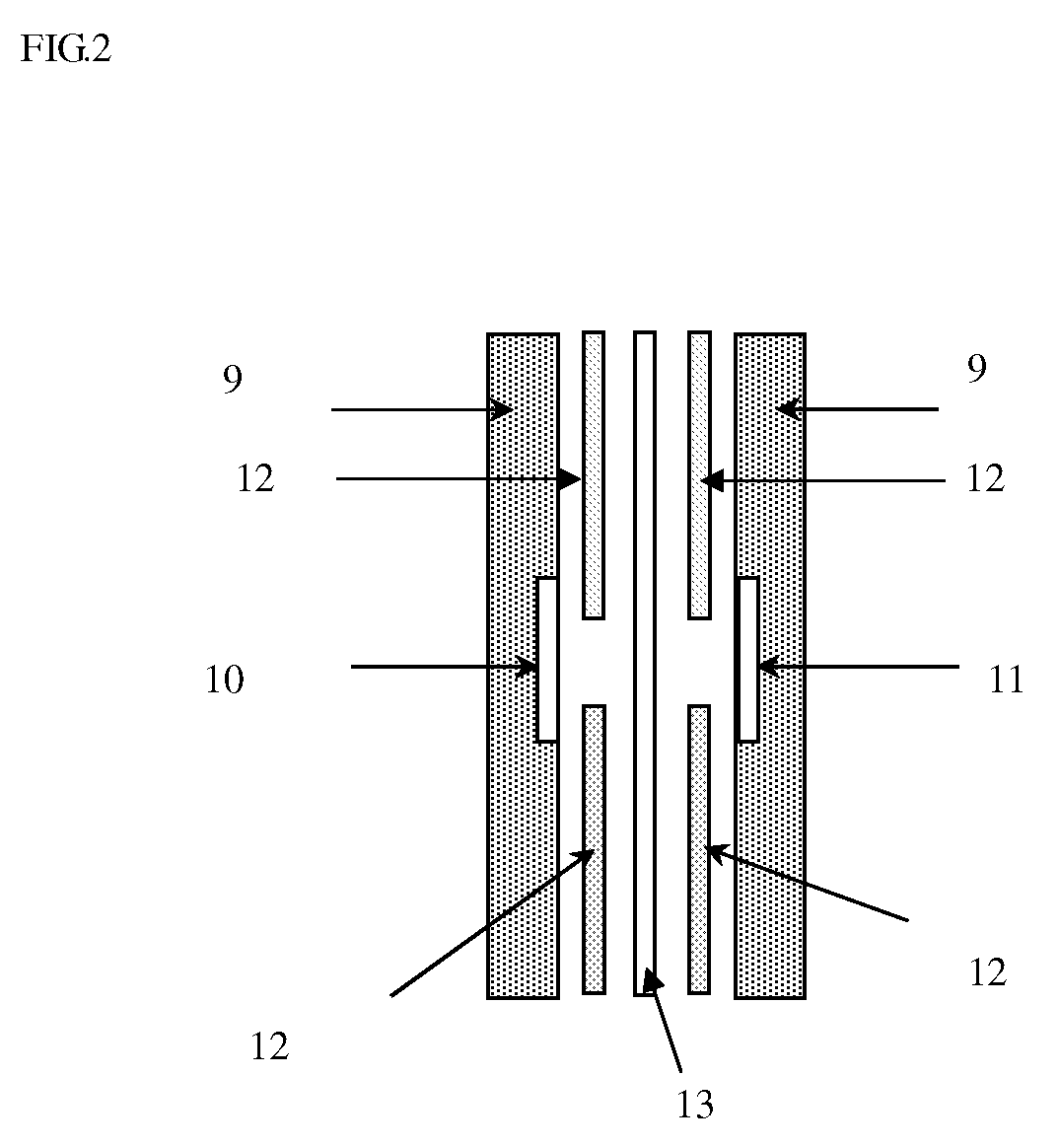
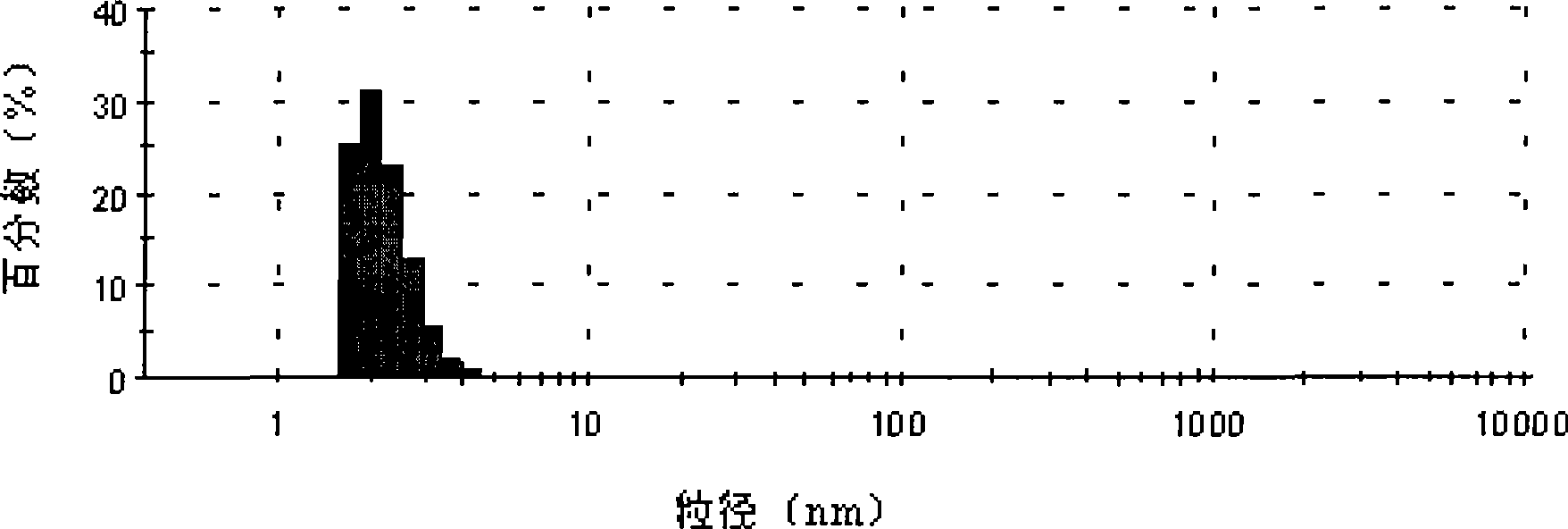
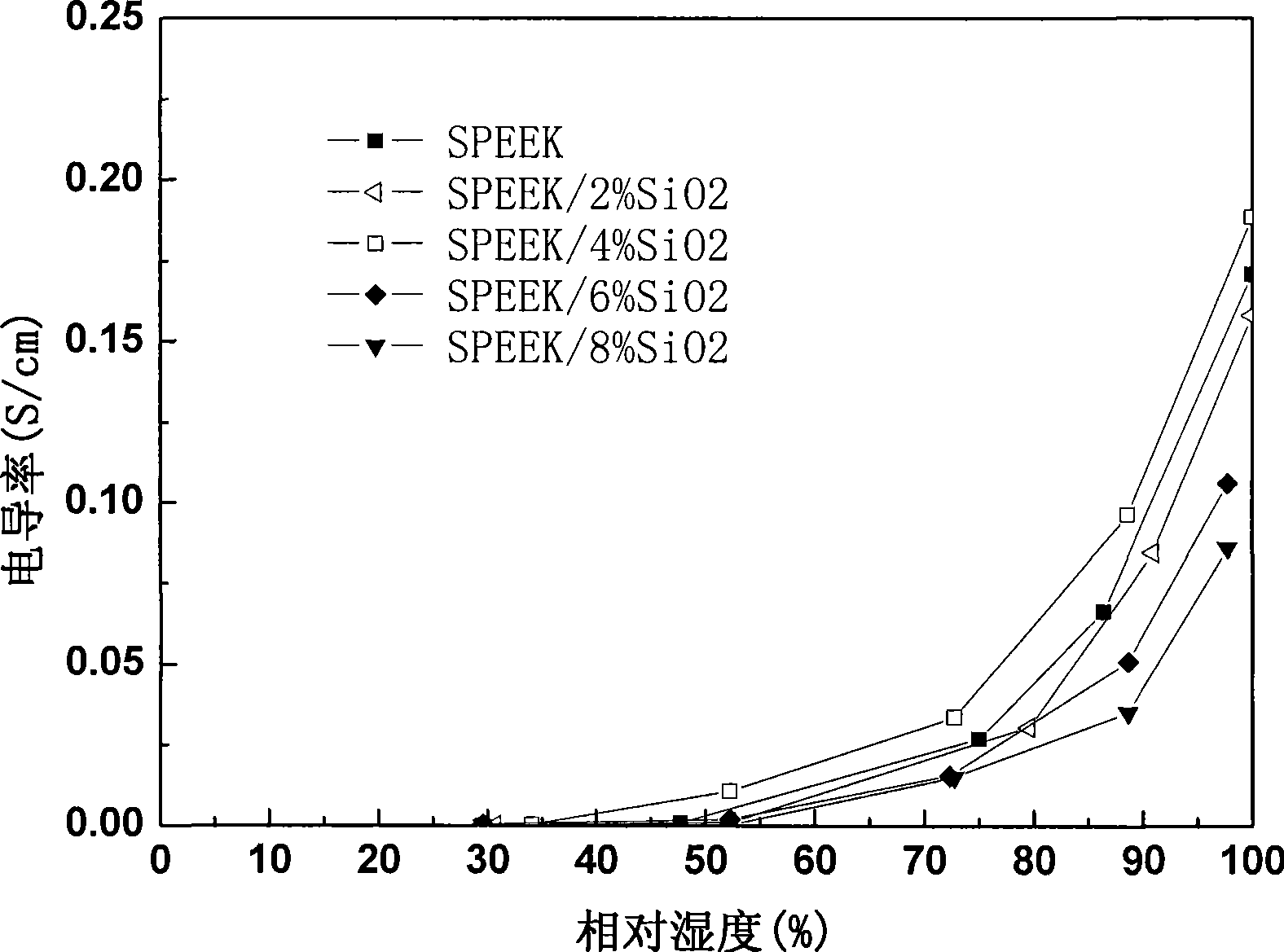
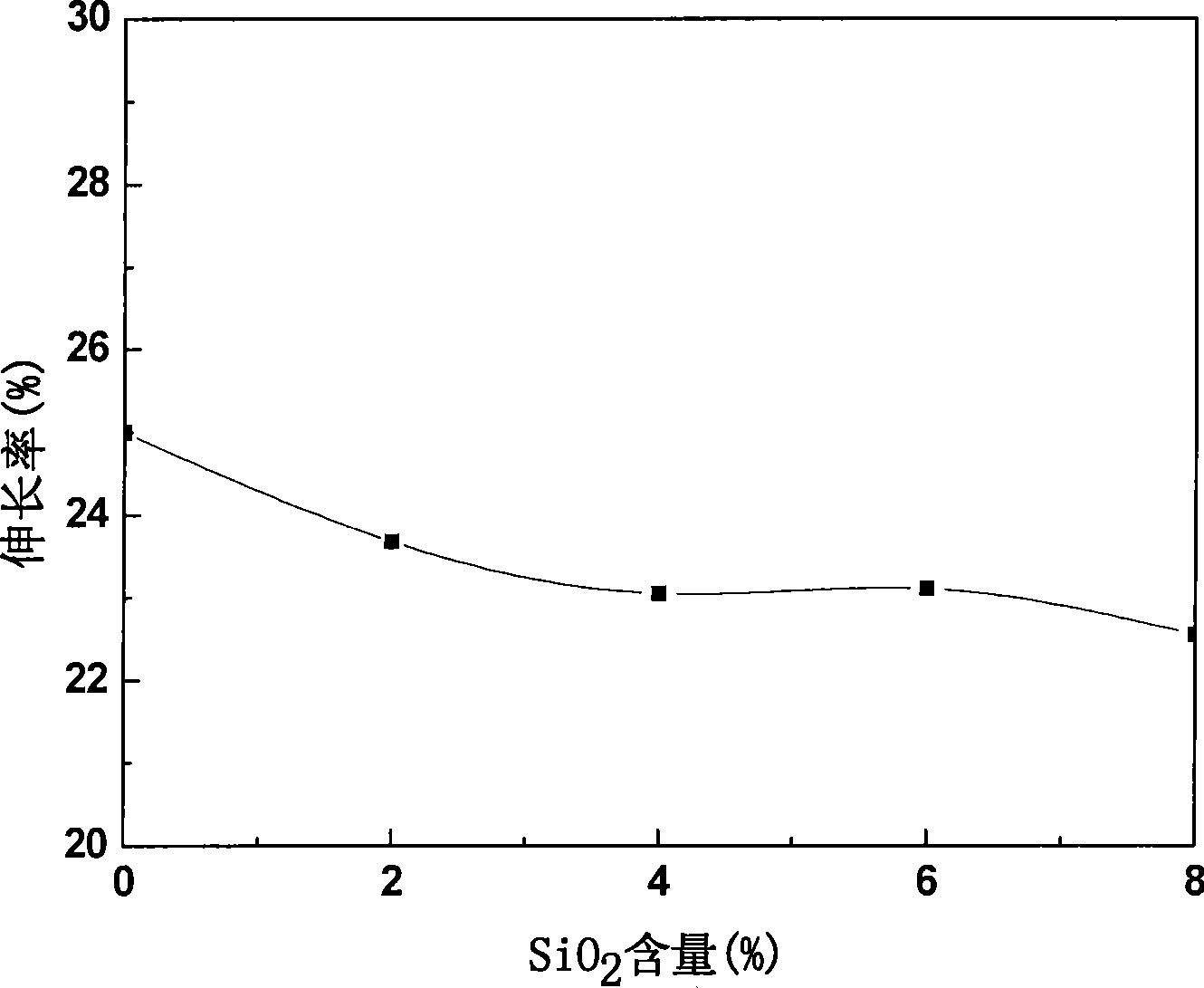
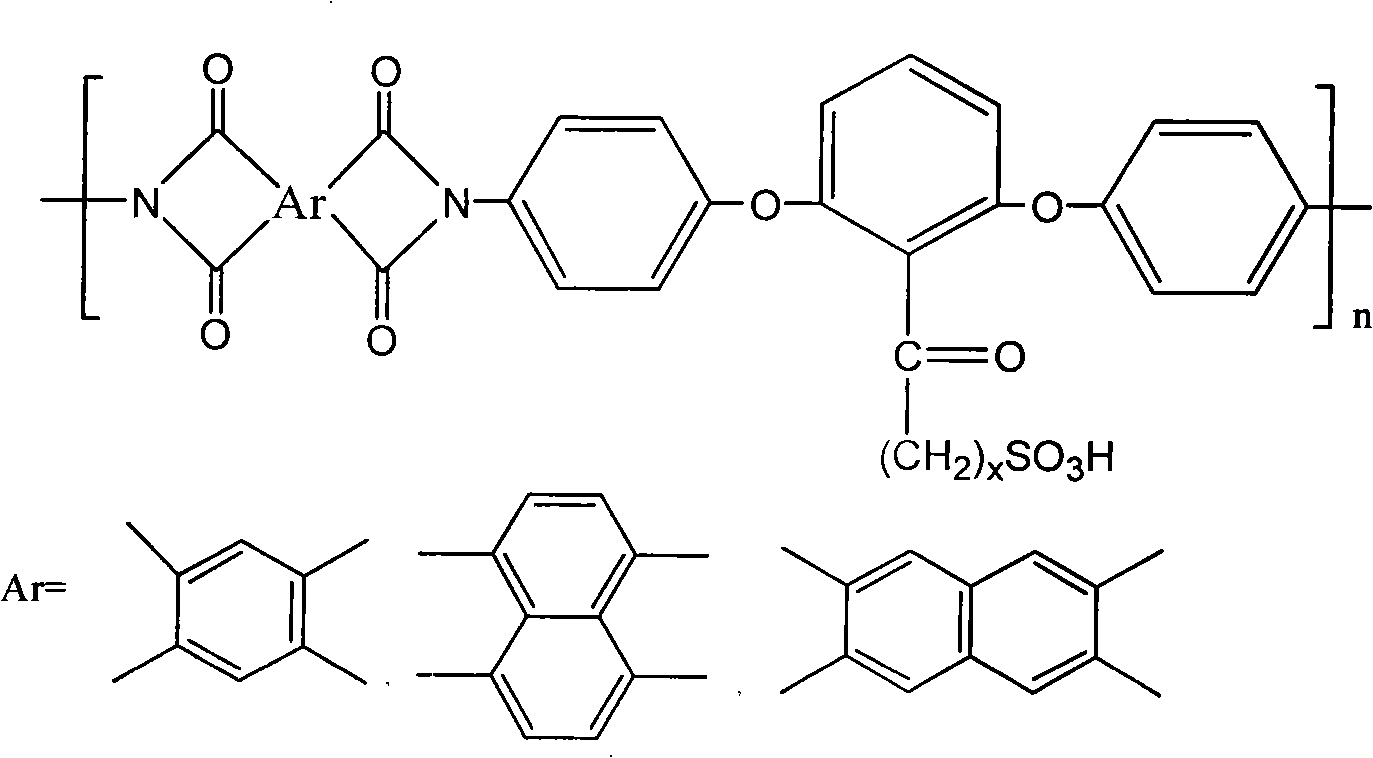
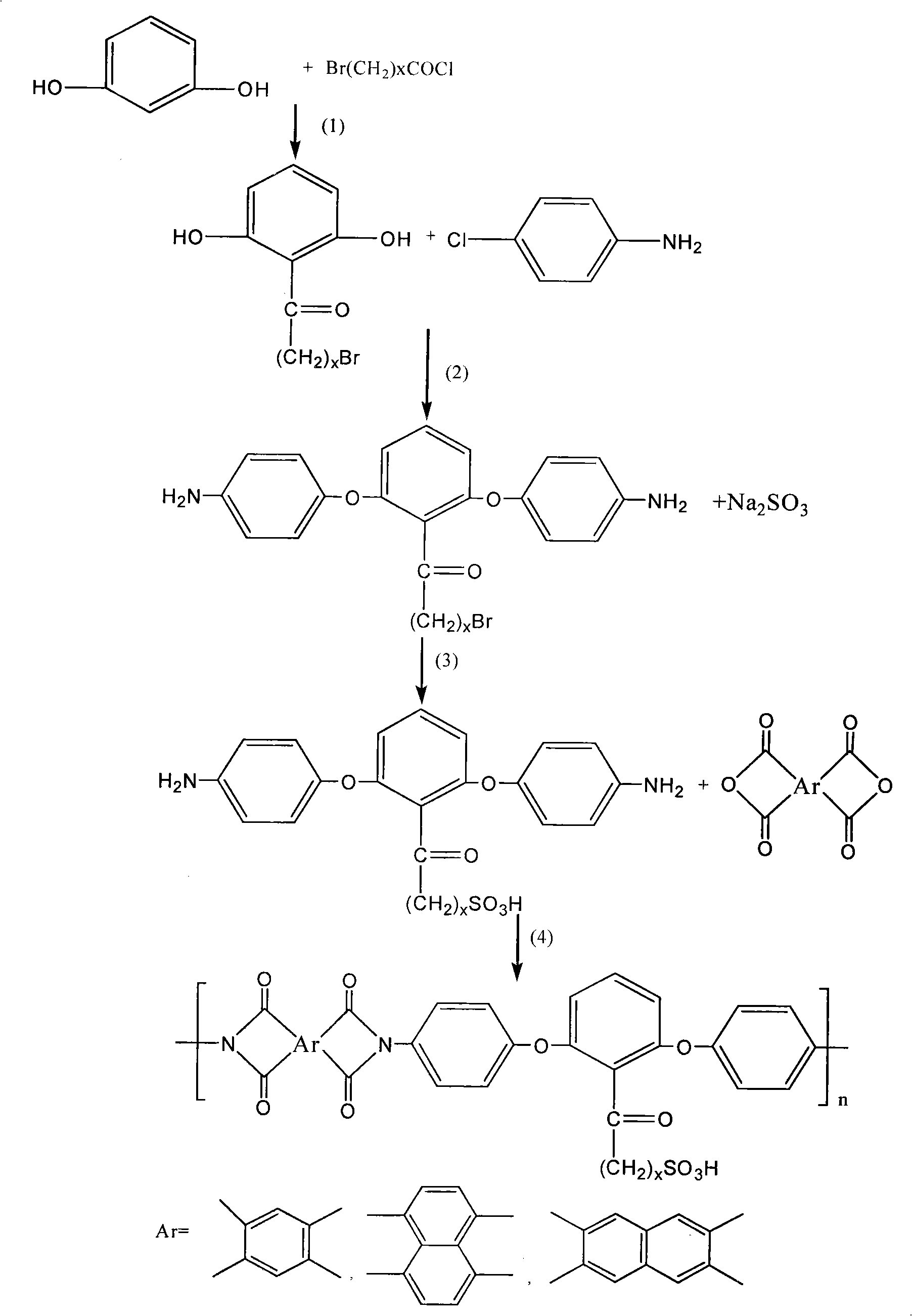
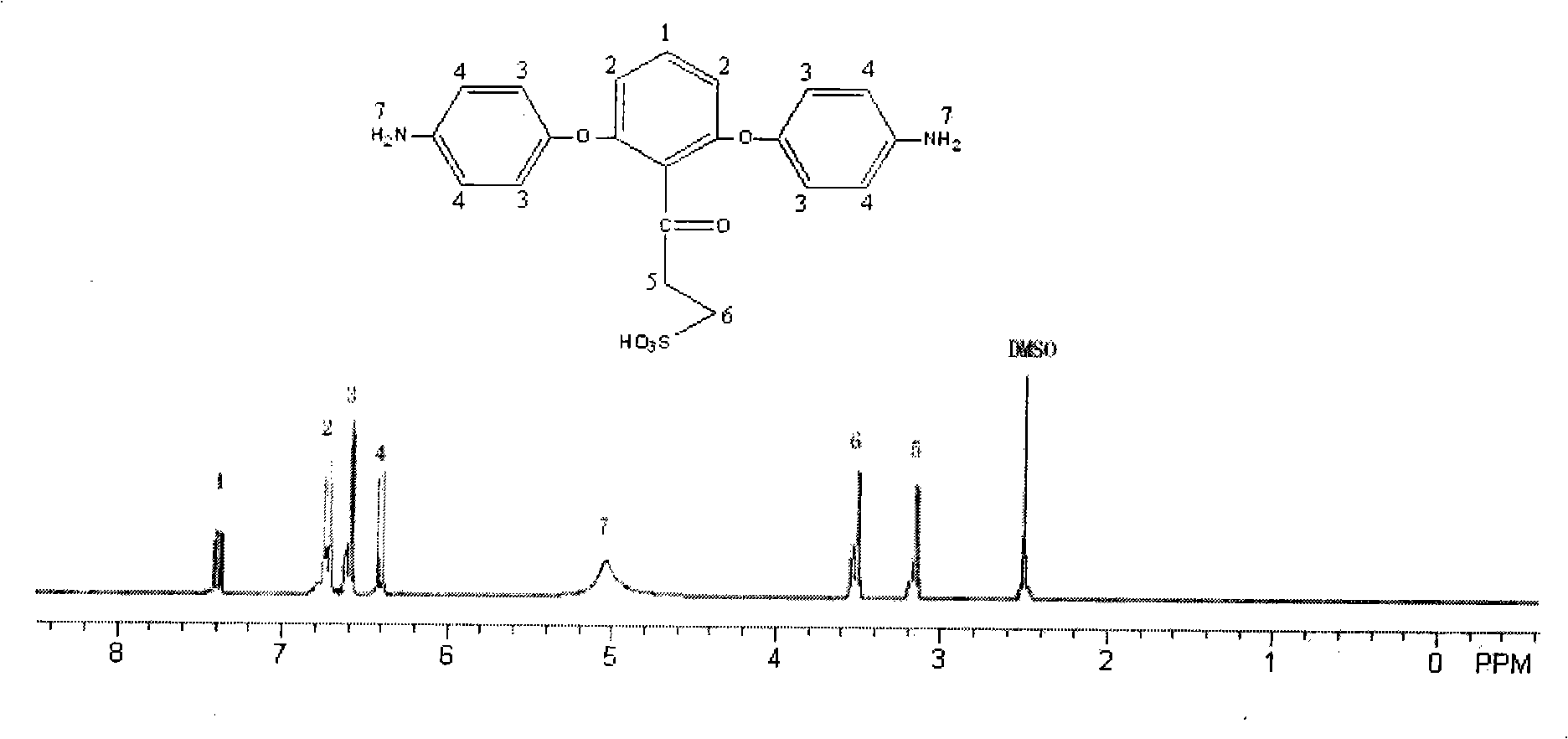
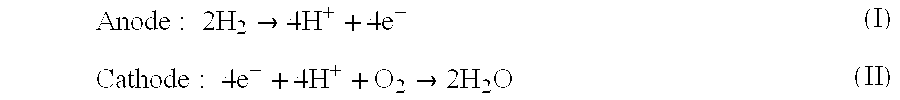Patents
Literature
104results about How to "Low methanol permeability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
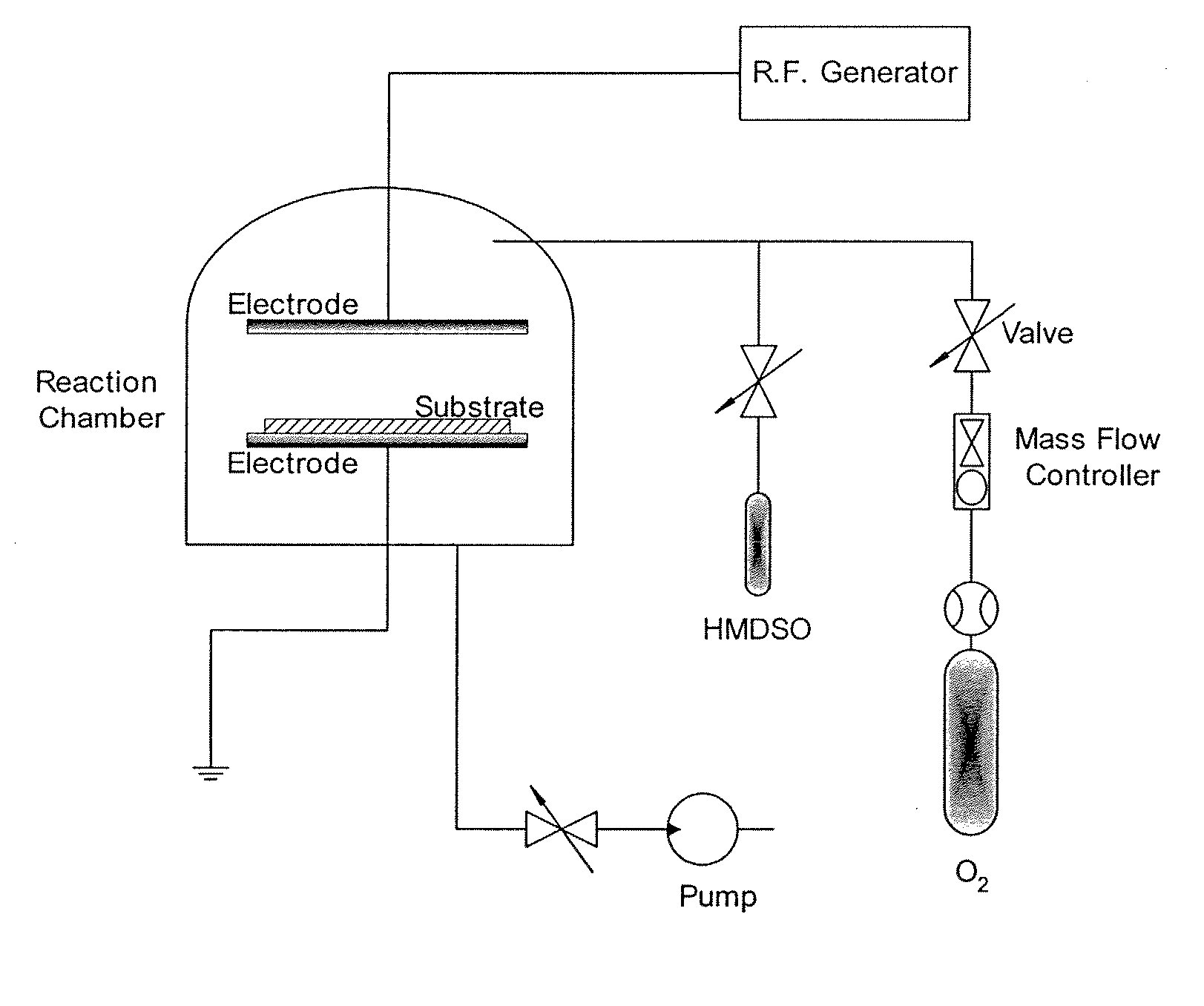
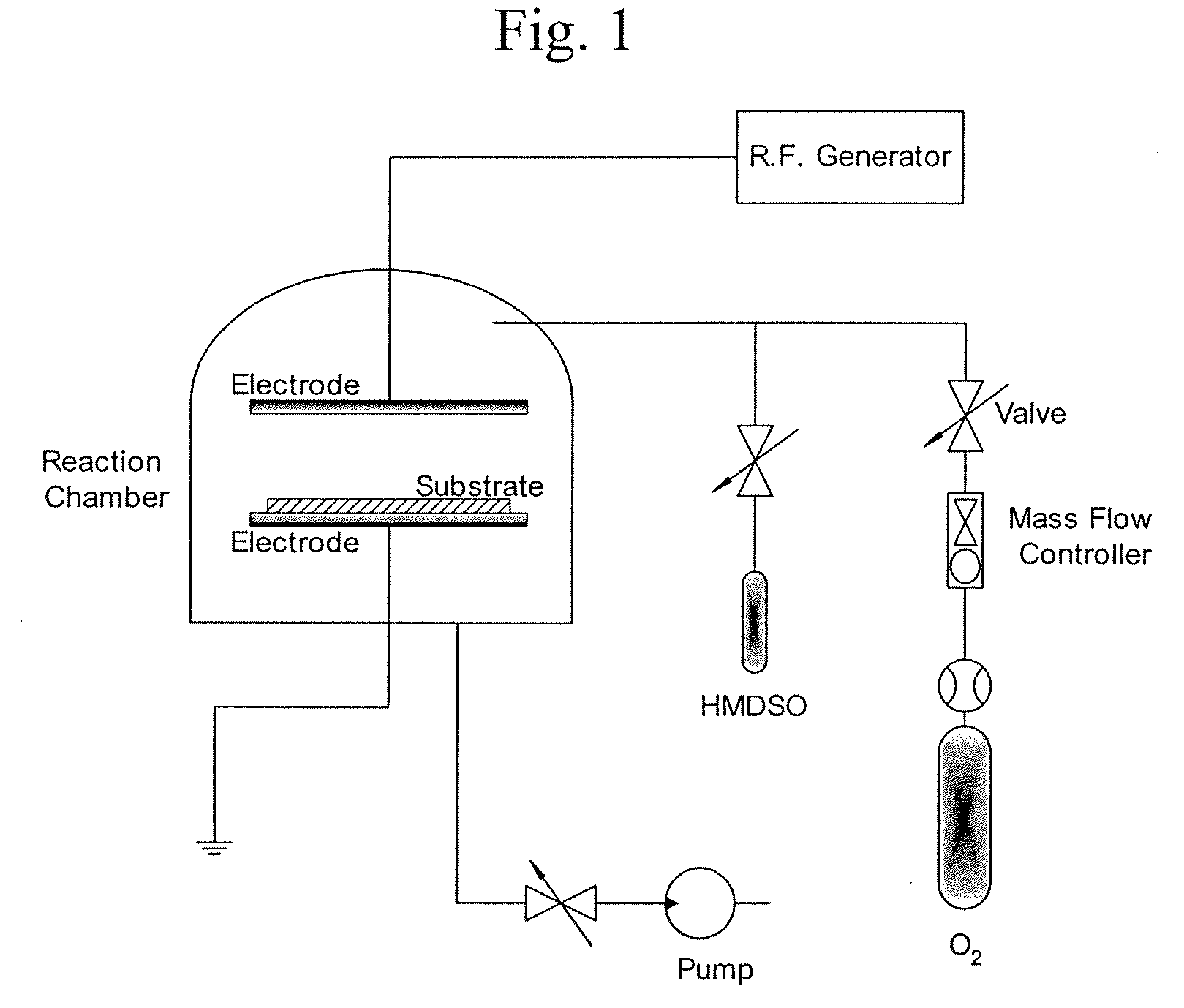
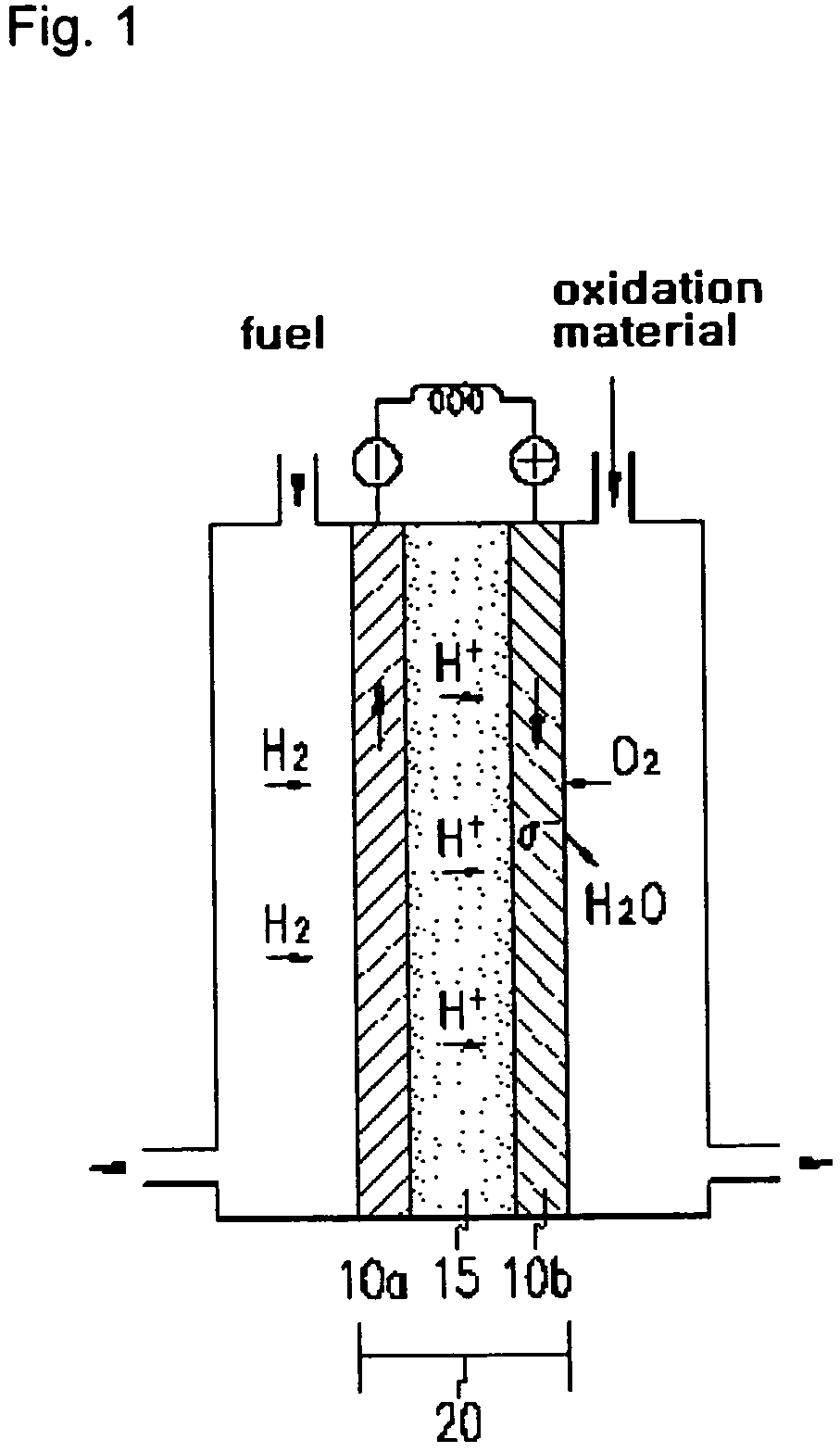
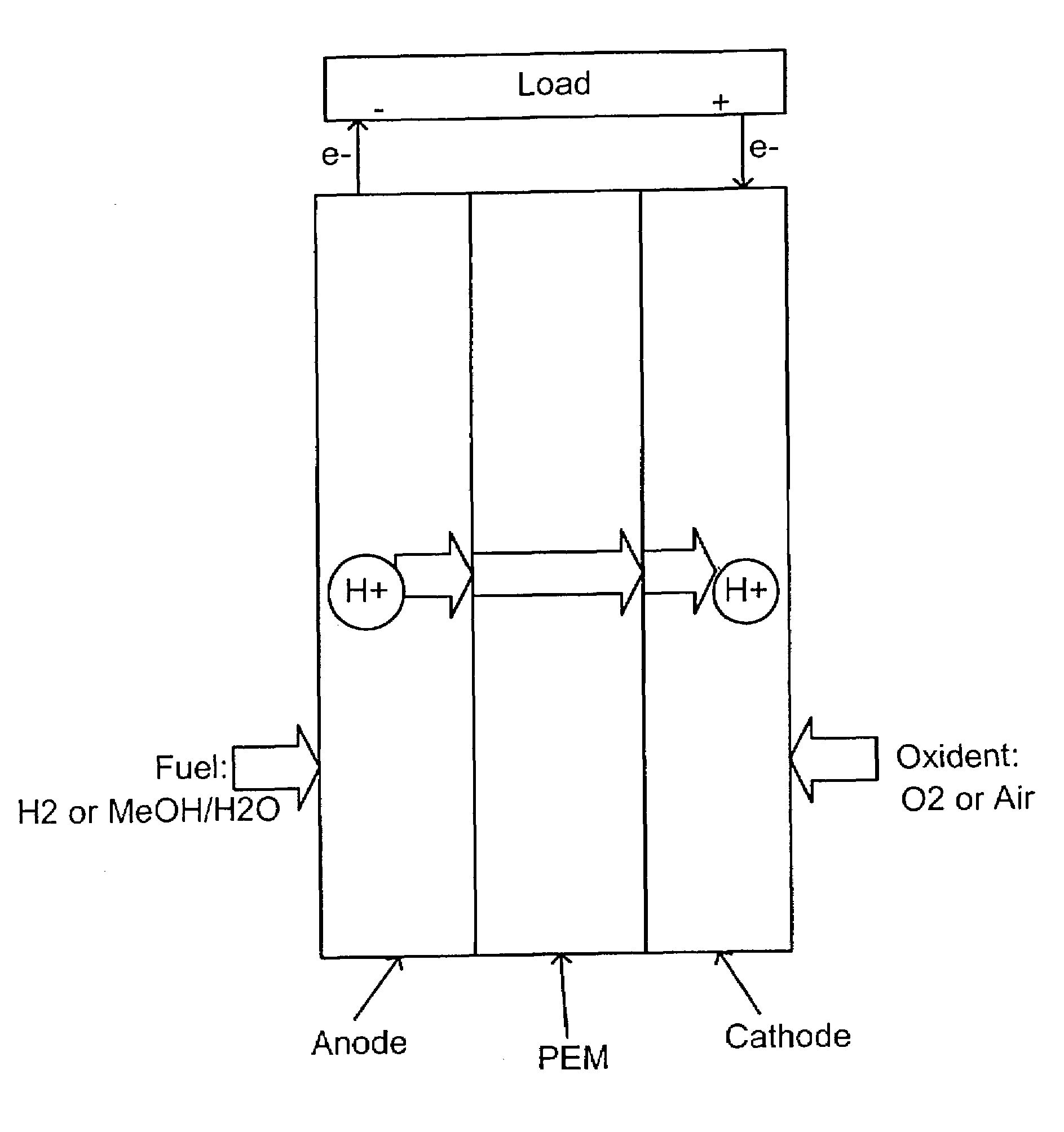
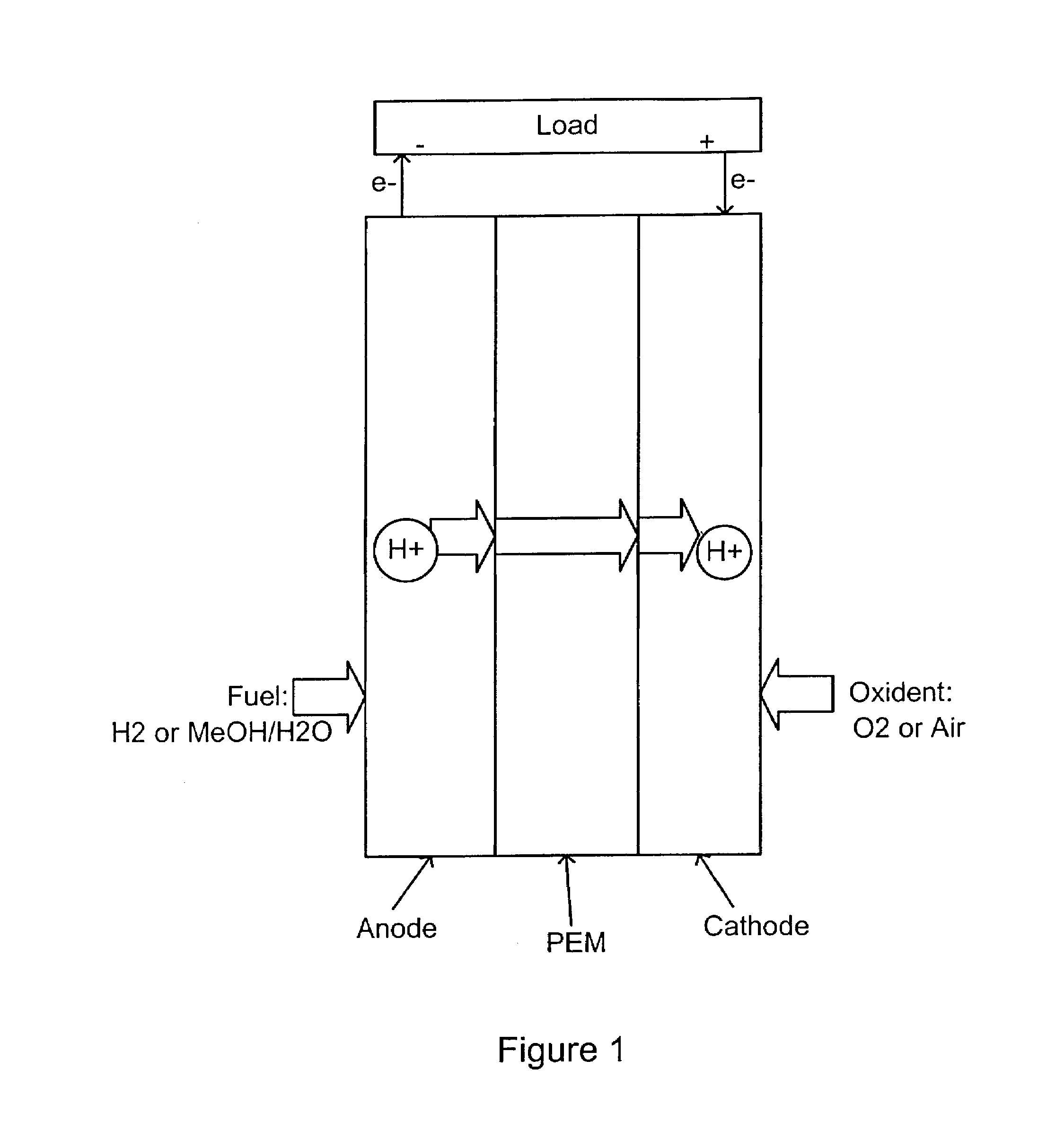
Method to manufacture composite polymer electrolyte membranes coated with inorganic thin films for fuel cells
InactiveUS20070231655A1Reduce conductivityLow methanol permeabilityMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureSilicon oxideMethanol crossover
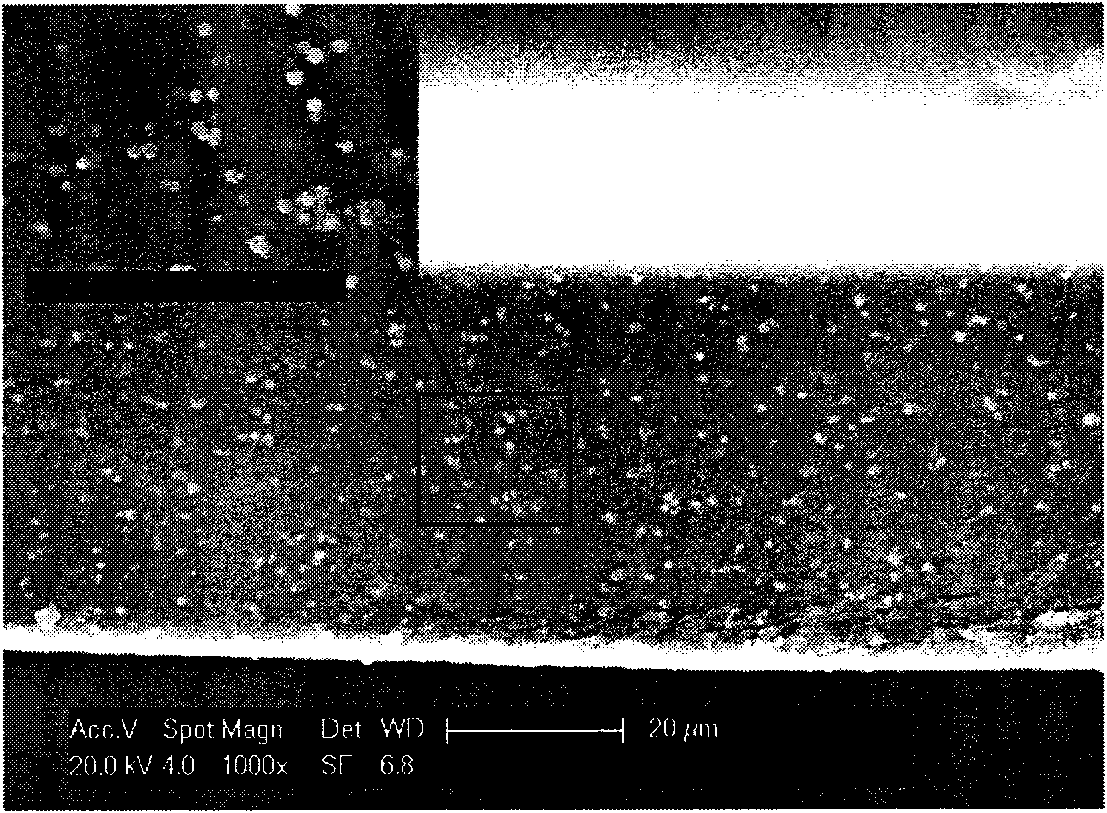
The present invention relates to a method for manufacturing composite polymer electrolyte membranes coated with inorganic thin films for fuel cells using a plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) method or a reactive sputtering method, so as to reduce the crossover of methanol through polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cells and enhance the performance of the fuel cells. The manufacturing method of composite polymer electrolyte membranes coated with inorganic thin films for fuel cells according to the present invention is characterized to obtain composite membranes by coating the surface of commercial composite polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cells with inorganic thin films using a PECVD method or a reactive sputtering method. The inorganic materials to form the inorganic thin films are chosen one or more from the group comprising silicon oxide (SiO2), titanium oxide (TiO2), zirconium oxide (ZrO2), zirconium phosphate (Zr(HPO4)2), zeolite, silicalite, and aluminum oxide (Al2O3). The present invention, by coating the polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cells with inorganic thin films via a PECVD method or a reactive sputtering method, reduces the methanol crossover sizably without seriously reducing the ionic conductivity of polymer electrolyte membranes, thereby, when applied to fuel cells, realizes a high performance of fuel cells.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
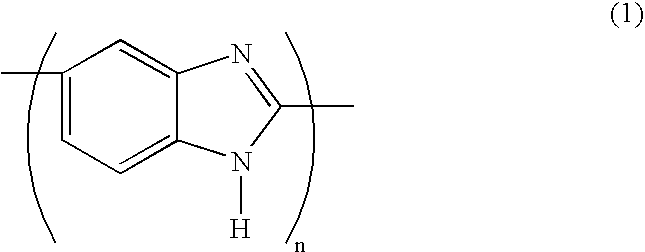
Method for preparing poly(2,5-benzimidazole)
InactiveUS7388035B2Improve proton conductivityLow methanol permeabilityNon-metal conductorsIon-exchanger regenerationPolymer electrolytesFuel cells
A method for preparing poly(2,5-benzimidazole) whereby 3,4-diaminobenzoic acid is polymerized using a dehydrating reagent containing P2O5 and CX3SO3H where X is H or F. The poly(2,5-benzimidazole) has good proton conductivity and low methanol permeability, and therefore can be used as a polymer electrolyte membrane for a fuel cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
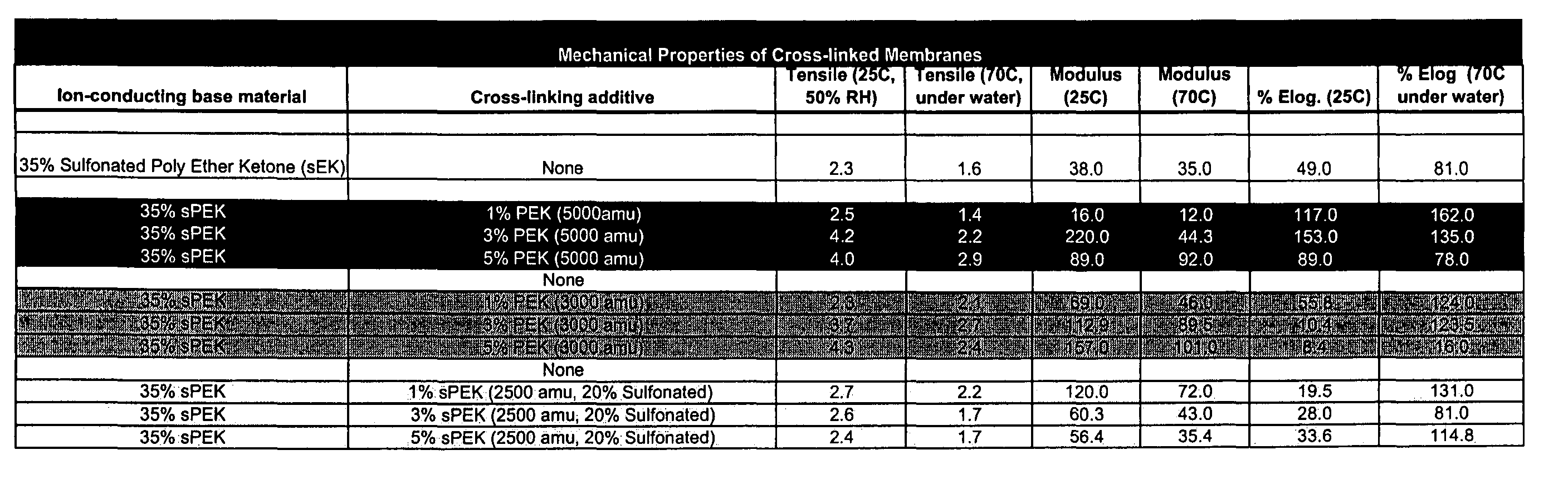
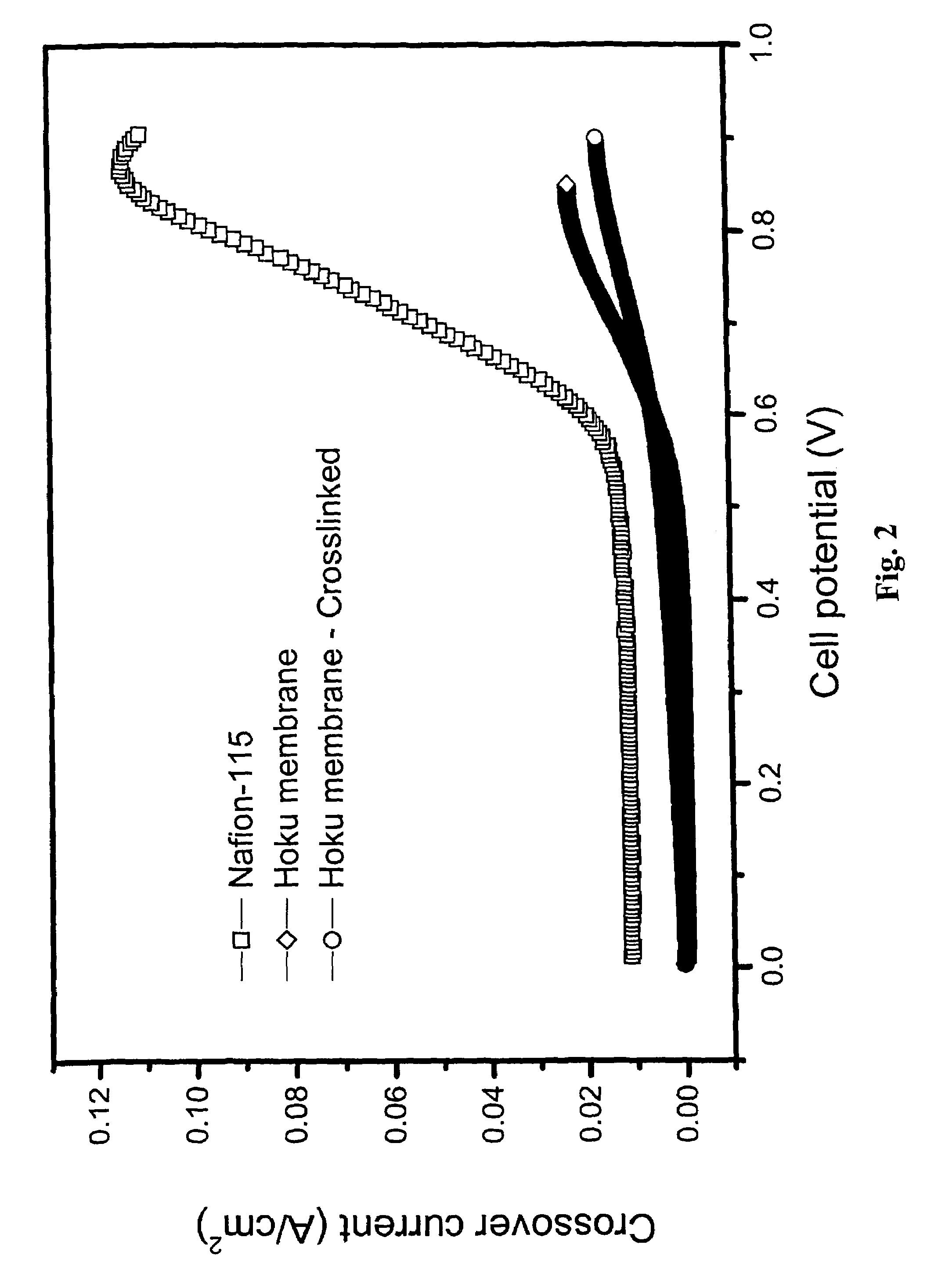
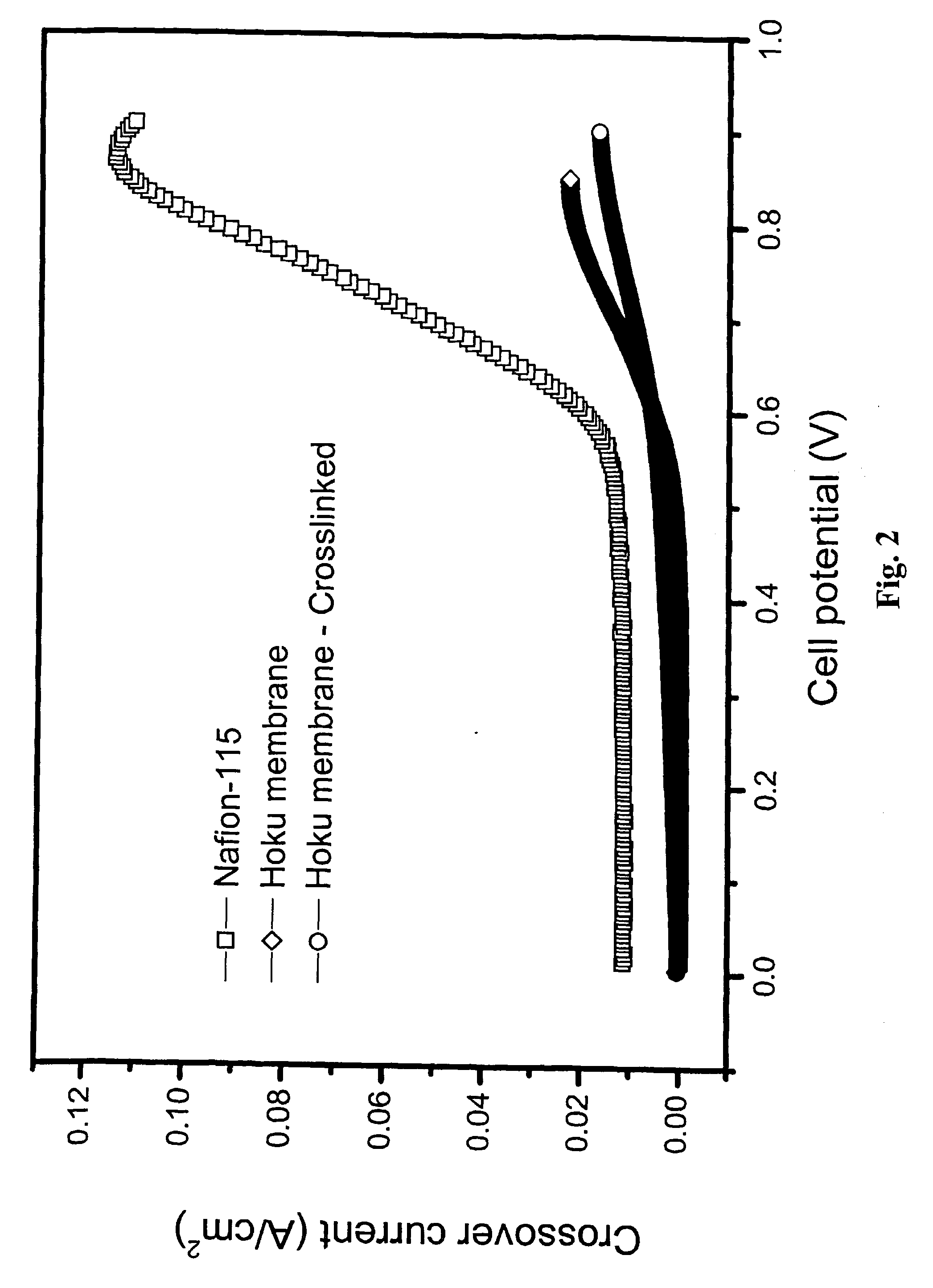
Composite electrolyte with crosslinking agents
InactiveUS6962959B2Sacrificing electrochemical performanceLow costSolid electrolytesIon-exchanger regenerationFuel cellsComposite electrolyte
A covalent crosslinking of ion-conducting materials via sulfonic acid groups can be applied to various low cost electrolyte membrane base materials for improved fuel cell performance metrics relative to such base material. This proposed approach is due, in part, to the observation that many aromatic and aliphatic polymer materials have significant potential as proton exchange membranes if a modification can increase their physical and chemical stabilities without sacrificing electrochemical performance or significantly increasing the material and production costs.
Owner:HOKU SCI
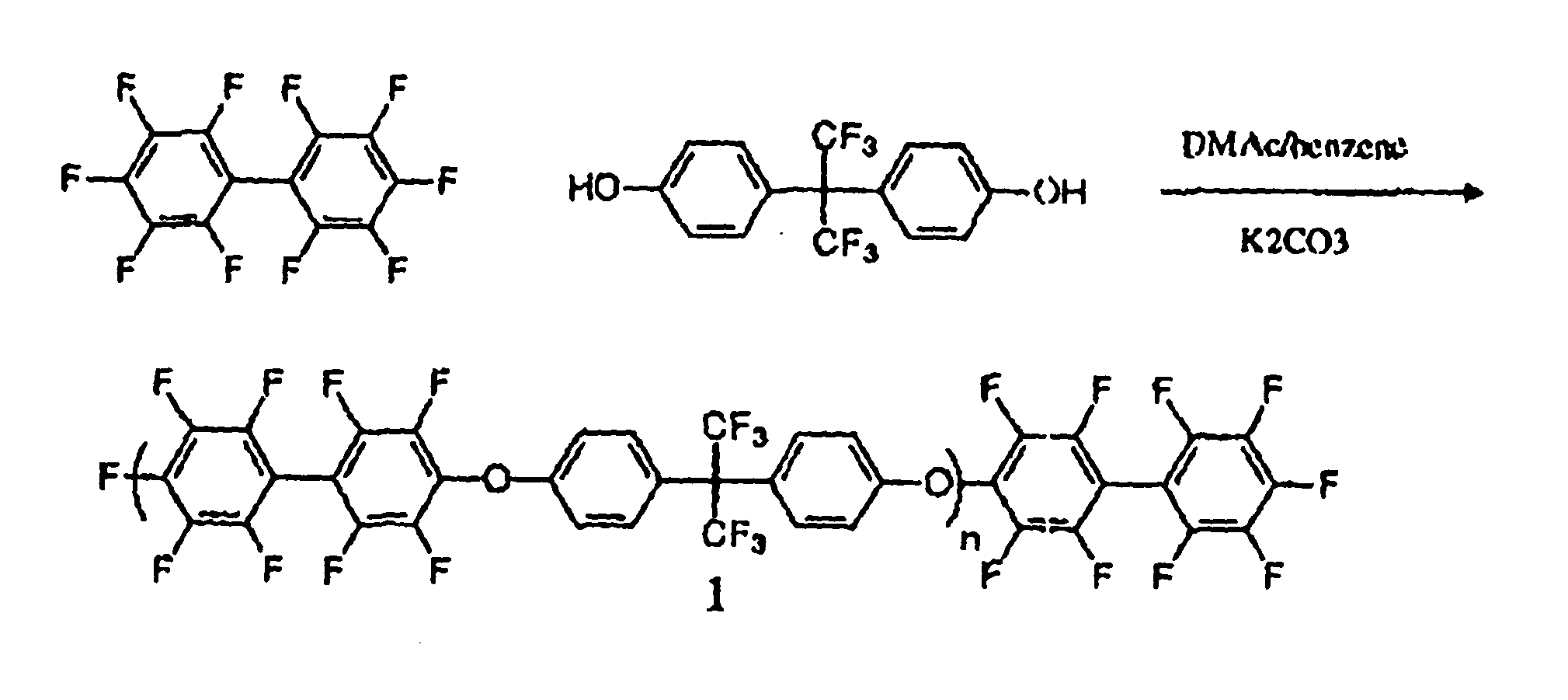
Multiblock Copolymers Containing Hydrophilic Hydrophobic Segments for Proton Exchange Membrane
InactiveUS20070292730A1Low methanol permeabilityImprove proton conductivitySolid electrolytesIon-exchanger regenerationPolymerElectrolyte
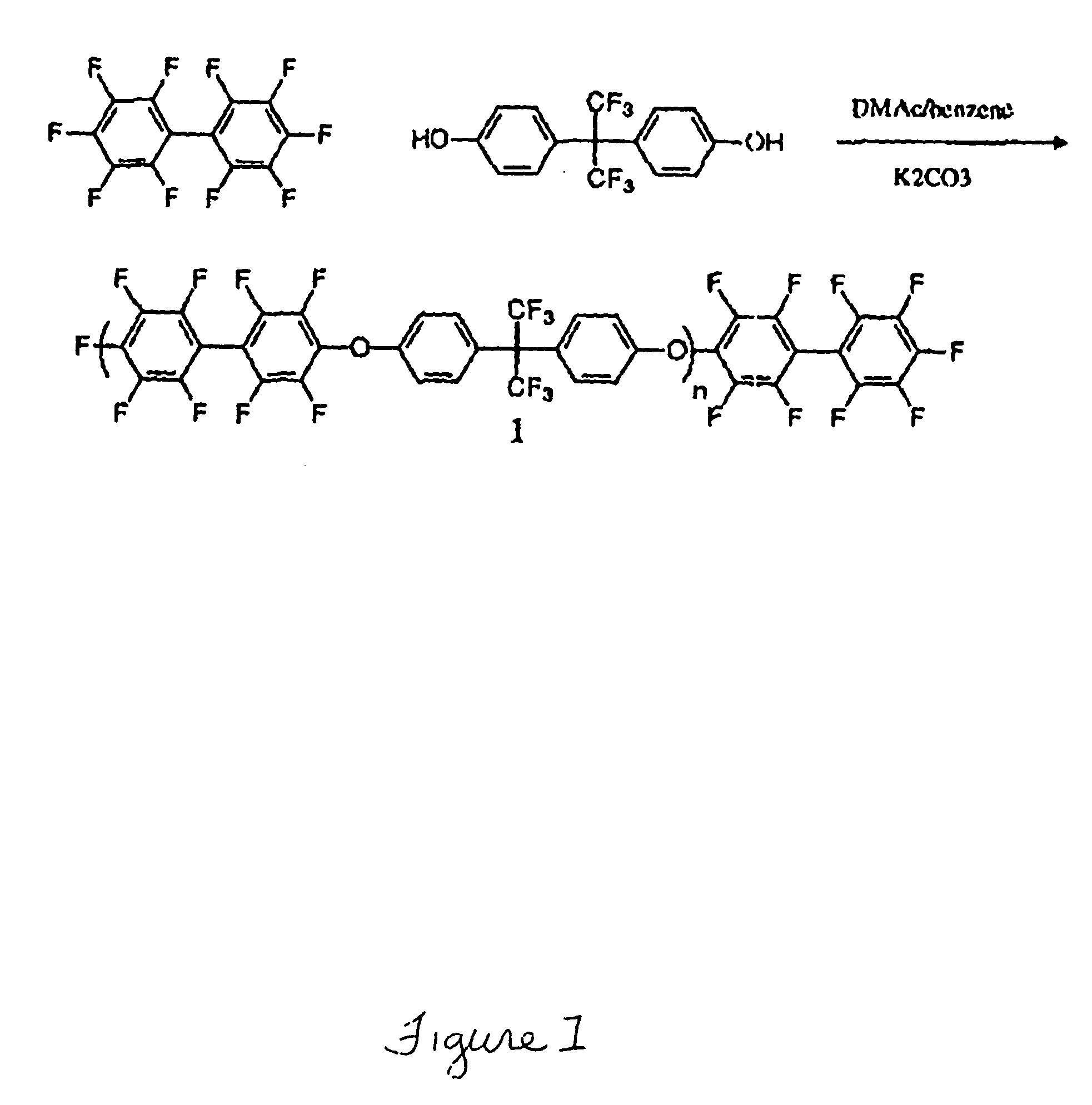
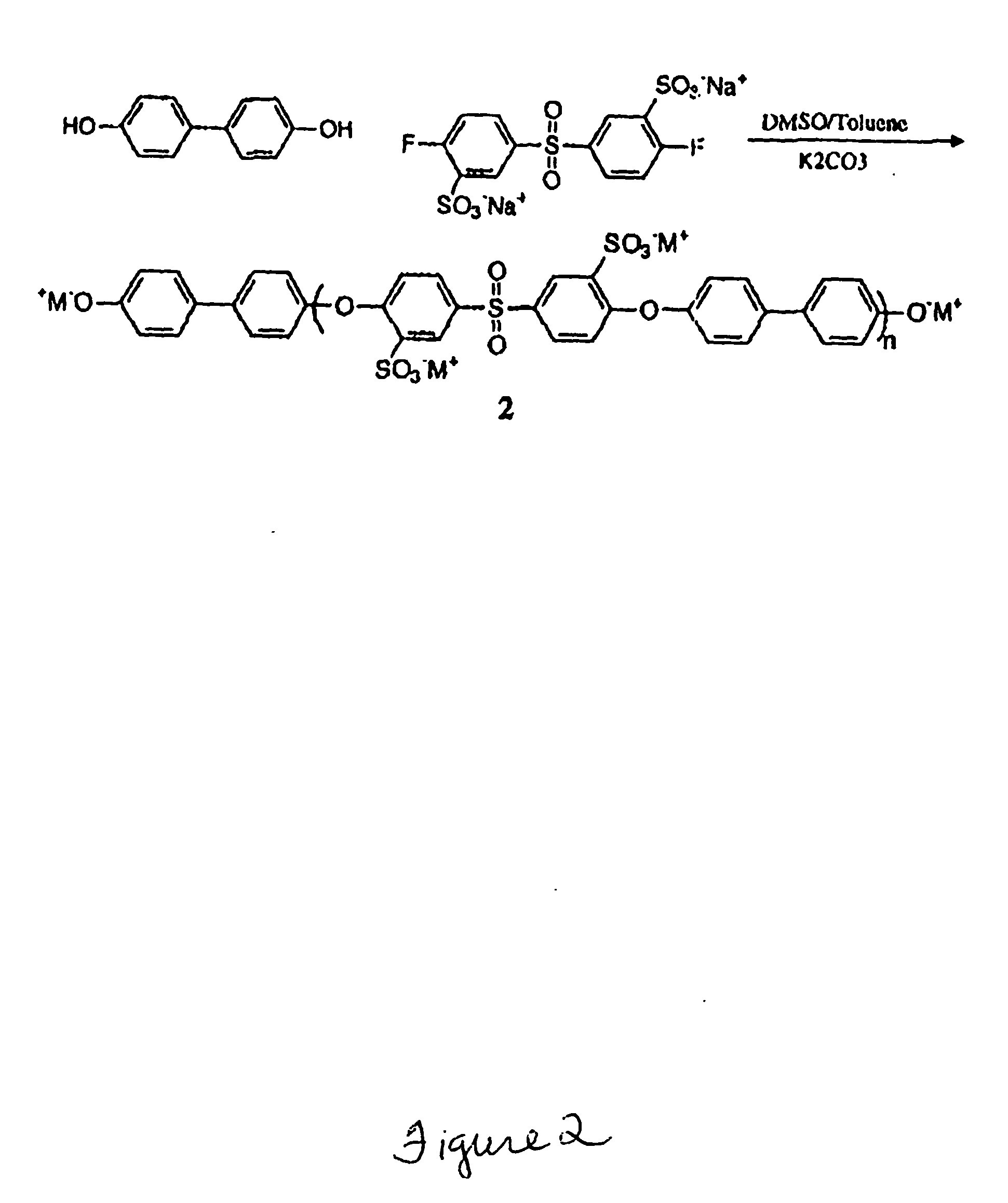
Novel multiblock copolymers containing perfluorinated poly(arylene ether) as a hydrophobic segment and disulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) as a hydrophilic segment are provided. The multiblock copolymers are used to form proton exchange membranes that are thermally and hydrolytically stable, flexible, and that exhibit low methanol permeability and high proton conductivity. The proton exchange membranes are thus well-suited for use for use as polymer electrolytes in fuel cells.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
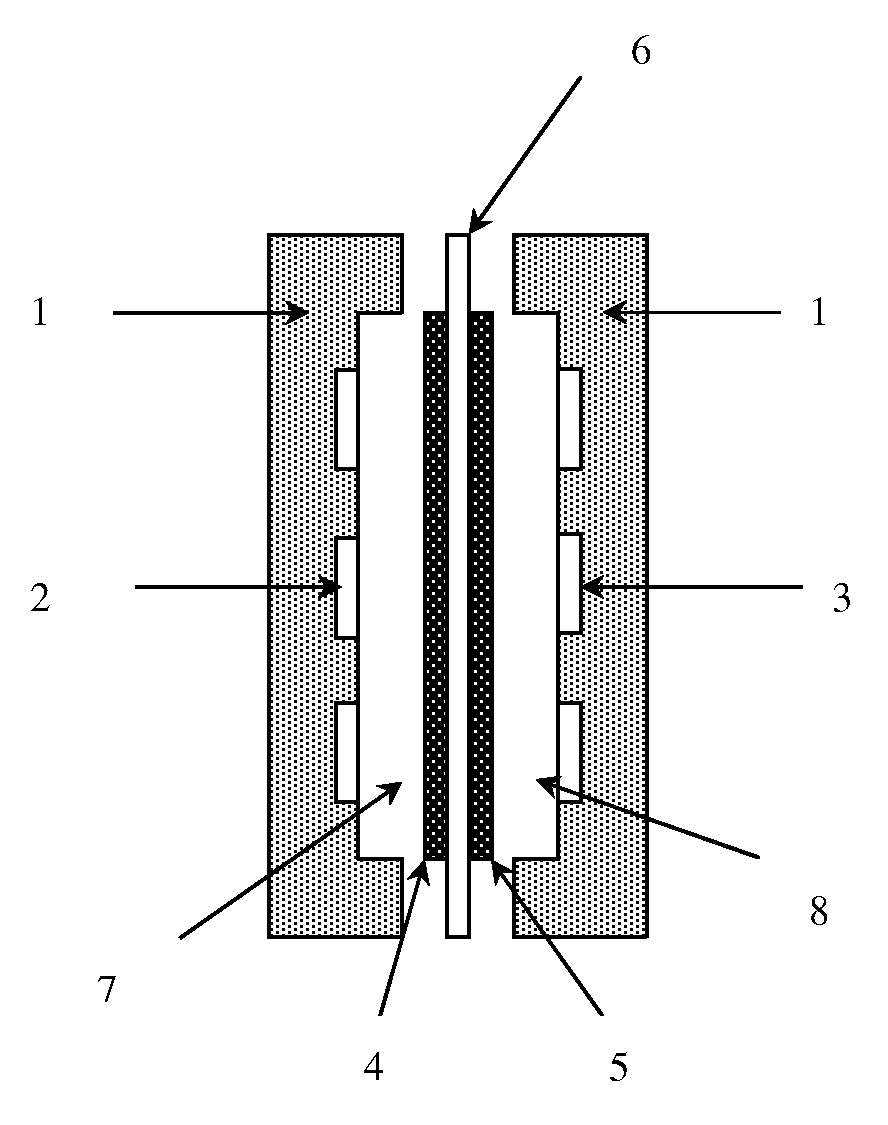
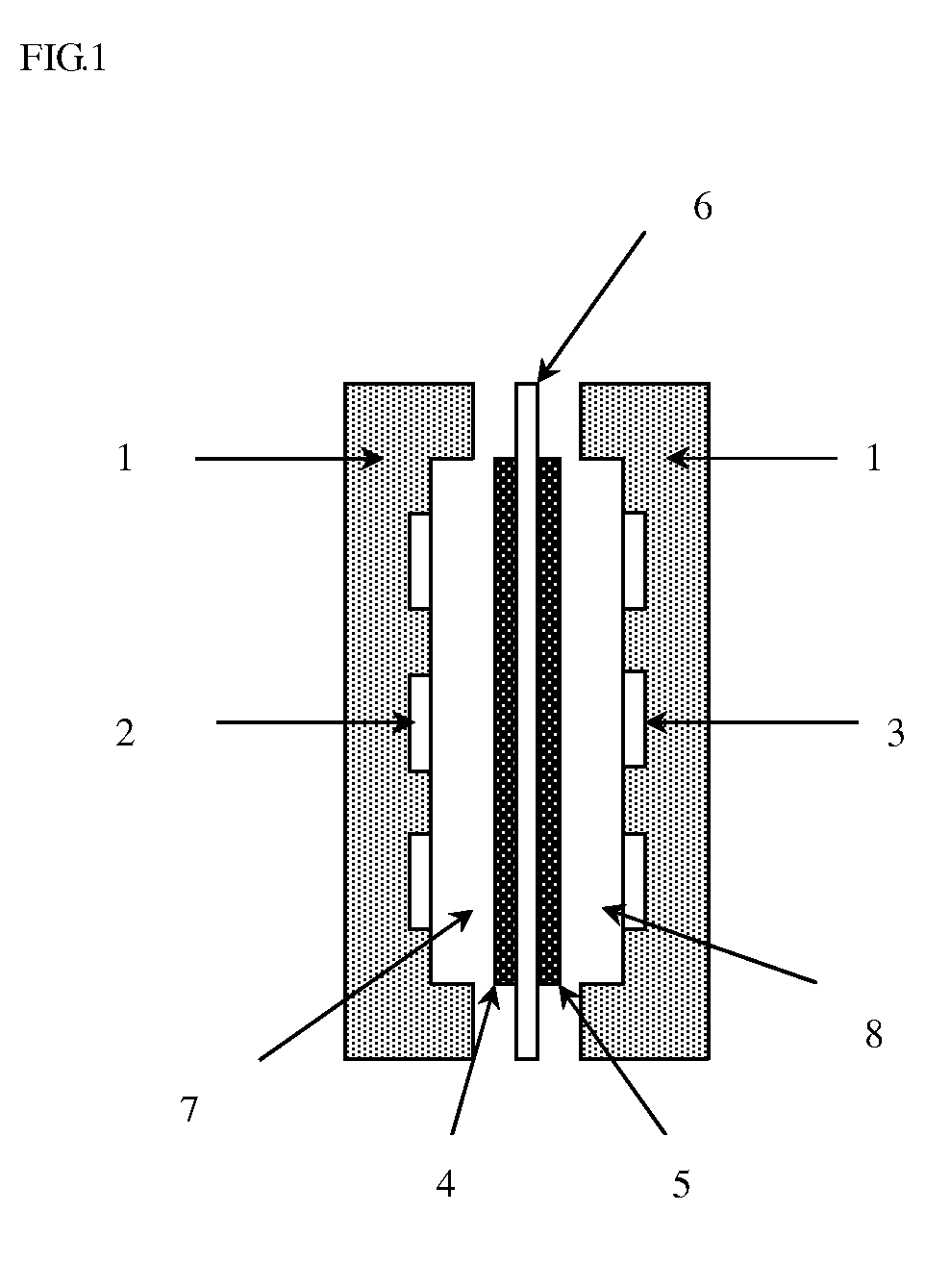
Direct alcohol fuel cell membrane electrode, and preparation and applications thereof
ActiveCN103840174AGuaranteed performanceLow methanol permeabilityCell electrodesFinal product manufactureFuel cellsAlcohol fuel
The invention relates to a direct alcohol fuel cell membrane electrode, and a preparation thereof. According to the preparation method, the direct alcohol fuel cell membrane electrode is formed by arranging an oxidized graphene layer between anode side of a proton exchange membrane and an anode catalyst layer; the oxidized graphene layer is composed of oxidized grapheme and Nafion at a mass ratio of 5:1-1:5. The direct alcohol fuel cell membrane electrode is capable of preventing methanol penetration without cell performance degradation effectively; and the preparation method is simple and convenient, and can be used for batch production.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Proton exchange polymer membrane using surface treatment technique based on direct fluorination, membrane-electrode assembly, and fuel cell comprising the same
InactiveUS20110014544A1Improve proton conductivityGood dimensional stabilityFinal product manufactureCell electrodesElectronegativityElectrochemistry
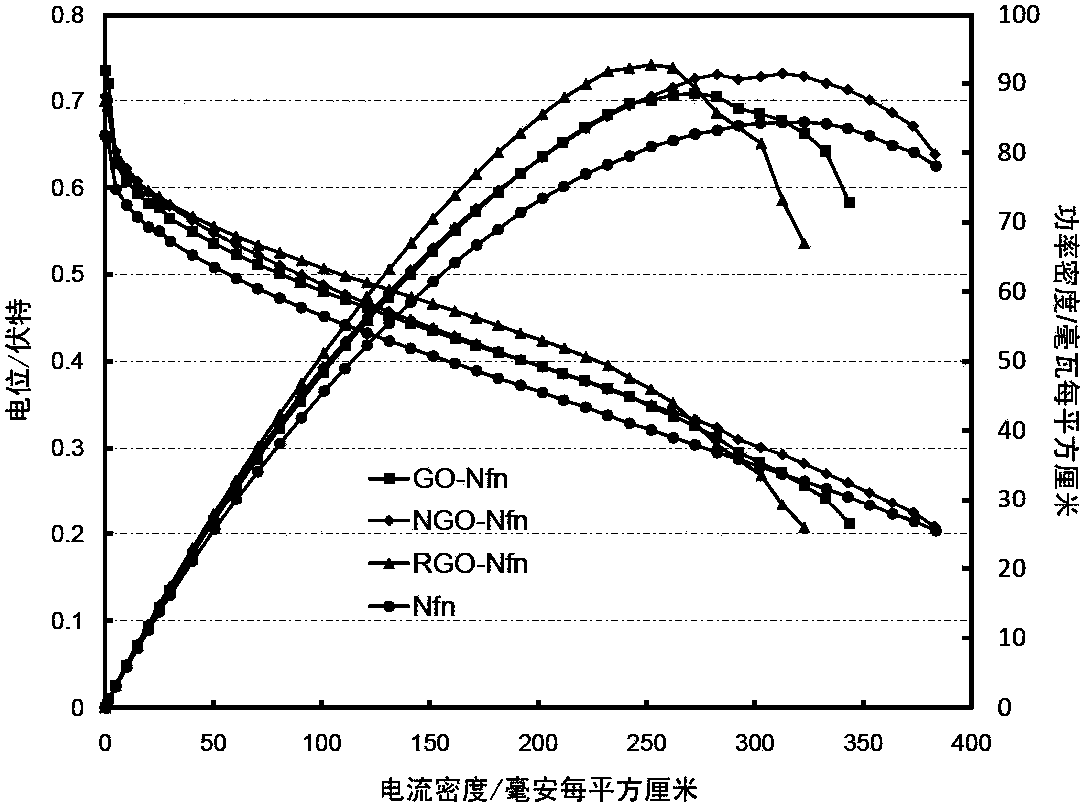
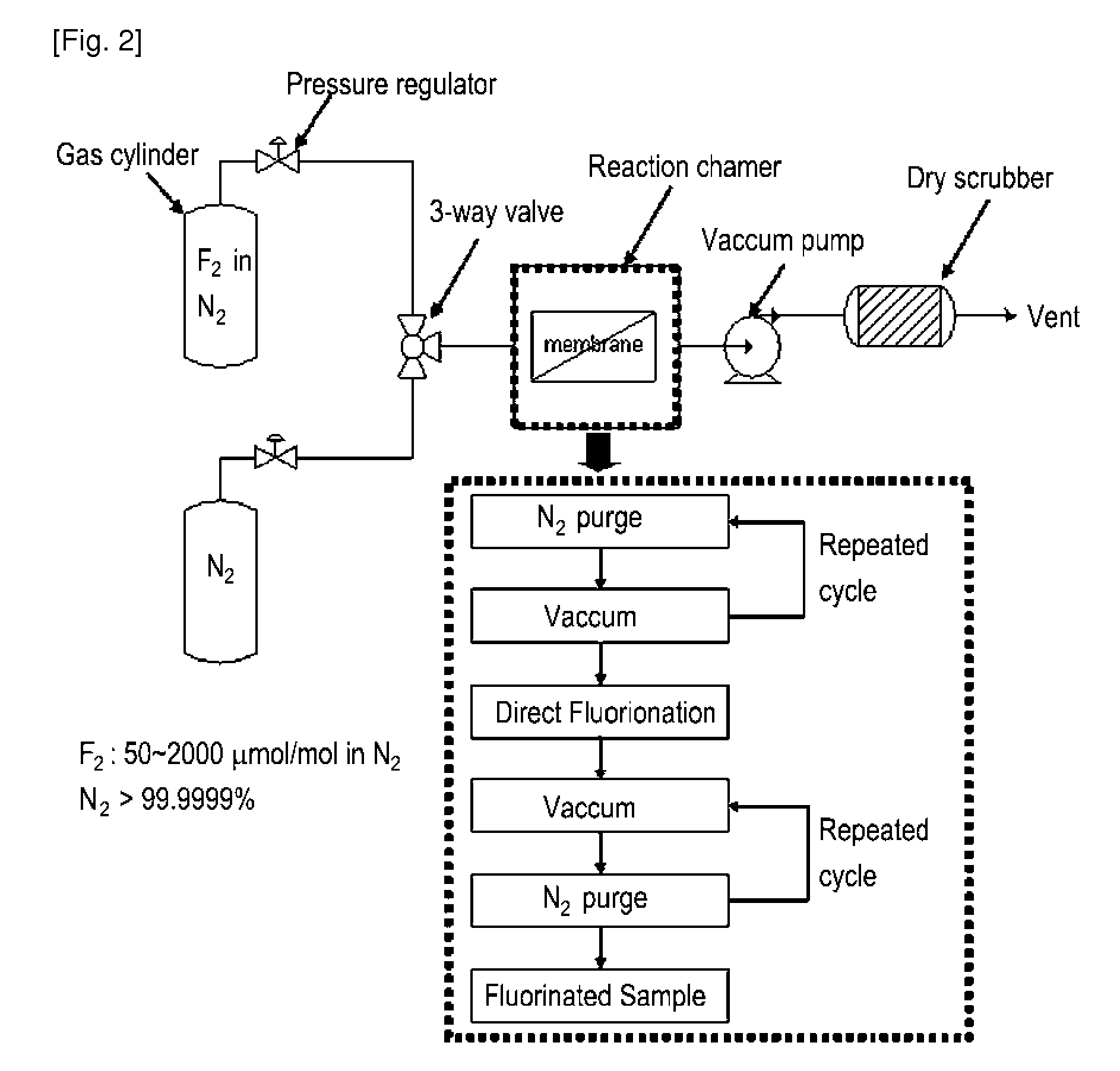
A proton exchange polymer membrane whose surface is treated by direct fluorination using a fluorine gas, a membrane-electrode assembly, and a fuel cell comprising the same are provided. The proton exchange polymer membrane of the present invention exhibits improved proton conductivity, high dimensional stability, and decreased methanol permeability through introducing hydrophobic fluorine having high electronegativity to the surface of the polymer membrane. Therefore, the proton exchange polymer membrane with excellent electrochemical properties of the present invention can be preferably utilized as polymer electrolyte membrane for fuel cell, generating electric energy from chemical energy of fuels.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUND HANYANG UNIV)
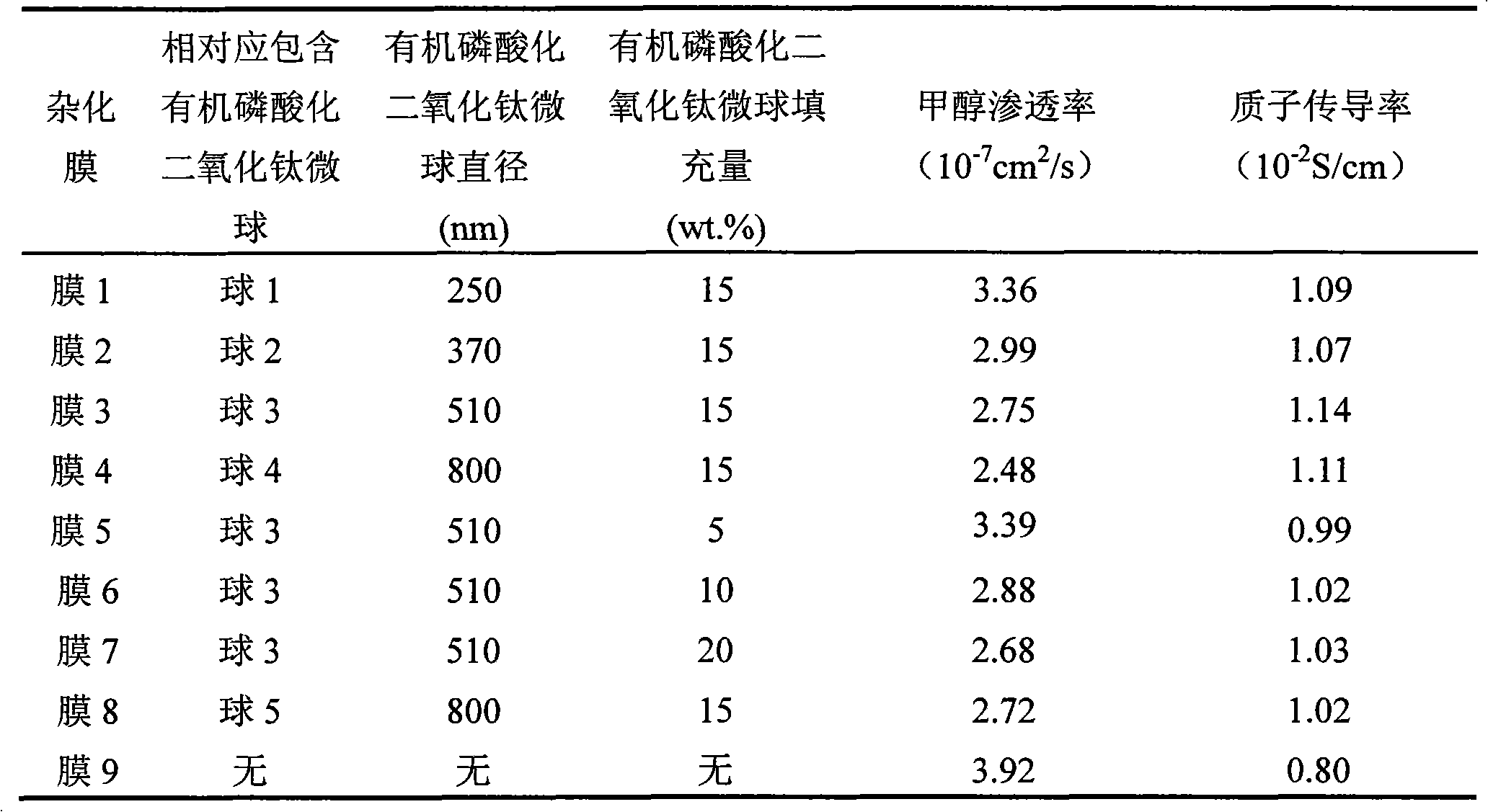
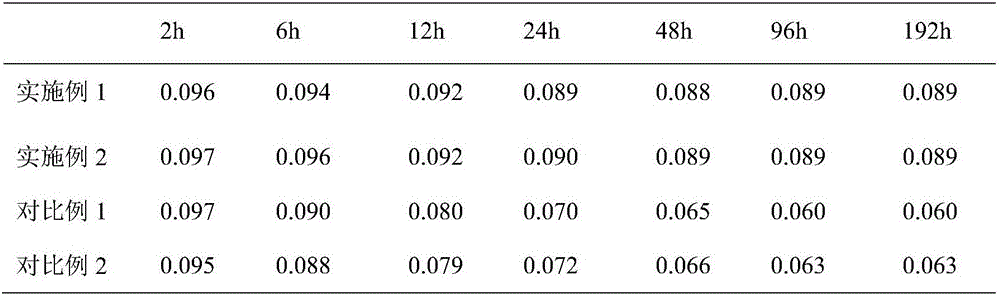
Organic phosphorylated titanium dioxide micrballon-filled chitosan hybrid membrane as well as preparation and application
InactiveCN101624449AEasy to makeUniform and controllable particle sizeCell component detailsSolid electrolyte fuel cellsO-Phosphoric AcidAqueous acetone
The invention relates to an organic phosphorylated titanium dioxide micrballon-filled chitosan hybrid membrane as well as a preparation and an application. The hybrid membrane is prepared by taking tetrabutyl titanate, glycol, organic phosphoric acid and chitosan as raw materials according to the following matching: the mole ratio of tetrabutyl titanate and glycol is 1:30-1:60 to prepare titanium dioxide micrballon, the mass volume ratio of titanium dioxide micrballon and organic phosphoric acid is 1:4-6, the mass ratio of titanium dioxide micrballon and chitosan is 0.05-0.2:1. The preparation method is as follows: the mixed solution of tetrabutyl titanate and glycol are precipitated in acetone water solution, washed and dried to obtain titanium dioxide micrballon which is put into organic phosphoric acid water solution for standing, the micrballon is put into glacial acetic acid water solution for ultrasound dispersion and is added with chitosan to obtain casting solution which subjects to casting on a substrate (glass plate) and is dried to form a membrane for crosslinking in sulphuric acid water solution, then washing and vacuum drying. The titanium dioxide micrballon and the membrane of the invention have rich source of raw materials, low cost and simple operation, and the prepared hybrid membrane has lower methanol permeability and higher proton conductivity, and can be used as direct methanol fuel cell membrane.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Modified nanometer material for improving stability of heteropoly acid in proton exchange membrane and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106750051AImprove conductivityLow methanol permeabilityMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureHalogenHeteropoly acid
The invention discloses a modified nanometer material for improving the stability of a heteropoly acid in a proton exchange membrane and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of organic modification of inorganic nanometer materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly coating nanometer material with dopamine hydrochloride, introducing active halogen atoms, and realizing graft polymerization of monomers with basic groups through an ATRP reaction on the nanometer material to obtain the modified nanometer material. The method is suitable for tubular nanometer materials and layered nanometer materials. The loss of the heteropoly acid in use is reduced by forming acid-base pairs between the basic groups carried on the nanometer material and the heteropoly acid and the hydrogen-bond interaction, and meanwhile the basic groups have good hydrophilicity, so the conductivity of the proton exchange membrane is improved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Separation membrane for direct liquid fuel type fuel cell & production method thereof
InactiveUS20100279204A1Improve heat resistanceHigh activitySolid electrolytesFinal product manufactureFuel cellsCounterion
Disclosed is a separation membrane for direct liquid fuel cells, which is composed of a quaternary ammonium-type anion exchange membrane. The quaternary ammonium-type anion exchange membrane is produced as follows: a polymerizable composition containing a styrene having a haloalkyl group, a crosslinking polymerizable monomer, a compound having an epoxy group and an effective amount of a polymerization initiator is brought into contact with a porous film, so that the pores of the porous film are filled with the polymerizable composition that is then polymerized therein; then a quaternary ammonium group is introduced into the bromoalkyl group; and then the counter ion of the quaternary ammonium group is ion-exchanged into a hydroxide ion. Also disclosed is a method for producing the quaternary ammonium-type anion exchange membrane.
Owner:TOKUYAMA CORP
Preparation of SiO2/organic polymer composite proton exchange membrane
InactiveCN101440167AReduce in quantityIncrease the number ofCellsFuel cell detailsPartial hydrolysisFuel cells
The invention provides a method for preparing SiO2 / organic polymer composite proton membrane. The method comprises the steps of subjecting ortho-silicate organic ester to partial hydrolysis and condensation under acid catalysis so as to synthesize SiO2-containing alcosol, compounding the alcosol with organic polymer proton conductive membrane liquid so as to prepare SiOx.(OH)y.(OR)z / organic composite proton exchange membrane, immersing the membrane in acidic water so as to completely hydrolyze OR radicals which are not hydrolyzed yet and preparing a SiOx.(OH)y / organic polymer composite proton exchange membrane. In the composite proton membrane prepared by the method, as SiOx.(OH)y is low in condensation degree, and as SiO2 exists as molecular groups not completely condensed and is completely dissolved in the membrane liquid and uniformly distributed in the composite membrane, the prepared composite membrane has the advantages of high composite-membrane mechanical strength, high proton conductivity, low water-absorption expansivity and low methanol permeation rate, and is a good fuel-cell proton membrane.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Crosslinkable aromatic resin having protonic acid group, and ion conductive polymer membrane, binder and fuel cell using the resin
InactiveUS7345135B2Increase productionOutput to deteriorateFinal product manufactureActive material electrodesConductive polymerPolymer network
The invention provides a crosslinkable aromatic resin having a protonic acid group and a crosslinkable group, suitable for electrolytic membranes and binders used in fuel cells, etc., and electrolytic polymer membranes, binders and fuel cells using the resin. The crosslinkable aromatic resin has a crosslinkable group, which is not derived from the protonic acid group and can form a polymer network without any elimination component. This resin exhibits excellent ion conductivity, heat resistance, water resistance, adhesion property and low methanol permeability. Preferably, the crosslinkable group is composed of a C1 to C10 alkyl group directly bonded to the aromatic ring and / or an alkylene group having 1 to 3 carbon atoms in the main chain in which at least one carbon atom directly bonded to the aromatic ring bonds to hydrogen, and a carbonyl group, or a carbon-carbon double bond or triple bond. The aromatic resins such as aromatic polyethers, aromatic polyamides, aromatic polyimides, aromatic polyamideimides, aromatic polyazoles, etc., which contain such a crosslinkable group, are preferred as the crosslinkable aromatic resins having a protonic acid group and a crosslinkable group.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Solid polyelectrolyte film, process for producing the same, and fuel cell
InactiveUS20090017358A1Low methanol permeabilityExcellent productivitySolid electrolytesFinal product manufacturePolymer chemistryPolyelectrolyte
A high-performance solid polyelectrolyte film is provided which is produced by the radiation-induced graft polymerization method without causing solution gelation and which is excellent in mechanical strength, chemical stability, and dimensional stability and reduced in methanol permeability. According to the present invention, the solid polyelectrolyte film is produced by graft-polymerizing either a polymerizable monomer having an alkoxysilyl group alone or the polymerizable monomer having an alkoxysilyl group and another polymerizable monomer with a resin film which has been irradiated with a radiation, followed by hydrolyzing the alkoxysilyl groups to conduct dehydrating condensation. In addition, this solid polyelectrolyte film is disposed between a fuel electrode and an air electrode to fabricate a fuel cell.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM CO LTD
Composite electrolyte with crosslinking agents
InactiveUS20050048341A1Improve fuel cell performanceGood chemical stabilitySolid electrolytesIon-exchanger regenerationFuel cellsComposite electrolyte
A covalent crosslinking of ion-conducting materials via sulfonic acid groups can be applied to various low cost electrolyte membrane base materials for improved fuel cell performance metrics relative to such base material. This proposed approach is due, in part, to the observation that many aromatic and aliphatic polymer materials have significant potential as proton exchange membranes if a modification can increase their physical and chemical stabilities without sacrificing electrochemical performance or significantly increasing the material and production costs.
Owner:HOKU SCI
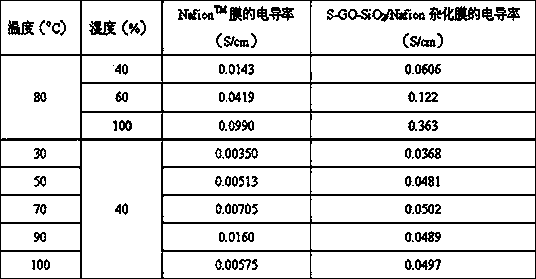
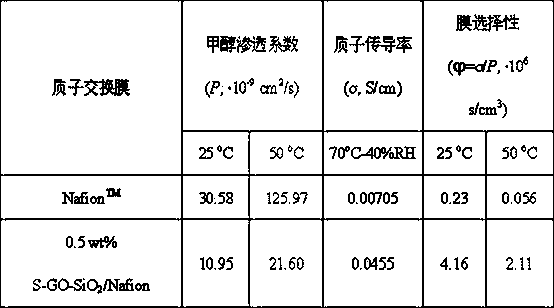
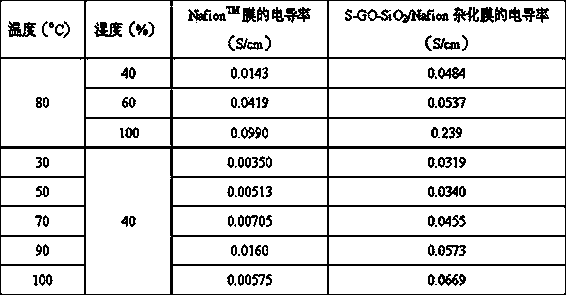
Sulfonated oxidized graphene-silicon dioxide composition/polymer hybridized proton exchange membrane and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103474681ALow methanol permeabilityGood dispersionFinal product manufactureSolid electrolyte fuel cellsPhysical chemistrySILICONE DIOXIDE
The invention belongs to the technical field of membranes, and specifically relates to a sulfonated oxidized graphene-silicon dioxide composition / polymer hybridized proton exchange membrane and a preparation method thereof. According to the invention, a sulfonated oxidized graphene-silicon dioxide composition is uniformly dispersed in a polymer matrix, and the proton conductivity of the sulfonated oxidized graphene-silicon dioxide composition / polymer hybridized proton exchange membrane prepared by the method is extremely improved compared with a pure polymer proton exchange membrane, and particularly, the proton conductivity is exponentially improved or even improved to an order of magnitudes under a high temperature environment and / or a low humidity environment. Meanwhile, even in the severe condition of high temperature and / or high methanol concentration, the methanol permeability is further greatly reduced, namely, the sulfonated oxidized graphene-silicon dioxide composition / polymer hybridized proton exchange membrane prepared by the method has extremely excellent selectivity. In addition, the method provided by the invention is simple in operational process, mild in preparation condition, lower in production cost and easy for massive and scaled production, and has a good industrial production basis and a wide application prospect.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Solid polymer electrolyte membrane and process for producing the same, and fuel cell
InactiveUS20060228609A1Improve ionic conductivitySmall methanol permeabilitySolid electrolytesIon-exchanger regenerationFuel cellsProton
The present invention relates to a solid polymer electrolyte membrane having both of a higher proton conductivity and a smaller methanol permeability, which can be produced by conducting a graft polymerization of a fluororesin thin membrane irradiated with a radiation with a monofunctional monomer and again irradiating the resulting film with a radiation, followed by conducting a graft polymerization thereof with a polyfunctional monomer; and a high-performance fuel cell comprising the solid polymer electrolyte membrane, a fuel electrode and an air electrode, said solid polymer electrolyte membrane being disposed between the fuel electrode and the air electrode.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Acid-base proton conducting polymer blend membrane
InactiveUS7534515B2Improve abilitiesReduced mechanical propertiesSolid electrolytesIon-exchanger regenerationConductive polymerProton
An acid-base proton conducting polymer blend membrane is provided. The acid-base proton conducting polymer blend membrane comprises a first acidic polymer having acidic subunits, a second basic polymer having basic subunits, and a third polymer containing one or more functional units for improving membrane conductivity, flexibility, water remaining ability, dimension stability, and methanol crossover. In one embodiment, the acid-base polymer blend membrane of the present invention comprises a first acidic polymer having acidic subunits, a second basic polymer having basic subunits, wherein at least one of the first acidic and second basic polymer comprises one or more functional units to improve the properties of the membrane. The functional units include hydrophilic units, methanol blocking units, methanol blocking units, dimensional stabilizer units, and flexible units.
Owner:POLYFUEL INC
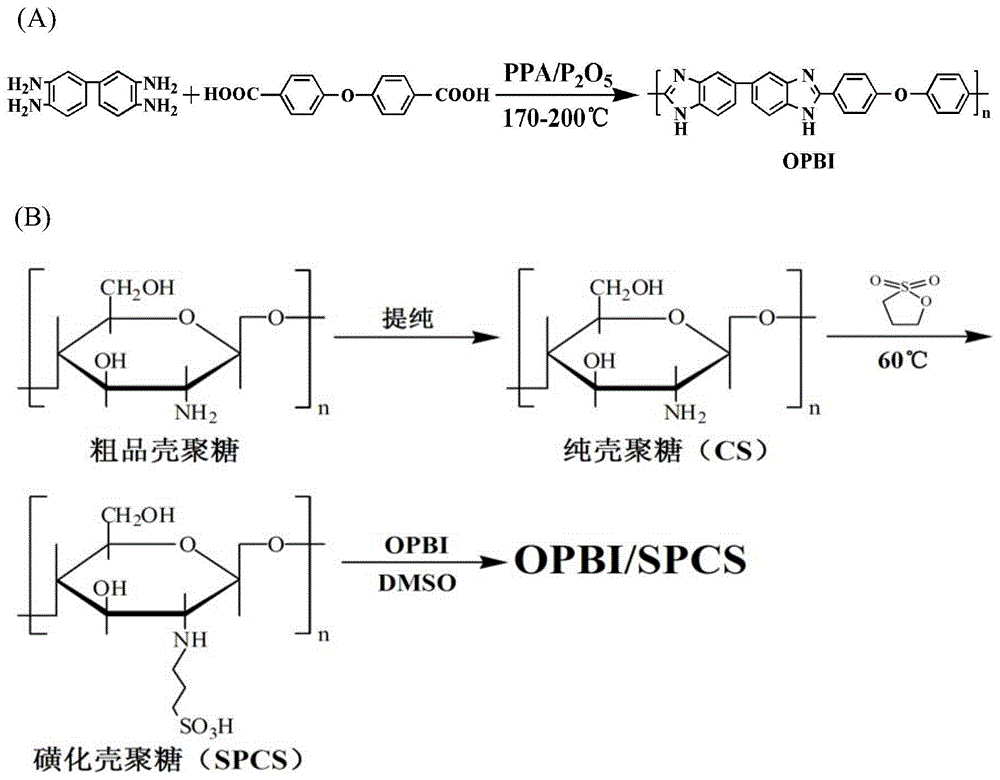
Preparation method of chitosan modification-polymer composite membrane
InactiveCN103601818AGood compatibilityImprove water retentionSolid electrolyte fuel cellsPolymer scienceMethanol fuel
The invention discloses a polybenzimidazole / sulfonated chitosan composite proton exchange membrane for a methanol fuel cell and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the steps of preparation of polybenzimidazole and sulfonated chitosan, preparation of composite dispersing liquid, solution casting and membrane formation and the like; the preparation process is simple and easy to control. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the prepared polybenzimidazole / sulfonated chitosan composite proton exchange membrane has relatively low methanol permeability and relatively high proton conductivity.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV +1
Curable resin composition for fuel cell electrolyte film and electrolyte film, process for producing the same, electrolyte film/electrode assembly, and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20070160888A1Reduce thicknessImprove ionic conductivityElectrolyte holding meansSolid electrolytesOligomerFuel cells
A curable resin composition for fuel cell electrolyte films characterized by comprising (1) 100 parts by mass of a monomer having at least one ethylenically unsaturated group per molecule and having, per molecule, either at least one, tonically conductive group or at least one precursor group capable of giving an tonically conductive group through a chemical reaction, (2) 10-400 parts by mass of an oligomer which has, per molecule, at least two reactive groups copolymerizable with the ethylenically unsaturated group of the ingredient (1) and has a number-average molecular weight of 400 or higher, (3) 10-400 parts by mass of a fluororesin, and (4) 0-2,000 parts by mass of a solvent.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Method of lowering permeability of proton exchange film methy alcohol contg fluorine sulfonic acid
InactiveCN1601790AAssembled preciselyHigh alcohol inhibition efficiencyPrimary cell electrodesFuel cell detailsPhotochemistryPolymer
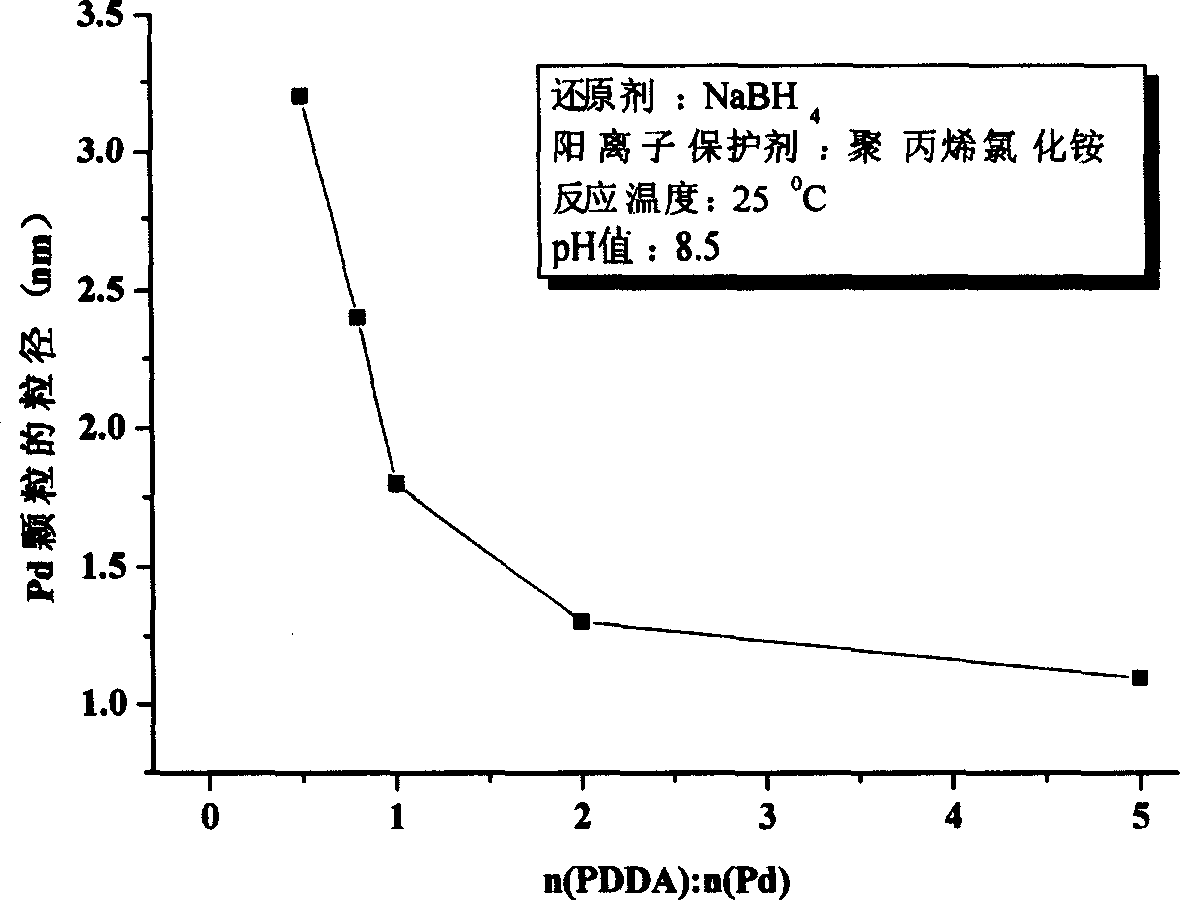
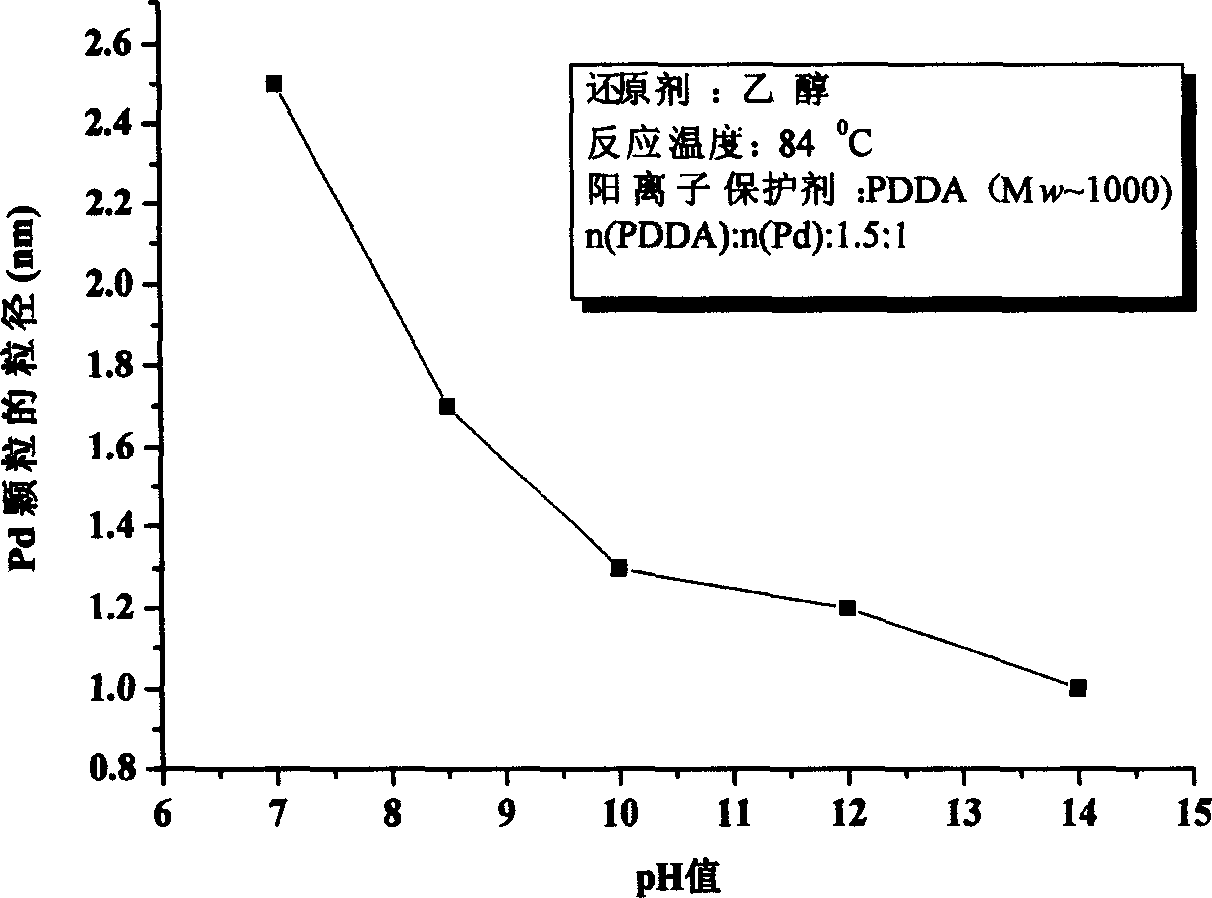
The method includes steps: first, positive ionized Nano Pd granules is synthesized from Pd salt deoxidized in aqueous solution of cation polymer in ammonium class and reducing agent; then, fluorosulfuric acid type proton exchange membrane is dipped in water decentralization liquid of positive ionized Nano Pd granules; thus, Pd granules are static self-assembled to exit and entrance of sulfonic acid radical group in methanol infiltration channels formed on surface of proton exchange membrane so as to reduce penetrability of methanol to membrane. Advantages are: less loading noble metal Pd, and no inference on proton conducting power basically.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) modified perfluorosulfonate proton exchange membrane and preparation method thereof
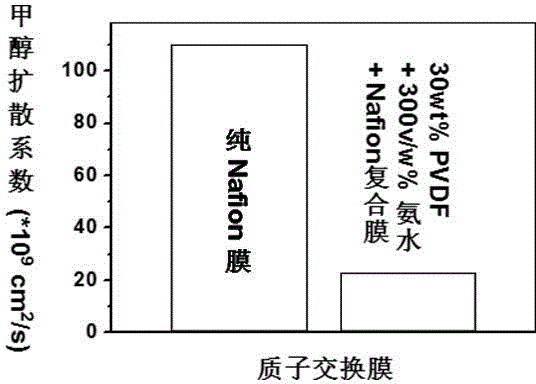
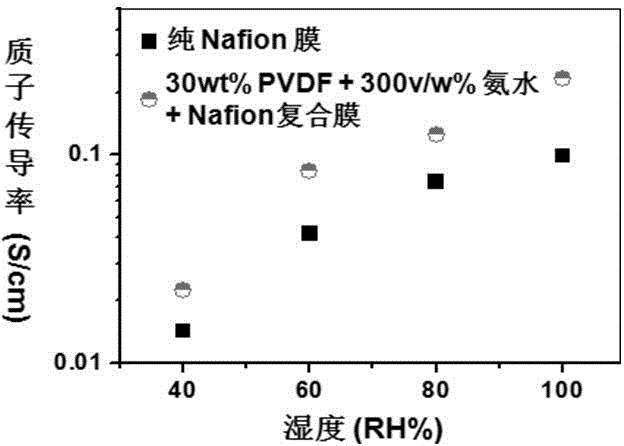
InactiveCN104558649ALow Methanol PermeabilityReduce manufacturing costPolyvinylidene fluorideChemistry
The invention belongs to the technical field of membranes and particularly relates to a PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) modified perfluorosulfonate proton exchange membrane and a preparation method thereof. PVDF is compounded with a perfluorosulfonate proton exchange membrane uniformly through the crosslinking of ammonia to prepare the PVDF modified perfluorosulfonate proton exchange membrane. The membrane permeability of the obtained PVDF modified perfluorosulfonate proton exchange membrane is reduced greatly compared with that of the perfluorosulfonate proton exchange membrane, and the membrane permeability of the PVDF modified perfluorosulfonate proton exchange membrane is reduced manyfold under the harsh conditions of high temperature and / or high concentration of methanol. In addition, the proton conductivity of the PVDF modified perfluorosulfonate proton exchange membrane is increased slightly under the same condition, and the mechanical stability and the dimensional stability of the compound proton exchange membrane are improved greatly. The preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple operation process, mild preparation condition and extremely low production cost, is suitable for batch production and scale production and has good industrial production basis and broad application prospect.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Low-swelling sulfonation polyimide proton exchanging membrane and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101343360AEnhance high temperature swelling stabilityLow methanol permeabilitySolid electrolyte fuel cellsDiamineChemistry
The invention relates to a low-swelling sulfonated polyimide proton exchange membrane and the preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the low-swelling sulphonation polyimide proton exchange membrane adopts the steps that novel diamine monomer with terminal sulfonic acid alkyl branched chain is obtained through friedel-acrafts acylation reaction, polycondensing and ether becoming reaction and sulfurous acid displacing reaction, then the novel diamine monomer and aromatic dianhydride monomer generate reaction, polyimide copolymer with sulfonic acid alkyl branched chain is obtained and dissolved in N-methyl-2-ketoyrrolidine, finally the solution is poured on a glass flat plate and coated in a flow-casting way, the vacuum drying operation is performed, and the low-swelling sulfonated polyimide proton exchange membrane is obtained. The low-swelling sulfonated polyimide proton exchange membrane obtained by utilizing the preparation method has the advantages of high proton conductivity and low methanol penetrability; simultaneously, good low-swelling property is provided, therefore, the low-swelling sulfonated polyimide proton exchange membrane has extensive application prospect in the methanol fuel cell field.
Owner:SHANGHAI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Preparation method of polymer matrix proton exchange membrane (PEM) with cross-linked structure
ActiveCN102775628AImprove performanceEffective graftingCell component detailsFuel cell detailsCross-linkPermeability coefficient
The invention relates to a preparation method of a polymer matrix proton exchange membrane (PEM) with a cross-linked structure, belonging to the field of battery electrolyte materials. The PEM is prepared by carrying out mechanical blending dispersion on matrix polymer material, unsaturated metal organic sulfonate, peroxide and auxiliary crosslinking agent, carrying out reaction in situ at the temperature of 140-200 DEG C, treating the product of the reaction by deionized water and sulfuric acid solution, and drying; and the PEM comprises the components in parts by weight: (1) 100 parts of matrix polymer material, (2) 20-150 parts of unsaturated metal organic sulfonate, (3) 1-20 parts of peroxide and (4) 0-5 parts of auxiliary crosslinking agent. In the molding process, organic solvent is not needed; and the preparation method is simple, high in efficiency, environment-friendly and low in cost. The prepared PEM has the proton conductivity approximate to Nafion (reaching up to the order of magnitude of 10<-2> / cm) and the methanol permeability coefficient far less than Nafion at the temperature of 20-80 DEG C, thus meeting the using requirement of a direct methanoi fuel cell.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Branched sulfonated polyaryletherketone containing benzoxazole ring side group, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103642032AGood dimensional stabilityLow methanol permeabilitySolid electrolyte fuel cellsFuel cell detailsOxidation stabilityMethanol
Belonging to the field of high polymer materials, the invention relates to branched sulfonated polyaryletherketone containing a benzoxazole ring side group, a preparation method and application thereof. The method includes: firstly conducting a nucleophilic polycondensation reaction, taking trifunctional 1, 3, 5-trifluorobenzene carbonylbenzene as a branching unit to prepare allyl-containing branched sulfonated polyaryletherketone of different sulfonation degrees and different branching degrees, and then introducing a benzoxazole ring into the side group position of the polymer. The branched sulfonated polyaryletherketone polymer film containing the benzoxazole ring side group provided by the invention has good dimensional stability, low methanol permeability, high oxidation stability and good proton conductivity, thus being able to satisfy the requirements of a fuel cell proton exchange membrane.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
High-temperature proton exchange membrane and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a preparation method of a high-temperature proton exchange membrane. The preparation method comprises the following steps of 1) preparing a bis-hydroxyethyl sulfone-4, 5-dicarboxyl imidazole polycondensate; 2) performing modification on the polycondensate; 3) carrying out casting and film forming; and 4) performing phosphoric acid doping. The invention also discloses the high-temperature proton exchange membrane prepared by the preparation method, and a proton exchange membrane fuel cell which takes the high-temperature proton exchange membrane as a polyelectrolyte membrane. Compared with the high-temperature proton exchange membrane in the prior art, the high-temperature proton exchange membrane prepared in the invention has higher proton conductivity, lower cost, lower methyl alcohol permeability, higher mechanical property, higher stability and high temperature resistance performance, and higher safety and environmental protection property in use.
Owner:福建永同丰超低能耗建筑研究院有限公司
Crosslinked polymer electrolyte and method for producing same
InactiveUS8211558B2Good water and solvent resistanceImprove heat resistanceSolid electrolytesCation exchanger materialsIon exchangeSolvent
There are provided a new crosslinked polymer electrolyte excellent in water resistance and solvent resistance, high in heat resistance, inexpensive and low in methanol permeability, and suitable for the proton conductive membrane of a fuel cell, by means of the crosslinked polymer electrolyte obtained by the following (1) or (2), and its production method.(1) A compound having two or three or more reactive groups is reacted with a polymer electrolyte.(2) A compound having two or three or more reactive groups is reacted with a polymer to obtain a crosslinked polymer and then an ion exchange group is introduced into the resultant polymer.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Crosslinked proton exchange membrane with specific oriented structure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102660120AImprove stabilityAvoid prone to phase separation problemsSolid electrolyte fuel cellsCross-linkIon-exchange resin
The invention discloses a crosslinked proton exchange membrane with a specific oriented structure and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the field of fuel cell polymer electrolyte materials. The crosslinked proton exchange membrane consists of an ion exchange resin containing a sulfonic acid group, wherein the ion exchange resin containing the sulfonic acid group is a sulfonated non-fluorohydrocarbon polymer with a proton exchange function. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: dissolving the ion exchange resin containing the sulfonic acid group into a solvent to prepare a solution; performing curtain coating and membrane forming; stretching the prepared membrane under the condition that the solvent is not removed completely; after stretching is completed, maintaining external force to keep the membrane in a stretching state; drying the stretched membrane to remove residual solvent; performing heat cross-linking in a vacuum drying oven; cooling at the room temperature; and removing external force. The membrane material has high proton conductivity and low methanol permeability, and can be taken as a polymer electrolyte material for being directly applied to methanol fuel cells.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Free-standing composite proton conducting film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101789278AReduce penetrationGood dimensional stabilityConductive layers on insulating-supportsLayered productsFuel cellsProton
The invention relates to a free-standing composite proton conducting film and a preparation method thereof in the technical field of a fuel cell. The free-standing composite proton conducting film is formed by overlapping an organic proton conducting film layer and an inorganic proton conducting film layer, wherein, the inorganic proton conducting film layer is metallic oxide or phosphorus-containing metallic oxide with proton conducting capacity, and the organic proton conducting film layer is polymer with the proton conducting capacity. The free-standing composite proton conducting film is obtained by dissolving a sacrificial layer, the problems of no flexibility of the inorganic proton conducting film layer and high methanol permeability of the organic proton conducting film layer are overcome, and the free-standing composite proton conducting film with proton conducting capacity and very low methanol permeability is obtained, so as to solve the technical problems in the prior art.
Owner:安徽元隽氢能源研究所有限公司
Semi-ipn (interpenetrating polymer network) proton exchange membrane and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103724643AEasy transferImprove proton conductivityFuel cell detailsGlycol methacrylateInterpenetrating polymer network
The invention belongs to the field of membrane science, and particularly relates to a semi-ipn (interpenetrating polymer network) proton exchange membrane and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises steps of dissolving sulfoacid polymer, 2-acrylamide-2-methyl propane sulfonic acid, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate and diphenyl ketone into polar solvent, heating the obtained solution at certain temperature so as to volatilize the solvent to obtain gel state membrane when a certain content of residual solvent is left, irradiating the obtained gel state membrane by an ultraviolet lamp for a certain time, soaking by dilute sulphuric acid and water so as to remove all left solvent, converting all sulfoacid group in the membrane into acid so as to obtain the semi-ipn proton exchange membrane. The proton exchange membrane material prepared by the method has high proton conductivity, low methanol permeability and reliable dimensional stability, and can be used in direct-methanol fuel cells.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Proton conductivity polymer, catalyst compsn.electrolytic memberane for fuel cell and fuel cell
InactiveCN1601793ALow methanol permeabilityReduce permeabilityNon-metal conductorsCell electrodesFuel cellsProton
The present invention is to provide an electrolyte membrane for fuel cell of low fuel permeability and high proton conductivity and to provide a fuel cell comprising the electrolyte membrane. According to the present invention, a polymer membrane including repeating unit of five-membered heterocyclic rings is used as an electrolyte membrane of the fuel cell. The electrolyte membrane has high proton conductivity with free from moves of the fuel or water when the proton conducts in the electrolyte membrane.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
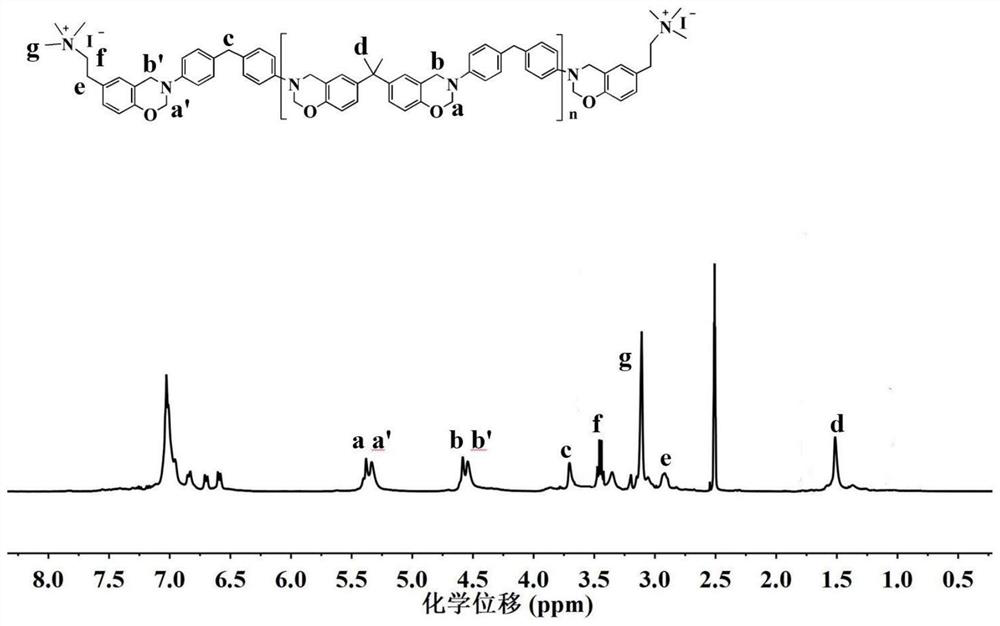
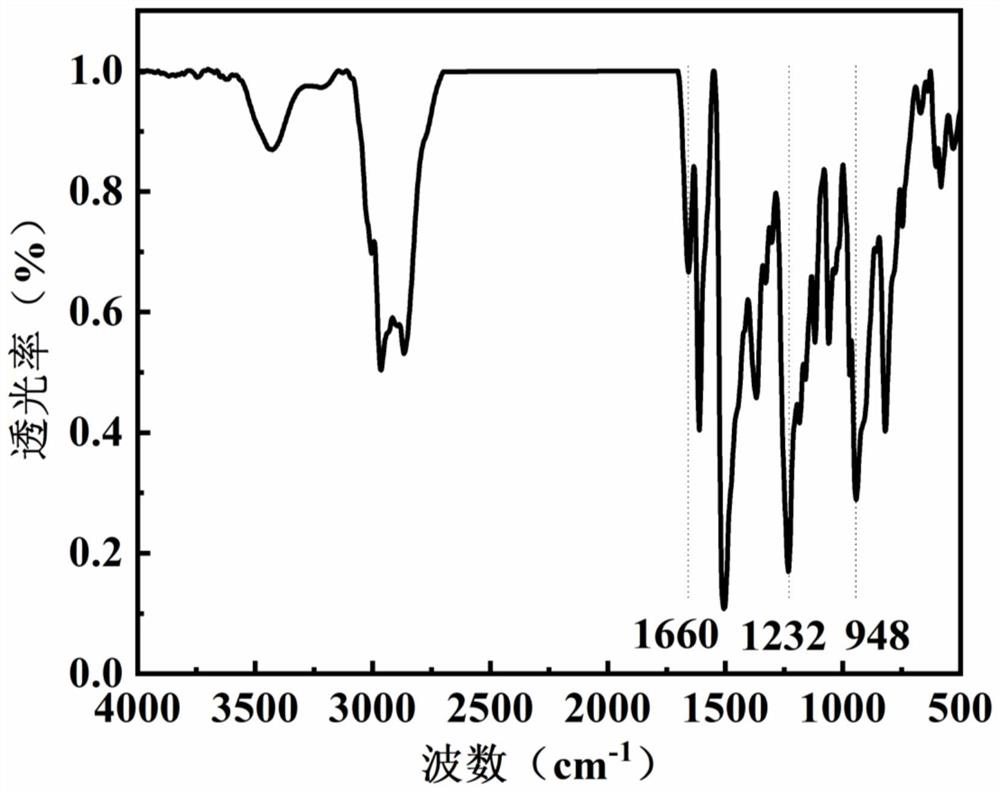
Benzoxazine resin containing quaternary ammonium group and preparation method and application of benzoxazine resin
The invention relates to benzoxazine resin containing a quaternary ammonium group and a preparation method and application of the benzoxazine resin. A main chain type benzoxazine containing the quaternary ammonium group is prepared from dihydric phenol, diamine, monohydric phenol and paraformaldehyde through Mannich reaction and quaternization reaction. And then thermocuring is performed to obtainthe polybenzoxazine film containing the quaternary ammonium group. The main chain type benzoxazine resin containing the quaternary ammonium group is designed and synthesized, so that the quaternary ammonium group can be simply and efficiently introduced into the benzoxazine resin, and the cross-linked polybenzoxazine film is obtained by taking the benzoxazine resin as a precursor. The membrane not only has good membrane-forming property, excellent alcohol resistance and thermal property, but also is low in cost, and is a powerful candidate in the field of fuel cells.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com