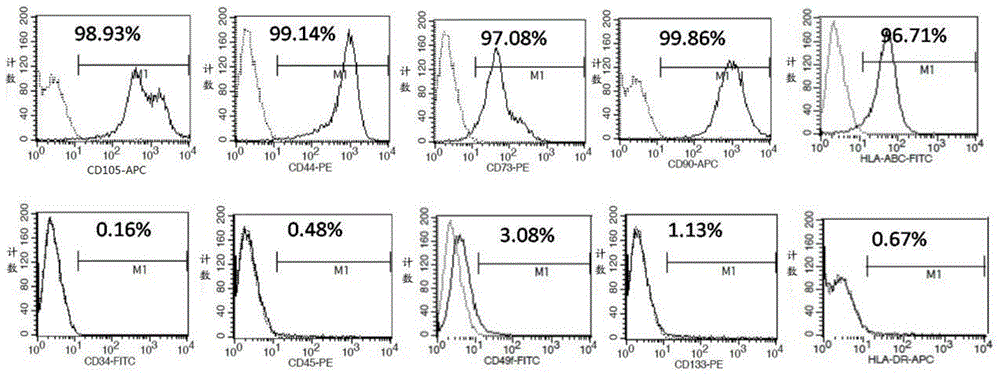
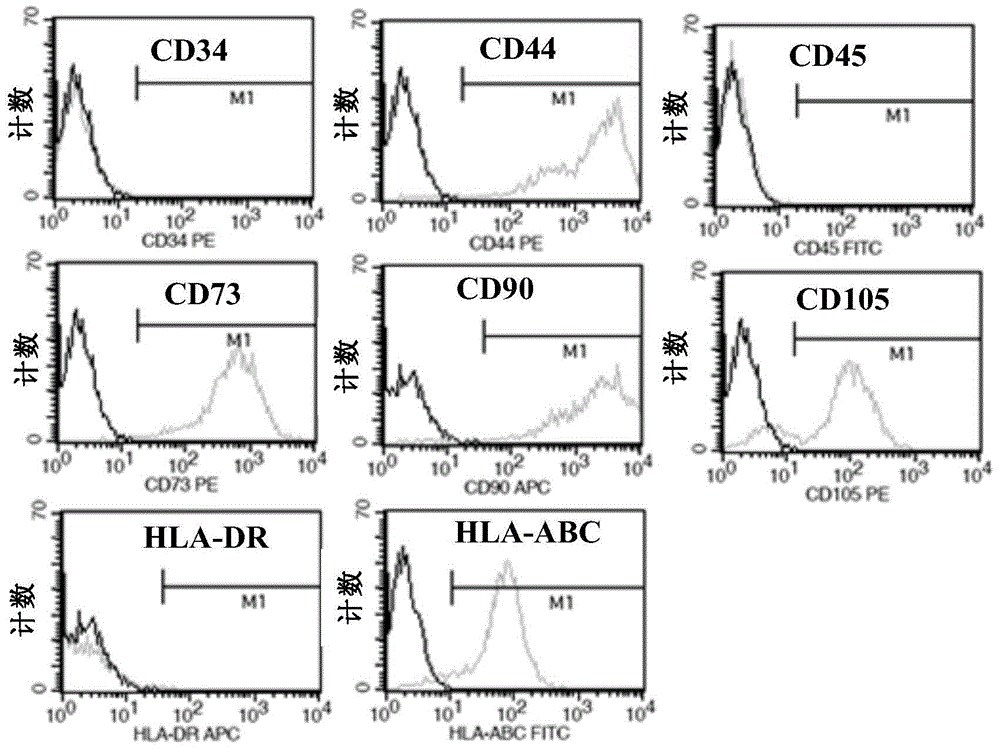
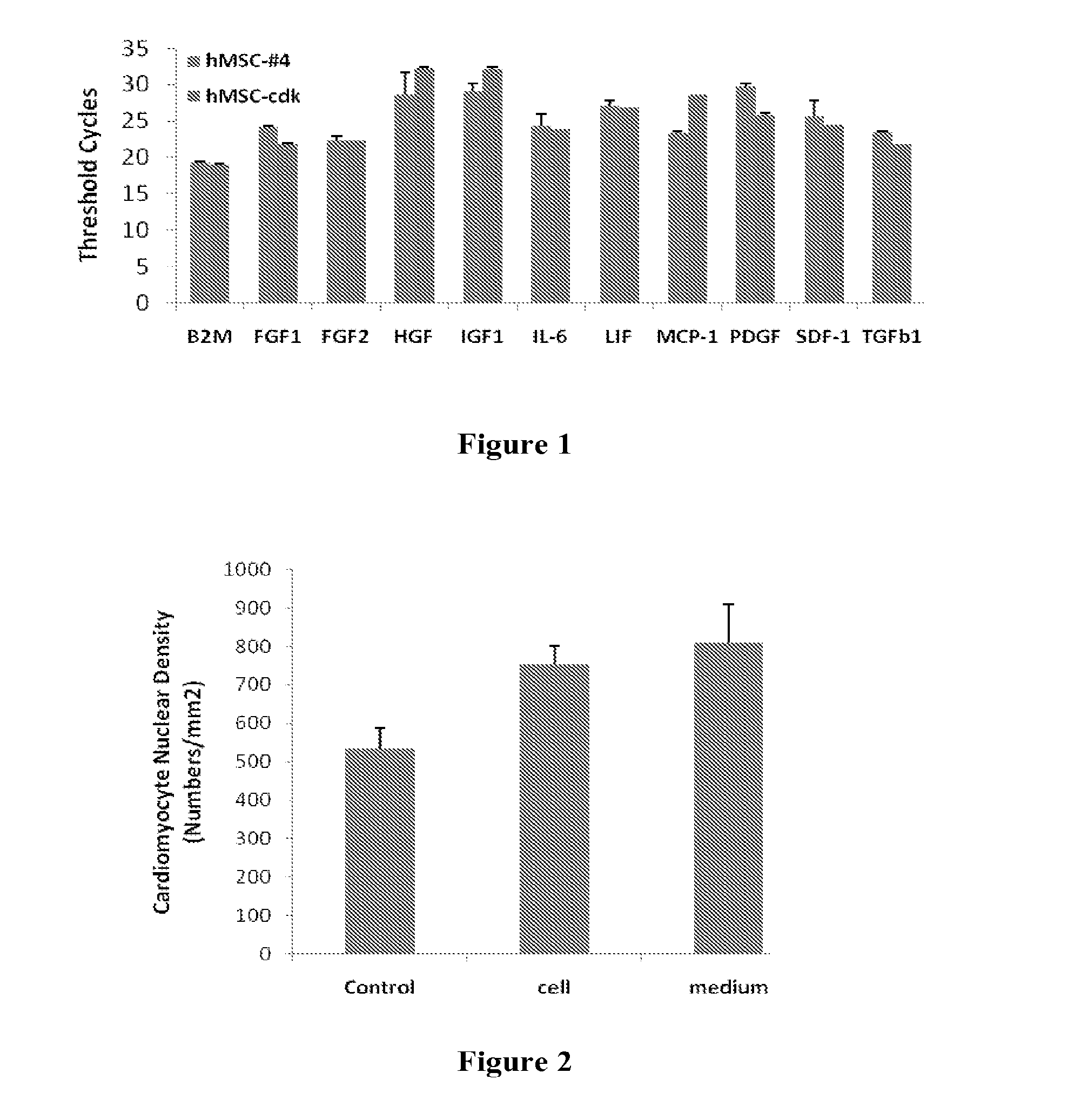
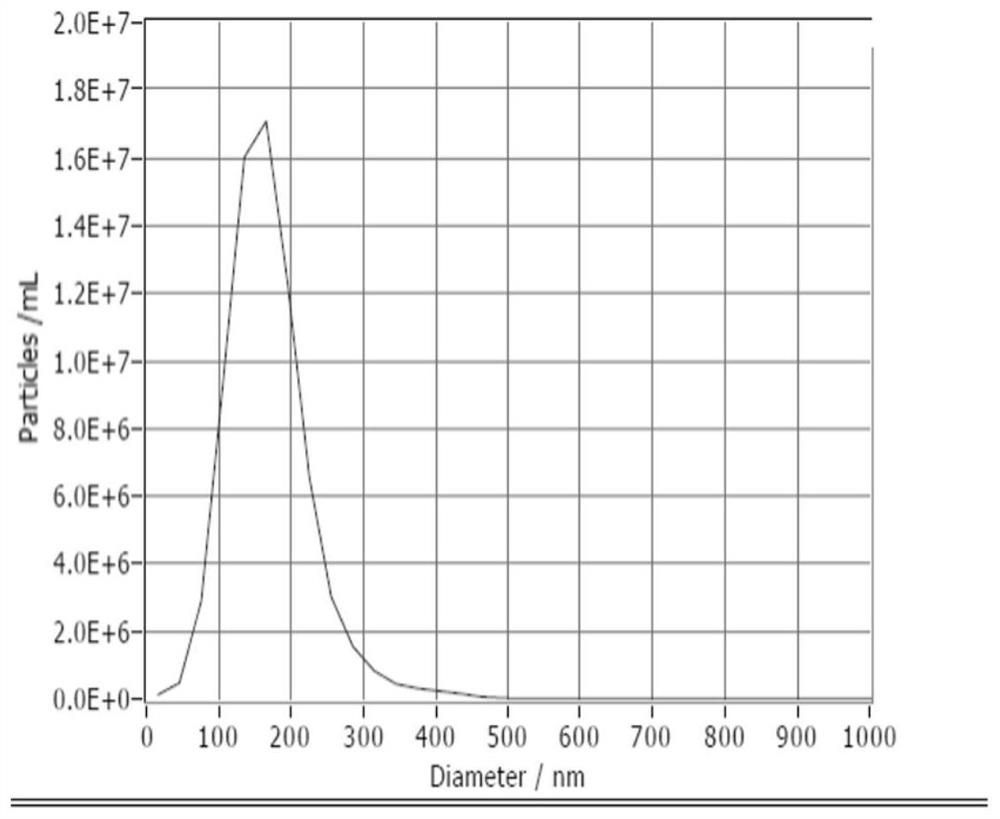
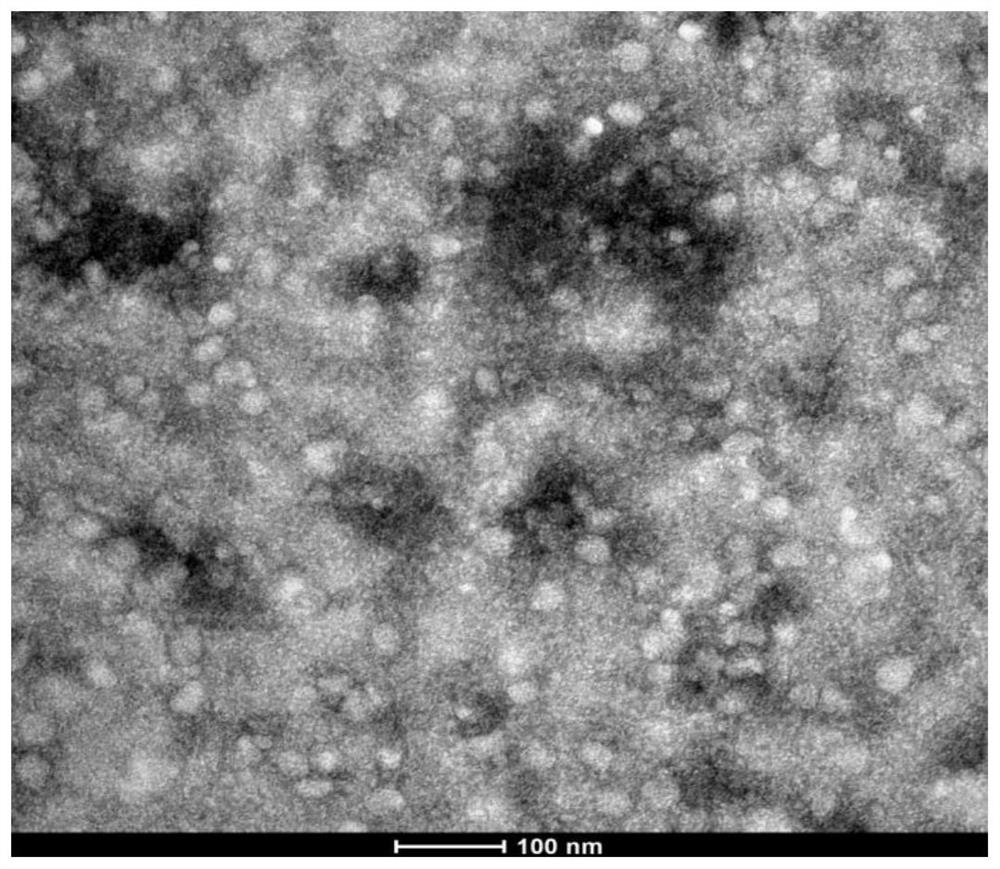
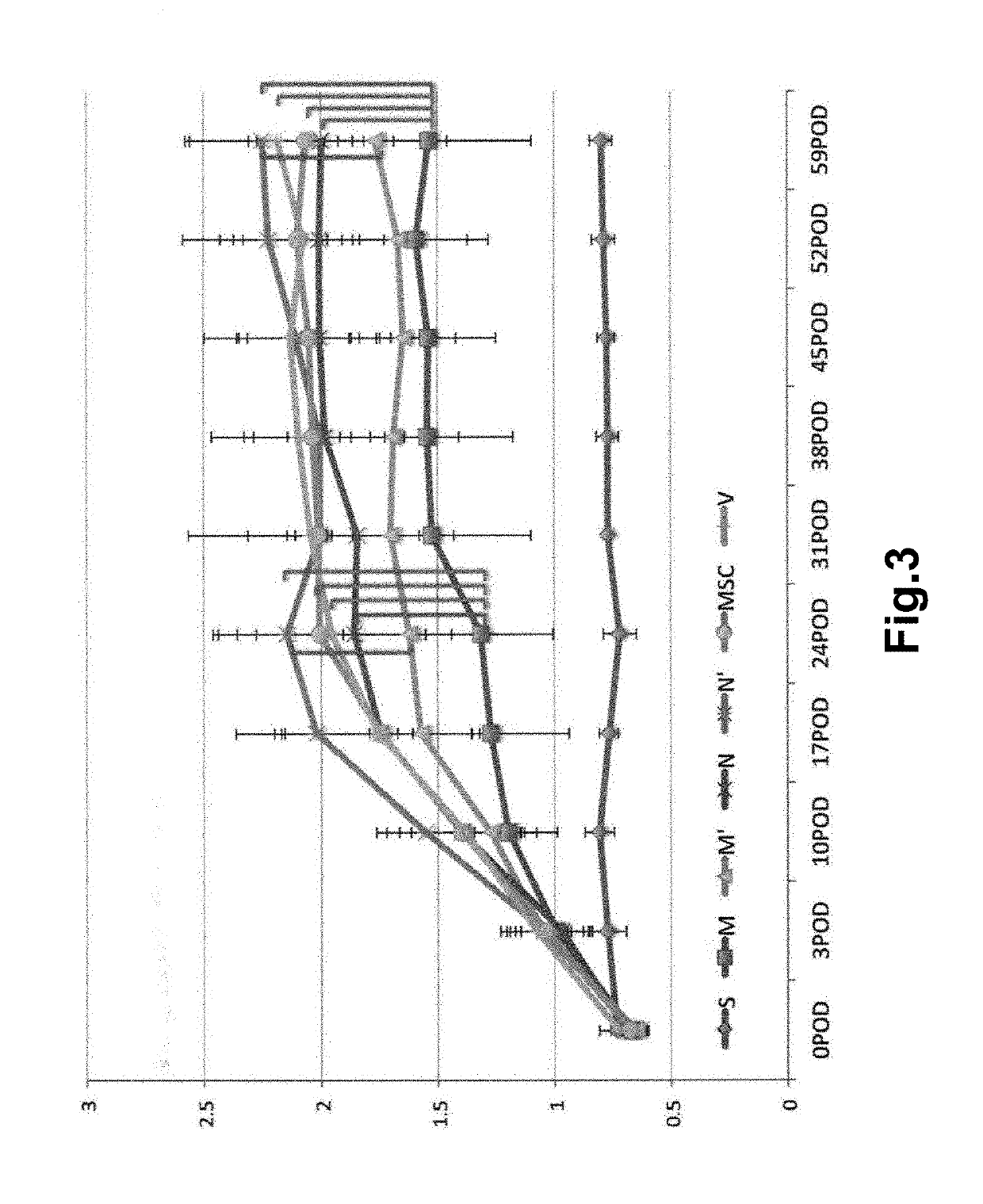
Patents
Literature
35results about How to "Non-tumorigenic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell injection and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104922059ANo immune rejectionNon-tumorigenicPharmaceutical delivery mechanismUnknown materialsHydroxyethyl starchFiltration
The invention relates to umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell injection and a preparation method and application thereof. The injection comprises umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and mixed solution; the mixed solution comprises balanced electrolyte solution, hydroxyethyl starch, adenosine disodium triphosphate-magnesium chloride, dimethyl sulfoxide and human serum albumin. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) fully and evenly mixing the balanced electrolyte solution, the hydroxyethyl starch and the human serum albumin, and performing filtration sterilization; (2) adding the umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; (3) adding the dimethyl sulfoxide; (4) performing split charging and frozen preservation to finish preparation; the invention also provides the application of the injection in the aspect of drugs for treating chronic ischemic heart diseases. The injection disclosed by the invention has a very good resuscitation effect after the frozen preservation, can be directly injected after being unfrozen and resuscitated, and has a remarkable effect on treatment on the chronic ischemic heart diseases.
Owner:北京青藤谷禧干细胞科技研究院有限公司
Stem-Cell Material and Method of Use
InactiveUS20130058903A1Process stabilityEliminating and minimizing riskBiocideGenetically modified cellsTissue repairMesenchymal stem cell
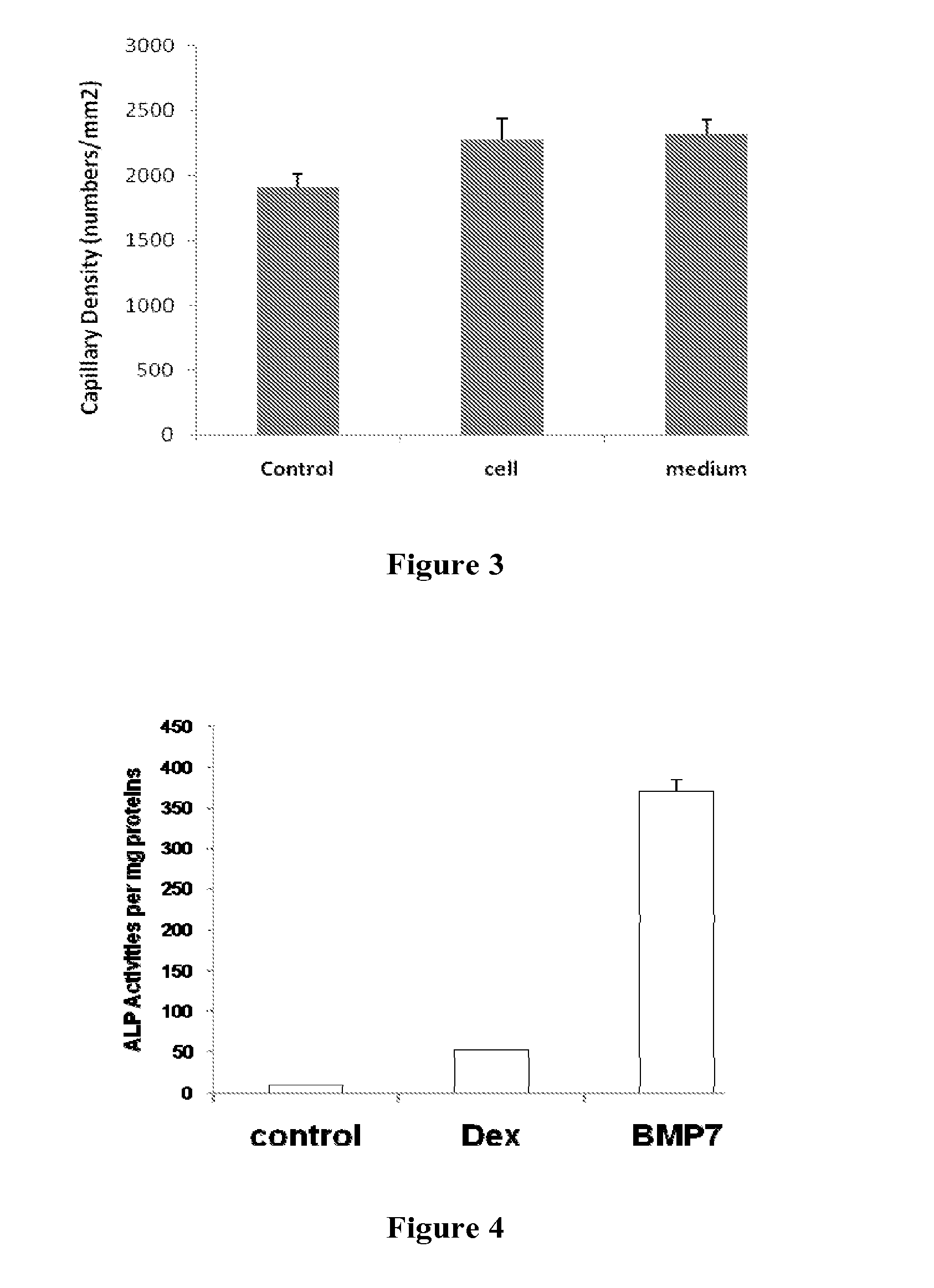
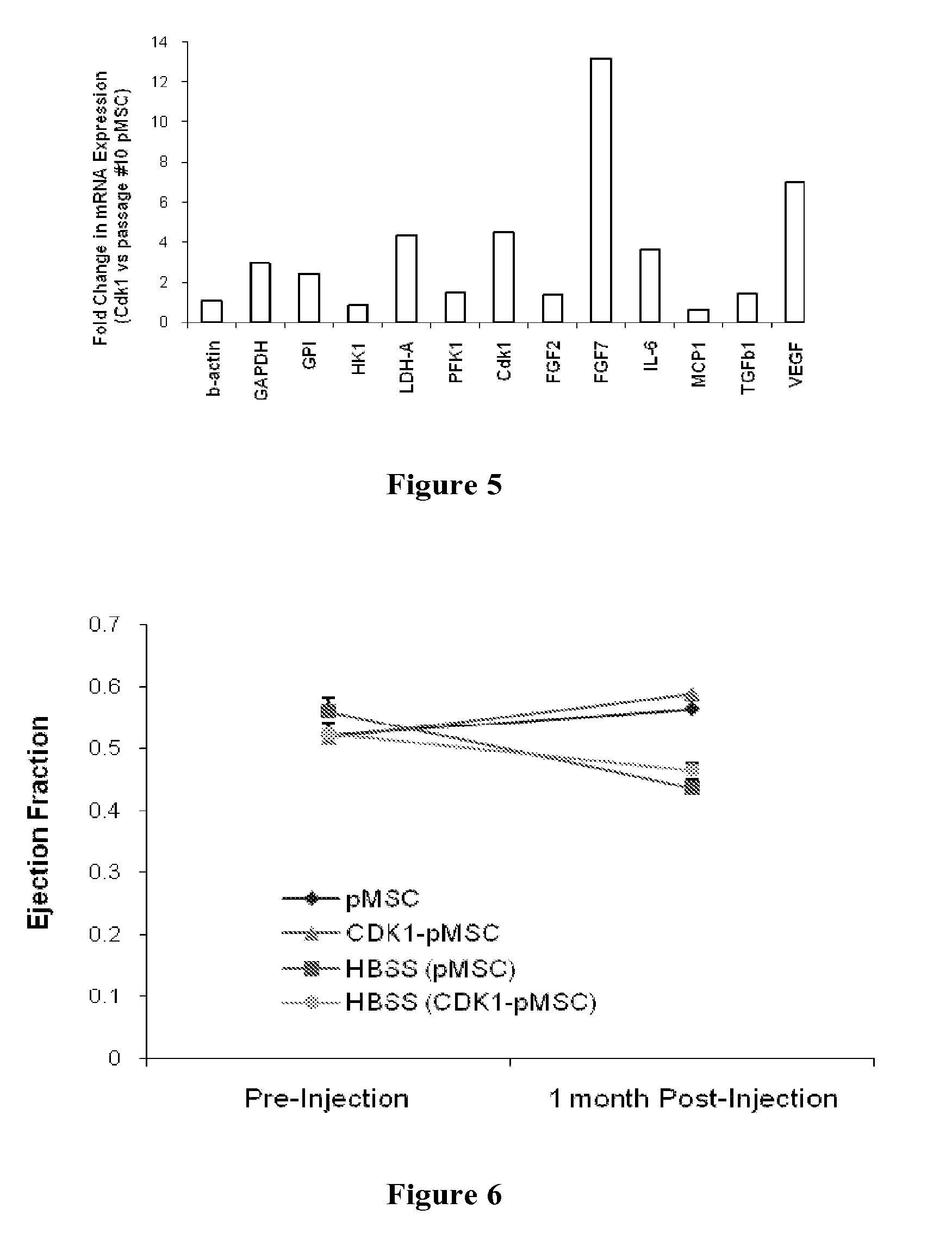
Provided herein are mesenchymal stem cells which have been modified by the introduction of polynucleotides encoding for a mammalian Cdk1 protein. These cells do not sense in culture and are non-tumorigenic thereby providing an ongoing source of cells as well as conditioned medium. The conditioned medium from these cells can be used for tissue repair. Also provided is a method of modifying mesenchymal stem cells which can be continuously propagated in culture and are non-tumorigenic.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method for preparing pseudorabies virus
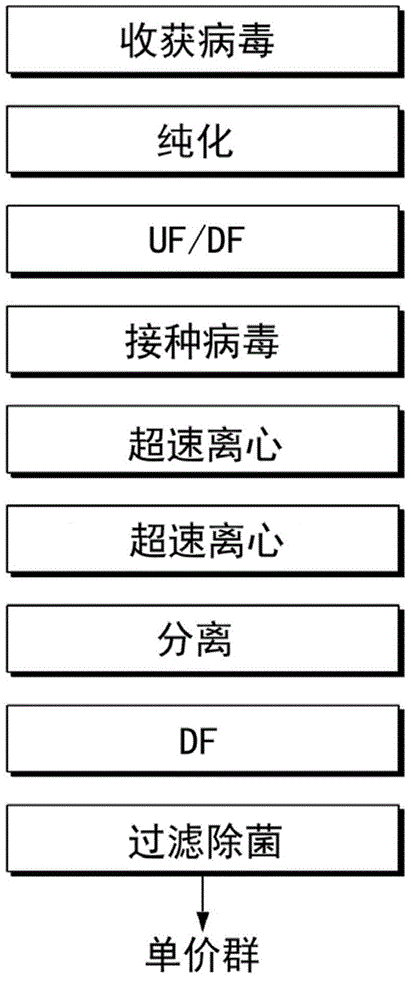
ActiveCN101979518ANo pollution in the processIncrease productionRecovery/purificationGene defectHigh density
The invention relates to a method for producing a gene defect pseudorabies virus by culturing a passage cell in a tidal biological reactor. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) subcultring a recovery cell; (2) performing high-density cell culturing by using a specific biological reactor and a carrier system, attaching the cell on a vector, circulating a culture medium, filling oxygen and adjusting pH value and glucose; (3) performing virus infection by using the biological reactor, replacing the culture medium by using a virus culture medium, and inoculating the virus into the virus culture medium so as to ensure that the virus is fully adsorbed on the cell; (4) culturing and amplifying the virus under a specific condition; and (5) harvesting viruses so as to realize mass production.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
Method for preparing pseudorabies vaccines
InactiveCN101979519ANo pollution in the processIncrease productionAntiviralsRecovery/purificationHigh densityVector system
The invention relates to a method for producing pseudorabies vaccines by culturing passage cells by using a tidal bioreactor, which comprises the following steps of: (1) subculturing recovered cells; (2) performing high-density culture on the cells by using the specific bioreactor and a vector system to attach the cells onto vectors, and performing circulation, oxygenation and pH value and glucose regulation on a culture medium; (3) performing virus infection by using the bioreactor, replacing the culture medium with a virus culture medium, inoculating viruses and completely absorbing the viruses onto the cells; (4) culturing and amplifying the viruses under specific condition; (5) harvesting the viruses; and (6) adding a lyophilization protecting agent, and performing uniform mixing, quantitative subpackaging and lyophilization to obtain the pseudorabies vaccines.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
Method and application of induced neural stem cells
ActiveCN110396499AMaintain propertiesGuaranteed stabilitySsRNA viruses negative-senseNervous disorderNeural stem cellPrecursor cell
The invention discloses a method of induced neural stem cells and a composition. Through the method and the composition, peripheral blood mononuclear cells can be induced to form neural stem cells. The neural stem cells can express neural stem cell related genes, and can disintegrate out nerve cells, astroglia cells and oligodendrocyte. Dopaminergic nerve precursor cells formed through in vitro induction and disintegration of the neural stem cells are transplanted into the striatum corpora of a PD mouse model, no tumors are formed, the ethology of a mouse Parkinson 's disease model can be improved, and the process of the Parkinson 's disease can be delayed. The neural stem cell inducing and disintegrating method provided by the invention is simple and quick to operate, small in traumatic occlusion and good in safety, and is hopefully used for treating the Parkinson 's disease.
Owner:WISEHEART MEDICAL VALLEY CO LTD
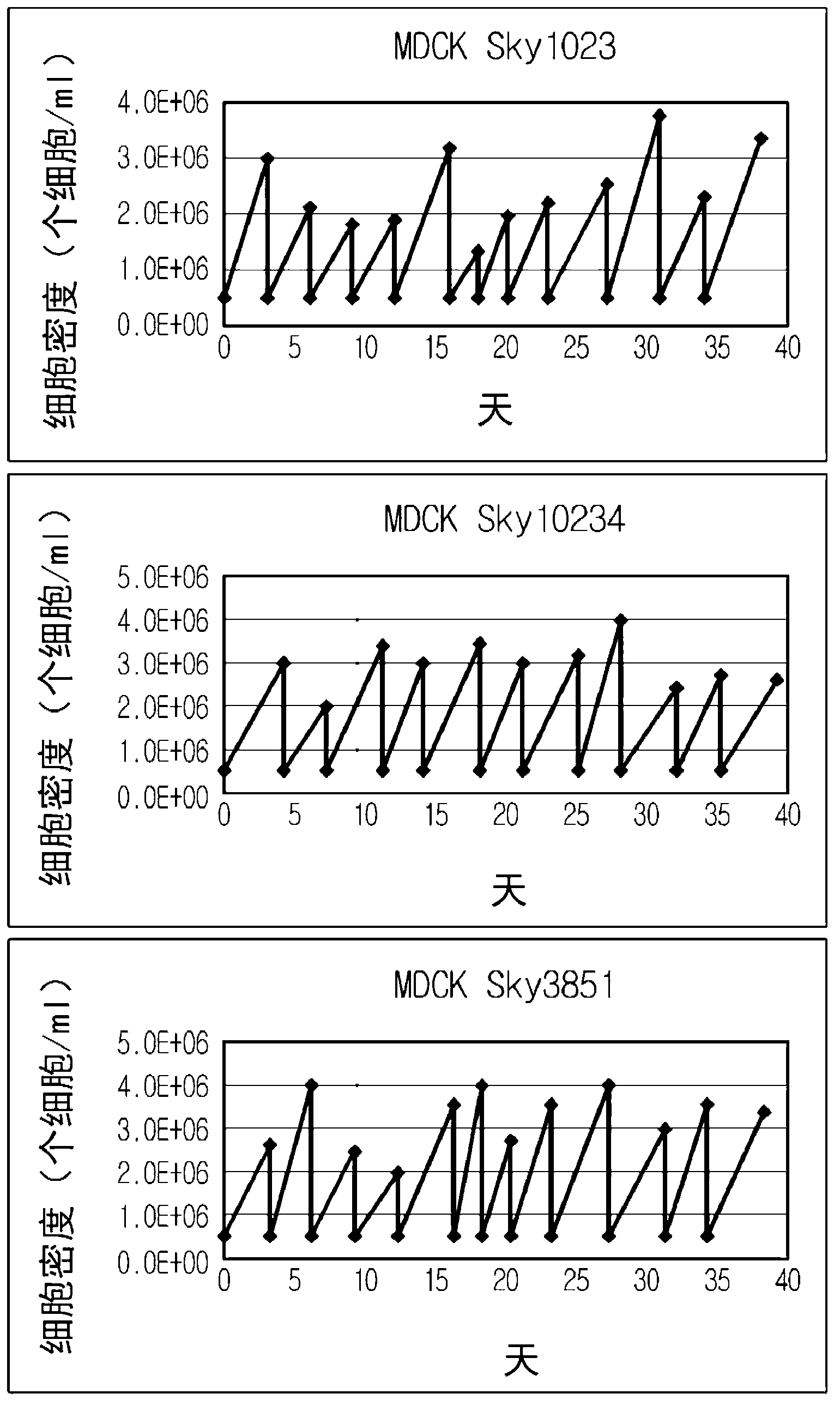
MDCK-derived cell lines adapted to serum-free culture and suspension culture and method for preparing vaccine virus using the cells
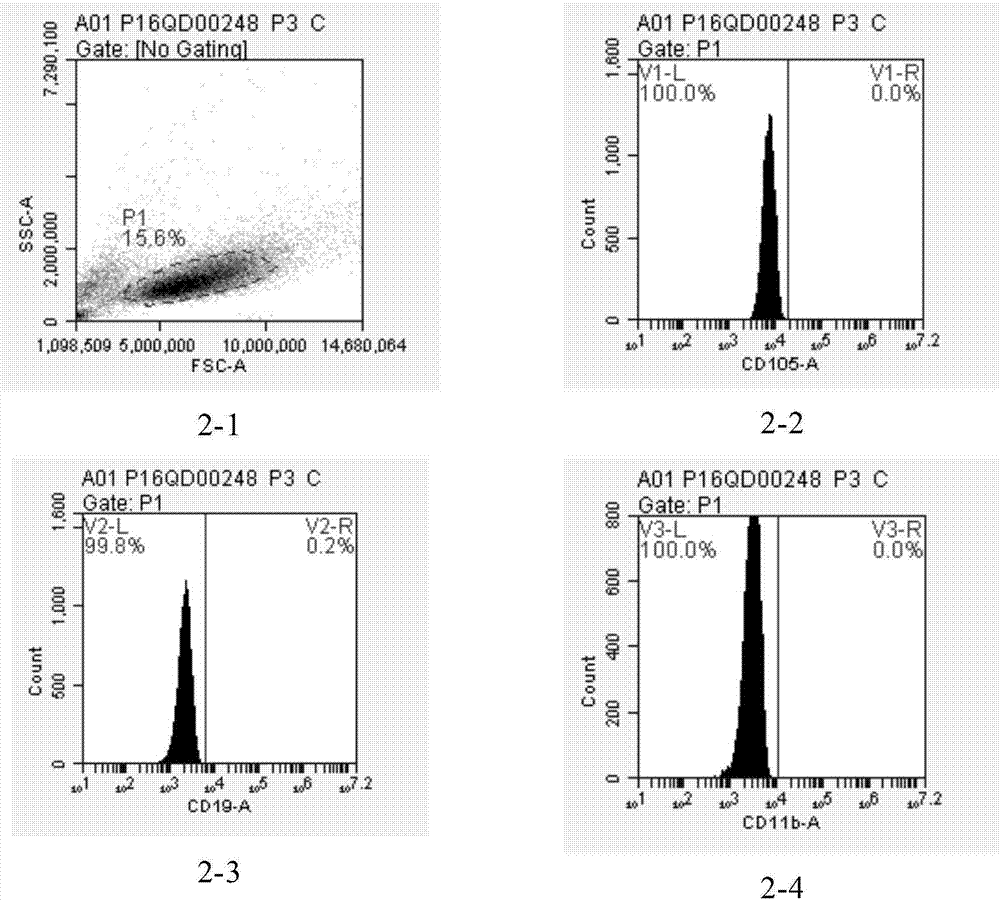
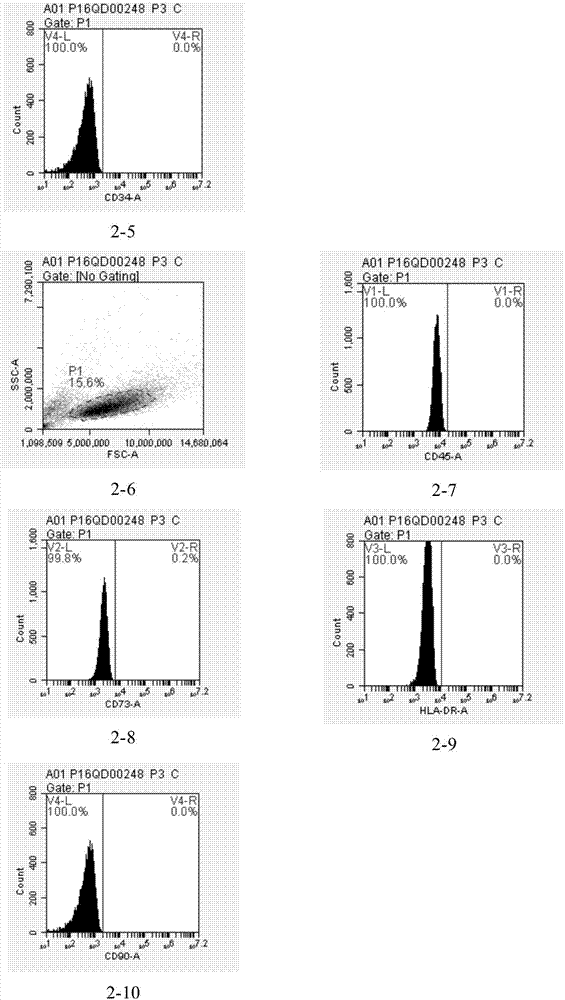
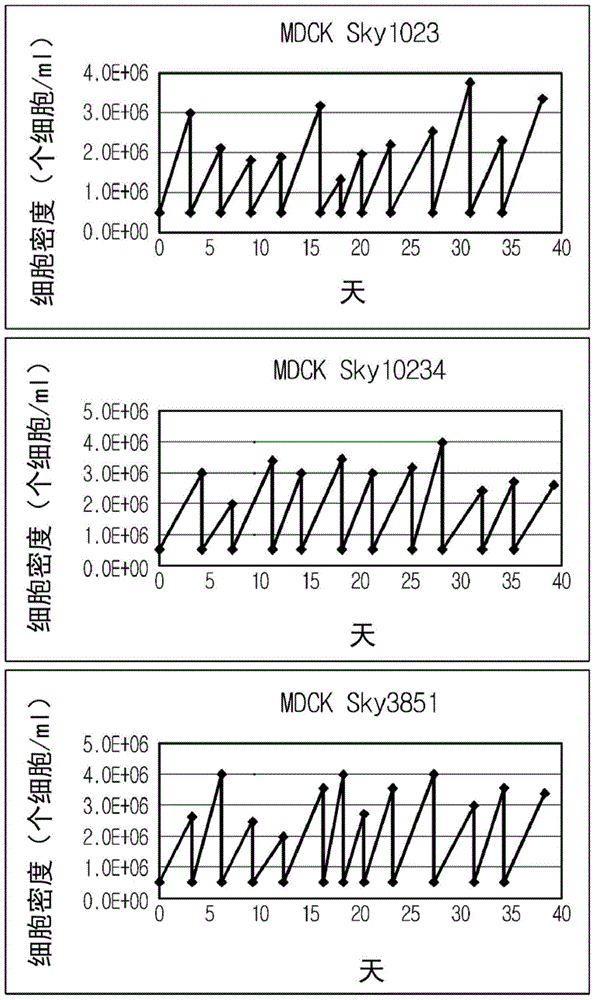
InactiveCN103154238AEffective proliferationNon-tumorigenicSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsCanine kidneySerum free
Disclosed is a Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK)-derived cell line. The MDCK-derived cell line is derived from MDCK cells deposited under accession number ATCC CCL-34. The MDCK-derived cell line can be prepared by serum-free culture and suspension culture. Preferably, the MDCK-derived cell line has low or no tumorigenicity. The MDCK-derived cell line is preferably selected from MDCK Sky1023, MDCK Sky10234 and MDCK Sky3851. Further disclosed are a culture method for growing the MDCK-derived cells and a method for producing a vaccine virus using the MDCK-derived cells.
Owner:SK CHEM CO LTD
Placenta mesenchymal stem cell injection, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106924285ALow immunogenicityNon-tumorigenicDigestive systemPharmaceutical delivery mechanismVitamin CHuman albumin
The invention relates to the technical field of stem cells and especially relates to a placenta mesenchymal stem cell injection, a preparation method and application thereof. The placenta mesenchymal stem cell injection comprises placenta mesenchymal stem cells, vitamin C, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), fetal calf serum (FBS), human albumin, rhizoma panacis majoris saponin and solvent. The placenta mesenchymal stem cell injection prepared according to the invention is characterized in that the materials are conveniently taken and the ethical violation problem is avoided; the injection prepared according to the invention can effectively preserve the activity of stem cells, can be directly used for recovery, need not be cleaned and centrifuged and is conveniently used; after the injection prepared according to the invention is fed back, the differentiation of the mesenchymal stem cells to the hepatic cells and the maturation of the hepatic cells can be boosted and the GVHD occurrence rate can be reduced.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Mdck-derived Cell Lines Adapted To Serum-free Culture And Suspension Culture And Method For Preparing Vaccine Virus Using The Cells
ActiveCN104862267AEffective proliferationNon-tumorigenicSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsCanine kidneySerum free
Disclosed is a Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK)-derived cell line. The MDCK-derived cell line is derived from MDCK cells deposited under accession number ATCC CCL-34. The MDCK-derived cell line can be prepared by serum-free culture and suspension culture. Preferably, the MDCK-derived cell line has low or no tumorigenicity. The MDCK-derived cell line is preferably selected from MDCK Sky1023, MDCK Sky10234 and MDCK Sky3851. Further disclosed are a culture method for growing the MDCK-derived cells and a method for producing a vaccine virus using the MDCK-derived cells.
Owner:SK BIOSCI CO LTD
Full-suspension culture method for avian influenza virus
ActiveCN107904215ANon-tumorigenicEasy to useSsRNA viruses negative-senseRecovery/purificationVirus multiplicationAvian influenza virus
The invention discloses a full-suspension culture method for avian influenza virus. The full-suspension culture method comprises the following steps: step 1, taking EB66 cells for growth culture; step2, when the density of the EB66 cells grows to be suitable for virus inoculation, utilizing a fed-batch fluid-replacement virus inoculation technology to inoculate avian influenza virus into the EB66cells and performing virus multiplication culture; step 3, 24h after virus inoculation, sampling every 12h to determine HV titer of the virus and obtaining and storing the virus when the virus HA titer reaches to the maximum to obtain cultured avian influenza virus. According to the full-suspension culture method disclosed by the invention, the EB66 cells are utilized to perform avian influenza virus culture, so that the defect that a lot of miscellaneous protein is prone to being introduced into when a traditional chick embryo culture technology is utilized for production is overcome, and occurrence of chicken immunity side reaction is effectively reduced; meanwhile, titer and purity of the cultured avian influenza virus are improved; furthermore, production quality of the avian influenza vaccine is improved.
Owner:ZHAOQING INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +2
Expression of recombination SARS virus gene in pleiomorphic Hansen yeast and its use
InactiveCN1475571AAvoid maladaptiveNon-tumorigenicOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAntigen epitopeAntigen
An expression of recombinant SARS virus gene in polymorphic Hanson yeast and its application are disclosed. In the procedure of industrially preparing the expressed product of SARS virus' genes S, S1and S2 and primary antigen epitope gene, the SARS virus' genes S, S1 and S2 and primary antigen epitope gene are redesigned according to the application method of the codon of high-expression gene for Hanson yeast. The high-expression product can be used as vaccine to prevent the atypical pneumatonitis caused by SARS virus. The designed gene can also be used for fusion expression with cholera toxin B subunit gene in Hanson yeast.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
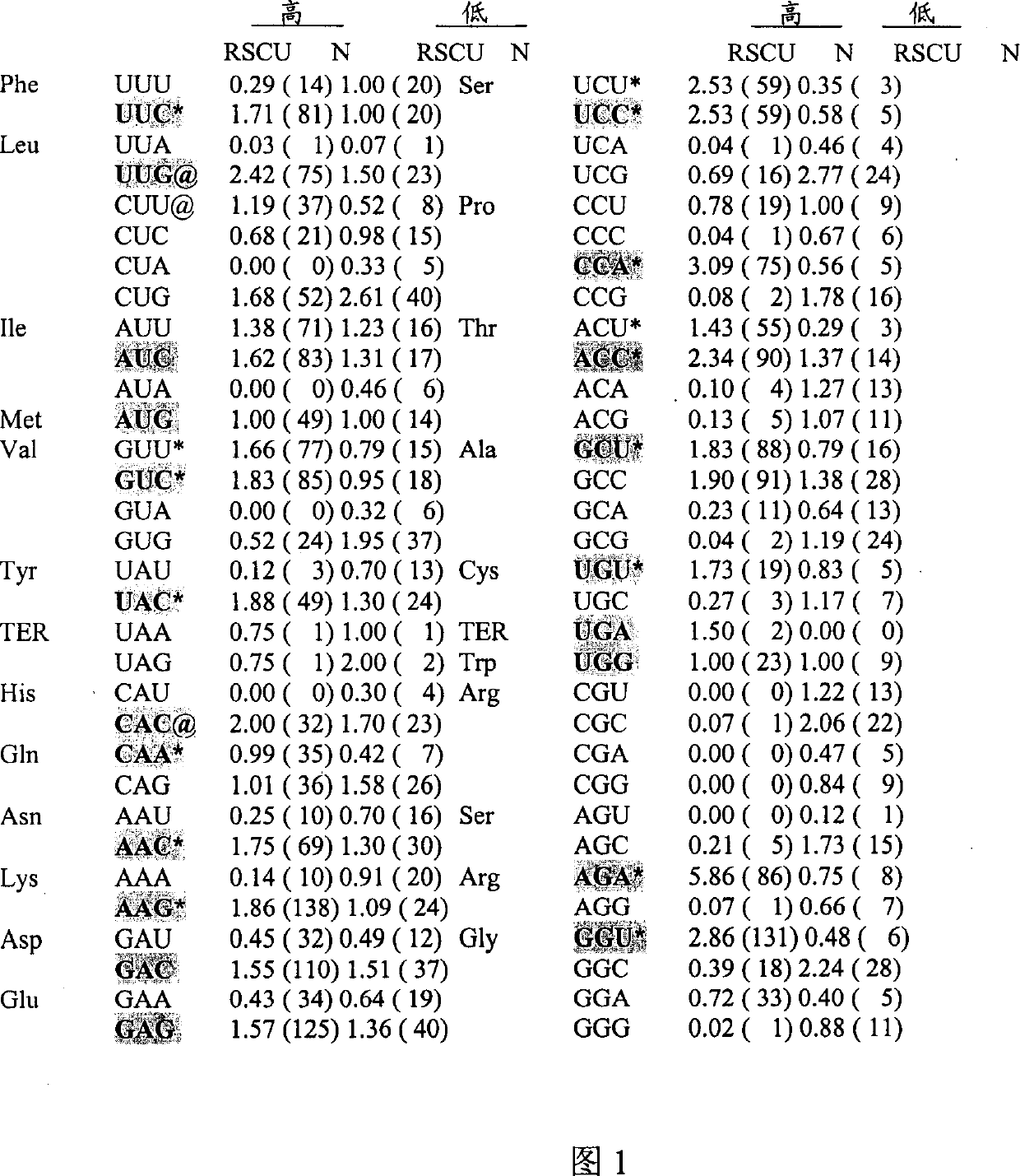
Preparation method of immortalized human intervertebral disc nucleus pulposus cell system
ActiveCN102093980AImprove the level of prevention and controlHave a normal growth rateEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionTelomeraseReverse transcriptase
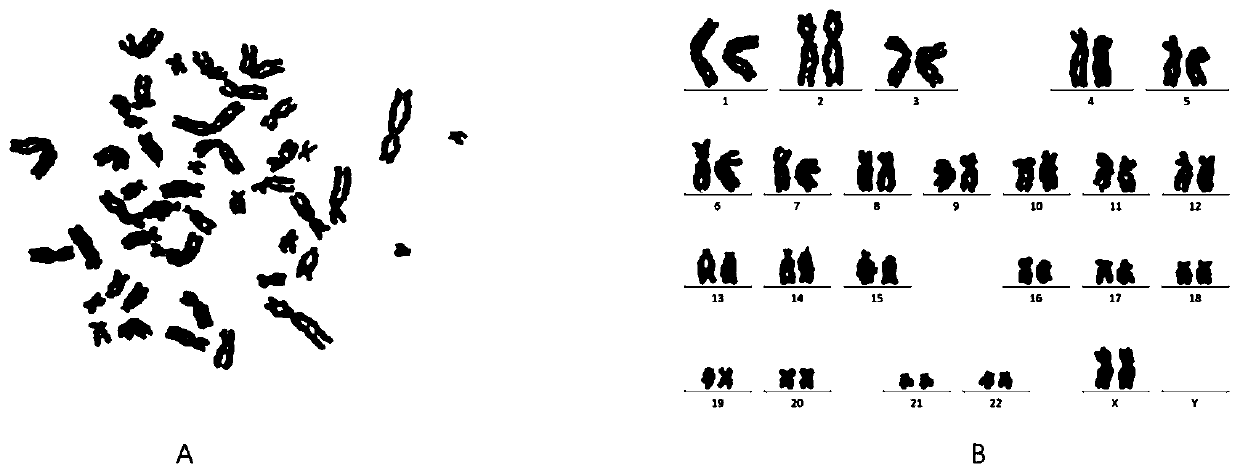
The invention discloses a preparation method of an immortalized human intervertebral disc nucleus pulposus cell system. The preparation method is as follows: extrinsic human telomerase reverse transcriptase is transfected into the human nucleus pulposus cell to activate telomerase and construct immortalized human nucleus pulposus cell line through induction immortalized human nucleus pulposus cell line, normal cells not transformed cells are used, wherein the cells have normal growth rate and karyotype, have contact inhibition, anchorage dependence and other safety properties and do not have carcinogenicity and soft agar cloning capability; and as same as the germline stem cells, the cells have real immortalization, thus the standard cell line can be provided for the further research of the pathogenic mechanism of the degenerative disc disease and a new idea is provided to increase the entire control level of the degenerative disc disease.
Owner:梁伟国
Medicament for treating osteonecrosis
ActiveCN101327223AAvoid and address deficienciesAvoid neoplasiaSkeletal disorderMammal material medical ingredientsHuman bodyOsteoblast
The invention relates to a medicine for curing osteonecrosis, belonging to the field of regenerative medicine engineering. Human amniotic mesenchymal cells (hAMCs) are used as cell source for cellular transplantation and tissue organization so as to cure the osteonecrosis and to provide a new way for repairing a damaged osseous tissue and reorganizing tissues. Based on the multi-lineage differentiation potential of the hAMCs, osteocytes, osseous tissues and vascular endotheliums can be differentiated in the human body, thereby completing the processes of osteanagenesis, bone remodeling and vascularization and forming a new osseous tissue integrated with the tissues of the patient.
Owner:北京科润维德生物技术有限责任公司
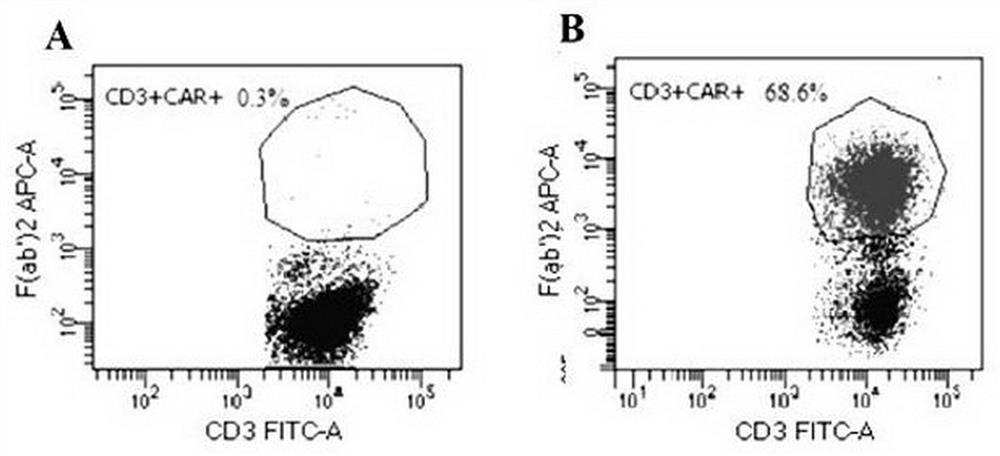
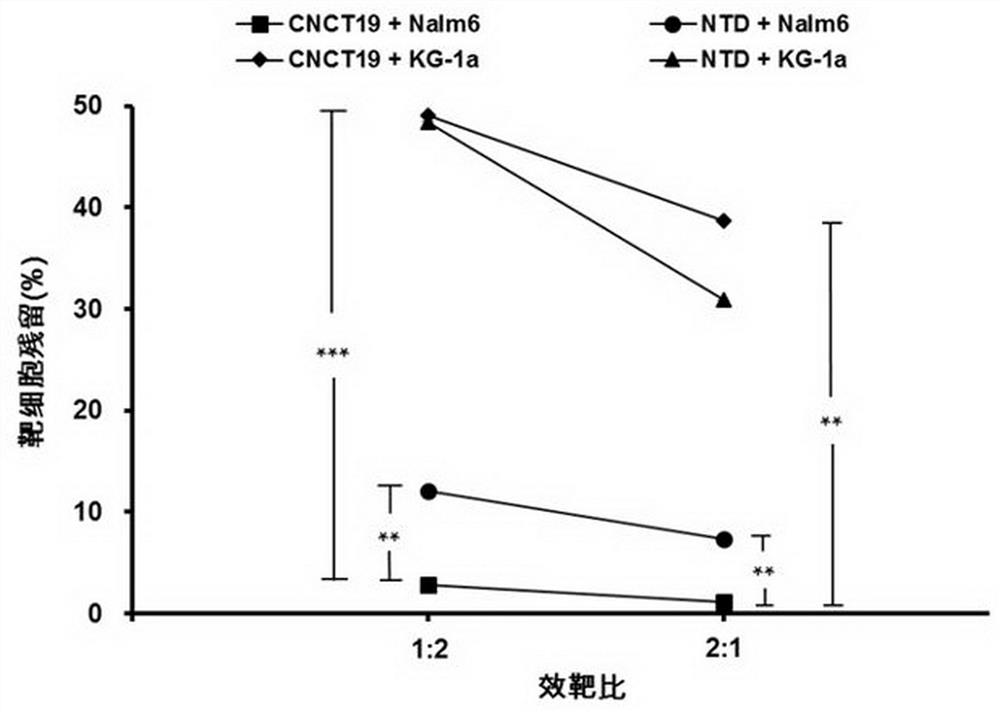
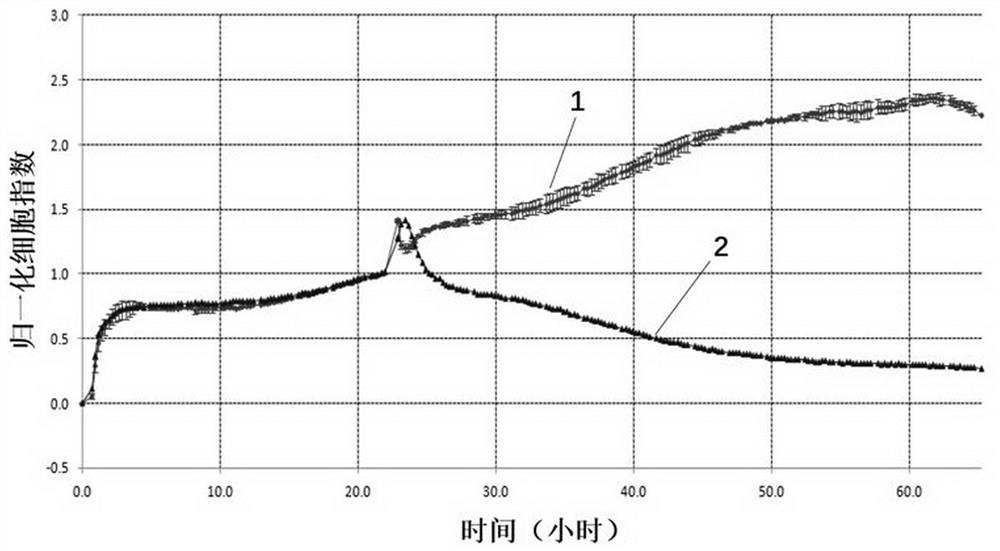
CD19 targeting chimeric antigen receptor and application thereof
ActiveCN112079934APromote secretionProlong survival timeNGF-receptor/TNF-receptor superfamilyImmunoglobulinsAntigen receptorImmune effector cell
The invention provides a chimeric antigen receptor. The chimeric antigen receptor comprises an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The application also provides nucleic acids encoding the chimeric antigen receptor, vectors comprising the nucleic acids, immune effector cells comprising the chimeric antigen receptor, the nucleic acid molecules and / or the vectors, methods of preparing the immune effector cells, compositions comprising the immune effector cells, and uses of the chimeric antigen receptor.
Owner:JUVENTAS CELL THERAPY LTD
Human normal renal tubule primary cell and in-vitro isolated culture and application thereof
ActiveCN110241071AStable traitsVigorous proliferationCell dissociation methodsMicrobiological testing/measurementCell separationRenal tubule
The invention discloses a human normal renal tubule primary cell and in-vitro isolated culture and application thereof. The cell is named human normal renal tubule primary cell XHRN-01, and the preservation number of the cell is CCTCC NO:C201970. An isolated culture method of the primary cell comprises the steps that the clinical postoperative excised tissue near the kidney cancer is acquired in vitro, no cancer cell infection is identified through the pathology, the blood vessels and adipose tissue in the tissue are removed, a tissue sample is subjected to collagenase / trypsin digestion, filtration and low-speed centrifugation to obtain cell pellets, after a red blood cell lysis buffer lyses red blood cells, a COMR complete medium is used for resuspending the cells, and a cell line is constructed through continuous cell culture. The cell can be applied in the physiological study on human normal cells, study on drug toxicity of in-vitro normal cells, study on the pathogenesis of the kidney cancer and related diseases including the renal cancer, chronic nephritis and infectious diseases and study on screening of therapeutic drugs.
Owner:武汉赛尔朗灵科技有限公司
Recombinant Marek's disease virus strain SCA13 strain and application thereof
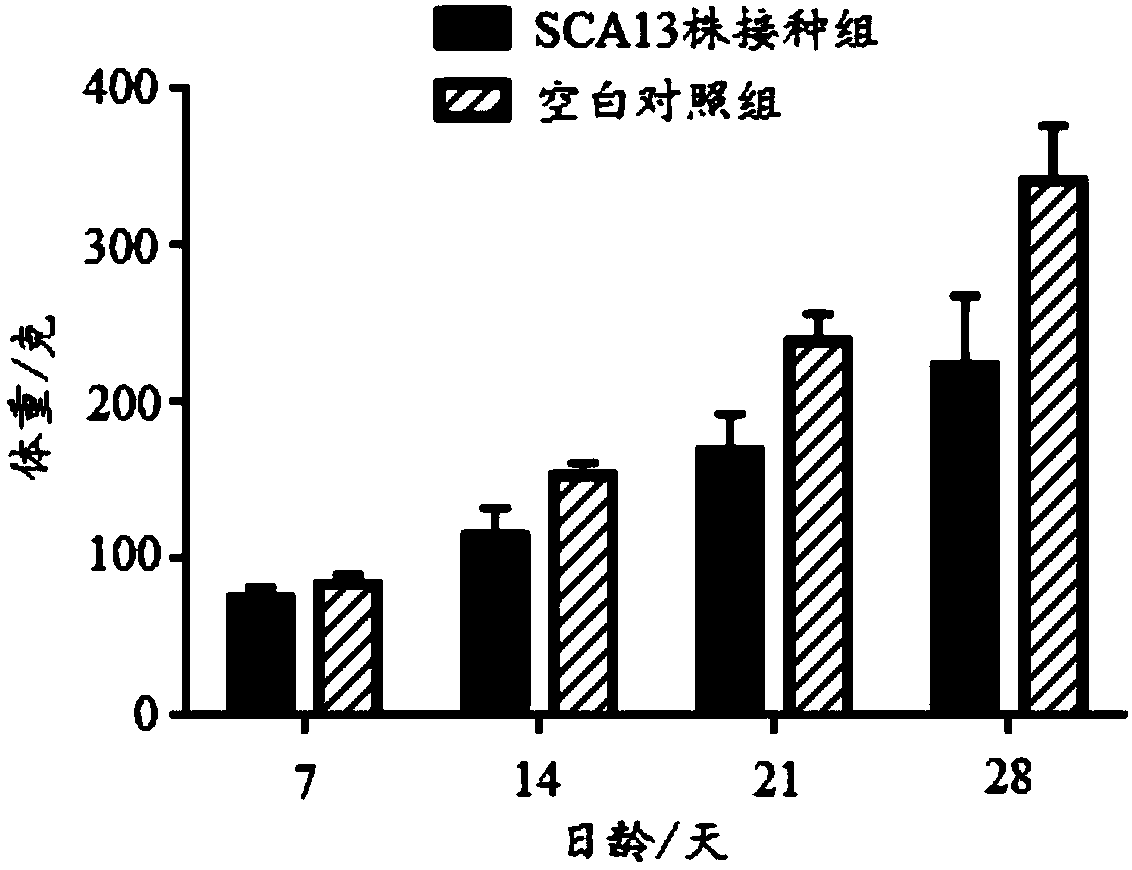
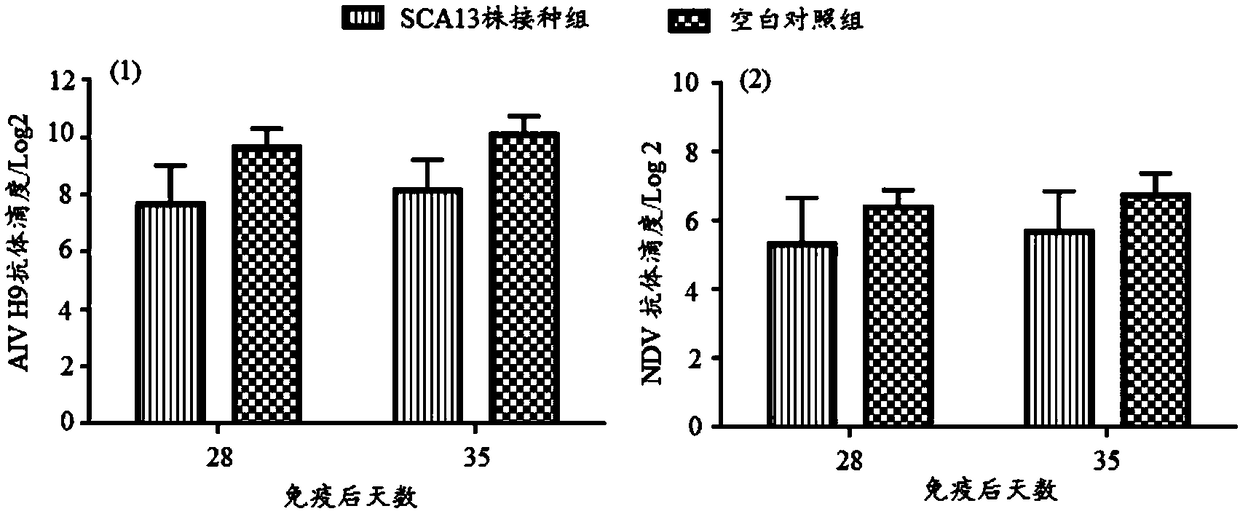
ActiveCN108342367ANon-tumorigenicGood immune protectionViral antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementBac cloneHorizontal transmission
The invention discloses a recombinant Marek's disease virus strain SCA13 strain. The biological preservation number of the strain is CGMCC NO.15285, and an SCA13 strain genome is integrated with ALV LTR and can exist stably. On the basis of BAC clone, and by means of the phenomenon that a Red E / T recombinant technology lacks meq and vTR genes, a deletion strain of the meq and vTR genes of the MDVSCA13 strain is built, the biological preservation number of the strain is CGMCC NO.15286, a double gene deletion strain built on the basis of the SCA13 strain completely loses lethality and tumorigenicity to chickens, the immunosuppressive property is lost, the strain has better biosecurity and better horizontal transmission capacity, the problem that in the MD vaccine immunity process, due to immunity leakage of the chickens, diseases occur can be solved, and the chickens are subjected to better immunoprotection in clinic.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Construction of down's syndrome cell model and cell bank of down's syndrome cell by employing hTERT gene recombination
InactiveCN104419676AReduce injuriesIncrease success rateMicroorganism librariesVector-based foreign material introductionEnzyme digestionAmpicillin
The invention relates to construction of a down's syndrome cell model and a cell bank of a down's syndrome cell by employing hTERT gene recombination applied to the field of medicines. The construction is mainly characterized by comprising the following processes: performing double-enzyme digestion on a plasmid pCIneo-hTERT and a carrier pLXSNneo by incision enzyme EcoR I and Xho I, and connecting hTERT and pLXSNneo enzyme-digested products which are processed by PCR amplification and gel electrophoresis separation with Ligation Mix; constructing a pLXSNneo-hTERT recombinant, and converting a DH5a competent cell for purifying amplifying and choosing ampicillin-resistant colonies to extract plasmids; transfecting down's syndrome cells which are subjected to in vitro passage by lipidosome and are in logarithmic growth; integrating the recombinants with the cell DNA, carrying out enlarging circulation, and screening cells containing positive recombinants by G418; and screening the cell of which cell morphology, growth curve, chromosome karyotype, nude mouse carcinogenicity test, transfected cell telomerase activity, hTERT mRNA expression, immumohistochemistry, cell generation cycle and cell apoptosis rate accord with the cell characteristics of an immortalized cell and are the same as or similar to those of a primary cell as an hTERT-mediated down's syndrome in-vitro study cell model and cryopreserved in liquid nitrogen, thus a foundation is laid for in vitro long-term research of pathogenesis from the cellular level.
Owner:翁炳焕
Immortalized human neural stem cell line and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108866005AStable and safe and effective immortalization coding strategyNormal formCulture processNervous system cellsL-myc GenesPrimary cell
The invention discloses an immortalized human neural stem cell line and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) isolating and culturing primary human hippocampus-derived neural stem cells; (2) constructing a recombinant lentiviral vector containing L-myc gene; (3) carrying out packaging production of the above recombinant lentiviral and collecting supernatant; (4) selecting virus supernatant with appropriate concentration for transfection and screening of stem cells and constructing the immortalized human neural stem cell line. The preparation method of immortalized cell line provided by the invention is a novel stable and safe and effective immortalized coding strategy; the prepared immortalized human neural stem cell line has all the biological characteristics of primary neural stem cells, and also has the feature of normal three-line differentiation at the same time, can be successfully differentiated into neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes,and the growth rate of such cell line and ability to form neurospheres are stronger than the growth rate of primary cells, and the cell line can still proliferate rapidly after 20 generations withouttumorigenicity.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Application of adipose-derived stem cell exosome in hair growth
PendingCN114410576AEase of mass productionIncrease the number ofCell dissociation methodsUnknown materialsUltrafiltrationIn vivo experiment
A preparation method of the adipose-derived stem cell exosome comprises the following steps: culturing 3rd to 6th generations of mouse adipose-derived stem cells in logarithmic growth by using a complete culture solution containing FBS until the cell density reaches 70 to 80 percent, and continuously culturing for 45 to 50 hours by using a DMEM culture solution containing exosome-free FBS, so as to obtain the adipose-derived stem cell exosome. And collecting a supernatant culture solution, centrifuging to remove cells and cell debris, centrifuging at 1500-2500g by using an ultrafiltration tube with the molecular weight of 100kDa for 30 minutes, concentrating, adding an exosome rapid extraction reagent into a concentrated solution, extracting, centrifuging, and collecting the mouse adipose-derived stem cell exosome. In-vitro and in-vivo experiments show that the mouse adipose-derived stem cell exosome can significantly promote hair growth and has an outstanding effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGJI HOSPITAL
Immortalized human neural stem cell line and preparation method thereof, and recombinant virus vector and application thereof
ActiveCN110229790ARapid ProliferationReduced stabilityCulture processNervous system cellsVirus typePrimary cell
The invention discloses an immortalized human neural stem cell line and a preparation method thereof, and a recombinant virus vector and an application thereof. The preparation method includes the following steps: (1) constructing the recombinant lentiviral vector pLenti-EF1a-EGFP-P2A-Puro-CMV-MYCL-3Flag of an L-myc gene; (2) packaging and producing lentivirus, and collecting supernatant; and (3)adopting the lentivirus supernatant to perform transfection, screening and construction of the immortalized human neural stem cell line on human neural stem cells. The preparation method is a novel, stable, safe and effective immortalization coding strategy; the prepared immortalized human neural stem cell line has all the biological characteristics of primary neural stem cells and also has normalcharacteristics of three-line differentiation, so that the cell line can successfully differentiate neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes; and the growth speed and the ability to become neurospheres of the cell line are stronger than primary cells, so that the cell line can still be rapidly propagated after the successful passing of 25 generations and has no tumorigenicity.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for preparing rabies vaccine for veterinary use
InactiveCN108144053AIncrease productionIncrease production capacitySsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsRabiesAdjuvant
The invention discloses a method for preparing rabies vaccine for veterinary use. According to the method, the rabies vaccine for veterinary use is cultivated and produced by a cell bioreactor total-suspension non-serum method. In particular, the method comprises the following steps: performing virus infection on a BHK-21 cell with certain density and adapted to a strain by utilizing a rabies strain PV / BHK-21 and performing virus harvesting for many times, wherein the BHK-21 cell is obtained by performing total-suspension, non-serum and continuous perfusion cultivation by the cell bioreactor;and performing filtering system treatment and deactivation on the harvested virus stock solution, adding an adjuvant to prepare the rabies inactivated vaccine with high immunity and high safety. Through total-suspension and continuous perfusion culture by the cell bioreactor, high-density cell culture can be realized and viruses can be harvested continuously; and through non-serum culture, serum source pollution can be avoided, the purification process can be simplified and allergic reaction of the organism caused by the serum can be reduced. By the method provided by the invention, mass production and popularization can be realized.
Owner:北京生科基因科技有限公司 +2
Construction of trisomy 18 syndrome cell model and cell bank thereof by hTERT transgenosis
InactiveCN104419677AReduce injuriesIncrease success rateMicroorganism librariesVector-based foreign material introductionAmpicillinEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to construction of an hTERT mediated trisomy 18 syndrome cell model and a cell bank thereof in the medical field. The construction is mainly characterized in that incision enzymes EcoR I and Xho I are used for carrying out double enzyme digestion on plasmid pCIneo-hTERT and carrier pLXSNneo, and Ligation Mix is used for connecting hTERT and pLXSNneo enzyme-digested products subjected to PCR amplification and gel electrophoresis separation to construct a pLXSNneo-hTERT recon; DH5a competent cells are transformed to purify, amplify and pick ampicillin-resistant bacterial colony extraction plasmids; trisomy 18 syndrome cells in logarithmic growth during in-vitro passage are subjected to lipofection transfection; the recons are integrated with cell DNAs and are subjected to amplification culture; positive recon colons are subjected to G418 screening; cells, which meet the immortalized cell characters in the aspects of cellular morphology, growth curve, karyotype, nude mice tumorigenesis test, transfected cell telomerase activity, hTERT mRNA expression, immunohistochemistry, and cell generation cycle and apoptosis rate and are as same as or similar to primary cells, are screened to be as the hTERT mediated trisomy 18 syndrome external research cell models to be frozen in liquid nitrogen. Therefore, the foundation of in vitro long-term research of pathogenesis of trisomy 18 syndrome based on the cellular level is established.
Owner:翁炳焕
Recombinant turkey herpesvirus expressing HA gene and application thereof
PendingCN110205308ABroad immunogenicityRecombination is fast and accurateSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsFowlNucleotide
The invention provides a recombinant turkey herpesvirus expressing HA gene and an application thereof. Based on a viral vector HVT- BAC as a platform, combined with a RED / ET recombination technology and a ccdB reverse screening technology, and the recombinant turkey herpesvirus expressing HA gene is prepared by a two-step recombination method, wherein, a nucleotide sequence of the HA gene is shownas SEQ ID No. 1. The beneficial effect is that the HA gene used in the present invention is derived from a H9N2 toxic strain widely prevalent in recent years in China, and has broad immunogenicity tobirds. A preparation method of the invention realizes rapid and accurate recombination of the exogenous gene, and a used screening marker is beneficial to reduce a screening step, and the obtained recombinant virus strain can be stably passaged. A vaccine prepared by the recombinant virus strain can stimulate the latent infection of the chicken body, causes lifelong immunity, provides technical support for effectively preventing and controlling H9N2 avian influenza and Marek's disease, and has important production guiding significance.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
A method for inducing neural stem cells and its application
ActiveCN110396499BMaintain propertiesGuaranteed stabilitySsRNA viruses negative-senseNervous disorderPeripheral blood mononuclear cellAstrocyte
Owner:WISEHEART MEDICAL VALLEY CO LTD
A kind of human normal renal tubule primary cell and its in vitro isolation culture and application
ActiveCN110241071BStable traitsVigorous proliferationCell dissociation methodsMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellRed blood cell
The invention discloses a primary human normal renal tubule cell and its in vitro isolation, culture and application. The cell is named primary human normal renal tubular cell XHRN‑01, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: C201970. The primary cell isolation and culture method is as follows: Obtain in vitro the tissue adjacent to the renal cancer after clinical surgery, no cancer cell invasion is detected by pathology, blood vessels and adipose tissue in the tissue are removed, the tissue sample is digested with collagenase / trypsin, filtered, The cell pellet was obtained by low-speed centrifugation. After the erythrocytes were lysed by the erythrocyte lysate, the cells were resuspended with COMR complete medium, and the cell line was constructed by subculture. The cells of the present invention can be used in the physiological research of normal human cells, the drug toxicity research of normal cells in vitro, the pathogenesis of kidney and related diseases including renal cancer, chronic nephritis and infectious diseases, and the application of drug screening research.
Owner:武汉赛尔朗灵科技有限公司
Prophylactic or therapeutic agent for vascular disorder
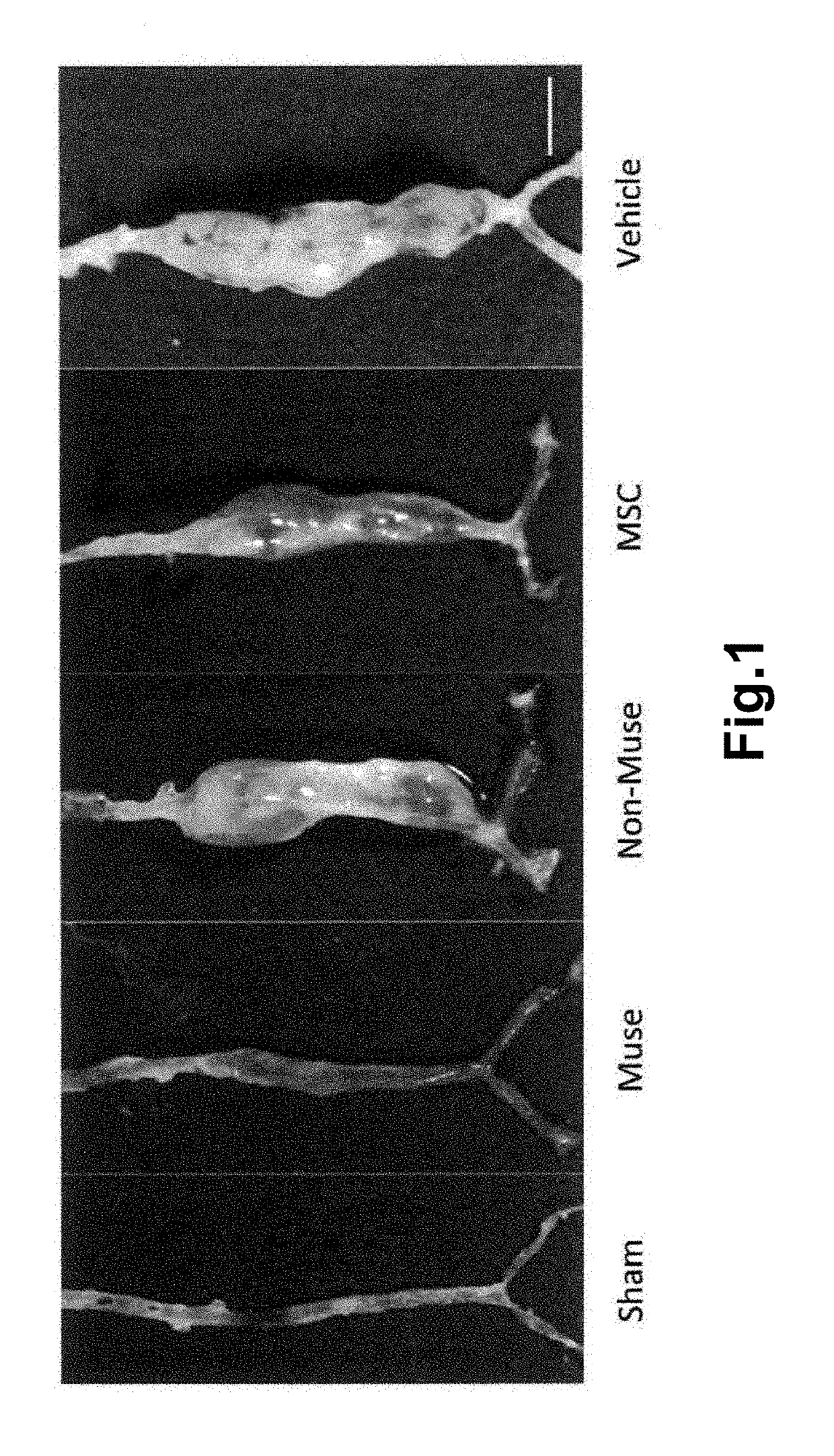
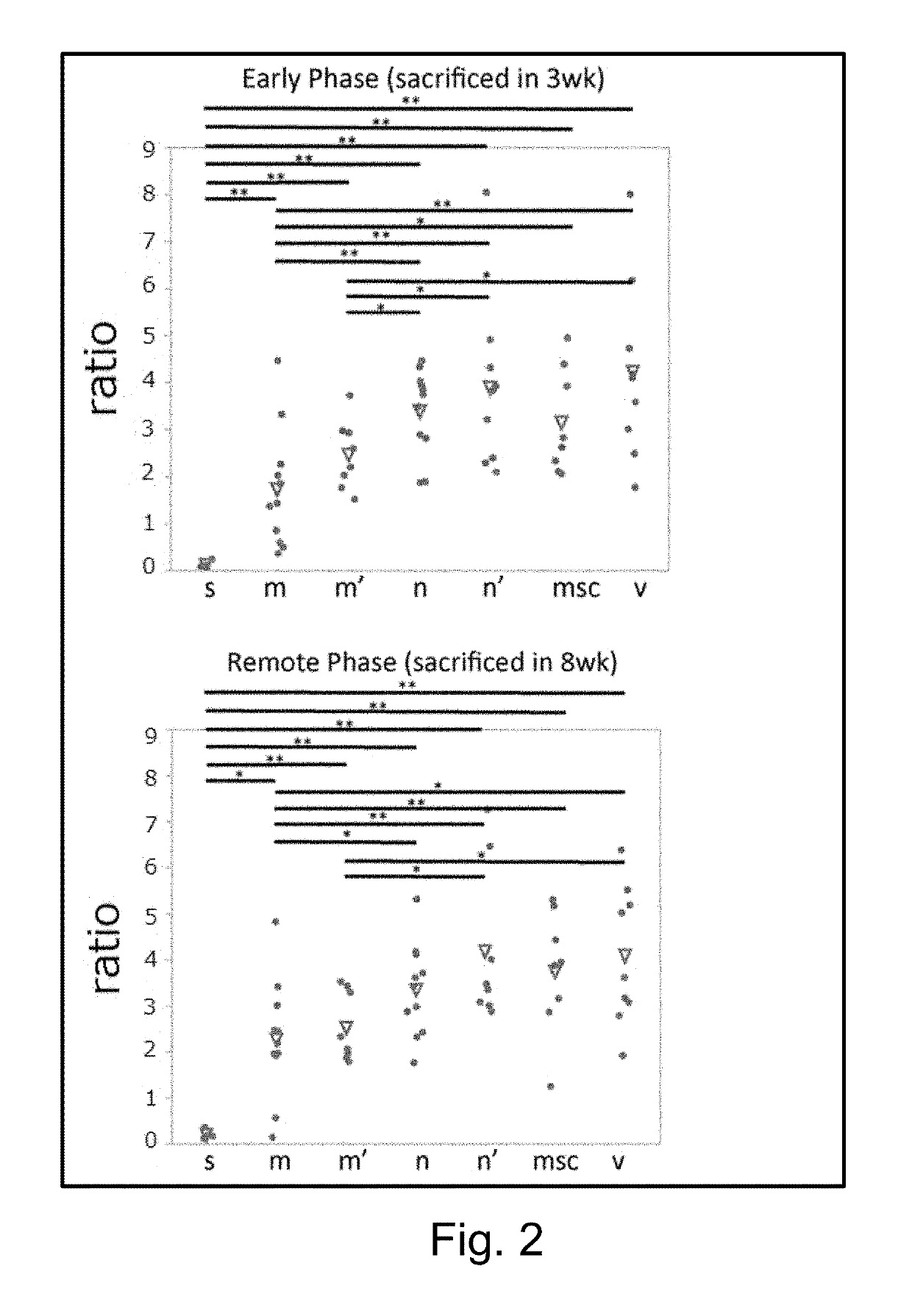
ActiveUS20190175662A1Improvement and recovery of functionEffect is exertedUnknown materialsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsVascular diseaseLiving body
A cell product for prevention and / or treatment of vascular disorders such as aortic aneurysm, comprising a SSEA-3-positive pluripotent stem cell derived from a mesenchymal tissue in a living body or a cultured mesenchymal cell (Muse cell).
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV +1
Application of human amniotic epithelial cells in preparation of medicine for preventing or treating senile asthenia
PendingCN111803525AThe separation method is simpleNo ethical issuesAntinoxious agentsMammal material medical ingredientsPharmaceutical drugAmniotic epithelial cells
The invention discloses application of human amniotic epithelial cells in preparation of a medicine for preventing or treating senile asthenia, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The senile asthenia comprises senile asthenia or the early stage of senile asthenia, an effective dose of human amniotic epithelial cells or cell preparations thereof are used independently or in combination with other medicines for preventing or treating senile asthenia, the human amniotic epithelial cells are cells collected without any treatment, partially purified cells or purified cells proliferated through artificial culture, and the effective dose of each time is 1*106-1*1010 cells. The human amniotic epithelial cells used in the application are simple and convenient in separation method, free of ethics problems and tumorigenicity, have multi-directional differentiation and immune regulation capacity, have good safety and effectiveness when used for preventing and treating senile asthenia, and improve the living state of senile asthenia people and the living quality of senile asthenia people.
Owner:上海安库生医生物科技有限公司
Preparation method of immortalized human intervertebral disc nucleus pulposus cell system
ActiveCN102093980BImprove the level of prevention and controlHave a normal growth rateEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionTelomeraseReverse transcriptase
The invention discloses a preparation method of an immortalized human intervertebral disc nucleus pulposus cell system. The preparation method is as follows: extrinsic human telomerase reverse transcriptase is transfected into the human nucleus pulposus cell to activate telomerase and construct immortalized human nucleus pulposus cell line through induction immortalized human nucleus pulposus cell line, normal cells not transformed cells are used, wherein the cells have normal growth rate and karyotype, have contact inhibition, anchorage dependence and other safety properties and do not have carcinogenicity and soft agar cloning capability; and as same as the germline stem cells, the cells have real immortalization, thus the standard cell line can be provided for the further research of the pathogenic mechanism of the degenerative disc disease and a new idea is provided to increase the entire control level of the degenerative disc disease.
Owner:梁伟国
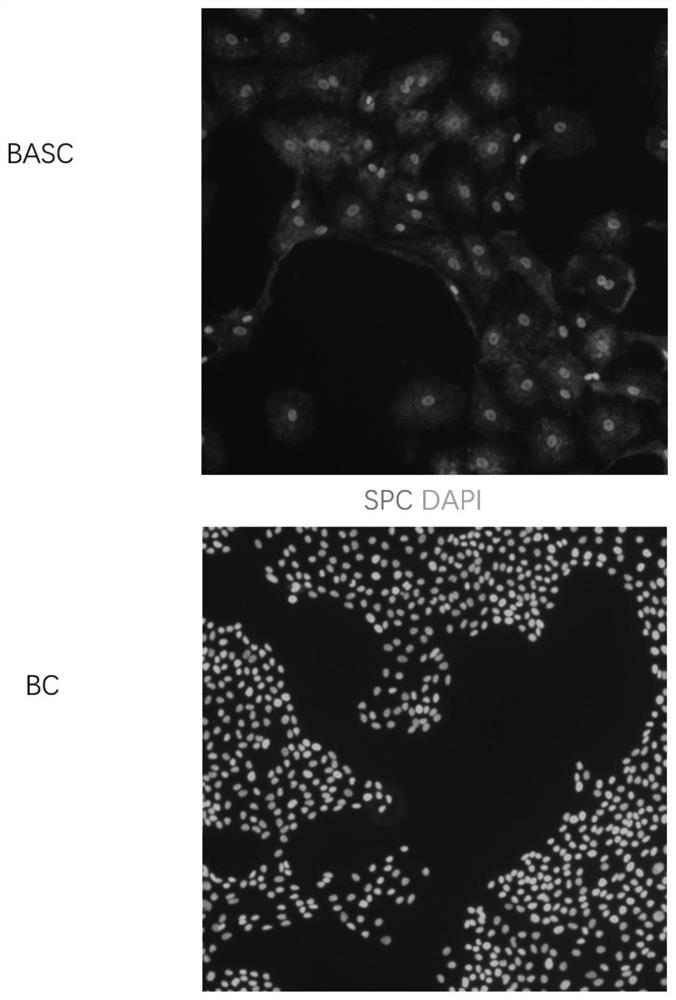
Culture medium and method for inducing airway basal stem cells to differentiate into bronchoalveolar stem cells
ActiveCN113025563AGood substituteHigh differentiation efficiencyCell culture active agentsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsGamma secretaseKeratinocyte growth factor
The invention provides a culture medium and a method for inducing airway basal stem cells to differentiate into bronchoalveolar stem cells, and relates to the technical field of stem cell induced differentiation. The culture medium comprises a primary induced differentiation culture medium and a secondary induced differentiation culture medium; the primary induced differentiation culture medium comprises the following components: a fibroblast growth factor 10, a keratinocyte growth factor and a glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitor; the secondary induced differentiation culture medium is prepared from the following components: a fibroblast growth factor 10, a keratinocyte growth factor, a keratinocyte growth factor, a gamma secretase inhibitor and a phosphodiesterase inhibitor. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the BC is subjected to induction culture by adopting the induction culture medium and can be efficiently converted into the BASC. According to the culture medium and the culture method, autologous airway basal stem cells can be successfully induced into bronchoalveolar stem cells, and the induction conversion rate is high.
Owner:中山大学深圳
A kind of whole suspension culture method of avian influenza virus
ActiveCN107904215BNon-tumorigenicEasy to useSsRNA viruses negative-senseRecovery/purificationTGE VACCINEVirus
The invention discloses a full-suspension culture method of avian influenza virus, which comprises the following steps: step 1: take EB66 cells for growth and culture; step 2: when the density of EB66 cells grows to be suitable for inoculation, inoculate with infusion fluid Process Inoculate avian influenza virus into EB66 cells, and carry out virus proliferation and culture; Step 3: After inoculation for 24 hours, take samples every 12 hours to measure the HA titer of the virus, and harvest the virus when the virus HA titer reaches the highest level, and store it to obtain Cultured avian influenza virus. The present invention uses EB66 cells for avian influenza virus culture, avoids the disadvantage of easily introducing a large amount of miscellaneous proteins during production by adopting the traditional chicken embryo culture process, effectively reduces the occurrence of immune side reactions in chickens, and simultaneously improves the titer and purity of the cultured avian influenza virus , thereby improving the production quality of avian influenza vaccines.
Owner:ZHAOQING INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +2
Method for constructing cell model and cell bank for chromosomal translocation by recombination of hTERT (human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase)
InactiveCN104419663AKeep chromosomesNormal differentiationMicroorganism librariesVector-based foreign material introductionElectrophoresis bandDNA Endonuclease
The invention relates to a method for constructing a cell model and cell bank for chromosomal translocation by recombination of hTERT (human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase), and belongs to the field of medical science. The method is mainly characterized by comprising the following steps of carrying out dual-enzyme digestion on a plasmid pCIneo-hTERT and a vector pLXSNneo by virtue of endonucleases EcoR I and Xho I to obtain hTERT and pLXSNneo enzyme-digested products by linking through Ligation Mix, carrying out PCR amplification and separating through gel electrophoresis, constructing a pLXSNneo-hTERT recombinant, transforming the recombinant with DH5a competent cells, purifying, amplifying and picking ampicillin-resistant colonies, extracting a plasmid, transfecting with a lipidosome, carrying out in-vitro passage on chromosomal translocation cells in logarithmic growth so that the recombinants and cell DNA are integrated, carrying out enlarge culture, cloning a cell containing positive recombinants screened through G418, screening the cell of which a cell morphology, a growth curve, a chromosome karyotype, carcinogenicity tests of naked mice, the activity of telomerase in transfected cells, expression products of hTERT mRNA, immunohistochemical staining, a cell proliferate cycle and an apoptosis rate are in line with characteristics of an immortalized cell and are same as or similar to those of a primary cell as the hTERT-mediated cell model for chromosomal translocation, and cryopreserving in liquid nitrogen. The cell model lays a foundation for in-vitro research on the pathogenesis of chromosomal translocation in a cellular level in a long term.
Owner:翁炳焕
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com