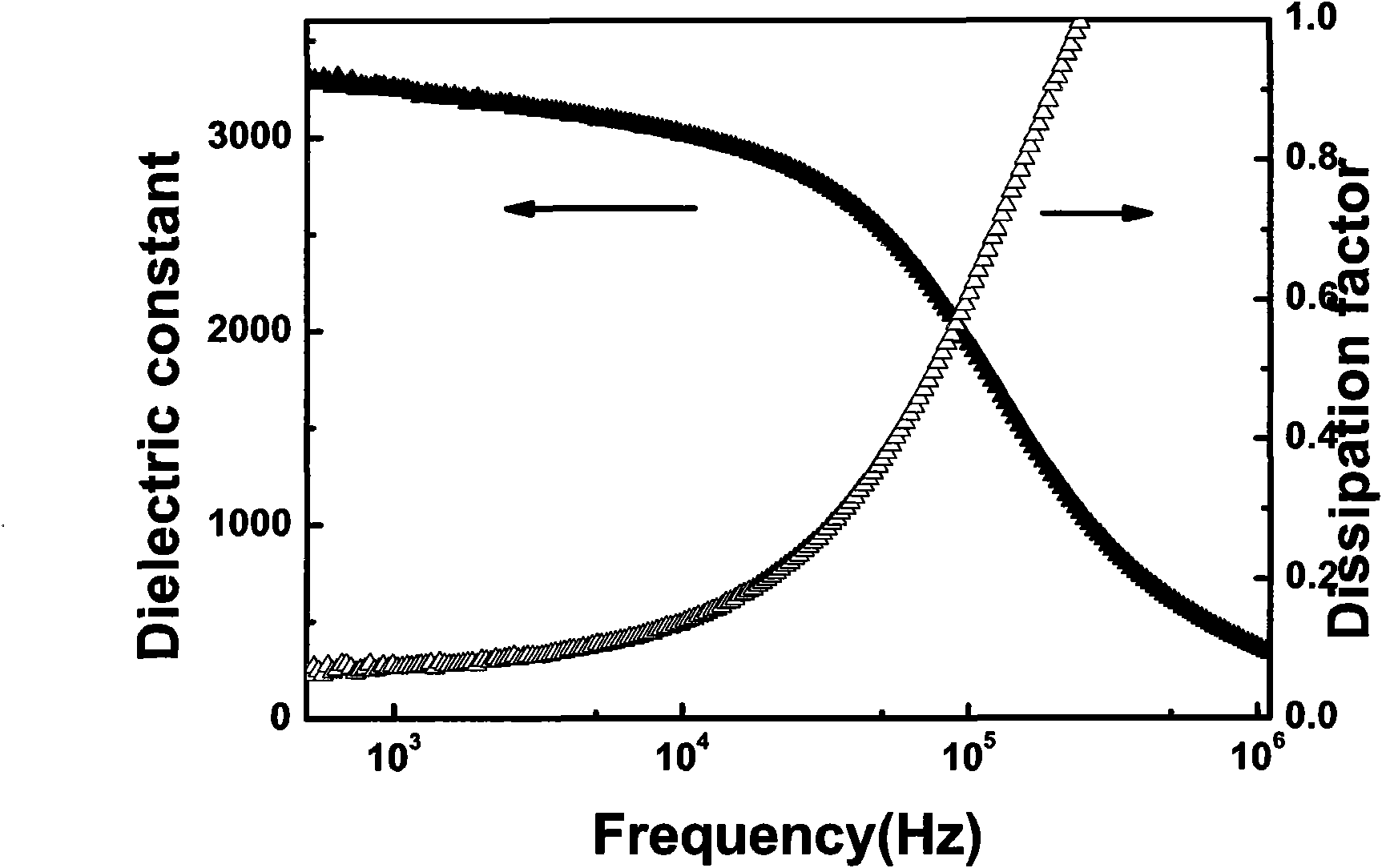
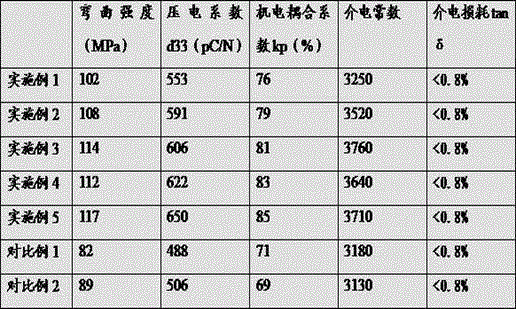
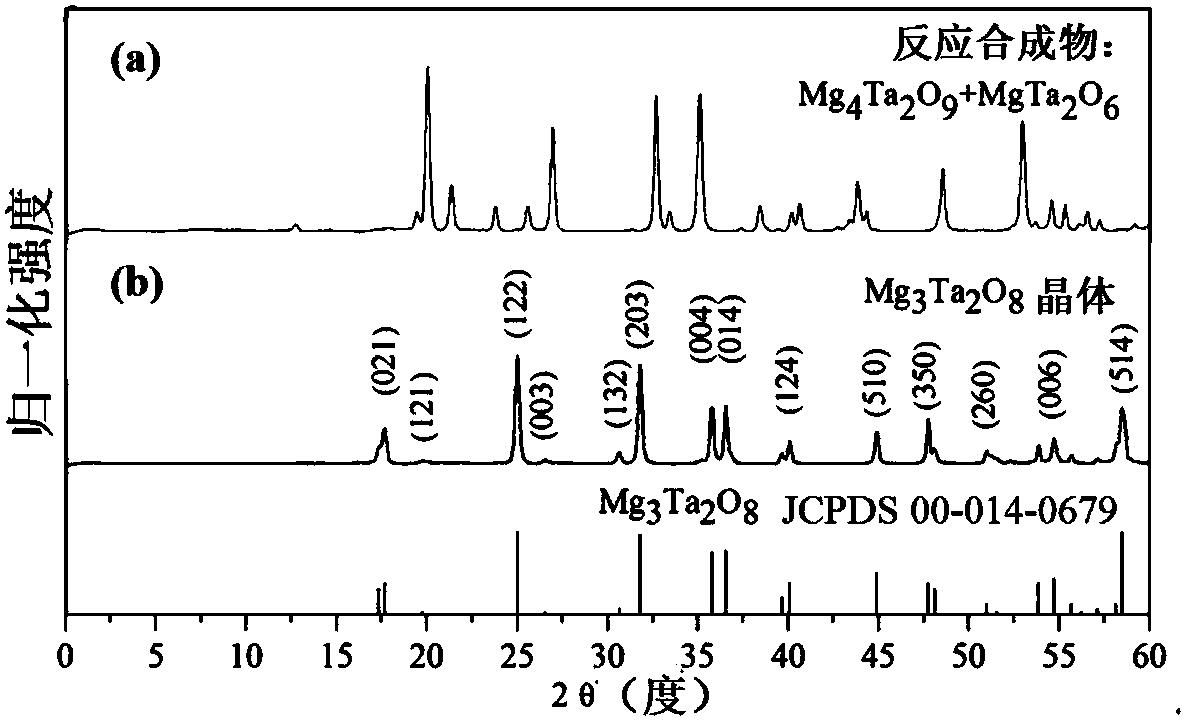
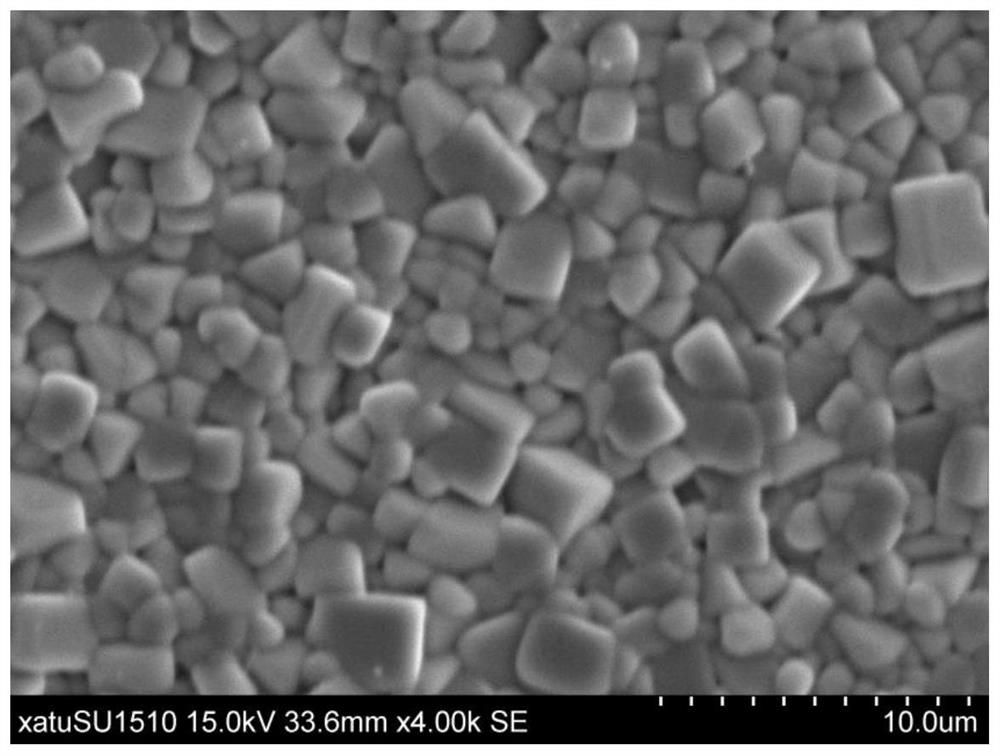
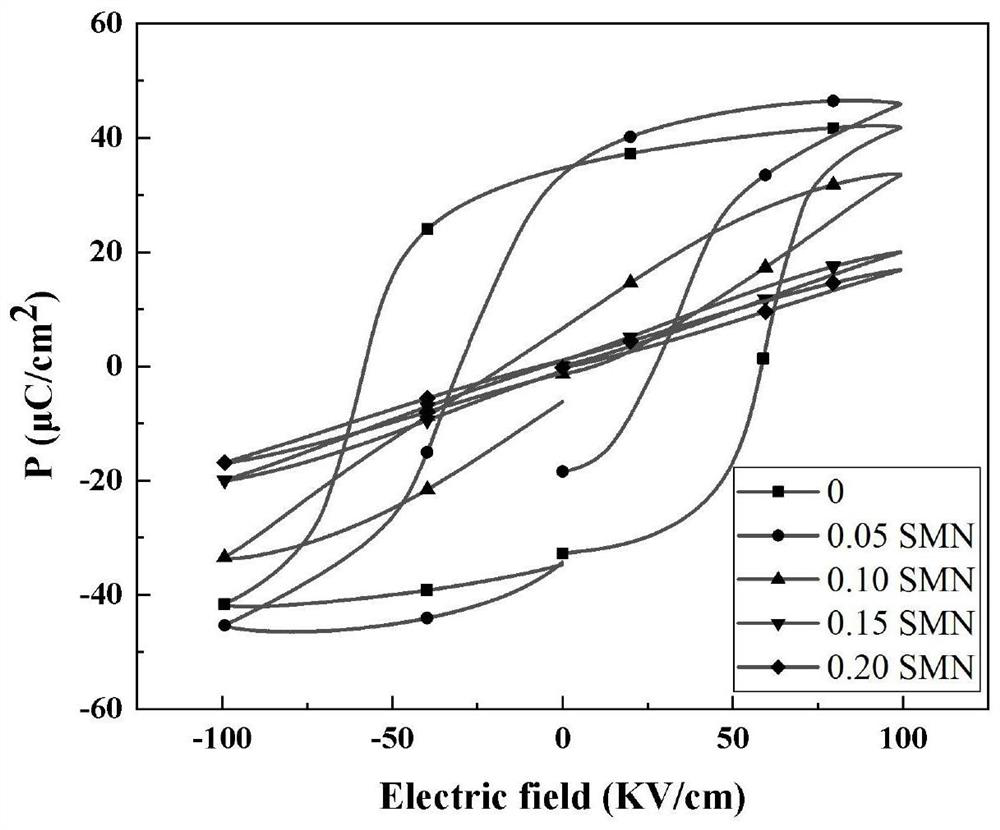
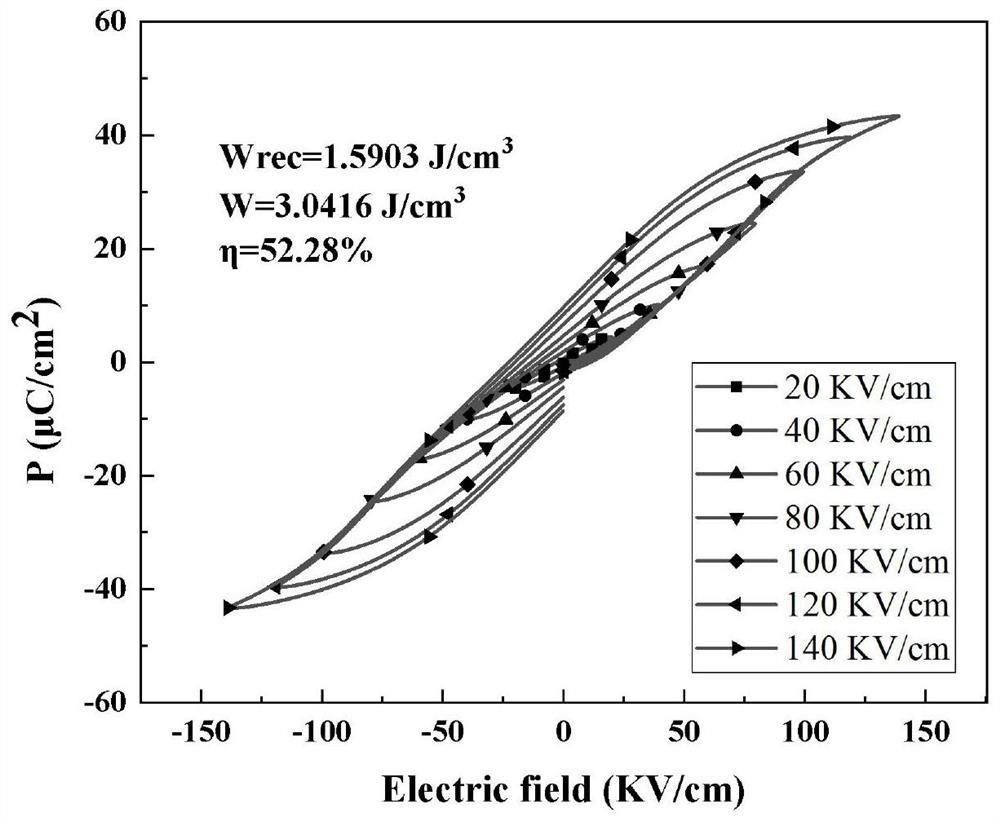
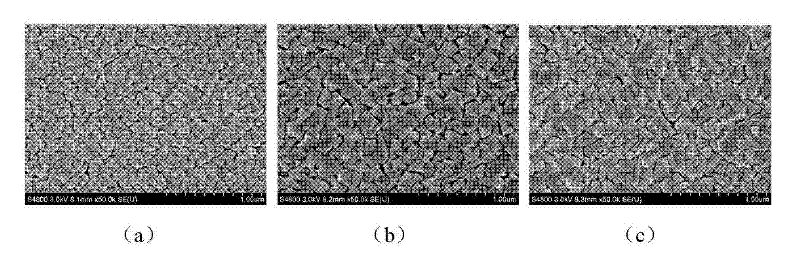
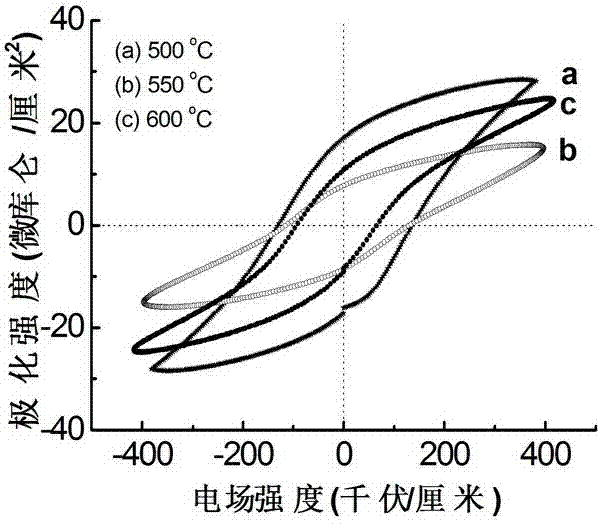
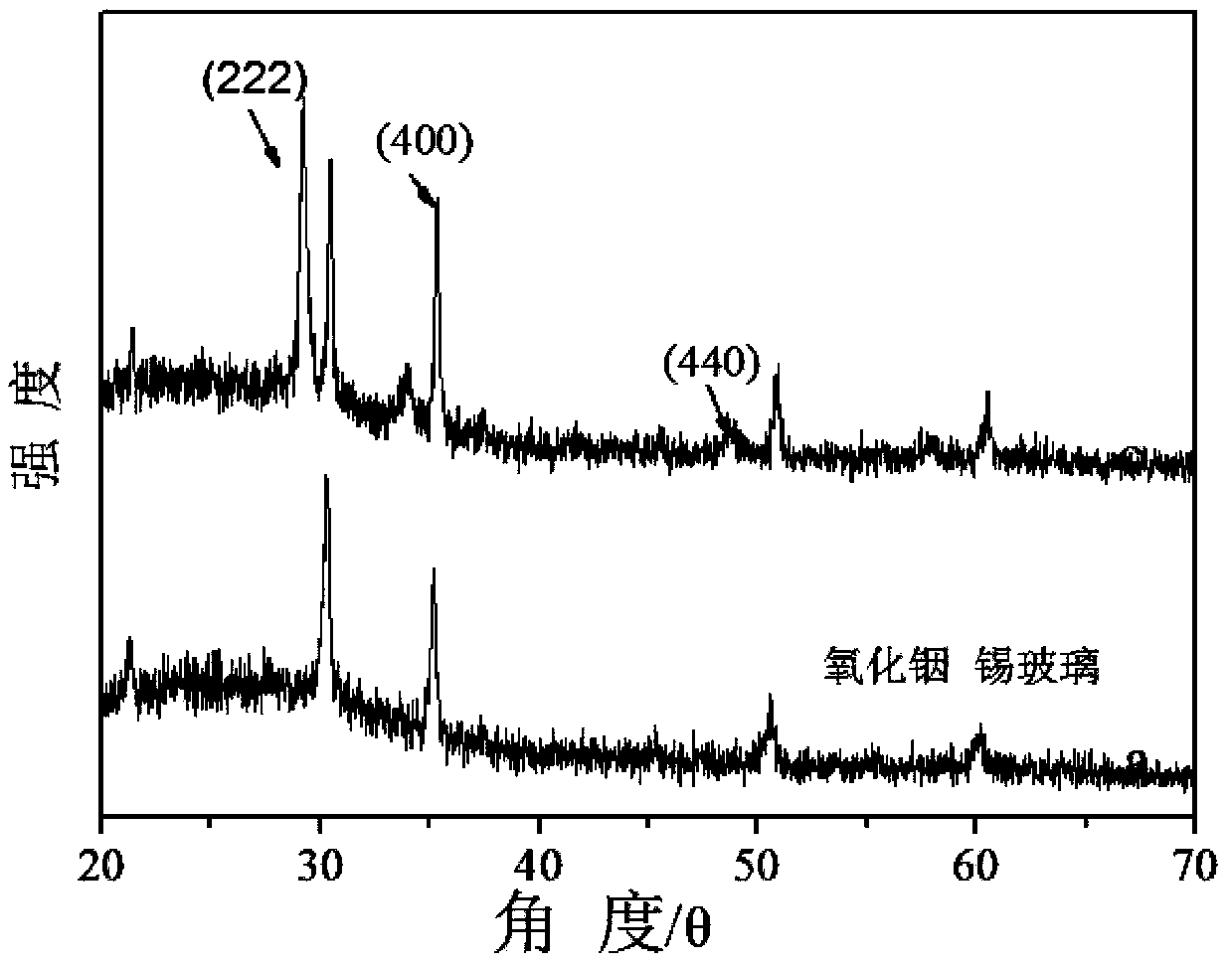
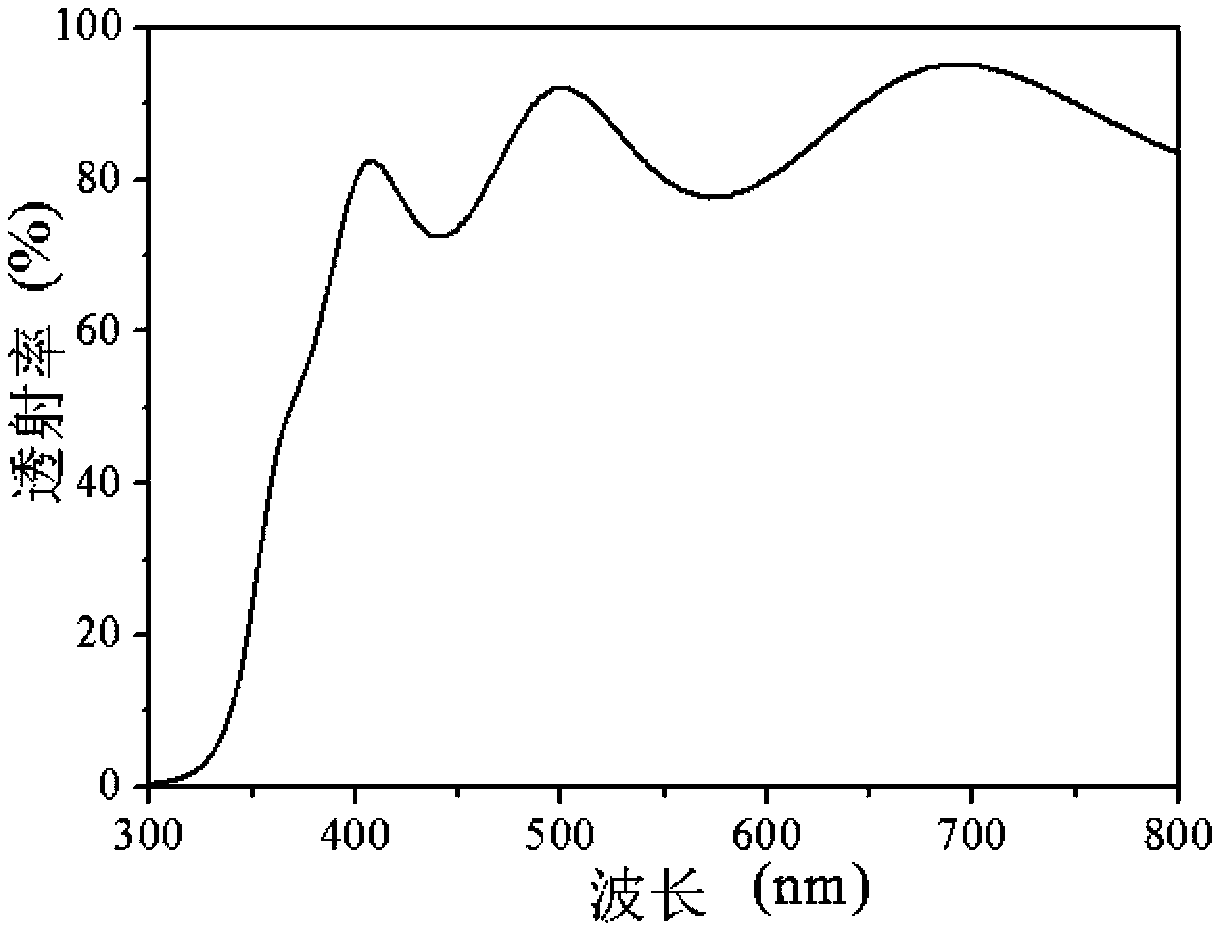
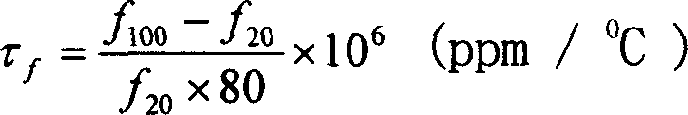Patents
Literature
33 results about "Magnesium niobate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lead magnesium niobate is a relaxor ferroelectric. It has been used to make piezoelectric microcantilever sensors. References This Condensed Matter Physics-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. This electromagnetism-related article is a stub. You ...
Magnesium removal from magnesium reduced metal powders
A method of producing a refractory metal powder that includes providing a metal powder containing magnesium tantalate or magnesium niobate; and heating the powder in an inert atmosphere in the presence of magnesium, calcium and / or aluminum to a temperature sufficient to remove magnesium tantalate or magnesium niobate from the powder and / or heating the powder under vacuum to a temperature sufficient to remove magnesium tantalate or magnesium niobate from the powder, the heating steps being performed in any order. The metal powder can be formed into pellets at an appropriate sintering temperature, which can be formed into electrolytic capacitors.
Owner:TANIOBIS GMBH
Method for preparing plumbum magnesium niobate-plumbum titanate ferroelectric film
InactiveCN101956166ASimple preparation processGood repeatabilityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingFerroelectric thin filmsPerovskite (structure)
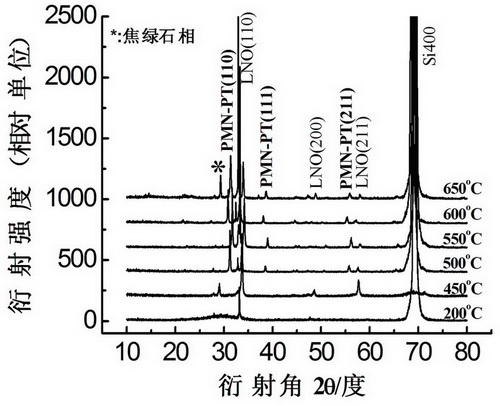
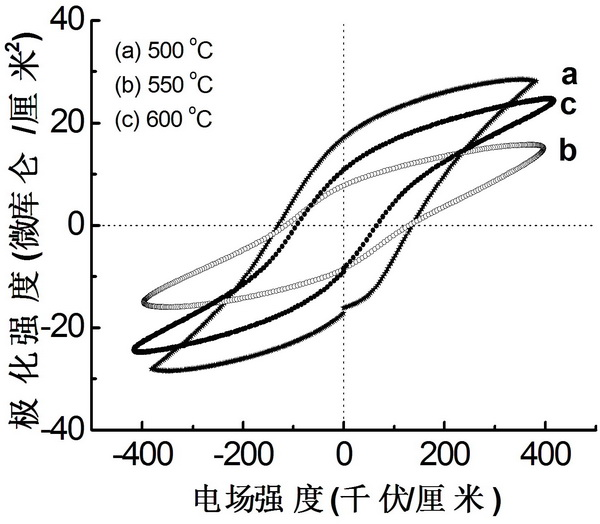
The invention belongs to the field of ferroelectric film materials and relates to a method for preparing a plumbum magnesium niobate-plumbum titanate (PMN-PT) ferroelectric film. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, preparing a PMN-PT ceramic target; secondly, cleaning a silicon (Si) substrate; thirdly, preparing a LaNiO3 conductive buffer layer; and finally, preparing the PMN-PT ferroelectric film. The method for preparing the PMN-PT ferroelectric film has the advantages of simple process, high repeatability, capacity of preparing the large-area PMN-PT film with pure perovskite structure preferred orientation on a cheap silicon substrate with an actual application value, compatibility with a Si integrated process, low preparation cost and contribution to mass production of devices. The prepared film has the advantages of high ferroelectric properties and suitability for ferroelectric-semiconductor integrated devices.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing magnesium niobate microwave ceramic powder on the basis of sol-gel technique
The invention discloses a method for preparing magnesium niobate microwave ceramic powder on the basis of sol-gel technique. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing the citric acid solution of niobium (Nb); (2) preparing the citric acid solution of magnesium (Mg); and (3) obtaining a Mg-Nb precursor solution, xerogel and nano-powder. The invention can overcome the disadvantages of high temperature and large particle size in the existing synthesis of magnesium niobate microwave ceramic powder on the basis of solid-phase method by preparing the magnesium niobate microwave ceramic powder with the average particle diameter being 40nm to 80nm under the condition that the calcination temperature is 550 to 850 DEG C.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Magnesium removal from magnesium reduced metal powders
A method of producing a refractory metal powder that includes providing a metal powder containing magnesium tantalate or magnesium niobate; and heating the powder in an inert atmosphere in the presence of magnesium, calcium and / or aluminum to a temperature sufficient to remove magnesium tantalate or magnesium niobate from the powder and / or heating the powder under vacuum to a temperature sufficient to remove magnesium tantalate or magnesium niobate from the powder, the heating steps being performed in any order. The metal powder can be formed into pellets at an appropriate sintering temperature, which can be formed into electrolytic capacitors.
Owner:TANIOBIS GMBH
Method for preparing lead-titanate-lead-magnesium niobate films by pulsed laser deposition assisted by oxygen plasmas
ActiveCN101892522AOptimizing Deposition Growth ConditionsCompact structurePolycrystalline material growthFrom condensed vaporsHigh energyCrystallinity
The invention provides a method for preparing lead-titanate-lead-magnesium niobate films by pulsed laser deposition assisted by oxygen plasmas, which is characterized by introducing high-activity oxygen plasmas to the process of preparing lead titanium-magnesium niobate films by pulsed laser deposition and improving the crystallinity and topography of the oxygen plasmas, thus obtaining the high-quality lead titanium-magnesium niobate films. The specific process is as follows: placing the lead-titanate-lead-magnesium niobate target and the substrate into a vacuum chamber; vacuumizing the vacuum chamber and heating the substrate to certain temperature; then pumping certain amount of high-purity oxygen and ionizing the oxygen by using a gas ionization system to apply high pressure to form the high-activity oxygen plasmas; ensuring the oxygen plasmas between the lead-titanate-lead-magnesium niobate target and the substrate; and using the high energy pulse laser to bombard the lead-titanate-lead-magnesium niobate target to generate the high energy plasmas and depositing the lead-titanate-lead-magnesium niobate films on the substrate. The films prepared by the invention have good crystallization quality, compact structure and excellent dielectric and ferroelectric properties.
Owner:中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所苏州研究院
High-performance piezoceramic material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106587992AImprove bending strengthImprove fracture toughnessPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesScandiumMaterials science
The invention discloses a high-performance piezoceramic material and a preparation method of the high-performance piezoceramic material. The high-performance piezoceramic material is prepared from the following raw materials: titanium tetrachloride, silver vanadate, barium nitrate, glutamic acid, scandium acetate, lithium aluminum tetrachloride, sodium zirconium silicate, terbium acetate hydrate, vanadium copper oxide, gallium telluride, phosphorus oxide, lithium tantalite, magnesium niobate, potassium chlorate, nickel citrate, methanol, deionized water and ethylene glycol. The piezoceramic material provided by the invention is higher in bending strength and greatly improved in fracture toughness, furthermore, piezoelectric properties of the piezoceramic material are all kept at high levels to meet performance requirements of the industry for the piezoceramic material. The piezoceramic material provided by the invention is good in comprehensive performances and has very good application market prospects.
Owner:SUZHOU AIBOMAIER NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
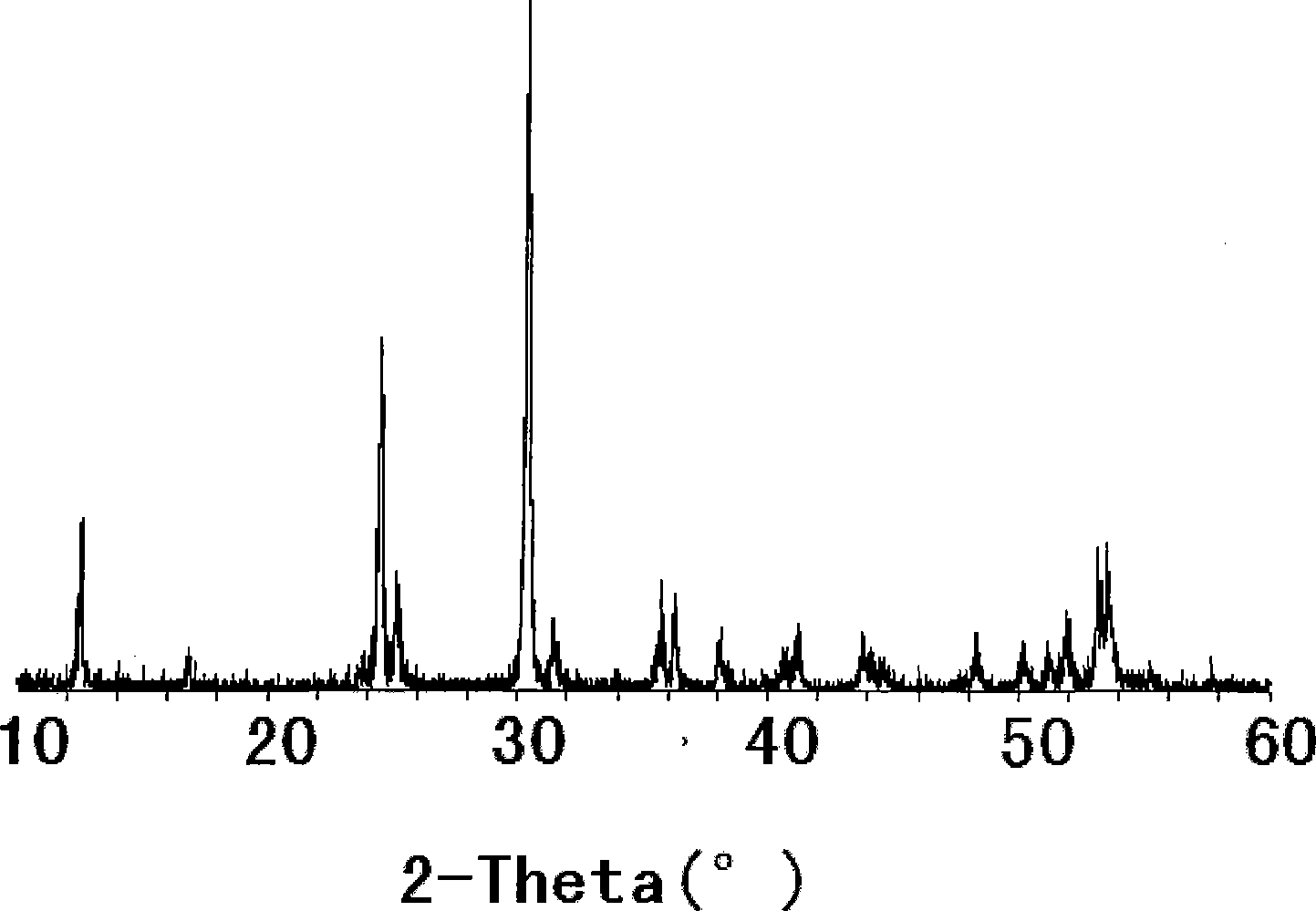
Magnesium niobate series crystals and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108203844AHigh crystalline integrityTransparent no macro defects noPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltSpontaneous nucleationSingle crystal
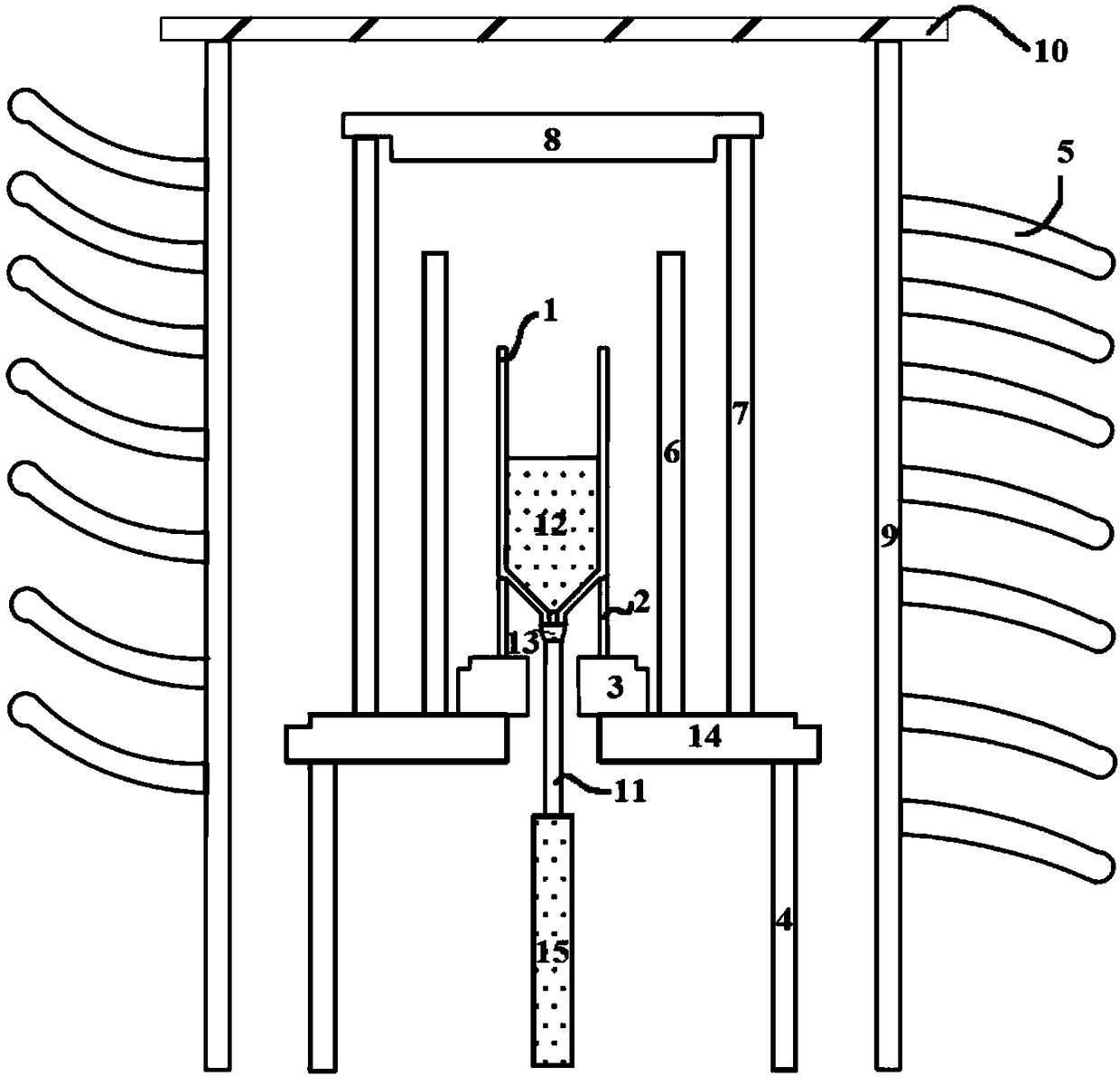
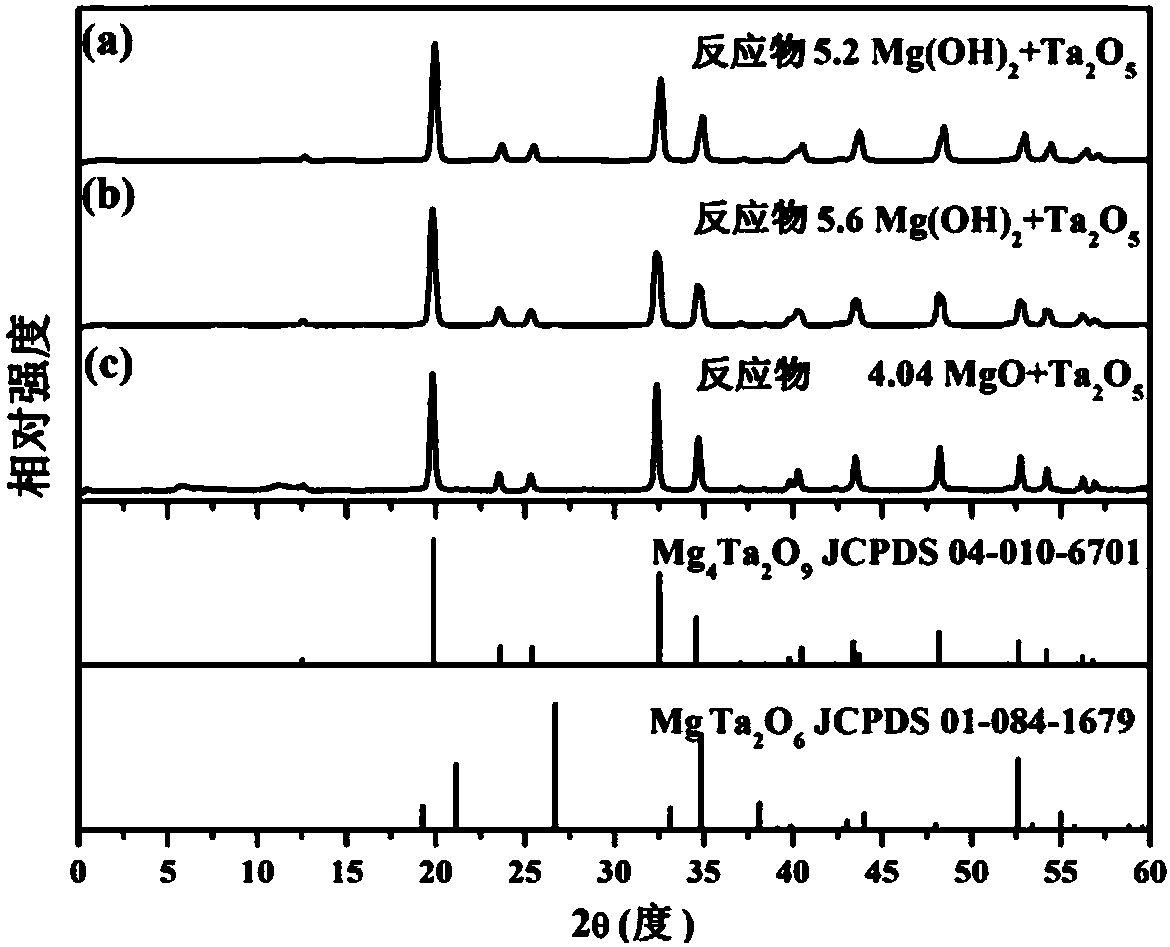
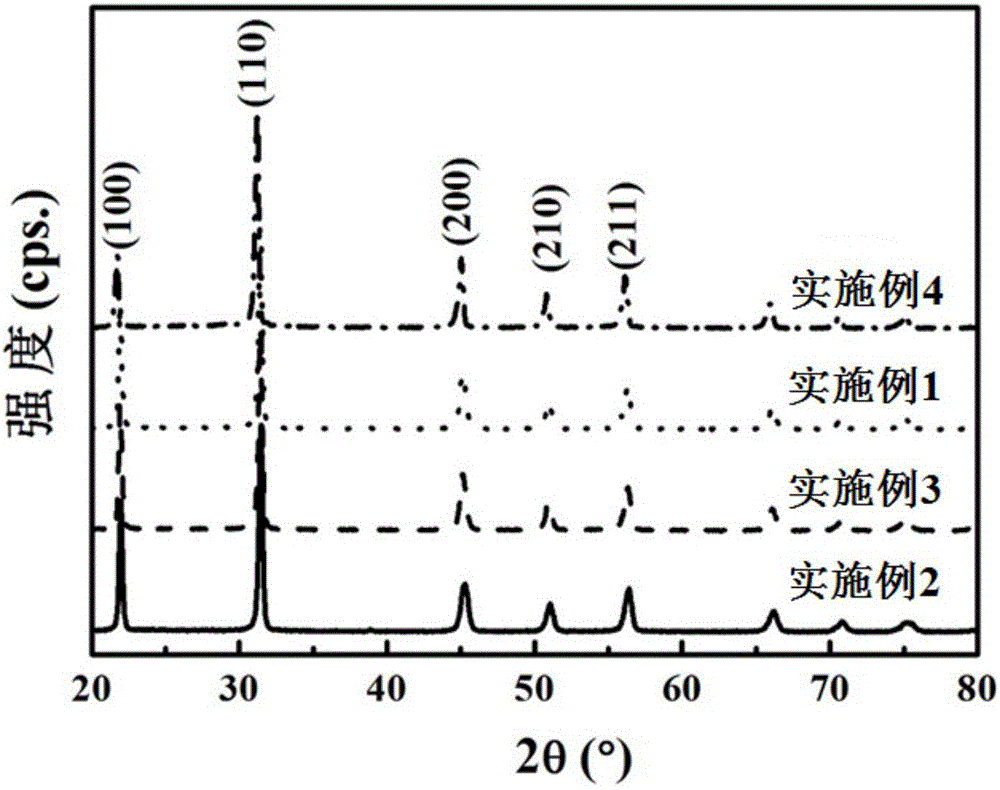
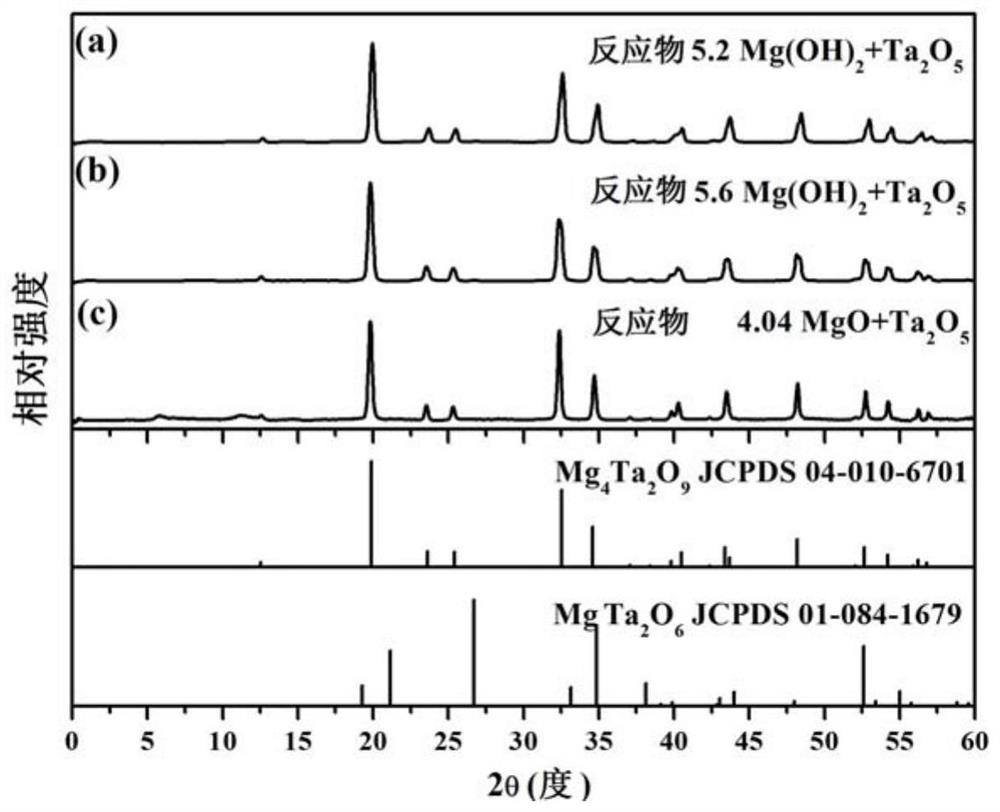
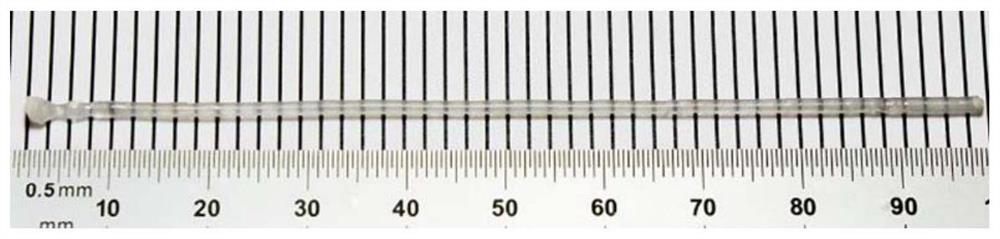
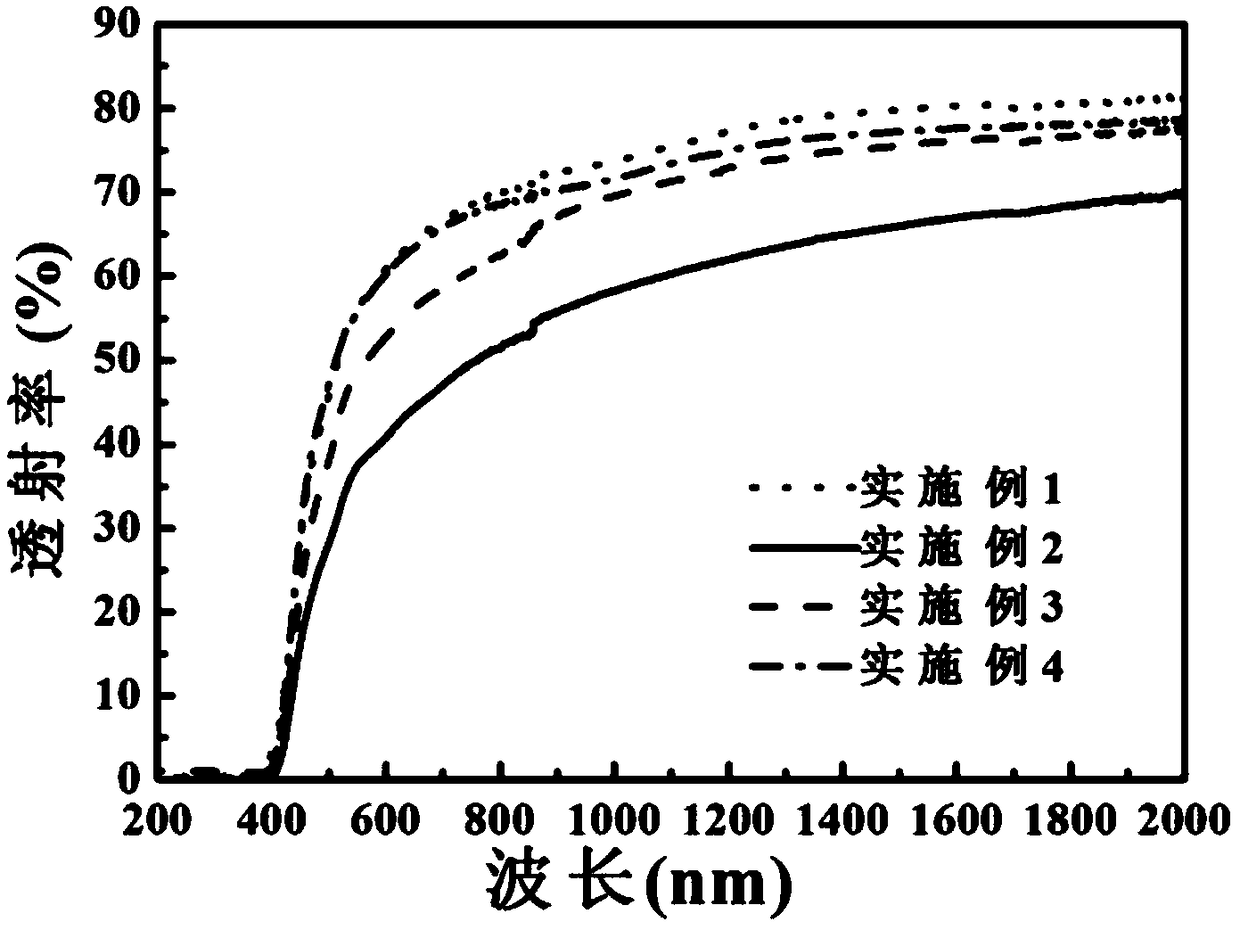
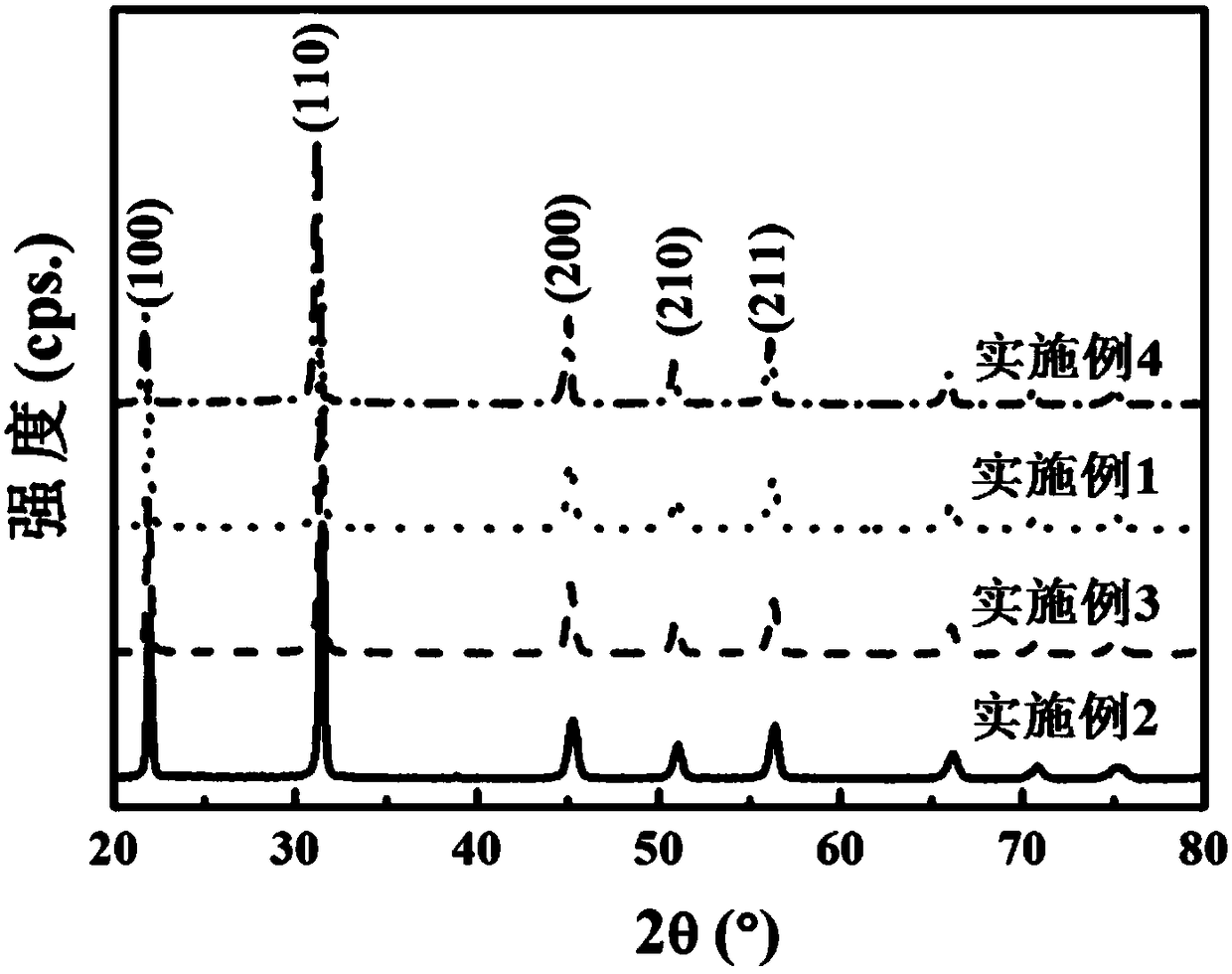
The invention discloses magnesium niobate series crystals, namely a MgO-Ta2O5 pseudo binary system. The magnesium niobate series crystals are Mg4Ta2O9, Mg3Ta2O8 and MgTa2O6, respectively. A method forpreparing the magnesium niobate series crystals is also provided. High-purity MgTa2O6 and Mg4Ta2O9 powders are synthesized by solid phase reaction using excess MgO or Mg(OH)2 component compensation,and the centimeter-scale rod-shaped MgTa2O6 and Mg4Ta2O9 single crystal is grown by a micro-downdraw method. Using Mg4Ta2O9 and MgTa2O6 as melting starting materials, a centimeter-scale rod-shaped Mg3Ta2O8 single crystal is grown on a MgTa2O6 ceramic seed rod by a spontaneous nucleation technique. According to the magnesium niobate series crystals, the micro-downdraw method is adopted, and the high temperature gradient near a growth interface is effectively utilized, to achieve rapid and high uniform crystallization; and a post-heater is effectively utilized to solve the cracking problem caused by excessive thermal stress.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Bismuth magnesium niobate modified potassium sodium niobate transparent ferroelectric ceramic material and preparation method thereof adopting low purity raw materials
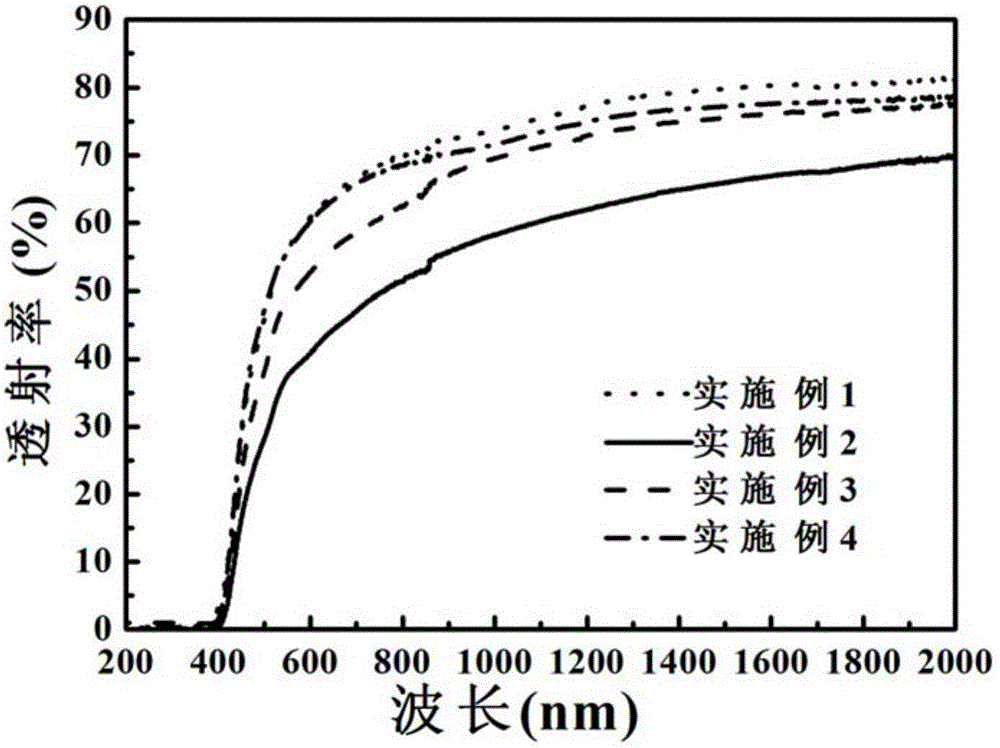
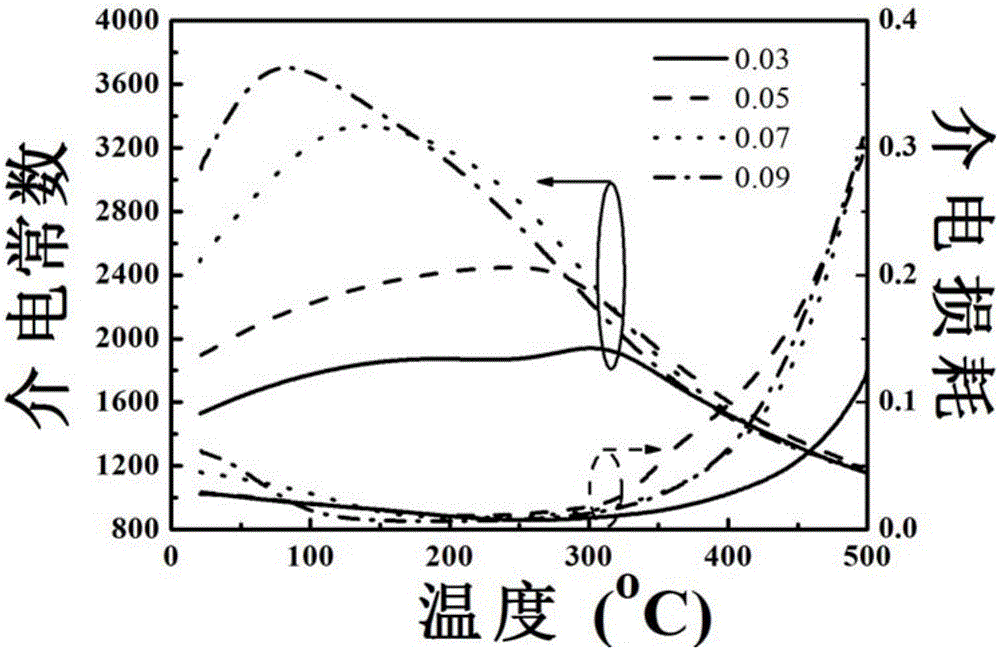
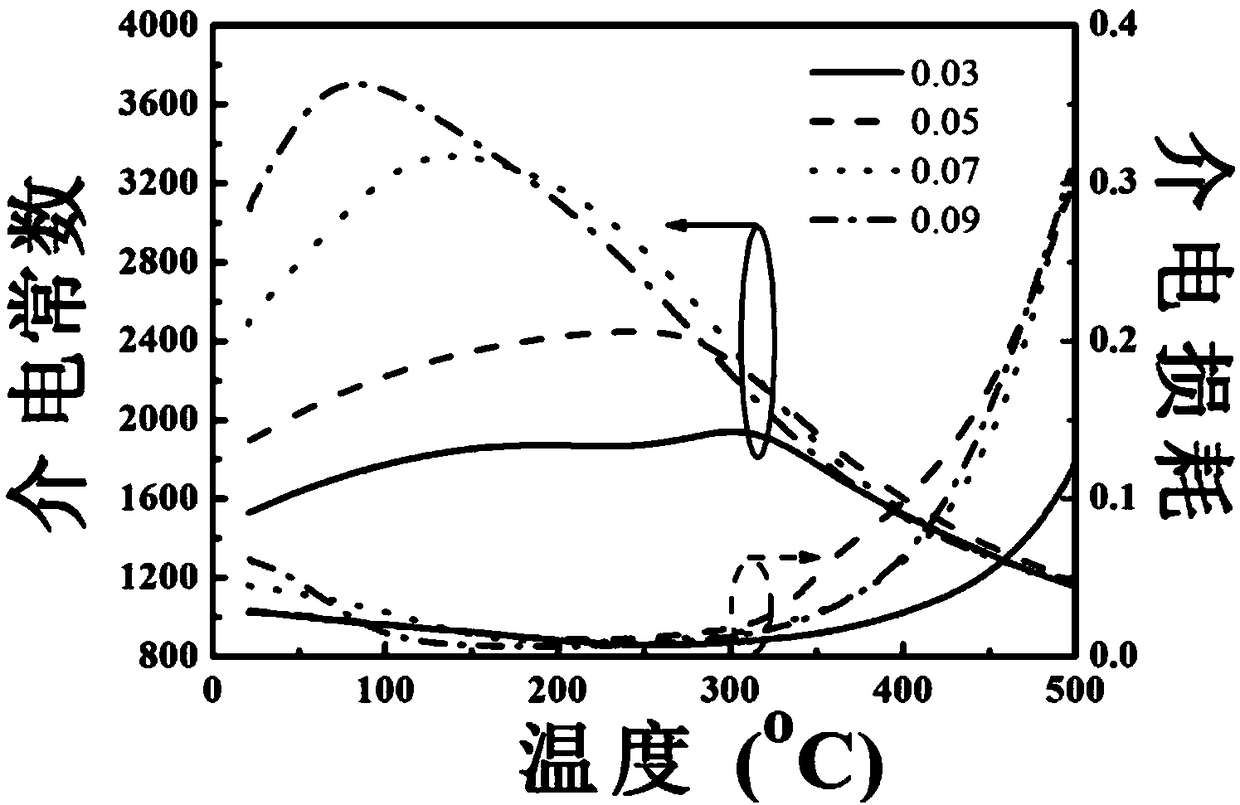
The invention discloses a bismuth magnesium niobate modified potassium sodium niobate transparent ferroelectric ceramic material and a preparation method thereof adopting low purity raw materials. The formula of the ceramic material is (1-x)(K<0.5>Na<0.5>)Nb<3-x>Bi(Mg<1 / 3>Nb<2 / 3>)O3, wherein x represents the mole number of Bi(Mg<1 / 3>Nb<2 / 3>)O3 and is in a range of 0.03 to 0.09. Low purity raw materials are used, the preparation method comprises steps of preparing raw materials, pre-burning, ball-milling, granulating, pressing, rubber discharging, pressure-free sealed sintering, polishing, and silver ink firing; the ceramic material has the advantages of high light transmission, optical isotropy, strong practicality, and easy production, moreover, the preparation method is simple, the repeatability is good, and the yield is high. The test results show that when x is equal to 0.07, the optical transmission rate of the ceramic material is 70% or more in the visible light and infrared areas, at the same time, the ceramic material has good electric properties: the maximal dielectric constant is 3337, the dielectric loss is less than 3%, the remnant polarization is 1.5 [mu]C / cm2, and the coercive field is 7.0 kV / cm.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Strontium magnesium niobate doped modified sodium bismuth titanate-based energy storage ceramic material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111978082AImproved breakdown fieldAvoid it happening againFree energiesSodium bismuth titanate
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
Method of preparing magnesium-niobate
InactiveCN101367552APrevent volatilizationShort reaction timeNiobium compoundsChemical reactionLead oxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing magnesium niobium oxide, which comprises the following steps: magnesium oxide (MgO) is mixed with niobium pentaoxide (Nb2O5) according to the dose of the mole ratio of 1:1, and the mixture is arranged inside a screw grinding machine to be ground for 6 to 11 hours; or after the magnesium oxide (MgO) is mixed with niobium pentaoxide (Nb2O5) at the same proportional ratio, the mixture is added with de-ionized water that can dip the mixture, and after the mixed solution is ground and uniformly mixed in a mortar, and the mixture is arranged into an oven to be dried until the mixture is slightly dry in the temperature of 80 to 100 DEG C; the slight dried mixture is ground in the screw grinding machine for 5 to 8 hours to get the magnesium niobium oxide with the ordinary chemical formula of MgNb2O6. The prepared magnesium niobium oxide can be reacted with lead monoxide to synthesize the magnesium niobium oxide lead iron electrical material, thus can greatly shorten the reaction time of the synthesis, and also can effectively prevent the volatilization of the lead composition in the reaction process, and can realize the pollution-free chemical reaction. The invention has the advantages of simple craftwork, easy operation, short preparation time, pure material phase, good dispersion, uniform particles, and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
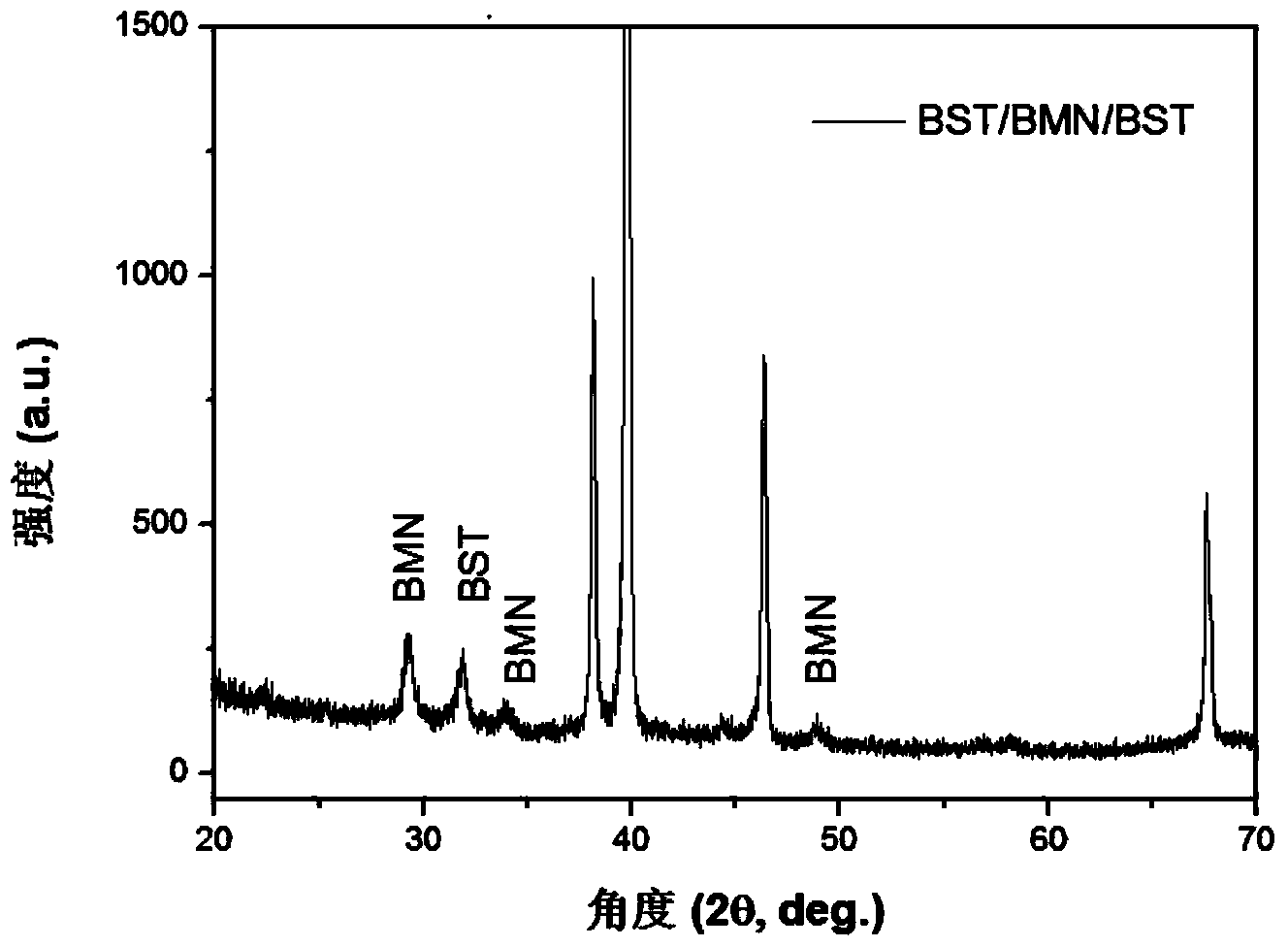
Preparation method of BST(barium strontium titanate)/BMN (bismuth magnesium niobate)/BST multilayer composite film
InactiveCN104029432AImprove performanceSimple processLayered productsTitanium compoundsStrontium titanateBarium strontium titanate
The invention discloses a preparation method of a BST (barium strontium titanate) / BMN / BST multilayer composite film. A layer of BMN dielectric layer with low loss is additionally arranged between two BST films, so that the dielectric loss of the film can be reduced. The method is characterized by comprising the steps: first preparing precursor sol of BST and BMN, then respectively dropping the precursor sol onto a substrate to prepare a corresponding film, carrying out post-annealing on the film at the temperature of 550 to 750 DEG C to obtain the BST / BMN / BST multilayer composite film. The barium titanate, strontium titanate and titanium dioxide are used as raw materials to substitute partial alcohol salt and tetrabutyl titanate, so that the production cost of the film is reduced. The magnesium carbonate is used for substituting the magnesium nitrate hydrate, so that the chemical proportioning is more precise; by adopting a novel improved sol-gel process, the composite film is excellent in performance, simple in process and wide in application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
BMN dielectric film microwave voltage-controlled capacitor preparation method
InactiveCN104064357AHigh quality factor (Q value)Moderate tuning rateCapacitor with voltage varied dielectricDielectricCapacitance
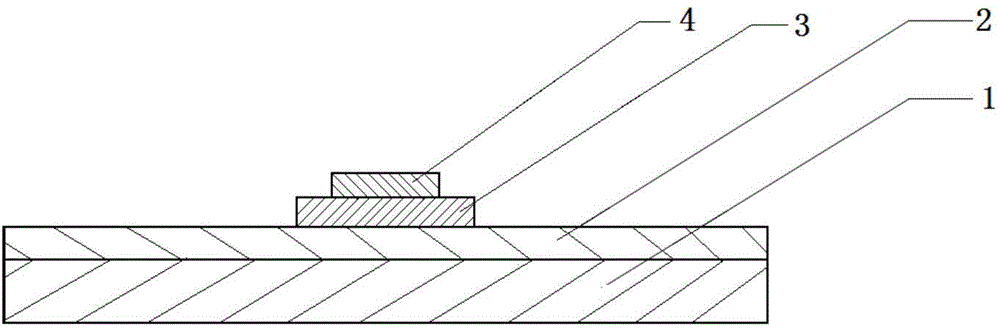
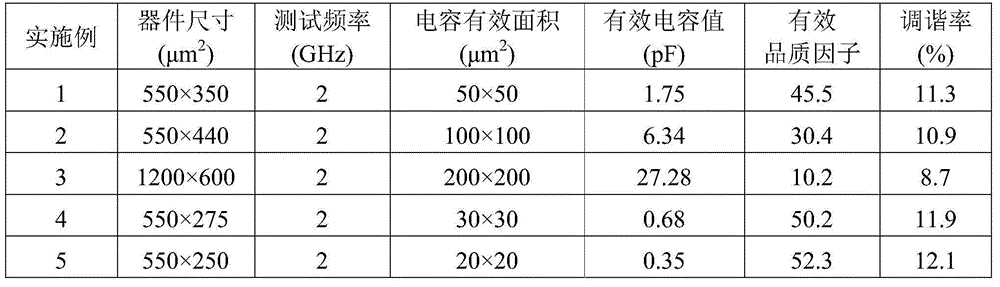
The invention discloses a BMN dielectric film microwave voltage-controlled capacitor preparation method. At first, a bottom electrode is prepared, then a bismuth magnesium niobate dielectric film layer is prepared through the spin-coating and heat treatment method, and then the dielectric film layer is patterned, and a top electrode is prepared on the patterned dielectric film layer; wherein the device size is (550-1200)*(250-600)mum<2>, and the capacitance effectively area is (20-200)*(20-200)mum<2>. The preparation process of the invention is simple and is easy to implement; the prepared product has the advantage of high quality factor (the Q value) in the microwave frequency band, and advantages of moderate tuning rate and good device stability can be realized, and a good device basis is provided for the development and application of a modern microwave communication system.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation for magnesium niobate microwave ceramic powder through sol-gel technology
The invention discloses a method for preparing magnesium niobate microwave ceramic powder through a sol-gel technology. The method comprises the following steps: (1), preparing a citric acid aqueous solution for niobium; (2), preparing a citric acid aqueous solution for magnesium; (3), obtaining a Mg-Nb precursor solution, xerogel and nano-powder. According to the invention, the defects that the magnesium niobate microwave ceramic powder synthesized through a solid phase method at present is high in temperature and large in particle size are overcome, and the magnesium niobate microwave ceramic powder, of which the average particle size is 40-80 nm, is prepared under the condition that the calcination temperature is 550-850 DEG C.
Owner:JINAN WEIBO NEW MATERIAL
Preparation method of bismuth ferrite-lead titanate-bismuth magnesium niobate ternary system high-temperature piezoelectric ceramic
PendingCN113307619ALower sintering temperaturePromote densificationPhysical chemistryPiezoelectric coefficient
The invention belongs to the field of piezoelectric ceramic materials, and particularly relates to a preparation method of bismuth ferrite-lead titanate-bismuth magnesium niobate ternary system high-temperature piezoelectric ceramic. The chemical formula is (1-x-y) BiFeO3-xPbTiO3-yBi (Mg2 / 3Nb1 / 3) O3, x and y are molar weights, and x is more than or equal to 0.20 and less than or equal to 0.40; 0.01 < = y < = 0.10; the auxiliary component is mBi2O3 + nPbO + zMnO, m, n and z are the mass percent of the total formula, and m is larger than or equal to 0 and smaller than or equal to 0.10; 0 < = n < = 0.10; 0 < = z < = 0.10. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, weighing the raw materials; s2, carrying out primary ball milling; step S3: drying; s4, performing solid-phase synthesis; step S5, carrying out secondary ball milling; step S6, granulating and forming; step S7, glue discharging; step S8; and step S9. The sintering temperature of a system can be reduced, ceramic densification is promoted, cracking and pulverization are avoided, the ceramic has the good sintering characteristic, the c / a ratio of the system is reduced, the material is easy to polarize, the ceramic obtains the large piezoelectric coefficient under the condition that the high Curie temperature is guaranteed, the insulativity and temperature stability of the material are improved, and the service life of the material is prolonged. And practical application of devices at high temperature is facilitated.
Owner:XIAN INT UNIV
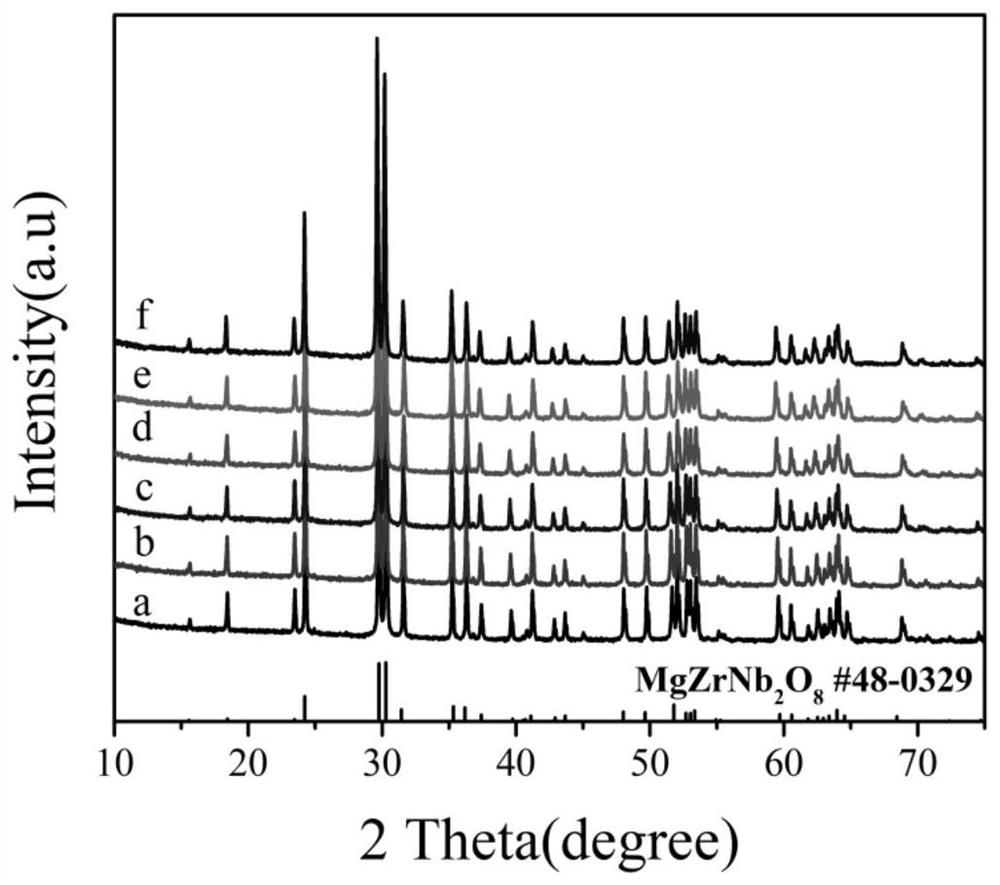
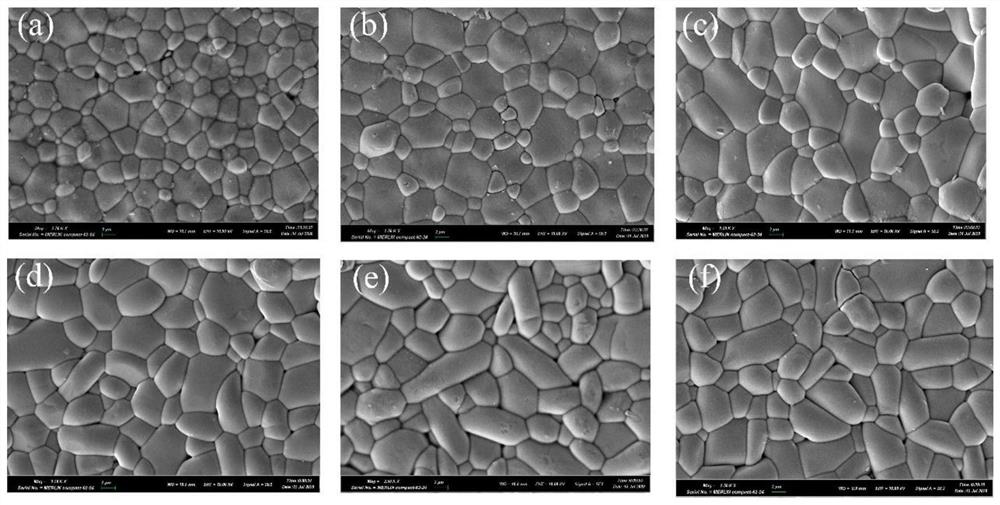
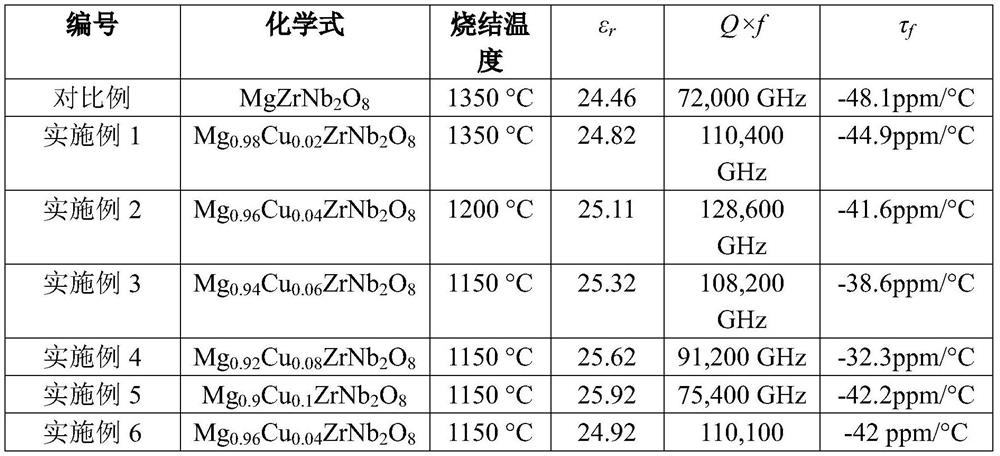
Ultralow-loss zirconium magnesium niobate system microwave dielectric ceramic material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112851346AHigh densityReinforcement energy and key energyChemical industryCeramicMagnesium niobate
The invention provides an ultralow-loss zirconium magnesium niobate system microwave dielectric ceramic material and a preparation method thereof, the chemical general formula is Mg1-xCuxZrNb2O8, x is more than 0 and less than or equal to 0.1, and the crystal phase is pure phase MgZrNb2O8; the microwave dielectric ceramic material is prepared from MgO, CuO, ZrO2 and Nb2O5 according to the general chemical formula of Mg (1-x) CuxZrNb2O8 according to certain stoichiometric ratio, wherein 0<x<=0.1; after first ball-milling and mixing, pre-sintering is carried out for 2-6 hours at the temperature of 1000-1100 DEG C, after ball-milling and mixing for the second time, granulating, forming, and sintering are carried out for 2-6 hours at the temperature of 1150-1350 DEG C to obtain the product. According to the invention, Mg site in MgZrNb2O8 ceramic is replaced by Cu ions, and a crystal structure is finely adjusted, so that lattice energy and bond energy are enhanced. Cu ion substitution improves the density of the ceramic and increases the grain size, thereby improving the quality factor of the ceramic material.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A strontium niobate magnesium doped modified bismuth sodium titanate based energy storage ceramic material and preparation method thereof
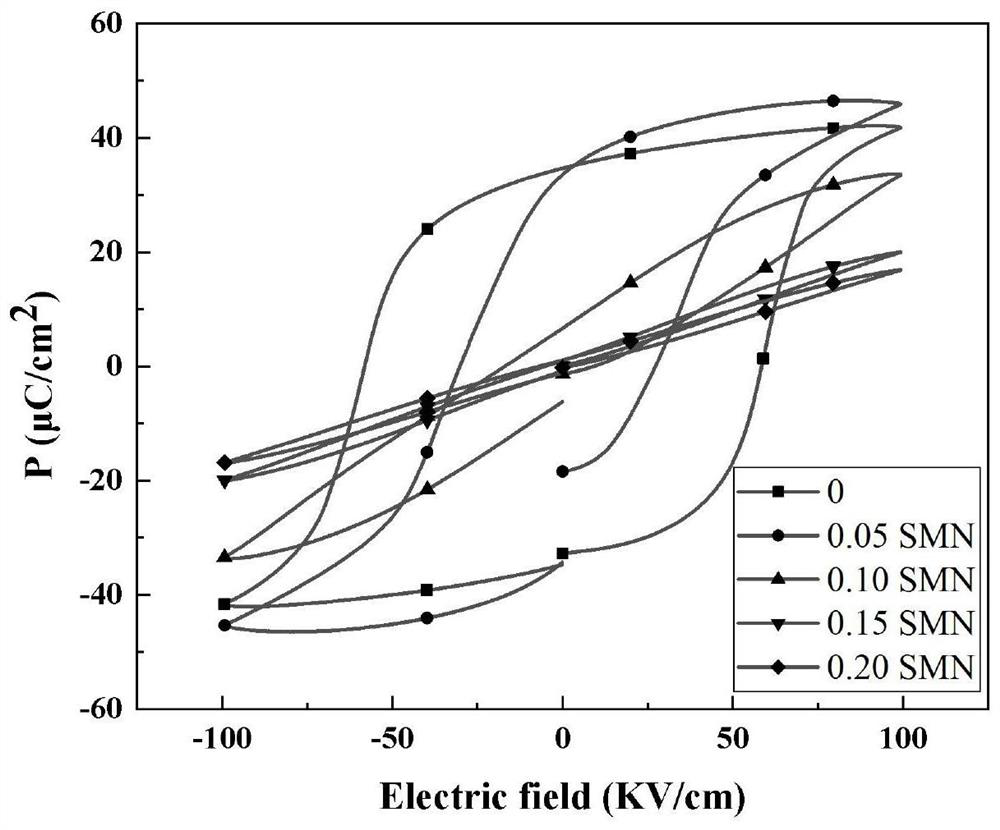
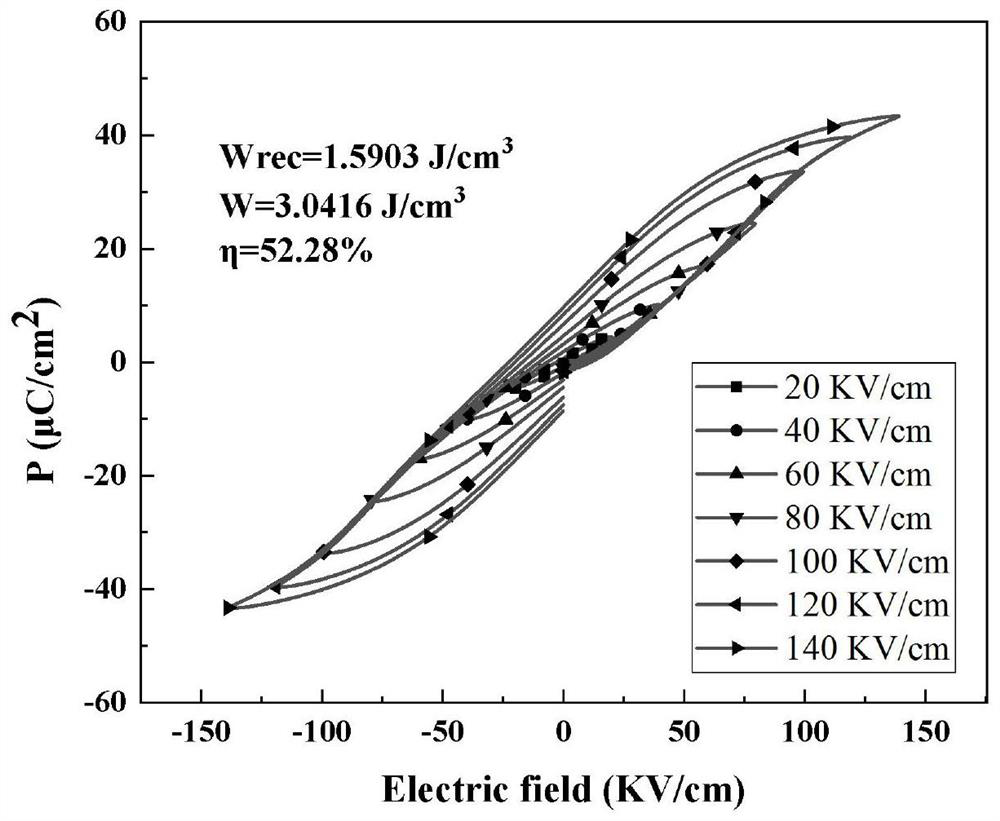
The invention discloses a strontium niobate-magnesium-doped modified bismuth-sodium titanate-based energy storage ceramic material and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the technical field of electronic ceramics; The formula of energy ceramic material is: (1‑x)(Bi 0.5 Na 0.5 )TiO 3 ‑xSr(Mg 0.3334 Nb 0.6666 )O 3 , (wherein 0≦x≦0.20); the present invention adopts the solid phase sintering method, weighs the raw materials according to the stoichiometric formula and mixes them uniformly to form the whole batching; the whole batching is sequentially ball milled, dried, ground and sieved to form the sieved material ; The sieved material was pressed into a sample, and the sample was sintered to successfully prepare energy storage ceramics with small grain size and uniform density. The energy storage ceramics prepared by the method of the present invention can obtain 1.59J / cm at a higher breakdown field strength (140KV / cm) 3 The recyclable energy storage density; and has the advantages of low cost, large output, simple preparation process and green environmental protection, and may become an important candidate material for lead-free energy storage capacitor materials.
Owner:XIAN TECH UNIV
Magnesium columbate microweve medium ceramic and its preparation process
InactiveCN1724464AImprove featuresExcellent microwave dielectric propertiesCeramicsLithium carbonateFluoride
A magnesium niobate ceramic as microwave medium is proportionally from magnesium niobate, V2O5 or VO2 and lithium carbonate (or fluoride or oxide) through proportional mixing, grinding, granulating, shaping and sintering at 900-1050 deg. C. Its advantages are high quality factor and dielectric performance and low sintering temp.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Preparation method of bismuth magnesium niobate nanometer powder
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Europium-doped barium magnesium niobate (BMN) red phosphor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109810705AUniform particle sizeGood chemical stabilityLuminescent compositionsColor rendering indexEuropium
The invention belongs to the field of light-emitting materials, and particularly relates to europium-doped barium magnesium niobate (BMN) red phosphor. The expression is Ba(1-x%)Eux%(Mg1 / 3Nb2 / 3)O3, wherein x is larger than or equal to 0.5 and smaller than or equal to 5. A preparation method comprises the steps: a peroxy-Nb-citric acid solution is prepared; a BMN:Eu precursor solution is prepared through an aqueous solution gel method; and after the BMN:Eu precursor solution is dried and calcined, the BMN:Eu phosphor is prepared. The obtained phosphor is even in particle size distribution and good in chemical stability, can emit red light with the high intensity and the good color purity under stimulation of near ultraviolet, and can be used for solving the problems that a WLED lacks in theefficient red phosphor, consequently the color rendering index is low, and the color temperature is high and is bias towards cold white.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing lead-titanate-lead-magnesium niobate films by pulsed laser deposition assisted by oxygen plasmas
ActiveCN101892522BOptimizing Deposition Growth ConditionsCompact structurePolycrystalline material growthVacuum evaporation coatingHigh energyHigh pressure
Owner:江苏先进无机材料研究院
Lead zirconate titanate-lead tantalum magnesium niobate piezoelectric ceramic material and preparation method thereof
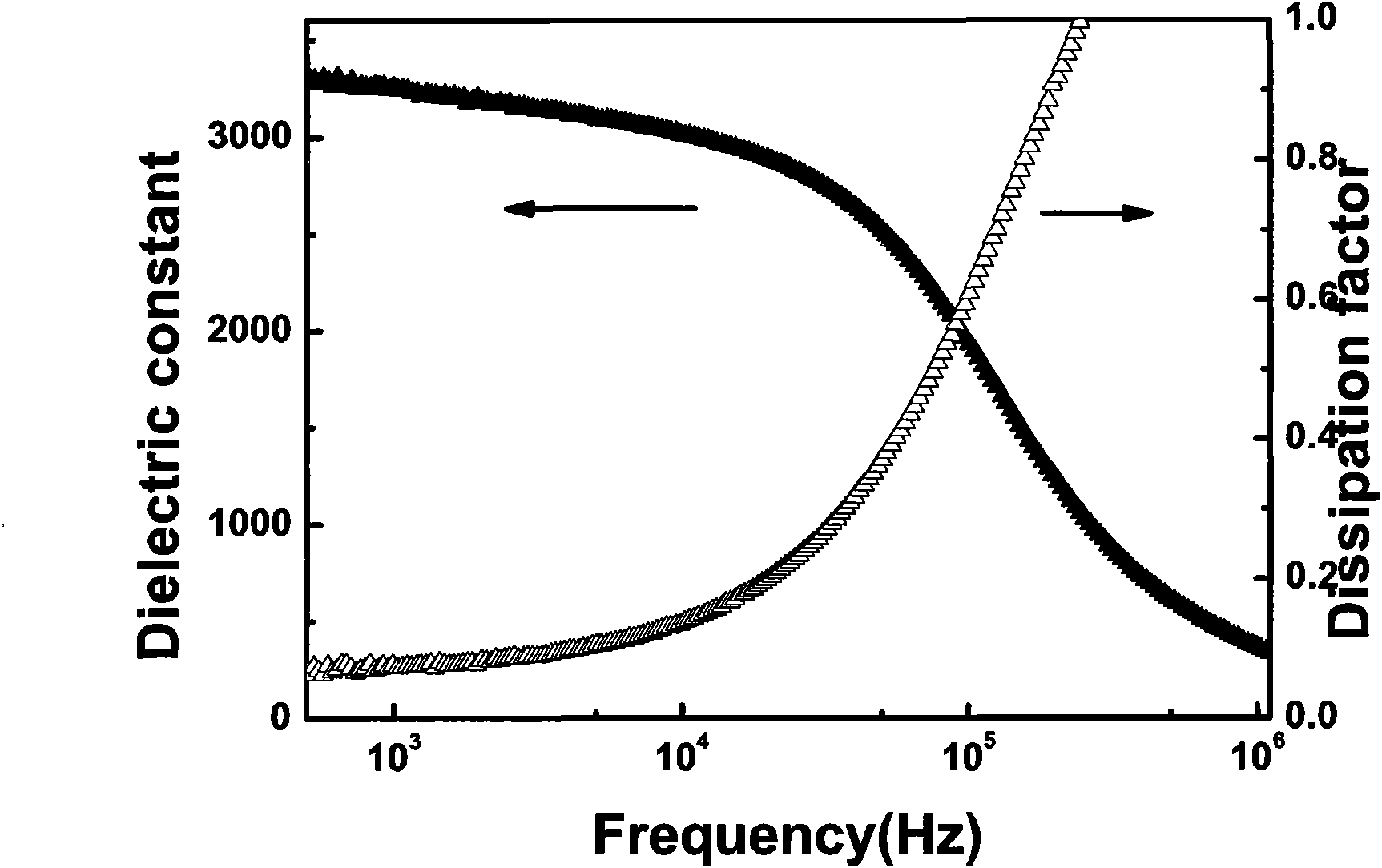
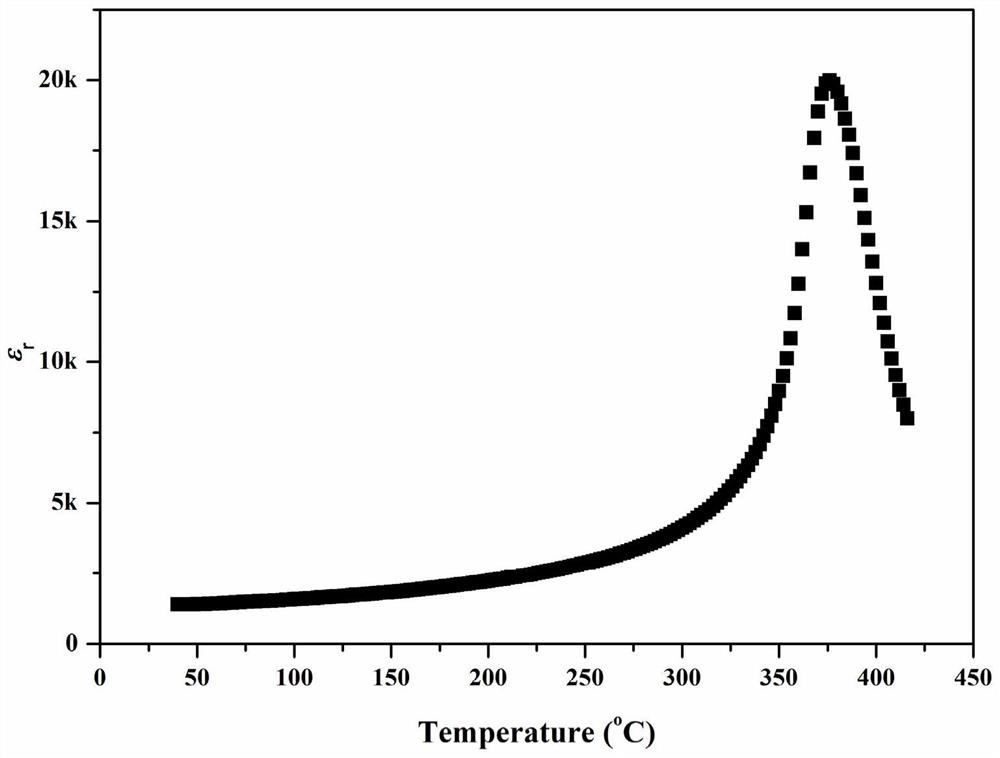
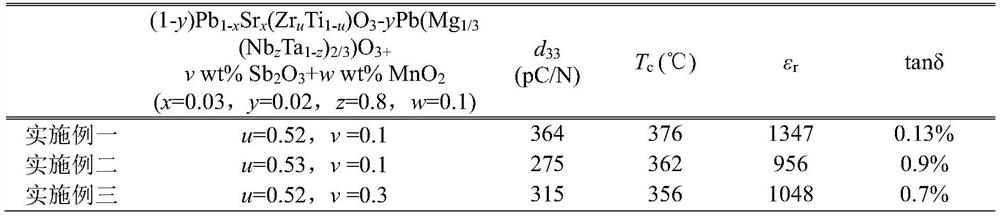
The invention discloses a lead zirconate titanate-lead tantalum magnesium niobate piezoelectric ceramic material and a preparation method thereof, the material takes a lead zirconate titanate Pb (ZruTi1-u) O3 solid solution as a main component, a second component Pb (Mg1 / 3 (NbzTa1-z) 2 / 3) O3 is added, and antimony trioxide Sb2O3 and manganese dioxide MnO2 are doped at the same time; strontium ions are doped at the A site of Pb (ZruTi1-u) O3 to replace part of lead ions; the stoichiometric formula is (1-y) Pb1-xSrx (ZruTi1-u) O3-yPb (Mg1 / 3 (NbzTa1-z) 2 / 3) O3 + v wt% Sb2O3 + w wt% MnO2, x and y are molar ratios, x is more than 0 and less than or equal to 0.3, y is more than 0 and less than or equal to 0.4, z is more than 0 and less than or equal to 0.8, u is more than 0.2 and less than or equal to 0.8, v is more than 0 and less than or equal to 0.4, and w is more than 0 and less than or equal to 0.2. The material has extremely low dielectric loss and dielectric constant, keeps better piezoelectric property, and can greatly reduce energy loss in an electromechanical transformation process. Meanwhile, the material has higher Curie temperature, so that the material has the possibility of being applied in a wider temperature range.
Owner:XIAMEN NIELL ELECTRONICS
A kind of barium magnesium niobate luminescent ceramic and its preparation method
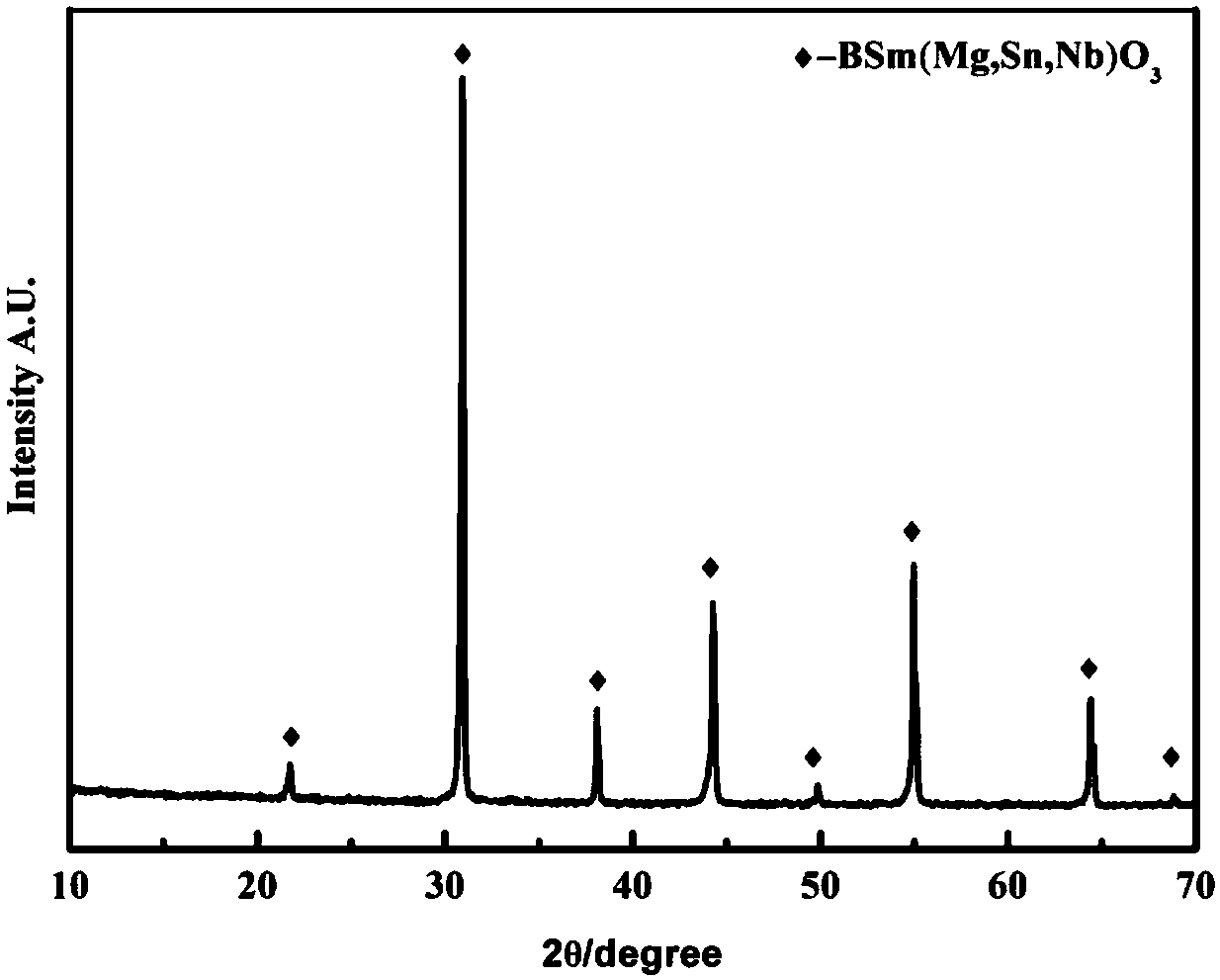
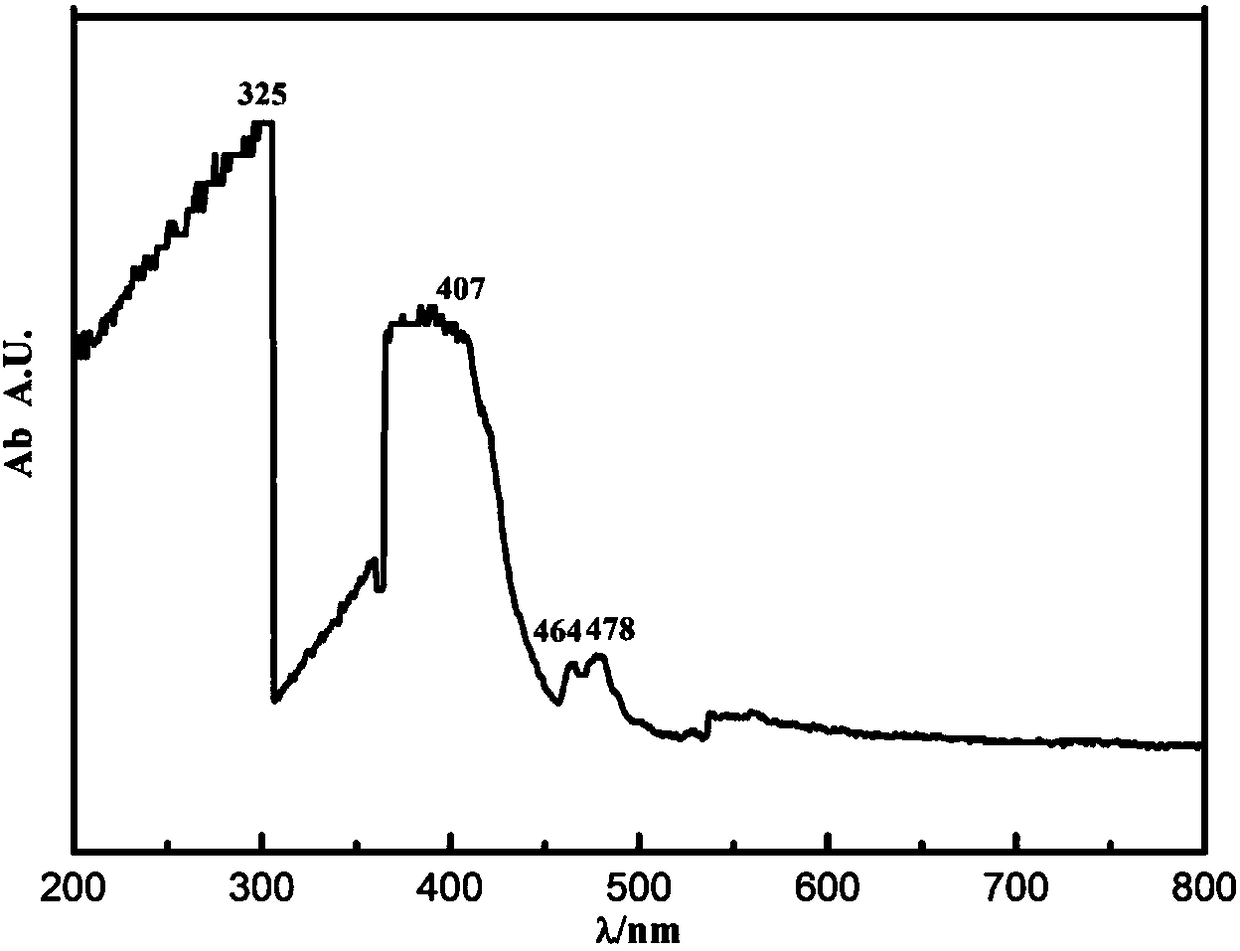
The invention relates to barium magnesium niobate light-emitting ceramics and a preparation method thereof.The formula of the barium magnesium niobate light-emitting ceramics is Ba(1-x)Smx(Sn0.1Mg0.3Mg0.3Nb0.6)O3, wherein 0.005< / =x< / =0.03.The preparation method includes the steps of firstly, performing ball milling on a barium-source compound, a samarium-source compound, a magnesium-source compound, a tin-source compound and a niobium-source compound according to the weight requirements of the formula, then sintering under 1300-1350 DEG C to obtain products, and performing secondary ball milling on the products to obtain ceramic powder; secondly, adding a polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution into the ceramic powder for pelleting, aging, crushing to obtain ceramic particles, forming the ceramic particles to obtain ceramic bodies, and preparing the ceramic bodies into even-pressure ceramic bodies through isostatic cool pressing; thirdly, sintering the even-pressure ceramic bodies under oxygen atmosphere after the even-pressure ceramic bodies discharge glue, cooling along with a furnace, and coarsely polishing and finely polishing to obtain the barium magnesium niobate light-emitting ceramics, wherein sintering temperature is 1500-1600 DEG C, and the temperature is kept for 48-60 hours.The barium magnesium niobate light-emitting ceramics have the advantages that the crystal boundary of the ceramics has no impurity phases, and the ceramics are good in compactness, even in grain size, high in chemical stability, and good in physical performances such as compressive strength; the ceramics have evident absorption peak in the visible light range, the quenching concentration can reach 2%mol, and high light-emitting intensity is achieved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
A multi-source regulated resistive memory with a multi-layer film structure and its preparation method
InactiveCN103811473BSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHeterojunctionElectricity
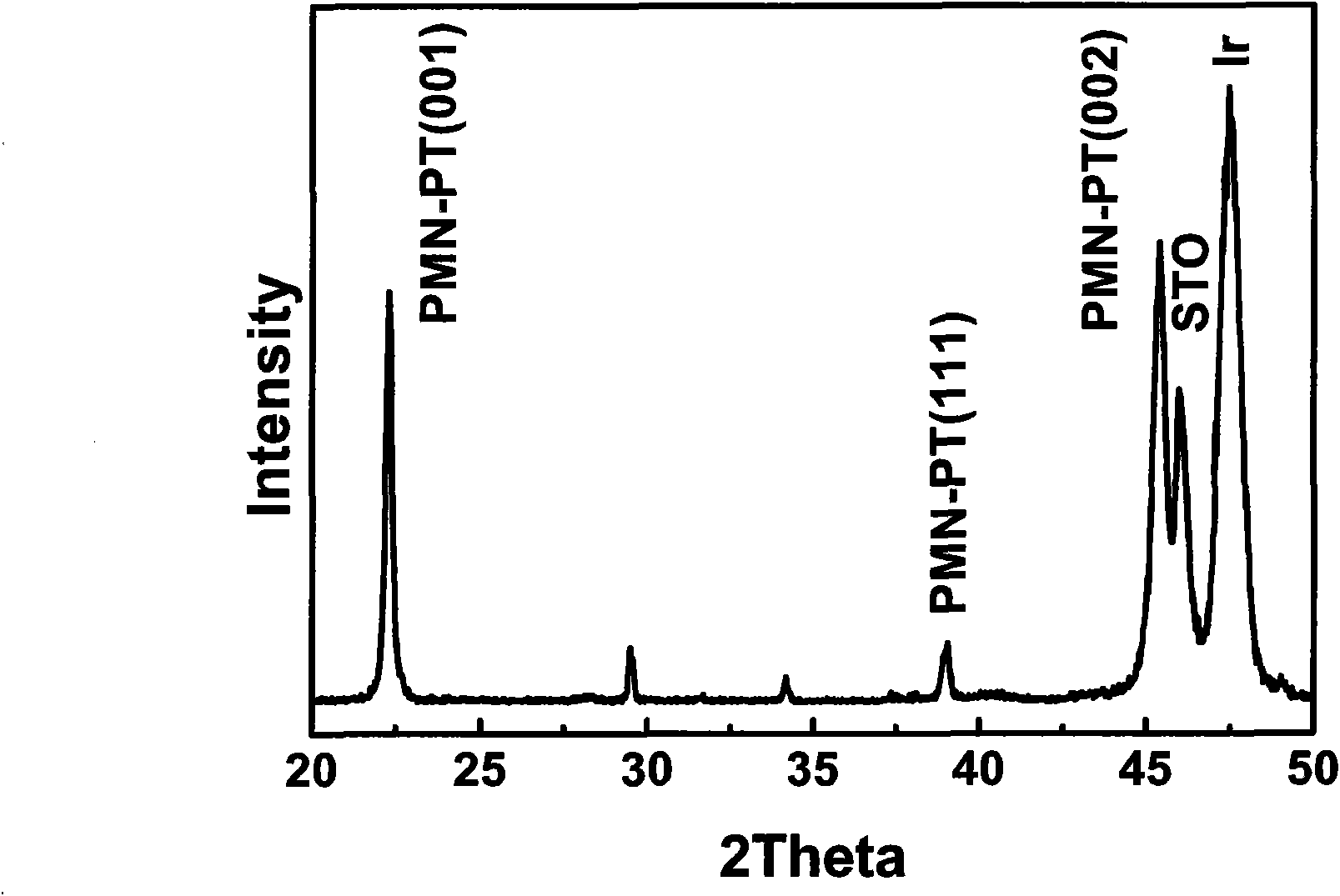
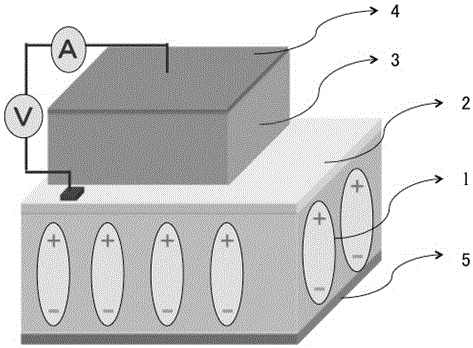
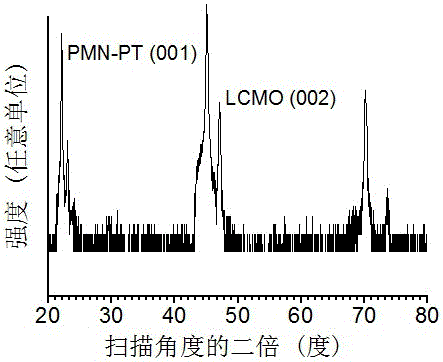
The invention discloses a multi-field controllable resistive random access memory with a multi-layer film structure and a preparation method thereof. The resistive random access memory is composed of a piezoelectric substrate, a conductive lower electrode, a ferroelectric thin film layer, an upper electrode thin film layer and a gate electrode, wherein the piezoelectric substrate is made from a PMN-PT (Plumbum Magnesium Niobate ) single crystal material; the conductive lower electrode is a manganite thin film; the ferroelectric thin film layer is a BaTiO3 or BiFeO3 ferroelectric thin film; the upper electrode layer and the gate electrode are Pt, Au or Al conductive thin films. The preparation method of the memory comprises the steps of depositing the conductive lower electrode thin film layer on the piezoelectric substrate, next, depositing the single ferroelectric thin film layer or a heterojunction, and finally, depositing the upper electrode thin film and the gate electrode. The memory of the structure has excellent electro-resistive effect, and the electro-resistance can be regulated dynamically by virtue of a field effect structure established with the piezoelectric substrate, and therefore, multi-field regulation and control of the resistive state of a memory device are realized and the design flexibility of the memory can be improved; the multi-field controllable resistive random access memory with the multi-layer film structure is significant for increasing the manufacturing quantity of data memory devices in China.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Europium-doped barium magnesium niobate red fluorescent powder and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109810705BUniform particle sizeGood chemical stabilityLuminescent compositionsColor rendering indexEuropium
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Magnesium tantalate series crystals and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108203844BPrevent volatilizationAvoid decompositionPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltSpontaneous nucleationSingle crystal
The invention discloses magnesium niobate series crystals, namely a MgO-Ta2O5 pseudo binary system. The magnesium niobate series crystals are Mg4Ta2O9, Mg3Ta2O8 and MgTa2O6, respectively. A method forpreparing the magnesium niobate series crystals is also provided. High-purity MgTa2O6 and Mg4Ta2O9 powders are synthesized by solid phase reaction using excess MgO or Mg(OH)2 component compensation,and the centimeter-scale rod-shaped MgTa2O6 and Mg4Ta2O9 single crystal is grown by a micro-downdraw method. Using Mg4Ta2O9 and MgTa2O6 as melting starting materials, a centimeter-scale rod-shaped Mg3Ta2O8 single crystal is grown on a MgTa2O6 ceramic seed rod by a spontaneous nucleation technique. According to the magnesium niobate series crystals, the micro-downdraw method is adopted, and the high temperature gradient near a growth interface is effectively utilized, to achieve rapid and high uniform crystallization; and a post-heater is effectively utilized to solve the cracking problem caused by excessive thermal stress.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Potassium sodium niobate transparent ferroelectric ceramic material modified by bismuth magnesium niobate and its preparation method using low-purity raw materials
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
A preparation method of bismuth-based thin film with high tuning rate
InactiveCN104087905BHigh crystallinityGood orientationVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingRutheniumPerformance tuning
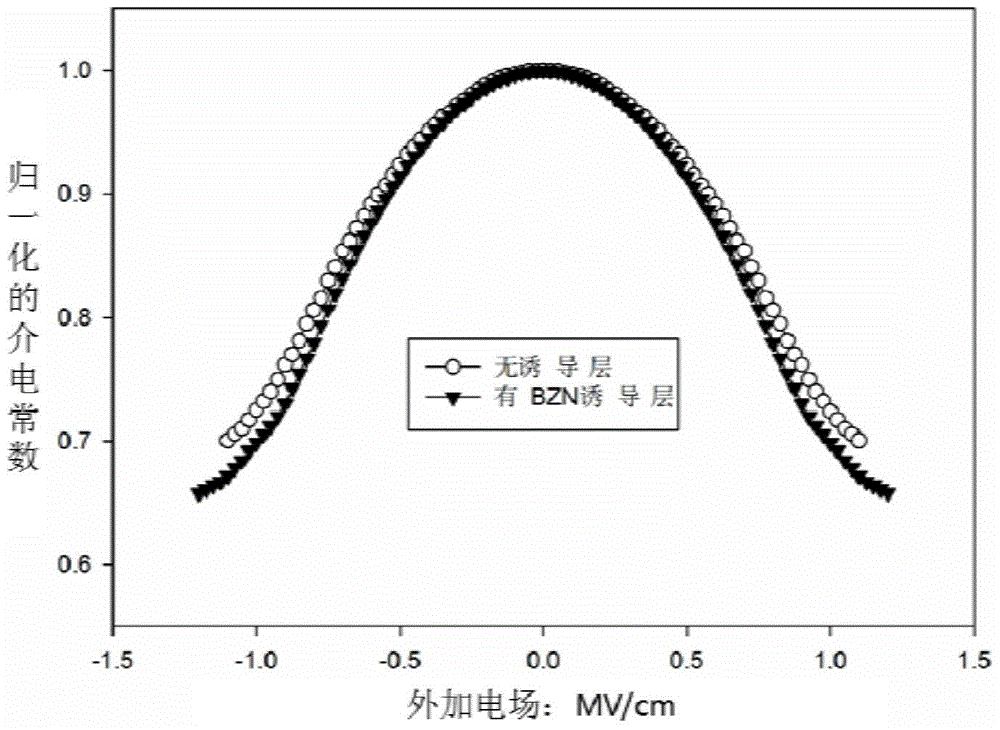
The invention discloses a preparation method of a bismuth-based thin film with a high tuning rate: first, a substrate is cleaned, and then a zinc-bismuth niobate induction layer is prepared on the substrate, and then annealing is performed at 650°C-750°C; Then deposit and prepare the magnesium bismuth niobate thin film layer on the substrate with the zinc bismuth niobate induction layer, and finally anneal at 750° C. to prepare the magnesium bismuth niobate thin film with high tuning rate bismuth base structure. Compared with the prior art, the invention has better crystallinity, significantly improved orientation and tuning performance, and the tuning rate increases from 30% to 35%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for preparing plumbum magnesium niobate-plumbum titanate ferroelectric film
InactiveCN101956166BSimple preparation processGood repeatabilityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingFerroelectric thin filmsPerovskite (structure)
The invention belongs to the field of ferroelectric film materials and relates to a method for preparing a plumbum magnesium niobate-plumbum titanate (PMN-PT) ferroelectric film. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, preparing a PMN-PT ceramic target; secondly, cleaning a silicon (Si) substrate; thirdly, preparing a LaNiO3 conductive buffer layer; and finally, preparing the PMN-PTferroelectric film. The method for preparing the PMN-PT ferroelectric film has the advantages of simple process, high repeatability, capacity of preparing the large-area PMN-PT film with pure perovskite structure preferred orientation on a cheap silicon substrate with an actual application value, compatibility with a Si integrated process, low preparation cost and contribution to mass production of devices. The prepared film has the advantages of high ferroelectric properties and suitability for ferroelectric-semiconductor integrated devices.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Magnesium Removal From Magnesium Reduced Metal Powders
A method of producing a refractory metal powder that includes providing a metal powder containing magnesium tantalate or magnesium niobate; and heating the powder in an inert atmosphere in the presence of magnesium, calcium and / or aluminum to a temperature sufficient to remove magnesium tantalate or magnesium niobate from the powder and / or heating the powder under vacuum to a temperature sufficient to remove magnesium tantalate or magnesium niobate from the powder, the heating steps being performed in any order. The metal powder can be formed into pellets at an appropriate sintering temperature, which can be formed into electrolytic capacitors.
Owner:H C STARCK INC
Preparation method of transparent magnesium bismuth niobate film voltage-controlled varactor
InactiveCN103397303BHigh transparencyModerate tuning rateVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingIndiumMetal electrodes
The invention discloses a preparation method of a voltage-controlled varactor made of transparent bismuth magnesium niobate thin films. The preparation method comprises following steps: Bi1.5MgNb1.5 O7 target material is prepared by solid state sintering method, wherein the firing temperature is 1150 to 1180 DEG C; a clean and dry indium tin oxid glass substrate is placed on a magnetron sputtering sample stage, Ar and O2 are used as sputtering gases, the Bi1.5MgNb1.5 O7 thin films are obtained by deposition, and then the Bi1.5MgNb1.5 O7 thin films are added into a furnace in oxygen atmosphere for post-annealing treatment; and metal electrodes are prepared on the Bi1.5MgNb1.5 O7 thin films by using mask version. Transparency of the varactor is high; tunability is moderate, device stability is high, preparation technologies are simple, electrode performances are excellent, no heavy metal poisoning or pollution is caused in preparation processes, and application prospect is promising.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com