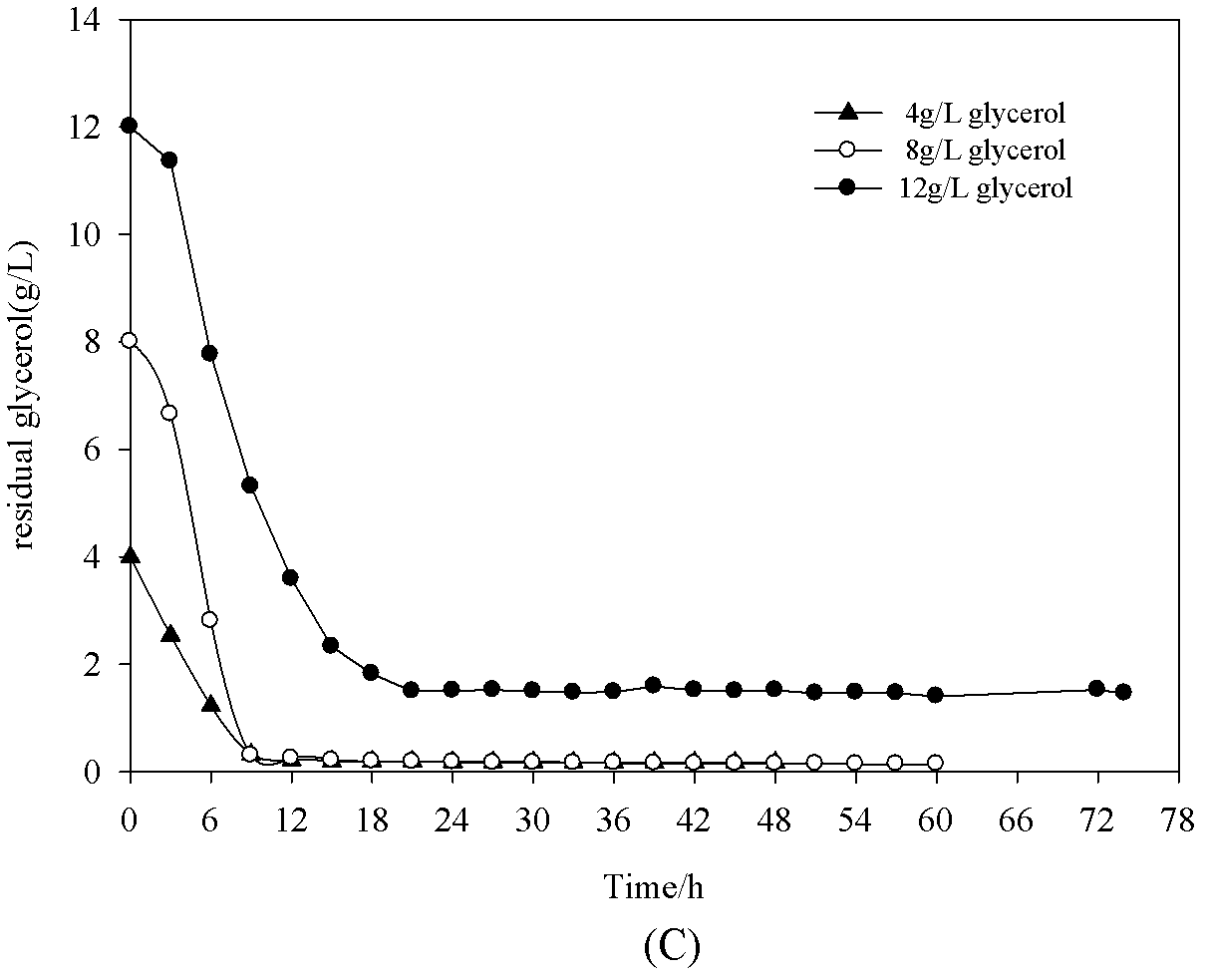
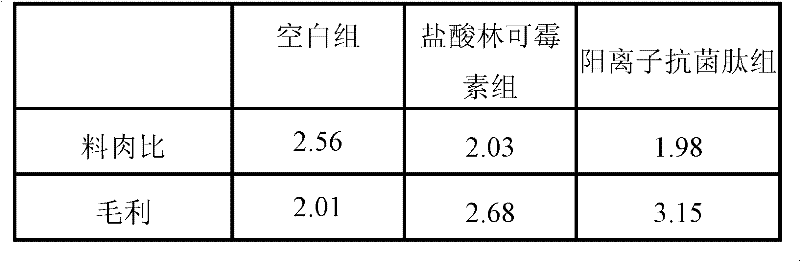
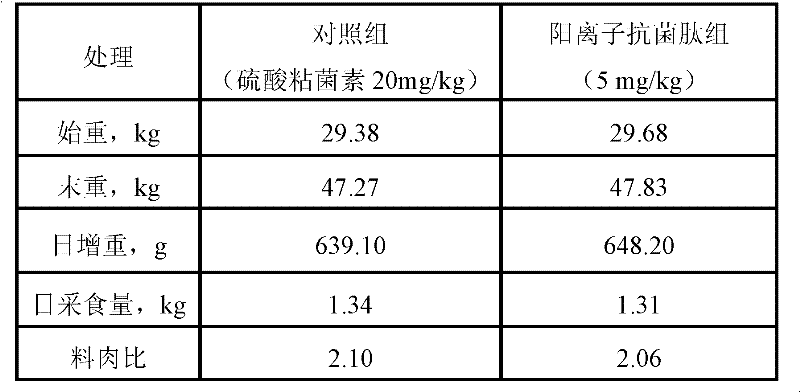
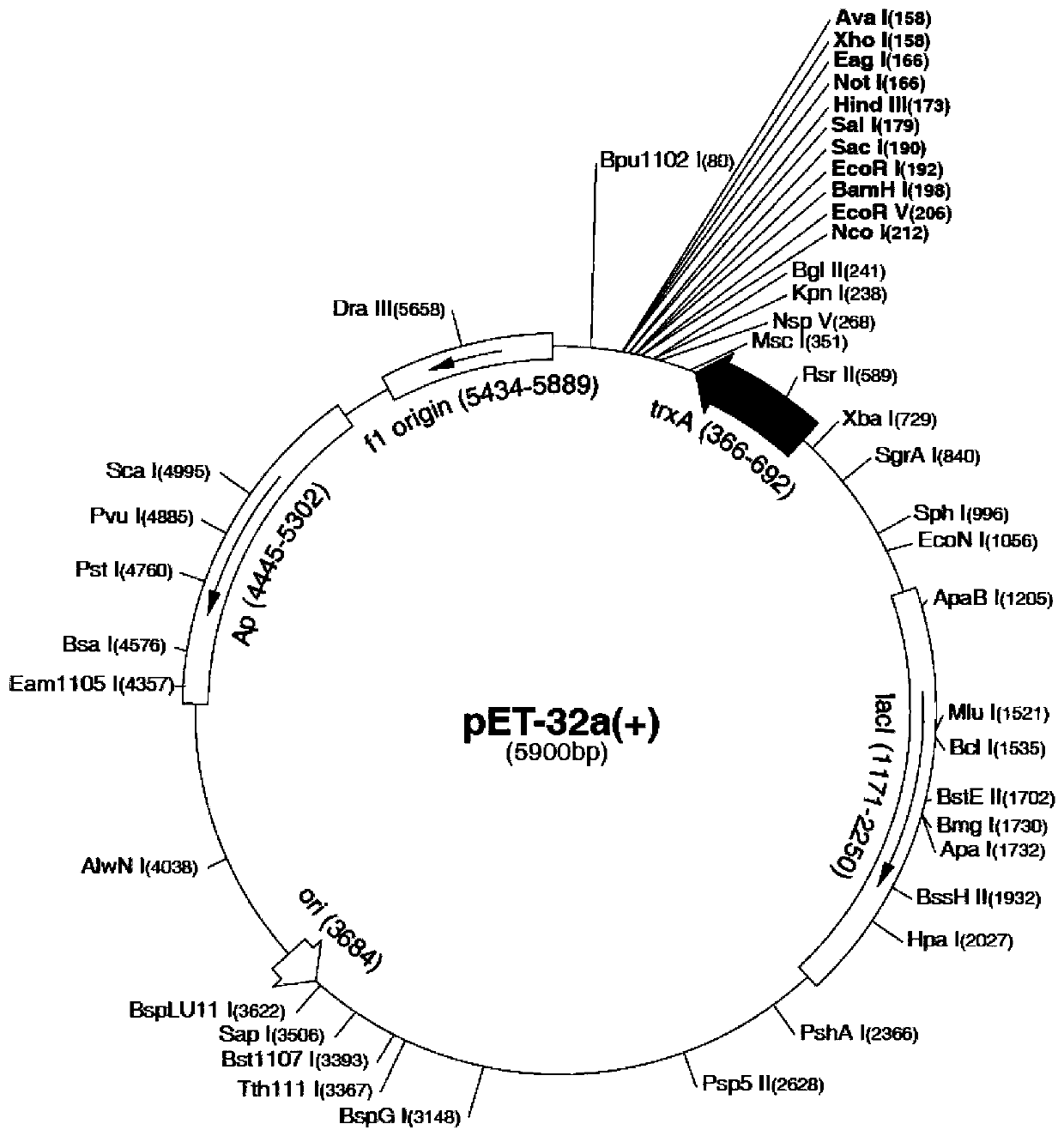
Patents
Literature
87 results about "Isopropyl Thiogalactoside" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Engineering bacterium producing 5-glycyl ethylformic acid and construction and application method thereof
InactiveCN101063105AIncrease productionSimple processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPropanoic acid
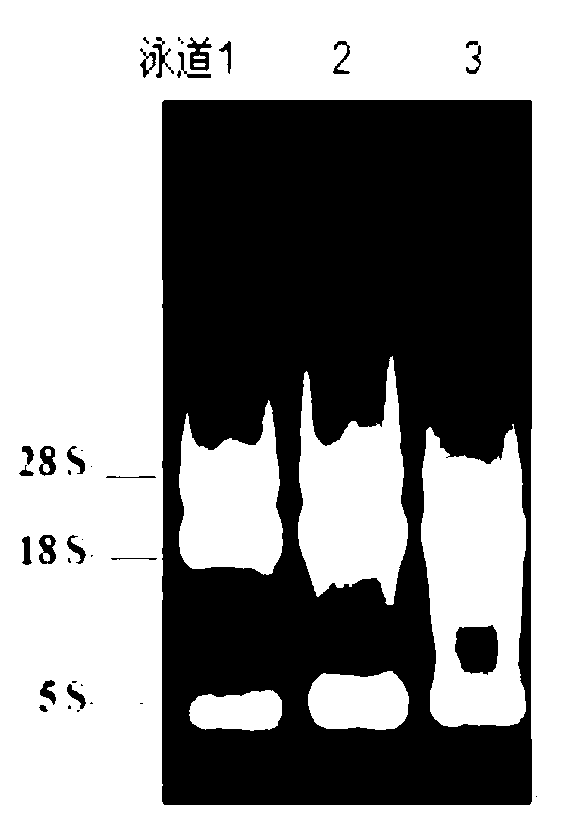
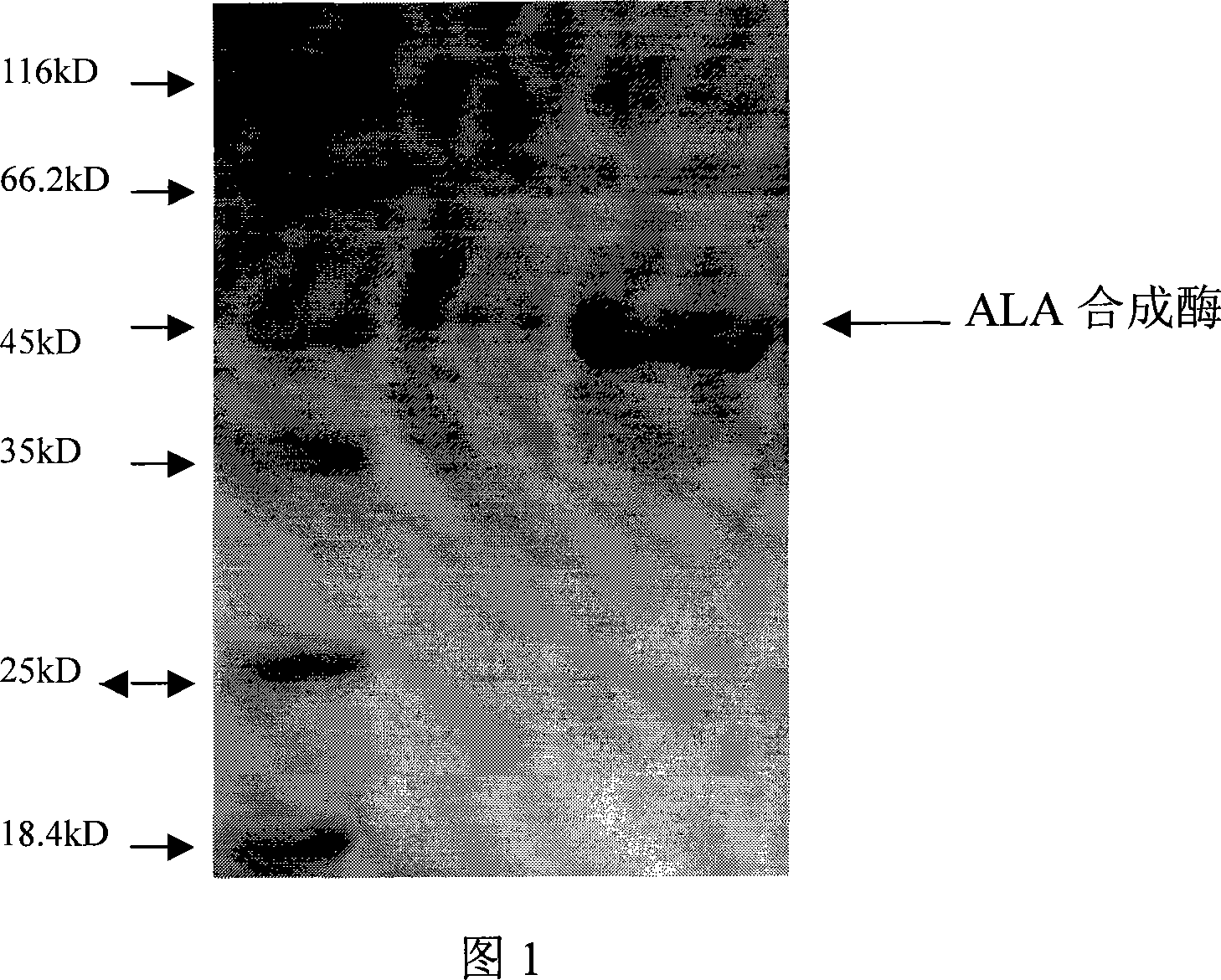
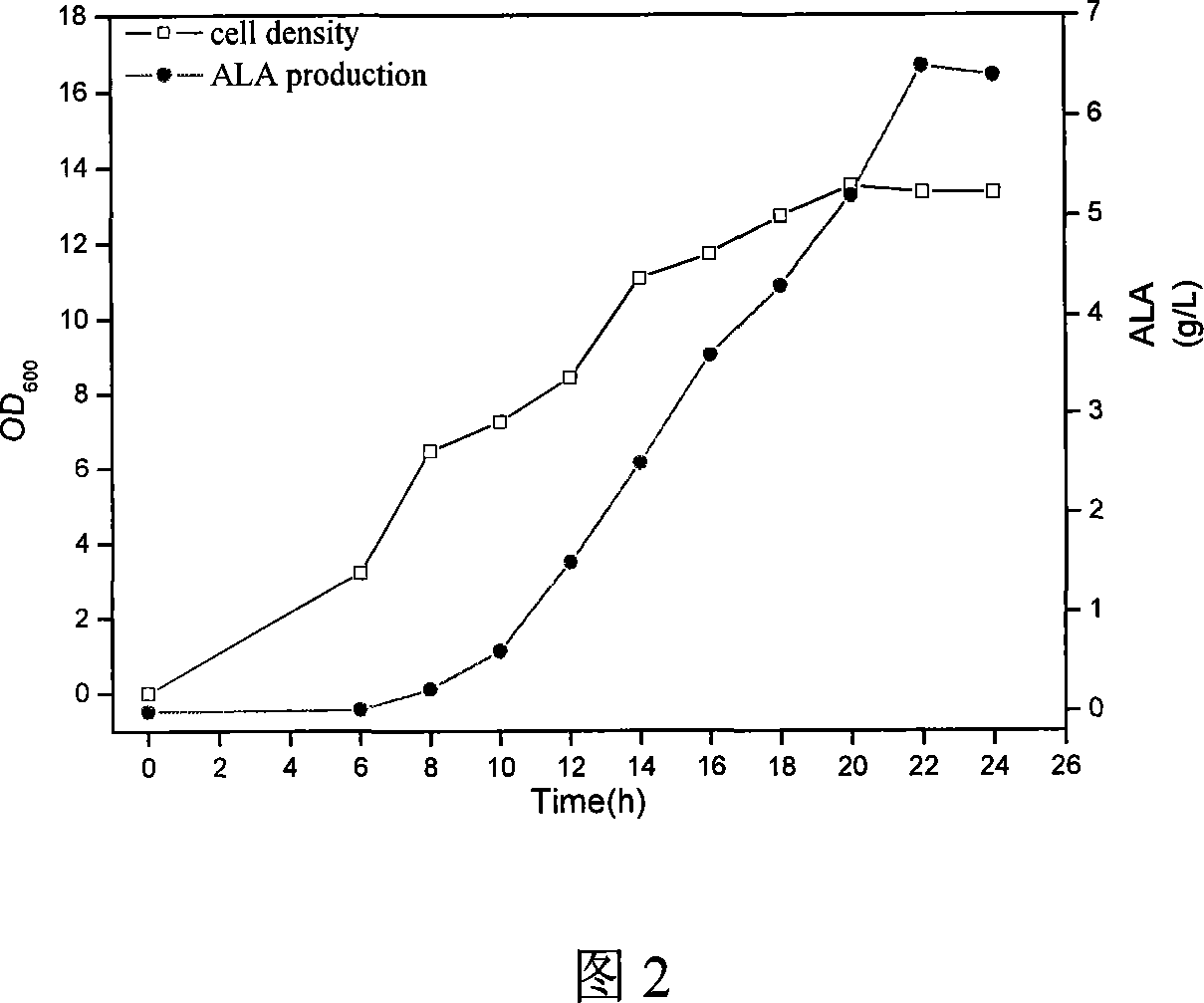
The invention discloses a method to prepare engineering bacteria of 5-glycyl propionic acid and methods for using them, which comprises the following steps: incorporating radial agrobacteriocin; setting the preserved number at CGMCC No. 1938; activating engineering bacteria with LB medium flat; getting monoclonal of the engineering bacteria; seeding to shake; culturing; getting first-grade seed; seeding the first-grade in shake; culturing; getting second-grade seed; seeding the second-grade seed in fermenter; culturing; cooling and evoking with isopropyl-beta-D-sulfo-galactose-glycoside; culturing continually; proceeding supplementing material culture. This engineering bacteria possesses higher ALA synthase expression, simple craft, low cost and good industrial prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Recombinant oral protein TAT-GH of tilapia, preparation method for recombinant oral protein TAT-GH and application of recombinant oral protein TAT-GH
ActiveCN102703483AGuaranteed accuracyIntegrity guaranteedBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses recombinant oral protein TAT-GH of tilapia, a preparation method for the recombinant oral protein TAT-GH and application of the recombinant oral protein TAT-GH. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting total messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) from a pituitary gland of male tilapia, performing reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) to obtain complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (cDNA), performing PCR amplification to obtain a growth hormone (GH) gene of the tilapia, and amplifying a TAT-GH gene by a PCR overlap extension method; constructing a recombinant plasmid pET-32a(+)-TAT-GH; and transforming Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) by using the recombinant plasmid pET-32a(+)-TAT-GH, efficiently expressing fusion protein TAT-GH in the form of an inclusion body under the induction of isopropyl thiogalactoside (IPTG), and purifying and renaturing to obtain active protein. The protein can effectively promote the growth and development of fries of the tilapia after being fed to the fries of the tilapia.
Owner:HUBEI TAIYANGHONG BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
B hepatitis virus X protein transduction system expression vector and its construction
InactiveCN1546668ARealize "quantitative" importAchieving Quantitative ImportMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCell membraneHepatitis B Virus-X
The invention discloses a type B hepatitis virus X protein transduction system expression vector and its construction, by constructing restructured plasmid pTAT-GFP-X through the X gene of the human hepatitis B virus and pTAT-GFP vector, wherein the constructed pTAT-GFP-X restructured plasmid can express the fusion protein containing X protein of hepatitis B viruse, and a vast amount of expression fusion proteins can be evoked from isopropylthiog-alactoside (IPTG), purification can be carried out through 6 histidines (His6), the TAT polypeptide has the structure capable of traversing cell membrane.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Galectin-3 binding protein, preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN102942624AAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsGalectin 3 binding proteinThiogalactosides
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology, and in particular to a galectin-3 binding protein, and preparation and application thereof. The galectin-3 binding protein is shown as an amino acid sequence SEQ ID No.1 in the sequence table. The preparation method is as below: using Cynoglossus semilaevis cDNA as a template; conducting PCR amplification by primers F1 and R1; connecting PCR products to an expression vector to obtain a plasmid pETG3BP; conversing BL21DE3 to obtain a transformant BL21 / pETG3BP; inducting by isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside; and purifying the recombinant protein with affinity chromatography column to obtain the galectin-3 binding protein. The galectin-3 binding protein has significant binding ability to various bacteria.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Genetically engineered bacterium used for biological catalysis of glucosidation of flavonoids
ActiveCN105087454AImprove solubilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
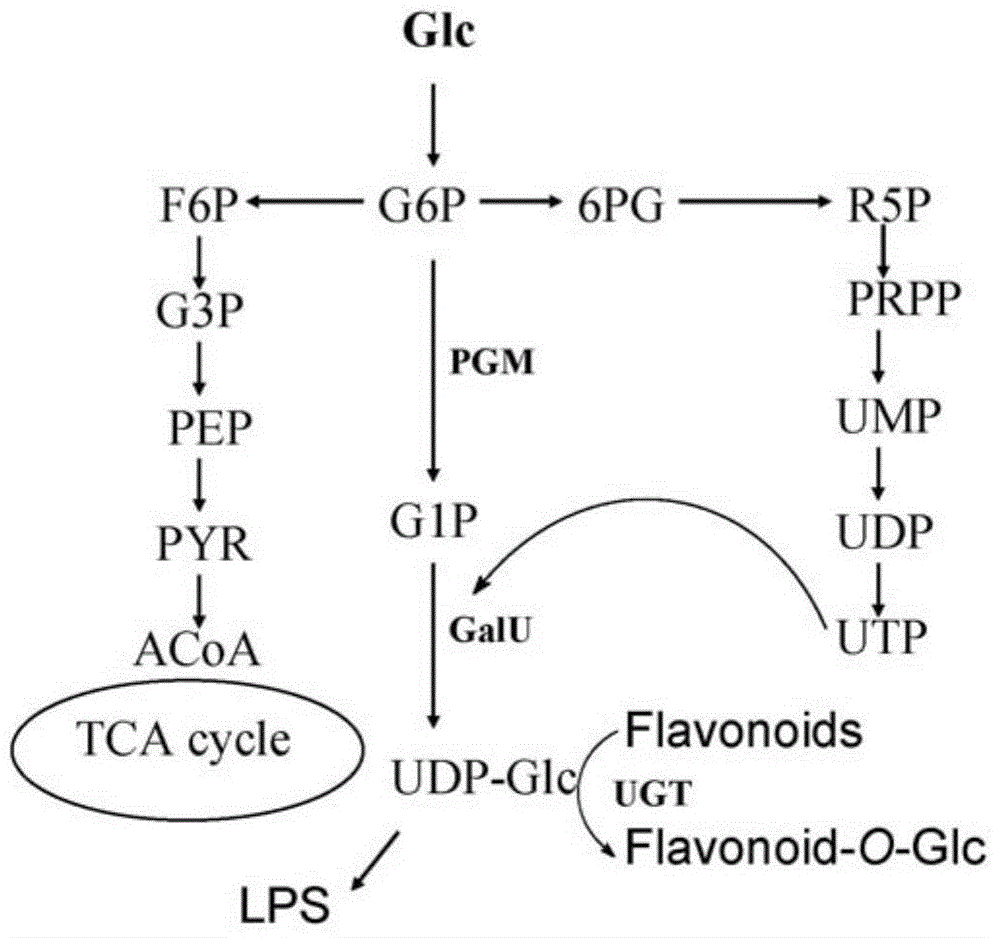
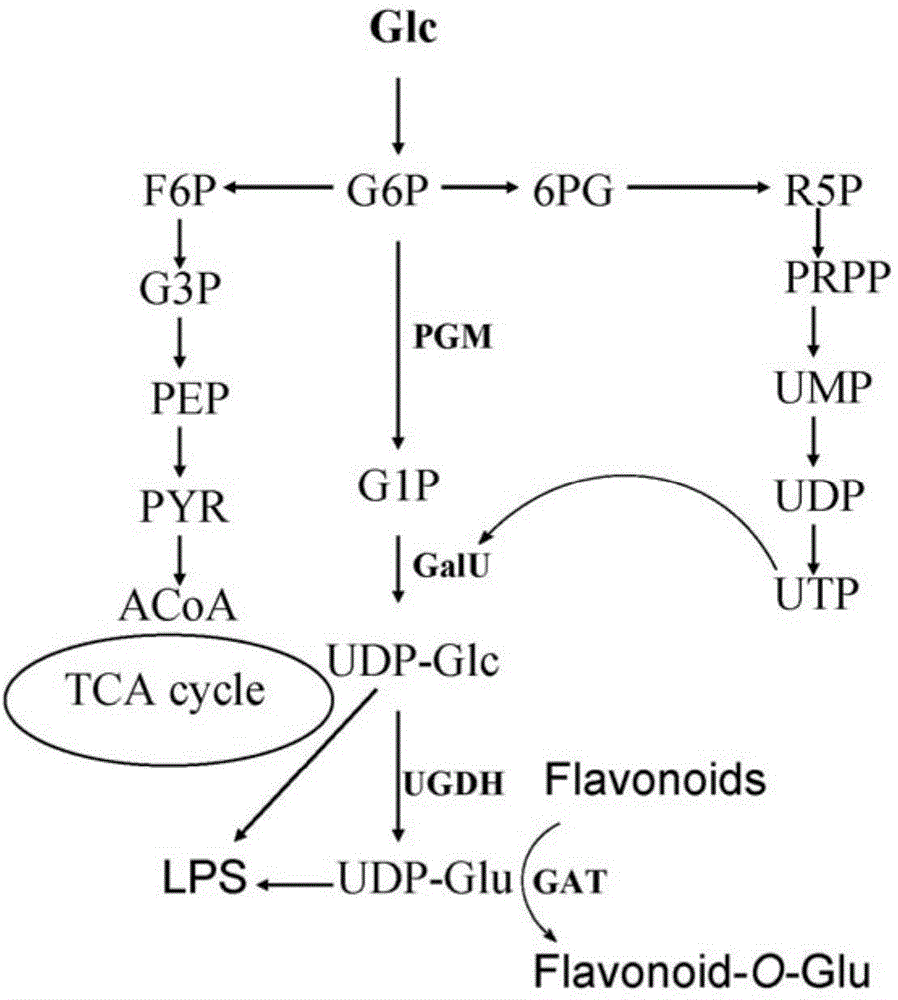
The invention relates to genetically engineered organisms, especially to microbes like Escherichia coli with activity in catalysis of glucosidation of flavonoids, and provides a genetically engineered bacterium used for biological catalysis of glucosidation of flavonoids. The genetically engineered bacterium is prepared by coexpression of three genes respectively coding phosphoglucomutase, uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase and uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase in a microbial cell and introduction of the functional enzyme genes into the cell through expression vectors. The genetically engineered bacterium induces expression of functional enzyme protein under the condition of addition of an inductive agent--isopropyl thiogalactoside (IPTG) and is directly used for biological catalysis of glucosidation of flavonoids; and the advantages of good cell growth, a short fermentation period and low cost are obtained.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Tibetan sheep myostatin recombinant expression protein
InactiveCN102286513AImprove meat performanceRegulate nutrient metabolismBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliMyostatin
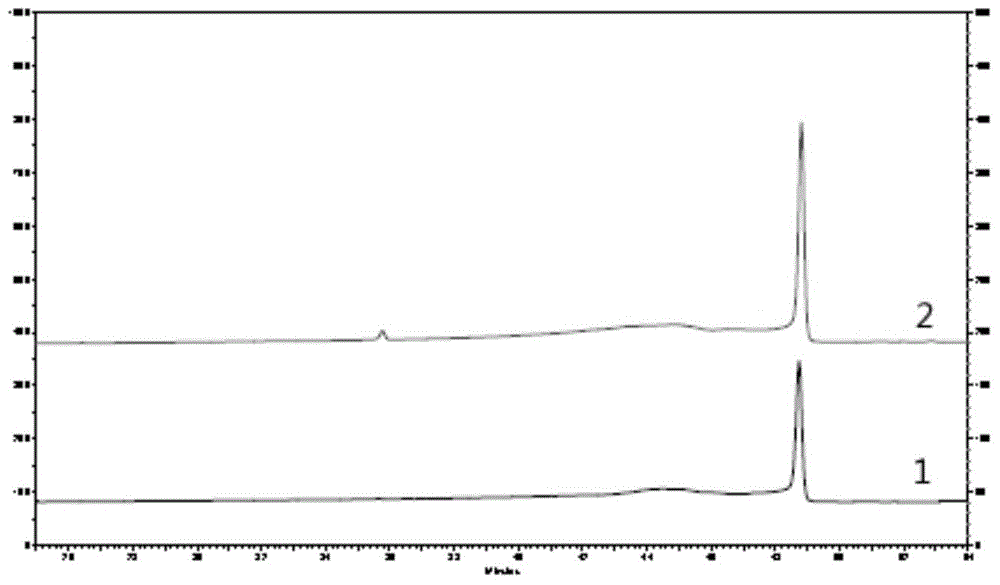
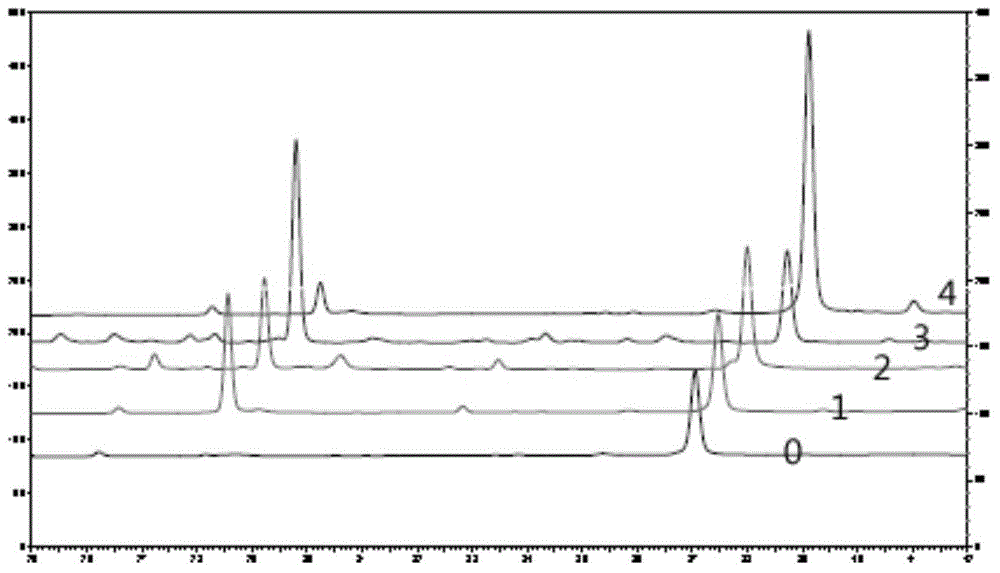
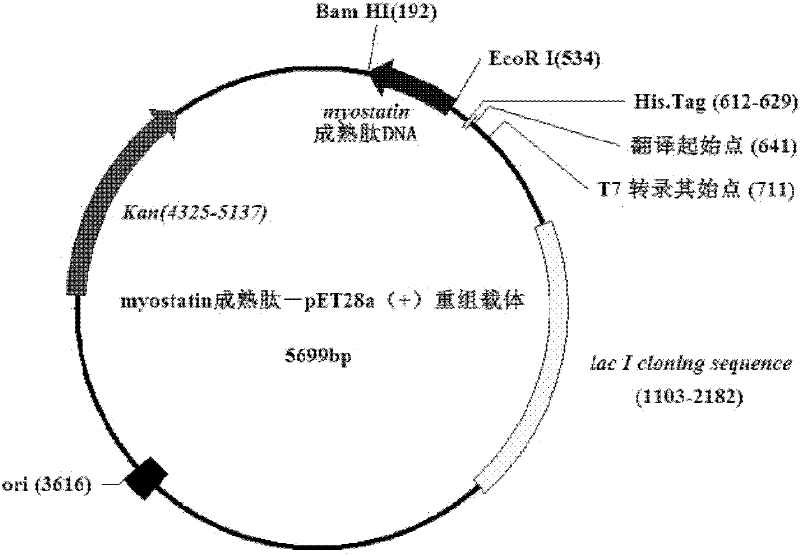
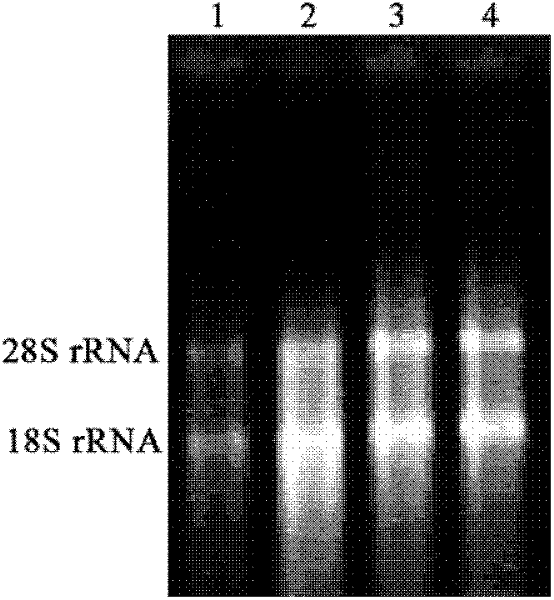
The invention discloses a recombinant Tibetan sheep myostatin protein. In the invention, a Tibetan sheep myostatin (MSTN) coding gene is cloned, the gene is used as a template for polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, the bioactive region of the MSTN coding gene is cloned, a recombinant expression vector is constructed, the cloned bioactive region is transferred into Escherichia coli to construct gene engineering bacteria, and the gene engineering bacteria are subjected to isopropyl thiogalactoside (IPTG) induced expression and purification of MSTN protein. Then the MSTN protein is used to actively immunize a domestic rabbit to prepare polyclonal antibody serum, and an indirect enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay (ELISA) is used to detect the immunogenicity of the MSTN protein. The recombinant Tibetan sheep MSTN protein is used to immunize a mouse actively so as to detect the influence of the recombinant MSTN protein on the growth of the mouse. The purity and immunogenicity of the recombinant Tibetan sheep MSTN protein provided by the invention are high, and the actively immunizing MSTN protein can obviously increase the diameter and area of muscle fibers of the mouse and promote the muscle fibers to increase. Thus, the recombinant Tibetan sheep MSTN protein can be used for active immunizing of Tibetan sheep and help to accelerate the growth of Tibetan sheep and to improve meat performance.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
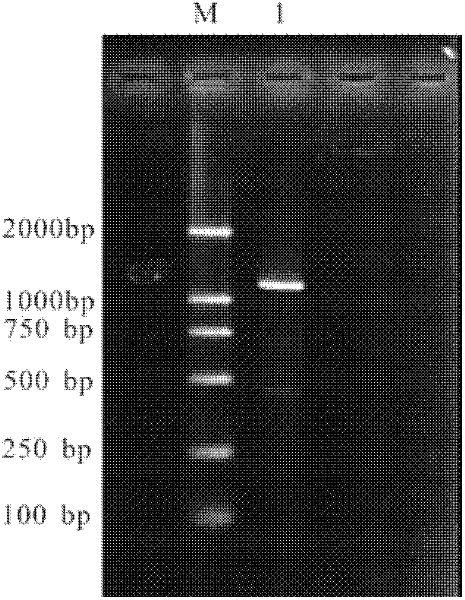
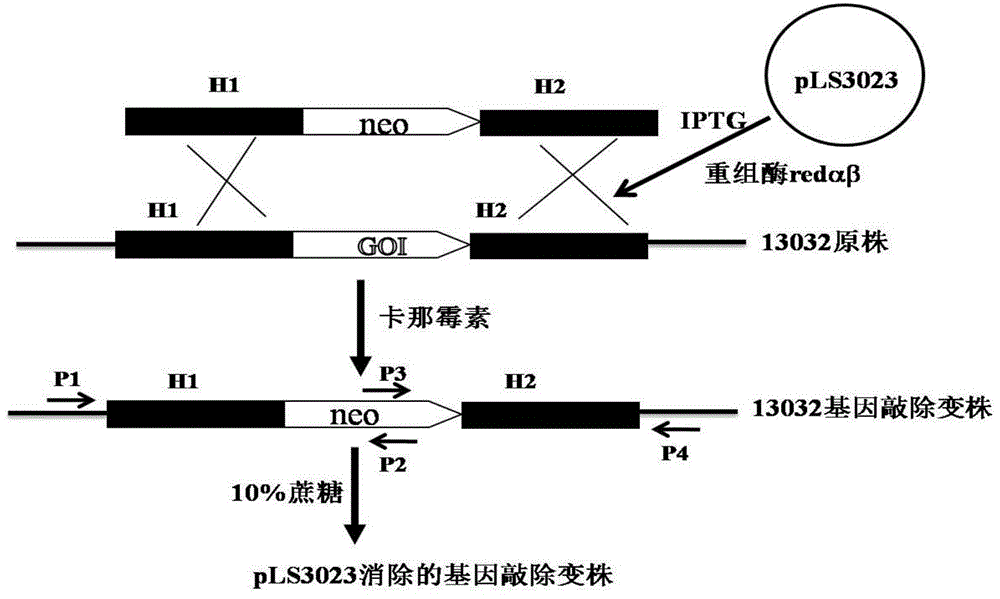
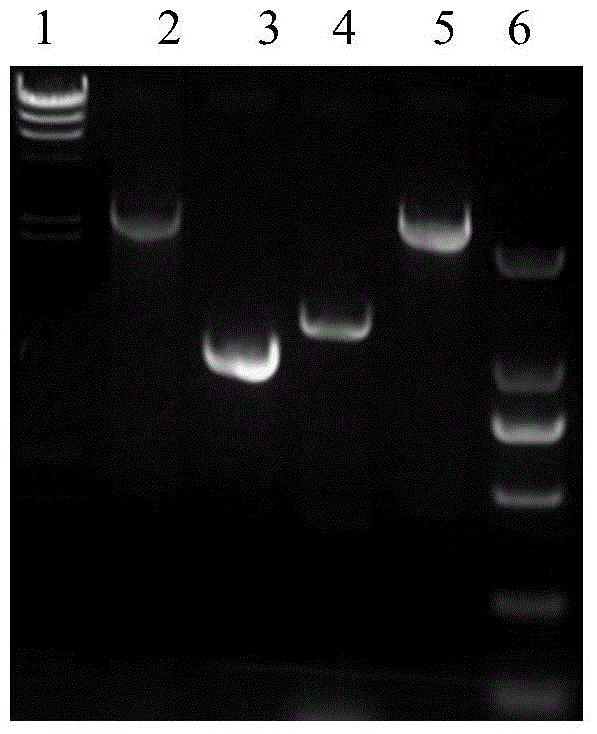
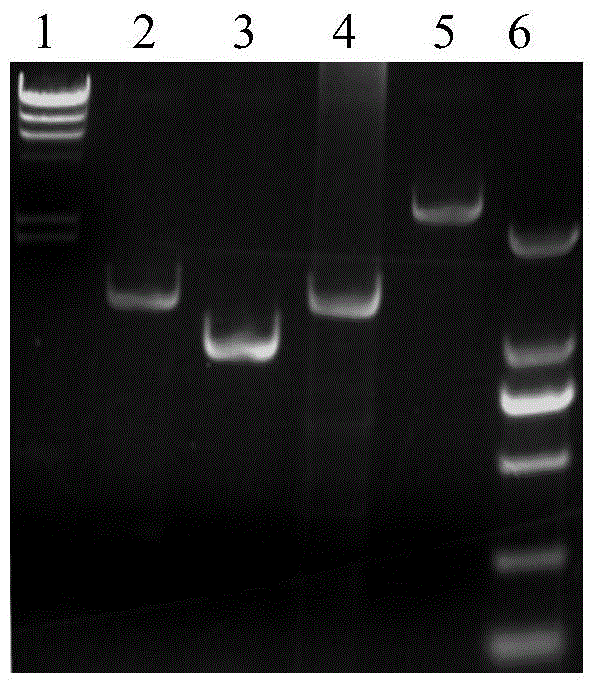
Recombineering-mediated gene knockout method of corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032
InactiveCN104561077AMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionSaccharumThiogalactosides
The invention relates to a recombineering-mediated gene knockout method of corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032. The gene knockout method comprises the following specific implementation steps: obtaining a DNA fragment which is provided with 500-bp homologous sequences on two sides aiming at genes to be knocked out and a kanamycin resistance gene in the middle through a polymerase chain reaction amplification; carrying out electrotransformation on the DNA fragment into a corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032 cell in which recombinase is induced to express by isopropyl-Beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside, and enabling the kanamycin resistance gene to replace the target gene through the resistance selection of kanamycin to obtain gene knockout strains; finally, cultivating mutant strains in a solid medium containing cane sugar to eliminate plasmids containing recombinase genes. The gene knockout method adopts simple PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) and electrotransformation supplemented by the resistance selection of kanamycin, is free of operating steps, such as gene cloning in molecular biology and other certain operating steps, and simple and rapid, and has important application in the aspects of researching gene functions and producing amino acid.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Bacillus subtilis gene engineering strain, construction method thereof and application in lactulose production
ActiveCN105255805AEasy to operateAvoid loss of enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesThiogalactosidesBio engineering
The invention discloses a method for producing lactulose by means of a recombinant bacillus subtilis, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering technology. The recombinant bacillus subtilis is used as the production strain, the recombinant bacillus subtilis includes cellobiose epimerase capable of catalyzing lactose for producing the lactulose, and induction expression is performed through the lactose or isopropyl-beta-D-isopropylthiogalactoside (IPTG) so as to use the lactose or whey as a substrate for a biological catalysis reaction. Bacillus subtilis wet cells or a fermentation solution is used for the catalysis reaction, the method is simple and easy to implement, and enzyme activity losses and cost waste in the enzyme separation and purification process are avoided; the food-grade bacillus subtilis is used as the production strain, the method is safe and reliable, and the effective references are provided for industrial and environment-friendly lactulose production.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing virus analogs of nervous necrosis viruses
ActiveCN101942496AHigh expressionLow costMicroorganism based processesPeptide preparation methodsNecrovirusPlasmid Vector
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to a method for preparing virus analogs of nervous necrosis viruses. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) performing expression of the virus analogs of the nervous necrosis viruses on escherichia coli of pQE30 plasmid vectors coded with nervous necrosis virus capsid protein genes under the pronucleus condition, wherein the expression is performed under the following conditions of: inoculating 1 mass percent of escherichia coli solution of which OD600 is equal to 1.5 into a culture medium, culturing the escherichia coli at 37 DEG C under 250rpm till the OD600 is 0.3 to 0.5, adding isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside into the escherichia coli solution till the final concentration of the isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside is 900muM, transferring the solution, and continuously culturing the escherichia coli for 3 to 4 hours at the temperature of between 25 and 30 DEG C at the rotational speed of 200rpm to finish the expression; and (2) after the expression is finished, breaking, separating and purifying the strains to obtain the virus analogs of the nervous necrosis viruses, wherein the plasmid coded genes also can be nervous necrosis virus capsid protein genes containing histidine tags, and the expression product of the genes can be purified by affinity chromatography. The method provided by the invention can obtain high virus analog expression amount; and the chromatography and purification method is simple and convenient and has low costs in required apparatuses and reagents.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
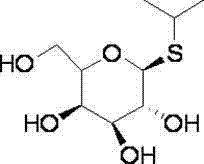
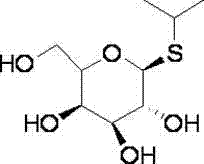
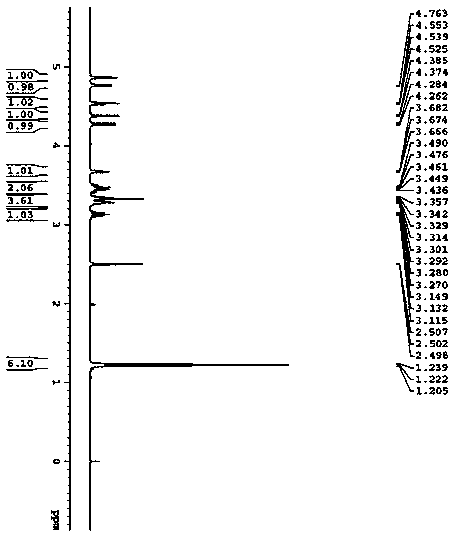
Isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside preparation method
ActiveCN103709209AImprove the safety factor and productionEasy to operateSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationSodium methoxideAcetic anhydride
The invention relates to the field of sugar compounds, and concretely relates to an isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside preparation method. The method comprises the following steps: adding acetic anhydride and a catalyst at room temperature, adding galactose, adding isopropyl mercaptan after the above reaction, and post-processing to obtain isopropyl thioacetylgalactosamine; and adding isopropyl thioacetylgalactosamine into methanol for dissolving, adding sodium methoxide, adding acetic acid after the above reaction to neutralize, and post-processing to obtain isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside. The method allows isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside to be synthesized through a two-step reaction process, and has the advantages of simple operation, easily available raw materials, and saving of the operation cost and materials.
Owner:济南尚博医药股份有限公司
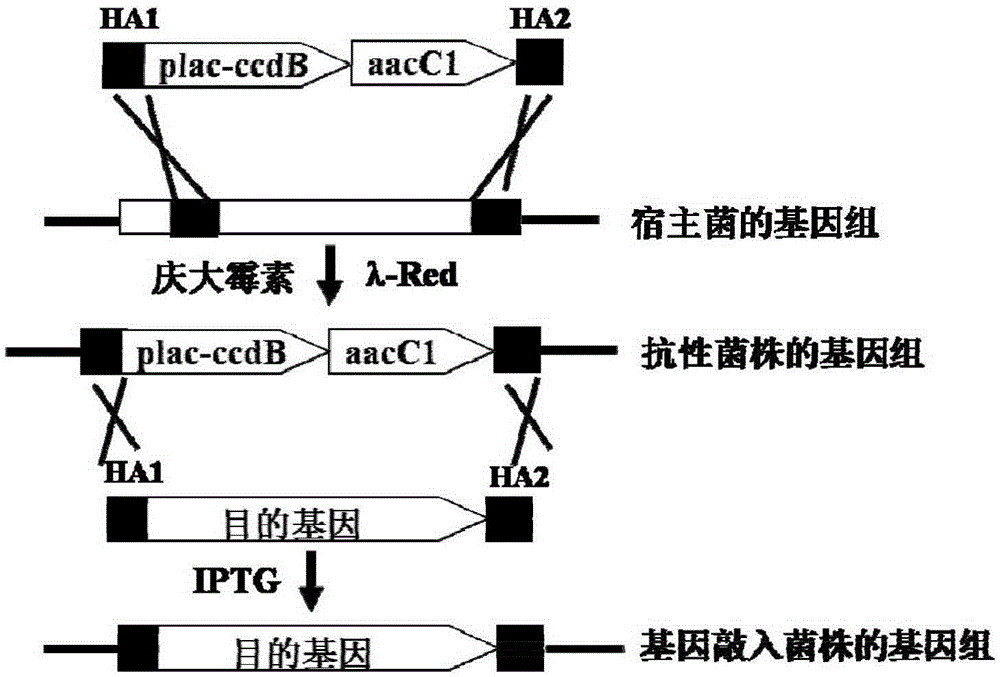
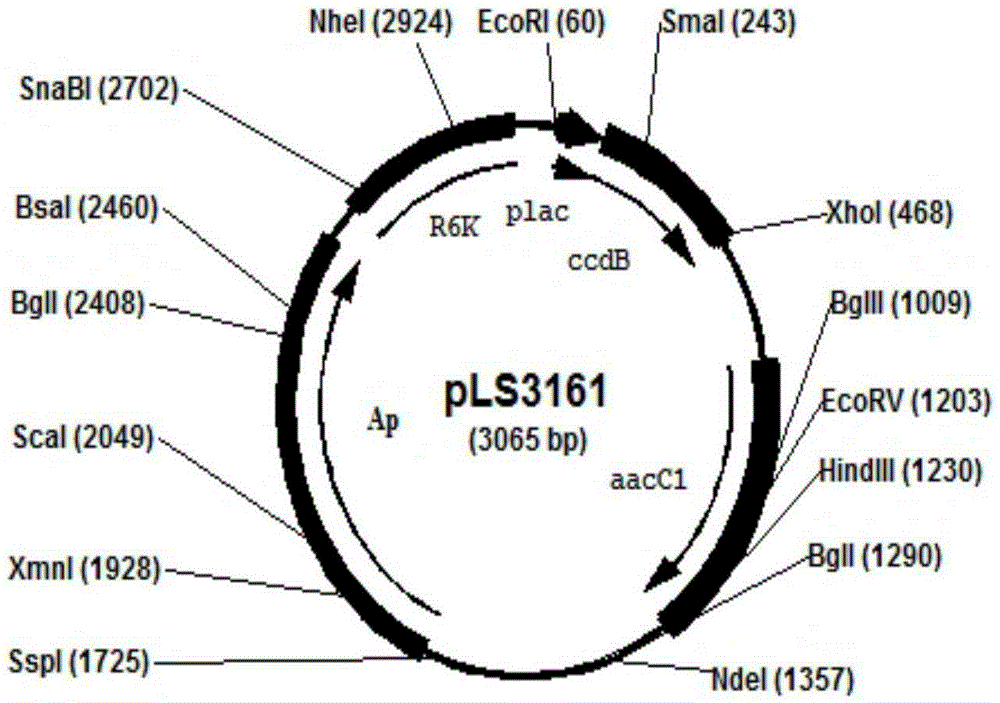
Negative selection marker for escherichia coli gene knock-in
InactiveCN105238820AConvenient researchStable introduction of DNAMicroorganism based processesThiogalactosidesDNA fragmentation
The invention relates to a negative selection marker for escherichia coli gene knock-in, namely, the virulent gene ccdB driven by a plac promoter, and plac-ccdB and the gentamicin resistance gene aacC1 form a gene cassette for gene knock-in. In the first step, DNA fragments containing homologous arms plac-ccdB and aacC1 are obtained through amplification, and electro-transformed into escherichia coli for expression of recombinase. Under gentamicin screening, recombinase catalyzes homologous recombination and the DNA fragments are integrated into escherichia coli genome. In the second step, same homologous arms are utilized for amplification of foreign DNA fragments, ccdB is expressed in the bacterial strains obtained in the first step during the electrotransformation for expression of recombinase under the screening of isopropyl-beta-d-isopropylthiogalactoside, the toxicity serves as the feature of the negative selection marker, recombinase catalyzes homologous recombination among homologous arms, and foreign DNA fragments replace a plac-ccdB-aacC1 gene cassette to realize gene knock-in.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Corynebacteria inducible promoter, expression vector comprising same, and application thereof
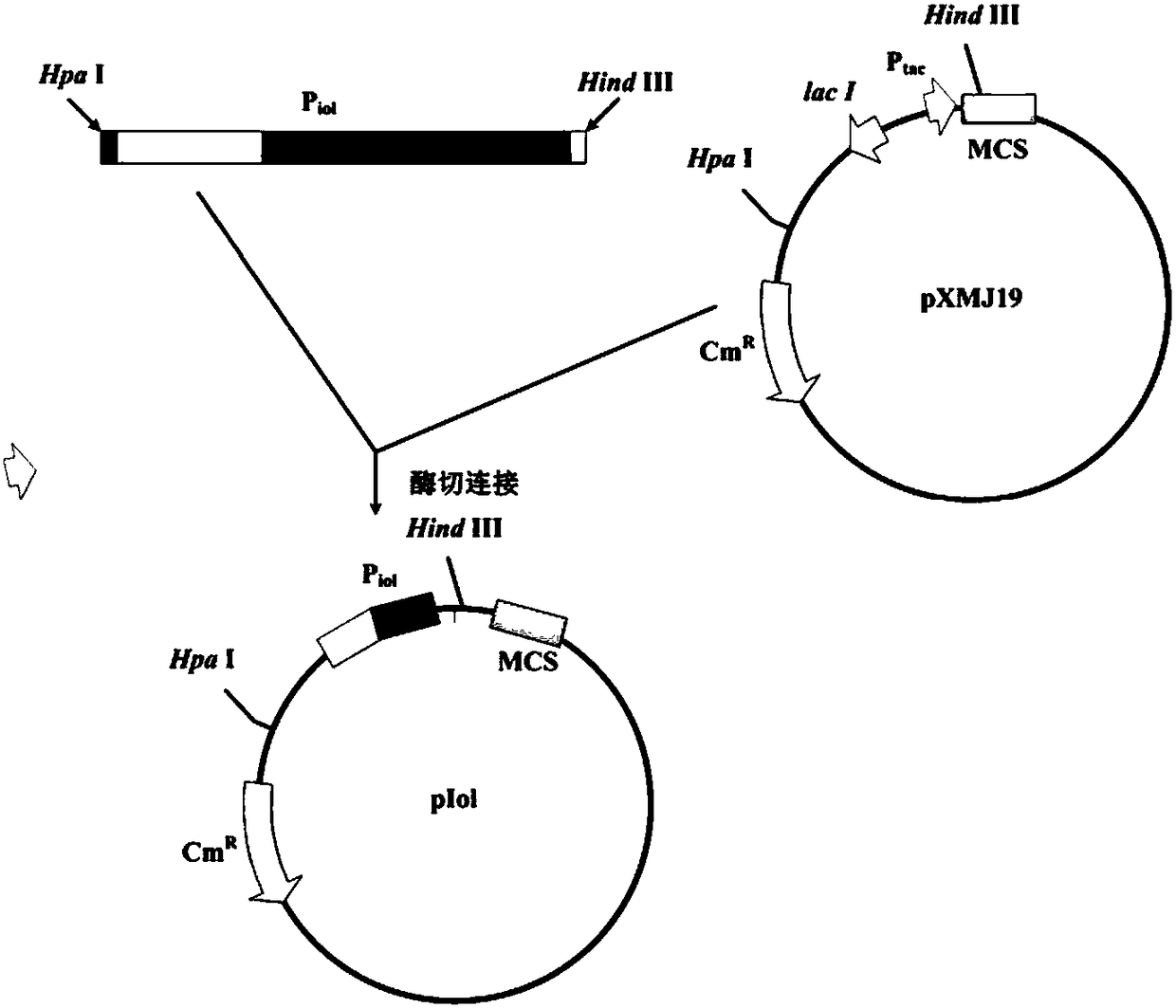
The invention relates to a Corynebacteria inducible promoter, an expression vector comprising same, and an application thereof, wherein the expression vector is converted to corynebacterium glutamicumto obtain a 5-aminolevulinic acid producing bacterial strain, by that 5-aminolevulinic acid can be produced through a fermentation method. The expression vector constructed from the promoter, throughcontrollable expression of gene through inositol induction, can overcome problems of inhibition effect on growth of bacterial cells with and high production cost due to high price of an inducing agent, (isopropyl[beta]-D-thiogalactoside, IPTG). The expression vector has characters such as stability. By integrating the promoter with genome of a host or converting the expression vector into the host, corynebacterium glutamicum, the 5-aminolevulinic acid producing bacterial strain is acquired, yield of the 5-aminolevulinic acid reaching 24.2 g / L.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
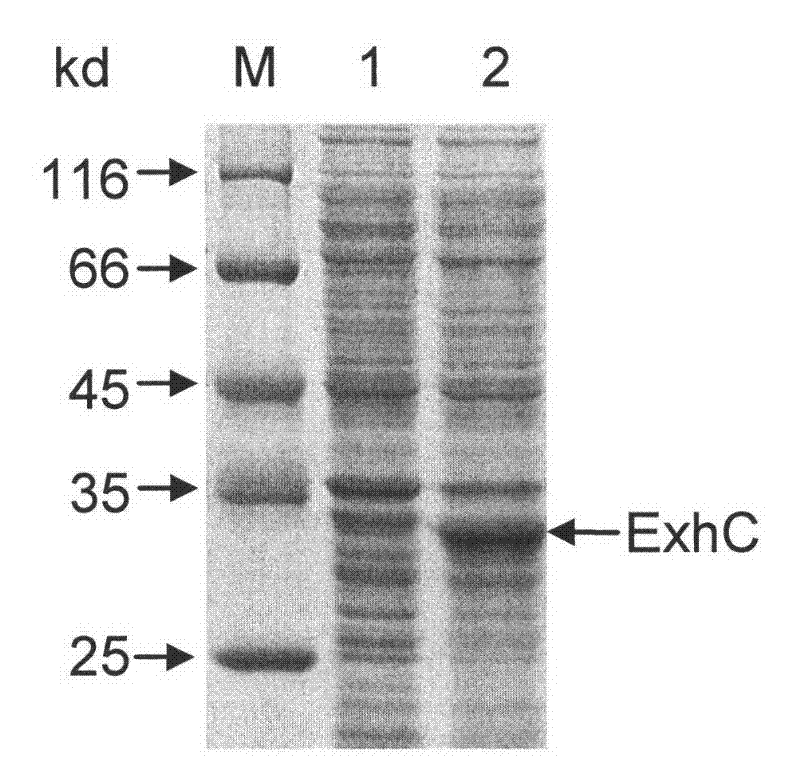
Preparation method of exfoliative toxin C (ExhC) proteins of staphylococcus sciuri
InactiveCN102174553AEfficient expressionImprove biological activityMicroorganism based processesPeptide preparation methodsEscherichia coliHigh concentration
The invention relates to a preparation method of exfoliative toxin C (ExhC) proteins of staphylococcus sciuri, which comprises the following steps of: (1) taking staphylococcus sciuri genome DNA as templates, amplifying the overall length of ExhC genes of the staphylococcus sciuri, and cloning the ExhC genes into prokaryotic expression vectors to obtain recombinant plasmids; (2) performing escherichia coli conversion on the recombinant plasmids, and expressing the recombinant plasmids through IPTG (isopropyl thiogalactoside) induced proteins; and (3) extracting the crude extract of the proteins, and purifying ExhC proteins. In the method, the efficient expression of ExhC in escherichia coli is realized successfully through a gene engineering technology, and high-purity and high-concentration ExhC with biological activities is obtained; moreover, the preparation method is simple to operate and low in cost.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Hepatitis B virus multi-epitope fusion protein and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102199217AHighly inhibitoryEfficient removalDigestive systemAntiviralsEscherichia coliFusion Protein Expression
The invention relates to a hepatitis B virus multi-epitope fusion protein and a preparation method and application thereof. The fusion protein is obtained by inserting hepatitis B virus multi-epitope fusion peptide (with the sequence shown as SEQIDNo.1) formed by serially connecting HBsAg313-321, HBsAg335-343, Pol150-159, Pol455-463 and Padre epitopes through connecting peptide between amino acidat the 78th position and amino acid at the 79th position of a hepatitis B virus core protein; and the preparation method comprises the following steps of: constructing a hepatitis B virus multi-epitope fusion protein expression plasmid pET28-HBc-HP; performing isopropyl thiogalactoside (IPTG) inducing expression by using an Escherichia coli expression system; and purifying by using affinity chromatography. The fusion protein carries a plurality of supertype epitopes of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg) and polymerase, is viral particles, has the advantages of strong immunogenicity, wide applicable range and the like, and can be used for preparing therapeutic hepatitis B vaccines.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Fermenting technology for improving expression amount of fusion protein of recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide
ActiveCN107177649AImprove expression levelReduce manufacturing costAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFermentationAmpicillinBiology
The invention discloses a fermenting technology for improving expression amount of fusion protein of recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide. The fermenting technology comprises the following steps of adding 18 to 20L of BHD culture medium, 65 to 80mL of glycerin, and ampicillin into a fermenting tank until the final concentration is 100mg / L; inoculating, adjusting the air ventilation amount until the dissolved oxygen content in the fermenting liquid is 30% to 50%, adjusting the pH (potential of hydrogen) value to 6.8 to 7.2, and culturing at the temperature of 37 DEG C; when OD600 is 10 to 15, adding isopropyl thiogalactoside until the final concentration is 0.5 to 1.0mmol / L, inducing, adding 150 to 300mL / A of supplementing liquid A into the fermenting tank, stopping fermenting culture after 3 to 6h, and harvesting bacteria. The fermenting technology has the advantages that the expression level of rhBNP fusion protein is obviously improved, the expression amount reaches up to 34.5% to 38.3%, and the good commercial development value and great success in commerce are obtained.
Owner:西藏诺迪康药业股份有限公司
PPA-linker-Thanatin fusion protein and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102241778AHigh clinical application valueHybrid peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliTwo step
The invention discloses a PPA-linker-thanatin fusion protein of which the amino acid sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the PPA-linker-thanatin fusion protein, comprising the following steps of: acquiring target genes of recombinant pinellia pedatisecta schott agglutinin and thanatin by a two-step PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method, cloning the target genes onto an E.coli expression vector pET-28a-c(+), and acquiring the expressed protein by IPTG (isopropyl thiogalactoside) induction, wherein the expressed protein is the PPA-linker-thanatin fusion protein, namely the expression product of the pinellia pedatisecta schott agglutinin-thanatin. The expression product of the pinellia pedatisecta schott agglutinin-thanatin has biological activity and has inhibiting effect on the growth of tumor cells.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Genetically engineered bacterium used for biological catalysis of glucuronidation of flavonoids
ActiveCN105087453AImprove efficacyGood water solubilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention relates to genetically engineered organisms, especially to microbes like Escherichia coli with activity in catalysis of glucuronidation of flavonoids, and provides a genetically engineered bacterium used for biological catalysis of glucuronidation of flavonoids. The genetically engineered bacterium is prepared by coexpression of four genes respectively coding phosphoglucomutase, uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase, uridine diphosphate glucose dehydrogenase and uridine diphosphate glucuronyltransferase in a cell and introduction of the functional enzyme genes into the cell through expression vectors. The genetically engineered bacterium induces expression of functional enzyme protein under the condition of addition of an inductive agent--isopropyl thiogalactoside (IPTG) and is directly used for biological catalysis of glucuronidation of flavonoids; and the advantages of good cell growth, a short fermentation period and low cost are obtained.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Method for improving expression of selenoprotein TrxR
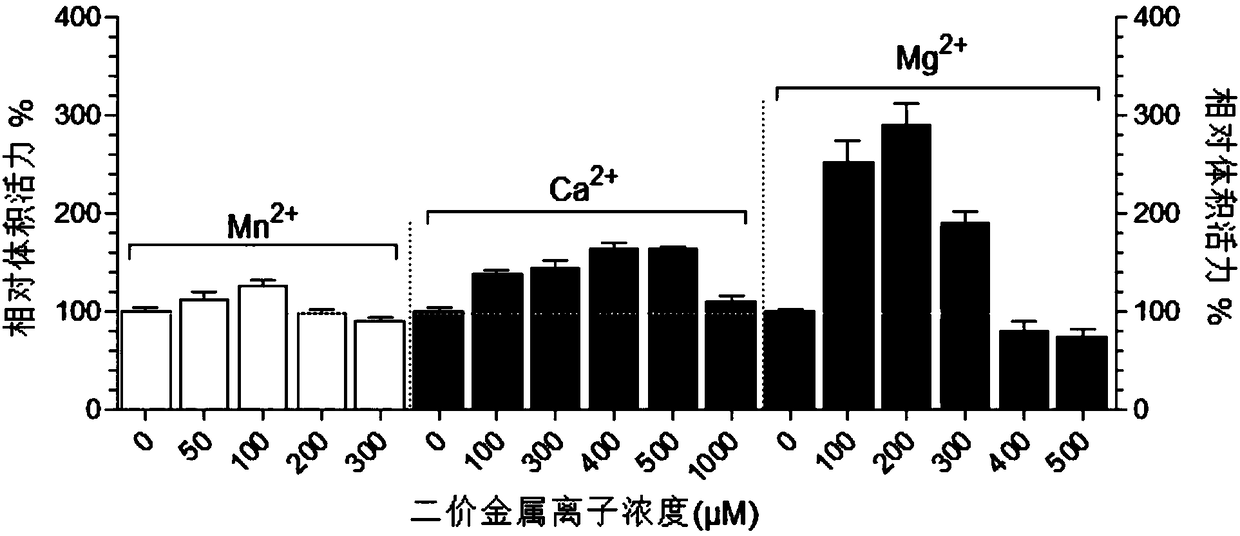
ActiveCN108546688AHigh expressionSimple methodOxidoreductasesProkaryotic expressionDivalent metal ions
A method for improving expression of selenoprotein TrxR is disclosed and belongs to the technical field of protein prokaryotic expression. In a prokaryotic expression process of the TrxR, an expression strain is first cultured under conditions of 37 DEG C and 220 rpm until the end of the logarithmic phase, then L-cysteine, sodium selenite, isopropyl thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG), and divalent metalions such as Mn<2+>, Ca<2+>, and Mg<2+> are added to the medium, and inducible expression under conditions of 24 DEG C and 220 rpm is performed for 24 h. The addition of the divalent metal ions suchas Mn<2+>, Ca<2+>, and Mg<2+> enhances the expression of the TrxR. The method is simple, raw materials are easily available, the cost is low, expression of the TrxR is obviously improved, and the method has high utilization value.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Genetic engineering kit for detecting environmental estrogen pollutants and application thereof
InactiveCN101975776AReduce demandImprove detection stabilityBacteriaMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorThio-Genetic engineering
The invention relates to a genetic engineering kit for detecting environmental estrogen pollutants and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of detection. The kit comprises the following components in part by volume: 2*10<4> parts of LB culture medium, 1 part of isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside, 20 parts of chloroform, 10 parts of solution of lauryl sodium sulfate, 20 parts of o-nitrophenyl-beta-D-galactoside and 100 parts of solution of sodium carbonate. A detection process of the genetic engineering kit is simple, convenient and quick, and results can be obtained within 2 to 3 hours; the genetic engineering kit does not have special requirements on instruments, demand quantity of samples is fewer, detection stability is high, and the detection sensitivity can reach n g / L; and the genetic engineering kit improves the analytical rate while reducing the analytical cost greatly.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Site directed mutagenesis thermoplasma acidophilum F3 factor recombinant protein and application thereof
InactiveCN102212511AEasy to prepareIncrease productionHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliThermoplasma acidophilum
The invention discloses site directed mutagenesis thermoplasma acidophilum F3 factor recombinant protein and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the recombinant protein is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The recombinant protein is prepared by the following steps of: connecting full-length segments of thermoplasma acidophilum F3 factor recombinant protein genes subjected to site directed mutagenesis (E101Q, N261T) to a modified expression vector pGL01; transforming escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) by a thermal shock method; inducing to efficiently express by using isopropyl thiogalactoside; and separating and purifying. The recombinant protein has protein active sites consistent with human aminopeptidase active sites, high enzyme activity and high thermal stability, can be used for evaluating the inhibition effect of the newly synthesized aminopeptidase inhibitor, and can replace commercial APN to screen inhibition activity of synthetic compounds.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside preparation technology
ActiveCN103709210AImprove the safety factor and productionEasy to operateSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationSodium methoxideAcetic anhydride
The invention relates to the field of sugar compounds, and concretely relates to an isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside preparation technology. The technology comprises the following steps: adding acetic anhydride and a catalyst at room temperature, adding galactose, adding isopropyl mercaptan after the above reaction, and post-processing to obtain isopropyl thioacetylgalactosamine; and adding isopropyl thioacetylgalactosamine into methanol for dissolving, adding sodium methoxide, adding acetic acid after the above reaction to neutralize, and post-processing to obtain isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside. The technology allows isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside to be synthesized through a two-step reaction process, and has the advantages of simple operation, easily available raw materials, and saving of the operation cost and materials.
Owner:济南尚博医药股份有限公司
Method for preparing isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside
ActiveCN103694286AImprove the safety factor and productionEasy to operateSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationSodium methoxideAcetic anhydride
The invention relates to the field of saccharide compounds, particularly a method for preparing isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside. The method comprises the following steps: adding acetic anhydride and a catalyst at room temperature, and adding galactose; after the reaction finishes, adding isopropyl mercaptan; after the reaction finishes, carrying out after-treatment to obtain isopropyl thioacetyl galactose; dissolving the isopropyl thioacetyl galactose in methanol, and adding sodium methoxide; and after the reaction finishes, adding acetic acid for neutralization, and carrying out after-treatment to obtain the isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside. The method synthesizes the isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside by a two-step reaction process, is simple to operate and accessible in raw materials, and saves the operating cost and materials.
Owner:济南尚博医药股份有限公司
Method for preparing isopropyl-beta-D-isopropylthiogalactoside
ActiveCN103665063AImprove the safety factor and productionEasy to operateSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationSodium methoxideAcetic acid
The invention relates to the field of sugar compounds and in particular relates to a method for preparing isopropyl-beta-D-isopropylthiogalactoside. The method comprises the following steps: adding acetic anhydride and a catalyst at room temperature, adding galactose, adding isopropyl mercaptan after the reaction is ended, and performing aftertreatment to obtain isopropylthiogalactoside after the reaction is ended; adding the isopropylthiogalactoside into methanol for dissolving, adding sodium methoxide, adding acetic acid for neutralizing after the reaction is ended, and performing aftertreatment to obtain the isopropyl-beta-D-isopropylthiogalactoside. According to the method, the isopropyl-beta-D-isopropylthiogalactoside is synthesized through a two-step reaction method, the operation is simple, the raw materials are readily available, and the operating cost and materials are saved.
Owner:济南尚博医药股份有限公司
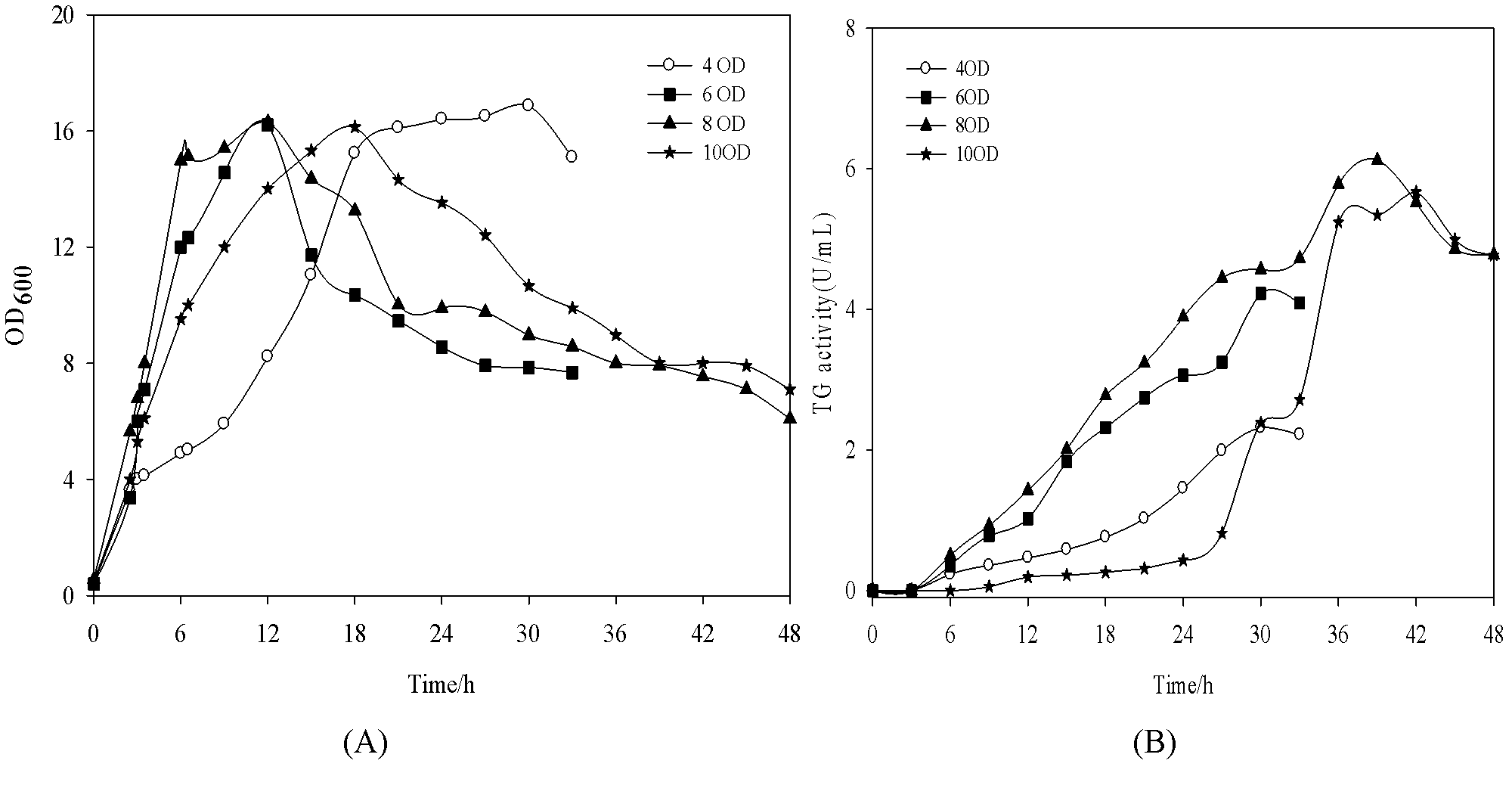
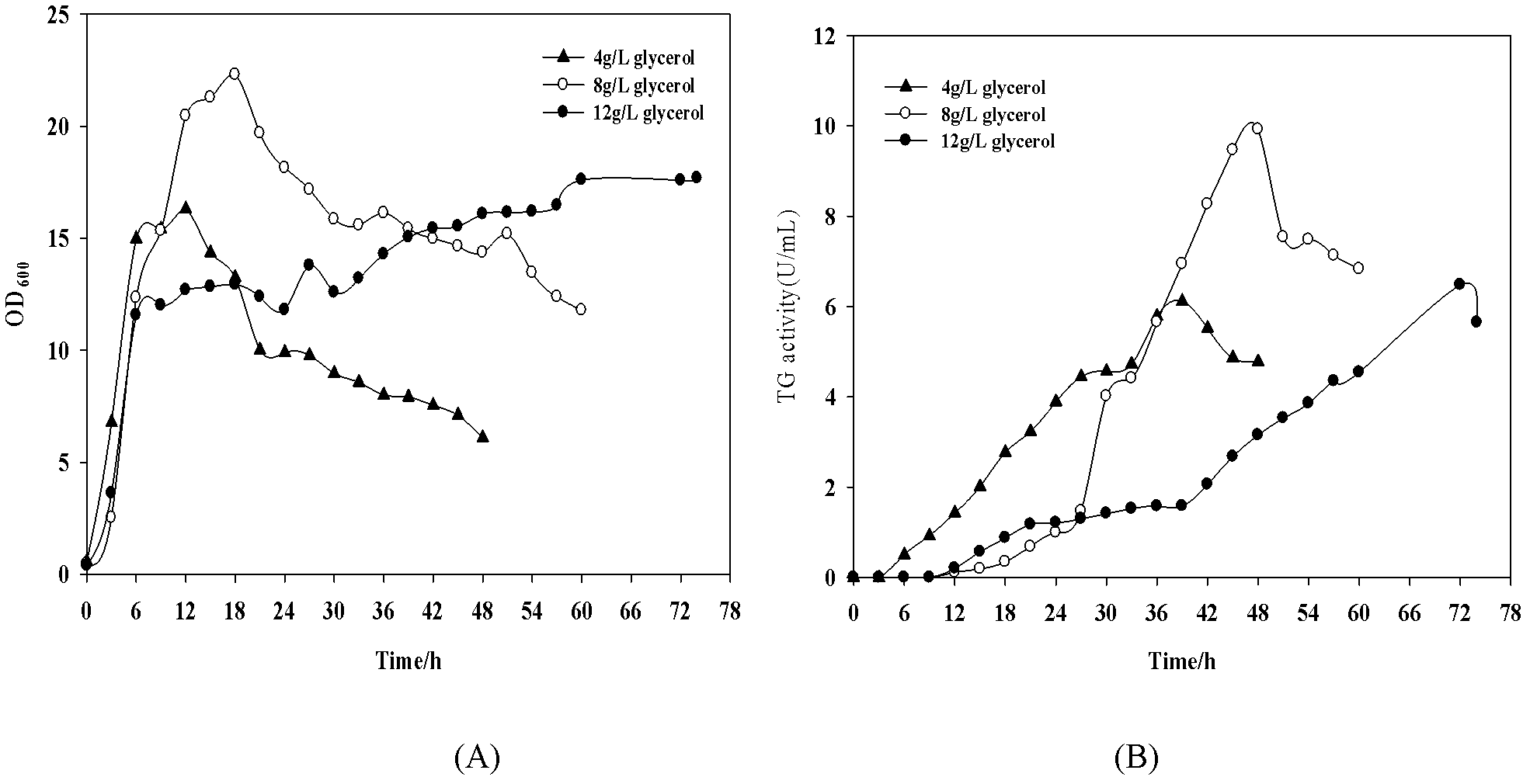
Method for efficiently producing pro-TGase through fermentation
The invention discloses a method for producing pro-TGase by adding isopropyl thiogalactoside (IPTG) and inducing to improve the fermentation of recombinant Escherichia Coli BL21(DE3) through a low temperature strategy. A secretary expression vector pET22b recombinant Escherichia Coli BL21(DE3) is taken as a fermentation strain, and the temperature is controlled to be 37DEG C in an initial growth stage; when thalli grow to reach a certain thallus concentration, cool induction is carried out, the IPTG at the final concentration of 0.4mM is added, the temperature is reduced to 20DEG C, and the expression of the pro-TGase is induced. The temperature of an induction stage is reduced in the fermentation process, and the aim of improving the yield of the pro-TGase is finally fulfilled. The method has the advantages that: the yield and the productivity of the pro-TGase can be effectively improved, the content of other proteins in a fermentation liquor is reduced, the efficiency during downstream extraction is improved, the product purity is improved, energy consumption is reduced, and the method is suitable for industrial large-scale production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method and application of animal-derived cationic antimicrobial peptides
ActiveCN102229666AConvenient purification workOmit refoldingAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntimicrobial drugAntibacterial activity
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of animal-derived cationic antimicrobial peptides. The preparation method comprises the following steps: cloning cationic antimicrobial peptide genes shown as SEQ ID NO.1 onto a carrier; transforming plasmids into genetic engineering strains; culturing for 12-16 hours on a culture medium; screening out bacterial colonies containing recombinant plasmids; selecting a single bacterial colony and placing in an LB (Load Balance) liquid culture medium; shaking and culturing till OD600 reaches 0.5-0.7; adding IPTG (Isopropyl Thiogalactoside), shaking and culturing for 3 hours and inducing protein expression; centrifuging for 10 minutes at 4 DEG C and collecting thallus; utilizing a lysis buffer solution to re-suspend the thallus, performing ice-bath, and ultrasonically breaking cells, thereby releasing protein; and utilizing a Chitin column to purify the protein. A test proves that the animal-derived cationic antimicrobial peptides have a broad spectrum antimicrobial function and an ultrahigh antimicrobial activity and can be used for replacing antibiotics for preventing and treating poultry and livestock bacterial infections. A new method for developing a novel clinic antimicrobial drug is demonstrated.
Owner:山东迅达康兽药有限公司
Recombinant vector, strain, and expression and purification method of Rhizoctonia solani effector protein
PendingCN110904139AIncrease concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesProtein solutionProtein target
The invention discloses a recombinant vector, a strain, and an expression and purification method of a Rhizoctonia solani effector protein, and belongs to the biotechnical field. The recombinant vector is used for expressing the Rhizoctonia solani effector protein; the recombinant vector is obtained by inserting a coding gene of the Rhizoctonia solani effector protein into a position between EcoRIand XhoI restriction enzyme cutting site of a pET-32a vector; the amino acid sequence of the Rhizoctonia solani effector protein is represented by SEQ ID NO:1 in a sequence table; and the nucleotidesequence of the coding gene of the Rhizoctonia solani effector protein is represented by SEQ ID NO:2 in the sequence table. The strain with the recombinant vector is subjected to activation culture, isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside is added to induce the expression of the target protein, the target protein is dissolved by using a protein dissolving buffer solution, and elution and dialysis treatments are carried out multiple times with different buffer solutions to obtain a high-concentration Rhizoctonia solani effector protein solution.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Bran coat source peroxidase anti-tumor active fragment as well as preparation method and application thereof
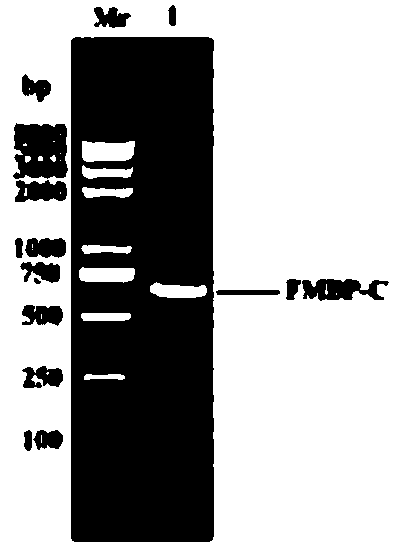
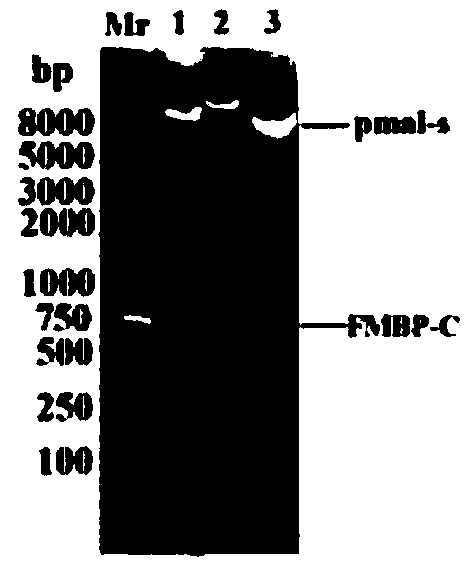
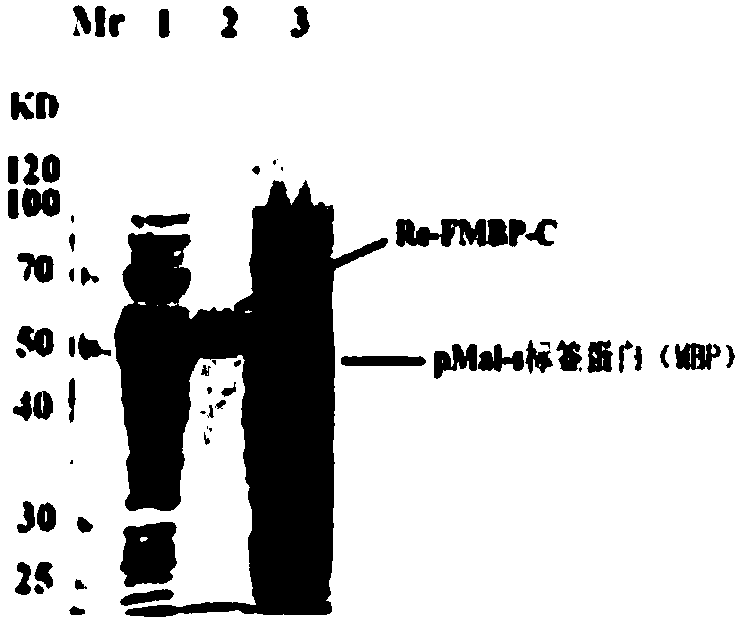
The invention provides a bran coat source peroxidase anti-tumor active fragment as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the fragment comprises the followingsteps: extracting mRNA of rice seedling tissues by a Trizol method, taking the mRNA as a template, performing enzymatic catalysis, and performing inverse transcription to obtain cRNA; obtaining a protein gene sequence in Genebank according to FMBP mass spectrum identification results of the rice anti-tumor active protein, respectively performing truncated screening according to different functional regions, determining a gene sequence of Ca<2+> binding sites as an anti-tumor effect structural domain, and designing a specific primer thereby; taking the rice cDNA as a template, and amplifying the FMBP-C gene sequence by a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method; respectively introducing BamH I and HindIII restriction enzyme sites at the upstream and downstream of the sequence, connecting thesites with a pMal-s vector, constructing a pMal-s-FMBP-C recombinant plasmid, transferring E.coli DH5alpha competent cells, and screening to obtain a positive transformant; performing induced expression on a target protein through IPTG (Isopropyl Thiogalactoside), performing affinity purification, desalting and concentrating, and detecting functions of resisting tumors and reversing multiple drugresistance of tumors by an MTT method. The results show that the active fragment has obvious activities of resisting tumors and reversing multiple drug resistance of the tumors.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
High density fermentation method of recombinant porcine interferon alpha 1 (rPoIFN alpha 1) gene engineering bacteria
ActiveCN103589769AEfficient expressionAvoid expressing the need for refolding problemsFermentationInclusion bodiesThiogalactosides
The invention discloses a high density fermentation method of recombinant porcine interferon alpha 1(rPoIFN alpha 1) gene engineering bacteria, and belongs to the technical field of fermentation engineering. The high density fermentation method of the recombinant porcine interferon alpha 1 (rPoIFN alpha 1) gene engineering bacteria is as follows: recombinant escherichia coli BL21 / pET-32a-rPoIFN alpha 1 which can construct and express rPoIFN alpha 1 by itself is used as a production bacteria strain for fermentation at 37 DEG C for 2-3h, inducer isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside (IPTG) with the concentration of 50 g / L-100 g / L is added into each liter fermentation solution by one time, fermentation is continued at 32 DEG C for 4-5 h, and then the fermentation process is completed. The high density fermentation method can realize the high-efficiency expression of the rPoIFN alpha 1, an objective protein expression amount accounts for more than 40% of the total bacteria protein, the potency can reach above 1*10<6>IU / ml, the protein is a soluble protein, denaturation and renaturation problems of inclusion body expression can be avoided, the production cycle is shortened, and the high density fermentation method provides a solid foundation for industrial production of the rPoIFN alpha 1.
Owner:王明丽 +1
High-stereoselectivity methionine adenosyltransferase as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112760303AHigh expressionHigh stereoselectivity with high expressionTransferasesFermentationEscherichia coliEnzyme digestion
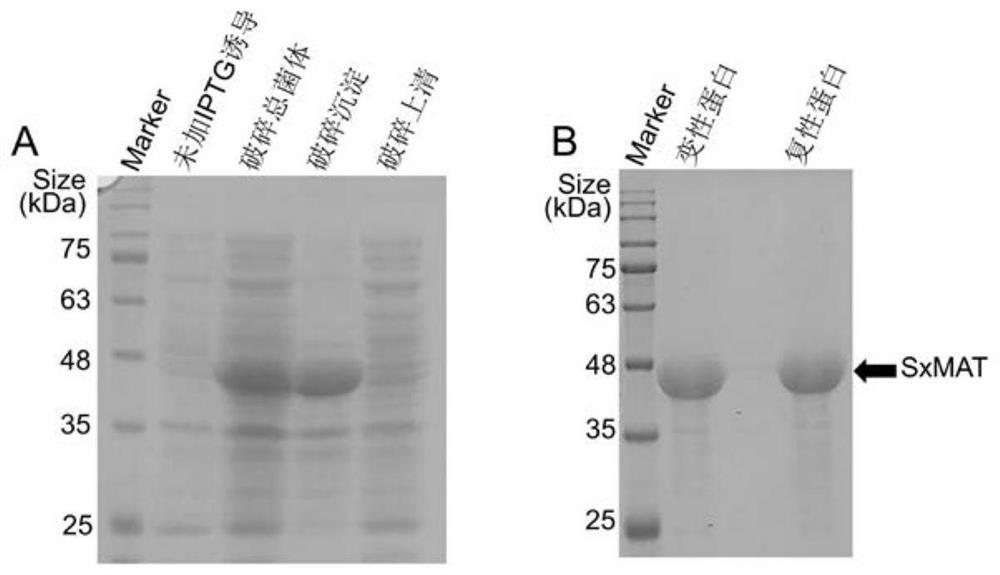
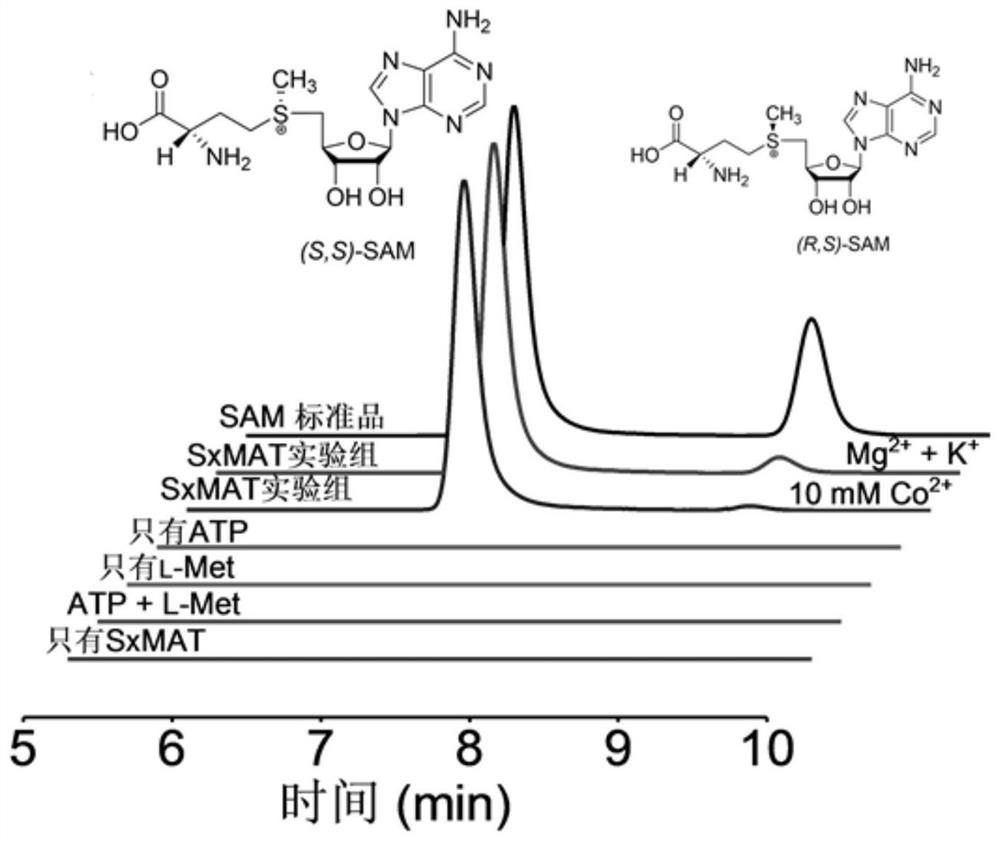
The invention discloses high-stereoselectivity methionine adenosyltransferase as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: extracting a genome of streptomyces xinghaiensis; by taking a genome as a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) template and adopting a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification technology, obtaining a gene sequence of methionine adenosyltransferase in the streptomyces xinghaiensis, namely a metK target fragment; carrying out double enzyme digestion on the metK target fragment and an expression vector pET-32a (+), and then connecting to construct a recombinant plasmid; transforming the recombinant plasmid into competent cells of escherichia coli BL21 by adopting a thermal activation method, and carrying out inducible expression by virtue of isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside, so as to obtain SxMAT. According to the invention, high-stereoselectivity methionine adenosyltransferase is subjected to denaturation and renaturation later to obtain high-purity SxMAT, the SxMAT is good in stability when the temperature is 25-55 DEG C and the pH value is 8-10.5, the optical purity (ee) of the product is higher than 90%, the yield is 80%, and the in-vitro double-enzyme cascade reaction is constructed by combining the SxMAT and the fluorinase, so that the understanding of people on a fluorination pathway in streptomyces is facilitated, and the application of fluorinated natural products is derived.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Hepatitis B virus multi-epitope fusion protein and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102199217BEfficient removalImproving immunogenicityDigestive systemAntiviralsEscherichia coliFusion Protein Expression
The invention relates to a hepatitis B virus multi-epitope fusion protein and a preparation method and application thereof. The fusion protein is obtained by inserting hepatitis B virus multi-epitope fusion peptide (with the sequence shown as SEQIDNo.1) formed by serially connecting HBsAg313-321, HBsAg335-343, Pol150-159, Pol455-463 and Padre epitopes through connecting peptide between amino acid at the 78th position and amino acid at the 79th position of a hepatitis B virus core protein; and the preparation method comprises the following steps of: constructing a hepatitis B virus multi-epitope fusion protein expression plasmid pET28-HBc-HP; performing isopropyl thiogalactoside (IPTG) inducing expression by using an Escherichia coli expression system; and purifying by using affinity chromatography. The fusion protein carries a plurality of supertype epitopes of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg) and polymerase, is viral particles, has the advantages of strong immunogenicity, wide applicable range and the like, and can be used for preparing therapeutic hepatitis B vaccines.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com