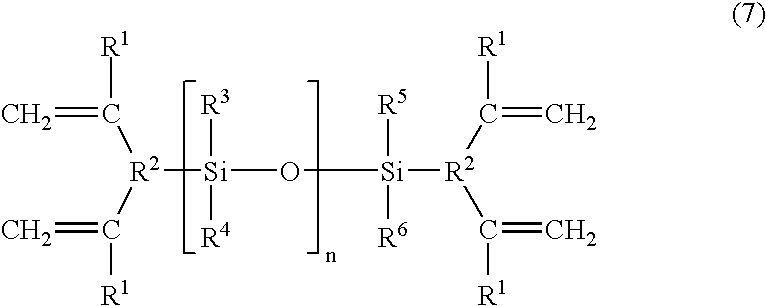
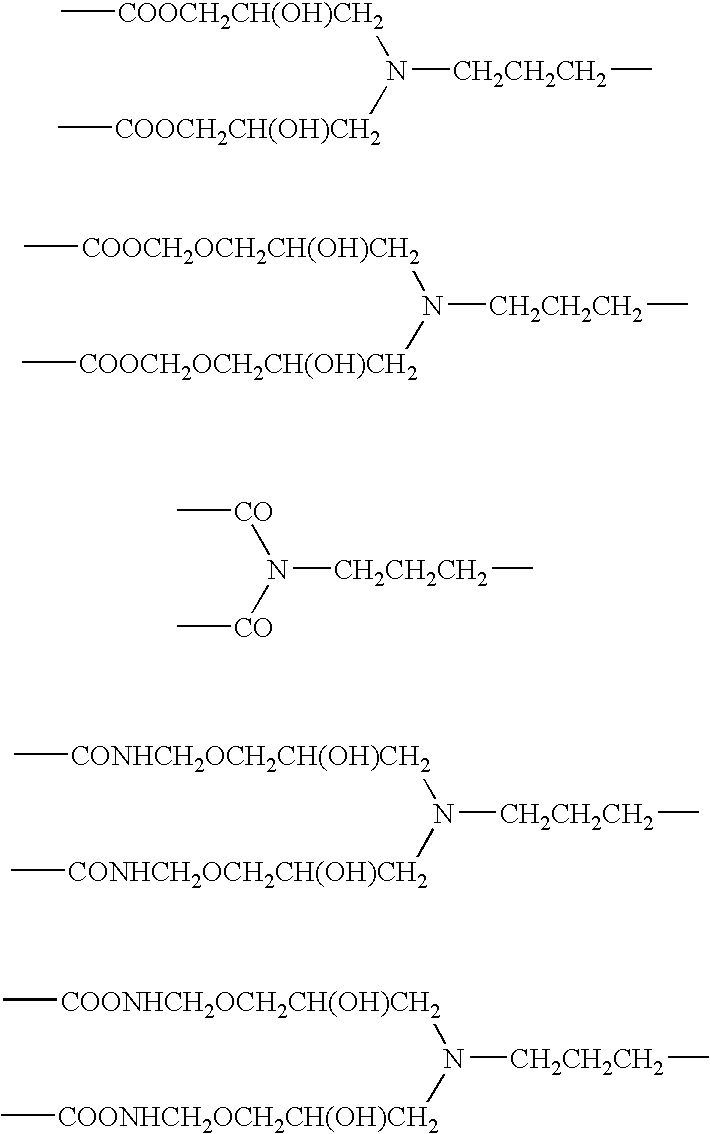Patents
Literature
68results about How to "High χ value" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
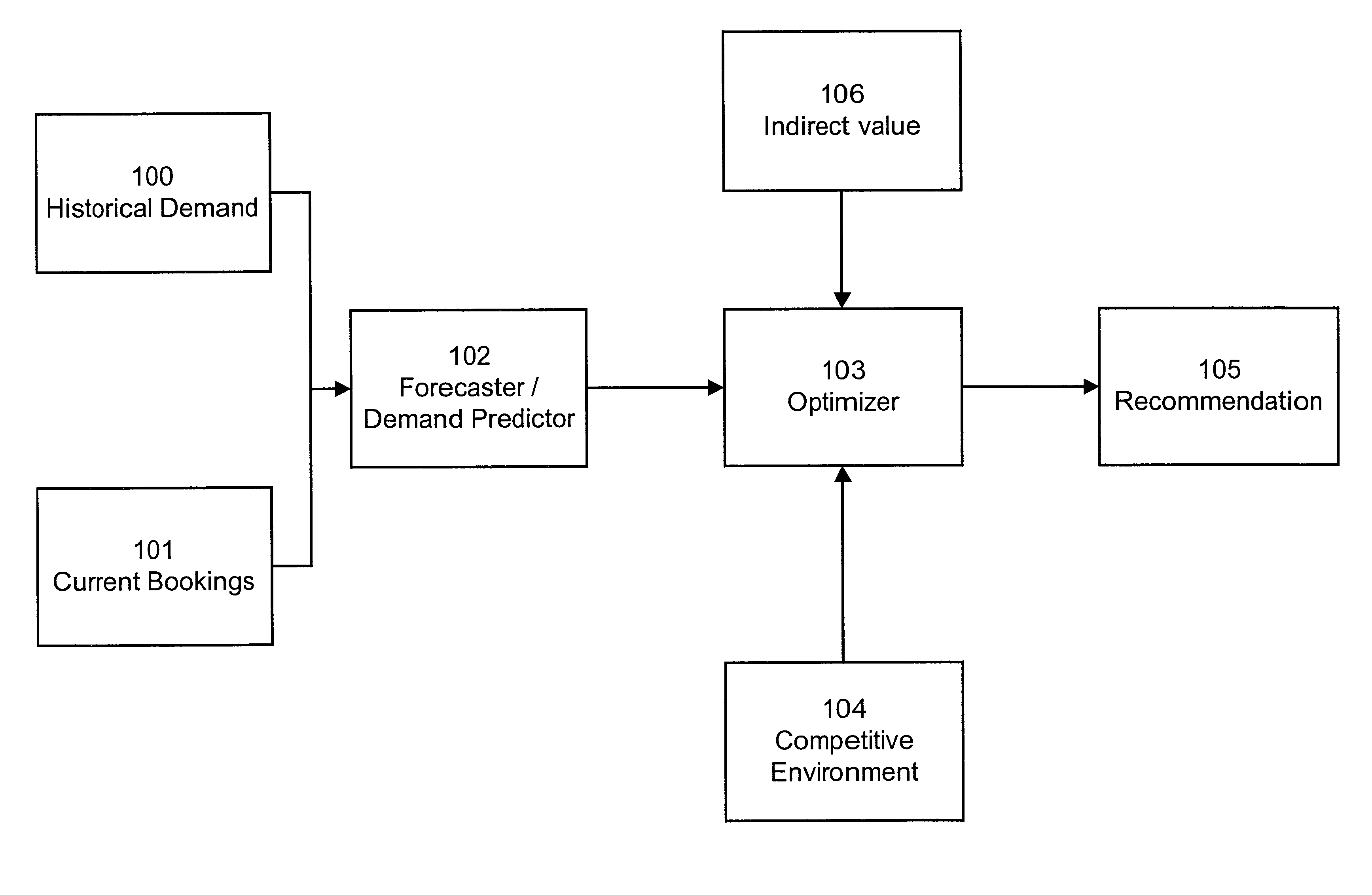
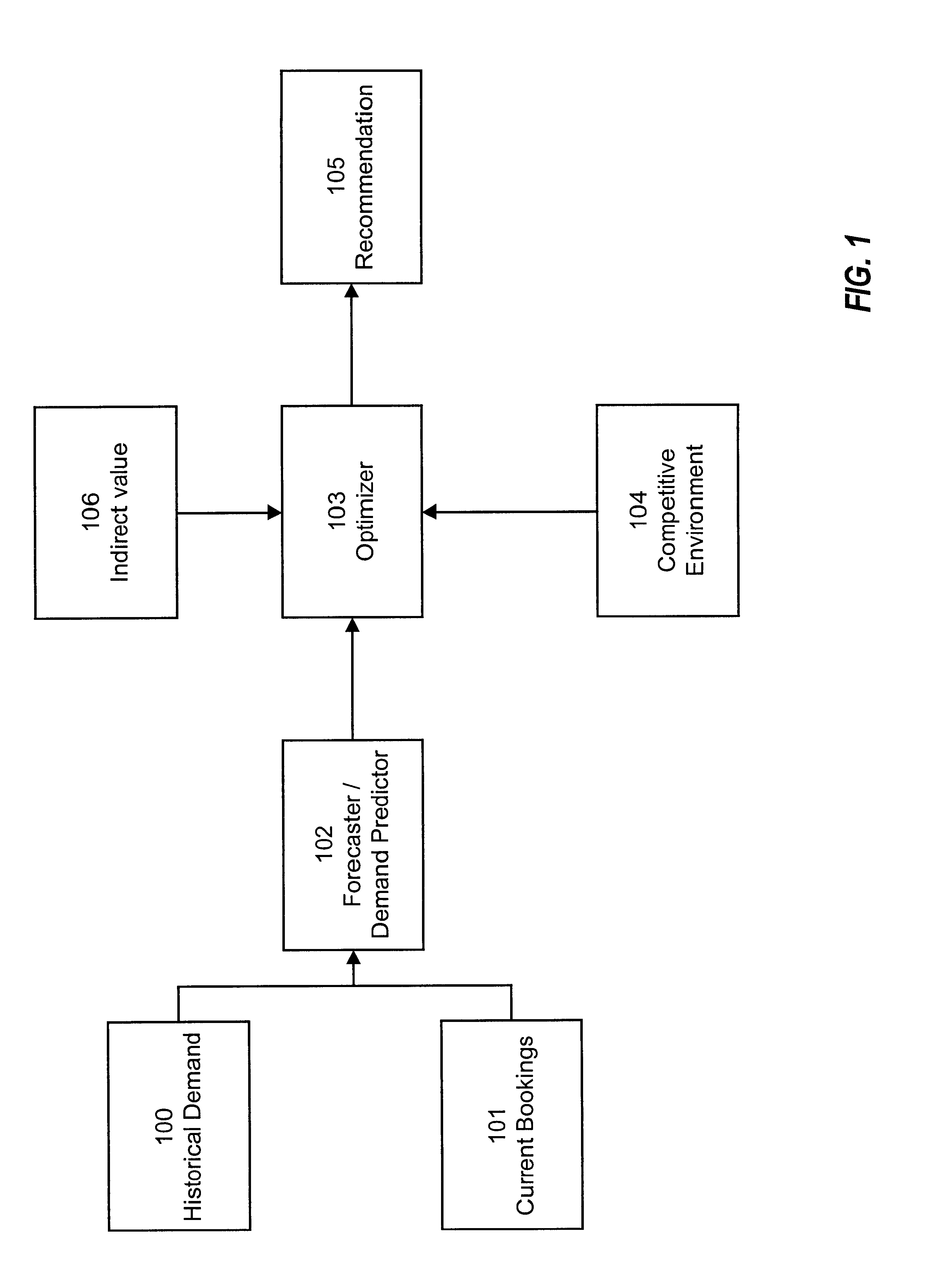
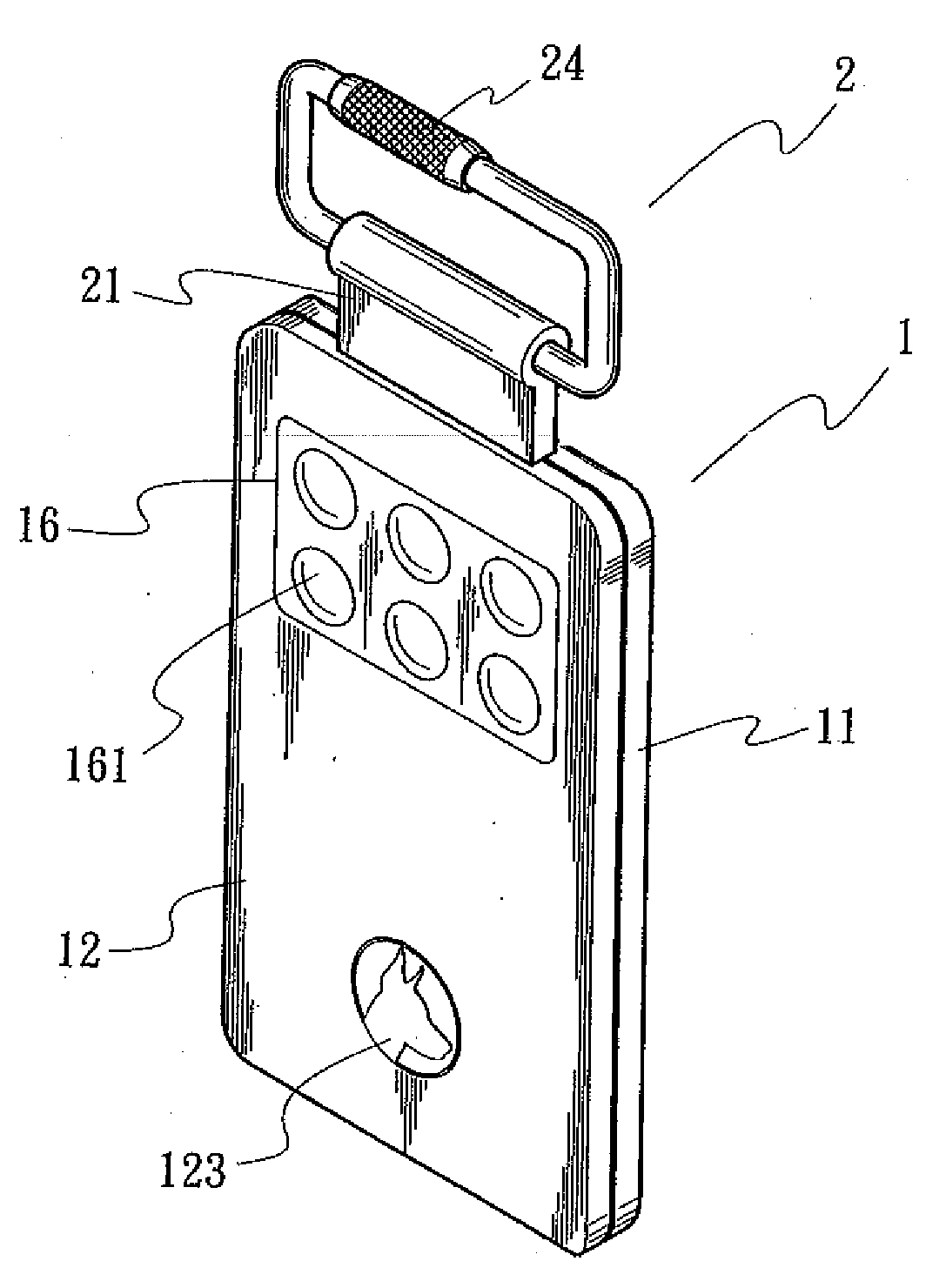
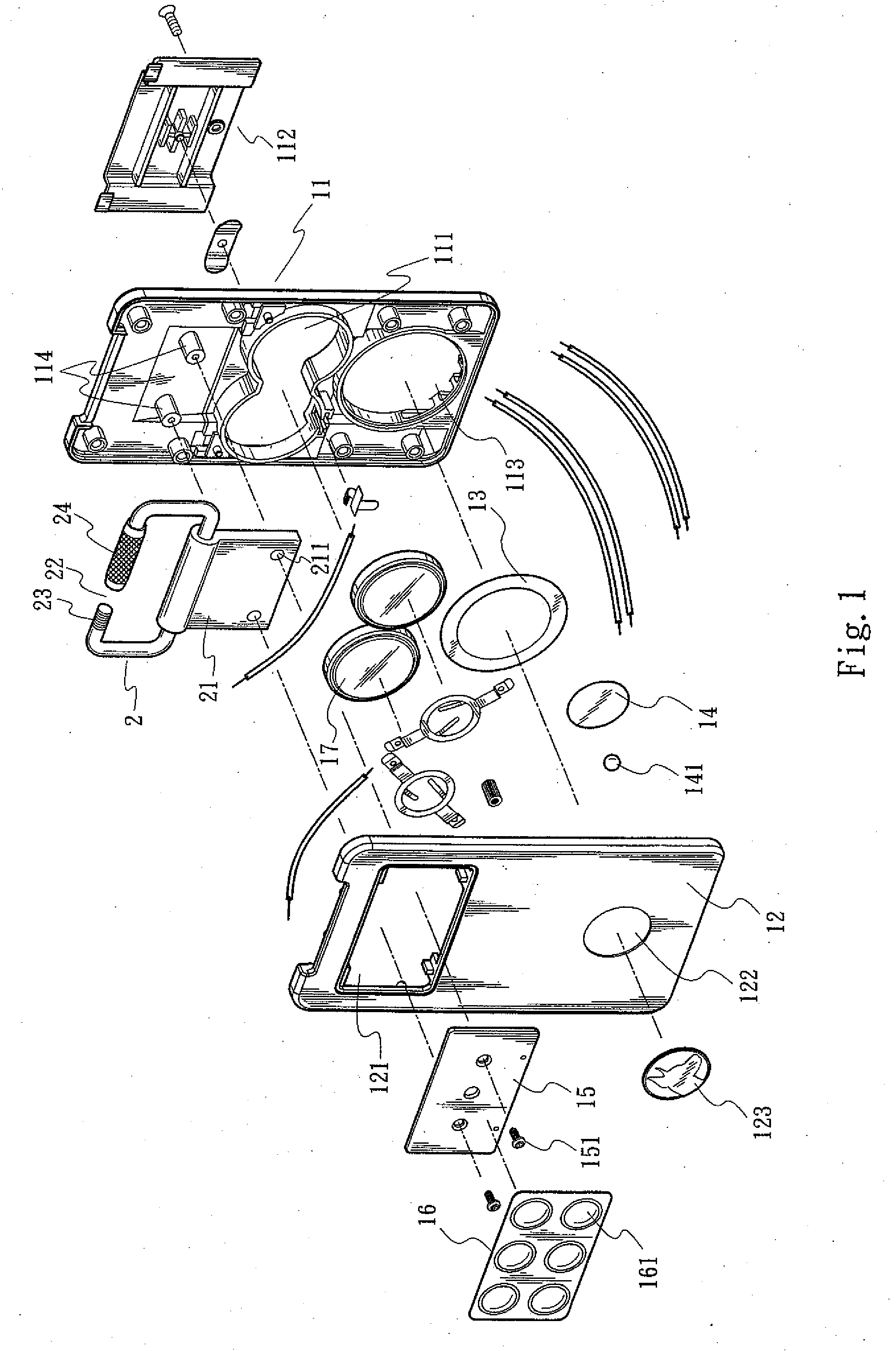
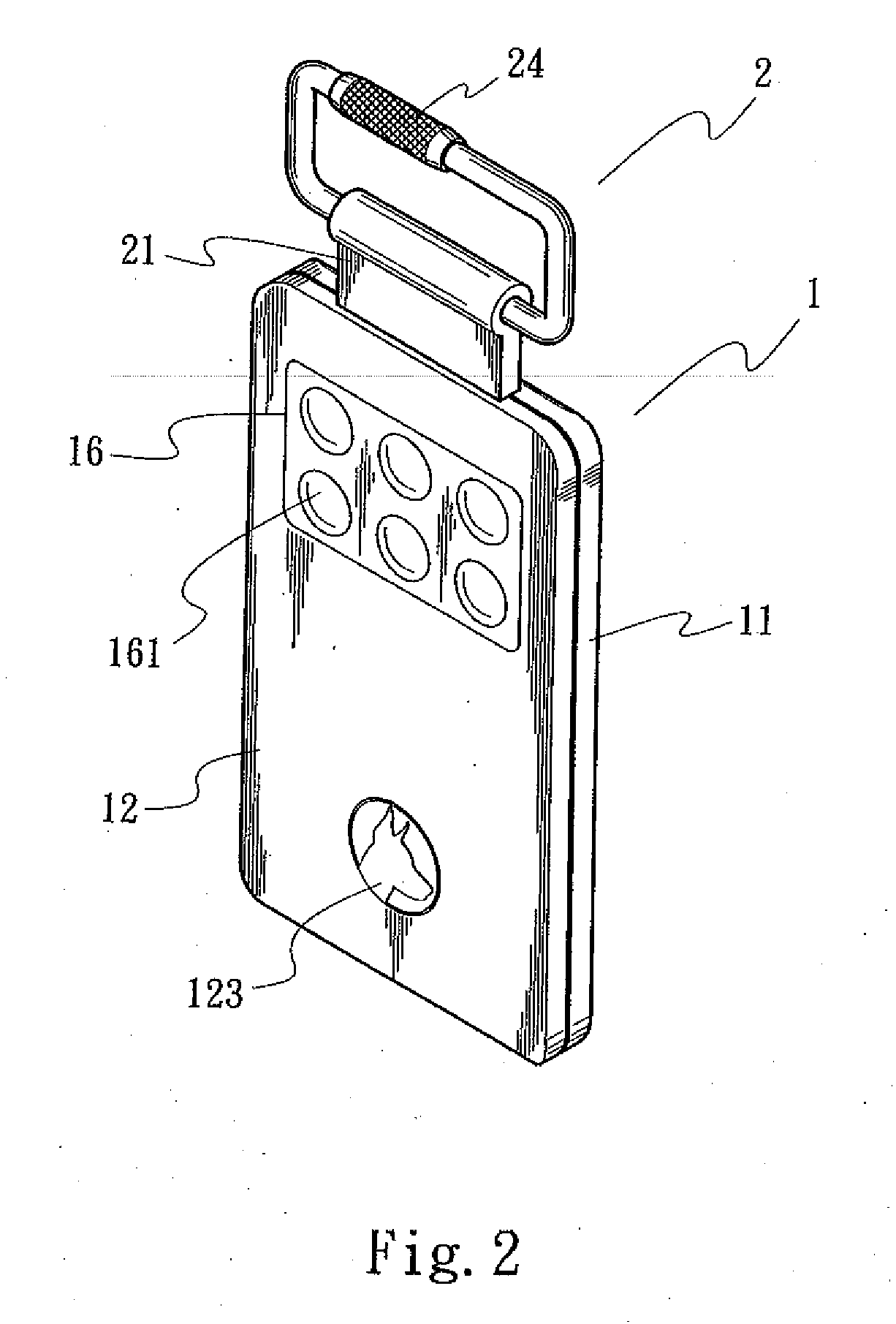
Resource price management incorporating indirect value
InactiveUS6993494B1Efficiently manageHigh valueMarket predictionsDiscounts/incentivesMarket conditionsResource management
A method and system of managing value from a resource such as hotel rooms by taking into account indirect value, such as gaming value, in determining recommended bid prices. Observed and / or estimated indirect value for customers is obtained. Recommended bid prices for instances of the resource, such as hotel rooms, are adjusted based on the obtained indirect value. Prices are further adjusted based on competitive market conditions.
Owner:CAESARS LICENSE CO LLC
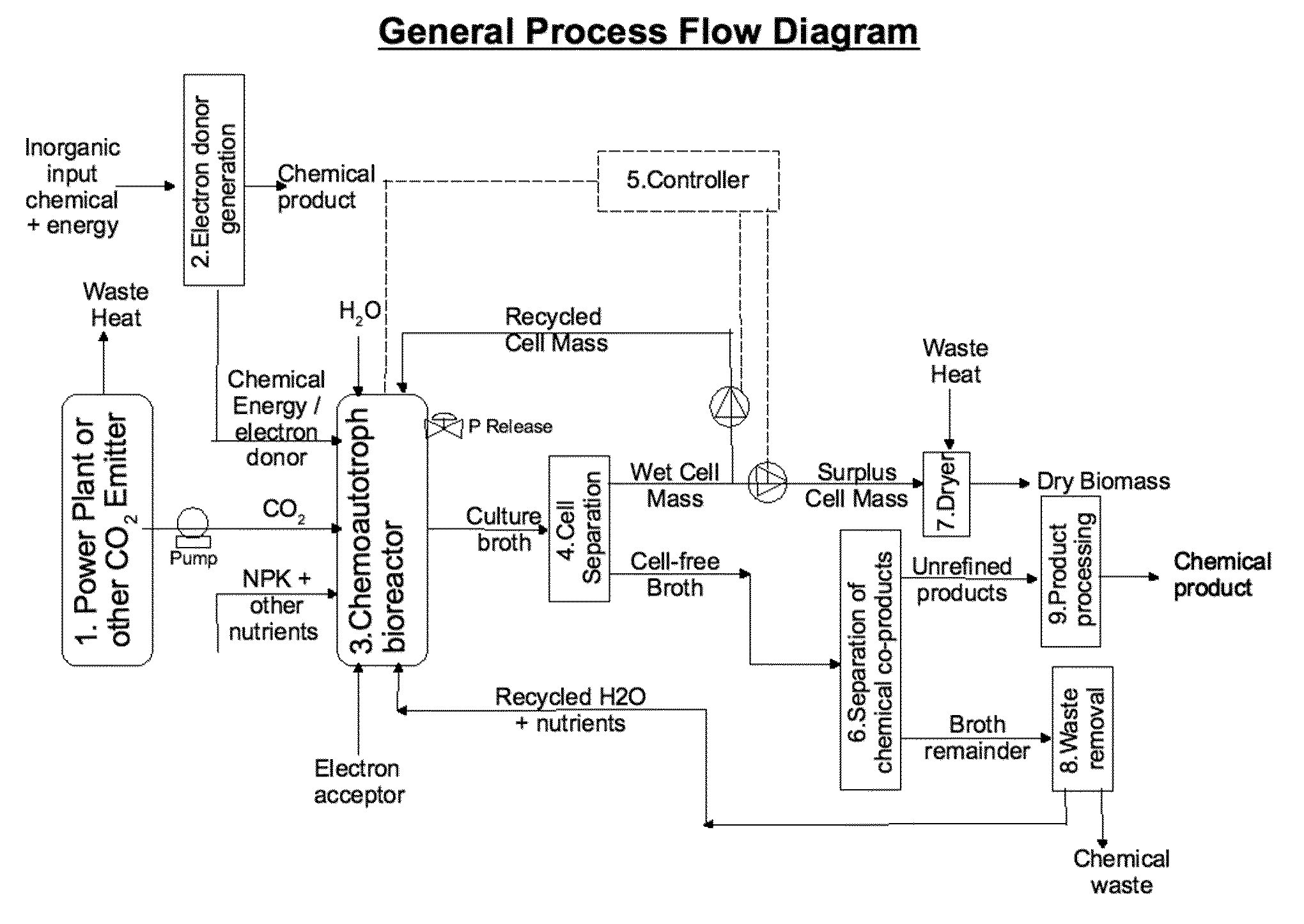
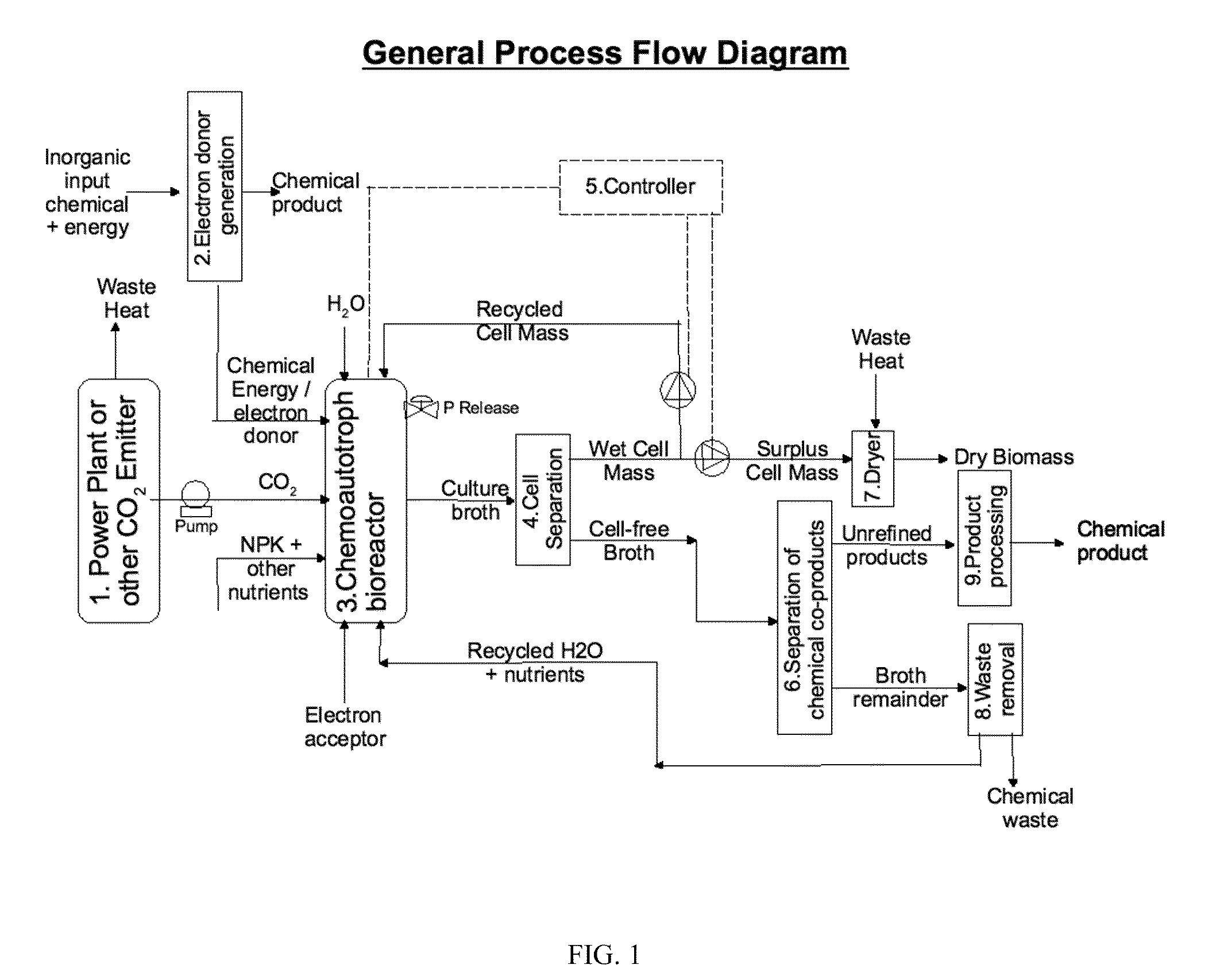
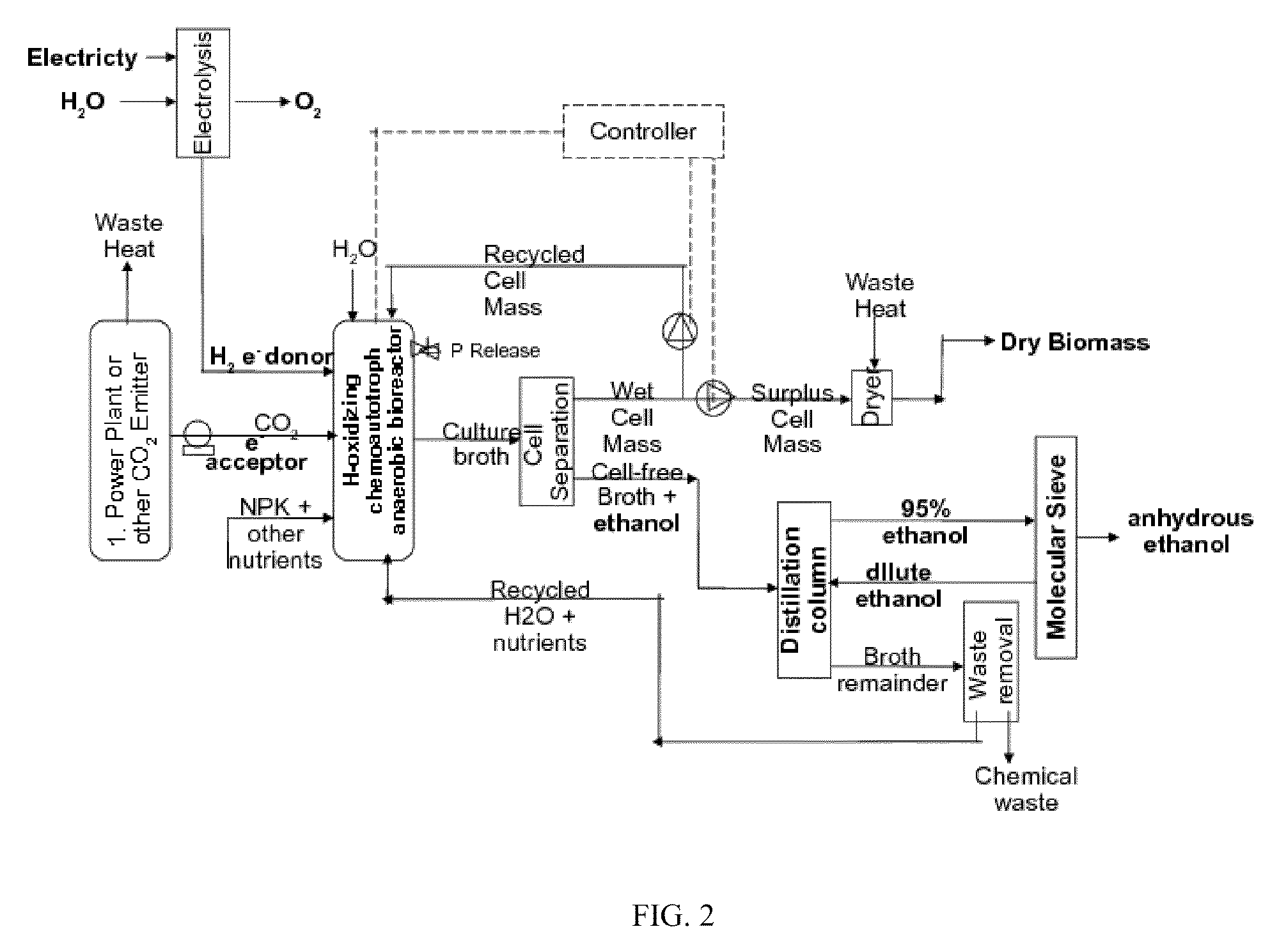
Biological and chemical process utilizing chemoautotrophic microorganisms for the chemosythetic fixation of carbon dioxide and/or other inorganic carbon sources into organic compounds, and the generation of additional useful products
InactiveUS20100120104A1High valueEfficient productionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBio-organic fraction processingCarbon dioxideCarbon source
The invention described herein presents compositions and methods for a multistep biological and chemical process for the capture and conversion of carbon dioxide and / or other forms of inorganic carbon into organic chemicals including biofuels or other useful industrial, chemical, pharmaceutical, or biomass products. One or more process steps in the present invention utilizes chemoautotrophic microorganisms to fix inorganic carbon into organic compounds through chemosynthesis. An additional feature of the present invention describes process steps whereby electron donors used for the chemosynthetic fixation of carbon are generated by chemical or electrochemical means, or are produced from inorganic or waste sources. An additional feature of the present invention describes process steps for the recovery of useful chemicals produced by the carbon dioxide capture and conversion process, both from chemosynthetic reaction steps, as well as from non-biological reaction steps.
Owner:KIVERDI INC
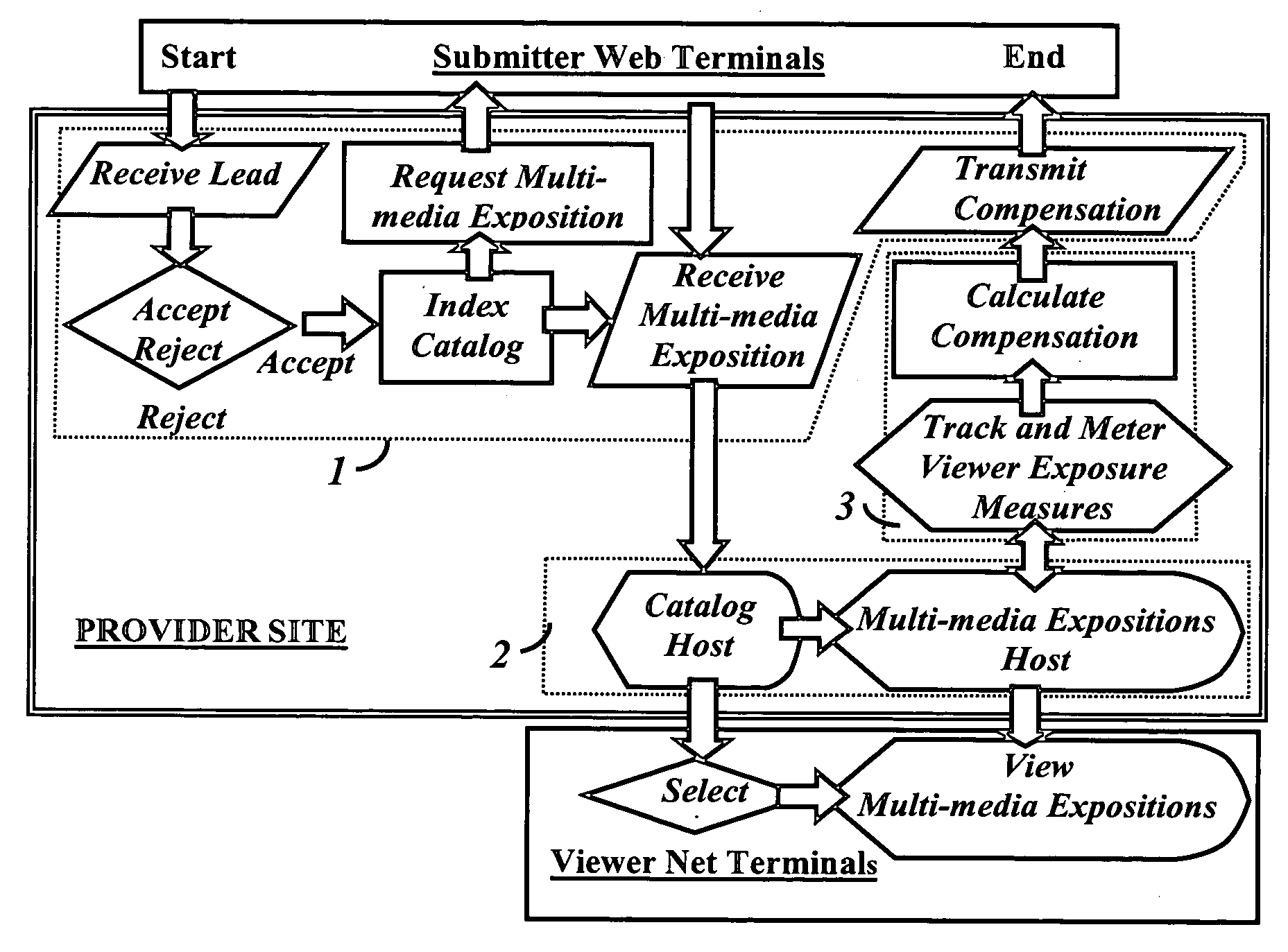
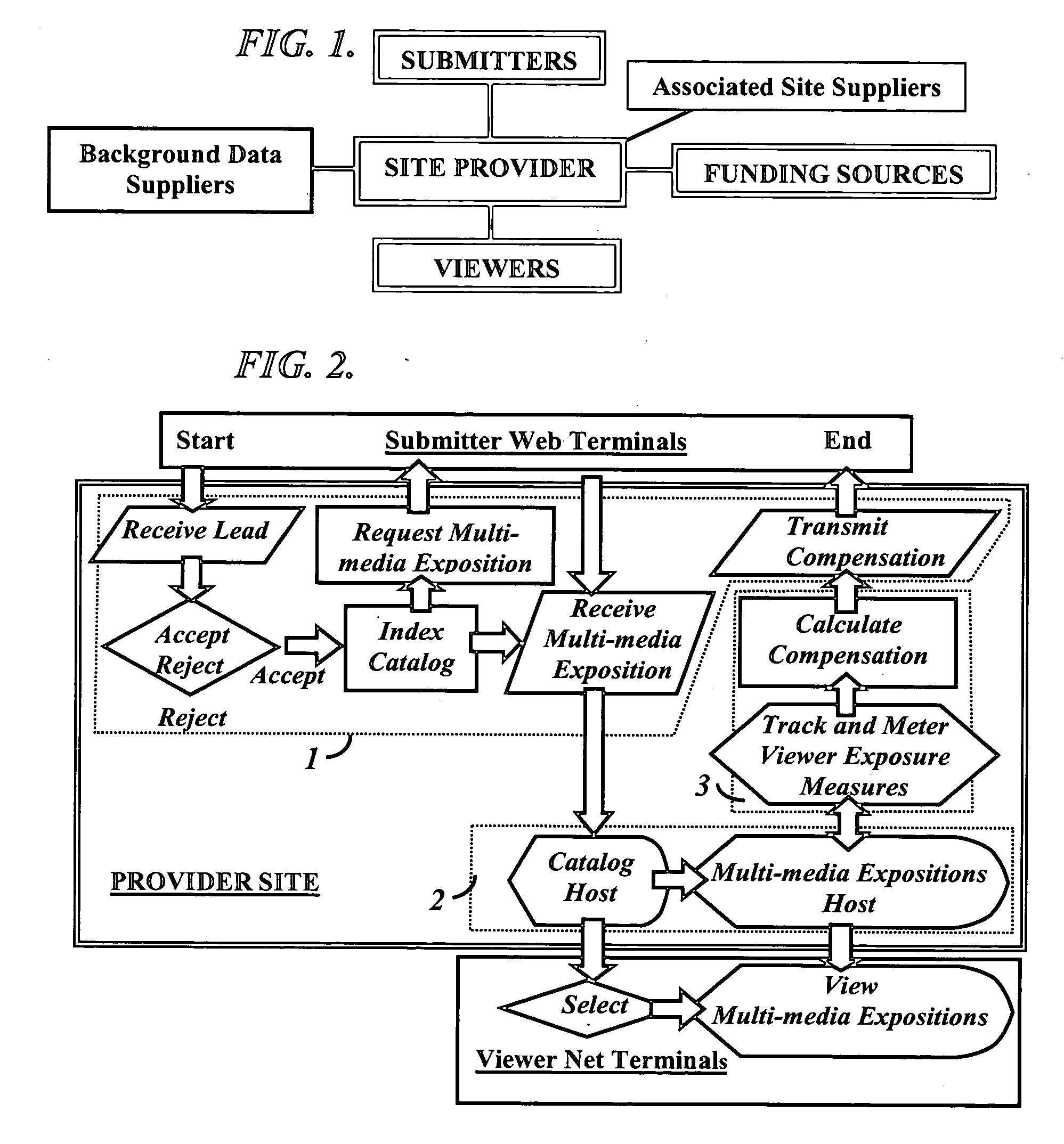
Internet news compensation system
InactiveUS20050049971A1High valueHigh chargeAdvertisementsComputer security arrangementsWeb siteCataloging
A computerized compensation system of disseminating a plurality of news and information items offered, contributed, and submitted by a plurality of independent submitters to an internet provider site. The provider site accepts, indexes, catalogs, tracks, meters, and calculates viewer exposure to each submitted news and information item chosen by a plurality of viewers. Compensation due individual submitters is transmitted in real time, as the submitter continues the submission to the provider web site. Billing of funding sources is provided.
Owner:BETTINGER DAVID S
Selected processing for non-equilibrium light alloys and products
InactiveUS20030183306A1High valueEffectiveVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingMagnesiumNet shape
A new class of light or reactive elements and monophase alpha'-matrix magnesium- and aluminum-based alloys with superior engineering properties, for the latter being based on a homogeneous solute distribution or a corrosion-resistant and metallic shiny surface withstanding aqueous and saline environments and resulting from the control during synthesis of atomic structure over microstructure to net shape of the final product, said alpha'-matrix being retained upon conversion into a cast or wrought form. The manufacture of the materials relies on the control of deposition temperature and in-vacuum consolidation during vapor deposition, on maximized heat transfer or casting pressure during all-liquid processing and on controlled friction and shock power during solid state alloying using a mechanical milling technique. The alloy synthesis is followed by extrusion, rolling, forging, drawing and superplastic forming for which the conditions of mechanical working, thermal exposure and time to transfer corresponding metastable alpha'-matrix phases and microstructure into product form depend on thermal stability and transformation behavior at higher temperatures of said light alloy as well as on the defects inherent to a specific alloy synthesis employed. Alloying additions to the resulting alpha'-monophase matrix include 0.1 to 40 wt. % metalloids or light rare earth or early transition or simple or heavy rare earth metals or a combination thereof. The eventually more complex light alloys are designed to retain the low density and to improve damage tolerance of corresponding base metals and may include an artificial aging upon thermomechanical processing with or without solid solution heat and quench and annealing treatment for a controlled volume fraction and size of solid state precipitates to reinforce alloy film, layer or bulk and resulting surface qualities. Novel processes are employed to spur production and productivity for the new materials.
Owner:HEHMANN FRANZ
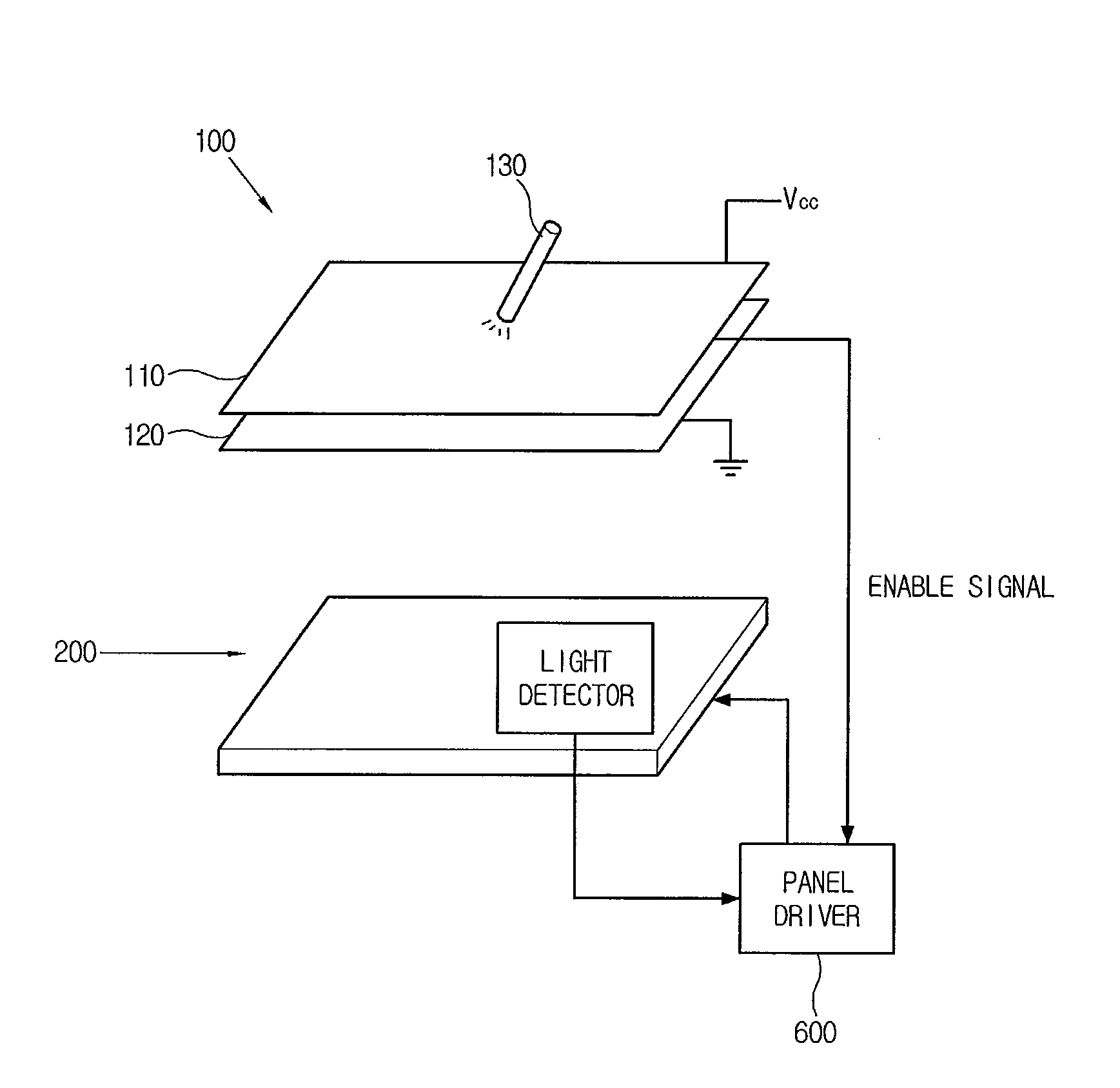
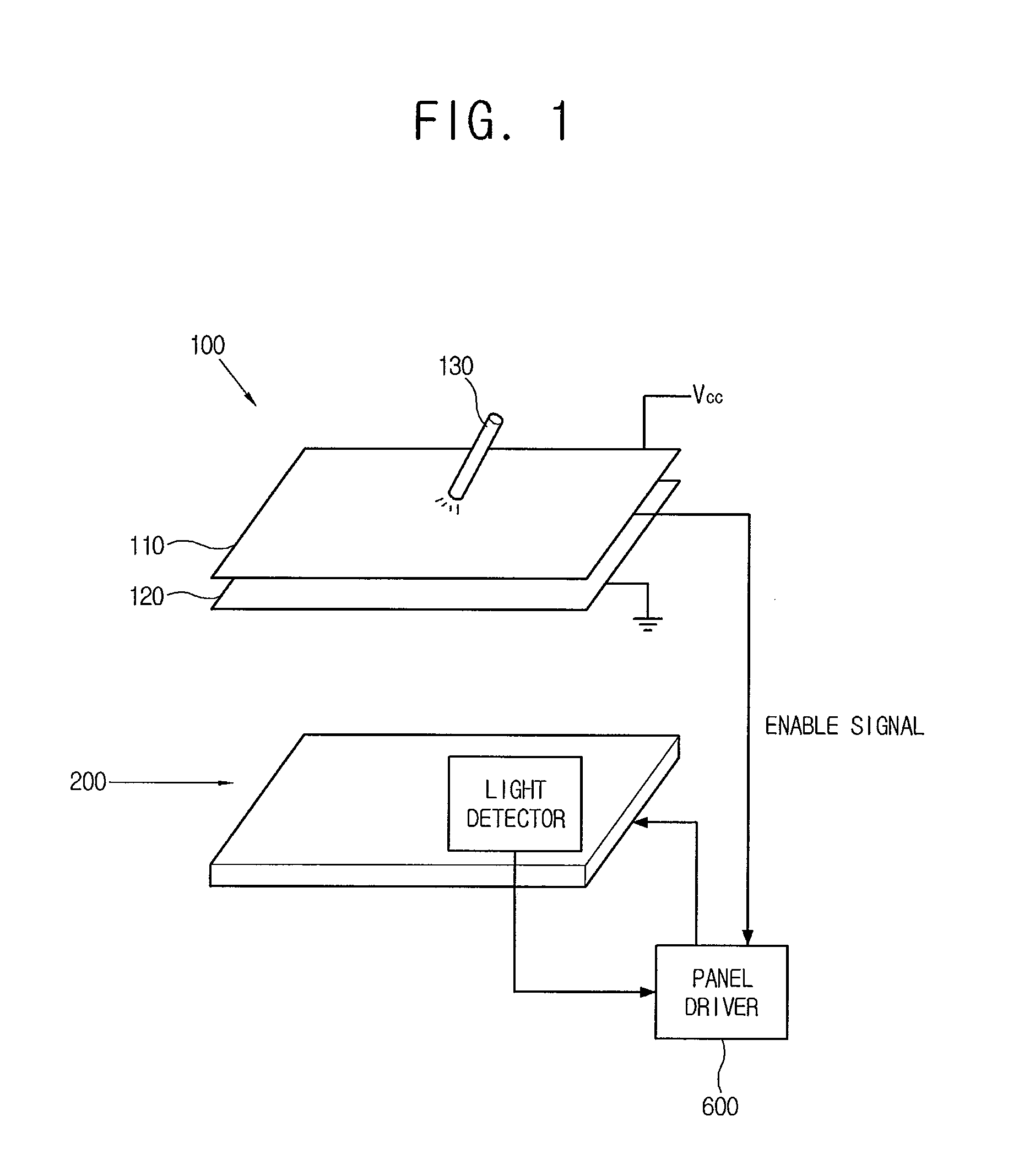
Display device
InactiveUS20080211786A1High valueLow valueNon-linear opticsInput/output processes for data processingSignal onTouch panel
A display device, includes: a touch panel which outputs a predetermined enable signal corresponding to an external pressure; a display panel which includes a light detector responding to external light and generating a predetermined electrical signal representing the position of the light; and a panel driver which forms an image corresponding to the electrical signal on the display panel if the enable signal is input.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Rate limiting barriers for implantable devices and methods for fabrication thereof
A method of coating an implantable medical device, such as a stent, is disclosed. The method includes applying a formulation on a first polymer layer containing a therapeutic substance to form a second layer. The formulation can contain a highly hydrophobic polymer or a solvent which is a poor solvent for the drug or the polymer of the first layer. The formulation can have a low surface tension value or a high Weber number value.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
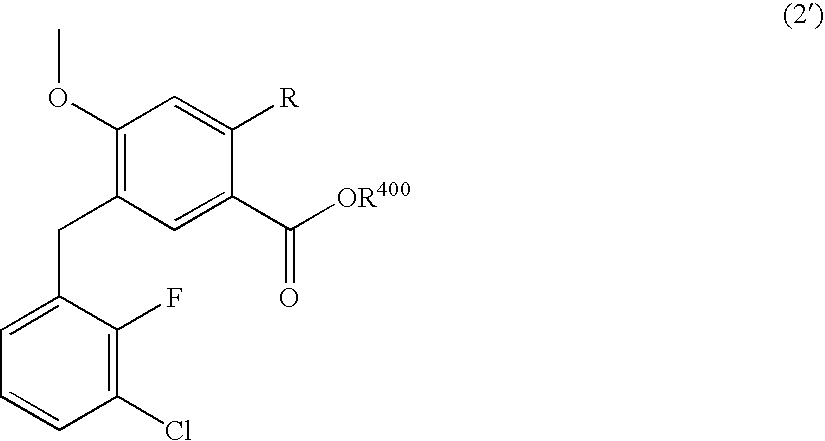
Method for producing 4-oxoquinoline compound
ActiveUS20090036684A1Decrease in yieldHigh valueOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationIntegrasesQuinolinium Compounds
The present invention provides a compound useful as a synthetic intermediate for an anti-HIV agent having an integrase inhibitory activity, and a production method thereof, and a production method of an anti-HIV agent using the synthetic intermediate. Specifically, for example, a compound represented by the formula (2′):wherein R is a fluorine atom or a methoxy group, and R400 is a hydrogen atom or a C1-C4 alkyl group, or a salt thereof, and a production method thereof, and a production method of an anti-HIV agent using the synthetic intermediate.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
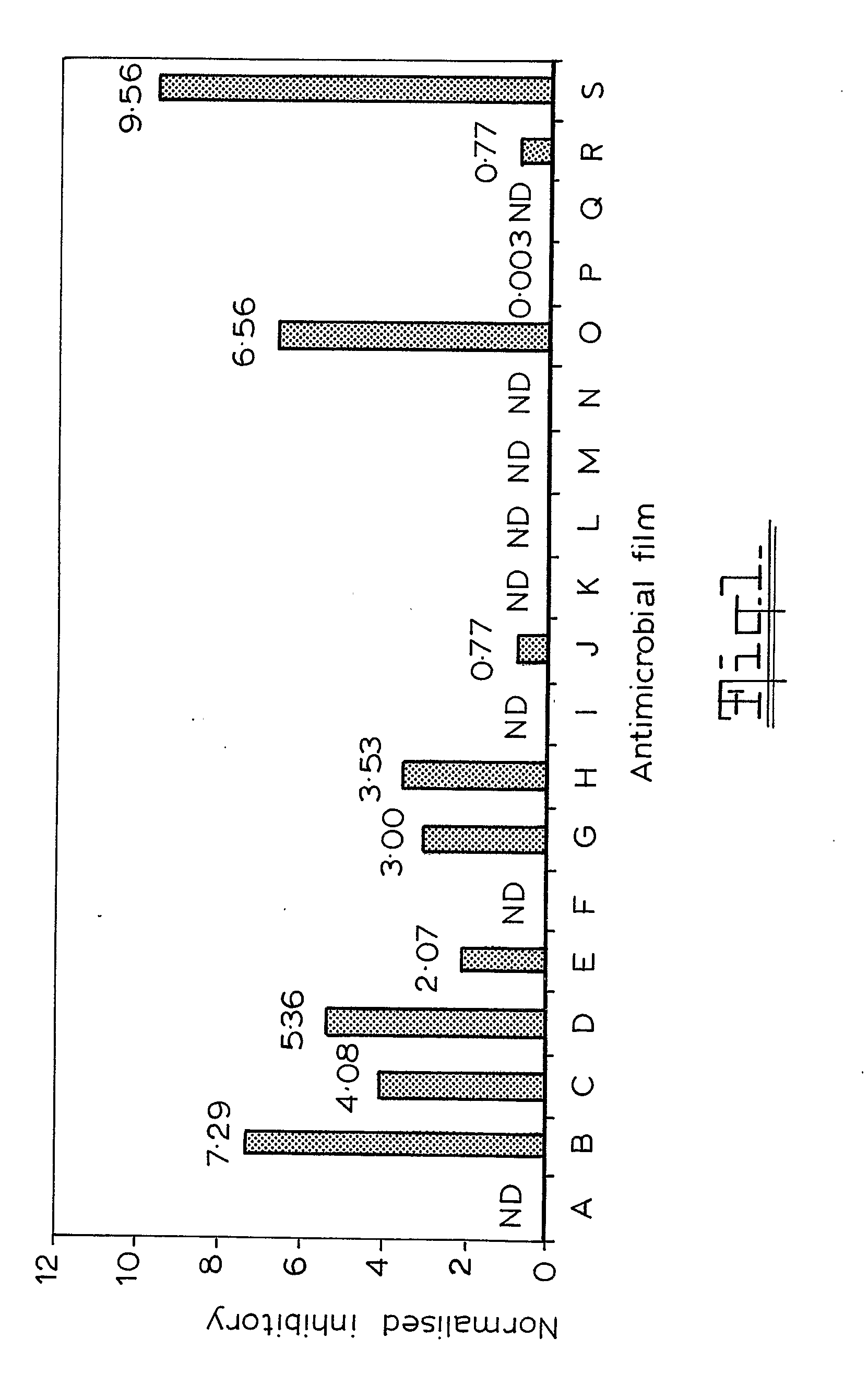
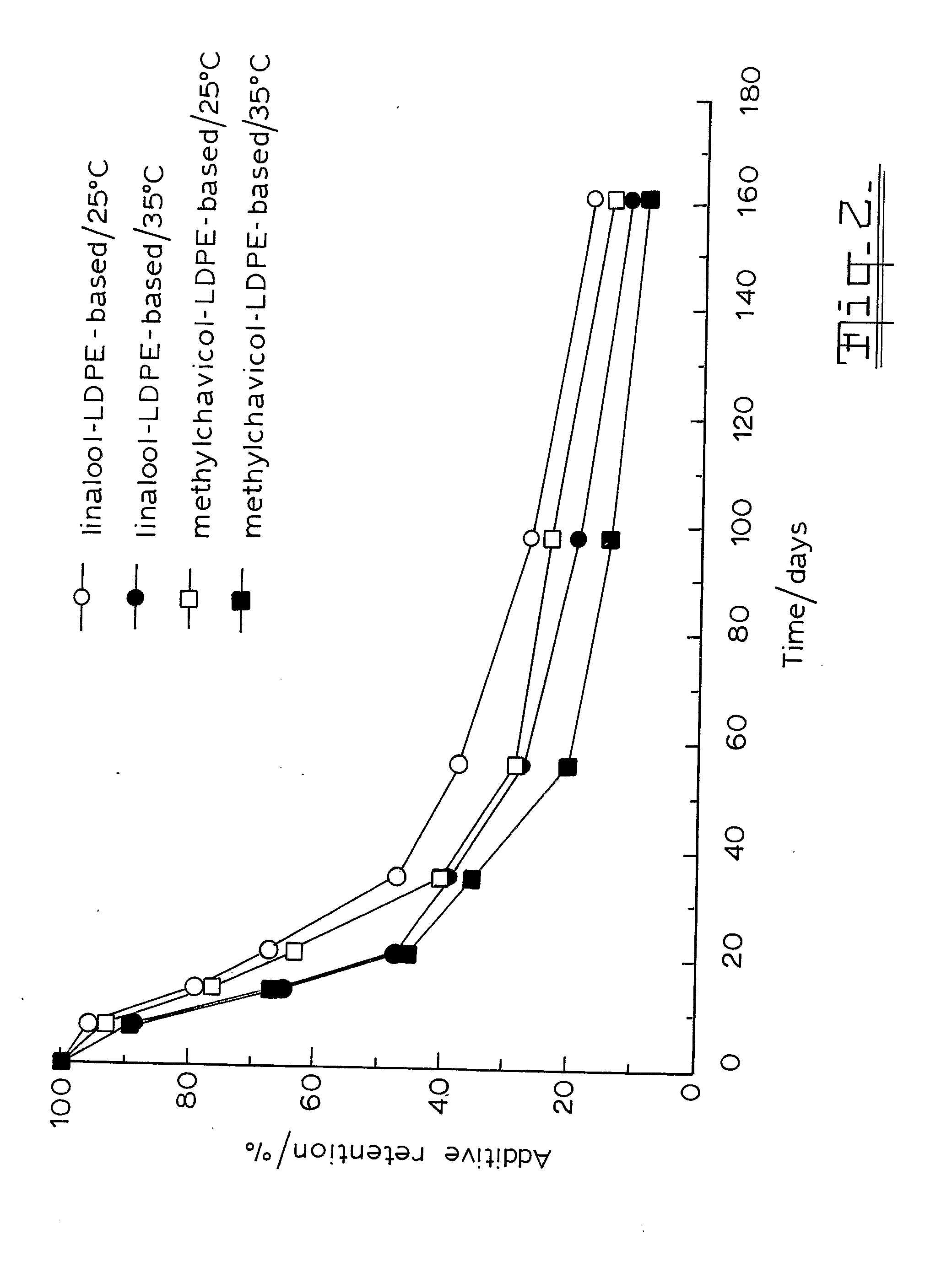
Antimicrobial Packaging Material
InactiveUS20080220036A1Release rate be controlHigh valueBiocideAntifouling/underwater paintsMethyl cinnamateMethyl acrylate
An antimicrobial packaging material for food stuffs containing from 0.05% to 1.5% by weight of a natural essential oil. The oil can be selected from primarily linalool and / or methylchavicol, but also from one or more of citral, geraniol, methyl cinnamate, methyl eugenol, 1,8-cineole, trans-a-bergamotene, carvacrol and thymol blended with one or more polymers selected from ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer, polyacrylates, including ethyl acrylate methyl methacrylate copolymers, lonomers, nylons and other hydrophilic polymers or polymers possessing functional groups capable of partially anchoring the additives and the blender mix is coated onto the food contact face of a food grade packaging film or incorporated into a food grade packaging film. A binding agent such as polyethylene glycol is added to the blend to improve the retention of the volatile oil in the polymer during processing. This material has no regulatory limitations and, at the referred concentrations, does not form detectable off-flavours.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA +1
Inductor having small energy loss
InactiveUS6894598B2Small energy lossHigh valueTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsSolid-state devicesInductorEnergy loss
An inductor has a laminated structure in which an insulating layer and a wiring layer are laminated alternately on a semiconductor substrate. The laminated structure includes at least two wiring layers and an insulating layer interposed between them. A first wiring layer has a first winding part and a second winding part in the same plane, adjacent each other, and wound. A second wiring layer has a wiring part having a single path from one terminal to the other. The first and second winding parts are electrically connected to the wiring part. When a voltage is applied between one terminal of the first winding part and one terminal of the second winding part, currents flow in the first and second winding parts in opposite directions.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Compositions and methods of using a synthetic Dnase I
Compositions and method for making and using a synthetic bovine DNase I are disclosed. More particularly, the sbDNase I of the present invention is a versatile enzyme that cleaves DNA nonspecifically to release 5′-phosphorylated nucleotides. The sbDNase I molecules of the present invention find particular use in a wide range of molecular biology applications, including: degradation of contaminating DNA after RNA isolation; RNA clean-up prior to, or in conjunction with, RT-PCR after in vitro transcription; identification of protein binding sequences on DNA (DNase I footprinting); prevention of clumping when handling cultured cells; tissue dissociation and creation of fragmented DNA for in vitro recombination reactions.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Tunnel barriers based on rare earth element oxides
InactiveUS20070053113A1High valueExcellent barrier performanceNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsCrystalline materialsRare-earth element
Magnetic tunnel junctions are disclosed that include ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic) materials and a bilayer tunnel barrier structure that includes a layer of a rare earth oxide. The bilayer also includes a layer of crystalline material, such as MgO or Mg—ZnO. If MgO is used, then it is preferably (100) oriented. The magnetic tunnel junctions so formed enjoy high tunneling magnetoresistance, e.g., much greater than 100% at room temperature.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method for forming a SiGe or SiGeC gate selectively in a complementary MIS/MOS FET device
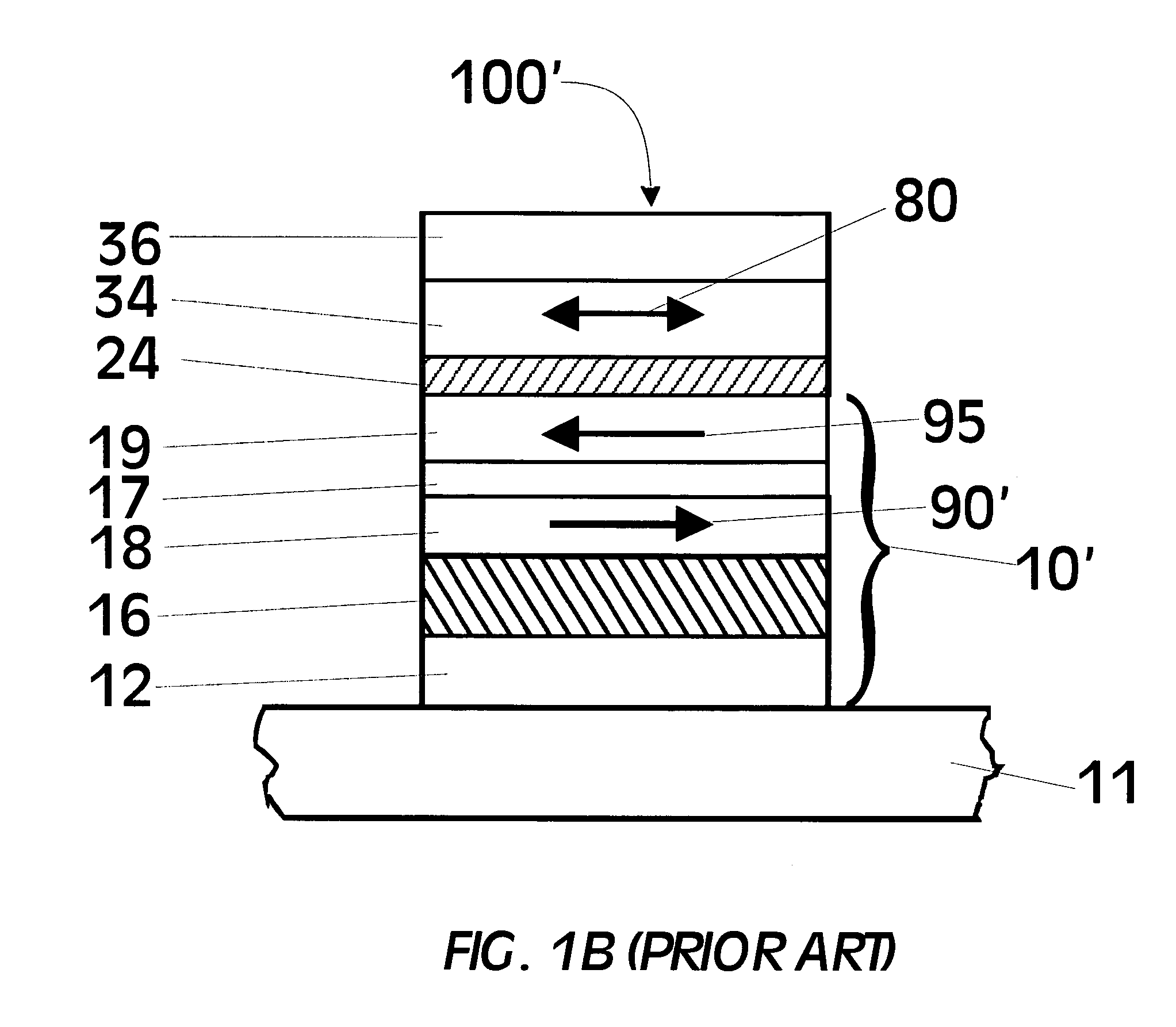
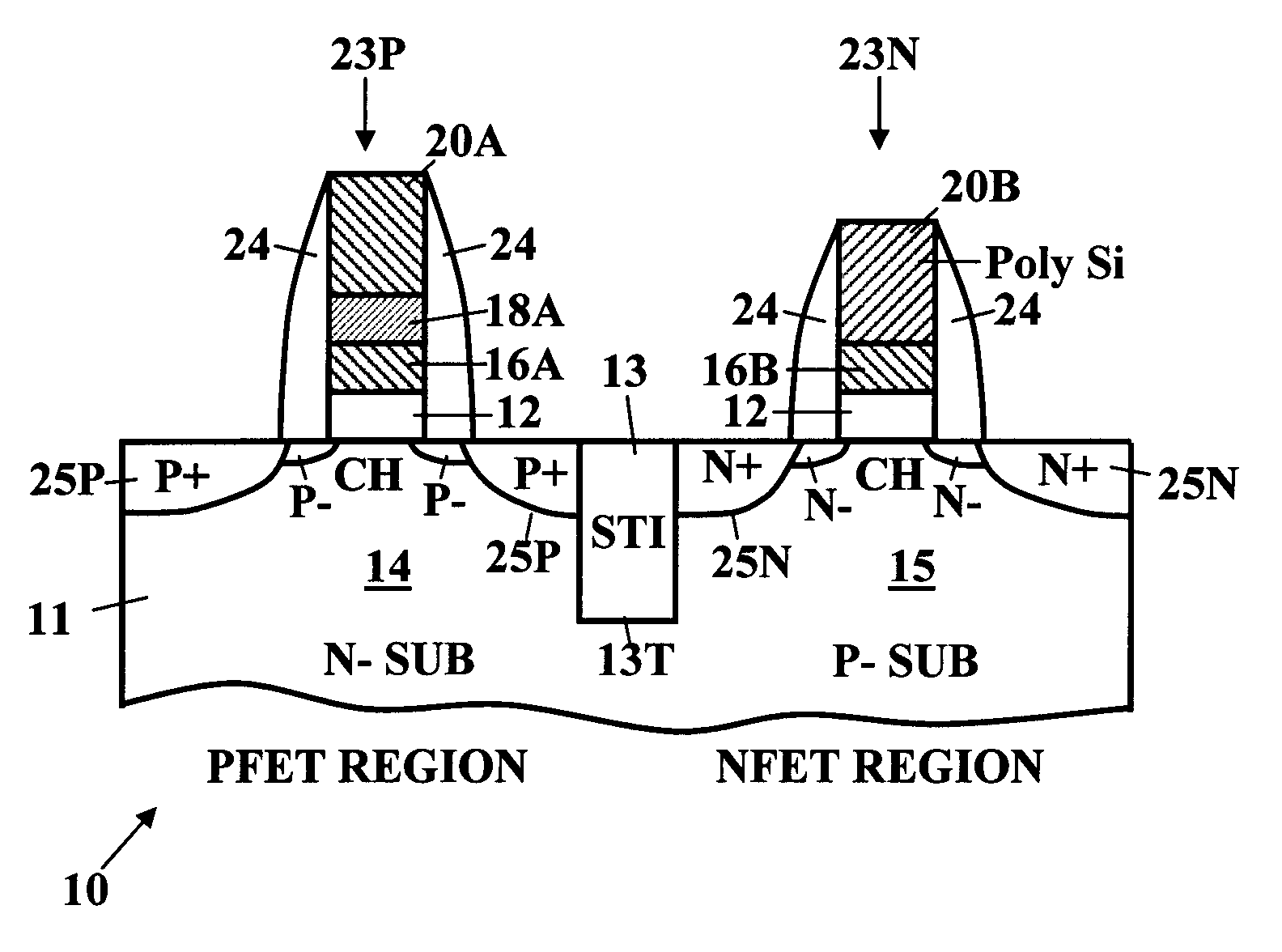
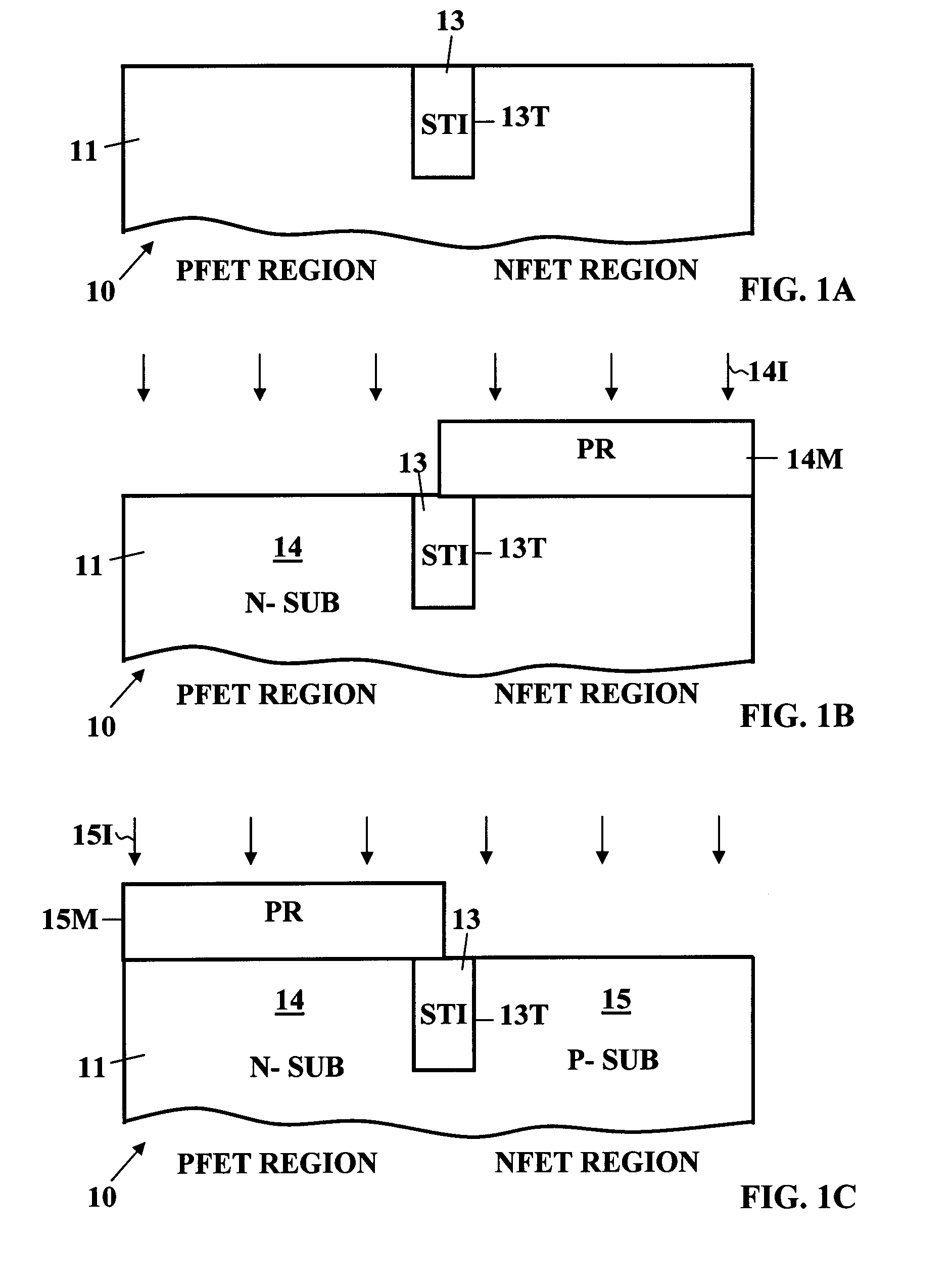
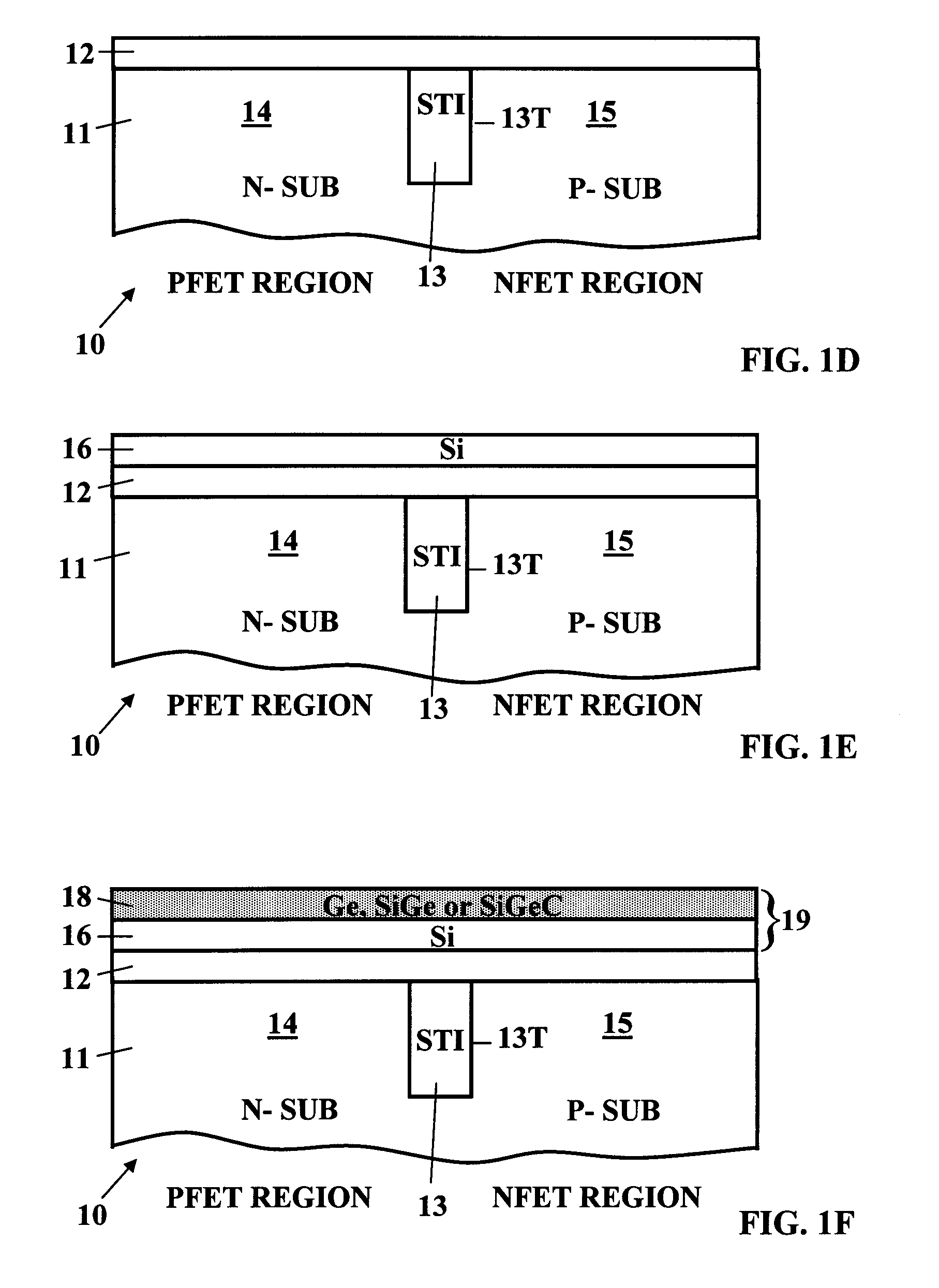
ActiveUS7132322B1High valueHigh levelSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPolycrystalline siliconSemiconductor
Form a dielectric layer on a semiconductor substrate. Deposit an amorphous Si film or a poly-Si film on the dielectric layer. Then deposit a SiGe amorphous-Ge or polysilicon-Ge thin film theteover. Pattern and etch the SiGe film using a selective etch leaving the SiGe thin film intact in a PFET region and removing the SiGe film exposing the top surface of the Si film in an NFET region. Anneal to drive Ge into the Si film in the PFET region. Deposit a gate electrode layer covering the SiGe film in the PFET region and cover the exposed portion of the Si film in the NFET region. Pattern and etch the gate electrode layer to form gates. Form FET devices with sidewall spacers and source regions and drains regions in the substrate aligned with the gates.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
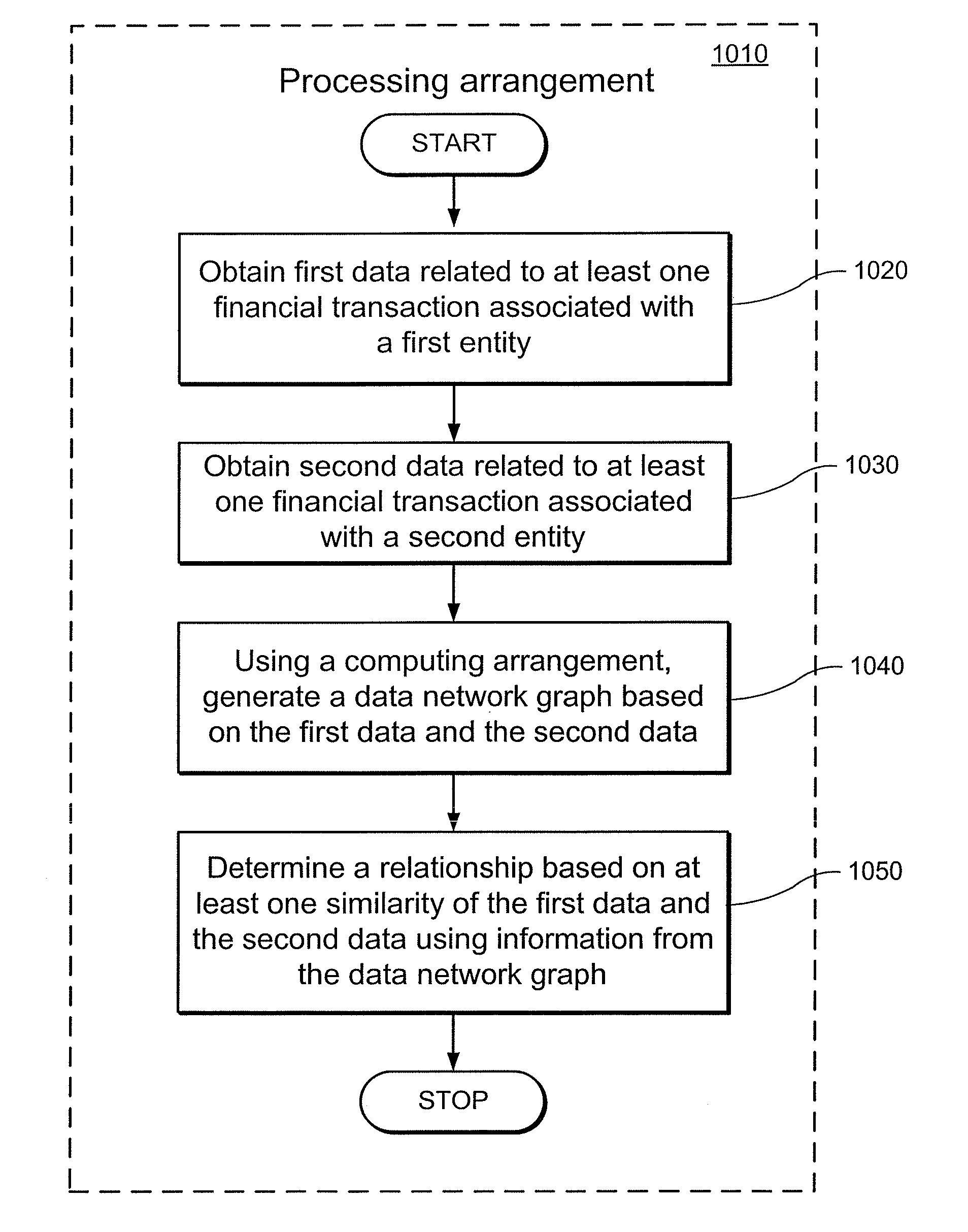
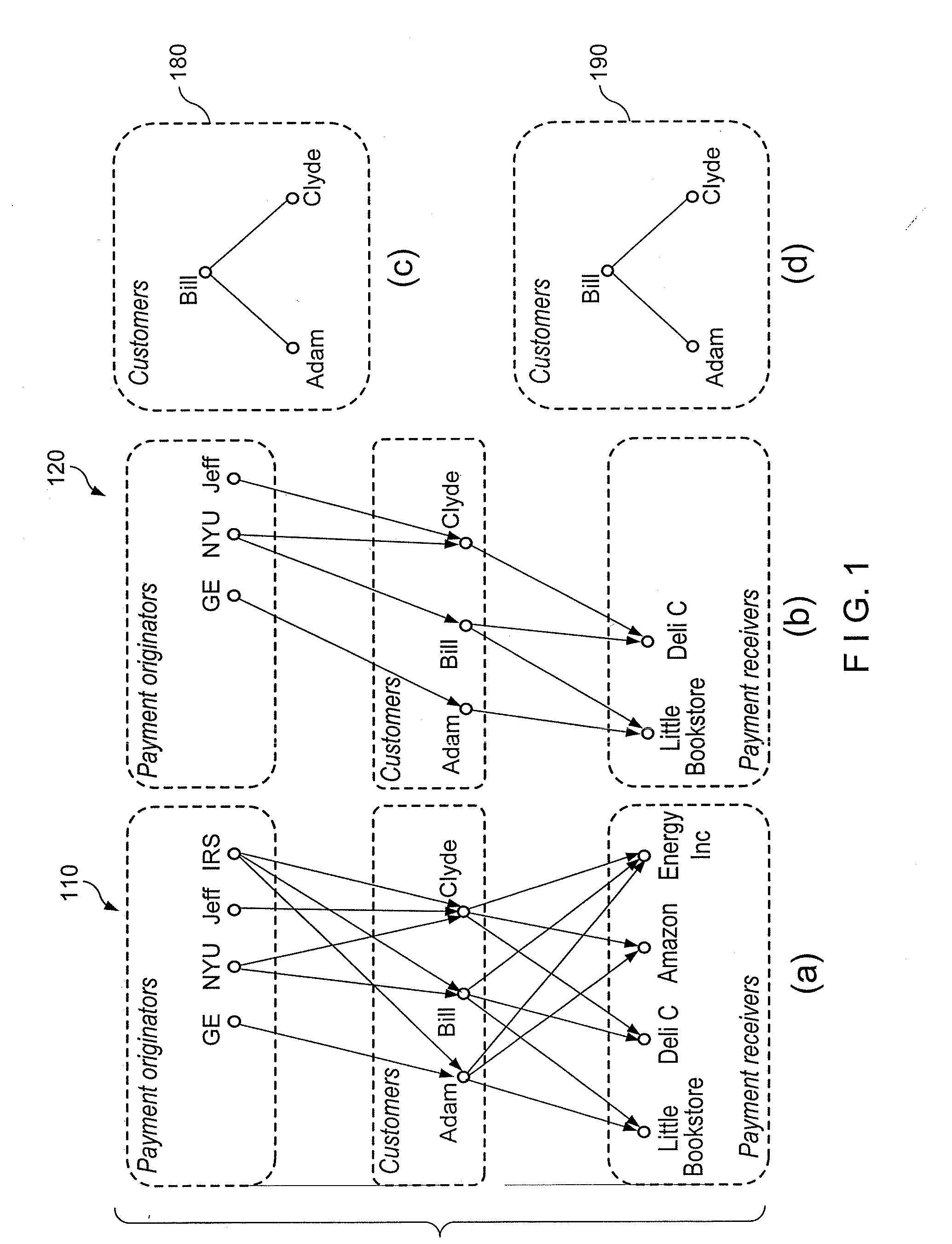
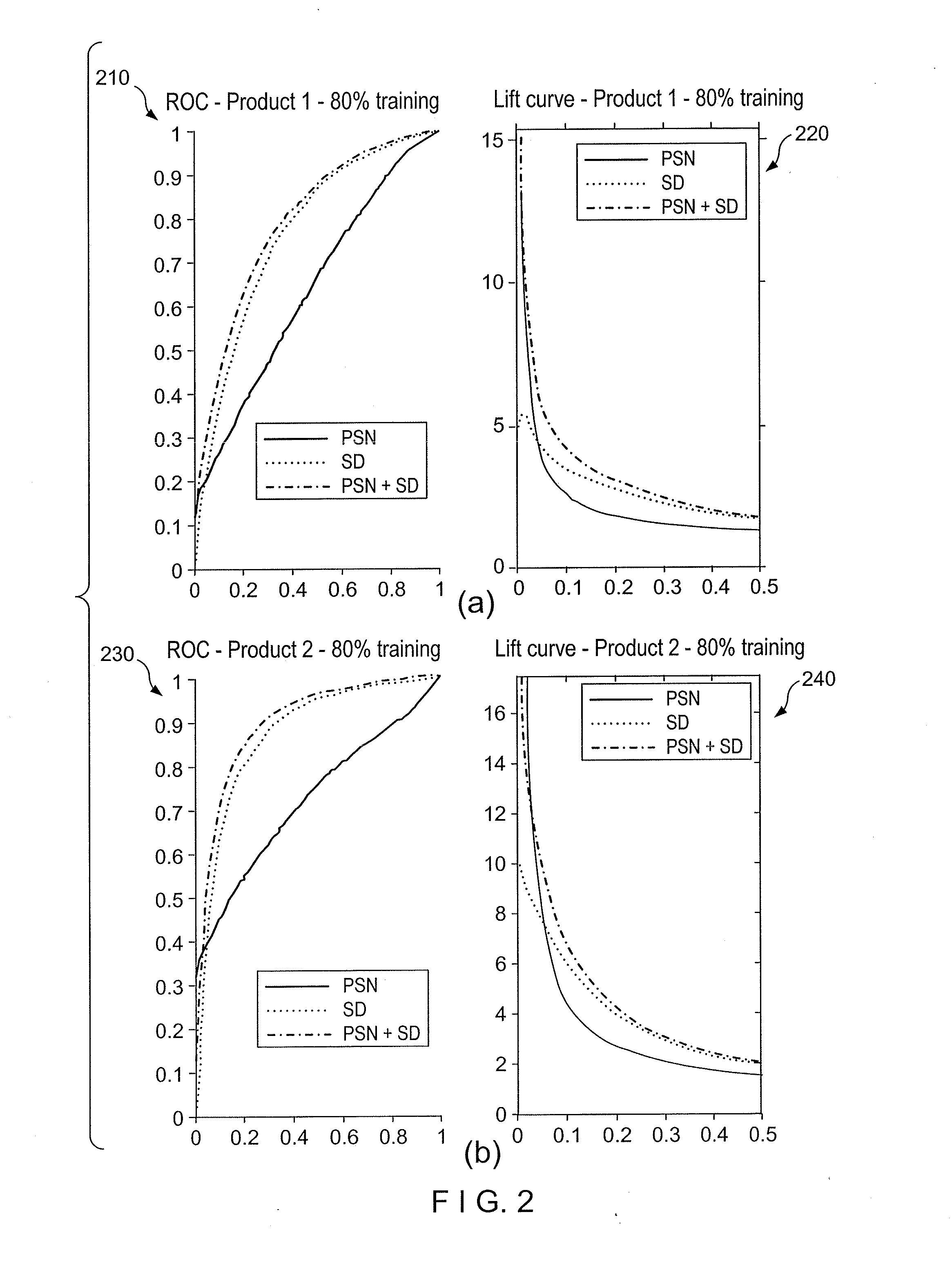
Methods, computer-accessible medium and systems for construction of and interference with networked data, for example, in a financial setting
Networked data can, e.g., define connections between similar entities. Such data can be valuable for, e.g., improving business revenue opportunities (e.g., increasing sales, reducing customer attrition / churn, etc.) as networked data can capture similarities that can be often hard to encapsulate in traditional variables such as, e.g., socio-demographics. For example, related research has generally focused on the case where social network data was obtained directly or indirectly from online data, or from offline call logs in a telecommunication setting. Results can be implemented when inferring the values of target variables over the networked data. Methods, computer-accessible medium and systems according to exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure for creating privacy-friendly pseudo-social networked (PSN) data from off-line banking data can be provided. Exemplary PSN in accordance with certain exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure can be used, e.g., for a variety of networked data-mining applications for banks and other financial institutions to increase revenue or manage risk, for example.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
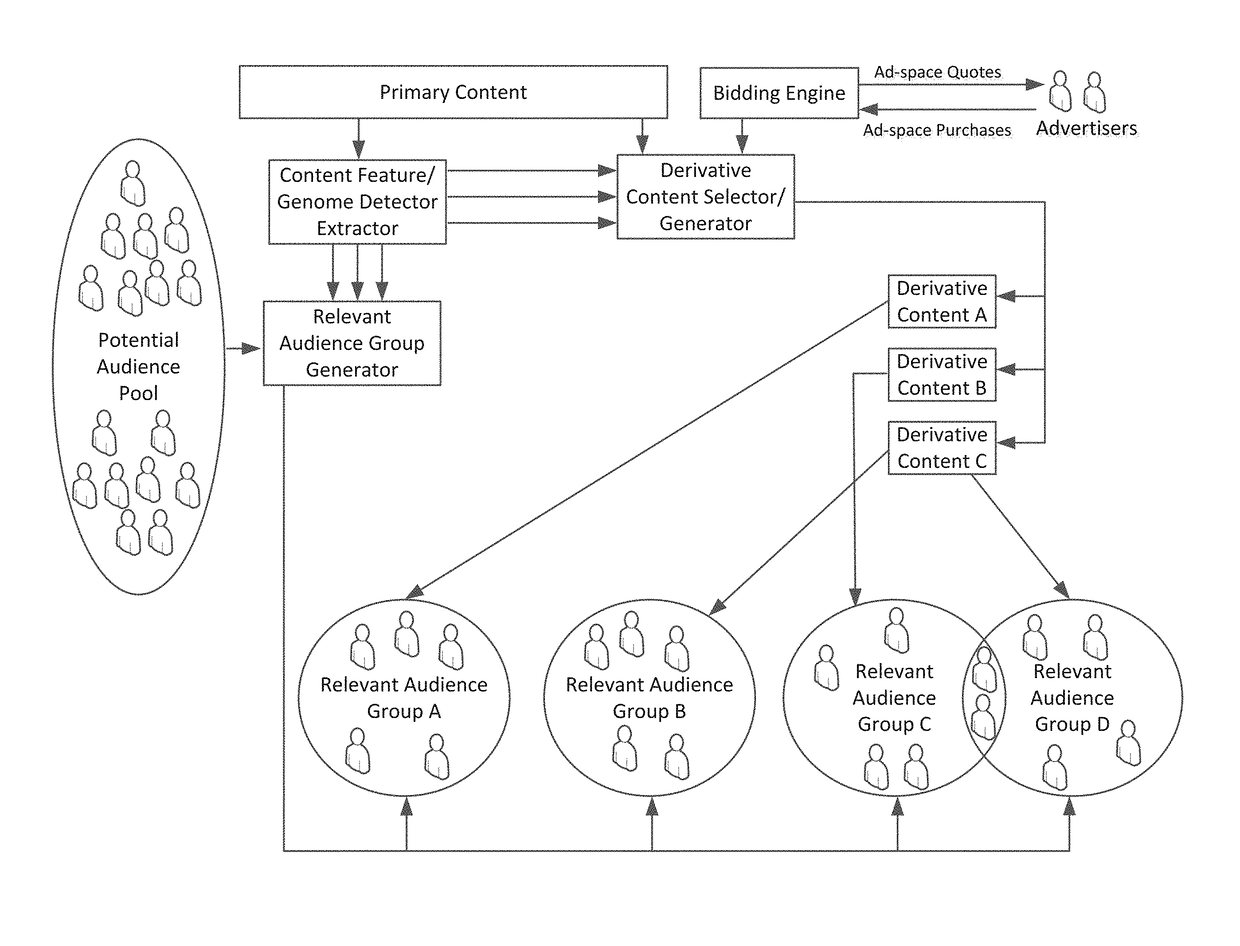
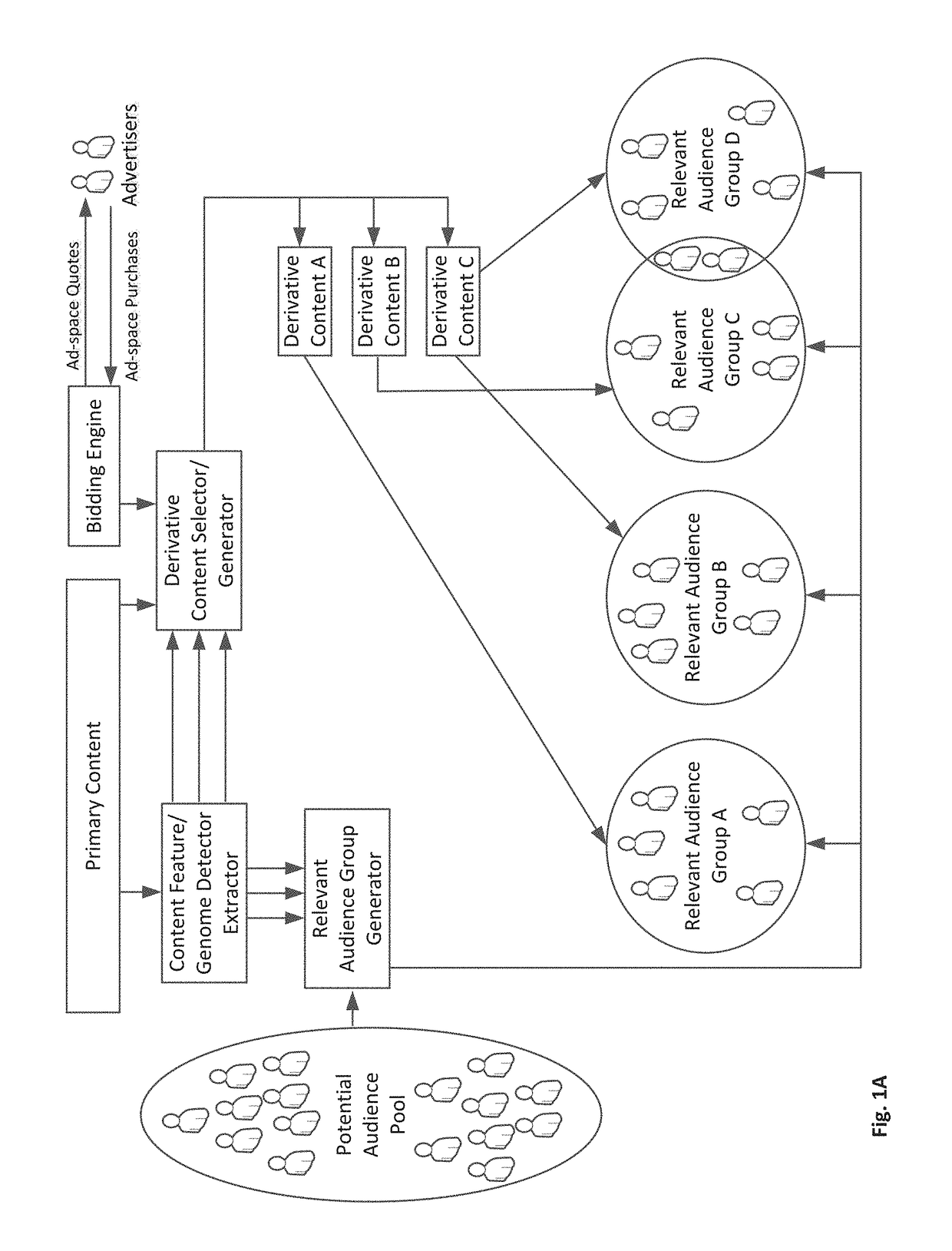
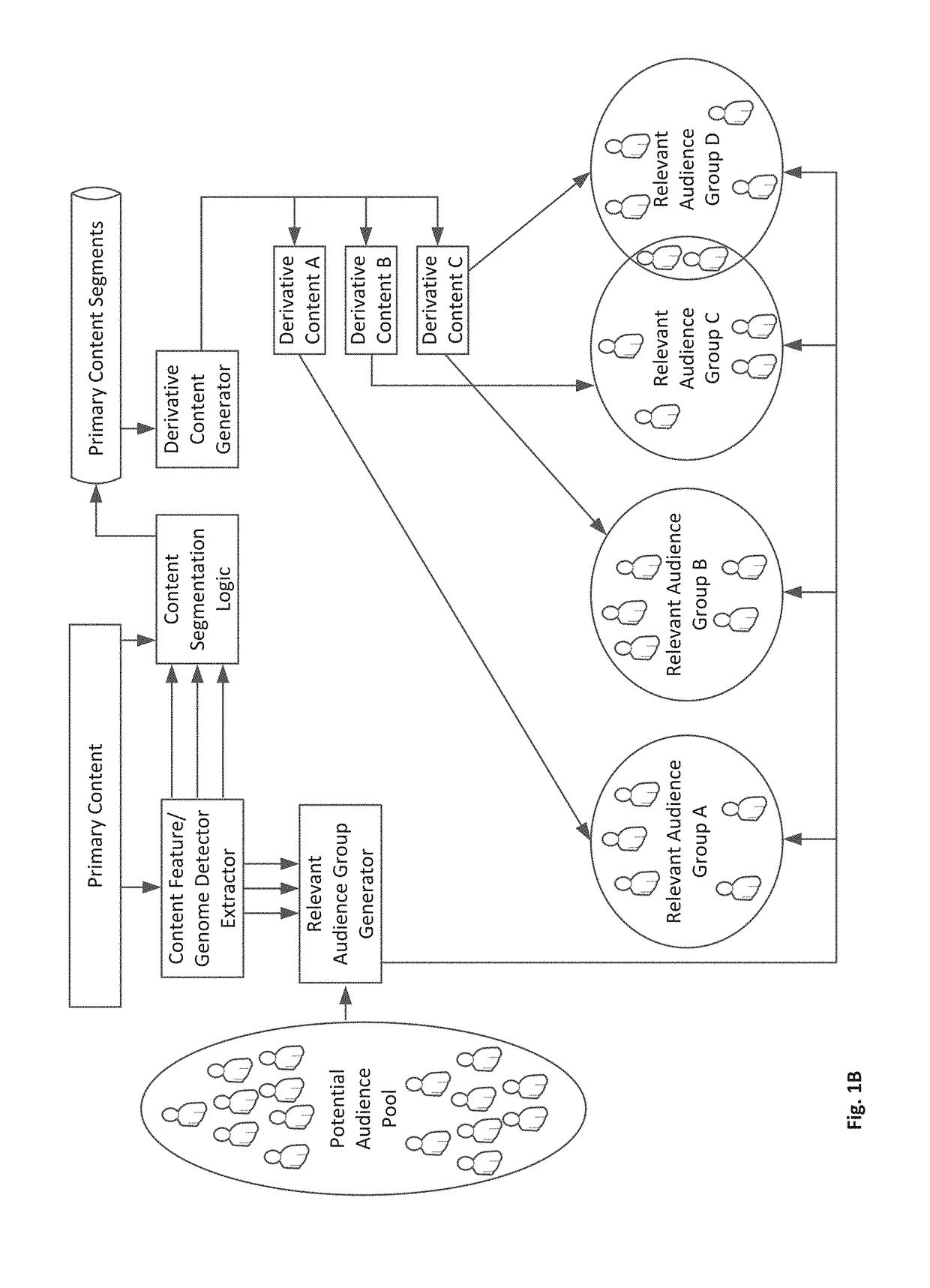
Methods Circuits Devices Systems and Associated Machine Executable Code for Taste-based Targeting and Delivery of Content
InactiveUS20170243244A1High valueFacilitate generationAdvertisementsSelective content distributionInformation retrievalUser profile
Disclosed is a digital content targeting and delivery system. The system includes an interface to receive a primary content for distribution to one or more audience groups and a content feature detector to extract content features relevant to each of one or more audience groups. A relevant audience set generator parses a pool of potential audience member records into one or more (target) audience group lists by matching extracted content features with content preference parameters / fields of taste user profiles within the potential audience member records. a derivative content delivery module delivers, to members of at least one audience group, a derivative of the primary content including content segments with content features matching at least one common preference of the members of the at least one audience group.
Owner:JINNI MEDIA
Unified parking management system and method based on optical data processing
InactiveUS20140344026A1High valueHigh confidenceTicket-issuing apparatusProgram planningOptical data processing
A system and method for unified parking management based on optical data processing from installed cameras. The invention can be used in both on-street and off-street parking situations. The system allows for economical dynamic pricing based on demand, profiles and loyalty, and how much a motorist is willing to pay at any given time for a parking space similar to frequent flier programs and seats on a flight. Prices can be constantly changing based on demand, which in turn can be based on time of day, convenience, services available and loyalty.
Owner:LIBERTY PLUG INS INC
Engineered CO2-Fixing Chemotrophic Microorganisms Producing Carbon-Based Products and Methods of Using the Same
Disclosed herein are microorganisms containing exogenous or heterologous nucleic acid sequences, wherein the microorganisms are capable of growing on gaseous carbon dioxide, gaseous hydrogen, syngas, or combinations thereof. In some embodiments the microorganisms are chemotrophic bacteria that produce or secrete at least 10% of lipid by weight. Also disclosed are methods of fixing gaseous carbon into organic carbon molecules useful for industrial processes. Also disclosed are methods of manufacturing chemicals or producing precursors to chemicals useful in jet fuel, diesel fuel, and biodiesel fuel. Exemplary chemicals or precursors to chemicals useful in fuel production are alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, fatty acid alcohols, fatty acid aldehydes, desaturated hydrocarbons, unsaturated fatty acids, hydroxyl acids, or diacids with carbon chains between six and thirty carbon atoms long. Also disclosed are microorganisms and methods using disclosed microorganisms for the production of butanediol and its chemical precursors in low-oxygen or anaerobic fermentation. Also disclosed are microorganisms and methods using disclosed microorganisms for generating hydroxylated fatty acids in microbes through the transfer of enzymes that are known to hydroxylate fatty acids in plants or microbes. Also disclosed are microorganisms and methods using disclosed microorganisms for the production of shorter-chain fatty acids in microbes through the introduction of exogenous fatty acyl-CoA binding proteins.
Owner:KIVERDI INC
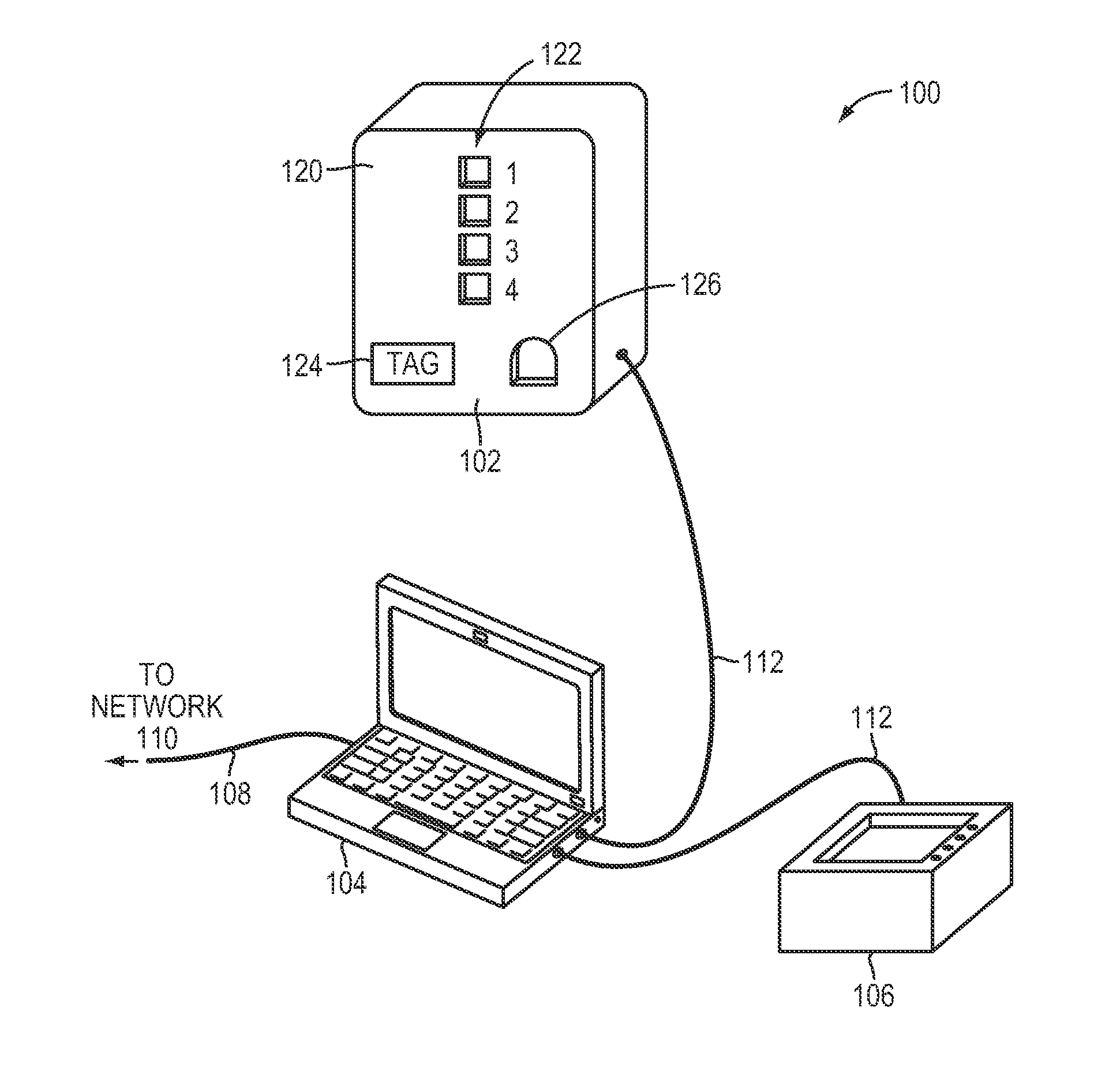
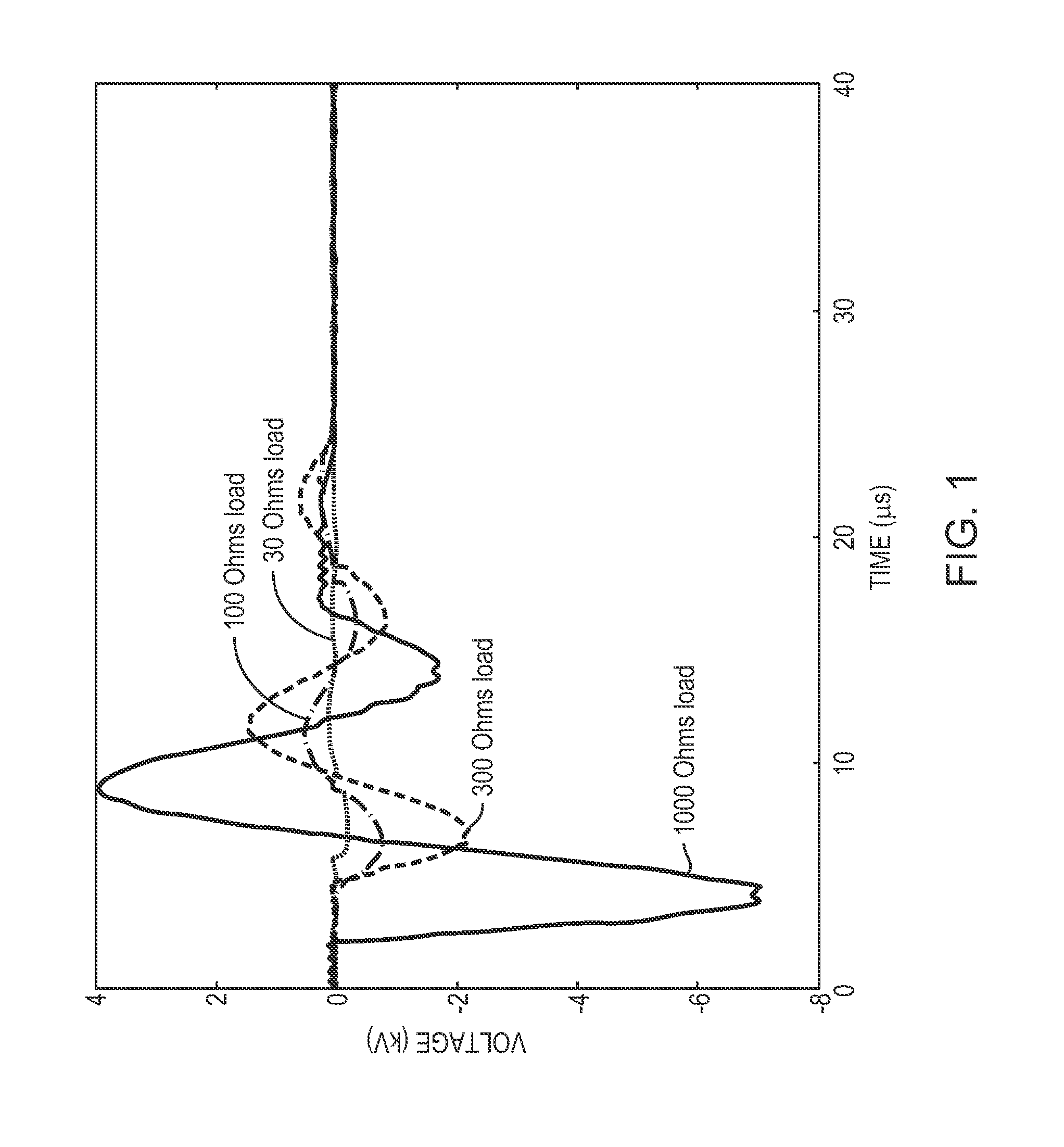
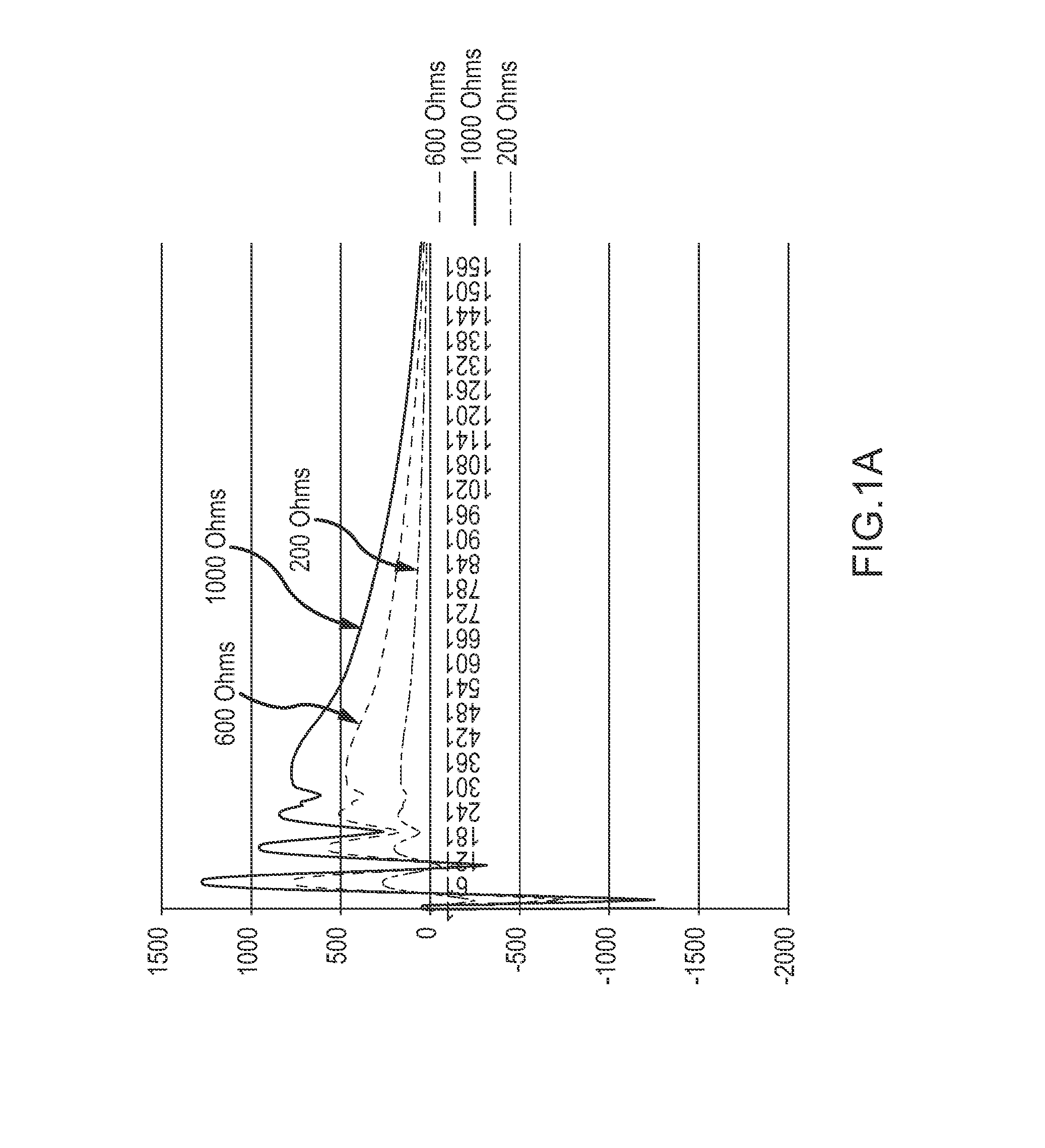
Stun device testing apparatus and methods
InactiveUS20140225630A1High valueResistance/reactance/impedenceWeapons typesEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A testing apparatus includes a housing having a port for receiving a discharge end of an electrical discharge device. A discharge-receiving circuit is operatively connected to the port, and is configured to receive a discharge from the electrical discharge device. The discharge-receiving circuit includes a default resistor and at least one supplemental resistor. When in a first setting, the discharge-receiving circuit is configured so as to pass the discharge automatically through at least the default resistor. When in a second setting, the discharge-receiving circuit is configurable so as to selectively pass the discharge through at least one of the plurality of resistors.
Owner:AEGIS IND INC
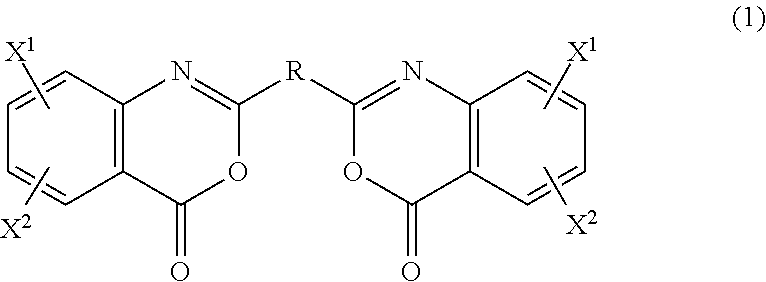
Black composition, black coating composition, resin black matrix, color filter for liquid crystal display and liquid crystal display
ActiveUS20070059612A1Prevention of decrease in yieldHigh valueLiquid crystal compositionsPhotosensitive materialsLiquid-crystal displayCrystallography
A black coating composition which gives a highly adhesive resin black matrix that exhibits a high OD value which was able to be attained only by metal thin film black matrices is disclosed. The black coating composition comprises as indispensable components a titanium nitride oxide and a resin. The X-ray intensity ratios R1 and R2 of the titanium nitride oxide represented by the Equations (1) and (2) below, respectively, satisfy the relationships represented by Formulae (3) and (4)below:R1=I3 / {I3+1.8(I1+1.8I2)} (1)R2=I2 / I1 (2)R1>0.70 (3)0.85<R2<1.80 (4)wherein I1 represents the maximum diffraction intensity of the titanium nitride oxide when the angle of diffraction 2θ, determined by using CuKα line as the X-ray source, is 25° to 26°, I2 represents the maximum diffraction intensity of the titanium nitride oxide when the angle of diffraction 2θ is 27° to 28°, and I3 represents the maximum diffraction intensity of the titanium nitride oxide when the angle of diffraction 2θ is 36° to 38°.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Biofuel production methods
InactiveUS20080184616A1High valueIncreasing supplyBiofuelsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsBiofuel feedstockChemistry
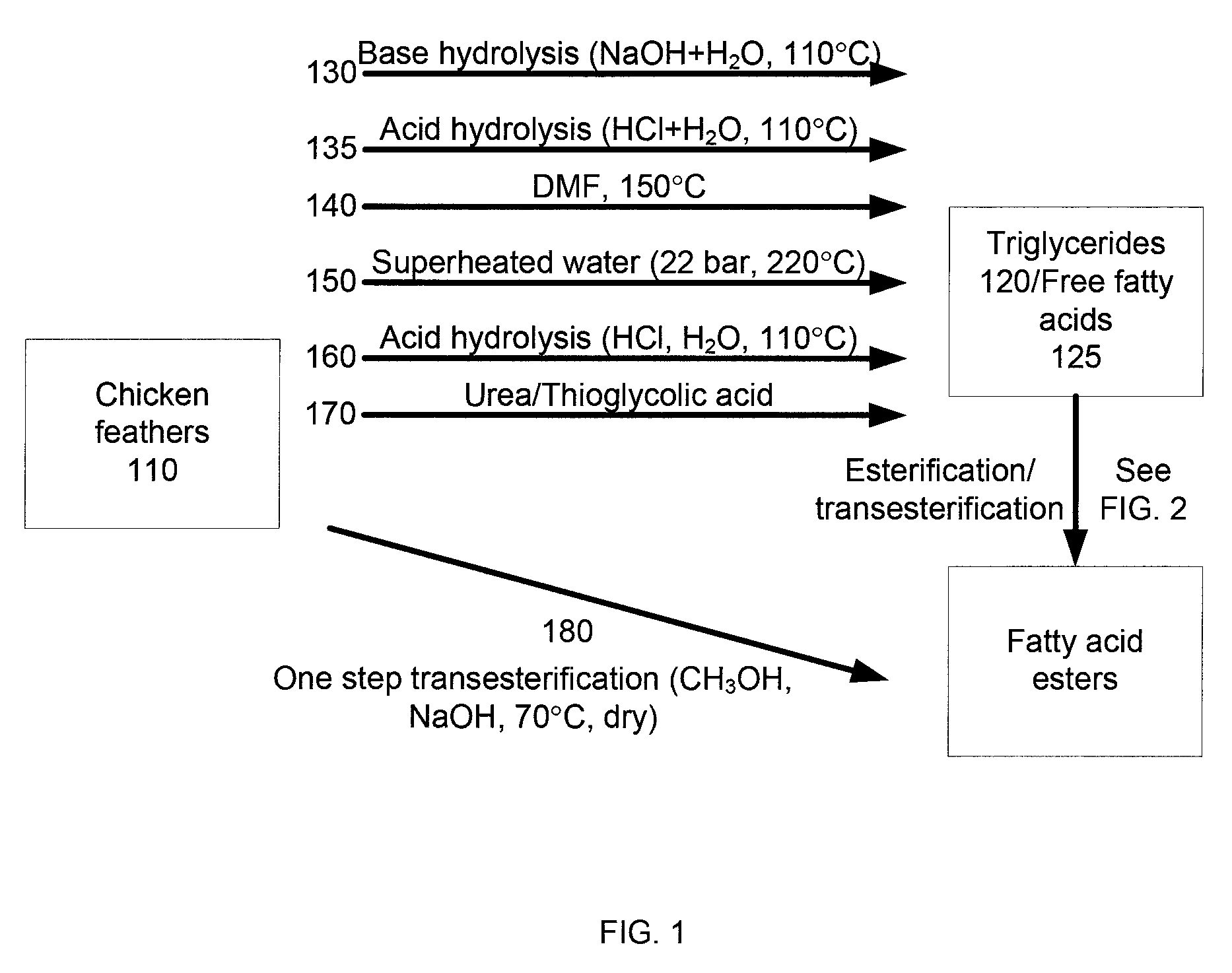
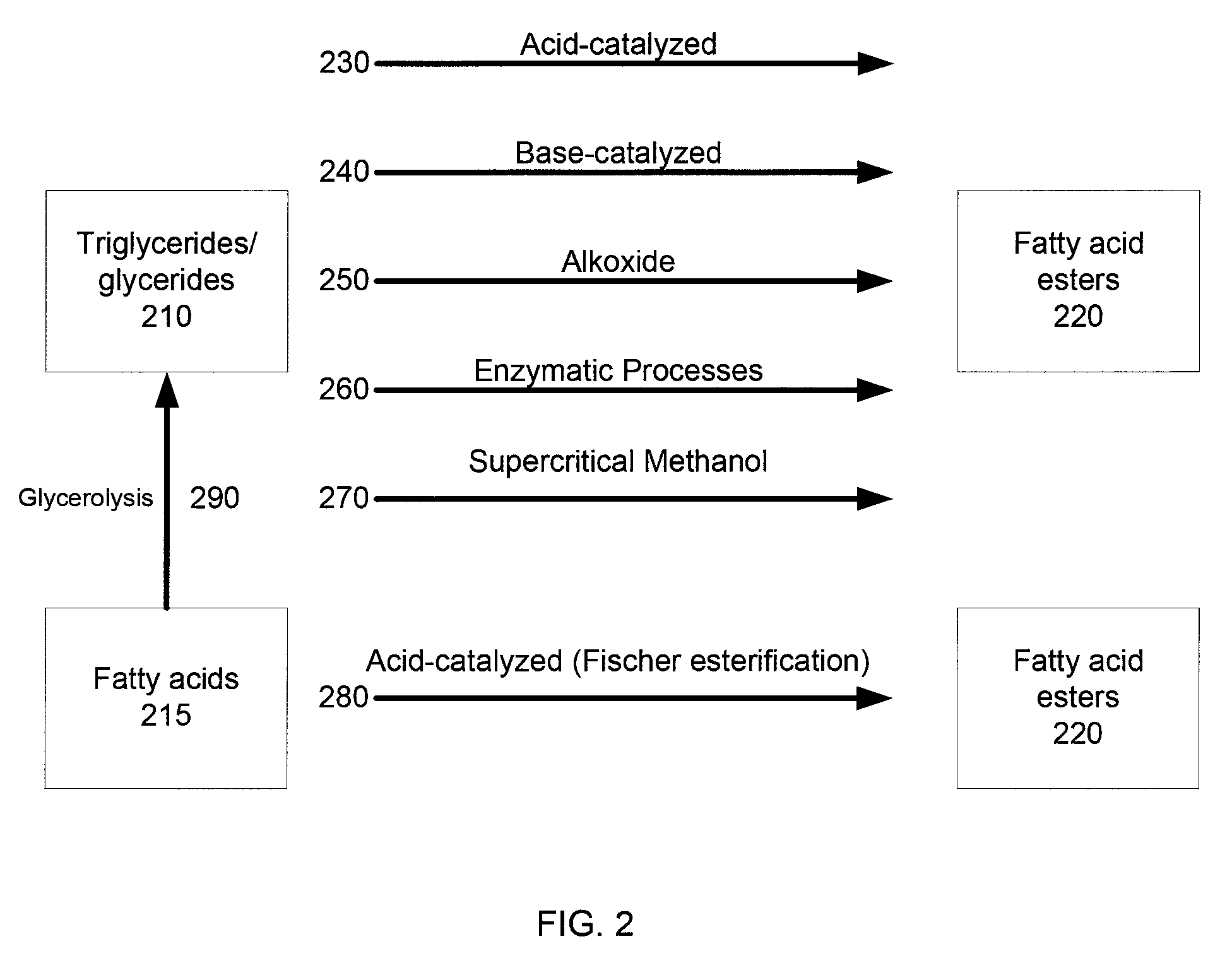
In some embodiments, the present disclosure provides methods for producing biofuel from a biological material that includes protein and a biofuel feedstock, such as triglycerides. In a specific example, the biological material is hydrolyzed to obtain the biofuel feedstock, such as by treatment with a base. Free fatty acids or triglycerides are then extracted using an organic solvent. The free fatty acids or triglycerides are converted to fatty acid esters, useable as biofuel, by esterification or transesterification, respectively. In a more specific example, the biological material is converted to a biofuel in a one step process by treating the biological material with base and an appropriate alcohol. In some implementations, a disclosed method uses chicken feathers obtained from a chicken processing operation as the biological material.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT NEVADA SYST OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF NEVADA RENO
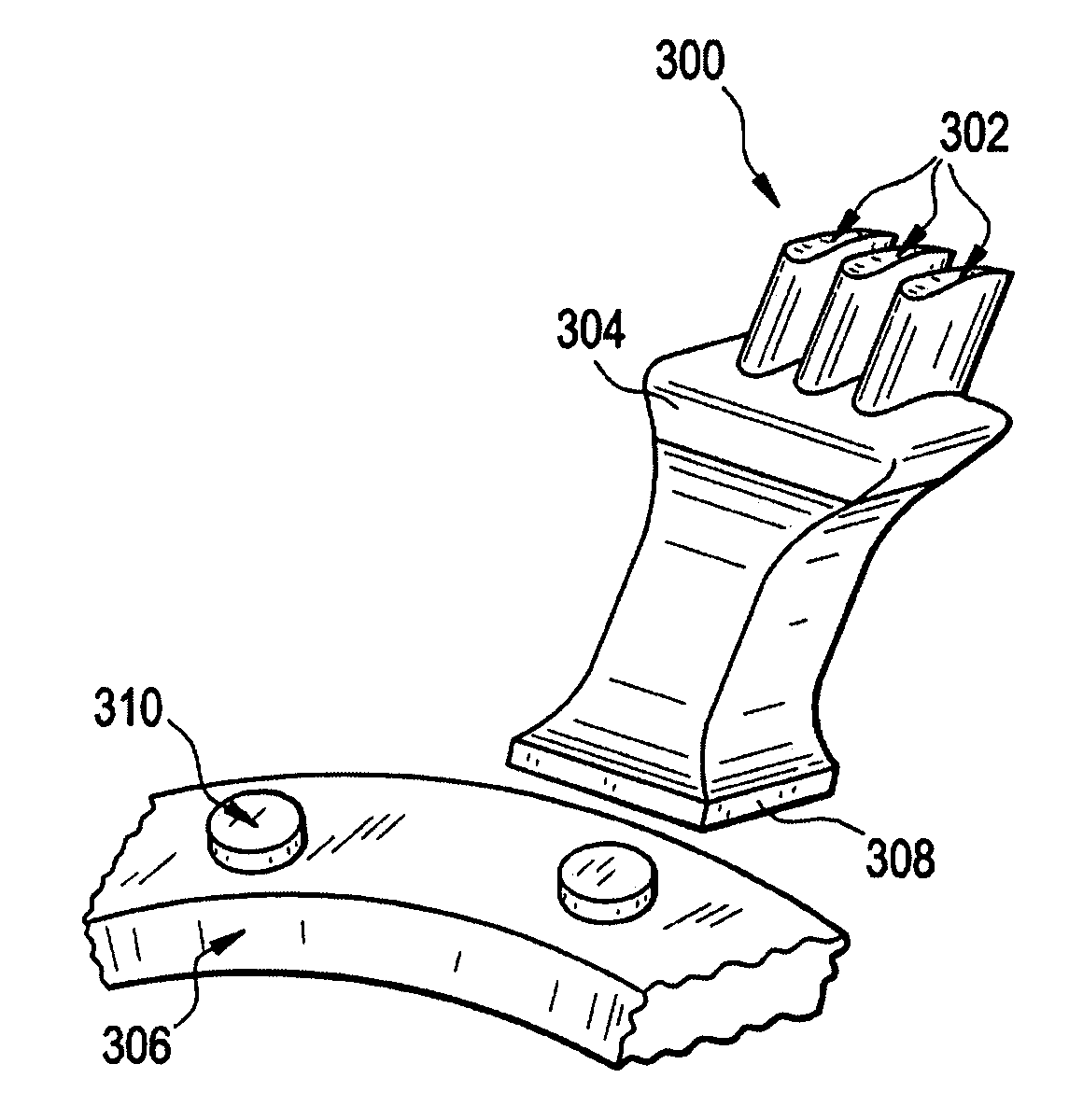
Disk rotor and method of manufacture
A disk rotor comprises a hub having a bore, and a plurality of spoke segments radially extending from the hub, each spoke segment including a base portion being attached to the hub and a rim portion, wherein the rim portion includes one or more airfoils integrally formed thereon, the plurality of spoke segments collectively forming a ring.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
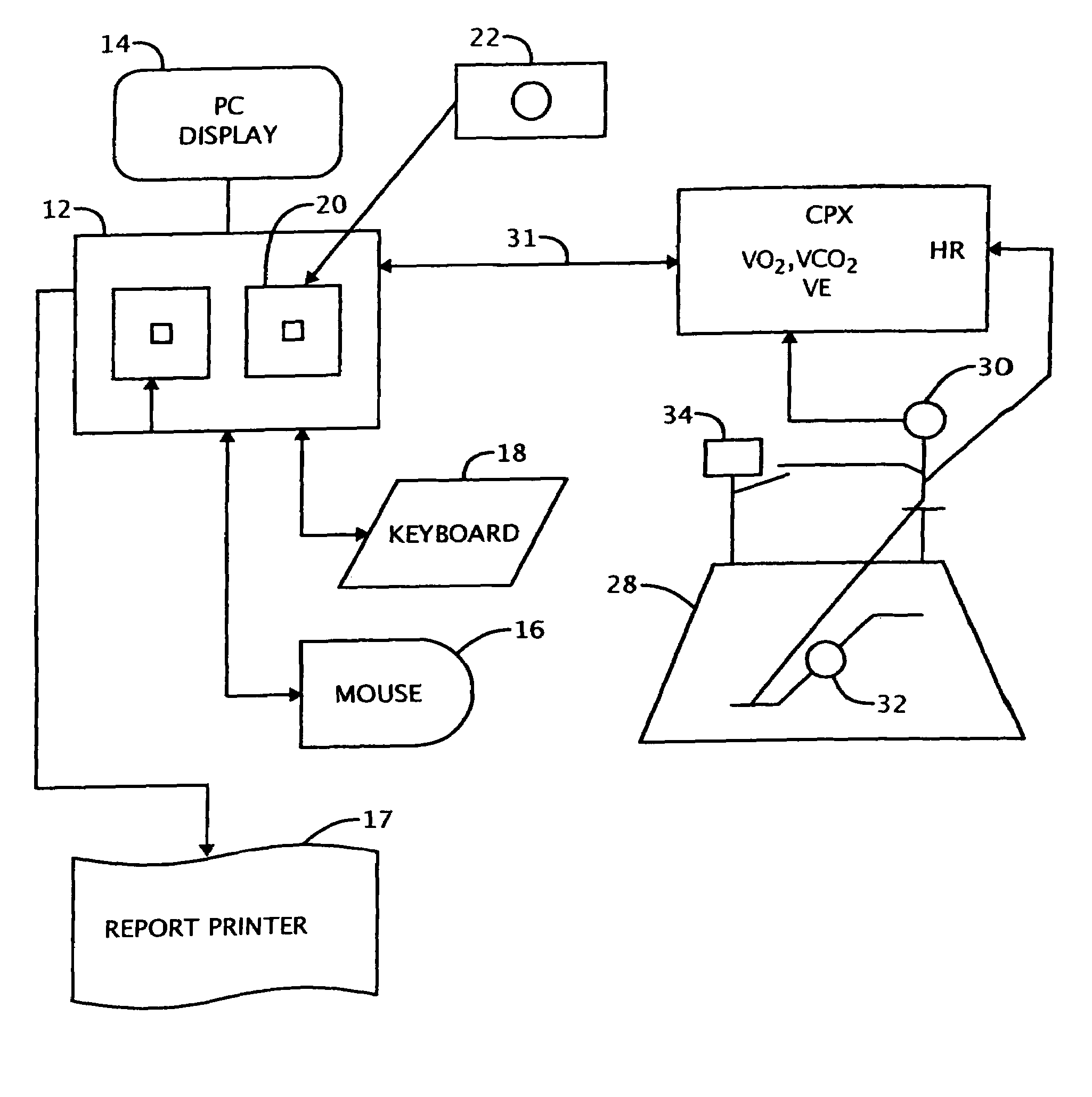
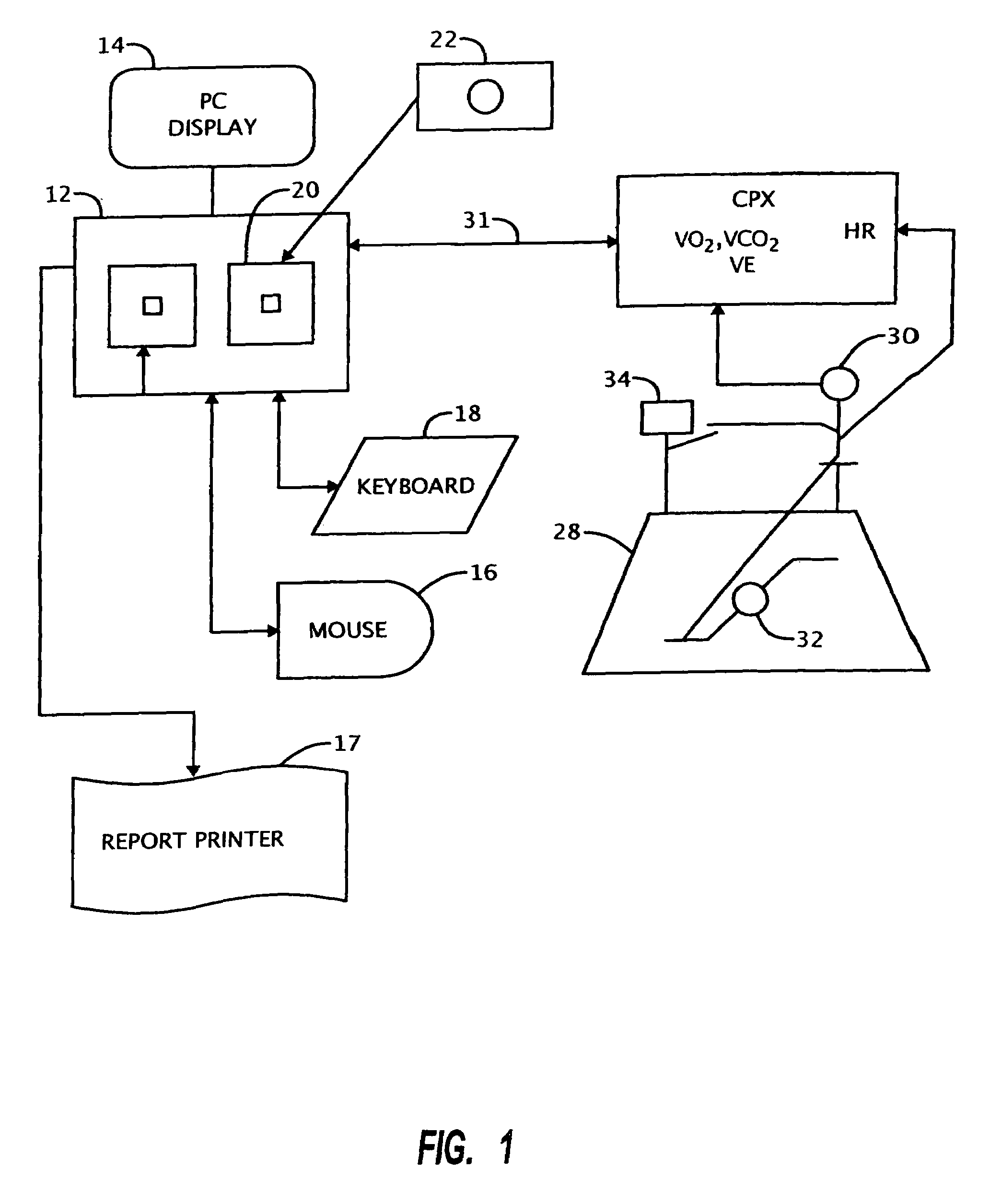
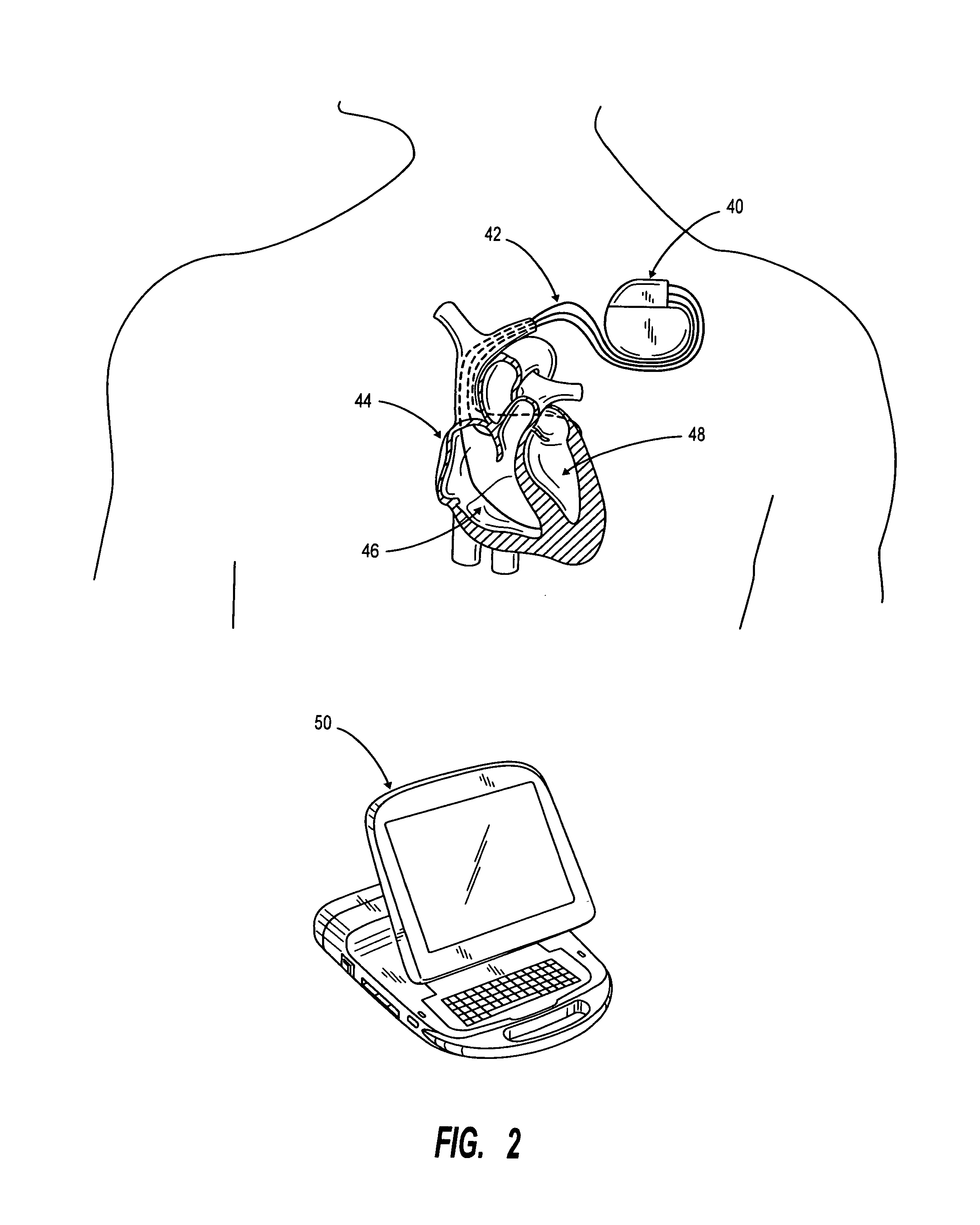
Method of optimizing patient outcome from cardiac resynchronization therapy
InactiveUS7225022B2High valueLow valueHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringCardiac pacemaker electrodeComputer-aided
A method of data management for optimizing the patient outcome from the provision of cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) is described. This method describes a process by which sets of dynamic cardiopulmonary dependent variables are measured during steady-state conditions, displayed, and translated into quantitative and qualitative measurements while the independent variables of CRT, device lead placement and atrial-ventricular and interventricular delay settings of bi-ventricular pacemaker systems, are altered by a physician. In combination with visual observation and computer-assisted ranking of the dependent variables, a physician can utilize the resulting information to render decisions on the optimal choice of the independent variables.
Owner:SHAPE MEDICAL SYST
Steam reforming catalyst composition and process
InactiveUS20050025701A1Efficient hydrogen generationHigh valueHydrogenCatalyst activation/preparationSteam reformingHydrocarbon
A method for producing novel catalysts comprising of Group VIII metal along with a partially reducible metal oxide, zirconium oxide, lanthanum oxide and aluminum oxide is disclosed. These novel catalysts retain their catalytic activity even in the presence of significant quantities of sulfur compounds. This makes them attractive in the conversion of hydrocarbons into hydrogen; a process for the same is also disclosed.
Owner:MILLENNIUM RES LAB
Mask Decomposition for Double Dipole Lithography
ActiveUS20100223590A1High valuePhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentDipoleDecomposition
Method and apparatus for generating a pair of layouts suitable for forming exposure mask to use in a double dipole lithographic process are disclosed. With some implementations, a y-dipole layout and an x-dipole layout are generated by decomposing a target layout. Subsequently, an optical proximity correction process is implemented on the y-dipole layout and the x-dipole layout. The decomposition may designate ones of the edge segments in the target layout at major edge segments and other ones of the edge segments as minor edge segments. A higher feedback value may then be assigned to the minor edges than the major edges. Subsequently, a few iterations of an optical proximity correction process that utilizes a smaller than intended mask rule constraint value and the assigned feedback values is implemented on the target layout. The minor edges separated by a distance of less than the intended mask rule constraint distance are then collapsed. After which, a few iterations of the optical proximity correction process are allowed to iterate. In further implementations, once the y-dipole and x-dipole layouts have been generated. An additional optical proximity correction process is implemented on the layouts. During this optical proximity correction process, a higher feedback values is again assigned to the minor edge segments. At a point during the optical proximity correction process, minor edges within portions of the layouts that have a bias value larger than a predetermined value are expanded back from their collapsed position.
Owner:SIEMENS PRODUCT LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
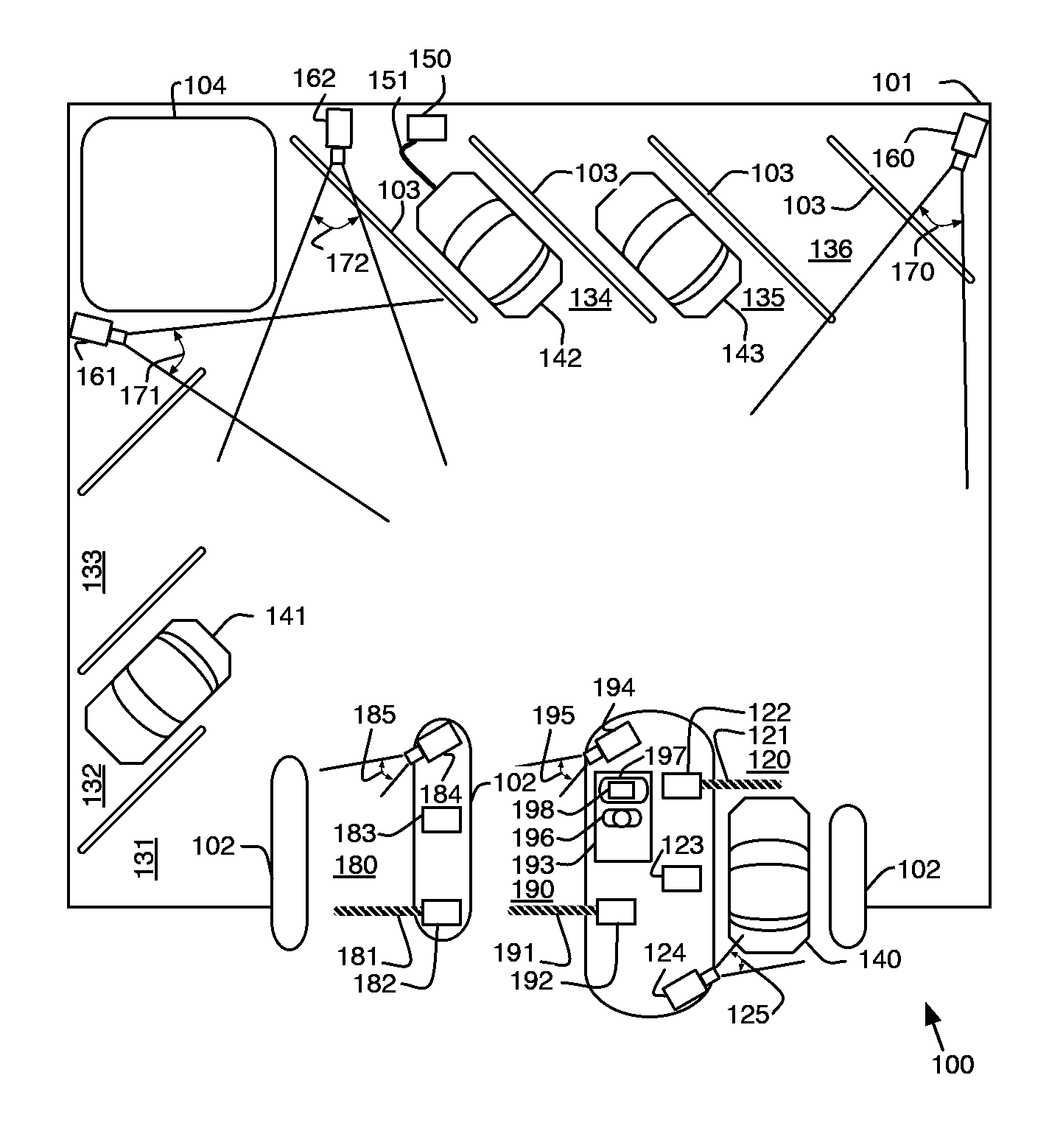
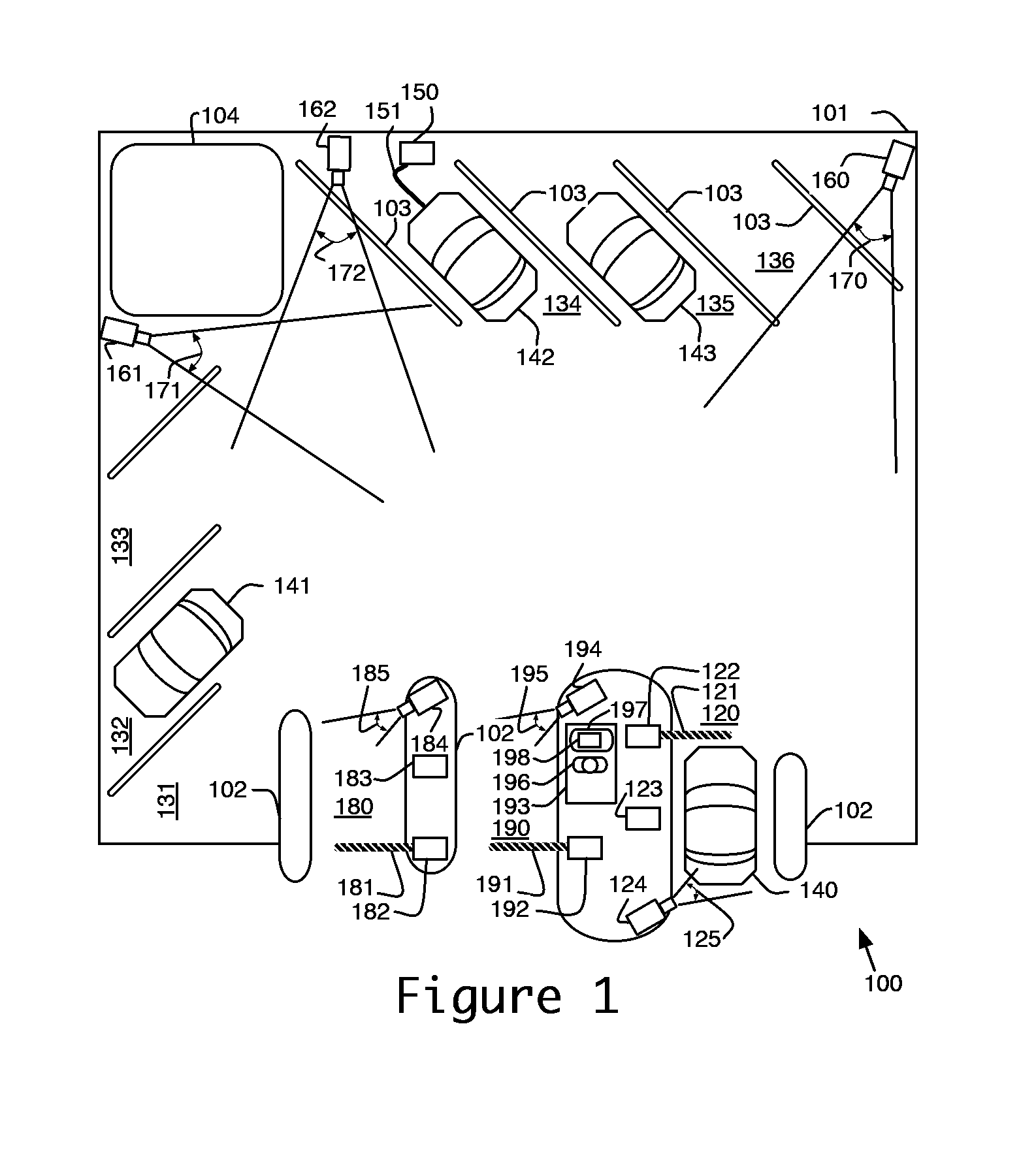
Geared motor for an active roll stabilizer
A slewing motor for an active roll stabilizer, which can be connected by its drive to one stabilizer half, and which can be connected on the stator side to another stabilizer half of a divided stabilizer. A torsion element, whose rotational rigidity is lower than the rotational rigidity of the stabilizer, is effectively arranged between the drive and the one stabilizer half.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Hot-Rolled High Strength Steel Sheet Having Excellent Ductility, Stretch-Flangeability, and Tensile Fatigue Properties and Method for Producing the Same
ActiveUS20090050244A1High valueImprove fatigue propertyFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesDuctilityAverage diameter
The present invention provides a hot-rolled high strength steel sheet in which, without using expensive Mo, by effectively using Ti which is an inexpensive element and the amount of precipitation hardening of which is large, both ductility and stretch-flangeability are improved at a tensile strength of 780 MPa or higher, and excellent tensile fatigue properties are exhibited; and a method for producing the hot-rolled high strength steel sheet. A hot-rolled high strength steel sheet having a composition including, in percent by mass, C: 0.06% to 0.15%, Si: 1.2% or less, Mn: 0.5% to 1.6%, P: 0.04% or less, S: 0.005% or less, Al: 0.05% or less, and Ti: 0.03% to 0.20%, the balance being Fe and incidental impurities, wherein the steel sheet has a structure in which the volume fraction of ferrite is 50% to 90%, the balance is substantially bainite, the total volume fraction of ferrite and bainite is 95% or more, precipitates containing Ti are precipitated in the ferrite, and the precipitates have an average diameter of 20 nm or less; and 80% or more of the Ti content in the steel is precipitated.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
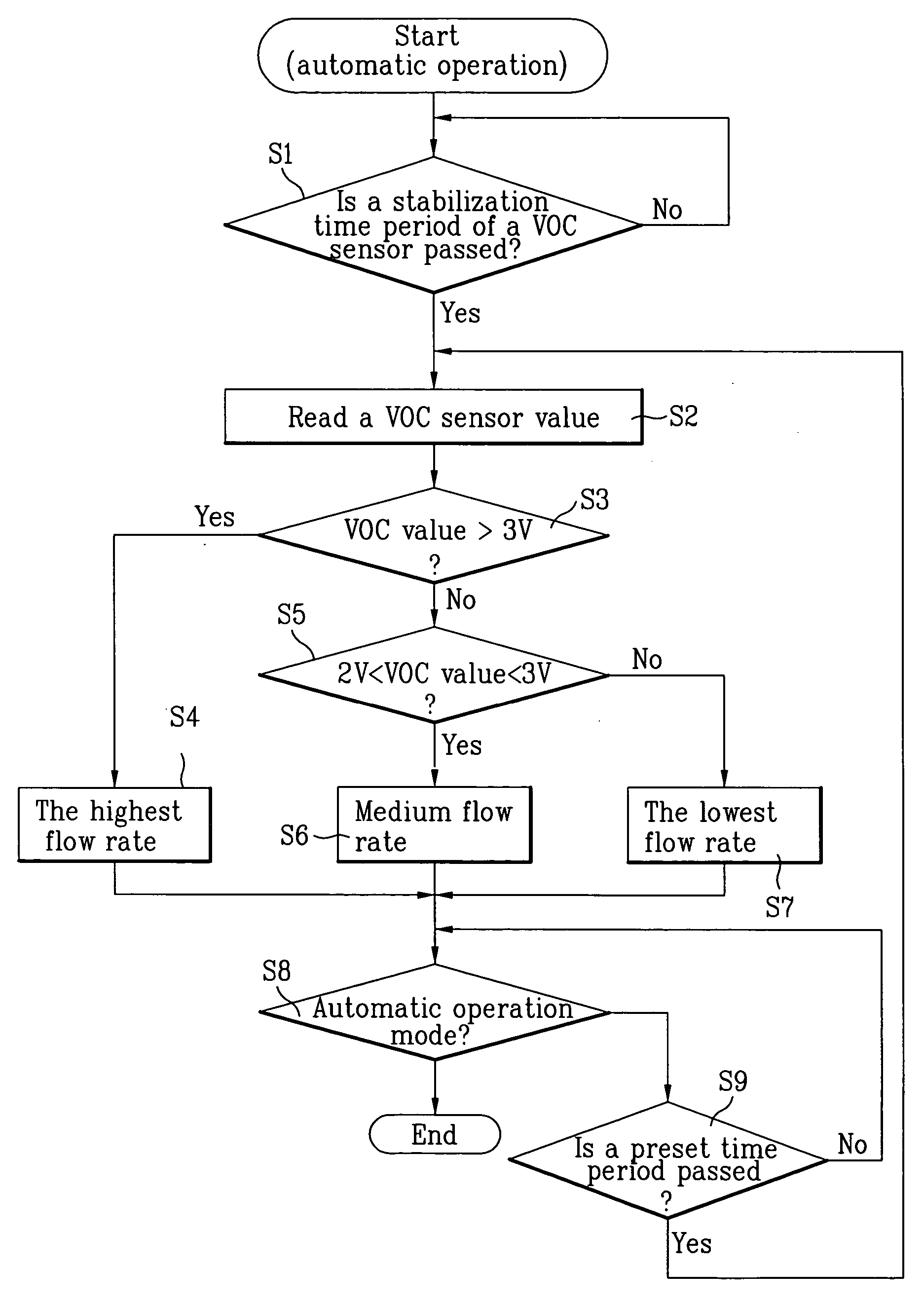
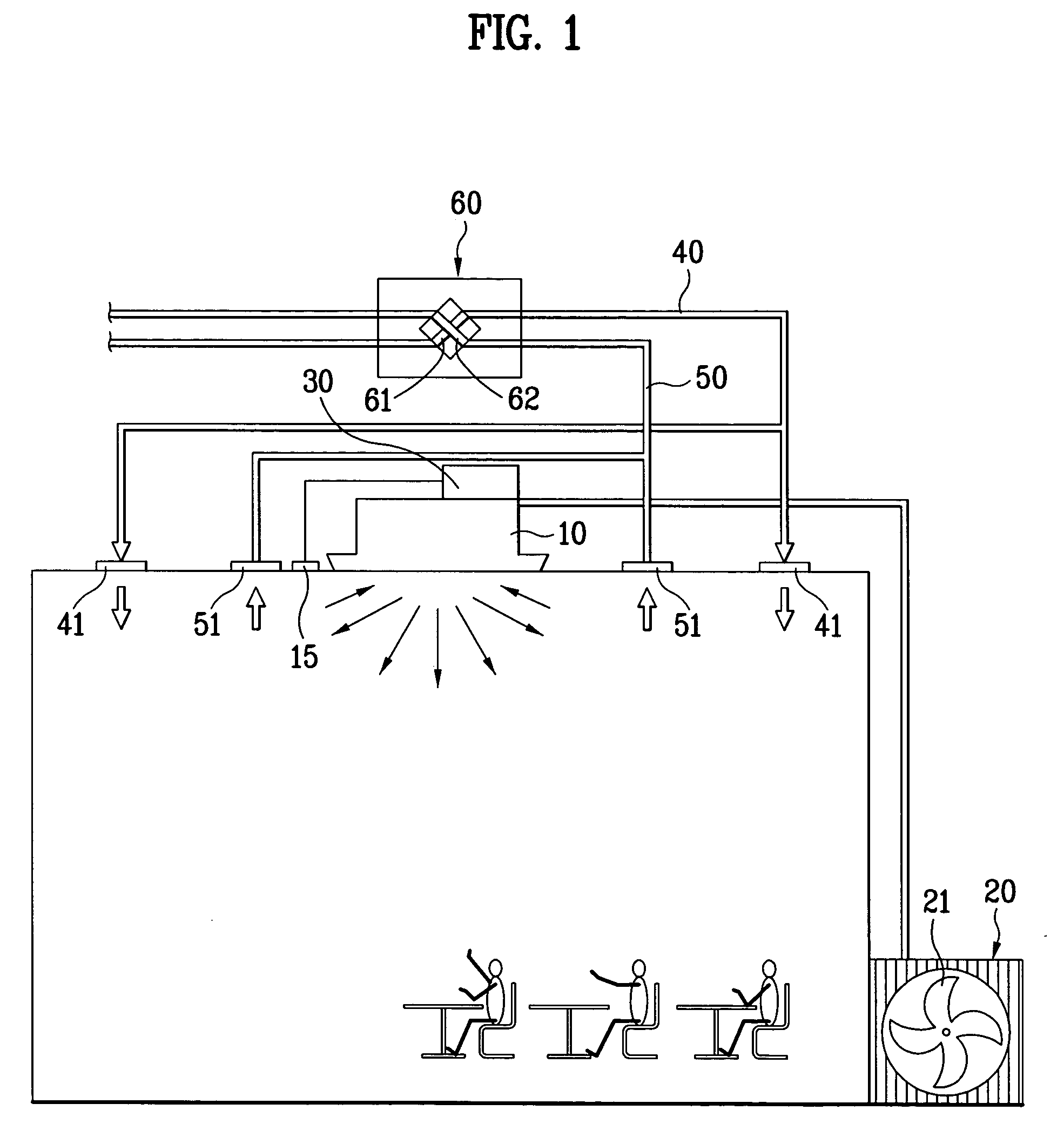
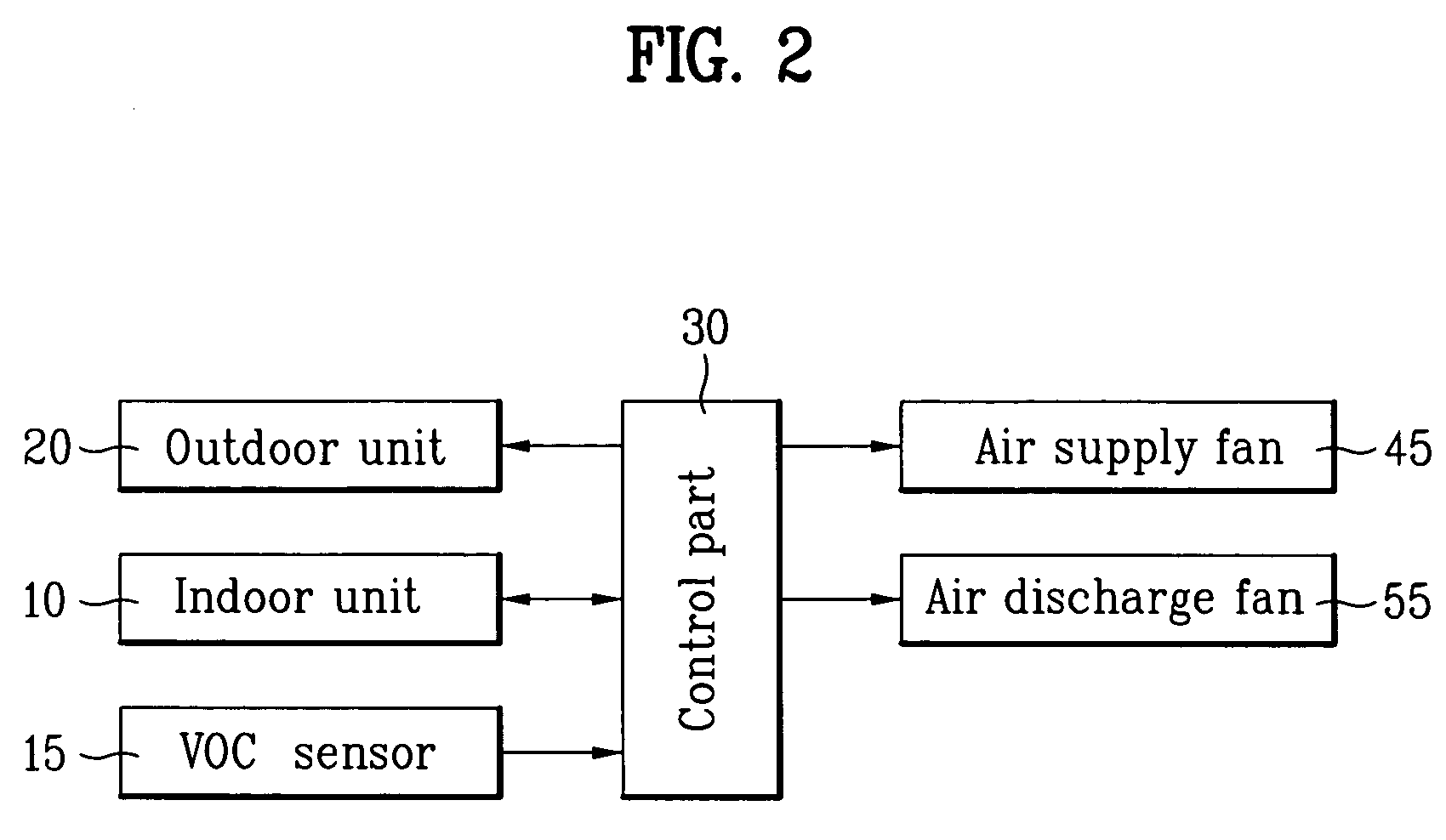
Method for controling air flow rate of air conditioning system
InactiveUS20050155366A1Low valueHigh valueMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsVolatile organic compoundAir volume
Method for controlling an air flow rate of an air conditioning system, including the steps of measuring a concentration of volatile organic compounds in air periodically, calculating a value of concentration change from concentration values measured at the present time and in the past, and controlling the flow rate of air for cleaning or ventilating a room with reference to the present concentration and value of concentration change, whereby controlling a flow rate of room cleaning or ventilating air to cope, not only with concentration of organic compounds, but also with rapid change of the concentration of the organic compounds in the air.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Laminated polyester film
InactiveUS20130337267A1Good adhesive propertyHigh valueSynthetic resin layered productsOptical articlesSurface functionPolycarbonate
The present invention can solve various problems posed by a triacetyl cellulose film, and provides a laminated polyester film which can exhibit a good adhesion property to adhesives as well as a good adhesion property to various surface functional layers, and can be suitably used as a protective film for a polarizing film, in particular, as a protective film disposed on a front surface of a front side polarizing plate. The laminated polyester film according to the present invention comprises a polyester film; and a coating layer formed on one surface of the polyester film which is obtained by applying a coating solution comprising a hydroxyl group-containing polycarbonate compound and an oxazoline compound onto the surface of the polyester film.
Owner:MITSUBISHI PLASTICS INC
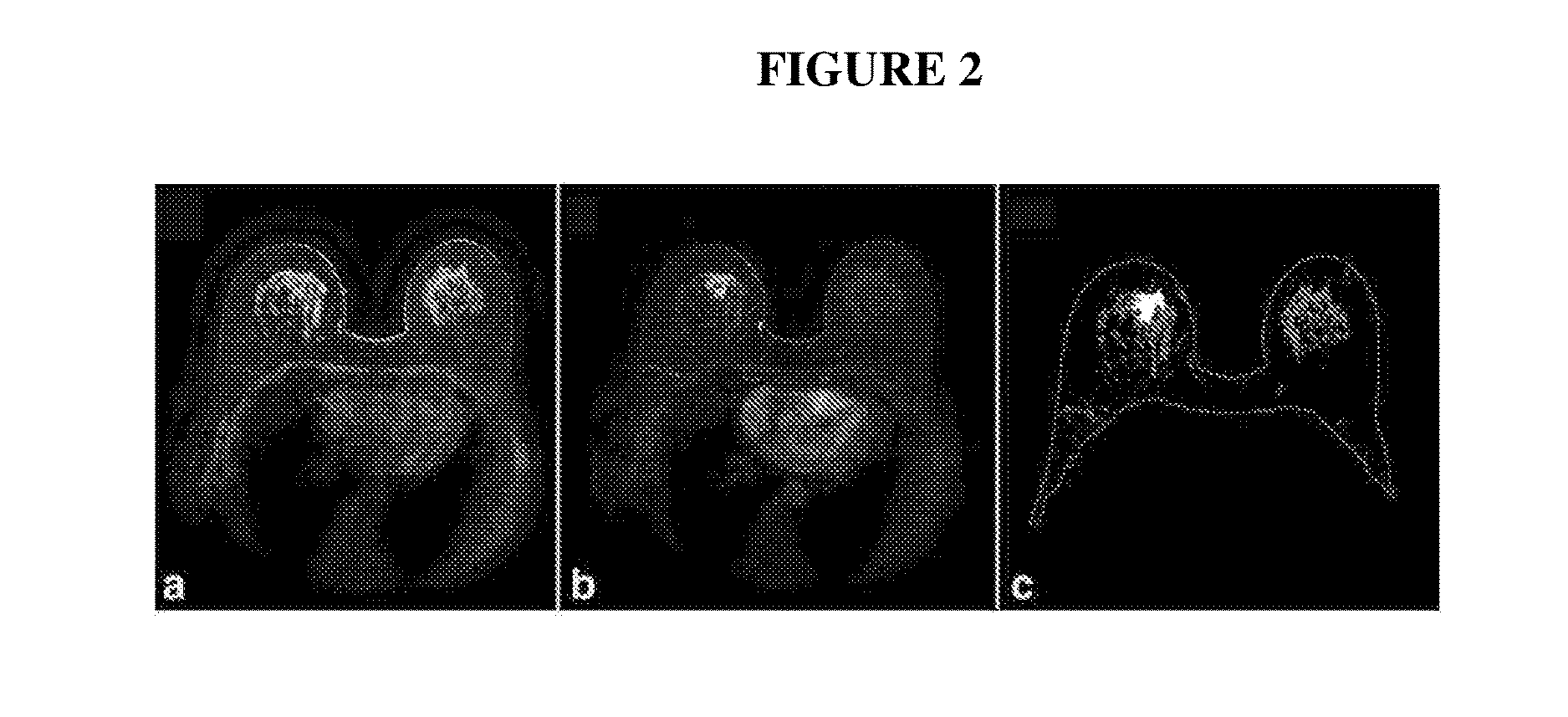
Systems and methods for extracting prognostic image features
ActiveUS20170014108A1Increase riskHigh valueImage enhancementMedical imagingImaging FeatureMagnetic Resonance Imaging Scan
Described herein are systems and methods for extracting image features from magnetic resonance imaging scans. These methods and systems are useful for both determining cancer lesion severity and disease prognosis. In particular, methods and systems are provided herein for extracting and analyzing imaging features that are correlated with breast cancer subtype and prognosis.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Multi-purpose portable alarm
Owner:CHEN MIKE
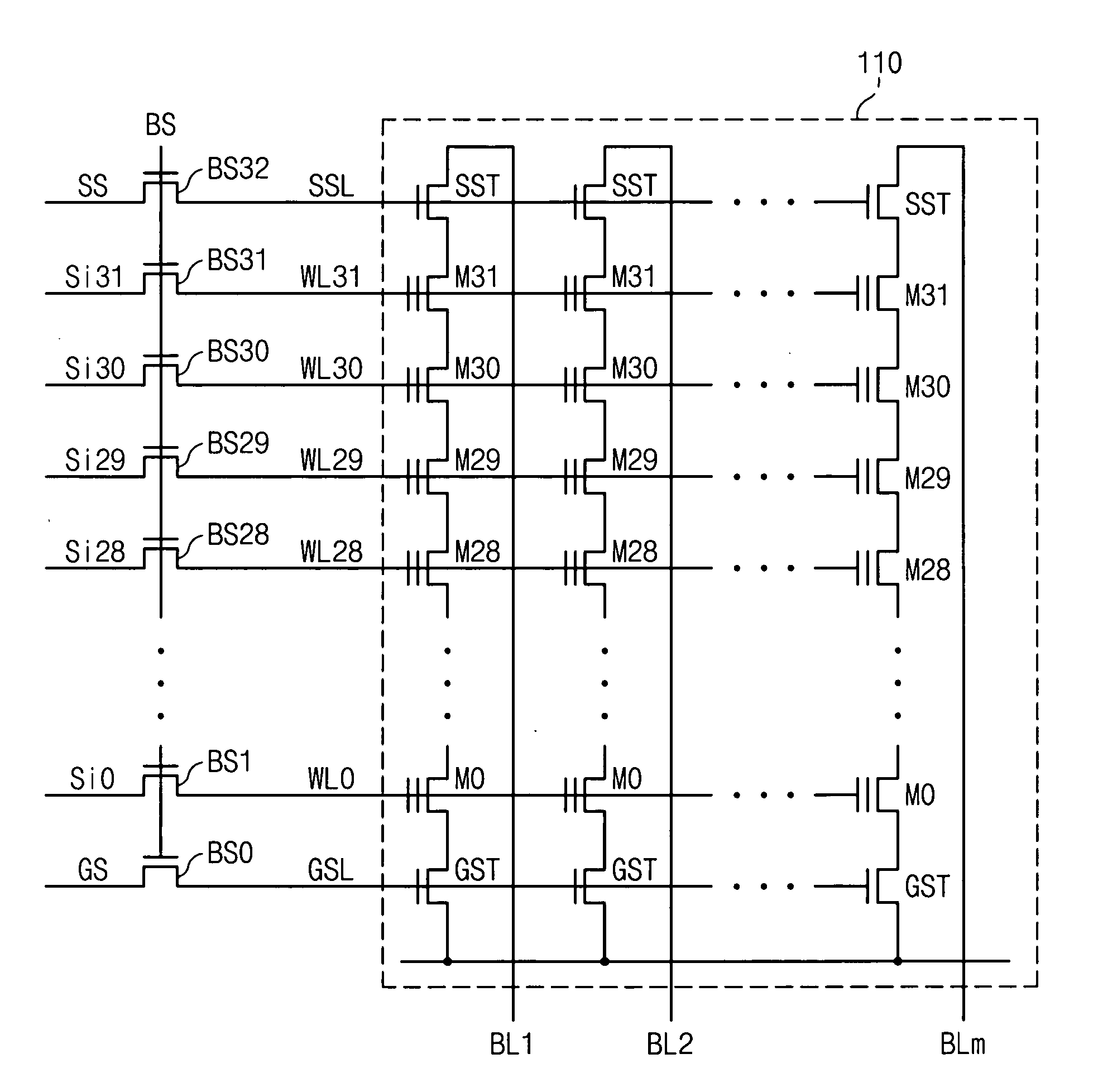
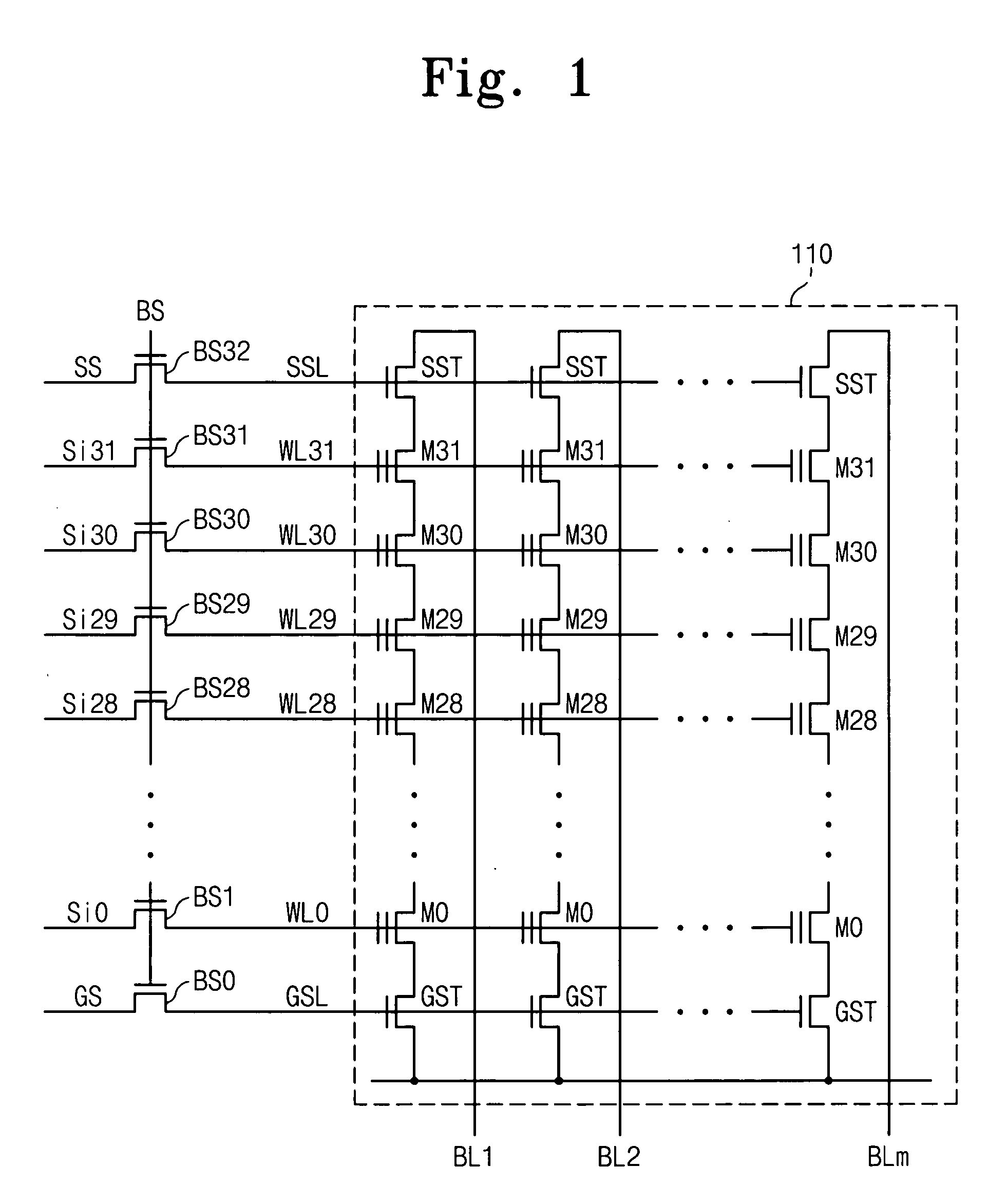
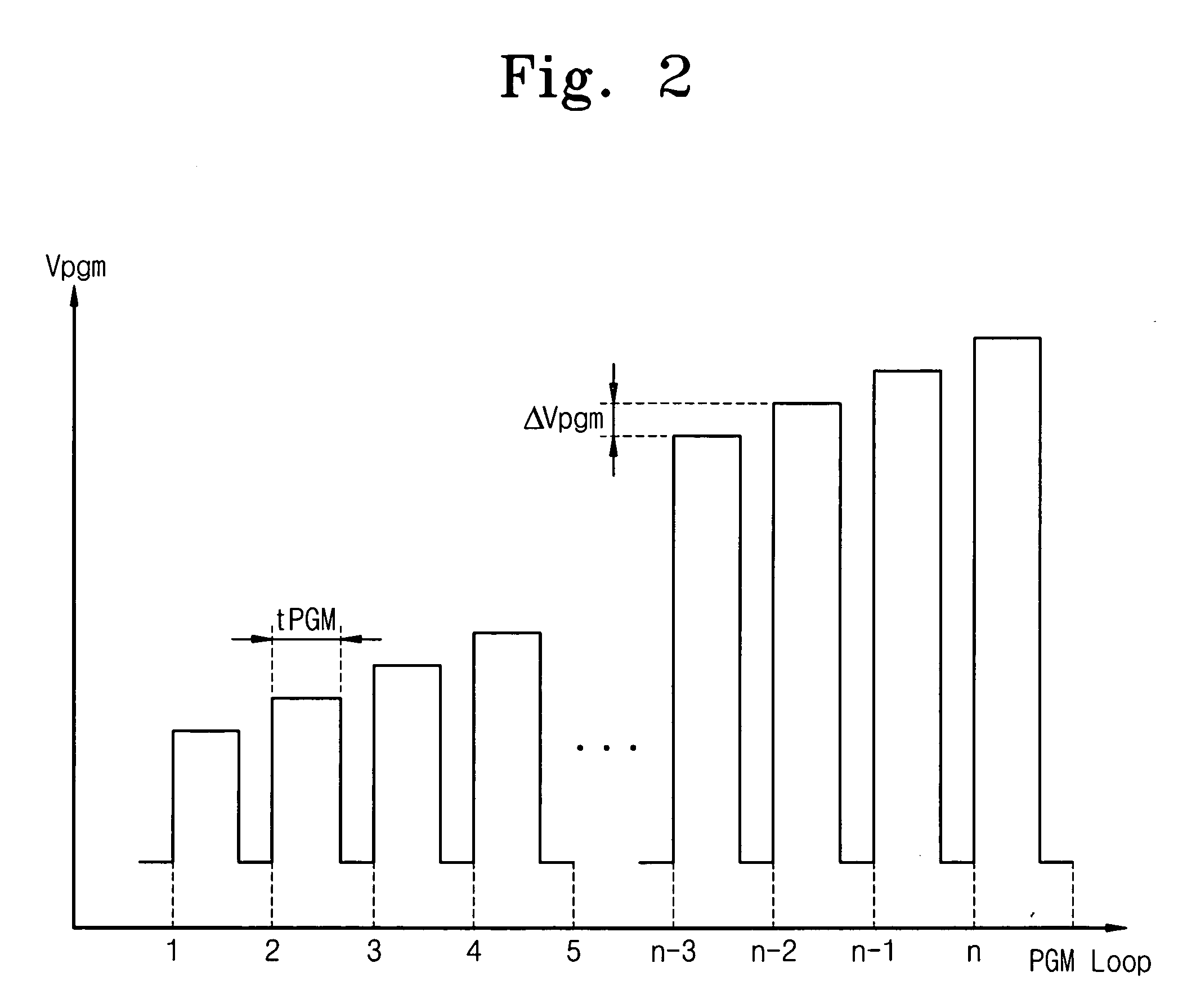
Nonvolatile memory devices and methods of controlling the wordline voltage of the same
A nonvolatile memory device includes an array of memory cells arranged in rows and columns, the array of memory cells having wordlines associated therewith. A wordline voltage controller determines the levels of wordline voltages to be supplied to the respective wordlines and a wordline voltage generator generates the wordline voltages at the determined levels. Related methods are also provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com