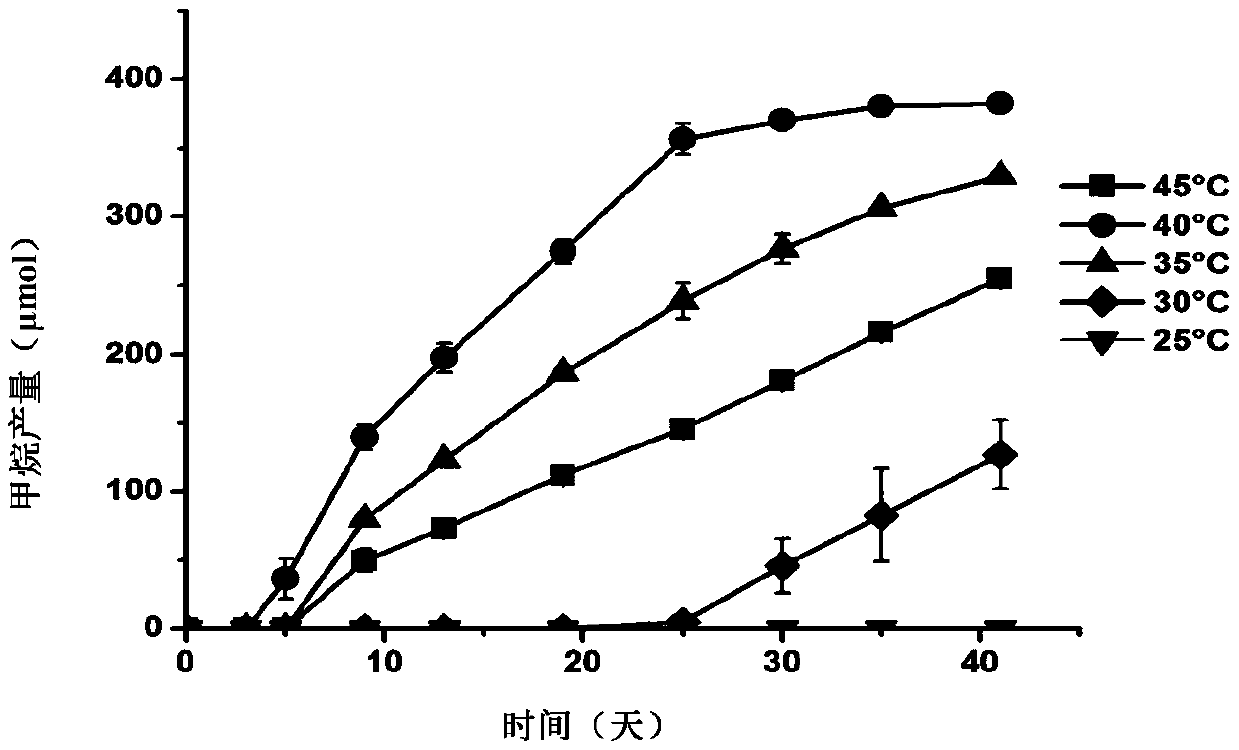
Patents
Literature
39 results about "Methanosaeta" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In taxonomy, Methanosaeta is a genus of microbes within Methanosaetaceae. Like other species in this family, those of Methanosaeta metabolize acetate as their sole source of energy. The genus contains two species, Methanosaeta concilii, which is the type species (type train GP6) and Methanosaeta thermophila. For a time, some scientists believed there to be a third species, Methanosaeta soehngenii, but because it has not been described from a pure culture, it is now called Methanothrix soehngenii.
Compound microbial bacterial preparation and application thereof
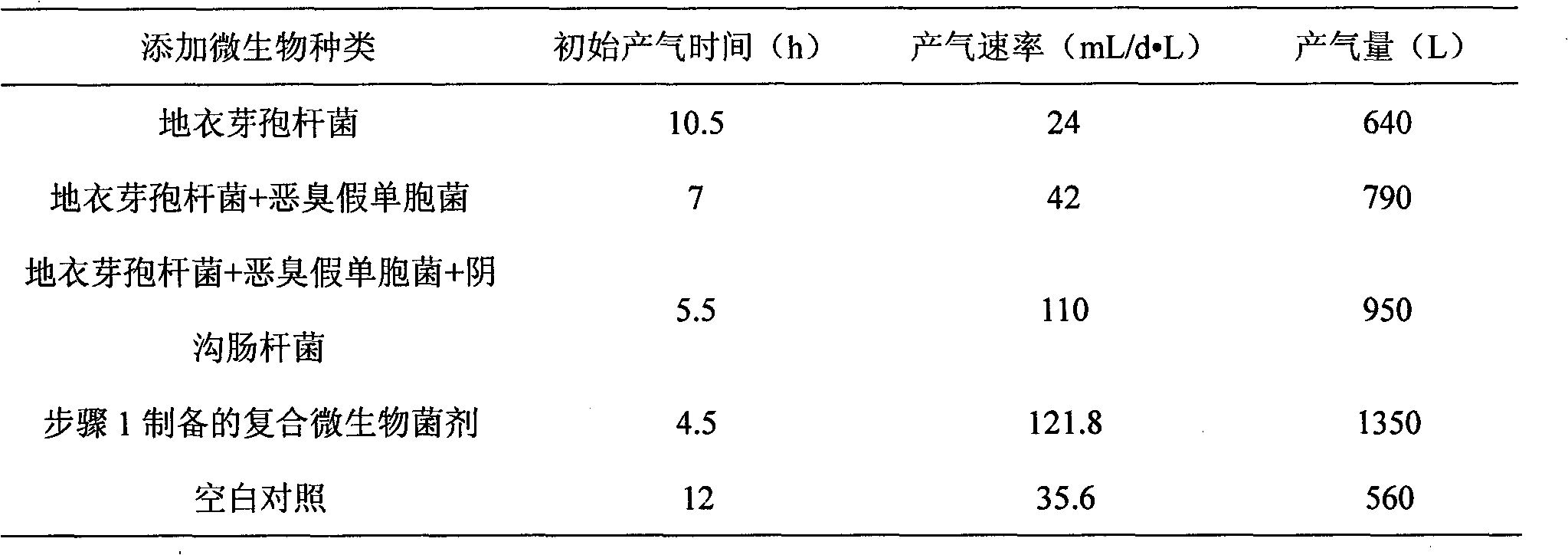
InactiveCN101864362AOvercoming the problem of only targeting a single organic wastePromote enrichmentFungiBacteriaCelluloseBacillus licheniformis
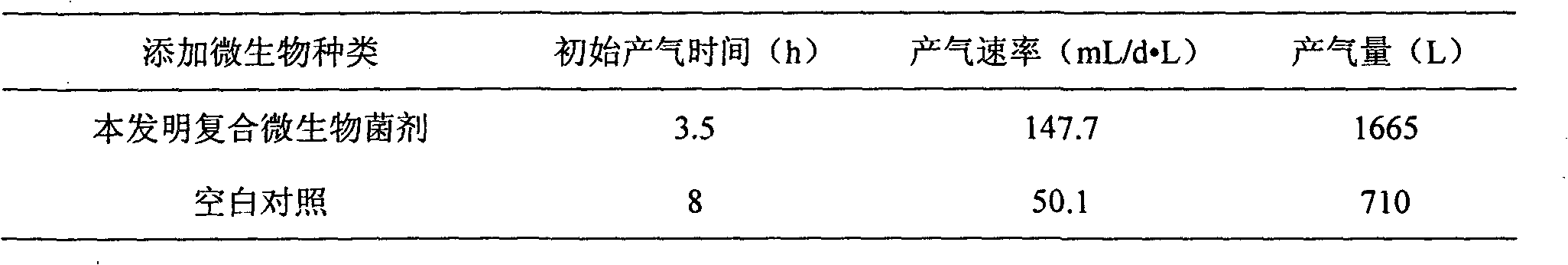
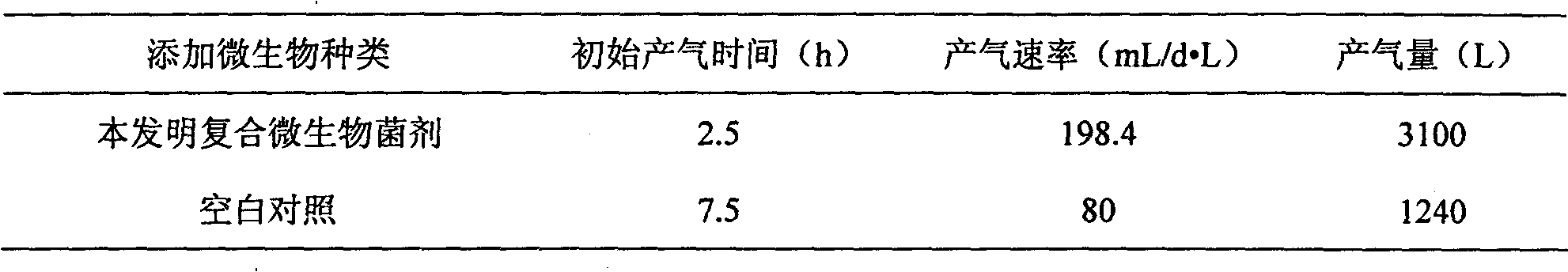
The invention belongs to the technical field of environment protection and discloses a compound microbial bacterial preparation and application thereof. The compound microbial bacterial preparation consists of fermentation liquor of four bacteria, i.e. Bacillus licheniformis, Pseudomonas putida, Enterobacter cloacae and Candida valida. The compound microbial bacterial preparation provided by the invention has strong digestion power for various types of cellulose, proteins and fat macromolecules. The addition of the compound microbial bacterial preparation into excess sludge and / or kitchen waste can quicken enrichment of methanogen, shorten anaerobic digestion time and improve methane yield. Moreover, the synergetic effect of the four microbial strains is superior to the effect of any one, two or three strains of microorganisms.
Owner:江苏加德绿色能源有限公司
Anaerobic cellulose-degrading methane producing composite bacterium
InactiveCN101475926AEfficient hydrolysisFermentation starts fastBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCelluloseFacultative
The invention discloses anaerobic degradation cellulose methane composite bacteria, which is composed of 13 strains that respectively belong to facultative anaerobic and strictly anaerobic fermentative bacteria, hydrogen-production and acetic acid-production bacteria and methane-producing bacteria. The composite bacteria can not only effectively perform anaerobic degradation to the cellulose, but also can use the degradation production of the cellulose to produce methane, which can be widely used in straw biogas fermentation, compost processing, and the like conversion processes.
Owner:BIOGAS SCI RES INST MIN OF AGRI
Preparation of composite bacteria
InactiveCN101481676APromote degradationPerformance unchangedMicroorganism based processesMicrobiology processesCelluloseMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for preparing composite bacterium, comprising the following steps: inoculating microorganism of zymogenous bacteria, hydrogen-producing acetogenic bacteria and methanogen respectively belonging to facultative anaerobic bacteria and strict anaerobic bacteria which are mixed according to a certain proportion into a culture solution containing cellulose, sealing and keeping standing to culture at a temperature of between 30 to 50 DEG C and pH value of 3 to 10, wherein the culture solution containing cellulose contains CaCO3, 0.3 to 0.7 percent of NaCl, 0.5 to 1 percent of cellulose, 0.1 to 0.4 percent of urea, 0.1 to 0.3 percent of peptone and 0.05 to 0.15 percent of yeast powder, and water is used as a solvent. The composite bacterium having effective cellulose degrading property and capable of generating methane is prepared by the method.
Owner:BIOGAS SCI RES INST MIN OF AGRI
Composite microbial inoculum used for anaerobic fermentation of kitchen wastes
ActiveCN103215213AAchieve synergyNormal fermentationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesBiotechnology
The invention discloses a composite microbial inoculum used for the anaerobic fermentation of kitchen wastes, belongs to the field of micro-organisms, and solves the problem of the lack of a microbial inoculum suitable for performing anaerobic fermentation by taking kitchen wastes as a main raw material at present. The composite microbial inoculum comprises, in parts by weight, 8-15 parts of acid production bacteroides DSM 15896 fermentation liquor, 25-35 parts of long-chain fatty acid syntrophic aeromonas DSM 18709 fermentation liquor, 15-25 parts of clostridium sordellii ATCC9714 fermentation liquor, 20-28 parts of combined methanosaeta JCM10134 fermentation liquor and 22-27 parts of methanospirllum hungatei DSM864 fermentation liquor, wherein the effective viable counts of the fermentation liquors of the five bacteria aforementioned achieve more than 10<9> per millilitre respectively. The composite microbial inoculum disclosed by the invention is suitable for an anaerobic fermentation process taking the kitchen wastes as the main raw material, and capable of playing the roles of stabilizing the pH value of a fermentation system, promoting to bring forward the peak of methanogenesis, and increasing the total amount of methanogenesis after being inoculated in the fermentation system.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG BAYI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
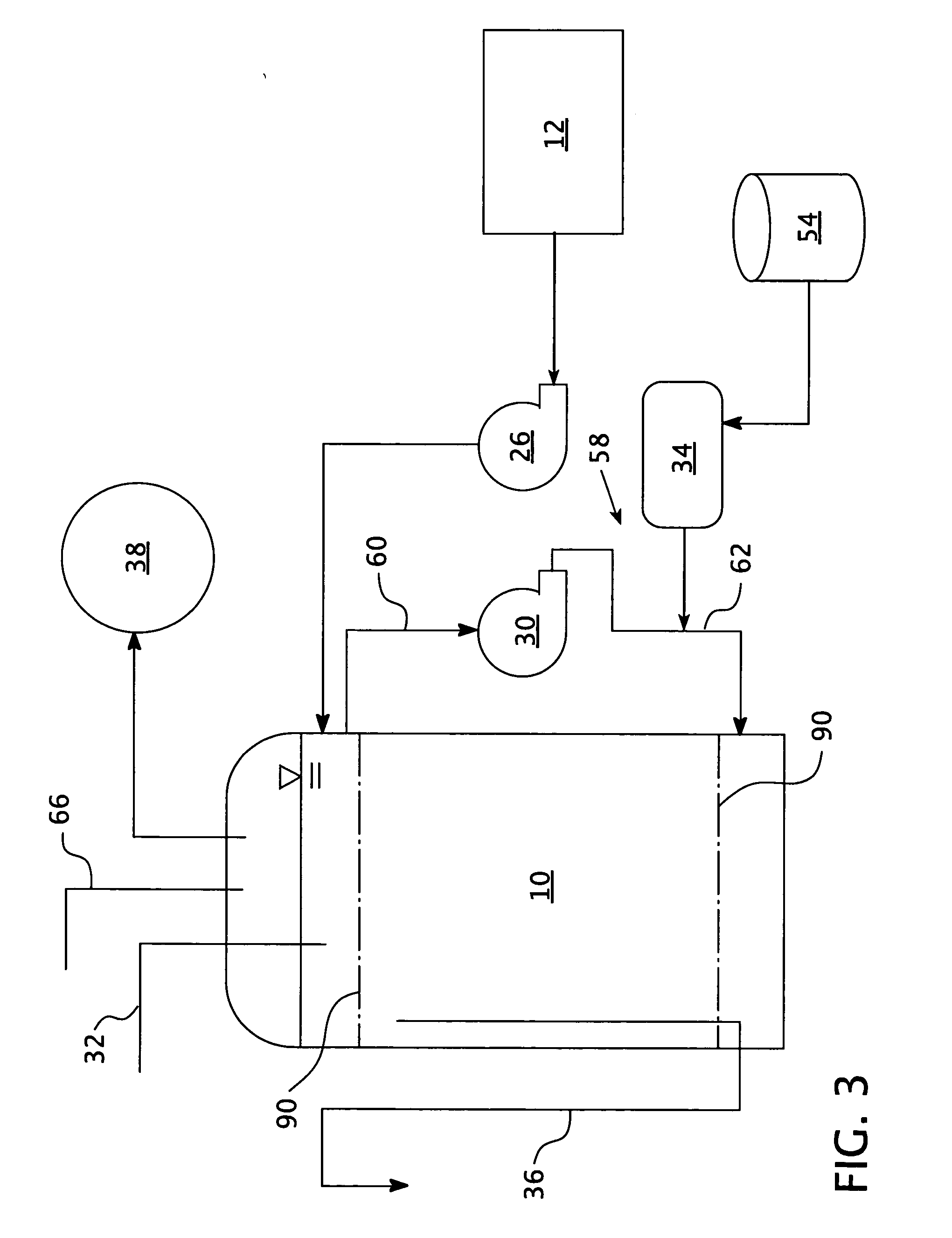
Bioelectrolytical methanogenic/methanotrophic coupling for bioremediation of ground water
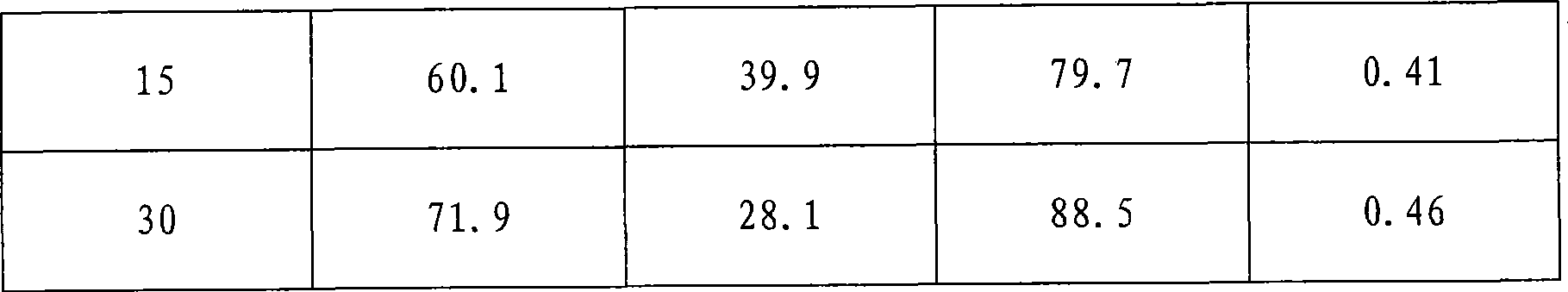
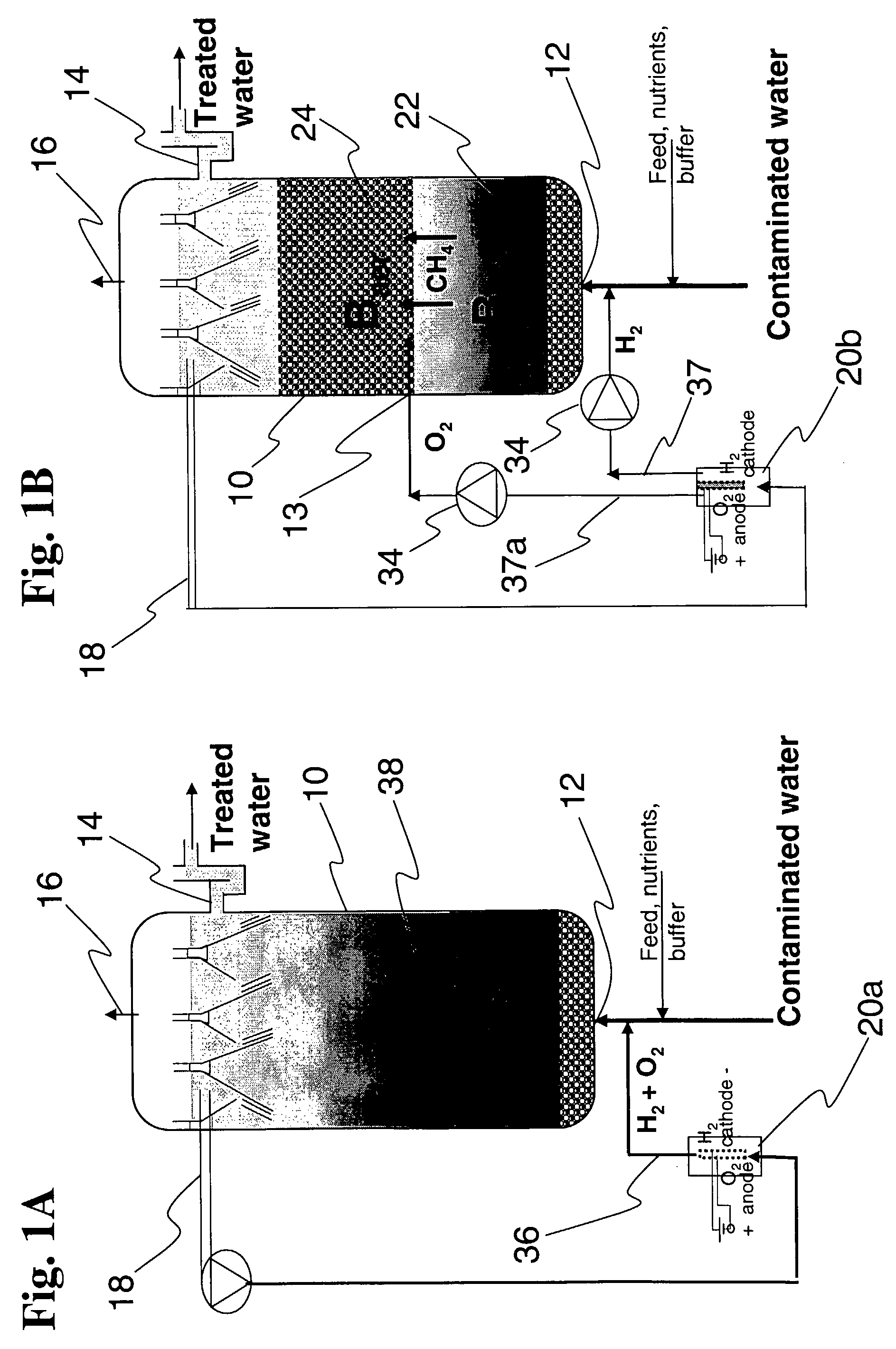
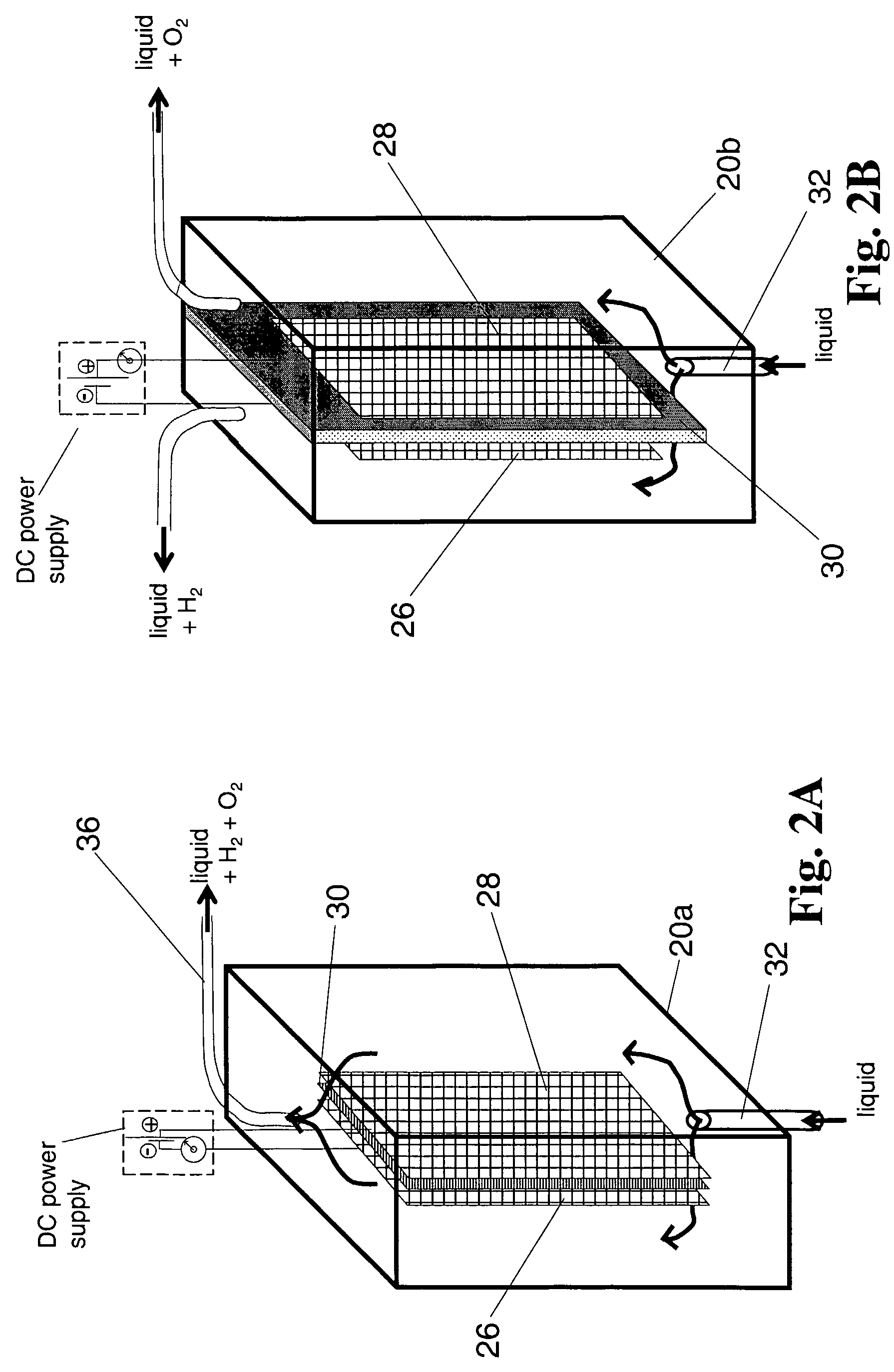
InactiveUS7682815B2Facilitated DiffusionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrolysisElectron donor
The invention disclosure is a method of bioremediation of wastewater, particularly groundwater, by utilizing coupled anaerobic and aerobic biological treatment, more specifically, methanogenic (strictly anaerobic) and methanotrophic (strictly aerobic) microbial populations, in combination with a supply of in-situ generated water-dissolved oxygen and hydrogen. Water electrolysis is used to produce water-dissolved oxygen and hydrogen. The immediate advantage of using H2 from the electrolysis is to provide electron donors to methanogens to reductively dechlorinate the chloroaliphatics, and to reduce the water carbonates and generate methane which is used as energy and carbon source for the methanotrophic bacteria. Oxygen is used as electron acceptor by the aerobic bacteria, including the methanotrophs. The addition of an organic carbon source can be minimized or even eliminated, so as to diminish the competition between methanotrophic bacteria and heterotrophic bacteria for oxygen.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Microbial agent for sewage treatment, attachment carrier of microbial agent and preparation method of microbial agent
The invention discloses a microbial agent for sewage treatment. The microbial agent comprises, by weight, 8-10 parts of clostridium acetobutylicum, 12-16 parts of bacillus licheniformis, 16-20 parts of bacillus subtilis, 5-7 parts of lactobacillus acidophilus, 5-7 parts of methanosarcina, 3-5 parts of methanosaeta, 6-8 parts of rhodopseudomonas palustris, 4-6 parts of cellulomonas flavigena, 8-10parts of streptococcus thermophilus, 8-10 parts of alcaligenes faecalis, 3-5 parts of bacillus amyloliquefaciens, 2-4 parts of bacillus nitrosomonas, 1-3 parts of issatchenkia orientalis and 3-5 partsof streptomyces bullis. Besides, the invention further discloses an attachment carrier of the microbial agent and a preparation method of the microbial agent. The microbial agent can be effectively attached to the carrier and accordingly has better activity. The microbial agent is reasonable in strain preparation and can be effectively attached to the attachment carrier to treat sewage, and the method for sewage treatment is simple, good in treatment effect and worthy of popularization.
Owner:ANJIEYU BEIJING OILFIELD TECHNICAL SERVICES CO LTD
Separation method of monoprop-oxidating hydrogen-producing acetogenic dominant bacterial flora
InactiveCN101768562AEasy to handleReduce shockBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationHydrogen
The invention relates to a separation method of monoprop-oxidating hydrogen-producing acetogenic dominant bacterial flora, in particular to a separation method of hydrogen-producing acetogenic bacteria, solving the problem of separation difficulty and low hydrogen-producing rate of hydrogen-producing acetogenic bacteria cultured by using the traditional separation method. The separation method comprises the following steps of: (1) primarily training anaerobic active mud; (2) preparing a bacterial suspension A; (3) enriching the bacterial suspension; (4) secondarily enriching and culturing the enriched bacterial suspension; (5) preparing a compound bacterial flora of monoprop-oxidating hydrogen-producing acetogenic bacteria and methane-producing bacteria; (6) preparing a monoprop-oxidating hydrogen-producing acetogenic bacterial flora; (7) transferring the monoprop-oxidating hydrogen-producing acetogenic bacterial flora into a monoprop culture substrate to be cultured; and (8) repeating the step (7) for 4-8 times for separation. The invention method has easy separation and simple operation, and the hydrogen-producing rate of the separated dominant bacterial flora is about 6-8 times that of the traditional hydrogen-producing bacteria. The dominant bacterial flora of the invention not only can degrade higher-concentration monoprop, but also can effectively improve the processing efficiency of high-concentration organic wastewater.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
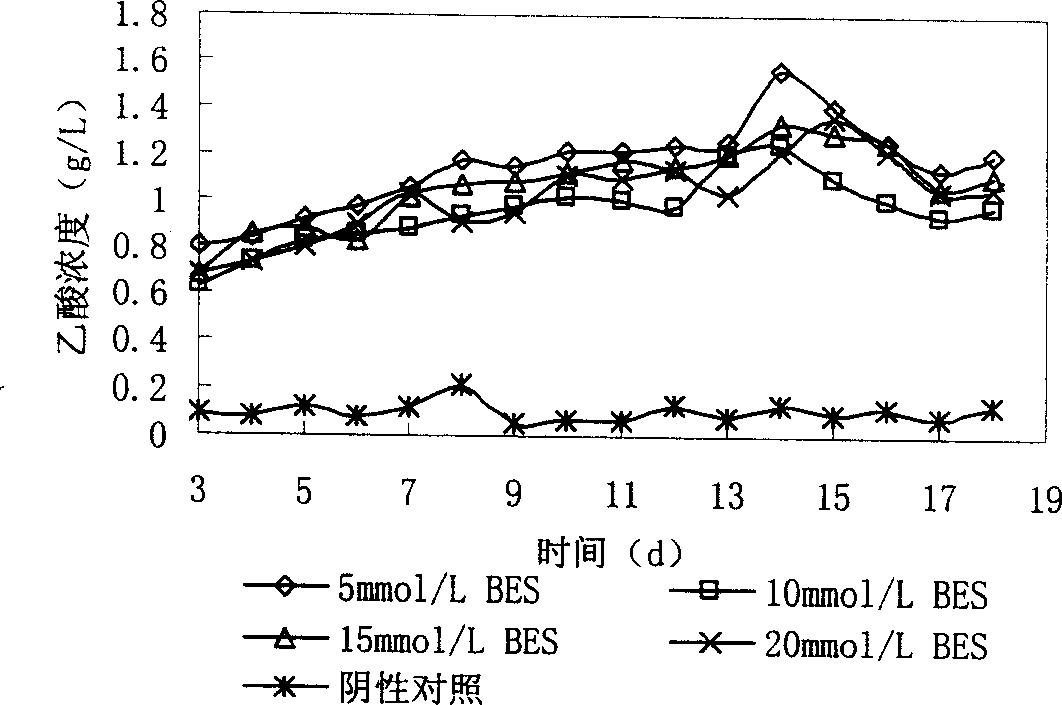
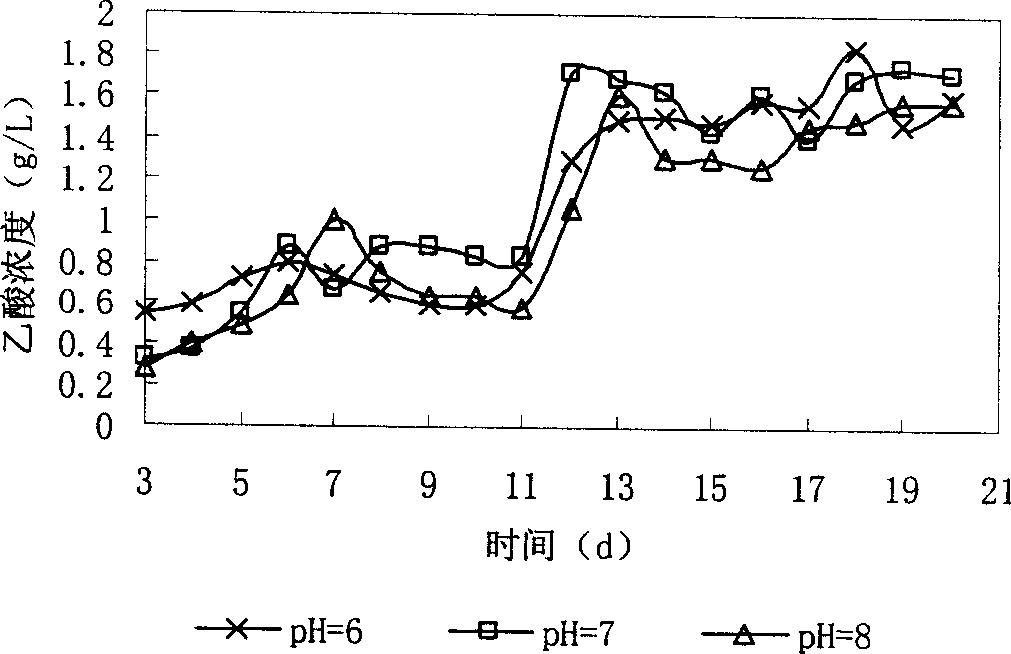
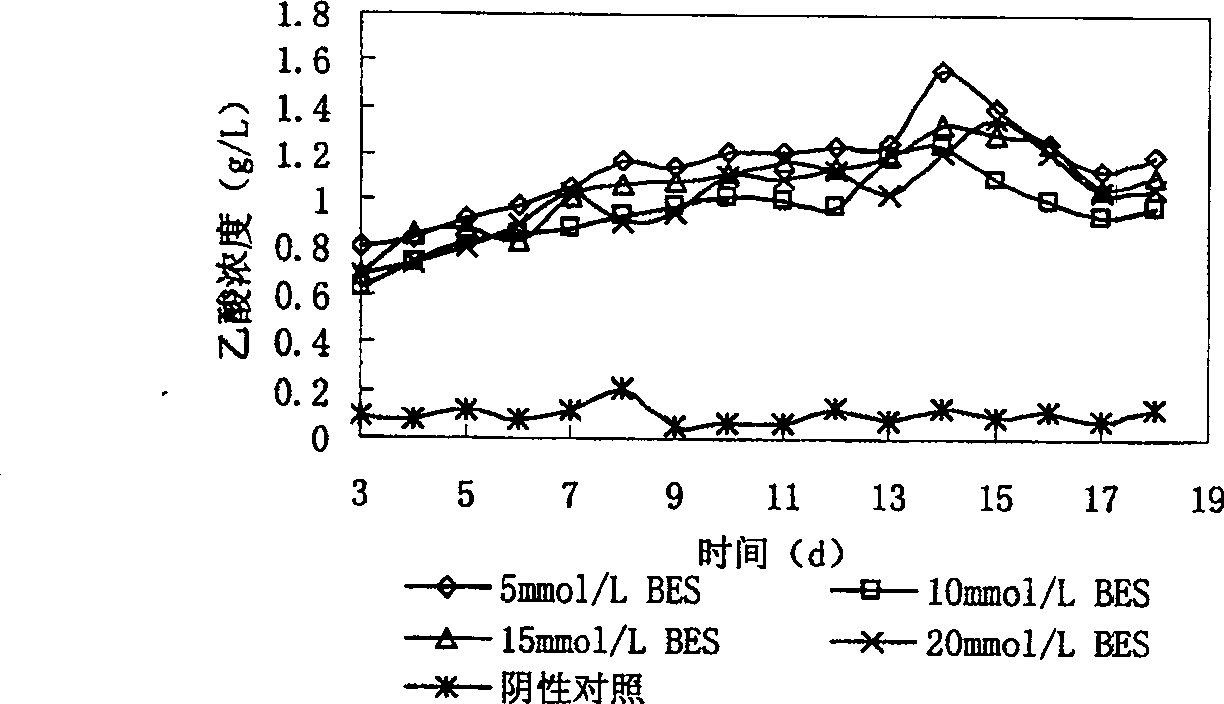
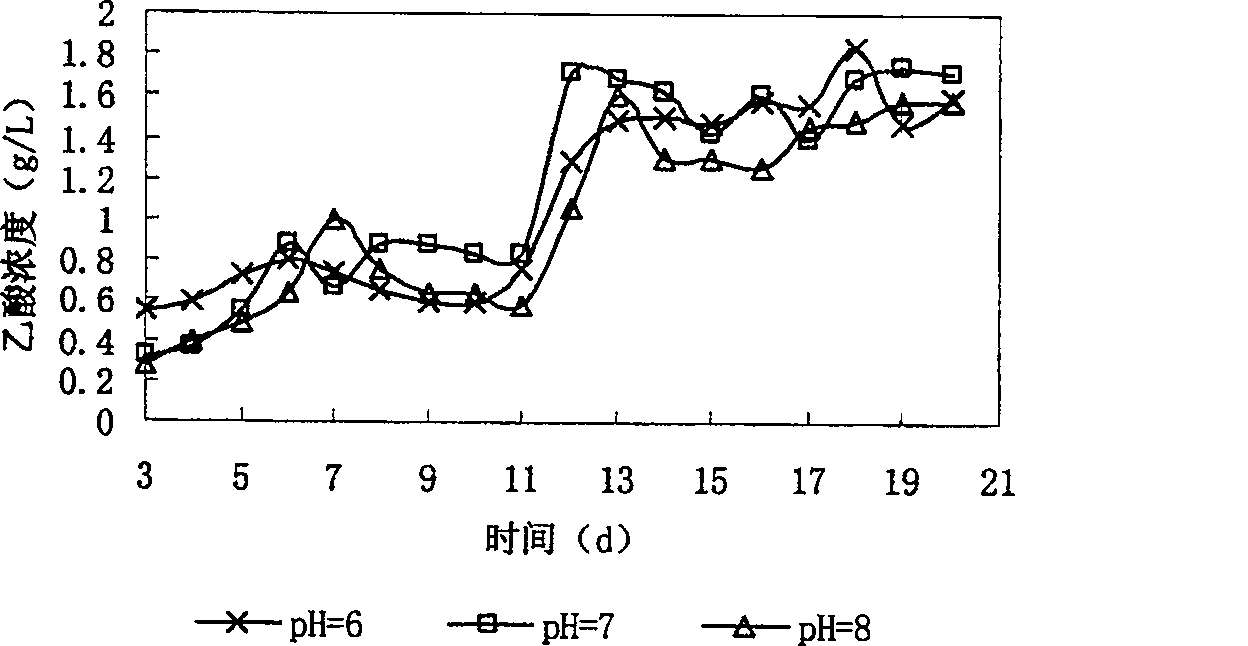
Oriented production of acetic acid in sludge anaerobic fermentation by methane-bacterium specific inhibitor
InactiveCN1896258AIncrease added valueMicroorganism based processesFermentationOrganic acidAcetic acid
The present invention provides a method of directional acetic acid production in anaerobic sludge fermentation using methanogenic bacteria-specific inhibitors which belongs to the sludge recycling field. This invention prepares the methanogenic bacteria-specific inhibitor, 2-bromethylsulfonate sodium into solution of certain concentration and adds the solution into the pretreated sludge. When the concentration of 2-bromethylsulfonate sodium is 5-20 mmol / L and the initial pH is 6-8, the maxmium concentration of acetic acid can achieve 1.84g / L after 15-20 day's fermentation, which is more than five times of the yield of acetic acid under natural conditions. The addition of 2-bromethylsulfonate sodium into anaerobic digestion system will inhibit methanogens and facilitates the accumulation of organic acids, especially acetic acid.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for sustained microbial production of hydrogen gas in a bioreactor using klebsiella oxytoca
InactiveUS20070048851A1Readily apparentBacteriaGas production bioreactorsMicroorganismKlebsiella oxytoca
The present invention provides a method of hydrogen production from microorganisms, wherein a bioreactor provides an environment conducive to the production of hydrogen from Klebsiella oxytoca and restrictive to the production of methane from methanogens. Klebsiella oxytoca metabolizes organic material at elevated temperatures and pH levels that are detrimental to methanogens. Particularly, the environment in the bioreactor is preferably maintained between about 3.5 and 6.0 pH. Further, the Klebsiella oxytoca metabolizes organic material in the organic feed material and produces hydrogen in substantially a 1:1 ratio with carbon dioxide.
Owner:DIZ HARRY R +2
Oriented production of acetic acid in sludge anaerobic fermentation by methane-bacterium specific inhibitor
InactiveCN100526469CIncrease added valueMicroorganism based processesFermentation2-bromoethanesulfonateOrganic acid
The present invention provides a method of directional acetic acid production in anaerobic sludge fermentation using methanogenic bacteria-specific inhibitors which belongs to the sludge recycling field. This invention prepares the methanogenic bacteria-specific inhibitor, 2-bromethylsulfonate sodium into solution of certain concentration and adds the solution into the pretreated sludge. When the concentration of 2-bromethylsulfonate sodium is 5-20 mmol / L and the initial pH is 6-8, the maxmium concentration of acetic acid can achieve 1.84g / L after 15-20 day's fermentation, which is more than five times of the yield of acetic acid under natural conditions. The addition of 2-bromethylsulfonate sodium into anaerobic digestion system will inhibit methanogens and facilitates the accumulation of organic acids, especially acetic acid.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Straw degradation and acidification fungicide and preparation method thereof
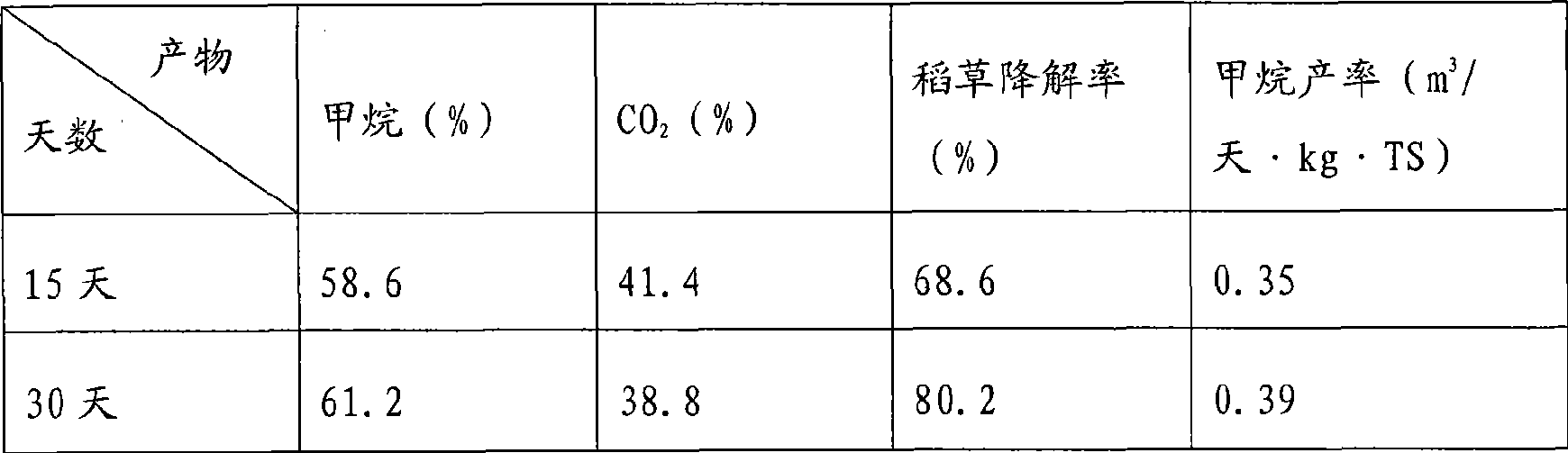
ActiveCN106811438AImprove degradation rateIncrease gas production rateFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyTrichoderma reesei
The invention provides a straw degradation and acidification fungicide and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the biological technical field. The straw degradation and acidification fungicide comprises trichoderma reesei fermentation liquor, trichoderma viride fermentation liquor, acetobacter aceti fermentation liquor and saccharomycetes fermentation liquor, wherein the volume ratio of the trichoderma reesei fermentation liquor to the trichoderma viride fermentation liquor to the acetobacter aceti fermentation liquor to the saccharomycetes fermentation liquor is 3: 3: 2: 2. The fungicide makes effective use of hydrolase which is produced by mildew and can efficiently hydrolyze cellulose and hemicelluloses and is matched with yeast strains and bacillus aceticus to quickly transform straw substances into organic acid such as acetic acid for producing methane bacteria; by the synergistic effect, the gas producing rate is increased, the methane fermenting time is shortened, the equipment utilization rate is increased, and the investment cost is reduced.
Owner:河南天冠纤维乙醇有限公司
Marsh gas fermentation material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104232726ASolve unhandled problemsReduce startup timeMicroorganism based processesWaste based fuelStart timeSludge
The invention discloses a marsh gas fermentation material and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of a biological fermentation method for preparing marsh gas. The marsh gas fermentation material comprises a fermentation main material and a fermentation initiator, wherein the fermentation main material is prepared from Flammulina velutipes residue, Enteromorpha, corn straw, fish pond sludge, wheat straw, animal manure and wine stillage; the fermentation initiator is prepared from fish pond sludge, wheat straw, animal manure and strains; the strains comprise Bacteroides succinogenes, Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens, Bacillus subtilis, microzyme, sarcina methanica and Methanosaeta in a ratio of 1:5:3:3:2:2; and the weight ratio of the fermentation main material to the fermentation initiator is (15-19):1. The marsh gas fermentation material fully utilizes the wastes Flammulina velutipes residue and Enteromorpha, and can greatly shorten the start time and increase the gas production quantity and gas production speed in the marsh gas fermentation process.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & ENVIRONMENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Methanomassiliicoccus sp. and application thereof
ActiveCN109609415AIncrease productionLow toxicityBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffBacterial strainTriethylamine-N-oxide
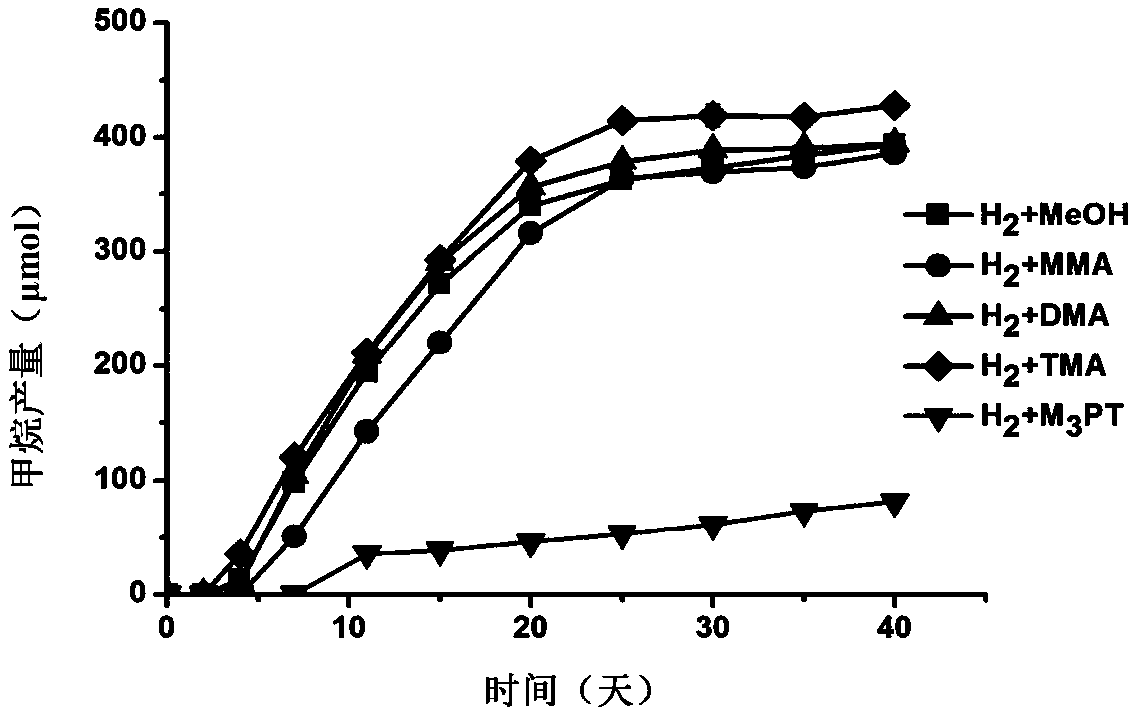
The invention discloses methanomassiliicoccus sp. The classification name of the methanomassiliicoccus sp. is methanomassiliicoccus sp. (methanomassiliicoccus sp.), the bacterial strain number is LGM-RCC1, the methanomassiliicoccus sp. is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the preservation time is at 24 October, 2018, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.16819. The invention also discloses an application of the methanomassiliicoccus sp. in fermentation production of methane, and an application of the methanomassiliicoccus sp. to preparation of a probiotic agent or a feed additive. The LGM-RCC1 can be used for generating the methane through reducing methanol, monomethylamine, dimethylamine, trimethylamine and methyl 3-methylthiopropionate through hydrogen, and the LGM-RCC1 can be used as an additive for increasing the yield of the methane in a methane-generating pit; and the LGM-RCC1 can utilize the trimethylamine in digestive tracts, toxicity of the LGM-RCC1 to human bodies or animals can be reduced, and the LGM-RCC1 is a potential probiotic for treating diseases and preventing cardiovascular diseases caused by trimethyl amine oxide.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method of producing isoprene monomer
ActiveUS20150275233A1Excellent for production of isopreneEasy to produceBacteriaTransferasesNitrosopumilusCorynebacterium efficiens
A host cell includes a heterogeneous expression unit including: (a) a polynucleotide encoding a mevalonate kinase derived from a microorganism belonging to a genus selected from Methanocella, Corynebacterium, Methanosaeta, and Nitrosopumilus, and (b) a promoter operatively linked to the polynucleotide. The host cell is used to produce mevalonate kinase, mevalonate-5-phosphate, and isoprenoid compounds.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Separation method of butyric acid oxidized hydrogen-producing acetogenic dominant microorganisms
InactiveCN101724595AHigh removal rateButyric acid concentration decreasedBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationActivated sludge
The invention discloses a separation method of butyric acid oxidized hydrogen-producing acetogenic dominant microorganisms, relating to a separation method of hydrogen-producing acetogenic bacteria and solving the problems that the traditional separation method is difficult to separate and the hydrogen-producing rate of the cultured hydrogen-producing acetogenic bacteria is low. The separation method comprises the following steps of: firstly, preliminarily domesticating anaerobic activated sludge; secondly, preparing a bacterial suspension A; thirdly, enriching a back bacterial suspension; fourthly, enriching and culturing the enriched back bacterial suspension again; fifthly, preparing compound microorganisms of butyric acid oxidized hydrogen-producing acetogenic bacteria and methanogen; sixthly, preparing the butyric acid oxidized hydrogen-producing acetogenic microorganisms; seventhly, transferring the butyric acid oxidized hydrogen-producing acetogenic microorganisms to a butyric acid culture medium for vibration velocity culture; and eighthly, repeating the step seven for 3-6 times and then separating. The method has easy separation and simple operation, and the hydrogen-producing rate of the separated dominant microorganisms is about 7-10 times of that of the hydrogen-producing bacteria. The advantageous bacterium group not only can degrade the butyric acid with higher concentration, but also can effectively improve the treating efficiency of organic wastewater with high concentration.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Inhibition of methane production during anaerobic reductive dechlorination
ActiveUS20140251900A1Affect competitionLower emission levelsWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsRed yeast riceHydrogen
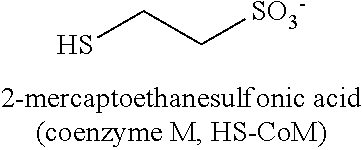
This method of restricting methane production in methanogenic bacteria, by the use of the enzyme and coenzyme inhibitors, works during anaerobic reductive dechlorination. Various compounds such as, but not limited to, red yeast rice, vitamin B10 derivatives, and ethanesulfonates are utilized to disrupt these different enzyme and coenzyme systems responsible for the production of methane. This method affects the competition of the methanogen and halo bacteria for the organic hydrogen donors that are injected in the soil and groundwater system during the remediation process.
Owner:INNOVATIVE ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
System for sustained microbial production of hydrogen gas in a bioreactor using klebsiella oxytoca
InactiveUS20070048850A1Readily apparentBacteriaGas production bioreactorsMicroorganismKlebsiella oxytoca
The present invention provides a system of hydrogen production from microorganisms, wherein a bioreactor provides an environment conducive to the production of hydrogen from Klebsiella oxytoca metabolism and restrictive to the production of methane from methanogens. Klebsiella oxytoca metabolizes organic material at elevated temperatures and pH levels that are detrimental to methanogens. Fixed colonies of Klebsiella oxytoca are contained within the bioreactor, providing a sustained level of hydrogen production. The Klebsiella oxytoca metabolizes organic material in the organic feed material and produces hydrogen in substantially a 1:1 ratio with carbon dioxide. The environment in the bioreactor is preferably maintained between about 3.5 and 6.0 pH.
Owner:DIZ HARRY R +2
Application of red yeast rice to reduction of methane discharged by ruminant such as sheep
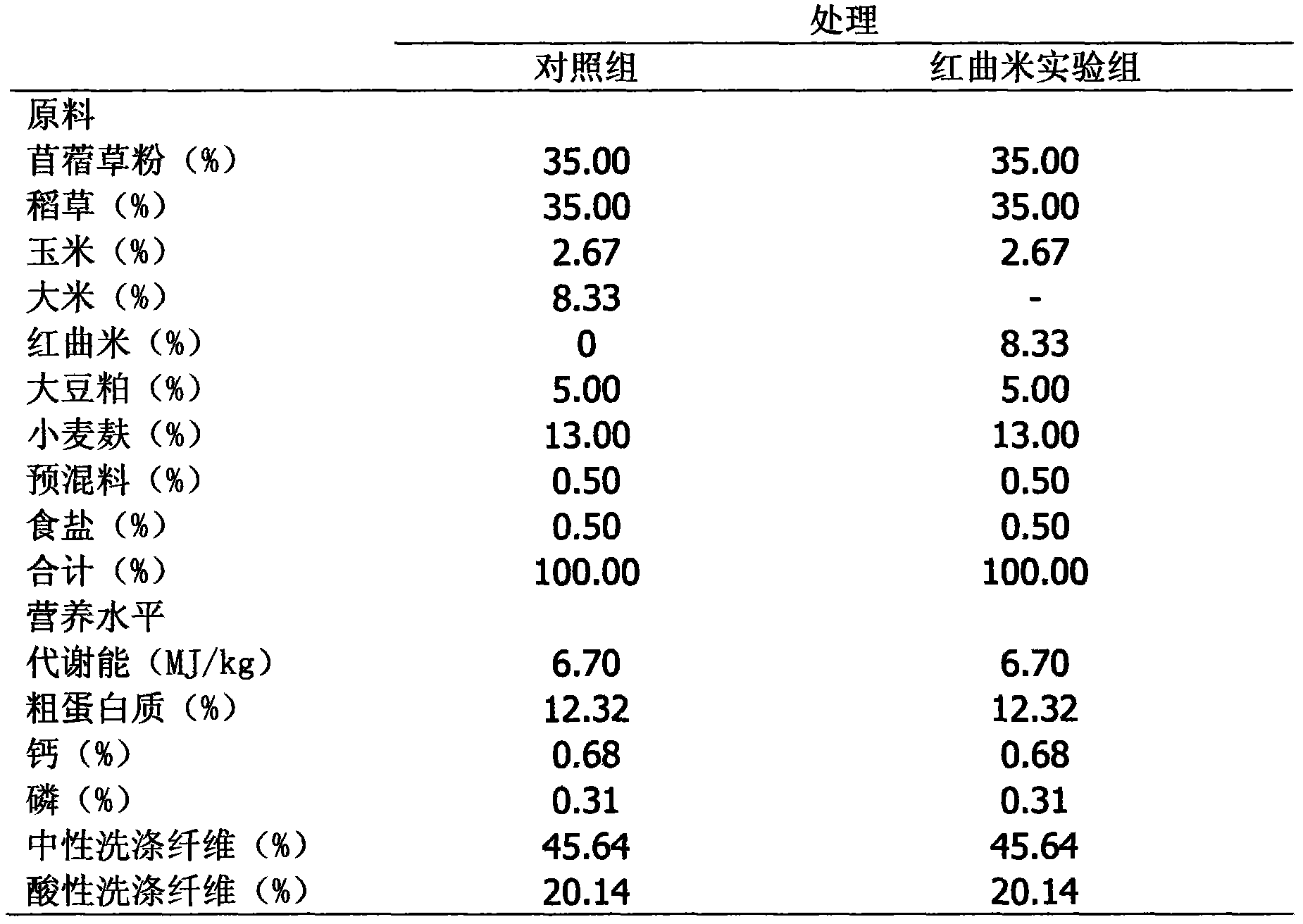
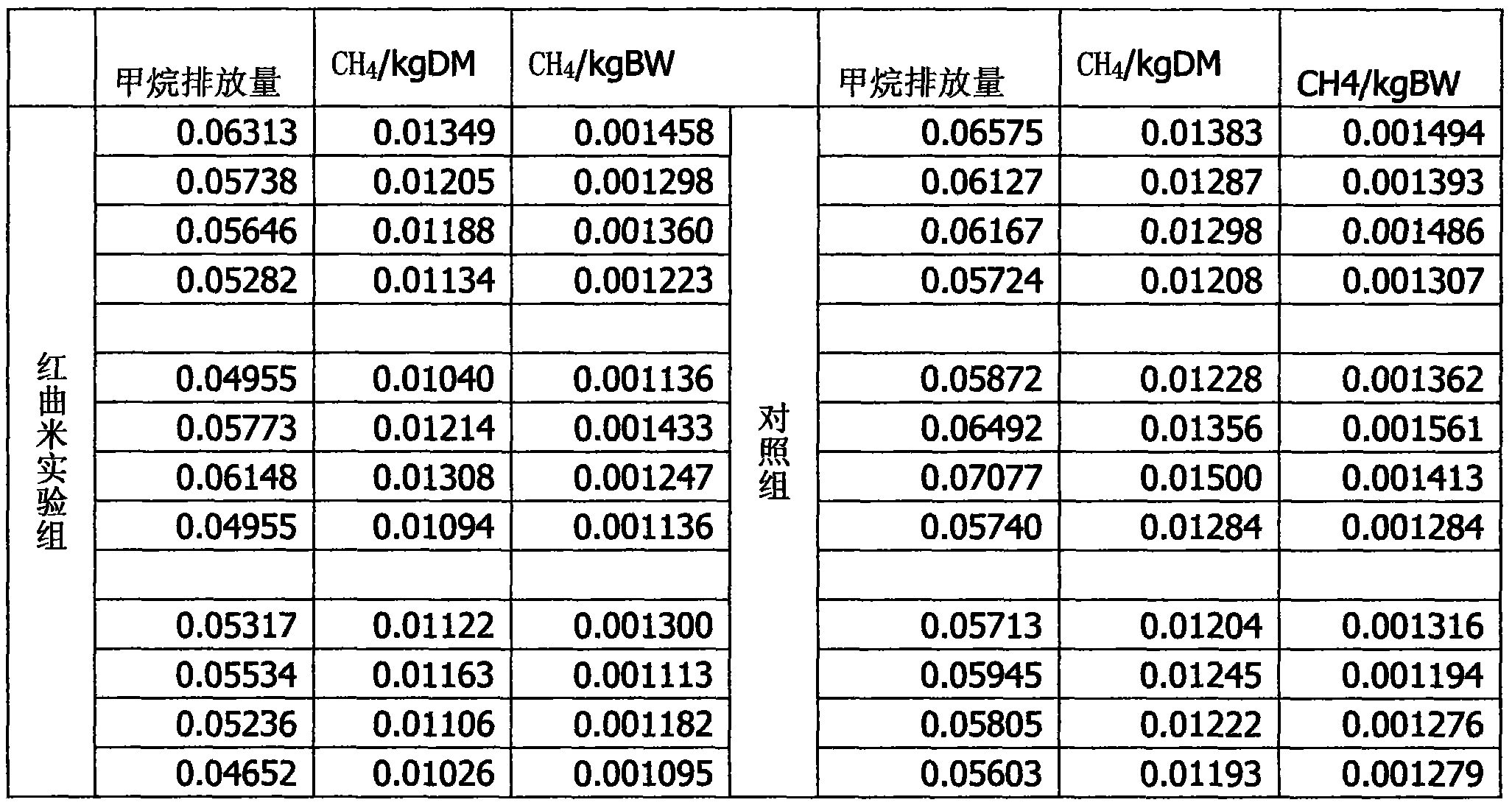
InactiveCN103829090AImprove nutrient utilizationGrowth inhibitionAnimal feeding stuffAgriculture gas emission reductionBiotechnologyRed yeast rice
The invention discloses application of red yeast rice to reduction of methane discharged by ruminant such as sheep. When the red yeast rice is added into ruminant feed to reduce methane discharged by ruminant, the additive amount of the red yeast rice in the daily ration of sheep depends on the average daily feed intake of the sheep, the content ratio of nutrients to lovastatin in the red yeast rice and the ratio of opening loops to closed loops of lovastatin. The red yeast rice is adopted for reducing methane discharged by sheep, and the added red yeast rice naturally containing lovastatin can competitively and powerfully inhibit 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase and cut off the passage for synthesizing methane bacteria membrane lipid, thereby effectively inhibiting the growth of methane bacteria and eventually reducing methane discharged by ruminant such as sheep.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Preparation of composite bacteria
InactiveCN101481676BPromote growthPromote proliferationMicroorganism based processesMicrobiology processesCelluloseStrict anaerobic bacteria
The invention discloses a method for preparing composite bacterium, comprising the following steps: inoculating microorganism of zymogenous bacteria, hydrogen-producing acetogenic bacteria and methanogen respectively belonging to facultative anaerobic bacteria and strict anaerobic bacteria which are mixed according to a certain proportion into a culture solution containing cellulose, sealing and keeping standing to culture at a temperature of between 30 to 50 DEG C and pH value of 3 to 10, wherein the culture solution containing cellulose contains CaCO3, 0.3 to 0.7 percent of NaCl, 0.5 to 1 percent of cellulose, 0.1 to 0.4 percent of urea, 0.1 to 0.3 percent of peptone and 0.05 to 0.15 percent of yeast powder, and water is used as a solvent. The composite bacterium having effective cellulose degrading property and capable of generating methane is prepared by the method.
Owner:BIOGAS SCI RES INST MIN OF AGRI
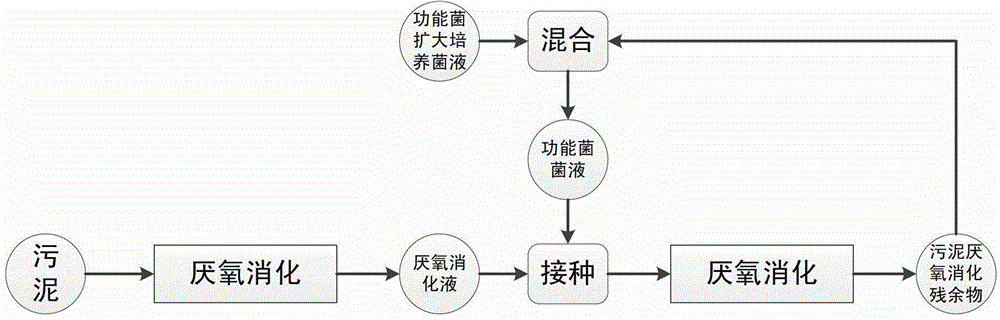
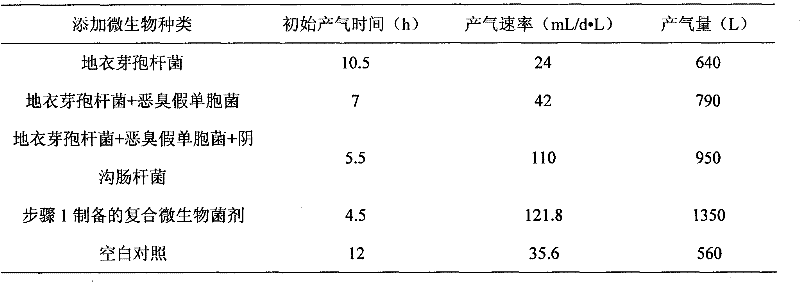
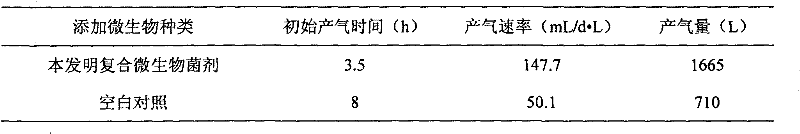
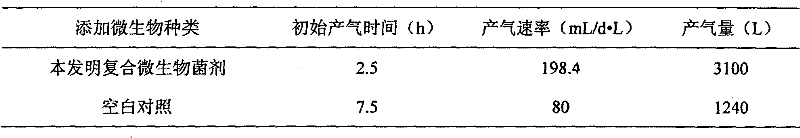
Method for improving anaerobic digestion performance of sludge and synchronously enlarging cultivation by functional bacteria
ActiveCN103058478BImprove the efficiency of anaerobic digestionPromote formationBacteriaWaste based fuelOrganic matterDigestion
The invention relates to a method for improving anaerobic digestion performance of sludge and synchronously enlarging cultivation by functional bacteria. The method comprises the following steps of: collecting and screening the functional bacteria; enlarging cultivation of the functional bacteria; preparing functional bacteria solution; inoculating the functional bacteria solution into an anaerobic digestion reactor containing sludge after carrying out anaerobic digestion for 10-15 days on the sludge, further carrying out anaerobic digestion on the sludge for 15-30 days, hydrolyzing protein which is difficult to degrade in the sludge into low molecular weight organic matters by the functional bacteria; hydrolyzing the low molecular weight organic matters to form methane by mathanogenic bacteria; and carrying out multiplication of bacteria cells by the functional bacteria, so as to finally obtain sludge digestion residue containing the methanogenic bacteria and the functional bacteria. Compared with the prior art, advantages enrichment and expansion of the functional bacteria are achieved by the method; the obtained sludge digestion residue contains target functional bacteria, and can be used as an inoculant to be applied to anaerobic digestion treatment of the sludge by circulating inoculation; and the anaerobic digestion efficiency of the sludge is lastingly improved, and the treatment cost is reduced.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Composite microbial inoculum used for anaerobic fermentation of kitchen wastes
ActiveCN103215213BNormal fermentationGuaranteed Filtration EfficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBacteroides
The invention discloses a composite microbial inoculum used for the anaerobic fermentation of kitchen wastes, belongs to the field of micro-organisms, and solves the problem of the lack of a microbial inoculum suitable for performing anaerobic fermentation by taking kitchen wastes as a main raw material at present. The composite microbial inoculum comprises, in parts by weight, 8-15 parts of acid production bacteroides DSM 15896 fermentation liquor, 25-35 parts of long-chain fatty acid syntrophic aeromonas DSM 18709 fermentation liquor, 15-25 parts of clostridium sordellii ATCC9714 fermentation liquor, 20-28 parts of combined methanosaeta JCM10134 fermentation liquor and 22-27 parts of methanospirllum hungatei DSM864 fermentation liquor, wherein the effective viable counts of the fermentation liquors of the five bacteria aforementioned achieve more than 10<9> per millilitre respectively. The composite microbial inoculum disclosed by the invention is suitable for an anaerobic fermentation process taking the kitchen wastes as the main raw material, and capable of playing the roles of stabilizing the pH value of a fermentation system, promoting to bring forward the peak of methanogenesis, and increasing the total amount of methanogenesis after being inoculated in the fermentation system.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG BAYI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Biogas fermentation initiator and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104152494AReduce startup timeIncrease gas productionMicroorganism based processesWaste based fuelGenus MethanosarcinaStart time
The invention discloses a biogas fermentation initiator and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biogas preparation through a biological fermentation method. The present problems of slow start, low gas yield efficiency, and no gas yield in the fermentation process are solved. The initiator is composed of the following raw materials: sludge in fishpond, wheat straw, animal manure, ammonium bicarbonate, and bacterium strains; wherein the bacterium strains are bacteroides succinoge-nes, butyrivibrio fibrisolvens, bacillus subtilis, saccharomycetes, methanosarcina, and methanosaeta. The biogas fermentation initiator is applied to biogas fermentation, can greatly shorten the start time (biogas can be produced after one day), and is capable of increasing the biogas yield and biogas generation speed.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & ENVIRONMENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Compound microbial bacterial preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101864362BStrong digestionOvercoming the problem of only targeting a single organic wasteFungiBacteriaBacillus licheniformisCellulose
The invention belongs to the technical field of environment protection and discloses a compound microbial bacterial preparation and application thereof. The compound microbial bacterial preparation consists of fermentation liquor of four bacteria, i.e. Bacillus licheniformis, Pseudomonas putida, Enterobacter cloacae and Candida valida. The compound microbial bacterial preparation provided by the invention has strong digestion power for various types of cellulose, proteins and fat macromolecules. The addition of the compound microbial bacterial preparation into excess sludge and / or kitchen waste can quicken enrichment of methanogen, shorten anaerobic digestion time and improve methane yield. Moreover, the synergetic effect of the four microbial strains is superior to the effect of any one, two or three strains of microorganisms.
Owner:江苏加德绿色能源有限公司
Acetate supplemention of medium for butanologens
The invention relates to the fields of industrial microbiology and alcohol production. More specifically, the invention relates to improved production of butanol isomers by recombinant microorganisms containing an engineered butanol pathway and disrupted activity of the genes in pathways for the production of by-products during the fermentation when the microorganisms are grown in a fermentation medium containing acetate. In embodiments, recombinant microorganisms have an increased growth rate in a fermentation medium containing acetate as a C2 supplement.
Owner:GEVO INC
Inhibition of methane production during anaerobic reductive dechlorination
ActiveUS9221699B2Affect competitionLower emission levelsWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsRed yeast riceHydrogen
This method of restricting methane production in methanogenic bacteria, by the use of the enzyme and coenzyme inhibitors, works during anaerobic reductive dechlorination. Various compounds such as, but not limited to, red yeast rice, vitamin B10 derivatives, and ethanesulfonates are utilized to disrupt these different enzyme and coenzyme systems responsible for the production of methane. This method affects the competition of the methanogen and halo bacteria for the organic hydrogen donors that are injected in the soil and groundwater system during the remediation process.
Owner:INNOVATIVE ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Microorganism bacterium agent for digesting sludge
InactiveCN106396325AEasy to synthesizeStrong acetic acid conversionFungiBacteriaEscherichia coliSynechococcus
The invention relates to the field of microorganism environmental protection and in particular relates to a microorganism bacterium agent for digesting sludge. The microorganism bacterium agent is prepared from aspergillus niger, escherichia coli, a mixed bacterial colony, bifidobacterium and the balance of nutrient substances in percentage by mass, wherein the mixed bacterial colony is composed of rhodospirillum rubrum, streptococcus thermophilus, salt denitrified virgibacillus and paracoccus denitrificans at the mass ratio of 1 to 1 to 1 to 1. The bacterium agent provided by the invention is simpler to synthesize, and comprises the mixed bacterial colony, the escherichia coli, the bifidobacterium and the aspergillus niger; microorganisms are mixed through self-culture, and then the nutrient substances for the growth of the microorganisms are added to obtain the bacterium agent; the microorganism bacterium agent is very convenient to produce, and can be used for converting organic acids including propionic acid and the like, which cannot be utilized by methanogenic bacteria after organic matters are decomposed through an enzyme, into acetic acid, and methane gas is generated; the amount of the methane generated through the sludge with the equivalent volume can be greatly improved and the efficiency is improved very well; the utilization rate of the sludge is increased and the sludge is recycled better.
Owner:安徽新季环保科技有限公司
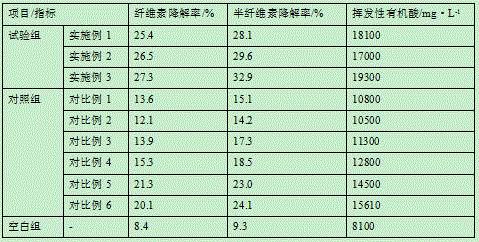
Method for producing methane through pre-fermenting and strengthening surplus sludge anaerobic digestion
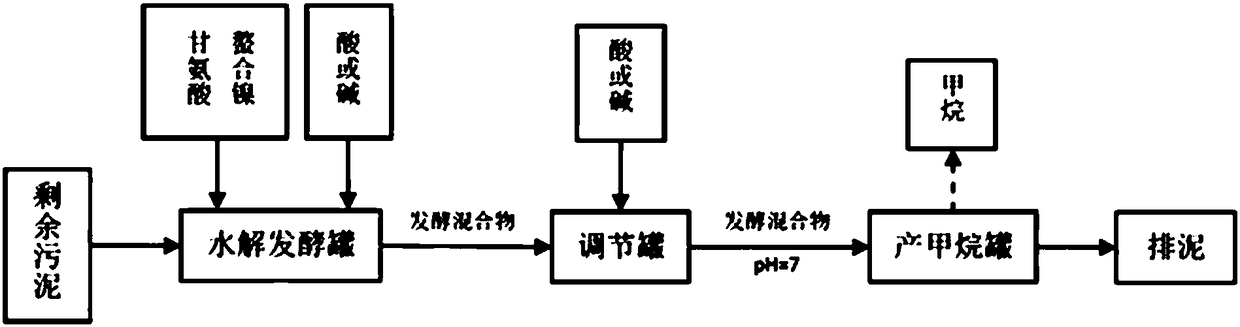
ActiveCN108249725AIncreased rate of hydrolytic acidificationOptimizing the Type of Fermentation Acid ProductionBiological sludge treatmentClostridiaHydrolysis
The invention provides a method for producing methane through pre-fermenting and strengthening surplus sludge anaerobic digestion. The method comprises the following steps of S1, precipitating and concentrating a sludge to obtain a sludge to be treated; S2, mixing an inoculating mud and the sludge to be treated obtained in the step S1 according to the proportion so as to obtain a fermented mixture, and adjusting pH of the fermented mixture to be acid; S3, mixing the fermented mixture obtained in the step S2 and chelate nickel glycinate according to the proportion, and carrying out hydrolysis fermentation. By using the chelate nickel glycinate under a weak acid condition, the relative abundance of acidogenic fermentation bacterium Clostridia can be improved, the sludge hydrolytic acidification speed is accelerated, and an acidogenic fermentation type is optimized for providing a beneficial substrate for methanogens; meanwhile, through a nickel element dissolved in the sludge, the relative abundance of the methanogens Methanosaeta can be also improved, and the performance for producing the methane through sludge anaerobic digestion is effectively improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Microbial agent for reducing sludge, carrier thereof and preparation method for carrier thereof
The invention discloses a microbial agent for reducing sludge. The microbial agent comprises the following components in parts by weight: 8-10 parts of clostridium acetobutylicum, 12-16 parts of bacillus licheniformis, 16-20 parts of bacillus subtilis, 5-7 parts of lactobacillus acidophilus, 5-7 parts of methanosarcina, 3-5 parts of methanosaeta, 6-8 parts of rhodopseudomonas palustris, 4-6 partsof cellulomonas flavigena, 8-10 parts of streptococcus thermophilus, 8-10 parts of alcaligenes faecalis, 3-5 parts of bacillus amyloliquefaciens, 2-4 parts of bacillus nitrosomonas, 1-3 parts of issatchenkia orientalis and 3-5 parts of streptomyces oxalis. The invention also discloses a carrier of the microbial agent for reducing sludge and a preparation method thereof. The carrier is capable of effectively attaching microorganisms and endowing microorganisms with higher activity. Strains are reasonably prepared in the microbial agent disclosed by the invention; the microbial agent is attachedto the carrier for treating sewage; when the method is used for treating sewage, the operation is simple, the treatment effect is excellent and sludge deposition is less; the method is worthy of popularization.
Owner:ANJIEYU BEIJING OILFIELD TECHNICAL SERVICES CO LTD
Vaccine pharmaceutical composition for transdermal administration
ActiveUS20170216431A1Improve complianceImprove the quality of lifeBacterial antigen ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsAntigenAcidocella
The present invention provides a vaccine pharmaceutical composition for transdermal administration which is safe, usable as a prophylactic or therapeutic agent for cancer or infectious diseases, and capable of safely and effectively inducing a systemic immune response. It can be administered to a human or animal skin, the vaccine pharmaceutical composition including: a lipopolysaccharide or its salt derived from at least one gram-negative bacterium such as Serratia, Lelercia, Rahnella, Acidicaldus, Acidiphilium, Acidisphaera, Acidocella, Acidomonas, Asaia, Belnapia, Craurococcus, Gluconacetobacter, Gluconobacter, Kozakia, Leahibacter, Muricoccus, Neoasaia, Oleomonas, Paracraurococcus, Rhodopila, Roseococcus, Rubritepida, Saccharibacter, Stella, Swaminathania, Teichococcus, Zavarzinia, Pseudomonas, Achromobacter, Bacillus, Methanoculleus, Methanosarcina, Clostridium, Micrococcus, Flavobacterium, Pantoea, Acetobacter, Zymomonas, Xanthomonas, and Enterobacter, as an immunostimulant; and at least one antigen, the vaccine pharmaceutical composition having a mass ratio between the immunostimulant and the antigen, the total mass of the immunostimulant / the total mass of the antigen, of 0.002 to 500.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
A Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide preparation that regulates rumen microflora
ActiveCN104273340BPromote the reproduction of degrading bacteriaIncrease concentrationAccessory food factorsBacteroidesFiber
The invention discloses a ganoderma polysaccharide preparation for regulating rumen microflora and a preparation method thereof. The invention extracts the ganoderma polysaccharide from ganoderma ganoderma residues, ganoderma processing leftovers or ganoderma, and adds a carrier to make a preparation. The preparation is added to the premix or total mixed ration at 5-50 mg / kg dry matter of the ration, and is used to feed cattle and sheep. Filamentous bacteria, Ruminococcus xanthus, Bacillus fibrinolyticus and total bacteria concentration, reduce the concentration of methane bacteria, increase the production of NH3-N, microbial protein and total volatile fatty acids, and at the same time enhance the immunity of cattle and sheep, and improve fiber feed Utilization, improve production performance. Moreover, the source is easy, the preparation process is simple, the use is convenient and safe, and there is no side effect. It can be used as a green additive for cattle and sheep feed, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com