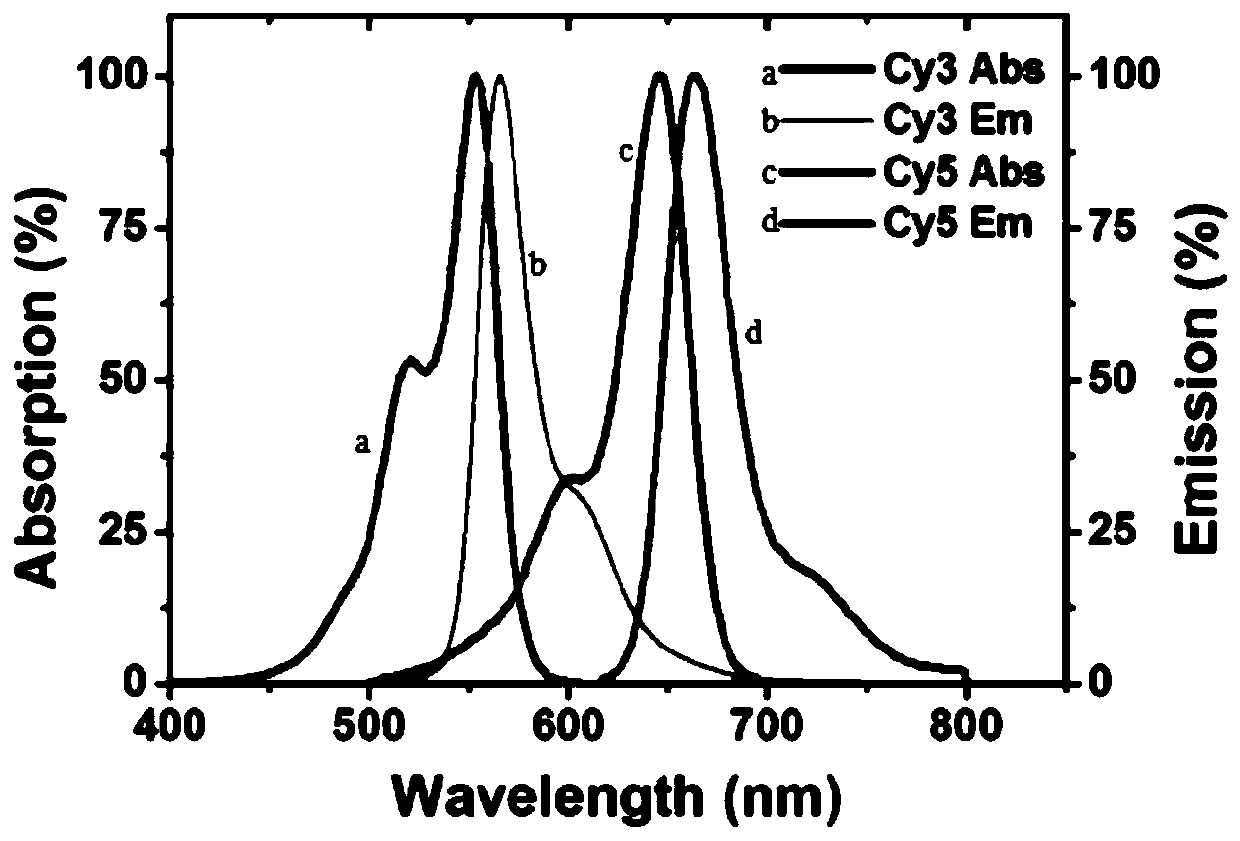
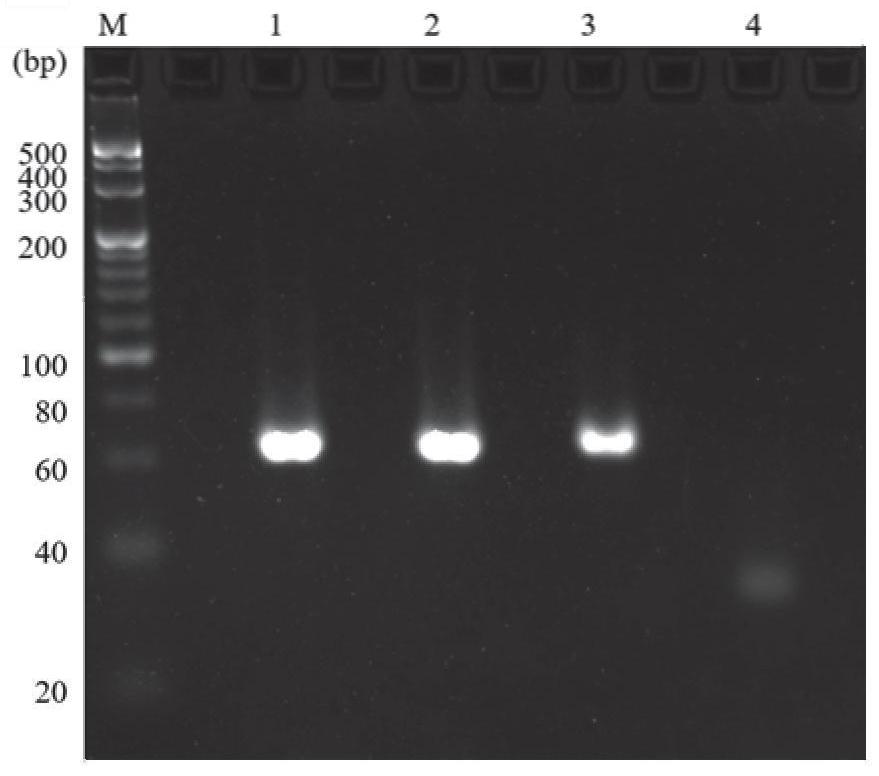
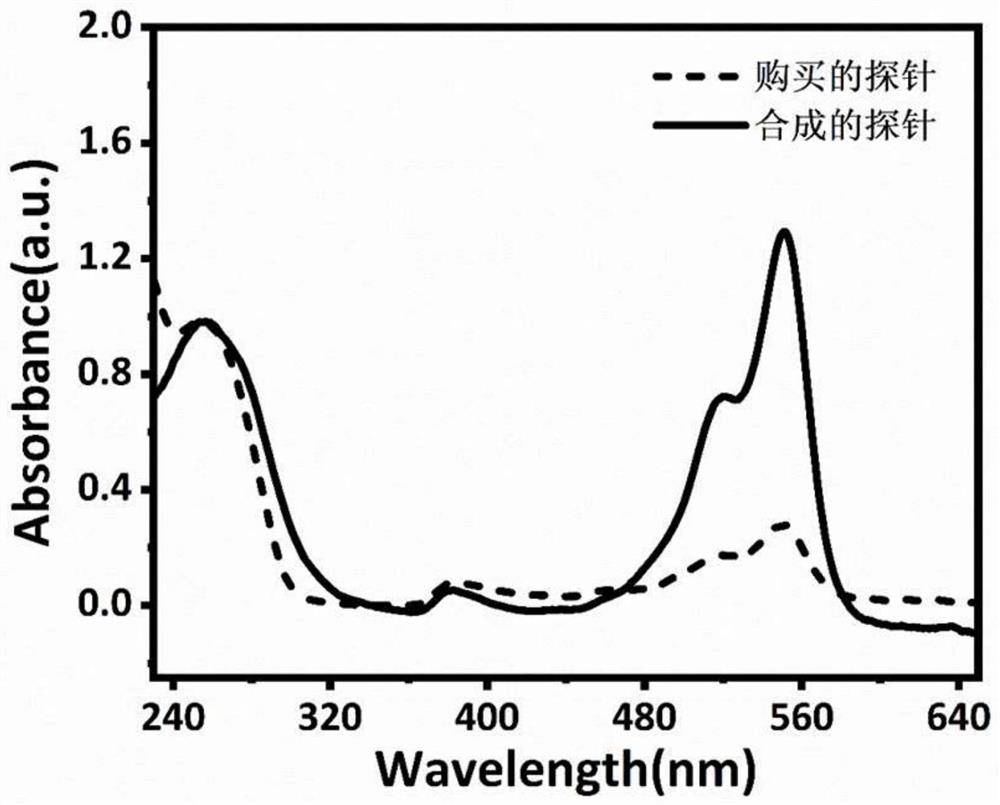
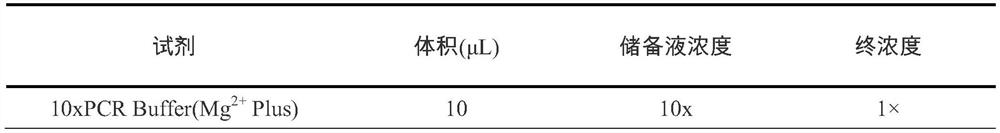
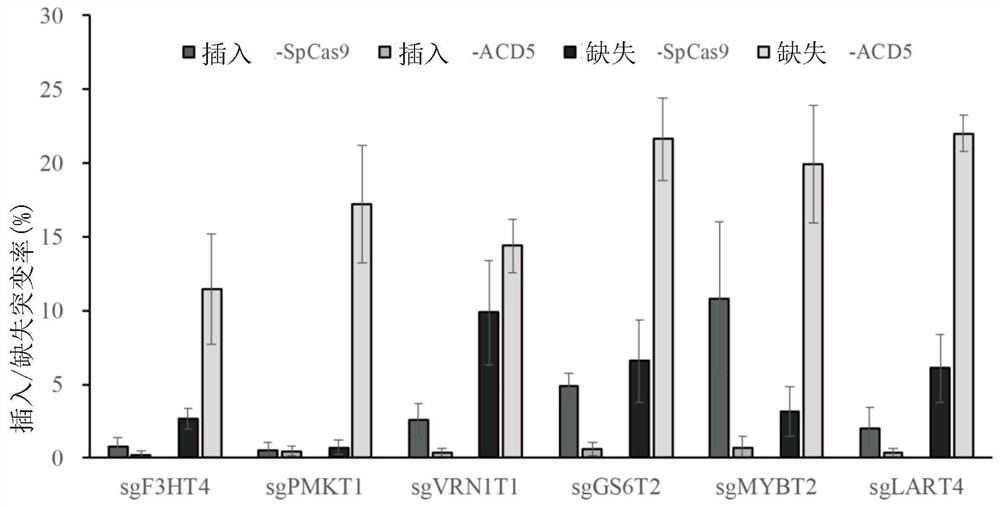
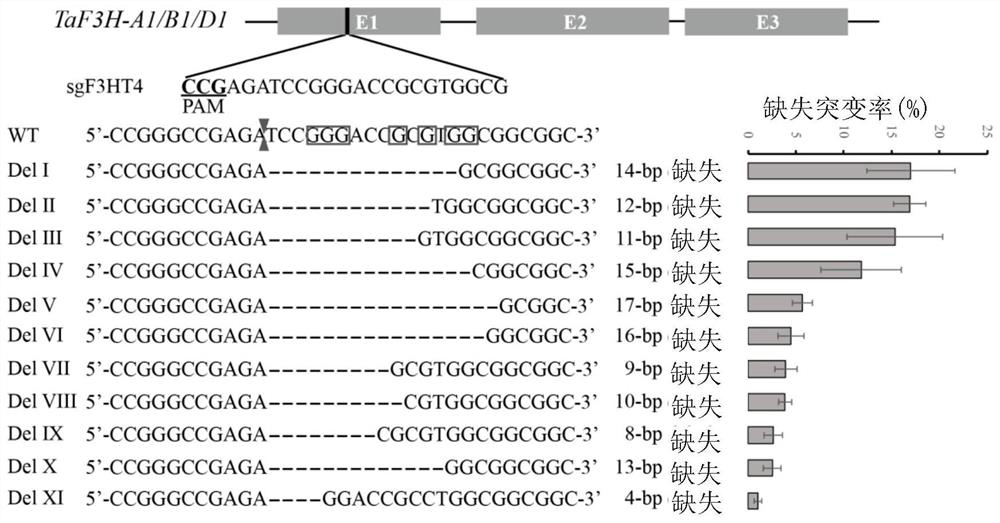
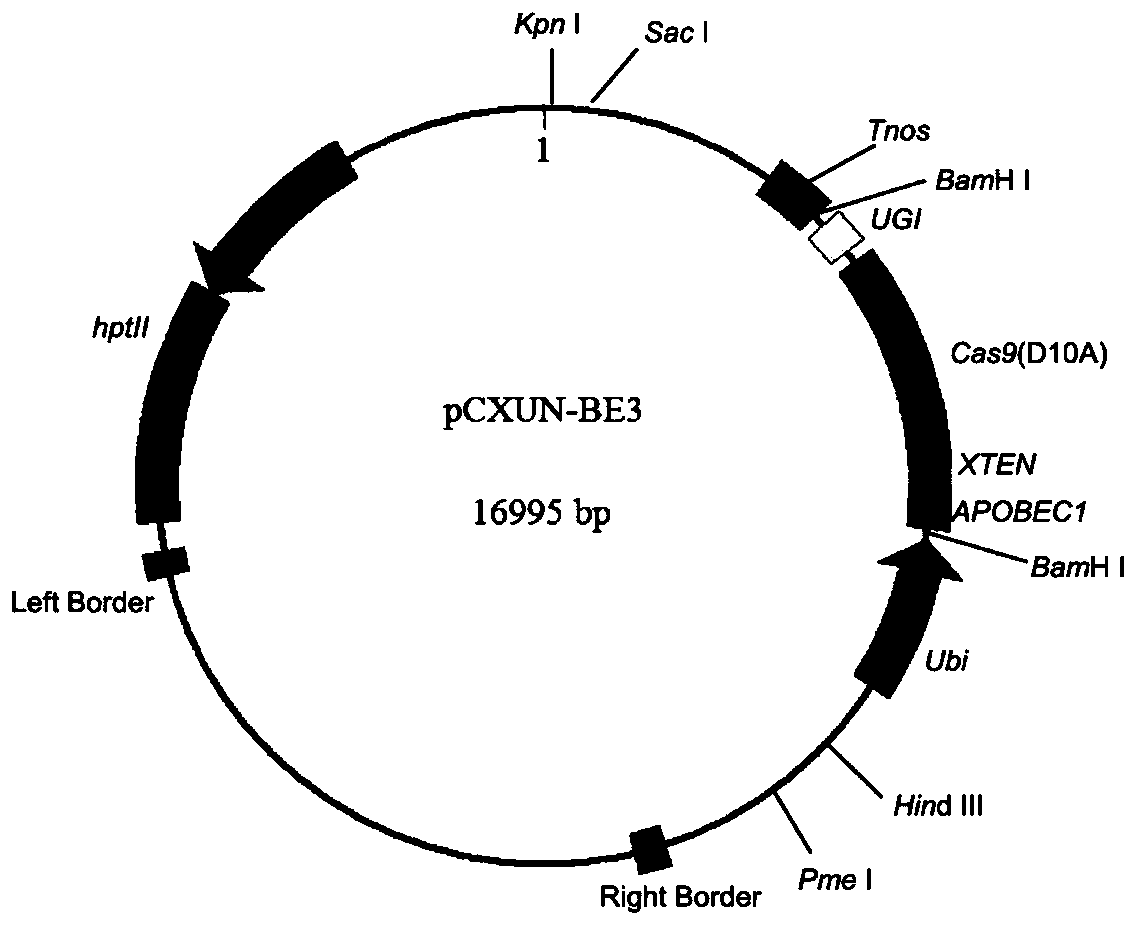
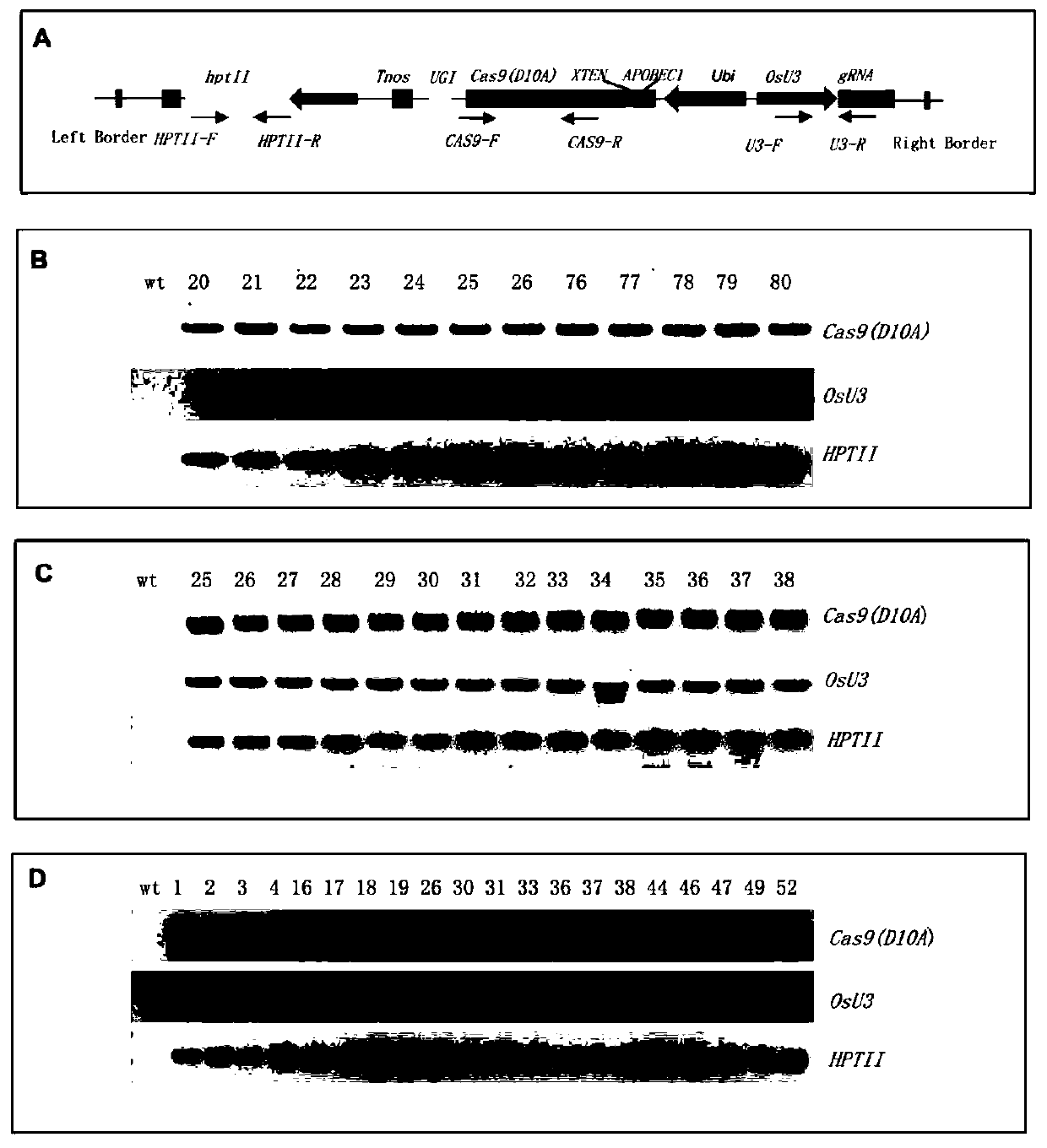
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Uracil in DNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
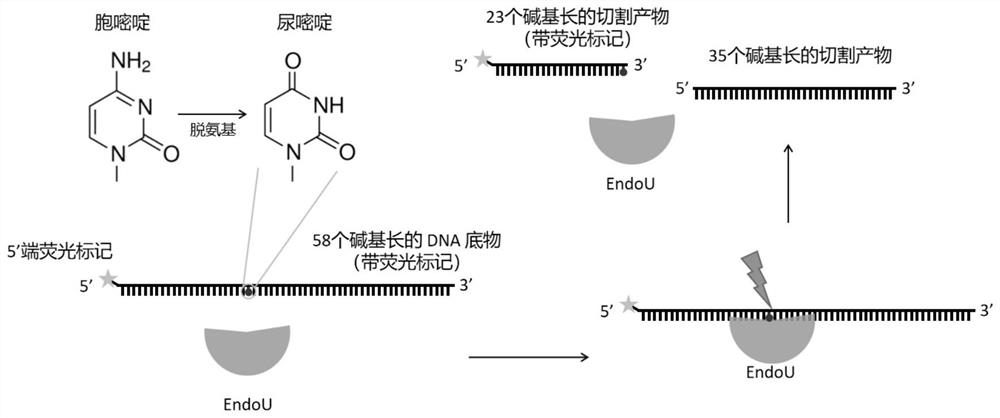
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms. The information in DNA is stored as a code made up for four nucleotides: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. During protein biosynthesis, DNA is transcribed into RNA, another type of ribonucleid acid. In RNA, the DNA base thymine is replaced by uracil, a fifth nucleotide which is almost chemically identical to thymine, but lacks its 5′ methyl group. Cytosine can deaminate spontaneously to produce uracil. This process is referred to as hydrolytic deamination. Therefore, if there was an organism that used uracil in DNA, the deamination of cytosine, would lead to formation of uracil during DNA synthesis. Uracil-DNA glycosylase excises uracil bases from double-stranded DNA. This enzyme would therefore recognize and cut out both types of uracil - the one incorporated naturally and the one formed due to cytosine deamination, which would lead to unnecessary and inappropriate repair processes. This problem is believed to have been solved in terms of evolution, i.e. by "tagging" uracil. Methylated uracil is identical to thymine.
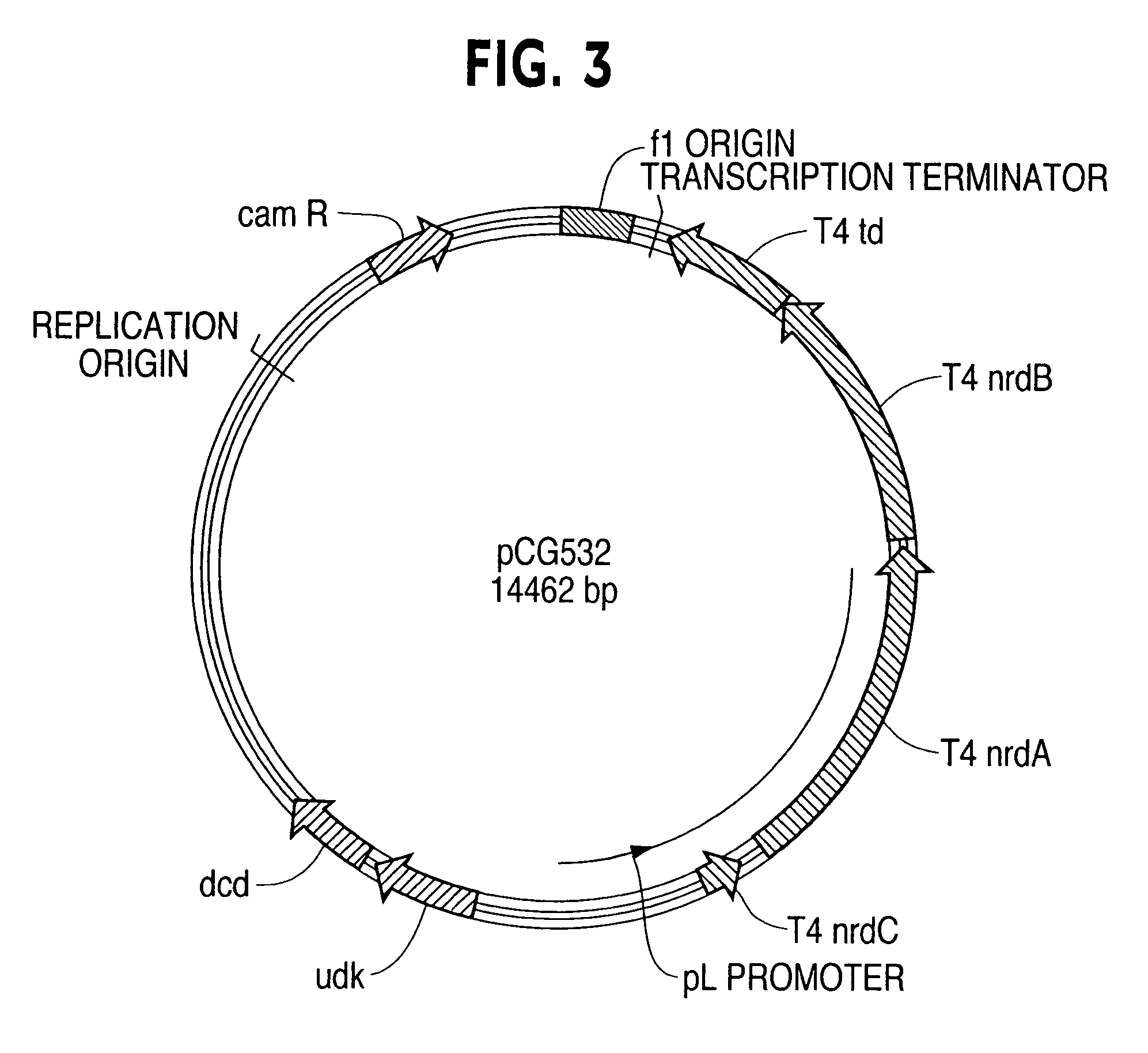
Vectors, cells and processes for pyrimidine deoxyribonucleosides production
Novel DNA constructs and host cells comprising the same are disclosed. DNA constructs comprise a transcription unit (e.g. operon) comprising DNA sequences encoding for ribonucleotide reductase and thioredoxin. In preferred embodiments, constructs further comprise DNA sequences encoding for thymidylate synthase and / or transcription units comprising sequences encoding for uridine kinase preferably together with dCTP deaminase. In particularly preferred embodiments, host cells comprising constructs having all of the above characteristics wherein the host cell displays repressed or no uracil DNA glycosylase activity. This may be achieved by removal of the host cell ung gene. Use of host cells in the manufacture of pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotides e.g. thymidine is also disclosed.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
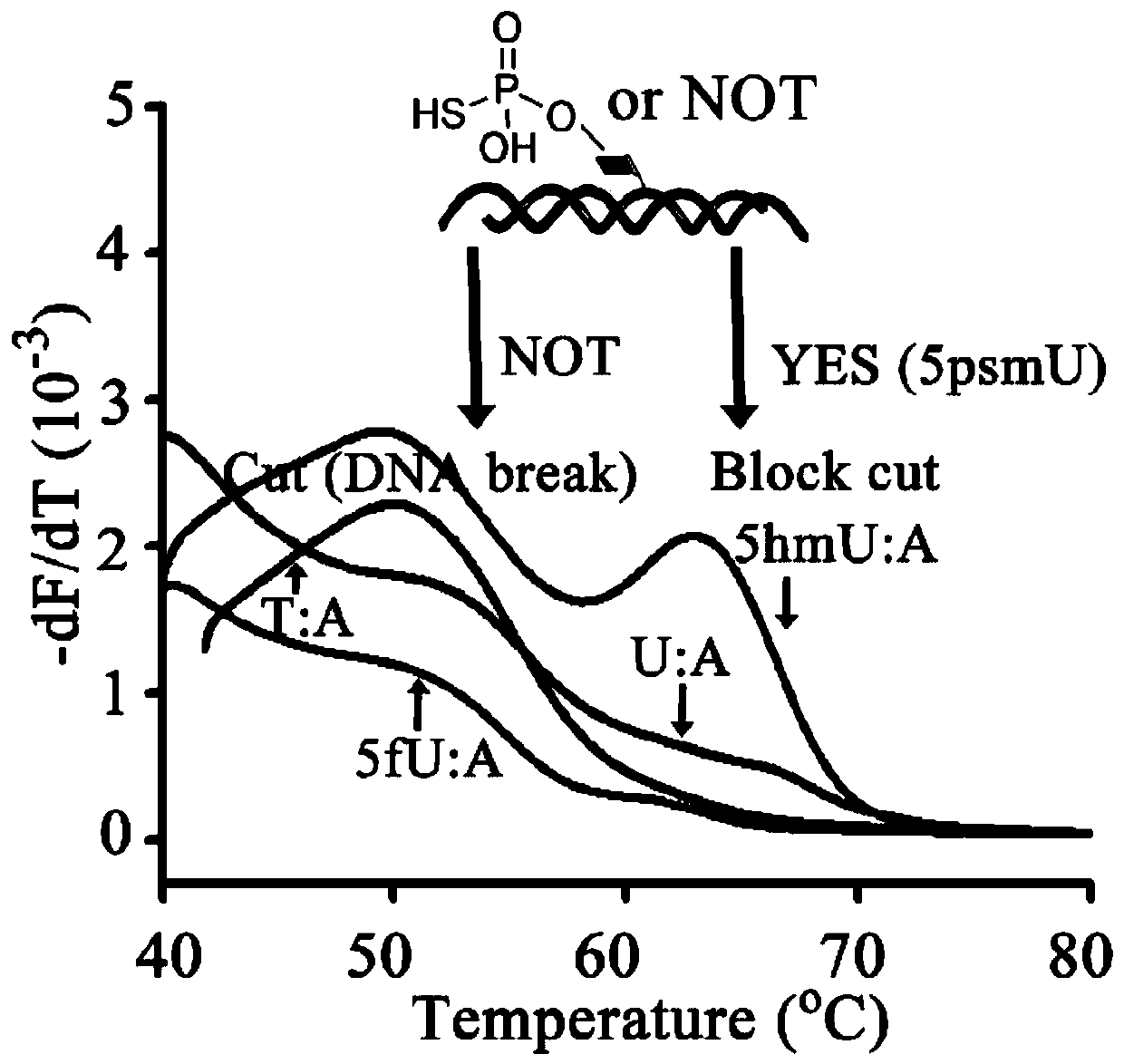
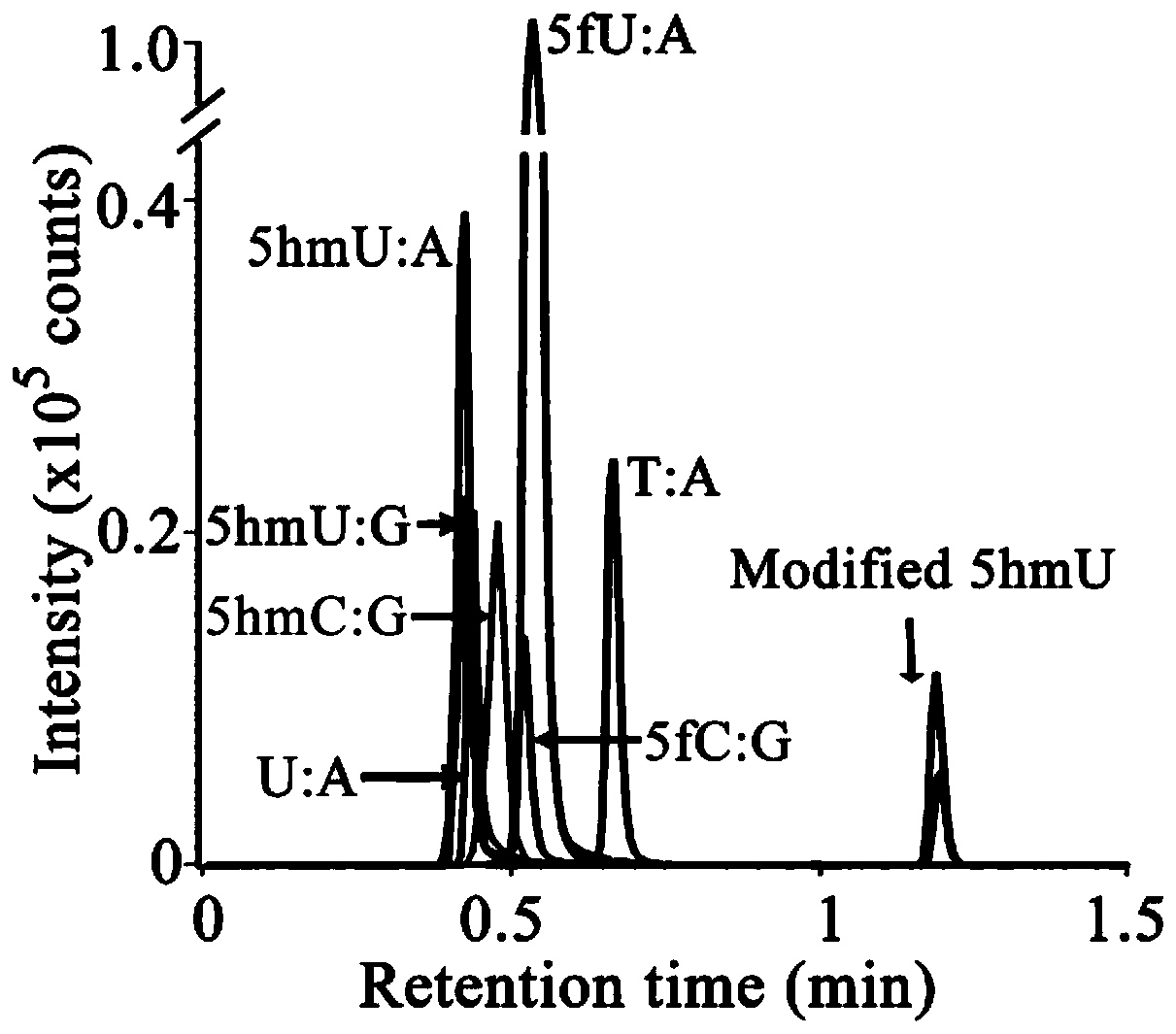
Specific marking method for 5-hydroxymethyluracil on DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
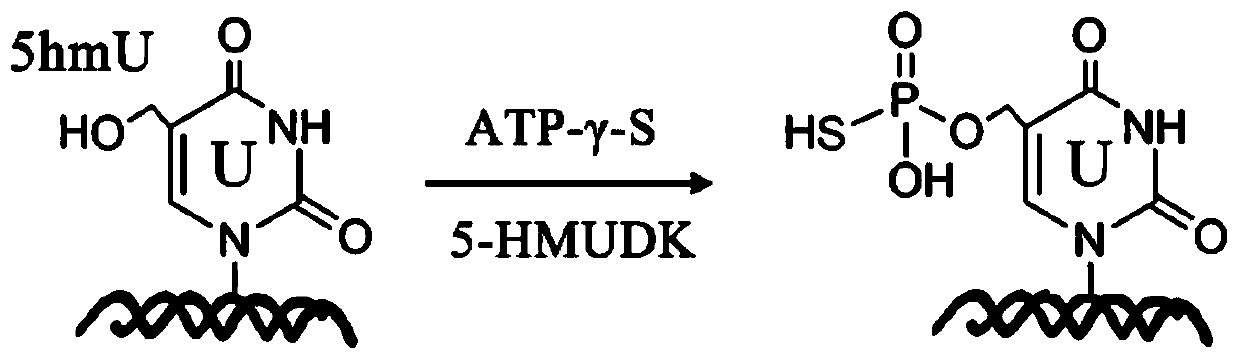
ActiveCN111088252AAvoid errorsAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationChemical reactionThio-
The invention discloses a specific marking method for 5-hydroxymethyluracil on DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. The specific marking method comprises the following steps: transferring gamma-thiophosphate to 5-hmU from 5-O-thiotriphosadenine by using 5-hmU separated from bacteriophage M6 of pseudomonas aeruginosa so as to generate 5-thiophosphoricacid methyluracil, representing the generated 5-thiophosphoric acid methyluracil by using a liquid chromatogram-tandem mass spectrometry method, and marking sulfydryl through crosslinking chemistry,so as to achieve specific marking on 5-hydroxymethyluracil on DNA. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, defects that a great amount of detection samples are needed, chemical reaction conditions are harsh, the reaction efficiency is low, and the like, can be effectively overcome.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Vectors, cells and processes for pyrimidine deoxyribonucleosides production
Novel DNA constructs and host cells comprising the same are disclosed. DNA constructs comprise a transcription unit (e.g. operon) comprising DNA sequences encoding for ribonucleotide reductase and thioredoxin or a uridine kinase gene and / or a dCTP deaminase gene. In preferred embodiments the constructs comprising DNA sequences encoding for ribonucleotide reductase and thioredoxin further comprise DNA sequences encoding for thymidylate synthase and / or transcription units comprising sequences encoding for uridine kinase preferably together with dCTP deaminase. In particularly preferred embodiments, the host cells comprise constructs having all of the above characteristics wherein the host cell displays repressed or no uracil DNA glycosylase activity. This may be achieved by removal of the host cell ung gene. Use of host cells in the manufacture of pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotides e.g. thymidine is also disclosed.
Owner:GLAXO SMITHKLINE LLC
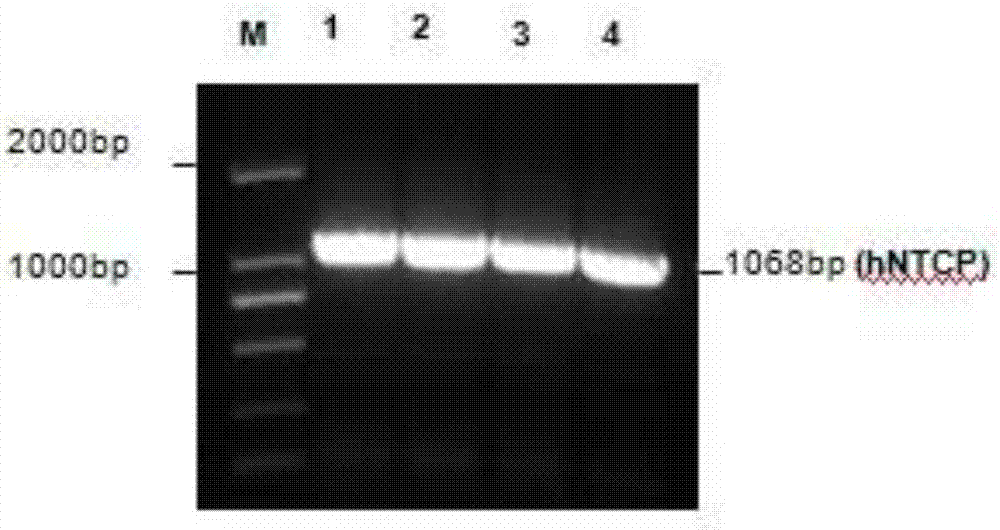
Labeling and detecting method of 5-acetenyl-2'-deoxyuridine of genomic DNA of hepatitis B virus
ActiveCN106929484AEasy to operateBright colorsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisFluorescenceGenomic DNA
The invention discloses a labeling and detecting method of 5-acetenyl-2'-deoxyuridine of a genomic DNA of hepatitis B virus. The method specifically comprises the following steps: (1) amplifying an NTCP gene, constructing an NTCP eukaryotic expression plasmid pcDNA-NTCP, and shifting the pcDNA-NTCP to an Hhh7 hepatoma carcinoma cell to construct a Huh7-NTCP cell line with NTCP stably expressed; (2) treating a HepG2.2.15 cell by using EdU, obtaining a cell supernatant containing EdU-HBV, performing treatment with PEG8000, and quantifying the copy number of HBV genome after concentration; and (3) performing subculture on the HBV cells till the cell convergence degree is 50-80%, infecting the Huh7-NTCP cell with EdU-HBV, and then performing EdU-HBV fluorescence detection. Compared with the prior art, the method is simple to operate, the image result does not need to be processed in the later stage, and the dyeing results do not interfere with each other.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
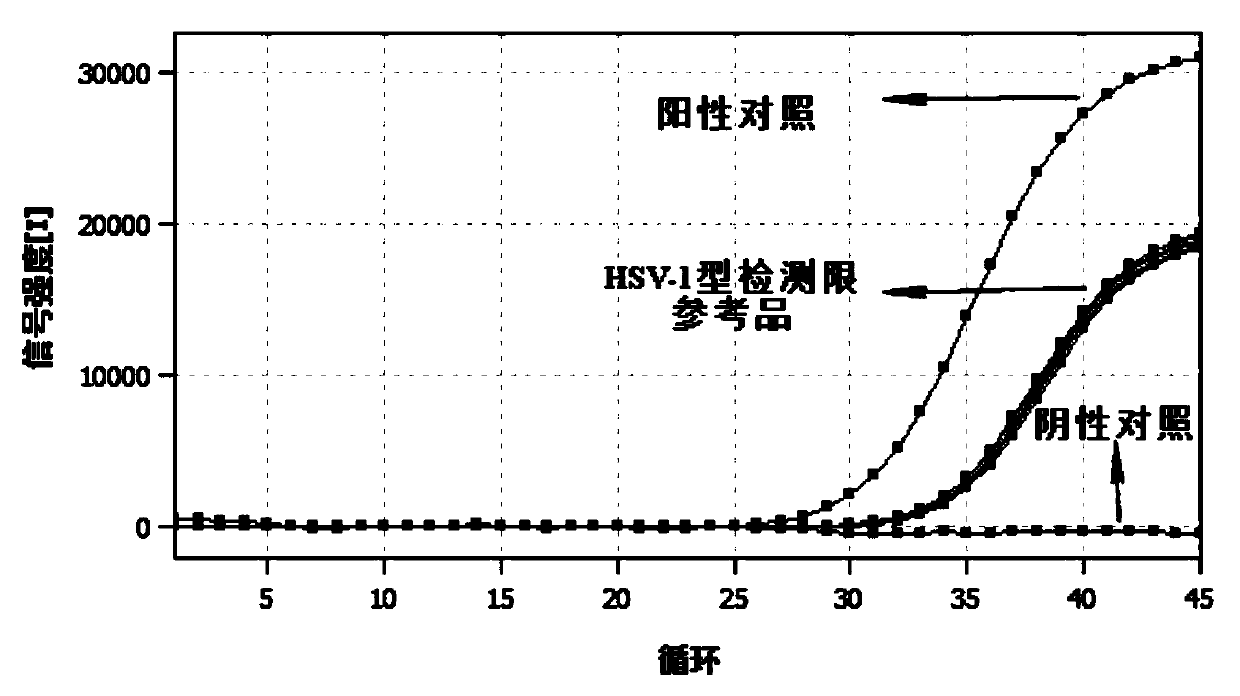
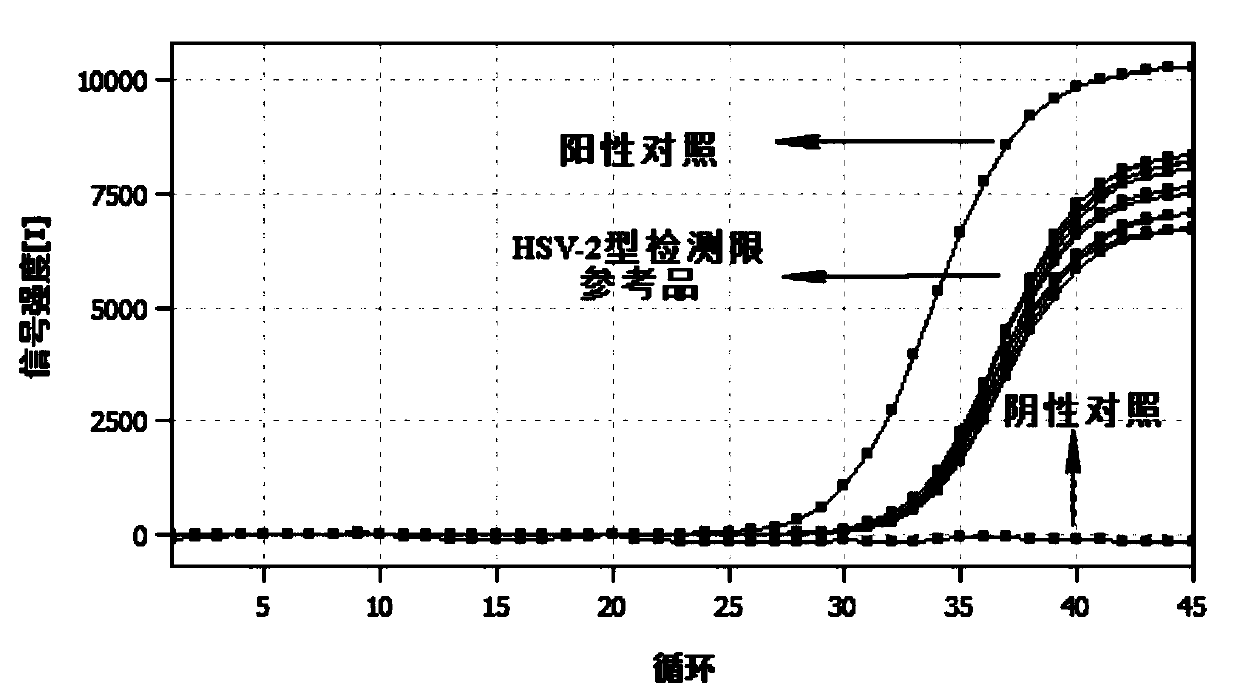
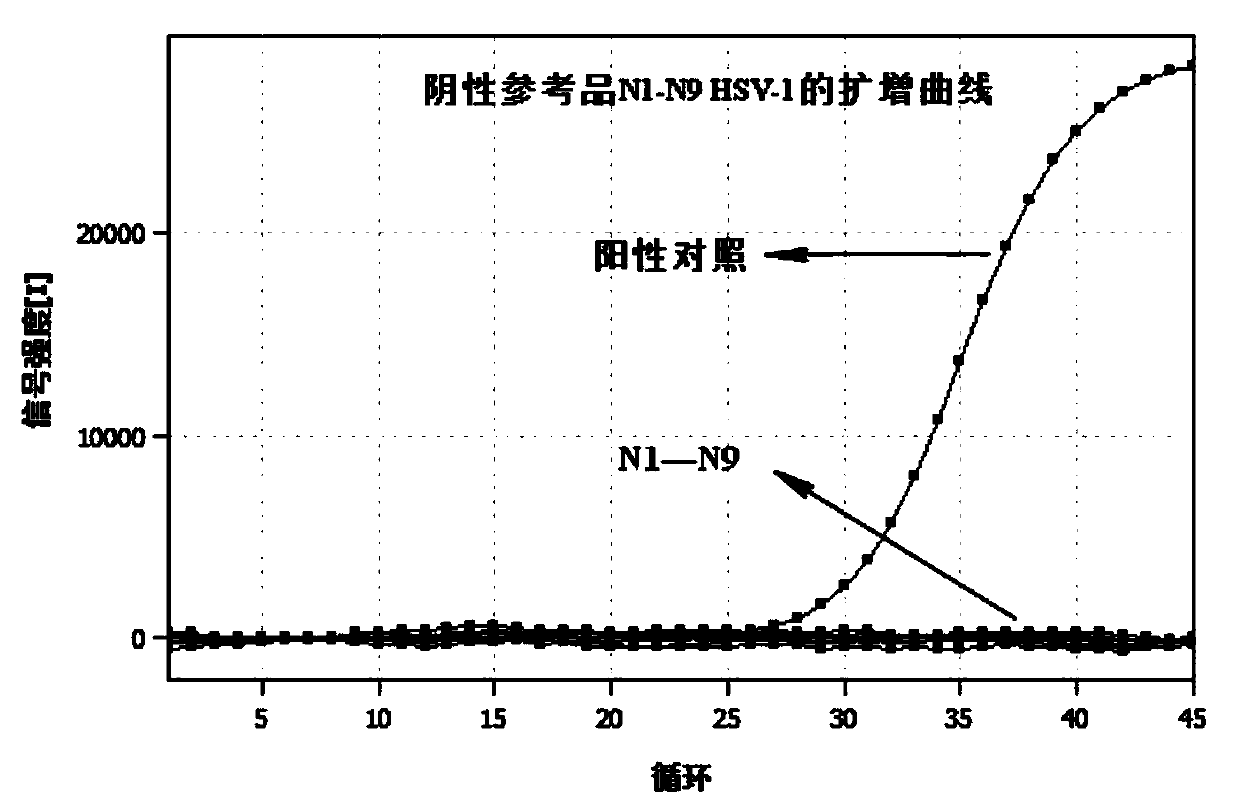
Herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 typing nucleic acid detection kit
PendingCN111172323AGuaranteed Assay SpecificityGuaranteed operation detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMANGANESE ACETATEUracil-DNA glycosylase
The invention provides a herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 typing nucleic acid detection kit which includes a PCR reaction solution 1, a PCR reaction solution 2, negative control and positive control. The PCR reaction solution 1 is prepared from a HSV-1 type upstream primer, a downstream primer, a fluorescent probe, a HSV-2 type upstream primer, a downstream primer, a fluorescent probe, DNA polymerase, uracil DNA glycosylase, dNTP, a PCR buffer, a PCR amplification enhancer, an antiseptic agent and water; and the PCR reaction solution 2 is prepared from manganese acetate, an antiseptic agent and water. The herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 typing nucleic acid detection kit is convenient to operate, the reagent is stored at 2-8 DEG C, the detection sensitivity is high, the specificity is good, the repeatability is high, and the detection result is fast. The herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 typing nucleic acid detection kit can be used to simultaneously perform typing fluorescence PCR qualitative detection on specific DNA nucleic acid fragments of herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 in a single tube, a reliable molecular diagnostic basis is provided for diagnosingherpes simplex virus infection.
Owner:AUTOBIO DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
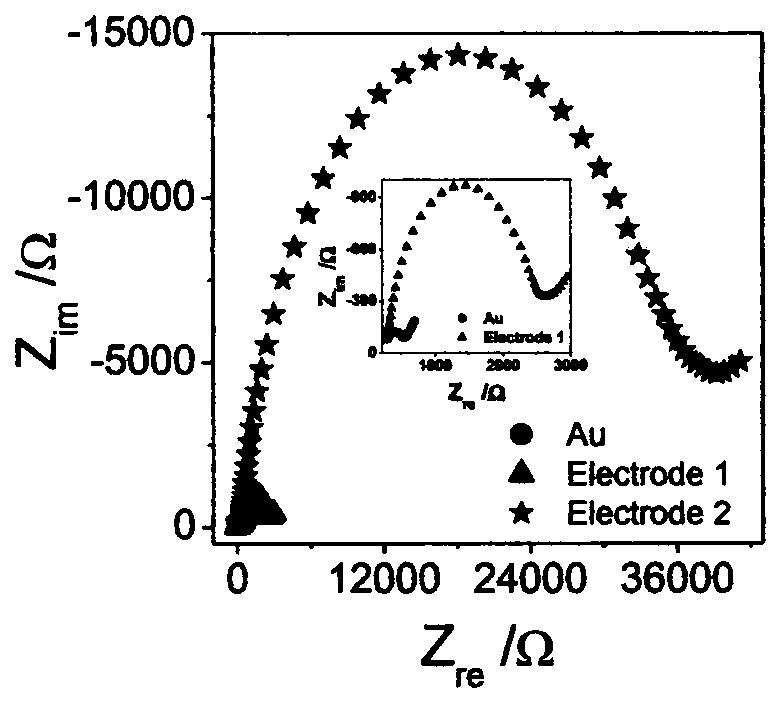
Electrochemical method for detecting activity of uracil-DNA glycosylase based on DNA NANOTREE
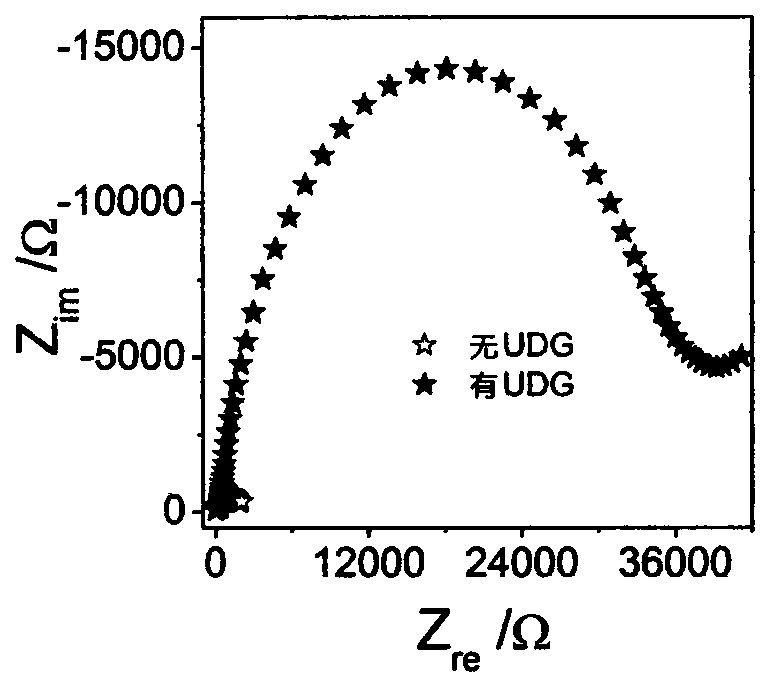
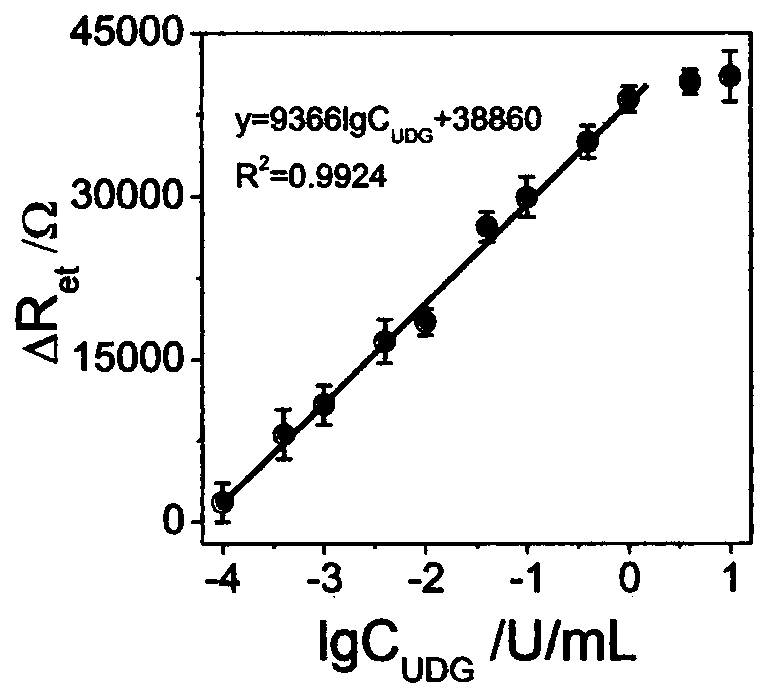
The invention discloses an electrochemical method for detecting the activity of uracil-DNA glycosylase based on a DNA NANOTREE. The method comprises the following specific steps of performing Au treatment, modifying Au with H0, opening a hairpin structure of chain initiation by utilizing the UDG, initiating HCR amplification along with the introduction of single-stranded DNA1, using TdT to catalyze extension of 3'-OH of H1 and H2, forming a G4 structure under the action of Pb<2+>, inserting hemin into the G4 structure, and under the biocatalytic effect of G4 / hemin, oxidizing 3,3-diaminobenzidine (DAB) by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to form non-conductive IP. As a result, electron transfer between an electrode interface and a redox probe is greatly impeded, thereby resulting in significant amplification of an electrochemical impedance signal. In a sensor preparation process, the UDG concentration and the inhibitor UGI concentration are changed, and the influences of a series of prepared sensors on the electrochemical impedance signal are explored. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity, high detection speed, accurate and reliable result and low cost.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Detection method of microRNA (micro Ribonucleic Acid)
InactiveCN105648098ARealize detectionLow backgroundMicrobiological testing/measurementBase JSodium ascorbate
The invention discloses a detection method of microRNA (micro Ribonucleic Acid), and belongs to the field of optical biosensing techniques. A to-be-detected sample is mixed with template DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid), an obtained first mixture is annealed and hybridized, a buffer solution containing polymerase Klenow fragment, deoxyuracil nucleoside triphosphate and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase is added into a reaction product, an obtained second mixture is caused to react for 4h at 35 DEG C in a water bath, so as to prepare a polyuracil base sequence; sodium ascorbate is added into a polyuracil base sequence solution obtained in the step (4), and then CuCl2 is added into an obtained third mixture, and an obtained fourth mixture is caused to react for 10min at a room temperature, so as to prepare a red-fluorescence copper nano cluster which uses the polyuracil base sequence as a template, thereby obtaining a solution containing the red-fluorescence copper nano cluster. The intensity of the red fluorescence of the solution including the red-fluorescence copper nano cluster is measured by adopting a spectrofluorophotometer; by comparing the result about the intensity of the red fluorescence with a standard relation curve, the concentration of the microRNA is calculated and obtained.
Owner:吴滨
Methods for the production of libraries for directed evolution
ActiveUS20160032280A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningHeteroduplexDouble stranded
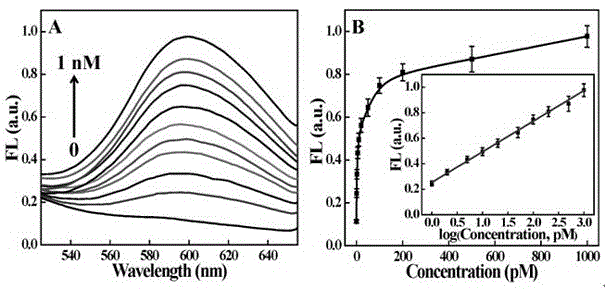
Disclosed herein is an efficient method of generating a library of variants of a sequence of interest, such as may be used in directed evolution, in one embodiment, the method includes an amplification reaction, e.g. error-prone PCR, to generate double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) variants of a sequence of interest, after which one strand of the dsDNA variants may be selectively degraded to produce single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) variants. The ssDNA variants may be hybridized to ssDNA intermediaries, e.g., uracilated circular ssDNA intermediaries, to form heteroduplex DNA, which may be transformed into cells, such as E. coli cells, yielding a library of variants. This method eliminates the inefficient sub-cloning steps and the need for costly primer sets required by many prior methods.
Owner:AXIOMX
Preparation method and application of DNA polymerase accelerant
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a DNA polymerase accelerant. The DNA polymerase accelerant is composed of three kinds of heat-stability protein which are uracil DNA glycosidase UDG, hypoxanthine DNA glycosidase AlkA and endonuclease IV respectively. UDG is in charge of cutting off dU basic groups generated in a PCR, AlkA is in charge of cutting off generated dI basic groups, and endonuclease IV is in charge of cutting off basic group removal loci. The joint action of the three kinds of protein can achieve the purposes that the inhibition effect of the dU / dI basic groups on the activity of B type DNA polymerase is released; the dU / dI basic groups are repaired and corrected, and the PCR faithfulness of the A type and B type DNA polymerase is improved. In addition, the activity of 3'-excision enzymes of endonuclease IV can provide deleted correction activity of the A type DNA polymerase. The DNA polymerase accelerant can effectively increase the PCR yield of the B type DNA polymerase by 1-3 times.
Owner:SUZHOU KUANGSHI JUNCHI BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
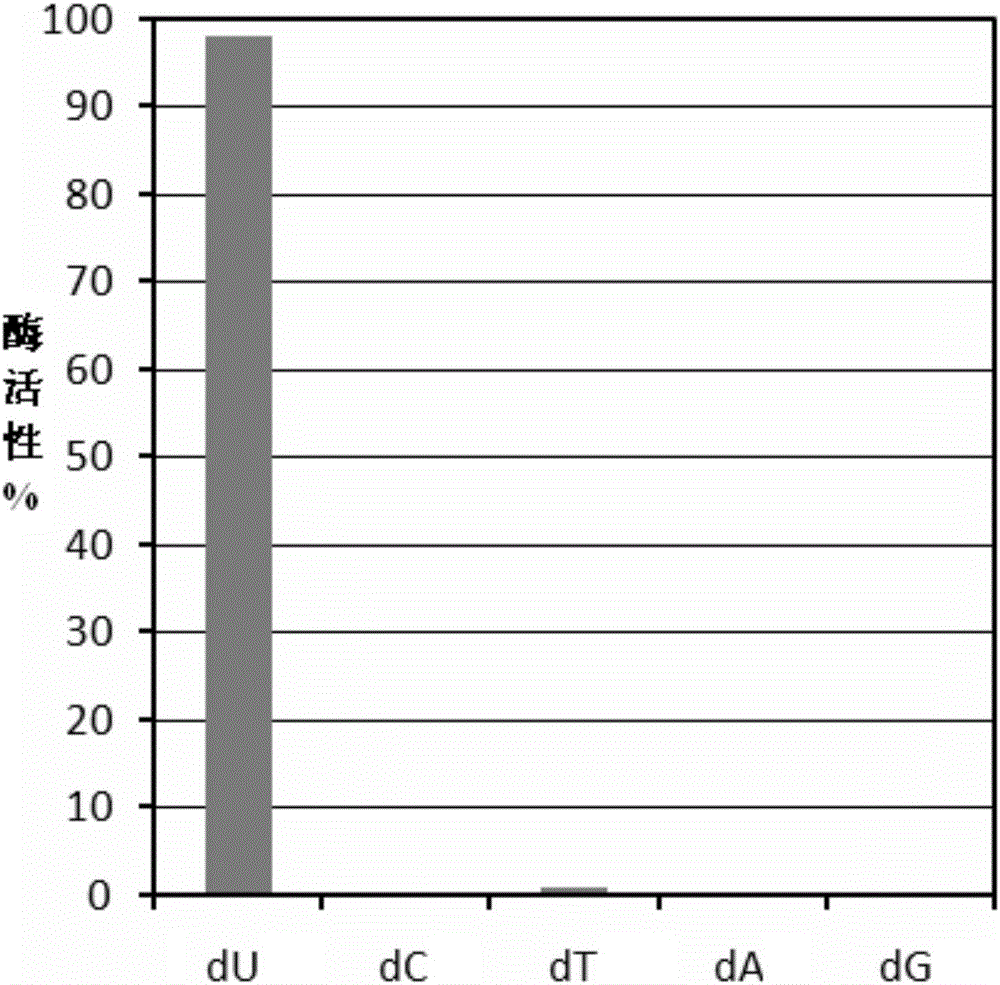
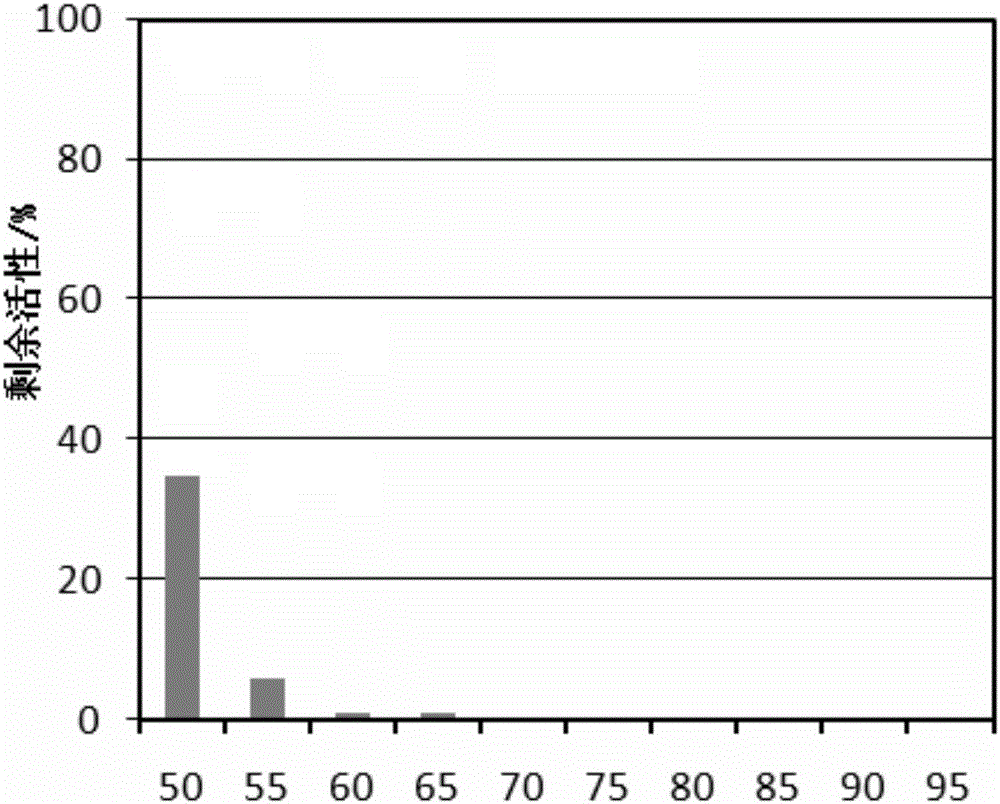
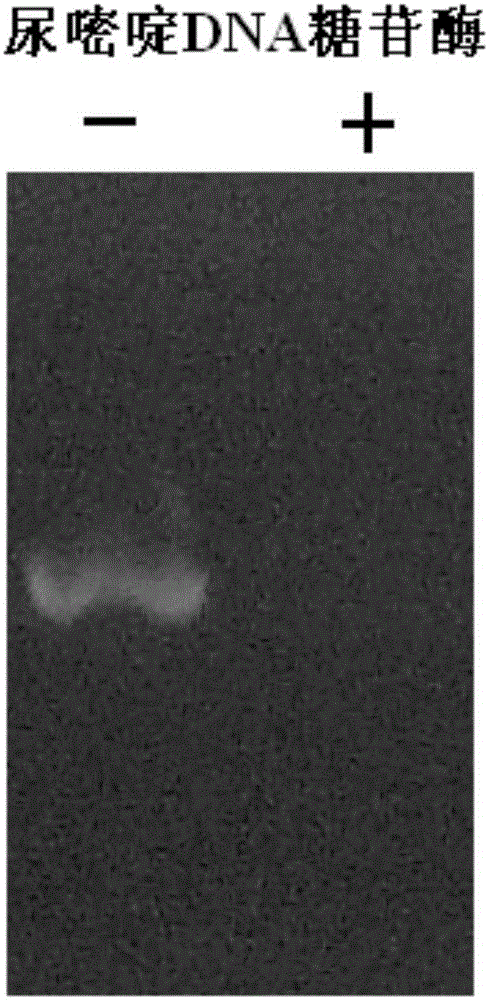
Preparation method and application of uracil DNA glycosidase
InactiveCN106754823AImprove accuracyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid vectorNucleic acid testHeat sensitive
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of uracil DNA glycosidase. The uracil DNA glycosidase prepared by using the method can be used for hydrolyze glucosidic bonds between uracil basic groups and deoxyriboses in DNA at the temperature of 20-37 DEG C; at the same time the glycosidase has a good heat sensitivity, when the temperature is higher than 60 DEG C, the glycosidase swiftly loses activeness, when the temperature reaches 60 DEG C for 5 minutes, the enzymatic activity loses by 99%; the prepared heat sensitive uracil DNA glycosidase can be used for preventing the sample DNA contamination in all types of nucleic acid detection reaction. The preparation method and application of uracil DNA glycosidase have the advantages being capable of both completely removing the contaminated DNA, and exerting no inhibition to the nucleic acid amplified reaction. The glycosidase can be used as a cleaning agent to the sample contamination in all types of nucleic acid amplified reaction (such as PCR), can remove the DNA contamination caused by the products of the previous amplified reaction, and increase the accuracy of nucleic acid test.
Owner:SUZHOU KUANGSHI JUNCHI BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
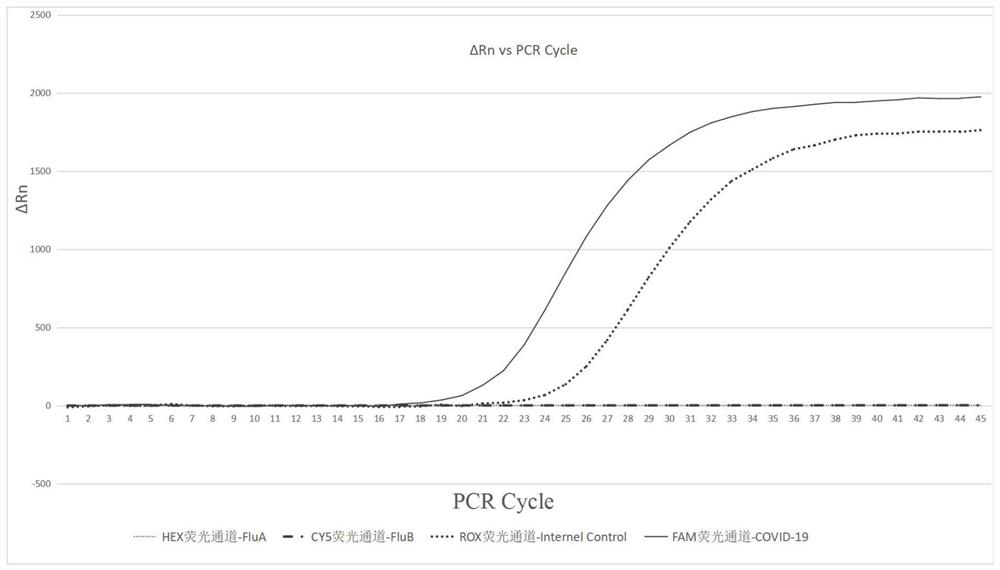
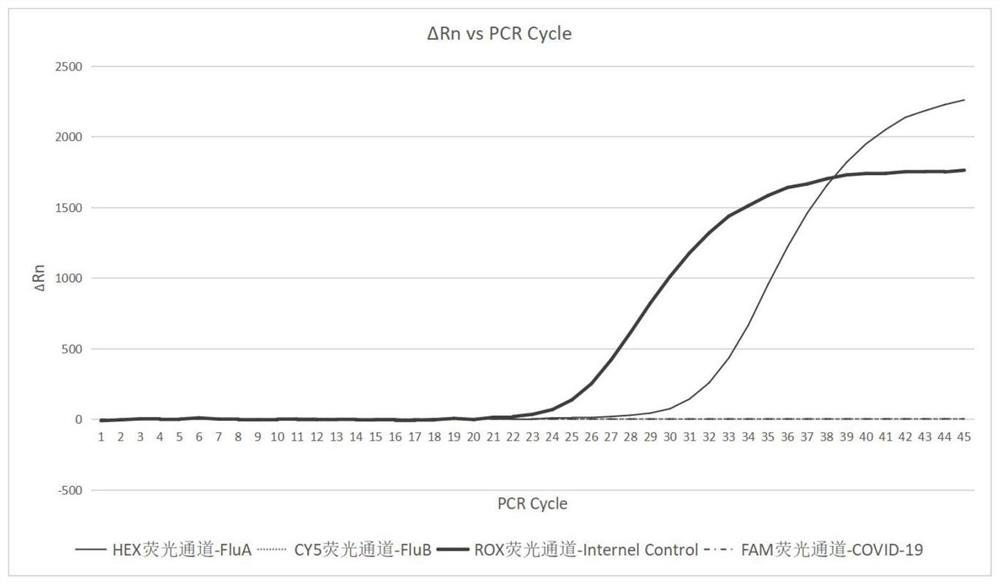
Freeze-dried PCR (polymerase chain reaction) reagent for detecting COVID-19, FluA and FluB viruses and preparation method thereof
PendingCN111647688ALow costNo risk of failureMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesViral testUracil in DNA
The invention discloses a freeze-dried PCR (polymerase chain reaction) reagent for detecting COVID-19, FluA and FluB viruses and a preparation method thereof. The freeze-dried PCR reagent is characterized in that three different upstream primers, downstream primers and TaqMan probes are designed according to the specific gene sequences of the COVID-19, FluA and FluB viruses, so that the freeze-dried PCR reagent can simultaneously detect three pathogens of COVID-19, FluA and FluB for patients with fever symptoms, and judge whether the pathogens capable of causing the fever symptoms are one or more of COVID-19, FluA and FluB. The reagent contains a uracil-DNA glycosylase anti-pollution system, and dUTP is used as a PCR raw material instead of dTTP; and during PCR amplification, the uracil-DNA glycosylase can digest the U-containing PCR product in the PCR product, thereby preventing the PCR product from aerosol pollution and ensuring the detection effect of the freeze-dried PCR reagent.
Owner:ANHUI GUOTAI GUORUI MEDICAL TREATMENT TECH CO LTD
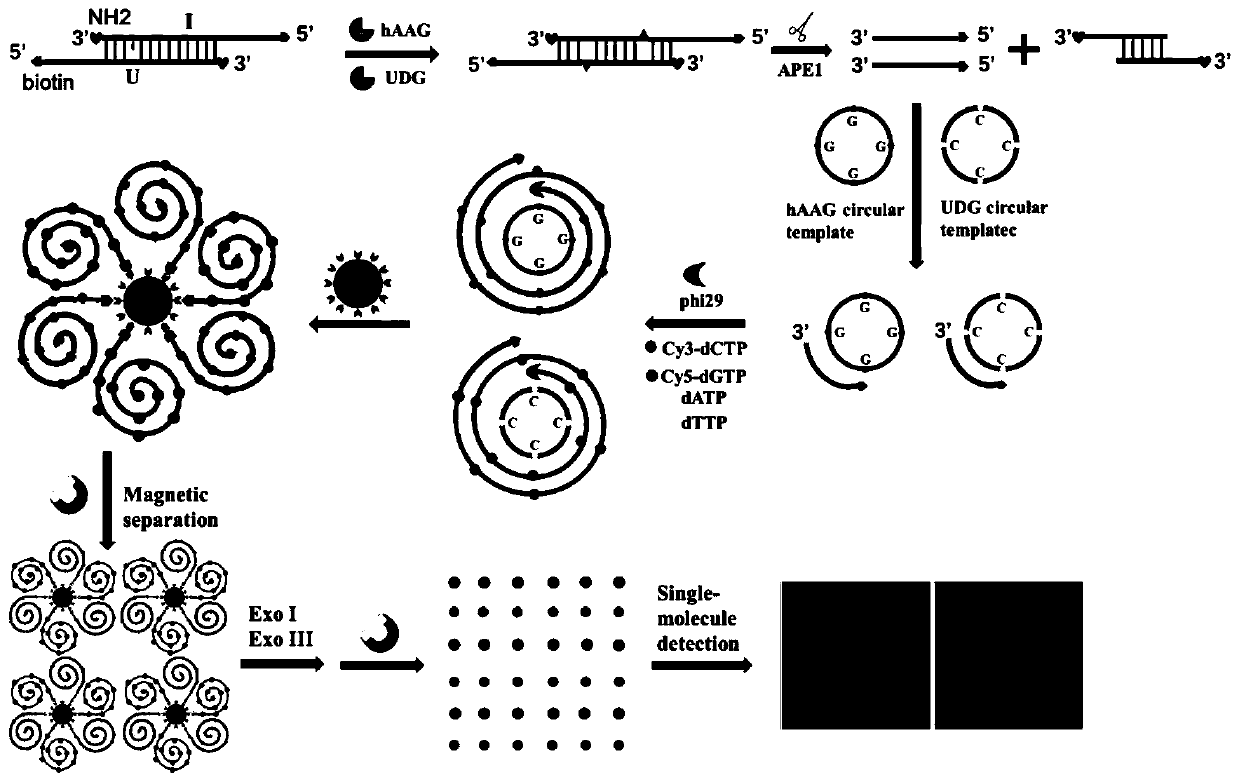
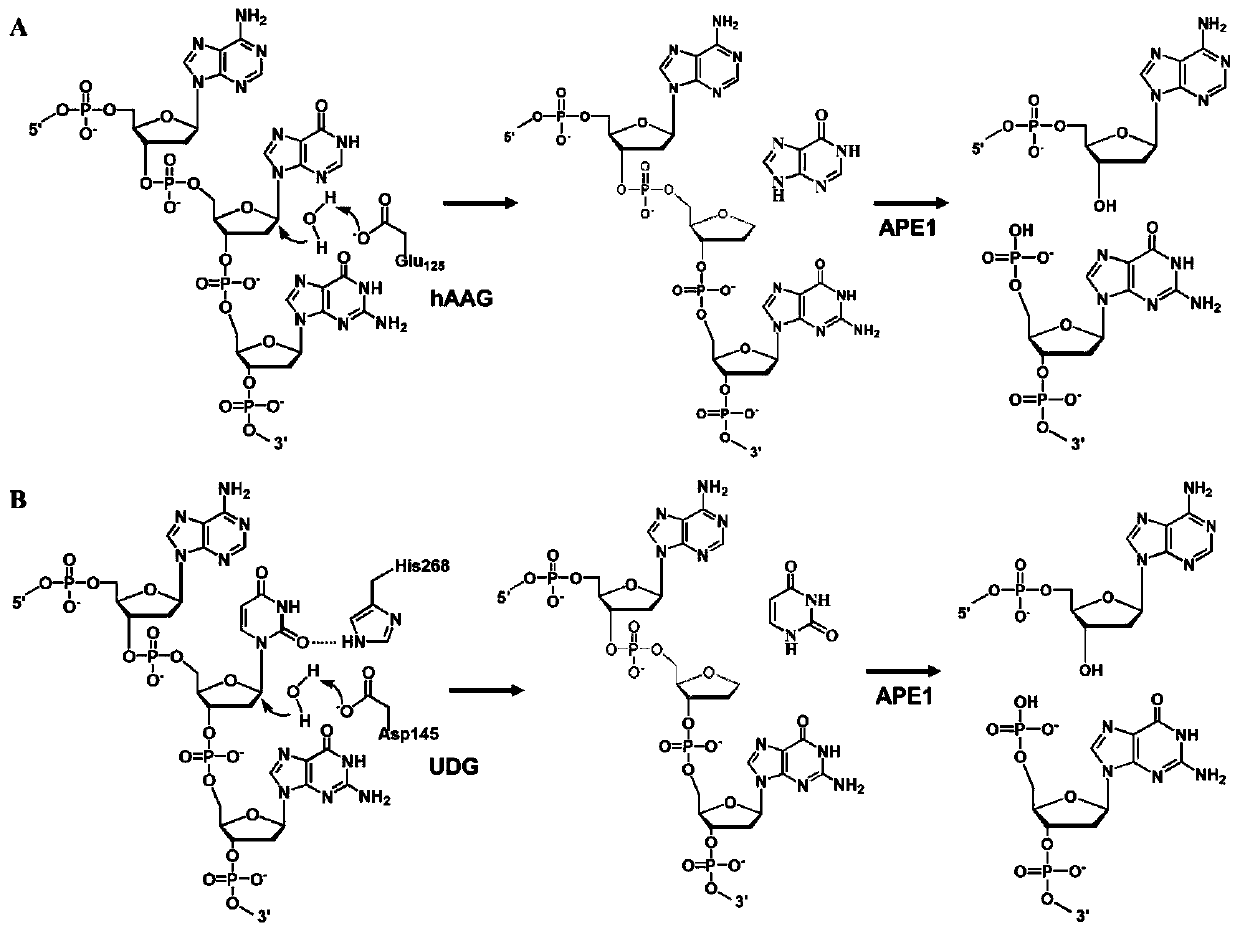
Fluorescent chemical sensor for synchronously detecting multiple DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) glycosylases and detection method and application of fluorescent chemical sensor
ActiveCN111154839AHigh amplification efficiencyImprove signal-to-noise ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellUracil-DNA glycosylase
The invention belongs to the technical field of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) glycosylase detection and in particular relates to a fluorescent chemical sensor for synchronously detecting multiple DNA glycosylases and a detection method and application of the fluorescent chemical sensor. The invention provides a method for simultaneously detecting multiple DNA glycosylases, the detection precision can be improved, the analysis and detection cost can be reduced, and the clinical application practicability can be improved. The invention provides a method for simultaneously detecting human alkyl adenine DNA glycosylase (hAAG) and uracil DNA glycosylase (UDG), monomolecular detection and rolling circle amplification driven fluorescent molecules of different codes are combined, multiple DNA glycosylases in cancer cells can be simultaneously detected at a monomolecular level, and normal cells and cancer cells can be also distinguished. The fluorescent chemical sensor can be further applied to analysis on enzyme kinetic parameters and screening on DNA glycosylase inhibitors, and has great potential in biomedical research, clinical diagnosis and medicine development.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Preparation method of multi-fluorescent nucleic acid probe and application thereof
PendingCN113150769AAchieve improvementHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementLuminescent compositionsNucleotidePhosphorylation
The invention relates to the technical field of nucleic acid detection material preparation, in particular to a preparation method and an application of a multi-fluorescent nucleic acid probe, 5-ethynyl-uracil deoxynucleotide (5-EdUTP) is used for replacing thymine deoxynucleotide (dTTP) for nucleic acid amplification, and high-density alkyne double-stranded DNA is obtained; after the obtained double-stranded DNA is treated by an excision enzyme Lambda Exonuclease, the 5'end phosphorylation labeled nucleic acid chain is digested, and the high-density alkyne single-stranded DNA is obtained; through a click reaction catalyzed by copper ions, a dye cy3-azide with an azide group is successfully modified to a single-chain DNA of high-density alkyne, and the multi-fluorescent nucleic acid probe is obtained. The fluorescent groups of the multi-fluorescent nucleic acid probe prepared by the invention are increased, signal amplification is realized structurally, the sensitivity of the fluorescent nucleic acid probe in researches such as analysis and detection, biological imaging and the like can be enhanced, and the practical value of the fluorescent nucleic acid probe is improved.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
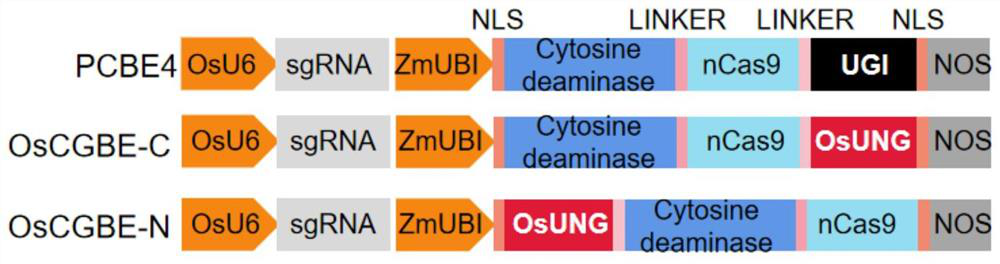
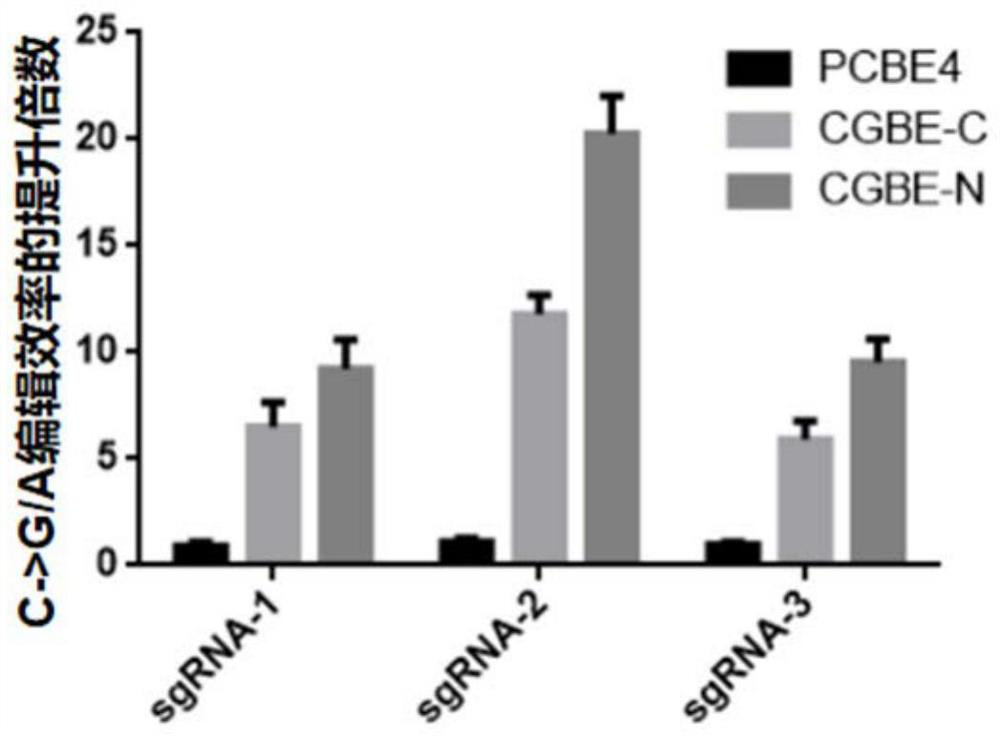
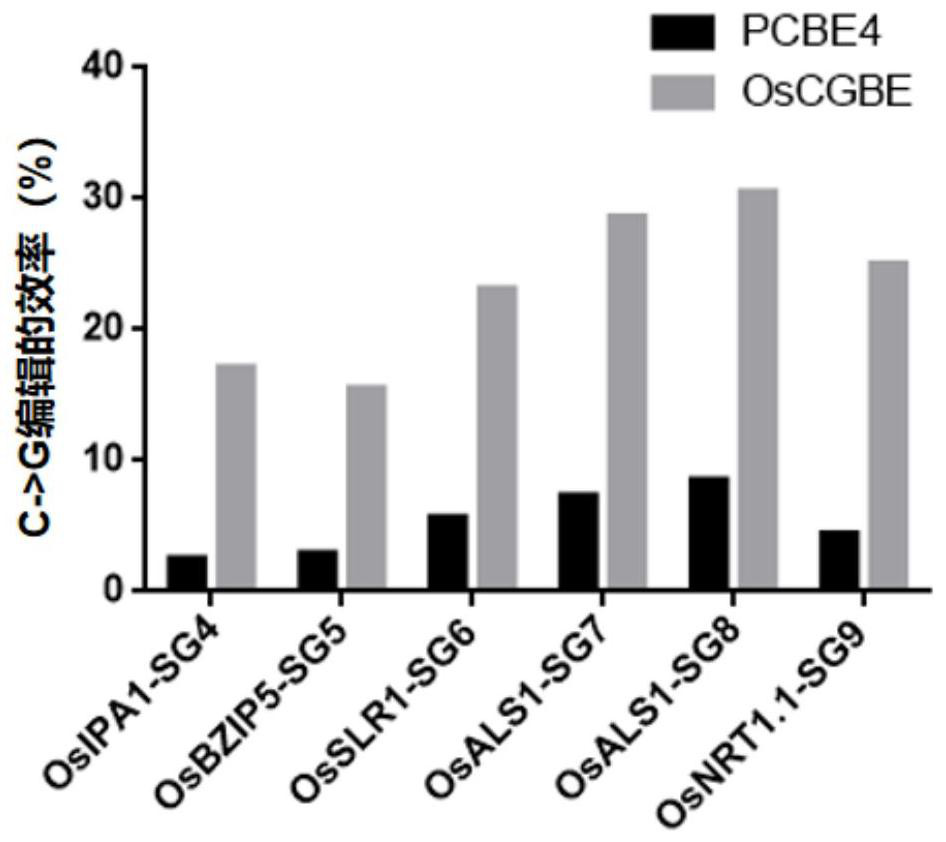
Rice uracil DNA glycosidase and application thereof in gene editing induction of plant single base diversity
The invention discloses rice uracil DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) glycosidase and application thereof in gene editing induction of plant single base diversity. The rice uracil DNA glycosidase is a protein composed of an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2; or a protein which is derived from the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2 and keeps the protein function shown in SEQ ID NO.2 through substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2. According to the application provided by the invention, a biological material containing the rice uracil DNA glycosidase UNG is constructed into a plant cytosine single-base editing vector OsCGBE containing the OsUNG sequence, the expression vector is introduced into a plant, a C base on DNA is induced to be mutated into T or G or A, plant single-base diversity is efficiently created, and the application range of a single-base editor is expanded.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
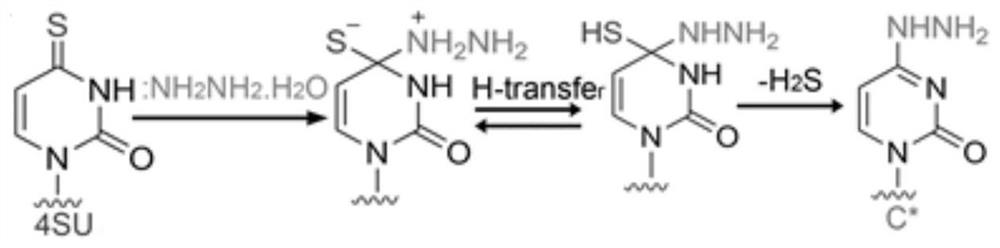
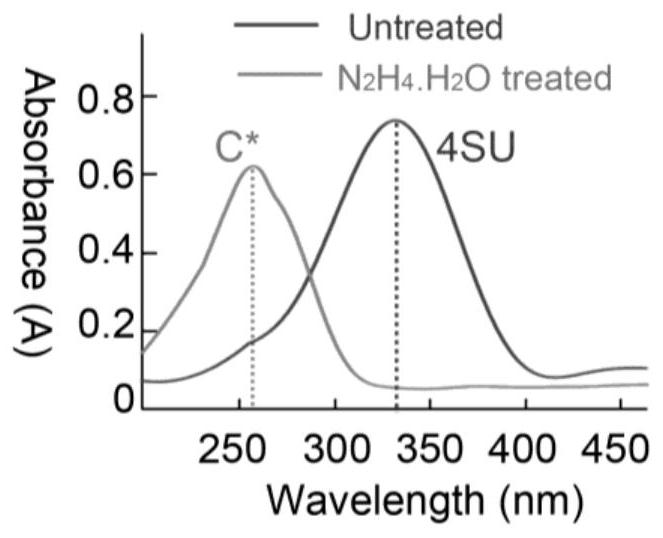
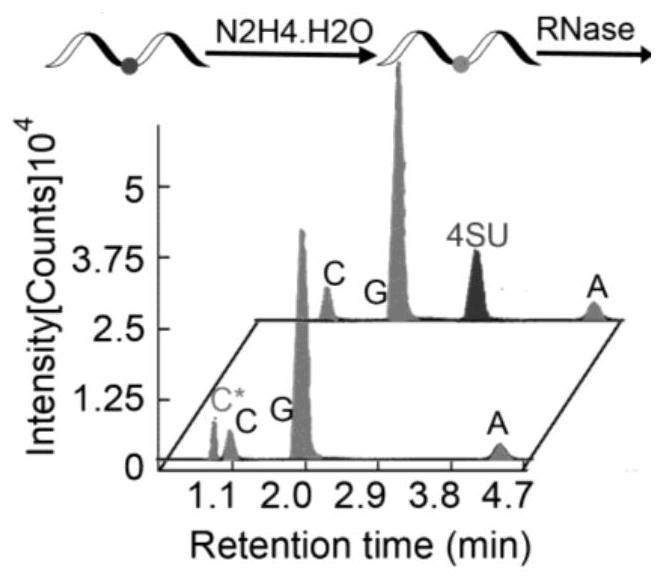
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) 4-mercaptouracil specific labeling method and application thereof
ActiveCN113293203AGood choiceStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBase JNucleic acid chemistry
The invention discloses an RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) 4-mercaptouridine specific labeling method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of nucleic acid chemistry. According to the method, a structure similar to cytosine (C) is generated under a mild condition by utilizing a reaction mechanism that hydrazine hydrate is used for carrying out addition elimination on RNA 4-mercaptouridine; in the reverse transcription process of RNA, the original A: T pairing at the position of 4sU is changed into C: G pairing, so that the position of 4sU is subjected to single base recognition. The method is combined with a sequencing technology and can be used for detecting the position of naturally existing 4sU and researching the dynamic state of a transcriptome.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Hydrosulfite-free whole genome methylation analysis
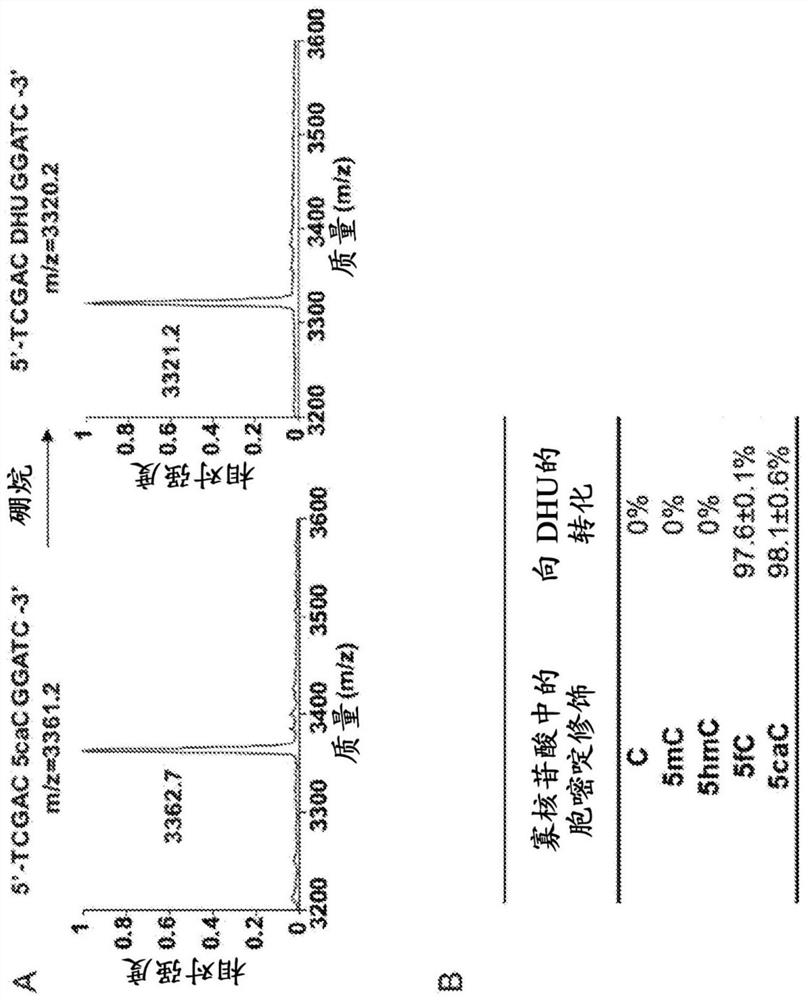
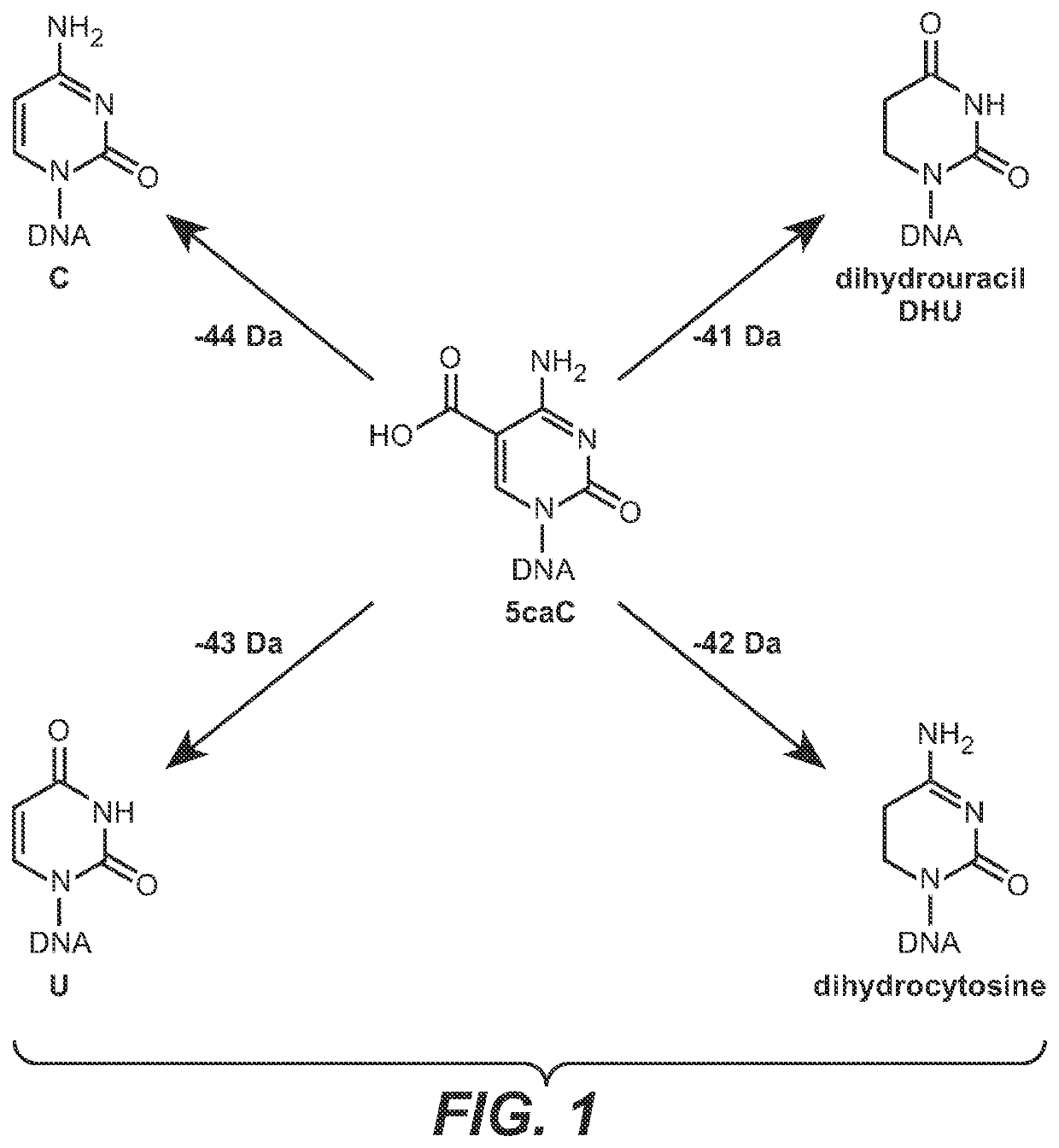
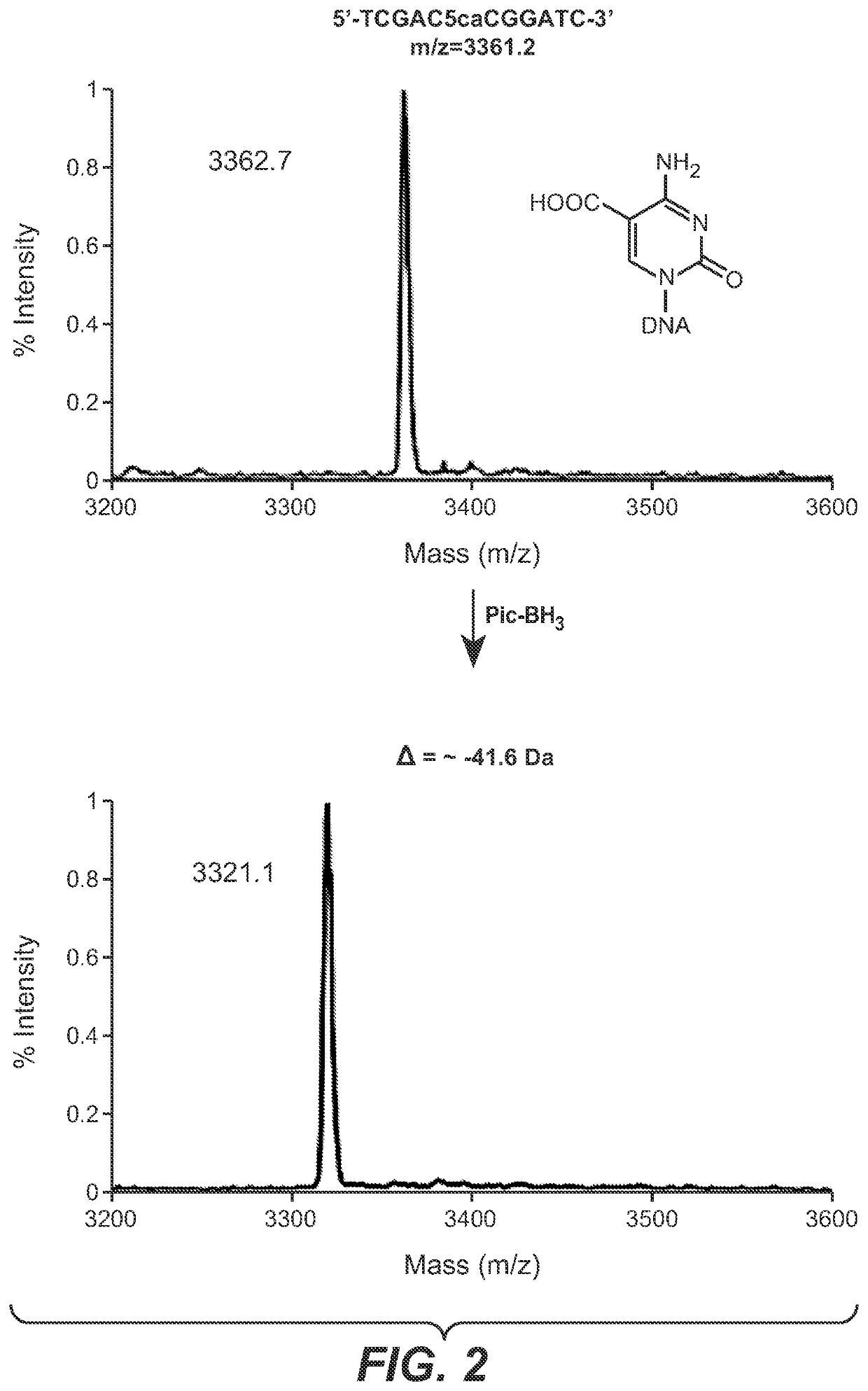
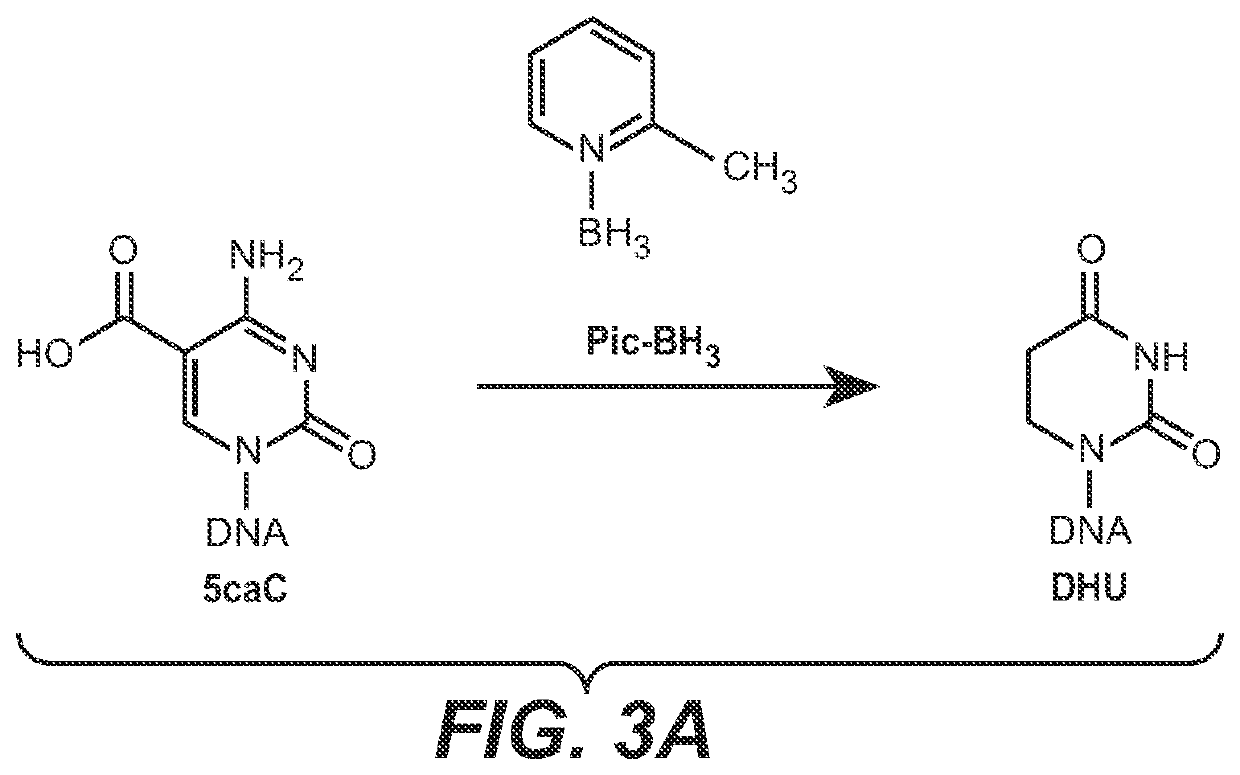
The present disclosure provides a method for the cost effective bisulfite-free identification of the position of one or more of 5-methylcytosine, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, 5-carboxycytosine, and 5-formylcytosine in DNA, including whole genome DNA, and a method for the cost effective bisulfite-free identification of the position of one or more of 5-methylcytosine, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, 5-carboxycytosine, and 5-formylcytosine. The methods described herein are based on the conversion of a modified cytosine (5mC, 5hmC, 5fC, 5caC) to a dihydrouracil (DHU), e.g. By a TET-assisted pyridine borane treatment, followed by cleavage of the DHU with an endonuclease and identification of a cleavage site corresponding to the position of the modified cytosine.
Owner:LUDWIG INST FOR CANCER RES
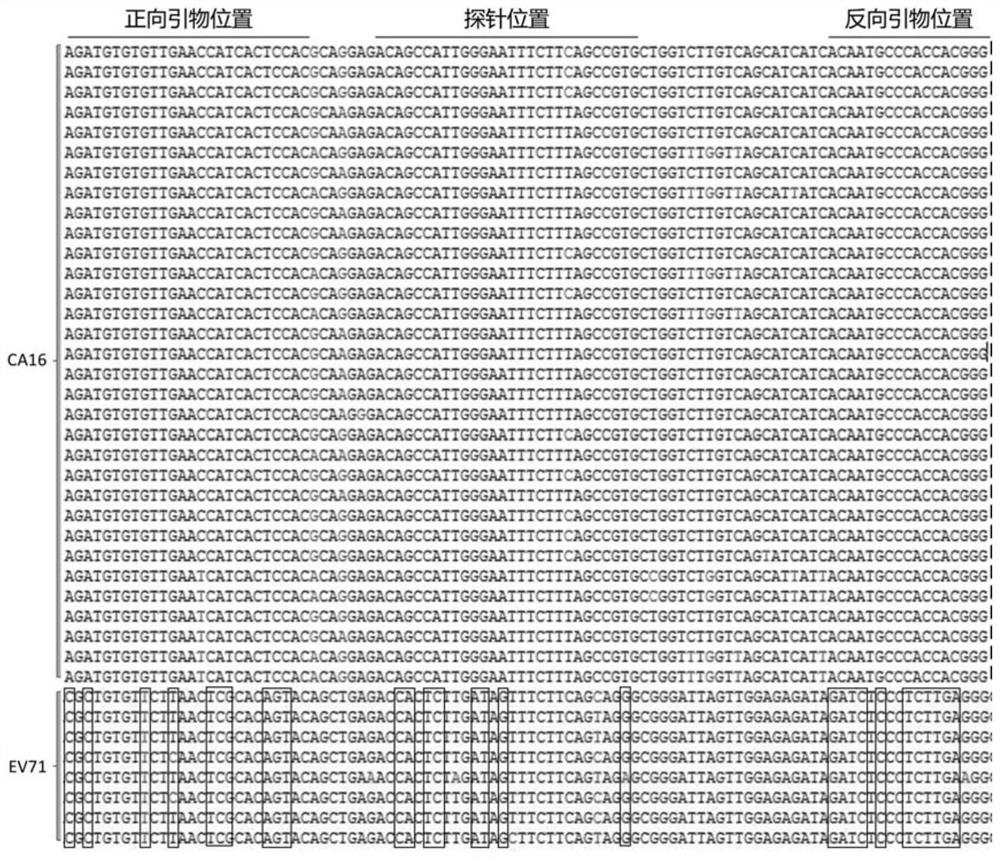
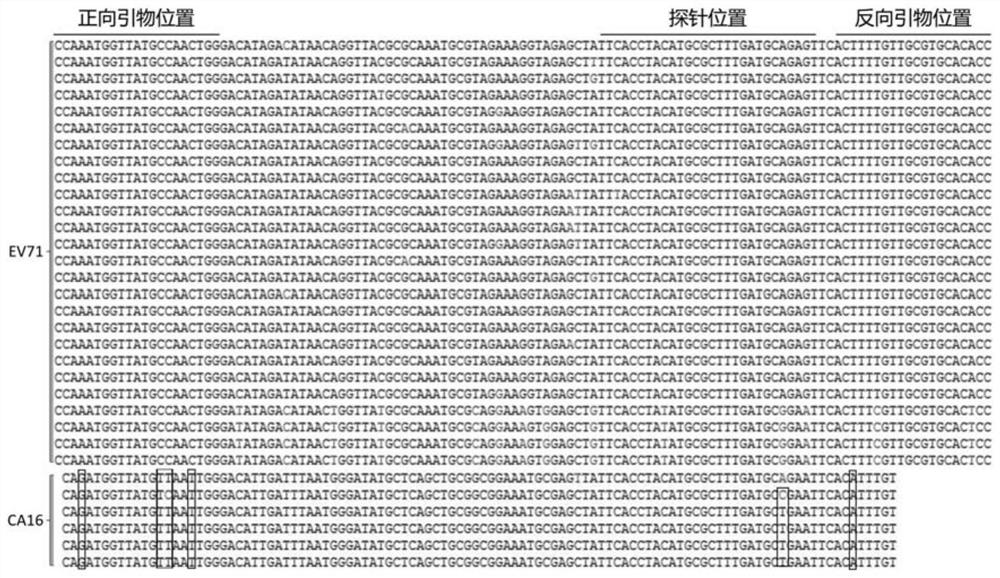
Fluorescent RT-PCR detection reagent and method for coxsackievirus A16 and enterovirus 71
PendingCN112813202AInclusiveImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFreeze-dryingUracil-DNA glycosylase
The invention provides a fluorescent RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) reagent and a method for detecting coxsackievirus A16 and enterovirus 71. A primer and a probe used by the fluorescent RT-PCR detection reagent for the coxsackievirus A16 and the enterovirus 71 provided by the invention are obtained by designing and screening based on the latest gene sequence information of the coxsackievirus A16 and the enterovirus 71 in a public gene sequence database, and have good inclusiveness, specificity and reaction performance; the reagent contains uracil DNA glycosylase and dUTP, so that a false positive result possibly caused by PCR product aerosol can be prevented, and the detection accuracy is further ensured; and besides, the fluorescent RT-PCR detection reagent for the coxsackievirus A16 and the enterovirus 71 is prepared into a freeze-dried reagent which can be stored at normal temperature through a freeze-drying technology, so that the risk that a conventional liquid fluorescent PCR detection reagent fails due to storage temperature change or repeated freeze-thawing is avoided, and the transportation and management cost is reduced.
Owner:深圳市赛格诺生物科技有限公司
Kit for guiding 5-fluorouracil medication
InactiveCN104862377AImprove targetingImprove predictabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural sciencePredictability
The present invention discloses a kit for guiding 5-fluorouracil medication. The invention provides a primer group, which comprises a primer pair A and a primer pair B, wherein the primer pair A comprises single-stranded DNA molecules represented by the sequence 1 and single-stranded DNA molecules represented by the sequence 2, and the primer pair B comprises single-stranded DNA molecules represented by the sequence 3 and single-stranded DNA molecules represented by the sequence 4. The present invention further provides the kit for identifying the IVSl4+lG>A point mutation of gene DPYD and the 665C>T point mutation of gene MTHFR, wherein the kit comprises the primer group. According to the present invention, the kit can be used for detecting the two SNP sites associated with the 5-fluorouracil sensitivity so as to be used to clinically guide the individualized use of the 5-fluorouracil, and improve the targeting property and the predictability of the clinical treatment.
Owner:北京奥维森基因科技有限公司
Gene polymorphism detection kit for predicting adverse reaction and curative effect of fluorouracil as well as detection method and application of gene polymorphism detection kit
PendingCN113755588ASimplify timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationUracil in DNAFluorouracilum
The invention discloses a gene polymorphism detection kit for predicting adverse reaction and curative effect of fluorouracil as well as a detection method and application of the gene polymorphism detection kit. The detection kit is used for detecting gene polymorphism of fluorouracil metabolism related genes TYMS, GSTP1, NQO1 and MTHFR, the kit designs specific amplification primers and sequencing primers for the TYMS, GSTP1, NQO1 and MTHFR. The kit comprises the following components: a sample treating fluid, magnetic beads, an amplification reagent 1, an amplification reagent 2, the TYMS, the GSTP1, the NQO1, an MTHFR sequencing primer and a positive control. According to the gene polymorphism detection kit for predicting the adverse reaction and the curative effect of the fluorouracil as well as the detection method and application of the gene polymorphism detection kit, rapid DNA preparation, constant-temperature PCR amplification and pyrosequencing technologies are combined to detect the gene polymorphism for predicting the adverse reaction and curative effect of the fluorouracil, and suggestions from the gene perspective are provided for clinical personalized medication.
Owner:菲思特(上海)生物科技有限公司
Library construction method based on promoter and library thereof
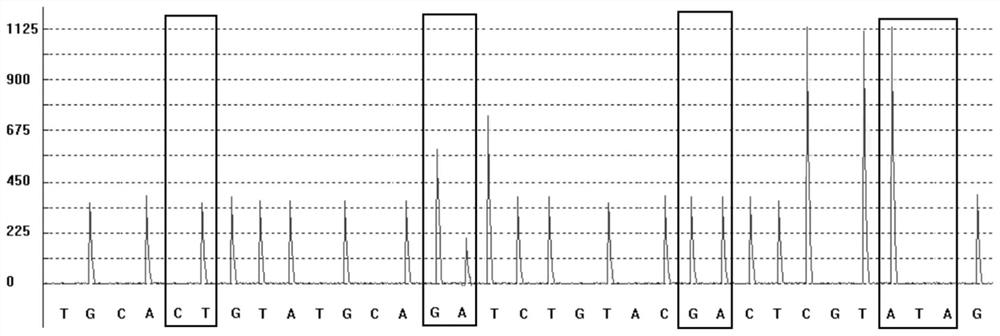
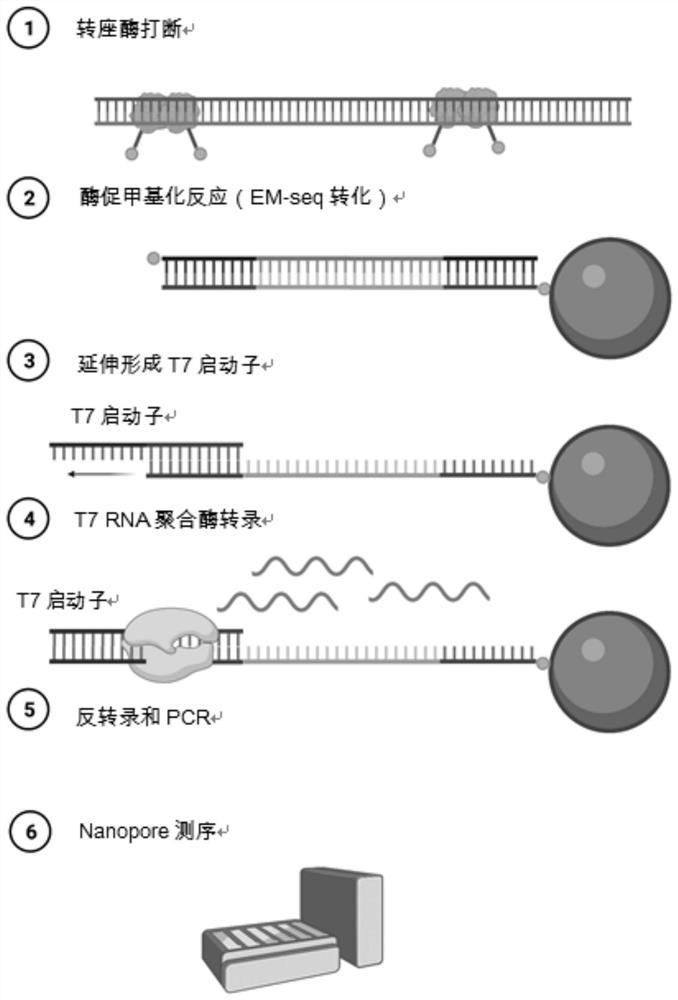
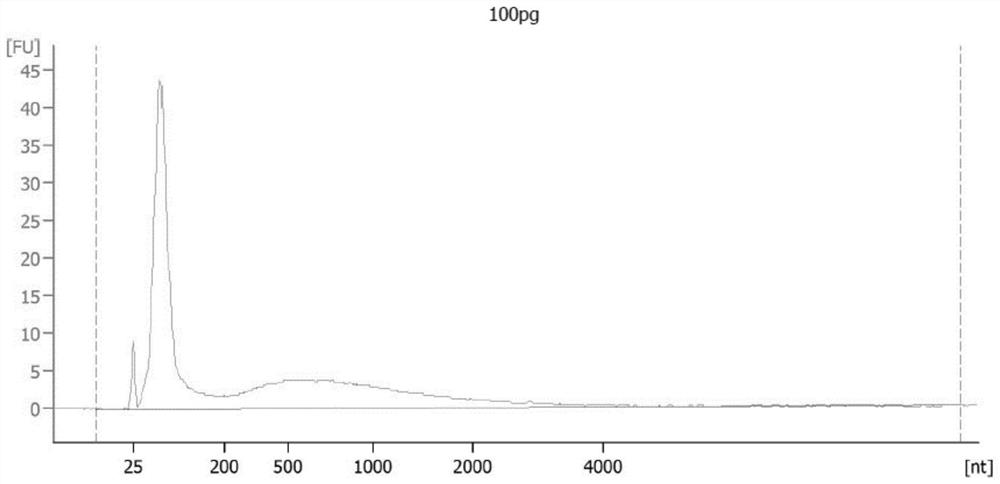
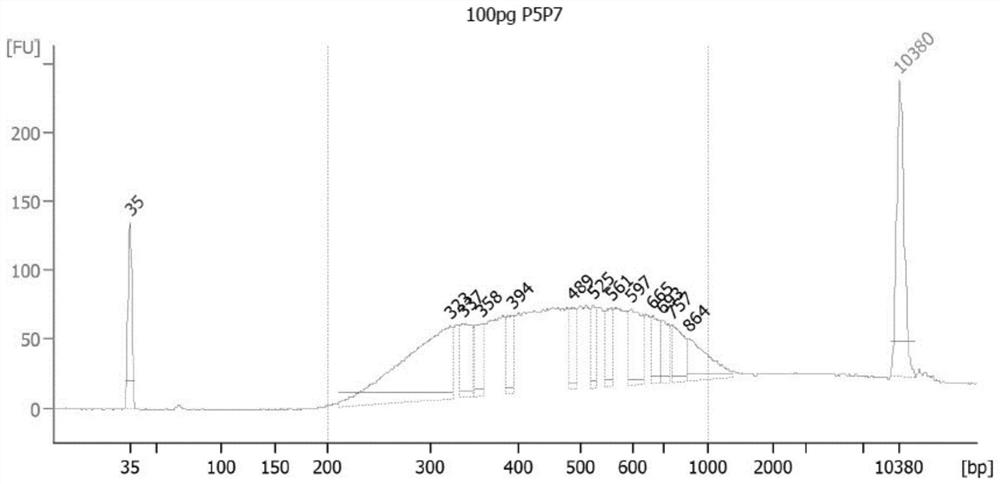
PendingCN114411266AUniform transcriptionIncrease coverageNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementUracil in DNAPromoter
The invention discloses a method for constructing a library based on a promoter and the library. The method comprises the following steps: a breaking step: breaking a to-be-detected sample to obtain a broken to-be-detected sample; carrying out enzymatic methylation conversion, namely carrying out enzymatic methylation conversion on the broken sample to be detected; connecting a T7 promoter, namely annealing the to-be-detected sample subjected to the enzymatic methylation conversion treatment and the T7 promoter, and reacting to obtain a to-be-detected sample connected with the T7 promoter; in-vitro transcription: transcribing the to-be-detected sample connected with the T7 promoter into RNA (Ribonucleic Acid); and reverse transcription and amplification: carrying out reverse transcription and PCR amplification on the RNA to obtain the library. Compared with direct PCR (polymerase chain reaction) in the prior art, transcription (aiming at DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) rich in uracil) of the T7 is more uniform, more RNA (ribonucleic acid) can be obtained by transcription to serve as a template for next cDNA amplification, and methylation coverage is greatly improved.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD
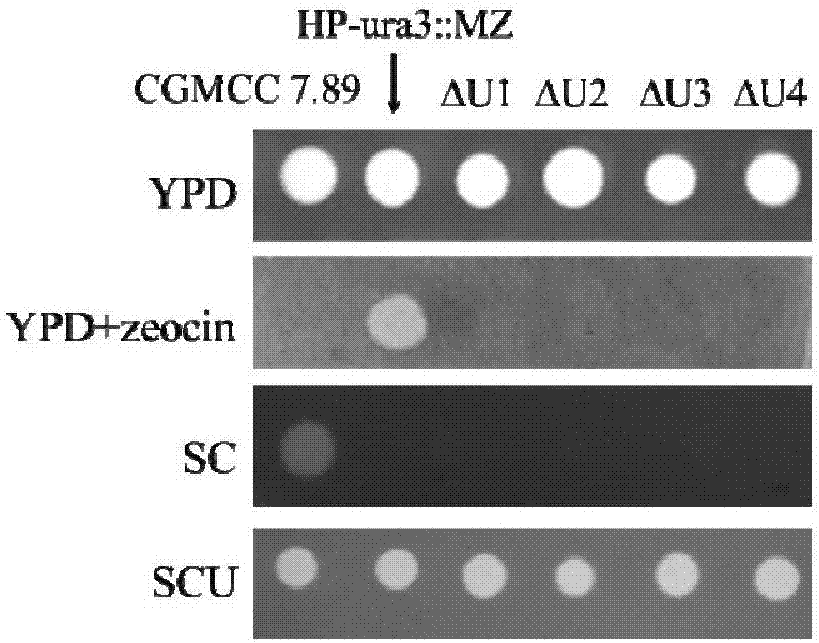
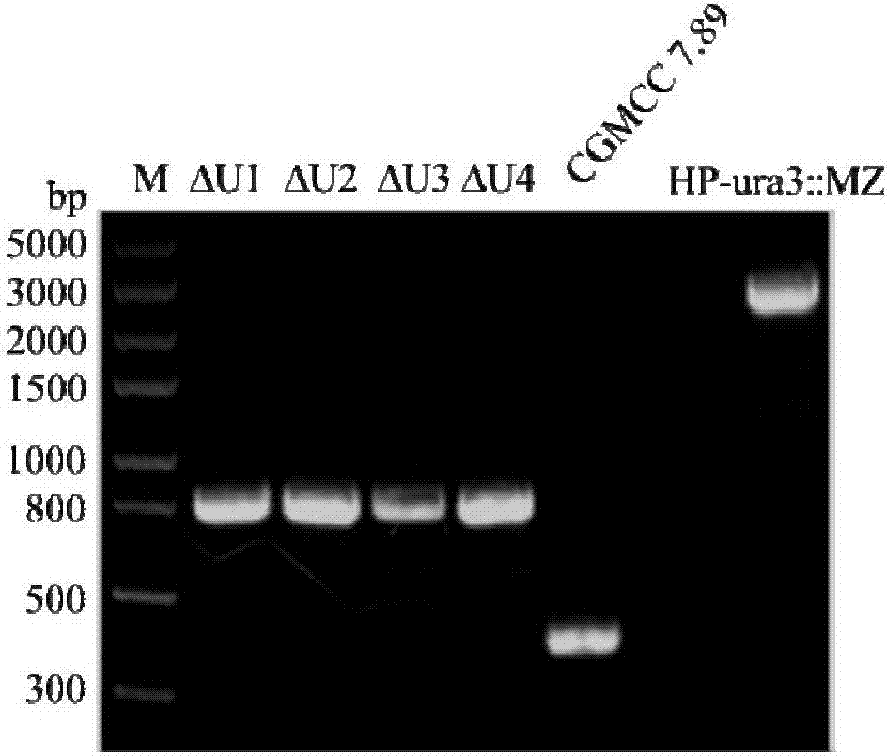
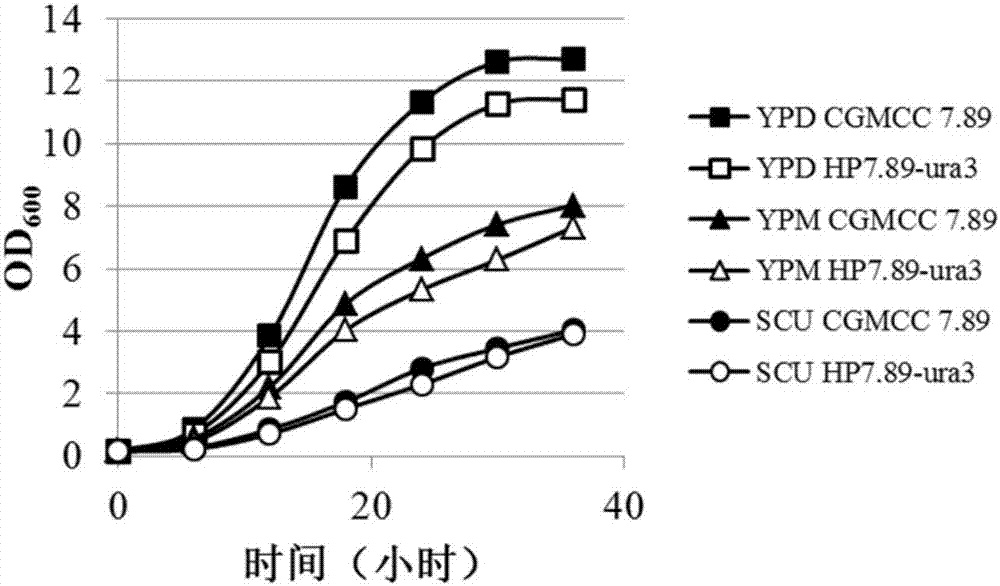
Uracil auxotrophic hansenula polymorpha and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses uracil auxotrophic hansenula polymorpha and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the uracil auxotrophic hansenula polymorpha comprises the steps that orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase genes in hansenula polymorpha original strains are knocked out, or the content of proteins coded by the orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase genes are reduced, or the proteins coded by the orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase genes are inactivated, and the uracil auxotrophic hansenula polymorpha is obtained, wherein knockout of the orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase genes are conducted with the steps that M1, coding of the orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase genes is early stopped; and M2, exogenous DNA fragments are inserted into the orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase genes. The built uracil auxotrophic hansenula polymorpha is stable in heredity, has no obvious difference from wild type strains in other growth characteristics, and can be used as transformed chassis cells in metabolic engineering or synthetic biology, and cell factories of efficient expression recombinant proteins.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
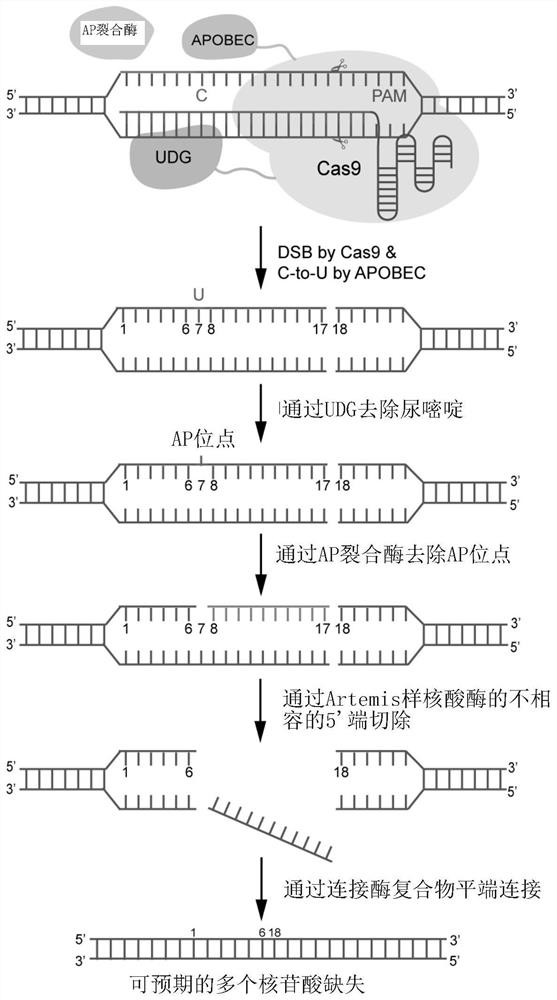
Improved gene editing system
Provided is a gene editing system for editing a target sequence in the genome of a cell, comprising a CRISPR nuclease, a cytosine deaminase, an AP lyase, a guide RNA and optionally an uracil-DNA glycosylase. Also provided are a method of producing a genetically modified cell, and a kit comprising the gene editing system.
Owner:SUZHOU QI BIODESIGN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
A CRISPR/NCas9-mediated site-directed base replacement in plants
ActiveCN107043779BRapid improvement of agronomic traitsImproved agronomic traitsVectorsVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyEnzyme inhibition
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Endonuclease and application thereof
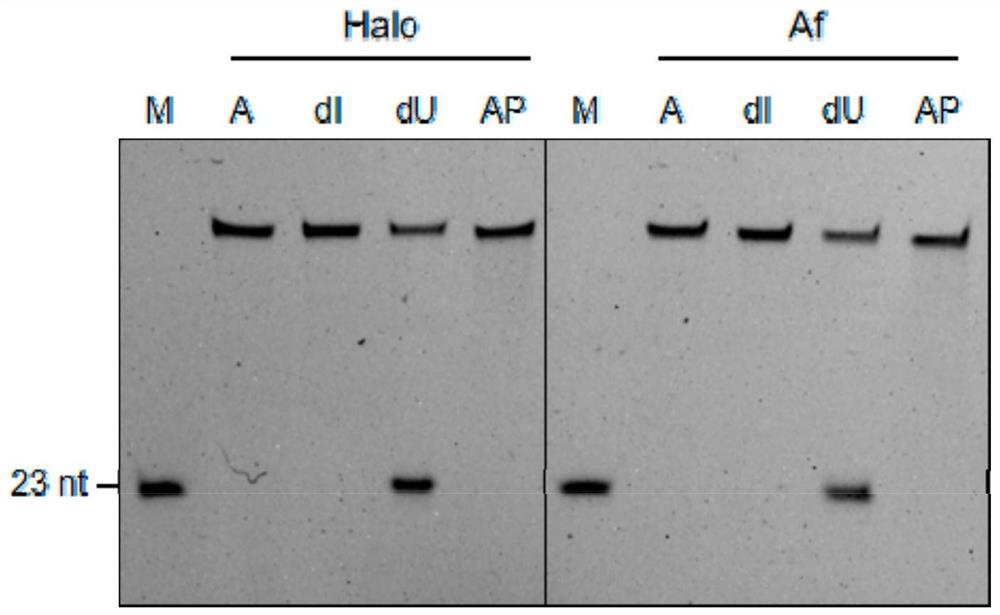
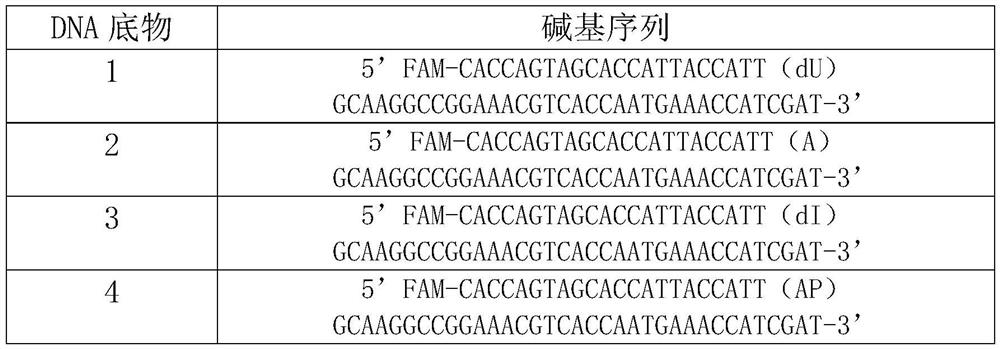
The invention discloses endonuclease and application thereof. An amino acid sequence of the endonuclease is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1 or SEQ ID NO: 2, or the amino acid sequence of the endonuclease and an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 1 or SEQ ID NO: 2 have at least 70% of sequence identity. The endonuclease can be used for directly and specifically recognizing deoxyuracil (deoxyuridine) on a DNA strand and cutting a first phosphodiester bond located at a 3'-terminal of the deoxyuracil is cut, cutting can be independently completed without combined action with other endonucleases with AP site lyase activity, and the endonuclease has wide application prospects in the fields of in-vitro molecular diagnosis of DNA damage mutation and the like. In addition, the invention provides a cutting site, i.e., the first phosphodiester bond located at the 3'-terminal of the deoxyuracil for the first time, and the cutting site is not reported in the prior art.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Methods for the epigenetic analysis of DNA, particularly cell-free DNA
ActiveUS20210262009A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEpigenetic AnalysisCell free
Methods are provided for the epigenetic analysis of cell-free DNA using organic boranes to convert oxidized 5-methylcytosine residues in the cell-free DNA to dihydrouracil (DHU) residues. Cell-free DNA is contacted with an organic borane selected to successively bring about reduction, deamination, and decarboxylation of oxidized 5-methylcytosine residues such as 5-carboxylcytosine and 5-formylcytosine, resulting in DHU residues in place thereof. Following amplification, the treated cell-free DNA is sequenced, with the DHU residues read as thymine residues. Reaction mixtures, kits and additional methods are also provided, as are related methods for the epigenetic analysis of DNA, including cell-free DNA.
Owner:CLEARNOTE HEALTH INC
Method and kit for non-specifically amplifying natural short-fragment nucleic acid
ActiveCN112301103AAchieve enrichmentAvoid damageMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationEnzyme digestionDeoxyuridine
The invention relates to a method for non-specifically amplifying natural short-fragment nucleic acid. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing terminal repair on the natural short-fragment nucleic acid to obtain terminal-repaired nucleic acid; (2) connecting the terminal-repaired nucleic acid with a double-chain connector to obtain a connection product, wherein each chain of the double-chain connector only comprises three basic groups; (3) performing PCR amplification on the connection product by using a PCR primer with a deoxyuridine marker to obtain a PCR product, wherein the PCR primer is completely or partially complementary to one chain of the double-chain connector and only comprises three basic groups; and (4) performing enzyme digestion on the PCR product by usingan enzyme with a deoxyuridine cutting function, and performing enzyme digestion by using an enzyme with 5'->3' polymerase activity and 3'->5' exonuclease activity in the presence of a deoxynucleotidesolution to obtain a non-specific amplification product of the natural short-fragment nucleic acid, wherein the deoxynucleotide solution only comprises complementary basic groups of the basic groups which are lacked by the primer. The invention also relates to a kit for implementing the method.
Owner:BERRYGENOMICS CO LTD
A method for labeling and detecting 5-ethynyl-2' deoxyuridine of hepatitis B virus genome dna
ActiveCN106929484BBright colorIncrease signal strengthMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisHepatitis B immunizationStaining
The invention discloses a labeling and detecting method of 5-acetenyl-2'-deoxyuridine of a genomic DNA of hepatitis B virus. The method specifically comprises the following steps: (1) amplifying an NTCP gene, constructing an NTCP eukaryotic expression plasmid pcDNA-NTCP, and shifting the pcDNA-NTCP to an Hhh7 hepatoma carcinoma cell to construct a Huh7-NTCP cell line with NTCP stably expressed; (2) treating a HepG2.2.15 cell by using EdU, obtaining a cell supernatant containing EdU-HBV, performing treatment with PEG8000, and quantifying the copy number of HBV genome after concentration; and (3) performing subculture on the HBV cells till the cell convergence degree is 50-80%, infecting the Huh7-NTCP cell with EdU-HBV, and then performing EdU-HBV fluorescence detection. Compared with the prior art, the method is simple to operate, the image result does not need to be processed in the later stage, and the dyeing results do not interfere with each other.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for detecting uridine monophosphate modification of protein
InactiveCN111505001AIncreased sensitivityValid identificationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryUracil in DNA
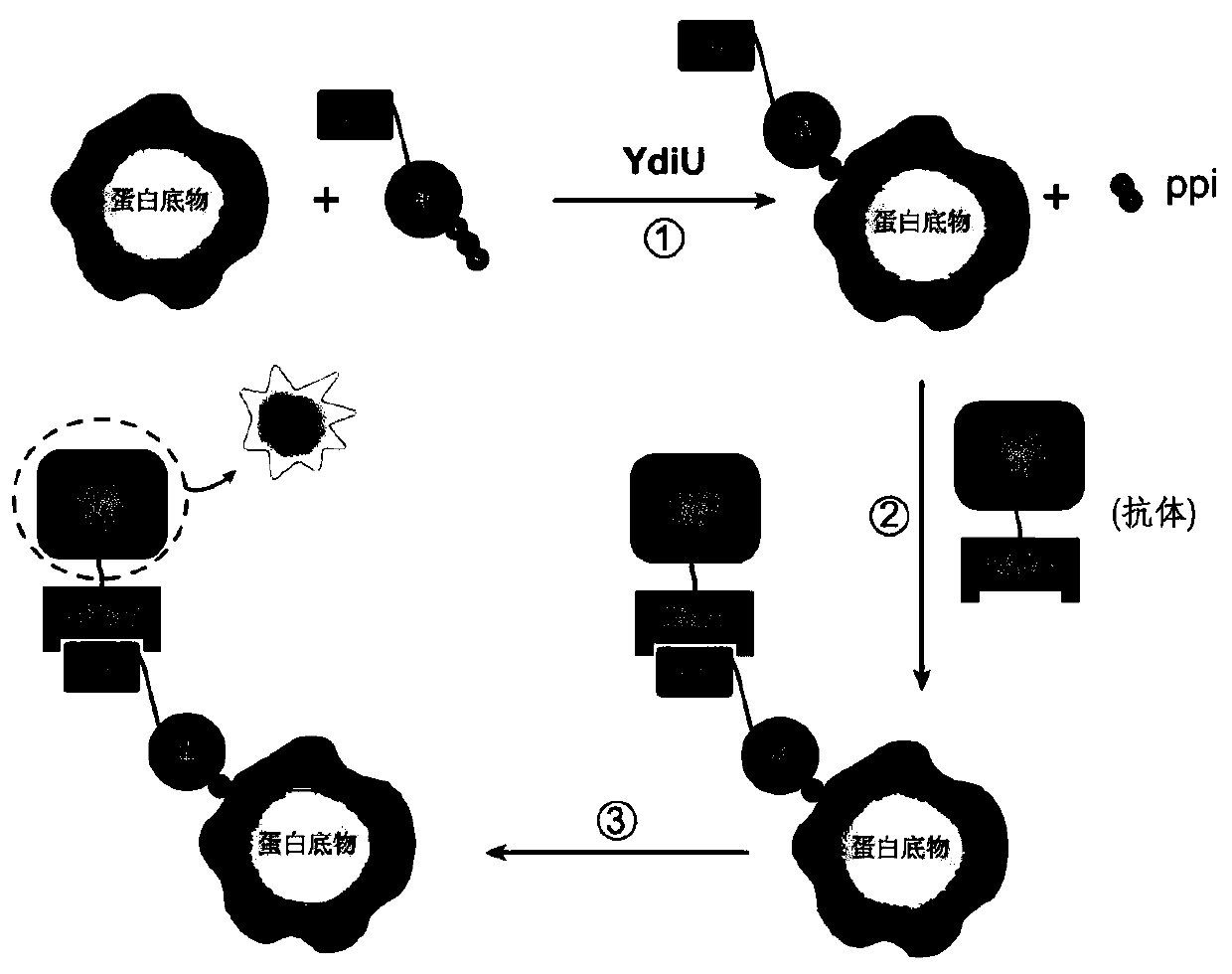
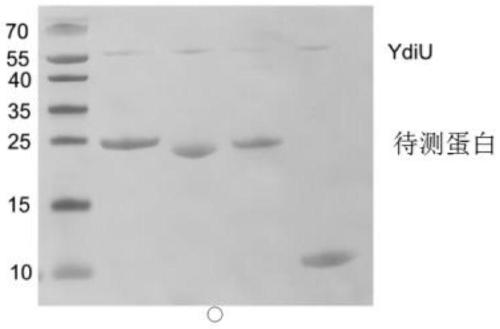
The invention discloses a method for detecting uridine monophosphate modification of protein. The method comprises the following steps: by using biotin-labeled UTP (Biotin-16-UTP) as a raw material, under the action of uridine monophosphate transferase YdiU, the protein occurring UMP modification having biotin labeling; and subsequently, verifying whether the protein to be detected has a biotin label or not by using a biotin-streptavidin imprinting method. The method has the characteristics of simplicity, convenience, high sensitivity and the like, can be used for high-throughput screening ofproteins subjected to uridine monophosphate acidification in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, can determine modification sites in combination with mass spectrometry detection, and provides an effective identification and research means for research of protein uracil mononucleotide modification.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICINE OF SAMS
Rapid DNA sulfite conversion reagent and method
PendingCN114574560AImprove conversion rateReduce lossesMicrobiological testing/measurementBulk chemical productionCytosineA-DNA
The invention relates to a rapid DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sulfite conversion reagent and a rapid DNA sulfite conversion method, and particularly discloses a DNA sulfite treatment method which comprises the following steps: DNA is contacted with a conversion reagent in a sulfite reaction system, and the conversion reagent comprises the following components: NaHSO3, (NH4) 2SO3 and NH4HSO3. The reagent disclosed by the invention can be used for quickly and efficiently converting non-methylated cytosine of DNA into uracil with high sensitivity.
Owner:上海长岛抗体诊断试剂有限公司
Gene cloning and site-specific mutagenesis method by utilizing high-fidelity polymerase and UDG
InactiveCN110964737AIncreased loyaltyPrevent genetic mutationVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliGenes mutation
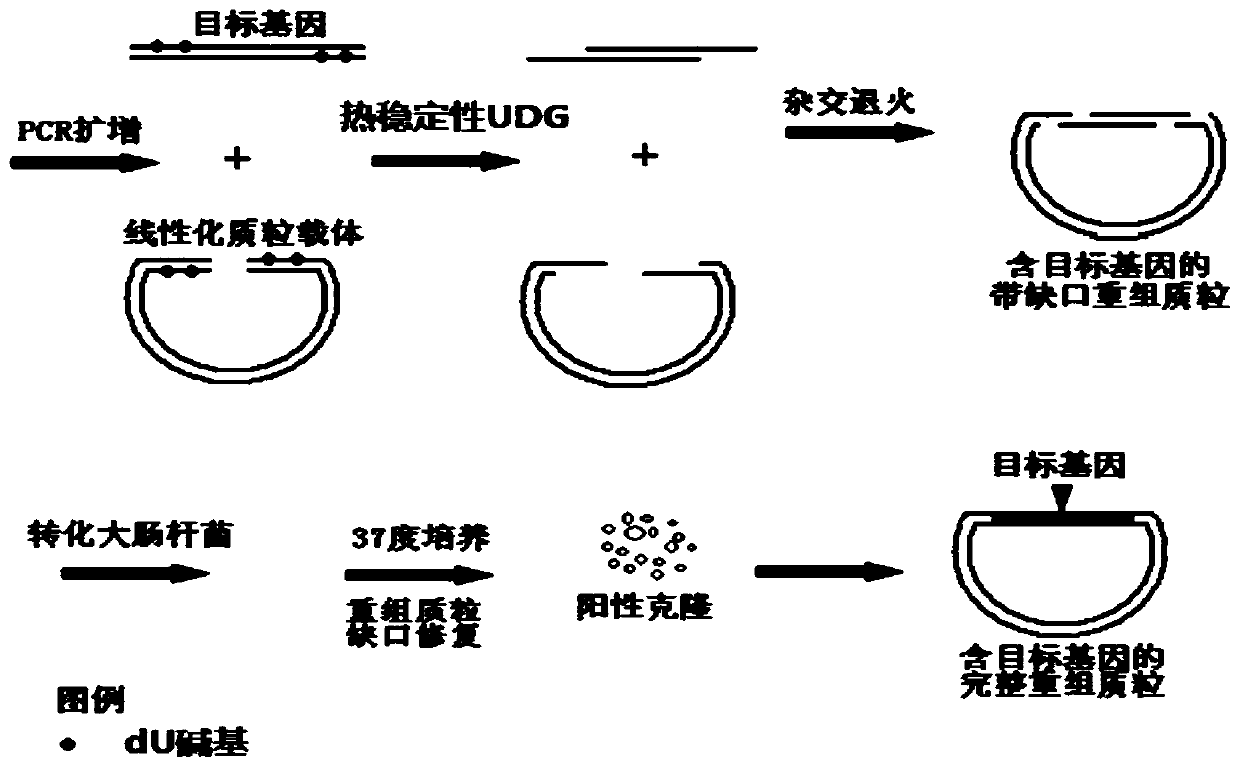
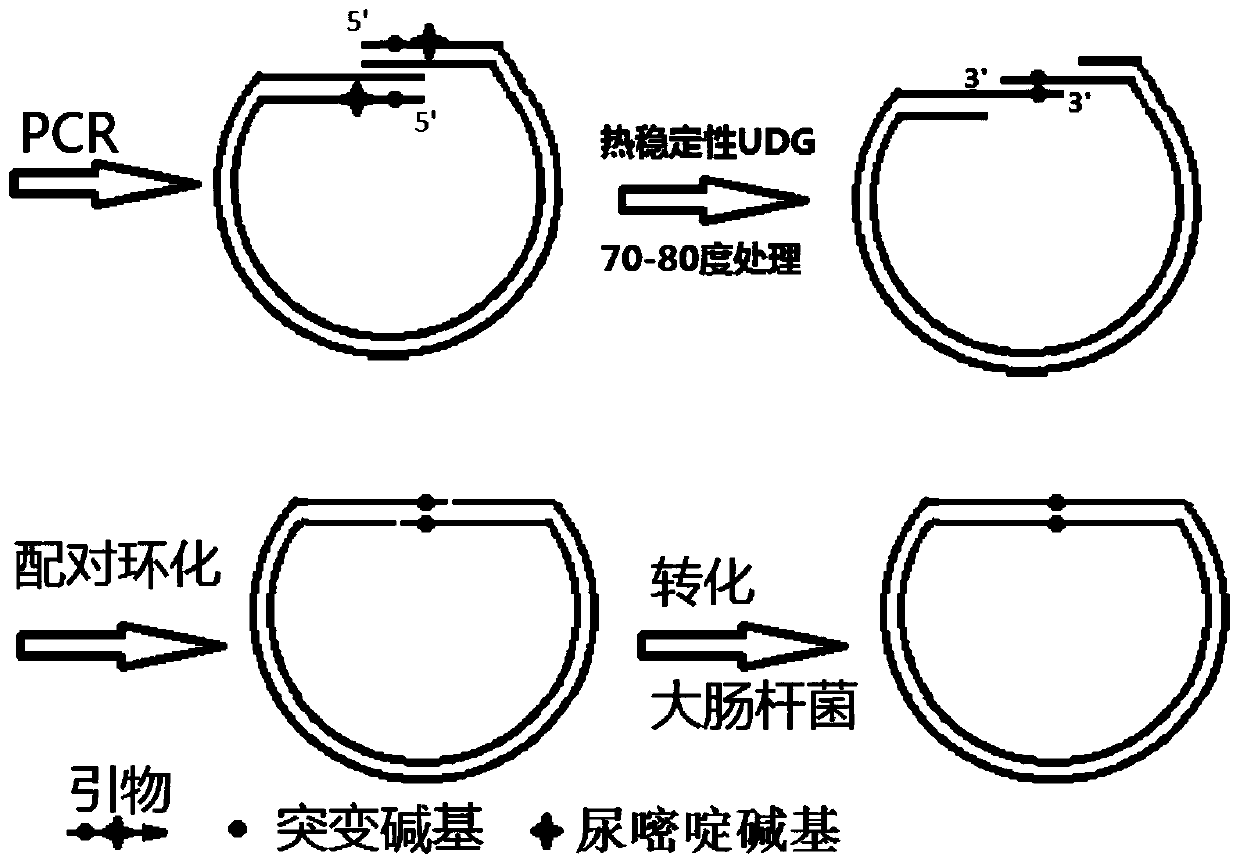
The invention discloses a gene cloning and site-specific mutagenesis method by using high-fidelity polymerase and UDG. The gene cloning and site-specific mutagenesis method comprises the following steps: amplifying a target gene and a plasmid vector by using a dU modified primer and dU tolerant high-faithfulness DNA polymerase; carrying out high-temperature treatment by using heat-stable uracil DNA glycosidase to obtain a target gene and a plasmid vector of which the 3'end is a single chain; mixing the target gene and the plasmid vector so that the target gene and single-stranded regions at the two ends of the plasmid vector are paired and connected to form a notched annular recombinant plasmid vector containing the target gene; after escherichia coli is transformed by the annular recombinant plasmid vector with the notch containing the target gene, repairing the notch, and obtaining the complete recombinant plasmid vector containing the target gene . By adopting the method, the faithfulness of an amplification reaction is remarkably improved, extra gene mutation caused by Taq DNA polymerase with low faithfulness is avoided, and the method is particularly suitable for vector construction with protein expression as a target; dU and dA bases are paired, the pairing result is equal to normal dT / dA pairing, and gene mutation caused by introduction of additional wrong bases into modified bases is avoided; the thermostable UDG has enzymatic activity at 60-80 DEG C, so that removal of dU bases and breakage of DNA chains are performed simultaneously, and alkali-adding thermal cracking operation is omitted.
Owner:苏州博睐恒生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com