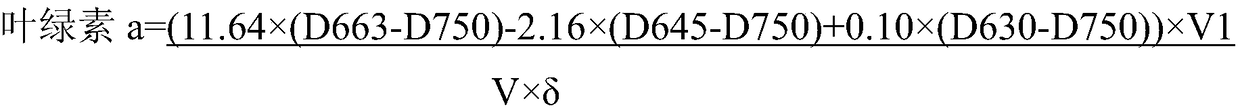Patents
Literature
88 results about "Cell biomass" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Continuous-Batch Hybrid Process for Production of Oil and Other Useful Products from Photosynthetic Microbes
InactiveUS20080118964A1Lower potentialIncreased complexityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismCarrying capacity
A process for cultivating photosynthetic microbes comprising Closed Systems for continuous cultivation and Open Systems for batch cultivation, in which (a) the Closed System Area occupies no more than 20% of the Total Land Area of the cultivation facility; (b) batch cultures in the Open Systems are initiated with an inoculum from the Closed Systems containing a cell biomass of no less than 5% of the carrying capacity of said Open System; (c) the doubling rate of said photosynthetic microbe is no less than once every 16 hours; and (d) the residence time of the batch culture in said Open System is no more than a period of 5 days.
Owner:CELLANA
Novel Strain of Schizochytrium limacinum useful in the production of lipids and Extracellular Polysaccharides and process thereof
The present disclosure provides a novel mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum having the Accession No. MTCC 5249, which produces lipids and extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) simultaneously. The disclosure further provides a process for simultaneous production of lipids and extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) from the novel mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum. The lipids produced from the novel mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum comprises docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). The disclosure also provides a food, feed, cosmetic, nutritional or therapeutic supplement for humans or animals comprising the cell biomass and extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) of the mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum. A cosmetic composition comprising the extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) of Schizochytrium limacinum is also provided that is useful as a base for cosmetics for topical application. The present disclosure further provides a pickle composition and a fat product having improved nutritive value.
Owner:ABL BIOTECH
Continuous-batch hybrid process for production of oil and other useful products from photosynthetic microbes
InactiveUS7770322B2Minimize complexityOperation minimizedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismCarrying capacity
Owner:CELLANA
Strain of Schizochytrium limacinum useful in the production of lipids and extracellular polysaccharides and process thereof
The present disclosure provides a novel mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum having the Accession No. MTCC 5249, which produces lipids and extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) simultaneously. The disclosure further provides a process for simultaneous production of lipids and extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) from the novel mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum. The lipids produced from the novel mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum comprises docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). The disclosure also provides a food, feed, cosmetic, nutritional or therapeutic supplement for humans or animals comprising the cell biomass and extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) of the mutant strain of Schizochytrium limacinum. A cosmetic composition comprising the extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) of Schizochytrium limacinum is also provided that is useful as a base for cosmetics for topical application. The present disclosure further provides a pickle composition and a fat product having improved nutritive value.
Owner:ABL BIOTECH
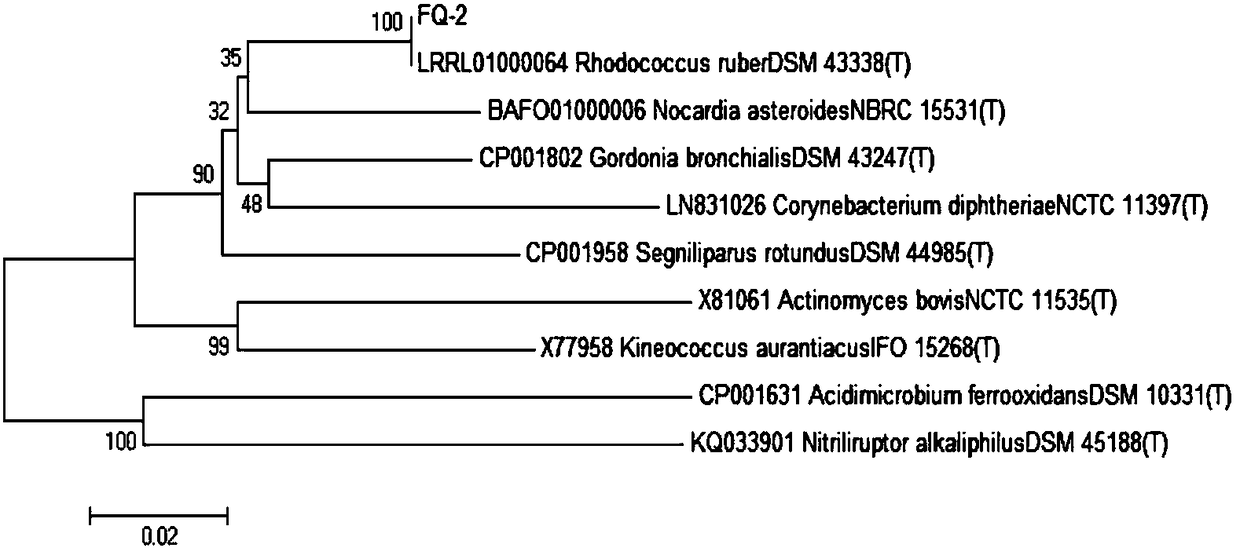
Rhodococcus ruber and application thereof in degradation of organic pollutants
The invention discloses rhodococcus ruber FQ-2 and an application thereof in degradation of acetone and other common industrial organic pollutants. The application method comprises the steps: an inorganic salt culture medium containing acetone and other common industrial pollutants is inoculated with the rhodococcus ruber FQ-2, a degradation reaction is carried out under the conditions of the temperature of 30 DEG C and the rotating speed of 160 r / min, and thus the organic pollutants are degraded; the common organic pollutants comprise acetone, n-hexane, carbon disulfide, chlorobenzene, butylacetate, ethyl acetate or alpha-pinene. The rhodococcus ruber FQ-2 is taken from activated sludge of an aeration tank of a pharmaceutical factory in Zhejiang province, has good degradation effect on VOCs organic pollutants, especially acetone, and can completely convert acetone into harmless substances such as CO2, H2O, cell biomass and the like; at the same time, the bacterial strain also can degrade common industrial pollutants such as carbon disulfide and chlorobenzene in different extent, so the bacterial strain has broad application prospects in biological purification of industrial wastegas and wastewater.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
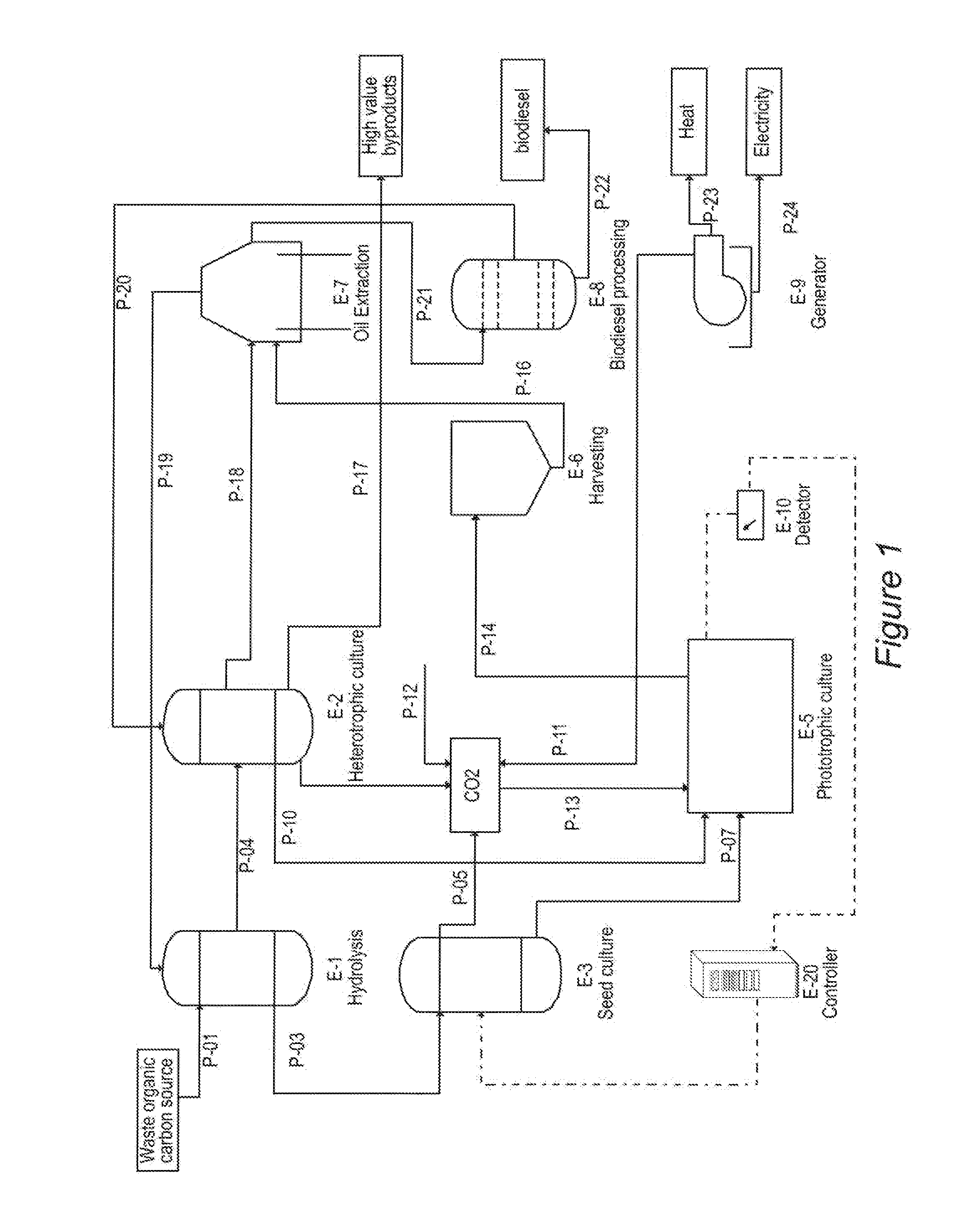
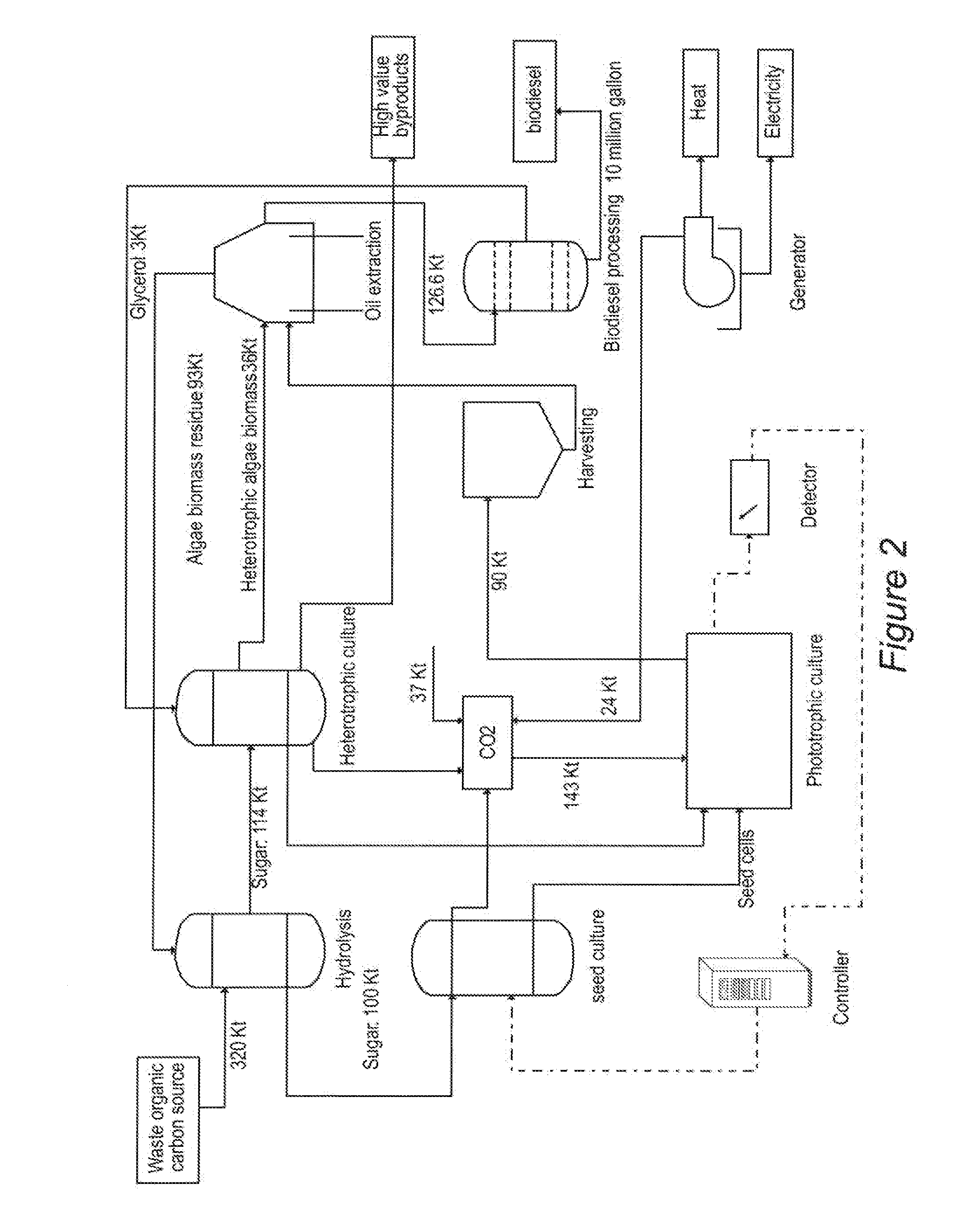
Integrated system for production of biofuel feedstock
InactiveUS20110027827A1Increase flexibilityReduces concern regarding contaminationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWaste streamBiofuel feedstock
Disclosed is a culture system for the production of algae biomass to obtain lipid, protein and carbohydrate. By integrating heterotrophic processes with a phototrophic process in parallel, this system provides year around production in colder climates. By integrating heterotrophic processes with a phototrophic process in series, this system creates a two-stage, separated mixed-trophic algal process that uses organic carbon and nutrients for the production of seed in the heterotrophic process, followed by release of cultured seed in large-scale phototrophic culture for cell biomass accumulation. Organic carbon source including waste materials can be used to feed the heterotrophic process. The production capacity ratio between the heterotrophic and the phototrophic processes can be adjusted according to season and according to the availability of related resources. The systems are used for producing and harvesting an algal biofuel feedstock as well as other potential high-value products. The sequence and approach enhances utilization of carbon and nutrient waste-streams, provides an effective method for controlling contamination, adds flexibility in regard to production and type of available products, and supplies greater economic viability due to maximized use of available growth surface areas.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY
Integrated system for productioin of biofuel feedstock
InactiveCN102089434AIncrease flexibilityReduce sizeUnicellular algaeBiofuelsBiotechnologyBiofuel feedstock
Disclosed is a culture system for the production of algae biomass to obtain lipid, protein and carbohydrate. By integrating heterotrophic processes with a phototrophic process in parallel, this system provides year around production in colder climates. By integrating heterotrophic processes with a phototrophic process in series, this system creates a two-stage, separated mixed- trophic algal process that uses organic carbon and nutrients for the production of seed in the heterotrophic process, followed by release of cultured seed in large-scale phototrophic culture for cell biomass accumulation. Organic carbon source including waste materials can be used to feed the heterotrophic process. The production capacity ratio between the heterotrophic and the phototrophic processes can be adjusted according to season and according to the availability of related resources. The systems are used for producing and harvesting an algal biofuel feedstock as well as other potential high-value products. The sequence and approach enhances utilization of carbon and nutrient waste-streams, provides an effective method for controlling contamination, adds flexibility in regard to production and type of available products, and supplies greater economic viability due to maximized use of available growth surface areas.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Process for producing, methods and compositions of glucuronoxylomannan as nutriceutical agent from higher basidiomycetes mushroom
InactiveUS6383799B1Decreased blood levelReduce riskOrganic active ingredientsFungiBiotechnologyTremella
The present invention describes new and distinct strains of higher Basidiomycetes mushrooms grown in submerged cultures. Specifically, the new strain of species of the genus Tremella offer superior yields of one-cell biomass and exocellular heteropolysaccharide glucuronoxylomannan, niacin and essential amino acids.
Owner:MEDMYCO
Pandora bacterium with dichloromethane degrading capability and application thereof
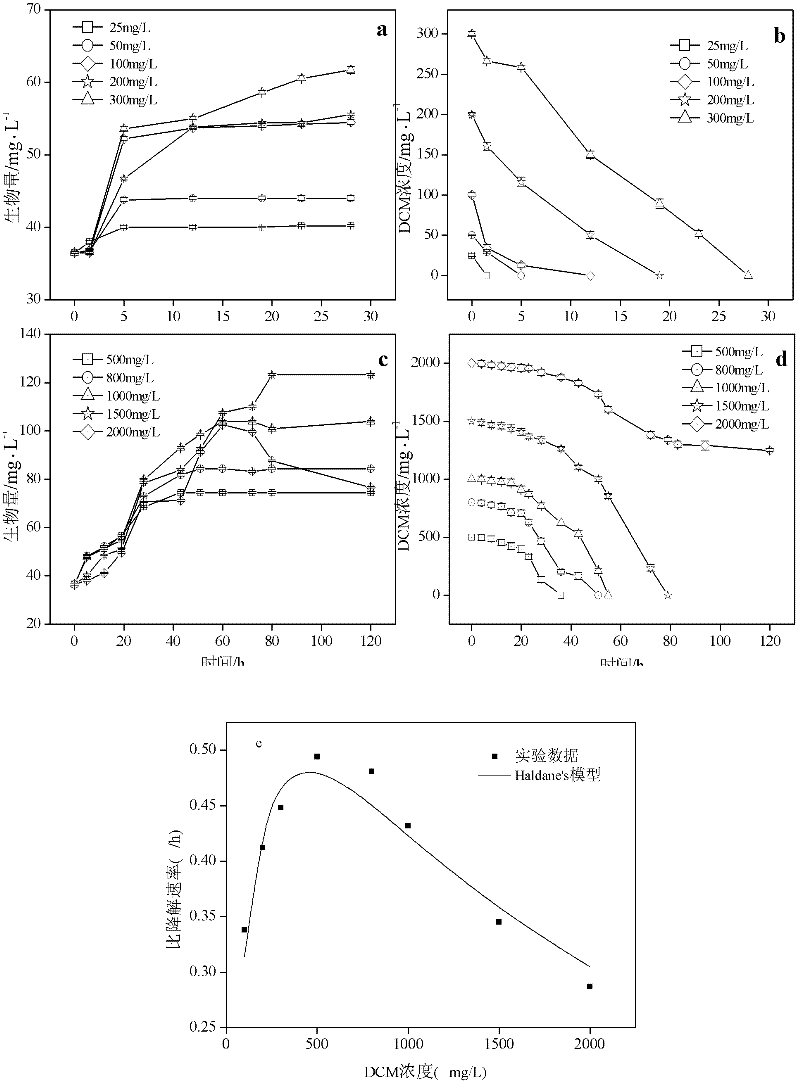
The invention provides a dichloromethane degrading bacterium, namely a pandoraeapnomenusa strain flx<-1>, and an application thereof. The strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection in Wuhan University (430072), Wuhan, China, the preservation number is CCTCC NO.: M 2011242, and the preservation date is July 8, 2011. The pandoraeapnomenusa strain flx<-1> is taken from a wastewater treatment unit and has good degrading effects on chlorinated hydrocarbon compounds, in particular on DCM (dichloromethane), and the DCM can be completely converted into CO2, H2O, biologic cells and other harmless substances. Meanwhile, benzene, toluene and other common industrial pollutants can be degraded to certain extent through the strain. Therefore, the strain has broad application prospects in biological purification of industrial exhaust gas and wastewater.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Surface-modified biomass, preparation method thereof, and method for recovering valuable metals using the same
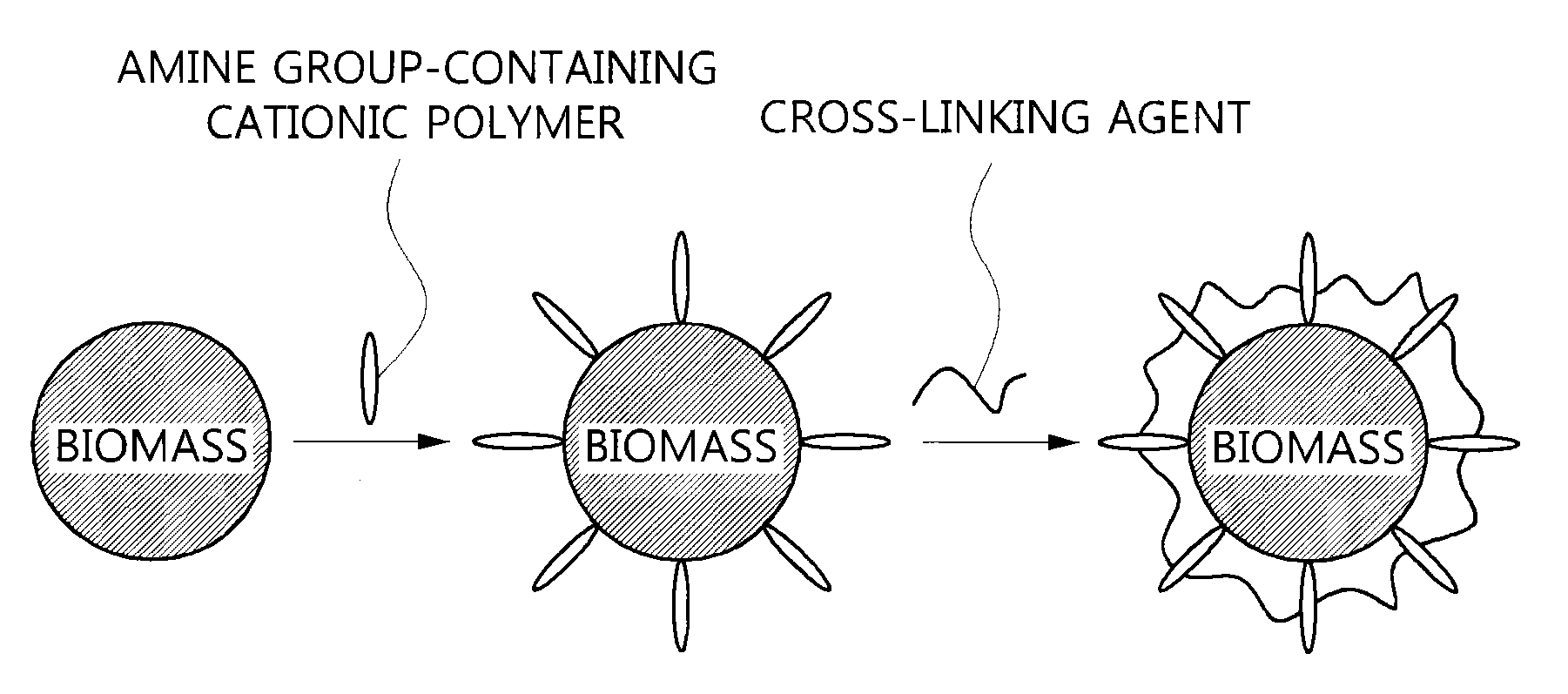
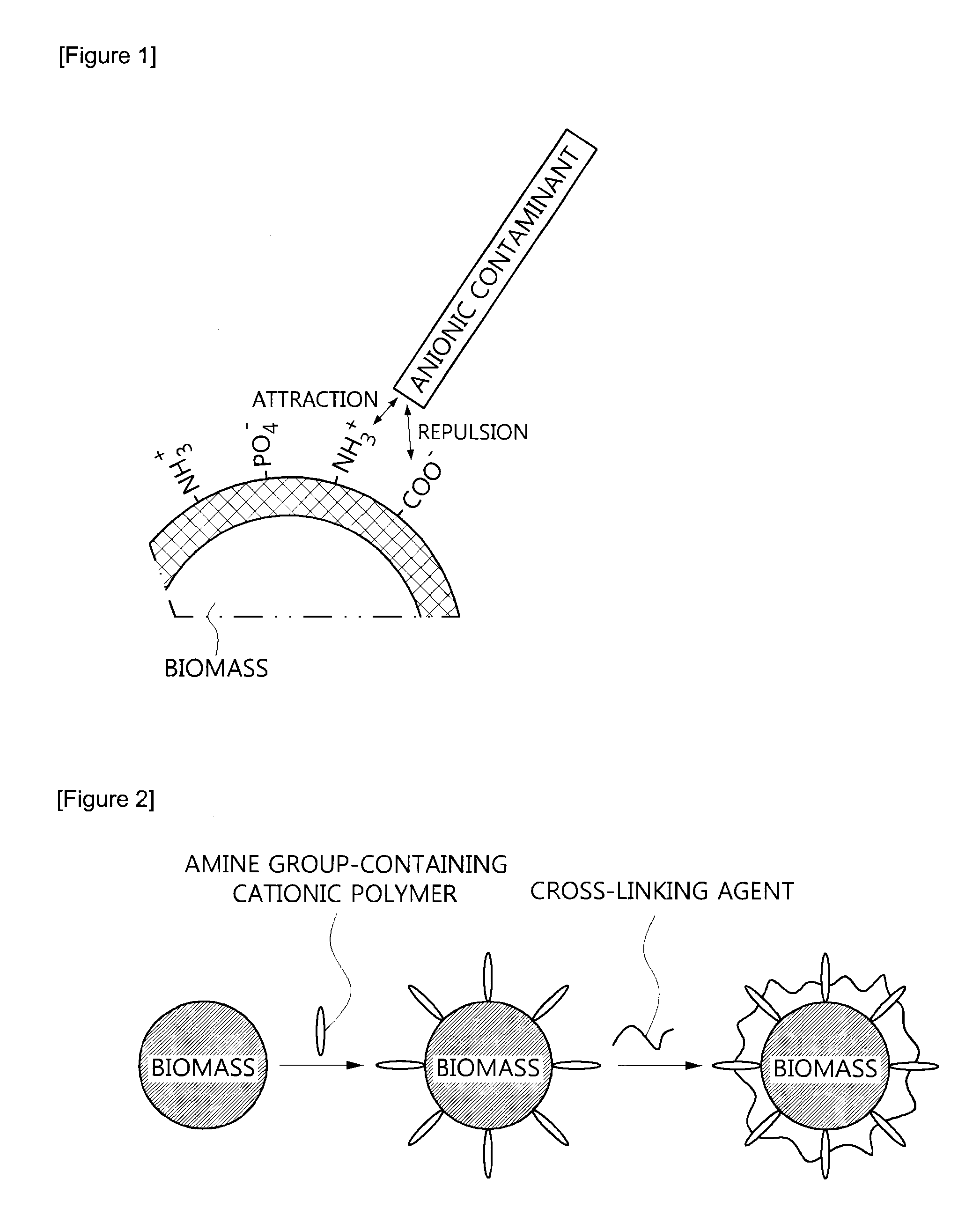
InactiveUS20120036962A1Easy to useImprove adsorption capacityMaterial nanotechnologyWater contaminantsRecovery methodPolymer
The present invention relates to a surface-modified biomass which is crosslinked with an amine group-containing cationic polymer on the surface of a cell biomass, its preparation method, and a method for recovering valuable metals using the same. The surface-modified biomass of the present invention has an advantage of improving adsorption of and affinity with anionic pollutants as a result of further introducing a cationic functional group by crosslinking of the amine group-containing cationic polymer on the surface of the biomass. In addition, the method for recovering valuable metals with the present invention is environment-friendly, economical, and harmless to the human body.
Owner:IND COOP FOUND CHONBUK NAT UNIV
Lactobacillus freeze-dried product and preparation method of same
ActiveCN102978143AHigh viable countImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLactobacillus rhamnosus
The invention relates to a preparation method of a freeze-dried powder preparation of Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus paracasei or lactobacillus rhamnosus, and provides a culture medium used in the freeze-drying process of Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus paracasei or lactobacillus rhamnosus products. The inventor combines two critical factors influencing bacterial fermentation together, and creatively carries out fermentation in a high-density fermentation process by means of combination of two-sectional pH and three-sectional temperature variation, so that the relatively single form of the maximum cell biomass and the highest fermentation activity is improved remarkably, meanwhile, the obtained freeze-dried preparation is high in viable count and excellent in stability. The invention also provides an excellent freeze-drying protective additive.
Owner:中创益科(上海)生物科技有限公司
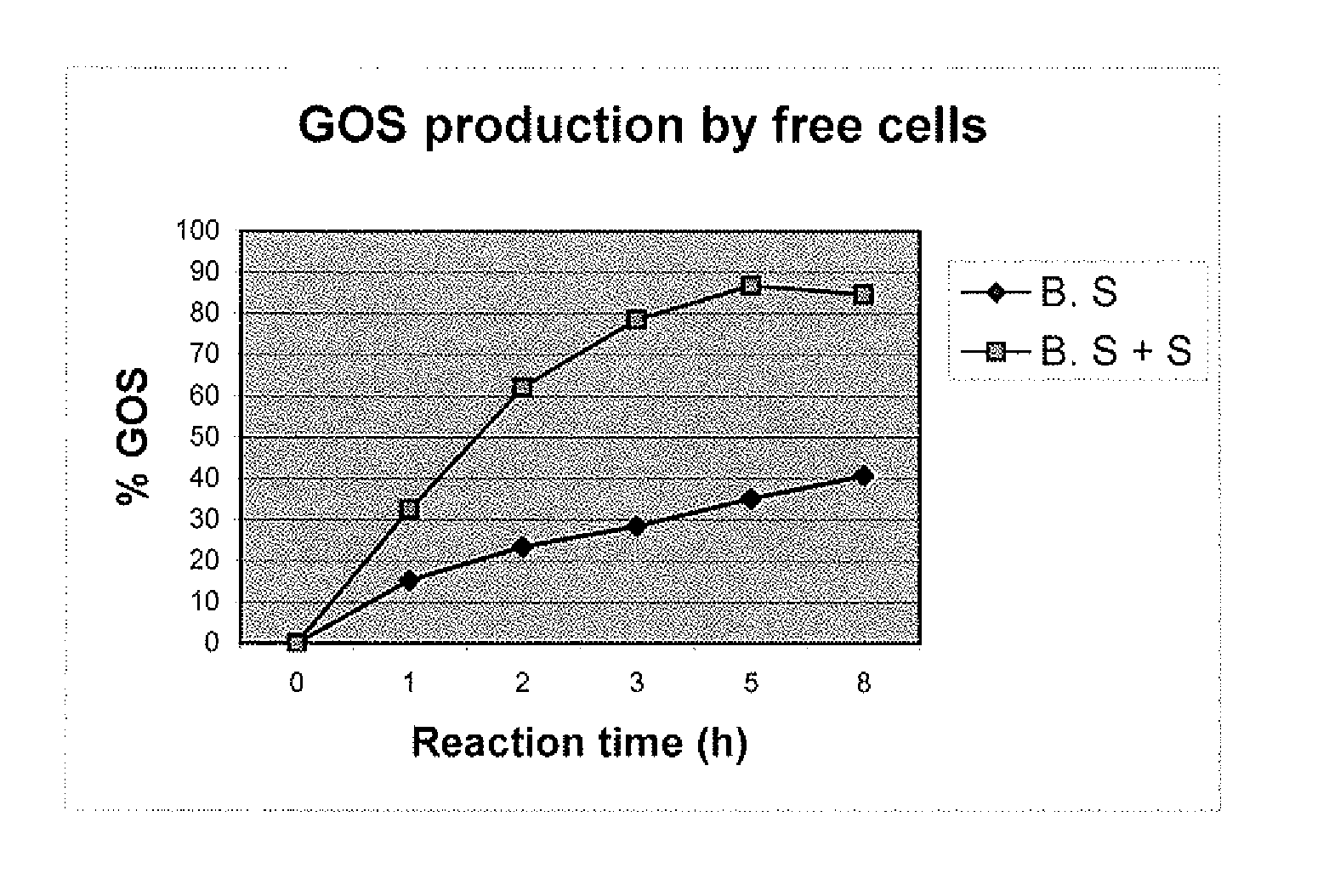
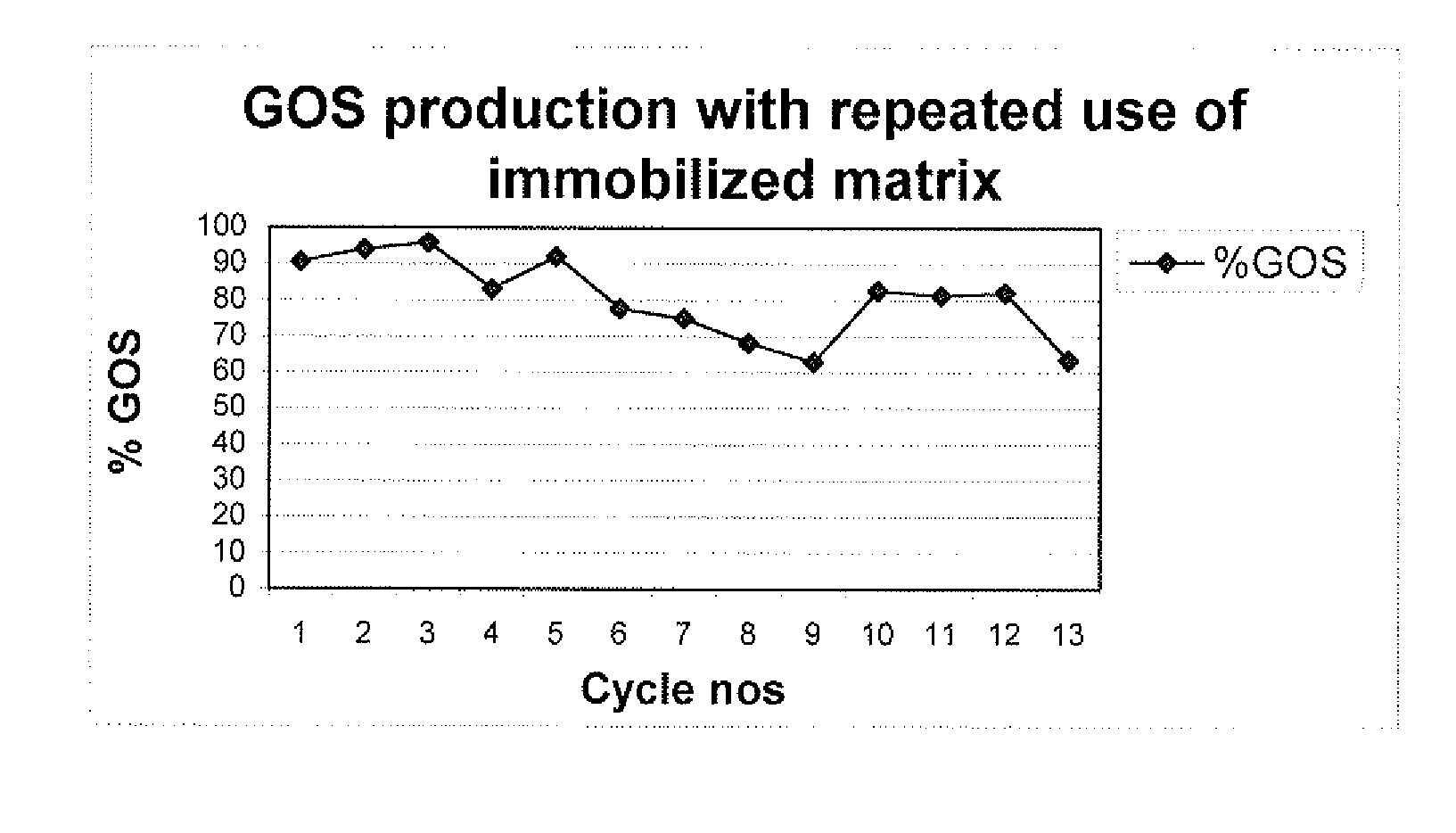
Process for production of galactooligosaccharides (GOS)
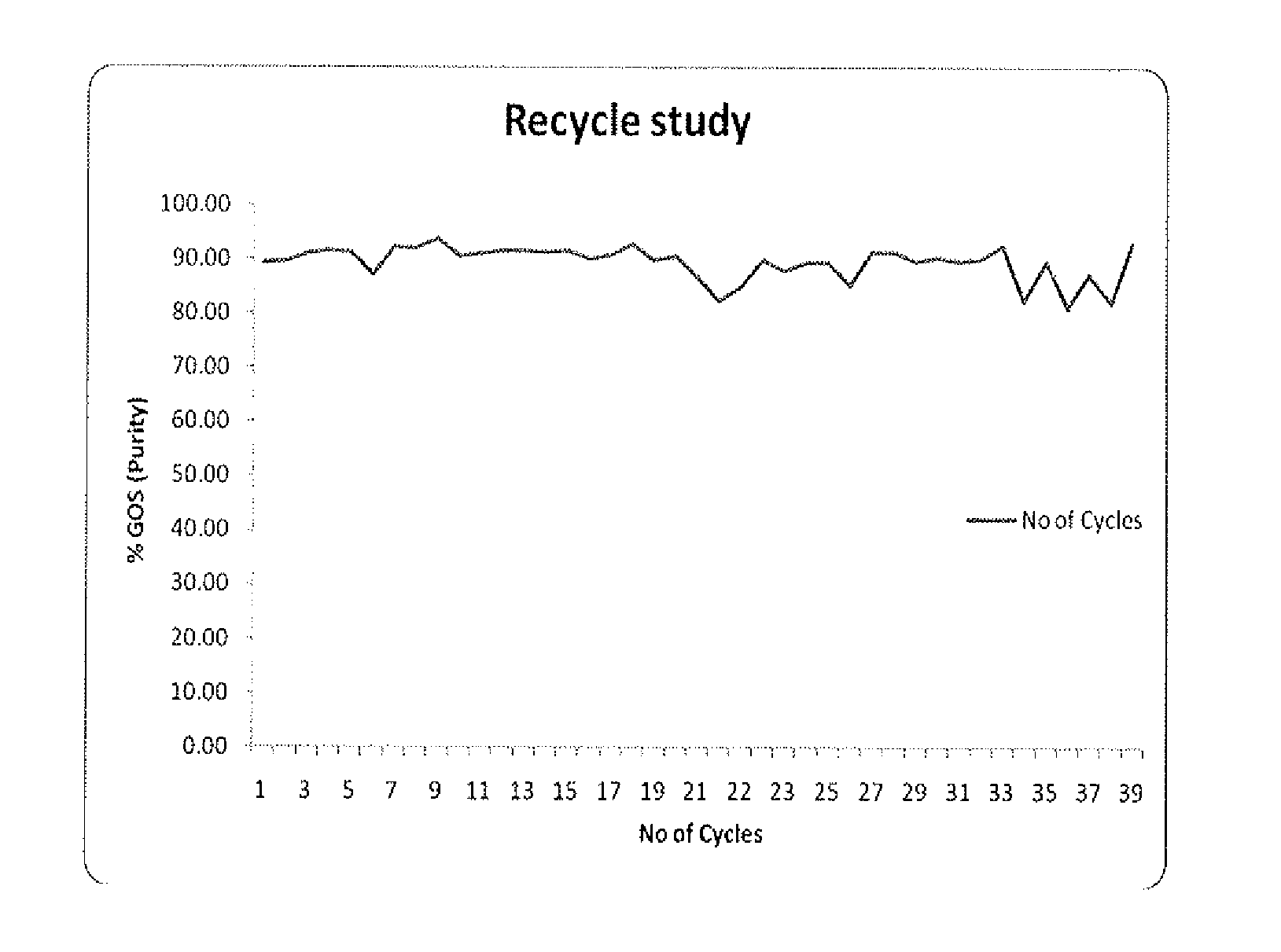
The present invention deals with an improved process for the production of high yield of pure Galactooligosaccharides using microbial whole cells in a reactor with cross flow hollow fiber microfiltration system. The process is economical as cell biomass is used repeatedly and eliminated the need to carry out downstream processing for the removal of mono and disacchacrides from the final product.
Owner:TATA CHEM LTD
Method of preparing lycopene from trispore Bruce mould
InactiveCN1920046AIncrease productionFast oxygen transferMicroorganism based processesFermentationLycopeneOxygen
The invention relates the method for fermenting trisporic Bang's fungus to produce lycopersicin. The carrier of oxygen is added into fermentation culture medium to provide a carrier of oxygen fermentation system, the invention improves the oxygen concentration without consuming excess energy source, and it improves cell biomass and lycopersicin content, and it improves the productivity of lycopersicin.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for culturing paenibacillus polymyxa at high density
The invention belongs to the field of microbial fermentation and particularly relates to a method for culturing paenibacillus polymyxa at high density, which can increase the yield of paenibacillus polymyxa. According to the method, paenibacillus polymyxa serving as a strain is activated and inoculated onto a culture medium. After being optimized, the cell biomass of paenibacillus polymyxa reaches 5.3 *10<9>cfu / mL which is 15.72 times higher than before (3.17*18<8>). Through study on culture medium formula and culture conditions, the method lays a foundation for industrial fermentation and further development and utilization of paenibacillus polymyxa.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Methods for extending the replicative capacity of somatic cells during an ex vivo cultivation process
InactiveUS20190024079A1Improve proliferative abilityReplication capacity can be improvedHydrolasesGenetically modified cellsTelomeraseADAMTS Proteins
Owner:UPSIDE FOODS INC
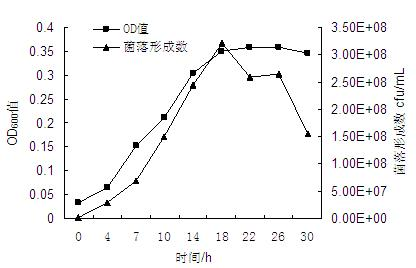
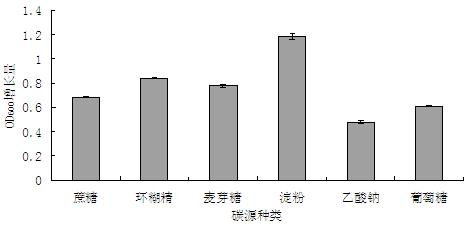
Method for carrying out high-density culture on bacillus subtilis
The invention belongs to the field of microbial fermentation, and particularly relates to a method for carrying out high-density culture on bacillus subtilis, which aims to improve the yield of the bacillus subtilis. According to the method for carrying out high-density culture on the bacillus subtilis, provided by the invention, the bacillus subtilis is adopted as strains, and is activated to be vaccinated into a fermentation culture medium so as to be cultured. Through optimization, the cell biomass of the bacillus subtilis can reach 4.32*109cfu / mL, which is 31.48 times higher than the cell biomass of the bacillus subtilis before optimization (1.33*108cfu / mL). Through research on culture medium formula and culture conditions, the method lays a foundation for industrial fermentation production and further development and utilization of the bacillus subtilis.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Immobilized alpha-amino-acid ester hydrolase, preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101525603AMany preparation stepsShort manufacturing cycleHydrolasesChemical industryCross-linkPenicillin
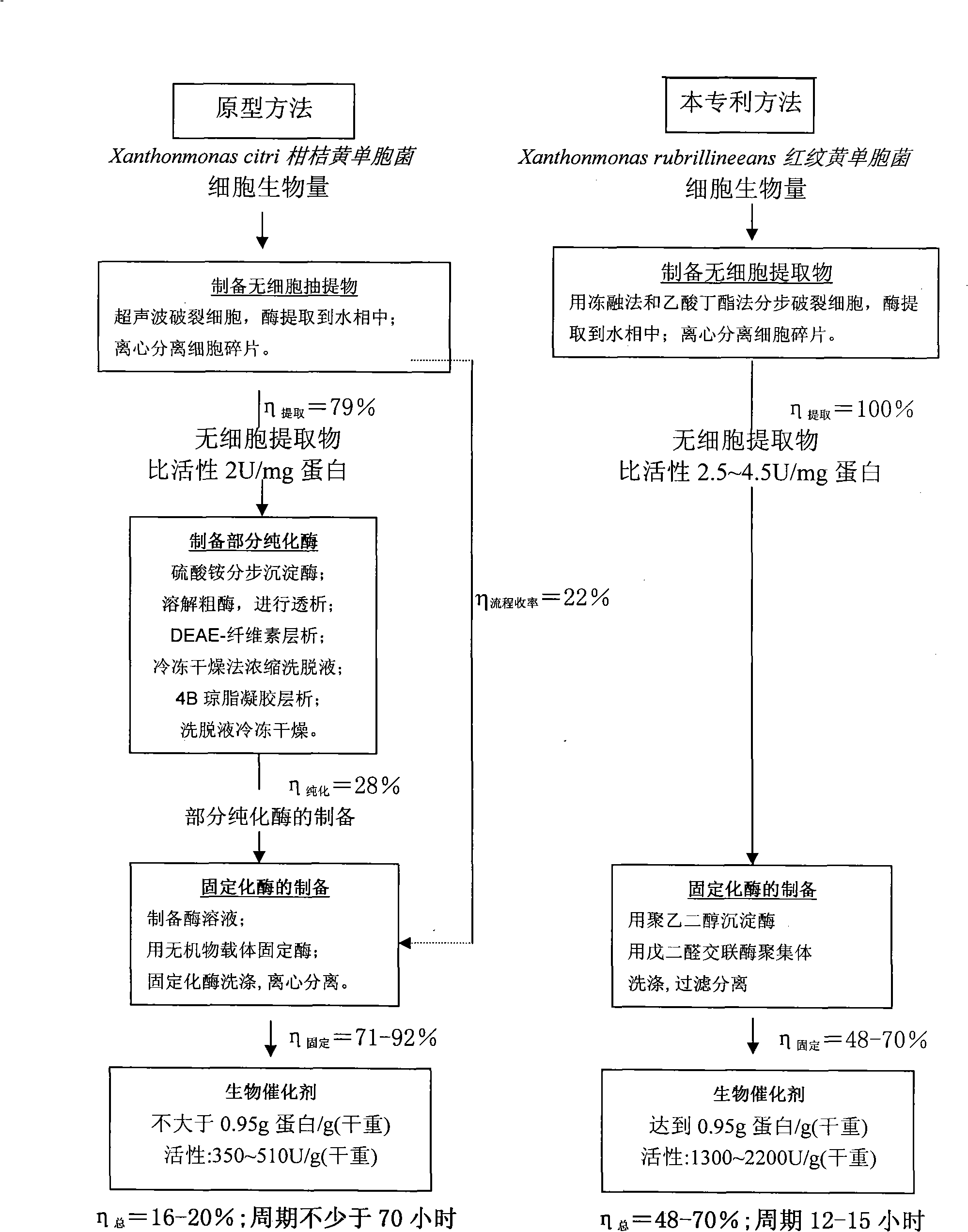
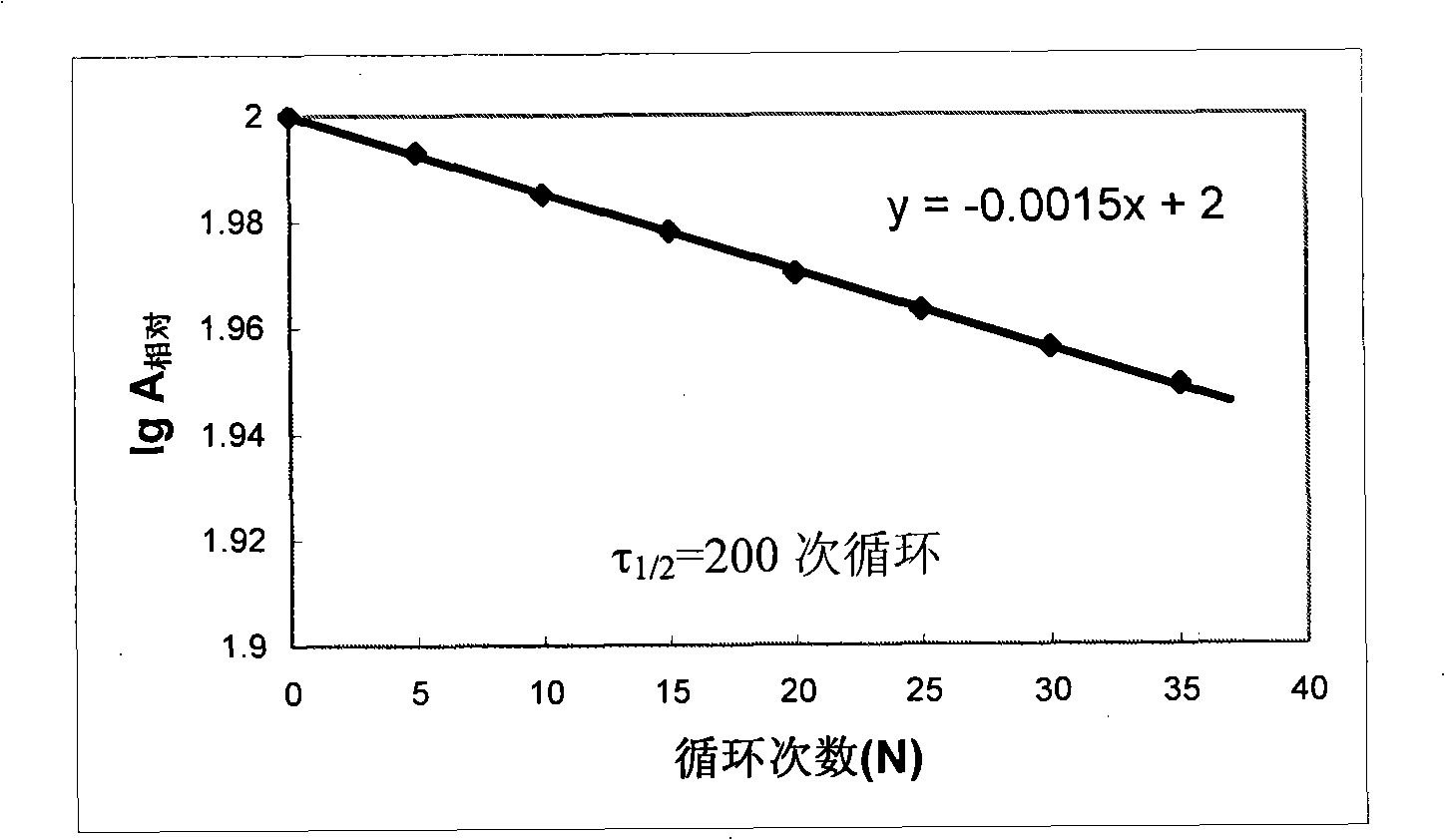
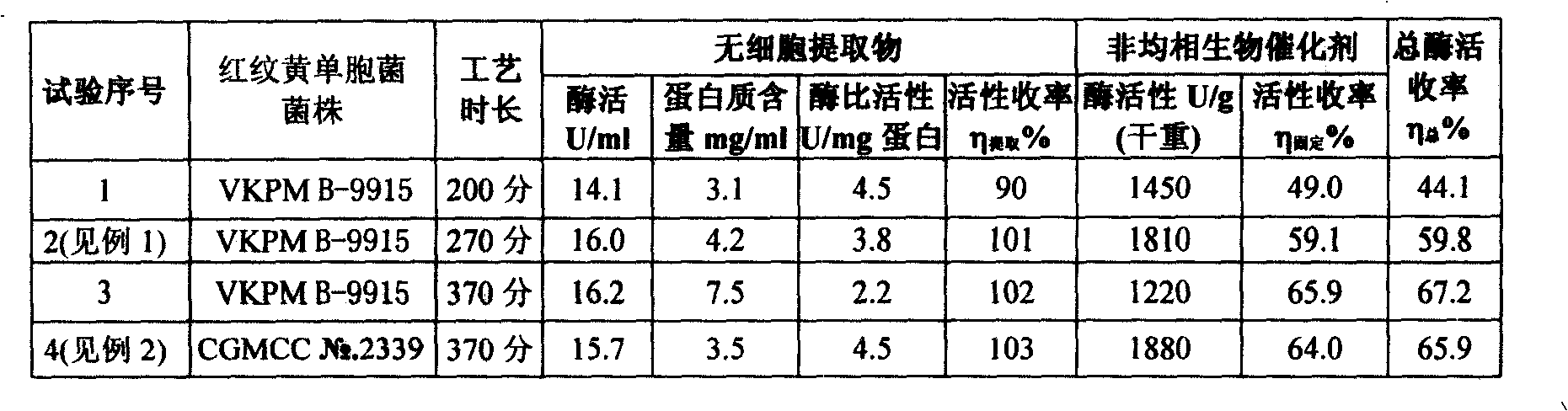
The invention discloses a heterogeneous biocatalyst taking alpha-amino-acid ester hydrolase as basis, a preparation method thereof and application in synthesizing amino beta-lactams. The activity of catalyst synthetase is 2,200 U / g by dry weight, and the content of protein is 0.95 g / g by dry weight; and xanthomonas rubrilineans cell biomass is processed in an organic solvent under a pH gradient through low temperature effect to extract enzyme, and enzyme aggregates are deposited and cross-linked to obtain the hydrolase. The alpha-amino-acid ester hydrolase as a catalyst can be synthesized into amino penicillin and amino cephalosporin drugs through acylating a beta-lactam compound by D-phenylglycine methyl ester derivatives in water or in a mixed medium of water and an organic solvent.
Owner:SICHUAN INDAL INST OF ANTIBIOTICS CHINA NAT PHARMA GROUP CORP +1
Method and system for producing heterotrophic alga in high density
InactiveCN101899481ALow costBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesLipid formationDocosahexaenoic acid
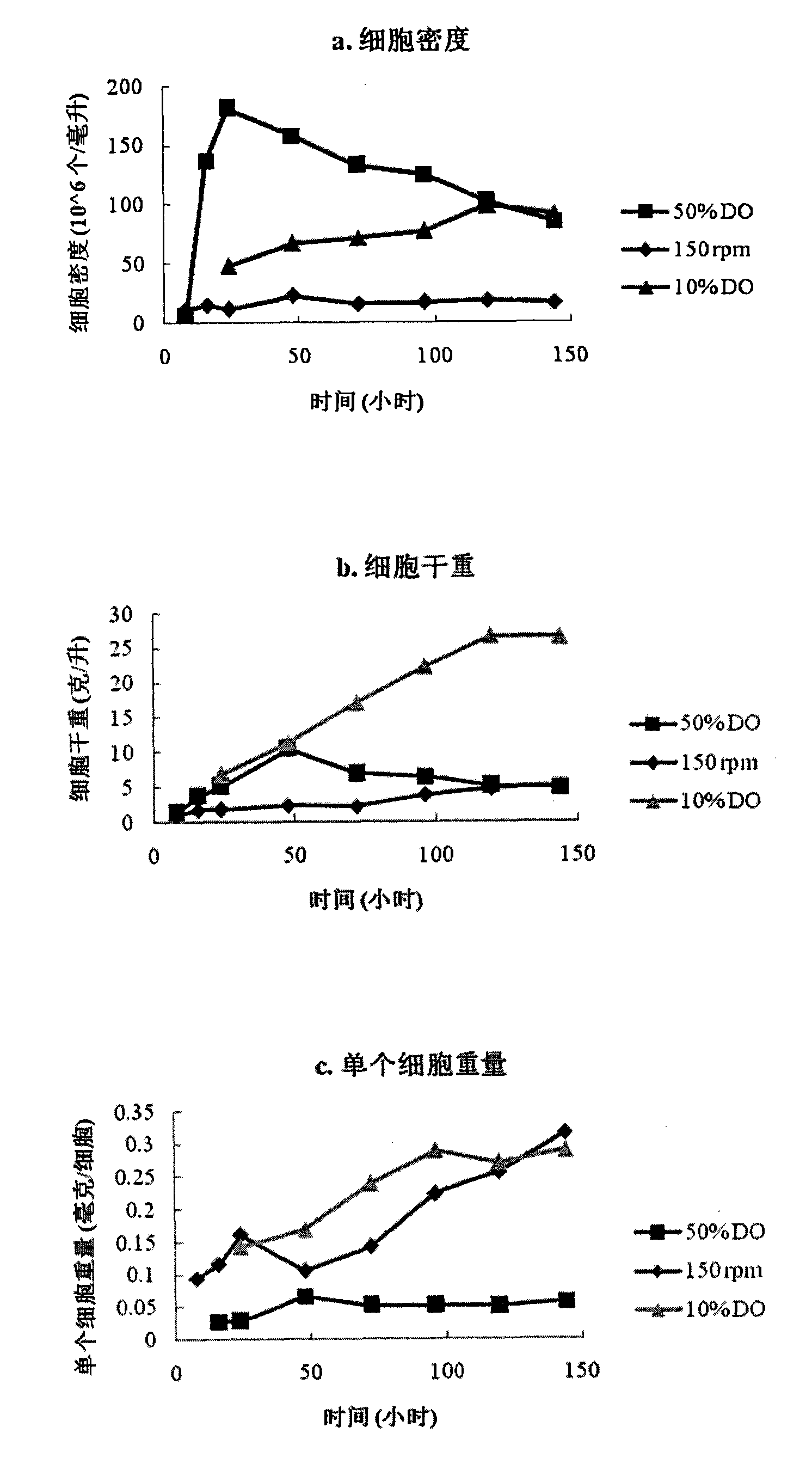
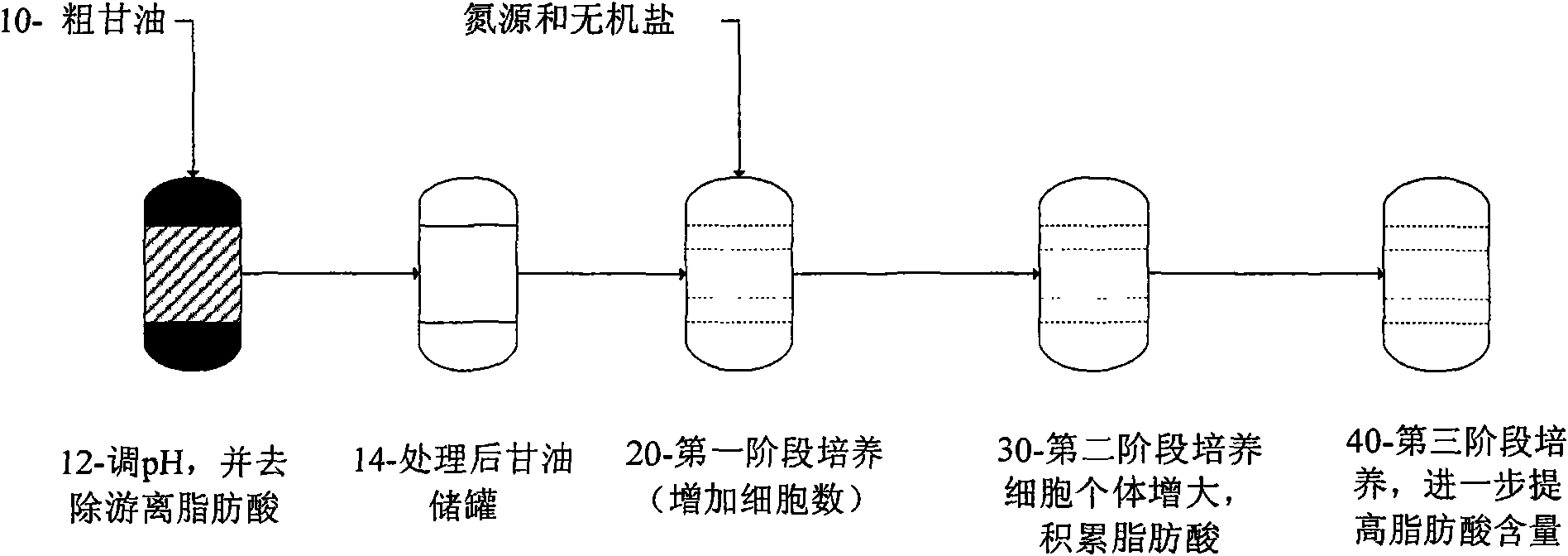
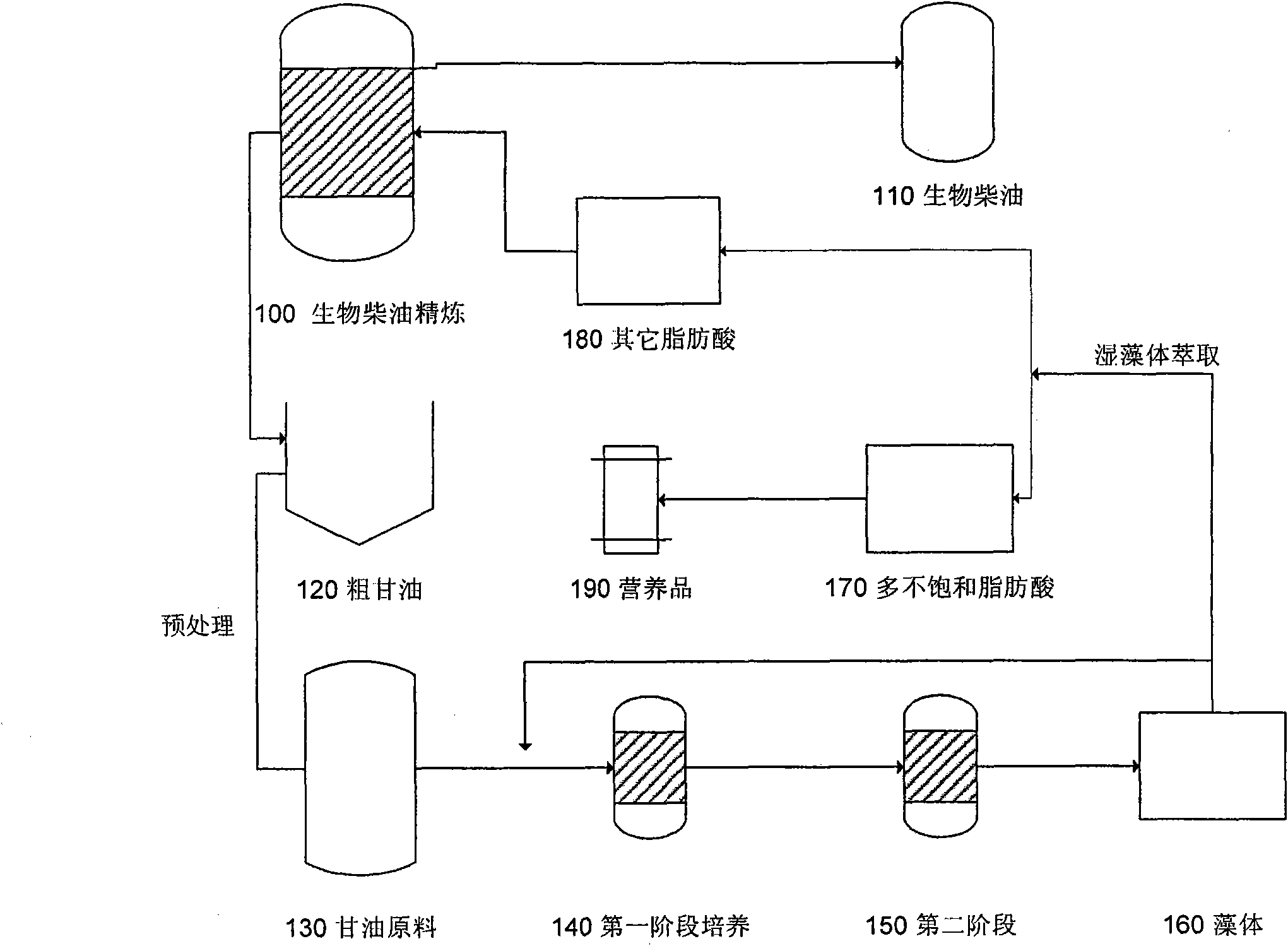
The invention provides a method and a system for producing heterotrophic alga in high density. In the method, unique biological characteristics of a microbial system are utilized, and the accumulation of lipid is increased by simulating cell division and the uncoupling of cell growth / amount. A process for producing polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) by microalgae fermentation comprises three different stages: (1) a cell proliferation stage for increasing the number of cells; (2) a biomass and lipid accumulation stage for increasing cell biomass, particularly the amount of the lipid; and (3) a lipid concentration increasing stage by refining for producing more PUFA by adjusting the steering of the lipid. Various variables such as the types and concentration of a carbon source and nutritional factors, dissolved oxygen and temperature are changed continuously through a three-stage alga growing process to produce maximum biomass, lipid and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) by final induction. Therefore, most cell viability leads to the cell division and the rapid formation of a large number of cells, so that the biomass and the lipid yield are integrally enhanced finally.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY +1
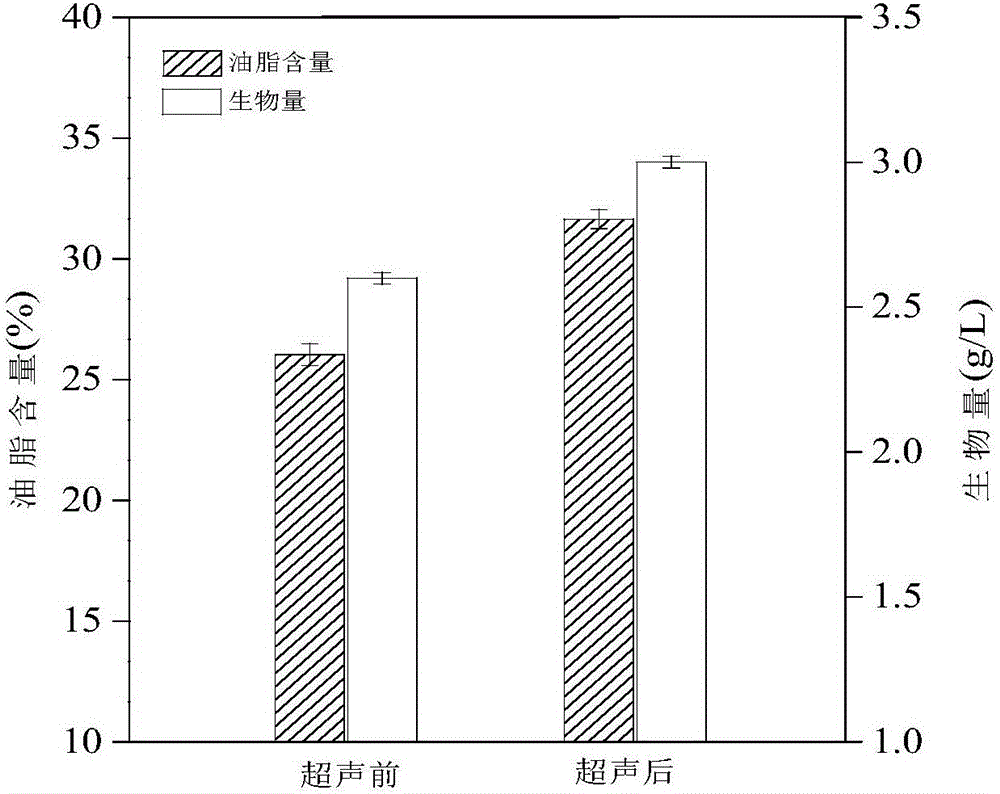
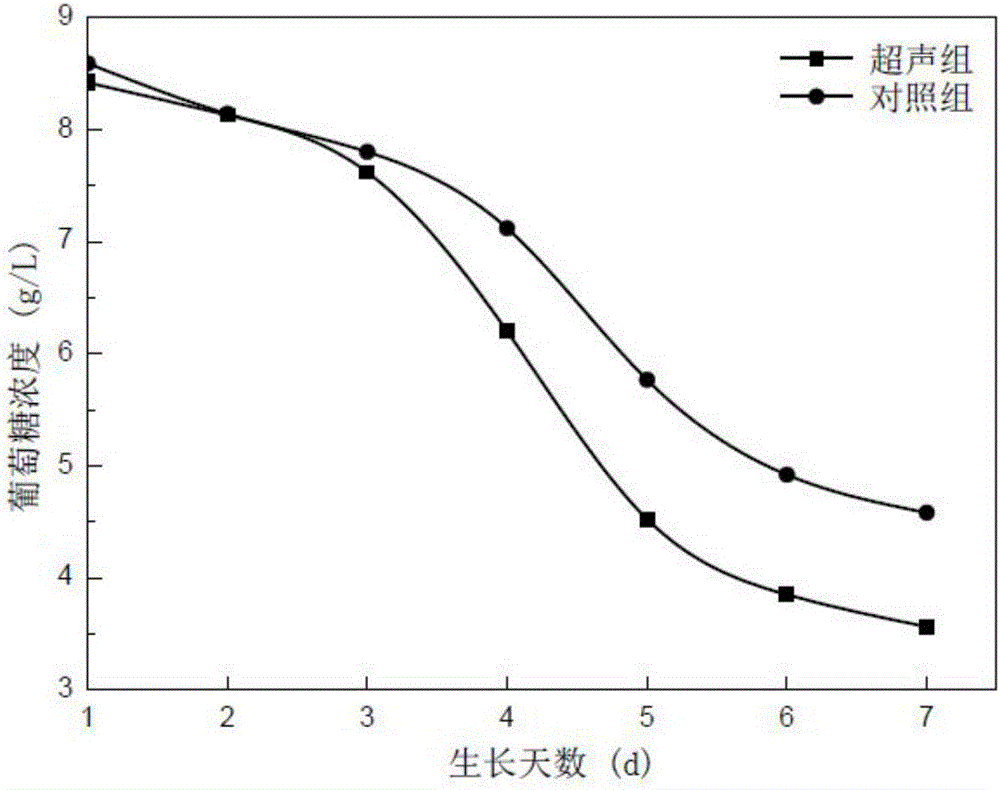
Method for promoting synthesis of microalgae oil by low frequency and low intensity ultrasound
ActiveCN106801072AIncrease intakePromote accumulationMicroorganism based processesFermentationMedicineSugar
The invention discloses a method for promoting the synthesis of microalgae oil by low frequency and low intensity ultrasound, aiming at the critical problem in the field of oil production from microalgae, i.e., the technical difficulty of how to improve the oil content in the microalgae. The method is characterized in that an ultrasonic probe is immersed in a microalgae culture solution which is cultured to a logarithmic phase; ultrasound is started to perform ultrasonic treatment on the microalgae, and circular treatment is carried out, wherein the ultrasonic frequency is 20-50kHz, the ultrasonic power is 10-30W / L, the ultrasonic treatment time is 15-35min / d, and the time interval of ultrasonic pulses is 1-6s; the treated microalgae are transferred to an illumination incubator for culture. The technique provides a new strategy for improving the oil content and cell biomass of the microalgae. The cultured microalgae has the advantages that not only is the synthesis amount of oil increased, but also the utilization rate of sugar and biomass are increased, which lays a good foundation for the industrialization development of the microalgae.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
METHOD OF PRODUCING MENINGOCOCCAL MENINGITIS VACCINE FOR NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS SEROTYPES A, C, Y, and W-135
InactiveUS20080318285A1Yield maximizationYield minimizationAntibacterial agentsBacteriaDiseaseSynechococcus
Owner:REDDY JEERI R
Method for culturing paenibacillus polymyxa at high density
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Microalgae cell biomass detection system for ship ballast water and method
InactiveCN108827891AQuick checkRapid determinationColor/spectral properties measurementsChlorophyll aFluorescence
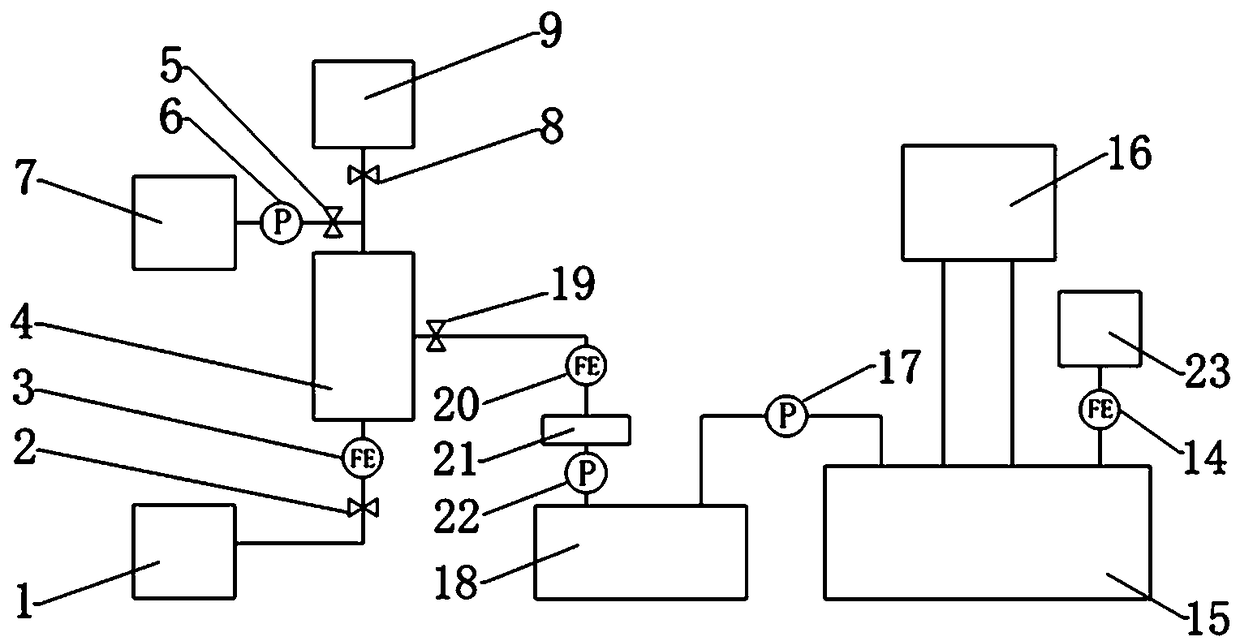
The invention discloses a microalgae cell biomass detection system for ship ballast water and a method. The system comprises a sample introduction chamber, a concentrating device, a wastewater tank, abackwashing device, a cracking chamber, a circulation tank and a recovery device and a spectrograph, wherein an inlet of the concentrating device is connected with an outlet of the sample introduction chamber; an inlet of the wastewater tank is connected with a first outlet of the concentrating device; an outlet of the backwashing device is connected with the first outlet of the concentrating device; an inlet of the cracking chamber is connected with a second outlet of the concentrating device; an inlet of the circulation tank is connected with an outlet of the cracking chamber; and an inletof the recovery device is connected with an outlet of the circulation tank. According to the system and the method, the system for detecting microalgae cell organisms with the particle size of 10 to 50 microns in the ship ballast water is designed by means of measuring chlorophyll a by spectrophotometry on the basis of a long-light-path circulation tank and has the advantages that the device structure is simple, the operation is convenient, the detection process is rapid and efficient, the dependence on fluorescent dyes is absent, the restrictions to ship swing and the like are absent, and a means for effectively and rapidly supervising the ballast water is provided for law-enforcing departments such as Department of Maritime Affairs, Department of Inspection and Quarantine and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Method for researching microbial degradation of petroleum pollutants under low-temperature high-salt conditions
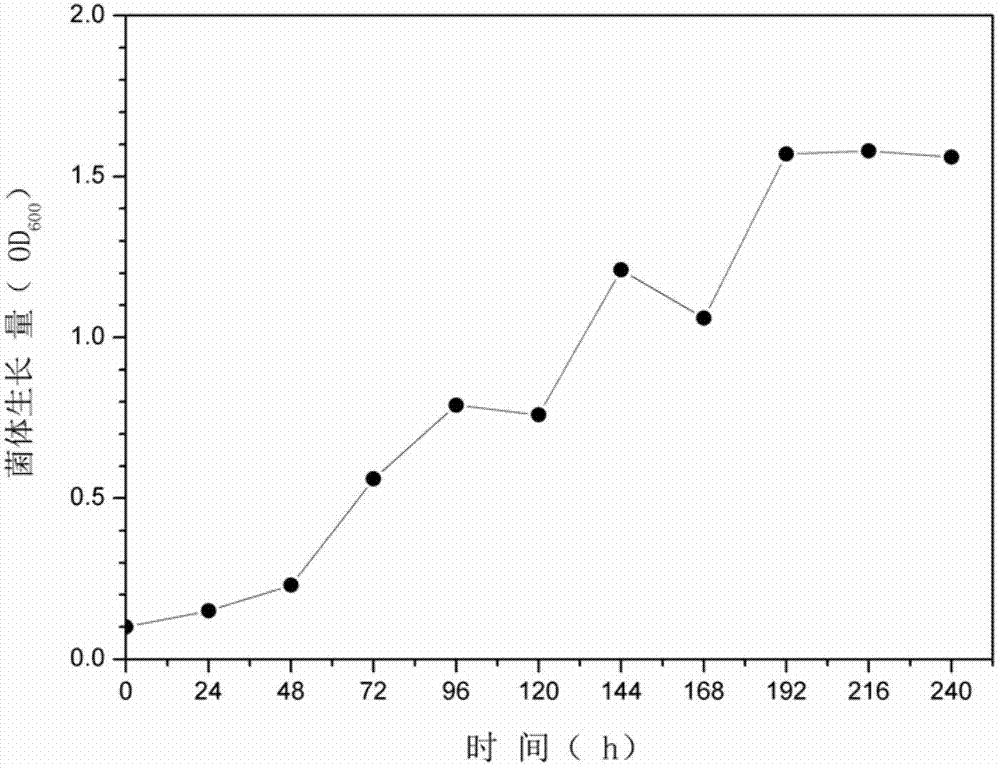
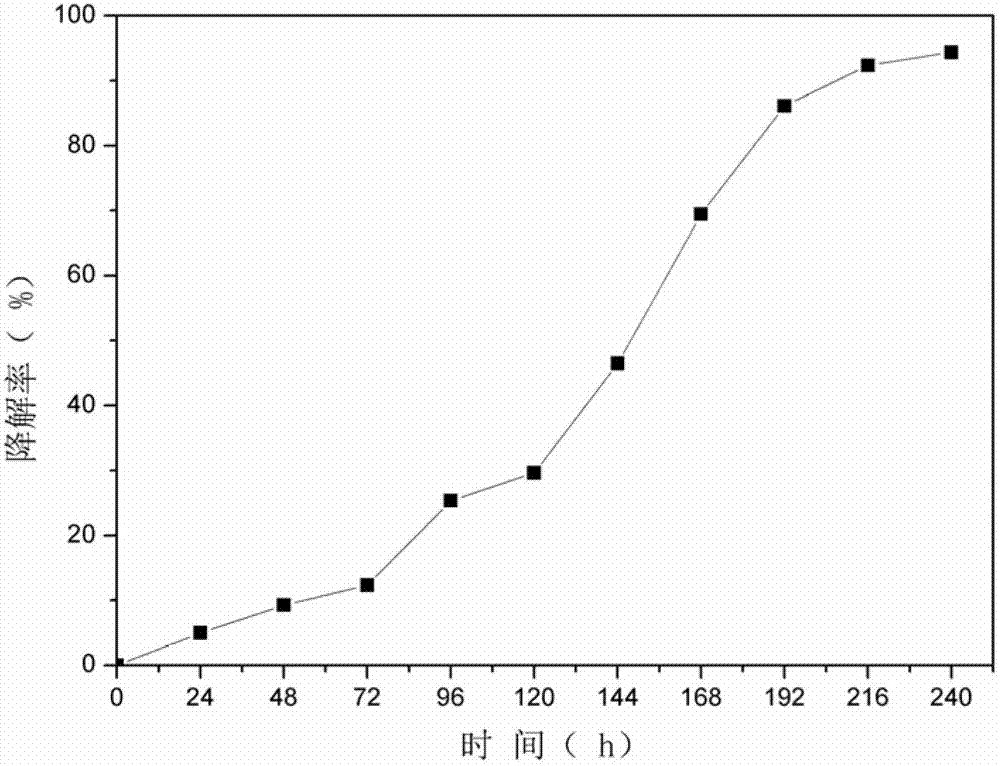
InactiveCN102888443AImprove degradation rateMicrobiological testing/measurementInorganic saltsMicrometer
The invention relates to a method for researching microbial degradation of petroleum pollutants under low-temperature high-salt conditions, which comprises the following steps: preparing a basic inorganic salt culture medium for degrading petroleum pollutants, filling 100mL of inorganic salt culture medium into a 250mL triangular flask, sealing, sterilizing at the high temperature of 121 DEG C for 20 minutes, and cooling to room temperature for later use; adding a low-temperature-resistant high-salt-tolerant strain into the inorganic salt culture medium, wherein the initial OD600 is 0.1; passing petroleum hydrocarbons through a 0.22-micrometer oil film to remove internal infectious microbes, and adding 0.5mL of the petroleum hydrocarbons into the inoculated inorganic salt culture medium; and after carrying out shake culture, taking samples every other 24 hours, and measuring the thallus concentration and remaining petroleum hydrocarbon concentration in the culture medium. The cell biomass variation of mycobacteria cp1 degrading petroleum hydrocarbons under the conditions of 10 DEG C, pH 7.2 and 200rpm proves that the OD600 reaches the maximum value 1.6 at the time of the 192nd hour, and remains constant until the 240th hour. The degradation rate for the petroleum hydrocarbons increases as the time changes, and reaches the maximum value 94.36% at the 240th hour.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for producing carotenoid through fermentation
InactiveCN105779551AImprove cold resistanceIncrease heat stressMicroorganism based processesFermentationFruit juiceCarotenoid
The invention discloses a method for producing carotenoid through fermentation. The method comprises the following steps: by taking yellow peach cannery trimmings as a main raw material, carrying out microwave fixation, frozen-breaking and biological enzymolysis to obtain fruit juice with relatively high carotenoid content, adjusting components to obtain a fermentation medium, inoculating oceanic red yeast producing the carotenoid with high yield into the fermentation medium, carrying out fractional inoculation and temperature shift fermentation so that maximization of proliferation of oceanic red yeast is realized, carrying out ultrahigh pressure homogenization, vacuum centrifugation and demulsification separation on fermentation broth to obtain emulsion, and extracting, separating and purifying the emulsion to obtain the carotenoid finished product, wherein the cell biomass of the fermentation broth is 38-52g / L, and the yield of the carotenoid is 47-61mg / L. The preparation method is simple, short in period, high in efficiency, energy-saving and environment-friendly, the whole course adopts a low temperature biologic processing technology, the production cost is reduced, the hidden environmental pollution danger is eliminated, and a solid foundation is laid for sustainable development of the technical field of deep processing of yellow peaches, so that the method disclosed by the invention has positive economic and social development significance.
Owner:BEIJING KEHUITONG WISDOM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method for lanthanon promoting saffron cell growth and increasing saffron essence content
InactiveCN1570087APromote growthHigh biomassUnknown materialsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologyRare-earth element
The invention relates to a method for promoting saffron growth and increasing crocin content by the application of rare earth element. It inoculates the saffron callus to the vegetable cell medium containing rare earth elements, cytomin and archusia, cultures for 15 to 30 days under 15DEG C-30DEG C, then again inoculates the callus to the vegetable cell medium containing rare earth elements, cytomin and archusia for culturing 15 to 30 days under 15DEG C-30DEG C. It can promote the saffron cell growth and obtain more saffron cell biomass in the same culturing time compared with the prior part. The crocin content is markedly increased and the crocin obtained does not easy to turn brown.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
METHOD OF PRODUCING MENINGOCOCCAL MENINGITIS VACCINE FOR NEISSERIA MENINGITIDIS SERO TYPES A,C,Y, and W-135
InactiveUS20080020002A1Yield maximizationYield minimizationAntibacterial agentsBacteriaConjugate vaccineSynechococcus
Methods for producing quadrivalent meningococcal meningitis polysaccharide and conjugate vaccines for serotypes A, C, Y and W-135 disclosed. Neisseria meningitidis fastidious medium was designed to maximize the yield of capsular polysaccharides and generate minimal cellular biomass and endotoxin in a short duration of fermentation. The crude polysaccharides are isolated, purified, and mechanically depolymerized by sonication. These purified polysaccharides were found in human clinical trials to be safe and immunogenic against meningococcal disease caused by N. meningitidis A, C, Y and W-135 serogroups in sub-Saharan Africa. In the preferred embodiment, the polysaccharides are conjugated to carrier proteins of diphtheria or tetanus toxiod to an average molecular size of 5100 to 9900 Daltons and provide broad spectrum protection to humans of all ages. Accelerated polysaccharide production and the efficacy of the resulting vaccine are demonstrated.
Owner:REDDY JEERI R
Method for effectively suppressing initial-stage browning phenomenon of liquorice cell suspension culture
InactiveCN103589679APromote growthThe relative degree of browning decreasedPlant cellsLiquoricesSuspension culture
The invention provides a method for effectively suppressing a browning phenomenon after liquorice cell solid-liquid transformation with simple operation, and belongs to the field of plant cell culture. The method comprises the steps of selecting and inoculating seed cells, culturing by controlling rotating speed in different stages, rinsing the cells and carrying out suspension culture. The browning phenomenon after the liquorice cell solid-liquid transformation process is obviously suppressed; cell biomass accumulation is obviously increased; compared with a control group (without addition of an inhibitor, rotating speed control at different stages and rinsing process), the relative browning degree of the suspension system is reduced by 55.8% maximally, and the biomass (wet weight) accumulation is at most increased by 35.2%. The obtained liquorice suspension cells are uniformly dispersed, well in growth situation, and can be used as the excellent seed cells for further propagation or an excellent scientific research material.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for detection of living cell biomass of phanerochaete chrysosporium under heavy metal stress
InactiveCN103424370AImprove processing efficiencyRegulating Processing EfficiencyColor/spectral properties measurementsColor reactionAbsorbance
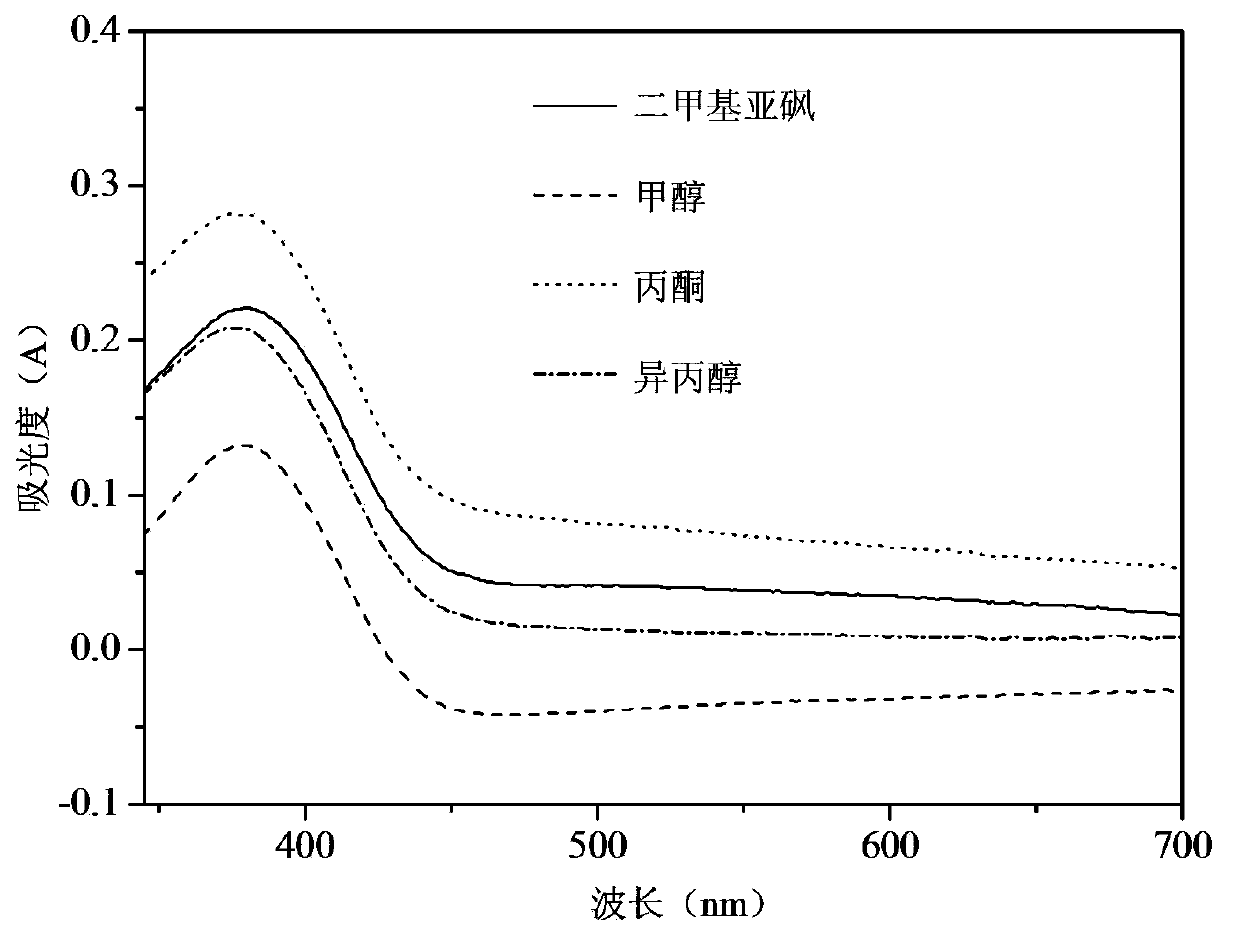
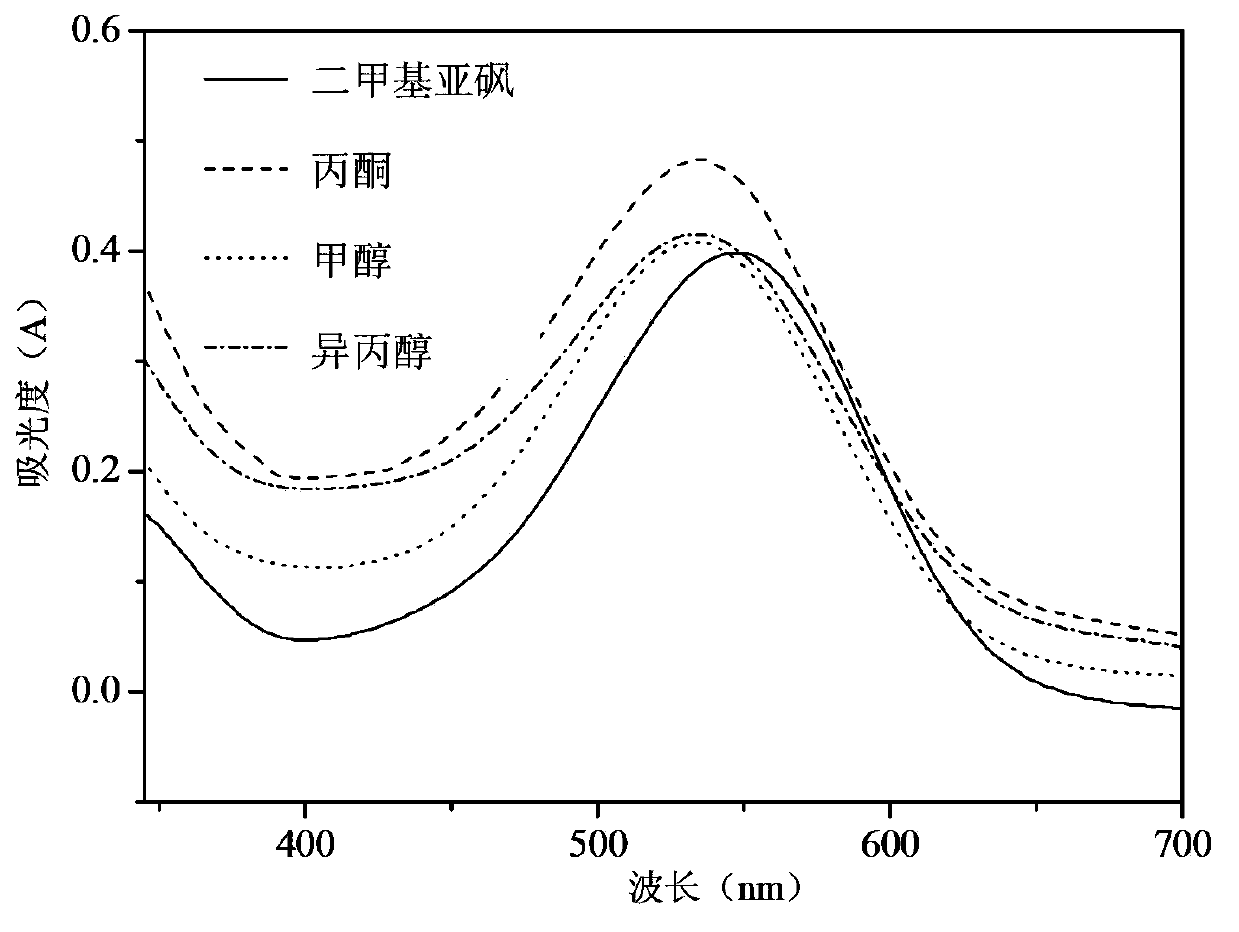
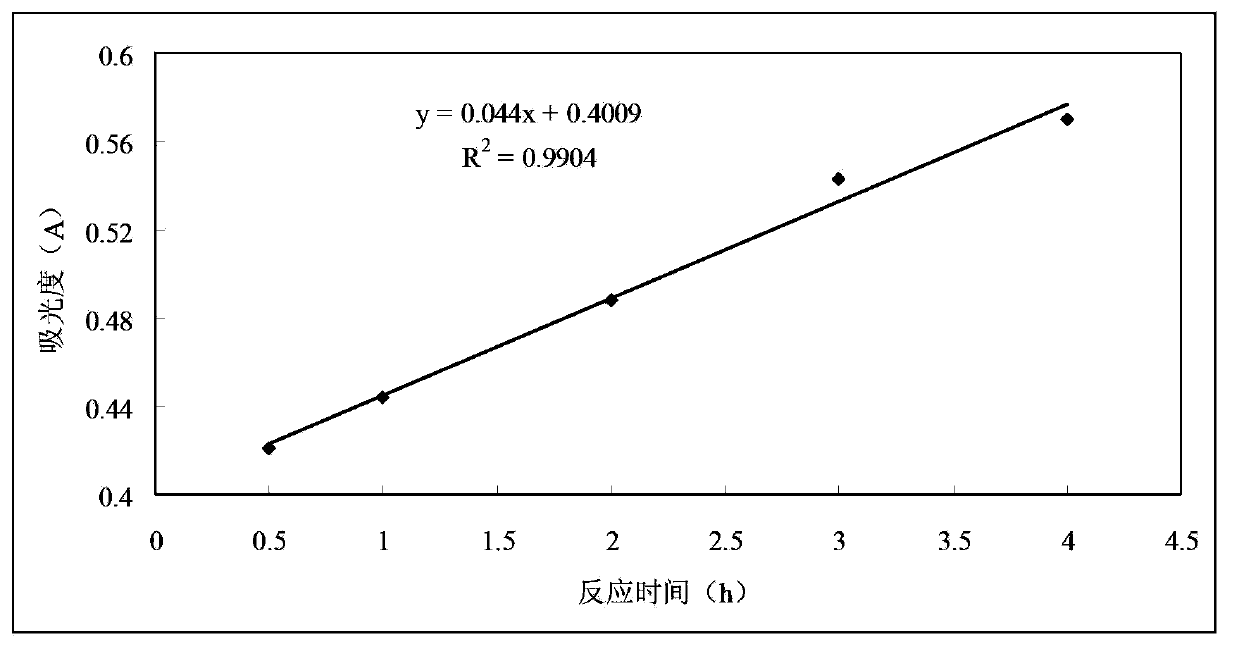
The invention discloses a method for detection of the living cell biomass of phanerochaete chrysosporium under the heavy metal stress. The method comprises the steps as follows: 1, pellet culturing: adding the phanerochaete chrysosporium into a liquid culture medium for constant-temperature culturing, and adding heavy metal solution for stress treatment; 2, chromogenic reaction: adding the phanerochaete chrysosporium pellets obtained after heavy metal stress into sterile MTT solution and performing chromogenic reaction for 0.5-4 h at the temperature of 30-50 DEG C, and then quickly adding hydrochloric acid solution to stop the reaction, so as to obtain the mixed liquor after reaction; 3, centrifugal treatment: performing centrifugal treatment on the mixed liquor to remove the liquid supernatant and obtain the lower sediment; 4, extracting detection: adding an extracting agent into the sediment for extraction, determining the absorbance of the extract liquor, and calculating the living cell biomass of the phanerochaete chrysosporium under the heavy metal stress. According to the invention, the detection method is simple and convenient, wide in application and strong in practicability.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for detecting microalgae content in ship ballast water
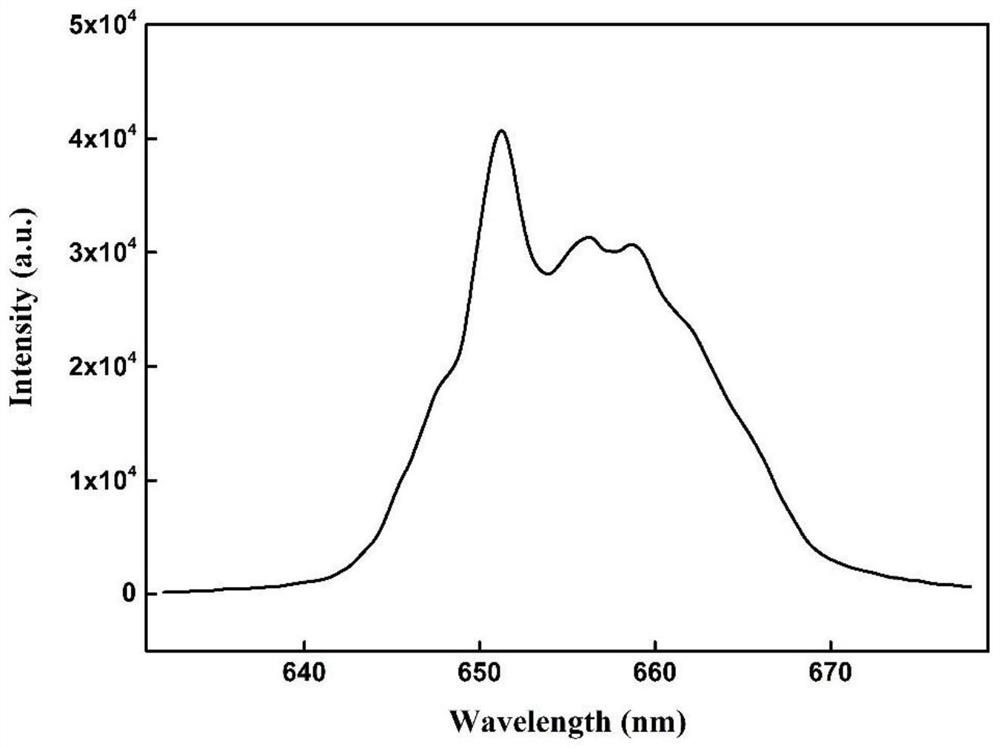
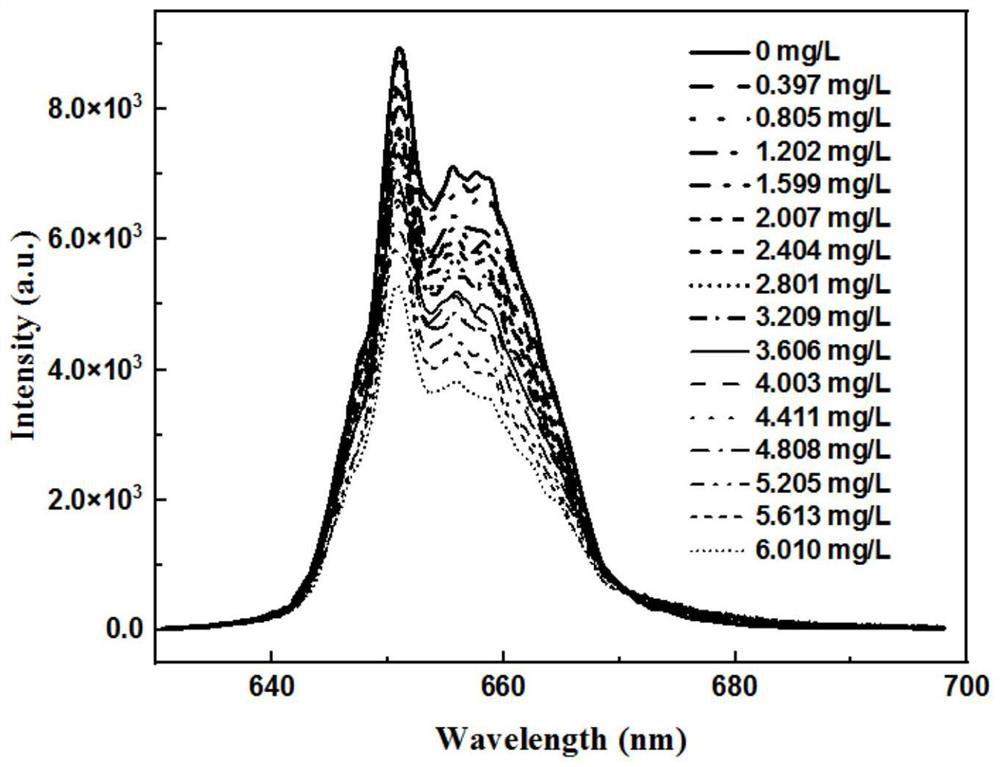
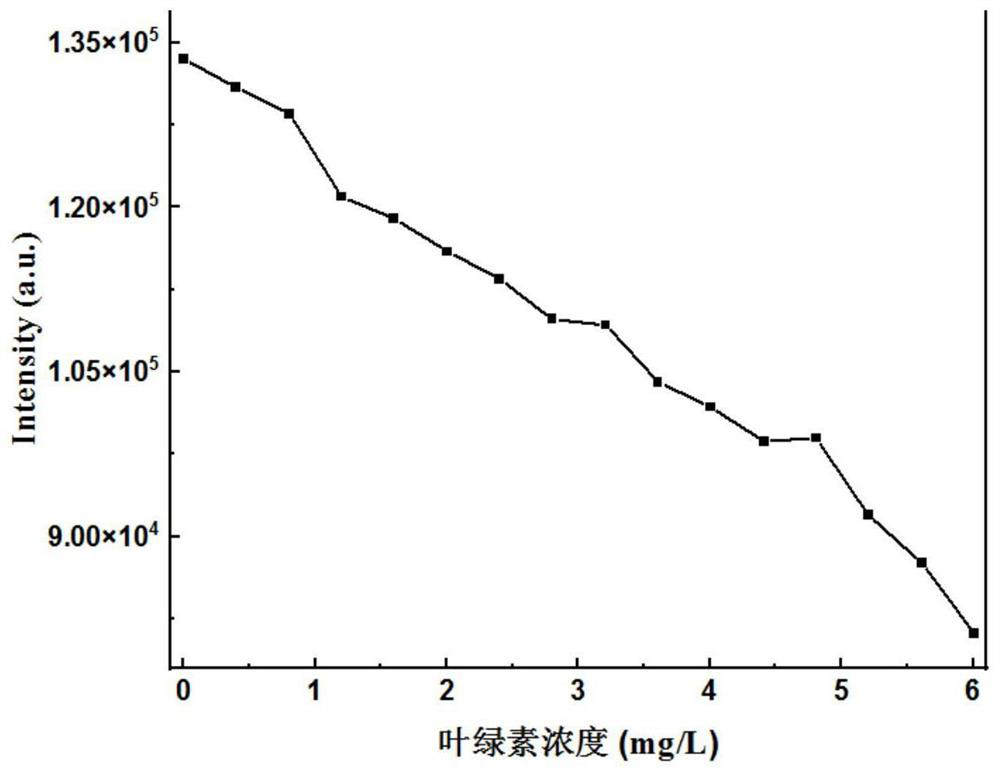
ActiveCN114563362ADoes not cause spontaneous background fluorescenceLight damage is smallColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesLuminous intensity
The invention belongs to the technical field of ship ballast water microalgae content detection, and particularly relates to an up-conversion nano fluorescent probe which realizes rapid detection of microalgae content through competitive emission. According to the method, a red up-conversion nano fluorescent probe is adopted, red luminescence of the fluorescent probe is highly overlapped with the maximum absorption peak of ballast water microalgae chlorophyll a under excitation of near-infrared light, a relation curve of luminescence intensity and the content of chlorophyll a is established through competitive luminescence measurement, and the content of the chlorophyll a is determined according to the corresponding relation of the content of the chlorophyll a and the microalgae cell biomass. And establishing a relation model between the luminous intensity and the microalgae cell biomass so as to calculate the microalgae biomass in the ballast water sample. According to the present invention, the rapid detection of the microalgae biomass can be achieved, the operation is simple and convenient, the sensitivity is high, the safe long wavelength near-infrared light is adopted as the excitation source, the light damage to the organism is reduced, the spontaneous background fluorescence of the microalgae cannot be caused, the detection sensitivity can be improved in the order of magnitude, and the method is suitable for promotion and application.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Method for producing carotenoid by utilizing canned yellow peach leftovers through fermentation
InactiveCN105755086AImprove cold resistanceIncrease heat stressFungiOrganic chemistryFruit juiceHigh pressure homogenization
The invention discloses a method for producing carotenoid by utilizing canned yellow peach leftovers through fermentation. The method comprises the following steps: by taking the canned yellow peach leftovers as main raw materials, obtaining juice with relatively high carotenoid content through microwave color fixation, frozen-breaking and biological enzymolysis; obtaining a fermentation culture medium after regulating components; carrying out fractional inoculation and variable-temperature fermentation on oceanic red yeast which is inoculated with high-yield carotenoid for proliferating the oceanic red yeast to the greatest extent; obtaining emulsion after carrying out high-pressure homogenization, vacuum centrifuging, and emulsion breaking separation on fermentation liquor; and extracting, separating and purifying the emulsion to obtain a finished product carotenoid, wherein cell biomass of the fermented liquor is 38-52g / L, and the yield of the carotenoid is 47-61mg / L. The preparation method is simple, is short in period, is high in efficiency, and is environmentally friendly, saves energy resources, adopts a low-temperature biological processing technology throughout the process, reduces the production cost, eliminates environmental pollution hidden trouble, lays a solid foundation for the sustainable development of the technical field of the yellow peach deep processing, and has positive economic and social development significance.
Owner:临沂市康发食品饮料有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com