Patents
Literature
173 results about "Mass transport" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mass transfer describes the transport of mass from one point to another and is one of the main pillars in the subject of Transport Phenomena. Mass transfer may take place in a single phase or over phase boundaries in multiphase systems.
Resonant cavity light emitting devices and associated method
InactiveUS20060118799A1Increase probabilityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResonant cavitySource material
A method may produce a resonant cavity light emitting device. A seed gallium nitride crystal and a source material in a nitrogen-containing superheated fluid may provide a medium for mass transport of gallium nitride precursors therebetween. A seed crystal surface may be prepared by applying a first thermal profile between the seed gallium nitride crystal and the source material. Gallium nitride material may be grown on the prepared surface of the seed gallium nitride crystal by applying a second thermal profile between the seed gallium nitride crystal and the source material while the seed gallium nitride crystal and the source material are in the nitrogen-containing superheated fluid. A stack of group III-nitride layers may be deposited on the single-crystal gallium nitride substrate. The stack may include a first mirror sub-stack and an active region adaptable for fabrication into one or more resonant cavity light emitting devices.
Owner:SORAA
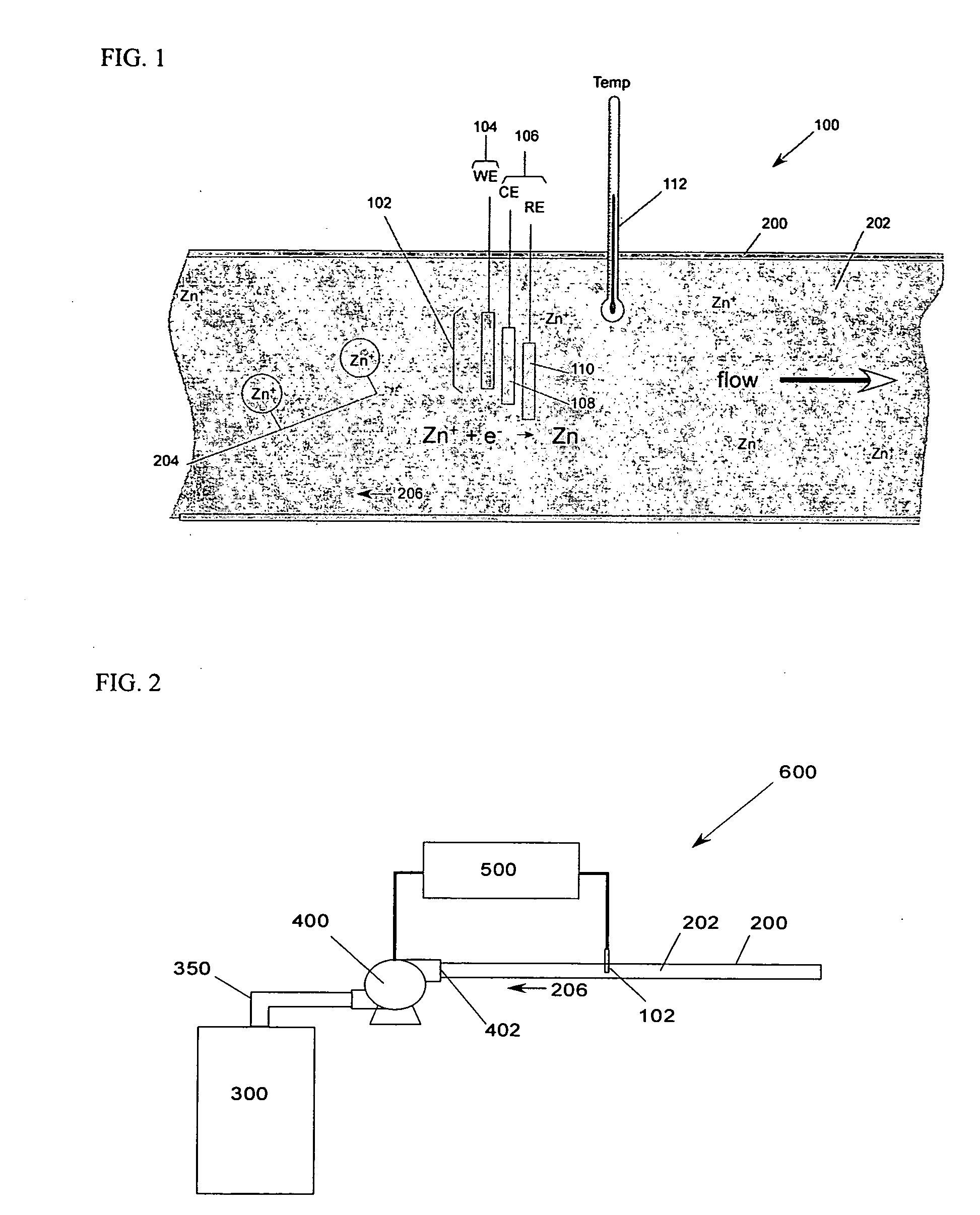
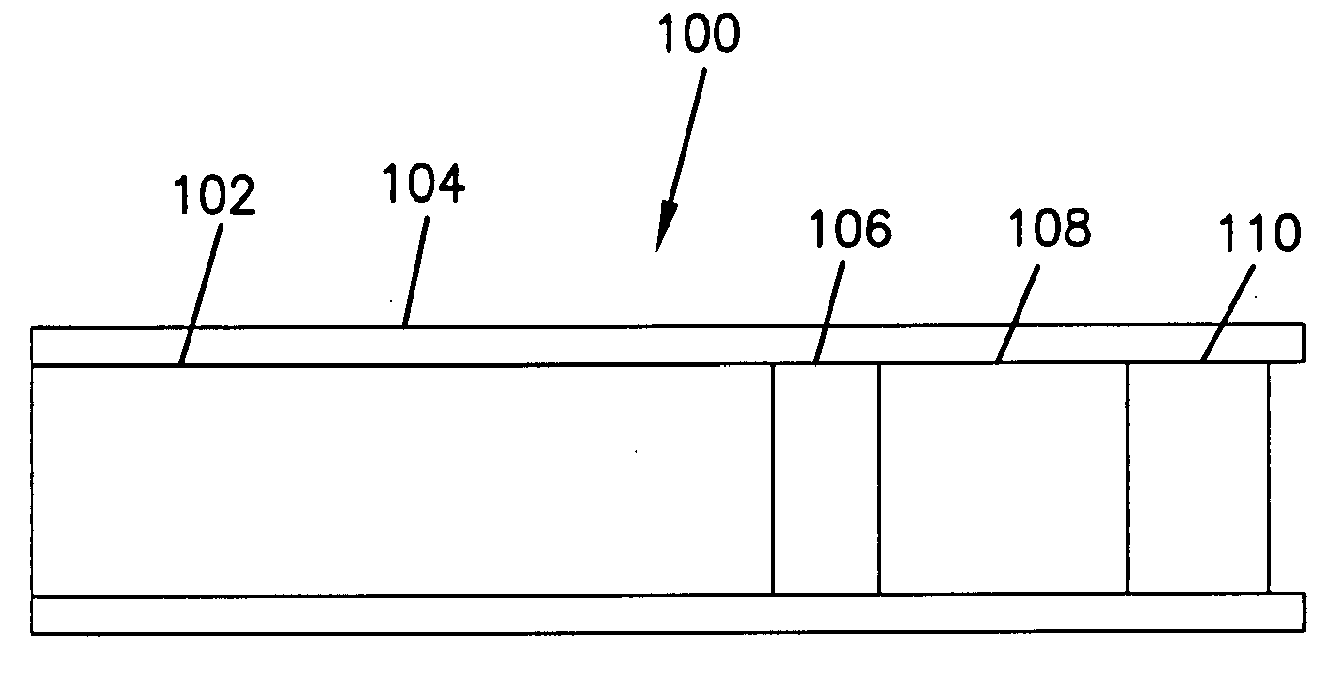
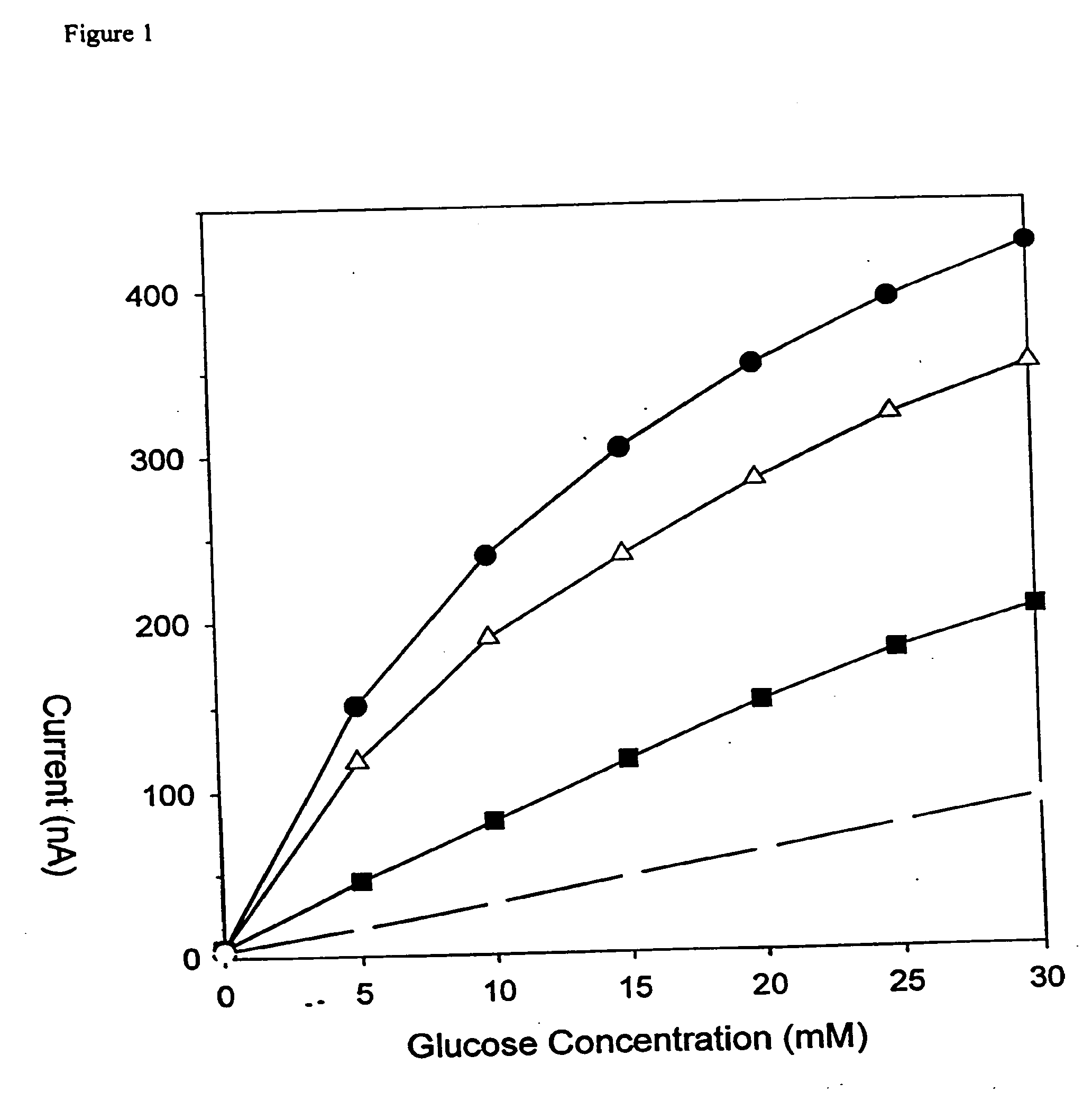
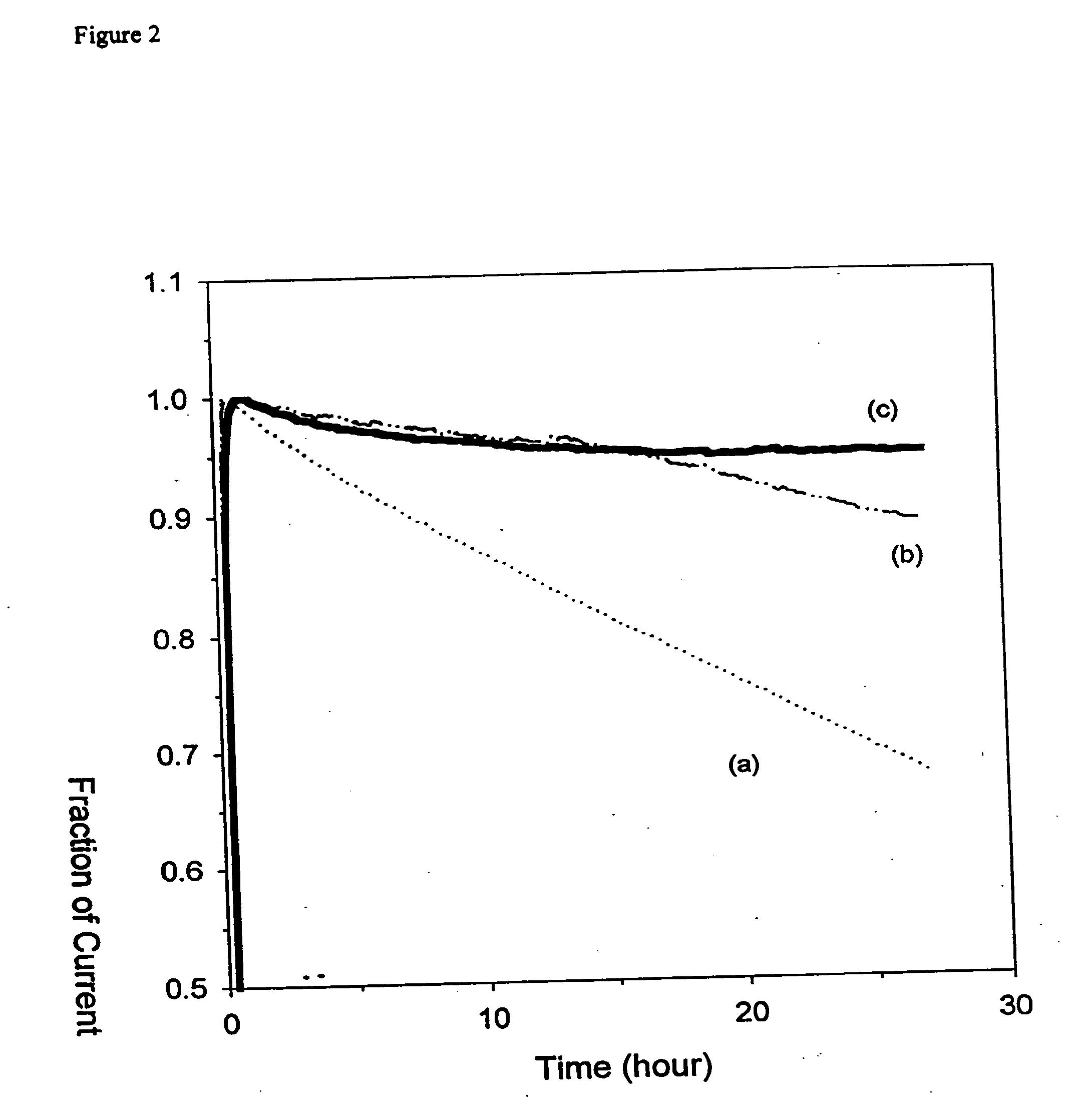
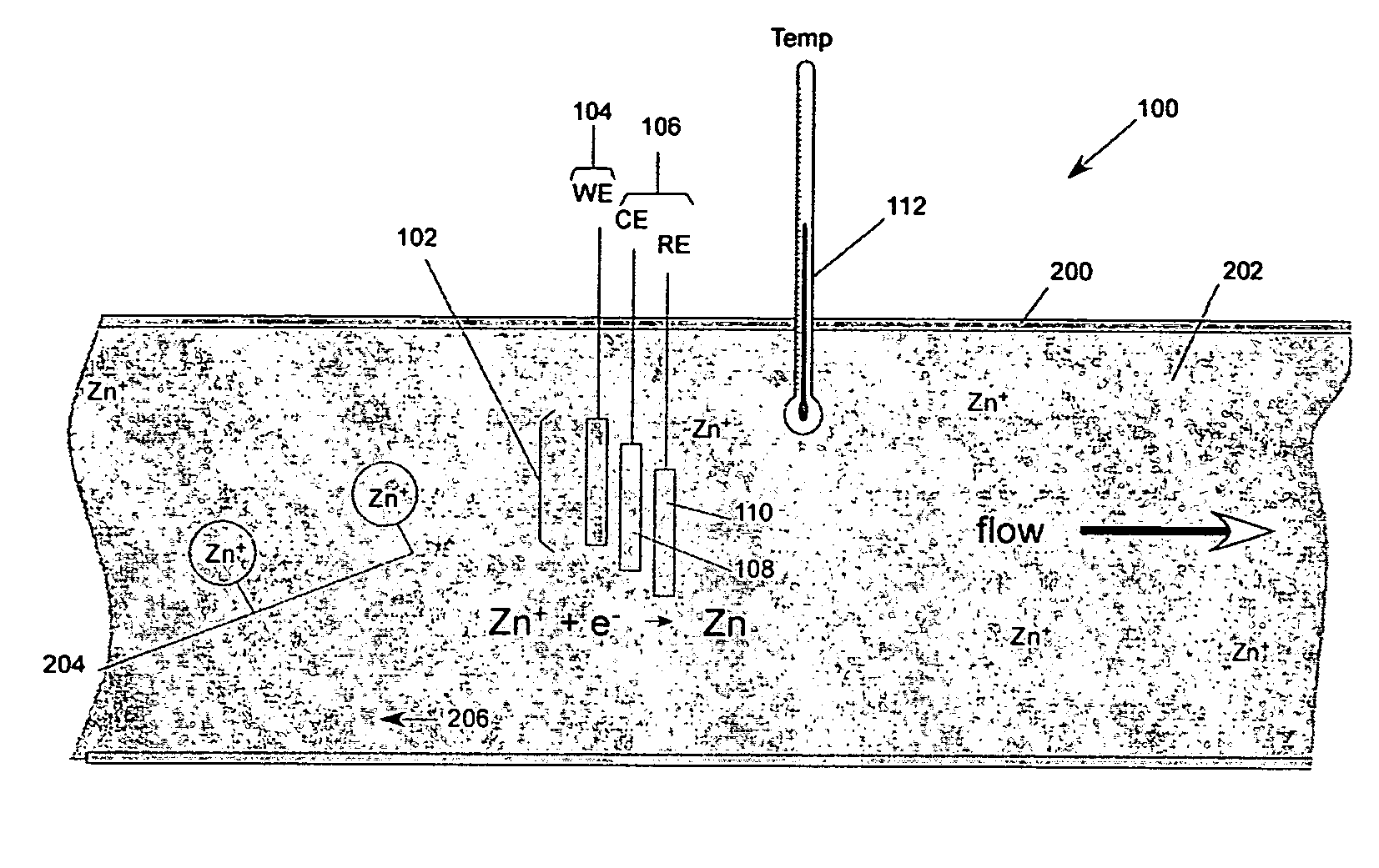
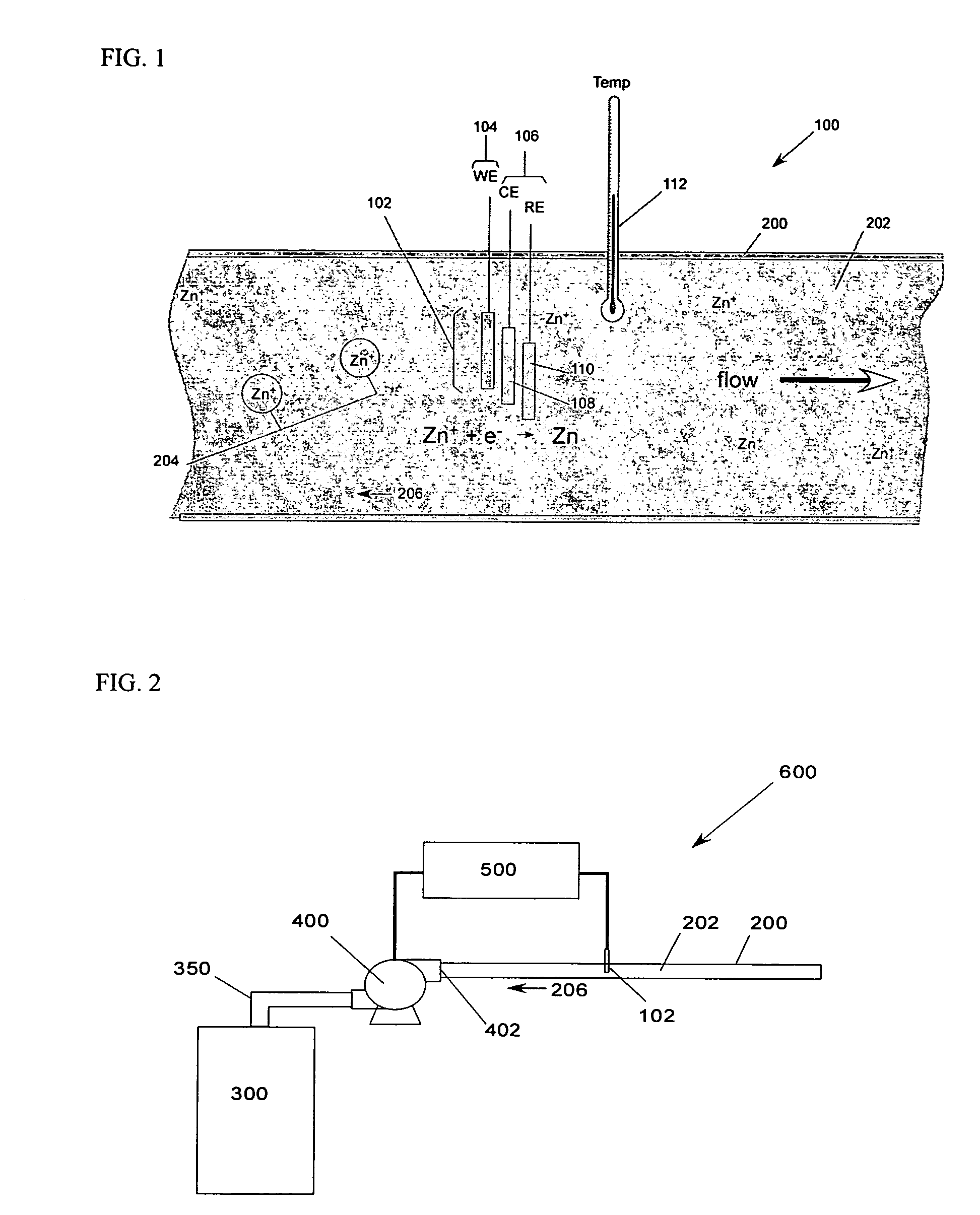
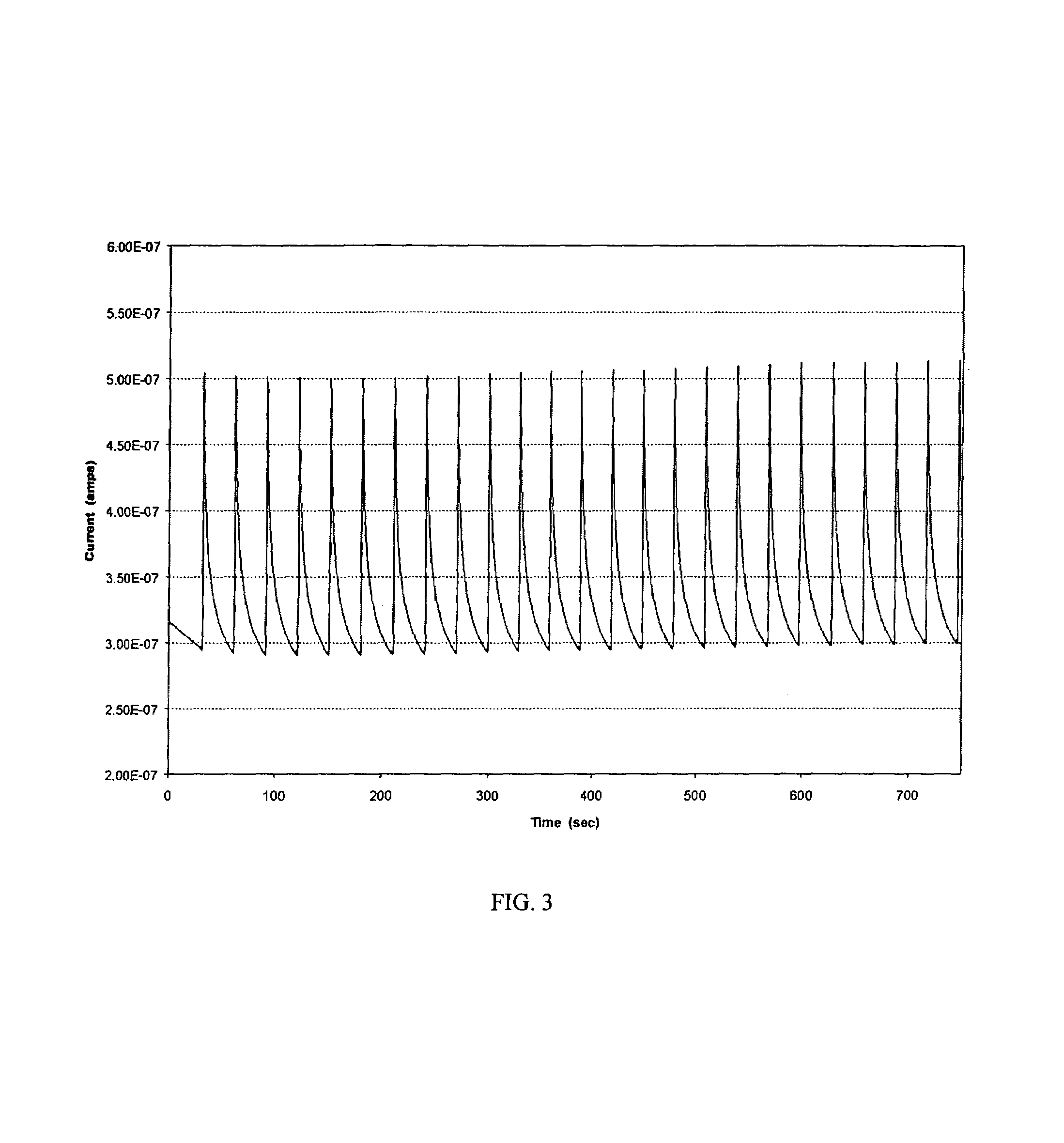
Mass transport limited in vivo analyte sensor
InactiveUS6975893B2Transport be restrictTransport be smallNanotechMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteIn vivo
An in vivo electrochemical sensor including a working electrode, and an analyte-responsive sensing layer proximate the working electrode. The sensing layer is exposed at an edge of the sensor, wherein the sensor signal is limited, at least in part, by mass transport of analyte to the sensing layer. The sensor is configured and arranged for implantation into the body of a mammal for contact with body fluids of the mammal. The analyte diffuses to the sensing element via the edge of the sensor, thereby restricting mass transport of the analyte to the sensing element. This is because the solution-contacting surface area of the sensor edge is much smaller than an open face of the sensing layer.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
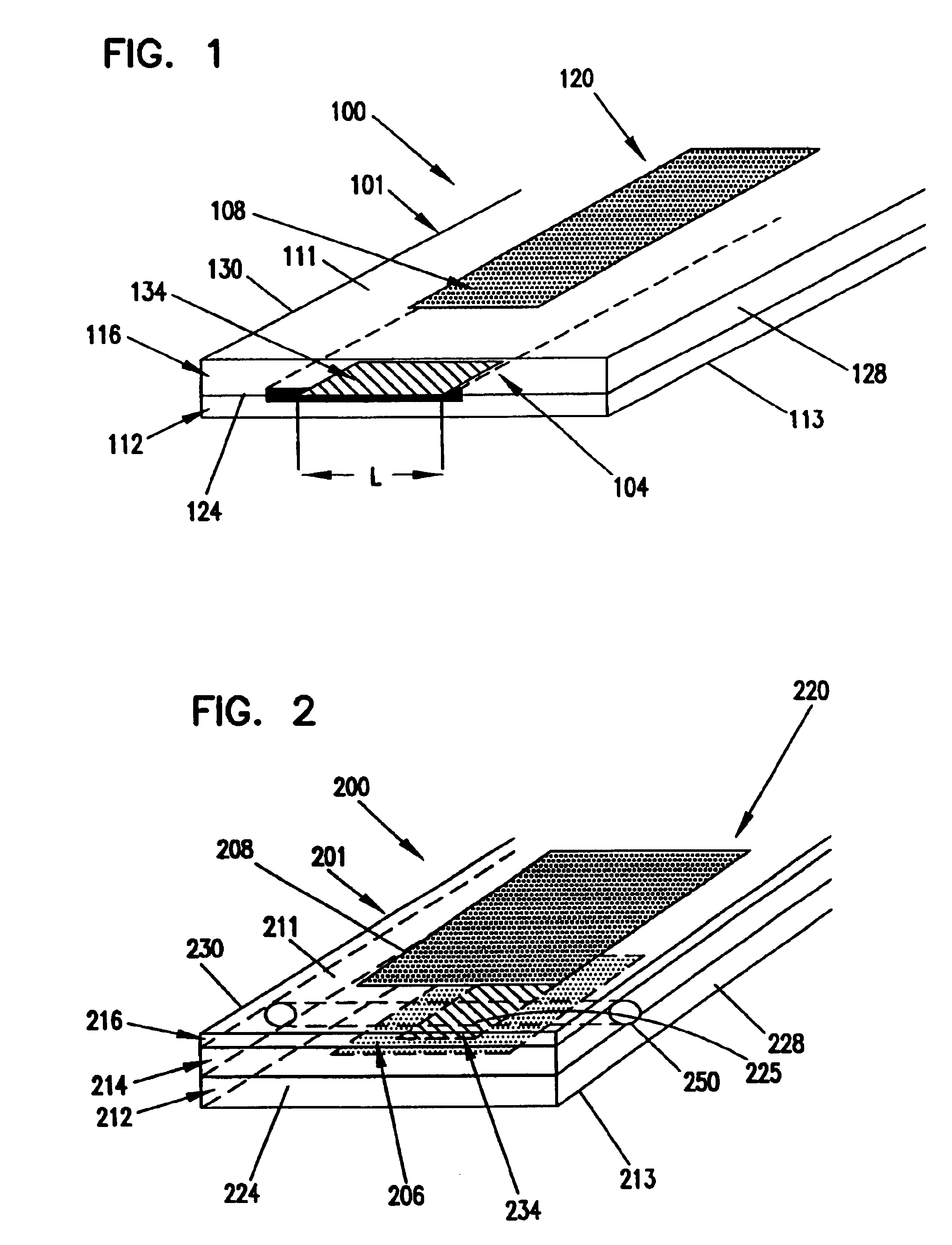
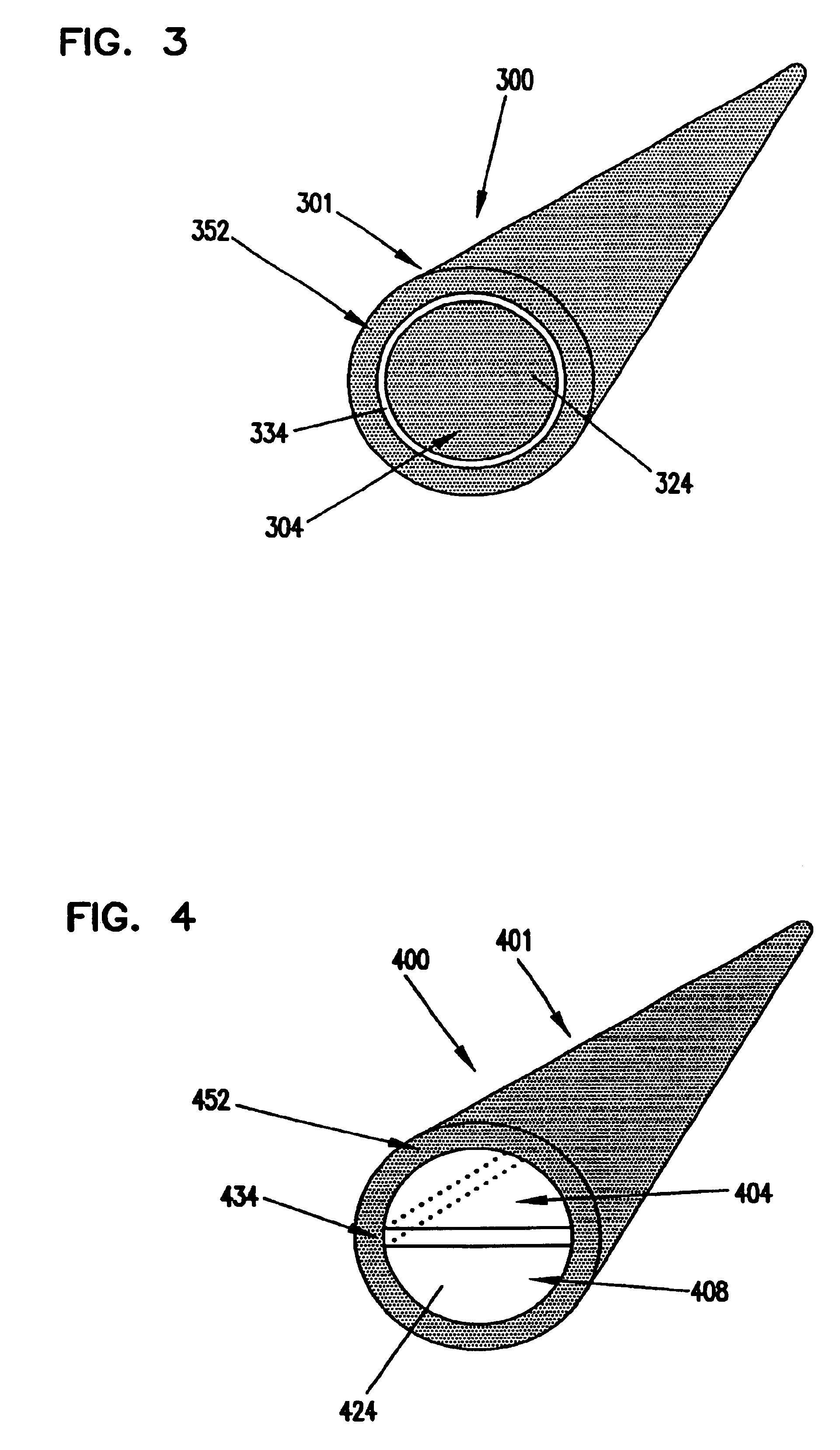
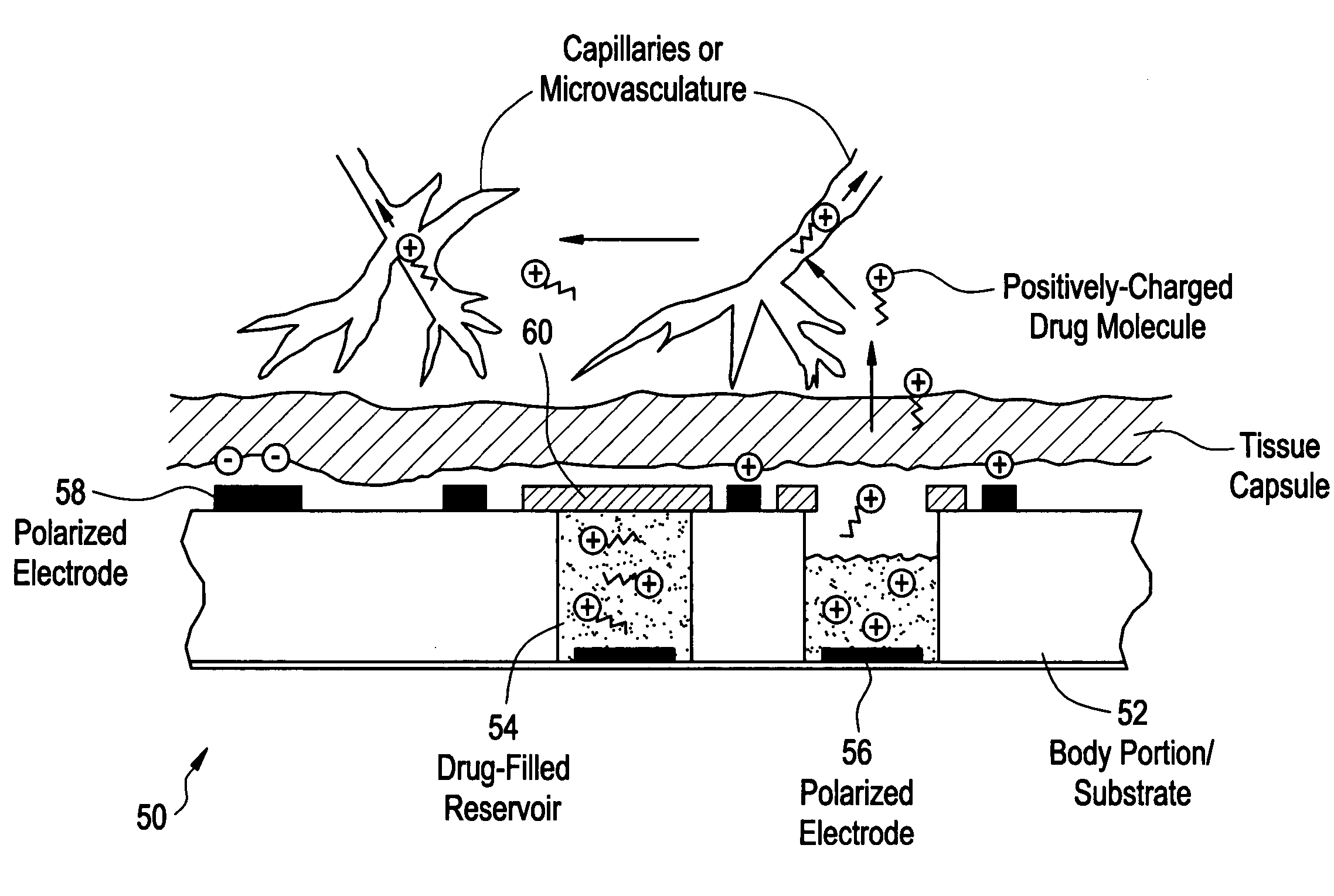
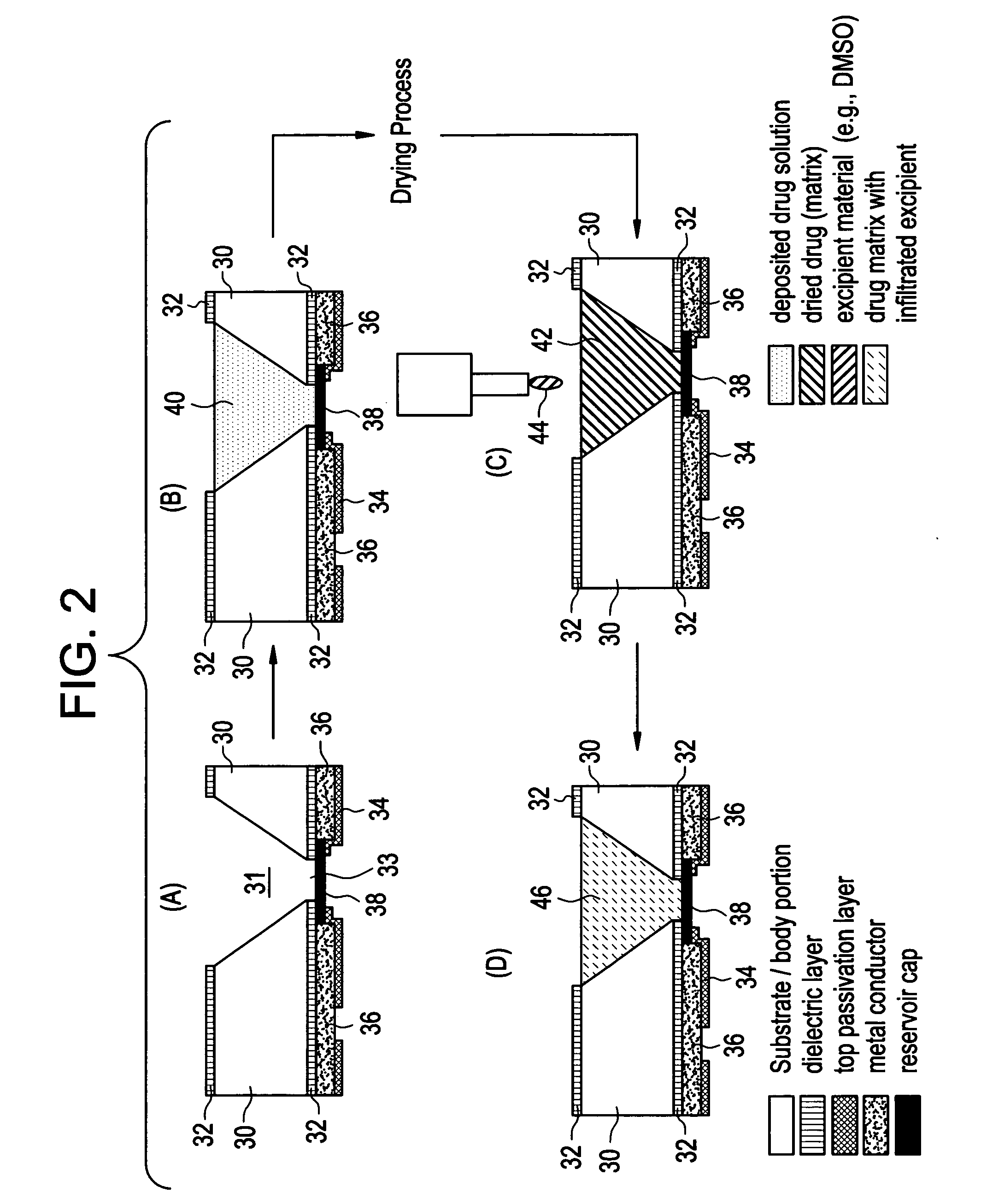
Devices and methods for measuring and enhancing drug or analyte transport to/from medical implant
InactiveUS20050267440A1Easy to transportEfficient propulsionElectrocardiographyAntipyreticControlled drugsAnalyte
Methods and devices are provided for enhancing mass transport through any fibrous tissue capsule that may form around an implanted medical device following implantation. Methods and devices are also provided to enhance vascularization around the implanted device, which also will aid in mass transport to / from the device. The device preferably comprises multiple reservoirs containing (i) a drug formulation for short- or long-term, controlled drug delivery, (ii) sensors for sensing an analyte in the patient, or (iii) a combination thereof.
Owner:MICROCHIPS INC
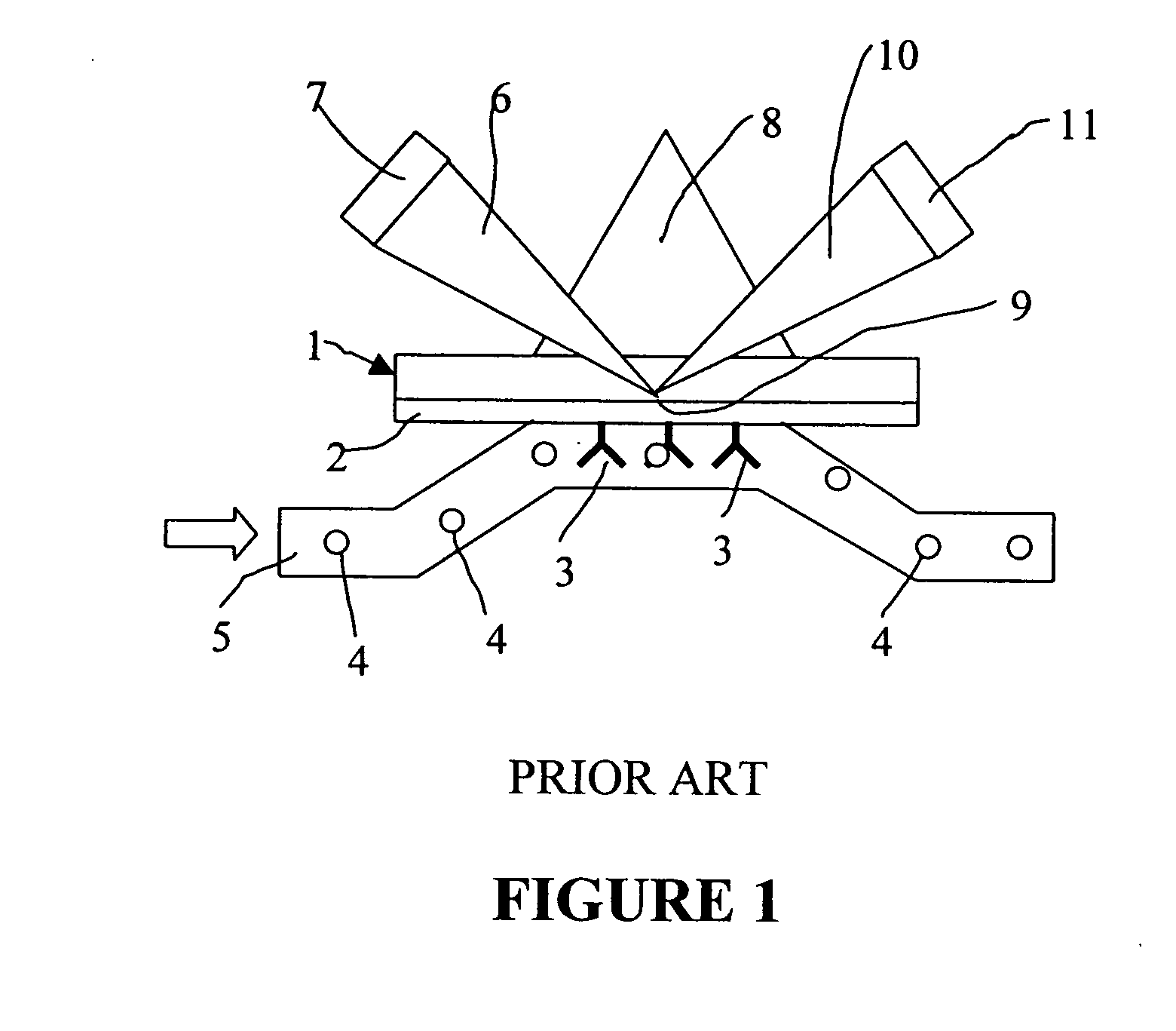
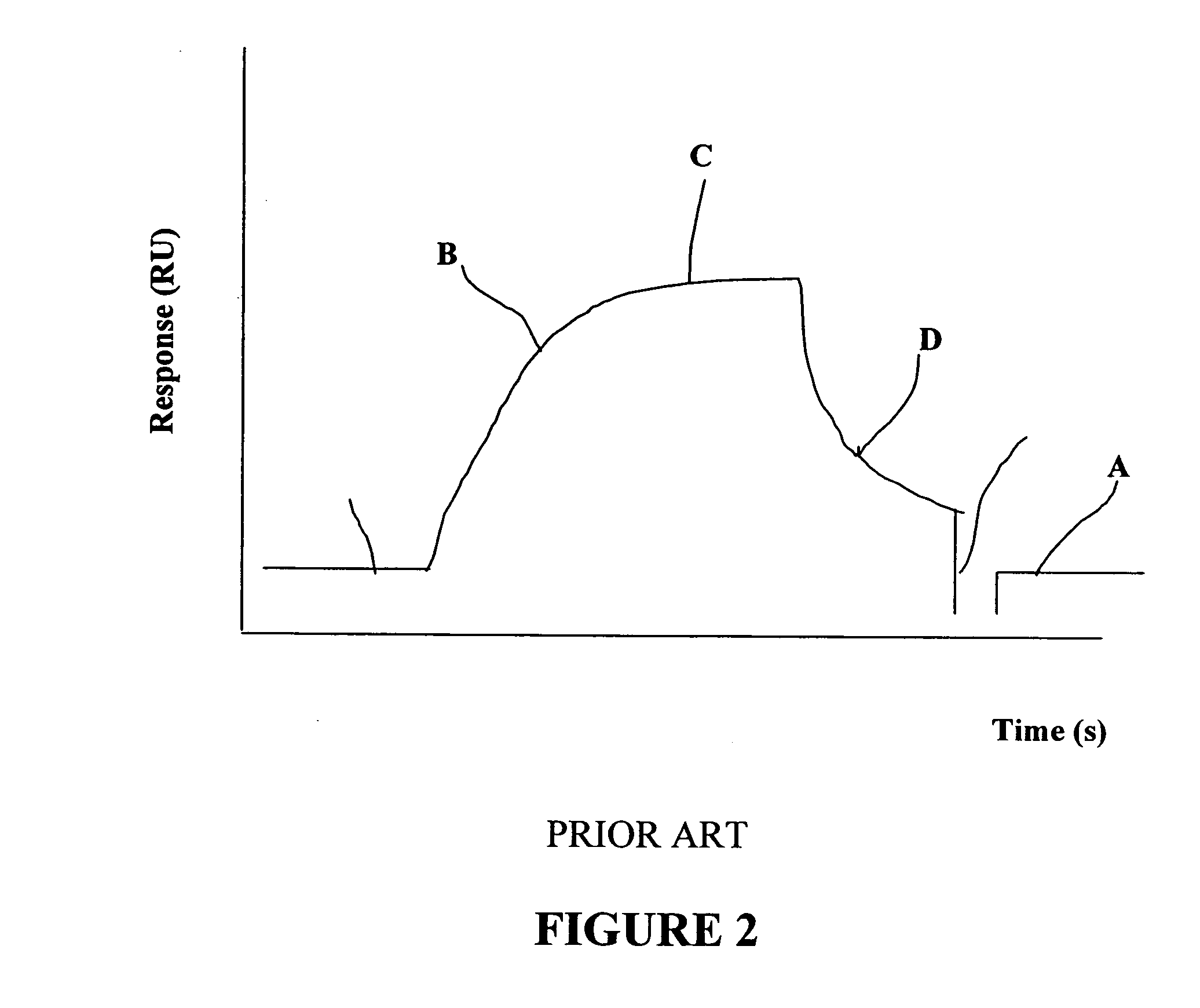
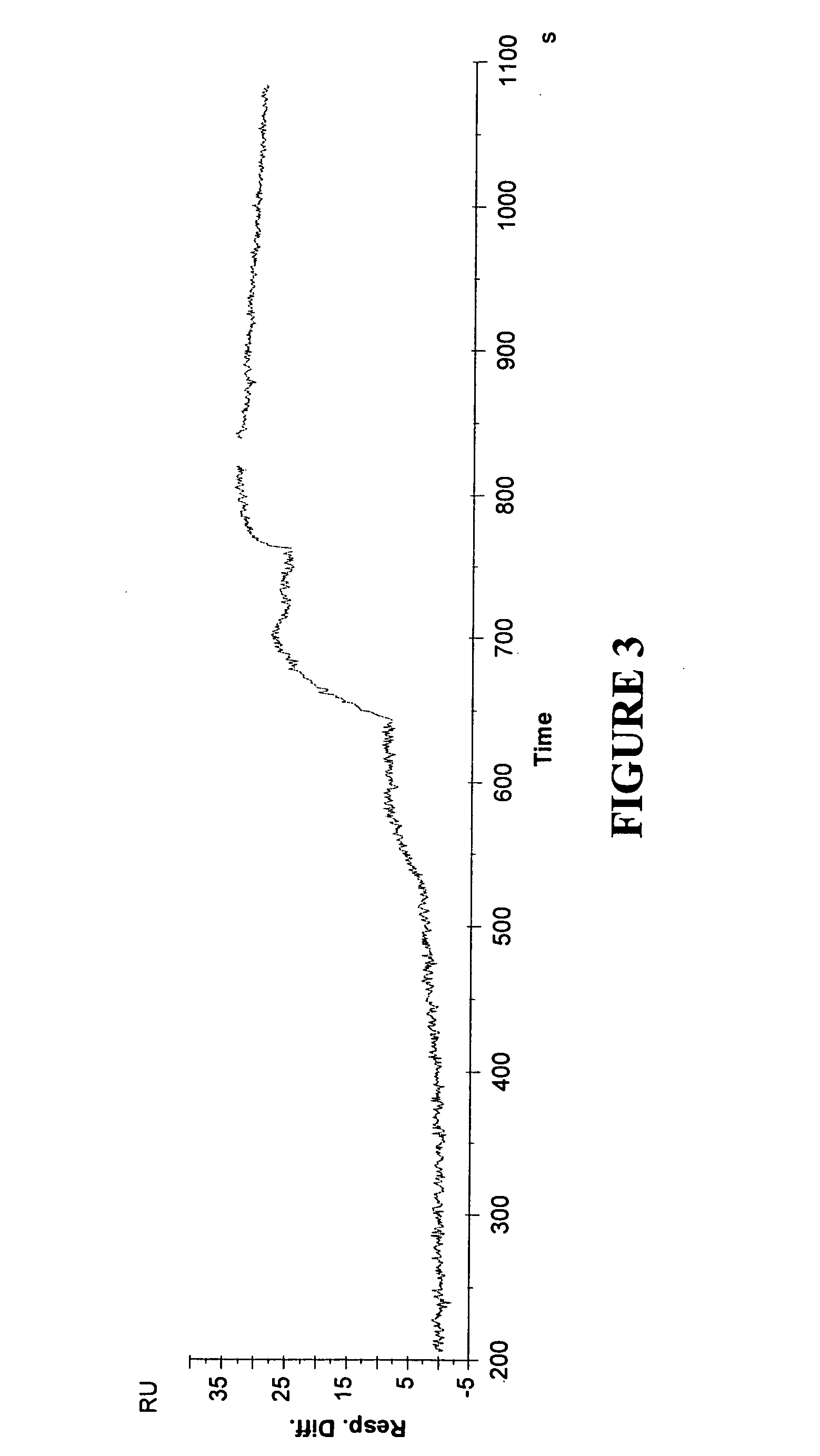
Method and system for determination of molecular interaction parameters
A method of determining kinetic parameters for a reversible molecular interaction between a ligand immobilized to a solid support surface and a binding partner to the ligand in solution, comprises sequentially, without intermediate regeneration or renewal of the immobilized ligand, flowing a plurality of fluid volumes containing different known concentrations of the binding partner over the solid support surface, monitoring the momentary amount of binding partner bound to the solid support surface related to time and solution concentration of binding partner and collecting the binding data, and determining the kinetic parameters by globally fitting a predetermined kinetic model for the interaction between the binding partner and the immobilized ligand to the collected binding data, which model allows for mass transport limitation at the solid support surface. An analytical system for carrying out the method, a computer program, a computer program product and a computer system for performing the method are also disclosed.
Owner:CYTIVA SWEDEN AB
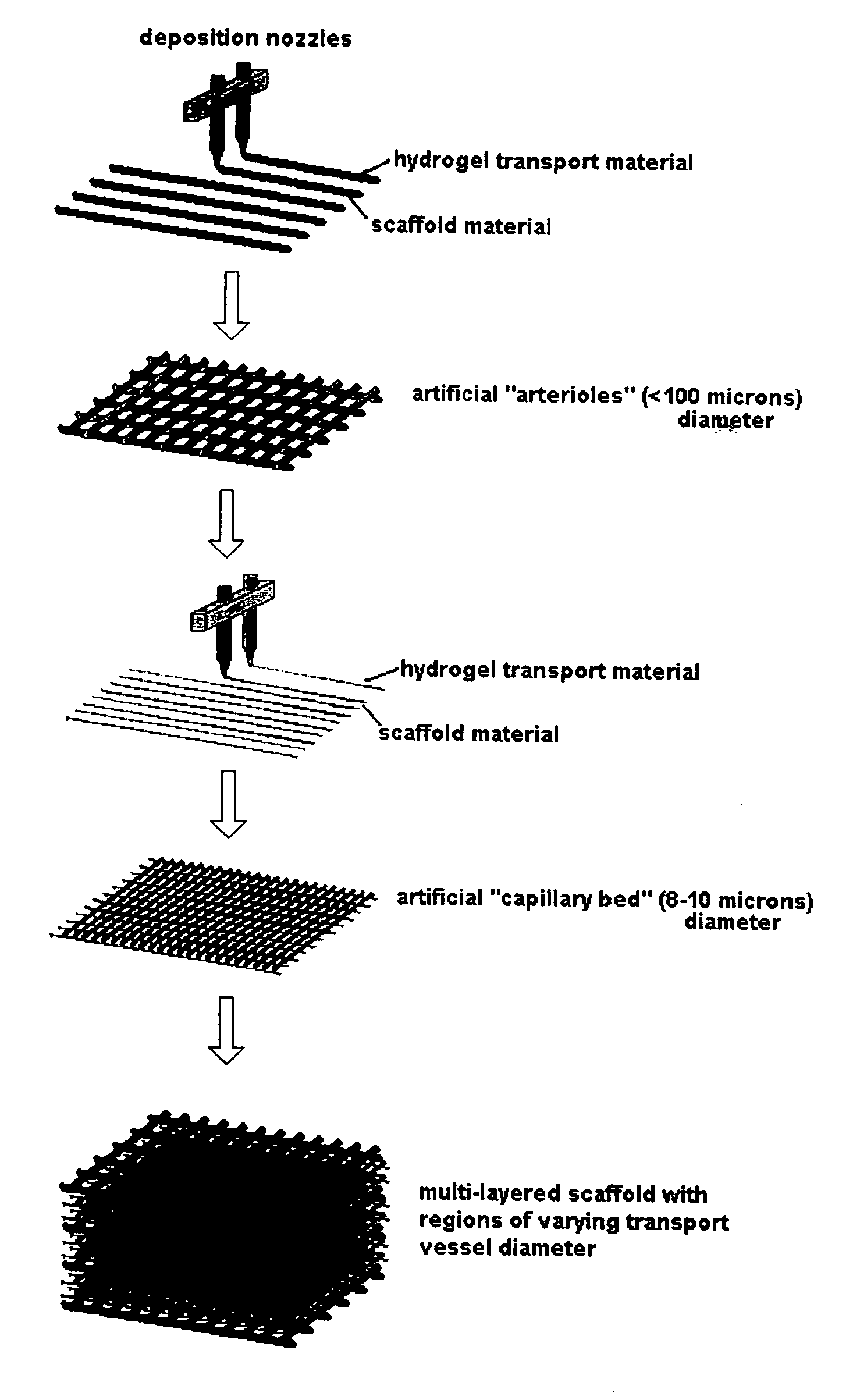
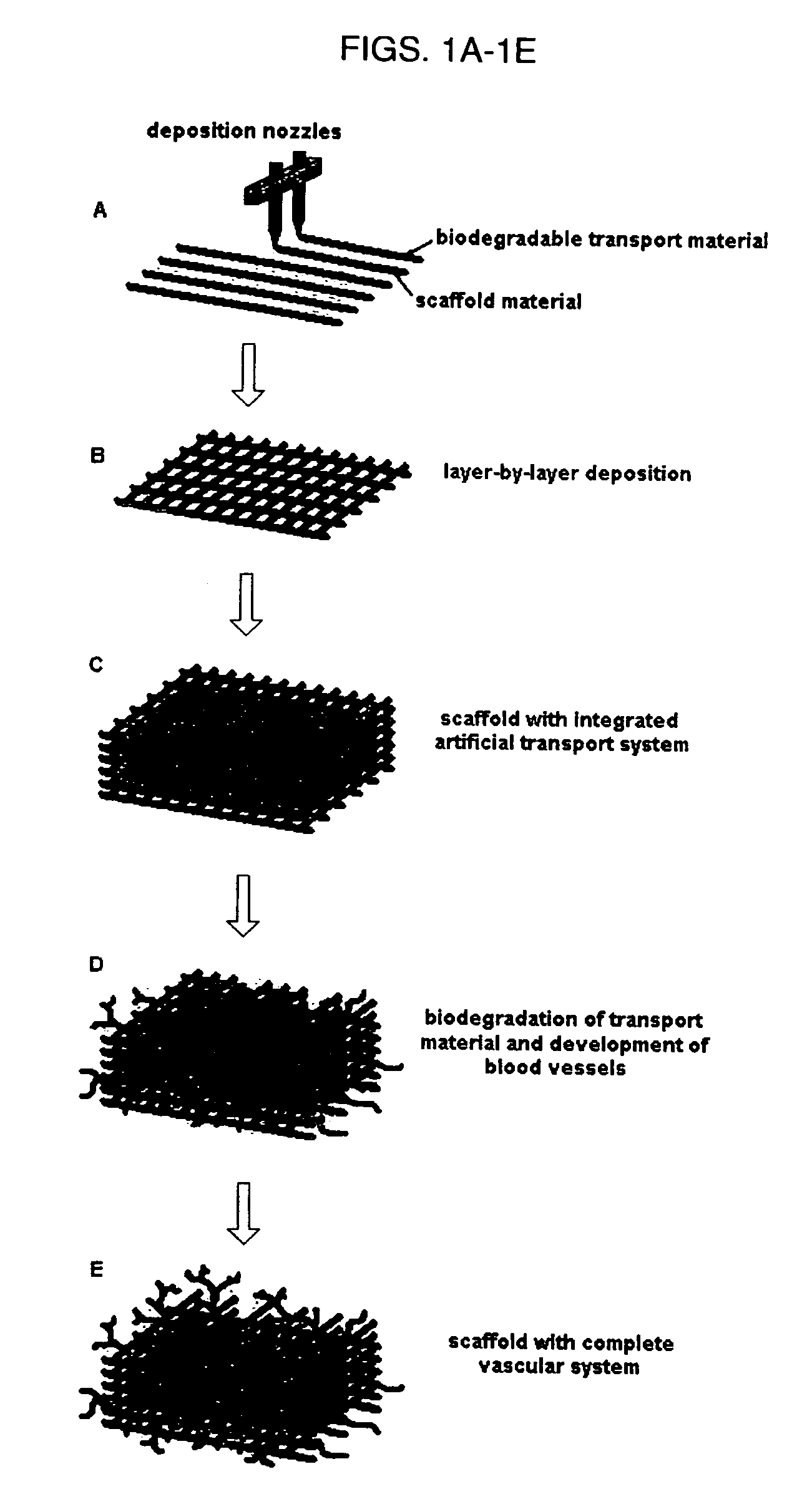
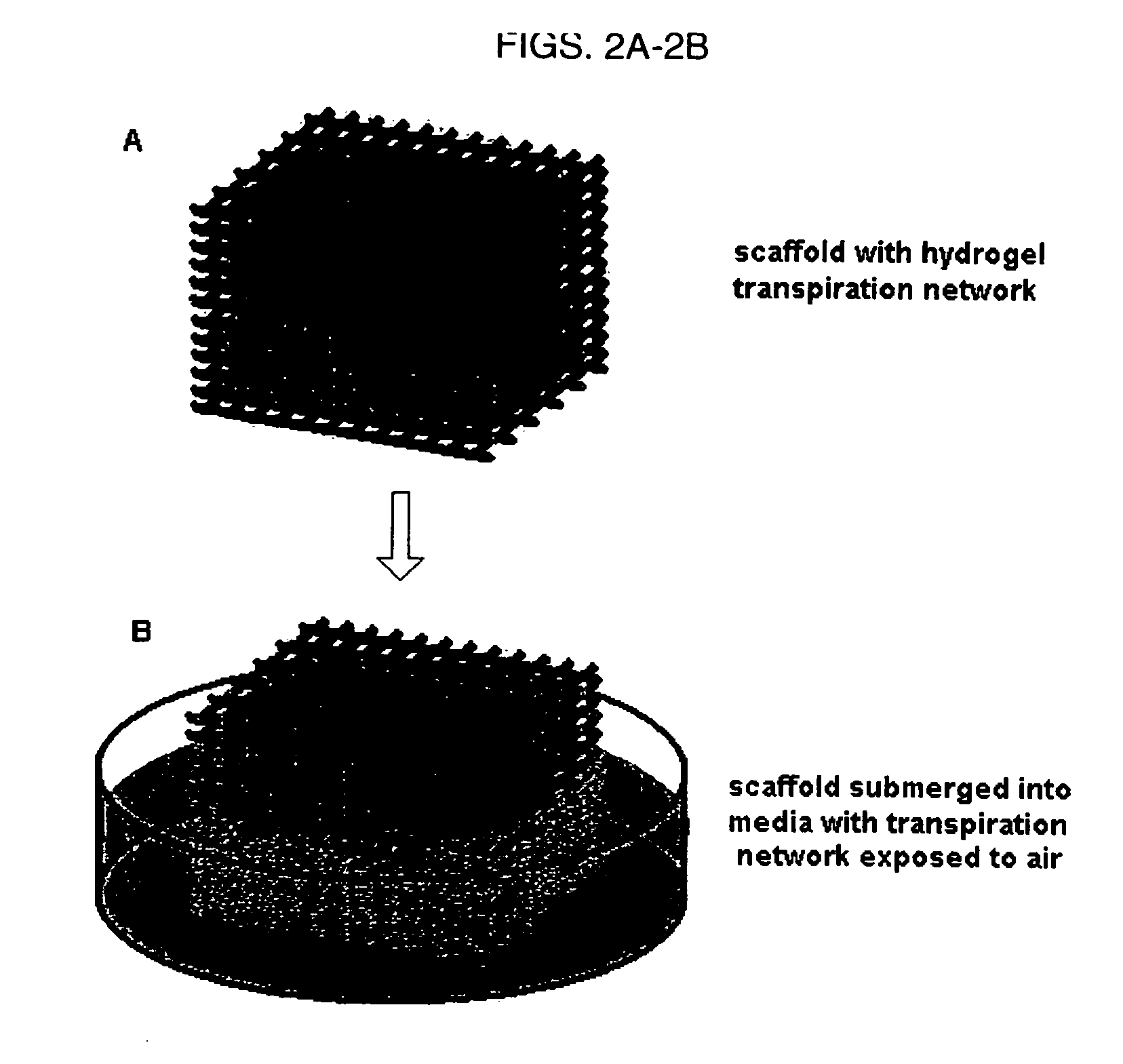
Method for creating an internal transport system within tissue scaffolds using computer-aided tissue engineering
ActiveUS20060195179A1Promote circulationFacilitated DiffusionTissue cultureBlood vesselsTransport systemEngineering
An artificial tissue including an internal mass transport network having a plurality of channels, wherein the channels are designed to substantially mimic naturally occurring vascular network and a method for creating an internal transport system within a tissue scaffold to improve circulation, diffusion, and mass transport properties by utilizing computer-aided tissue engineering (CATE). The artificial tissue has the internal mass transport network of channels embedded, deposited, or molded within a scaffold, wherein the channels are made from a biodegradable transporting material and the scaffold is made from a scaffold material. The artificial tissue of the invention includes a basic circulatory system embedded within the tissue scaffold. This system provides mass transport throughout the entire scaffold and degrades after the new circulatory system develops.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Devices and methods for use in assessing a flow condition of a fluid
InactiveUS20050249606A1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMicrocontrollerElectrochemical response
A device for use in assessing a flow condition of a fluid, or a fluid in a flow path, is provided. The device comprises at least one electrochemical cell, comprising a working electrode and at least one other electrode, sufficient for communication with the fluid, or sufficient for communication with a flow path, such that when sufficient fluid is in the flow path, the cell is in communication with the fluid. The fluid comprises a component sufficient to affect a mass-transport limited electrochemical reaction at the working electrode. The device also comprises at least one microcontroller operably connected to the at least one electrochemical cell for providing a potential or a current to the working electrode and for assessing the electrochemical reaction. A method of assessing a flow condition of a fluid, or a fluid in a flow path, is also provided. The device and the method of the present invention may be used in connection with the delivery of a fluid-borne or fluidized drug or medicament to a subject.
Owner:THERASENSE
Engineered Scaffolds for Intervertebral Disc Repair and Regeneration and for Articulating Joint Repair and Regeneration
ActiveUS20080195211A1Eliminate needDesired effective mechanicalAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone implantProperty distributionMR - Magnetic resonance
Methods for the engineering and preparation of intervertebral disc repair scaffolds and articulating joint repair scaffolds are disclosed. The methodology utilizes either magnetic resonance images or combined magnetic resonance and computed tomography images as a template for creating either the intervertebral scaffold or the joint repair scaffold (e.g., osteochondral scaffold) with fixation to the underlying bone. The disc scaffold design may include an outer annulus that may contain desired structures and a central nucleus pulposus region that could either contain a designed microstructure or a contained hydrogel. The osteochondral scaffold may include a bone compartment interface with a cartilage compartment. The bone compartment may interface with a cutout portion of the bone through fixation components. Different microstructure designs may be created for the bone and cartilage compartment to represent desired mechanical and mass transport properties. The scaffolds are designed with a microstructure that controls elastic and permeability property distribution within the scaffold.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
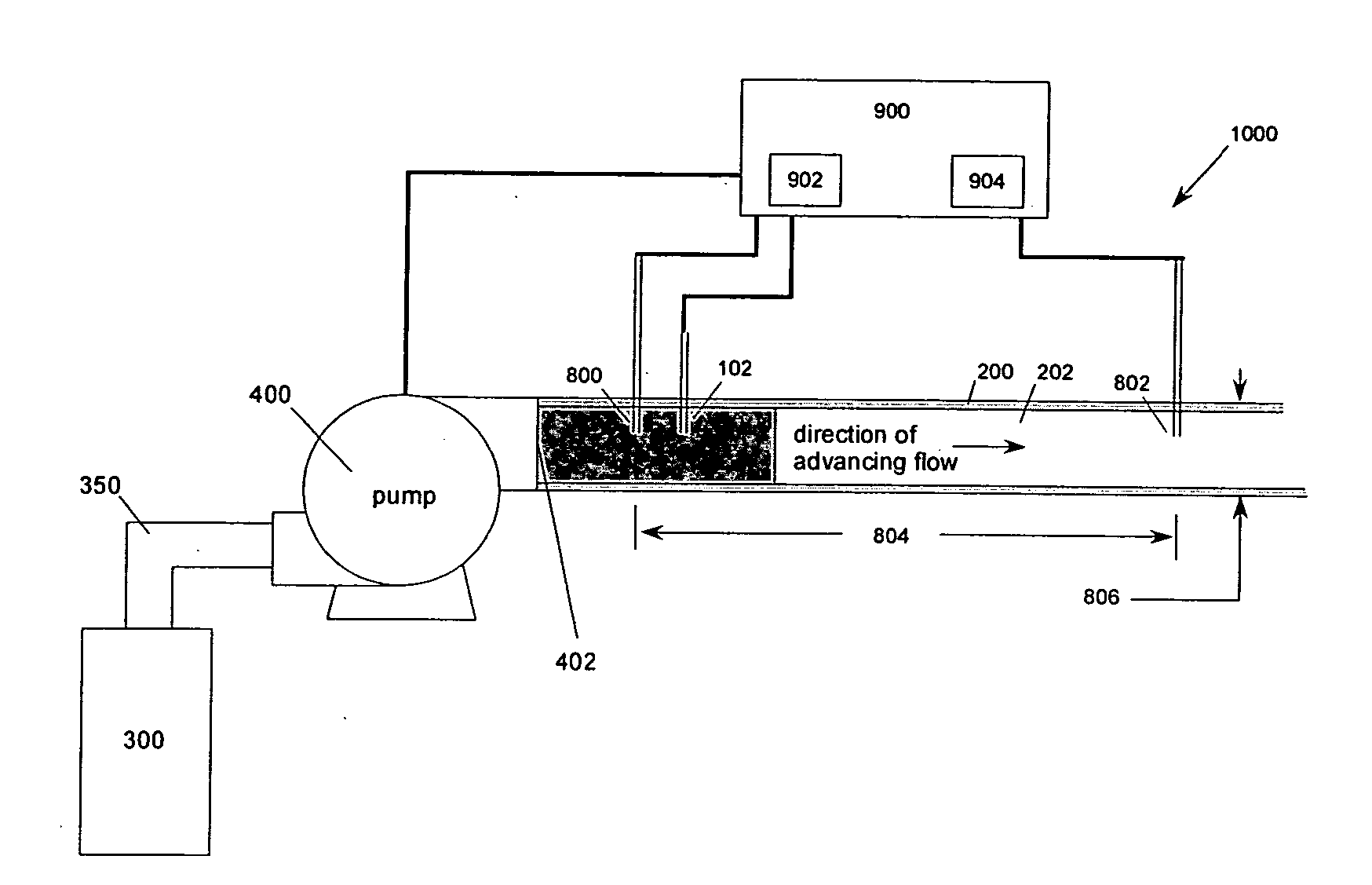
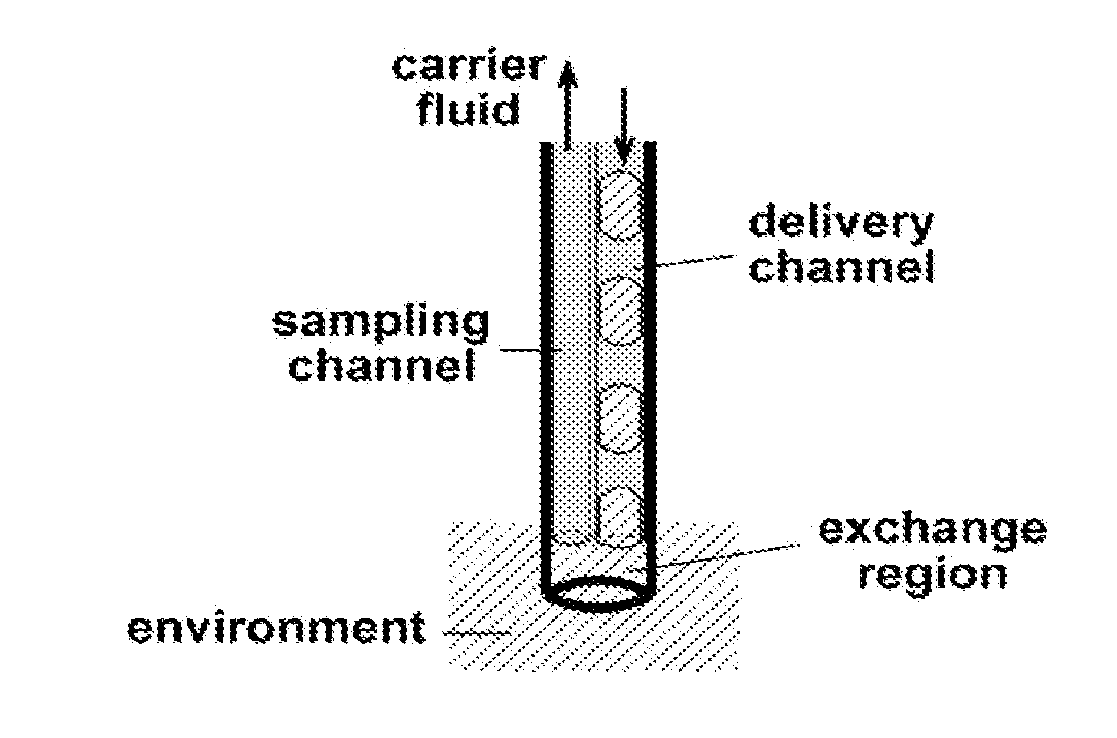
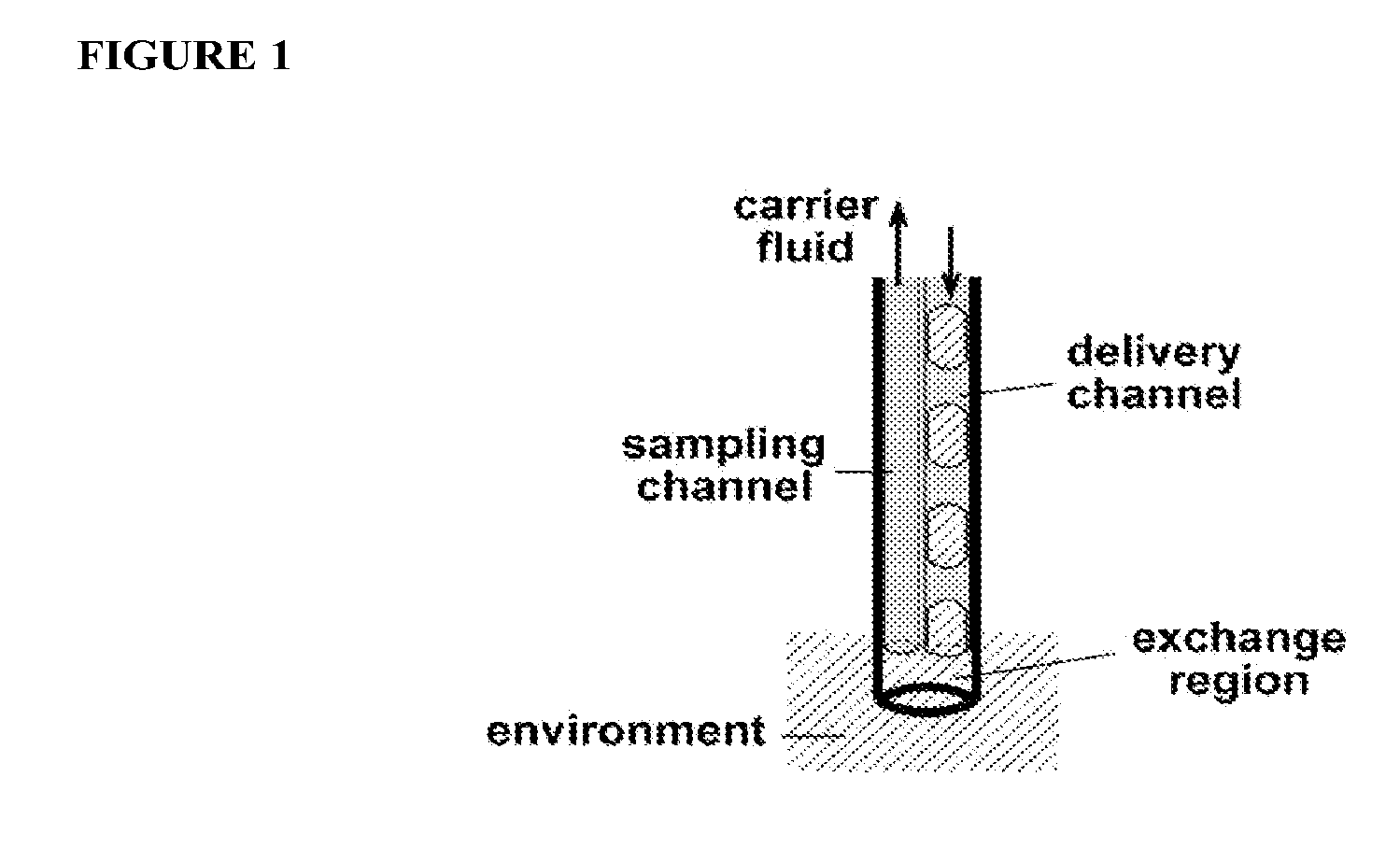
Sampling device and method for measuring fluid flow and solute mass transport
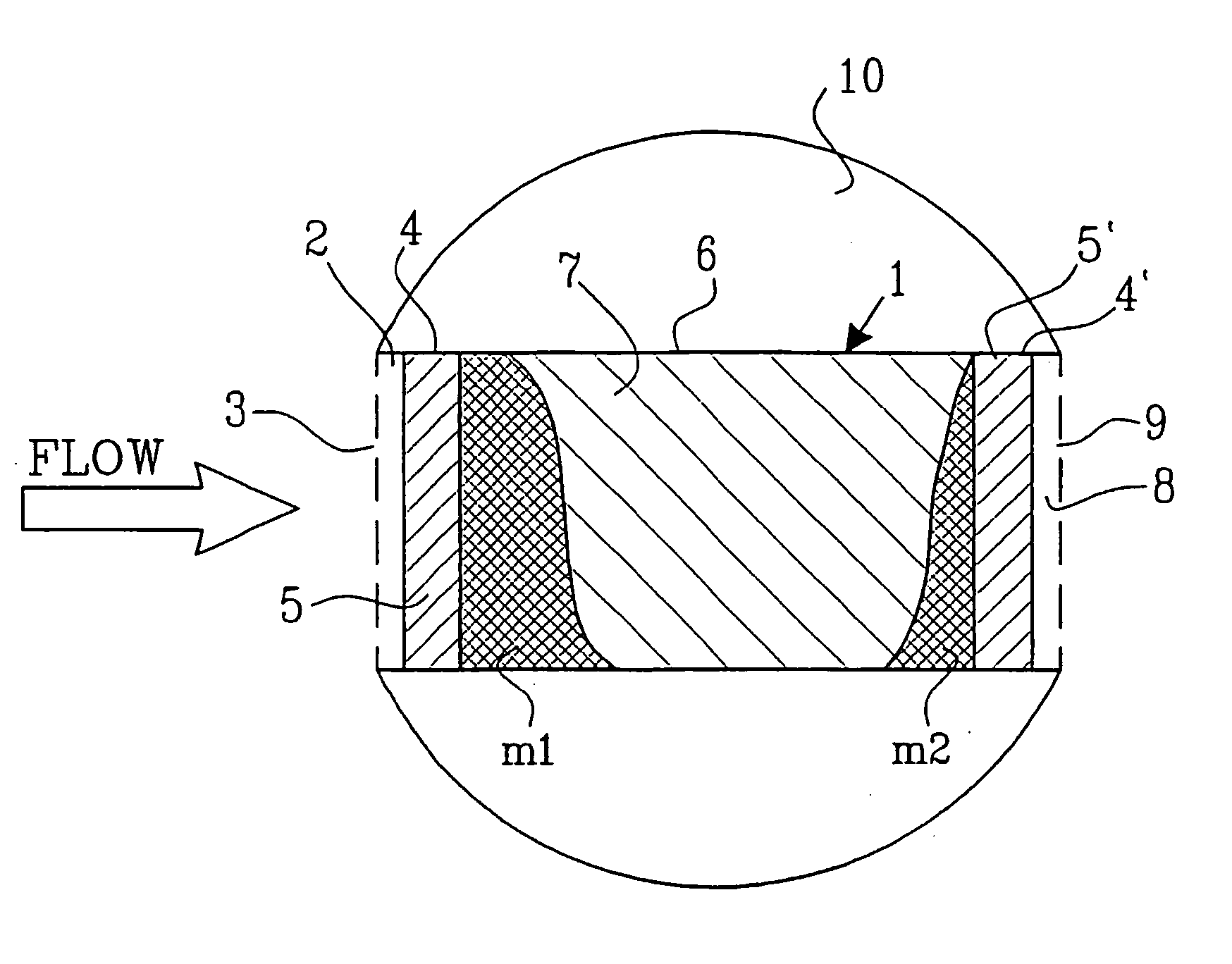
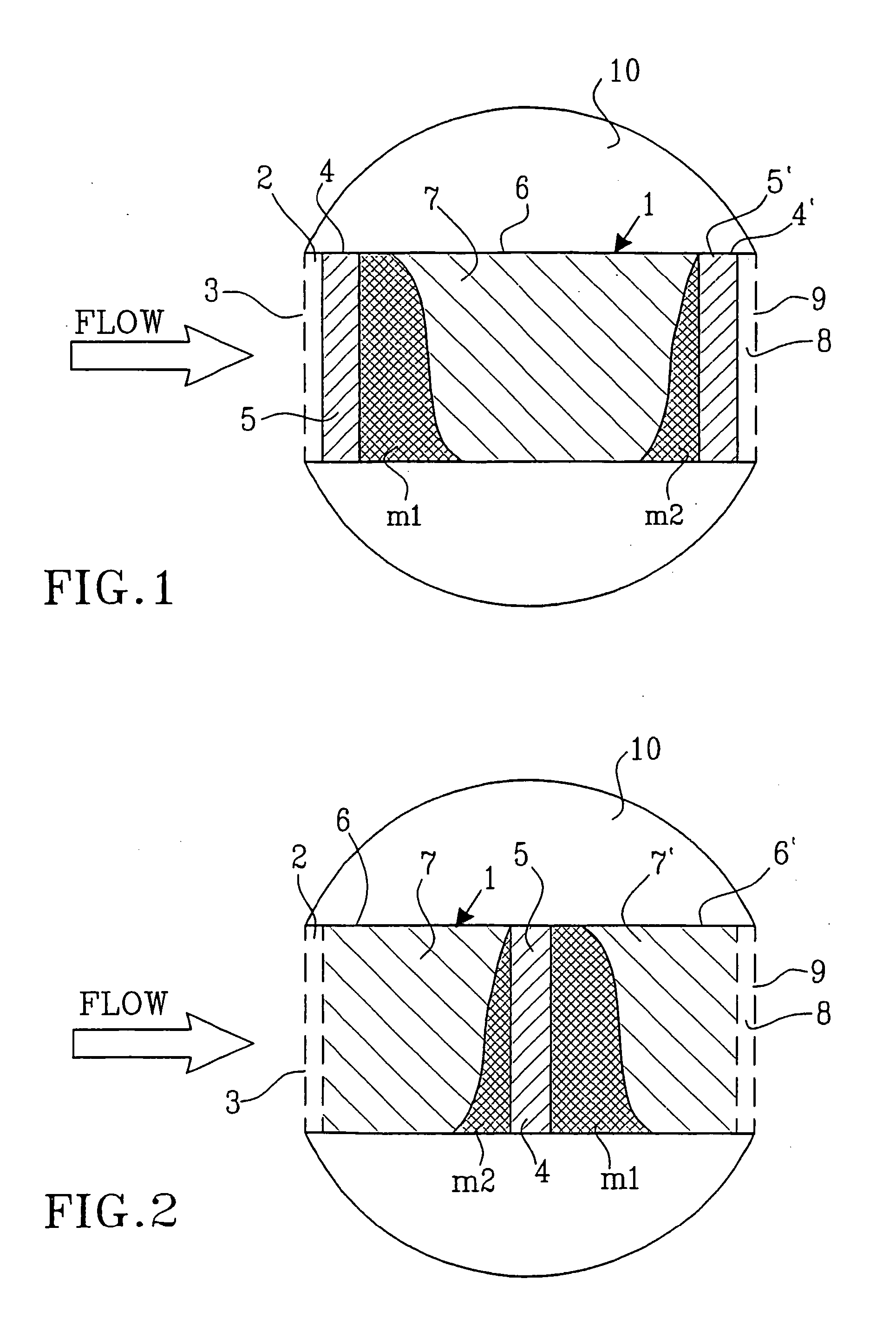
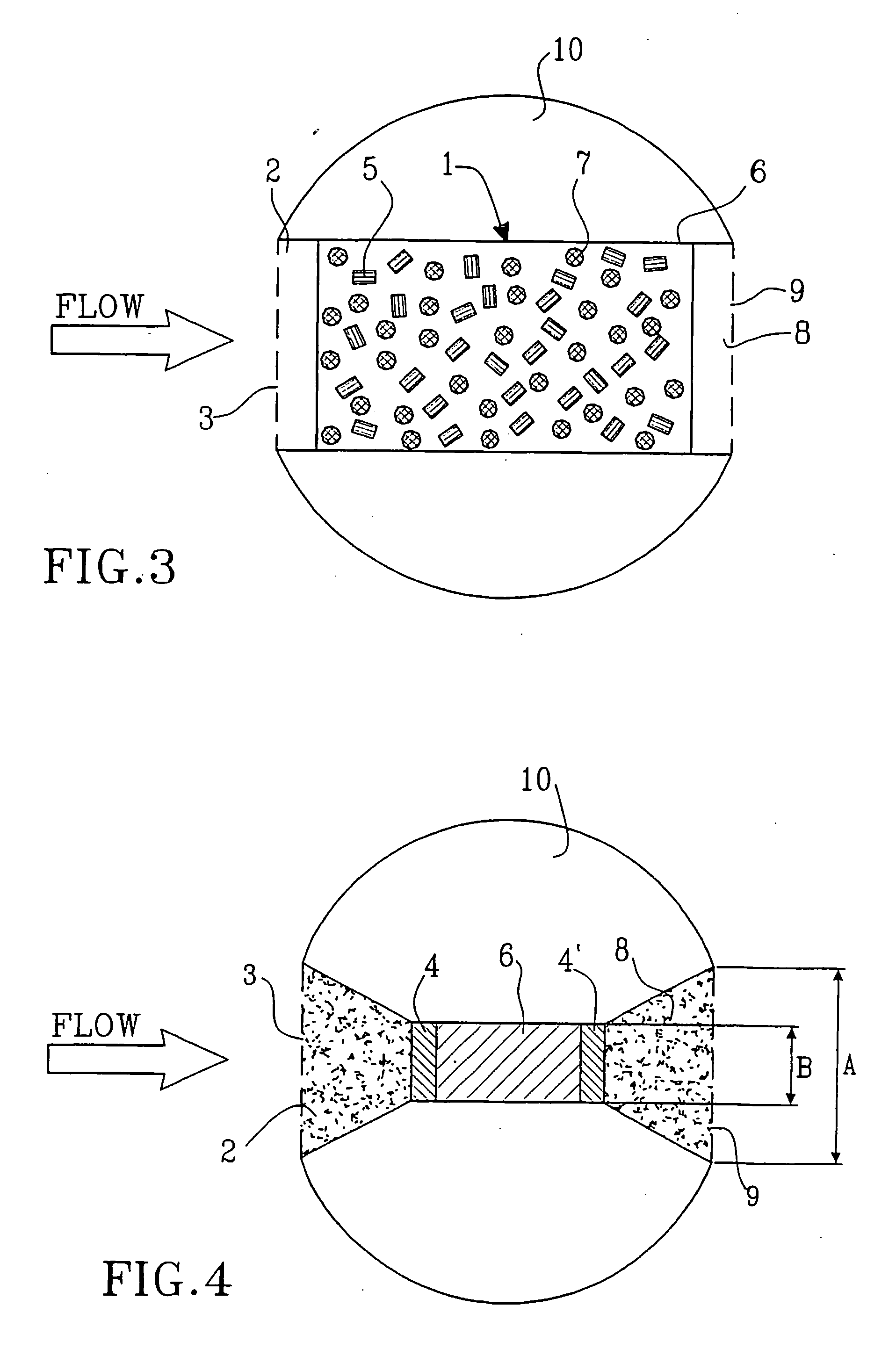
ActiveUS20050235757A1Accurate measurementComponent separationWithdrawing sample devicesSorbentStream flow
A device and a method for measuring fluid flow and solute mass transport in flow systems includes a casing (1) having inlet (3) and outlet (9) openings and a fluid passageway therebetween, the casing containing at least one fluid permeable insoluble adsorbent matrix (7) and at least one tracer material (5, 5′) located in the fluid passageway. The tracer material (5,5′) is a fluid permeable partially soluble material which at least prior to installation is not physically or chemically bonded to the adsorbent matrix (7) and is either mixed with the adsorbent matrix or is located in at least one section (4,4′) of the casing (1) separate from but in contact with at least one section (6,6′) of the casing holding the insoluble adsorbent matrix (7,7′). The device is intended to be installed in a medium having a fluid path therein.
Owner:AARHUS UNIV
Engineered scaffolds for intervertebral disc repair and regeneration and for articulating joint repair and regeneration
ActiveUS8275594B2Eliminate needDesired effective mechanical and mass transport propertyAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone implantProperty distributionMass transport
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
Gas Separator Apparatus
ActiveUS20080134895A1Speed up heat transferGood choiceMembranesSemi-permeable membranesChemical speciesProduct gas
An apparatus for separating at least one component from a mixture of a plurality of chemical species is provided. The apparatus comprises a membrane structure comprising a plurality of pores disposed within a matrix material to allow mass transport from a first surface of the membrane structure to a second surface of the membrane structure. The matrix material has a thermal conductivity of at least about 10 W / m / K; and a functional material disposed within at least a portion of the plurality of pores. The functional material has the property of promoting selective transport of at least one species through the membrane structure from the first surface to the second surface.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
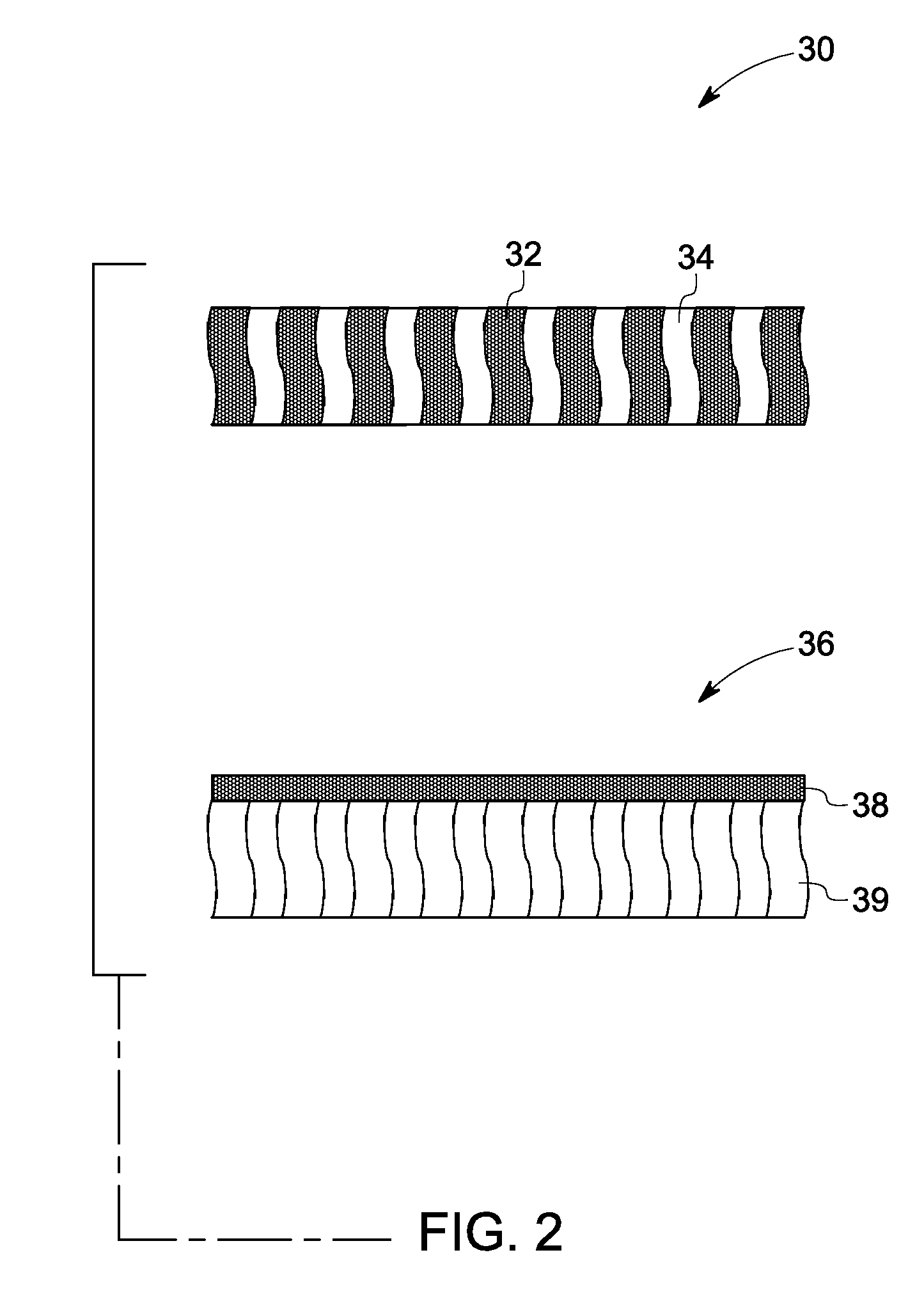
Redox and plating electrode systems for an all-iron hybrid flow battery
A system for a flow cell for a hybrid flow battery, comprising: a redox plate comprising a plurality of electrolyte flow channels; conductive inserts attached to the redox plate between adjacent electrolyte flow channels; a redox electrode attached to a surface of the redox plate; a plating electrode, comprising: a plurality of folded fins with an oscillating cross-section, the plurality of folded fins comprising: a first planar surface; a second planar surface, parallel to the first planar surface; a plurality of ridges intersecting the first and second planar surfaces such that the plurality of ridges divide the first planar surface into a first plurality of strips, and divide the second planar surface into a second plurality of strips; and a membrane barrier. In this way, the capacity and performance of hybrid flow batteries may be maximized, through decreasing the reaction kinetics, mass transport and ohmic resistance losses at both electrodes.
Owner:ESS TECHNOLOGY
Method for creating an internal transport system within tissue scaffolds using computer-aided tissue engineering
An artificial tissue including an internal mass transport network having a plurality of channels, wherein the channels are designed to substantially mimic naturally occurring vascular network and a method for creating an internal transport system within a tissue scaffold to improve circulation, diffusion, and mass transport properties by utilizing computer-aided tissue engineering (CATE). The artificial tissue has the internal mass transport network of channels embedded, deposited, or molded within a scaffold, wherein the channels are made from a biodegradable transporting material and the scaffold is made from a scaffold material. The artificial tissue of the invention includes a basic circulatory system embedded within the tissue scaffold. This system provides mass transport throughout the entire scaffold and degrades after the new circulatory system develops.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
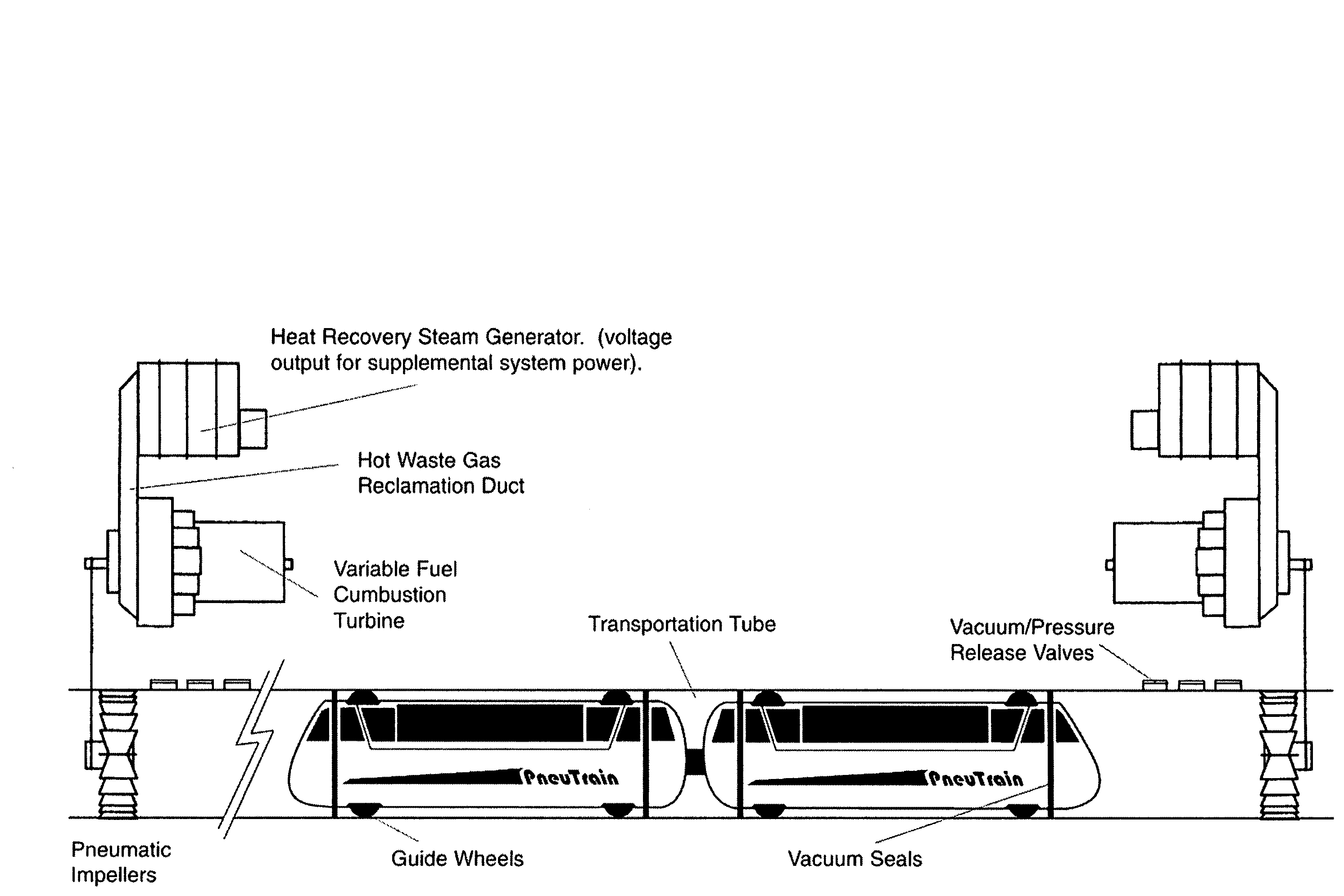
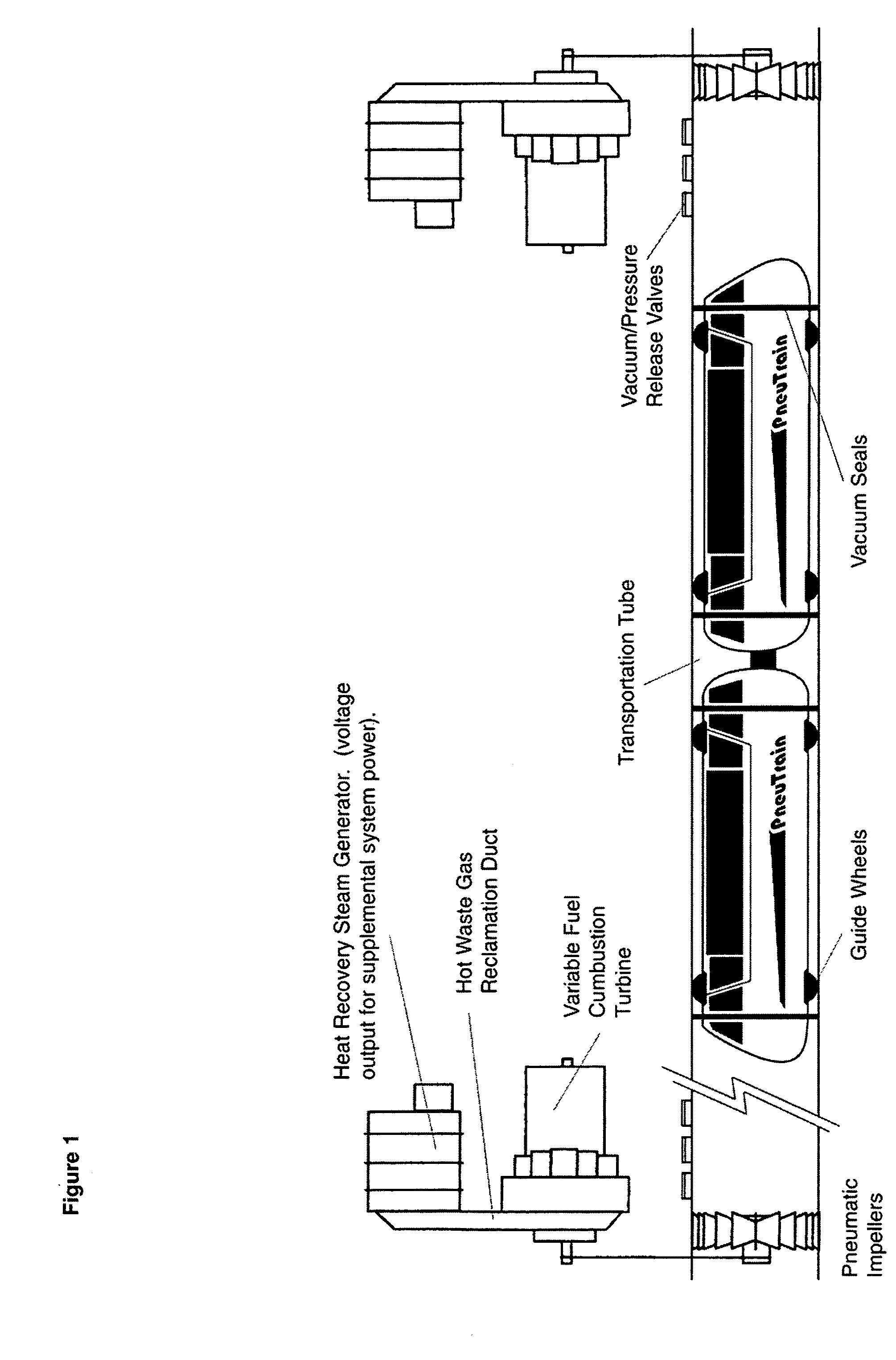
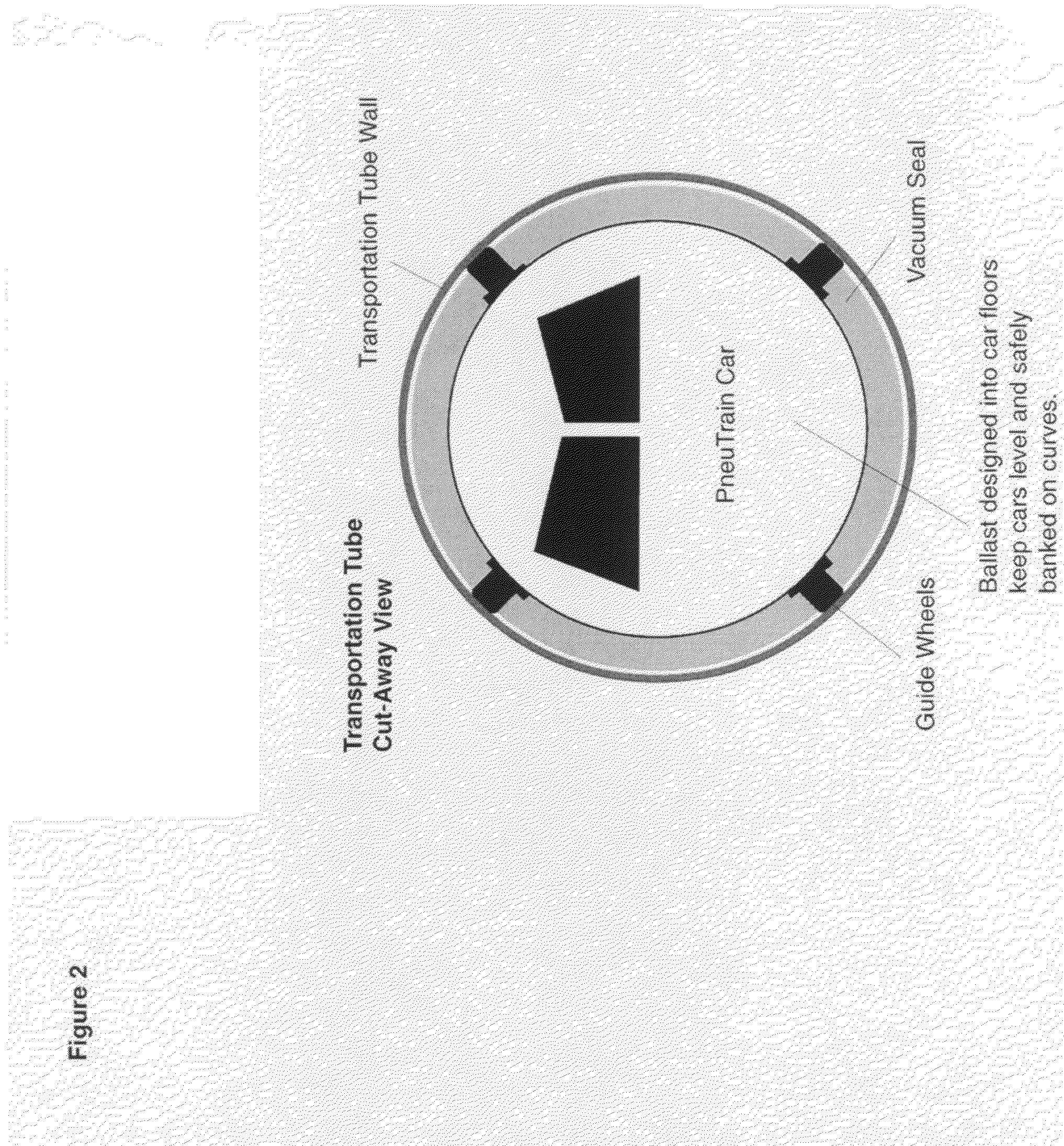
Pneutrain pneumatic mass transportation system
This invention is a pneumatic mass transportation system on the cutting edge of technology employing a combined cycle turbine power system with digital controls to effect acceleration, deceleration and train propulsion. The combustion turbines can be adapted to use alternative fuels including bio fuels as they are developed. The heat recover steam generator will recycle the hot exhaust gasses from the turbines to generate electricity to be used by the system. The multi-car train is propelled by differential air pressure forward and aft of the vehicle in the pneumatic tube. Air propulsion is achieved by large in-tube impellers driven by the turbines. A digital control system will operate the pitch of the impeller blades and the vacuum / pressure release valves in the tubes to produce full movement control of the trains.
Owner:FLYNN PATRICK JOSEPH
Electrodes With Multilayer Membranes And Methods Of Making The Electrodes
A sensor including a sensing layer is disposed over an electrode or an optode and a layer-by-layer assembled mass transport limiting membrane disposed over the sensing layer. The membrane includes at least one layer of a polyanionic or polycationic material. The assembled layers of the membrane are typically disposed in an alternating manner. The sensor also optionally includes a biocompatible membrane.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
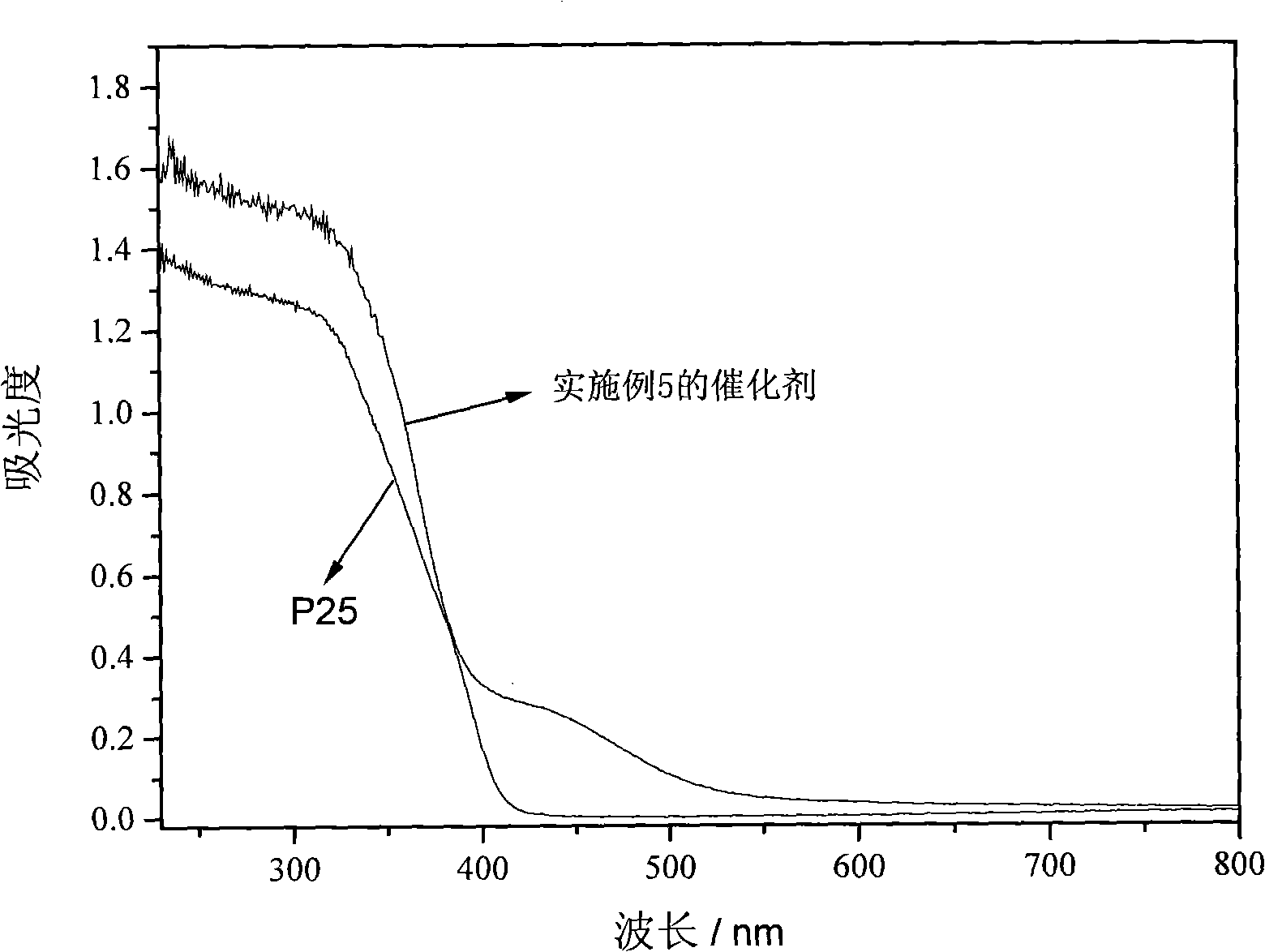
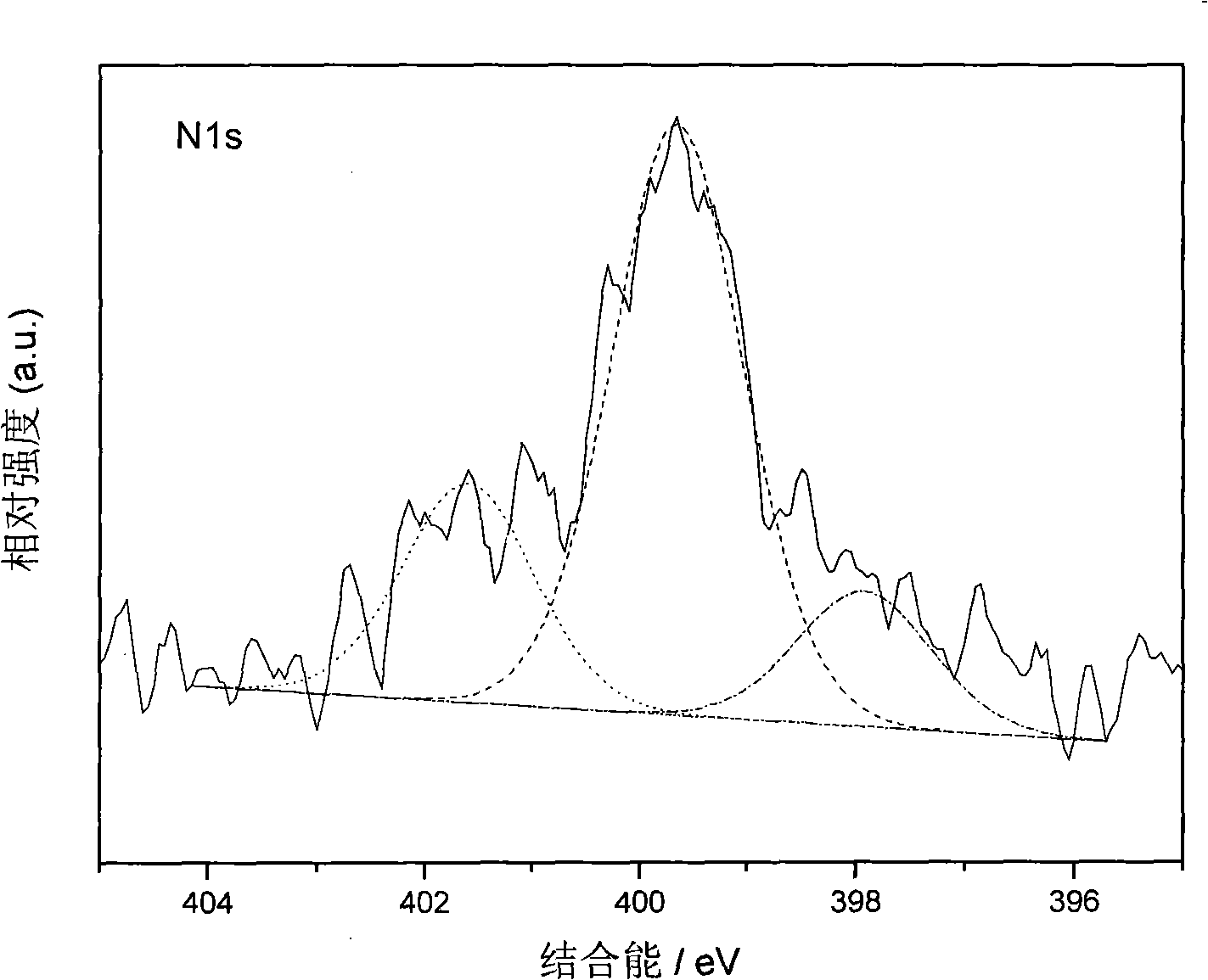
Load type nitrogen intermingle with one-dimensional structure TiO2 and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101279250ALarge specific surface areaEnhanced mass transferPhysical/chemical process catalystsDeodrantsIon exchangeActive point
The invention discloses a photocatalyst of loaded nonmetal nitrogen doping one-dimensional TiO2 for exciting visible light and a preparation method thereof. In the method, a metal Ti plate and concentrated alkaline solution is taken as the main raw materials, visible light photocatalyst of the loaded nonmetal nitrogen one-dimensionally doping TiO2 is prepared by acidification, ion exchange and following heat treatment and by hydrothermal technology. The photocatalyst prepared by the invention is characterized in that the doping of nitrogen leads the catalysis to absorb the visible light and the absorption wavelength red shift is 600nm; the catalyst self is a in loaded style, which solves the defect that granulated catalyst is easy to fall off; the catalyst has a one-dimensional structure, large specific surface and abundant active points, which is favorable for strengthening reaction and mass transport process, thus realizing the degradation of typical indoor air contamination, compared with granulated nitrogen doping TiO2, the activity is higher to 1.2-3.0 times.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ZHONGDE IND
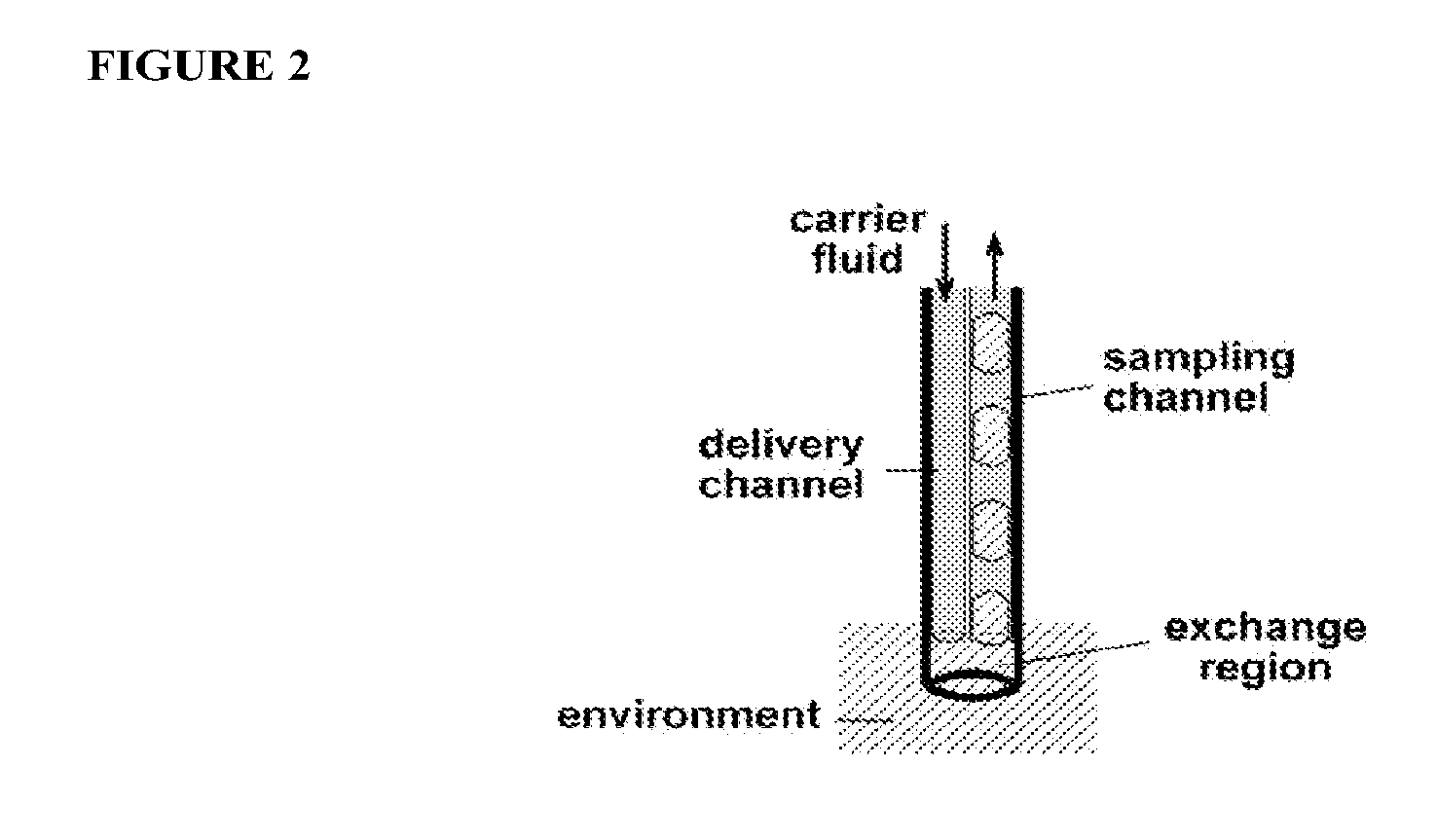
Chemistrode, a plug-based microfluidic device and method for stimulation and sampling with high temporal, spatial, and chemical resolution
A method for sampling and / or introducing a matter to an environment comprises introducing a first array of plugs through a first microchannel of a device into an exchange region of the device in which mass transport between the environment and the plug fluid of at least one plug in the first array of plugs occurs and a second array of plugs is formed. The exchange region is in fluid communication with the first microchannel. The method further comprises directing the second array of plugs into a second microchannel downstream of and in fluid communication with the exchange region.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Methods for use in assessing a flow condition of a fluid
InactiveUS7399401B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMicrocontrollerElectrochemical response
A device for use in assessing a flow condition of a fluid, or a fluid in a flow path, is provided. The device comprises at least one electrochemical cell, comprising a working electrode and at least one other electrode, sufficient for communication with the fluid, or sufficient for communication with a flow path, such that when sufficient fluid is in the flow path, the cell is in communication with the fluid. The fluid comprises a component sufficient to affect a mass-transport limited electrochemical reaction at the working electrode. The device also comprises at least one microcontroller operably connected to the at least one electrochemical cell for providing a potential or a current to the working electrode and for assessing the electrochemical reaction. A method of assessing a flow condition of a fluid, or a fluid in a flow path, is also provided. The device and the method of the present invention may be used in connection with the delivery of a fluid-borne or fluidized drug or medicament to a subject.
Owner:THERASENSE
Nanoscale relaxation oscillator
InactiveUS20060118782A1Mechanical force is largeHigh frequencyNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesIndiumCarbon nanotube
A nanoscale oscillation device is disclosed, wherein two nanoscale droplets are altered in size by mass transport, then contact each other and merge through surface tension. The device may also comprise a channel having an actuator responsive to mechanical oscillation caused by expansion and contraction of the droplets. It further has a structure for delivering atoms between droplets, wherein the droplets are nanoparticles. Provided are a first particle and a second particle on the channel member, both being made of a chargeable material, the second particle contacting the actuator portion; and electrodes connected to the channel member for delivering a potential gradient across the channel and traversing the first and second particles. The particles are spaced apart a specified distance so that atoms from one particle are delivered to the other particle by mass transport in response to the potential (e.g. voltage potential) and the first and second particles are liquid and touch at a predetermined point of growth, thereby causing merging of the second particle into the first particle by surface tension forces and reverse movement of the actuator. In a preferred embodiment, the channel comprises a carbon nanotube and the droplets comprise metal nanoparticles, e.g. indium, which is readily made liquid.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Vacuum low temperature microscopic visualizer
InactiveCN101231249AAccurate observationComprehensive observationMaterial analysis by optical meansMaterial thermal analysisEngineeringData treatment
The invention relates to a vacuum low temperature micro visualize, which comprises a sight chamber, a cold trap, a refrigeration system, a vacuum system, and a control and teat recording system. A microscope, an electronic scale, a cooling and heating element, a winding lens shielding mechanism, a temperature sensing element, and a pressure sensing element are arranged in the sight chamber. A low temperature condensing coil is arranged in a cold trap chamber, the refrigeration system is connected with a heating refrigeration board and a nozzle of the sight chamber as well as the condensing coil of the cold tap chamber. A vacuum pump is connected with a pumping hole of the cold trap chamber, the computer control and teat recording system is connected with a thermocouple, the electronic scale, and the sight chamber, and is connected with an image collector above the microscope through an image data processor. The invention can be used for studying the heat-transfer and mass-transport process of various solids and liquid materials under the condition of low temperature and vacuum, and for timely and continuously observing the mass, the temperature, the pressure, and the micro image of the observed materials, which are recorded and stored by a computer, thereby realizing the numeralization operation.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method and system for determination of molecular interaction parameters
A method of determining kinetic parameters for a reversible molecular interaction between a ligand immobilized to a solid support surface and a binding partner to the ligand in solution, comprises sequentially, without intermediate regeneration or renewal of the immobilized ligand, flowing a plurality of fluid volumes containing different known concentrations of the binding partner over the solid support surface, monitoring the momentary amount of binding partner bound to the solid support surface related to time and solution concentration of binding partner and collecting the binding data, and determining the kinetic parameters by globally fitting a predetermined kinetic model for the interaction between the binding partner and the immobilized ligand to the collected binding data, which model allows for mass transport limitation at the solid support surface. An analytical system for carrying out the method, a computer program, a computer program product and a computer system for performing the method are also disclosed.
Owner:CYTIVA SWEDEN AB
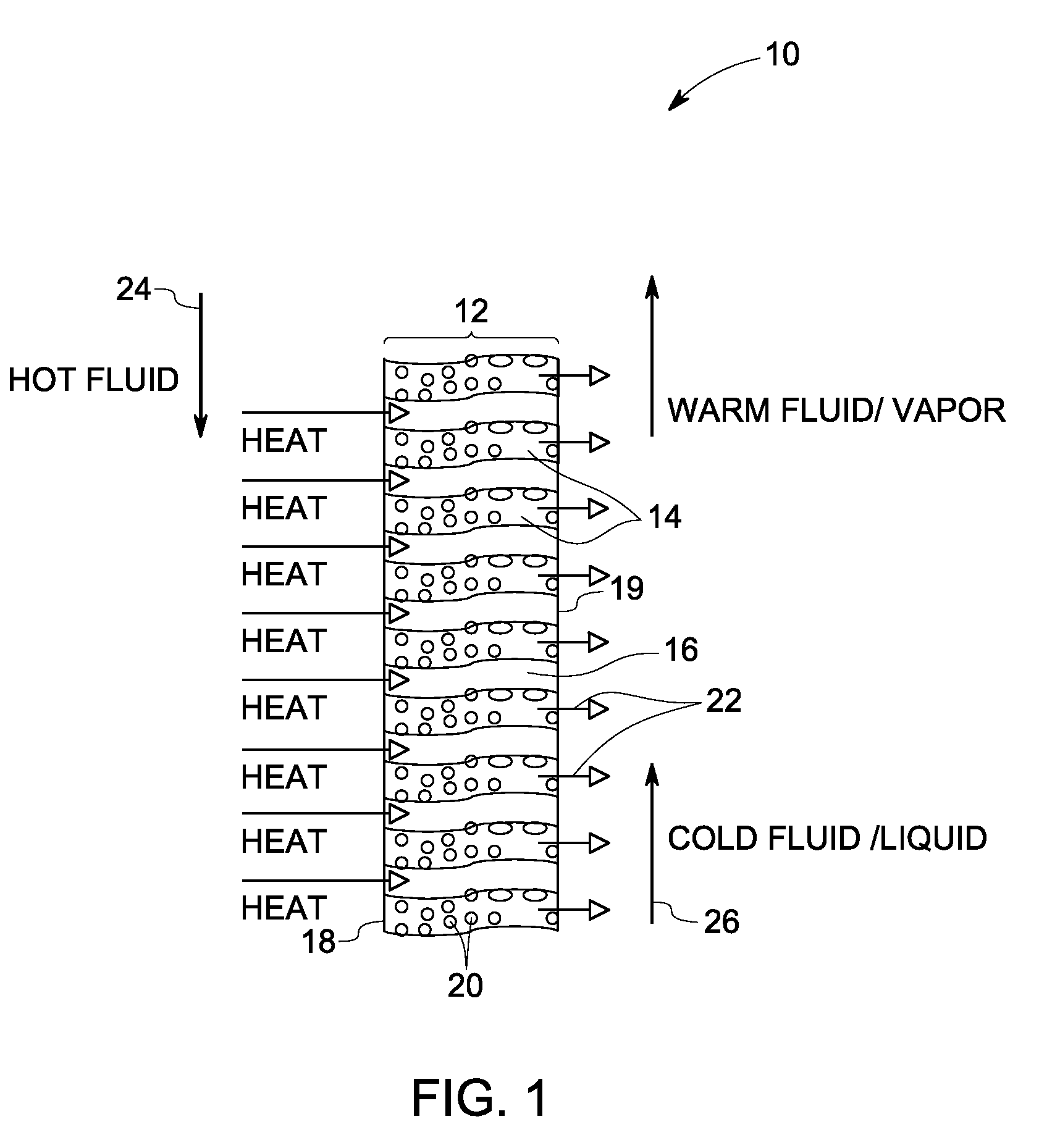
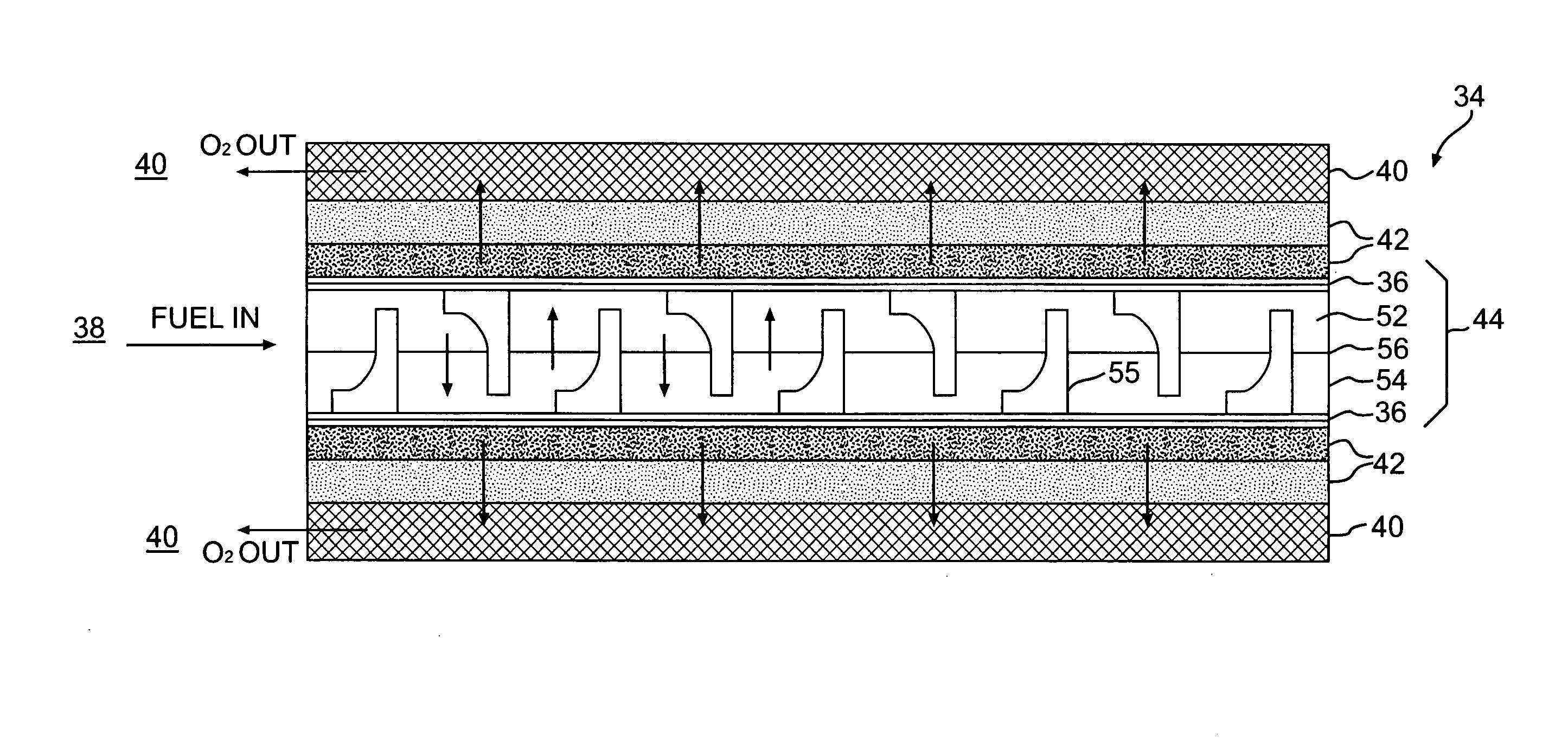
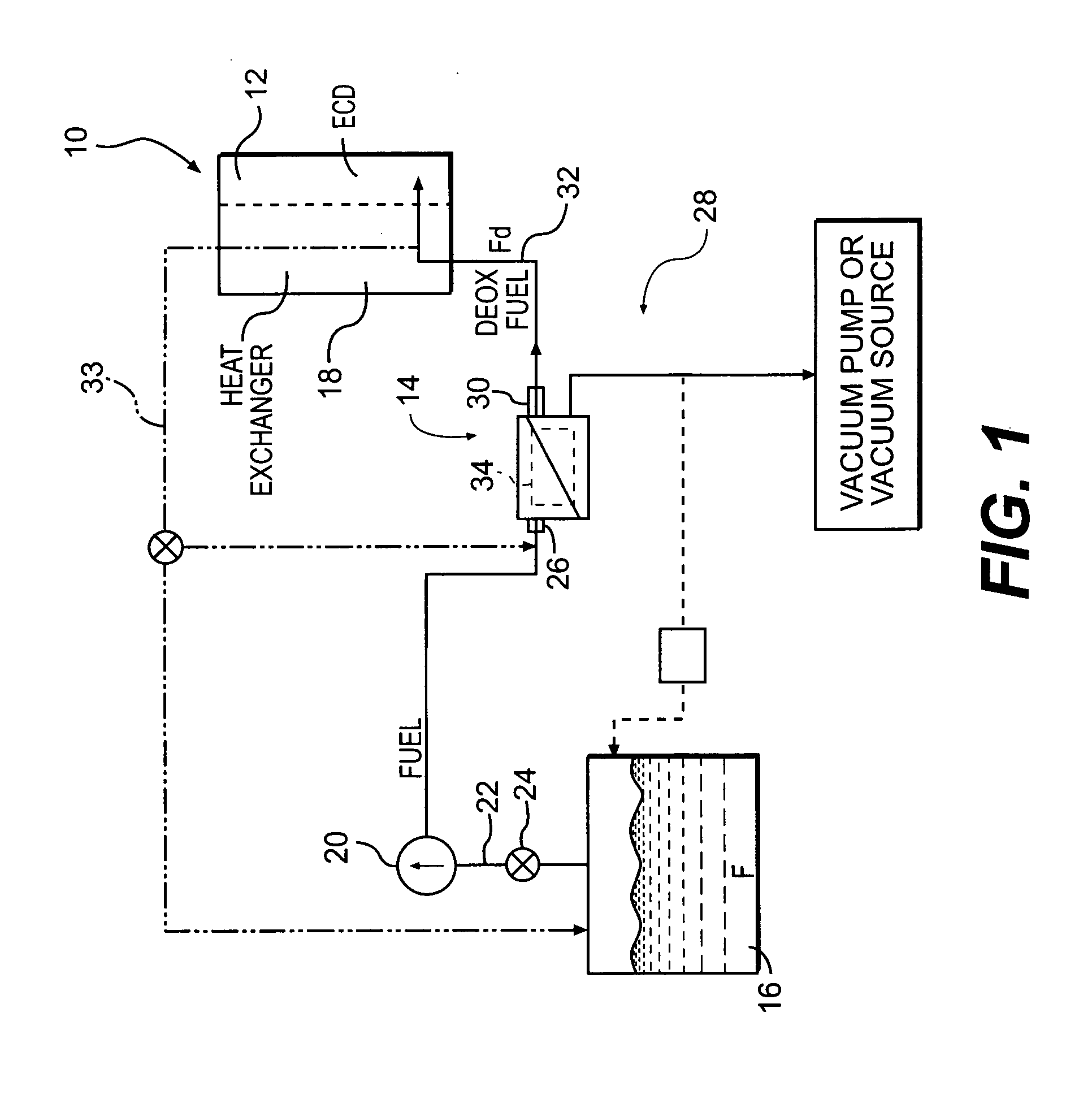
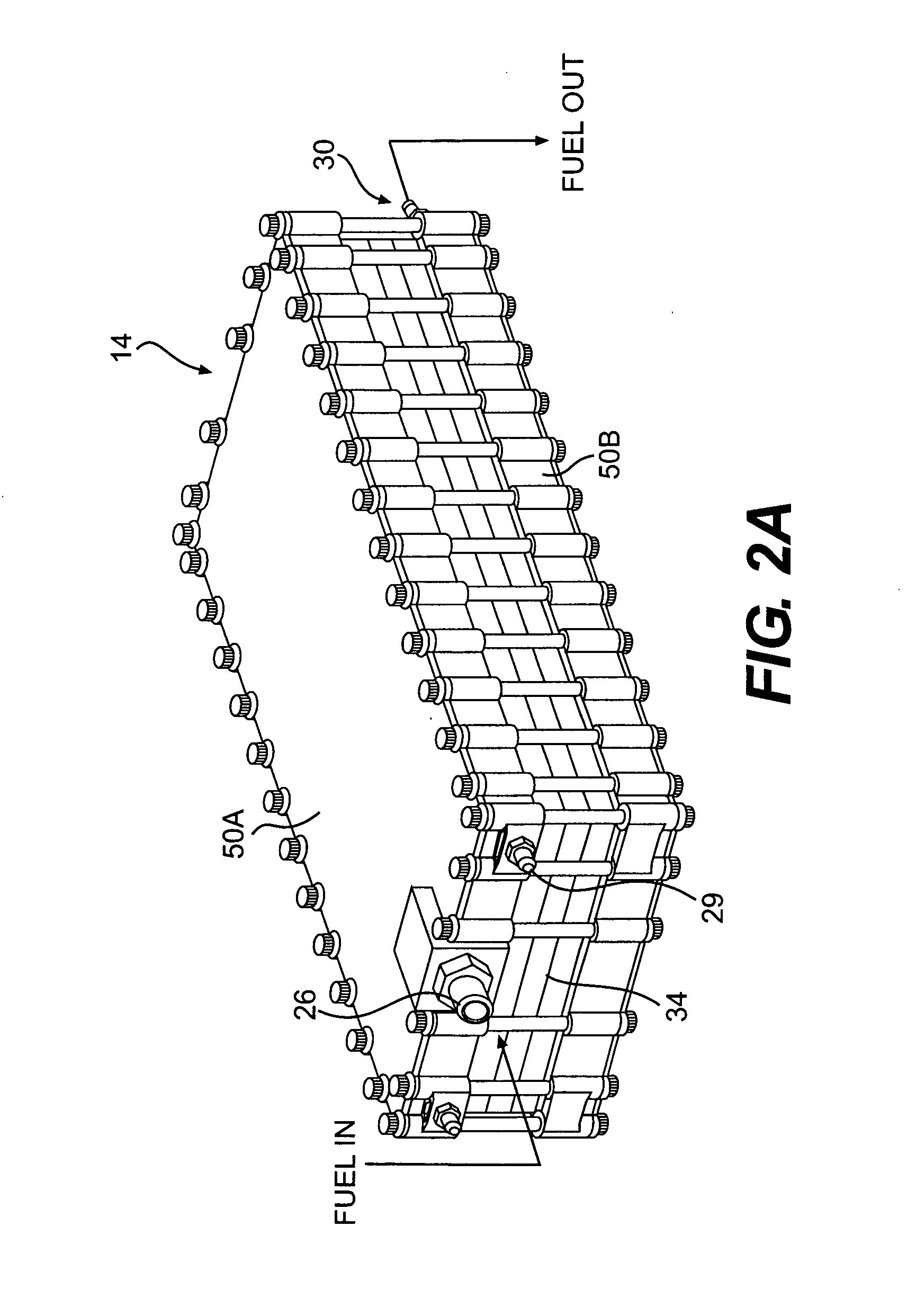
Method for enhancing mass transport in fuel deoxygenation systems
ActiveUS7824470B2Increase mass transportEasy to transportSemi-permeable membranesFlow mixersMembrane surfaceEngineering
A fuel system for an energy conversion device includes a deoxygenator system with a multitude of flow impingement elements which are interleaved to provide a fuel channel with intricate two-dimensional flow characteristics. The flow impingement elements break up the boundary layers and enhance the transport of oxygen from the core of the of the fuel flow within the fuel channel to the oxygen permeable membrane surfaces by directing the fuel flow in a direction normal to the oxygen permeable membrane. The rapid mixing of the relatively rich oxygen core of the fuel with the relatively oxygen-poor flow near the oxygen permeable membrane enhances the overall removal rate of oxygen from the fuel. Because this process can be accomplished in fuel channels of relatively larger flow areas while maintaining laminar flow, the pressure drop sustained is relatively low.
Owner:RTX CORP
Shutter mechanism for fuel cell
A shutter mechanism for use with a direct oxidation fuel cell system is provided within a fuel cell system between the reactant to be controlled and the MEA of the fuel cell. On the anode side, the shutter mechanism can disposed in the vapor gap between a passive mass transport barrier and the anode current collector. This embodiment of the shutter mechanism of the present invention operates in z-axis plane perpendicular to the plate itself and perpendicular to the general direction of fuel flow. In this manner, additional lateral volume is not required for movement of the shutter plate. In accordance with another aspect of the invention, one part of the shutter mechanism is integrated into the current collector, the fuel cell housing, or other component of the fuel cell. In other words, the moving shutter plate has features that correspond with openings in either the anode or the cathode current collector, and such features can be used in conjunction with the current collector to provide control of substances travelling into and out of the fuel cell. The present invention can also be used for heat transfer within the fuel cell system.
Owner:MTI MICROFUEL CELLS
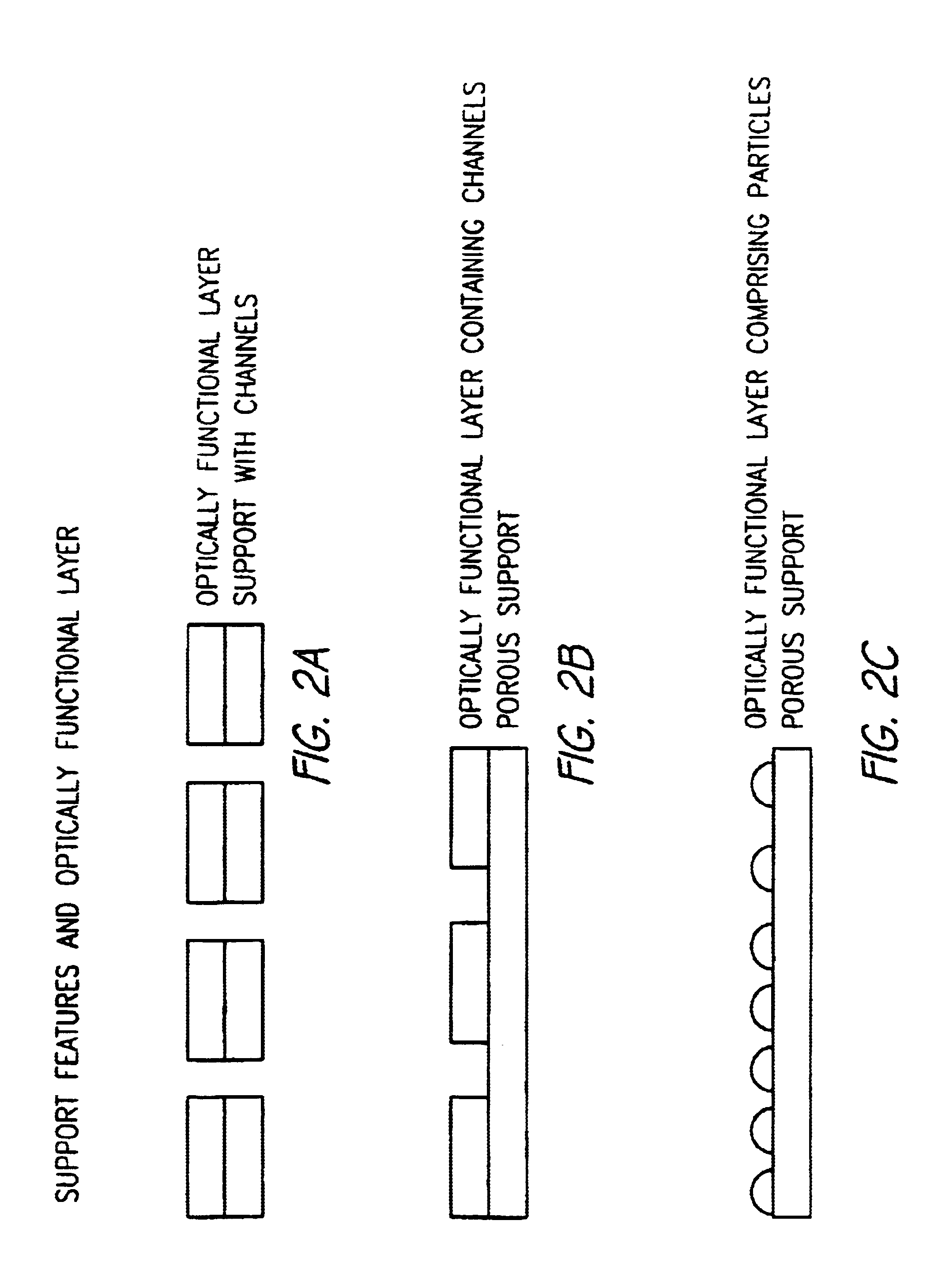
Device for mass transport assisted optical assays
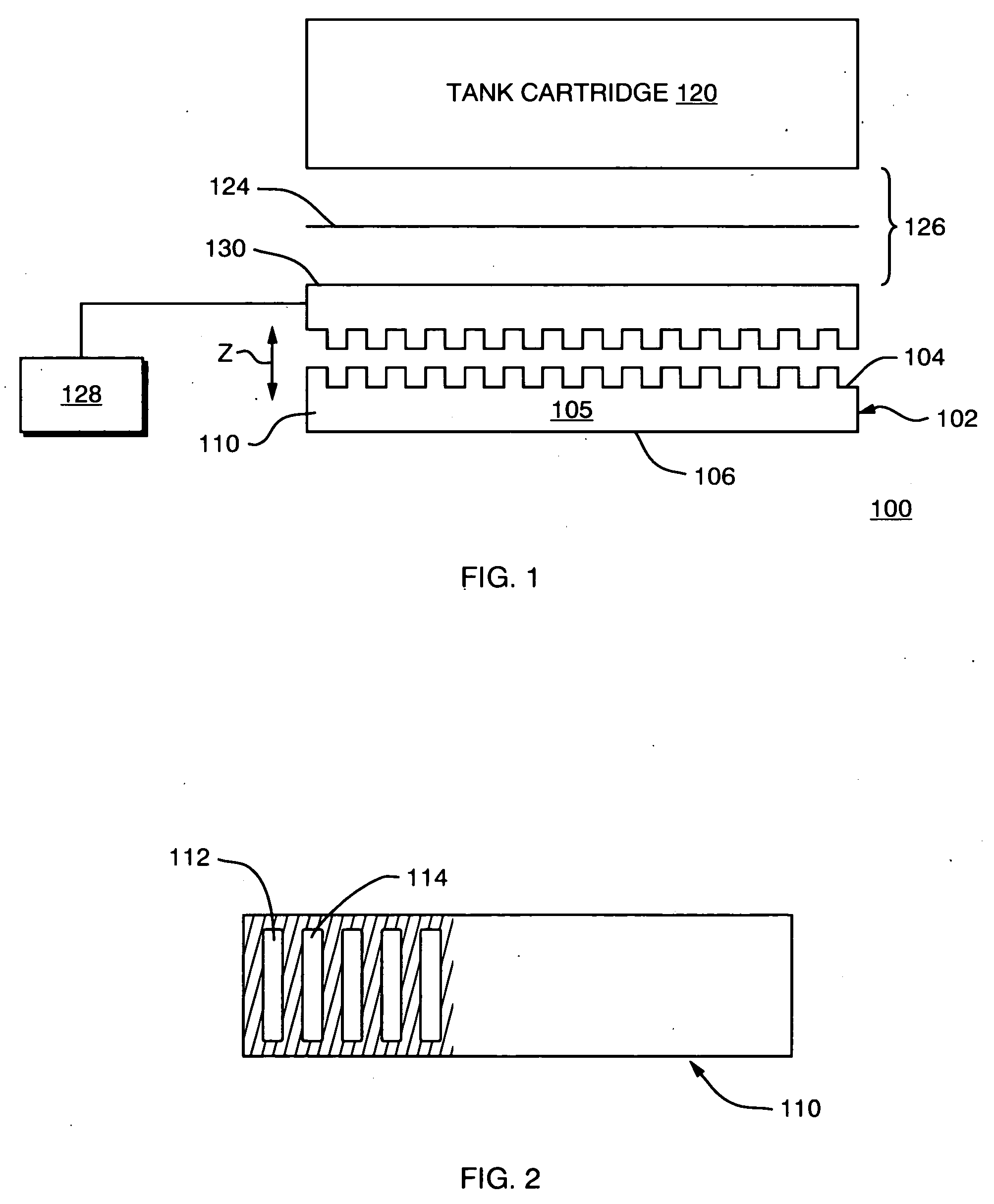
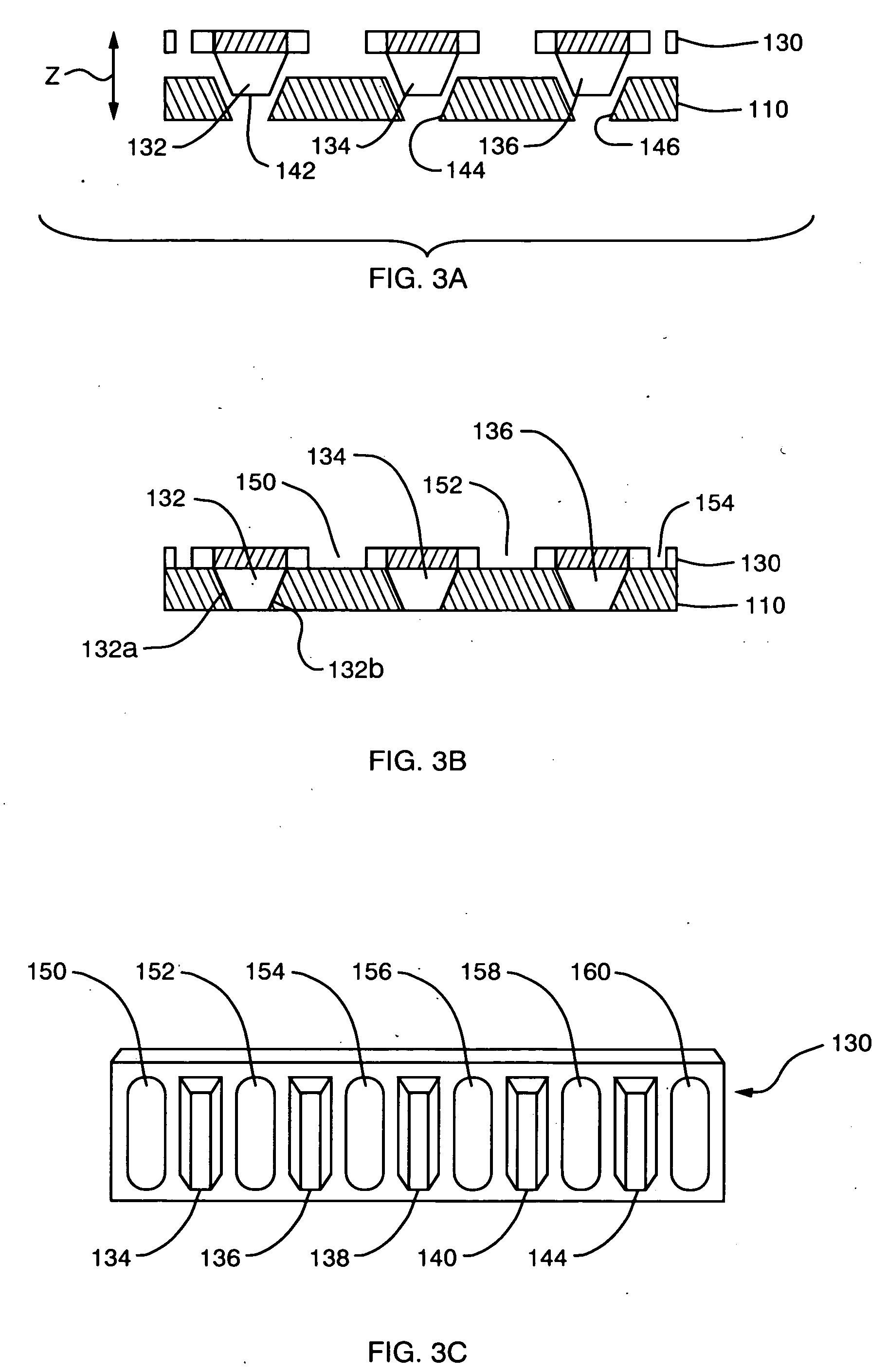
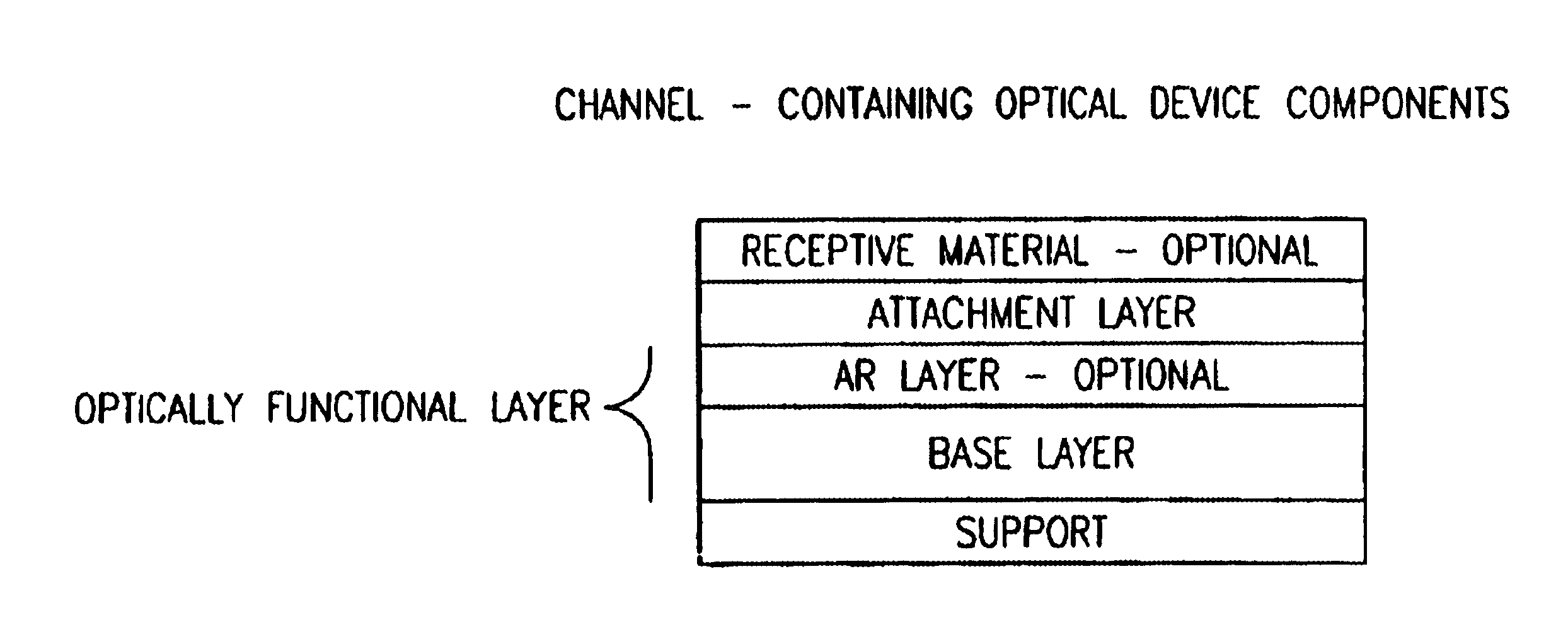
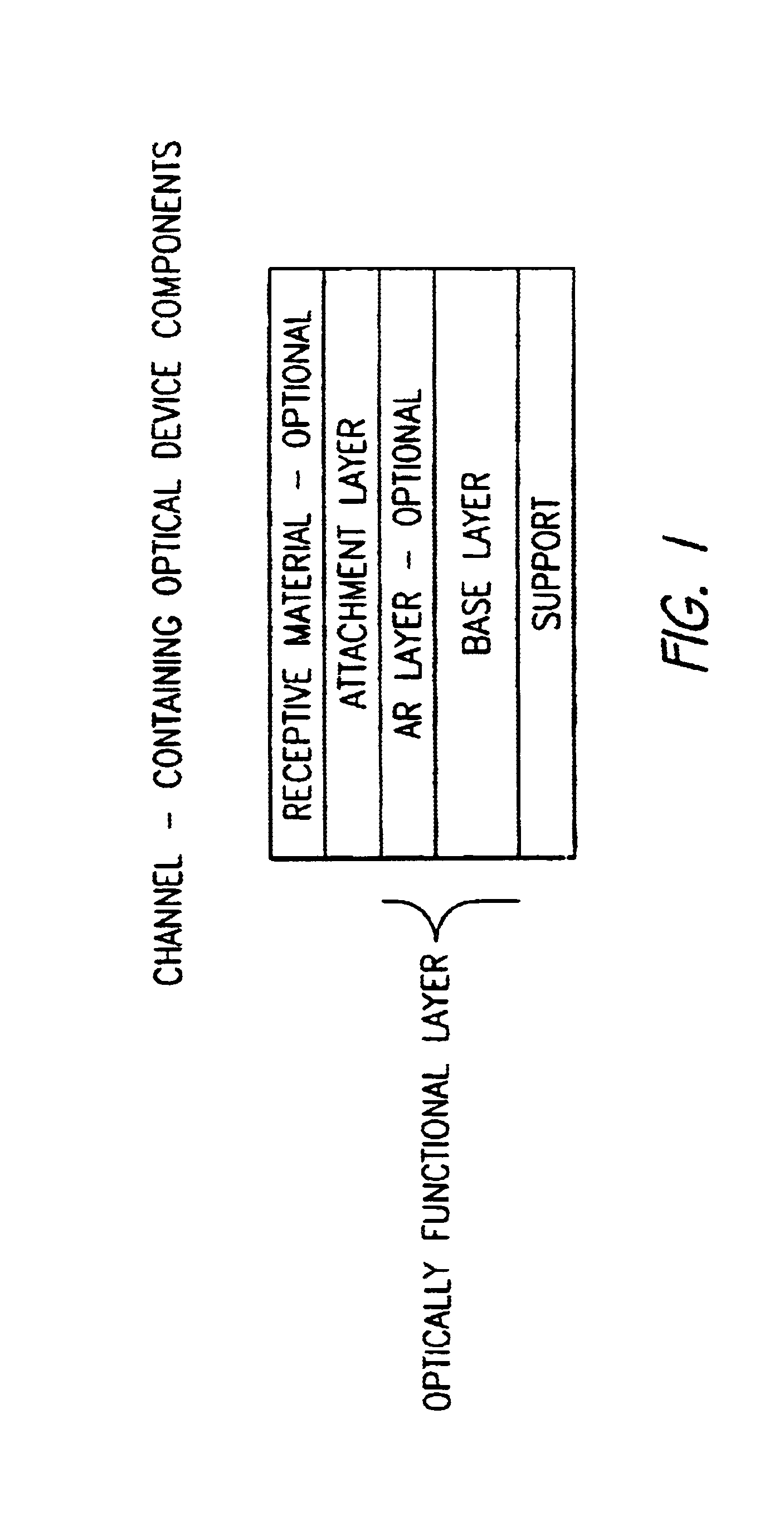
InactiveUS6933112B1High sensitivityHigh analytical sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteMass transport
An optical assay device for the detection of an analyte of interest in a sample comprising a support containing channels, an optically functional layer positioned on the support such that the optically functional layer and the support allow for laminar flow of the sample through layers of the device, an attachment layer positioned on the optically functional layer, and an analyte specific receptive layer positioned on the attachment layer.
Owner:INVERNESS MEDICAL - BIOSTAR
Micro gap flow through electrochemical devices with self adjusting reactive surfaces
Contemplated electrochemical devices and methods include an electrolyte flow path in which substantially all of the electrolyte has laminar flow. A segmented electrode contacts the electrolyte, and each of the segments in the segmented electrode is preferably coupled to a control device to provide control over the flow of current to and / or from the electrolyte. Thus, it should be appreciated that the redox state of the electrolyte can be changed in a single-pass through the flow path, which effectively eliminates problems associated with mass transport phenomena and reduced current efficiency.
Owner:CLARKE RICHARD
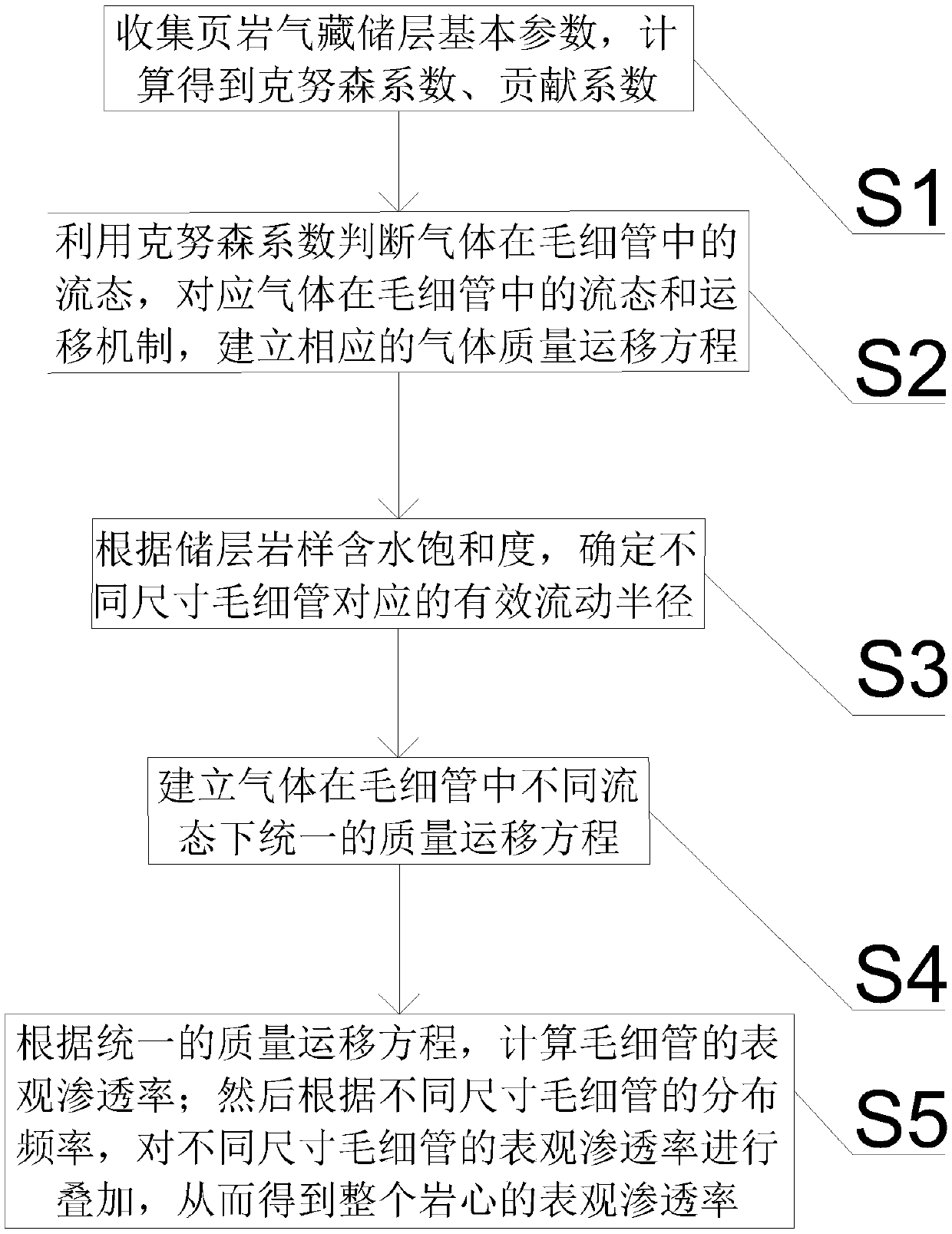
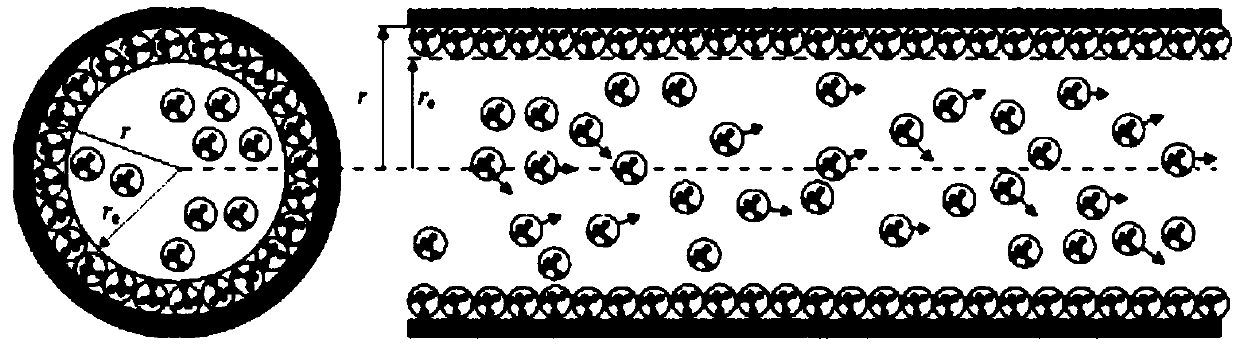
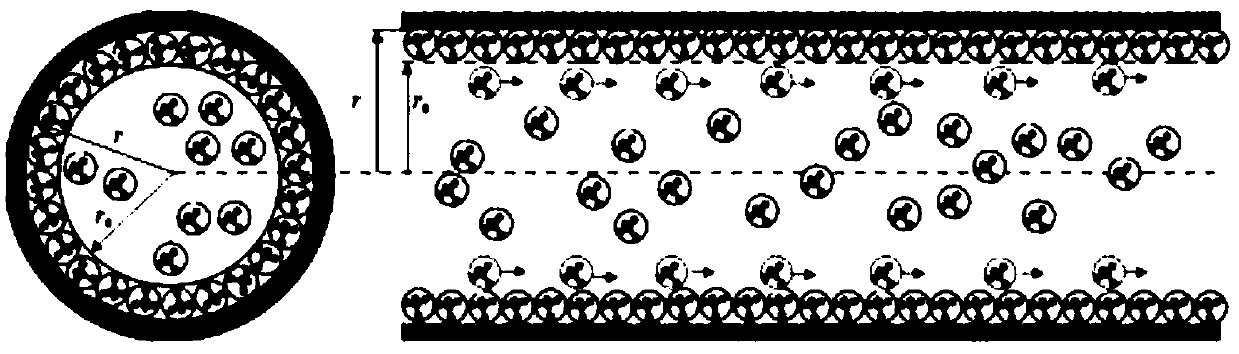
Method for calculating apparent permeability of porous media of shale reservoir
ActiveCN108710723AApparent permeability is accurateAccurate calculation of apparent permeabilityDesign optimisation/simulationPermeability/surface area analysisPorous mediumUnconventional oil
The present invention belongs to the technical field of unconventional oil and gas development, and relates to a method for calculating apparent permeability of porous media of shale reservoir. The method includes the steps of: S1, collecting basic parameters of shale gas reservoir, calculating to obtain a Knudsen coefficient and a contribution coefficient; S2, utilizing the Knudsen coefficient tojudge the flow state of the gas in the capillary tube, and establishing the corresponding gas mass transport equation; S3, according to the water saturation of the reservoir rock sample, determiningthe effective flow radius corresponding to the capillaries of different sizes; S4, establishing unified mass transport equation of gas in different flow states in capillary tubes; S5. according to theunified mass transport equation, calculating the apparent permeability of the capillary tube, and superposing the apparent permeabilities of the capillary tubes with different sizes to obtain the apparent permeability of the whole shale core. The method of the invention takes into account the influence of different capillary sizes, distribution frequencies and water saturation of shale, and the method provided by the invention is closer to the real situation of the reservoir and obtains more accurate data.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
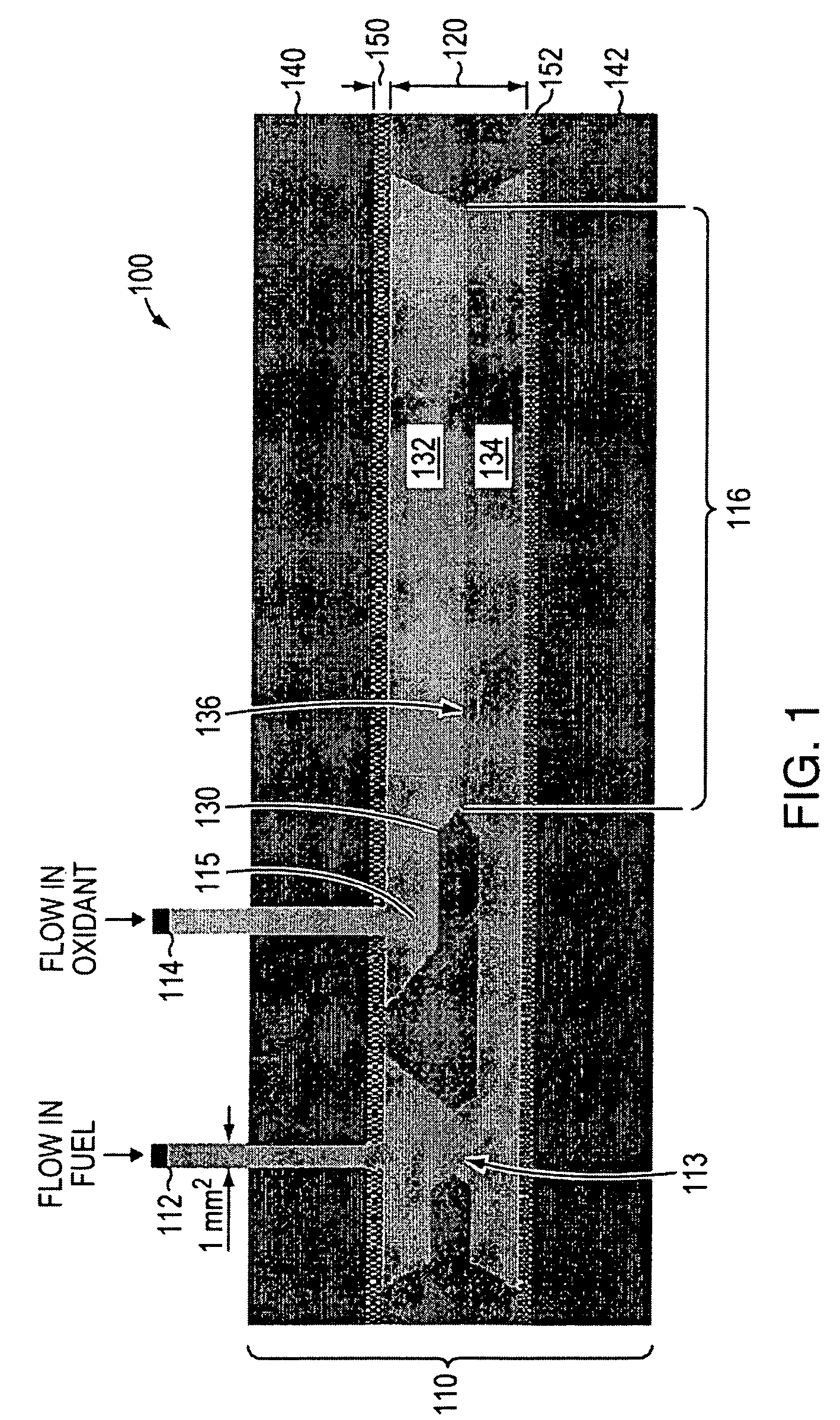
Planar membraneless microchannel fuel cell
A planar microfluidic membraneless flow cell. The design eliminates the need for a mechanical membrane, such as a polyelectrolyte membrane (PEM) in a fuel cell, by providing a flow channel in which laminar flow regimes exist in two fluids flowing in mutual contact to form a “virtual interface” in the flow channel. In the flow cell, diffusion at the interface is the only mode of mass transport between the two fluids. In a fuel cell embodiment, a planar design provides to large contact areas between the two streams, which are fuel and oxidant streams, and between each stream and a respective electrode. In some embodiments, silicon microchannels, of fixed length and variable width and height, have been used to generate power using formic acid as fuel and oxygen as oxidant. Power densities on the order of 180 μW / cm2 have been obtained using this planar design.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
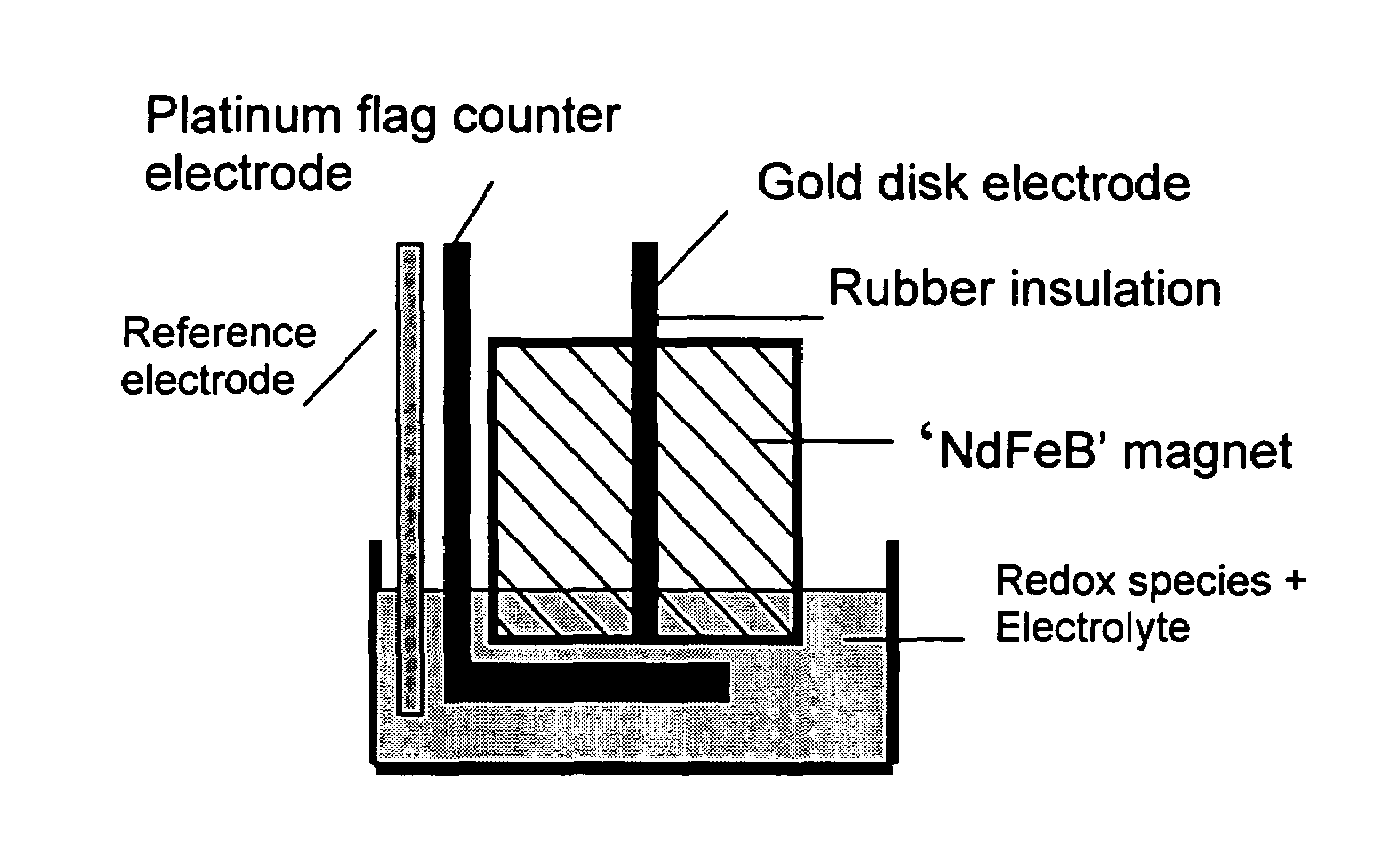
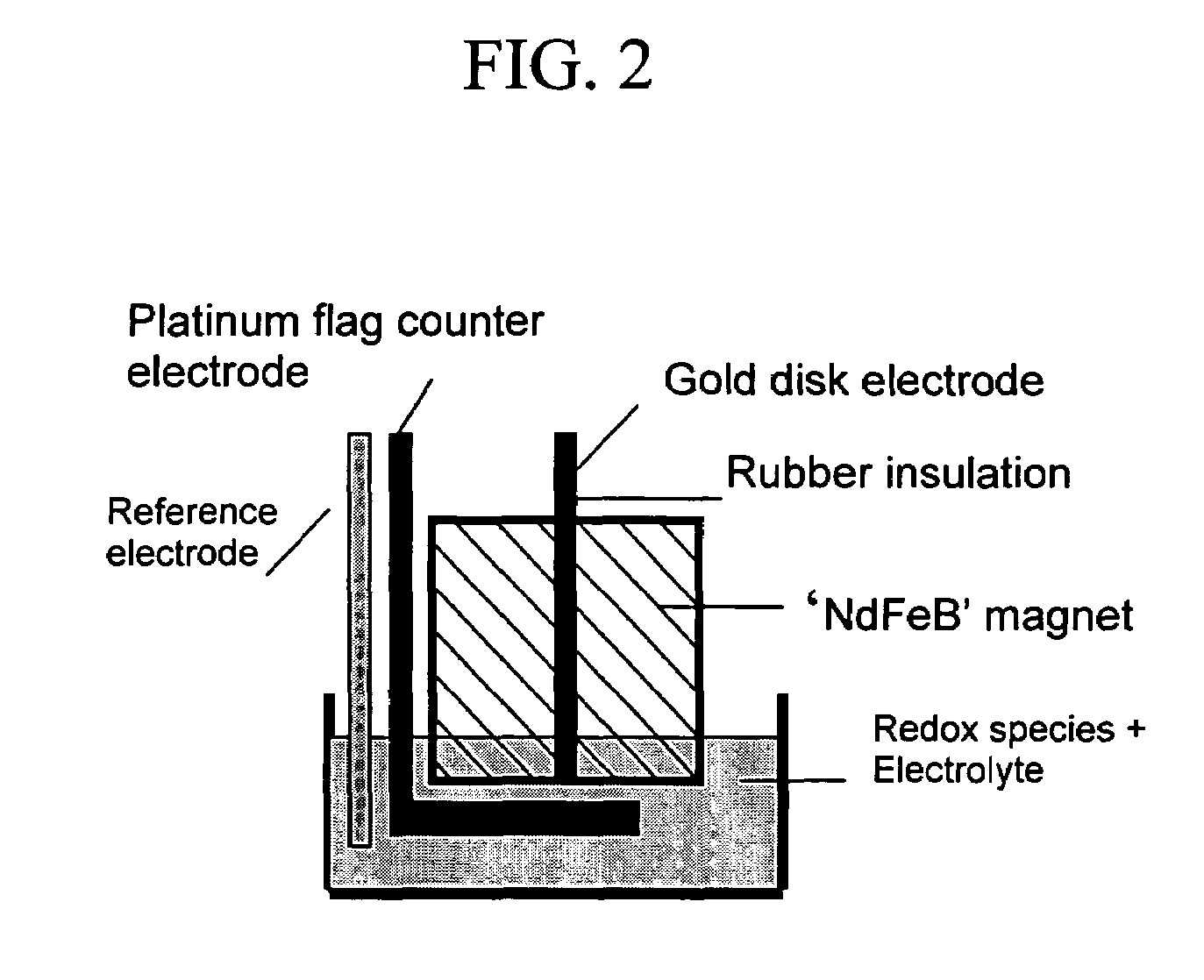
Electrochemistry using permanent magnets with electrodes embedded therein
InactiveUS7572355B1Well mixedLow voltage requirementRotary stirring mixersTransportation and packagingHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsLab-on-a-chip
Devices and methods of enhancing mass transport proximate a surface of an electrode immersed in a liquid are disclosed. One aspect of the device comprises an electrode embedded in a sintered or bonded magnetic material. The device is contacted with a solvent containing a redox material dissolved therein. An external voltage or current is applied to the electrode, which external voltage or current is sufficient to enhance mass transport proximate the surface of the electrode. Magnetic field effects can be effectively applied to the microstirring of fluids in conjunction with microelectrochemical systems in a lab-on-a-chip format. Suitable applications include bioassays, drug discovery, and high throughput screening, and other applications where magnetohydrodynamics can enhance chemical detection and / or reagent mixing, which otherwise rely on diffusional processes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Plasmon assisted control of optofluidics
ActiveUS20080245430A1Easy to makeHighly controllableCircuit elementsPressure pumpsEngineeringProduct gas
A method of microfluidic control via localized heating includes providing a microchannel structure with a base region that is partially filled with a volume of liquid being separated from a gas by a liquid-gas interface region. The base region includes one or more physical structures. The method further includes supplying energy input to a portion of the one or more physical structures within the volume of liquid in a vicinity of the liquid-gas interface region to cause localized heating of the portion of the one or more physical structures. The method also includes transferring heat from the portion of the one or more physical structures to surrounding liquid in the vicinity of the liquid-gas interface region and generating an interphase mass transport at the liquid-gas interface region or across a gas bubble while the volume of liquid and the gas remain to be substantially at ambient temperature.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Heat and water management device and method in fuel cells
A method and device for fuel cell heat and water management is provided. A thermally and electrically conductive hydrophilic heat and mass transport element is provided to the fuel cell spanning from inside to outside the cell. The transport element is deposited between current collector and gas diffusion layers, where heat is transported along the transport element from an interior portion of the element inside the cell to an exterior portion of the element outside the cell. Liquid water is transported along the element into or out of the cell, and heat is removed from the exterior portion by any combination of radiation, free convection and forced convection, and where the liquid water is removed from the exterior portion by any combination of convection driven evaporation and advection. The water is added to the cell from the exterior to the interior by any combination of advection and capillary wicking.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Mesoporous metal oxides, preparation and applications thereof
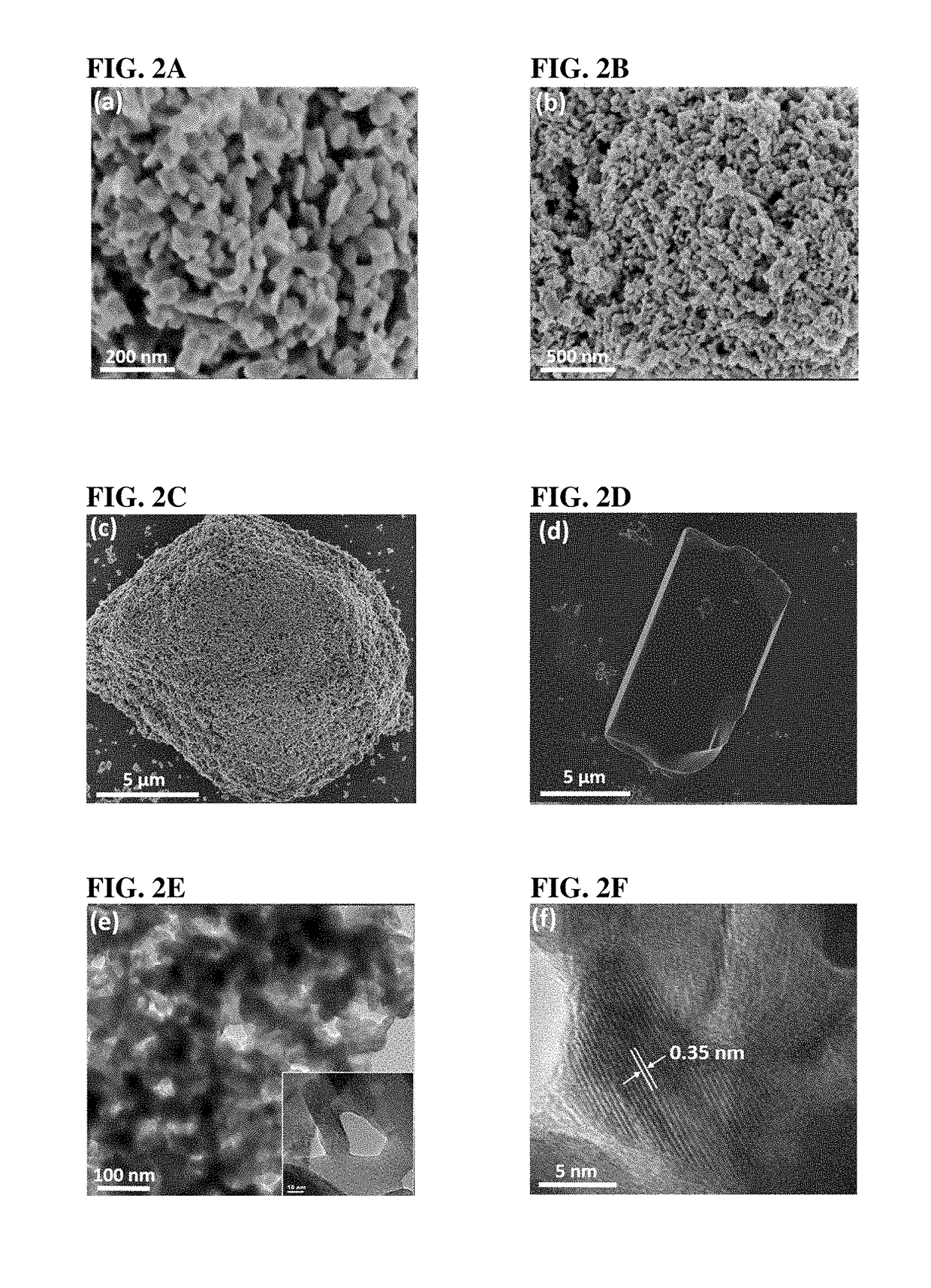
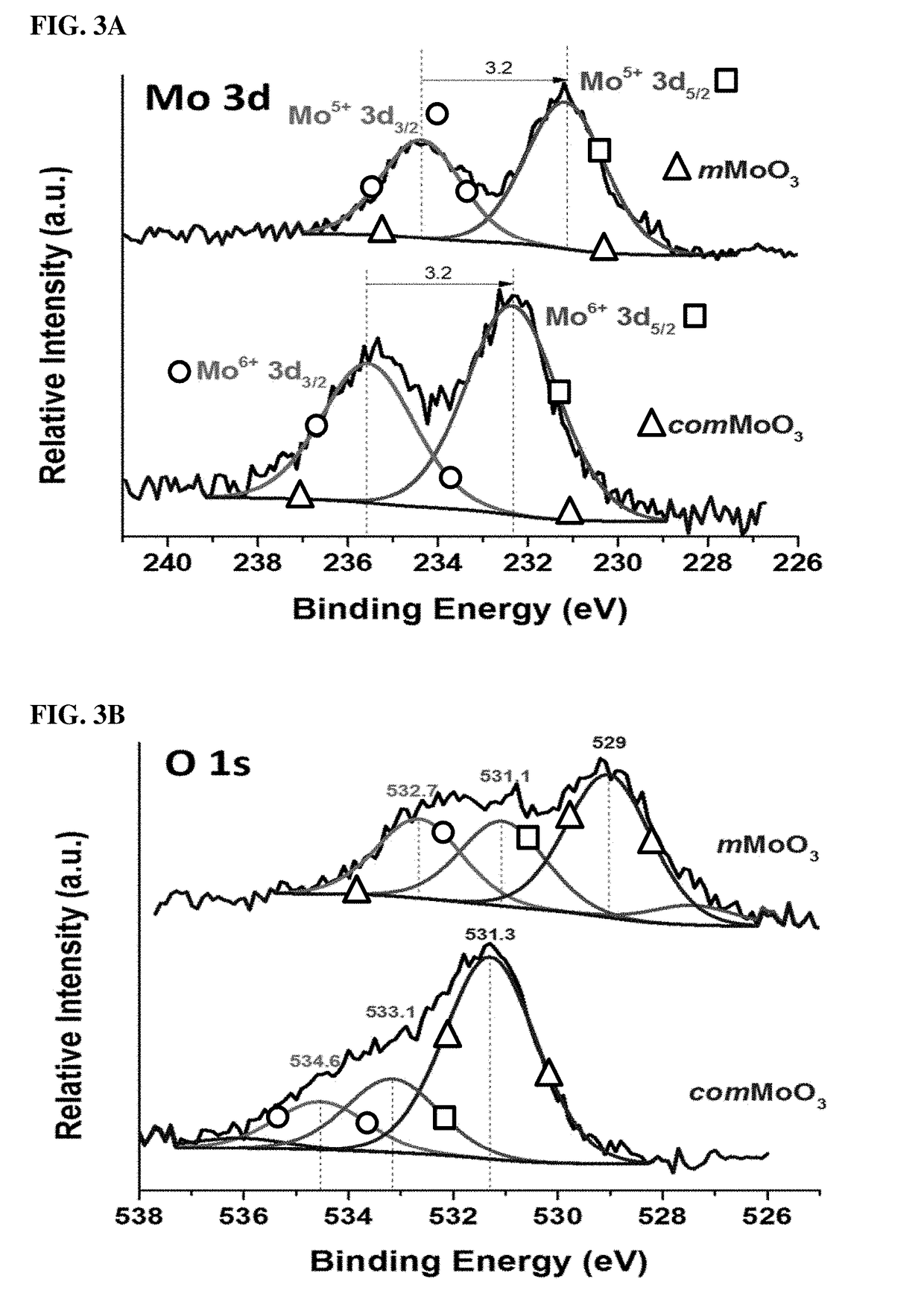
ActiveUS20170349447A1High catalytic activityHybrid capacitor electrodesCell electrodesOxygen vacancyOxygen deficient
This disclosure provides a unique approach for the synthesis of non-stoichiometric, mesoporous metal oxides with nano-sized crystalline wall. The as-synthesized mesoporous metal oxide is very active and stable (durability>11 h) electocatalyst in both acidic and alkaline conditions. The intrinsic mesoporous metal oxide serves as an electrocatalyst without the assistant of carbon materials, noble metals, or other materials, which are widely used in previously developed systems. The as-synthesized mesoporous metal oxide has large accessible pores (2-50 nm), which are able to facilitate mass transport and charge transfer. The as-synthesized mesoporous metal oxide requires a low overpotential and is oxygen deficient. Oxygen vacancies and mesoporosity served as key factors for excellent performance.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com