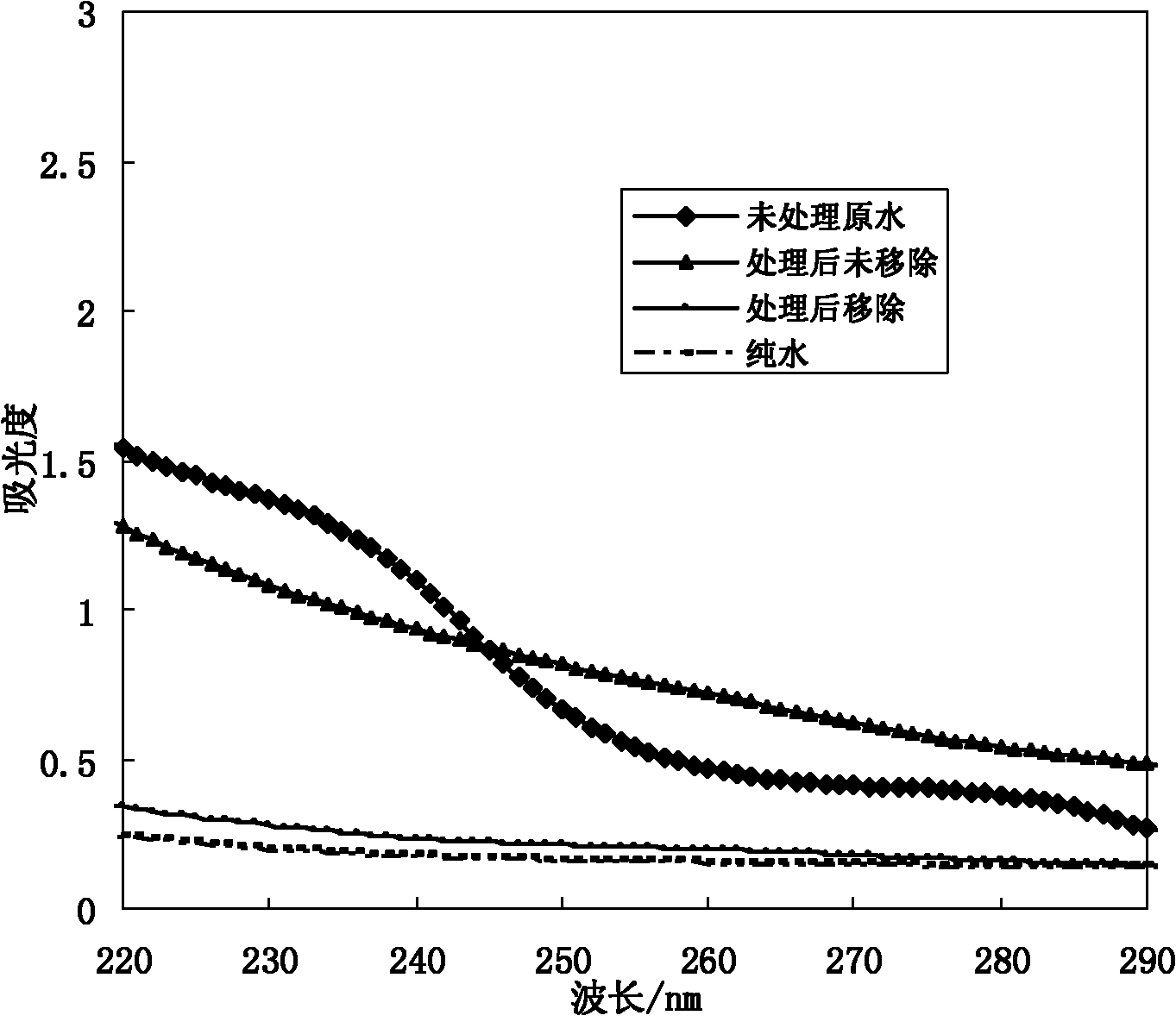
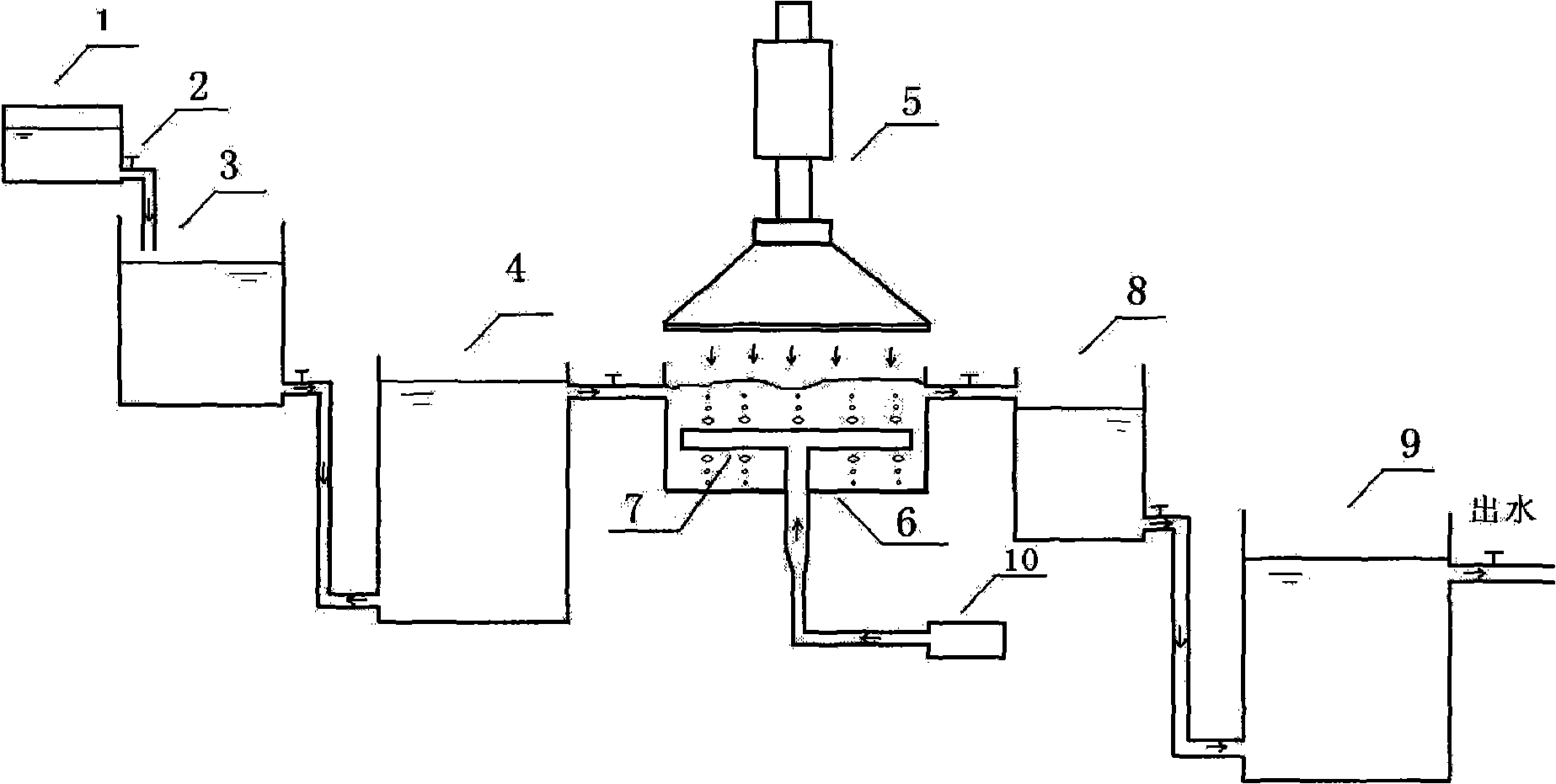
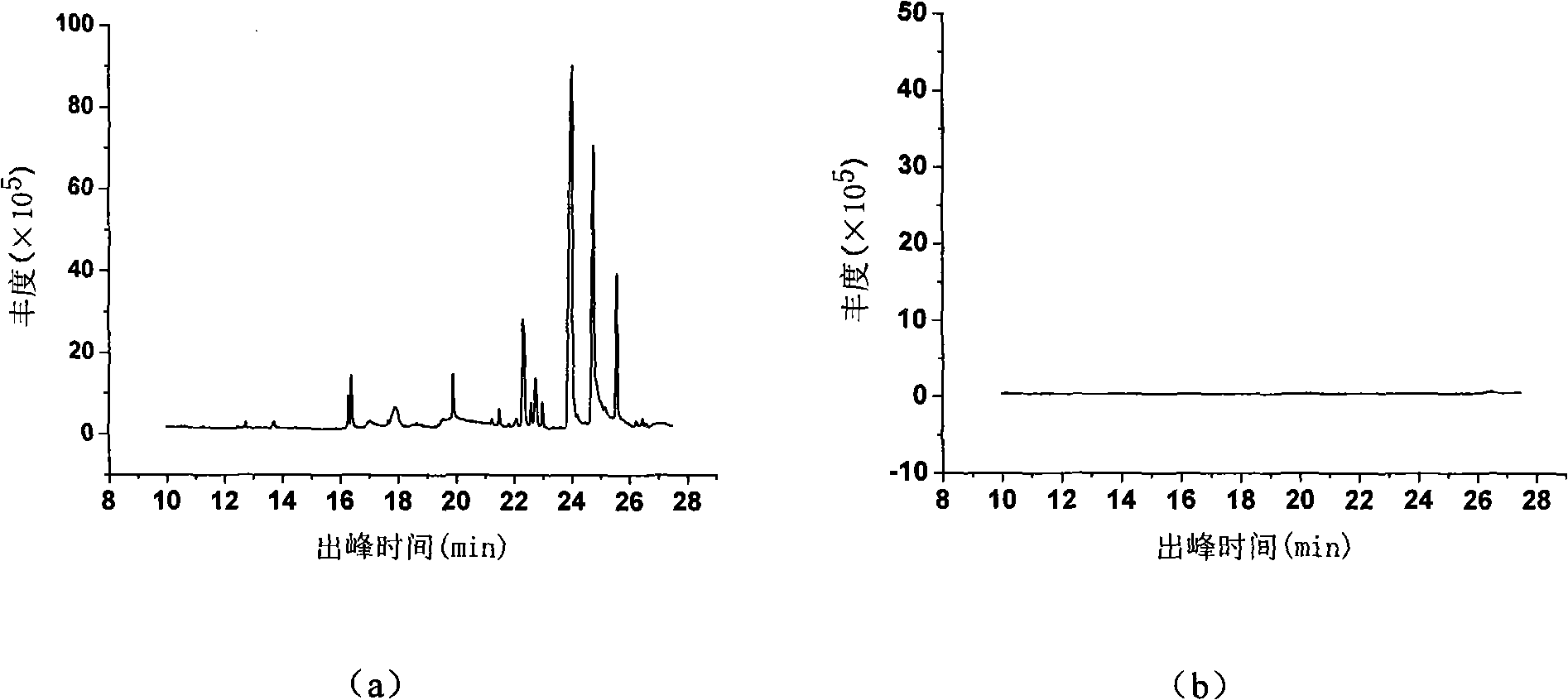
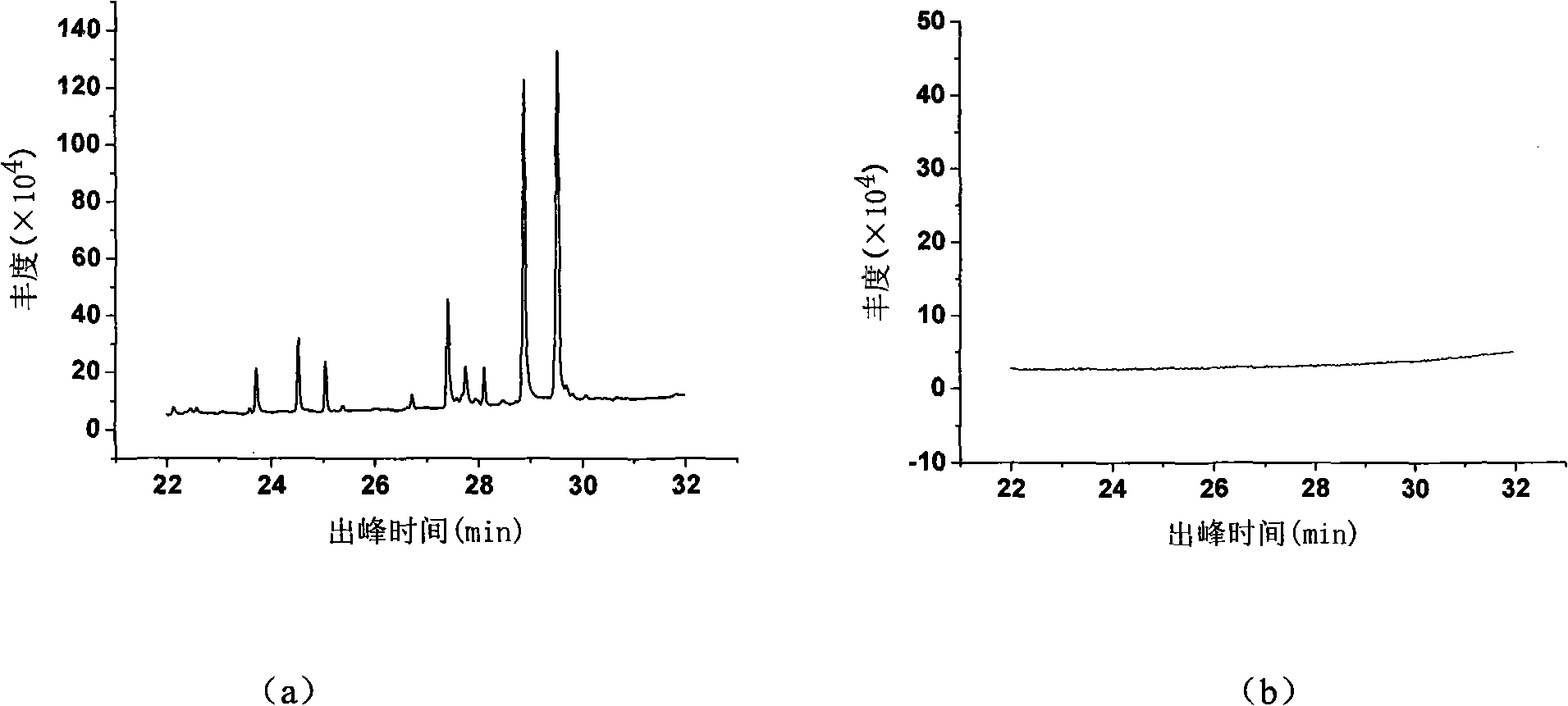
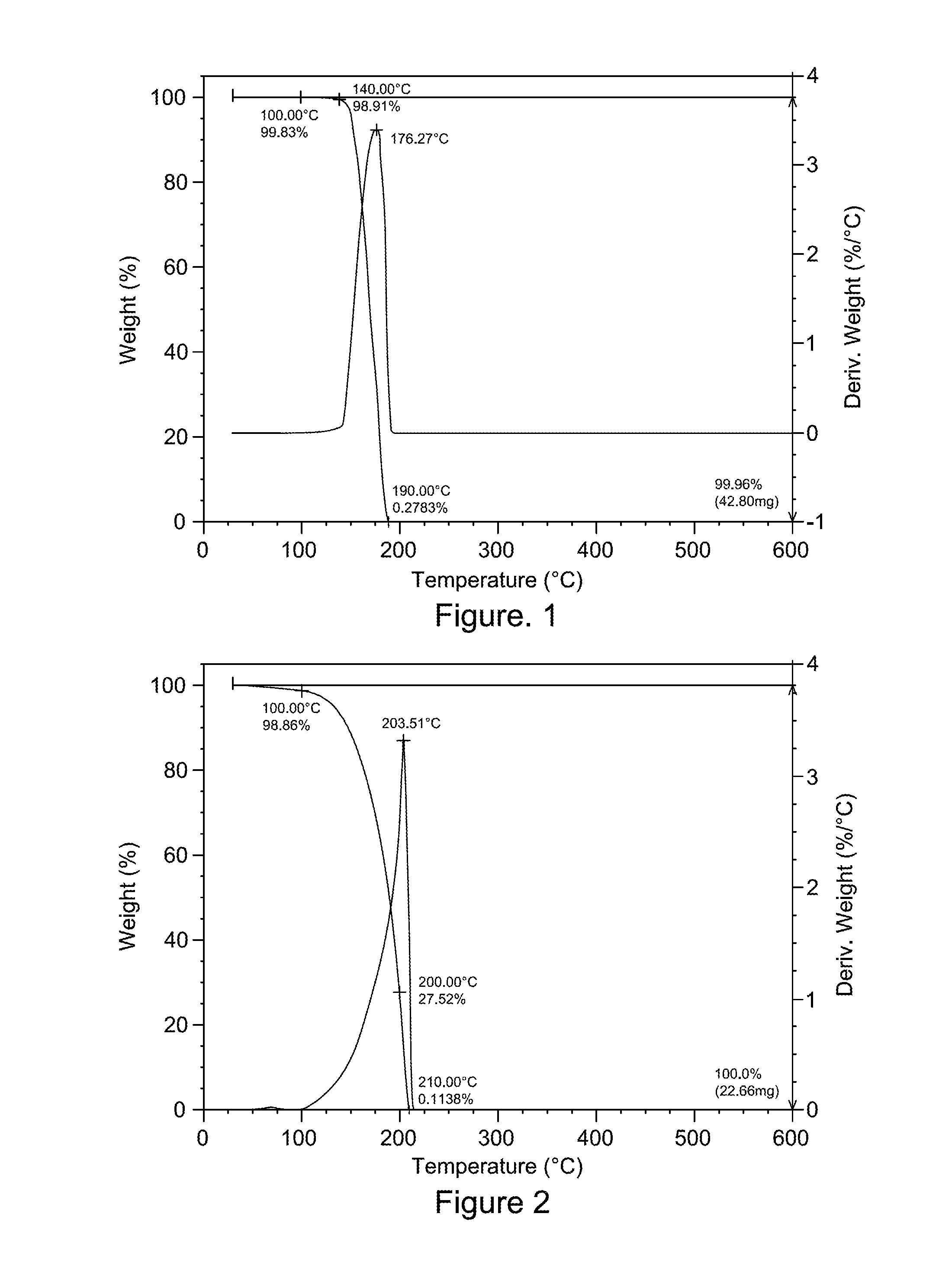
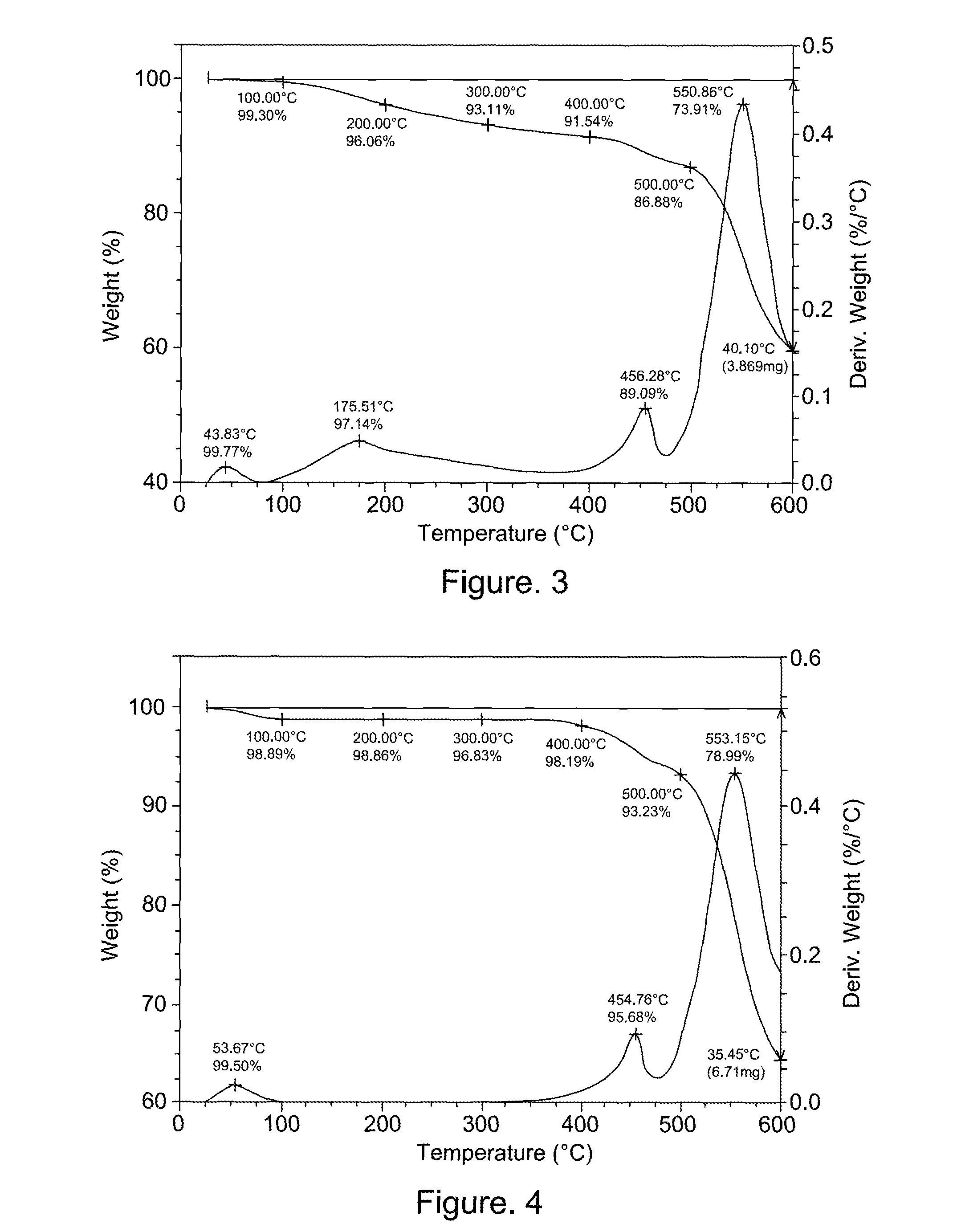
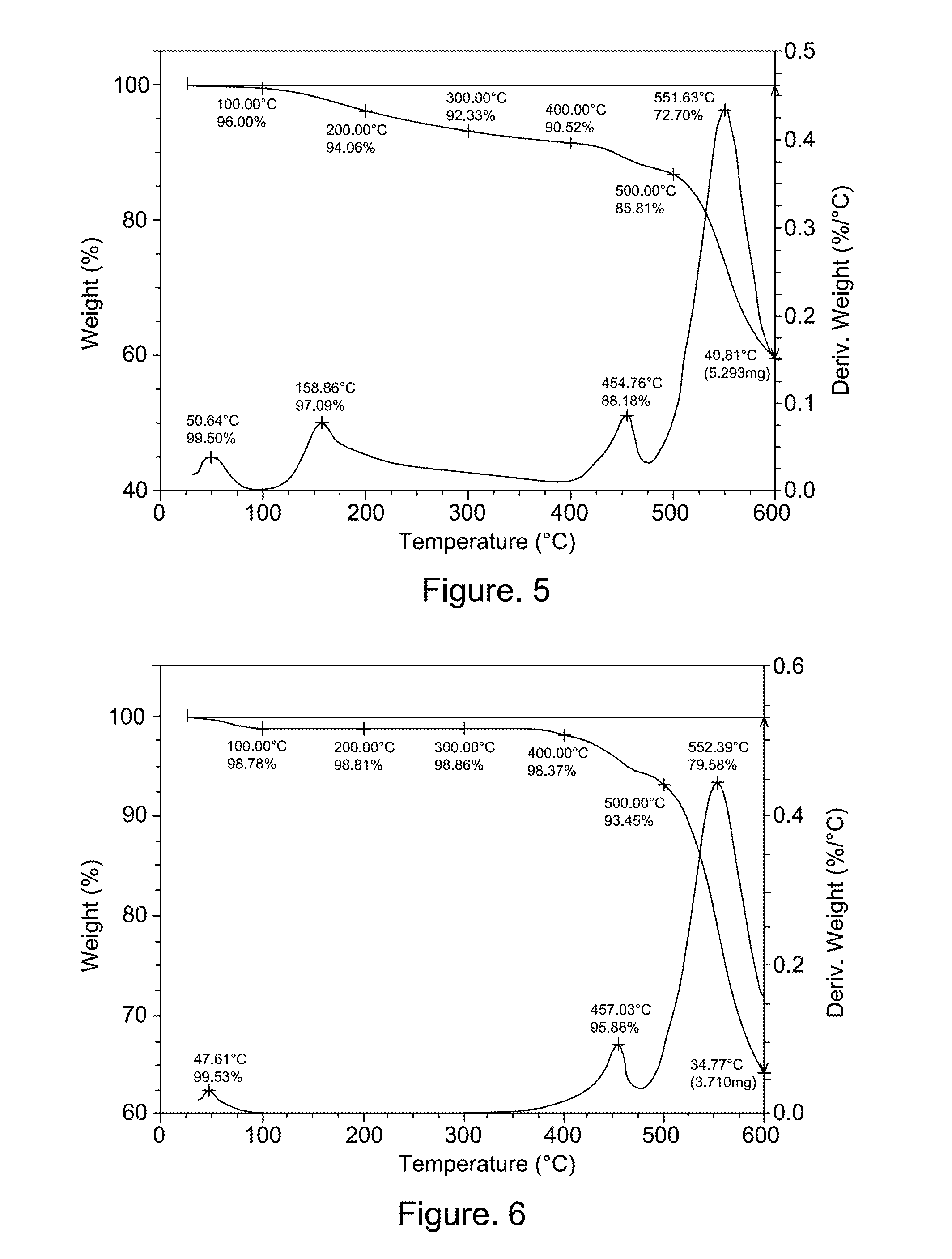
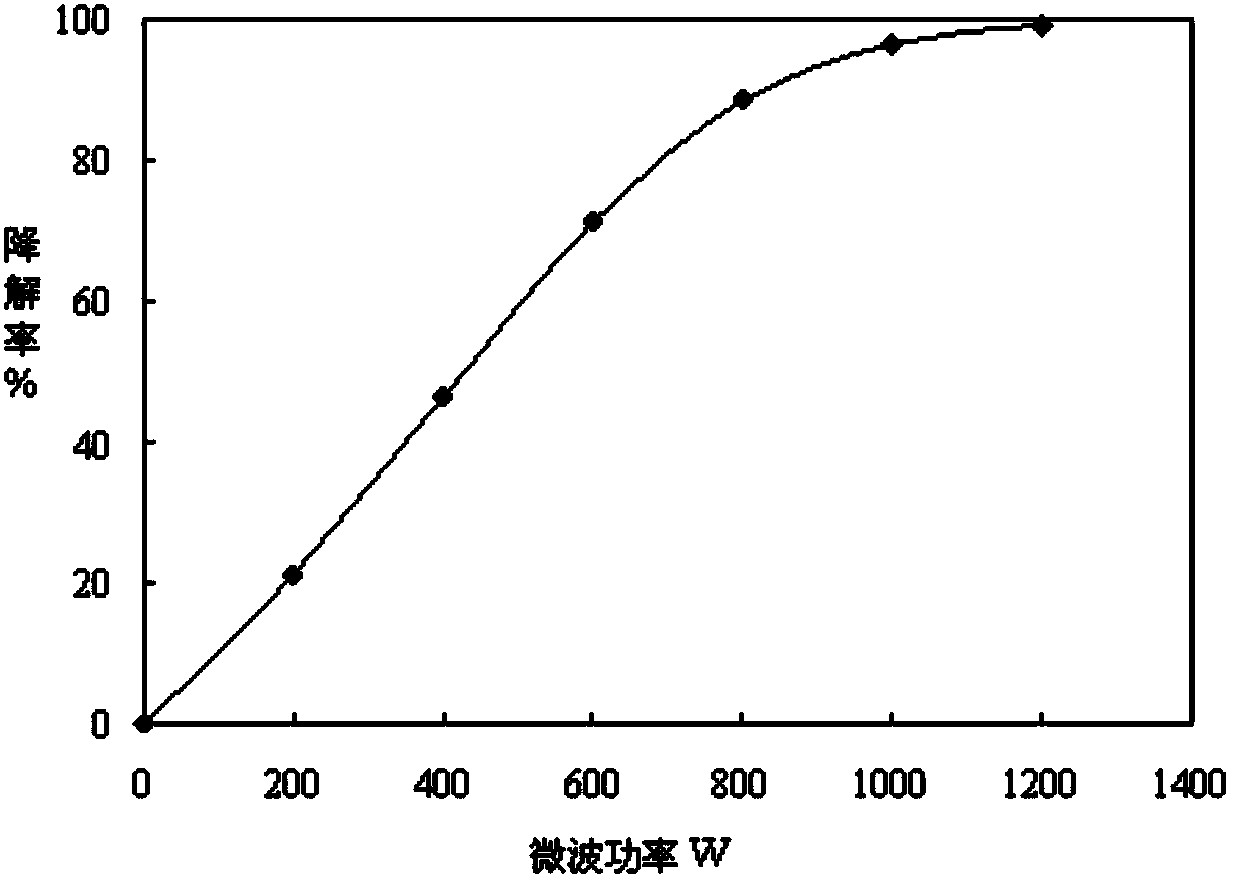
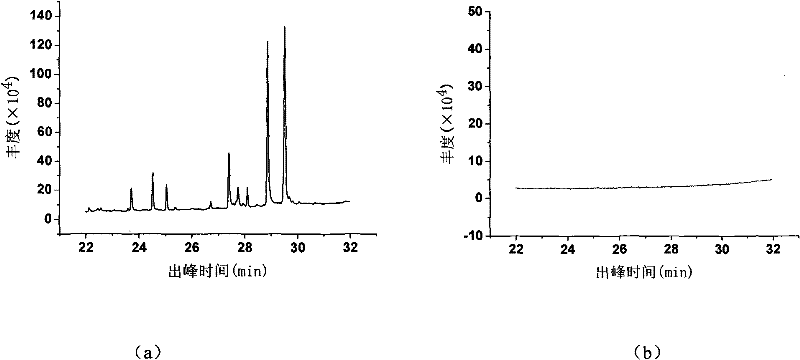
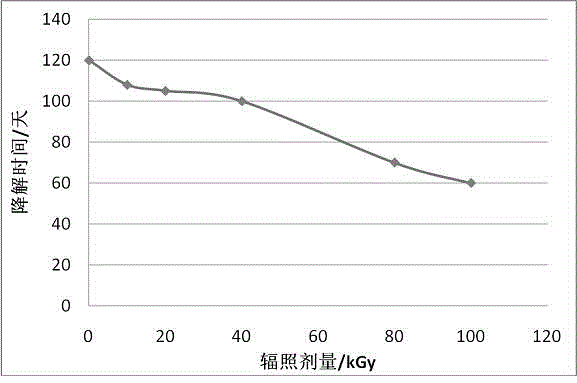
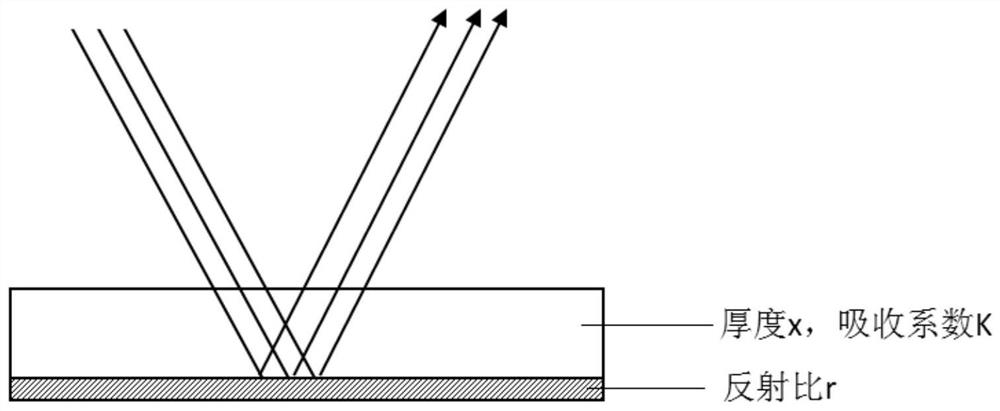
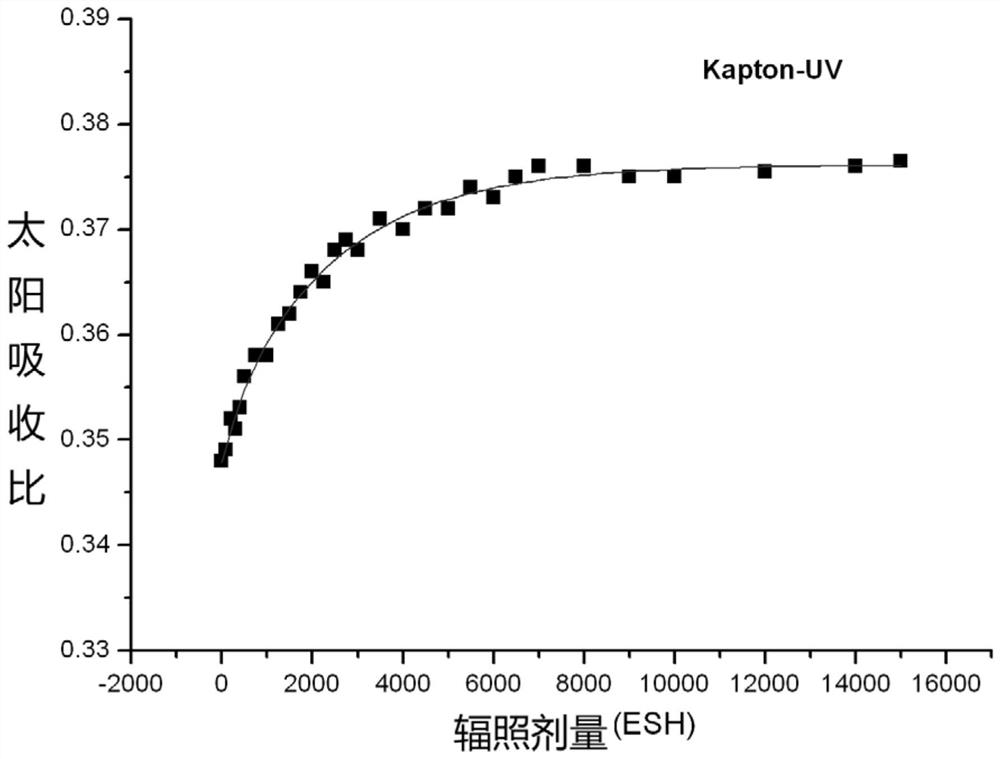
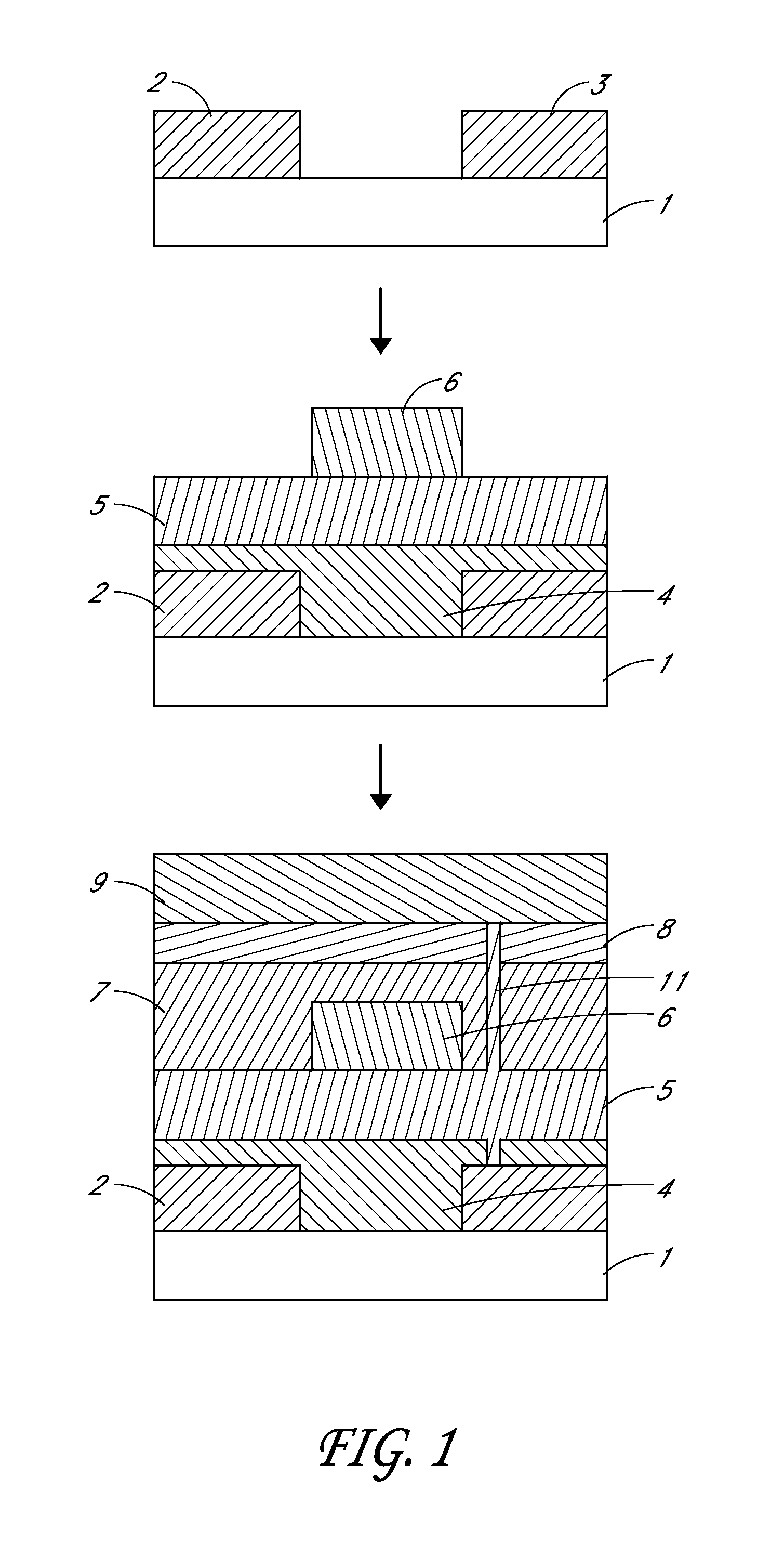
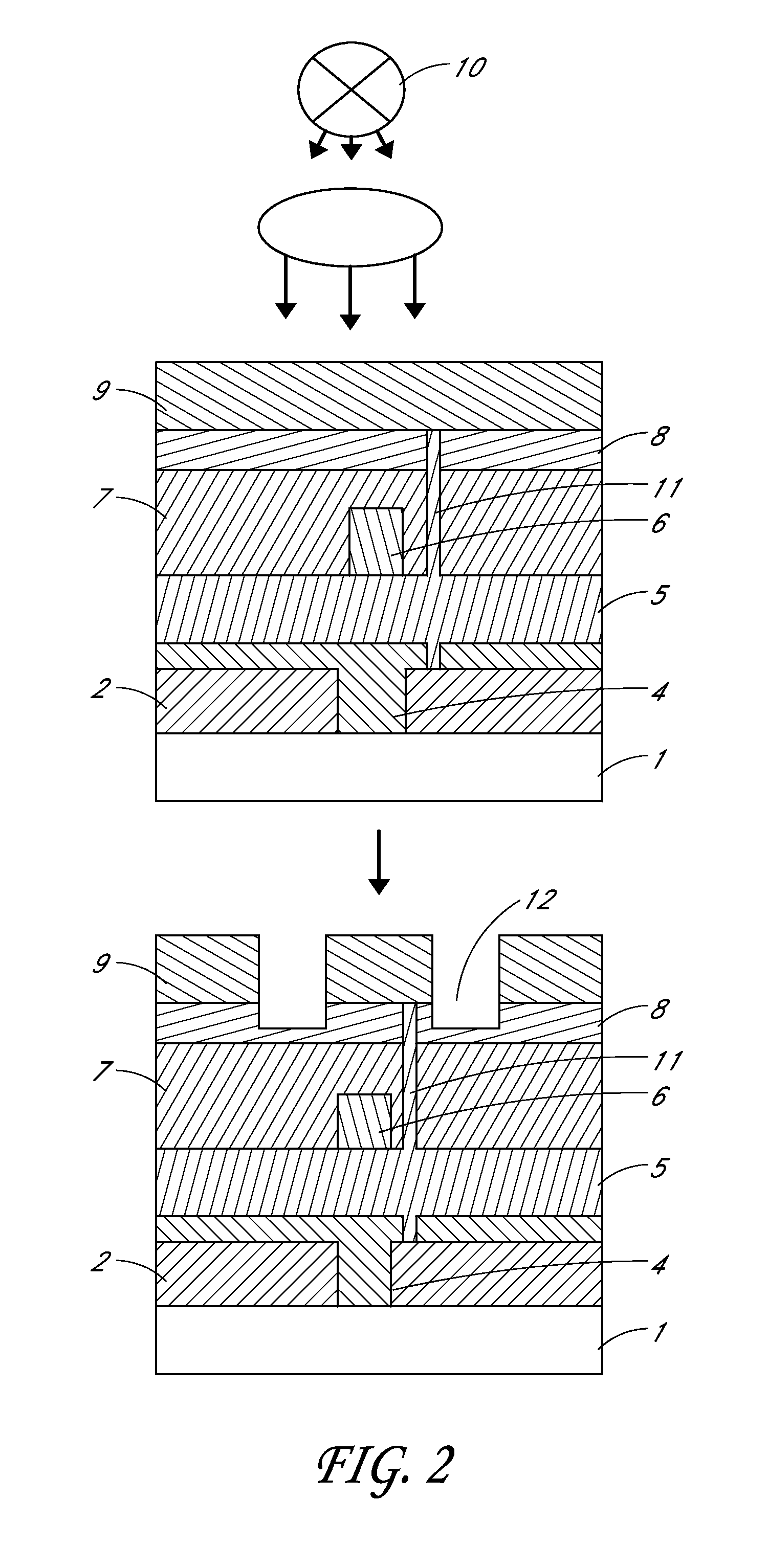
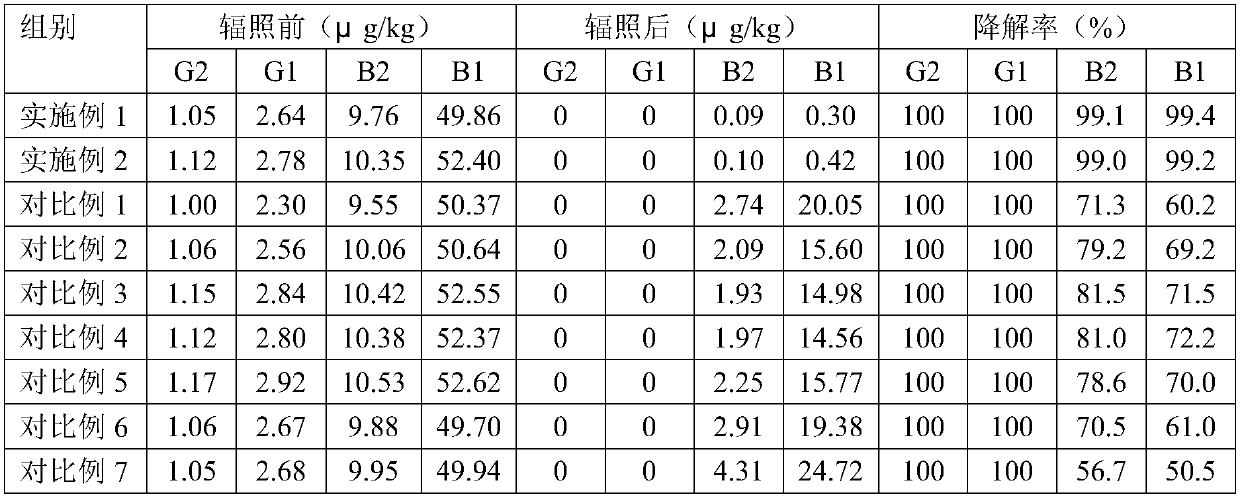
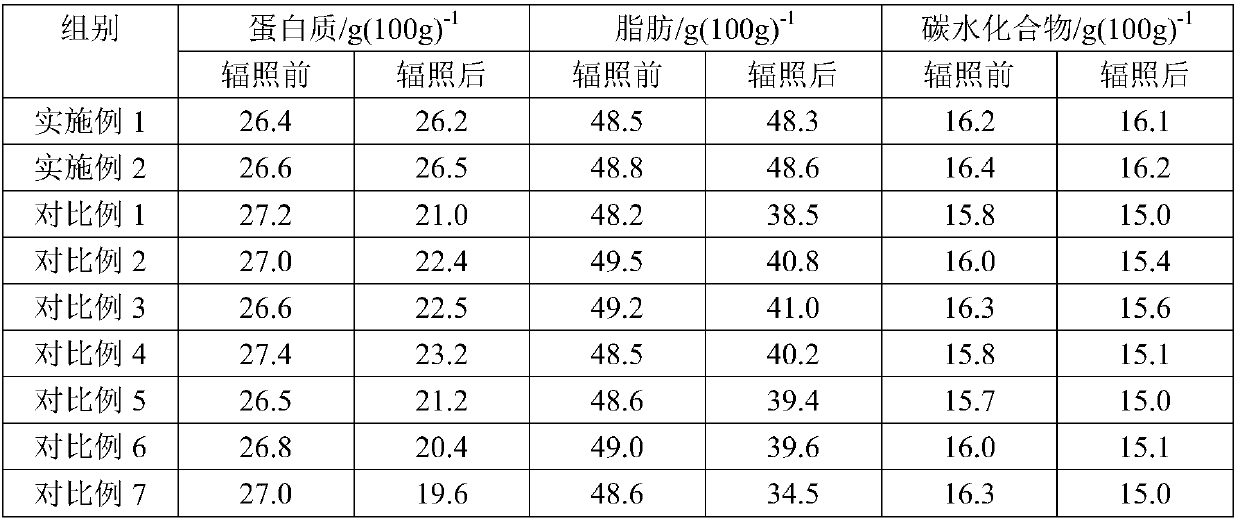
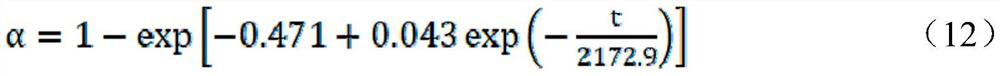Patents
Literature
51 results about "Radiation degradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Preparing low molecular weight chitosan by sensitizing radiation degradation method
The sensitizing and readiation degrading process of preparing low molecular weight chitosan includes the following steps: mixing refined solid chitosan with water solution of sensitizer to form semi-solid sample, regulating pH to 4 with inorganic acid or organic acid and reaching chitosan concentration of 16-25 wt% and sensitizer concentration of 15-30 wt%, gamma ray irradiation in the dosage of 1-10 kGy to degrade at room temperature, and spray drying or vacuum drying to obtain low molecular weight chitosan. Adding the sensitizer can lower the irradiation dosage greatly, and obtain chitosan product with narrow molecular weight distribution and small molecular weight. The present invention can obtain chitosan with molecular weight as low as 3000, and the process is convenient, safe, economic, practical, high in yield and environment friendly.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for preparing chitosan into water-soluble chitosan oligosaccharide
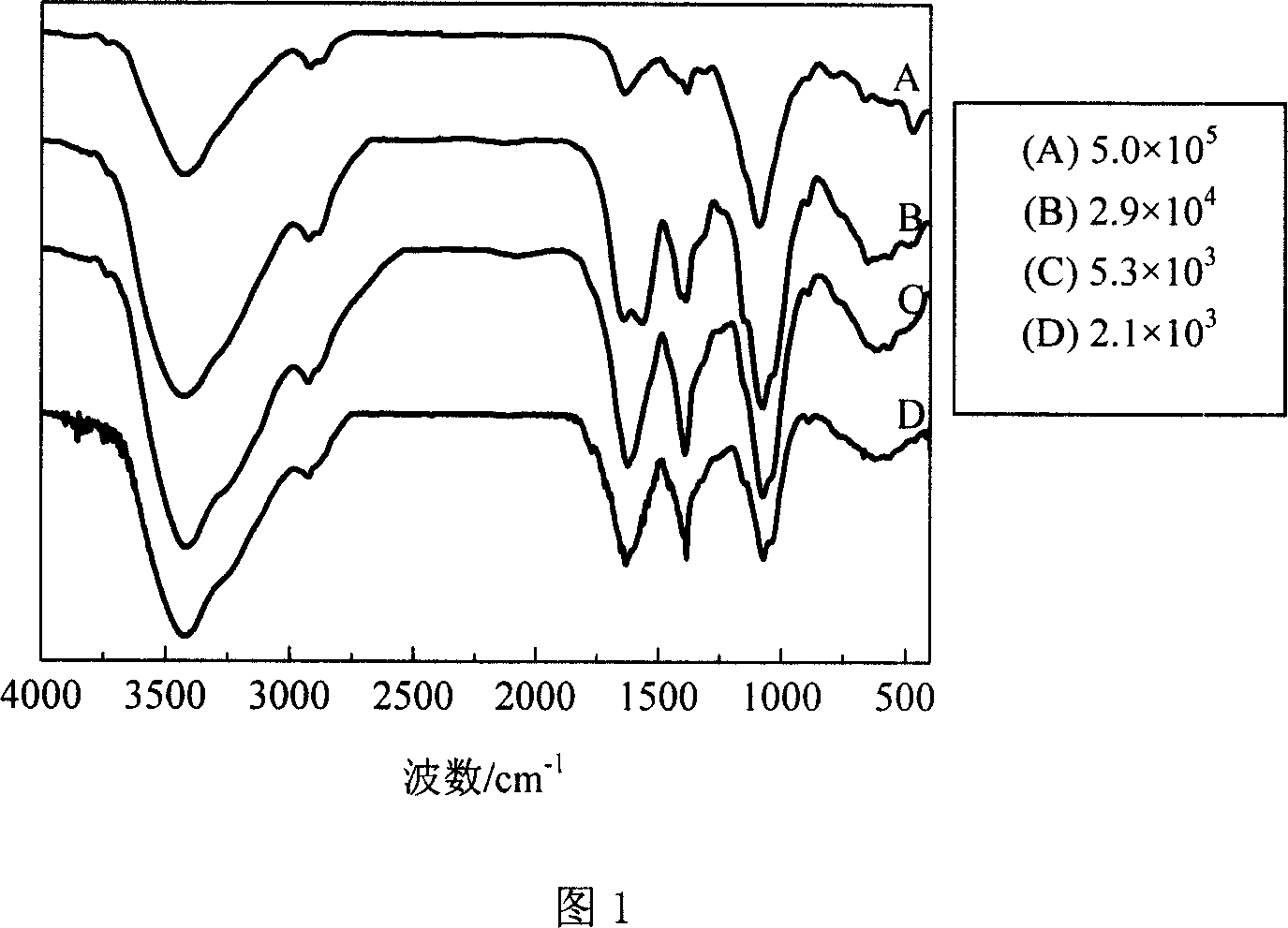
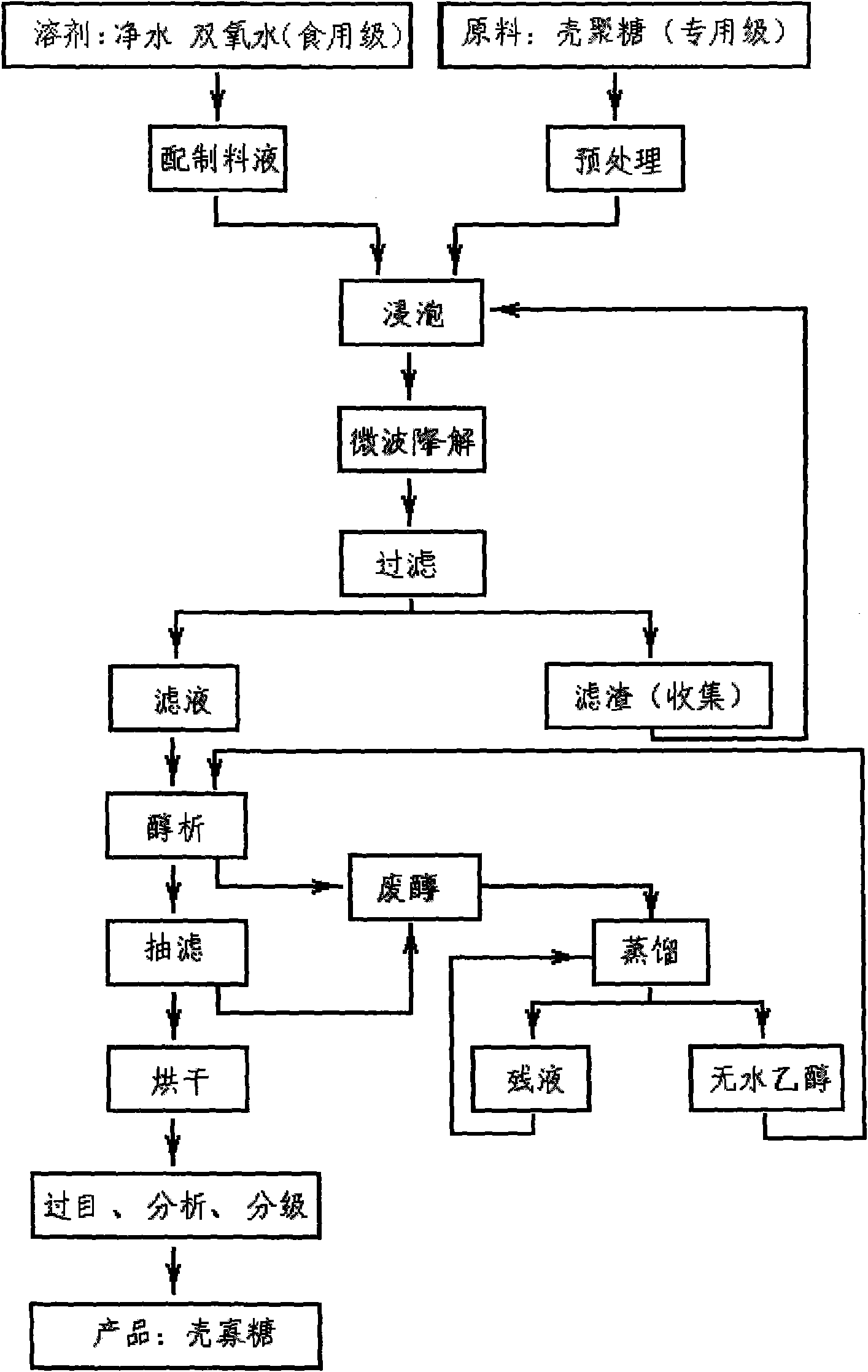
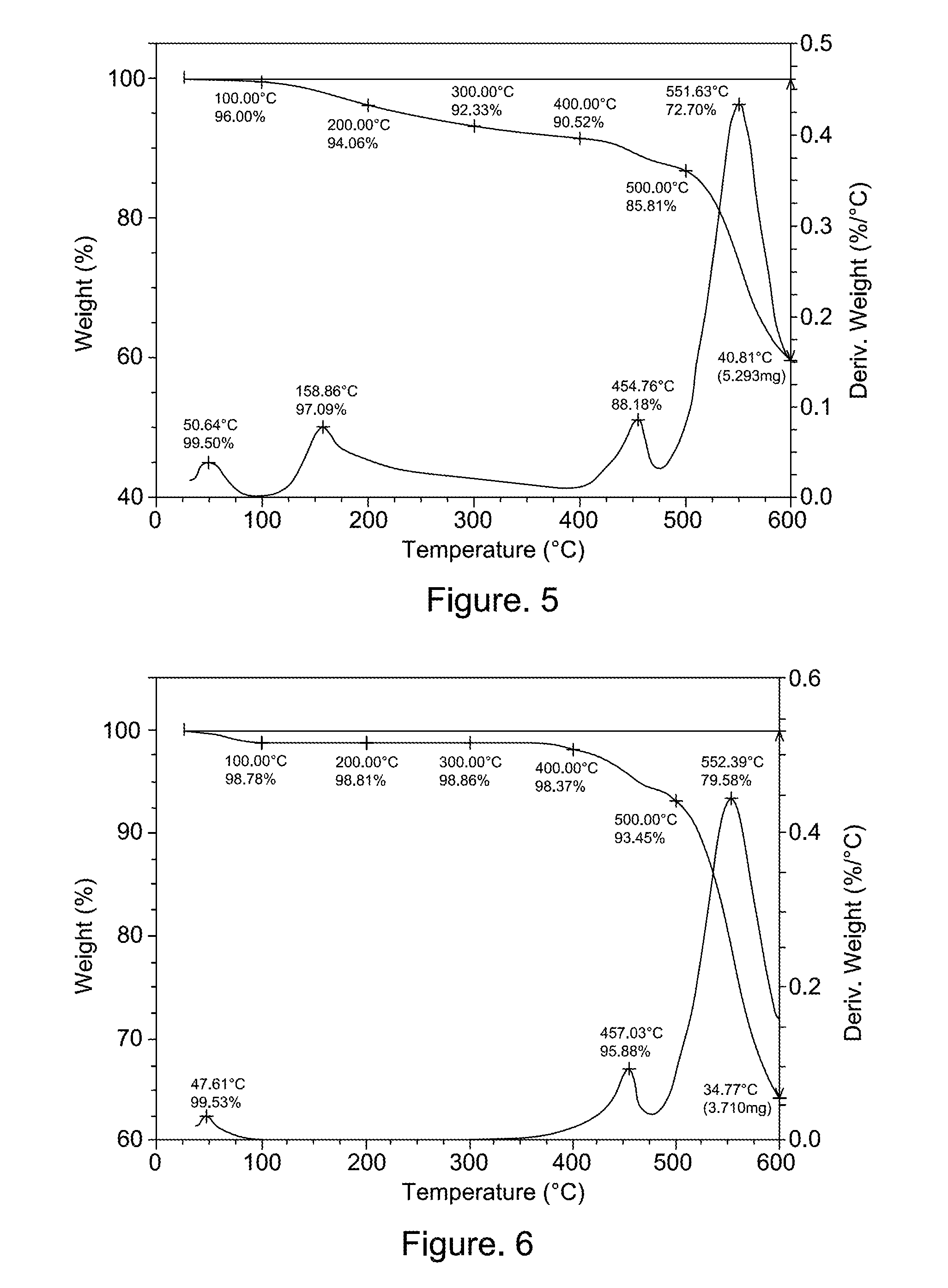
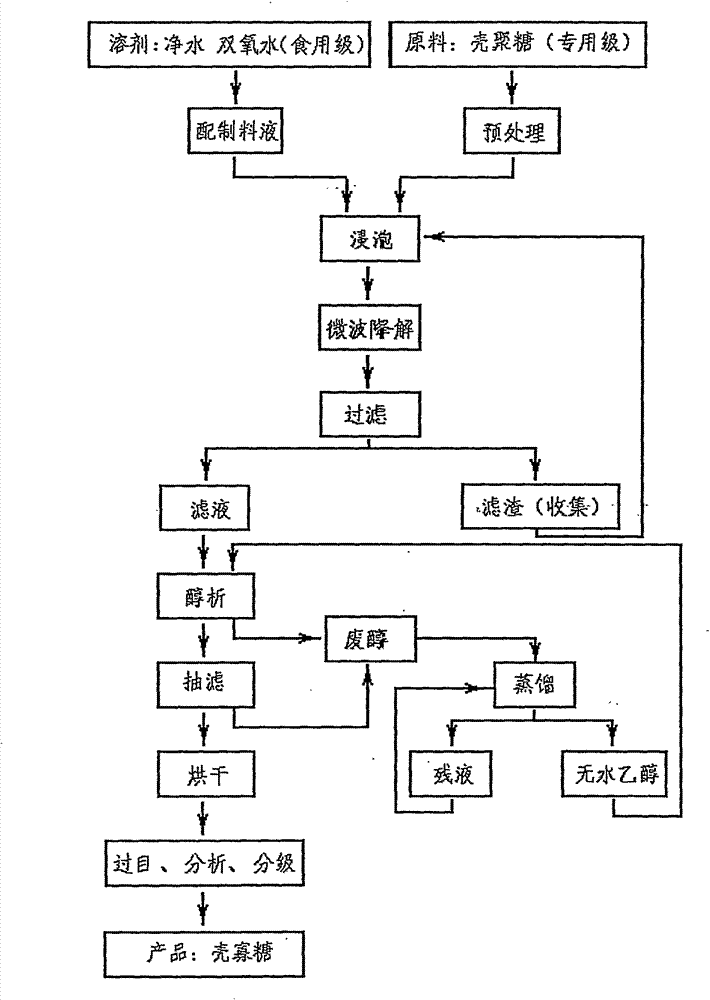
The invention relates to a method for preparing chitosan into water-soluble chitosan oligosaccharide, which takes the chitosan as raw material and comprises the following steps of: treating the chitosan by rinsing and drying technique, and then soaking in material liquid prepared by purified water and food grade hydrogen peroxide; carrying out microwave radiation degradation treatment, and formingthe mixed liquid of low molecular weight chitosan oligosaccharide which can be dissolved in the material liquid and chitosan part of which is not dissolved; after that, filtering and obtaining the residue of the chitosan and the chitosan oligosaccharide solution; and finally, adding the chitosan oligosaccharide solution into absolute alcohol for alcohol precipitation, and then carrying out suction filtration and drying, thus obtaining the finished product of the water-soluble chitosan oligosaccharide. By adopting the microwave radiation degradation treatment technology and exciting energy bya physical method, the higher molecular weight chitosan is degraded into the low molecular weight water-soluble chitosan oligosaccharide with stable structure, no reaction by-product is generated in the degradation process, and no contaminant is produced; furthermore, compared with the preparation method in the prior art, the method has the advantages of advanced technique, simple working procedures, little production facility investment, high purity of the product, stable quality and the like, thus opening up wide market application prospect for preparing the chitosan oligosaccharide by taking the chitosan as raw material.
Owner:SHANGHAI 007 MOTIVE TECH DEV
Polymers, polymer membranes and methods of producing the same
A method for preparing a polymeric material includes: providing a polymeric matrix having at least one polymer and at least one porogen; and degrading the at least one porogen at a temperature T≦1.1 Tg, where Tg is a glass transition temperature of the polymeric matrix. The degrading step includes exposing the polymeric matrix to thermal degradation, chemical degradation, electrical degradation and / or radiation degradation, wherein the polymeric material has a permeability at least 1.2 times a permeability of the polymeric matrix for a gas, and a selectivity of the polymeric material is at least 0.35 times a selectivity of the polymeric matrix for a gas pair. The method preferably provides gas separation membranes that exceed Robeson's upper bound relationship for at least one gas separation pair. Novel polymeric materials, gas separation membranes and fluid component separation methods are also described.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Antimicrobial radiation-preventing formaldehyde-degrading ecological diatom wall material
The invention discloses a wall material belonging to the field of building decoration, and specifically relates to antimicrobial radiation-preventing formaldehyde-degrading ecological diatom wall material paint and a preparation process and construction process of the wall material. The wall material is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 21-29% of kieselguhr, 15-20% of quartz sand, 0.1% of fiber, 7-8.6% of bentonite, 3-5% of attapulgite, 12-17% of sierozem, 6-8% of water-retaining agent, 8-12% of nano titanium dioxide, 3-6.1% of nano zinc oxide, 3-5% of zeolite, 3-5% of micro silicon powder, 3-5% of grammite and 3-7% of anion powder. The wall material disclosed by the invention has the effects of adsorbing toxic and harmful gas, resisting bacteria, preventing radiation and degrading formaldehyde, and diatom ooze enables the product to have the powerful characteristics of breathing, conditioning and purifying air; and the wall material has the functions of fire resistance, flame retardance, sound insulation, noise reduction, warm keeping and heat insulation. Thus, the wall material is an ideal wall decoration material combining an environmental protection function and artistic modeling.
Owner:广东太氧谷环保科技有限公司
Method for preparing chitosan into water-soluble chitosan oligosaccharide
The invention relates to a method for preparing chitosan into water-soluble chitosan oligosaccharide. The method is as below: rinsing and drying a raw material chitosan, soaking chitosan into a feed liquid prepared from clean water and food grade hydrogen peroxide, conducting microwave radiation degradation treatment to form a mixed solution of low molecular chitosan oligosaccharide dissoluble in the feed liquid and non-degraded chitosan, then filtering to obtain by chitosan residue and a chitosan oligosaccharide solution, subjecting the chitosan oligosaccharide solution to alcohol precipitation in ethanol, and conducting suction filtration and drying to obtain the water-soluble chitosan oligosaccharide product. Due to the microwave radiation degradation treatment technology and physical method for lasing energy, polymer chitosan degrades into low molecular water- soluble chitosan oligosaccharide with stable structure; and in the degradation process, no other reaction by-products or pollutants are generated. Compared with the preparation method in the prior art, the method has the advantages of advanced technology, simple process, less investment in production facilities, high product purity and stable quality, and opens broad market prospect for chitosan prepared from chitin as raw material.
Owner:殷国铭 +1
Method for preparing water-soluble chitosan through radiation process
The invention belongs to a method for preparing water-soluble chitosan through a radiation process. Small molecular weight or water-soluble chitosan is obtained by carrying out radiation degradation on a refined solid or solution of high molecular weight chitosan by using 60Cogamma rays, and carrying out post-processing steps of a degradation product, such as dissolving, decolourizing and the like. The method is convenient to operate, rapid, simple, convenient, high in yield, good in repeatability, easy to control molecular weight, environment-friendly, low in pollution and low in cost. The method not only can be used for rapidly preparing a few water-soluble chitosan samples but also has further industrial possibility. The obtained chitosan is multifunctional and can be used as an agricultural output increasing agent, a food drying agent, a natural antibacterial material, a biomedical material and the like.
Owner:DALIAN CHUANGDA TECH TRADE MARKET
Degradation method of algal polysaccharides
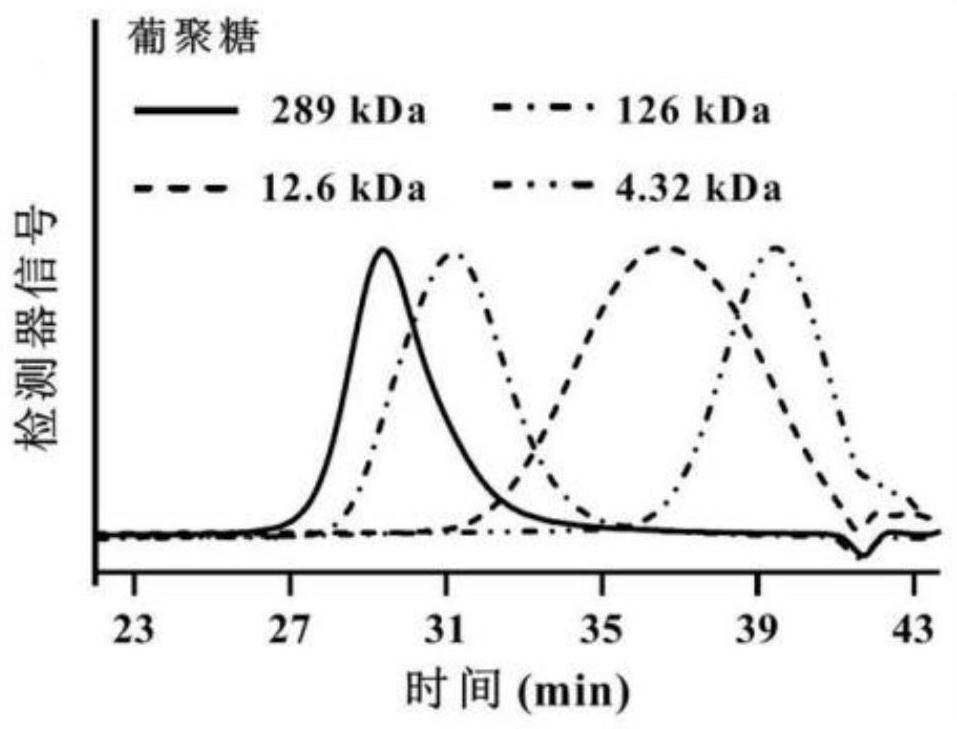
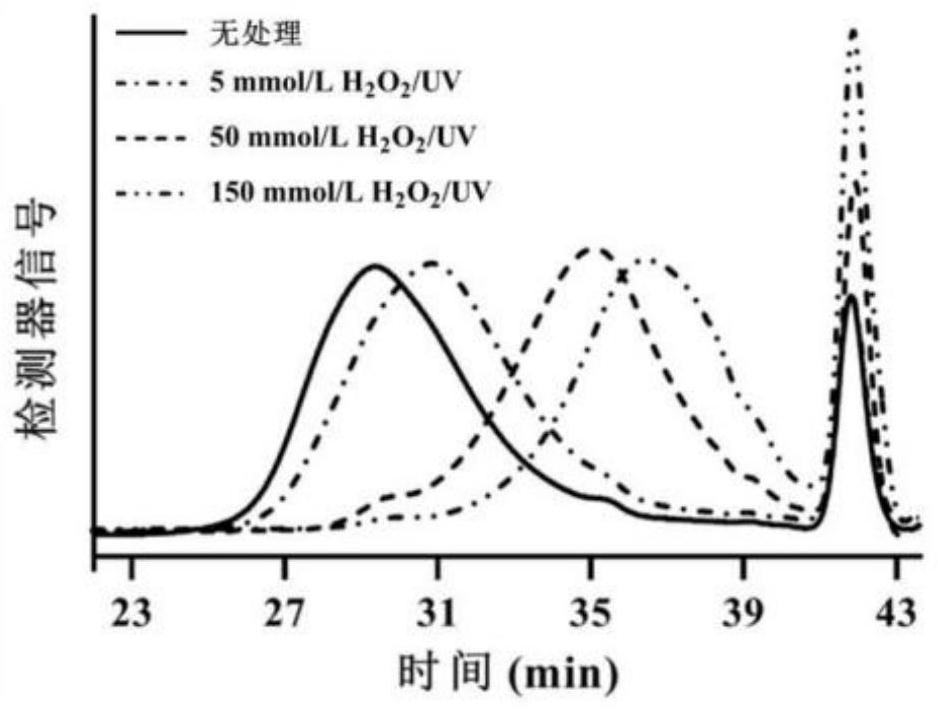
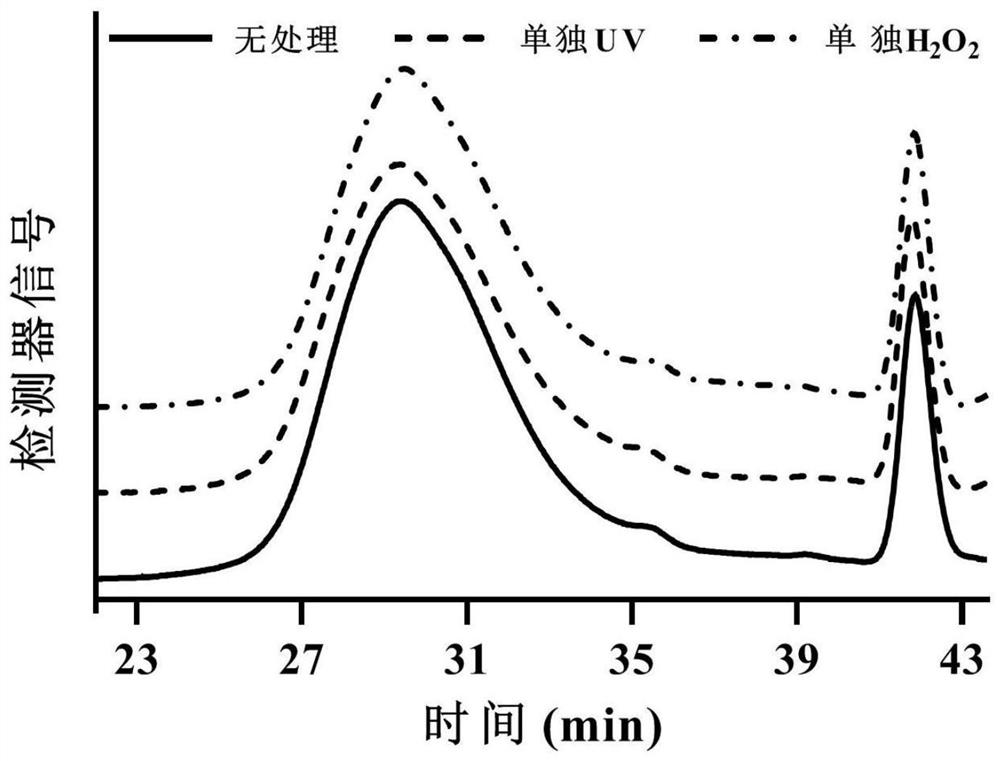
The invention provides a degradation method of algal polysaccharides, and belongs to the technical field of marine chemical engineering. The degradation method comprises the following steps: mixing algal polysaccharides, water and H2O2 to obtain a mixed solution; and carrying out radiation degradation on the mixed solution by adopting ultraviolet light to obtain a degradation product. According to the method, the algal polysaccharides are degraded by combining UV with H2O2, an acidic or alkaline solvent is not involved in the operation process, the process is safe and environmentally friendly, the cost is low, the operation is simple and time-saving, the degradation effect is relatively good, and the method has a good application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Device for degrading pollutant with electron beam radiation
ActiveCN102500305AWell mixedImprove performanceEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesFour-way valveRadiation reaction
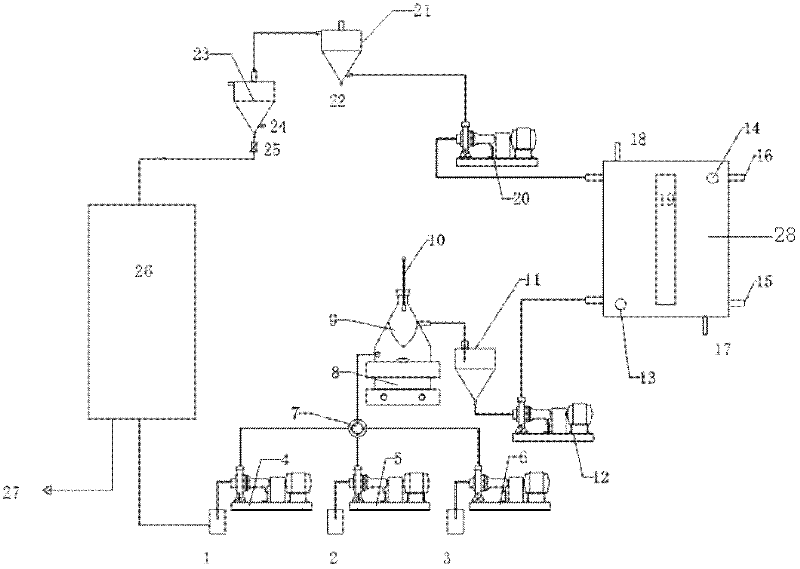
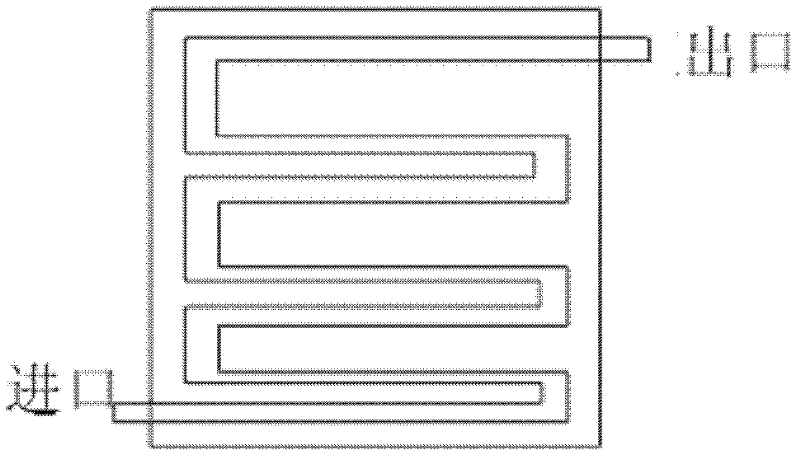
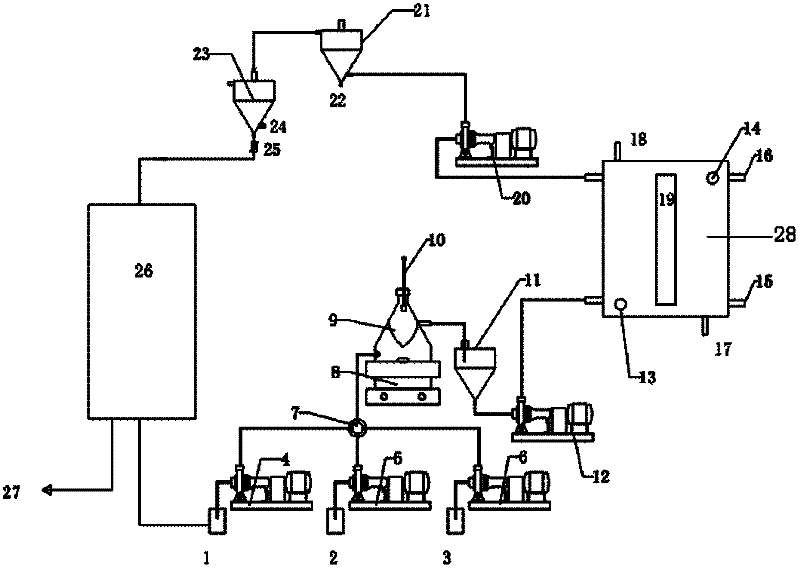
The invention discloses a device for degrading a pollutant with electron beam radiation. An injection pump is used for injecting solvent, absorbent and liquid to be treated in a liquid storage tank into a mixer after the solvent, absorbent and liquid to be treated in the liquid storage tank are mixed by a four-way valve in different proportion; the mixed liquid is fully mixed under the action of a magnetic stirrer; a liquid buffer tank receives the mixed liquid which effuses from the upper outlet of the mixer; and a compression pump at a liquid inlet pumps the mixed liquid in the liquid buffer tank into a radiation reaction box to degrade the mixed liquid with radiation. The device can automatically and continuously radiate to degrade organic halogen which is difficult to degrade; and a matched remote control system and a working condition system are independently developed for self-fault diagnosis and manual remote safety monitoring, so that all the performances of the radiation degradation device can be improved.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for degrading venlafaxine in water by utilizing electron beam irradiation
InactiveCN108585319AStrong handling toxicityRefractory ToxicityWater treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsNuclear technologyHigh energy
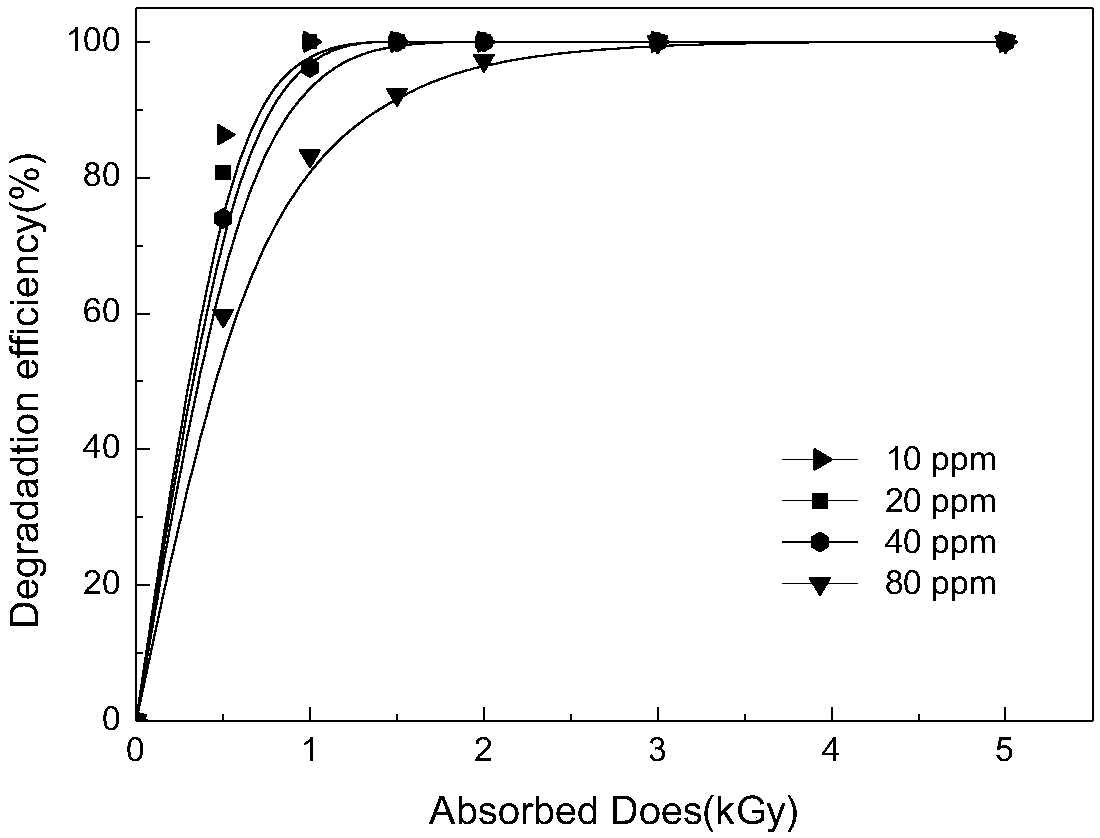
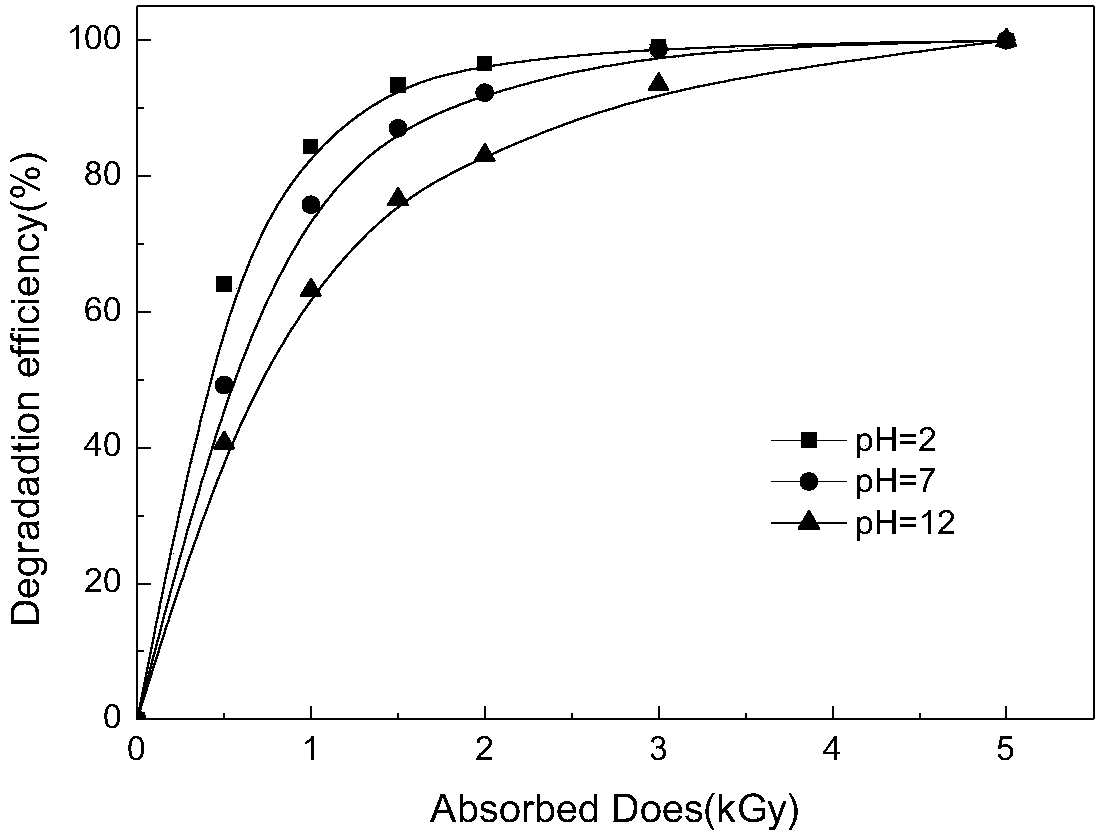
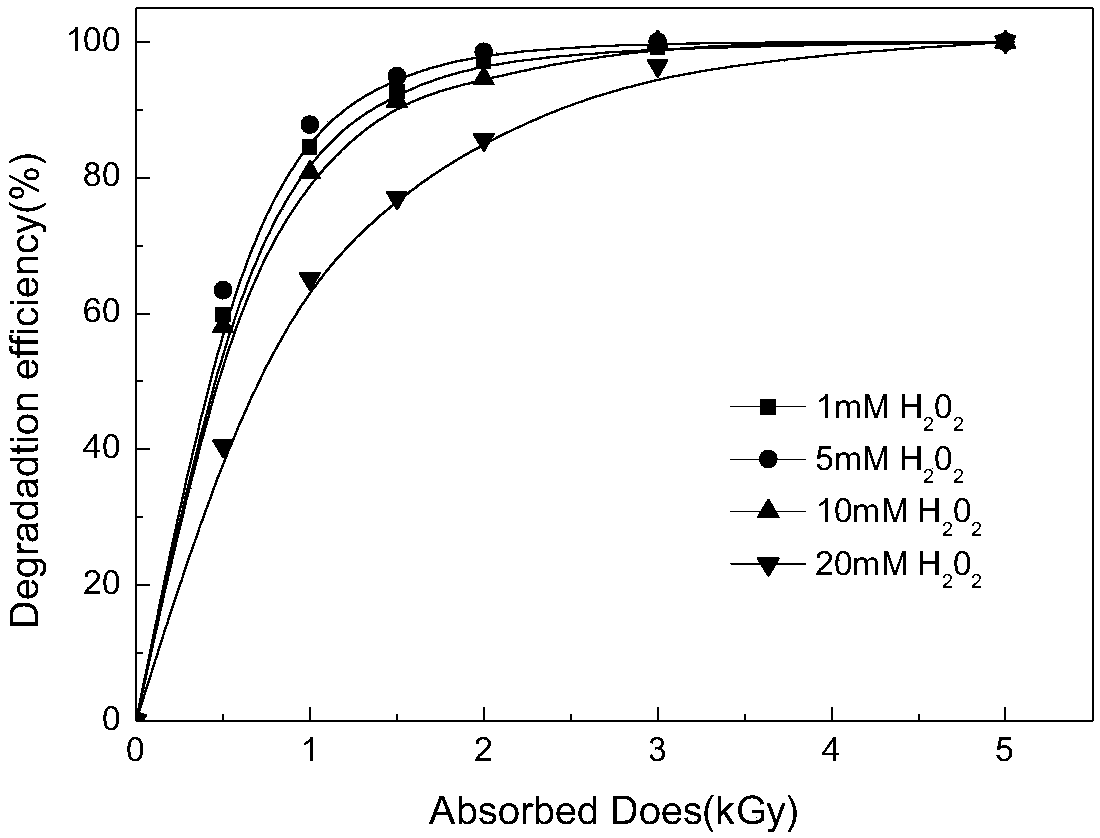
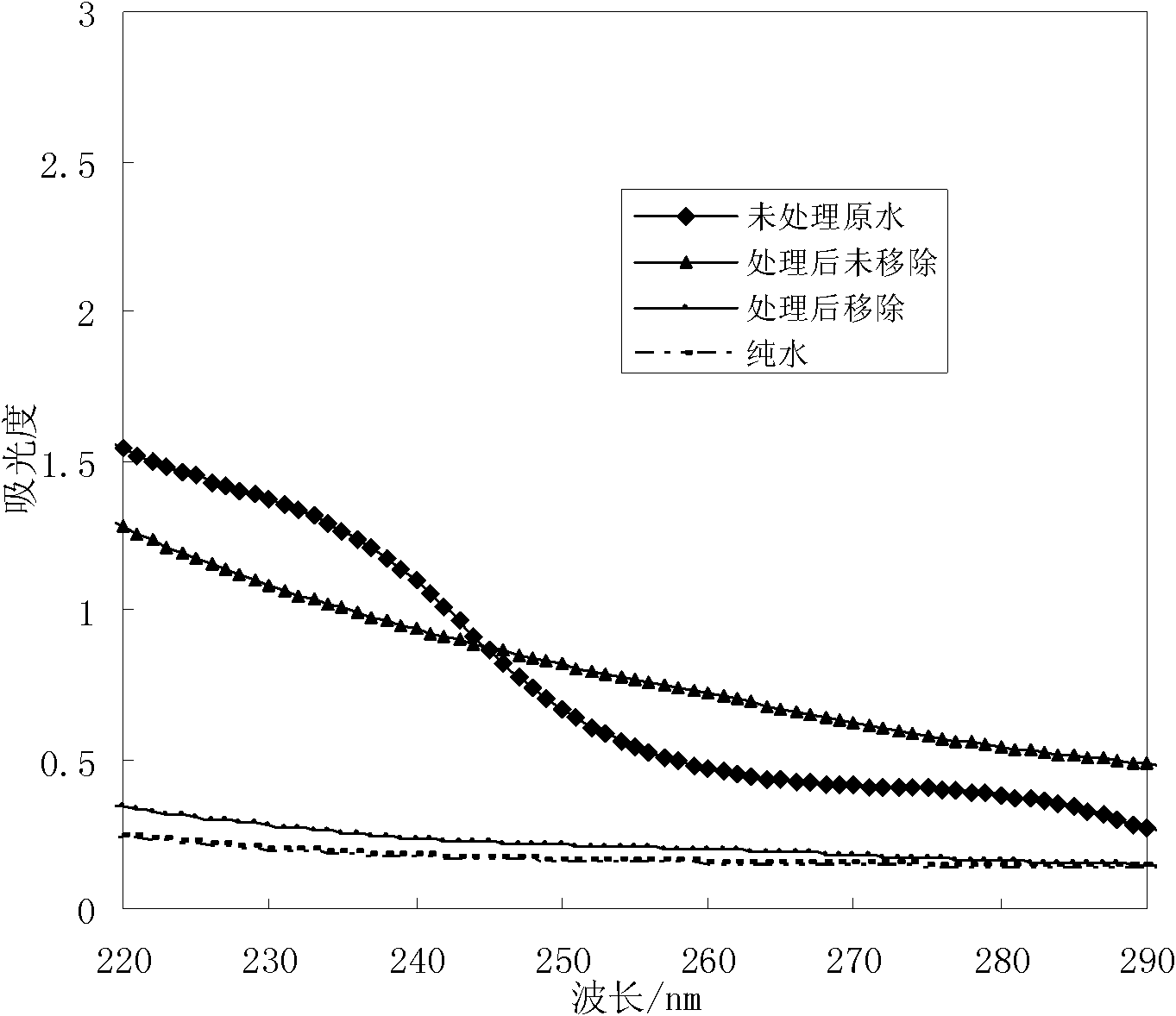
The invention discloses a method for treating an antidepressant venlafaxine in water by utilizing electron beam irradiation, particularly electron irradiation, and belongs to the technical fields of nuclear technology application, water treatment and environmental protection. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a water body containing the venlafaxine is treated by utilizing high energy electrons generated under electron accelerator radiation conditions to degrade the venlafaxine. An electron accelerator adopted in the method disclosed by the invention has an electron irradiation dose of 0.5-5 KGy. Concentrated sulfuric acid is added in a used sample pretreatment solution of the venlafaxine to regulate the pH value of the solution to reach 2-7, and 1-5 mM of hydrogen peroxide is added into the solution, so that a radiation degradation effect is promoted; moreover, the irradiation dose can be properly reduced. The method disclosed by the invention can remove the venlafaxine drug pollution in the water body, is high in reaction speed and high in degradation efficiency, has better applicability when being compared with other traditional methods and is an efficient and energy-saving water treatment technology.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for removing high-concentration dimethyl phthalate through radiation
InactiveCN102219280ATo achieve the purpose of degradationStrong penetrating powerWater/sewage treatment by irradiationHigh concentrationHigh energy
The invention discloses a method for removing high-concentration dimethyl phthalate through radiation. In the method, the dimethyl phthalate at the concentration of 300 to 5,000 mg / L is subjected to high-dose radiation treatment by high-energy rays; and then solid substances are separated and removed from the solution. By the method, the removal rate of the dimethyl phthalate is over 95 percent; radiation degradation products can be removed directly; chemical aids are not required; and energy is saved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
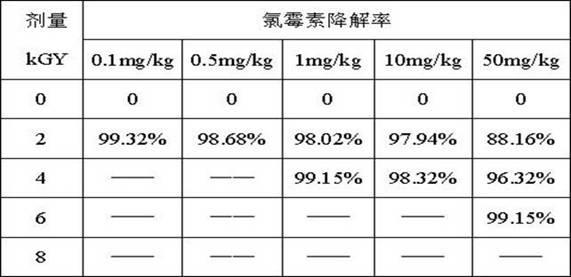
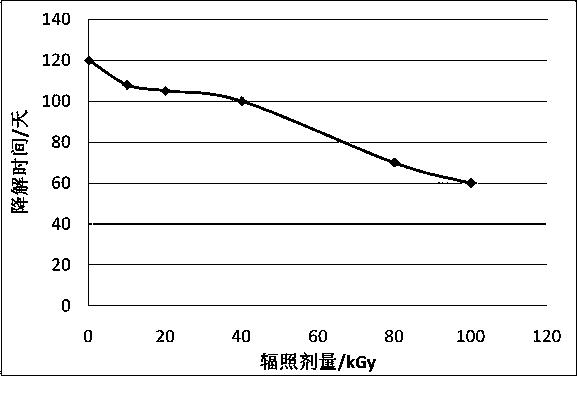
Method for radiation treatment of chloromycetin wastewater
InactiveCN101560031ALow toxicityImprove protectionWater/sewage treatment by irradiationMultistage water/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationEmission standard
The invention relates to a method for radiation treatment of high concentration chloromycetin-containing organic wastewater discharged in the production process of chloromycetin medicament and belongs to the technical field of organic wastewater treatment and environmental protection. The method uses special wastewater radiation treatment devices to degrade chloromycetin molecules in the wastewater through radiation by a high-energy electron beam into harmless small molecules, so that the wastewater can meet the requirements of a national standard for effluent discharge. The method mainly uses wastewater treatment devices including an electron accelerator, a wastewater reaction tank and a blower system and uses an aeration device which is a glass sand core arranged in the reaction tank to realize uniform blowing and aeration so as to improve radiation degradation effect of the wastewater under radiation of the electron beam produced in the electron accelerator. The method is simple in process, convenient in operation and capable of treating high-concentration refractory toxic organic wastewater with high efficiency and low consumption.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Radiation-induced degradation method for chloramphenicol in natural casing
InactiveCN102550639AOrganizational performance impactPlay a role in degradationSausage casingsEngineeringProcessing cost
The invention relates to a radiation-induced degradation method for chloramphenicol in natural casing, belonging to the technical field of radiation degradation. The method is characterized by carrying out radiation at normal temperature on a natural casing containing chloramphenicol obtained after pickling, draining, bagging of finished products, and selecting an automatic turning over back and forth power-and-free hanging chain continuous radiation mode with a hanging chain speed electrical parameter of 12-24 Hz to radiate for 2-12 h, wherein the radiation dose of each casing is 2-9 kGy, and the non-uniformity of the same batch of products processed by the same radiation dose is 1.1-1.4. The motion mode of the radiation bagged casing is automatically controlled, thus the radiation efficiency is raised, the processing cost is reduced, and pesticide and veterinary drug residues in food can be effectively degraded. According to the invention, the radiation-induced degradation for chloramphenicol has the advantages of low cost and convenient operation, the radiation has no significant influence on color difference of casings, tensile strength, and shear strength, the adverse influence on the casings caused by external environmental conditions can be effectively overcome, the color of the casings is protected, the economic loss is reduced, and the production benefit is increased.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Preparation method for controllable biodegradable material
The invention discloses a preparation method for a controllable biodegradable material. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1) starch radiation modification; 2) mixing: adding a nanometre assistant, polyvinyl alcohol, stearic acid, polylactic acid, a radiation sensitizer and an accelerant in the treated modified starch, adequately stirring, and uniformly mixing; 3) radiation copolymerization: placing the mixed sample in an aluminium foil bag carrying out packaging and sealing treatment in a vacuum or by charging nitrogen, and then carrying out radiation treatment on the packaged sample; 4) granulation / membrane preparation: uniformly pouring the mixture subjected to radiation copolymerization in a double-screw double-exhaust extrusion granulator group or a double-screw double-exhaust extrusion pelletizer group, and carrying out extrusion granulation or pelletizing; 5) radiation degradation rate control: radiating the product obtained by granulation / membrane preparation while controlling the dosage to be 10-100 kGy and controlling the dosage non-uniformity U of the product to be not greater than 1.3. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the problems of cumbersome process, high-temperature energy consumption, and inevitably-brought pollutant discharge of a common chemical method are overcome, and the object of controlling the decomposition rate is realized.
Owner:赵永富
Radiation degradation method for residual chloromycetin in honey
InactiveCN1666639ANo significant change in activityLess nutrient lossFood preservationFood preparationChloramphenicolRadiation degradation
The invention relates to a radiation degradation method for residual chloromycetin in honey which comprises the following steps, loading bee honey or royal jelly into sealed container, filling nitrogen, sealing the container, subjecting the sealed bee honey or royal jelly to radiation process with gamma beams, the dose range of the radiation degradation additive is 4KGy-10KGy. The method can be applied for degrading the aquamycetin in the bee honey.
Owner:安徽省农业科学院原子能农业应用研究所
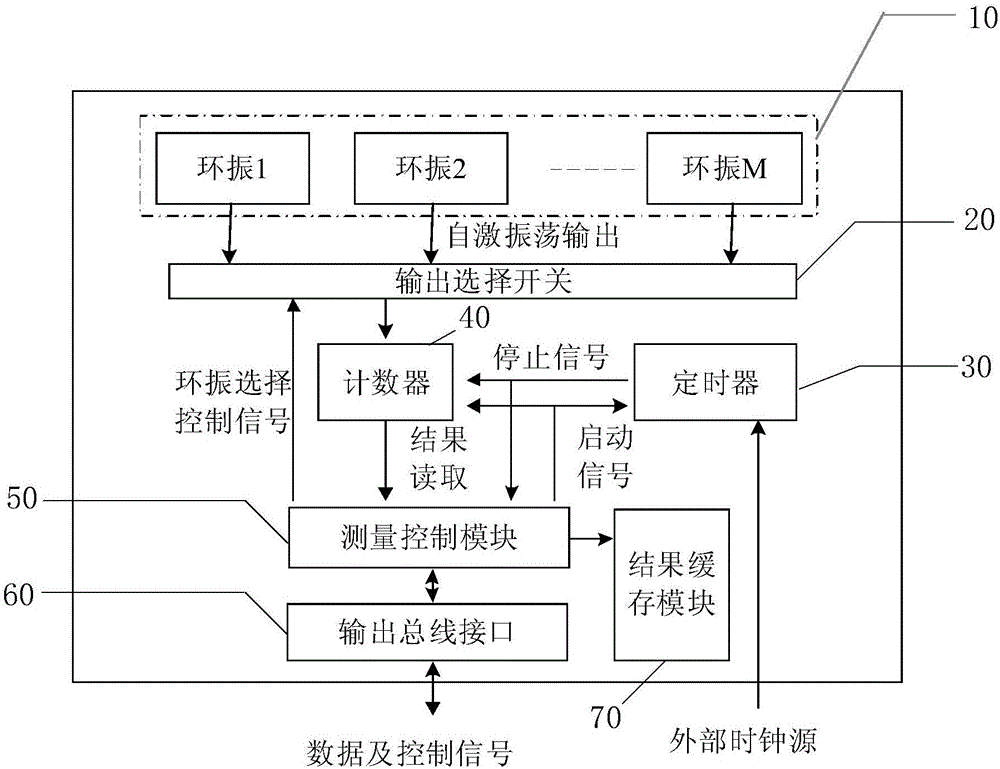
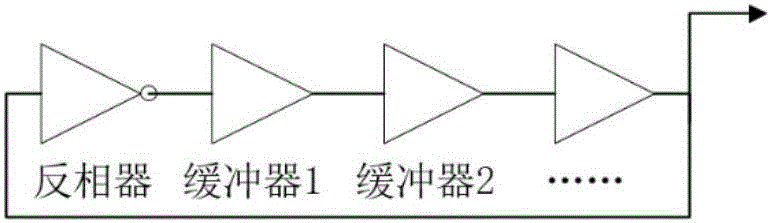
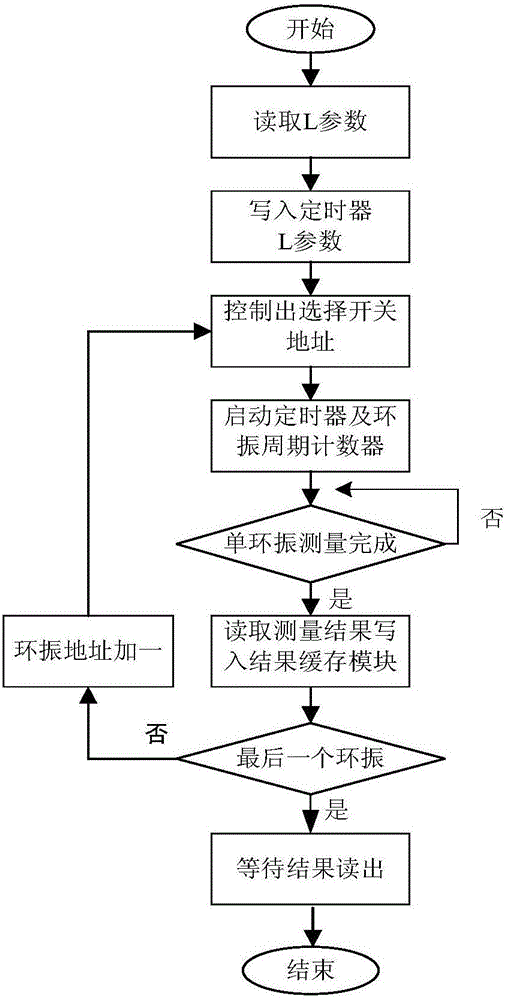
Spacecraft information processing unit radiation degradation measuring device and method
ActiveCN106443420AWeight effectCircuit Complexity ImpactDigital circuit testingElectric discharge tubesInformation processingMeasurement device
The present invention relates to a spacecraft information processing unit radiation degradation measuring device and method. According to an existing test method, an externally connected measuring device is required, and as a result, the method is not suitable for the actual use condition of a satellite, while, with the spacecraft information processing unit radiation degradation measuring device and method of the invention adopted, the above condition can be avoided. The spacecraft information processing unit radiation degradation measuring device includes a ring vibration group, an output selection switch, a counter, a timer, a measurement control module and an output bus interface; the output selection switch is used for selecting one of ring vibration units, so that the selected ring vibration unit can provide frequency signals for the counter, wherein the frequency signals are used for reflecting the degradation degree of an FPGA device; after the timing duration of the timer is over, the timer sends stopping signals to the counter and the measurement control module; the measurement control module can send startup signals to the counter and the timer; and the output bus interface is used for reading the frequency signals in the measurement control module to a bus. The invention also includes a spacecraft information processing unit radiation degradation measurement method. The present invention is applicable to a spacecraft.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Preparing method of water-soluble ocean oligo-polysaccharides
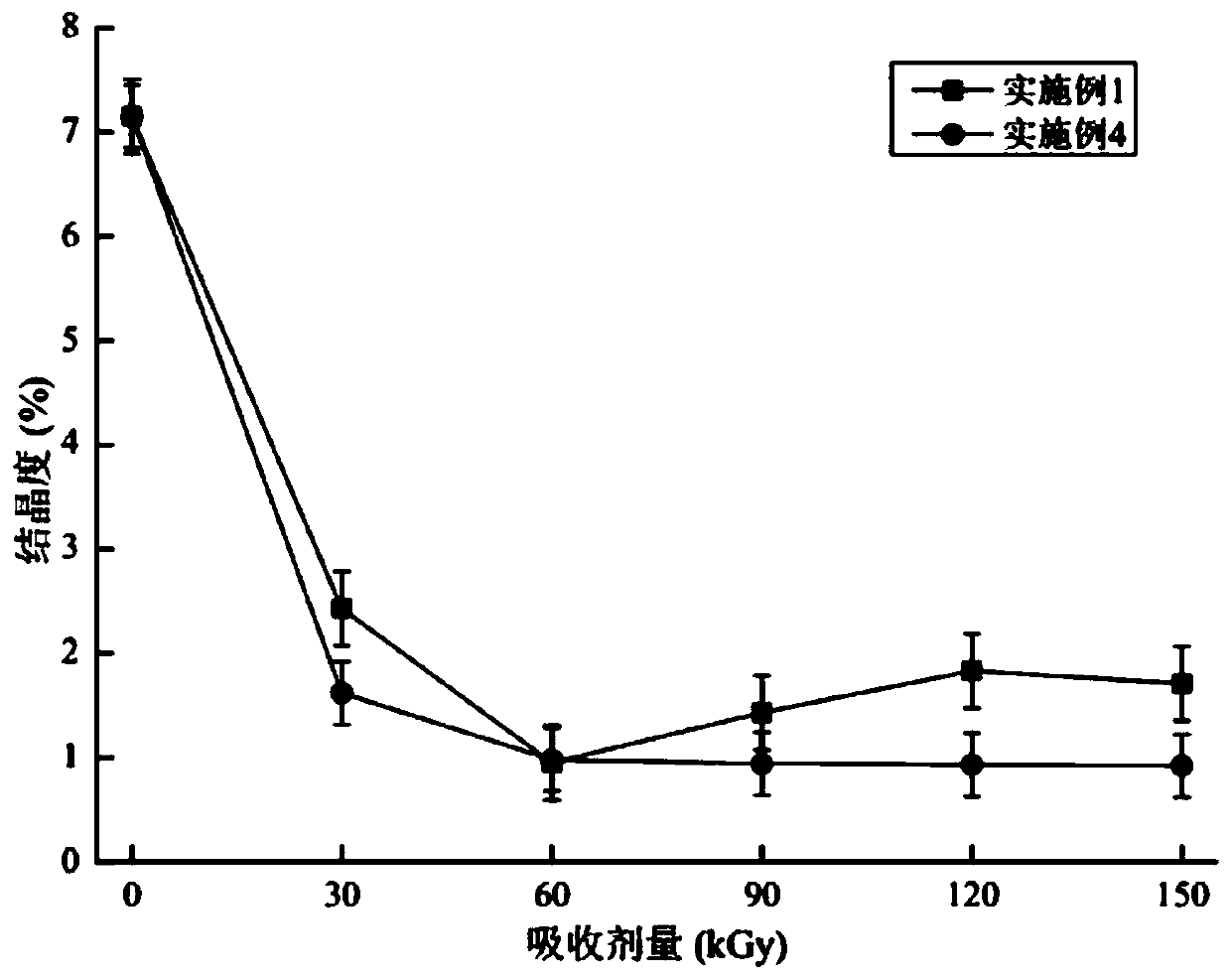
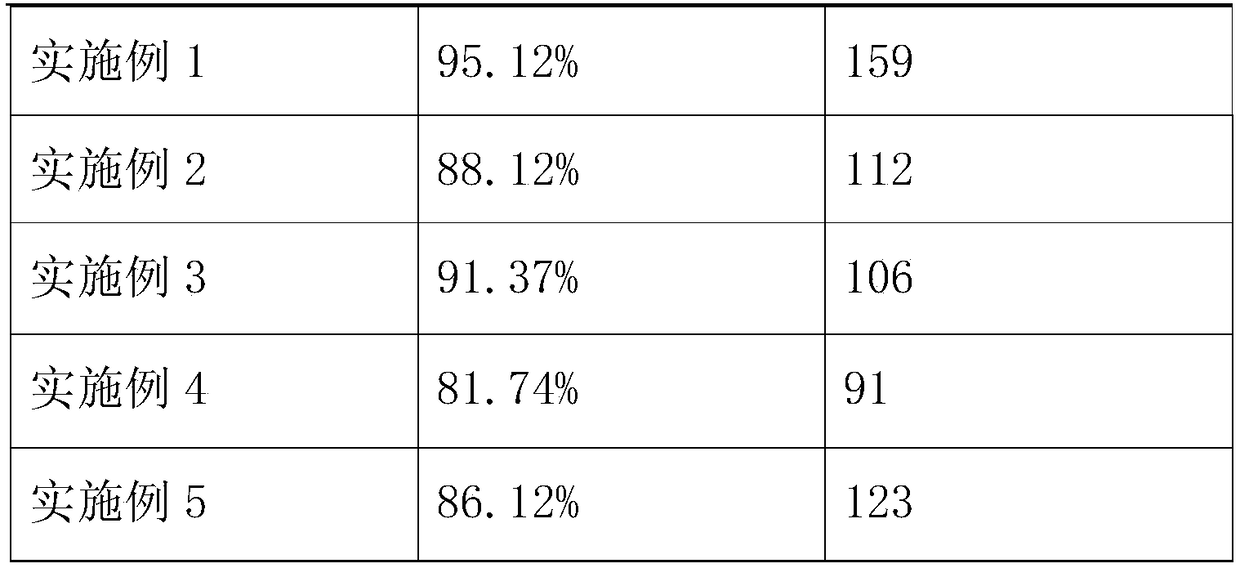
The invention provides a preparing method of water-soluble ocean oligo-polysaccharides, and belongs to the technical field of oceans. The method comprises the steps of providing ocean polysaccharideswith the high molecular weight; providing electron flow, wherein polysaccharide radiation degradation is performed on polysaccharides through the electron flow; performing separation and purificationto obtain the oligo-polysaccharides with the good water solubility. By adopting electron flow irradiation instead of introducing inorganic salt, the purpose of simplifying the steps is achieved, the repeatability and controllability are good, no environment contamination is caused, the degrading efficiency is high, the degrading effect and product uniformity are good, the water-soluble polysaccharides with the low molecular weight can be obtained under the low absorbent amount, the product crystallinity can be lowered, the water soluble performance is improved, and energy consumption and the production cost can be lowered.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Formula, preparation method and application of high-temperature-resistant hot melt adhesive
InactiveCN112080227AHigh viscosityReduce liquidityNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesPolymer scienceAntioxidant
The invention discloses a formula of a high-temperature-resistant hot melt adhesive. The high-temperature-resistant hot melt adhesive comprises the following components in parts by mass: 30 to 60 parts of a radiation crosslinking base material, 10 to 50 parts of a radiation-degradable base material, 8 to 20 parts of a tackifier and 1 to 3 parts of an antioxidant. Correspondingly, the invention discloses a preparation method of the high-temperature-resistant hot melt adhesive, which comprises the following steps: taking the radiation crosslinking base material, the radiation-degradable base material, the tackifier and the antioxidant in parts by weight, mixing, blending, extruding at the extrusion temperature of 80 to 170 DEG C, cooling, and granulating to obtain the high-temperature-resistant hot melt adhesive. The prepared high-temperature-resistant hot melt adhesive is applied to an inner adhesive layer material of a double-wall heat-shrinkable sleeve, so that the double-wall heat-shrinkable sleeve can achieve the effects of rapid shrinkage and insulation sealing protection when being heated, and the effect that the inner adhesive layer material does not flow obviously in a high-temperature environment can be achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGYUAN ELECTRONICS MATERIAL
Method for preparing microcrystalline cellulose by electron beam irradiation
The invention discloses a method for preparing microcrystalline cellulose by electron beam irradiation. The method is characterized by using natural cellulose pulp as a raw material, microcrystallinecellulose is prepared by a combination process of gamma ray or a high-energy electron beam radiation degradation technology and a mechanochemical acidolysis technology. The preparation process has thefollowing conditions: the absorbed dose is 10-200 kGy, the mass fraction of a dilute acid aqueous solution is 0.5%-2.0%, and the mass ratio of the dilute acid aqueous solution to the natural cellulose pulp is 0.5-2.0: 1.0, the kneading temperature is 60 to 110 DEG C, and the kneading time is 30 to 120 minutes. Compared with a conventional acid hydrolysis method, the preparation method has a largereduction in the amount of acid, and the water consumption in a washing process is greatly reduced, and the washing wastewater can be simply treated to realize no pollution discharge.
Owner:HENAN KEGAO RADIATION CHEM TECH
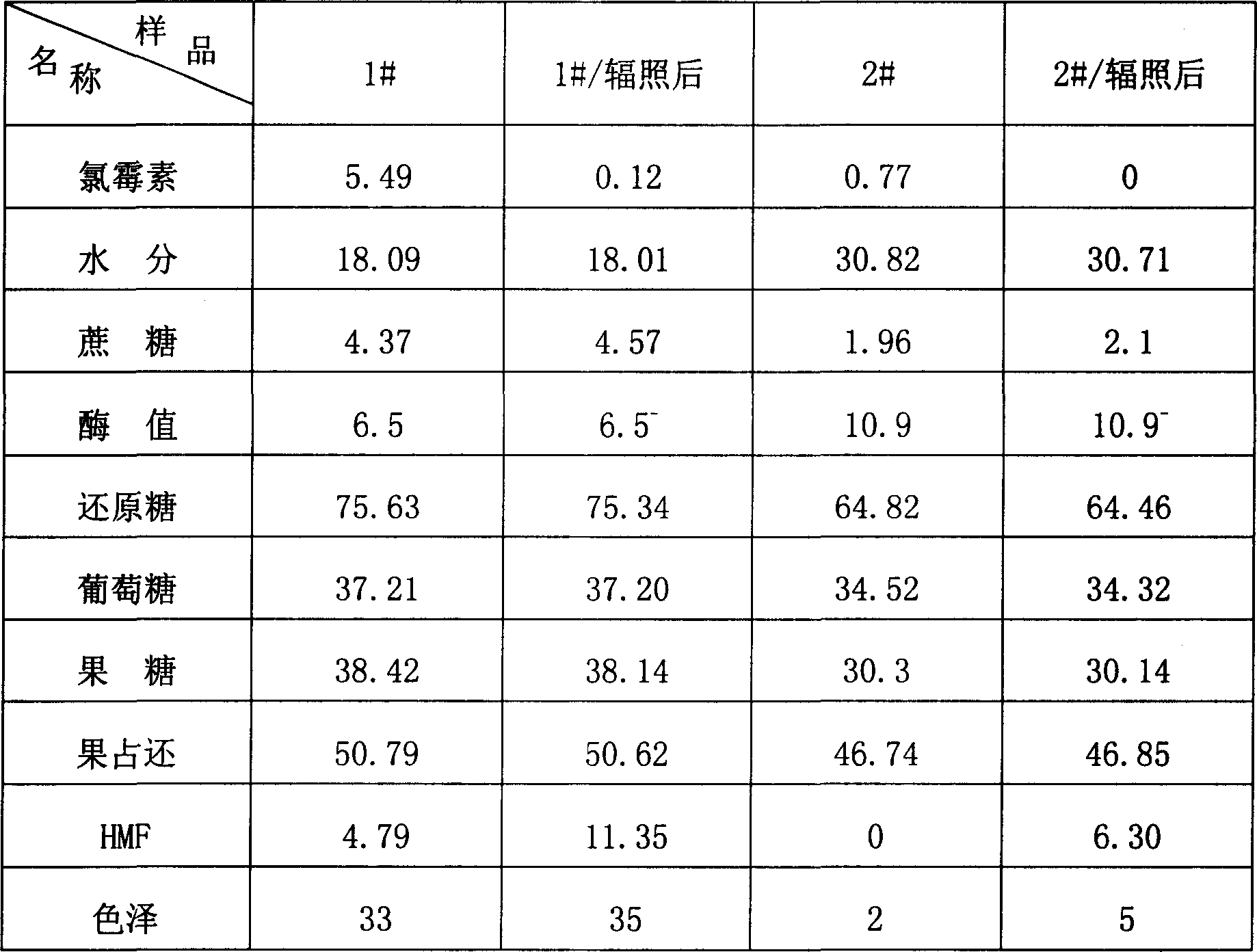
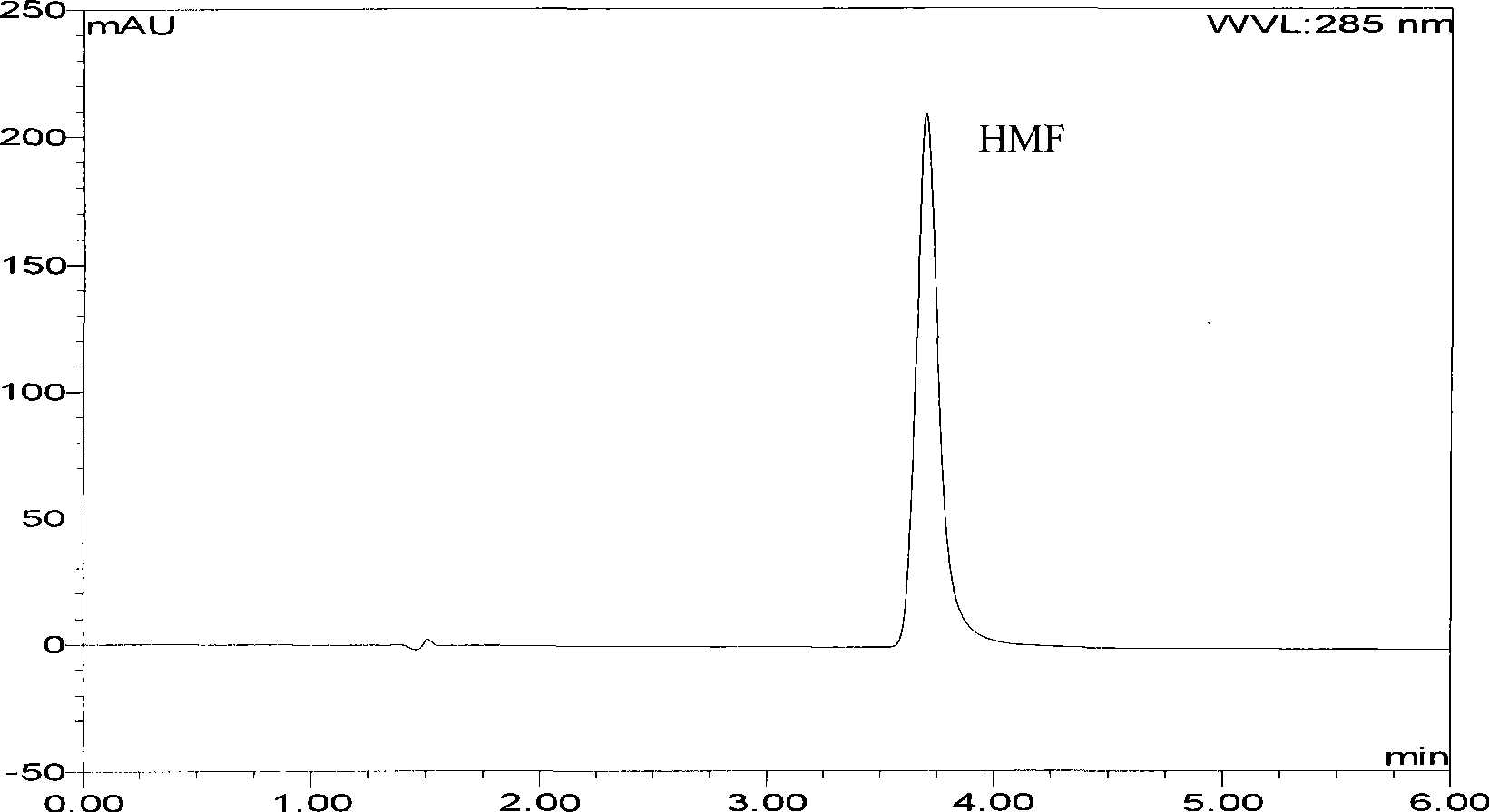
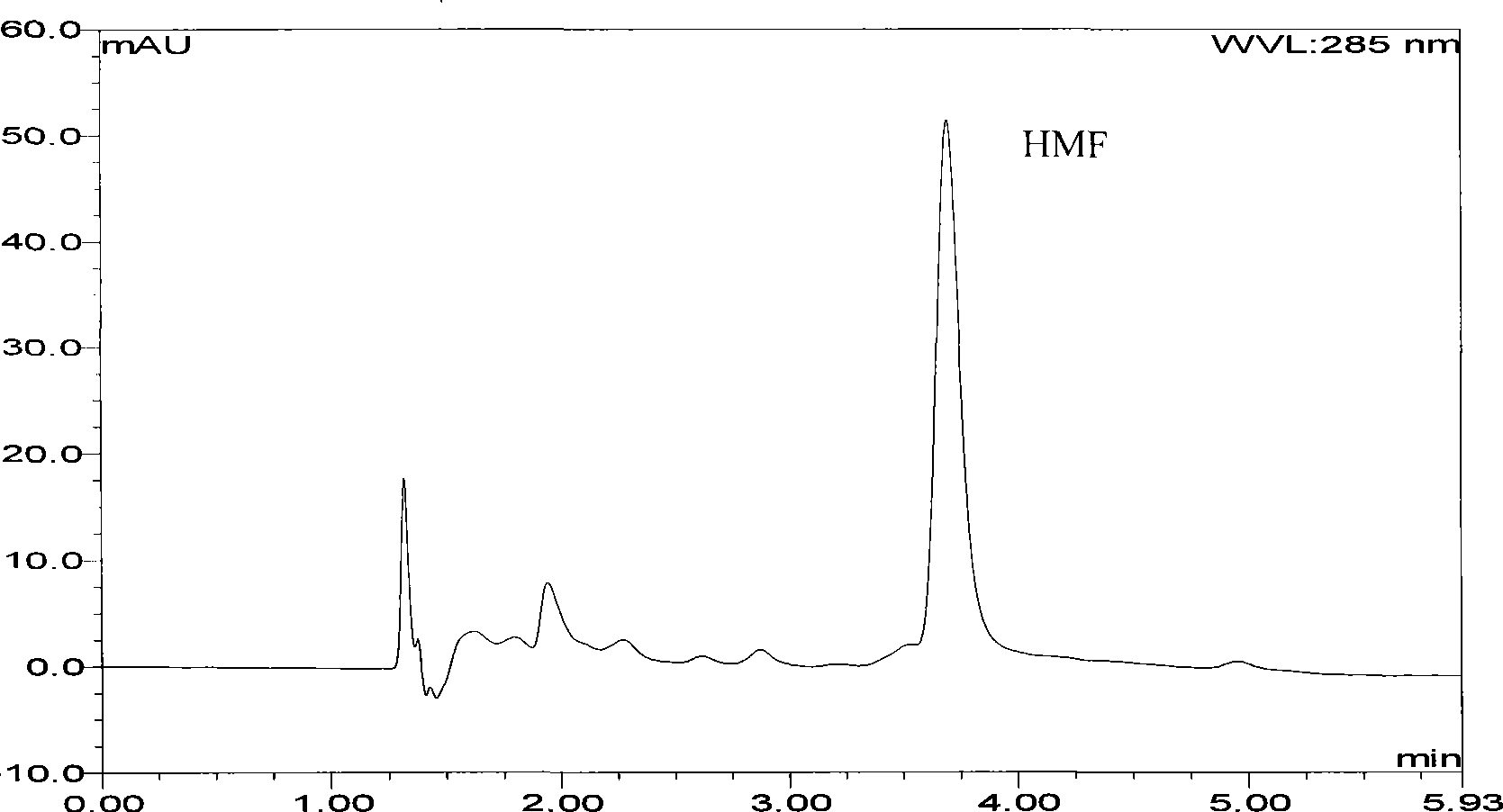
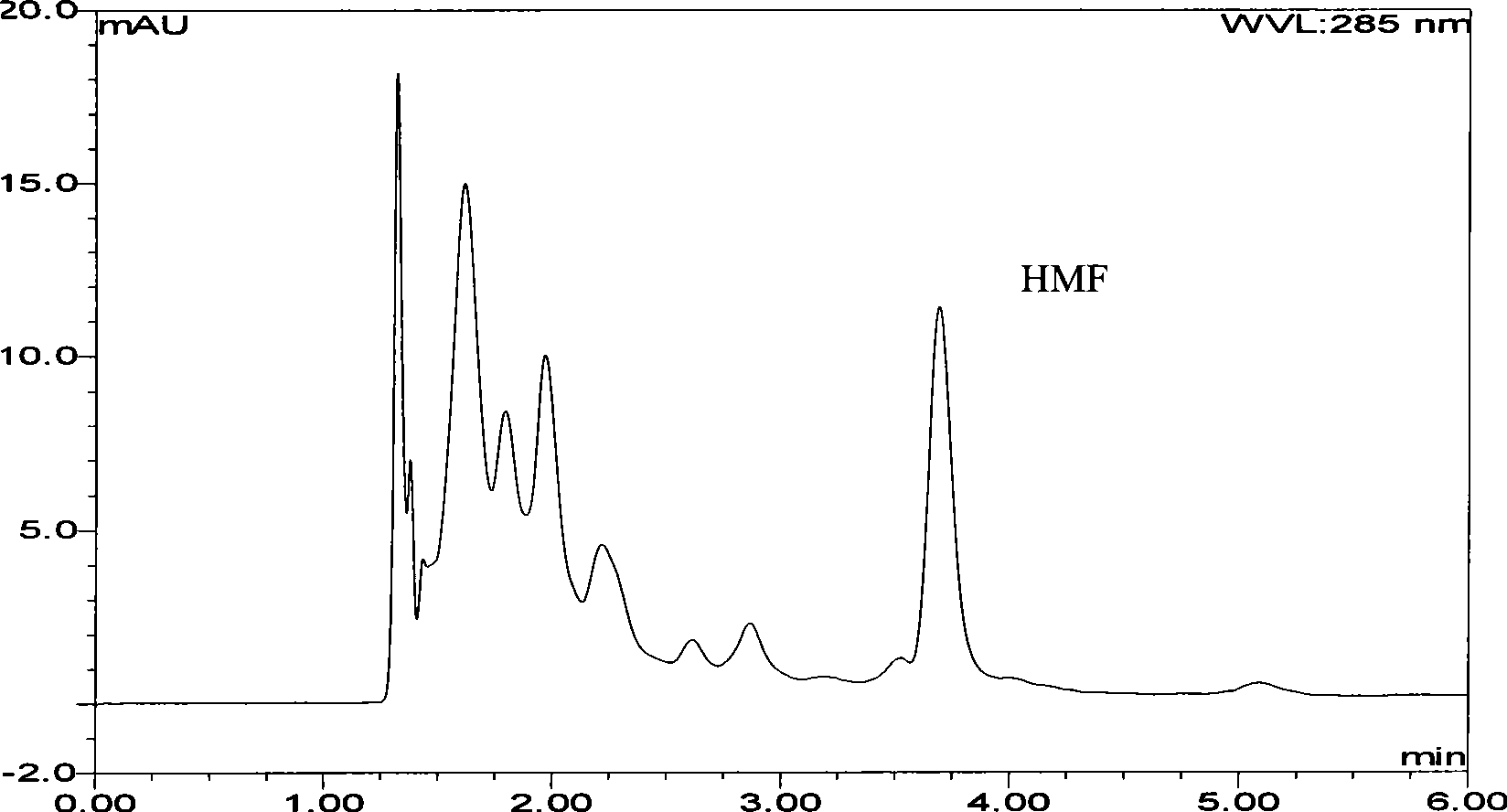
Radiation degradation method for 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in bee honey
The invention relates to a 5 - hydroxymethyl-furfural irradiation degradation method in honey, wherein the 5 - hydroxymethyl-furfural is subjected to irradiation degradation by using Gamma-ray and the irradiation dose is 5KGy-15KGy. The method not only degrades the HMF content in honey to below 10mg / kg and the degradation rate of the 5 - hydroxymethyl-furfural is more than 90%, but also contents of various sugars and the various enzymatic activities are basically kept and the inherent appearance color and flavor are kept. In addition, the operation method is simple and the cost is low and application is wide.
Owner:BEE RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
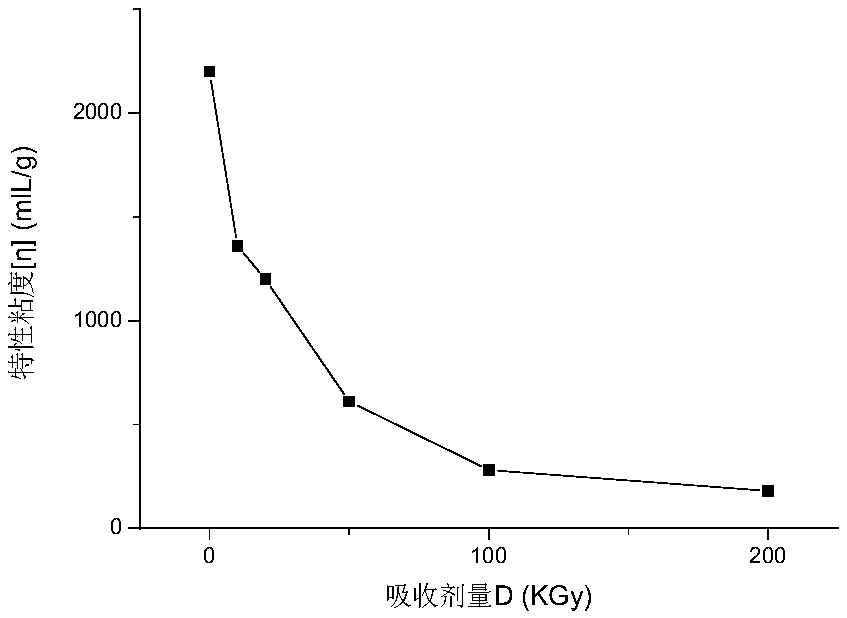
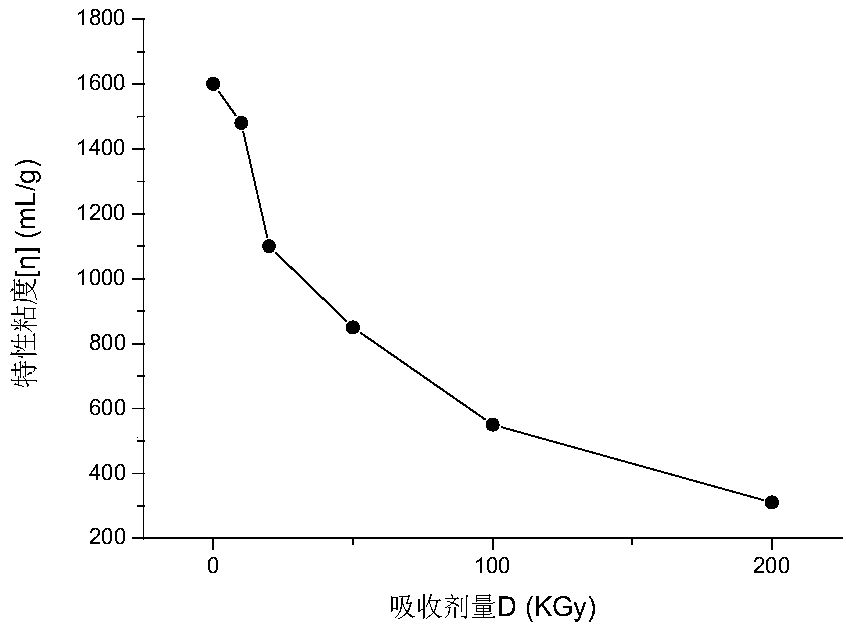
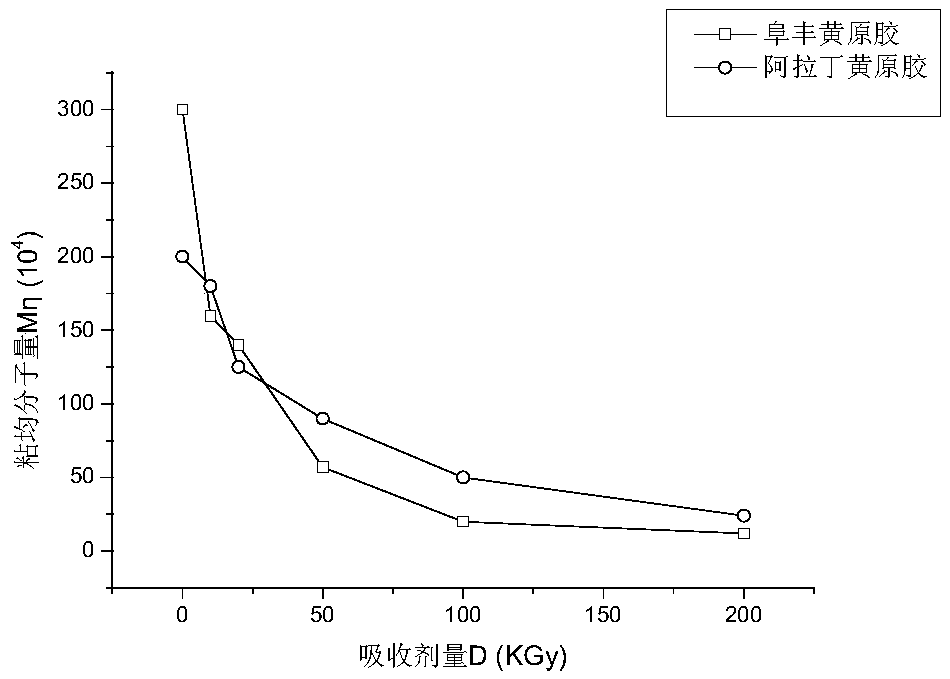
Method for radiation degradation of xanthan gum through electron beams
The invention discloses a method for radiation degradation of xanthan gum through electron beams. According to the method, the xanthan gum is radiated by virtue of the electron beams and is solid-state xanthan gum or liquid-state xanthan gum; by carrying out radiation through the electron beams, particularly the viscosity average molecular weight Meta can be decreased from about 3000000 to about 20000 during the radiation of the liquid-state xanthan gum when the absorbed doses D is only 2.5KGy, and the intrinsic viscosity is decreased from over 2000mL / g to 47.5mL / g. Besides, the oxidation resistance of the degraded xanthan gum is greatly increased relative to that of undegraded xanthan gum, the reducing power is increased by over 300%, and the DPPH free radical scavenging rate is increasedby over 100%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ENERGY & NUCLEAR TECH APPL RES INST
Printing and dyeing wastewater decolorizing process technique
InactiveCN101269859AImprove processing efficiencyQuick resultsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWaste water treatment from textile industryPhotocatalytic reactionRadiation degradation
The invention relates to a dye wastewater decolor treatment technology, which is characterized in that microwave-light is utilized to catalyze and couple as well as degrade organic wastewater, reaction solution is heated through the pretreatment of the microwave before the light catalytic reaction, so the reaction time of the light catalytic degradation method is shortened; five important factors influencing the degradation dye effect of the microwave radiation degradation method are found, and the best technological condition of the microwave degradation method is determined through orthogonality experiment. The technology of the invention has the advantages of the biological treatment method and the physical treatment method, the treatment efficiency is highly efficient and quick, the investment of the required equipment is less, the effect is taken fast, and the decolor ratio to particularly color thicker organic wastewater reaches up to more than 90 percent.
Owner:JIANGSU HUAJIA SILK
Polymers, polymer membranes and methods of producing the same
A method for preparing a polymeric material includes: providing a polymeric matrix having at least one polymer and at least one porogen; and degrading the at least one porogen at a temperature T≦1.1 Tg, where Tg is a glass transition temperature of the polymeric matrix. The degrading step includes exposing the polymeric matrix to thermal degradation, chemical degradation, electrical degradation and / or radiation degradation, wherein the polymeric material has a permeability at least 1.2 times a permeability of the polymeric matrix for a gas, and a selectivity of the polymeric material is at least 0.35 times a selectivity of the polymeric matrix for a gas pair. The method preferably provides gas separation membranes that exceed Robeson's upper bound relationship for at least one gas separation pair. Novel polymeric materials, gas separation membranes and fluid component separation methods are also described.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
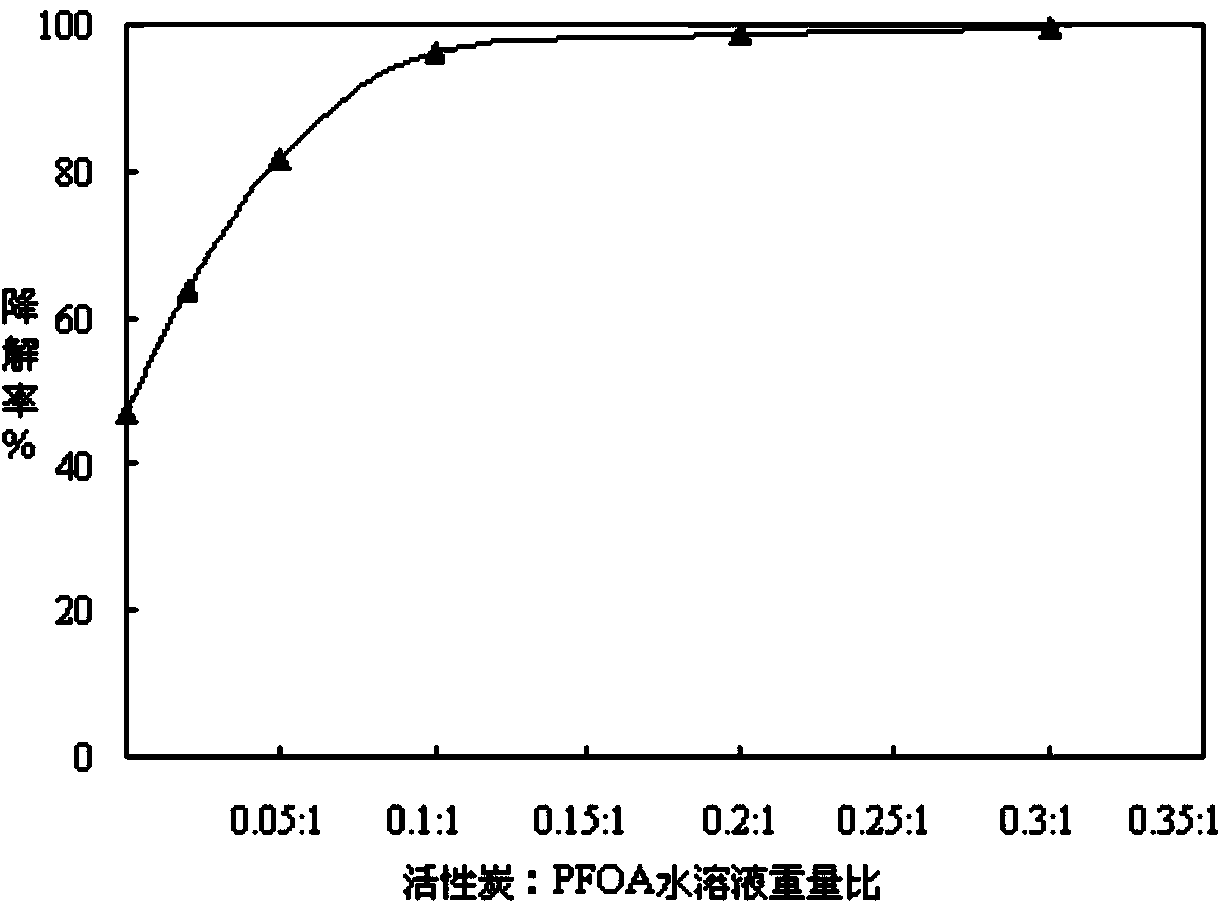
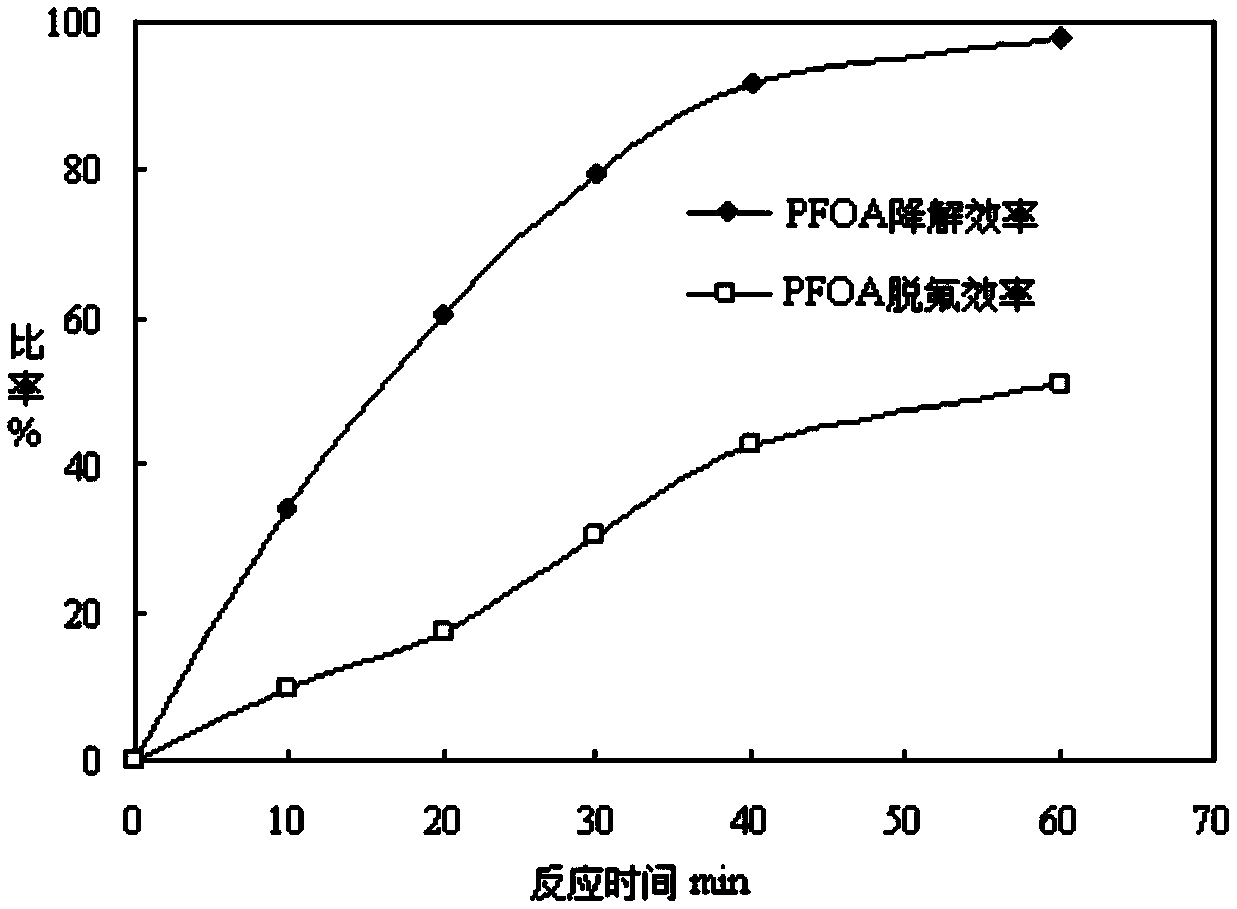
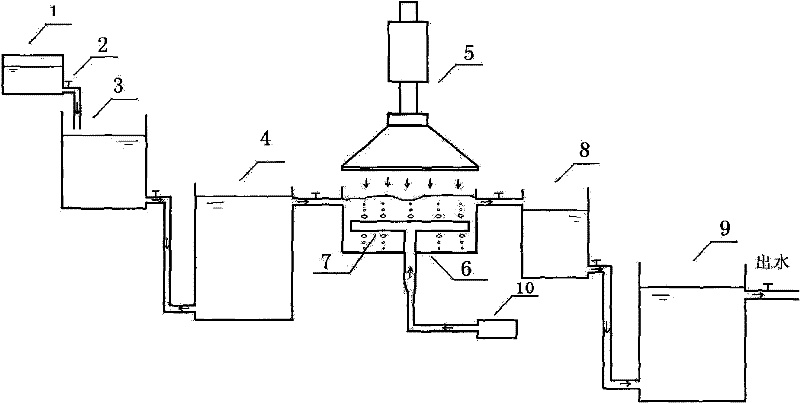
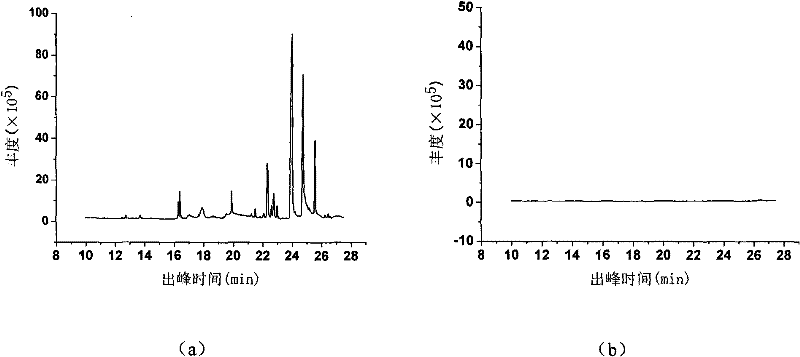
Method for degrading perfluorocarboxylic acid pollutant by utilizing microwave radiation
InactiveCN103936096ASimple methodImprove degradation efficiencyWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsUltrafiltrationFirst-order reaction
The invention belongs to the technical field of perfluorocarboxylic acid pollutant treatment and relates to a method for degrading a perfluorocarboxylic acid pollutant by utilizing microwave radiation. The method for degrading the perfluorocarboxylic acid pollutant by utilizing the microwave radiation comprises the following steps: firstly putting coconut shell activated carbon into a perfluoro caprylic acid aqueous solution, and stirring, so that a mixed solution is obtained; then transferring the mixed solution into a microwave digestion tank with polytetrafluoroethylene as lining, and carrying out reaction for 30-40 minutes while power of the microwave radiation is 800-1000W; then taking 2ml sample every 5-10 minutes, separating the activated carbon in the samples by adopting a centrifugal machine, taking supernate, then filtering the supernate by adopting an ultrafiltration membrane with the pore diameter of 0.22 microns, and finally analyzing concentration of the perfluoro caprylic acid in the supernate by adopting a high performance liquid chromatography method, so that degradation of the perfluorocarboxylic acid is realized. The method for degrading the perfluorocarboxylic acid pollutant by utilizing the microwave radiation is simple, safe and reliable, degradation efficiency is high, a microwave radiation degradation reaction accords with a first-order reaction kinetics equation, a reaction half-life period is short, no secondary pollution is produced, and environmental friendliness is realized.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for radiation treatment of chloromycetin wastewater
InactiveCN101560031BLow toxicityImprove protectionWater/sewage treatment by irradiationMultistage water/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationEmission standard
The invention relates to a method for radiation treatment of high concentration chloromycetin-containing organic wastewater discharged in the production process of chloromycetin medicament and belongsto the technical field of organic wastewater treatment and environmental protection. The method uses special wastewater radiation treatment devices to degrade chloromycetin molecules in the wastewater through radiation by a high-energy electron beam into harmless small molecules, so that the wastewater can meet the requirements of a national standard for effluent discharge. The method mainly useswastewater treatment devices including an electron accelerator, a wastewater reaction tank and a blower system and uses an aeration device which is a glass sand core arranged in the reaction tank torealize uniform blowing and aeration so as to improve radiation degradation effect of the wastewater under radiation of the electron beam produced in the electron accelerator. The method is simple inprocess, convenient in operation and capable of treating high-concentration refractory toxic organic wastewater with high efficiency and low consumption.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Controllable biodegradable material preparation method
The invention discloses a preparation method for a controllable biodegradable material. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1) starch radiation modification; 2) mixing: adding a nanometre assistant, polyvinyl alcohol, stearic acid, polylactic acid, a radiation sensitizer and an accelerant in the treated modified starch, adequately stirring, and uniformly mixing; 3) radiation copolymerization: placing the mixed sample in an aluminium foil bag carrying out packaging and sealing treatment in a vacuum or by charging nitrogen, and then carrying out radiation treatment on the packaged sample; 4) granulation / membrane preparation: uniformly pouring the mixture subjected to radiation copolymerization in a double-screw double-exhaust extrusion granulator group or a double-screw double-exhaust extrusion pelletizer group, and carrying out extrusion granulation or pelletizing; 5) radiation degradation rate control: radiating the product obtained by granulation / membrane preparation while controlling the dosage to be 10-100 kGy and controlling the dosage non-uniformity U of the product to be not greater than 1.3. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the problems of cumbersome process, high-temperature energy consumption, and inevitably-brought pollutant discharge of a common chemical method are overcome, and the object of controlling the decomposition rate is realized.
Owner:赵永富
A method for predicting performance degradation of thin-film thermal control coatings under near-ultraviolet radiation
ActiveCN109490179BImprove test efficiencyReduce testing costsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceDesign optimisation/simulationThin membraneEngineering
The invention discloses a film thermal control coating near ultraviolet radiation performance degradation predicating method. The film thermal control coating near ultraviolet radiation performance degradation predicating method helps study the law of performance degradation under near ultraviolet radiation under the condition of grasp of the near ultraviolet radiation degradation mechanism to establish a performance degradation model, and takes the results of a short cycle on the ground as the basis to extrapolate the degradation result of material performance under long-time near ultravioletradiation in space; the film thermal control coating near ultraviolet radiation performance degradation predicating method can predict the performance degradation of a long-life aircraft film thermalcontrol coating under near ultraviolet radiation through a short-cycle ground-based simulation test, thereby improving the testing efficiency, saving the testing cost and providing technical supportfor reliability design of the film thermal control coating.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SPACE TECH
A combined degradation method of zearalenone and ochratoxin a in a solution
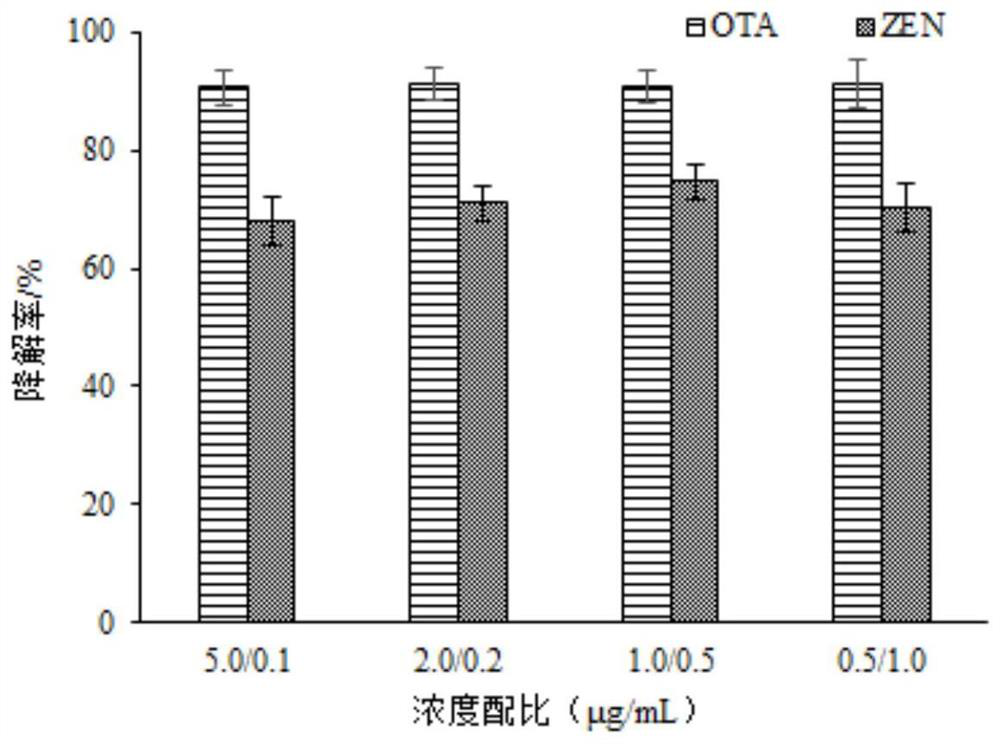
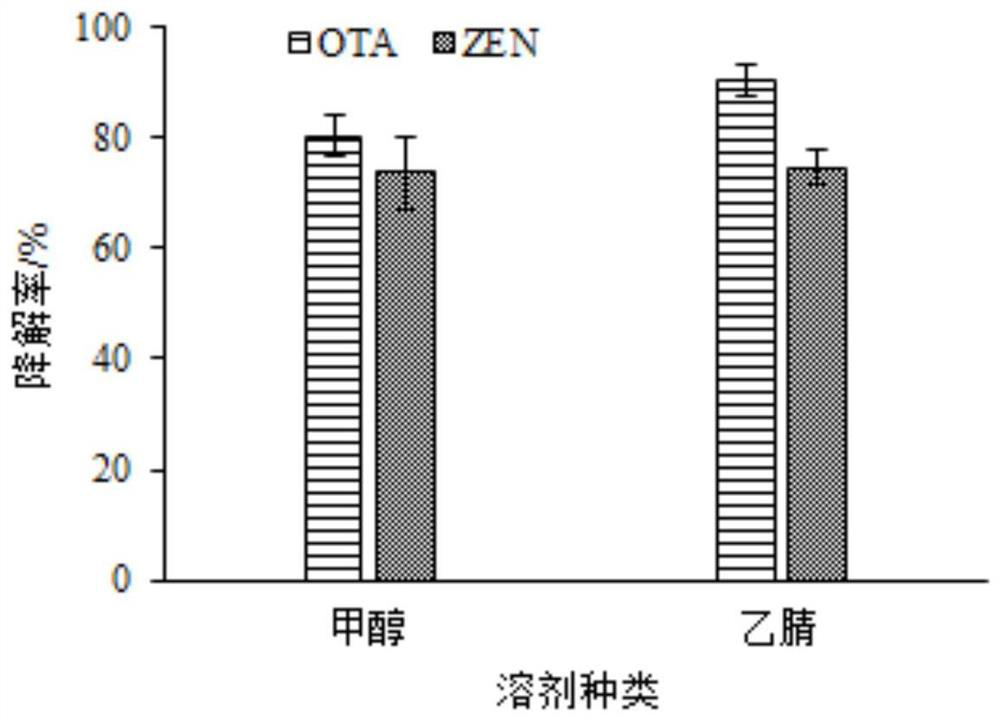
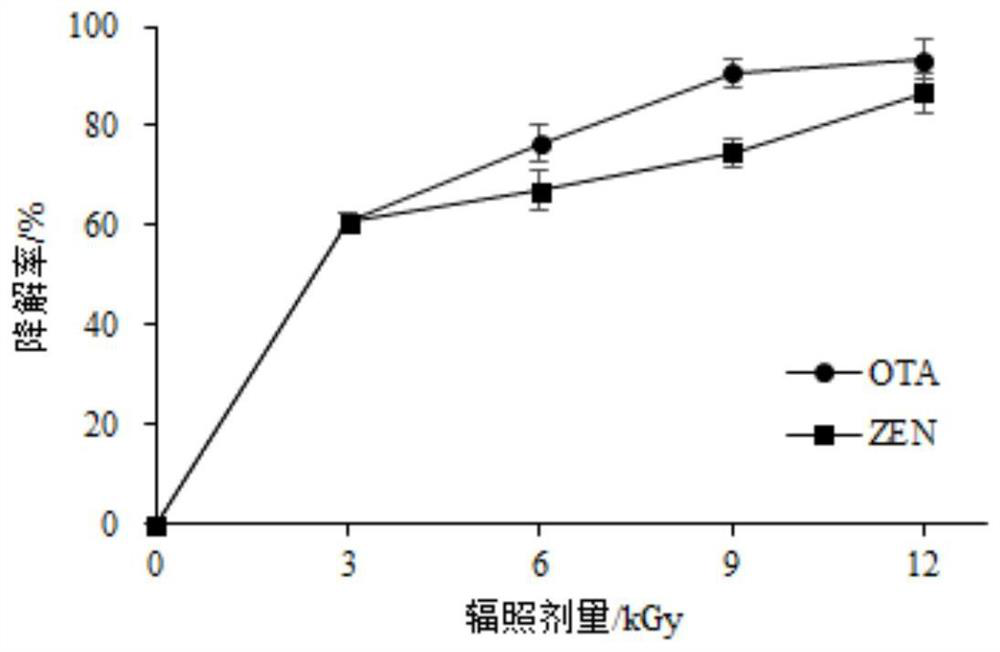
ActiveCN108225884BPromote degradationEfficient degradationComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationBiotechnologyRadiation degradation
The invention discloses a combined degradation method of zearalenone and ochratoxin A in a solution, and belongs to the technical field of the degradation of fungaltoxin in food and the environmentalprotection. The invention is the novel technology in the fungaltoxin combined subduction loop in the crops of grain and the like, the feature is that an electronic beam produced by an electronic accelerator is used for performing radiation degradation on the mixed solution of the ZEN and the OTA. The experimental process verifies that the effect of degrading the ZEN and OTA in the mixed solution by the electronic beam is obvious; the concentrations of the ZEN and the OTA in the mixed solution is 1.0 and 0.5 microgram / mL, the radiation degradation effect is the most obvious, the degradation rate of the ZEN and OTA in the acetonitrile solution at 12kGy is 86.70% and 93.35%. That means that the electronic beam radiation changes or eliminates the toxicity sites in the ZEN and OTA molecules, and the aim of efficient degradation is achieved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
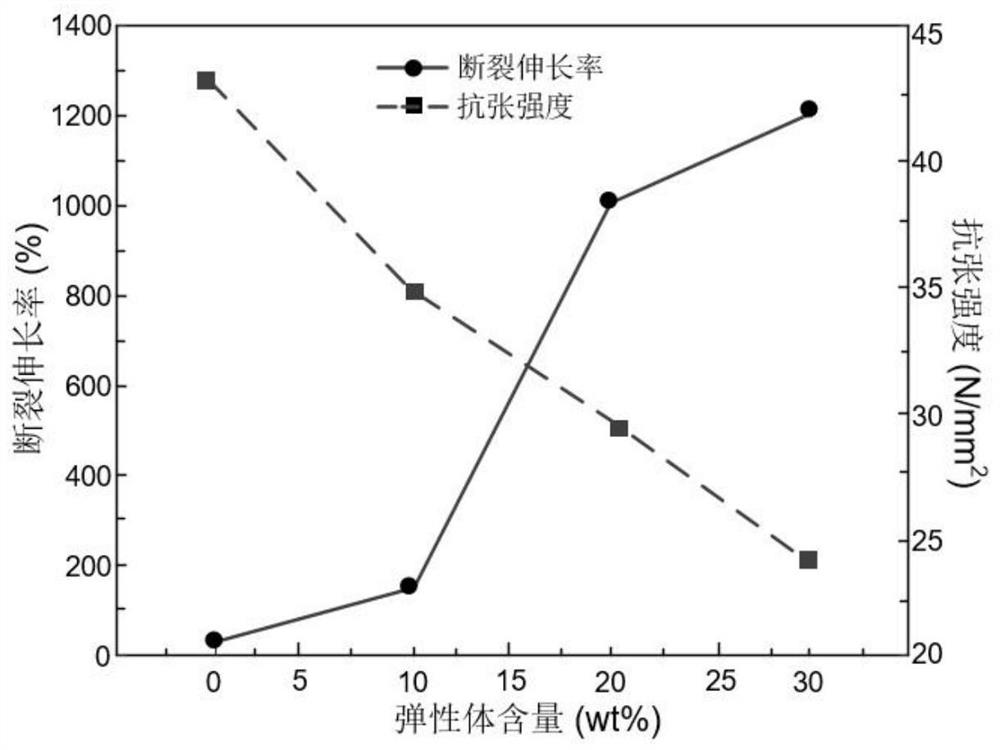
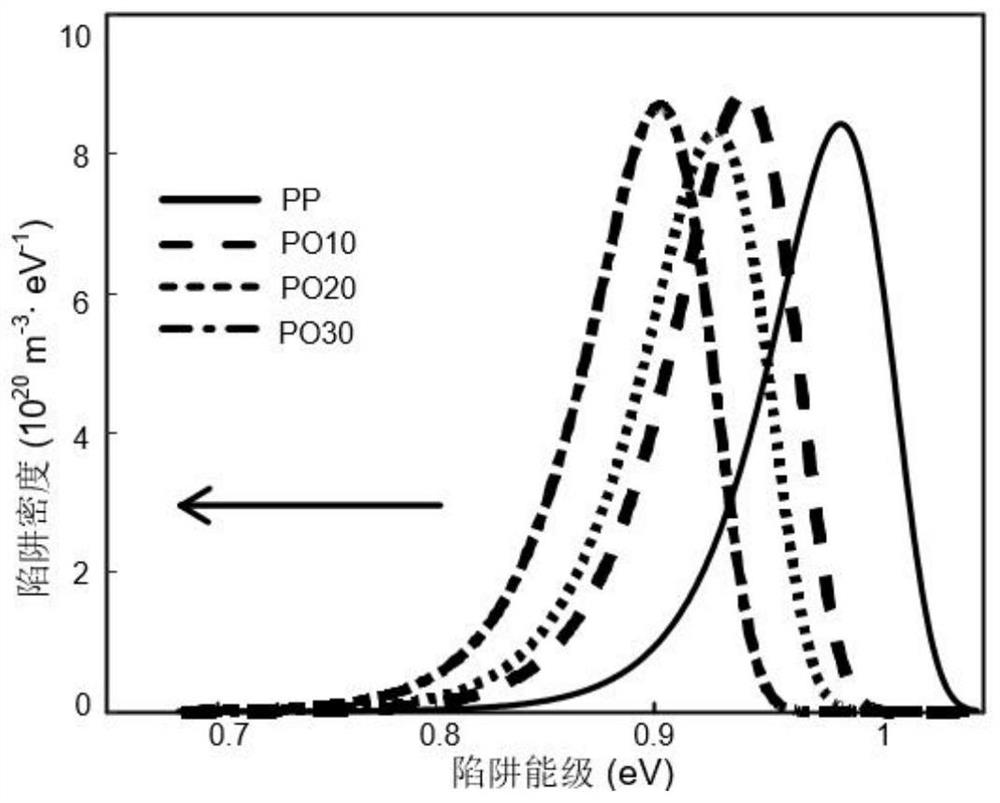
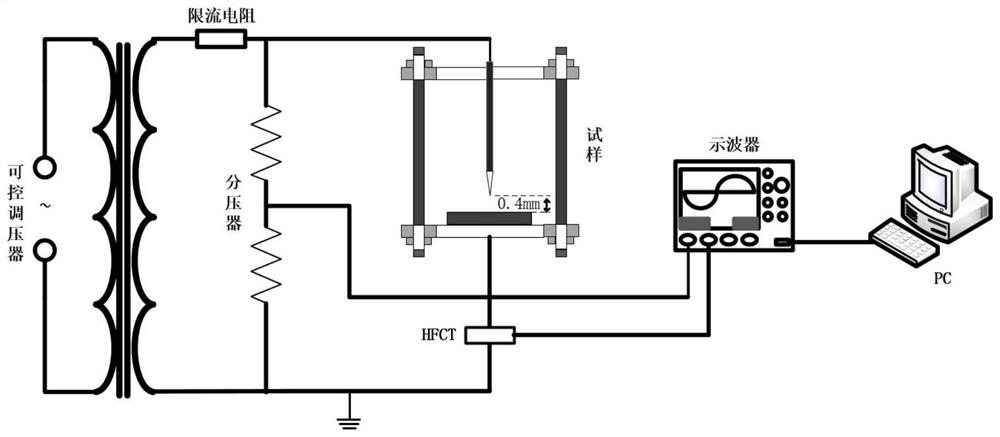
Preparation method of elastomer-based polypropylene insulating material with high partial discharge tolerance
The invention relates to a preparation method of an elastomer-based polypropylene insulating material with high partial discharge tolerance, which is characterized in that by adding an octylene elastomer, the elasticity modulus of the polypropylene insulating material is reduced, the polypropylene insulating material is easy to deform under the bombardment of partial discharge high-energy particles, and the energy of charged particles is relieved; the partial discharge tolerance of polypropylene is improved; the added octylene elastomer has better ultraviolet radiation tolerance, and can relieve the associated ultraviolet radiation degradation phenomenon in the partial discharge process, so that the partial discharge tolerance of polypropylene is improved; the trap depth of the polypropylene insulating material added with the octylene ethylene elastomer is reduced, dissipation of charges accumulated on the surface of polypropylene is accelerated, the proportion of direct bombardment of charged particles on the surface of the polypropylene material is weakened, and then the partial discharge tolerance of polypropylene is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Electrode patterning
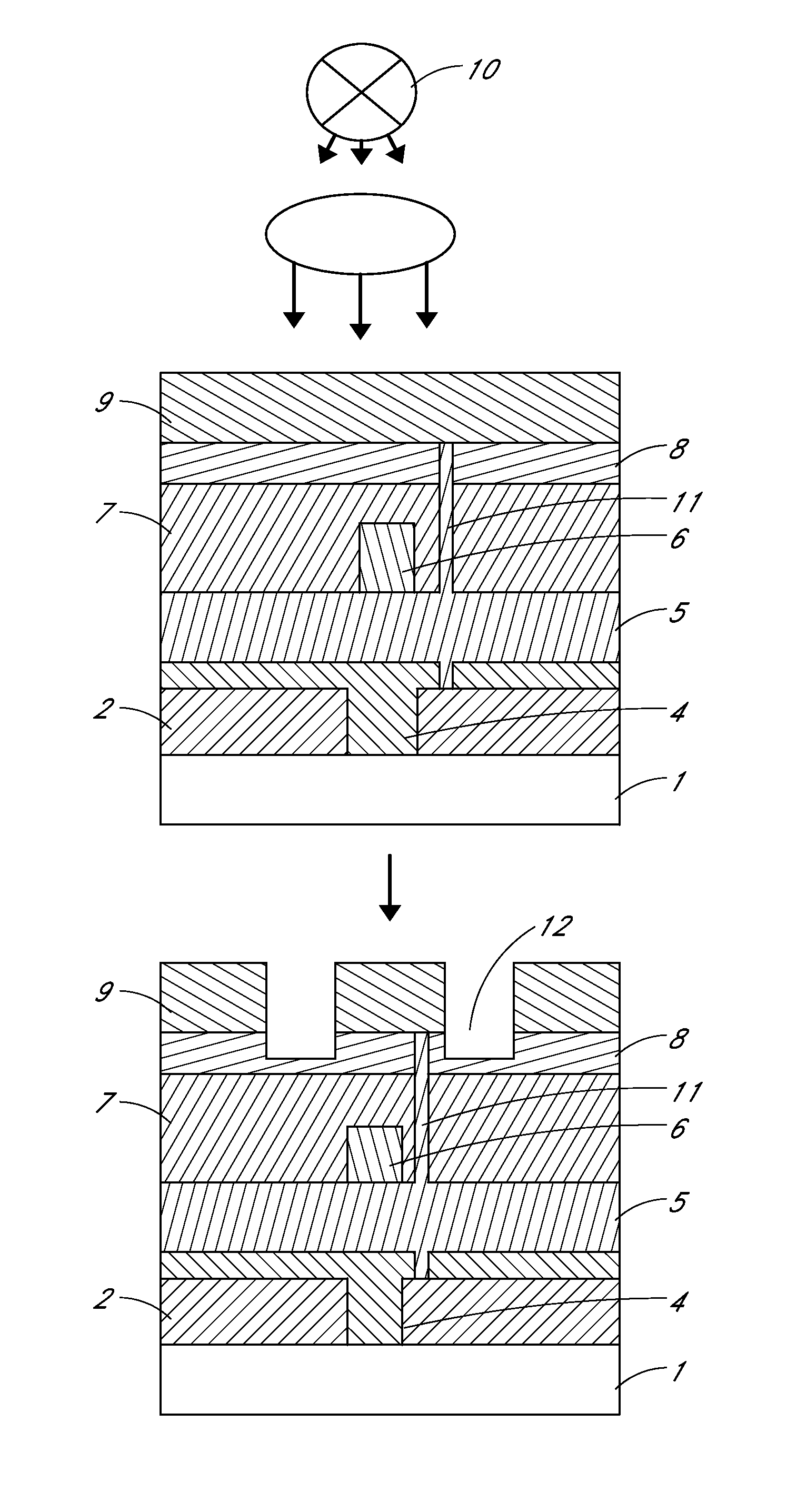
InactiveUS8684779B2No excess debrisSimple methodSolid-state devicesVessels or leading-in conductors manufactureSelf limitingElectricity
A method is provided to isolated conductive pads on top of a multi-layer polymer device structure. The method utilizes laser radiation to ablate conductive material and create a non-conductive path, electrically isolating the conductive pads. The process is self-limiting and incorporates at least one layer within the stack that absorbs the radiation at the required wavelength. The prevention of radiation degradation of the underlying layers is achieved, as absorption of radiation occurs primarily on the surface of the structure, but not in any of the radiation sensitive underlying layers of the electronic device. The method preferably uses low energy infrared radiation which has been shown to produce little debris and no device degradation.
Owner:FLEXENABLE LTD
A kind of radiation degradation method for aflatoxin in Baiziren
ActiveCN107455459BReduce pollutionGuaranteed food safetySeed preservation by irradiation/electric treatmentPorous starchGamma ray
The invention relates to a method for irradiation degradation of aflatoxin in cypress kernels. Before irradiation, the method needs to carry out crude product treatment on the cypress kernels to be treated, that is, the surface of cypress kernels is uniformly coated with stabilizer The porous corn starch layer is then irradiated with 60Co-γ rays at a radiation dose of 1-10 kGy. Finally, the irradiated cypress kernels are repeatedly soaked and washed with ethanol, and the alkali lignin, corn porous starch, and stabilizer on the surface of the cypress kernels are cleaned, and then dried. Aflatoxin. The results show that this method can effectively remove the aflatoxin contamination of the cypress kernels, and at the same time minimize the loss of nutrients in the cypress kernels, so that the levels of fatty acids and proteins in the oil-rich cypress kernels are almost the same before and after irradiation. Changes occur, and do not involve chemical reagents, there is no residue problem, and food safety is guaranteed.
Owner:广州华大生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com