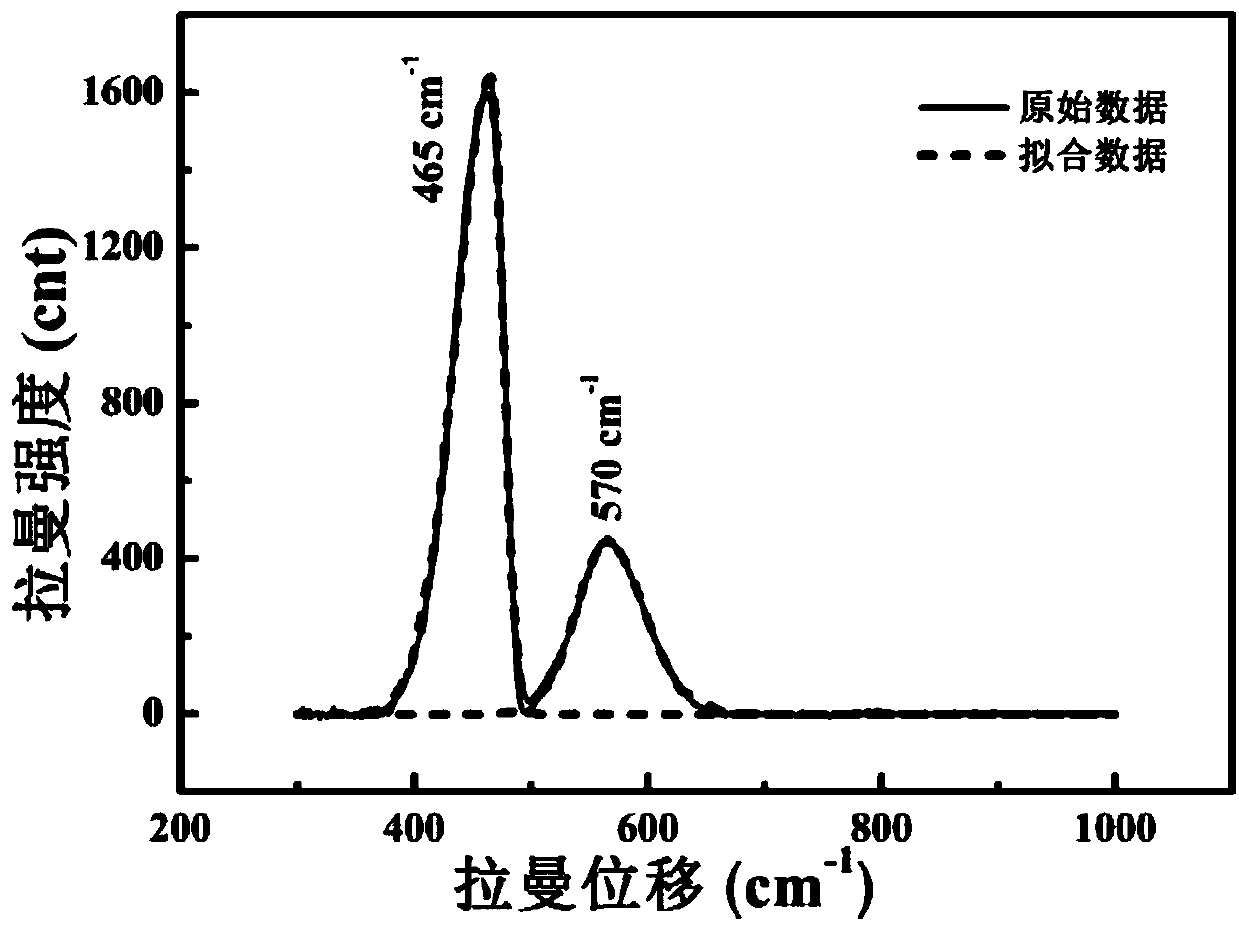
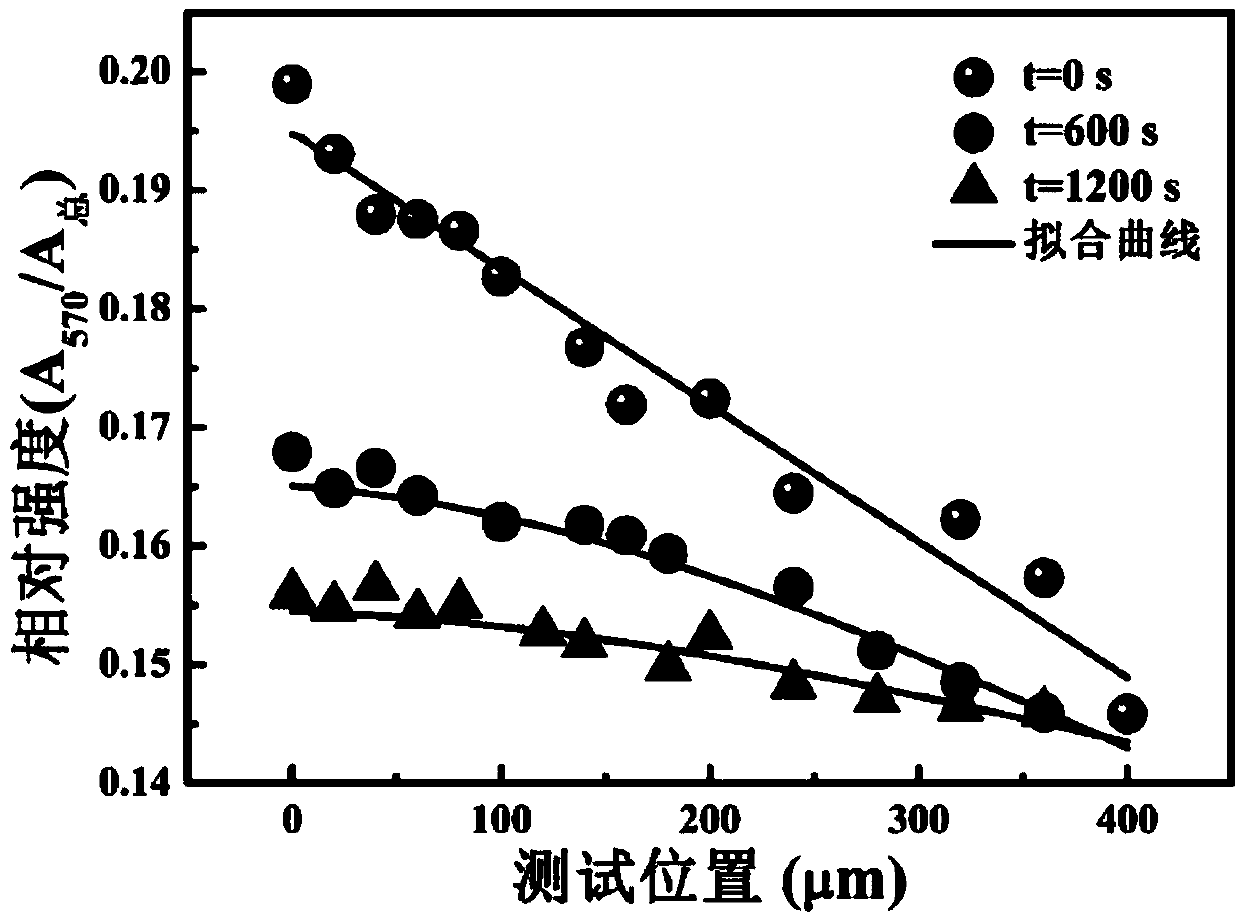
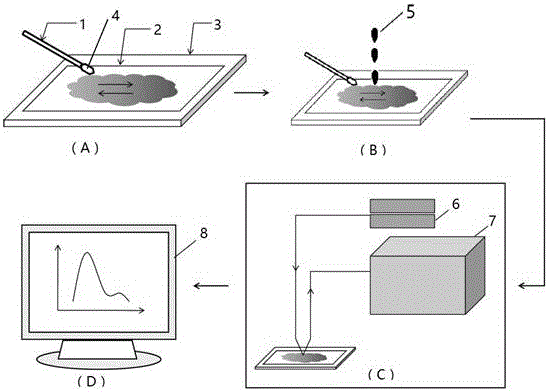
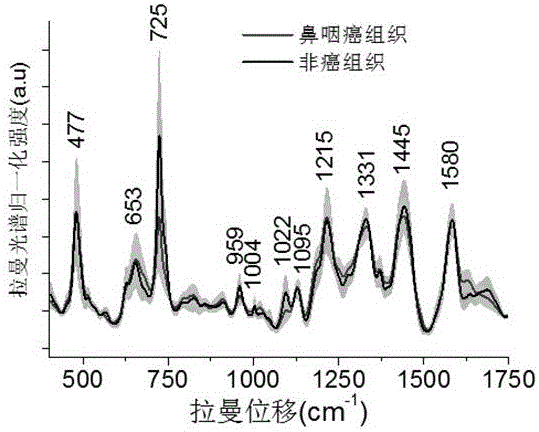
Patents
Literature
74 results about "Micro raman spectroscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
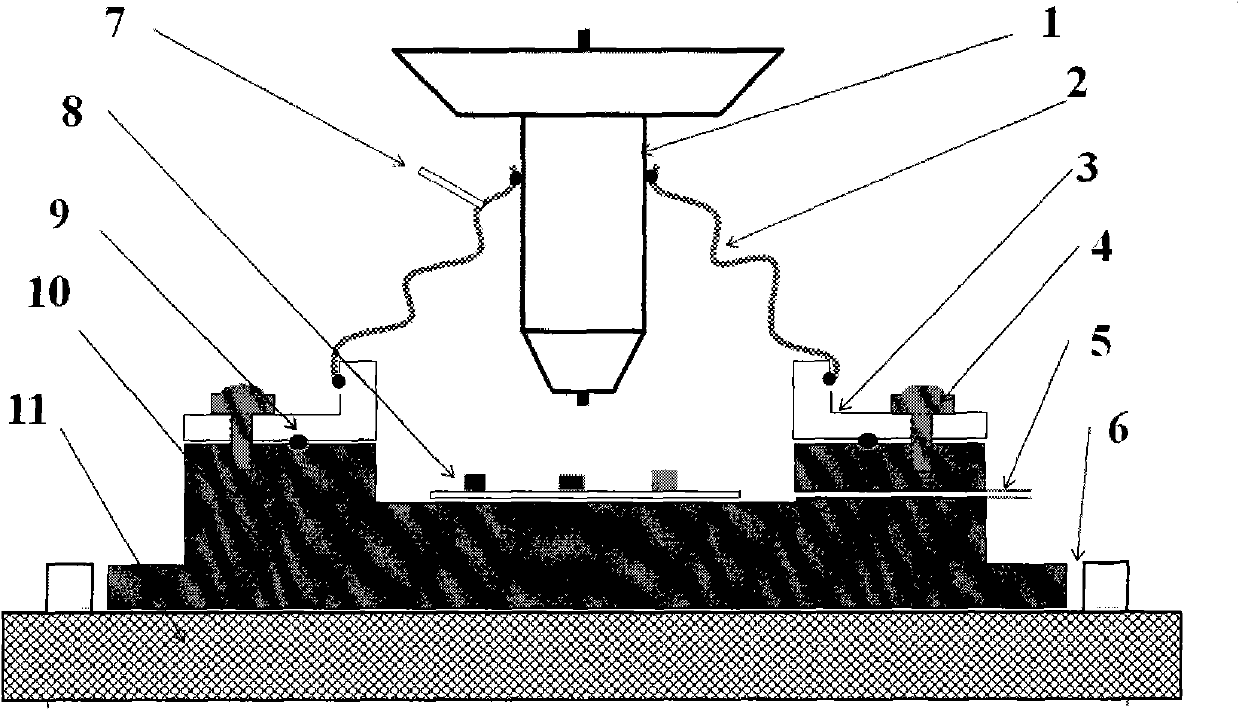
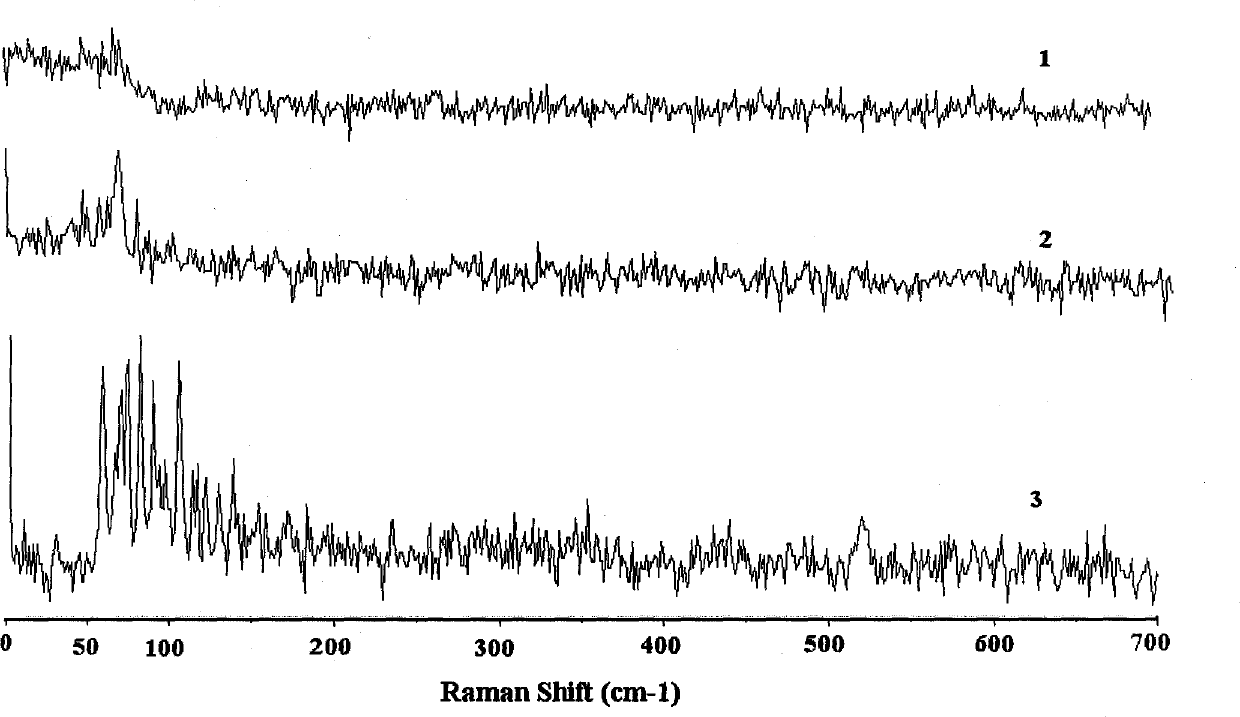
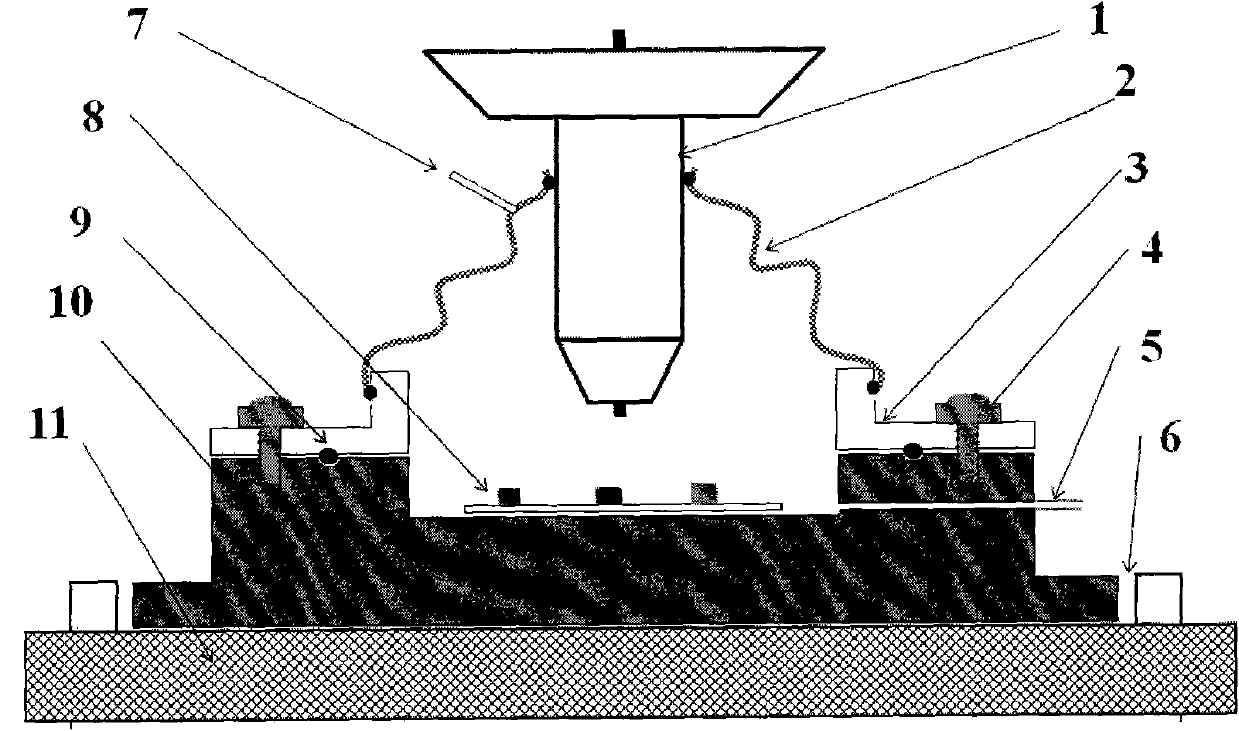
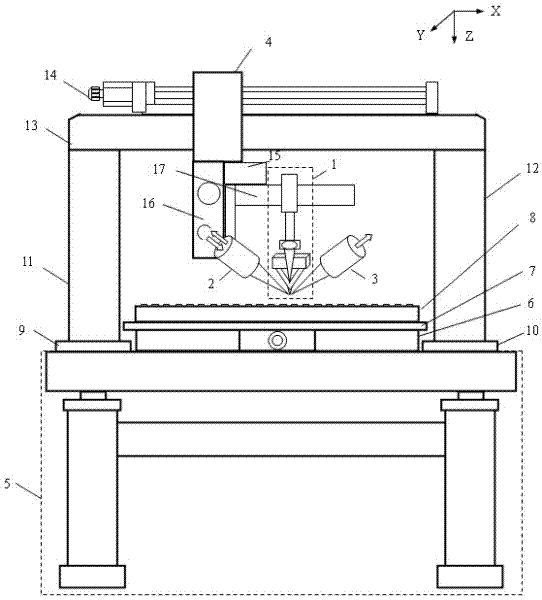
Micro Raman spectroscopy is a technique that uses a specialized Raman spectrometer to measure the Raman spectra of microscopic samples. In general terms, a Raman spectrometer is integrated with a Raman microscope. Different excitation laser wavelengths may be used to excite a microscopic sample so that the micro Raman spectrometer can collect...
Fabrication of ZnO nanorod-based hydrogen gas nanosensor
InactiveUS8263002B1High sensitivityEasy transferMaterial analysis by optical meansMaterial resistanceEnergy dispersionElectron
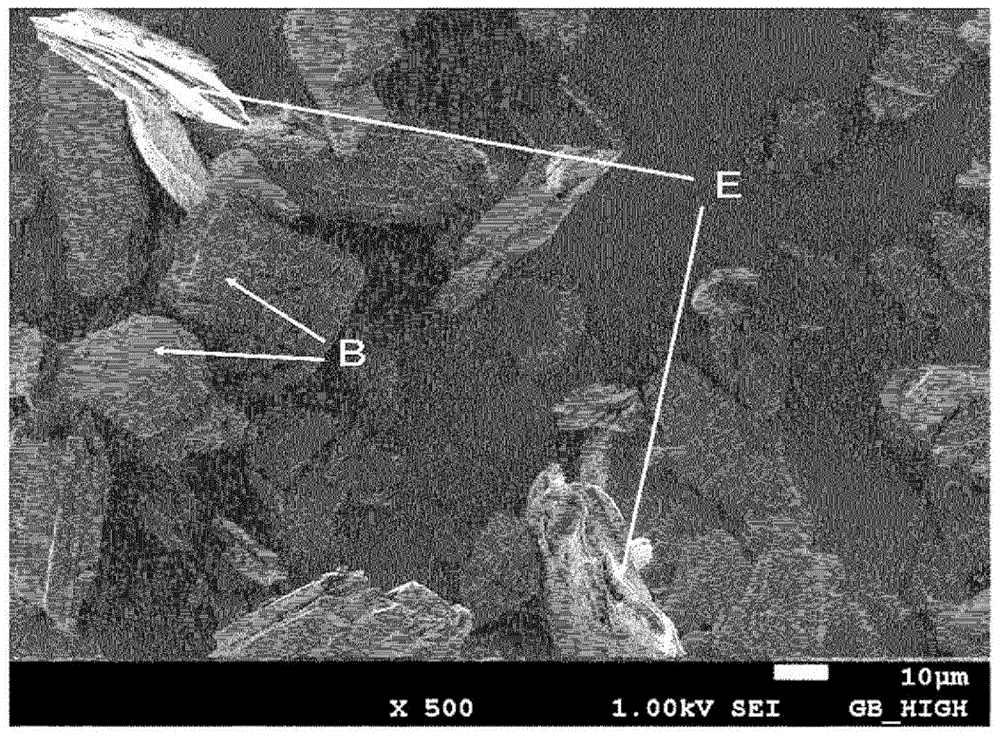
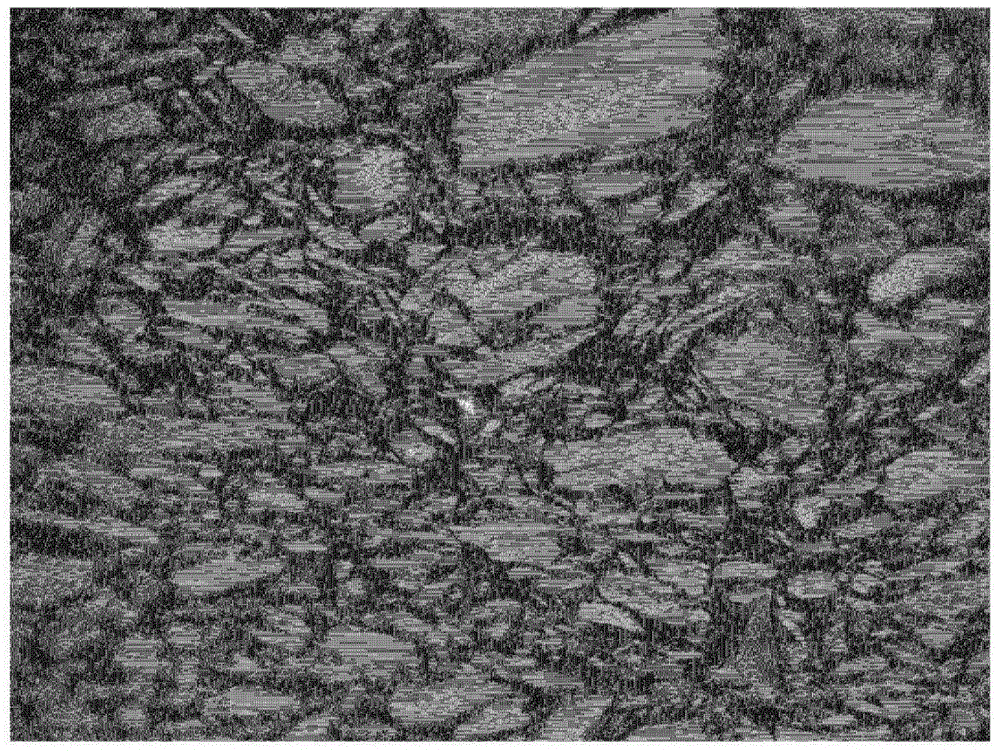
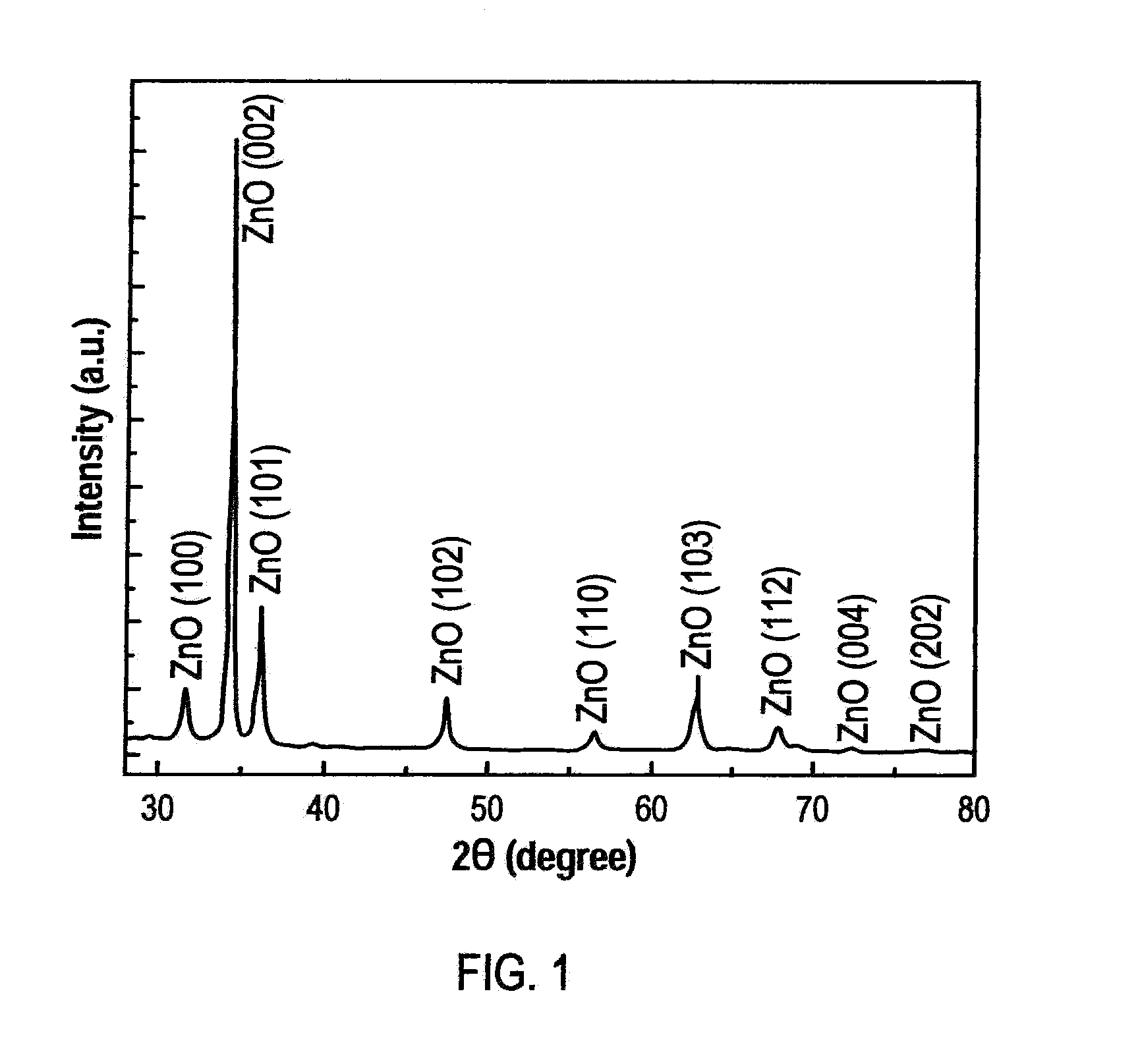
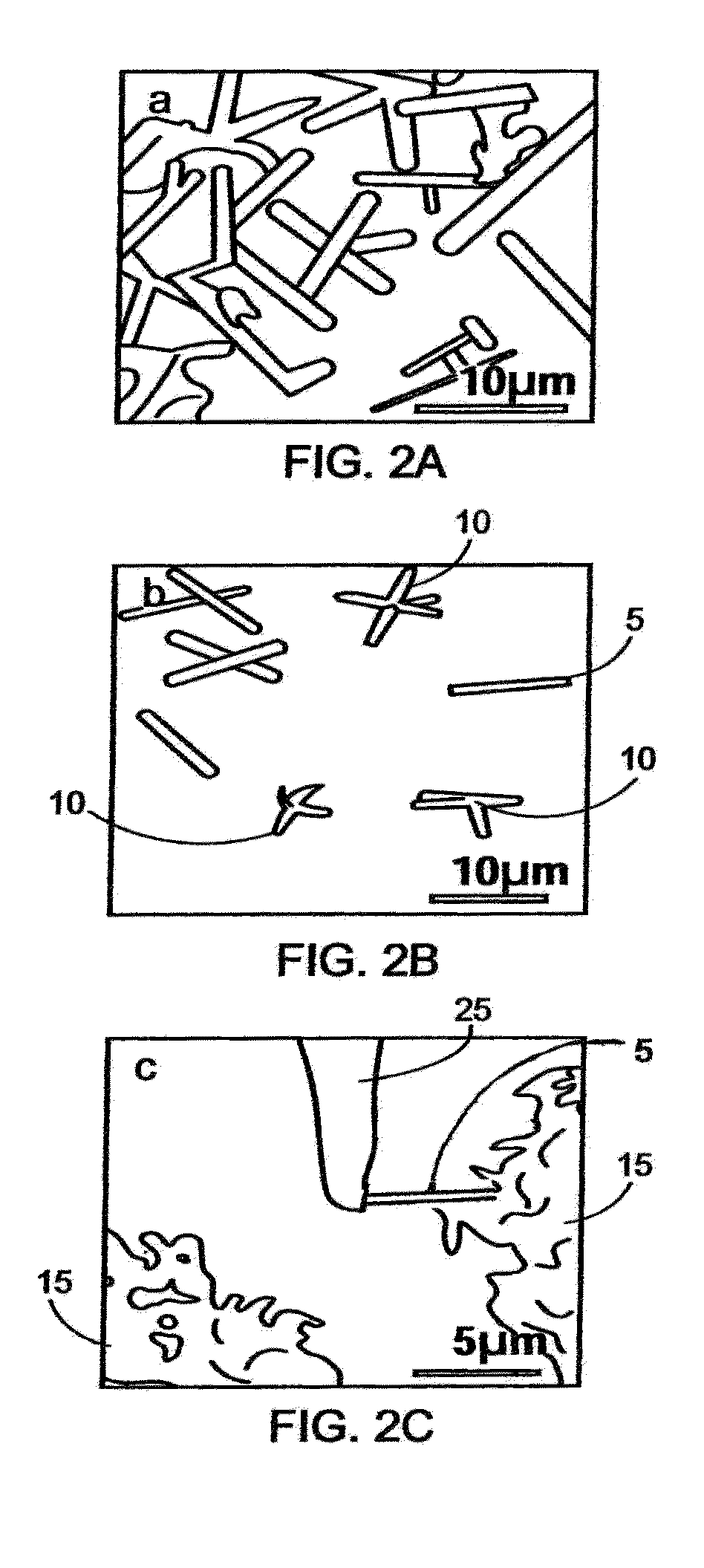
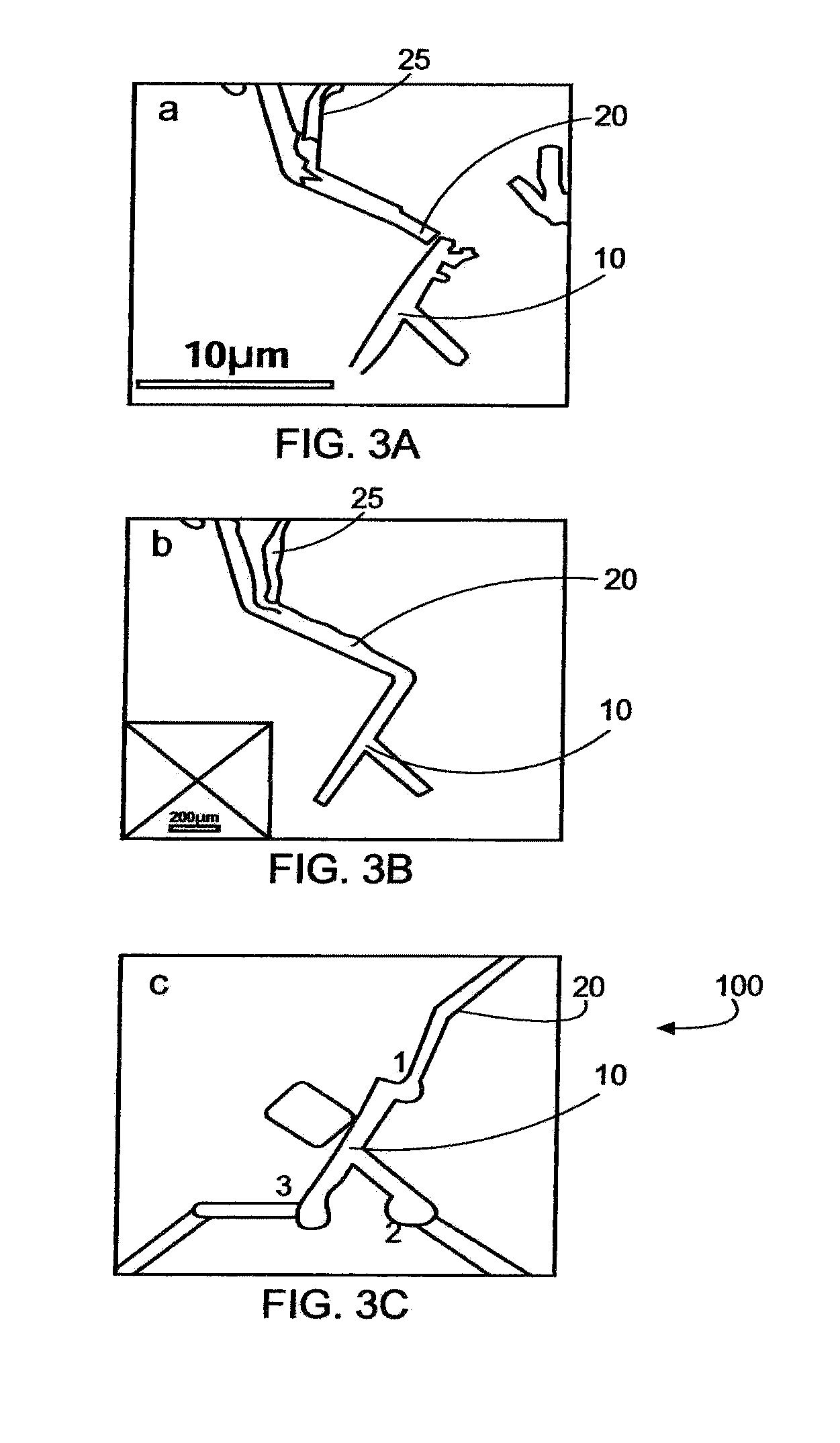
The nanofabrication of a hydrogen gas nanosensor device from single straight and branched, tripod shaped ZnO nanorods using in-situ lift-out technique, performed in the chamber of a focused ion beam (FIB) system is disclosed. Self-assembled ZnO branched nanorods have been grown by a cost-effective and fast synthesis route using an aqueous solution deposition method and rapid thermal processing. The properties of the ZnO nanorod structures were analyzed by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersion X-ray spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy and micro-Raman spectroscopy. High quality ZnO nanorods were obtained with a 90% success rate for building nanodevices. The fabricated nanosensor can gauge 150 ppm hydrogen gas in the air at room temperature. The nanosensor has selectivity for other gases such as oxygen, methane, carbon monoxide and liquid propane gas. The ZnO nanorod sensors of the present invention also operate at low power of less than 5 microwatts.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
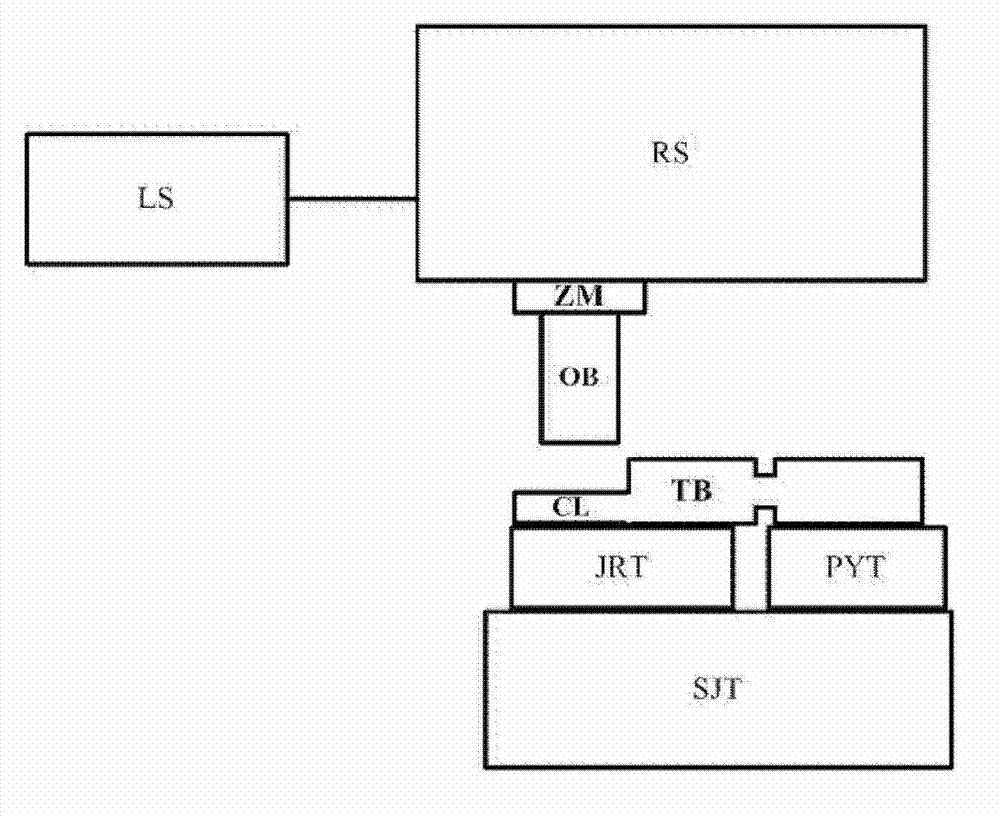
Confocal microscopic Raman spectrometer with angle resolution capacity
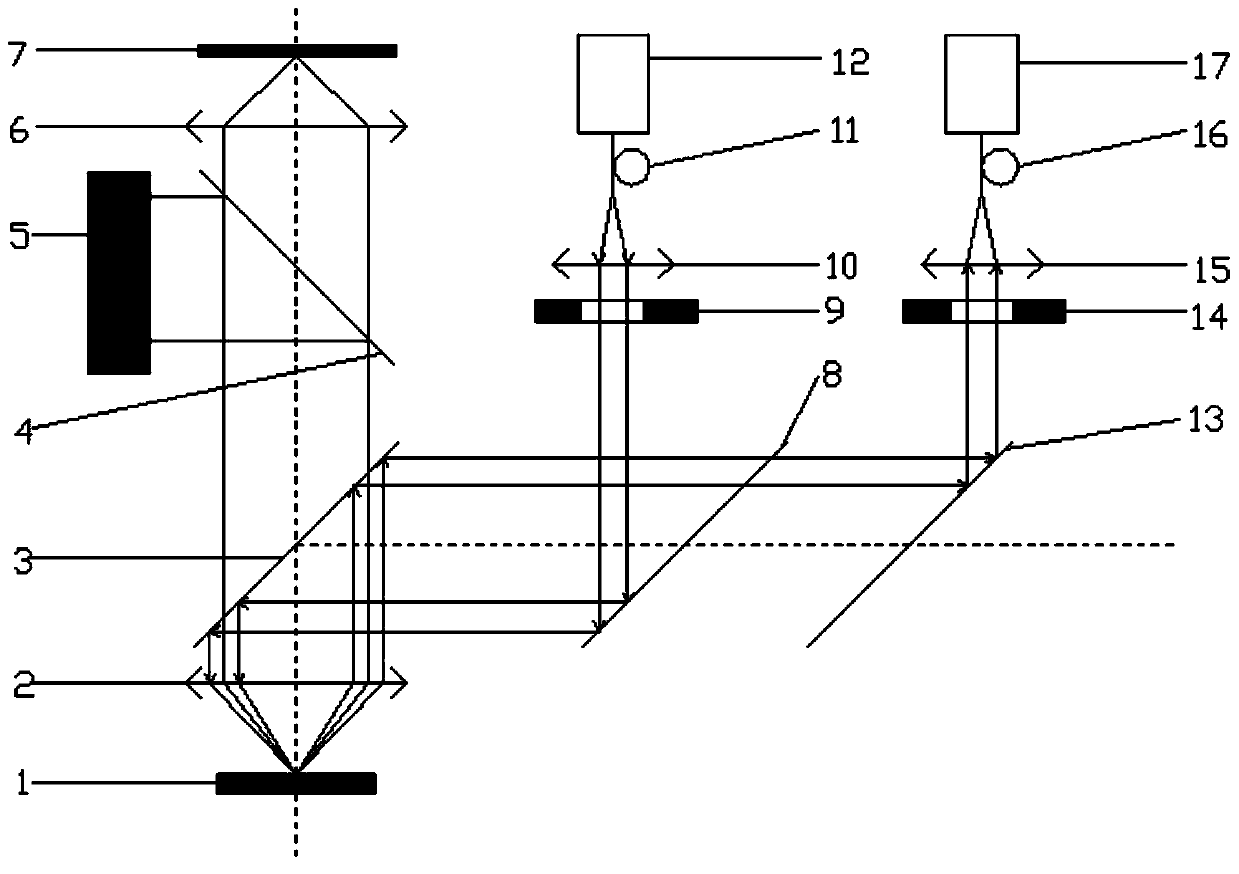
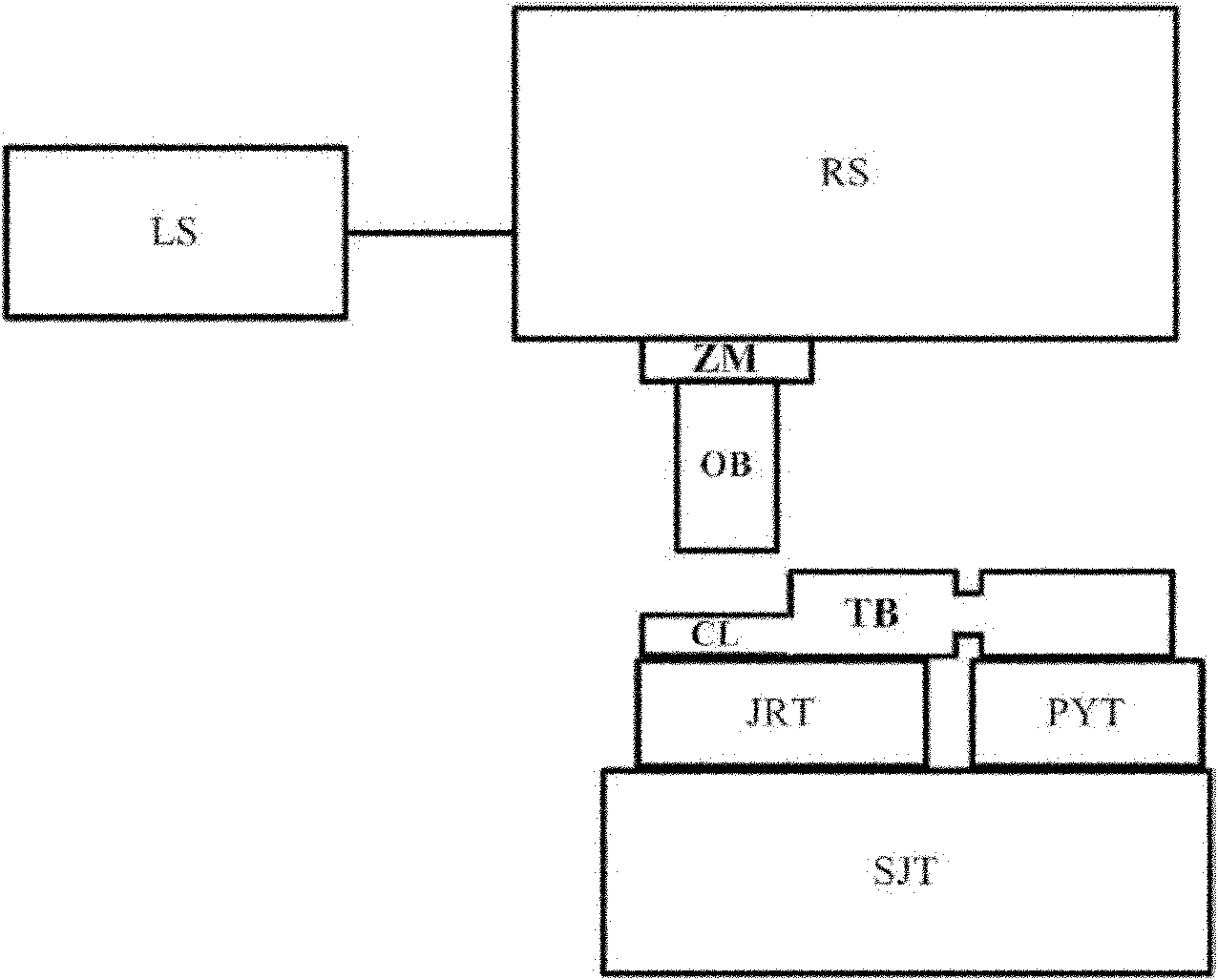
The invention discloses a confocal microscopic Raman spectrometer with angle resolution capacity and relates to Raman spectrometers. The confocal microscopic Raman spectrometer comprises a microscope objective, a low-pass light filter, a high-pass light filter, a reflector, a beam splitter, adjustable diaphragms, a collimating lens, an optical fiber and a corresponding laser light source, a spectral signal detector, an illuminating light source and a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera, wherein light emitted by the laser light source enters the microscope objective through the optical fiber, the collimating lens, the high-pass light filter and the low-pass light filter, the positions of the incident parallel beams can be adjusted by moving the high-pass light filter from left to right along the horizontal direction, and an angle of exciting light which reaches the sample surface is adjusted. The first adjustable diaphragm can control the pore diameter of the incident parallel beams, and the positions of emergent parallel beams can be adjusted by moving the reflector from the left to right along the horizontal direction, so that an angle of Raman scattering light collected from the sample surface is adjusted; and the second adjustable diaphragm can control the pore diameter of the Raman scattering light beams, and the sample can be imaged through the illuminating light source, the beam splitter and the CCD camera.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
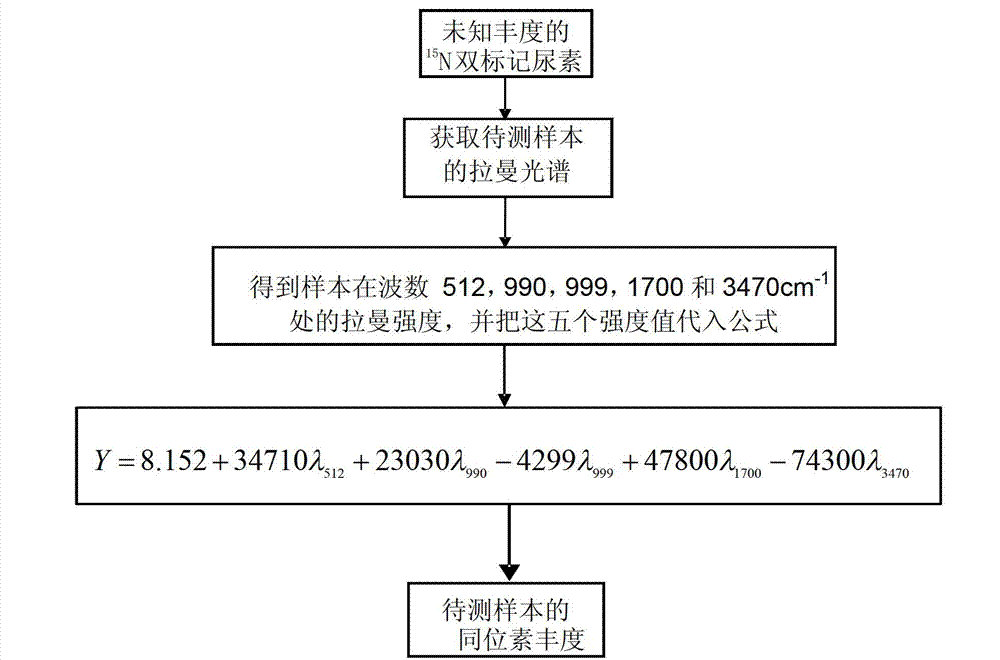
Urea isotopic abundance rapid detection method based on Raman spectrum
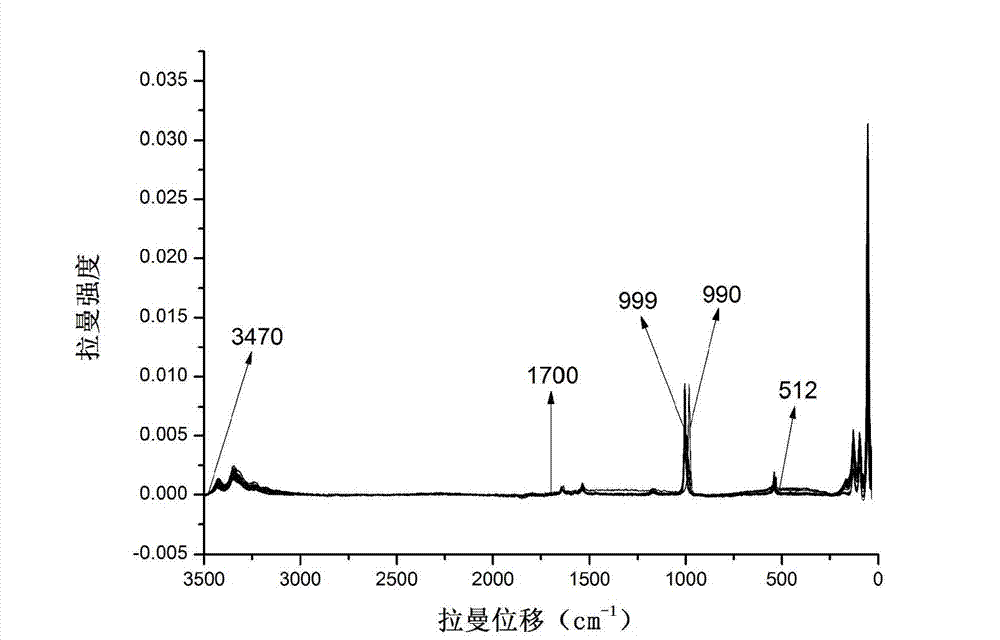
The invention relates to a urea isotopic abundance rapid detection method based on Raman spectrum. A traditional detection method is slow in speed and complex in operation. 15N double-tagging urea to be tested is placed at the center of a glass slide directly and pressed slightly by cover glass to enable the 15N double-tagging urea to be smooth in surface so as to obtain a sample. The sample is fixed on an objective table below a lens of a microscope of a Raman spectrometer, magnification times of the microscope is adjusted so as to enable the sample to make imaging clearly in an eyepiece field, and a laser is used for acquiring the Raman spectrum in a range of 3500cm<-1>-34.4cm<-1>. Finally, on the basis of the Raman spectrum of the sample in the range of 3500cm<-1>-34.4cm<-1>, a specific fingerprint waveband is screened out by adopting the successive projections algorithm, an intensity value of the Raman spectrum at the waveband is obtained, and isotopic abundance is calculated by using the intensity value of the Raman spectrum. The urea isotopic abundance rapid detection method based on the Raman spectrum is convenient to use and can measure plant 15N tracer isotope abundance rapidly and effectively.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Device for regulating test atmosphere of microscope Raman spectrometer
InactiveCN102033060AImprove test intensityRegulating the atmosphere of the test sampleRaman scatteringHigh numerical apertureEngineering
The invention provides a device for regulating test atmosphere of a microscope Raman spectrometer, and relates to the technical field of microscope Raman spectrometers. The device comprises a sample stage base and an objective lens, wherein a seal flange is fixed on the sample stage base, and a seal ring is arranged between the seal flange and the sample stage base; a seal cover is made of a flexible transparent material, one end of the seal cover is connected with the objective lens, and the other end of the seal cover is fixed on the seal flange; and an air passage upper port is arranged onthe seal cover, and an air passage lower port is arranged on the sample stage base. The device realizes that the objective lens with high numerical aperture and ultra-short work distance can be used in the Raman spectrum test in different atmospheres and intensifies the detection intensity of a Raman signal; a mobile seal embedded sample stage structure design is adopted to ensure that a closed space can be formed between the sample stage and the objective lens, and the sample stage and the objective lens can freely move relatively in three-dimensional direction without any window barrier, and the objective lens can be directly attached to the sample surface; and the upper and lower air passage ports can meet the requirement that gases in different specific gravities sweeping from different directions.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Raman atomic force microscopic detection device and method
InactiveCN102384985ASimple structureTechnical conditions are easy to achieveRaman scatteringScanning probe microscopyAtomic force microscopyOptical table
The invention discloses a Raman atomic force microscopic detection device and method. A first support post and a first fixing block are sequentially arranged on one side of an optical platform from top to bottom, a second support post and a second fixing block are sequentially arranged on the other side of the optical platform from top to bottom, a support cross beam is fixedly arranged at the upper ends of the first support post and the second support post, an X-direction stepping electric control transverse moving table is arranged above the support cross beam, a slide block is arranged on the X-direction stepping electric control transverse moving table, the lower end of the slide block is provided with a Z-direction moving rail, an L-shaped fixing block is arranged on the Z-direction moving rail, an atomic force microscopic probe cross beam is arranged on the L-shaped fixing block, an atomic force microscopic probe is arranged on the atomic force microscopic probe cross beam, both sides of the atomic force microscopic probe are respectively provided with a Raman spectrum microscopic probe and an optical microscope, and a Y-direction stepping electric control transverse moving table, a sample table and a sample to be measured are sequentially arranged on the optical platform from bottom to top. The micro nanometer form structure information and the microscopic Raman spectrum information of the samples can be obtained in real time on line.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
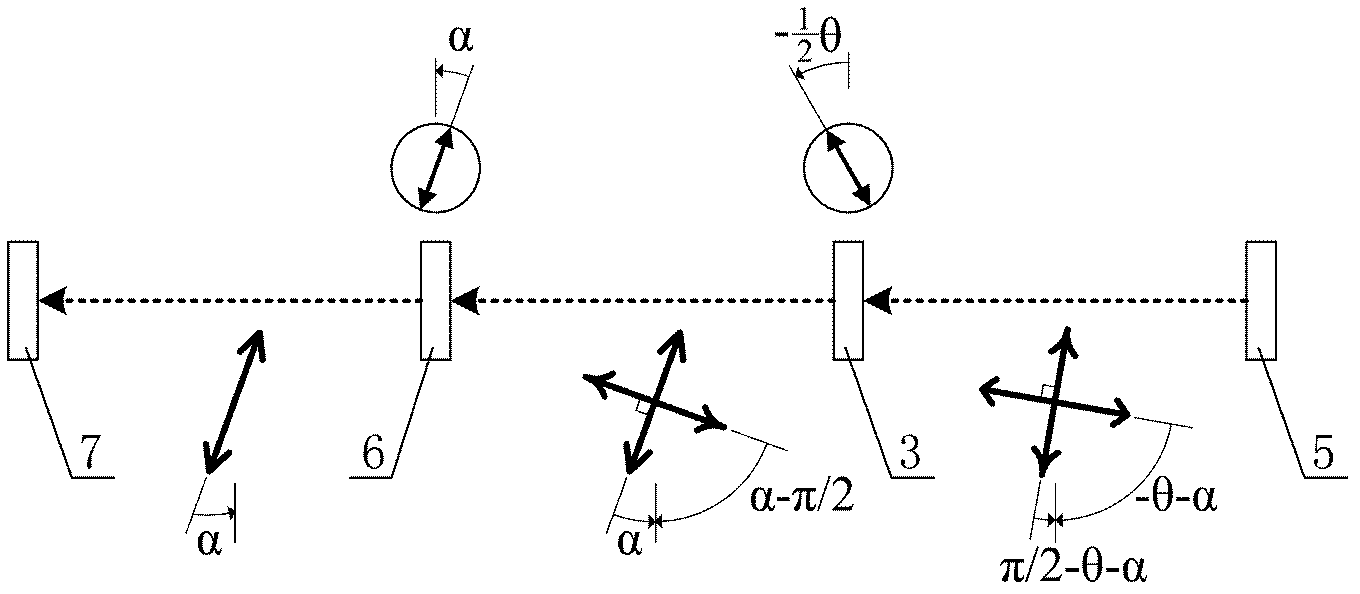
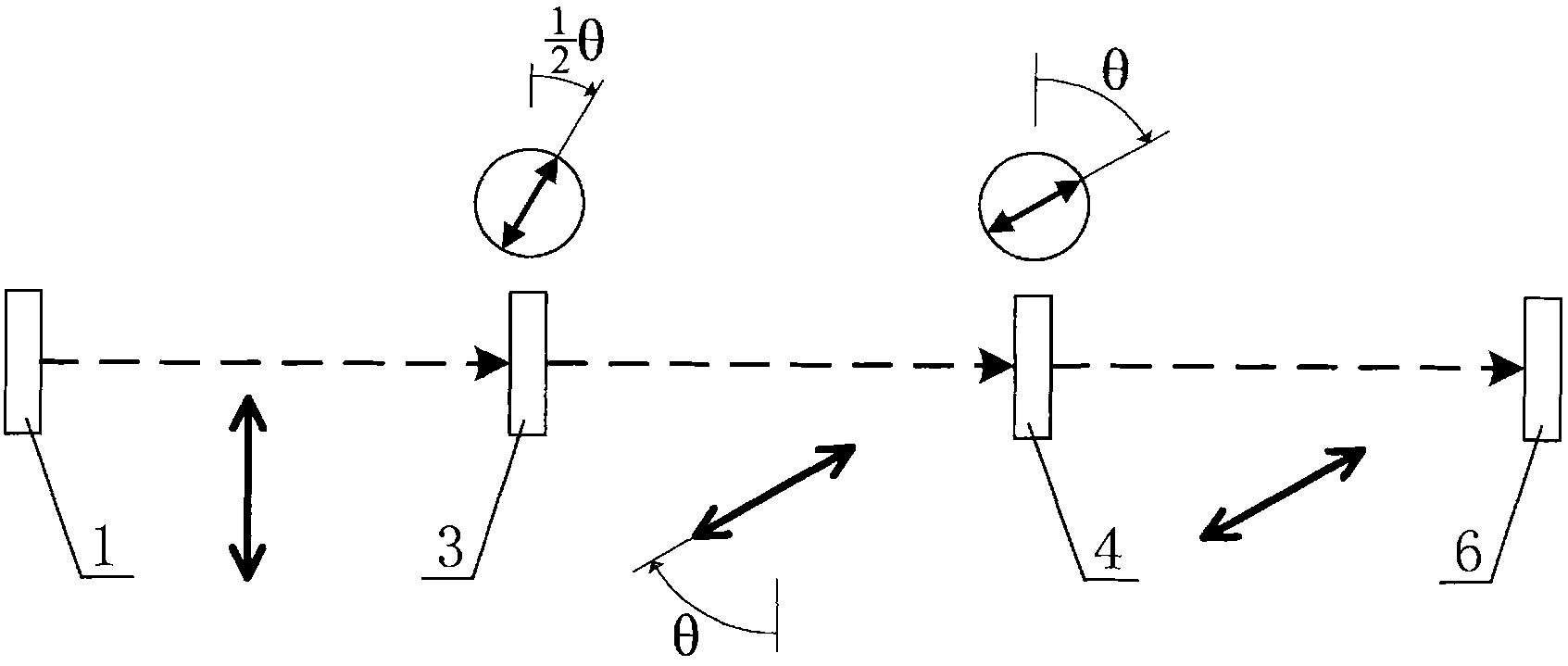
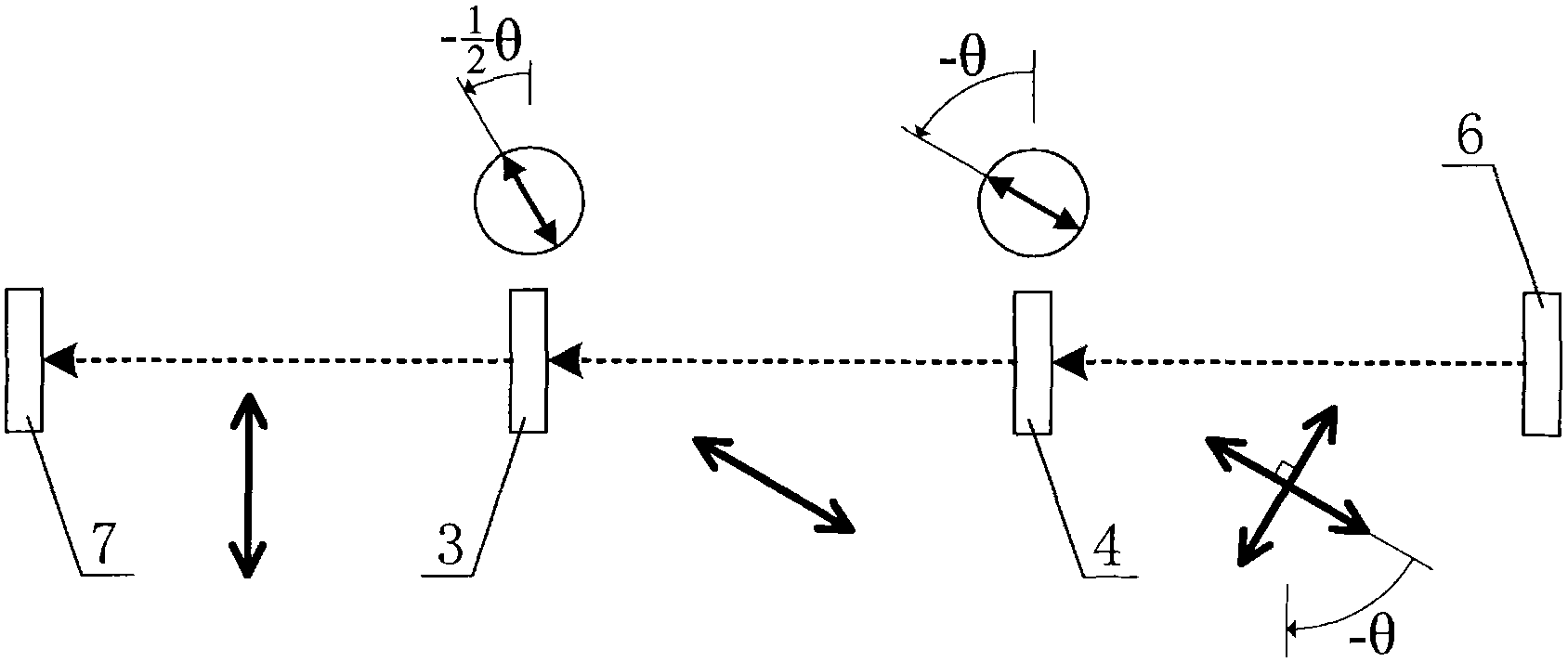
Micro-raman spectrum experiment apparatus for adjustable polarization direction continuous collaboration/covariation
The invention discloses a micro-raman spectrum experiment apparatus for adjustable polarization direction continuous collaboration / covariation. A micro-raman spectrum system is composed of a laser machine, an Edge optical filter, a microscope and a Raman spectrograph, a polarization collaboration / covariation adjusting module is composed of a half-wave plate and a polaroid sheet. The laser emitted by the laser machine is performed Edge optical filter reflection, half-wave plate transmission and microscope focusing incidence on the surface of the measured object. The diffusion light collected by the microscope transmits through the half-wave plate, the Edge optical filter and the polaroid sheet and then enters in the Raman spectrograph for photorecording the spectrum information. By setting the vibration detection angle of the polaroid sheet as zero or nonzero value-alpha, the fast optical axis angle of the half-wave plate is adjusted to be half of the rotation angle in the polarization direction, so that collaboration regulation or alpha angle covariation regulation of polarization direction of incidence light and scattered light can be realized. On the basis of unchanged functions and precision of the traditional micro-raman spectrum experiment system, the modularization and simplification of controlling polarization collaboration / covariation can be realized, and the manufacture cost can be reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
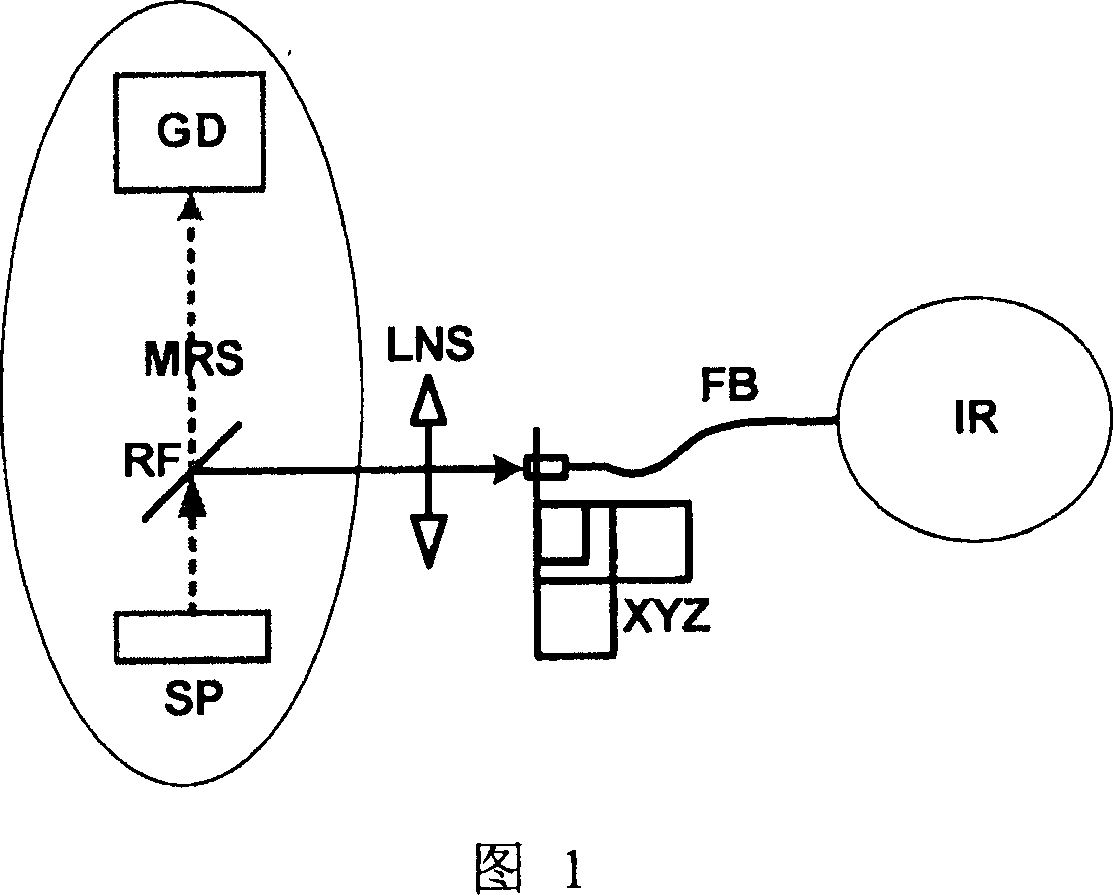
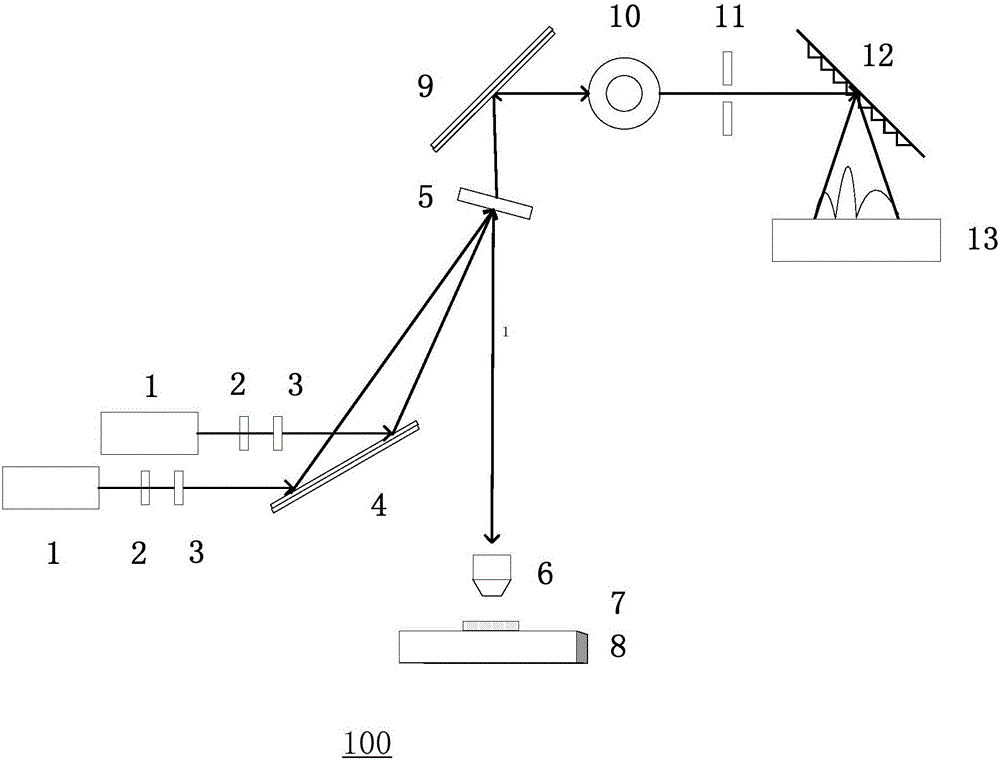
Combined test system of micro-Raman spectroscopy and near infrared spectrometer
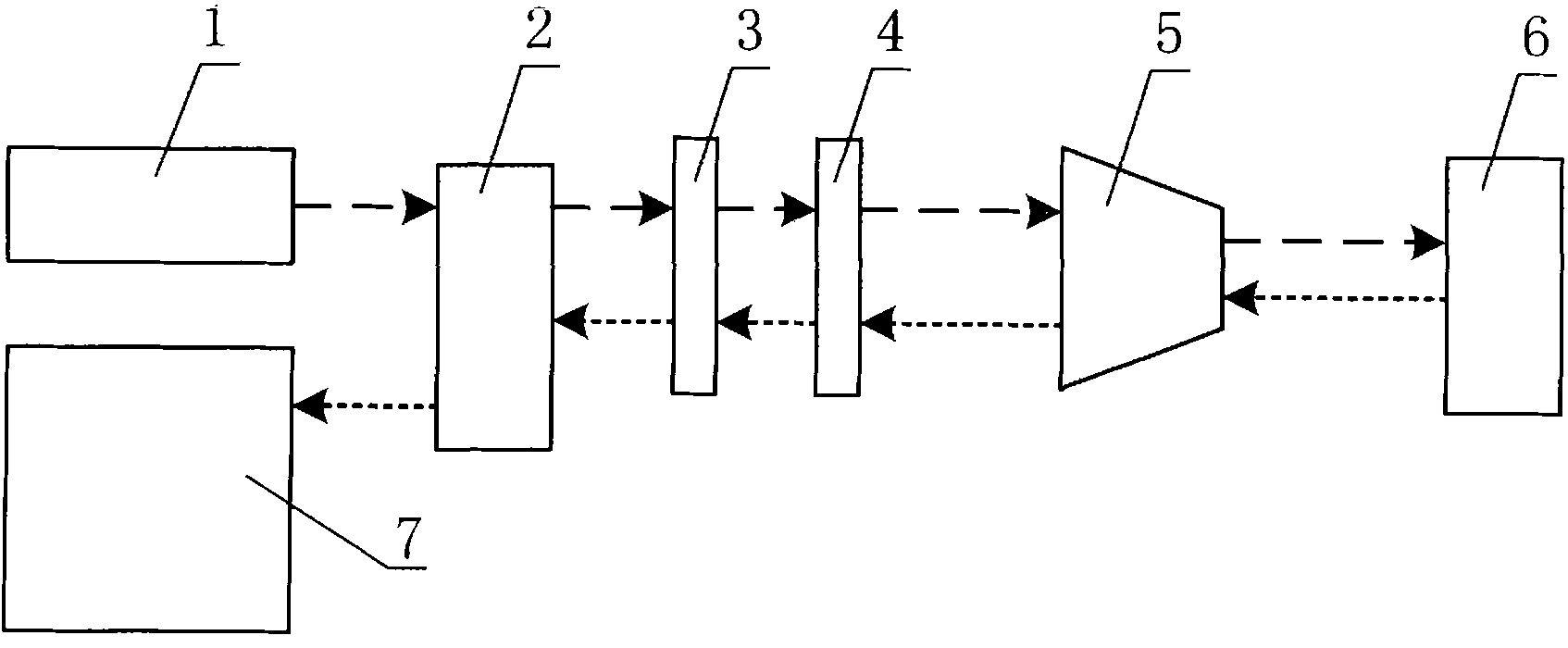
A couple test system of microscope Laman spectrometer and near infrared spectrometer comprises a visible microscope Laman spectrometer which comprises a sample platform and a detector in visible range, a mirror on the path of the visible microscope Laman spectrometer, a lens on the reflective path of the mirror, a three-dimension adjusting support on the path of the lens, a multi-model quartz fiber with one end fixed on the three-dimension adjusting support while another end is connected with a near infrared spectrometer. The mirror shifts the fluorescence signal emitted from the sample on the visible microscope Laman spectrometer, and the fluorescence signal is focused by the lens to be radiated into the core of the multi-mode quartz fiber which position is adjusted accurately by the three-dimension adjusting support, and the multi-mode quartz fiber transmits the signal to the near infrared spectrometer to measure fluorescence spectrum.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
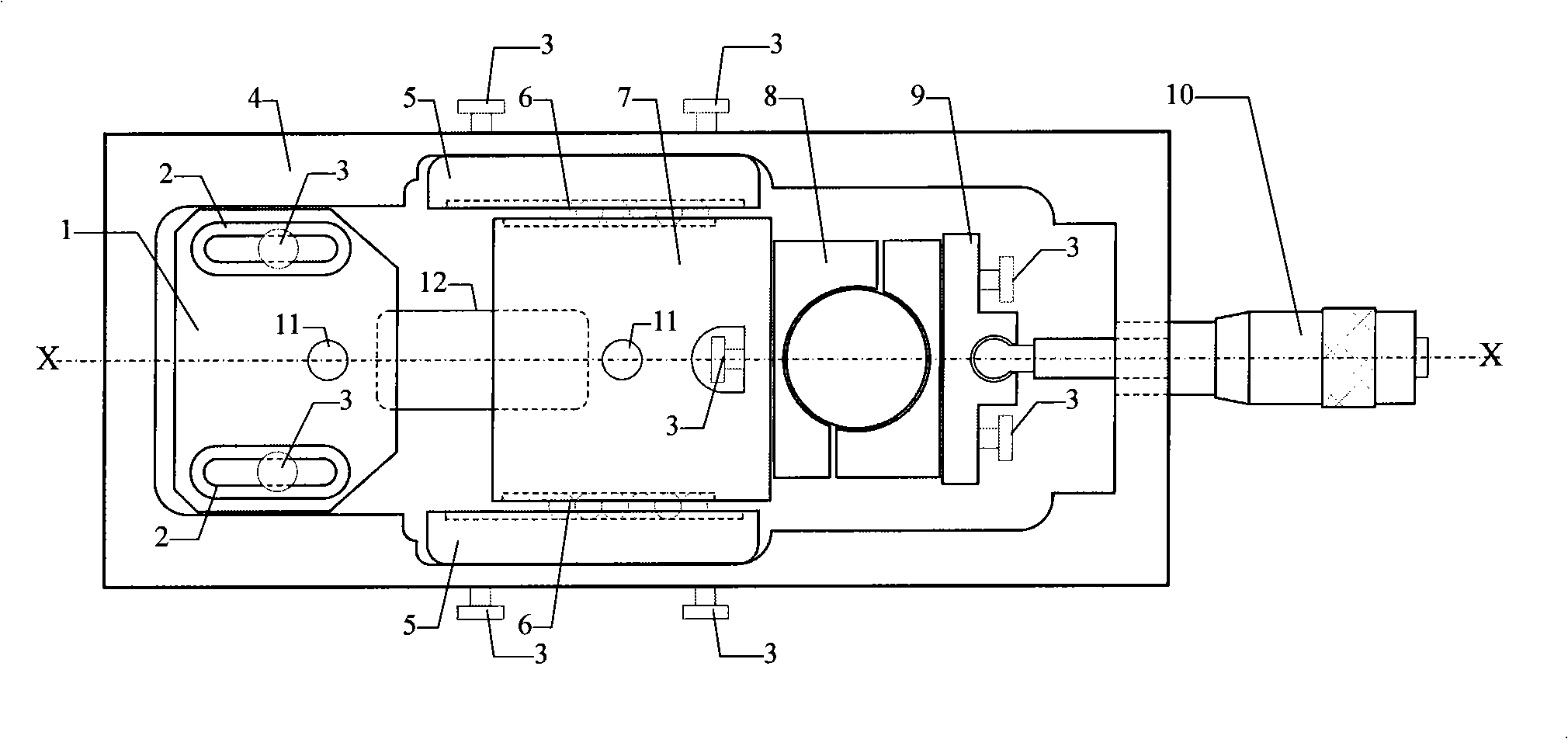
Multifunctional loading unit for objective table of microscope
InactiveCN101303450AReduce resistanceSpectrum investigationForce measurement by measuring optical property variationDiffractometerMicrometer
The invention relates to a multi-functional loading device for an object stage of microscopes, which comprises a force sensor, a fixing clamp splice, a moving clamp splice, a micrometer screw rod, and the like; the fixing clamp splice is provided with two long circular empty grooves; a screw goes through the empty grooves to connect the fixing clamp splice and a framework; two roll ball slideways are fixed in a frame slot by screws; the roll balls are installed in the grooves at both sides and are connected with the grooves in a sliding manner; the moving clamp splice is fixedly connected with the force sensor by the screws; a rotation / translation shifting block is fixed with the force sensor by the screws; the micrometer screw rod goes through the framework and is installed on the rotation / translation shifting block; the displacement loading information can be read from the scale on the micrometer screw rod and the force loading signal is sent out by a signal wire connected with the force sensor. The multi-functional loading device of the invention can be universally used in the object stages of Micro-Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffractometer and various microscopes, the volume thickness is only 16mm and the observation of the microscopic appearance of samples, the collection of diffraction spectrum and the acquisition of stress / strain information are realized when tension and compression load are exerted on the samples.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Agricultural product pesticide residue detection method
InactiveCN107727637AAchieve specific identificationEnvironmentally friendlyRaman scatteringPesticide residueTest sample
The invention discloses an agricultural product pesticide residue detection method. The method comprises the following steps that template molecules, chitosan, hydroxyethyl acrylate, polyethyleneimineand deionized water are taken, imprinted hydrogel with the template molecules is synthesized; pretreatment of to-be-detected vegetables is completed, and a to-be-detected sample solution is prepared;the template molecules of the obtained imprinted hydrogel are removed; a standard Raman spectrogram of the template molecules is made; the imprinted hydrogel obtained after the template molecules areremoved is soaked in the to-be-detected sample solution and fished out, after confocal micro-Raman Spectrum detection is conducted, the obtained Raman Spectrum is compared with the standard Raman spectrogram, and then whether the template molecules are contained in samples or not is judged, and the content range of the molecules is judged preliminarily. Accordingly, the hydrogel with the specificrecognition function is prepared through a molecular imprinting technology, after the to-be-tested samples are adsorbed and enriched by the hydrogel, spectra collection is conducted by means of a portable Raman spectroscope, and whether the samples contain pesticide or not is judged by comparing with the standard Raman spectrogram.
Owner:云南技师学院
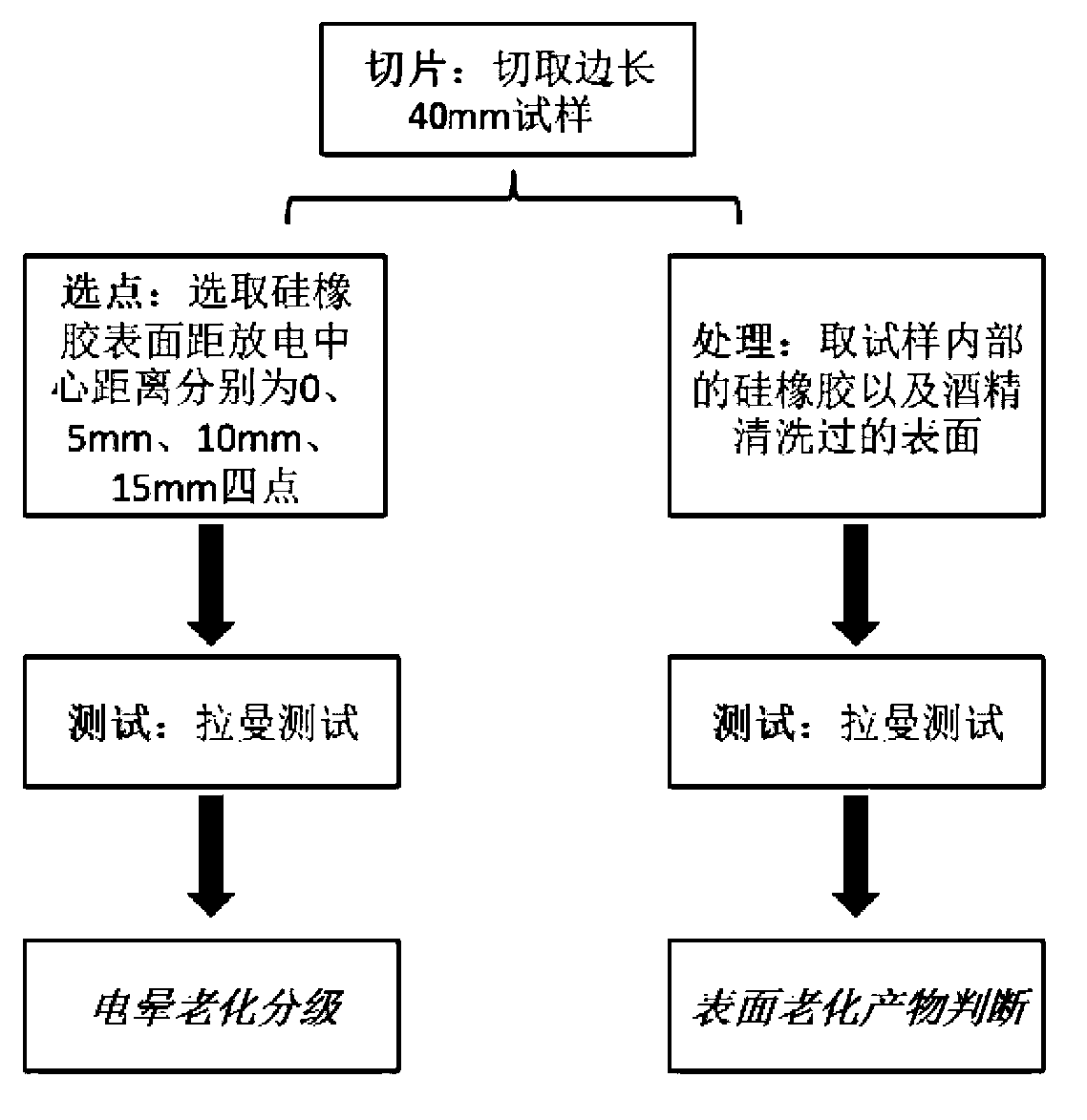
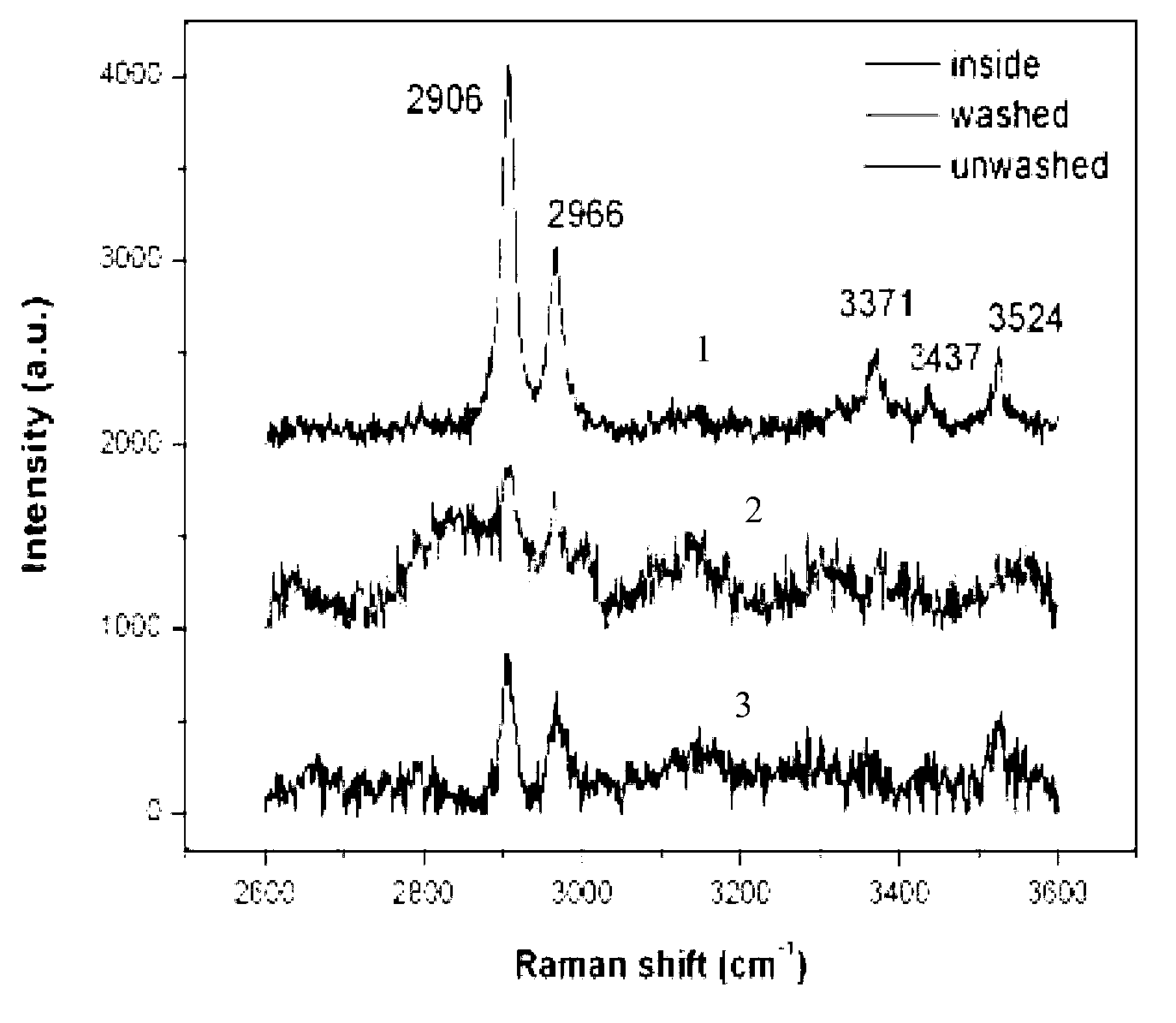
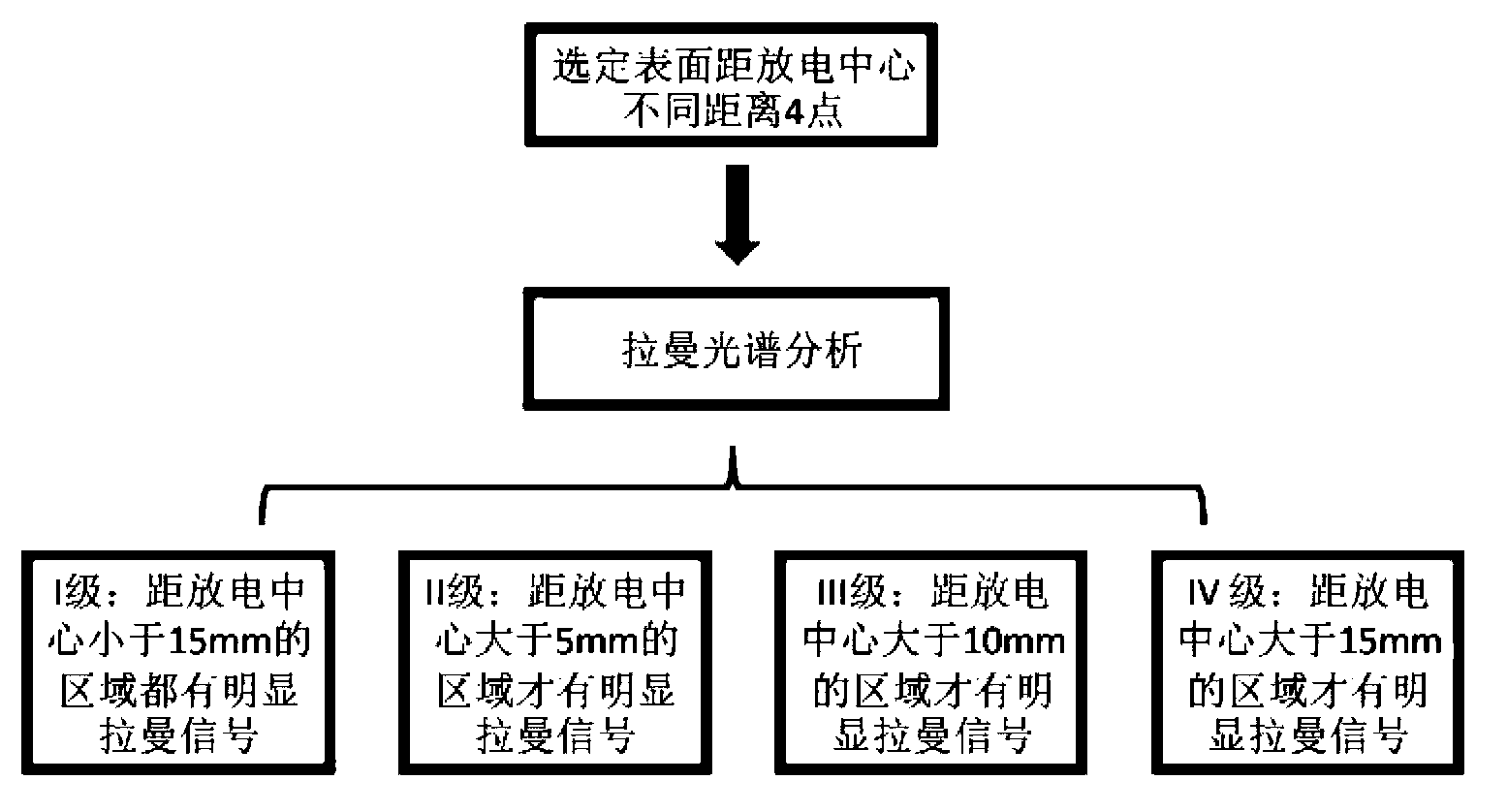
Method for detecting electrical aging of silicone rubber composite insulator
ActiveCN103267937AFew samplesShort test timeTesting dielectric strengthRaman scatteringElectricityComposite insulators
The invention discloses a method for detecting electrical aging of a silicone rubber composite insulator. The method for detecting the electrical aging of the silicone rubber composite insulator includes a first step of taking a high-voltage-side shed of the silicone rubber composite insulator of a running line as a sample, and a second step of collecting micro-Raman spectra on the surface of the sample, and judging the degree of the electrical aging of the sample according to the fact that whether an obvious Raman peak exists at the position of 2906cm-1, 2966cm-1, 3371cm-1, 3437cm-1, 3524cm-1. The method for detecting the electrical aging of the silicone rubber composite insulator has the advantages of being less in sample, short in detection time and easy and convenient to conduct. Detection can be finished without the need of complicated treatment of the sample. The Raman peak is used as a tool of analysis of the electrical aging of the silicone rubber composite insulator, so that subjective factors such as a man-made factor and an environment factor are eliminated and the accuracy is improved.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID +1
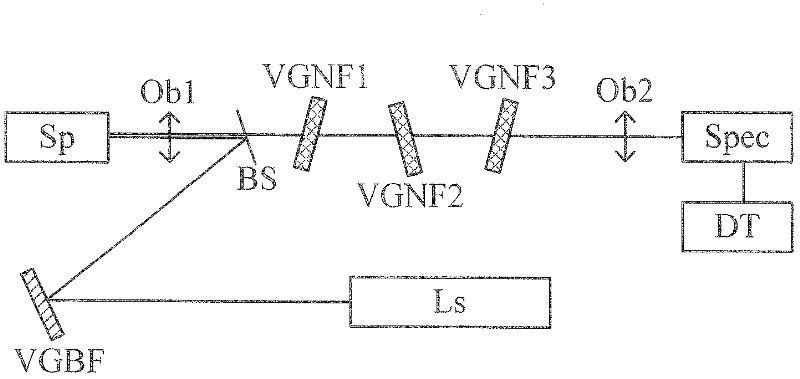
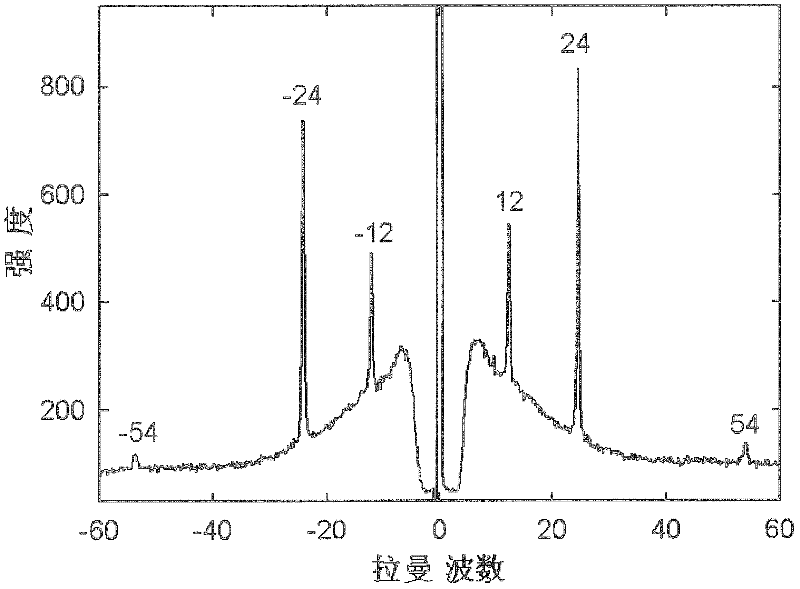
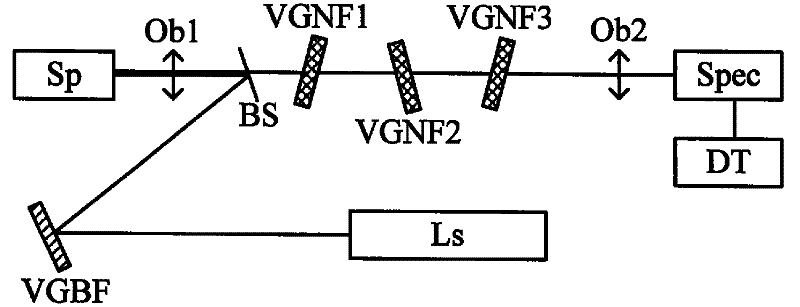
Single-grating Raman spectrum testing system for measuring low-wave-number Raman signals
InactiveCN102374901ARadiation pyrometrySpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsBandpass filteringBeam splitter
The invention discloses a single-grating Raman spectrum testing system for measuring low-wave-number Raman signals. The system comprises a laser source, a volume grating bandpass filter, a beam splitter, a microscope objective, three volume grating notch fibers, a focusing lens and a single-grating spectrometer, wherein the volume grating bandpass filter is positioned on a laser optical path, and is used for filtering plasma lines of laser light and purifying laser lines; the beam splitter is positioned on the light path of laser light reflected by the volume grating bandpass filter, and is used for reflecting the laser light purified by the volume grating bandpass filer onto the microscope objective; the microscope objective is used for focusing the laser light onto a sample for exciting Raman spectrum signals; the three volume grating notch fibers are arranged in sequence, and are positioned on a light path on which sample Raman signal light is collected by using microscope objective and passes through the beam splitter; the focusing lens is used for converging the Raman signals into the inlet of the single-grating spectrometer; and the single-grating spectrometer comprises a detector, and is used for collecting Raman signals. The system can be used for detecting Raman spectrum signals of which the wave numbers are as small as 5, so that a microscopic Raman spectrometer has remarkable advantage on the aspect of measuring low-wave-number Raman spectrums than an infrared spectrometer.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
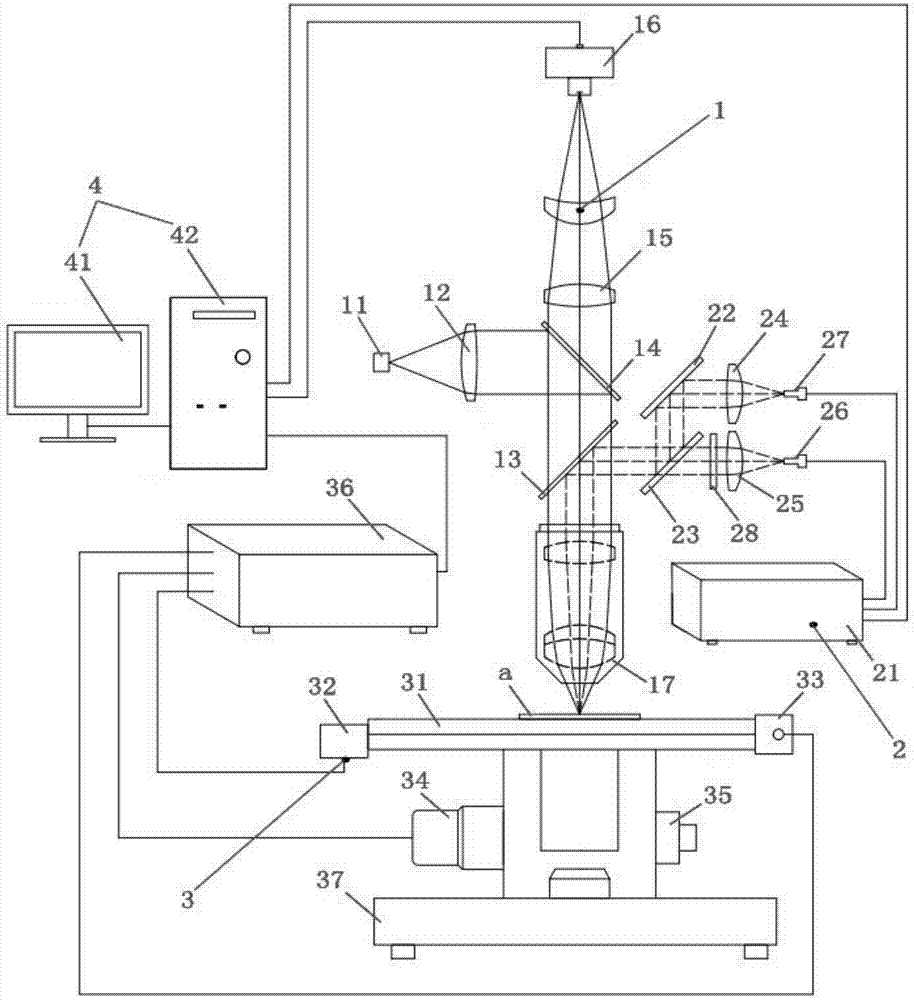
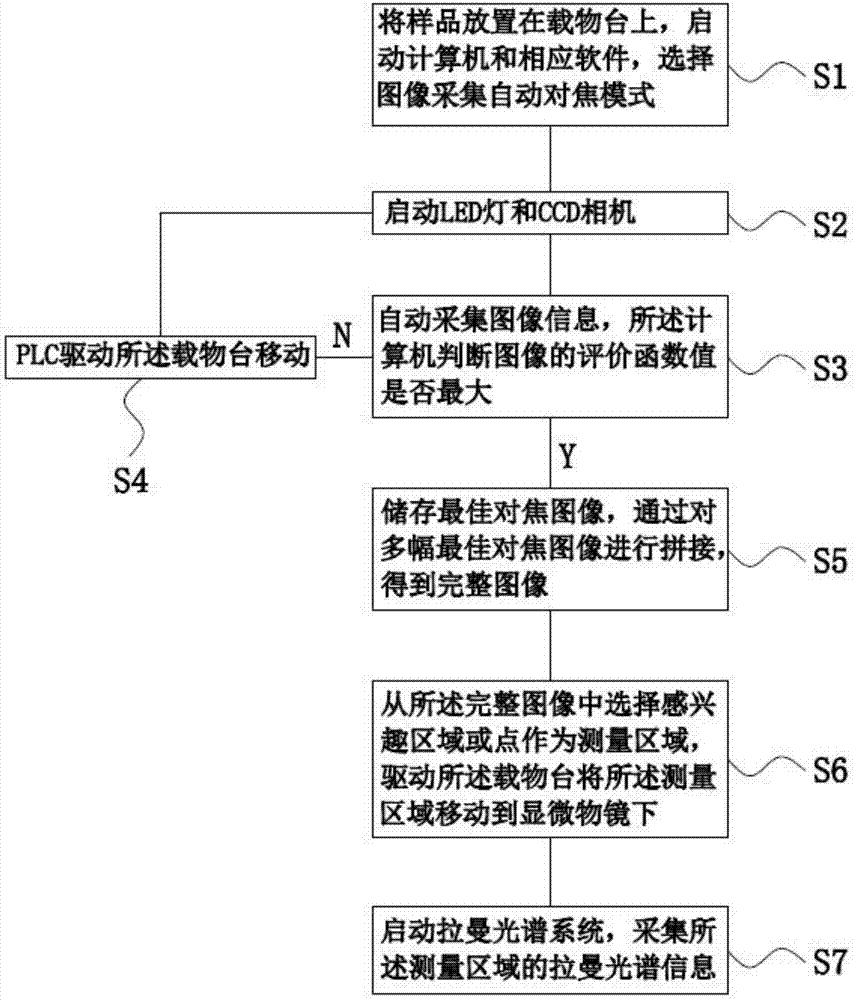
Quick automatic focusing microscopic Raman spectrometer and application method thereof
PendingCN107884388AImprove test resultsImprove spatial resolutionRaman scatteringMicroscopesOptical spectrometerMaterials science
The invention discloses a quick automatic focusing microscopic Raman spectrometer and an application method thereof. The quick automatic focusing microscopic Raman spectrometer comprises a microscopicimaging system, a Raman spectrum system, a control apparatus and a computer system, wherein the control apparatus is connected with the computer system, the microscopic imaging system is located above the control apparatus, and the Raman spectrum system is located on one side of the microscopic imaging system. The quick automatic focusing microscopic Raman spectrometer is compact in structure, comprehensive in function and capable of automatically focusing, and can acquire spectrum information of a local area of a sample, acquire complete object image information under a high-resolution microscope and acquire Raman spectrum information, thereby greatly improving the test efficiency and test effect of the Raman spectrometer.
Owner:奥谱天成(厦门)光电有限公司
Graphene sheet intercalation compound preparation method and in situ microRaman representation system
InactiveCN102156116AEasy to manufactureCreate pollutionPreparing sample for investigationRaman scatteringCuvetteAlcohol
The invention discloses a graphene sheet intercalation compound preparation method and an in situ micro-Raman representation system. The preparation method comprises the following steps: respectively placing the graphene sheet and ferric trichloride into a glass tube and a cuvette which are connected ang communicated with each other; vacuumizing the glass tube and the cuvette by a molecular pump; sealing the vacuumized glass tube and cuvette by an alcohol lamp; heating to 340 DEG C and keeping the temperature for 6 to 24 hours; and cooling to the normal temperature. The in situ micro-Raman representation system comprises the glass tube and the cuvette which contain the graphene sheet and the ferric trichloride and sealed from the outside and communicated with each other, a laser, a Raman spectrometer, a heating platform, a lifting platform, a translational platform and two scanners. The graphene sheet / ferric trichloride intercalation compound preparation method is simple and practical; and the in situ micro-Raman representation system can be used for in situ representing the micro-Raman spectrum of a graphene / ferric trichloride intercalation compound, and in situ monitoring the formation condition of the graphene / ferric trichloride intercalation compound.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Simple coordinate regulation device for regulating polarization direction of Micro-Raman spectrum system
The invention discloses a technology and a device which is applied to the Micro-Raman spectrum system for simple and coordinated regulation of polarization direction of incidence light and scattered light. A laser device, an incidence and emergent light interface, a microscope and a Raman Spectrometer constitute a Micro-Raman spectrum system while a half-wave plate and a polaroid constitute a polarization regulation assembly. Laser emitted from the laser device sequentially pass through the incidence and emergent light interface, the half-wave plate and the polaroid before passing through the microscope and reaching the surface of an object to be detected.Back scattered light collected by the microscope sequentially passes through the polaroid and the half-wave plate before passing through the incidence and emergent light interface and entering the Raman Spectrometer to form spectral information. In the invention, the fast optical axis angle of the half-wave plate and polarization detection angle of the polaroid are respectively adjusted to be half of the rotation angle in the polarization direction and to be equal to the rotation angle in the polarization direction, so that coordinate regulation of polarization direction of incidence light and scattered light can be realized. In the invention, modularization of polarization control is realized, so that acquisition of the maximum grating diffraction efficiency of the scattered light entering the spectrometer can be ensured and the optimal light spectrum contrast ratio can be obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
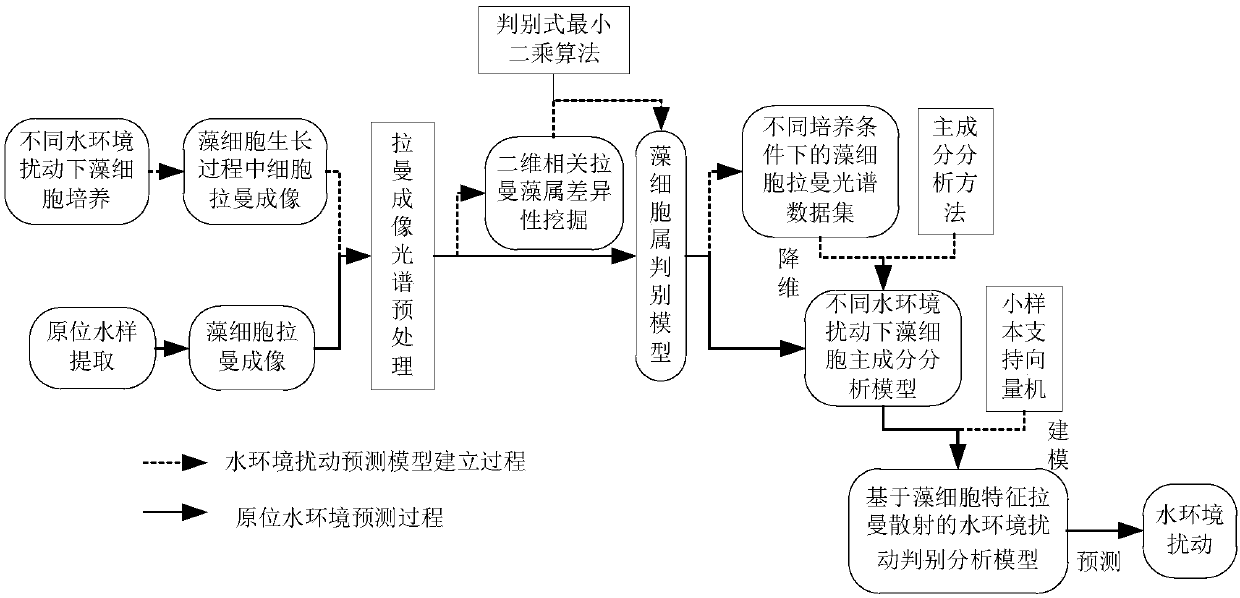
Method for evaluating water environment disturbance based on characteristic Raman scattering of alga cells
InactiveCN107941783ARapid assessmentRaman scatteringCharacter and pattern recognitionRaman imagingBiology
The invention relates to a method for evaluating the water environment disturbance based on characteristic Raman scattering of alga cells, belonging to the technical field of water environment evaluation. The method comprises the following steps: (S1) culturing alga cells under different simulated water environment disturbance factors; (S2) carrying out sampling representation on alga liquid in aculturing period, carrying out Raman imaging on the alga cells by virtue of a confocal microscope Raman spectrometer, and carrying out pretreatment on a Raman spectrum of the alga cells; (S3) analyzing characteristic Raman spectrums of the alga cells under different culturing conditions, so as to obtain the Raman difference of characteristic fingerprints of the alga cells, and determining the category of the alga cells; (S4) establishing a water environment disturbance evaluation model based on the characteristic Raman scattering of the alga cells; and (S5) evaluating and predicting a water environment according to the water environment disturbance evaluation model established in the steps (S4). According to the method, the characteristic Raman spectrum of the alga cells is established andis utilized for predicting the disturbances of different environments, so that the rapid evaluation of the water environment disturbance is realized.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for testing ion diffusion coefficient in solid electrolyte
ActiveCN108562517AQuick testTest accurateSurface/boundary effectRaman scatteringDiffusionGrain boundary diffusion coefficient
The invention provides a method for testing an ion diffusion coefficient in a solid electrolyte. The method comprises the following steps: applying an electric field to to-be-tested solid electrolyteat a certain temperature, enabling ion concentration in a material to be in graded distribution, then removing an electric field, and testing the Raman spectrum of the material at regular intervals byusing a laser confocal microscopic Raman spectrometer in the direction of the electric field at a certain distance; and taking the ratio of the integral area of a Raman spectrum characteristic peak position of to-be-tested ions to the total integral area as ion concentration so as to obtain ion concentration distribution at different times after the electric field is removed; and finally, carrying out fitting by using a function relationship of the ion concentration, time and space positions to obtain an ion diffusion coefficient. The method is simple and convenient to operate, and the diffusion coefficient of ions in the solid electrolyte can be measured rapidly and accurately.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for detecting biochemical components of throat swab sample by adopting surface enhanced micro-Raman spectroscopy
InactiveCN105738343AHigh feasibilityShort detection timeRaman scatteringSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopySpectral signature
The invention relates to a method for detecting component information of a throat swab sample by adopting surface enhanced micro-Raman spectroscopy. The method comprises preparation of a surface enhancement reagent, treatment of the throat swab sample, measurement of a surface enhanced Raman spectrum of the sample and processing and analysis of Raman spectrum data. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps: preparing the enhancement reagent for enhancing the Raman spectrum of the sample; smearing the throat swab sample on a smooth and clean pure aluminum sheet, dripping the surface enhancement reagent, and naturally air-drying the pure aluminum sheet at room temperature to prepare a throat swab-surface enhanced Raman test sheet; performing micro-Raman spectroscopic test on the throat swab-surface enhanced Raman test sheet to acquire the surface enhanced micro-Raman spectrum of the throat swab sample, and analyzing biochemical component information and features of the throat swab sample by virtue of spectral features. The method has the advantages of short detection time, low cost, convenience and rapidness in process and the like, and rich biochemical component information of the throat swab sample can be obtained, so that a rapid and effective analysis method can be provided for biochemical features and changes of intracavity mucous tissues.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Automatic detection system of circulating tumor cells based on Raman spectrum
InactiveCN106769693AThere is no false positive problemRich varietyBiological particle analysisMaterial analysisMicro imagingTumor cells
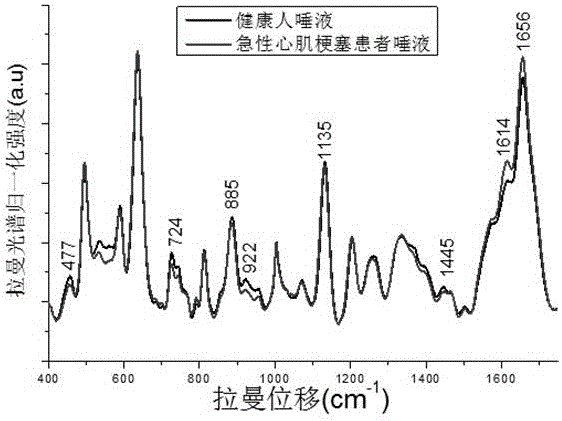
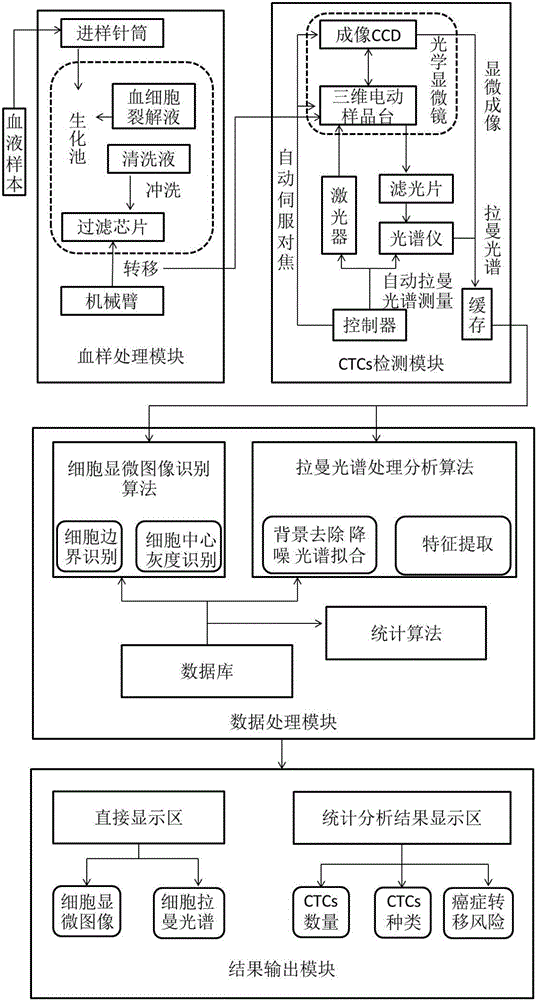
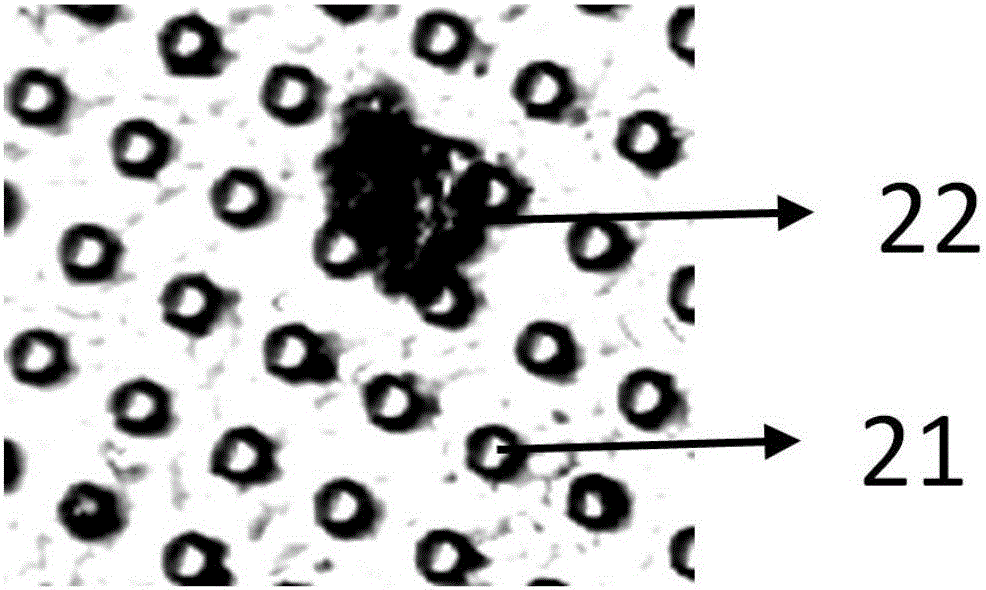
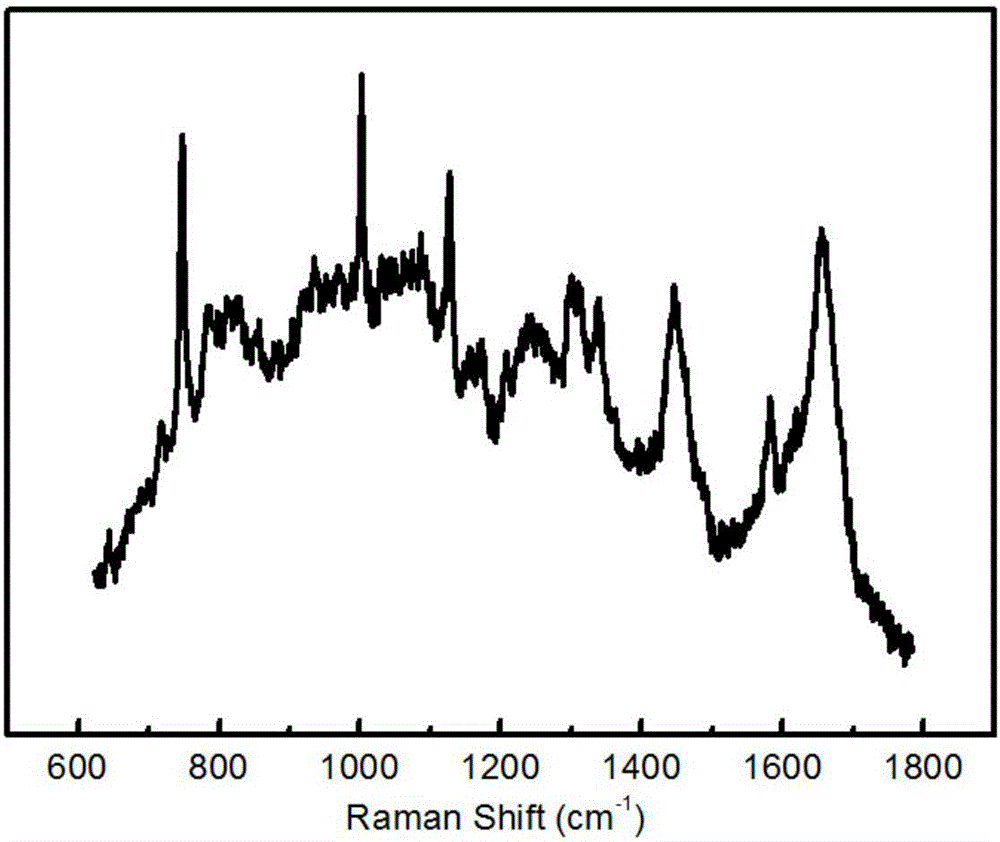
The invention provides an automatic detection system of circulating tumor cells based on a Raman spectrum. The system is composed of a blood sample processing module, a circulating tumor cell detection module, a data processing module and a result output module, wherein the blood sample processing module is mainly based on an enriching effect on circulating tumor cells of a microporous filter chip, the circulating tumor cell detection includes optical microimaging detection and micro-Raman spectrum detection, and detection data are compared with a database, so that information such as the quantity, kind, period and the like of the circulating tumor cells (CTC) are obtained ultimately.The system has the advantages of high integration level, simplicity in operation and good specificity of the Raman spectrum, a detection result can be obtained when a blood sample is directly put in the system, and the system can be widely applied to the fields of clinical blood test, early diagnosis and prognosis monitoring of cancer, basic scientific research and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
System for rapid assessment of water quality and harmful algal bloom toxins
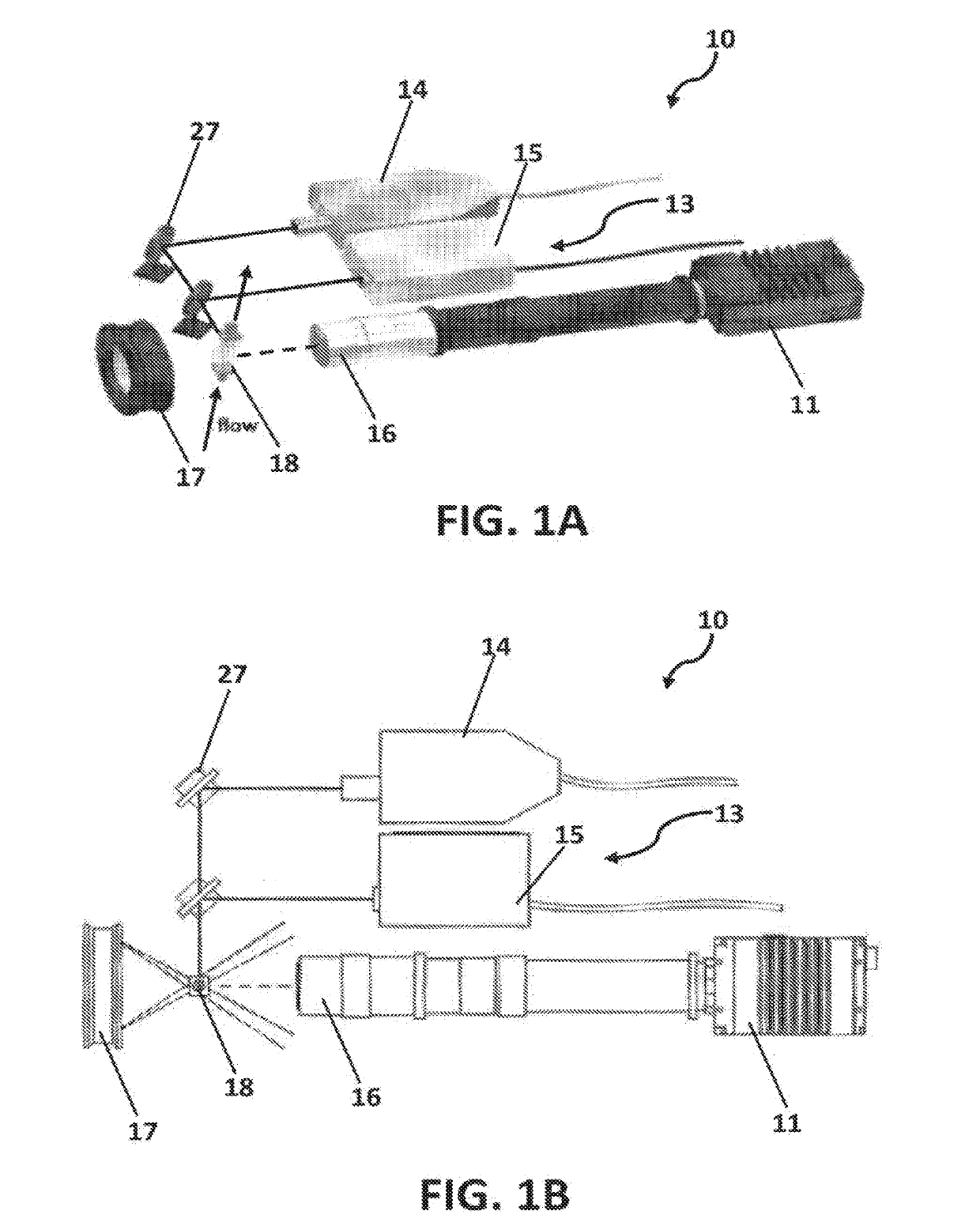
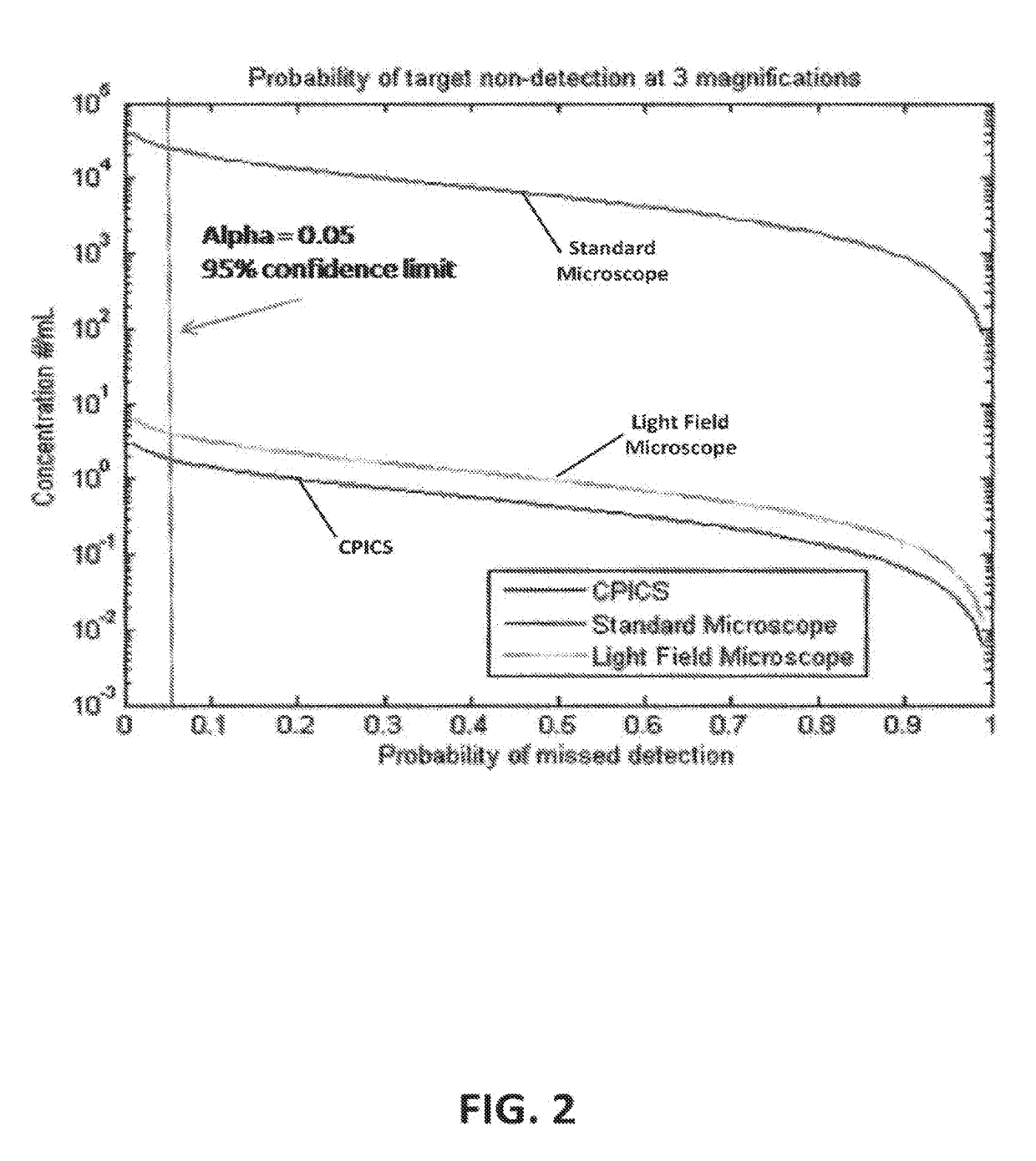
The present invention is directed toward the early detection of harmful algal blooms. The system employs the ability of whole cell non-contact micro Raman spectroscopy to detect cell pigmentation in such a way that distinct patterns or fingerprints can be assembled. Light field microscopy will provide a fundamentally innovative increase in image and sample volume. Furthermore, darkfield microscopy is employed to capture high-resolution, color images of the detected plankton to increase the accuracy of species identification and classification. Together, this new instrument will provide a powerful yet elegantly simple solution to detection of HAB cells and characterization of environmental conditions.
Owner:WOODS HOLE OCEANOGRAPHIC INSTITUTION
Polarization direction continuous collaborative regulating device for micro-Raman spectroscopy
The invention discloses a device for continuously and collaboratively regulating the incident light and scattered light polarization direction for a micro-Raman spectroscopy. A transmission gear is respectively meshed with a driving gear and the large gear of a double-link gear. A half-wave plate and a polaroid gear are hollow gear rings, and the hollow circles thereof are respectively inlaid into a half-wave plate and a polaroid. The half-wave plate gear and the polaroid gear share the same center of circle. A transition gear is arranged between the small gear of the double-link gear and the half-wave plate gear, the polaroid gear is meshed with the large gear of the double-link gear, and two positioning gears are meshed with the half-wave plate gear and the polaroid gear. Being a box-like structure, the device is implanted into the public optical path of incident light and scattered light of the Raman spectroscopy, a manual turntable serves as a control part, variable speed transmission is implemented through the transmission and the rotation of the gear structure and the double-link gear, the polarizer angle of the half-wave plate and the polarization angle of the Polaroid are collaboratively controlled through one-step operation, so as to conveniently realize the continuous collaborative regulation of the incident light and scattered light polarization direction with high precision.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
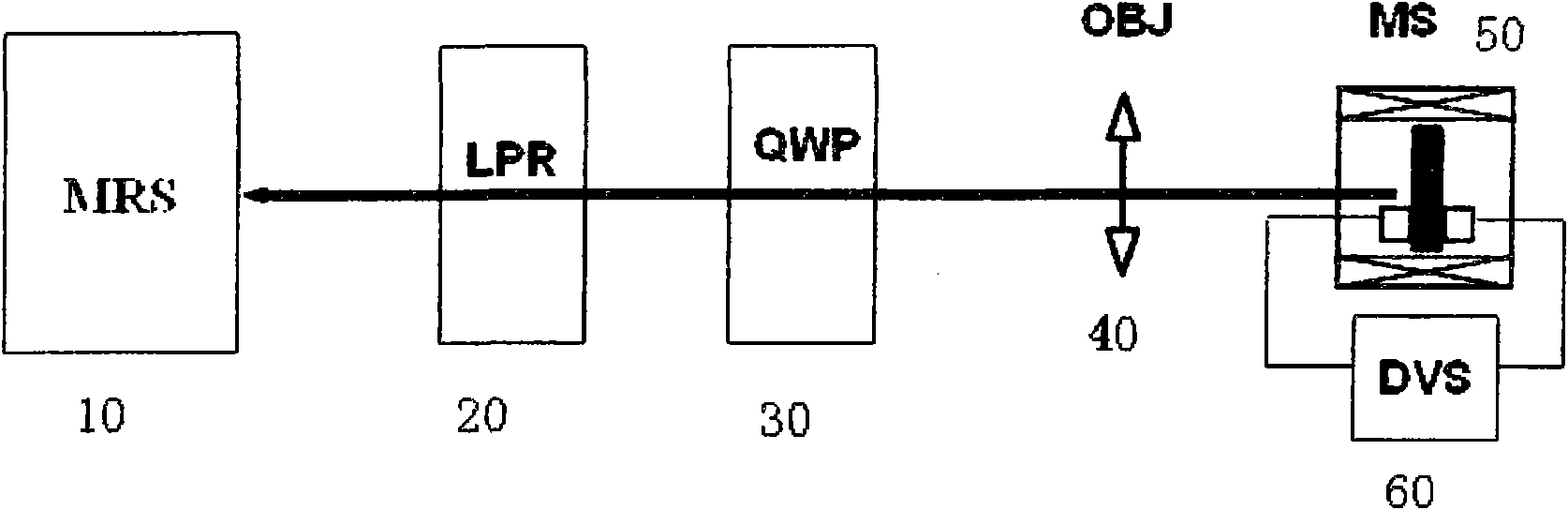
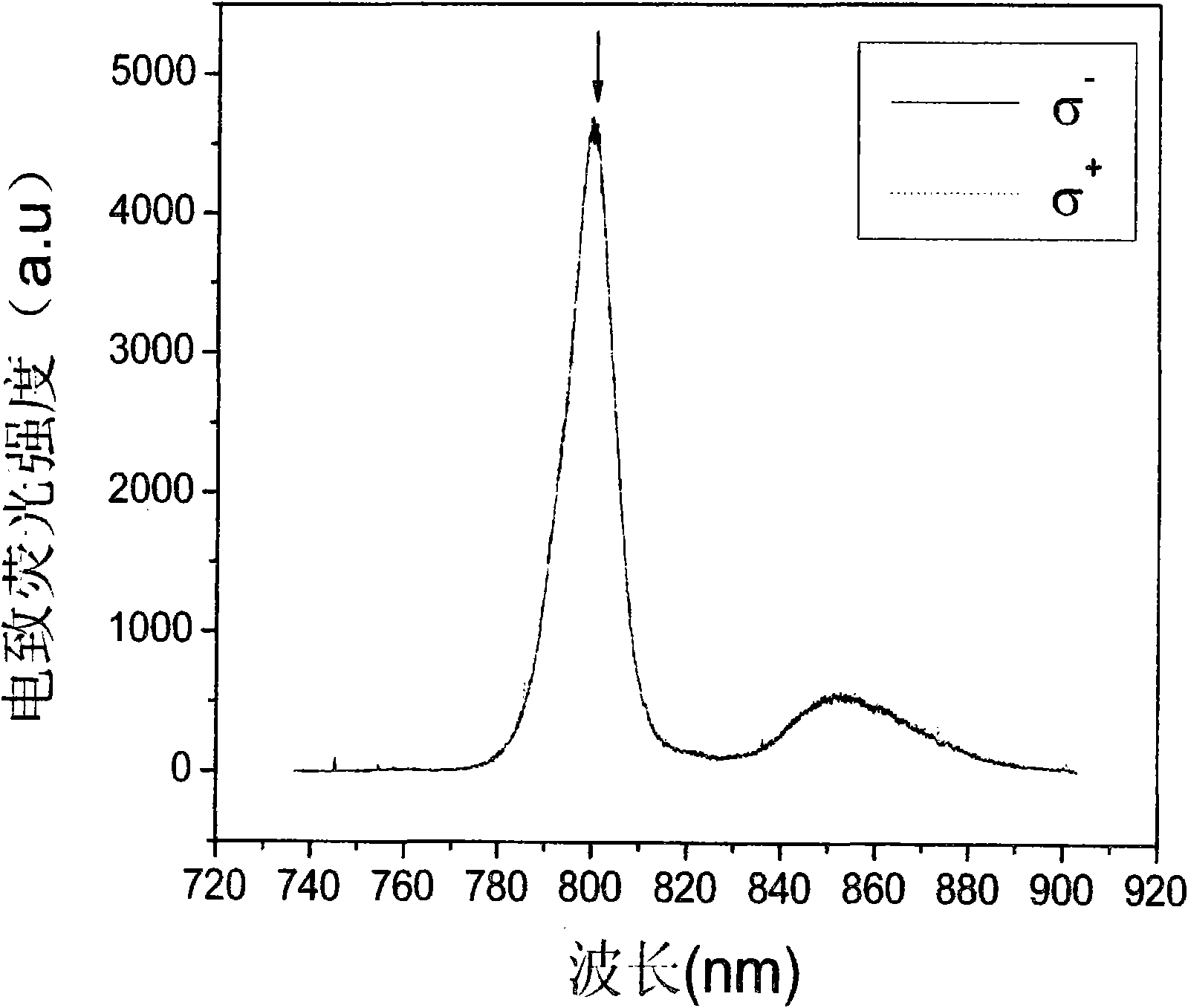
Micrometering system for measuring electro-spin fluorescence
The invention relates to a micrometering system for measuring electro-spin fluorescence, which is characterized by comprising a micro Raman spectrometer, a broad-band line polaroid sheet, a broad-band one-fourth wave plate, a magnet system, a digital voltage source meter and an over-long operating distance microobjective. The micro Raman spectrometer, the broad-band line polaroid sheet and the broad-band one-fourth wave plate are spaced by preset distances and positioned in a same light path; the digital voltage source meter is connected in parallel with the magnet system; and the over-long operating distance microobjective is positioned between the broad-band one-fourth wave plate and the magnet system and is in the same light path with the broad-band one-fourth wave plate and the magnet system.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
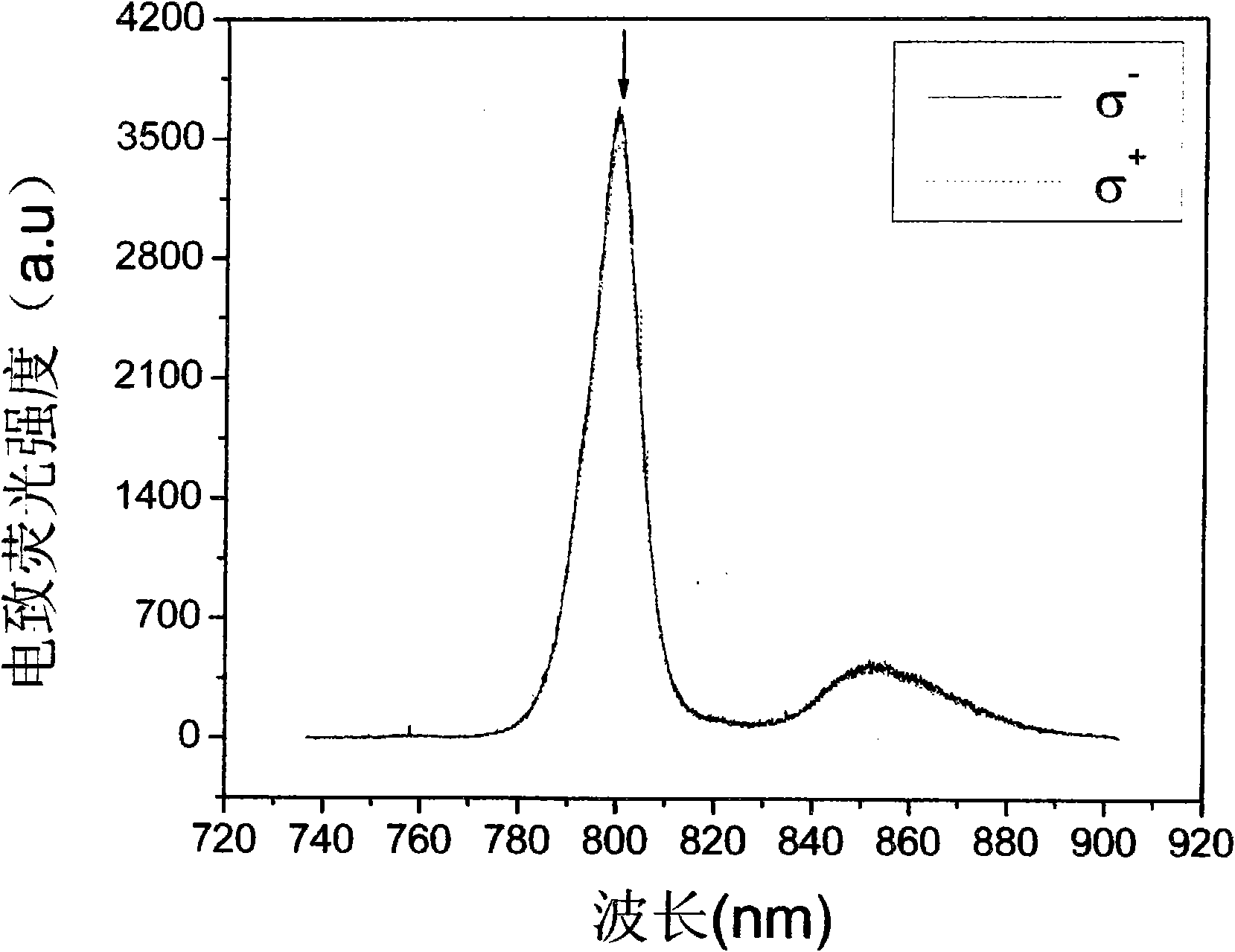
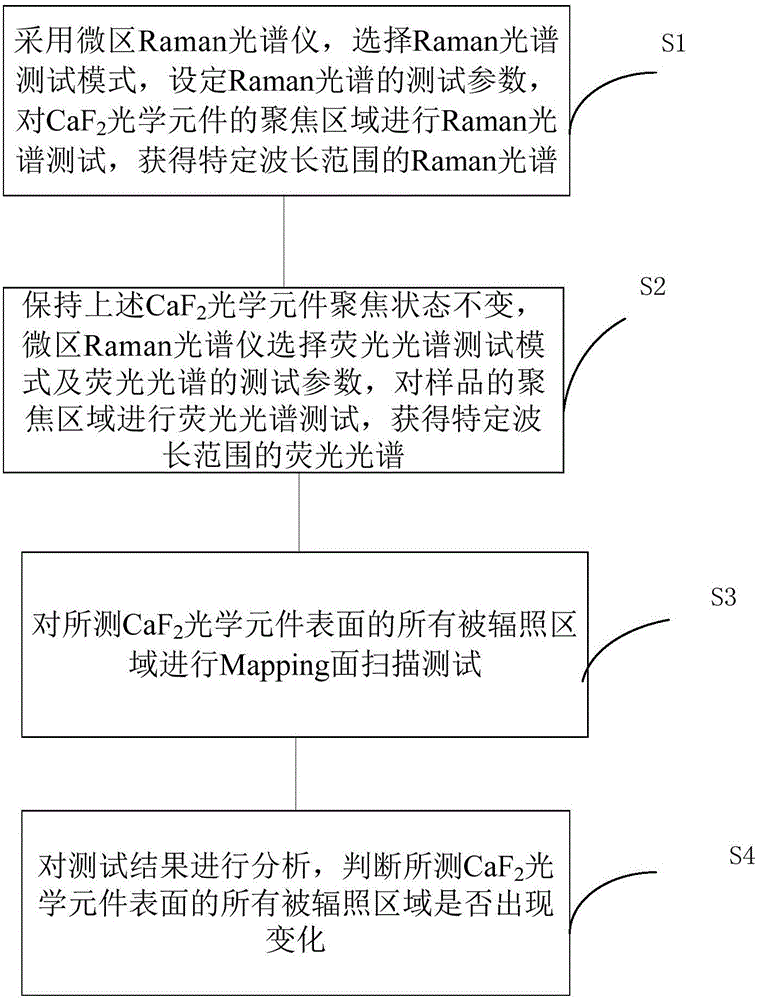
Method for detecting deep ultraviolet laser radiation induction surface change of CaF2 optical substrate
ActiveCN106404745AHigh precisionImprove accuracyRaman scatteringFluorescence/phosphorescenceUltravioletFluorescence spectrometry
The invention discloses a method for detecting a deep ultraviolet laser radiation induction surface change of a CaF2 optical substrate. The method comprises the following steps: S1, carrying out a Raman spectrum test on a focus area of a CaF2 optical element by using a micro Raman spectroscopy, selecting a Raman spectrum test mode and setting a Raman spectrum test parameter; S2, selecting a fluorescence spectrum test mode and a fluorescence spectrum test parameter by the micro Raman spectroscopy, and carrying out a fluorescence spectrum test on the focus area of a sample; S3, carrying out a Mapping surface scanning test on all irradiated areas of the surface of the tested CaF2 optical element; S4, analyzing test results and judging whether all irradiated areas of the surface of the tested CaF2 optical element change. The method for detecting the deep ultraviolet laser radiation induction surface change of the CaF2 optical substrate provided by the invention can improve the detection precision and the detection accuracy.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Detection method of melamine in milk and milk powder
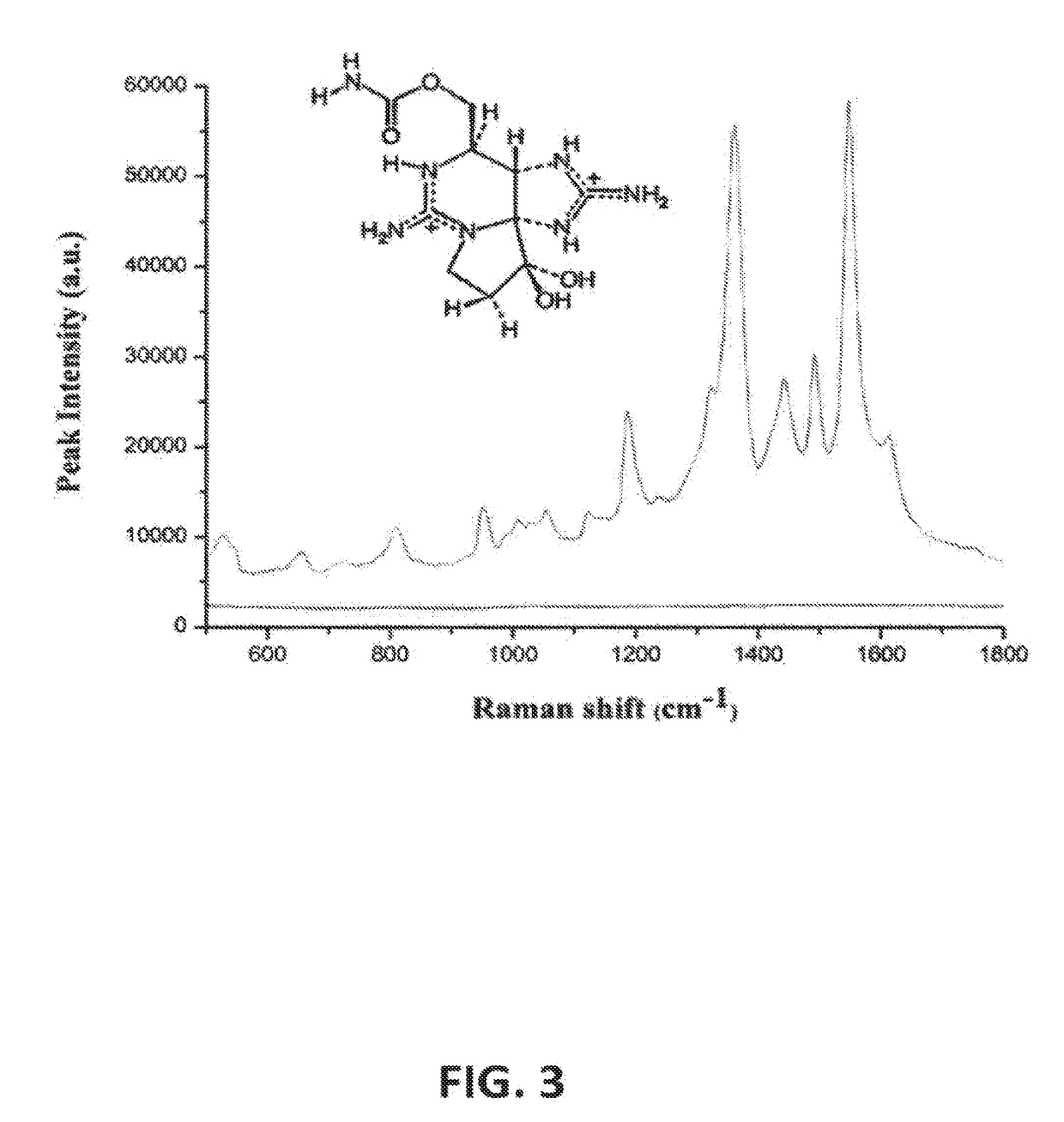
The invention discloses a detection method of melamine in milk and milk powder. Separation and enrichment characteristics of coffee-ring effect and high resolution detection of confocal micro-raman spectroscopy are fully combined, and a new detection method of low-concentration melamine in milk and milk powder is provided. The new detection method is simple and shortcut and has advantages of low cost and accurate result. Only by normal evaporation process, low-cost detection can be realized. The method is beneficial to large-batch low-cost rapid screening. The invention provides a new technical means for detection of melamine in milk and milk powder products.
Owner:河北伊诺光学科技股份有限公司
Carbon material, carbonaceous material for battery electrode, and battery
InactiveCN104039697AImprove Coulombic efficiencySmall thickness change rateGraphiteCell electrodesX-rayAqueous electrolyte
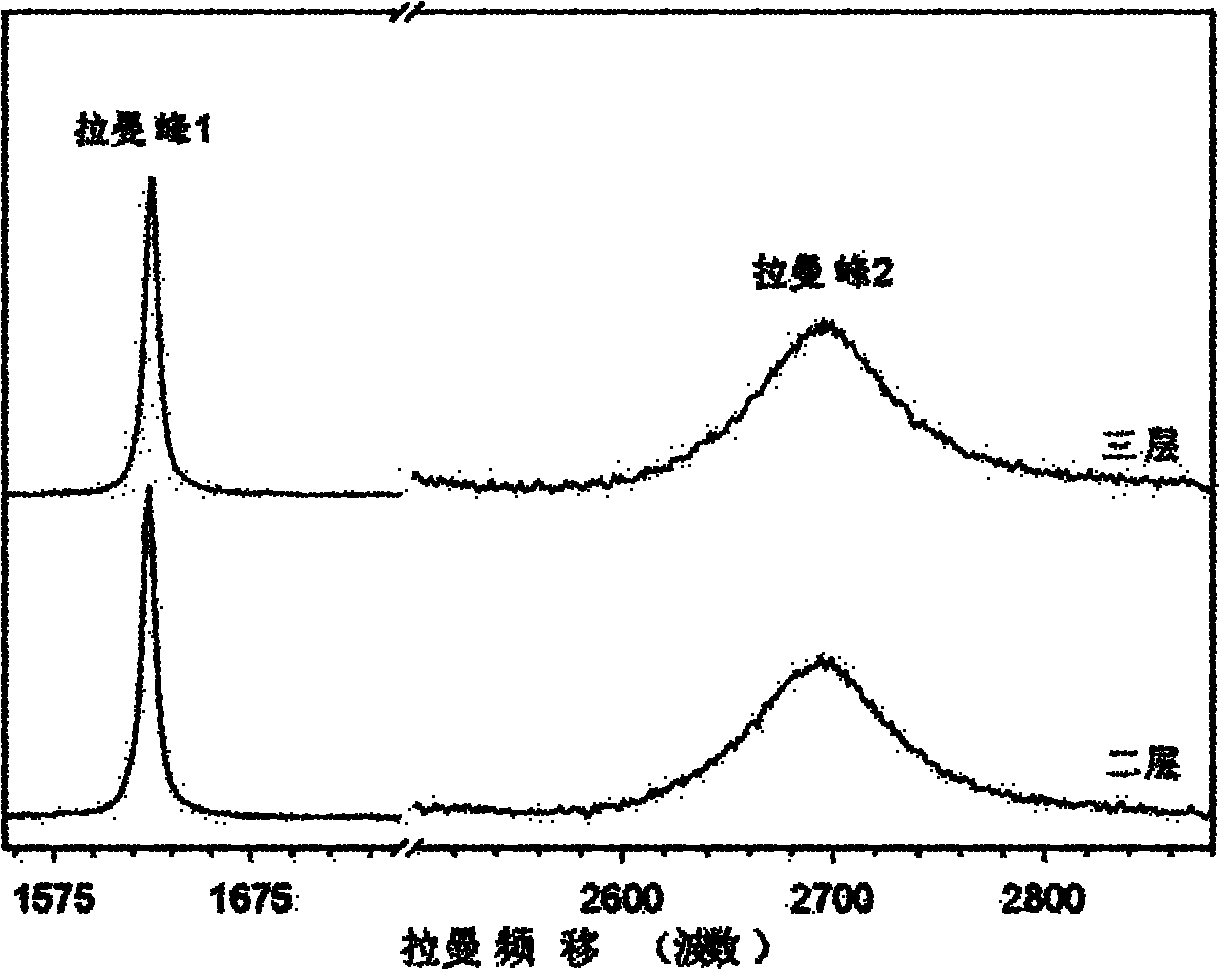
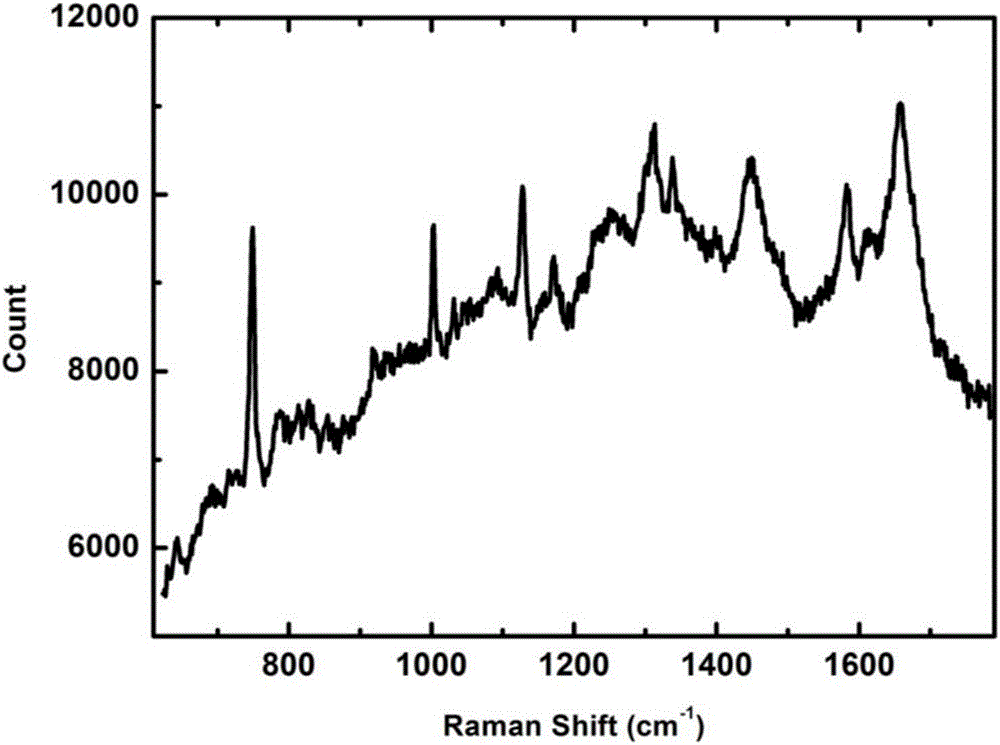
Provided is a flake-like carbon material that is suitable for use as an electrode material for an aqueous-electrolyte secondary battery. When the end surface of a particle of the carbon material is measured by using a micro-Raman spectrometer, the peak area (ID) of the peak measured in the 1300-1400 cm-1 range of the Raman spectrum, and the peak area (IG) of the peak measured in the 1580-1620 cm-1 range of the Raman spectrum have a IG / ID intensity ratio (G value) that is 5.2-100 inclusive. The average plane spacing (d002) of the (002) planes, as measured by X-ray diffractometry, is equal to or less than 0.337nm. The material has an optical structure of a specific shape. Also provided are a method for manufacturing the carbon material, a carbonaceous material for a battery electrode that includes the carbon material, a paste for an electrode, and a secondary battery that exhibits superior charge / discharge cycle properties and heavy-current carrying properties.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Method and device for in-situ online determination of solubility of CO2 in alkane
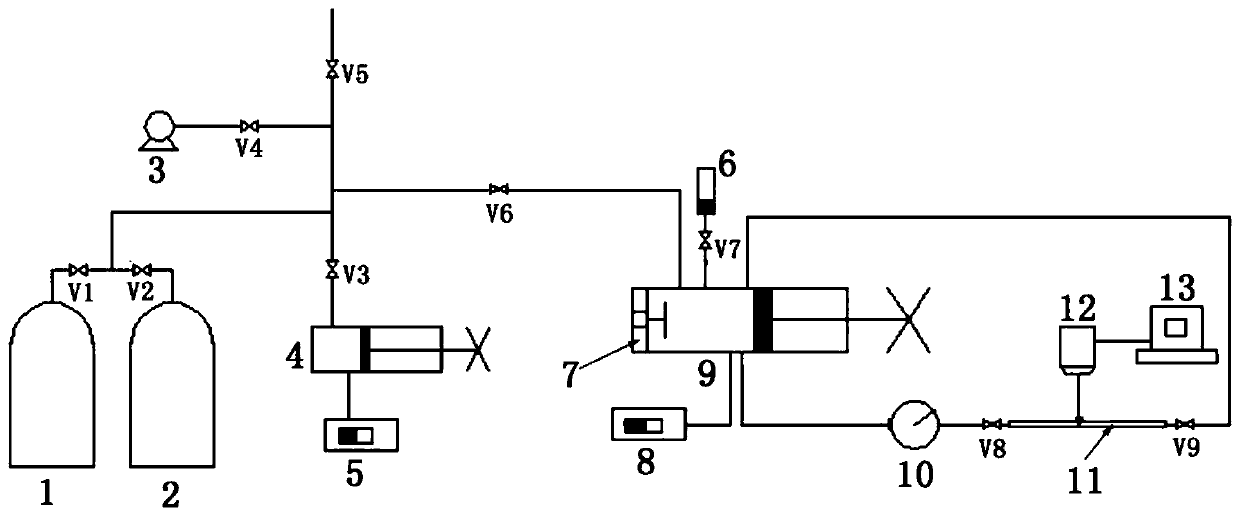
PendingCN111157510AEnsure consistencyGuaranteed accuracyPreparing sample for investigationRaman scatteringAlkaneOptical spectrometer
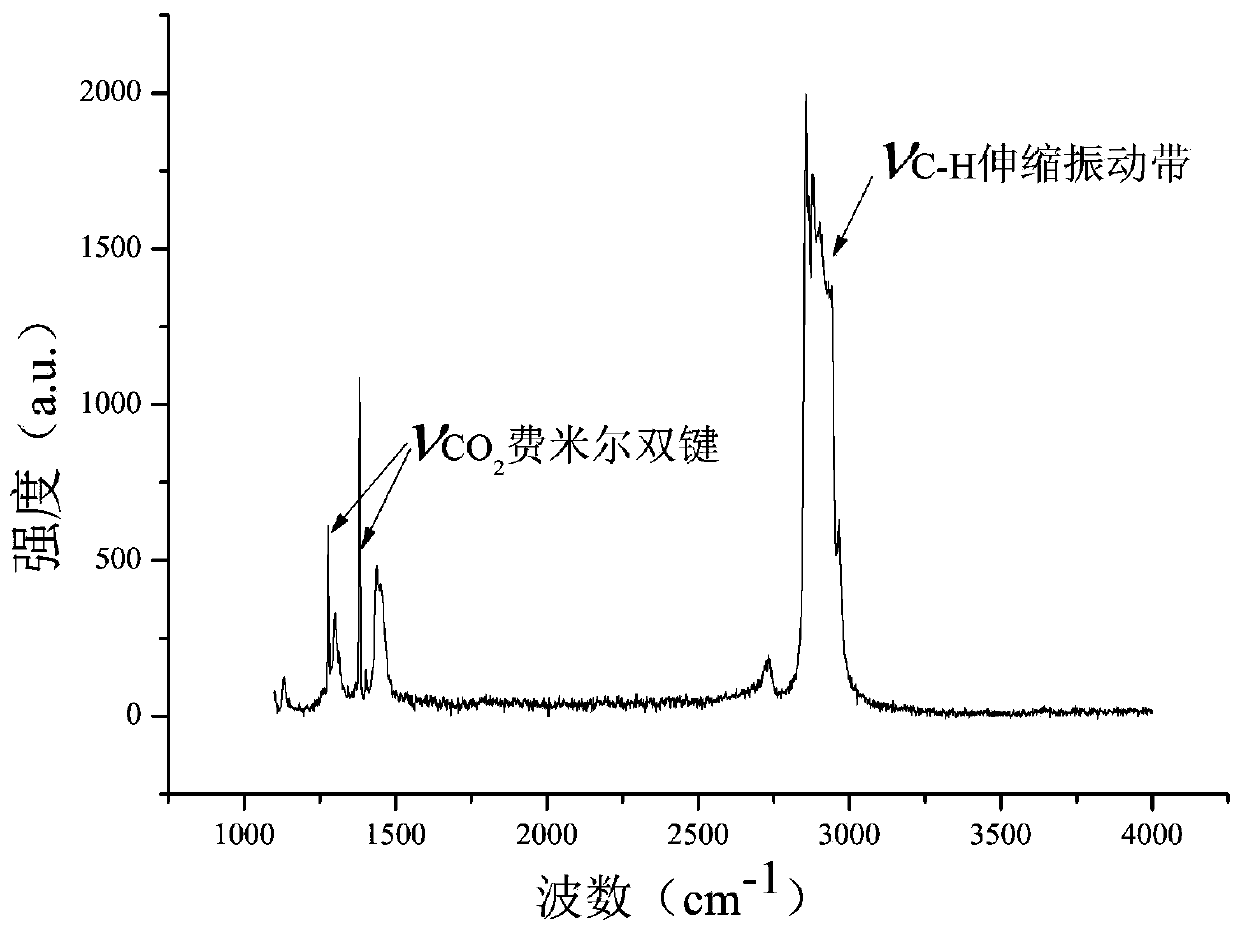
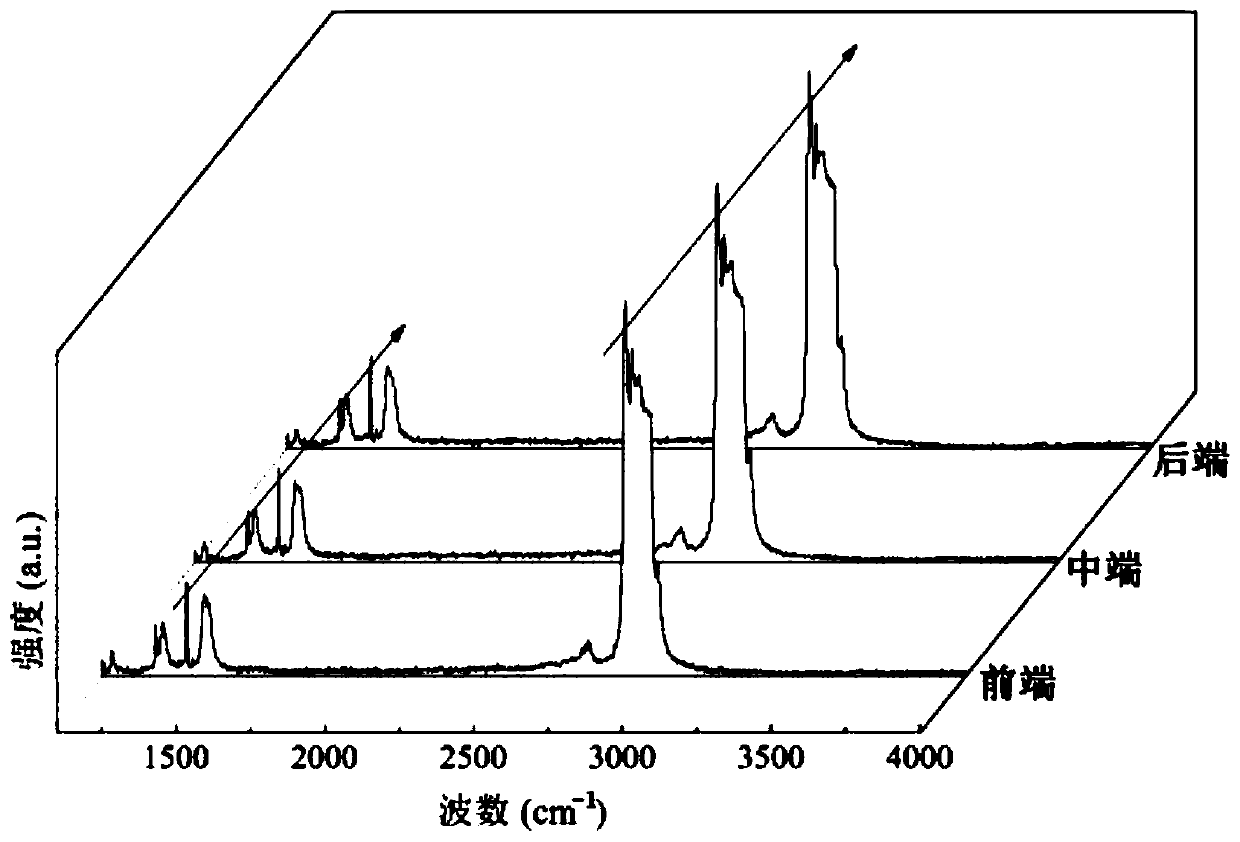
The invention discloses a method and a device for in-situ online determination of solubility of CO2 in alkane. The device comprises a confocal microscopic Raman spectrometer, a high-pressure ventilation pipeline, a circulation balance pipeline system, a cooling and heating table and the like. Because the property of the alkane is changed due to temperature change, an electric heating device is arranged on the phase equilibrium kettle, and a pipeline of the circulation equilibrium pipeline system is coated with a heat preservation layer so as to keep the consistency of the temperature of the system. According to the method disclosed by the invention, CO2 is quantitatively injected into a CO2-alkane system in batches by utilizing a high-pressure ventilation pipeline; the method further includes detecting and recording peak-height ratio values of C-H telescopic vibration peaks of CO2 Fermi double bonds and alkane in the CO2-alkane system under the CO2 gradient concentration, drawing a standard curve taking the CO2 concentration as an abscissa and the peak-height ratio as an ordinate, and then determining the solubility of CO2 in alkane. The method provided by the invention has the characteristics of high data credibility, no need of sampling, safety, high efficiency, intuition, strong operability, repeated operation and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
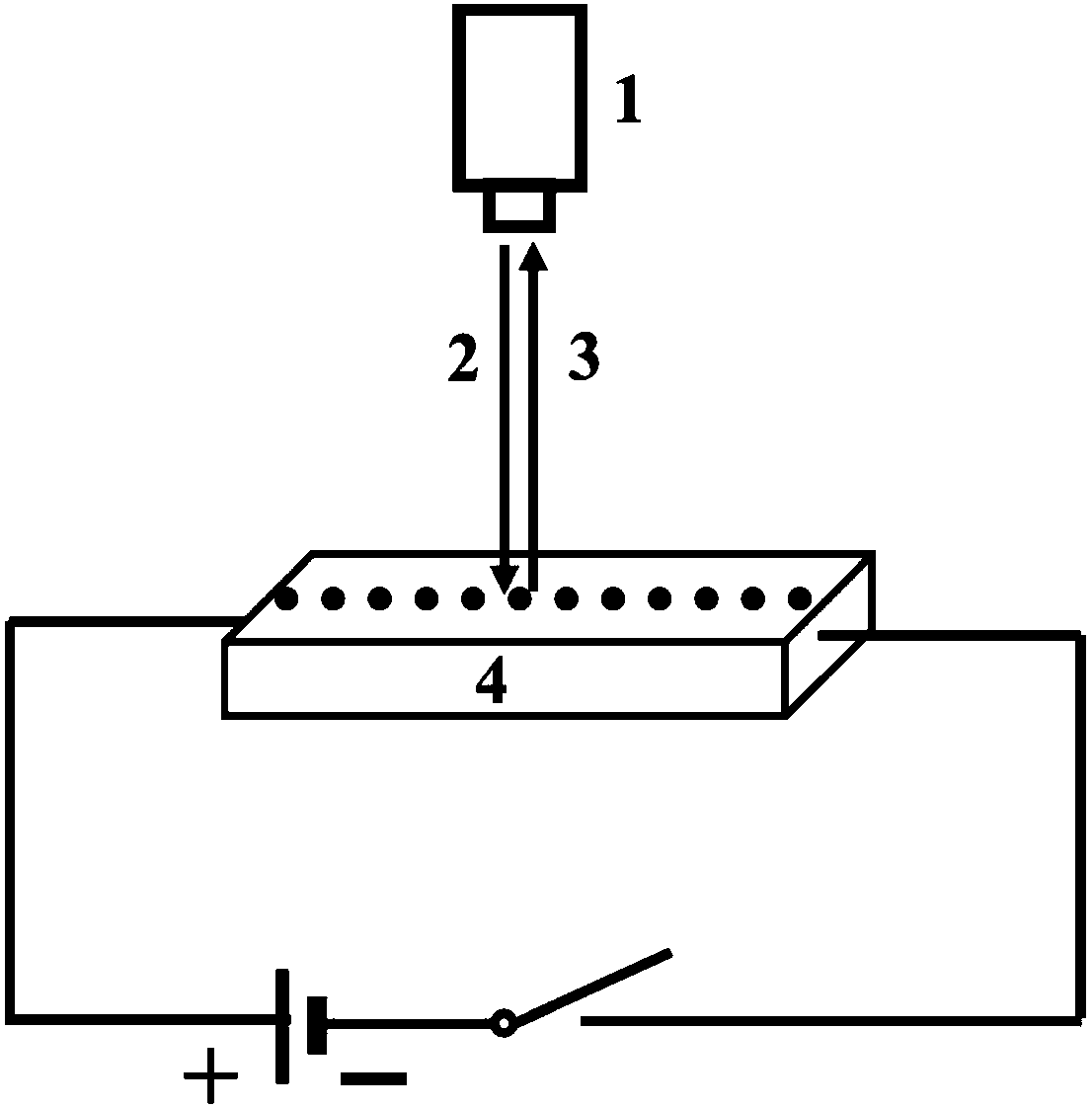
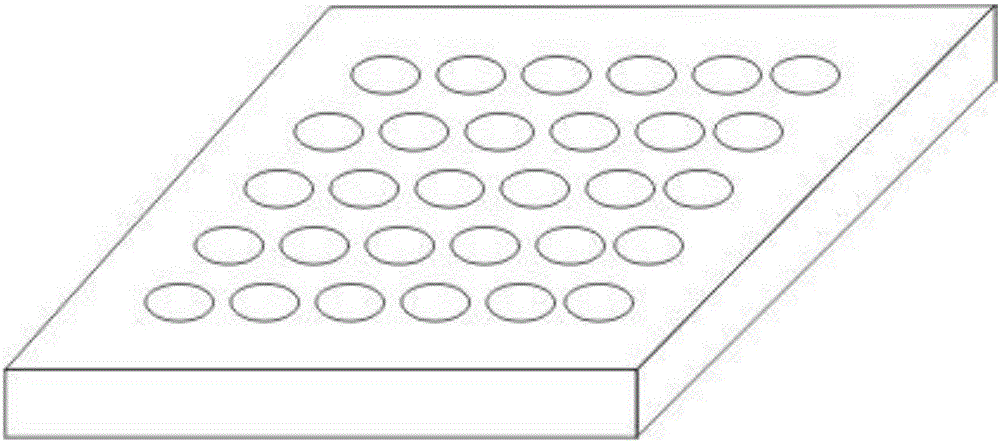
Living single cell Raman spectrum detection chip
InactiveCN106442462AGuaranteed stabilityEasy to useRaman scatteringMicrofluidicsComplex control system
The invention provides a living single cell Raman spectrum detection chip. The living single cell Raman spectrum detection chip is formed by a substrate with micro-pit arrays and without Raman scattering characteristic peaks. Living single cells are dripped on the surface of the chip, after moving and falling into micro-pits, the cells are allowed to remain motionless, then Raman spectrum measurement is conducted by a microscope, and thus Raman spectrum of the living single cells is obtained. The chip is used for living single cell Raman spectrum measurement, and during the measurement, a complex control system required by microfluidic control is not needed. The living single cells can be added by dripping, the operation is simple, and the chip can be widely used in the field of biomedical detection.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
In situ microscopic Raman characterization system
The invention discloses an in situ microscopic Raman characterization system which comprises: a glass tube and a colorimetric ware, which respectively contain ferric trichloride and graphene flakes and are hermetically communicated with each other; a laser; a Raman spectrometer; a heating table; a lifting platform; a translation stage; and two vibrating mirrors. The in situ microscopic Raman characterization system provided by the invention can be used for in situ characterization of microscopic Raman spectrum of a graphene flake / ferric trichloride intercalation compound and is capable of in situ monitoring of the formation situation of the graphene flake / ferric trichloride intercalation compound.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
In-situ spectrum analysis pool for gas-sensitive sensing exploration and applications
InactiveCN113866095AFlexible connectionPrecise Electrical TestingComponent separationRaman scatteringTemperature controlOptical spectrometer
The invention discloses an in-situ spectrum analysis pool for gas-sensitive sensing exploration and applications, wherein the in-situ spectrum analysis pool is suitable for in-situ spectrum analysis of equipment such as an infrared spectrometer and a micro-Raman spectrometer, an optical window is arranged at the top of a cavity, and a sealing ring is arranged between a cavity top cover and a bottom in-situ pool main body; a sample temperature control table containing a temperature control element and a temperature measuring element is arranged in the closed in-situ spectrum analysis pool, and the height of the sample temperature control table can be adjusted; a sample test area is arranged on the sample temperature control table, and a plurality of electrical probes are arranged around the sample test area and used for measuring the electrical characteristics of a sample to be tested; the closed in-situ spectrum analysis pool is provided with a plurality of gas inlets and outlets and is used for vacuumizing treatment, and after various gases are mixed according to a specific proportion through a gas distributor, the gases are introduced and discharged. According to the invention, the sample to be measured is placed in the in-situ pool, gas entering the cavity of the in-situ pool through the gas guide tube skims over the surface of the sample, spectral information in the gas-solid reaction process can be collected in situ, and the electrical characteristics of the gas sensor are measured.
Owner:QUZHOU RES INST OF ZHEJIANG UNIV
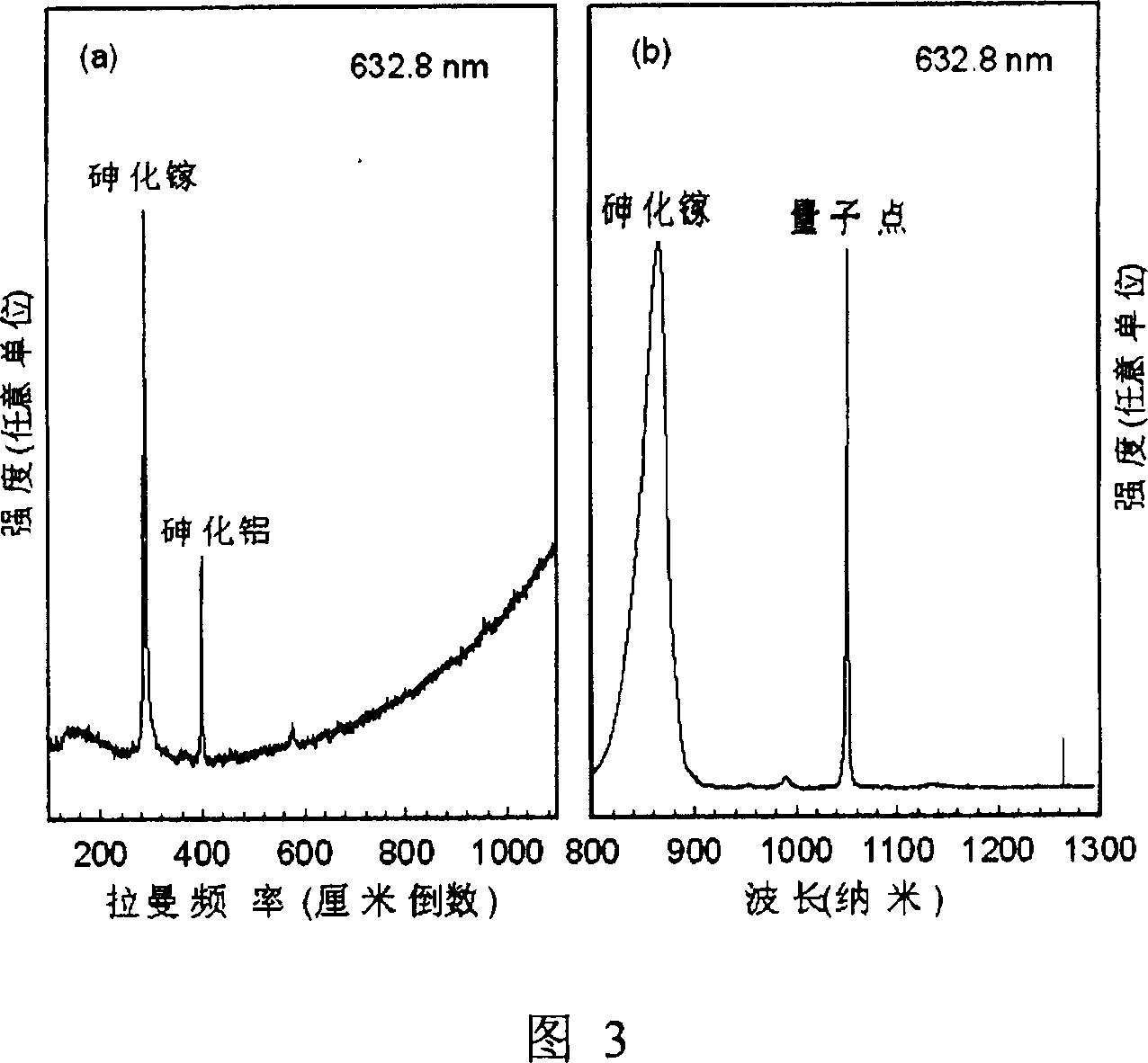
Control method resonant cavity enhancement detector cavity film
InactiveCN101471396AEffectively exert the resonance enhancement effectImprove quantum efficiencyRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringResonant cavityAluminium arsenide
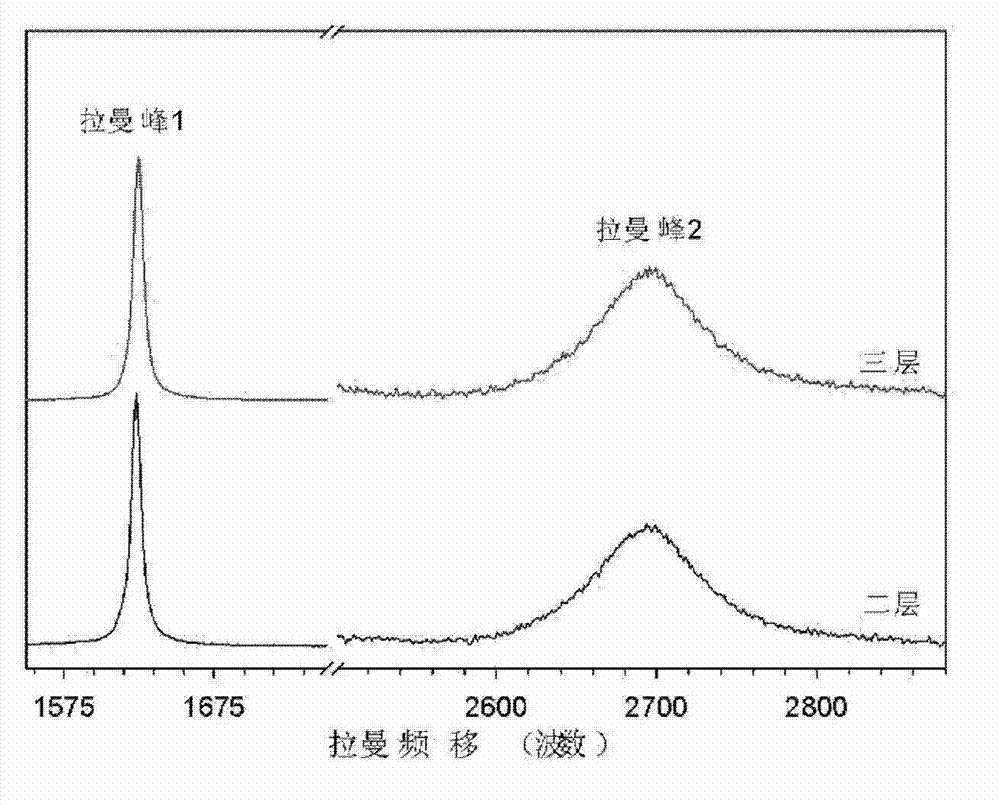
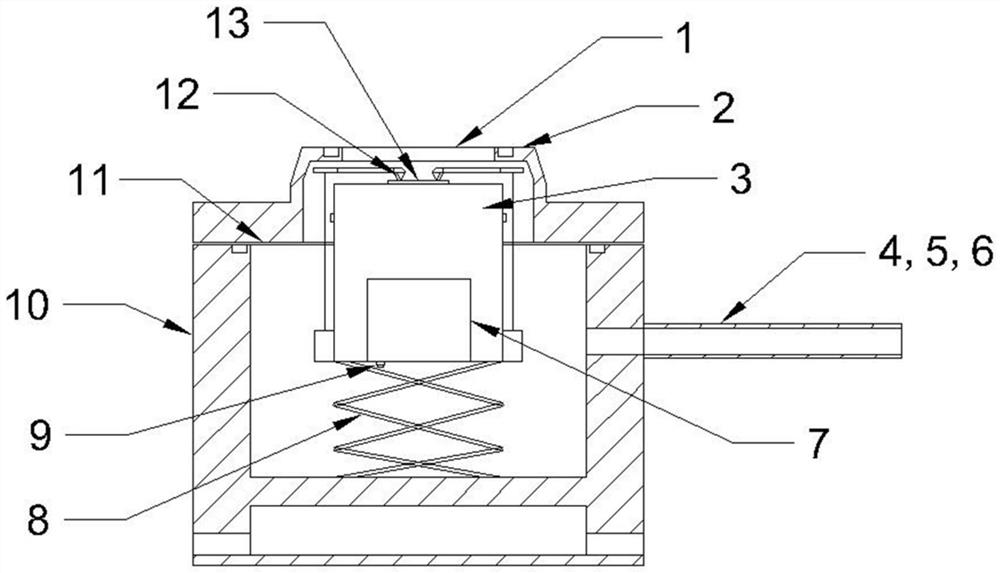
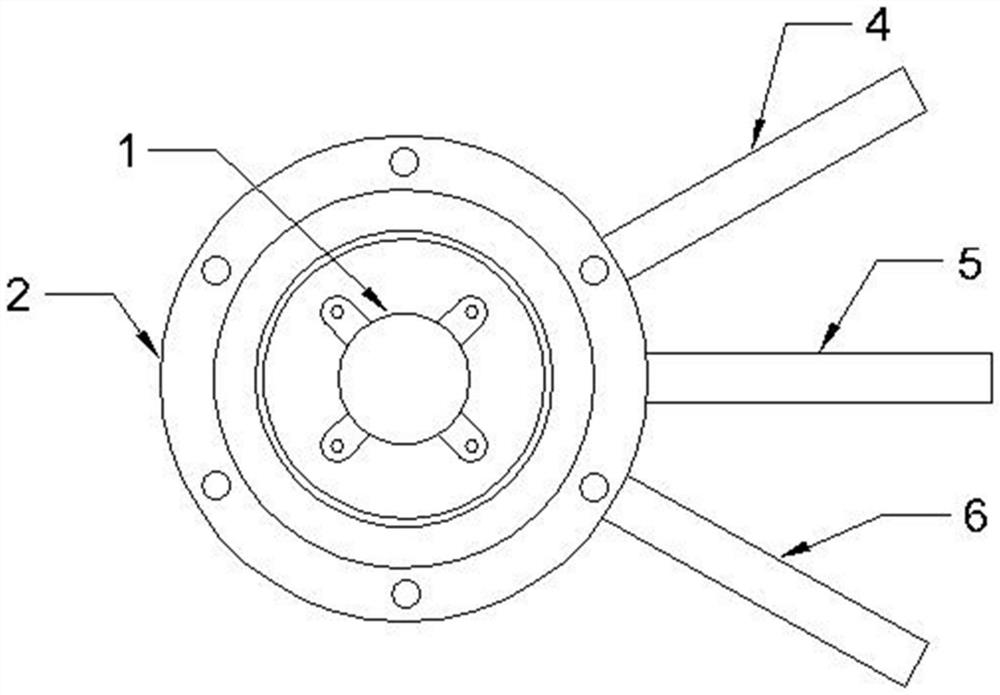
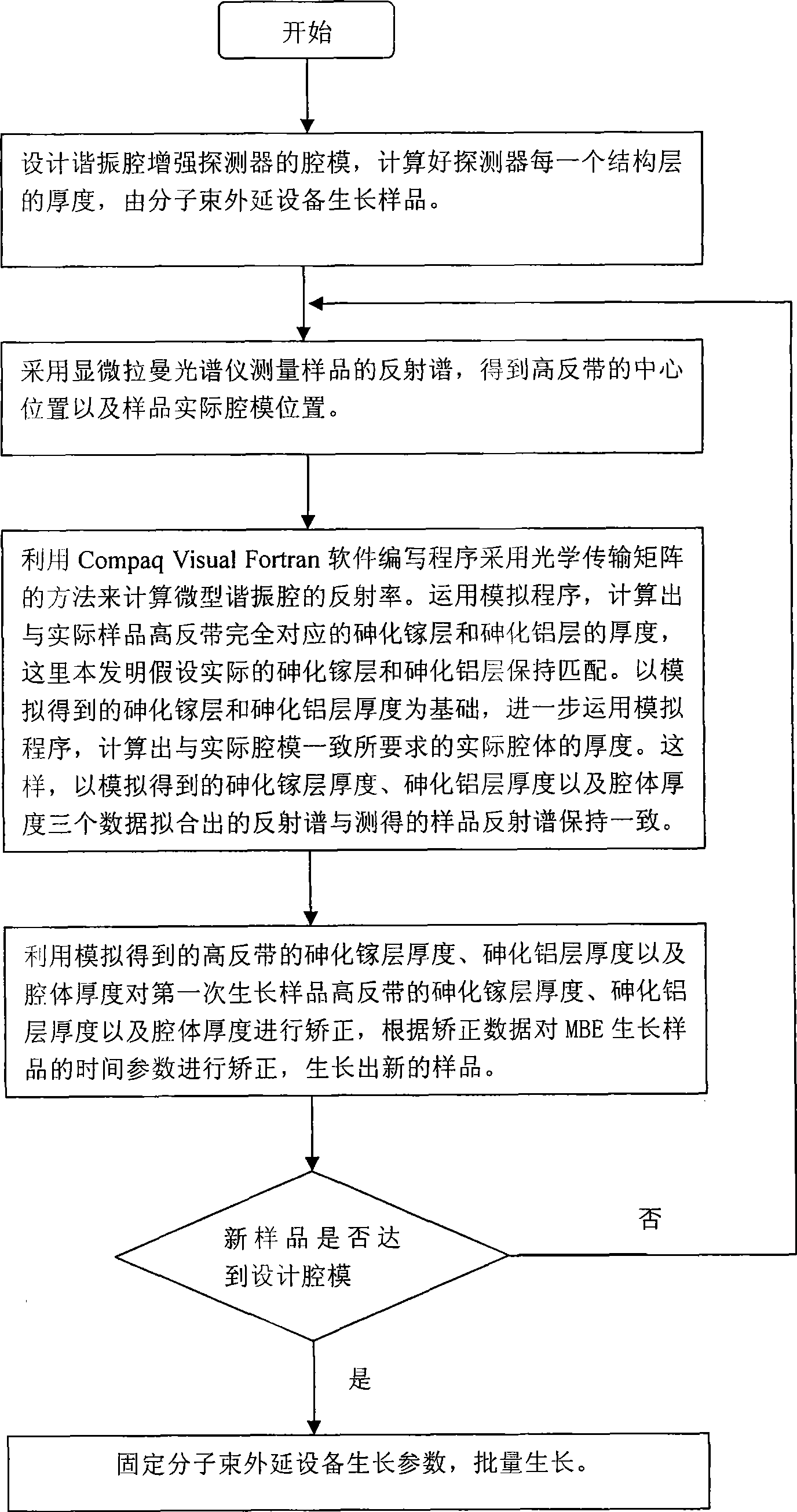
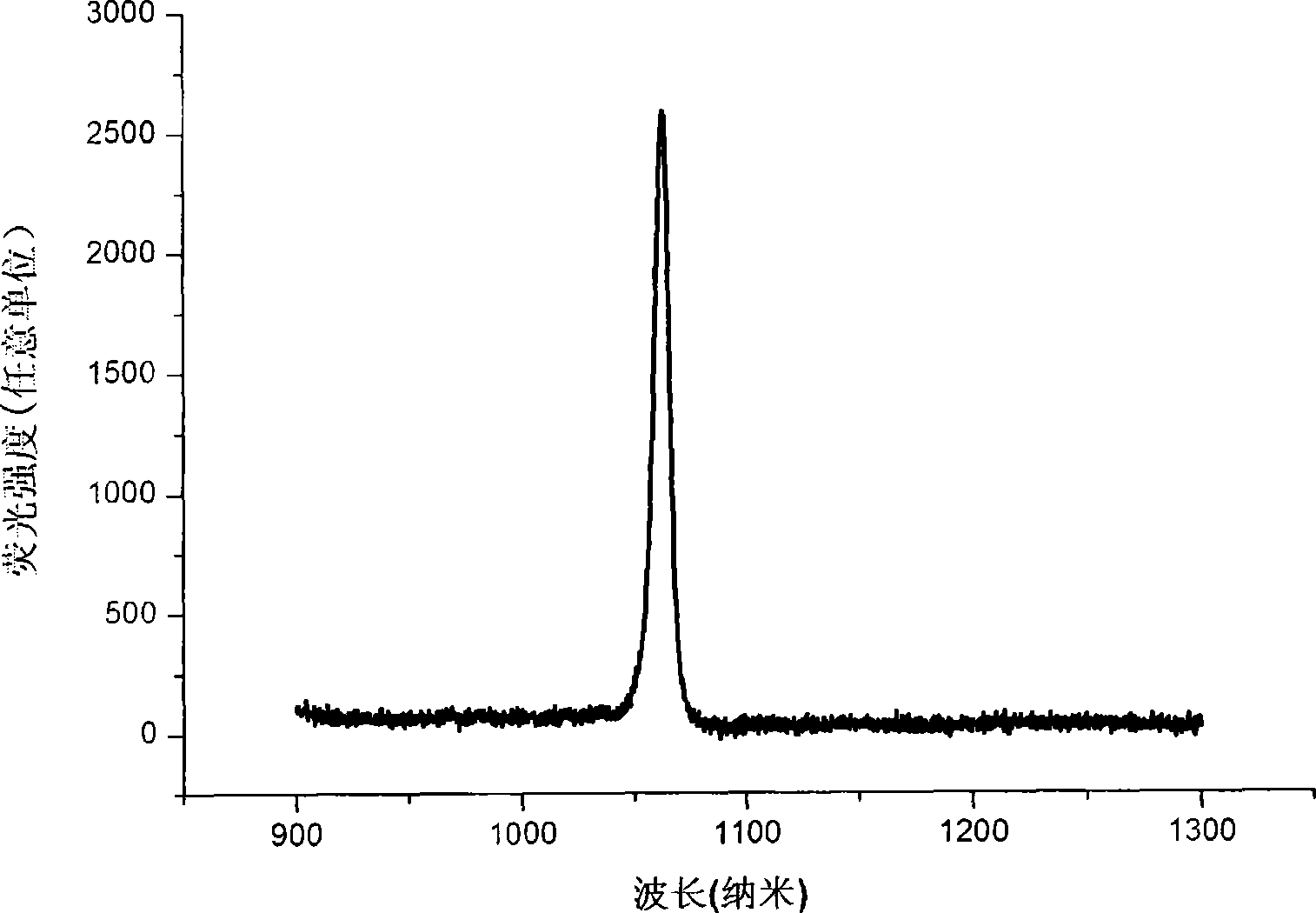
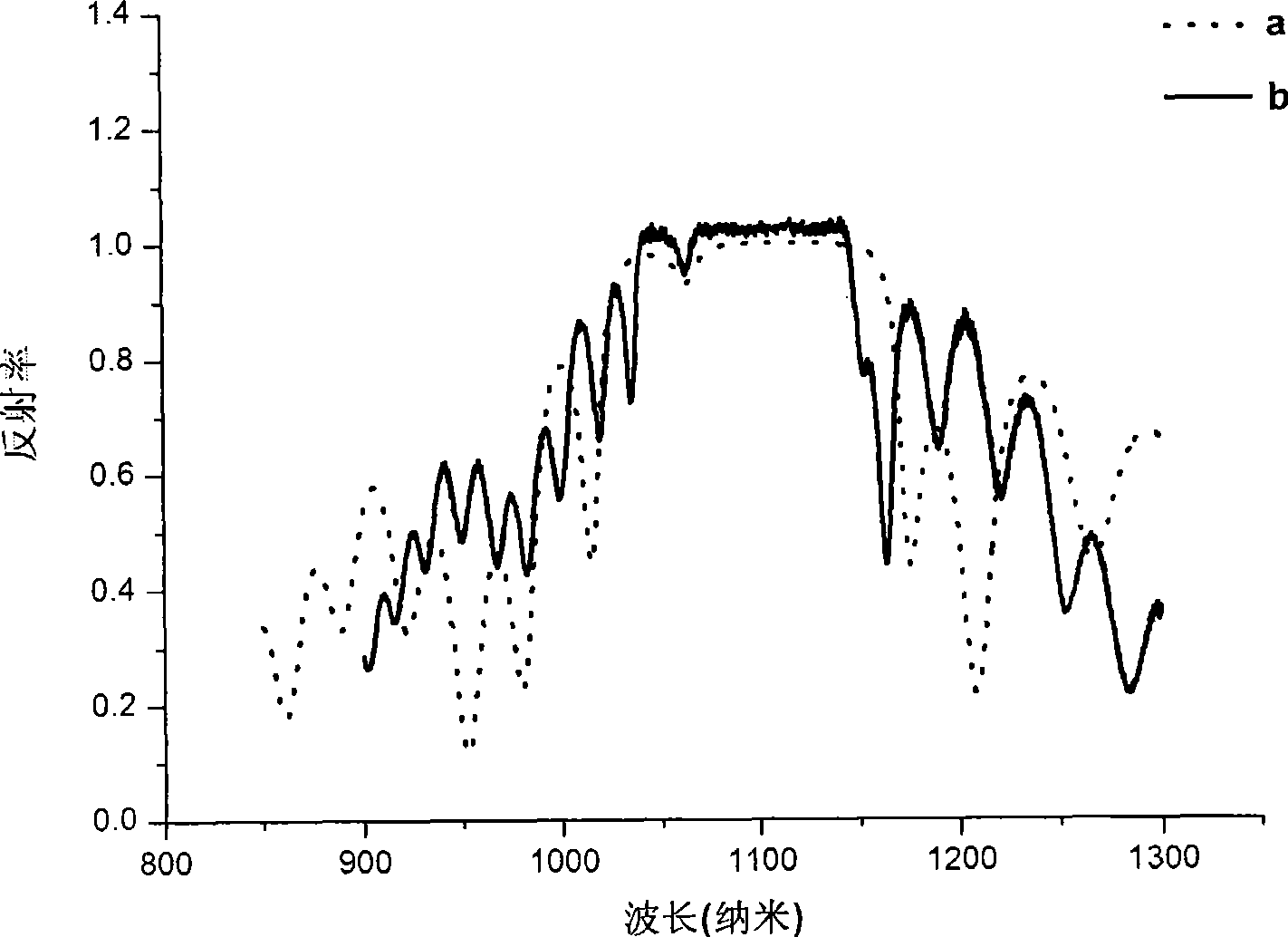
The invention relates to a method for controlling a cavity module of a resonant cavity reinforcing detector, which comprises: firstly, designing a cavity module of the resonant cavity reinforcing detector, initially setting the thickness of each structure layer of the detector, and leading samples to grow on a molecular beam epitaxy device, secondly, adopting a confocal laser Raman microscopy to measure reflectance spectrums of samples, and getting central positions of a high reflectivity belt and an actual cavity module position of a sample, thirdly, adopting an analog procedure, calculating out the thickness of a gallium arsenide layer which is totally corresponding to the high reflectivity belt of an actual sample, the thickness of an aluminium arsenide layer and the thickness of an actual cavity body, required by totally corresponding to the actual cavity module, fourthly, correcting the thickness of the gallium arsenide layer of the high reflectivity belt where samples firstly grow, the thickness of the aluminium arsenide layer and the thickness of the cavity body according to the data got through the step three, and correcting time parameters for growing samples on the molecular beam epitaxy, and leading new samples to grow, fifthly, adopting the confocal laser Raman microscopy to measure reflectance spectrums of new samples.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Raman characteristic spectrum peak extraction method based on improved principal assembly analysis
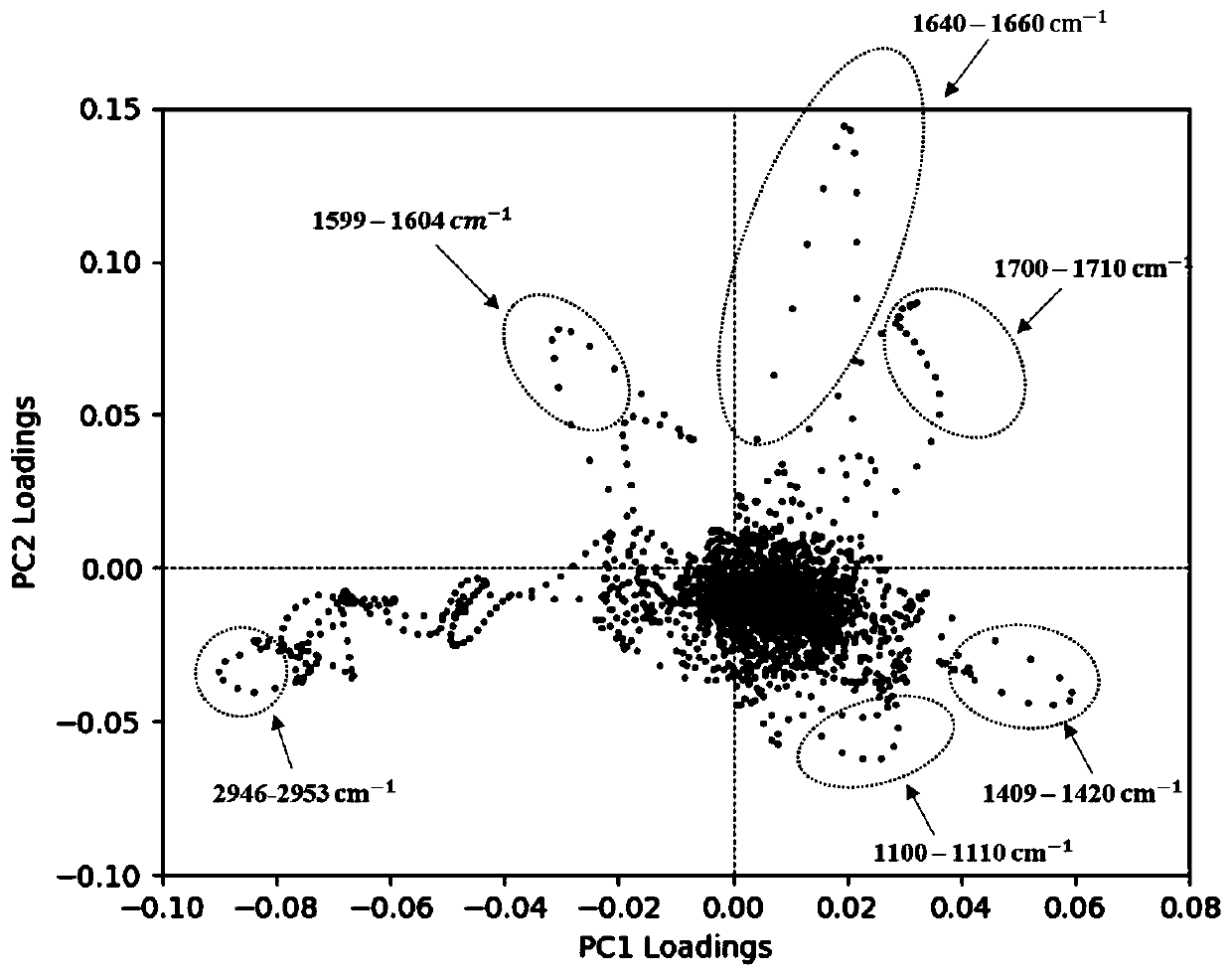
ActiveCN110672582AImprove accuracyFast classificationRaman scatteringTesting foodPork meatPrincipal component analysis
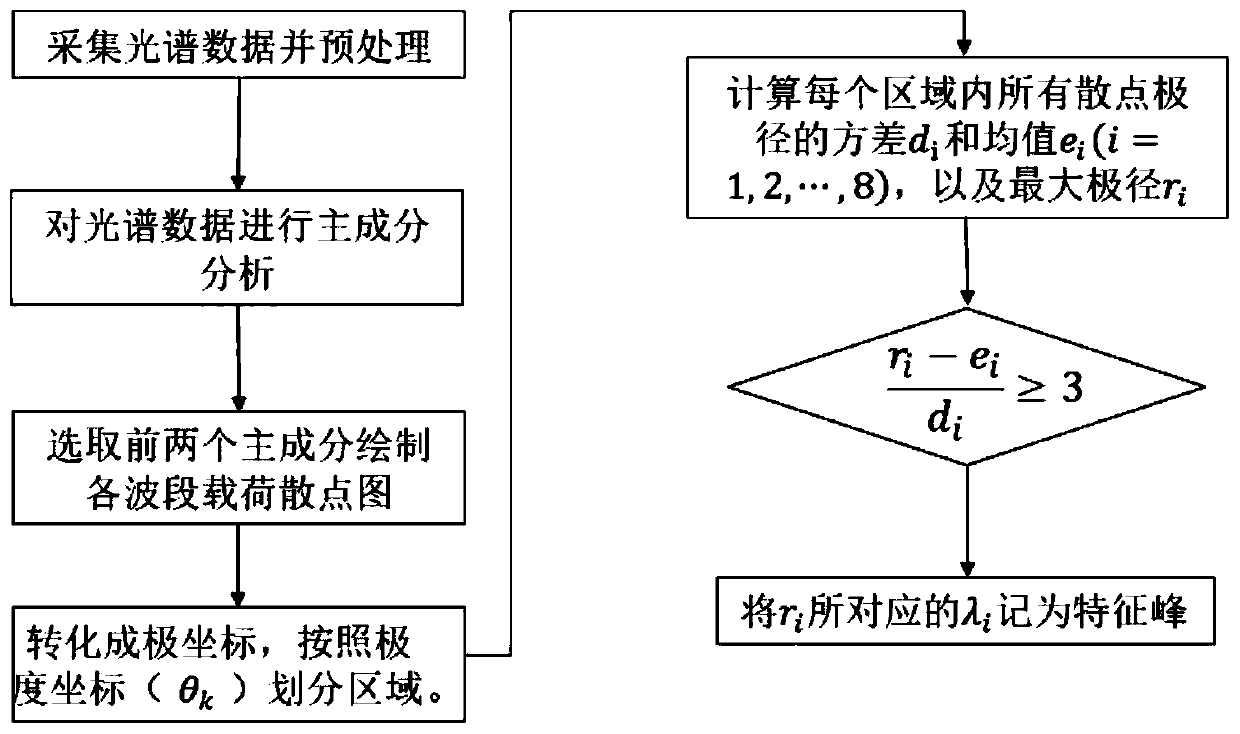
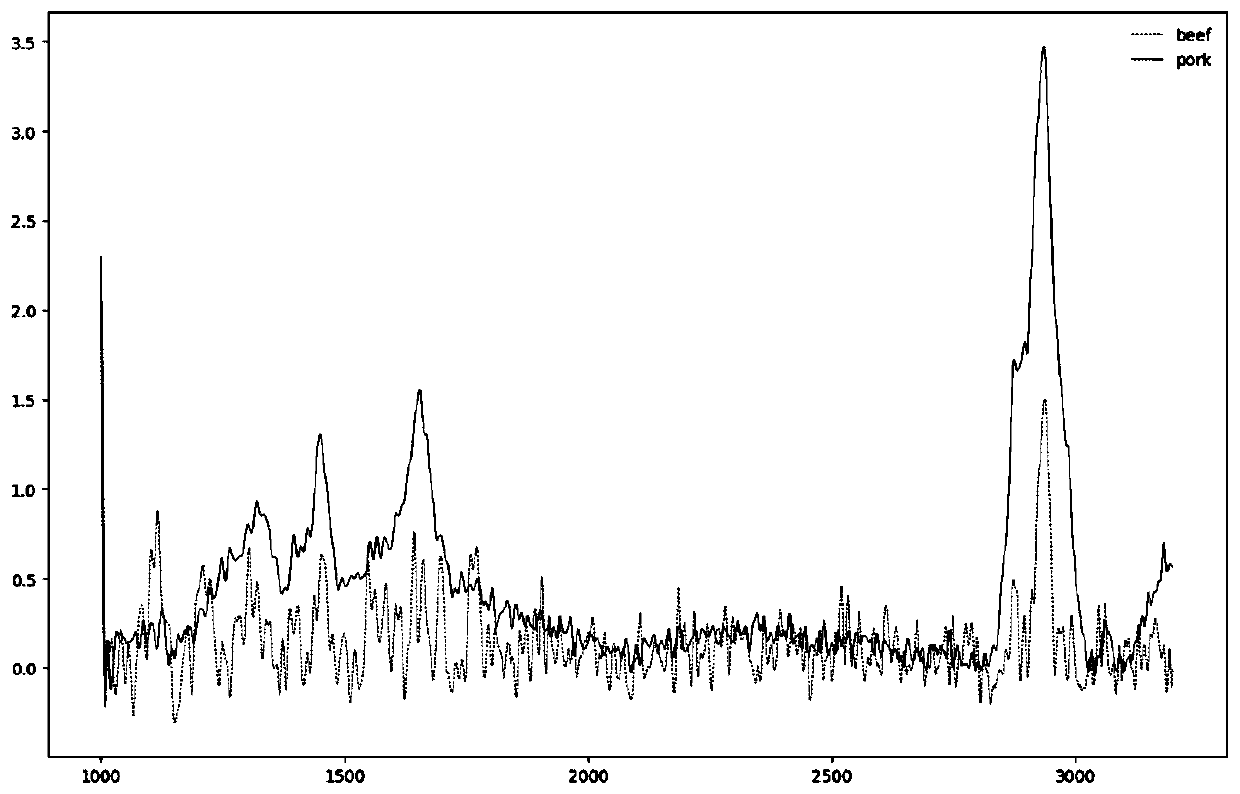
The invention discloses a Raman characteristic spectrum peak extraction method based on improved principal assembly analysis. The method comprises the following steps of collecting Raman spectrum dataof the surfaces of pork and beef samples by a confocal microscopic Raman spectrometer; preprocessing the Raman spectrum data, performing principal component analysis, establishing a principal component load scatter diagram, analyzing and extracting scatter point characteristics of the principal component load scatter diagram, and screening a Raman characteristic spectrum peak according to the scatter point characteristics. The method extracts the Raman characteristic spectrum peaks of the beef and the pork and substitutes the Raman characteristic spectrum peaks into a classifier for classification, so that higher accuracy rate is achieved, and the classification speed is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com