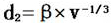Patents
Literature
59 results about "Dendrite (metal)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
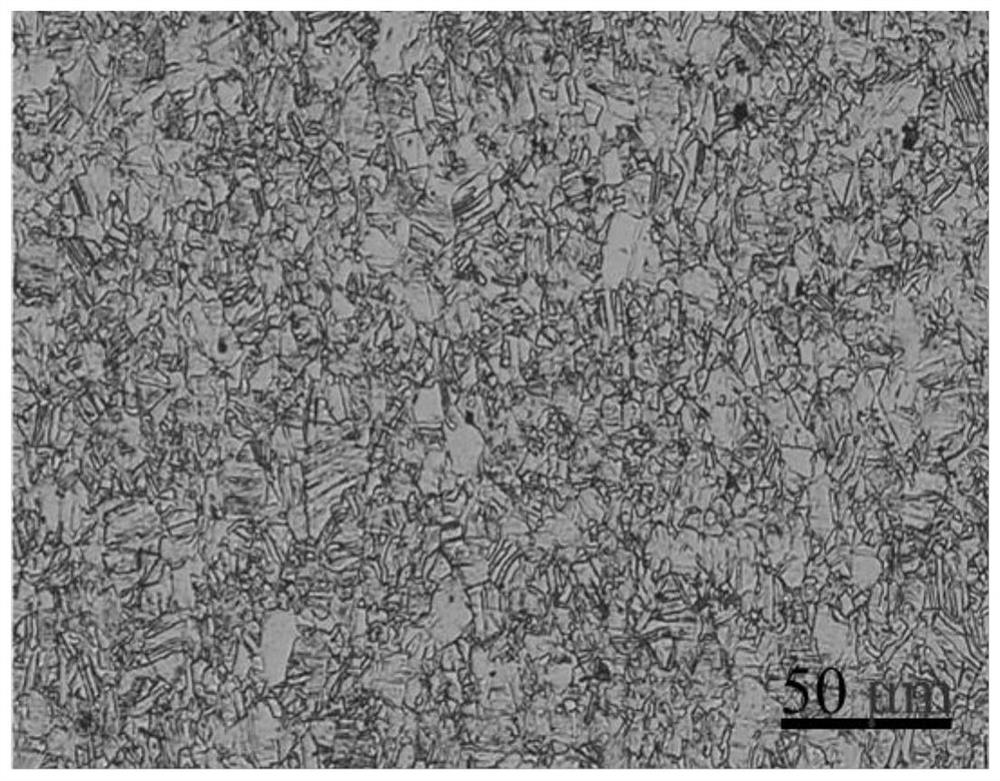
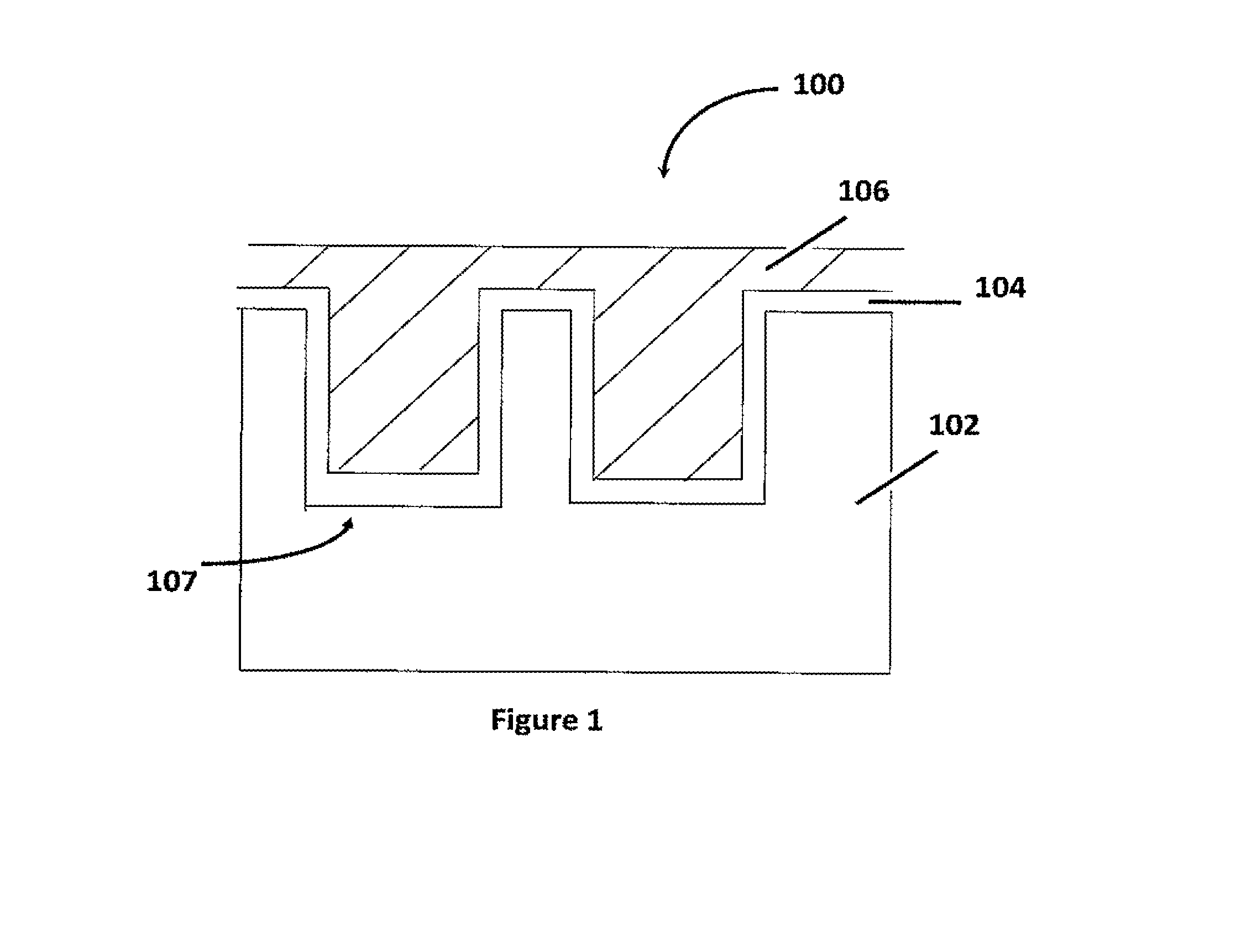
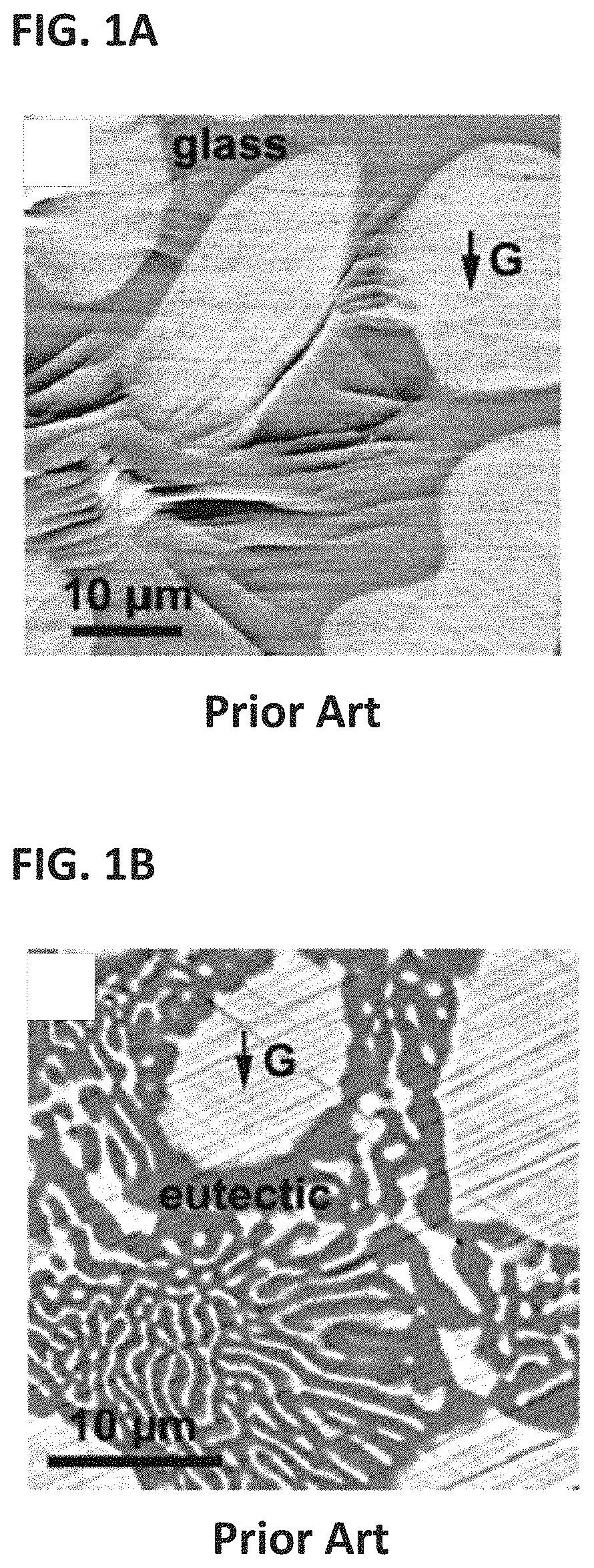
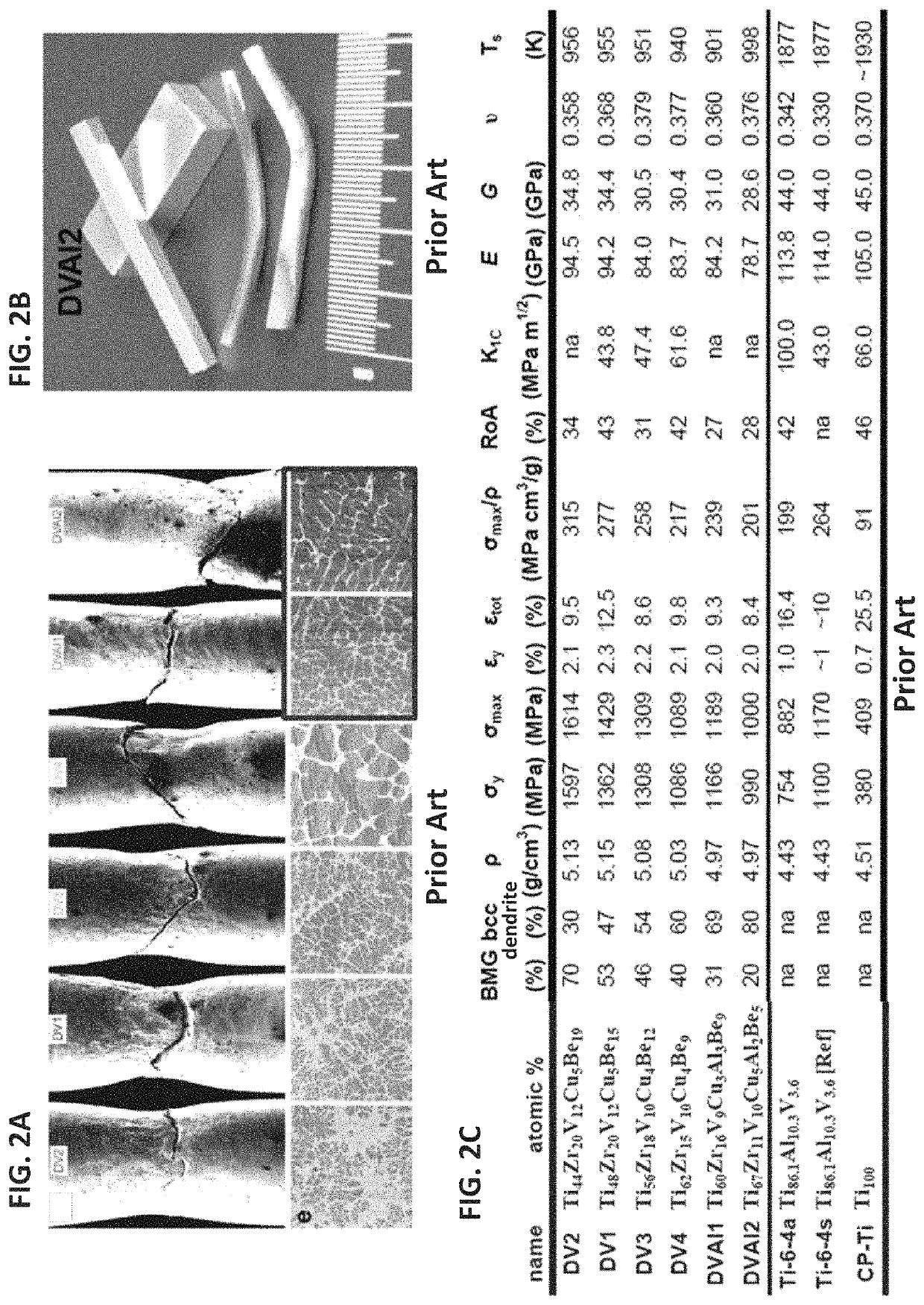
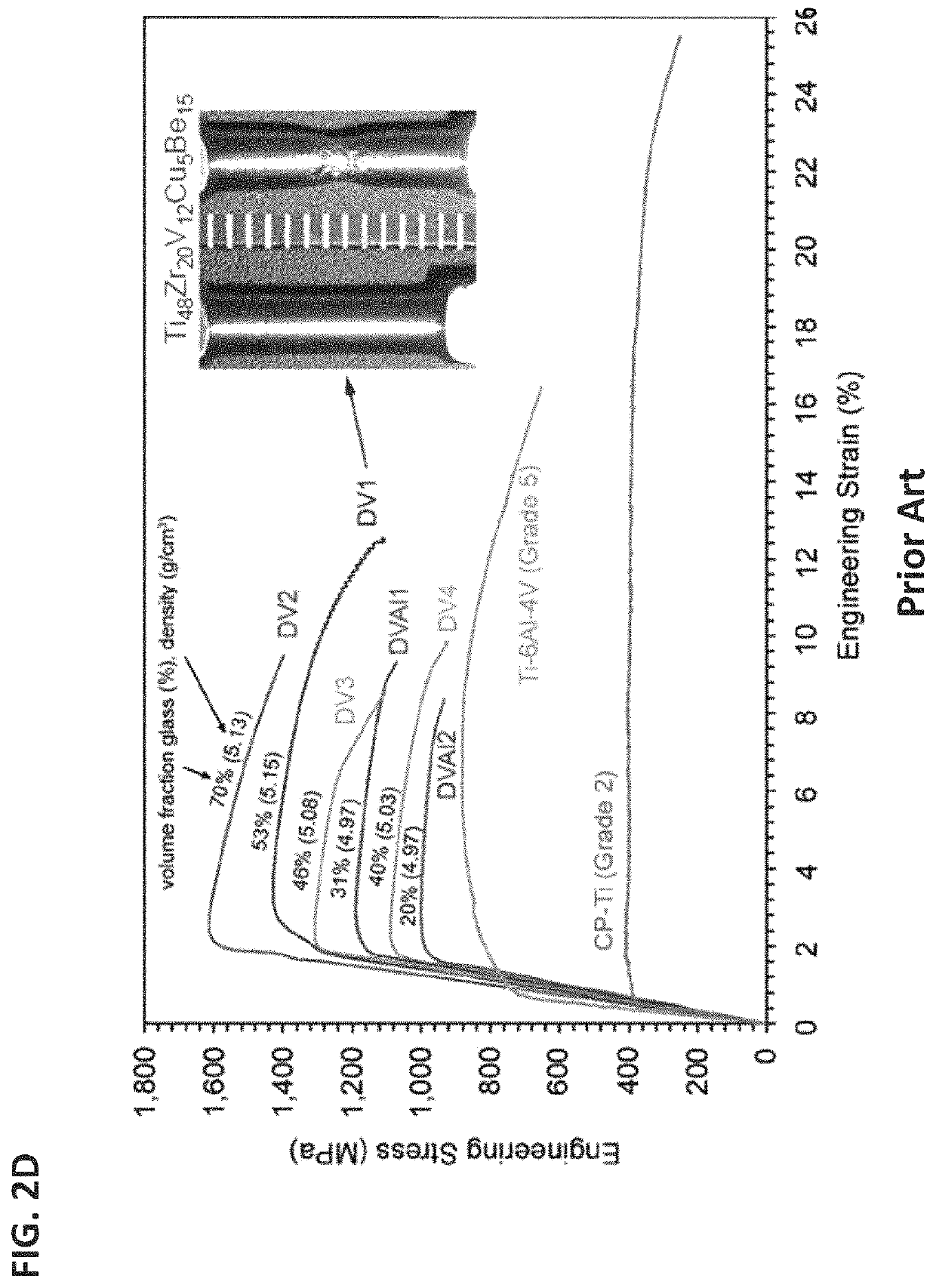
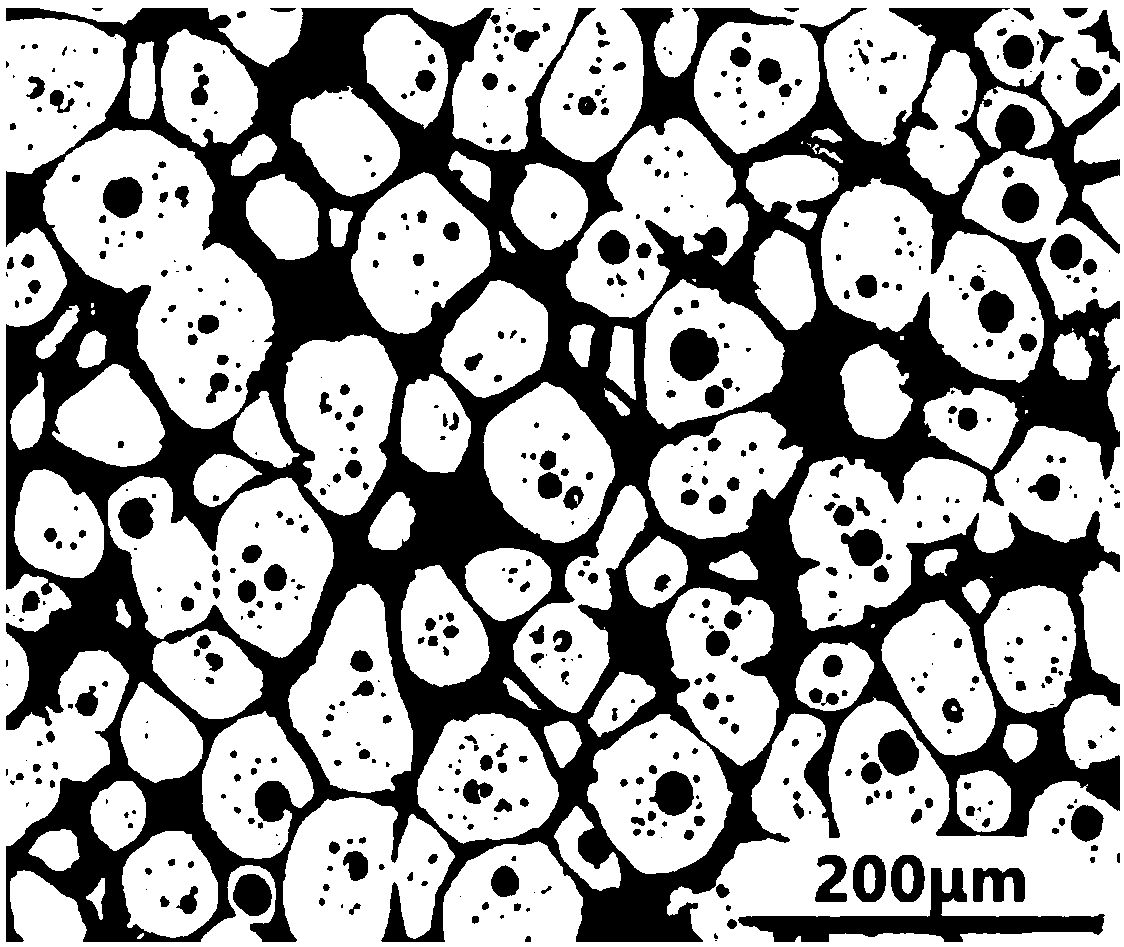
A dendrite in metallurgy is a characteristic tree-like structure of crystals growing as molten metal solidifies, the shape produced by faster growth along energetically favourable crystallographic directions. This dendritic growth has large consequences in regard to material properties.
Casting of non-ferrous metals
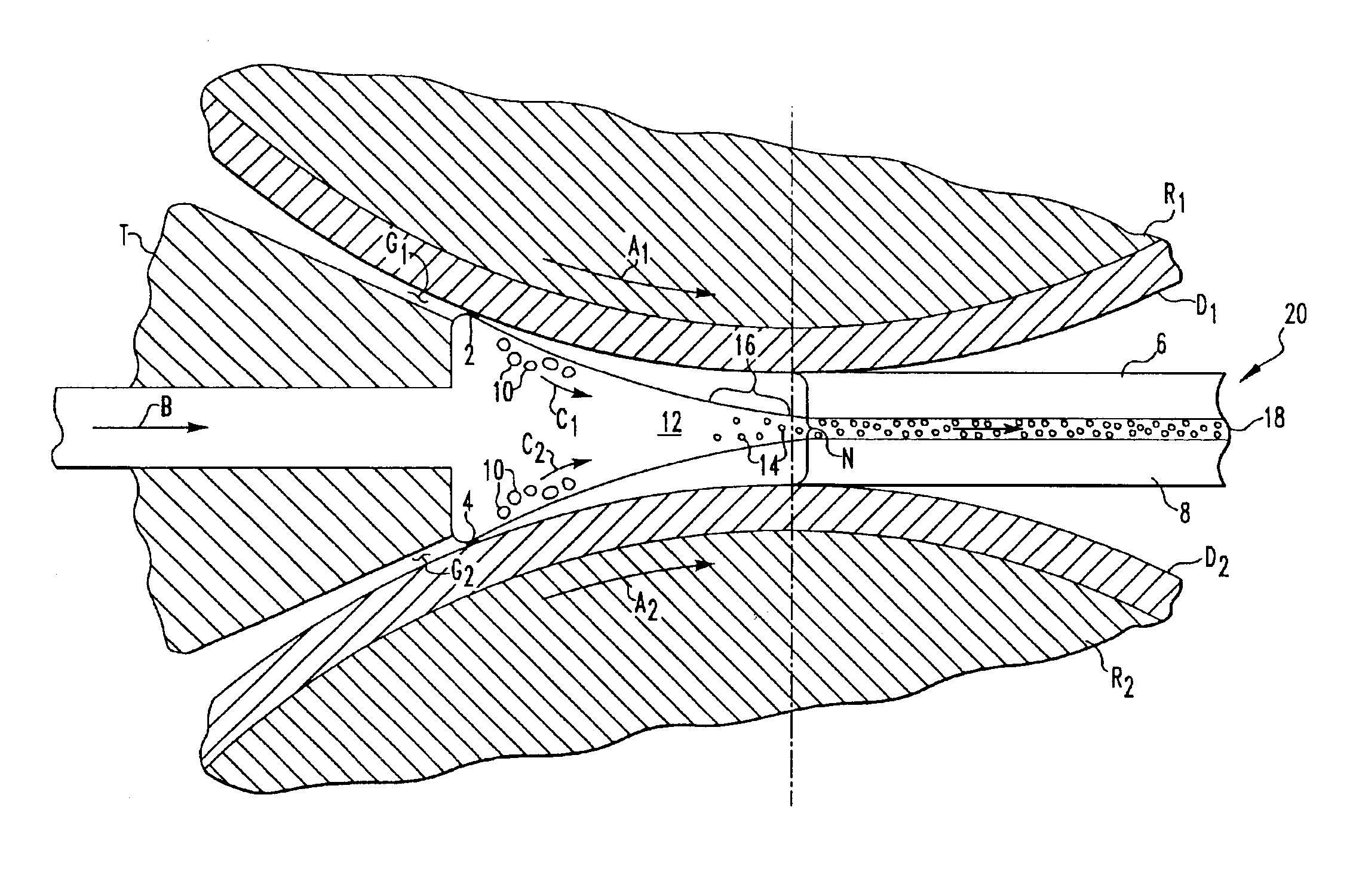
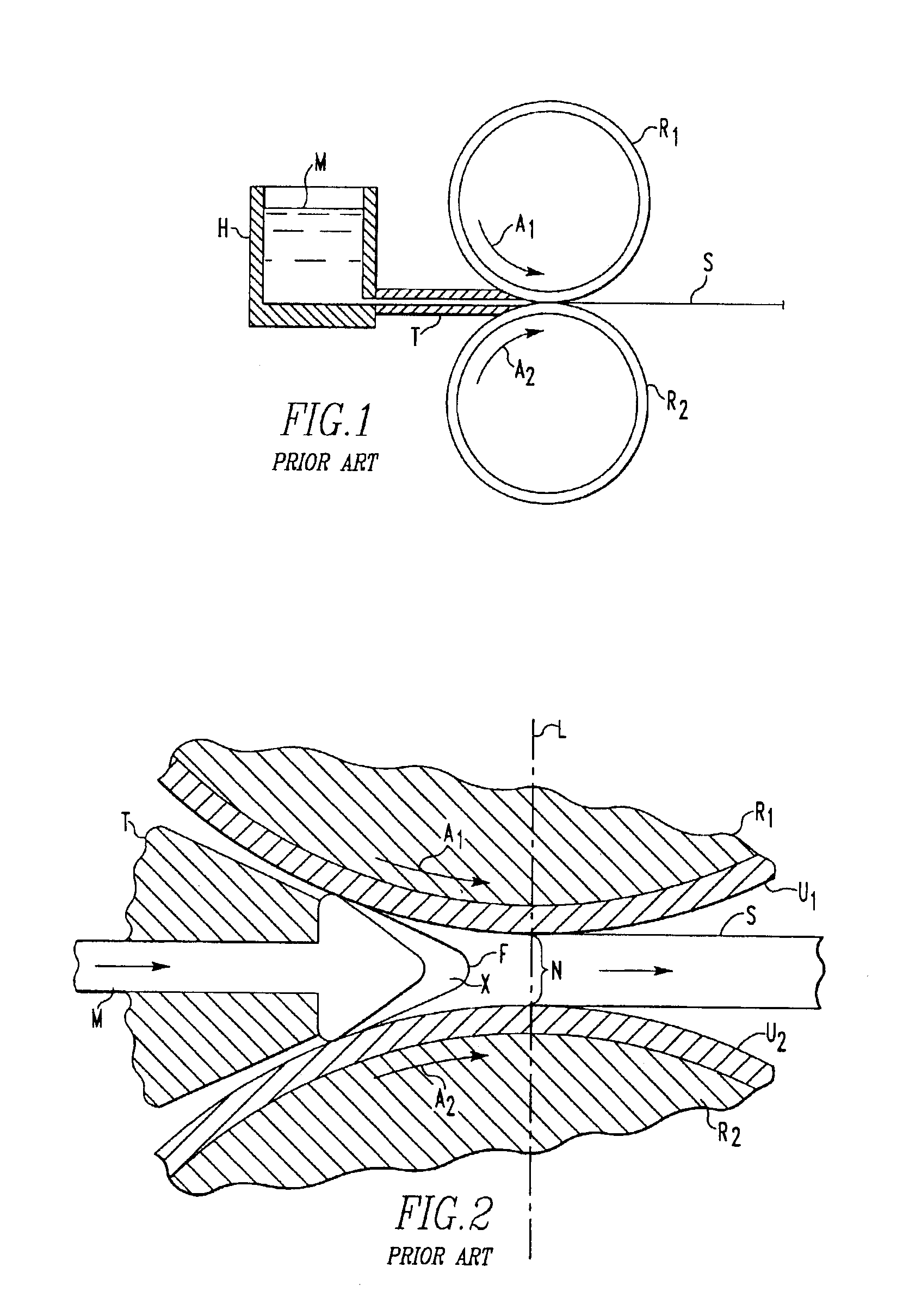
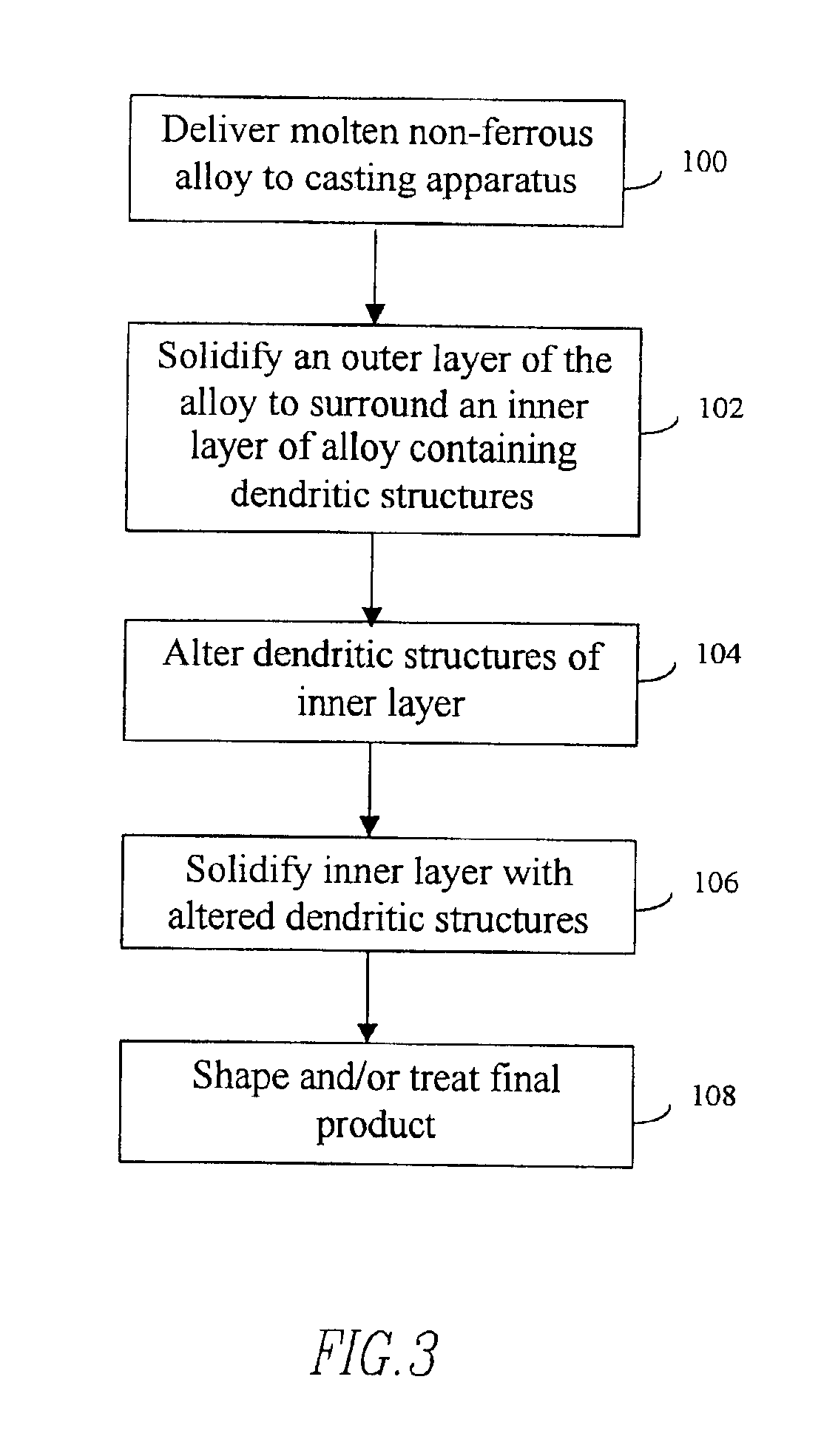
InactiveUS7125612B2Avoids and minimizes centerline segregationFurnace typesThin material handlingSolid componentNonferrous metal
A method of continuous casting non-ferrous alloys which includes delivering molten non-ferrous alloy to a casting apparatus. The casting apparatus rapidly cools at least a portion of the non-ferrous alloy at a rate of at least about 100° C. thereby solidifying an outer layer of the non-ferrous alloy surrounding an inner layer of a molten component and a solid component of dendrites. The dendrites are altered to yield cast product exhibiting good resistance to cracking.
Owner:ARCONIC TECH LLC
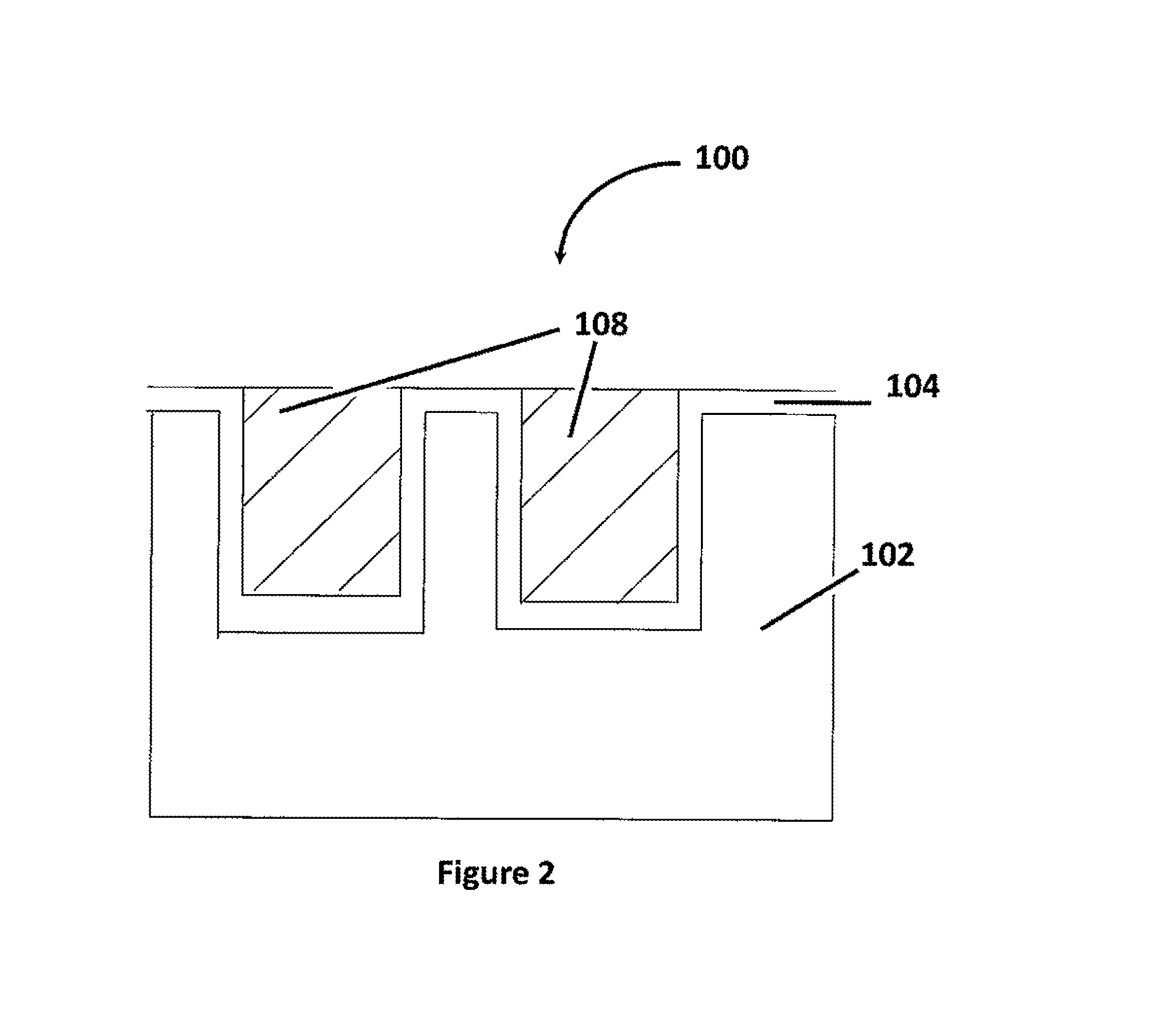
BEOL integration scheme for copper CMP to prevent dendrite formation
ActiveUS20140065815A1Eliminate exposureAvoid formingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectroless depositionDendrite
Disclosed herein are various methods of forming copper-based conductive structures on integrated circuit devices by performing a copper deposition process to fill the trench or via with copper, which can be performed by fill, plating or electroless deposition. Copper clearing of copper overburden is performed using CMP to stop on an existing liner. Copper in the trenches or vias is recessed by controlled etch. An Nblok cap layer is deposited to cap the trenches or vias so that copper is not exposed to ILD. Nblok overburden and adjacent liner is then removed by CMP. Nblok cap layer is then deposited. The proposed approach is an alternative CMP integration scheme that will eliminate the exposure of copper to ILD during CMP, will prevent any dendrite formation, can be used for all metal layers in BEOL stack, and can be utilized for multiple layers, as necessary, whenever copper CMP is desired.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
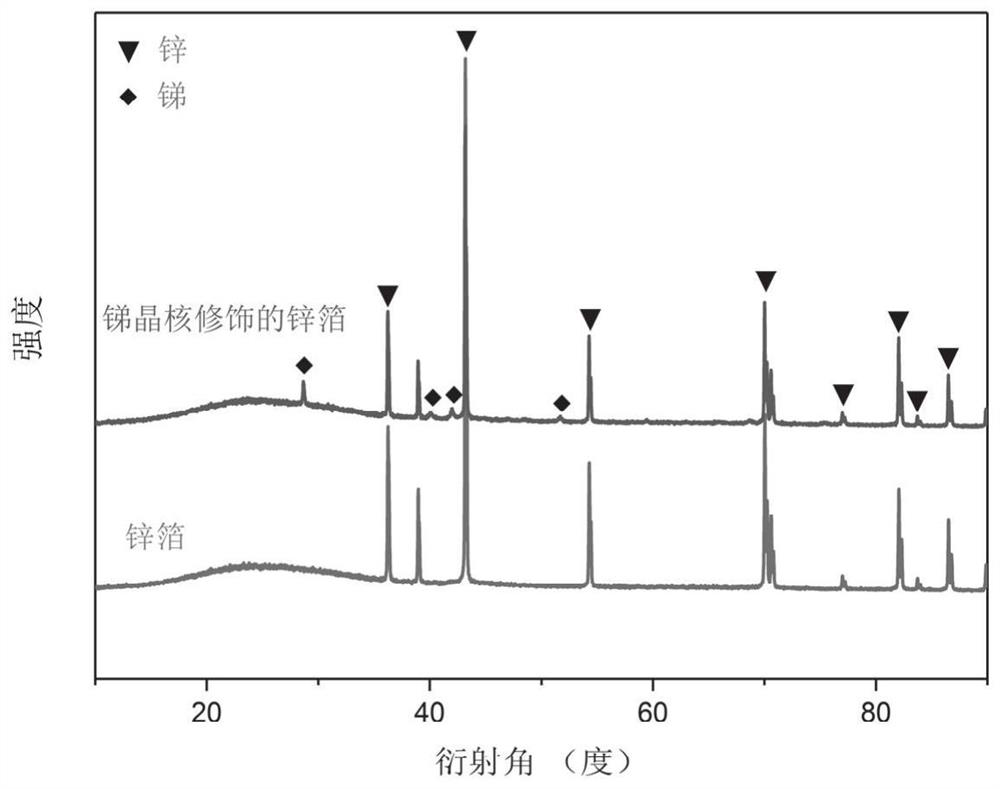
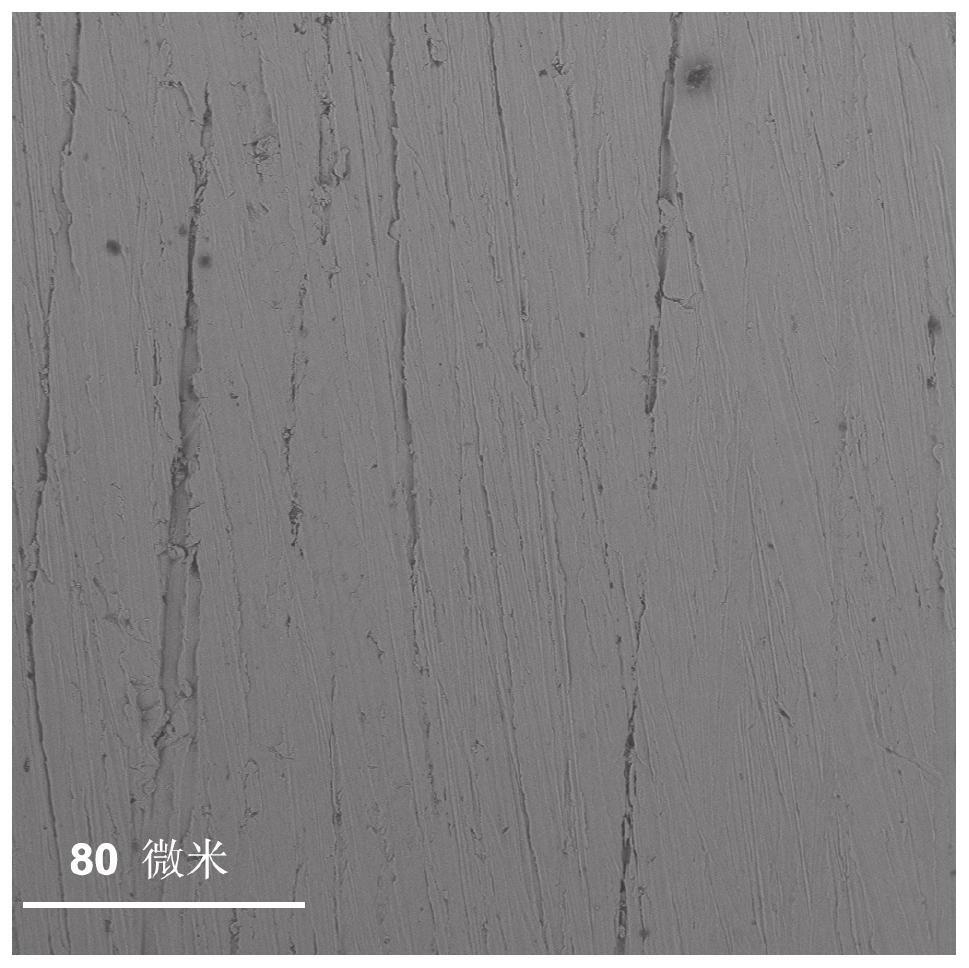
Composite material of metal zinc foil and zinc-affinity crystal nucleuses and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111926313AReduce volumeAvoid negative effectsCell electrodesSecondary cellsDendrite (metal)Zinc
The invention provides a composite material of metal zinc foil and zinc- affinity crystal nucleuses and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation of the composite material includesthe steps that metal salt solution is prepared as deposition solution, the metal zinc foil is placed in the deposition solution, and the composite material is obtained after in-situ chemical deposition. The volume of the zinc-affinity crystal nucleuses is smaller, thin crystal nucleuses can evenly cover the surfaces of the zinc foil, the unique structure can effectively inhibit zinc dendrite, furthermore, due to the fact that the thickness of the crystal nucleuses covering the surfaces of the zinc foil is comparatively thin, the zinc electrode reaction surface area is further maintained at alarge extent, so that the adverse impact on zinc negative electrode materials by modification can be prevented, and the circulating performance of a battery can be improved greatly.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Preparation method of high-strength and high-toughness CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy homogeneous fine-grain thin plate
The invention belongs to the technical field of metal materials, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a high-strength and high-toughness CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy homogeneous fine-grain thin plate. The preparation method comprises the five steps of vacuum smelting, alloy ingot annealing, hammer cogging and drawing-out and high-temperature back-and-forth rolling forming. Accordingto hammer cogging and drawing-out, upsetting and drawing-out forging treatment is carried out on an annealed alloy cast ingot to prepare a plate blank; and the upsetting rate is 50-200 mm / s, and the drawing-out forging ratio is 2-10. According to the method, hammer cogging and drawing-out treatment is carried out after annealing, a large number of dendrites in an as-cast structure can be completely broken through severe plastic deformation in a short time, a fine and uniform grain structure is obtained, and metallurgical defects such as pores and looseness are reduced; and a high-temperature back-and-forth rolling process method is adopted, the grain size and the structure are refined, the strength, plasticity and toughness of materials are improved, and the anisotropy problem of an CrCoNimedium-entropy alloy is obviously reduced.
Owner:GUIZHOU AEROSPACE XINLI CASTINGSAND FORGINGS
Dendrite-reinforced titanium-based metal matrix composites
ActiveUS11014162B2Additive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyDendrite (metal)Titanium
Ti-based metal matrix composites, methods of their additive manufacture, and parts manufactured therefrom and thereby are provided. Method include layer-by-layer additive manufacturing for fabricating Ti-based metal matrix composite parts thicker than 0.5 mm, in layers with thickness between 10-1000 micrometers. The parts formed may have one or more of the following properties: a tensile strength greater than 1 GPa, a fracture toughness greater than 40 MPa m1 / 2, a yield strength divided by the density greater than 200 MPa cm3 / g, and a total strain to failure in a tension test greater than 5%.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for inhibiting zinc dendritic crystal growth by using polydopamine film
PendingCN112349893AEffective control of thicknessPolymerization reaction conditions are easy to controlCell electrodesSecondary cells servicing/maintenanceMedicineDendrite (metal)
A method for inhibiting zinc dendritic crystal growth by using a polydopamine film comprises the steps: a zinc foil is soaked in a dopamine solution, and a polydopamine film layer is formed on the surface of zinc by adjusting the concentration of dopamine, the pH value of the solution, the polymerization time and the reaction temperature; the dopamine-modified zinc foil is used as the negative electrode of the secondary battery, and structural characterization after charge-discharge circulation shows that the surface of the electrode is smooth, and no obvious dendritic crystal is generated; and the polydopamine has strong metallophilicity, a stable protective layer is formed on the surface of the zinc foil, and the deposition of zinc is limited in a limited space, so that the growth of zinc dendrites is effectively inhibited, and the cycle life of the zinc negative electrode is prolonged. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in process, easy in reaction condition control, environment-friendly and beneficial to performance optimization and practical application of the zinc negative electrode.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
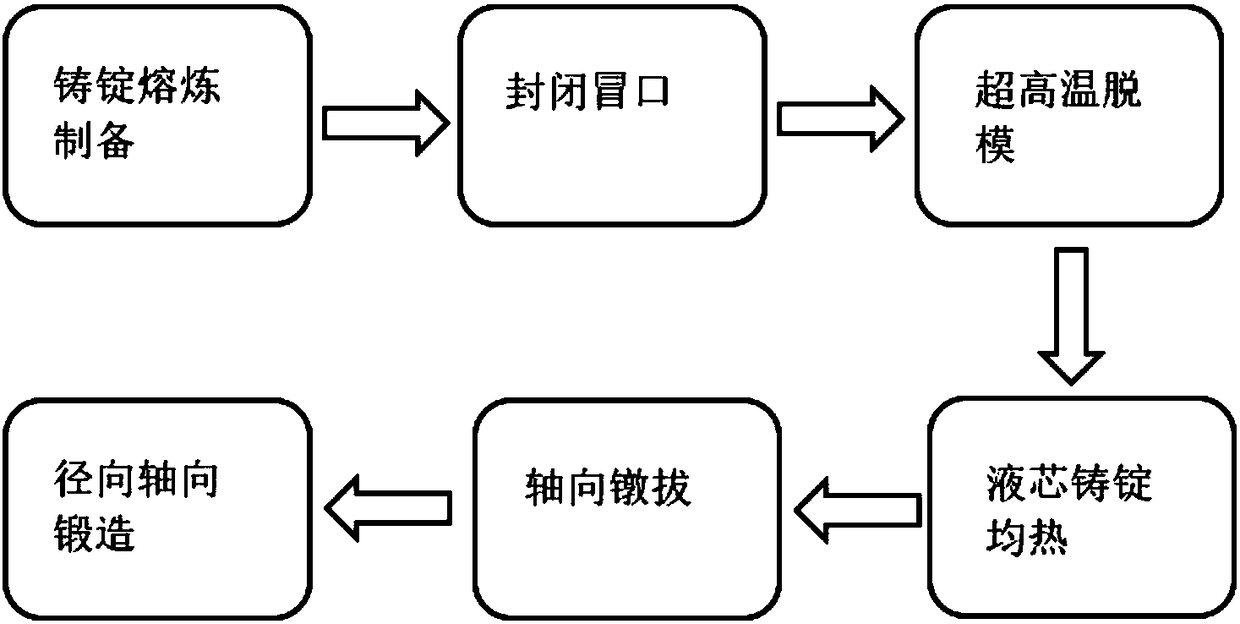
High-uniformity short-process forming method for large metal component
The invention relates to the field of metal forming, in particular to a high-uniformity short-process forming method for a large metal component. Firstly, a cast alloy cast ingot is subjected to superhigh temperature demolding; then soaking is conducted on the liquid core cast ingot, precise control of the liquid fraction of the core part of the cast ingot is achieved, axial upsetting and rollingare conducted on the cast ingot under a forging press, dendrite at the liquid core of the cast ingot is fully crushed and balled, and a uniform and tiny semisolid structure is formed; and finally radial and axial forging is conducted on the cast ingot, and the cast ingot is forged into the needed large metal component structure. Through the high-uniformity short-process forming method, the problems such as shrinkage cavity and porosity and dendritic segregation in the cast ingot are solved, the central mechanical performance of the large metal component can reach the surface performance level,and uniformity of the overall performance of the component is improved. The core part of the cast ingot forms the uniform and tiny semisolid structure, and thus the final forge piece has good comprehensive performance. Forming pressure is small, the requirement for ability of forging equipment is lowered, the technological process is shortened, and production cost can be lowered effectively.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
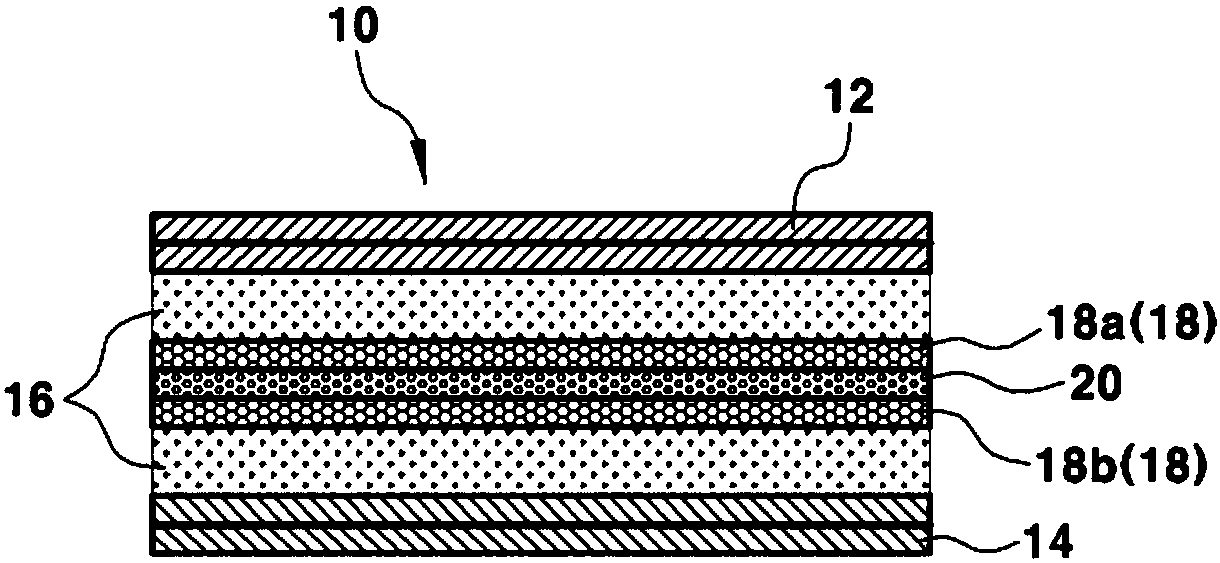
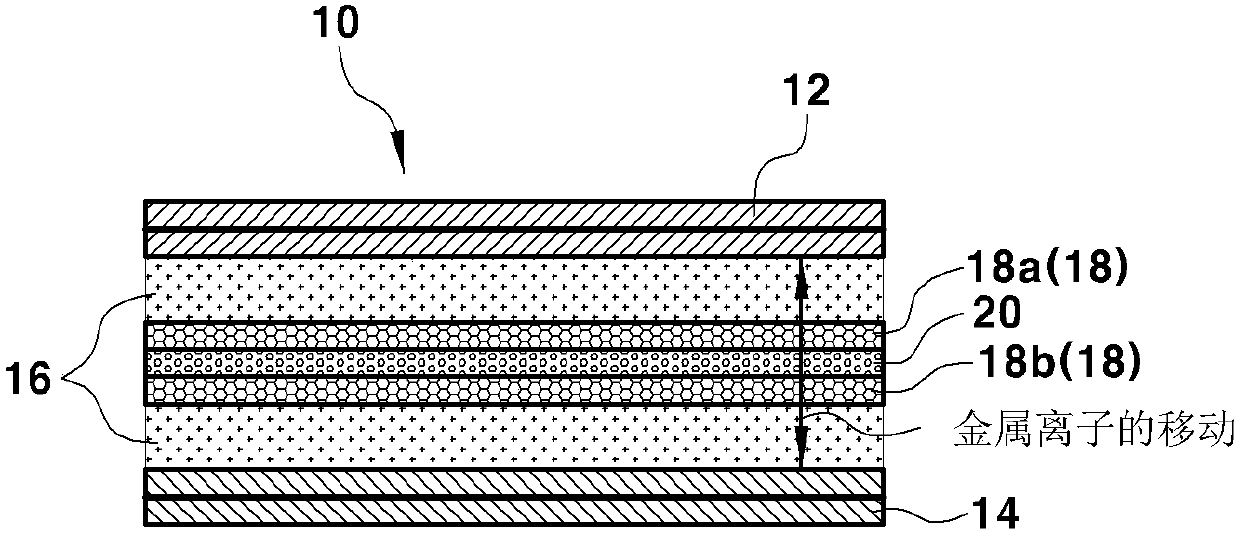
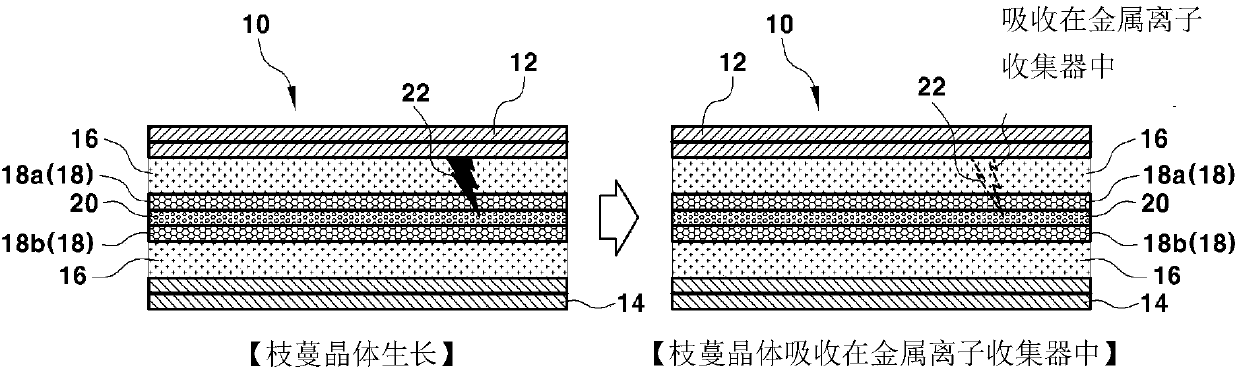
Secondary battery preventing dendrite growth
InactiveCN109713201AFinal product manufactureNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesDendrite (metal)Battery cell
The present invention provides a secondary battery that includes a metal ion receptor, which can absorb metal dendrites generated on the surface of a cathode while the battery is used, in a battery cell, whereby it is possible to improve safety by suppressing growth of dendrites and preventing a short due to a dendrite by making metal dendrites be absorbed in the metal ion receptor before the dendrites growing on the surface of the cathode reach the surface of an anode.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Application of metal dendritic crystal inhibition additive, electrolyte containing same and battery
InactiveCN110828896AStrong electrostatic effectStronger electrostatic interactionNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsSecondary cells servicing/maintenanceElectrolytic agentElectrical battery
The invention discloses application of a metal dendritic crystal inhibition additive, an electrolyte containing the same and a battery. The dendritic crystal inhibition additive provided by the invention is used as an additive of an electrolyte of a metal-based battery. The additive comprises a compound with an electrophilic group in a molecular structure or capable of dissociating organic cationsin the electrolyte. The metal-based battery containing the metal dendritic crystal inhibiting additive is provided, in the charging process of the battery, electrophilic groups in the additive or organic cations dissociated after being dissolved in electrolyte can be adsorbed on the small bulges on the surface of a metal negative electrode under the action of electrostatic force, and metal ions are prevented from being deposited on the small bulges, so that the growth of dendrites is inhibited, the service life of the battery is prolonged, and the coulombic efficiency of the battery is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Microstructured ion-conducting composites and uses thereof
ActiveCN110099950ACell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersCell electrodesPolymer scienceNano structuring
A composite membrane with nanostructured inorganic and organic phases is applied as an ion-selective layer to improve processability, prevent dendrite shorting, and increase power output of lithium-metal anodes through better Li-ion conductivity. Nanoconfinement, as opposed to macroscale confinement, is known to dramatically alter the properties of bulk materials. Control over a ceramic's size, shape, and properties is achieved with polymer templates. This is a new composition of matter and unique approach to composite membrane design.
Owner:SEPION TECH INC +1
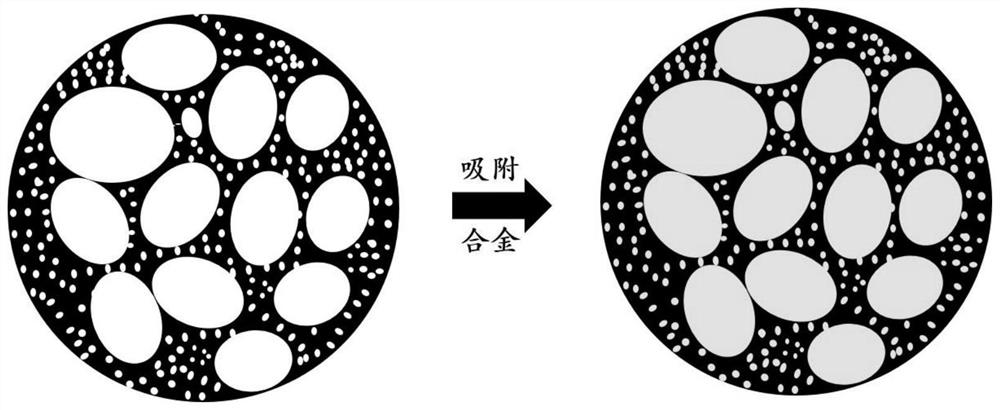
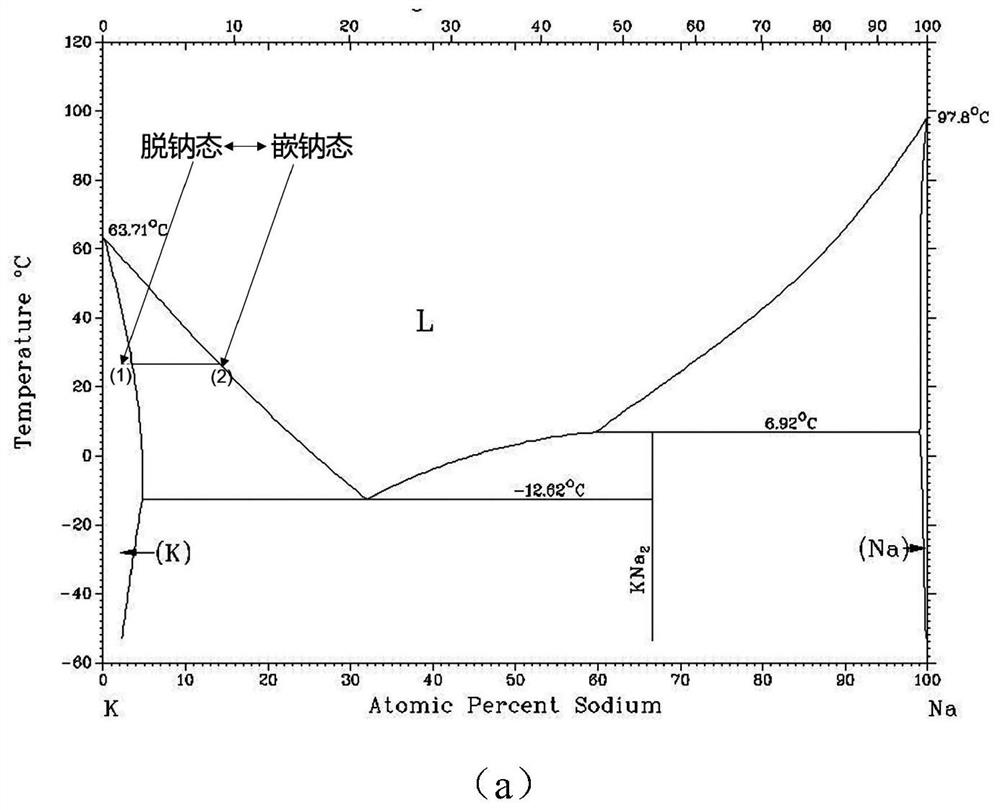
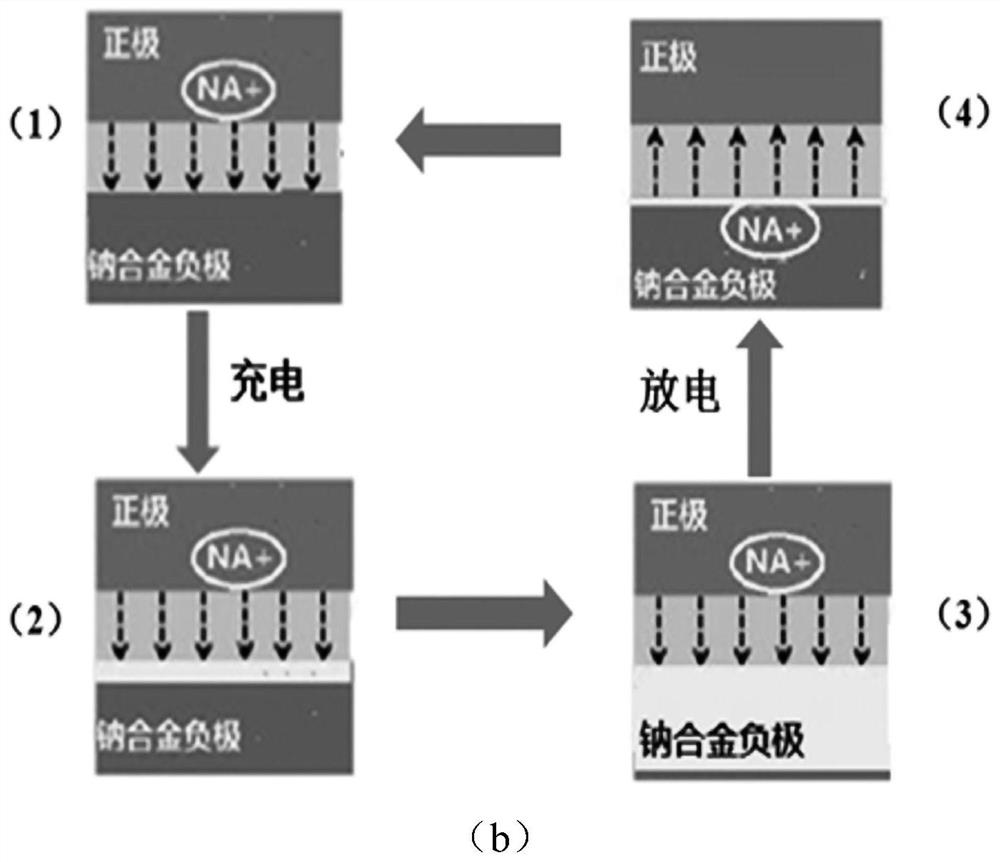
Dendrite-free alloy negative electrode with solid-liquid phase conversion mechanism and preparation method of dendrite-free alloy negative electrode
ActiveCN113258035AEnhanced wettingImprove adsorption capacityFilling tube/pocket electrodesNegative electrodesDendrite (metal)Liquid alloy
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
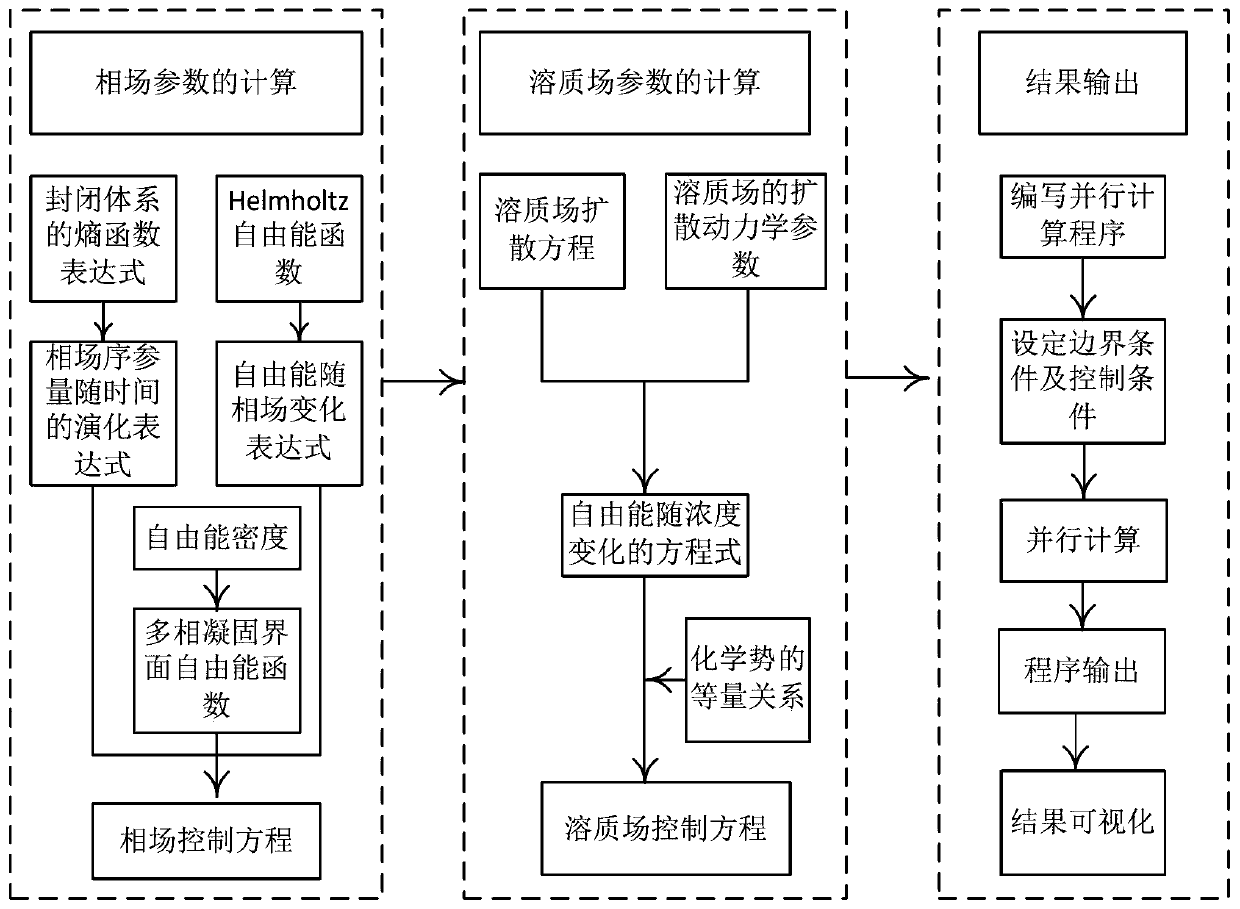
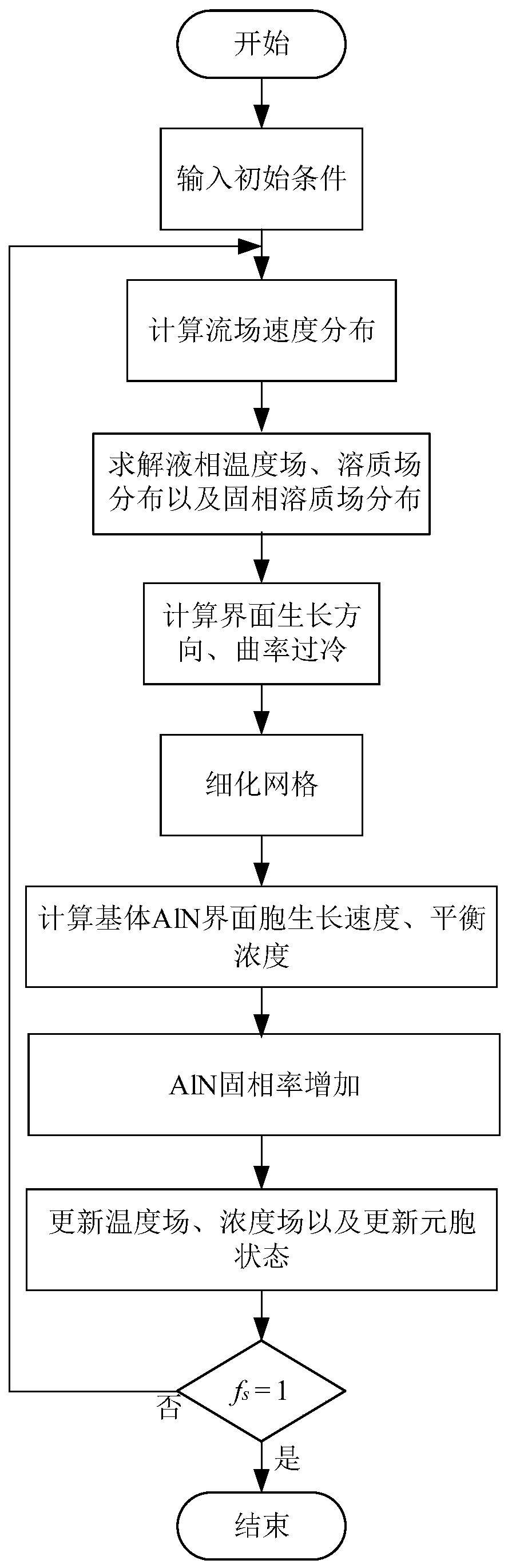
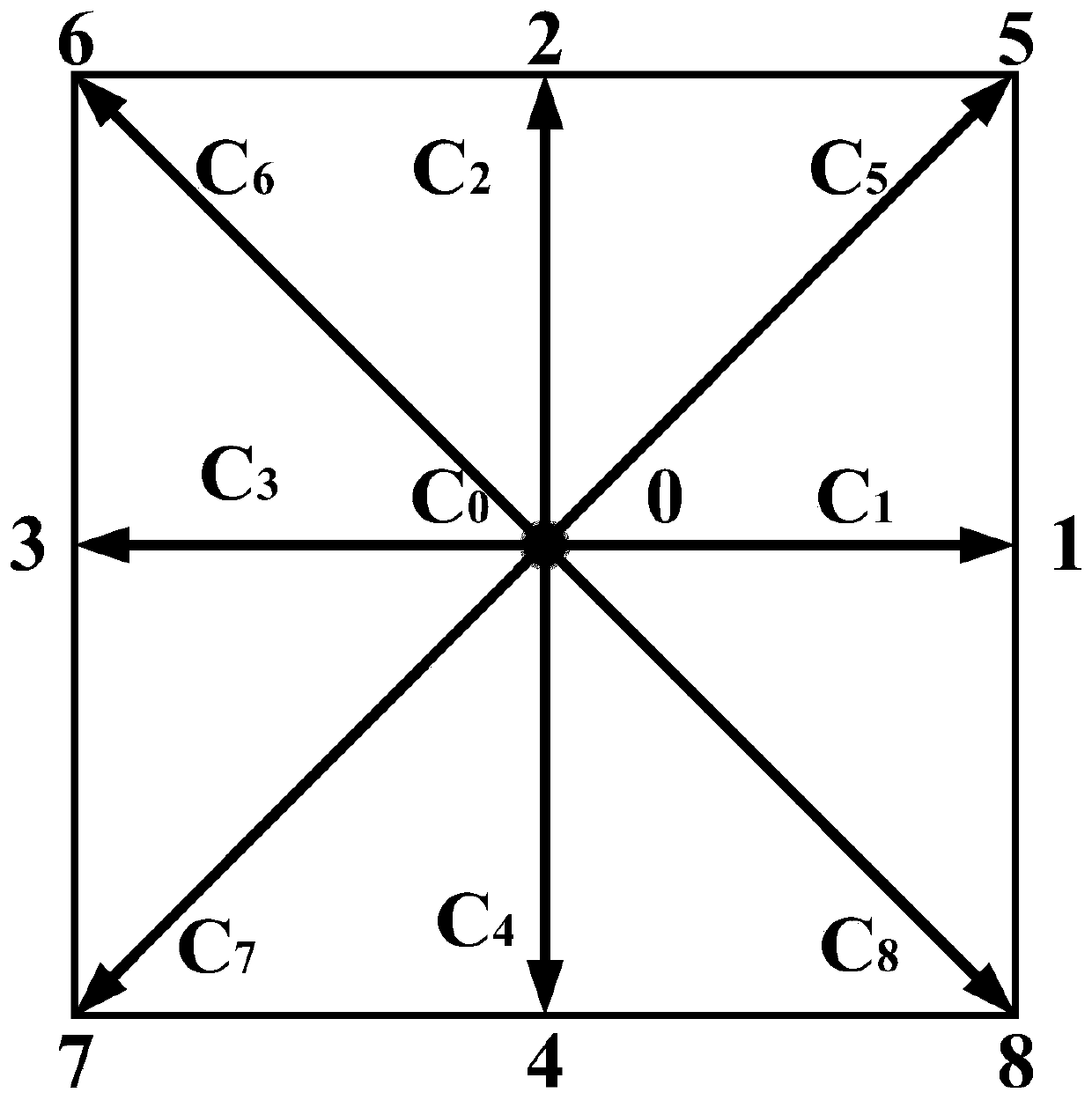
Prediction method for dendritic crystal growth in static molten steel based on parallel computing
PendingCN110993038AHigh precisionHigh cost of solutionResource allocationForecastingConcurrent computationMaterials science
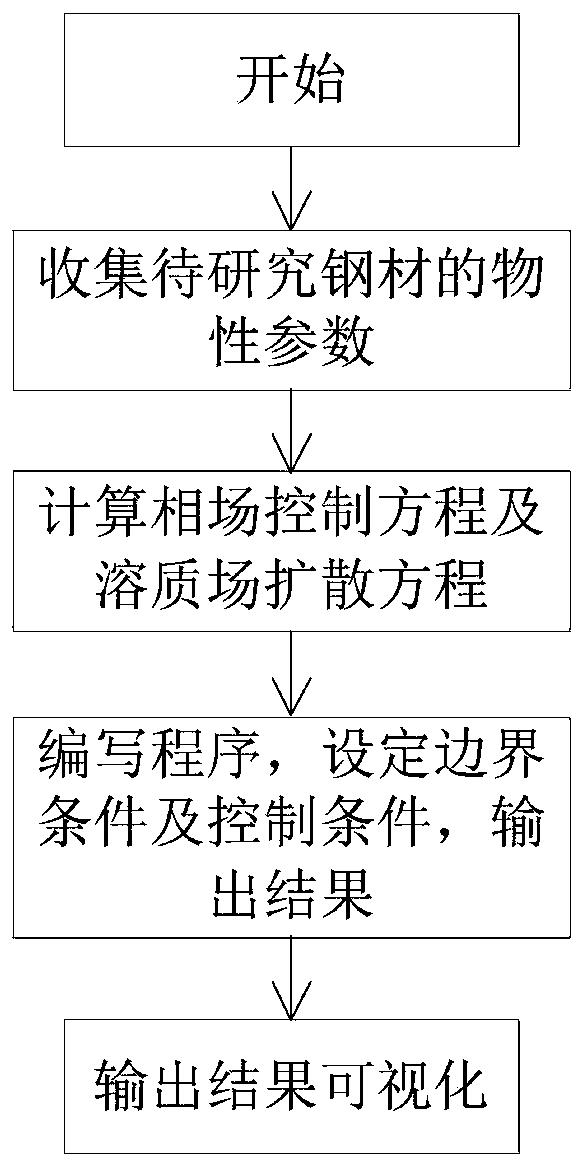
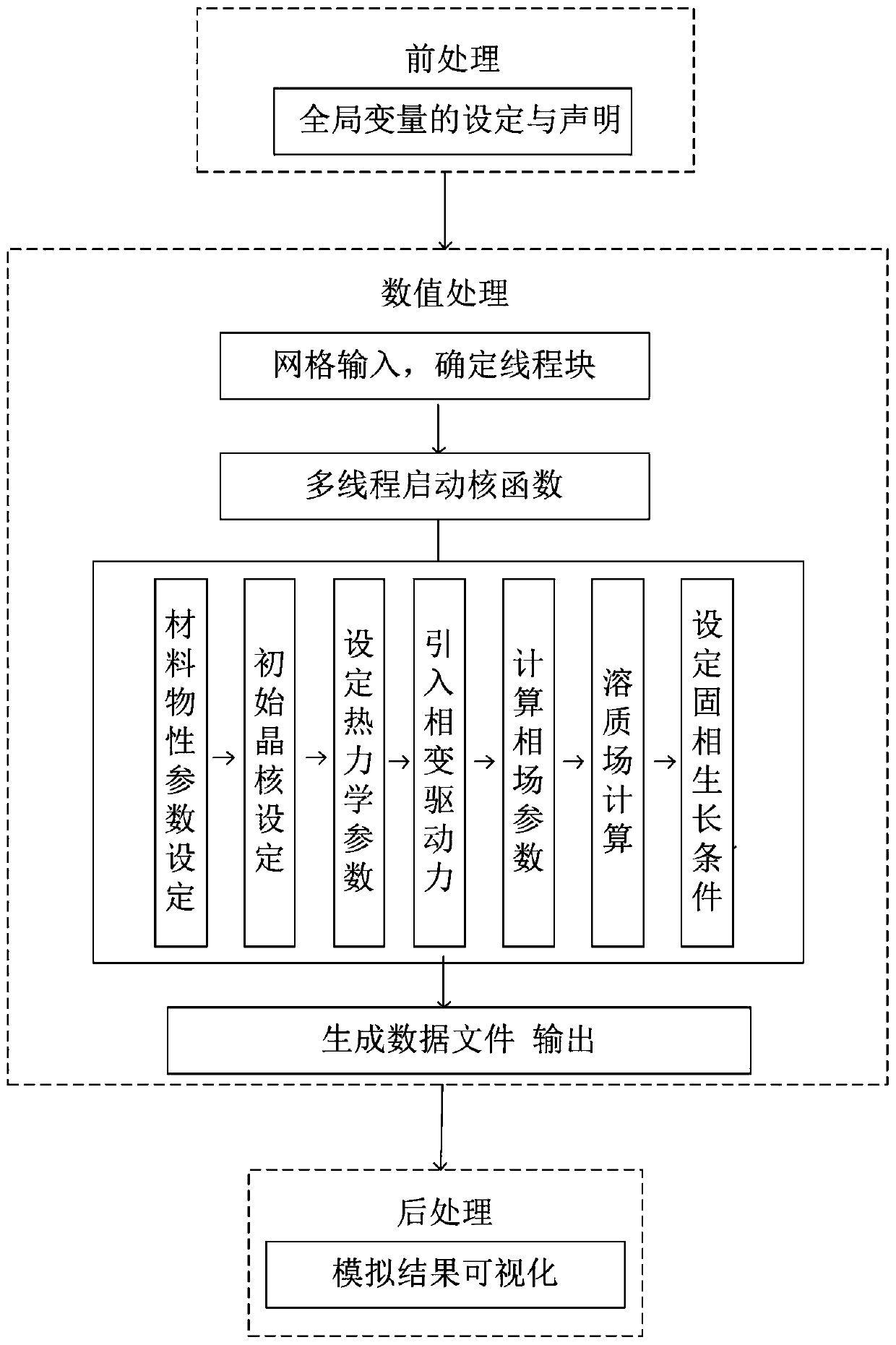
The invention relates to the technical field of metallurgy continuous casting, and provides a prediction method for dendritic crystal growth in static molten steel based on parallel computing. The method comprises the following steps: collecting physical property parameters of to-be-studied steel and proportion data of each component; calculating a control equation of a phase field and a solute field according to the collected physical property parameter data and a phase field method model: writing multi-thread program codes based on parallel calculation, distributing a phase field variable and a concentration calculation process of an i-th node to an i-th thread, and setting a boundary condition and a control condition; enabling the n threads to execute the multi-thread program codes based on parallel computing at the same time, and enabling the i-th thread to output the phase field variable and concentration of the i-th node to an (n + 1)-th thread; and enabling the (n + 1)-th threadto convert the phase field variables and concentrations of the n nodes into an image form to obtain the growth process of dendrites in the static molten steel. According to the method, the growth process of the dendritic crystal in the static molten steel can be reproduced, and the dendritic crystal growth prediction accuracy and calculation efficiency are improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for reducing metal dendrites in manganese electrodeposition
ActiveCN113445076AImprove deposition morphologyReduce generationPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsElectrolysisManganese
The invention discloses a method for reducing metal dendrites in manganese electrodeposition, which comprises a direct-current power supply, a circuit system, electrodes and an electrolytic bath. A circuit is added to a manganese metal electrolysis device, the amplitude and frequency of electrochemical oscillation in the manganese metal electrolysis process can be effectively reduced, the chaos state of an electrolysis system is weakened, the current density is homogenized, and therefore generation of cathode metal dendrites is restrained.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Simulation method for predicting solidification process of vacuum consumable melting cast ingot
PendingCN114091248AUniform compositionSolve liquidity problemsDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsMetallurgyMathematical model
The invention discloses a simulation method for predicting the solidification process of a vacuum consumable melting cast ingot, and relates to the technical field of vacuum consumable arc melting. The simulation method comprises the following steps: establishing a mathematical model related to an electromagnetic field and a flow field, carrying out mesh generation on a geometric model, adopting an Eulerian-Eulerian method, setting three phases: molten metal, equiaxed dendrites and columnar crystals, and obtaining related material attributes; setting relevant boundary conditions and relevant dynamic grid parameters, and simulating flowing and solidification of molten metal in the vacuum consumable arc melting process and distribution of an electromagnetic field and a solidification structure. According to the method, the rising process of the molten pool and the solidification process of the cast ingot in the vacuum self-consuming arc melting process are simulated, the flowing form of the molten metal in the solidification process is obtained, the capacity of predicting macrosegregation of the cast ingot is achieved, and the method plays an important guiding role in optimizing the vacuum self-consuming arc melting process to obtain the cast ingot with uniform components; and the method is of great significance to actual production.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
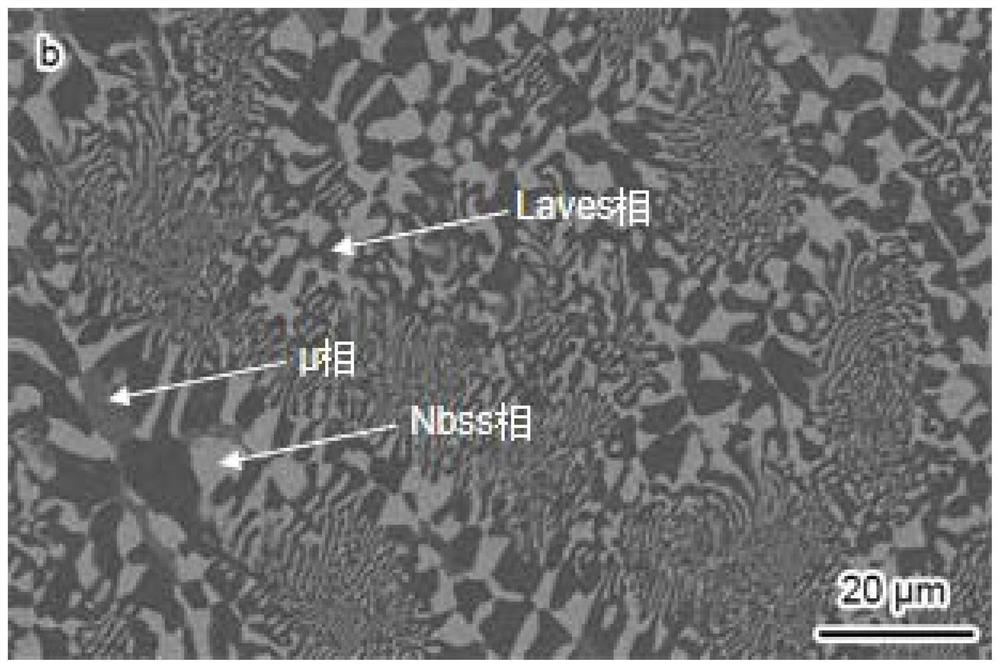
Laves phase eutectic alloy with high strength, high hardness and high thermal stability and preparation method of laves phase eutectic alloy
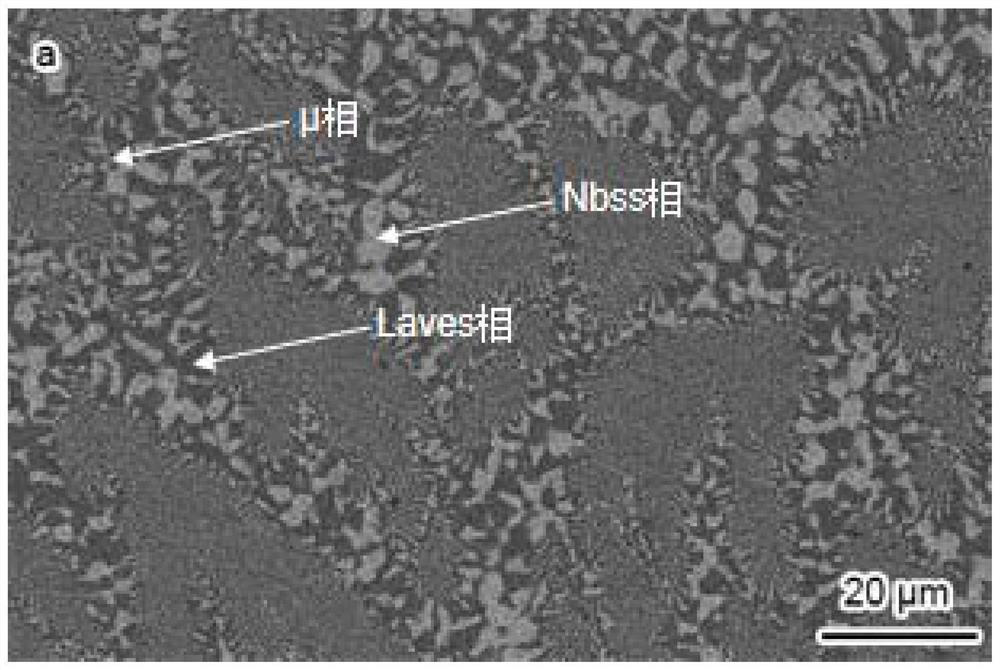
The invention discloses a Laves phase eutectic alloy with high strength, high hardness and high thermal stability and a preparation method of the Laves phase eutectic alloy. The preparation method comprises the following steps that 1, high-purity metal raw materials are polished and cleaned, and proportioning is conducted according to chemical components Cr-22.93 Fe-53.68 Nb (at.%); and 2, the metal raw materials are sequentially put into a water-cooled copper crucible of a non-consumable electric arc melting furnace according to the sequence that the melting points are from low to high, the vacuum degree of a furnace body is increased to 3 * 10 <-3> Pa to 6 * 10 <-3> Pa, high-purity argon is introduced, the air pressure in the furnace is controlled to be 0.05 Pa, and in an electric arc melting process, an alloy ingot is turned over and remelted five times to obtain an eutectic alloy product. According to the eutectic alloy, in a microscopic structure, a full eutectic Laves phase / Nbss phase is arranged in dendrites, a full eutectic Laves phase / mu phase / Nbss phase is arranged among the dendrites, the eutectic alloy has high strength, high hardness and high thermal stability, meanwhile, low-cost Fe is adopted for replacing Cr, the material cost is low, the manufacturing process is simple, rapid and efficient, the eutectic alloy has the advantages of being small in crystallization temperature interval, good in fluidity, small in component segregation and the like, and is suitable for preparing large-size high-quality components with uniform components and structures.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
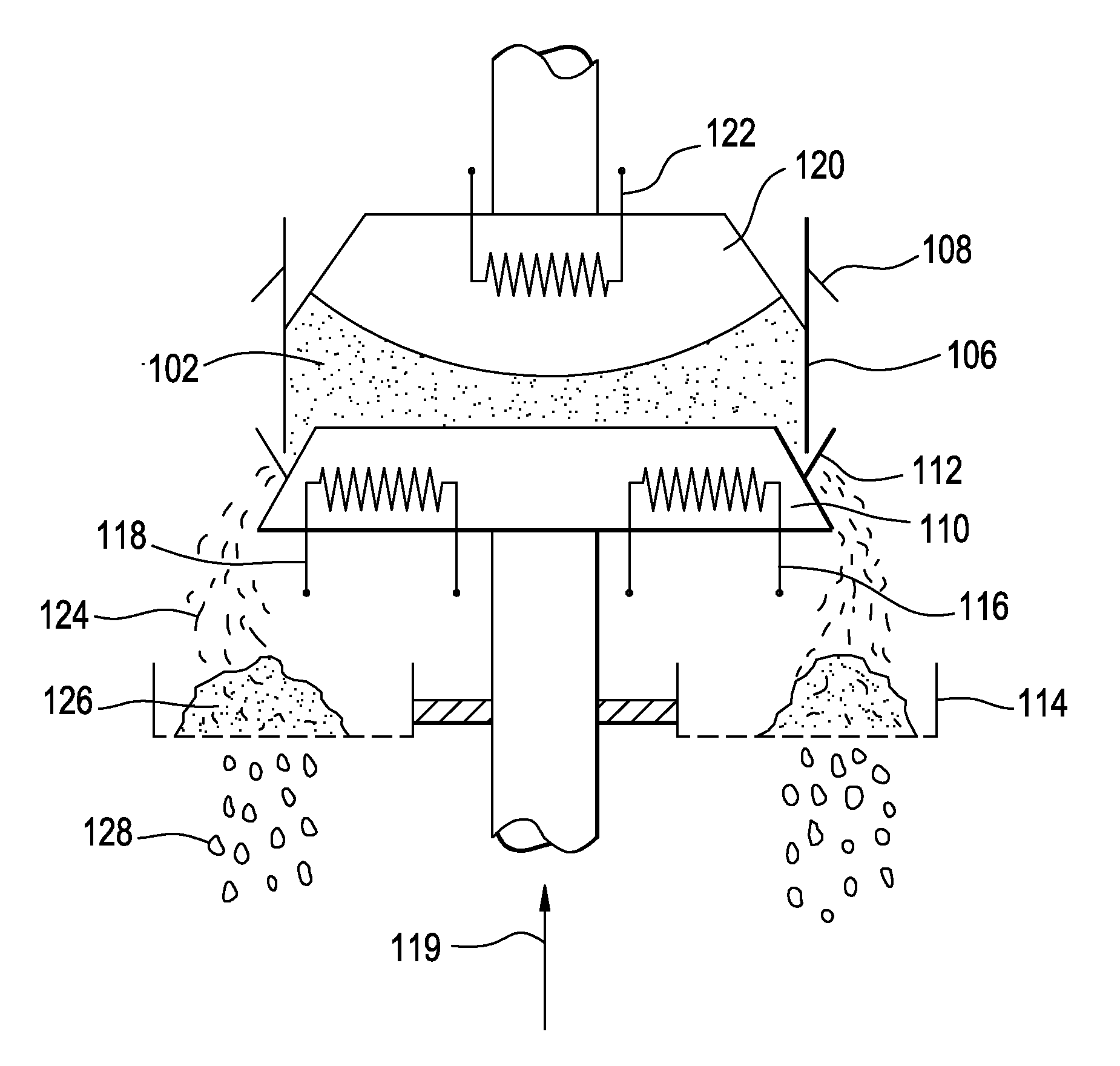
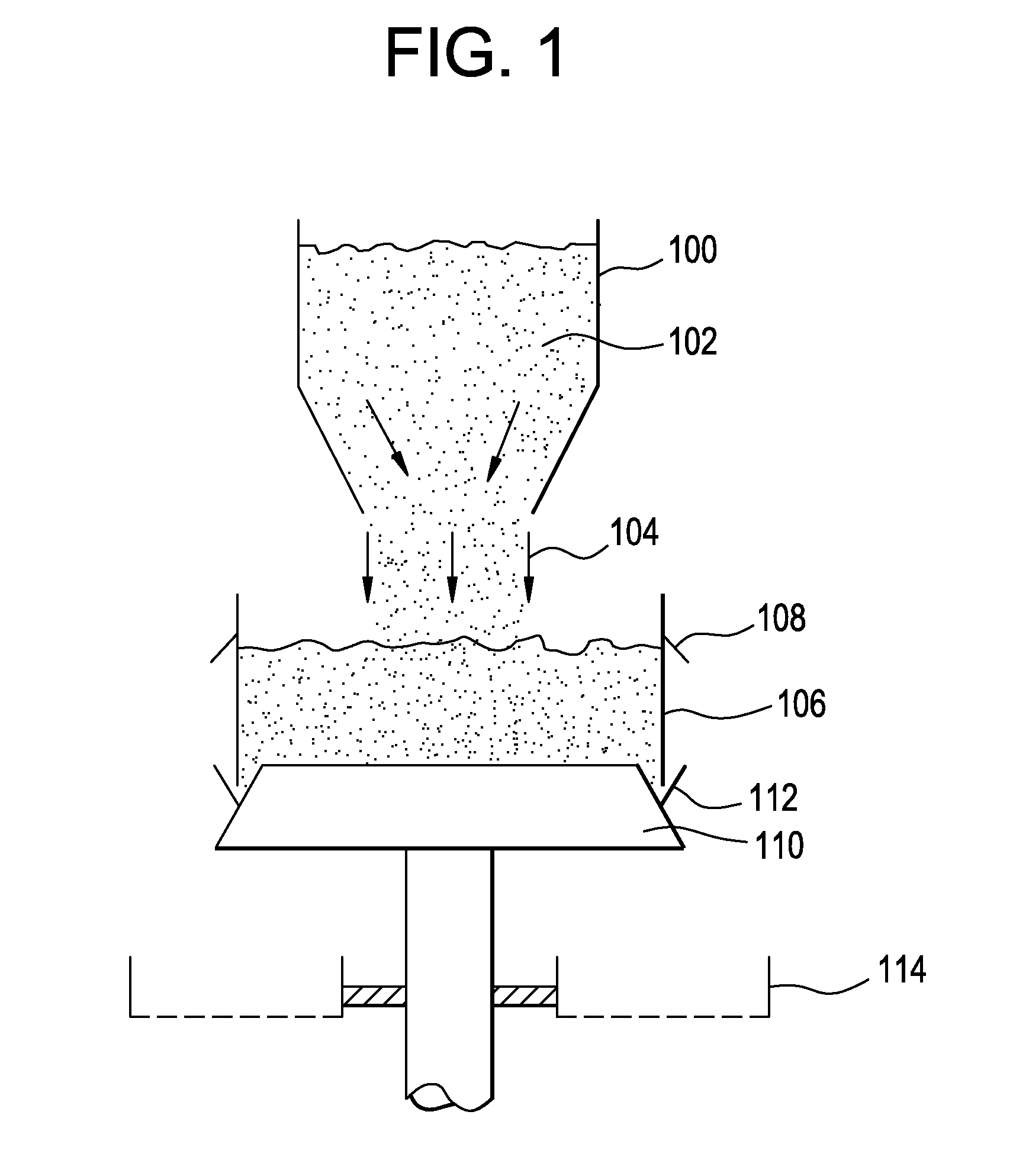
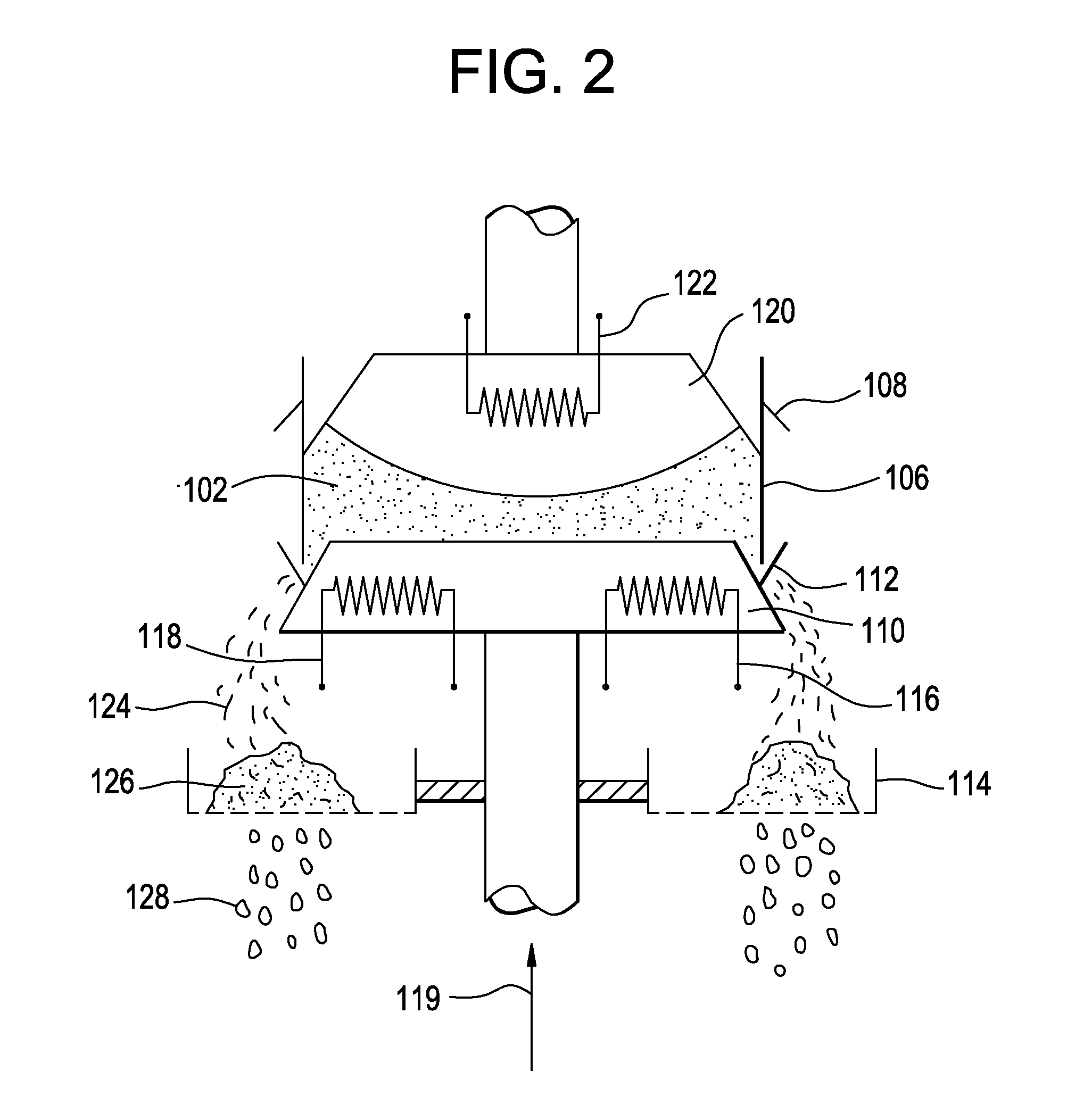
Mechanical press system and method of removing salt using the same
A method of removing salt from a dendritic mixture includes loading the dendritic mixture into a mechanical press system. The dendritic mixture includes a metallic dendrite and salt dispersed within the metallic dendrite. The dendritic mixture is heated to liquefy the salt without volatilizing one or more metals of the metallic dendrite. The dendritic mixture is also compressed to obtain a fluidic mixture and an ingot of the metallic dendrite. The fluidic mixture may include molten salt and residual metallic dendrite. The fluidic mixture may be filtered to separate the residual metallic dendrite from the molten salt.
Owner:GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY AMERICAS
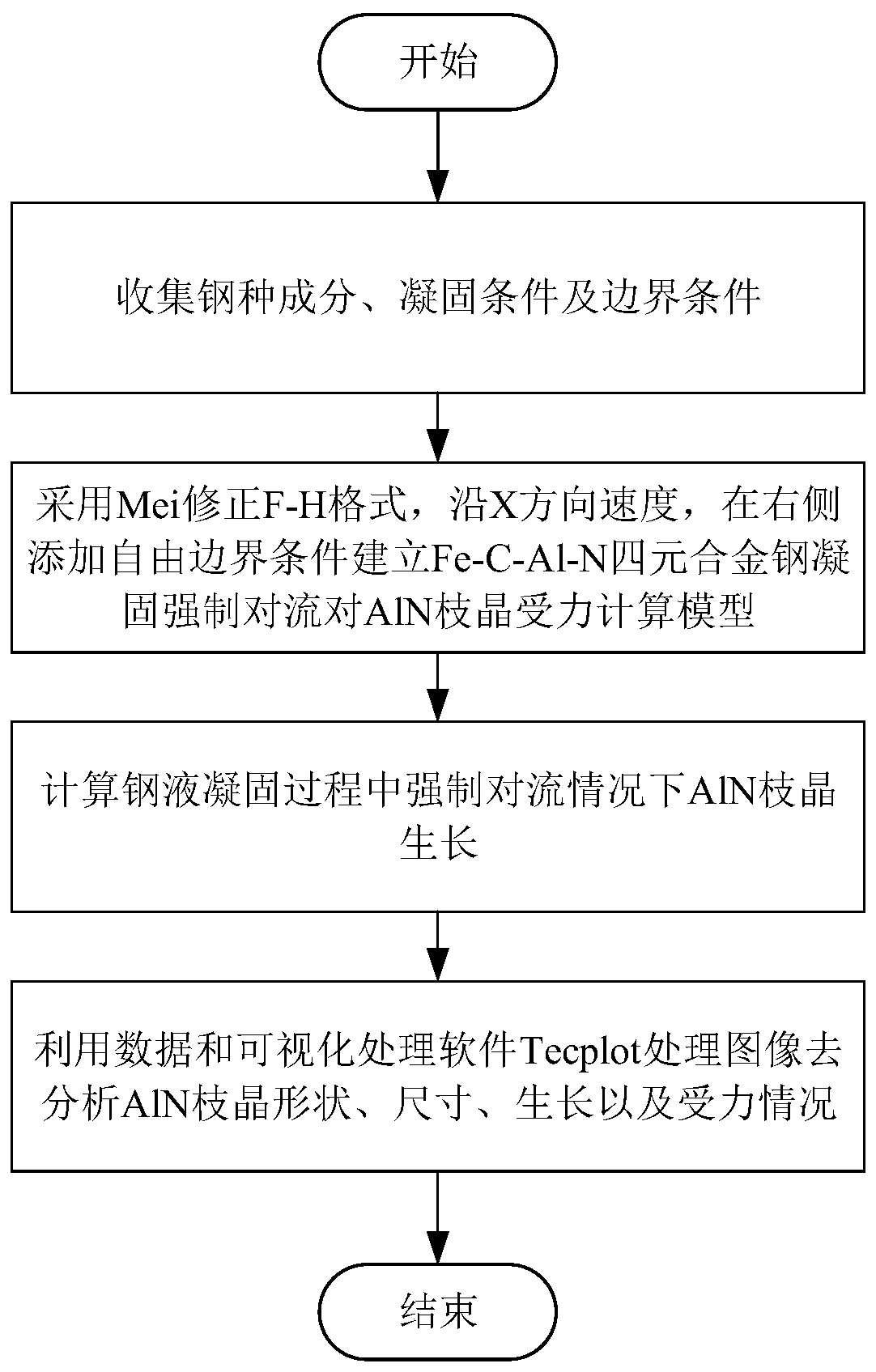
Method for calculating stress of forced convection on AlN dendrites in molten steel solidification process in field of metallurgy
PendingCN110970095AImprove calculation accuracyImprove billet qualityChemical processes analysis/designComputational theoretical chemistryDendrite (metal)Forced convection
The invention provides a method for calculating the stress of forced convection on AlN dendrites in the molten steel solidification process in the field of metallurgy, and relates to the field of metallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: firstly collecting steel grade components and solidification conditions; secondly calculating heat transfer and mass transfer in the solidification process, growth of interface cells in the solidification process and nucleation and growth of AlN in the solidification process, and further establishing an AlN precipitation model in Fe-C-Al-N quaternary alloy solidification; according to the continuous casting process conditions such as casting temperature, solute components and cooling rate, predicting the precipitation rule through the established AlN precipitation model, displaying the precipitation position, size, shape and size of AlN in a data imaging mode through data analysis and visual processing software, and quantifying the AlN precipitation number. According to the prediction method for the precipitation situation of the AlN inclusions in the molten steel solidification process, the theoretical guidance is provided for optimizing the solidification technology, controlling the size of the AlN inclusions in steel and improving the quality of a casting blank.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
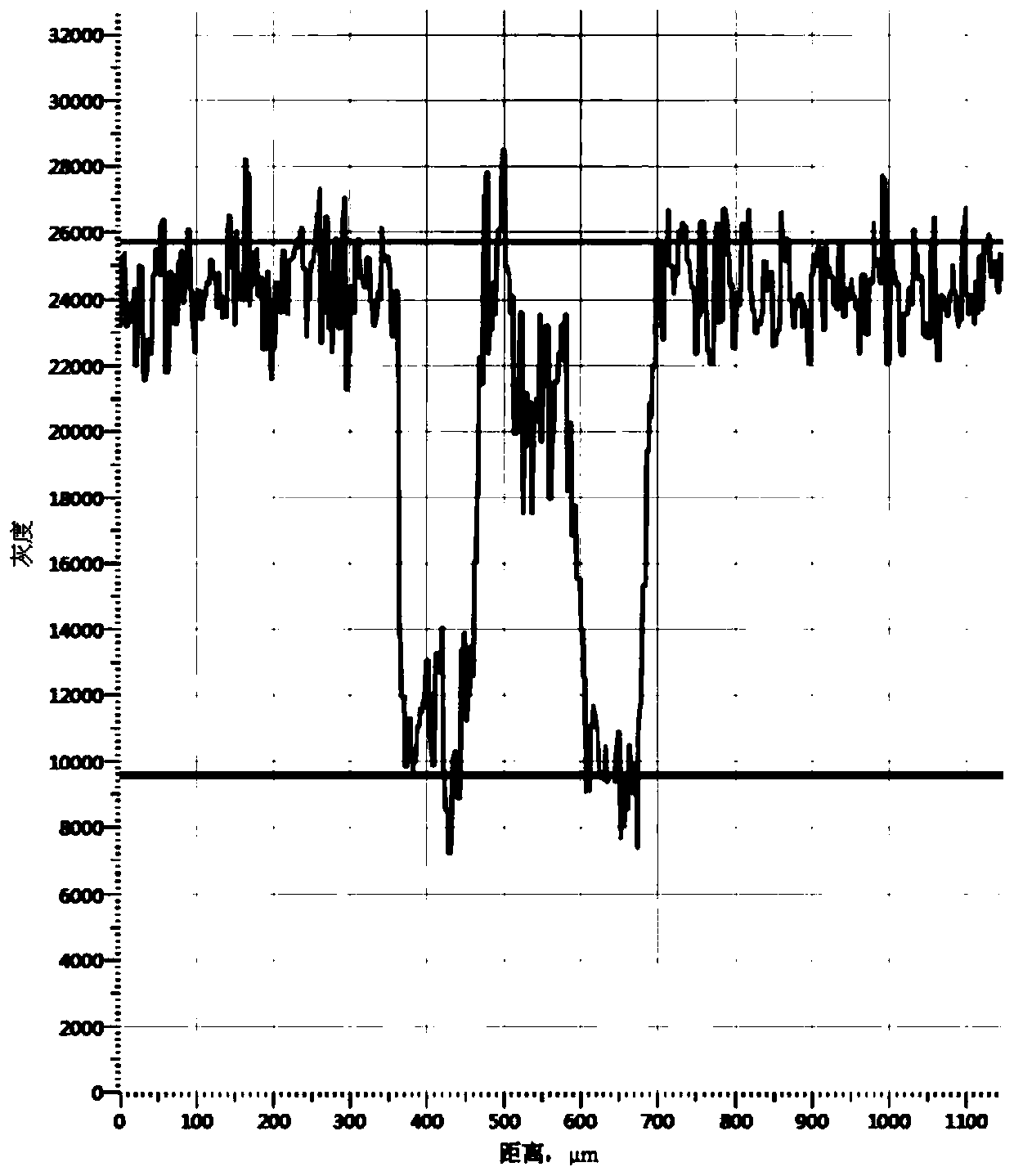
Method for measuring dendritic crystal spacing of chalcogenide free-cutting steel continuous casting billet
ActiveCN111024741AAccurate measurementDetermination method is simpleMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationUsing wave/particle radiation meansStatistical analysisMetallic materials
The invention discloses a method for measuring dendritic crystal spacing of a chalcogenide free-cutting steel continuous casting billet, and belongs to the technical field of metal material detection.The method comprises the following specific steps and parameters: firstly, cleaning, grinding and polishing a sample, and then putting into an electron microscope for analysis; then carrying out automatic statistical analysis on the non-metallic inclusions; adjusting the current of the probe to enable the dead time of the free-cutting steel sample under the electron beam to reach 20-30%; and thelike; carrying out closed operation image processing to obtain an inclusion distribution diagram spliced by all fields of view, screening according to elements and content information of the inclusiondistribution diagram, and judging the inclusion with the S content of more than or equal to 0.1 percent and the Mn content of more than or equal to 0.1 percent as manganese sulfide inclusion; obtaining a manganese sulfide inclusion distribution diagram; and finally, averaging more than or equal to 10 positions to obtain a final measurement value of the secondary dendrite spacing. The method has the advantages that the method is simple and convenient, the measured dendrite spacing value is accurate, the analysis scanning areas can be continuously spliced, and the measurement area is more than100mm < 2 >.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Metal structures
PendingUS20220074024A1Good fluid permeabilityReduce twistMaterial nanotechnologyMetallurgyDendrite (metal)
A method for producing a metal structure comprising a porous inter-dendritic matrix defining a network of dendritic channels, the method comprising the steps of: preparing an alloy melt comprising a metal element and at least one alloying element, cooling the alloy melt to a solid alloy, wherein the cooling promotes formation of a network of dendrites rich in the at least one alloying element within an inter-dendritic matrix rich in the metal, dealloying the solid alloy to remove alloying element from the dendrites and the inter-dendritic matrix to obtain the metal structure.
Owner:ROYAL MELBOURNE INST OF TECH
Electrolytic cell for metal electrowinning
InactiveUS20160024670A1High overvoltageImprove conductivityPhotography auxillary processesDiaphragmsElectrowinningMetal
The invention relates to a cell for metal electrowinning equipped with a device useful for preventing the adverse effects of dendrite growth on the cathodic deposit. The cell comprises a porous conductive screen, positioned between the anode and the cathode, capable of stopping the growth of dendrites and avoiding that they reach the anode surface.
Owner:IND DE NORA SPA
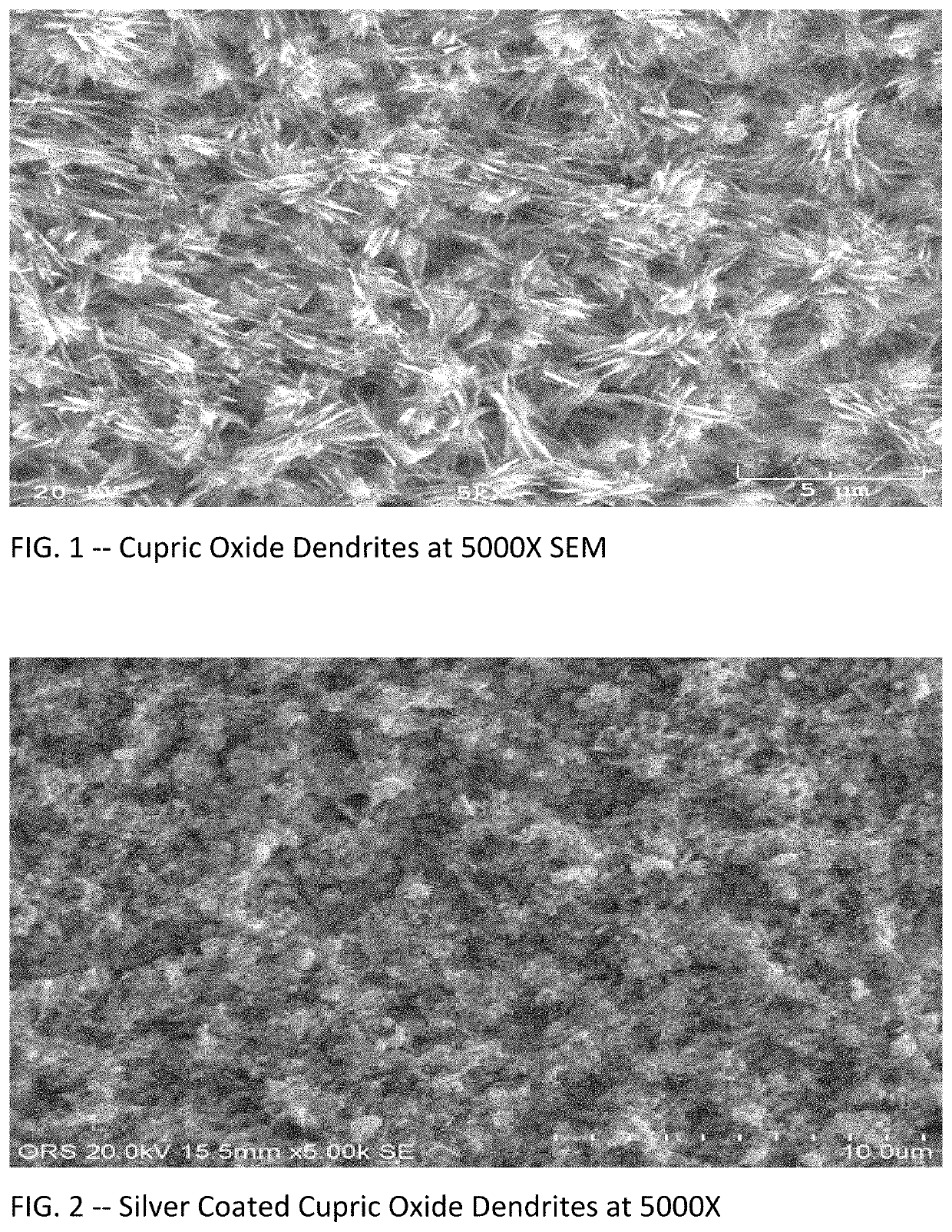
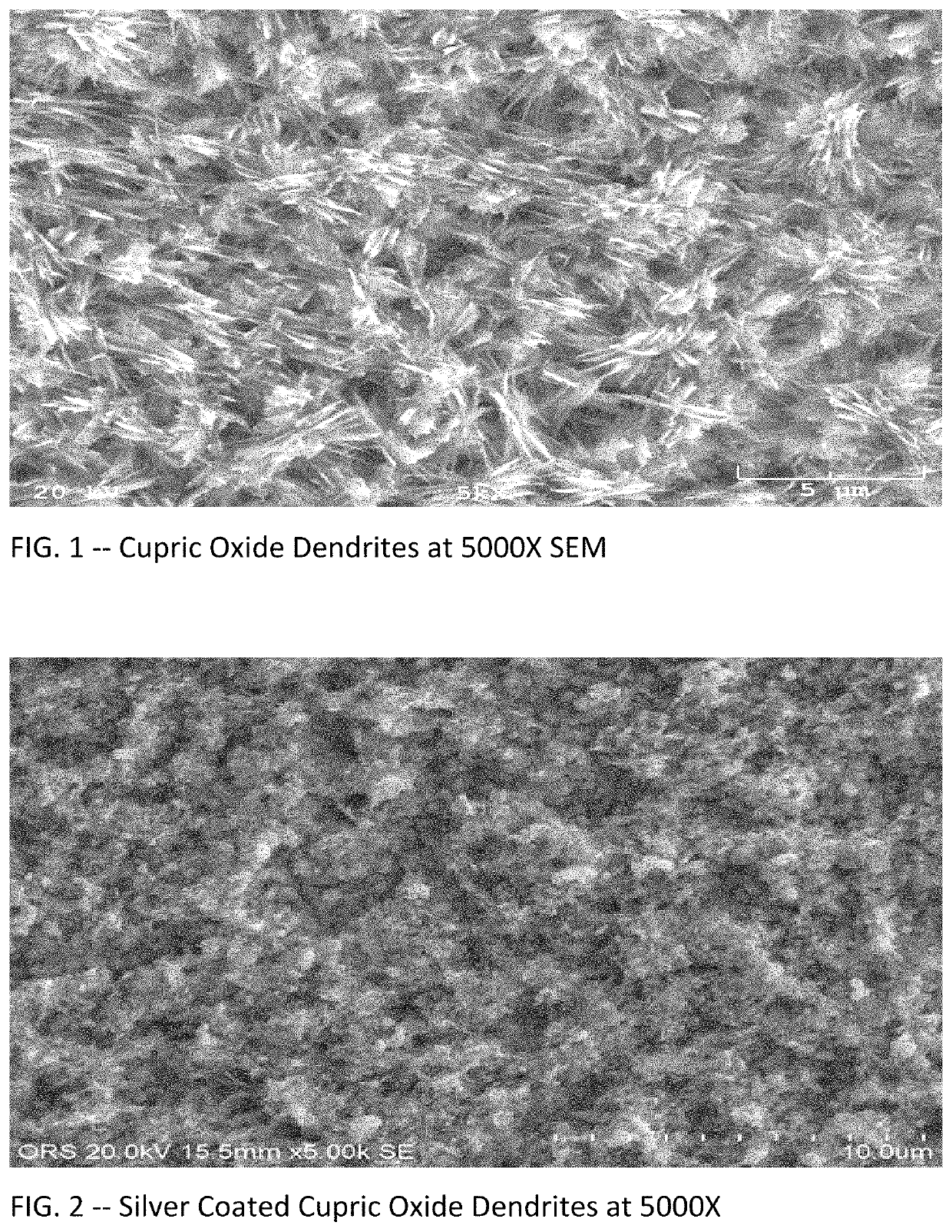
Process for producig nanostructured metal substrates for use in surface enhanced raman spectroscopy or similar applications
ActiveUS20200071812A1Ease of mass productionCost effectiveMaterial analysis by optical meansSolid state diffusion coatingMetal coatingSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
A framework of copper oxide dendrites is formed on a copper substrate, and these are then coated or plated with silver, gold, or an equivalent metal to create metal-coated dendrites with nano-structures, favorably in range of 50 to 200 nanometers. The framework of metal-coated dendrites are well suited for use in surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and other practical applications.
Owner:PLOOF LLOYD +2
Metal continuous casting process and metal continuous casting device based on electromagnetic excitation combined with mechanical stirring
The invention discloses a metal continuous casting process of electromagnetic excitation combined mechanical stirring. When the alloy melt is solidified, the electromagnetic excited combined mechanical stirring technology is used to generate microscopic and macroscale strong shear flow to break dendrites. In this way, the goal of refining the solidification structure, fully equiaxed crystallization, and reducing the degree of solute segregation can be achieved, thereby improving the performance of the alloy. The invention also provides a metal continuous casting device, which is realized by a device composed of a main crystallizer, a rotor stirring paddle, a runner, a program-controlled motor, a magnetic field generator, a coil, and a voltage-regulated and frequency-regulated AC power supply. The present invention uses the microscopic flow generated by electromagnetic excitation and the macroscopic flow generated by mechanical stirring to form a very complex chaotic flow, forming a strong shear flow, breaking dendrites, promoting the proliferation of crystal nuclei, reducing the temperature gradient, and obtaining ultra-fine Fully equiaxed crystal structure, while significantly reducing or even completely inhibiting the segregation of alloy elements, the energy consumption of the present invention is significantly lower than that of conventional electromagnetic stirring, and the energy saving effect is remarkable.
Owner:新兴发展集团有限公司
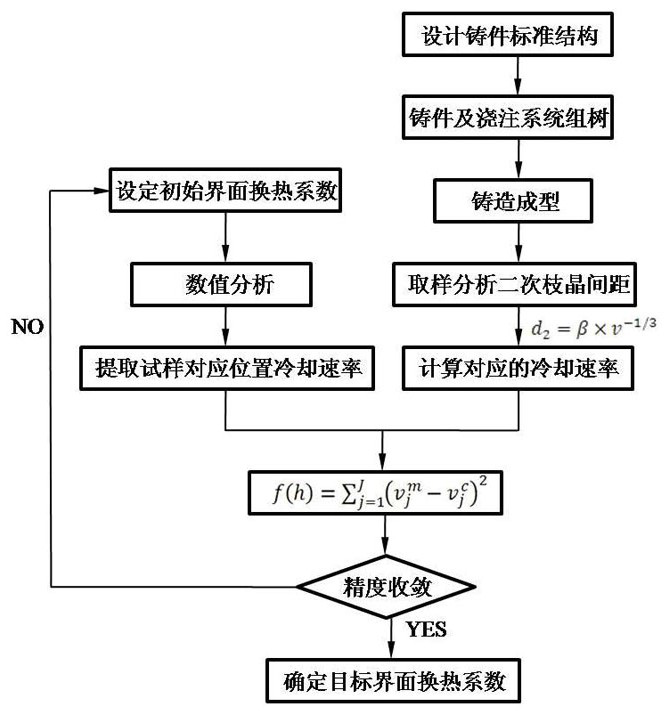
A Simple Back Calculation Method for Measuring Casting Interface Heat Transfer Coefficient
ActiveCN108108529BOmit the temperature measurement processLow costDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsThermal coefficientDendrite (metal)
The invention discloses a simple back calculation method for measuring the heat transfer coefficient of a casting interface, comprising the steps of: 1) designing a standard casting structure; 2) designing a casting process scheme and molding the casting; 3) sampling different positions on the surface of the standard casting, And after numbering in sequence, do metallographic analysis to obtain the secondary dendrite spacing data of each sample; 4) Calculate the cooling rate corresponding to the secondary dendrite spacing of each sample; 5) Calculate the temperature field value of the casting process plan Simulation analysis, and set the initial interface heat transfer coefficient, extract the cooling rate of the mushy zone; 6) According to the back calculation principle, the cooling rate calculated by the experiment and the simulated cooling rate are fitted and back calculated to solve the required interface heat transfer coefficient. This method can effectively measure and back-calculate the interface heat transfer coefficient without the temperature measurement process, and is convenient to implement and has high accuracy. It is also a general method for the interface heat transfer coefficient of various casting methods.
Owner:DONGFANG TURBINE CO LTD
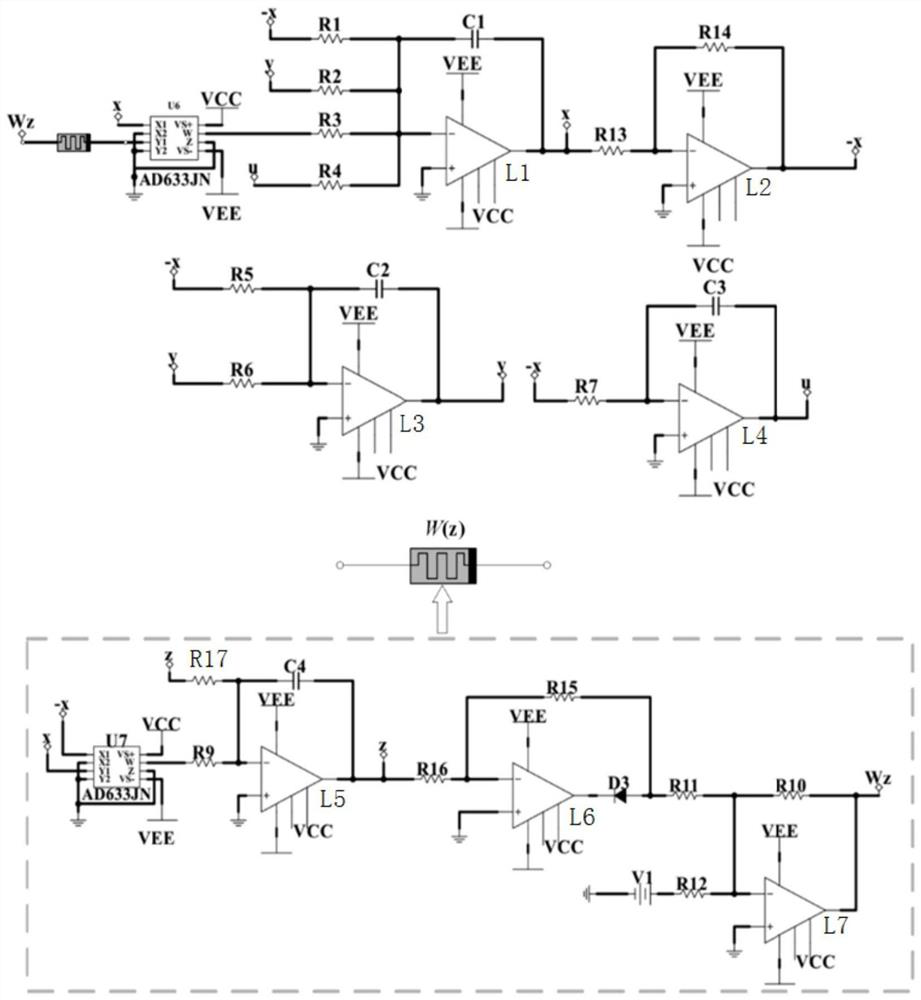
Spot welded joint and spot welding method
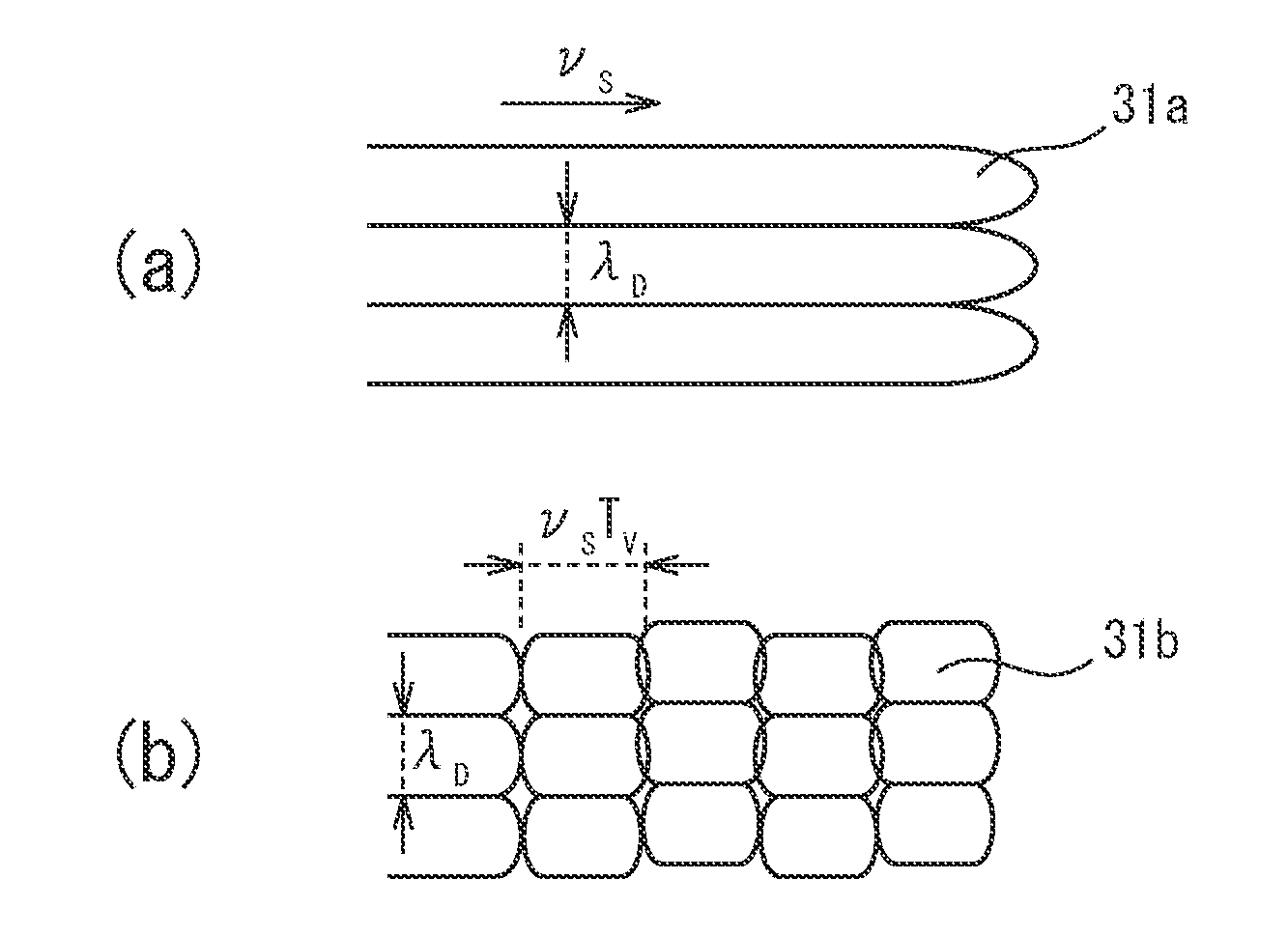
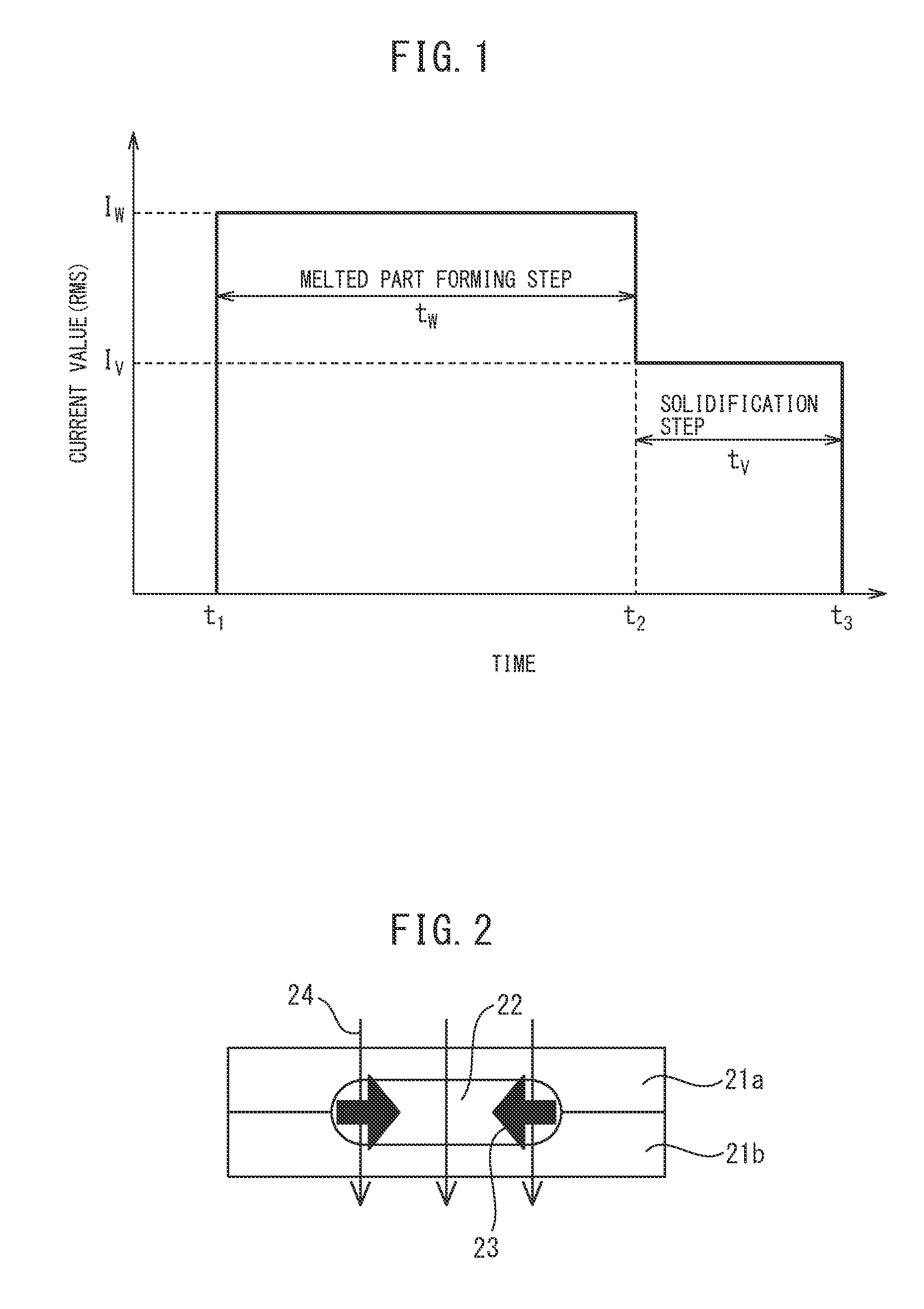
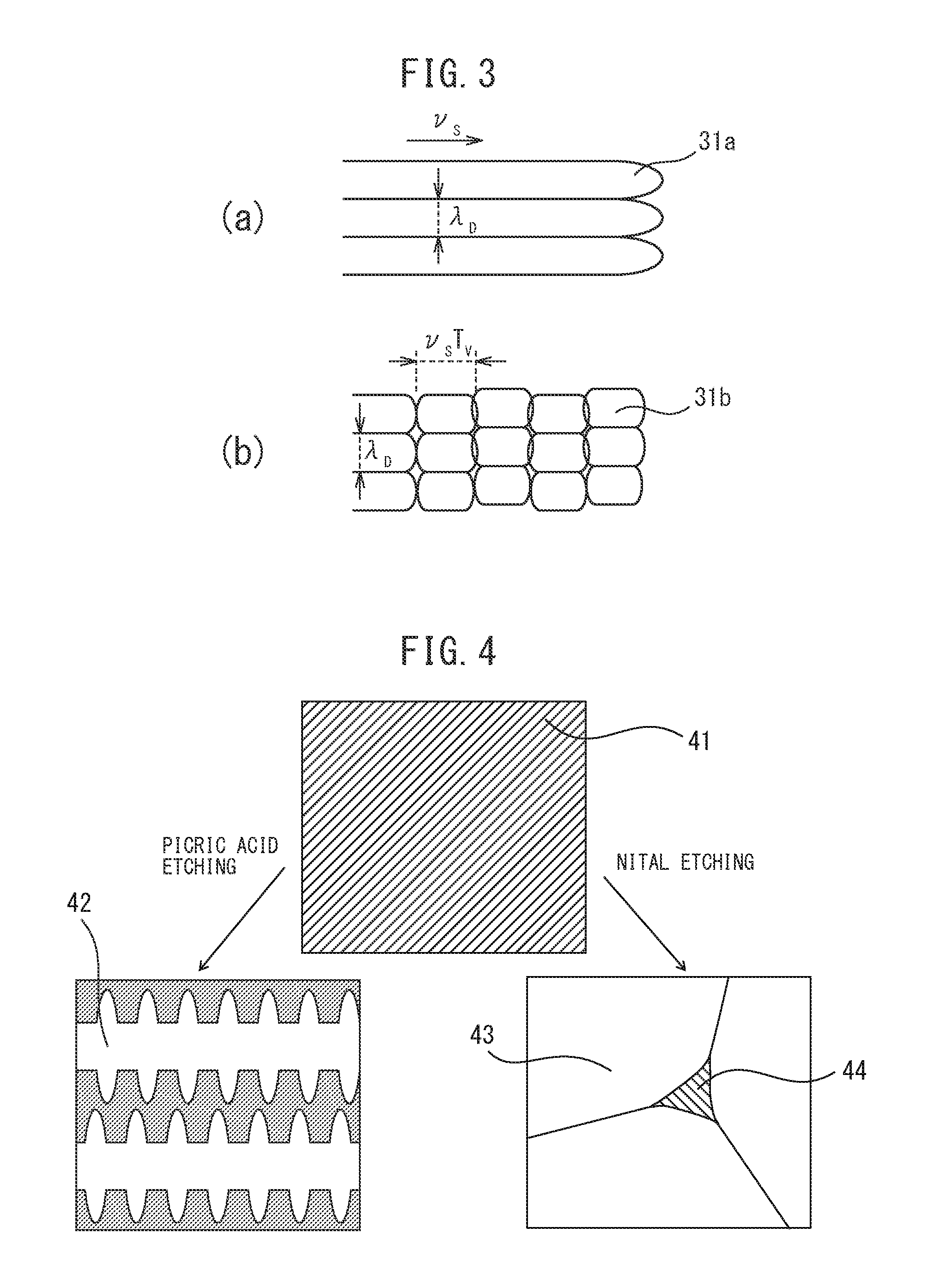
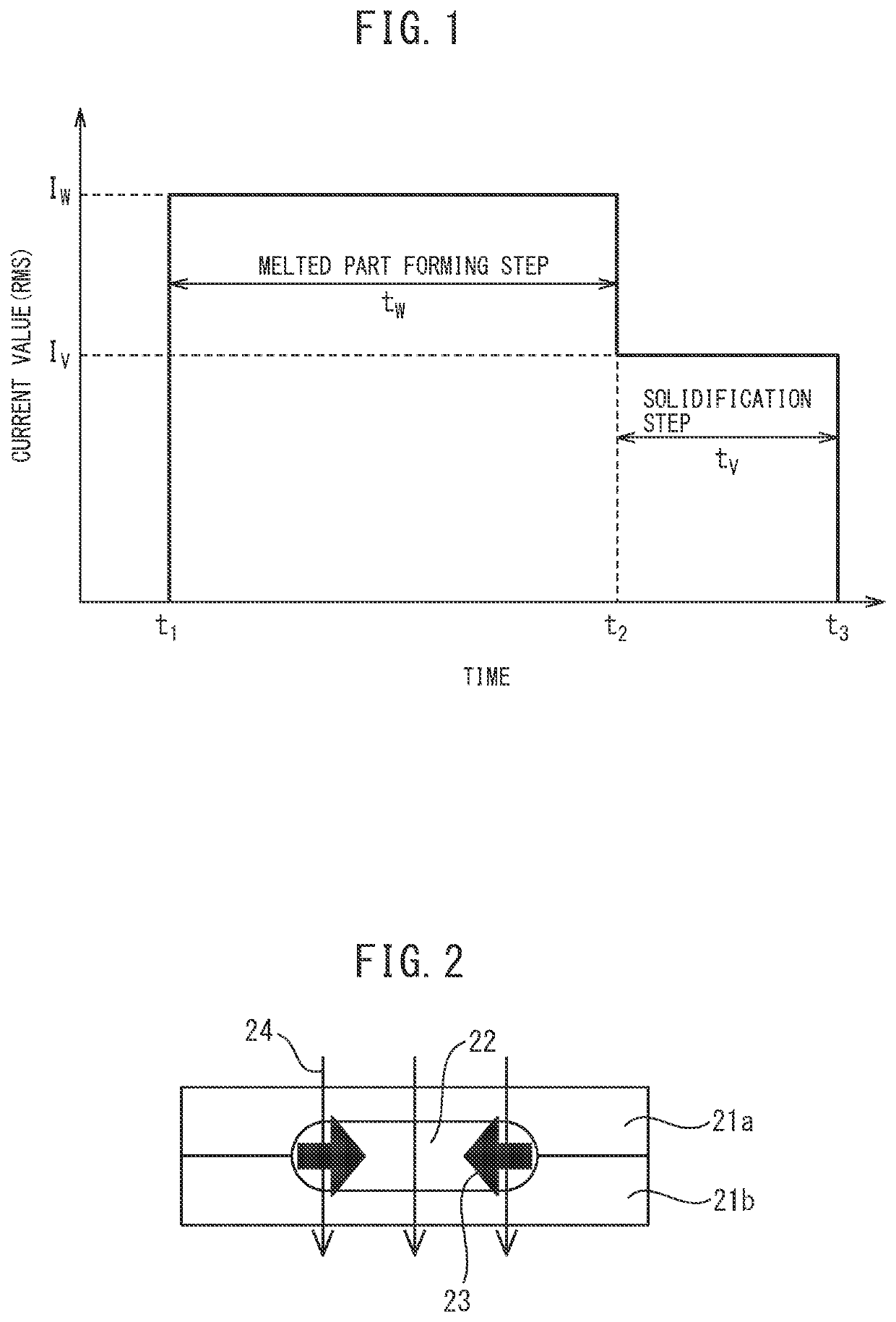
ActiveUS20160263694A1Improve reliabilityImprove toughnessVehicle componentsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesSpot weldingUltimate tensile strength
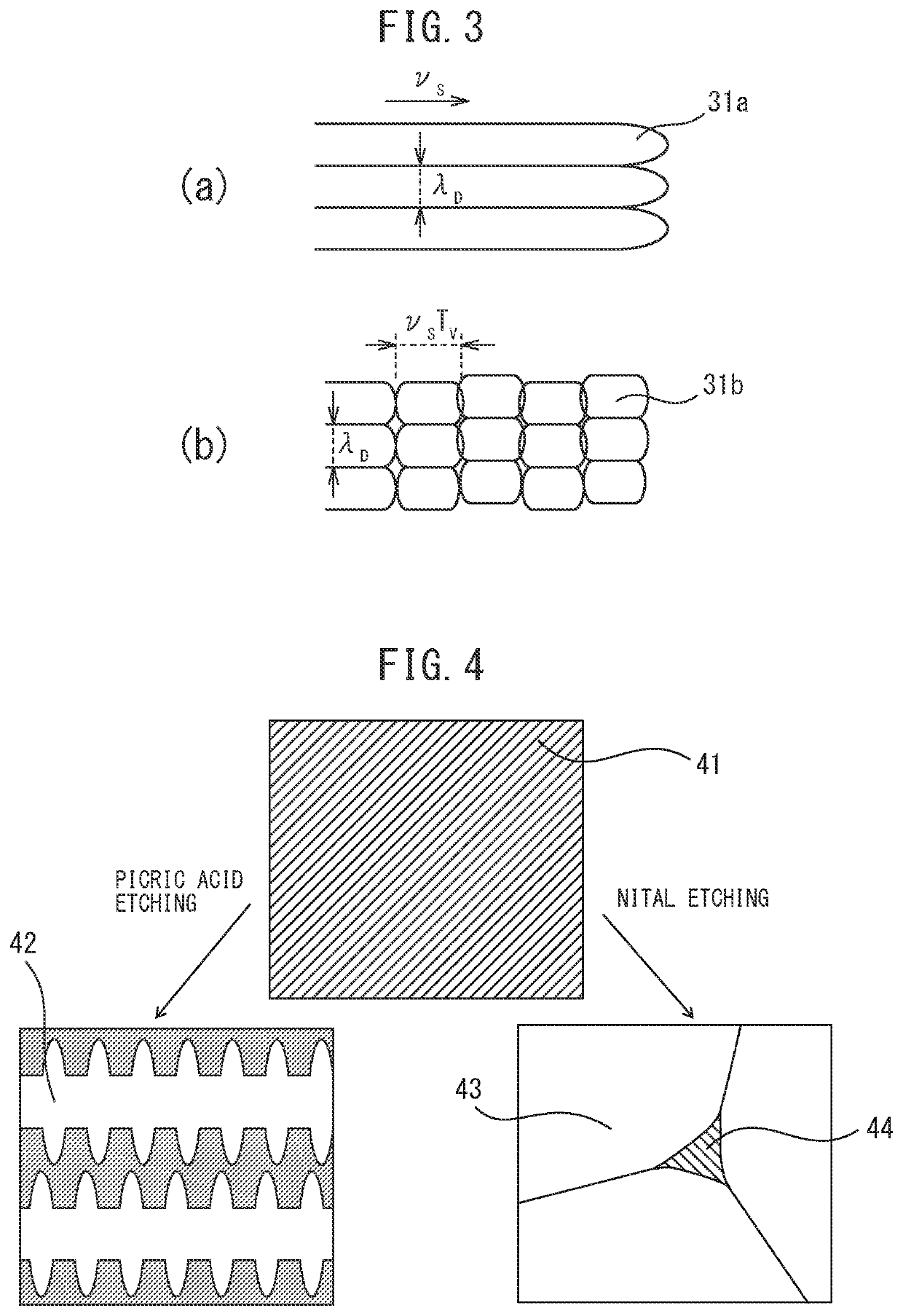
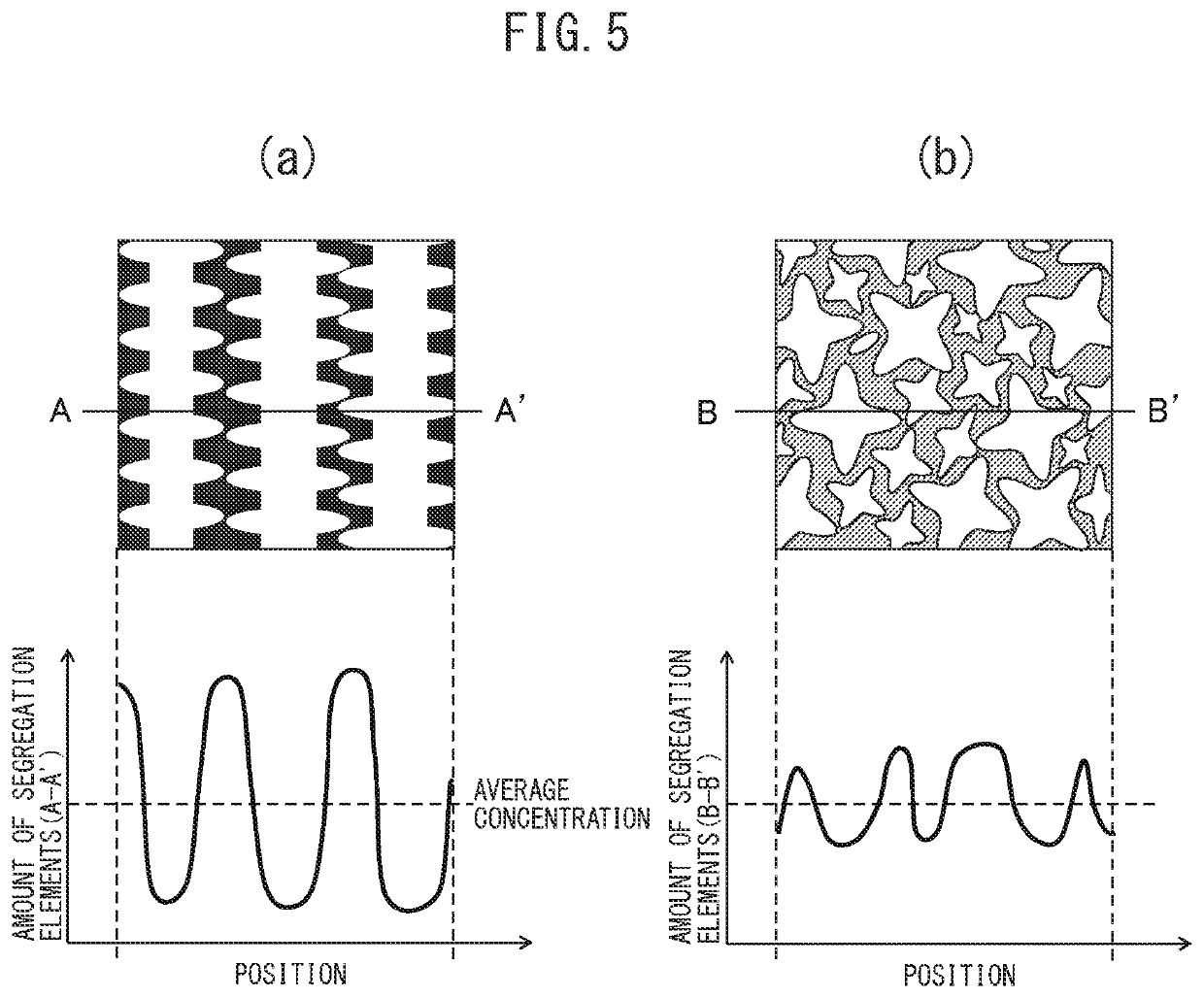
The present invention has as its object to provide a spot welded joint and spot welding method which raise the fracture toughness of spot welded metal to raise the strength of the spot welded joint. In the present invention, there is provided a spot welding method comprising a melt zone forming step forming a melt zone by conduction and, after the melt zone forming step, a solidification step of running a current lower than the current run in the melt zone forming step so as to cause the melt zone to solidify, wherein, in the solidification step, electromagnetic vibration is applied to the melt zone, and a frequency fV of the electromagnetic vibration, a solidification speed νS when the melt zone solidifies, and an arm interval of dendrites λD when the melt zone solidifies satisfy 0.2≦νS / (λD·fV)≦4.0.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Spot welded joint and spot welding method
ActiveUS10646949B2Improve toughnessHighly reliable spot welded jointVehicle componentsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesDendrite (metal)Spot welding
The present invention has as its object to provide a spot welded joint and spot welding method which raise the fracture toughness of spot welded metal to raise the strength of the spot welded joint. In the present invention, there is provided a spot welding method comprising a melt zone forming step forming a melt zone by conduction and, after the melt zone forming step, a solidification step of running a current lower than the current run in the melt zone forming step so as to cause the melt zone to solidify, wherein, in the solidification step, electromagnetic vibration is applied to the melt zone, and a frequency fV of the electromagnetic vibration, a solidification speed νS when the melt zone solidifies, and an arm interval of dendrites λD when the melt zone solidifies satisfy 0.2≤νS / (λD·fV)≤4.0.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Process for producing nanostructured metal substrates for use in Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy or similar applications
ActiveUS10829846B2Ease of mass productionCost effectiveMaterial analysis by optical meansSolid state diffusion coatingMetal coatingMetallurgy
Owner:SQUARE ONE COATING SYST LLC
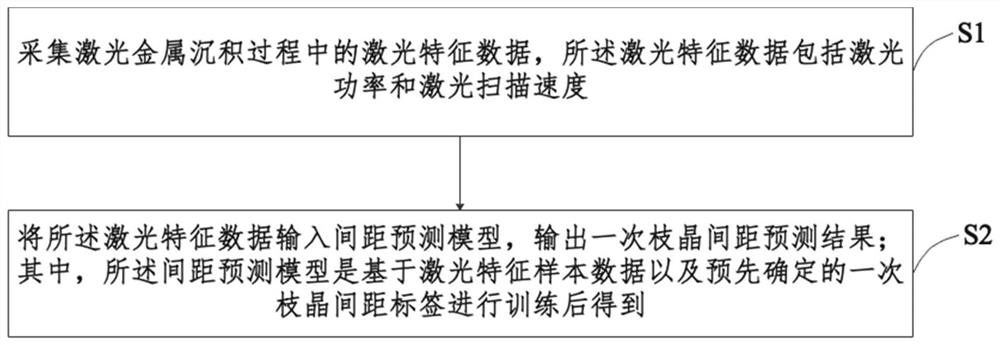
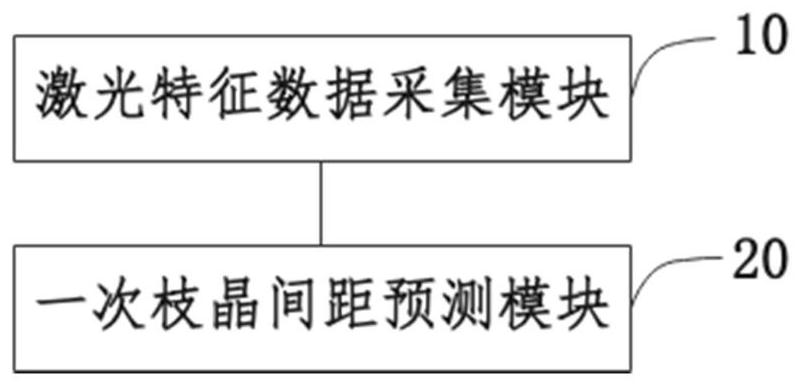
Laser metal deposition primary dendrite spacing prediction method and system
ActiveCN112949208BRealize real-time controlPrediction is accurateAdditive manufacturing apparatusDesign optimisation/simulationLaser scanningDendrite (metal)
The present invention provides a method and system for predicting primary dendrite spacing in laser metal deposition, wherein the prediction method includes: collecting laser characteristic data during laser metal deposition, the laser characteristic data including laser power and laser scanning speed; The feature data is input into the spacing prediction model, and the primary dendrite spacing prediction result is output; wherein, the spacing prediction model is obtained after training based on laser characteristic sample data and a predetermined primary dendrite spacing label. In the present invention, the primary dendrite spacing prediction data can be obtained by inputting the laser power and laser scanning speed into the spacing prediction model. The spacing prediction model is obtained after training based on the laser characteristic sample data and the predetermined primary dendrite spacing label. The invention provides The method has high precision and good timeliness, which is conducive to realizing real-time control of microstructure in industrial applications.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
A continuous casting method for eliminating dendrite band segregation near the surface of alloy spring steel wire rod
ActiveCN110508771BAvoid crack defectsImprove fatigue performancePreparing sample for investigationTesting metal structuresWire rodWater flow
The invention discloses a continuous casting method for eliminating dendrite strip segregation near the surface of an alloy spring steel wire rod. The method comprises the control of the superheat degree of molten steel in a continuous casting tundish, the control of the casting speed of a continuous casting slab, and the control of electromagnetic stirring in a crystallizer. , crystallizer water flow control and vibration parameter control process; the superheat of molten steel in the tundish is controlled at 15-25°C through the electromagnetic induction heating equipment of the tundish; 150~300A, frequency 1.5~2.5Hz; adopt hydraulic vibration, amplitude 2.3~2.7mm, vibration frequency 100~130cpm, liquid level fluctuation is controlled within ±2mm. The φ5.5-20mm alloy spring steel wire rod produced by the continuous casting method of the present invention has no near-surface dendrite band segregation through dendrite corrosion detection, and the surface layer metallographic structure is uniform after heat treatment, effectively preventing the dendrite band segregation caused by dendrite band segregation. Early fatigue fracture of the spring.
Owner:XINGTAI IRON & STEEL
Dendrite etchant and corrosion method for large ingot modified in617 alloy
The invention relates to a dendritic crystal etchant of a large ingot type modified IN617 alloy and a corrosion method thereof, belongs to the technical field of metallographic sample preparation, andsolves the technical problem that the existing etchant cannot corrode a clear dendritic crystal structure of the ingot type modified IN617 alloy in the prior art. The dendritic corrosion agent of thelarge ingot type modified IN617 alloy comprises 80-120 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid, 9-15 ml of concentrated nitric acid, 100-130 ml of water and 10-20 ml of ethanol. The etchant provided bythe invention can rapidly and clearly corrode the dendritic structure in the as-cast state and the homogenized heat treatment state of the modified IN617 alloy, measure the dendritic spacing, measurethe components between dendrites and dendrite arms through energy spectrum, analyze the segregation degree of the dendrites, evaluate the elimination effect of the as-cast structure and the homogenized heat treatment of the modified IN617 alloy on the dendritic segregation, and provide an important basis for formulating the homogenization process before forging.
Owner:TIANJIN HEAVY EQUIP ENG RES +1
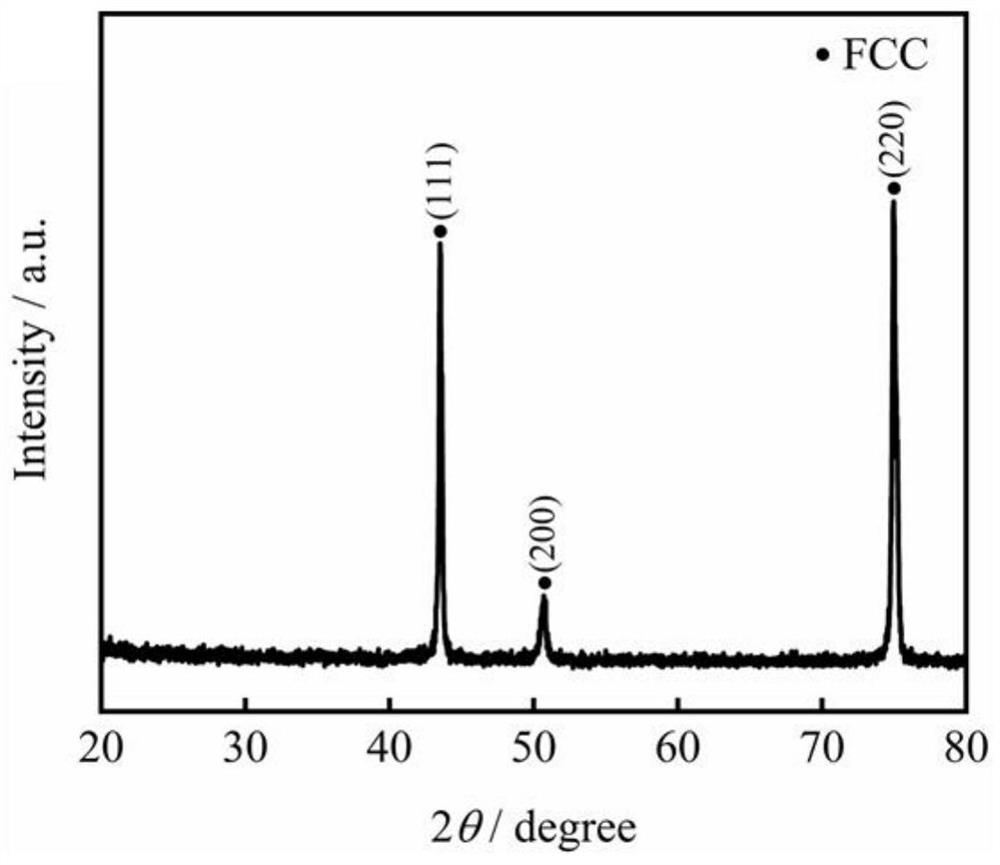
A method of cutting and preparing cast single crystal superalloy seed crystal
A method for cutting and preparing cast single crystal superalloy seed crystals. Based on the strict correspondence between the growth direction of single crystals and crystal directions, the directions of primary dendrites and secondary dendrites are precisely cut and calibrated, and standard dendrites are constructed based on the dendrite directions. The FCC crystal structure can cut out the (001) crystal plane of the single crystal test rod, and then use the crystal plane angle formula of the FCC crystal to calculate the angle θ between the target crystal plane and the (001) crystal plane, and according to the FCC crystal structure Features Mark the intersection line between the target crystal plane and the (001) crystal plane on the (001) crystal plane, and cut out the target crystal plane along the intersection line with an angle of θ with the (001) crystal plane; cut perpendicular to the target crystal plane A seed crystal with the target orientation is obtained. The invention adopts metallographic observation and directional cutting to directly cut seed crystals with any crystal orientation on cast single crystal test rods, has simple equipment and operation steps, and the orientation deviation of cut out seed crystals is less than 5°.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com