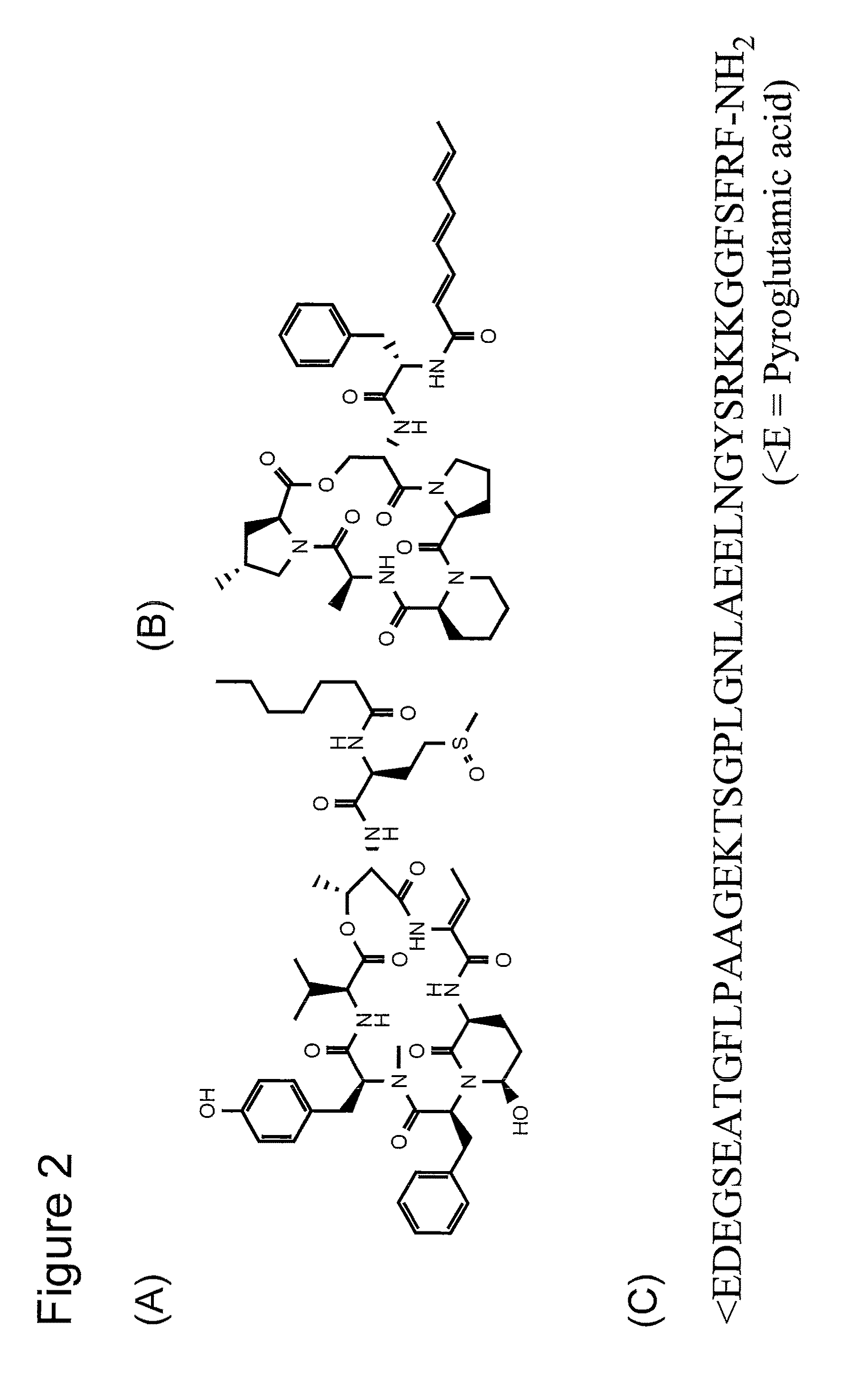
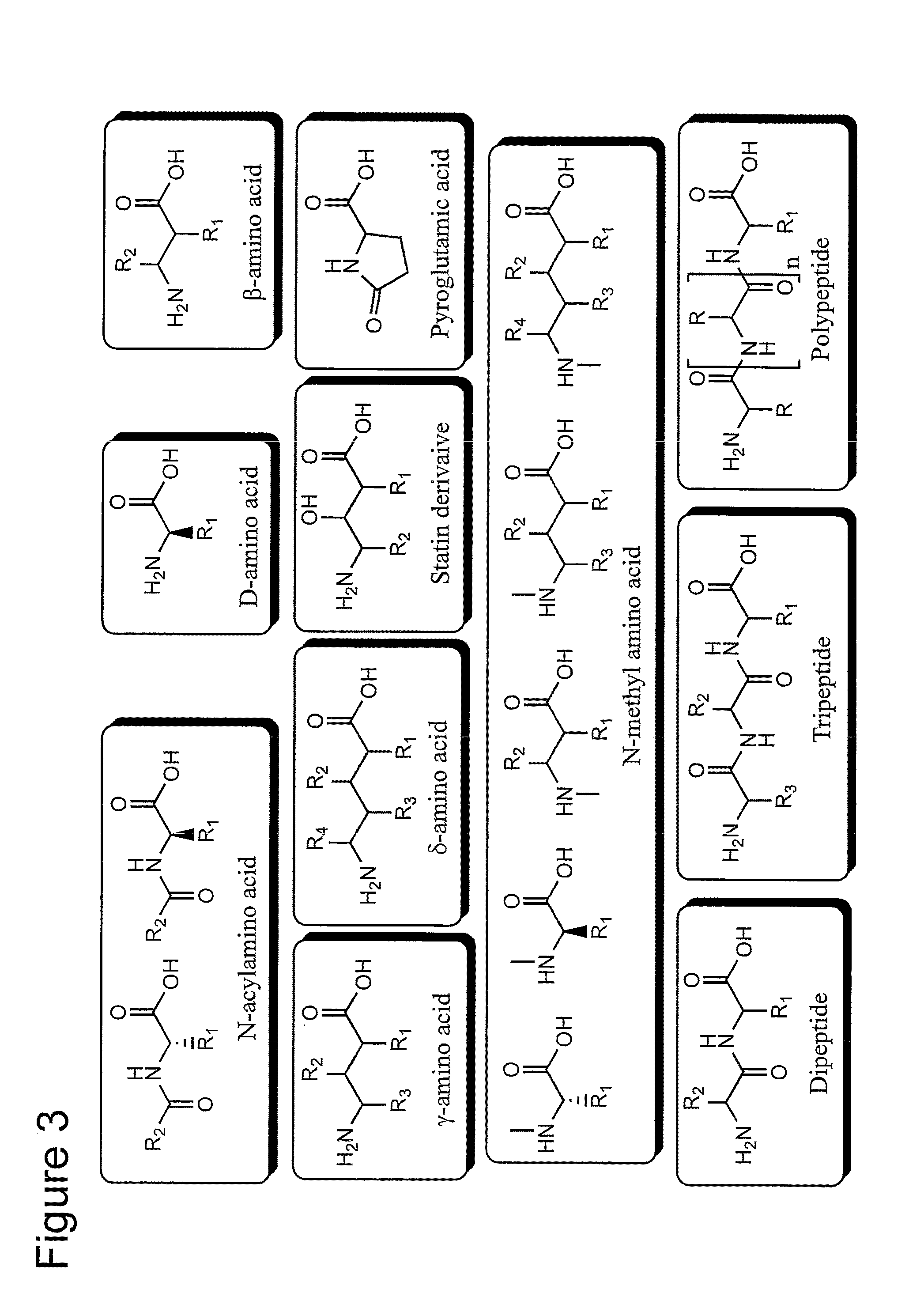
Patents
Literature
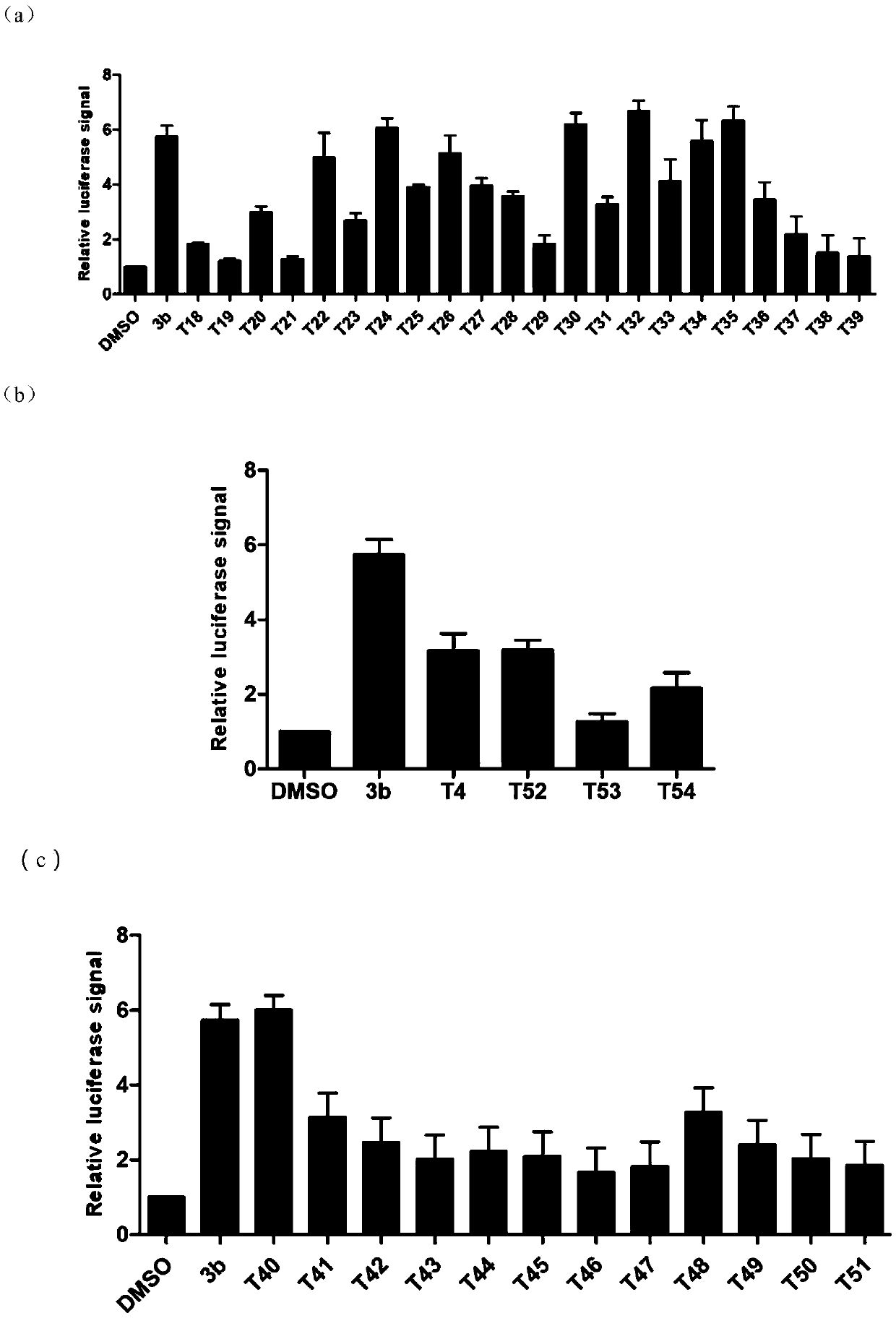
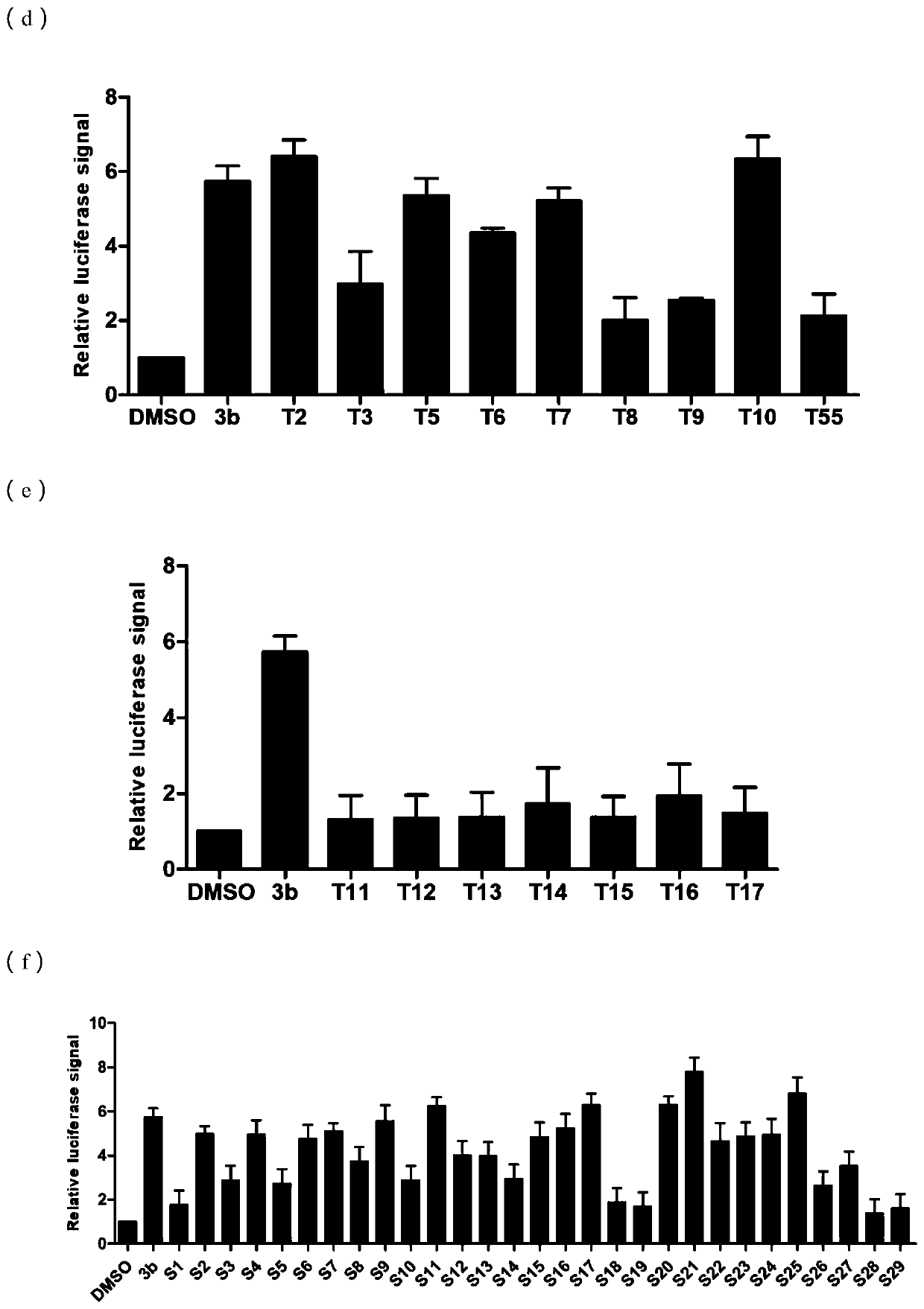
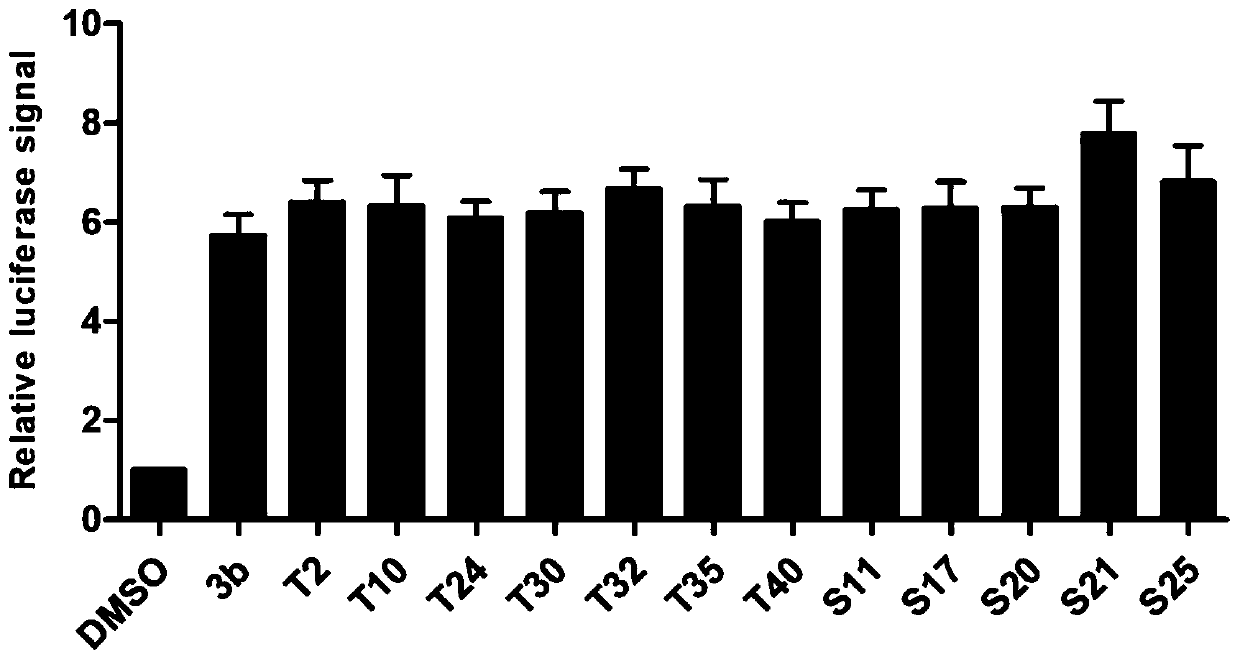
58 results about "Biosynthetic process" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of substances; typically the energy-requiring part of metabolism in which simpler substances are transformed into more complex ones. [GOC:curators, ISBN:0198547684]
Bacterial cellulose membrane with gradient structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103233050AThe preparation process is easy to controlWide variety of sourcesMicroorganism based processesFermentationWound dressingFermentation
The invention discloses a bacterial cellulose membrane in a gradient structure and a preparation method of the bacterial cellulose membrane. The bacterial cellulose membrane is prepared by the steps of adding crop starch in a fermentation culture solution, heating for gelatinizing the mixture, adding a thickening agent into the gelatinized mixture, and carrying out static culture; and the bacterial cellulose membrane has a gradient structure with continuous transition from a compact upper surface downwards to a loose lower surface. The in-site fast controllable preparation of the gradient structure of the bacterial cellulose membrane can be realized by adjusting the proportion of the crop starch to the thickening agent. The preparation method of the bacterial cellulose membrane disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the resources of raw materials are wide, biosynthesis process is mild and pollution-free, and the product is environment-friendly, safe, low in production cost, controllable in process and designable and has a bright large-scale production prospect. The bacterial cellulose membrane with the gradient structure is suitable for the fields of cosmetics and biomedical materials including a facial mask, a cooling paste, a wound dressing, an artificial skin and the like.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method for producing epsilon-poly-L-lysine
ActiveCN102363797AIncreases anabolic activityPromote accumulationMicroorganism based processesFermentationGlycineIntermediate stage
The invention relates to a method for producing epsilon-poly-L-lysine. The method is characterized in that a medium containing 1-10g / L of glycine is added at an early or middle stage of culture. By adding glycine in a fermentation process in the invention, glycine which enters a folic acid metabolism approach allows sufficient one-carbon groups to be supplied to a biosynthesis process, the anabolism activity of bacterial strains to be improved, the synthesis of a precursor L-lysine and epsilon-poly-L-lysine to be increased, and the accumulation amount of epsilon-poly-L-lysine to be 20-50% higher than the accumulation amount obtained through original technologies.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SILVER ELEPHANT BIO ENG
White magnolia extract-containing skin brightening and whitening cosmetic lotion and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108272679ABlock the biosynthetic processImprove autoimmunityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsPolyolWhitening Agents
The invention discloses a white magnolia extract-containing skin brightening and whitening cosmetic lotion and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of facial care. The white magnoliaextract-containing skin brightening and whitening cosmetic lotion comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 0.1-5 parts of a white magnolia extract, 1-10 parts of polyol, 1-10 parts of a moisturizing agent, 0.2-3 parts of an anti-allergic soothing agent, 0.3-3 parts of a skin conditioner, 2-8 parts of a whitening agent, 0.1-1 part of a preservative, 0.05-0.1 part of an essence and0.1-0.4 part of an essence solubilizer, wherein deionized water is added till 100 parts. Through addition of a new generation of mild and environment-friendly whitening active component, the skin brightening and whitening cosmetic lotion prevents the biosynthesis process of melanin by starting from inhibition of melanin formation, so that skin is continuously moisturized, the own immunity of skincells is enhanced and the skin elasticity is restored while skin brightening and whitening effects are achieved.
Owner:DOCTOR PLANT GUANGDONG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
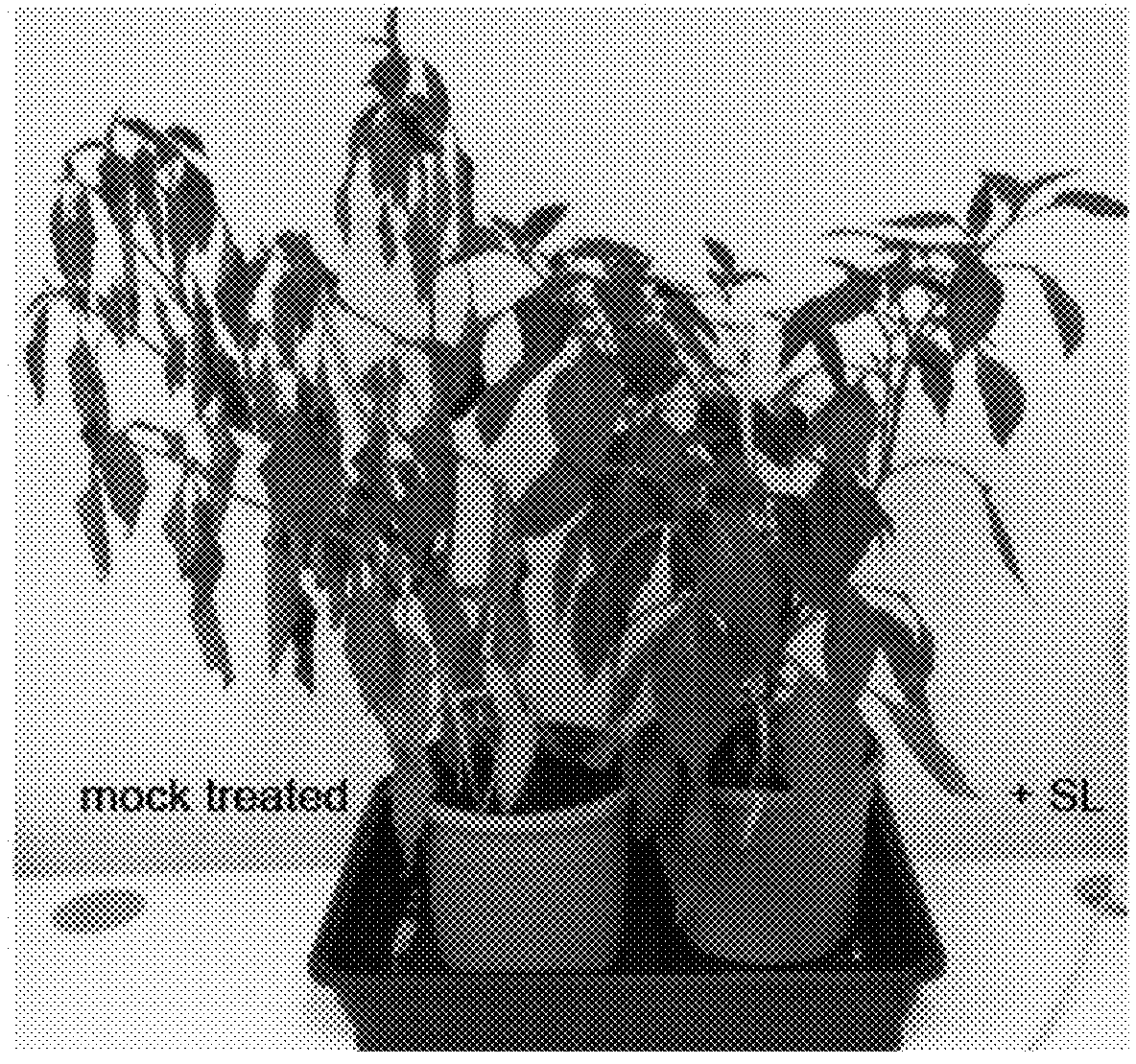
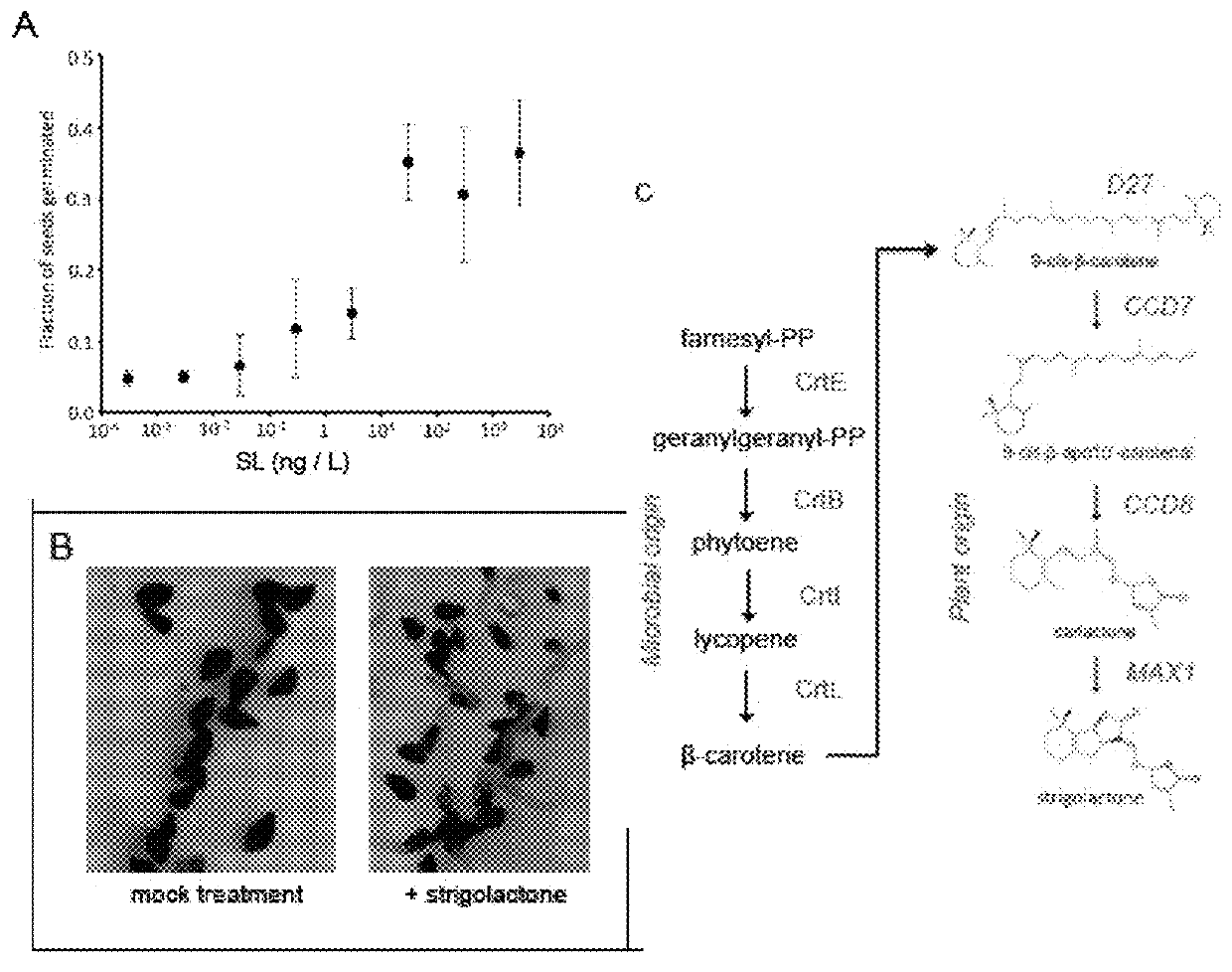
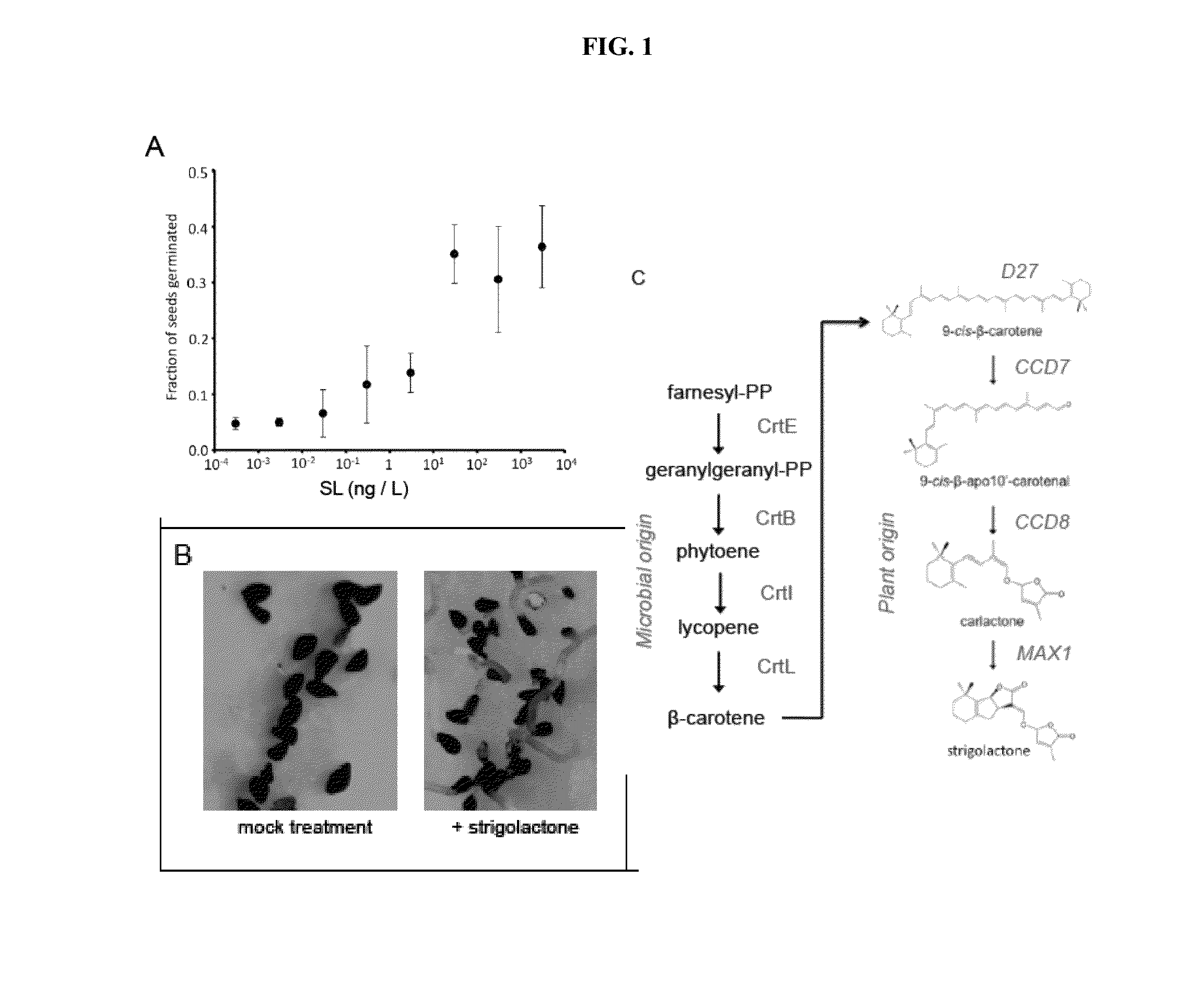
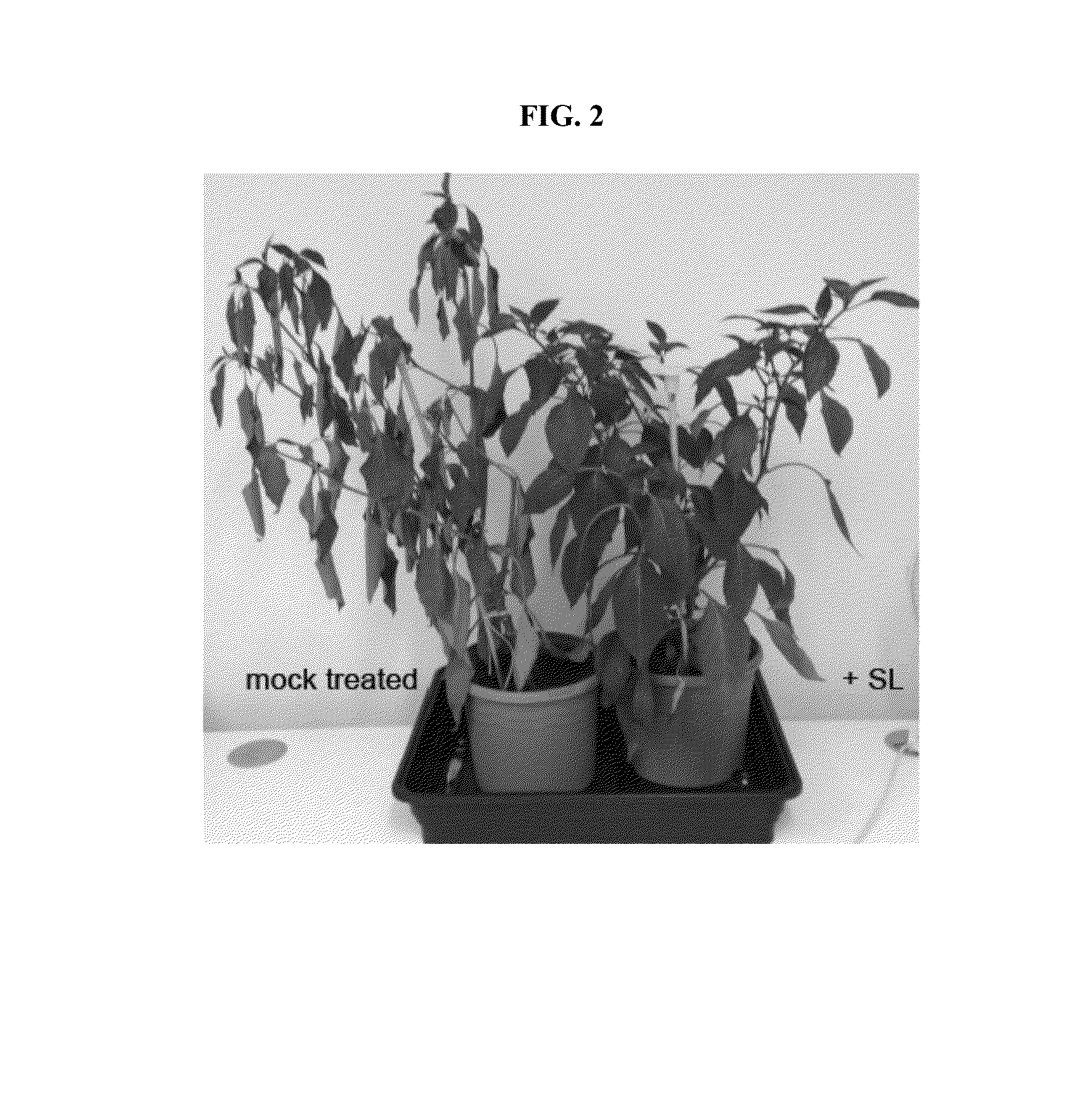
Strigolactone formulations and uses thereof
Disclosed herein plant propagation materials, methods of manufacturing, formulations and uses thereof. The plant propagation materials disclosed herein may comprise a strigolactone obtained by a biosynthetic process. The plant propagation material may comprise a chemical mimic of a strigolactone. The strigolactone may be 5-deoxystrigol. Methods of manufacturing the plant propagation materials may comprise a chemical process. Alternatively, methods of manufacturing the plant propagation material may comprise a biosynthetic process. The methods may comprise use of one or more polynucleotides. The polynucleotides may encode a metabolite. The polynucleotides may comprise one or more genes encoding one or more components of a strigolactone pathway.
Owner:SOUND AGRI CO
Biologic synthesis of perylene quinone compound
InactiveCN1680562ABiosynthesis process optimizationIncrease expansionMicroorganism based processesFermentationPeryleneWheat Brans
Biosynthesis of quinine compound and its optimizational ferment process. Strain is Ascomycetes Hypomyces(Fr) Tul.sp. Solid medium contains maize flour, wheat bran and bean dregs. Strain is switched in the medium after disinfection. Ferment at 24-25deg.C above 7 days. Fungus containing quinine compound is obtained. Break and dry the fungus, then extract to obtain the product.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Apparatus for aerobic liquid-phase fermentation
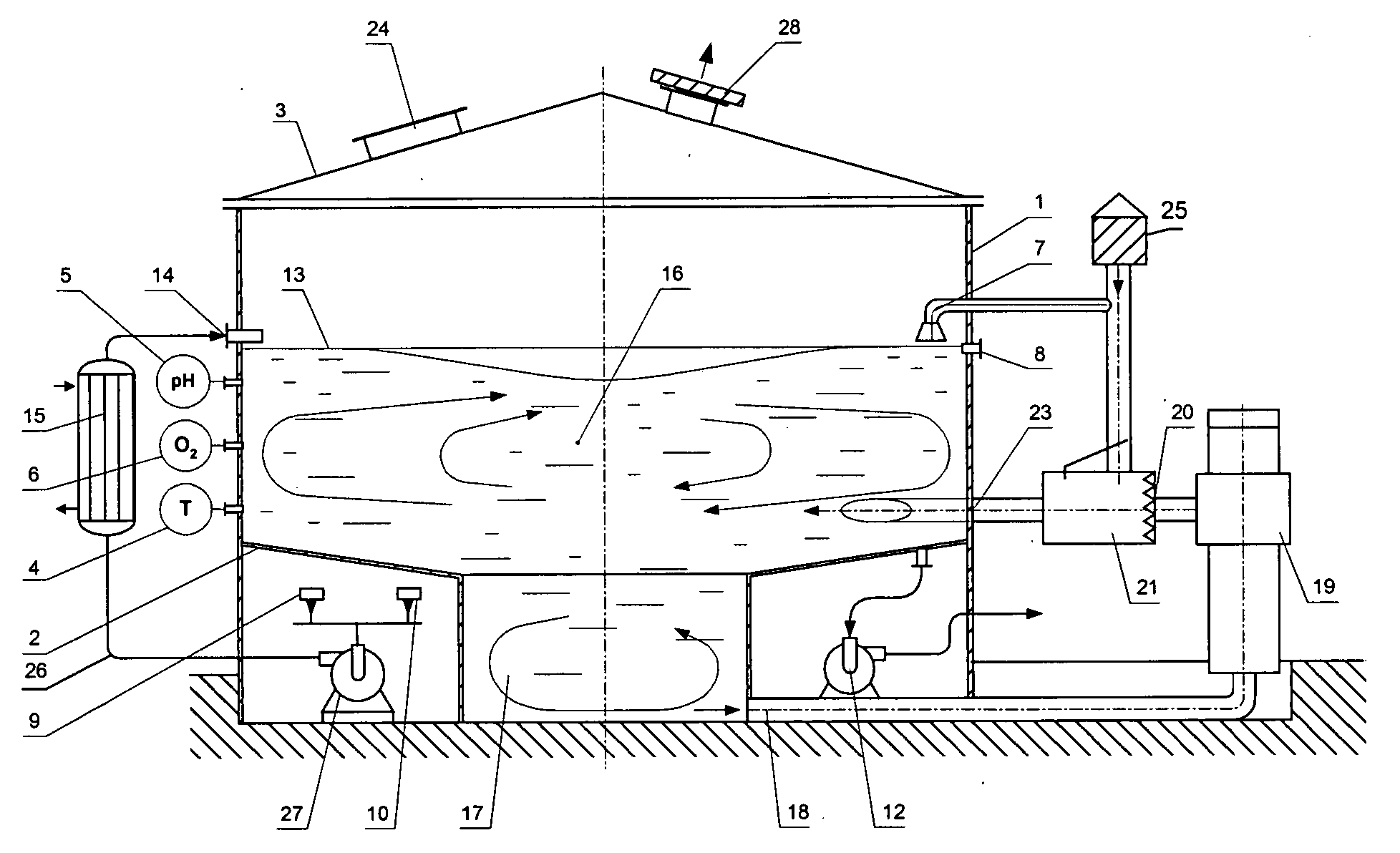
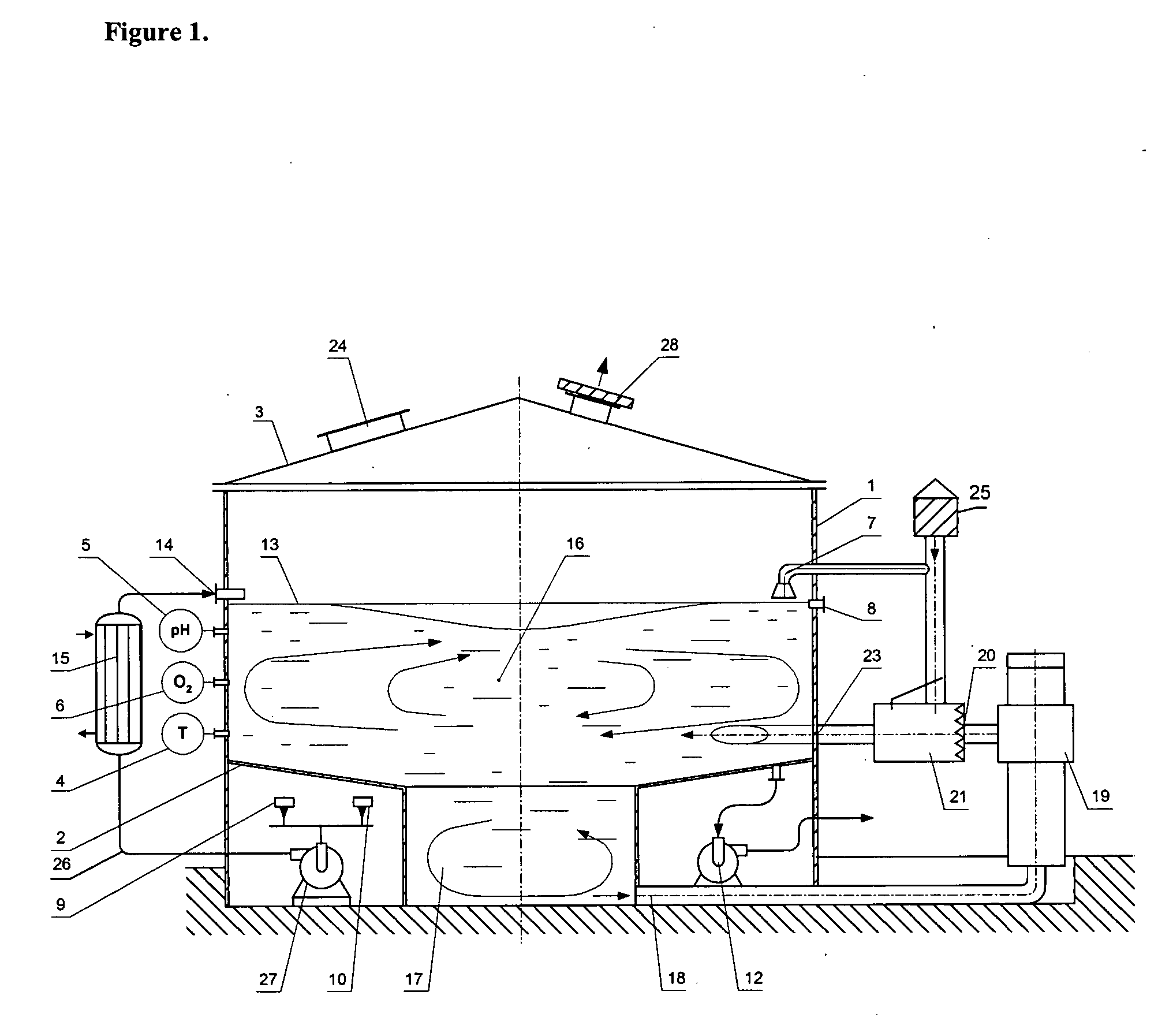
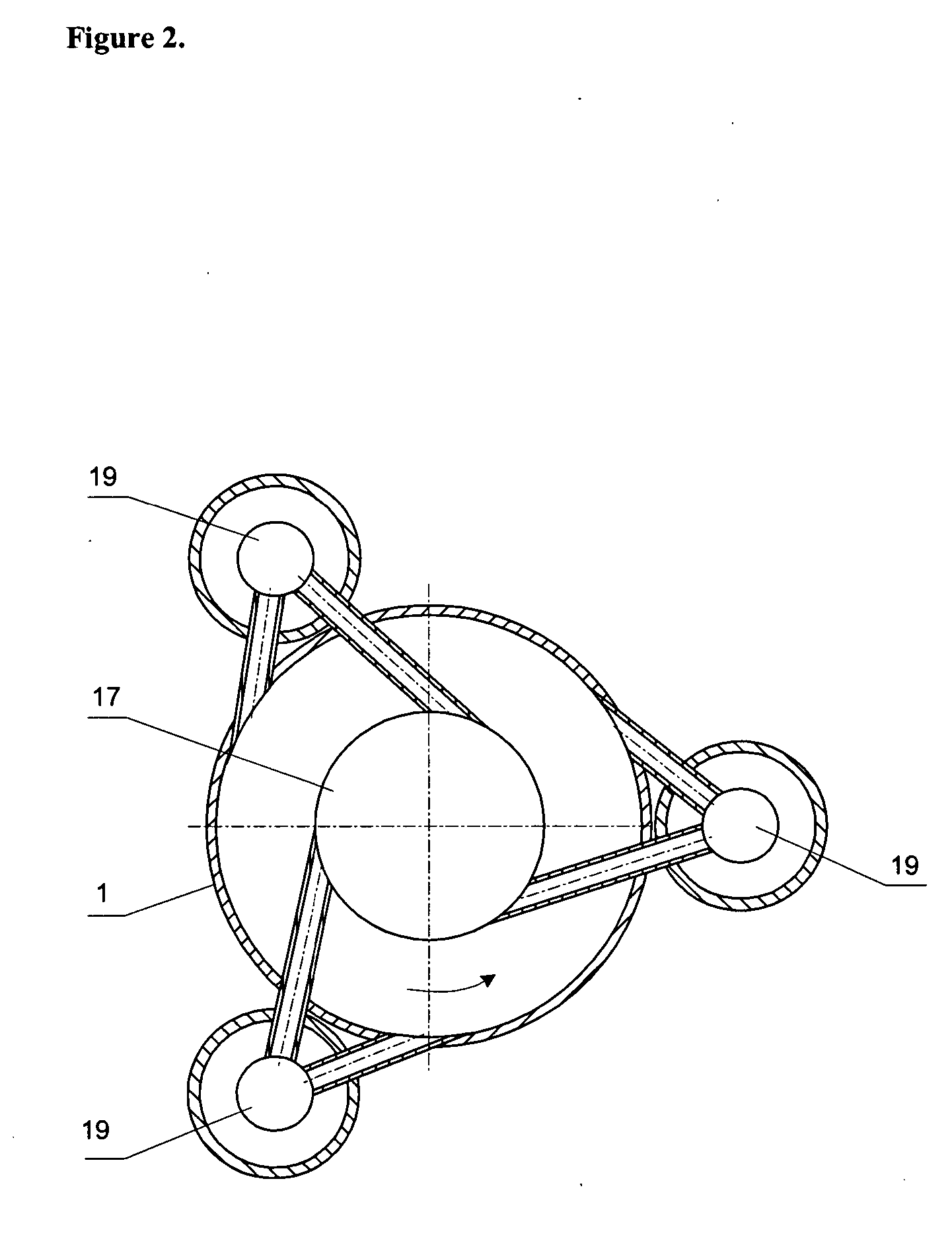
InactiveUS20050059142A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLiquid mediumEngineering
The present invention describes the apparatus for aerobic liquid-phase fermentation. The present invention relates to the field of chemical, physical and physical-chemical processes carried out in apparatus with an aeration and intermixing of a liquid medium, namely: processes of biosynthesis of various biological products, processes of processing waste from various productions, processing of semi-products, and processes of clearing of waste water that could also can be used in food, medical, microbiological, petrochemical industries, and also in an ecological remediation of an environment from various wastes.
Owner:VINAROV ALEXANDER +4
Strigolactone Compositions And Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20150274690A1Increase productionExtended contact lifeBiocideOrganic chemistryBiotechnologyMetabolite
Disclosed herein plant propagation materials, methods of manufacturing, formulations and uses thereof. The plant propagation materials disclosed herein may comprise a strigolactone obtained by a biosynthetic process. The plant propagation material may comprise a chemical mimic of a strigolactone. The strigolactone may be 5-deoxystrigol. Methods of manufacturing the plant propagation materials may comprise a chemical process. Alternatively, methods of manufacturing the plant propagation material may comprise a biosynthetic process. The methods may comprise use of one or more polynucleotides. The polynucleotides may encode a metabolite. The polynucleotides may comprise one or more genes encoding one or more components of a strigolactone pathway.
Owner:ASILOMAR BIO
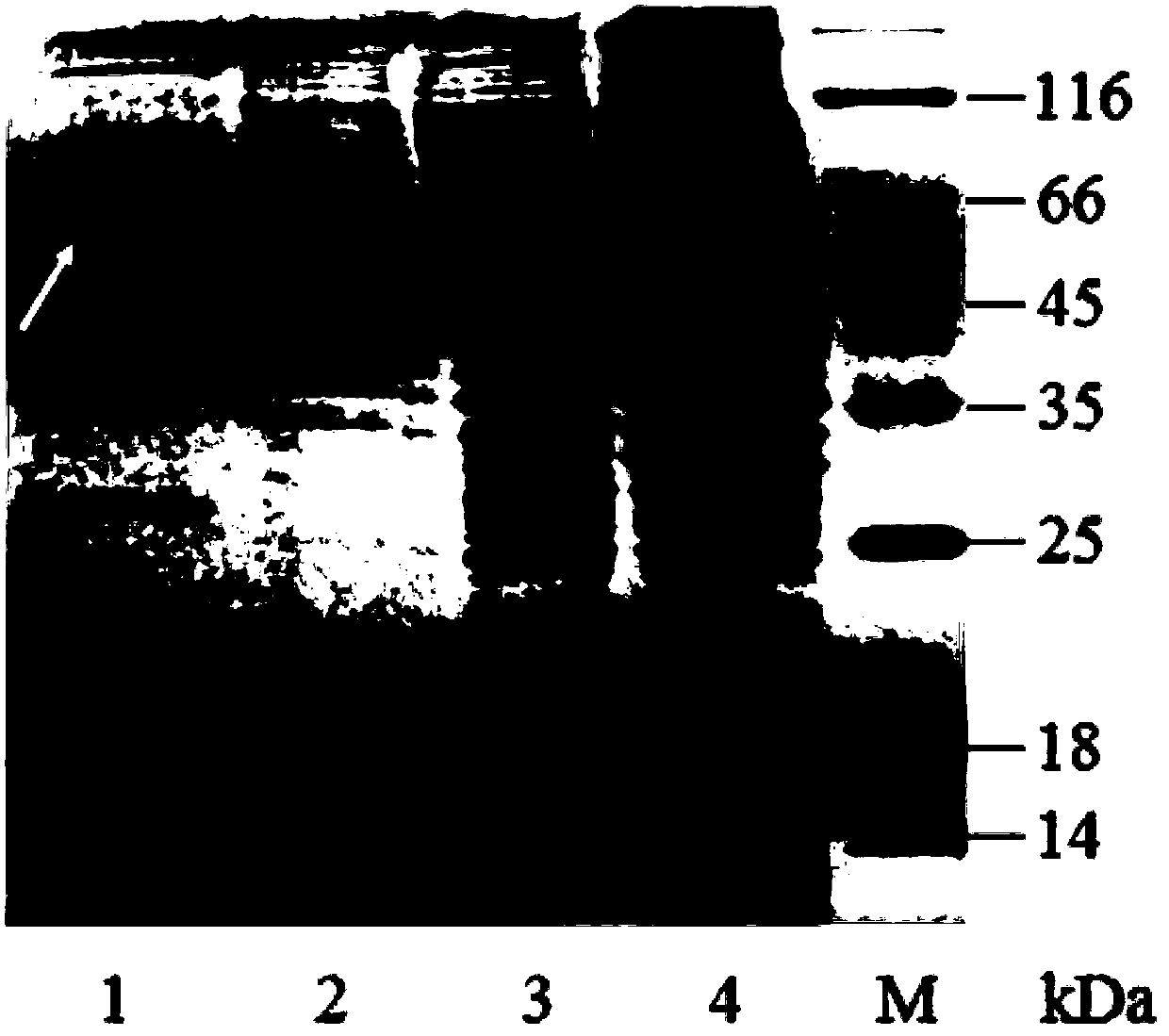
Spider dragline silk protein and biosynthesis method thereof
InactiveCN107805283AEasy to produce by fermentationEasy to operateConnective tissue peptidesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention provides a spider dragline silk protein and a biosynthesis method thereof. The spider dragline silk protein comprises an 'ABA-type' triblock copolymer of a spider silk protein and a collagen-like protein, the amino acid sequence and the nucleotide sequence of the spider dragline silk protein are SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2, and the collagen-like protein is a tripolymer (Pro-Gly-Pro)15 and positioned at two ends of the spider silk protein. The biosynthesis method includes the steps: (1) designing and optimizing a spider dragline silk protein gene; (2) building a gene expression vector; (3) converting, fermenting and culturing engineering bacteria; (4) inducing expression; (5) extracting and purifying products. The spider dragline silk protein has good biocompatibility, directing properties and fibroblast potential and can meet requirements of artificial spider silk fiber molecular weight, and the spider dragline silk protein is mild in biosynthetic process and simple in process and provided with a potential protein fiber material and has a broad prospect of industrial implementation.
Owner:JINGGANGSHAN UNIVERSITY
Photosynthesis process of forming characters and pattern on honey peach
InactiveCN1930945ANo loss of nutrientsReduce manufacturing costDecorative surface effectsCultivating equipmentsEngineeringChlorophyll
The present invention relates to agricultural cultivation technology, and is especially photosynthesis process of forming text and pattern on honey peach. The process includes the following steps: forming text or pattern in a computer, making plate, printing the text or pattern with the plate on transparent adhesive paper, adhering the paper to the opening of the honey peach bag in the sunlight side before the honey peach matures, forming text or pattern on the honey peach through sun irradiation and taking off the bag. The present invention can raise the decoration value of honey peach greatly while maintaining the nutritious components and taste of honey peach.
Owner:邹玉琴 +1
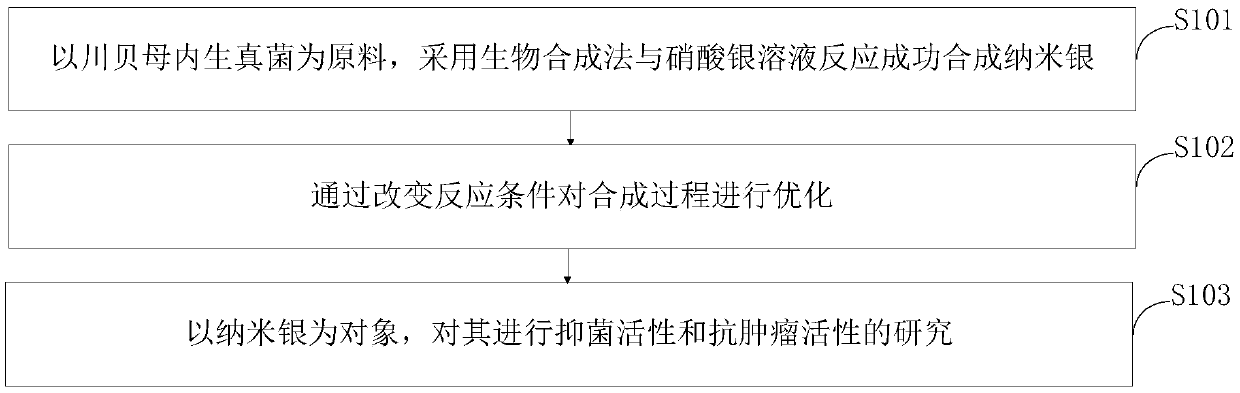
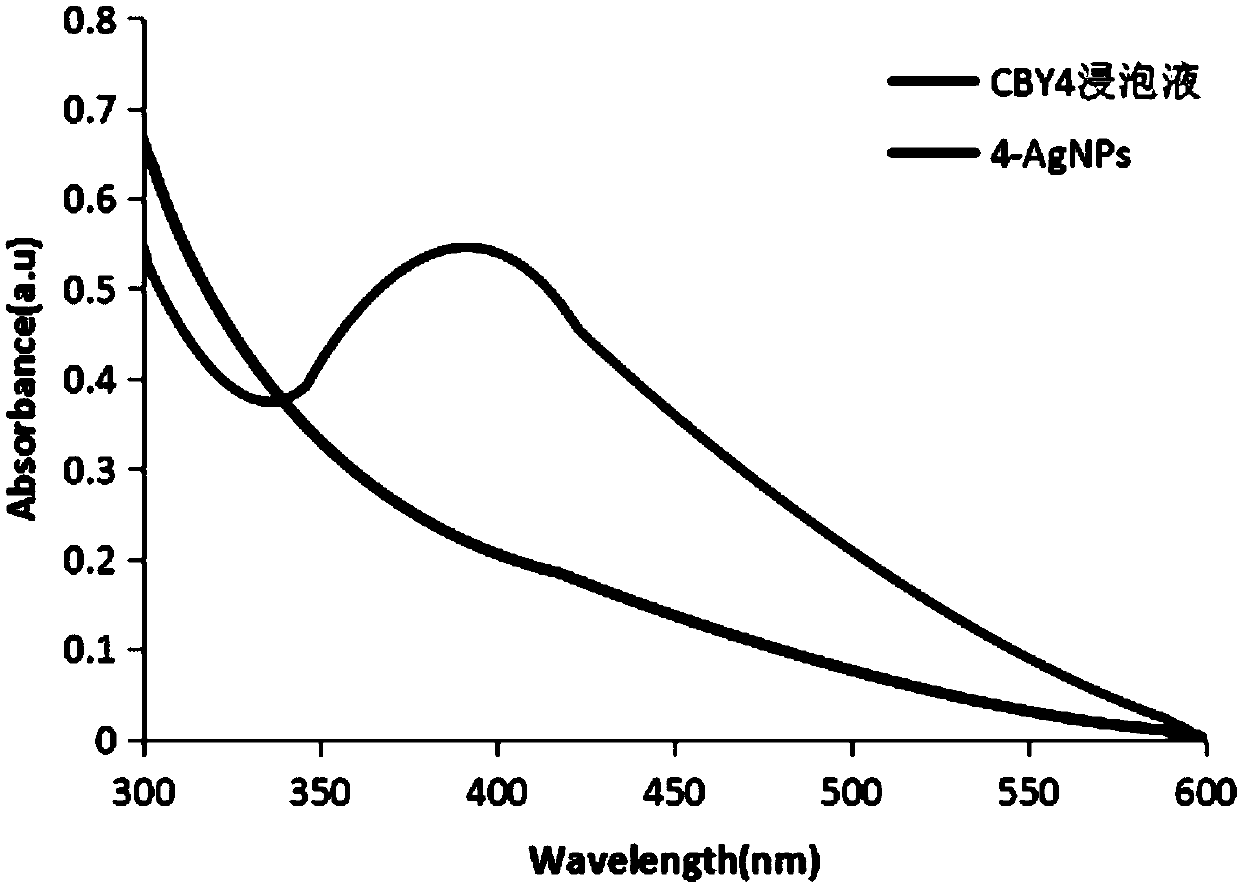
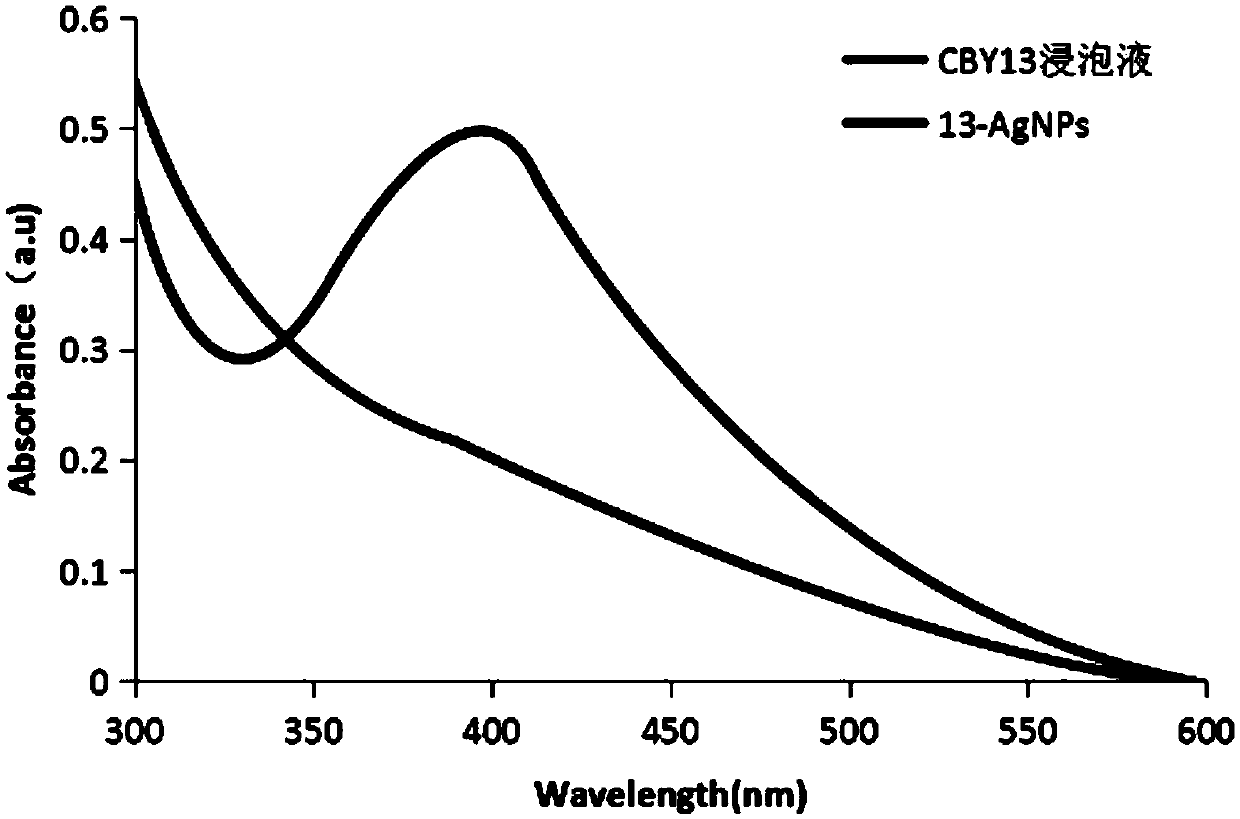
Biosynthetic method and application of bulbus fritillariae cirrhosae endophytic fungus mediated nano-silver
InactiveCN109097405AHas antibacterial activityHas antitumor activityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEndophytic fungus
The invention belongs to the technical field of biosynthesis and discloses a biosynthetic method and an application of bulbus fritillariae cirrhosae endophytic fungus mediated nano-silver. A bulbus fritillariae cirrhosae endophytic fungus soak solution and a silver nitrate solution are subjected to a reaction, and nano-silver 4-AgNPs and 13-AgNPs are prepared from bulbus fritillariae cirrhosae endophytic fungi CBY4 and CBY13 with the biosynthetic method after 15 bulbus fritillariae cirrhosae endophytic fungi are screened primarily; in the biosynthetic process, the synthetic conditions are as follows: pH is 3-11, concentration of the silver nitrate solution is 2 mmol / L, illumination intensity is 2000 Lux, and the temperature is 50 DEG C. It is discovered for the first time that the endophytic fungi CBY4 and CBY13 separated from bulbus fritillariae cirrhosae have nano-silver synthesizing capacity, the reaction conditions more suitable for nano-silver synthesis are obtained by optimization, and synthesized nano-silver has certain bacteriostatic and antitumor activity.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Isolated enzymatic manufacture of semiconductor nanoparticles
InactiveUS20170335309A1Material nanotechnologyCarbon-sulfur lyasesCell free supernatantSemiconductor Nanoparticles
Novel semiconductor nanoparticles and methods of biosynthesizing the same are provided by biosynthetic processes using cell-free supernatants and isolated enzymes.
Owner:LEHIGH UNIVERSITY
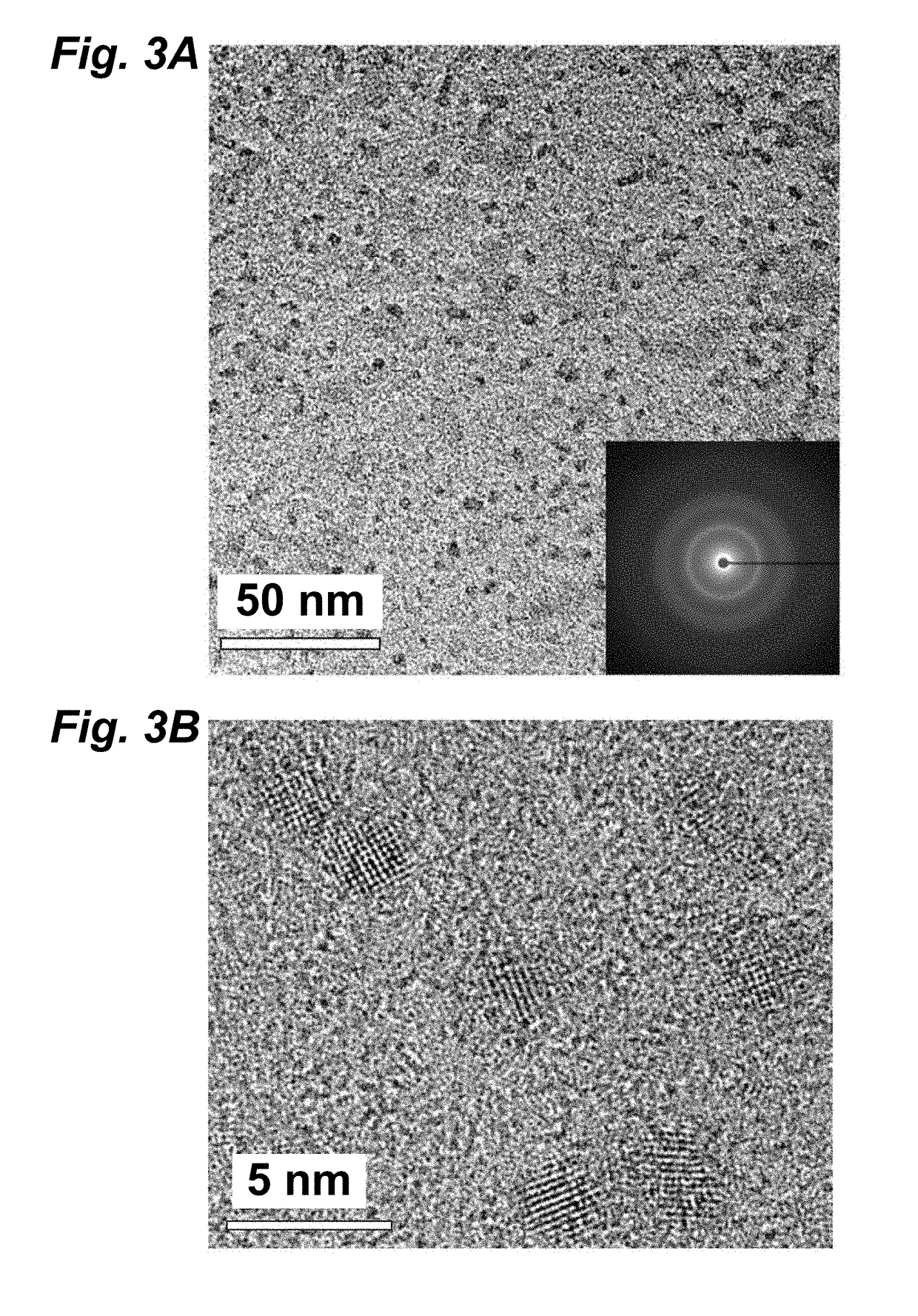
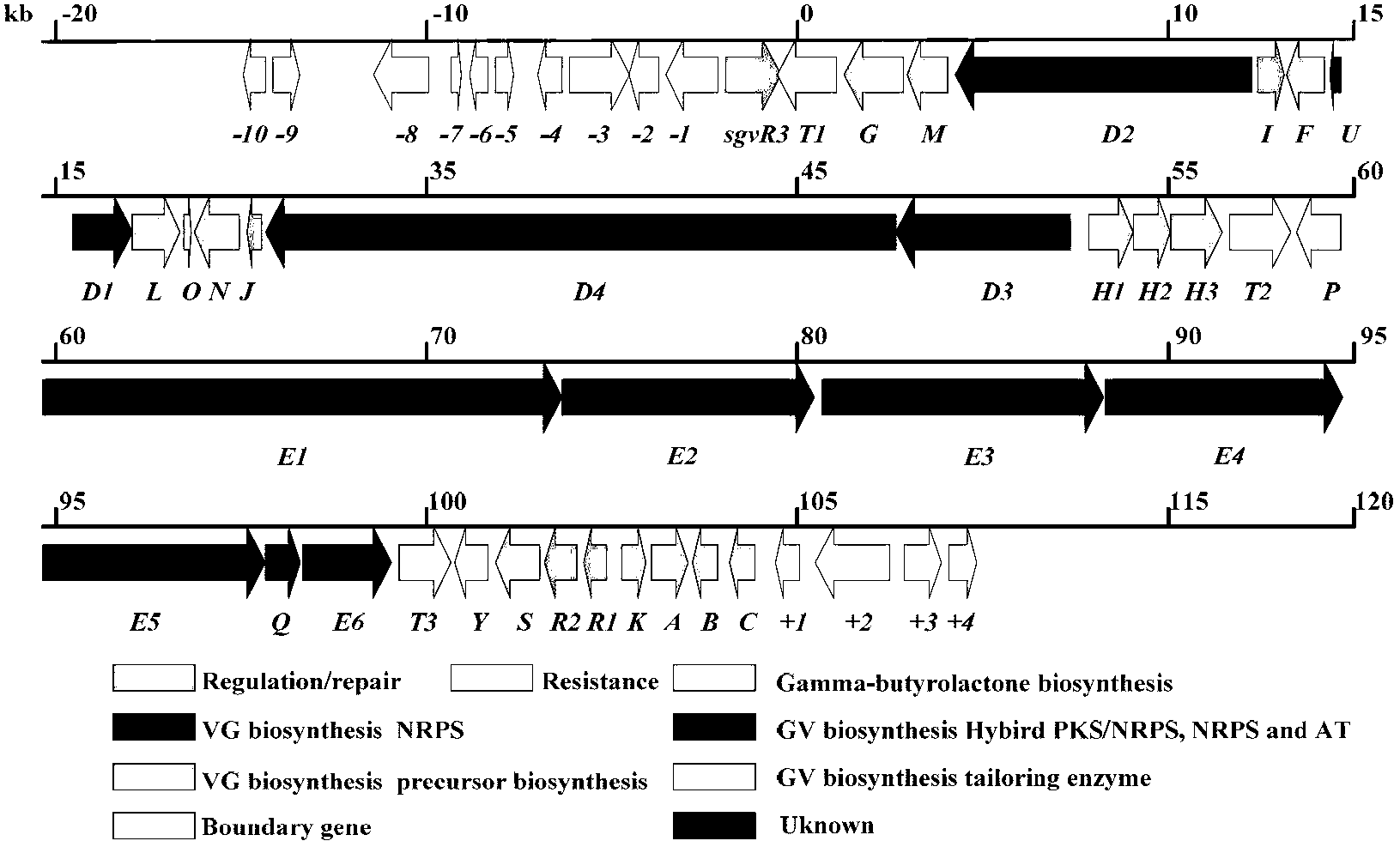
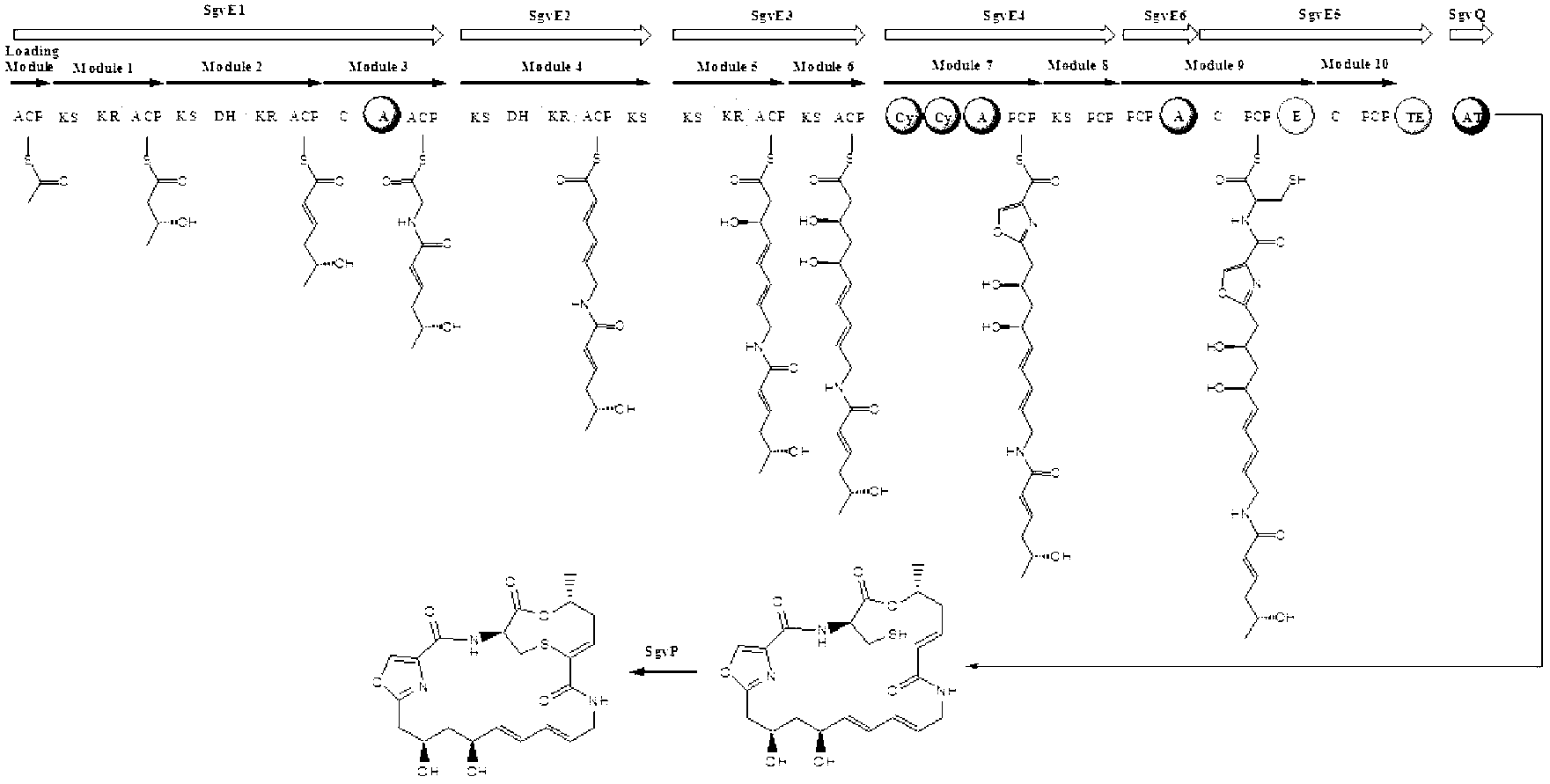
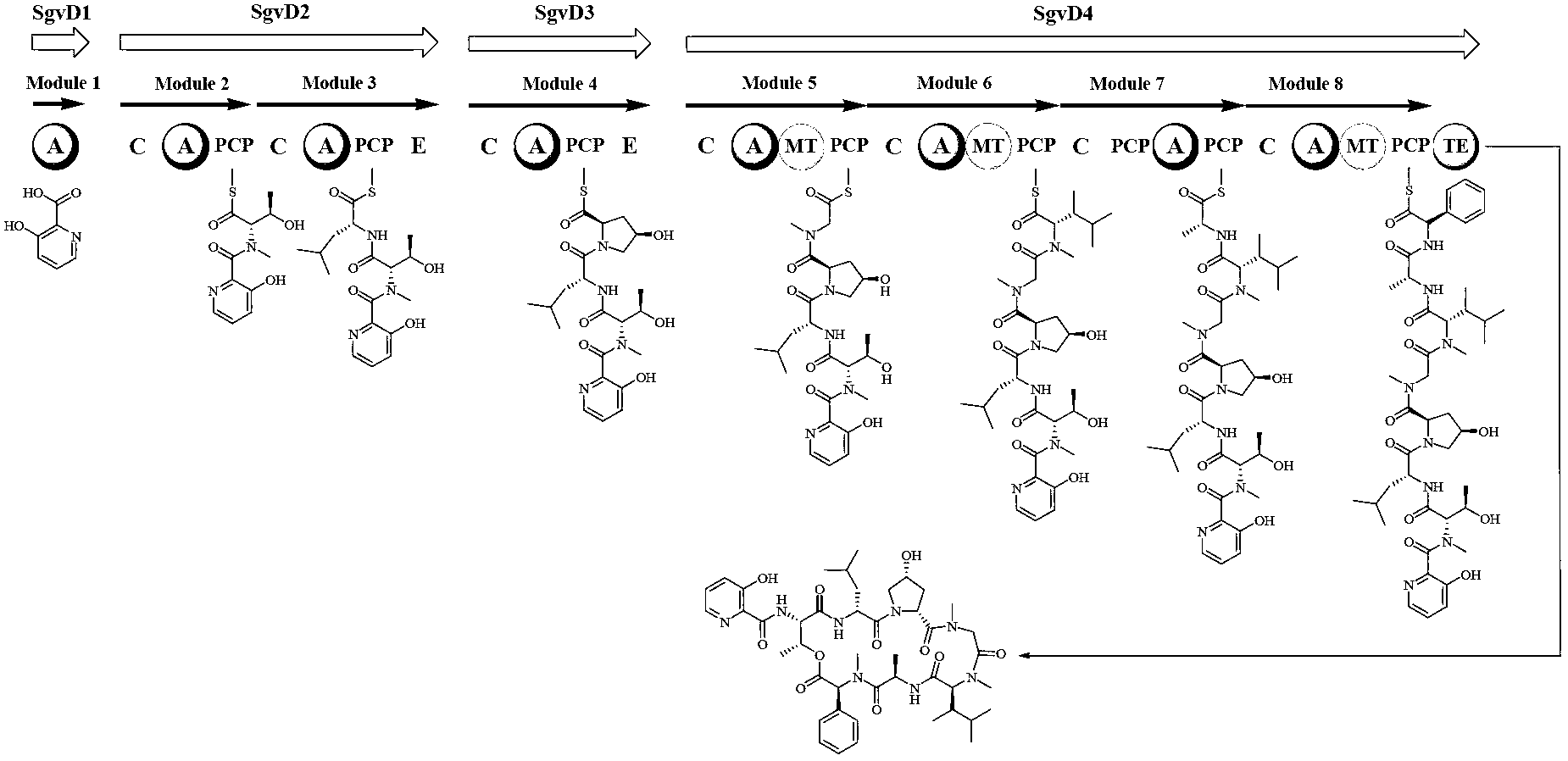
Biosynthesis gene cluster of griseoviridin and viridogrisein and application of biosynthesis gene cluster
The invention discloses a biosynthesis gene cluster of griseoviridin and viridogrisein and application of the biosynthesis gene cluster. A nucleotide sequence of the biosynthesis gene cluster is shown as 13530-118200 bits in a SEQ ID NO.1, the biosynthesis gene cluster includes 36 genes which comprise genes being responsible for framework synthesis and post-tranlational modification of griseoviridin macrolide, the genes being responsible for the framework synthesis of viridogrisein ring lipopeptid, the genes related to coding of gamma-butyrolactone compound synthesis protein and camp receptor protein, the genes for coding and regulating son protein and transportors, the genes for coding precursor synthesis protein of the viridogrisein, the genes for coding dehydrogenase, the genes for coding griseoviridin and viridogrisein biosynthesis process repairing and viridogrisein adjustment and other proteins with unclear functions.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
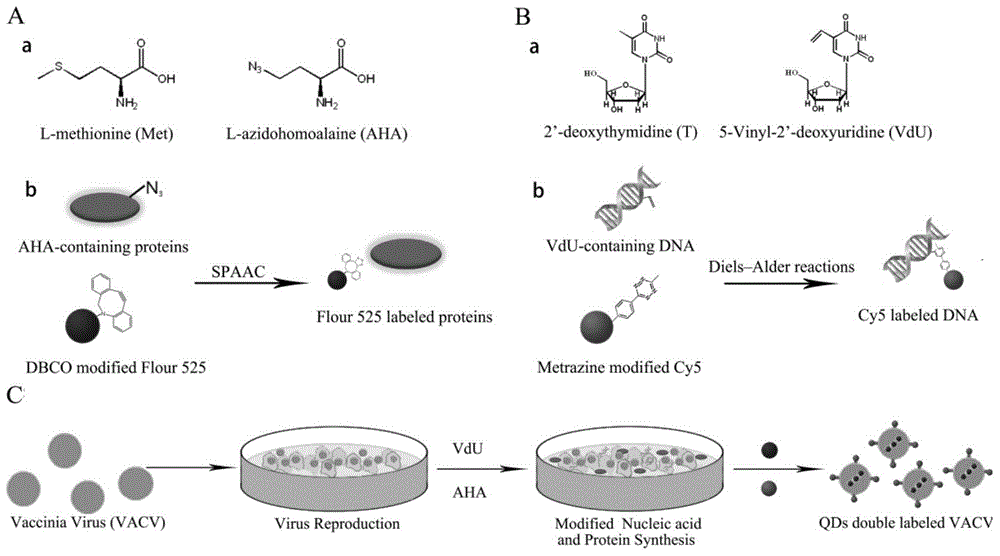
Novel virus double-fluorescence labeling method based on nucleic acid and protein biosynthesis
InactiveCN104894295ALittle effect on activitySimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical reactionViral nucleic acid
The invention relates to a novel virus double-fluorescence labeling method based on nucleic acid and protein biosynthesis, and belongs to the field of chemistry and biomedicine. The method comprises specific steps as follows: a methionine analogue methionine azide and a deoxythymidine analogue ethylene deoxyuridine are synthesized; viruses are added to host cells for infection, methionine azide and ethylene deoxyuridine are added respectively, vinyl derivation of viral nucleic acid and azido derivation of protein are realized with biosynthesis processes of nucleic acid and protein; double-fluorescence labeling of viral nucleic acid and protein is naturally realized through two biological orthogonal reactions including a Diels-Alder reaction of tetrazine-oefin and a copper-free catalytic click chemical reaction of azido-cyclooctyne. The labeling method is simple, convenient and reliable, can be applied to all DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) viruses including single-stranded DNA viruses, double-stranded DNA viruses, enveloped viruses and non-enveloped viruses, and is a universal virus fluorescence labeling method on an absolute basis.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
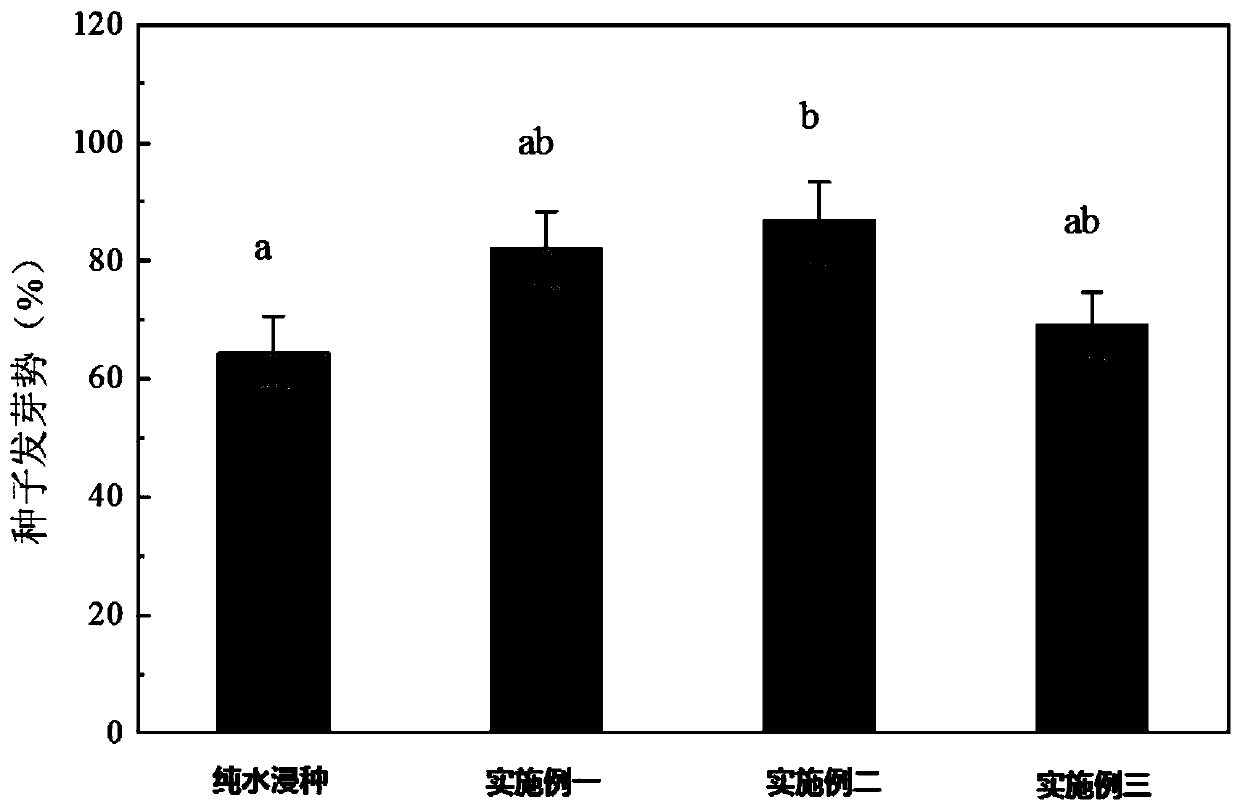
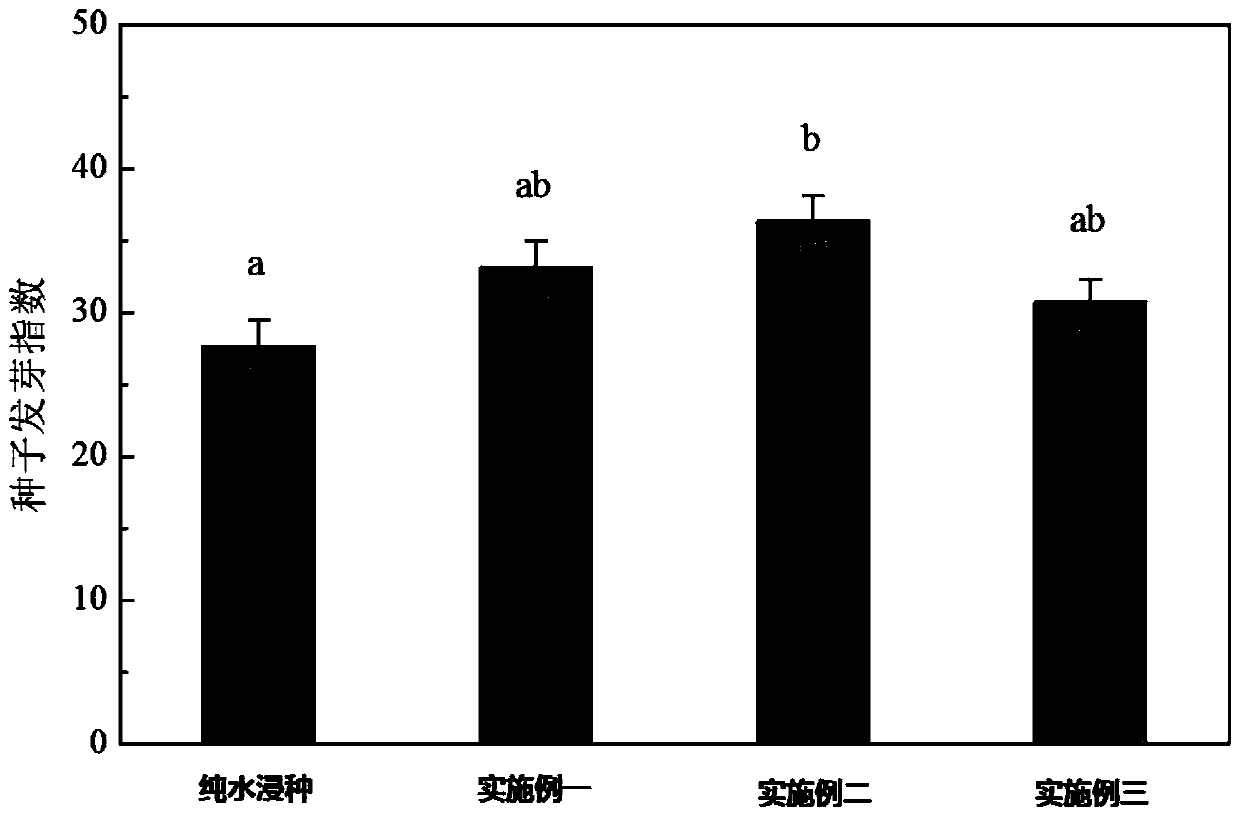
Method for improving germination and growth of corn seeds
InactiveCN110337857AShorten the timeImprove germination rateCereal cultivationSeed immunisationUridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylaseMetabolite
The invention discloses a method for improving germination and growth of corn seeds and relates to the field of crop planting. The method aims to solve the technical problems of low germination rate and long germination period of existing corn seeds. The method comprises the steps of 1, sterilizing the surfaces of the seeds; 2, preparing a seed soaking agent; 3, performing vibrated seed soaking treatment. The method can shorten the average time of seed germination and increase the germination rate, germination vigor, germination index and vigor index of the seeds. The growth and elongation ofa root system and germs are boosted; the activity of hexokinase and uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase is obviously increased, the activity of aldolase is reduced, the activity of phosphofructokinase is maintained at a relatively normal level, the glycolysis metabolism and the biosynthesis process of cell walls are promoted, and metabolic products and energy are provided for the germination and growth of the seeds. The method is used for promoting the germination and growth of the corn seeds.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
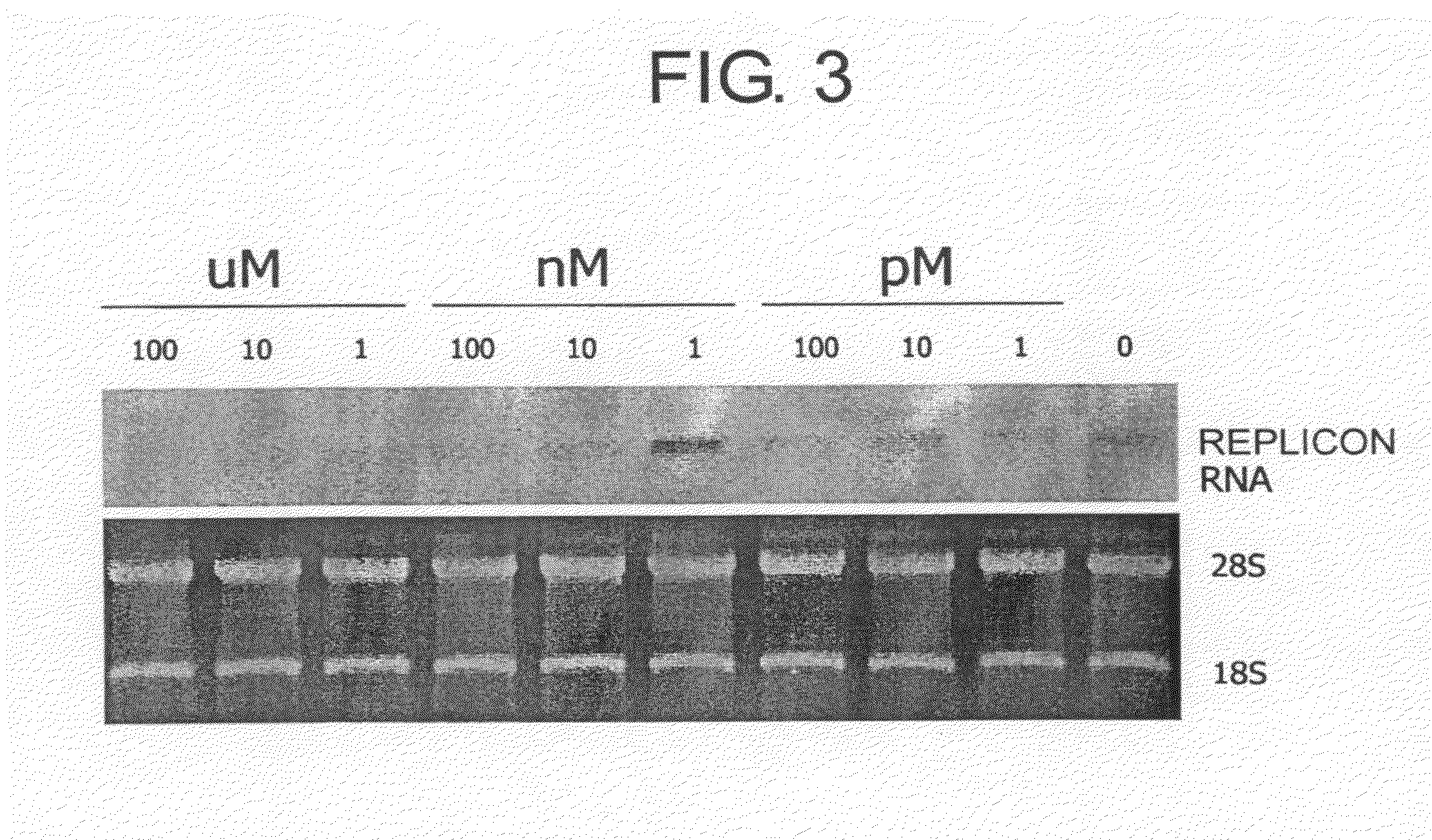
Pharmaceutical agents for treating HCV infections
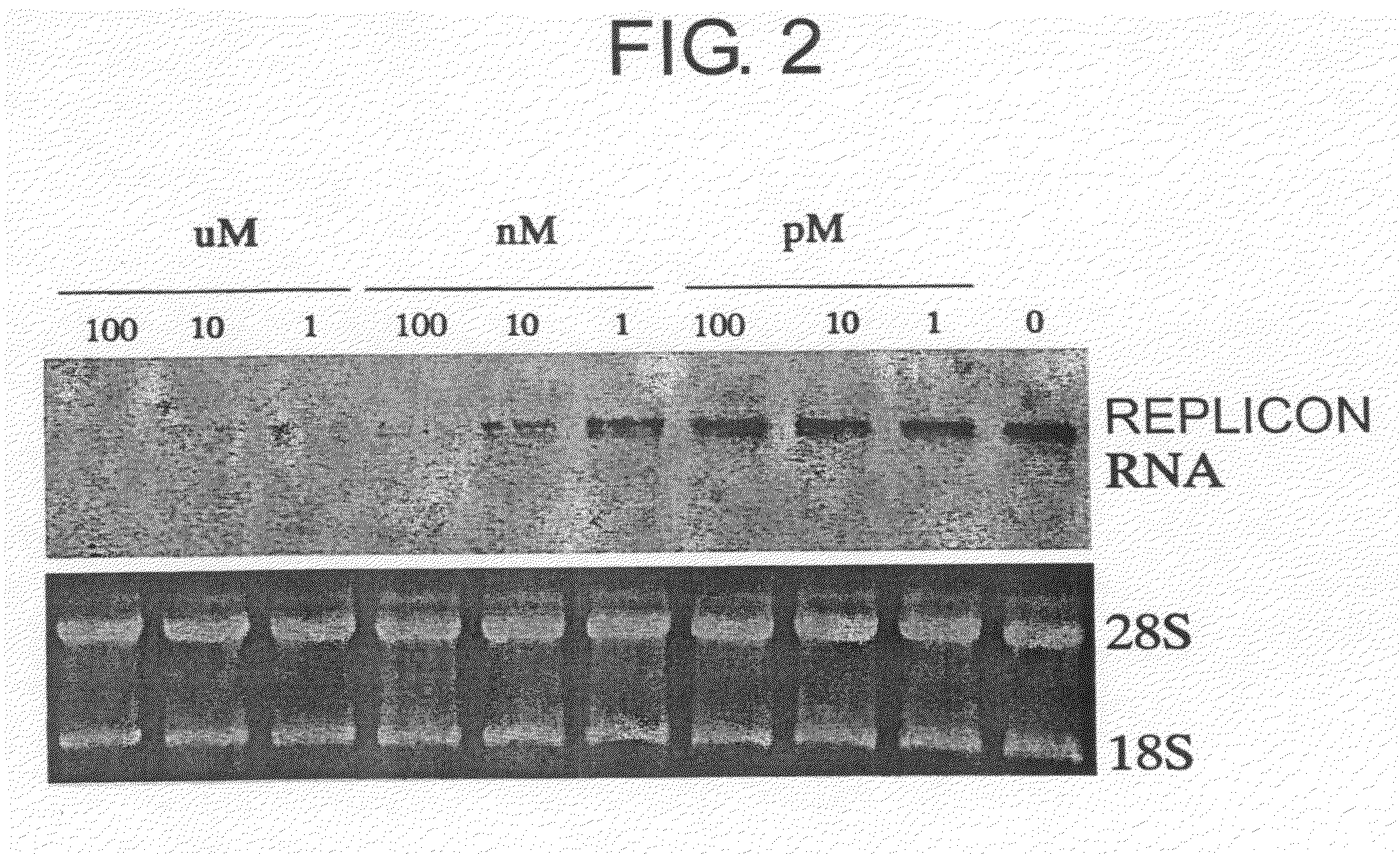
InactiveUS8183005B1Decreasing replicon RNAReduce expressionOrganic active ingredientsSsRNA viruses positive-senseMicroorganismMyriocin
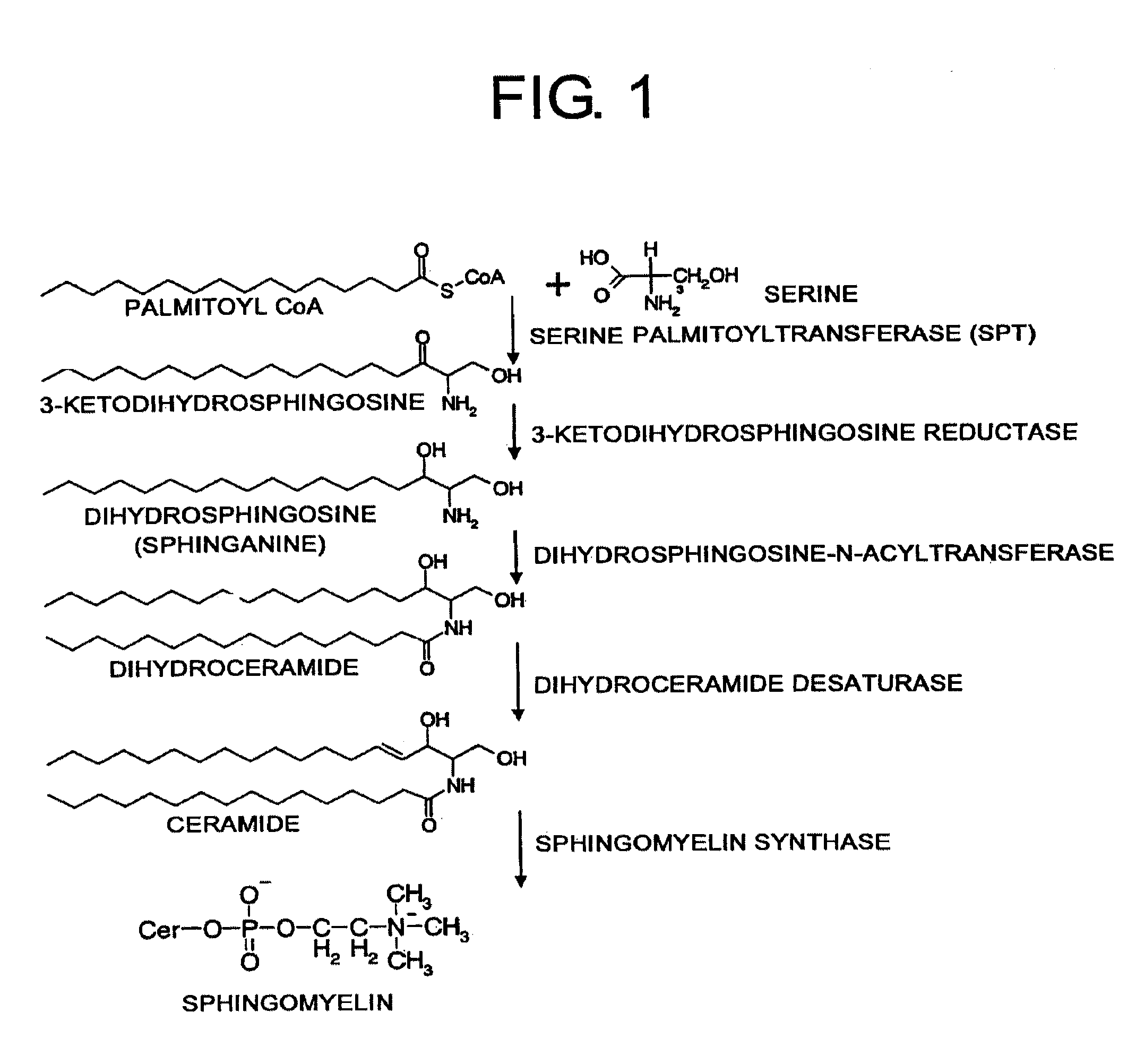
The present inventors examined the inhibitory activity against HCV replicon of myriocin, fumonisin B1, and ceramide trafficking inhibitor HPA-12, which are compounds derived from microorganisms such as those of the genus Aureobasidium, and found that these compounds have the effect of inhibiting the replication of HCV replicon RNAs or inhibiting the expression of HCV proteins. The present inventors further performed serine palmitoyltransferase knockdown experiments using siRNAs, and results showed that HCV replicon activity and HCV protein expression were significantly inhibited in cells with suppressed LCB1 expression. Thus, sphingolipid biosynthesis was found to be involved in HCV infection. This showed that HCV infection can be treated or prevented by inhibiting enzyme activities involved in the process of sphingolipid biosynthesis by adding compounds or knocking down a gene.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
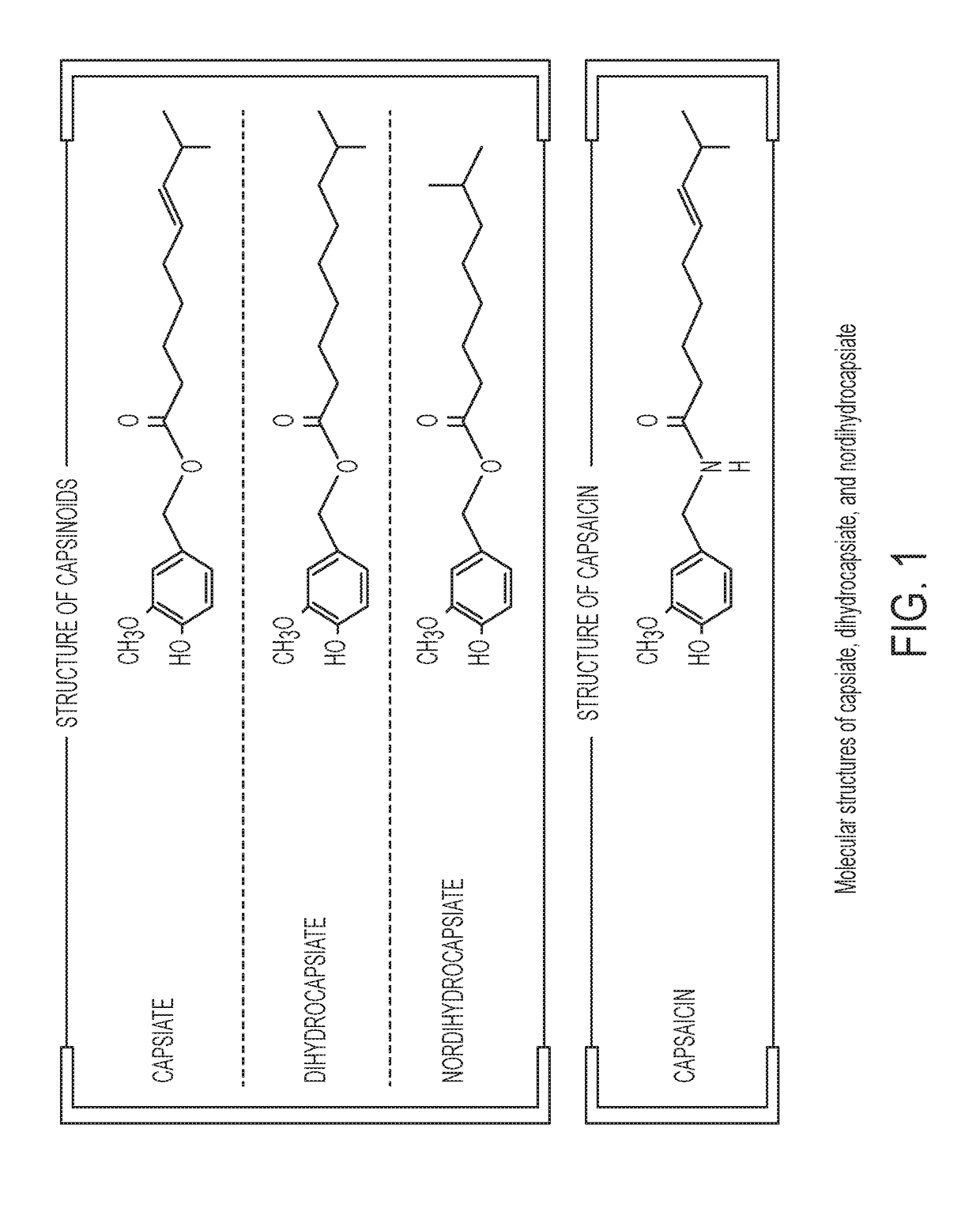
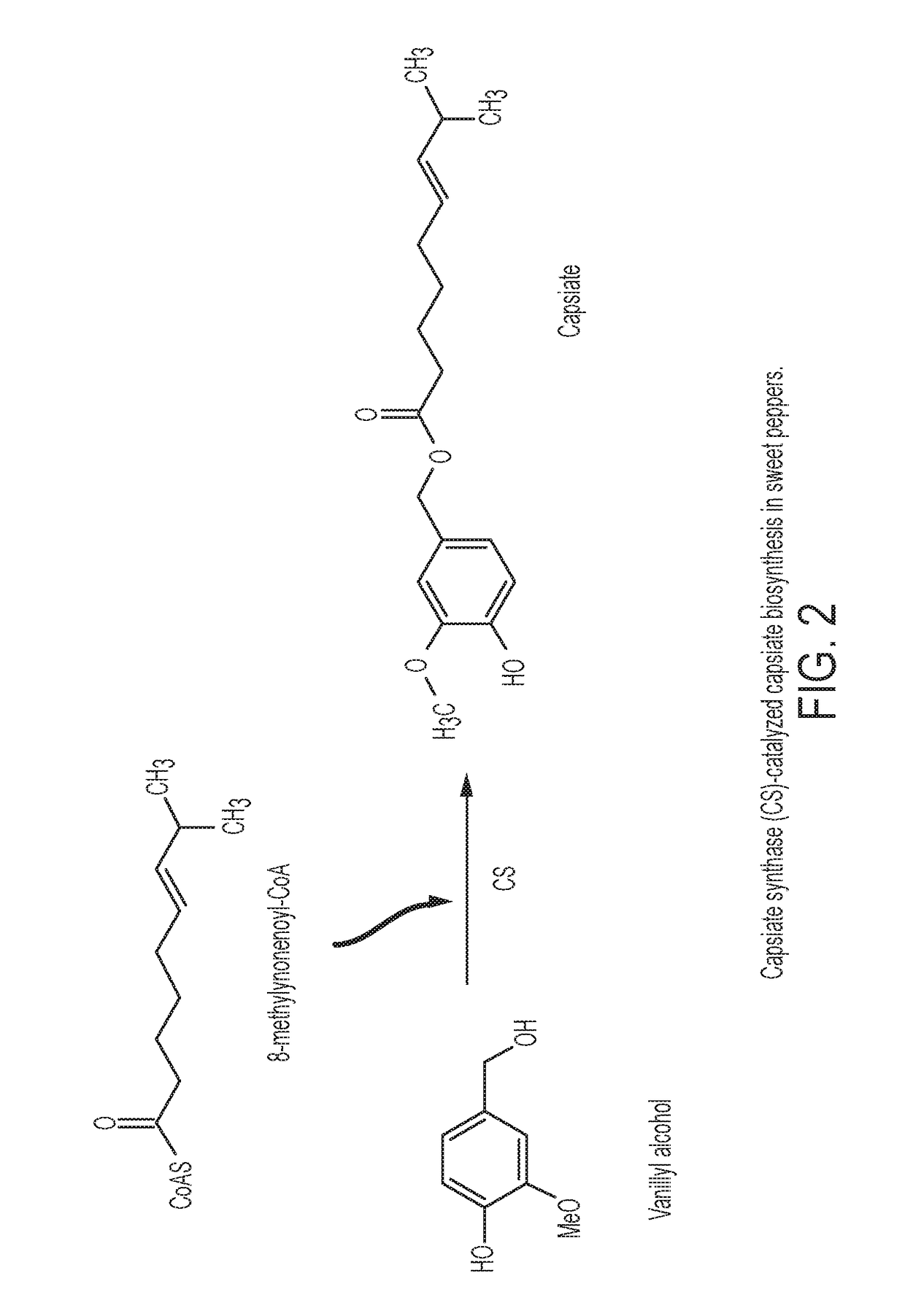
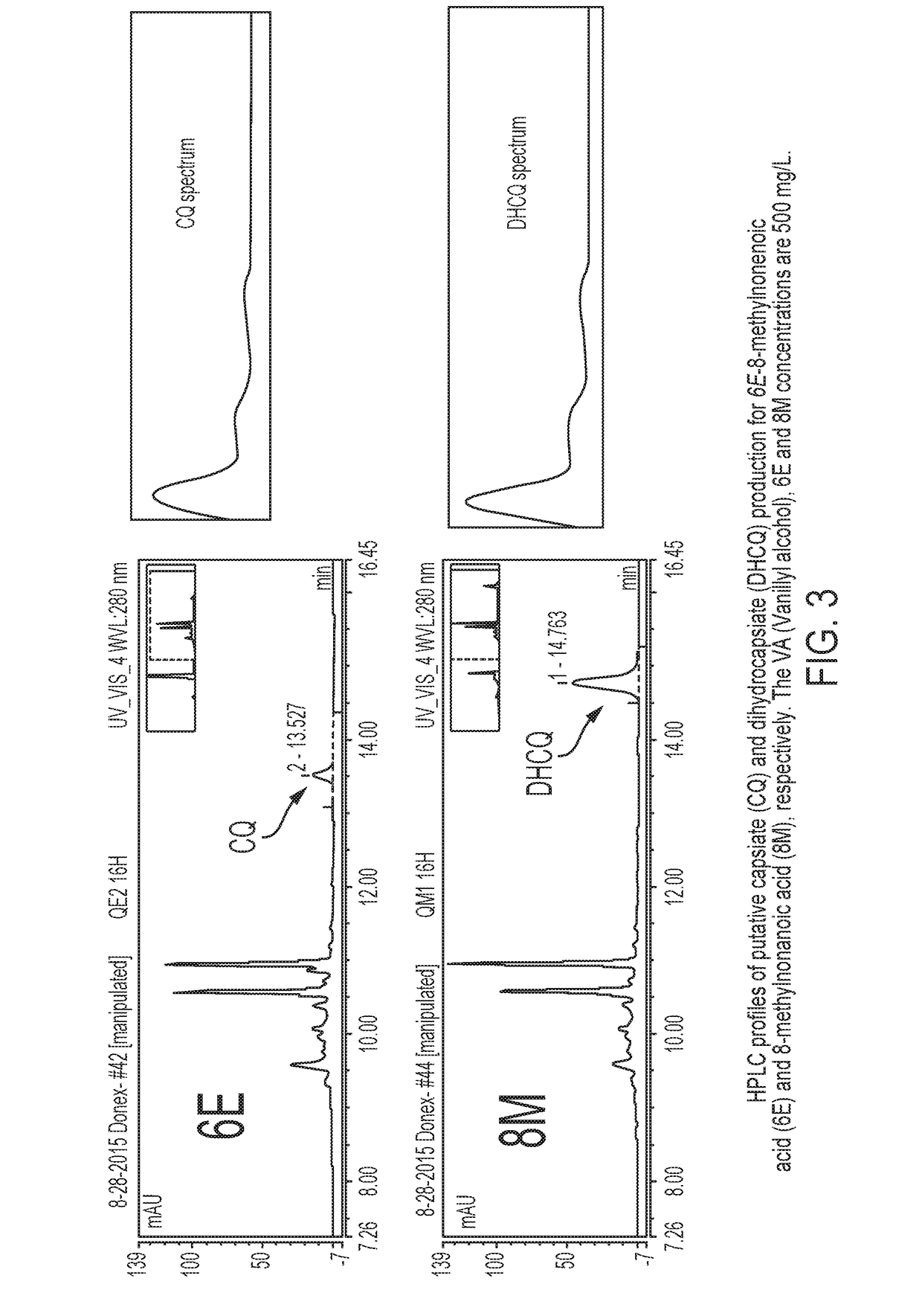
Methods of making capsinoids by biosynthetic processes
ActiveUS20190010522A1Organic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationCellulose biosynthetic processCapsaicin
Provided herein are methods of making capsinoids including providing a capsiate synthase in a mixture or cellular system, feeding 8-methyl-6-nonenoyl-CoA, 6E-8-methylnonenoic acid or 8-methylnonanoic acid into the mixture or cellular system, feeding vanillyl alcohol into the mixture or cellular system, and collecting capsinoids from the mixture or cellular system.
Owner:CONAGEN INC
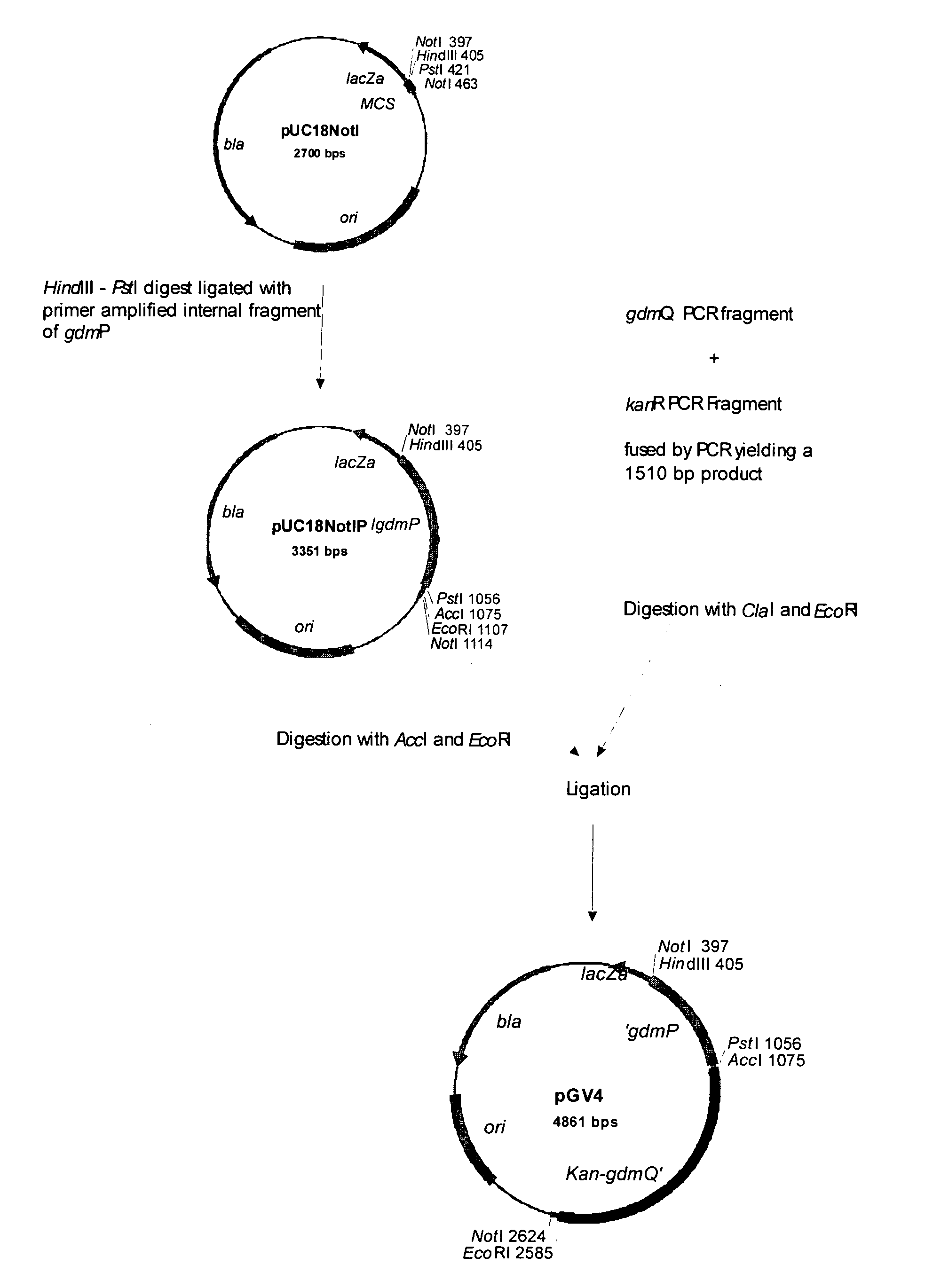
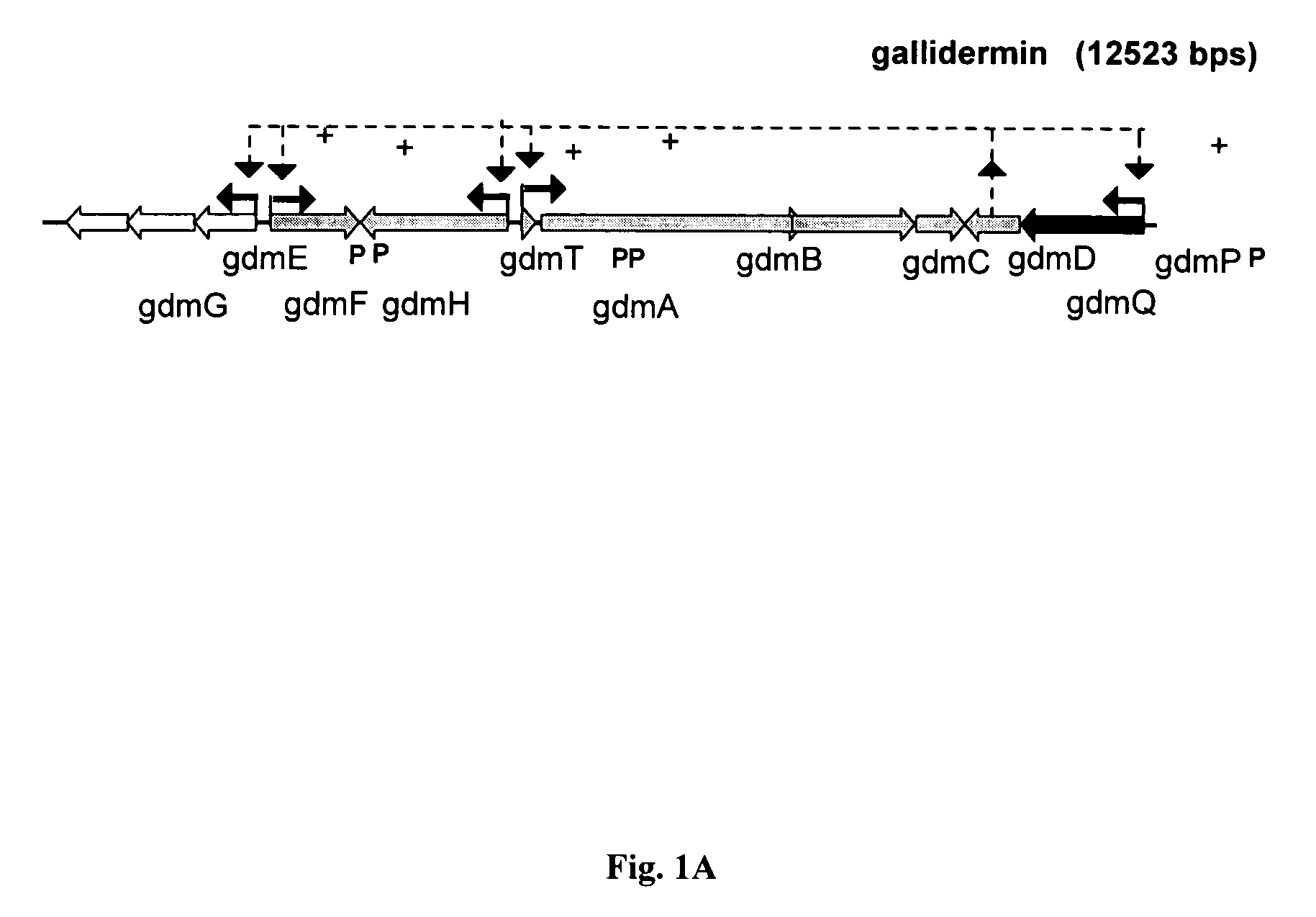
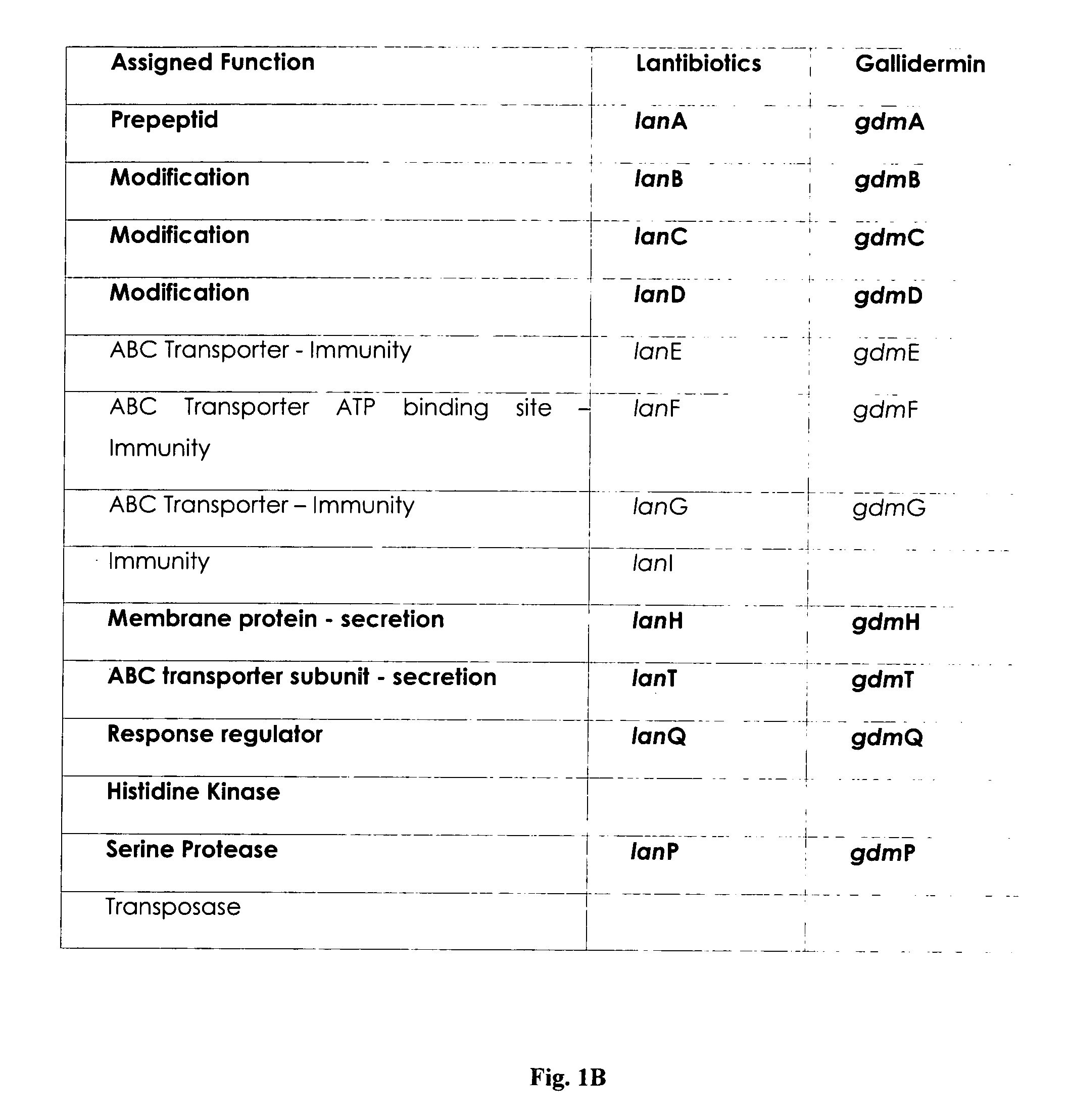
Biosynthetic process for the preparation of gallidermin
A process for the production of gallidermin comprises fermentative production of the respective biologically in-active and non-toxic pre-form(s) by either genetically engineered producer organism or mutants of the natural producer organism that are deficient for the extracelluar gallidermin pathway specific serine-pro tease. The process includes a downstream process in which a pre-form of gallidermin is isolated from the fermentation and bio-catalytically activated, followed by purification of the mature and active gallidermin.
Owner:BIOTECH CONCEPTS
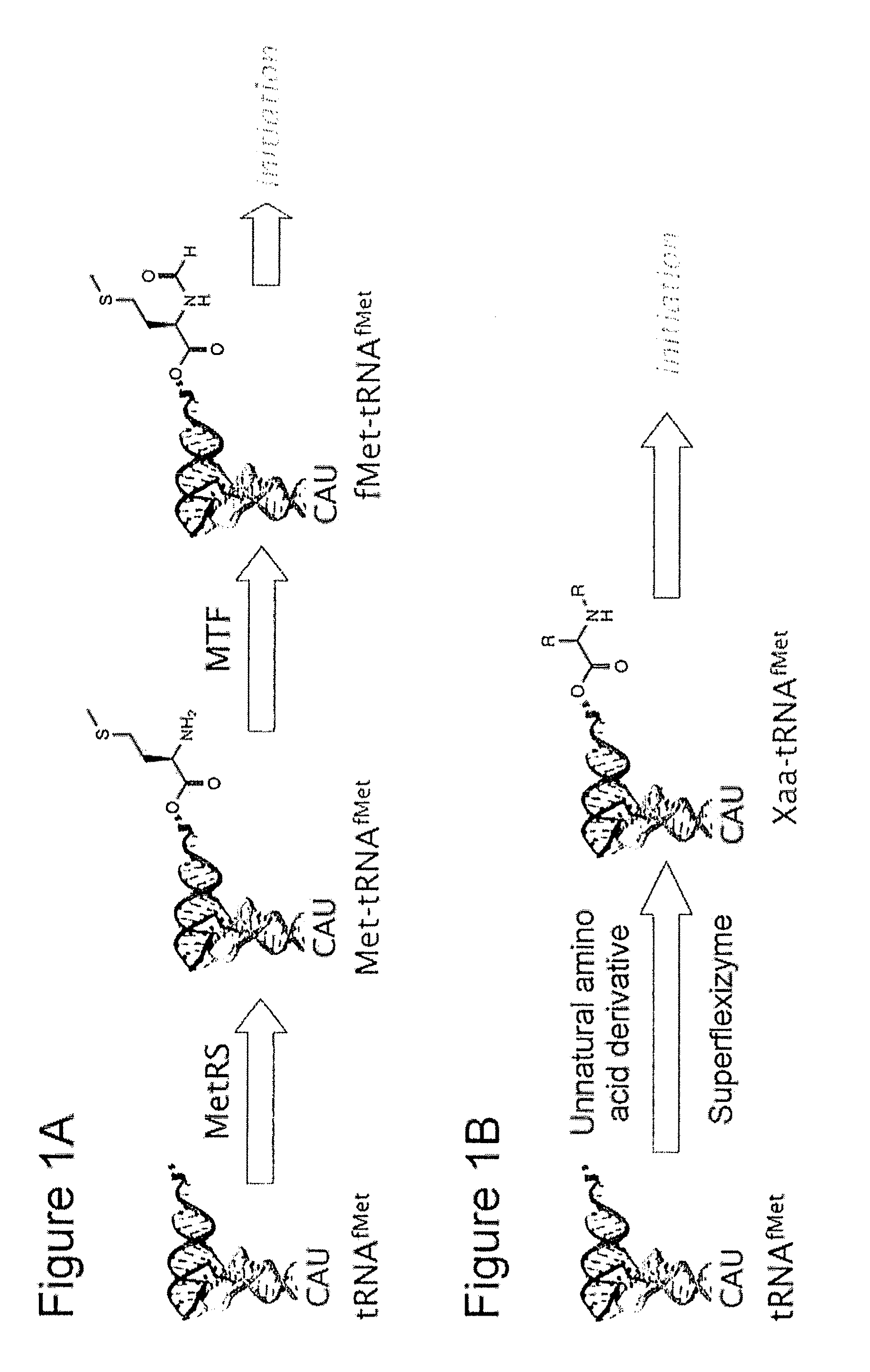
Methods for ribosomal synthesis of polypeptides containing unnatural n-terminal groups and applications thereof
The present invention aims to synthesize a polypeptide having an unnatural structure at the N-terminus via a biosynthetic process by translation of amino acid sequence information encoded by a nucleic acid. A polypeptide having any amino acid at the N-terminus is synthesized by using an ARS ribozyme that catalyzes the acylation of tRNA with any amino acid to attach any amino acid to an initiator tRNA, thereby initiating a translation with the initiator tRNA.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
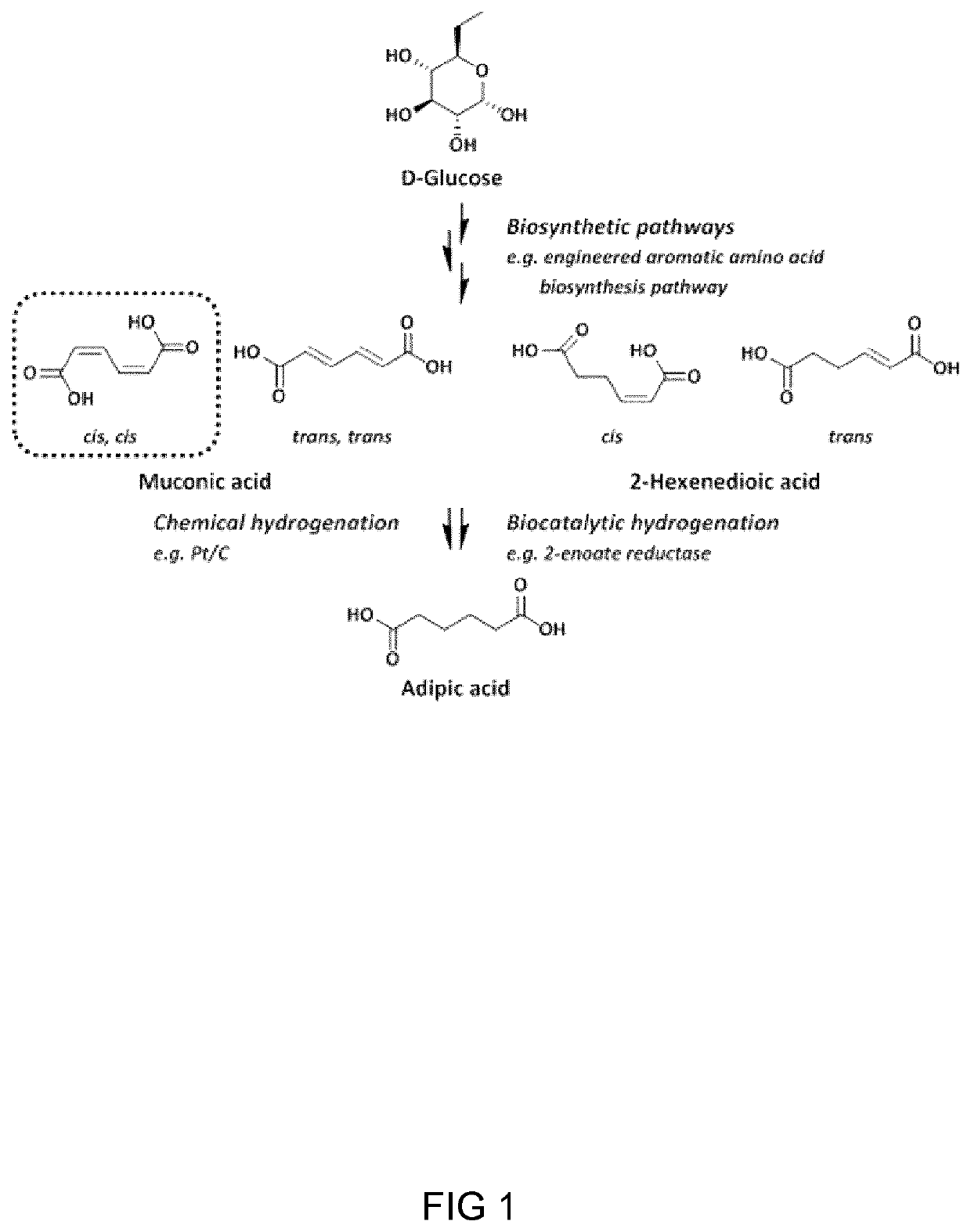
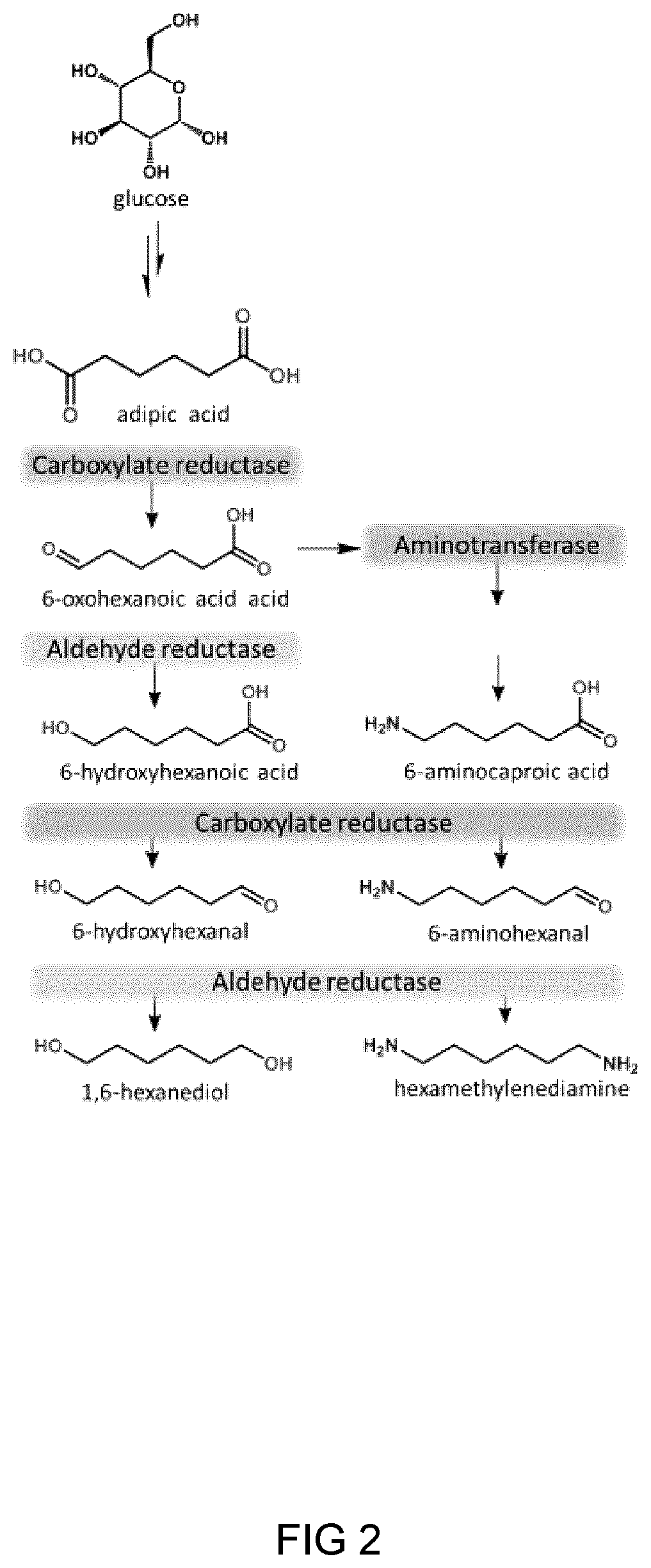
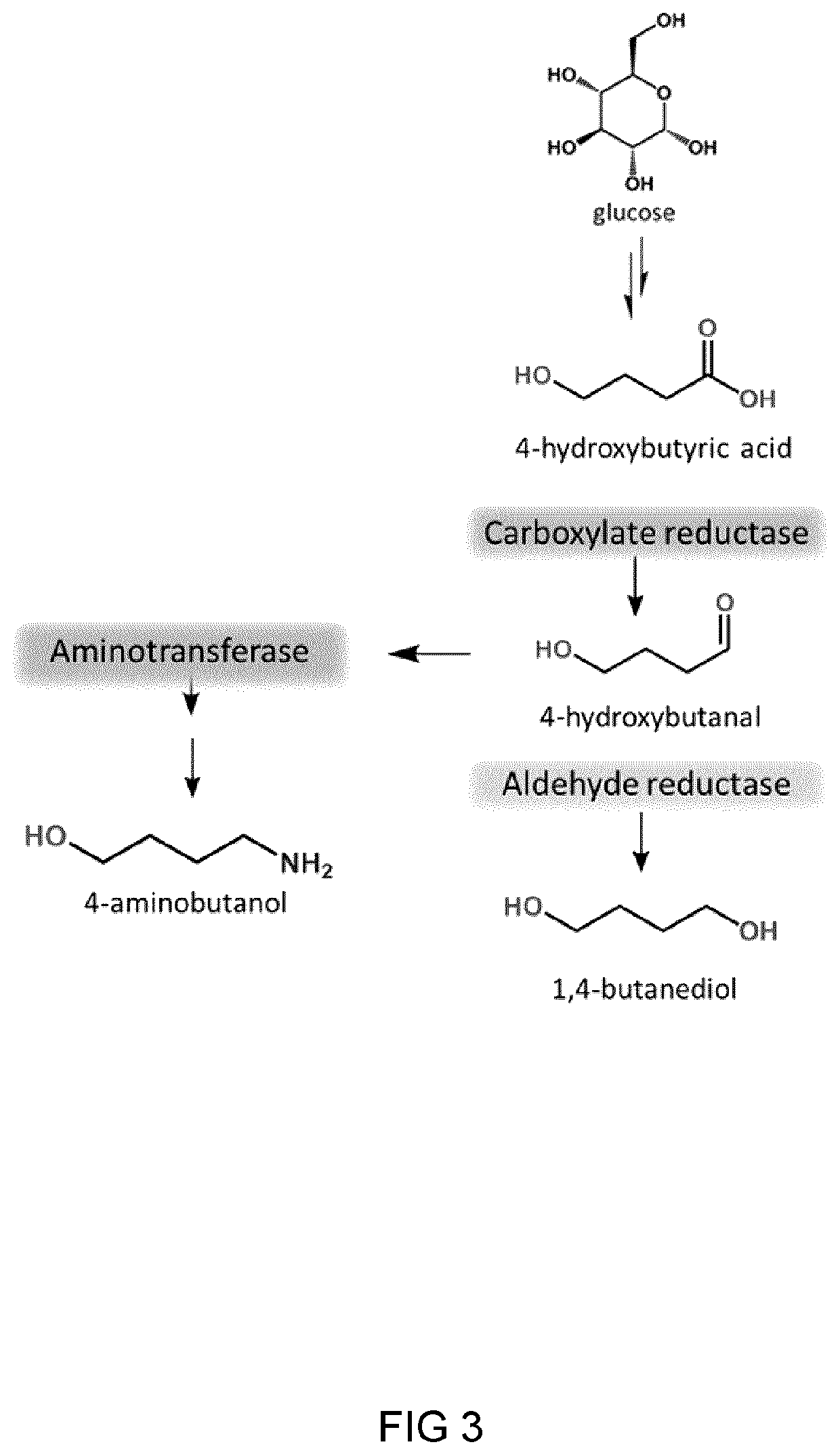
Process And Microorganism For Synthesis Of Adipic Acid From Carboxylic Acids
A method for biosynthesis of polymer precursors, including, adipic acid, 1,6-hexanediol, 6-hydroxyhexanoic and 6-aminocaproic acids from carboxylic acids is provided. A method for biosynthesis of adipic acid from six-carbon dicarboxylic acids having α, β-enoate reductase activity by treatment with an enzyme is provided. The biocatalytic conversion of aliphatic and hydroxycarboxylic acids to corresponding aldehydes, alcohols, and amines using novel carboxylate reductases, aldehyde reductases, and aminotransferases is described. Also provided are genetically engineered microorganisms for use in the biosynthetic processes.
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO
Pavlova-viridis-derived delta-6 desaturase new gene
The invention relates to a Pavlova-viridis-derived delta-6 desaturase new gene. Polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and dehydroacetic acid (DHA), are important nutrient substances which are necessary for the human body and can not be synthesized by the human body. In view of the microalga-Pavlova viridis capable of naturally synthesizing EPA and DHA, a conserved region sequence amplification-RACE combined method is used for for cloning to obtain the new delta-6 fatty acid desaturase gene. The acquisition of the gene provides references for further recognizing and utilizing the biosynthesis process of the EPA and DHA which have high practical significance.
Owner:广州诺晶生物技术有限公司
miRNA biosynthesis inhibitor
The invention provides a compound shown as a formula I, or a conformational isomer thereof, or an optical isomer thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The compound can be tightly combined with related binding proteins in an miRNA biosynthesis process and can effectively inhibit the synthesis of miRNA-21. The prepared active compound provided by the invention can be used as an miRNA-21 inhibitor, and further as a potential drug for treating malignant tumors. The formula I is shown in the description.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Protein related to Perilla frutescens L. terpene substance biosynthesis, encoding gene of protein, and application
InactiveCN112746062AIncrease terpenoid contentTransferasesFermentationNicotiana tabacumPlant terpene
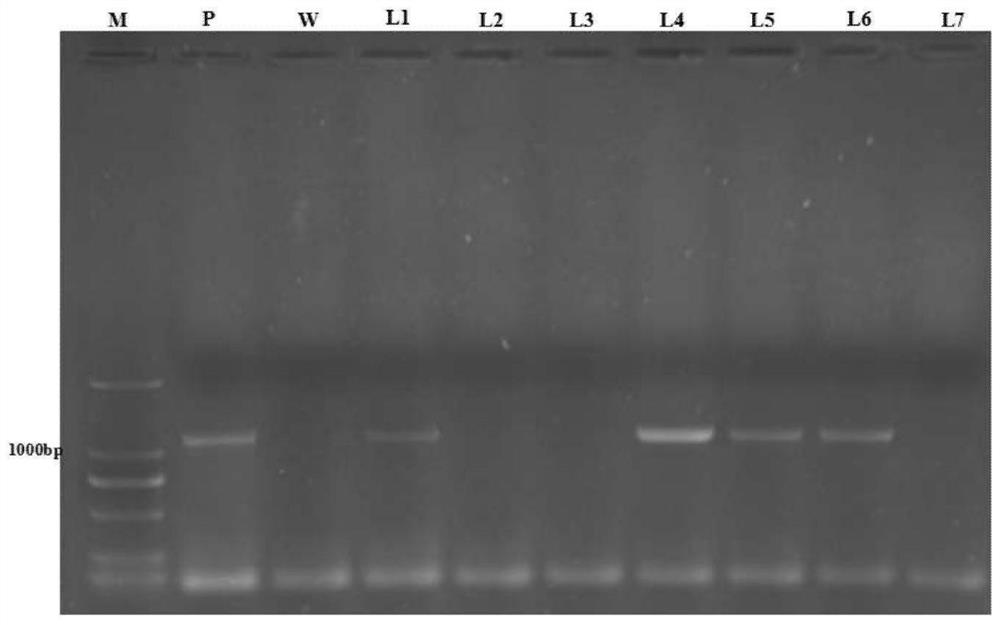
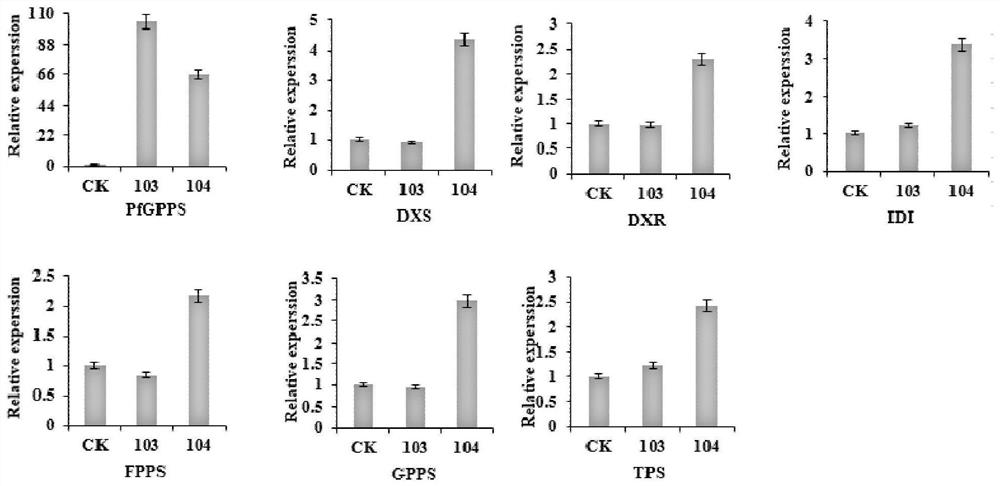
The invention discloses a protein related to Perilla frutescens L. terpene substance biosynthesis, an encoding gene of protein, and application, and is the protein consisting of an amino acid sequence disclosed by a sequence 2 in a sequence table, and a gene which encodes the protein related to the Perilla frutescens L. terpene substance biosynthesis, and the encoding sequence of the gene is a DNA molecule disclosed by a sequence 1 in the sequence table. The invention provides a pfGPPS protein and an encoding gene thereof, the encoding gene is imported into tobaccos to obtain a tobacco plant which carries out overexpression on a pfGPPS gene, then, the transgenosis tobacco plant is subjected to pot culture, during a mature period, transgenosis tobacco leaves are harvested, and the content of terpene substances is detected through GC-MS. Compared with wild tobaccos, the content of the terpene substances in the transgenosis tobacco is obviously improved. Therefore, the pfGPPS gene and the protein encoded by the pfGPPS gene perform an important function in a plant terpene substance biosynthesis process. The pfGPPS gene provided by the invention and the protein encoded by the pfGPPS gene have an important application value in research of improvement of the content of the plant terpene substances.
Owner:河北省农林科学院经济作物研究所
Recombinant expression vector, genetically engineered bacterium containing recombinant expression vector and application of genetically engineered bacterium
PendingCN112877349AReduce inhibitionIncrease consumptionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMetaboliteTransformation efficiency
The invention discloses a recombinant expression vector. The recombinant expression vector comprises a specific gene of p-coumaroyl-CoA ligase and a specific gene of stilbene synthetase. When the recombinant expression transformant containing the recombinant expression vector is applied to the biosynthesis process of the denisolin, the inhibition of an intermediate metabolite cinnamyl-coenzyme A and the denisolin on cinnamic acid conversion can be effectively reduced, the consumption of a substrate cinnamic acid is increased, and the conversion efficiency from the cinnamic acid to the denisolin is greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Biosynthesis method of perylenequinonoid compounds
InactiveCN105624226AIncrease profitIncrease productivityMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyBrick
The invention discloses a biosynthesis method of perylenequinonoid compounds, in particular a biosynthesis method of perylenequinonoid compounds and specifically relates to optimization of a fermentation process in a biosynthesis process. A fungus, which grows in Yunnan western mountainous area and is identified to belong to ascomycetes, hypocreaceae and hypornyces, serves as a strain and a solid mixture, which contains maize powder, wheat bran and bean drges, is taken as a solid-state culture medium. The solid-state culture medium is sterilized and the strain is inoculated, and fermentation is conducted at 21-23 DEG C for no less than 9 days, so that a brick-red solid fermented product containing the perylenequinonoid compounds is obtained, therefore a bacterium block containing the perylenequinonoid is obtained through biosynthesis, wherein the bacterium block contains biosynthesis products of the invention, namely such perylenequinonoid compounds as elsinochrome A, hypocrellin A, hypocrellin B, hypomycin A and B, and the like. A finished perylenequinonoid compound product can be obtained by drying and crushing the bacterium block and by extracting and separating. According to the biosynthesis method disclosed by the invention, the total amount of the perylenequinonoid compounds in the finished product is improved.
Owner:赵建英
New delta12 desaturase gene derived from Pavlova viridis
The invention provides a new delta12 desaturase gene derived from Pavlova viridis. Polyunsaturated fatty acids such as conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and the like are necessary important nutrient substances of human bodies. Aiming at microalgae, namely Pavlova viridis which is capable of naturally synthesizing lots of polyunsaturated fatty acids, a new delta12 desaturase gene is cloned by combining conservative region sequence amplification with RACE (rapid-amplification of cDNA ends), thereby providing the basis further knowing and utilizing biosynthesis processes of linoleic acid and conjugated linoleic acid which have great practical significances.
Owner:江苏桂龙生物技术有限公司
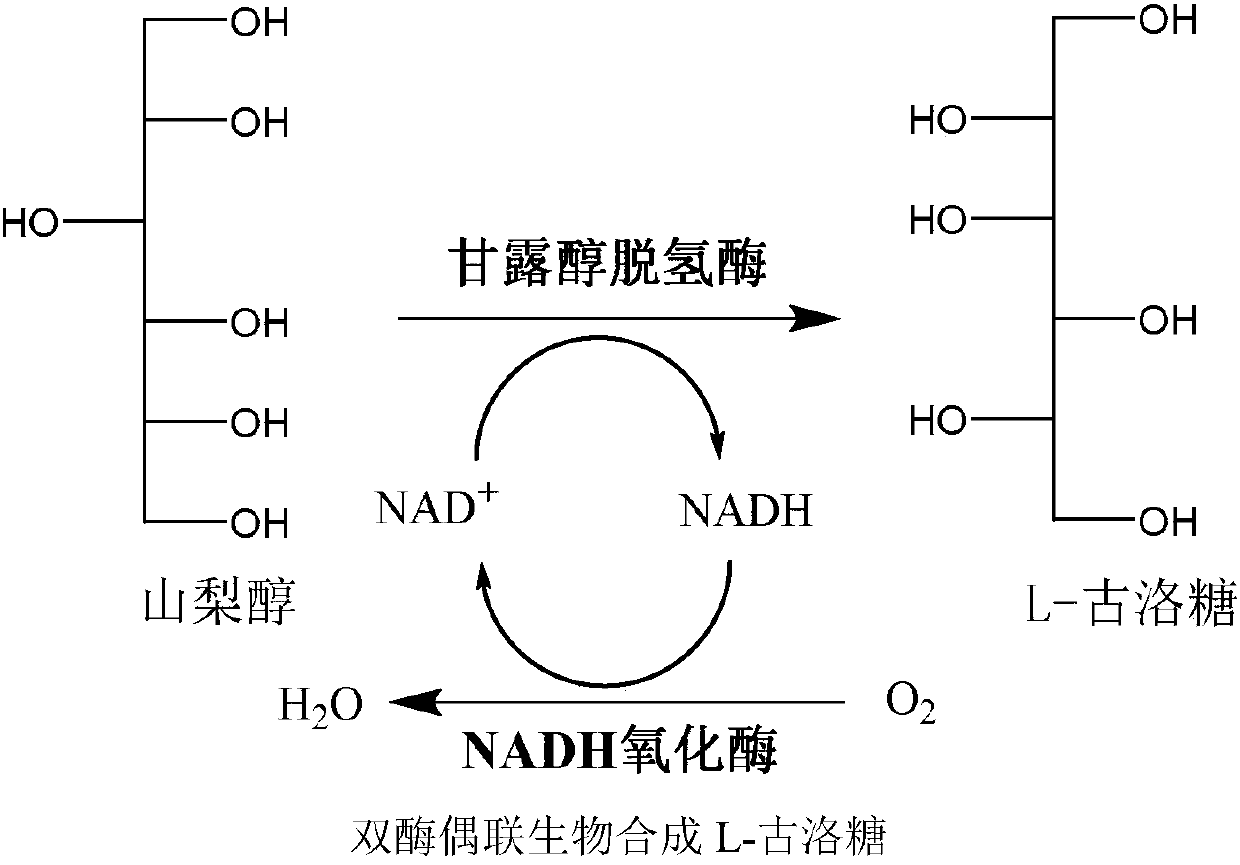
Preparation method for L-gulose
InactiveCN107937455AEfficient Green BiosynthesisAchieve inhibitionFermentationEscherichia coliVitamin C
L-gulose is a rare aldohexose, which can be used as a synthetic precursor of vitamin C and a drug intermediate for the synthesis of nucleoside antiviral drugs, with high potential economic value. In view of the shortcomings of the existing gulose synthesis process, the present invention co-expressed NAD+-dependent mannitol dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase in Escherichia coli to construct a whole-cell biocatalyst. A green biosynthetic process for the preparation of L-gulose.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
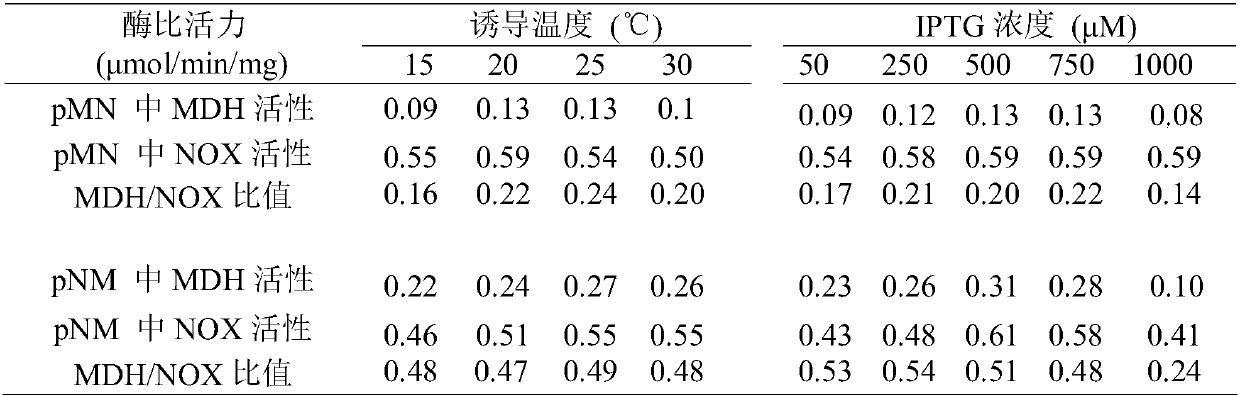
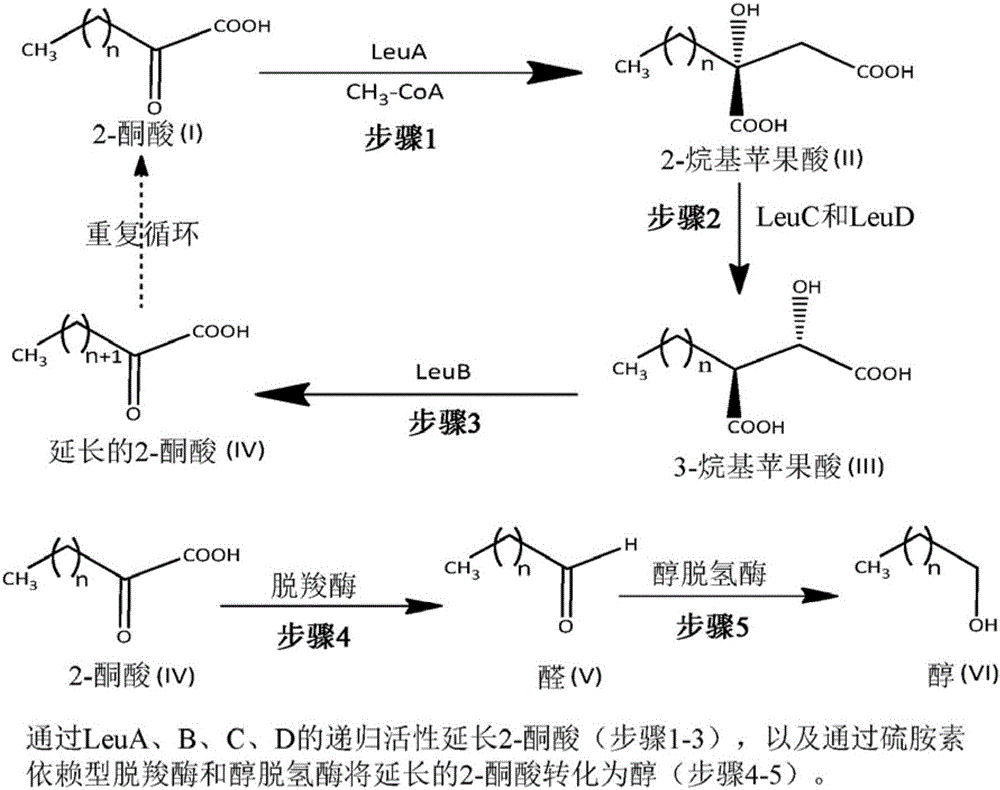
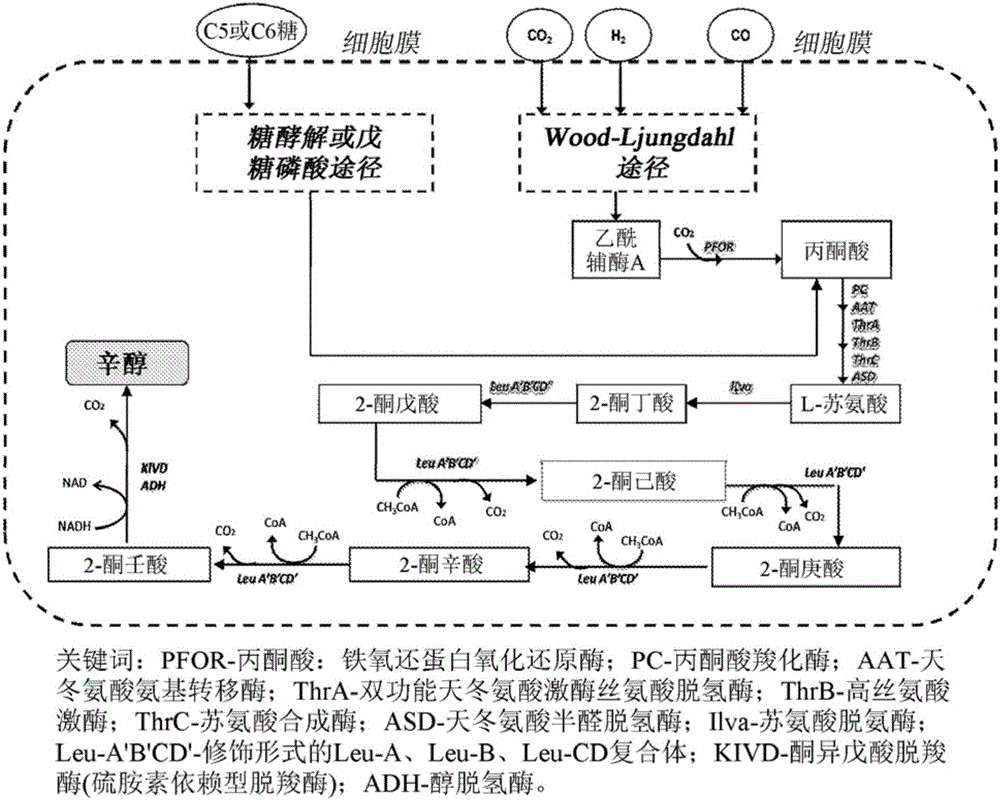
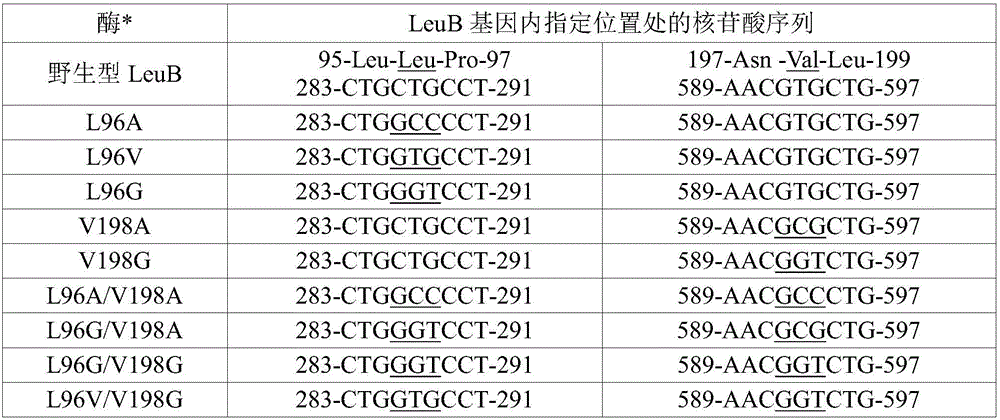
Processes to prepare elongated 2-ketoacids and c6-c10 compounds therefrom via genetic modifications to microbial metabolic pathways
Modification of metabolic pathways includes genetically engineering at least one enzyme involved in elongating 2-ketoacids during leucine biosynthesis, and preferably at least isopropylmalate dehydrogenase or synthase (LeuB or LeuA in E. coli), to include at least such non- native enzyme, enzyme complex, or combination thereof to convert 2-ketobutyrate or 2-ketoisovalerate to a C7-C11 2-ketoacid, wherein the production of such is at a higher efficiency than if a purely native pathway is followed. The C7-C11 2-ketoacid may then be converted, via a native or genetically engineered thiamin dependent decarboxylase, to form a C6-C10 aldehyde having one less carbon than the C7-C11 2-ketoacid being converted. In some embodiments the C6-C10 aldehyde may then be converted via additional native or genetically engineered enzymes to form other C6-C10 products, including alcohols, carboxylic acids, and alkanes. This genetic engineering offers the opportunity for commercial scale of in vivo biosynthetic processes that may be more cost-efficient than non- biobased approaches to produce the same products.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Application of sphingolipid inhibitor for preparing medicine of inhibiting iron overload disease
InactiveCN109432076AOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsSphingolipid metabolismIsrapafant
The invention discloses application of a sphingolipid inhibitor for preparing a medicine of inhibiting an iron overload disease. The sphingolipid inhibitor is Myriocin. A new mechanism of ferroptosisis that excessive iron ions accelerate the synthesis of sphingolipid and activates a PDK1-SGK1 signal path to cause cell death. In addition, Myriocin inhibits serine palmitoyl transferase in a sphingolipid biosynthesis process to inhibit the synthesis of sphingolipid so as to rescue cell ferroptosis. The invention provides a theoretical basis for treating the iron overload disease which takes theferroptosis as a target, and especially provides a basis for researching and developing diseases caused by chronic iron overload.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method of saccharomycetes bio-synthesing, producing optical pure adenosine methionine and its culture solution
InactiveCN1955306ALow costSimple manufacturing methodFungiFermentationBiotechnologyS-Adenosyl-l-methionine
This invention provides a yeast fungus biosynthesis preparation of optical rotation adenosyl methionine. Biosynthesis of adenosyl methionine is conducted using yeast fungus by importing air into nutrient solution containing carbon source, methionine and vitamin, stirring and add carbon source during the biosynthetic process. This invention also discloses a preparation of producing optical rotation adenosyl methionine with above-mentioned method, and provides a nutrient solution for yeast fungus biosynthetic optical rotation adenosyl methionine. The level of biosynthetic adenosyl methionine will reach 10g / l, and the purity of the products is over 98.5%, with containing more than 97.0% (S,S)-type. This method is simple and of low cost, so it is easy to produce in great scale.
Owner:SHANGHAI DUOMIRUI BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD +1
Novel regulation protein
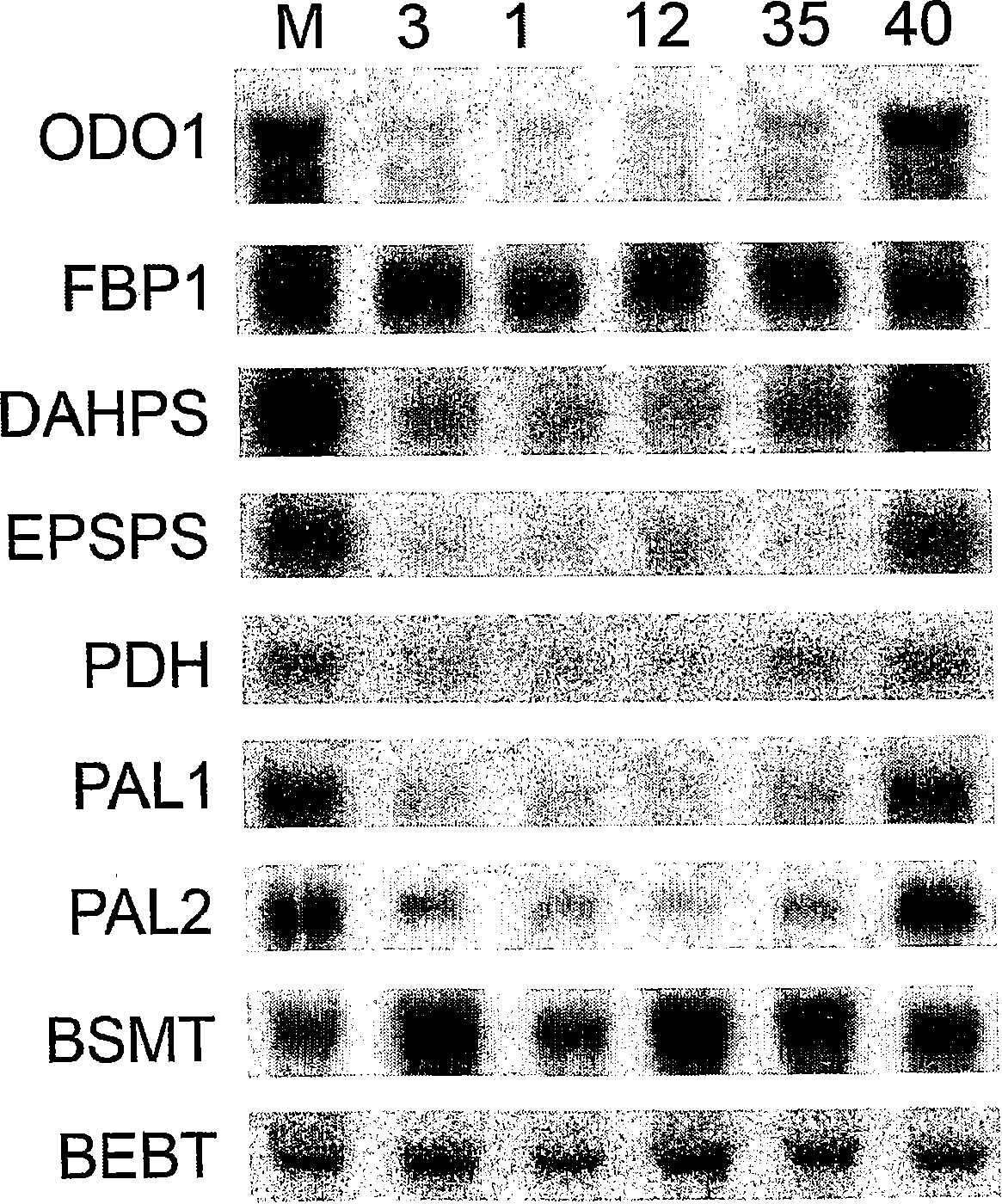
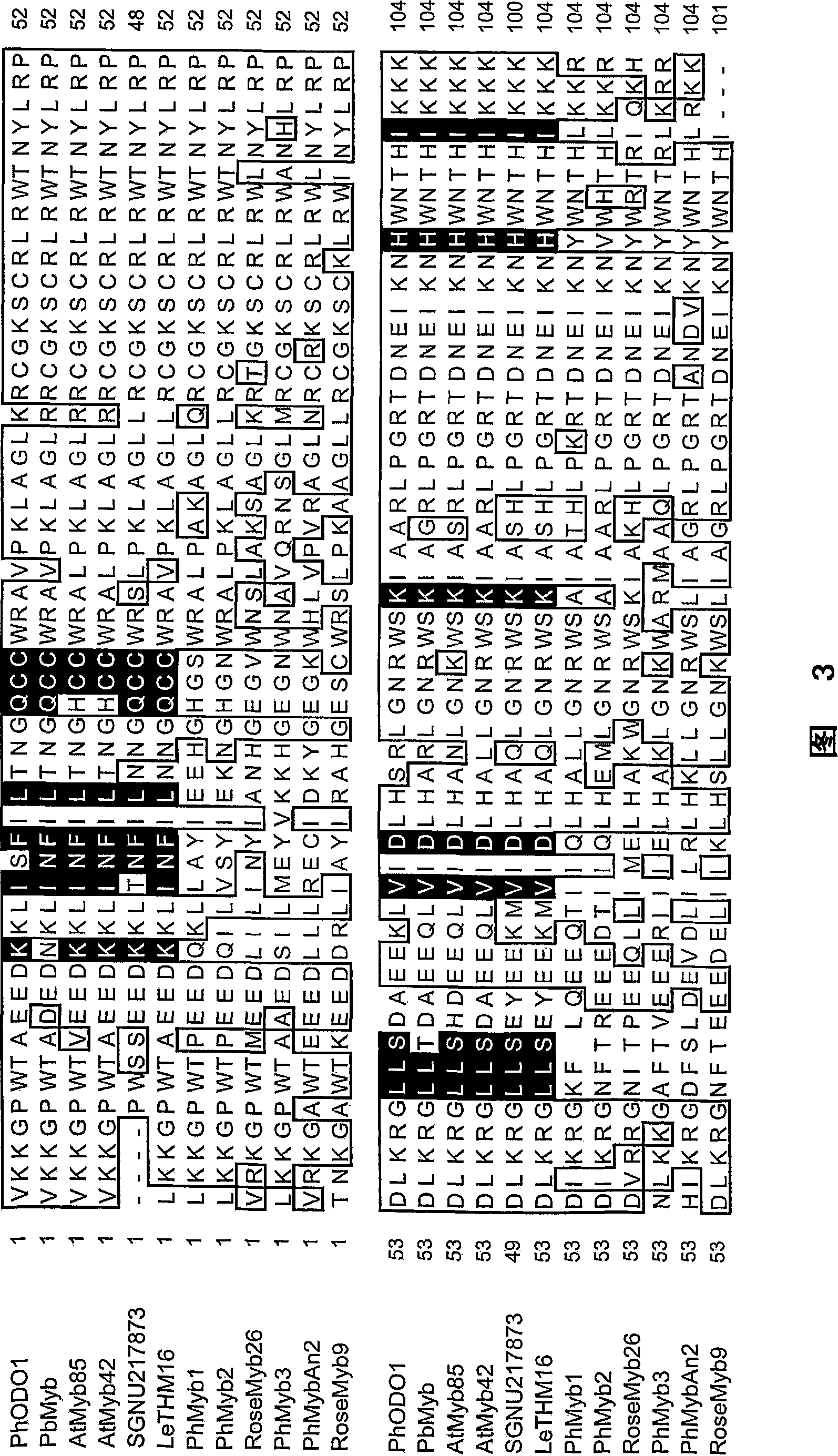
The present invention relates to a polypeptide which belongs to the R2R3-type MYB family and which regulates the shikimate pathway towards the production of benzenoids. The shikimate pathway is a biosynthesis pathway through which the three essential aromatic amino acids tyrosine, phenylalanine and tryptophane are synthesized in plants, bacteria and fungi. The present inventiont provides for the first time a regulatory protein in the shikimate pathway and a means to regulate the biosynthesis of these three essential amino acids which cannot be produced by mammals. At the same time, it opens up the way for the regulation of the biosynthesis of aromatic and-non- aromatic compounds which are derived from these essential amino acids. A polypeptide or polynucleotide of the invention may be used in a method for manipulating the transcript levels of the genes of the shikimate pathway towards benzenoids for instance the genes of 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase (DAHPS), 5-enol-pyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS), L- phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) and chorismate mutase (CM). Through these enzymes, biosynthetic processes at lower levels may be influenced. For instance, compounds of the invention may be used in a method to regulate scent in flowers or to regulate resistance to pest insects or pathogenic organisms.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com