Patents
Literature
50 results about "Extracellular metabolite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bacillus amyloliquefacien for degrading aflatoxin B1 in peanut meal
ActiveCN103966147AGrowth inhibitionInhibitionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismBacillus amyloliquefaciens
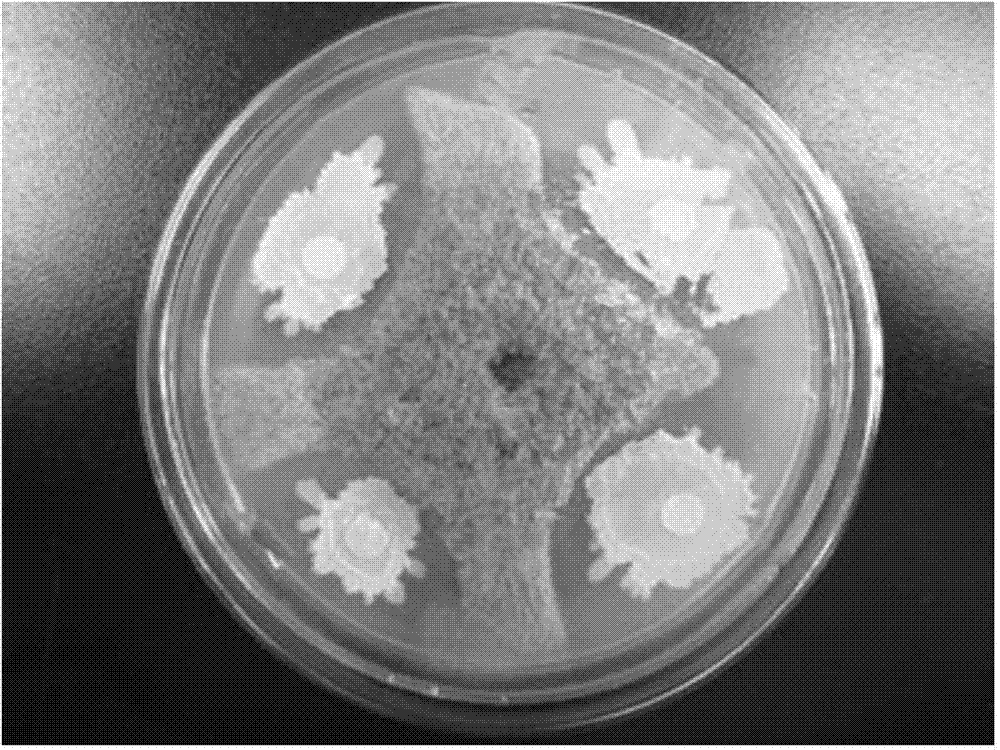
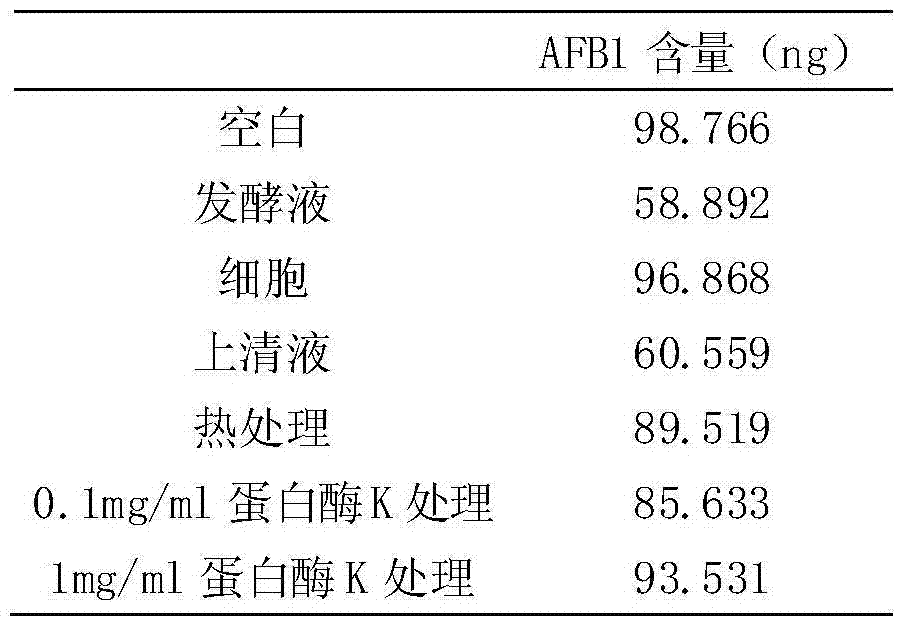
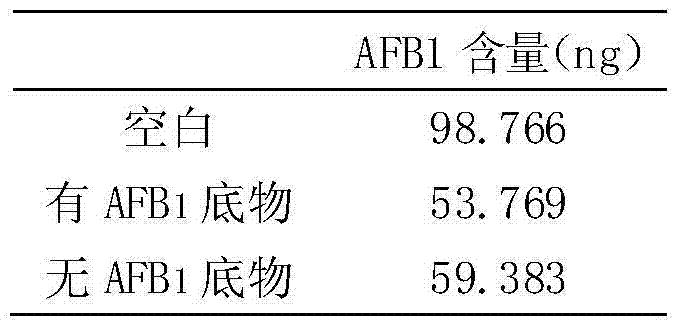
The invention discloses a bacillus amyloliquefacien for degrading aflatoxin B1 in peanut meal, and belongs to the technical field of applied microbiology. According to the invention, a bacillus amyloliquefacien capable of significantly inhibiting the growth of Aspergillus flavus and efficiently degrading aflatoxin B1 can be obtained by screening and the content of aflatoxin B1 in detoxified peanut meal is lower than the national limited standard and achieves the safe feeding level after the bacillus amyloliquefacien is applied to moldy peanut meal. Furthermore, the detoxification mechanism of the strain is the degradation effect of extracellular metabolites, and generation of the active substance is of a non-induced type, which is an inherent attribute of the strain. The features of the strain provide the possibility for biocontrol of Aspergillus flavus and aflatoxin B1 in industries such as feed and foods and the strain has very high application values.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for promoting chlorella growth and oil accumulation by carrying out co-culture of alga and bacterium
ActiveCN109609382ANormal growthEfficient oil productionBacteriaUnicellular algaeBacteroidesNormal growth
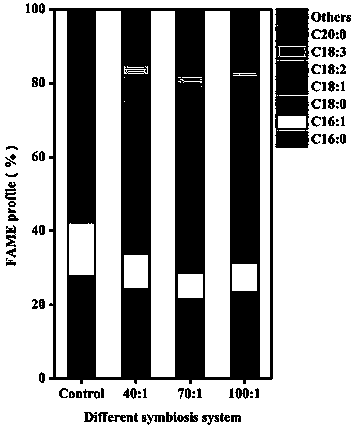
The invention discloses a method for promoting chlorella growth and oil accumulation by carrying out co-culture of an alga and a bacterium. The method for promoting chlorella growth and oil accumulation by carrying out co-culture of the algae and the bacterium specifically comprise a step of co-culturing chlorella with Mesorhizobium sp. (a nitrogen-fixing bacterium) in certain proportion, so that,oxygen and extracellular metabolites released by the chlorella during growth process can be consumed by the Mesorhizobium sp. while carbon dioxide is metabolized by the Mesorhizobium sp. for photosynthesis of the chlorella cells; moreover, growth stimulators, including vitamins, glycopeptides and the like, are also released so as to promote growth of the chlorella. In addition, nitrogen-fixing capability of the Mesorhizobium sp. is further utilized so as to realize limited nitrogen supply; and thus, normal growth of the chlorella is ensured with efficient oil production of the chlorella cellsrealized.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Bacillus atrophaeus for prevention and control of cotton boll blight, and microbial agent thereof
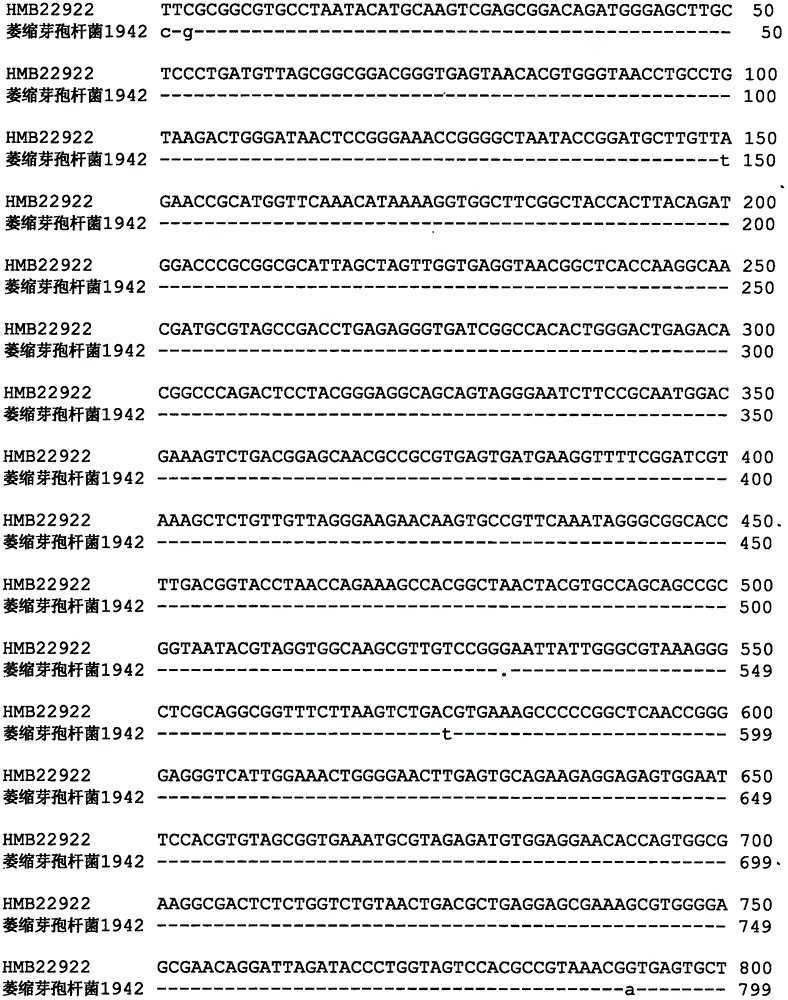
The present invention discloses a strain of Bacillus atrophaeus HMB22922 for prevention and control of cotton boll blight, wherein the strain is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on December 20, 2011, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.5614. The present invention further discloses a microbial agent produced by using the strain, and a preparationmethod thereof. Active ingredients of the microbial agent are HMB22922 thallus and extracellular metabolites thereof. The HMB22922 strain of the present invention provides special prevention and control effects for cotton boll blight, wherein the prevention and control efficiency is high, and the average prevention and control efficiency is more than 80%. The microbial agent of the present invention is safe for human and animals, and does not cause environmental pollution. Drug resistance is not easily generated when the strain and the microbial agent are adopted to prevent and control the cotton boll blight. In addition, the preparation method for the microbial agent of the present invention has characteristics of simpleness, low cost, and easy use.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Soil bacilli for preventing and controlling fruit tree crown gall and inocula thereof and preparation method
InactiveCN101451112AImprove efficiencyNo pollution in the processBiocideBacteriaMetaboliteTherapeutic effect
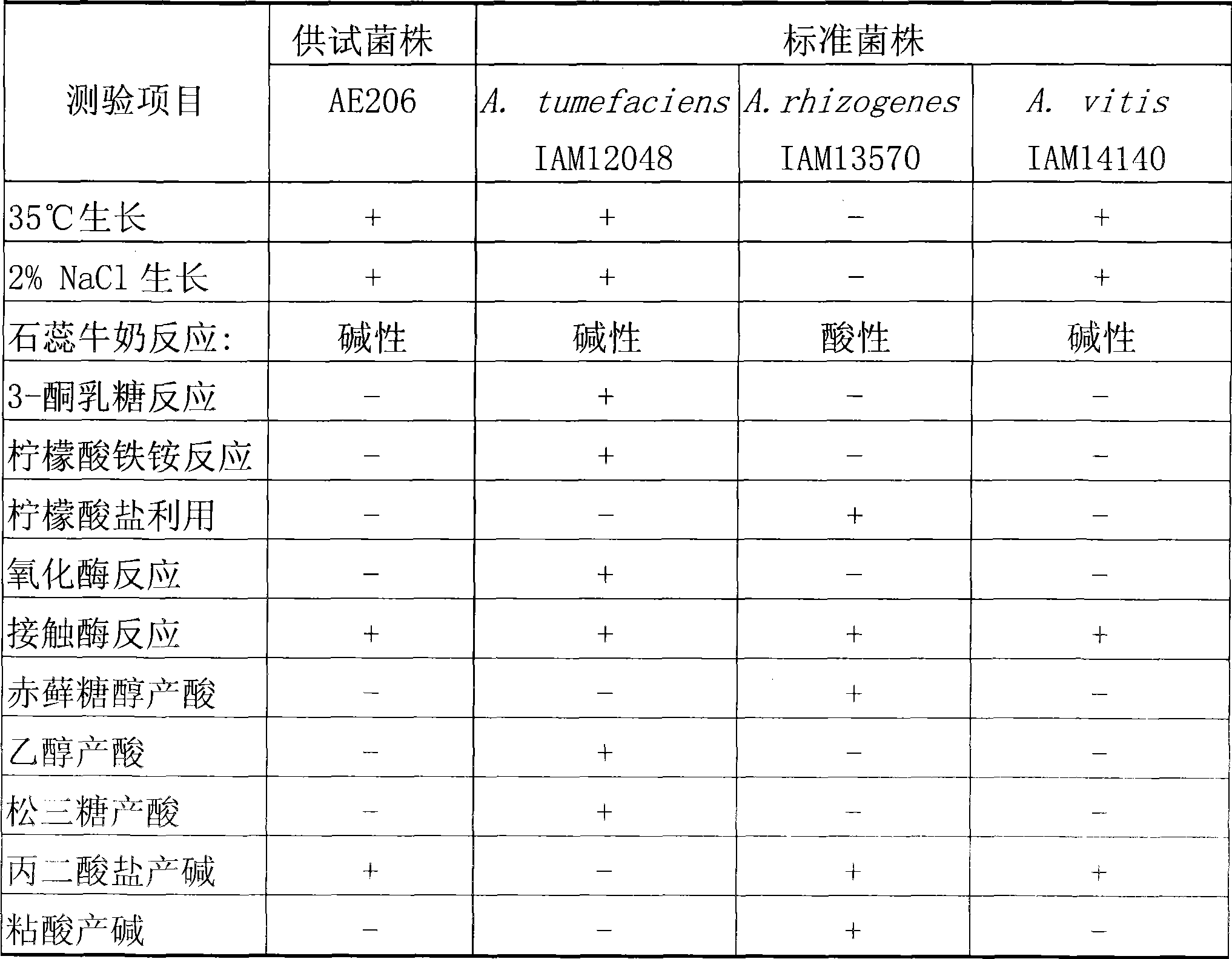
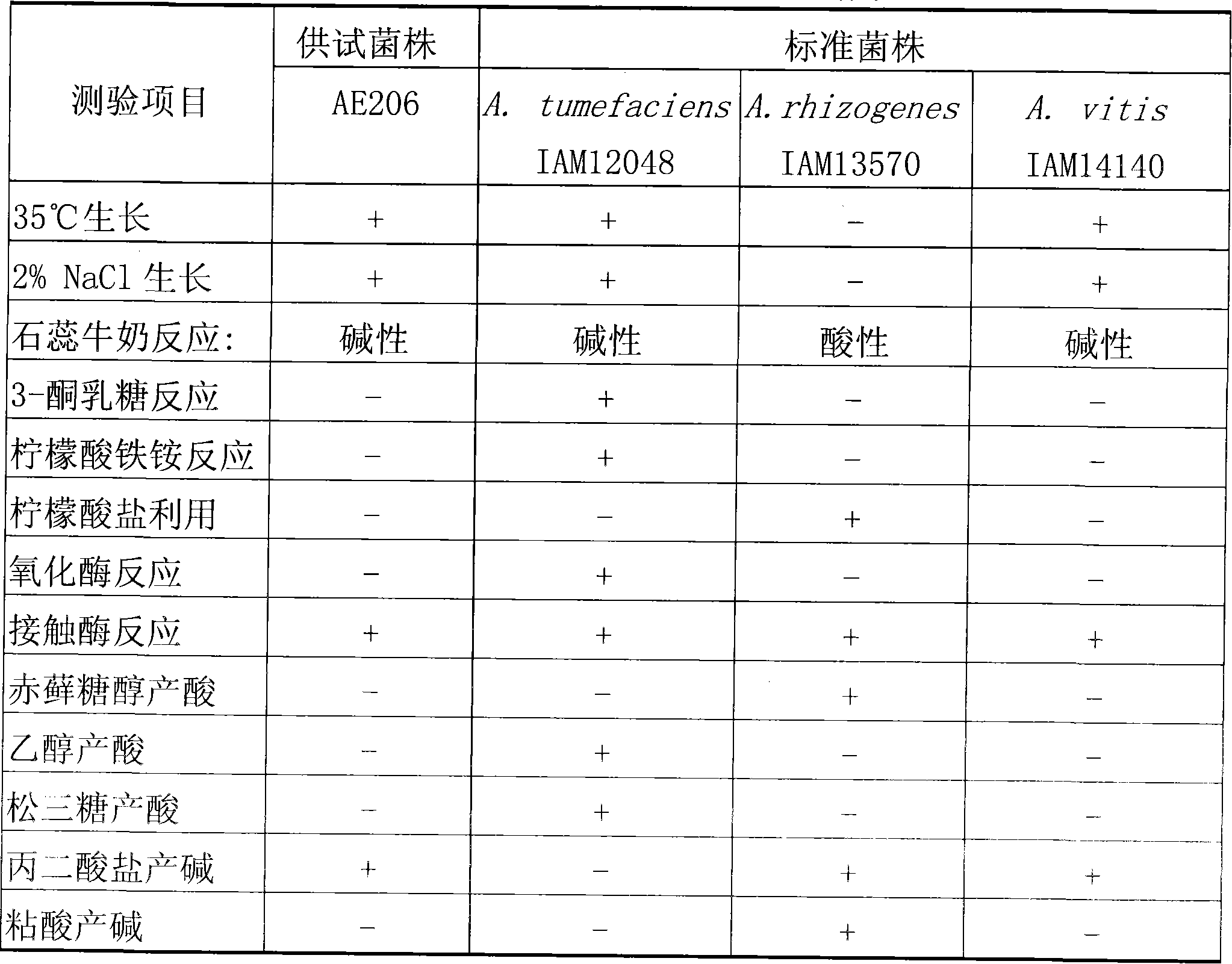
The invention discloses an agrobacterium vitis strain AE206. The strain is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, and has a preserving registration number of CGMCC No.2408. The invention also discloses a microbial preparation and a preparation method thereof. The active ingredients of the preparation are AE206 thalli and extracellular metabolite of the AE206 thalli. The agrobacterium vitis AE206 has good prevention and treatment effect on grape crown gall, has wide antimicrobial spectrum, and has good prevention effect on peach crown gall and cherry crown gall. Moreover, the microbial preparation belongs to a biological agent, and has the characteristics of non-pollution, non public nuisance, low cost and so on.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Bacillus mojavensis and microorganism bacterium agent thereof for controlling cucumber downy mildew
The invention discloses a Bacillus mojavensis strain HMB20199 for controlling cucumber downy mildew, wherein the Bacillus mojavensis strain HMB20199 is preserved in China Microbial Culture Collection Management Center on December 20th, 2011, with the preservation number of CGMCC No.5617. The invention also discloses a microorganism bacterium agent produced by using the HMB20199 and a preparation method of the microorganism bacterium agent. Active components of the microorganism bacterium agent are the Bacillus mojavensis HMB20199 thallus and extracellular metabolites thereof. The HMB20199 strain disclosed by the invention is strong in specificity in controlling of the cucumber downy mildew and high in control efficiency, wherein the average control efficiency is over 85 percent; and moreover, the drug resistance is not easily generated by controlling the cucumber downy mildew through the Bacillus mojavensis strain HMB20199. In addition, the microorganism bacterium agent has no harm topeople or livestock and does not pollute the environment. The preparation method of the microorganism bacterium agent is simple, low in cost and convenient in use.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Biological storage agent for edible fungi, preparation method of biological storage agent and edible fungi preservative paper
ActiveCN103651774AExtended shelf lifeEfficient storageFruit and vegetables preservationBiotechnologyBiological storage
The invention relates to a biological storage agent for edible fungi, and in particular relates to the biological storage agent for edible fungi, a preparation method of the biological storage agent and a piece of edible fungi preservative paper. The biological storage agent comprises extracellular metabolite containing bacillus subtilis BSD-2 which is preserved in Chinese Common Microbe Bacterial Preservation Administration Center with the preservation No. of CGMCC No.8440, and the preservative paper with excellent preservation effect is developed. The biological storage agent can be applied to storage of the edible fungi, so as to obviously reduce brown stain of the edible fungi, and prolong the preservation time for 8-15 days at low temperature. The biological storage agent is free from other chemical components and pollution, is environment-friendly and safe, and further suitable for postharvest preservation and freshness of other vegetables and fruit, and can be widely popularized and applied.
Owner:河北绿茵生化科技有限公司
Microbial preparation for degrading aflatoxin and application
ActiveCN109161497AEfficient degradation abilityPromote degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyExtracellular metabolite
The invention discloses a microbial preparation for degrading aflatoxin and application, and belongs to the technical field of aflatoxin detoxification. An active ingredient of the microbial preparation for degrading the aflatoxin, which is disclosed by the invention, is a bacillus siamensis bacterium suspension or a culture of a bacillus siamensis whole culture solution or a crude extract of bacillus siamensis or an extracellular metabolite of the bacillus siamensis; and the bacillus siamensis is bacillus siamensis A2025 and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture CollectionCenter on April 12, 2018, the preservation number is CGMCC NO:15611, the address is No. 3, No. 1 Courtyard, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, and the preservation requiring institution is Shandong Peanut Research Institute. The bacillus siamensis A2025 disclosed by the invention has a high-efficiency degrading effect on the aflatoxin.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
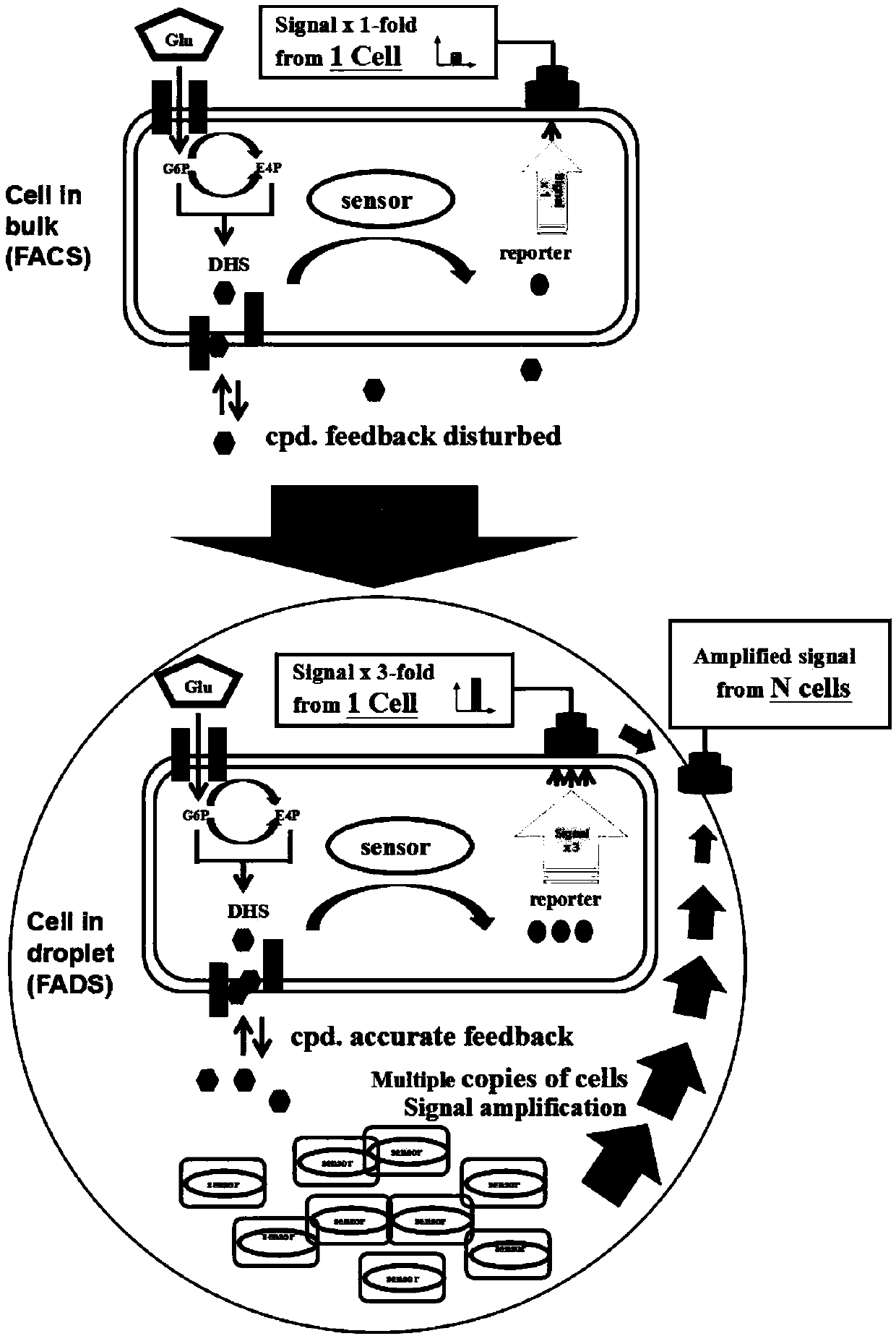
High-flux screening method based on biosensor
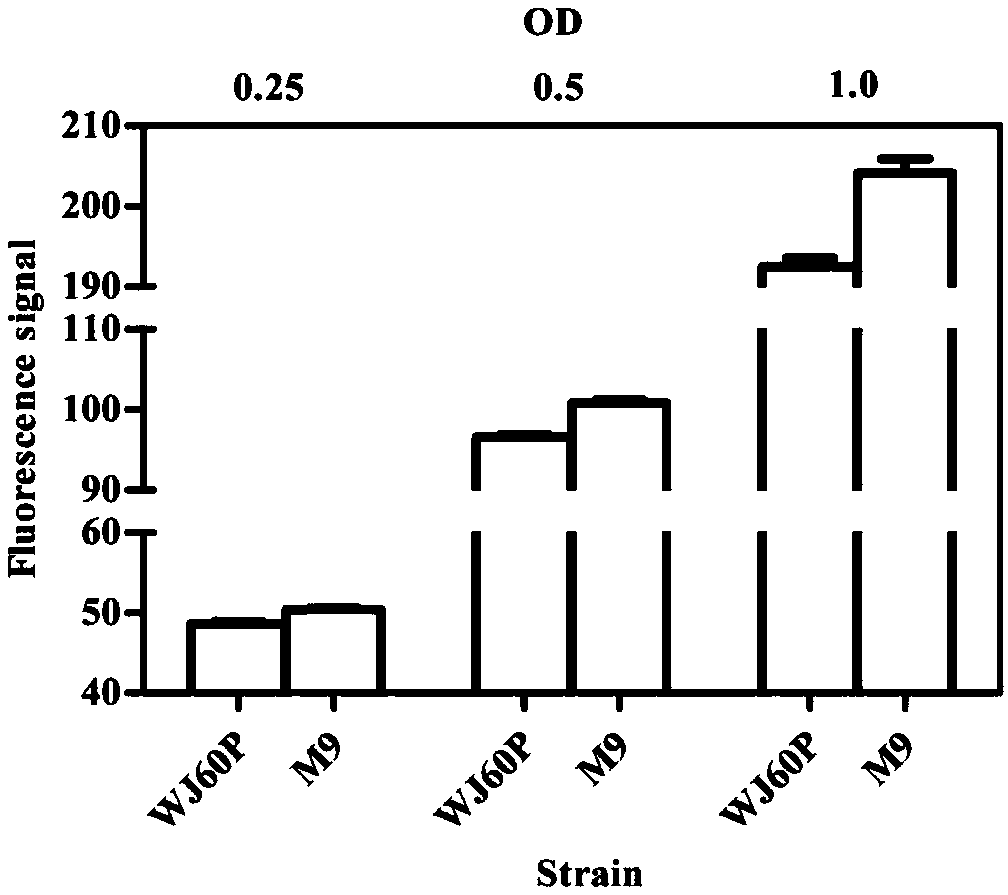
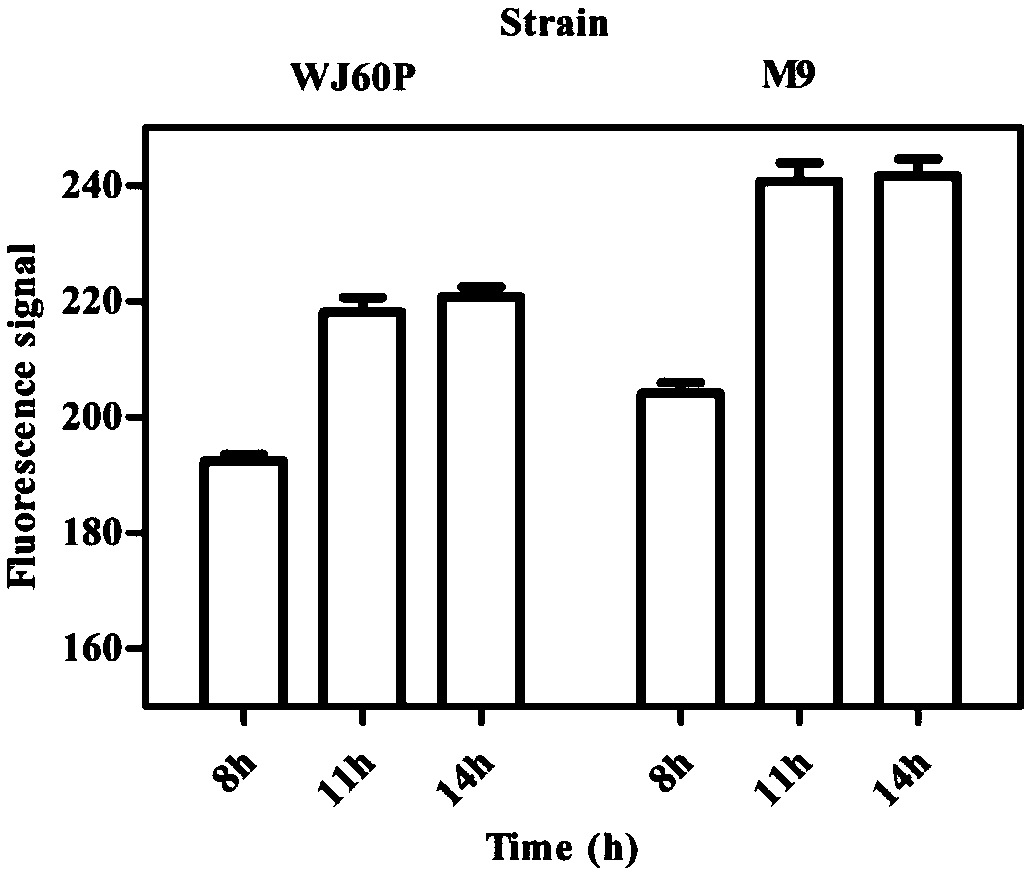
ActiveCN109679886AImprove the level ofFluorescence signal difference, increased fluorescence signal difference between dropletsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFluorescenceHigh flux
The invention discloses a high-flux screening method based on a biosensor, and belongs to the technical field of high-flux screening. A way of embedding biosensor-containing cells by liquid drops is adopted to carry out high-flux screening on a metabolite micromolecule 3-dehydrogenation shikimic acid cell factory to realize the efficient enrichment of 3-dehydrogenation shikimic acid high-yield bacterial strains. Compared with a single cell level screening method for combining the biosensor with a flow cytometer, on the one hand, the high-flux screening method disclosed by the invention utilizes the augmentable enrichment characteristics of cells in the liquid drops to enlarge an inter-unicellular fluorescence signal difference for N times to a difference among cell groups; on the other hand, through the characteristics that the liquid drops are used for isolating single cells and secretory products thereof, the influence of other cells and secretory products is eliminated, reductive cells and extracellular metabolite secreted by the reductive cells are truly communicated and fed back; through the above improvement, the screening sensitivity of the profitable positive clone bacterial strains can be effectively improved, and the enrichment efficiency of the profitable positive clone bacterial strains is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
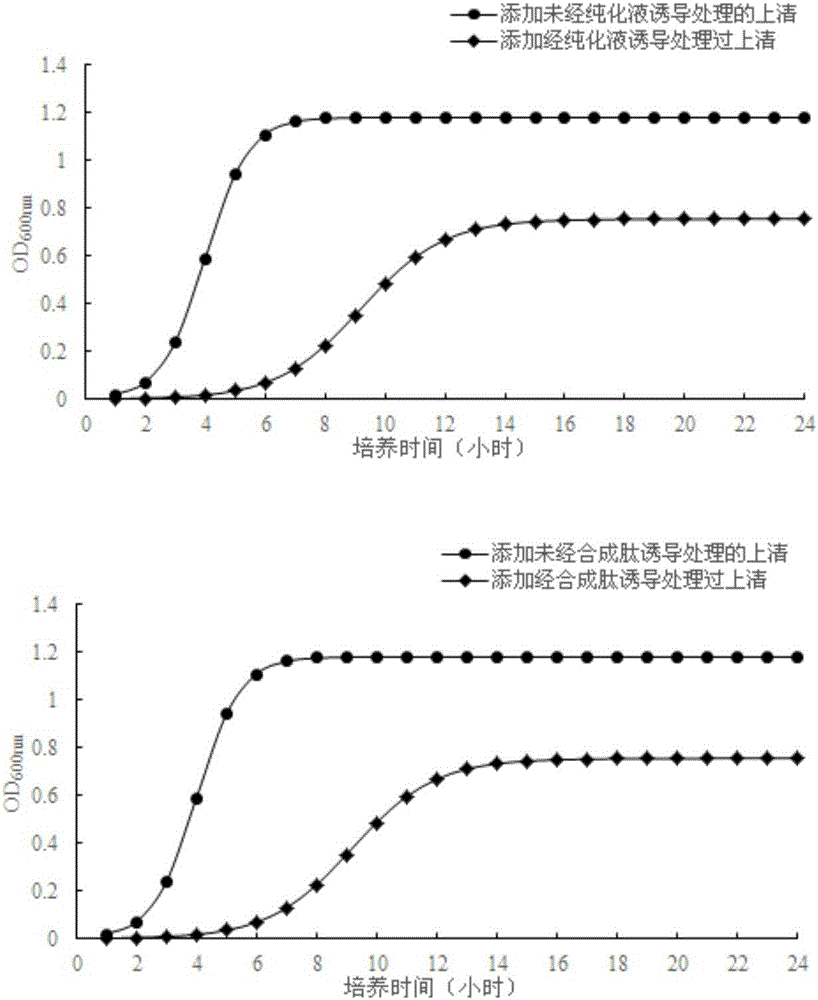
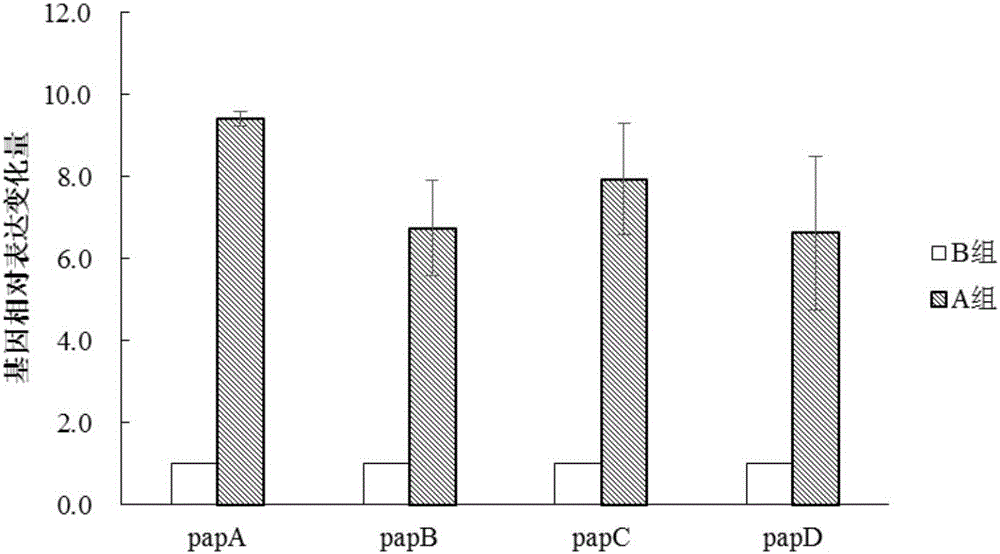
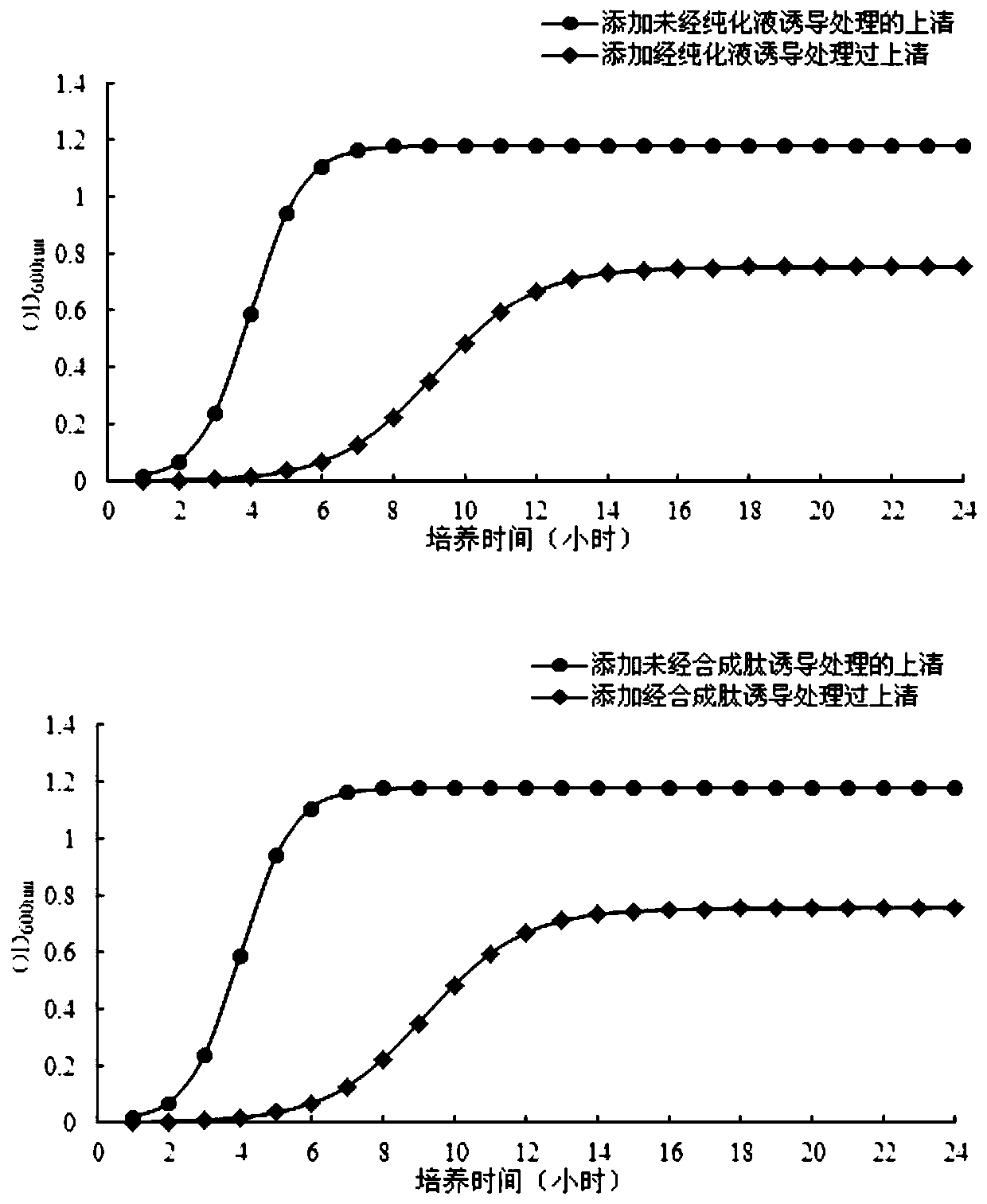
Polypeptide and lactobacillus plantarum extracellular metabolite, application thereof, method for inducing lactobacillus plantarum to produce bacteriocin and identification method
ActiveCN106188252AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
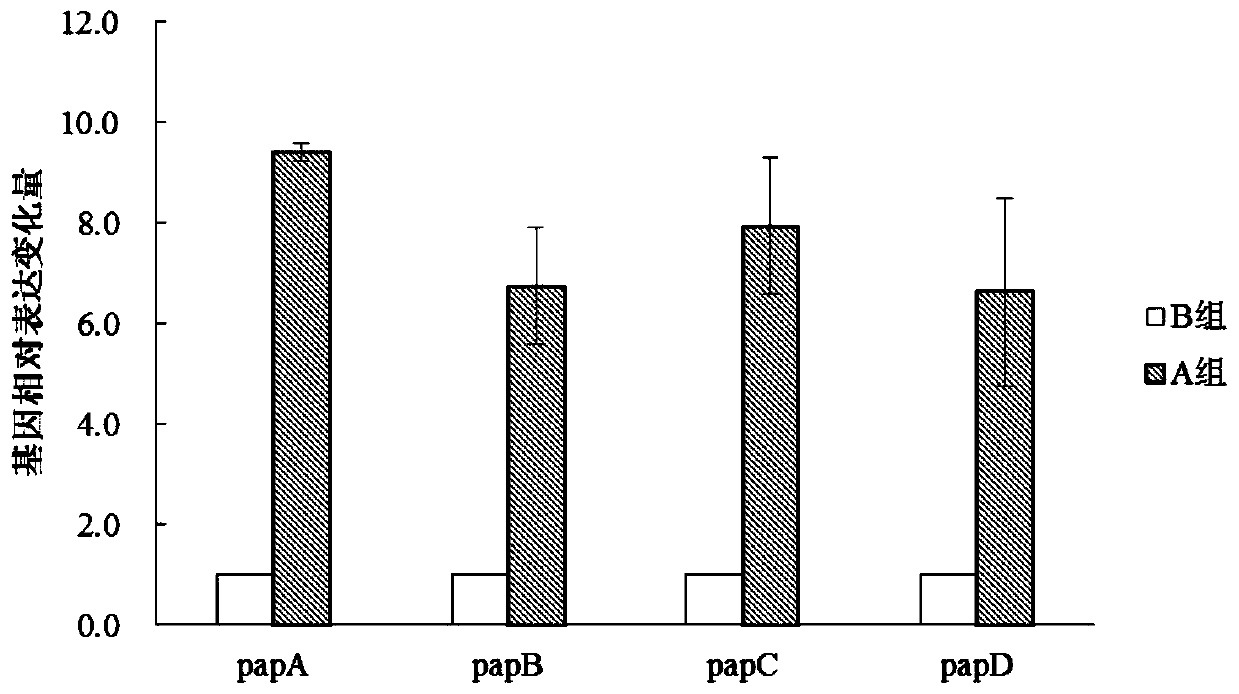
Relating to the field of microorganism, the invention discloses a polypeptide and a lactobacillus plantarum extracellular metabolite, application thereof, a method for inducing lactobacillus plantarum to produce bacteriocin and an identification method. The invention specifically relates to a polypeptide shown as SEQ ID NO:1, a lactobacillus plantarum extracellular metabolite containing the polypeptide and a preparation method, application of the polypeptide and / or lactobacillus plantarum extracellular metabolite in inducing lactobacillus plantarum to produce bacteriocin, a method for inducing lactobacillus plantarum to produce bacteriocin and an identification method of bacteriocin-producing lactobacillus plantarum. The polypeptide and / or lactobacillus plantarum extracellular metabolite can induce lactobacillus plantarum to express bacteriocin, the expression levels of the four genes papA, papB, papC gene and papD related to bacteriocin production in a lactobacillus plantarum gene are respectively increased by 9.41, 6.75, 7.94 and 6.63 times, thus indicating that adding of the polypeptide and / or lactobacillus plantarum extracellular metabolite can induce the expression of related genes in lactobacillus plantarum.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI
Microecological preparation used for preventing and treating apostichopus japonicus putrid skin syndrome and preparation method of microecological preparation
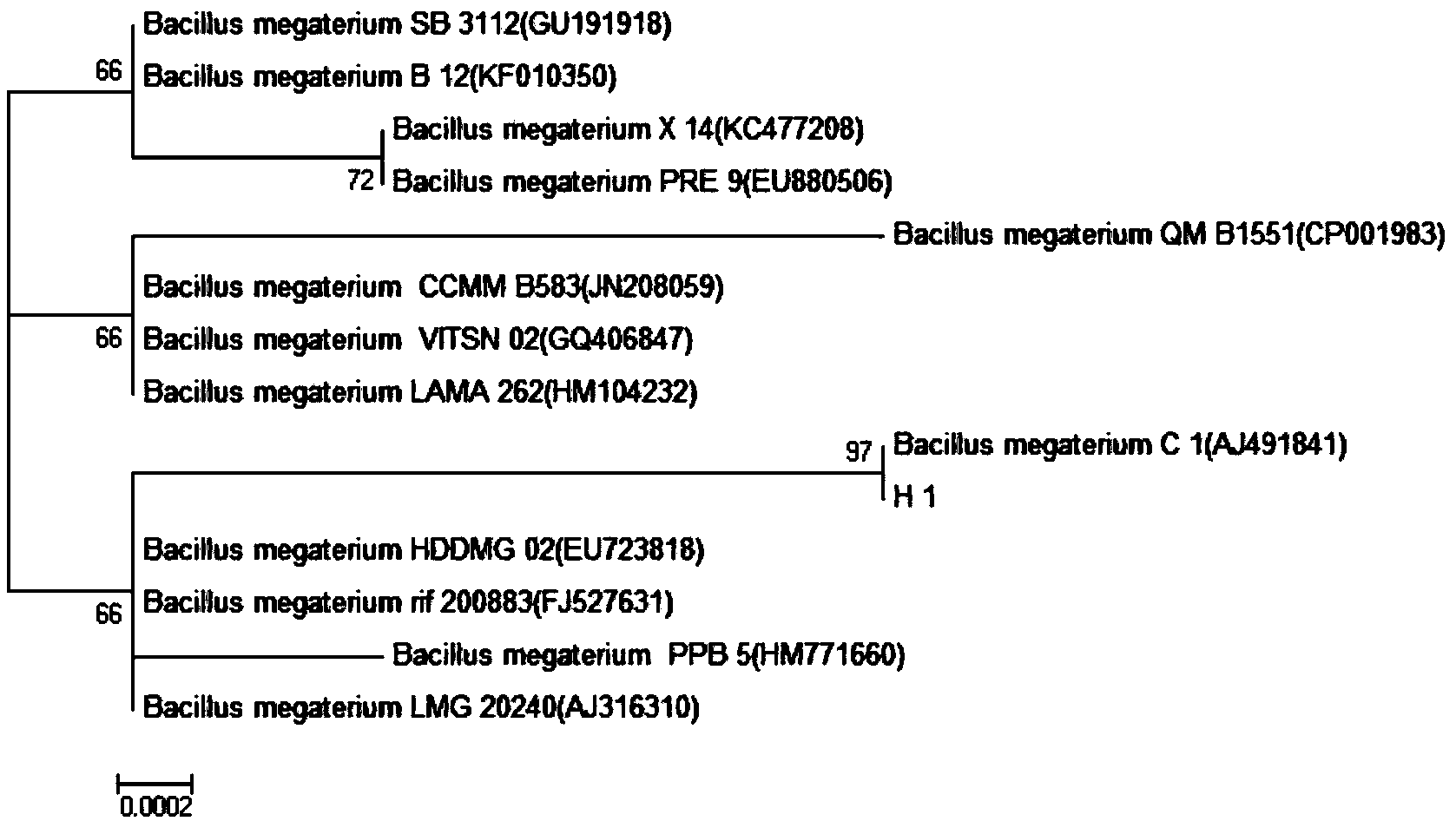
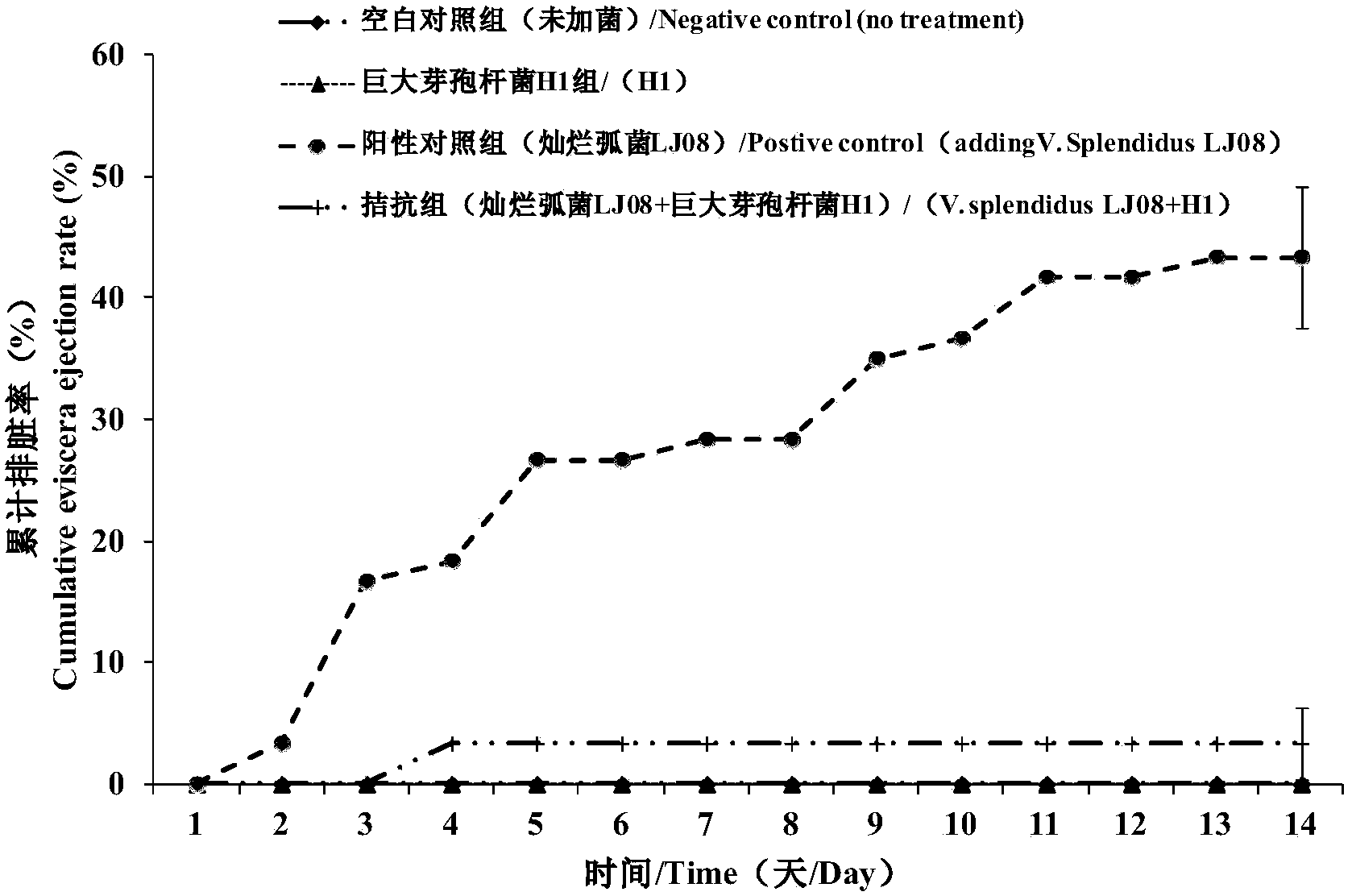
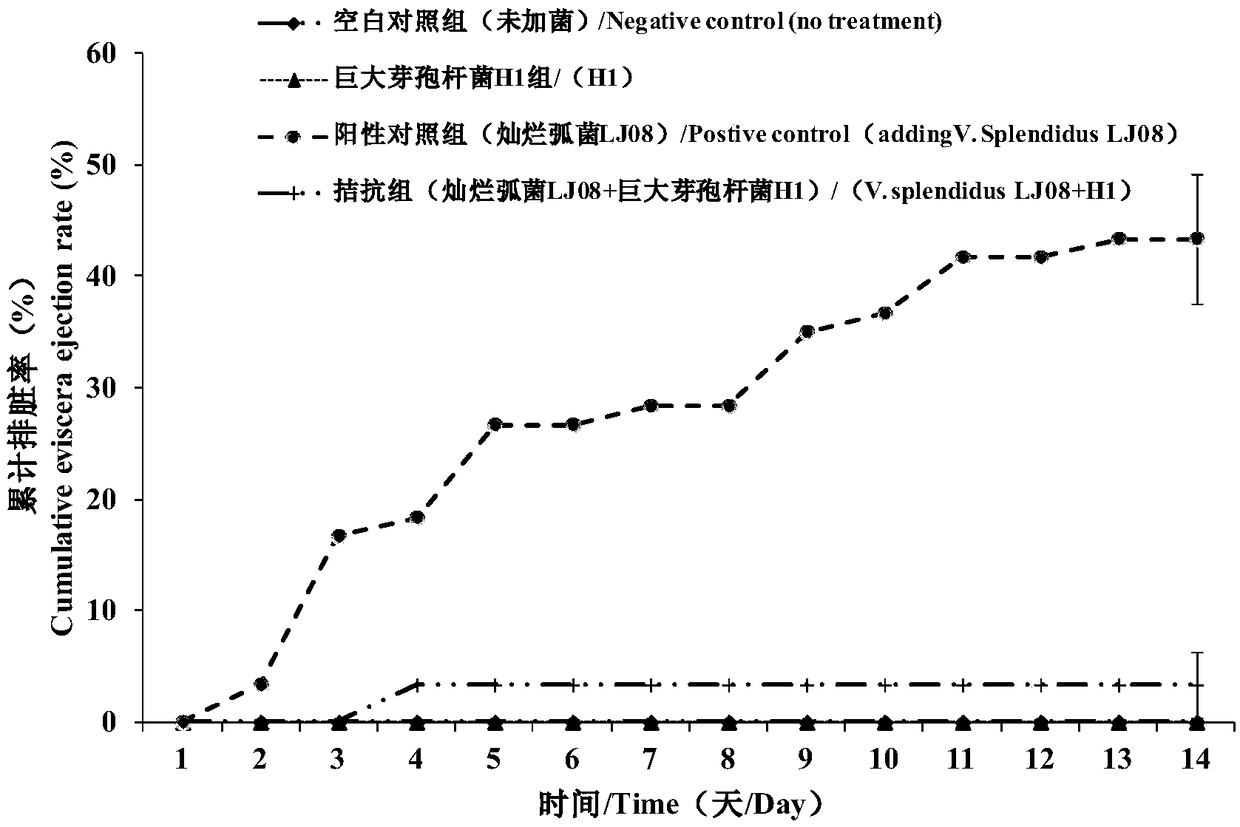
The invention relates to a microecological preparation used for preventing and treating apostichopus japonicus putrid skin syndrome and a preparation method of the microecological preparation and belongs to the field of aquatic microorganisms. Active ingredients of the microecological preparation are thalli of bacillus megatherium H1 and extracellular metabolites of the bacillus megatherium H1; the bacillus megatherium strain is separated from intestinal tract excrement of apostichopus japonicus which is healthily cultivated in Penglai, Shandong, detection of safety, bacteriostatic activity and toxicity and artificial antagonistic vibrio splendidus experiments verify that the bacillus megatherium H1 is antagonistic to vibrio splendidus, young apostichopus japonicus is effectively protected, the bacillus megatherium H1 can be used for preventing and treating apostichopus japonicus 'putrid skin syndrome' caused by vibrio splendidus and survival rate of an apostichopus japonicus seedling protecting stage is increased.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Special substrate for seedling of celeries
InactiveCN107522561AAdd application methodKeep aliveExcrement fertilisersBioloigcal waste fertilisersProlonium iodideSericulture
The invention mainly relates to the technical field of planting and discloses a special substrate for seedling of celeries. The special substrate is prepared from the following raw materials: straws, sheep manure, pig manure, fallen leaves, saw dust, bagasse, waste vegetable leaves, sericulture leftovers, plant ash, vermiculite, perlite, EM bacteria and prolonium iodide. The special substrate is balanced in nutrition and is favorable for absorption of seeds, so that the celery seeds germinate 2-3 days in advance, the germination rate is 84.7%, and the planting efficiency of the celeries is obviously improved; the straws, the sheep manure, the pig manure, the fallen leaves, the saw dust and the bagasse are smashed and then are transplanted into the EM bacteria for high-temperature fermentation, so that the multiplication of thalli is promoted, and the fermentation time is shortened; the waste vegetable leaves, the sericulture leftovers and the plant ash are added, and then the temperature is lowered for continuous fermentation, so that the accumulation of extracellular metabolites is promoted, the absorption of the seeds is facilitated, embryos are stimulated to grow, and the germinating time of the seeds is shortened.
Owner:界首市鸿飞家庭农场
Predicting the metabolic condition of a cell culture
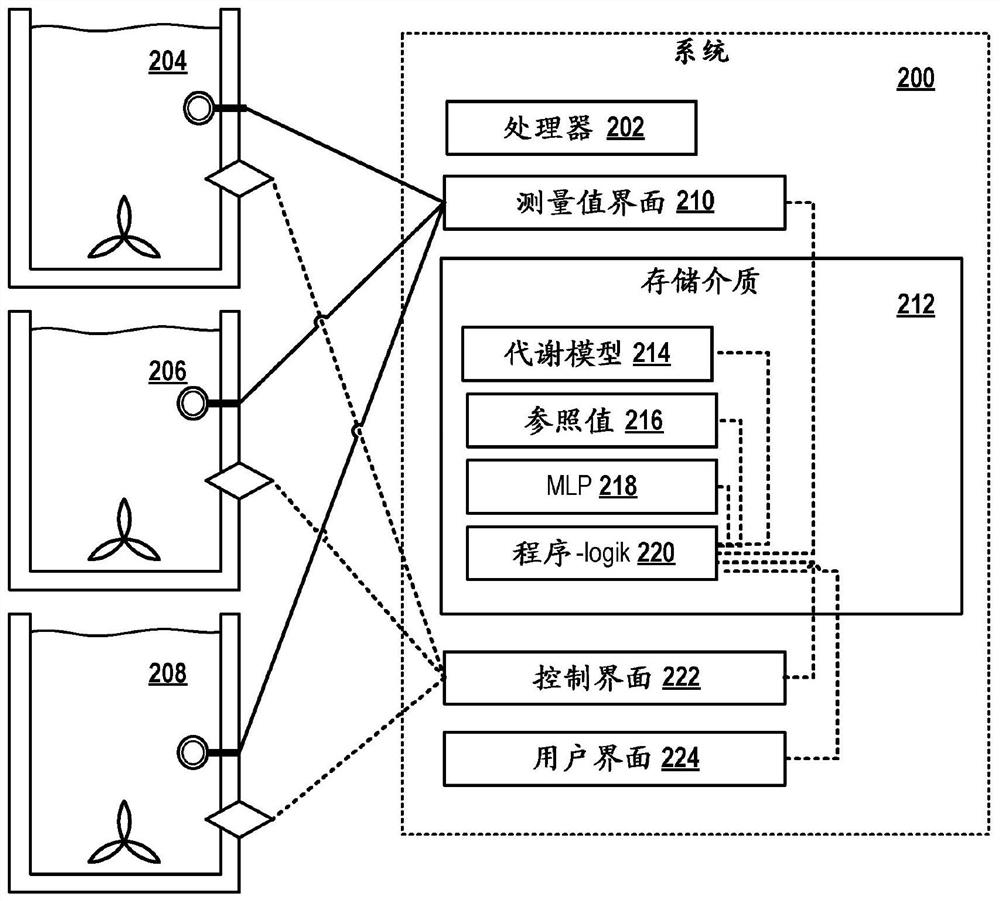
PendingCN112119306AReal-time prediction of metabolic statusBiochemistry apparatusCell culture mediaMetabolic ModelCell type specific
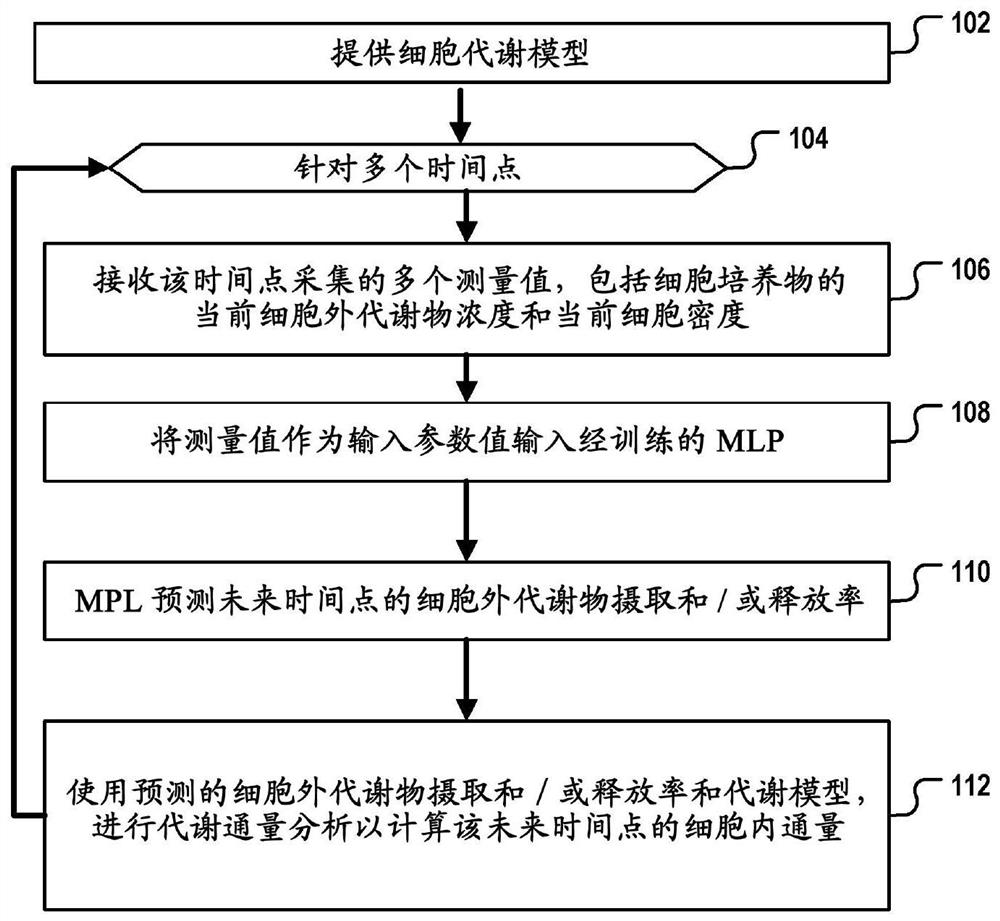
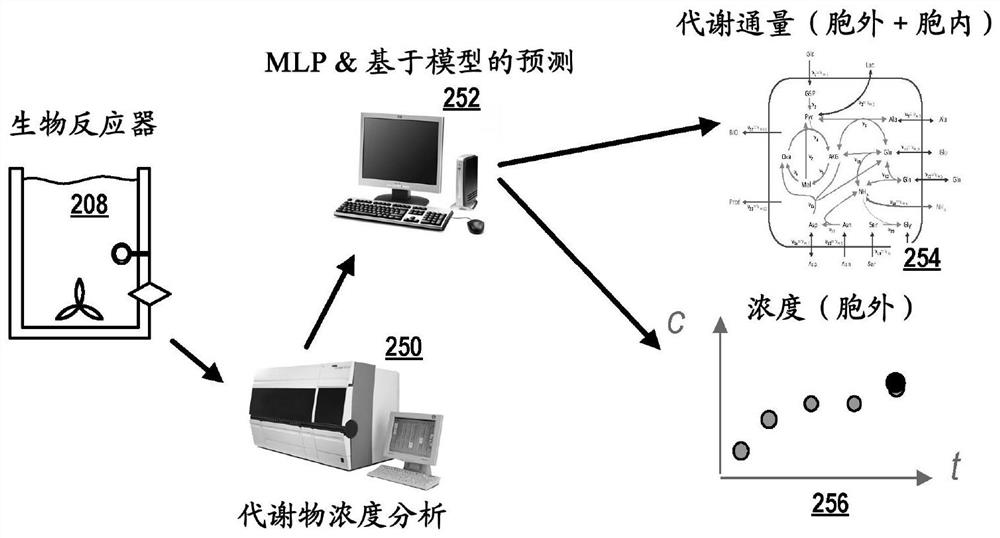
The invention relates to a method for predicting the metabolic condition of a cell culture of cells of a specific cell type. The method comprises providing (102) a metabolic model (402) of a cell of the specific cell type and carrying out the following steps at each of a plurality of points in time during the cultivation of the cell culture: receiving (106) measured concentrations of several extracellular metabolites and a measured cell density in the culture medium; inputting (108) the received measured values as input parameter values into a trained machine learning program logic-MLP (218);predicting (110) extracellular flows (408) of the extracellular metabolites at a future point in time by means of the MLP; carrying out (112) a metabolic flow analysis for calculating the intracellular flows at the future point in time on the basis of the predicted extracellular flows and the stoichiometric equations of the metabolic model.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Bacillus subtilis for preventing and treating cucumber ampho disease, and microbial agent thereof
The invention discloses a Bacillus subtilis strain HMB20428 for preventing and treating cucumber ampho disease, and the Bacillus subtilis strain HMB20428 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on December 20, 2011, and the preserving registration number is CGMCC No.5616. The invention further discloses a microbial agent prepared by the strain and a preparationmethod thereof. The active ingredients of the microbial agent are Bacillus subtilis HMB20428 thalli and extracellular metabolite of the Bacillus subtilis HMB20428 thalli. The strain HMB20428 has strong specificity for the cucumber ampho disease; the control effect is high; and the average control effect can reach above 85%; through the method provided by the invention for preventing and treating the cucumber ampho disease, drug resistance is difficult to generate; the microbial agent is safe to human and livestock, and is free of environment pollution; and the preparation method is simple, the cost is low, and the microbial agent is convenient to use.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Method for separating metabolite capable of inducing cucumber resisting powdery mildew from molecule modifying trichoderma harzianum
The invention relates to a process which is capable of inducing cucumbers to resist powdery mildew metabolites separated from trichoderma harzianum with lecular modification, which takes advantages of gene integration technique of restriction endonuclease mediated, constructs transformant of trichoderma harzianum by preparing strain protoplast of trichoderma harzianum and extracting plasmid, then the transformant is cultivated and fermented, extracellular metabolites of trichoderma harzianum transformant capable of systematic performance to induce cucumbers to resist powdery mildew are selected from the fermentation liquid. The extracellular metabolites of trichoderma harzianum transformant of the invention can overcome the weakness that living trichoderma harzianum is not stable in induced resistance effect. The invention not only has remarkable control effect to powdery mildew, but also facilitates growth of cucumber seedlings, and provides an efficient process for rapidly and highly efficiently selecting novel microbial pesticide guide compound from trichoderma harzianum for preparation of green molecular pesticide.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
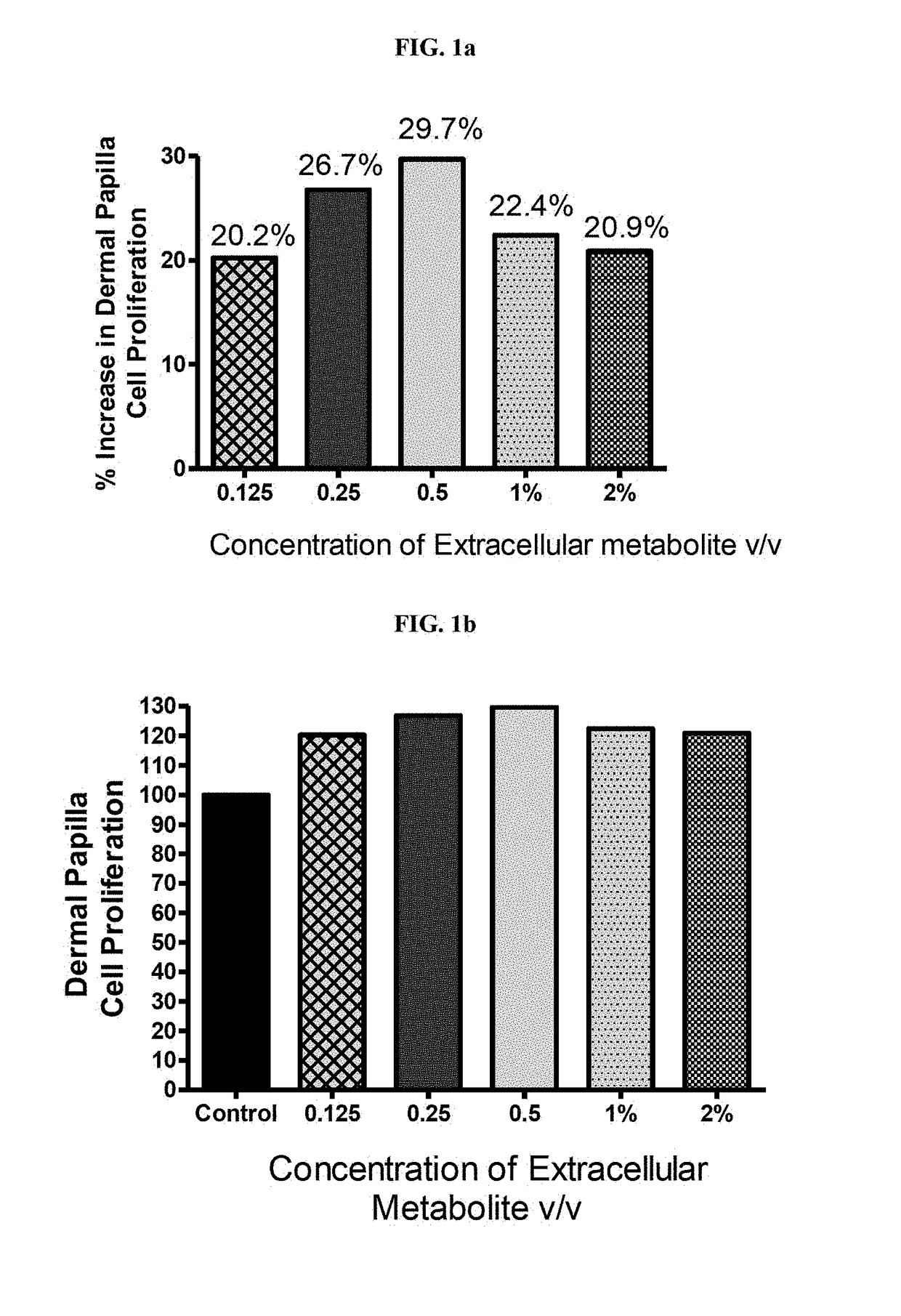
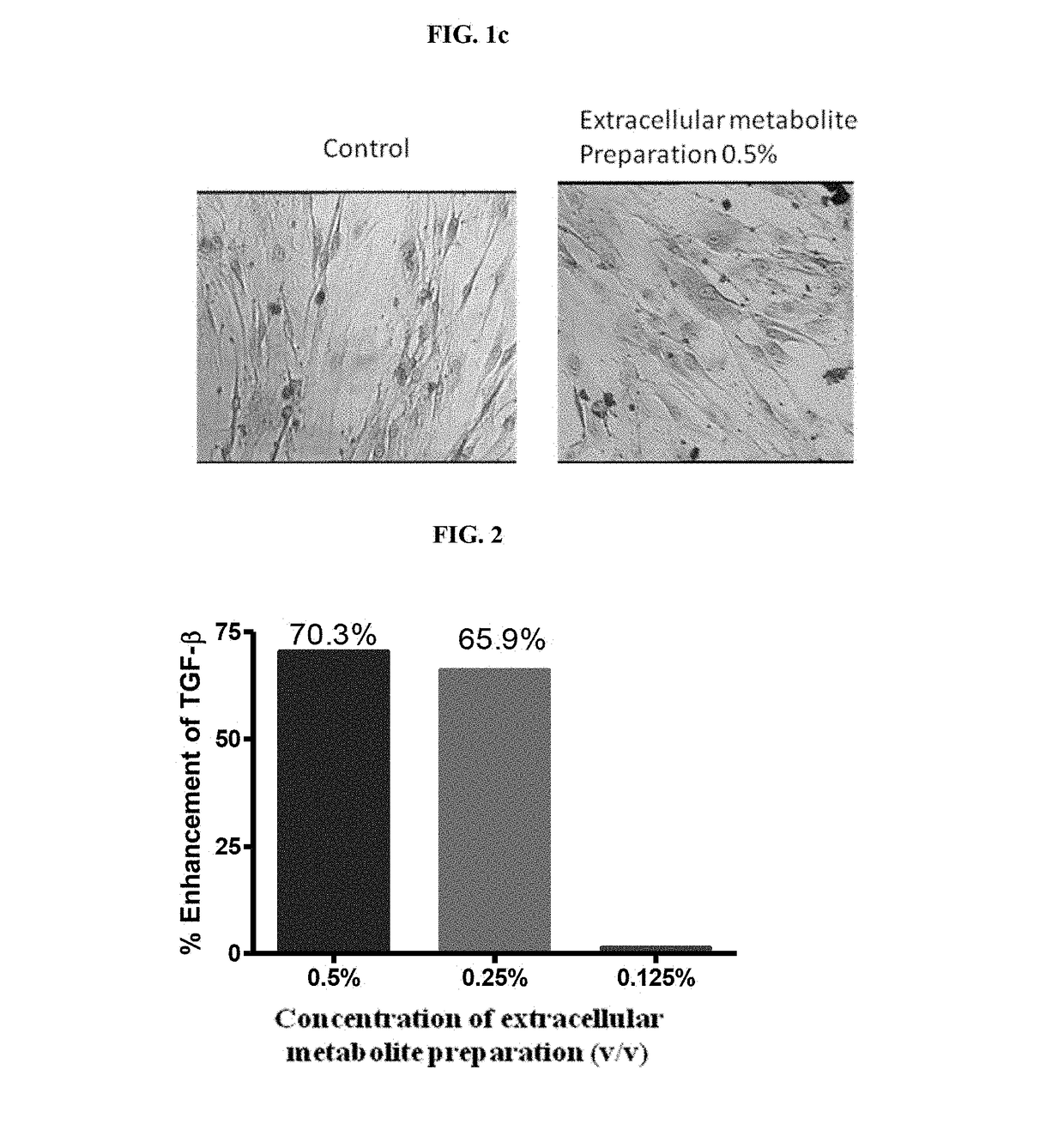
Anti-aging potential of extracellular metabolite isolated from bacillus coagulans mtcc 5856
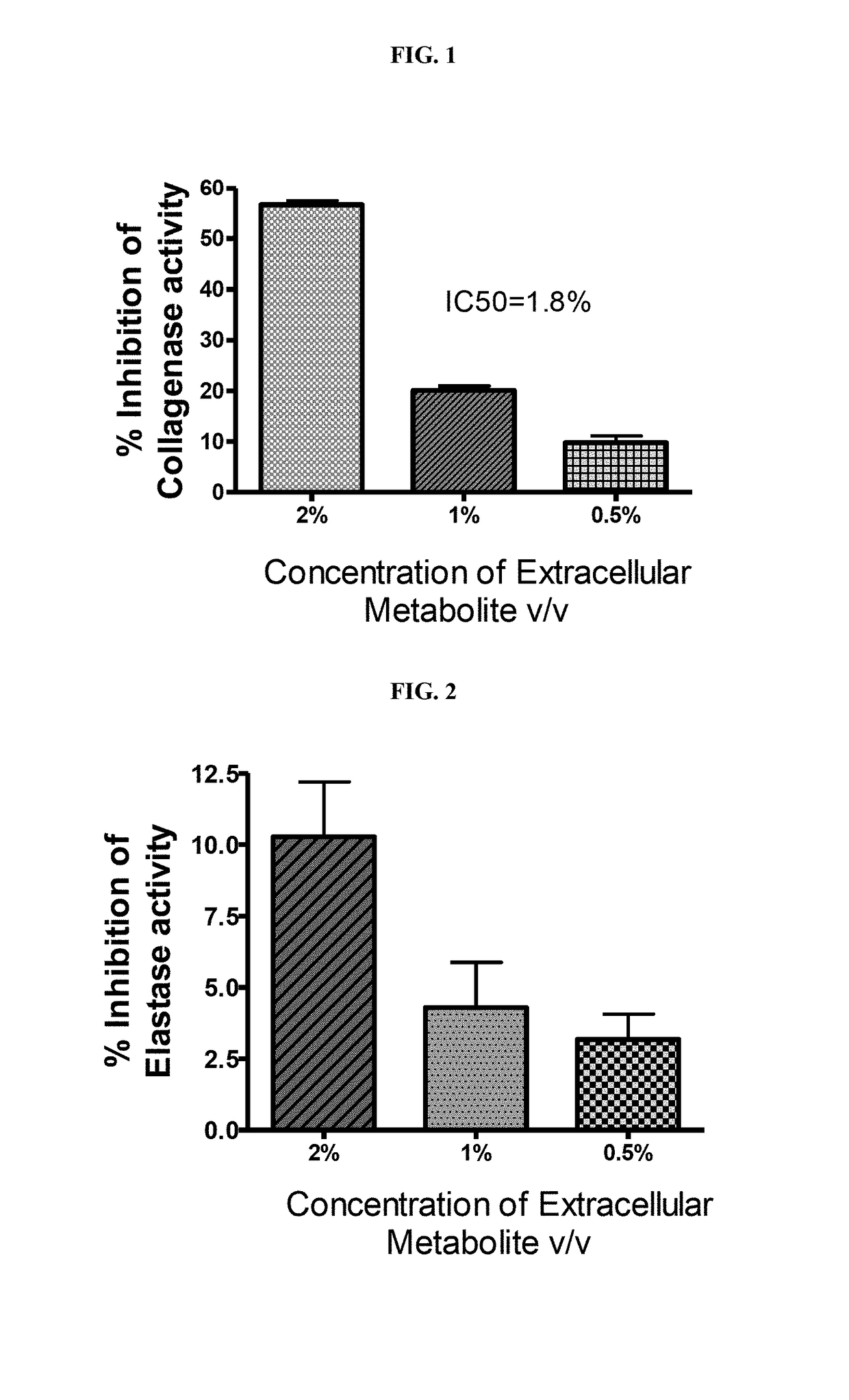
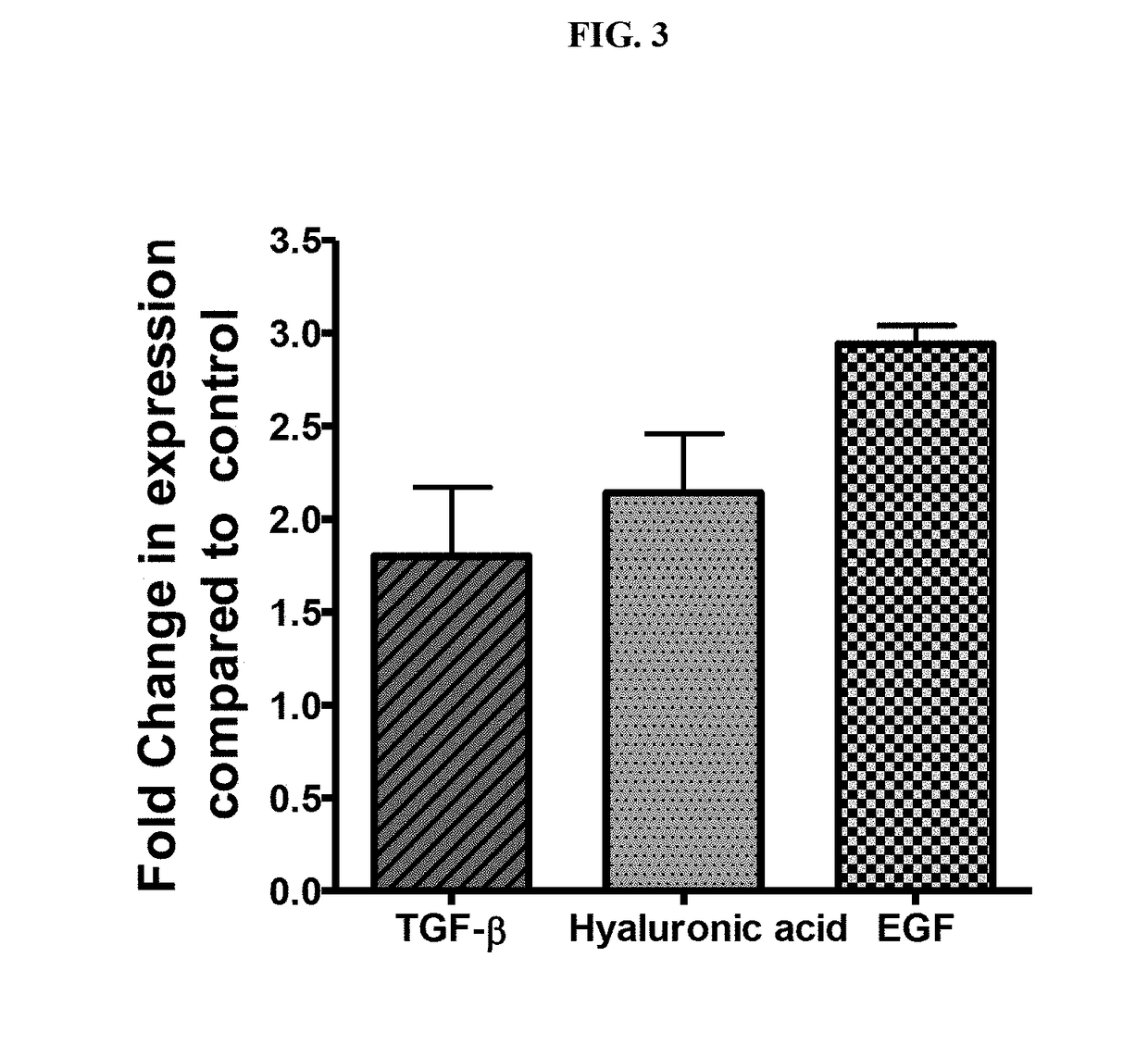
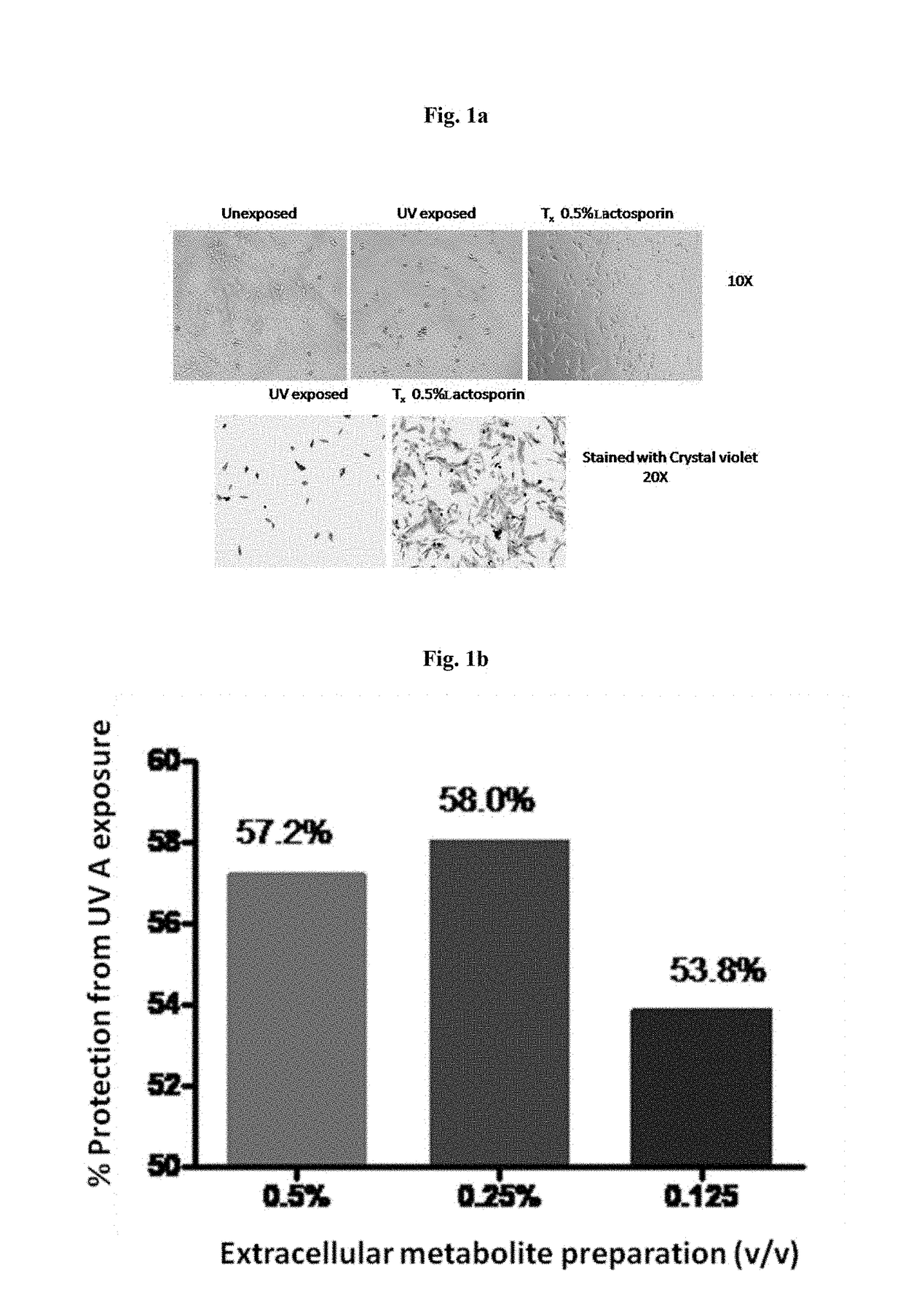
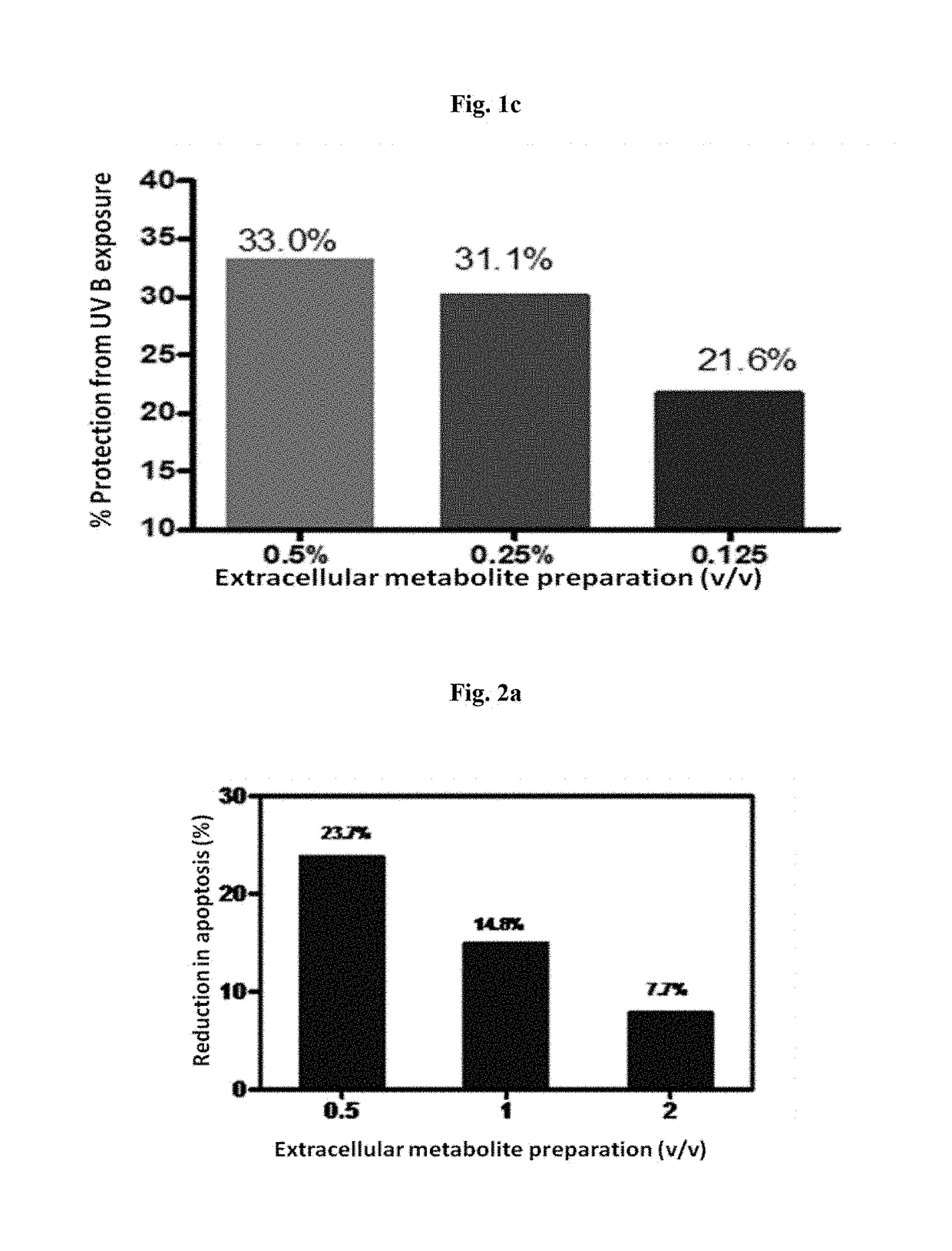
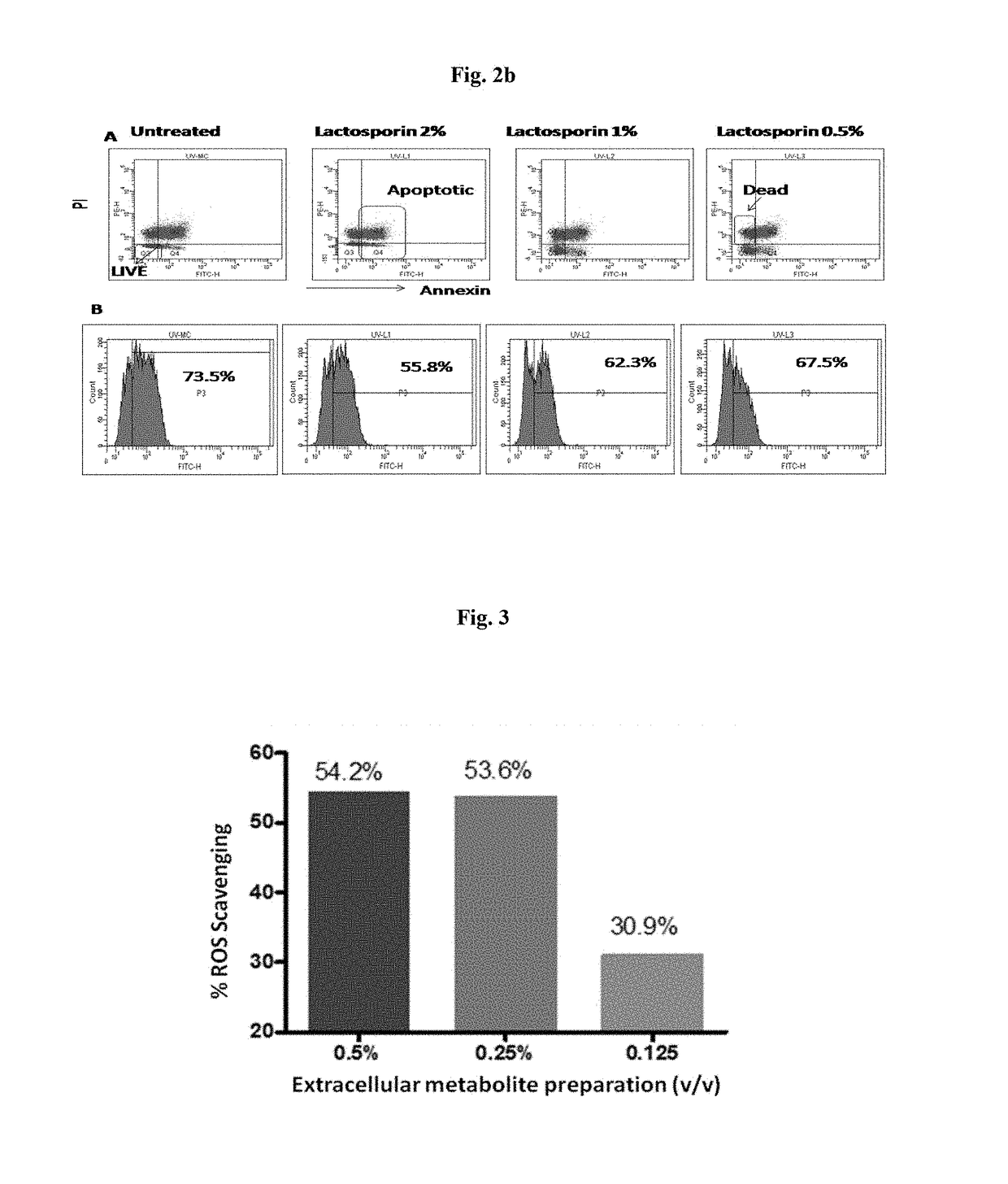
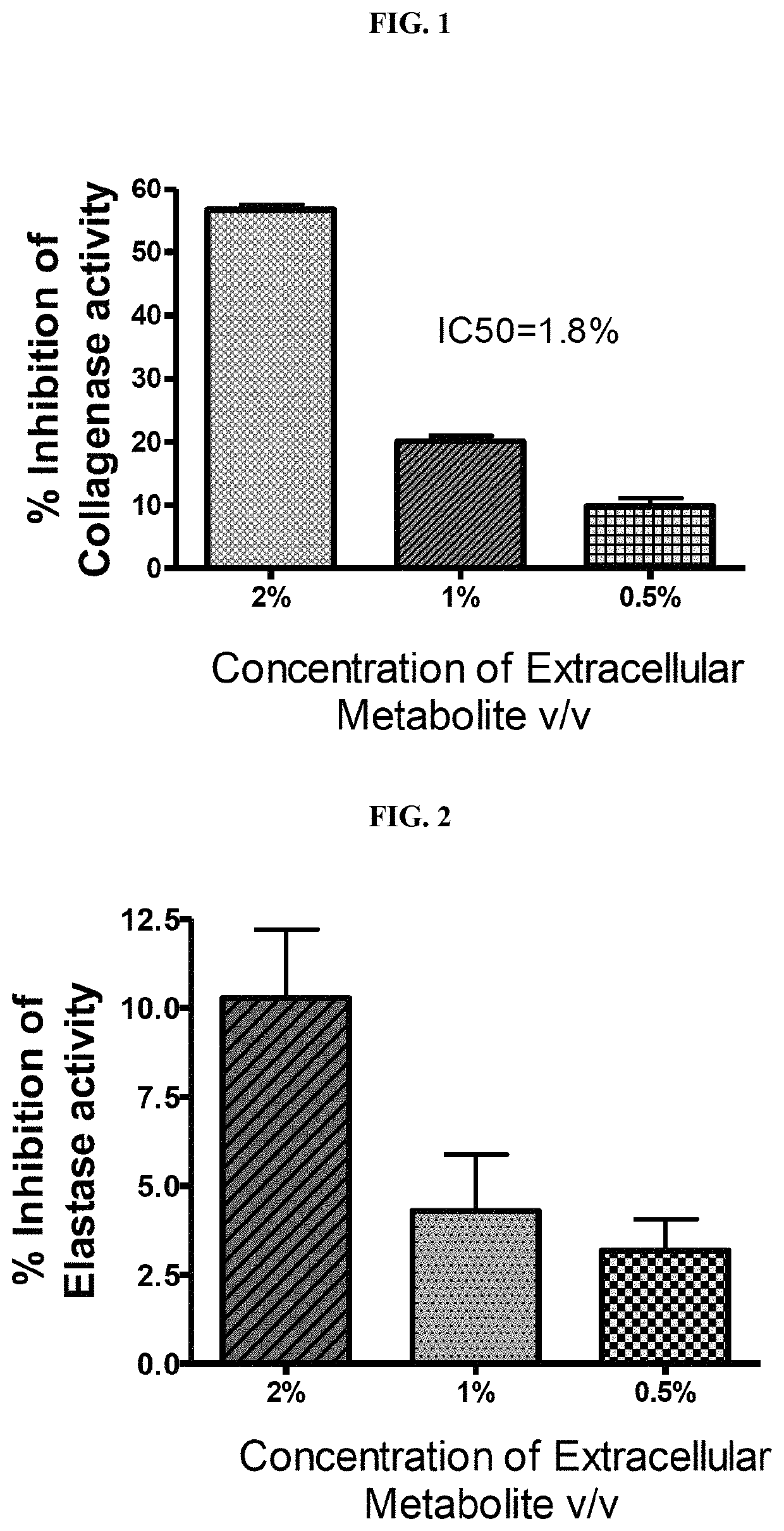
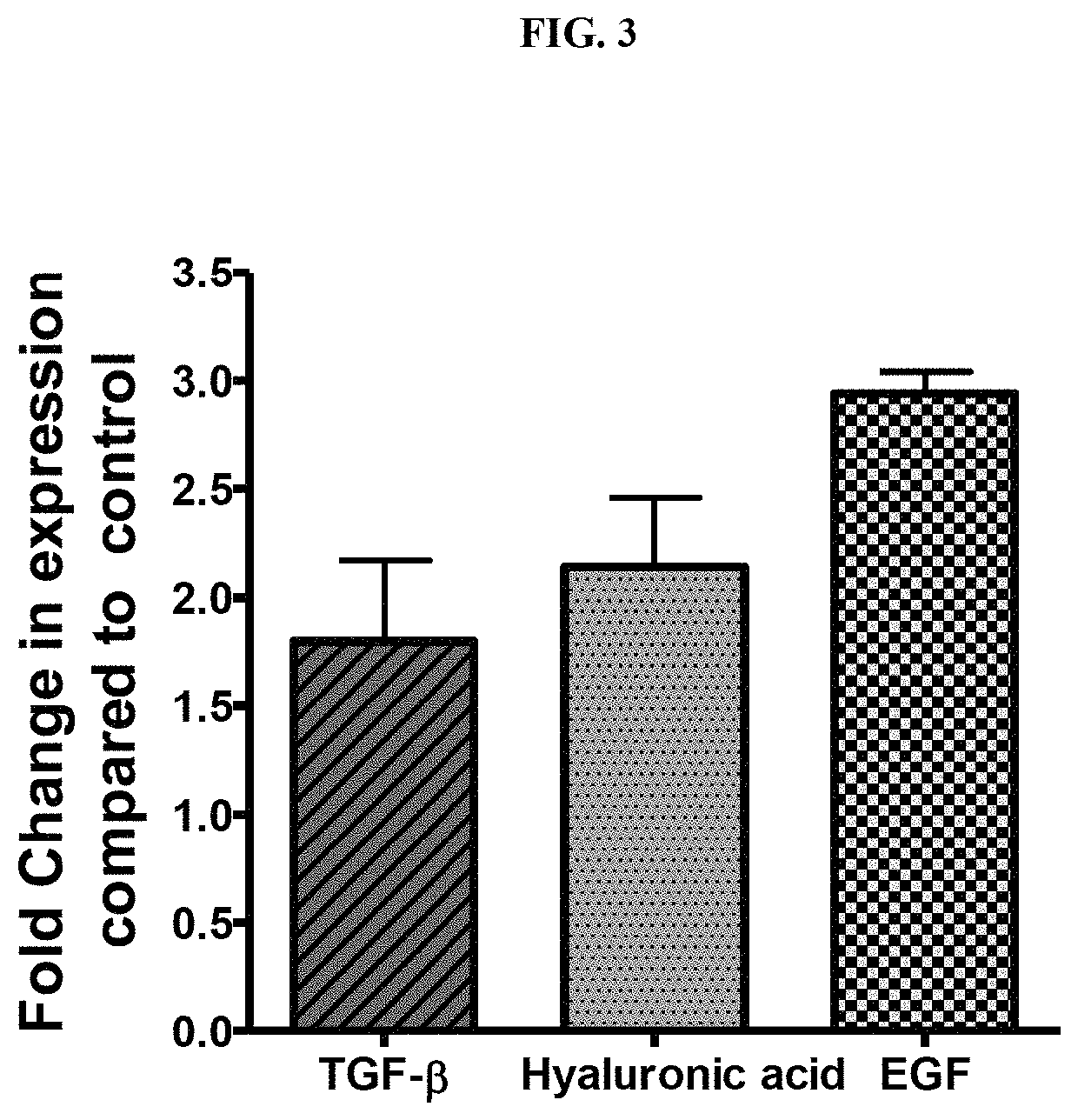
ActiveUS20180344628A1Prevent skin agingCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsExtracellular metaboliteHuman skin fibroblast
Disclosed is the use of partially purified extracellular metabolite isolated from Bacillus coagulans MTCC 5856 to prevent skin aging. More specifically the invention discloses the anti-collagenase, anti-elastase, anti-glycation activity and enhancement of TGF-β, epidermal growth factor and hyaluronic acid expression in human dermal fibroblasts, of extracellular metabolites isolated from Bacillus coagulans MTCC 5856.
Owner:SAMI LABS LTD
Skin care applications of extracellular metabolites from bacillus coagulans
Disclosed are the skin care applications of a composition containing the partially purified extracellular metabolite isolated from Bacillus coagulans MTCC 5856. More specifically, the invention discloses the ability of the partially purified extracellular metabolite isolated from Bacillus coagulans MTCC 5856 to confer protection to the skin fibroblasts against UV induced cell damage and apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammation.
Owner:SAMI LABS LTD
Preparation method of live chlorella suspension capable of improving human immunity
InactiveCN108504580AThe proportion of biologically active substances is highImprove immunityUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesDiseaseMetabolite
The invention discloses a preparation method of a live chlorella suspension capable of improving human immunity. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a culture medium; 2) performinginitial culture: inoculating a strain suspension into the culture medium and culturing the strain suspension for 4 d continuously to obtain an initial chlorella suspension; 3) preparing concentrated chlorella suspension: (1) preparing concentrated chlorella suspension cell biomass; (2) preparing a concentrated chlorella culture solution; (3) preparing the concentrated chlorella suspension: preparing the concentrated chlorella suspension from the concentrated chlorella suspension cell biomass and the concentrated chlorella culture solution by mixing. The mixed suspension based on live cells andextracellular metabolites of a chlorella strain is formed by effectively using the extracellular metabolites decomposed into the culture solution, and the suspension reserves all bioactive substancesof chlorella, is easily absorbed by a human body, has the advantages of long storage period and the like and particularly has the functions of improving human immunity and preventing diseases.
Owner:GANSU DEFU BIOTECH
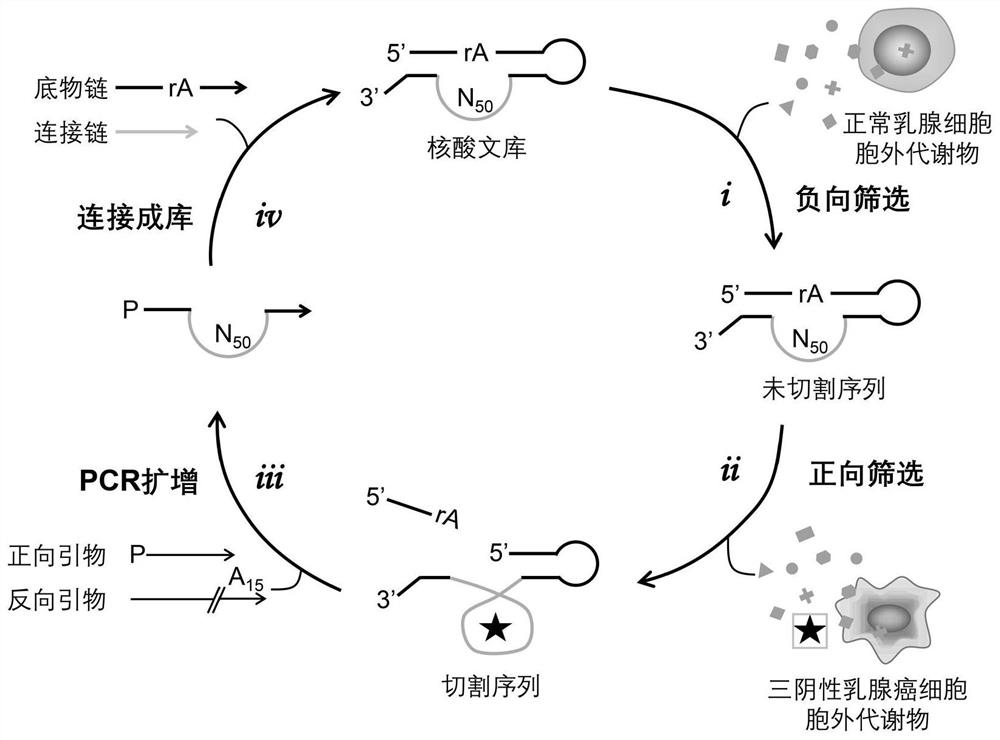
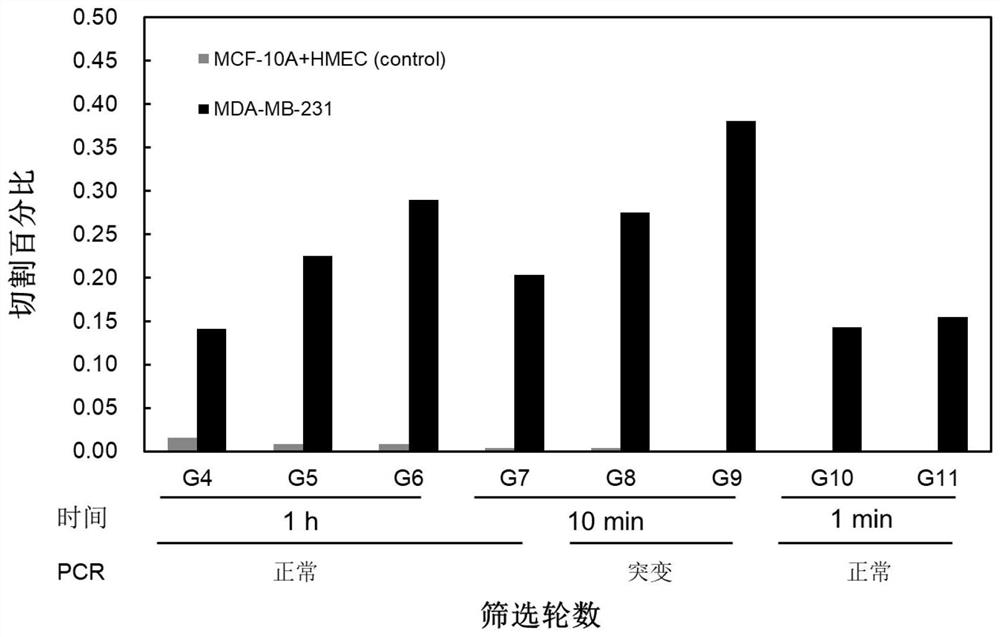
Differential screening of deoxyribozyme probe for specifically sensing triple negative breast cancer
PendingCN113046353AIncreased cleavage signalBiological material analysisDNA preparationOncologyExtracellular metabolite
The invention discloses a deoxyribozyme probe for specifically sensing triple negative breast cancer and a screening method. According to the invention, the deoxyribozyme probe for specifically sensing the extracellular metabolite of the TNBC cell line MDA-MB-231 is obtained through a'hedging counteracting 'difference screening strategy under the condition that a target molecule is unknown. The probe has the characteristics of high recognition speed and good specificity, and provides a new idea for subsequent development of rapid diagnosis of triple-negative breast cancer.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV SHANGHAI CANCER CENT
Hair care compositions containing extracellular metabolite preparation from bacillus coagulans
ActiveUS20180344781A1Promote growthIncreased proliferationCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsMetaboliteAndrogen
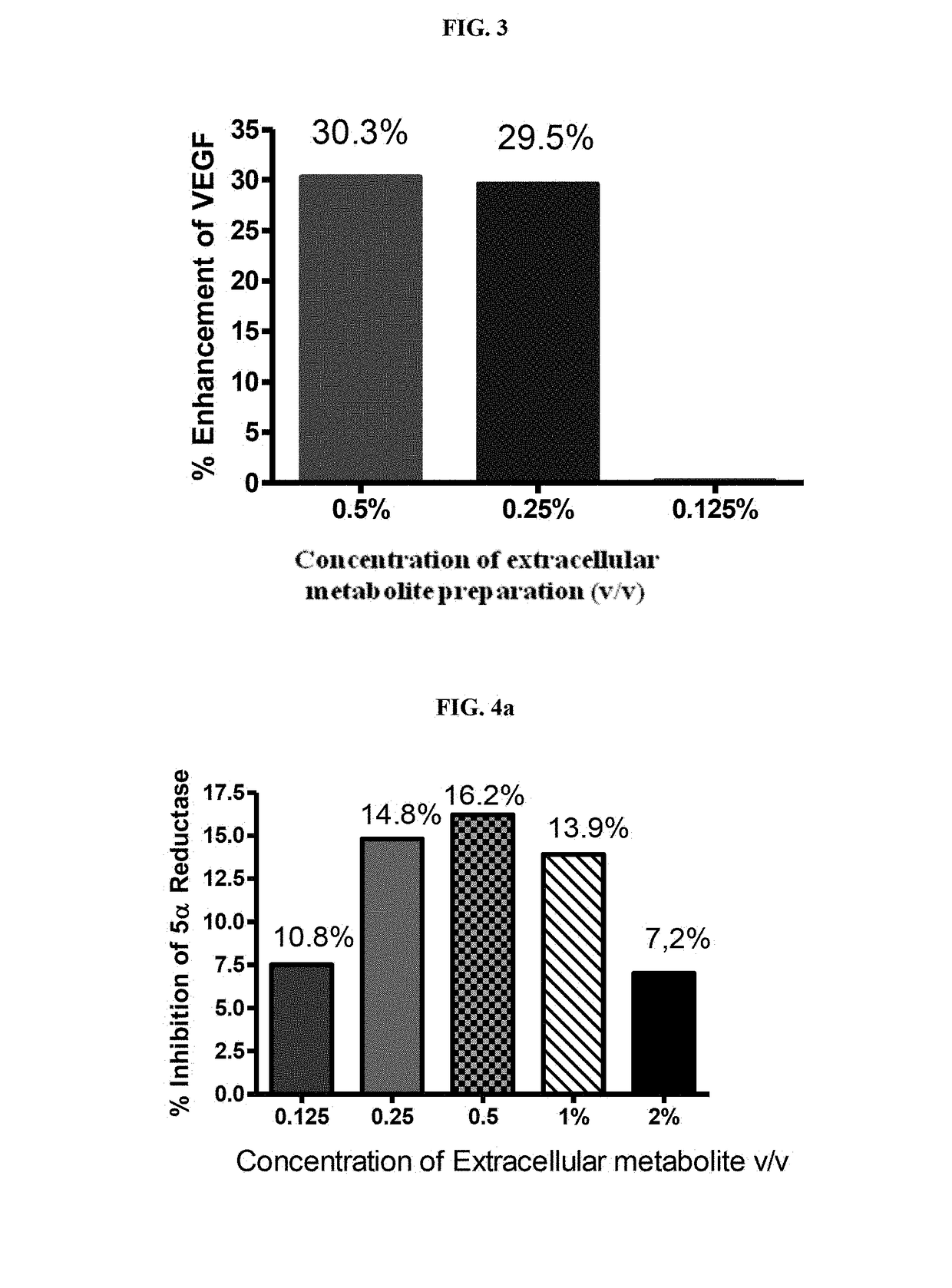
Disclosed are hair care compositions containing partially purified extracellular metabolite preparation from strains of Bacillus coagulans. Specifically, the uses of compositions containing extracellular metabolite preparation from a strain of Bacillus coagulans for increasing hair growth, inhibition of 5α-reductase and proliferation of follicle dermal papilla cells and in the management of androgenic alopecia, are disclosed.
Owner:SAMI LABS LTD
Yeast cell active metabolite capable of promoting growth and anti-stress capability of animals and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104046650AEasy to shapePromote growthMicroorganism based processesAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyAnti stress
The invention discloses a yeast cell active metabolite capable of promoting the growth and anti-stress capability of animals and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the yeast cell active metabolite capable of promoting the growth and anti-stress capability of animals comprises the following steps of firstly obtaining a fermentation broth of which the yeast dry weight is greater than 30g / L through aerobic fermentation; carrying out anaerobic fermentation for 4-24 hours in environment with an extreme temperature, an extreme pH value or an extreme osmotic pressure to obtain an extracellular metabolite; breaking the wall of the yeast in an autolyzing manner by addition of protease, releasing an intracellular metabolite; centrifuging, filtering, separating and purifying the active metabolite product of which the molecular weight is less than 30,000 daltons in the supernatant. The yeast cell active metabolite prepared by the invention can be used as an feed additive for feeding animals, has the effects of improving the morphology of intestinal mucosa of animals, maintaining the balance of intestinal flora, increasing the utilization rate of the feed, promoting the growth of animals and improving the anti-stress capacity of animals and has the characteristics of safe feeding, small addition and no residue.
Owner:CHANGCHUN BORUI FEED
Bacillus subtilis for preventing and treating cucumber ampho disease, and microbial agent thereof
ActiveCN102533610BNo pollution in the processStrong specificityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMetaboliteMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a Bacillus subtilis strain HMB20428 for preventing and treating cucumber ampho disease, and the Bacillus subtilis strain HMB20428 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on December 20, 2011, and the preserving registration number is CGMCC No.5616. The invention further discloses a microbial agent prepared by the strain and a preparationmethod thereof. The active ingredients of the microbial agent are Bacillus subtilis HMB20428 thalli and extracellular metabolite of the Bacillus subtilis HMB20428 thalli. The strain HMB20428 has strong specificity for the cucumber ampho disease; the control effect is high; and the average control effect can reach above 85%; through the method provided by the invention for preventing and treating the cucumber ampho disease, drug resistance is difficult to generate; the microbial agent is safe to human and livestock, and is free of environment pollution; and the preparation method is simple, the cost is low, and the microbial agent is convenient to use.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Bacillus pumilus for controlling cottonbollblight and microorganism bacterium agent thereof
ActiveCN102732444BStrong targetingImprove efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMetaboliteMicrobiological culture
The invention discloses a Bacillus pumilus strain HMB22277 for controlling cottonbollblight which is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on December 20, 2011 with the preservation number of CGMCC NO. 5615. The invention further discloses a microorganism bacterium agent produced by using the microbe and a preparation method thereof. The active component of the microorganism bacterium agent is Bacillus pumilus HMB22277 thalli and its extracellular metabolite. According to the invention, the Bacillus pumilus HMB22277 has strong targeted performance on cottonbollblight with high control effect, wherein the average control effect is higher than 77%; secondly the microorganism bacterium agent of the invention is safe for human and animals and has no environmental pollution and doesn't easily develop drug resistance; in addition in addition, the preparation method of the microorganism bacterium agent is simple, the cost is low and the application is convenient.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Soil bacilli for preventing and controlling fruit tree crown gall and strain agent thereof and preparation method
InactiveCN101451112BImprove efficiencyNo pollution in the processBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyMicrobiological culture
The invention discloses an agrobacterium vitis strain AE206. The strain is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, and has a preserving registration number of CGMCC No.2408. The invention also discloses a microbial preparation and a preparation method thereof. The active ingredients of the preparation are AE206 thalli and extracellular metabolite of the AE206 thalli. The agrobacterium vitis AE206 has good prevention and treatment effect on grape crown gall, has wide antimicrobial spectrum, and has good prevention effect on peach crown gall and cherry crown gall. Moreover, the microbial preparation belongs to a biological agent, and has the characteristics of non-pollution, non public nuisance, low cost and so on.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Microecological preparation and preparation method for preventing and treating rotting skin syndrome of sea cucumber
The invention relates to a microecological preparation used for preventing and treating apostichopus japonicus putrid skin syndrome and a preparation method of the microecological preparation and belongs to the field of aquatic microorganisms. Active ingredients of the microecological preparation are thalli of bacillus megatherium H1 and extracellular metabolites of the bacillus megatherium H1; the bacillus megatherium strain is separated from intestinal tract excrement of apostichopus japonicus which is healthily cultivated in Penglai, Shandong, detection of safety, bacteriostatic activity and toxicity and artificial antagonistic vibrio splendidus experiments verify that the bacillus megatherium H1 is antagonistic to vibrio splendidus, young apostichopus japonicus is effectively protected, the bacillus megatherium H1 can be used for preventing and treating apostichopus japonicus 'putrid skin syndrome' caused by vibrio splendidus and survival rate of an apostichopus japonicus seedling protecting stage is increased.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Polypeptides and extracellular metabolites of Lactobacillus plantarum and their application, method and identification method for inducing Lactobacillus plantarum to produce bacteriocin
ActiveCN106188252BMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismExtracellular metabolite
Relating to the field of microorganism, the invention discloses a polypeptide and a lactobacillus plantarum extracellular metabolite, application thereof, a method for inducing lactobacillus plantarum to produce bacteriocin and an identification method. The invention specifically relates to a polypeptide shown as SEQ ID NO:1, a lactobacillus plantarum extracellular metabolite containing the polypeptide and a preparation method, application of the polypeptide and / or lactobacillus plantarum extracellular metabolite in inducing lactobacillus plantarum to produce bacteriocin, a method for inducing lactobacillus plantarum to produce bacteriocin and an identification method of bacteriocin-producing lactobacillus plantarum. The polypeptide and / or lactobacillus plantarum extracellular metabolite can induce lactobacillus plantarum to express bacteriocin, the expression levels of the four genes papA, papB, papC gene and papD related to bacteriocin production in a lactobacillus plantarum gene are respectively increased by 9.41, 6.75, 7.94 and 6.63 times, thus indicating that adding of the polypeptide and / or lactobacillus plantarum extracellular metabolite can induce the expression of related genes in lactobacillus plantarum.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI
Anti-aging potential of extracellular metabolite isolated from Bacillus coagulans MTCC 5856
Disclosed is the use of partially purified extracellular metabolite isolated from Bacillus coagulans MTCC 5856 to prevent skin aging. More specifically the invention discloses the anti-collagenase, anti-elastase, anti-glycation activity and enhancement of TGF-β, epidermal growth factor and hyaluronic acid expression in human dermal fibroblasts, of extracellular metabolites isolated from Bacillus coagulans MTCC 5856.
Owner:SAMI LABS LTD
Compound biopesticide for preventing and curing rice sheath blight disease and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104351258AImprove fertilizer efficiencyEnhance N fertilizer use efficiencyBiocideFungicidesPaecilomyces lilacinusNitrifying bacteria
The invention discloses a compound biopesticide for preventing and curing a rice sheath blight disease and a preparation method thereof. The pesticide can improve the soil fertilizer efficiency at the same time and is a biopesticide with the effects of both a fertilizer and a pesticide. The pesticide is an aqueous solution or powder, the active ingredients in the aqueous solution or powder comprise bacillus subtilis B-2103 and paecilomyces lilacinus BS-003, and the weight ratio of the bacillus subtilis B-2103 to the bacterial strain of the paecilomyces lilacinus BS-003 is 1:(0.0005-1000). The bacillus subtilis B-2103 to the bacterial strain of the paecilomyces lilacinus BS-003 are compounded, the extracellular metabolite has an excellent effect of preventing the rice sheath blight disease and nitrobacteria, the bacterial strain of the paecilomyces lilacinus BS-003 play the synergistic effect, so that the rate of preventing and curing the rice sheath blight disease is more than 82%, meanwhile, the fertilizer efficiency of the soil is improved, and the utilization efficiency of the soil fertilizer N is strengthened.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH LIAONING
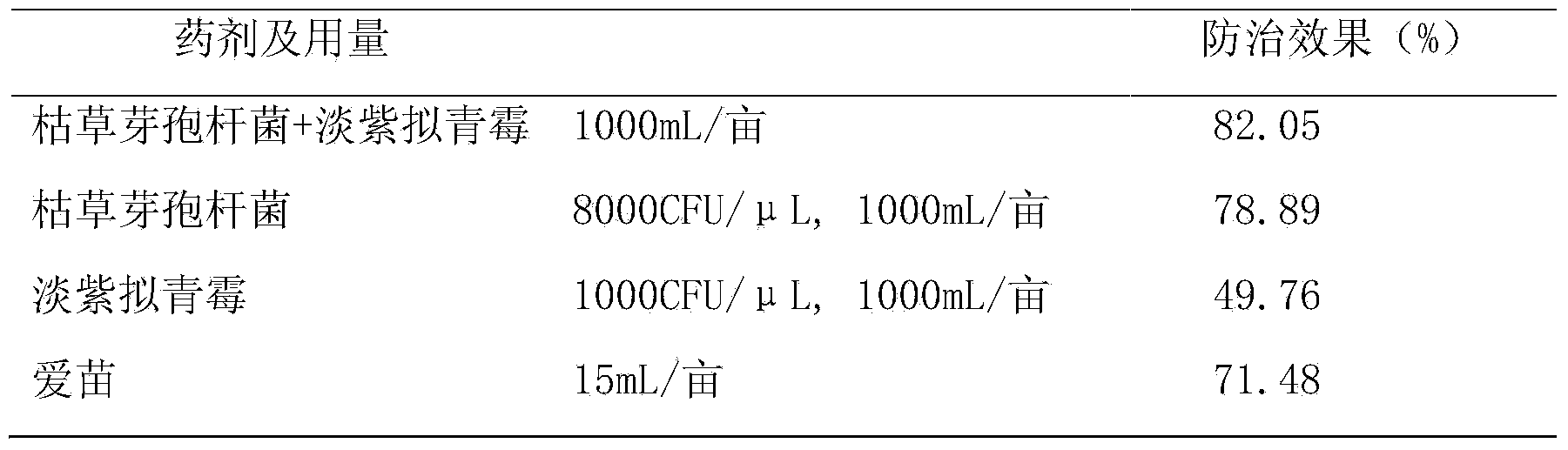
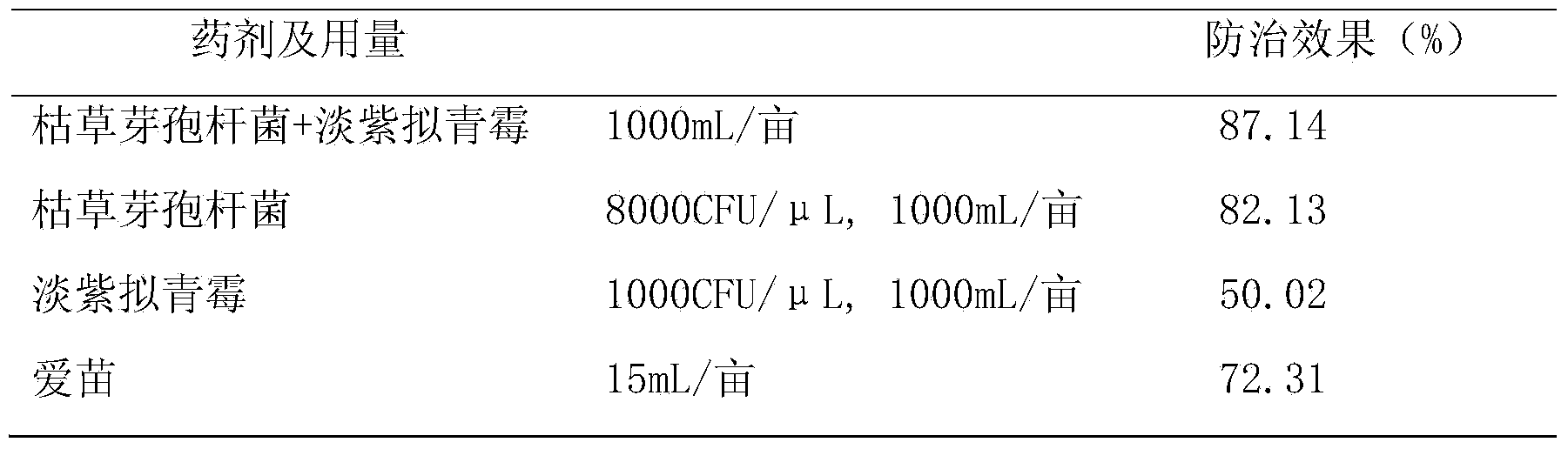
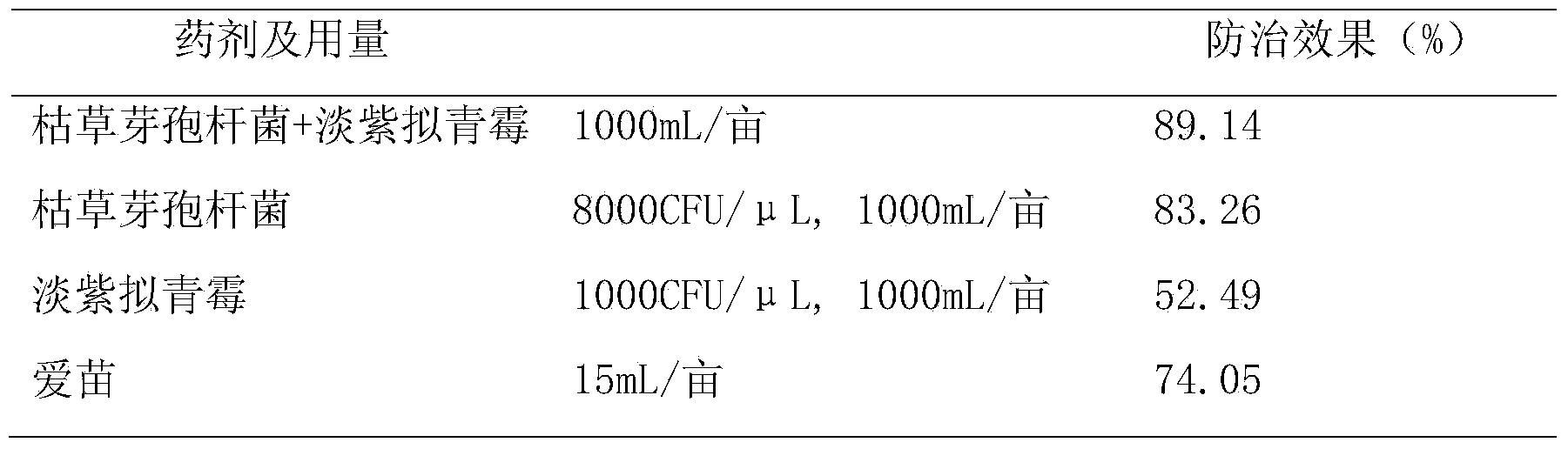
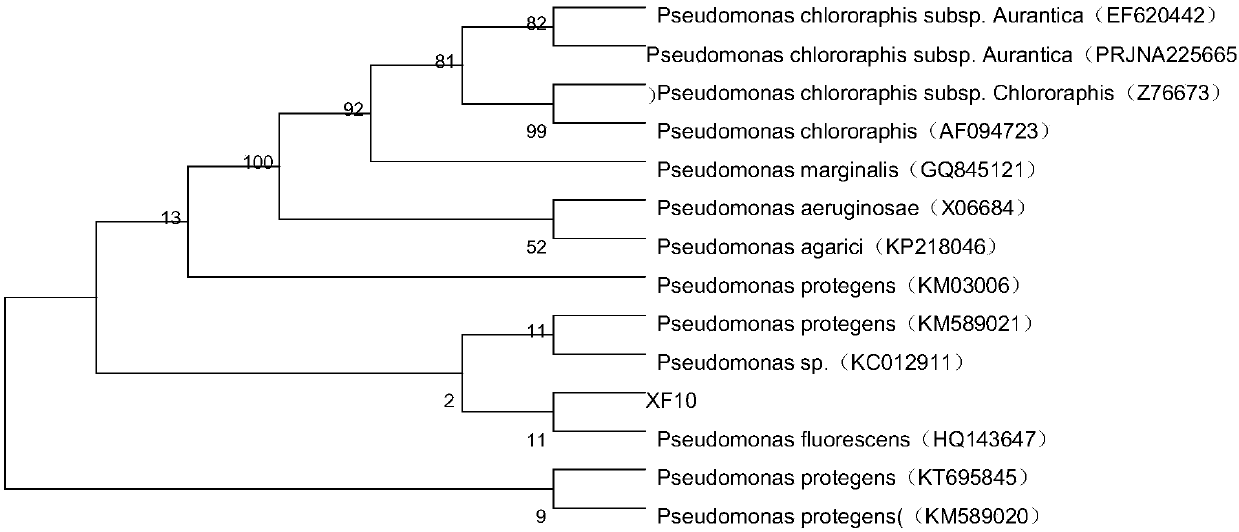
Pseudomonas fluorescens and its application in prevention and control of tobacco black shank
InactiveCN107828677AHighly active and stableEfficient killingBiocideDead plant preservationNicotiana tabacumMetabolite
The invention provides a Pseudomonas fluorescens XF10 with the preservation number being CGMCC No.13703. The bacterial liquid, the extracellular metabolites and the volatile products of the Pseudomonas fluorescens can effectively inhibit the tobacco black shank. The Pseudomonas fluorescens screened in the invention has high activity and is stable, and the fermentation broth, the extracellular metabolites and the volatile products of the Pseudomonas fluorescens can effectively kill Phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae; a root irrigation manner is adopted, so the operating process is simple; and the Pseudomonas fluorescens has no pollution, and has no harms to the environment.
Owner:陈德鑫 +7
A kind of processing method of waste acrylic fabric
ActiveCN107419355BGood decolorization effectGood colorFibre typesBiochemical treatment with enzymes/microorganismsMicroorganismSpinning
The invention mainly relates to the technical field of textiles, and discloses a processing method of waste acrylic cloth. The processing method comprises the following steps: sorting, removing impurities, decoloring, sterilizing, melting at a high temperature, reinforcing fibers, spinning and shaping. The method is simple, the obtained renewable acrylic fibers are high in strength, the decoloring rate is up to 85.7 percent, no toxic reagent is contained used in the preparation process, and health and environmental protection can be realized; the waste acrylic cloth is cleaned after being sorted, and impurities are removed, so that the subsequent treatment is facilitated; and the primarily selected cloth is arranged in a decoloring pool, a fermentation solution and zymophyte are added to firstly perform the fermentation at a high temperature and to promote the proliferation of the bacteria, various microorganisms perform the metabolism, a great amount of extracellular metabolites are generated, the combination capacity of the dye and cloth is reduced, the decoloration is facilitated, and then the fermentation solution is replaced to perform the low-temperature fermentation, so that the decoloration effect of the waste acrylic fibers is obviously improved, the application range of the renewable acrylic fibers is enlarged, and the safety and health of the renewable acrylic fibers can be improved.
Owner:JIESHOU TIANZHU TEXTILE MATERIAL
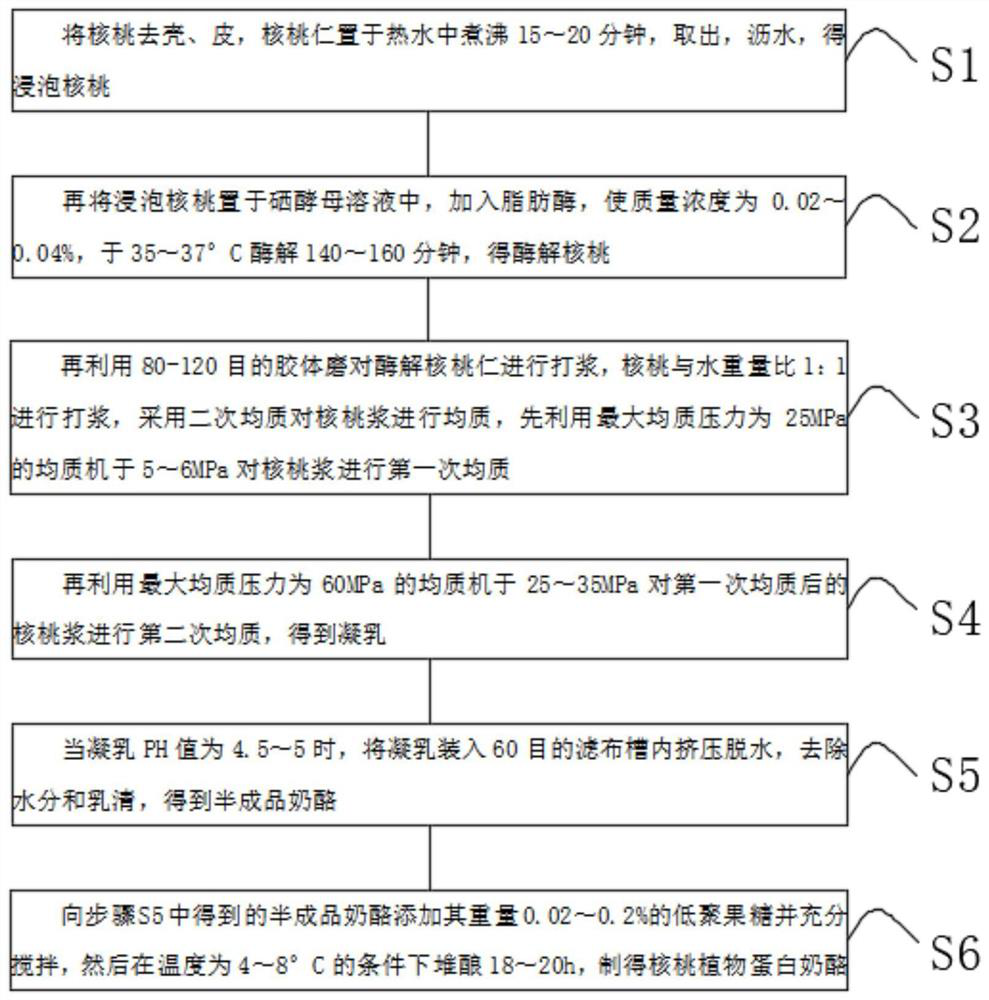
Development method of walnut vegetable protein cheese
PendingCN112869025AReduce fatIncrease the fragranceCheese manufactureFood scienceBiotechnologyLactic bacteria
The invention discloses walnut vegetable protein cheese, and belongs to the technical field of vegetable protein cheese. The walnut vegetable protein cheese is prepared from walnuts, a microorganism complex microbial inoculant, lactic acid, table salt, emulsifying salt and an enzyme additive through the steps of peeling, water adding and pulping, material mixing, homogenizing, sterilizing, enzymolysis, fermentation and after-ripening. The walnut kernels are boiled in hot water, a small amount of fat in the walnut kernels can be leached out, meanwhile, the walnut kernels are cured, and the walnut fragrance is increased; after being soaked, the walnuts are added into a selenium yeast solution for lipase enzymolysis, so that the content of organic selenium in the walnuts is increased, fat in the walnuts is reduced, the health-care function of the walnuts is enhanced, the walnuts are prevented from being oxidized, and the shelf life is prolonged; and after enzymolysis, the walnuts are placed in a sucrose solution to be boiled again, the flavor of the walnuts is increased, fat in the walnuts is leached out, lactic acid bacteria are inoculated for fermentation after boiling, the leached fat is decomposed, the sour and sweet taste is palatable, the greasy feeling of the walnuts is removed, and extracellular metabolites generated through fermentation can promote digestion.
Owner:KUNMING BIOLOGICAL MFG RES INST CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com