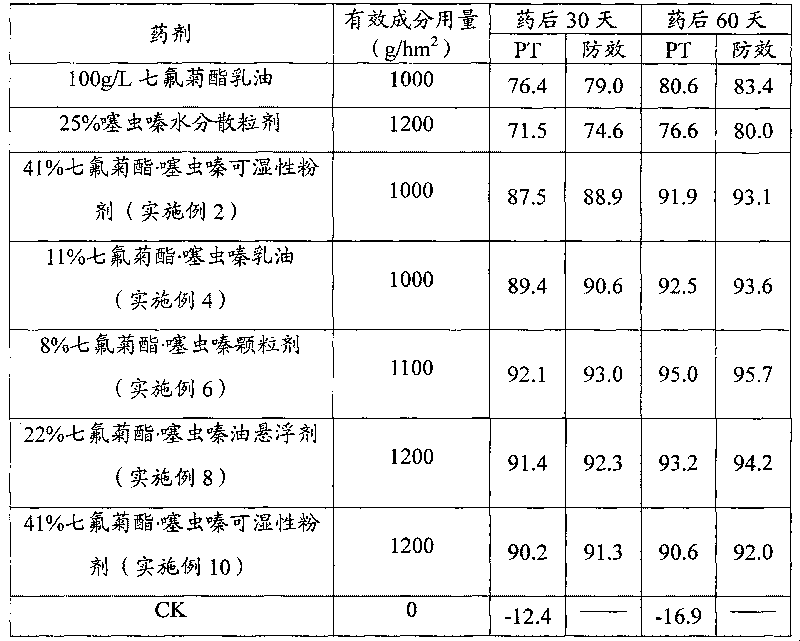
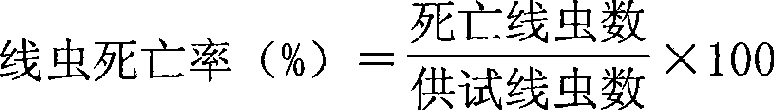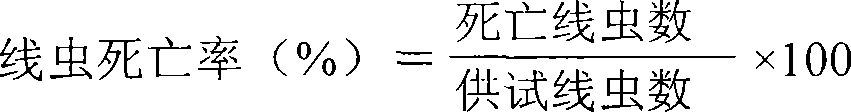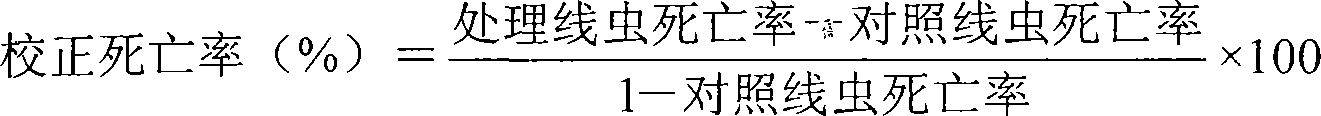Patents
Literature
117 results about "Dauer larva" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dauer (German "die Dauer", English "the enduring", "the duration" in the meaning of "a length of time", from A.G. Fuchs (1937) Neue parasitische und halbparasitische Nematoden bei Borkenkäfern und einige andere Nematoden, English New Parasitic and Half-parasitic Nematodes with Bark-Beetles and Some Other Nematodes) describes an alternative developmental stage of nematode worms, particularly rhabditids including Caenorhabditis elegans, whereby the larva goes into a type of stasis and can survive harsh conditions. Since the decision to enter the dauer stage is dependent on environmental cues, it represents a classic and well studied example of polyphenism. The Dauer state is given other names in the various types of nematodes such as ‘diapause’ or ‘hypobiosis’, but since the C. elegans nematode has become the most studied nematode, the term ‘dauer stage’ or 'dauer larvae' is becoming universally recognised when referring to this state in other free-living nematodes. The dauer stage is also considered to be equivalent to the infective stage of parasitic nematode larvae.
Aspergillus niger fungus capable of poisoning plant parasitic nematodes, preparation method and application thereof
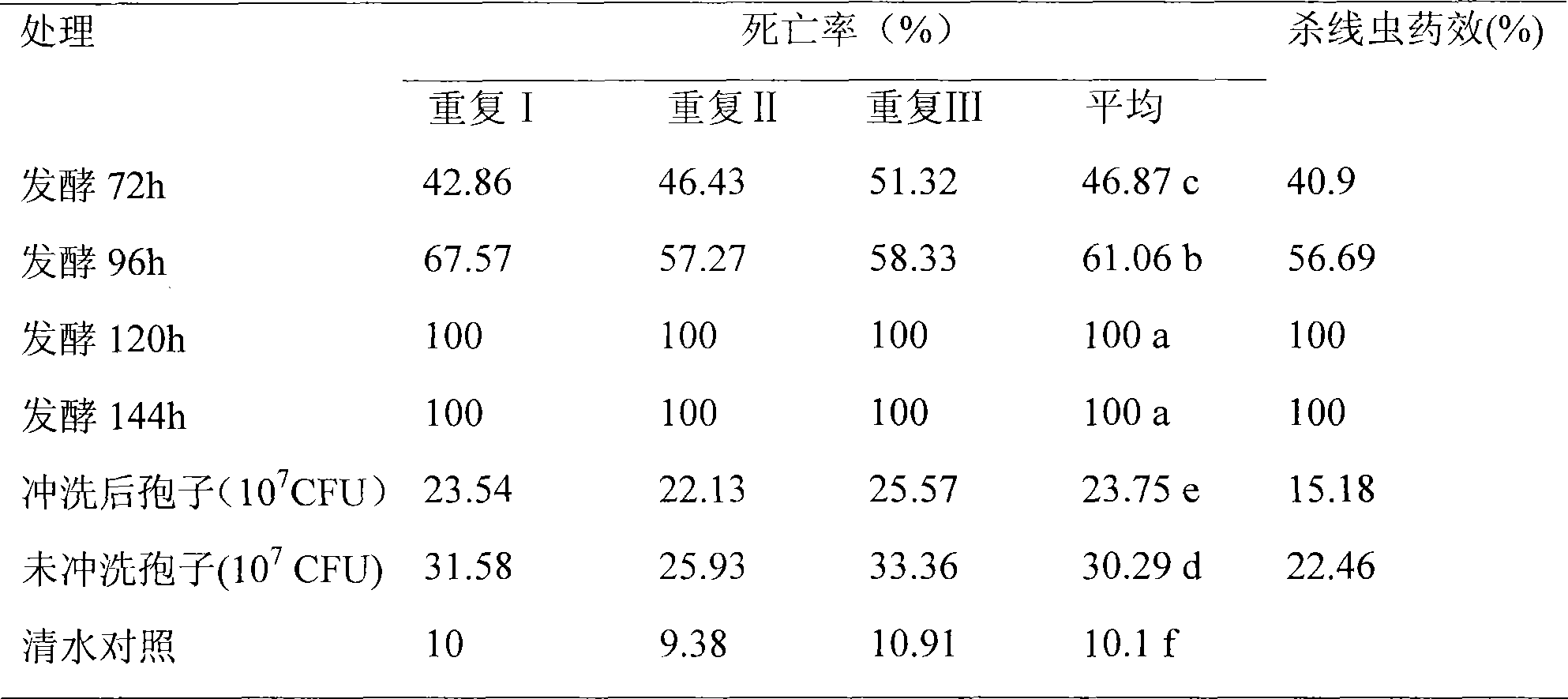
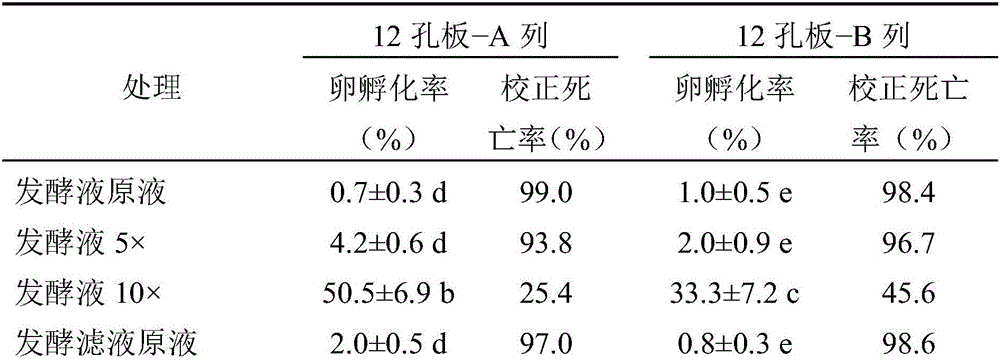
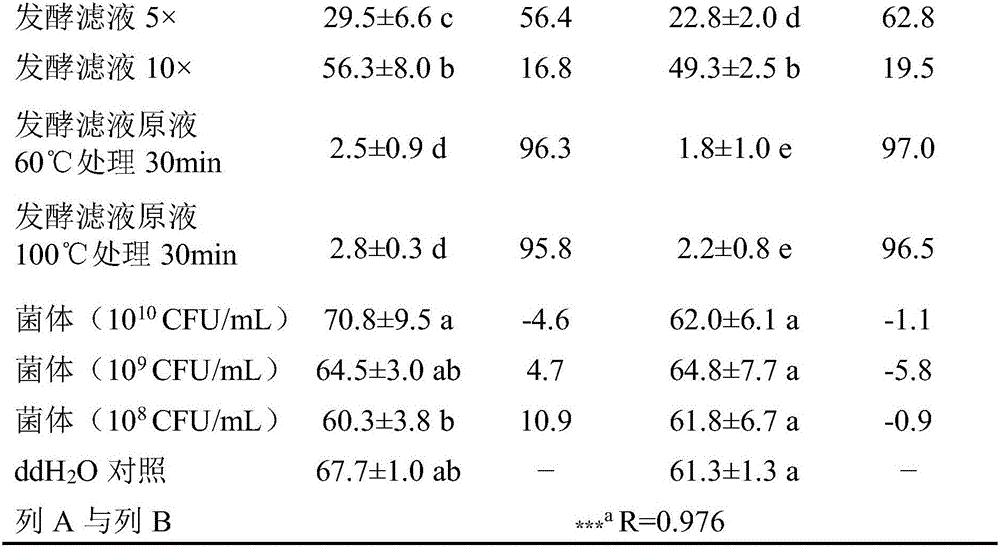
The invention relates to a culture method of a fungus capable of poisoning plant parasitic nematodes, and a preparation method of a metabolite thereof and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microbial pesticides. A fungus strain (Aspergillus niger Y-61) related in the invention was collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on August 7, 2008, and the collection number is CGMCC No.2631. The taxonomic status of the Y-61 is a mitosporic fungus, hyphomycetes, moniliales, moniliaceae, aspergillus and aspergillus niger. The fungus metabolite is prepared by liquid fermentation and culture, has outstanding characteristics of high toxicity to the plant parasitic nematodes, especially root-knot nematodes, and has obvious nematodes killing effect; and the influence of the strain fermentation broth on Meloidogyne incognita juveniles (J2) and oocyst hatching is determined indoors. Treatment of the fermentation broth with different diluted concentrations is significantly different from the aseptic water treatment, and the preventive effect of the fermentation broth with less than one-fifth concentration is be equivalent to that of 10mug / ml of cadusafos. The fungus has good application and development prospects.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Insecticidal composition for controlling underground pest
ActiveCN101755817AImprove the effect of prevention and controlReduce pollutionBiocideNematocidesMeloidogyne incognitaSynergy
The invention discloses an insecticidal composition which comprises an active substance A and an active substance B which are used as effective components, wherein A is tefluthrin, B is one of neonicotine insecticides comprising acetaniprid, imidacloprid and thiamethoxam, and the mass ratio of A to B is 60:1-1:80. The composition of the invention has obvious synergy, can lower the consumption of the effective components and reduce the insecticide applying times, is used for controlling various agricultural pests, and is especially suitable for controlling scarab larvae, flea beetle larvae androot-knot nematode.
Owner:SHENZHEN NOPOSION AGROCHEM
Drug controlling plant nematodes
ActiveCN105145633AAvoid harmImprove the effect of prevention and controlBiocideFungicidesPlant nematodeBegonia aptera
The invention discloses a drug controlling plant nematodes. Effective ingredients comprise natural saponin, and the natural saponin is one or more of soapnut saponin, gleditsioside, tea saponin, saikosaponin, esculentoside, ursolic acid, vulgarsaponin and begonia yunnanensis Levl. saponin. Preferably, the drug also comprises lysobacter antibioticus, possseses relatively good killing effect on plant nematodes, nematode host cerambycidae ovum and larva and the like, and additionally, is extremely excellent in controlling effect on fruit tree gummosis. The exploited drug is environment-friendly type, is increased in controlling effect, also avoids environment harm caused by usage of a large amount of severely toxic pesticides, and possesses great reality meaning for protecting our country forest resource and ecological environment and recovering economic loss.
Owner:北京泰克美高新技术有限公司
Preparation method of streptomyces having activity for poisoning plant nematodes and uses thereof
The invention relates to a culturing method of streptomyces with the function of poisoning plant menatodes and a preparation method and application of the metabolin, belonging to the technical field of microbial pesticides. The streptomyces bacterial strain Snea253 is Streptomyces venezuelae, stored in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on January 18, 2008 (address: Datun Road, Zhaoyang District, Beijing; post code: 100101) with CGMCC No.2348. The streptomyces bacterial strain Snea253 is classified in species Streptomyces venezuelae, genus streptomyces, order actinomycetales, class actinomycetales, phylum actinomycetales. The culturing method of streptomyces with the function of poisoning plant menatode has the advantages that: through liquid fermentation culture preparation, the metabolites can poison plant parasitic nematodes, in particular Heterodera glycines, Meloidogyne spp. and Aphelenchoides besseyi with distinct effects; the fermentation liquid of the bacterial strain has higher poisonous activity to second instar larva of Heterodera glycines, and can remarkably restrain cyst hatching; the treatment of fermentation liquid with different diluted concentration is significantly different from the treatment of sterile water; the insecticidal effects of stock fermentation solution can reach above 90%, and the effects of greenhouse experiment are obvious; at the same time, the bacterial strain can remarkably poison the Meloidogyne spp. and Aphelenchoides besseyi with good application and development prospects.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
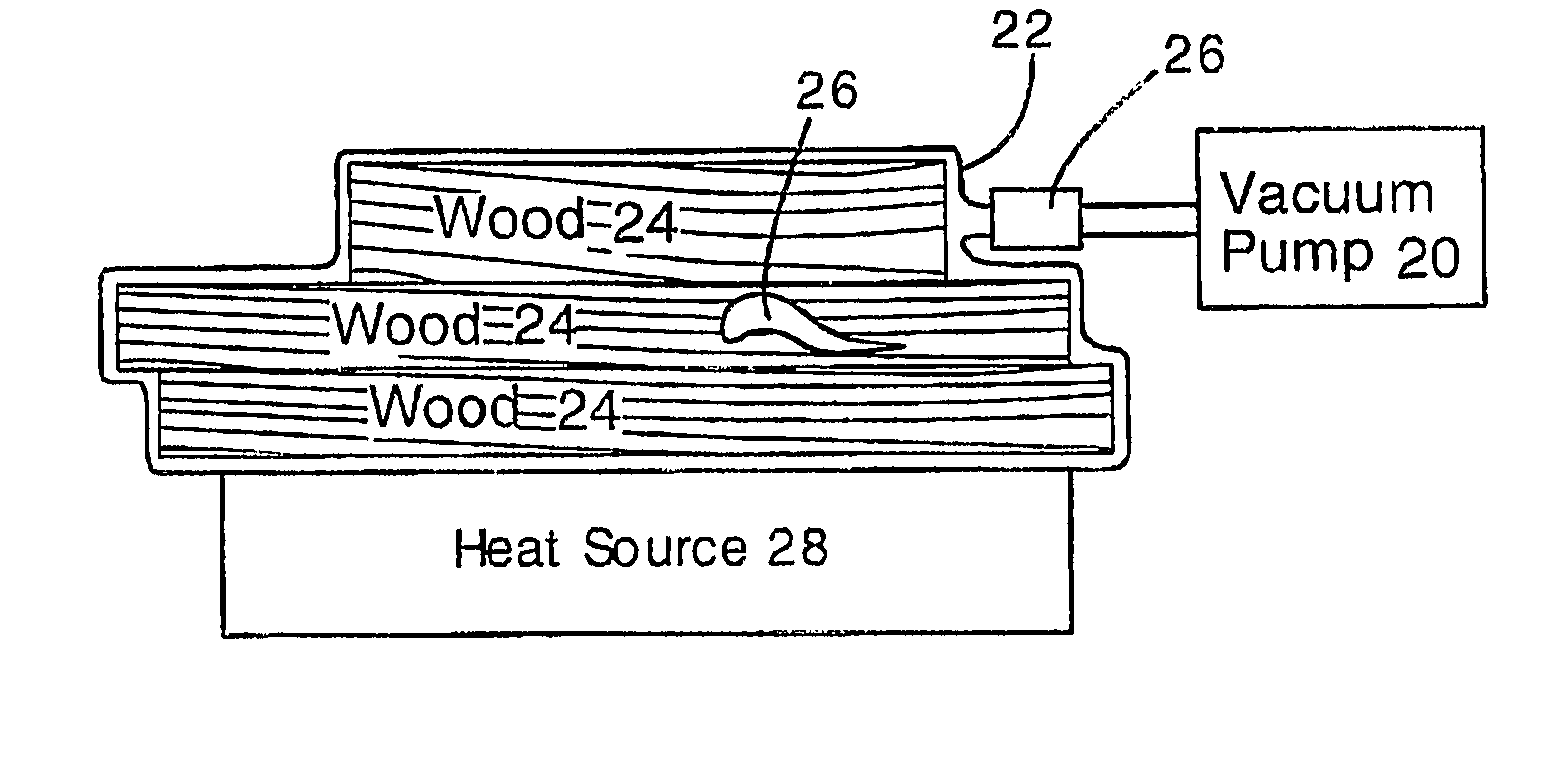
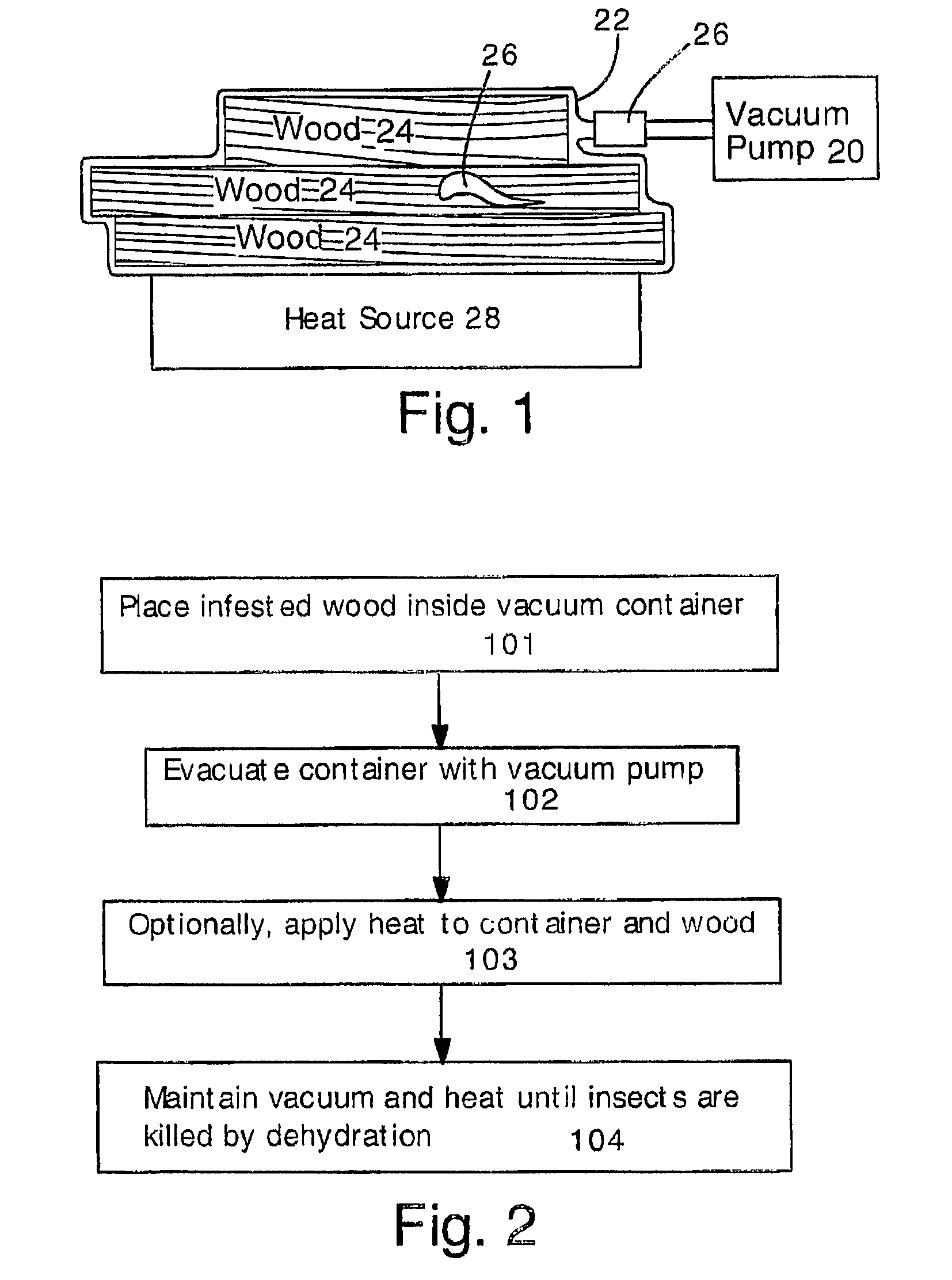
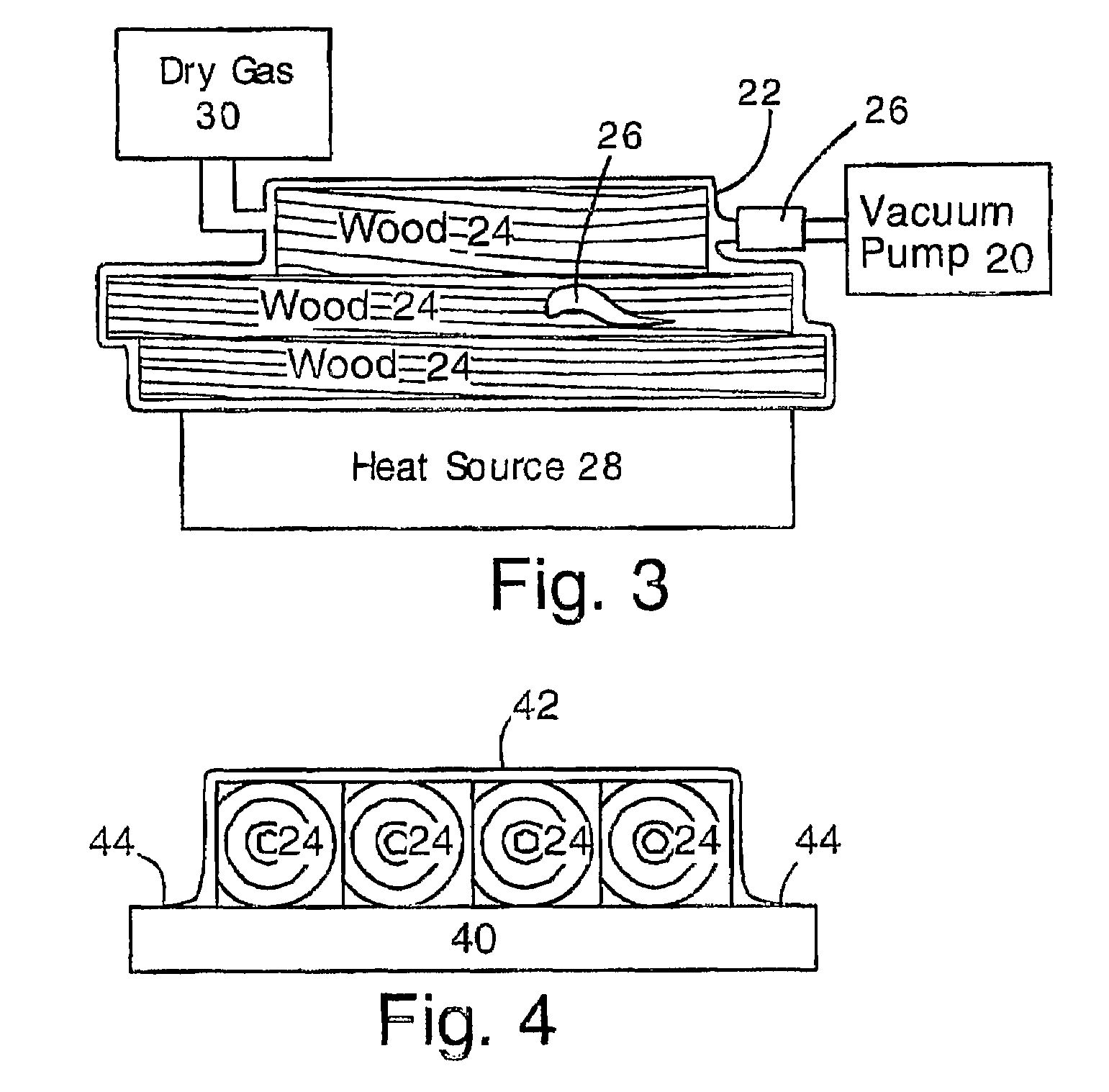
Killing insect pests inside wood by vacuum dehydration
InactiveUS7739829B2Faster and reliable destructionReduce moisture contentBiocideDrying solid materials with heatSolid woodNematode
Insect pests can be transported around the world in wooden shipping containers. To prevent the spread of wood-borne insect pests, it is necessary to kill insects within the wood. The wood is placed in a vacuum container having a flexible wall. The flexible wall presses against the wood and enables the wood to be heated by conduction. The wood and flexible wall can to be heated by contact with ambient or heated air, for example. Desiccant or dry air can be used to increase the rate of dehydration. Insects in the wood are typically killed after losing 25-50% of their body weight by dehydration. This technique will kill beetle larvae, nematodes and other invasive and destructive insects that live inside solid wood, and is particularly applicable for rendering wood acceptable for use in pallets and other containers shipped internationally.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
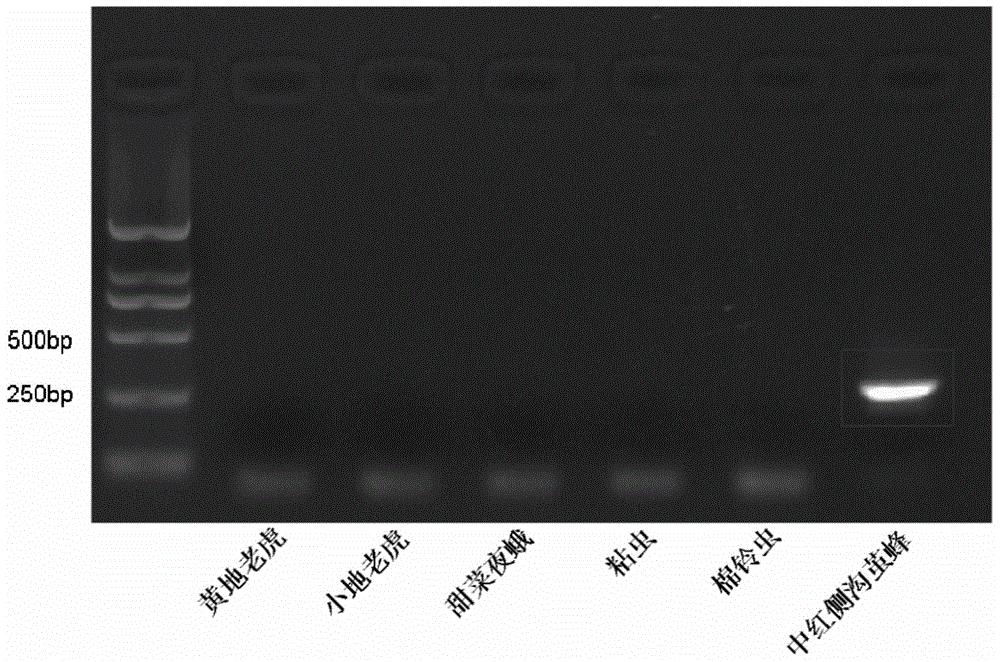
Method for assisting in identifying root-knot nematodes and special primer pair thereof
InactiveCN102102100AShorten purification culture timeHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyRoot-knot nematode
The invention discloses a method for assisting in identifying root-knot nematodes and a special primer pair thereof. The invention provides a special primer consisting of a primer pair A and a primer pair B, wherein the primer pair A consists of DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) shown as a sequence 1 in a sequence table and DNA shown as a sequence 2 in the sequence table; the primer pair B consists of DNA shown as a sequence 3 in the sequence table and DNA shown as a sequence 4 in the sequence table; and the special primer can be used for assisting in identifying the root-knot nematodes. The method provided by the invention can be used for correctly distinguishing four common root-knot nematodes, has high sensitivity, and can be used for identifying the types of root-knot nematodes by using a single egg capsule or a single second stage juvenile. The root-knot nematode can be directly separated from diseased tissues without purification culturing, the purification culturing time of the nematodes can be greatly shortened, and the detection efficiency can be improved.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Rapid inspection for nematode larva of dormant pine wood
InactiveCN1645135AImprove the detection rateEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementInsect catchers and killersPotassium nitrateNematode
A quick quaratine method of dormant nematoda larva in pine wood includes cutting wood into pieces and packing them by etamine to put it in container with culture solution, placing the container at 20-41 deg.c for separation culture, filtering the solution with 100 M and 500M screen mesh and collecting nematode from the solution by 500m screen mesh for being detected with microscope. The culture solution is prepared as using hydrogen peroxide as base solution then adding one or multiple of nutrition solution, gibberellin, potassium nitrate and clenbuterol hydrochloride for combination.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE COMPREHENSIVE TECH CENT JIANGXI ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
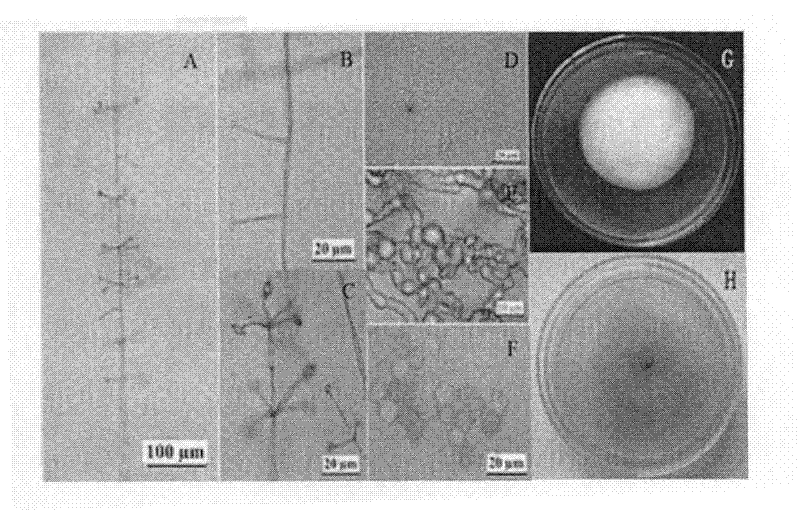
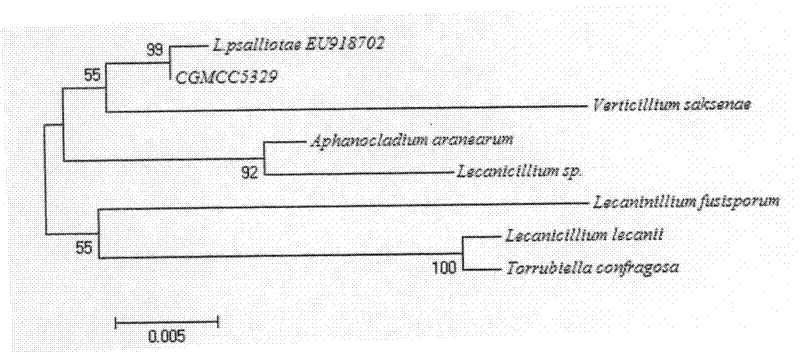
Lecanicillium psalliotae strain
InactiveCN102417886AIncrease enzyme activityIncreased parasitic abilityBiocideFungiDegradative enzymeLife stage
The invention discloses a lecanicillium psalliotae strain with the preservation number of CGMCC NO: 5329. The strain can colonise spawns, two-year-old larvae and female adults at different life stages of rootknot nematode. Activations of chitinous substance degradative enzyme and excisionenzyme generated by the strain can be respectively determined through an N-acetyl glucosamine method and a p-nitrobenzene method, the enzymatic activities thereof can reach 3.98 U / h.mL and 0.38 U / h.mL, and higher activity of the produced chitinous substance enzyme can be detected at different temperature (27 DEG C-75 DEG C) and different pH (3.0-7.0); and the influence of chitinous substance enzyme extract produced by the strain on eclosion of rootknot nematode spawns is determined in vitro, and the inhibition ratio and the destruction ratio of enzyme solution on relative eclosion of the spawns are respectively 94.52 percent and 84.32 percent. The lecanicillium psalliotae strain disclosed by the invention is applied to biological control of crop rootknot nematodiasis, provides an effective way for protecting sweet potatoes, fruits, vegetables in north China and particularly controlling destructiverootknot nematodiasis, and has obvious ecological benefit, economic value and social value.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Biological medicament for preventing and treating plant parasitic nematode and uses thereof
ActiveCN101508968AHigh poisonous activityInhibition hatchingBiocideBacteriaMetaboliteBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention discloses a biological medicine for preventing and curing plant parasitic nematode and application thereof. The active ingredient of the biological medicine is Streptomyces rubrogriseus HDZ-9-47 CGMCC No 2878. The plant parasitic nematode is prevented and cured by using the biological medicine in the invention, and the results show that the Streptomyces rubrogriseus HDZ-9-47 CGMCC No 2878 and the metabolite thereof have very strong toxic activity for eggs of Meloidogyne incognita and can obviously inhibit hatching of eggs, and have obvious parasitization for eggs and egg capsules of Meloidogyne incognita; when Streptomyces rubrogriseus HDZ-9-47 CGMCC No 2878 and the metabolite thereof are mixedly used, the effect of insect disinfestation on Meloidogyne incognita can reach 100%. The greenhouse experimental results of tomatoes show that the Streptomyces rubrogriseus HDZ-9-47 CGMCC No. 2878 has very good effect of killing nematode. The biological medicine in the invention has good application development prospect for prevention and cure of plant parasitic nematode.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Plant insecticide for preventing and treating vegetable root nematodes and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105901038AImprove immunityImprove stress resistanceBiocidePest repellentsBiotechnologyAntibiosis
The invention discloses a plant insecticide for preventing and treating vegetable root nematodes and a preparation method thereof. The plant insecticide is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 20-30 parts of garlic juice, 15-25 parts of cortex granati, 15-25 parts of fructus cnidii, 10-20 parts of picrorhizae, 5-10 parts of onion juice, 2-5 parts of melia azedarach leaves and 2-5 parts of polygonum hydropiper. The plant insecticide adopts a plurality of types of natural compound active substances, has insect killing, insect repelling, larva growth and development inhibiting, sterilizing and antibacterial effects, and also has the effect of preventing diseases and disinfecting. The plant insecticide has good insect killing and insect repelling effects and strong selectivity, is safe and stable for people and livestock, has no pollution to the environment, and has no damages to crops.
Owner:方有历
Ochrobactrum pseudogrignonense and applications of Ochrobactrum pseudogrignonense in prevention and control of plant parasitic nematodes
ActiveCN106244480AHas a growth-promoting effectSynergisticPlant growth regulatorsBiocideAbove groundMicrobial agent
The present invention provides a strain of Ochrobactrum pseudogrignonense NC1 and applications of the biocontrol microbial agent of Ochrobactrum pseudogrignonense NC1. According to the present invention, the results of the biological test of Ochrobactrum pseudogrignonense NC1 fermentation broth on the egg and the second instar larvae of Melanogyne incognita show that the strain can inhibit the Melanogyne incognita egg hatching and the second instar larvae activity through the volatile nematode killing active substance in the fermentation broth; after the biocontrol microbial agent prepared by using the Ochrobactrum pseudogrignonense NC1 as the active component is applied on potted tomatoes, the test results show that the strain can significantly increase the tomato above-ground part fresh weight, achieves the Melanogyne incognita prevention effect of 62.5%, and has the effect equivalent to the nematode killing agent 10% fosthiazate; and the Ochrobactrum pseudogrignonense NC1 and the biocontrol microbial agent thereof provide good application prospects in prevention and control of root-knot nematode in vegetables.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bacillus firmus for killing plant parasitic nematodes, and preparation method and application thereof
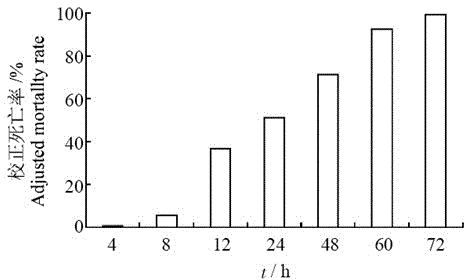
The invention relates to blastema firmus for killing plant parasitic nematodes, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The blastema firmus for killing the plant parasitic nematodes is a wild type strain of the blastema firmus YBf-10 which is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection in June 14th, 2012, with a preservation number of CCTCCNO. M2012233. The invention also provides the preparation method and the application of blastema firmus for killing the plant parasitic nematodes. Metabolic product of the blastema firmus YBf-10 is prepared by the fermentation of the blastema firmus YBf-10 in a common bacteria culture medium, and can be applied to kill root-knot nematodes. A corrected mortality rate of 24 h is over 50% and the corrected mortality rate of 72 h can reach 100% when the metabolic product acts on second-stage larvas; and inhibited egg hatching rate of 48 h is over 80% when the metabolic product acts on the eggs of the root-knot nematodes.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
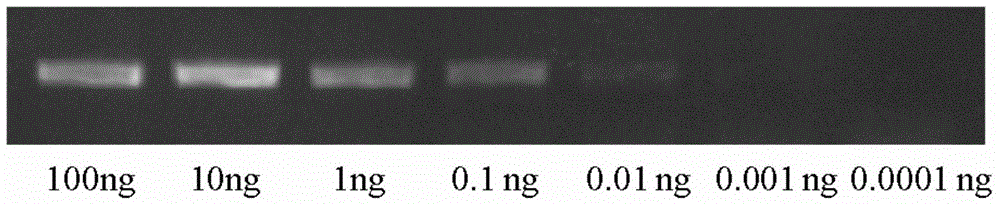
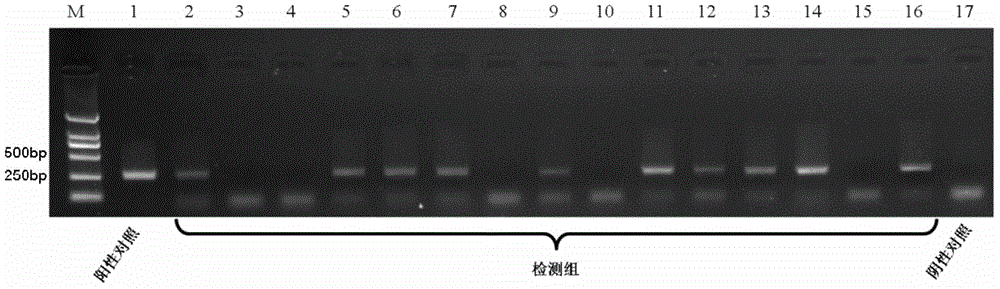
LAMP (Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification) primer group and method for rapidly detecting ditylenchus destructor from complex samples
ActiveCN107988383AEasy to detectEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPlant tissueDitylenchus destructor
The invention discloses an LAMP (Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification) primer group and method for rapidly detecting ditylenchus destructor from complex samples. The LAMP primer group comprises a pair of outer primers F3 / B3, a pair of inner primers FIP / BIP and a loop primer LF, and sequences of the primers are sequentially shown as SEQ ID NO. 1-5. The LAMP primer group and the detection method thereof disclosed by the invention have excellent specificity and sensitivity for detecting the ditylenchus destructor, individuals of the ditylenchus destructor in different insect stages (such as eggs, larva, female and male) can be detected, the ditylenchus destructor can be directly detected from multiple nematode mixed samples, plant tissue samples and soil samples, and the detection sensitivity can reach 1 / 1000 individual DNA. A novel detection method is provided for rapid detection and identification and early diagnosis of the ditylenchus destructor, and the method has the advantages ofbeing accurate, sensitive, stable and intuitive in result judgment. The LAMP primer group disclosed by the invention is simple and convenient to operate and high in practicality, and has important significances and application value on quarantine on ports and transfer and origin monitoring operations.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Bacillus cereus for preventing and controlling plant nematodes and application thereof
ActiveCN108676761AHigh poisonous activityReduce in quantityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPlant nematodeTriticeae
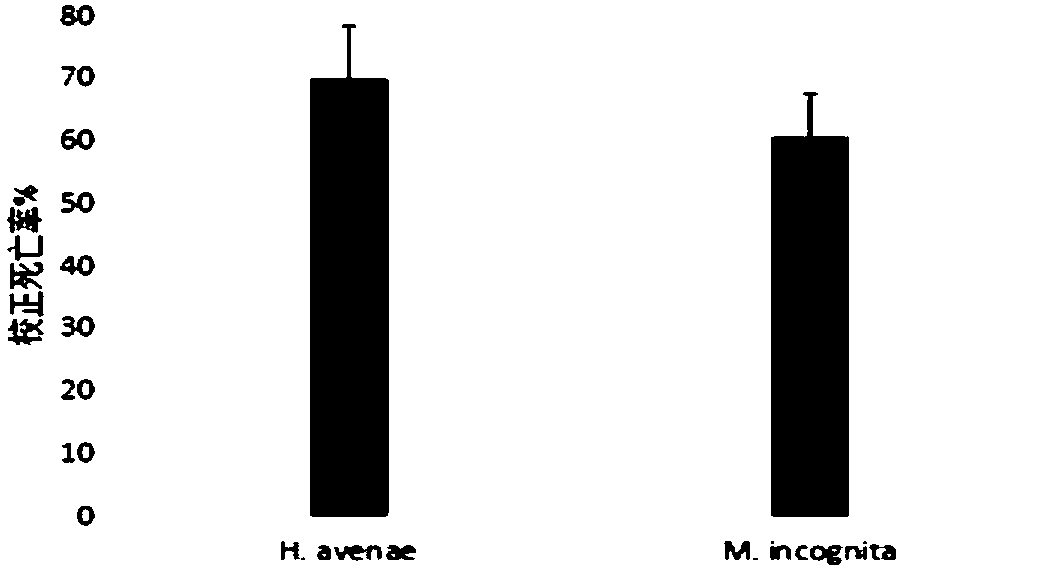
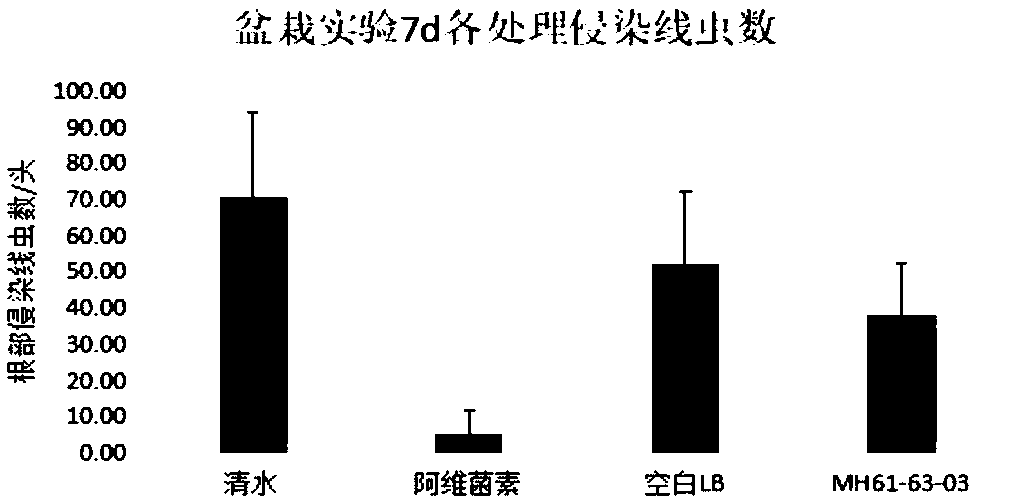
The invention discloses bacillus cereus for preventing and controlling plant nematodes and application thereof. The name of the bacillus cereus is MH61-63-03; the collection number is CGMCC No.15616.Experimental results prove that the bacillus cereus has the advantages that a fermenting filtrate of the bacillus cereus MH61-63-03 has higher toxic activity on second instar larvae of the plant nematodes; the number of nematodes in wheat roots treated by the fermenting filtrate MH61-63-03 is greatly reduced 7 days after the second instar larvae of the cereal cyst nematode are inoculated, and thereduction rate of insect is 26.82%; the number of sporocysts of each wheat plant treated by the fermenting filtrate MH61-63-03 is obviously reduced 65 days after the second instar larvae of the cerealcyst nematode are inoculated; the biological agent has good application and development prospect in the preventing and controlling of the plant nematodes.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for verifying anti-chalk disease traits of swarm by SNP marker
InactiveCN104498608AEasy to identifyRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementItalian beeDisease
The invention relates to a method for verifying anti-chalk disease traits of a swarm by an SNP marker. The method comprises the following steps: collecting larva samples from Italian swarms to be observed, extracting larva DNA, synthesizing a target primer, carrying out PCR with each extracted individual DAN as a template, carrying out electrophoresis detection on a PCR product, sequencing, finally comparing and analyzing the obtained sequencing result, and verifying the anti-chalk disease traits by judging whether the occurrence frequency PC of a C allele of randomly captured larva individuals from the swarm has difference with the occurrence frequency PT of a T allele in the SNP marker C2587245T. According to the invention, aiming at the problem that the Italian swarms are severely affected by the chalk disease, the SNP (C2587245T) marker related to anti-chalk disease of Italian bee larva provided from the molecular biology level for scientifically, accurately and quickly verifying the strength of the anti-chalk disease performance of the Italian swarms, the breeding cycle of the anti-chalk disease breeding of the Italian bees can be greatly shortened, the bee breeding speed is accelerated and the loss in the beekeeping industry caused by the chalk disease is reduced.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
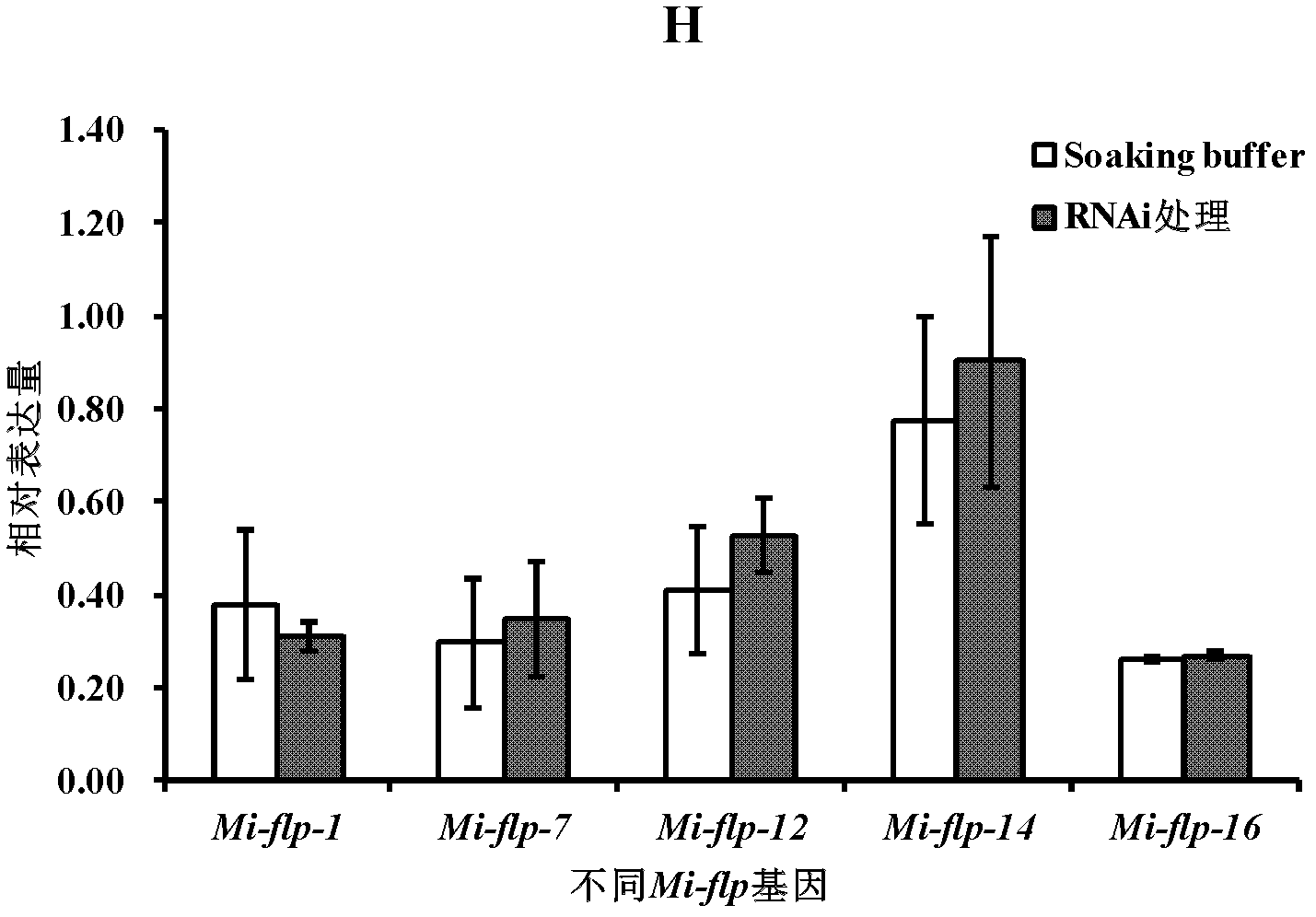
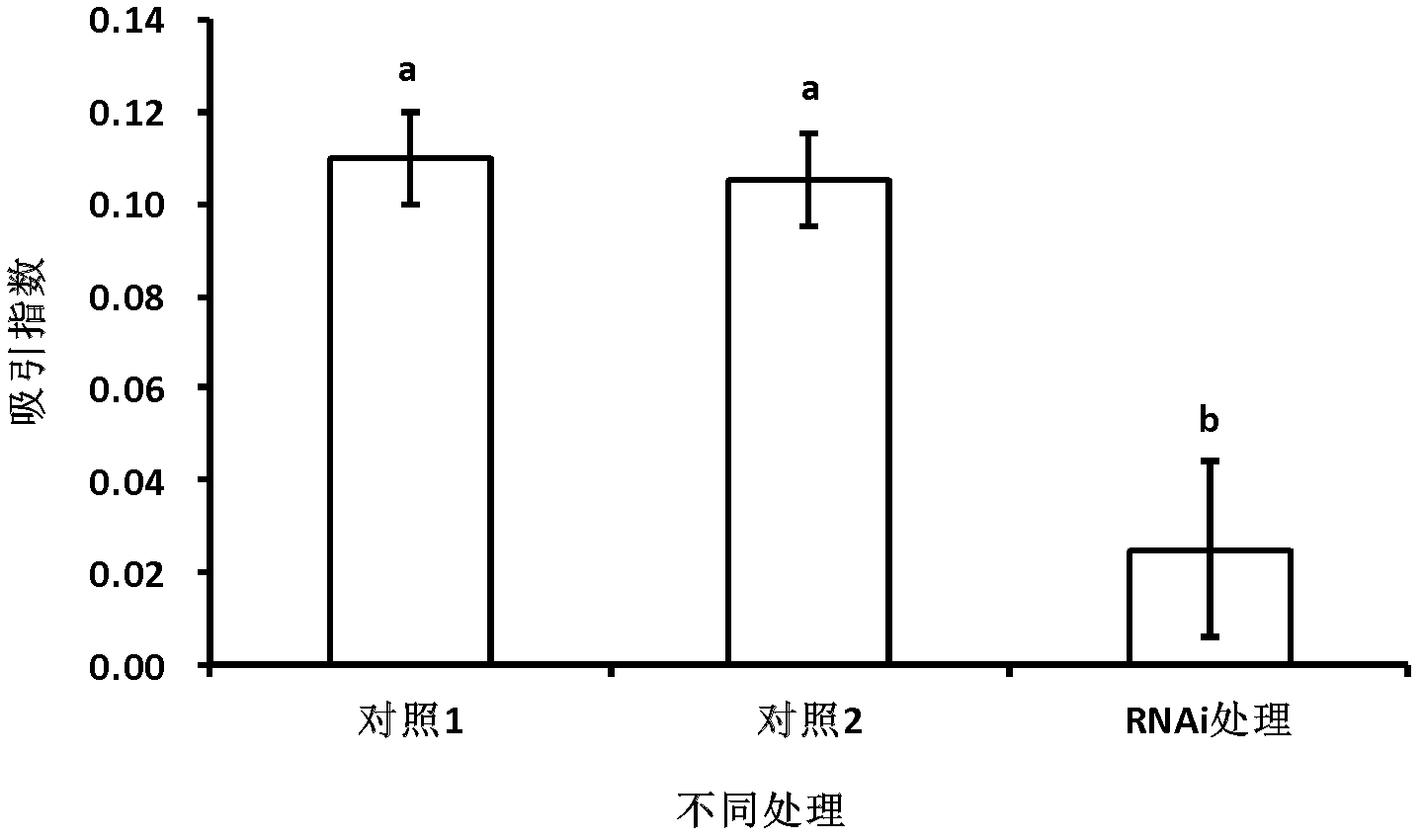
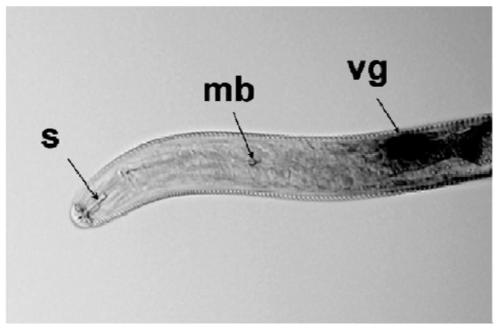
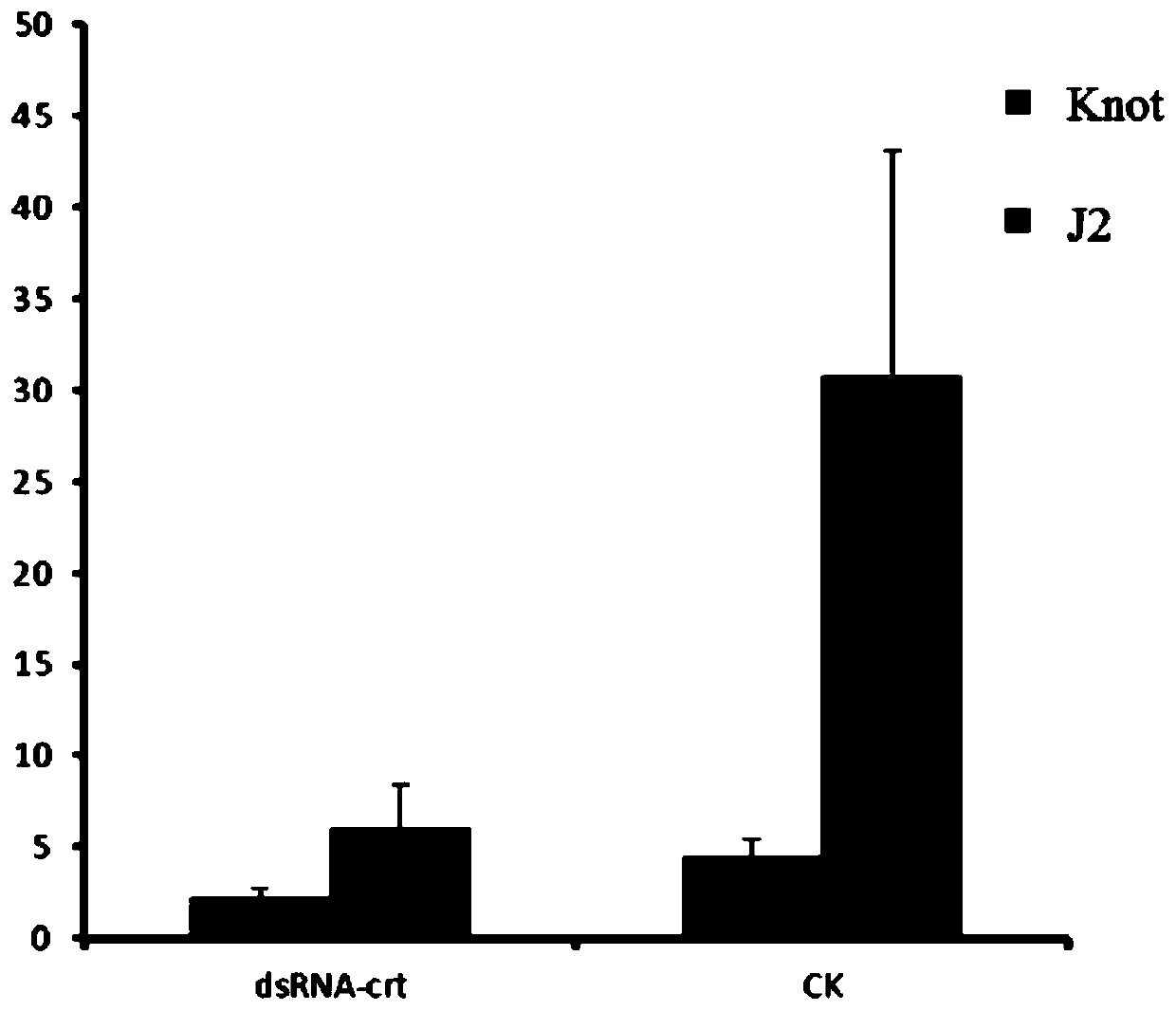
dsRNA (ribonucleic acid) capable of inhibiting FLPs neuropeptide gene and application thereof
The invention discloses dsRNA (ribonucleic acid) capable of inhibiting FLPs neuropeptide gene and application thereof. The dsRNA provided by the invention is double-chain RNA consisting of nucleotide represented by a sequence 1 in a sequence table and nucleotide represented by a sequence 2 in the sequence table. The experiment in the invention shows that dsRNA (ribonucleic acid) is provided by the invention, 2nd instar larvas of southern plant root-knot nematode are soaked, after RNAi, the tendency migration of southern plant root-knot nematode to a host plant is effectively avoided, the infestation of southern plant root-knot nematode on the host plant is reduced, and the propagation of nematode is also inhibited; and from the point of view of biological safety, dsRNA can not generate functional protein, has the characteristic of specifity, and is capable of reducing the influence on non-target organisms.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
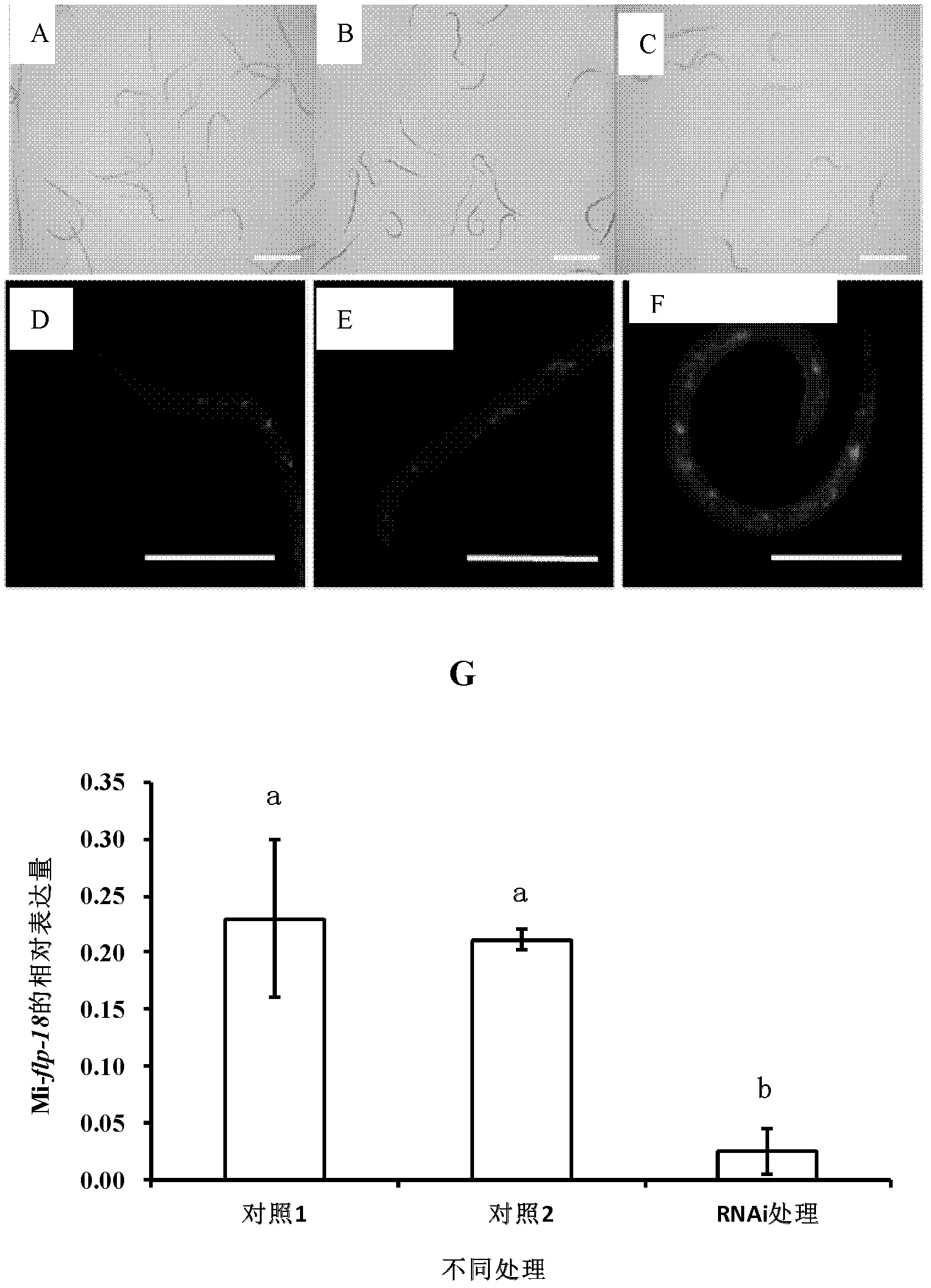
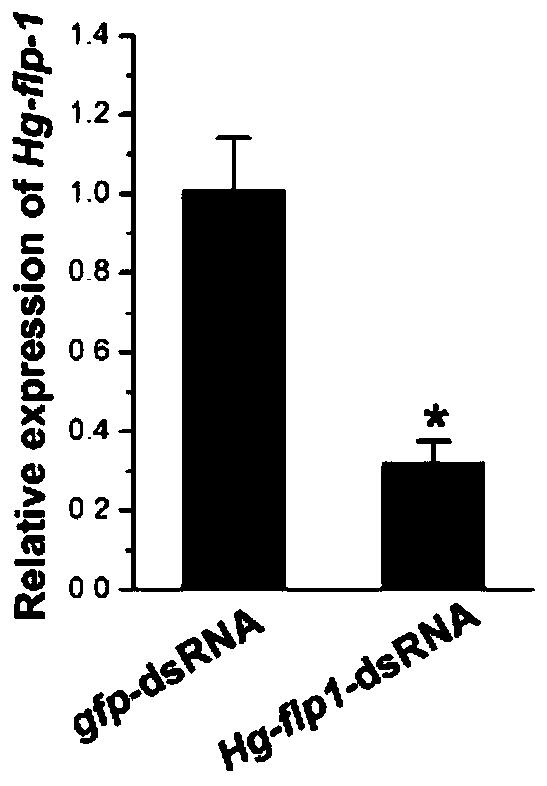
Soybean cyst nematode Hg-flp-1 gene, and encoding protein and application thereof
The invention discloses a soybean cyst nematode Hg-flp-1 gene as well as an encoding protein and application thereof, and relates to a soybean cyst nematode neuropeptide gene as well as an encoding protein and application thereof. The invention aims to solve the problem of environmental pollution in the existing chemical control method of soybean cyst nematode. The nucleotide sequence of the geneis shown as SEQ ID NO: 1 in a sequence table. The amino acid sequence of the encoded protein is shown as SEQ ID NO: 2 in a sequence table. After the neuropeptide gene Hg-flp-1 is subjected to dsRNA treatment, the number of second-stage instar larvae in infected roots and the number of root surface female insects after 21 days of infection are reduced by 25% and 28.9% respectively. The soybean cystnematode Hg-flp-1 gene disclosed by the invention is applied to the field of soybean cyst nematode prevention and control.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Microplitis mediator MmedCO I gene and application thereof
ActiveCN105861512AAvoid statistical errorsStatistically accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCotton bollwormMolecular level
The invention relates to the field of parasitoid detection, and specifically provides a Microplitis mediator MmedCO I gene sequence (as shown in SEQ ID No.1), and specific amplification primers, which are designed based on the sequence, and provides a molecular level method for rapid detection of parasitic cotton bollworm larvae of the Microplitis mediator. The invention facilitates quick and accurate calculation of the egg laying amount of parasitic wasps or parasitism rate of host larvae. The invention can effectively detect the parasitized state of host larvae 24 hours after parasitism of the host larvae, reduce detection time, avoid statistical error due to abnormal death of host larvae and improve the accuracy of statistics.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Apparatus for providing an environment of controlled water activity for storage of nematodes
Third stage juvenile (J3) entomopathogenic nematodes are prepared for storage by being induced into a state of cryptobiosis. The induction of cryptobiosis is effected by mixing an aqueous cream of the J3 nematodes with anhydrous, small particles of non-fibrous cellulose. The cryptobiotic J3 nematodes are stored in a container, fitted with an attachment which maintains the water activity in the container at a required value. The attachment includes a rigid tube that connects the interior of the container with a chamber that is vented to ambient atmosphere by small apparatus. The chamber contains water-absorbent material saturated with water or with a saturated salt solution, and the tube contains an air-permeable plug. An alternative attachment comprises a plastic envelope as the chamber, one face of which is stuck to the wall of the container. Small aperatures in the face are aligned with apertures in the container wall. Small apertures in the other face connect the inside of the envelope to ambient atmosphere.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Biocontrol strain SFC-3 for controlling nematode disease and application thereof
InactiveCN109207381AReduce requirements for pollution-free productionMeet the requirements of pollution-free productionBiocideFungiDiseaseBiotechnology
The invention relates to a biocontrol strain SFC-3 for controlling nematode disease and application thereof, which can effectively solve that problem of unstable control effect and high use cost of existing biocontrol strain for controlling root-knot nematode diseases, and is classify and named as Trichoderma asperellum (CGMCC NO. 16097), which is a biocontrol strain SFC-3. At the concentration of1 * 109 CFU / mL, the egg hatching and the second instar larvae of root-knot nematode are inhibited. The strain can remarkably reduce the invasion of nematodes, and the control effect on root-knot nematode diseases is 78.51%. The strain can be used for irrigating roots when vegetable seedlings are transplanted, and has the growth promoting effect.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF SCI INST OF BIOLOGY LIABILITY
Calprotectin gene of Meloidogyne graminicola and application of calprotectin gene
ActiveCN111187774AReduce in quantityControl of infested cropsBiocideNematocidesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a calprotectin gene of Meloidogyne graminicola and application of the calprotectin gene, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The calprotectin gene is a calprotectingene MgCRT, disclosed for the first time, of the Meloidogyne graminicola, a nucleotide sequence of the calprotectin gene MgCRT is represented by SEQ ID NO.1, and an amino acid sequence of an expression protein of the calprotectin gene MgCRT is represented by SEQ ID NO.2. Experiments prove that the gene is expressed in subabdominal esophageal glands of the Meloidogyne graminicola, dsRNA of the geneis designed and synthesized, Meloidogyne graminicola larvae are steeped in a dsRNA solution, are washed and are inoculated to rice, and after the gene MgCRT of the Meloidogyne graminicola is silencedby virtue of a method, nematodes invading rice are remarkably decreased, so that the calprotectin gene MgCRT of the Meloidogyne graminicola is relevant with invasion hosts of the Meloidogyne graminicola, and the gene MgCRT can be utilized as a target for preventing and controlling the invasion of the Meloidogyne graminicola on crops by virtue of an RNA interference technique.
Owner:SUZHOU CITY INVASIVE PEST PREVENTION & CONTROL TECH CENT
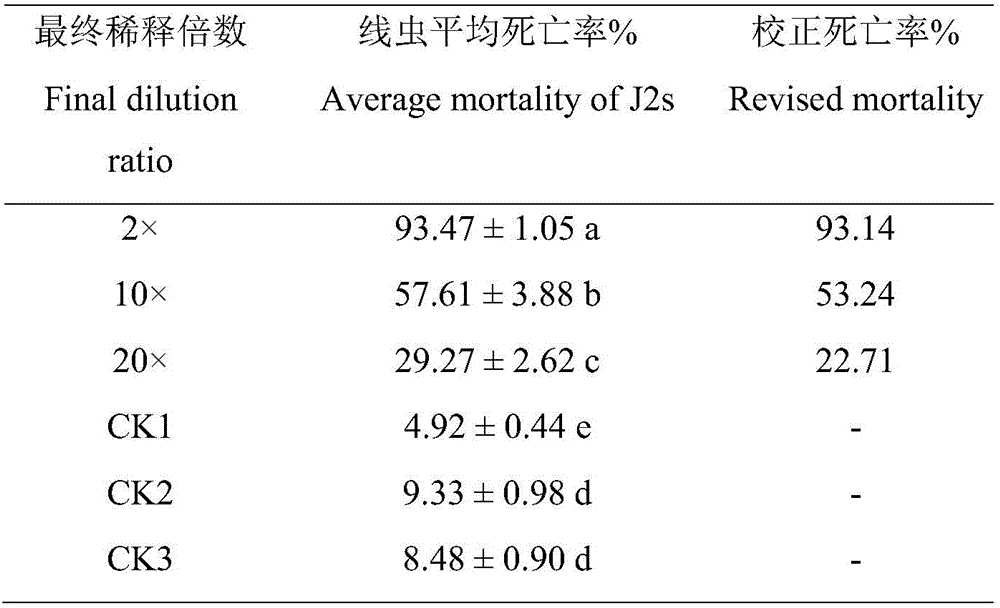
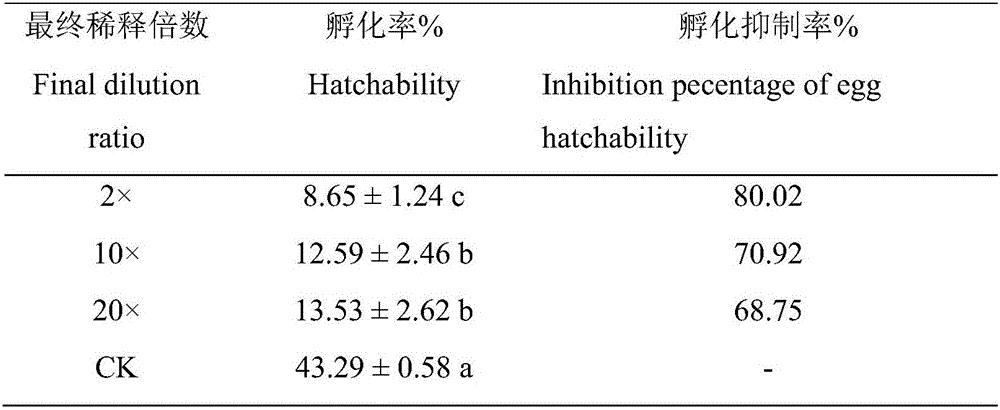
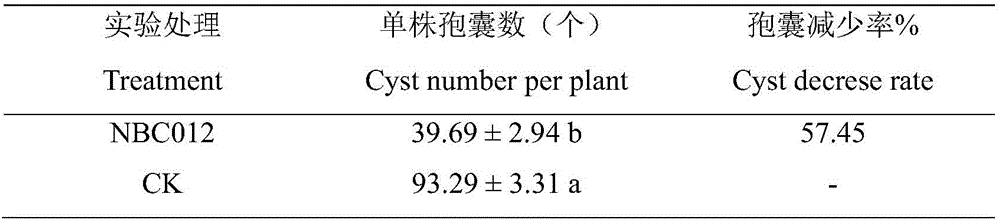
Nematicidal-activity P. oxalicum NBC012 and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to nematicidal-activity P. oxalicum NBC012 and a preparation method and application thereof. A high-activity fungus strain P. oxalicum NBC012 is isolated and screened from wheat cyst nematode group from stfold, Norway and is collected under CGMCC No. 12474. Nematicidal-activity P. oxalicum NBC012 is prepared by liquid fermentation culturing, fermentation broth of P. oxalicum NBC012 has significant poisoning action for plant parasitic nematodes. Indoor determination shows that the fermentation broth of the strain has effect on age-2 larvae and egg hatching of soybean cyst nematode. Fermentation broths with different dilution concentrations all show poisoning action for age-2 larvae and significant inhibitory action for egg hatching. Fermentation original broth may cause a decrease of 57.45% in amount of soybean cyst, and P. oxalicum NBC012 has a promising development and application prospect.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for high-throughput screening of pine wood nematode inhibitor
The invention relates to the field of biological pest control, in particular to a method for high-throughput screening of a pine wood nematode inhibitor. Pine trees are the most important afforestation tree species in China, but pine wood nematode diseases are always first forest diseases and insect pests in nearly thirty years, the harm is very serious, but the prevention and control drugs are limited, so that more prevention and control drugs need to be supplemented and screened urgently for more effective prevention and control. The invention aims to provide technical support for screeningmore pine wood nematode control agents. The method for high-throughput screening of the pine wood nematode inhibitor comprises the following steps: 1) collecting pine wood nematode, namely separatingpine wood nematode from epidemic wood, and carrying out enlarged culture; (2) pine wood nematode screening, namely distinguishing and counting cultured nematodes according to adults and larvae; (3) test board manufacturing, namely setting a contrast and test area in a microwell plate and preparing a reagent with a certain concentration; and (4) data recording and processing, namely recording deadand alive changes of the nematodes along with time, counting drug effects and screening.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY ACAD
Breeding method for improving commercial value of galleria mellonella
PendingCN112167181AIncrease commodity rateReduce the ratioFood processingAnimal feeding stuffAnimal scienceNematode
The invention discloses a breeding method for improving the commercial value of galleria mellonella. The galleria mellonella is bred by combining specific culture temperature, feed additive amount, egg density and population density and using the breeding method, the proportion of mature larvae which are less than 0.100 g and can pupate quickly can be reduced compared with the prior art. Accordingto the galleria mellonella bred by the method, the ratio of the larva which can be directly used for measuring the invasion rate of nematodes and is larger than 0.151 g and the larva which can be used for living nematode propagation, nematode recovery and other purposes and is 0.101-0.150 g is relatively high; and compared with the prior art, the operation is relatively simple, the commodity rateof the galleria mellonella can be remarkably improved, and the method has a wide practical value for breeding of the galleria mellonella, and has a wide practical value for the commercial breeding ofthe galleria mellonella.
Owner:INST OF SOIL & FERTILIZER XINJIANG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Molecular marker method for cerambycidae larvae of different families
The invention discloses a molecular marker method for cerambycidae larvae of different families. The method is realized by the steps of: selecting two pairs of specific primers to carry out PCR reaction, and extracting genomic DNA from to-be-detected cerambycidae individuals and parents of different families by DNA extraction; taking the genomic DNA as the template, and carrying out two rounds of PCR amplification on the selected two pairs of primers respectively; subjecting the PCR product to 1.5% agarose electrophoresis detection, performing ethidium bromide staining, then conducting observation under ultraviolet, and photographing the electrophoresis result; and constructing a phylogenetic tree by a neighbor-joining method. According to the method provided by the invention, the genetic distances of 33 cerambycidae COI genes indicate that: the genetic distance between different genuses is obviously larger than that of a same genus, the COI gene is in full compliance with the inspection standard of DNA bar code validity, and the fragment can well distinguish different species of cerambycidae's different genuses, and can be used for rapid identification of cerambycidae.
Owner:太仓海关综合技术服务中心
Application of target gene in shellfish larva metamorphosis development process researched by RNA interference technology
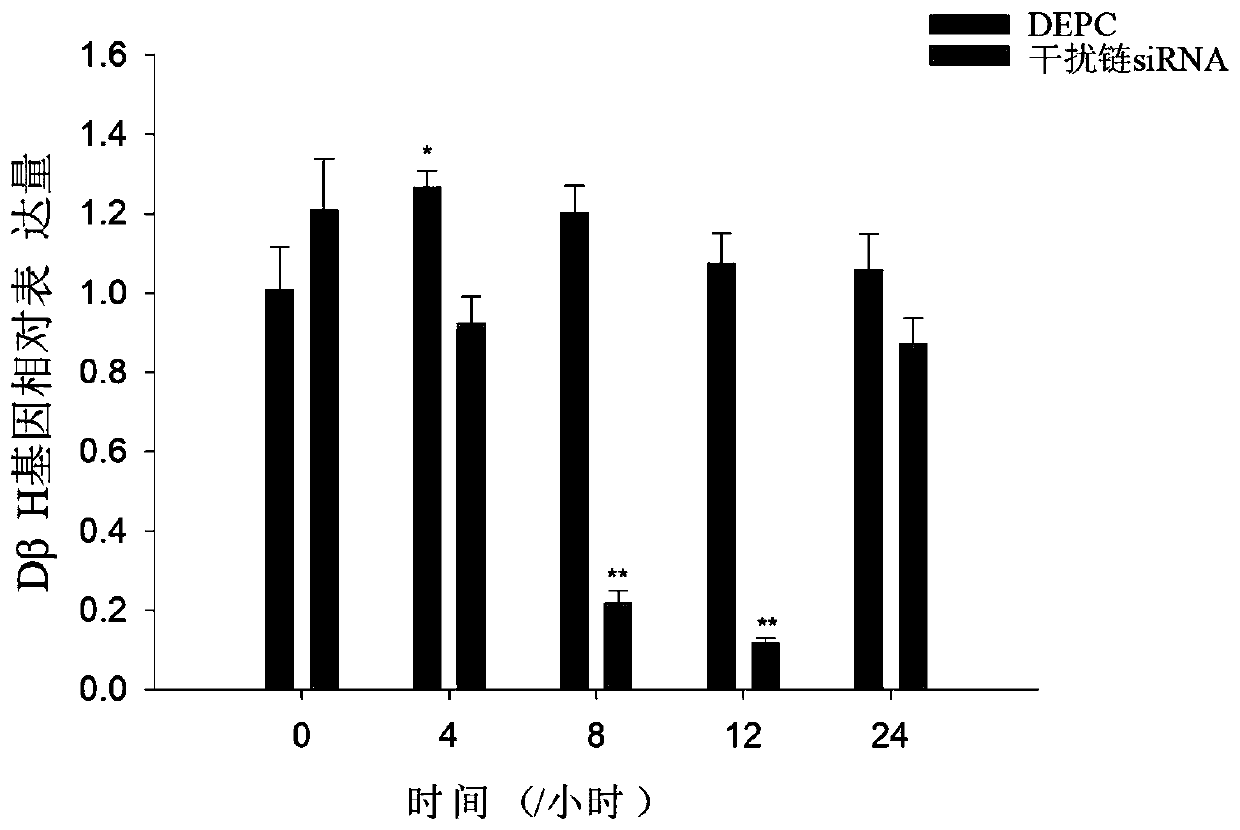
ActiveCN111500577AAchieve knockdownAccurate researchMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationMicrobiologyIn vivo
The invention provides an application of an RNA interference technology in researching a target gene in a shellfish larva metamorphosis development process. Specifically, sinonovacula constricta is selected as a research object; dopamine beta-hydroxylase is used as a target gene; siRNA is designed, a method for soaking larvae in vitro by adopting siRNA is employed. The metamorphosis rate, the survival rate and the target gene expression quantity change of larvae are detected; namely, in the sinonovacula constricta larva development period, siRNA effectively reduces the expression level of target genes, the metamorphosis rate and the survival rate of the larvae are remarkably reduced, so that the feasibility of the in-vitro siRNA soaking method is indicated; the in-vitro soaking method adopted by the invention breaks through the limitation of injecting siRNA in vivo, and realizes the application of an RNA interference technology in shellfish larva research; the experimental operation issimple and easy to implement, is not limited by experimental conditions, and can eliminate the interference of other genes, thereby more accurately implementing the research on the single target gene.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Entomogenous fungus strain with high pathogenicity to prodenia litura and application thereof
The invention belongs to the field of plant protection and particularly relates to the field of biological control. An excellent strain SCAUYZ-16 with high pathogenicity to prodenia litura is obtained through screening research, the SCAUYZ-16 is preserved in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center on November 19, 2020, and the preservation number is GDMCC No: 61300. Experiments show that the virulence of the strain at 10<8> spores / mL to second-stage larvae of prodenia litura reaches 70.71%, the pathogenicity of the strain is more stable than that of other tested strains, and the strain has great potential to be used for biological control of prodenia litura.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV +1
Root-knot nematode lure attraction agent and application thereof
InactiveCN105638740AImprove the effect of root-knot nematode controlLow costBiocideBacteriaDiseaseAbamectin
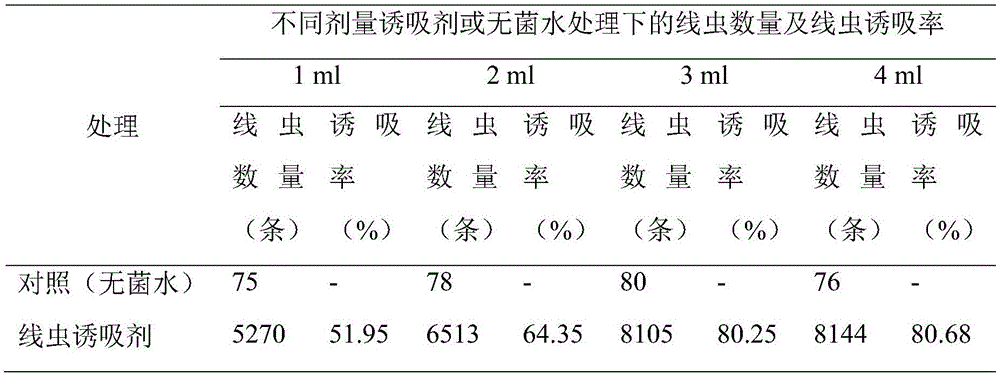
The invention relates to a root-knot nematode lure attraction agent and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of plant disease prevention and treatment. The biological lure attraction agent is obtained from Bacillus methylotrophicus Mo-TB strain with the culture preservation number being CGMCC No.11851 through the steps of test tube slant seed culture, liquid culture, fermentation pot mass culture and lure attraction agent preparation. The lure attraction agent is applied to lure attraction of root-knot nematode second-stage larvae in soil. The biological lure attractive agent and abamectin and fosthiazate chemical pesticides are mixed and then applied in prevention and treatment of the root-knot nematode disease. The root-knot nematode lure attraction agent has the advantages that the lure attraction rate of the biological lure attraction agent for root-knot nematode second-stage larvae in soil within one centare is 80% or above; the effect of preventing and treating the root-knot nematode disease is improved due to the fact that the biological lure attraction agent is used by being mixed with abamectin and fosthiazate chemical pesticides; the biological lure attraction agent is low in cost, free of residue and safe for human and livestock, and the prevention effect of conventional nematode killing pesticide can be significantly improved.
Owner:莫明和
Method for preventing pine wood nematode diseases
InactiveCN111066823AImprove diapause rateReduce transmissionBiocideAnimal repellantsNematodeEthyl palmitate
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural pest control, and particularly relates to a method for controlling pine wood nematode disease. The invention discloses a method for preventing and treating pine wood nematodes. On the basis of a scheme for preventing and treating pine wood nematode disease by using ethyl palmitate in the prior art; fluorite nano powder modified by juiceof selected succulent plants is added into ethyl palmitate; under the condition that the application amount of the low-dosage ethyl palmitate of the pine tree body is 0.5 to 5mu l / m <3>; the diapauserate of the pine wood nematodes is further improved, a large number of pine wood nematodes stop breeding, diffusion type pine wood nematodes (including diffusion type three-year-old larvae (LIII) anddiffusion type four-year-old larvae (LIV)) are formed, propagation of vector insects during eclosion of monochamus alternatus in January to May of the next year is reduced, and pine wood nematode diseases can be effectively prevented.
Owner:HEZE UNIV
Arthrobotrys oligospora strain N and application thereof
The invention provides an arthrobotrys oligospora strain N, the preservation number of which is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.5508. The strain is a mutagenic strain obtained by injecting low-energy nitrogen ion beams into arthrobotrys oligospora. The strain has the characteristics that the growth and reproduction are quick, spore production is early, the quantity of produced spores is large, and the capacity for catching and feeding on third-stage larva of nematode is strong, so that the strain can be used for biological control on livestock parasitic nematode.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com