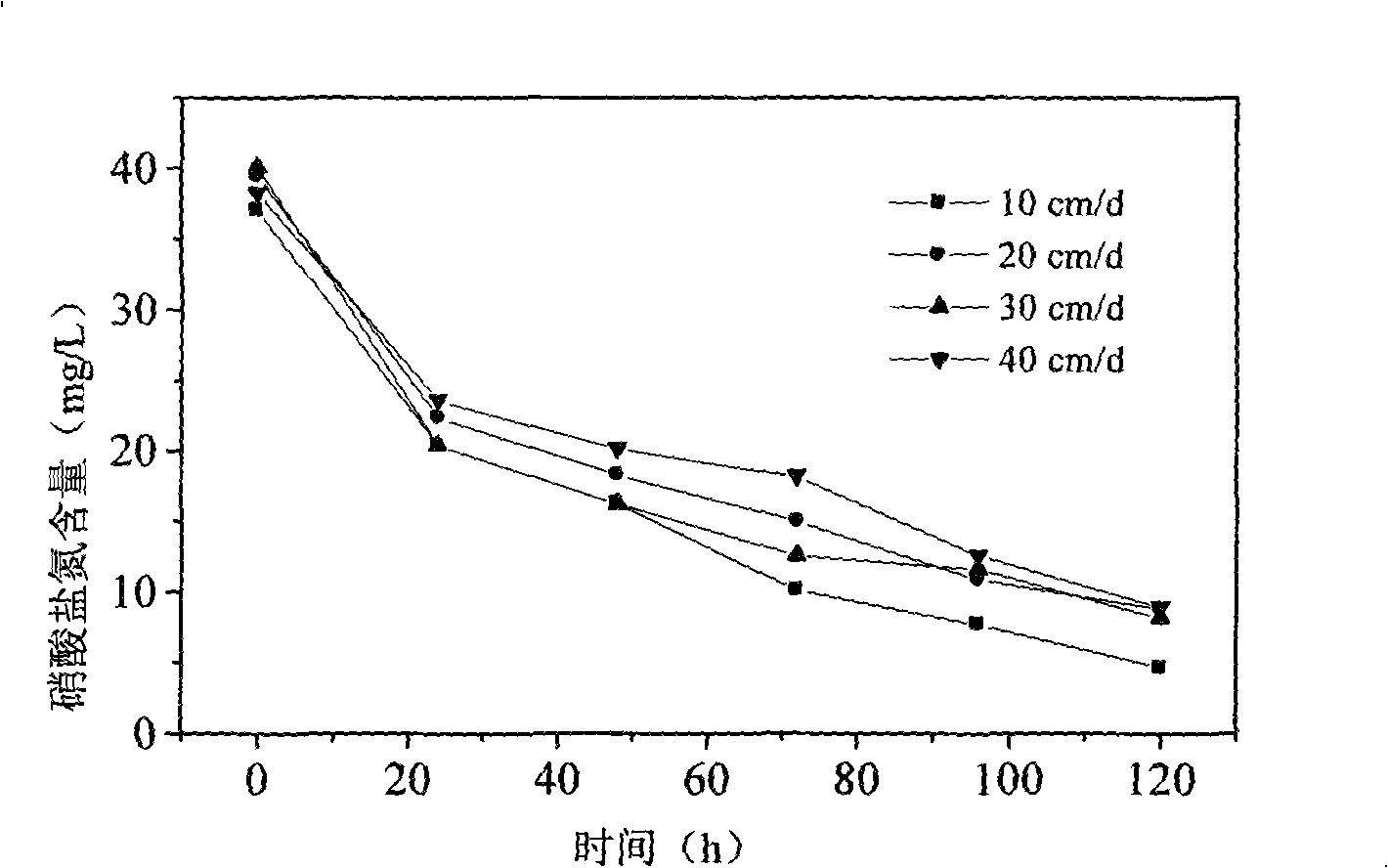
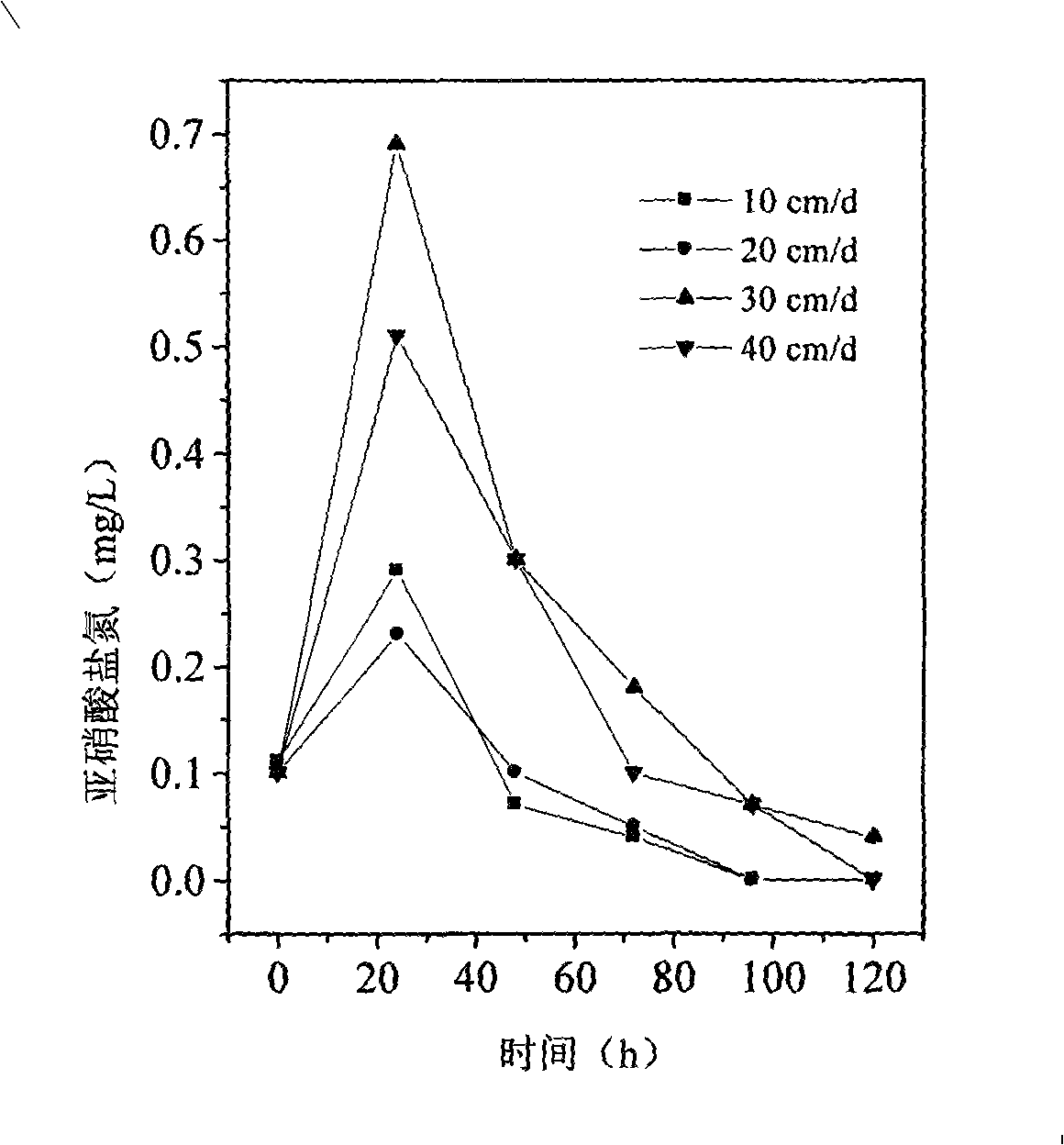
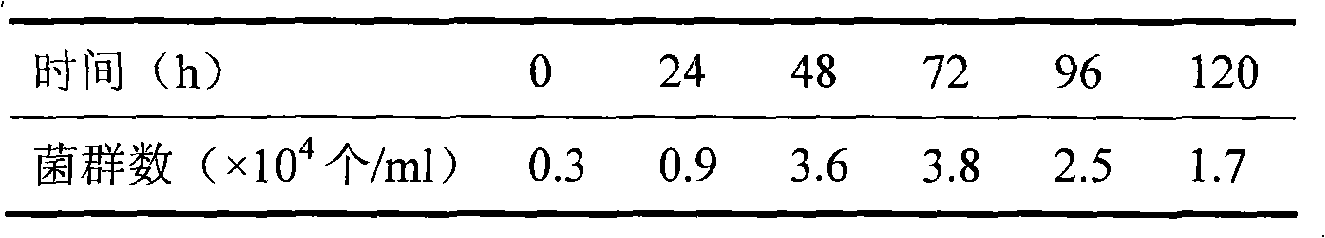
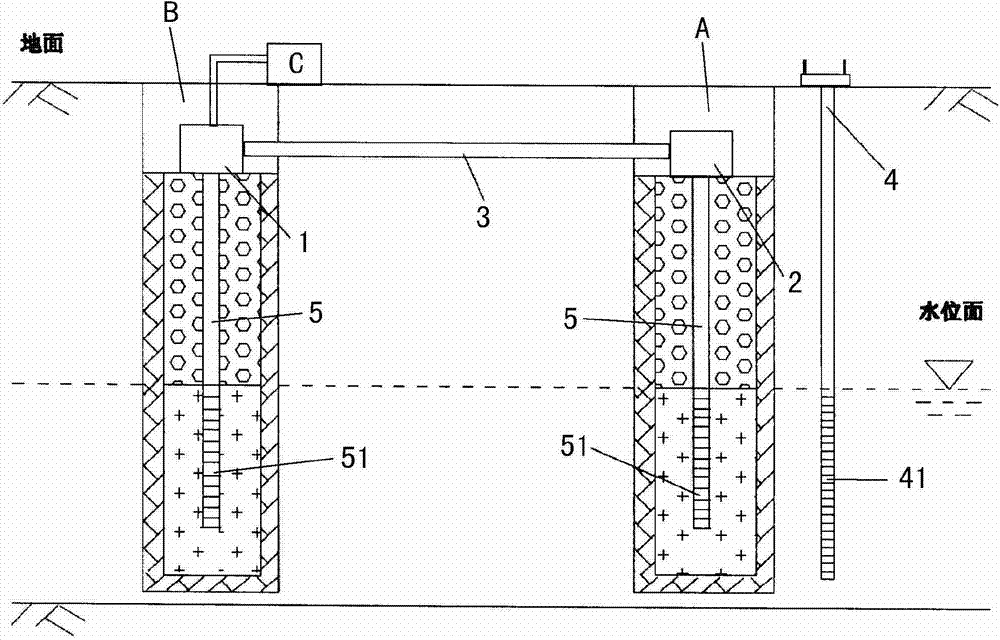
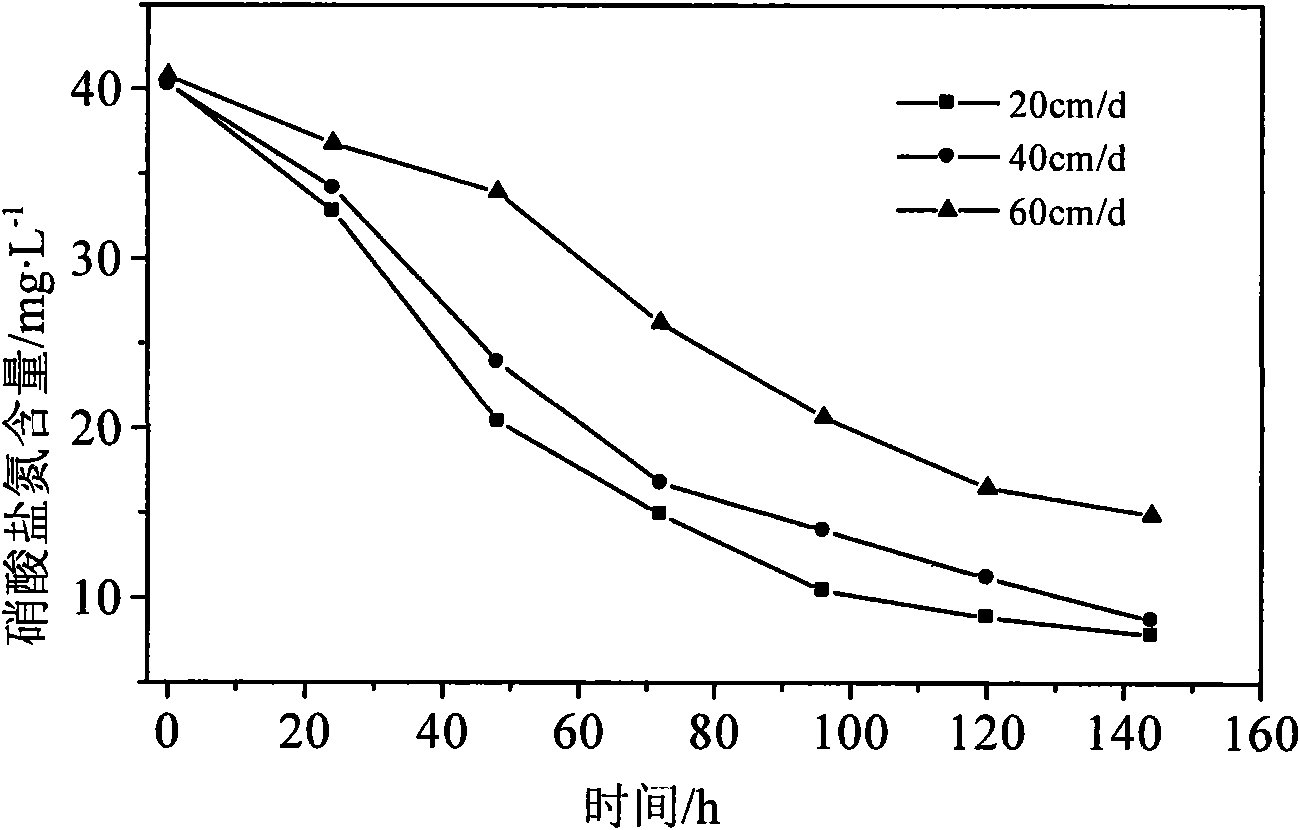
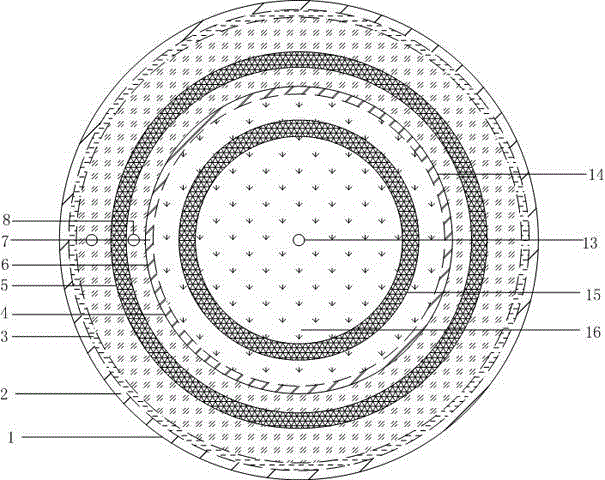
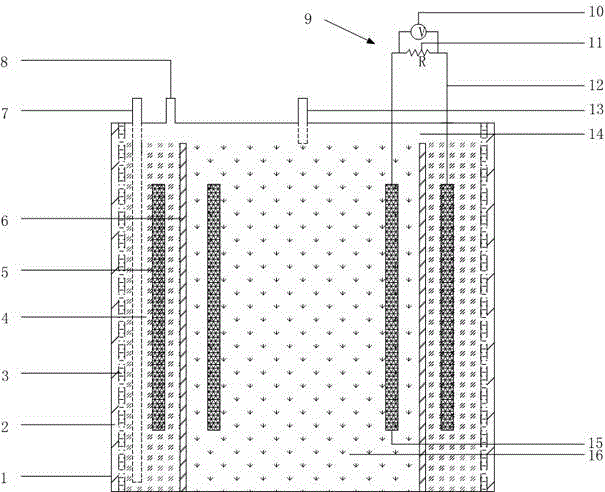
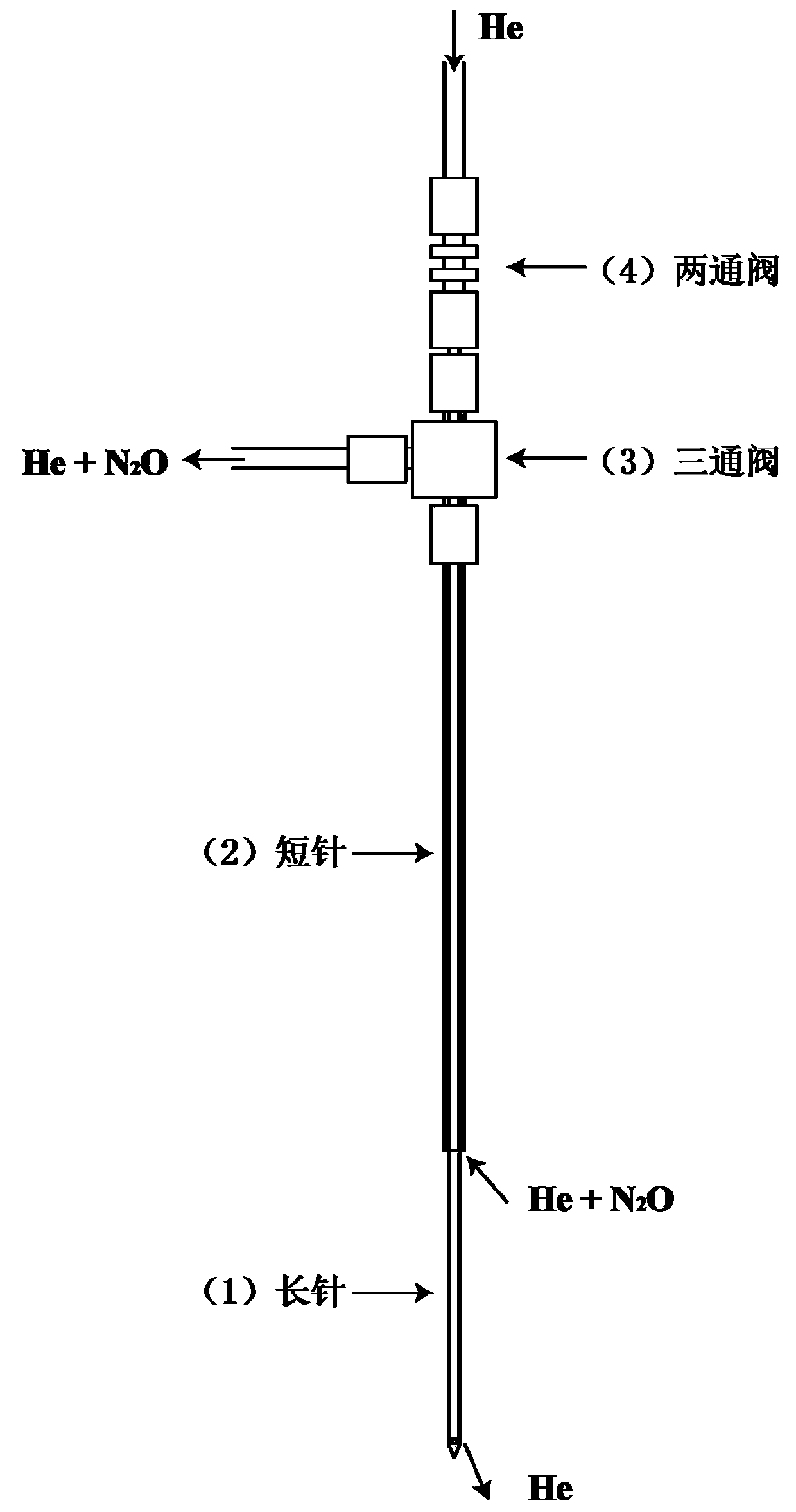
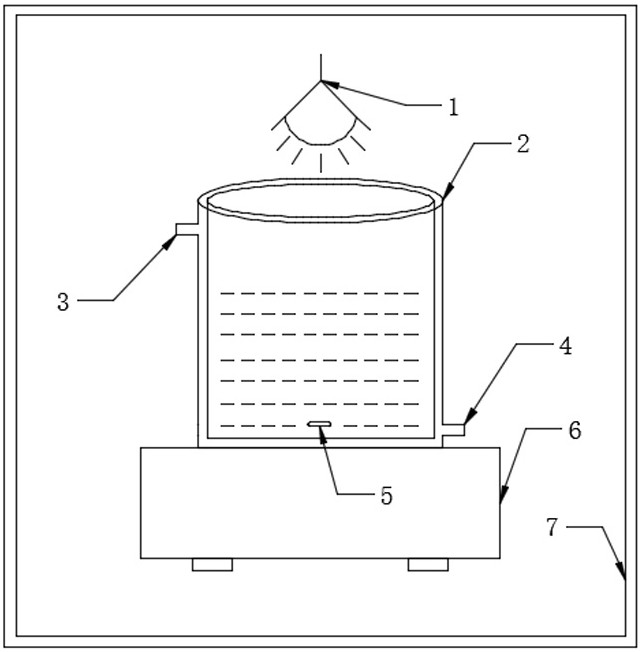
Patents
Literature
70 results about "Nitrate pollution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nitrate pollution. Water contamination caused by the presence of excessive amounts of nitrates washed out from inorganic fertilizers (the ones most commonly sold and used). These compounds cause eutrophication and are suspected in instances of blood poisoning in infants and stomach cancer in older persons.
Method for in situ restoring groundwater azotate pollution with corn stalk
InactiveCN101492206ASolve pollutionSolve the use problemTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesGroundwater nitrateHydrolysate
The invention relates to a method for remedying the nitrate pollution of underground water in situ with maize straws, which is characterized in that maize straws or a maize straw hydrolysate serving as a denitrification carbon source and flora-enriched liquid rich in denitrifying bacteria florae are added in nitrate polluted underground water to remove nitrate nitrogen from underground water through bio-denitrification. The method realizes the harmless use of biomass maize straws and remedies the nitrate pollution of underground water effectively.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Carbon source carrier filler for repairing nitrate pollution of underground water
InactiveCN102689982AAvoid churnAvoid missingWater contaminantsTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesGroundwater nitrateTrace element
The invention provides a carbon source carrier filler for repairing nitrate pollution of underground water. The carbon source carrier filler is formed by cladding biological ceramsite surface with an organic carbon source coating. The coating of the carbon source carrier filler comprises the following main components of: by weight, 10-50% of a natural carbon source material powder, 10-20% of a solvent, 1-5% of trace element, 10% of animal glue, 0-5% of a deoxidant, 0-5% of a pH conditioning agent and 0-2% of a surfactant. The carbon source carrier filler prepared in the invention has good mechanical properties and biological endophilicity, can achieve the aim of long-acting sustained release of carbon source, is suitable for underground water in-situ and ex-situ remediation technologies, and can be used to effectively avoid the secondary pollution problem of additional carbon sources.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Catalyst for photocatalysis and degradation of benzene and nitrates
InactiveCN101385981APromote degradationAbility to increase nitrateWater/sewage treatment by irradiationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsBenzeneNitrate
The invention discloses a catalyst which can optically catalyze and degrades benzene and nitrate, a preparation method and application of the catalyst. The catalyst is dual-metal A-B-TiO2-typed catalyst carried by TiO2; wherein, metal A is Pd, Pt or Au; metal B is Cu, Ag or Ni. The preparation method comprises the steps as follows: TiO2 is added into solution of A salt or B salt, dipped and dried by steaming; the catalyst is subsequently gained by a reduction method under the conditions of H2 and high temperature. The invention takes TiO2 carried by dual metals as catalyst; when the optical catalysis is carried out, the benzene and nitrate pollutant in water can be degraded; the operation is simple, the raw material is easily gained, furthermore, the catalyst has no secondary pollution, the disposal effect is obvious and the catalyst has wide application prospect in micro-polluted water disposal field.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
In-situ remediation method for nitrate pollutions in groundwater
ActiveCN104129850AReduce solubilityDoes not change the compositionTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesContaminated groundwater/leachate treatmentParticulatesAnaerobic microorganisms
The invention discloses an in-situ remediation method for nitrate pollutions in groundwater, which is characterized by comprising the steps of crushing low-grade siderite ores, and screening the obtained object so as to obtain particles with a particle size of 0.1-1 mm; excavating a groove in an aquifer perpendicular to the flow direction of groundwater, and filling the siderite particles into the groove so as to build an underground permeable wall; and injecting nitrate-dependent iron oxidizing bacteria liquid for oxidizing siderites and reducing nitrates in the presence of iron oxidizing bacteria of anaerobic microorganism depended nitrates. New iron oxides also have a function of absorbing other pollutants in purified water.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for culturing denitrifying bacterium and determining water body nitrate nitrogen isotope composition
ActiveCN102732466AGood effectReduce the cost of trainingBacteriaMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCulture fluidIsotope
The invention relates to the technical field of water body nitrate pollution treatment and control, and is a method for culturing a denitrifying bacterium and using the bacterium to determine water body nitrate nitrogen isotopic composition. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out enrichment culture of the denitrifying bacteria, (2) detecting whether the denitrifying bacteria completely converse NO3- in a culture fluid, (3) concentrating of the denitrifying bacteria, (4) adding the concentrated cell culture to a sample bottle, purifying an upper space and removing N2O in the denitrifying bacterium liquid, (5) conversing NO3- in the sample to N2O, (6) determining the N2O nitrogen isotope, and (7) correcting the nitrogen isotope determination result to complete the test. The positive effects of the invention are as follows: the culture of the denitrifying bacteria can be completed by using only a common saline bottle or a triangular flask, the detection of sulfanilamide color development improves the reliability of the determination result, and the determination cost is reduced. For the current situation that severe water body nitrate pollution is urgently needed to be treated, the method of the invention has the advantages of scientificalness, simplicity, and high maneuverability, and has a broad popularization prospect.
Owner:INST OF ENVIRONMENT & SUSTAINABLE DEV IN AGRI CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Device and method for repairing underground water nitrate pollution
InactiveCN102923838AImprove permeabilityStrong water storage functionBiological water/sewage treatmentGroundwater nitrateFilling materials
A device for repairing underground water nitrate pollution mainly comprises a pumping well and at least one water injection well, wherein a water suction pump is installed in a well pipe of the pumping well, a boosting pump is installed at the top of a well pipe of the water injection well, and the well pipe of the water injection well is connected with a pipeline for conveying carbon sources; well sieves are installed on the parts of the well pipes of the pumping well and the water injection well under the water level; a water conveying pipeline is connected between the water suction pump and the boosting pump; and the well pipes of the pumping well and the water injection well are respectively installed in respective protecting walls with pores of the pumping well and the water injection well, and filling materials are filled between the well pipes and the protecting walls to form a permeable reaction wall. The invention further discloses a method for repairing underground water nitrate pollution by utilizing the device.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Organism remediation method of underground water nitrate pollution for solving nitrite accumulation problem
InactiveCN102690012AComplete denitrificationReduce disruptionWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesGroundwater nitrateNitration
The invention relates to a method for remediating nitrate pollution in underground water, and the advantage of the method lies in that nitrite accumulation problem caused by conventional microorganism remediation methods is solved. According to the method, a biological reaction wall portion and an aerobic well portion are comprised. The biological reaction wall consists of a solid-phase carrier medium serving as an organic carbon source that can slowly release organic carbon and oxygen capturing agent. The aerobic well is filled with solid filler that can slowly release oxygen, or a suspension of a medium that slowly release oxygen is poured into the aerobic well. The oxygen is released into underground environment by using the aerobic well, so that dissolved oxygen in the environment is improved. Nitration is carried out under an aerobic condition, so that accumulated nitrite is converted into a small mount of nitrate again. The method effectively solves the problem of excessive nitrite in effluent, nitrate content in the final effluent is small, and the concentration of the nitrate in the final effluent is lower than the III classification standard in Quality standard for ground water GB / T 14848-1993, so that no secondary pollution on the underground water will happen.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Isotope and dating combined shallow groundwater nitrate source analysis method
ActiveCN111272960AQuick identificationAccurate identificationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansTesting waterGroundwater nitrateSoil science
The invention provides an isotope and dating combined shallow groundwater nitrate source analysis method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) setting a monitoring sampling point and a background value sampling point according to environmental characteristics of a determination area; and (2) monitoring the age of the underground water by using an isotope dating method, and carrying out qualitative identification and quantitative analysis on the nitrate source of the underground water in combination with a nitrogen-oxygen stable double isotope tracing method, research area land utilization and pollution source information. According to the invention, underground water dating and isotope tracing methods are creatively combined. A pollution source can be quickly and accurately identified, the isotope method has the advantage of being slightly influenced by the concentration change of water environment factors, and meanwhile, the average residence time of the underground water ismeasured and compared with the formation time of the pollution source to trace back the industry category which may cause potential pollution, so that the nitrate pollution of the underground water isquickly and accurately traced back.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Permeable reaction medium material for nitrate pollution of underground water
ActiveCN103803704AReduce dissolved oxygen contentCause secondary pollutionTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesContaminated groundwater/leachate treatmentGroundwater nitrateWater quality
The invention relates to a permeable reaction material for nitrate pollution of underground water. The permeable reaction medium material consists of quartz sand, denitrifying bacteria, chitosan, CaCl2, sodium alginate, coated nano iron and a Na2HPO4-NaH2PO4 buffering solution with the pH value of 7 at a mass ratio of (1-3):(0.1-0.5):(1-3):(1.5-3):(0.5-1):(0.5-1.5):50. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the permeable reaction material. By adopting the permeable reaction medium material, not only can the carbon source be released for the growth of microorganisms, but also the reducing environment of the underground water can be enhanced, the denitrifying rate is increased, the water quality is purified, and the secondary pollution problem of the nitrate reduction product can be effectively avoided.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
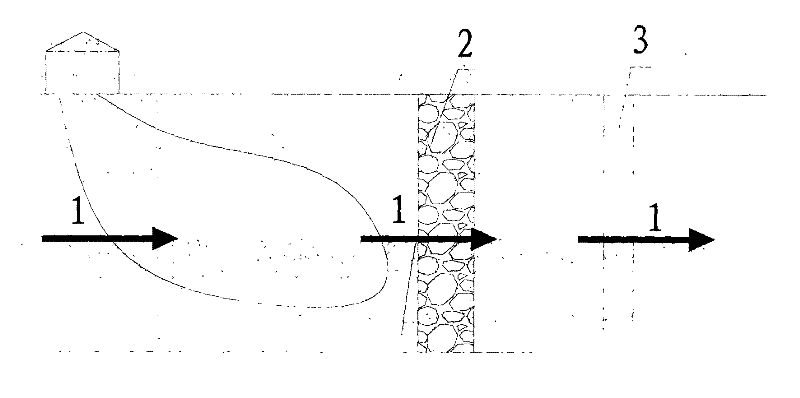
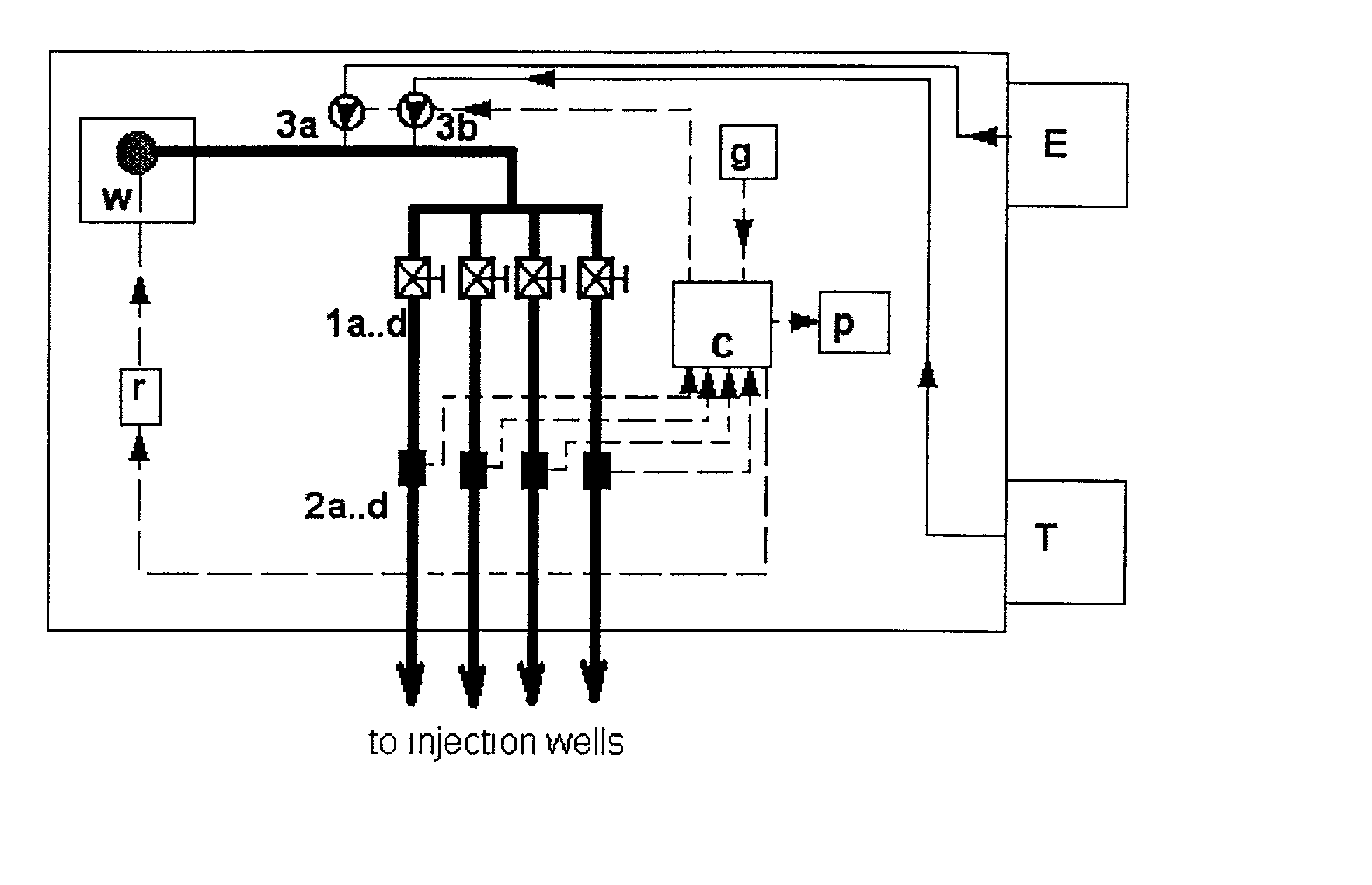
Bioremediation of nitrate contaminated groundwater
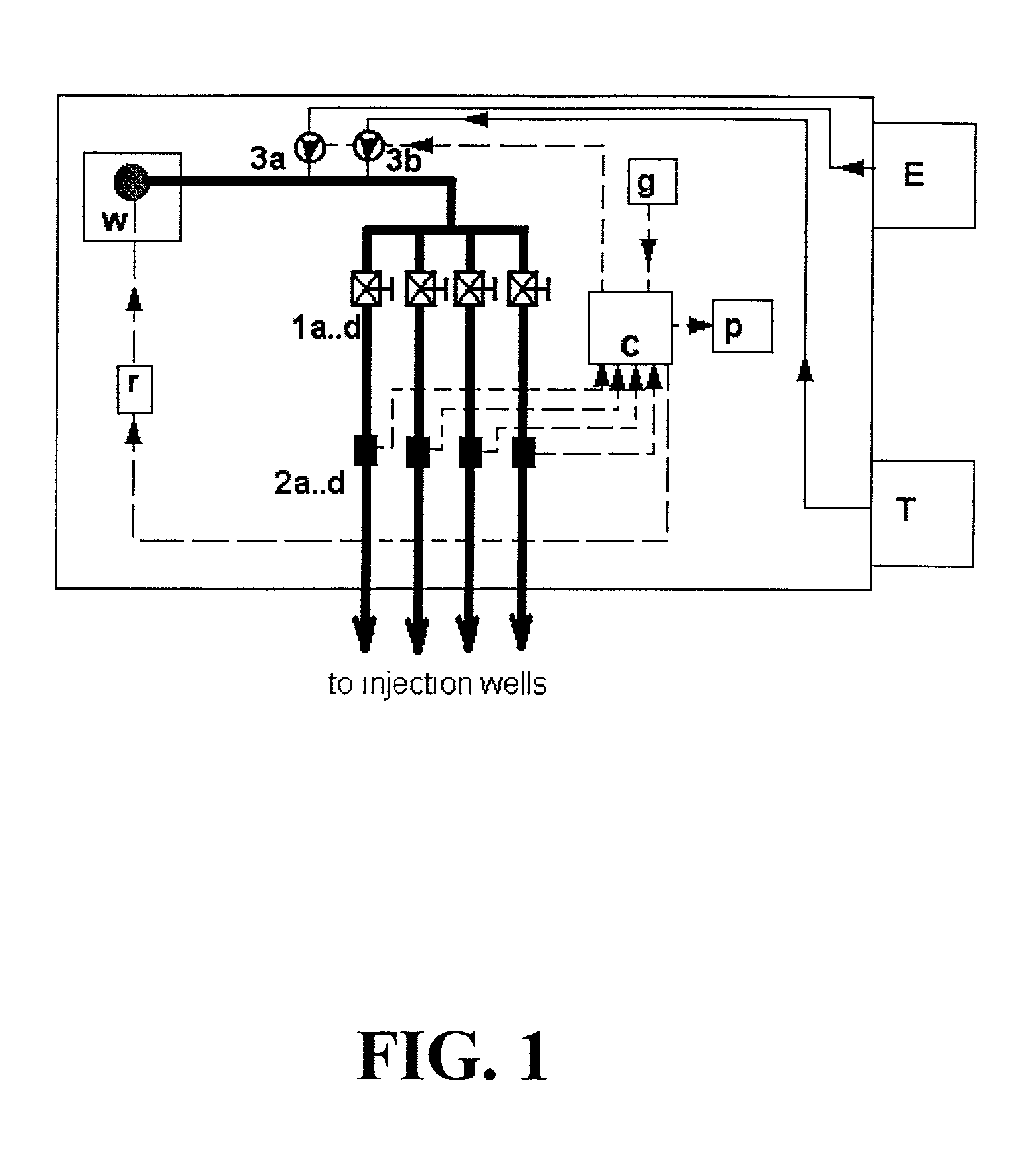
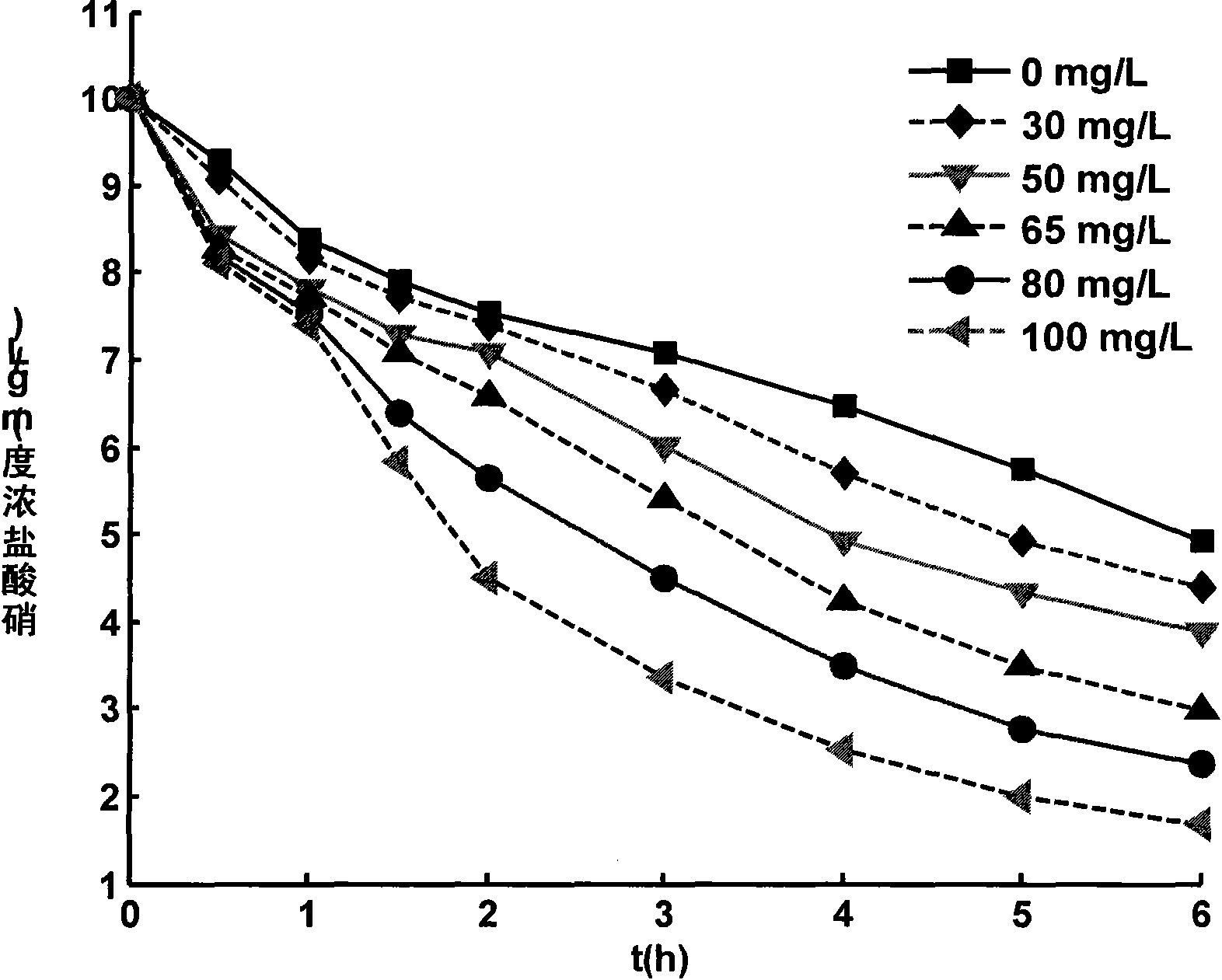
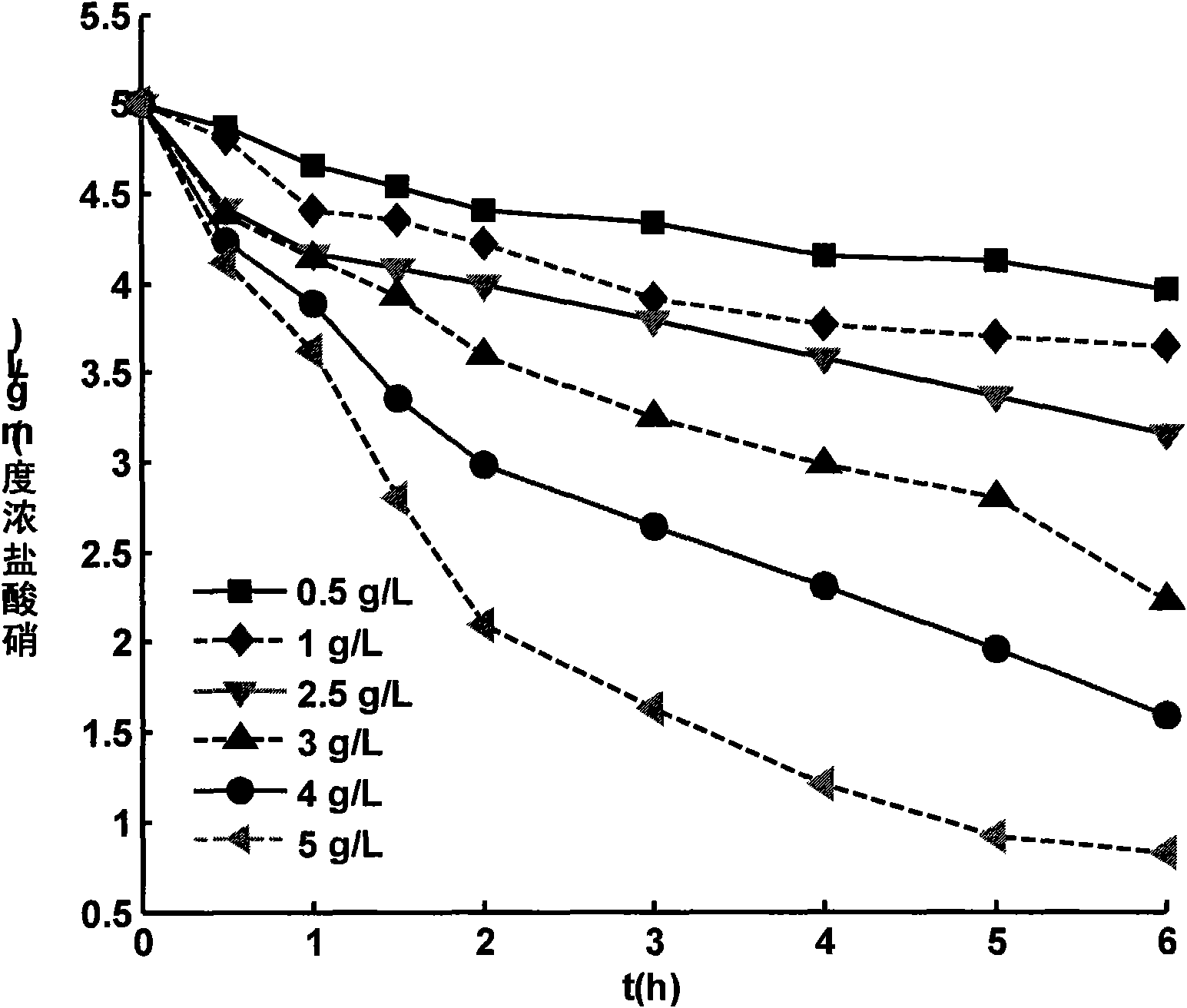
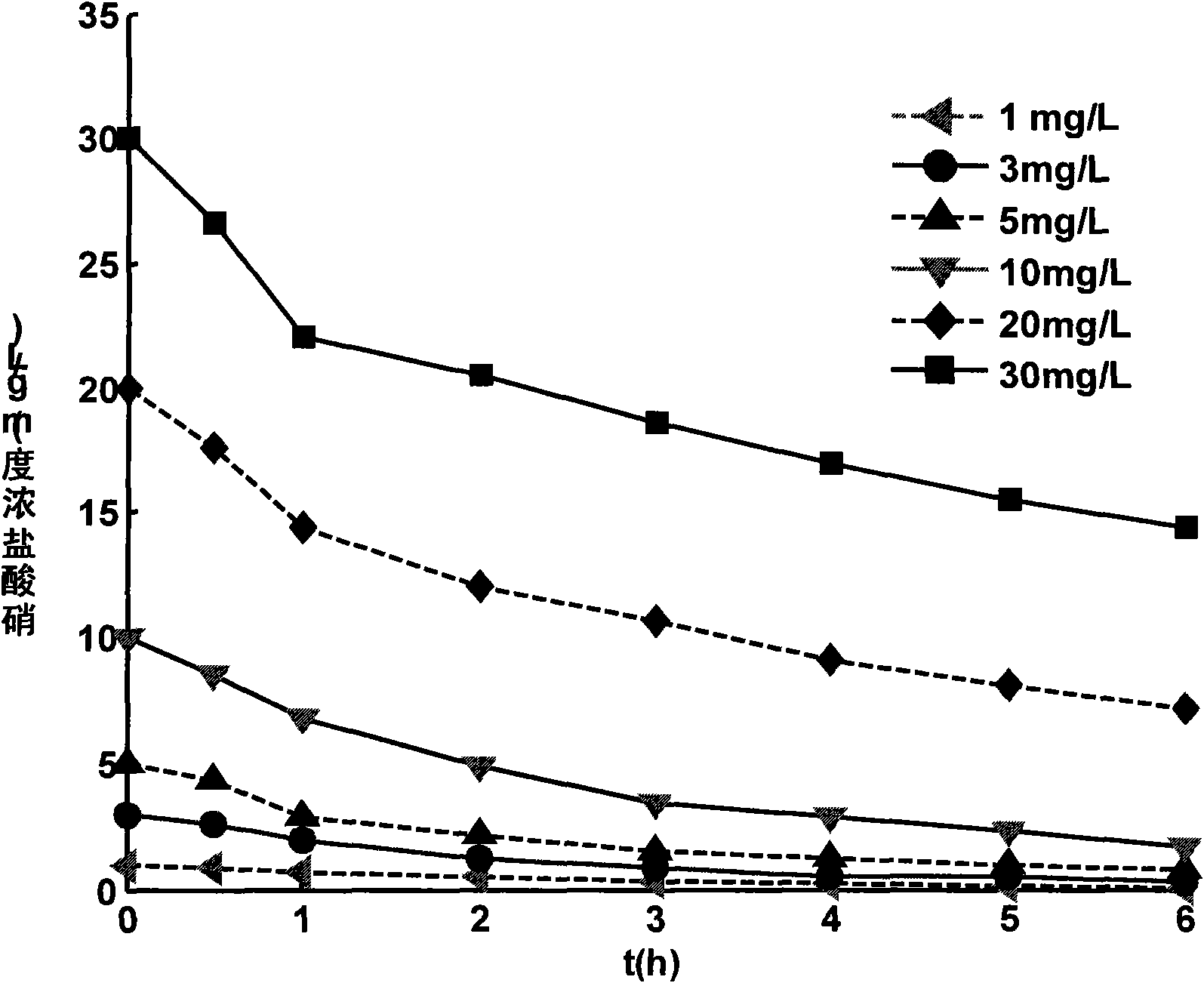
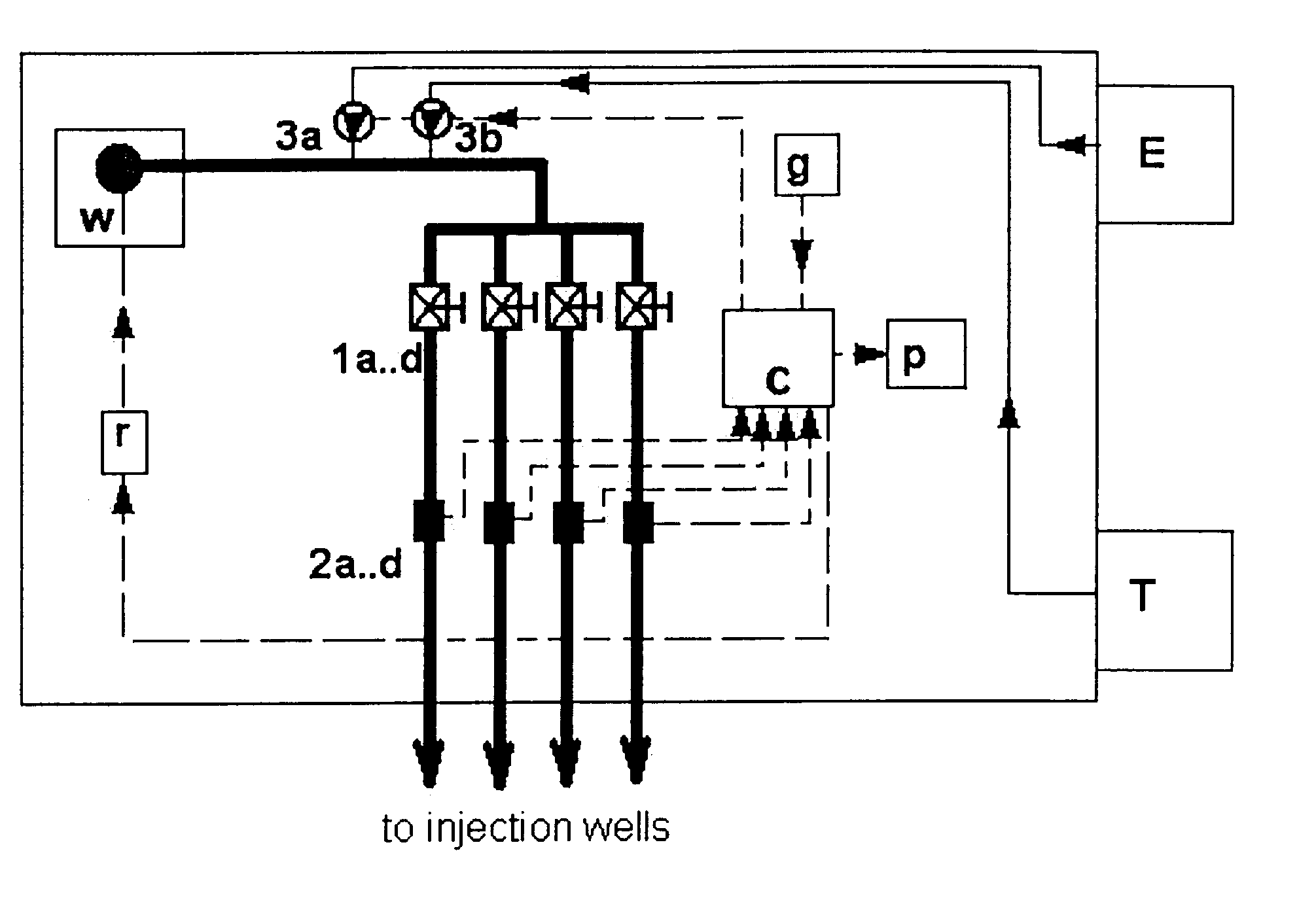
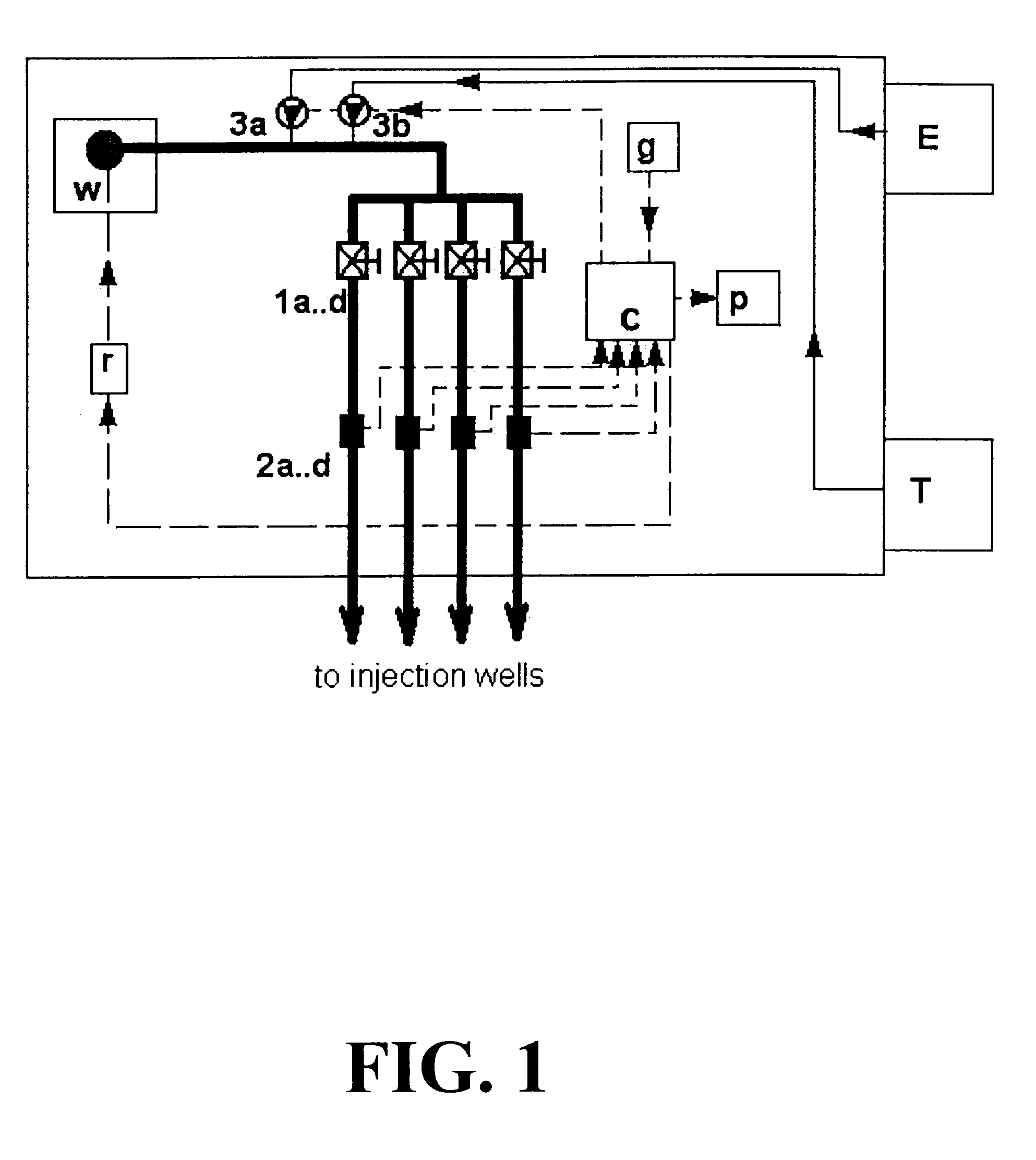
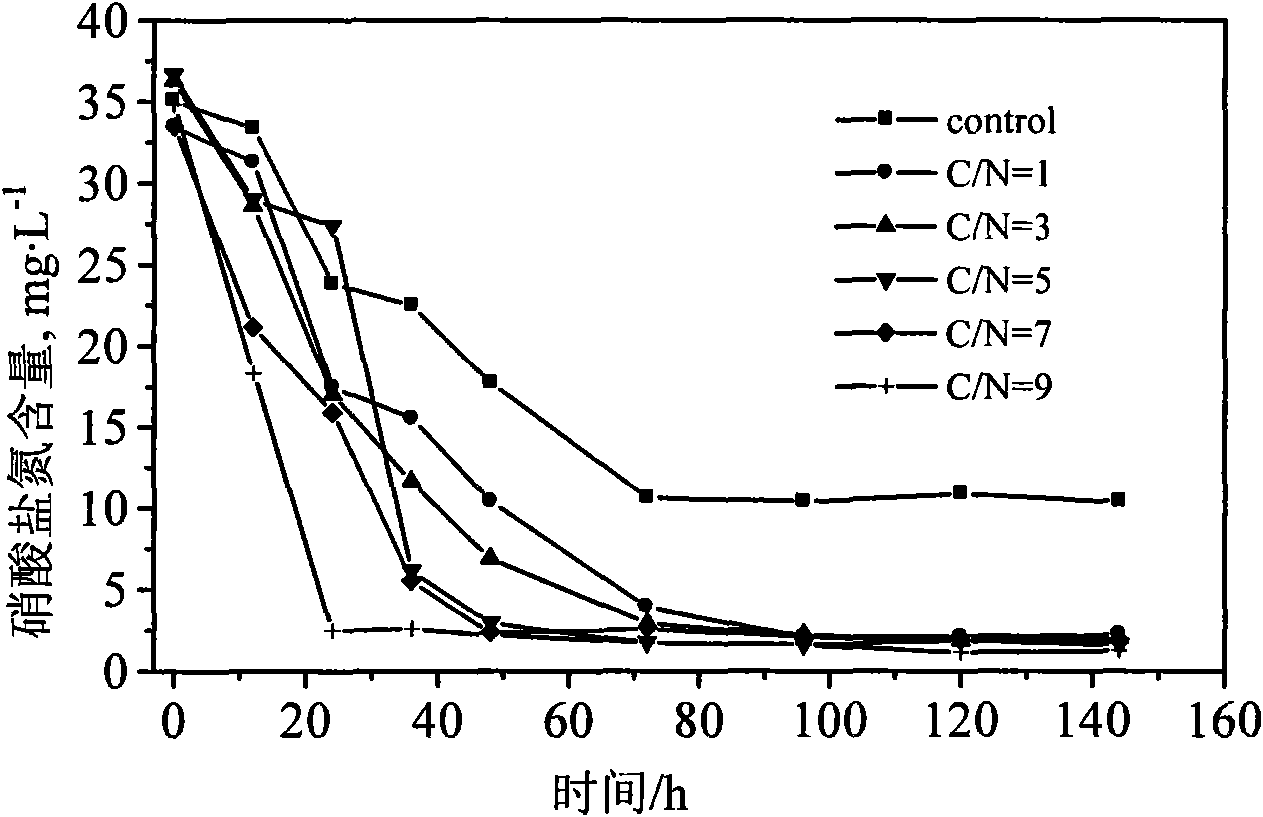
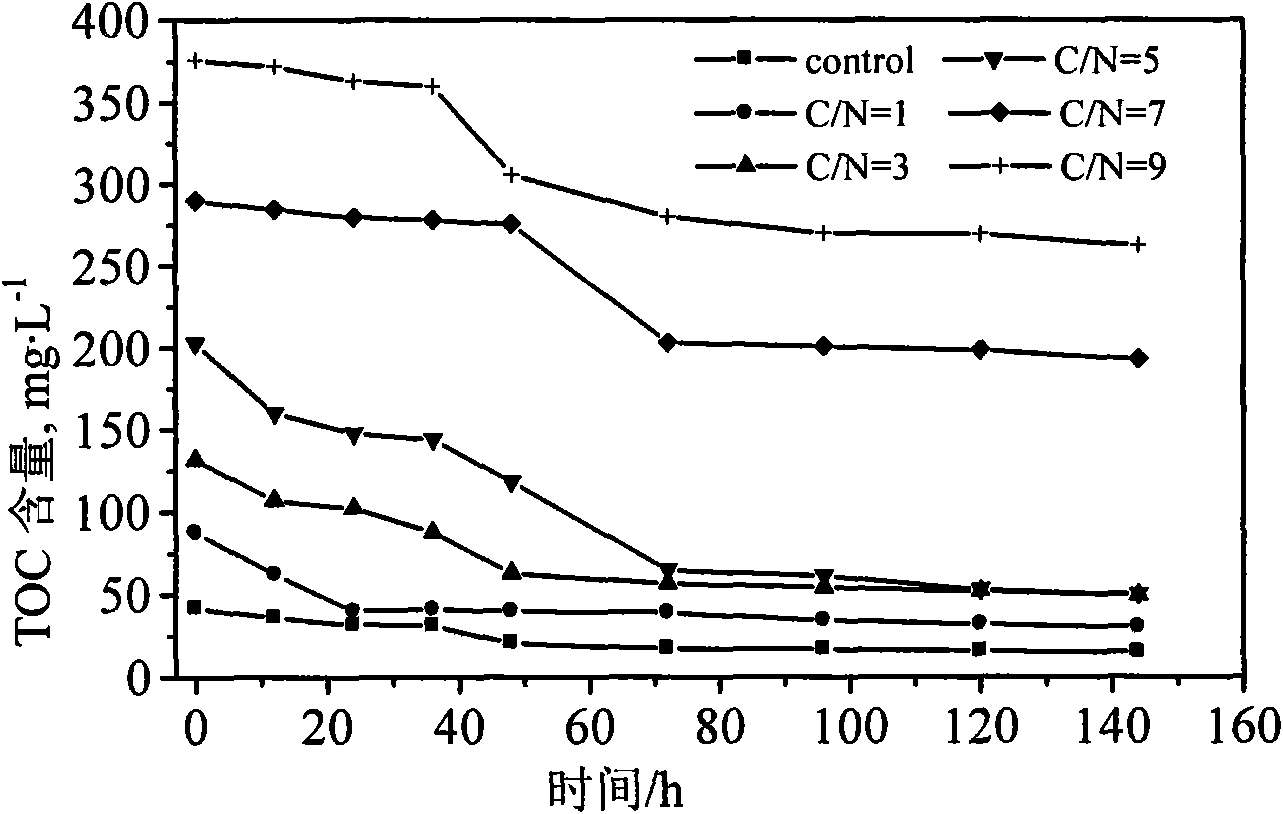
The invention disclosed relates to a method and apparatus for the denitrification of groundwater in situ in an aquifer under substantially anaerobic conditions, the method comprising (a) providing a network, including an extraction well for removal of groundwater from the aquifer and a plurality of injection wells for returning groundwater to the aquifer, the injection wells being arranged in a line substantially perpendicular to the direction of groundwater flow, the extraction well being located downstream or upstream of the line of injection wells, and the spacing of the wells and the number of injection wells being determined by the mathematical relationship <math-cwu id="MATH-US-00001"> <number>1< / number> J = C p + nC 1 W → min ( 1 ) <mathematica-file id="MATHEMATICA-00001" file="US20020020664A1-20020221-M00001.NB" / > <image id="EMI-M00001" wi="216.027" he="18.00225" file="US20020020664A1-20020221-M00001.TIF" imf="TIFF" ti="MF" / > < / math-cwu> where J is the cost of treatment, Cp and C1 are the costs of extraction and injection wells, respectively; n is the number of injection wells, and W is the distance across the protected area, and wherein the water stream is evenly distributed between injection wells, according to the relationship: <paragraph lvl="0"><in-line-formula>Fl=Fe / n=const (2) < / in-line-formula>where F is the water flow rate (e-extraction well, i-injection well) and n is the number of injection wells, (b) removing groundwater from the aquifer by the extraction well, (c) adding a carbon source to the groundwater in a controlled manner, (d) returning the carbon source amended groundwater to the aquifer by the injection wells in even distribution, the water flow rate being controlled, and (e) monitoring the nitrate concentration of the groundwater removed from the extraction well, a decrease in nitrate concentration being indicative of denitrification.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Application of composite synergist into Southern double cropping rice
InactiveCN102653491AReduce manufacturing costEasy to acceptFertilising methodsAgriculture gas emission reductionN-Acetylmuramic acidAgricultural science
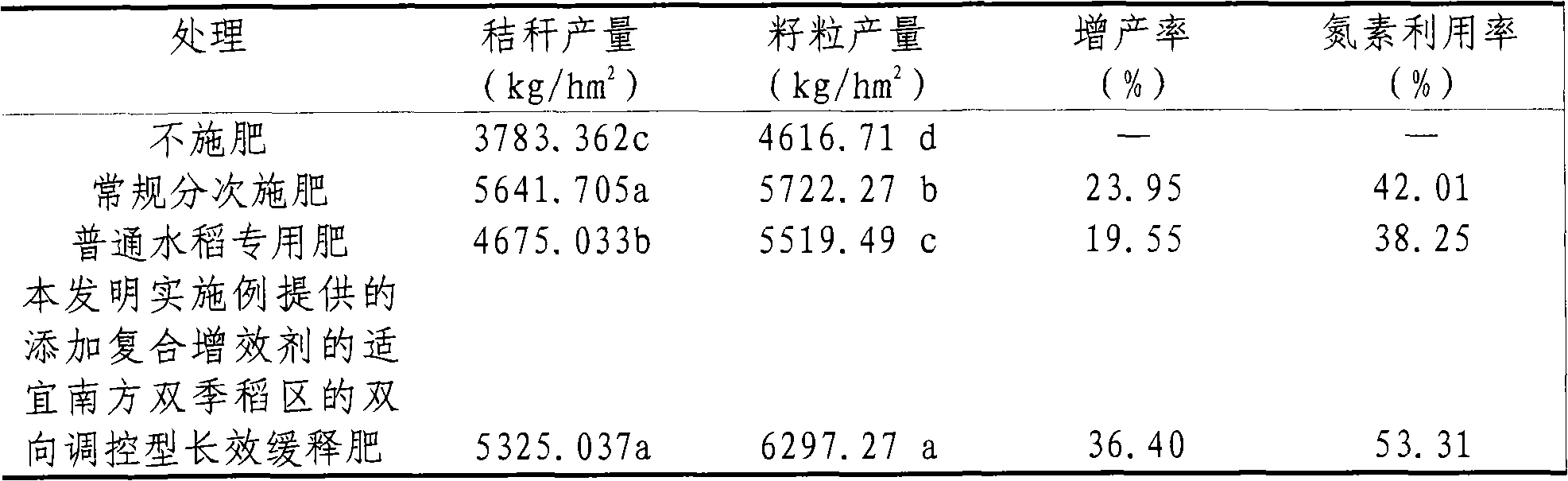
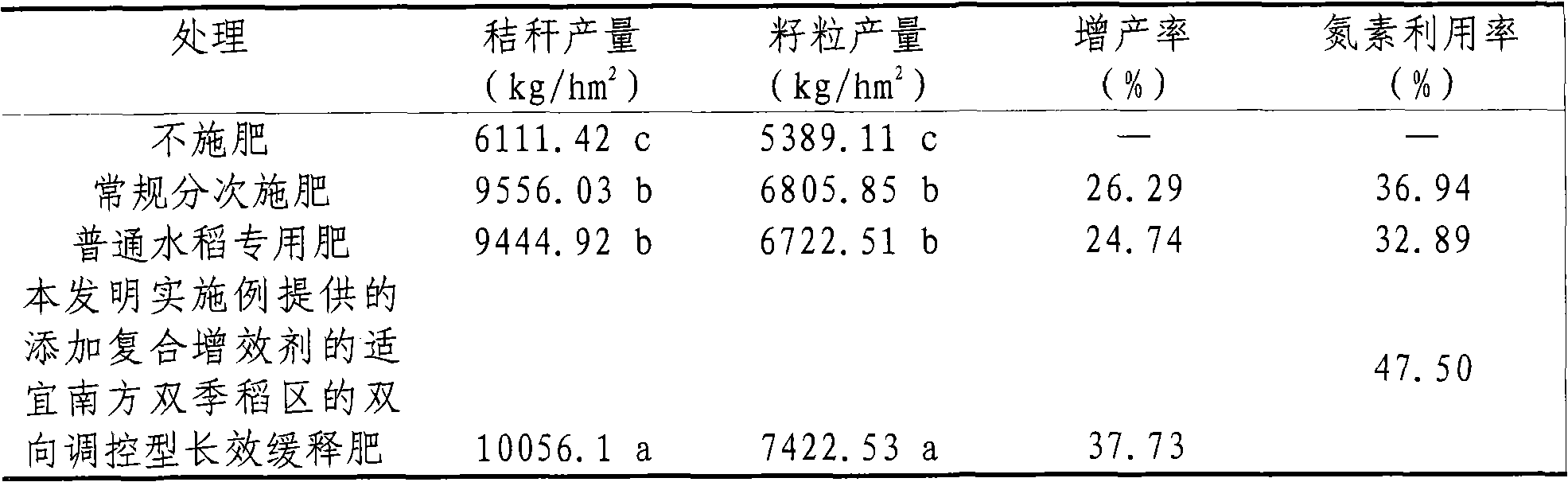
The invention relates to the field of fertilizer production, particularly application of a composite synergist into Southern double cropping rice. The composite synergist NAM (N-acetylmuramic acid) is used as a synergist applicable to slow release fertilizers for Southern double cropping rice seedlings. After the composite synergist is compounded with the slow release fertilizer, the compound fertilizer applied to the Southern double cropping rice field can greatly enhance the rice yield, is convenient for production and use, obviously reduces the greenhouse gas emission in the rice field, lowers the nitrate pollution, and has the advantages of strong technical compatibility, low cost and the like. The invention can receive favorable economic, social and ecological effects.
Owner:SHIKEFENG CHEM IND
Packing medium for permeable reactive barrier and application of packing medium to aspect of in-situ treatment on underground water nitrate pollution and method thereof
ActiveCN105347515ARaw materials are easy to getReduced operating requirementsWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsGroundwater nitrateNitrate salts
The invention provides a packing medium for a permeable reactive barrier and application of the packing medium to an aspect of in-situ treatment on underground water nitrate pollution, and a method thereof. The packing medium is formed by evenly mixing polyhydroxyalkanoate and ceramsite with the grain sizes of 4-6.5mm and 5-8mm respectively according to a ratio; raw material components of the packing medium are simple, and simple and easy to obtain. The invention also provides the application of the packing medium to an aspect of treatment on underground water nitrate pollution, in particular to the application to an aspect of in-situ treatment on underground water nitrate pollution. In addition, the invention also provides a method for in situ removal of underground water nitrate pollutants; the method takes a mixture of the polyhydroxyalkanoate and the ceramsite as the packing medium for the permeable reactive barrier. The method has the advantages of being simple and practicable, low in cost, long in service life, and small in secondary pollution, not easily causing aquifer blocking, and the like.
Owner:四川发展环境科学技术研究院有限公司
Method for preventing and controlling nitrate leaching loss of soil in dry farming land of North China Plain by utilizing mode of interplanting corn and soybean
InactiveCN103141248AReduce leachingReduce the risk of contaminationHorticultureMonocroppingNorth china
The invention discloses a method for preventing and controlling nitrate leaching loss of soil in a dry farming land of North China Plain by utilizing a mode of interplanting corn and soybean. Aiming at the problems that a dry farming land of the North China Plain is rainy and hot synchronously, the fertilizing amount of single culture of corn is large, the residual quantity of nitrate nitrogen in soil is large, the risk of nitrogen leaching loss is very high, the method effectively controls nitrate leaching loss of soil by interplanting corn and soybean summer sowing season. According to the invention, appropriate irrigation is performed during sowing; open type management is adopted during the growing period of crops; optimized fertilization is performed to corn bands and soybean bands respectively; the fertilizing amount is subjected to the local recommended fertilizing amount of corresponding crops, and fertilizer is applied between rows of corresponding crops; and during the critical growing period of the crops, if rain water is sufficient, irrigation is not performed, and if no rain comes or rain water is insufficient, appropriate irrigation is performed. The method can be implemented to effectively prevent and control the risk of nitrate pollution of a dry farming land of North China Plain, and has relatively remarkable economic benefits and environmental benefits.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for removing nitrate nitrogen, corresponding combination preparation, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101613148AStrong chemical stabilityImprove removal efficiencyWater contaminantsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPollutantChemistry
The invention relates to a method for removing nitrate nitrogen which can effectively improve the rate of the reaction that nitrate in water is reduced with nano-iron and the removal rate of nitrate nitrogen by adding nano-iron and aluminum salt or iron salt catalyst in nitrate to react. A combination preparation is prepared by the method that firstly nano-iron and aluminum salt or iron salt catalyst are added in a sealed container containing acetone and then the container is irradiated by ultrasound and stirred. The combination preparation has good chemical stability, can directly remove the nitrate pollutants in water and has simple process and convenient operation.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Bioremediation of nitrate contaminated groundwater
The invention disclosed relates to a method and apparatus for the denitrification of groundwater in situ in an aquifer under substantially anaerobic conditions, the method comprising(a) providing a network, including an extraction well for removal of groundwater from the aquifer and a plurality of injection wells for returning groundwater to the aquifer, the injection wells being arranged in a line substantially perpendicular to the direction of groundwater flow, the extraction well being located downstream or upstream of the line of injection wells, and the spacing of the wells and the number of injection wells being determined by the mathematical relationshipwhere J is the cost of treatment, CP and CI are the costs of extraction and injection wells, respectively; n is the number of injection wells, and W is the distance across the protected area, and wherein the water stream is evenly distributed between injection wells, according to the relationship:where F is the water flow rate (e-extraction well, i-injection well) and n is the number of injection wells,(b) removing groundwater from the aquifer by the extraction well,(c) adding a carbon source to the groundwater in a controlled manner,(d) returning the carbon source amended groundwater to the aquifer by the injection wells in even distribution, the water flow rate being controlled, and(e) monitoring the nitrate concentration of the groundwater removed from the extraction well, a decrease in nitrate concentration being indicative of denitrification.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Method for remedying nitrate pollution in groundwater by adopting Klebsiella sp. DB-2
InactiveCN101613156AReduce nitrogen contentImprove metabolic activityBacteriaWater contaminantsGroundwater nitrateIn situ remediation
A method for remedying nitrate pollution in groundwater by adopting Klebsiella sp. DB-2 is characterized by taking soluble carbonaceous organic materials as carbon sources and the purified Klebsiella sp. DB-2 as a bioremediation strain. The method comprises in-situ remediation and ex-situ remediation. The method of the invention can be effectively used for bioremediation of the nitrate pollution in the groundwater.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Microbial fuel cell for in-situ remediation of nitrate pollution of underground water
ActiveCN104681844AAchieve continuous operationAvoid problems such as cloggingBiochemical fuel cellsBiological water/sewage treatmentExhaust pipeDenitrification
The invention discloses a microbial fuel cell for in-situ remediation of nitrate pollution of underground water. The microbial fuel cell is in an integral cylindrical structure and comprises an anode chamber, a cathode chamber, an anion-exchange membrane assembly and an external circuit system, wherein the anode chamber is externally arranged at the outer side of the cathode chamber in a sleeving manner, a water inlet pipe and an exhaust pipe are arranged on the top of the anode chamber, a biological anode is arranged in the anode chamber, anaerobic electricity-generating microorganisms are attached to the biological anode, the anode chamber is filled with an anode liquid and the anode liquid is organic wastewater; a water outlet pipe is arranged on the top of the cathode chamber, a biological cathode is arranged in the cathode chamber, electric active denitrification microorganisms are attached to the biological cathode, the cathode chamber is filled with a cathode liquid, and the cathode chamber is inoculated with efficient anaerobic denitrification microorganisms; the anion-exchange membrane assembly comprises an anion-exchange membrane and a carrying layer; the external circuit system comprises an external circuit, a lead and an electric signal collecting recorder. The microbial fuel cell disclosed by the invention has triple functions of removing organic wastes, generating electricity by the microorganisms and carrying out the in-situ remediation on the nitrate pollution of the underground water, is simple and compact in structure, is economic and efficient, and can continuously and stably operate.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Measurement method of nitrogen and oxygen stable isotope of nitrate in seawater
ActiveCN104181247AGood training effectImprove training effectComponent separationContinuous measurementOxygen
The invention belongs to the technical field of water nitrate pollution treatment and control, and in particular relates to a measurement method of nitrogen and oxygen stable isotope of nitrate in seawater. The method comprises the steps of carrying out off-line treatment on the nitrate in the seawater to be measured by denitrifying bacteria without N2O reductase activity, and then converting the treated nitrate into nitrous oxide gas; and carrying out on-line continuous measurement on the nitrogen and oxygen stable isotope by combining a trace gas pre-concentrating apparatus (Precon) and gas chromatography (GC)-isotope ratio mass spectrometer (MS). After the measurement method is used, a culture method of the denitrifying bacteria is optimized, a formula of a culture medium is improved, the nitrate is not added, the cultivation effect is relatively good, the growth of the bacteria is stable, whether the culture medium has the residual nitrate or not after enrichment culture is not required to be tested, and the pollution is not caused in the subsequent sample treatment; the culture medium is good in bacteria enrichment effect, short in bacterial culture period and high in efficiency, and the cultivation cost is reduced.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Greenhouse soil nitrate pollution modifying agent, and preparation method and using method thereof
InactiveCN103525426AReduce the risk of contaminationRealize the role of pollution prevention and controlAgriculture tools and machinesContaminated soil reclamationGroundwater nitrateAgricultural pollution
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural pollution prevention and control, and in particular relates to a greenhouse soil nitrate pollution modifying agent used for comprehensively modifying greenhouse soil nitrate pollution and effectively preventing and controlling underground water nitrate pollution risk in intensive vegetable planting regions, and a preparation method and a using method thereof. The greenhouse soil nitrate pollution modifying agent consists of composite liquid and effective microorganism (EM) bacteria liquid with equal mass ratio, wherein the composite liquid is prepared from sodium humate and dicyandiamide through composite proportioning; the EM bacteria liquid is bacterial liquid of fermented EM bacteria; and the composite liquid and the EM bacteria liquid are mixed according to the mass ratio of 1:1. The composite liquid and the EM bacteria liquid are combined to be irrigated and applied to soil, so that the greenhouse soil nitrate pollution can be prevented and controlled through biological and chemical control technological means, the nitric nitrogen content of the greenhouse soil can be reduced by above 10 percent, and the nitrogen utilization ratio of crops can be increased by above 15 percent.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG ACAD OF SCI INST OF NATURAL RESOURCES
Purifying agent for nitrates in water and application of purifying agent
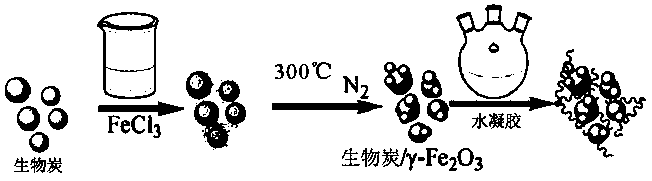
PendingCN110104833AOvercome adsorptionLarge specific surface areaWater contaminantsTreatment involving filtrationWater sourceExisting Treatment
The invention discloses a purifying agent for nitrates in water and application of the purifying agent, and aims to solve the technical problems that in an existing treatment technology, application is limited, secondary pollution is caused, and the nitrogen removal efficiency is low. The preparation method of the purifying agent for the nitrates in the water comprises the steps that biomass is ground and screened to prepare charcoal; iron-modified charcoal is prepared by adding a FeCl3 solution; the purifying agent for the nitrates in the water is prepared by adding acrylamide, N,N-methylenebisacrylamide and ammonium persulfate. The invention further provides a treatment method of the nitrates in a water system. The treatment method comprises the steps that pH and temperature of to-be-treated disposal sewerage are adjusted; the purifying agent for the nitrates in the water is added, and then the nitrates can be removed. The purifying agent for the nitrates in the water can be used for treating production wastewater, has the effect of preventing and controlling agricultural non-point source pollution and can be further used for treating nitrate pollution to drinking water, relieving harm, caused by the drinking water high in nitrate content, to the human health, preventing further deterioration of the water and providing an effective measure for protection of a water source.
Owner:AGRO ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION INST OF MIN OF AGRI
Method for removing nitrates in underground water through utilizing rice straws and entrapping denitrifying bacteria
InactiveCN102976484ARealize comprehensive utilizationHigh removal rateTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesCelluloseSolid carbon
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
P. denitrificans/S. oneidensis/graphene/calcium alginate denitrifying gel microsphere as well as preparation method and application thereof
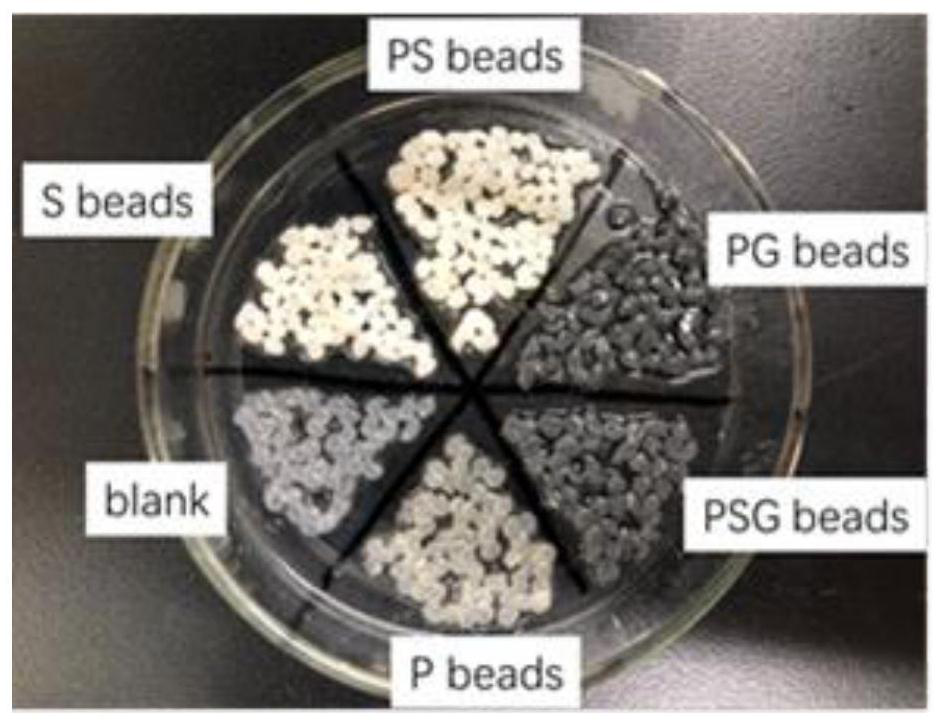
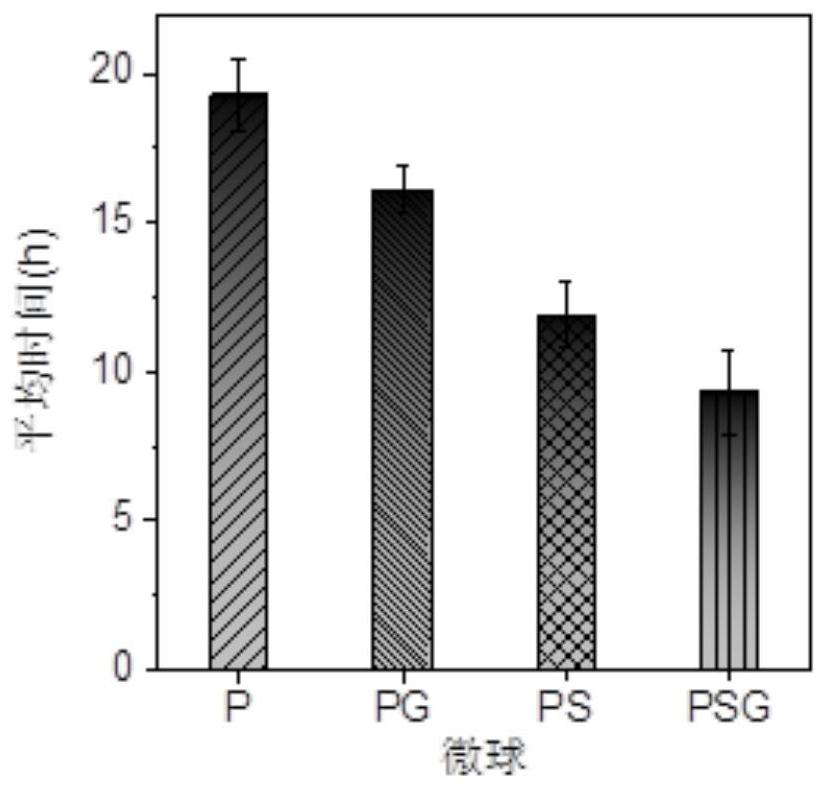
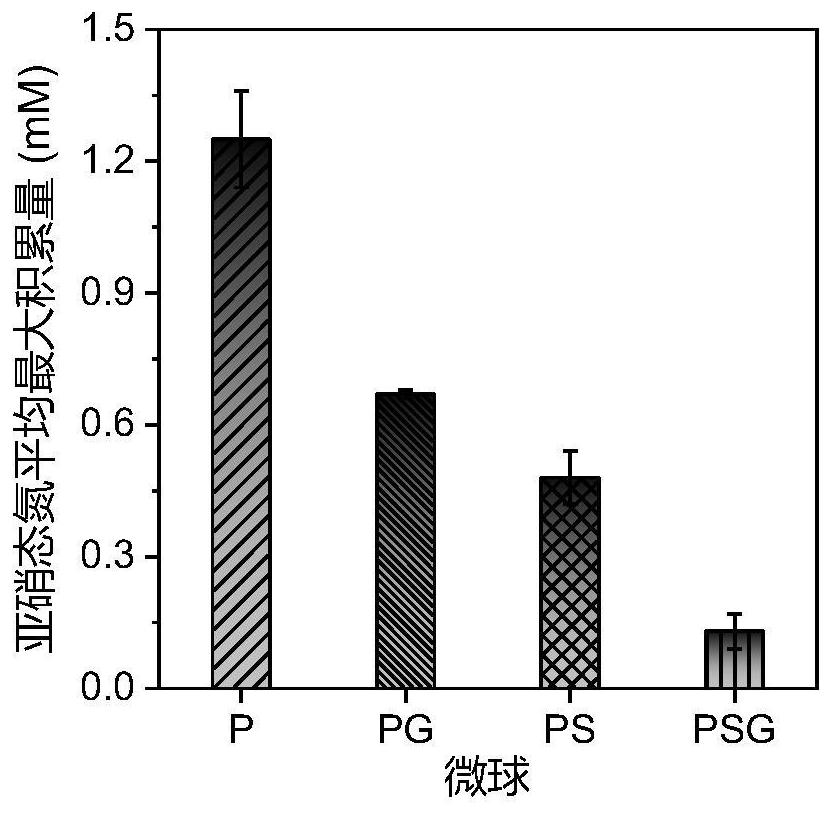
PendingCN112048500AIncrease the rate of electron transferAccelerate the efficiency of anaerobic denitrificationWater contaminantsMicroorganism based processesMicrosphereNitration
The invention discloses P. denitrificans / S. oneidensis / graphene / calcium alginate denitrifying gel microsphere as well as preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical fieldof environmental protection. According to the invention, calcium alginate is adopted to embed denitrifying microorganisms P. denitrifians, S. oneidensis MR-1 and graphene to form P. denitrifians / S. oneidensis MR-1 / graphene / calcium alginate denitrifying gel microspheres, and the prepared microspheres have strong resistance to toxic and harmful environmental impact, and can realize recycling of strains and materials. When the microsphere is applied to an anaerobic denitrification system polluted by nitrate or co-polluted by nitrate, the time required by reaching 90% of nitrate removal rate can be greatly shortened, and the accumulation of intermediate products nitrite and nitrous oxide is reduced.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Treatment method of stainless steel pickling wastewater
InactiveCN103523957ARepair pollutionWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater bathsIron powder
The invention relates to a wastewater treatment method, and discloses a treatment method of stainless steel pickling wastewater. The treatment method of the stainless steel pickling wastewater comprises the following steps: firstly, using 0.05mol / L dilute sulfuric acid for cleaning iron powder for 1 ~ 2 times, then cleaning with deionized water, drying for standby use; adding the iron powder to the stainless steel pickling waste water for water bath heating, stirring evenly, and filtering with a 0.22 mum microfiltration membrane. The treatment method can remove nitrate in the wastewater, can remove Cu <2+>, Ni <2+>, Cr <6+> and other heavy metal ions to a certain extent, and can be widely used for the repair of nitrate pollution in groundwater.
Owner:SHAANXI SHENGMAI PETROLEUM
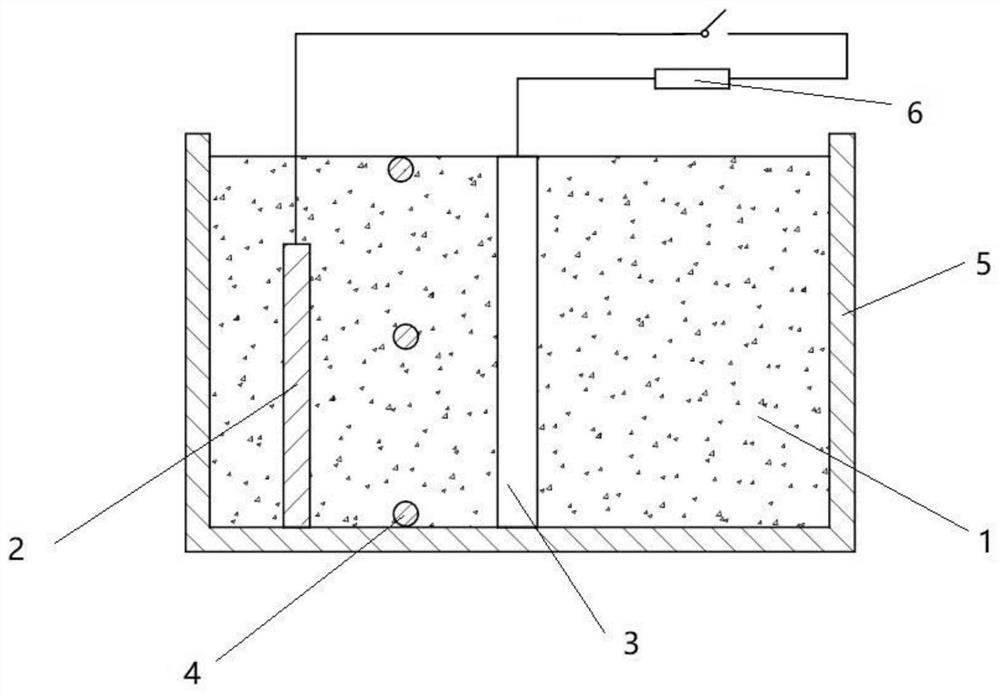
Method and device for in-situ remediation of groundwater pollution by electrically driven biological PRB (permeable reactive barrier)
ActiveCN113929206ARepair pollutionContinuous degradationTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater contaminantsHalohydrocarbonWater quality
The invention discloses a method and a device for in-situ remediation of groundwater pollution by electrically driven biological PRB (permeable reactive barrier). The device comprises a PRB, microorganisms, an anode, a cathode and an external circuit element device, the anode is mounted in the PRB and forms a biological PRB anode region together with the microorganisms; a water guide wall is arranged between the biological PRB anode region and the biological PRB cathode for separation; the cathode and the anode are connected with an external circuit element to jointly form an external circuit; the external circuit adopts closed-open-closed cycle operation, and generates and regenerates an iron oxide oxidation zone and an iron oxide reduction zone in situ according to pollutant properties and water quality requirements; and a filler of the PRB is a mixed filler of a conductive carbon material and a zero-valent iron material, and the mass ratio of the conductive carbon material to the zero-valent iron material is 0.1%-50%. According to the method provided by the invention, underground water petroleum hydrocarbon, halogenated hydrocarbon and nitrate pollution can be remarkably resolved, the cost is low, and the risk of secondary pollution does not exist.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
PRB (permeable reactive barrier) repair material applied to repairing of underground water nitrate pollution and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107555610AReduce churnGood field applicabilityWater contaminantsContaminated groundwater/leachate treatmentGroundwater nitrateSodium Bentonite
The invention discloses a PRB (permeable reactive barrier) repair material applied to the repairing of underground water nitrate pollution. The PRB repair material is characterized by being prepared from the following ingredients by weight percent: 30% to 40% of oxygen trapping reducing agent, 10% to 15% of stabilizing and curing adhesive, 5% to 10% of autotrophic denitrification microbial agent,25% to 35% of microbial carrier material, 10% to 15% of sand and the balance of water. According to the PRB repair material disclosed by the invention, combined action of all the ingredients is utilized to achieve the effect that a filling material for repairing underground water nitrate by PRB has the functions of high efficiency, stability and better field adaptability; increasing apposition growth environment supply for microorganisms in underground water is facilitated; meanwhile, an effect of the adhesive can reduce loss of autotrophic denitrification microorganisms and reducibility ironpowder along with underground water flow and further can form a growth environment suitable for autotrophic microorganisms; iron ions formed in a repairing process can be absorbed by bentonite, so that effects of excessively releasing iron ions to downstream is reduced, and occurrence of secondary pollution is avoided; in addition, the characteristics of environmental friendliness and low cost ofthe PRB filling materials are achieved.
Owner:北京市可持续发展科技促进中心 +1
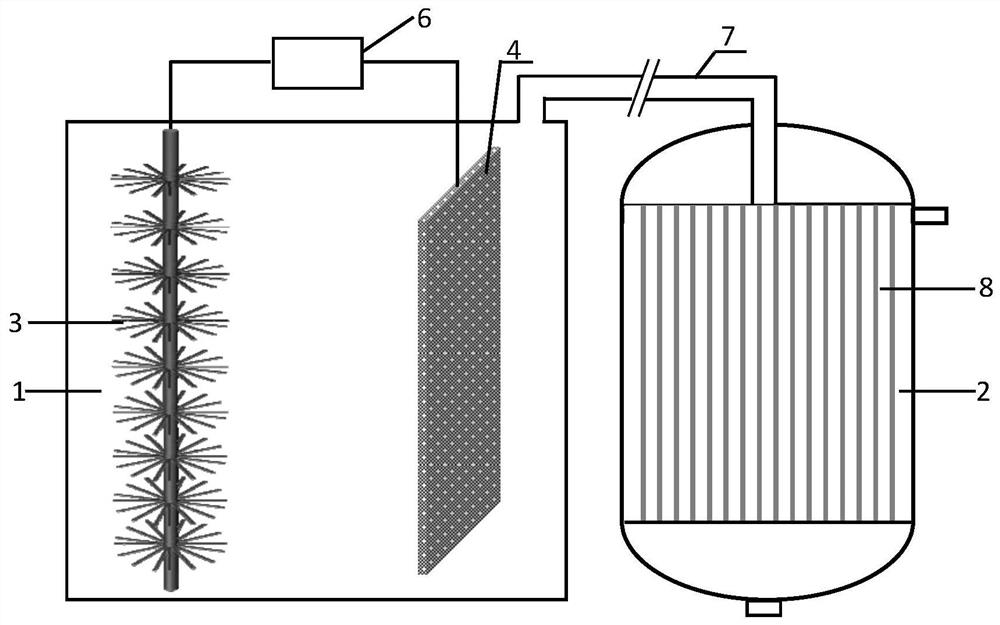
Heterotopic electron compensation hydrogen autotrophic denitrification nitrogen removal device
ActiveCN112250163AImprove solubilityIncrease profitTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater contaminantsNitrogen removalGaseous diffusion
The invention discloses a heterotopic electron compensation hydrogen autotrophic denitrification nitrogen removal device, and relates to an autotrophic denitrification nitrogen removal device. The invention aims to solve the problems of low denitrification efficiency and low rate of nitrate polluted water body lack of electron donors. The device consists of a hydrogen production chamber, a denitrification chamber, an anode, a cathode, a gas diffusion film and a direct-current power supply, wherein the hydrogen production chamber and the denitrification chamber are separated through the gas diffusion film; or the device comprises a gas diffusion device, wherein the gas diffusion device is arranged at the gas outlet end of the hydrogen conveying pipeline. According to the device, hydrogen generated by the bioelectrochemical system is heterotopic used for hydrogen autotrophic denitrification, the inherent limitation on the electrode spacing during denitrification is broken through, the total nitrogen removal rate can be increased, the utilization rate of electrons recovered by the anode is increased, and secondary pollution to a water body is avoided. The device is suitable for sewagetreatment.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
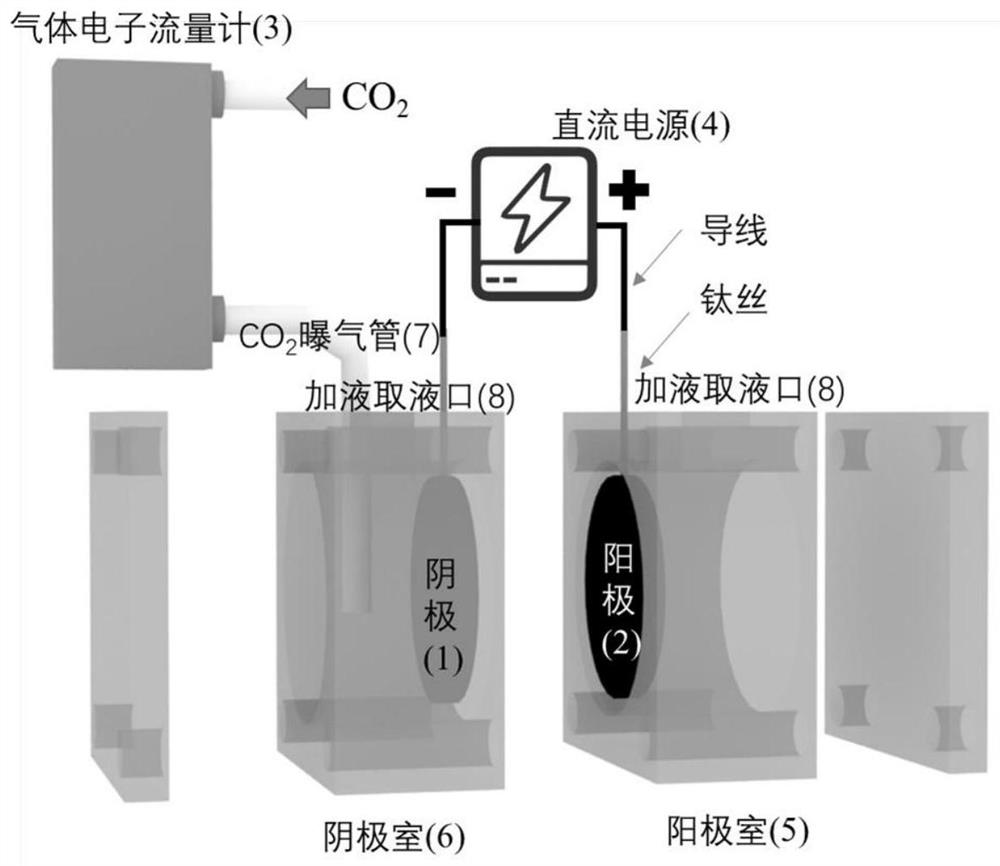
Device and method for preparing ammonium bicarbonate by using carbon dioxide waste gas and nitrate wastewater
PendingCN114875423AEmission reductionAvoid pollutionCellsGas treatmentAmmoniacal nitrogenAmmonia production
The invention relates to a waste water and waste gas resource utilization technology, in particular to a device and a method for preparing ammonium bicarbonate by utilizing carbon dioxide waste gas and nitrate waste water. The device provided by the invention comprises a cobalt oxide / foamy copper cathode, a dimensionally stable anode, a carbon dioxide aerator pipe, a gas electronic flowmeter, a cathode chamber, an anode chamber, a direct-current power supply and a liquid adding and taking port. The highest yield of ammonium bicarbonate produced by the device is 34.2 mg cm <-2 > h <-1 >; according to the method provided by the invention, CO2 is introduced into the nitrate wastewater, the cobalt oxide / foamy copper cathode is promoted to electrochemically reduce nitrate to synthesize ammonia, and the ammonia production selectivity is 38.2% higher than that when CO2 is not introduced. According to the method, emission of CO2 in the waste gas is reduced, nitrate pollutants in the waste water are removed, the environment is protected, CO2 and ammonia nitrogen are stored as raw materials in the form of ammonium bicarbonate, subsequent synthesis of other economic products is facilitated, and resource utilization of the waste gas and the waste water is achieved.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
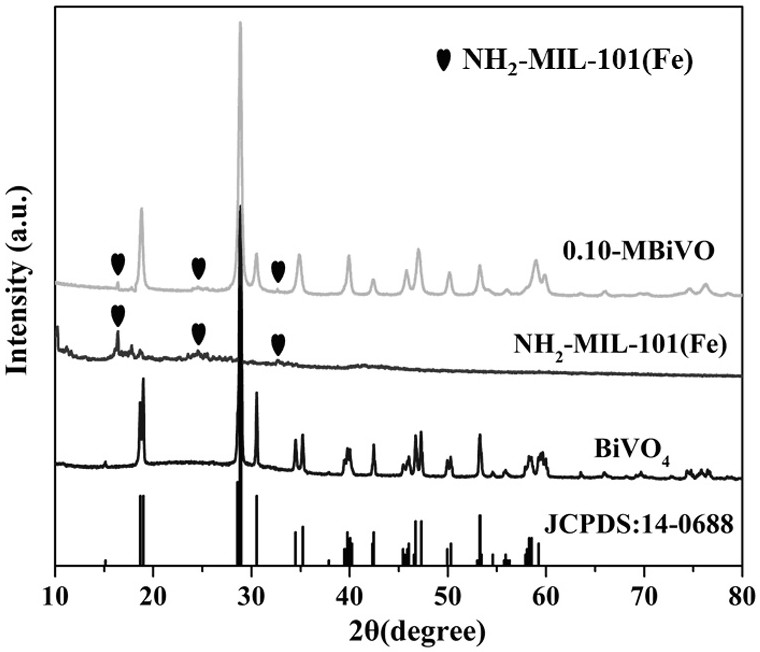
Preparation method and application of photocatalyst for selectively reducing nitrate into N2
ActiveCN113457745AAchieve removalLarge specific surface areaWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsNanoparticleNitrate salts
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a photocatalyst for selectively reducing nitrate into N2. According to the technical scheme, the preparation method of the photocatalyst comprises the following steps: step 1, preparing NH2-MIL-101 (Fe) porous octahedral nanoparticles by adopting a solvothermal method; and step 2, preparing the NH2-MIL-101 (Fe) / BiVO4 flower-ball-shaped heterojunction photocatalyst by a hydrothermal synthesis method. The photocatalyst is used for efficiently and selectively performing photocatalytic reduction on nitrate in a water body into nitrogen. The beneficial effects are that the prepared photocatalyst overcomes the defects that photon-generated carriers of a traditional photocatalyst are easy to compound and secondary pollutants are easy to generate, has the characteristics of stable chemical property, low cost, high reduction catalytic activity, good N2 selectivity and the like, can selectively convert nitrate into non-toxic and harmless N2, and thus the treatment of the nitrate pollutants in the wastewater is realized economically, efficiently and environmentally friendly.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
A combined isotopic and dating method for nitrate source apportionment in shallow groundwater
ActiveCN111272960BAccurate analysisMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansTesting waterGroundwater nitrateSoil science
The invention provides a shallow groundwater nitrate source analysis method combining isotope and dating, said method comprising the following steps: (1) setting monitoring sampling points and background value sampling points according to the environmental characteristics of the measurement area; (2) ) using the isotope dating method to monitor the age of groundwater, combined with the nitrogen and oxygen stable double isotope traceability method, and the land use and pollution source information in the study area to conduct qualitative identification and quantitative analysis of groundwater nitrate sources. The present invention innovatively combines groundwater dating with isotope traceability methods to realize rapid and accurate identification of pollution sources. The isotope method has the advantage of being less affected by changes in the concentration of water environmental factors. Compared with time, the industry categories that may cause potential pollution can be traced back, and the rapid and accurate traceability of groundwater nitrate pollution can be realized.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Preparation method of sulfur autotrophic denitrification bacterium immobilized particles
PendingCN108913623AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGroundwater nitrateStart time
The invention belongs to field of biological treatment of nitrate pollution in groundwater, and particularly relates to a preparation method of sulfur autotrophic denitrification bacterium immobilizedparticles. The preparation method of the sulfur autotrophic denitrification bacterium immobilized particles comprises the following steps that S1, polyvinyl alcohol and xanthan gum are added into deionized water, agricultural waste and sulfide which are subjected to biofilm culturing are added, and thus a material A is formed; S2, boric acid and calcium chloride are molten in the deionized water,a sodium hydroxide solution is added to adjust the pH value, then a supernatant is taken, and thus a solution B is formed; and S3, the material A is taken to be dripped into the solution B to form embedded particles, and after a cross-linking reaction is conducted, the sulfur autotrophic denitrification bacterium immobilized particles are obtained. According to the preparation method of the sulfur autotrophic denitrification bacterium immobilized particles, the mechanical properties and salt stability of the sulfur autotrophic denitrification bacterium immobilized particles can be improved, the denitrification start time is shortened, the denitrification efficiency is improved, and meanwhile, a new idea is provided for secondary utilization of the agricultural waste.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com