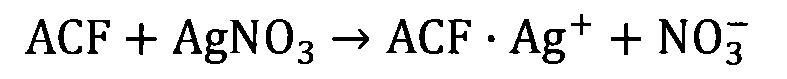Patents
Literature
186results about How to "Short build time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
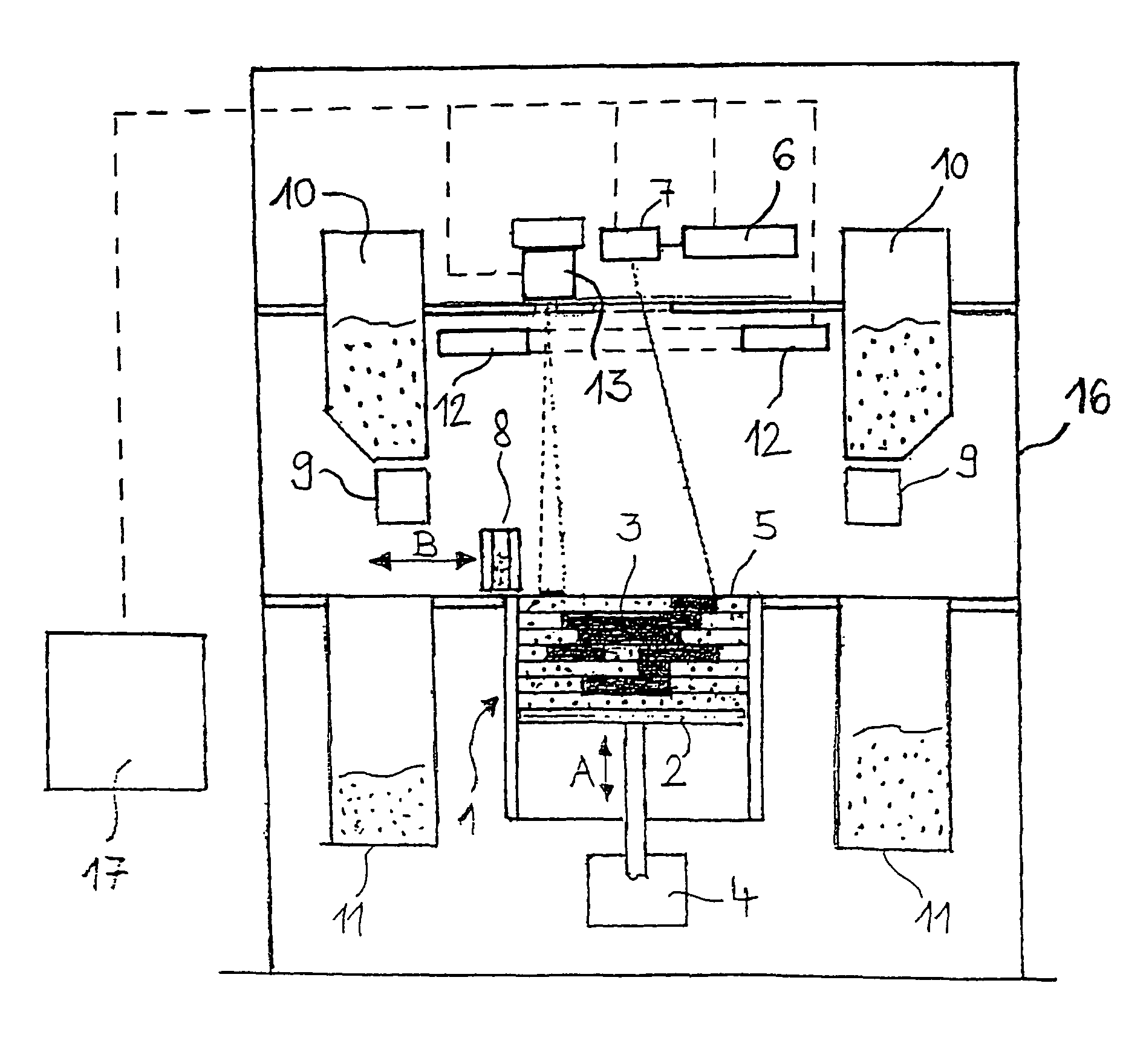
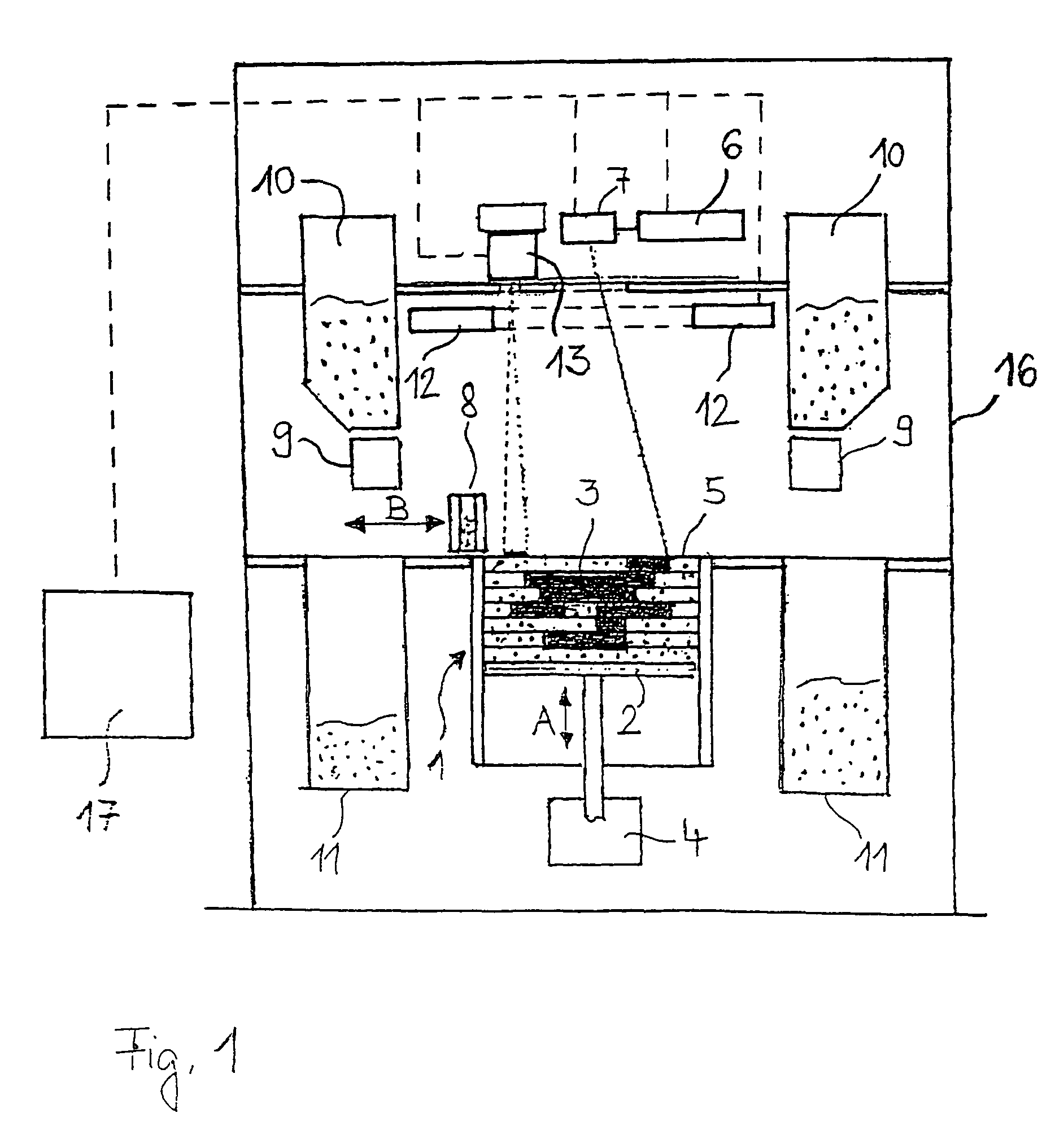
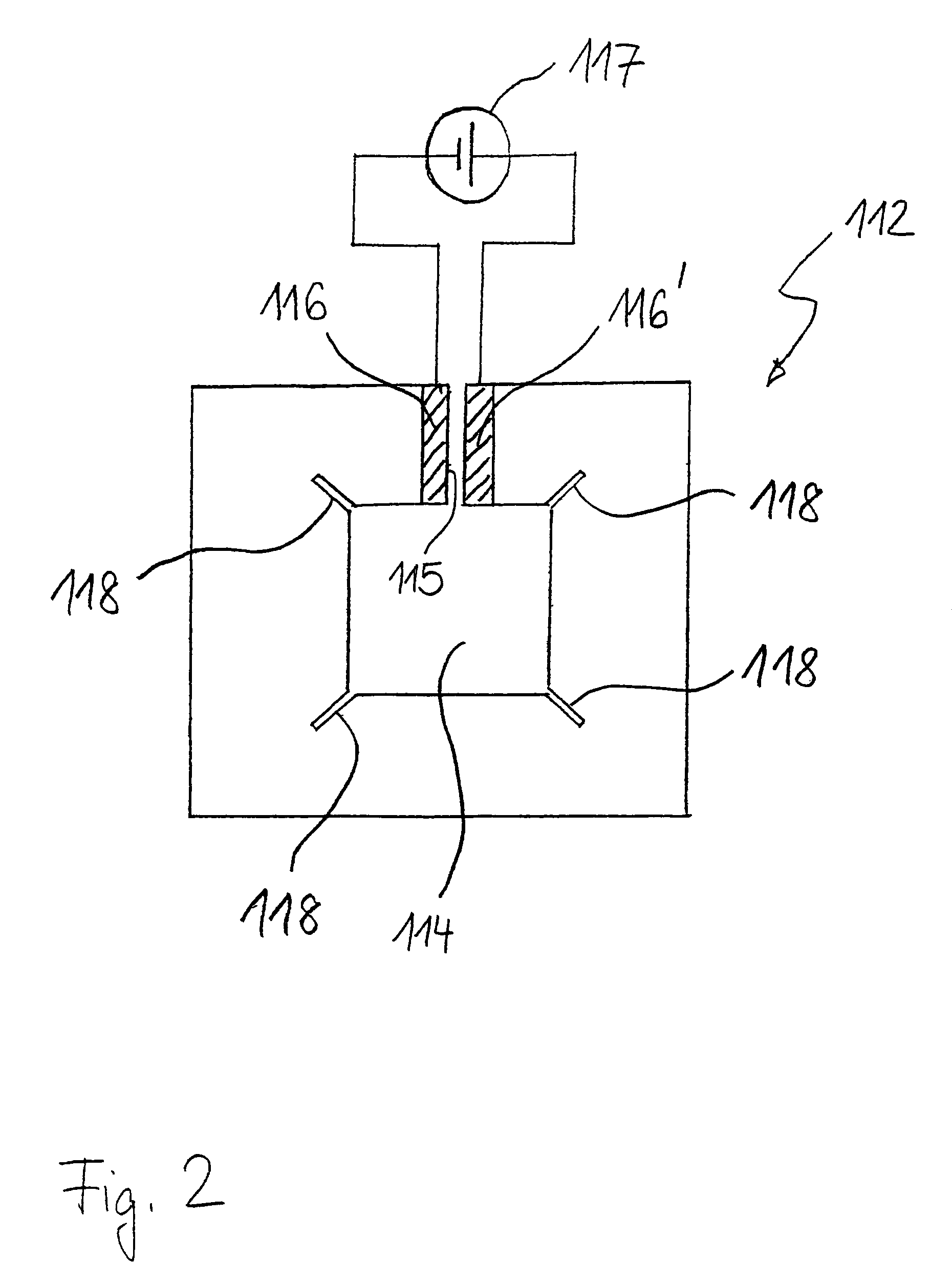
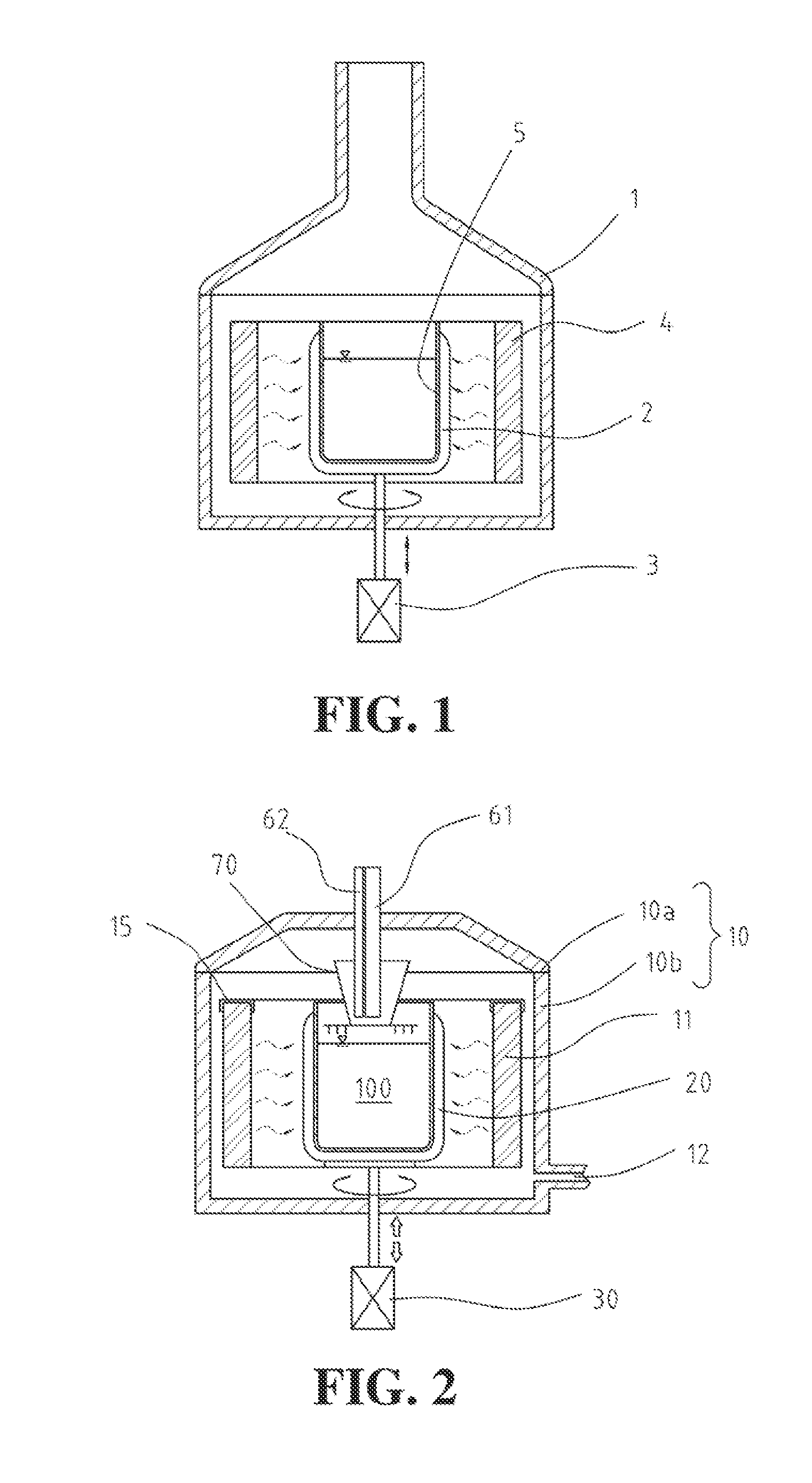
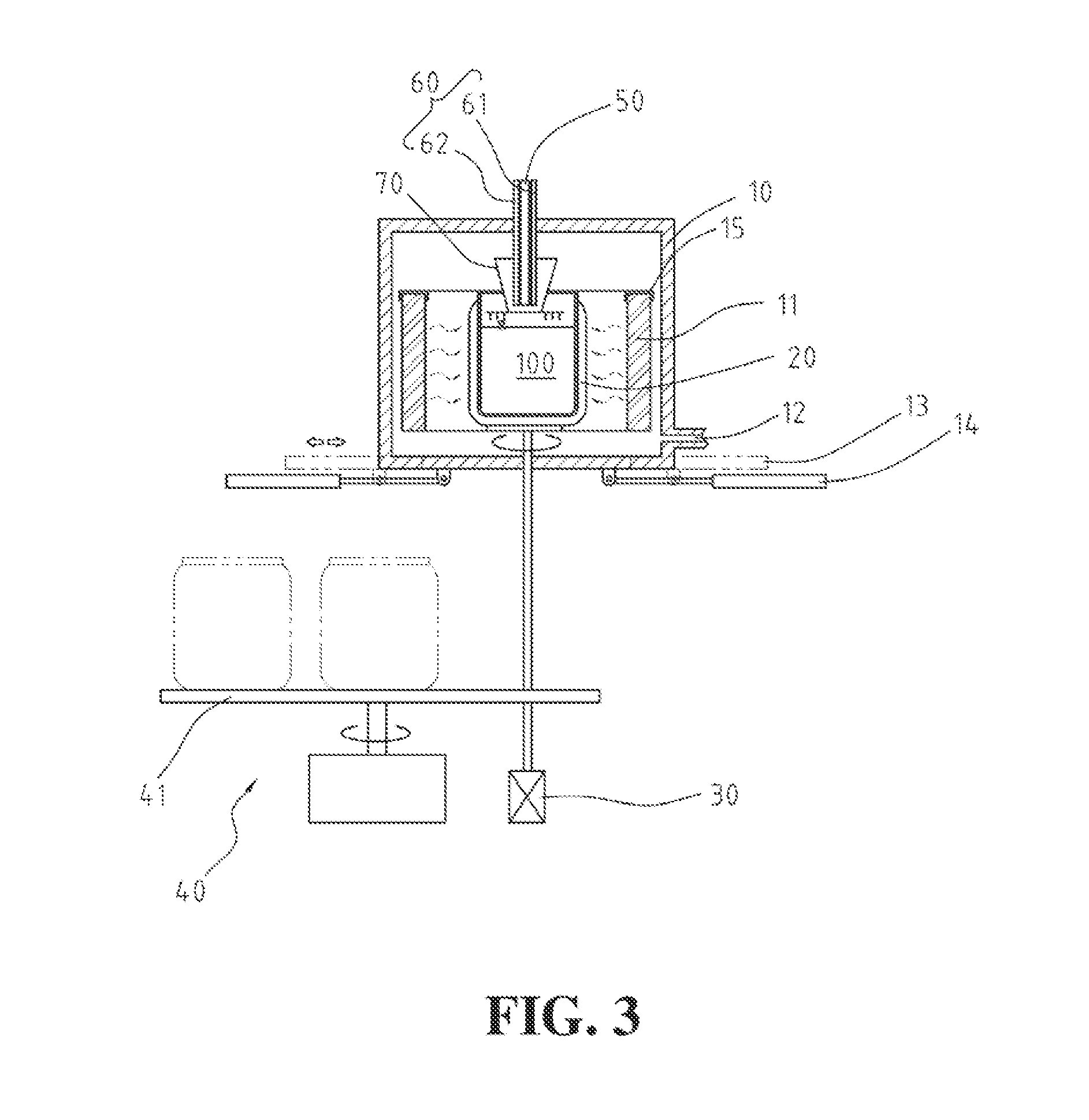
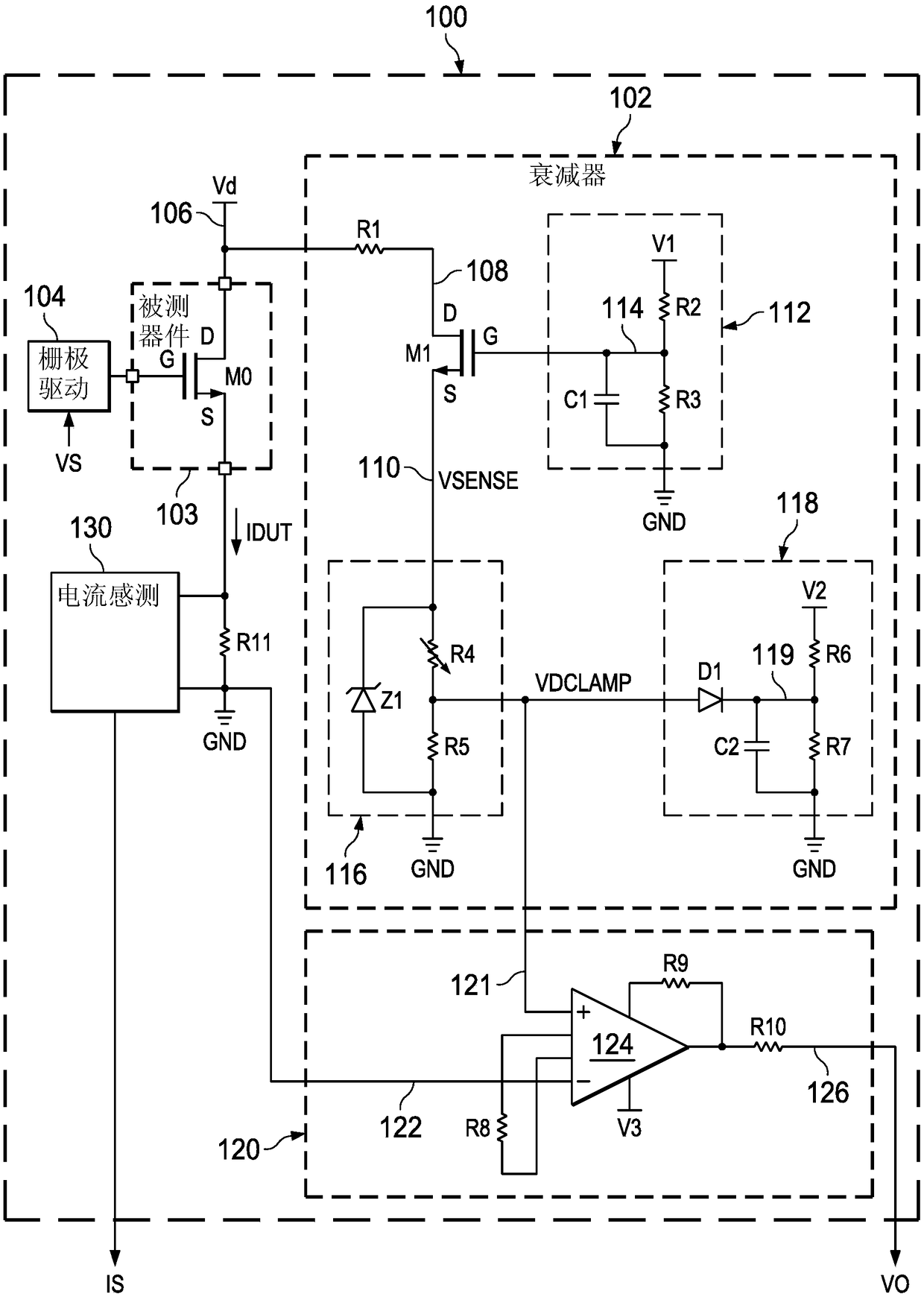
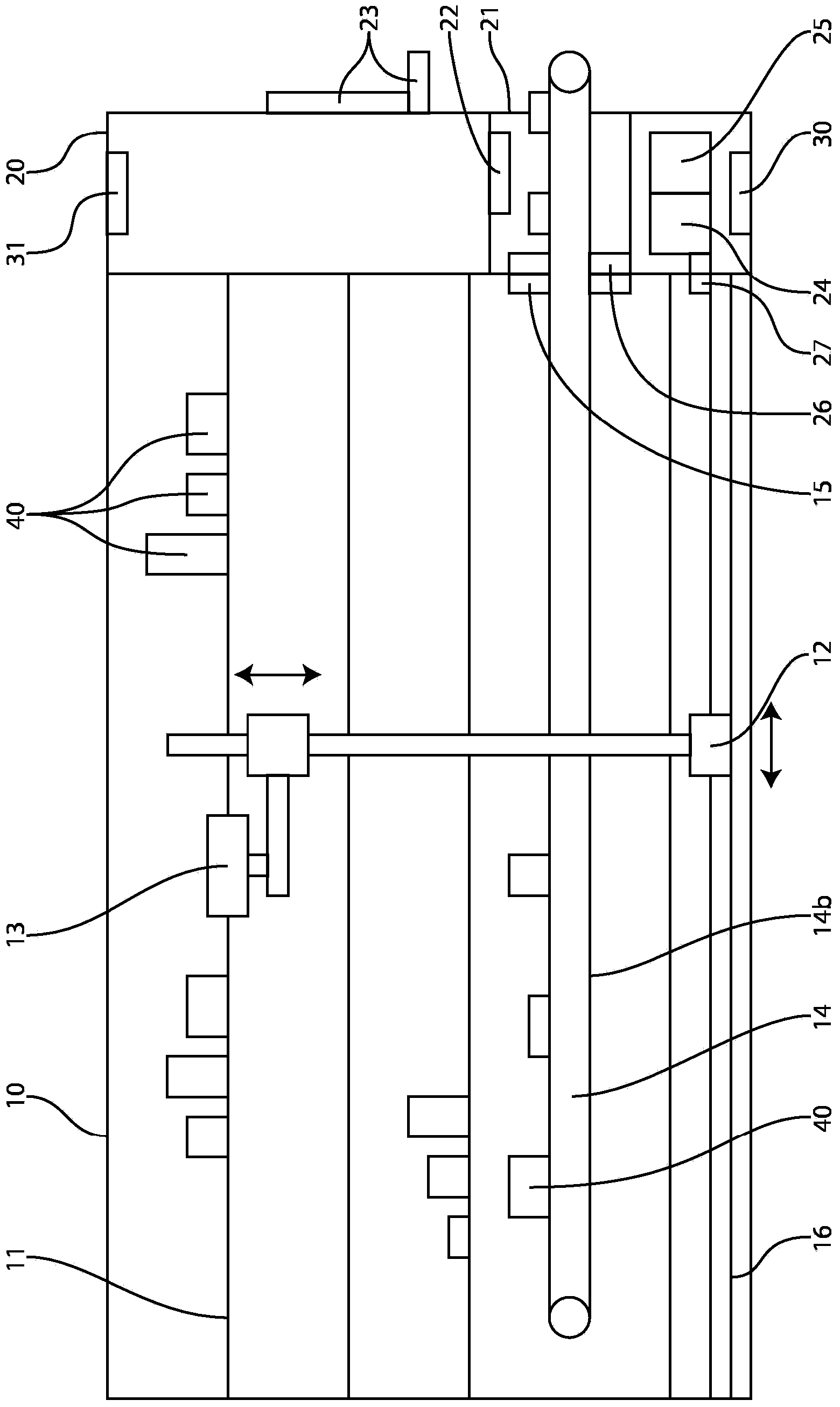
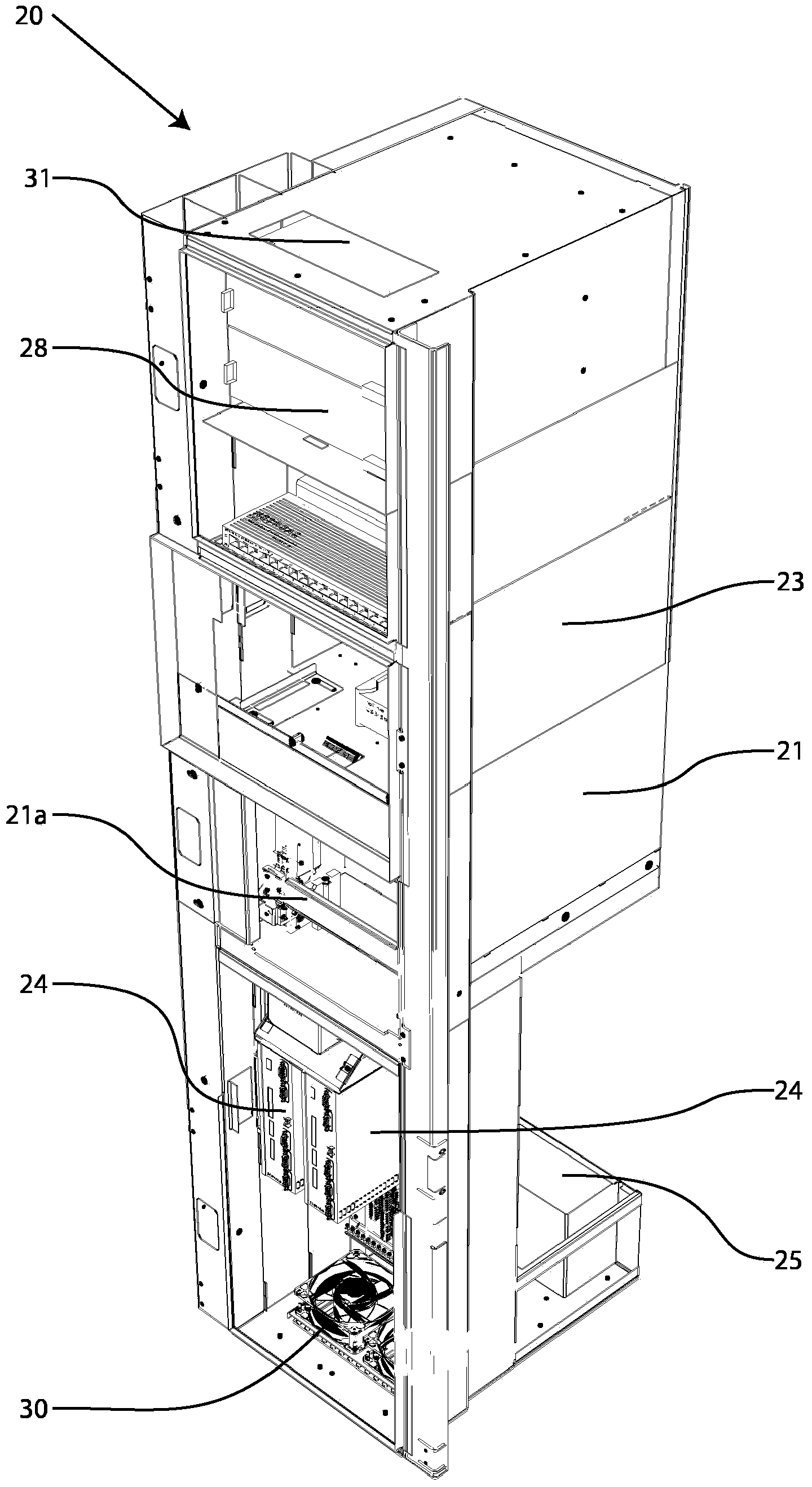
Radiant heater for heating the building material in a laser sintering device
InactiveUS8073315B2Reduce the temperatureThermal inertiaDomestic stoves or rangesDrying solid materials with heatRadiant heaterMetallurgy
A radiant heating for heating the building material in a laser sintering device and a laser sintering device having such a radiant heating are described. The radiant heating has a sheet-like heat radiating element (113, 213, 313), which is characterized in that it is made of a material, that has a low thermal inertia with a thermal diffusivity of preferably more than 1.5·10−4 m2 / s and preferably has a thickness of 2 mm or less.
Owner:EOS ELECTRO OPTICAL SYST
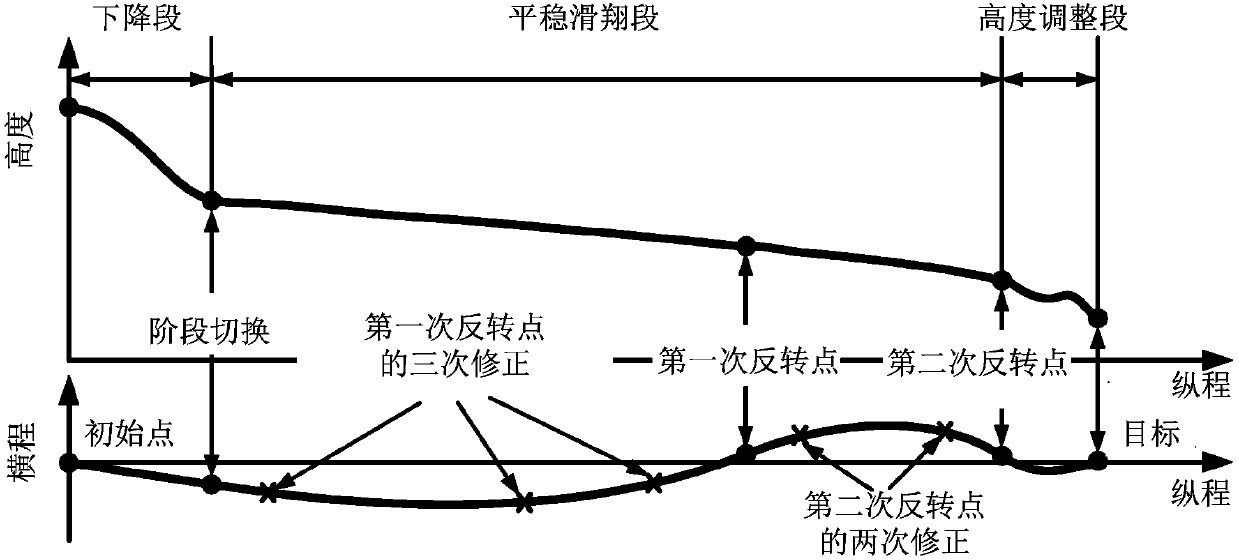
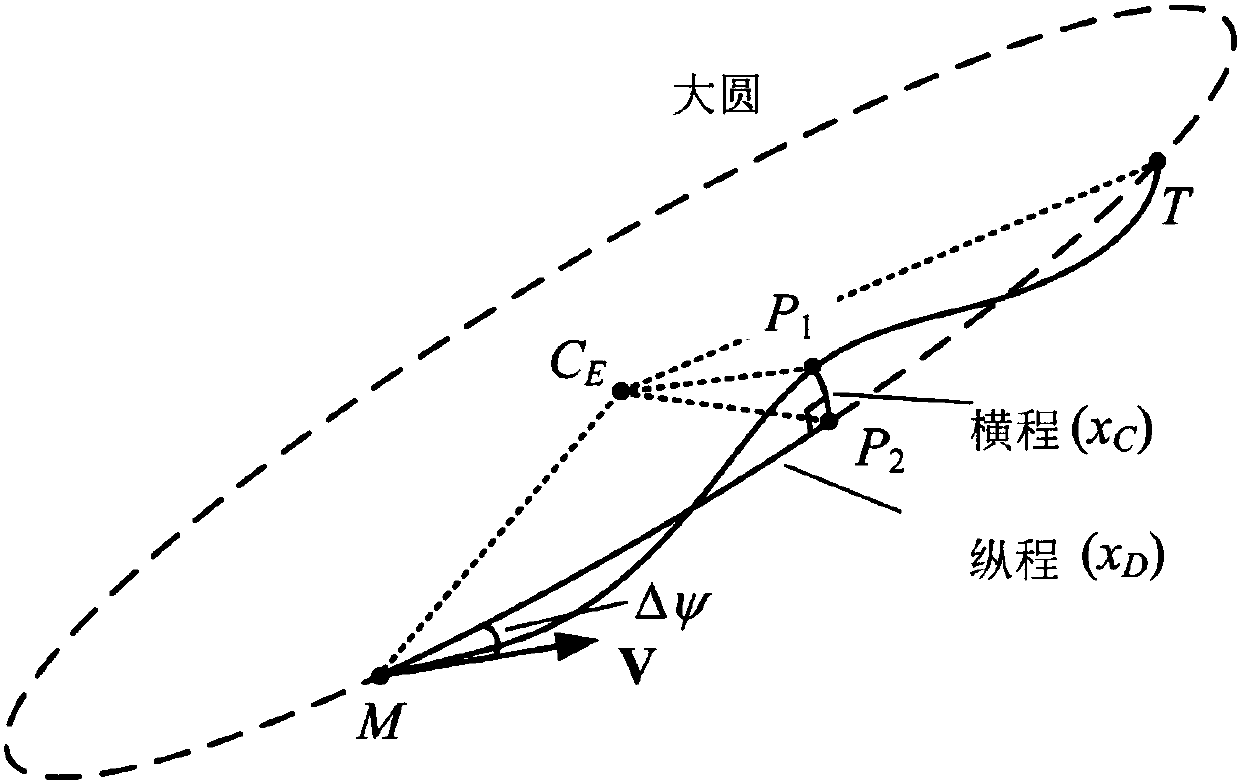
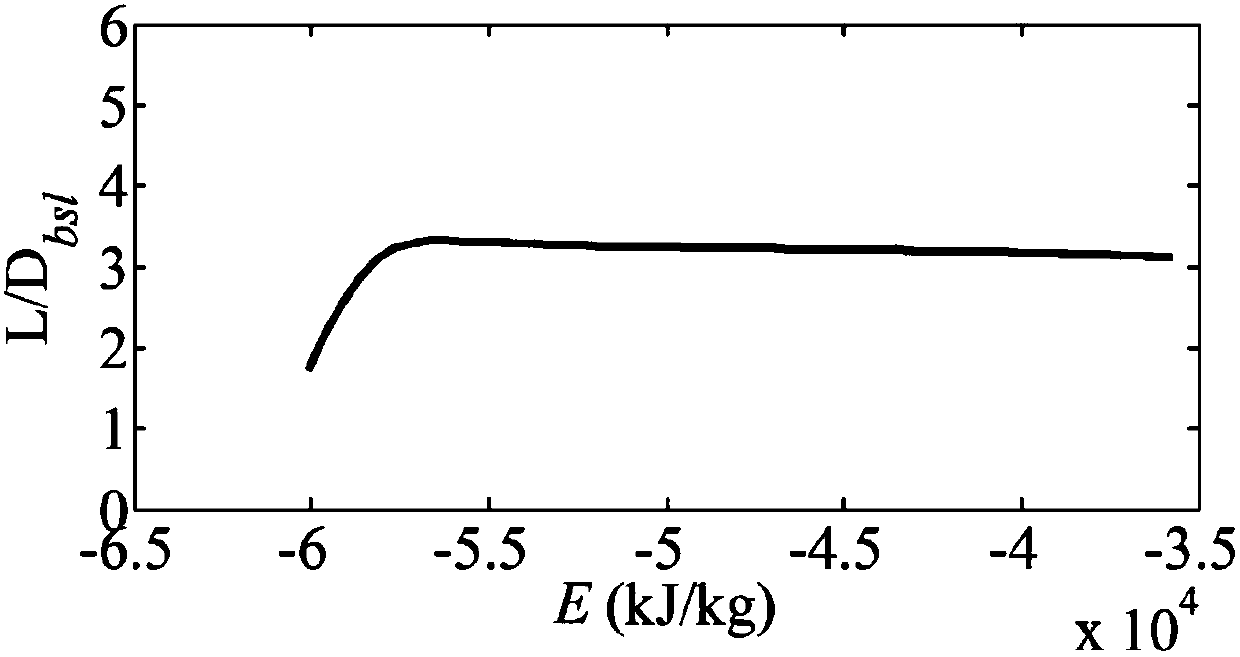
Full-firing-direction autonomous reentry guidance method based on three-dimensional reentry trajectory analytical solution
ActiveCN108036676AOscillation suppressionReduce peakGeometric CADSustainable transportationHeat fluxEarth's rotation
The invention discloses a full-firing-direction autonomous reentry guidance method based on a three-dimensional reentry trajectory analytical solution. The full-firing-direction autonomous reentry guidance method comprises the following steps of 1, building of a kinematical equation and a dynamical equation, 2, summarizing of the reentry guidance method, 3, descent stage guidance strategies, 4, steady gliding stage guidance strategies and 5 height-adjustment stage guidance strategies. The full-firing-direction autonomous reentry guidance method has the advantages that reentry guidance of an aircraft with the large lift-drag ratio can be guided effectively, low-damping and long-period trajectory oscillation caused by the high lift-drag ratio can be restrained effectively, the peak value ofthe heat flux density is reduced, and tracking of a reference track is facilitated; inertia force caused by earth rotation and actual aerodynamic force are combined into equivalent aerodynamic force,an equivalent aerodynamic section is planned through the analytical solution, and thus the aircraft has the omni-directional reentry task processing capability; and an equivalent aerodynamic section fitting formula based on the inverse proportional function is put forward, the reentry trajectory analytical solution based on the complex equivalent aerodynamic section form is further deduced, and thus high precision, all-dimensional applicability and high robustness are achieved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
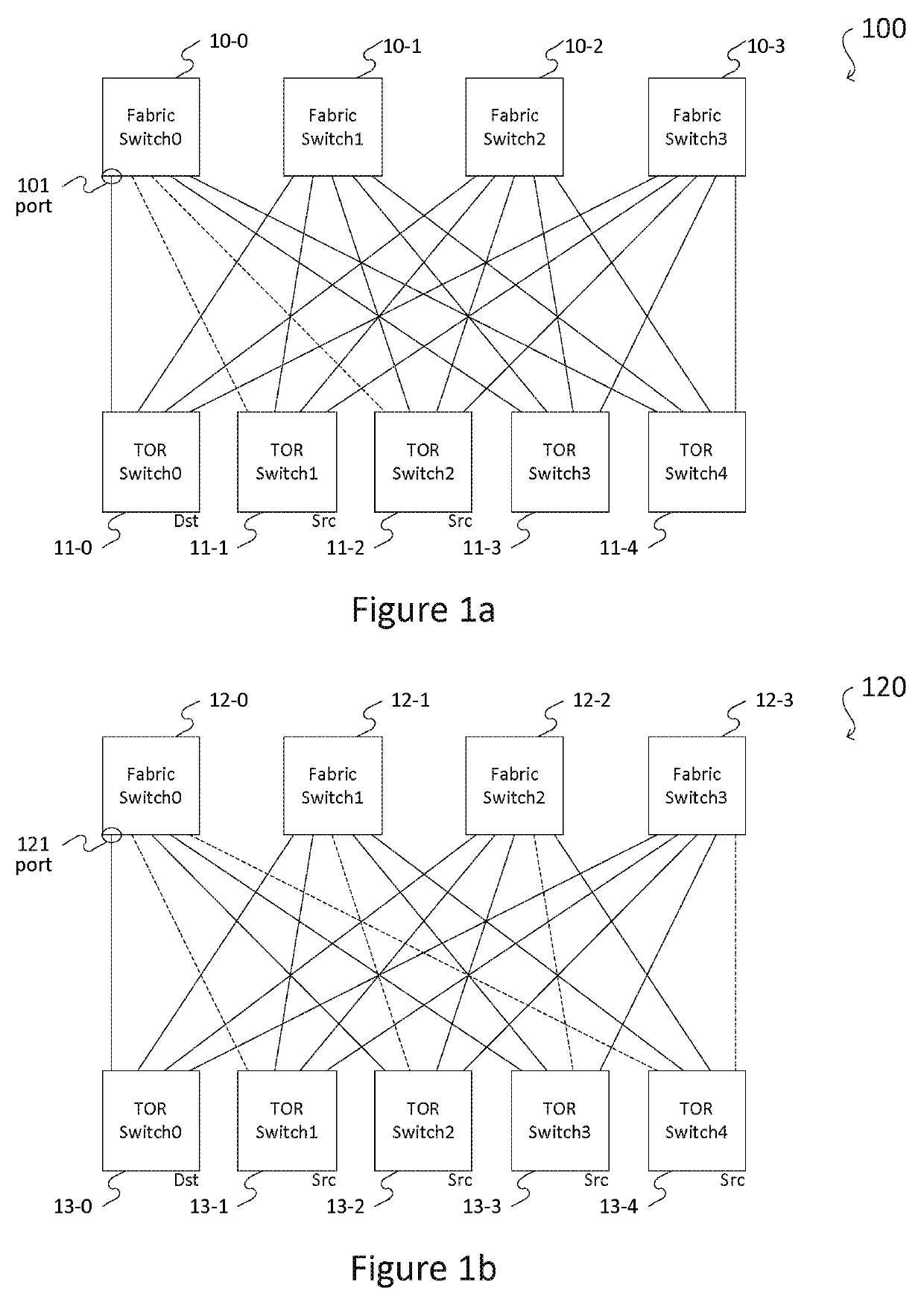
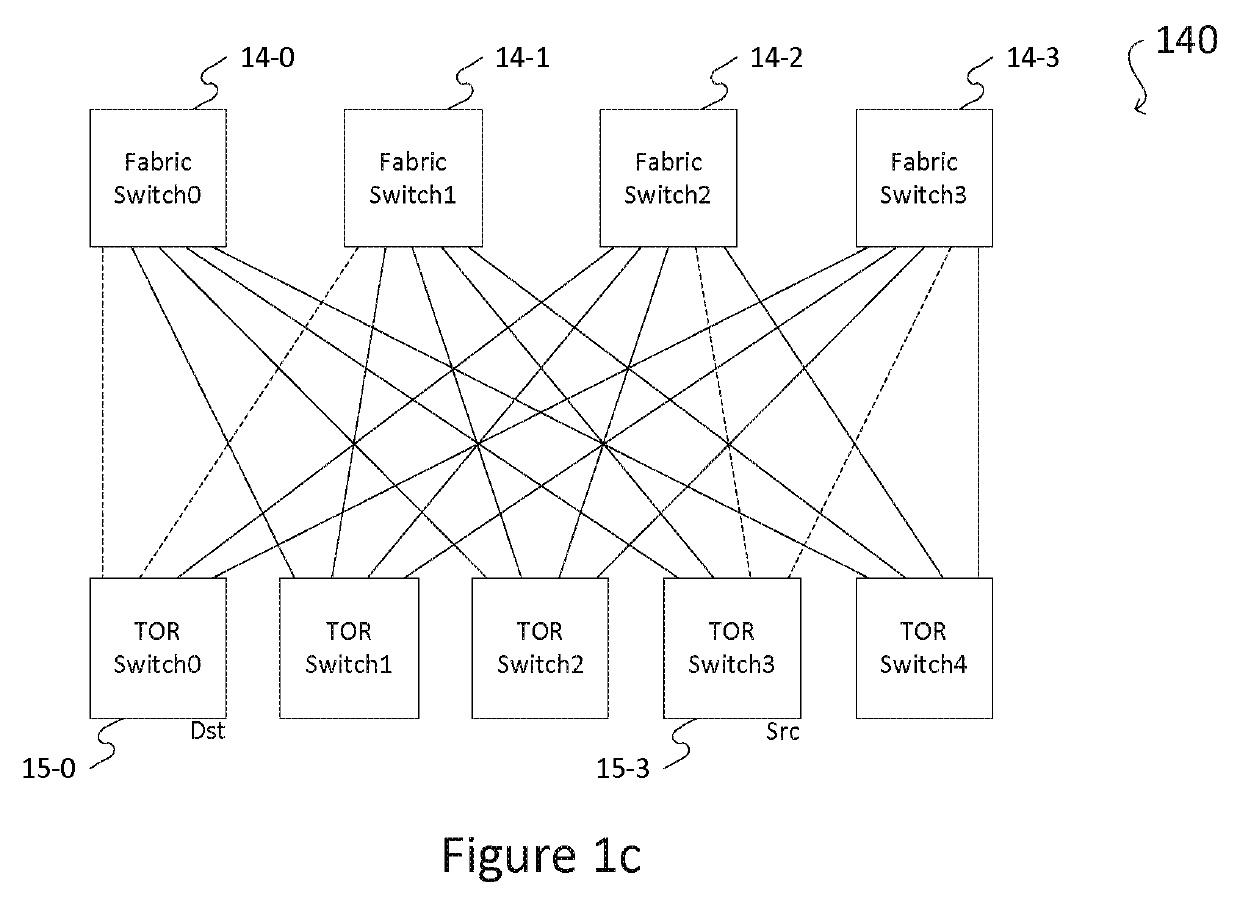
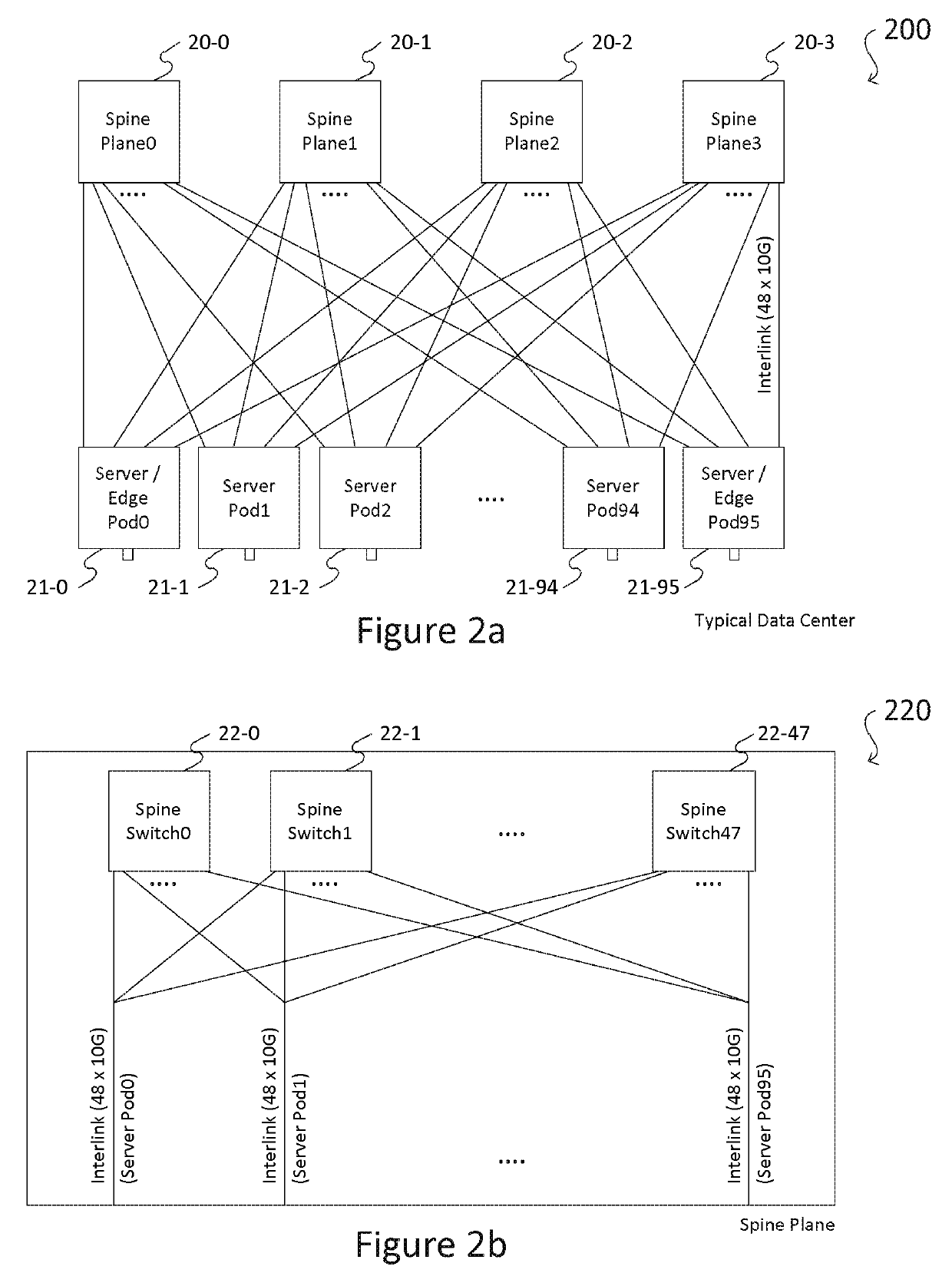
Network interconnect as a switch
ActiveUS20190245751A1Simple processLow hardware requirementsMultiplex system selection arrangementsStar/tree networksMulti unitData center
An interconnect as a switch module (“ICAS” module) comprising n port groups, each port group comprising n−1 interfaces, and an interconnecting network implementing a full mesh topology where each port group comprising a plurality of interfaces each connects an interface of one of the other port groups, respectively. The ICAS module may be optically or electrically implemented. According to the embodiments, the ICAS module may be used to construct a stackable switching device and a multi-unit switching device, to replace a data center fabric switch, and to build a new, high-efficient, and cost-effective data center.
Owner:WONG DAVID I KEONG
Method for preparing in situ crystallization type catalytic cracking catalyst
ActiveCN101537368AReduce build timeShort build timeMolecular sieve catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationMolecular sieveIn situ crystallization
The invention provides a method for preparing an in situ crystallization type catalyst by adding components with a silicon-aluminum structure unit in a certain proportion. The method is characterized in that: kaoline with meso position grain diameter used as a raw material is added with water to form a pulp, the pulp undergoes spray forming to form an earth ball, and the earth ball is roasted to form a roasted earth ball. The roasted earth ball undergoes the crystallized reaction with sodium silicate, the components with the silicon-aluminum structure unit, a guiding agent and the like to from a crystallized product of which the content of NaY zeolite is between 15 and 60 percent and the silicon-aluminum ratio is 3.5-5.5; and the crystallized product is exchanged and roasted to obtain the catalyst needed. Because the components with the silicon-aluminum structure unit are used as sources of partial silicon, aluminum and sodium, the method has the advantages of realizing the preparation of the in situ crystallization type molecular sieve in a short period of time, further shortening flow, improving yield and lowering production cost.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method and system for testing reliability of electric spindle in machining center
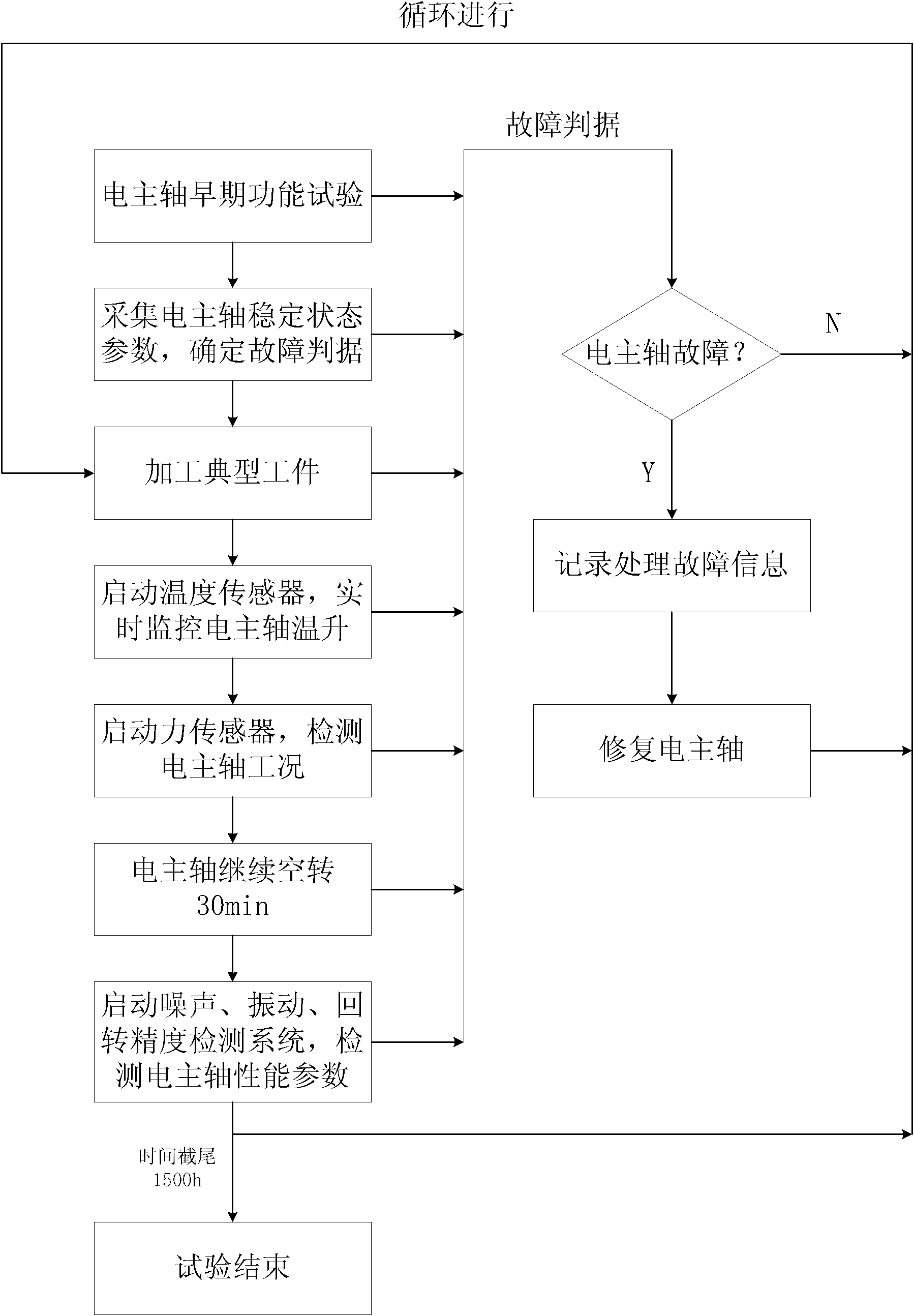
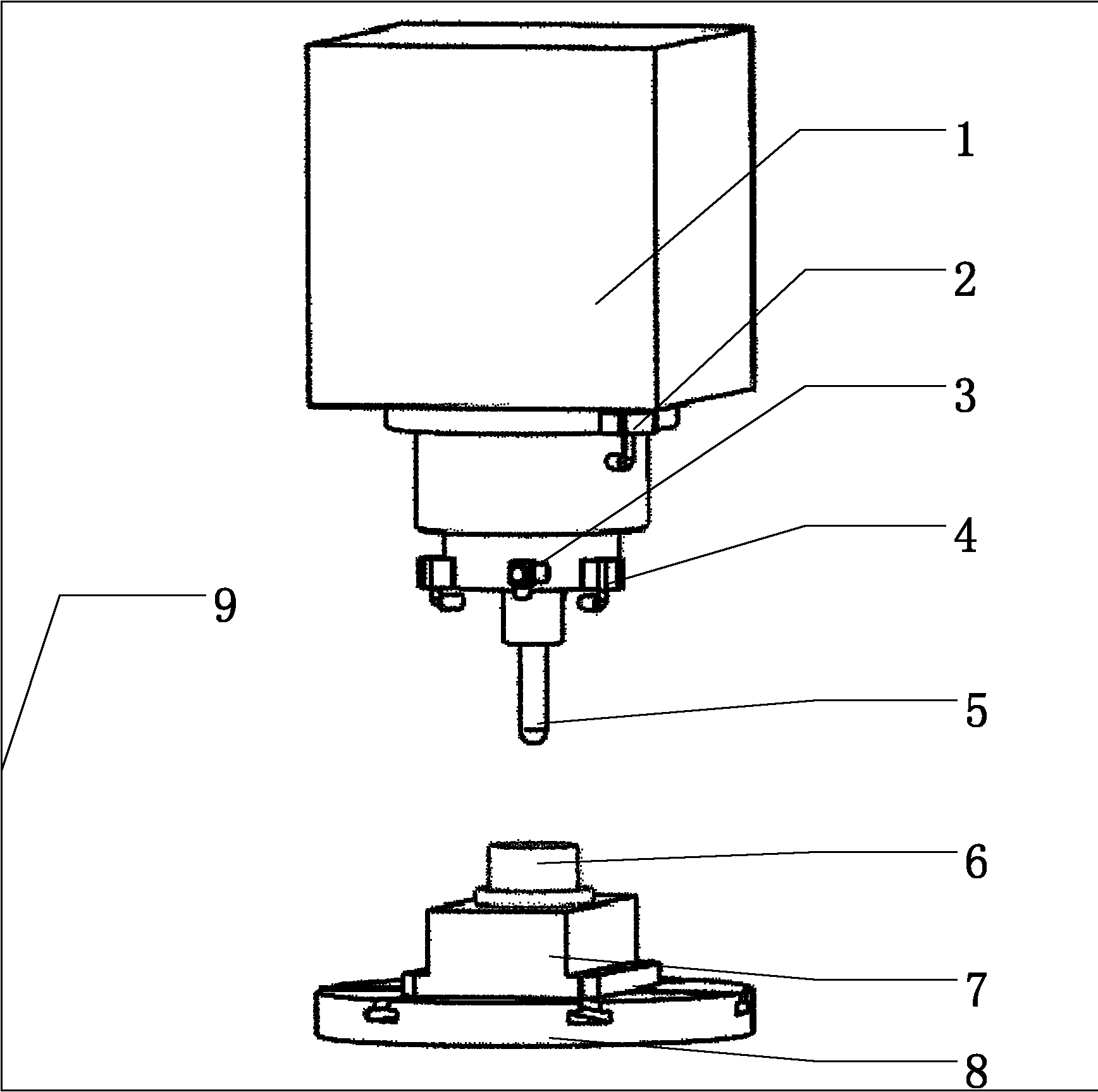
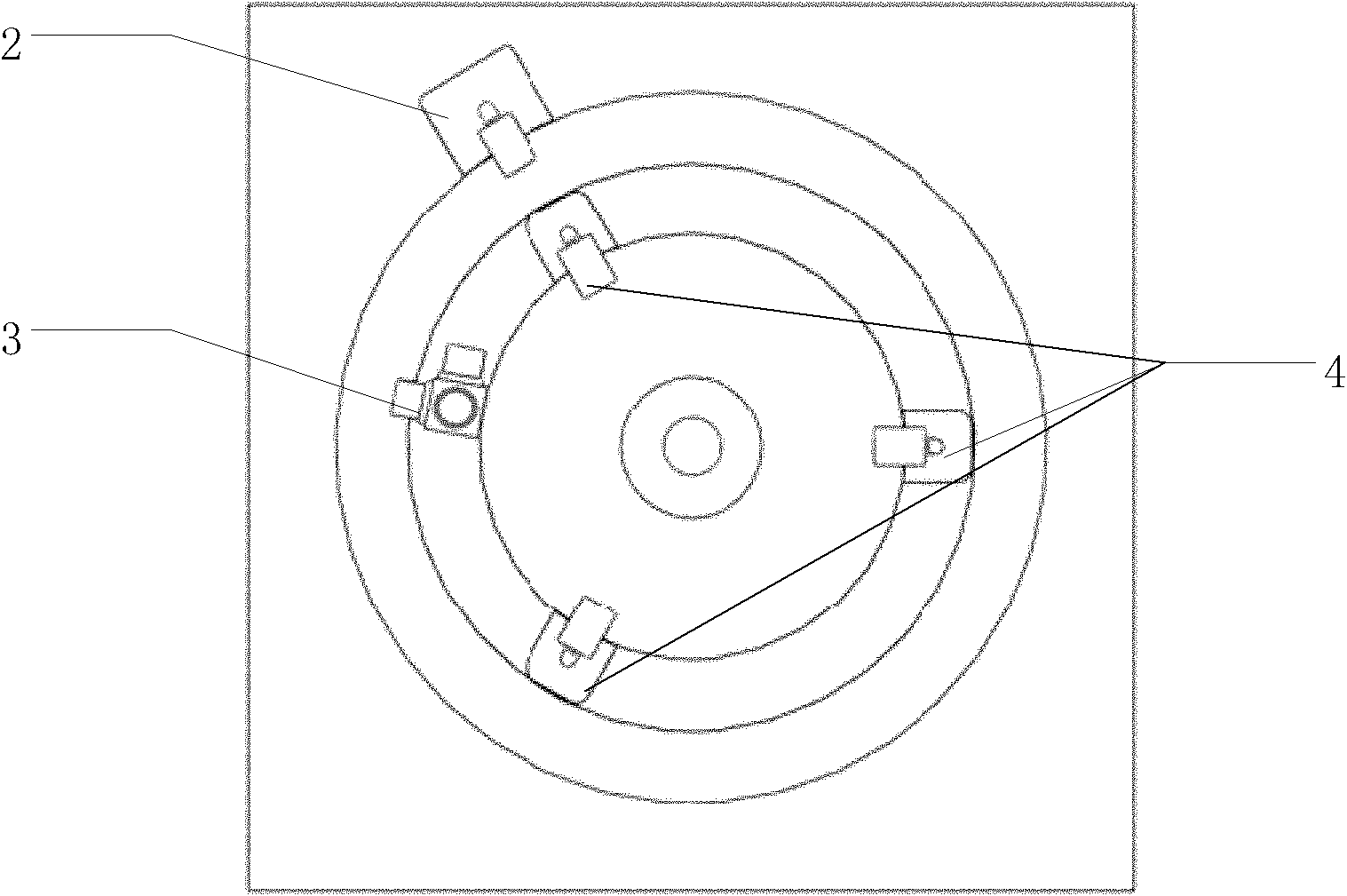
InactiveCN102012286ALow costShort build timeSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementForce measurementStable stateTested time
The invention discloses a system and a method for testing the reliability of an electric spindle in a machining center. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, establishing the system for testing the reliability of the electric spindle in the machining center; 2, determining test environment and test time; 3, performing a function test on the electric spindle to remove early failures; 4, acquiring the performance parameter of the electric spindle in a stable state and determining a failure criterion; and 5, circularly machining a typical workpiece, monitoring the state and performance parameter of the electric spindle and judging the failures. The system comprises a temperature sensor, a noise sensor, a force sensor, an eddy current displacement sensor, a vibration sensor, and a control unit connected with the parts. The system has the advantages of simple and compact structure, low cost, simple principle, convenience of operation, high test accuracy and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
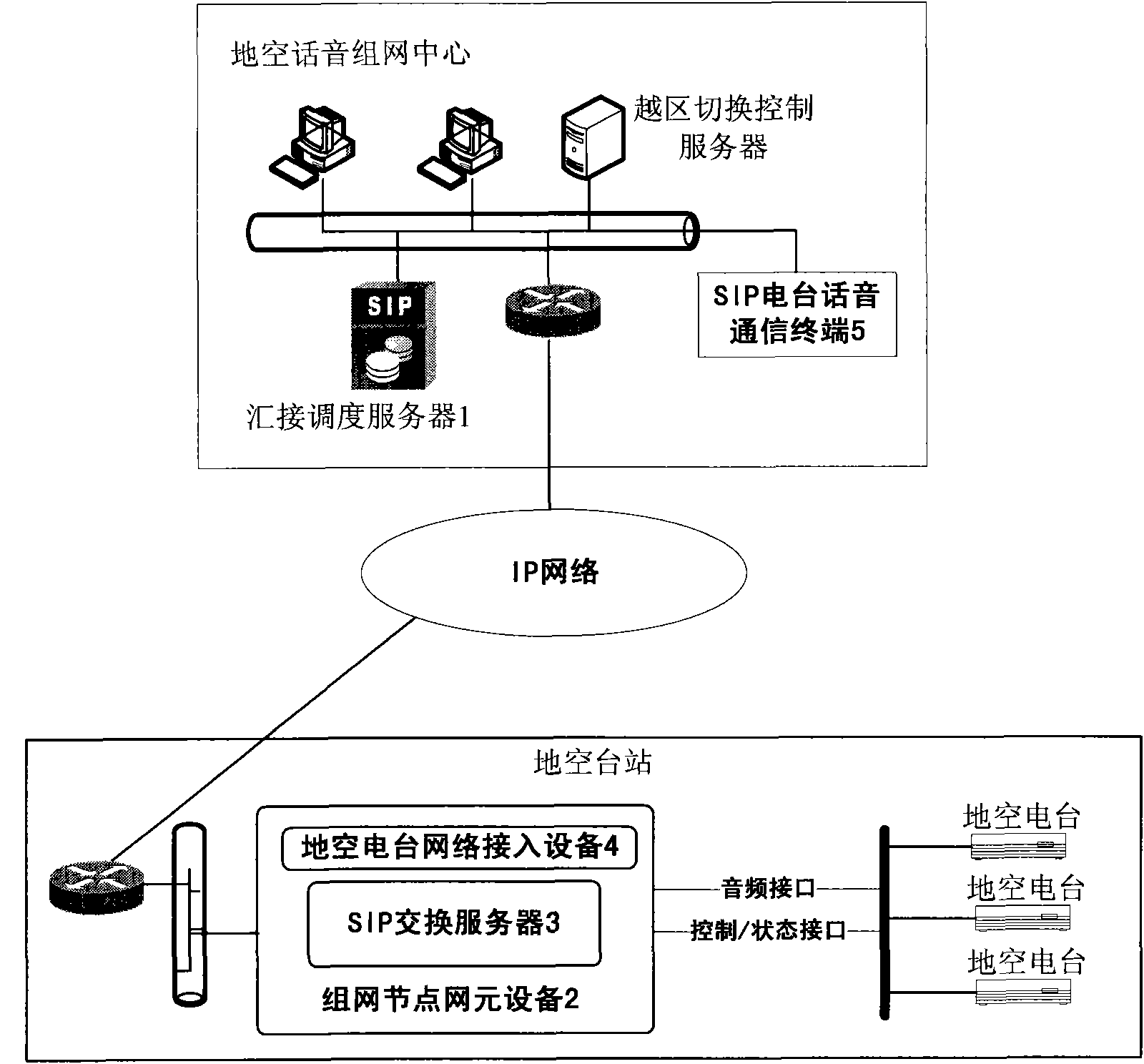
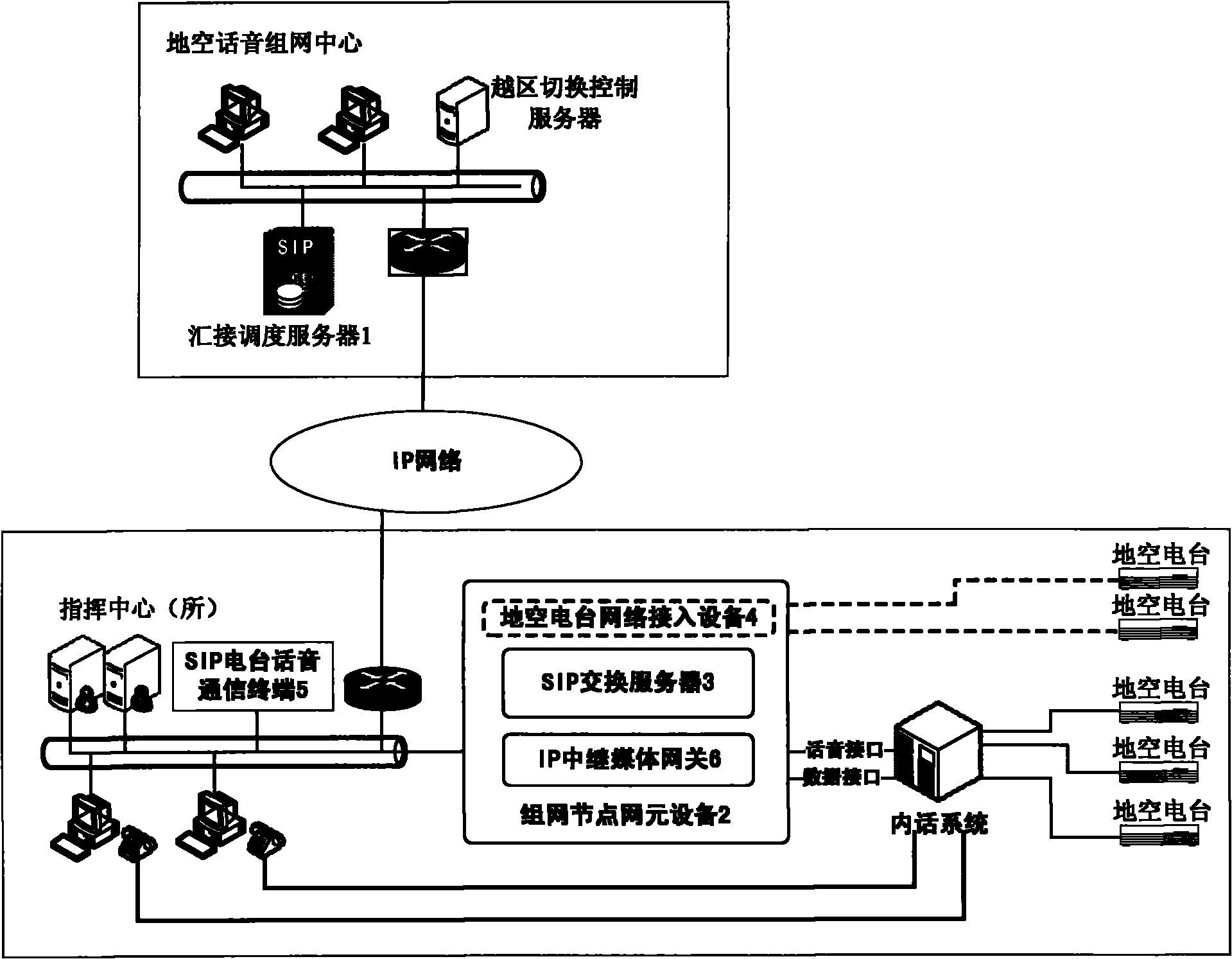
SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)-based regional ground-to-air radio station voice networking system and implementation method thereof
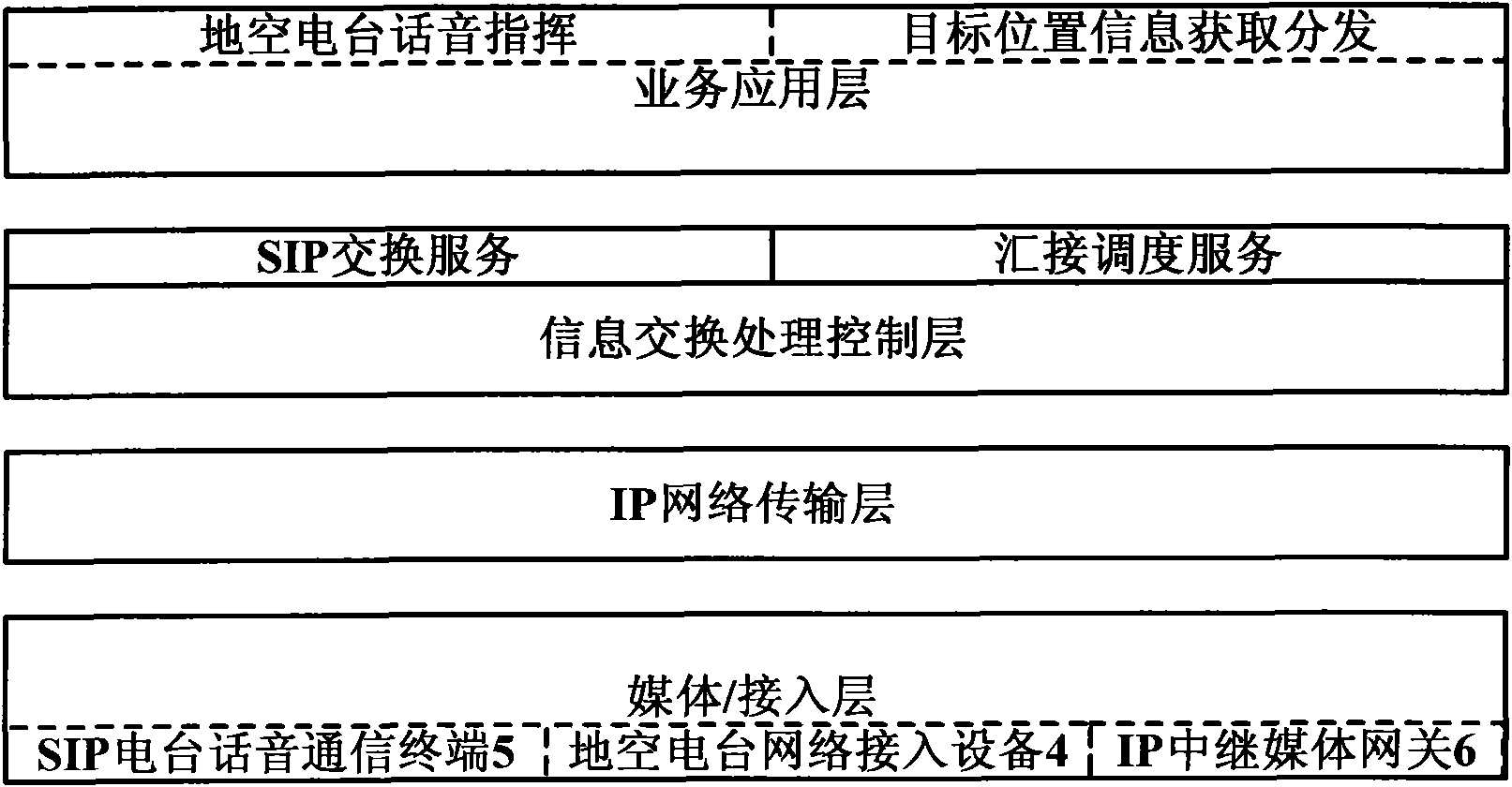
ActiveCN102065076ARealize integrationShort build timeInterconnection arrangementsData switching by path configurationSession Initiation ProtocolTelecommunications link
The invention discloses an SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)-based regional ground-to-air radio station voice networking system which comprises a plurality of ground-to-air radio stations and also comprises a tandem scheduling server, an SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) radio station voice communication terminal and a networking node network element device, wherein the networking node network element device is connected between the tandem scheduling server and the SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) radio station voice communication terminal and connected with the ground-to-air radio stations.The SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)-based regional ground-to-air radio station voice networking system can realizes integration with a ground-to-air data link system and can realize goal-oriented ground-to-air voice command which is compatible and coordinated with ground-to-air data link system; and a commander can synchronously obtain the voice command control capacity when seeing a target. Moreover, a communication link for directly implementing the voice command control on first-line task aircrafts is provided for a remote high-level command center within shorter setup time and in more flexible setup mode so that commands of chief executives can reach the first-line aircrafts immediately and the effect that a link can be uses as long as set up is achieved.
Owner:THE 28TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
Electromagnetic flow sensor
InactiveUS20050000300A1Short build timeLarge flow rangeVolume/mass flow by electromagnetic flowmetersFlow transducerCoupling
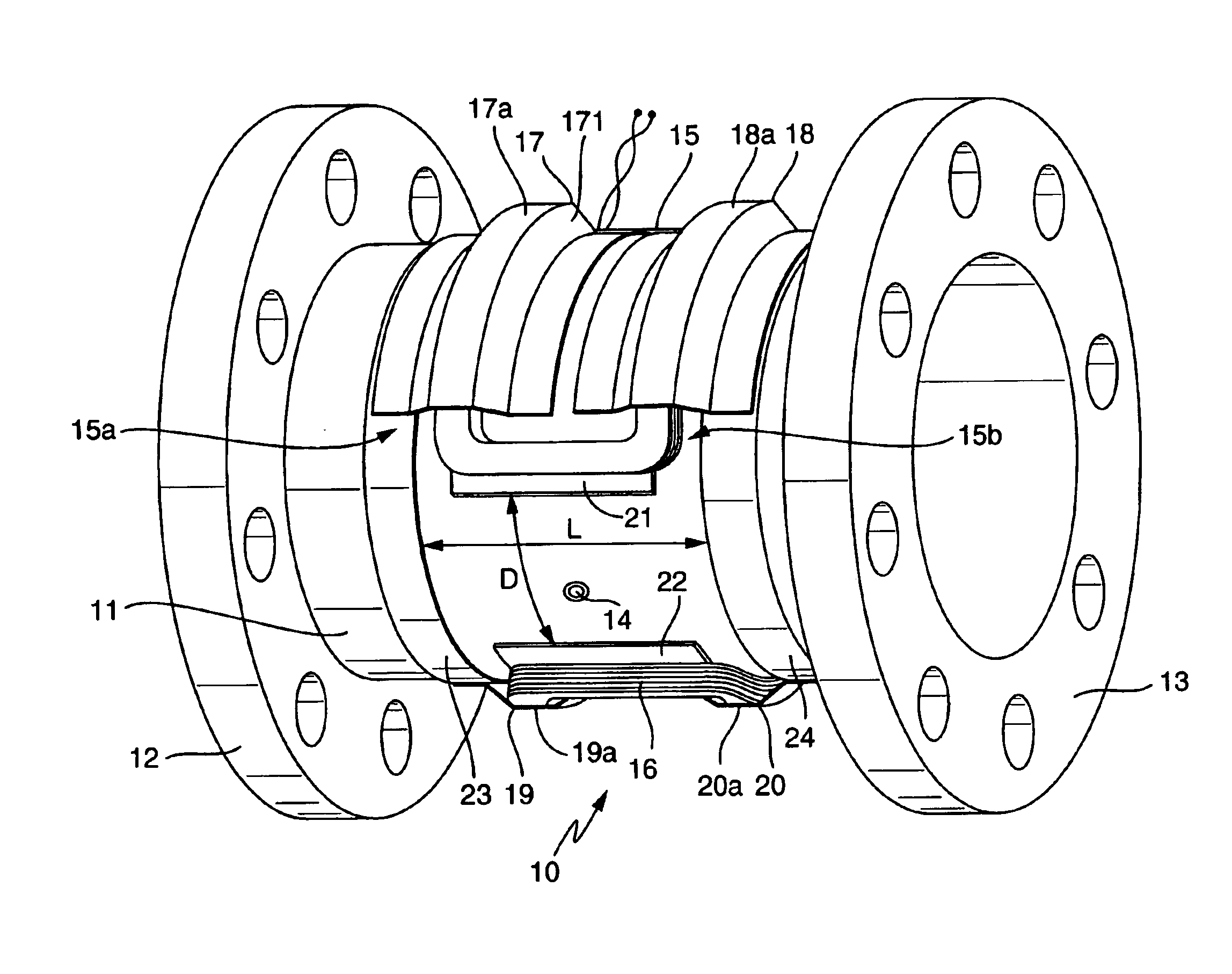
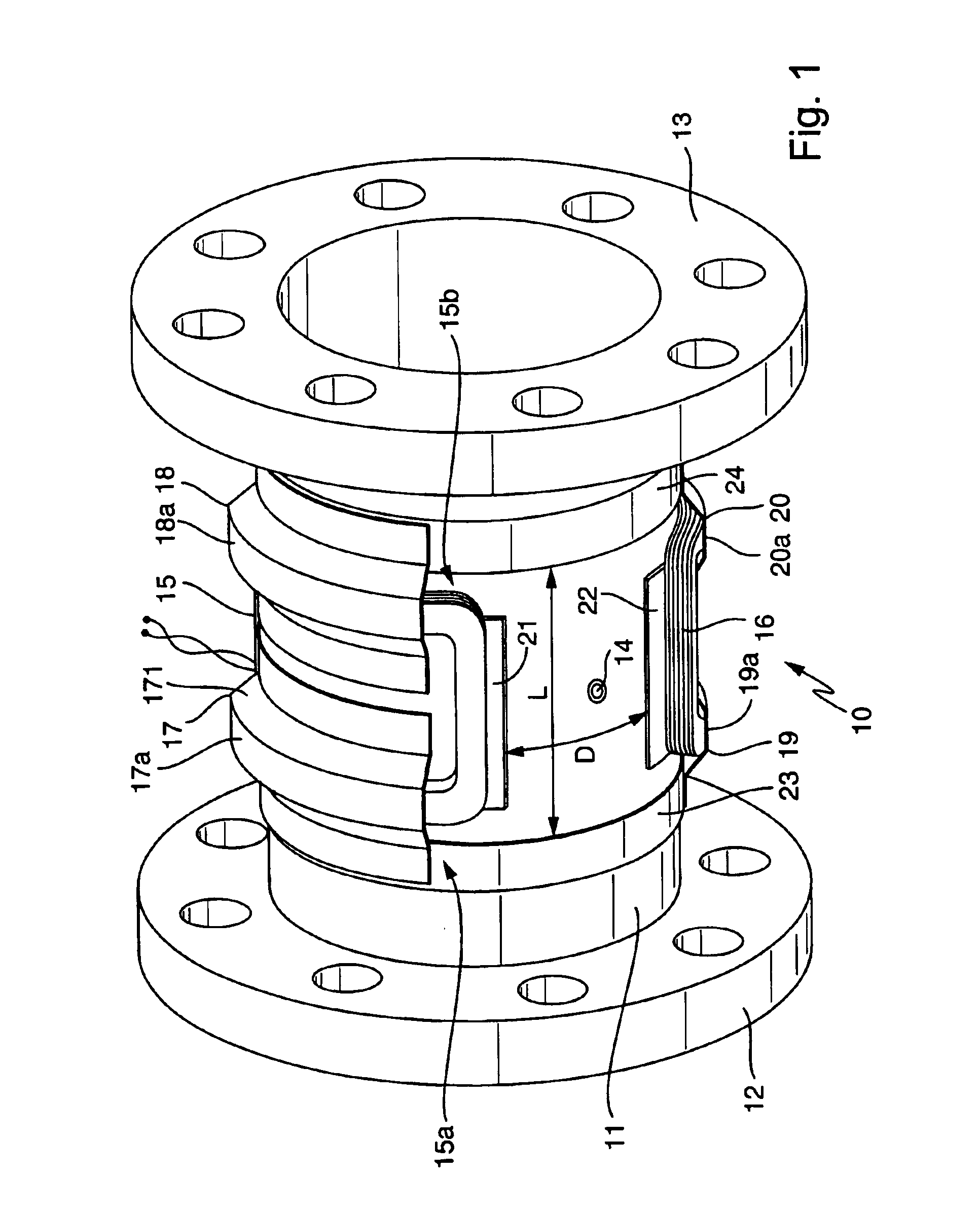
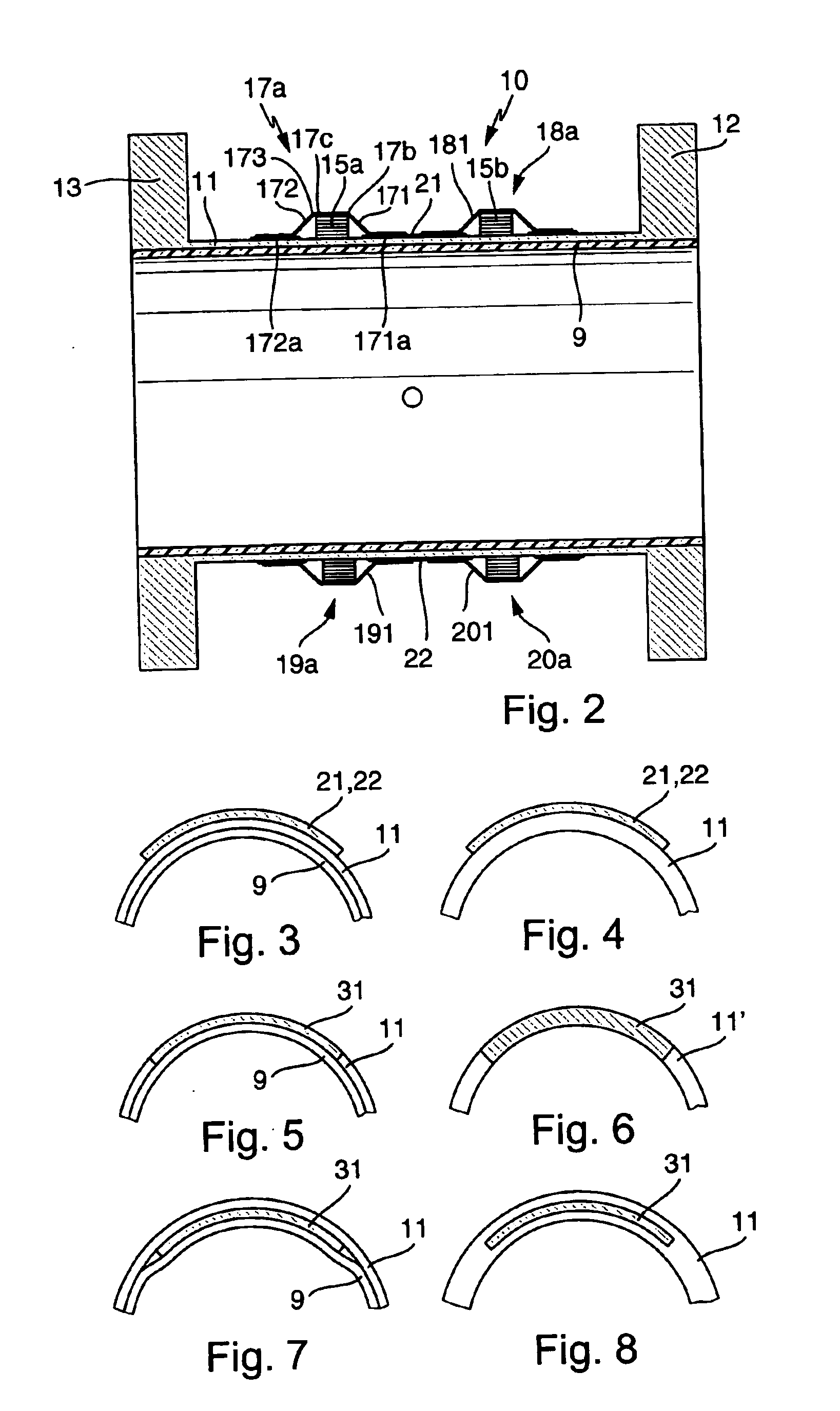
The flow sensor serves to measure an electrically conductive fluid flowing in a pipe. It comprises a flow tube designed to be inserted into the pipe for conducting the fluid, the flow tube being electrically nonconductive at least on a fluid-contacting inner side, an electrode arrangement consisting of at least two measuring electrodes disposed on the flow tube for picking up a voltage induced in the fluid, and a magnetic field system likewise disposed on the flow tube. The magnetic field system comprises at least two saddle-shaped field coils for producing a magnetic field cutting the fluid during operation of the flow sensor, a respective ferromagnetic pole piece for each of the two field coils, as well as at least one ferromagnetic return path extending around the flow tube upstream of the two field coils and at least one ferromagnetic return path extending around the flow tube downstream of the two field coils for directing the magnetic field around the flow tube. The pole pieces are magnetically coupled to the return paths by means of ferromagnetic coupling elements. Each of the, preferably identically shaped, coupling elements has at least one essentially trough-shaped cover segment which receives a first winding section of the respective associated field coil, lying essentially on a first periphery of the flow tube, or a second winding section of the associated field coil, lying essentially on a second periphery of the flow tube.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
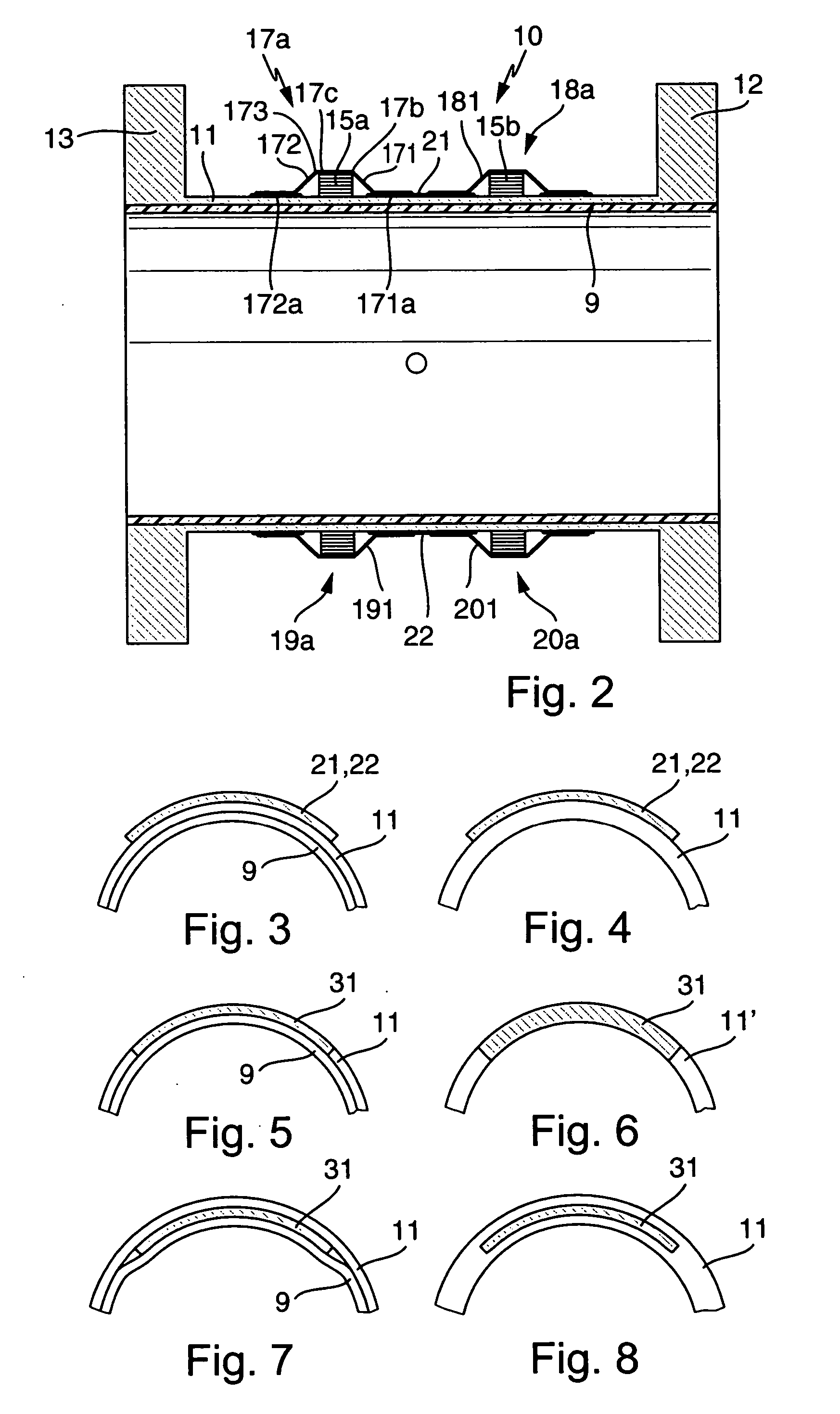
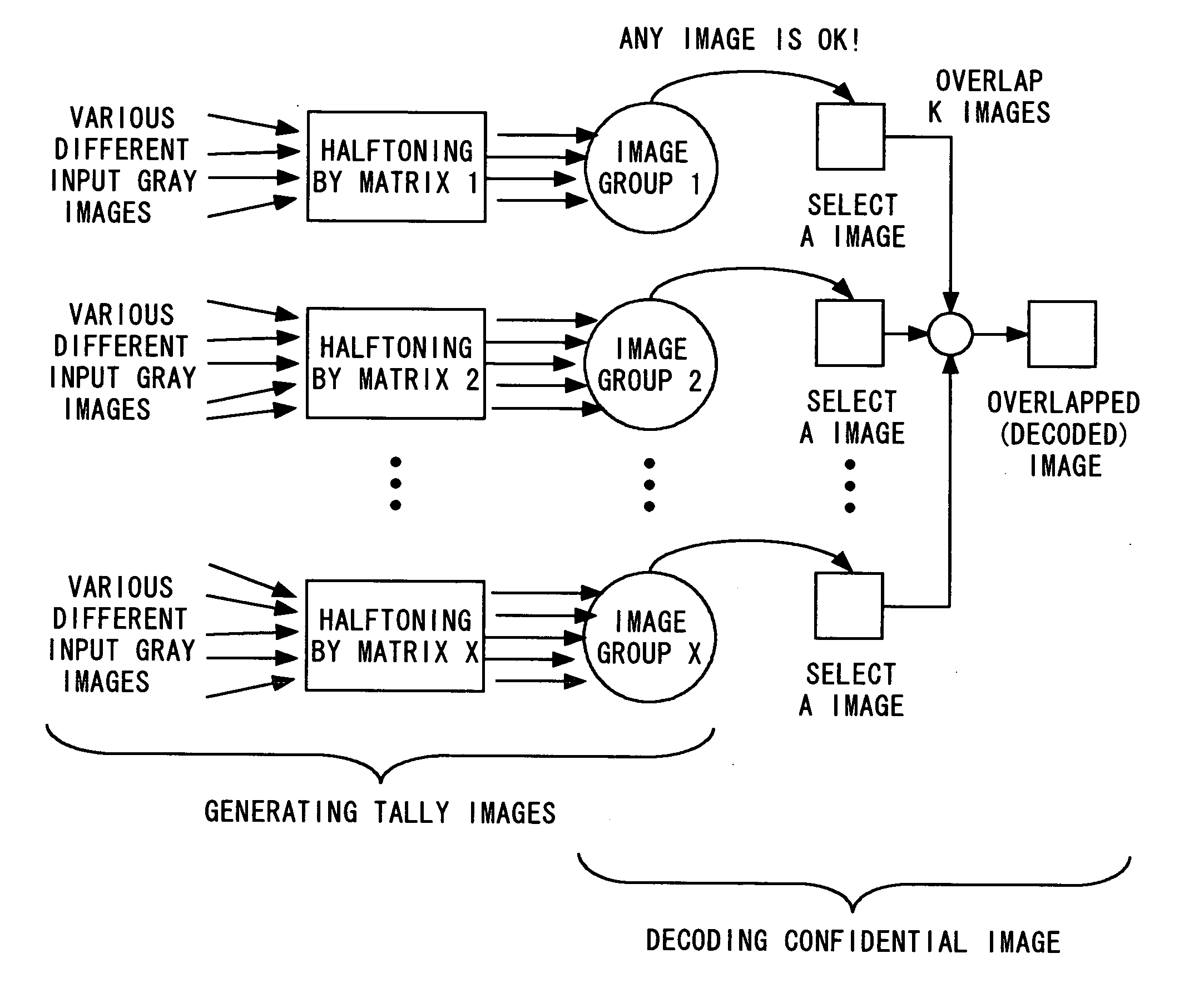
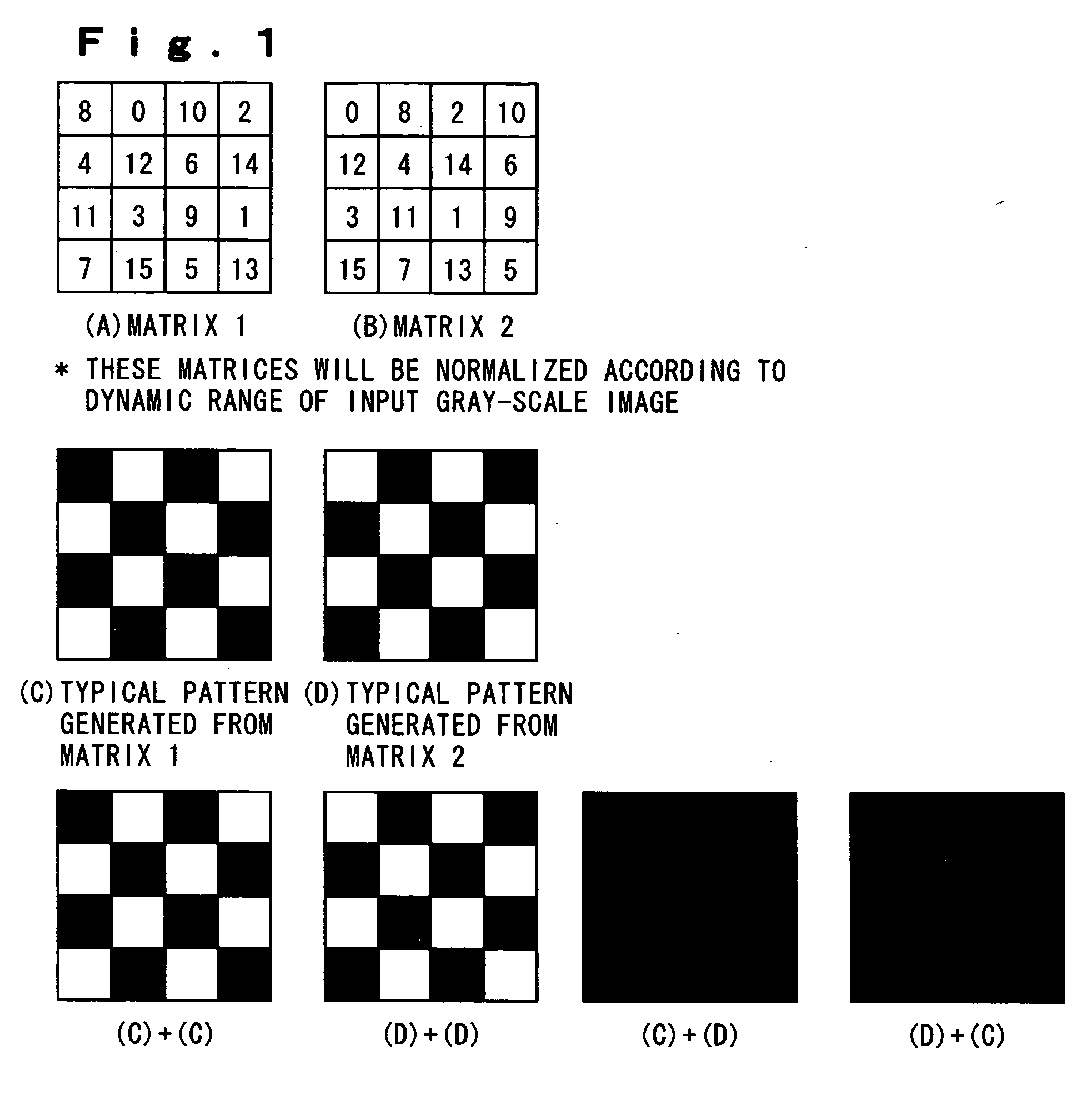
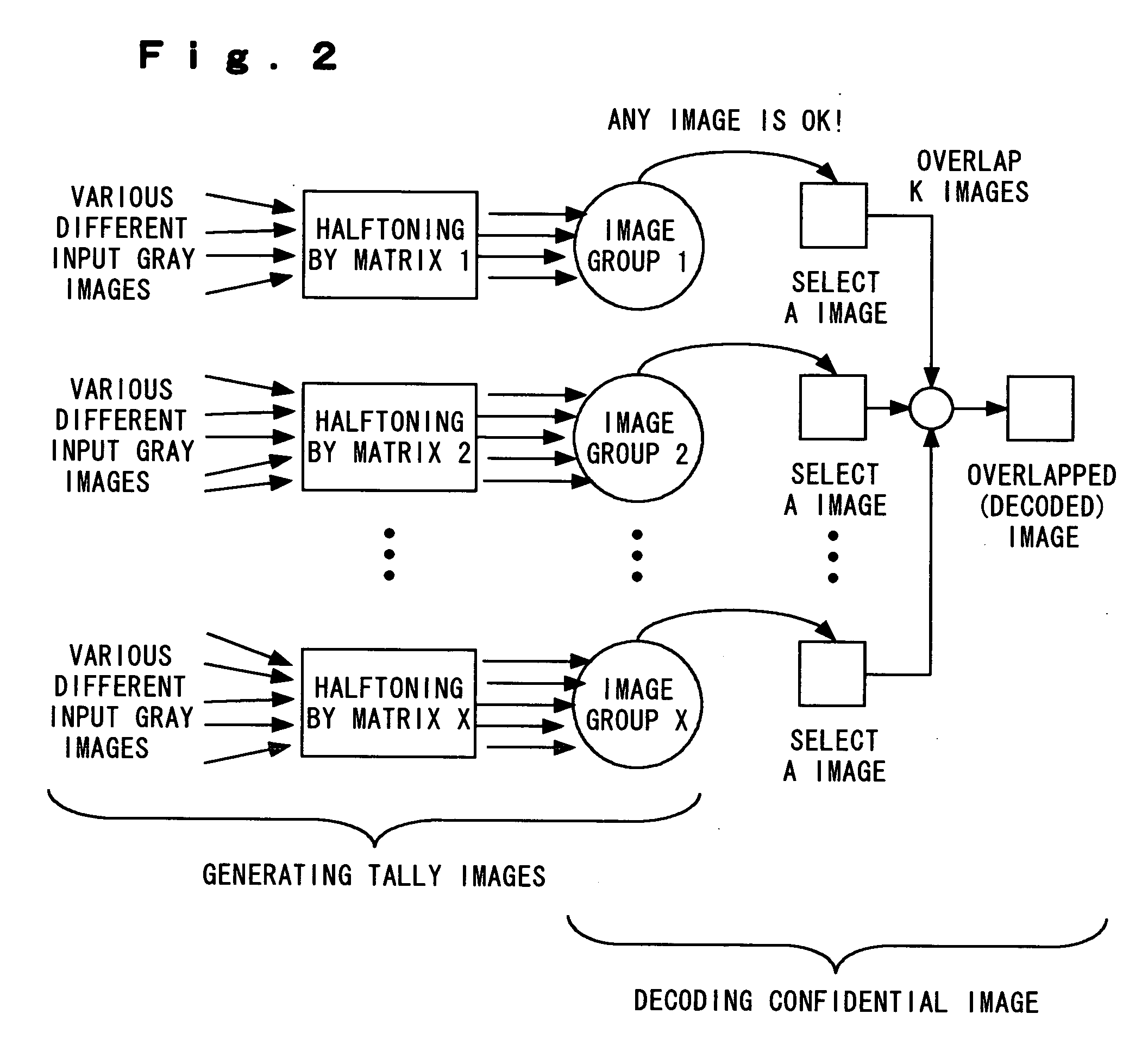
Tally image generating method, decoding method, tally image generator, and decoder
InactiveUS20060197990A1Improve visibilityQuality improvementCharacter and pattern recognitionVisual presentationPattern recognitionDecoding methods
Owner:KDDI CORP
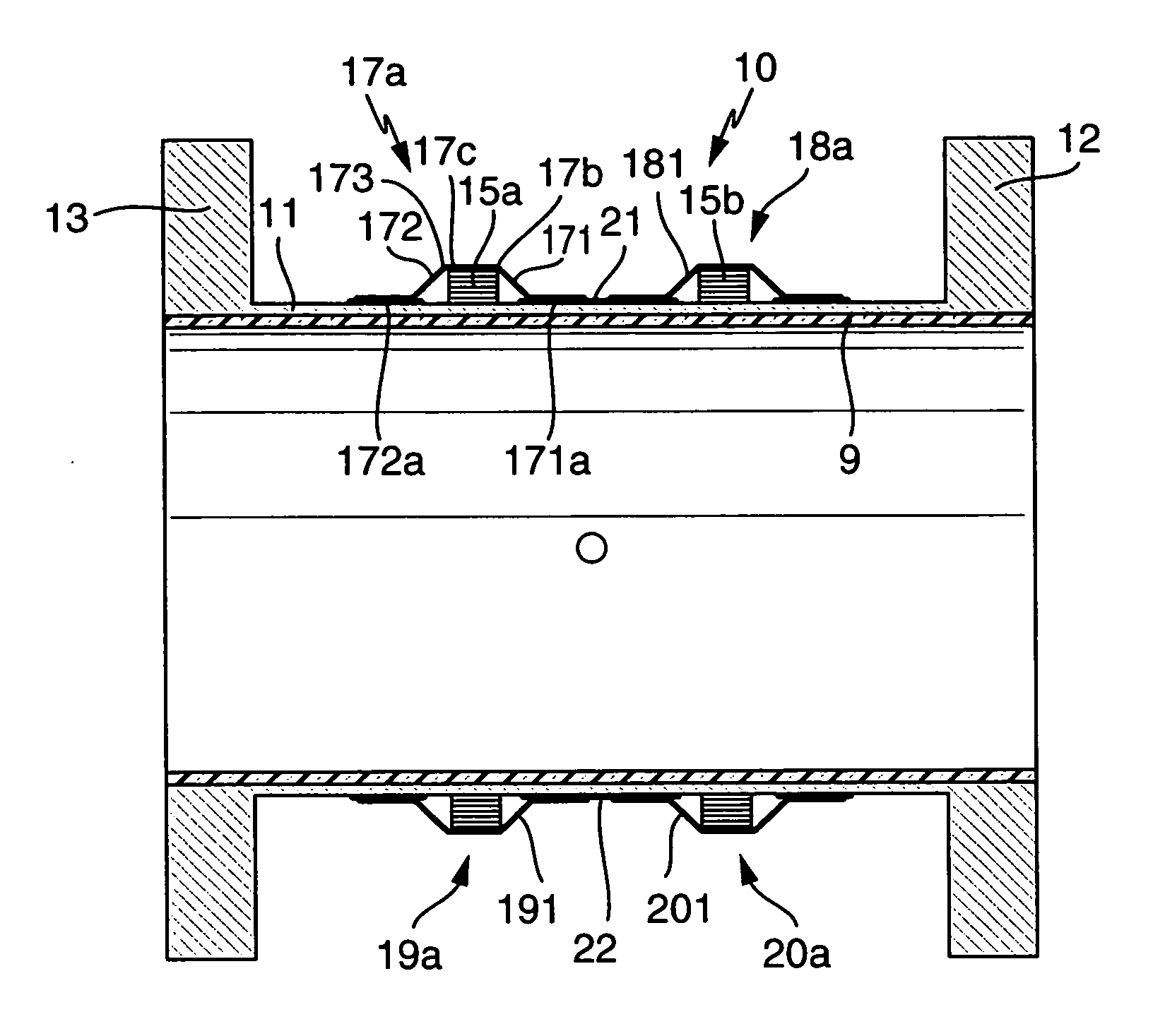
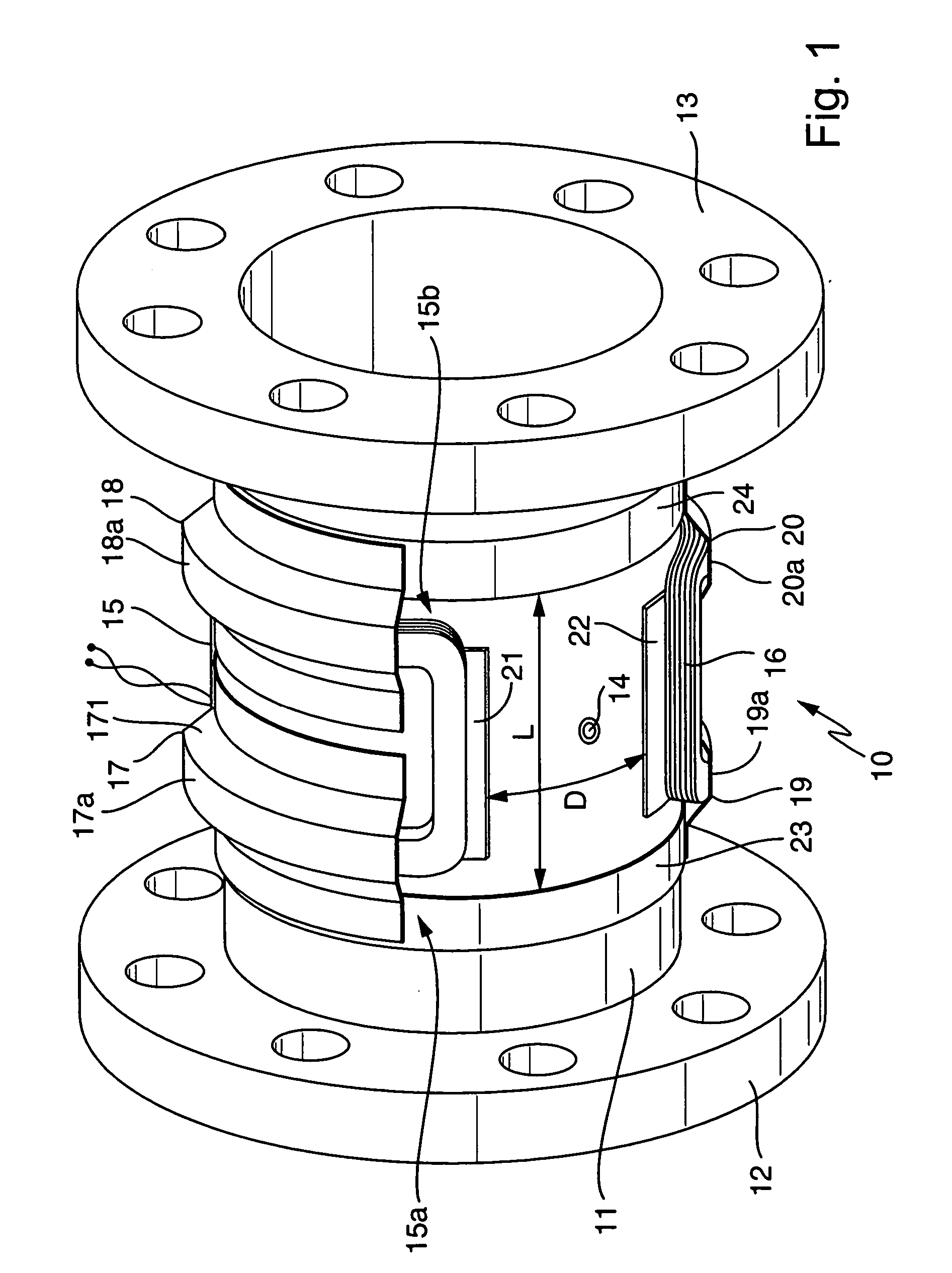
Magnetically inductive flow rate sensor
InactiveCN1973187AReduce leakage inductanceShort build timeVolume/mass flow by electromagnetic flowmetersCouplingConductor Coil
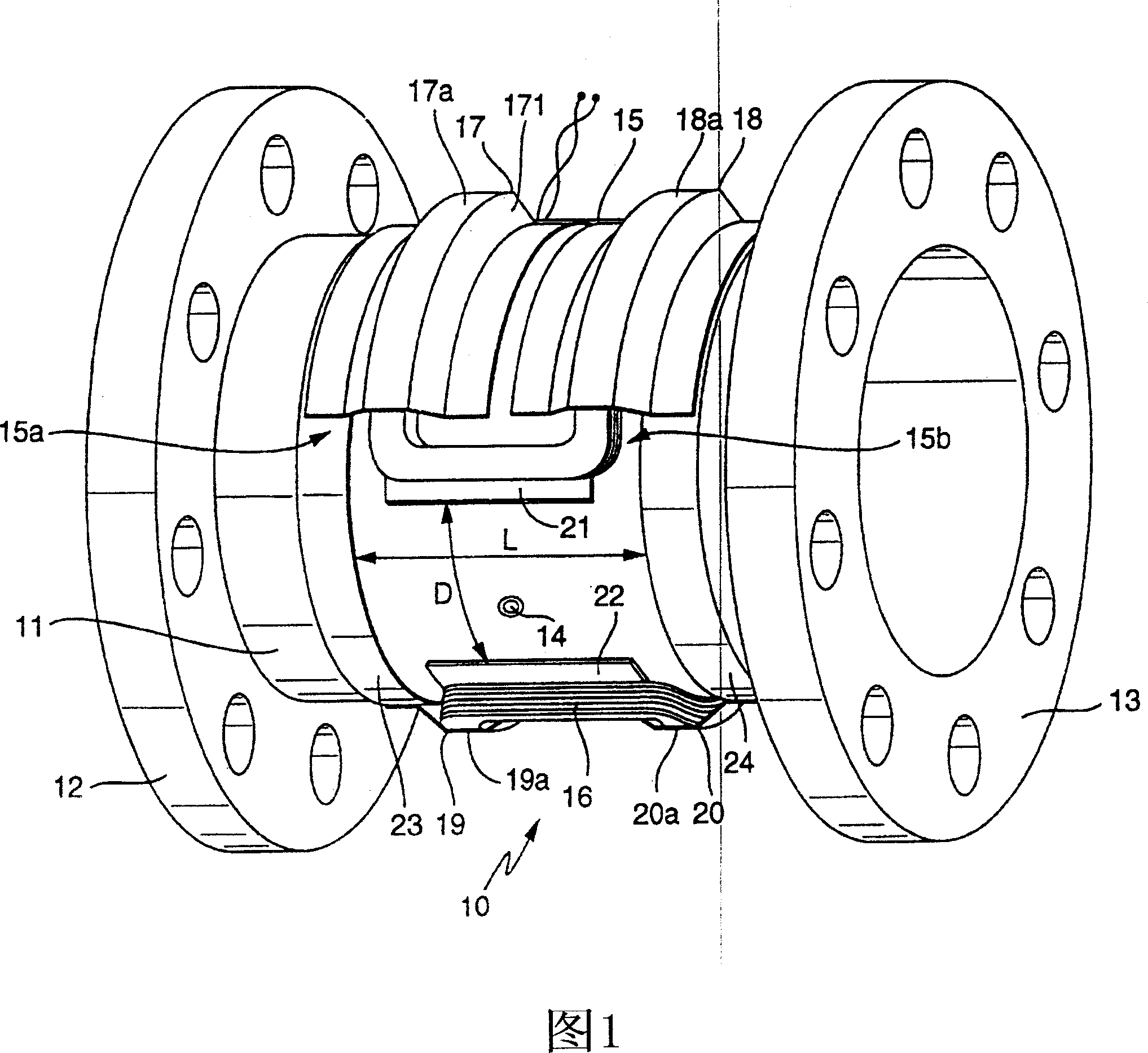
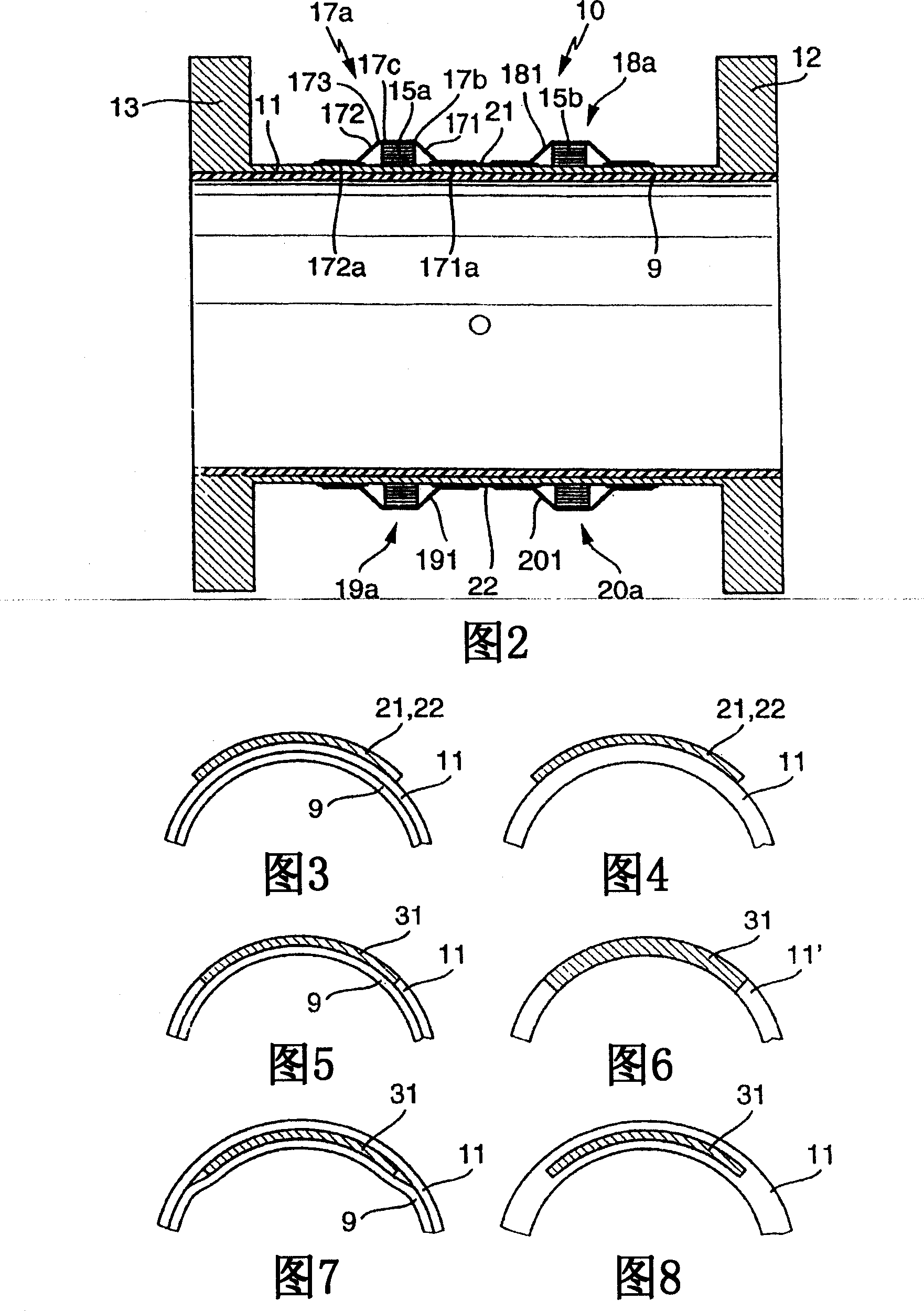
The invention relates to a flow rate sensor (10), which is designed to measure an electrically conductive fluid that flows in pipework. Said sensor comprises a measuring tube (11), which can be inserted into the run of pipework to conduct the fluid, said measuring tube (11) being electrically non-conductive on at least one inner face that comes into contact with the fluid, an electrode assembly (14) comprising at least two measuring electrodes that are located on the measuring tube and tap an electric voltage that is induced in the fluid, in addition to a magnetic field system that is also located on the measuring tube (11). The magnetic field system of the inventive flow rate sensor is equipped with at least two saddle-shaped field coils (15, 16), for generating a magnetic field that penetrates the fluid when operational, a respective ferromagnetic pole shoe (21, 22) for the field coils, for conducting the magnetic field towards the fluid and at least one ferromagnetic feedback element running around the measuring tube upstream of the two field coils and at least one ferromagnetic feedback element (23, 24) running around the measuring tube downstream of the two field coils, for conducting the magnetic field around said measuring tube. The pole shoes are magnetically coupled to the feedback elements by means of respective ferromagnetic coupling elements (17, 18, 19, 20). Each of said coupling elements, which are preferably configured in a standard manner, comprises at least one substantially gully-type cover segment (17a, 18a, 19a, 20a), which receives a first winding section of the respective field coil, said section essentially lying on a first circumferential segment of the measuring tube, or a second winding section (15a, 15b) of the respective field coil, said section essentially lying on a second circumferential segment of the measuring tube.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
Light-load transient enhanced circuit and low-voltage-difference linear voltage stabilizer integrated with circuit
InactiveCN104407662ASimple structureImprove stabilityElectric variable regulationLow voltageEngineering
The invention discloses a light-load transient enhanced circuit and a low-voltage-difference linear voltage stabilizer integrated with the circuit. The light-load transient enhanced circuit comprises a dynamic bias voltage generation circuit, a load current control switch, a voltage stabilizing capacitor, a discharging circuit and an output circuit; when the light-load transient enhanced circuit has a light load, no static current is consumed; when the low-voltage-difference linear voltage stabilizer is switched to the light load from a heavy load, gradually-reduced load current is provided by the light-load transient enhanced circuit, and the establishing time of the low-voltage-difference linear voltage stabilizer is greatly shortened, so that the problem that the establishing time for switching the current low-voltage-difference linear voltage stabilizer from the heavy load to the light load is too long is solved; secondly, extra auxiliary circuits are not needed so that the structure is simple and the transient response performance of the low-voltage-difference linear voltage stabilizer can be enhanced when the load is light, and furthermore, the light-load transient enhanced circuit can be applicable to ultralow-power-consumption medical electronics application.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Priority-based inter-domain resource reservation method
InactiveCN101715151AShort service establishment timeImprove network performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsTraffic capacityTwo step
The invention provides a resource reservation protocol-traffic engineering (RSVP-TE)-based resource reservation method capable of allocating priorities to services requiring connection and processing according to the priority, namely a priority-based inter-domain resource reservation method, which is applied to an all-optical network with a multi-layer multi-domain control sub-network. The technical key points are that different priorities are allocated to the services requiring connection, and a resource reservation process is completed by two steps of temporary reservation and definite reservation. The method has lower service blocking rate than a forward reservation protocol (FRP), has shorter service connection establishing time than a backward reservation protocol (BRP), greatly optimizes network performance, overcomes the defect that the conventional resource reservation methods cannot adapt to the multi-layer multi-domain optical network environment, and effectively establishesLSP in the multi-layer multi-domain network with wavelength conversion capacity. Meanwhile, service priority differentiation is supported, and the service with higher priority request the resource reservation in priority; and the method meets the requirement of development of future ASON networks.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Electromagnetic flow sensor
InactiveUS6983661B2Short build timeLarge flow rangeVolume/mass flow by electromagnetic flowmetersCouplingPole piece
The flow sensor serves to measure an electrically conductive fluid flowing in a pipe. It comprises a flow tube designed to be inserted into the pipe for conducting the fluid, the flow tube being electrically nonconductive at least on a fluid-contacting inner side, an electrode arrangement consisting of at least two measuring electrodes disposed on the flow tube for picking up a voltage induced in the fluid, and a magnetic field system likewise disposed on the flow tube. The magnetic field system comprises at least two saddle-shaped field coils for producing a magnetic field cutting the fluid during operation of the flow sensor, a respective ferromagnetic pole piece for each of the two field coils, as well as at least one ferromagnetic return path extending around the flow tube upstream of the two field coils and at least one ferromagnetic return path extending around the flow tube downstream of the two field coils for directing the magnetic field around the flow tube. The pole pieces are magnetically coupled to the return paths by means of ferromagnetic coupling elements. Each of the, preferably identically shaped, coupling elements has at least one essentially trough-shaped cover segment which receives a first winding section of the respective associated field coil, lying essentially on a first periphery of the flow tube, or a second winding section of the associated field coil, lying essentially on a second periphery of the flow tube.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
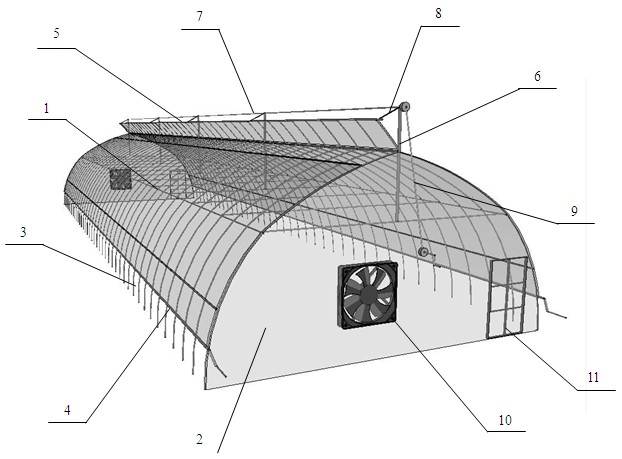
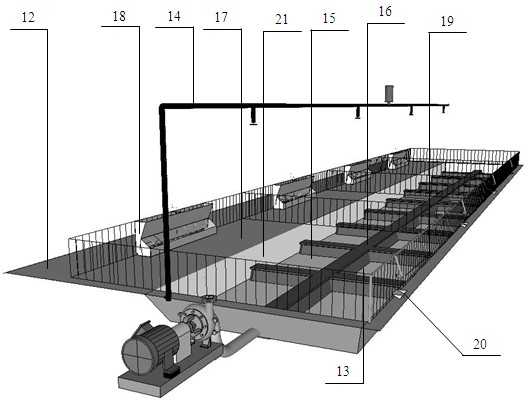
Application of low-carbon saving type pig house
The invention relates to application of a low-carbon saving type pig house, belonging to the field of application of a pig house. The pig house adopts a galvanized steel pipe greenhouse structure, and the roof of the pig house is covered with a plastic light transmission film and a sun-shading net material; a ventilation opening which can be opened and closed is arranged on each of a south wall body and a north wall body, a retractable ventilation skylight facing toward the south is arranged at the top of the pig house and is pulled and retracted through a longitudinal scroll at the top of the pig house; a fan is arranged on each of an east gable and a west gable of the pig house for supplementing ventilation; and a medium pressure atomization spraying system is arranged above a pigpen inthe pig house, a fermentation bed is arranged on the south side of the interior of the pigpen, fermentation bed padding is laid in a fermentation bed padding pit, an aeration fermentation system pipeline is buried at the bottom of the pit. The pig house adopts steel pipe materials and the structure which is helpful for convection and ventilation, and utilizes time-delay atomization spraying technology, fermentation bed pig raising technology and the aeration fermentation technology at the bottom of the fermentation bed, so that the pig house reduces construction cost and use cost, is energy-saving and environment-friendly, and reduces carbon emissions.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for loading nano silvery on activated carbon fibre
The invention designs a method for loading nano-silver on active carbon fiber through an electrochemical deposition method. In the method, a silver ion is absorbed by the absorption capacity of active carbon fiber, and is reduced to silver element by a cathodic reduction method; and nano-silver is directly fixed on the surface of the active carbon fiber while the nano-silver is generated by controlling operation condition. The method is applicable to various conductive active carbon fiber materials with fast preparation speed; the obtained nano-silver is firmly combined with the active carbon fiber with even particle diameter; and the product can be used in drinking water purification, medical sanitation and other fields.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for fast establishing DSE and plant symbiosis cultivation system and uses thereof
InactiveCN101263778AShort build timeImprove efficiencyFungiCultivating equipmentsNutrient solutionOxygen
The invention relates to a method for the fast establishment of DSE and plant symbiotic culture system and the application of the method, in particular to a method for the fast establishment of dark septate endophytes and plant symbiotic culture system and the application of the method, belonging to the field of applied microbiology, plant nutrition and ecology. The invention is characterized in that, based on the biological characteristics of DSE of wide carbon utilization and aerobe, riversand with good air permeability is used as the solid substrate; improved MS culture medium is added as the nutrient solution, and early nutritional growth requirements for the formation of DSE-plant symbiotic system are satisfied; the invention utilizes plant seedlings and DSE as materials; by inoculating DSE and plant seedlings on an aseptic culture medium, symbiotic relationship is formed. The method of the invention has the advantages of short setup time of the DSE and plant symbiotic culture system, high efficiency and other excellences; the invention can be applied to the study of the relationship between DSE and plants, the study of DSE morphology, the initial detection of suspected DSE bacterial strains and the application of DSE inoculation.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
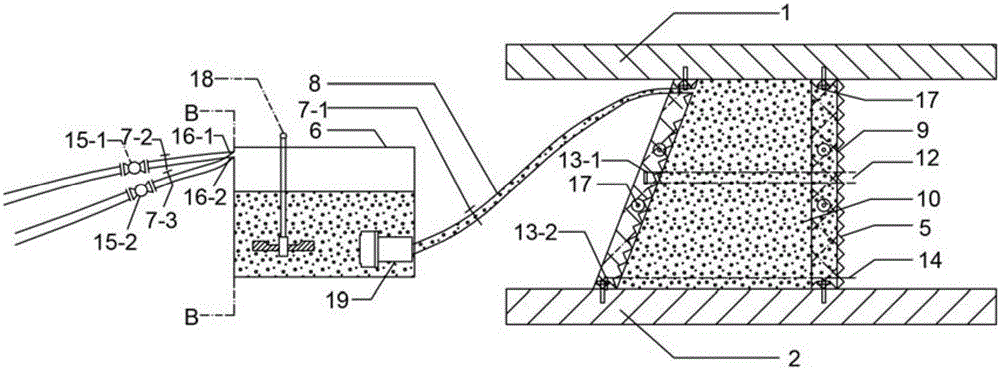
Modern arch type bamboo bridge and construction method thereof
InactiveCN104594175AImprove power transmissionImprove mechanical performanceBridge erection/assemblyArch-type bridgeDuctilityStructural element
The invention discloses a modern arch type bamboo bridge. The modern arch type bamboo bridge is characterized by comprising bamboo arch ribs, bamboo beams, diagonal bracings, bamboo panels and steel shoes, wherein the bamboo arch ribs, the bamboo beams, the diagonal bracings and the bamboo panels are made of reconsolidated bamboo materials; the steel shoes are made of steel materials. The invention further discloses a construction method of the modern arch type bamboo bridge. The construction method of the modern arch type bamboo bridge is characterized in that the bamboo arch ribs, the bamboo beams, the diagonal bracings, the bamboo panels and the steel shoes are prefabricated, installation of the steel shoes and a bridge abutment skewback is finished, then installation of the bamboo arch ribs and the steel shoes is finished, the bridge abutment skewback is poured, and finally the bamboo beams, the diagonal bracings and the bamboo panels are installed. The construction method of the modern arch type bamboo bridge has the advantages that the manufacturing process is simple, the cost is low, factorization and standardization of structural components are good, the assembly degree is high, the building time is short, the structural intensity is high, rigidity is large, ductility is good, and the seismic performance is good, and the obtained arch type bamboo bridge has the effects of being environmentally friendly and low in carbon.
Owner:CHONGQING JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
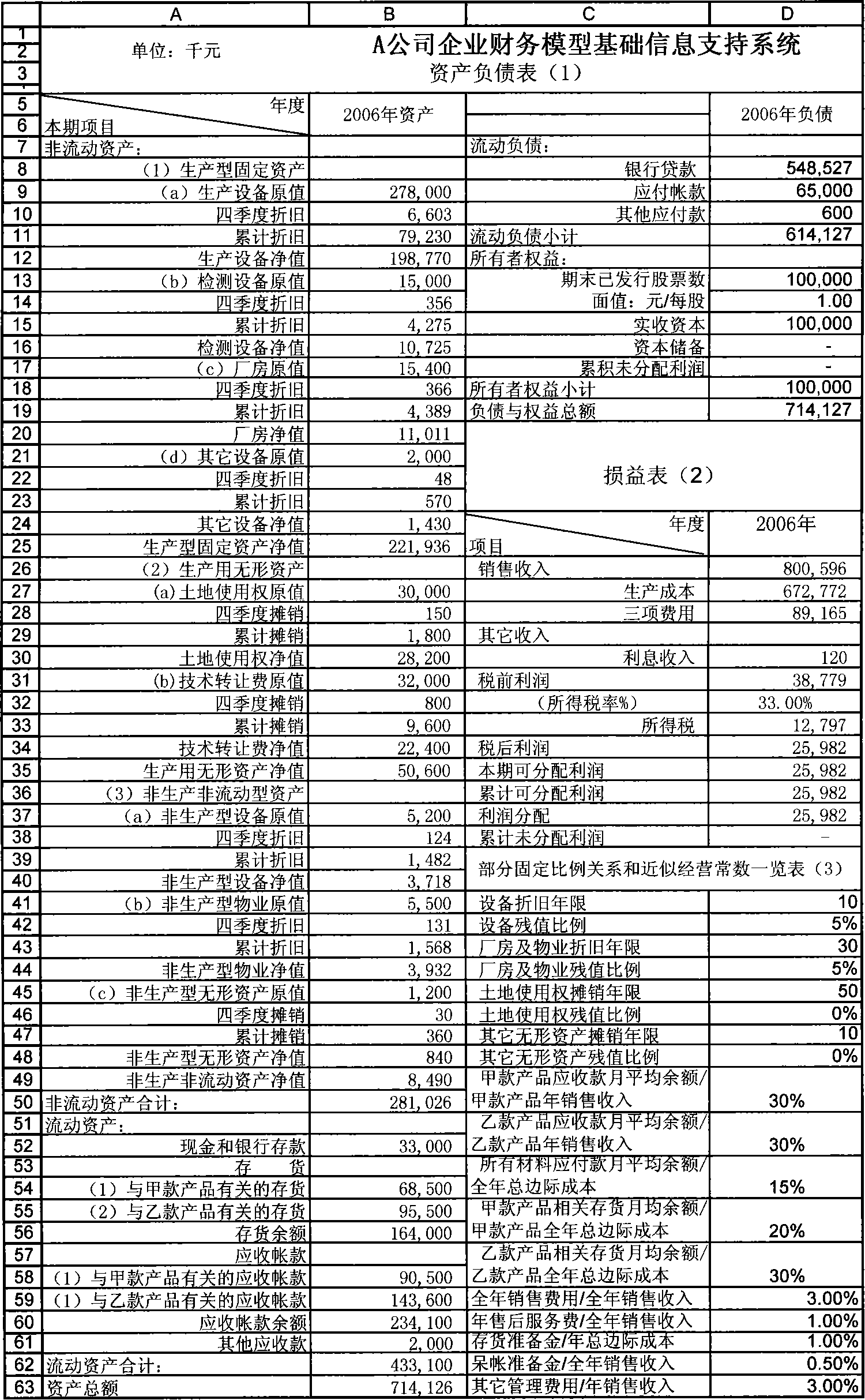
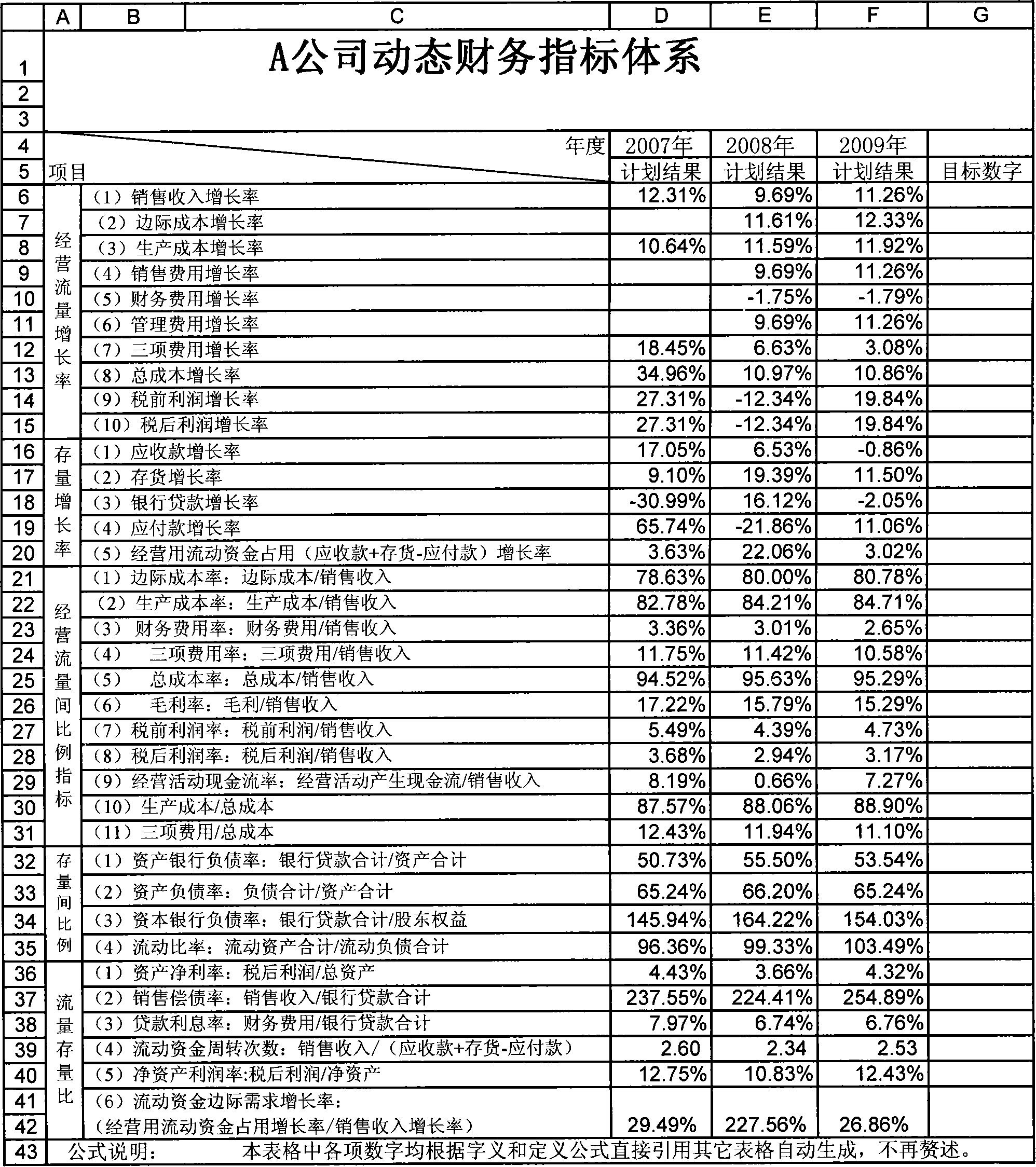
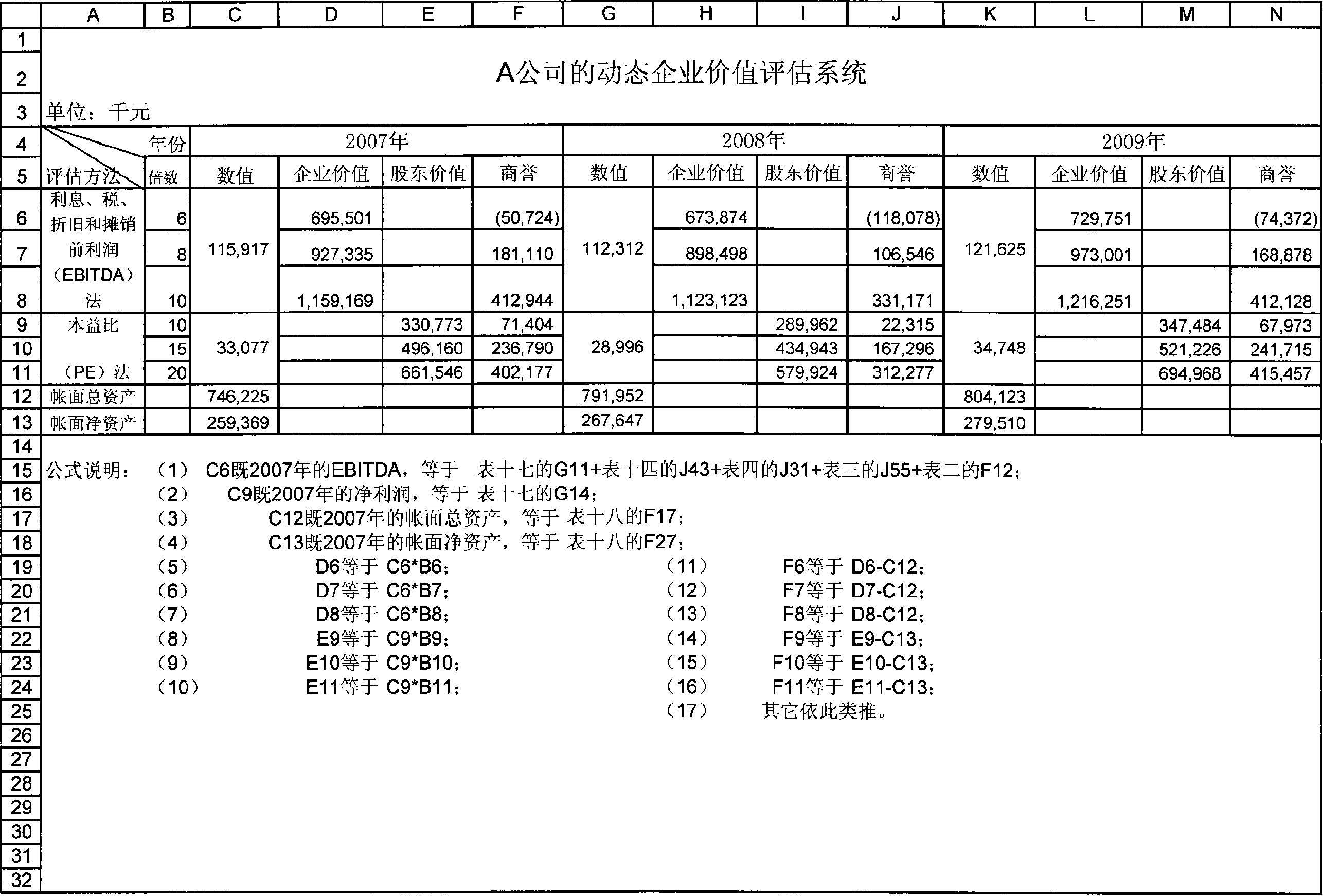
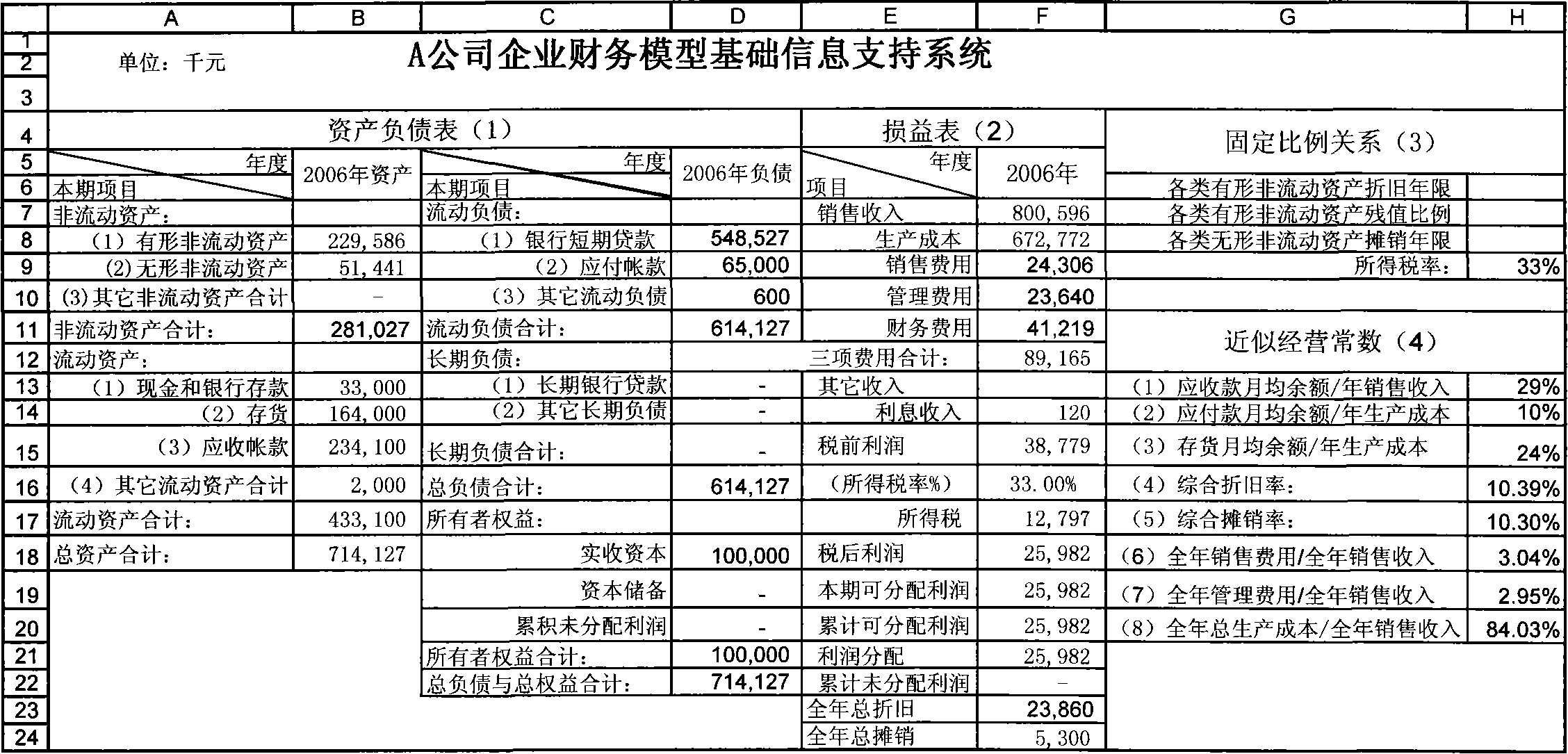
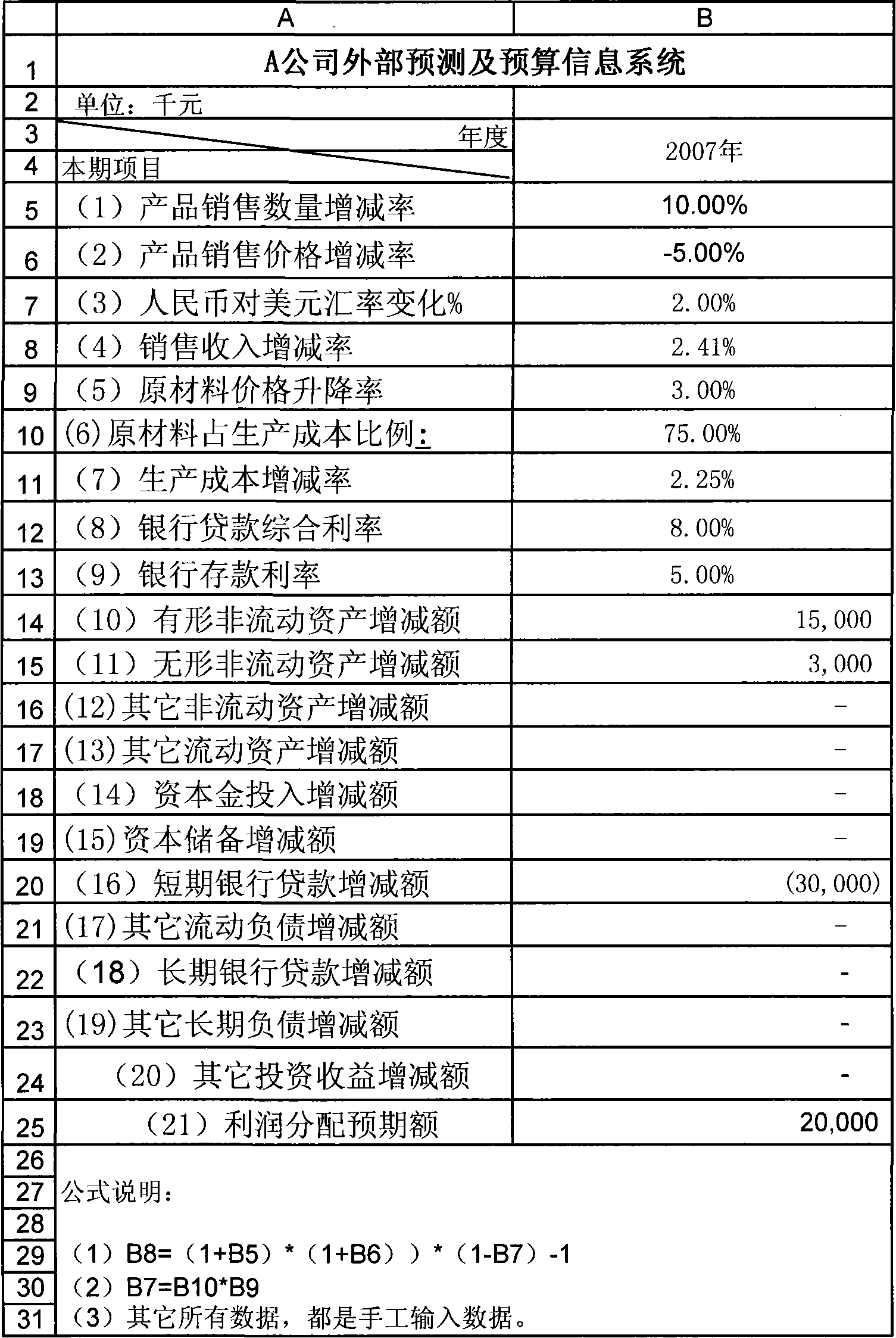
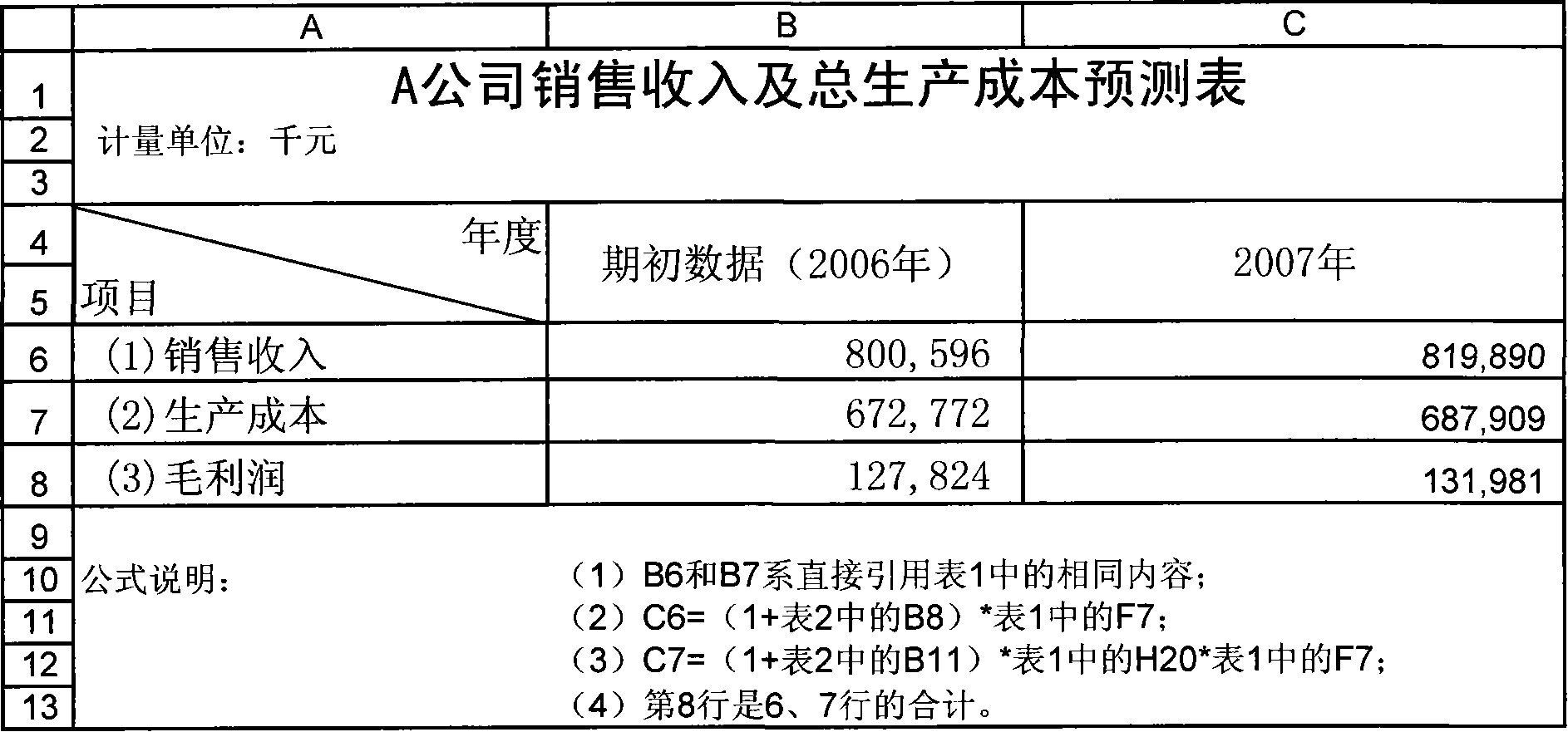
Complete information based dynamically interactive type enterprise finance model construction and operation method
A construction method of dynamic interactive enterprise financial module based on complete information, build up basic information supporting system according to the beginning financial data, fixed ratio relationship and approximate operating constant of applicable enterprise; combined external predictive data with internal predictive data, use accounting principles , mathematical knowledge, logical thinking, function relation, time relation and operating constant factor to design form and content of corporation financing, main business, cost control, capital management and financial statements five sub-module. And it provides operating method of dynamic interactive enterprise financial module based on complete information. The invention is of short module construction time, simple in operation, a single operational level, can integrated with abstract means, rapidly,comprehensively and effectively simulate,plan and evaluate future specific business of enterprise.
Owner:佟辛
Concrete formwork support device
InactiveCN105625710AWon't tiltAvoid piercing operationsForms/shuttering/falseworksAuxillary members of forms/shuttering/falseworksInterior spaceFloor slab
Owner:张海文
Hanging type movable working platform for storage tank maintenance
ActiveCN103352559APrevent camberImprove the safety of useBuilding support scaffoldsAgricultural engineeringHanging basket
The invention discloses an aerial maintenance working device, and particularly relates to a hanging type movable working platform for storage tank maintenance. The hanging type movable working platform for the storage tank maintenance can effectively save materials, and is short in building time, low in building cost, free of external power for supporting, and high in using safety. The hanging type movable working platform comprises a working hanging basket set, a first walking mechanism and a second walking mechanism, the first walking mechanism is arranged on the top of the working hanging basket set and relatively slides on a wind resistant ring of a storage tank through a pulley, the second walking mechanism is arranged on the side face of the working hanging basket set, the top end of the second walking mechanism abuts against and presses the outer wall of the storage tank through a pulley and relatively slides, the working hanging basket set comprises at least two working hanging baskets connected end to end, and a crawling ladder is arranged between the working hanging baskets.
Owner:SINOCHEM ZHOUSHAN XINGHAI CONSTR
Apparatus for purifying metallurgical silicon for solar cells
InactiveUS20110198336A1Ensure safetyImprove purification efficiencyPolycrystalline material growthElectric discharge heatingCelsius DegreeCrucible
A system for forming high quality silicon material, e.g., polysilicon. In a specific embodiment, the melted material comprises a silicon material and an impurity, e.g., phosphorous species. The system includes a crucible having an interior region. In a specific embodiment, the crucible is made of a suitable material such as a quartz material or others. The quartz material is capable of withstanding a temperature of at least 1400 Degrees Celsius for processing silicon. In a specific embodiment, the crucible is configured in an upright position and has an open region to expose a melted material. In a specific embodiment, the present system has an energy source. Such energy source may be an arc heater or other suitable heating device, including multiple heating devices, which may be the same or different. The arc heater is configured above the open region and spaced by a gap between the exposed melted material and a muzzle region of the arc heater to cause formation of a determined temperature profile within a vicinity of a center region of the exposed melted material while maintaining outer regions of the melted material at a temperature below a melting point of the quartz material of the crucible. In a specific embodiment, the system produces a melted material comprising a resulting phosphorous species of 0.1 ppm and less, which is purified silicon.
Owner:HOSHINO MASAHIRO +1
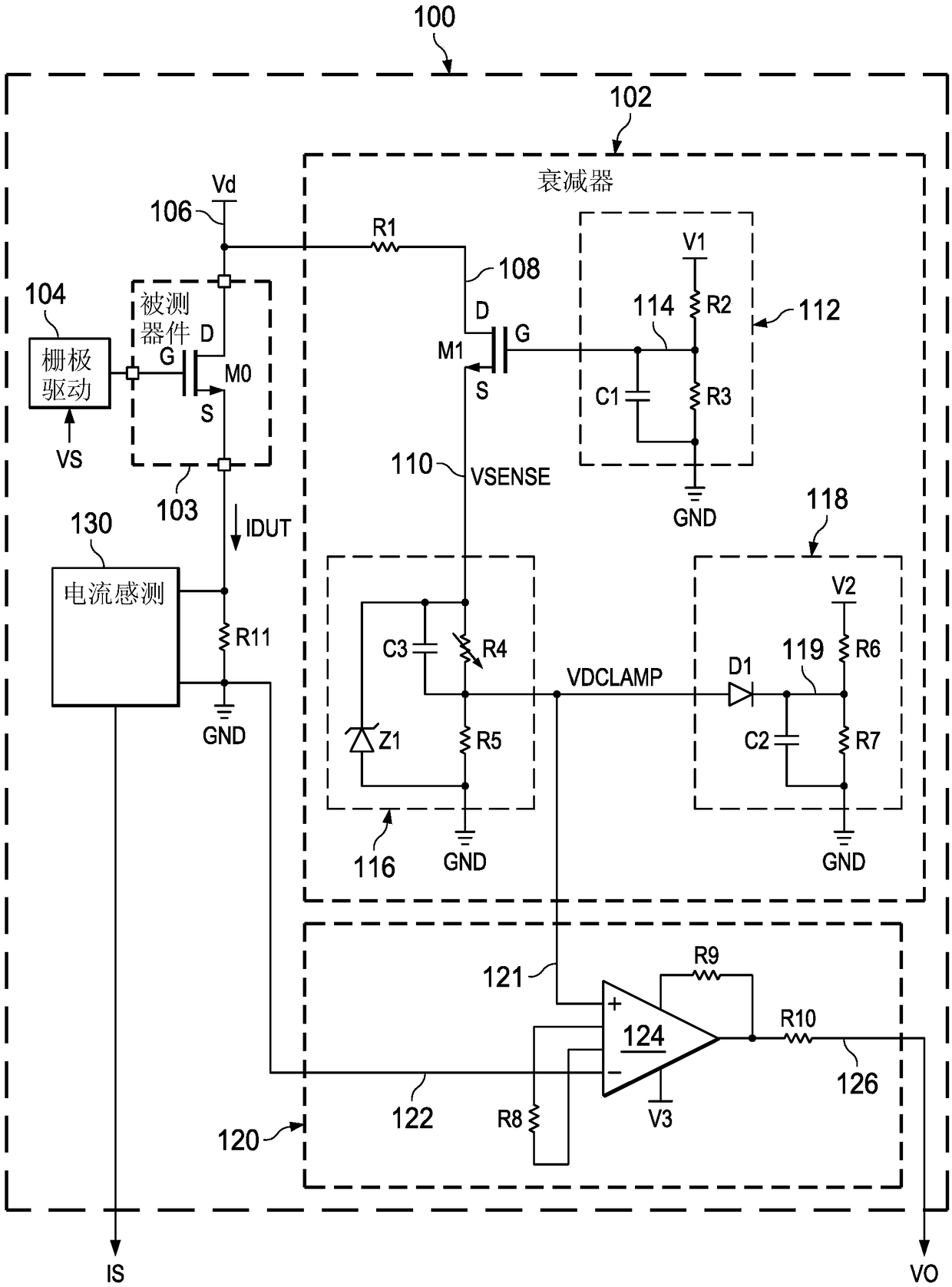
High-resolution power electronics measurements
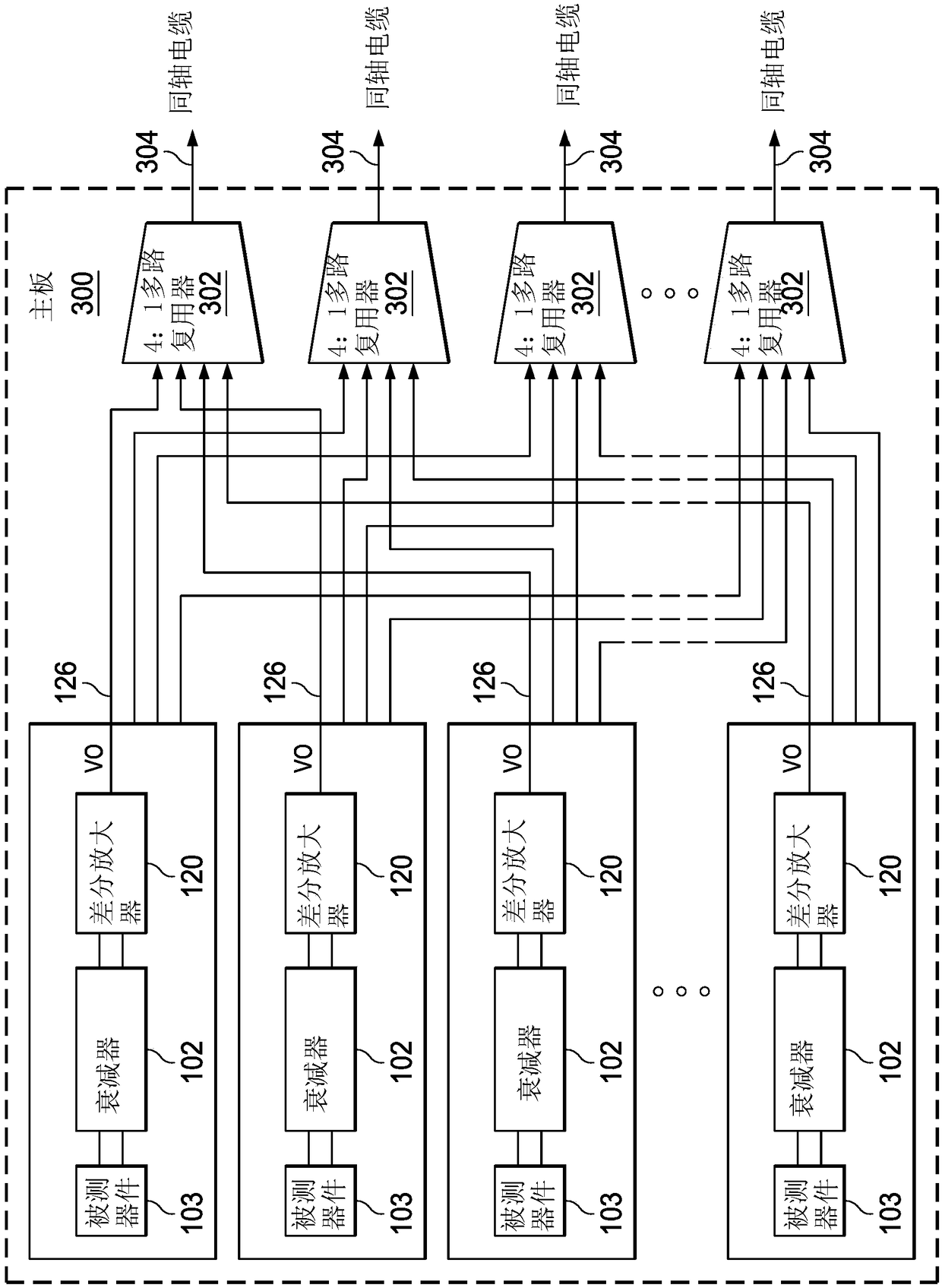
ActiveCN108738350AEasy to measureShort build timeResistance/reactance/impedenceVoltage dividersComputational physicsDifferential amplifier
In described examples of a measurement circuit to measure a drain voltage of a drain terminal (106) of the high voltage transistor (M0) during switching, the measurement circuit includes an attenuatorcircuit (102) to generate an attenuator output signal (VDCLAMP) representing a voltage across the high voltage transistor (M0) when the high voltage transistor (M0) is turned on, and a differential amplifier (124) to provide an amplified sense voltage signal (VO) according to the attenuator output signal (VDCLAMP). The attenuator circuit (102) includes a clamp transistor (M1) coupled with the drain terminal (106) of the high voltage transistor (M0) to provide a sense signal (VSENSE) to a first internal node (110), a resistive voltage divider circuit (116) to provide the attenuator output signal (VDCLAMP) based on the sense signal (VSENSE), and a first clamp circuit (Z1) to limit the sense signal voltage (VSENSE) when the high voltage transistor (M0) is turned off.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Three-particle cooperative optimization method applied to vector quantization-based speaker recognition
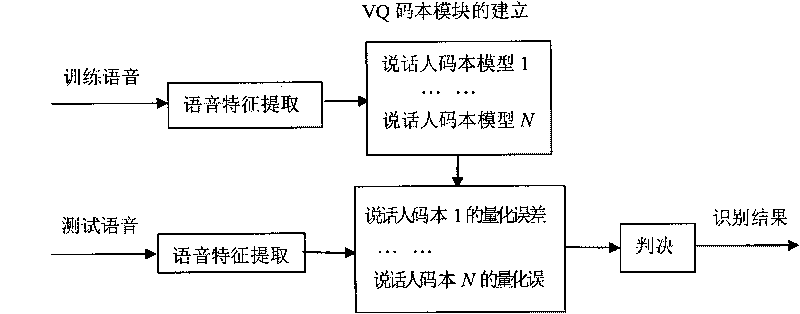
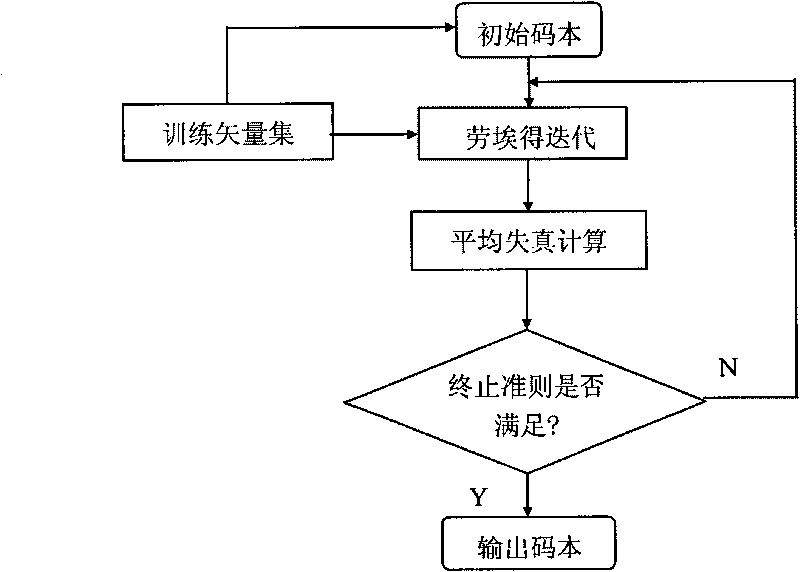
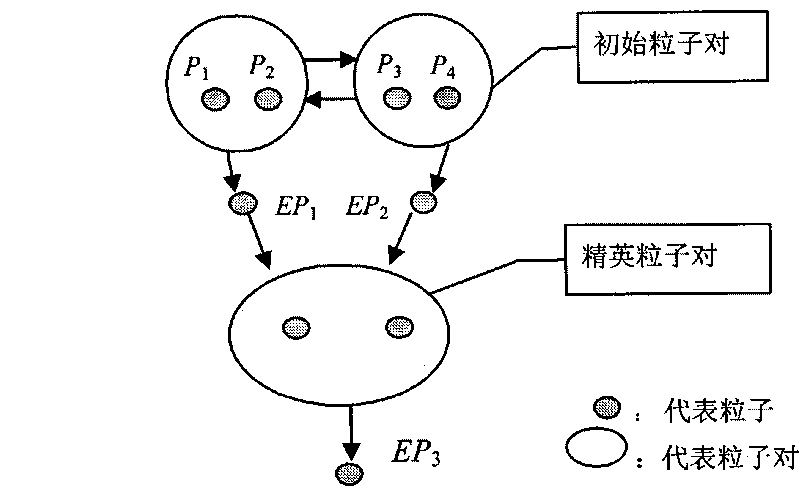
InactiveCN101740029AAvoid falling intoIncrease diversitySpeech recognitionSub populationsGlobal information
The invention relates to a three-particle cooperative optimization method applied to speaker recognition, which is an optimization design method for a vector quantization speaker codebook model and comprises the following steps: dividing an initial population of six particles into two sub-populations, wherein each particle represents a codebook and each sub-population consists of three particles named three-particle; adopting different particle update parameters by two three-particles so as to realize global exploration and local exploration; executing updating of speed and position of PSO and operation of an LBG algorithm with an iteration number of three by the particles in each iteration; when the iterations reach mixing update times, mixing and dividing the particles into new three-particles to realize global information exchange and cooperative evolution; when a condition of the maximum iteration number of the initial population is met, selecting two particles from the two three-particles to continue searching until the maximum iteration number of the elite particles is achieved; and using the optimized one as the speaker codebook model. The three-particle cooperative optimization method applied to the speaker recognition better solves the problem that an initial codebook influences the optimization result, and obviously improves the performance of short-voice speaker recognition.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Method for constructing oil drilling waste mud solidification pool
ActiveCN101979781AImprove anti-seepage effectWill not puncture the polyethylene geomembraneArtificial islandsUnderwater structuresGeomembraneWell drilling
The invention provides a method for constructing an oil drilling waste mud solidification pool and relates to the technical field of oil and gas exploration drilling pollution control. A scheme of the method comprises the following steps of: excavating the solidification pool on site, wherein the slope of a pool wall is 45 to 60 DEG, and the pool height is 2.0 to 2.5 m; performing seepage control on a pool bottom by adopting clay-(non-woven geotextile)-(high-density polyethylene geomembrane)-(non-woven geotextile); continuously packaging solid waste to a top part by using the clay-(non-woven geotextile)-(high-density polyethylene geomembrane)-(non-woven geotextile); and capping the top part by using C20 concrete so as to prevent a solidified body from seeping. The process is simple and easy, the cost investment is small, the construction period is short, and the drilling waste mud is propelled to be solidified rapidly and timely so as to effectively prevent the waste mud from overflowing and polluting the environment in the drilling operation process.
Owner:CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP CHUANQING DRILLING ENG CO LTD +1
Multifunctional safety and environment-friendly type skid-mounted fuel-servicing equipment
InactiveCN102737447ASmall footprintLess investmentLarge containersUnderwater structuresServicing equipmentAutomatic control
The invention relates to multifunctional safety and environment-friendly type skid-mounted fuel-servicing equipment. The equipment comprises a sledge body pedestal, functional facilities and a ceiling. Functional facilities are arranged on the sledge body pedestal; the functional facilities comprise an oiling machine, a vacuum dust-absorbing system, an automobile tyres air-ejecting system, an automatic vending system, a bank automatic teller and deposit system that being arranged in parallel, and an oil tank, an oil gas recovery and processing apparatus, an auxiliary system, an automatic monitoring system, an automatic control system and a black box are arranged at the rear of the functional facilities; According to the invention, an integrated service of oil storage, oiling, automatic depositing and withdrawing money, automatic selling goods, air-ejecting of automobile tyres, dust-absorbing and cleaning of the automobile and the like.
Owner:北京福吉长安防爆材料盐城有限责任公司 +1
Parameterized configuration for a programmable logic device
ActiveUS8347243B2Run-time partShort build timeCAD circuit designProgram controlProgrammable logic deviceTheoretical computer science
The invention relates to a method and a tool for generating a parameterized configuration for a Field Programmable Gate Array from a Boolean function, the Boolean function comprising at least one parameter argument, comprising the steps generating at least one tunable logic block from the Boolean function and from at least one parameter argument, and mapping the at least one tunable logic block to the Field Programmable Gate Array. This is advantageous since a parameterized configuration can be generated faster than with conventional tools.
Owner:UNIV GENT
Public information based dynamically interactive type enterprise finance model construction and operation method
InactiveCN101149833AShort build timeGuaranteed uptimeData processing applicationsInformation supportFixed ratio
The dynamic interaction-type enterprise financial module constitution method based public information includes: constitute a basic information support system according to the financial data suitable to enterprise opening to the public, fixed ratio relation and approximate operation constant; constitute an external prediction and budget information system according to relative information of external personnel and organizations of the enterprise; design the form and content of main form of the enterprise financial module by using accounting principle, mathematics general knowledge, logic thinking, function relation, ratio relation, time relation and approximate operation constant, determine the formula relationship of all data of the form itself and between one another to form a dynamic inter-action type enterprise financial module. The method for operating the module is also disclosed. Advantage: short constitution time, simple and independent operation.
Owner:佟辛
Pharmacy picking device comprising a universal supply-and-control module
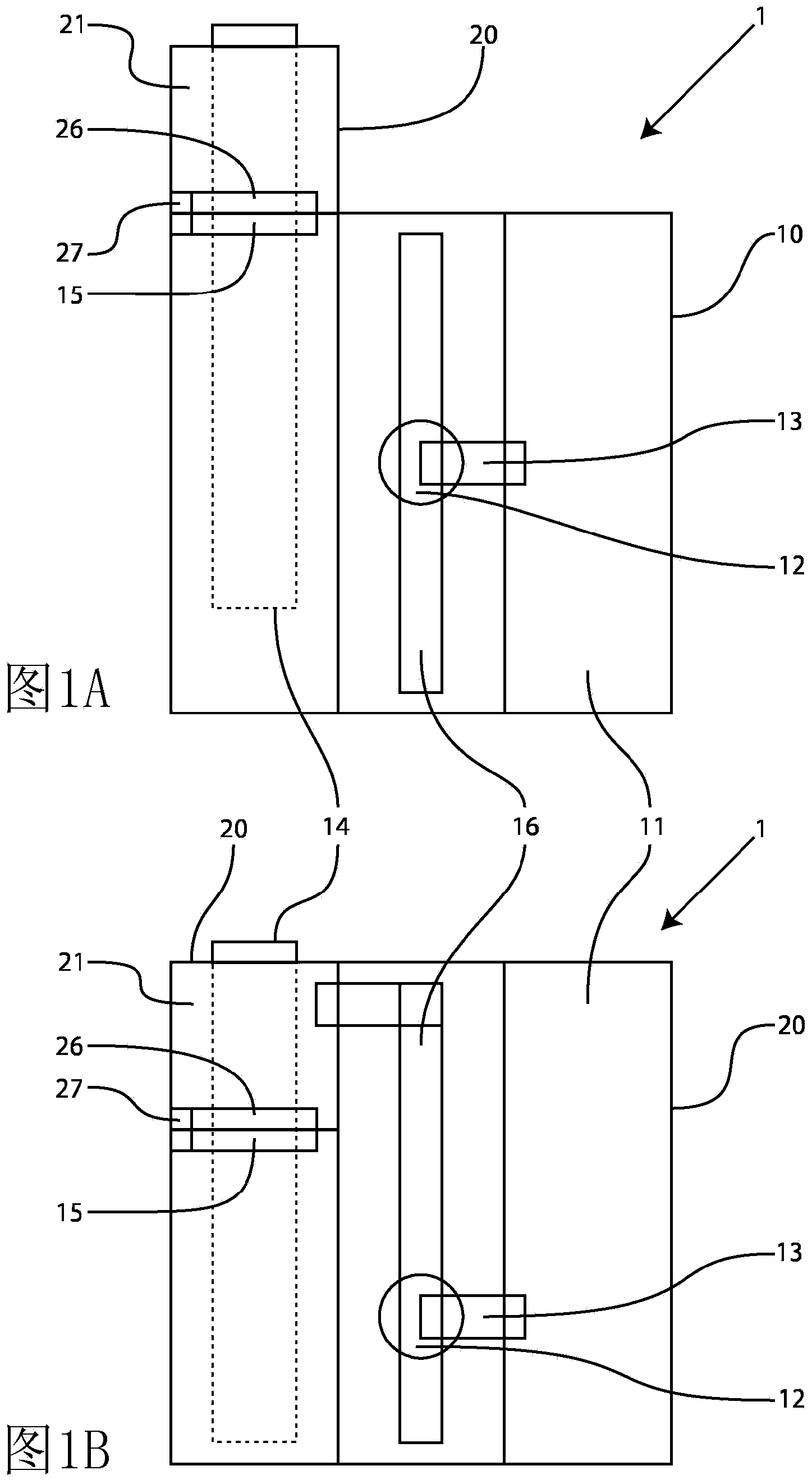
The invention relates to a pharmacy picking device (1) comprising a housing (10) with a plurality of shelf bases (11) disposed one above the other, at least one operating device (12), a conveyor device (14), a housing-coupling interface (15), and a universal supply-and-control module (20). This universal supply-and-control module (20) comprises a feed device (21), an identification and measurement device (22), operator input / output devices (23), an electronic controller (24) and a voltage supply assembly (25), as well as a housing-coupling interface (15) and an electrical interface (27), said supply-and-control module (20) being arranged adjacent to the housing (10) such that a mechanical coupling is produced by said housing-coupling interface (15) and module-coupling interface (26), in such a manner that drug packages in or on the supply-and-control module (20), which are to be deposited, are delivered to a position on the conveyor device (14) which is known to the electronic controller.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON ROWA GERMANY GMBH
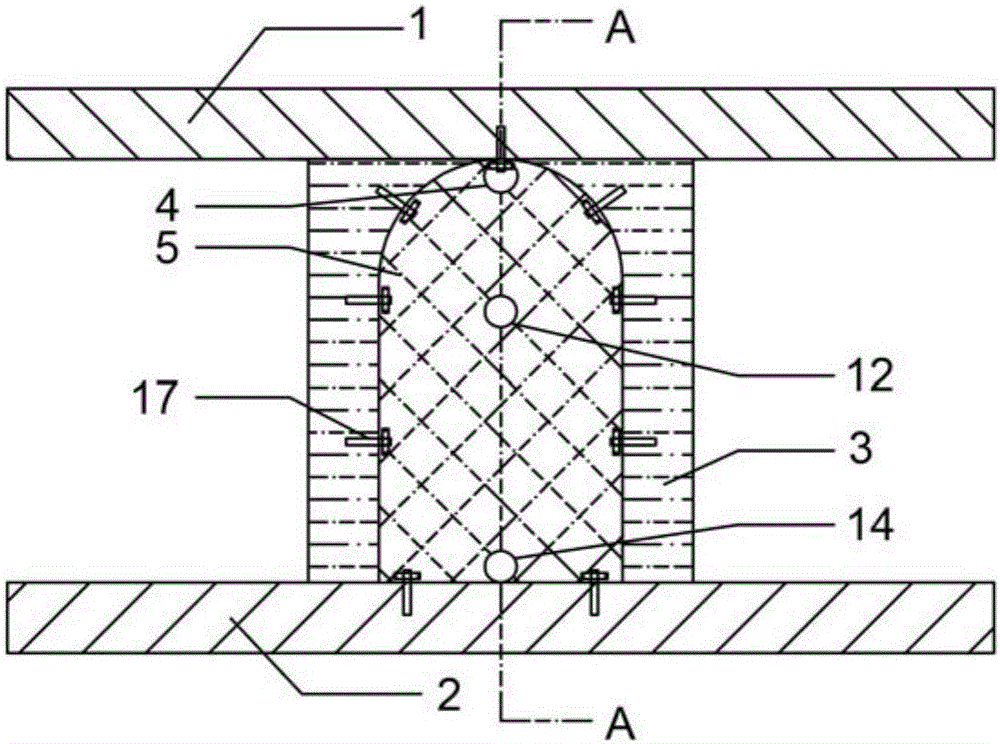
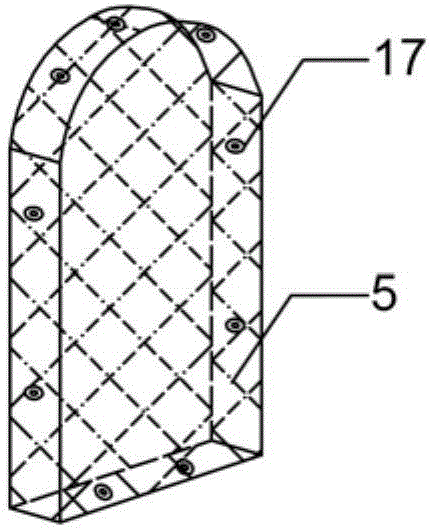
Mine anti-explosion trapezoidal sealing wall and construction method thereof
ActiveCN106837418AOvercome the shortcomings of poor security and stabilityEasy accessMining devicesUnderground chambersStructural engineeringDrainage tubes
The invention relates to a mine anti-explosion trapezoidal sealing wall and a construction method thereof. The mine anti-explosion trapezoidal sealing wall is suitable for the situation that when heat power disasters such as an explosion and a fire occur in a roadway, a traditional sealing wall is too late to be built or a mine with large gas emission quantity. A top plate and a bottom late of the roadway are at the top end and the bottom end correspondingly, and the roadway wall is on the two sides; metal anchor nets are arranged on surrounding rock through expansion bolts, the two metal anchor nets are mutually connected through iron wires; sealing cloths are arranged on the inner sides of the metal anchor nets and connected with the metal anchor nets through iron wires; filling body materials are injected into a cavity formed by the sealing cloths and the surrounding rock through a grouting hole, and the sealing wall is formed after filling; the grouting hole is connected with a filling device through a grouting pipe; and a pouring pipe made of a fire preventing and extinguishing material and penetrating through the wall is reserved in the middle of the sealing wall, and a water draining pipe penetrating through the wall is reserved at the bottom of the sealing wall.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
CMOS operation amplifier with great direct-current open-loop voltage gain
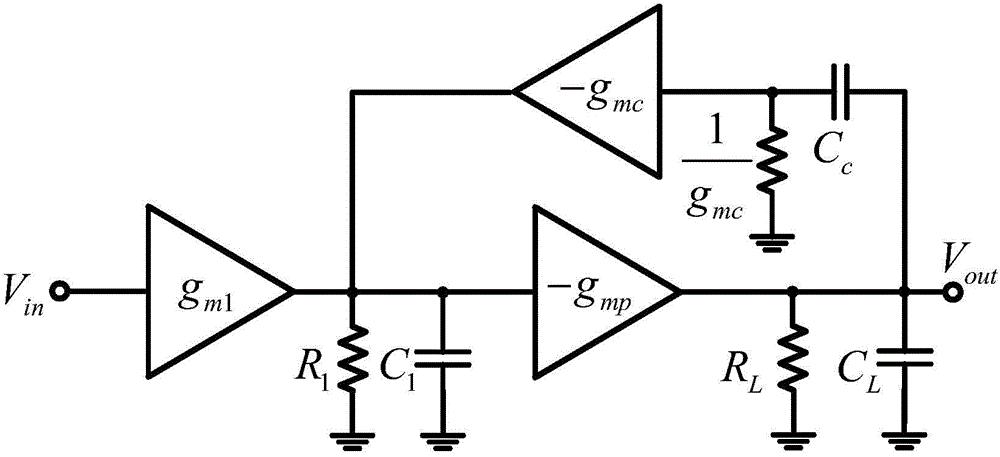
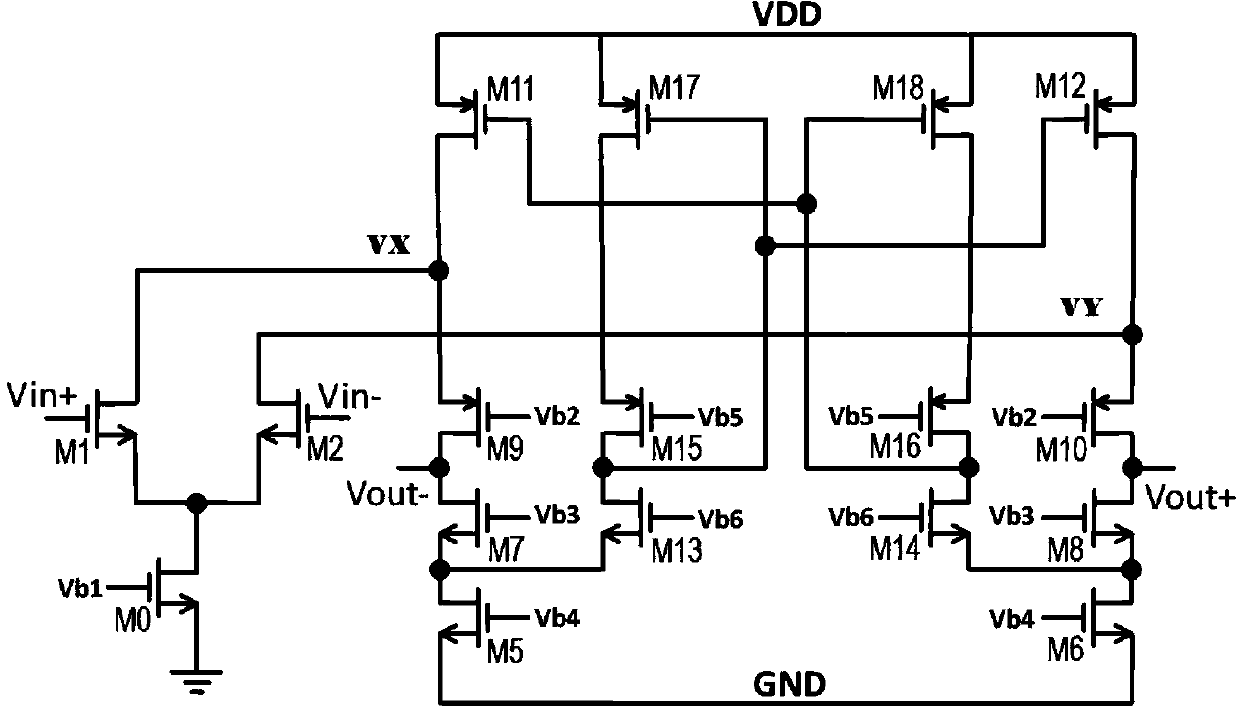
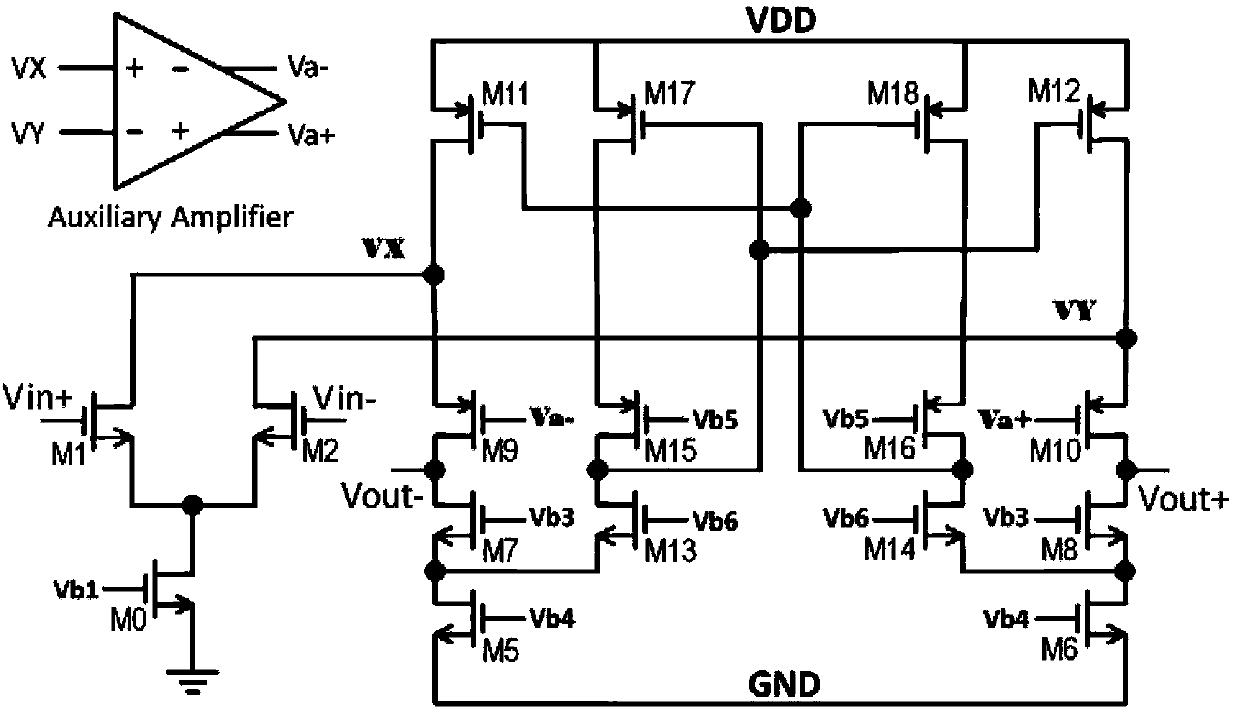
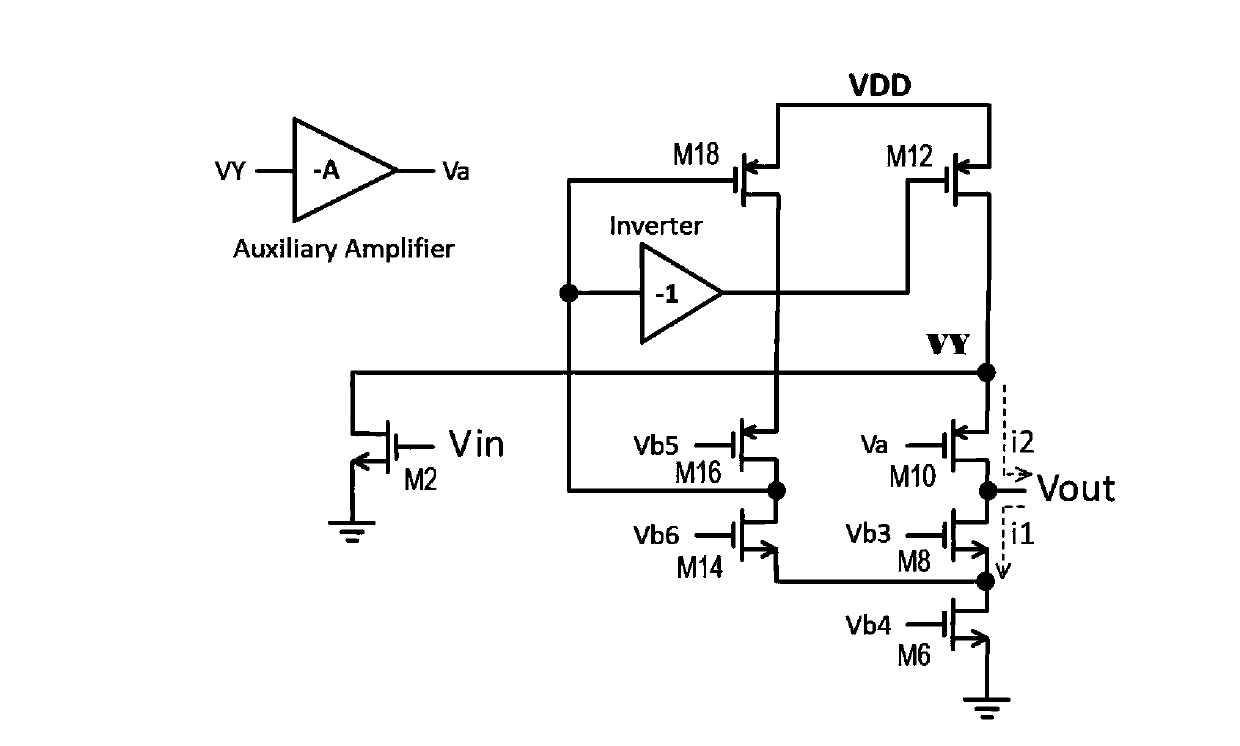
ActiveCN103973243ALarge DC open-loop voltage gainHigh DC open-loop voltage gainDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesCMOSAudio power amplifier
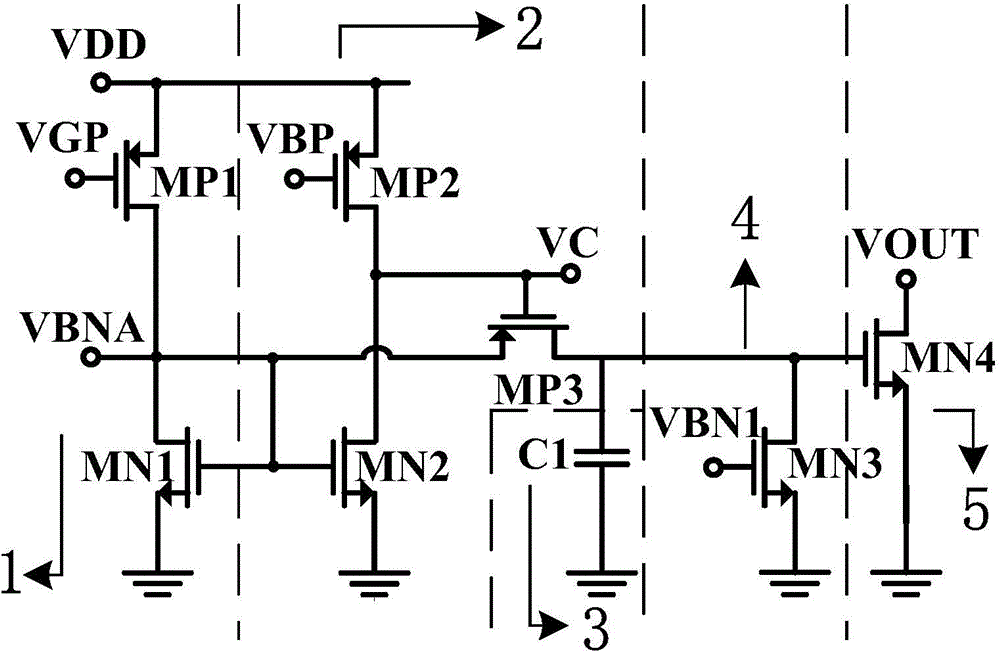
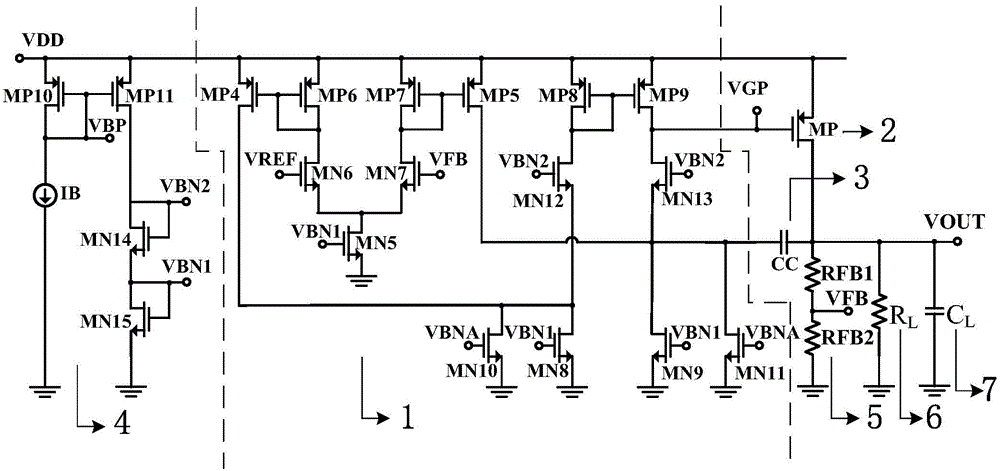
The invention provides a CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) operation amplifier with great direct-current open-loop voltage gain. The CMOS operation amplifier comprises a first transistor M0, a second transistor M1, a third transistor M2, a fifth transistor M5, a sixth transistor M6, a seventh transistor M7, an eighth transistor M8, a ninth transistor M9, a tenth transistor M10, an eleventh transistor M11, a twelfth transistor M12, a thirteenth transistor M13, a fourteenth transistor M14, a fifteenth transistor M15, a sixteenth transistor M16, a seventeenth transistor M17 and an eighteenth transistor M18. A feedback loop is formed by the operation amplifier through the transistors M13-M18. Compared with a traditional folding common-source and common-gate amplifier, the CMOS operation amplifier has the advantages of high DC open-loop voltage gain, wide unit gain band width, short built-up time and less power consumption.
Owner:西安电子科技大学重庆集成电路创新研究院
Full-integration UHF-RFID reader-writer radio frequency reception front end circuit working in 860-960MHz
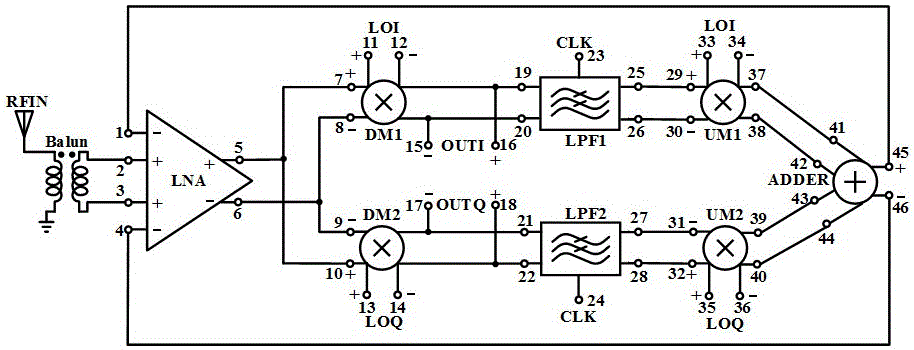
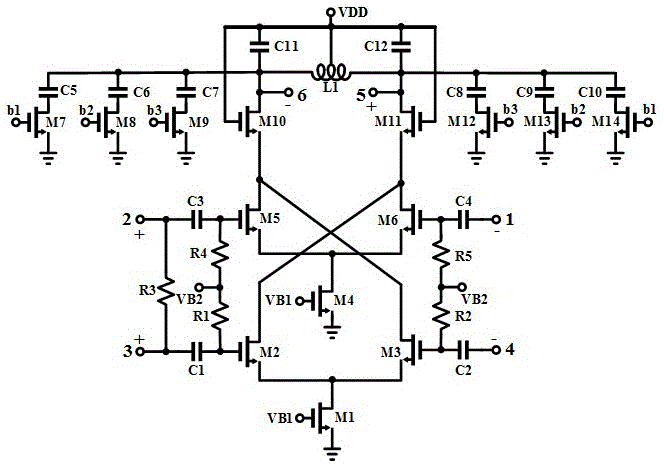
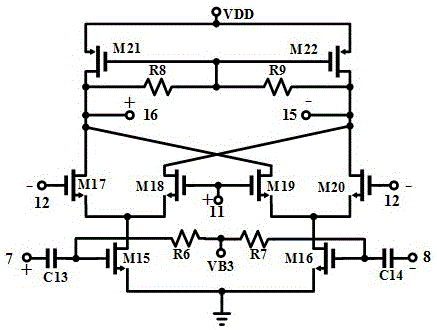
ActiveCN105139049AImprove linearityHigh sensitivityCo-operative working arrangementsFrequency mixerReader writer
The invention discloses a full-integration UHF-RFID reader-writer radio frequency reception front end circuit working in 860-960MHz, consisting of four-input cross coupled difference low noise amplifier LNA, an I path lower mixer DM1, a Q path lower mixer DM2, a I path low-pass filter LPF1, a Q path low-pass filter LPF2 and an orthogonal upper mixer, wherein the orthogonal upper mixer comprises an I path upper mixer UM1, a Q path upper mixer UM2 and a summator ADDER. The invention mixes carrier leakage and label signals downwardly to low frequency, and the label signals are removed through the low-pass filter to maintain direct current; the direct current is converted to a carrier frequency band through the upper mixer; the carrier frequency band and the label signal containing the carrier leakage go through the difference low noise amplifier, and the carrier leakage signal is offset and the label signal is amplified. In the 10 dBm carrier leakage situation, the conversion gain in the working frequency band of 860-960MHz is higher than 26dB, the noise coefficient is smaller than 24dB, the sensitivity is superior to -86dBm, the time consumed by the carrier for offset is smaller than 15Mus, and all requirements for communication speed of the UHF RFID are satisfied.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com