrolyzed slowly in vivo, and effectively reduces the in-vivo toxicity. The PTX drug precursor has good solubility in water. The targeting property of the PTX drug precursor is increased. Hyaluronic acid is modified with anhydride and then is grafted to paclitaxel. The polymer has good injection safety, self-aggregation characteristics and drug loading capacity.
Owner:YANCHENG TEACHERS UNIV +1
Polycationic nucleic acid compound nano-particles as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104257630APrevent proliferationRealize deliverySenses disorderGenetic material ingredientsVascular proliferationNanoparticle
The invention relates to the technical field of medicines for treating vascular proliferation and in particular relates to a polycationic nucleic acid compound for treating vascular proliferation as well as a preparation method and application thereof. According to the polycationic nucleic acid compound nano-particles for treating vascular proliferation disclosed by the invention, the nano-particles comprise polycationic nucleic acid materials and genetic substances, wherein a mass ratio of the polycationic nucleic acid materials to genetic substances is (1-100):1. The polycationic nucleic acid compound nano-particles for treating vascular proliferation comprise the polycationic nucleic acid materials and the genetic substances. Compared with the prior art, the nano-particles can effectively inhibit vascular proliferation and realize delivery of the genetic substances, and the problems of in-vivo toxicity and in-vivo immunogenicity are solved. Moreover, because the nano-particles are neutrally charged, adhesion of in-vivo non-target tissues can be avoided, and in-vivo pathological cell targeting is realized, so that the targeting effect is effectively improved, and endocytosis of in-vivo pathological cells is not influenced.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Sorbic acid-tea polyphenol composite nanoparticles and application thereof
InactiveCN107223849AEnsure safetySimple structurePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsComposite nanoparticlesSafety testing
A sorbic acid-tea polyphenol composite nanoparticle and application thereof, the invention relates to the technical field of nanocomposite particle synthesis; its preparation method is as follows: 1. preparing composite nanoparticle; 2. detecting the encapsulation efficiency and Drug loading, the prepared composite nanoparticles have been tested for functional response performance, and qualified composite nanoparticles have been obtained; 3. Safety performance testing of composite nanoparticles: starting from the overall safety of composite nanoparticles, through the hemolytic test , In vitro cytotoxicity test and mouse acute toxicity test to study the in vitro and in vivo toxicity of composite nanoparticles, to initially understand the intensity and nature of their toxicity, and to obtain the dose-effect relationship; 4. Apply composite nanoparticles to the development of fresh-keeping health care. The safety performance of the composite nanoparticles is guaranteed, which provides an important guarantee for later application, and has a wide range of applications, providing a new application for the existing fresh-keeping health care field.
Owner:JIANGSU TIANCHENG BIOCHEM PROD
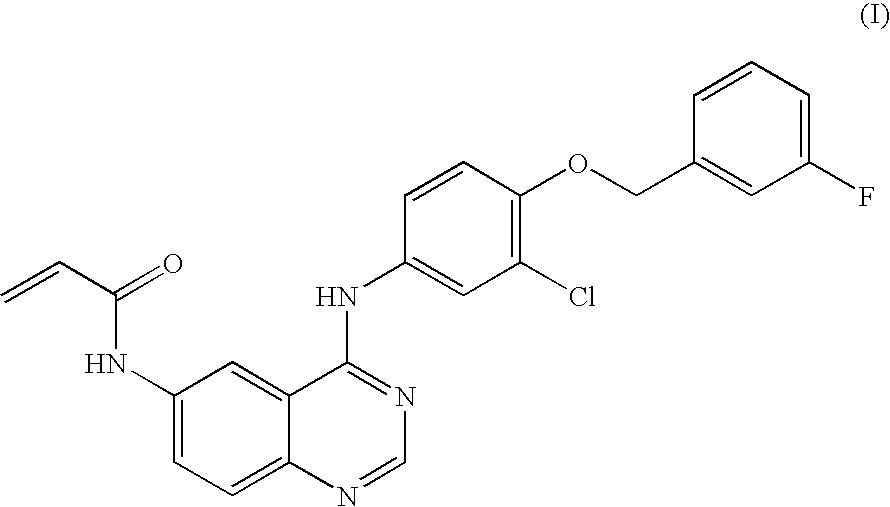
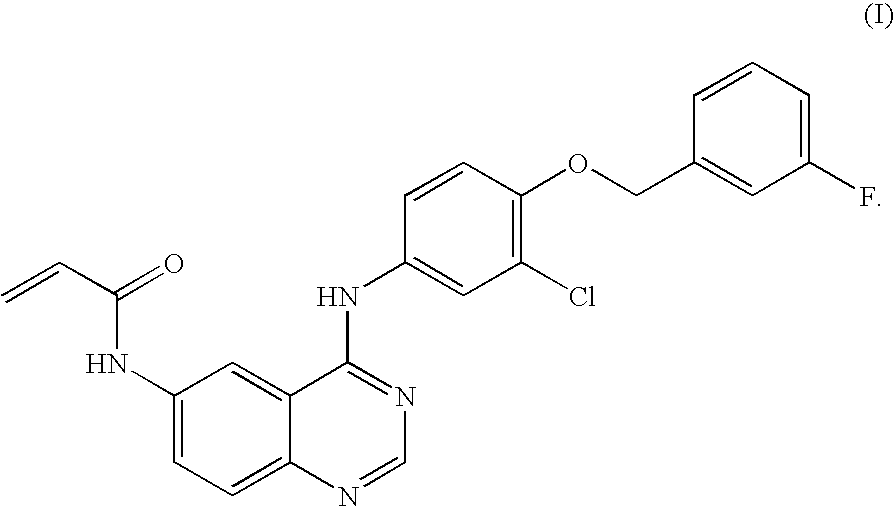
Salts of 4-aniline quinazoline derivative
ActiveUS20100168142A1Excellent tumor inhibitory activityImprove bioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideBioavailabilityAniline
The present invention relates to salt forms of N-{4-[3-chloro-4-(3-fluoro-benzyloxy)phenylamino]-quinazolin-6-yl}-acrylamide, methods for preparation thereof, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same and their use thereof. The salt forms of the present invention, which possess excellent tumor inhibitory activity, good bioavailability and low toxicity in an animal body, are suitable for the use of preparation of anti-tumor medicaments.
Owner:SHANGHAI ALLIST PHARM CO LTD
Acid-responsive mesoporous silica nano-based drug as well as preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN109464671AHigh biosecurityGood biocompatibilityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsNanoparticleMesoporous silica
The invention relates to an acid-responsive mesoporous silica nano-based drug as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The nano-based drug takes mesoporous silica nanoparticles as carriers, acid-responsive functional molecules are coupled on the mesoporous silica nanoparticles, a drug is coupled on the acid-responsive functional molecules, and a drug made from dopamine and used forvascular normalization is used. The acid-responsive mesoporous silica nano-based drug can stably exist during in vivo transportation, pH response can be realized when the drug reaches weakly acidic tumor sites, and the drug made from the dopamine and used for prompting the vascular normalization is released, thereby achieving the effects of reducing in vivo toxicity, improving biological safety and obviously prompting the normalization of in situ tumor vessels. Furthermore, the preparation method of the acid-responsive mesoporous silica nano-based drug is simple and easy to operate, high in stability and high in repetition rate.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Metal beta-lactamase inhibitor pyridine dicarboxylic acid amine derivative and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113461606ALow cytotoxicity in vitroLow toxicity in vivoAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsMeropenemAmidase activity
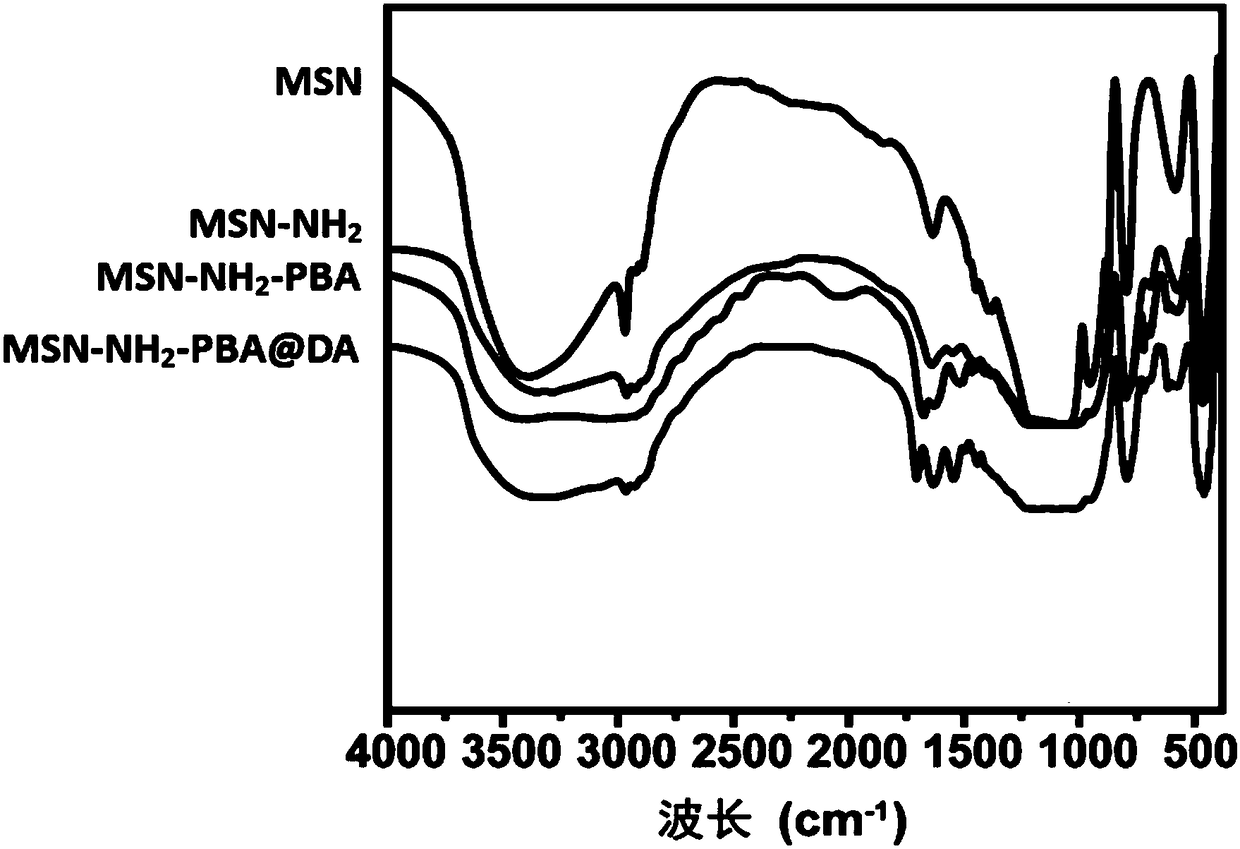
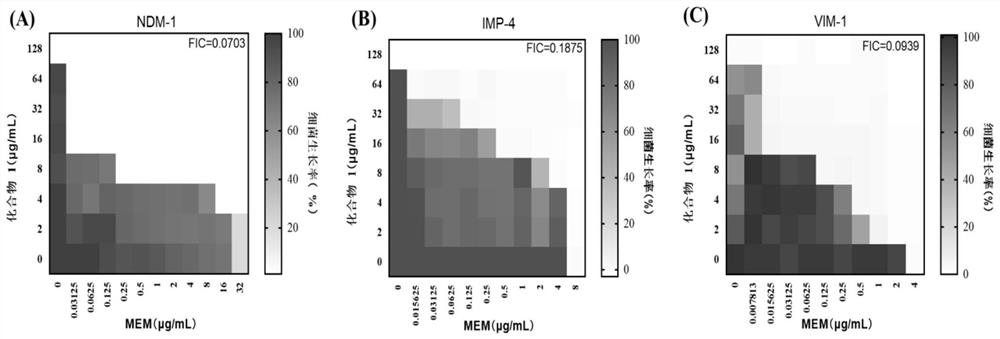
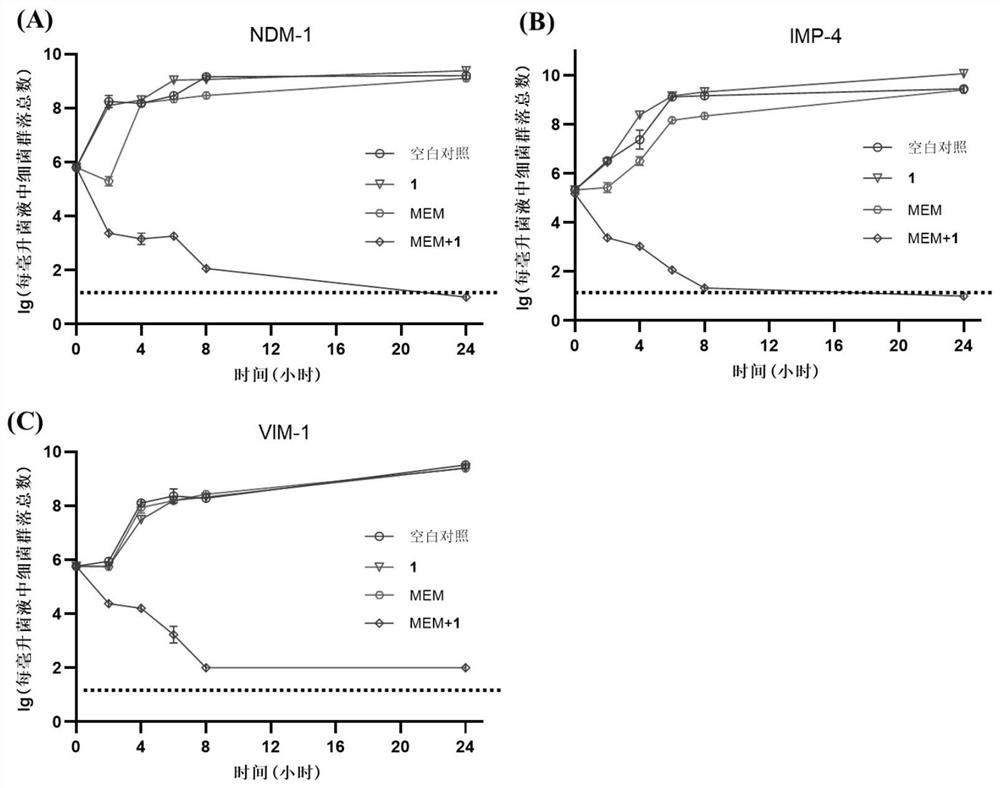
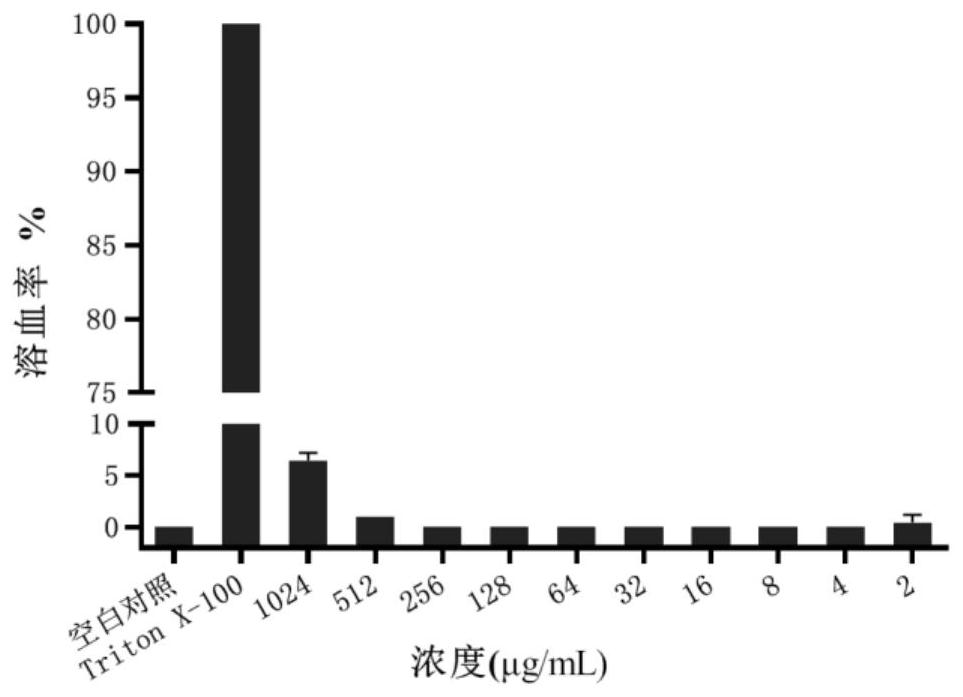
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicinal chemistry, and relates to a metal beta-lactamase inhibitor pyridine dicarboxylic acid amine derivative, a preparation method thereof and an application thereof in the antibacterial field. The derivative has the following structural formula: the compound has better inhibition activity on metal beta-lactamase (NDM-1, IMP-4 and VIM-1), and can recover the antibacterial activity of engineering strains for producing metal beta-lactamase and clinically separated enterobacteriaceae bacteria on carbapenem antibiotics; and the drug effect of meropenem on carbapenem-resistant Escherichia coli (NDM-1-producing metal beta-lactamase) can be improved by at least 1024 times to the maximum extent. The compound 1 and meropenem are combined for use, so that strains capable of producing MBL can be quickly killed. A compound toxicity experiment proves that the compound has very small in-vitro cytotoxicity and in-vivo toxicity, and a mouse in-vivo experiment shows that the survival rate of a mouse infected with metal-producing beta-lactamase klebsiella pneumoniae can be remarkably improved through combined treatment of the compound and meropenem. The product can be used as a candidate drug of a novel metal beta-lactamase inhibitor.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Novel medicine for treating tumors and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112870267AImprove immunityInhibit growthAmphibian material medical ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsTumor therapyEfficacy
The invention relates to the technical field of tumor treatment, and discloses a novel medicine for treating tumors, and the medicine is mainly prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 15 to 30 percent of astragalus membranaceus, 10 to 20 percent of ganoderma lucidum, 10 to 60 percent of oldenlandia diffusa and 15 to 30 percent of sculellaria barbata. According to the novel medicine for treating tumors, astragalus membranaceus and ganoderma lucidum are used as main medicines, so that the effects of strengthening body resistance, tonifying yin, enhancing organism immunity and inhibiting virus breeding and growth are achieved; oldenlandia diffusa, sculellaria barbata, honeysuckle, coptis chinensis, dried toad skin and rabdosia rubescens are used as adjuvants, so the traditional Chinese medicine composition has the effects of eliminating evil and resisting cancer, attacking hard mass and removing stasis, promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis, clearing away heat and toxic materials, tonifying yin and nourishing blood, softening and moistening tendons and vessels, and promoting spleen to remove stasis; salvia miltiorrhiza has the functions of clearing away heat and toxic materials, tonifying spleen and qi and regulating the drug effect, a plurality of drugs are all taken from natural plants and animal bodies, the toxicity and adverse reaction are far lower than those of traditional chemoradiotherapy drugs, and when the two drugs are used together, the drug is expected to become a substitute drug or an important biological drug for cancer treatment.
Owner:荆文斌
MODIFIED CpG OLIGODEOXYNUCLEOTIDE WITH IMPROVED IMMUNOREGULATORY FUNCTION
InactiveUS20090214530A1Enhance immune regulation functionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAnticarcinogenPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The present invention relates to a modified CpG oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN) which is prepared by coupling a consecutive sequence of deoxyribothymine (dT) to the 3′-terminus of CpG ODN having immunoregularory function, thereby improving immunoactivity of splenocytes, macrophages and peripheral mononuclear cells, and therefore, can be effectively used as a vaccine adjuvant for preventing and treating hepatitis B or an anticancer agent. Since the phosphorothioate CpG ODN having the consecutive sequence of dT at its 3′-terminus shows high activity inducing Th-1 immune response and does not elicit in vivo toxicity with guaranteeing its safety, it can be effectively used as a vaccine adjuvant.
Owner:YONSEI UNIVERSITY
Medicament for the treatment of diseases caused by parasitic protozoa
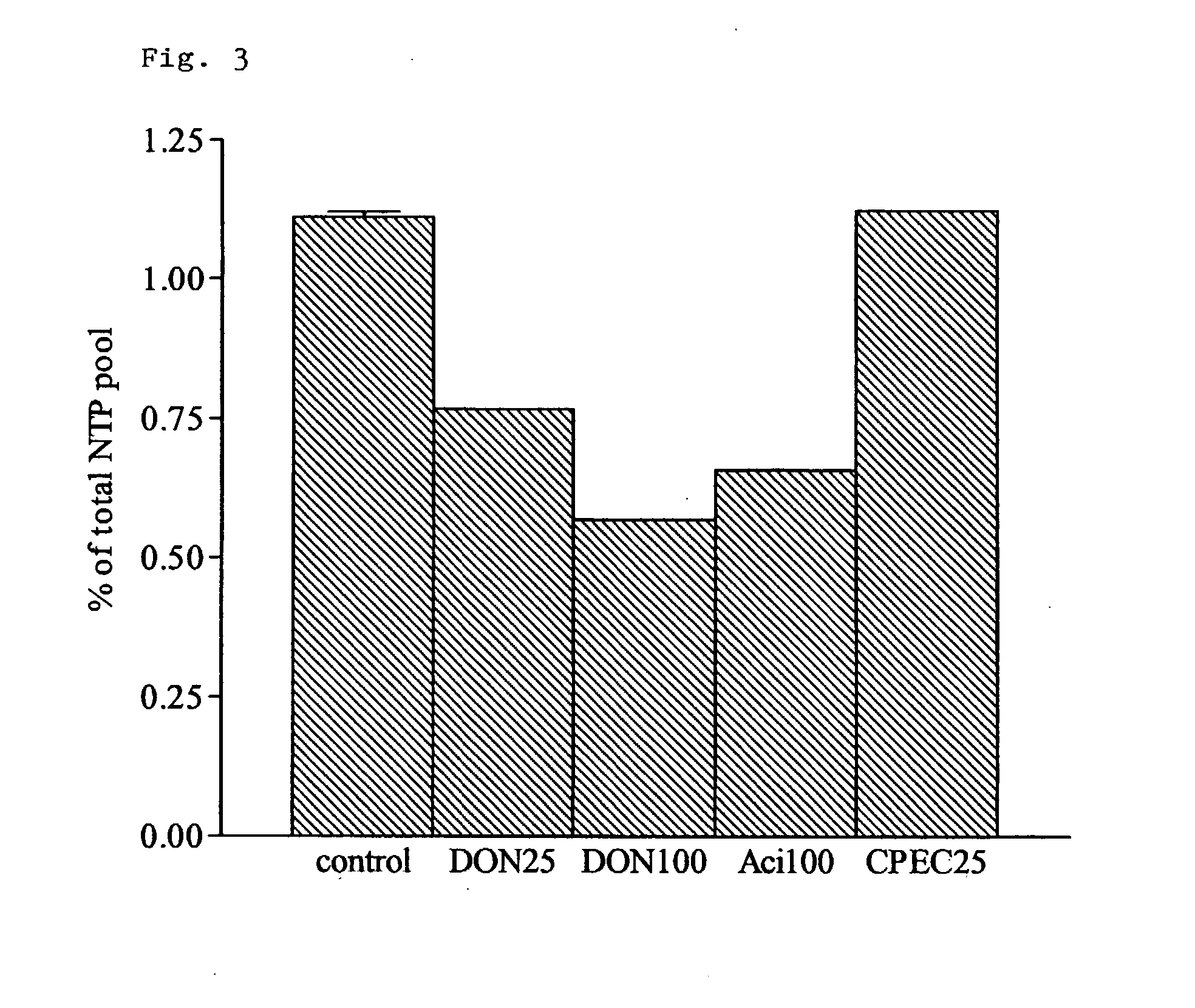
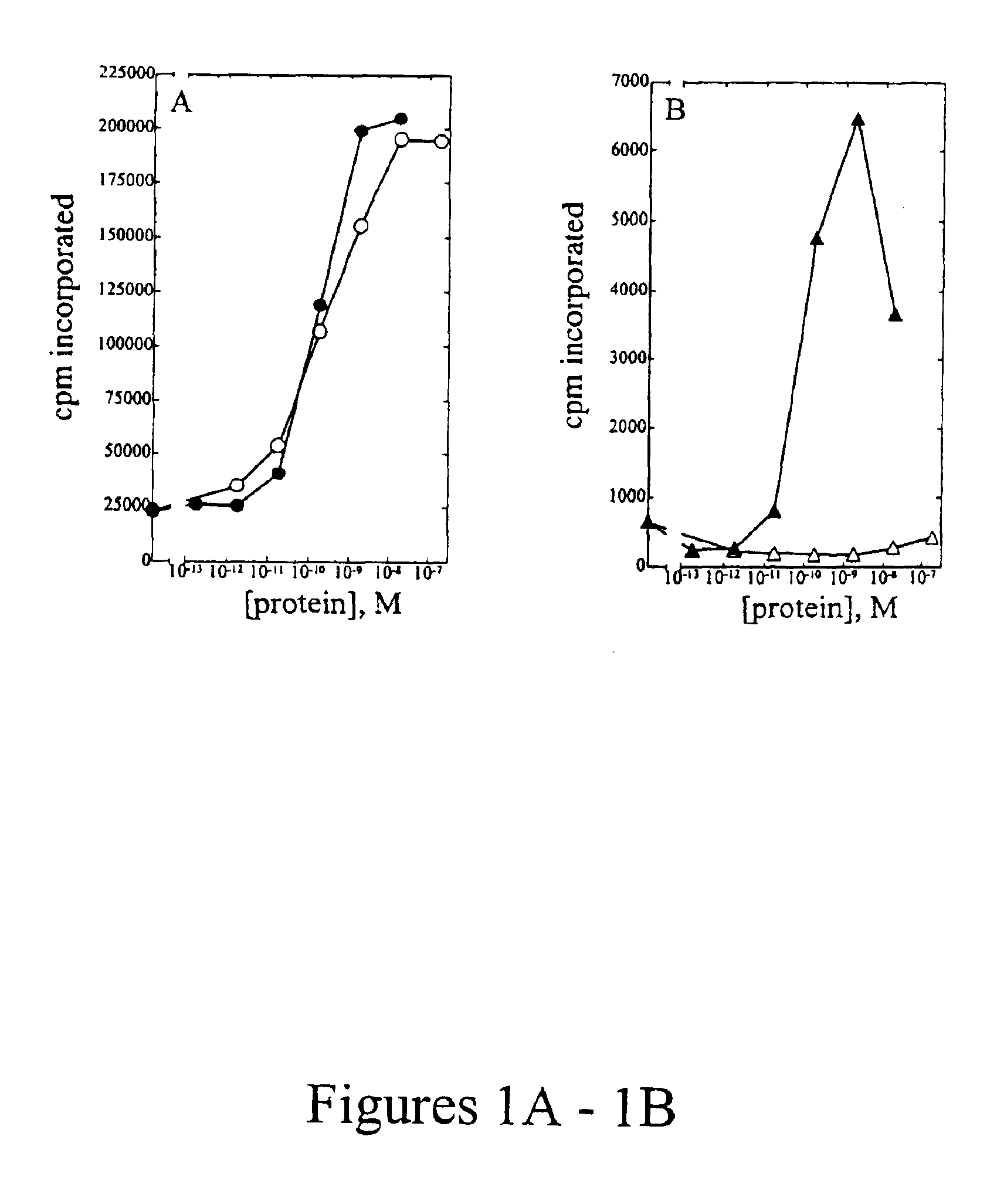
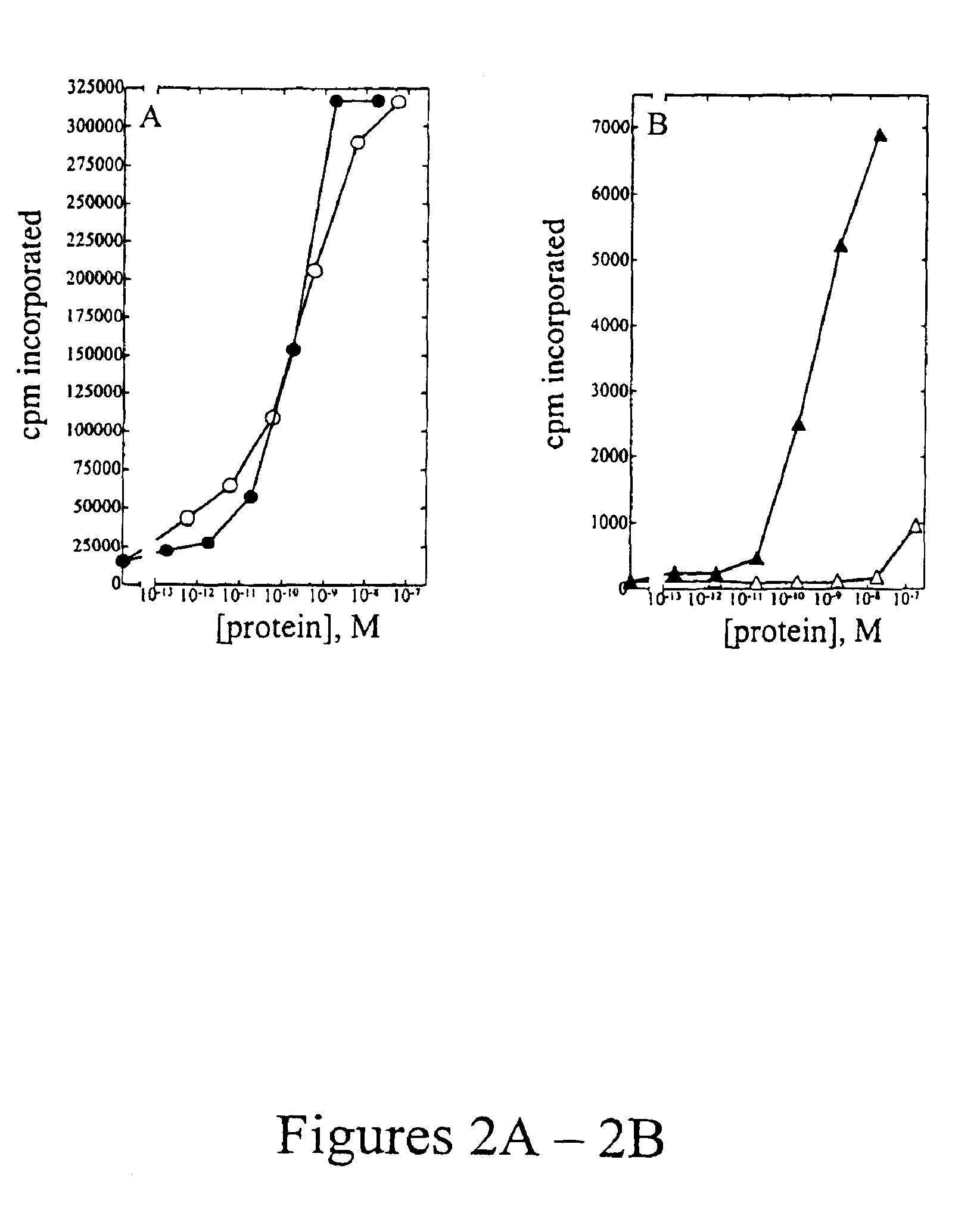
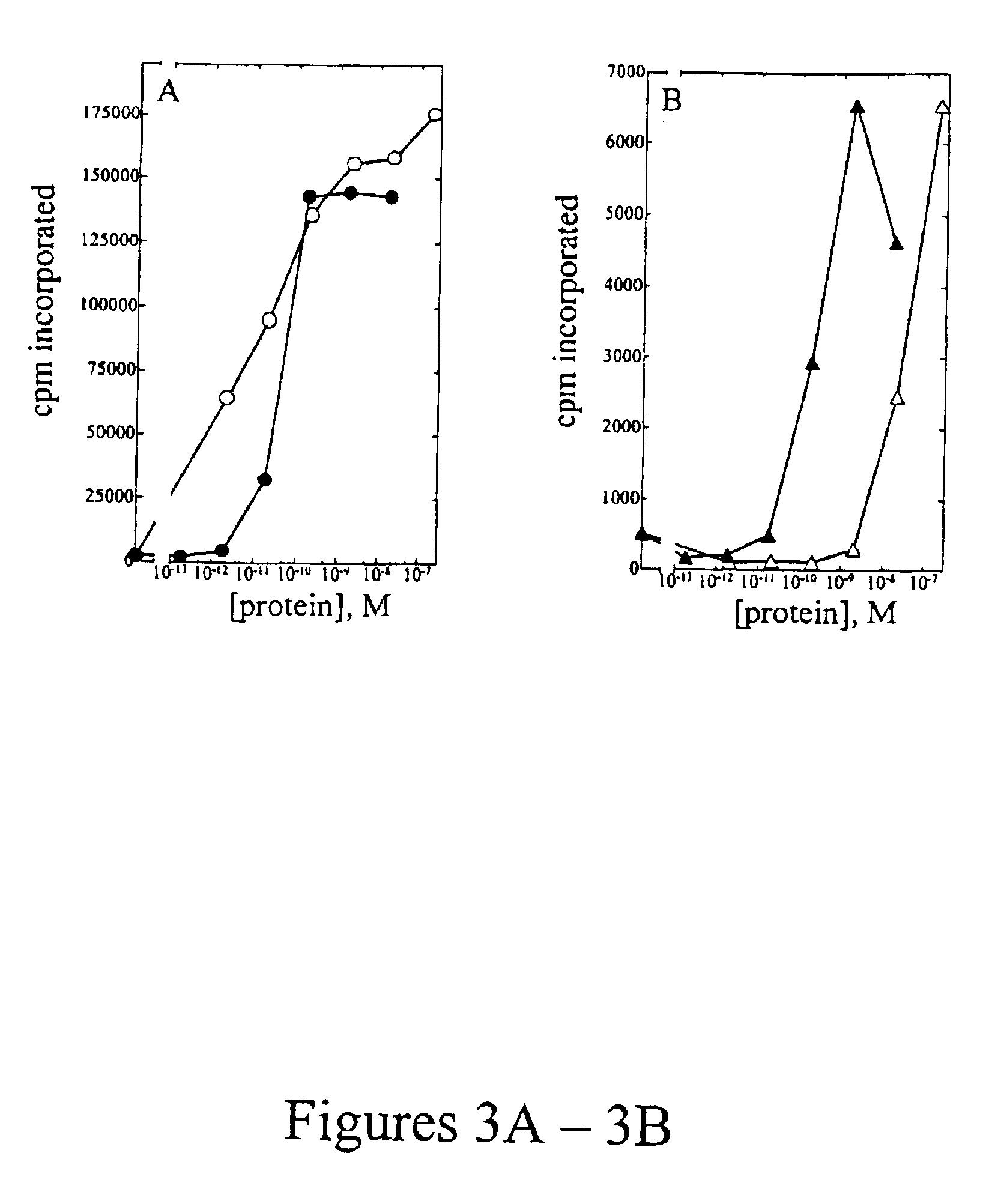
The present invention relates to the use of an inhibitor of CTP synthetase, such as a glutamine analogue, and a substance capable of suppressing toxic effects thereof in vivo, in the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment of a disease caused by a parasitic protozoa. More specifically, said substance capable of suppressing toxic effects may be a nucleobase, such as a purine base or a nucleoside, while the glutamine analogue advantageously is 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine (DON). The invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition as such for the treatment and / or prevention of a disease caused by a parasitic protozoa, wherein the disease is selected from the group consisting of malaria, leishmaniasis and trypanosomiasis, e.g. American trypanosomiasis (Chaga's disease), or African trypanosomiasis (African sleeping sickness).
Owner:HOFER +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com


![Aziridinyl quinone antitumor agents based on indoles and cyclopent[b]indoles Aziridinyl quinone antitumor agents based on indoles and cyclopent[b]indoles](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/d3d26f69-9bf8-4af9-97bf-bf399977eec9/US20030139609A1-20030724-C00001.png)
![Aziridinyl quinone antitumor agents based on indoles and cyclopent[b]indoles Aziridinyl quinone antitumor agents based on indoles and cyclopent[b]indoles](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/d3d26f69-9bf8-4af9-97bf-bf399977eec9/US20030139609A1-20030724-C00002.png)
![Aziridinyl quinone antitumor agents based on indoles and cyclopent[b]indoles Aziridinyl quinone antitumor agents based on indoles and cyclopent[b]indoles](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/d3d26f69-9bf8-4af9-97bf-bf399977eec9/US20030139609A1-20030724-C00003.png)