Patents
Literature
38results about How to "Increased biomass accumulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Transgenic plants used as a bioreactor system
ActiveUS20060259998A1Efficient assimilationIncreased biomass accumulationOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationChemistryAntibody
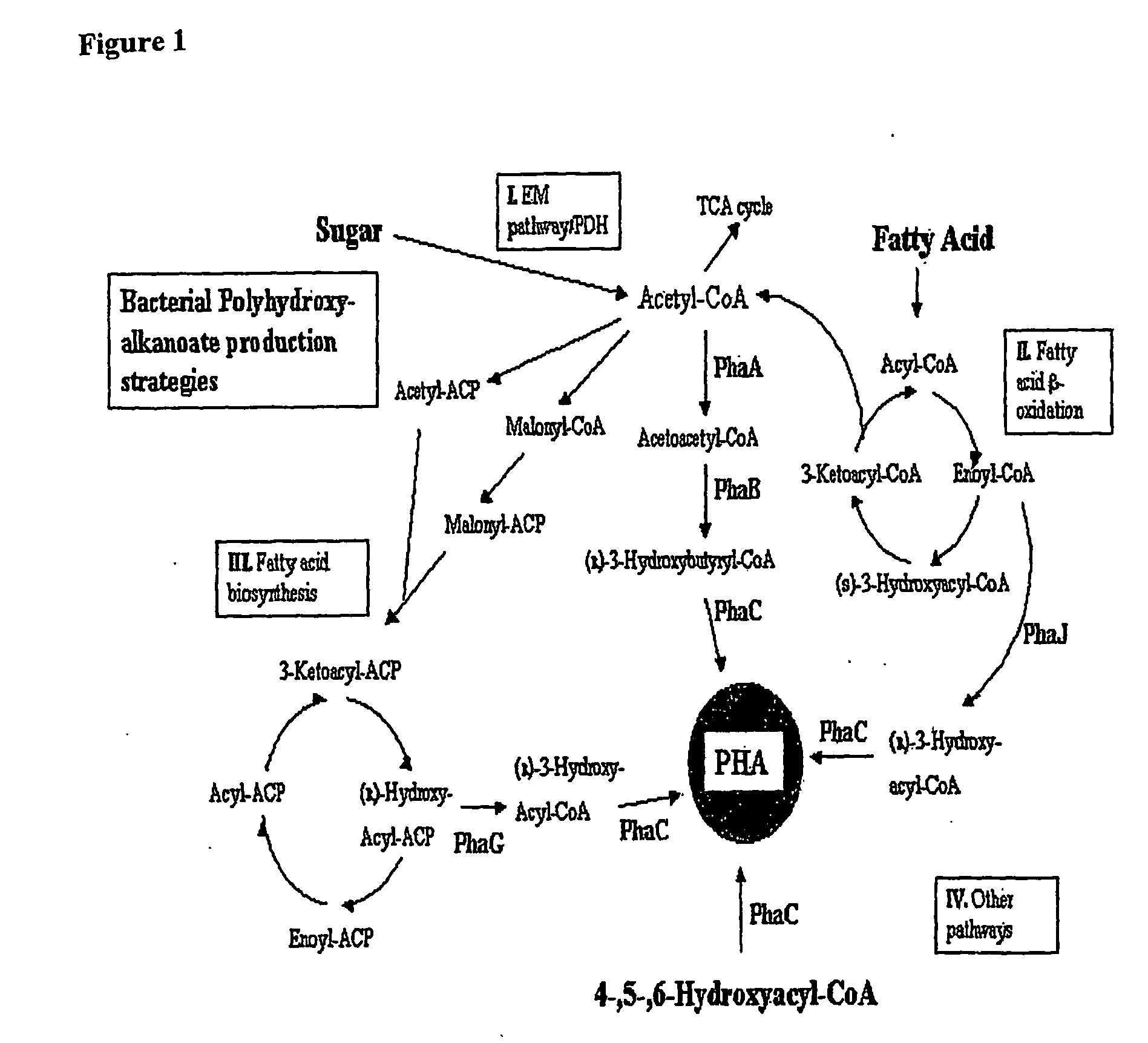
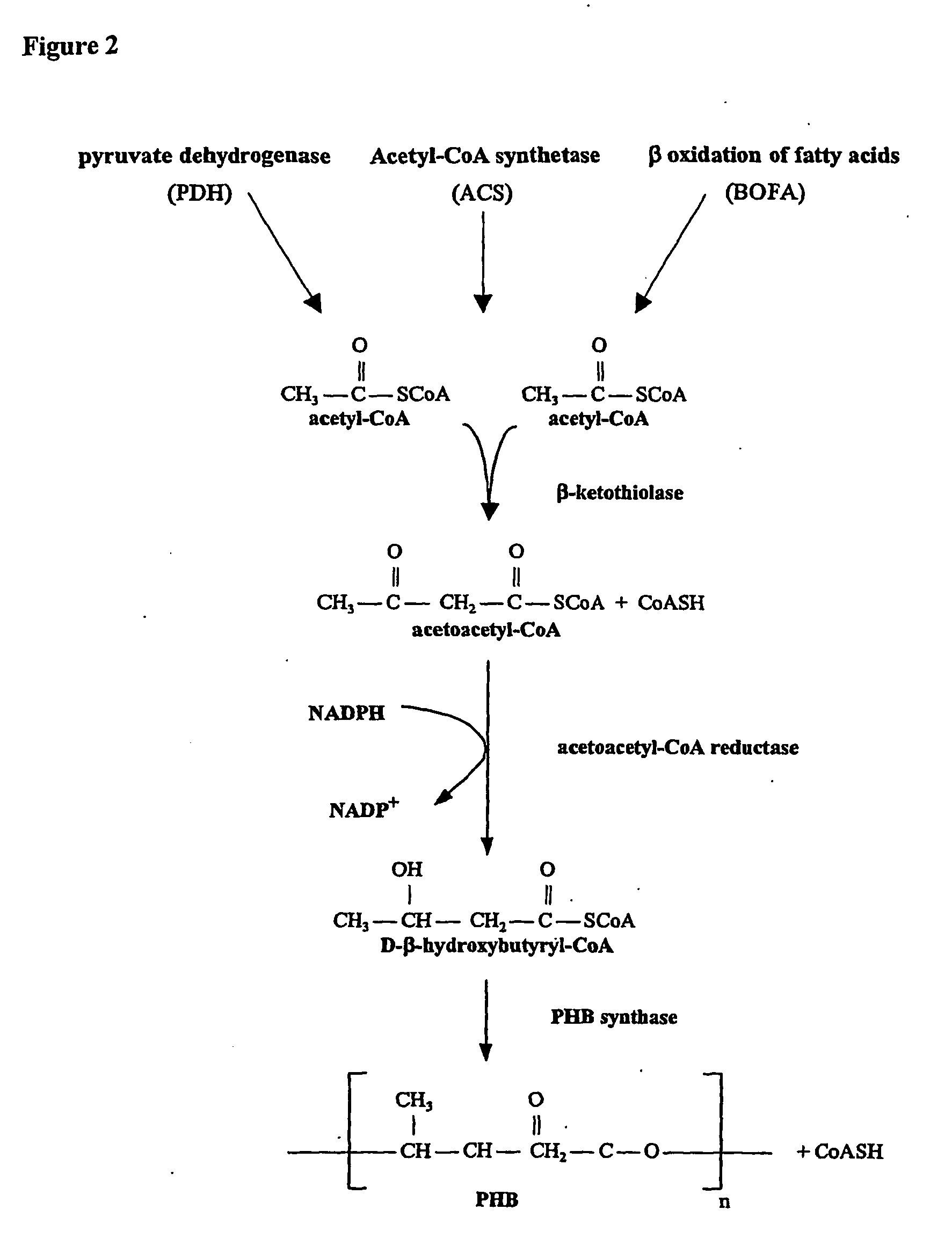
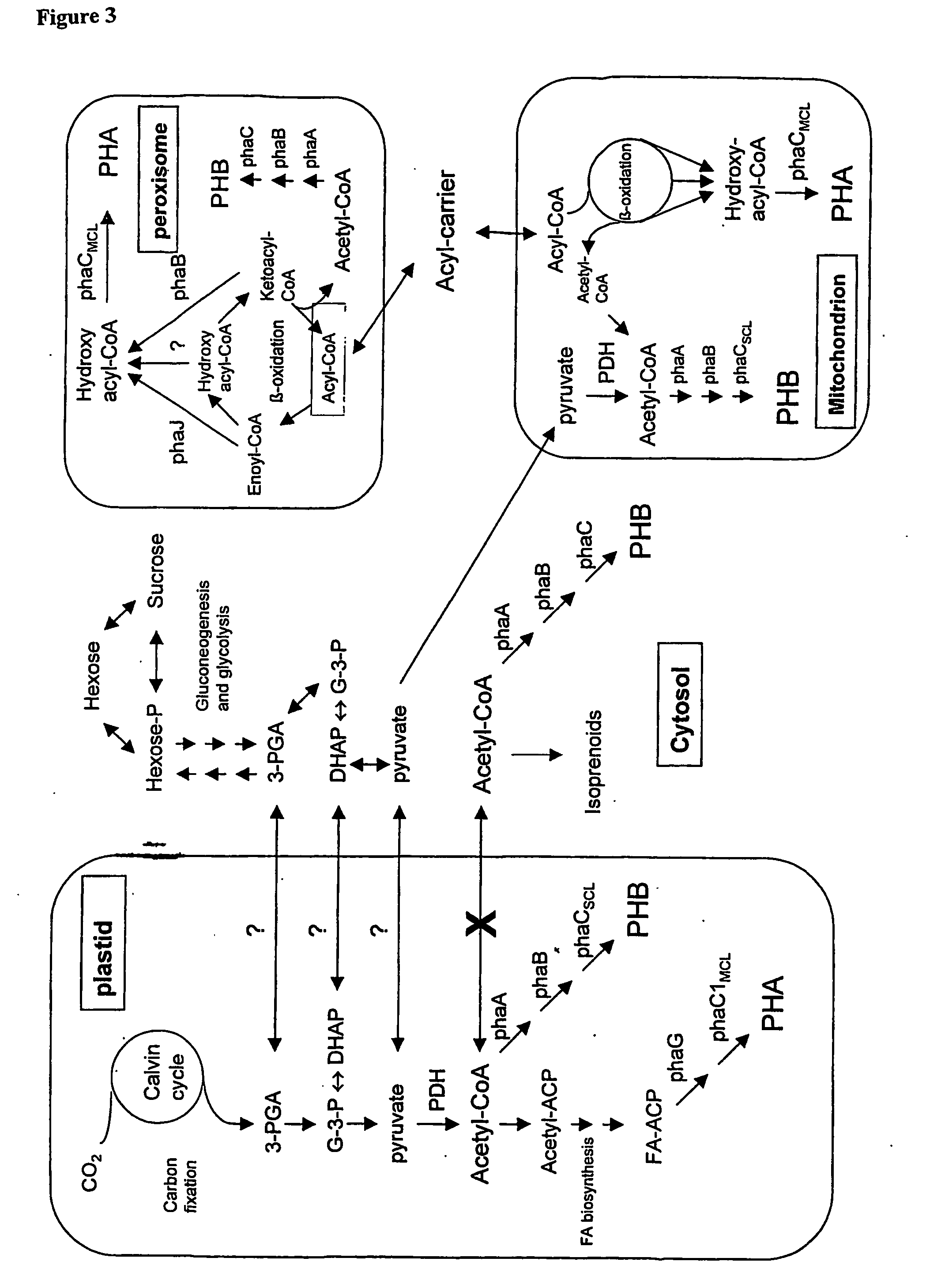
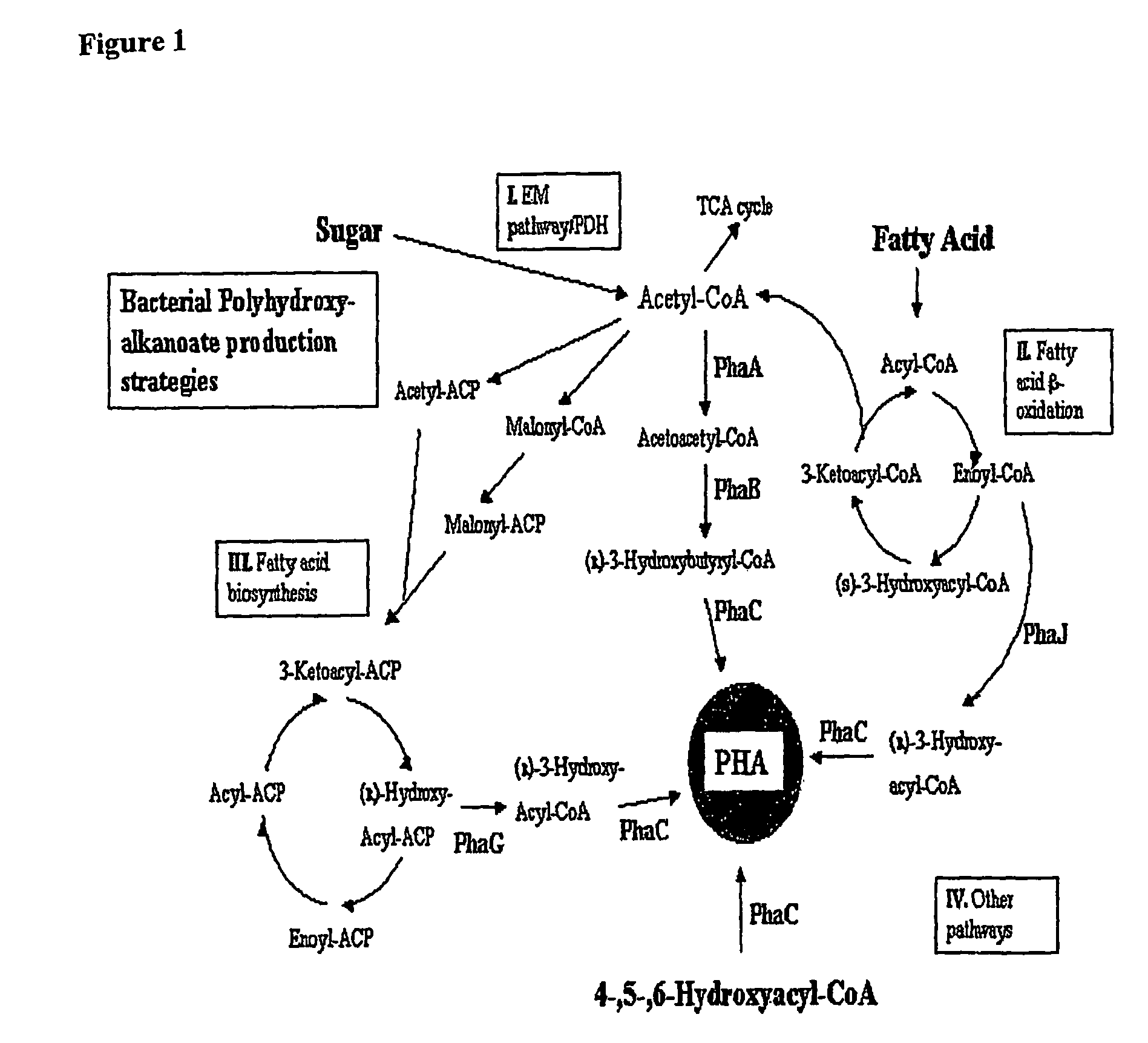
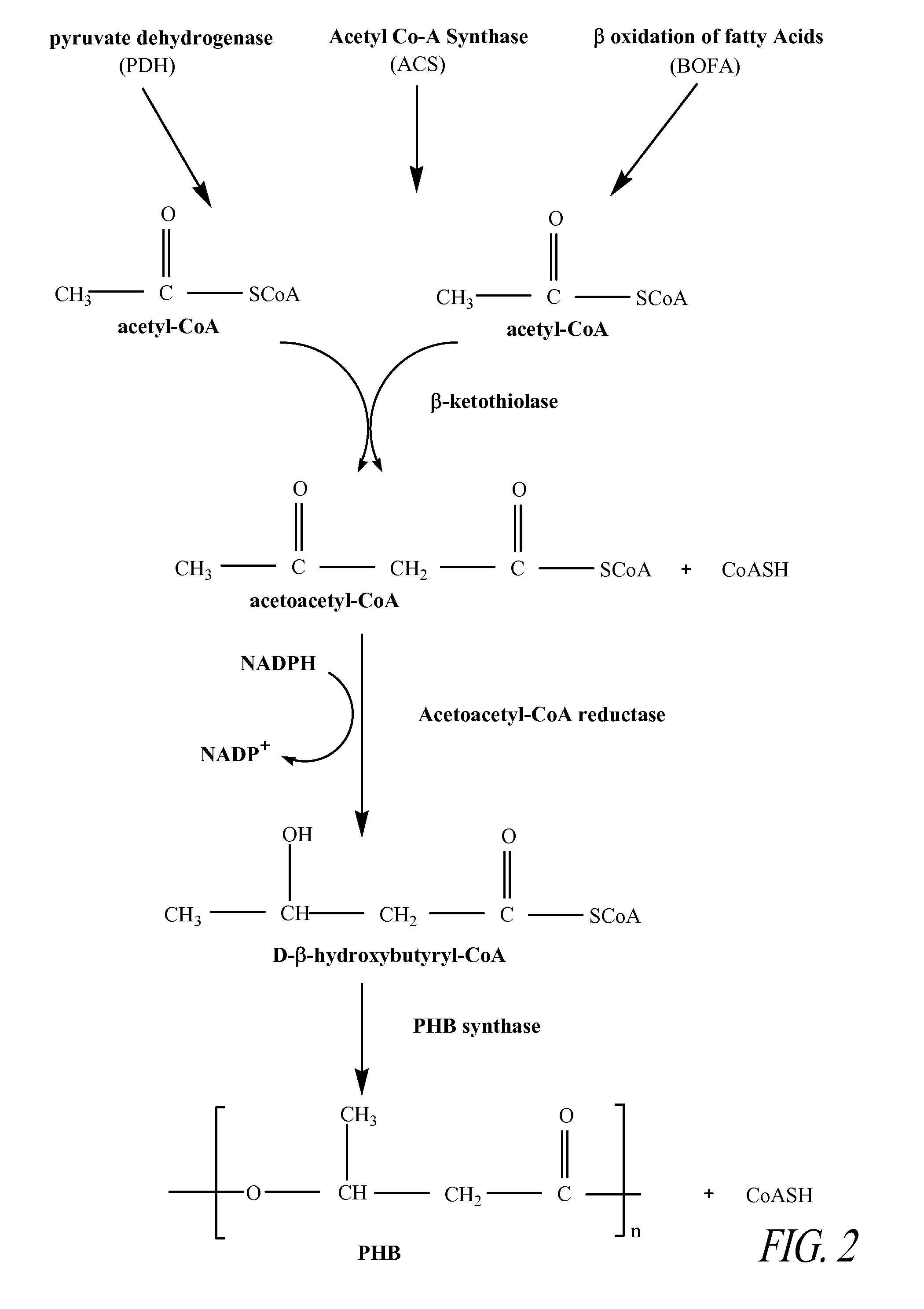
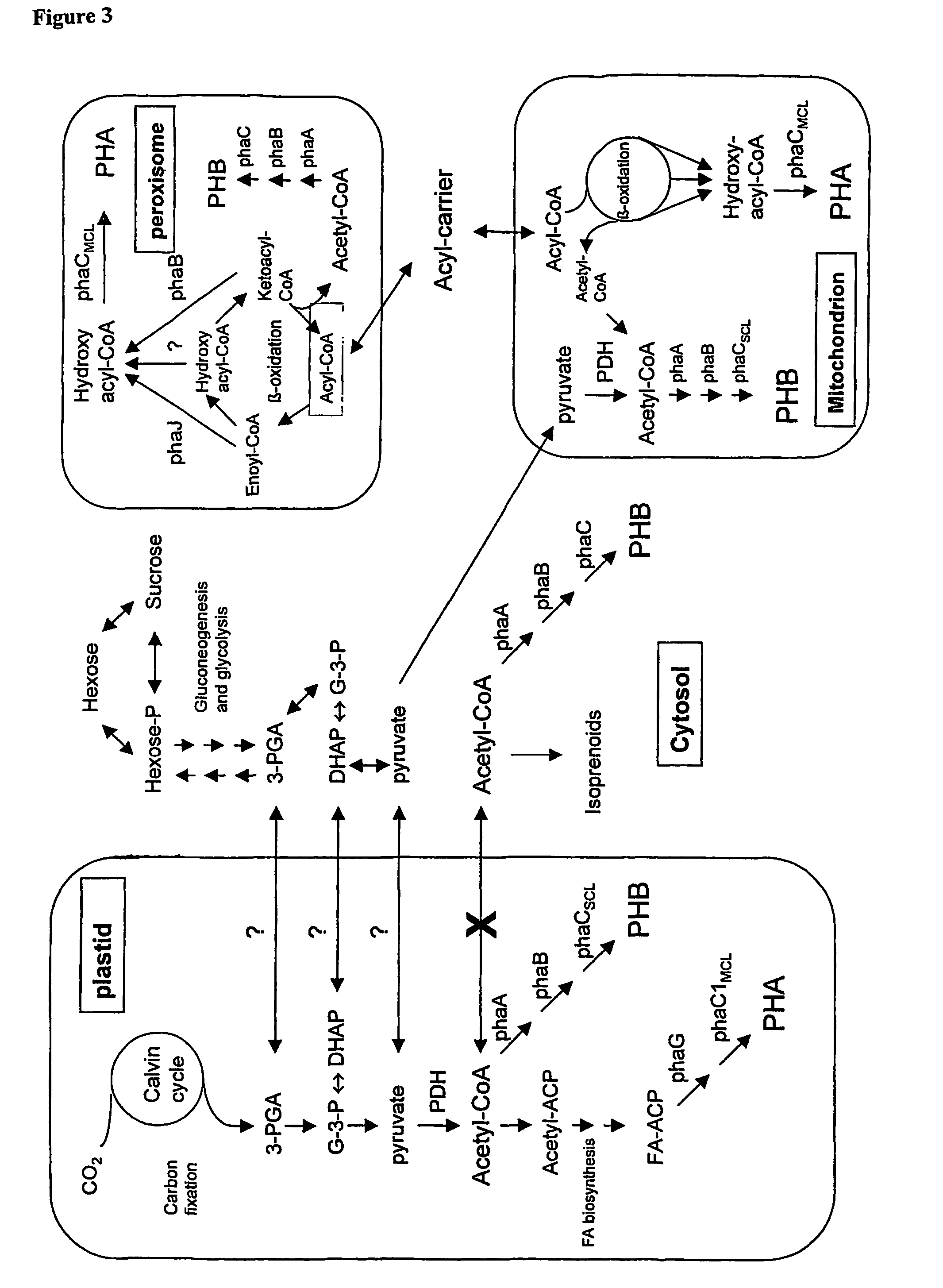
The present invention relates generally to the use of plants as bioreactors for the production of molecules having useful properties such as inter alia polymers, metabolites, proteins, pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals. More particularly, the present invention contemplates the use of grasses, and even more particularly C4 grasses, such as sugar-cane, for the production of a range of compounds such as, for example, polyhydroxyalkanoates, pHBA, vanillin, indigo, adipic acid, 2-phenylethanol, 1,3-propane-diol, sorbitol, fructan polymers and lactic acid as well as other products including, inter alia, other plastics, silks, carbohydrates, therapeutic and nutraceutic proteins and antibodies. The present invention further extends to transgenic plants and, in particular, transgenic C4 grass plants, capable of producing the compounds noted above and other products, and to methods for generating such plants. The ability to utilize the high growth rate and efficient carbon fixation of C4 grasses is advantageous, in that it obviates the significant growth penalties observed in other plants, and results in high yields of desired product without necessarily causing concomitant deleterious effects on individual plants. In addition, the C4 grass, sugarcane, is particularly advantageous, as in addition to the features common to all C4 grasses, this plant accumulates sucrose. This sucrose store provides a ready supply of carbon based compounds and energy which may further obviate any deleterious effects on the growth of the plant associated with the production of the product. The present invention provides, therefore, a bioreactor system comprising a genetically modified plant designed to produce particular metabolic or biosynthetic products of interest.
Owner:SUGAR RES AUSTRALIA +1
Malus hupehensis MhWRKY40a gene and applications thereof
InactiveCN103387994AImprove germination rateHigh expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySalt resistance
The invention discloses a malus hupehensis MhWRKY40a gene and applications thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the malus hupehensis MhWRKY40a gene is shown as the SEQ ID NO.1. The MhWRKY40a gene is capable of applying to the production of novel species, which are salt resistant and low temperature resistant, and / or plant variety improvement. A novel MhWRKY40a gene is cloned from malus hupehensis for the first time, and the homology between the gene sequence and the arabidopis thaliana, grape and barley is 50.89%. But the protein tertiary structure of the MhWRKY40a is prominently different from the homologous gene of the model plant arabidopis thaliana; the former has 5 beta-folds, while the latter has 4 beta-folds. The MhWRKY40a transgenetic tobacco has the properties of salt resistance and low-temperature resistance, raises the resistance-associated gene expression, and therefore the fact, which the MhWRKY40a gene has the function of improving the salt resistance and low-temperature resistance properties of the plants, is testified.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Microorganisms engineered for increased productivity
ActiveUS20170067069A1Improve productivityIncreased biomass accumulationBiofuelsAlgae/lichens peptidesMicroorganismWild type
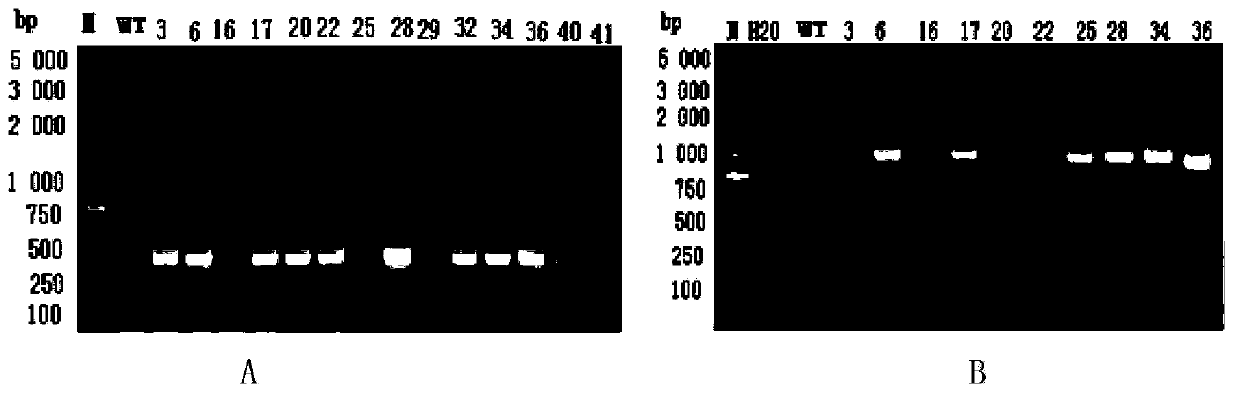
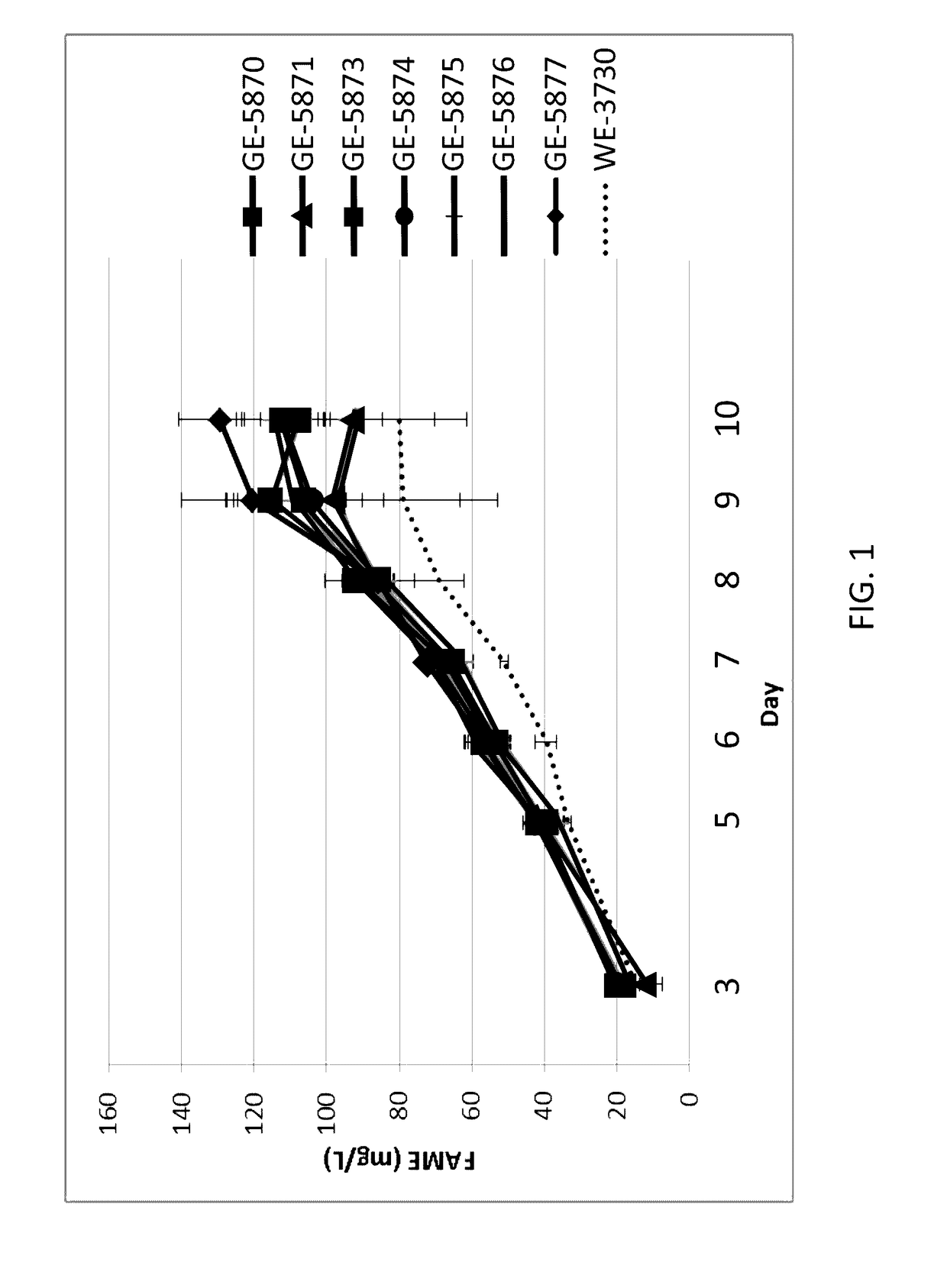
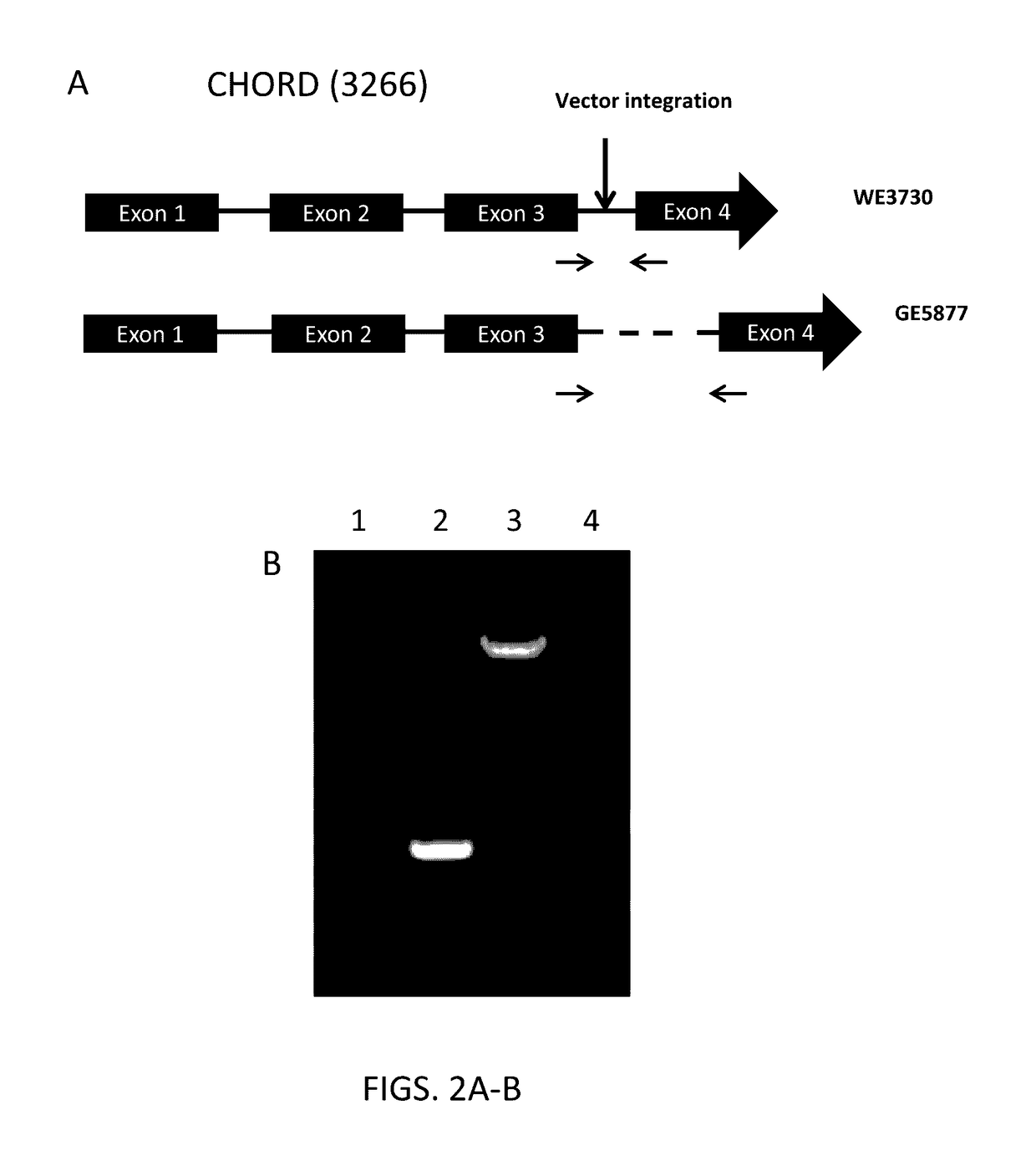
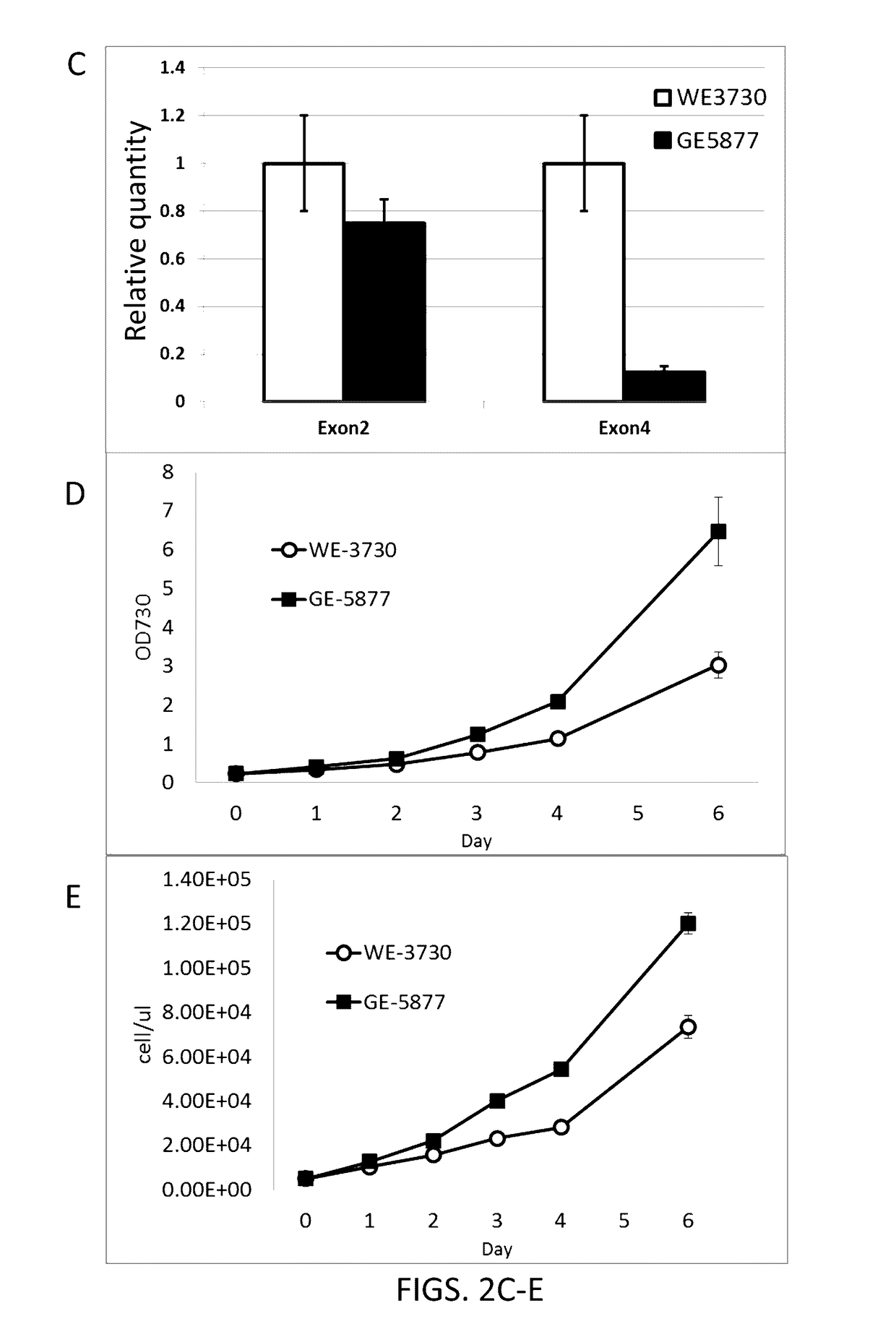
The application provides recombinant microorganisms with increased productivity with respect to control or wildtype microorganisms. The recombinant microorganisms can include a non-native gene encoding a SKP1 polypeptide or a CHORD-derived polypeptide. Increased productivity can be increased biomass or lipid productivity. These recombinant microorganisms can be used to produce products of interest.
Owner:SYNTHETIC GENOMICS INC
Plant culture substrate conditioner, method for using conditioner for preparing composite culture substrate and prepared culture substrate
InactiveCN106083354AEasy to prepareEasy to operateBioloigcal waste fertilisersOrganic fertiliser preparationFiberGrowth plant
The invention discloses a plant culture substrate conditioner and a preparation method thereof and a method for using the conditioner for preparing a composite culture substrate. The substrate conditioner comprises alga residues, coconut fibers and phosphorite. The composite culture substrate prepared through the substrate conditioner is balanced in nutrition, high in nutrient content, stable in physical property and reasonable in nutritional structure. The prepared composite culture substrate has good cation exchangeability and adsorbability, can adsorb a large amount of salt with a buffer effect, has a buffer effect and can obstruct rapid changes of pH values and EC values, the acid-base environment of the substrate is regulated, the effect that nutrients are slowly released is achieved, breathing and growth of plant root systems are promoted, absorption of the nutrients by the root systems is promoted, plant growth requirements are met, the survival rate of plant culture is raised, and the appreciation effect is improved.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for increasing yield of flask shaking fermentation euglena gracilis klebs through feeding method
InactiveCN108148763ARaise the level of fermentationImprove single-batch fermentation intensityUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesEuglena gracilisHigh concentration
The invention relates to a method for increasing the yield of flask shaking fermentation euglena gracilis klebs through a feeding method. According to the method, by feeding a mixed nitrogen source, the fermentation level of the euglena gracilis klebs in a shake up flask in the middle and later periods can be greatly improved; by feeding a high-concentration carbon source, the requirement for thecarbon source in the middle and later periods of euglena gracilis klebs flask shaking fermentation can be greatly guaranteed, and single batch fermentative strength in the shake up flask can be improved; in this way, accumulation of euglena gracilis klebs biomass in the flask shaking fermentation process is greatly improved; important reference data is provided for test batch, pilot batch and production of the euglena gracilis klebs, and great significance is achieved for large-scale cultivation of the euglena gracilis klebs.
Owner:QINGDAO XUNON BIOLOGICAL ENG
Method for improving tribonema biomass and metabolites by using magnetic field intervention
ActiveCN109536484AUnleash economic potentialIncrease growth rateUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesLipid formationMetabolite
The invention belongs to the technical field of aquatic product processing or biophysical processing, and relates to a method for improving tribonema biomass and metabolites by using magnetic field intervention. The specific steps are as follows: firstly, preparing a BG11 culture medium, pouring the culture medium into a column reactor, and inoculating the culture medium with tribonema sp. in logarithmic phase; placing the reactor in a climate incubator, setting a certain temperature, illumination intensity and illumination time, introducing a certain amount of air containing CO2, and carryingout culturing; and after 1 day of culturing, applying additional magnetic field treatment, continuing the culturing, and detecting biomass and oil accumulation after 7 days of culturing. The method can increase the content of lipids, saccharides, proteins or natural metabolites with natural biological activity in the cells by adding a magnetic field to a culture system of filamentous microalgae such as the tribonema, and can fully exert the economic potential of the filamentous microalgae.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
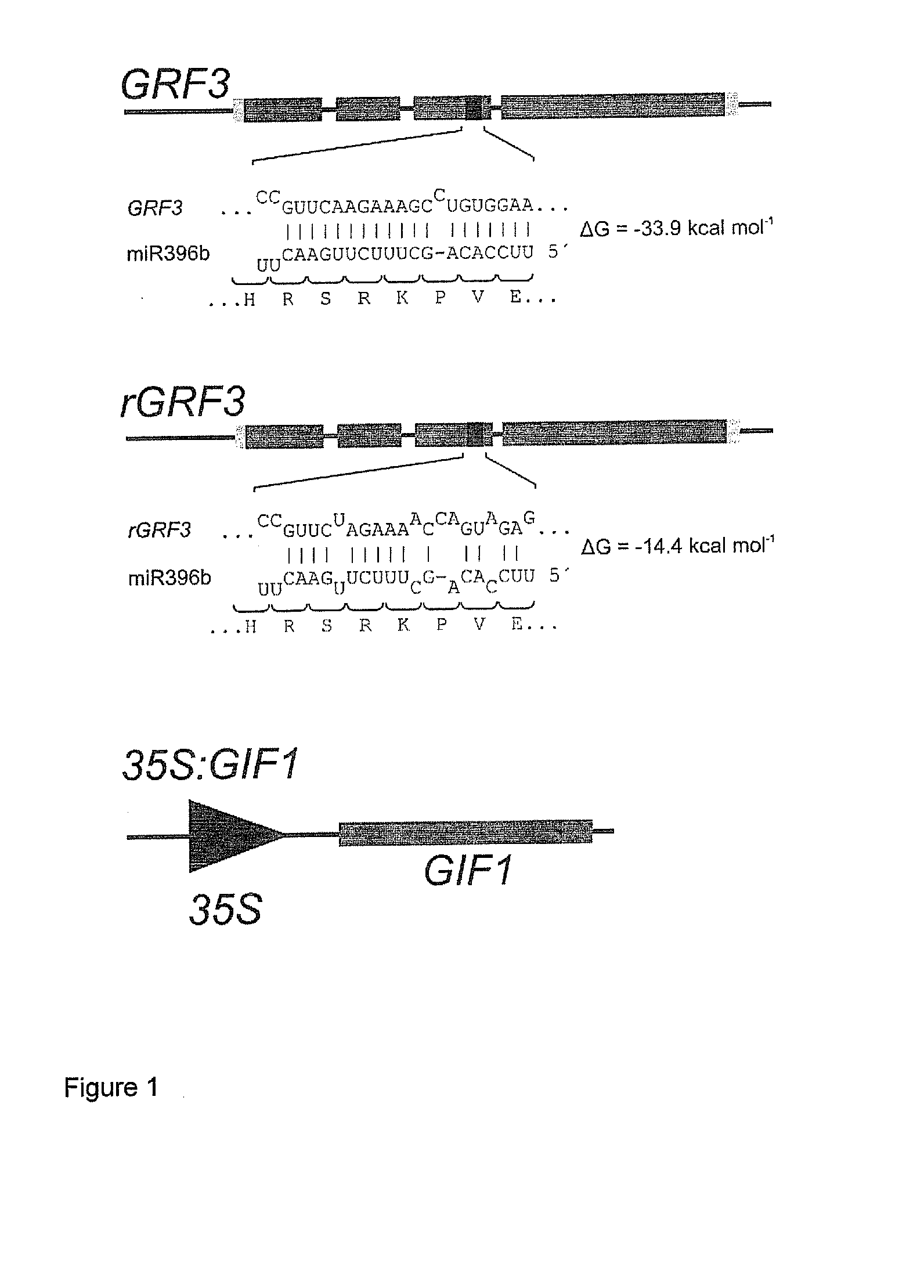
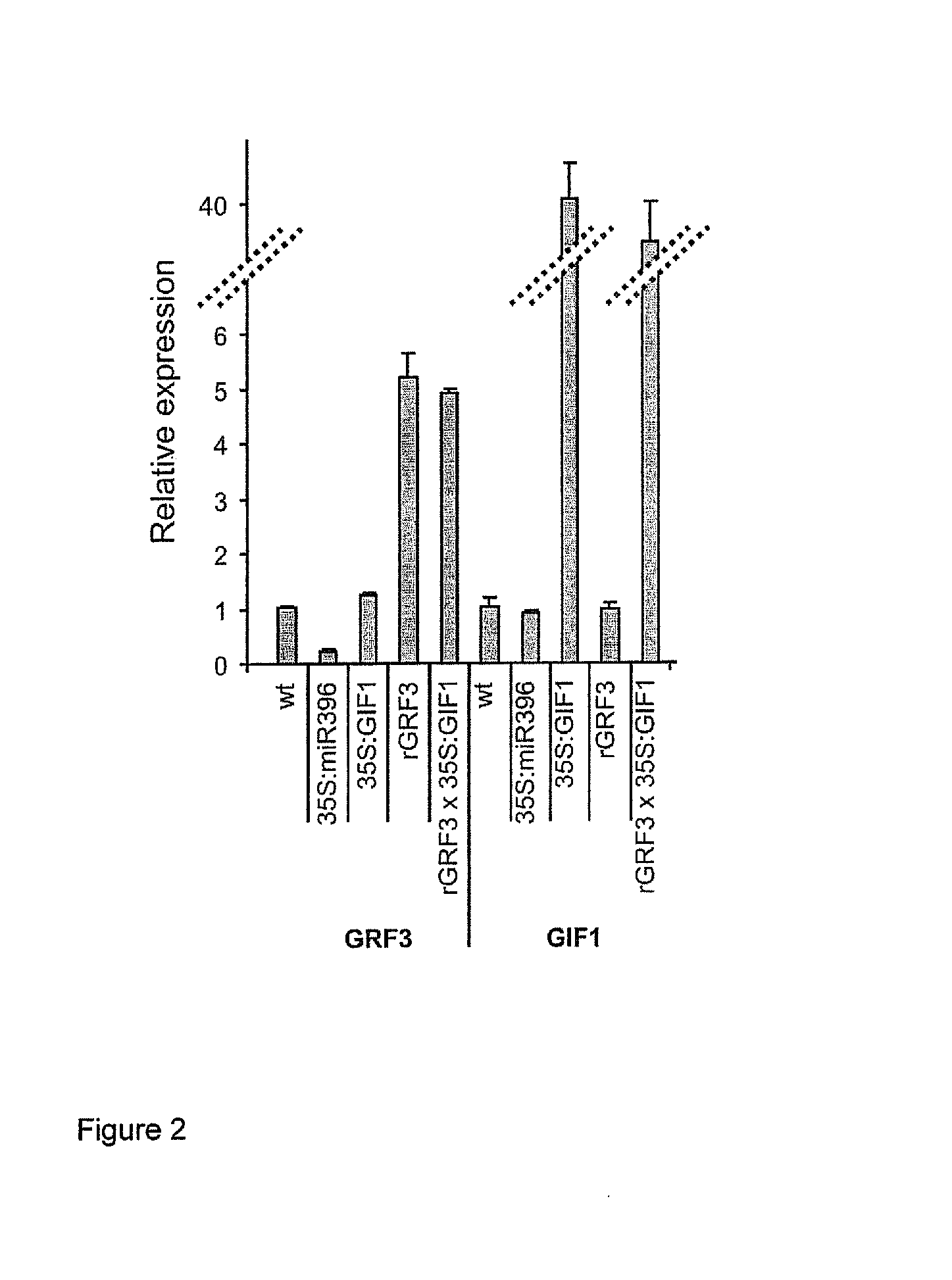
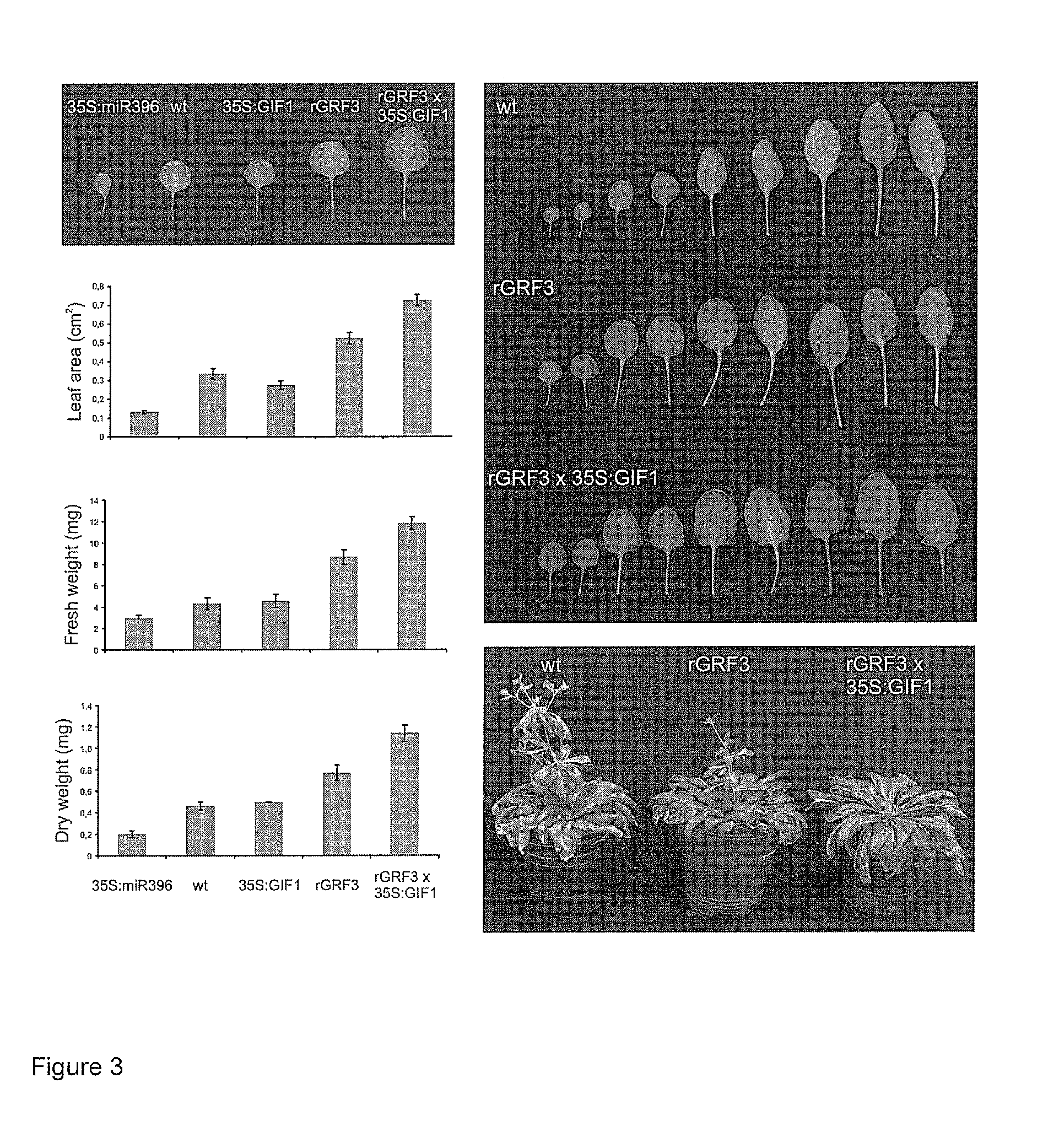
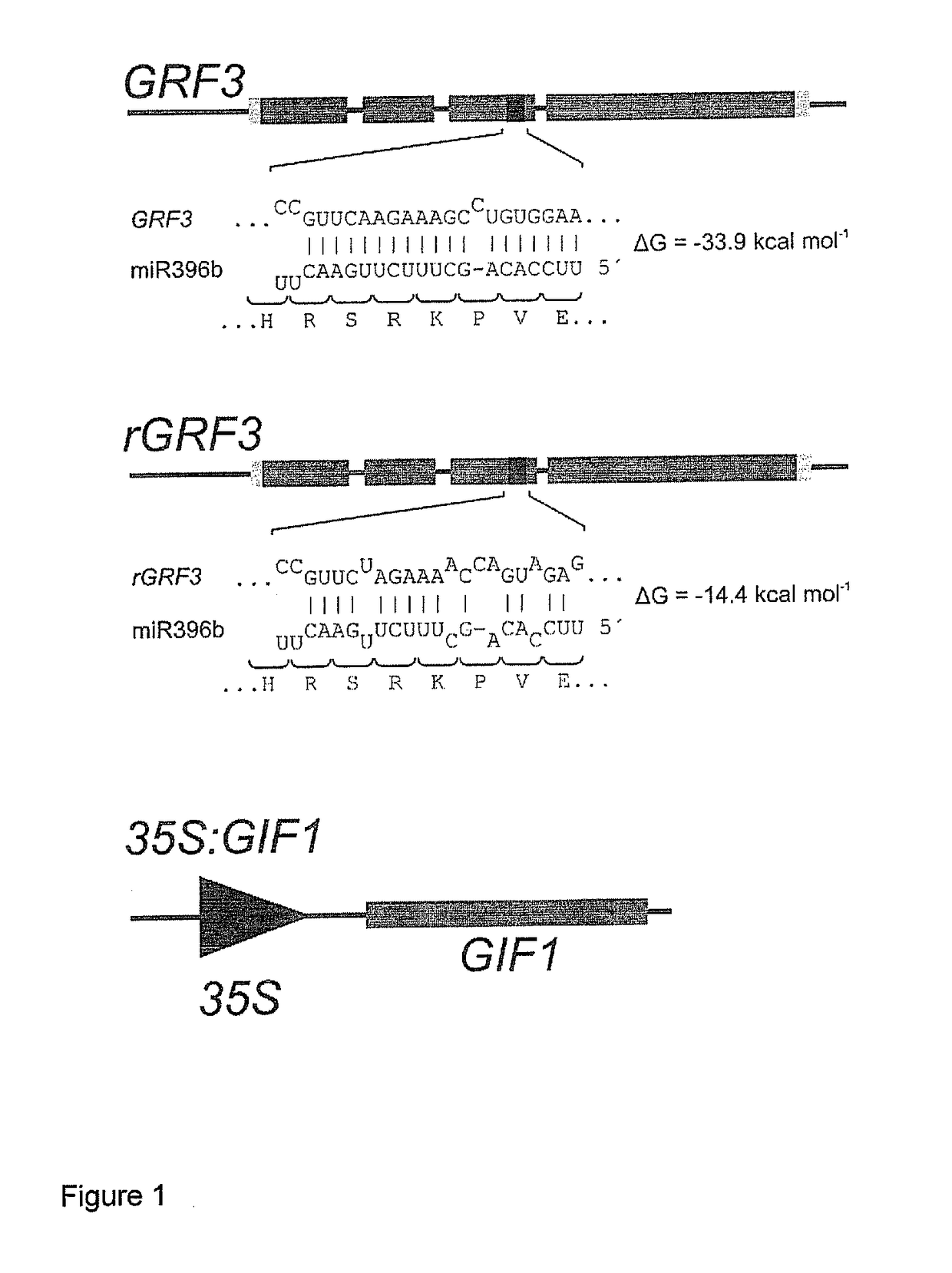
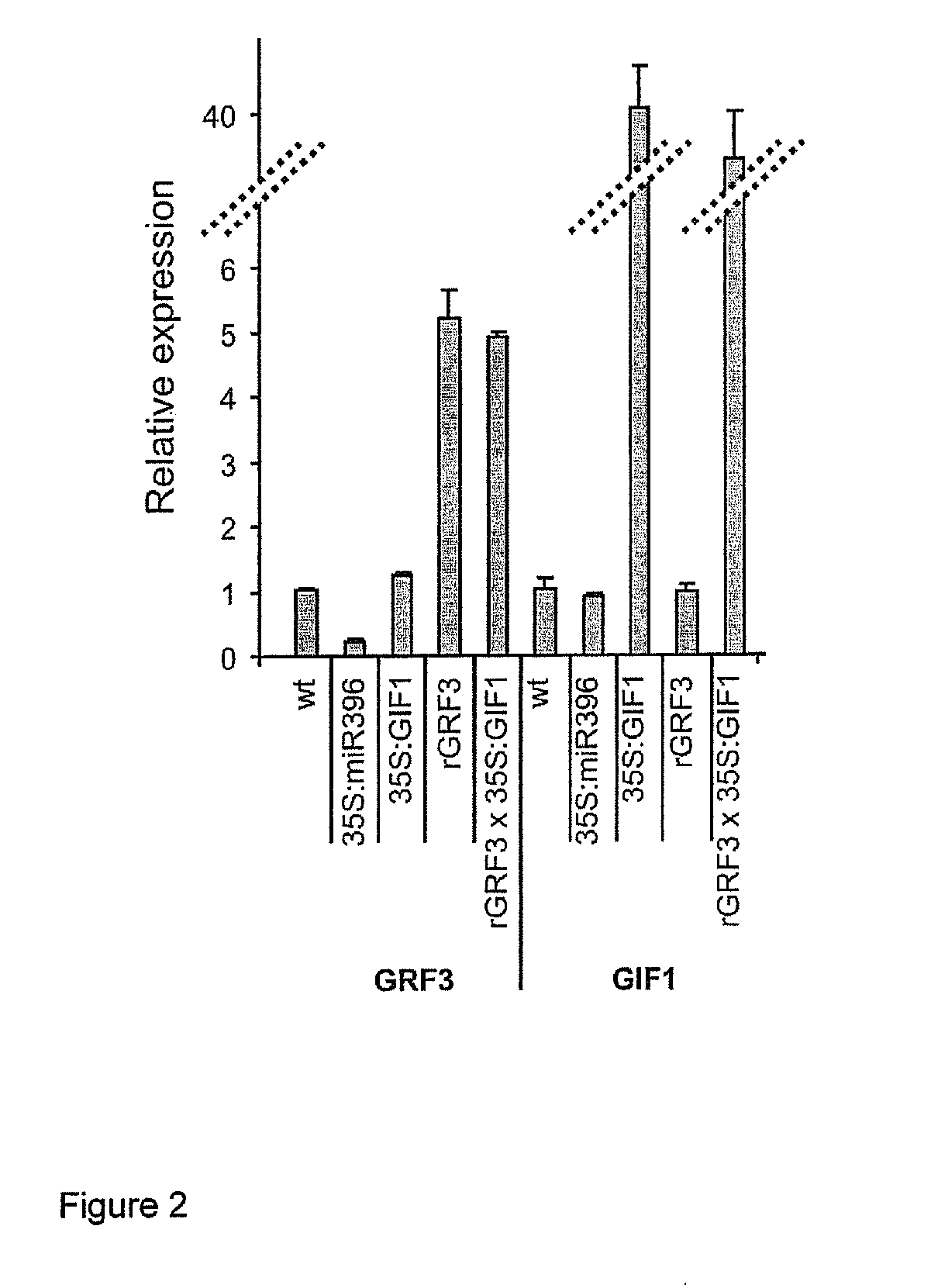
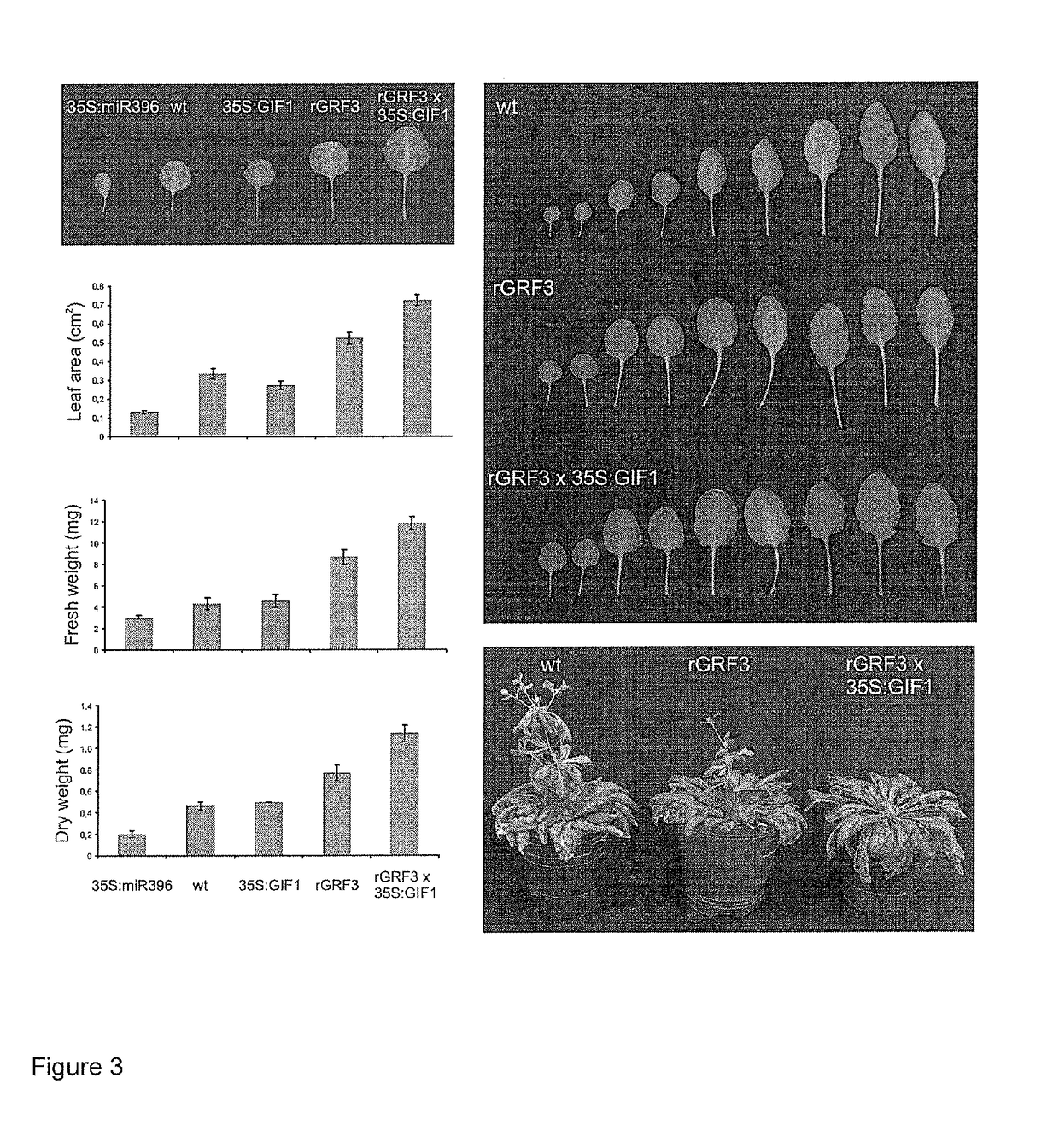
GRF3 Mutants, Methods and Plants
ActiveUS20150033413A1Increase productivityHigh yieldSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationRoot growthMutant
The present disclosure provides a novel modified gene, rGRF3, or an orthologue thereof, which is shown to be decoupled from control by miR396, particularly in the presence of over-expression of at least one GIF gene, such as GIF1, AtGIF 2, AtGIF 3, Os11g40100, Os12g31350, Os03g52320 or combinations thereof. When present in a plant, the rGRF3 results in a phenotype of increased productivity (e.g. increased yield, increased biomass, increased stress resistance, increased seed production, increased seed yield, increased root growth, increased root elongation speed, delayed leaf senescence or increased drought tolerance and combinations thereof).
Owner:UNIV NACIONAL DE ROSARIO +1
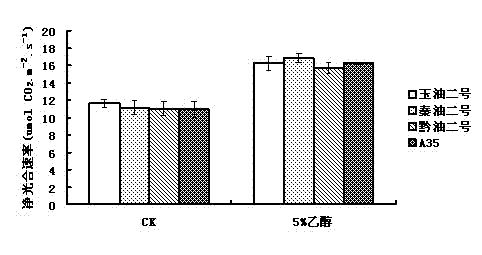
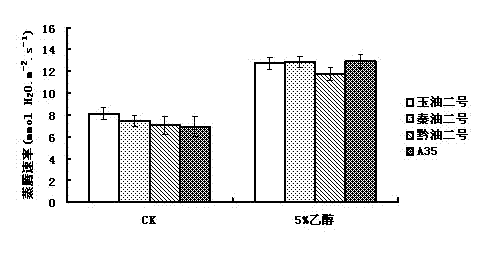
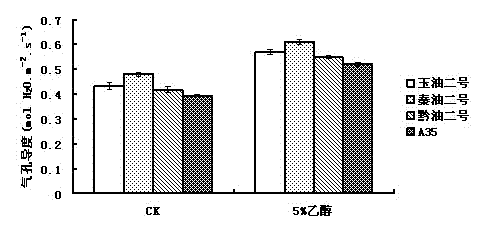
Application of ethanol in promoting plant growth
The invention discloses a new application of ethanol, namely, an application of ethanol as a treating agent in promoting plant growth, wherein when used, 2-8% of volume percent of ethanol solution is used for spraying leaves of plant seedlings growing for 2-3 weeks twice a week; continuously treating for 4-8 weeks, and observing the growth index of the plant; it is shown by experimental result that the photosynthesis ability of the plant seedlings after being treated by ethanol is strengthened, and the chlorophyll content, the net photosynthetic rate, the transpiration rate, the stomatal conductance and the intercellular CO2 concentration are increased notably; the ethanol treating agent can promote plant growth, and increase accumulation of the plant biomass (dry weight of overground part and dry weight of underground part).
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
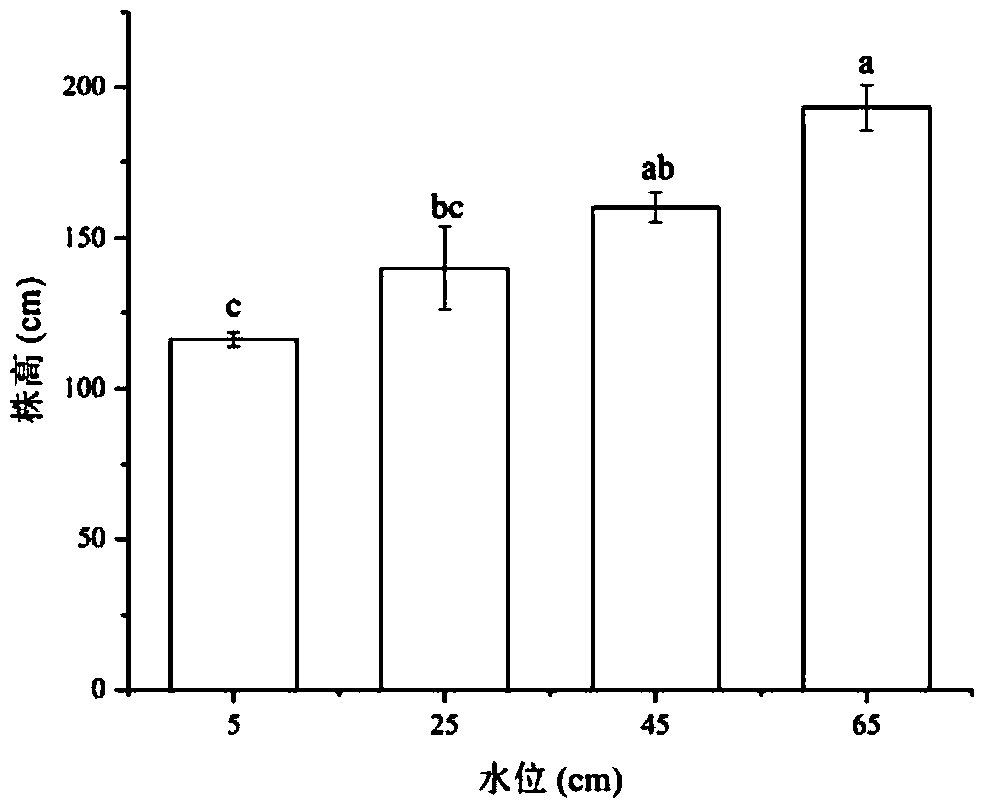
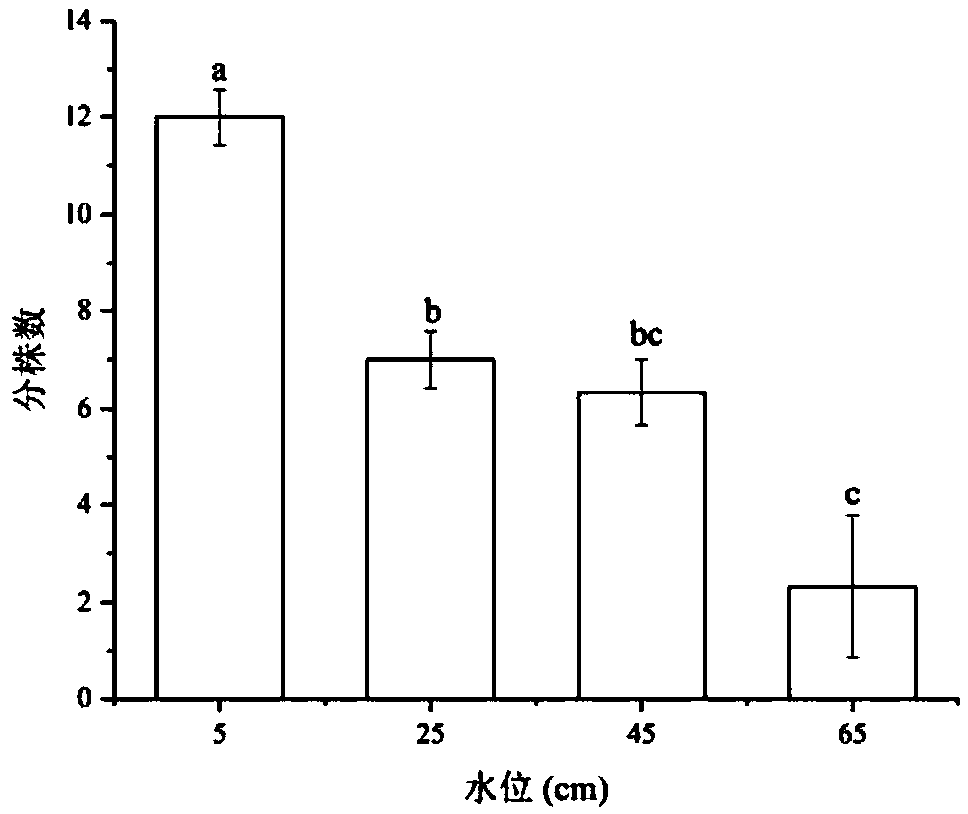
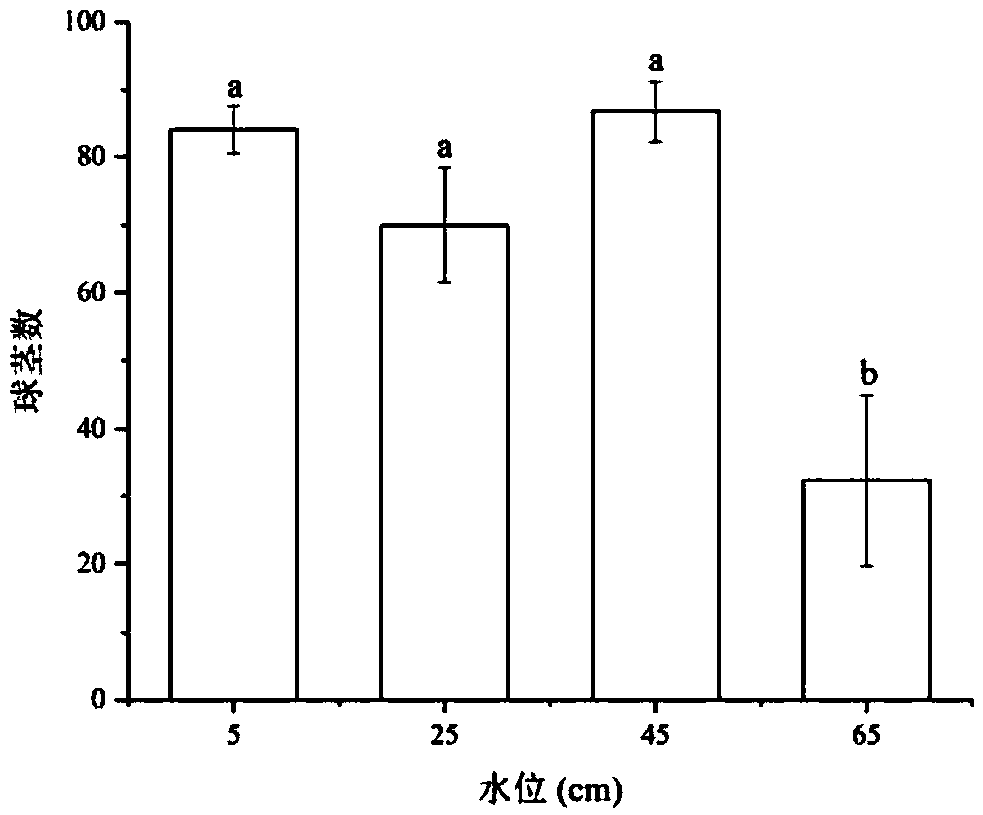
Method for optimizing water level height of Sanjiang currant seedling and method for rapidly recovering degraded saline-alkali wetland plants
InactiveCN109463211AIncreased biomass accumulationPromote accumulationPlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsRecovery methodWater level
The invention relates to a method for optimizing the water level height of a Sanjiang currant seedling and a method for rapidly recovering degraded saline-alkali wetland plants, belonging to the technical field of ecological restoration and aiming at determining the influence of the water level height on the growth of the three-river currant seedling. The method for optimizing the water level height comprises the following steps of: 1, collecting the corms of the field three-river currant; secondly, indoor seedling raising; 3, preparing a substrate; fourthly, setting a plurality of water levelgradients, and respectively culturing the Sanjiang currant seedlings; 5, calculating the relative growth rate of the seedlings, and measuring the biomass of the currant; and 6, measuring and analyzing. The quick recovery method comprises the following steps of: injecting water into a recovery area until the water depth is between 40cm and 50cm when the Sanjiang currant bulb grows out and the height of the Sanjiang currant seedlings is between 12 and 18cm. According to the method for optimizing water level height of Sanjiang currant seedling and method for rapidly recovering degraded saline-alkali wetland plants , the optimal water level height of the growth of the Sanjiang currant seedlings is determined by researching the influence of the water level on the growth of the three-river currant seedlings, so that the accumulation of the biomass of the Sanjiang currant is effectively improved, and the rapid planting and construction of the Sanjiang currant population are facilitated.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
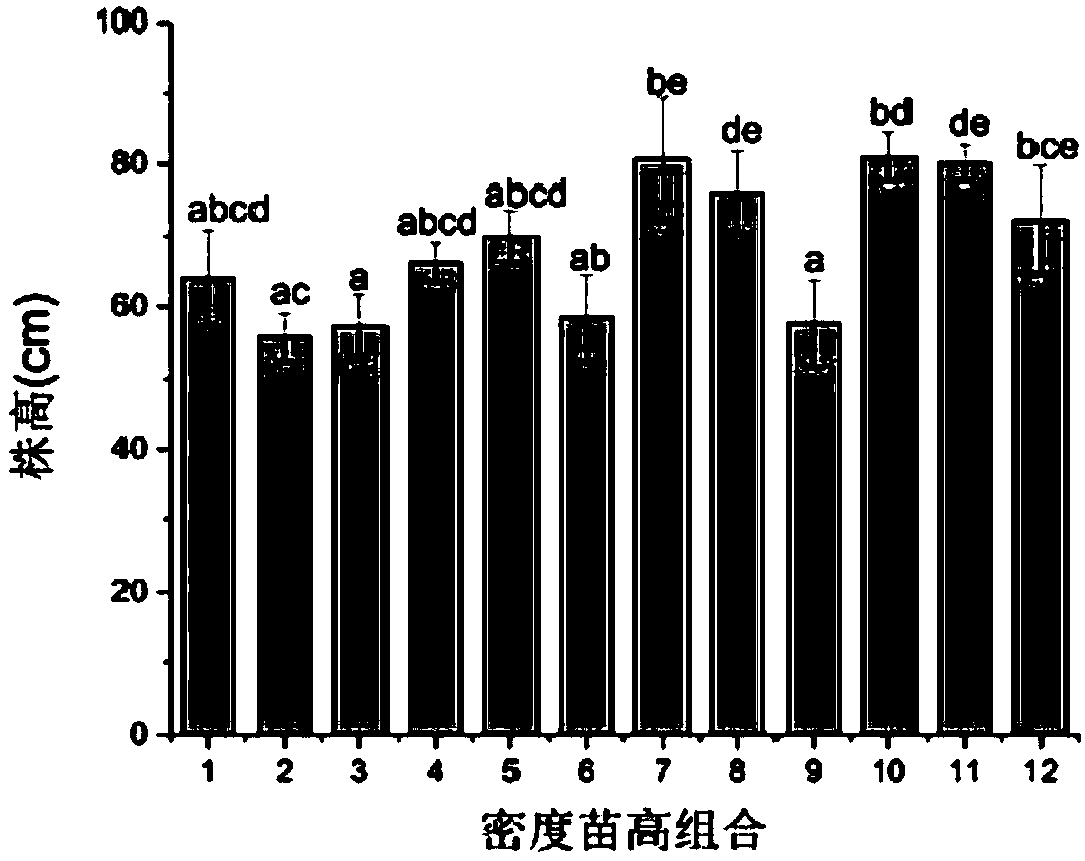
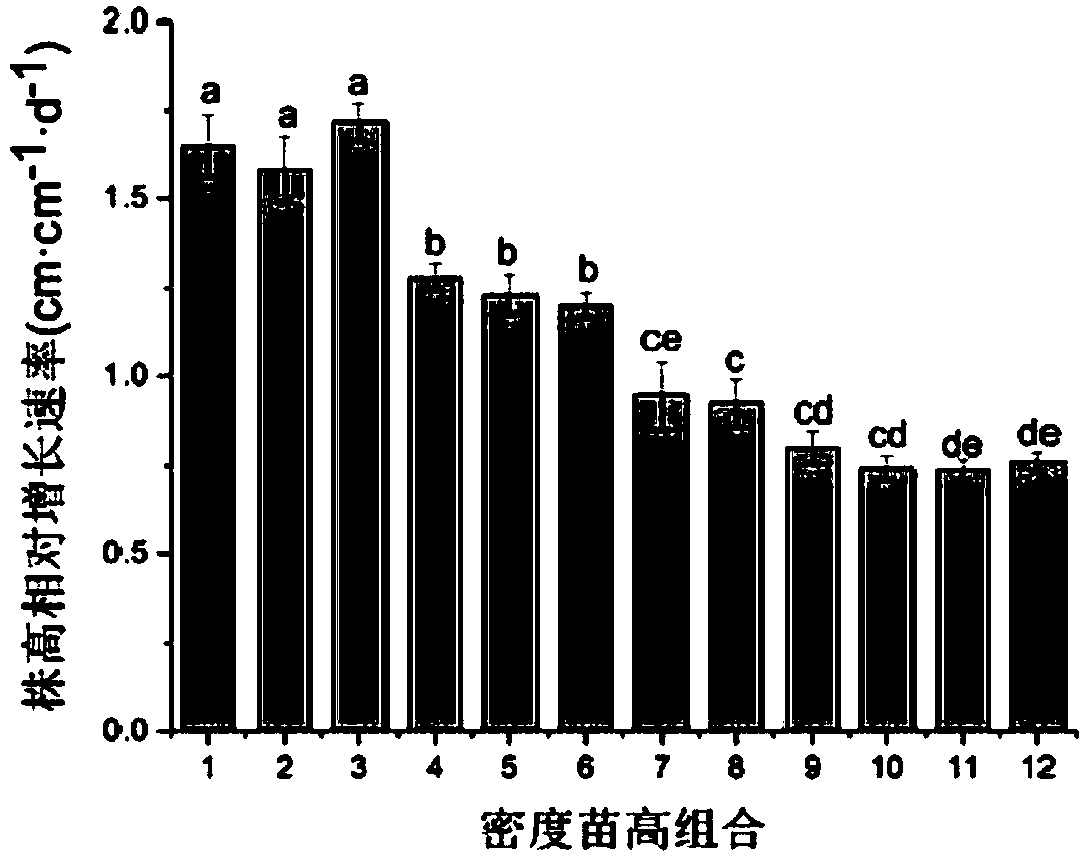
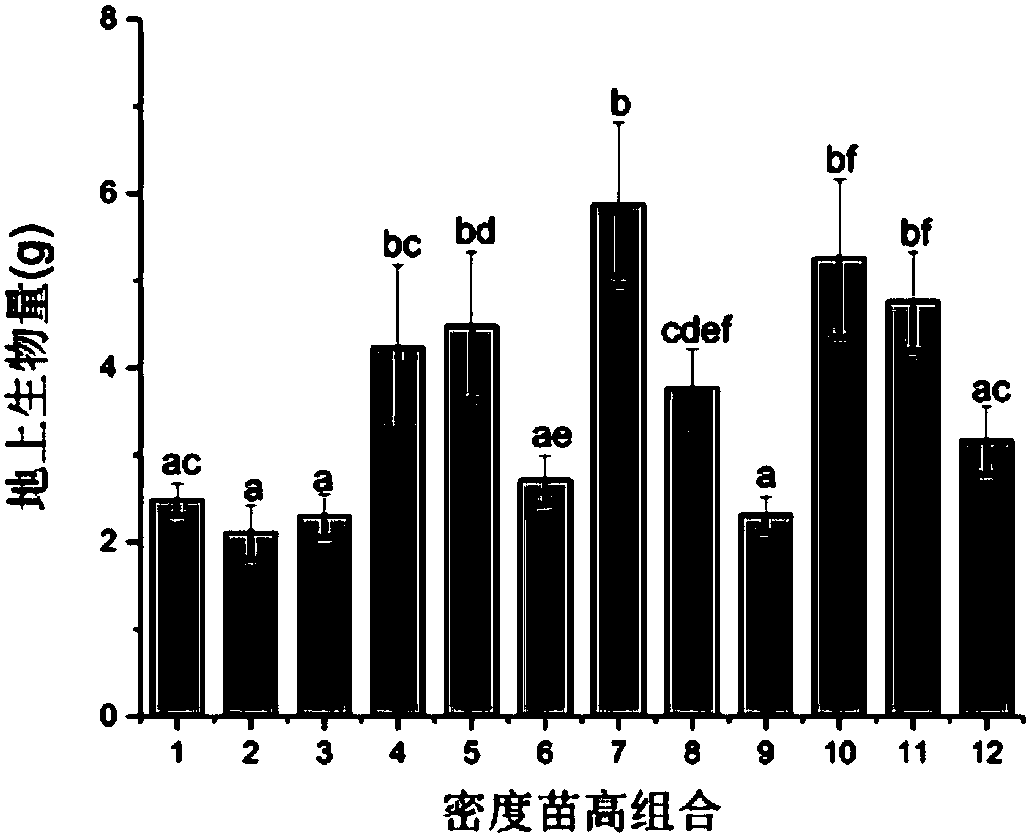
Method for obtaining optimal transplanting density and initial planting height of reed seedlings
InactiveCN108551983ALow costShorten the overall cyclePlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsVegetationObserved Survival
The invention discloses a method for obtaining optimal transplanting density and initial planting height of a reed seedling, and relates to the technical field of ecological restoration. The method isused for restoring rapidly the vegetation in the degraded saline-alkali wetlands. The method aims at solving the problems of low survival rate and slow seedling growth of the reed in the degraded reed wetlands. The method includes the following steps of first, collection of reed root-like stem; second, indoor seedling; third, seedling cultivation at different seedling heights and different plantdensities; fourth, measurement and settlement; fifth, analysis of optimal transplanting density and initial planting height. The method has the advantages that the cost and the cycle of the seedling transplanting are reduced, the plant height and the biomass accumulation of the reed seedlings are increased, and the high relative growth rate is maintained, so that the rapid restoration of the reedwetlands is facilitated. The method is mainly used for obtaining the optimal transplanting density and the initial planting height of the reed seedlings.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
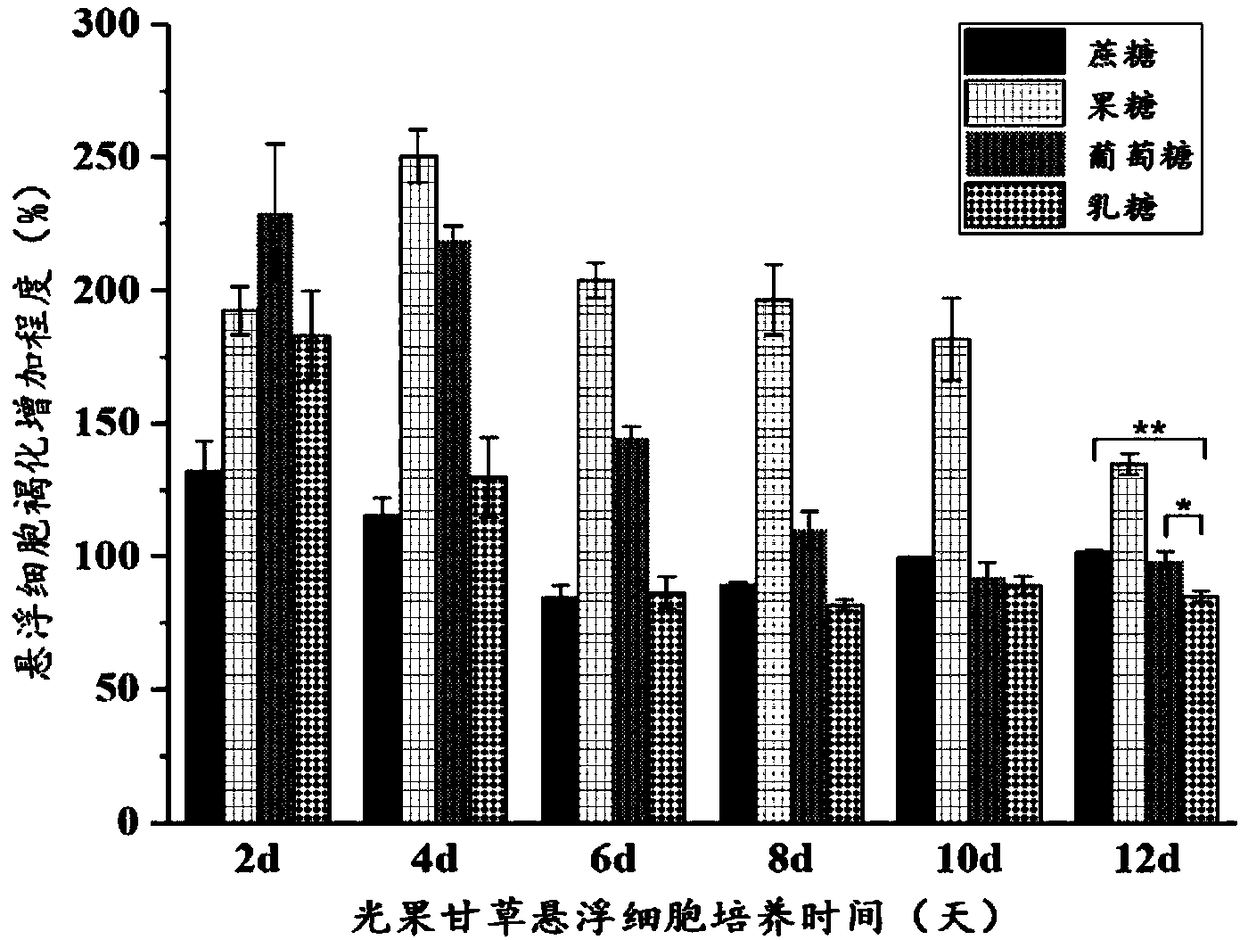
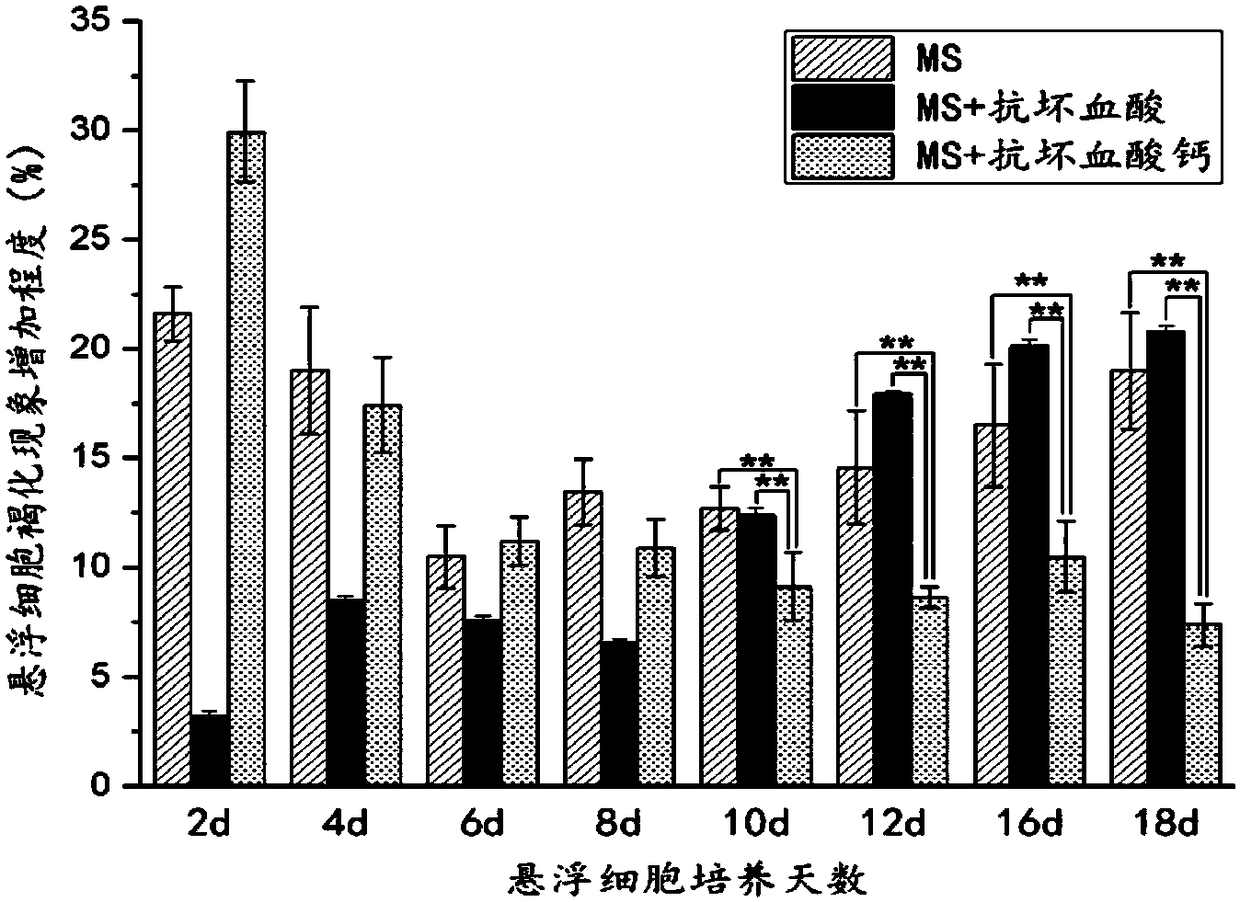
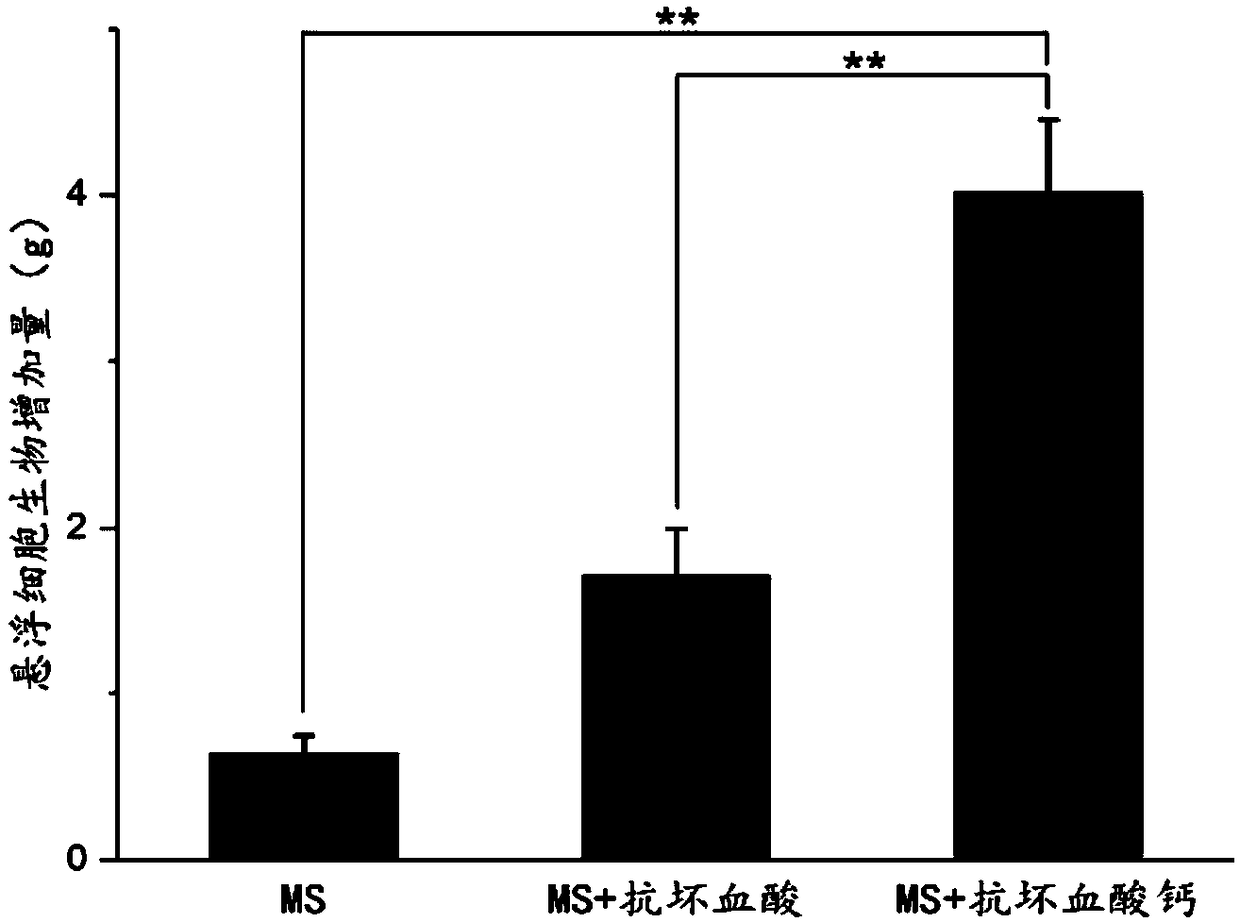
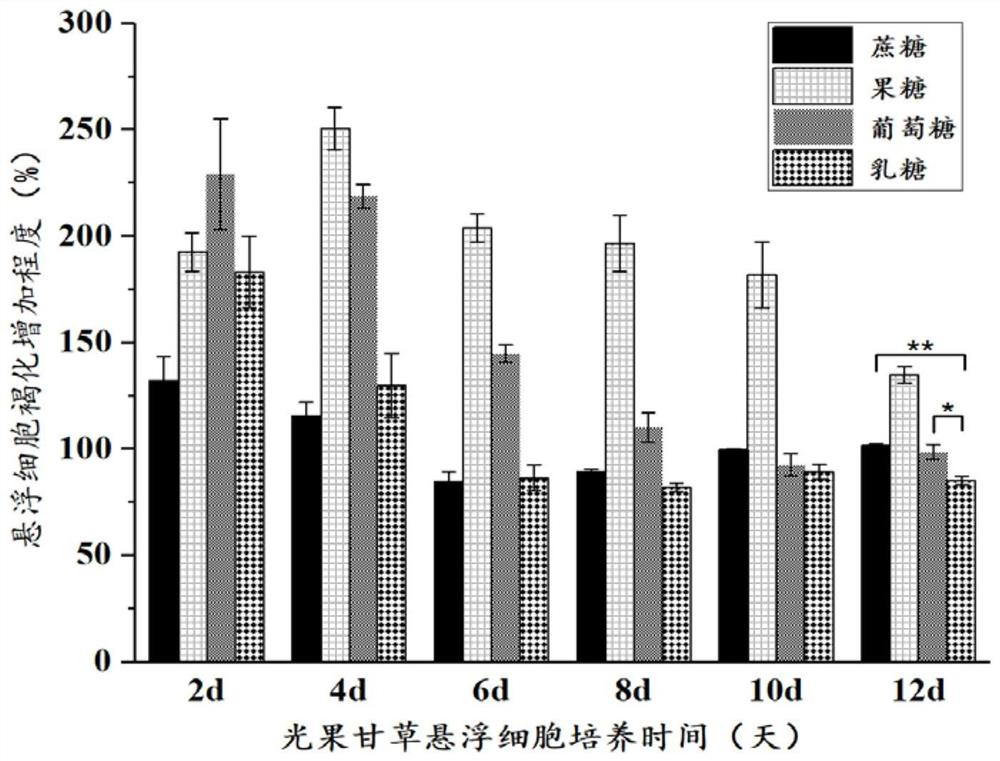
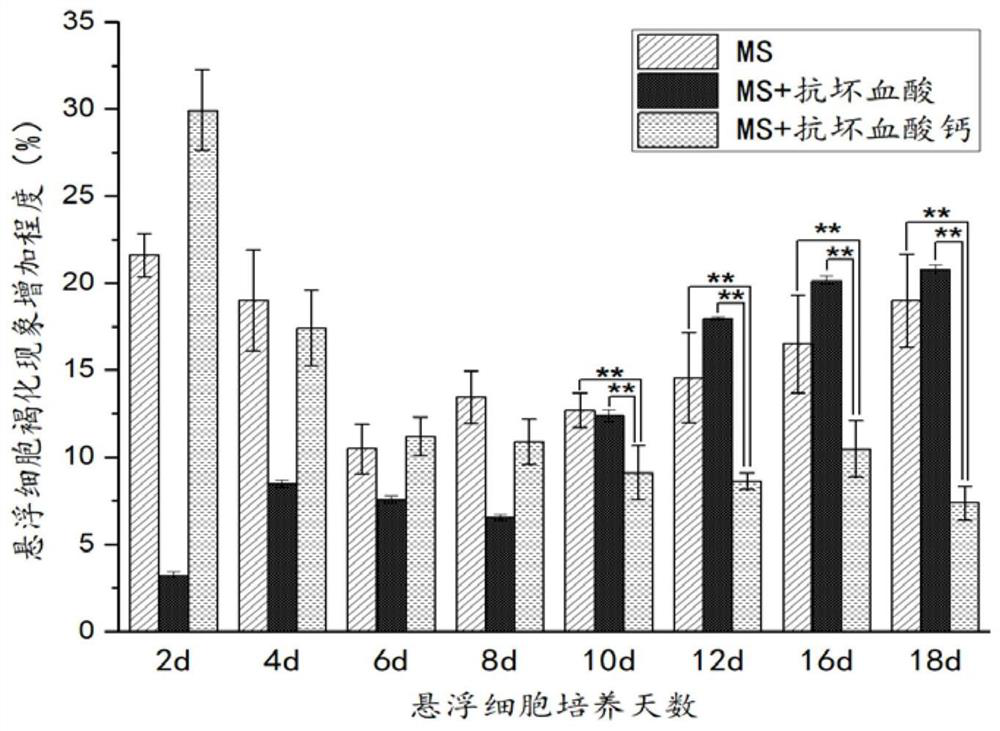
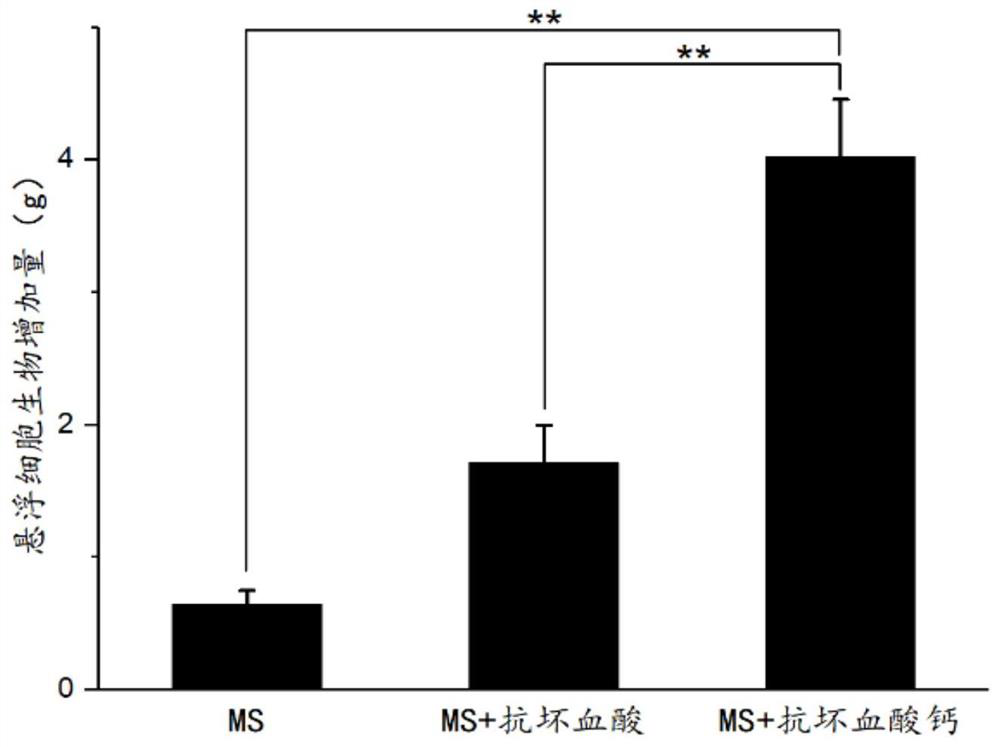
Method for inhibiting browning in glycyrrhiza glabra suspension cell culture process for long time
The invention discloses a method for inhibiting browning in glycyrrhiza glabra suspension cell culture process for long time, and aims at inhibiting browning in the glycyrrhiza glabra suspension cellculture process for long time. The method is characterized in that an ascorbic acid derivate (calcium ascorbate) is adopted to replace ascorbic acid as a browning resisting agent, and meanwhile, lactose is screened to replace saccharose as a carbon source in the culture of glycyrrhiza glabra suspension cells. The result shows that the activity of polyphenol oxidase in the suspension cells can be inhibited for long time (20d) by the culture method, and the browning in the glycyrrhiza glabra suspension cell culture process can be inhibited; and meanwhile, the biomass accumulation of the suspension cells is obviously increased. Additionally, the method is simple to operate; the obtained glycyrrhiza glabra suspension cells are high in dispersing performance and good in growing state. An effective technical mean is provided for amplification culture of glycyrrhiza glabra cells.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
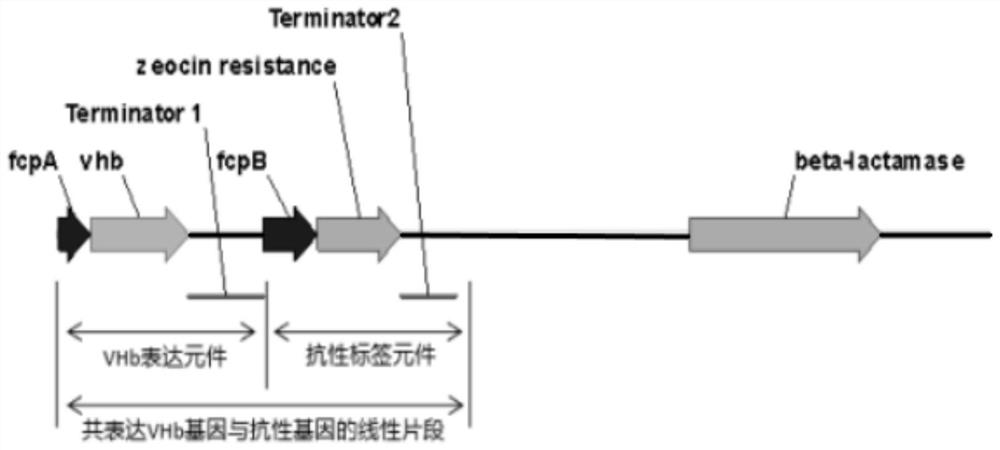
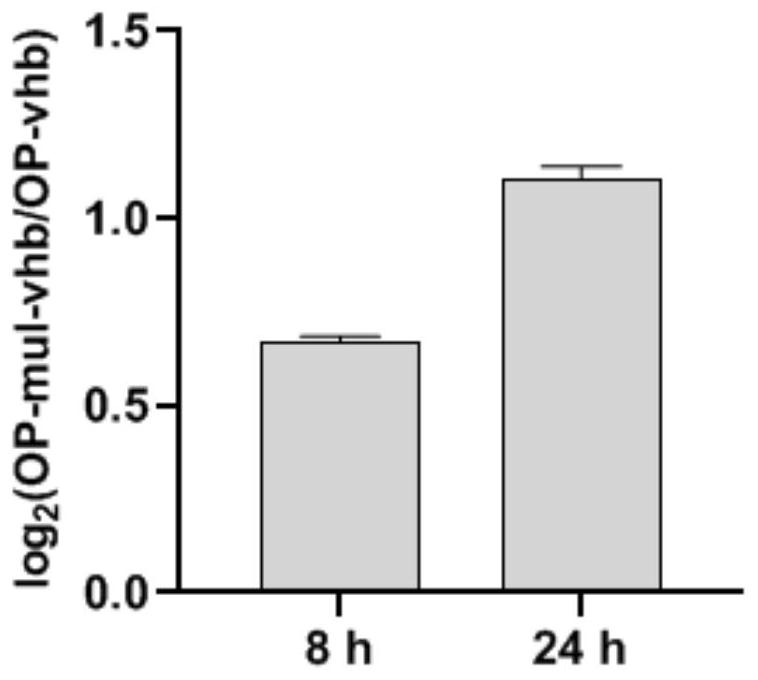
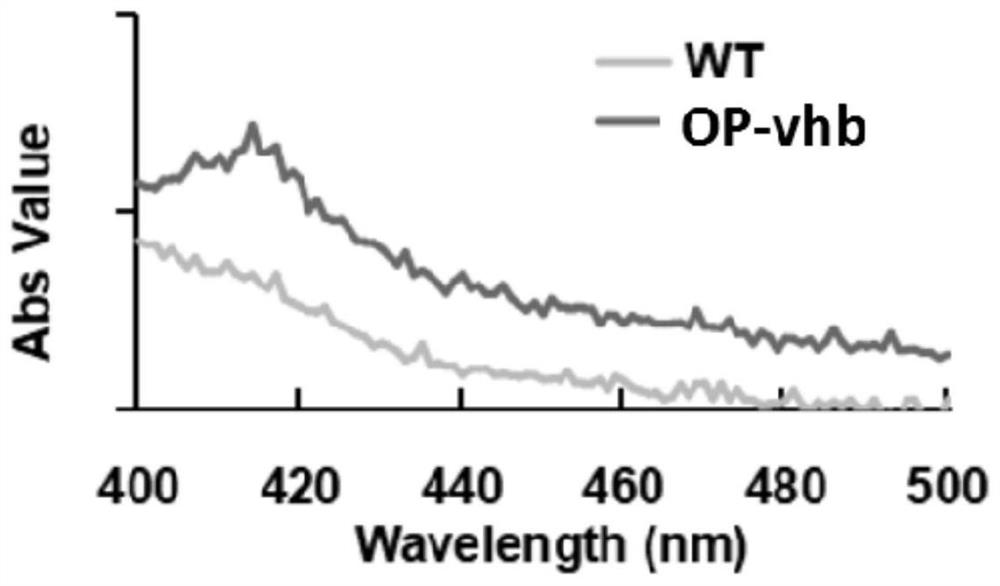
Method for expressing vitreoscilla hemoglobin in phaeodactylum tricornutum for autotrophic and mixotrophic culture
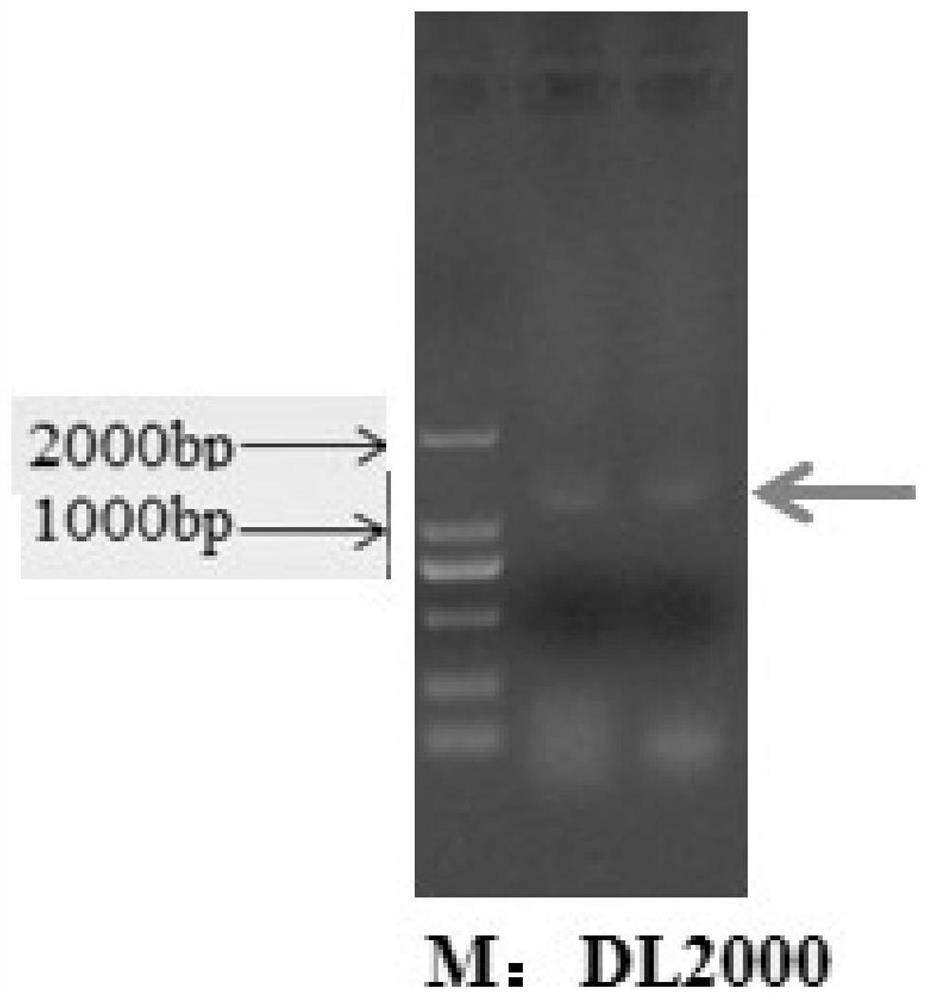
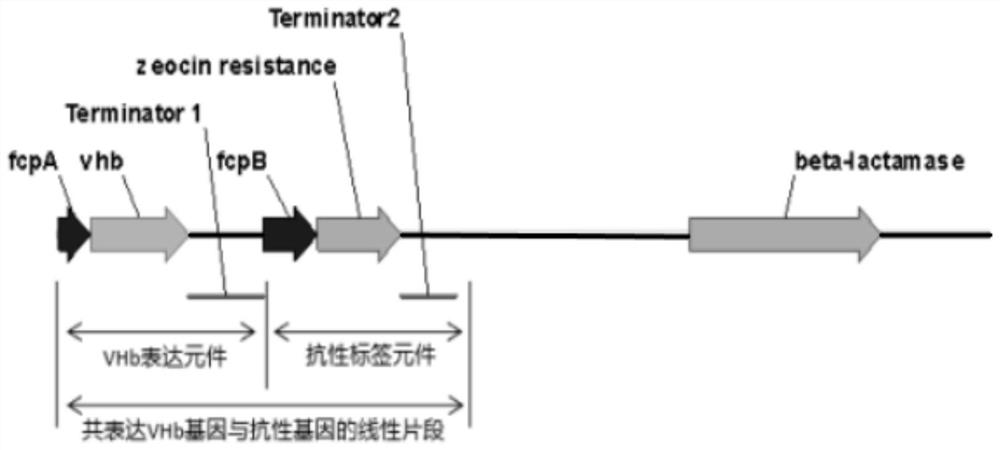
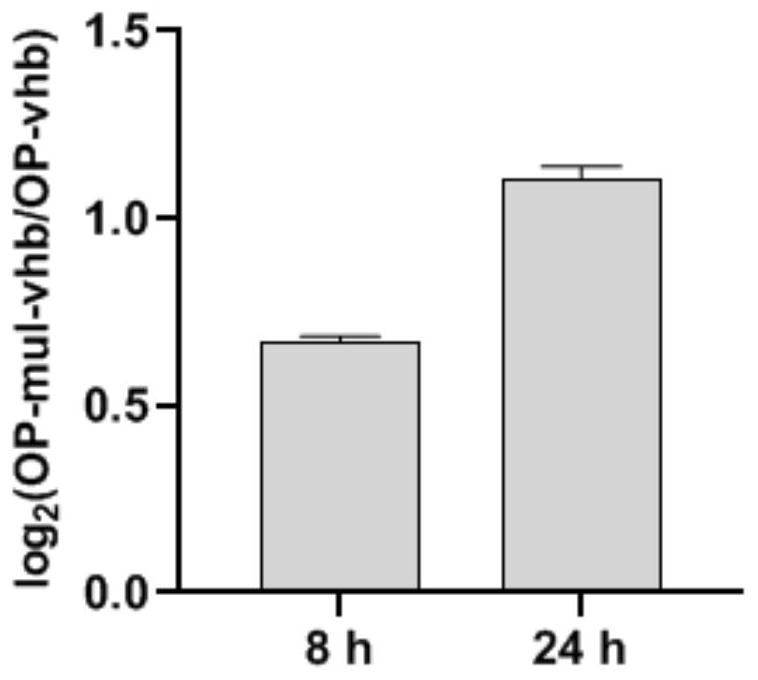
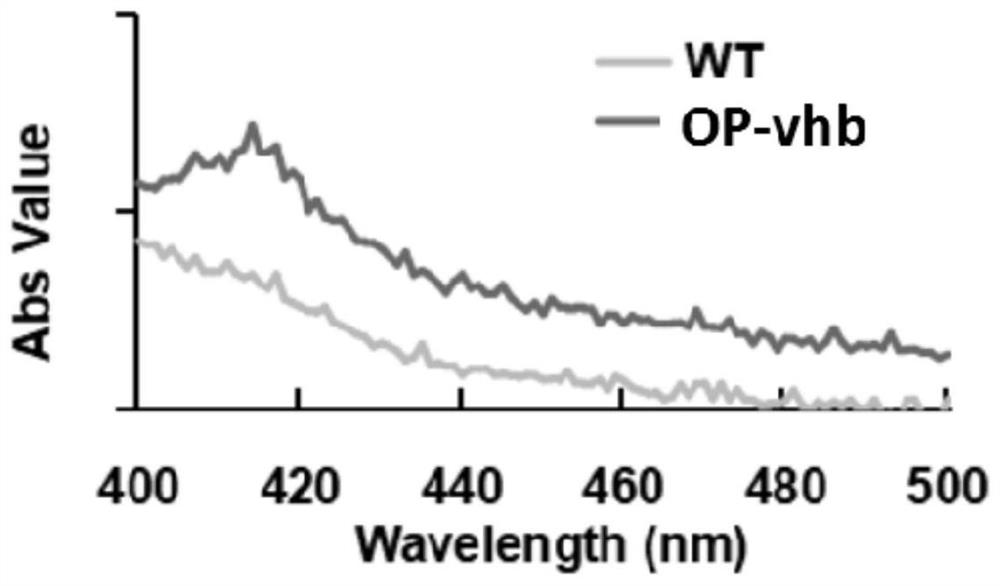
ActiveCN111893137AImprove expression efficiencyReduce oxidative damageHaemoglobins/myoglobinsUnicellular algaeVitreoscilla hemoglobinTransgene
The invention provides a method for expressing vitreoscilla hemoglobin in phaeodactylum tricornutum for autotrophic and mixotrophic culture. codon optimization of a VHb gene and construction of an expression vector are mainly performed; the VHb expression vector is constructed, and is introduced into a cell in an electrotransformation manner by utilizing PCR amplification linearized fragments, andtransgenic algal strains are obtained by screening; the transgenic algal strains obtained by the invention can continuously improve the gene in the aspects of the growth efficiency of phaeodactylum tricornutum under autotrophic and mixotrophic culture conditions and the yield of high added-value products.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
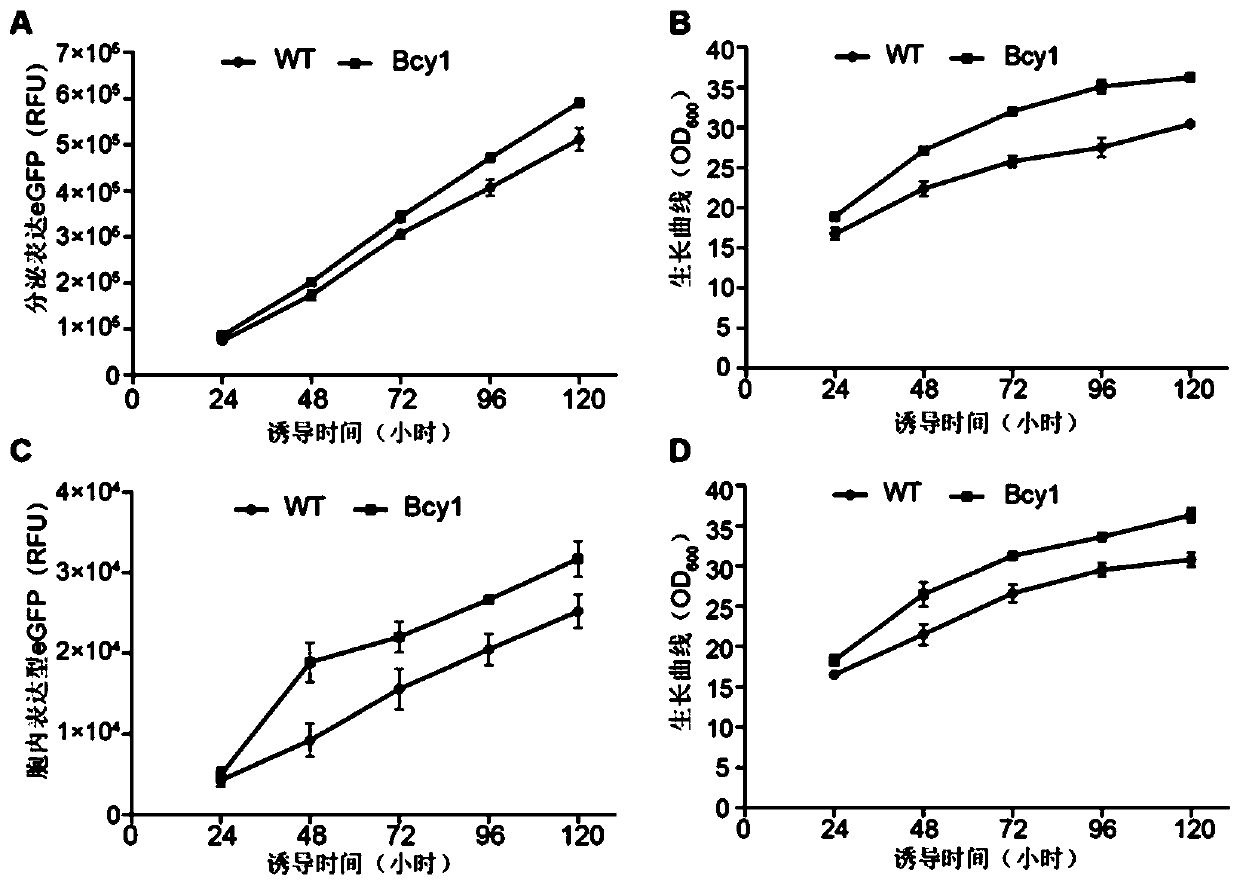
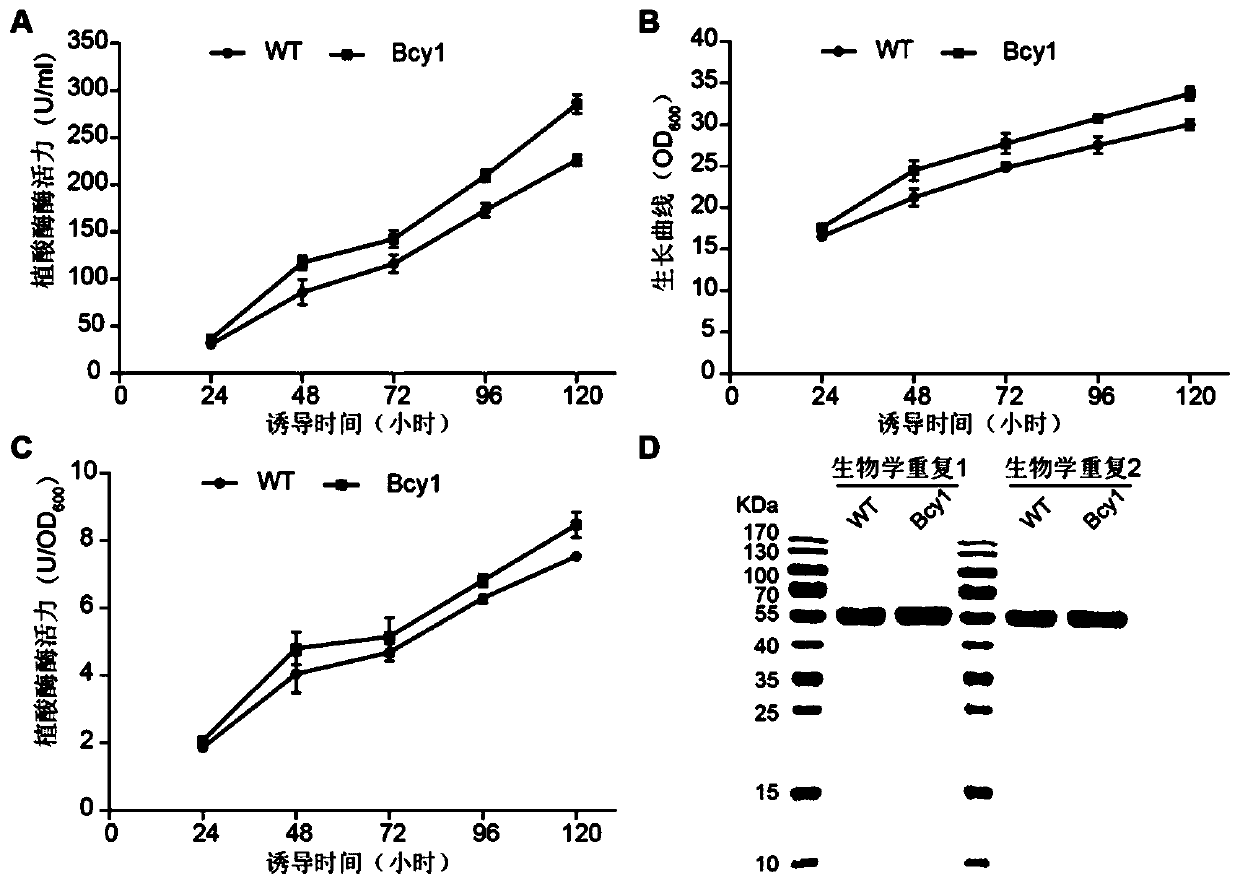
Application of pichia pastoris translation correlation factor Bcy1 to foreign protein expression
The invention discloses application of a pichia pastoris translation correlation factor Bcy1 to foreign protein expression. According to application, it is discovered that the biomass in the cell fermentation process can be significantly improved by the pichia pastoris translation correlation factor Bcy1 (annotation: protein kinase A regulated subunit), the expression quantity of enhanced green fluorescence protein eGFP is improved, the expression quantity of phytase Phy is improved, the cell growth of pichia pastoris during stable fermentation can be promoted, cell biomass accumulation is increased, it is indicated that the pichia pastoris translation related factor Bcy1 has the high universality, and the pichia pastoris translation related factor Bcy1 has good application prospects to aspects of cell biomass accumulation during fermentation and foreign protein yield improvement.
Owner:拜斯特药业(广州)有限公司 +1
Seed dressing agent for promoting premature germination of peanuts and preparation method of seed dressing agent
ActiveCN113712033AIncrease productionPromote growthBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyGibberellin
The invention discloses a seed dressing agent for promoting premature germination of peanuts and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of biological agents. The seed dressing agent for promoting premature germination of peanuts disclosed by the invention comprises at least one selected from melatonin and gibberellin, and further comprises a bactericide and an adhesive. When the seed dressing agent is used for treating peanut seeds, growth of peanut root systems can be promoted, nutrient absorption of plants is improved, biomass accumulation is increased, and finally, peanut yield is increased.
Owner:HENAN INST OF SCI & TECH
Transgenic plants used as a bioreactor system
ActiveUS7754943B2Efficient assimilationIncreased biomass accumulationOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationMetabolite1,3-Propanediol
The present invention relates generally to the use of plants as bioreactors for the production of molecules having useful properties such as inter alia polymers, metabolites, proteins, pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals. More particularly, the present invention contemplates the use of grasses, and even more particularly C4 grasses, such as sugar-cane, for the production of a range of compounds such as, for example, polyhydroxyalkanoates, pHBA, vanillin, indigo, adipic acid, 2-phenylethanol, 1,3-propane-diol, sorbitol, fructan polymers and lactic acid as well as other products including, inter alia, other plastics, silks, carbohydrates, therapeutic and nutraceutic proteins and antibodies. The present invention further extends to transgenic plants and, in particular, transgenic C4 grass plants, capable of producing the compounds noted above and other products, and to methods for generating such plants. The ability to utilize the high growth rate and efficient carbon fixation of C4 grasses is advantageous, in that it obviates the significant growth penalties observed in other plants, and results in high yields of desired product without necessarily causing concomitant deleterious effects on individual plants. In addition, the C4 grass, sugarcane, is particularly advantageous, as in addition to the features common to all C4 grasses, this plant accumulates sucrose. This sucrose store provides a ready supply of carbon based compounds and energy which may further obviate any deleterious effects on the growth of the plant associated with the production of the product. The present invention provides, therefore, a bioreactor system comprising a genetically modified plant designed to produce particular metabolic or biosynthetic products of interest.
Owner:SUGAR RES AUSTRALIA +1
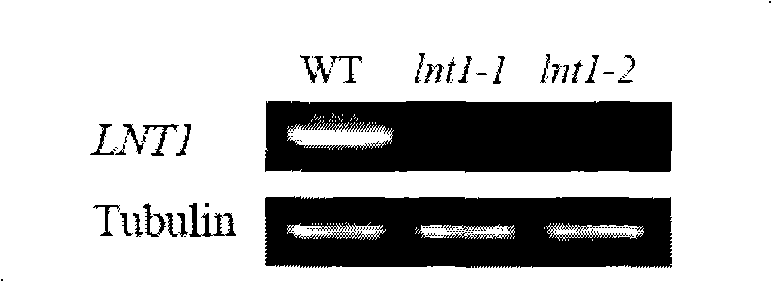
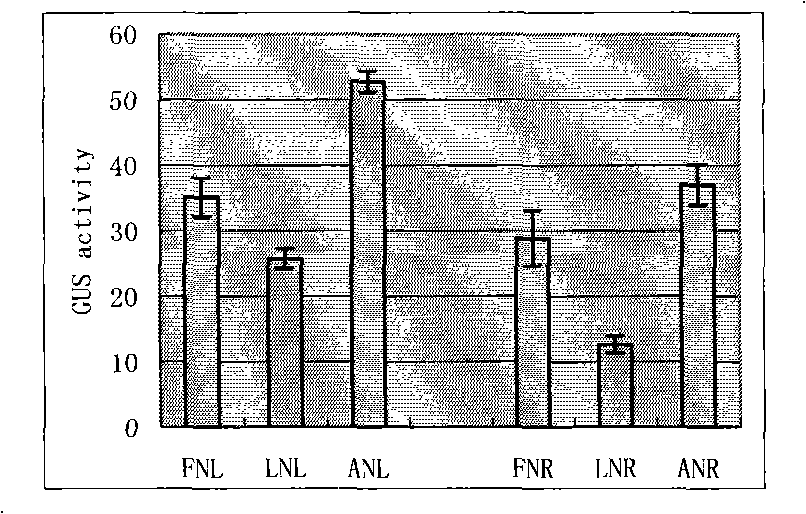
Method for accelerating vegetation in low-nitrogen condition
InactiveCN101270355AIncreased biomass accumulationHigh in nitrogenFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionVegetationLow nitrogen
The invention discloses a method for promoting the growth of plants under low-nitrogen conditions, which comprises adopting the general gene engineering method to inactivate AtLNT1 genes or disenable AtLNT1 genes to be expressed. With the method, the number of the branch roots of plants can be increased under low-nitrogen conditions, and the capability of absorbing nitrogen nutritive elements of plants is improved; the nitrogen white content of plants can be improved; and the photosynthesis of plants is improved. On the whole, the method disclosed by the invention is remarkably effective for promoting the growth of plants under low-nitrogen conditions.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing whole cells of gluconobacter oxydans by using glycerol as carbon source
InactiveCN109097314AReduce manufacturing costIncreased biomass accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesInorganic saltsGlycerol
The invention discloses a method for preparing whole cells of gluconobacter oxydans by using glycerol as a carbon source. The method includes performing genetic engineer transformation on wild-type gluconobacter oxydans to make the wild-type gluconobacter oxydans grow with the glycerol as the carbon source, to make a recombinant gluconobacter oxydans DeltaGOX1068DeltaGOX0854, and then inoculatingthe obtained recombinant gluconobacter oxydans in a glycerol inorganic salt medium, to obtain the whole cells of gluconobacter oxydans after shaking culture through a shaking table at 30+ / -1 DEG C. Experiments prove that the process of preparing the whole cells in the method is simple and convenient, a prepared whole cell biocatalyst has catalytic efficiency equivalent to that of a gluconobacter oxydans 621H whole cell biocatalyst prepared in a sorbitol complex medium, and the biocatalyst has a low preparation cost and has good application values.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Improved culture medium suitable for vegetative growth of nostoc sphaeroids kutz and preparation method
InactiveCN112662583ANutritional balanceLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHydration reactionSolvent
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Application of rape BnLAC2 gene in improvement of cold-resistant early blossoming
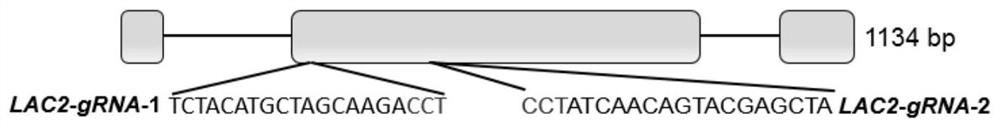
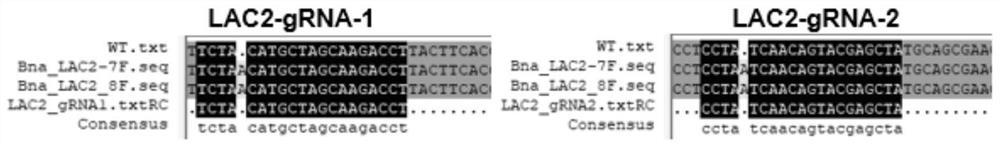
The invention discloses application of an oilseed rape BnLAC2 gene in improving cold-resistant early flowering of oilseed rape, sgRNA specifically targeting the oilseed rape BnLAC2 gene is designed, the sgRNA is prepared into an oligo dimer, the oligo dimer and a Cas9 skeleton construct a gene editing carrier, the gene editing carrier is introduced into cabbage type oilseed rape hypocotyl callus through an agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation technology and regenerated into seedlings, and the cold-resistant early flowering of the oilseed rape is improved. Cas9 nuclease edits a BnLAC2 gene on a genome A under the guidance of sgRNA to generate insertion mutation, phenotypic identification finds that the biomass of the oilseed rape subjected to cold injury treatment of a homozygous mutant strain is improved, and the oilseed rape blooms two weeks ahead of time.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Formula for feeding black-bone chicken by blending with traditional Chinese medicinal materials
InactiveCN110447786ASpread evenlyIncrease resistanceFood processingAnimal feeding stuffPaulowniaMedicine
The invention discloses a formula for feeding black-bone chicken by blending with traditional Chinese medicinal materials. The raw materials by weight include: 4-9 parts of radix bupleuri, 3-8 parts of wrinkled giant hyssop, 6-16 parts of coptis, 8-15 parts of leaf of fortune paulownia, 10-15 parts of dandelion, 12-21 parts of isatis root, 15-20 parts of Radix Astragali, 10-15 parts of Chinese magnoliavine, 20-35 parts of barley, 17-38 parts of sorghum, 10-25 parts of soybean meal, and 30-60 parts of water. A preparation method of the formula comprises the step of selecting appropriate amountof radix bupleuri, wrinkled giant hyssop, coptis, leaf of fortune paulownia, dandelion, isatis root, Radix Astragali and Chinese magnoliavine, The invention relates to the technical field of black-bone chicken feeding. According to the formula, the traditional Chinese medicinal materials are added to the grain normally eaten by the black-bone chicken, the product can prevent diseases, increase theresistance of black-bone chickens, reduce the frequency of disease occurrence, and increase the accumulation of biomass in black-bone chickens. The preparation method is simple, the product can promote the growth of black-bone chicken, is suitable for feeding the black-bone chicken, and improves the quality of the black-bone chicken.
Owner:安徽西山湖农业发展有限公司
Method for accelerating vegetation in low-nitrogen condition
InactiveCN101270355BIncreased biomass accumulationHigh in nitrogenFermentationPlant phenotype modificationVegetationLow nitrogen
The invention discloses a method for promoting the growth of plants under low-nitrogen conditions, which comprises adopting the general gene engineering method to inactivate AtLNT1 genes or disenableAtLNT1 genes to be expressed. With the method, the number of the branch roots of plants can be increased under low-nitrogen conditions, and the capability of absorbing nitrogen nutritive elements of plants is improved; the nitrogen white content of plants can be improved; and the photosynthesis of plants is improved. On the whole, the method disclosed by the invention is remarkably effective for promoting the growth of plants under low-nitrogen conditions.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
An endophytic fungus of the genus Phoma and its application
InactiveCN104293681BSlow down or delay the symptoms of salt damageIncreased biomass accumulationAgriculture tools and machinesFungiOchrobactrum triticiGenus Phoma
The invention discloses an endophytic fungus of the genus Phoma and its application. The Phoma sp. endophytic fungus is named as Phoma sp. KDZ-5, and the preservation number is CCTCC No.M 2014162. The application is the application of the endophytic fungus of the Phoma genus in improving the salt tolerance of rice or wheat. The present invention finds for the first time that Phoma sp. KDZ-5 can improve the resistance ability of rice and wheat to salt stress. The test shows that after establishing a co-cultivation system with KDZ-5 strain and rice seedlings, the KDZ-5 strain can significantly Promote the growth of rice seedlings on salt-added MS plates; after establishing a co-culture system with wheat seedlings under nutrient solution hydroponic and soil pot conditions, KDZ-5 strains can significantly slow down or delay the salinity of wheat in saline-alkali soil damage symptoms, while greatly increasing the biomass accumulation of wheat.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Combined antibiotic application method for haematococcus pluvialis pure culture
PendingCN113717917AIncrease growth rateIncreased biomass accumulationUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesIron sulfateAmpicillin
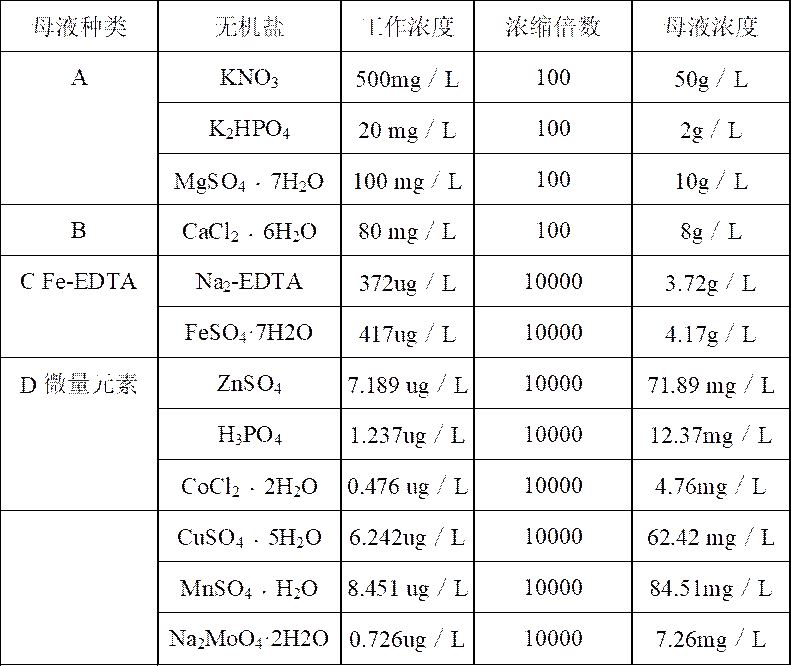
The invention relates to a combined antibiotic application method for haematococcus pluvialis pure culture. A haematococcus pluvialis culture medium MCM culture medium used in an experiment is as follows: a formula of a solution A comprises 500mg / L of potassium nitrate, 20mg / L of dipotassium phosphate and 100mg / L of magnesium sulfate heptahydrate; a formula of a solution B comprises 80 mg / L of calcium chloride hexahydrate; a formula of a solution C comprises 372 [mu]g / L of disodium ethylene diamine tetraacetate and 417 [mu]g / L of ferric sulfate heptahydrate; a formula of a solution D comprises 7.189 [mu]g / L of zinc sulfate, 1.237 [mu]g / L of phosphoric acid, 0.476 [mu]g / L of cobalt chloride dehydrate, 6.242 [mu]g / L of copper sulfate pentahydrate, 8.451 [mu]g / L of manganese sulfate monohydrate and 0.726 [mu]g / L of sodium molybdate dehydrate; formula solvents are tap water, and after high-pressure sterilization, the solution A, the solution B, the solution C and the solution D dissolve in the solvents in sequence; and four antibiotics, namely streptomycin, kanamycin, gentamicin and ampicillin are combined for use, the pH value is adjusted to 6.99-7.03 and the concentration of the antibiotics are 600mu g / ml, culturing is performed on a shaker in a light box for 3 days, and purifying and inspecting are performed by combining with a solid culture medium to obtain the pure haematococcus pluvialis.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
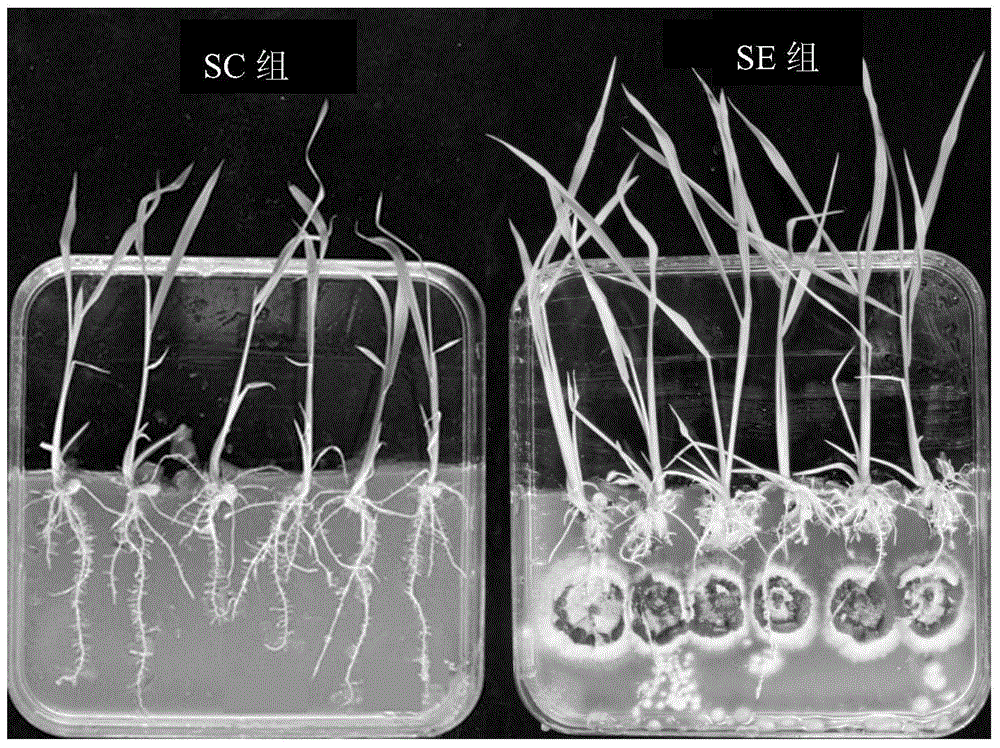
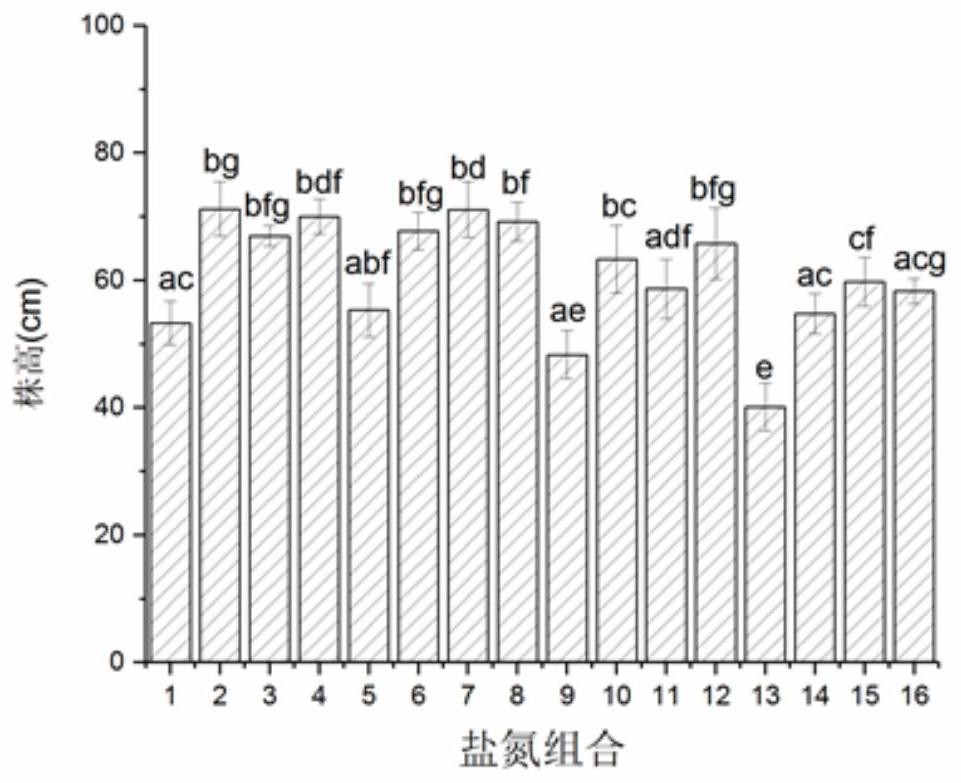
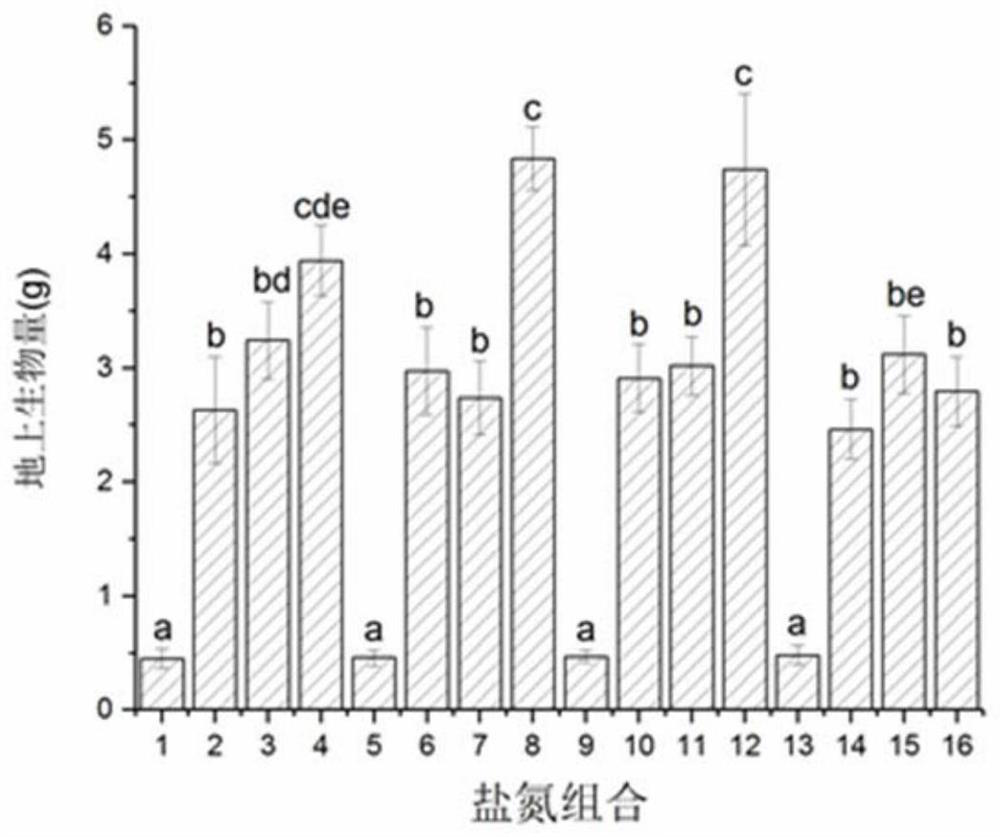
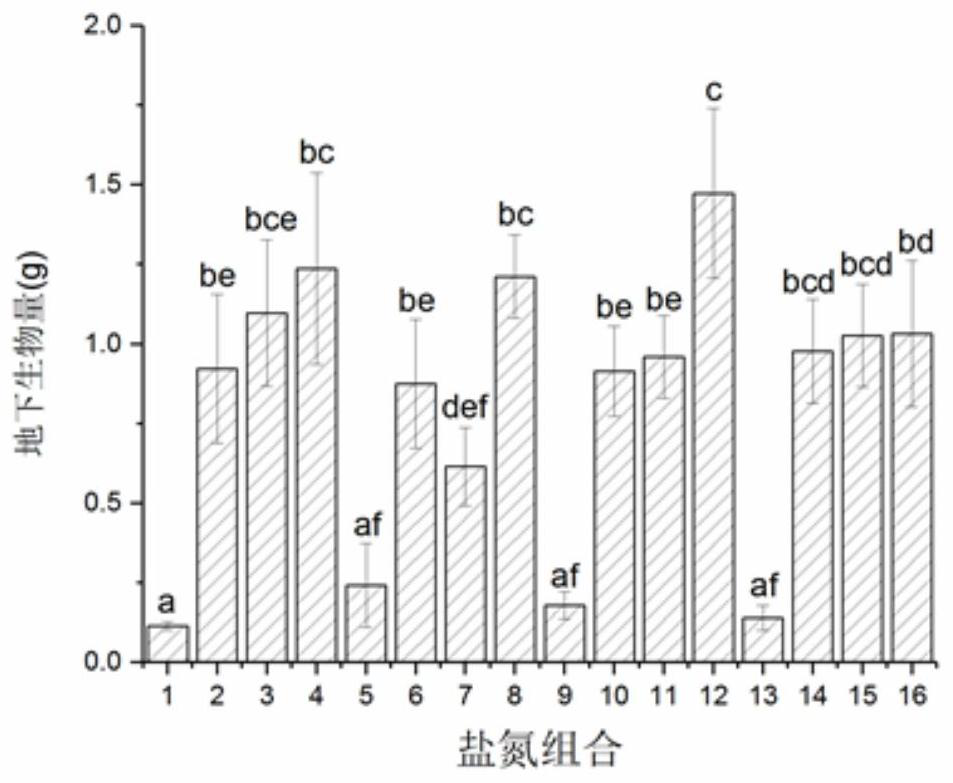
A Screening Method for Optimum Salt and Nitrogen Conditions of Reed Seedlings
ActiveCN109122067BIncrease plant heightIncreased biomass accumulationCultivating equipmentsPlant cultivationPlantletRhizome
The invention discloses a screening method for optimal salt and nitrogen conditions of reed seedlings, which belongs to the technical field of ecological restoration, and specifically relates to a screening method for optimal salt and nitrogen conditions of reed seedlings in saline-alkali wetlands. The purpose of the invention is to solve the problems of low survival rate of transplanted reeds and slow growth of seedlings in the existing degraded reed wetlands. A screening method for optimal salt and nitrogen conditions for reed seedlings: 1. Collection of reed rhizomes; In the case of nitrogen concentration / nitrogen addition concentration combination, the seedlings were cultivated respectively; 4. Detection and analysis: according to the plant height of reed seedlings, the biomass of aboveground plants of reed seedlings, the biomass of underground rhizomes of reed seedlings, and the total biomass of reed seedlings, SPSS 19.0 was used One-way analysis of variance was carried out, and finally the optimal salt and nitrogen conditions for reed seedlings were obtained. Advantages: The survival rate of transplanted reed seedlings reaches 100%. The invention is mainly used for rapid recovery and reconstruction of reeds in saline-alkali wetlands.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Compound fertilizer for cordate houttuynia and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN113354478APromote growth and developmentIncrease contentAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersSoil scienceHouttuynia
The invention provides a compound fertilizer for cordate houttuynia and a preparation method thereof, the compound fertilizer comprises the following components in parts by weight: 30-36 parts of urea, 40-48 parts of potassium sulfate, 10-16 parts of industrial monoammonium and 0.6-1 part of trace elements, and also comprises 6-10 mg / Kg of polyurethane and 0.08-0.12 mg / Kg of intelligent hearing. The fertilizer also comprises laxogenin, and the content of the laxogenin in the fertilizer is 0.2-0.6 mg / kg; and the content of the potassium brownish yellow rot in the fertilizer is 6-10mg / kg. The compound fertilizer provided by the invention contains a large number of nutrient elements and trace elements required by the growth of cordate houttuynia crops, and polyurethane peptide, smart hearing aid, potassium brownish fulvic acid and laxogenin are added as required, so that the compound fertilizer is relatively comprehensive in nutrients, can better promote the growth and development of the cordate houttuynia crops, and can improve the yield of the cordate houttuynia crops.
Owner:HUAQIANG CHEM GRP
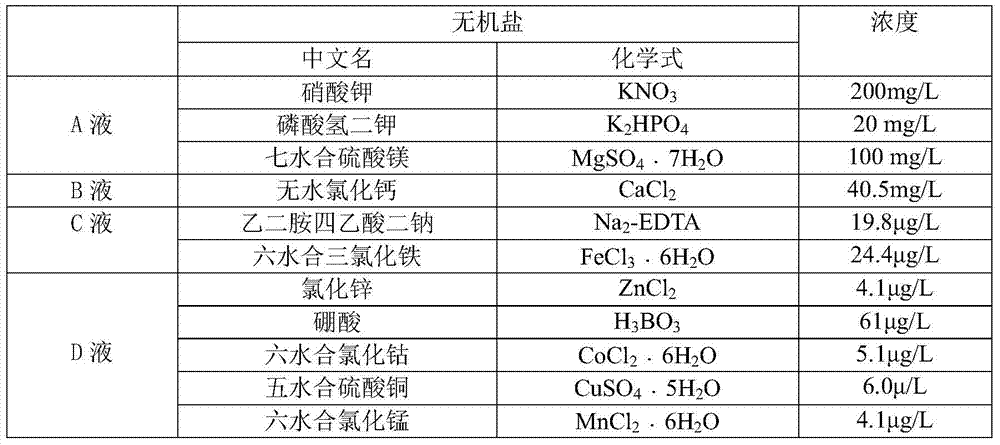
An improved medium suitable for the vegetative growth of Haematococcus pluvialis and its preparation method
InactiveCN104862232BNutritional balanceLow costUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesNutritionDipotassium phosphate
The invention discloses an improved culture medium applicable to Haematococcus pluvialis vegetative growth and a preparation method of the improved culture medium. The preparation method of the improved culture medium comprises the following steps: firstly, respectively preparing mother liquor of a solution A, mother liquor of a solution B, mother liquor of a solution C and mother liquor of a solution D, wherein the solution A comprises potassium nitrate with the concentration of 200 mg / L, dipotassium phosphate with the concentration of 20 mg / L and magnesium sulfate heptahydrate with the concentration of 100 mg / L; the solution B is anhydrous calcium chloride with the concentration of 40.5 mg / L; the solution C comprises ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt with the concentration of 19.8 [mu]g / L and ferric trichloride hexahydrate with the concentration of 24.4 [mu]g / L; the solution D comprises zinc chloride with the concentration of 4.1 [mu]g / L, boric acid with the concentration of 61 [mu]g / L, cobalt chloride hexahydrate with the concentration of 5.1 [mu]g / L, copper sulfate pentahydrate with the concentration of 6.0 [mu]g / L, manganese chloride hexahydrate with the concentration of 4.1 [mu]g / L, and ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate with the concentration of 38 [mu]g / L; sterilized tap water serves as a solvent; secondly, during use, dissolving the fixed amount of the solution A, solution B, solution C and solution D into the solvent in sequence, adjusting the pH value to be 6.9-7.1, and inoculating the culture medium with strains of the Haematococcus pluvialis. The improved MCM culture medium provided by the invention is balanced in nutrition, low in cost, simple to operate during preparation, and high in growth rate and biomass accumulation of cultivated strains, can be stored, and facilitates the improvement of industrialized production efficiency.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
A long-term method for inhibiting the browning phenomenon of Glycyrrhizae glabra suspension cell culture
The invention discloses a long-term method for inhibiting the browning phenomenon in the suspension cell culture process of Glycyrrhizae glabra. In order to be able to suppress the browning phenomenon in the suspension cell culture process of Glycyrrhiza glabra over a long period of time, the present invention selects ascorbic acid derivatives (calcium ascorbate) instead of ascorbic acid as the anti-browning agent, and simultaneously screens out lactose instead of sucrose as a carbon source for glazing. Glycyrrhiza glabra suspension cells were cultured, and it was found that this culture method can inhibit the activity of polyphenol oxidase in suspension cells for a long time (20 days), thereby inhibiting the occurrence of browning of Glycyrrhiza glabra suspension cells, and at the same time, the biomass accumulation of suspension cells obviously increase. In addition, the method of the invention is simple to operate, and the obtained licorice glabra suspension cells have good dispersibility and good growth state. The proposal of the invention provides an effective technical means for the enlarged culture of Glycyrrhiza glabra cells.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
A method for improving carbon fixation efficiency of microalgae and transgenic Chlamydomonas and application
ActiveCN109825441BDoes not affect normal growthIncrease growth rateUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses a method for improving the carbon fixation efficiency of microalgae. Chlamydomonas chloroplast-type glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene was overexpressed to enhance the ability of Chlamydomonas photosynthetic carbon fixation. It specifically includes the construction of a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene recombinant expression vector, and transforming the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene recombinant expression vector into Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cells by electric shock transformation, and screening to obtain glyceraldehyde-3 ‑Phosphate dehydrogenase enhanced expression in transgenic Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Microalgae can synthesize biomass such as oil, protein, starch, and carotenoids through photosynthetic carbon fixation, and accelerating the production efficiency of microalgal biomass plays an important role in downstream industries. The invention transfers the target gene into Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, accelerates the carbon fixation efficiency and increases its growth rate, and has significant application prospects in the field of microalgae bioengineering.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method for expressing Vitiligo hyaline hemoglobin in Phaeodactylum tricornutum for autotrophic and syntrophic culture
ActiveCN111893137BIncrease growth rateHigh fat contentHaemoglobins/myoglobinsUnicellular algaeIntracellularHemoglobin hb
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
GRF3 mutants, methods and plants
ActiveUS9890388B2Increase biomassImprove stress resistanceClimate change adaptationPlant peptidesRoot growthMutant
Owner:UNIV NACIONAL DE ROSARIO +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com