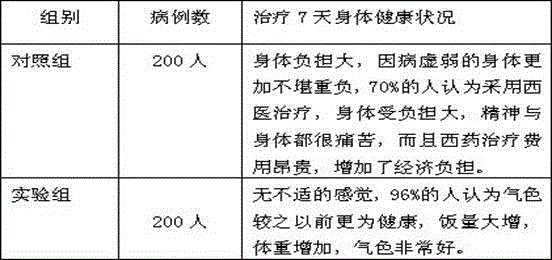
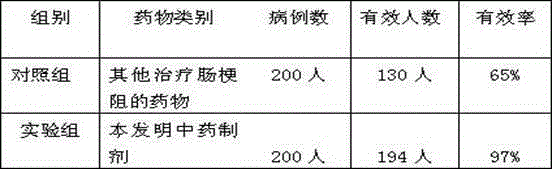
Patents
Literature
88 results about "Intestine obstruction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Any impairment, arrest, or reversal of the normal flow of intestinal contents toward the anus.
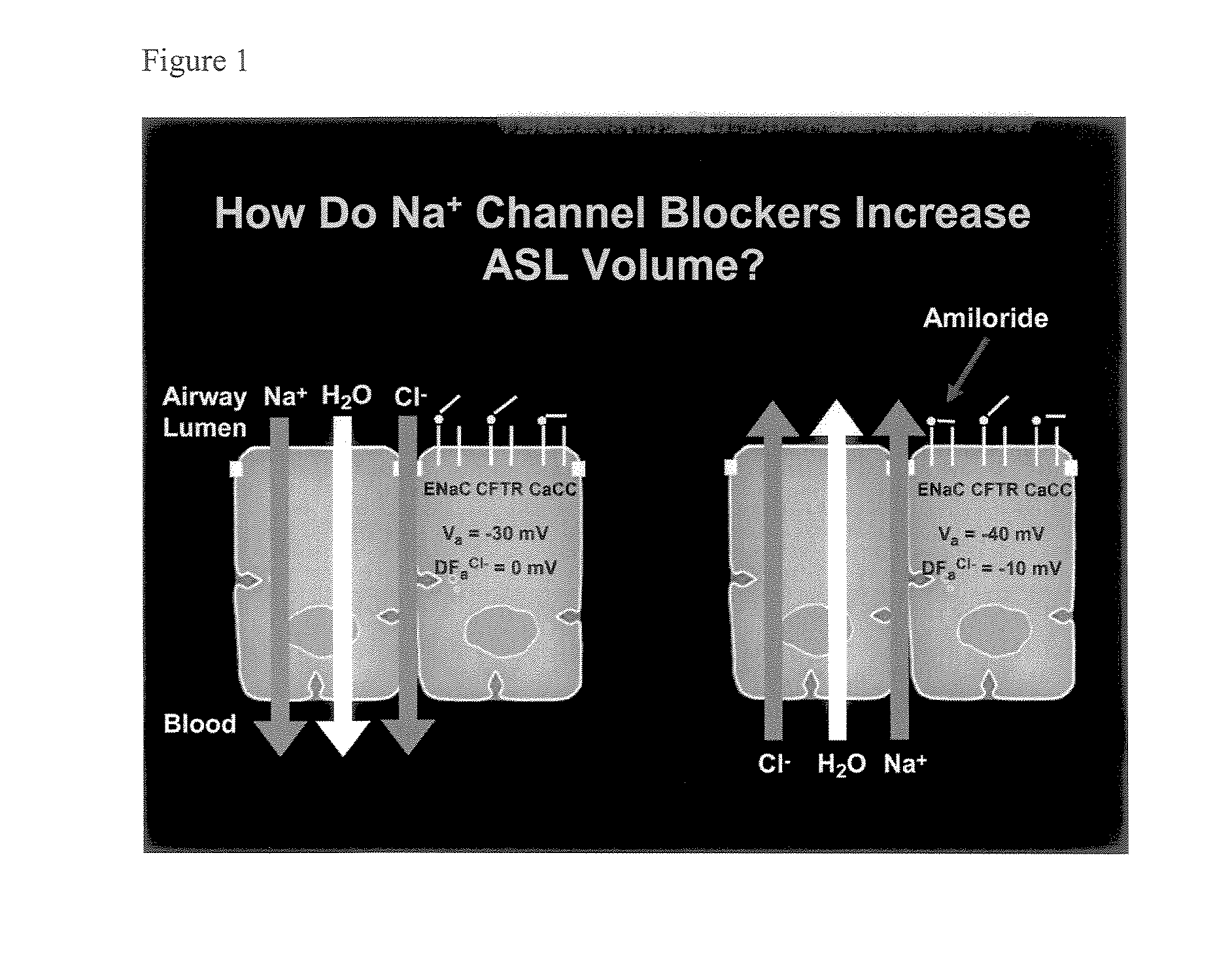
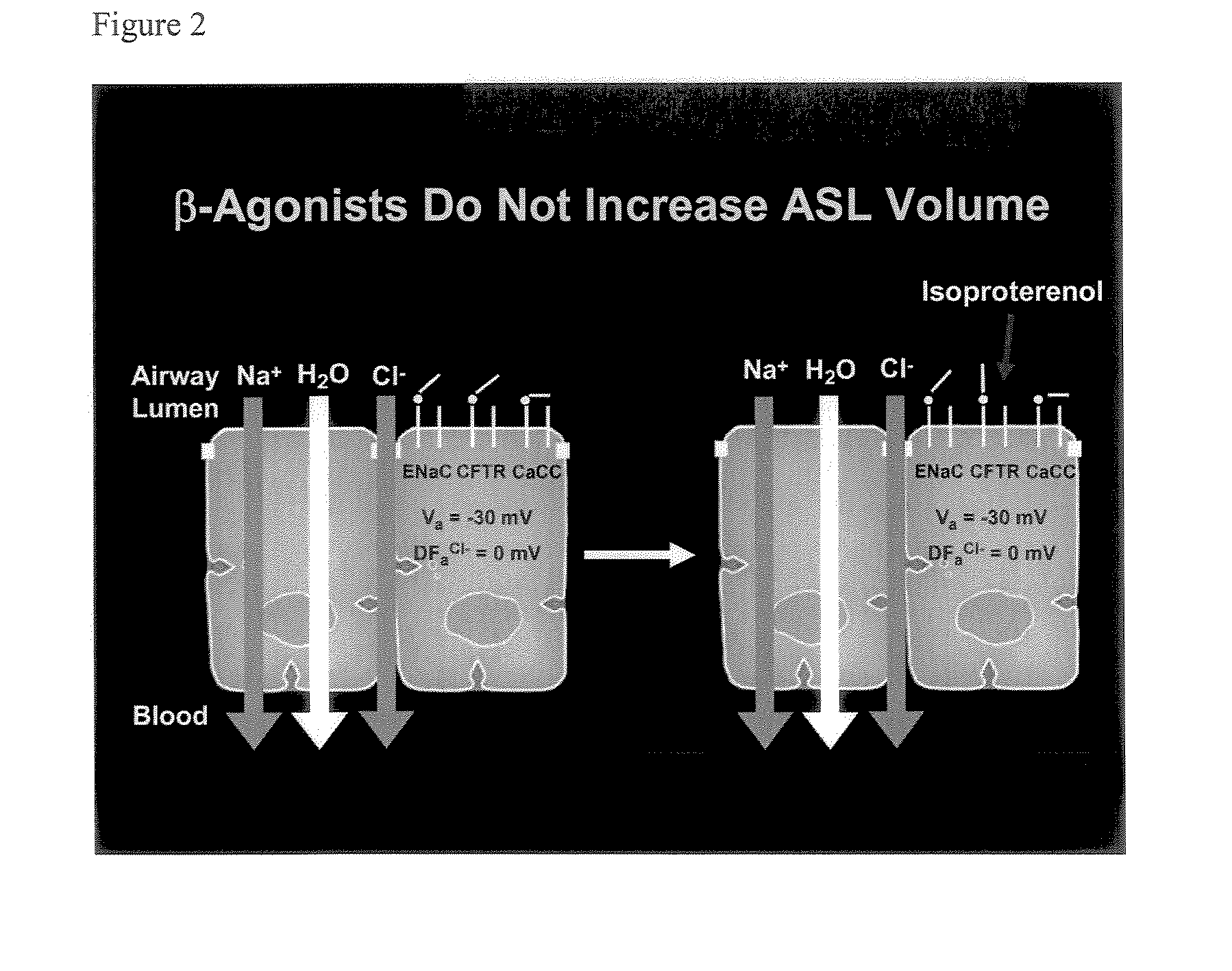
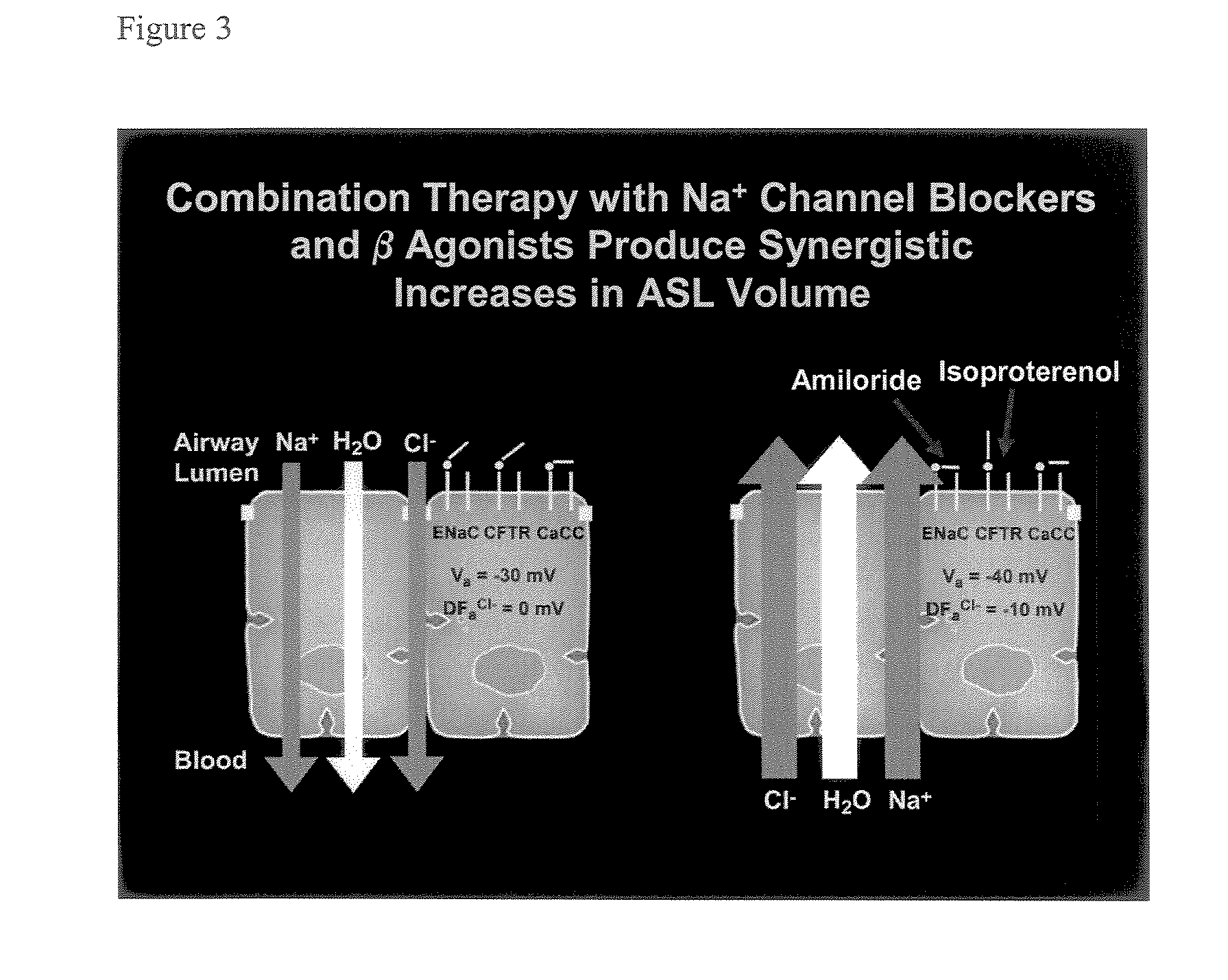
Aliphatic pyrazinoylguanidine sodium channel blockers with beta agonist activity
ActiveUS8324218B2More potent and/or absorbed less rapidlyLess reversibleOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseSinusitis
The present application provides sodium channel blockers exemplified by the following structure:The compounds of the invention useful for treating chronic bronchitis, cystic fibrosis, sinusitis, vaginal dryness, dry eye, Sjogren's disease, distal intestinal obstruction syndrome, dry skin, esophagitis, dry mouth (xerostomia), nasal dehydration, ventilator-induced pneumonia, asthma, primary ciliary dyskinesia, otitis media, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, emphysema, pneumonia, constipation, and chronic diverticulitis, for example.
Owner:PARION SCI DURHAM NC
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating colon cancer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101757566AImprove self-coordinationEffective treatmentHeavy metal active ingredientsAnthropod material medical ingredientsTARAXACUM OFFICINALE ROOTMedicinal herbs
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating colon cancer and a preparation method thereof. The traditional Chinese medicine composition mainly comprises the following raw medicinal herbs: indigo naturalis, tuckahoe, coix seed, taraxacum officinale root, herba violae, Mangnolia officinalis, houttuynia cordata, patrinia, angelica sinensis, radix paeoniae alba, Chinese lobelia herb, radix sophorae falvescentis, dried orange peel, medicated leaven, rhizoma cyperi, aspongopus, prepared frankincense, prepared myrrh, corydalis tuber, manis pentadactyla, raw astragalus mongholicus, radix notoginseng, charred sanguisorba officinalis, rhizoma sparganii, curcuma zedoary and the like. The Traditional Chinese medicine composition can be prepared into any one common oral preparation according to a conventional traditional Chinese medicine composition method. The invention can remarkably improve symptoms of frequency increase of defecate, blood and mucus brought in the defecate, bellyache, diarrhea or astriction, intestinal obstruction and malaise, weight reduction, anemia and the like, and has accurate clinical treatment effect, remarkable treatment effect and rapid effect taking. Because of being combined by basically adopting medicinal and edible medicines specified in National Formulary, the traditional Chinese medicine composition has the advantages of low cost, basic no toxic and side effect, and the like.
Owner:TAIYI HEPU BEIJING RES INST OF TCM
Enema mixture for treating ileus and method for preparing same
InactiveCN1883594AReduce capacityRelieve pressureDigestive systemSulfur/selenium/tellurium inorganic active ingredientsTreatment effectMedicine
The invention provides an enteroclyster mixture for treating intestinal obstruction, which is prepared from magnolia bark, radish seeds, rhubarb horsetails, peach kernels, mirabilite, radix paeoniae rubrathe, immature bitter orange, banksia rose and herba patriniae through the steps of charging the medicinal materials into water, boiling three times, merging filtrate, filtering, stewing and taking the supernatant fluid, concentrating, homogenizing, finally split charging and sterilizing.
Owner:李平 +1
Traditional Chinese medicinal composition for treating adhesive intestinal obstruction
InactiveCN104491381AImprove conservative cure rateLong-lasting effectDigestive systemSulfur/selenium/tellurium inorganic active ingredientsSenna LeavesGleditsia triacanthos
The invention relates to a traditional Chinese medicinal composition for treating adhesive intestinal obstruction. The traditional Chinese medicinal composition is mainly prepared from the following medicinal raw materials, by weight, magnolia cortex, bitter orange, radish seed, banksia rose, the root of three-nerved spicebush, green tangerine peel, Chinese angelica, radix paeoniae rubrathe, peach kernel, raw rhubarb, saltcake, unprocessed Radix Kansui, senna leaf, safflower, tree peony bark, corydalis tuber, Radix Codonopsis, Radix Ophiopogonis, Chinese honey locust, inula flower, red sage root, Ligusticum wallichii, licorice, leech, rhizoma alismatis, Poria cocos, rhizoma corydalis, hemp seed, ginger processed pinellia and caulis bambusae in taeniam (added for patients with emesis and nausea), and honeysuckle flower and Radix Astragali (added for patients with fever). The traditional Chinese medicinal composition has advantages of little toxic and side effect, long duration of drug effect, minimal injury, low cost and the like.
Owner:周广生
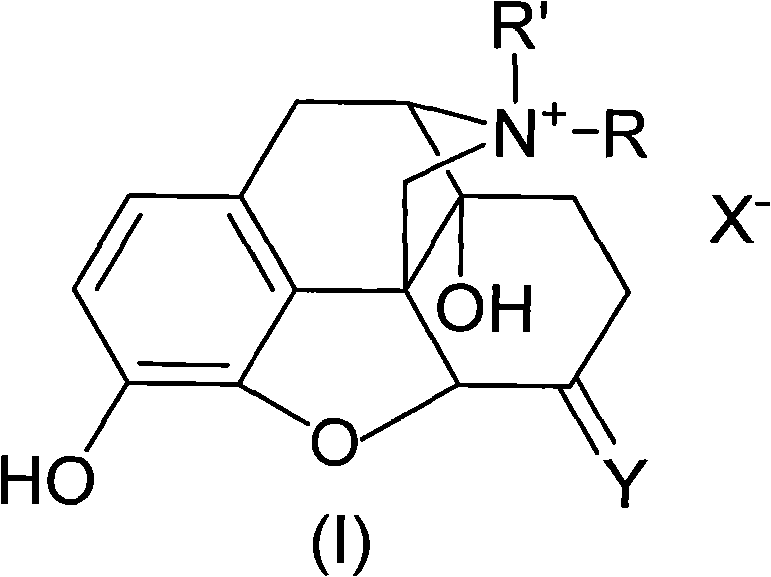
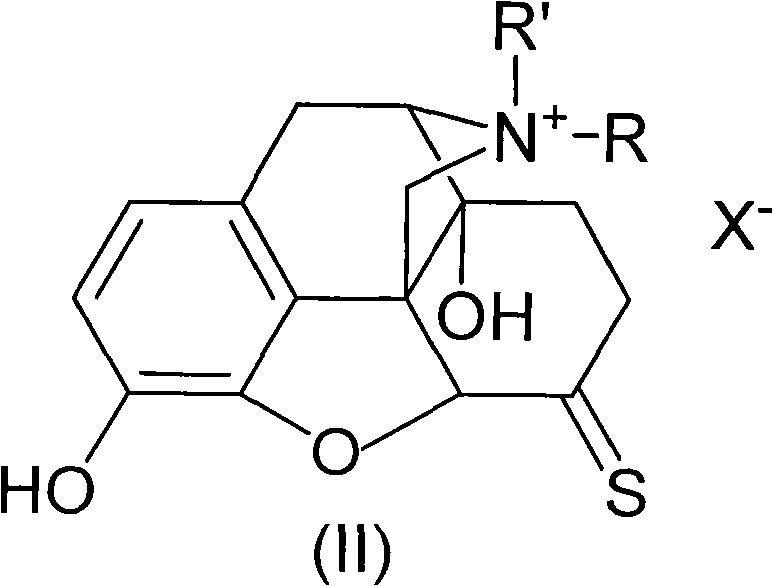
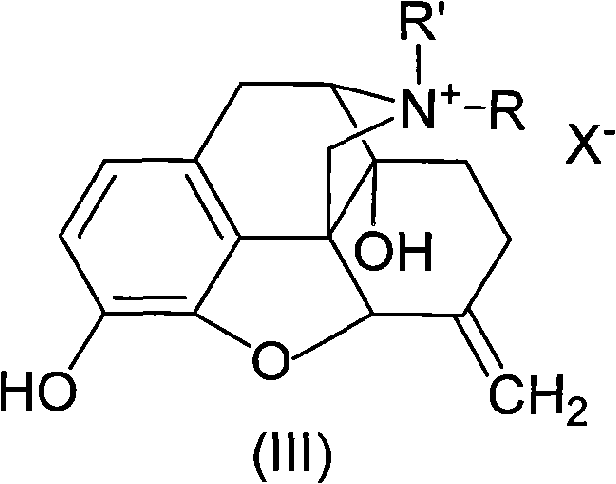
Morphinone quaternary ammonium salt derivatives and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101570539AEasy to operateFew reaction stepsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderIntestinal ObstructionsIntestinal peristalsis
The invention provides morphinone quaternary ammonium salt derivatives which are prepared through the following steps: obtaining morphinone derivatives from morphine as the starting material through demethylation, oxidation, reduction, condensation and other chemical reactions; and obtaining the morphinone quaternary ammonium salt derivatives from the morphinone derivative through the reaction with halocarbon. The preparation method of the invention has the characteristics of few technological steps, low production cost, simple operation, stable quality and the like. The compounds provided by the invention have obvious contraction effect on the morphine-dependent guinea pig ilea, thereby promoting the intestinal peristalsis, the compounds are applicable to the preparation of drugs for curing constipation and intestinal obstruction; and the compounds provided by the invention further have obvious inhibiting effect on the conditioned place preference (CPP) of morphine-induced rats to the drug-paired compartment, therefore, the compounds can be used for preparing anti-relapsing drugs and effectively reducing the relapse rate, and the invention is favorable for the all-round promotion of rehabilitation and anti-relapsing work.
Owner:HANGZHOU ADAMERCK PHARMLABS INC
Traditional Chinese medicine suppository and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101099784AAvoid destructionEasy to useDigestive systemSuppositories deliveryIntestinal ObstructionsCITRUS MEDICA FRUIT
The invention is concerned with the Chinese traditional medicine suppository and the preparation method for treating and defending intestine paralysis, intestine conglutination and intestinal obstruction, composes of bark of official magnolia, rhubarb and fruit of immature citron that compounds with weight, which is by distill, filtration, concentration, dryness, crush to get dry cream powder, melts and mixes with the suppository base, irrigate module, cooling, gets the suppository. The invention is fast effect and dramatic curative effect.
Owner:JINAN KANGZHONG PHARMA TECH DEV
Medicinal composition for treating intestinal obstruction and method for preparing the same
The present invention discloses a pharmaceutical composition for treating intestinal obstruction and the preparation method, which is composed of the active ingredients of 7 raw materials of rhubarb, officinal magnolia bark, immature bitter orange, matrii sulfas exsiccatus, red paeony root, peach seed and radish seed, the mix ratio by weight of all the raw materials are: 3.81 to 38.0 parts of rhubarb, 3.81 to 38.0 parts of officinal magnolia bark, 3.04 to 30.4 parts of immature bitter orange, 1.0 to 10.0 parts of matrii sulfas exsiccatus, 3.81 to 38.0 parts of red paeony root, 3.04 to 30.4 parts of peach seed and 7.61 to 76.1 parts of radish seed respectively. Compared with the prior art, the present invention is characterized by significant efficacy, easy administration, no side effects and moderate price; the present invention has the functions of dredging intestines, promoting qi and removing blood stasis, which is used for intestinal obstruction, and the prevention and treatment of abdominal postoperative tympanites and intestinal adhesion.
Owner:广西壮族自治区药物研究所有限公司
Traditional Chinese medicine preparation for treating adhesive intestinal obstruction and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine preparation for treating adhesive intestinal obstruction. The traditional Chinese medicine preparation comprises the following various raw material medicines: 10-20 parts of semen raphani, 10-20 parts of very light blue, 10-20 parts of fingered citron, 10-20 parts of acute turpinia leaf, 10-20 parts of delavay schefflera root, 10-20 parts of soya-bean oil, 10-20 parts of liriope spicata, 10-20 parts of Chinese hawthorn leaf, 1-10 parts of alangium platanifolium flower, 1-10 parts of kalimeris indica, 1-10 parts of clove bark, 1-10 parts of myristica fragrans, 1-10 parts of majoram, 1-10 parts of hericium erinaceus, 1-10 parts of honeysuckle, 1-10 parts of mint, 1-10 parts of quispualis indica, and 1-10 parts of rhizoma kaempferiae. The traditional Chinese medicine preparation disclosed by the invention has the effects of smoothing qi and lubricating intestines, dispelling wind and removing dampness, promoting qi circulation and dissipating blood stasis, smoothing circulation, and dredging food retention in intestines. The traditional Chinese medicine preparation disclosed by the invention is simple and convenient in production process, low in toxic and side effects, convenient to administrate, easy to manufacture, and low in cost.
Owner:杜卫兵
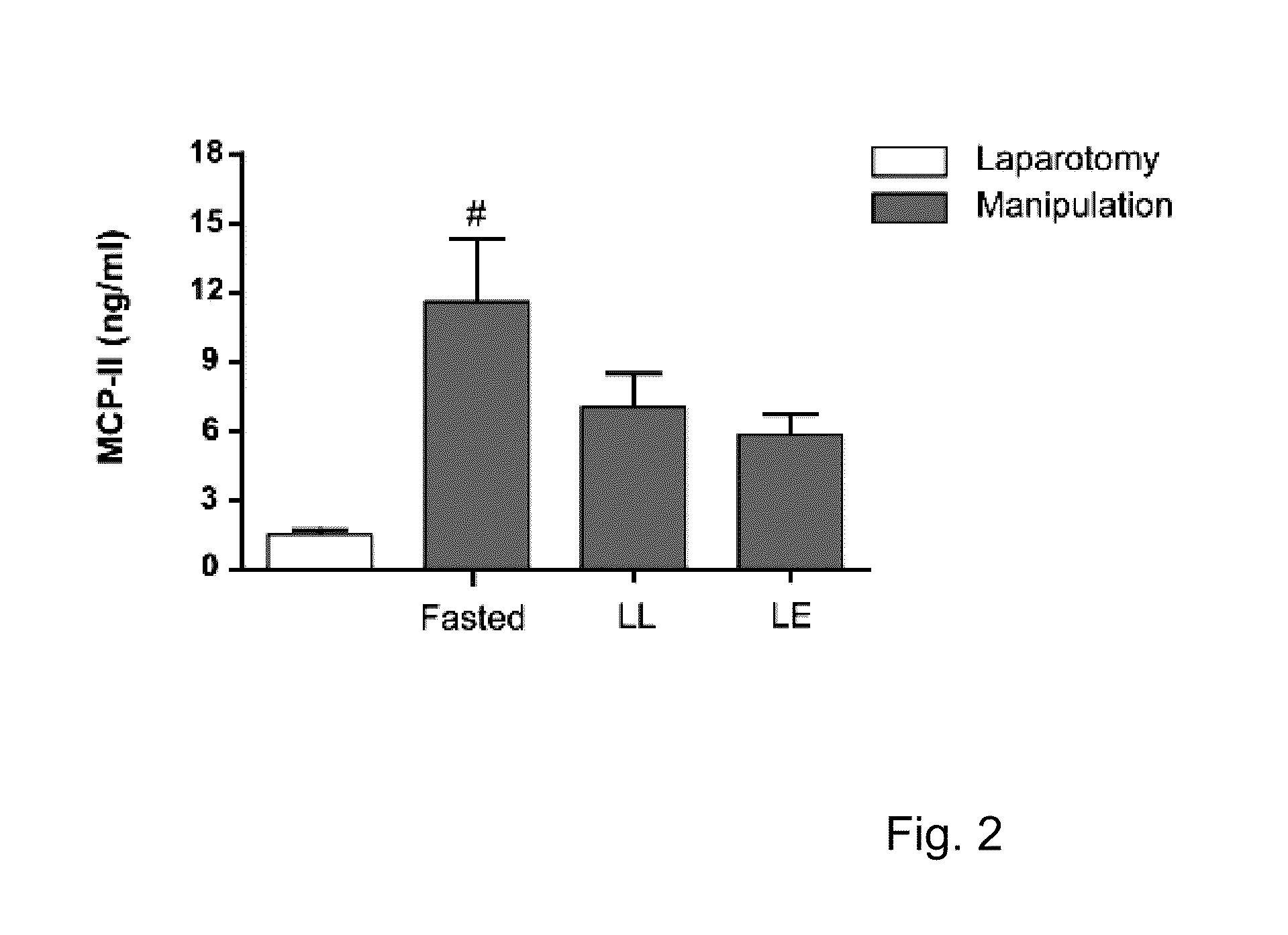
Use of Lipid-Rich Nutrition for the Treatment of Post-Operative Ileus
InactiveUS20110034376A1Avoid large quantitiesGood componentPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderPeritoneal LavagesNutrition
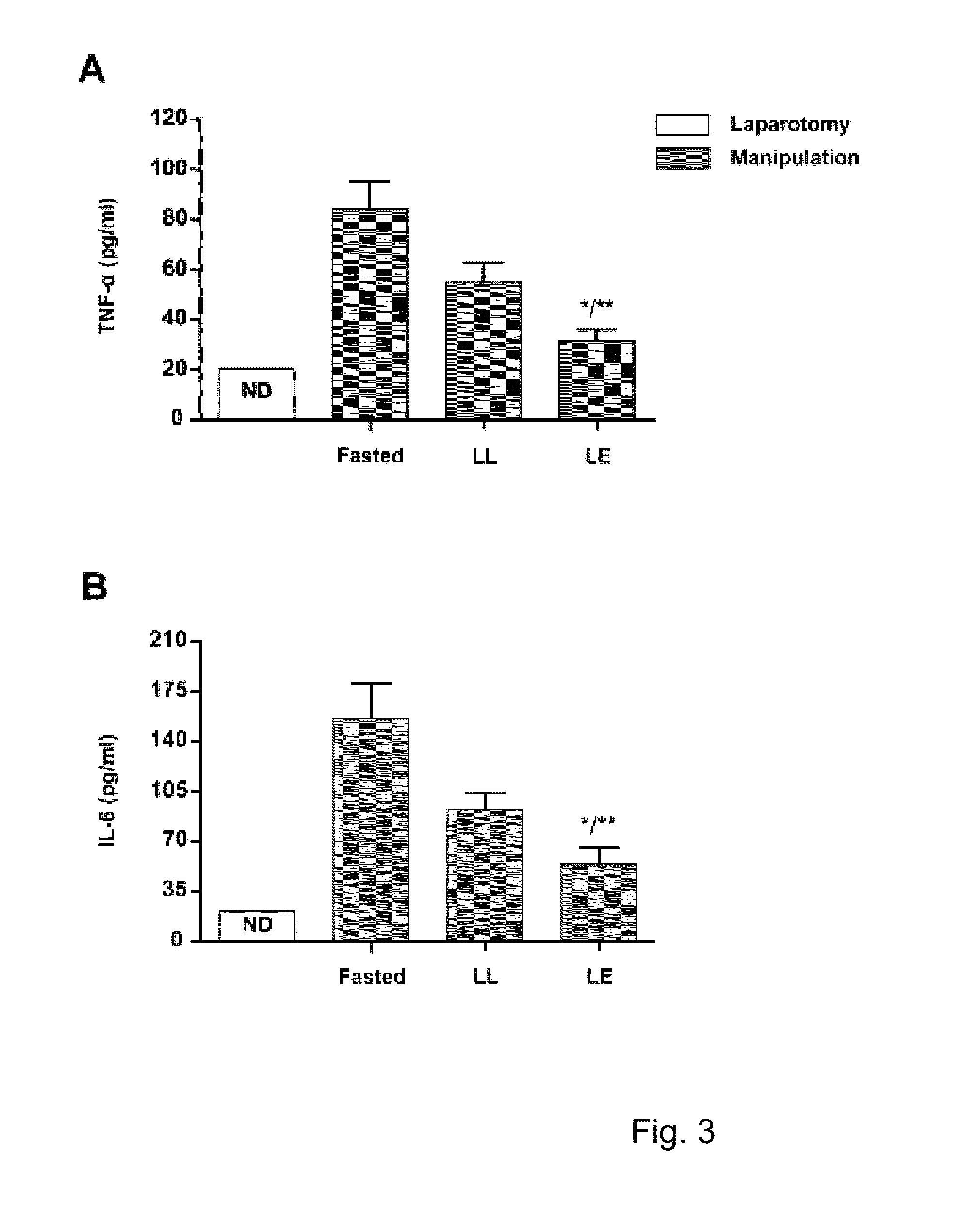
The invention pertains to the use of a lipid-rich nutrition for the manufacture of a composition for the prevention and / or treatment of post-operative ileus. The lipid fraction inhibited IL-6 and TNF-α levels in peritoneal lavage fluid, and / or wherein the lipid fraction prevents influx of neutrophils in the intestinal muscularis following intestinal manipulation. The nutritional composition comprises at least a lipid fraction which accounts for 42 to 90%, preferably between 45 and 70% of the total energy of the composition. The lipid fraction preferably contains 8 to 50 wt % of phospholipids.
Owner:NUTRICIA
Lotus leaf extract, monomer component and application thereof
InactiveCN101712649BImprove learning and memory abilityOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderBiotechnologyDisease
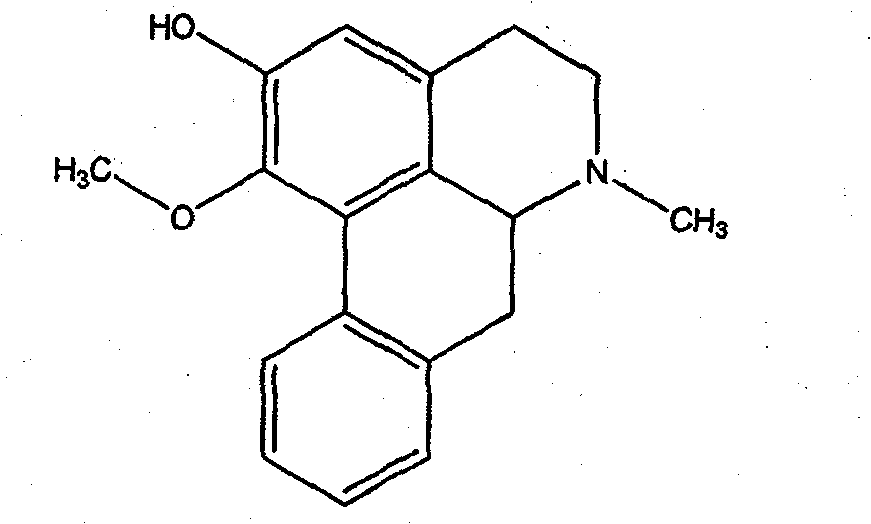
The invention relates to a lotus leaf extract, a monomer component and application thereof. An active monomer component of the extract is aporphine alkaloid and comprises 2-hydroxy-1-methoxy-aporphine, nuciferine and N-nornuciferine. The lotus leaf extract and the monomer component have good inhibition to acetylcholinesterase, and can be developed into medicaments for treating the diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, glaucoma, asthenic bulbar paralysis, intestinal obstruction and the like.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Ileus dredging device
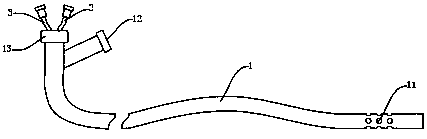
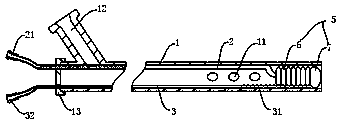
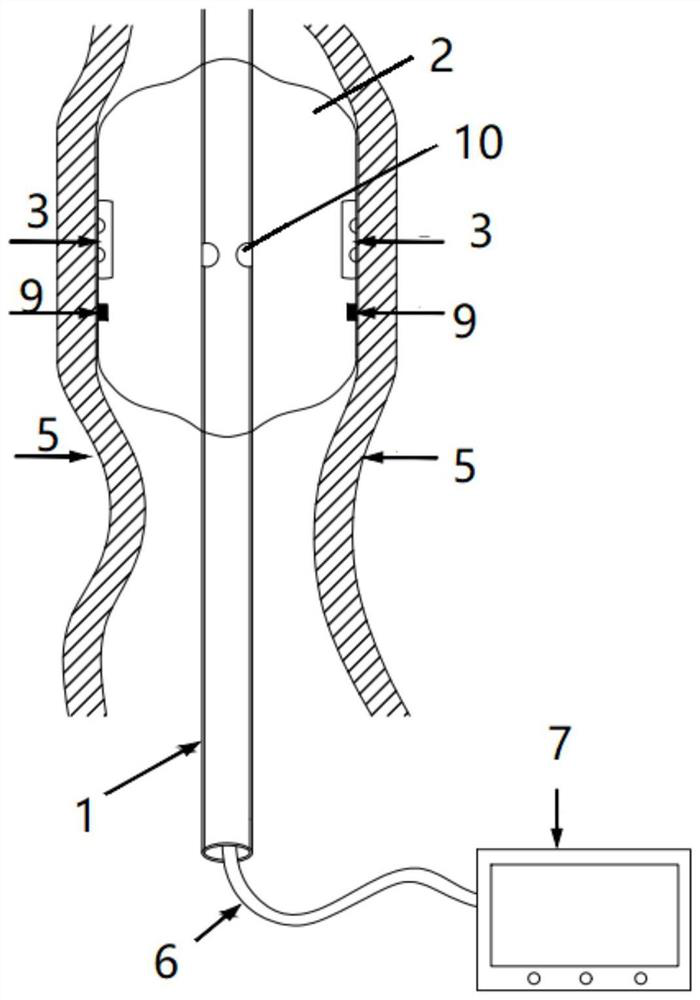
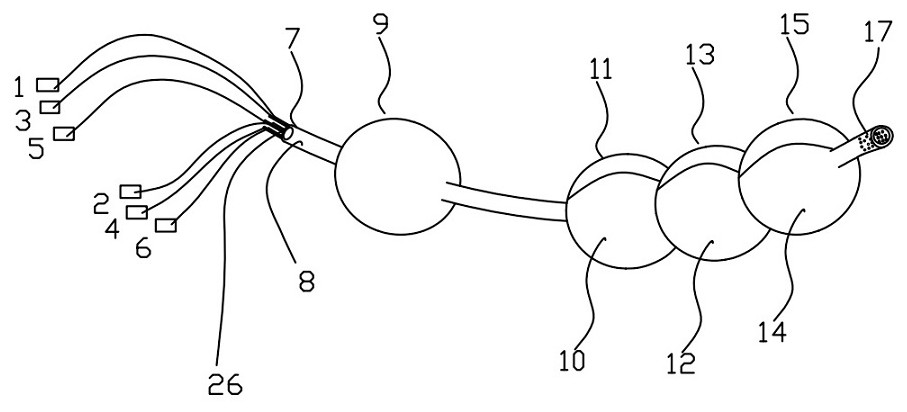
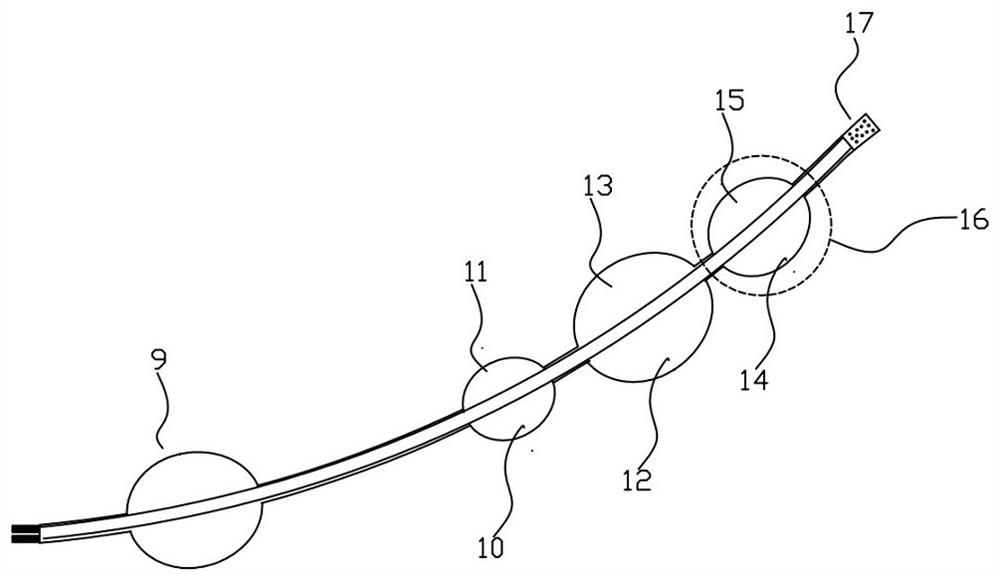
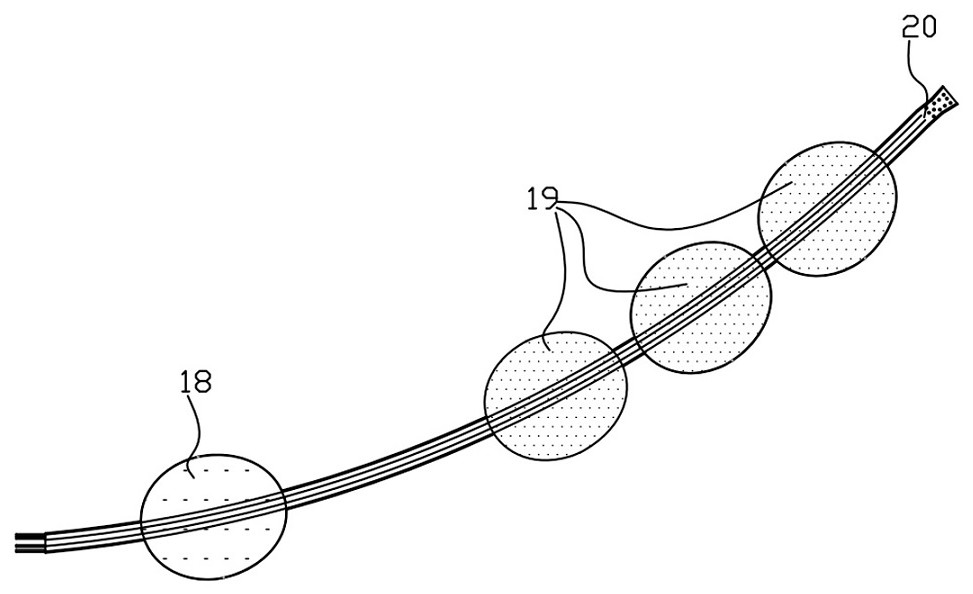
InactiveCN111298218AClearly show where you areThere is no problem of difficult extractionBalloon catheterIntravenous devicesIntestinal wallsCatheter
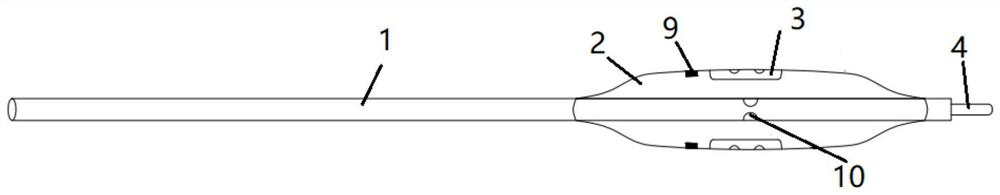
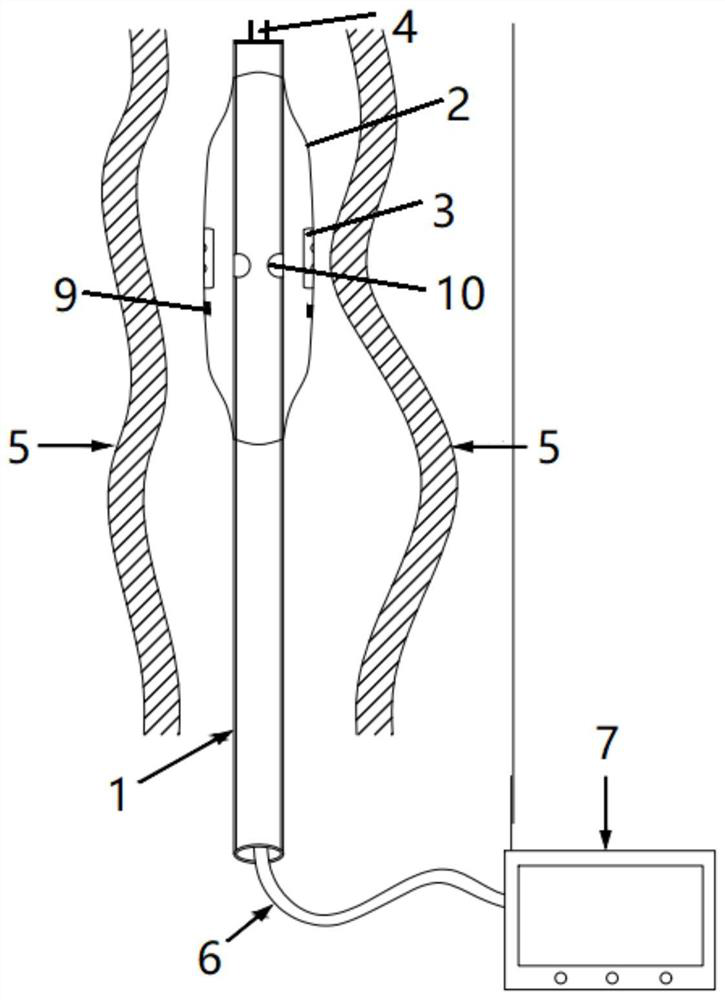
The invention discloses an ileus dredging device which comprises a conduit, wherein a side hole is formed in the front end pipe wall of the conduit, an outer guide hole is formed in the rear end of the conduit, a pneumatic guide head is disposed on the front end of the conduit body, the pneumatic guide head comprises a pneumatic telescopic body and an elastic balloon which are connected integrally, and the elastic balloon is located on the front end of the pneumatic telescopic body; and the pneumatic telescopic body and the elastic balloon are connected to a telescopic body pipe and a balloonpipe respectively, the telescopic body pipe and the balloon pipe penetrate out from the tail part of the conduit, a telescopic body pipe joint and a balloon pipe joint used for air inflation and air deflation are disposed at the tail end of the telescopic body pipe and the tail end of the balloon pipe respectively, and the balloon pipe is an X-ray development pipe. The ileus dredging device is applied to depressurization, discharge of pneumatosis and hydrops and liquid medicine injection for an ileus patient. During use, when the conduct cannot be advanced normally due to obstruction obstacles, the pneumatic guide head can be operated to drag the conduit to advance and pass through the obstacles step by step to reach a drainage part. The flexible telescopic body pipe and the soft balloon pipe can look for clearance automatically when being inflated to extend, the passing capability is strong, the intestinal wall is not damaged, and operations are convenient, safe and reliable.
Owner:伦俊杰
Drug for treating paralytic ileus and promoting stomach and intestine function recovery after abdominal operation and preparation method thereof
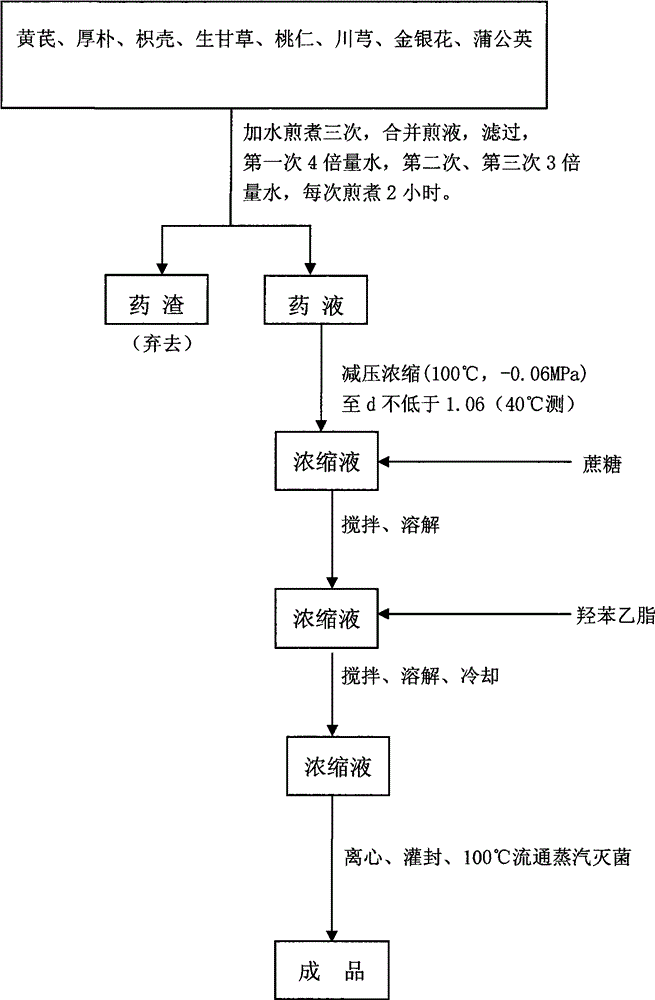
ActiveCN103977109AAdjust stress statePromote recoveryDigestive systemPlant ingredientsFormularyRadix Astragali seu Hedysari
The invention relates to a drug for treating paralytic ileus and promoting stomach and intestine function recovery after an abdominal operation and a preparation method thereof. The drug is prepared from 20 parts by weight of radix astragali, 10 parts by weight of magnolia cortex, 10 parts by weight of bitter orange, 20 parts by weight of raw licorice root, 15 parts by weight of peach seed, 20 parts by weight of ligusticum wallichii, 25 parts by weight of honeysuckle flower and 25 parts by weight of dandelion. The drug is a claybank decoction and has a light traditional Chinese medicine fragrance. The preparation method comprises the following steps of a, weighing the above raw materials according to a formula, b, decocting the above eight medicines by water three times, for 2h each time, wherein in the first decoction process, the amount of used water is four times that of the medicines, and in the second and third decoction processes, the amount of used water is three times that of the medicines, merging the decoctions and carrying out filtration, and c, removing decoction residues, carrying out reduced-pressure condensation on the decoction, carrying out stirring, carrying out dissolution, cooling the solution, carrying out centrifugation, carrying out encapsulation, carrying out steam disinfection, carrying out packaging and carrying out warehousing. The drug can adjust a human stress state after an operation, can improve and keep stability of the inner environment, can promote stomach and intestine function recovery after an abdominal operation, is conducive to human body recovery after the operation and is safe and convenient in use.
Owner:邵阳市中医医院
Traditional Chinese medicine composition used after abdominal surgical operation
InactiveCN103920094AThe party is rigorousCompatibility scienceDigestive systemDermatological disorderPatriniaSurgical operation
The invention relates to a traditional Chinese medicine composition used after abdominal surgical operation. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is prepared from cassia seeds, lalang grass rhizome, dried orange peel, rhizoma zedoariae, angelica dahurica, perilla leaf, parched rhizoma atractylodis macrocephalae, parched fructus aurantii, lotus leaves, burdock, jasmine, bamboo leaves, radix scutellariae, rheum officinale, beautiful sweetgum fruit, elecampane, dendrobe, patrinia, folium mori, dandelion, glechoma hedracea, rhizoma cyperi, ligusticum wallichii, rhizoma corydalis and liquorice. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is precise in formula and scientific in compatibility of medicines and can be used for treating tissue adhesion and intestinal obstruction caused by abdominal surgical operation and promoting wound healing.
Owner:王志伟
Covered stent, preparation method and weight-losing stent system comprising covered stent
InactiveCN110974504AMalleableSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismIntestinal ObstructionsDiet habits
The invention discloses a weight-losing stent system. The system comprises a covered stent and a conveying device, the covered stent is conveyed to the stomach through the conveying device. The covered stent achieves a mass effect through the self-expansion force, so that the intragastric volume is reduced. The diet amount of obese patients can be reduced through the mass effect, and diet controlis achieved in the aspect of food saving. After a period of time, due to the fact that the personal diet habit is formed due to the food control effect, the rice amount is greatly reduced from the original, and finally a recovery sheathing pipe is directly connected to a covering film and compresses and recovers the covering film. The conveying-type weight-losing stent system does not need a traumatic operation and can effectively solve complications such as intestinal obstruction and the like caused by existing products. The covered stent comprises a stent and tectorial membrane clothes attached to the surface of the stent. The conveying device comprises a conveying catheter and a conveying sheath, the conveying sheath and the conveying catheter are mainly made of nylon and polyurethane high polymer materials, and the conveying sheath is located in the conveying catheter and connected to the covered stent.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SUN SHING BIOTECH CO LTD
Traditional Chinese medicine composition containing honeysuckle stems and leaves for preventing and treating constipation, preparation method and application
InactiveCN106619777AStable sourceThe effect is accurateDigestive systemNatural extract food ingredientsDiseaseIntestinal Obstructions
The invention provides a traditional Chinese medicine composition for preventing and treating constipation. The raw materials of the traditional Chinese medicine composition comprise honeysuckle stems and leaves. The traditional Chinese medicine composition can be used for preparing drug or health-care food which is clinically used for promoting peristalsis and preventing and treating constipation, , and is used for preventing, controlling and treating diseases such as intestinal obstruction caused by poor peristalsis and constipation and colonic ulcer and complications of the diseases. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is simple in preparation process, low in energy consumption, pollution-free, safe and convenient and easy to store, has definite effects, and is easy to produce industrially.
Owner:河北京阳生物医药科技有限公司
Three-ring bionic artificial anal sphincter protective sleeve for preventing tissues from proliferating inwards
PendingCN111973314AReduce contact surfaceImprove inward wrappingAnti-incontinence devicesLigamentsIntestinal ObstructionsArtificial anus
The invention relates to a three-ring bionic artificial anal sphincter protective sleeve for preventing tissues from proliferating inwards. The three-ring bionic artificial anal sphincter protective sleeve comprises an outer shell matched with a three-ring bionic artificial anus, two silica gel films and an elastic rope, wherein one sides of the two silica gel films are connected through the elastic rope, and the other sides of the two silica gel films are respectively attached to the inner sides of an upper ring and a lower ring of the three-ring bionic artificial anus through pressing sheets. The three-ring bionic anal sphincter protective sleeve is simple in overall structure, small in size, light in weight and good in sealing performance, the contact surface between an external intestinal tract and the inner part of the three-ring bionic anal sphincter prosthesis can be effectively reduced, and the problems that external tissue is proliferated and wrapped inwards, and intestinal obstruction is caused when the intestinal tract falls into the prosthesis through two ends of a port are solved; and a relatively independent closed space is formed in the prosthesis, the phenomenon that a middle ring swing arm cannot reach a specified clamping position due to tissue proliferation and intestinal obstruction is relieved, and the service life of the prosthesis is prolonged.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method of surgical treatment of intestinal obstructions in narrow and large intestine and device for its implementation
This invention relates to medicine, more specifically, to the surgical treatment of intestinal obstructions using the minimum invasive (endoscopic) method. The invention provides the possibility of the surgical treatment of intestinal obstructions along the entire length of the intestine by means of stenting. The technical result achieved by the first and second subjects of the invention is providing the total surgical treatment of intestinal obstructions in the narrow and large intestine by installing a stent at an intestine obstruction location in a manner allowing further moving the stent during its positioning or removal and avoiding damage to the intestine as a result of the surgical manipulations. Said technical objective is achieved with the first subject of the invention, i.e. the method, as follows. The method of surgical treatment of intestinal obstructions in narrow and large intestine comprises the movement of the endoscope across the entire length of the narrow and large intestine and delivering the dilatation balloon and stent system to the obstructed section of the intestine. After the dilatation balloon and stent system is delivered to the obstructed section of the intestine, the dilatation balloon is installed at the intestine obstruction location, and the normal intestine section is restored by inflating the dilatation balloon. Then the volume of the dilatation balloon is reduced, the balloon is retracted to the endoscope, and the stent is installed at the intestine obstruction location. The movement of the dilatation balloon and stent is controlled using a hydraulic piston mechanism. Said technical objective is achieved with the second subject of the invention, i.e. the device, as follows. The endoscope for the total surgical treatment of intestinal obstructions in narrow and large intestine comprises a hydraulic endoscope movement drive and an endoscope case installed in the outer tube. Said endoscope case comprises channels for the supply of gas and liquid into the intestine cavity, an optical channel, a light channel and two manipulation channels. The stent is installed at the distal end of one of said manipulation channels at the central portion of the manipulation shaft which is rigidly mounted on the stent extension piston and has stopping balloons at both ends. The distal end of the other manipulation channel comprises the dilatation balloon mounted on a hollowed manipulation shaft which in turn is rigidly mounted on the dilatation balloon extension piston. The proximal ends of said manipulation channels comprise hydraulic piston mechanisms acting on said dilatation balloon extension piston and on said stent extension piston. Said dilatation balloon and said stent stopping balloons are connected via said gas supply channels to said hydraulic piston mechanisms installed at the proximal ends of said manipulation channels.
Owner:GLOBETEK 2000 +1
Novel disposable leakage-proof tubular anastomat
PendingCN111493962AReduce incidenceReduce consumptionSurgical staplesIntestinal wallsIntestine obstruction
The invention discloses a novel disposable leakage-proof tubular anastomat, which comprises an annular knife arranged in a knife body assembly and a nail propping seat connected with the knife body assembly, and is characterized by further comprising an annular gasket concentrically arranged in the knife body assembly and the nail propping seat; wherein the cutter body assembly is provided with two groups of annular cutters comprising an outer-ring annular cutter and an inner-ring annular cutter; the tip of the outer-ring annular cutter is in contact with the outer contour surface of the annular gasket, and the inner-ring annular cutter penetrates through the inner ring of the annular gasket. The intestinal anastomat has the advantages that the redundant intestinal wall of the anastomoticnear-end intestinal canal droops, the anastomotic stoma is protected, the anastomotic stoma cannot crack due to too high pressure in the intestinal cavity, anastomotic stoma leakage is avoided, and the intestinal anastomotic near-end intestinal canal is suitable for intestinal anastomosis under the condition of intestinal obstruction. Operation risks can be reduced, medical resource consumption isreduced, and the risk of enterostomy of a patient is reduced.
Owner:闫兆鹏
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating susceptible intestinal obstruction after colon tumor operation
InactiveCN104352992AReasonable formulaEasy to takeDispersion deliveryDigestive systemIntestine obstructionSargentodoxa cuneata
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine for treating susceptible intestinal obstruction after colon tumor operation. The traditional Chinese medicine is a medicament prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 5-15 parts of Chinese angelica, 10-20 parts of red paeony root, 5-15 parts of szechuan lovage rhizome, 10-20 parts of rehmannia glutinosa, 5-15 parts of peach seed, 3-10 parts of safflower, 5-15 parts of curcuma zedoary, 10-20 parts of immature bitter orange, 3-10 parts of costustoot, 3-10 parts of combined spicebush root, 3-10 parts of areca nut, 10-30 parts of astragalus membranaceus, 5-15 parts of largehead atractylodesrhizome and 10-30 parts of sargentgloryvine stem. A traditional Chinese medicine composition disclosed by the invention takes the effects of promoting blood circulation and removing stasis, promoting the circulation of qi and removing stagnation, removing swelling and relieving pain, and dredging the intestines as treatment principles, adopts qi tonifying medicaments such as Chinese angelica, astragalus membranaceus, red paeony root and the like in an auxiliary way, has a reasonable formula, is convenient to take, can be used for effectively treating intestinal obstruction, and especially can be used for treating intestinal obstruction caused by the colon tumor operation.
Owner:黄红妹
Oral Chinese patent medicine for intestinal obstruction and decocting method thereof
InactiveCN113197965AAvoid the pain of surgeryLow costDispersion deliveryDigestive systemAsparagus cochinchinensisWarm water
The invention relates to the field of medicine, in particular to an oral Chinese patent medicine for intestinal obstruction and a decocting method thereof, and the oral Chinese patent medicine comprises the following raw materials: radix asparagi, rehmannia, ginseng, astragalus membranaceus, plantain herb, rheum officinale, immature bitter orange and pericarpium citri reticulatae. The preparation method comprises the following steps: soaking grabbed dry herbal medicines in warm water for 30-60 minutes by adopting dosage and pre-soaking; decocting: transferring the pre-soaked medicines into a decocting pot, boiling with strong fire, and then decocting with soft fire; and cooling: decocting the medicine by adopting a method of taking out the decocted medicine, wherein an operation is not needed, the pain caused by the operation is avoided, the medicine is safe and efficient, the effect is instantly achieved, and the medicine can be taken once only by adding the decoction. The traditional Chinese medicine has the advantages of high efficiency, rapidness, low cost, no pain, no side effect, safety and reliability.
Owner:王植星
Traditional Chinese medicine compound preparation for preventing and treating intestinal adhesion and uses
InactiveCN1278718CIncrease exerciseImprove microcirculationPowder deliverySurgical drugsAdjuvantBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention relates to a traditional Chinese medicine compound preparation for preventing and treating intestinal adhesion and a preparation method thereof. The traditional Chinese medicine compound preparation for preventing and treating intestinal adhesion disclosed by the invention is an oral preparation composed of extracts containing active ingredients of rhubarb, citrus aurantium, magnolia officinalis, mirabilite and raspberry active ingredients and pharmaceutical auxiliary materials. The medicine of the present invention has the functions of dredging the interior, invigorating the spleen, drying dampness, promoting qi and relieving pain, and is mainly used for treating abdominal pain, abdominal distension, vomiting, constipation and other diseases caused by abdominal surgery and simple adhesive intestinal obstruction; The role of intestinal adhesions after abdominal surgery.
Owner:GUIYANG XINTIAN PHARMA CO LTD
Anti-blocking device for transanal intestinal obstruction catheter
ActiveCN112827047AReduce laborAccurate judgmentMedical devicesCatheterCatheter blockageIntestinal Obstructions
The invention discloses an anti-blocking device of a transanal intestinal obstruction catheter, which comprises a catheter body, one end of the catheter body is communicated with a suction tube, the outer end of the suction tube is communicated with a Y-shaped catheter connector, the outer end of the catheter body is provided with an anti-blocking dredging device used for dredging catheter blockage, any outer end of the Y-shaped catheter connector is connected with an automatic water injection assembly used for cleaning the catheter, the catheter body can be dredged through the anti-blocking dredging device, the blockage condition in the catheter body can be detected, whether blockage of the catheter body is removed or not is effectively judged, compared with manual bending and extruding of the catheter by personnel, the labor capacity of the personnel is greatly reduced, meanwhile, blockage removal judgment is more accurate, use by the personnel is facilitated, and smooth proceeding of medicine perfusion and drainage is guaranteed.
Owner:SECOND MEDICAL CENT OF CHINESE PLA GENERAL HOSPITAL
Traditional Chinese medicine preparation used for treating intestinal obstruction, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104998144AEasy to prepareEasy to takeDigestive systemPlant ingredientsInflammatory edemaIntestino-intestinal
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine preparation used for treating intestinal obstruction. The traditional Chinese medicine preparation is prepared from following main raw materials, by weight, 10 to 16 parts of pericarpium citri reticulatae viride, 5 to 12 parts of malt, 6 to 12 parts of magnolia obavata, 5 to 15 parts of folium sennae, 10 to 20 parts of ricinus communis, 3 to 8 parts of betel nut, 4 to 8 parts of szechwan Chinaberry fruit, 10 to 20 parts of pericarpium citri reticulatae, 8 to 16 parts of semen raphani, 9 to 13 parts of black soya bean, 5 to 15 parts of hawthorn, 1 to 5 parts of Sedum aizoon, and 4 to 6 parts of cortex cinnamomi. The traditional Chinese medicine preparation is capable of invigorating spleen and warming the middle warmer, activating qi for lowering adverse qi, removing food retention and promoting purgation, purgating heat and bowels, relieving swelling and pain, resolving hard lump, removing blood stasis and stimulating the menstrual flow, relieving intestinal adhesion, promoting gastrointestinal motility, improving intestinal blood circulation, reducing capillary permeability, protecting intestinal mucosal barrier and reducing bacterial translocation, and promoting inflammatory edema extinction. It is confirmed by clinical experiments that curative effect is excellent, application is convenient, economical, and safe; patient compliance is high; and the traditional Chinese medicine preparation is worthy of clinical expansion.
Owner:李伟
External traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating intestinal obstruction
ActiveCN110833575AHydroxy compound active ingredientsDigestive systemIntestinal ObstructionsCodonopsis pilosula
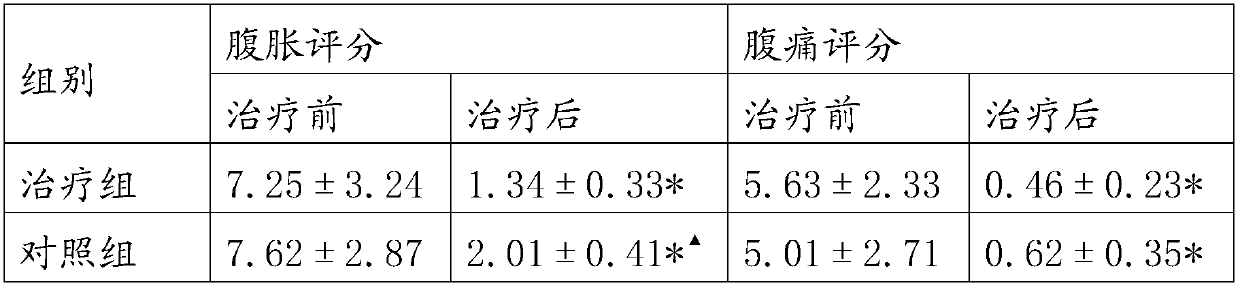
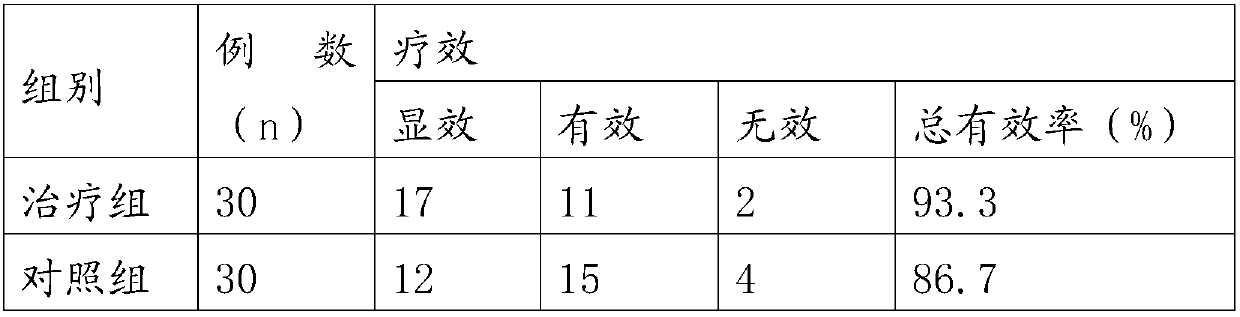
The invention provides an external traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating intestinal obstruction. The external traditional Chinese medicine composition is prepared from the following raw material medicines: ligusticum wallichii, salviae miltiorrhizae, borneol and codonopsis pilosula. The clinical experiment research results show that the total clinical effective rate of the traditional Chinese medicine composition is 93.3%, and abdominal distension and abdominal pain symptoms of patients with intestinal obstruction can be remarkably improved.
Owner:WANGJING HOSPITAL OF CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
Near infrared spectrum continuous rectum tissue oxygen saturation monitor
PendingCN114642428AGuaranteed accuracyAvoid interferenceDiagnostics using spectroscopyCatheterIschemic hypoxiaEngineering
The invention provides a rectum tissue oxygen saturation monitor which comprises an electrode, a balloon and an in-vitro monitoring component, the electrode comprises a near infrared spectrum electrode, the electrode is attached to the inner wall of the balloon, and the near infrared spectrum electrode is connected with the in-vitro monitoring component through a cable. The monitor disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively early warning ischemia and hypoxia phenomena of local tissues and intervening oxygen supply and demand imbalance of the local tissues, so that complications such as endotoxemia related to postoperative intestinal obstruction and intestinal barrier damage caused by ischemia and hypoxia of intestinal tracts in a perioperative period are prevented; and the method has important clinical value for accelerating postoperative intestinal function recovery and rapid ingestion and drinking.
Owner:王天龙
Medicine for treating intestinal obstruction of infants and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105012773AQuick effectHigh recovery rateDigestive systemUnknown materialsIntestinal ObstructionsSide effect
The invention discloses a medicine for treating intestinal obstruction of infants and a preparation method thereof. The medicine comprises the following raw herbal materials: Chinese buckeye seeds, securidaca inappendiculata, tender catchweed bedstraw, helicteres isora, calophyllum membranaceum, jasminum laurifolium, portulaca oleracea, fructus cannabis, pericarpium arecae, edible fat made from milk, vernonia andersonii, stephania longa, orobanche coerulescens, fruit of highland barley malt, ixeris denticulata, pericarpium citri reticulatae viride, fructus aurantii, patrinia heterophylla, eretmochelys imbricata, rumexpatientia, scutellaria barbata, crotalaria tetragona, sida szechuensis, tuber or root of smilax stans, semen cassia, olibanum, astilbe chinensis, breynia fruticosa, perilla fruit, vigna umbellata, angelica sinensis, euonymus phellomana, red peony root and buckwheat. The medicine has the benefits as follows: the medicine has the efficacy of regulating qi, removing stasis, activating blood, moistening the intestines and relieving dyspepsia, meanwhile, has the effects of clearing heat, cooling blood, guiding qi downwards, removing intestinal obstruction, and resisting infection, and has the advantages of quick action, high improvement rate, definite curative effect, short treatment course, no toxic or side effect, low cost and the like.
Owner:JINAN SHUNHAO BIOTECH CO LTD
Material and methods for the treatment of gastro-intestinal disorders
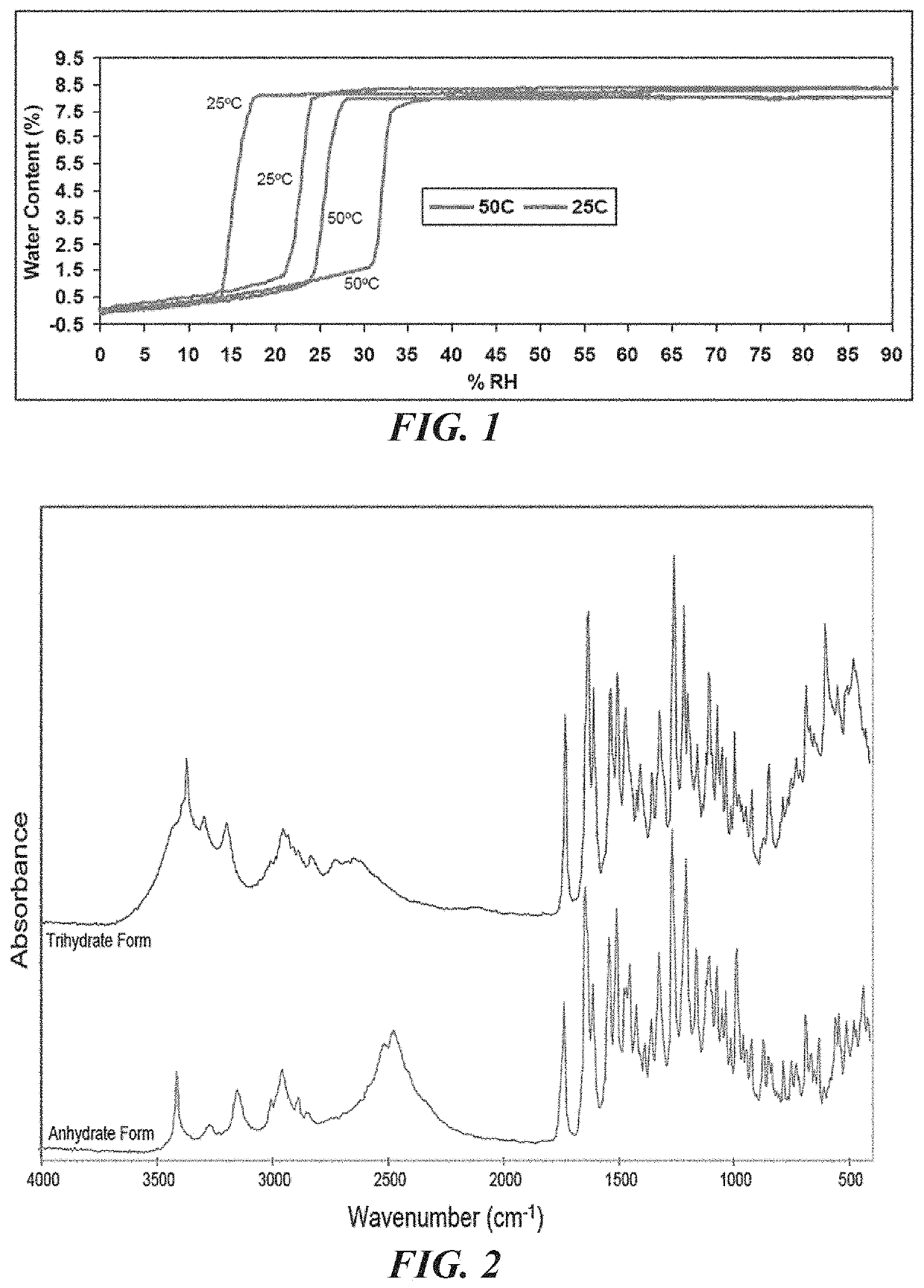
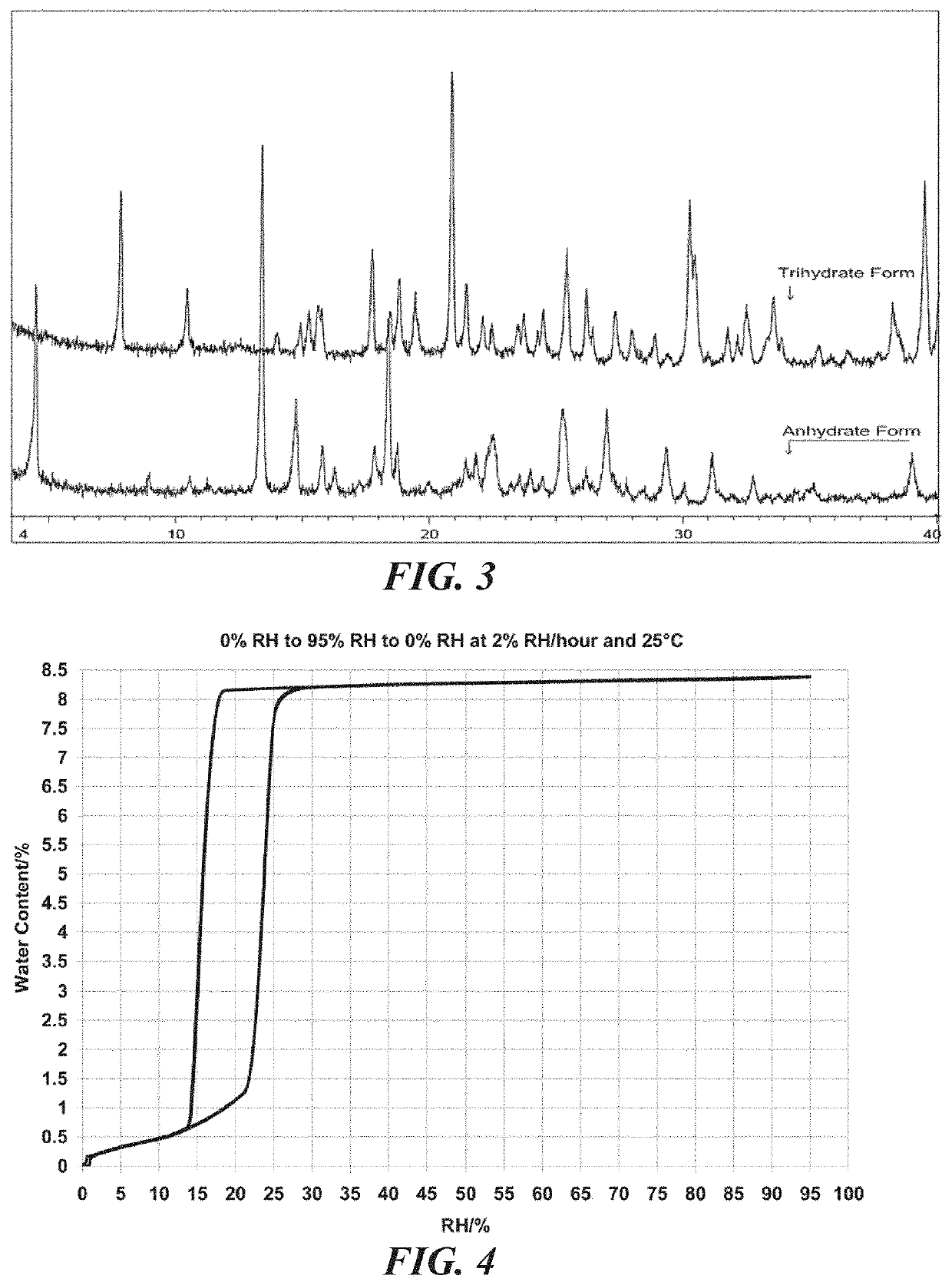
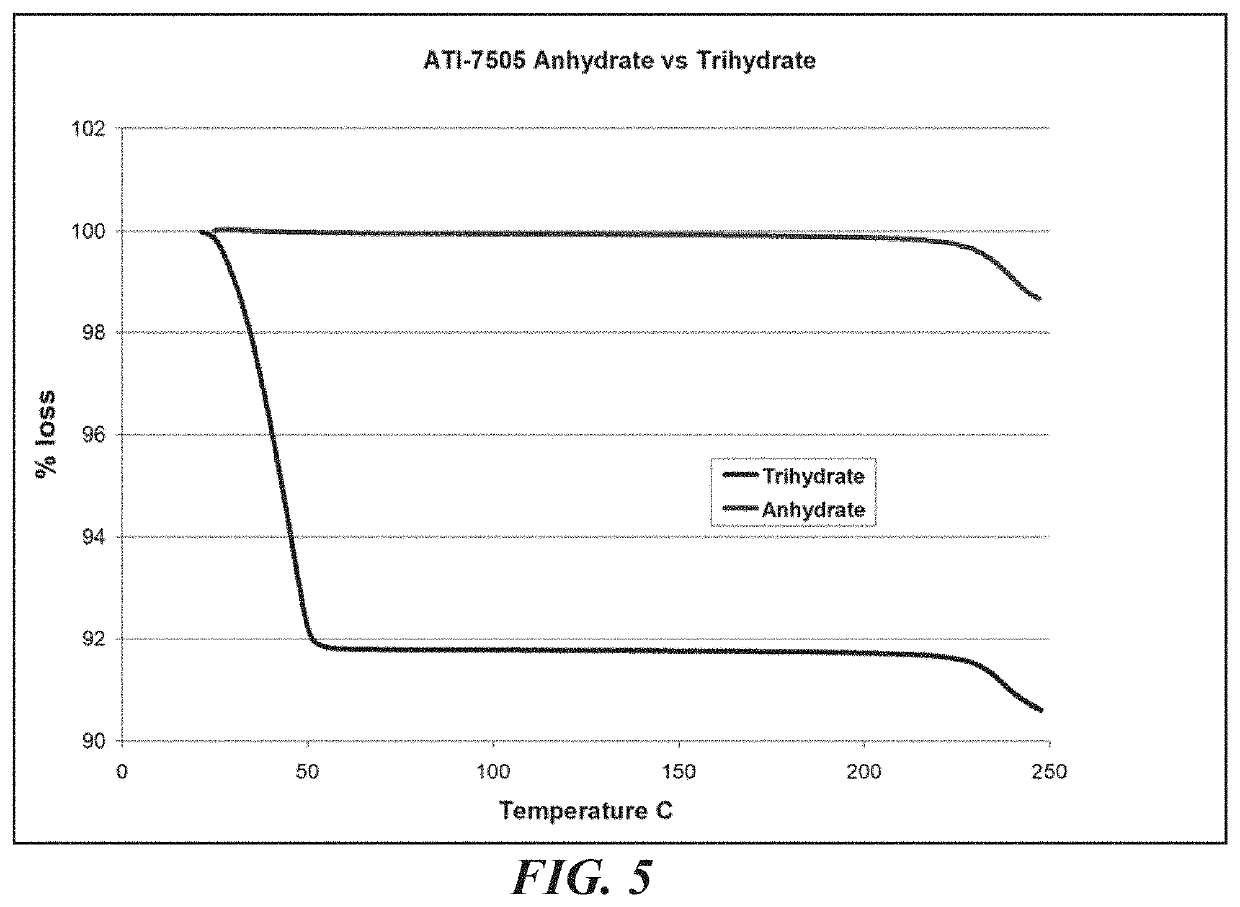
Provided herein is a bulk composition comprising the trihydrate form of (3S, 4R, 3′R)-6-[4-(4-amino-5-chloro-2-methoxy-benzoylamino)-3-methoxy-piperidin-1-yl]-hexanoic acid 1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3′-yl ester di-hydrochloride salt. Provided are also pharmaceutical compositions and dosage forms comprising the trihydrate form, and methods and uses for treating a gastrointestinal disorder in a subject with the trihydrate form. In some embodiments, the gastrointestinal disorder is gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), dyspepsia (such as functional dyspepsia or functional motility disorder), gastroparesis, paralytic ileus, post-operative ileus, emesis, nausea, heartburn, intestinal pseudo-obstruction, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), constipation, enteral feeding intolerance (EFI), or esophagitis. In some embodiments, the gastrointestinal disorder is post-operative ileus, chronic grass sickness, constipation, megacolon, gastritis, gastrointestinal stasis, or abomasal emptying defect.
Owner:RENEXXION LLC
Eccentric multi-cavity smooth type rectum high-pressure high-capacity pelvis compression water bag and using method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of medical instruments, and particularly relates to an eccentric multi-cavity smooth type rectum high-pressure high-capacity pelvis compression water bag which comprises an expandable assembly, a liquid injection assembly and a drainage pipeline, the drainage pipeline is a supporting component, and a plurality of parallel expansion bag sets are distributed on the outer side of the drainage pipeline. Each expansion bag set is composed of a plurality of compression water bags, the drainage pipeline is a smooth pipeline and penetrates through the middle of the expansion bag sets, the head end of the drainage pipeline is a drainage opening, and the tail end of the drainage pipeline is a dischare opening. By means of noninvasive implantation, convenience and rapidness are achieved, operation is easy, taking out is convenient, the pain of a patient can be relieved, and no further injury is caused; Alternate compression can be guaranteed through multiple cavities, different positions in front of the sacrum can be compressed, more targeted compression on one side can be guaranteed through eccentricity, defecation and exhaust functions of the rectum are reserved through the drainage pipeline, the drainage function is achieved, and intestinal obstruction caused by rectum blockage can be reduced.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU CENT HOSPITAL
Defecating apparatus for removing intestinal obstruction
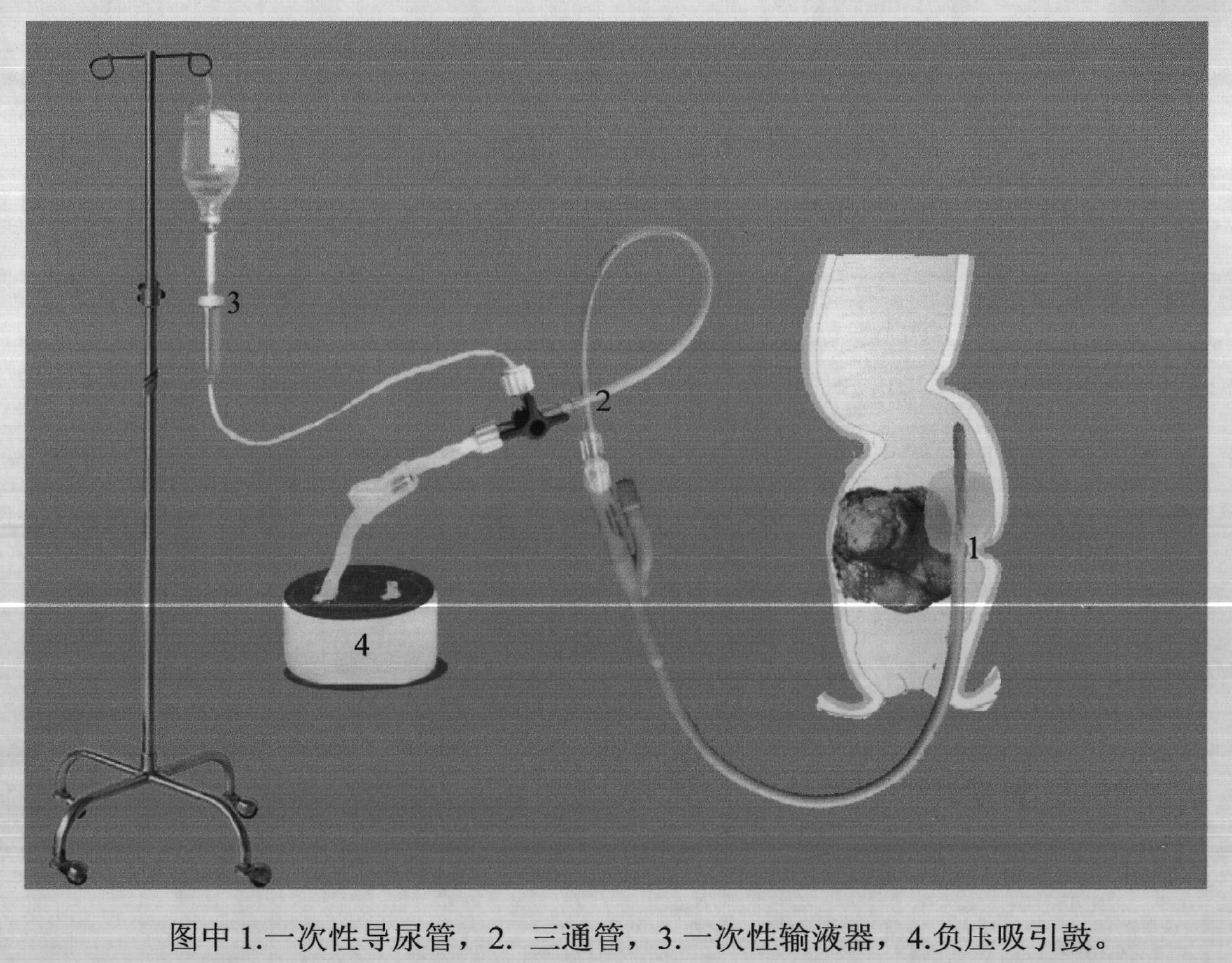
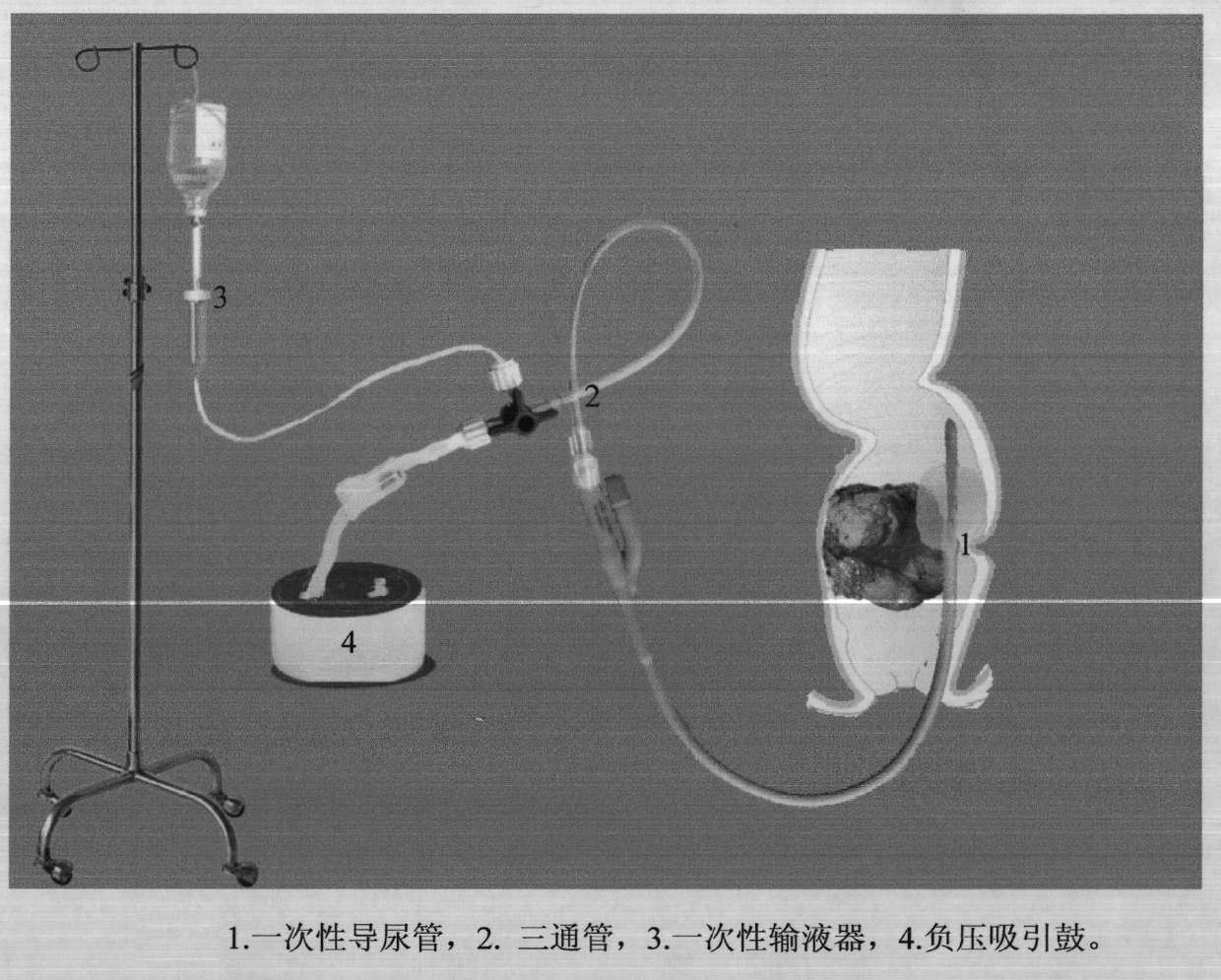
InactiveCN102553010AAvoid damageEasy dischargeEnemata/irrigatorsUrinary catheterIntestinal Obstructions
A defecating apparatus for removing intestinal obstruction is characterized in that a disposable catheter, a negative-pressure aspiration drum and a disposable infusion set are connected by a three-way pipe. The defecating apparatus is favorable for exhausting intestinal gas excretion and defecating, is convenient in operation, low in price, light in traumatic effect and free of repeated operation and effectively treats intestinal obstruction caused by rectostenosis.
Owner:陈净
Intestinal tract decompression device for intestinal obstruction patient during operation
PendingCN113425924AEasy resectionFit closelyDiagnosticsSurgeryIntestinal ObstructionsIntestinal walls
The invention discloses an intestinal tract decompression device for an intestinal obstruction patient during an operation. The intestinal tract decompression device comprises a far-end side, a storage section and a near-end side, wherein the far-end side is provided with a far-end buckle assembly used for releasing contents in a storage bag; the storage section is provided with storage scales for observation; the near-end side is provided with a near-end zipper and a near-end opening formed in the side part of the near-end zipper; and the two ends of the storage section are connected with the far-end side and the near-end side, respectively. The intestinal canal does not need to be dissected after laparotomy, and the near-end opening of the device is directly sewed on the intestinal wall close to an obstruction point, so that in-situ decompression of the intestinal canal is realized; the far-end side, the storage section and the near-end side are matched for operation, the pressure reduction time is shortened, and then the time for intestinal toxin absorption is shortened; the possibility of serious abdominal cavity pollution caused by a large amount of intestinal contents flowing into the abdominal cavity is reduced; the pressure can be fully reduced regardless of the quantity and the character of intestinal contents, so that the intestinal canals can be conveniently cut and anastomosed, and the risk of postoperative anastomotic fistula is reduced; and a sealing device can reduce overflow of odor, can keep fresh air in an operating room, and is easy to operate.
Owner:中国人民解放军海军军医大学第一附属医院 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com