Patents
Literature
56 results about "3T3 cells" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
3T3 cells come from a cell line established in 1962 by two scientists then at the Department of Pathology in the New York University School of Medicine, George Todaro and Howard Green. The 3T3 cell line has become the standard fibroblast cell line. Todaro and Green originally obtained their 3T3 cells from Swiss albino mouse embryo tissue.
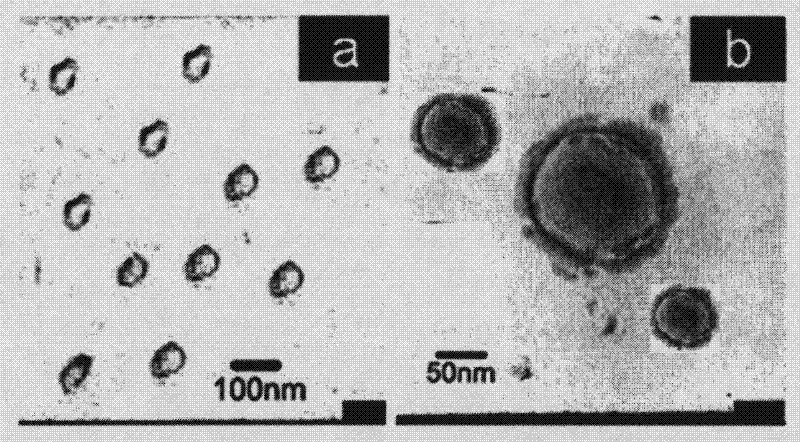
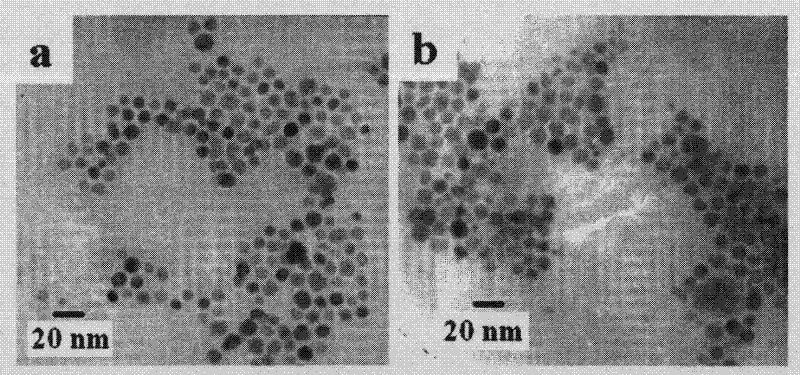
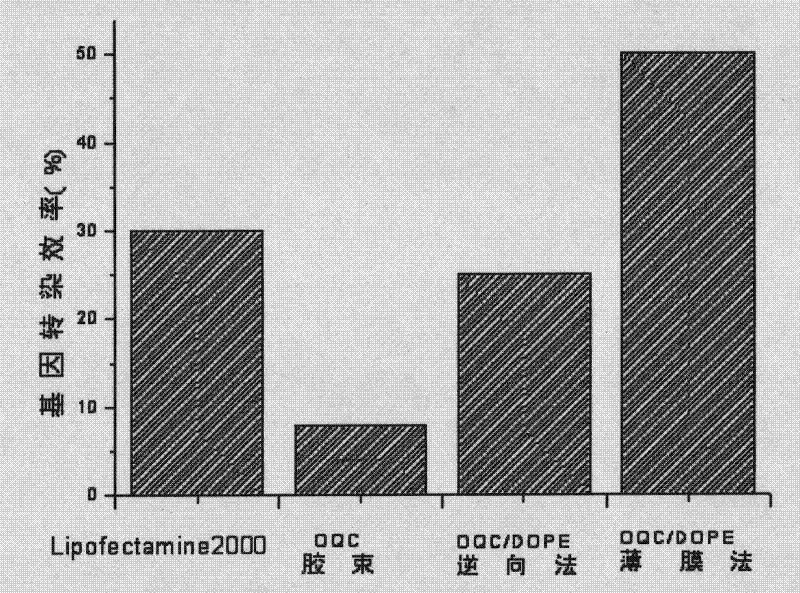
Target quaternary ammonium salt cationic polymer lipid gene carrier, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102234658ARich varietyHigh transfection efficiencyGenetic material ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsPositive controlQuaternary ammonium cation
The invention discloses a target quaternary ammonium salt cationic polymer lipid gene carrier, a preparation method and an application thereof. The target quaternary ammonium salt cationic polymer lipid genetic carrier is characterized in that: a polymeric quaternary ammonium salt and lipid are adopted for preparing a quaternary ammonium salt cationic polymer lipid genetic carrier according to a mass ratio, wherein the mass ratio of the polymeric quaternary ammonium salt to the lipid is 0.05-20:1; then a assembly method or a modification method is adopted for modifying to prepare a folic acid or EGFR antibody modified cationic polymer lipid gene carrier. Results of gene transfection experiments show that: gene transfection efficiencies of the target quaternary ammonium salt cationic polymer lipid gene carrier in 293T cells and NIH-3T3 cells are the same as the gene transfection efficiencies of positive control lipofectamine of lipofectamine<TM>2000 in the 293T cells and the NIH-3T3 cells; the gene transfection efficiencies of the EGFR antibody modified cationic polymer lipid genetic carrier in liver cancer Huh-7 cells and breast cancer MCF-7 cells are higher than the gene transfection efficiencies of the lipofectamine<TM>2000 in the liver cancer Huh-7 cells and the breast cancer MCF-7 cells. The cationic polymer lipid genetic carrier system provided by the present invention has good biocompatibility and low cytotoxicity, and can be as an excellent non-viral gene delivery carrier.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ONCOLOGY
Water soluble mitochondrial targeting imaging probe and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105777637AGood water solubilityGood photobleaching resistanceOrganic chemistryIn-vivo testing preparationsHigh resistanceSolubility
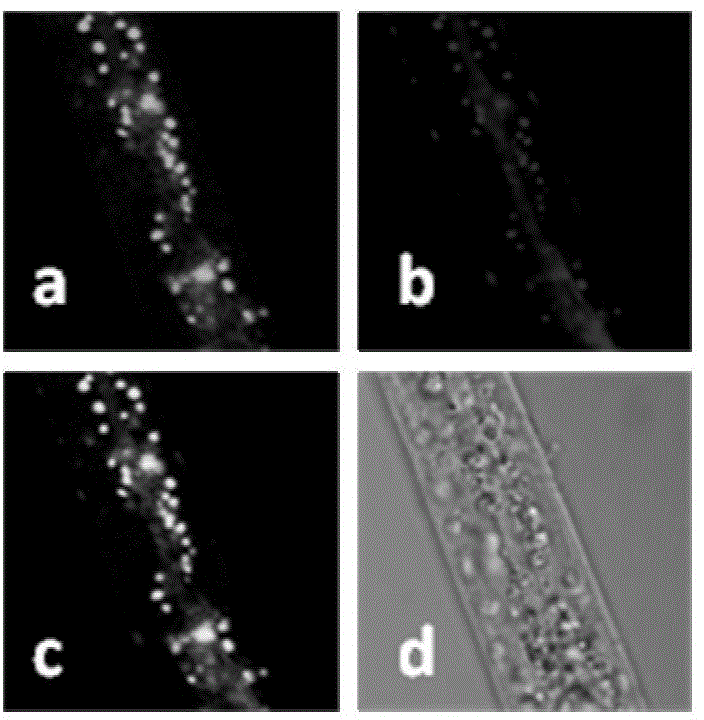
The invention discloses a water soluble mitochondrial targeting imaging probe and a preparation method thereof. The structural formula of compounds that form the water soluble mitochondrial targeting imaging probe can be formula (I), (II), (III), (IV), (V), or (VI). The water soluble mitochondrial targeting imaging probe has the characteristics of good water solubility, high resistance to photo-bleaching, high thermal stability, low toxicity, and high sensitivity. Hela, MCF-7, and NIH-3T3 cells are taken as the models to observe the distribution situation of the fluorescent probe in cells through a laser con-focal microscopy technology; the results show that the probe is mainly distributed in mitochondrial, and the targeting property is good. The test results show that the provided probe has the characteristic of strong mitochondrial targeting imaging performance on cancer cells and non-cancer cells; thus an effective means is provided for quantitatively research superoxide radicals in cells in time and space, and thus the pathologic and physiological mechanisms of active oxygen radicals can be researched.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Targeting metabolic enzymes in human cancer
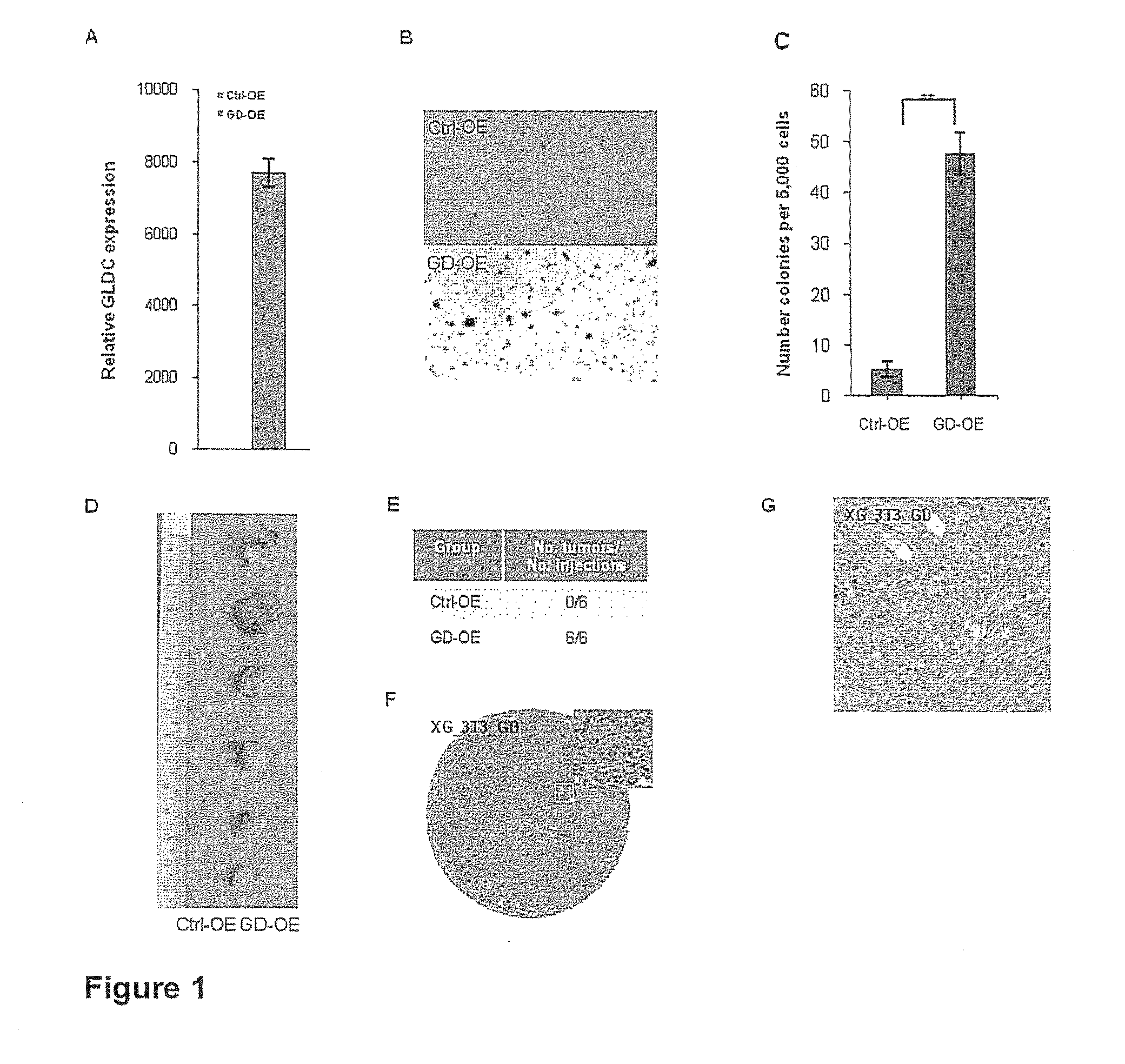
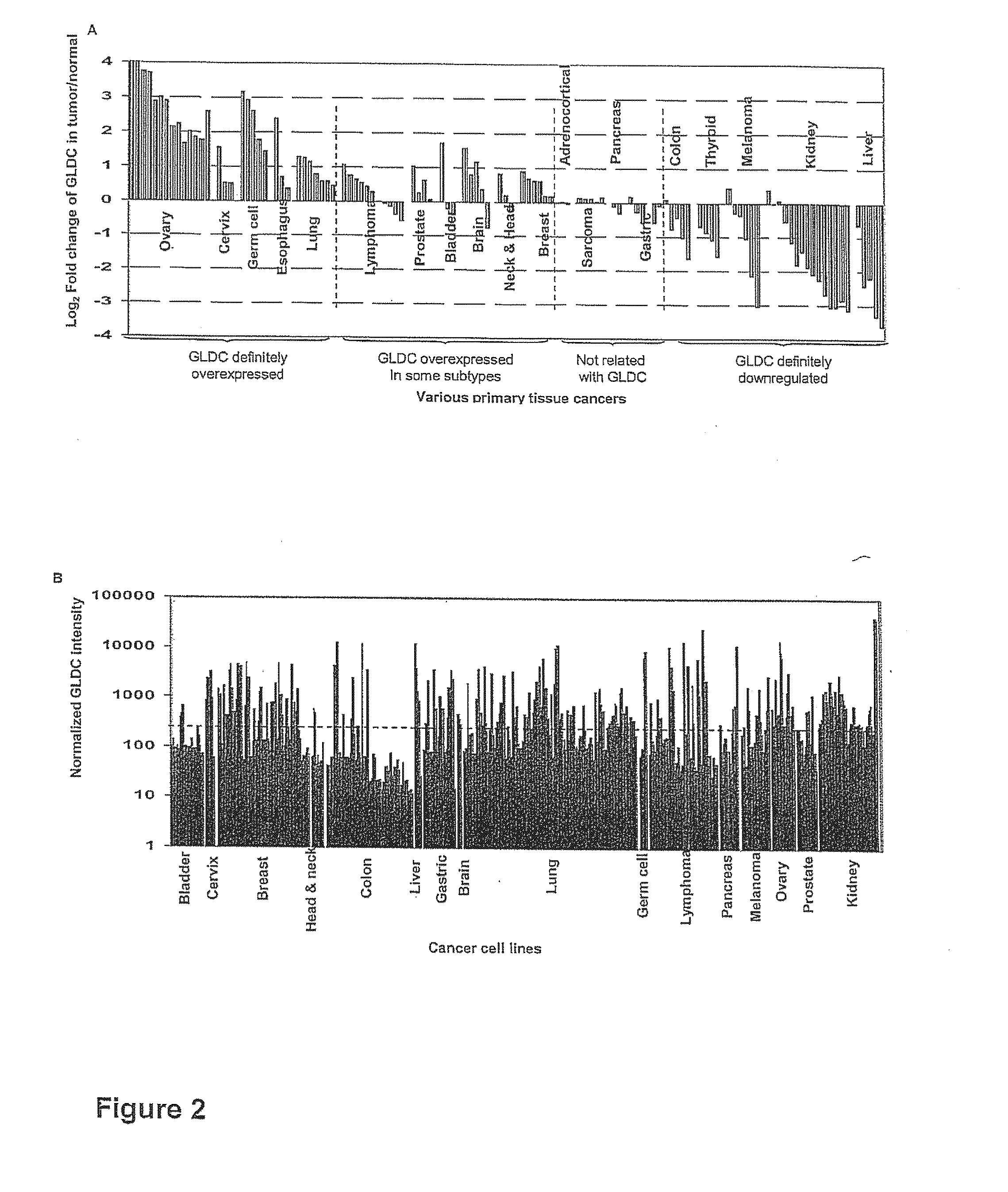
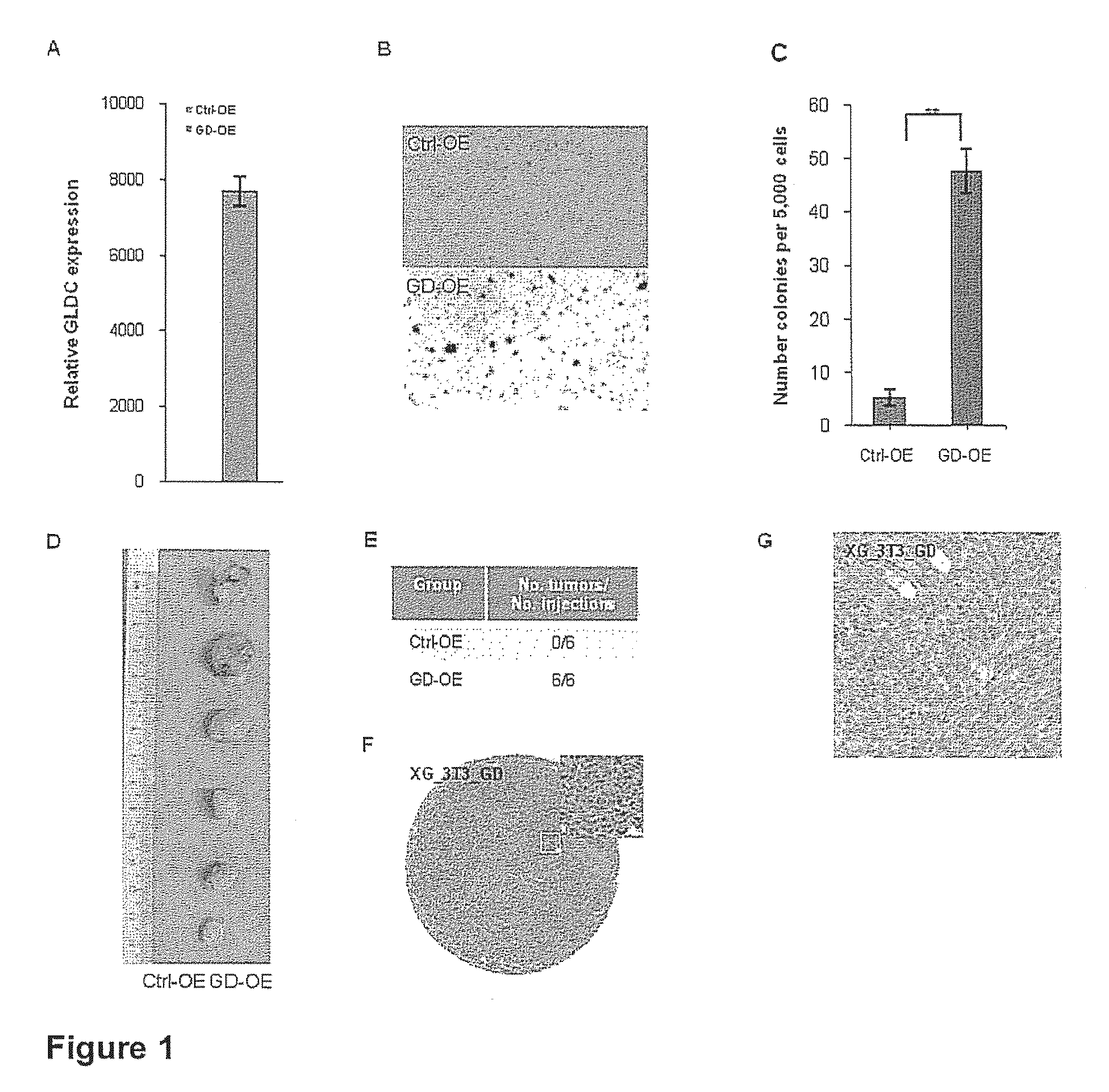
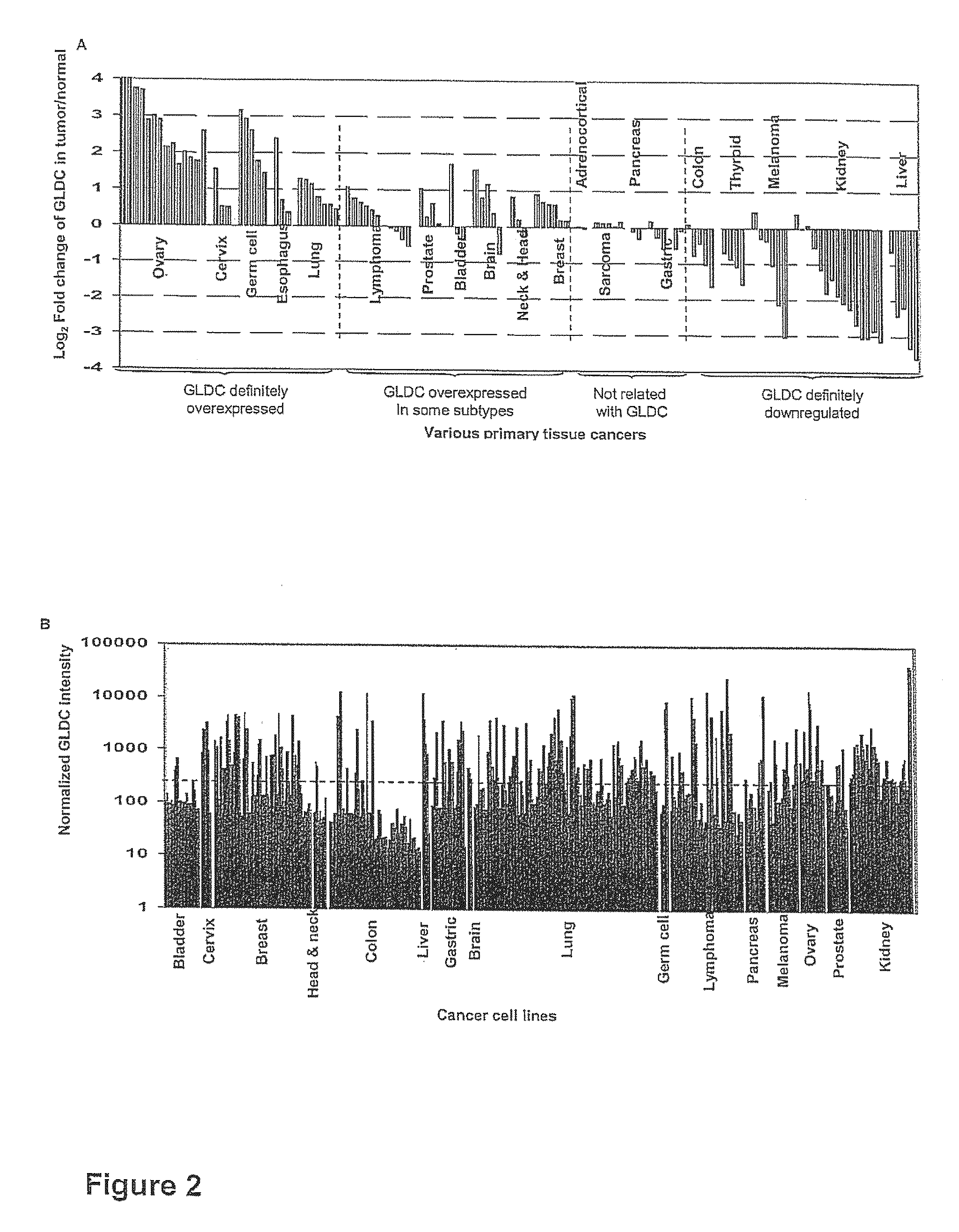
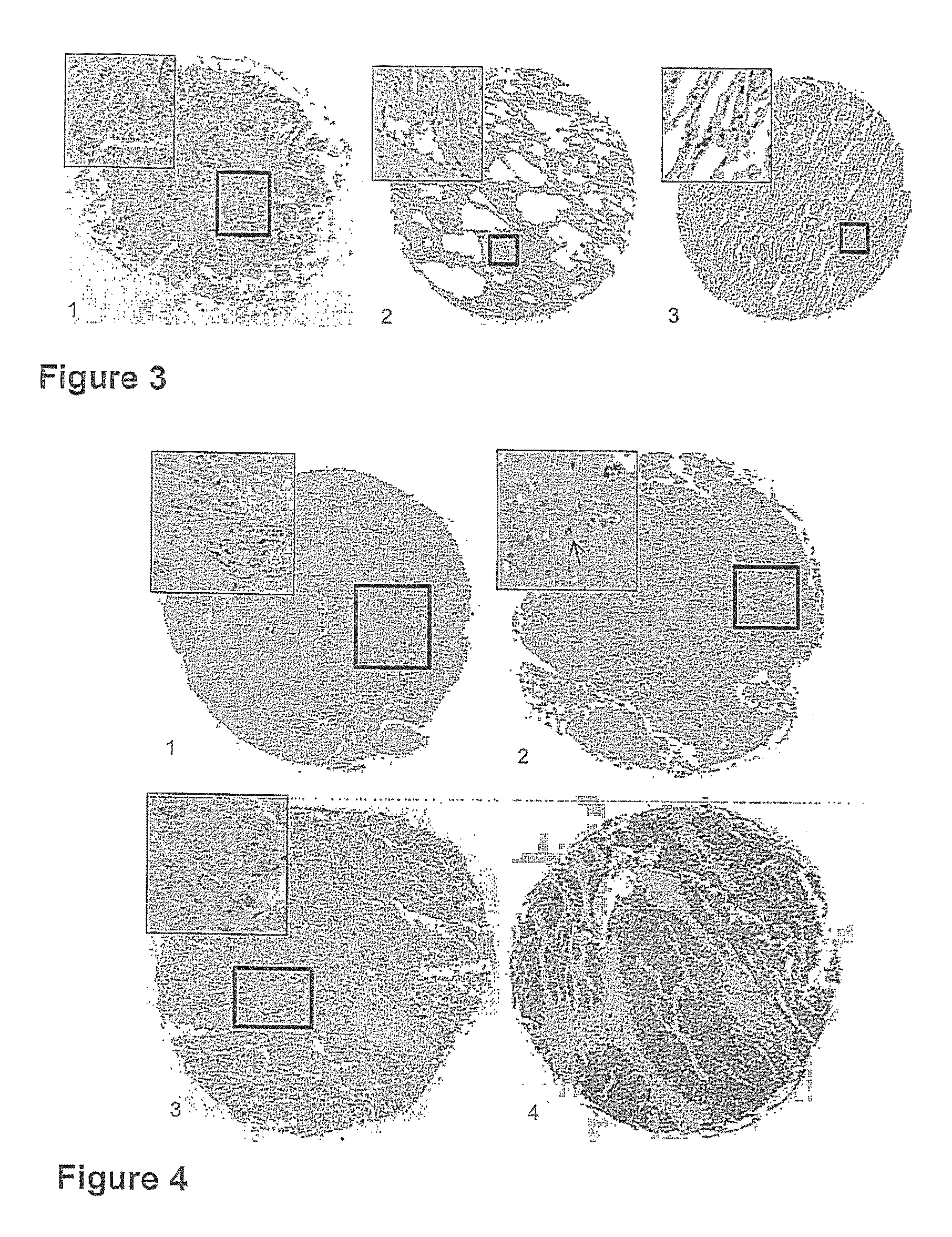
Targeting metabolic enzymes in human cancer Abstract Lung cancer is a devastating disease and a major therapeutic burden with poor prognosis. The functional heterogeneity of lung cancer (different tumor formation ability in bulk of tumor) is highly related with clinical chemoresistance and relapse. Here we find that, glycine dehydrogenase (GLDC), one of the metabolic enzyme involved in glycine metabolism, is overexpressed in various subtypes of human lung cancer and possibly several other types of cancers. GLDC was found to be highly expressed in tumor-initiating subpopulation of human lung cancer cells compared with non-tumorigenic subpopulation. By array studies we showed that normal lung cells express low levels of GLDC compared to xenograft and primary tumor. Functional studies showed that RNAi inhibition of GLDC inhibits significantly the clonal growth of tumor-initiating cells in vitro and tumor formation in immunodeficient mice. Overexpression of GLDC in non-tumorigenic subpopulation convert the cells to become tumorigenic. Furthermore, over-expression of GLDC in NIH / 3T3 cells and human primary lung fibroblasts can transform these cells, displaying anchorage-independent growth in soft agar and tumor-forming in mice. Not only is GLDC is expressed human lung cancer, it is also up-regulated in other types of cancer, such as colon cancer. RNAi knockdown of GLDC in colon cancer cell line, CACO-2 cells, can also inhibit the tumor formation in mice. Thus GLDC maybe a new metabolic target for treatment of lung cancer, and other cancers.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Establishment method of positive screening system based on gene knockout cells
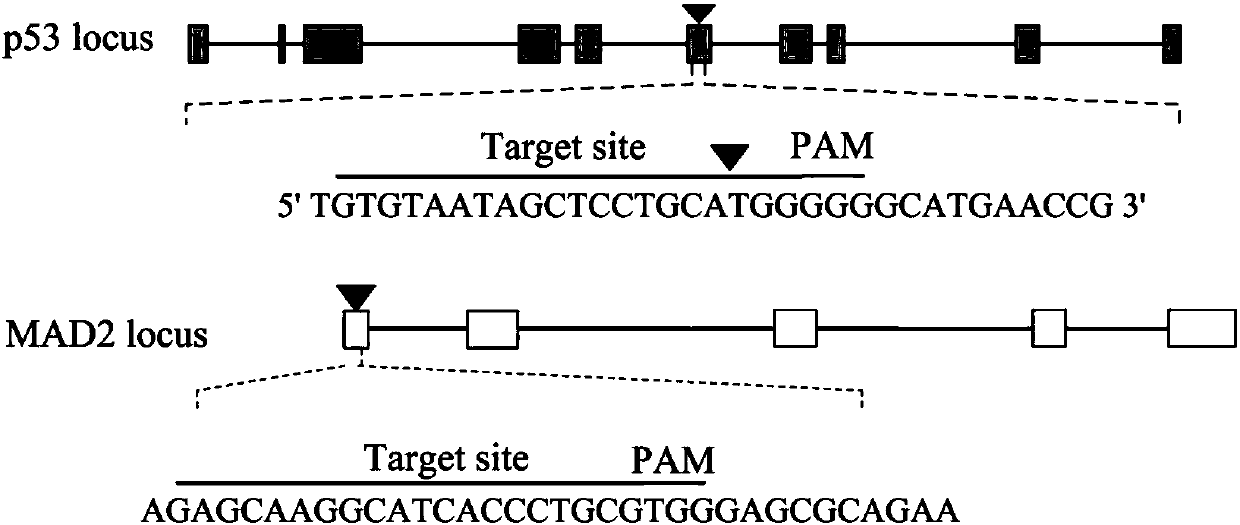
The invention belongs to the technical field of zoobiology, and relates to an establishment method of a positive screening system based on gene knockout cells; on the basis of the established system,p53 and MAD2 genes are knocked out in NIH / 3T3 cells, and the cells, which undergo gene knockout, are subjected to positive screening. According to the establishment method, target sequences of the sixth exon of the p53 gene and the first exon of the MAD2 gene are subjected to site-directed knockout in an NIH / 3T3 gene line, and in the combination with a green fluorescent protein gene and a puromycin gene, the cells, which undergo p53 and MAD2 gene knockout, are subjected to positive screening; and by virtue of the established positive screening system, the p53 and MAD2 genes are simultaneouslyedited in living mouse liver, so that a mouse liver cancer model is finally obtained. The method provided by the invention lays a foundation for related researches on editing the p53 and MAD2 genes ina living mouse.
Owner:SHANGHAI PUBLIC HEALTH CLINICAL CENT
Oligopeptide derivative capable of combination of basic fibroblast growth factor, and application thereof
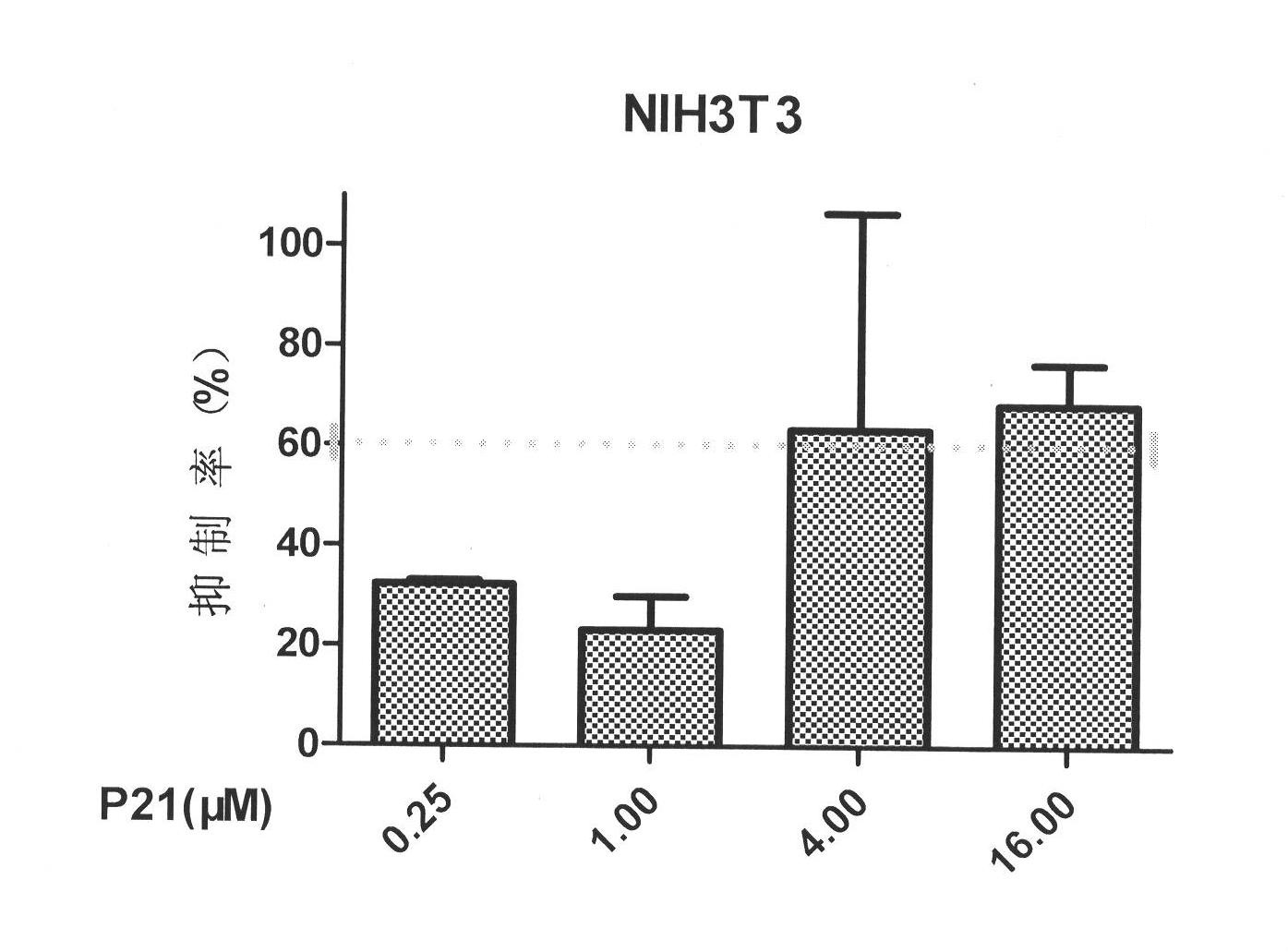
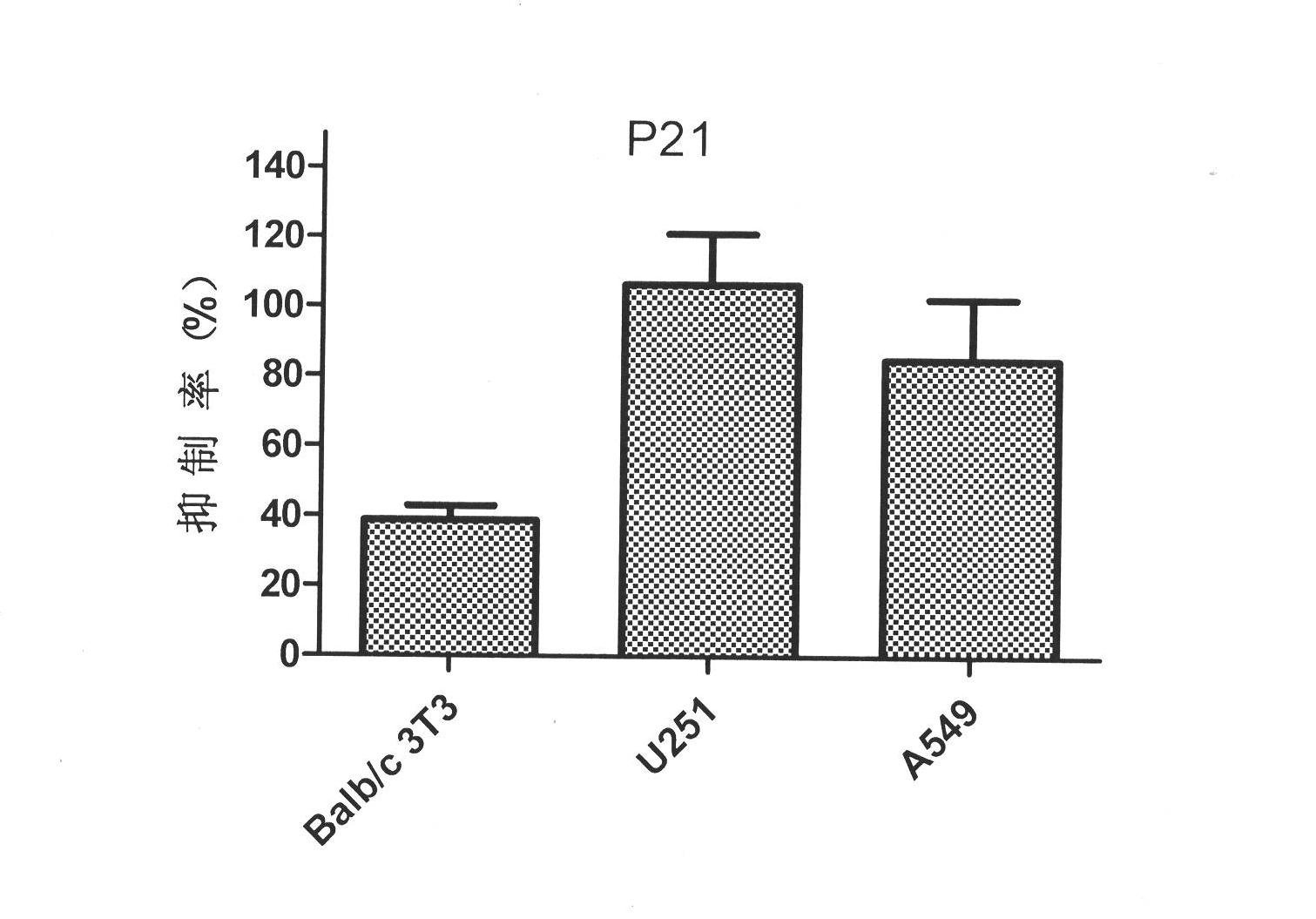
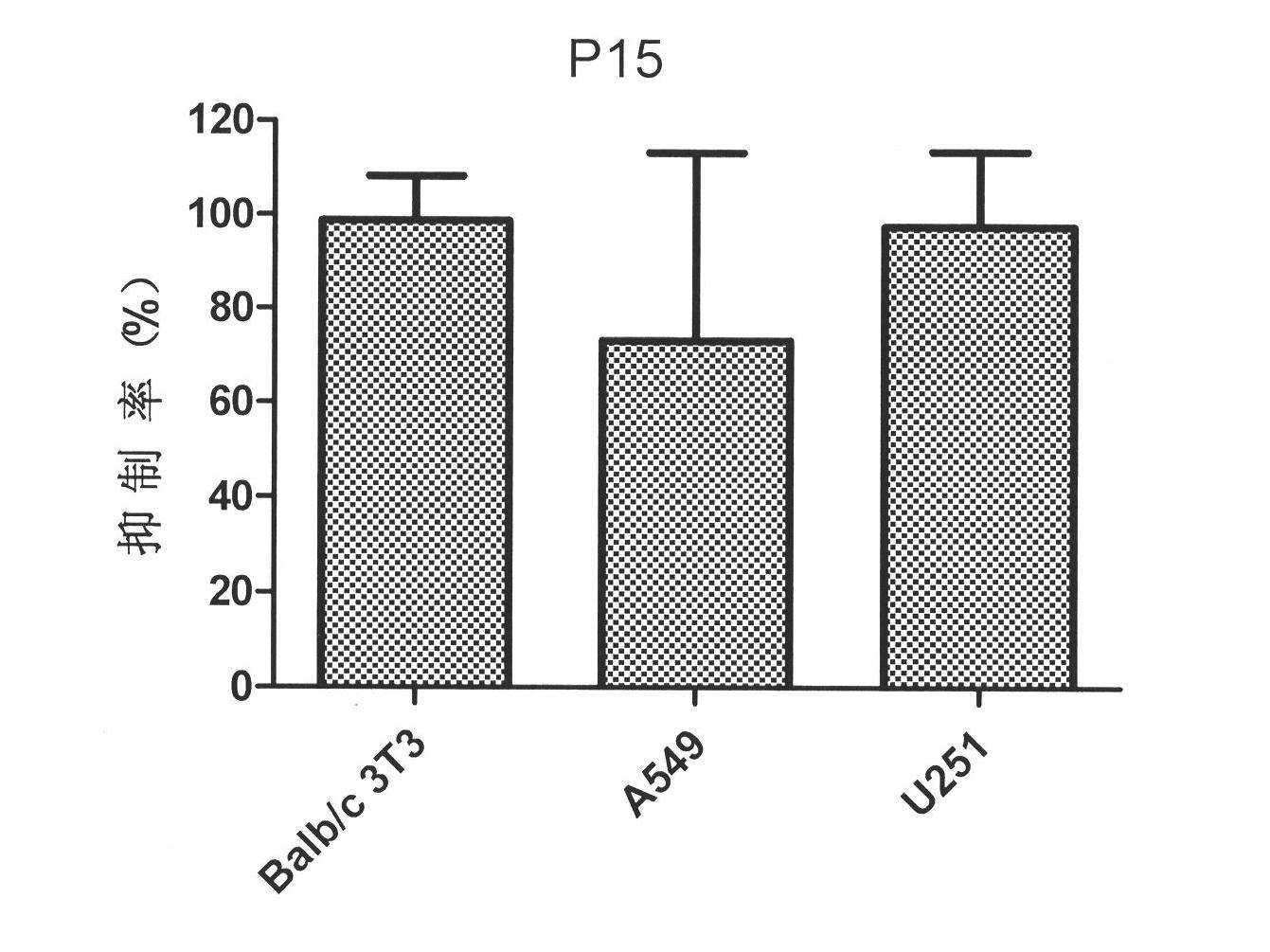
The invention belongs to the technical fields of medicinal chemistry and polypeptide biology, and relates to an oligopeptide derivative P15 capable of combination of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), wherein the sequence of the P15 is N'-PILQAGLGGGS-NH2-C'. The invention specifically relates to the sequence of the P15, and an application of the P15 in fields of basic research and medicine. The present invention further comprises various peptide derivatives of the P15, wherein the P21 is the peptide derivative of the P15, and the sequence of the P21 is N'-PLLQA TA GGGS-NH2-C'. With combination of the bFGF, the P15 and the P21 can provide good inhibition activities for bFGF-induced NIH3T3 cell proliferation and bFGF-induced Bable / C 3T3 cell proliferation, can significantly inhibit proliferations of bFGF-induced lung cancer A549 cells and bFGF-induced glioma U251 cells, and provide prospects for development into anti-tumor peptide drugs.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
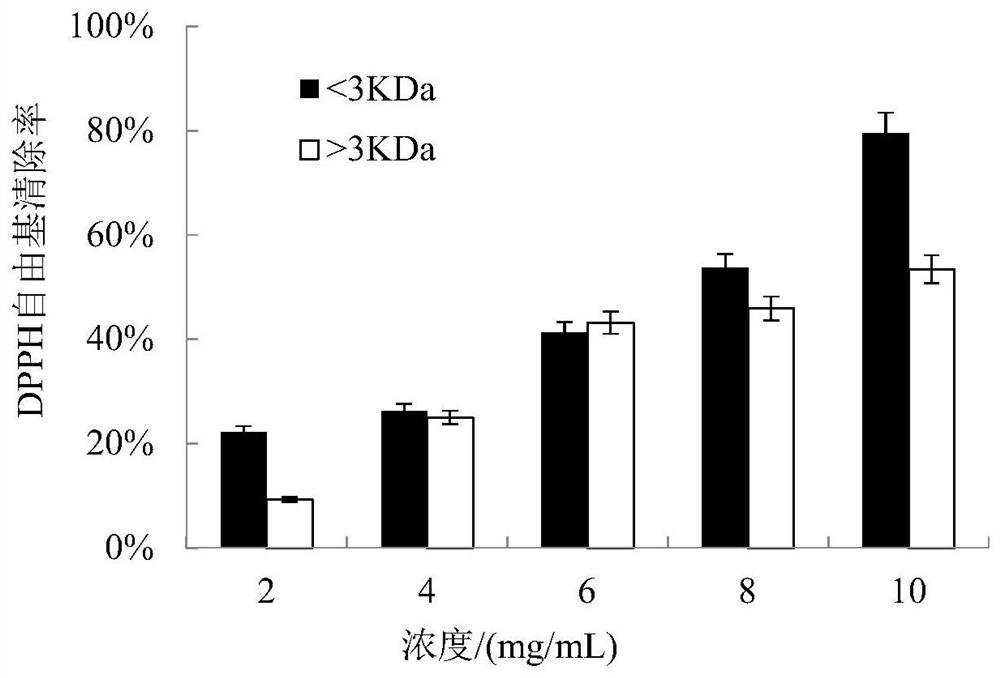
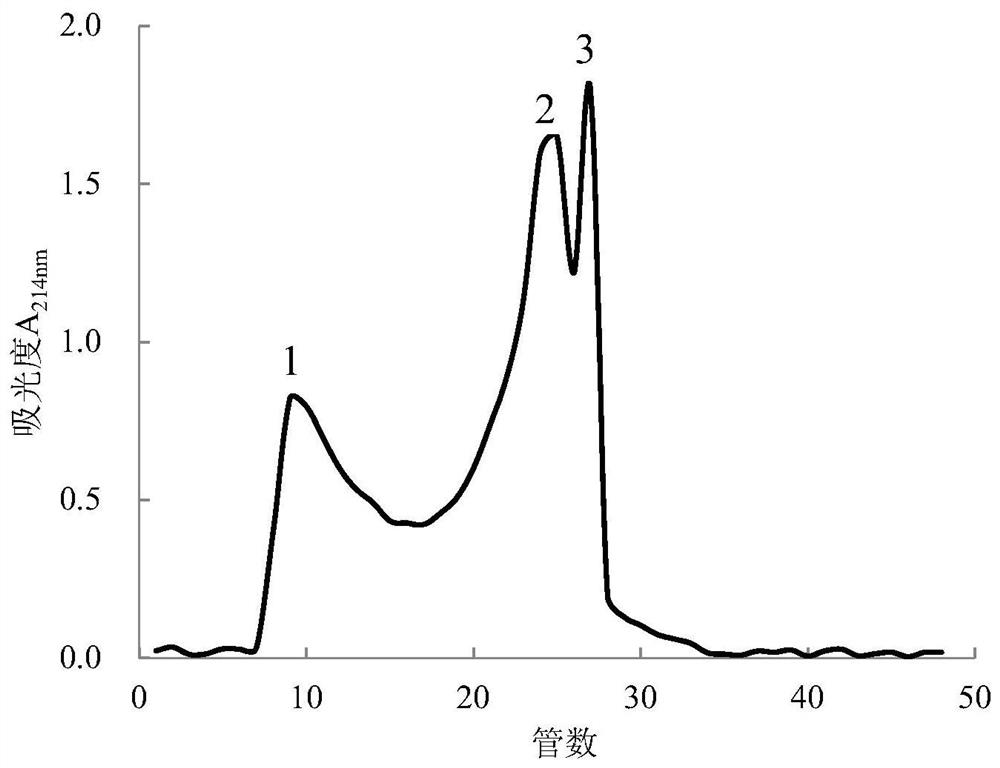
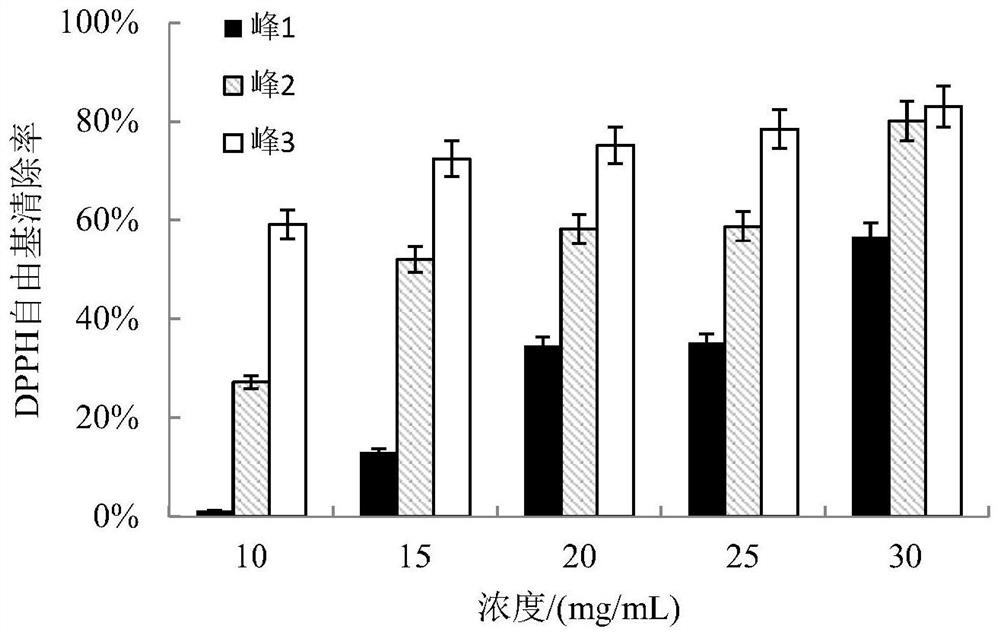
Antioxidant peptide and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111647072AImproves antioxidant activityRealize high-value utilizationConnective tissue peptidesAntinoxious agentsMyofibrillaOxygen radical absorbance capacity
The invention discloses an antioxidant peptide and a preparation method and application thereof, and aims to provide an antioxidant peptide which is derived from chicken breast myofibrillar protein and has high-efficiency antioxidant activity, and a preparation method and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the antioxidant peptide is ITTNPYDY or IGWSPLGSL. The preparation method of theantioxidant peptide comprises the following steps of: extracting the myofibrillar protein from fresh chicken breast serving as a raw material; performing enzymolysis on the obtained myofibrillar protein by using pepsin; and performing separation, purification and synthesis to obtain the antioxidant peptide. The antioxidant peptide is a novel antioxidant peptide, and has high antioxidant activitythrough detection; under the measuring condition, the iron ion reducing capacity and the oxygen radical absorbing capacity of the antioxidant peptide are obviously higher than those of glutathione; and meanwhile, the antioxidant peptide has an obvious effect of inhibiting the oxidative damage of NIH-3T3 cells. The antioxidant peptide belongs to a natural antioxidant, is safer to eat, and can be applied to food, health-care products and medicaments with antioxidant functions.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF COMMERCE
Recombinant human fibronectin III1-C, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111217903AIncrease productionShorten the production cycleCosmetic preparationsConnective tissue peptidesBALB/cCell adhesion
The invention discloses a recombinant human fibronectin III1-C (rhFNIII1-C), and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: optimizing a targetgene segment of the target protein according to codon expression preference, and inserting the obtained gene segment into pET-32a to construct a recombinant plasmid; transforming and introducing therecombinant plasmid into an expression vector BL21(DE3), and carrying out screening to obtain positive clone bacteria capable of realizing efficient soluble expression; carrying out enlarging fermentation culture on the positive clone bacteria, carrying out induced expression, performing crushing and centrifuging to obtain a supernatant, and carrying out purification through elution with a His-tagaffinity chromatography column, dialysis, filtration and other steps to obtain a high-quality rhFNIII 1-C solution with a protein concentration of 1.0 mg / mL or above and a purity of 90% or above. According to detection and observation results of cell adhesion promoting tests, the rhFNIII1-C has the performance of obviously promoting adherence and adhesion of MDBK cells and Balb / c / 3T3 cells and rapid division and growth of the cells, which indicates that the rhFNIII1-C has huge potential of being used as a raw material and a finished product for cosmeceuticals and medical skincare.
Owner:ANHUI MEDICAL UNIV
Vitamin B2 modified IONzyme, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109602914AGood dispersionEasy to manufactureHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsRos scavengingOral ulcers
The invention provides a vitamin B2 modified IONzyme, and in particular to vitamin B2 modified nano-scale ferriferrous oxide particles. The invention further provides a preparation method of a vitaminB2 modified IONzyme and a composition for promoting oral ulcer healing. The vitamin B2 modified IONzyme provided by the invention has higher catalase activity and superoxide dismutase activities thanthe IONzyme; and compared with the individually used vitamin B2 and IONzyme, the vitamin B2 modified IONzyme presents better protection effect for BALB / 3T3 cells and HOK cells in a hydrogen peroxideenvironment, better ROS clearance at a cellular level, and better ability to reduce IFN-gamma and IL-6 in ulcers. The vitamin B2 modified IONzyme has a better therapeutic effect on oral ulcers and canbe used to prepare effective drugs for promoting the healing of oral ulcers.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Scid mouse model of electromagnetic radiation carcinogenesis and constructing method thereof
InactiveCN101838633AGood effectSimple stepsElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentEmbryonic cellsAbnormal tissue growthElectromagnetic radiation
The invention relates to a Scid mouse model of electromagnetic radiation carcinogenesis and a constructing method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: culturing an NIH / 3T3 cell and carrying out passage; exposing the cell in the presence of the electromagnetic radiation of 30-90W / m<2> and culturing for 4-6 weeks; and carrying out a soft agarose culturing experiment and inoculating the cultured soft agaroes into a Scid mouse for carrying out an oncogeen experiment. The result shows that a cell colony is formed in the soft agarose experiment and Scid mice in the oncogeen experiments all generate tumors. By using the method, the Scid mouse model with tumors induced by using the electromagnetic radiation can be established; and the method has the advantages of remarkable effect, simple steps and favorable repeatability. An in vitro cell transformation experimental model established by the method can be used for simulating the vicious transformation of an in vivo cell and provides a favorable experimental model and a powerful technical means for the research on a pathogenesis and prevention and treatment measures of the tumor induced by the electromagnetic radiation. The method can be applied to the carcinogenic risk pre-evaluation on the electromagnetic radiation in the industry, science, medical treatment and daily life and has an important value of preventing the long-term harm of the electromagnetic radiation on the human health.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
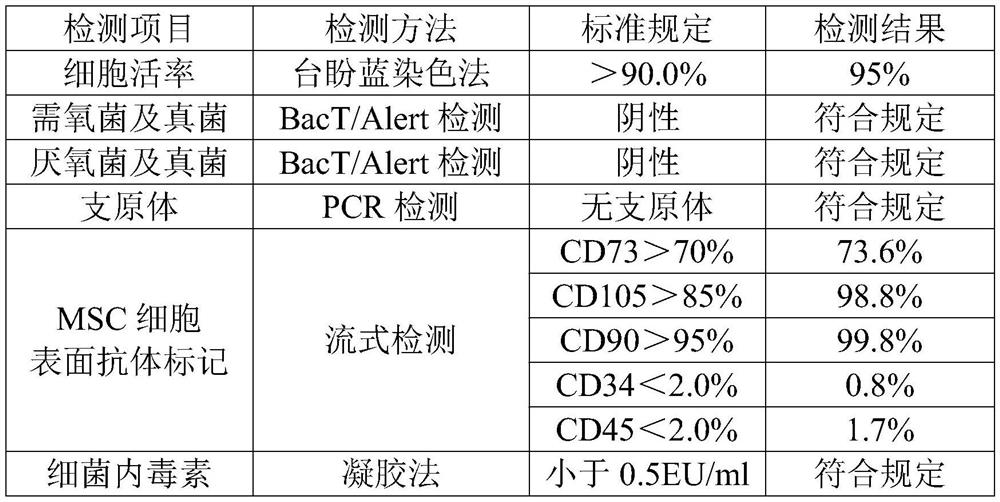
Purification preparation method and application of mesenchymal stem cell secreted factors
ActiveCN113425619AEliminate wrinklesShrink poresCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSECRETOR FACTORChemistry
The invention provides a purification preparation method and an application of mesenchymal stem cell secreted factors. The purification preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing MSC supernate; (2), purifying the mesenchymal stem cell secreted factors, including filtration and concentration, heparin affinity chromatography, and heparin affinity chromatography elution peak 5kD ultrafiltration or G-25 desalination column desalination; and (3) using the purified MSC secretion factors in the step (3) to prepare masks. According to the invention, a heparin affinity chromatography medium is adopted to specifically adsorb mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) secreted factors and purify substances with an effect of stimulating NIH 3T3 cell proliferation in MSC secretions, and the substances are potentially used for repairing refractory wounds and are added to cosmetics as an additive. The effects of repairing damaged skin, eliminating skin wrinkles, shrinking pores, improving complexion and the like can be achieved.
Owner:铜仁市泛特尔生物技术有限公司
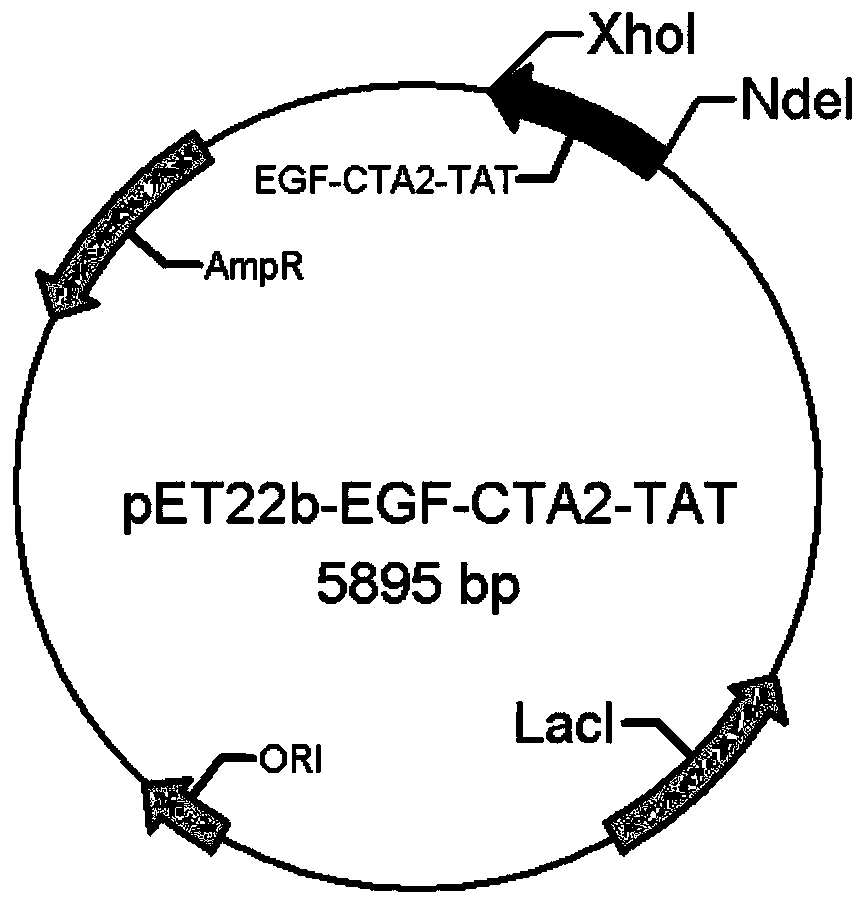
EGF-like protein and construction method thereof, and chimeric protein as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110078835ASignificant pro-growth effectBiologically activePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifNervous disorderBALB/c3T3 cells
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and particularly relates to EGF-like protein and a construction method thereof, and chimeric protein as well as a preparation method andapplication thereof. The invention provides the EGF-like protein; the EGF-like protein is EGF-CTA2-TAT protein; the nucleotide sequence of the EGF-CTA2-TAT protein is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The EGF-CTA2-TAT protein is chimeric with EGF protein with a repair effect, cell-penetrating peptide assisting transdermal absorption, and a cholera toxin A2 subunit (CTA2) with the ability of penetrating cellmembranes; it is shown by a cell activity experiment test result that the EGF-CTA2-TAT protein has obvious effect of promoting the growth of BALB / c 3T3 cell strains, and has bioactivity.
Owner:广东格烯生物科技股份有限公司
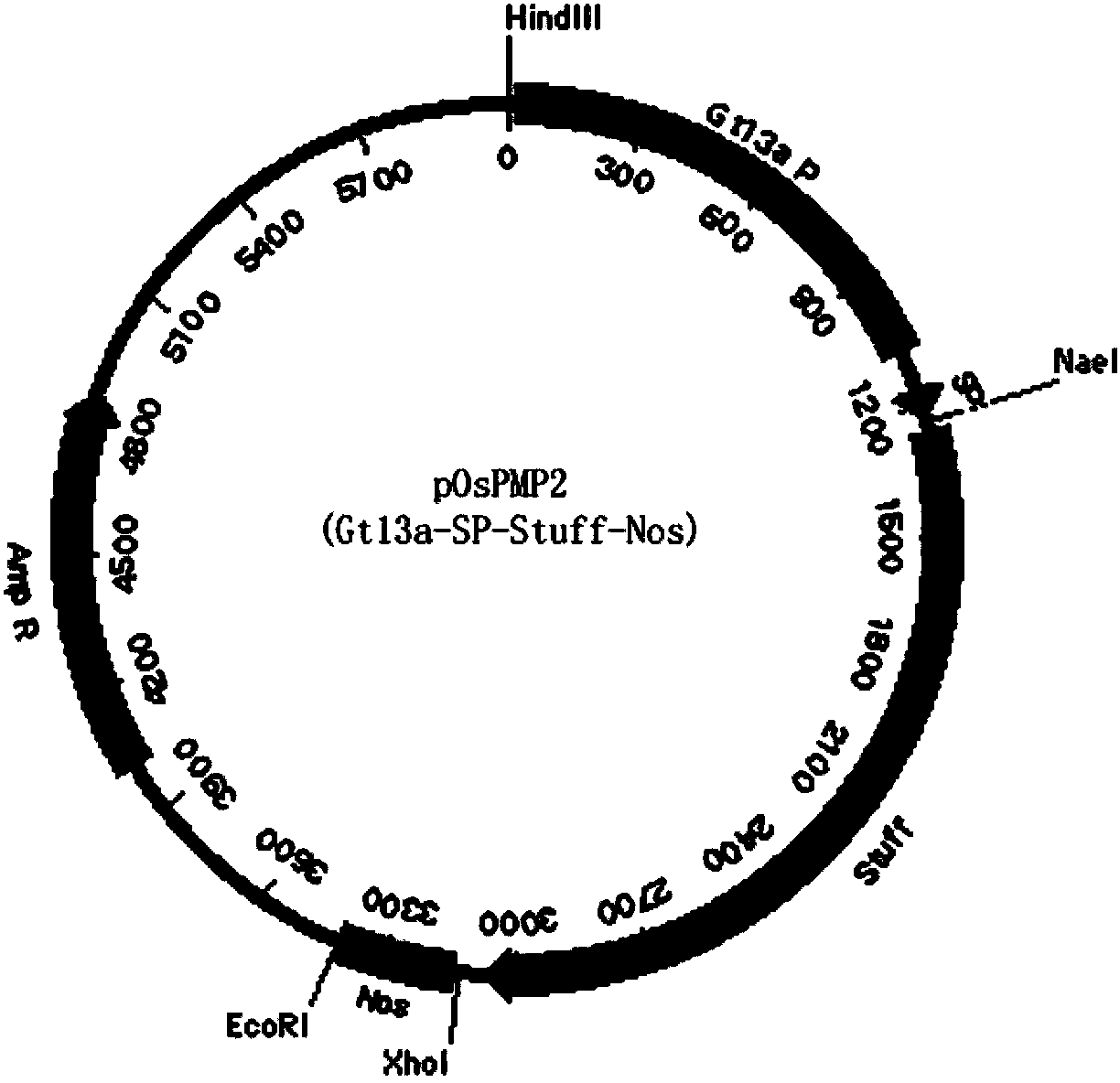
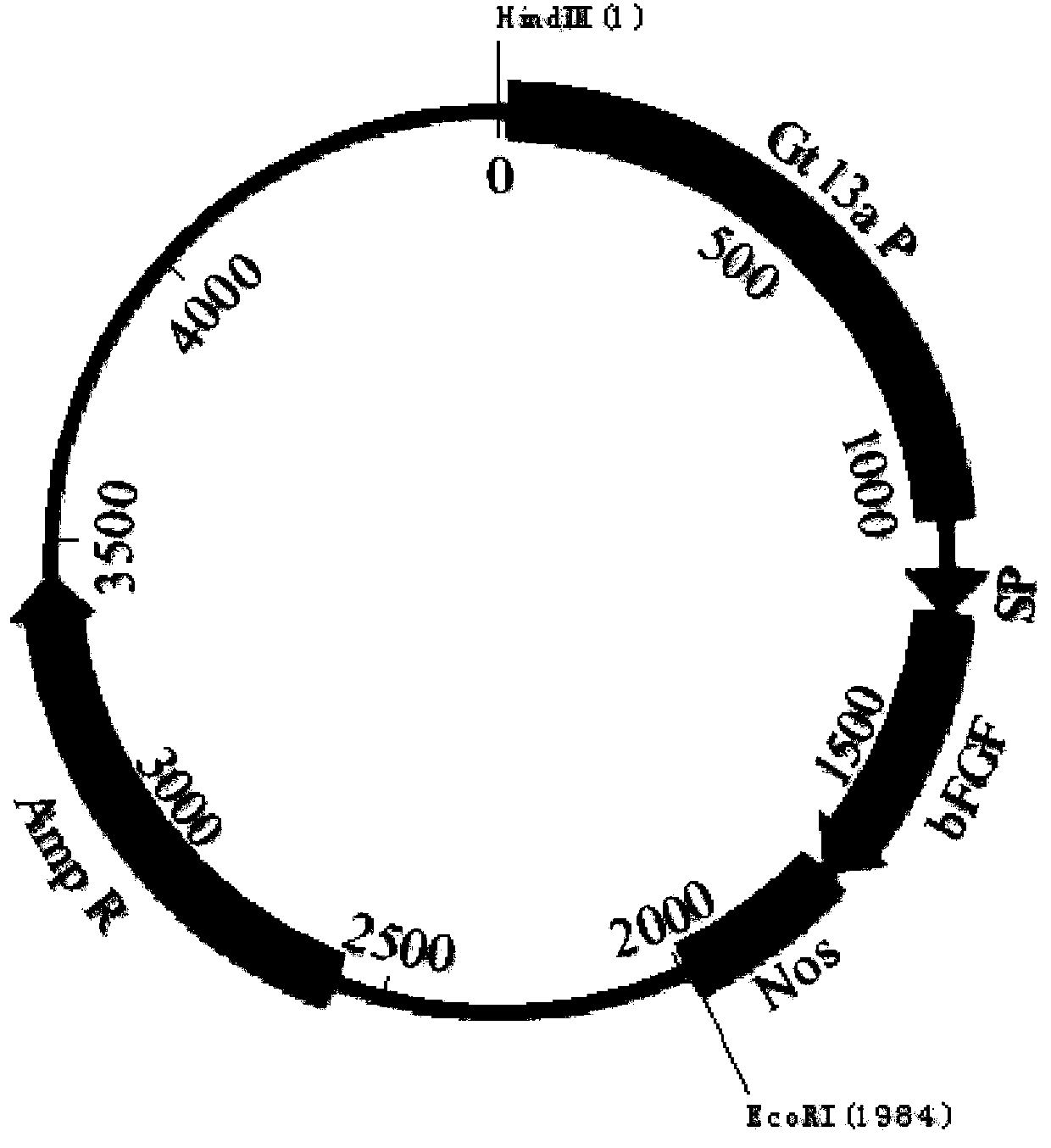
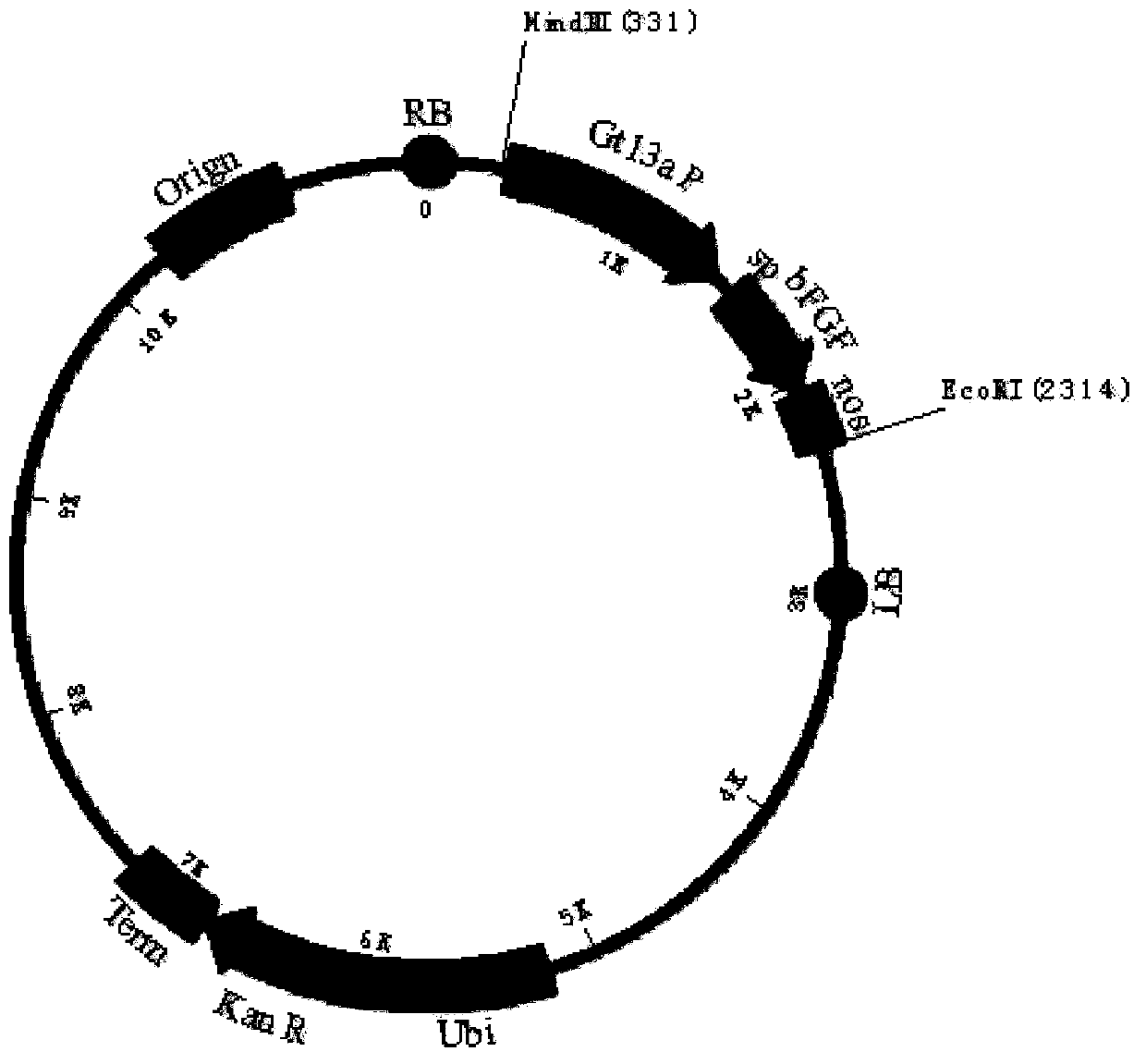
Method for producing recombinant human basic fibroblast growth factor from paddy rice seeds
InactiveCN103865932AActivePeptide preparation methodsFibroblast growth factorGenetically modified rice3T3 cells
The invention provides a OsrbFGF gene optimized by paddy rice genetic codon, correlated vectors, a method for preparing OsrbFGF transgenic paddy rice seeds, and a separation purification method of OsrbFGF. The OsrbFGF transgenic paddy rice seed is prepared through specific expression of OsrbFGF by paddy rice endosperm cells, and OsrbFGF is separated and purified. The purity of obtained OsrbFGF is 95%, and obtained OsrbFGF has the activity of promoting NIH / 3T3 cell proliferation in vitro and promoting wound healing in vivo.
Owner:WUHAN HEALTHGEN BIOTECHNOLOGY CORP
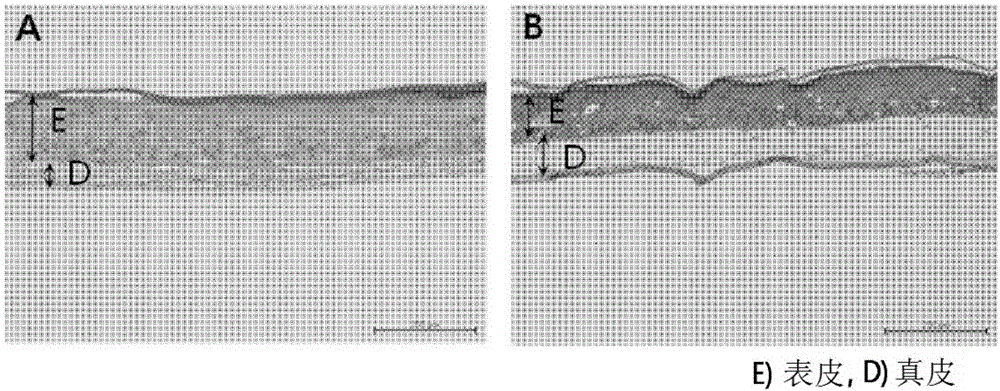
Method for making three-dimensional cultured skin model including dermis and epidermis, and three-dimensional cultured skin model made thereby
InactiveCN106573087AInhibition of contractionAvoid degradationEpidermal cells/skin cellsArtificial cell constructsCollagen shrinkageCuticle
The present invention relates to a method for making a three-dimensional cultured skin model comprising a dermis and an epidermis, which comprises: a step of preparing the dermis using a composition comprising a mouse-derived fibroblast, a native collagen or a combination of a native collagen and an atelocollagen; and a step of forming the epidermis using a keratin cell. Also, the present invention relates to a three-dimensional cultured skin model which comprises: a dermis made by a composition comprising a mouse-derived fibroblast, a native collagen, or a combination of a native collagen and an atelocollagen; and an epidermis formed from a keratin cell. The three-dimensionally cultured skin model of the present invention may be used widely in toxicity and efficacy experiments of medicines or cosmetics, and in the field of alternative experiments for animal experiments since the three-dimensionally cultured skin model is excellent in formation and differentiation of a dermis and an epidermis through use of a mouse-derived 3T3 cell for making the skin model and use of a mixture of an atelocollagen and a native collagen, and has a structure similar to a natural skin layer by inhibiting collagen shrinkage and degradation phenomenon of the dermis.
Owner:全世华
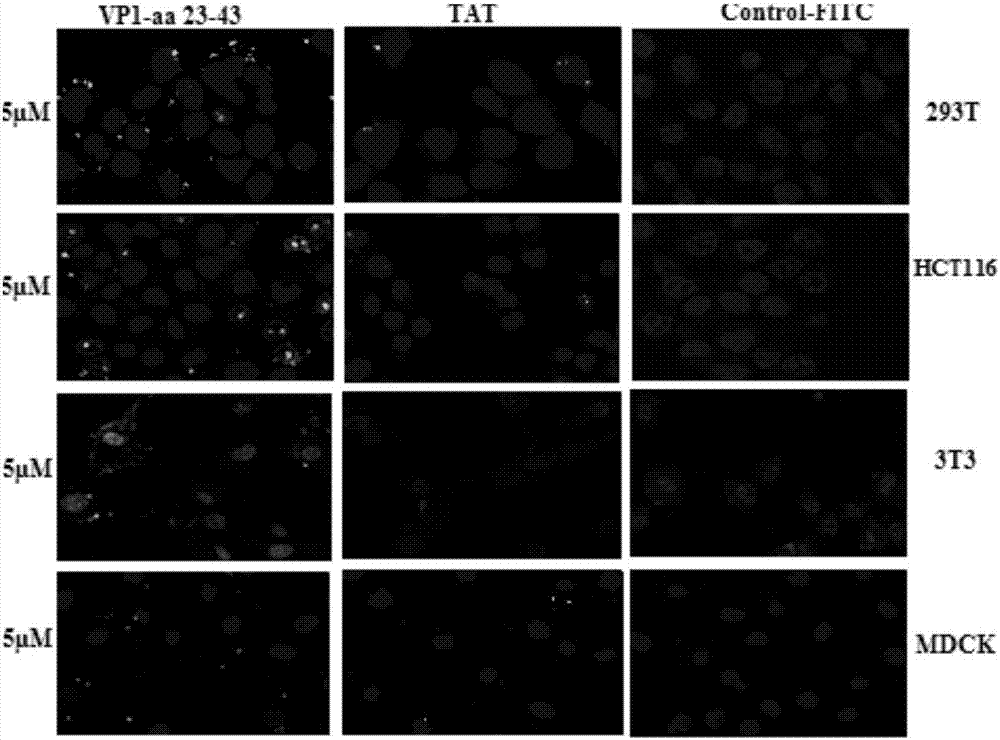
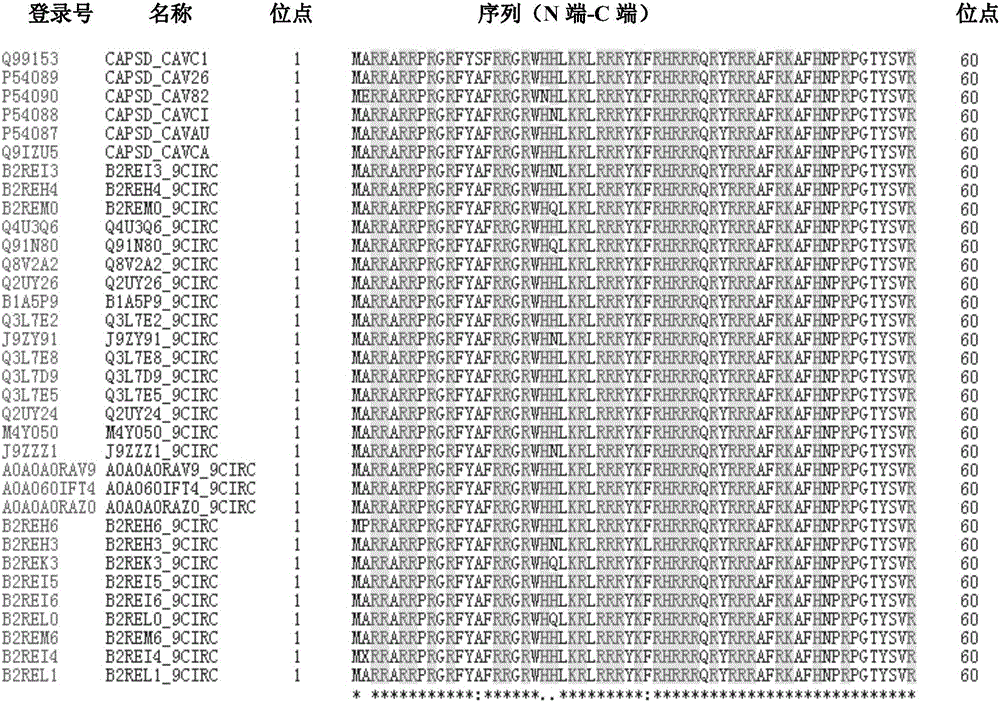
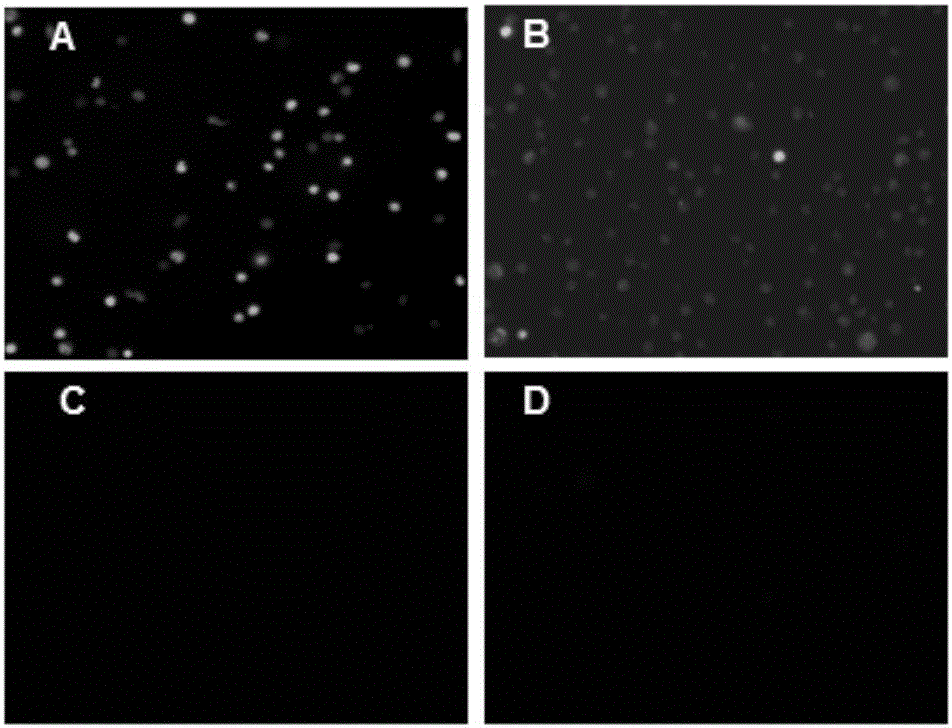
Application of chicken anemia virus (CAV)-derived VP1-aa 23-43 polypeptide as efficient cell penetrating peptide
ActiveCN106995487AHigh membrane penetration efficiencyVirus peptidesSsDNA viruses3T3 cellsConfocal microscopy
The invention relates to application of a chicken anemia virus (CAV)-derived VP1-aa 23-43 polypeptide as an efficient cell penetrating peptide. The sequence of the VP1-aa 23-43 polypeptide is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The polypeptide can carry FITC to enter a 293T cell, an HCT-116 cell, a 3T3 cell, an MDCK cell and an MSB1 cell within 30min; furthermore, the cell penetrating efficient is positively correlated to the concentration of the cell penetrating peptide; the key feature is that the polypeptide can efficiently enter suspension culture cells. The results of a laser scanning confocal microscope and a flow cytometry indicate that the cell penetrating efficiency of the CAV VP1-aa 23-43 polypeptide is over 2 times higher than that of a TAT oligopeptide at 10Mu M.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Cell culture layer and application in culture of human primary cancer cells thereof
InactiveCN103898043ARaise the ratioEasy to getArtificial cell constructsTumor/cancer cellsBottleCulture mediums
The invention discloses a cell culture layer which is prepared by the following methods: culturing BALB3T3 cells by adopting a DMEM culture medium, performing cell adherent culture until 70-80 percent of a culture bottle is full, and irradiating; performing X-ray irradiation by taking 3000cGy as a radiation dose; culturing by using an improved F culture medium after irradiation; culturing for 8 hours, and obtaining the culture, namely the cell culture layer. The cell culture layer can be used for culturing human primary cancer cells or cancer stem cells. The invention also discloses improvement of cell types of the cell culture layer as well as a preparation method of the cell culture layer. Compared with J2 cells, the 3T3 cells for preparing the culture layer are easily obtained, and the cell concentration and state can be easily controlled in the culture process. When the cell culture layer is used for culturing the human primary cancer cells or cancer stem cells, growth of the primary cancer cells can be well promoted, and human cancer stem cells in a higher ratio are obtained (the number of CD44 positive cells is improved by about 80 percent).
Owner:山东大学附属千佛山医院
Nucleophosmin/B23-binding peptide to inhibit tumor growth and regulate transcriptional activity of p53
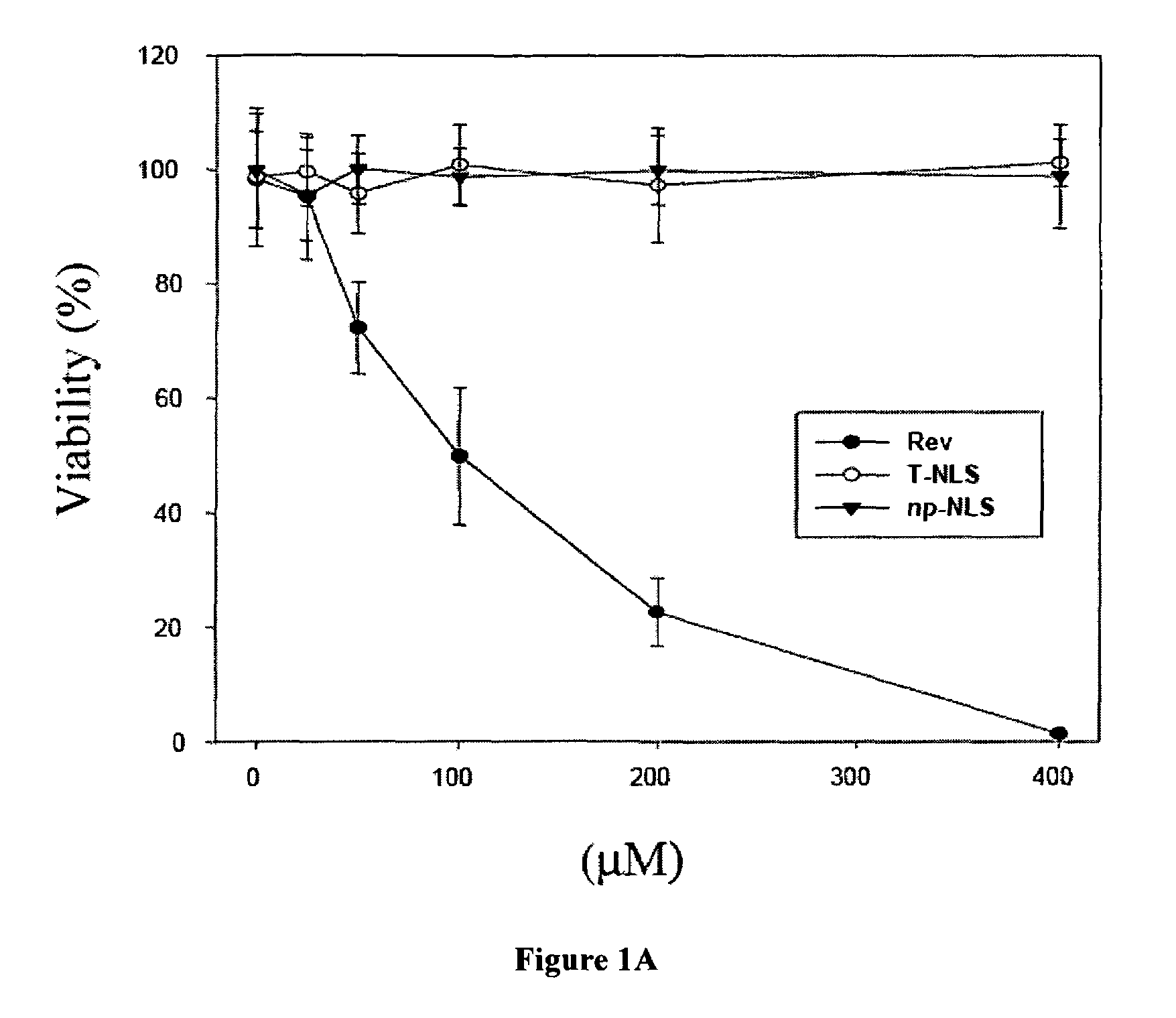
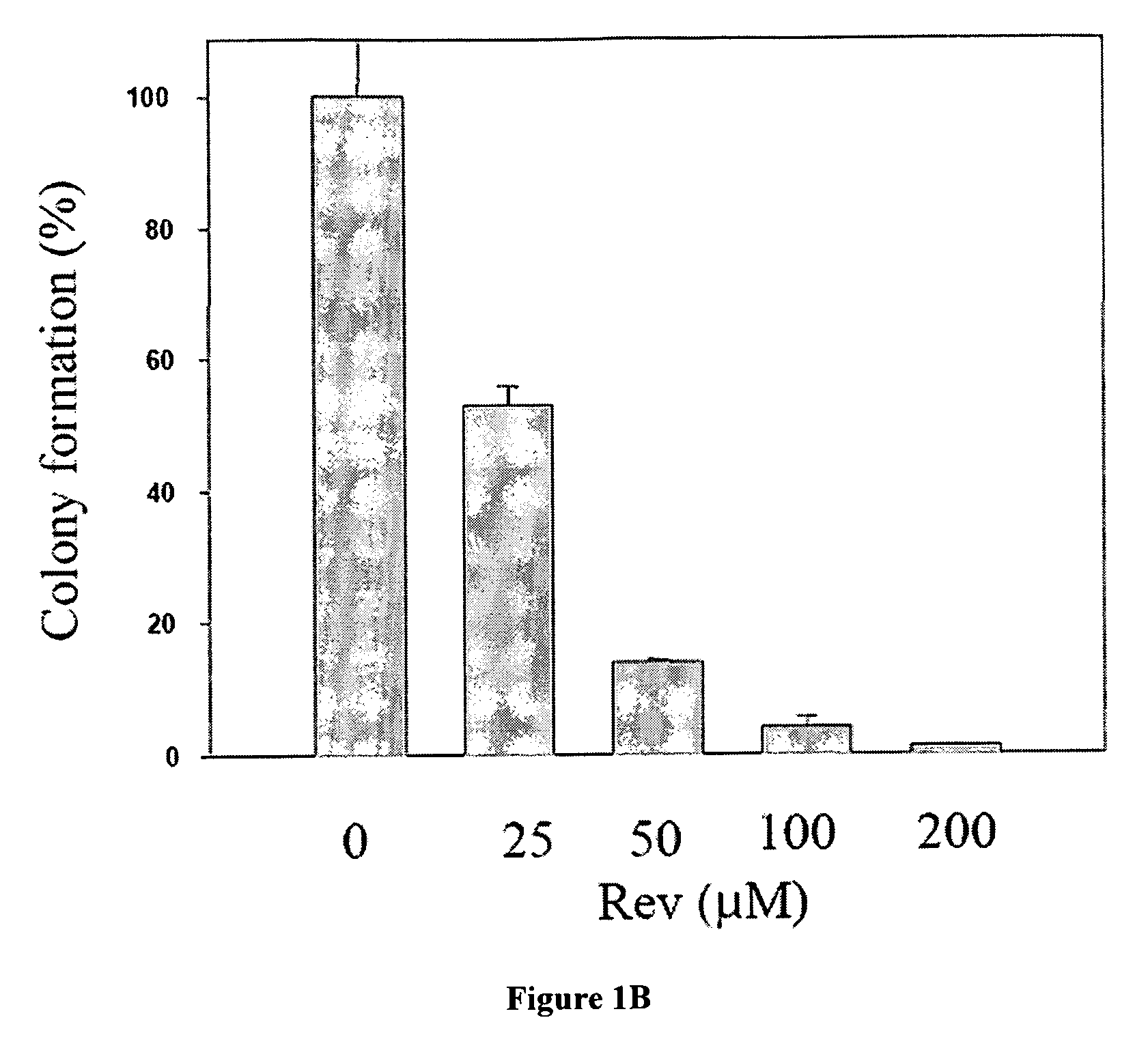
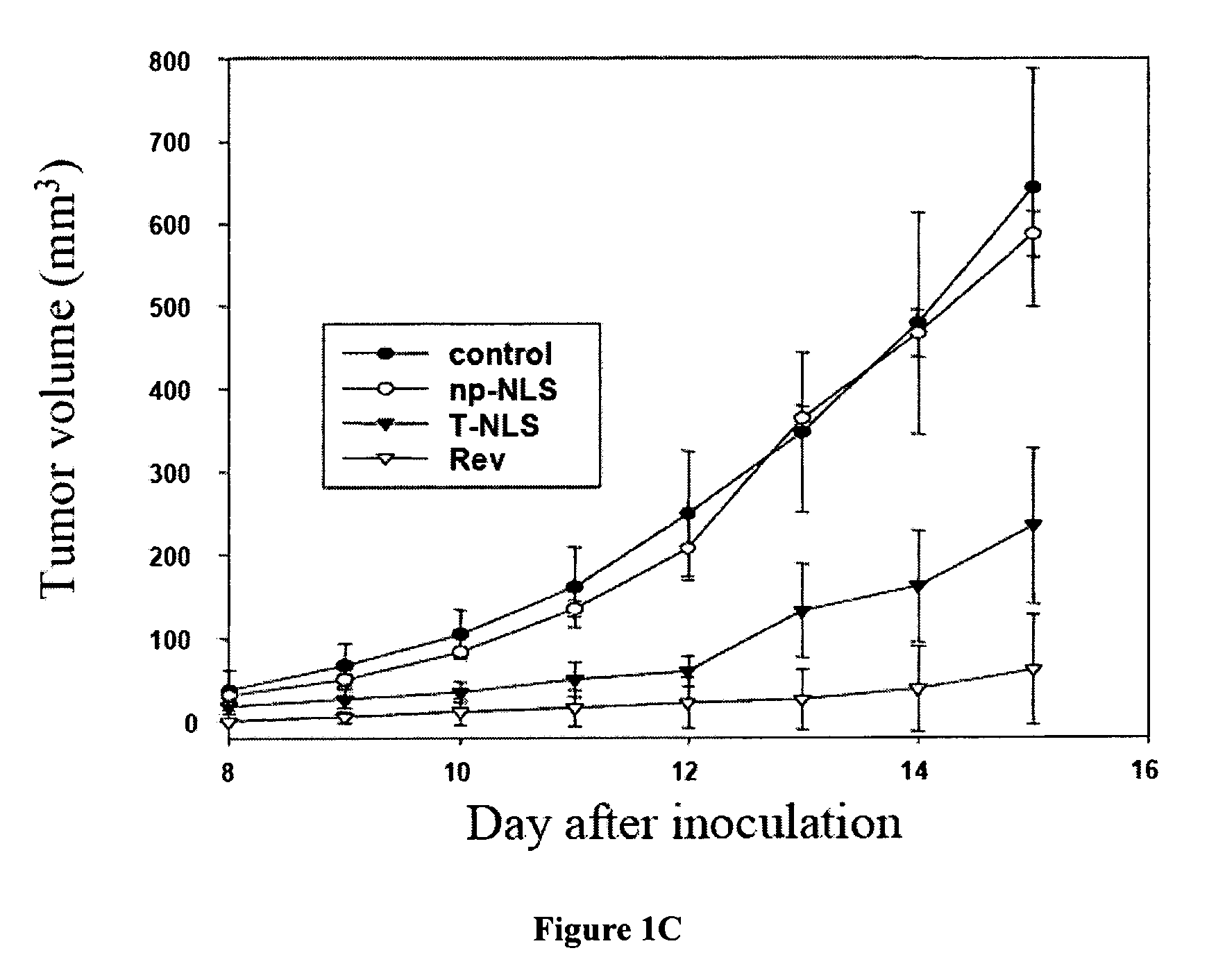
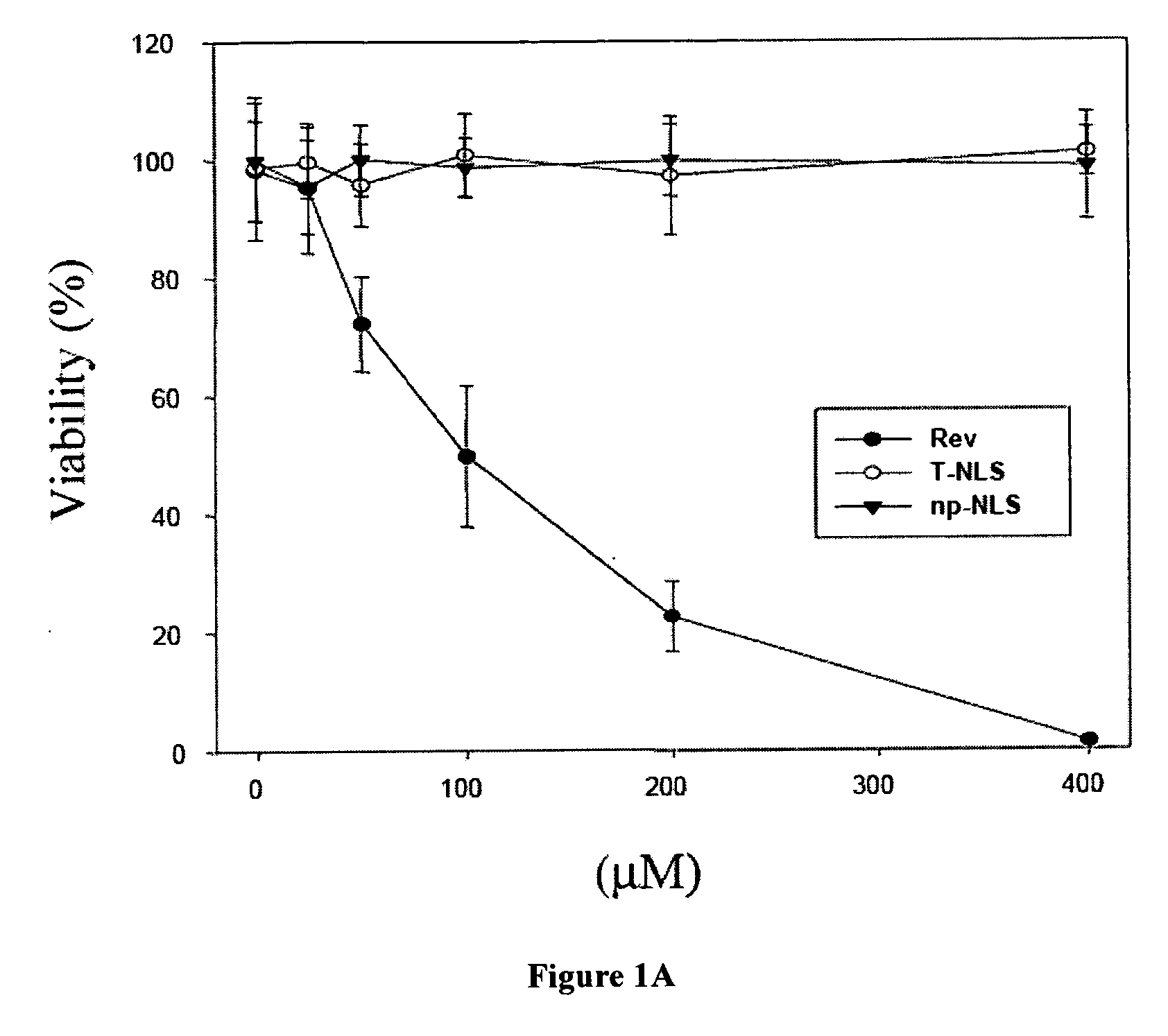
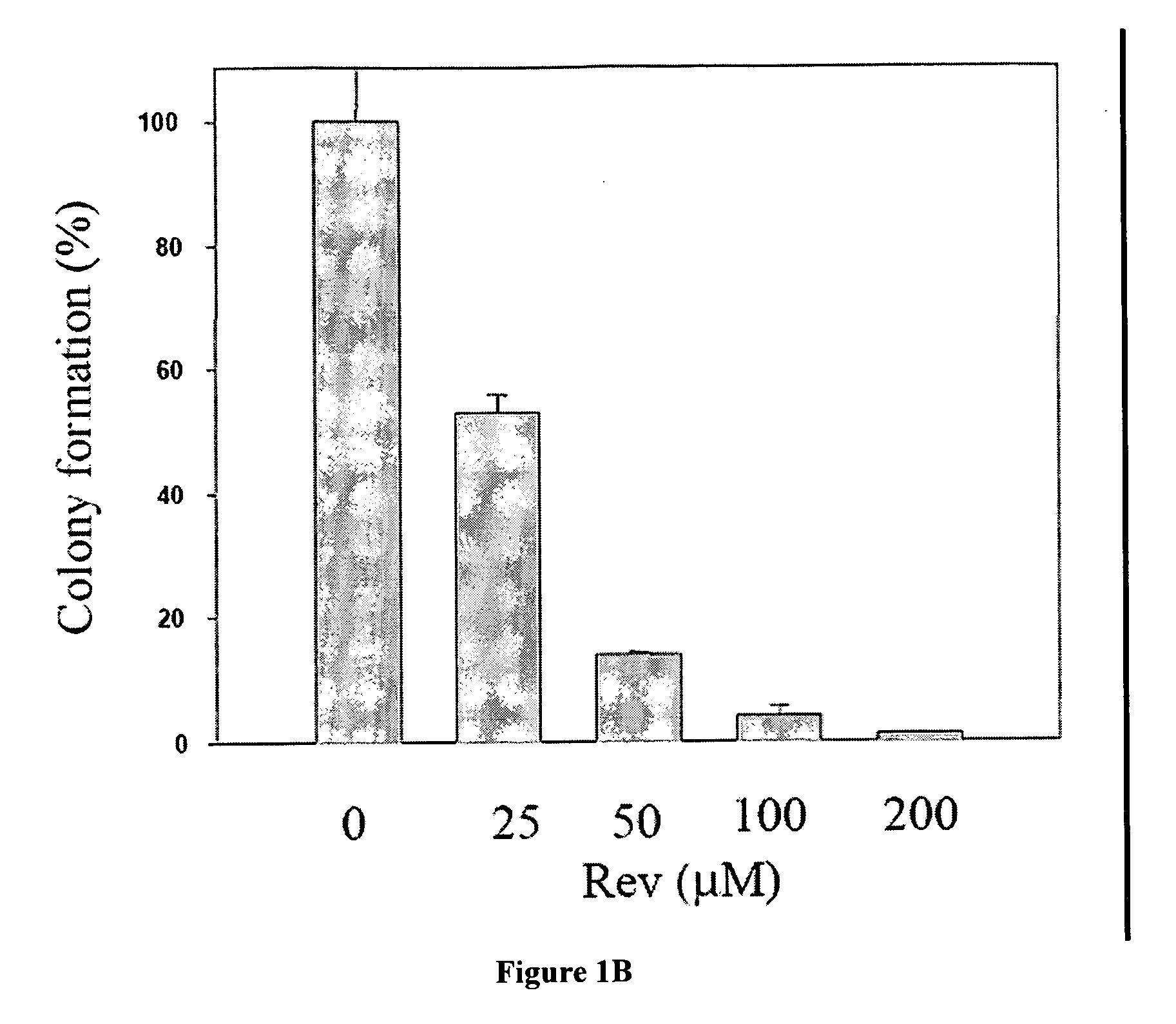
The Rev peptide that binds to nucleophosmin / B23 with the highest affinity exhibits the greatest cytotoxicity on Ras-3T3 cells and inhibits tumor growth most effectively in nude mice. The efficiency of colony formation in soft agar of Ras-3T3 cells is significantly inhibited by treatment with Rev peptide. In addition, Rev peptide can potentiate the doxorubicin-induced decrease of cellular viability in U1 bladder cancer cells and inhibition of tumor growth in nude mice. Treatment of Rev peptide increases protein expression and transcriptional activity of p53 and inhibits the nucleophosmin / B23-mediated PCNA promoter activation. Peptides having high affinity of binding to molecular targets such as nucleophosmin / B23 represent a useful approach to anti-cancer biotherapeutics.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
Human protein with function of promoting 3T3 cell conversion and its coding sequence
The present invention discloses one kind of human protein with 3T3 cell conversion promoting function, polynucleotides encoding the polypeptide and the recombinant process of producing the polypeptide. The present invention also discloses the agonist resisting the polypeptide and its treatment effect. The present invention also discloses the application of the polynucleotides encoding the human protein with 3T3 cell conversion promoting function.
Owner:NEWORGEN
Nucleophosmin/B23-binding peptide to inhibit tumor growth and regulate transcriptional activity of p53
InactiveUS20070254845A1High binding affinityInhibit tumor growthAntibacterial agentsBiocideCytotoxicityBinding peptide
The Rev peptide that binds to nucleophosmin / B23 with the highest affinity exhibits the greatest cytotoxicity on Ras-3T3 cells and inhibits tumor growth most effectively in nude mice. The efficiency of colony formation in soft agar of Ras-3T3 cells is significantly inhibited by treatment with Rev peptide. In addition, Rev peptide can potentiate the doxorubicin-induced decrease of cellular viability in U1 bladder cancer cells and inhibition of tumor growth in nude mice. Treatment of Rev peptide increases protein expression and transcriptional activity of p53 and inhibits the nucleophosmin / B23-mediated PCNA promoter activation. Peptides having high affinity of binding to molecular targets such as nucleophosmin / B23 represent a useful approach to anti-cancer biotherapeutics.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
New human protein having mouse NIH/3T3 cell conversion promoting function and its code sequence
A novel human protein with the function of promoting mouse NIH / 3T3 cell conversion, the polynucleotide for coding the polypeptide, the process for preparing the said polypeptide by recombination, theantagon of the said polypeptide and its medical action, and the application of said polynucleotide are disclosed.
Owner:NEWORGEN
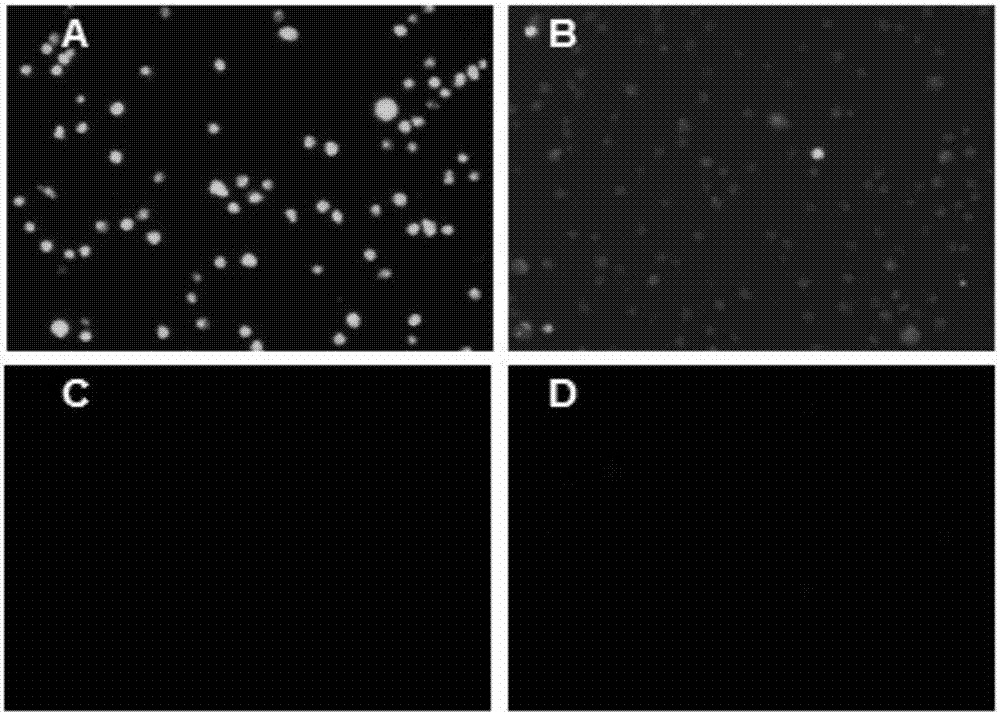
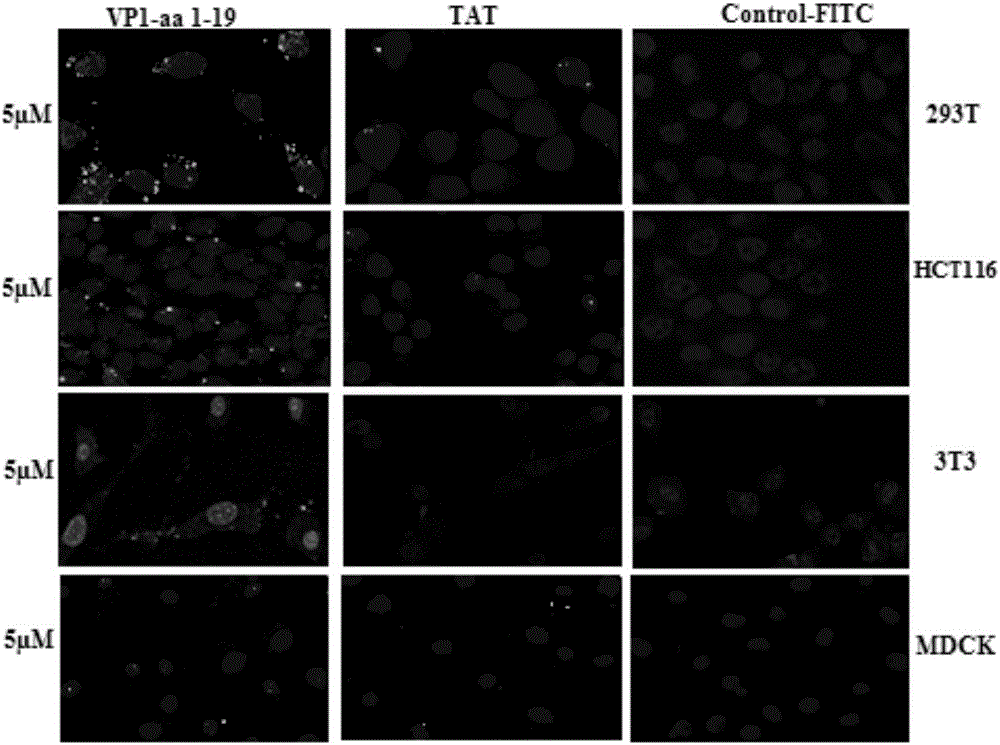
Use of chicken anemia virus (CAV) VP1-aa 1-19 polypeptide as highly efficient cell-penetrating peptide
ActiveCN106831957AHigh membrane penetration efficiencyVirus peptidesSsDNA viruses3T3 cellsConfocal microscopy
The invention relates to a use of a chicken anemia virus (CAV) VP1-aa 1-19 polypeptide as a highly efficient cell-penetrating peptide. The VP1-aa 1-19 polypeptide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The polypeptide can carry FITC and enter 293T cells, HCT-116 cells, 3T3 cells, MDCK cells and MSB1 cells in 30min, and the cell-penetrating efficiency is positively correlated with the concentration of the cell-penetrating peptide. The VP1-aa 1-19 polypeptide can efficiently enter suspension culture cells. The laser confocal microscope and flow cytometry result shows that the CAV VP1-aa 1-19 polypeptide has cell-penetrating efficiency significantly higher than that of a TAT short peptide.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
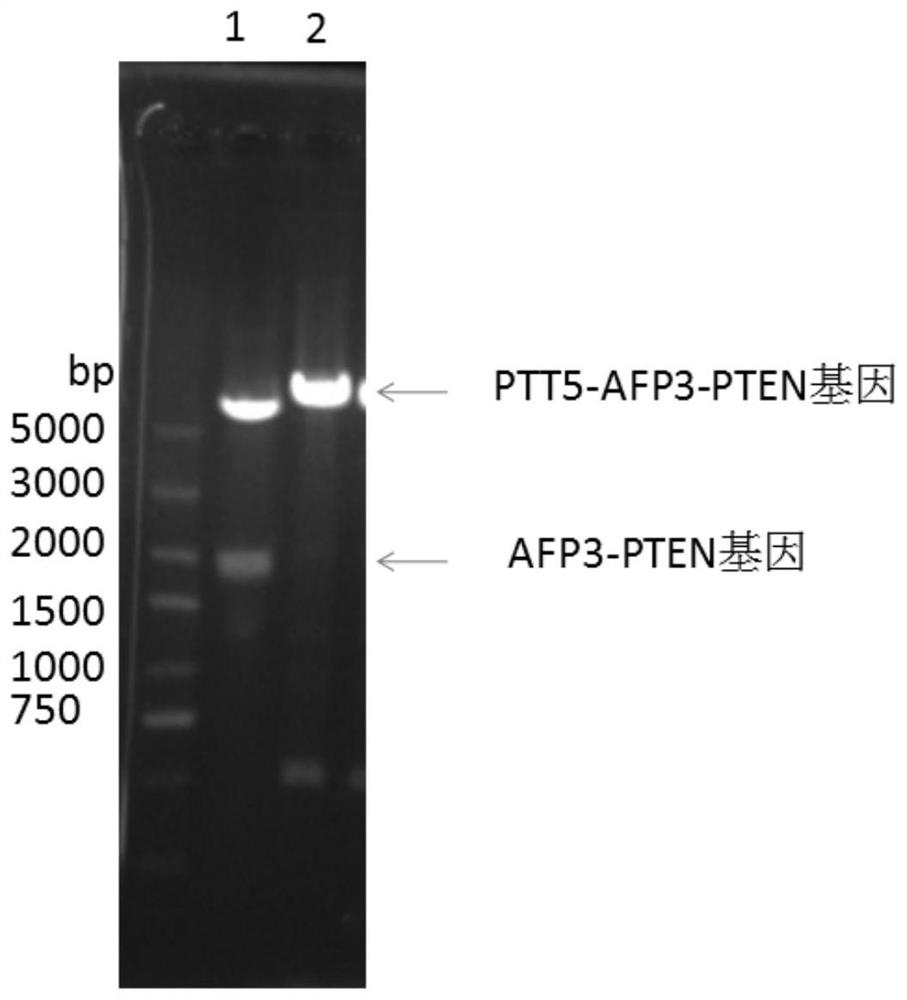
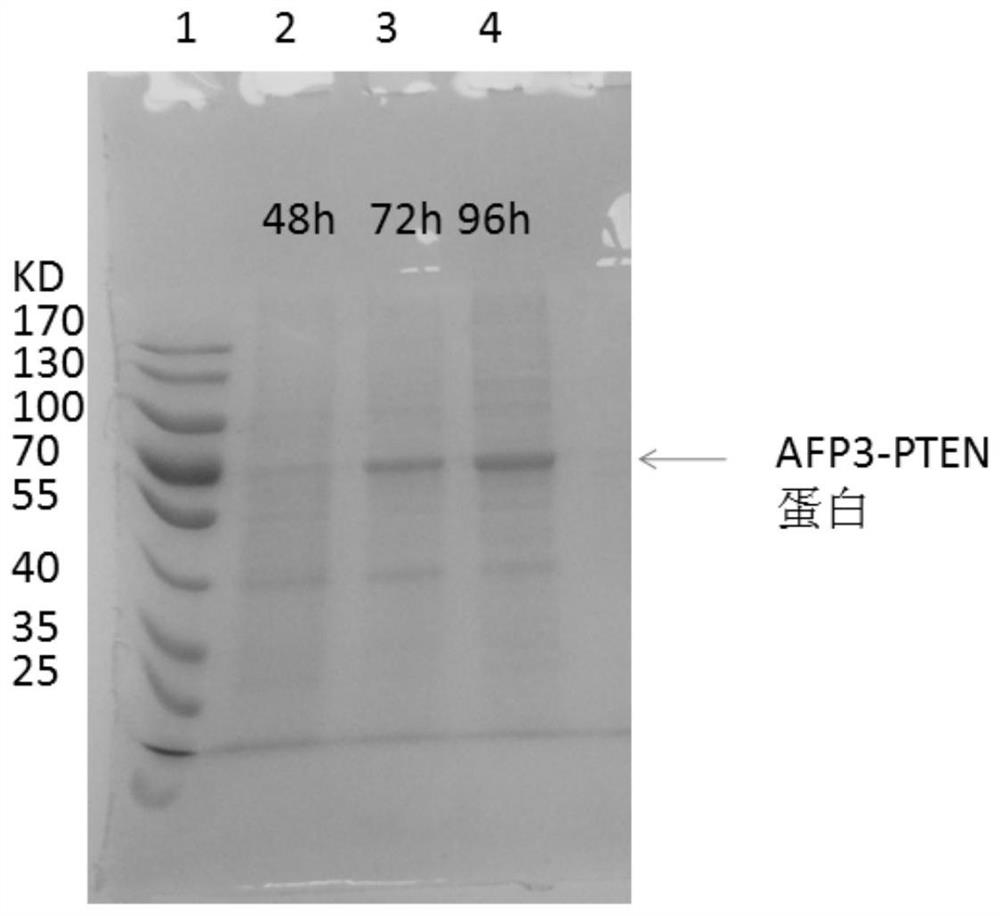
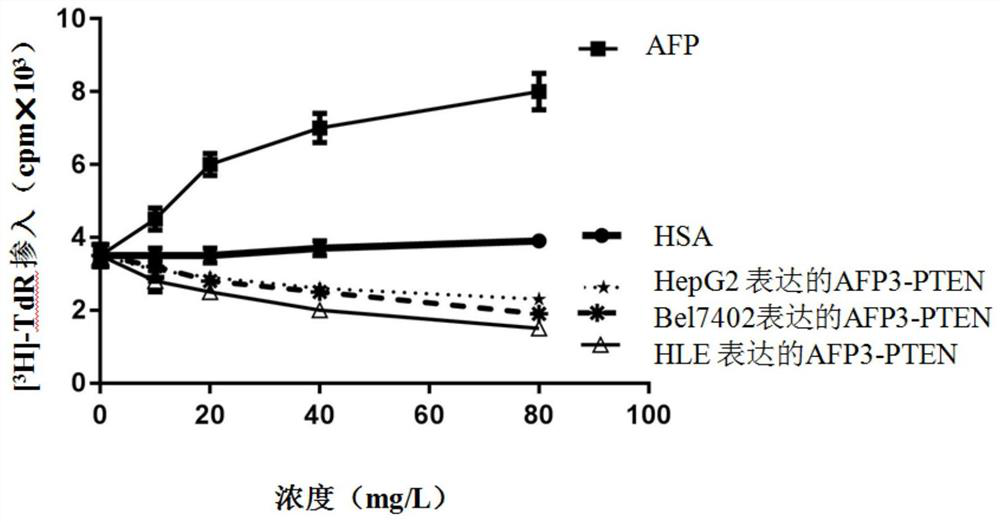
Method for efficiently expressing AFP3-PTEN fusion protein
The invention discloses a method for efficiently expressing an AFP3-PTEN fusion protein, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The method comprises the steps of cloning an HBx gene to a constructed expression vector, enabling the constructed vector to be transfected with human liver cancer cells, after expressing HBx proteins in the liver cancer cells, enabling the third structured domainof AFP and an overall-length PTEN gene to be connected to the expression vector and transfected into the human liver cancer cells expressing the HBx proteins, expressing the HBx proteins in the livercancer cells, promoting efficient secretory expression of a human AFP3-PTEN fusion protein through the HBx proteins, and concentrating and purifying culture mediums to obtain the AFP3-PTEN fusion protein. The AFP3-PTEN fusion protein expressed by the liver cancer cells can restrain cell proliferation and can enable the cell proliferation capacity of NIH 3T3 cells to be reduced by 15%-60%. But a reference protein AFP enables cell proliferation capacity to be obviously increased by 22-125%. Serum proteins do not have notable capacity for promoting NIH 3T3 cell proliferation. The obtained AFP3-PTEN fusion protein can be used for researching tumor treatment.
Owner:HAINAN MEDICAL COLLEGE
Cell membrane microvesicles targeting inflammation region and application of cell membrane microvesicles
InactiveCN113262212AMaintain stabilityMaintain biological activityAntipyreticAnalgesicsCell membraneGenetic engineering
The invention relates to a cell membrane microvesicle targeting an inflammation region and application of the cell membrane microvesicle, and solves the technical problem that an existing material does not have the characteristic of efficiently targeting the inflammation region. A preparation method of the cell membrane microvesicle comprises the following steps: transfecting an MC-3T3 cell through CXCR4 gene overexpressing lentivirus by utilizing genetic engineering, and proliferating the transfected cell to obtain cells with overpressed membrane receptor CXCR4; culturing the over-expressed CXCR4 MC-3T3 cells, conducting washing, conducting treating with cytochalasin B, and carrying out vortex separation on the cells and cell membrane microvesicles; centrifuging the mixture, separating the cells from the cell membrane microvesicles, collecting supernate, and conducting centrifuging for the second time to obtain the cell membrane microvesicles of the targeted inflammation region. The invention also provides an application of the cell membrane microvesicle of the targeted inflammation region in preparation of a targeted inflammation region material. The method can be used in the field of preparation of drug loading materials.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SCHOOL OF STOMATOLOGY
Cationic macromolecular proteolipid gene medicine carrier, preparation method and application
InactiveCN102716500ARich varietyHigh transfection efficiencyGenetic material ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsLipid formationPositive control
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ONCOLOGY
New human protein with mouse NIH/3T3 cell transformation improving function and its code sequence
The present invention discloses a new kind of human protein with 3T3 cell transformation improving function, polynucleotides encoding this polypeptide and recombination process to produce the polypeptide. The present invention also discloses the agonist resisting the polypeptide and its treatment effect. The present invention also discloses the application of the polynucleotides encoding this human protein with 3T3 cell transformation improving function.
Owner:NEWORGEN
A kind of water-soluble mitochondria-targeted imaging probe and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105777637BGood water solubilityGood photobleaching resistanceOrganic chemistryIn-vivo testing preparationsNon cancerSolubility
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for establishing transgenic removable human skin fibroblast feeder cell line
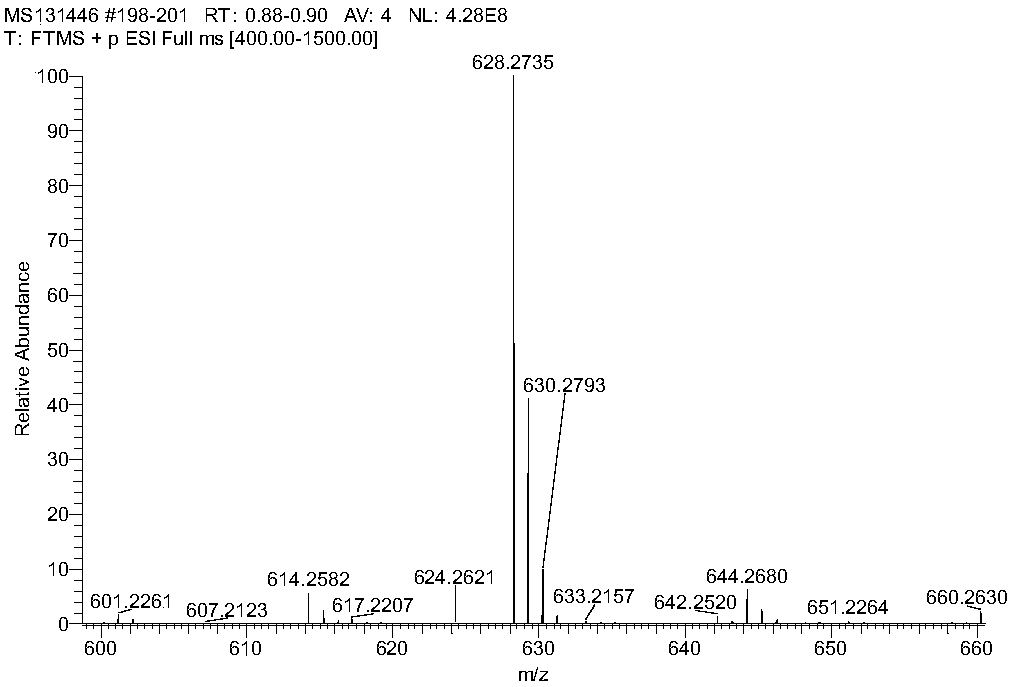
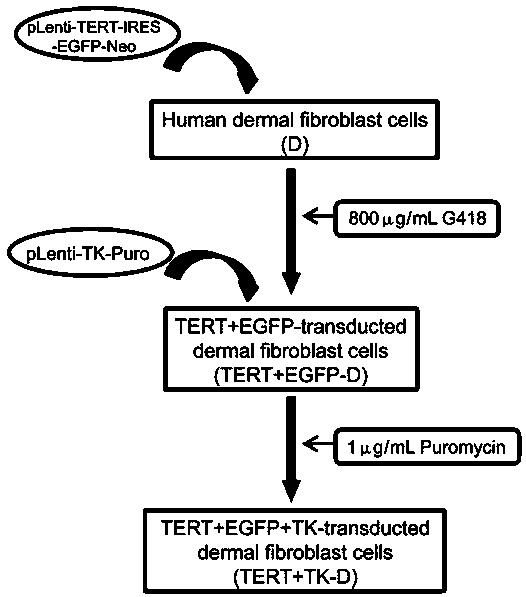
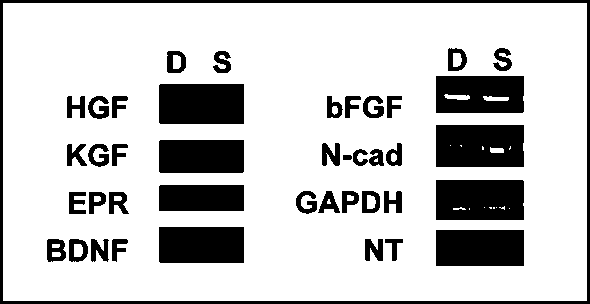
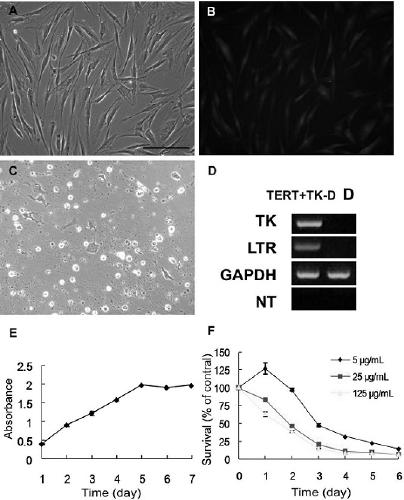
InactiveCN111575240AStrong ability to splitEpidermal cells/skin cellsNervous system cellsTelomeraseMitomycin C
The invention discloses a method for establishing a transgenic removable human skin fibroblast feeder cell line. By utilizing a retrovirus-mediated gene transfer way, the production tool introduces areinforced green fluorescent protein gene, a telomerase reverse transcriptase gene and a herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene into human skin fibroblasts to establish a fluorescence-labeled immortalization-removable TERT + TK-D human feeder cell line. After being treated by mitomycin C, the established cell line serving as feeder cells is co-cultured with human limbal stem cells, and the culture result is compared with a culture result of 3T3 feeder cells. Transgenic fluorescence-labeled immortalization-removable human skin fibroblast feeder cells are expected to replace the 3T3 cells for corneal regeneration therapy.
Owner:SHENZHEN HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Targeting metabolic enzymes in human cancer
Targeting metabolic enzymes in human cancer Abstract Lung cancer is a devastating disease and a major therapeutic burden with poor prognosis. The functional heterogeneity of lung cancer (different tumor formation ability in bulk of tumor) is highly related with clinical chemoresistance and relapse. Here we find that, glycine dehydrogenase (GLDC), one of the metabolic enzyme involved in glycine metabolism, is overexpressed in various subtypes of human lung cancer and possibly several other types of cancers. GLDC was found to be highly expressed in tumor-initiating subpopulation of human lung cancer cells compared with non-tumorigenic subpopulation. By array studies we showed that normal lung cells express low levels of GLDC compared to xenograft and primary tumor. Functional studies showed that RNAi inhibition of GLDC inhibits significantly the clonal growth of tumor-initiating cells in vitro and tumor formation in immunodeficient mice. Overexpression of GLDC in non-tumorigenic subpopulation convert the cells to become tumorigenic. Furthermore, over-expression of GLDC in NIH / 3T3 cells and human primary lung fibroblasts can transform these cells, displaying anchorage-independent growth in soft agar and tumor-forming in mice. Not only is GLDC is expressed human lung cancer, it is also up-regulated in other types of cancer, such as colon cancer. RNAi knockdown of GLDC in colon cancer cell line, CACO-2 cells, can also inhibit the tumor formation in mice. Thus GLDC maybe a new metabolic target for treatment of lung cancer, and other cancers.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Novel human protein with function for promoting mouse NIH/313 cell transformation and coding sequence thereof
The present invention discloses a novel human protein with the function of promoting 3T3 cell transformation, polynucleotide for coding said polypeptide and the method for producing said polypeptide by means of recombination technology. Said invention also discloses the agonist for resisting said polypeptide and its therapeutic action. Said invention also discloses the application of the polynucleotide coding said human protein with the function of promoting 3T3 cell transformation.
Owner:NEWORGEN
Human Protein for promoting transform of 3T3 cell and its coding sequence
A novel human protein with the function of promoting 3T3 cell transform, the polynucleotide for coding the peptide, the process for preparing said polypeptide by recombination, the antagon of said polypeptide and its medical action, and the application of said polynucleotide are disclosed.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ONCOLOGY
New human protein with function of improving mouse NIH/3T3 cell transformation and its encoding sequence
The present invention discloses a new kind of human protein with the functions of promoting 3T3 cell transformation, polynucleotides encoding this polypeptide and recombination process to produce the polypeptide. The present invention also discloses the agonist resisting the polypeptide and its treatment effect. The present invention also discloses the application of the polynucleotides encoding this new kind of human protein with the functions of promoting 3T3 cell transformation.
Owner:NEWORGEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com