Patents
Literature
35 results about "Pingyangmycin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pingyangmycin (also known as bleomycin A₅) is an antitumor glycopeptide antibiotic belonging to the bleomycin family, which is produced by Streptomyces verticillus var. pingyangensis n.sp., a variety of Streptomyces verticillus. It was discovered in 1969 at Pingyang County of Zhejiang Province in China, and was brought into clinical use in 1978.
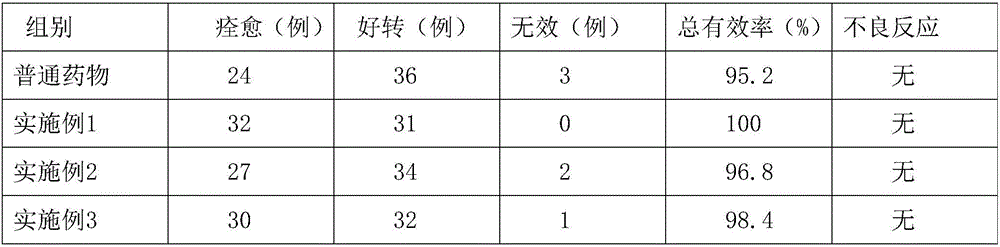
Pharmaceutical composition for treating embolism and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101670095AIncrease concentrationReduce concentrationSurgerySaccharide peptide ingredientsEmbolization AgentDouble bond
The invention provides a pharmaceutical composition for treating embolism and a preparation method thereof, the pharmaceutical composition comprises a hydroxyl-contained biocompatible polymer materialand a monomer containing unsaturated double bonds and anion groups, as well as a polymer generated by polymerization reaction of an optional vinyl monomer, wherein the polymerization is initiated through free radicles, and bleomycin or pingyangmycin is combined on the anion groups of the generated polymer. The preparation method combines the bleomycin or the pingyangmycin on a carrier of the polymer, thereby being capable of fully playing the dual effects of an anti-tumor antibiotic and a hardening agent owned by the bleomycin or the pingyangmycin during the embolism treatment. The anion partof the polymer can be properly combined with the bleomycin or the pingyangmycin which is rich in amino groups, thereby not only realizing the higher drug loading, but also leading the drug in an emboliaztion agent to be exchanged by cation in human body, and further realizing the slow release. In addition, the embolic carrier of the polymer has the advantages of simple prepration technology andlow cost, thereby being applicable to large-scale industrial production.
Owner:HYGEA MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Method for directionally screening salt-tolerant body through peanut in vitro mutagenesis
ActiveCN103070076AImprove germination rateHigh polymorphismHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBone Alkaline PhosphataseGermplasm
The invention provides a method for directionally screening a salt-tolerant body through peanut in vitro mutagenesis. The method mainly comprises the following steps: sterilizing the surface of peanut embryo; separating a leaflet, inoculating into a somatic embryo induction and mutagenesis medium added with 2,4-D and pingyangmycin, and performing mutagenesis culture treatment; and transferring a survival explant on which a somatic embryo is formed to a somatic embryo germination and screening culture medium added with bone alkaline phosphatase (BAP) and NaCl, and directionally screening the salt-tolerant body. The salt-tolerant body is directionally screened by combining in vitro mutagenesis and tissue culture, and plenty of manpower, materials and financial resources can be saved; and the salt-tolerant body is regenerated in an embryogenesis way, an somatic embryo is derived from a cell, and the chimerism of the salt-tolerant body can be avoided. A peanut mature seed is taken as a mutagenic material and cannot be limited by seasons, the operation is convenient, a novel salt-tolerant peanut germplasm can be created, the peanut genetic basis is enriched, and the difficulty that new high-yield salt-tolerant varieties are difficult to breed due to the lack of high salt-tolerant germplasm resources in peanut cultispecies is overcome.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Preparation method of ointment for treating infantile hemangioma
InactiveCN106729614AAvoid bleedingPromote circulationOrganic active ingredientsAerosol deliveryVitamin CVitamin B12
The invention relates to a preparation method of an ointment for treating infantile hemangioma. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding timolol hydrogenmaleate, propranolole hydrochloride, tacrolimus, pingyangmycin, vitamin C, vitamin E and vitamin B12 to water according to certain mass ratio, heating to 30-85 DEG C of the temperature, adding a thickener, imiquimod and a wetting agent according to certain mass ratio after stirring and dissolving, and uniformly stirring, and preparing the ointment for treating the infantile hemangioma after cooling. The ointment for treating the infantile hemangioma is an external used medicine, particularly suitable for the infants inconvenient for taking medicines and injection.
Owner:刘腾
Sodium alginate microballoon vein suppository containing hemangioma-resisting medicant, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101536987AGood treatment effectReduce systemic side effectsSurgeryPharmaceutical product form changeEmbolization AgentBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a sodium alginate microballoon vein suppository containing hemangioma-resisting medicant, a preparation method and an application thereof. The sodium alginate microballoon vein suppository comprises carrier sodium alginate and hemangioma-resisting medicant; the sodium alginate covers the hemangioma-resisting medicant; the weight ratio of the sodium alginate to the hemangioma-resisting medicant is 5:1-60:1; and the hemangioma-resisting medicant is pingyangmycin, sodium morrhuate, carbamide or bleocin. The raw materials used in the invention have favorable mechanical strength, biocompatibility, biological degradability and stability, have no organic solvent, and are basically harmless to functions of hemopoietic system and immune system, thereby suppository can be industrially produced.
Owner:BEIJING SHENGYIYAO SCI & TECH DEV
Injection for curing angiomatous
InactiveCN101284127AOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDexamethasoneCurative effect
The invention relates to an injection for treating hemangioma, which is prepared from interferon, dexamethasone, adrenaline, lidocaine and water for injection. The preparation method comprises dissolving pingyangmycin (8 mg) into 2% lidocaine injection to reach volume of 3 ml; dissolving interferon (3,000,000 unit) into water for injection to reach volume of 3 ml; mixing diluted pingyangmycin (2 ml), diluted interferon (1 ml), dexamethasone (1 ml), adrenaline (0.5 ml), 2% lidocaine (2.5 ml) and water for injection (3 ml); and making into injection. The injection has good curative effect on hemangioma, convenient application, and no restriction to medical treatment condition.
Owner:广水市第一人民医院
Method for improving salt-tolerant properties of Brassicaceae crops
The invention provides a method for improving salt-tolerant properties of Brassicaceae crops, which comprises the following steps of: processing sterile seeds of the crops by using pingyangmycin and the like; performing NaCl stress screening for layer-upon-layer elimination during the germination period of the seeds, the isolated culture period of the stem apex and the induction period of rhizogenesis respectively; and after strains are obtained, performing extended propagation according to the strains, and adding the NaCl stress screening for one time after subculture every three times in the process of extended propagation to increase the obtaining frequency of the salt-tolerant strains of the crops and accelerate the process of the salt-tolerant breeding of the crops. The method is simple to implement and easy to master, the whole screening process is performed under the controlled condition of completely-consistent laboratory rooms, so that screening results are real and reliable, and the strains obtained by screening have high stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
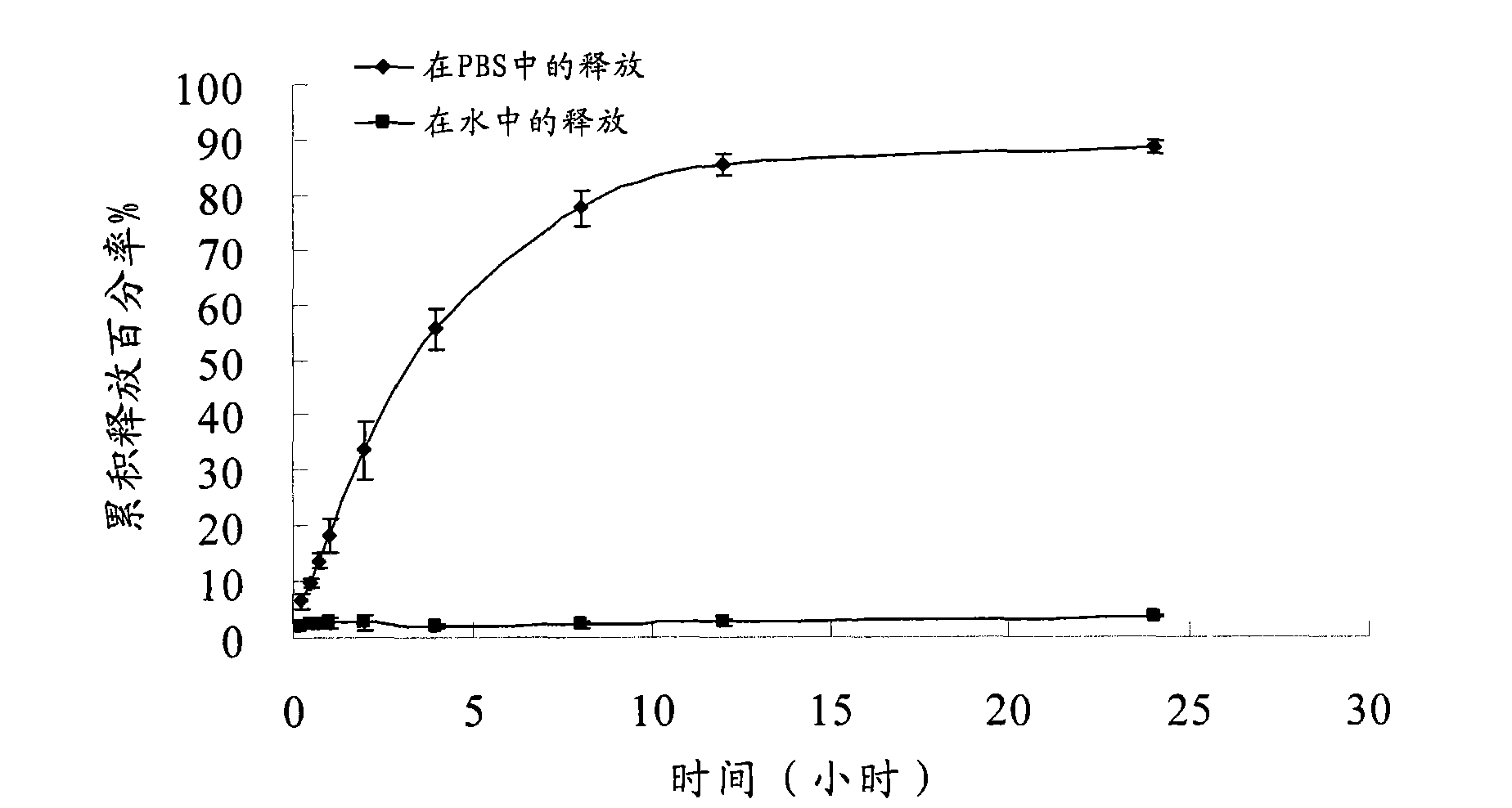
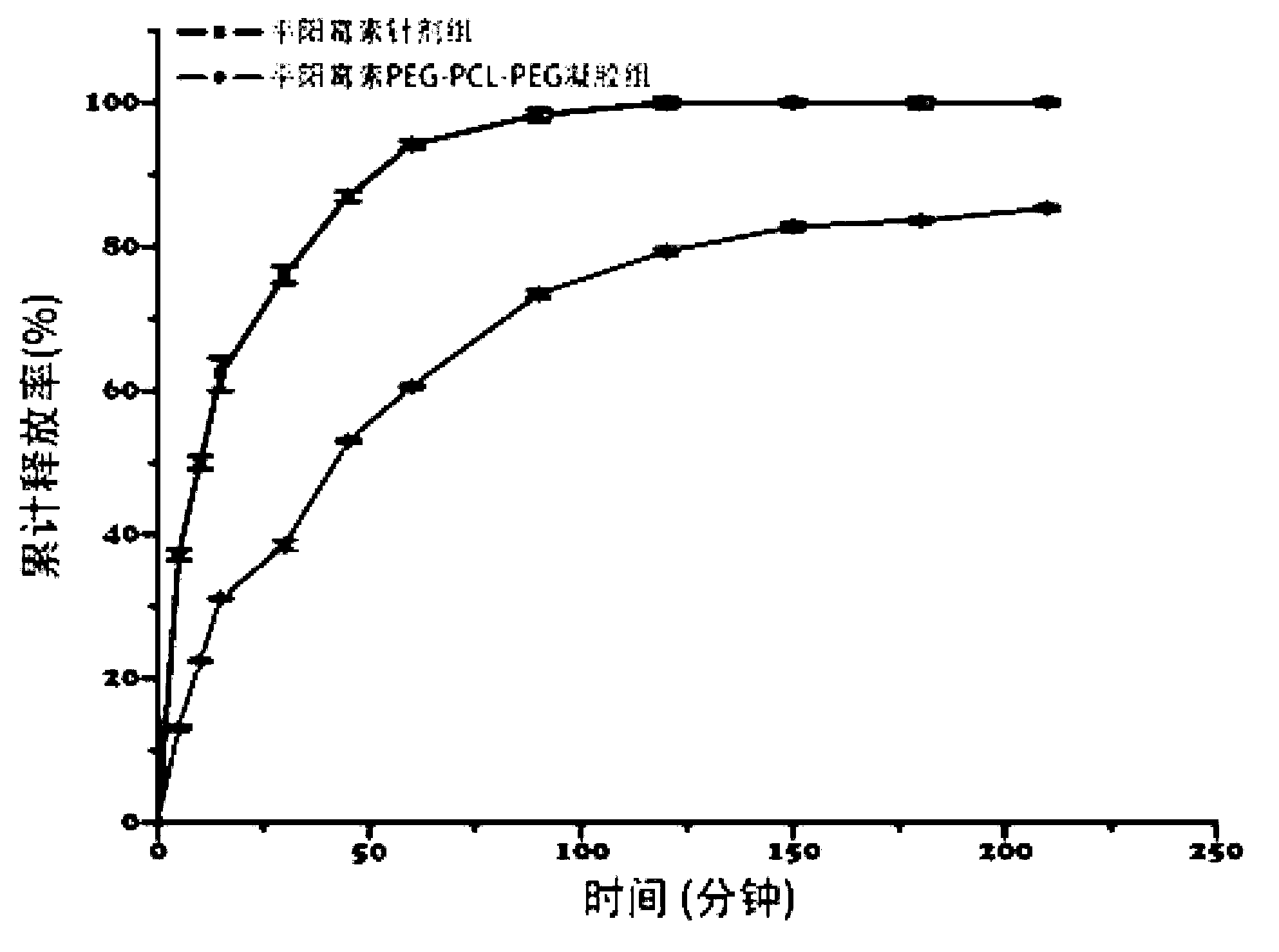
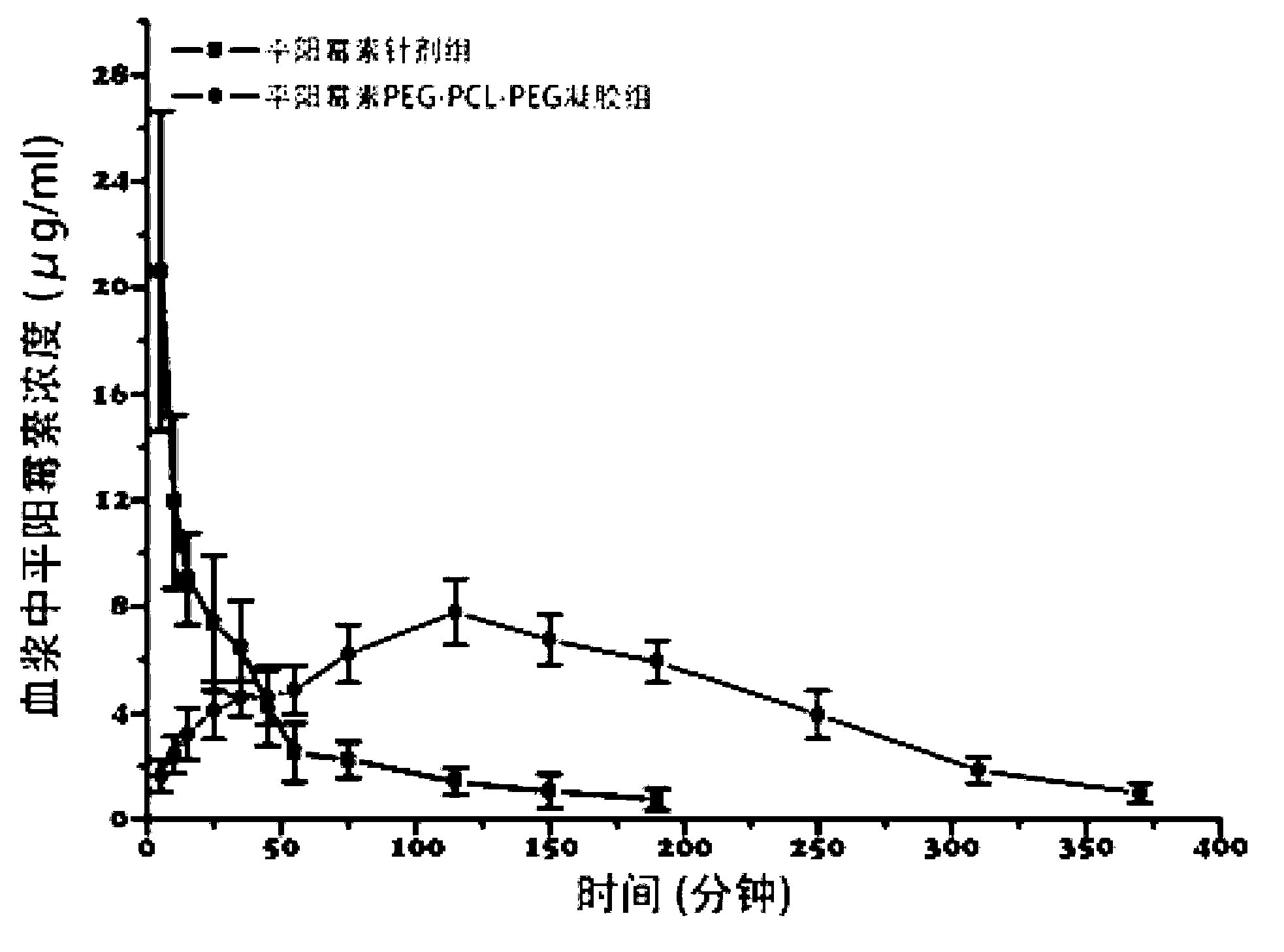
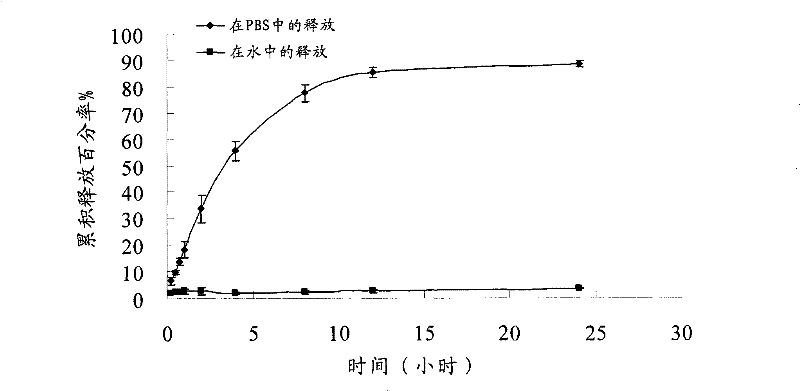
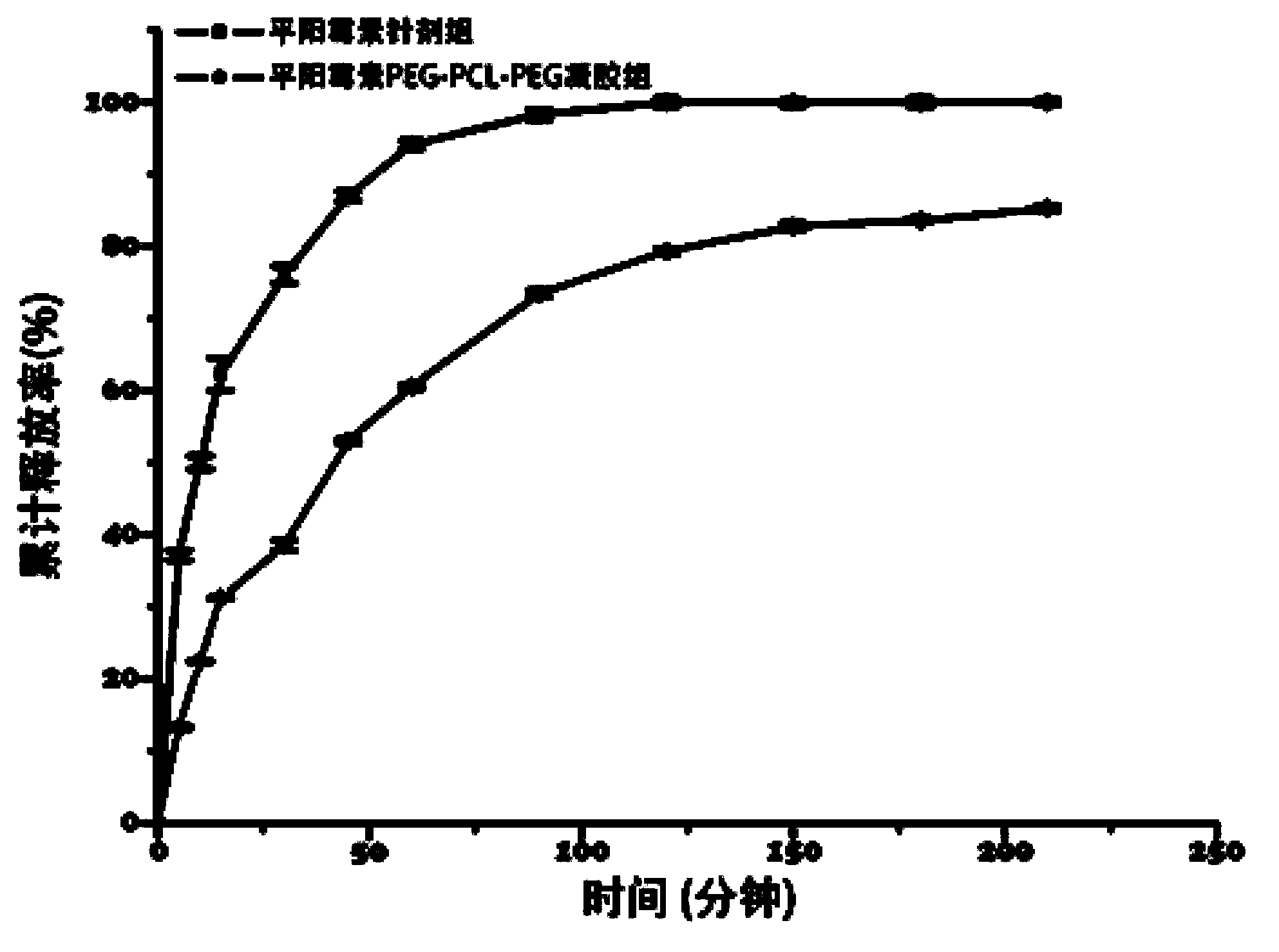
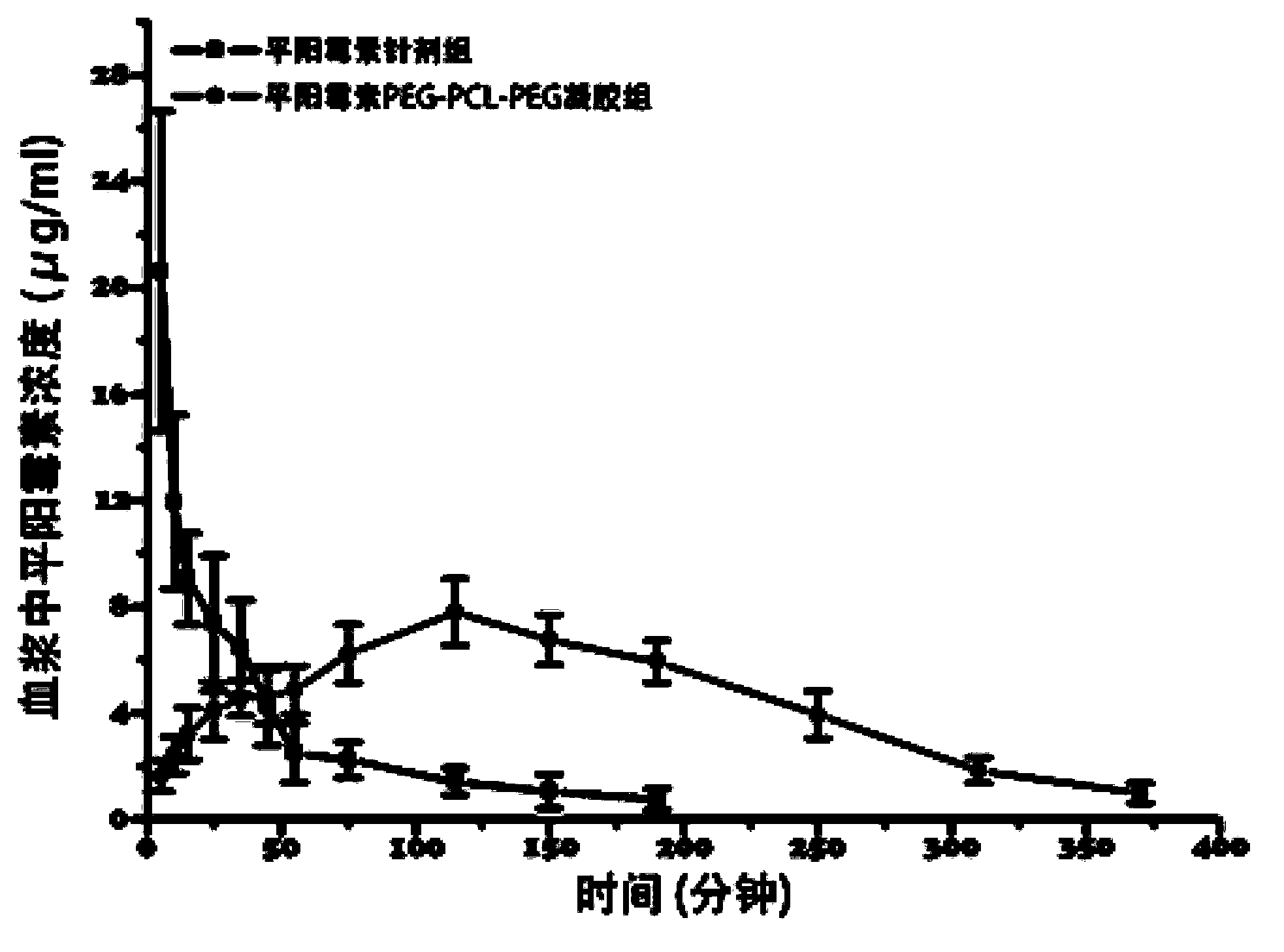
Pingyangmycin polyethylene glycol (PEG)-polycaprolactone (PCL)-polyethylene glycol (PEG) temperature-sensitive slow-release gel, as well as preparation method and application of same
ActiveCN102836418AExtended half-lifeExtension of timeAerosol deliveryOintment deliverySide effectHalf-life
The invention discloses a pingyangmycin polyethylene glycol (PEG)-polycaprolactone (PCL)-polyethylene glycol (PEG) temperature-sensitive slow-release gel, as well as a preparation method and the application of the gel. The Pingyangmycin PEG-PCL-PEG temperature-sensitive slow-release gel mainly consists of two parts comprising PEG (polyethylene glycol)-PCL (polycaprolactone)-PEG (polyethylene glycol) co-polymer and Pingyangmycin, is liquid at room temperature, and is solid gel under the in vivo 37 DEG C condition; the gel system has significant slow-release effect, thereby having functions in prolonging the half-life period and the acting time of the Pingyangmycin, reducing drug concentration in plasma, and reducing systemic toxic and side effects. The gel can be formed in situ after the medicine is injected in a high-flow-speed vessel, and then location embolism is realized, and so as to realize the, and muscularization and closing of muscle is caused, so that the sclerotherapy and the interventional therapy are combined effectively, the gel has excellent biocompatibility and degradability, is beneficial for treating hemangiomas, vascular malformations and cancers, particularly, a new selection is provided to the treatment of the vein malformation and partial malformation of cancers.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
External traditional Chinese medicinal composition for treating xerophthalmia and preparation method thereof
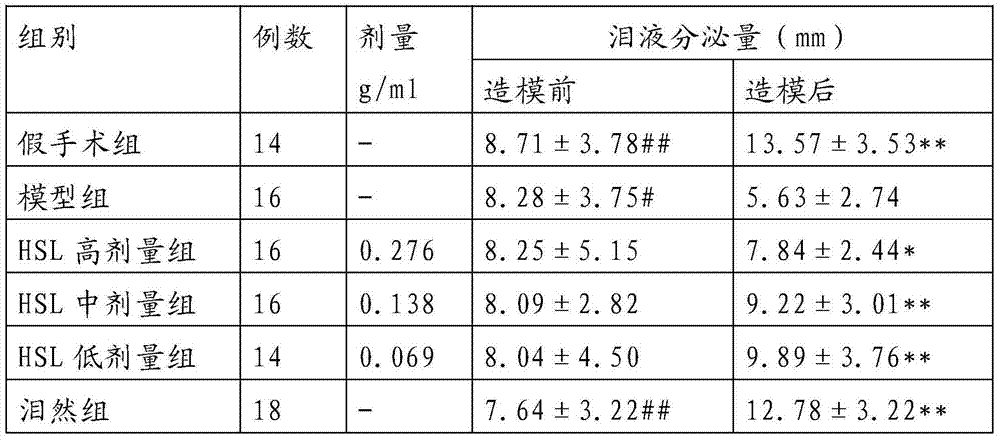
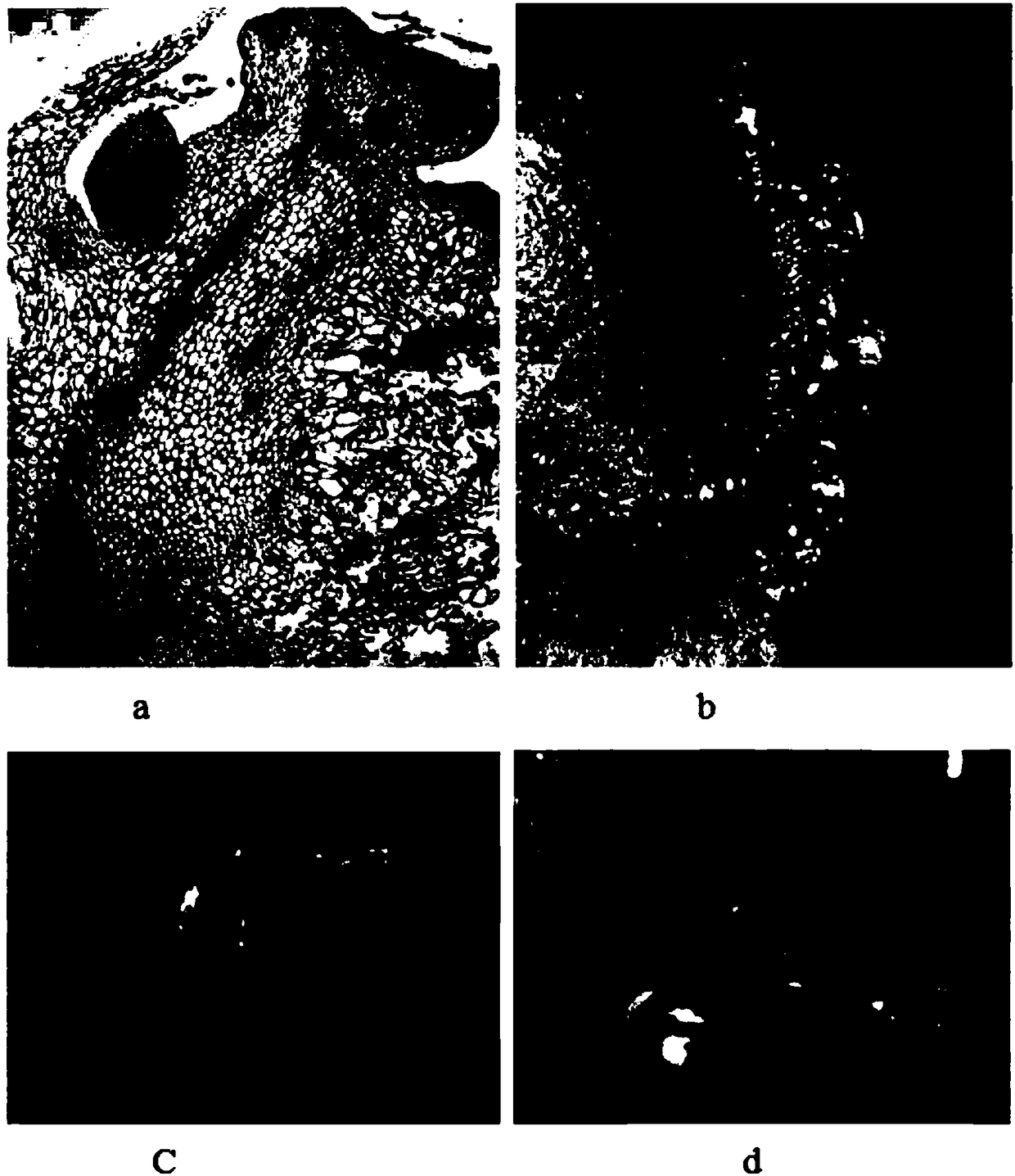
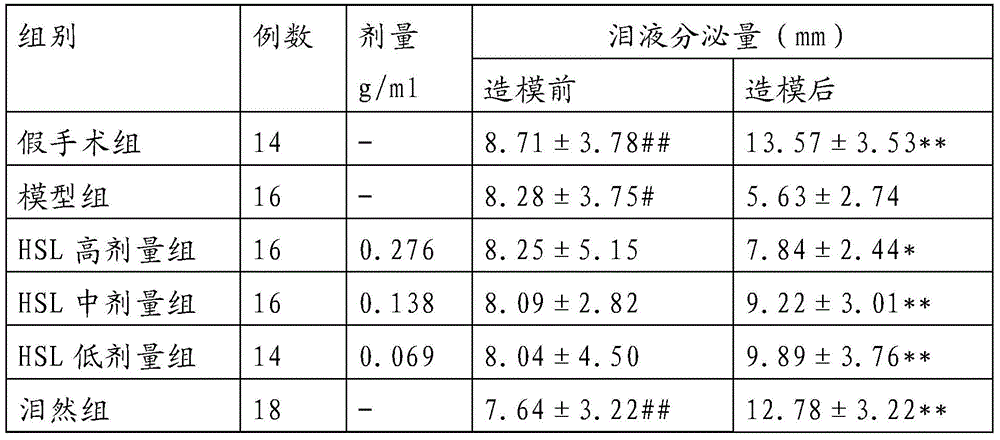
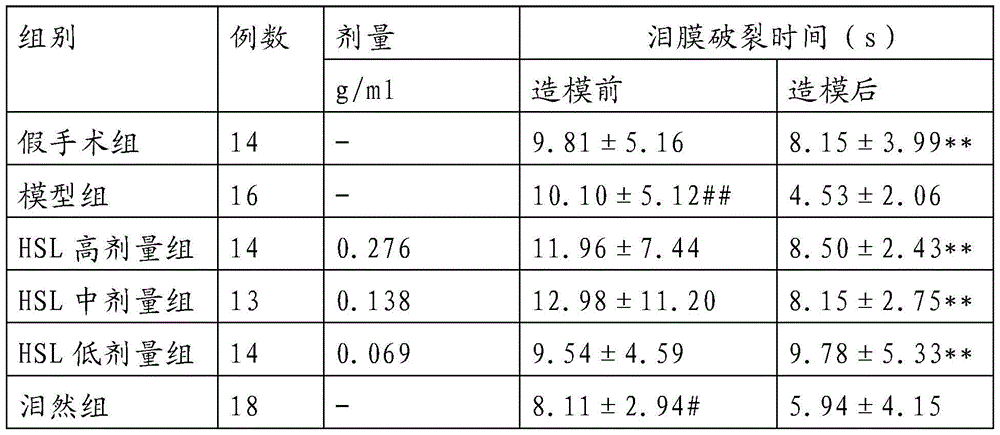
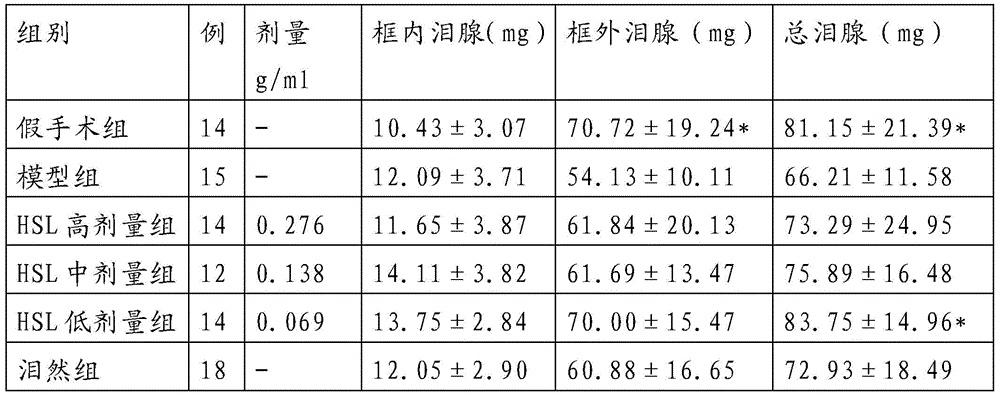
The invention provides an external traditional Chinese medicinal composition for treating xerophthalmia and a preparation method thereof. The external traditional Chinese medicinal composition for treating the xerophthalmia is prepared from the following raw materials: wolfberry, chrysanthemum, salviae miltiorrhizae, cortex phellodendri, pearl powder, borneol and menthol. The external traditional Chinese medicinal composition for treating the xerophthalmia has the advantages that pathological changes of lacrimal gland tissues of an experimental xerophthalmia mouse, lacrimal glands of which are damaged by injected pingyangmycin, in morphology can be obviously alleviated, quantity of tear fluid can be obviously increased, breakup time of a tear film is prolonged, and quantity of the tear fluid secreted by a normal domestic rabbit can be obviously increased.
Owner:陕西新视明医药生物科技有限公司
Method for cultivating high-oil peanut varieties
InactiveCN108353790AReduce pollutionReduce the number of operationsGraftingFabaceae cultivationHydroxyprolineGreenhouse
The invention provides a method for cultivating high-oil peanut varieties. The method mainly comprises the following steps: young peanut leaves with seedling age of 5-7 days are cultivated in an induction and mutagenesis medium with NAA, BAP and pingyangmycin for in-vitro mutagenesis culture; surviving explants are transferred to an adventitious bud differentiation and high-oil body directional screening medium supplemented with BAP and hydroxyproline for culture; obtained high-oil seedlings are transplanted to plastic greenhouses or high-temperature greenhouses after aseptic grafting, and normal seeds are obtained; progeny of the obtained high-oil bodies are bred with pedigree selection, and by combination with generation increasing in Hainan island and high-temperature greenhouses, 3 generations can be planted each year. The high-oil bodies are screened by in-vitro mutagenesis and in-vitro directional screening, and the problems of low mutagenesis frequency and incapability of directional breeding in conventional mutagenesis breeding are solved. The high-oil bodies are directionally screened and non-high-oil bodies are eliminated in the medium, and the problem of consumption of alarge quantity of manpower, material resources and financial resources in the identification of mutant progeny is solved.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Method for producing suppository for treating uterus adenomyosis
InactiveCN101015504ALow priceEasy to manufacturePharmaceutical product form changeSaccharide peptide ingredientsGelatin spongeEmbolization Agent
A preparation method of suppository for treating uterine adenomyosis mainly solves the problem of suppository material source and product cost. the preparation method comprises (1) cutting aseptic gelatin sponge into thin slices, overlaying, scissoring one end of the sponge into multiple filaments, scissoring into fine particle until to the other end of the sponge, packaging, sterilizing with oxirane, and standing for 2 weeks; (2) dissolving Pingyangmycin 24 mg in physiological saline for operation; and (3) inserting the conduit into one side of the uterine artery, putting the gelatin sponge into a 20mL disposable syringe, decimating the Pingyangmycin physiological saline solution repeatedly, and injecting with the conduit. The method has the advantages of easily-accessible raw materials, low cost, and high security.
Owner:赵传林 +4
Application of pingyangmycin combined with sodium hyaluronate in drug for treating lymphatic malformation
InactiveCN103330945AShort duration of actionGuaranteed specificitySaccharide peptide ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsLymphatic vesselLymphatic malformations
The invention discloses an application of pingyangmycin combined with sodium hyaluronate in a drug for treating lymphatic malformation, as well as a drug for treating lymphatic malformation, in particular to a drug for treating microcystic lymphatic malformation. According to the application, the pingyangmycin combined with the sodium hyaluronate is adopted and has better effects in the aspects of inhibiting human lymphatic malformation endothelial cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis while compared with pure pingyangmycin, wherein the molecular weight of the sodium hyaluronate is 600,000 Dalton-1,500,000 Dalton, and concentrations of the pingyangmycin and the sodium hyaluronate are 100 mu g / mL and 300 mu g / mL respectively.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV QILU HOSPITAL
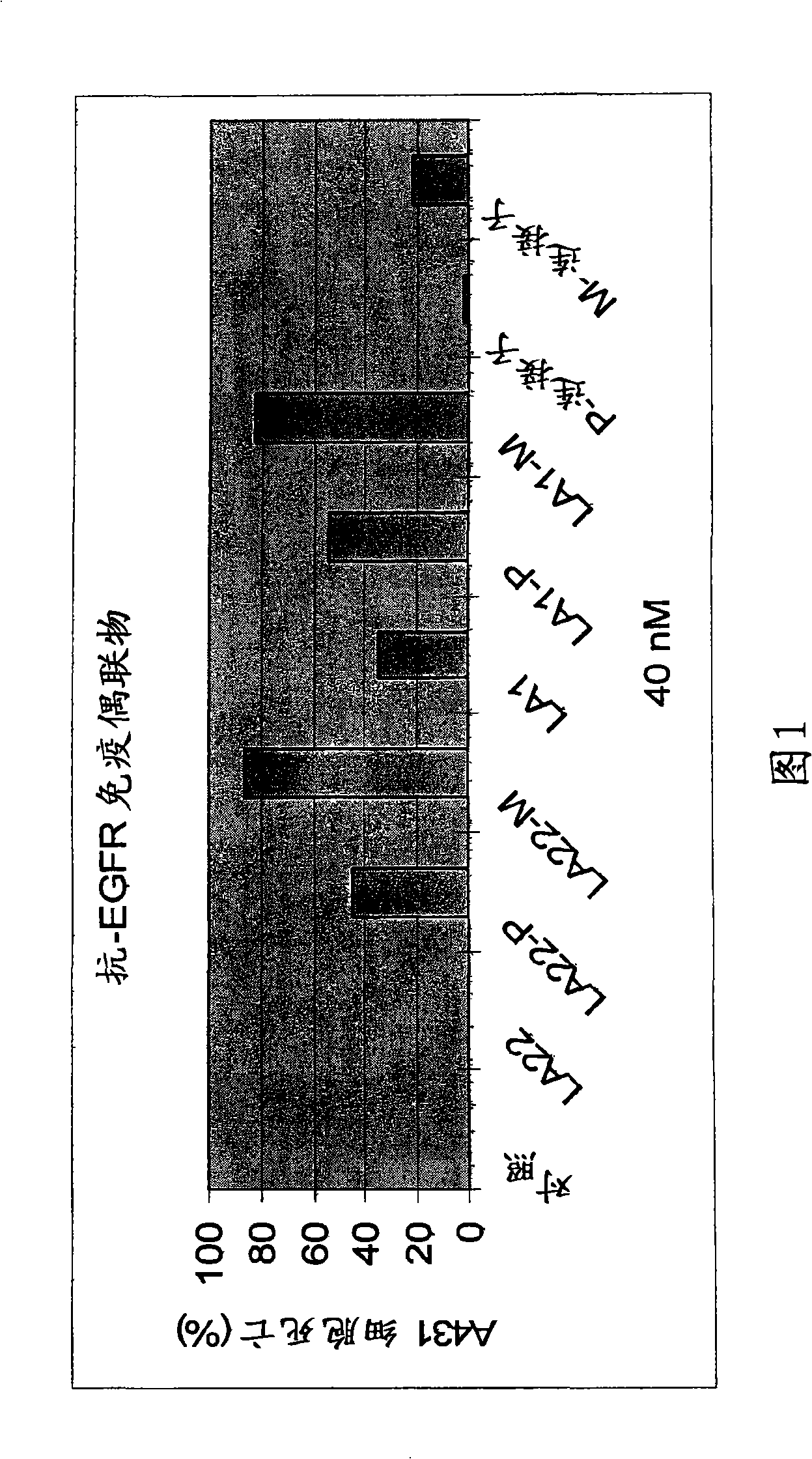
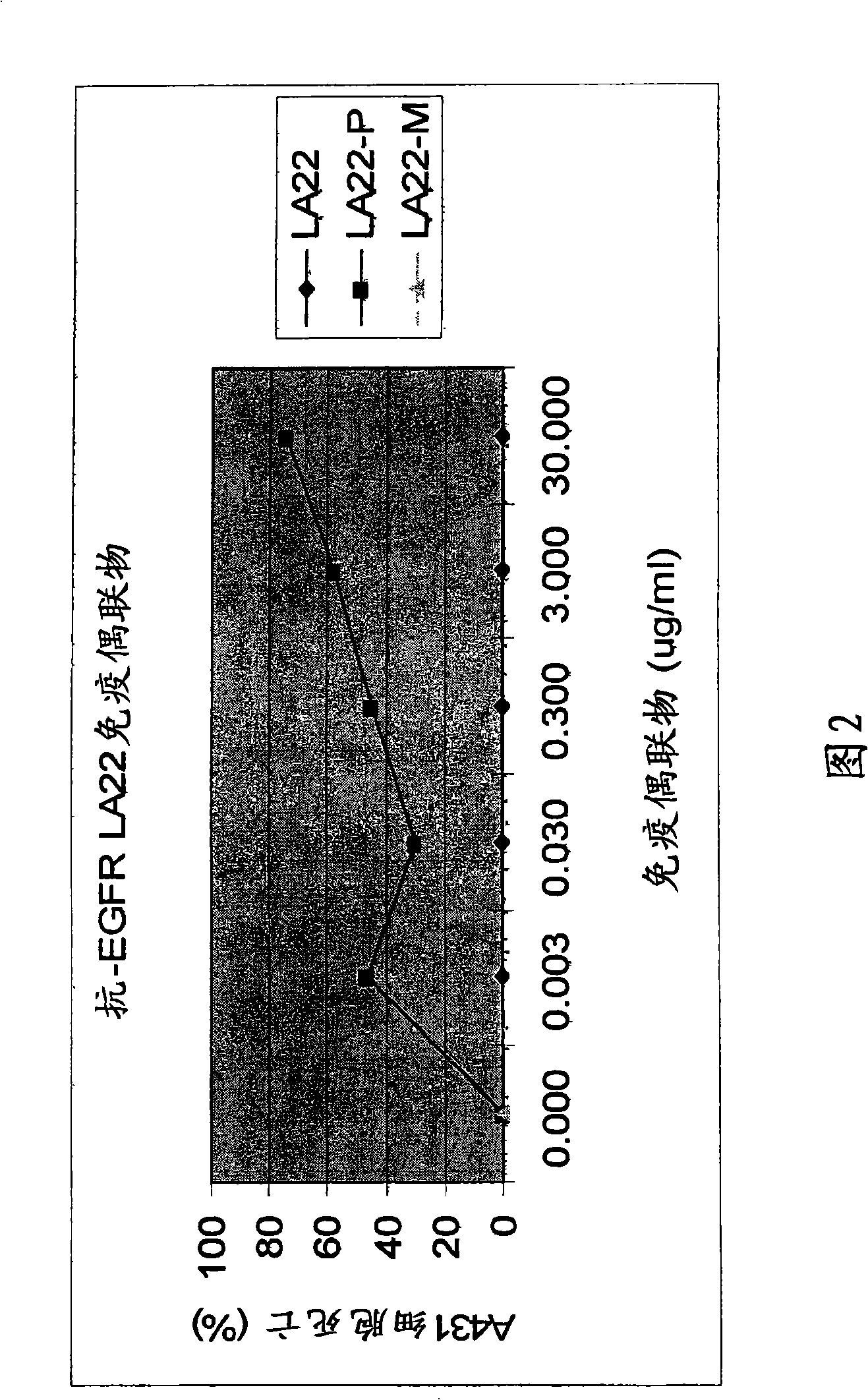
Antibodies for the treatment of cancers
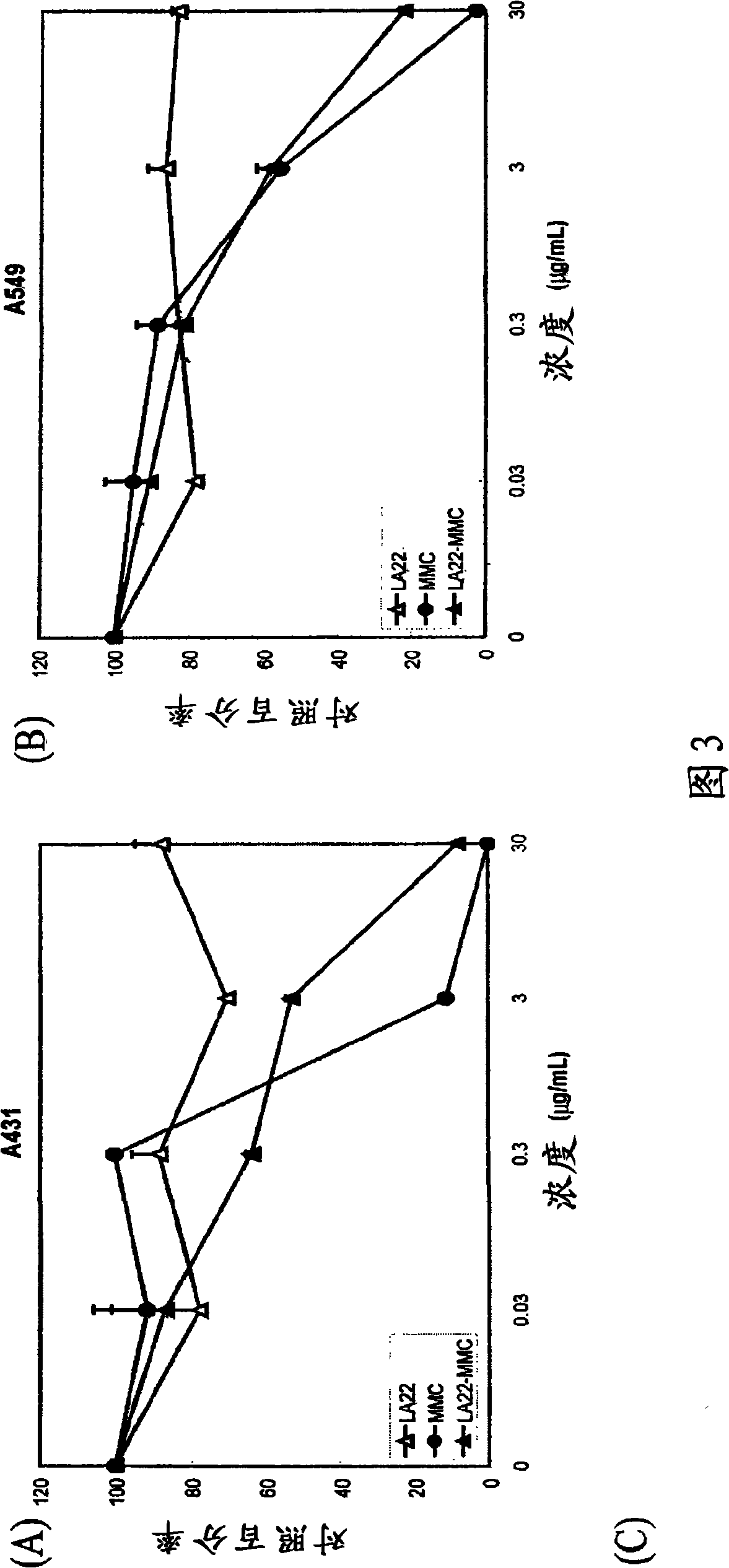
The present invention features monoclonal antibodies LA1 or LA22 conjugated with mitomycin C, pingyangmycin or other anti-cellular agents. The present invention also features other anti-EGFR antibodies conjugated with mitomycin C or pingyangmycin. The antibodies of the present invention can be used to treat cancers, including but not limited to, those of epithelial origin, such as glioblastoma or cancer of the lung, breast, head and neck, and bladder.
Owner:WELSON PHARMA
Purifying method for copper chelate of pingyangmycin and same-family compounds thereof
The invention discloses a purifying method for copper chelate of pingyangmycin and of same-family compounds thereof. The purifying method comprises the following steps: independently using monodisperse polystyrene / divinyl benzene chromatography media or combining the monodisperse polystyrene / divinyl benzene chromatography media with monodisperse polymethacrylate hybrid type cation exchange chromatography media so as to use as stuffing to carry out chromatography. The purifying method can be used for overcoming the defects that the original process is long in period, low in efficiency and low in product purity to obtain the copper chelate of high-purity pingyangmycin and same-family compounds thereof, wherein the purity is measured by virtue of an HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography), and the purity is over 97% in area percentage. After removing copper from the copper chelate, the high-purity pingyangmycin and same-family compounds thereof are obtained, so that the safety of clinical medication is improved.
Owner:哈尔滨莱博通药业有限公司
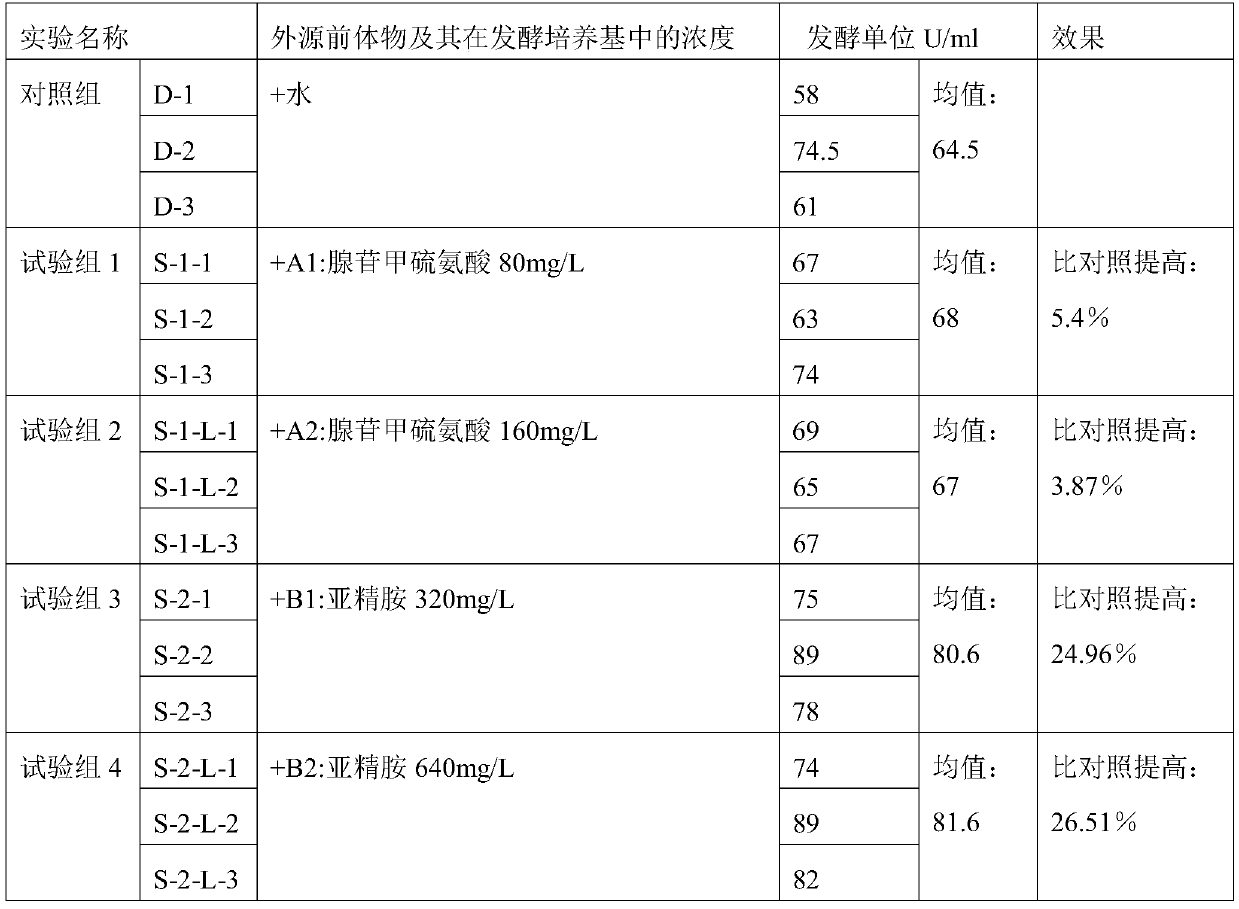
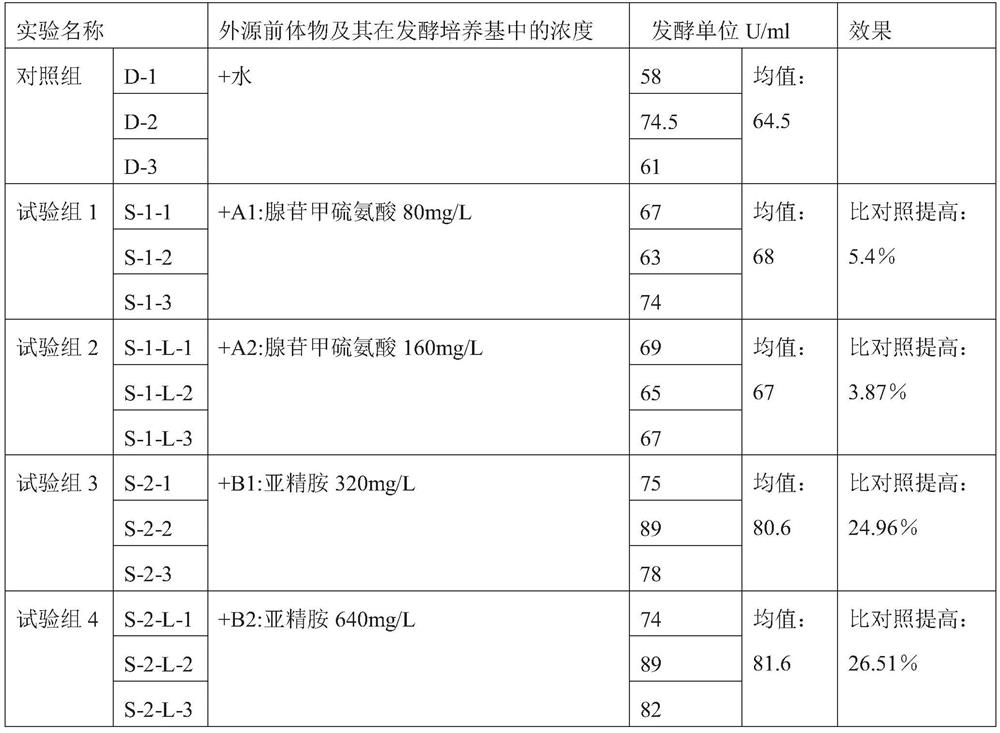
Method for producing pingyangmycin by fermentation
ActiveCN110699409AIncrease productionIncrease the level of fermentation productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyS-Adenosyl-l-methionine
The invention discloses a method for producing pingyangmycin by fermentation. The method for producing pingyangmycin by fermentation comprises the steps that streptoverticillium is fermented in a fermentation medium, an exogenous precursor is added into the fermentation medium during the fermentation to obtain pingyangmycin-containing fermentation product, and the pingyangmycin is isolated and obtained from the fermentation product; the exogenous precursor is a substance A and / or a substance B, the substance A is adenosylmethionine or a similar amino acid derivative of the adenosylmethionine,and the substance B is spermidine or a spermidine salt. The method for producing the pingyangmycin by fermentation is simple, effective, the level of pingyangmycin fermentation production can be quickly increased, the production cost is lowered, additional devices and manpower are not required, the level of pingyangmycin industrial fermentation can be greatly increased, and the method is suitablefor industrial scale production.
Owner:JILIN AODONG PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRY GROUP YANJI CO LTD
Pharmaceutical composition for treating embolism and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101670095BPlay a hardening roleHigh drug loadingSurgeryX-ray constrast preparationsDual effectDouble bond
The invention provides a pharmaceutical composition for treating embolism and a preparation method thereof, the pharmaceutical composition comprises a hydroxyl-contained biocompatible polymer material and a monomer containing unsaturated double bonds and anion groups, as well as a polymer generated by polymerization reaction of an optional vinyl monomer, wherein the polymerization is initiated through free radicles, and bleomycin or pingyangmycin is combined on the anion groups of the generated polymer. The preparation method combines the bleomycin or the pingyangmycin on a carrier of the polymer, thereby being capable of fully playing the dual effects of an anti-tumor antibiotic and a hardening agent owned by the bleomycin or the pingyangmycin during the embolism treatment. The anion part of the polymer can be properly combined with the bleomycin or the pingyangmycin which is rich in amino groups, thereby not only realizing the higher drug loading, but also leading the drug in an emboliaztion agent to be exchanged by cation in human body, and further realizing the slow release. In addition, the embolic carrier of the polymer has the advantages of simple prepration technology andlow cost, thereby being applicable to large-scale industrial production.
Owner:HYGEA MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
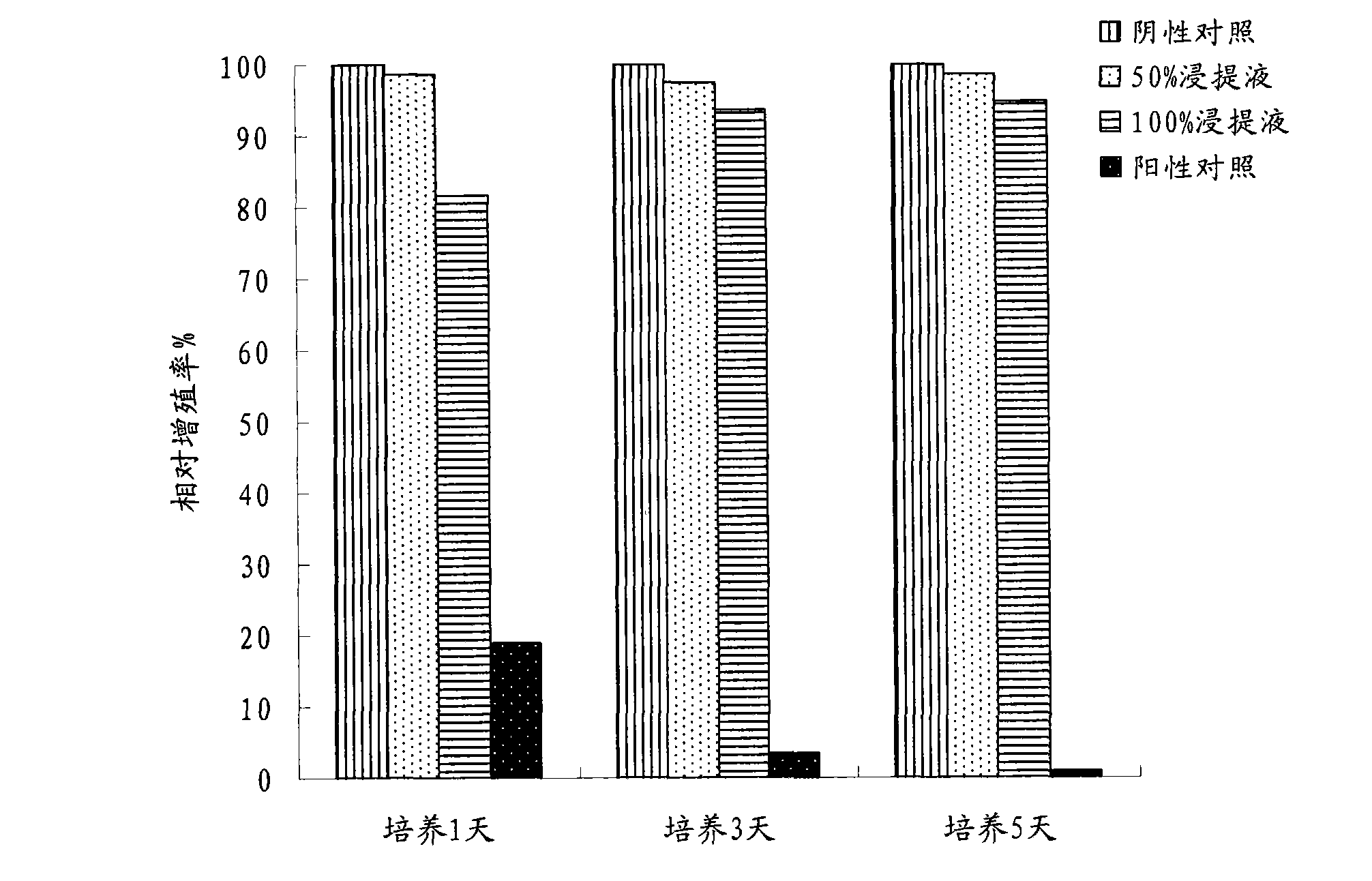
Preparation method for porous slow-release microsphere of chitosan graft copolymer
InactiveCN102784112BEvenly distributedGood dispersionOrganic active ingredientsSaccharide peptide ingredientsEndcappingPolymer science
Provided is a preparation method for porous slow-release microspheres of chitosan grafting poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide / acrylamide). The method includes: first taking chitosan as a base material, adding a terminated polyethylene glycol porogenic agent, forming chitosan porous microspheres by inverse suspension dispersion and chemical cross-linking solidification, and conducting further graft copolymerizing with N-isopropyl acrylamide / acrylamide by taking the porous microspheres as substrates to obtain chitosan grafting poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide / acrylamide) porous slow-release microspheres. The microspheres have temperature sensitivity and a porous characteristic, and are uniform in pore distribution, good in dispersibility, controllable in particle size, and mild in preparation process. The microspheres can be used for embedding drug pingyangmiein. Using a microsphere dosage form helps to improve drug curative effects and reduce toxic and side effects.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Fermentation medium and fermentation method for producing Bleomycin A5
ActiveCN112391432AIncrease productionLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyInorganic salts
The invention discloses a fermentation medium and a fermentation method for producing Bleomycin A5. The fermentation medium for producing the Bleomycin A5 comprises a carbon source, a nitrogen source,inorganic salt, and water; the content of the nitrogen source is 4.5-5.9%; the nitrogen source consists of soybean cake powder and corn steep liquor; and the content of the corn steep liquor is greater than 0.75% and less than 2.2%, wherein the percentage is mass percentage calculated on basis of the mass of the fermentation medium. Being adopted for fermenting the Bleomycin A5, the fermentationmedium disclosed by the invention can greatly increase yield of the Bleomycin A5 (to 2.47 times compared with a fermentation medium in the prior art), and remarkably reduce fermentation cost; and thus, a good foundation is laid for industrial production of the Bleomycin A5.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND +1
Method for cultivating new Rosa sp. variation variety by using chemical mutagenic agent
InactiveCN113575414AIncrease mutation rateIncrease variabilityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureChemical mutagensRosa arvensis
The invention discloses a method for cultivating a new Rosa sp. variation variety by a using chemical mutagenic agent. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: storing Rosa sp. seeds in sand, germinating, sowing in a hole tray, mixing pingyangmycin and a phosphate buffer solution to prepare a pingyangmycin solution, and mixing the pingyangmycin and an MS liquid culture medium to prepare an MS nutrient solution; when young seedlings come out of the soil, cotyledons are flattened and true leaves germinate, putting the young seedlings into the MS nutrient solution for carrying out hydroponic treatment, treating the growing points of the stem tips of the young seedlings by adopting the pingyangmycin solution, treating once in the morning, at noon and at night every day, continuously treating for 2-4 days, washing the growing points of the stem tips of the young seedlings and the roots of the young seedlings with clear water after the treatment is completed, and transferring the young seedlings into the MS liquid culture medium for culture; and after the Rosa sp. is treated for one month, the leaves of the Rosa sp. are gradually varied, and after variation is stable, plants with variation characters are subjected to conventional management in a greenhouse. According to the method, the chemical mutagenic agent is adopted to treat the growing points of the stem tips of plants and the root tips of the plants, operation is easy, a plant mutagenesis rate is high, a mutagenesis effect is good, and the survival rate of the plants is high.
Owner:TAISHAN RES INST OF FORESTRY +1
A kind of method for obtaining red potato mutant and used mutagenesis medium
ActiveCN104381127BAvoid problemsHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSolanum tuberosumRelative humidity
The invention relates to a method for acquiring a red potato mutant and a mutagenesis medium used by the method and belongs to the technical field of agriculture Biotechnology. The mutagenesis medium is obtained by use of 30-40mg / L of pingyangmycin in a regenerated medium. The method comprises the following steps of putting purple potato square pieces into the mutagenesis medium, carrying out culture for 15 days, transferring the purple potato square pieces to a regenerated medium, and carrying out culture under culture conditions of a temperature of 22+ / -2 DEG C, illumination intensity of 700lx, illumination time of 8h / d and relative humidity of 65-75%. Through the mutagenesis medium and method, after mutagenesis for 15 days, the purple potato can produce mutation and through further culture, a potato regeneration seedling which can produce red stem tubers is obtained.
Owner:VEGETABLE RES INST OF SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Application of pingyangmycin combined with sodium hyaluronate in drug for treating lymphatic malformation
InactiveCN103330945BShort duration of actionGuaranteed specificitySaccharide peptide ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsLymphatic vesselLymphatic malformations
The invention discloses an application of pingyangmycin combined with sodium hyaluronate in a drug for treating lymphatic malformation, as well as a drug for treating lymphatic malformation, in particular to a drug for treating microcystic lymphatic malformation. According to the application, the pingyangmycin combined with the sodium hyaluronate is adopted and has better effects in the aspects of inhibiting human lymphatic malformation endothelial cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis while compared with pure pingyangmycin, wherein the molecular weight of the sodium hyaluronate is 600,000 Dalton-1,500,000 Dalton, and concentrations of the pingyangmycin and the sodium hyaluronate are 100 mu g / mL and 300 mu g / mL respectively.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV QILU HOSPITAL
A new application of traditional Chinese medicine composition
The invention provides a new application of a traditional Chinese medicinal composition and in particular relates to an application of a traditional Chinese medicinal composition in preparation of a medicine used for treating xerophthalmia, and raw materials of the traditional Chinese medicinal composition comprise wolfberry, chrysanthemum, salviae miltiorrhizae, cortex phellodendri, borneol, pearl powder and menthol. The traditional Chinese medicinal composition has the advantages that pathological changes of lacrimal gland tissues of an experimental xerophthalmia mouse, lacrimal glands of which are damaged by injected pingyangmycin, in morphology can be obviously alleviated, quantity of tear fluid can be obviously increased, breakup time of a tear film is prolonged, and quantity of the tear fluid secreted by a normal domestic rabbit can be obviously increased; and meanwhile, the traditional Chinese medicinal composition has obvious anti-inflammation and anti-oxidation effects.
Owner:郑州市新视明科技工程有限公司
A method for directed selection of salt-tolerant body by in vitro mutagenesis
ActiveCN103070076BImprove germination rateHigh polymorphismPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBone Alkaline PhosphataseGermplasm
The invention provides a method for directionally screening a salt-tolerant body through peanut in vitro mutagenesis. The method mainly comprises the following steps: sterilizing the surface of peanut embryo; separating a leaflet, inoculating into a somatic embryo induction and mutagenesis medium added with 2,4-D and pingyangmycin, and performing mutagenesis culture treatment; and transferring a survival explant on which a somatic embryo is formed to a somatic embryo germination and screening culture medium added with bone alkaline phosphatase (BAP) and NaCl, and directionally screening the salt-tolerant body. The salt-tolerant body is directionally screened by combining in vitro mutagenesis and tissue culture, and plenty of manpower, materials and financial resources can be saved; and the salt-tolerant body is regenerated in an embryogenesis way, an somatic embryo is derived from a cell, and the chimerism of the salt-tolerant body can be avoided. A peanut mature seed is taken as a mutagenic material and cannot be limited by seasons, the operation is convenient, a novel salt-tolerant peanut germplasm can be created, the peanut genetic basis is enriched, and the difficulty that new high-yield salt-tolerant varieties are difficult to breed due to the lack of high salt-tolerant germplasm resources in peanut cultispecies is overcome.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Water-soluble substrate suitable for preparing water-soluble preparations of bleomycin and homologues thereof
InactiveCN102120032AReduce wasteEasy to wash offAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryIrritationWater soluble
The invention discloses a water-soluble substrate suitable for preparing water-soluble preparations of bleomycin and homologues thereof. The water-soluble substrate is prepared by co-melting and uniformly mixing the following components in part by weight: 30 to 40 parts of polyoxyethylene (40) stearate and 60 to 70 parts of fatty alcohol-polyoxyethylene ether (peregal O). The invention also discloses the application of the water-soluble substrate in the preparation of a water-soluble preparation of the bleomycin, a water-soluble preparation of pingyangmycin, a water-soluble preparation of boanmycin or a water-soluble preparation of boningmycin. The water-soluble substrate does not contain water, but can be dissolved in water, so that the medicinal preparations prepared by the water-soluble substrate are convenient to wash and remove; and when the medicinal preparations are used, the user does not need to directly touch the medicinal preparations by hands, so that the waste of the medicinal preparations is reduced and the irritation to the hands is reduced.
Owner:济南市皮肤病防治院
A kind of pingyangmycin peg-pcl-peg temperature-sensitive slow-release gel and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN102836418BExtended half-lifeExtension of timeSaccharide peptide ingredientsSide effectHalf-life
The invention discloses a pingyangmycin polyethylene glycol (PEG)-polycaprolactone (PCL)-polyethylene glycol (PEG) temperature-sensitive slow-release gel, as well as a preparation method and the application of the gel. The Pingyangmycin PEG-PCL-PEG temperature-sensitive slow-release gel mainly consists of two parts comprising PEG (polyethylene glycol)-PCL (polycaprolactone)-PEG (polyethylene glycol) co-polymer and Pingyangmycin, is liquid at room temperature, and is solid gel under the in vivo 37 DEG C condition; the gel system has significant slow-release effect, thereby having functions in prolonging the half-life period and the acting time of the Pingyangmycin, reducing drug concentration in plasma, and reducing systemic toxic and side effects. The gel can be formed in situ after the medicine is injected in a high-flow-speed vessel, and then location embolism is realized, and so as to realize the, and muscularization and closing of muscle is caused, so that the sclerotherapy and the interventional therapy are combined effectively, the gel has excellent biocompatibility and degradability, is beneficial for treating hemangiomas, vascular malformations and cancers, particularly, a new selection is provided to the treatment of the vein malformation and partial malformation of cancers.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
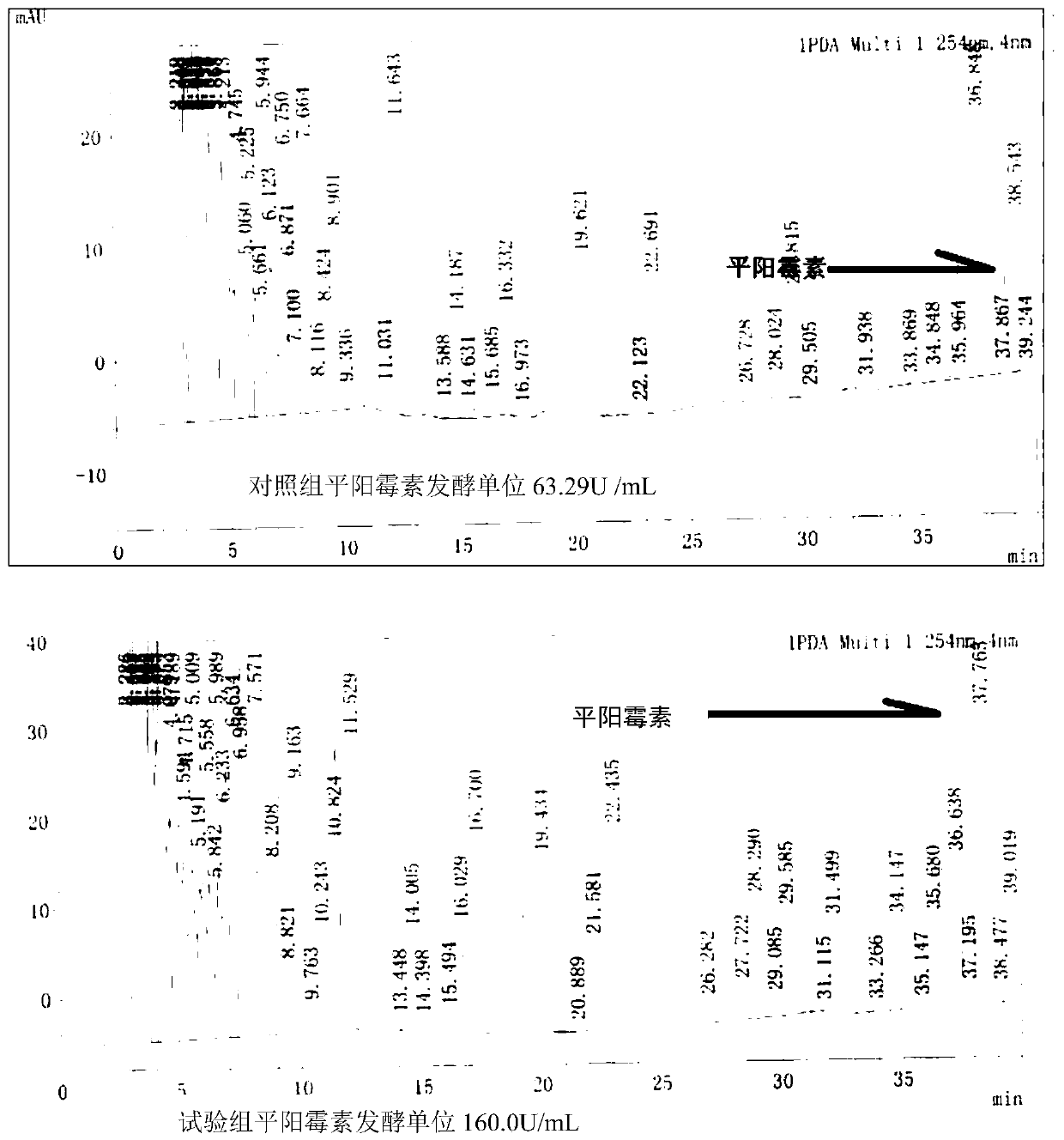
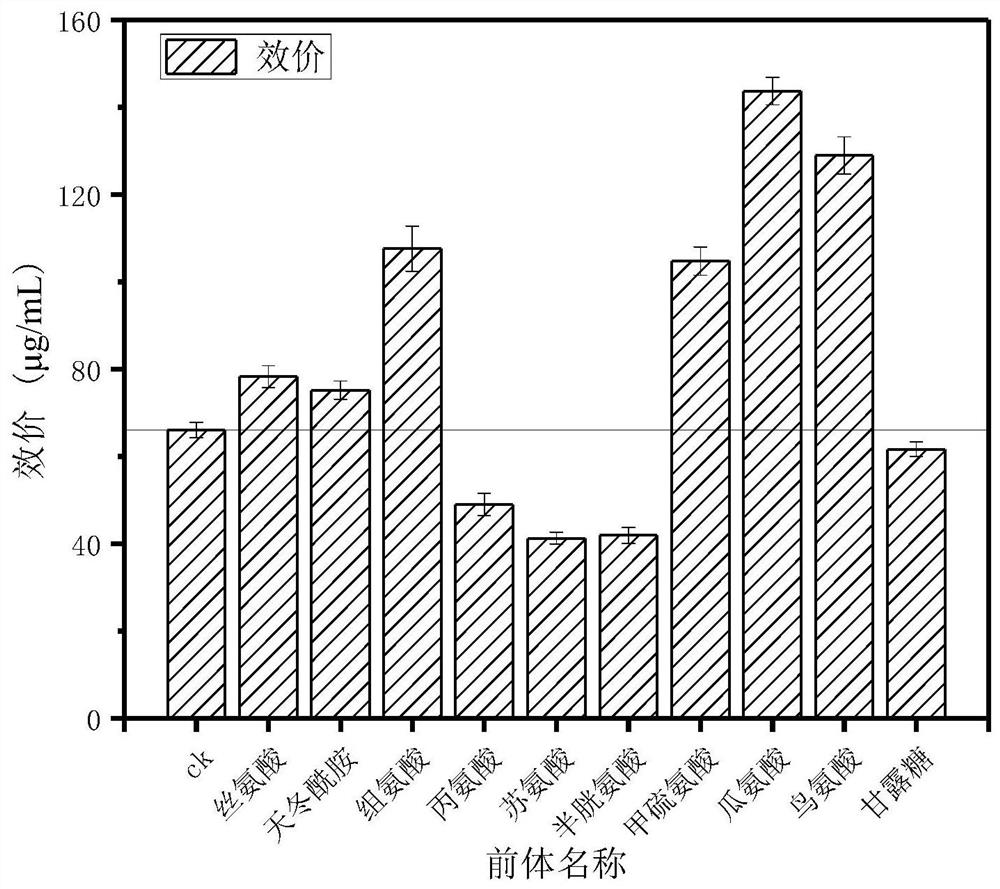
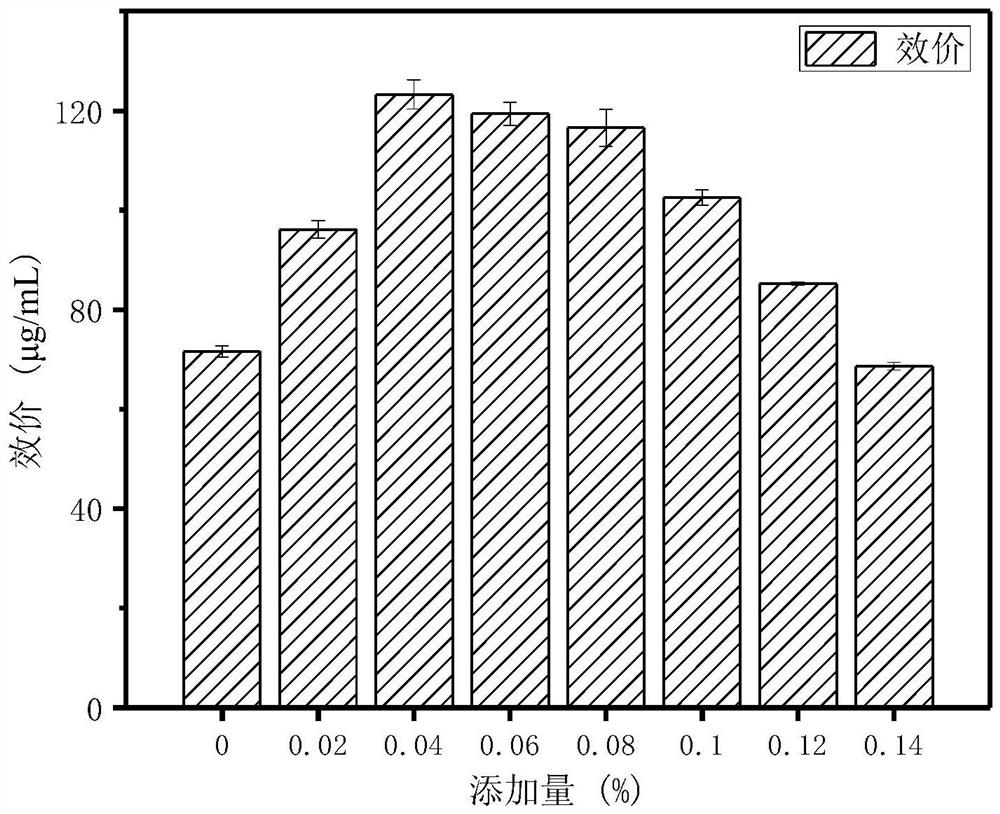
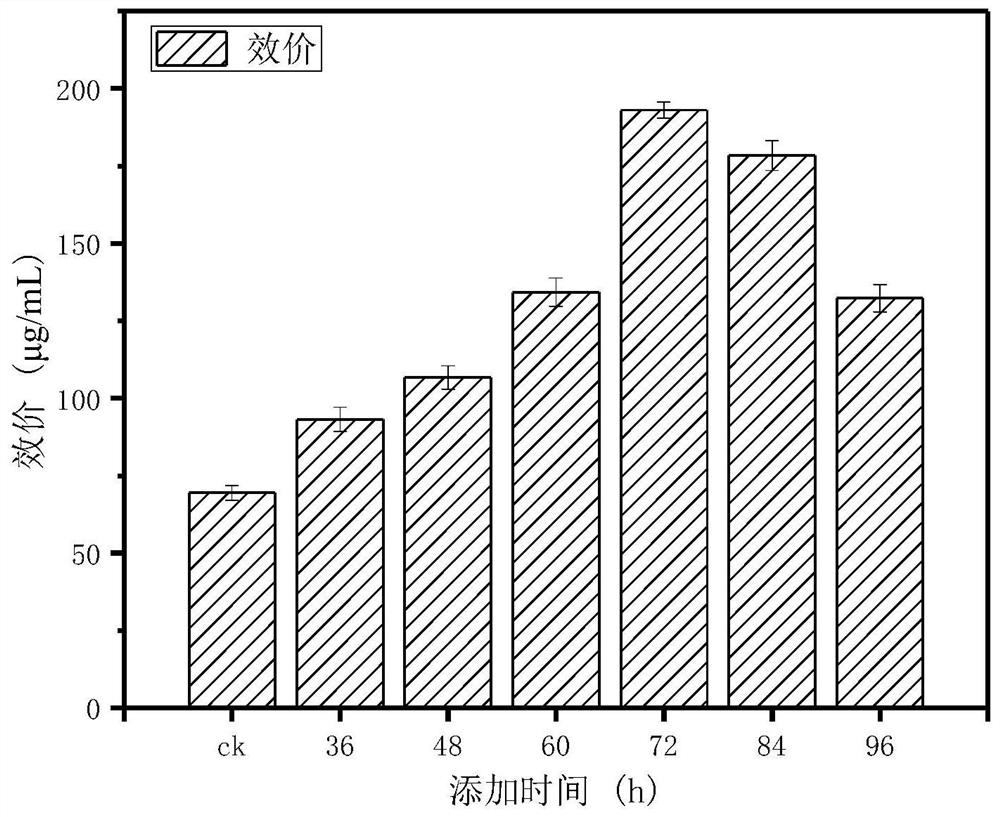
Method for improving biosynthesis efficiency of pingyangmycin
ActiveCN112176013AIncrease productivityMicroorganism based processesPeptidesOrganic chemistryAmino acid
The invention provides a method for improving the biosynthesis efficiency of pingyangmycin. The invention reveals for the first time that a proper amount of specific amino acid is added in a proper stage of fermentation of a pingyangmycin producing strain, so that the synthesis efficiency of pingyangmycin biosynthesis can be remarkably improved, and the yield is greatly increased. According to thetechnical scheme, on the basis that the cost of a fermentation culture medium is not remarkably increased, the biosynthesis yield of the pingyangmycin is remarkably increased; and meanwhile, the shortening of the biosynthesis period of the pingyangmycin becomes possible.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
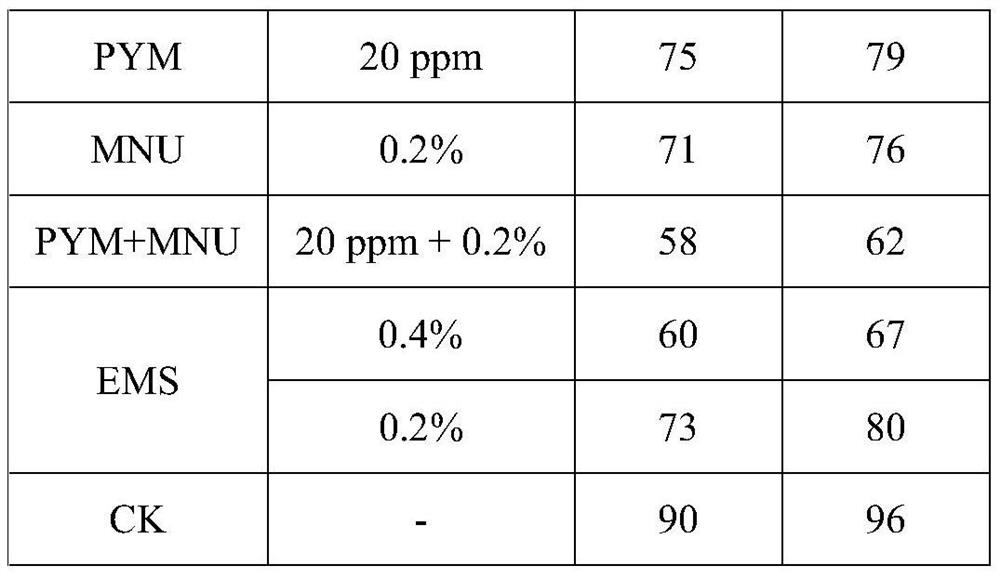
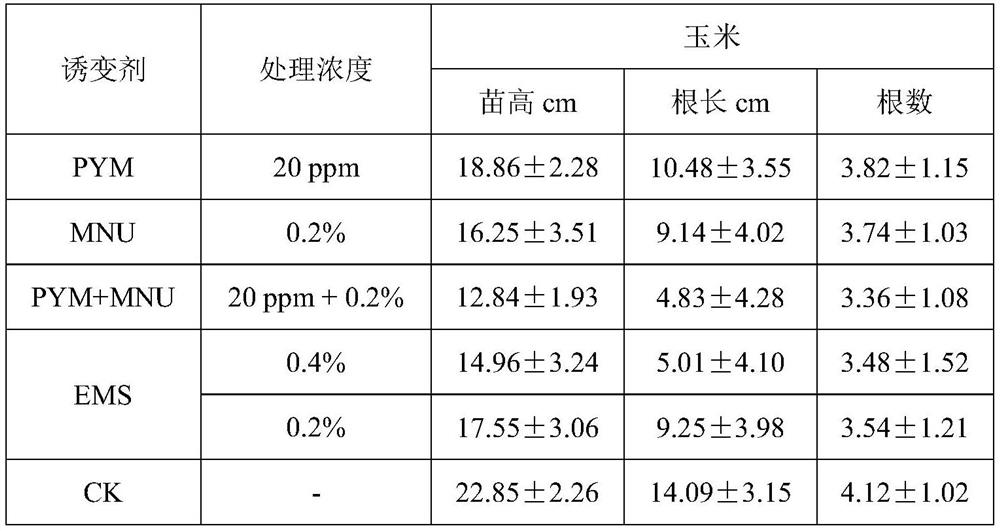
A chemical mutagen for genetic breeding of maize
ActiveCN111567527BEnhanced inhibitory effectSimple processing methodBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyChemical mutagens
The invention provides a kind of chemical mutagen that is used for corn genetic breeding, described chemical mutagen is the combination of Pingyangmycin and N-methyl-N-nitrosourea; Wherein the concentration of Pingyangmycin is 20ppm, The concentration of N-methyl-N-nitrosourea is 0.2%. The chemical mutagen can be used in corn genetic breeding.
Owner:SOUTH SUBTROPICAL CROPS RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
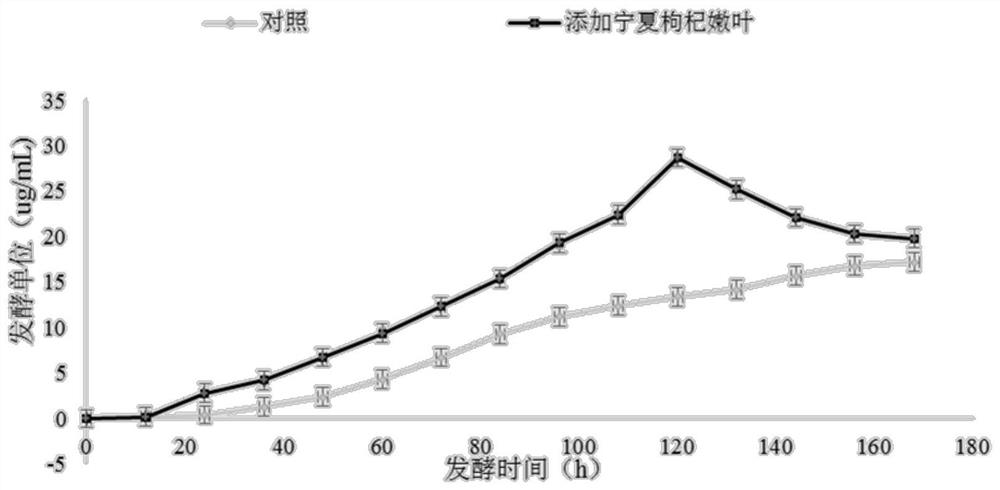
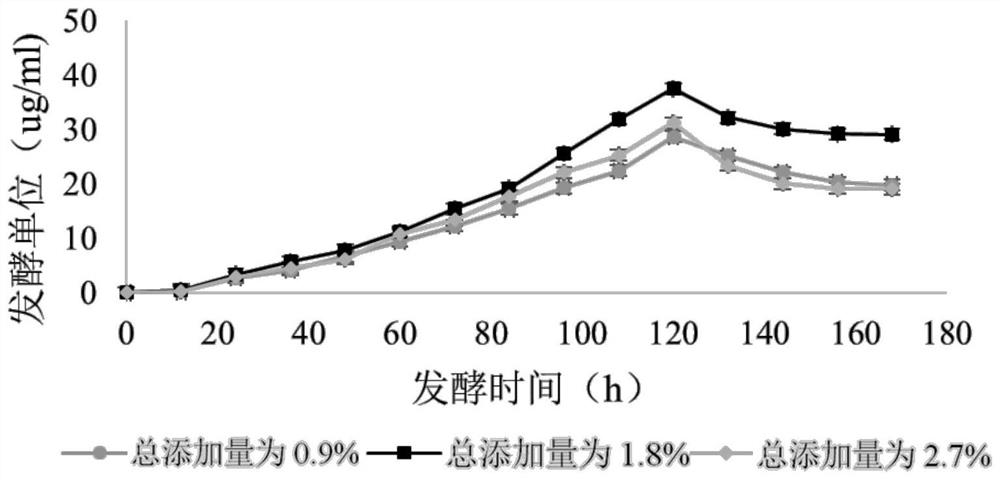
Fermentation medium for producing pingyangmycin and fermentation methods
ActiveCN112391430AImprove fermentation yieldShorten the fermentation cycleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesInorganic saltsMicrobiology
The invention discloses a fermentation medium for producing pingyangmycin and fermentation methods. The medium comprises the following components of a nitrogen source, a carbon source, inorganic salt,trace elements and water; the nitrogen source accounts for 3.55%-9.25% of the mass of the fermentation medium; the nitrogen source comprises cold-pressed soybean cake powder and a botanical drug; thebotanical drug is one or more of ningxia chinese wolfberry, ningxia chinese wolfberry tender leaves and coix seeds; and the botanical drug accounts for 0.1%-1.5% of the mass of the fermentation medium. The carbon and nitrogen sources in the fermentation medium are agricultural and sideline products, the price is low, the chemical property is stable, the sources are wide, the transportation and storage are convenient, no toxic and harmful substance residues exist in the fermentation process, the yield of the pingyangmycin is increased, the fermentation period is shortened, and the industrial production is facilitated.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND CO LTD +1
Snake venom cytotoxin, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN100548314CLittle side effectsHigh affinityReptile material medical ingredientsRespiratory disorderSide effectCancer cell
The invention discloses a snake poison cytotoxin, the preparation method and the application. The method of preparing the snake poison cytotoxin in the invention includes the following steps: firstly, the snake poison is conducted an ion-exchange chromatography and then the eluent between a first absorption peak and a second absorption peak on the absorbance curve with a detection wavelength of 280nm in the eluent is gathered; secondly, the eluent obtained in the first step is conducted an exclusion chromatography, water is used as a moving phase, and the second absorption peak on the absorbance curve with a detection wavelength of 280 nm in the eluent is gathered to obtain the snake poison cytotoxin. The saw-scale viper poison cytotoxin in the invention can induce the human laryngeal cancer cell Hep-2 to an apoptosis and the capability of inducing Cell Hep-2 to an apoptosis is stronger than Pingyangmycin with a viscosity of 100 Mug / ml when the snake poison cytotoxin has a concentration of 0.01 mg per milliliter. In addition, experiments of undue toxicity prove that the cytotoxin has slight side effects. The saw-scale viper poison cytotoxin in the invention can be used as an anti-cancer drug to turn biological anti-cancer drugs into a reality.
Owner:JINZHOU AHON PHARM CO LTD
A kind of traditional Chinese medicine composition for external use for treating dry eye and preparation method thereof
The invention provides an external traditional Chinese medicinal composition for treating xerophthalmia and a preparation method thereof. The external traditional Chinese medicinal composition for treating the xerophthalmia is prepared from the following raw materials: wolfberry, chrysanthemum, salviae miltiorrhizae, cortex phellodendri, pearl powder, borneol and menthol. The external traditional Chinese medicinal composition for treating the xerophthalmia has the advantages that pathological changes of lacrimal gland tissues of an experimental xerophthalmia mouse, lacrimal glands of which are damaged by injected pingyangmycin, in morphology can be obviously alleviated, quantity of tear fluid can be obviously increased, breakup time of a tear film is prolonged, and quantity of the tear fluid secreted by a normal domestic rabbit can be obviously increased.
Owner:陕西新视明医药生物科技有限公司
A method for fermenting and producing Pingyangmycin
ActiveCN110699409BIncrease productionIncrease the level of fermentation productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyS-Adenosyl-l-methionine
The invention discloses a method for producing pingyangmycin by fermentation. The invention discloses a method for fermenting and producing Pingyangmycin, which comprises fermenting Streptomyces verticillium in a fermentation medium, and adding exogenous precursors to the fermentation medium during the fermentation process to obtain the fermentation medium containing Pingyangmycin The product is isolated from the fermentation product to obtain Pingyangmycin; wherein, the exogenous precursor is substance A and / or substance B, and the substance A is adenosylmethionine or its similar amino acid derivatives, The substance B is spermidine or a salt of spermidine. The fermentative production method of Pingyangmycin provided by the present invention is simple and effective, can rapidly improve the fermentation production level of Pingyangmycin, reduce production cost, does not need additional equipment and manpower, can greatly improve the industrial fermentation level of Pingyangmycin, and is suitable for industrial scale production.
Owner:JILIN AODONG PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRY GROUP YANJI CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com