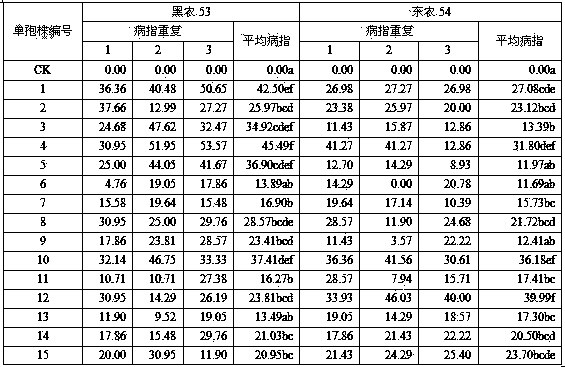
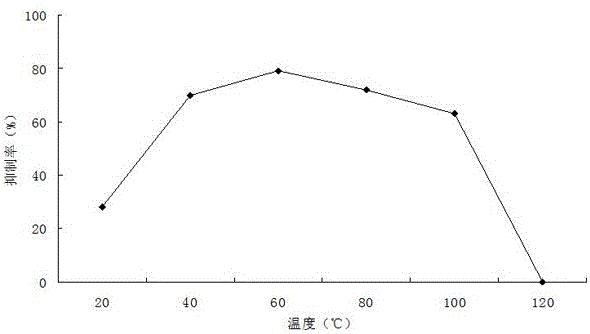
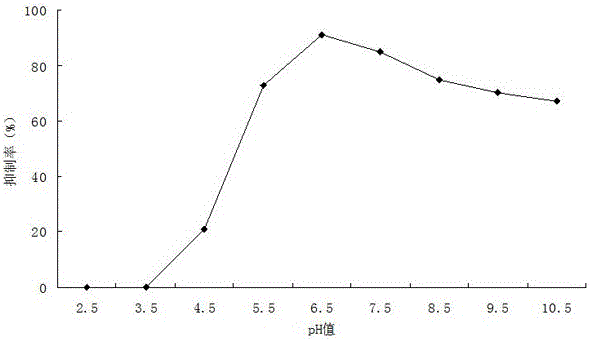
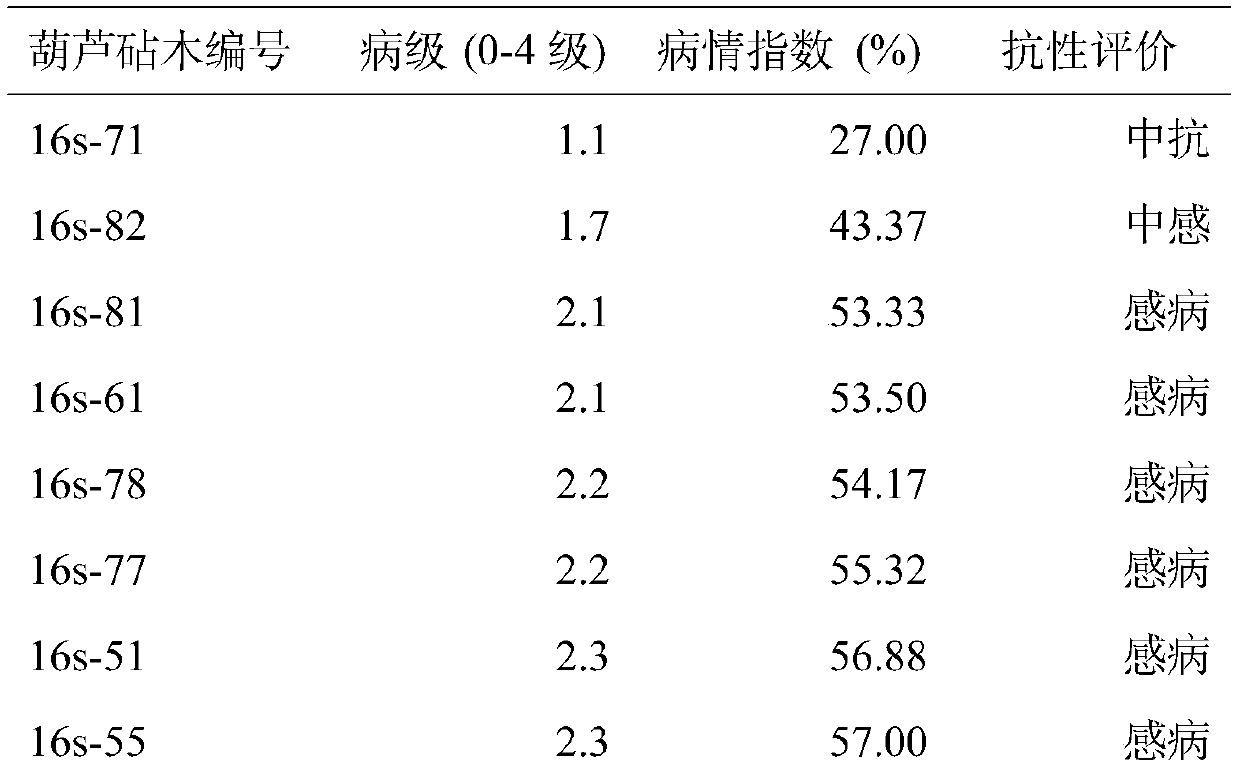
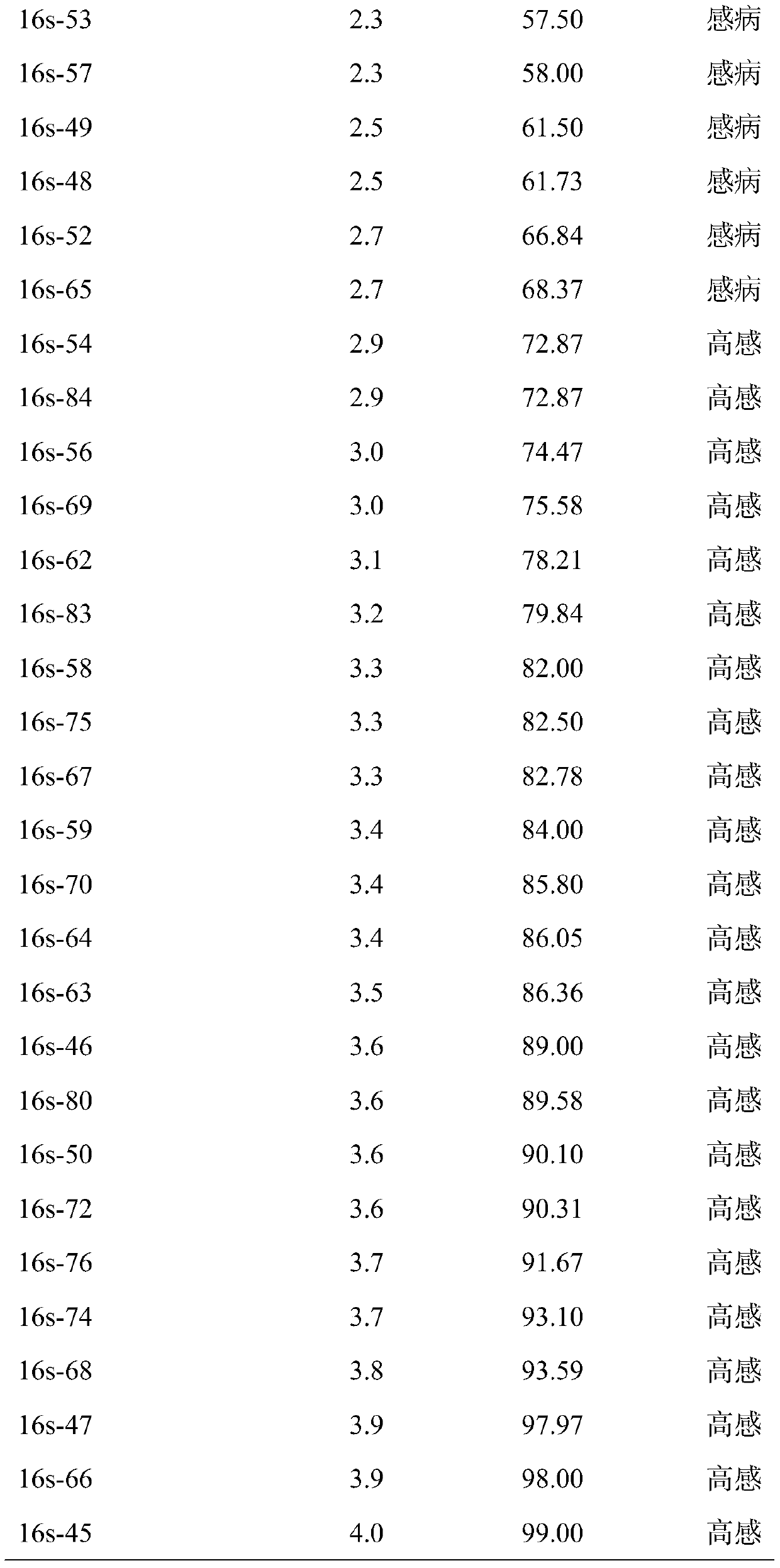
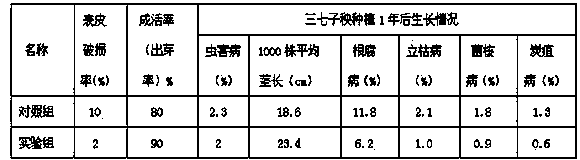
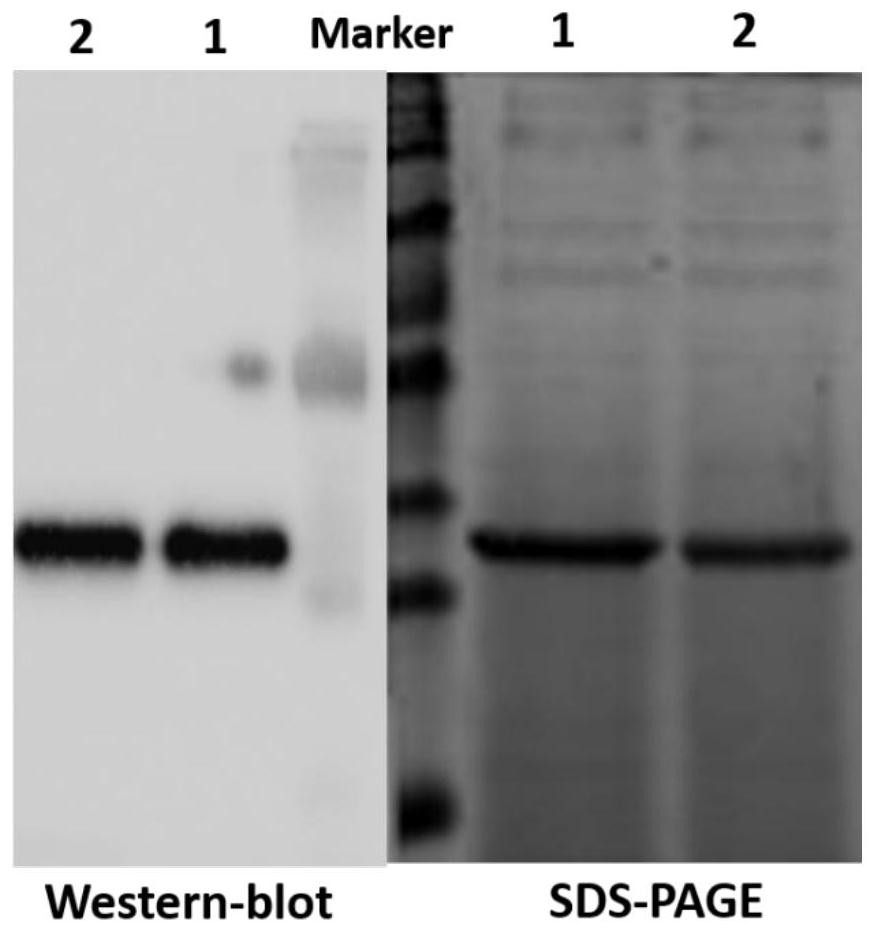
Patents
Literature
41 results about "Phymatotrichum omnivorum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phymatotrichum omnivorum Duggar, (1916) Texas root rot (also known as Phymatotrichopsis root rot , Phymatotrichum root rot , cotton root rot , or, in the older literature, Ozonium root rot ) is a pathogen fairly common in Mexico and the southwestern United States that causes sudden wilt and death of affected plants , usually during the warmer ...
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and application thereof
InactiveCN105018385ABroad antibacterial spectrumEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideBacteriaScreening methodMycelial cord
The invention relates to bacillus amyloliquefaciens, the preservation number of which is CCTCC M 2015299, and which is named as bacillus amyloliquefaciens XK-2. The invention further provides a screening method of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens XK-2 and an application of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens XK-2 in inhibiting watermelon fusarium oxysporum, rhizoctonia solani and walnut root rot pathogenic bacteria as well as a bacillus amyloliquefaciens XK-2 bactericide. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens XK-2 is a watermelon endophytic bacterial which is safe to the human beings, animals and crops, environment-friendly, relatively wide in antibacterial spectrum, has a good inhibition effect on common soil-borne pathogen,watermelon fusarium oxysporum, rhizoctonia solani and walnut root rot pathogenic bacteria, has a significant control effect on watermelon fusarium wilt, has an obvious inhibition effect on the growth of watermelon fusarium oxysporum hypha, slows down the growth of hypha, facilitates the distortion syndrome of the hypha and is wide in application prospect in biological control of plant diseases.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Bacillus pumilus NMCC 46 and application thereof
InactiveCN101760439AGood control effectPromote growthBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention relates to Bacillus pumilus NMCC 46, which is preserved in CGMCC with preservation date as November 2, 2009, and preservation number as CGMCC No.3378. The Bacillus pumilus NMCC 46 CGMCC No.3378 in the invention is a biological control bacillus separated from grass root surrounding soil near Namco Lake in Tibet, which can grow at 10 DEG C, is favorable for exerting growth promotion and biological control effects, can restrain soybean root pythium myriotylum and saccharomycetes, can boost growth of Arabidopsis and soybean, has a prevention and control effects on soybean root pythium myriotylum as high as 85%, can increase yield of soybean to 24%, and has good application prospect.
Owner:NANJING HOUJI BIO TECH
Trichoderma koningiopsis T5-1 bacterial strain and application thereof in improvement of growth of panax notoginseng and prevention and control of root rot
ActiveCN106566777ANothing producedPromote growthBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyBacterial strain
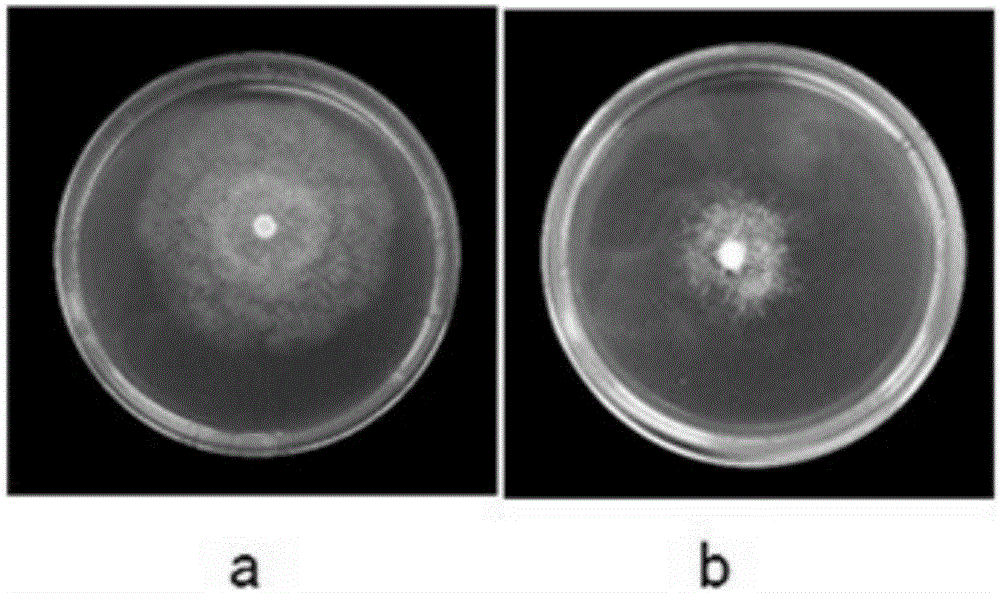
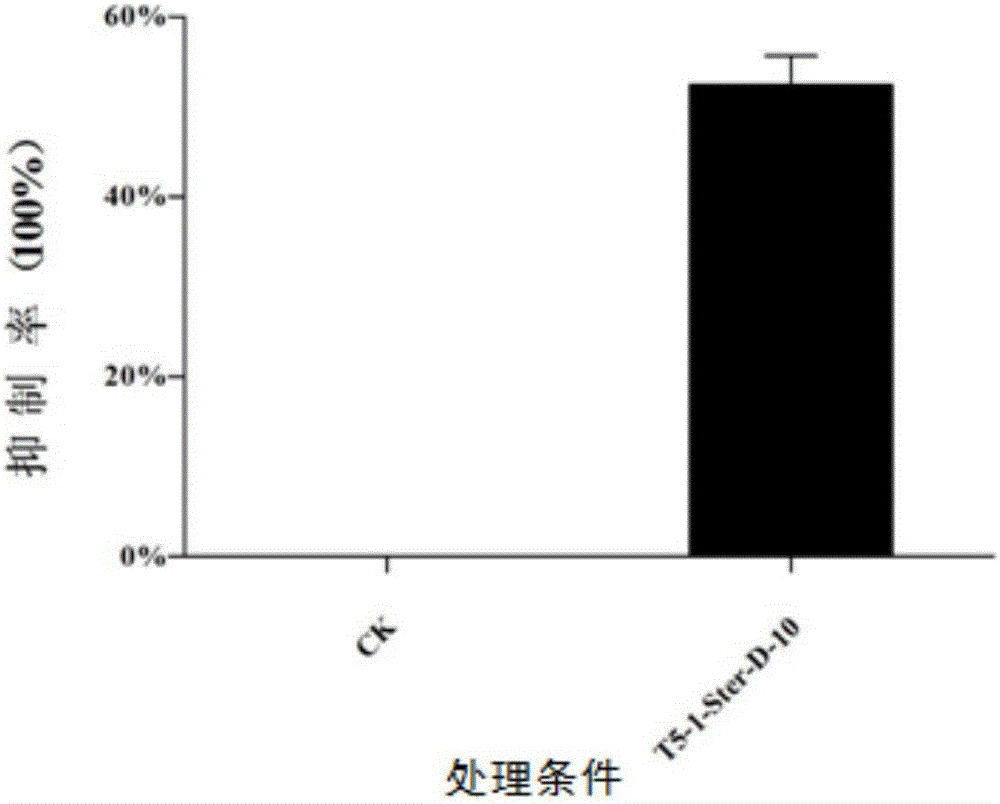
The invention belongs to the technical field of prevention and control of plants diseases and particularly relates to a trichoderma koningiopsis T5-1 bacterial strain and an application thereof in improvement of growth of panax notoginseng and prevention and control of root rot. The bacterial strain is named trichoderma koningiopsis, and is assigned the accession number of CGMCC No. 12779 in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center. The trichoderma koningiopsis T5-1 bacterial strain has developed mycelia and fluffy and dense aerial mycelia, and is free of generation of pigments. The trichoderma koningiopsis T5-1 bacterial strain can improve growth of panax notoginseng and also can inhibit growth of root rot fungus. The bacterial strain can be hyper-parasitized on the root rot fungus, so that spore production of the root rot fungus is inhibited by means of volatile organic compounds from the bacterial strain in a sealed condition. The bacterial strain lays a good foundation for development and utilization of bio-bacterial fertilizers.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV +2
Anti-bacterial protein PBR1 as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103724407ABroad-spectrum inhibitionStrong cracking abilityBiocidePeptide preparation methodsBiotechnologyGaeumannomyces
The invention discloses an anti-bacterial protein PBR1 as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of molecular biology and biological pesticides. The amino acid sequence of the anti-bacterial protein PBR1 is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The anti-bacterial protein PBR1 has a superior effect on preventing and curing plant diseases such as cruciferous plasmodiophoromycetes, paddy rice magnaporthe oryzae, curvularia lunata, fusarium oxysporum f. sp. dianthi, fusarium oxysporum vasinfectum, konjac foot rot bacteria, panax notoginseng root rot pathogen, pomegranate wilt pathogen, gaeumannomyces gramini, cylindrosporium pomi brooks, alternaria alternata and / or botrytis cinerea. A pesticide taking the anti-bacterial protein PBR1 as an active ingredient is a novel environment-friendly biological pesticide, is safe to people and livestock, protects the environment, and has a favorable development prospect.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Areca nut root rot fungicide taking lysinibacillus boronitolerans as base cells
ActiveCN111100806AGuaranteed outputEffectively prevent production loss and even deathBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyEcological environment
The invention relates to an application of lysinibacillus boronitolerans in inhibiting growth of cerrena unicolor. The lysinobacterium boronitrotolarans not only can reduce occurrence of areca nut root rot to a great extent, but also has no threat to the ecological environment, is expected to be used as a high-quality base microorganism for synthetic biology research, and thus brings a new direction to prevention and treatment of areca nut root rot.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Panax notoginseng seedling protection film, and preparation method and application thereof
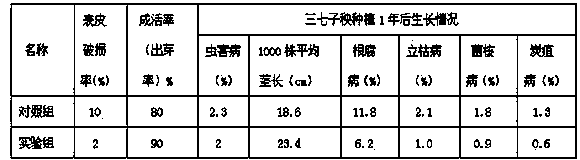
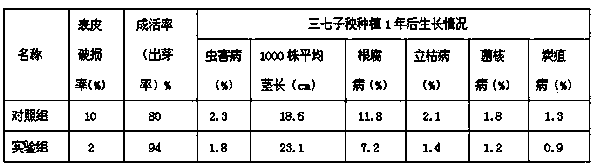
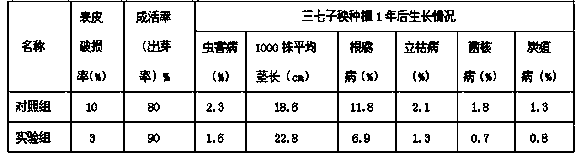
ActiveCN103392693AReduce skin breakage rateAverage stem length increaseBiocidePlant growth regulatorsSclerotiniaRoot growth
The invention relates to a panax notoginseng seedling protection film, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The film provided by the invention is a water-soluble gel prepared by using a water-soluble film-forming material, panax notoginseng polysaccharide, a root growth promoter, a preservative, and a pesticide. With the material, a protection film can be formed on the surface of a panax notoginseng seedling. With the panax notoginseng seedling protection film provided by the invention, water loss of panax notoginseng seedling during a transplanting process can be reduced, and seedling surface skin damage caused by abrasion during transportation or during transplanting can be reduced. Therefore, fungal infection or insect attack caused by damages after transplanting can be reduced, occurrence rate of panax notoginseng root rot, sclerotinia stem rot, sheath blight, anthracnose, and blight can be reduced, and panax notoginseng survival rate can be improved. The panax notoginseng seedling protection film provided by the invention has good physiochemical performances such as film-forming performance, water resistance, air permeability, water permeability, and the like. Therefore, healthy growth of crops can be protected.
Owner:YUXI WINHEY BIO TECH
Seedling-stage root rot resistance identification method for vigna unguiculata
InactiveCN105409613AAvoid conditionsAvoid environmental problemsFungiMicroorganism based processesDiseaseSpore
The invention belongs to the field of disease resistance detection of horticultural crops and relates to a seedling-stage root rot resistance identification method for vigna unguiculata. The method comprises the steps of carrying out germination hastening on vigna unguiculata seeds, carrying out sowing and seedling raising, carrying out special strain inoculating so as to carry out screening, preparing a vigna unguiculata root rot bacterium spore suspension, carrying out pathogenic bacterium infestation, carrying out onset examination and the like. Root systems of young seedlings are soaked and infested by adopting a bacterial solution so as to subject the vigna unguiculata young seedlings to artificial root rot bacterium infection; and the vigna unguiculata seeds are cultured in seedling raising matrixes until each young seedling has two leaves and one heart, and then, the young seedlings are drawn out for infestation, so that the growth vigor and size of the vigna unguiculata young seedlings are easily controlled, the vigna unguiculata young seedlings are easily drawn out, and the consistency and reliability of identification results are guaranteed. Special indicator strains are obtained through screening, the infesting effect is better by adopting appropriate time of infestation and appropriate root rot bacterium spore suspension concentration, the bacterium inoculating is uniform, and the onset is rapid. According to the method, by only injuring roots of different plants of consistent growth vigor through directly and naturally rubbing the roots and then infesting the roots with the indicator strains, the root rot resistance of a large amount of vigna unguiculata breeding materials can be identified simply, conveniently, rapidly and reliably, so that the efficiency of variety resistance identification is increased.
Owner:WUHAN VEGETABLE RES INST
Fusarium oxysporum single spore isolation method for soybean root rot
InactiveCN104357333AAvoid easy separationIncrease in sizeFungiMicroorganism based processesIsolation effectSpore
The invention discloses a fusarium oxysporum single spore isolation method for the soybean root rot. The fusarium oxysporum single spore isolation method is provided for solving the problems that a soybean fusarium oxysporum single spore is small, is in light color and is not easy to isolate. The fusarium oxysporum single spore is enlarged in size after germinating, then dilution is carried out until a spore suspension with only 1-2 spores in average every 10 <Mu>L is obtained, and isolated conidium is further confirmed in a round hole grid in a 96-mesh cell culture plate cover through an inverted microscope to be a single spore. Compared with other single spore isolation methods, the method is good in operability, high in accuracy, high in speed, excellent in isolation effect, and simple in equipment. The method is accurate, simple and feasible, and a large batch of fusarium oxysporum single spores can be isolated within a short period of time in a lab. Therefore, the method is suitable for promotion and application.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Marine bacteria BA-3 (Bacillus amyloliquefaciens-3) and application thereof in orchid disease prevention and treatment
ActiveCN106399187APlay a preventive roleEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideBacteriaDiseaseMicroorganism
The invention relates to marine bacteria BA-3 (Bacillus amyloliquefaciens-3) and application thereof in orchid disease prevention and treatment, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The preservation number for the marine bacteria BA-3 is CGMCC No.12745. The marine bacteria BA-3 capable of preventing and treating plant diseases, caused by stalk rot pathogens and root rot pathogens, of orchids can grow together with the orchids especially, can survive stably in orchid plants and can prevent and treat stalk rot diseases or root rot diseases of the orchids effectively.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION FAAS
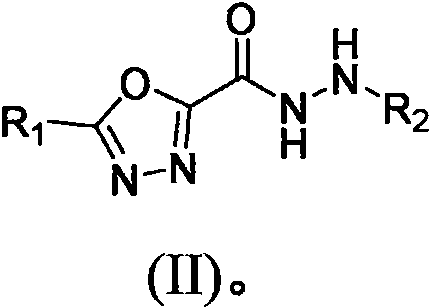
Heterocyclic substituted 1, 3, 4-oxadiazole hydrazide compound and preparation method and application thereof
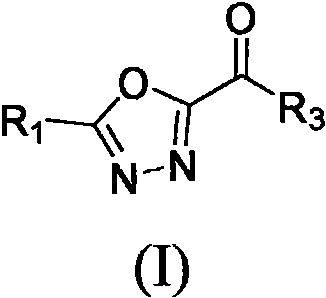
The invention relates to heterocyclic substituted 1, 3, 4-oxadiazole hydrazide compounds and a preparation method and application thereof. The compound has a structure shown as a general formula (I). The compound has a relatively good inhibition effect on pathogenic fungi and bacteria; and the compound has good inhibition effects onfusarium graminearum, potato late blight bacteria, blueberry root rot bacteria, pepper fusarium wilt, sclerotinia sclerotiorum, colletotrichum gloeosporioides, botryosphaeria dothidea, rhizoctonia solani, xanthomonas oryzae pv., ralstonia solannacearum, Xanthomonas citri, kiwi canker bacteria, Xanthomonas oryzae cucumber, Xanthomonas oryza konjak, Botryosphaeria dothidea, tomato canker pathogens, apple canker pathogens and the like.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
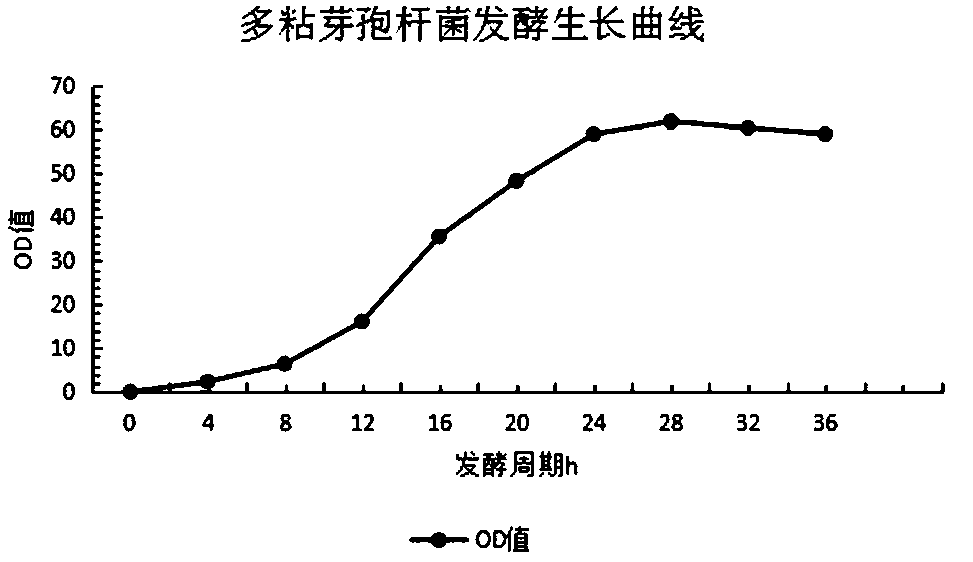
High-yield paenibacillus polymyxa strain and application thereof
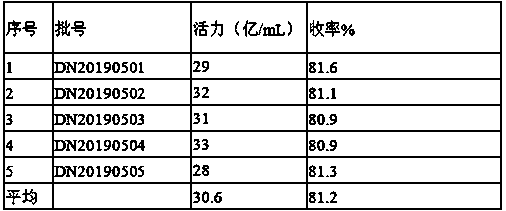
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological fermentation engineering, and specifically relates to a high-yield paenibacillus polymyxa strain and an application thereof. Paenibacillus polymyxa YSD7 is preserved at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on December 5, 2019, and a preservation number is CGMCC 19087. The paenibacillus polymyxa YSD7 can prevent and treaterwinia carotovora, taro soft rot bacteria, phytophthora nicotianae, flower root rot bacteria, bipolaris sorokiniana, cercospora personata, or polygonatum root rot bacteria. The inventors finally obtain the paenibacillus polymyxa strain YSD7 with relatively good growth vigor through the combination application of ultraviolet mutagenesis and diethyl sulfate mutagenesis technology, and qualitativescreening breeding based on the existing strain. Preliminary experimental results show that the highest fermentation activity of the YSD7 strain can reach 9.5 billion / mL, the YSD7 strain shows relatively good growth effects, and a good technical foundation for the preparation of paenibacillus polymyxa microbial preparation products can be laid.
Owner:河南新仰韶生物科技有限公司
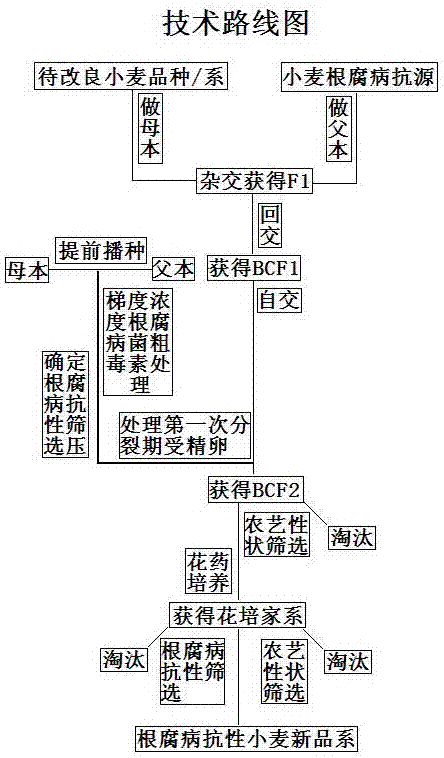
Breeding method for rapidly screening resistant varieties of wheat root rot by using root rot fungus crude toxin
InactiveCN107211882AImprove work efficiencyImprove accuracyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyTriticeae
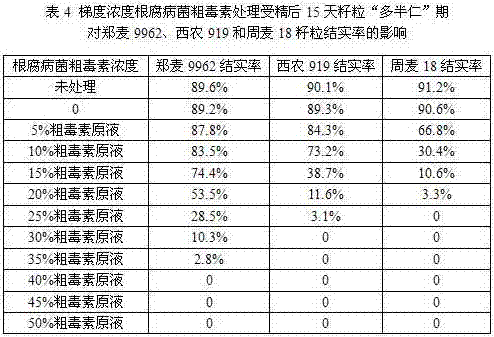
The invention discloses a breeding method for rapidly screening resistant varieties of wheat root rot by using root rot fungus crude toxin. The method comprises the following steps of (1) selecting to-be-improved wheat variety / strain and wheat root rot resistance source and hybridizing to obtain F1; (2) backcrossing the F1 to obtain BCF1; (3) sowing male and female parents and the BCF1 at different stages; (4) treating the male and female parents by using root rot fungus crude toxin of gradient concentrations and selecting resistance screening pressure of the root rot; (5) treating the BCF1 by using the resistance screening pressure of the root rot to obtain BCF2; and (6) taking BCF2 for anther culture to obtain an anther culture family and screening according to root rot resistance and agronomic characters to obtain a new wheat strain with root rot resistance. Hybrid species are treated by selecting the root rot fungus crude toxin with a proper concentration at the hypersensitive stage of the root rot fungus crude toxin and the first division stage of zygote, thereby specifically screening the resistance wheat family for the root rot and greatly improving the work efficiency and the accuracy of resistant breeding of the root rot.
Owner:尹纪岩
Burkholderiaspp.and application thereof in preventing and treating main pathogenic bacteria of panax notoginseng root rot
ActiveCN112646754APromote degradationPromote growthPlant growth regulatorsBiocidePANAX NOTOGINSENG ROOTMicrobiology
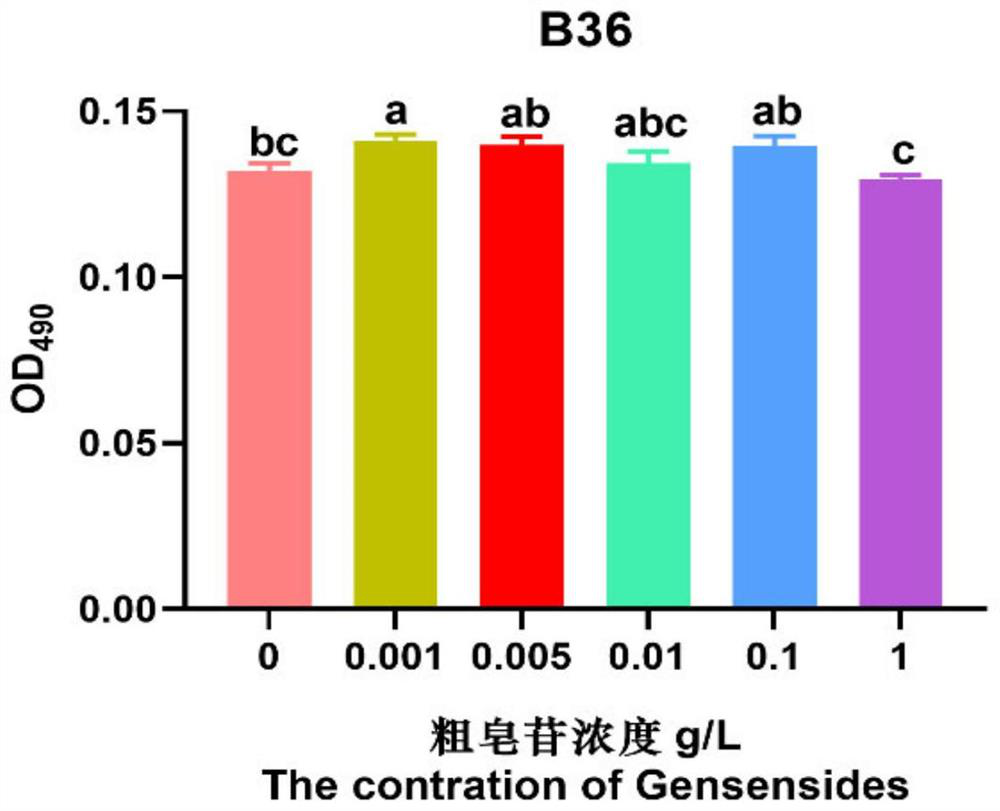
The invention provides Burkholderiaspp.B36. The strain has relatively strong inhibitory activity on main root rot bacteria of panax notoginseng, namely rust rot bacteria, has relatively obvious degradation on main saponin autotoxins (R1, Rg1, Re, Rb1 and Rd) of panax notoginseng, and especially has significant degradation activity on saponins Rb1 and Rd. The Burkholderiaspp.B36 has a broad application prospect.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Engineering strain producing anti-fungal protein genes and application
The invention discloses an engineering strain producing anti-fungal protein genes and a construction method and application thereof. The strain is pET32a(+)-Ap1-BL21, and the preservation serial number is CGMCC No.11542. According to the construction method, double enzyme digestion is carried out on anti-fungal protein AP1 genes and plasmid pET32a(+) through BamH I and XholI, and the anti-fungal protein AP1 genes and the plasmid pET32a(+) are connected through T4DNA ligase and then converted into E.coli BL21 competent cells to obtain the engineering strain pET32a(+)-Ap1-BL21 with the anti-fungal protein genes. The gene engineering strain contains the anti-fungal protein genes, induction time at the temperature of 30 DEG C is short, the expression rate (43.2%) is high, the purification protein yield (124.82 mg / L) is high, the recovery rate (92%) is high, protein has a good inhibiting effect on phytopathogen such as soybean root rot bacteria and fusarium fujikuroi after ITPG inducting, HIS column purifying and enterokinase restriction enzyme digesting are carried out, and the strain provides a novel strain resource for research and development of recombinant protein pesticide.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF SCI
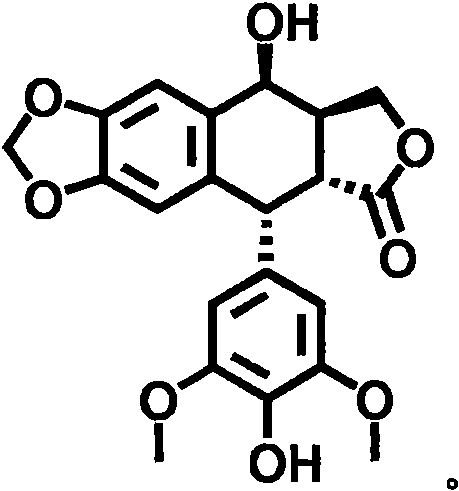
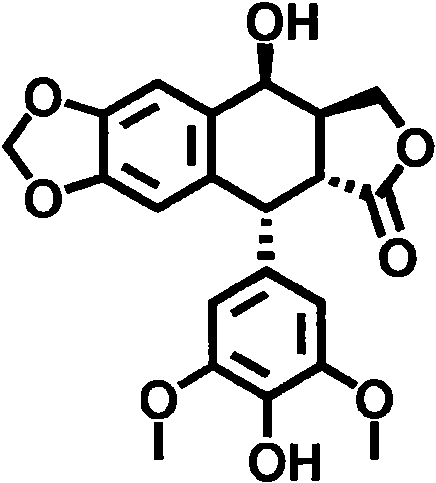
Application of 4'-demethyl epipodophyllotoxin as agricultural bactericide
The invention relates to application of 4'-demethyl epipodophyllotoxin as an agricultural bactericide. The compound has a relatively good inhibition effect on pathogenic bacteria and fungi; the invention aims at rice bacterial leaf blight, tobacco bacterial wilt, cucumber bacterial leaf blight, konjac bacterial leaf blight, citrus canker pathogen, grape canker pathogen, tomato canker pathogen, kiwi canker pathogen, apple canker pathogen, cucumber botrytis cinerea, pepper fusarium wilt pathogen, sclerotinia sclerotiorum, wheat gibberellic disease, potato late blight pathogen, and blueberry root rot bacteria, and the compound has a good inhibition effect.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Preparation containing bacillus subtilis YL13 for antagonizing diseases and/or promoting growth of plants and application of the preparation
ActiveCN108684711AGood effectPromote growthPlant growth regulatorsBiocideMutagenic ProcessChlorothalonil
The invention discloses a preparation containing bacillus subtilis YL13 for antagonizing diseases and / or promoting growth of plants and an application of the preparation. The strain, bacillus subtilisYL13, is assigned the accession number CCTCC No. M2018008 and is a broad-spectral antagonistic strain that can antagonize the plant diseases and is obtained through mutagenesis for the first time. The strain has significant effect of inhibition of colletotrichum camelliae, fusarium proliferatum, agaricodochium camelliae, colletotrichum truncatum, colletotrichum fructicola, alternaria solani, fusidium coccineum and rhizoctonia solani. A novel water-dispersing granular of the mutagenesis strain YL13 is researched, which not only can improve capability of resisting diseases, such as anthracnoseand root rot, but also can promote seedling growth. Test on prevention and treatment effect in forest shows that the YL13 microbial agent has excellent prevention and treatment effect on camellia oleifera anthracnose and can reach more than 80% in forest prevention and treatment effect, which is comparable with that of chemical preparations, such as chlorothalonil.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
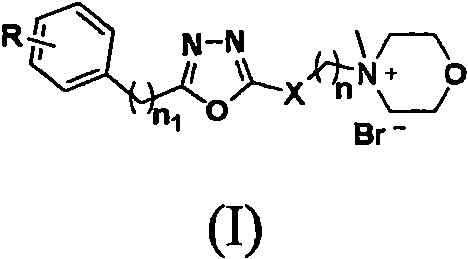
1, 3, 4-oxadiazole compound containing morpholine group as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN113636984AEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideOrganic chemistryBiotechnologyXanthomonas axonopodis
The invention relates to 1, 3, 4-oxadiazole compounds containing a morpholine group as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The compound has a structure as shown in a general formula (I) which is described in the specification. On the basis of a derivative containing a 1, 3, 4-oxadiazole group, a morpholine group capable of improving the biological activity of a target compound is introduced into the system. The compound has a good inhibition effect on pathogenic fungi and bacteria, such as Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae, Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri, fusarium oxysporum, and blueberry root rot.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Seedling-stage identification method for zucchini root rot resistance
ActiveCN110331185ASignificantly distinguish the difference between resistance and sensitivityEasy to operateFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementSporeGourd
The invention relates to a seedling-stage identification method for zucchini root rot resistance, and belongs to the technical field of crop disease resistance identification. The method comprises thefollowing steps of: firstly, preparing a root rot fungus spore suspension by taking zucchini root rot fungus, wherein the concentration is 10<6> / mL; after zucchini seedling cotyledons are flattened,injecting the zucchini root rot fungus spore suspension at the root for inoculation; and after 20 days, investigating the disease stages of each plant, calculating the disease index, and evaluating the disease resistance of zucchini rootstock germplasm resources against the root rot fungus. The invention establishes a seedling-stage identification method for zucchini rootstock root rot resistance.The identification method is seedling-stage identification, is simple to operate, fast and efficient, has accurate and reliable identification result, can obviously distinguish the difference of theresistance of different zucchini rootstock materials to root rot, is suitable for identifying and screening root rot disease resistance of mass materials, and improves the screening efficiency of germplasm resource materials.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Special culture medium for separating pathogen of soybean root rot
InactiveCN101475913ALow pollution rateEasy to separateFungiMicroorganism based processesPhytophthora sp.Mildew
The invention discloses a special substrate for separating the soybean phytophthora root rot, which is a substrate obtained by adding 3-hydroxy-5-methyl isoxazolyl and [6R [6alpha, 7beta(Z)]]-3-[[(1,2,5,6-tetrahydrochysene-2- methyl-5,6-dioxo-1,2,4-triazine-3-yl) thio] methyl]-7-[[(2-amino-4-thiazolyl) (methoxyimino) acetyl] amino]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo [4.2.0] oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid disodium triple hemigydrate, which corespondingly have a final concentration of 0.3-0.6g / L and 0.1-0 .3 g / L in the special substrate for separating the soybean phytophthora root rot. The inventive substrate can effectively inhibit the growth of bacteria and mildew, and has good separation efficiency, simple composition and low cost. Accordingly, the present inventive substrate can be used for large-scale separation of soybean phytophthora root rot.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
Panax notoginseng seedling protection film, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103392693BReduce skin breakage rateAverage stem length increaseBiocidePlant growth regulatorsSclerotiniaRoot growth
Owner:YUXI WINHEY BIO TECH
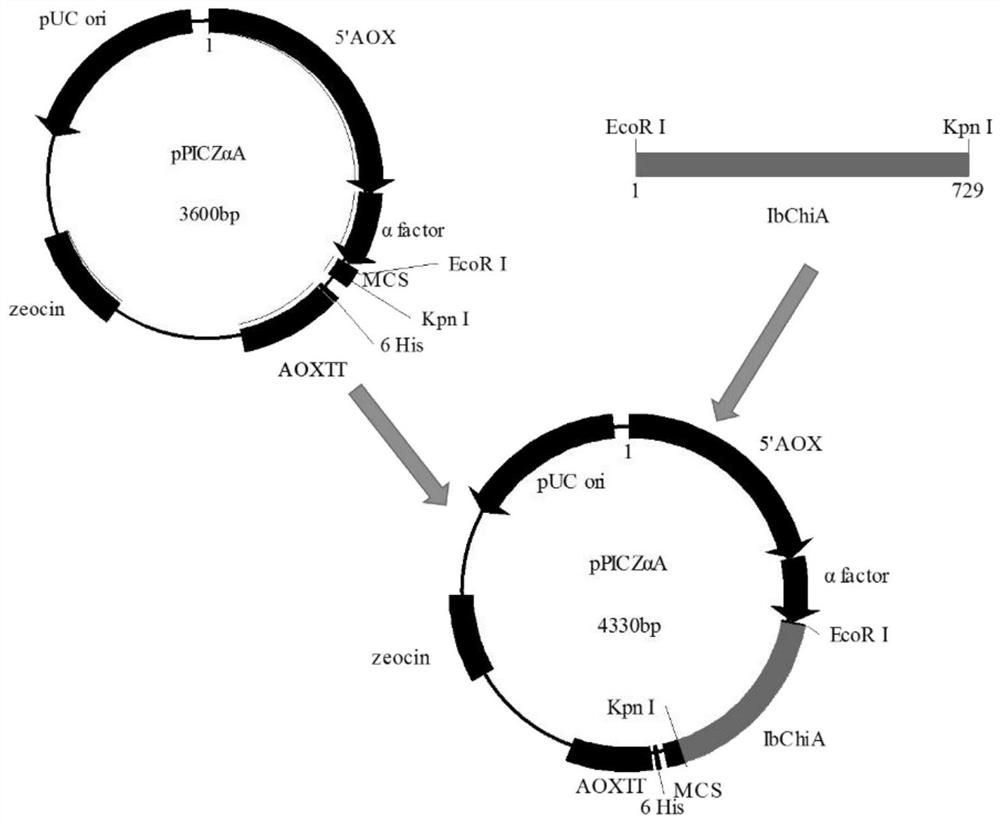
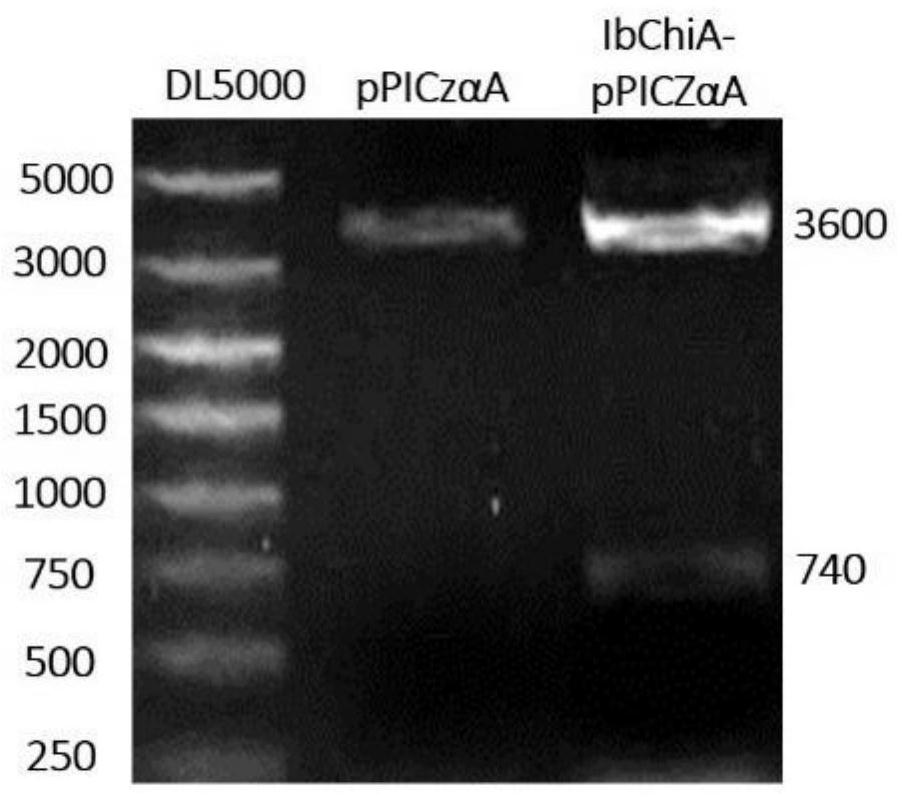
A strain of recombinant Pichia pastoris, its expression product and its application
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
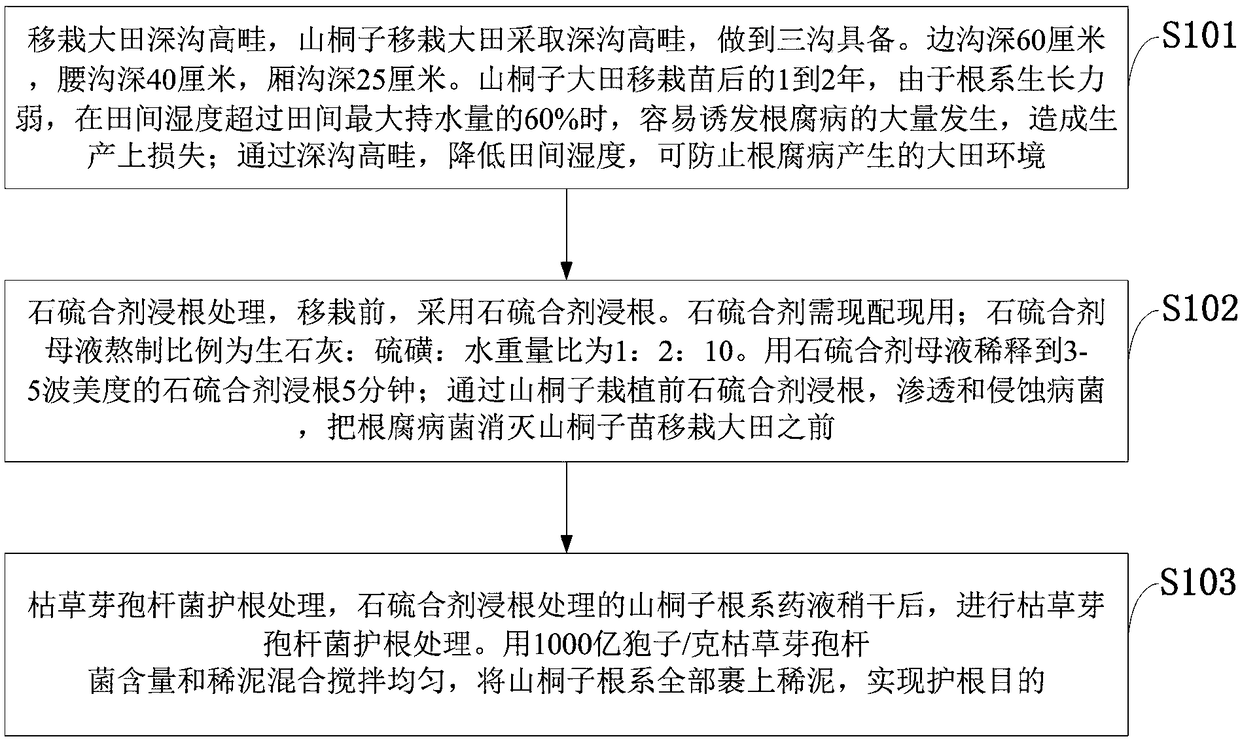
Prevention and treatment method for root rot of idesia polycarpa maxim seedlings transplanted in field
InactiveCN108738947AEffective in killing root rot fungiFree from harmPlant protectionPolycarpaSpore structure
The invention belongs to the technical field of root rot, and discloses a prevention and treatment method for root rot of idesia polycarpa maxim seedlings transplanted in a field. Through deep furrowsand high ridges, the field humidity is reduced, and the field environment generated by the root rot is prevented; lime sulphur is used for soaking roots before idesia polycarpa maxim is transplanted,funguses are permeated and eroded, and root rot funguses are eliminated before then idesia polycarpa maxim seedlings are transplanted in the field; bacillus subtilis protects roots to protect the idesia polycarpa maxim from being damaged by pathogenic bacteria and kill the root rot funguses, so that the whole growth period of the idesia polycarpa maxim is no longer subject to the damage of funguses. The bacillus subtilis grows and propagates through nutrition competition, thereby preventing the growth of plant pathogenic bacteria through a mode of occupying living space, a layer of high-density protective film can be formed on the plant surface, so that the pathogenic bacteria cannot obtain the living space, and crops are protected from being damaged by the pathogenic bacteria. The bacillus subtilis can secretes antifungal substances, inhibit the germination of pathogen spores and the growth of hyphae, thereby achieving the purpose of prevention and treatment; the prevention and treatment rate of the root rot reaches 98%.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV FOR NATITIES
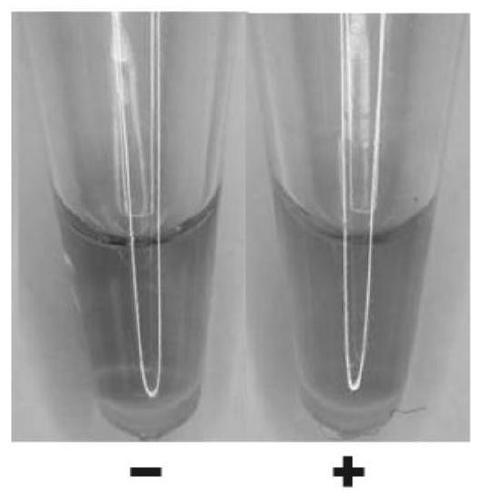
Detection of Phytophthora cedarii Root Rot Pathogen by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (Lamp) Technology Based on Color Judgment
InactiveCN106636371BQuick judgmentImprove practicalityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPhytophthora sojae
The invention discloses a molecular detection method for detecting phytophthora sojae of cedar by the color determination-based loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) technology and a primer thereof. The primer sequence is as shown respectively in SEQ ID NO.1 to SEQ ID NO.5. The detection system can be used for quickly, conveniently, efficiently, specifically and sensitively detecting the phytophthora sojae of cedar under a 62 DEG C isothermal condition, a complicated instrument is not required, a new technical platform is provided to detection of phytophthora sojae of cedar, and field detection on phytophthora sojae of cedar can be well fulfilled. The method is applicable to inspection and quarantine of imported and exported plants and plant products and investigation, quick diagnosis, detection and the like of diseases, and has an important meaning for preventing phytophthora sojae of cedar from being introduced into China. Furthermore, the establishment of the system provides technical guidance and theoretic base to detection of other pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:中华人民共和国昆山出入境检验检疫局
Thiazole hydrazide compound as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a thiazole hydrazide compound as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The compound has a structure as shown in a general formula (I). The compound has a relatively good inhibition effect on pathogenic fungi and bacteria; and has a good inhibition effect onfusarium graminearum, potato late blight bacteria, blueberry root rot bacteria, pepper fusarium oxysporum, sclerotinia sclerotiorum, colletotrichum oryzae, botryosphaeria dothidea, rhizoctonia solani, xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae, ralstonia solanacearum, citrus canker germs, kiwi fruit canker germs, cucumber xanthomonas oryzae pv. Cucumerinum, Xanthomonas oryzae of konjac, Botryosphaeria dothidea, tomato canker pathogen, apple canker pathogen and the like.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Effect of borrelidin for controlling soybean phytophthora root rot
InactiveUS20140011867A1Inhibit mycelial growthOrganic active ingredientsBiocideMetalaxylPhytophthora sp.
The present invention discloses use of borrelidin for preventing and controlling phytophthora root rot of soybean. The present invention also discloses formulations of borrelidin seed coating agents and wettable powders and preparation methods thereof. Borrelidin exhibits significant effects on Phytophthora sojae. As compared with the conventional fungicide metalaxyl which is used for preventing and controlling phytophthora root rot of soybean, the mycelial growth inhibition assay indicates that the IC50 and IC95 values of borrelidin are 1 / 62 and 1 / 263, respectively, of those of metalaxyl. In the indoor pot-culture experiment, the seed coating agent and wettable powder exhibit significant controlling effects on phytophthora root rot of soybean.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HISUN PHARMA CO LTD
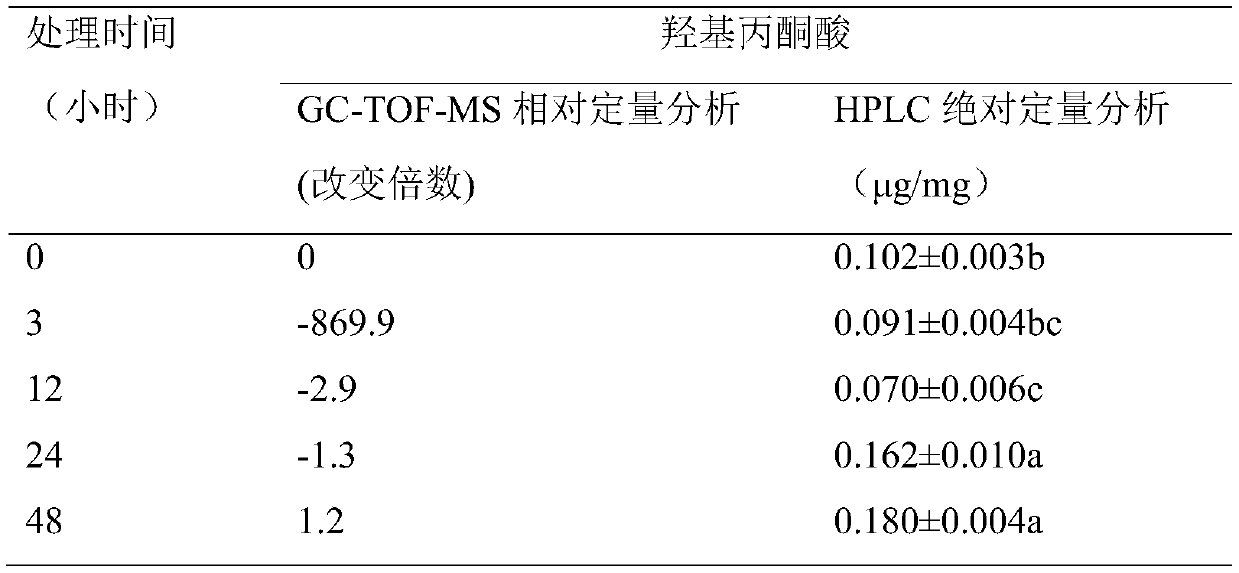
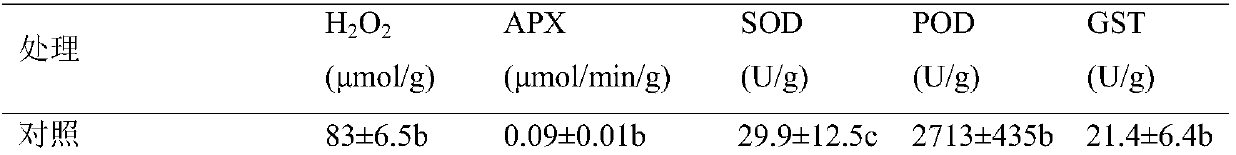
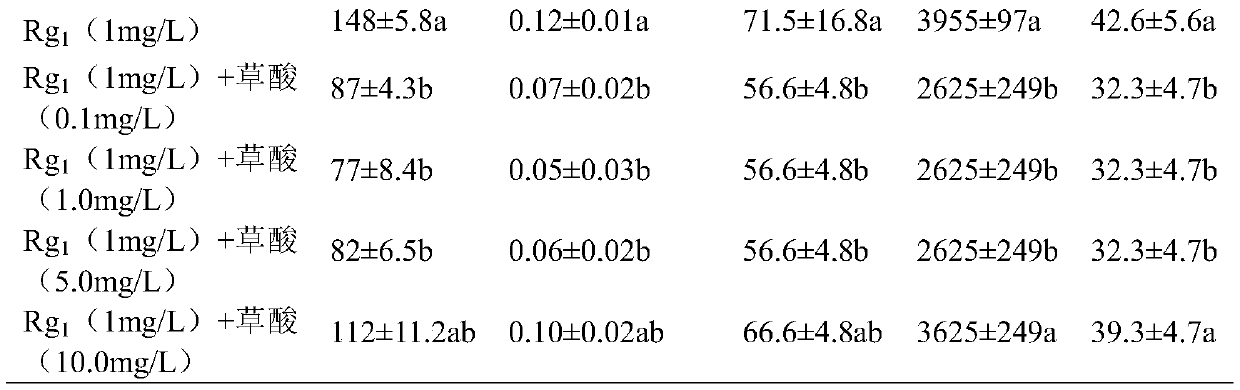
A method for alleviating the autotoxic injury of Panax notoginseng by using oxalic acid
ActiveCN106577649BIncrease resistanceImprove qualityBiocideAnimal repellantsContinuous croppingOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATE
The invention discloses a method for alleviating panax notoginseng self-poisoning injuries by using oxalic acid. The method particularly comprises the following steps: preparing an oxalic acid solution of which the concentration is 0.1 to 5.0mg / L by using deionized water containing 0.01% of Tween 80 in percent by volume, carrying out root-irrigation once after panax notoginseng is sowed or transplanted for 7 days; then continuously irrigating for 3 times by using the oxalic acid solution with the same concentration when the germination rate of panax notoginseng seeds reaches 10%, wherein irrigation is carried out at an interval of 7 days, and the root-irrigation amount for each panax notoginseng is 5mL. The method for alleviating the panax notoginseng self-poisoning injuries by using the oxalic acid disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects of solving the problem of decreased oxygen free radical scavenging abilities for the reduced oxalic acid taken as a panax notoginseng rhizosphere antioxidant substance caused by saponin autotoxins, improving the emergence rate and growth potentials of the panax notoginseng seeds and seedlings, enhancing the panax notoginseng resistance, lowering the probability in increasing of root rot damage for cell damage caused by the autotoxins in the growth process of the panax notoginseng and reducing the use amount of pesticides, thereby being an ecological, safe and effective measure for alleviating continuous cropping obstacles. The method disclosed by the invention is of great significance to improve the quality of the panax notoginseng and lower pesticide residues.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Trulaspora delbrueckii MP023 with bacteriostatic effect and application thereof
The invention discloses a strain of torulaspora delbrueckii MP023 with a bacteriostatic effect and an application of the torulaspora delbrueckii MP023. The torulaspora delbrueckii is classified and named as torulaspora delbrueckii, the torulaspora delbrueckii is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, and the preservation number of the torulaspora delbrueckii is CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) NO: M 2022264. The torulaspora delbrueckii MP023 or gas generated by the torulaspora delbrueckii MP023 can inhibit the growth of various phytopathogens such as rhizoctonia solani, strawberry root rot, alternaria alternata, botrytis cinerea and fusarium oxysporum, so that the torulaspora delbrueckii MP023 can be prepared into a biocontrol preparation for preventing and treating plant diseases caused by the phytopathogens; good market application prospects are realized.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
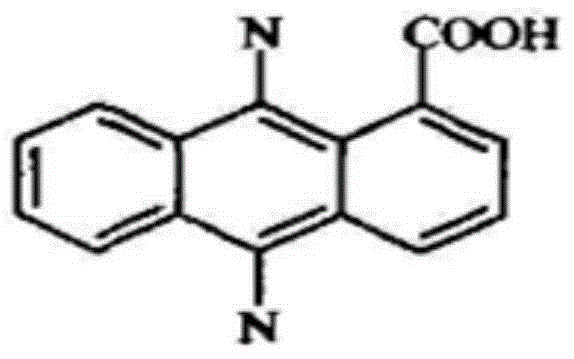
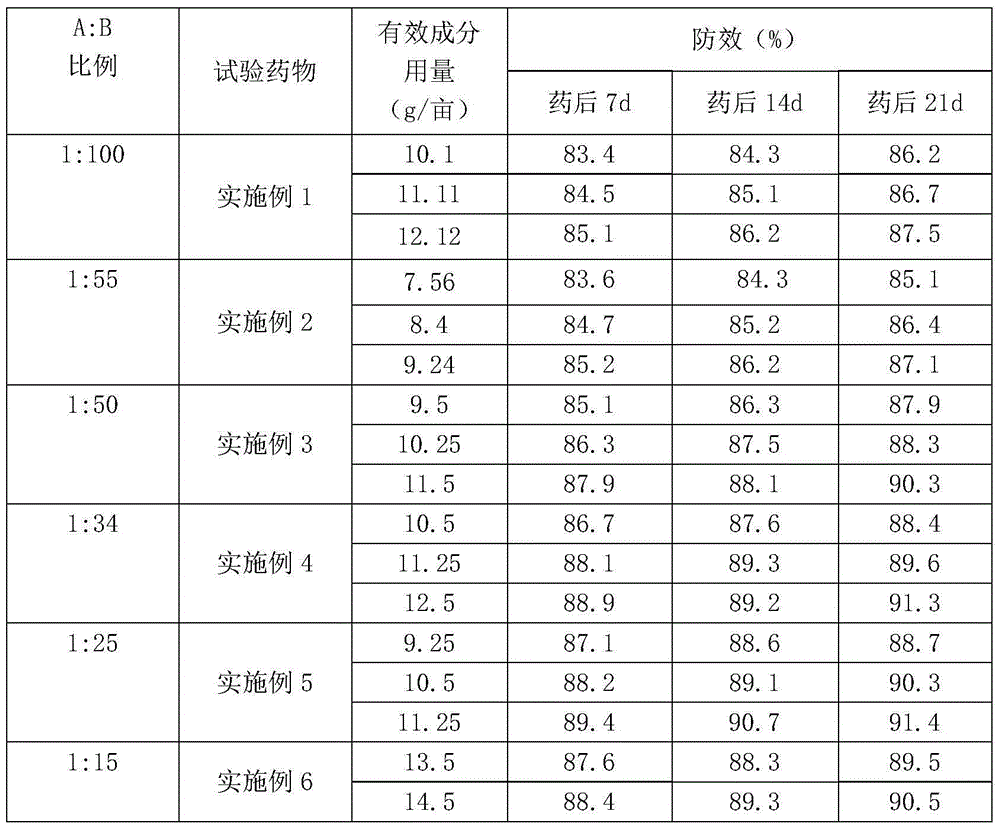
Bactericidal composition and application thereof
ActiveCN104957157AGood synergyImprove the effect of prevention and controlBiocideDead animal preservationCarbamateCarboxylic acid
Relating to the technical field of pesticide compounding, the invention discloses a bactericidal composition and application thereof. The effective component of the bactericidal composition contains phenazine-1-carboxylic acid A and a carbamate bactericide B, wherein the carbamate bactericide B is one or more of propamocarb and its hydrochloride or diethofencarb and its hydrochloride, and the weight ratio of A to B is 1:100-100:1. Compounding of the effective component A and B has an obvious synergistic effect, and can effectively reduce the dosage of each single agent. The bactericidal composition has good effect on expansion of the bacteriocidal spectrum and delaying of plant resistance to drugs, also can prolong the lasting period, and has obvious promotion value. The composition can be added with other pesticide adjuvants to be processed into any dosage form. The bactericidal composition can effectively control sheath blight, rice blast, Ustilaginoidea virens, rust disease, root rot, sclerotinia sclerotiorum, smut, and blight, etc.
Owner:LIER CROPSCIENCE CO LTD
A kind of actinomycetes with inhibitory effect on peanut soil-borne pathogenic fungus and its screening method
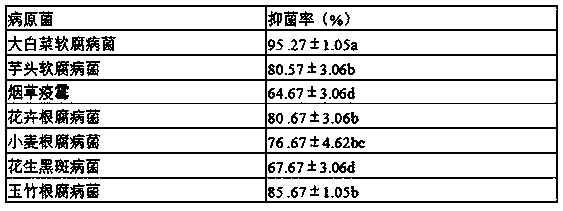
The invention discloses a Streptomyces luteus ( Streptomyces lute overticillatus ) strain, its preservation number is CCTCC No: M2020262. The fermentation liquid of this strain has inhibitory effects on peanut spp., peanut root rot and peanut crown rot. The inhibition rates of the three pathogenic bacteria are 77.71%, 42.62% and 63.18% after the fermentation liquid is diluted 5 times. At present, there is no report in China that the same biocontrol bacteria can also treat three soil-borne fungal diseases of peanuts. The bacterium has no pathogenicity to humans and animals, can be safely used for biological control of peanut soil-borne fungal diseases, can reduce the use of chemical pesticides, reduce environmental pollution, and promote the development of green agriculture, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
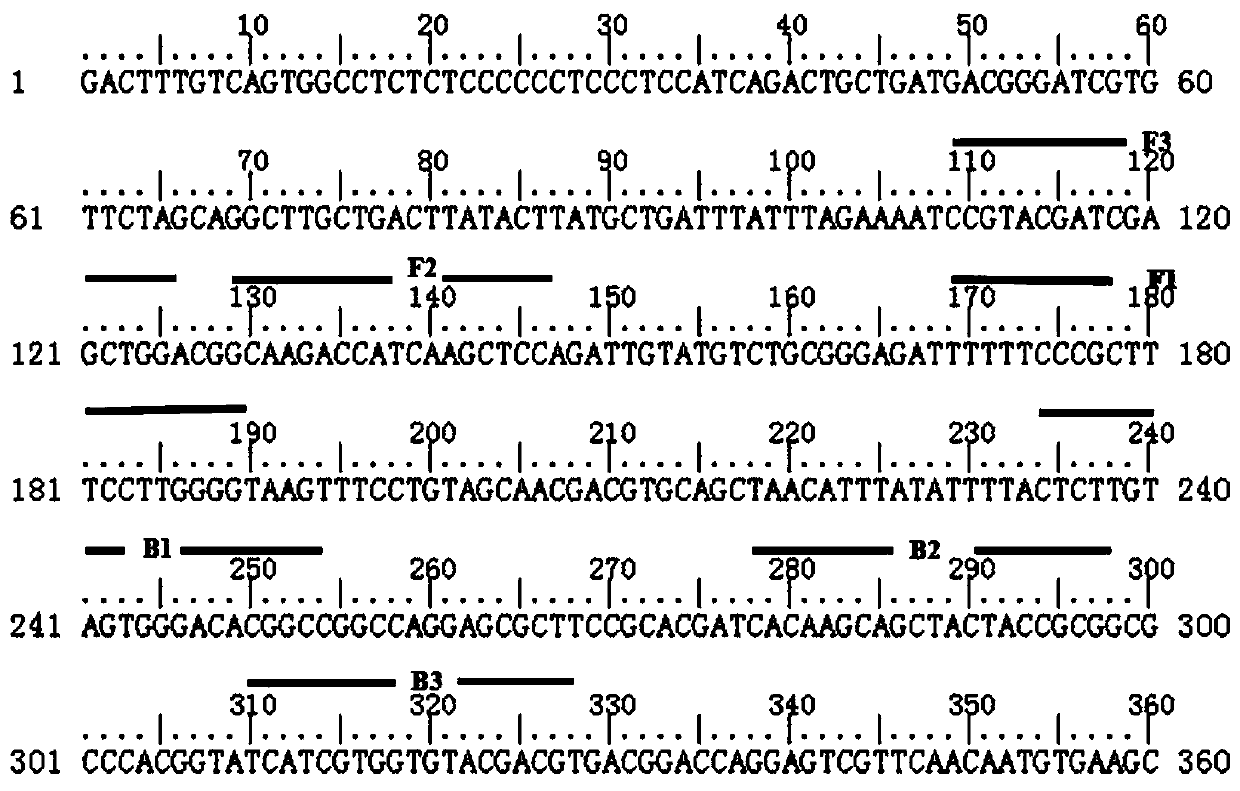
Primer group, kit and application of primer group in rapid identification of pepper root rot bacteria
InactiveCN113999926AHigh amplification efficiencyStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyRapid identification
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular detection, and discloses a primer group and a kit containing the primer group. The primer group comprises an upstream primer F1 and a downstream primer R1, and the sequences of the upstream primer F1 and the downstream primer R1 are as follows: the upstream primer F1 is 5'-CGTGTCGCAGAAGAGGG-3'; the downstream primer R1 is 5'-AATAGGAAGCCGCTGAGC-3', and the invention also discloses an application of the primer group or the kit in rapid identification of pepper root rot bacteria. The application comprises the following steps: S1, extracting sample DNA; S2, taking the sample DNA as a template, and carrying out PCR amplification reaction by utilizing the primer group to obtain a PCR amplification product; and S3, analyzing a PCR amplification product. The primer group provided by the invention can specifically identify fusarium solani, and achieves the characteristics of high amplification efficiency, strong specificity and high accuracy; meanwhile, the rapid identification method established in combination with the primer group is quite simple, and fusarium solani can be identified without morphological identification and DNA sequencing.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION SICHUAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com