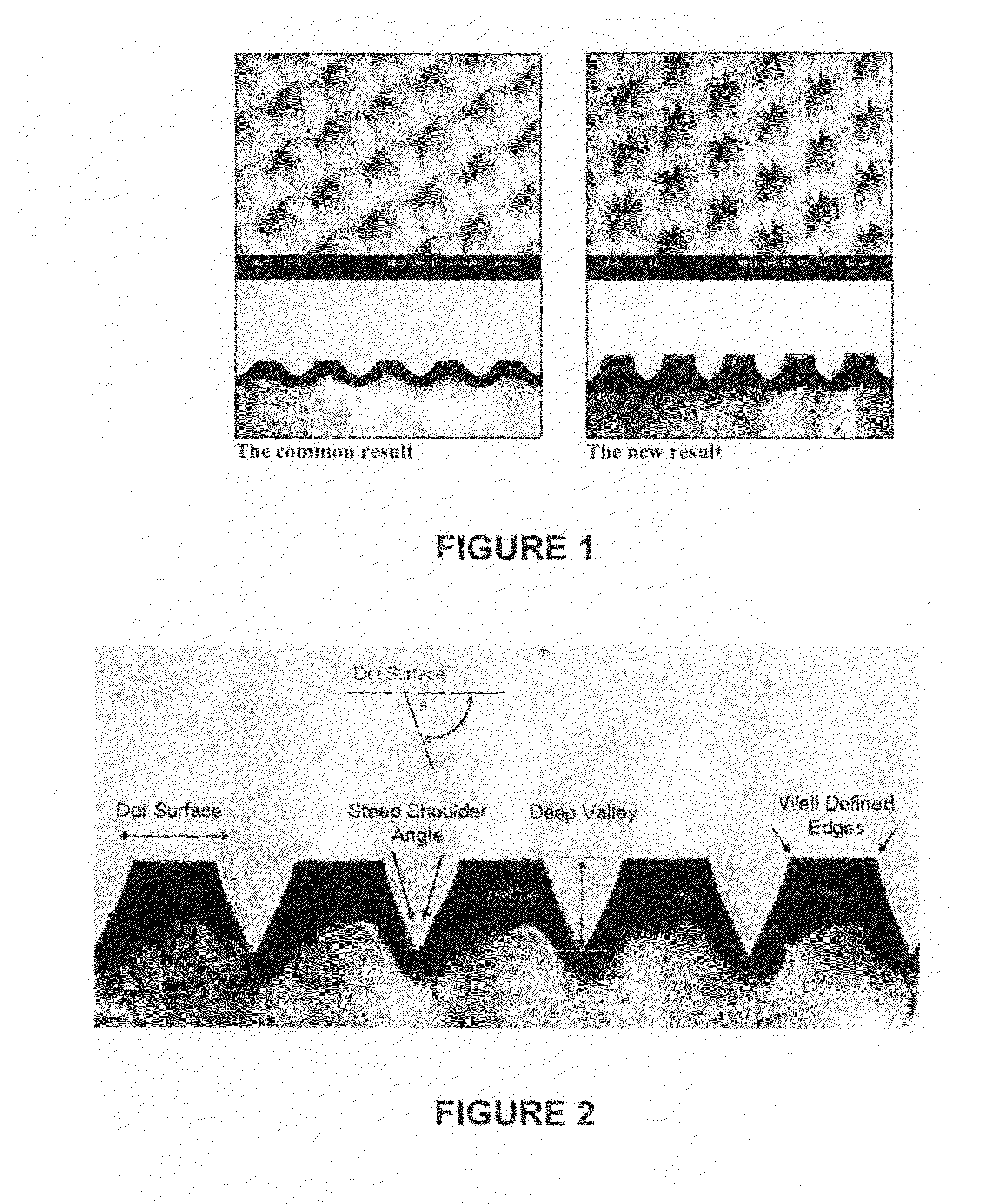
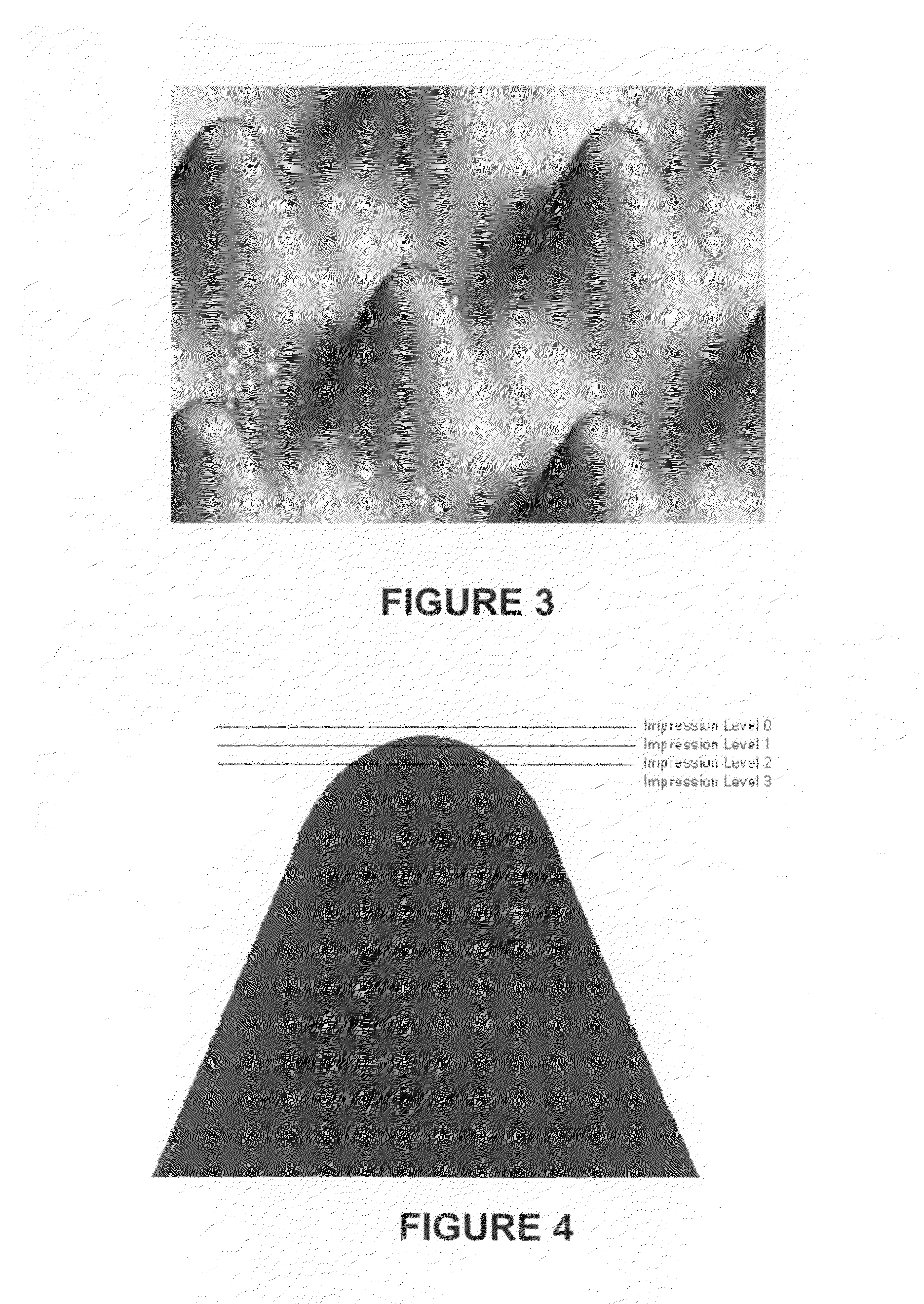
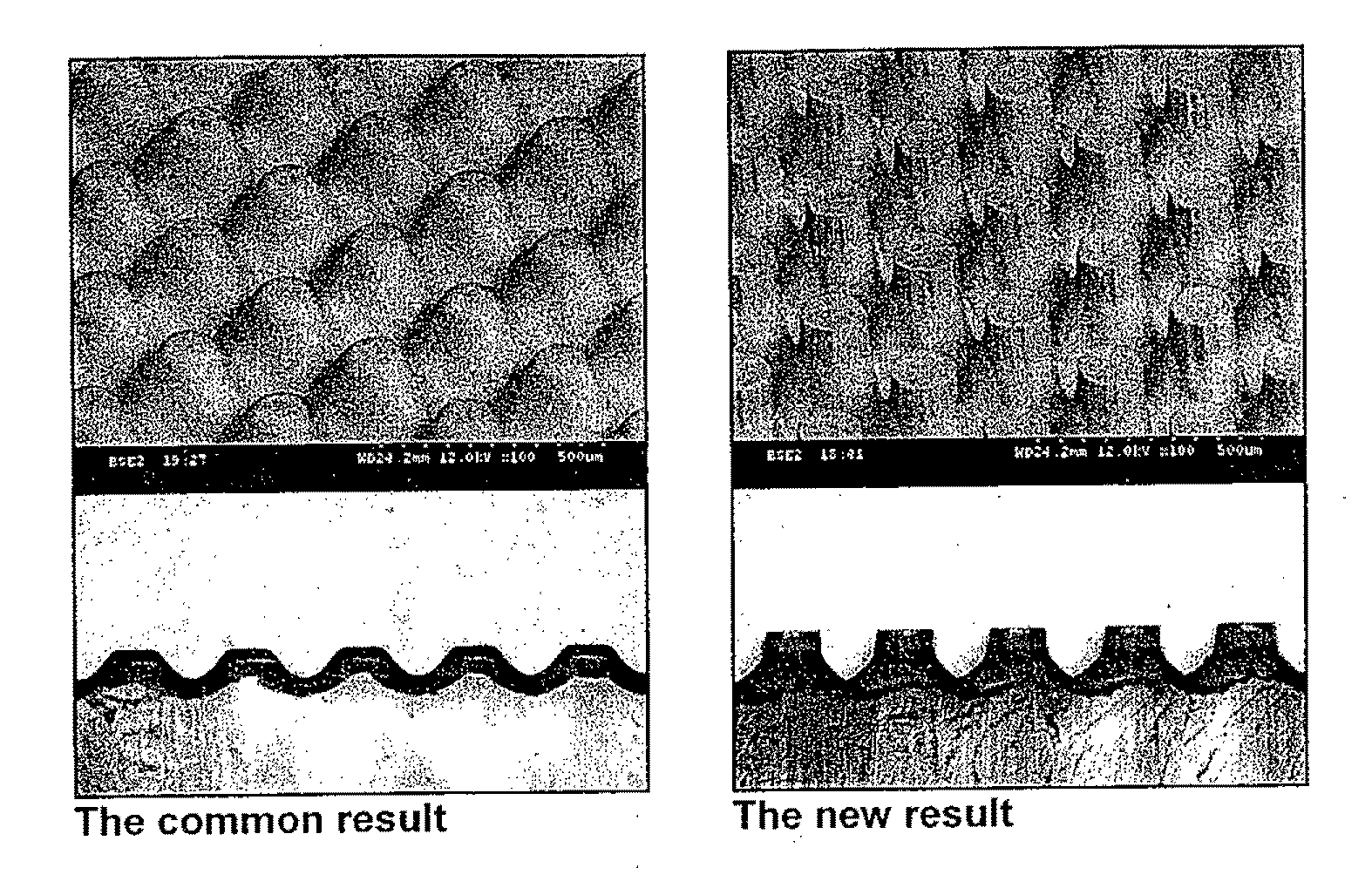
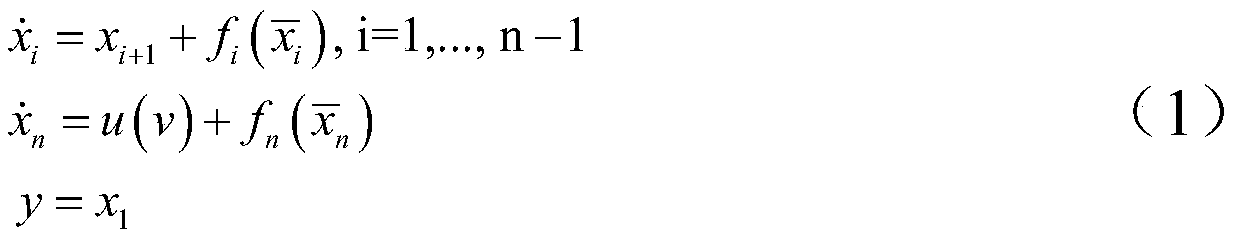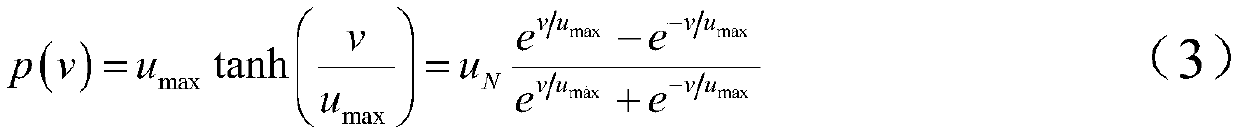Patents
Literature
149results about How to "Control roughness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
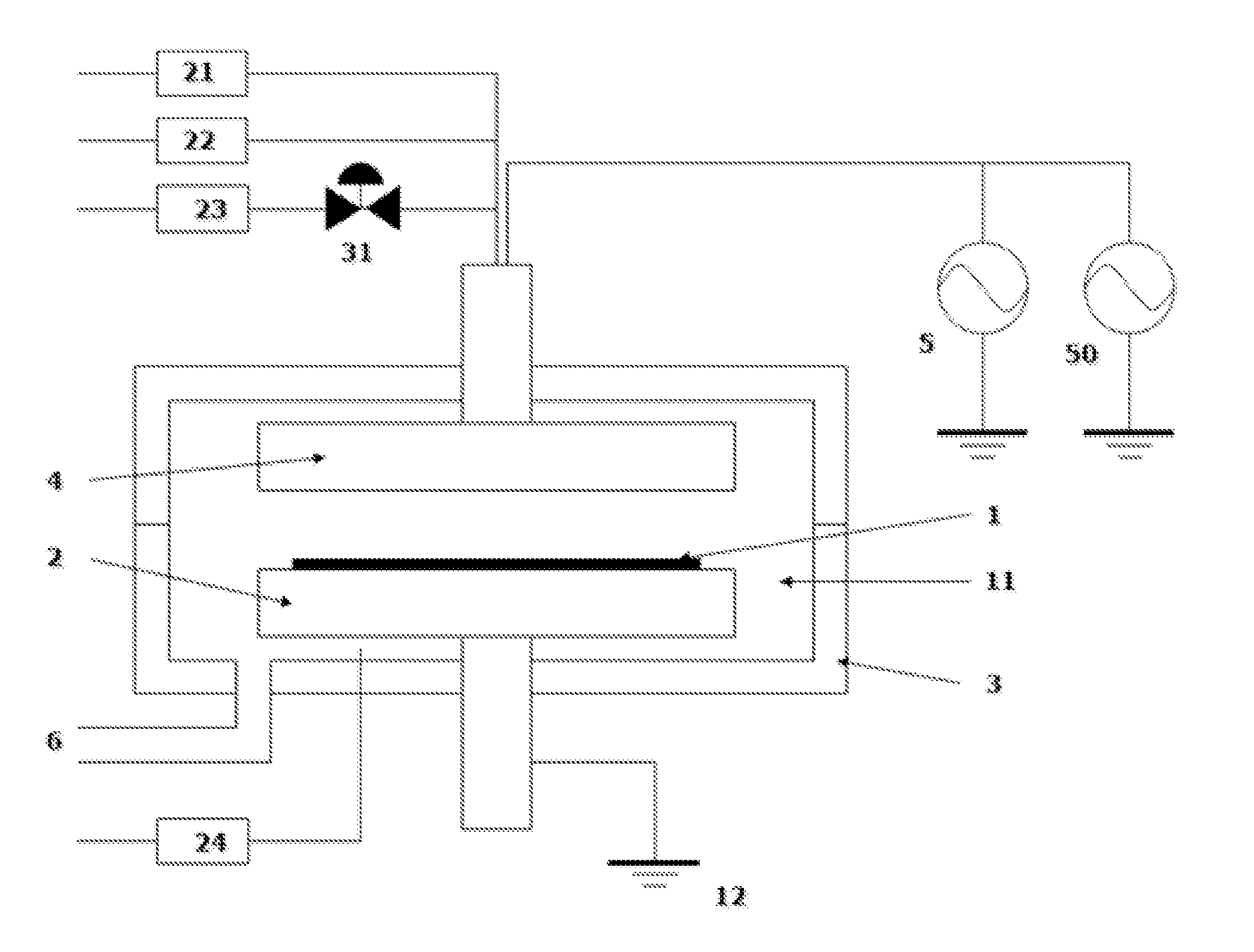
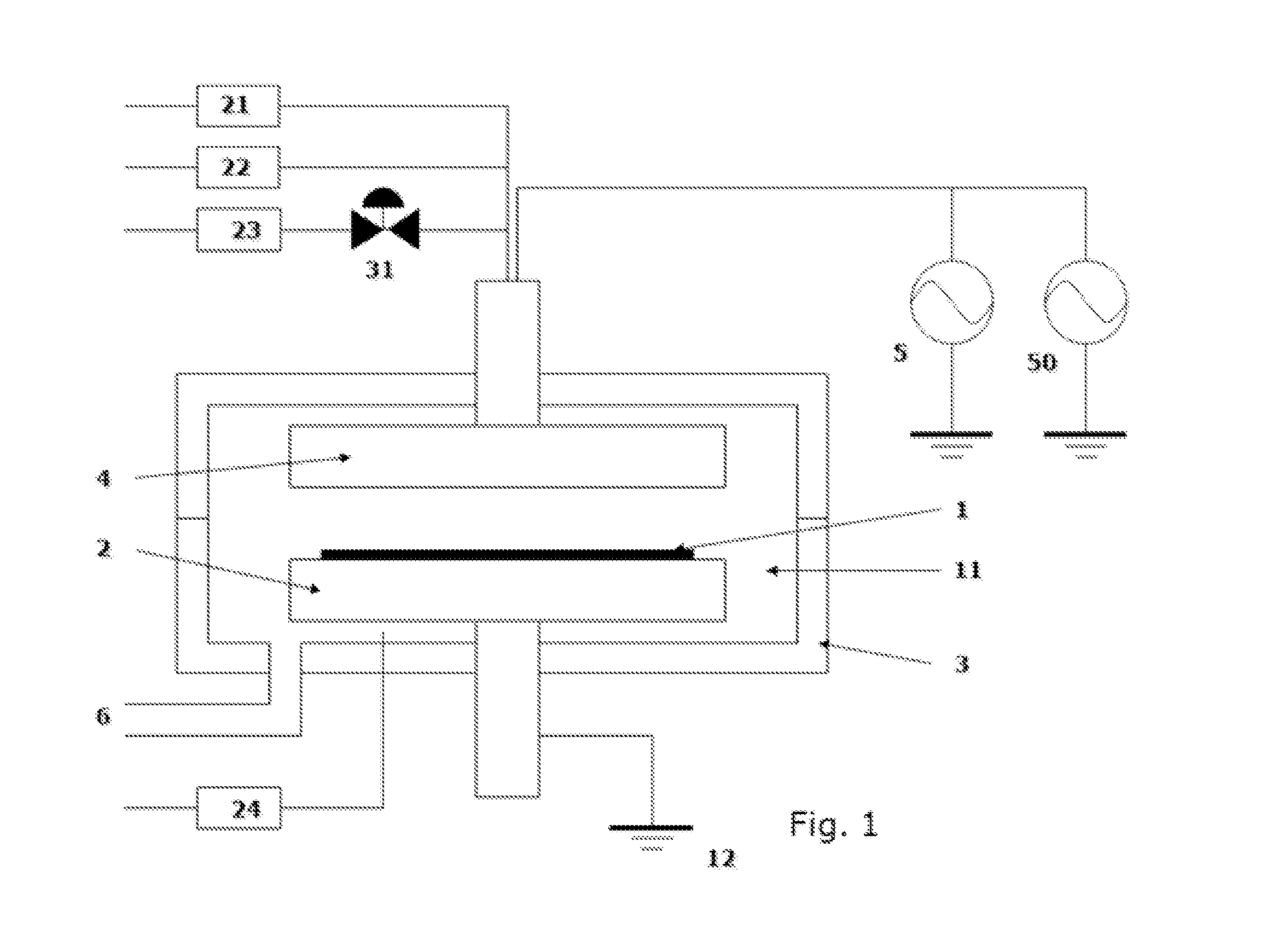
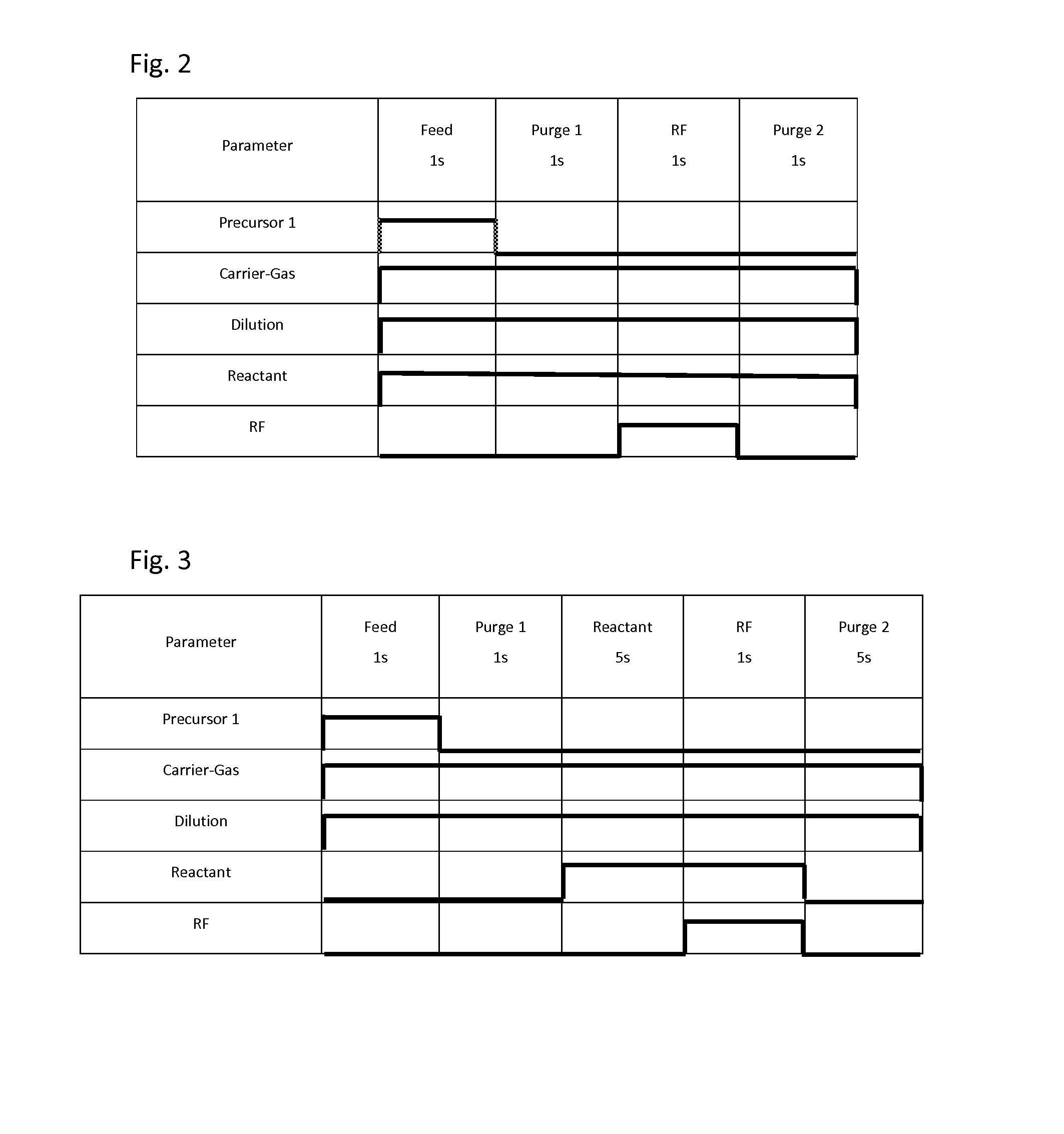
Method for depositing metal-containing film using particle-reduction step
InactiveUS20160168699A1Reduce surface roughnessSolve the lack of resistanceChemical vapor deposition coatingPlasma techniqueAMINO BASENitride
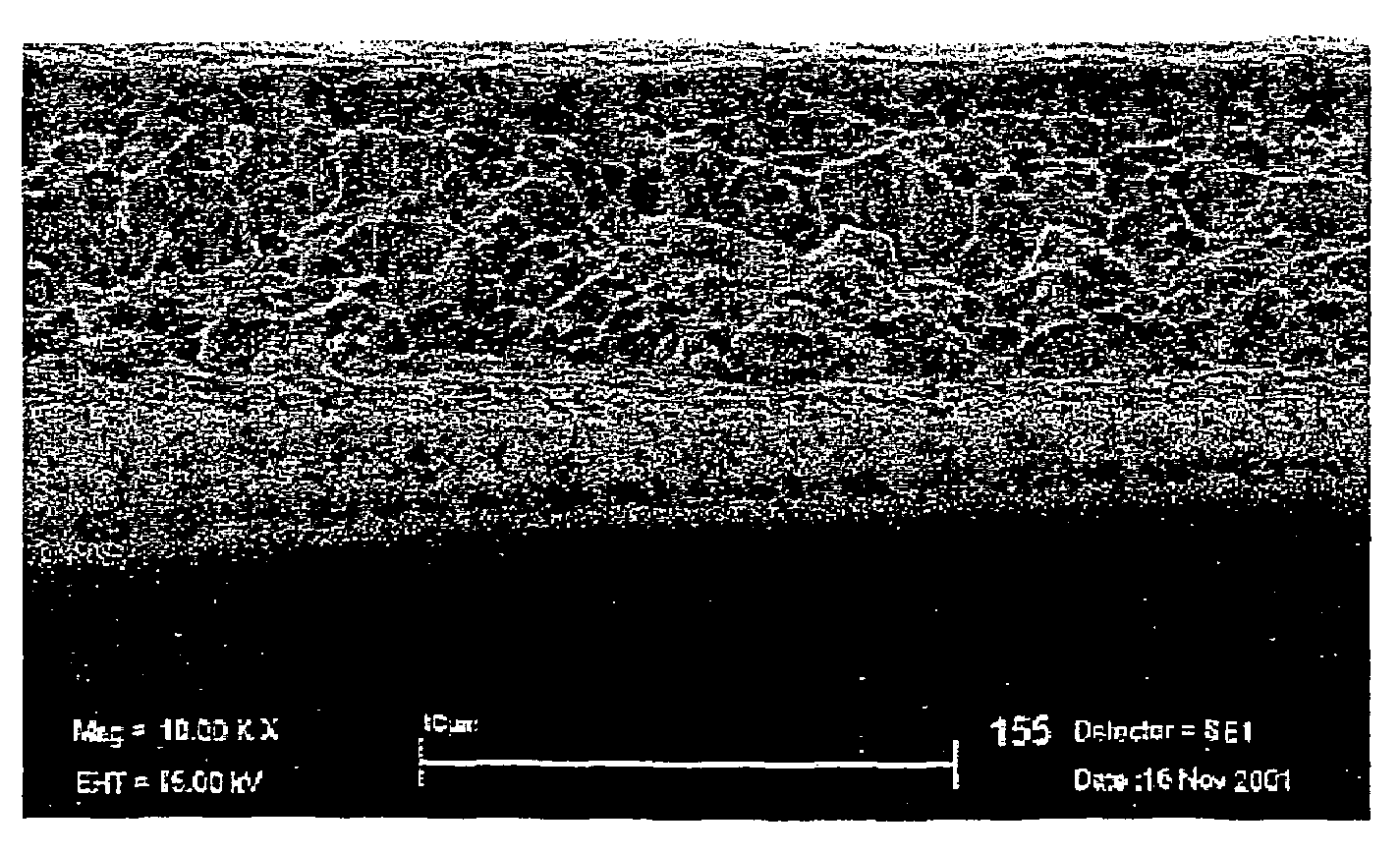
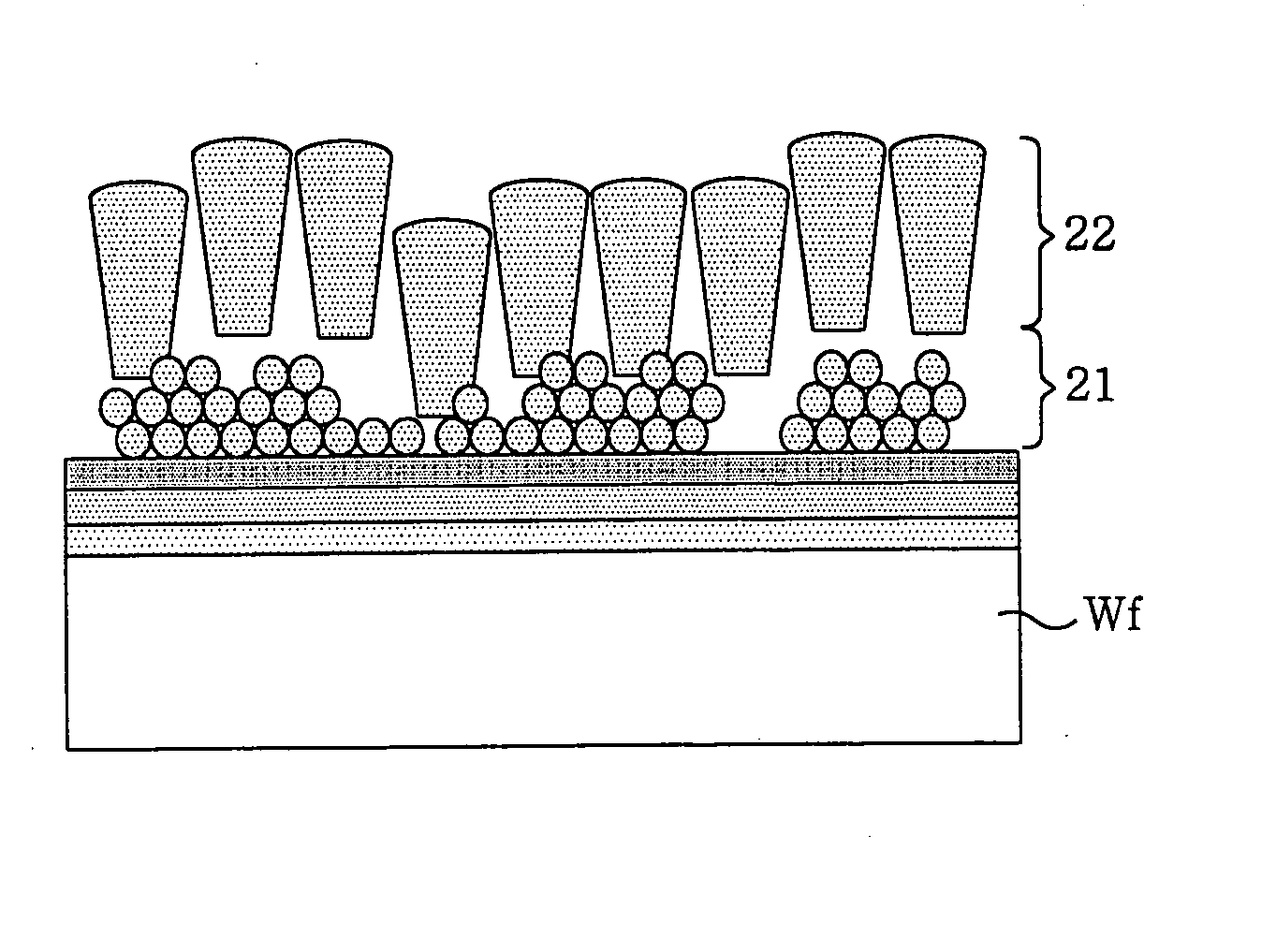
A method for forming a metal oxide or nitride film on a substrate by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD), includes: introducing an amino-based metal precursor in a pulse to a reaction space where a substrate is placed, using a carrier gas; and continuously introducing a reactant gas to the reaction space; applying RF power in a pulse to the reaction space wherein the pulse of the precursor and the pulse of RF power do not overlap, wherein conducted is at least either step (a) comprising passing the carrier gas through a purifier for reducing impurities before mixing the carrier gas with the precursor, or step (b) introducing the reactant gas at a flow rate such that a partial pressure of the reactant gas relative to the total gas flow provided in the reaction space is 15% or less.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method of improving print performance in flexographic printing plates
ActiveUS20110079158A1Promote resultsReduces print flutingLayered productsPlate printingCross-linkEngineering
A method of making a relief image printing element from a photosensitive printing blank is provided. A photosensitive printing blank with a laser ablatable layer disposed on at least one photocurable layer is ablated with a laser to create an in situ mask. The printing blank is then exposed to at least one source of actinic radiation through the in situ mask to selectively cross link and cure portions of the photocurable layer. Diffusion of air into the at least one photocurable layer is limited during the exposing step and preferably at least one of the type, power and incident angle of illumination of the at least one source of actinic radiation is altered during the exposure step. The resulting relief image comprises a plurality of dots and a dot shape of the plurality of dots that provide optimal print performance on various substrates, including corrugated board.
Owner:MACDERMID PRINTING SOLUTIONS
Magnetic tape
InactiveUS20120196156A1Good electromagnetic characteristicGood characteristic frictionMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageMagnetic tapeNon magnetic
An aspect of the present invention relates to a magnetic tape comprising, on one surface of a nonmagnetic support, a nonmagnetic layer containing a nonmagnetic powder and a binder, and thereon, a magnetic layer containing a ferromagnetic powder and a binder, whereinthe magnetic layer contains a nonmagnetic filler the average particle diameter φ of which satisfies relation (I) below with a thickness t of the magnetic layer:1.0≦φ / t≦2.0 (I);the thickness t of the magnetic layer ranges from 30 to 200 nm;the nonmagnetic layer has a thickness ranging from 30 to 200 nm;a composite elastic modulus as measured on a surface of the magnetic layer ranges from 6.0 to 8.0 GPa; anda centerline average surface roughness Ra of the surface of the magnetic layer, as measured by an optical three-dimensional profilometer, ranges from 0.2 to 1.5 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method of improving print performance in flexographic printing plates
ActiveUS8158331B2Promote resultsReduces print flutingPhotosensitive materialsDuplicating/marking methodsCross-linkEngineering
Owner:MACDERMID PRINTING SOLUTIONS
Method of Improving Print Performance in Flexographic Printing Plates
ActiveUS20110081614A1Promote resultsReduces print flutingPhotosensitive materialsDuplicating/marking methodsCross-linkEngineering
A method of making a relief image printing element from a photosensitive printing blank is provided. A photosensitive printing blank with a laser ablatable layer disposed on at least one photocurable layer is ablated with a laser to create an in situ mask. The printing blank is then exposed to at least one source of actinic radiation through the in situ mask to selectively cross link and cure portions of the photocurable layer. Diffusion of air into the at least one photocurable layer is limited during the exposing step and preferably at least one of the type, power and incident angle of illumination of the at least one source of actinic radiation is altered during the exposure step. The resulting relief image comprises a plurality of dots and a dot shape of the plurality of dots is produced that is highly resistant to print fluting for printing on corrugated board.
Owner:MACDERMID PRINTING SOLUTIONS
All-solid battery and manufacturing method therefor
ActiveUS20140134483A1Suppress the generation of carbon residueSuppress internal short circuit of the all-solid batterySolid electrolytesElectrode thermal treatmentSetterSurface roughness
A method for manufacturing an all-solid battery that includes preparing a first green sheet as a green sheet for at least any one of a positive electrode layer and a negative electrode layer and a second green sheet as a green sheet for a solid electrolyte layer, stacking the first green sheet and the second green sheet to form a stacked body, and firing the stacked body with a setter placed in contact with at least one surface of the stacked body. The setter in contact with the at least one surface of the stacked body is 0.11 μmRa or more and 50.13 μmRa or less in surface roughness.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Diffusing film comprising transparent resin and scatterers
InactiveUS20030147140A1Controlled surface roughnessImprove viewing angle characteristicsDiffusing elementsPolarising elementsRefractive indexPolymer chemistry
A diffusing film comprises a transparent resin in which scatterers are dispersed. The difference between the refractive index of the transparent resin and that of the scatterers is in the range of 0.04 to 1.5. The scatterers are flat particles having sizes of 0.1 to 50 mum.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
High strength vacuum deposited nitinol alloy films and method of making same
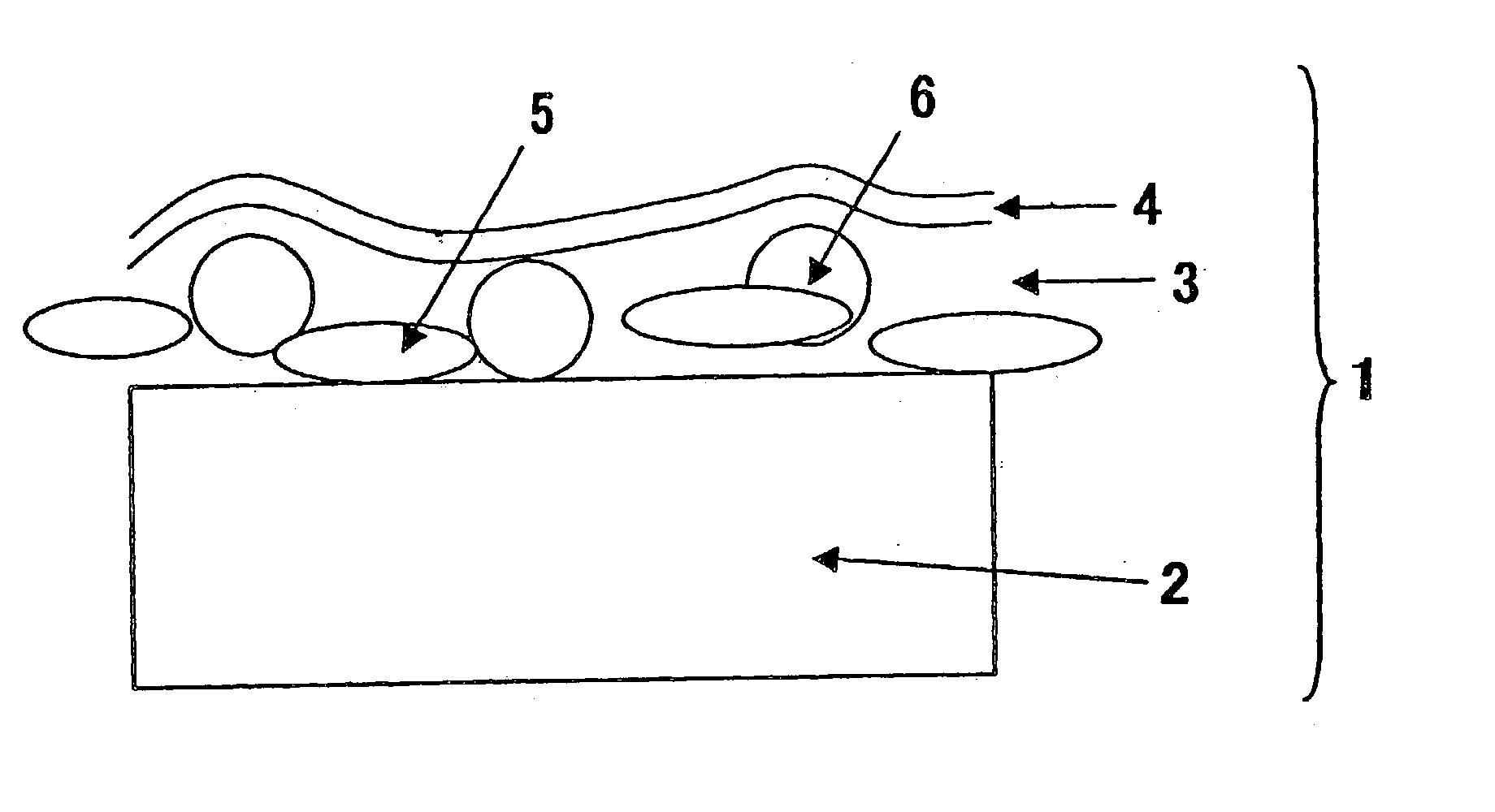
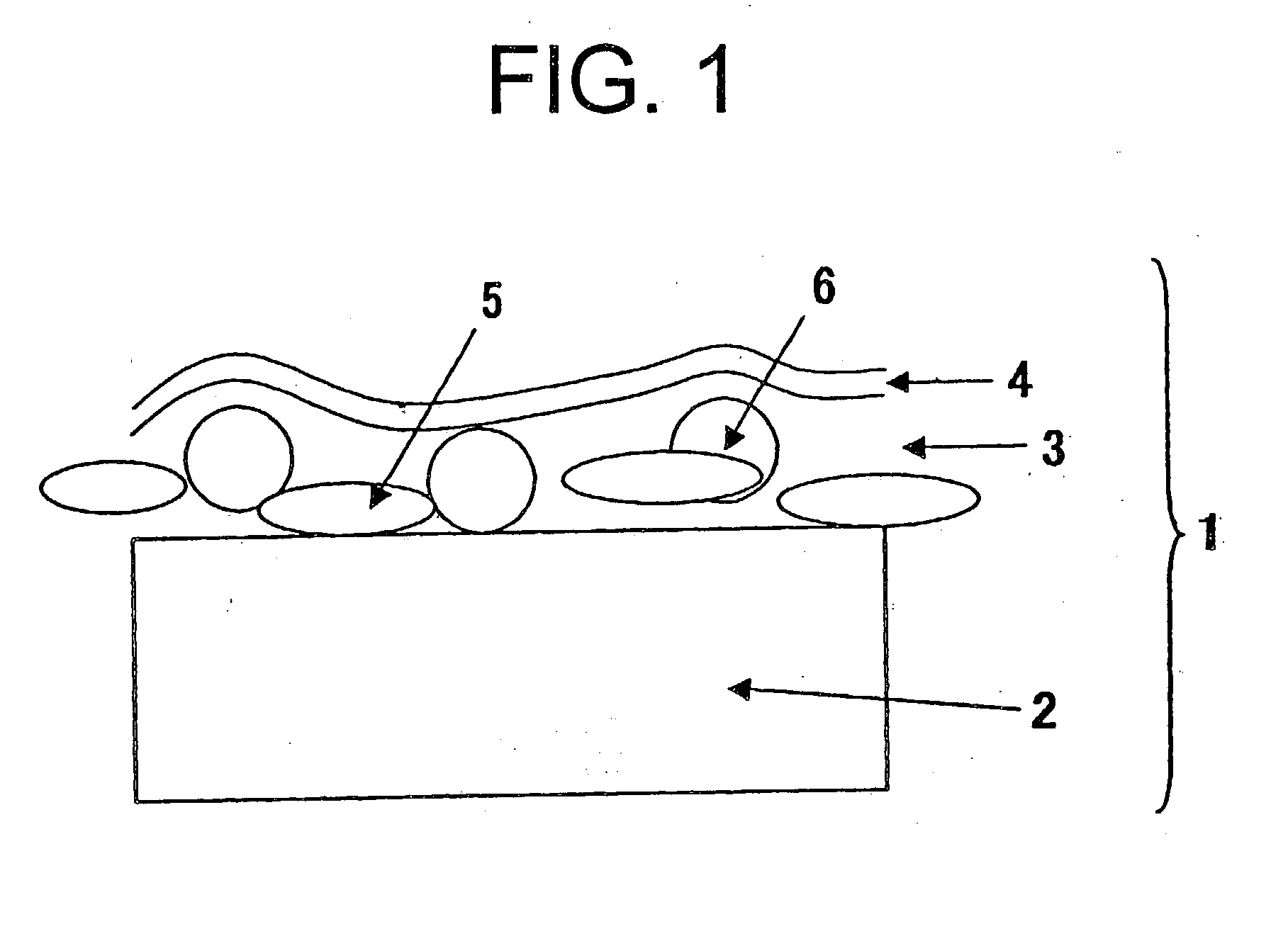
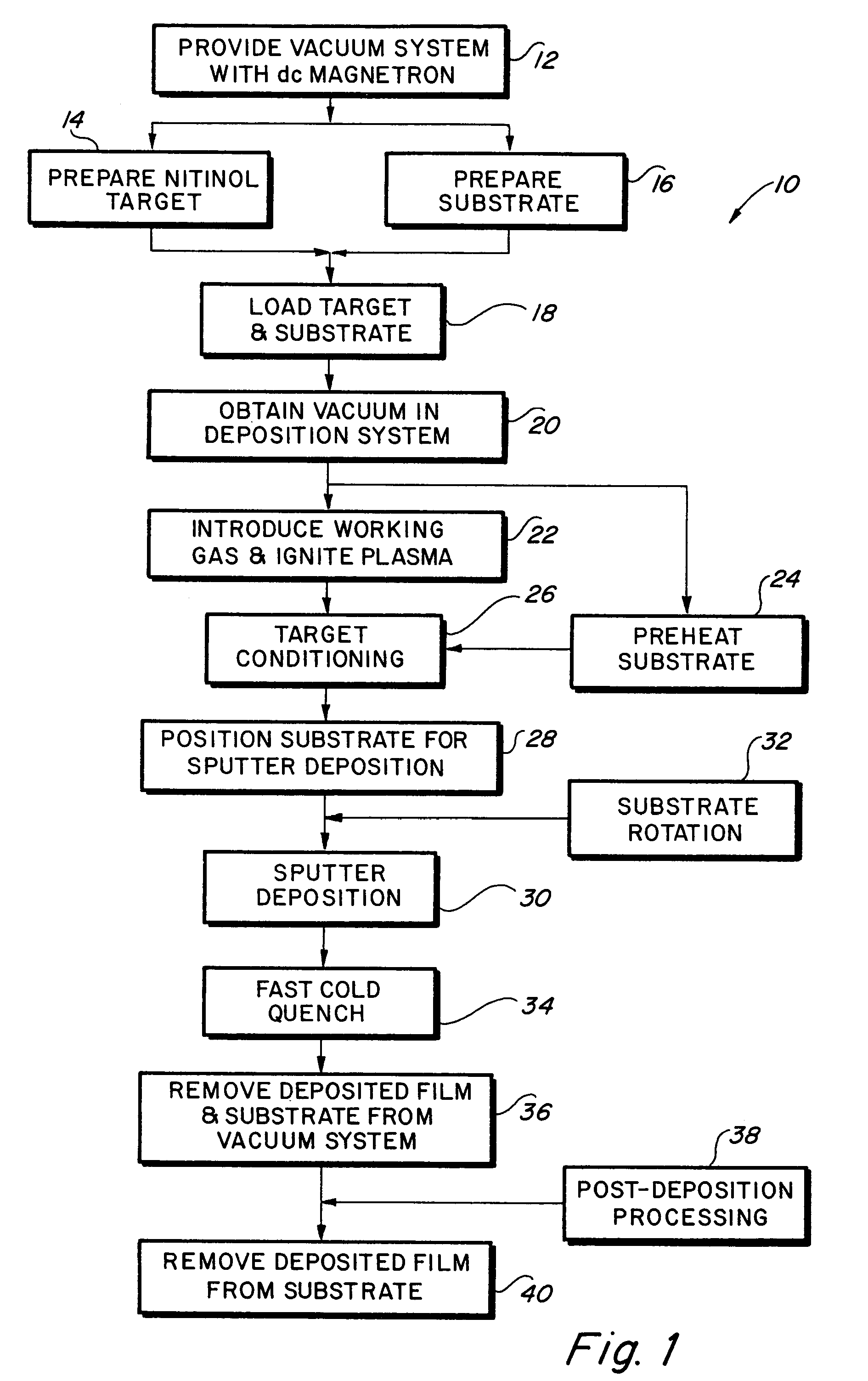
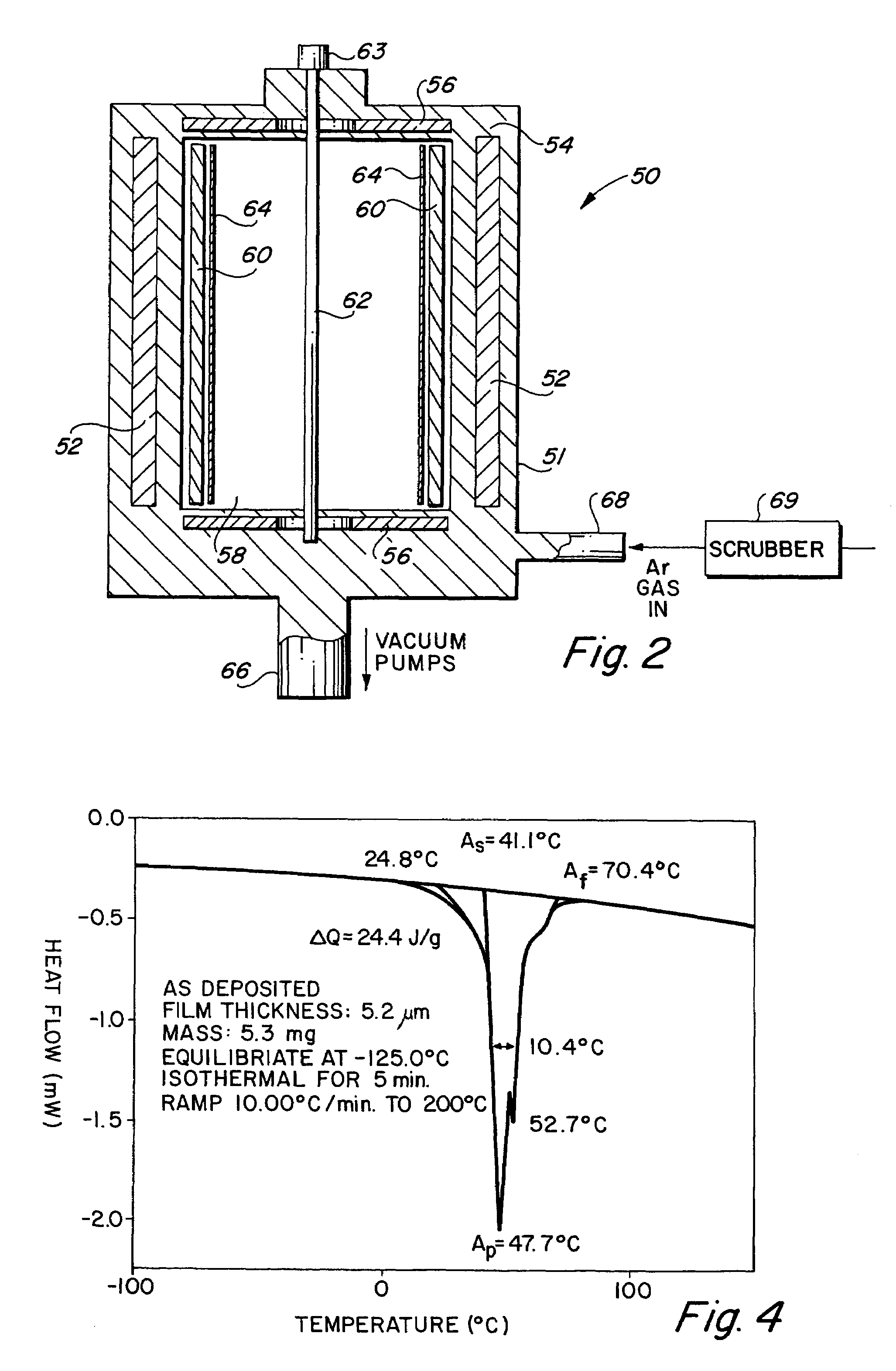
InactiveUS7335426B2Minimise scatteringControlled surface roughnessPig casting plantsThermometers using material expansion/contactionThin membraneTitanium
A vacuum deposition method for fabricating high-strength nitinol films by sputter depositing nickel and titanium from a heated sputtering target, and controlling the sputter deposition process parameters in order to create high-strength nitinol films that exhibit shape memory and / or superelastic properties without the need for precipitation annealing to attenuate the transition conditions of the deposited material. A vacuum deposited nitinol film having high-strength properties equal to or better than wrought nitinol films and which are characterized by having non-columnar crystal grain structures.
Owner:VACTRONIX SCI LLC
Diffusing film comprising transparent resin and scatterers
InactiveUS6710923B2Prevent surfaceWiden perspectiveDiffusing elementsPolarising elementsRefractive indexPolymer chemistry
A diffusing film comprises a transparent resin in which scatterers are dispersed. The difference between the refractive index of the transparent resin and that of the scatterers is in the range of 0.04 to 1.5. The scatterers are flat particles having sizes of 0.1 to 50 mum.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Heat treatment jig for semiconductor wafer
ActiveUS7331780B2Suppress generationSurface planarity and roughnessCharge supportsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface roughnessSemiconductor
A heat treatment jig by the invention comprising: the diameter of a disk-type structure being 60% or more of that of loaded semiconductor wafers; the thickness being 1.0 mm or more but 10 mm or less; the surface roughness Ra of 0.1 μm or more but 100 μm or less at a contacting surface with the wafers; and the surface planarity being specifically controlled in the concentric direction as well as in the diametrical direction, otherwise in place of above planarity, comprising a controlled maximum height in such a way that the maximum height is obtained by the flatness measurement at the multiple positions and the difference between said maximum height and the hypothetical-average-height-plane thus set is 50 μm or less, can reduce the slip generation due to the close adhesion of the wafers and the jig. Owing to this, even if the wafers having large tare weight should be heat-treated, the slip generation can be effectively prevented, thus enabling the jig to be widely used as the reliable heat treatment jig for semiconductor substrates.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Photoelectrochemical etching for chip shaping of light emitting diodes
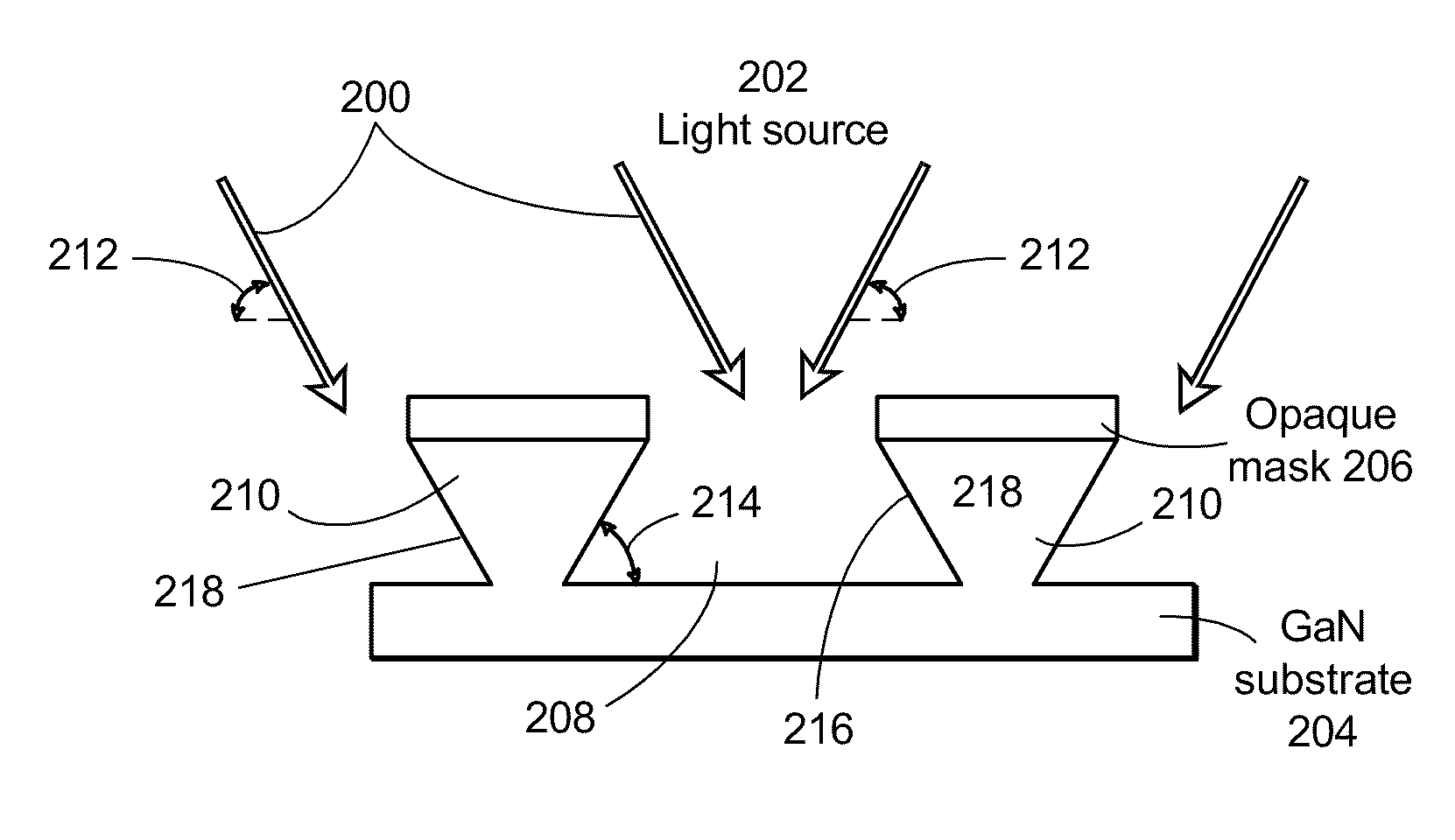
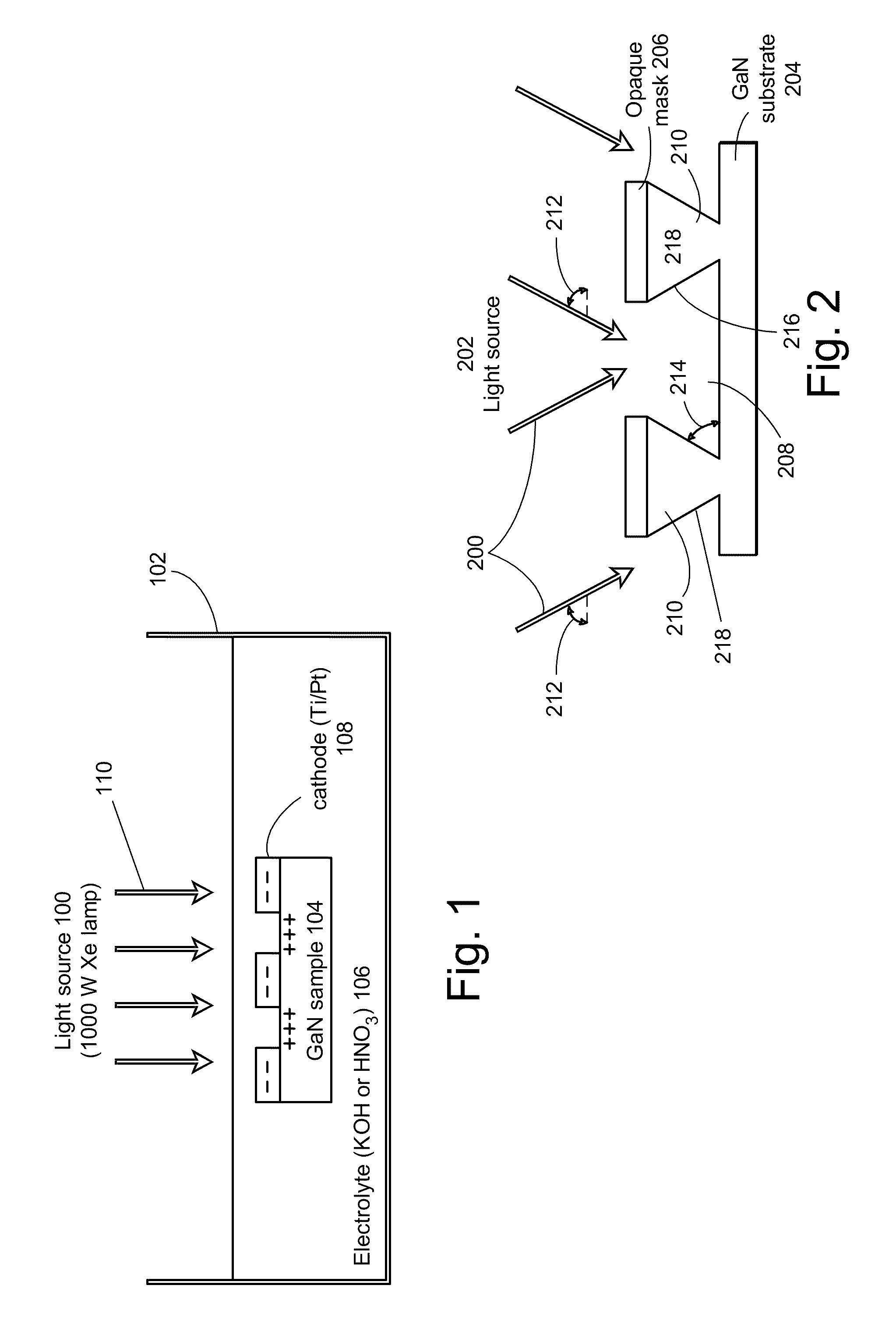
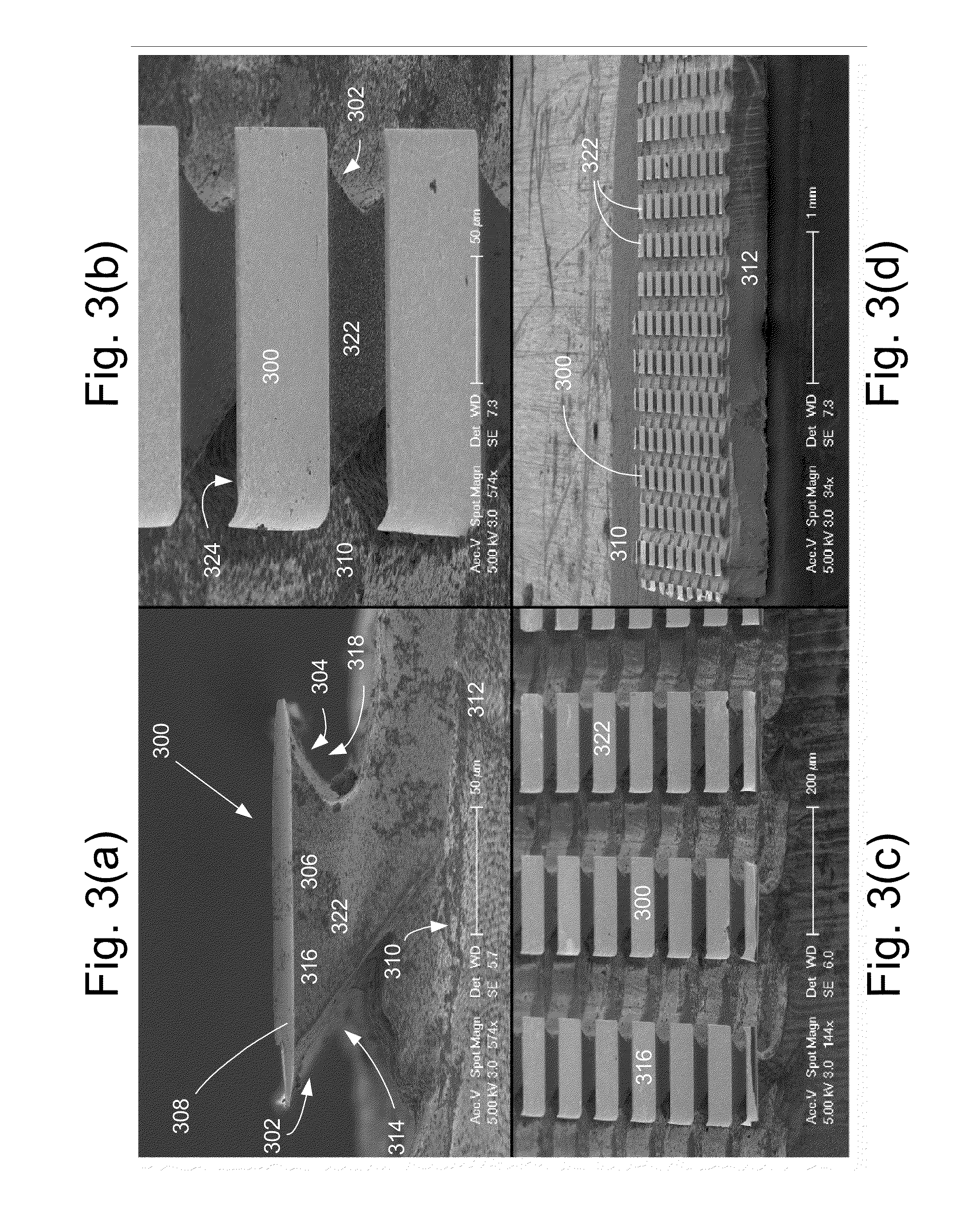
InactiveUS20100090240A1Speed up the extraction processControl roughnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsPhotoelectrochemical etching
A photoelectrochemical (PEC) etch is performed for chip shaping of a device comprised of a III-V semiconductor material, in order to extract light emitted into guided modes trapped in the III-V semiconductor material. The chip shaping involves varying an angle of incident light during the PEC etch to control an angle of the resulting sidewalls of the III-V semiconductor material. The sidewalls may be sloped as well as vertical, in order to scatter the guided modes out of the III-V semiconductor material rather than reflecting the guided modes back into the III-V semiconductor material. In addition to shaping the chip in order to extract light emitted into guided modes, the chip may be shaped to act as a lens, to focus its output light, or to direct its output light in a particular way.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for cutting a block of material and forming a thin film
InactiveUS7029548B2Weaken energyReduce distractionsDecorative surface effectsSolid-state devicesThermal treatmentChemistry
A process for cutting out a block of material includes a step of introducing ions in the block thereby forming an embrittled zone and defining at least one superficial part of the block. The method also includes a step of forming at least one separation initiator at the level of the embrittled zone, wherein the step of forming the separation initiator includes implanting ions of an ionic nature different from that introduced during the preceding step. The method further includes a step of separating at the level of the embrittled zone the superficial part of the block from a remaining part of the block from the separation initiator, wherein the separation step includes at least one of a thermal treatment and the application of mechanical forces acting between the superficial part and the embrittled zone.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Article Coated With an Ultra High Hydrophobic Film and Process For Obtaining Same
InactiveUS20080304008A1Control roughnessImprove surface roughnessFouling preventionPretreated surfacesPolymer scienceSurface roughness
The present invention relates to an article having at least one surface, wherein said surface is at least partially coated with a ultra high hydrophobic film having a surface roughness such that the film exhibits a static water contact angle at least equal to 115°, preferably 120°, even better 125°, and wherein said film is a nanostructured film comprising a first layer comprising nanoparticles bound by at least one binder adhering to the surface of the article, and a second layer of an anti-fouling top coat at least partially coating said first layer. The present invention also concerns a process for preparing the above article.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110207294A1Avoid crackingConstant polishing rateEdge grinding machinesBelt grinding machinesEngineeringSemiconductor
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device makes it possible to efficiently polish with a polishing tape a peripheral portion of a silicon substrate under polishing conditions particularly suited for a deposited film and for silicon underlying the deposited film. The method includes: pressing a first polishing tape against a peripheral portion of a device substrate having a deposited film on a silicon surface while rotating the device substrate at a first rotational speed, thereby removing the deposited film lying in the peripheral portion of the device substrate and exposing the underlying silicon; and pressing a second polishing tape against the exposed silicon lying in the peripheral portion of the device substrate while rotating the device substrate at a second rotational speed, thereby polishing the silicon to a predetermined depth.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP +1
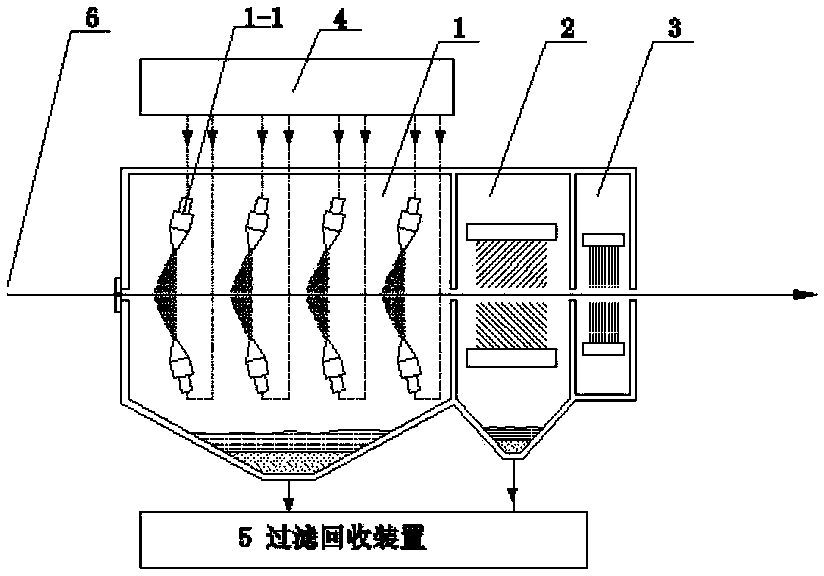
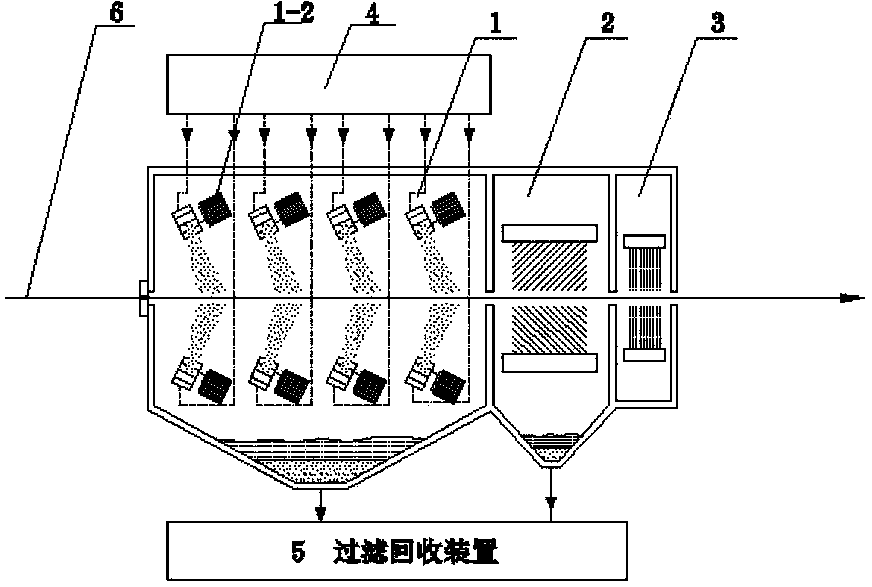
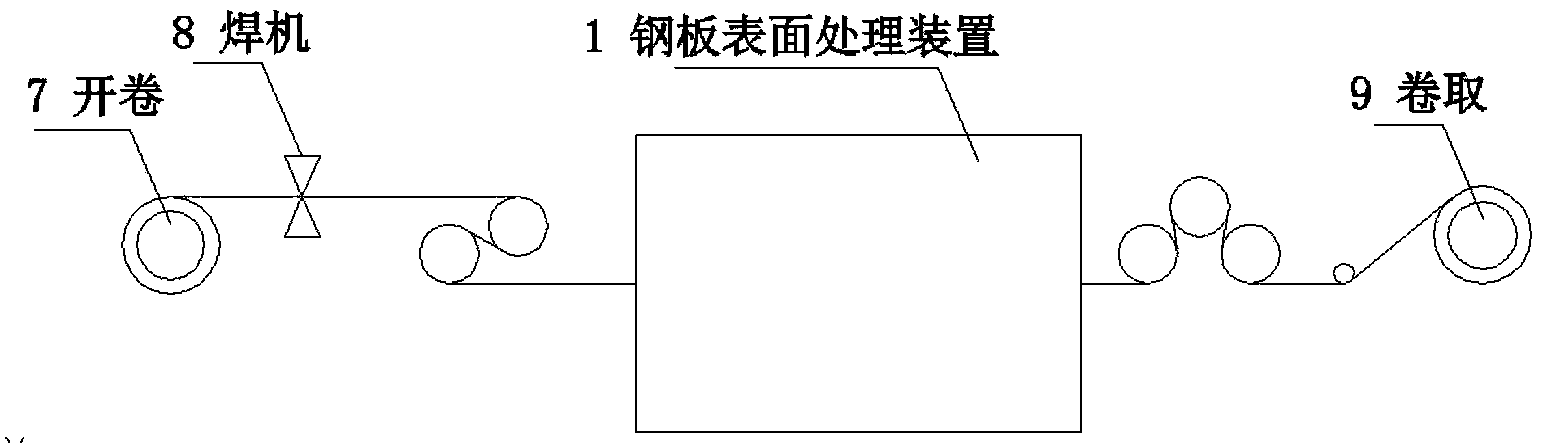
Steel plate surface treatment method and device
ActiveCN104056865AImprove cleanlinessReduce loadWork cleaning devicesMetal rolling arrangementsProcess functionSheet steel
An apparatus for treating a surface of a steal plate, sequentially comprising: a strip steel surface treatment unit (1) provided with a high-pressure ejection device (1-1) or a centrifugal throwing device (1-2), a strip steel surface cleaning unit (2), and a strip steel surface drying unit (3), one or both of the high-pressure ejection device and the centrifugal throwing device being arranged, and slurry, namely a mixture of solid abrasive and water, being sprayed onto the surface of the strip steel; and further comprising a slurry supply unit (4) and an abrasive filtering and recovery unit (5). Also disclosed is a method for treating a surface of a steal plate. In the treatment method, by spraying the solid mixed abrasive onto the surface of the strip steel, the surface roughness of the strip steel is controlled, and further, the oil, iron oxide scales and some dirty things on the surface of the strip steel can be cleared, thereby fully or partially replacing the smoothing process function.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Method to Fabricate a Redirecting Mirror in Optical Waveguide Devices
InactiveUS20090020499A1Reduce roughnessEasy to controlElectric discharge tubesOptical articlesResistWaveguide
A method of fabricating a turning mirror for an optical device includes the steps of depositing on a substrate, which defines a plane in which an optical signal propagates in a propagating direction, a photoresist layer sensitive to electrons and to UV radiation. The material in which the photoresist layer is formed, has a contrast not larger than 3. A first portion of the photoresist layer is exposed to an electron beam, wherein the electron dose of the electron beam exposure is varied within the first portion according to a selected pattern, and wherein the electron does to which a given region in the photoresist is exposed, depends on the resulting photoresist height in the given region after development. A second portion of the photoresist layer is exposed to UV radiation; the first and the second portions are overlapped at least in a third portion. The photoresist layer is developed so as to form in the third portion of the photoresist layer exposed to both electron beam and to UV radiation a first surface having an angle relative to the propagating direction. The substrate and the photoresist are etched so that a second angled surface is formed in the substrate in correspondence to the third portion. The second surface forms an angle with the propagating direction.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Yttria sintered body and component used for plasma processing apparatus
ActiveUS20110129684A1Reducing plasma etch rateImprove the level ofOptical articlesThin material handlingPorosityHalogen
To provide a high-purity Yttria sintered bodies having a high strength, a low dielectric loss and high plasma corrosion resistance of halogen gas during wide range surface roughness (Ra).SolutionAn Yttria sintered body having a dielectric loss tan δ of 1×10−4 or less in the frequency range from 1 to 20 GHz, wherein the Yttria sintered body contains Yttria of 99.9% by mass or more, has a porosity of 1% or less and an average crystal grain size of 3 μm or less, and the cumulative frequency ratio calculated from the following formula (1) is 3 or less:Cumulative frequency ratio=D90 / D50 (1)In the above-described formula (1), the meanings of the individual symbols are as follows:D90: The crystal grain size (μm) at which the cumulative number of grains as calculated from the smaller grain size side is 90% in the grain size distribution of the crystal grains in terms of the number of grains.D50: The crystal grain size (μm) at which the cumulative number of grains as calculated from the smaller grain size side is 50% in the grain size distribution of the crystal grains in terms of the number of grains.
Owner:FERROTEC CERAMICS CORP
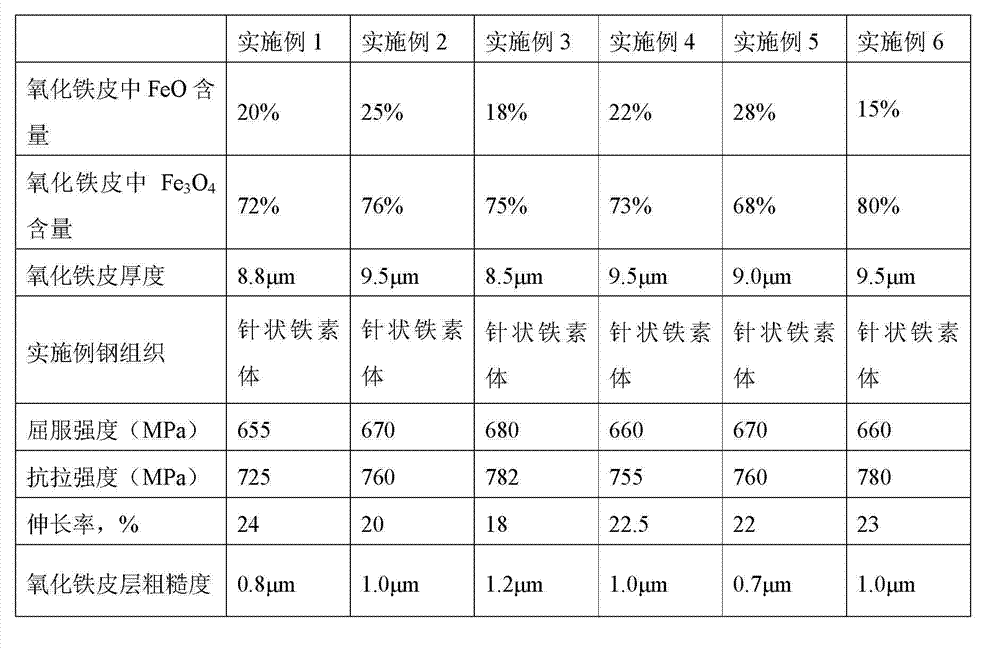
Steel with stable oxide layer for pretreatment-free high-strength container and manufacture method of steel
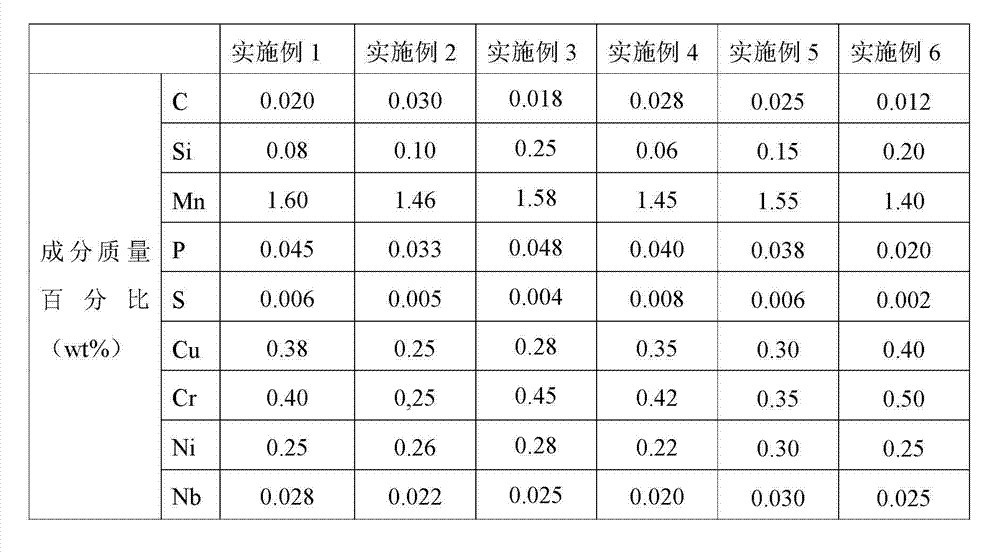
The invention discloses steel with a stable oxide layer for a pretreatment-free high-strength container and a manufacture method of the steel disclosed by the invention. The steel disclosed by the invention comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.01-0.03% of C, 0.05-0.25% of Si, 1.4-1.6% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.008% of S, less than or equal to 0.05% of P, 0.25-0.40% of Cu, 0.25-0.50% of Cr, 0.22-0.30% of Ni, 0.02-0.03% of Nb and the balance of iron and inevitable impurities. The manufacture method of the steel disclosed by the invention is carried out according to the general pure steel process and comprises the following steps of: desulfurizing molten iron, smelting via a converter, refining via an LF (ladle furnace), refining via an RH (Rockwell Hardness) furnace, heating plate blanks, performing hot continuous rolling, cooling back section and reeling. The practice proves that the steel disclosed by the invention has the advantages of good integral corrosion resistance and high strength; meanwhile, the steel disclosed by the invention can be directly used for coating in the process of manufacturing the container without the pre-treating non-environmentally friendly pretreatment processes of blasting sand and blasting shots and has no negative influence on the coating quality and the coating property; and an oxide iron layer and a coating system are closely combined, so that the steel is good in compatibility. The manufacture method of the steel disclosed by the invention is simple in process flows and low in production cost.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Giant non-standard trapezoidal thread processing method
ActiveCN101266476AImprove processing productivityImprove processing quality and precisionNumerical controlProcessing accuracyHigh pressure
The invention relates to a processing method of high-pressure exterior cylinder component of million grade super critical steam turbine, especially to a processing method of S2099*P50 giant nonstandard trapezoidal thread. A processing method of giant nonstandard trapezoidal thread uses a numerically controlled machine to execute processing, which is carried out according to the following sequences: executing mathematics modeling to the screw thread type wire; using coarse and fine processing methods, determining suitable radius lathe cutters respectively adopted by the coarse and fine processing methods according to required processing wire and required surface accuracy and roughness concentration, and determining suitable deepness allowance of the line face after the coarse processing; determining the coarse processing lathe cutter center track area and the fine processing lathe cutter center track area, and modeling for the cutter center track boundary; determining spacing of every layer during processing and spacing of every cutter in a same layer according to the material to be cut, the selected cutter, machine performance and cutting position; programming the coarse and fine processing lathe cutter walking procedure; and executing the process according to the programmed procedure. The inventive processing method has high process efficiency and high machine precision.
Owner:SHANGHAI ELECTRIC POWER GENERATION EQUIPMENT CO LTD
Method of forming dielectric film
ActiveUS20060008969A1Controlled surface roughnessReduce surface roughnessTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectricResidence time
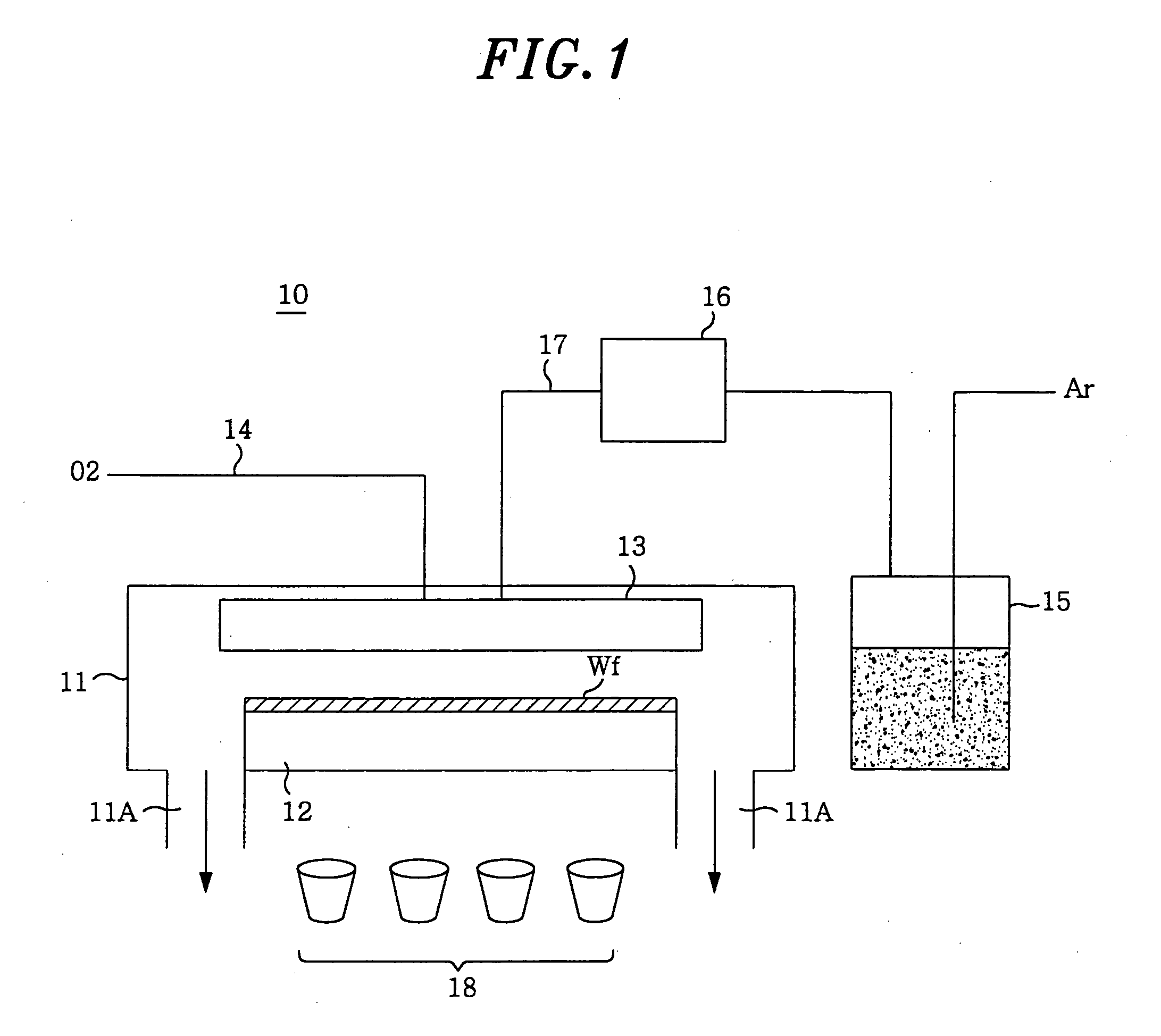
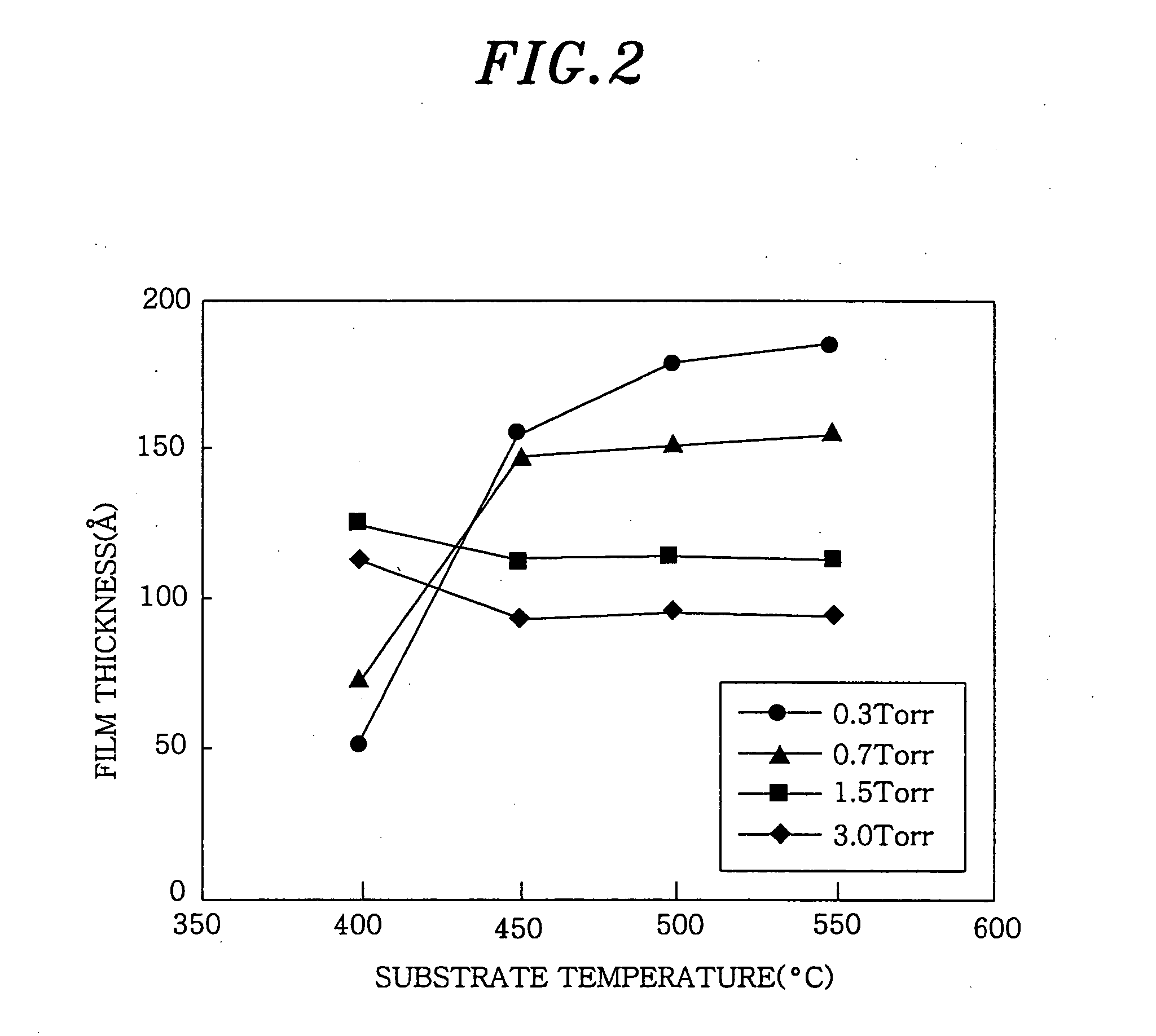
A method of forming a dielectric film by an organic metal CVD method, comprising the step of supplying an organic metal compound into a treating container having a substrate to be treated held therein to form the dielectric film on the substrate, wherein the dielectric film forming step comprises the first step of depositing, in the treating container, the dielectric film under a first condition so set as to allow the residence time of the organic metal compound to extend to a first value, and the second step of further depositing, after the first step and in the treating container, the dielectric film under a second condition so set as to allow the residence time of the organic metal compound to extend to a second value smaller than the first value.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
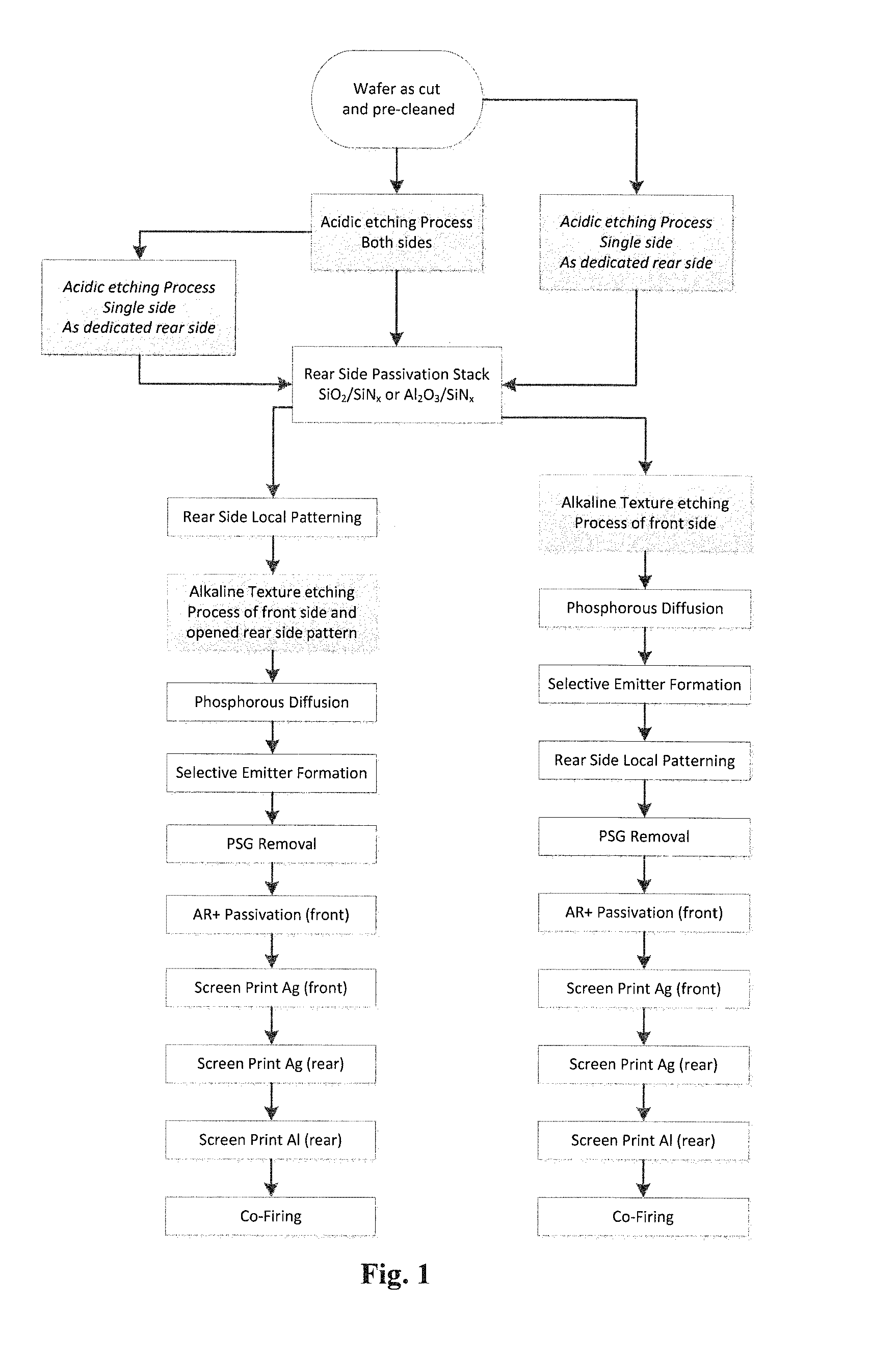
Acidic etching process for si wafers
InactiveUS20150040983A1Improve effectivenessControl roughnessFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsAlkaline etchingSilicon
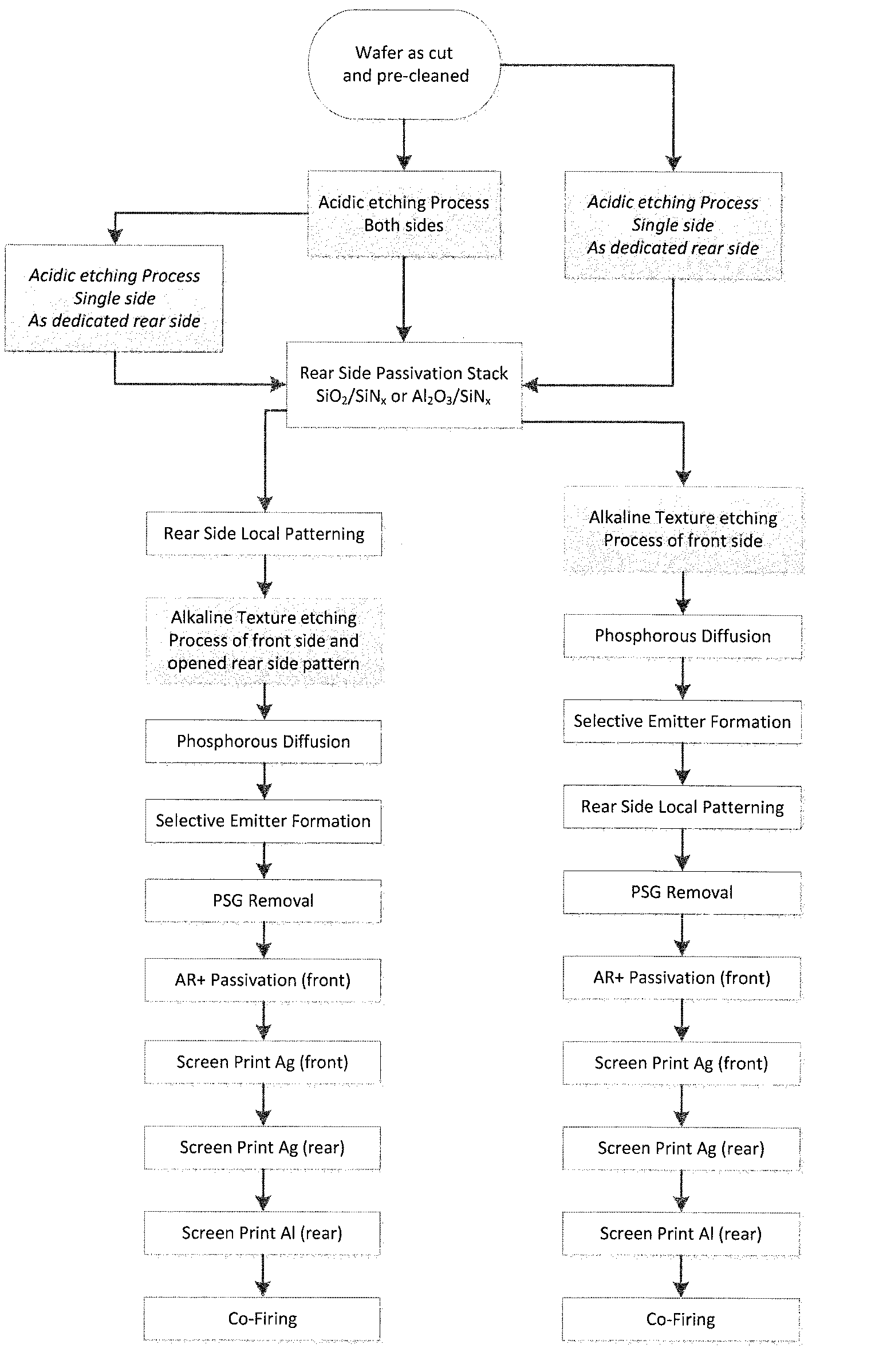
The present invention relates to a method for acidic surface etching of a silicon wafer, such as those used for solar cells, comprising contacting at least one surface of a silicon wafer as cut with an acidic etching agent, provided that the wafer is, prior to the acidic etching, not subjected to an alkaline etching step or process. Further, the present invention is directed to Si wafer, photovoltaic cells, PERC photovoltaic cells and solar modules produced according to the method of the present invention.
Owner:SOLARWORLD AMERICAS
Method for detecting non-planeness defect
InactiveCN1388354AControl roughnessReduce the influence of roughness measurementUsing electrical meansElectric/magnetic roughness/irregularity measurementsEngineeringAngular sector
The object of the invention is a process for detecting latent flatness defects in a band product (2) applied under tensile load to an angular sector (A) of measuring roll (1) comprising a plurality of detection zones (4) spaced apart each comprising a transmission sensor (3), at each rotation, of a measurement signal having a value under load (i) which is compared, at each rotation, with a reference value, in order to assess, in each longitudinal zone of the band (2), information representative of the tensile load applied in this zone. According to the invention, two values in empty condition (i1, i2) of the signal transmitted by each sensor (3) are measured, respectively before and after the corresponding detection zone passes through the angular application sector (A) of the band and the reference value (i0) to which is compared, at each rotation, the value under load (i) of the signal transmitted by each sensor is obtained by combination of said values in empty condition, respectively preceding (i1) and subsequent (i2).
Owner:CLECIM SAS
Automatic production line for AG anti-dazzle panel display glass
ActiveCN105645777AQuality improvementFinely control the amount of chemical polishingControl signalDrive motor
The invention provides an automatic production line for AG anti-dazzle panel display glass and relates to AG anti-dazzle panel display glass production equipment. The automatic production line comprises station regions and a DCS (Distributed Control System), wherein the station regions are sequentially a feeding region, an acid pickling region, two etching regions, a panel turning region, at least one washing region, at least one thinning and polishing region, a washing suck-drying region, an air drying region and a discharging region; each station region is provided with a rack and an independent driving system; each driving system is provided with a driving motor, a chain-drive mechanism, a drive shaft, at least one nail gear drive pair and at least one drive roll; the panel turning region comprises a panel turning mechanism; the panel turning mechanism is provided with a servo motor, a gear case, a tray, a tray overturning shaft, a magnetic controller and an angle controller; the acid pickling region is provided with an acid tool; the washing suck-drying region is provided with an upper water suction roll and a lower water suction roll; the air-drying region is provided with a blower and an air knife; the control signal output end of the DCS is respectively connected with the servo motor of the panel turning mechanism and the driving motor of the driving system in each station region and a liquid feeding pump of a liquid feeding system in each station region.
Owner:张源兴
Method for preparing polyvinyl butyral rubber sheet
InactiveCN101108532AControl Surface PatternControl roughnessFlat articlesPolyvinyl butyralSheet film
A method of preparing polyethylene glycerol film, which comprises the following procedures: firstly, mix polyethylene glycerol resin and addition agent to produce plasticized polyethylene glycerol resin; secondly, add the plasticized polyethylene glycerol resin produced in the procedure (1) to an extruding machine to smelt, and proceed flux extruding; the extruded flux is delivered into a extruding plate module head, a polyethylene glycerol film is extruded between the two module lips of the extruding plate module head, the gap between the module lips is controlled between 0.65 to 0.95mm during the process, at the same time control the temperature of the surface of the module lips lower by 20 to 55 DEG C. than the flux. The method provided in the invention can conveniently realize the surface decoration design and roughness of the PVB film, which doesn't need special assistance operation, and realize the control to the decoration design and roughness of the film.
Owner:浙江利丰塑胶有限公司
Multi-dimensional nano-particle modified super-hydrophobic oil-absorbing foam material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a multi-dimensional nano-particle modified super-hydrophobic oil-absorbing foam material and a preparation method thereof. According to the method, nano particles of different dimensions are grafted on the surface of a three-dimensional foam material by covalent bonds through a dual-functional group chemical modification method, and further, hydrophobic modification is performed by using a simple silane coupling agent, so that the super-hydrophobic oil-absorbing foam material is acquired. In the method, particle adhesion is improved effectively through chemical grafting, multi-layer modification by nano particles is realized by grafting repeatedly, so as to regulate the surface roughness of the material. The super-hydrophobic oil-absorbing foam material overcomes defects of single size of particles and poor adhesion on a matrix, is prepared through a simple process, is low-cost, and can be produced in a large scale.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
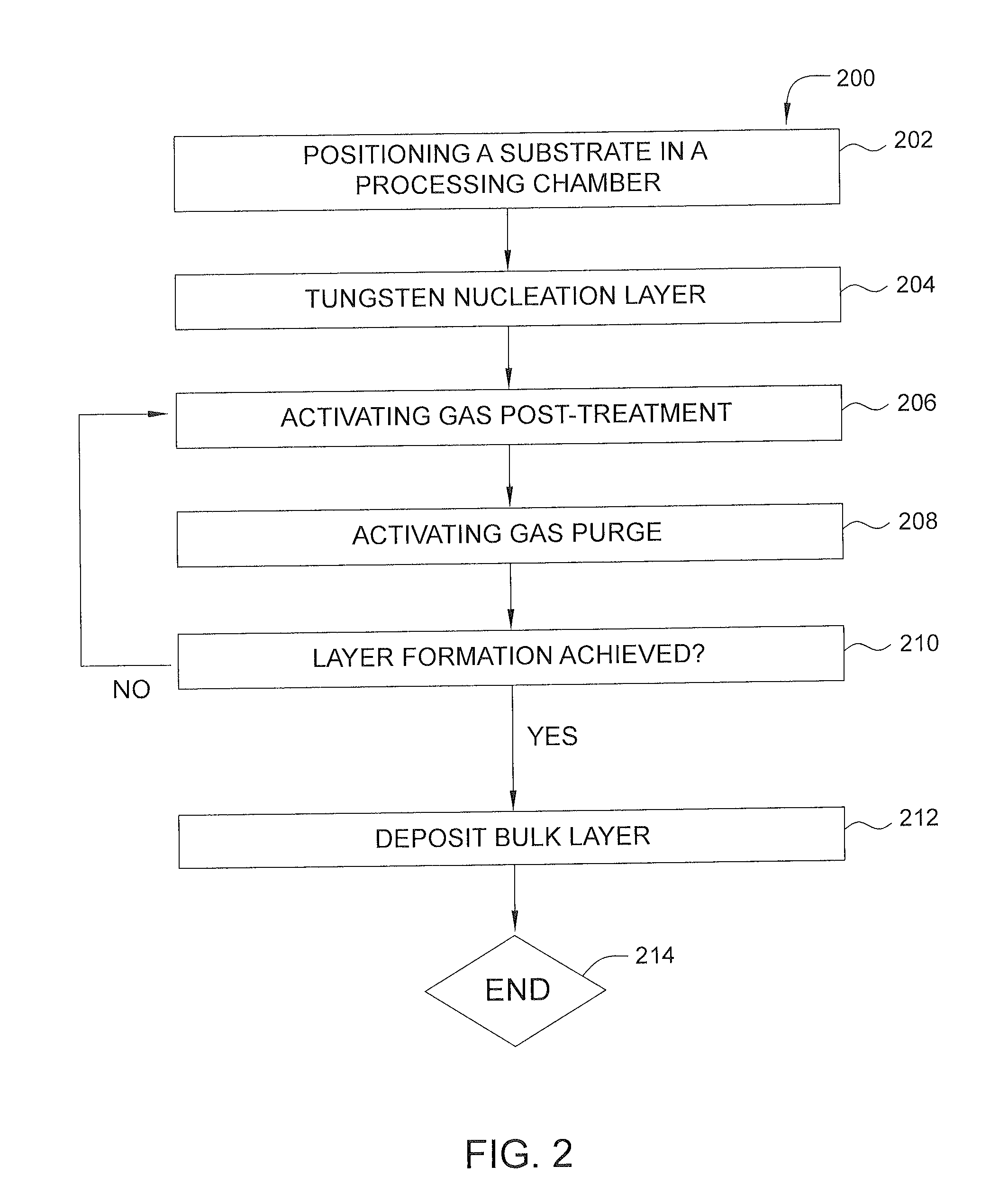
Method of reducing tungsten film roughness and resistivity
InactiveUS20140147589A1Low resistivityReduce roughnessChemical vapor deposition coatingDeposition temperatureNucleation
Methods for controlling crystal size in bulk tungsten layers are disclosed herein. Methods for depositing a bulk tungsten metal layer can include positioning a substrate with a barrier layer in a processing chamber, forming a tungsten nucleation layer, post-treating the nucleation layer with one or more treatment gas cycles including an activating gas and a purging gas, heating the substrate to a deposition temperature, and depositing a bulk tungsten layer with alternating nitrogen flow on the nucleation layer. The post-treatment cycling can be applied optionally to the bulk metal deposition with alternating nitrogen flow.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Aqueous, acid bath and method for the electrolytic deposition of copper
ActiveUS8679316B2Good effectControl roughnessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPrinted circuit manufactureElectrolysisCopper
An aqueous, acid bath for the electrolytic deposition of copper contains at least one copper ion source, at least one acid ion source, at least one brightener compound, and at least one leveler compound, and generates a very uniform copper deposit in particular in blind micro vias (BMVs) and trenches. The leveler compound is selected from among synthetically produced non-functionalized peptides, synthetically produced functionalized peptides, and synthetically produced functionalized amino acids.
Owner:ATOTECH DEUT GMBH
Adaptive event trigger control method for nonlinear uncertain system
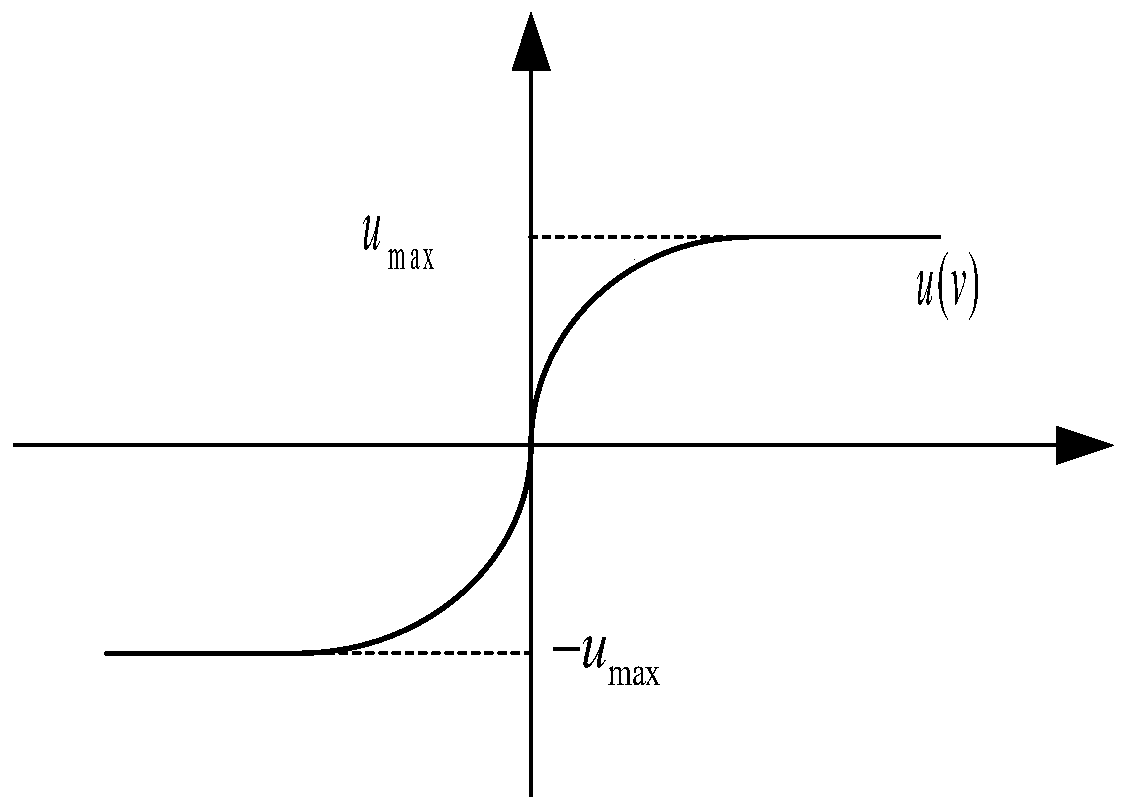
ActiveCN110687784AControl roughnessAvoid roughnessAdaptive controlControl engineeringEvent triggered
The invention discloses an adaptive event trigger control method for a nonlinear uncertain system, which comprises the steps of firstly, for an input saturation phenomenon, adopting a smooth hyperbolic tangent function to approximate the saturation characteristic of system control input so as to avoid the phenomenon of unsmooth control input and facilitate the subsequent design; secondly, for an uncertain part of the system, improving the traditional Fuzzy Logic Systems (FLSs) to a certain extent, and taking the time-varying approximation error of an approximation system into consideration; finally, providing an event trigger control mechanism of a dynamic threshold for the bandwidth constraint existing in the actual system, wherein the trigger threshold changes along with the change of the control quantity at the last moment, so that more precise and flexible control can be realized, and the system bandwidth resources can be better saved on the basis of ensuring the control effect.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Manufacturing method for anti-glare (AG) panel display glass
The invention provides a manufacturing method for AG panel display glass, belonging to the technical field of deep processing of glass. An automatic AG panel display glass production line is adopted in the invention. The manufacturing method comprises the following process flow: feeding; pickling; etching; turnover of panels; washing; thinning and polishing; washing and drying through sucking; and air drying. Through pickling, impurities adhered on the surface of a glass flake can be cleaned, so a clean glass surface is obtained for acid etching. Through corrosion of strong acid, honeycomb corrosion pits are formed in the surface of glass, so surface roughness of glass is improved. Chemical polishing is employed for fine processing control of the acid etched surface of the AG glass, and a DCS control system is used for realization of automatic operation of whole flow; thus, accurate control of technological parameters is realized, and product quality is improved.
Owner:福建和达玻璃技术有限公司
Plasma display panel and method for making a plasma display panel
InactiveUS20050264212A1Controlled surface roughnessEnhance electron emissionAddress electrodesSustain/scan electrodesPhosphorSurface roughness
A plasma display panel comprising first and second substrates positioned substantially parallel to each other, facing each other and separated from each other by a predetermined distance is disclosed. A plurality of address electrodes are formed on the first substrate. A first dielectric layer covers the address electrodes on the first substrate. A plurality of barrier ribs having predetermined heights are mounted on the first dielectric layer, creating discharge spaces between the first and second substrates. Phosphor layers are formed within the discharge spaces. A plurality of discharge sustain electrodes are formed on the second substrate and are positioned perpendicular to the address electrodes on the first substrate. A second dielectric layer is formed on the second substrate covering the discharge sustain electrodes. A MgO protection layer having a surface roughness (Rms) ranging from about 60 to about 250 {acute over (Å)} covers the second dielectric layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com