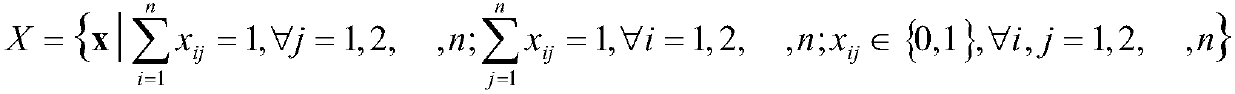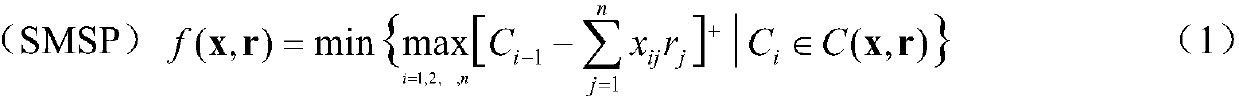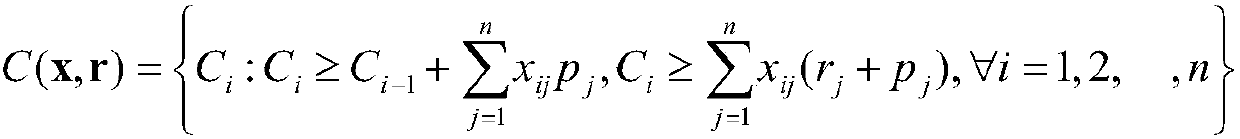Patents
Literature
47results about How to "Guaranteed high performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
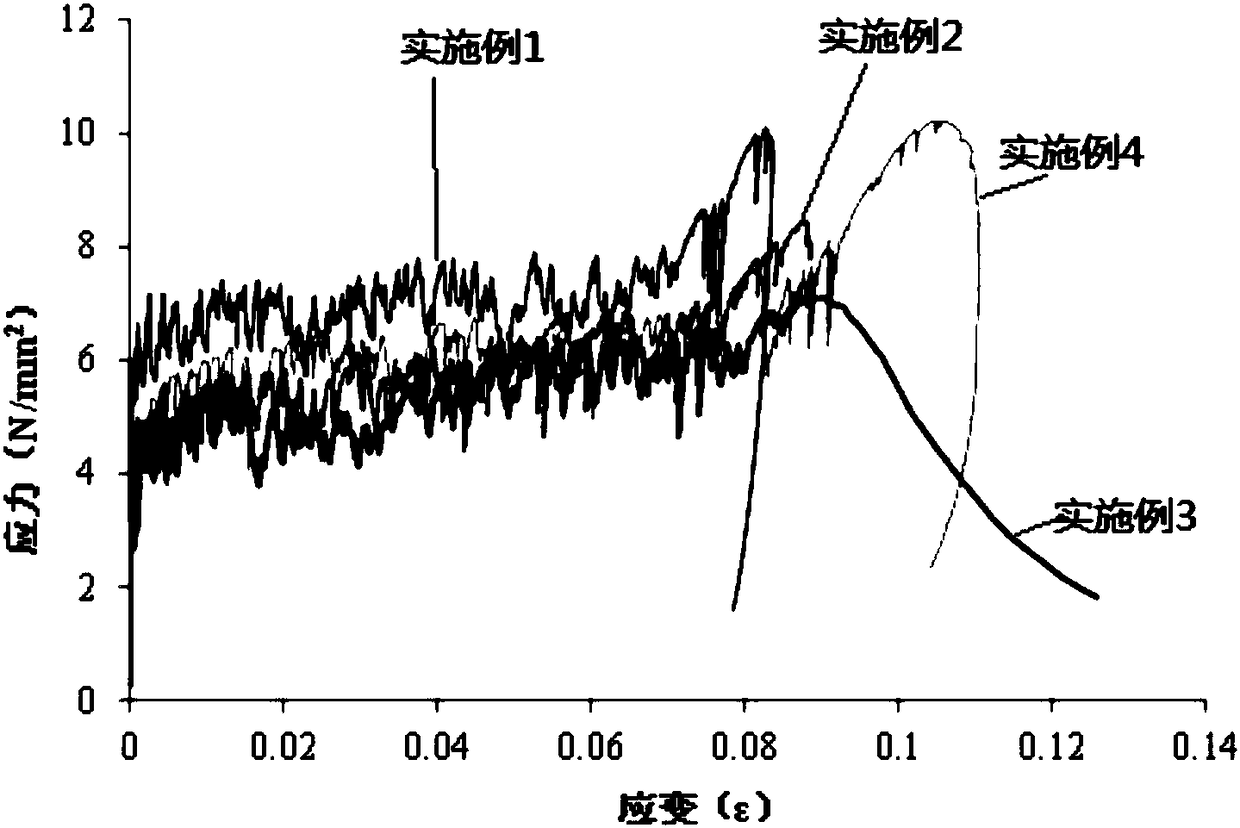
Noble metal-rare-earth catalyst for purifying waste gas and its preparation
InactiveCN1473651AIncreased durabilityIncreased chance of collisionDispersed particle separationCatalyst activation/preparationMischmetalMixed oxide
The catalyst includes alumina, RE metal oxide, composite Al-La oxide, and active metal Pt, Pd and Rh. It features that the mixed oxide grain with aluina, cerium oxide and Al-La oxide carries at least one of Pt and Pd as well as Rh. The mixed oxide grain is prepared through dissolving salt of Al, Ce and La in water, adding NH3OH to produce precipitate, and heating to decompose the precipitate. The catalyst preparing process includes carrying mixed oxide grains onto the carrier, carrying least one of Pt and Pd onto the mixed oxide grains, and carrying Rh finally. The catalyst is especially suitable for purifying automobile tail gas of gasoline engine near the theoretical air / fuel ratio, and has the features of lasting use, less noble metal consumption, high purifying efficiency and powerful sulfur poison resistance.
Owner:昆明贵研催化剂有限责任公司
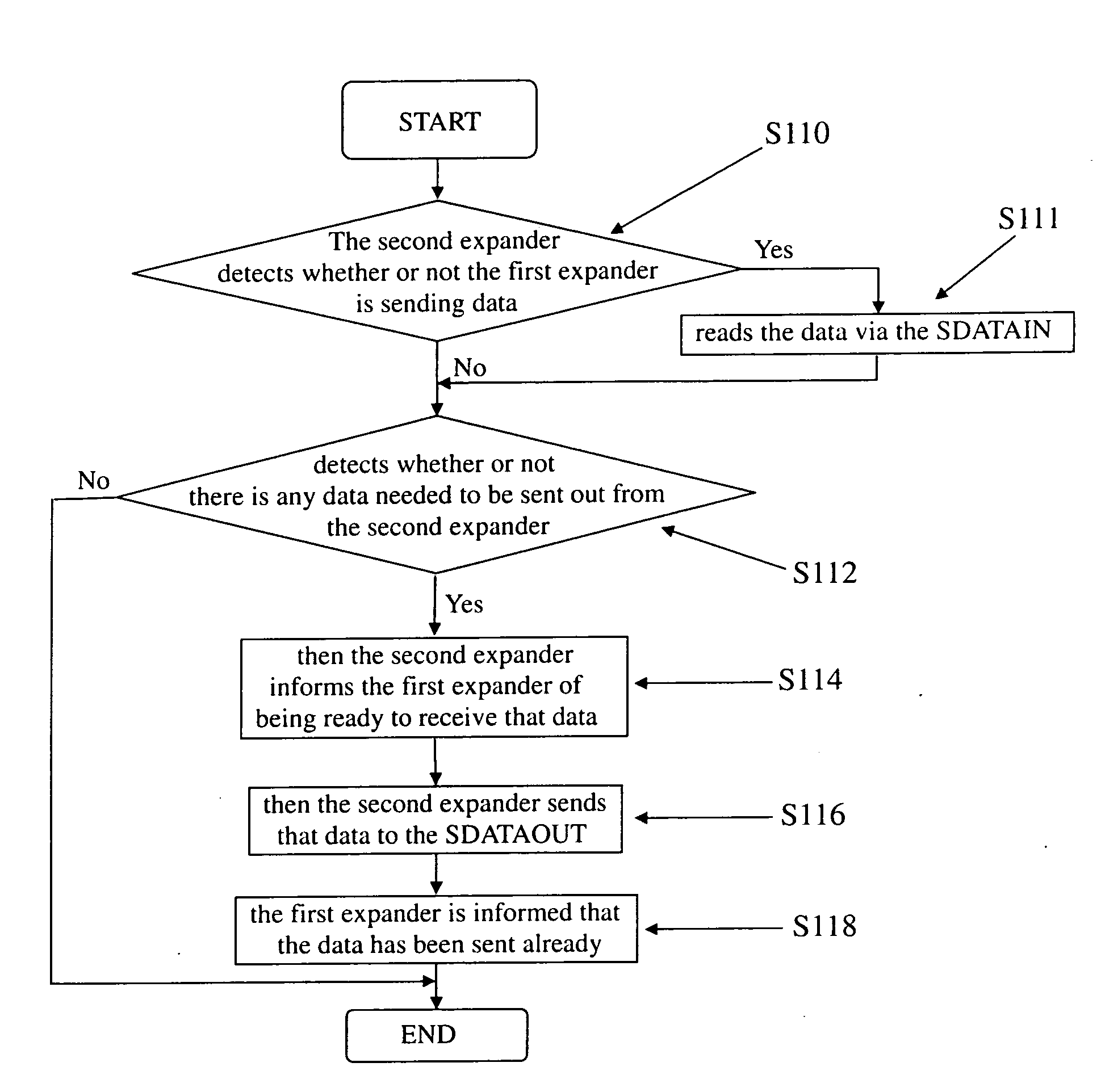
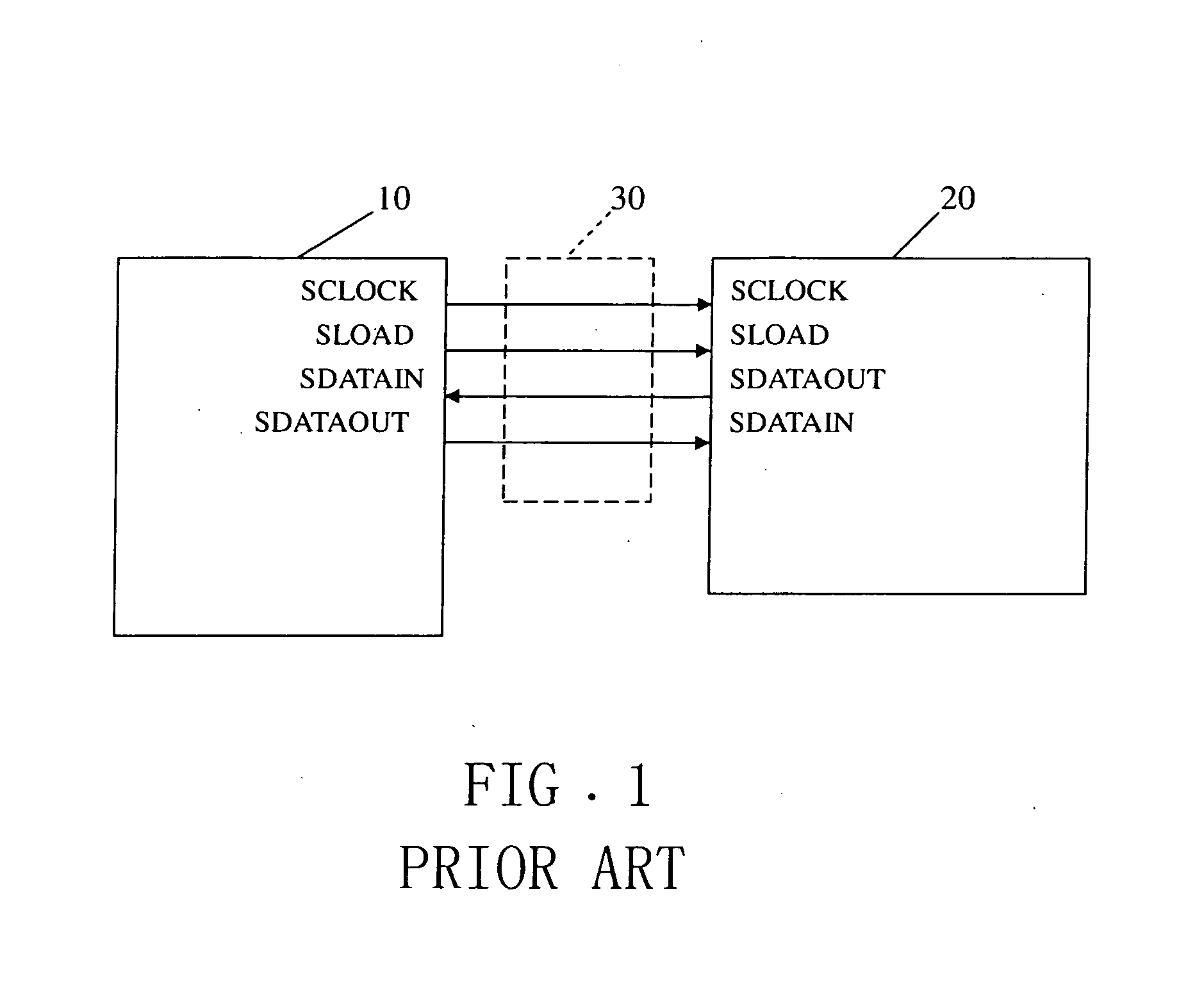
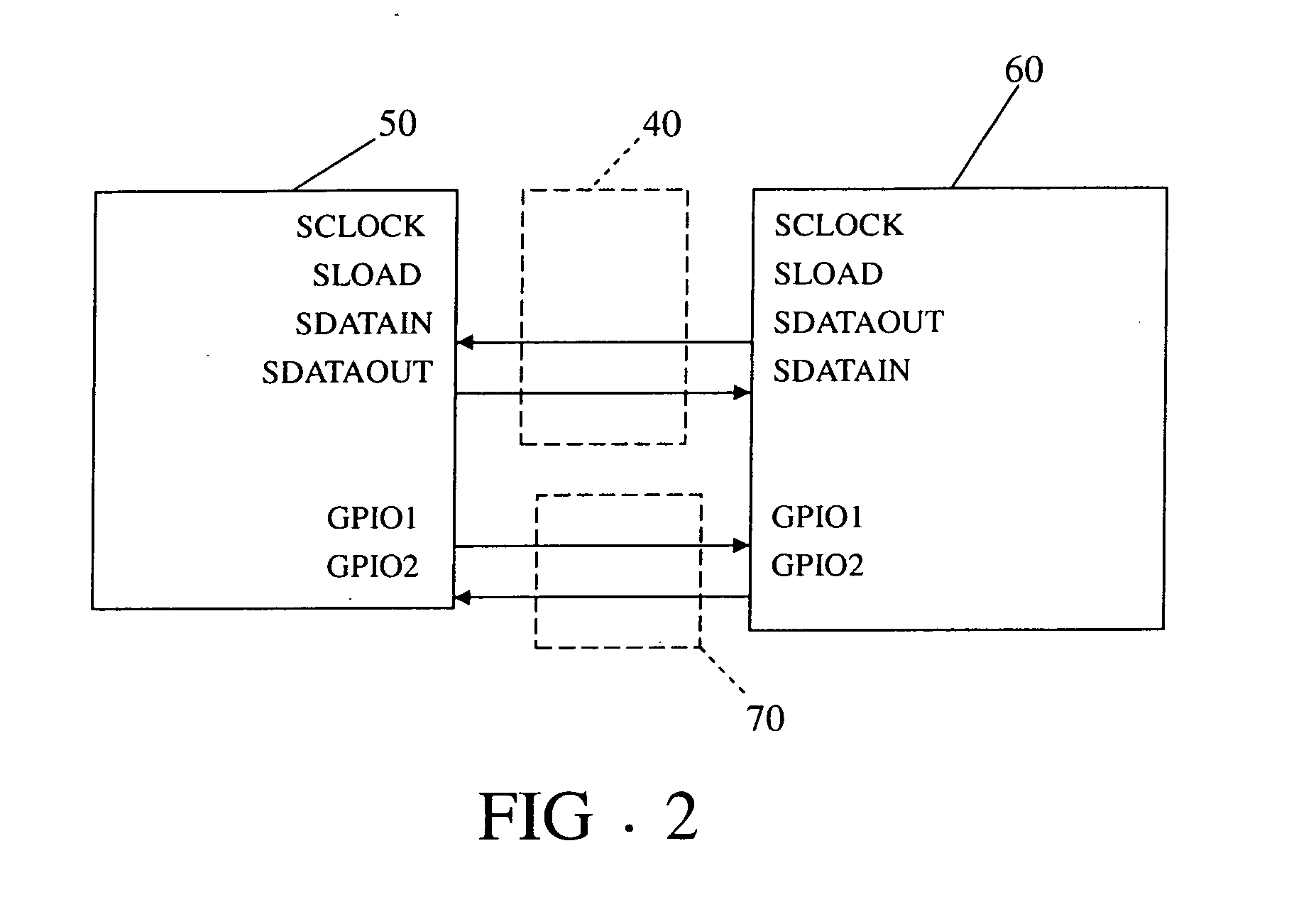
Data transmission system and method thereof
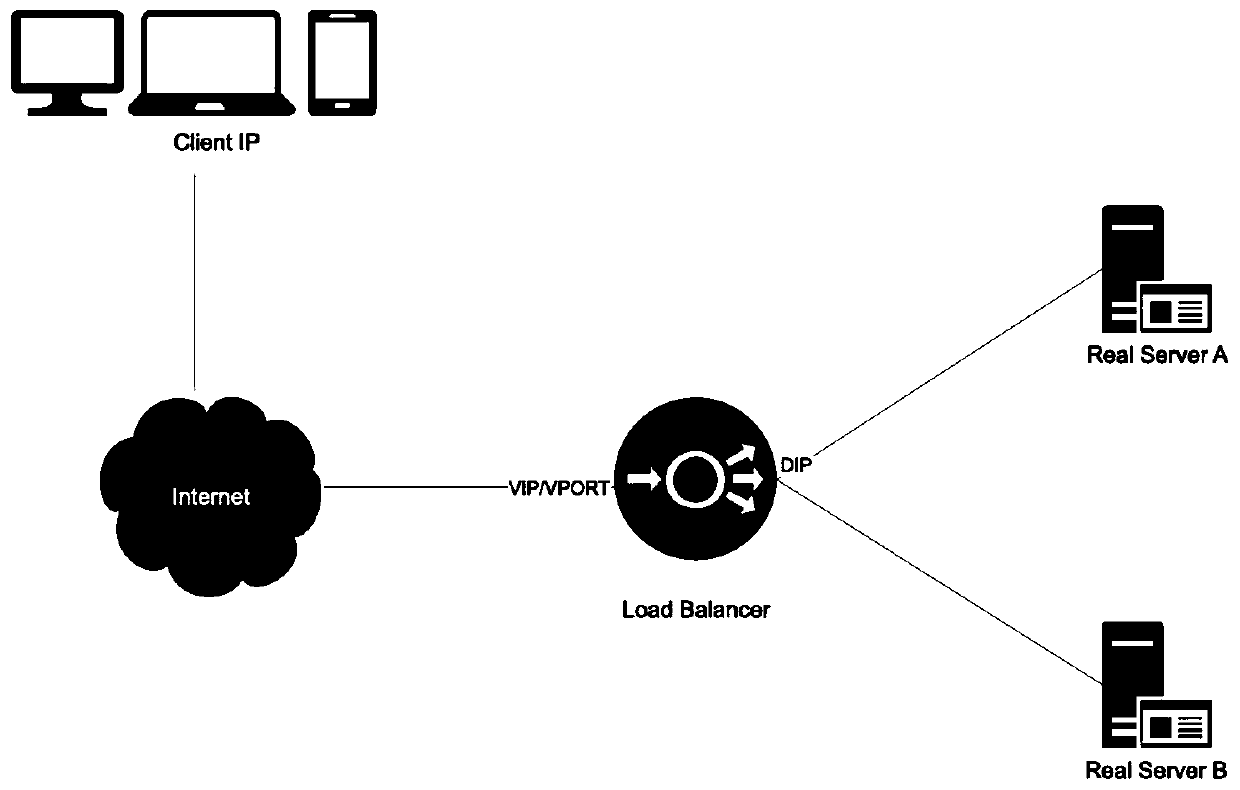
InactiveUS20090089473A1Improve communication performanceGuaranteed high performanceElectric digital data processingComputer hardwareTransmitter
The invention uses a SGPIO bus as an optional route for the communication between the two SAS expanders to guarantee high communication performance. Furthermore, two GPIO buses are used respectively as receiver and transmitter of the SGPIO so as to achieve synchronous data transmission between two SAS expanders.
Owner:UNIVERSAL SCI IND CO LTD
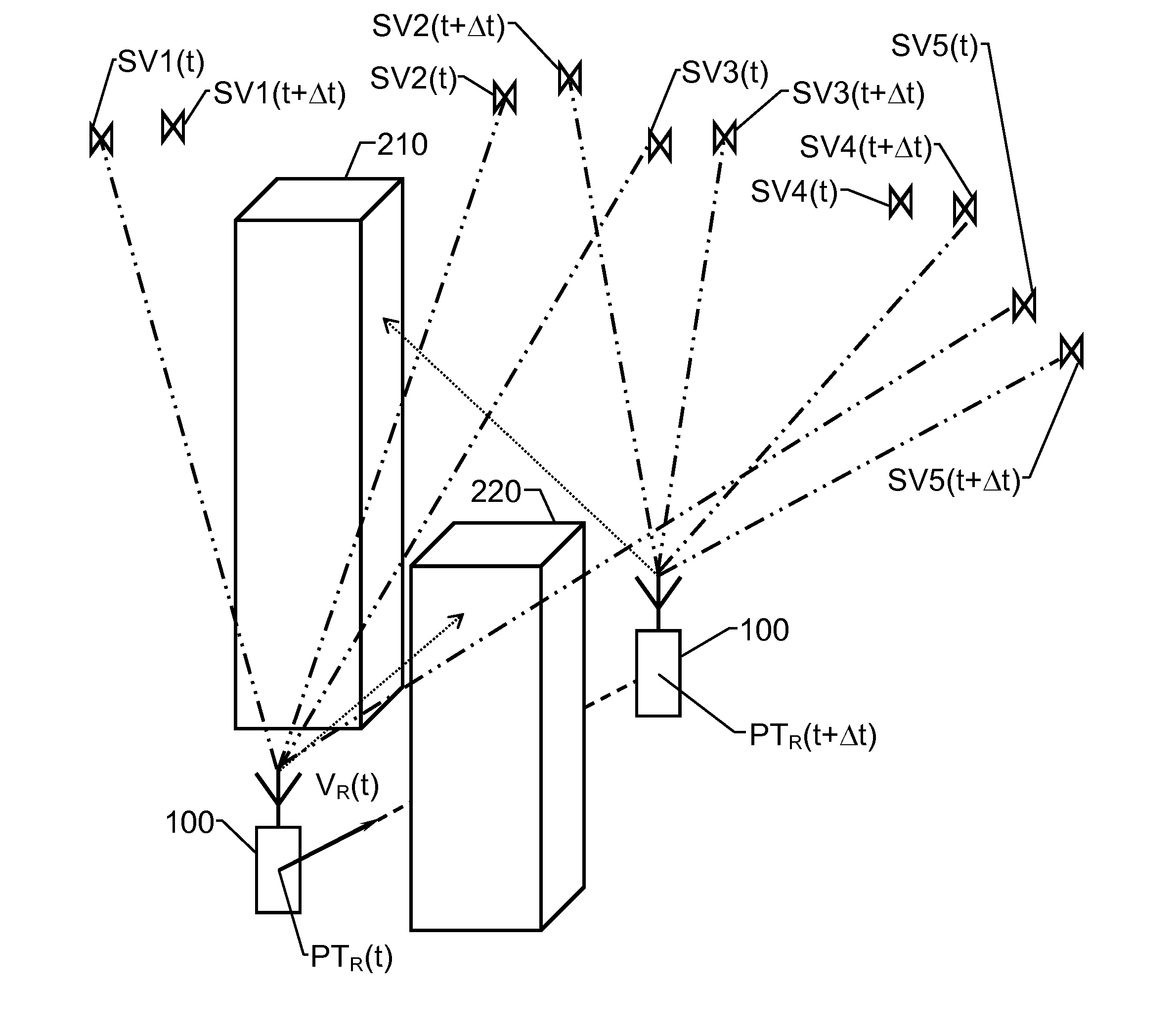
GNSS receiver and operating method
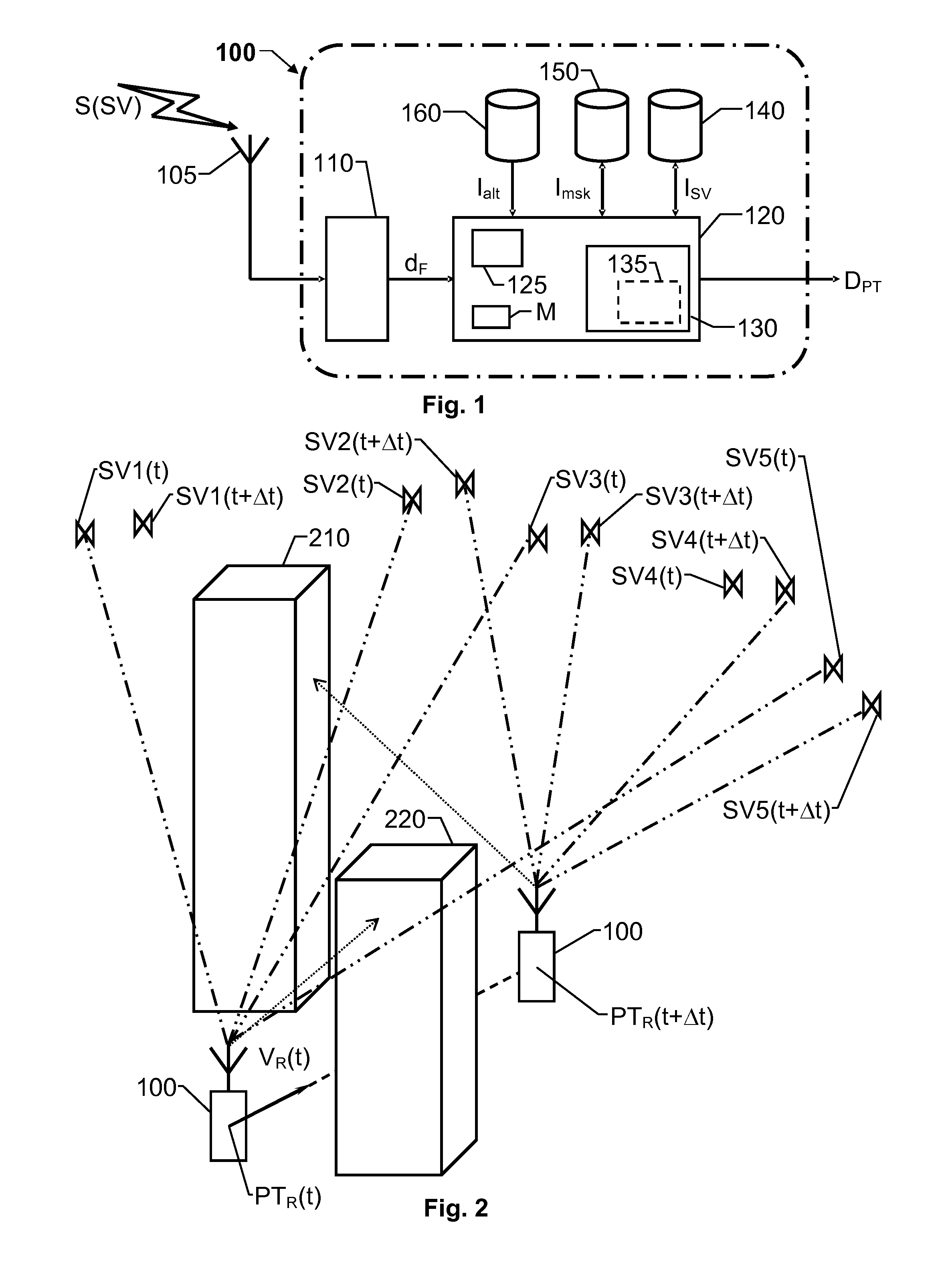
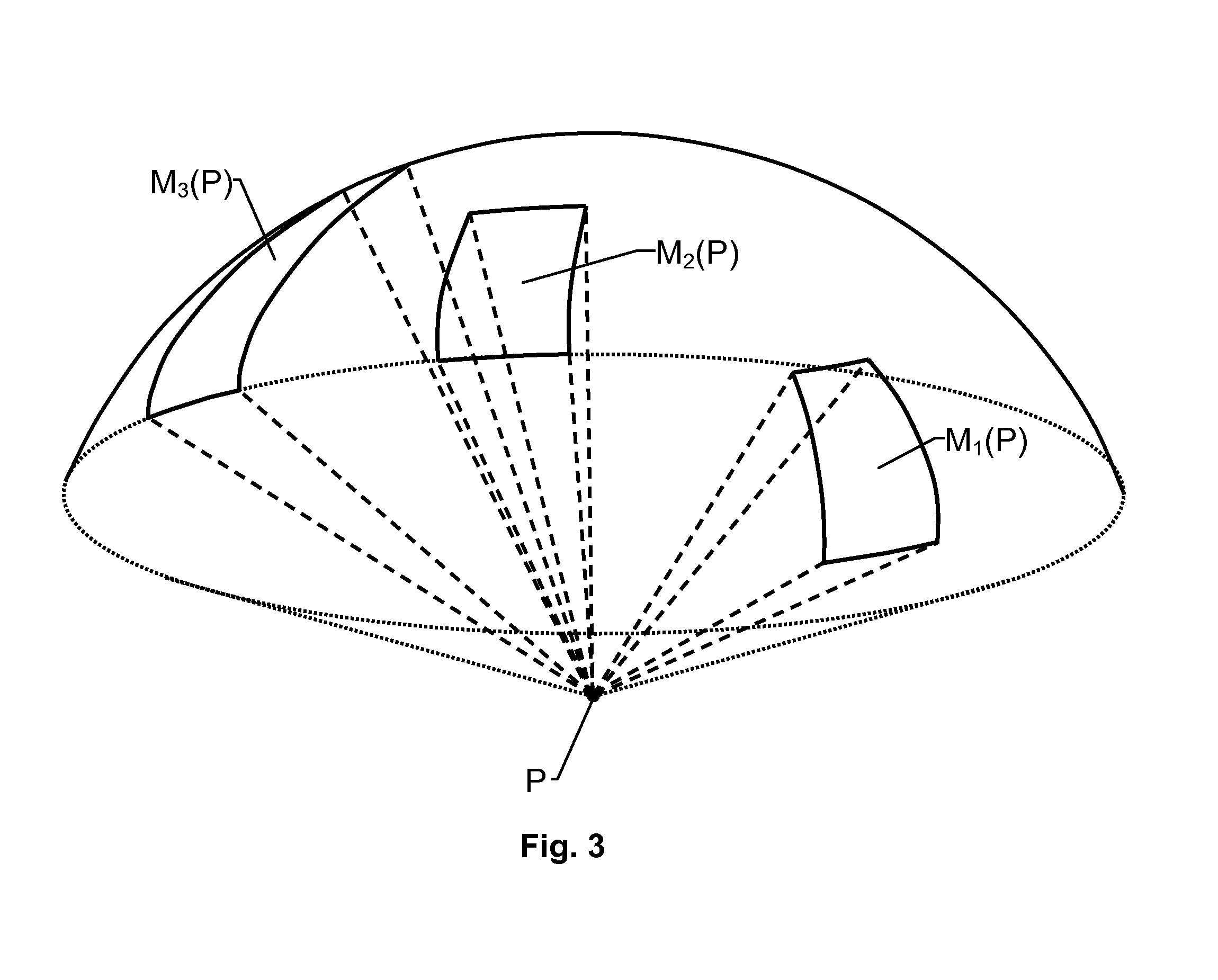
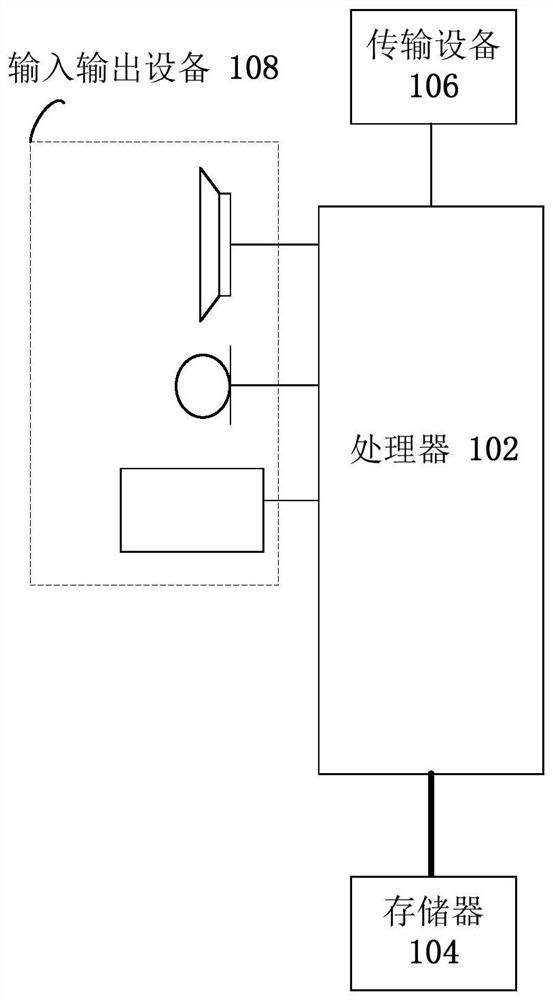
InactiveUS20120188124A1Efficient and robustIncrease chanceSatellite radio beaconingDerived DataTime signal
A GNSS receiver (100) receives radio signals (S(SV)) transmitted from an active set of signal sources (SV1, SV2, SV3, SV5) and based thereon produces position / time related data (DPT). The receiver (100) has a tracking channel resource for each signal source (SV1, SV2, SV3, SV5) in the active set, and the tracking channel resources process the radio signals (S(SV)) in parallel with respect to a real-time signal data rate of the signals. The receiver (100) also includes a signal-source database (140), a signal-masking database (150) and a control unit (130). The signal-source database (140) describes the movements of the signal sources (SV1, SV2, SV3, SV4, SV5) over time relative to a given reference frame, and the signal-masking database (150) reflects, for positions (P) within a predefined geographic area, visibility / blockage to the sky with respect to a direct line of sight in terms of spatial sectors (M1(P), M2(P) M3(P)). The control unit (130) derives data describing a current position / time (PTR(t)) and a current velocity vector (VR(t)) for the receiver (100) based on the position / time related data (DPT); and derives an estimated visibility of the signal sources (SV1, SV2, SV3, SV5) in the active set at a second position / time (PTR(t+Δt)) representing an expected future position / time for the receiver (100) based on the signal-source and signal-masking databases (140; 150). If at least one signal source (SV1) in the active set is estimated not to be visible at the second position / time (PTR(t+Δt)), the control unit (130) initiates a modification of the active set aiming at replacing the at least one non-visible signal source (SV1) with at least one signal source (SV4) which, based on the signal-source and signal-masking databases (140; 150), is estimated to be visible at the second position / time (PTR(t+Δt)).
Owner:QUALCOMM TECH INT
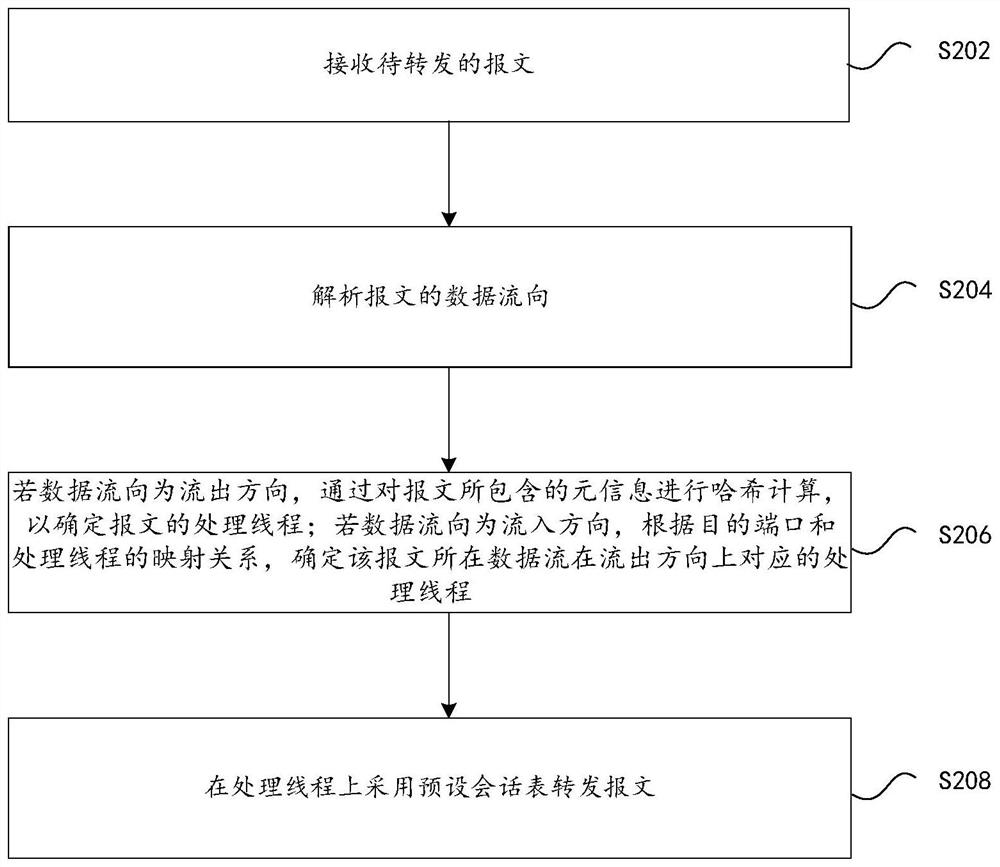
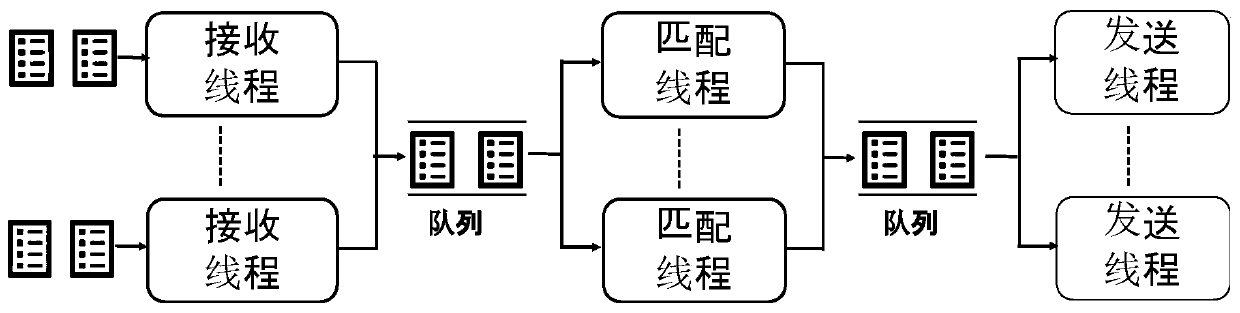
Message forwarding method and device, storage medium and electronic equipment
PendingCN112965824ATo achieve load balancingAvoid read-write lock mechanismResource allocationData switching networksEngineeringReal-time computing
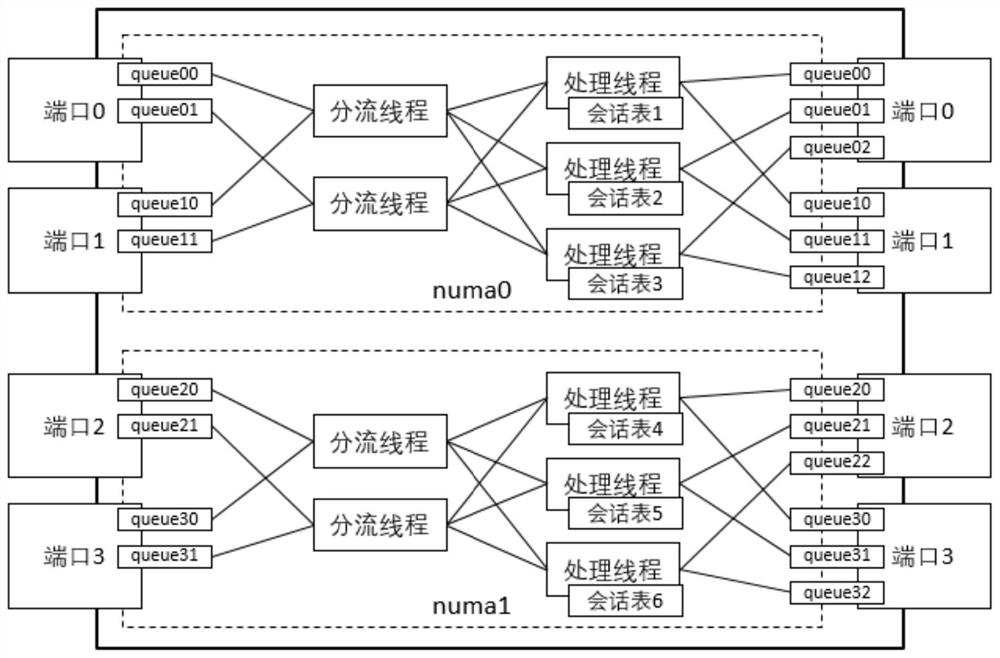
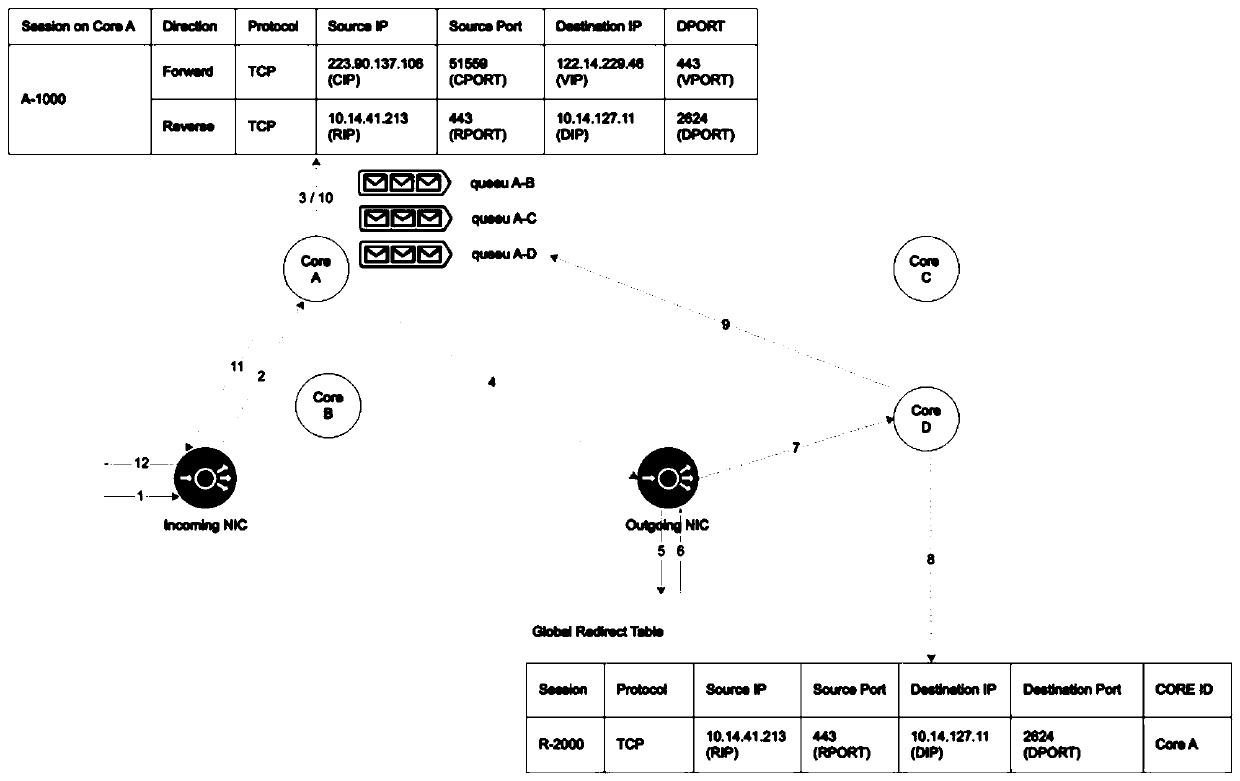
The invention discloses a message forwarding method and device, a storage medium and electronic equipment, and belongs to the field of communication. The method comprises the following steps: receiving a message to be forwarded; analyzing the data flow direction of the message; if the data flow direction is an outflow direction, performing hash calculation on meta-information contained in the message to determine a processing thread of the message; if the data flow direction is an inflow direction, determining a processing thread corresponding to the data flow where the message is located in an outflow direction according to a mapping relationship between a destination port and the processing thread, each processing thread being bound with a processor core; and forwarding the message on the processing thread by adopting a preset session table. Through application of the message forwarding method and device, the technical problem of low message forwarding efficiency of a multi-core CPU in related technologies is solved, and the message forwarding speed and the message processing efficiency are improved.
Owner:BEIJING KINGSOFT CLOUD NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Computer implemented systems and methods for improving renewable energy systems performance guarantees
InactiveUS20090132302A1Expand their offeringGuaranteed accuracyMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlRenewable energy systemRenewable power generation
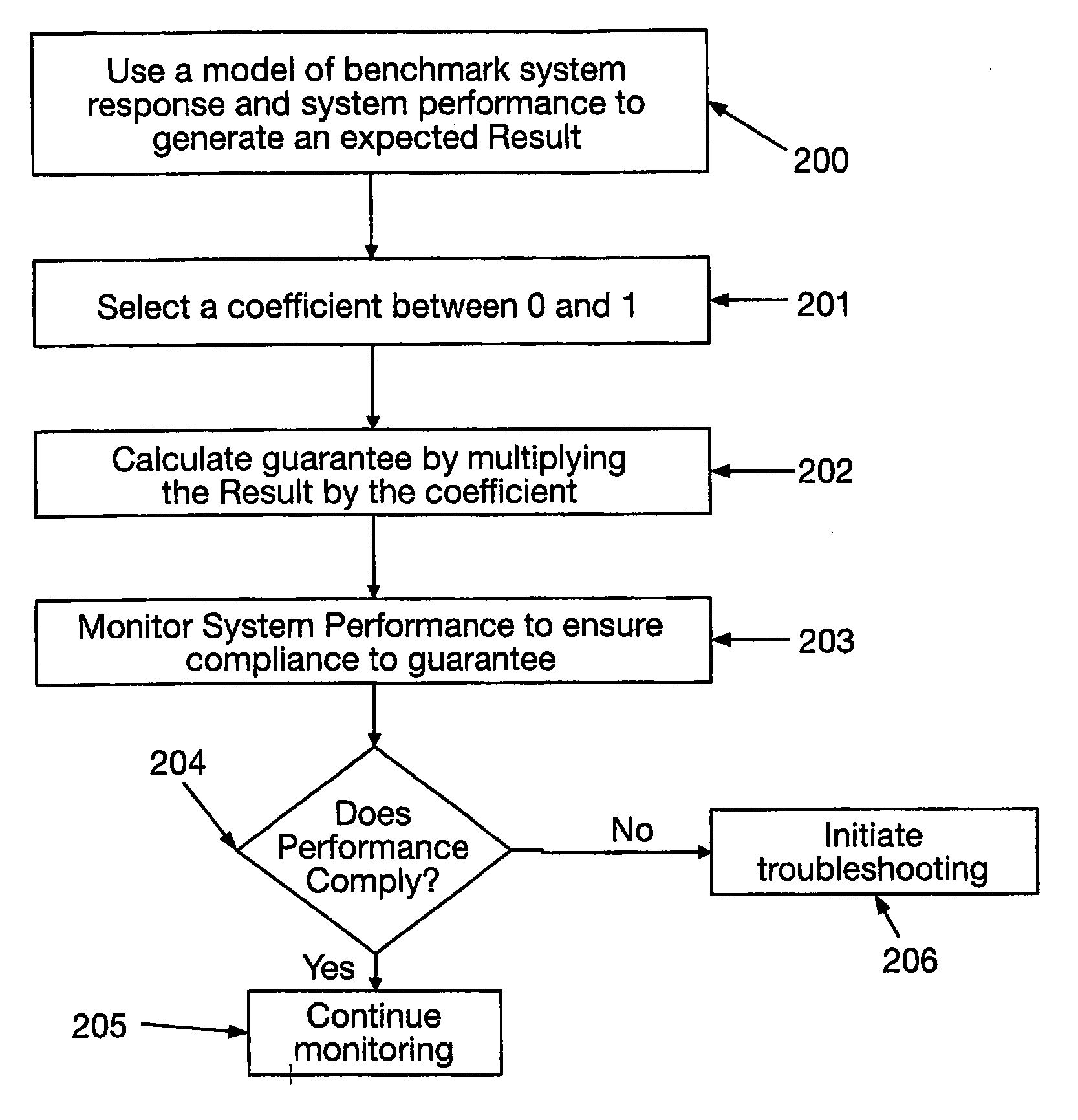
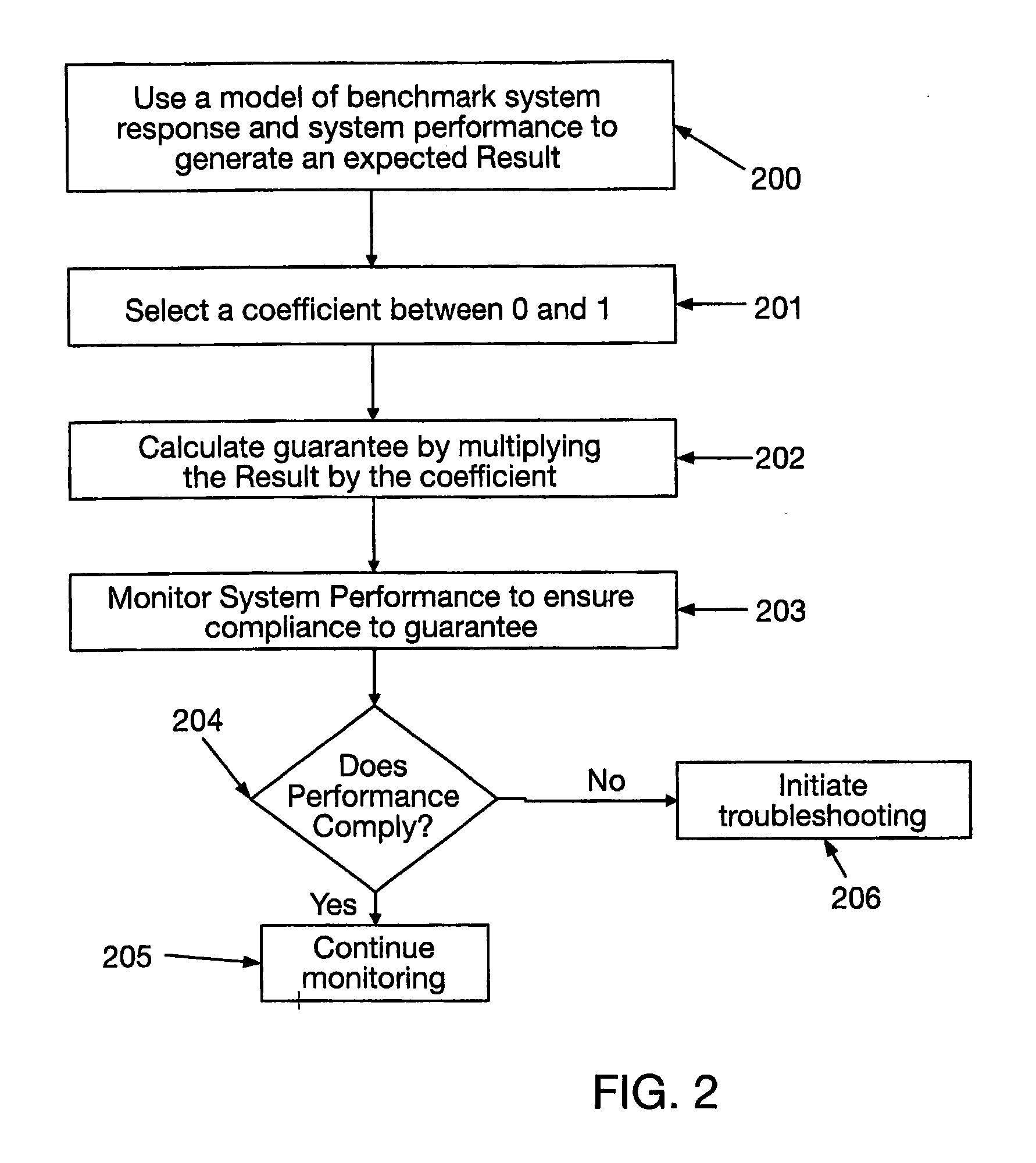
Systems and methods are provided for collecting, aggregating, and analyzing data associated with the installation and deployment of systems. Energy systems, (300) specifically renewable energy generation systems, are used as examples. The aggregated data serve as the basis for a variety of services that facilitate the adoption and deployment of these systems. Services are provided that aid in the modeling and establishment of improved System Performance Guarantee commitments. Additionally, services are provided that improve the system performance, improve the installation, lower the cost, and provide monitoring and service to maintain improved performance.
Owner:POWER ONE RENEWABLE ENERGY SOLUTIONS
Solid-state welding production method of high-performance conducting rod
InactiveCN101740987AGuaranteed high performanceNo interferenceLine/current collector detailsNon-electric welding apparatusElectrical conductorEngineering
The invention discloses a solid-state welding production method of a high-performance conducting rod. The electrical resistivity of a forging aluminum LD2CS welding joint is lowered to be about 8.1*10-8omega.m from 6.7*10-7omega.m during melting, the tensile strength is improved to be about 290 MPa from 186 MPa, the welding process has no interference on silver coatings, and the production efficiency is 10-50 times of that of MIG welding. The invention takes momentum moment or thermal coupling generated by the instant precise weaving of rotary and movable welding pieces as welding energy, so that the method does not need other energy and assistant material consumption, has no pollution and is an efficient energy-saving environmental-friendly industrial technology with good quality. A high voltage power transmission and distribution conducting rod has the following solid-state welding parameters: the friction velocity is 950-1150 rpm, the friction pressure is 16-25 MPa, the friction time is 6-10s, the upsetting force is 75-95 MPa, and the dwell time is 4-8 s; on a friction welder, the joint or the conductor of the conducting rod is tightly clamped in a rotary clamp, a tube is tightly clamped in a movable clamp, and PLC is utilized to realize advanced manufacturing technology operation.
Owner:SHAANXI BORDER ELECTRICAL EQUIP MFGCO
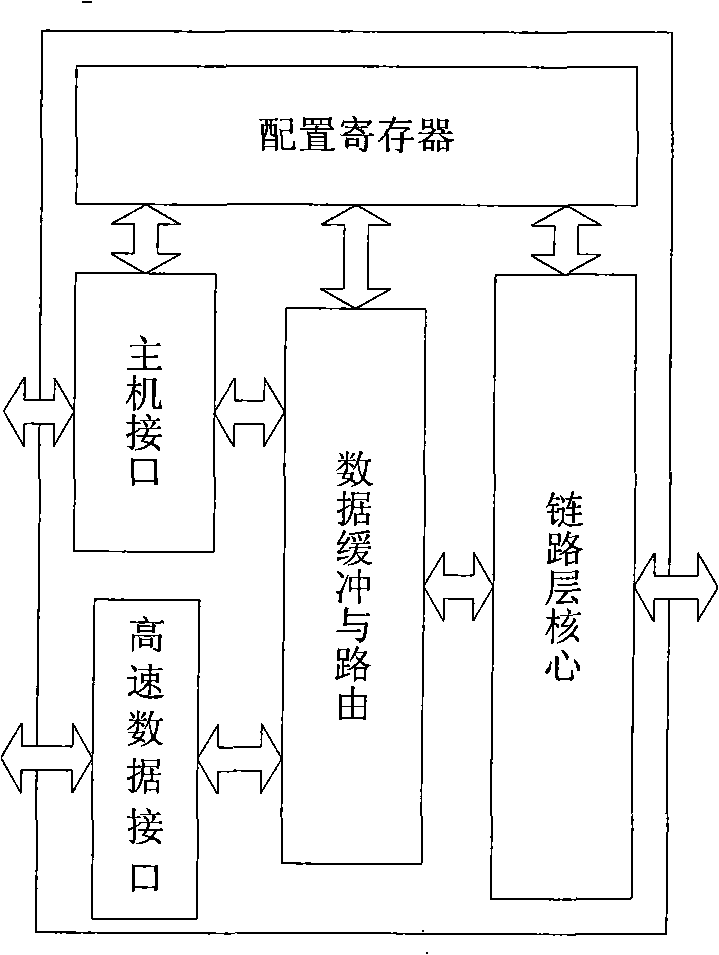
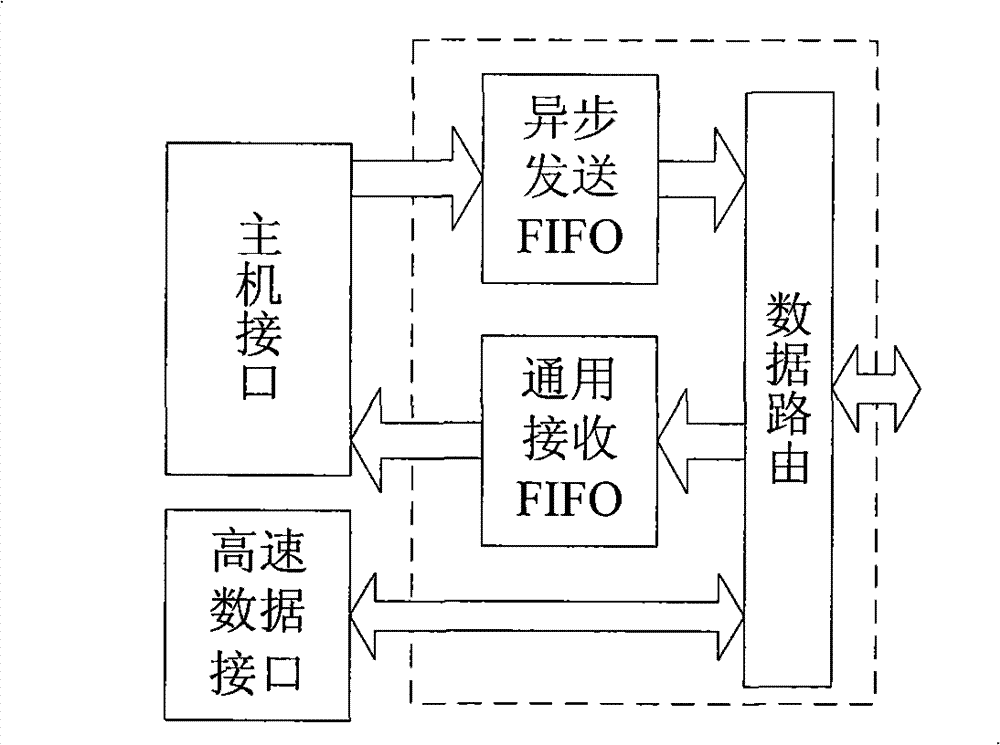
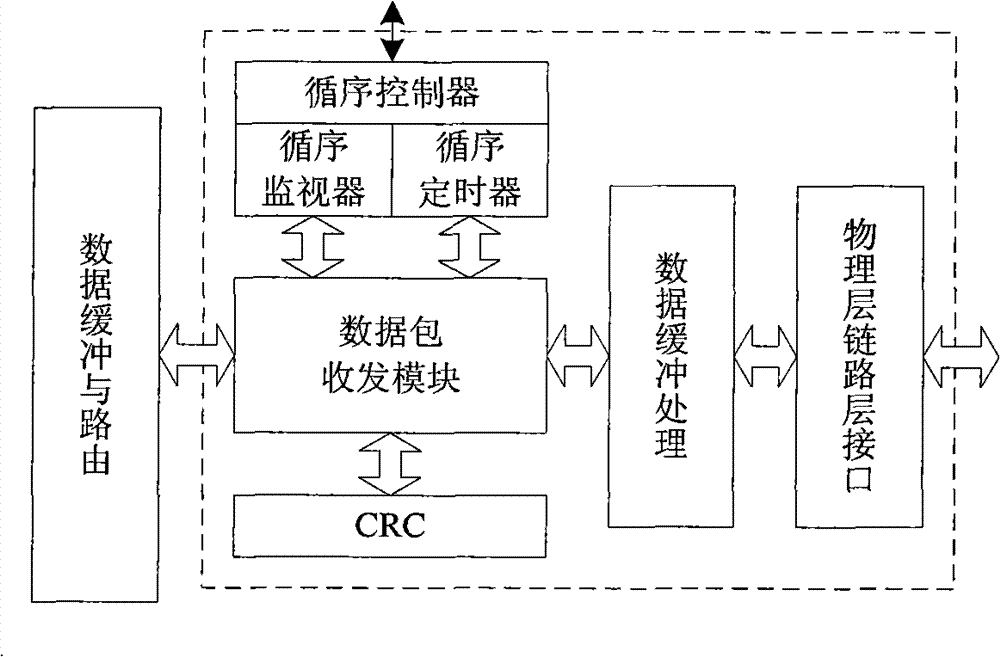
Link layer controller of IEEE1394 bus
InactiveCN101764795AImprove reliabilityImprove versatilityBus networksHandoff controlProcessor register
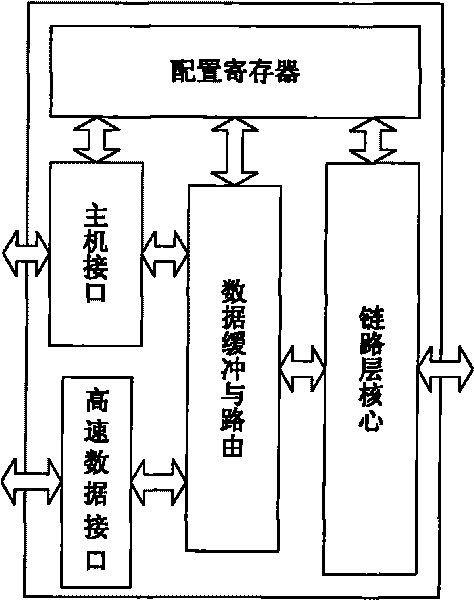
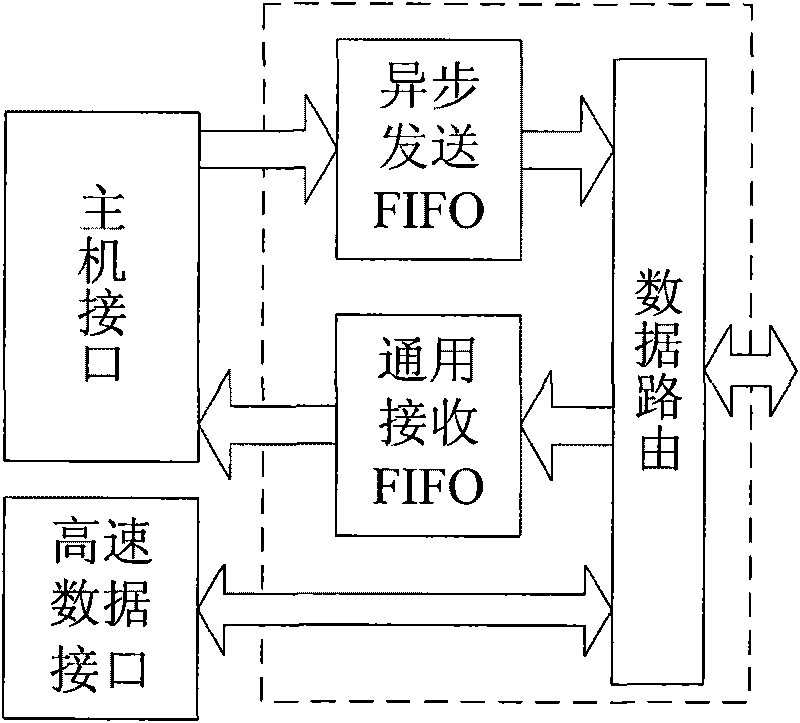
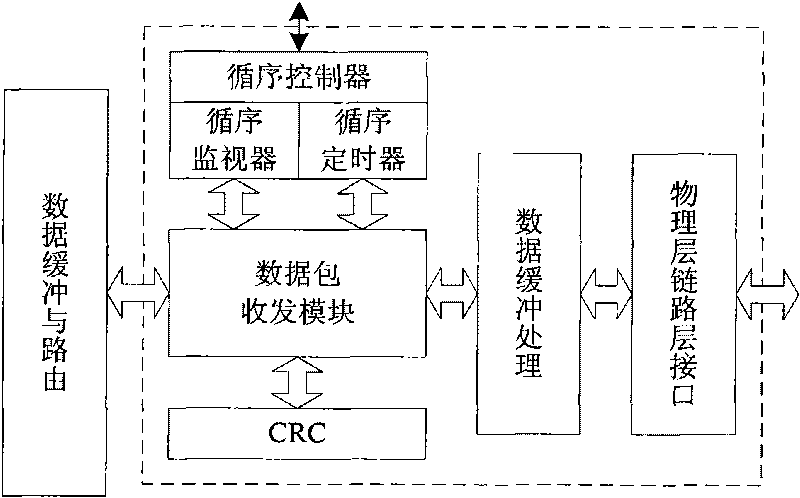
The invention relates to a link layer controller of an IEEE1394 bus, which comprises a host computer interface, a link layer core module, a data buffering and routing control module, a high-speed data interface module and a configuration register, wherein an external CPU (central processing unit) can read and write data buffering areas in the configuration register and the access data buffering and routing control module by the host computer interface; the data buffering and routing control module is positioned among the link layer core module and the host computer interface and a high-speed data interface, used for providing the switching control among different data receiving and sending channels and also provided with two asynchronous first-in first-out memories which are respectively used for the buffering of receiving and sending data and the synchronization of cross-clock domain data; and the configuration register is used for providing initial configuration and control for the link layer core module and the data buffering and routing control module and controlling and acquiring the working states of all modules of the link layer controller by the host computer interface reading and writing configuration register, and has good portability.
Owner:CENT FOR SPACE SCI & APPLIED RES
Microwave-fuel combined heating-type coal-based direct reduction method and rotary hearth furnace
The invention discloses a microwave-fuel combined heating-type coal-based direct reduction method and a rotary hearth furnace. The method comprises the following steps of drying and pre-heating materials, reducing the materials by a fuel combustion method, and further reducing the materials by a microwave radiation method, wherein a reducer for reducing the metal oxide into metal is fixed carbon in the materials. The rotary hearth furnace is used by the above method. The rotary hearth furnace has the advantages of simple structure, low cost, high metallization rate, and realization and popularization easiness.
Owner:ZHONGYE-CHANGTIAN INT ENG CO LTD
Supersonic synergic nano light catalytic air-sterilizing-purifying apparatus
InactiveCN1850283AImprove performanceImprove dust removal efficiencyDeodrantsRadiationAir cleaningPhotocatalysis
The present invention relates to an ultrasonic synergistic nano photocatalytic air sterilization and purification equipment. It includes the following several portions: shell body, upper water tank, lower water tank, water inlet valve, water outlet valve, miniature water pump, filtering screen, ultrasonic air energy transducer, filter, photocatalysis three-dimensional screen, ultrasonic reflecting plate and sterilization UV-light. Said invention also provides the connection mode of all the above-mentioned portions and the working principle of said air sterilization and purification equipment.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Water jet propulsion pump
InactiveCN103527521AGuaranteed working noiseGuaranteed high performance and long lifePump componentsPropulsive elementsImpellerWater jet
The invention belongs to the field of pumps and particularly relates to a water jet propulsion pump which comprises a pump body and a pump shaft assembly arranged at a pump cavity of the pump body. The pump shaft assembly at least comprises a pump shaft and an impeller wheel arranged on the pump shaft; the pump shaft is of a simply supported beam structure with bearings at the two ends of the pump shaft fixedly connected, the tail end of the pump shaft and a power source of the water jet propulsion pump are in normal-running fit, and the head end of the pump shaft extends in the axial direction and is in bearing fit with a bearing assembly arranged on the pump body; bounded by an impeller wheel body, the water jet propulsion pump is divided into a water inlet area and a water outlet area, wherein the water inlet area is communicated with a liquid inlet of the pump body, and the water outlet area is used for discharging water; a reflux passageway used for reducing the hydraulic thrust at the bearing assembly is arranged between the water inlet area and the water outlet area, and the water inlet area of the pump body, the water outlet area of the pump body, gaps to be lubricated of the bearing assembly and the reflux passageway are sequentially communicated and form a circular flow channel. The water jet propulsion pump is reasonable and practical in structure, wide in working usage range and long in service life, and high-efficiency work of components within the whole water outlet area of the pump body can be effectively guaranteed.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
Preparation method of high-performance permanent magnet ferrite magnet and magnet
InactiveCN107382303AImprove performanceInhibit growthInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureRemanenceStrontium
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-performance permanent magnet ferrite magnet and the magnet, belonging to the technical field of magnetic materials. The method comprises the steps of mixing and grinding a strontium ferrite pre-sintered material and an La-Ca-Sr-Co ferrite pre-sintered material in a certain weight proportion, wherein the La-Ca-Sr-Co ferrite material is prepared from the following components: La0.6Ca0.4-xSrxOn (Fe1-yCoy)2O3, wherein the x is more than or equal to 0.1 and is less than or equal to 0.4, the y is more than or equal to 0.2 and is less than or equal to 0.3, the n is more than or equal to 5.0 and is less than or equal to 6.0, the strontium ferrite material is prepared from the component of SrO.6(Fe2O3). When the strontium ferrite pre-sintered material is mixed with the La-Ca-Sr-Co ferrite pre-sintered material, the minimum remanence Br of the prepared permanent magnet ferrite is 418.7mT, and the maximum is 429.1mT; the minimum intrinsic coercivity is 350.3kA / m, and the maximum is 388.6kA / m, which fully meets the requirements of current use: the remanence Br is 415mT to 430mT, and the intrinsic coercivity is 350kA / m to 380kA / m.
Owner:MAANSHAN GAOKE MAGNETIC MATERIAL
Urban sewage strengthening treatment method in cold area based on multi-point feed water adjustment
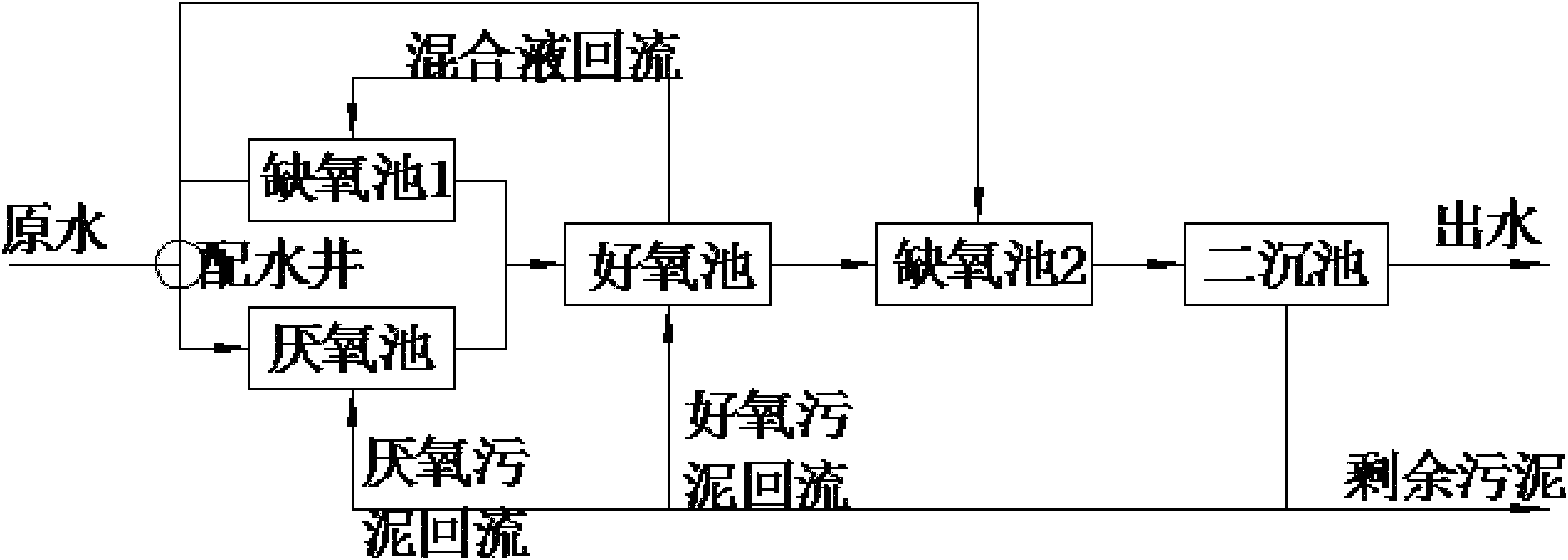
InactiveCN102001791AExtended staySmall volumeMultistage water/sewage treatmentNitrogenTherapeutic effect
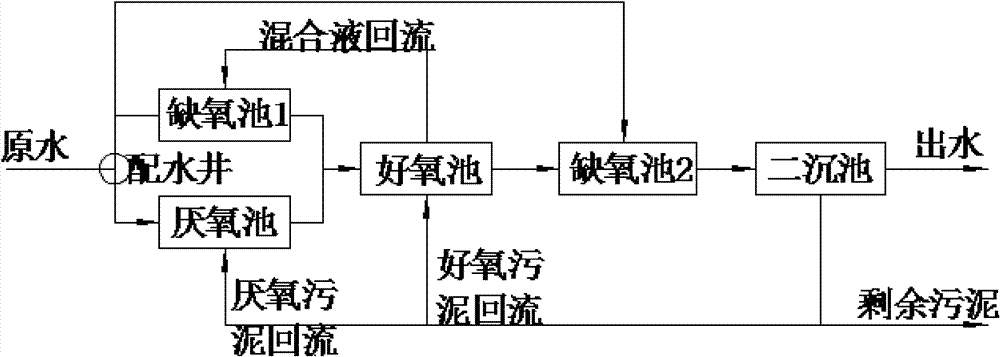
The invention discloses an urban sewage strengthening treatment method in a cold area based on multi-point feed water adjustment, which relates to an urban sewage strengthening treatment method and solves the problems of incapability of synchronous and efficient denitrogenation and dephosphorization, poor treatment effect, high running cost and unsuitability for treating urban sewage in the cold area in the traditional technology of treating the urban sewage. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, primary precipitation of sewage: dividing effluent of a primary settling tank into two parts or three parts through a distribution well for distribution; and secondly, synchronously introducing the effluent mixing liquid of an anaerobic tank and an anoxic tank 1 and the reflowing sludge at the head end of an aerobic tank into the aerobic tank, introducing the effluent of the aerobic tank into an anoxic tank 2, introducing the effluent of the anoxic tank 2 into a secondary settling tank through water drop, discharging a supernatant as treated purified water, reflowing a part of sludge at the lower layer, and discharging the rest as the remaining sludge. The invention can synchronously carry out efficient denitrogenation and dephosphorization, has favorable treatment effect and low running cost and is suitable for treating the urban sewage in the cold area.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Ultrathin half-wall short-circuit circular polarization top end radiation antenna
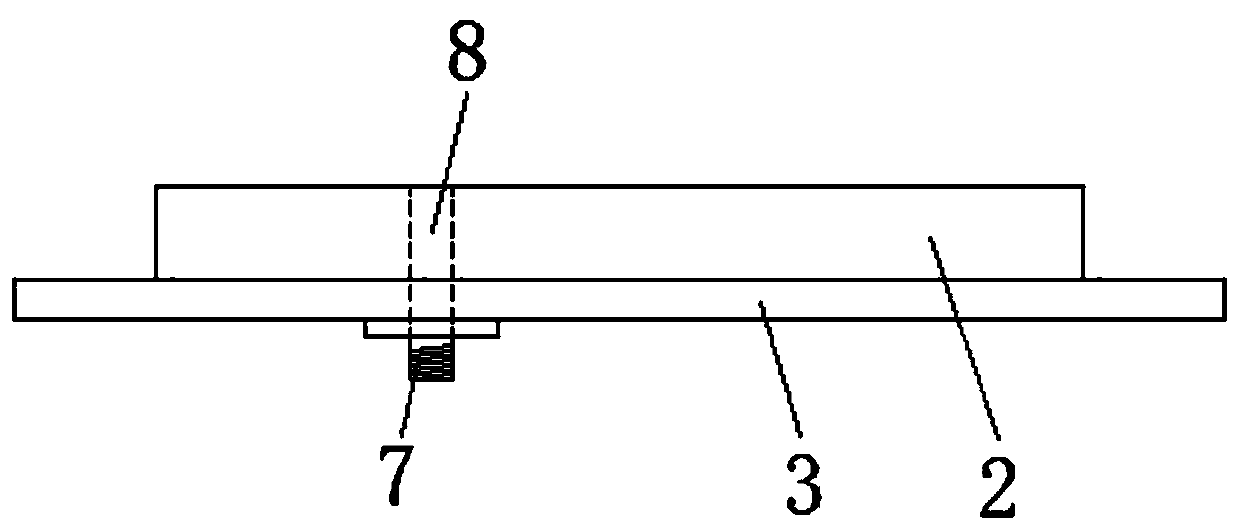
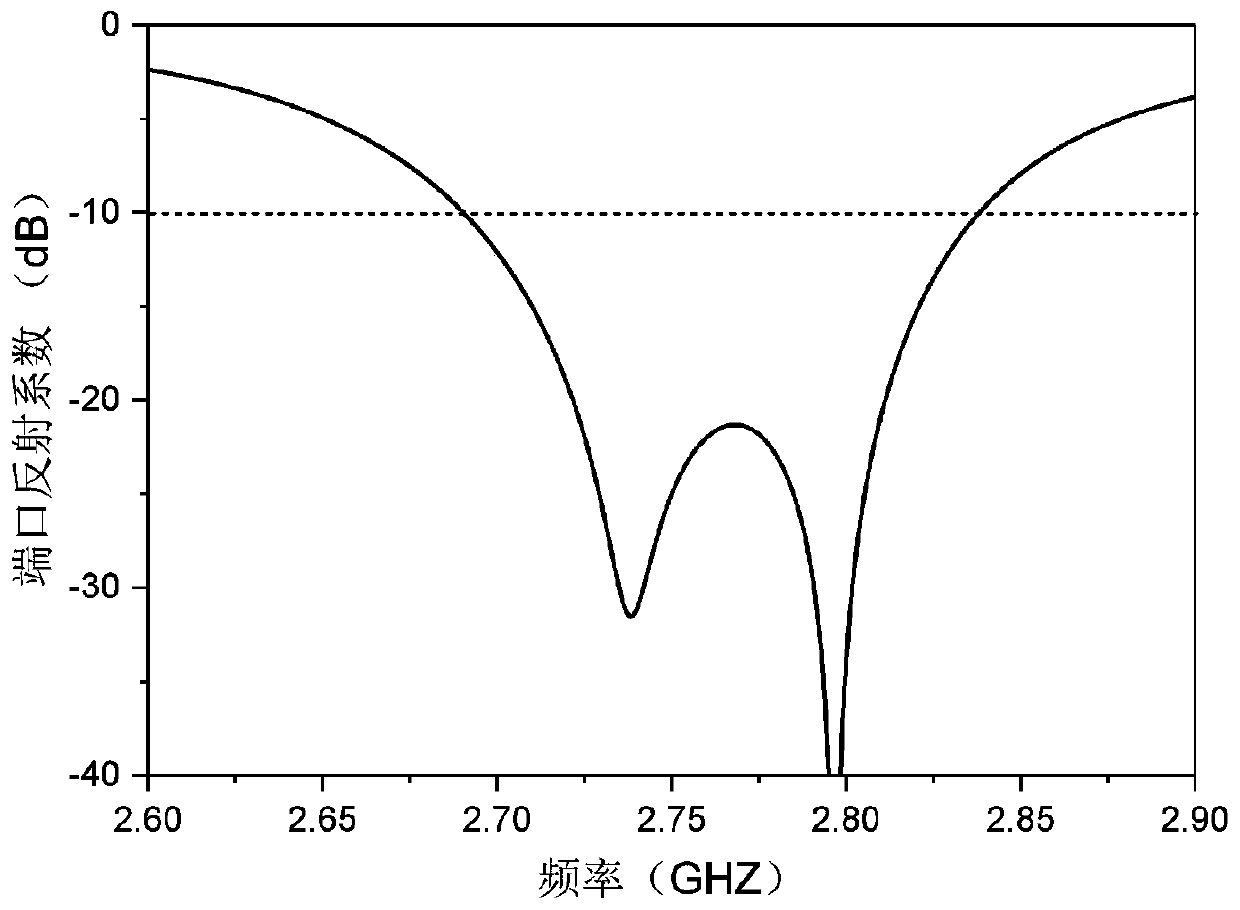
ActiveCN110492242AReduce section sizeLow profileRadiating elements structural formsAntennas earthing switches associationCoaxial probeDielectric substrate
The invention provides an ultrathin half-wall short-circuit circularly polarized top radiating antenna. The antenna comprises a rectangular radiation microstrip patch, a dielectric substrate, a metalbottom plate, four first metal short-circuit pins and a radio frequency connector, wherein the rectangular radiation microstrip patch is attached to one side surface of the dielectric substrate. The other side surface of the dielectric substrate is fixedly connected with the metal bottom plate; the four first metal short-circuit pins penetrate through the rectangular radiation microstrip patch, the dielectric substrate and the metal bottom plate and are connected with the metal bottom plate. The radio frequency connector is installed on the other side, opposite to the dielectric substrate, ofthe metal bottom plate, and a coaxial probe in the radio frequency connector penetrates through the dielectric substrate to be connected with the rectangular radiation microstrip patch in a welded mode. The problems that a single-layer short-circuit wall patch antenna of an existing radiation antenna is low in efficiency, unstable in directional diagram and the like under the condition of single-point feeding are solved.
Owner:西安利芯电子科技有限公司
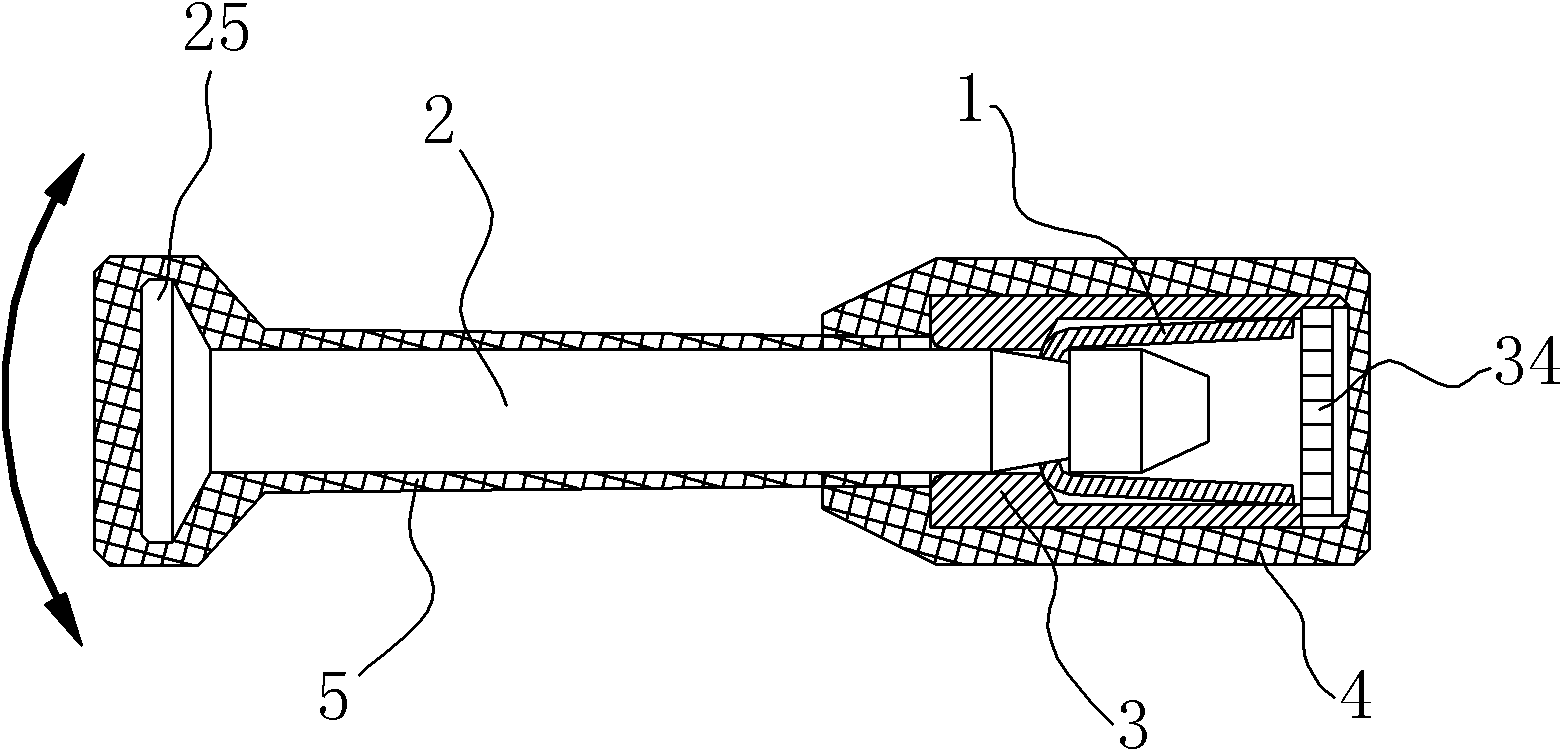
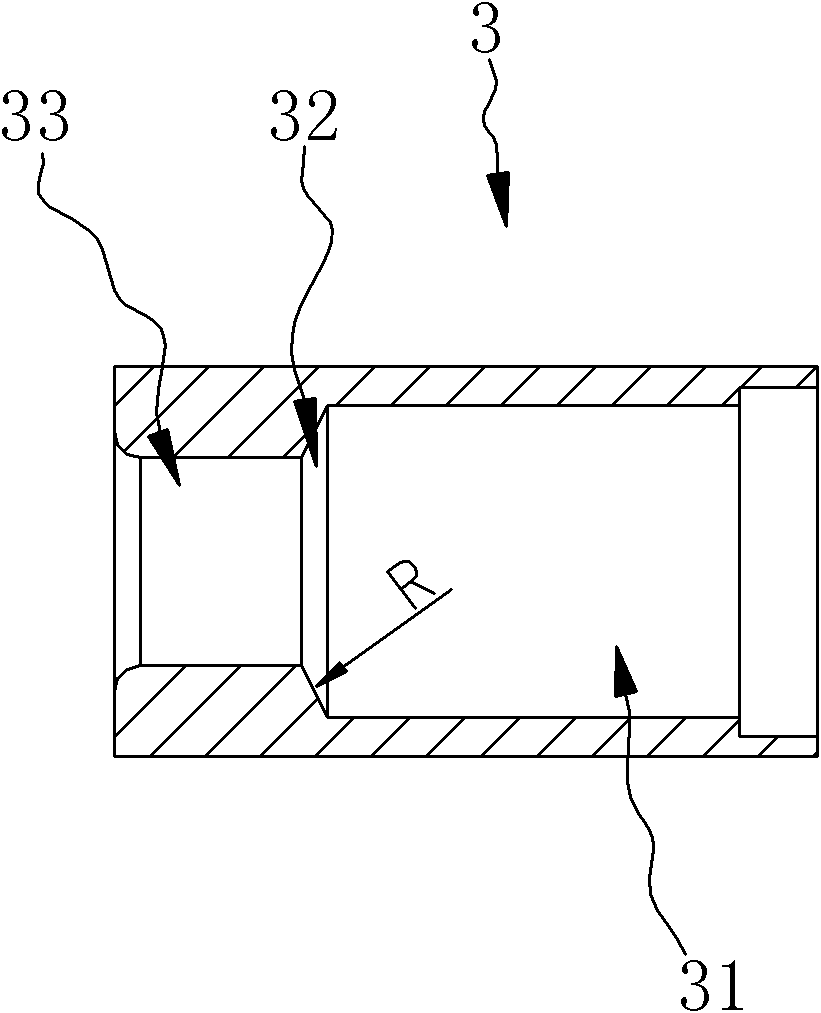
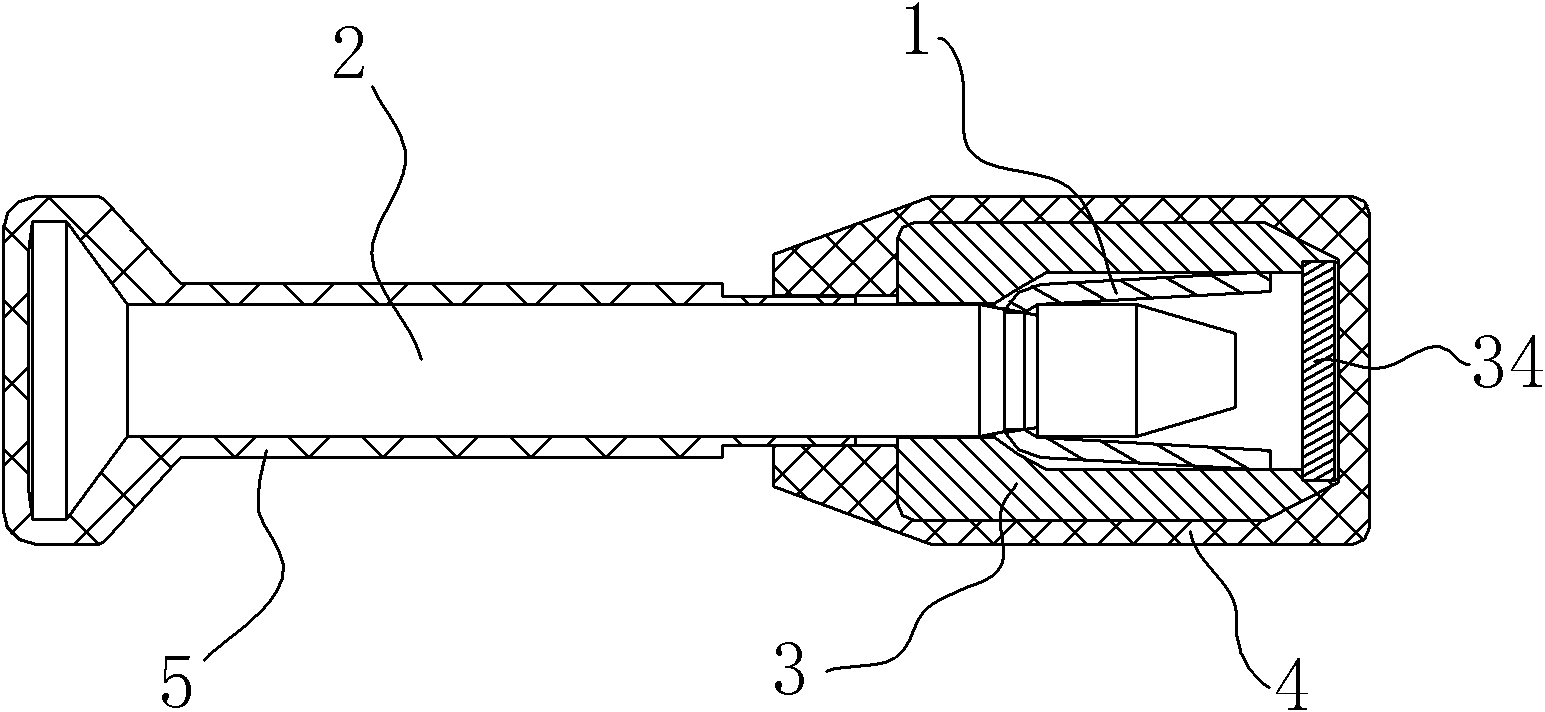
High-protection high-safety seal
The invention relates to the field of anti-theft locks, in particular to a disposable safety seal used for containers and cargo boxes. The disposable safety seal comprises a lock rod and a lock sleeve; a snap spring is arranged in the inner cavity of the lock sleeve; the snap spring is elastically blocked and matched with the inner wall of the lock sleeve; the front end of the lock rod is inserted in the inner cavity of the lock sleeve; and a necking part at the front end of the lock rod is elastically blocked and matched with a bayonet of the snap spring; and the radial size of the rear end of the lock rod and the radial size of the lock sleeve are larger than that of a body of the lock rod. The disposable safety seal is characterized in that: the front end of the inner cavity of the lock sleeve is thick, the rear end is thin, and the middle part is a reducing transition section; the size of the snap spring along the coaxial direction of the lock rod is smaller than the coaxial sizes of the middle part and the front part of the inner cavity of the lock sleeve; the snap spring driven by the lock rod can move front and back in the middle part and front part of the inner cavity of the lock sleeve along the coaxial direction of the lock rod; and the transition section has stronger centering capacity on the snap spring and the lock rod and the function of tightening the snap spring, and can guarantee to clamp the necking part of the lock rod. The seal has high stability and high safety.
Owner:黄山亿利工贸集团有限公司
Robust single machine scheduling method based on interval uncertainty
ActiveCN108181810AImprove performanceReduce decision riskAdaptive controlAlgorithmSingle-machine scheduling
The invention provides a robust single machine scheduling method based on interval uncertainty, and belongs to the field of production scheduling and operations research. The method includes: establishing a robust optimization model RSMSP of single machine scheduling, wherein an optimization target is to search an optimal workpiece machining sequence to enable the maximum waiting time of the sequence to be minimum in a poorest scene; during solution, converting the model RSMSP to a mixed linear integer programming model P; and solving the model P by employing a two-stage heuristic solution algorithm to obtain the optimal machining sequence, namely an optimal scheme of robust single machine scheduling. According to the method, uncertain parameters are expressed by employing the mode of interval estimation, a method for recognizing finite possible poorest scenes in an infinite scene set, which is in more accordance with the production reality, is firstly proposed, and decision risks canbe reduced to the maximum and the system performance can be guaranteed in the condition of poor information.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
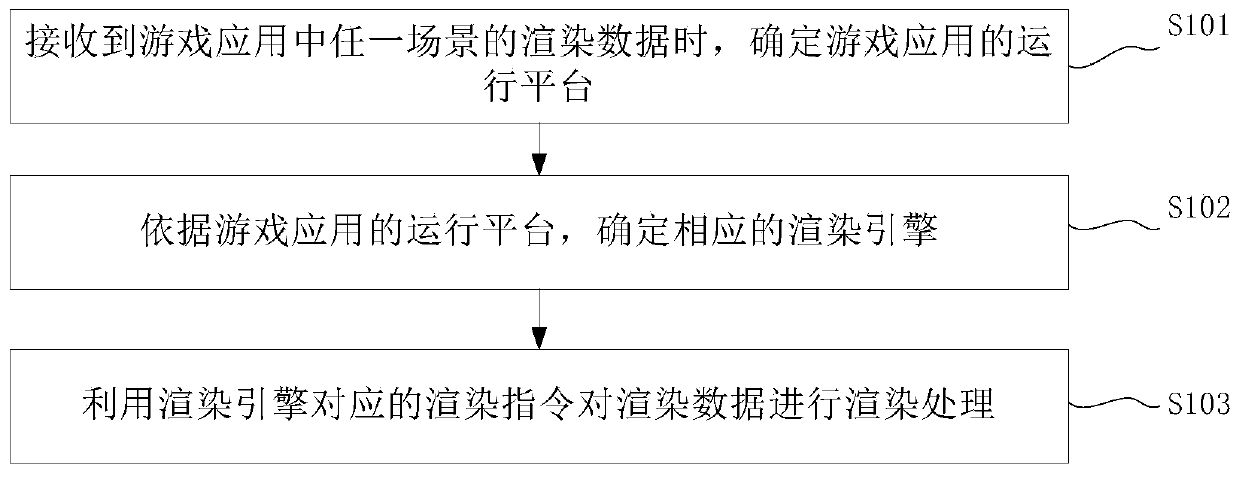
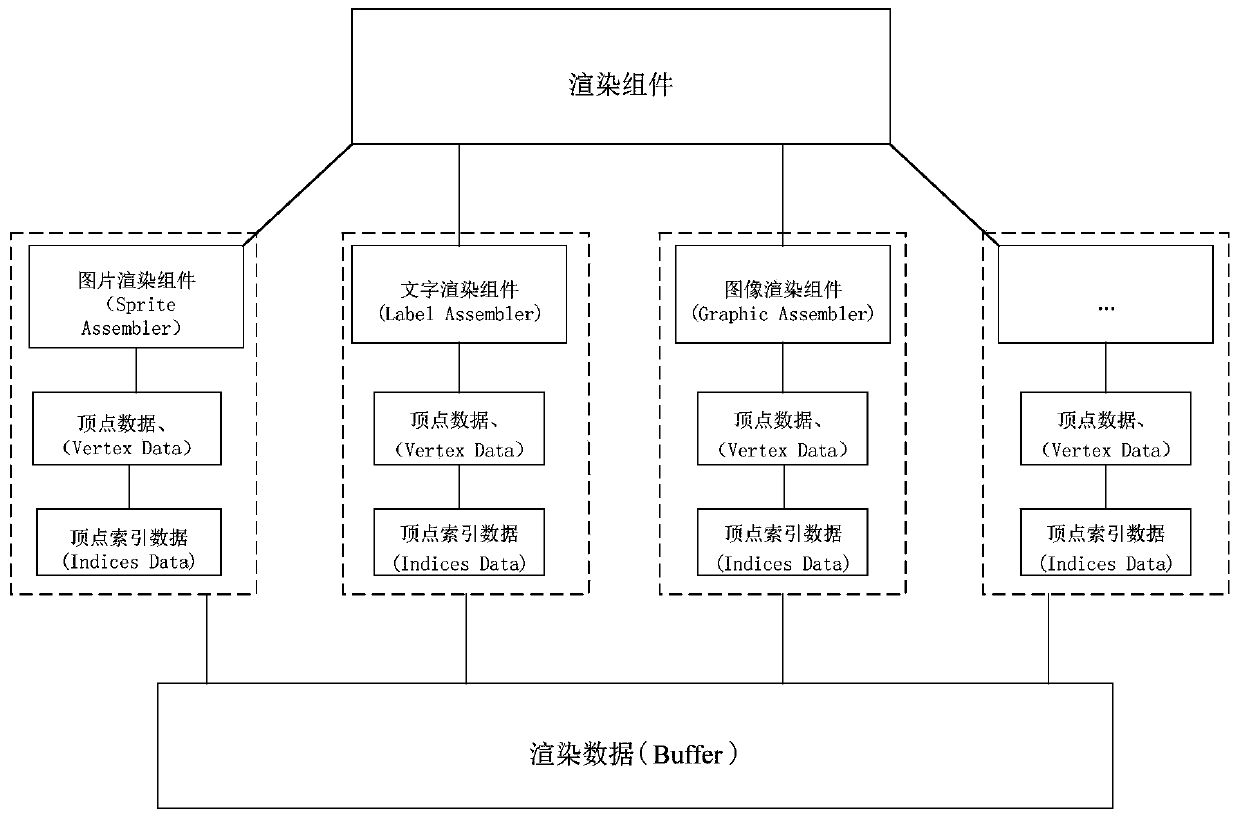
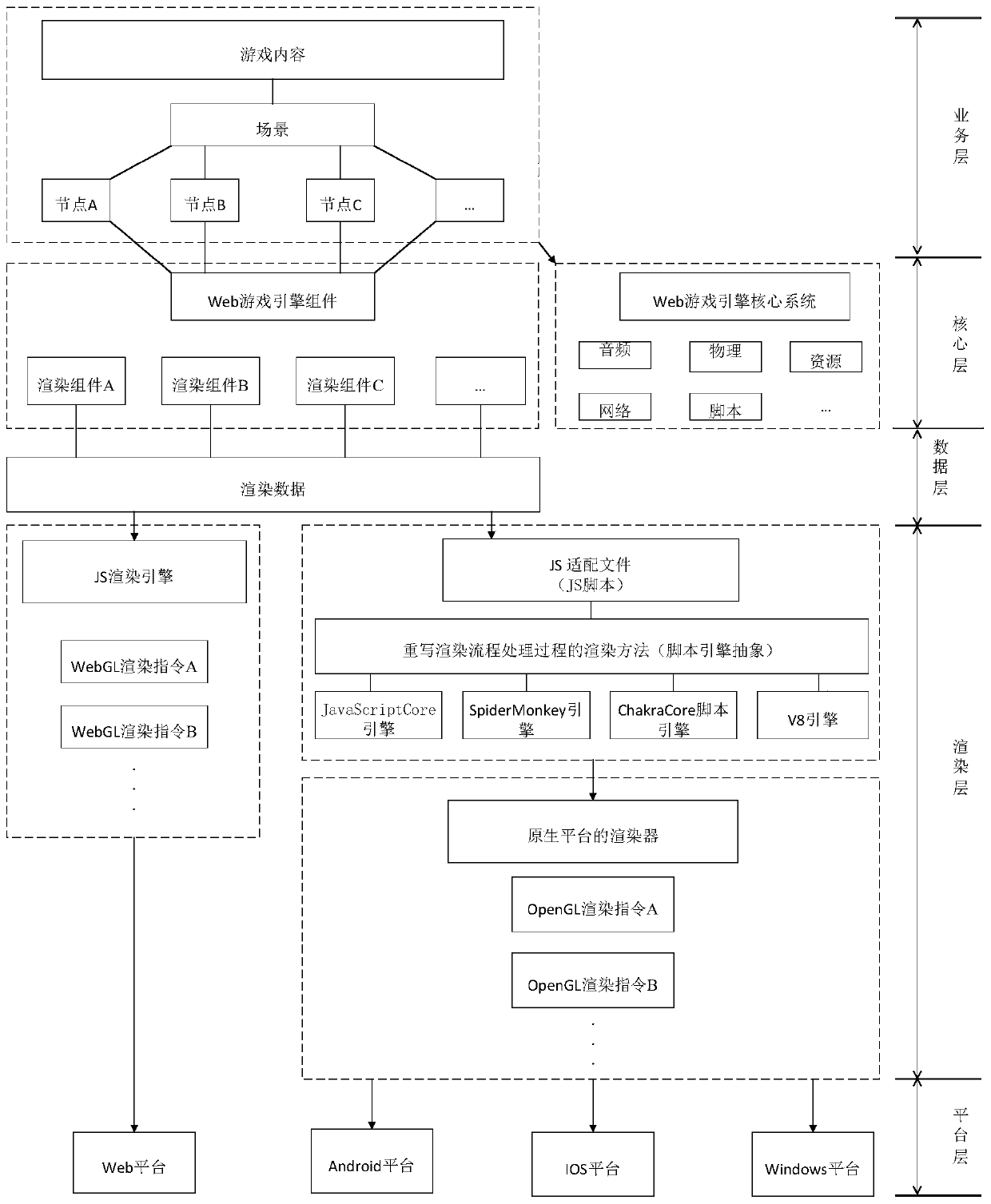
Rendering method and device based on game engine and electronic equipment
ActiveCN111408138AReduce development costsReduce maintenance costsVideo gamesEnergy efficient computingComputer graphics (images)Game based
The embodiment of the invention provides a rendering method and device based on a game engine and electronic equipment. The method comprises the steps of: when rendering data of any scene in a game application are received, determining an operation platform of the game application; determining a corresponding rendering engine according to the operation platform of the game application; and performing rendering processing on the rendering data by utilizing a rendering instruction corresponding to the rendering engine. According to the embodiment of the invention, different rendering engines areadopted for different platforms, the purpose of ensuring the high-performance performance of the same game application on different platforms is achieved, a game developer does not need to research and develop different game applications for different platforms, and the development and maintenance cost of the game applications is reduced.
Owner:XIAMEN YAJI SOFTWARE
Integrated high-voltage power IGBT device monolithic LED driving chip
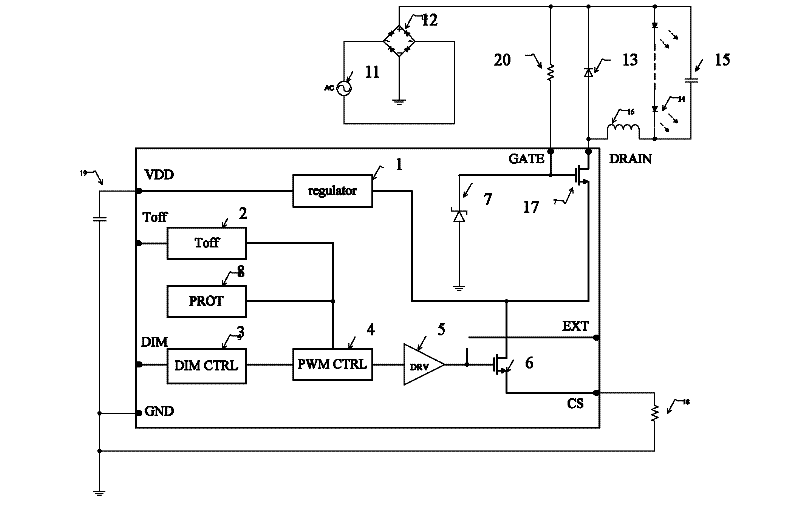
InactiveCN102523652AReduce complexityWork reliablyElectric light circuit arrangementEnergy saving control techniquesLow voltageDimmer
An integrated high-voltage power IGBT device monolithic LED driving chip relates to an integrated circuit technology. A regulator linear adjuster, a Toff turn-off time timer, a DIM light-dimmer controller, PWM signal generator, a DRV power tube driving module, a low voltage power device, a grid setting circuit of an external high voltage power device, a protection circuit and an IGBT high voltage power device are integrated on the chip. The regulator linear adjuster is connected with an output terminal of the IGBT high voltage power device. The Toff turn-off time timer, the DIM light-dimmer controller and the protection circuit are connected with the PWM signal generator. The PWM signal generator is connected with a grid electrode of the low voltage power device through the DRV power tube driving module. The grid electrode of the IGBT high voltage power device is connected with the grid setting circuit. The output terminal is connected with an input terminal of the low voltage power device. According to the invention, an innovation framework is used. The chip can work stably and reliably in a general alternating current input scope of 85VAC to 265 VAC. High performance of the system can be guaranteed.
Owner:成都成电硅海科技股份有限公司
Preparation method of high-performance M type calcium-strontium ferrite and product
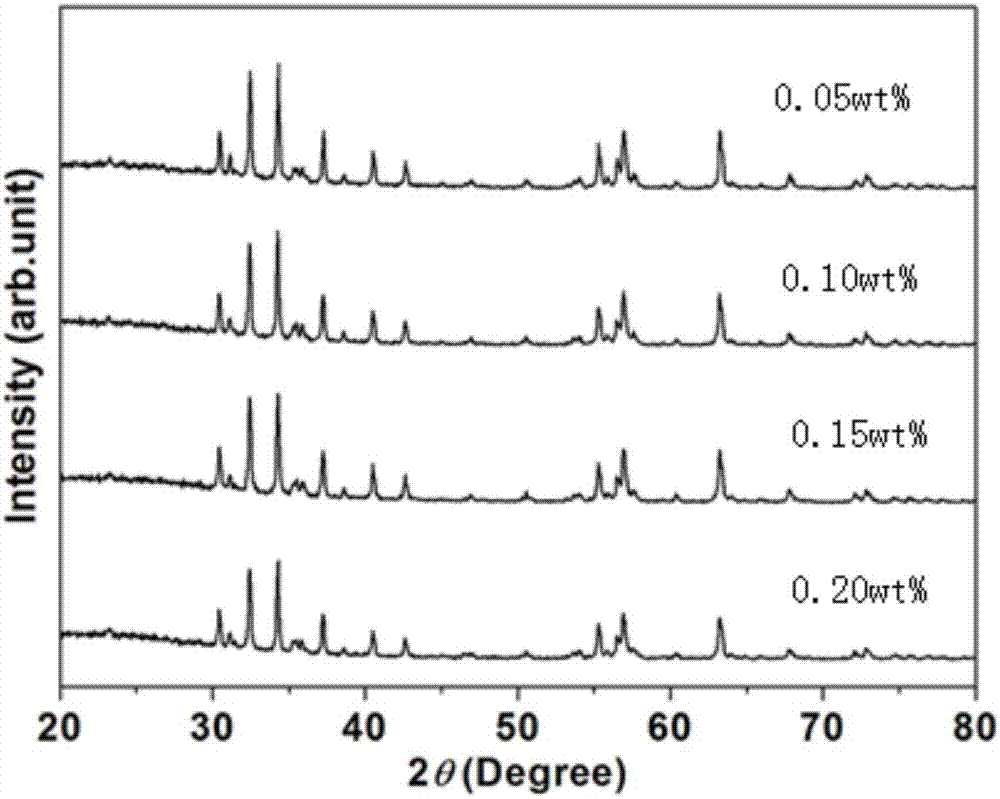
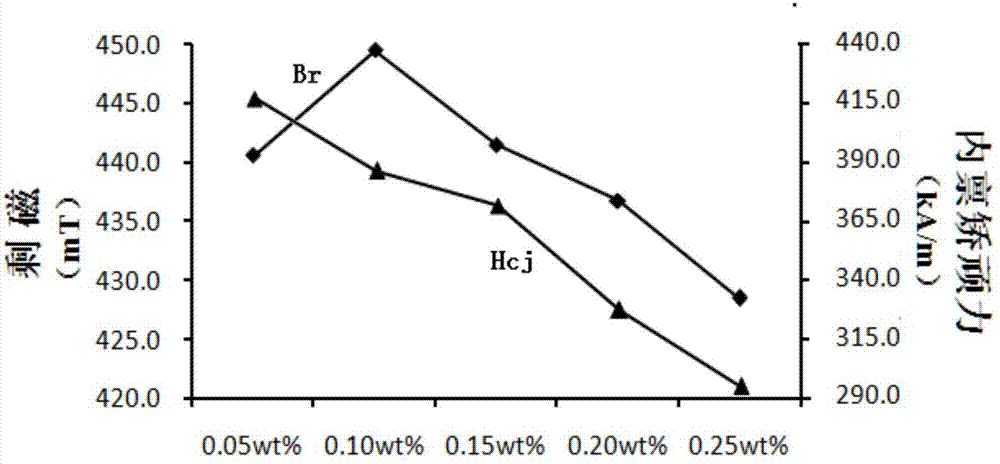
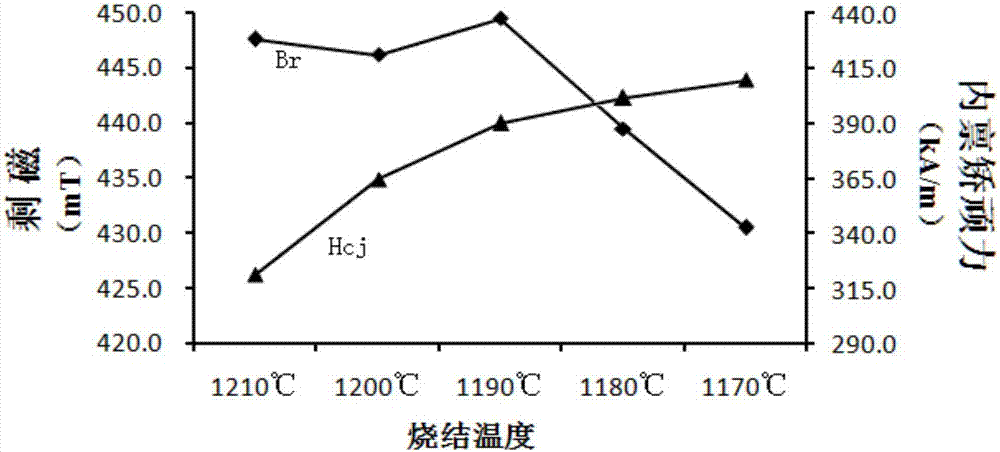
InactiveCN107473724AHigh residual magnetic inductionImprove crystal structureLithium carbonateStrontium
The invention discloses a preparation method of high-performance M type calcium-strontium ferrite and a product and belongs to the technical field of magnetic materials. The method comprises a pre-sintering process, and lithium carbonate powder is added to a pre-sintered material after pre-sintering and accounts for 0.05wt%-0.25wt% of the pre-sintered material by weight. According to the method, the pre-sintered material can be subjected to ball-milling firstly and then is mixed with the lithium carbonate powder; the pre-sintered material can also be subjected to mixed ball-milling together with the lithium carbonate powder. With the adoption of the preparation method of the high-performance M type calcium-strontium ferrite, a single type additive is adopted, so that control of a production process is convenient, residual magnetic flux density (Br) and intrinsic coercive field (Hcj) of the calcium-strontium ferrite are improved, the cost of the single type additive is low, and the production cost is reduced accordingly.
Owner:SINOSTEEL TIANYUAN MAANSHAN TONGLI MAGNETIC MATERIAL
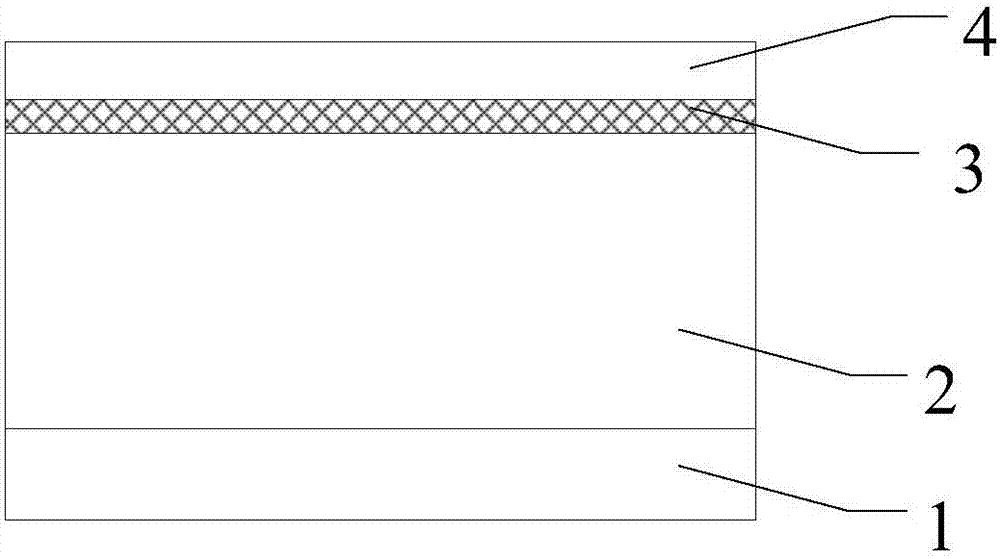
Fabrication method of vertical double-diffused metal-oxide-semiconductor (VDMOS) device
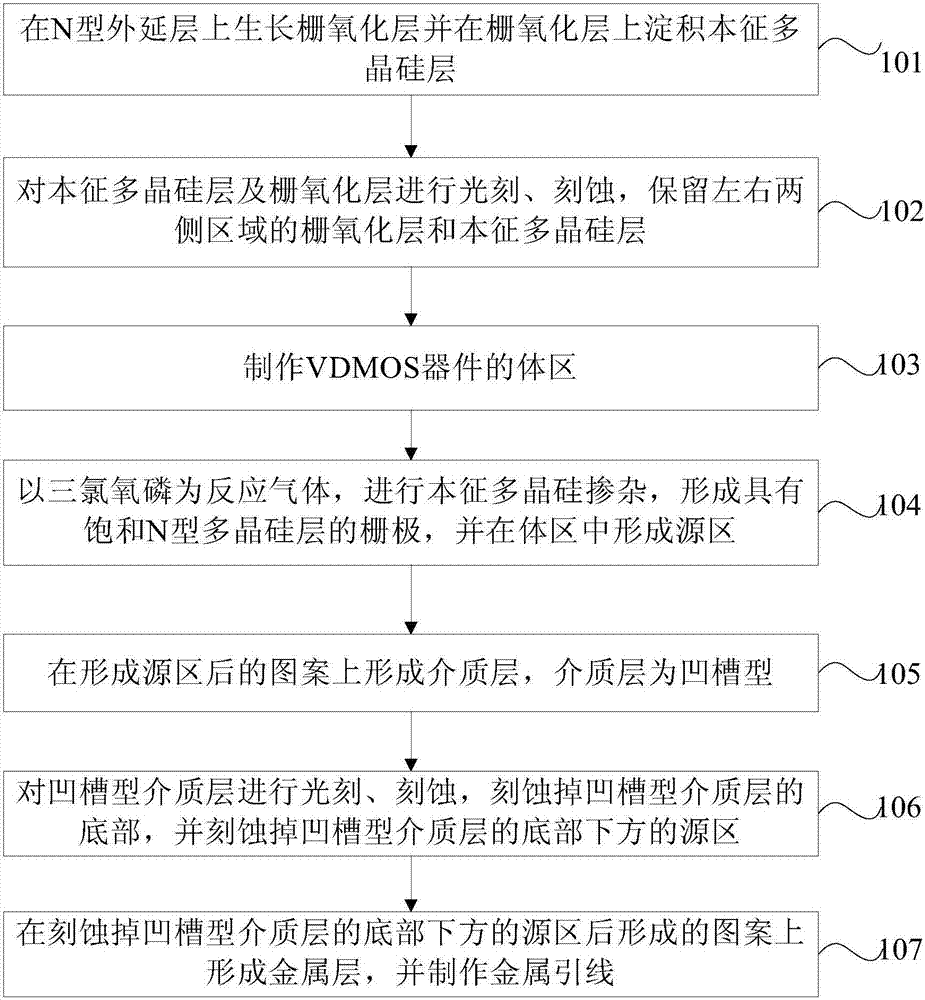
InactiveCN107342224AReduce repetitive production linksReduce manufacturing costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate oxideBody region
The invention provides a fabrication method of a vertical double-diffused metal-oxide-semiconductor (VDMOS) device. The method comprises the steps of growing a grid oxide layer on an N-type epitaxial layer, and depositing an intrinsic poly-silicon layer on the grid oxide layer; photoetching and etching the intrinsic poly-silicon layer and the grid oxide layer, and reserving the grid oxide layer and the intrinsic poly-silicon layer on a left-side region and a right-side region; fabricating a body region of the VDMOS device; performing intrinsic poly-silicon doping by taking POCl3 as a reaction gas to form a grid with a saturated poly-silicon layer, and forming a source region in the body region; forming a dielectric layer on a pattern after the source region is formed, wherein the dielectric layer is in a groove shape; photoetching and etching the groove-shaped dielectric layer to etch a bottom part of the groove-shaped dielectric layer, and etching the source region below the bottom part of the groove-shaped dielectric layer; and forming a metal layer on a pattern formed after the source region below the bottom part of the groove-shaped dielectric layer is etched, and fabricating a metal lead. By the fabrication method, high performance of the VDMOS device is ensured.
Owner:PEKING UNIV FOUNDER GRP CO LTD +1
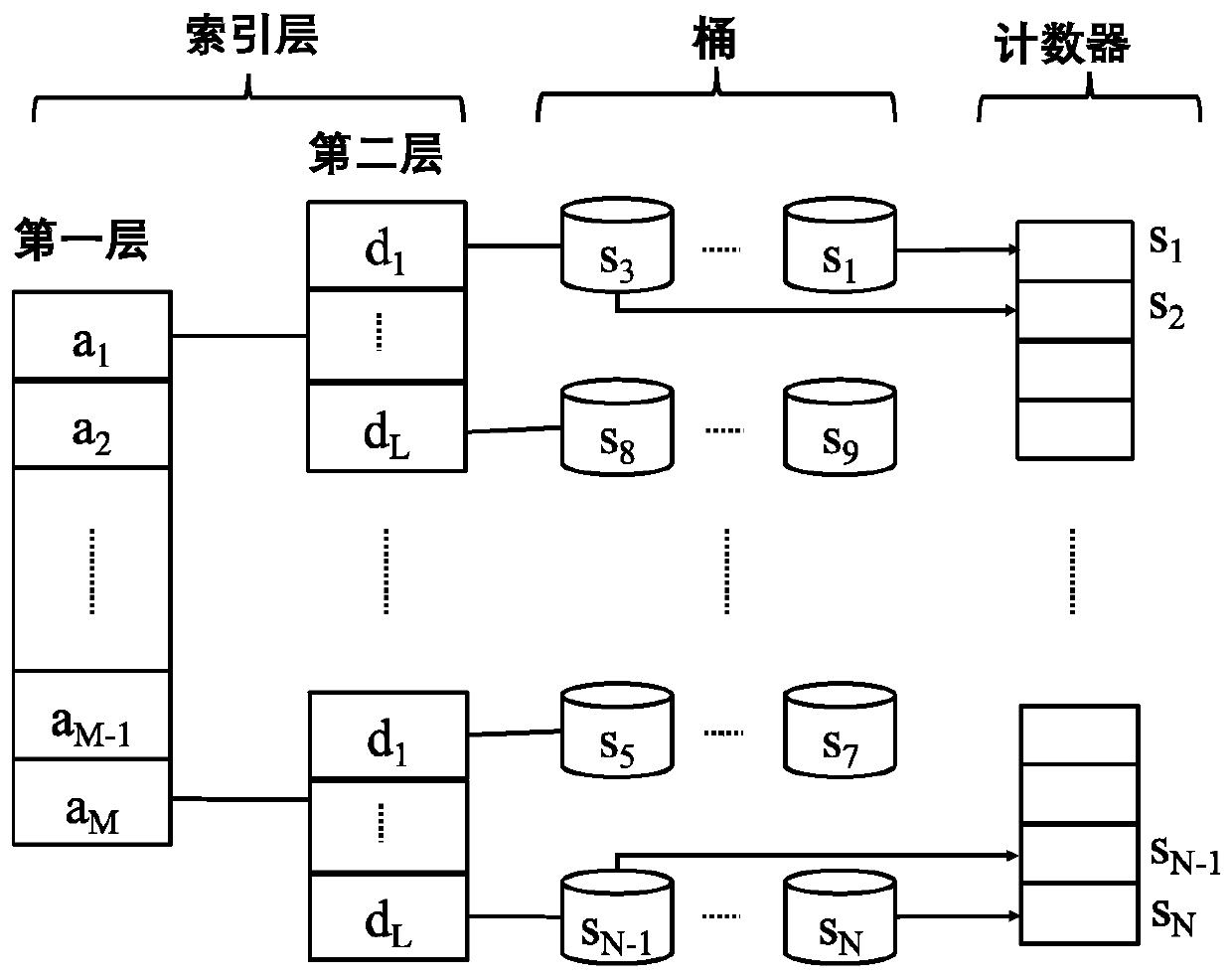
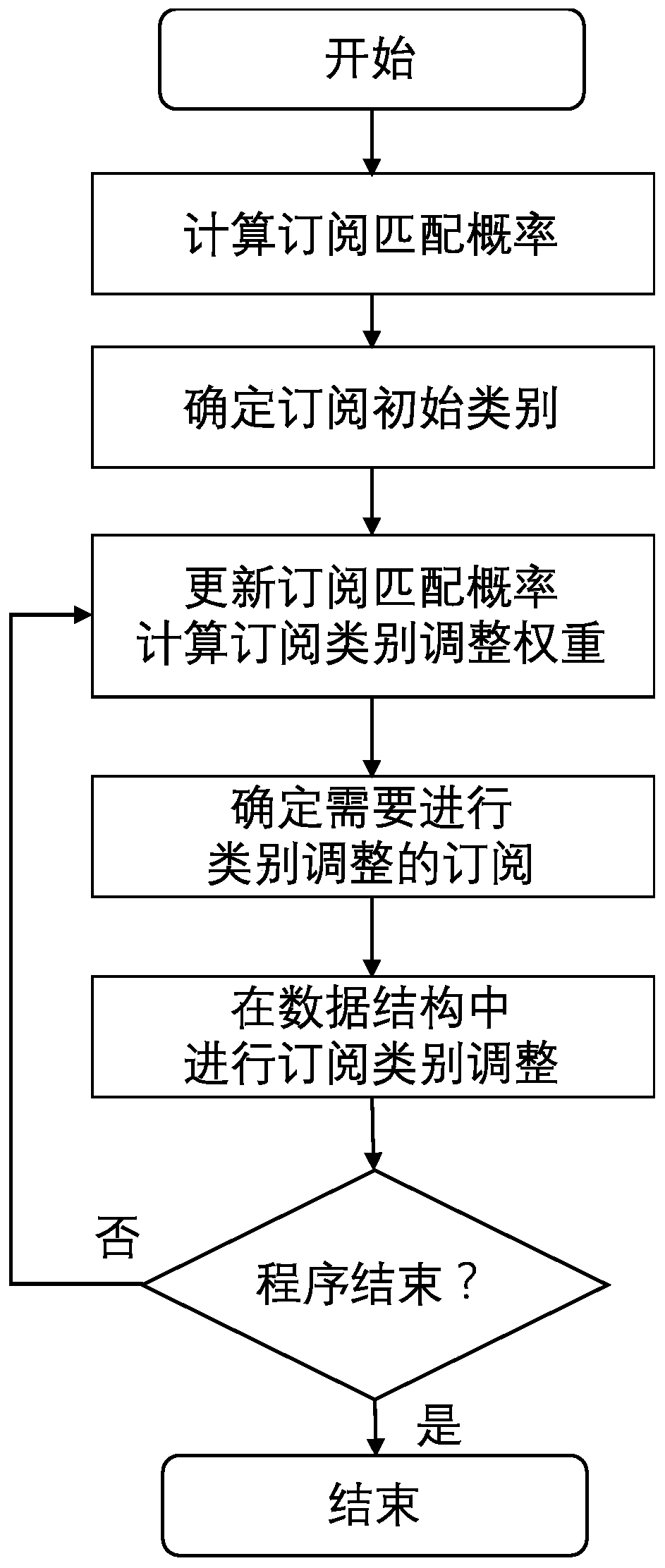
Optimization method and system based on matching real-time performance in publish-subscribe system
ActiveCN110413927AImprove performanceImprove efficiencyWeb data indexingWebsite content managementGroup typeData mining
The invention provides an optimization method and system based on matching real-time performance in a publish-subscribe system, and the method comprises the steps: calculating the matching probabilityof subscriptions and events, carrying out differential treatment of subscriptions according to the matching probability, and forming subscription grouping types; and establishing a structure index ofthe data structure based on the subscription grouping category, and adjusting the subscribed grouping category and the position of the subscribed grouping category in the structure index in real timeaccording to the subscription matching probability change so as to improve the matching efficiency. Subscriptions with high matching probabilities are firstly processed in the matching process, so that subscriptions matched with events are determined earlier, and the real-time performance of event distribution is improved. A concise classification scheme is defined to group the subscriptions according to the matching probability of the subscriptions and the events. A lightweight subscription dynamic adjustment mechanism is established. An effective greedy algorithm is provided to solve the adjustment scheme. The high efficiency of a subscription classification and structure layering method (SCSL) is ensured, the efficiency is optimized and the invention can be configured to meet differentapplication requirements.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
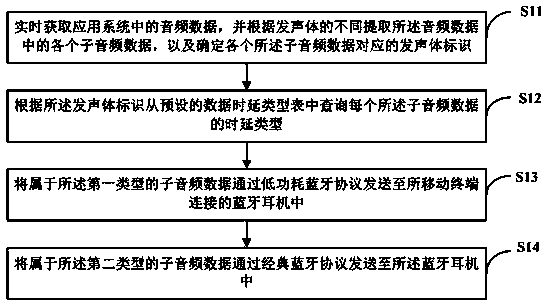
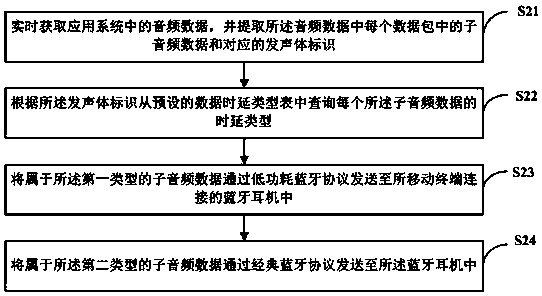
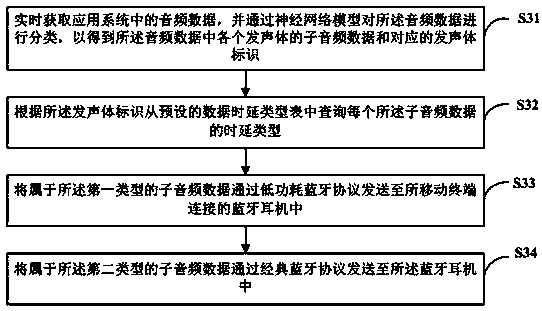
Audio data transmission method and device, readable storage medium and mobile terminal
InactiveCN110933216AGuaranteed timelinessGuaranteed high performanceSubstation speech amplifiersTransmissionComputer hardwareEngineering
The invention discloses an audio data transmission method and device, a readable storage medium and a mobile terminal, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining the audio data in an application system in real time, extracting each piece of sub-audio data in the audio data according to the difference of sound production bodies, and determining a sound production body identification corresponding to each piece of sub-audio data; querying a time delay type of each sub-audio data from a preset data time delay type table according to the sound production body identification, the time delay types including a first type and a second type, and the data timeliness requirement of the first type being higher than that of the second type; sending the sub-audio data belonging to the first type to aBluetooth earphone connected with a mobile terminal through a low-power Bluetooth protocol; and sending the sub-audio data belonging to the second type to the Bluetooth earphone through a classic Bluetooth protocol. According to the invention, the transmission real-time performance of the first type of audio data and the transmission high-efficiency performance of the second type of audio data can be realized.
Owner:南京雷鲨信息科技有限公司
Message sending method and device, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium
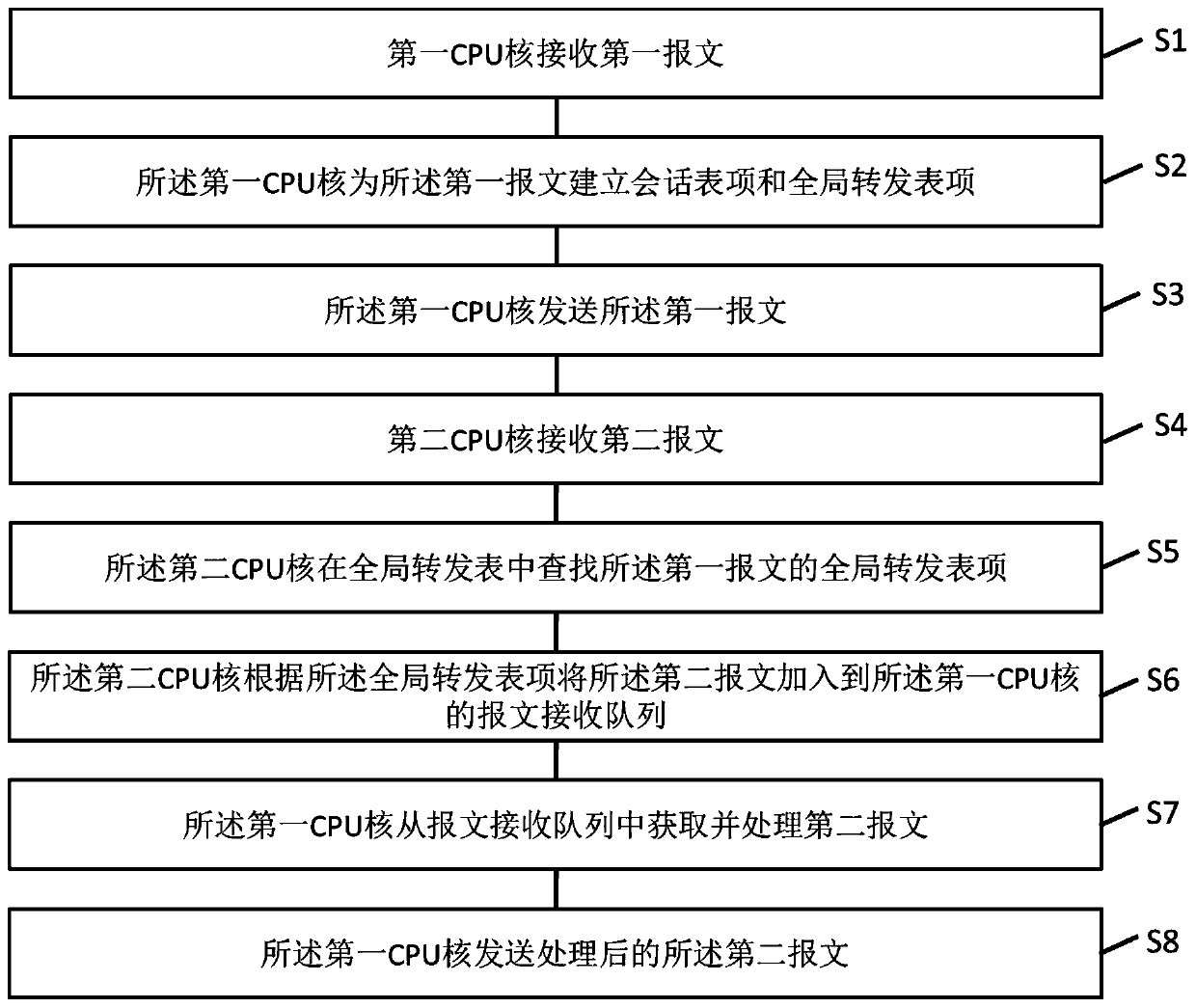
ActiveCN110177047AGuaranteed high performanceGuaranteed independenceData switching networksMessage processingDistributed computing
The invention discloses a message sending method and device, electronic equipment and a computer readable storage medium. The message sending method comprises the steps that a first CPU core receivesa first message and establishes a session table entry and a global forwarding table entry for the first message; a second CPU core receives a second message and adds the second message to a message receiving queue of the first CPU core according to the global forwarding table entry; and the first CPU core obtains, processes and sends the second message from the message receiving queue. According to the embodiment of the invention, by establishing the shared global forwarding table and the non-shared message receiving queue, a load balancing scheme independent of a specific flow filtering ruleis realized, and the independence of each CPU core is kept, so that the high performance of message processing is ensured.
Owner:BEIJING BYTEDANCE NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Switching type multi-power management circuit with extremely low power consumption
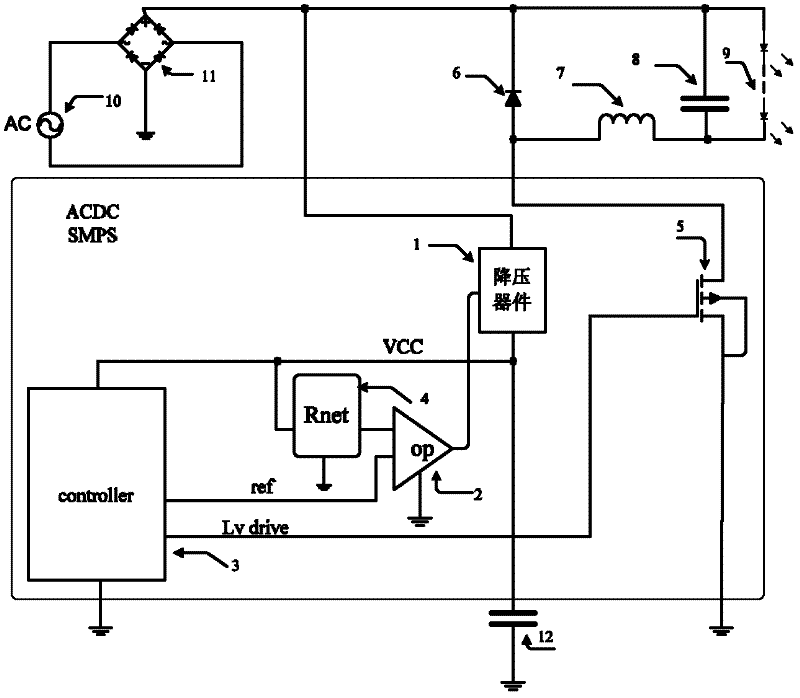
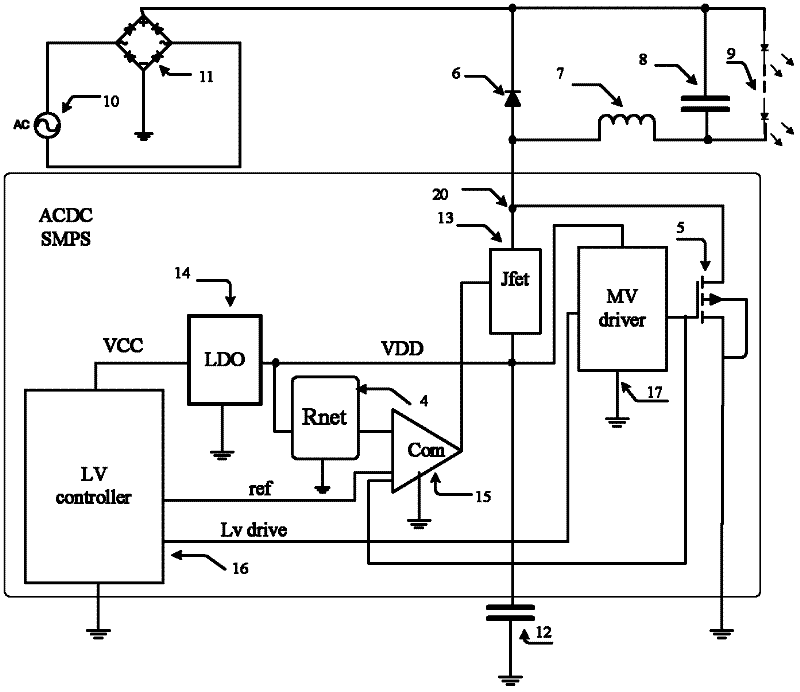
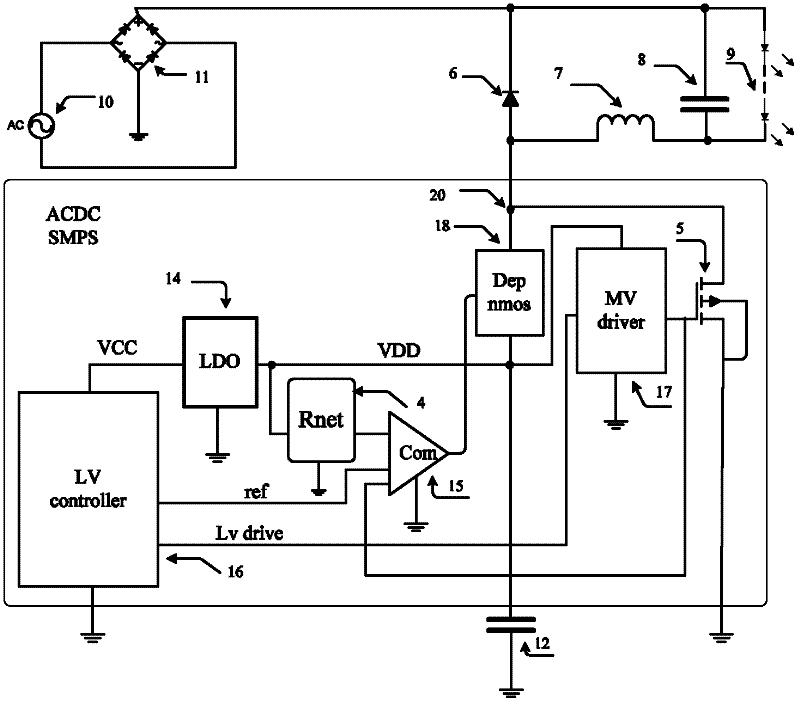
InactiveCN102420535ACan work stably and reliablyGuaranteed high performanceAc-dc conversion without reversalIntegrated circuitNetwork module
The invention discloses a switching type multi-power management circuit with extremely low power consumption, and relates to an integrated circuit technology. The switching type multi-power management circuit comprises a resistor network module and a power transistor, and further comprises a step-down transformer, an internal low-dropout voltage modulator, a comparator, a low-voltage control module and an intermediate voltage module, wherein the VCC end of the low-voltage control module is connected to a first connection point through the internal low-dropout voltage modulator; the first connection point is connected to the first input end of the comparator through the resistor network module; the low-voltage control module is also connected with the second input end of the comparator; the first connection point is connected with the intermediate voltage module which is connected with the gate of the power transistor; the gate of the power transistor is also connected to the third input end of the comparator of which the output end is connected to the control end of the step-down transformer; and one end of the step-down transformer is connected with the first connection point, and the other end of the step-down transformer is connected with an output point which is connected with the power transistor. The switching type multi-power management circuit can work stably and reliably within the universal alternating current input range of 85 to 265VAC, and high system efficiency can be ensured.
Owner:成都成电硅海科技股份有限公司
Urban sewage strengthening treatment method in cold area based on multi-point feed water adjustment
InactiveCN102001791BExtended staySmall volumeMultistage water/sewage treatmentNitrogenTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses an urban sewage strengthening treatment method in a cold area based on multi-point feed water adjustment, which relates to an urban sewage strengthening treatment method and solves the problems of incapability of synchronous and efficient denitrogenation and dephosphorization, poor treatment effect, high running cost and unsuitability for treating urban sewage in the cold area in the traditional technology of treating the urban sewage. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, primary precipitation of sewage: dividing effluent of a primary settling tank into two parts or three parts through a distribution well for distribution; and secondly, synchronously introducing the effluent mixing liquid of an anaerobic tank and an anoxic tank 1 and the reflowing sludge at the head end of an aerobic tank into the aerobic tank, introducing the effluent of the aerobic tank into an anoxic tank 2, introducing the effluent of the anoxic tank 2 into a secondary settling tank through water drop, discharging a supernatant as treated purified water, reflowing a part of sludge at the lower layer, and discharging the rest as the remaining sludge. The invention can synchronously carry out efficient denitrogenation and dephosphorization, has favorable treatment effect and low running cost and is suitable for treating the urban sewage in the cold area.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Polyethylene fiber-reinforced zeolite-fly ash-based geopolymer with ultra-high molecular weight and preparation method of polyethylene fiber-reinforced zeolite-fly ash-based geopolymer
The invention relates to a polyethylene fiber-reinforced zeolite-fly ash-based geopolymer with an ultra-high molecular weight and a preparation method of the polyethylene fiber-reinforced zeolite-flyash-based geopolymer. The polyethylene fiber-reinforced zeolite-fly ash-based geopolymer comprises the following raw materials of: in parts by weight, 493-542 parts of low-calcium fly ash, 124-136 parts of high-calcium fly ash, 203 parts of quartz sand, 0-61 parts of zeolite, 160 parts of water, 38 parts of sodium hydroxide, 173 parts of sodium silicate and 5-50 parts of polyethylene fiber with anultra-high molecular weight, and the preparation method comprises the following steps of: adding the low-calcium fly ash, high-calcium fly ash, quartz sand and zeolite to a stirring pot, and performing even stirring to obtain a No.1 mixture; mixing the water, sodium hydroxide and sodium silicate evenly in a beaker to obtain an alkali activator, adding the alkali activator to the stirring pot so as to mix the alkali activator with the No.1 mixture to obtain a No.2 mixture, adding the polyethylene fiber with an ultra-high molecular weight to the No.2 mixture, performing stirring until the fiberis evenly dispersed, putting the obtained slurry into a mould, then performing curing in an oven, and then performing curing at room temperature so as to achieve molding. When the preparation methodis compared with the prior art, the product has the advantages of low cost, good material performance and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Link layer controller of IEEE1394 bus
InactiveCN101764795BImprove reliabilityImprove versatilityBus networksProcessor registerData interface
The invention relates to a link layer controller of an IEEE1394 bus, which comprises a host computer interface, a link layer core module, a data buffering and routing control module, a high-speed data interface module and a configuration register, wherein an external CPU (central processing unit) can read and write data buffering areas in the configuration register and the access data buffering and routing control module by the host computer interface; the data buffering and routing control module is positioned among the link layer core module and the host computer interface and a high-speed data interface, used for providing the switching control among different data receiving and sending channels and also provided with two asynchronous first-in first-out memories which are respectively used for the buffering of receiving and sending data and the synchronization of cross-clock domain data; and the configuration register is used for providing initial configuration and control for the link layer core module and the data buffering and routing control module and controlling and acquiring the working states of all modules of the link layer controller by the host computer interface reading and writing configuration register, and has good portability.
Owner:CENT FOR SPACE SCI & APPLIED RES
FTP (file transfer protocol) file transfer method based on asynchronous read-write and FTP client
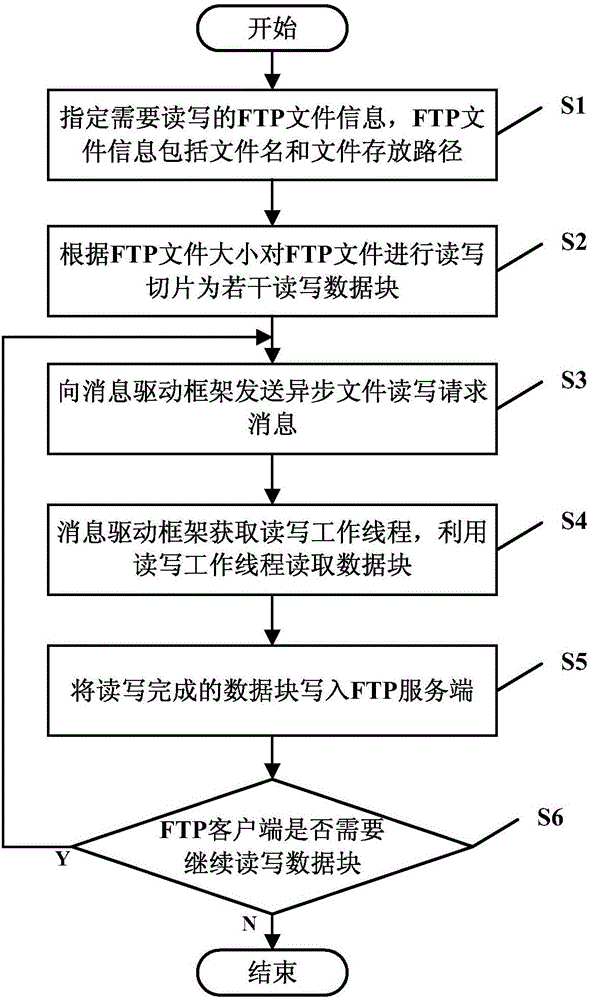
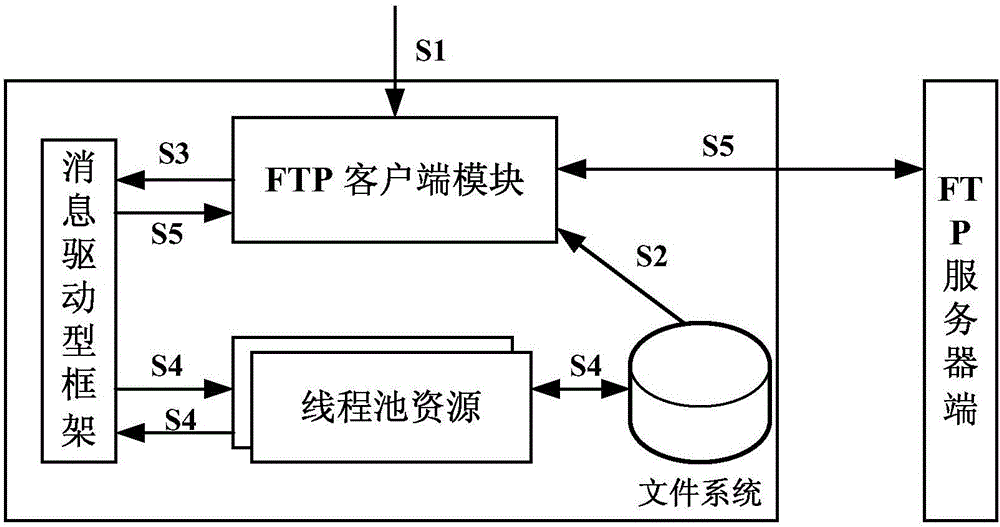
ActiveCN106790709AGuaranteed high performanceGuaranteed high efficiencyTransmissionThread poolFile transfer
The invention discloses an FTP (file transfer protocol) file transfer method based on asynchronous read-write and an FTP client and relates to the field of FTP configuration. The method comprises the following steps: the FTP client acquires FTP file sizes locally according to FTP file information needing to be read or written; FTP files are split into a plurality of read-write data blocks according to the file sizes; the FTP client sends an asynchronous file read-write request message to a message drive framework, and the message drive framework acquires a read-write worker thread in a preset thread pool; data blocks needing to be read or written in the FTP files are read by means of the read-write worker thread according to the asynchronous file read-write request message. According to the method, basic functions of FTP cannot be affected while high efficiency of the message drive framework is guaranteed, FTP is brought into the message drive type software framework perfectly, and the method is quite suitable for being popularized.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
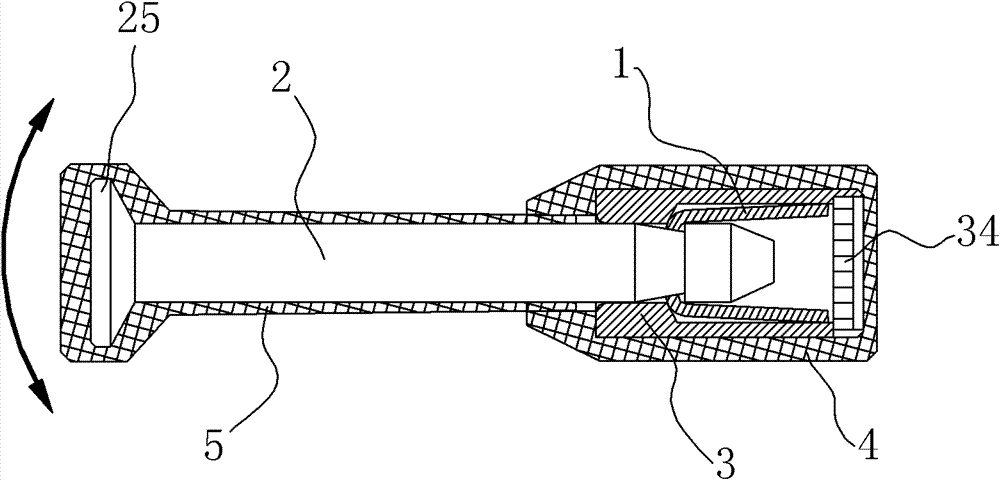
High-protection high-safety seal
The invention relates to the field of anti-theft locks, in particular to a disposable safety seal used for containers and cargo boxes. The disposable safety seal comprises a lock rod and a lock sleeve; a snap spring is arranged in the inner cavity of the lock sleeve; the snap spring is elastically blocked and matched with the inner wall of the lock sleeve; the front end of the lock rod is inserted in the inner cavity of the lock sleeve; and a necking part at the front end of the lock rod is elastically blocked and matched with a bayonet of the snap spring; and the radial size of the rear end of the lock rod and the radial size of the lock sleeve are larger than that of a body of the lock rod. The disposable safety seal is characterized in that: the front end of the inner cavity of the lock sleeve is thick, the rear end is thin, and the middle part is a reducing transition section; the size of the snap spring along the coaxial direction of the lock rod is smaller than the coaxial sizesof the middle part and the front part of the inner cavity of the lock sleeve; the snap spring driven by the lock rod can move front and back in the middle part and front part of the inner cavity of the lock sleeve along the coaxial direction of the lock rod; and the transition section has stronger centering capacity on the snap spring and the lock rod and the function of tightening the snap spring, and can guarantee to clamp the necking part of the lock rod. The seal has high stability and high safety.
Owner:黄山亿利工贸集团有限公司
Ultrahigh-precision optical fiber gyroscope structure
ActiveCN113804177AImmune to magnetic field interferenceGuaranteed high performanceSagnac effect gyrometersGyroscopeMiniaturization
The invention relates to an ultrahigh-precision optical fiber gyroscope structure. A mounting base, a mounting upper cover, a mounting flange and an outer cover form a double-layer magnetic shielding design, so that effective magnetic field shielding is provided for an optical fiber ring coil, and the optical fiber ring is prevented from being interfered by a magnetic field. A multi-layer structure is formed, an optical fiber is subjected to heat insulation design through the multi-layer structure and by utilizing an optical fiber ring base and an optical fiber ring inner cover, the influence of environment temperature change on the optical fiber ring coil is reduced, and the measurement precision and stability of the optical fiber gyroscope are improved. The whole structure is miniaturized, so that the gyroscope has excellent performance and meets the miniaturization requirement at the same time.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE TIMES OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH
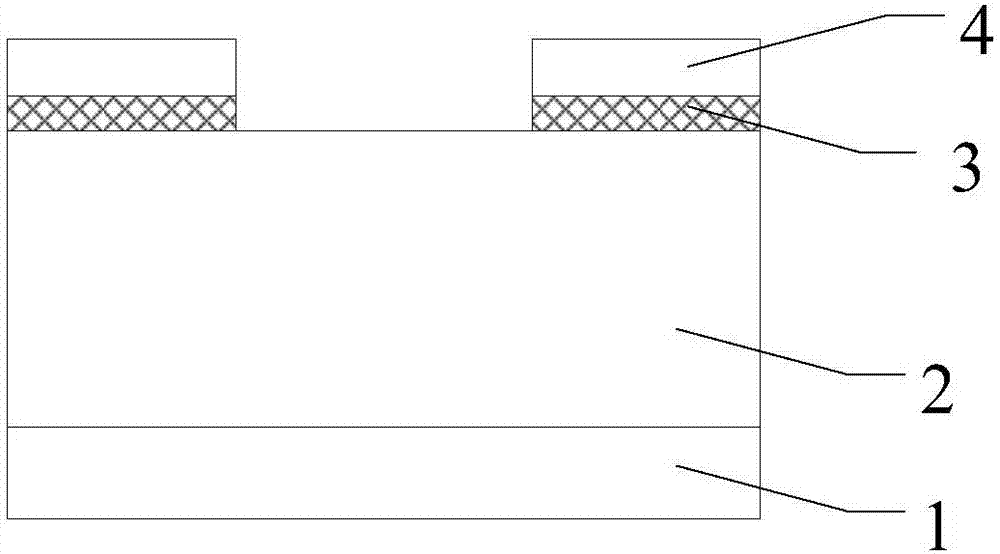
Method for manufacturing lateral double-diffused metal oxide semiconductor (LDMOS) device
InactiveCN102931088AEliminate PeelingImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxide semiconductorPolycrystalline silicon
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a lateral double-diffused metal oxide semiconductor (LDMOS) device. The method comprises the following steps of: providing a substrate; forming a gate dielectric layer, a polycrystalline silicon layer and a metal silicide layer on the substrate in sequence; performing rapid thermal annealing on the substrate; etching the polycrystalline silicon layer and the metal silicide layer to form a polycrystalline silicon and metal silicide gate electrode; and forming a channel region and a drift region in the substrate. By the method for manufacturing the LDMOS device, stress between the polycrystalline silicon layer and the metal silicide layer is relieved through rapid thermal annealing after the polycrystalline silicon layer and the metal silicide layer are formed, and the peeling phenomenon of metal silicide in the subsequent high temperature annealing process of forming the channel region and the drift region is avoided; and in addition, gradient impurity distribution of the channel region and self-aligned implantation of the drift region can be realized, so that the performance of the LDMOS device can be improved, and process complexity is reduced.
Owner:CSMC TECH FAB1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com