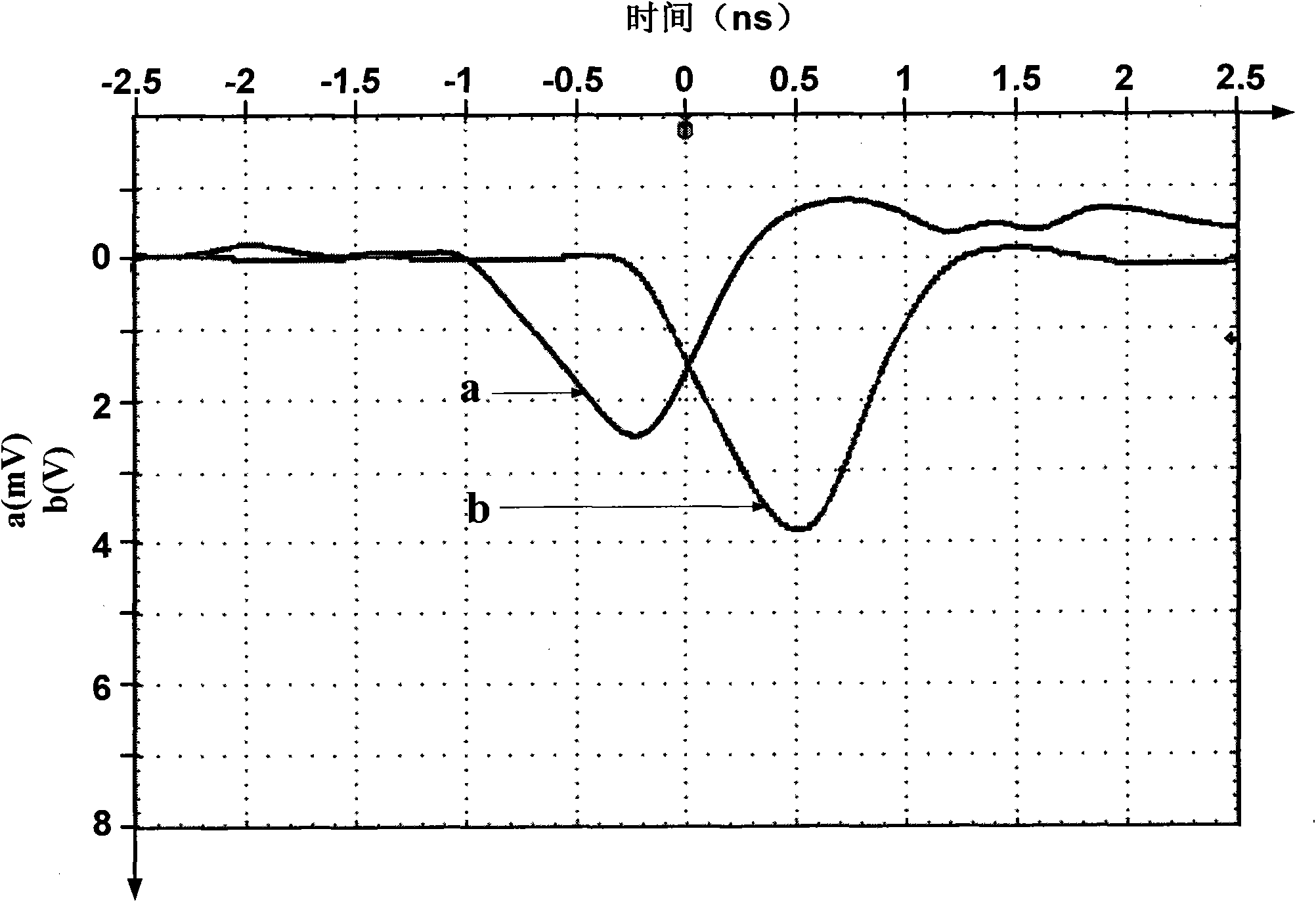
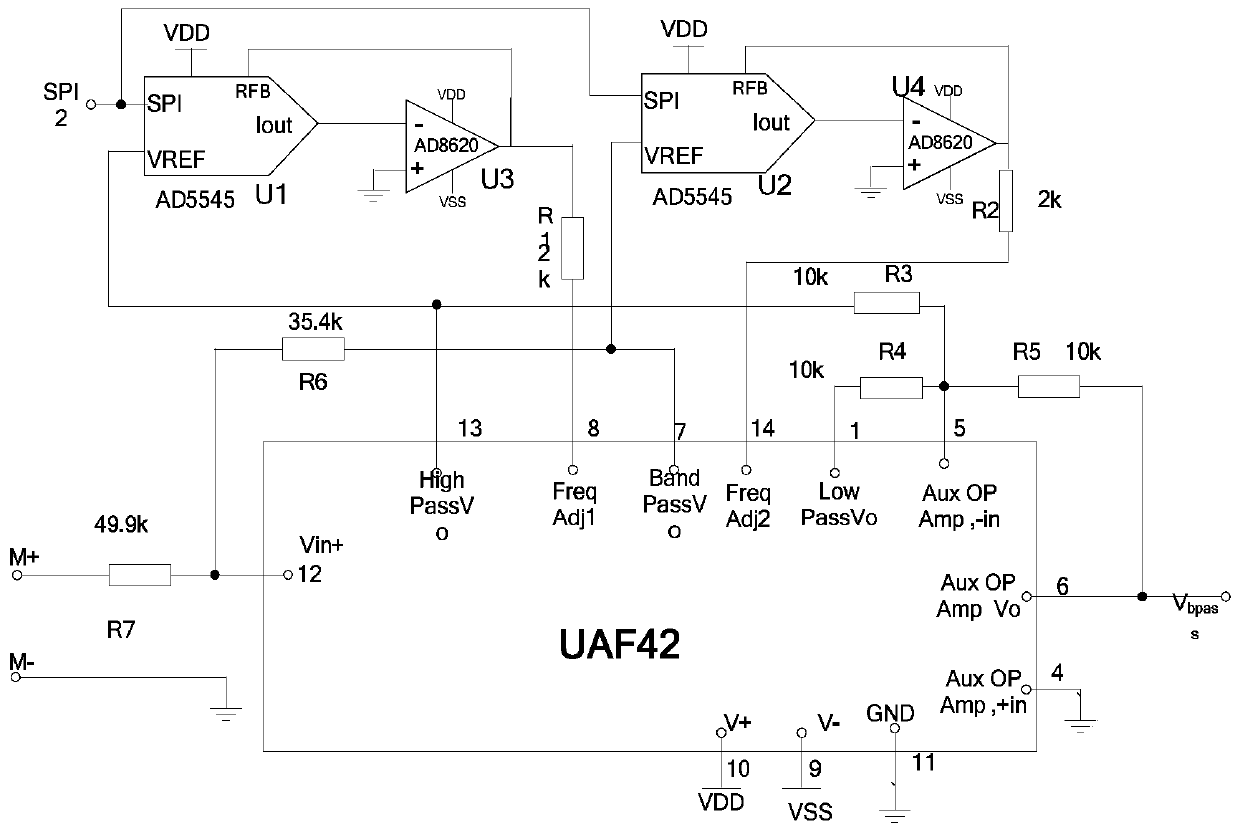
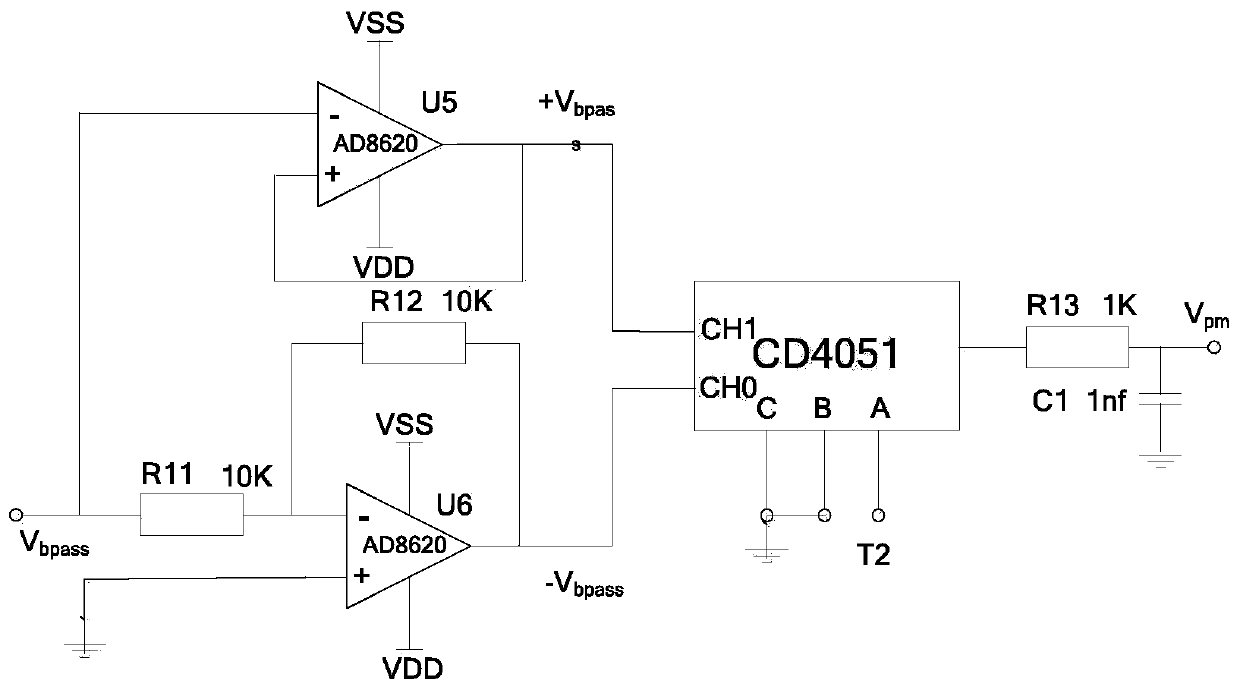
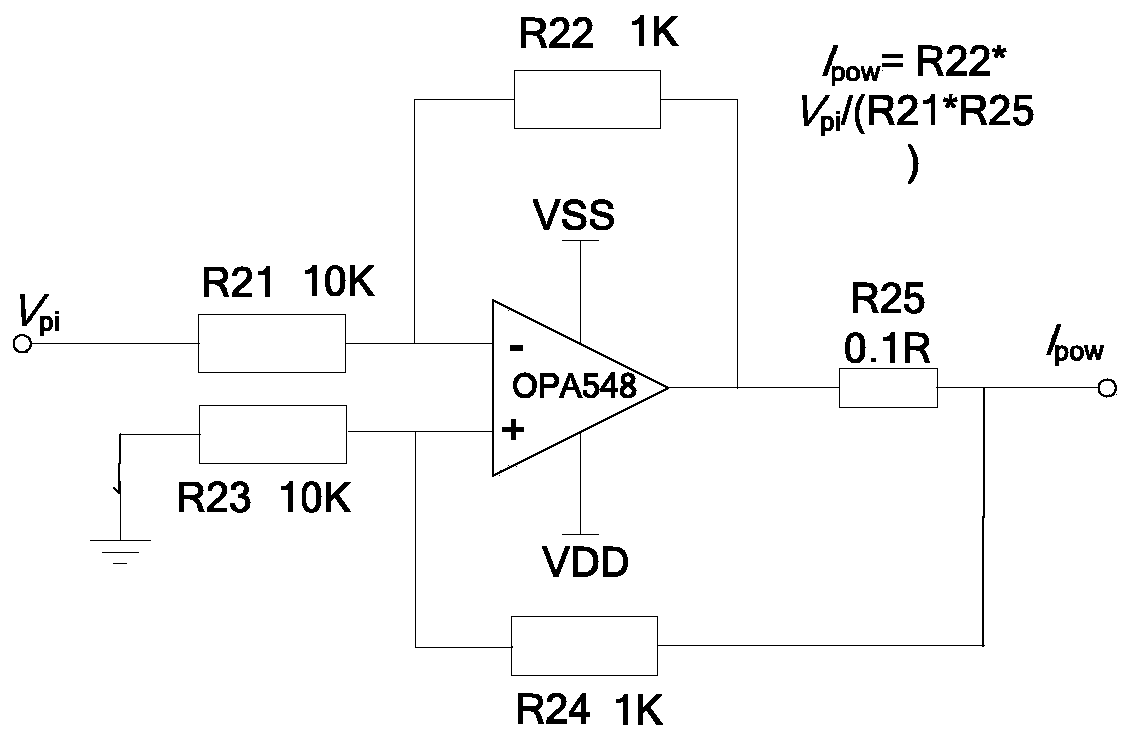
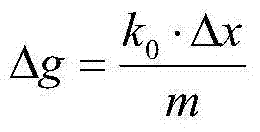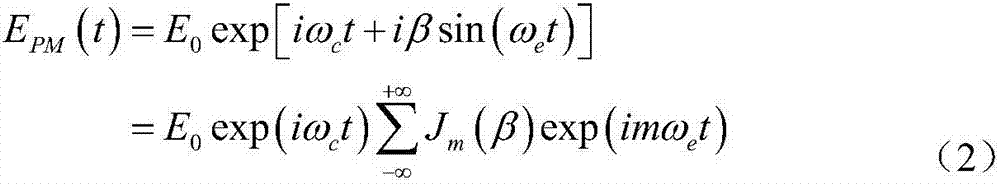Patents
Literature
67results about How to "Increased measurement bandwidth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
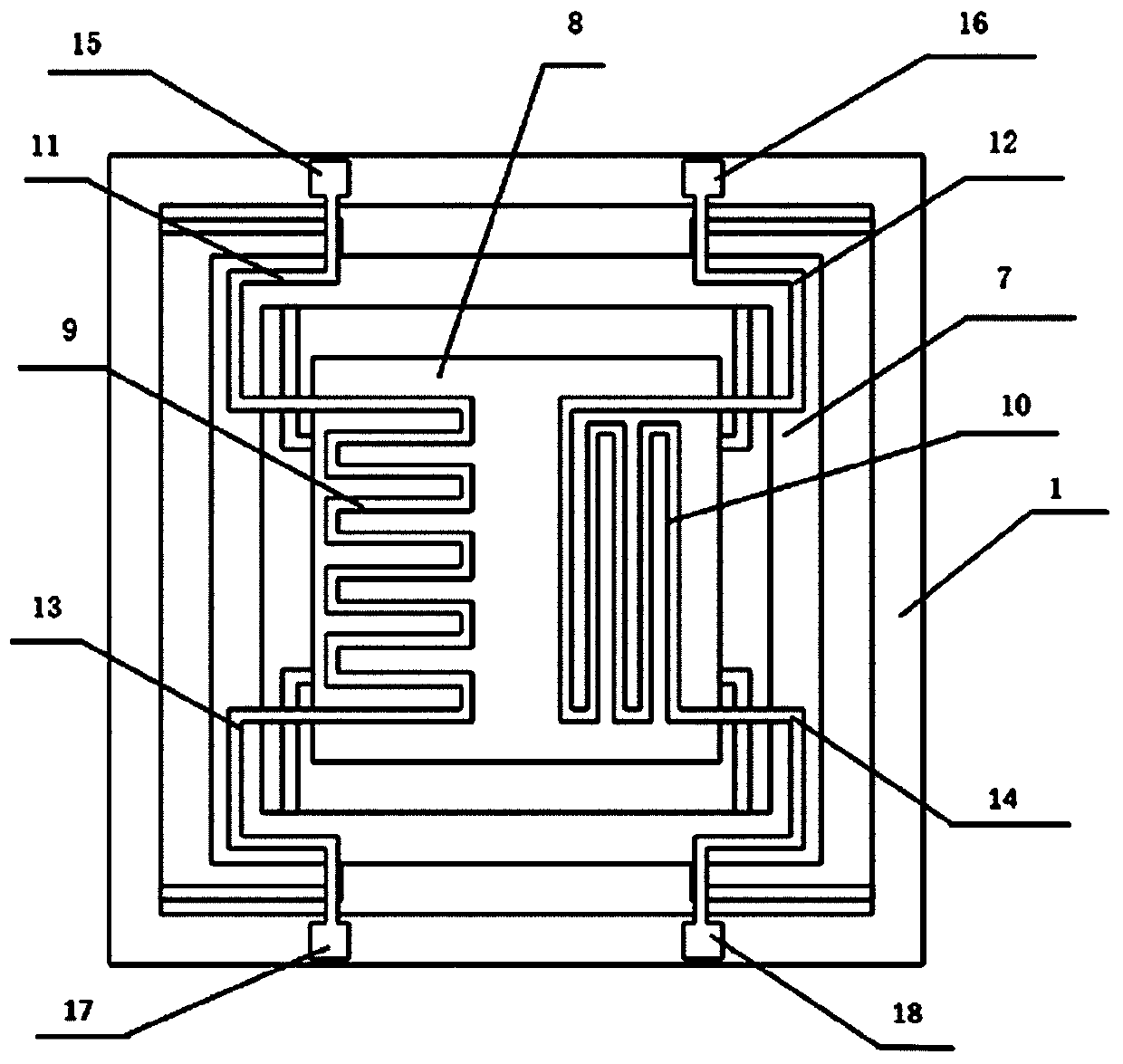
Micro sensor for electrochemically monitoring residue in micro channels
InactiveUS7332902B1Reduce effectExtend measurement bandwidthElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementMicroelectronicsAspect ratio
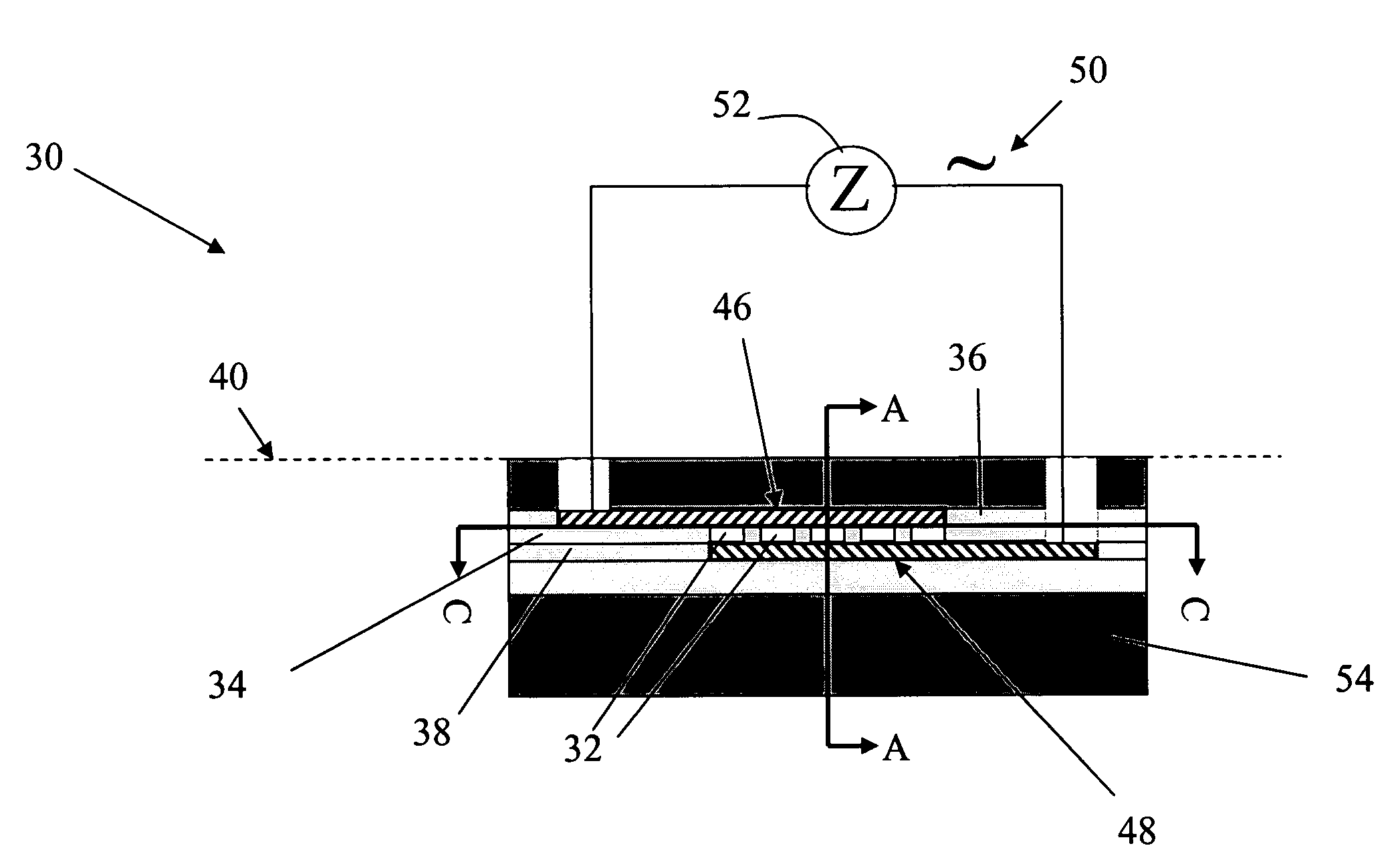
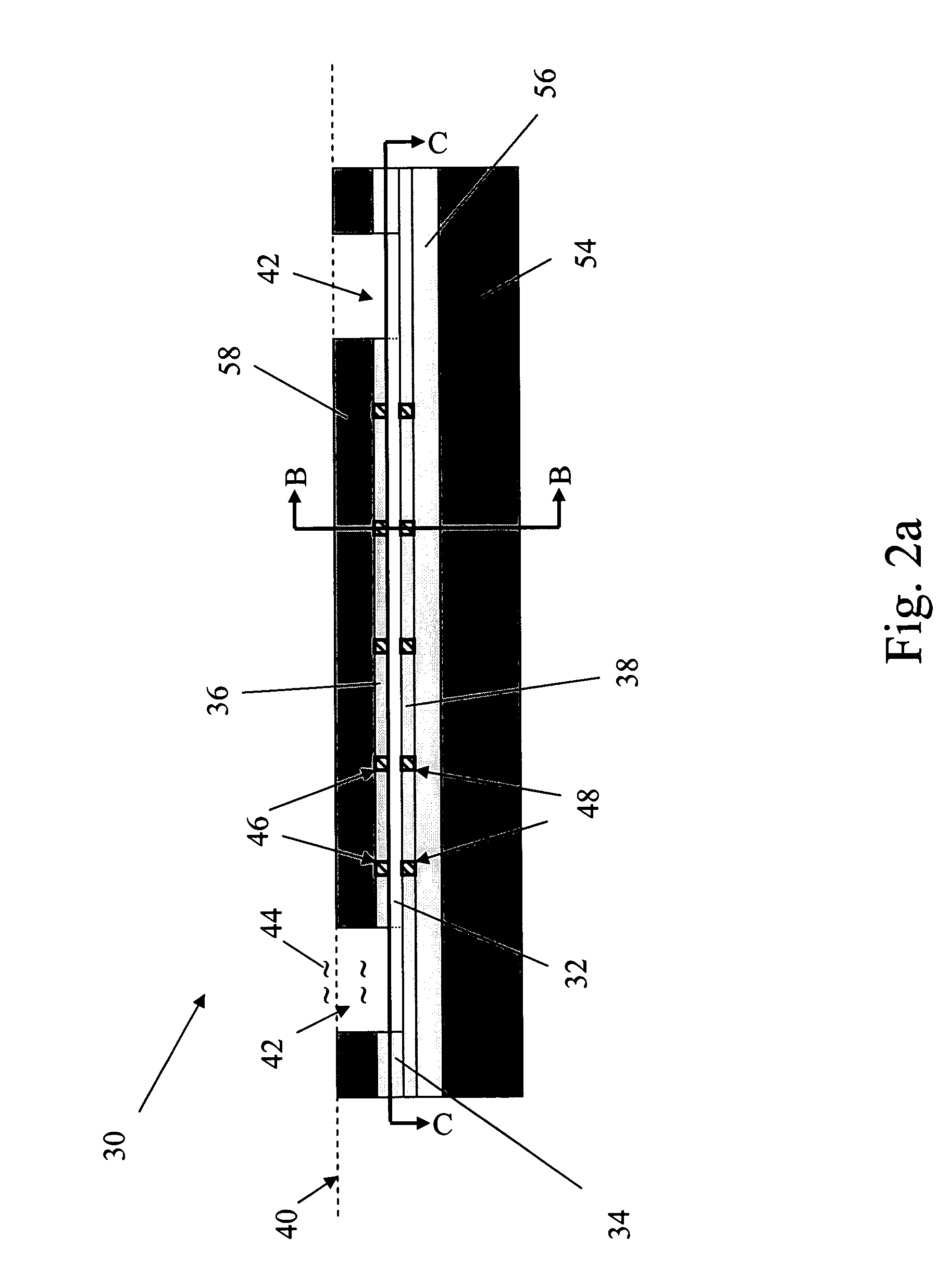
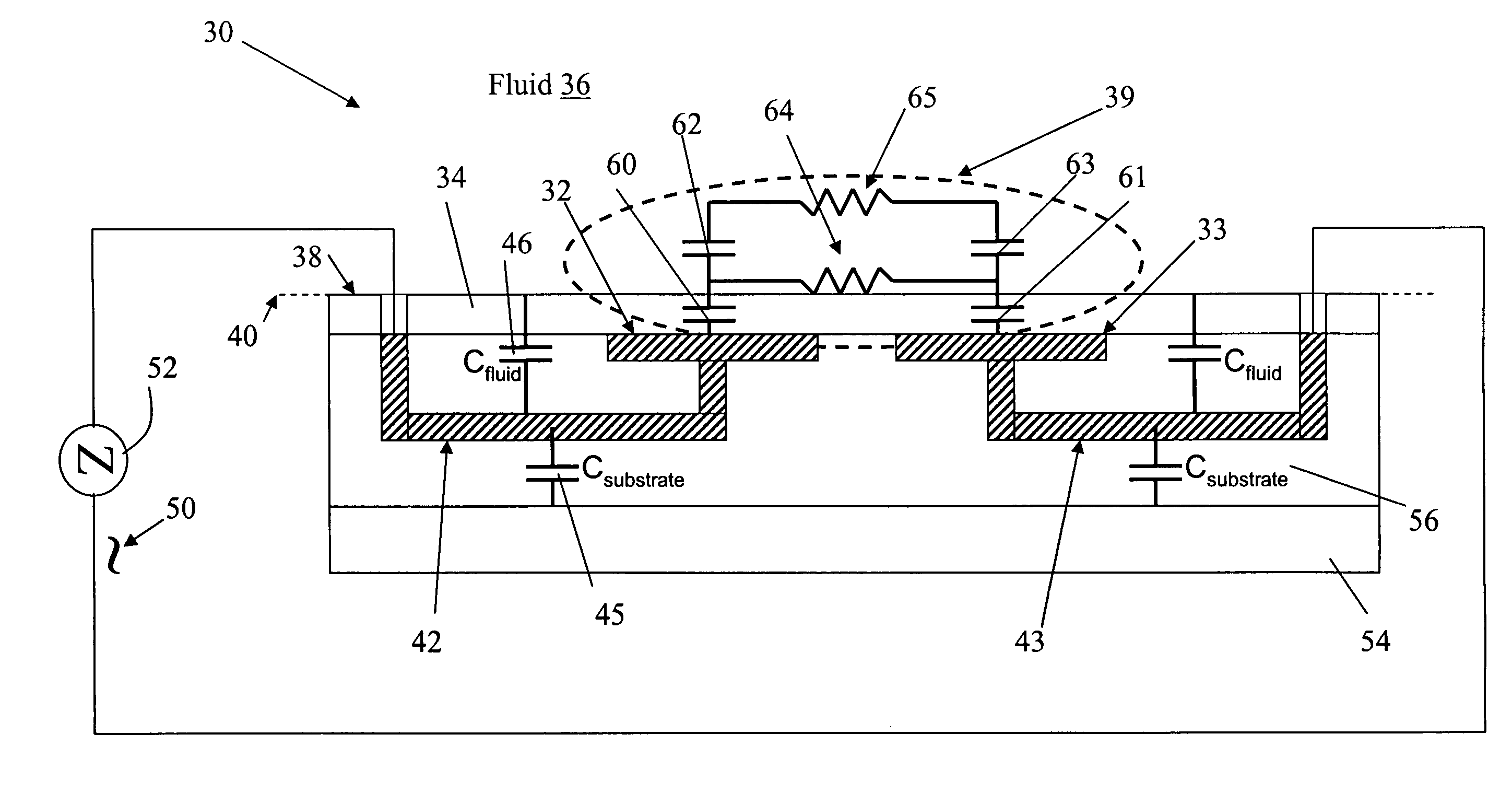
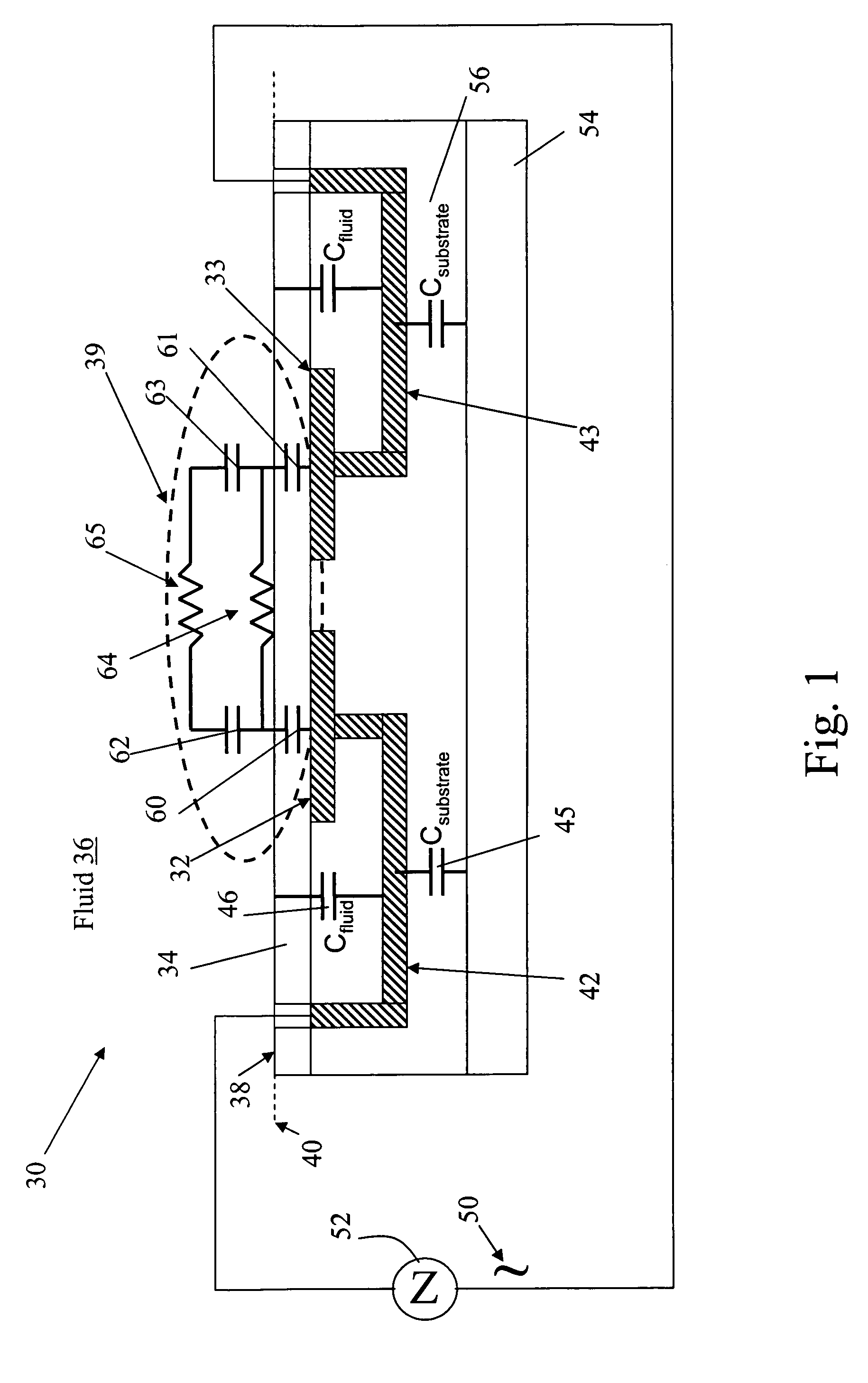
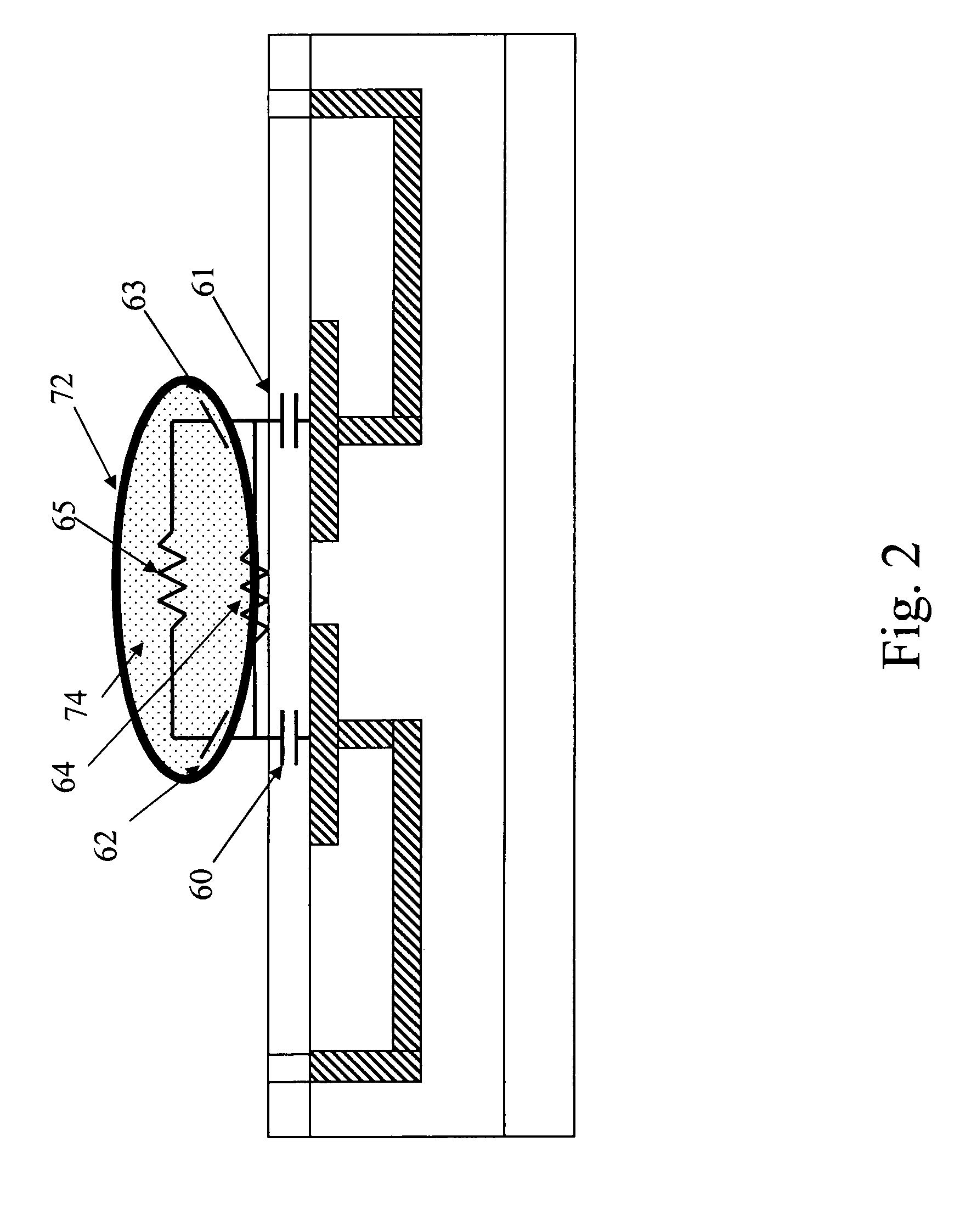
The present invention provides a micro sensor for monitoring the cleaning and drying processes for very high aspect ratio micro channels in dielectric films oriented parallel to the fluid-solid interface during the manufacture of ICs, MEMS and other micro-devices. The micro sensor can be used to monitor “vertical” micro features common in microelectronics fabrication or “horizontal” micro features found in MEMS or microfluidic fabrication. By forming the micro channels parallel to the interface, the channels can be made with much higher and well controlled aspect ratios. In addition, multiple sensors can sense the impedance at various points along the micro features. The addition of a guard reduces the effects of any parasitic capacitance, which extends the measurement bandwidth of the sensor.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL METROLOGY CORP
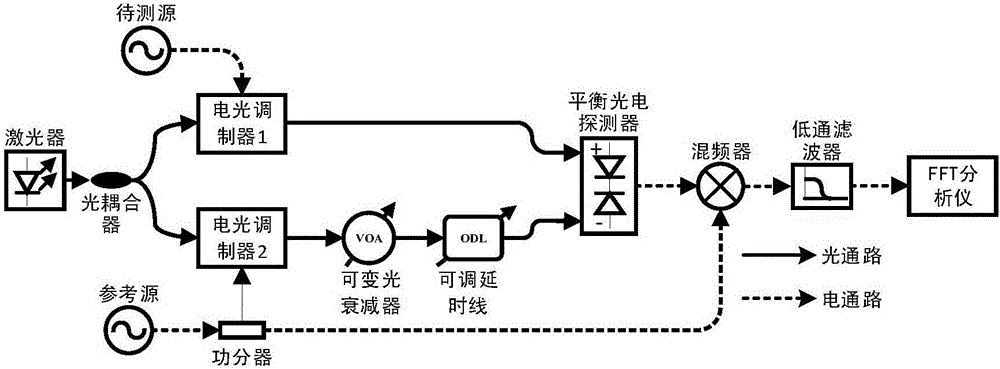
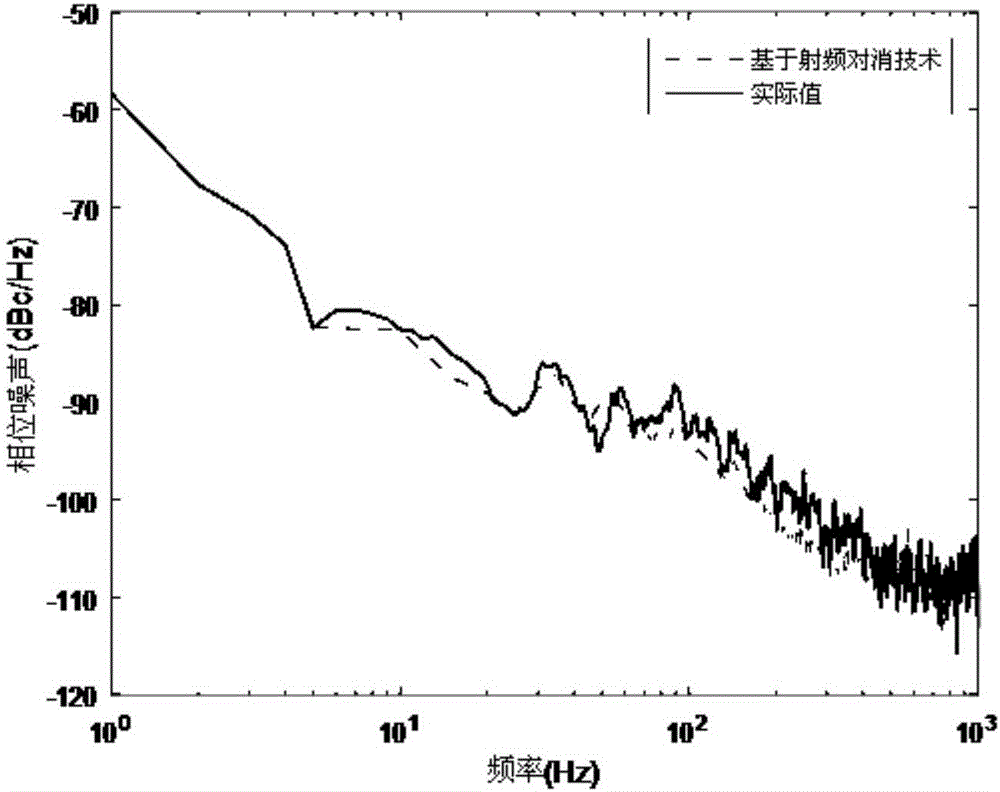
Phase noise measurement method and device based on radio frequency cancellation
InactiveCN106338658AHigh measurement sensitivityCarrier suppressionNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementPhase noiseMeasurement device
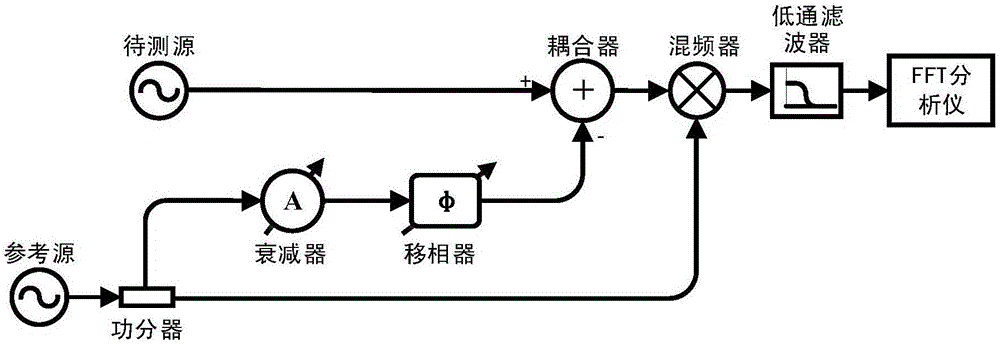
The invention discloses a phase noise measurement method based on radio frequency cancellation. The method comprises the following steps: dividing reference microwave signals at the same frequency as to-be-measured microwave signals into two channels; using one channel of reference microwave signals to cancel the to-be-measured microwave signals so as to convert carrier phase modulation by phase noise into suppression of carrier amplitude modulation; then, performing coherent demodulation on the canceled signals and the other channel of reference microwave signals; and finally, making a spectrum analysis of the low-frequency component of the signals after coherent demodulation to get the phase noise of the to-be-measured microwave signals. The invention further discloses a phase noise measurement device based on radio frequency cancellation. Compared with the prior art, the measurement sensitivity is higher, and the calibration process is easier.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
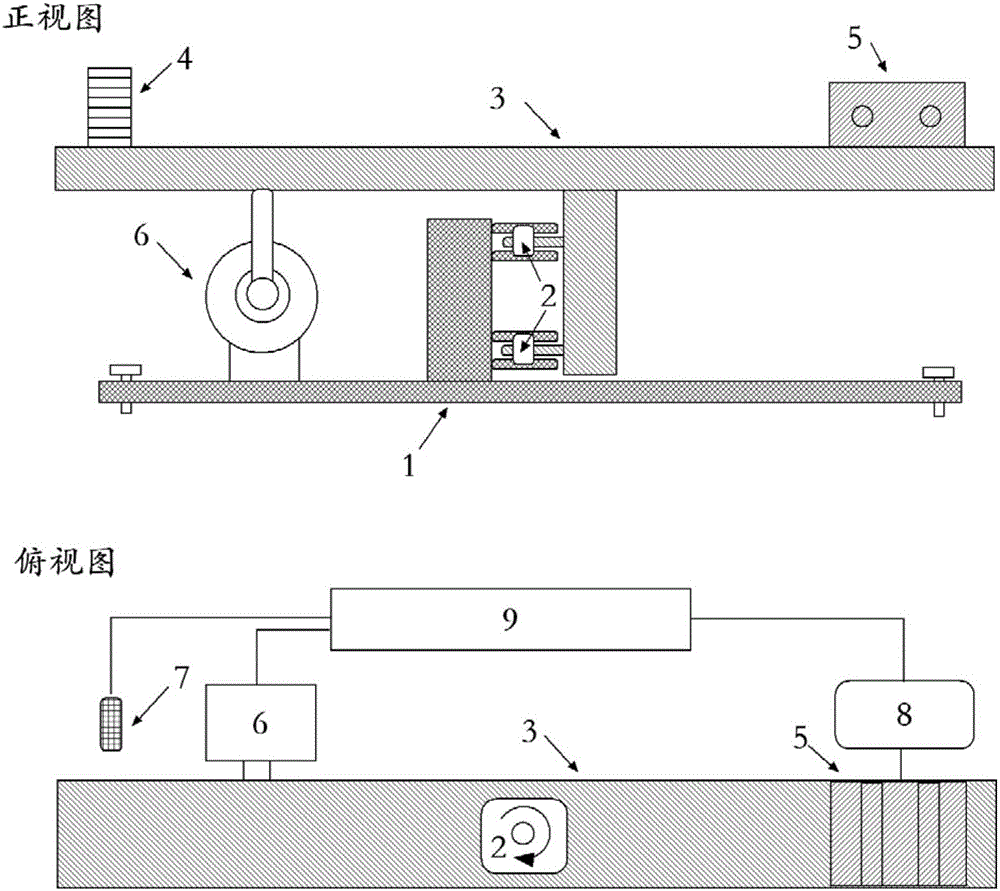
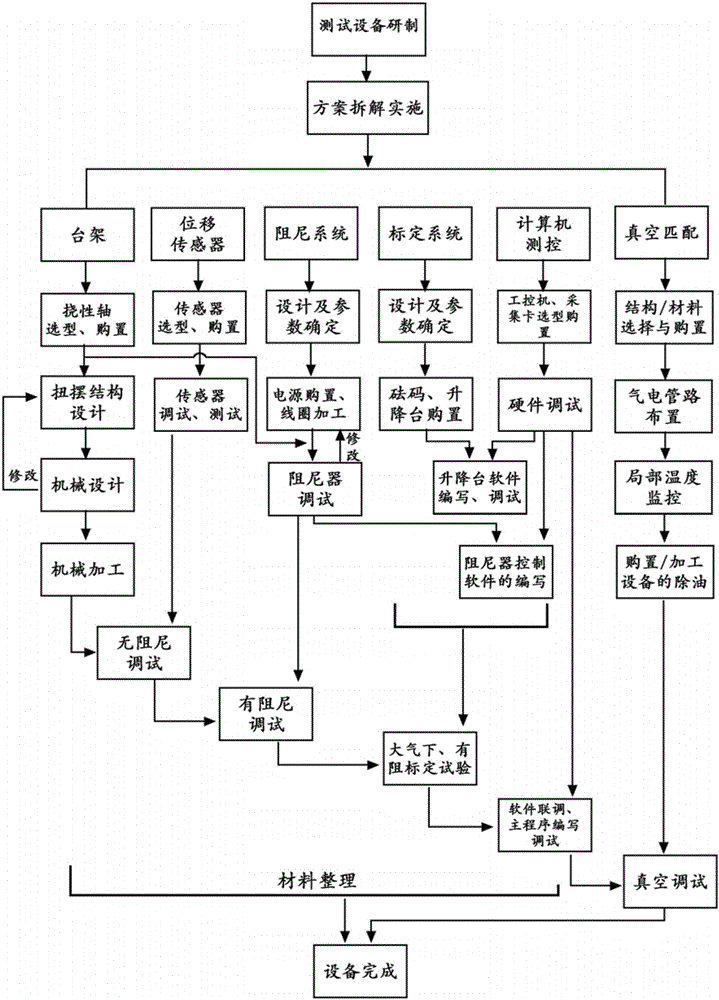
Micro thrust test system and method
InactiveCN105784237AIncreased measurement bandwidthHigh measurement accuracyApparatus for force/torque/work measurementForce/torque/work measurement apparatus calibration/testingData acquisitionDisplay device
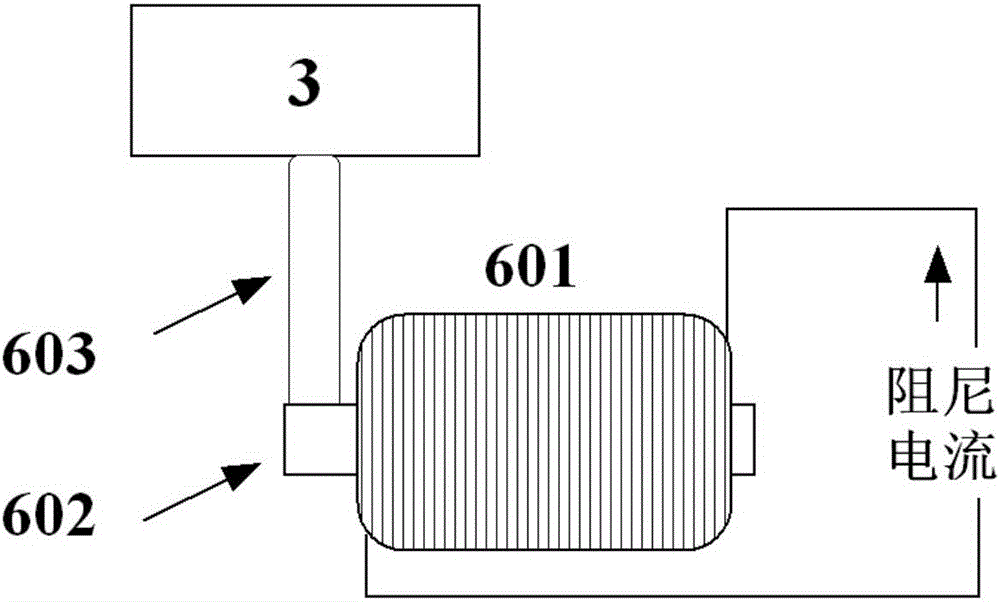
The invention discloses a micro thrust measuring system. The micro thrust measuring system is applied to tests according to which micro thrusts range from 1 mN to 1000 mN and a thrust-weight ratio ranges from 10<-5> to 10<-2>. With the micro thrust measuring system adopted, measurement accuracy can be greatly improved under the condition that measurement bandwidth is enough. The micro thrust measuring system comprises a bench, a displacement sensor, an online calibration assembly, a damping system and computer measurement and control equipment; the computer measurement and control equipment includes a high-frequency data acquisition card, an industrial personal computer and a display device which are connected with one another; the displacement data of the reflection-type laser displacement sensor are processed through the industrial personal computer, and the processed displacement data are displayed through the display device; the industrial personal computer controls the height of a lifting platform, measures thrust response under the loading of a standard weight and achieves steady thrust calibration; and the industrial personal computer controls the damping system to make the bench stand still. The invention also provides a test method using the device.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System for GIS (Global Information System) partial discharge measurement and VFTO (Very Fast Transient Overvoltage) measurement
ActiveCN102590718AReduce monitoring costsImprove straightnessTesting dielectric strengthCurrent/voltage measurementFrequency bandPhysics
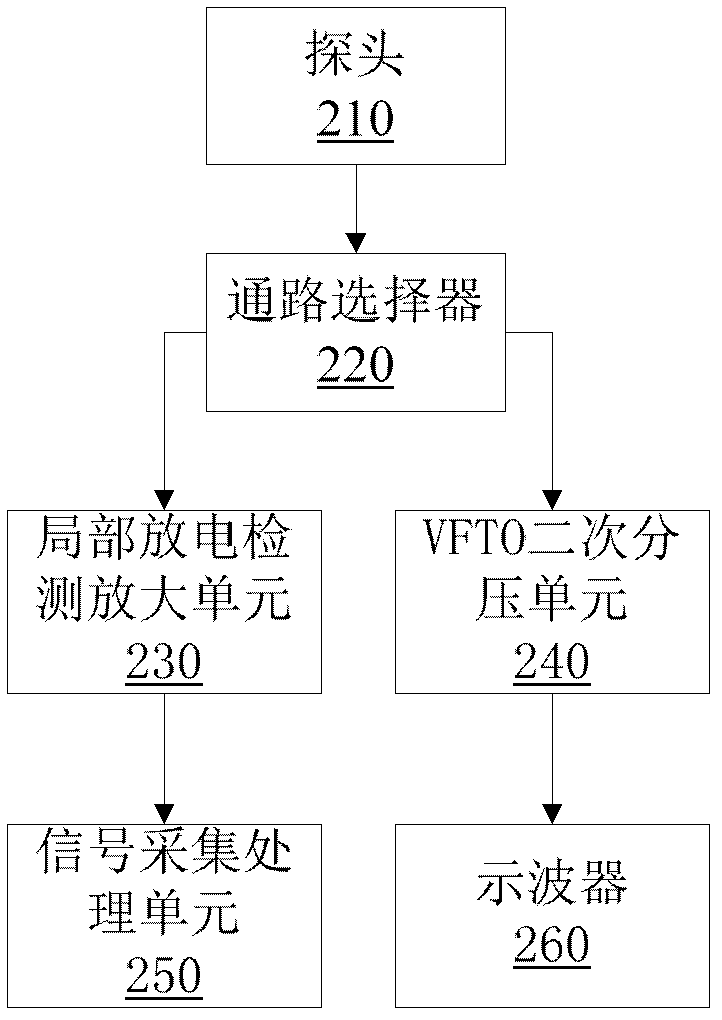
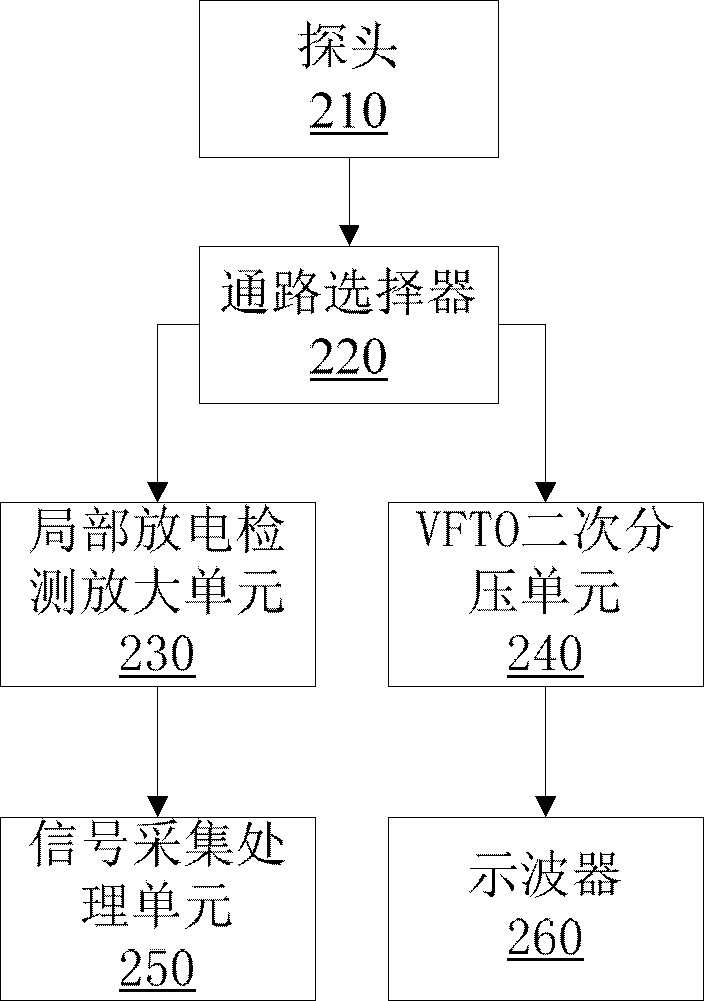
The invention discloses a system for GIS (Global Information System) partial discharge measurement and VFTO (Very Fast Transient Overvoltage) measurement in the technical field of online monitoring systems of electric equipment. The system comprises a probe, a circuit selector, a partial discharge detection amplifying unit, a VFTO secondary partial pressure unit, a signal collecting and processing unit and an oscilloscope. The measurement system can use one probe to perform GIS partial discharge and VFTO measurement, and the two original systems are combined to the same system to reduce the GIS monitoring cost; the special probe design improves the measurement sensitivity of partial discharge; and the preferable VFTO secondary unit design improves the glancing flatness of wide frequency band measurement of a VFTO sensor.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING) +1
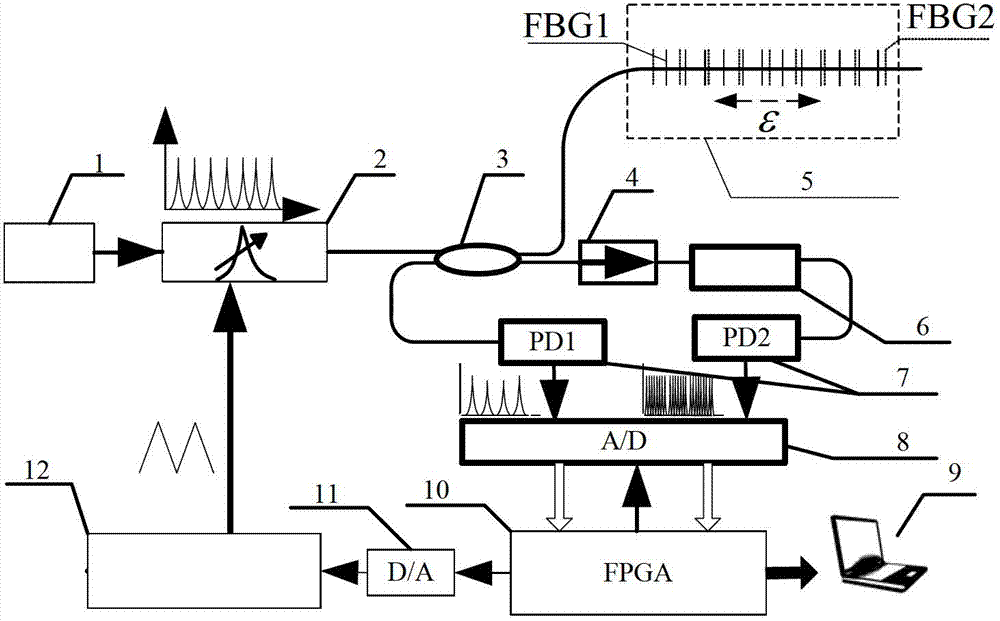
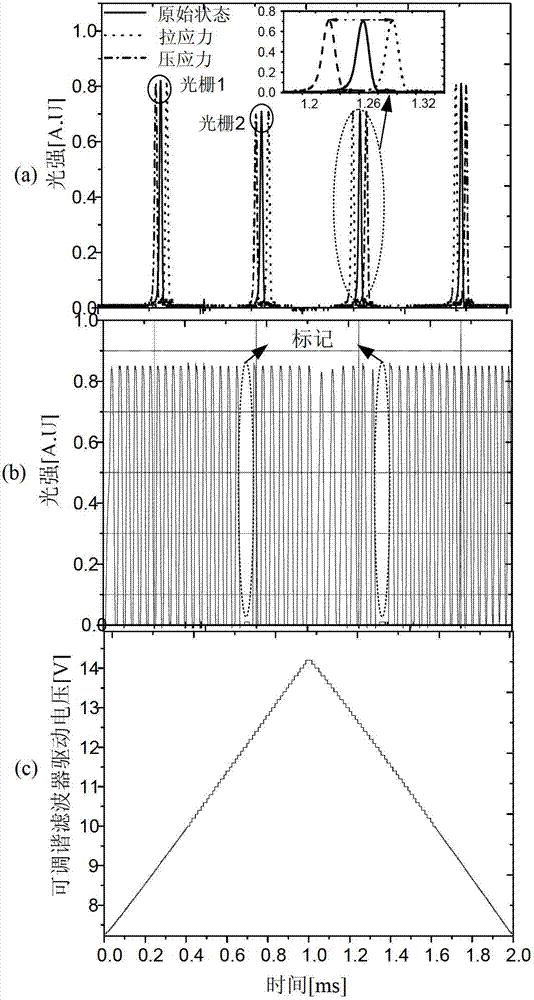
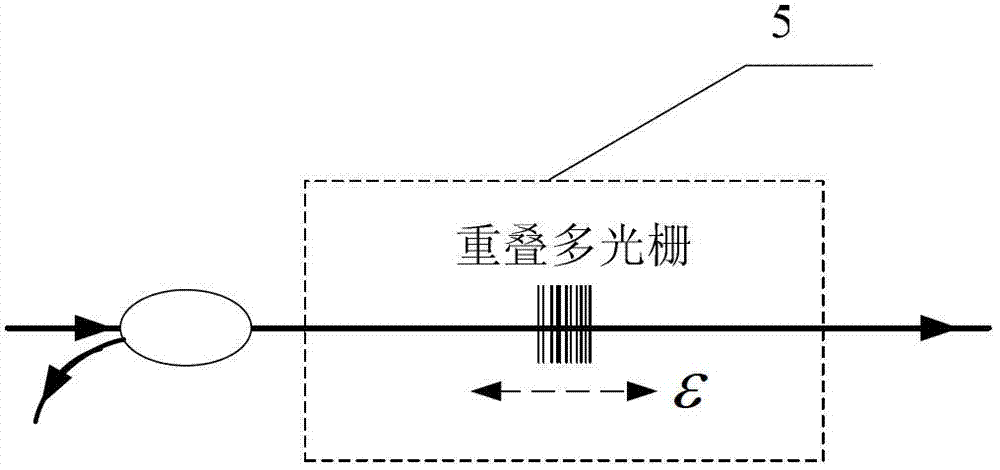
Dynamic strain measurement instrument based on multiple overlapped gratings
ActiveCN102818531AIncreased measurement bandwidthHigh wavelength resolutionUsing optical meansGratingPeak value
The invention provides a dynamic strain measurement instrument based on multiple overlapped gratings. The dynamic strain measurement instrument comprises the multiple overlapped gratings, a wideband light source, a tunable filter, a positioning coupler, an etalon, a photoelectric detector and a demodulation and control circuit. The multiple overlapped gratings are formed in a way that a plurality of sensing gratings with center wavelengths being distributed at equal intervals are inscribed in an overlapped manner in a same area on a sensing optical fiber by selecting different phase templates, wherein the center wavelengths of a fiber Bragg grating, which are inscribed in the overlapped together, are continuously distributed at equal intervals within a wavelength scanning range of the tunable filter, so that sensing information of the same physical quantity to be measured can be continuously obtained for a plurality of times within each wavelength scanning period, and a peak value position and wavelength variation of each sensing grating in the multiple overlapped gratings, namely reconfigurable original dynamic strain signals, can be recorded. Therefore, the purpose of improving a measurement bandwidth of the dynamic strain signals based on a grating demodulation system of the tunable filter can be realized. According to the dynamic strain measurement instrument provided by the invention, the sensed measurement bandwidth of the fiber Bragg grating based on the tunable filter can be effectively improved, so that the high-speed and high-precision simultaneous measurement requirement of the dynamic strain signals can be met.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Quantum dot array spectrum sensor
InactiveCN106768331AHigh wavelength resolutionThe number of encoding bits increasesSpectrum investigationPhotovoltaic detectorsLight sensing
The invention discloses a quantum dot array spectrum sensor, comprising: a quantum dot colloidal array film and an array photoelectric detector; the quantum dot colloidal array film is used for bearing a quantum dot colloidal array; the quantum dot colloidal array includes a plurality of quantum dot colloidal units, wherein at least one quantum dot colloidal unit has a different absorbing or transmitting spectrum from other quantum dot colloidal units; the side of the quantum dot colloidal array film bearing the quantum dot colloidal array is opposite to a light-sensing side of the array photoelectric detector; after measured light of measured spectrum irradiates the quantum dot colloidal array film, transmitting light passing through the quantum dot colloidal array is detected by the light-sensing side. With the cooperation of the quantum dot colloidal array and the array photoelectric detector, the quantum dot array spectrum sensor has great bandwidth, high wavelength resolution and good sensitivity to weak light, and properties of existing instruments are improved greatly.
Owner:杭州盗火者科技有限公司
TMR (Tunneling magnetoresistance) accelerometer based on gap change
ActiveCN106645797ASimple structural schemeCompact structureAcceleration measurement using interia forcesGiant magnetoresistanceAccelerometer
The invention discloses a TMR accelerometer based on gap change. The accelerometer comprises a top structure, a bottom structure and first and second anchor points, and the top structure is supported over the bottom structure via the first and second anchor points arranged at the two ends of the bottom layer respectively. The accelerometer detects acceleration signals by utilizing a high-sensitivity TMR effect, has the advantages of low saturated magnetic field, small working magnetic field, high sensitivity, low temperature coefficient, large measuring bandwidth and the like, and is also simple and compact in structure, smaller in size and high in measuring precision.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
System for Young modulus measurement of film
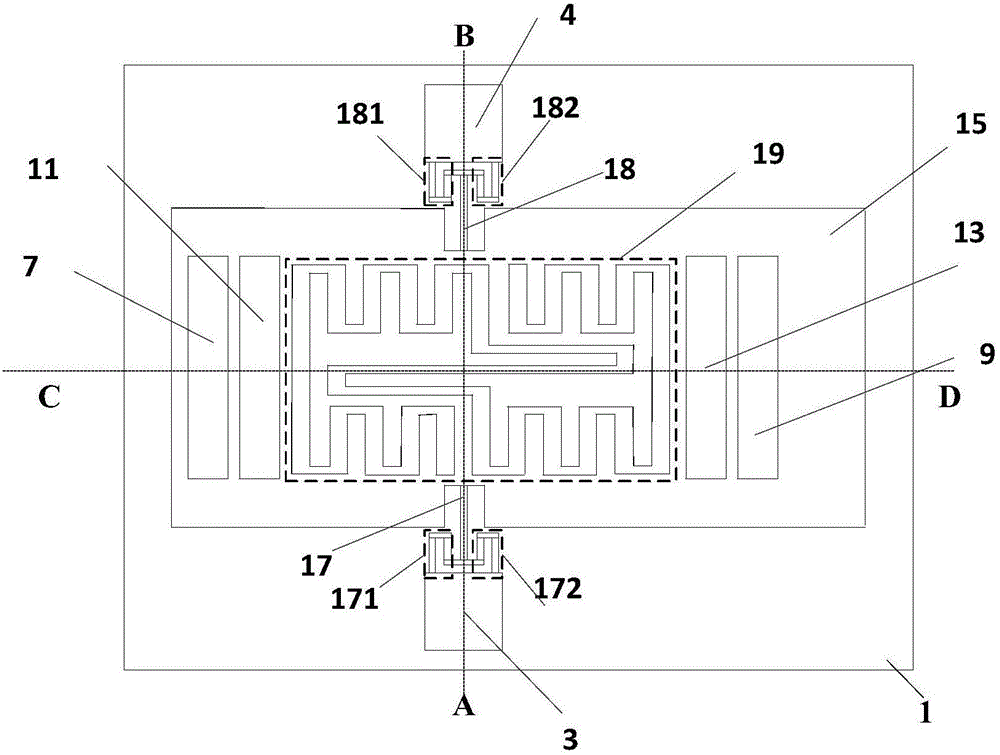
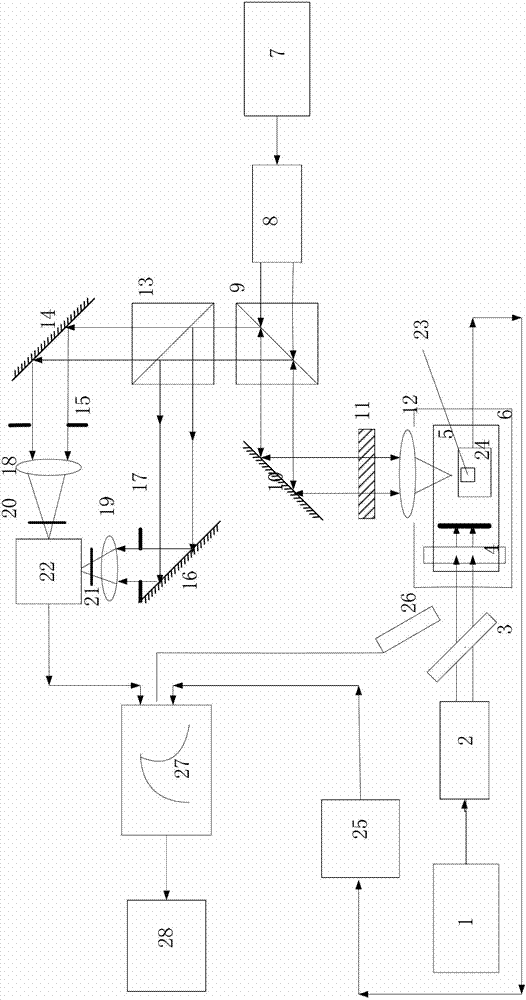
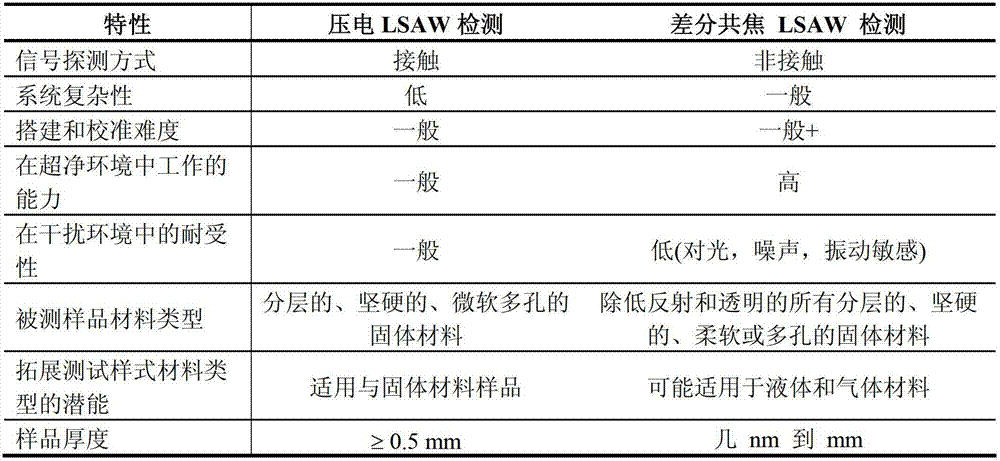
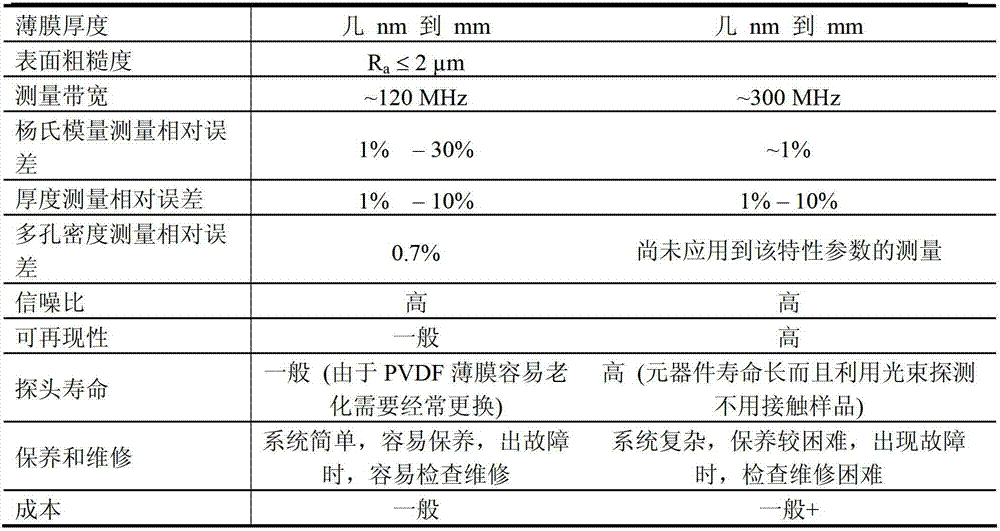
InactiveCN102768184ALarge signal amplitudeImprove applicabilityMaterial analysis by optical meansElectricityBeam expander
The invention discloses a system for Young modulus measurement of a film. The system comprises a pulsed laser, wherein the pulsed laser emits pulse laser, which is divided into 7 / 10 pulse laser and 3 / 10 pulse laser by a 3:7 spectroscope after being collimated and broadened by a first beam expander, and the 7 / 10 pulse laser is focused on the surface of a sample under test through a cylinder focusing lens to generate an acoustic surface wave signal under excitation; and the acoustic surface wave signal is converted into an electrical signal through a first detection channel and / or a second detection channel, and the electrical signal is output to a computer for processing after being displayed by an oscillograph. The system not only has the advantages of large signal amplitude, high applicability in testing environment with large disturbance and the like of the piezoelectric laser acoustic surface wave detection technology, but also inherits the advantages of rapid, accurate and non-contact measurement and high signal to noise ratio and the like of the difference confocal laser acoustic surface wave detection technology; and the system has higher applicability and wider range of applicability. Meanwhile, based on the advantage of high measurement bandwidth of the difference confocal laser acoustic surface wave detection technology, the measurement resolution is greatly improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Surface micro sensor and method
InactiveUS7489141B1Reduce effectExtend measurement bandwidthResistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMicroelectronicsElectricity
The present invention provides a micro sensor for monitoring the cleaning and drying processes of surfaces of dielectric films, micro features in porous dielectric films and biologic or other cells common in microelectronics fabrication, MEMS fabrication or microbiology test system fabrication. By embedding electrodes in the surface of a supporting dielectric, the sensor can probe the surface and pores of a covering dielectric or a cell on the covering dielectric. The addition of a guard reduces the effects of any parasitic capacitance, which extends the measurement bandwidth of the sensor and allows it to be manufactured at the scale of a single cell, a feature that is particularly important for applications in microbiology.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL METROLOGY CORP
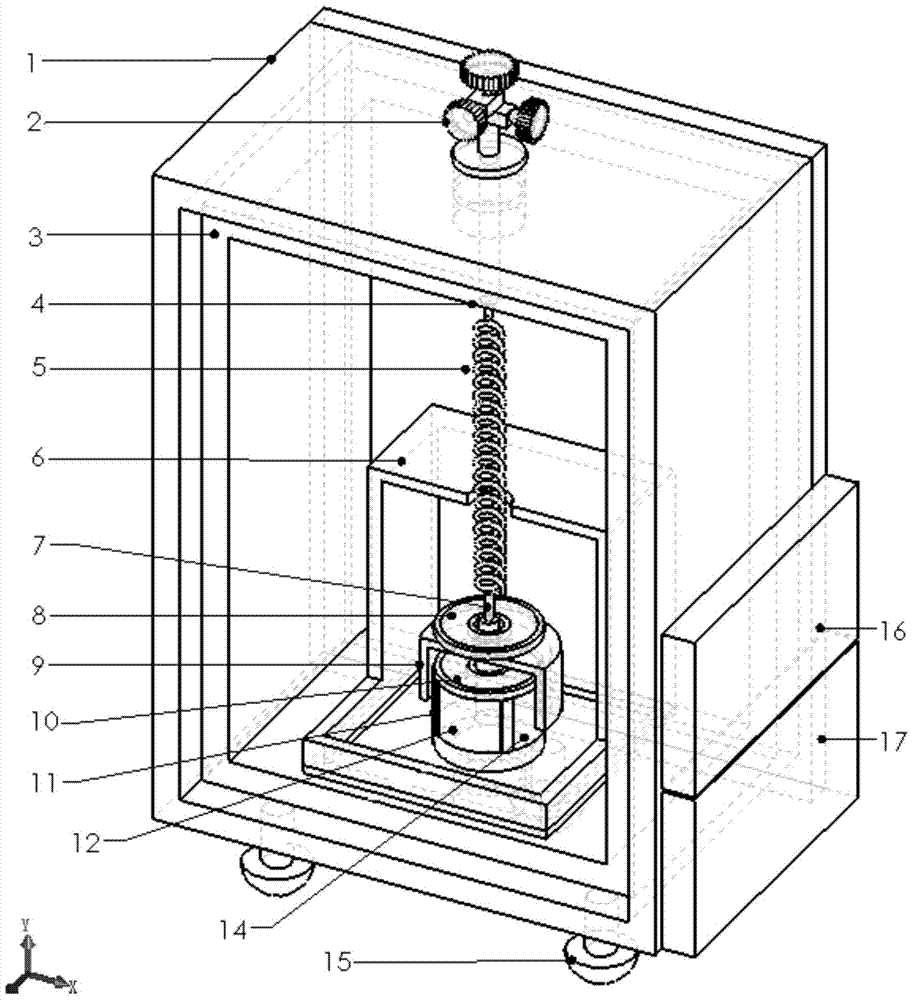
Sensitive probe and precise vertical spring portable type gravity meter
ActiveCN104502988ASimple structureEasy to operateUsing electrical meansGravitational wave measurementEngineeringDual function
The invention discloses a sensitive probe and a precise vertical spring portable type gravity meter. The sensitive probe at least comprises a swing body and an insulating electrode frame. The electrode frame comprises a bottom opening, an erect cylinder, an insulating frame body and an insulating plate. The shape of the insulating plate is identical with the shape of the top of the frame body. The shape of the swing body is identical with that of the frame body. Even number pairs of electrode plates are plated on the lateral wall of the frame body. At least one pair of electrode plates are plated on the top wall of the frame body and the insulating plate. The swing body is located between the top wall of the frame body and the insulating plate. The distances from the swing body to all the electrode plates are equal. The gravity meter uses the sensitive probe and is a high-precision vertical-swing clinometer, relative gravity acceleration and two-dimensional crustal inclination signal measuring are achieved at one step, and double functions of an existing high-precision gravity meter and an clinometer are achieved.
Owner:INST OF GEODESY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
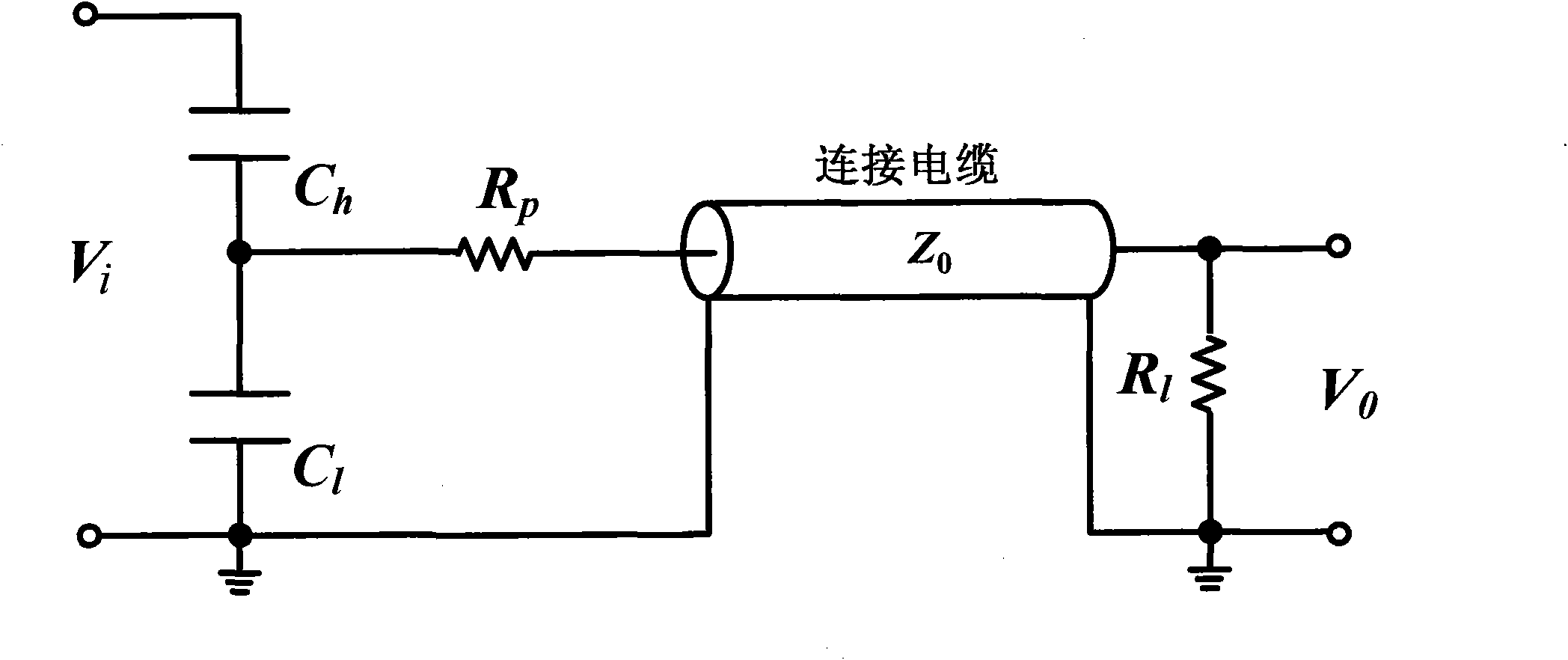
Subnanosecond high-voltage pulse measurement system
ActiveCN101839939AEasy to installEasy to operateCurrent/voltage measurementVoltage dividersCapacitanceVoltage pulse
The invention discloses a subnanosecond high-voltage pulse measurement system and relates to a device for measuring subnanosecond high-voltage pulse signals transmitted in a coaxial cable. The measurement system mainly comprises a coaxial capacitive voltage divider, a noninductive resistor, and an oscilloscope. The coaxial capacitive voltage divider in the device effectively uses stray parameters between inner and outer conductors of the structure and the coaxial cable. By adopting the crimping mode to connect the components, the lead-in inductance is effectively reduced, and the system measurement bandwidth is improved. The subnanosecond high-voltage pulse measurement system have the advantages of simple structure, convenient installation, no change of the signal transmission medium structure in the coaxial cable, and no influence on the originally transmitted signals, and can be widely applied to the measurement of high-voltage pulse signals in the coaxial cable.
Owner:REMEDICINE CO LTD
AC/DC zero-flux fluxgate current sensor and program control configuration and calibration method thereof
ActiveCN111323632AReduce production processReduce manufacturing costElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingSignal tracerCurrent sensor
The invention discloses an AC / DC zero-flux fluxgate current sensor, which comprises a fluxgate current sensor body and a configuration and calibration circuit for configuring and calibrating the fluxgate current sensor body. The fluxgate current sensor body comprises a first iron core, a second iron core, an excitation winding, a feedback winding and a measurement winding. The configuration and calibration circuit comprises a processor, a crystal oscillator, an RS232 interface circuit, an excitation source amplification drive circuit, a programmable compensation signal tracker, a programmablefilter, a phase-sensitive demodulation circuit, a PI control circuit and a power amplifier. The invention discloses a program control configuration and calibration method of an AC / DC zero-flux fluxgate current sensor. According to the invention, the offset current caused by inconsistent parameters of the two iron cores can be automatically matched, the requirement on the process consistency of thetwo fluxgate iron cores can be greatly reduced, the optimal performance of the fluxgate sensor can be realized, the practicability is strong, and the popularization and use values are high.
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGXI ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD RES INST +2
Optical fiber acoustic vibration sensor based on gold-plated vibration film and manufacturing method thereof
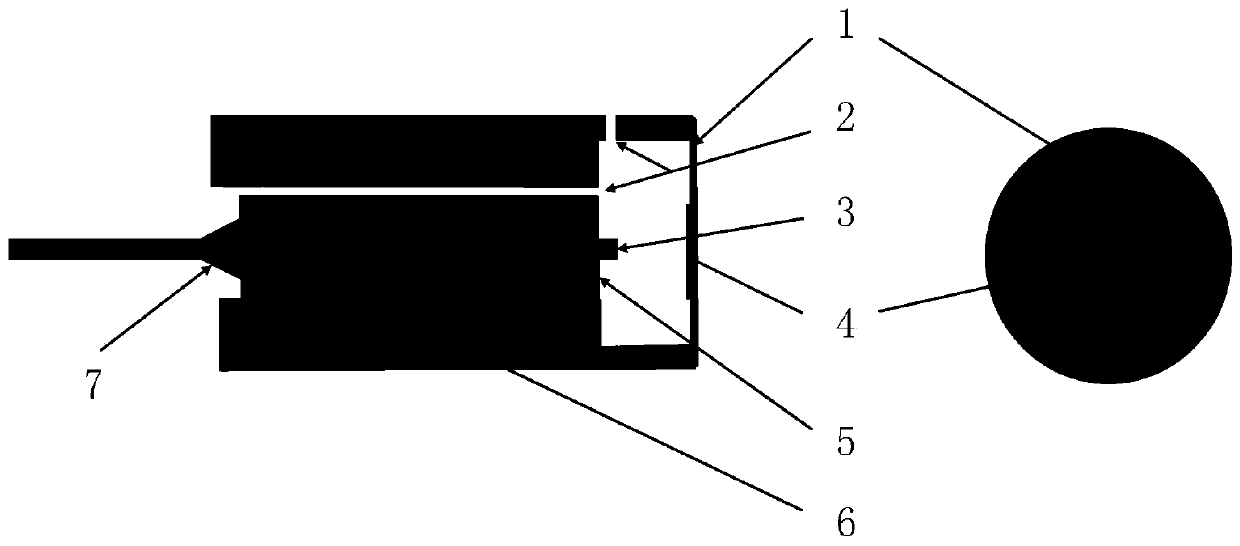
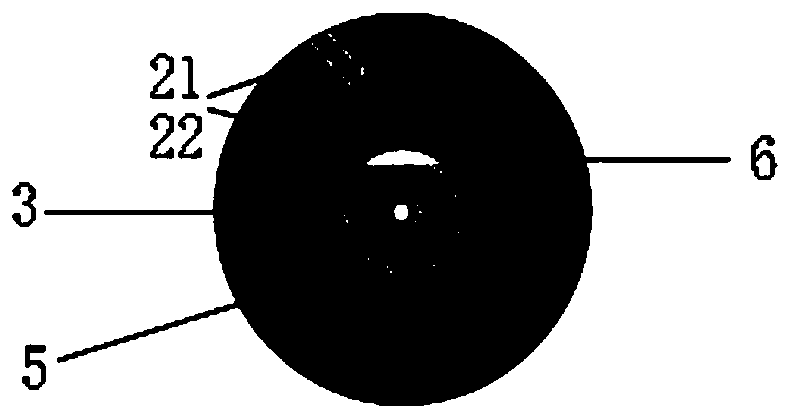
InactiveCN111044137AImprove reflectivityIncreased measurement bandwidthSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansAcoustic vibrationTube Capillary
The invention discloses an optical fiber acoustic vibration sensor based on a gold-plated vibration film and a manufacturing method thereof. The optical fiber acoustic vibration sensor comprises a vibrating diaphragm (1), a single-mode optical fiber (3) having the end surface containing a tantalum pentoxide coating, and a supporting structure of a sensing head; a gold plating layer (4) is arrangedon the inner surface of the vibrating diaphragm (1); and a through hole (2) is arranged between the vibrating diaphragm (1) and the single-mode optical fiber (3) with the tantalum pentoxide coating on the end face. The supporting structure of the sensing head is composed of the through hole (2), a D-shaped tube (5), a capillary tube (6) and an epoxy resin adhesive layer (7), and a resonance microcavity is formed between the single-mode optical fiber (3) with the tantalum pentoxide coating on the end face and the vibrating diaphragm (1). According to the invention, the high reflectivity is effectively ensured, the effective measurement bandwidth is improved, and the interference signal quality is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
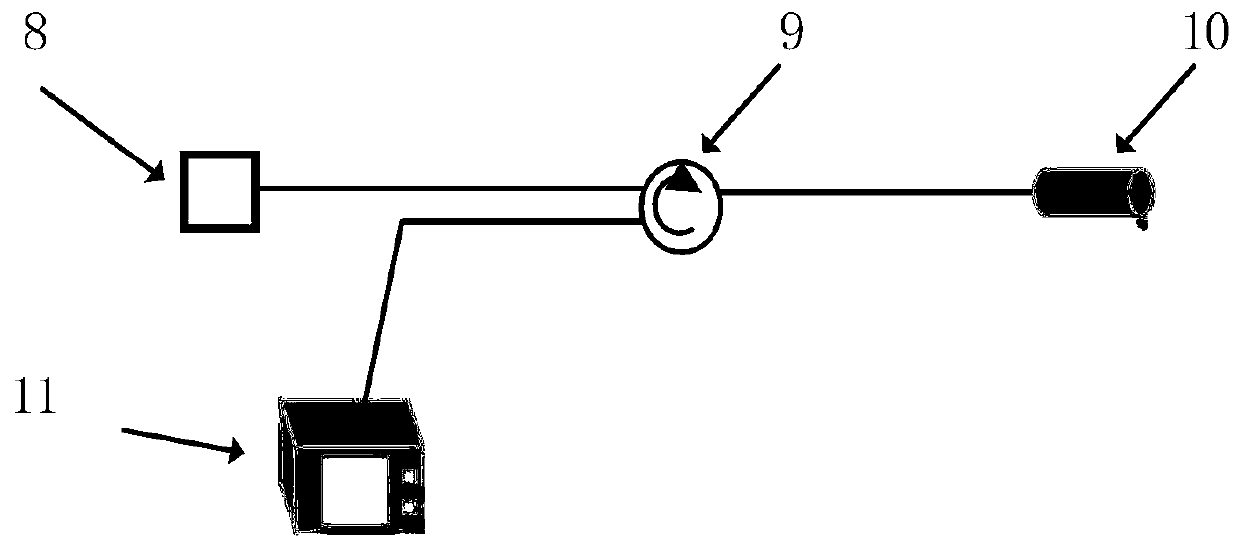
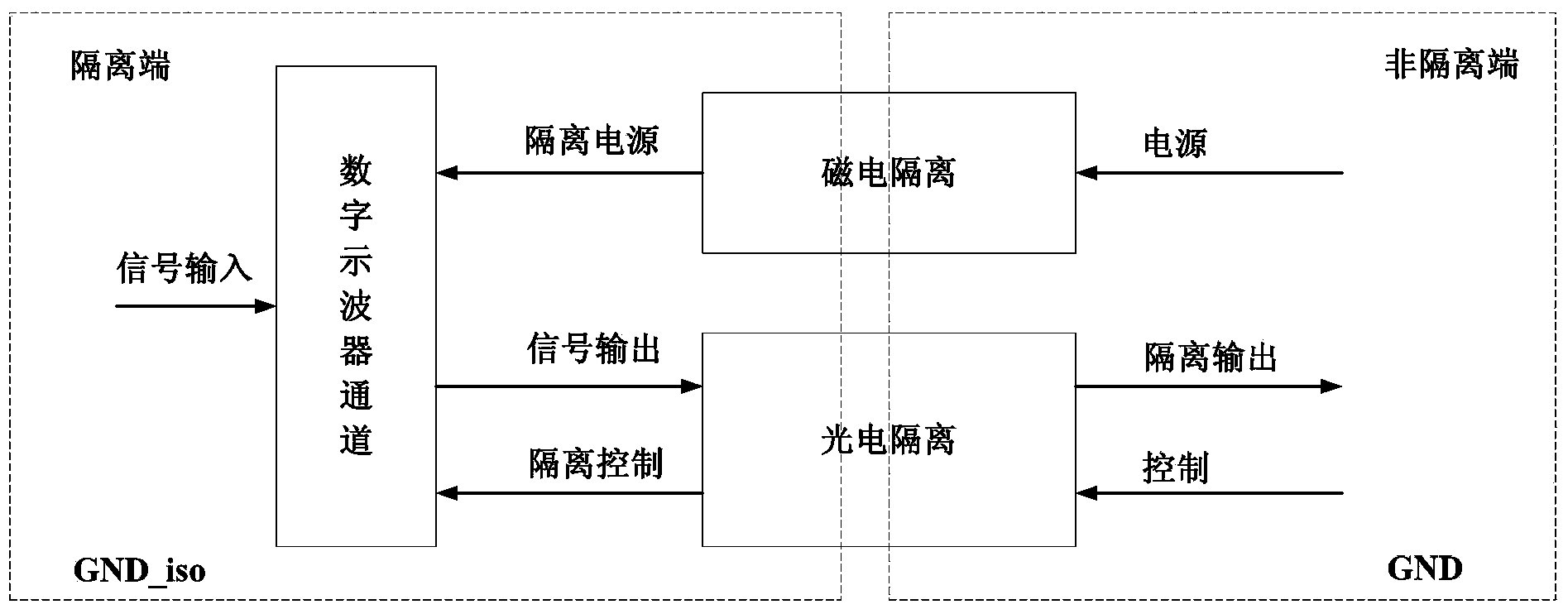
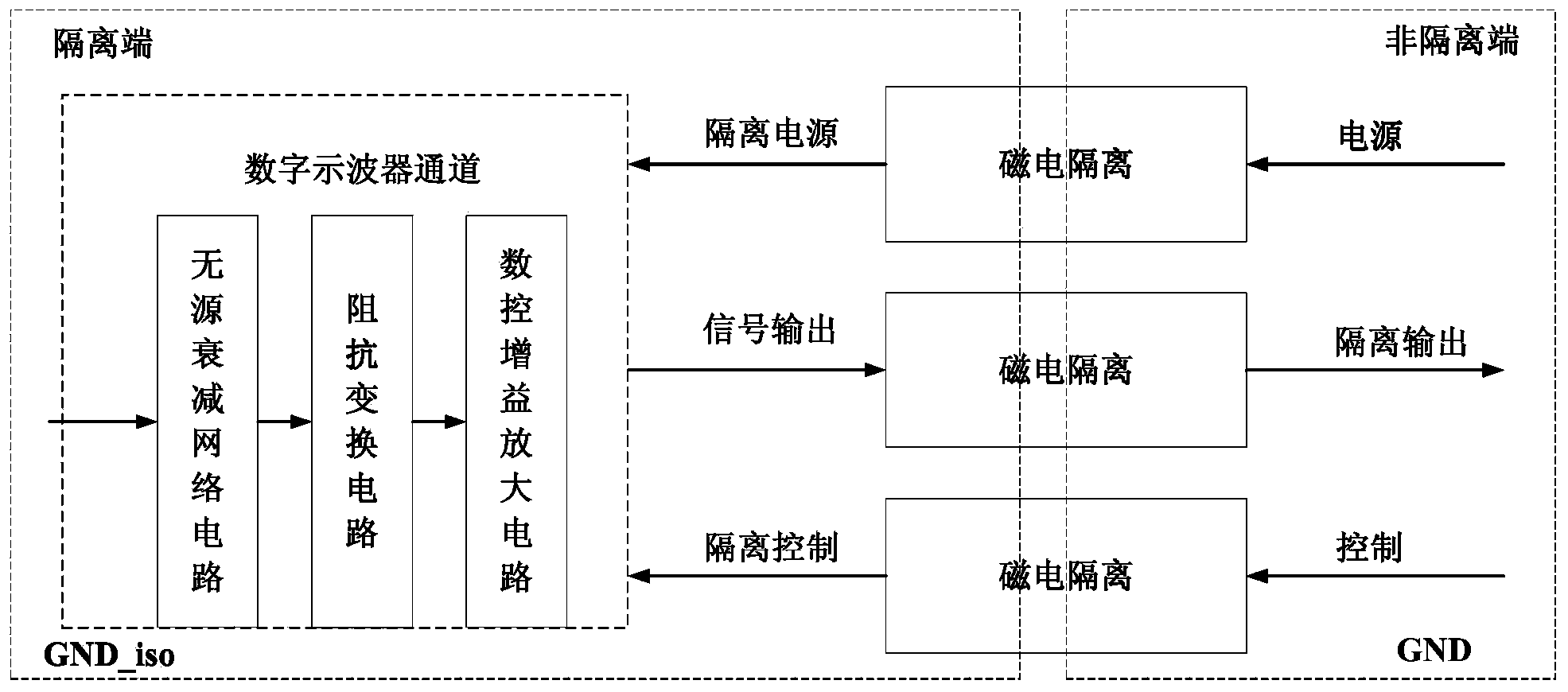
Digital oscilloscope isolation channel circuit
InactiveCN103487624AIncreased measurement bandwidthLarge floating isolation safety levelDigital variable displayNumerical controlGalvanic isolation
The invention belongs to the technical field of digital oscilloscopes, and particularly discloses a digital oscilloscope isolation channel circuit which comprises a passive attenuation network circuit, an impedance conversion circuit, a numerical control gain amplification circuit and an isolation circuit. The isolation circuit comprises a power isolation circuit, a digital isolation circuit and an analog signal isolation circuit, and the power isolation circuit, the digital isolation circuit and the analog signal isolation circuit are used for isolating a power supply from the ground, digital control signals and analog input signals respectively. A magneto-electricity isolation technology is adopted, the complete electrical isolation between the input end and the output end of a digital oscilloscope is achieved, and the isolation safety level reaches 1000V CATII. The measurement bandwidth ranges from DC to 200MHz, and smooth amplitude-frequency responses are maintained. The vertical sensitivity ranges from 2Mv / div to 100V / div. The digital oscilloscope isolation channel circuit has the advantages of being large in isolation bandwidth, high in floating isolating safety level, large in dynamic range, high in measurement precision, good in linearity and the like.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Multi-bridge tunnel magnetic resistance biaxial accelerometer
ActiveCN110780088AEasy to integrateEliminate static magnetic interferenceAcceleration measurement using interia forcesAccelerometerMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a multi-bridge tunnel magnetic resistance biaxial accelerometer, which comprises a support frame I, a support frame II, an X-axis mass block, a Y-axis mass block, an X-axis tunnel magnetic resistance element, a Y-axis tunnel magnetic resistance element, an X-axis inflection coil and a Y-axis inflection coil. The X-axis inflection coil and the Y-axis inflection coil are fixedly arranged on the X-axis mass block; the two ends of the X-axis inflection coil and the two ends of the Y-axis inflection coil are connected with corresponding electrodes on the support frame I through wires respectively; the X-axis tunnel magnetic resistance element and the Y-axis tunnel magnetic resistance element are fixedly arranged on the support frame II; the X-axis tunnel magnetic resistance element is arranged right above the X-axis inflection coil; and the Y-axis tunnel magnetic resistance element is arranged right above the Y-axis inflection coil. Multi-bridge circuit structures are arranged in the tunnel magnetic resistance elements. With the biaxial MEMS accelerometer based on the multi-bridge tunnel magnetoresistance, the limit detection capability and the detection sensitivity of the accelerometer are greatly improved.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
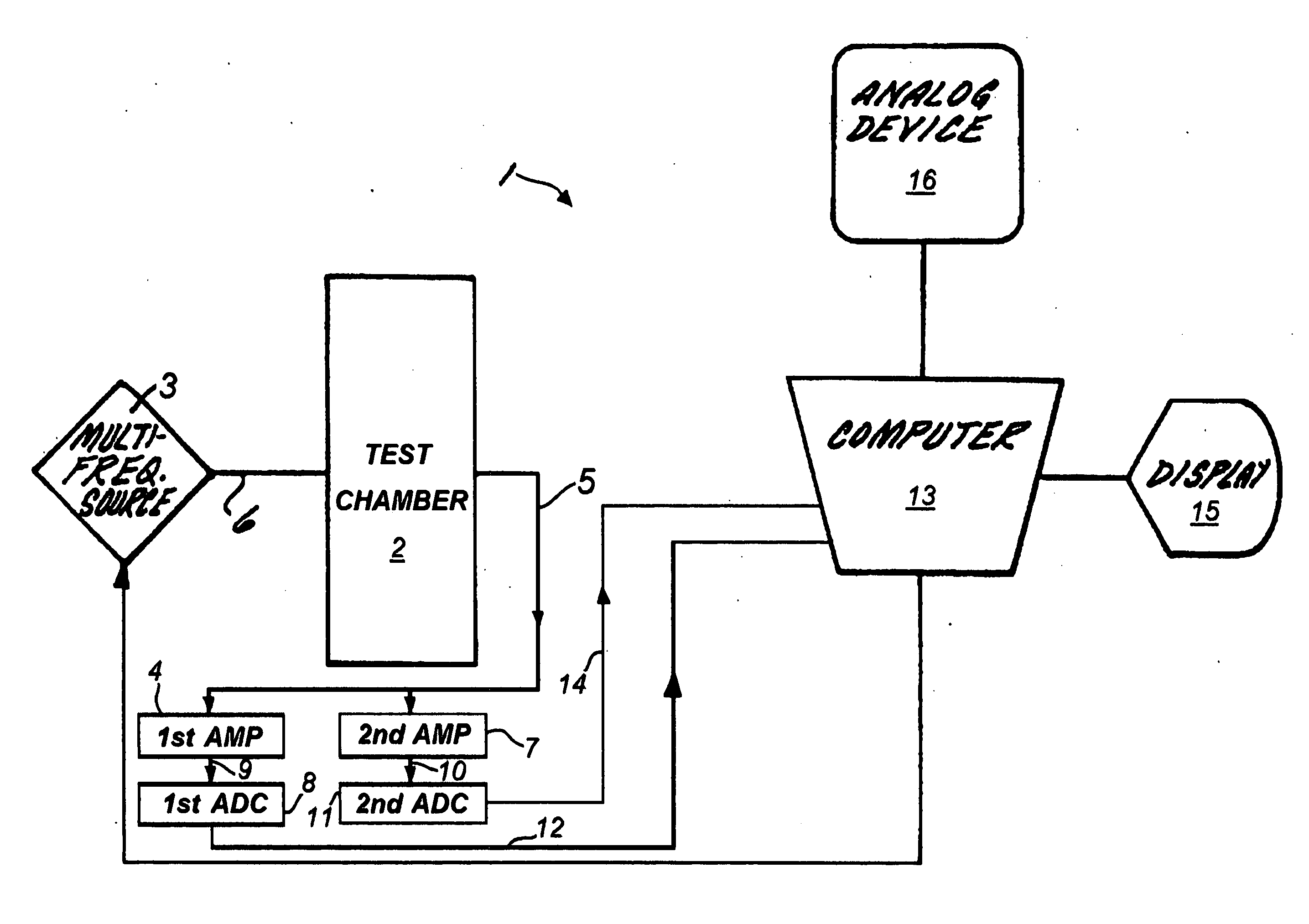
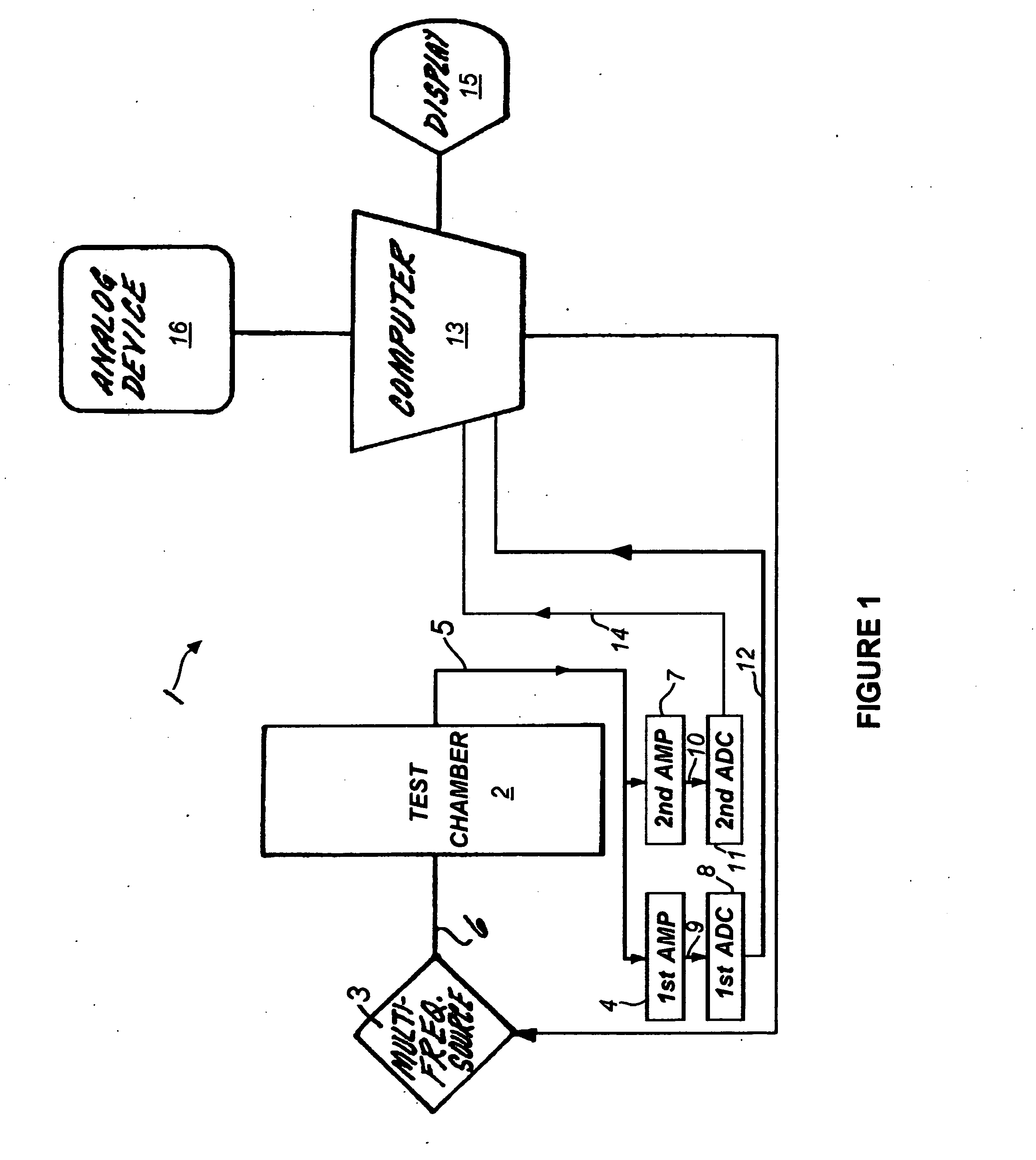
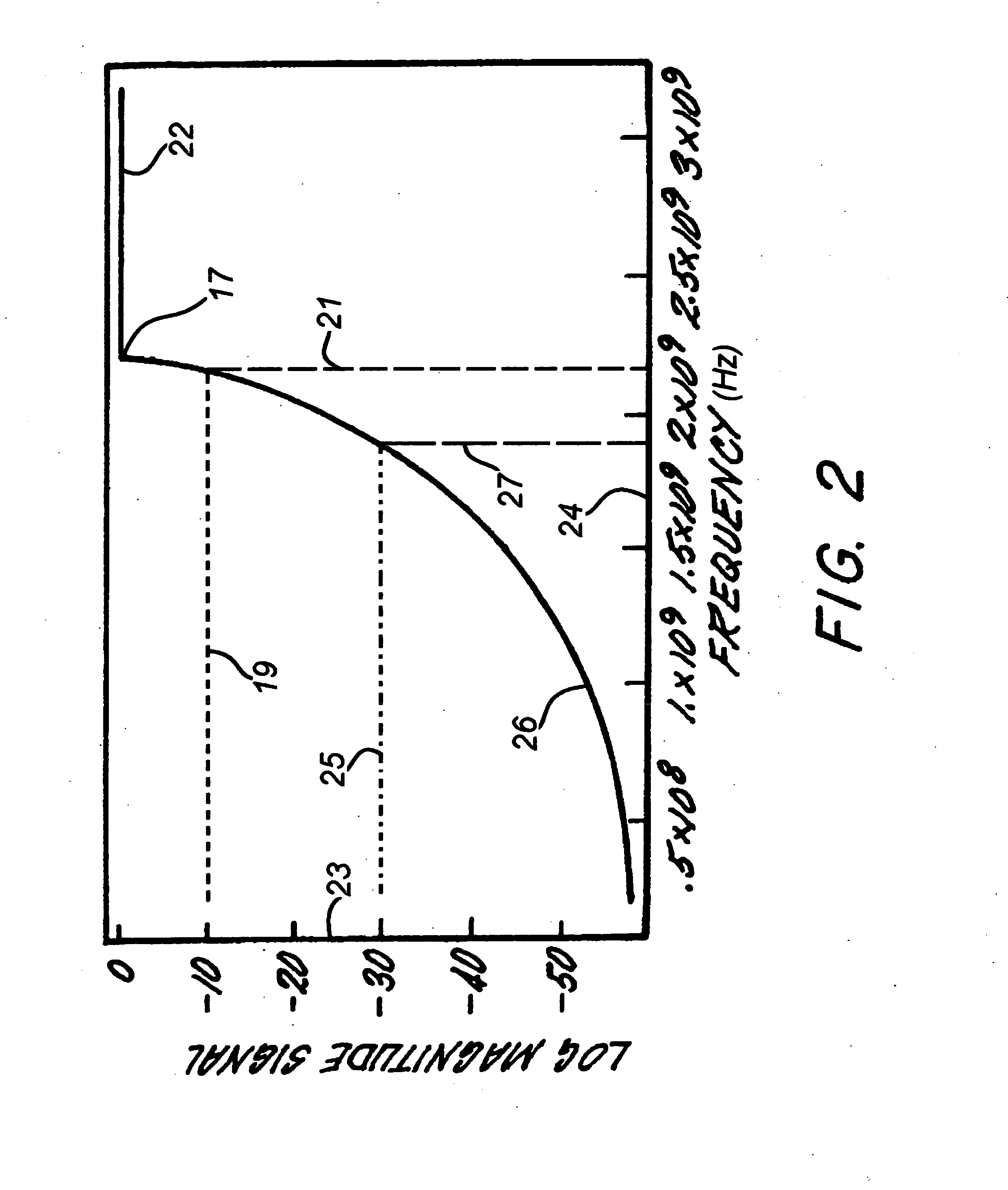
Signal processing in guided wave cutoff spectroscopy
ActiveUS20130024150A1Eliminate needHigh resolutionSpectral/fourier analysisResistance/reactance/impedenceDigital signal processingMaterial under test
The present invention includes a guided microwave spectroscopy system (1) that eliminates the need for an automatic gain control feature by providing multiple signal processing paths having differing fixed voltage gains. An emitted signal which exits a test chamber (2) containing a material under test is simultaneously amplified by at least a first fixed gain amplifier (4) and a second fixed gain amplifier (7). The output signal of each amplifier is separately digitized and then normalized for further digital signal processing by a computer (13) in order to determine parameters of the material under test which may have variable microwave radiation characteristics that are a function of the frequency of the signal emitted into the test chamber. During the signal processing step a system clock (121) causes the computer to sample only an integral number of complete output signal cycles. A calibration protocol (136-154) is conducted based on laboratory samples of each potential material to be processed by the system (1).
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
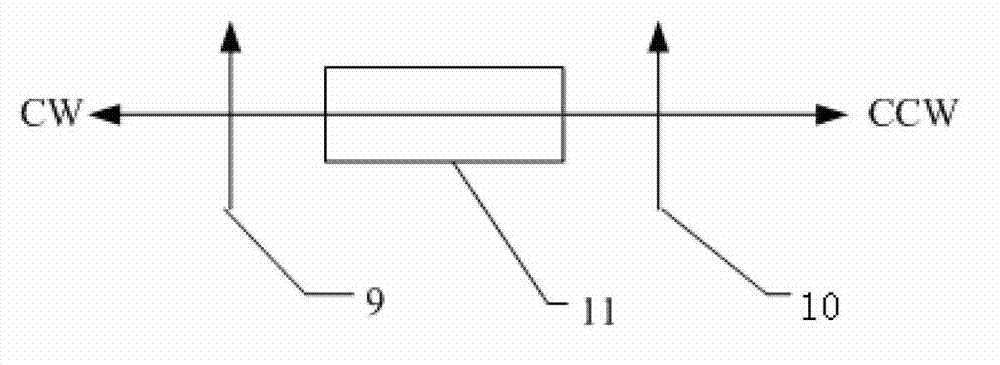
Laser gyroscope offset frequency method based on external cavity feedback
InactiveCN103033178AReduce complexityEliminate mechanical noiseSagnac effect gyrometersPath lengthPhase difference
The invention relates to a laser gyroscope offset frequency method based on external cavity feedback. The method particularly comprises the following steps of: establishing a feedback external cavity outside a laser gyroscope cavity, and reflecting clockwise beams into a laser resonant cavity; and arranging a nonreciprocal optical device in an external cavity light path, so that feedback light waves of clockwise and anticlockwise light waves have phase difference, and frequency offset is established between the clockwise and anticlockwise light waves of the laser gyroscope. A path length modulation part is arranged in the feedback external cavity light path, and the external cavity light path is modulated, so that the frequency offset of the laser gyroscope is modulated, and an effect similar to mechanical dither is obtained. A modulation signal in a laser gyroscope reading device is filtered by employing a filtering technology, so that an angular velocity signal of laser gyroscope measurement is obtained. According to the method, mechanical noise is not generated, and extremely high modulation frequency can be adopted, so that a response speed of the laser gyroscope is increased.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
X-ray pulsar navigation method based on dynamic pulse accumulation window
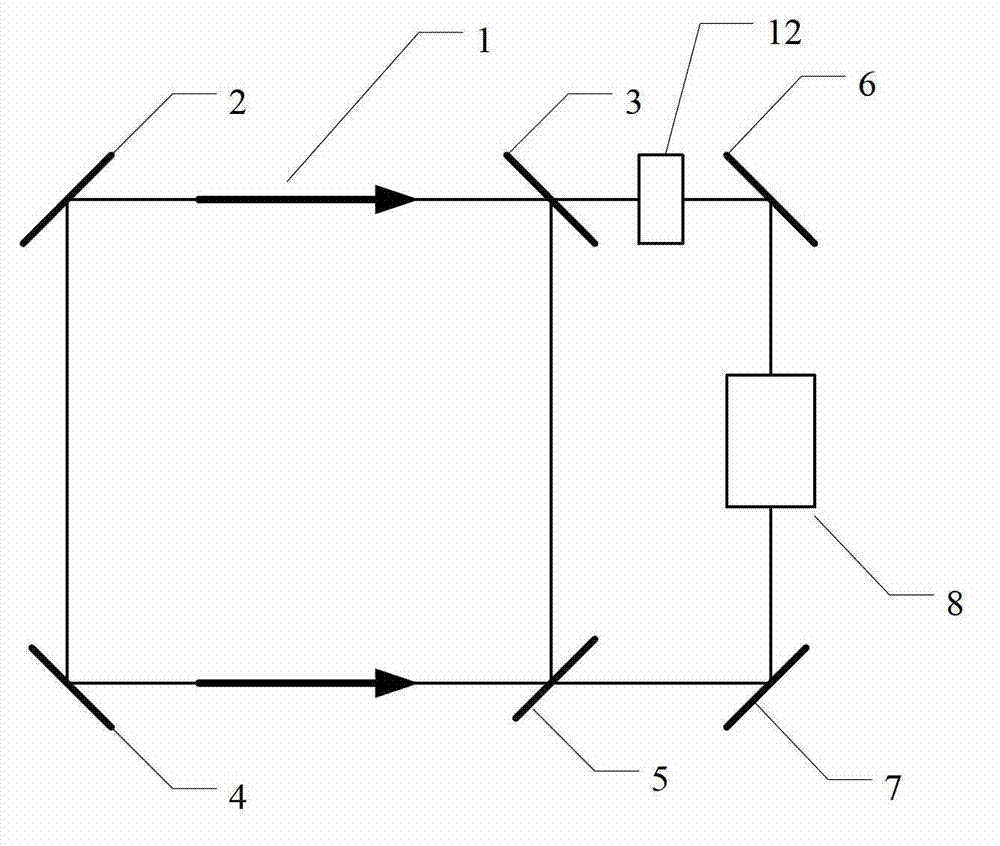
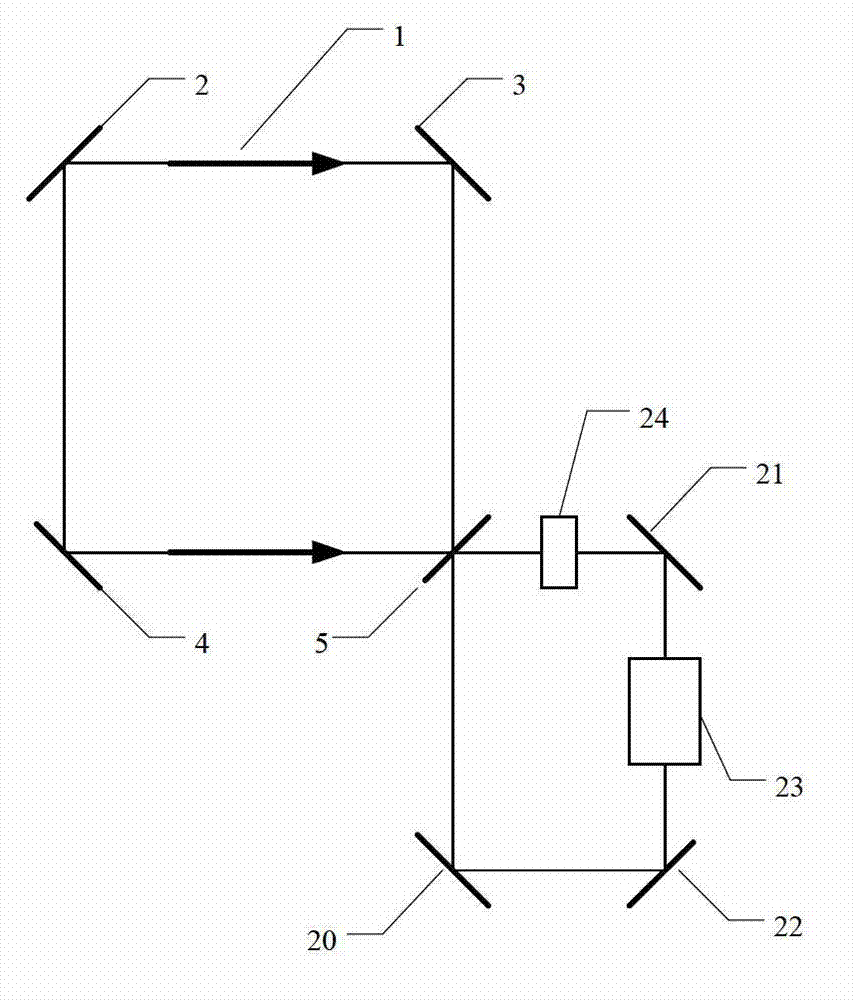
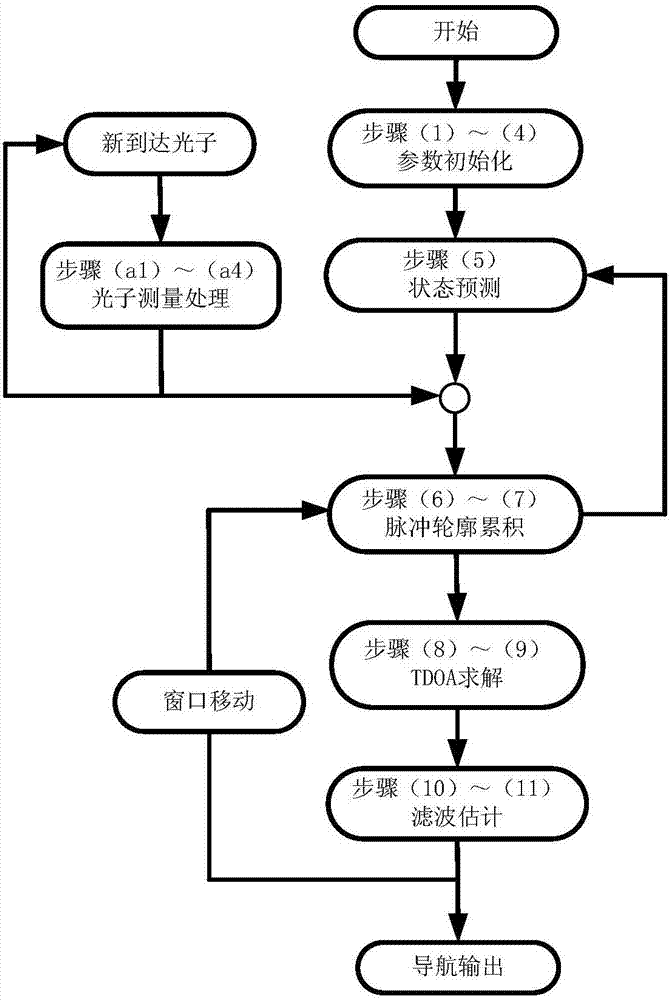
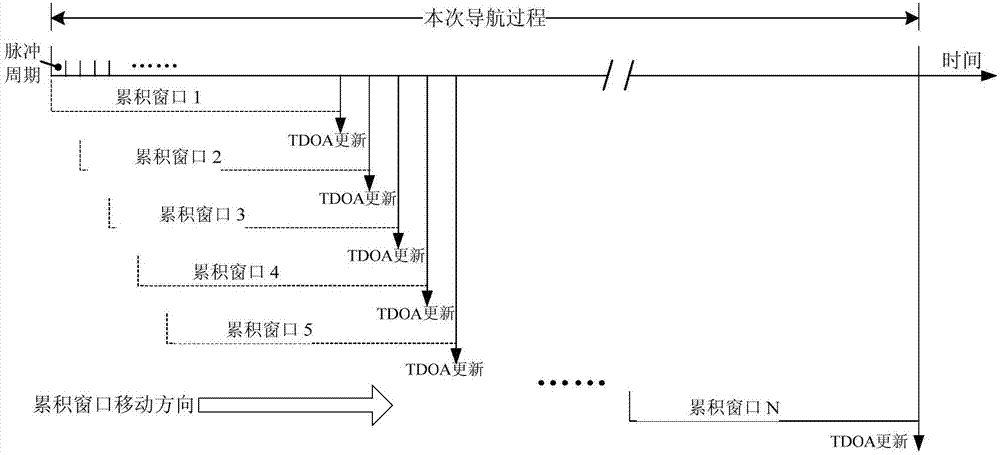
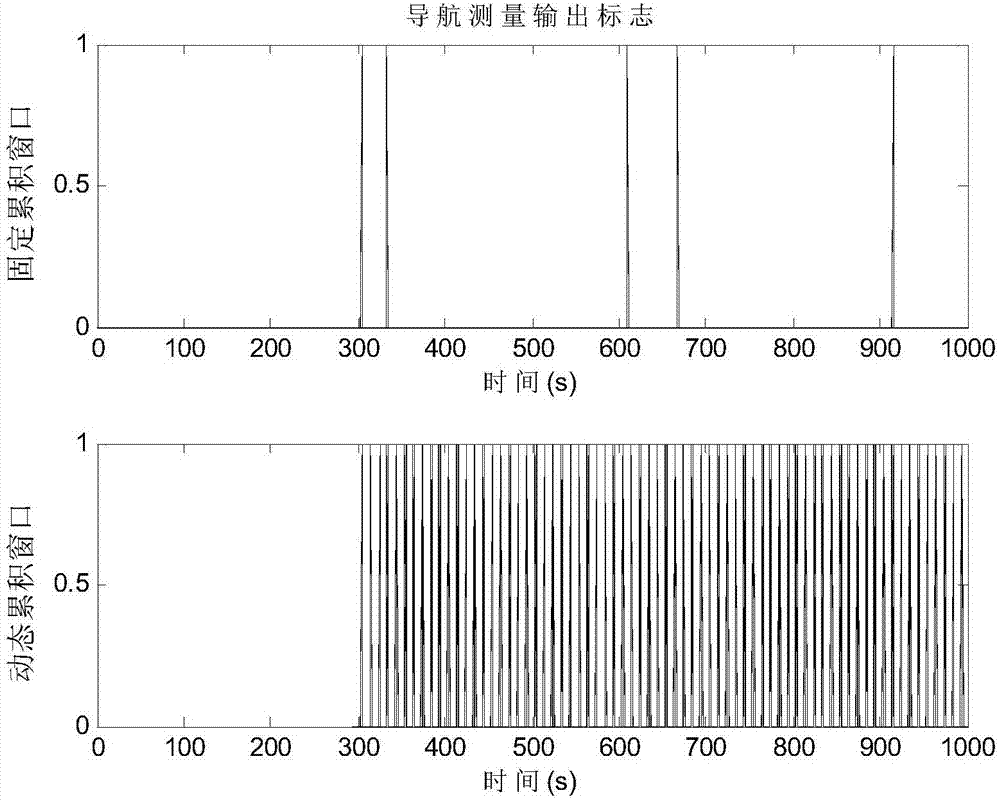
ActiveCN107328409AIncreased measurement bandwidthIncrease measurement update frequencyNavigation by astronomical meansSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Photonics
The invention relates to an X-ray pulsar navigation method based on a dynamic pulse accumulation window, belongs to the fields of spacecraft guidance, navigation and control, and is different from a mode that an X-ray pulsar photonic signal is subjected to fixed window accumulation in a present X-ray pulsar navigation method. The X-ray pulsar navigation method provided by the invention adopts the dynamically arranged pulse accumulation window, so that the position of the accumulation window can be synchronously regulated with a filtering recursive calculation process according to the needs of a signal accumulation signal-to-noise ratio and observation updating frequency along with the update of the X-ray photon pulse sampling; meanwhile, pulse profile cumulative data is updated, and the navigation observation updating frequency is improved. According to the X-ray pulsar navigation method, the problems that the random error cannot be effectively restrained, the orbit extrapolation error has great influence, the arrangement of the pulse accumulation window is inflexible and the like in the traditional X-ray pulsar photonic signal fixed window accumulation mode are effectively solved, and the navigation accuracy and stability are improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Method and system for achieving real-time measurement of big bandwidth optical signal radio frequency spectrums
InactiveCN107315108AIncreased measurement bandwidthReal-time measurementSpectral/fourier analysisElectromagnetic transmissionRadio frequencyOptical coupler
The invention relates to a method and a system for achieving real-time measurement of big bandwidth optical signal radio frequency spectrums. The system comprises an ultrashort pulse source, a first big chromatic dispersion unit, a polarization controller, an optical coupler, a non-linear device, an optical filter, a second big chromatic dispersion unit, a photoelectric detector and a real-time oscilloscope. According to the invention, when the radio frequency spectrum of the signal is changed from the MHz to the GHz, real-time measurement of the frame rate speed can be achieved directly on the radio frequency information of a to-be-measured signal in the time domain; by directly converting the radio frequency measurement of light carriers from the measurement in the electrical domain into the measurement in the optical domain, broadband limitations of the photoelectric detector are avoided; and the method and the system are characterized by capability of measuring the big radio frequency broadband of 100GHz or above.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Transient magnetic field recorder
InactiveCN102495382AAchieve captureRealize point measurementMagnetic measurementsSignal conditioningEngineering
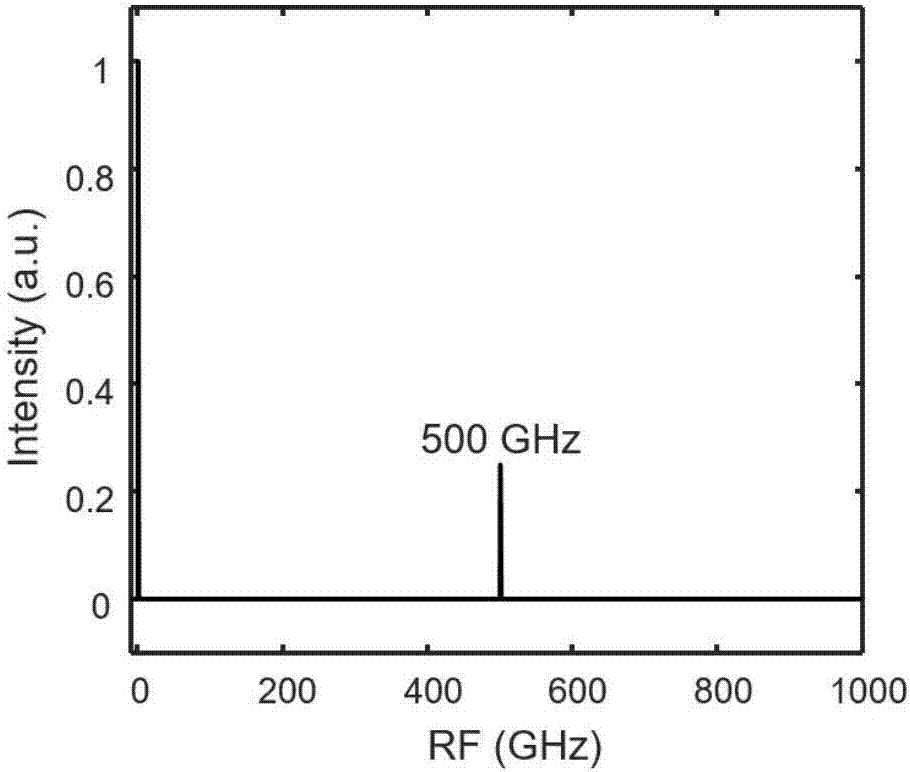
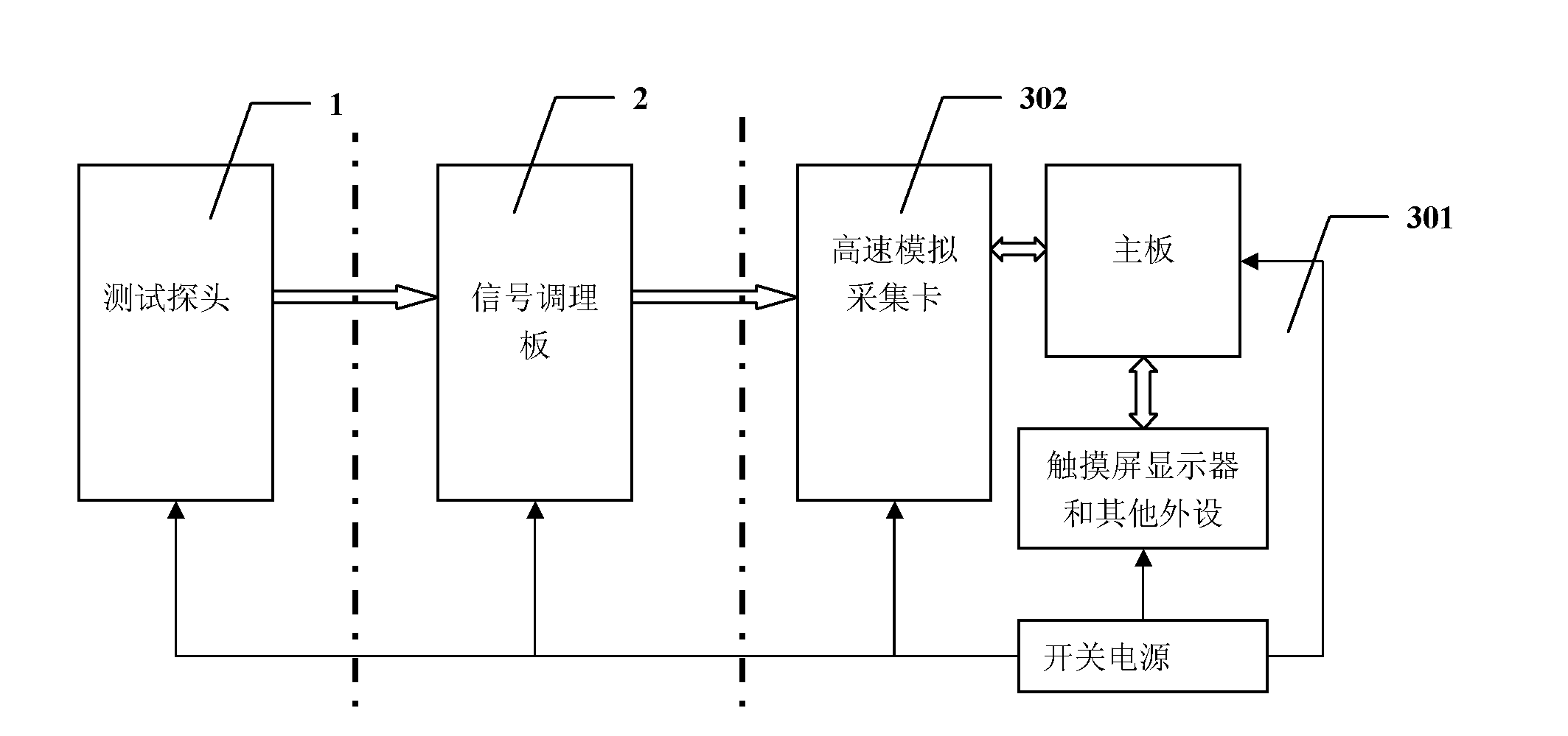
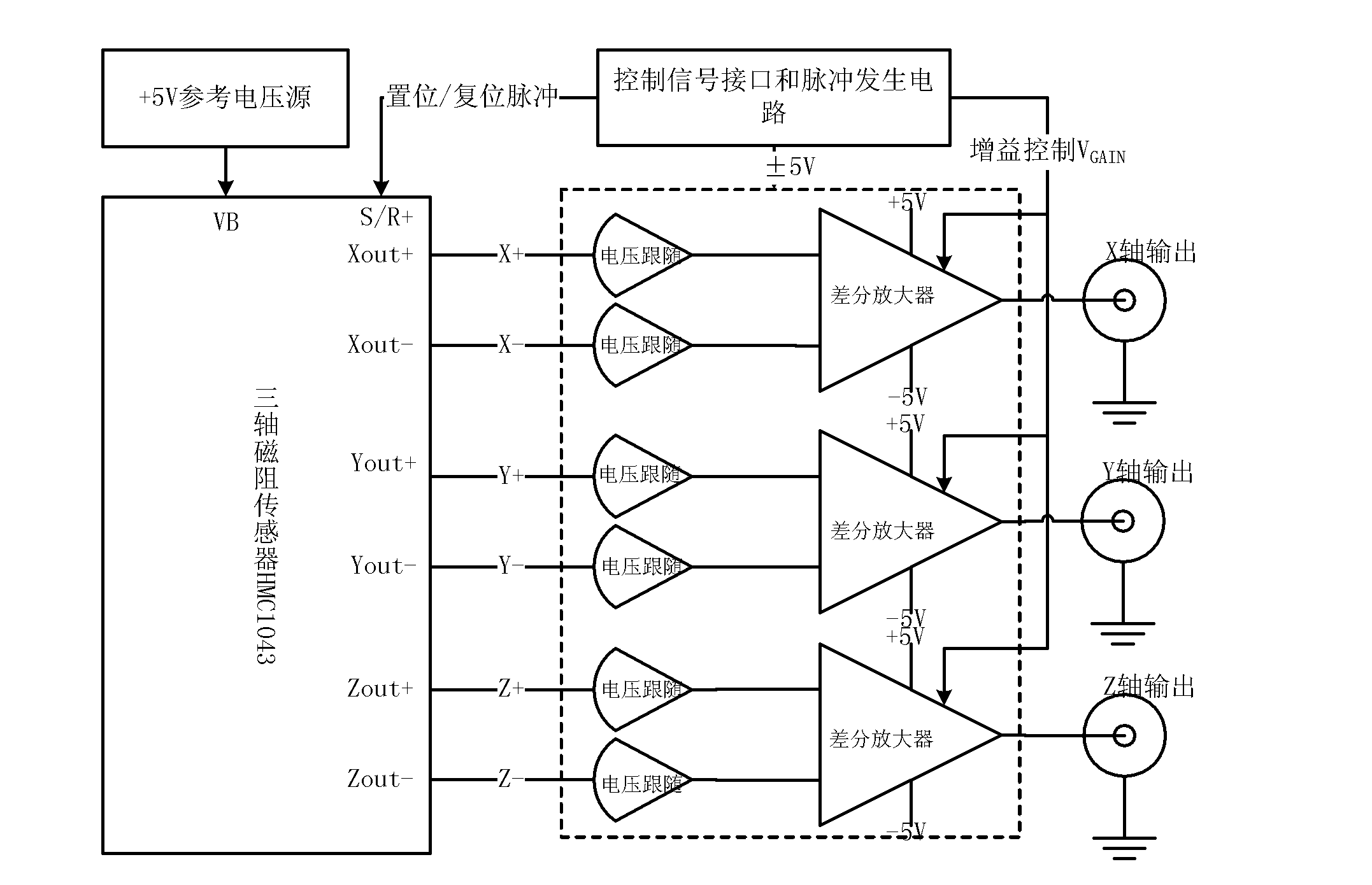
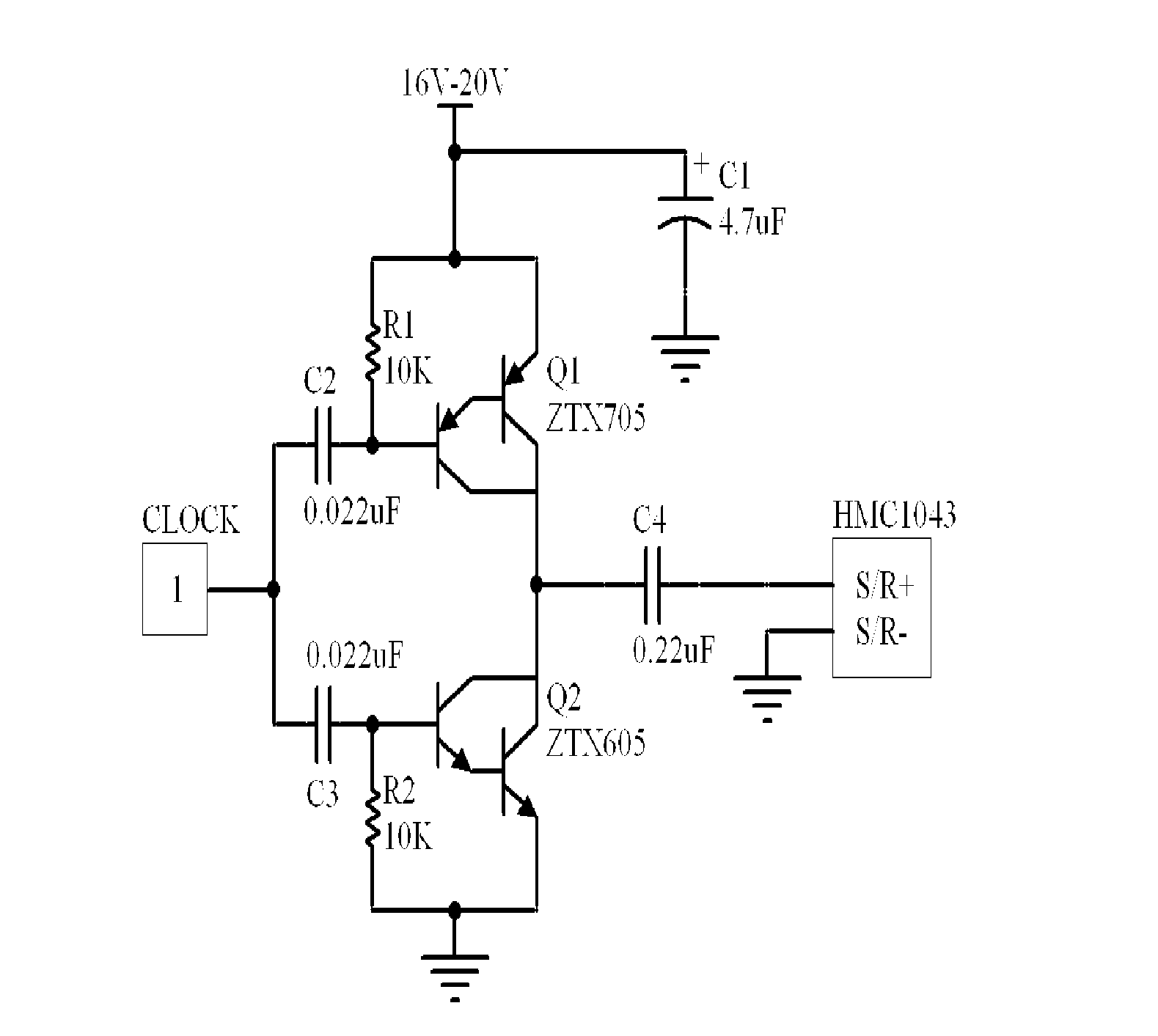
The invention discloses a transient magnetic field recorder which comprises a test probe, a signal conditioning plate and an intelligent processing system which is formed by a computer and a high speed simulation acquisition card. A space magnetic induction intensity vector is converted into electric quantity signals in X, Y and Z directions, proportion amplification, lossless transmission and operation are carried out, and the intelligent processing system carries out acquisition, display and record treatments on the processed electric quantity signals in X, Y and Z directions and electric quantity which is directly proportional to magnetic induction intensity. Since the test probe carries out conversion of a magnetic signal into an electrical signal through a triaxial magnetic resistance sensor, point measurement is realized, a measurement bandwidth is high and can reach DC-5MHz, thus capturing a transient abnormal magnetic field can be realized, and a plurality of traditional inherent defects that using an induction coil to capture a magnetic field can not realize the point measurement of the magnetic field, respond to contradiction among a constant magnetic field, the bandwidth and sensitivity and satisfy a transient magnetic field test requirement well are overcome.
Owner:STATE GRID SICHUAN ELECTRIC POWER CORP ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Multi-band wireless channel measurement calibration method and system
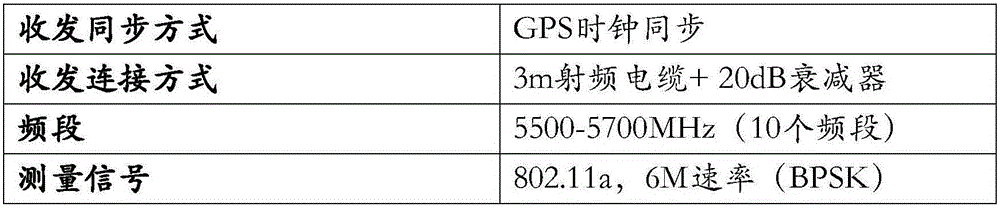
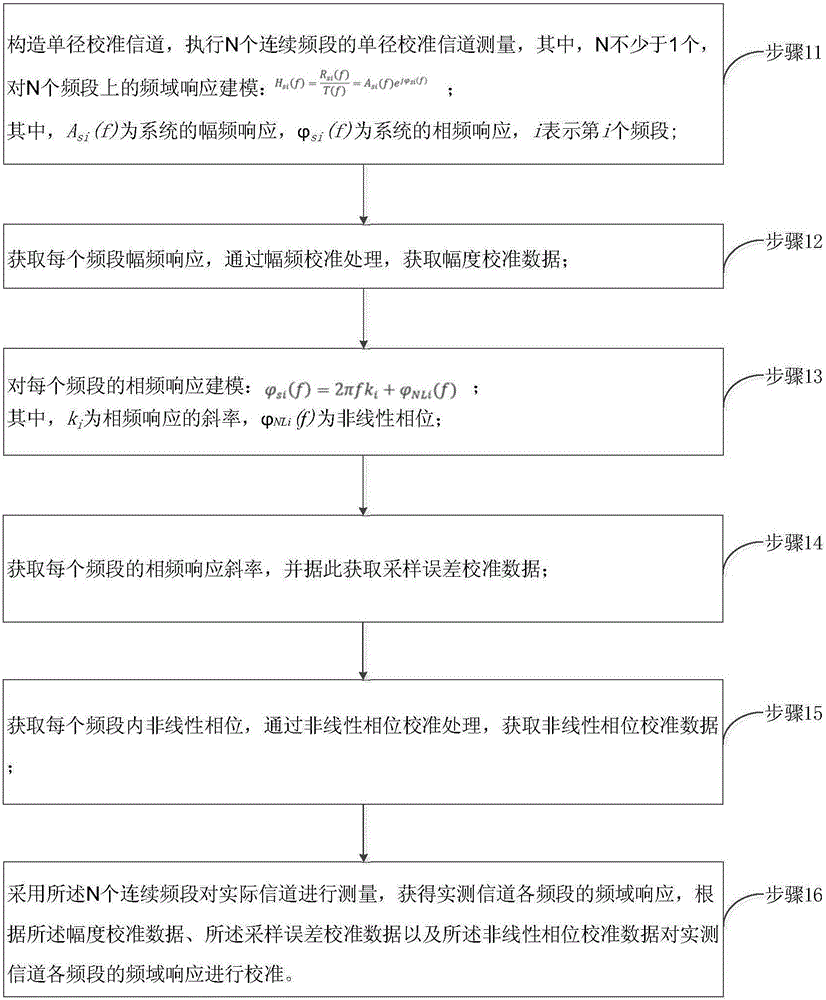
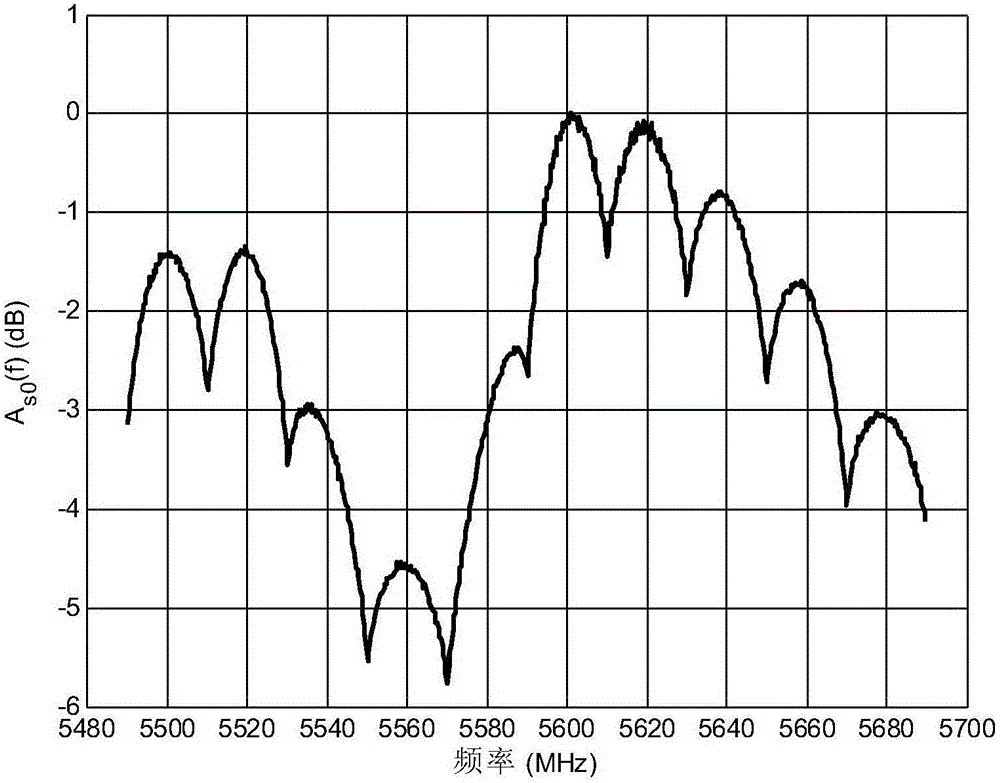
ActiveCN106160882AIncreased measurement bandwidthHigh latency resolutionTransmission monitoringWireless communicationMulti bandComputer science
The embodiment of the invention provides a multi-band wireless channel measurement calibration method and system. The method comprises the steps of establishing a single-path calibration channel, and performing single-path calibration channel measurement of N continuous bands, wherein the N is more than or equal to 1; obtaining the amplitude-frequency response of each band, and obtaining amplitude calibration data through amplitude-frequency calibration processing; obtaining the phase frequency response slope of each band, and obtaining sampling error calibration data according to the phase frequency response slope; obtaining the non-linear phase in each band, and obtaining non-linear phase calibration data through non-line phase calibration processing; measuring a practical channel through adoption of the N continuous bands, thereby obtaining the frequency domain response of each band of the actual measurement channel; and calibrating the frequency domain response of each band of the actual measurement channel according to the amplitude-frequency calibration, the sampling error calibration data and the non-linear phase calibration data. According to the method and the system, on the premise of not increasing hardware costs, the measurement bandwidth is multiplied, and the higher delay resolution is obtained.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
High-potential current acquisition system with rain-proof function
ActiveCN108303571AHigh measurement accuracyGuaranteed electrical insulationBatteries circuit arrangementsNon-electrical signal transmission systemsLow voltageControl line
The invention relates to a high-potential current acquisition system with a rain-proof function, which comprises a data acquisition box, a data receiving device and a trigger device, wherein the dataacquisition box comprises a shielding box, a data acquisition case and an adjustable resistor, the data acquisition case and the adjustable resistor are installed in the shielding box, the shielding box is connected with a high voltage wire and hung on a cross arm through an insulator, one end of the adjustable resistor is electrically connected with the shielding box, the other end is electrically connected with a discharge electrode below the shielding box through a conductive copper strip which is externally provided with an insulating layer, a resistance control line and a voltage measurement cable of the adjustable resistor are connected with the data acquisition case, and the data acquisition case exchange information with the data receiving device and the trigger device through an optical fiber. According to the invention, the data acquisition part of the high voltage side is placed in the metal shielding box, and information transmission between the high voltage side and the low voltage side is realized through the optical fiber, thereby not only being capable of shielding various types of electromagnetic interference and ensuring the electrical insulation between the highvoltage side and the low voltage side, but also being suitable for being used in a rain condition and creating favorable conditions for the research on air gap discharge under the raining state.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
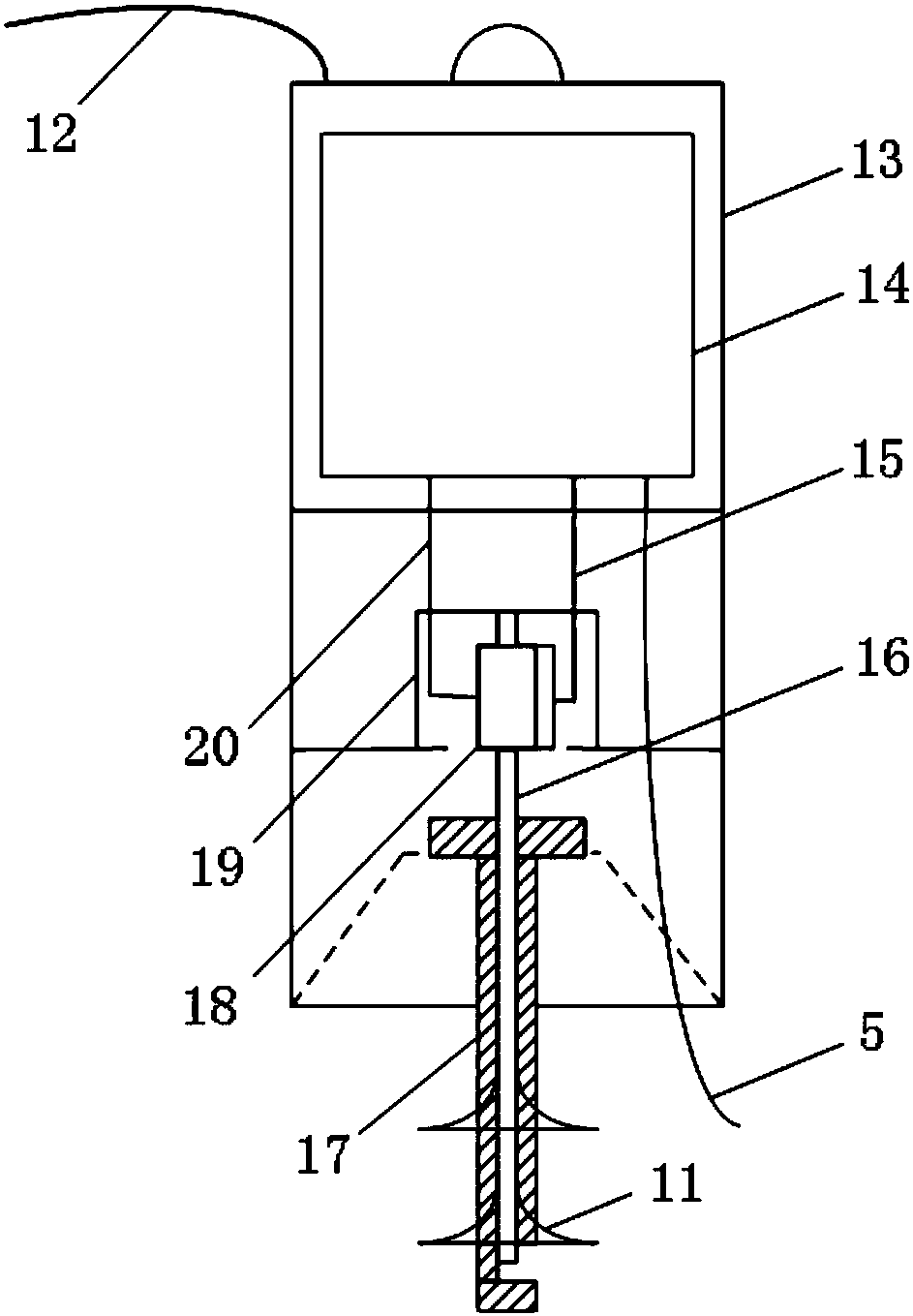
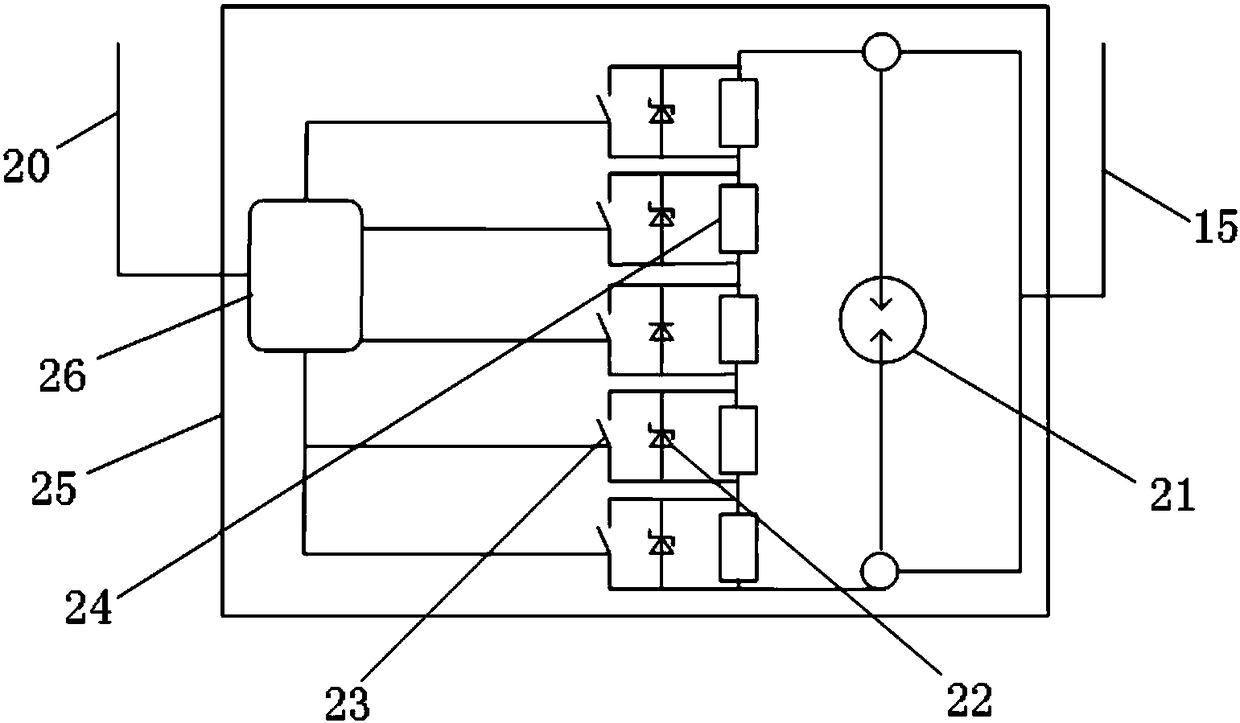
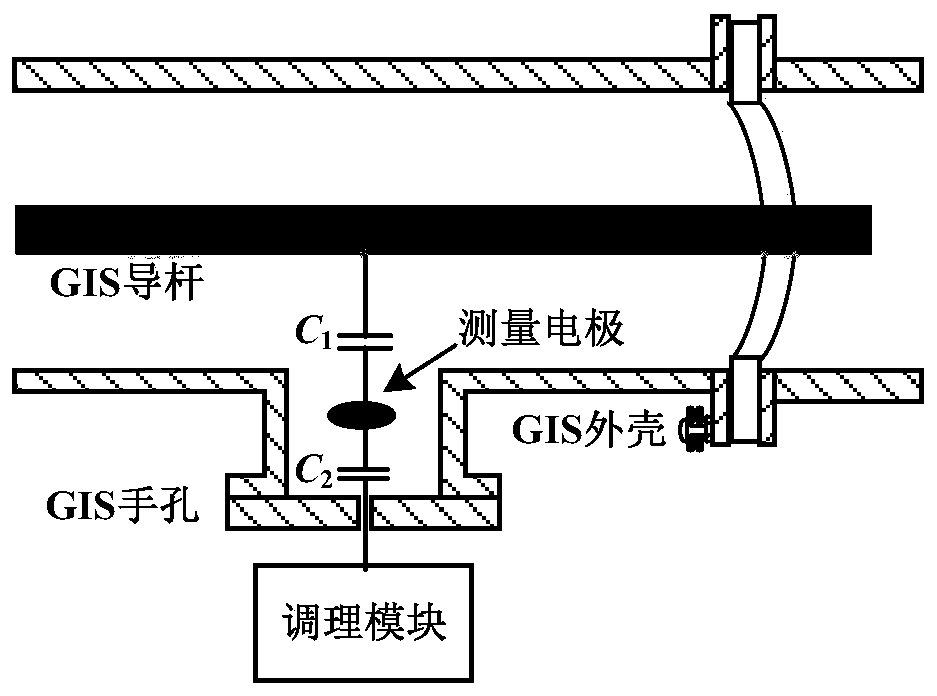
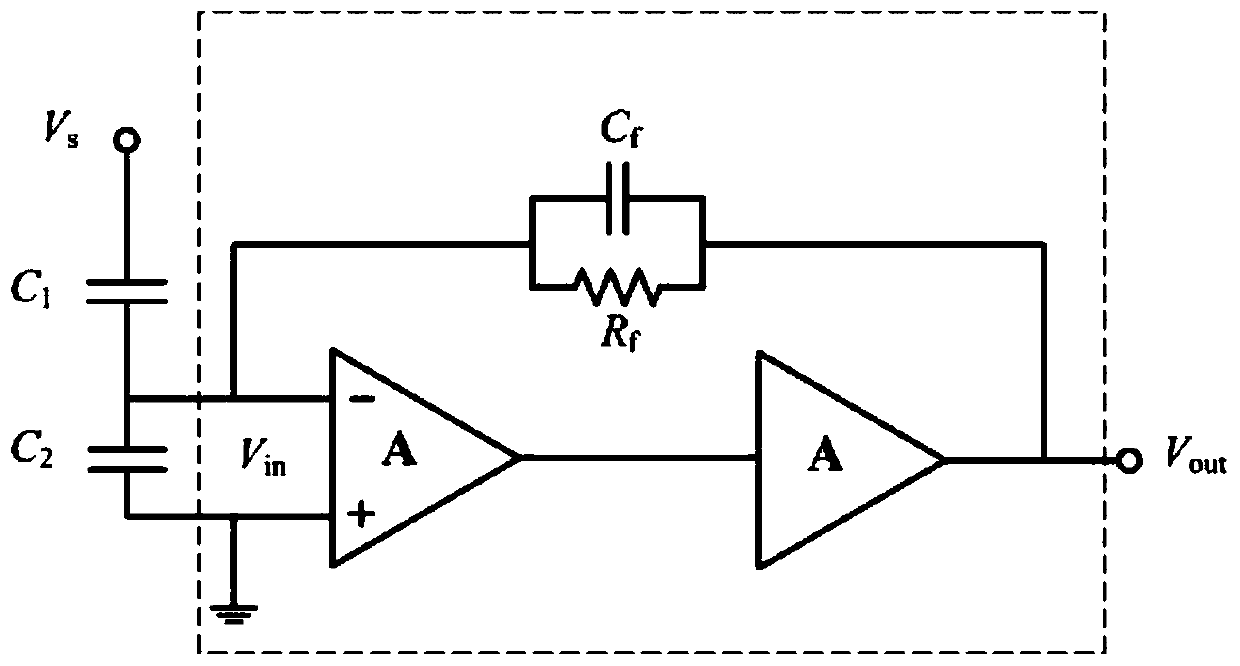
Wideband GIS electronic voltage transformer device and measurement method
ActiveCN110426547AEasy to adjustChange the voltage signal transmission relationshipVoltage/current isolationVoltage measurements onlyCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a wideband GIS electronic voltage transformer device and a measurement method. The device comprises a built-in measurement electrode module, a conditioning module, a sampling module and a control module, wherein a measurement electrode of the built-in measurement electrode module is arranged in a GIS hand hole, and the measurement electrode penetrates through a GIS shell through a wire to be connected with a forward input end of a wideband amplifier of the conditioning module; a conditioning resistor and a conditioning capacitor of the conditioning module are connectedin parallel between a negative input end and a negative output end of the wideband amplifier; the sampling module performs analog sampling and analog-digital conversion to obtain a digital output voltage; and the control module calculates a GIS primary voltage value according to a voltage division ratio and the digital output voltage. Through the device and the method, electrode size miniaturization is realized, measurement bandwidth is expanded, transient characteristics are improved, the voltage transformation ratio is easy to regulate, and it is not needed to set secondary voltage division.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
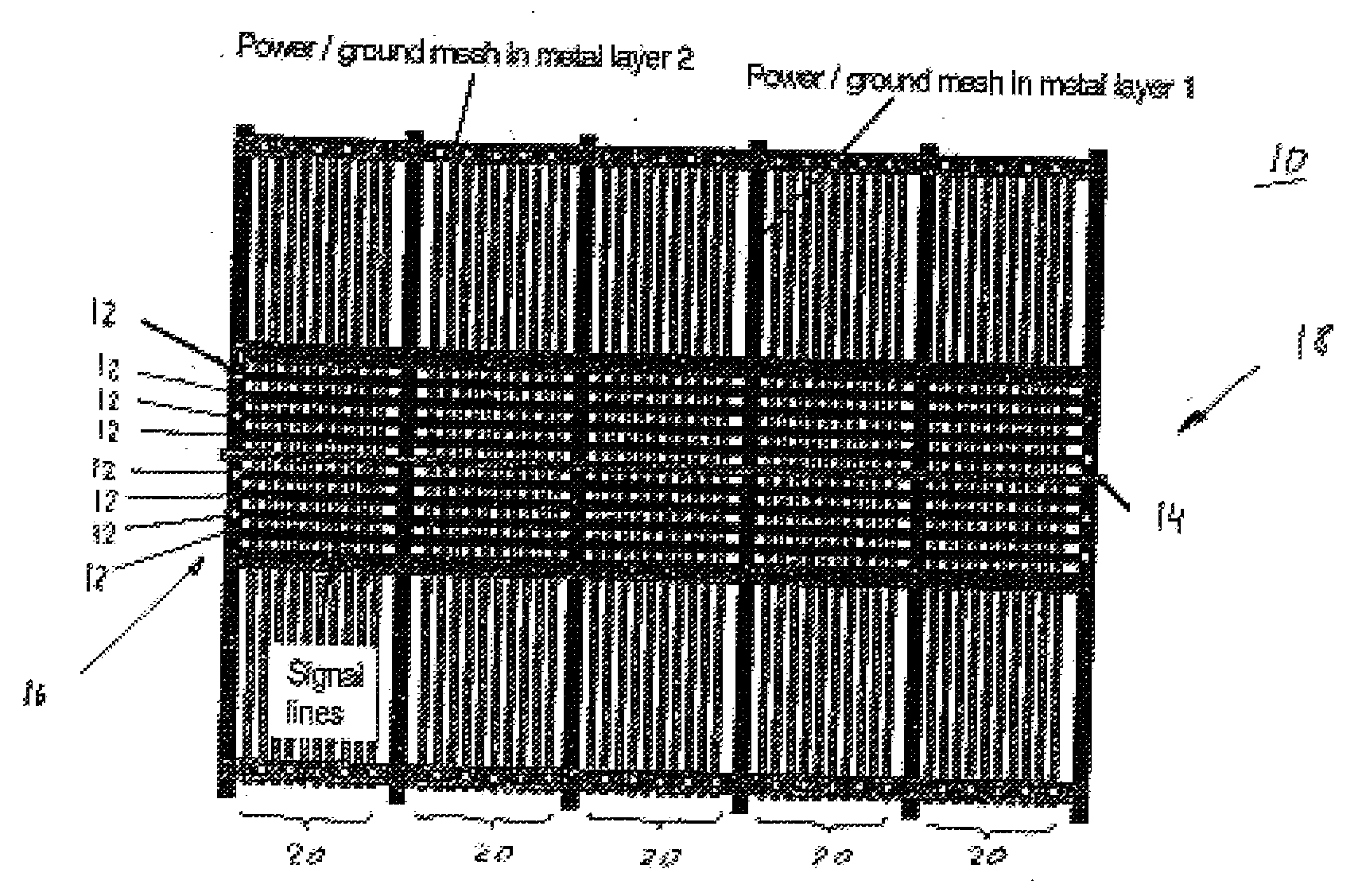
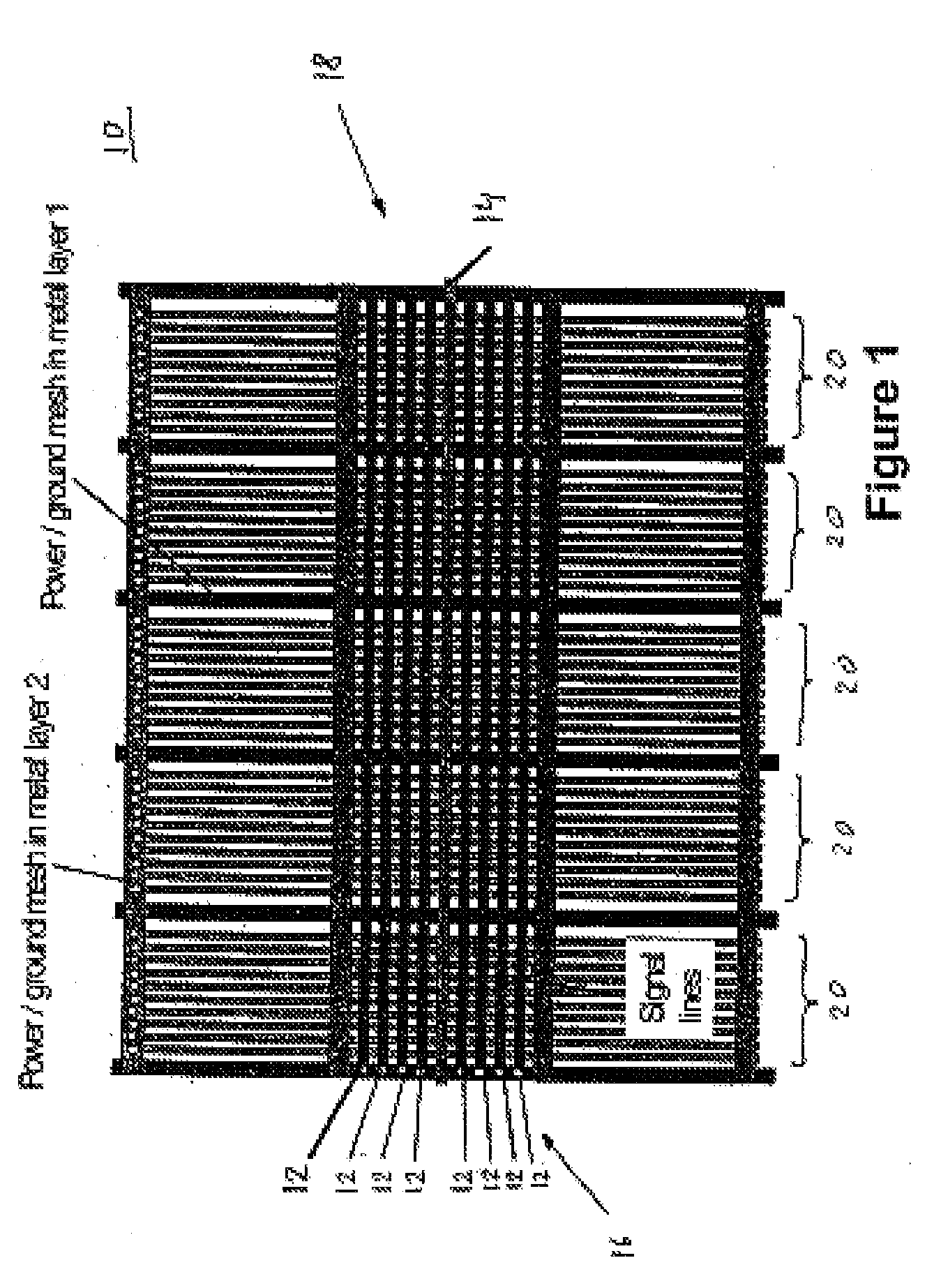
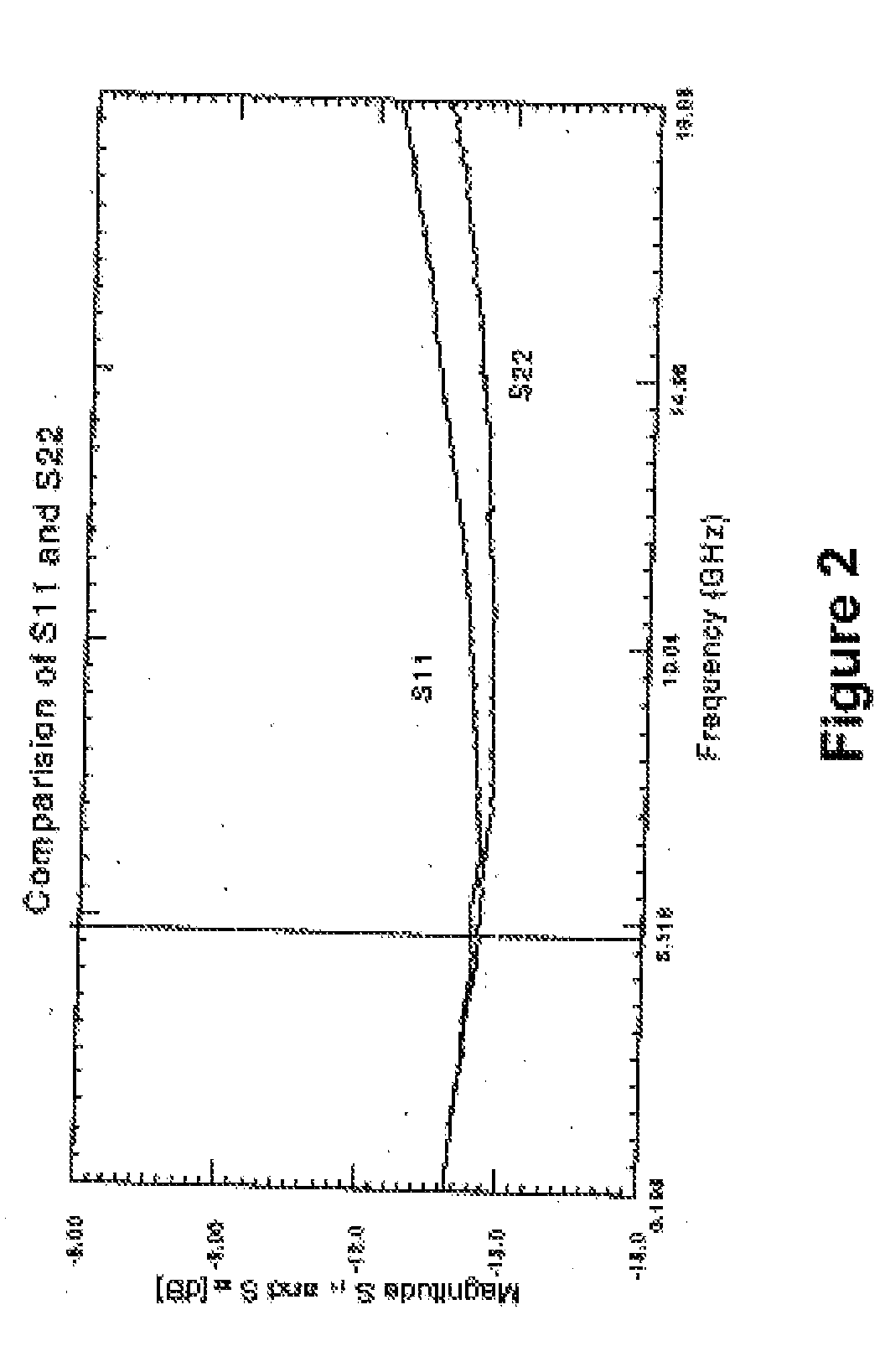
Measurement Arrangement for Determining the Characteristic line Parameters by Measuring Scattering Parameters
InactiveUS20080136423A1Increased measurement bandwidthLarge gainResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical testingElectricityMeasurement device
The present invention relates to a measurement arrangement for determining the characteristic line parameters by measuring the S-parameters as a function of the frequency of an electrical signal line that achieves an increased measurement bandwidth, namely a measurement bandwidth >4 GHz. To achieve this the electrical signal line under test has several neighboring signal lines which are connected to ground on one side and left open on the opposite side in an alternating manner.
Owner:IBM CORP
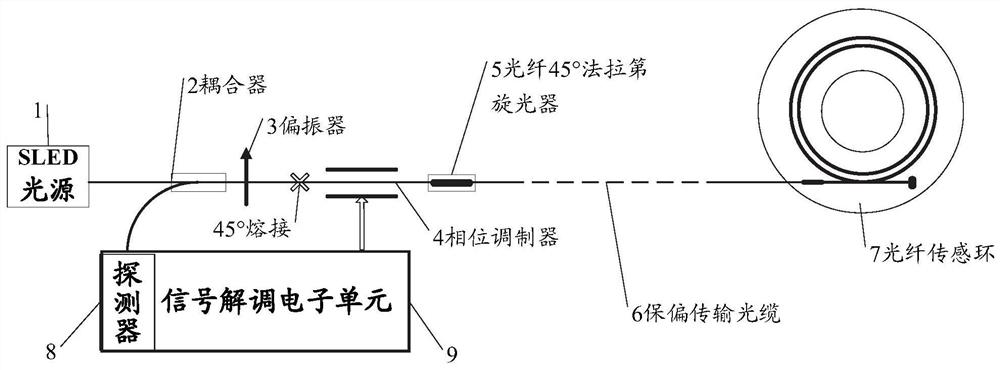
Optical fiber current sensor for realizing non-reciprocal dynamic phase modulation and corresponding signal demodulation method
ActiveCN111751610AReduce noiseExpand the measurement rangeVoltage/current isolationNon-linear opticsCurrent sensorPolarizer
The invention relates to an optical fiber current sensor for realizing non-reciprocal dynamic phase modulation. The optical fiber current sensor comprises a low-polarization SLED light source, an optical fiber coupler, an optical fiber polarizer, a straight waveguide phase modulator, a Faraday rotator, a polarization-maintaining transmission optical cable, an optical fiber sensing ring, a detectorand a signal demodulation electronic unit, wherein the low-polarization SLED light source is connected to the optical fiber coupler through a single-mode optical fiber; and the optical fiber coupleris welded with the optical fiber polarizer. The invention also relates to a signal demodulation method for realizing non-reciprocal dynamic phase modulation. The optical fiber current sensor for realizing non-reciprocal dynamic phase modulation and the corresponding signal demodulation method are adopted, modulation of fixed phase bias can be achieved, modulation of dynamic feedback can also be achieved, noise caused by frequent modulation of the current sensor can be lowered, small signal measurement precision can be improved, meanwhile, high measurement bandwidth can be obtained, dynamic modulation can be conducted according to the magnitude of current detected in real time, and the measurement range of the current sensor is widened.
Owner:浙江康阔光智能科技有限公司
High-dynamic force balance control method of MEMS (micro-electro-mechanical system) resonant gyroscope
ActiveCN110440779AGuaranteed measurement accuracy and stabilityExtended dynamic range and measurement bandwidthSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopes/turn-sensitive devicesAnti jammingControl variable
The invention discloses a high-dynamic force balance control method of an MEMS (micro-electro-mechanical system) resonant gyroscope. The method approximately comprises steps as follows: firstly, an augmentation form of a gyroscope resonant model is obtained and serves as a calculation model of an MPC (model predictive controller); then, the optimal balance force sequence is calculated in real timeat each sampling moment under the condition that balance force output constraint of the controller is met , and a first value of a vector of the sequence is taken as a controlled variable of the nextmoment. Such cycle calculation is performed, and finally, one optimal balance force sequence can be obtained, so that output of the gyroscope resonant model approaches a resonant output given value,coriolis force is counteracted, and force balance is realized. Accurate control of amplitude and frequency of the MEMS resonant gyroscope can be realized, accurate modal drive is provided for the gyroscope, and measurement accuracy and stability of the gyroscope are guaranteed. Meanwhile, the dynamic range and the measurement bandwidth of the gyroscope are enlarged, linearity and anti-jamming capability of scale factors are improved, and the sensitivity and the overall performance of the MEMS resonant gyroscope are improved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Broadband AC/DC current measuring device
ActiveCN112986654ABroaden current measurement bandwidthHigh precisionElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingBroadbandSelf excited oscillation
The invention discloses a broadband AC / DC current measuring device, which comprises two iron core frameworks, a non-magnetic framework, four windings and an affiliated compensation circuit, a double-iron-core structure self-oscillation fluxgate sensor and a Rogowski coil current sensor structure are combined, a direct current magnetic flux compensation circuit is matched, alternating current detection can be completed, direct current detection can also be completed, and the double-iron-core structure fluxgate method current sensor is used for measuring low-frequency current. The Rogowski coil current sensor is used for measuring the power frequency current, the current measurement bandwidth is greatly widened, and the detection precision of the alternating current containing the direct current component is superior to that of an electromagnetic current sensor. Meanwhile, when the low-frequency current is measured, the measurement precision of the low-frequency current can be effectively improved through a direct-current magnetic potential compensation and excitation frequency adjustment method. Therefore, the technical problems that when alternating current and direct current are measured in the prior art, high-frequency and low-frequency alternating current and direct current measurement cannot be considered at the same time, and the measurement error is large are solved.
Owner:CHINA SOUTH POWER GRID ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
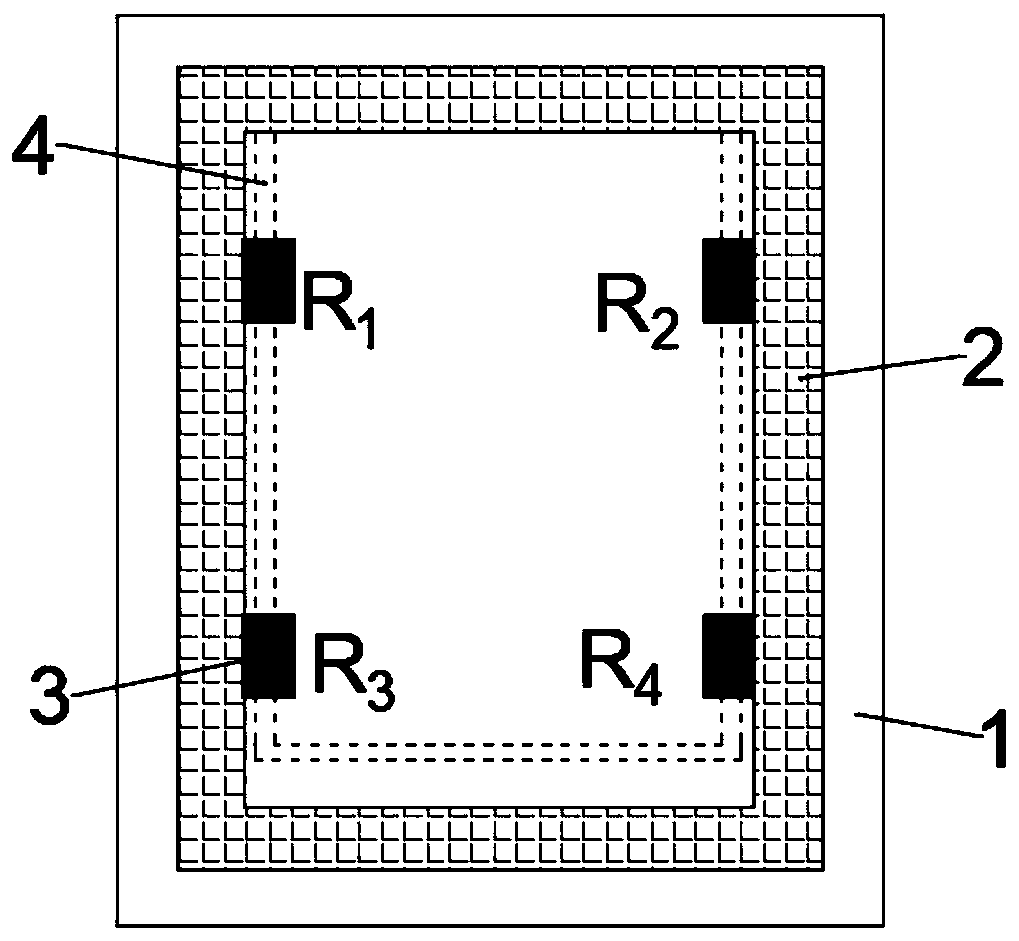
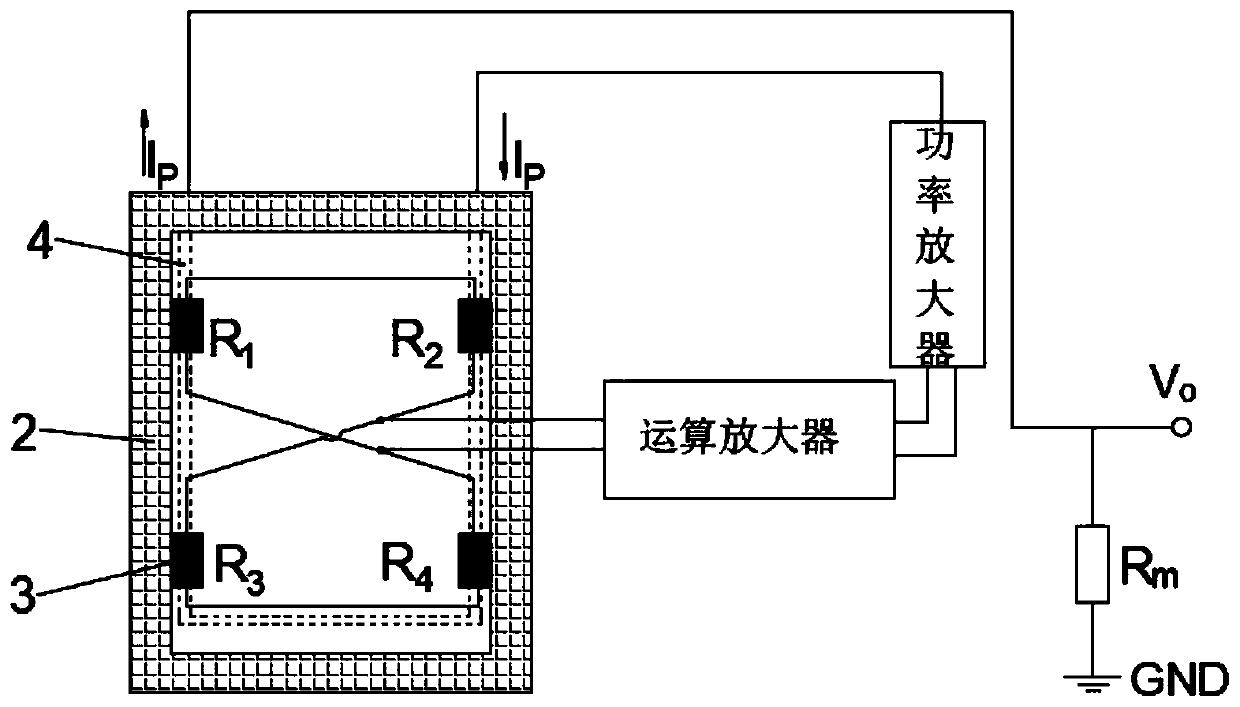
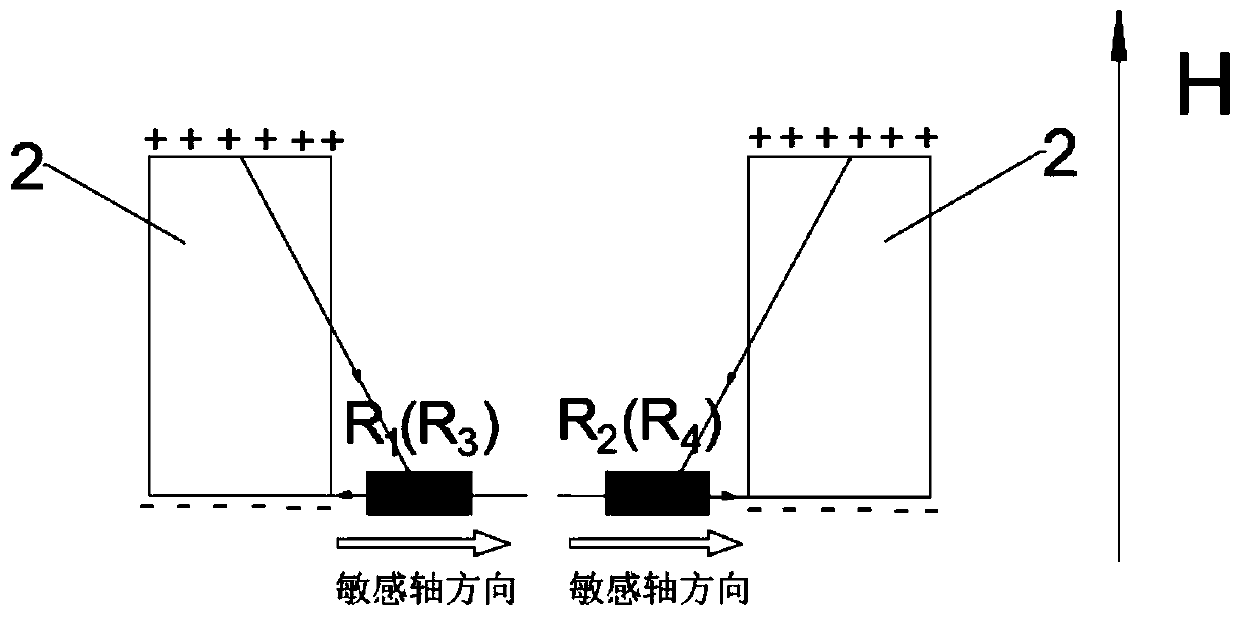
Vertical sensitive magnetic sensor closed-loop on-chip in-place feedback device
InactiveCN110398703AIncreased measurement bandwidthReduce power consumptionMagnetic measurementsClosed loop feedbackPush pull
The invention discloses a vertical sensitive magnetic sensor closed-loop on-chip in-place feedback device, comprising a silicon-based substrate, a flux guider, four identical magnetoresistors, a signal feedback coil, an operational amplifier and a power amplifier, since a on-chip in-place feedback coil is disposed on a push-pull type vertical sensitive magnetic sensor chip, when feedback current is supplied, magnetic field signals having the same magnitude and opposite directions are generated in a sensitive axis direction of two pairs of magnetoresistors above the feedback coil to respectively counter the original signal magnetic fields and to form a closed-loop feedback structure, and the design of the on-chip in-place feedback device can effectively improve the sensor output linearity,improve the measurement accuracy and reduce the power consumption, thereby having an important application value.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Radar System For Detecting Profiles Of Objects, Particularly In A Vicinity Of A Machine Work Tool
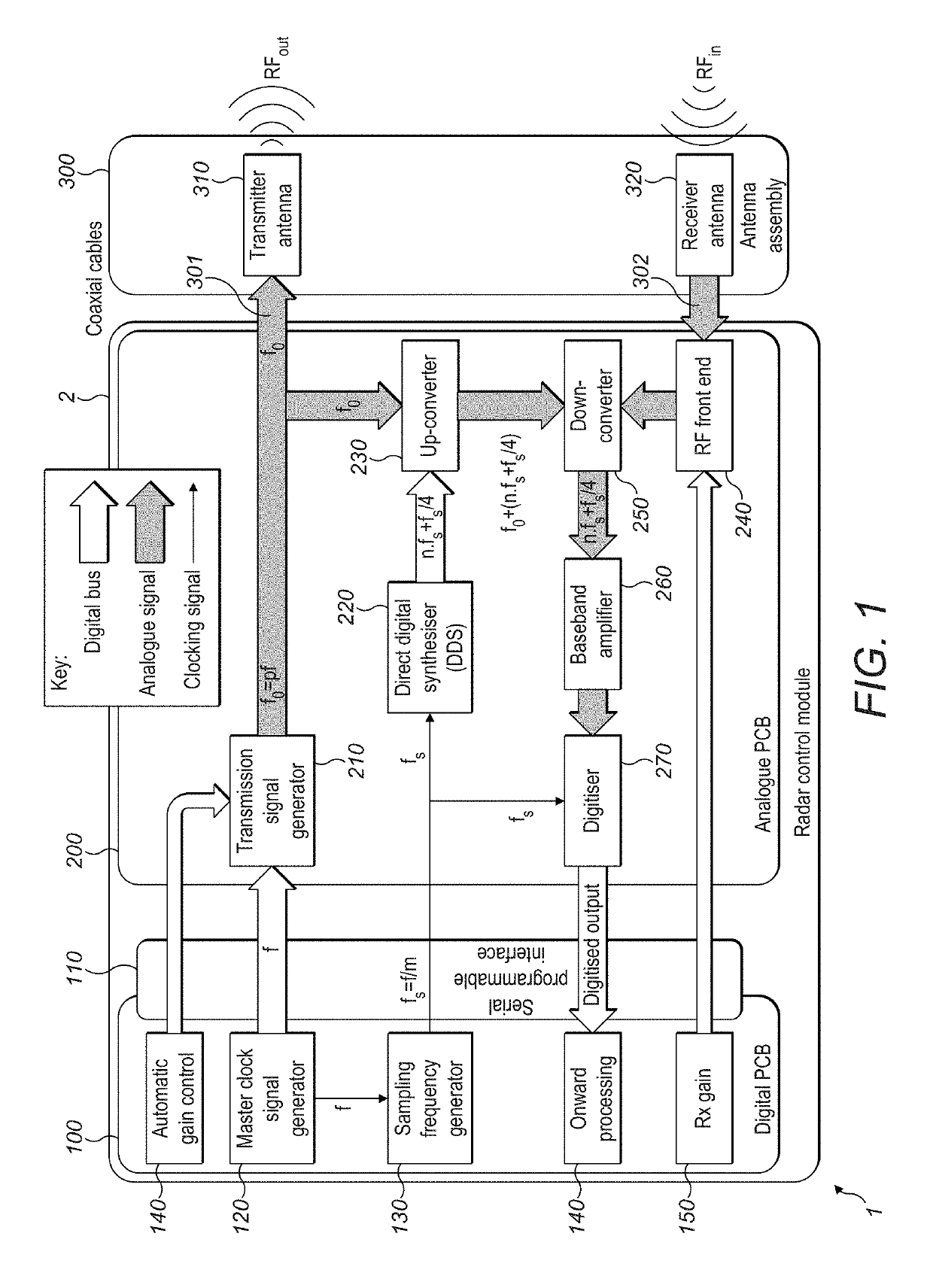
ActiveUS20190129001A1Low bandwidthReduce the sampling frequencyMechanical machines/dredgersGain controlFrequency changerData stream
A radar system is disclosed for detecting profiles of objects, particularly in a vicinity of a machine work tool. The radar system uses a direct digital synthesiser to generate an intermediate frequency off-set frequency. It also uses an up-converter comprising a quadrature mixer, single-side mixer or complex mixer to add the off-set frequency to the transmitted frequency. It further uses a down-converter in the receive path driven by the off-set frequency as a local oscillator. The radar system enables received information to be transferred to the intermediate frequency. This in turn can be sampled synchronously in such a way as to provide a complex data stream carrying amplitude and phase information. The radar system is implementable with a single transmit channel and a single receive channel.
Owner:RODRADAR LTD
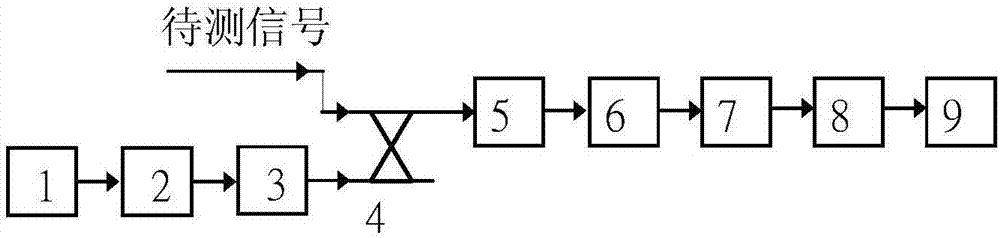
Phase modulator frequency response measurement method and device
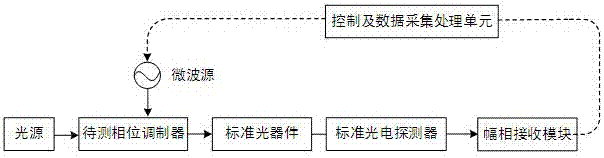
InactiveCN107219062ASolve the problem that the beat frequency cannot be directly passed by the standard photodetectorSimple structureTesting optical propertiesPhase responseMeasurement device
The invention discloses a phase modulator frequency response measurement method. Microwave signals are modulated on optical carriers by using a phase modulator to be measured so as to generate optical phase modulation signals; the optical phase modulation signals are enabled to pass through a standard optical device so that at least partial optical phase modulation signals are enabled to be converted into optical intensity modulation signals; the output optical signals of the standard optical device are converted into electric signals by using a standard photoelectric detector and the amplitude and phase information of the electric signals is extracted, wherein the frequency response of the amplitude and the phase of the standard optical device and the standard photoelectric detector is known; the frequency of the microwave signals is changed and the process is repeated so that the combined frequency response of the amplitude and the phase of the phase modulator to be measured, the standard optical device and the standard photoelectric detector can be obtained; and finally the amplitude and phase response of the standard optical device and the standard photoelectric detector is removed from the combined frequency response so that the amplitude and phase frequency response of the phase modulator to be measured can be obtained. The invention also discloses a phase modulator frequency response measurement device.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com