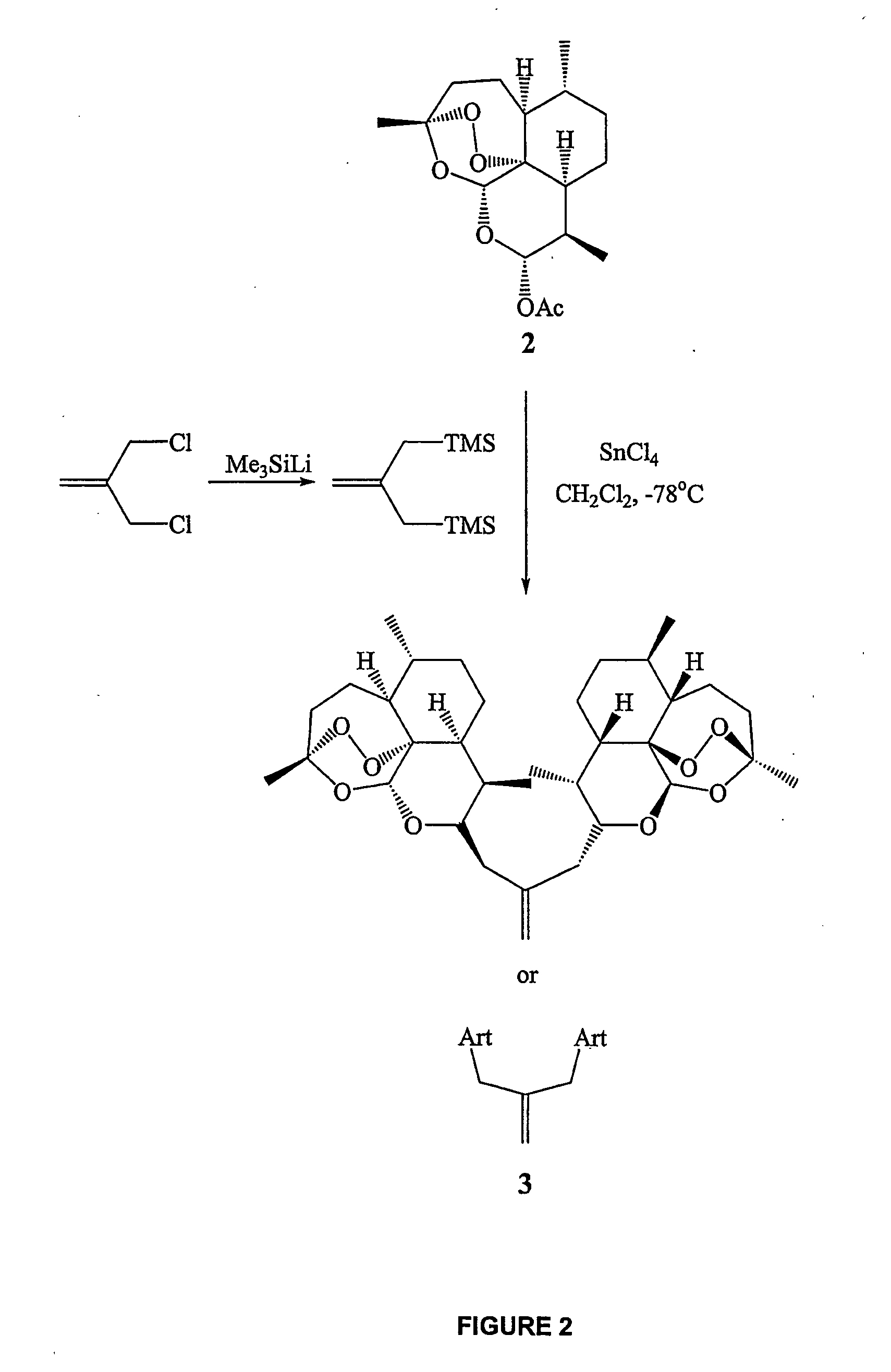
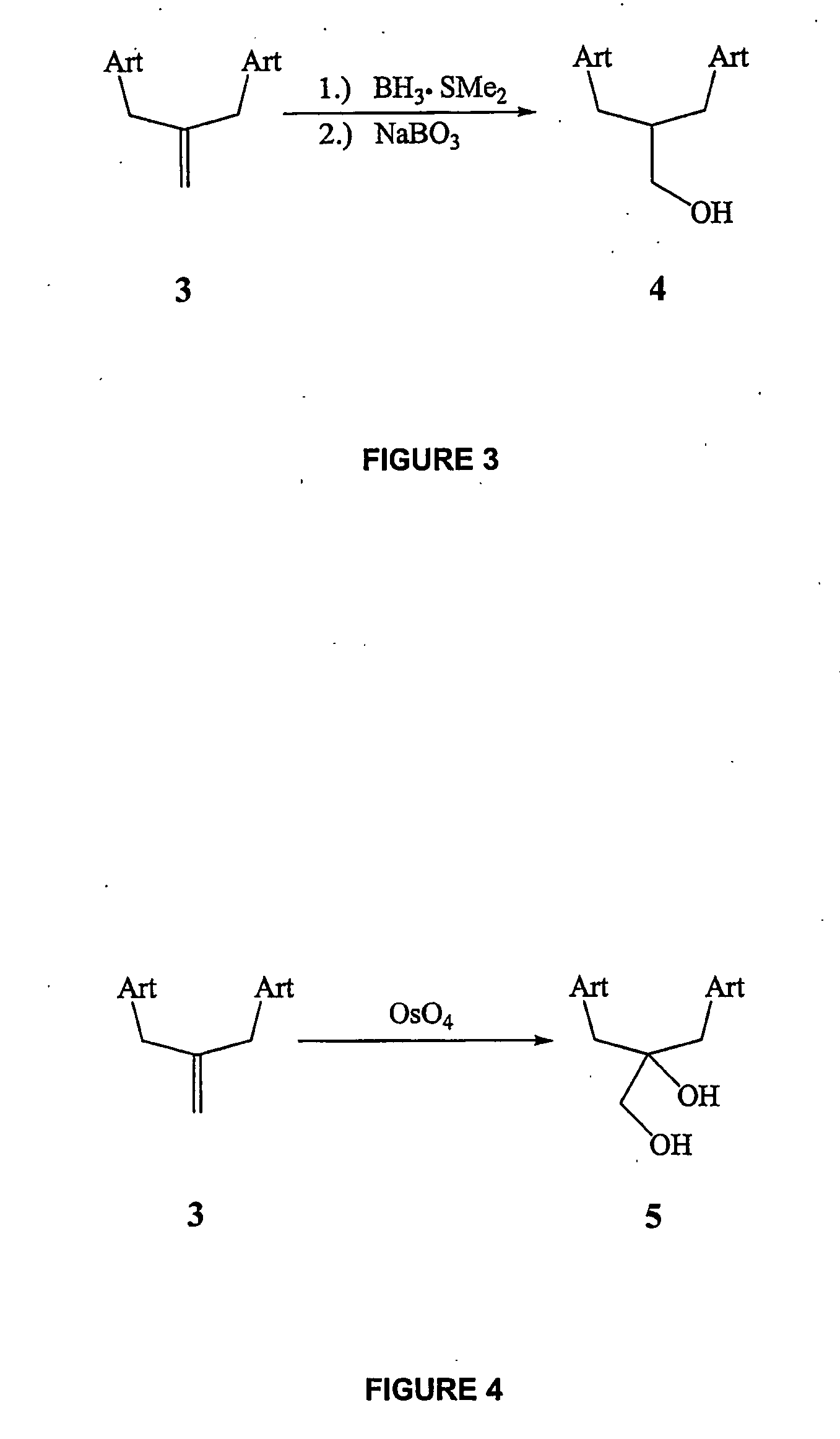
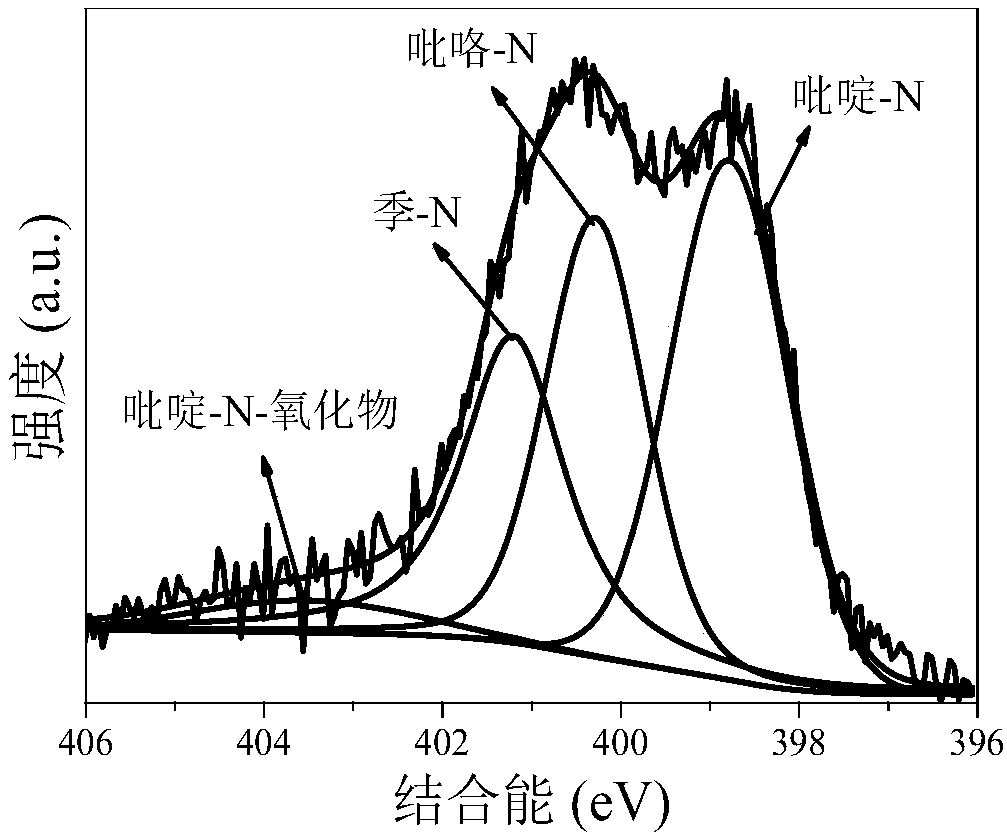
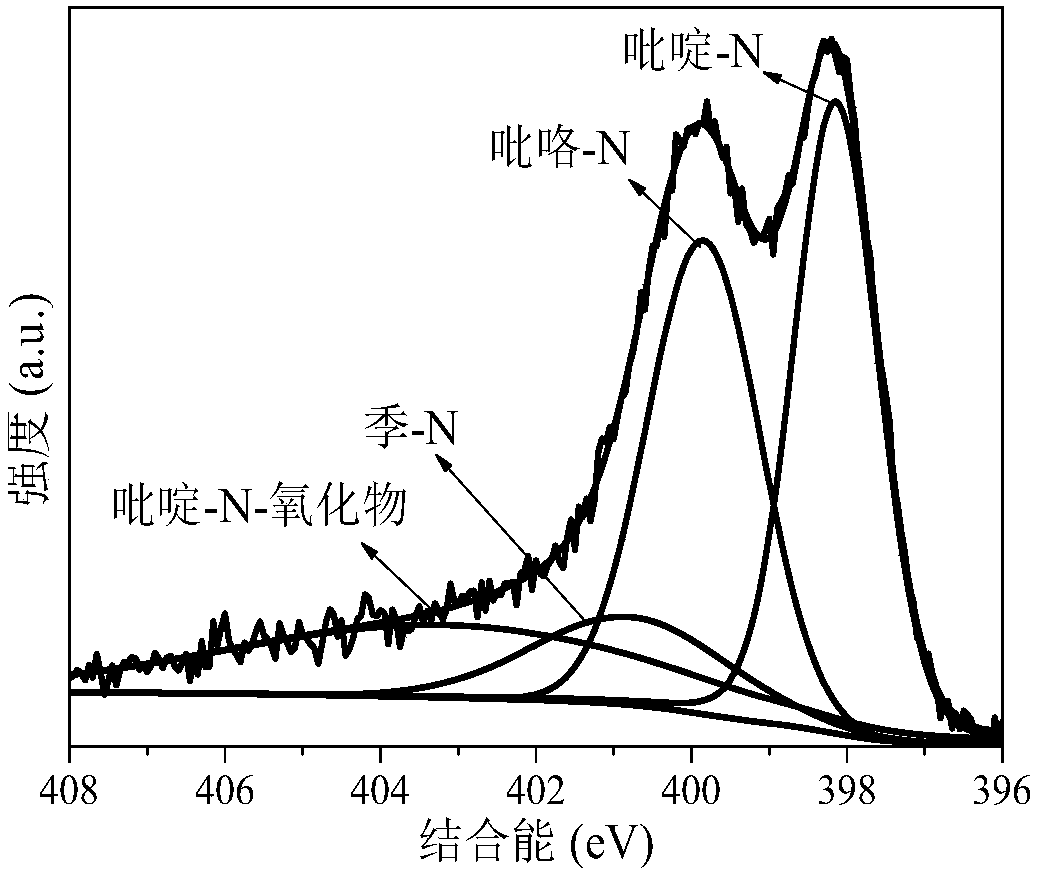
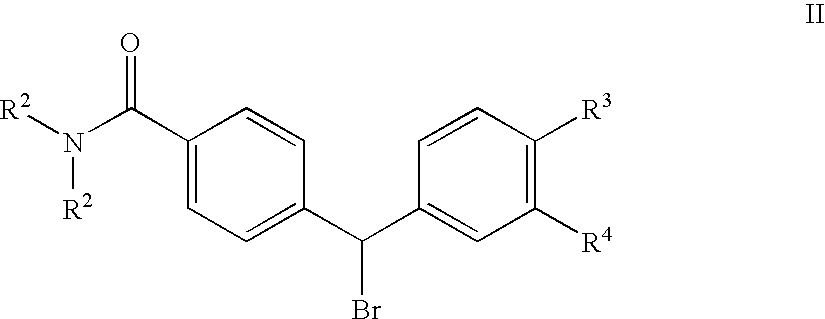
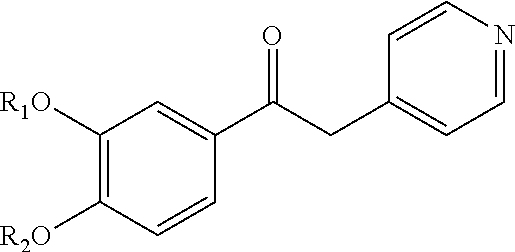
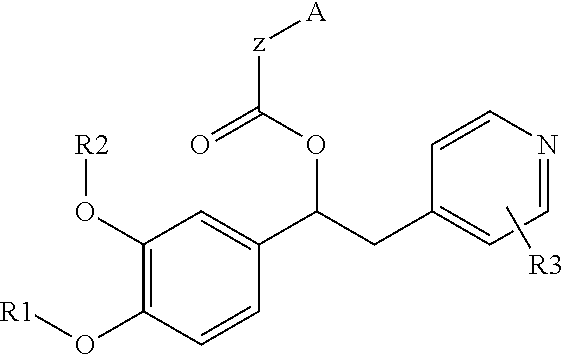
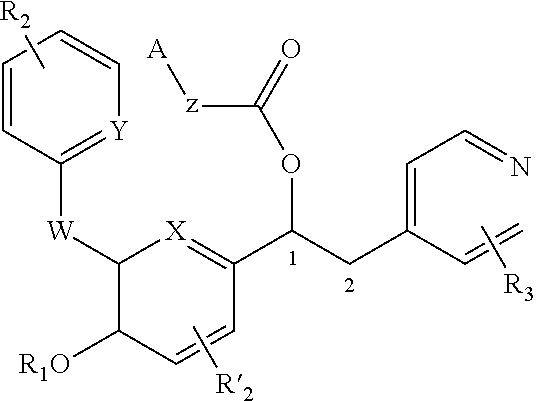
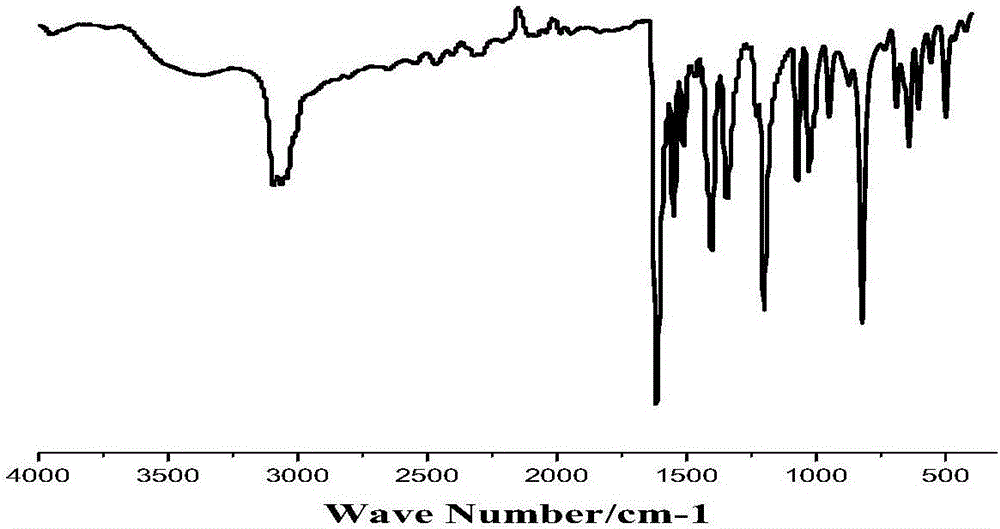
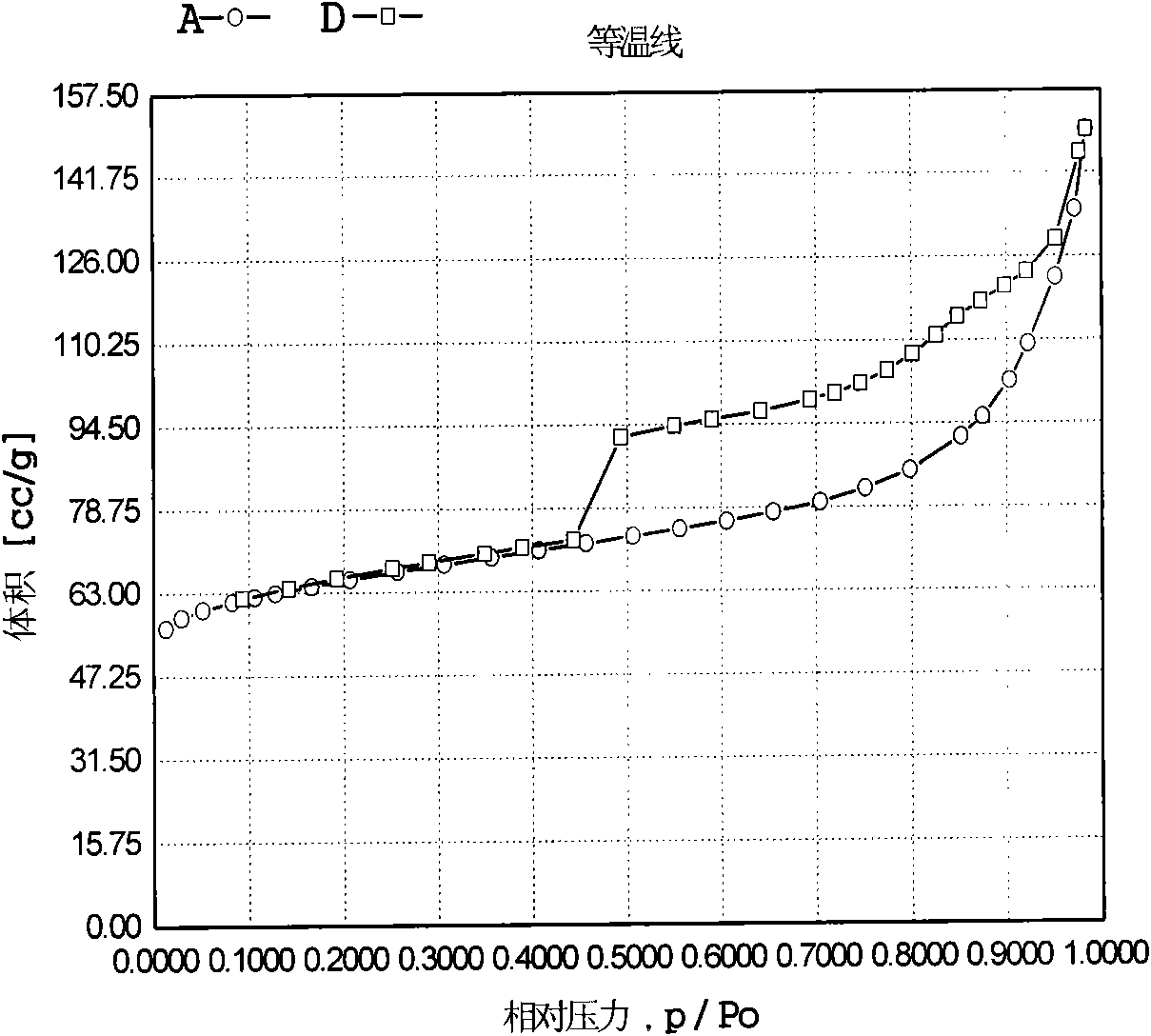
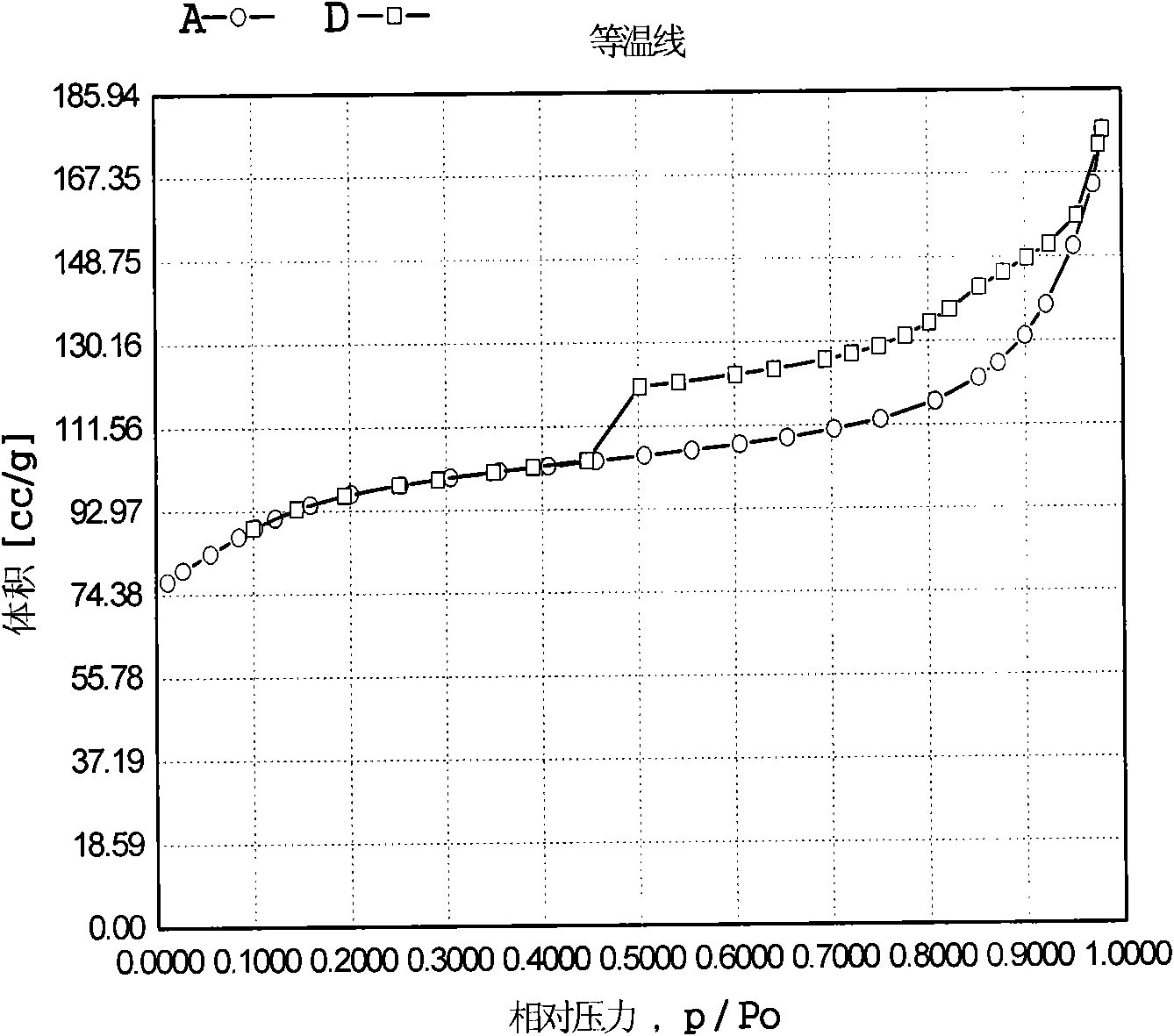
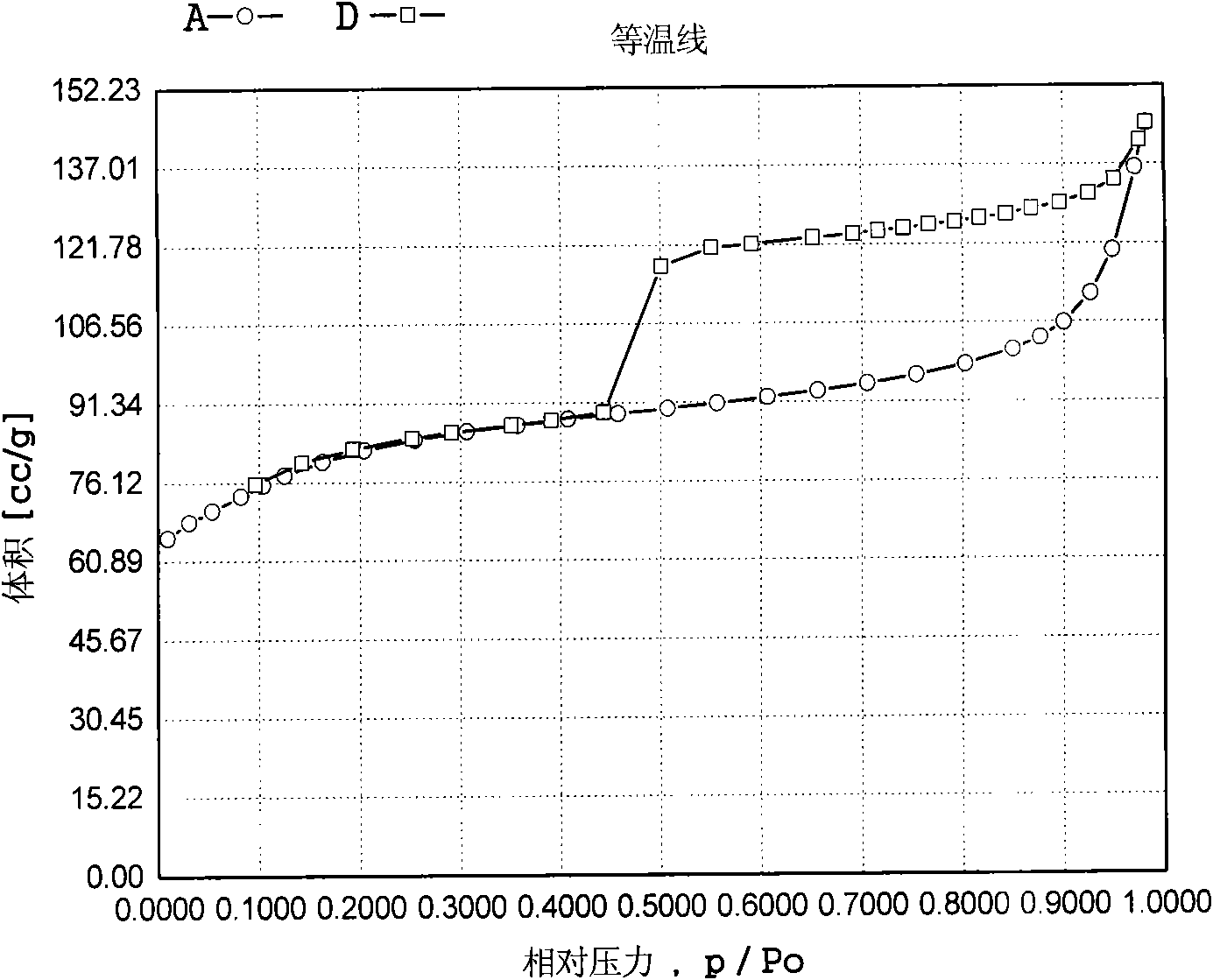
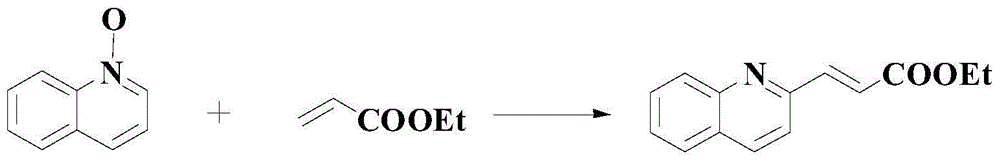Patents
Literature
97 results about "Pyridine-N-oxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
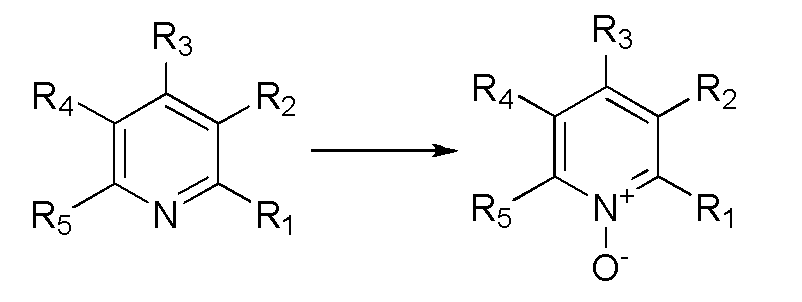
Pyridine-N-oxide is the heterocyclic compound with the formula C₅H₅NO. This colourless, hygroscopic solid is the product of the oxidation of pyridine. It was originally prepared using peroxyacids as the oxidising agent. The molecule is planar. The compound is used infrequently as an oxidizing reagent in organic synthesis. It also serves as a ligand in coordination chemistry.
Composition and use
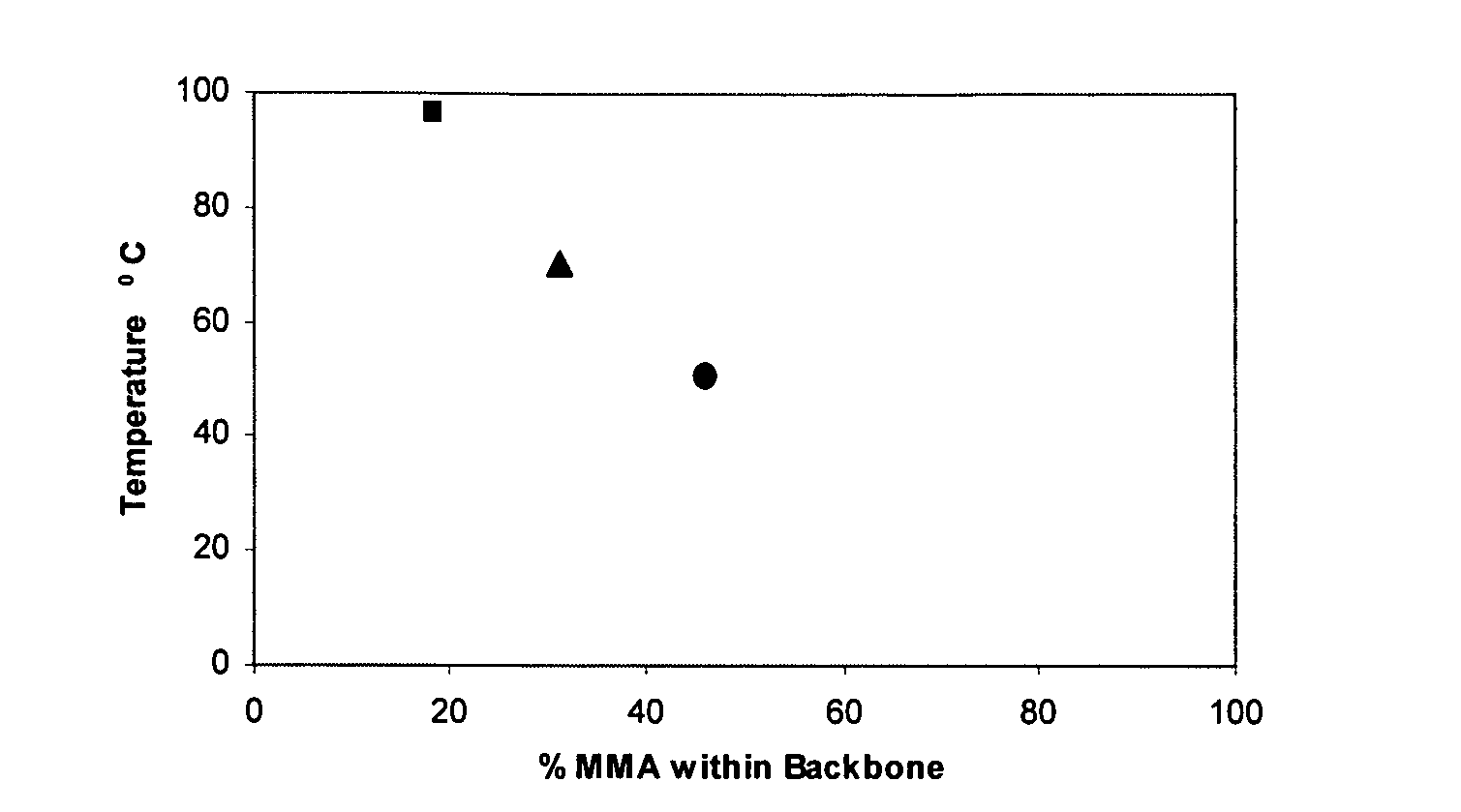
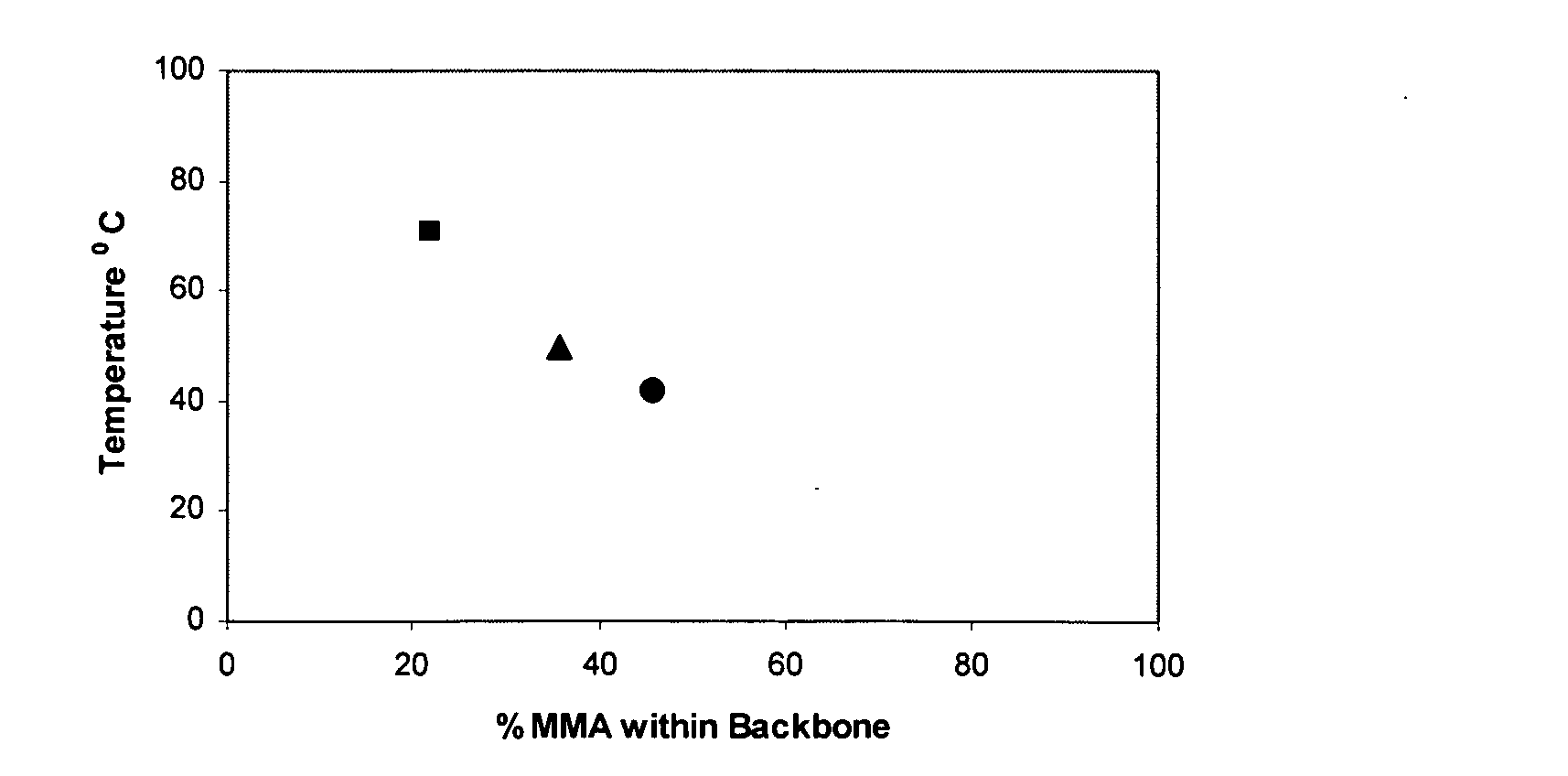
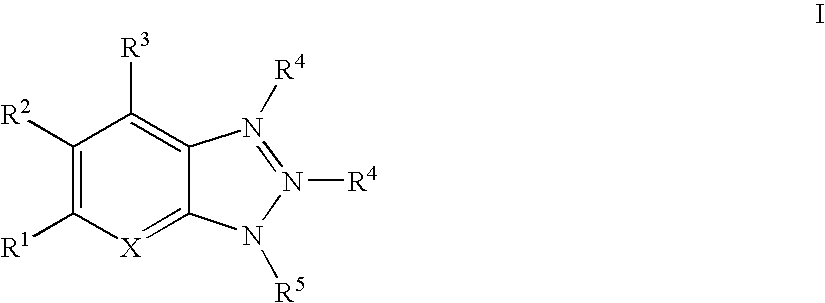
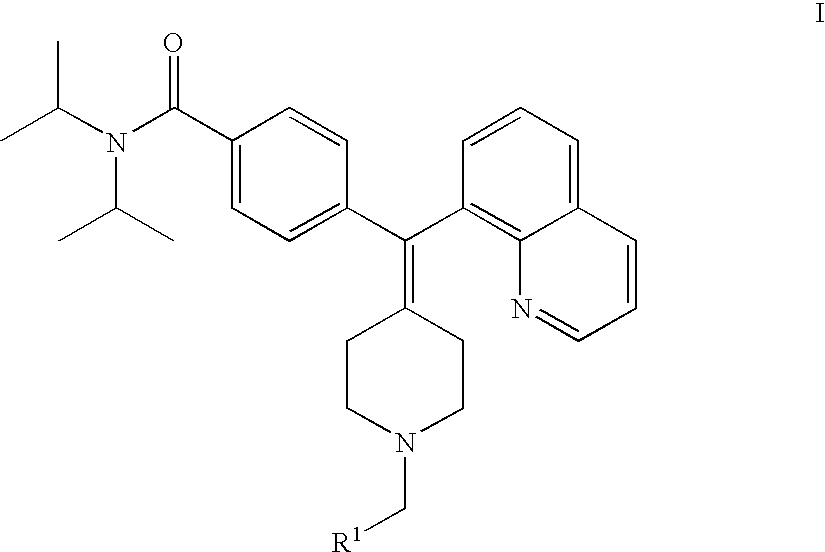
The present invention relates to a composition comprising: (i) an anti-microbial agent comprising a polymeric biguanide, alone or in combination with at least one other microbiologically active component selected from the group consisting of quaternary ammonium compounds, monoquaternary heterocyclic amine salts, urea derivatives, amino compounds, imidazole derivatives, nitrile compounds, tin compounds or complexes, isothiazolin-3-ones, thiazole derivatives, nitro compounds, iodine compounds, aldehyde release agents, thiones, triazine derivatives, oxazolidine and derivatives thereof, furan and derivatives thereof, carboxylic acids and the salts and esters thereof, phenol and derivatives thereof, sulphone derivatives, imides, thioamides, 2-mercapto-pyridine-N-oxide, azole fungicides, strobilurins, amides, carbamates, pyridine derivatives, compounds with active halogen groups, and organometallic compounds; and (ii) an amphoteric co-polymer of the Formula (1): wherein:[A] is of Formula (9), [B] is of Formula (10), [C] is of Formula (12), [D] is of Formula (13), and X is of Formula (11), wherein [A], [B], [C] and [D] may occur in any order; T is an optionally substituted substituent; L, G and Z each independently is an optionally substituted linking group; R1, R2 and R3 are each independently H, optionally substituted C1-20-alkyl or optionally substituted C3-20-cycloalkyl; R4 and R5 are each independently H or C1-4-alkyl; q is 15 to 1000; p is 3 to 50; J is an optionally substituted hydrocarbyl group; F is an acidic substituent; E is a basic substituent; m is 0 to 350; n is 1 to 75; v is 0 to 100; y is 1 to 100; b is 0, 1 or 2; s is 0 or 1; w is 1 to 4; and provided that at least one of R4 and R5 is H.
Owner:ARCH UK BIOCIDES LTD
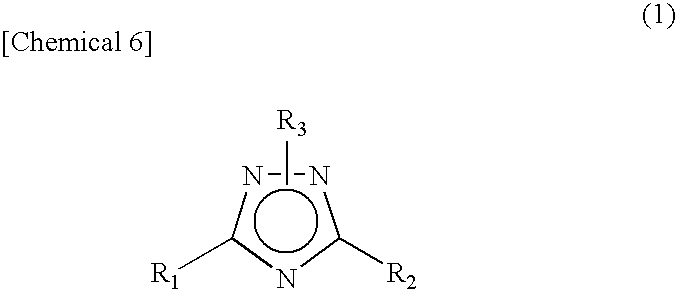
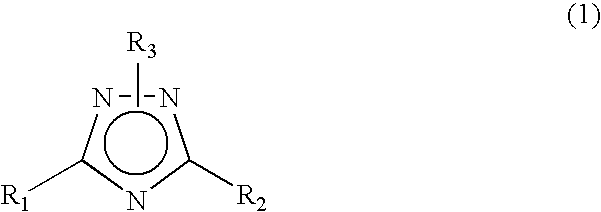
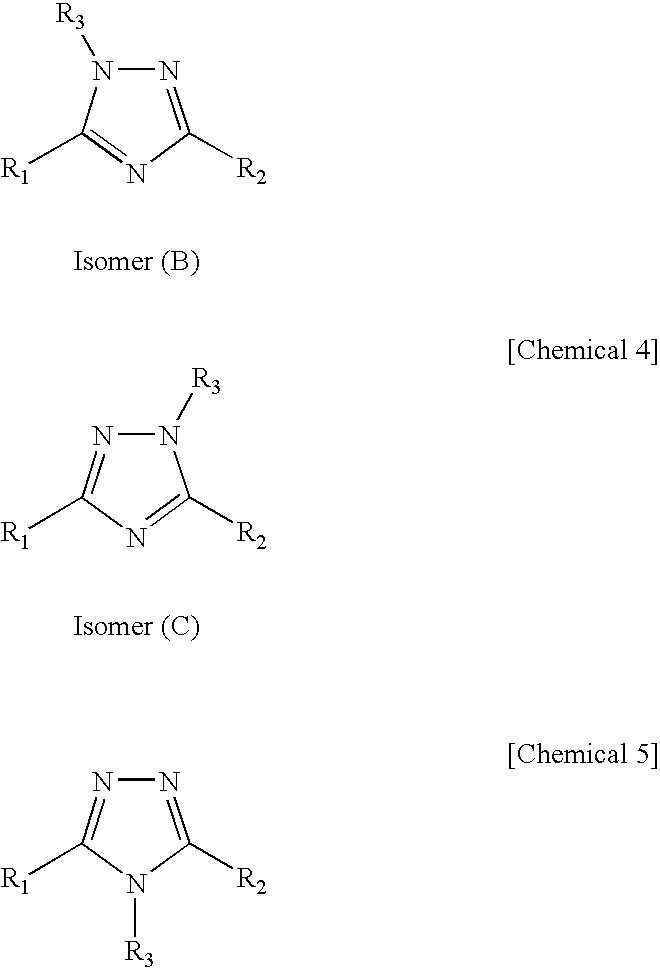
1 2 4-triazole compound
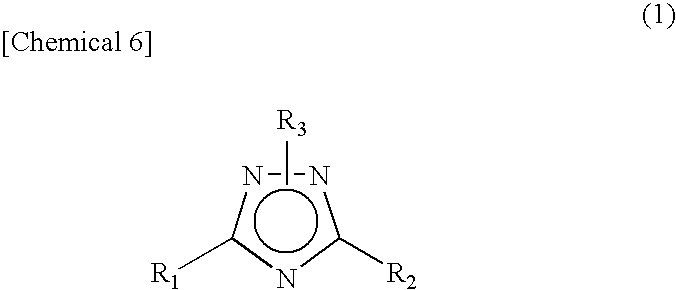
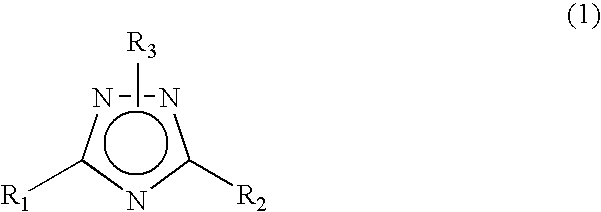
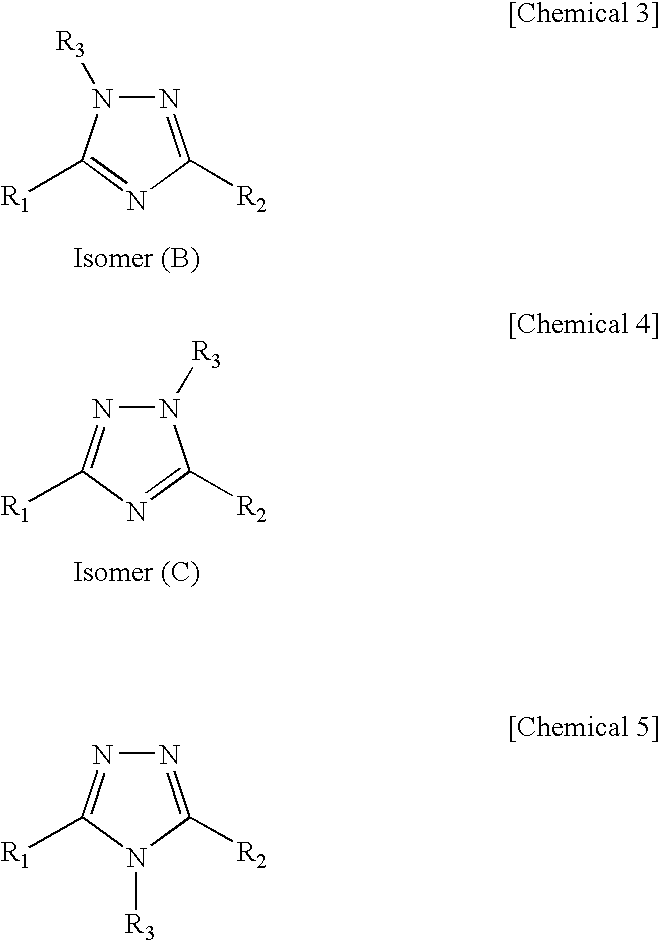
A novel 1,2,4-triazole compound which is useful as a therapeutic agent for hyperuricemia and gout due to hyperuricemia is provided. A compound is represented by the following general formula (1):wherein R2 represents an unsubstituted or substituted pyridyl group, R1 represents a similar pyridyl group, a pyridine-N-oxide group corresponding to these pyridyl groups, or a phenyl group, and R3 represents hydrogen or a lower alkyl group substituted with pivaloyloxy group and R3 bonds to a nitrogen atom in the ring. A process for production of a compound by reacting a nitrile and a hydrazide, and a therapeutic agent, particularly a xanthine oxidase inhibitor are also provided.
Owner:FUJI YAKUHIN CO LTD
Peroxo-containing metal complexes having amine oxide, phosphine oxide, arsine oxide, pyridine N-oxide or pyridine ligands as epoxidation catalysts
InactiveUS6054407AOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsOrganic chemistry methodsPyridine-N-oxideOxygen
PCT No. PCT / EP96 / 03888 Sec. 371 Date Mar. 11, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Mar. 11, 1998 PCT Filed Sep. 4, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 10054 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 20, 1997Olefins can be epoxidized using catalysts I where M is a metal of the 4th to 7th transition group of the Periodic Table of the Elements, L1 is an amine oxide, phosphine oxide, arsine oxide, pyridine N-oxide or pyridine ligand of the formula II, III, VII or VIII, L2 is a customary auxiliary ligand or a further ligand L1 or a free coordination site, X is oxo oxygen or an imido ligand, m is 1 or 2, and n is 1, 2 or 3.
Owner:BASF AG
Pipecolinic acid derivatives, method of manufacturing the same and therapeutic agents containing these compounds
The present invention provides a compound of the general formula (I) or a pharmaceutical salt thereof, wherein, when R1 and R2 are the same they are represented by =O, =N, -OR9 (where R9 is hydrogen, lower alkyl or benzyl), when R1 and R2 are different and one of R1 and R2 is represented by hydrogen, the other is represented by -R5-R6-, (where R5 is -O-, -NH-, -NHCO-, or -NHSO2-, and where R6 is hydrogen, lower alkyl, -Ph-R7, -(CH2)n-O-Ph-R7, (where n=1-6, R7 is hydrogen, hydroxy, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, halogen, nitro, or pyridyloxy), indolyl, N-oxidepyridyl, phthalimide, thienyl, or pyridyl); R3 represents -COOH, -COOEt, -COOMe, -CH2N(OH)CHO, or -CONHOH; R4 represents lower alkyl, thienyl, -Ph-R8 (where R9 represents hydroxy, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, nitro, halogen, pyridyloxy, or phenyl group substituted hydrogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, hydroxy, and halogen), and methods of making compounds within the class of the general formula (I).
Owner:KOTOBUKI PHARMA CO LTD
Condensed Imidazole Compound And Use Thereof
InactiveUS20080167314A1Maintain good propertiesBiocideSenses disorderVascular diseaseAutoimmune disease
The present invention relates to a compound represented by the formula [I]wherein X1, X2 and X3 are each an optionally substituted CH or a nitrogen atom, and any one of X1, X2 and X3 is a nitrogen atom, X4 is an optionally substituted CH, R1 is an optionally substituted phenyl group or an optionally substituted heterocyclic group, and R2 is an optionally substituted pyridin-4-yl group, an optionally substituted pyridine-N-oxide-4-yl group or an optionally substituted pyrimidin-4-yl group, or a salt thereof. The compound has superior p38 MAP kinase inhibitory activity and MMP-13 production inhibitory activity, and is useful as an agent for the prophylaxis or treatment and the like of an inflammatory disease, an autoimmune disease, a debilitating disease, an osteoarticular degenerative disease, a neurodegenerative disease, a vascular disease, a neoplastic disease or an infectious disease.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Processes and reagents for oligonucleotide synthesis and purification
The present invention relates to processes and reagents for oligonucleotide synthesis and purification. One aspect of the present invention relates to compounds useful for activating phosphoramidites in oligonucleotide synthesis. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of preparing oligonucleotides via the phosphoramidite method using an activator of the invention. Another aspect of the present invention relates to sulfur-transfer agents. In a preferred embodiment, the sulfur-transfer agent is a 3-amino-1,2,4-dithiazolidine-5-one. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of preparing a phosphorothioate by treating a phosphite with a sulfur-transfer reagent of the invention. In a preferred embodiment, the sulfur-transfer agent is a 3-amino-1,2,4-dithiazolidine-5-one. Another aspect of the present invention relates to compounds that scavenge acrylonitrile produced during the deprotection of phosphate groups bearing ethylnitrile protecting groups. In a preferred embodiment, the acrylonitrile scavenger is a polymer-bound thiol. Another aspect of the present invention relates to agents used to oxidize a phosphite to a phosphate. In a preferred embodiment, the oxidizing agent is sodium chlorite, chloroamine, or pyridine-N-oxide. Another aspect of the present invention relates to methods of purifying an oligonucleotide by annealing a first single-stranded oligonucleotide and second single-stranded oligonucleotide to form a double-stranded oligonucleotide; and subjecting the double-stranded oligonucleotide to chromatographic purification. In a preferred embodiment, the chromatographic purification is high-performance liquid chromatography.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
Synthesis of pyridine-N-oxide
Synthesis of pyridine-N-oxide is carried out by preparing sodium tungstate into carrier phosphate-tungstic acid by wetting method, vacuum drying to generate anhydrous product, putting anhydrous product and carrier into container, formulating solution by deionized water, agitating to remove water content, drying at high-temperature, activating to obtain catalyst, putting catalyst and pyridine into flask, oxidation reacting by hydrogen peroxide, filtering out catalyst and decompress distilling to obtain the final product. It's simple, fast and cheap and has less solvent.
Owner:天津维智精细化工有限公司
Use of polymers in dishwashing compositions for the removal of grease and oil from plastic dishware, and dishwashing compositions
InactiveUS20070272277A1Easy to cleanHigh molecular weightOrganic detergent compounding agentsAnionic surface-active compoundsAdditive ingredientPyridine-N-oxide
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Catalytic oxidation method of pyridine
The invention discloses a catalytic oxidation method of pyridine. Under oxidation reaction conditions, pyridine, an oxidant, a solvent and a catalyst are mixed and subjected to a contact reaction so as to prepare pyridine-N-oxide. The method is characterized in that the catalyst is a soluble zinc salt modified heteroatom molecular sieve. Under the circumstance of comparable selectivity, the catalytic oxidation activity of the method is improved compared with the prior art.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
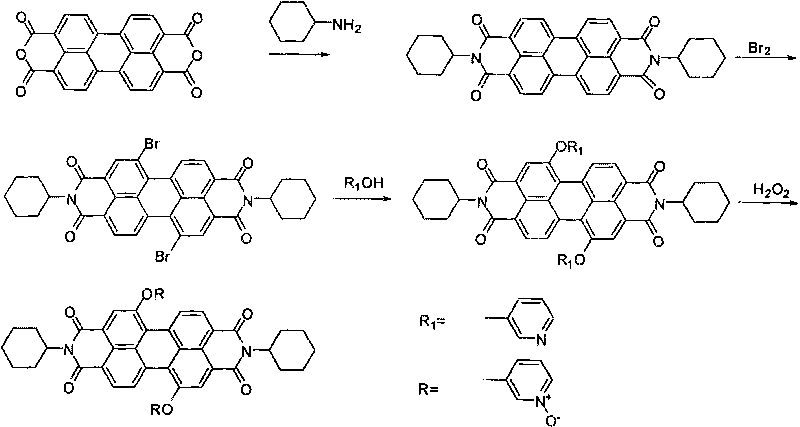
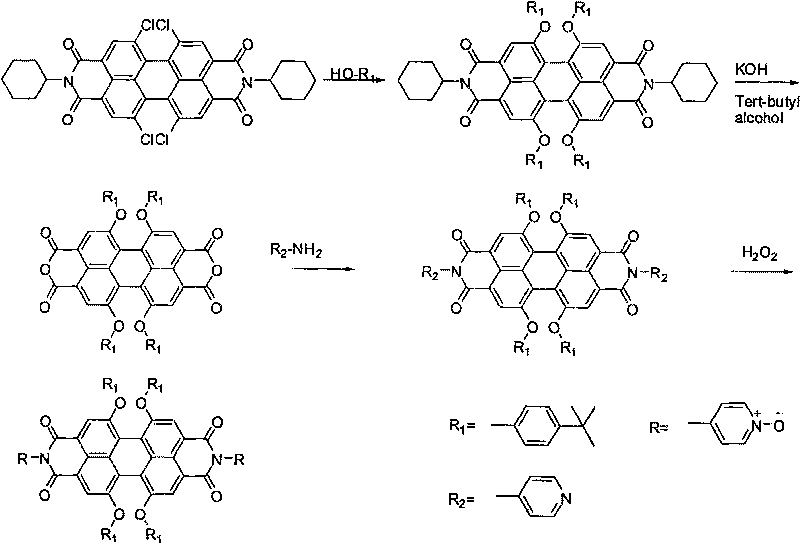
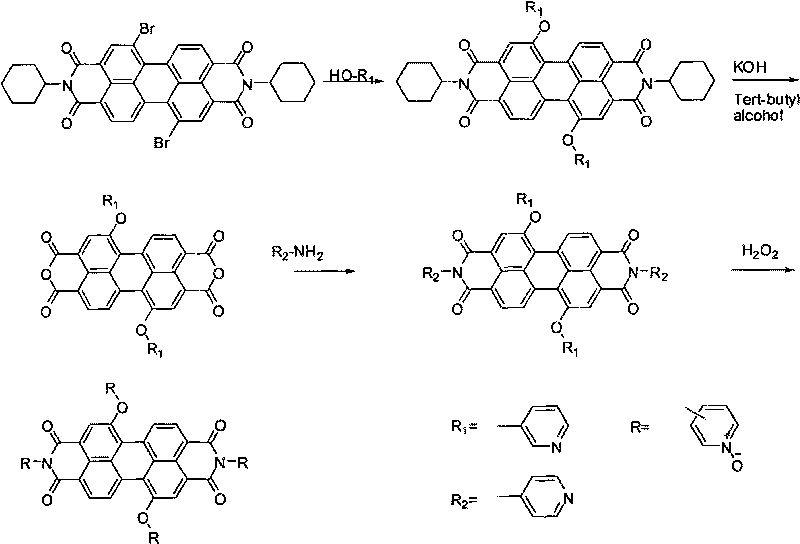
Water-soluble perylene diimide derivatives containing N-pyridine oxide groups and synthetic method thereof
InactiveCN101704816ALow toxicityHigh fluorescence quantum yieldOrganic chemistryLuminescent compositionsQuantum yieldPyridine-N-oxide
The invention discloses water-soluble perylene diimide derivatives containing N-pyridine oxide groups and a synthetic method thereof. In the general structural formula of the water-soluble perylene diimide derivatives containing N-pyridine oxide group, R'=OR or H, the substituents R are same or different and are independently selected from an N-pyridine oxide group or a hydrocarbon group, and at least one substituent R is an N-pyridine oxide group; and the hydrocarbon group is an alkyl group or aryl group. The water-soluble perylene diimide derivatives are oxidized with oxydol after halogenated perylene diimide derivatives react with a substituent reagent containing hydroxyl groups. The invention has the advantages of easily controlled preparation method and conditions, mild reaction, economical raw materials, small toxicity and high fluorescence quantum yield.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
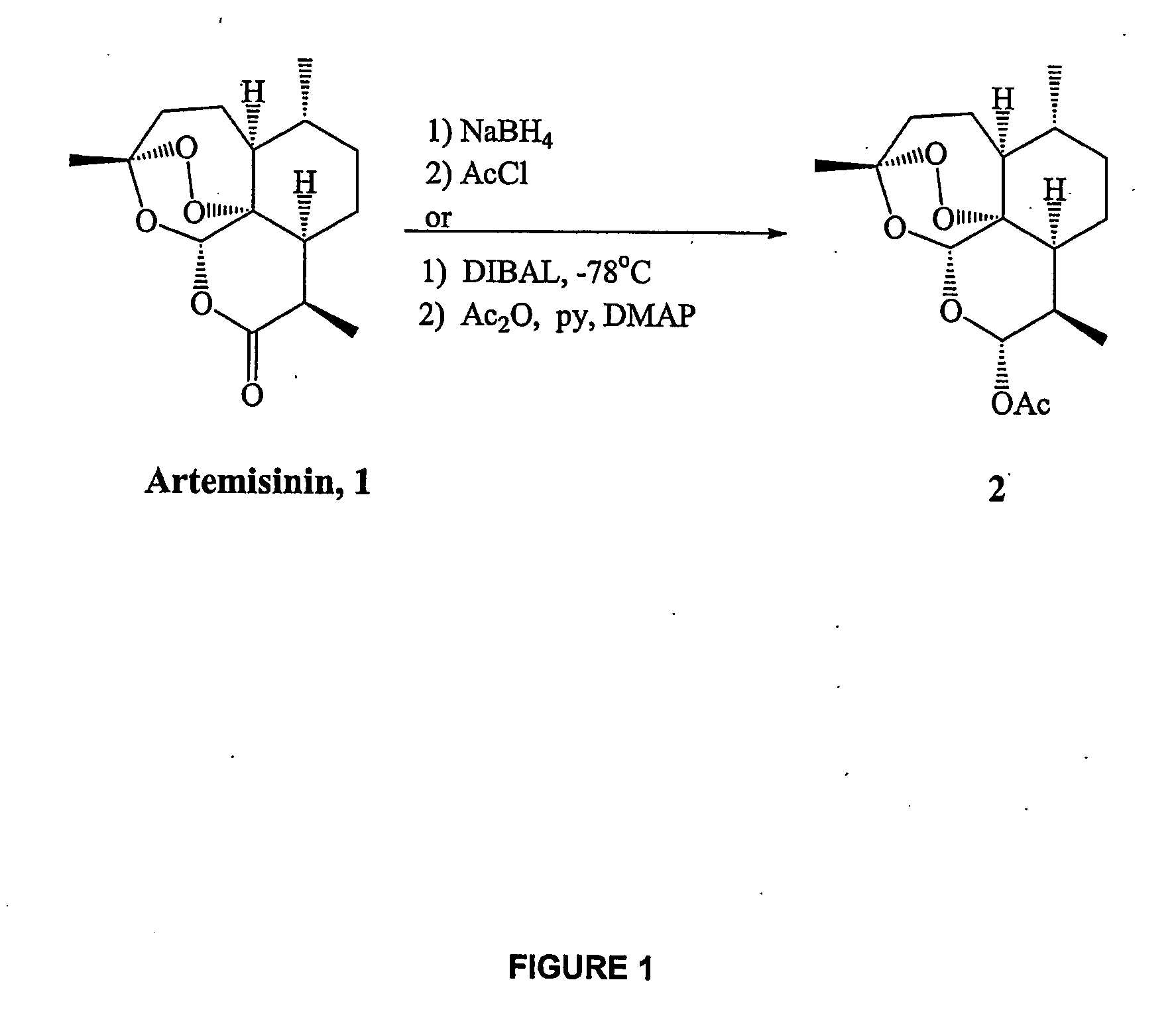
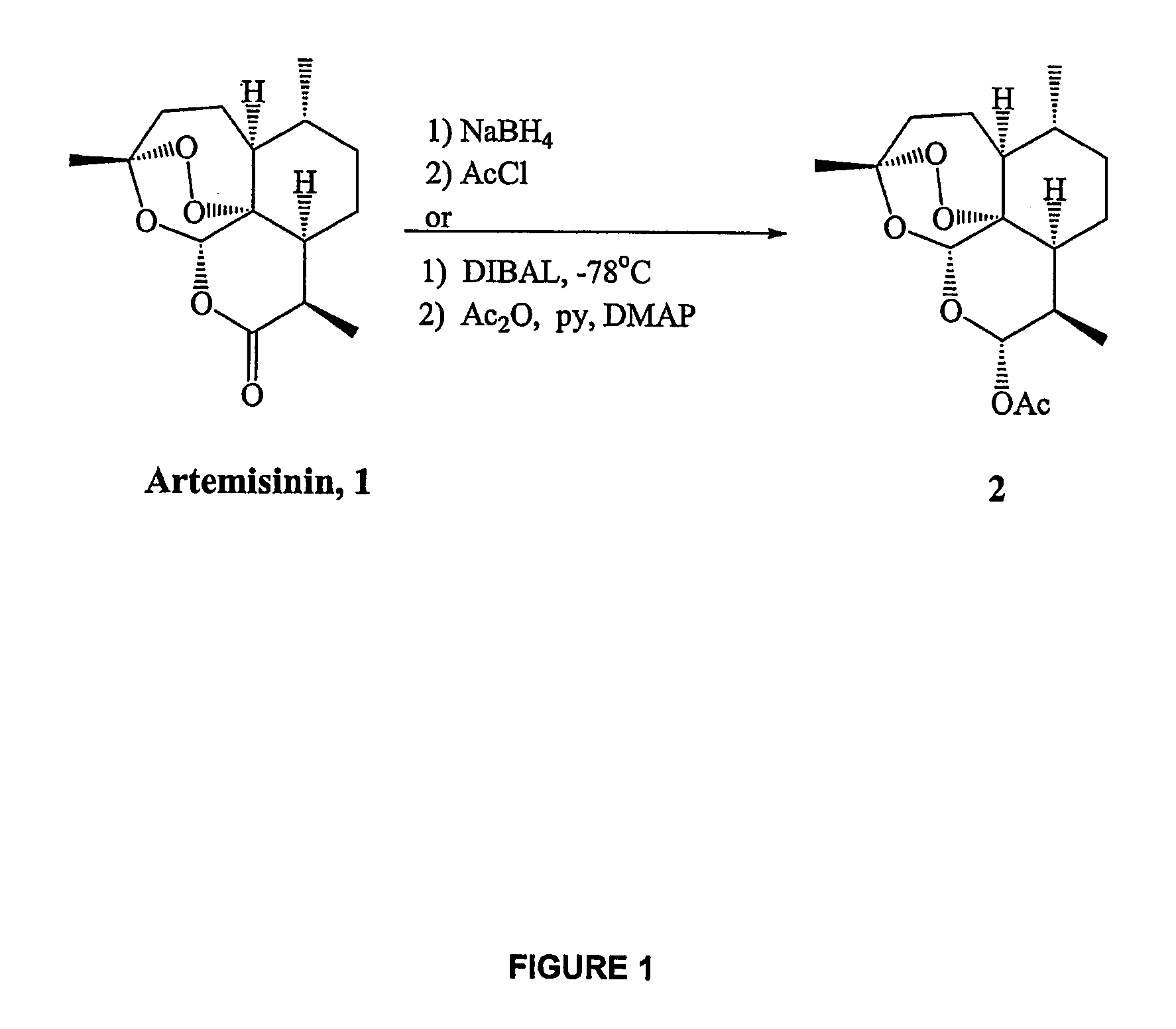
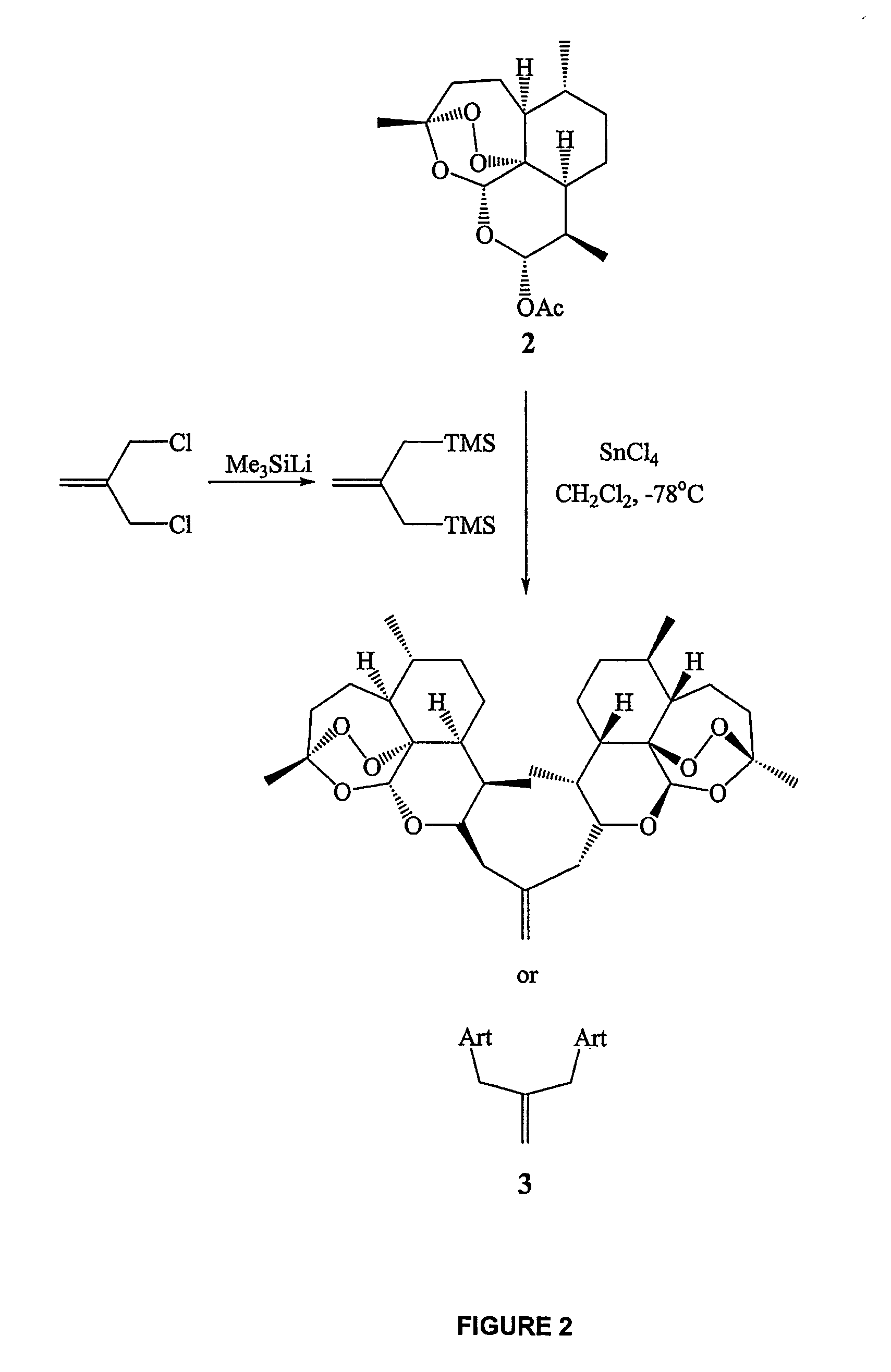
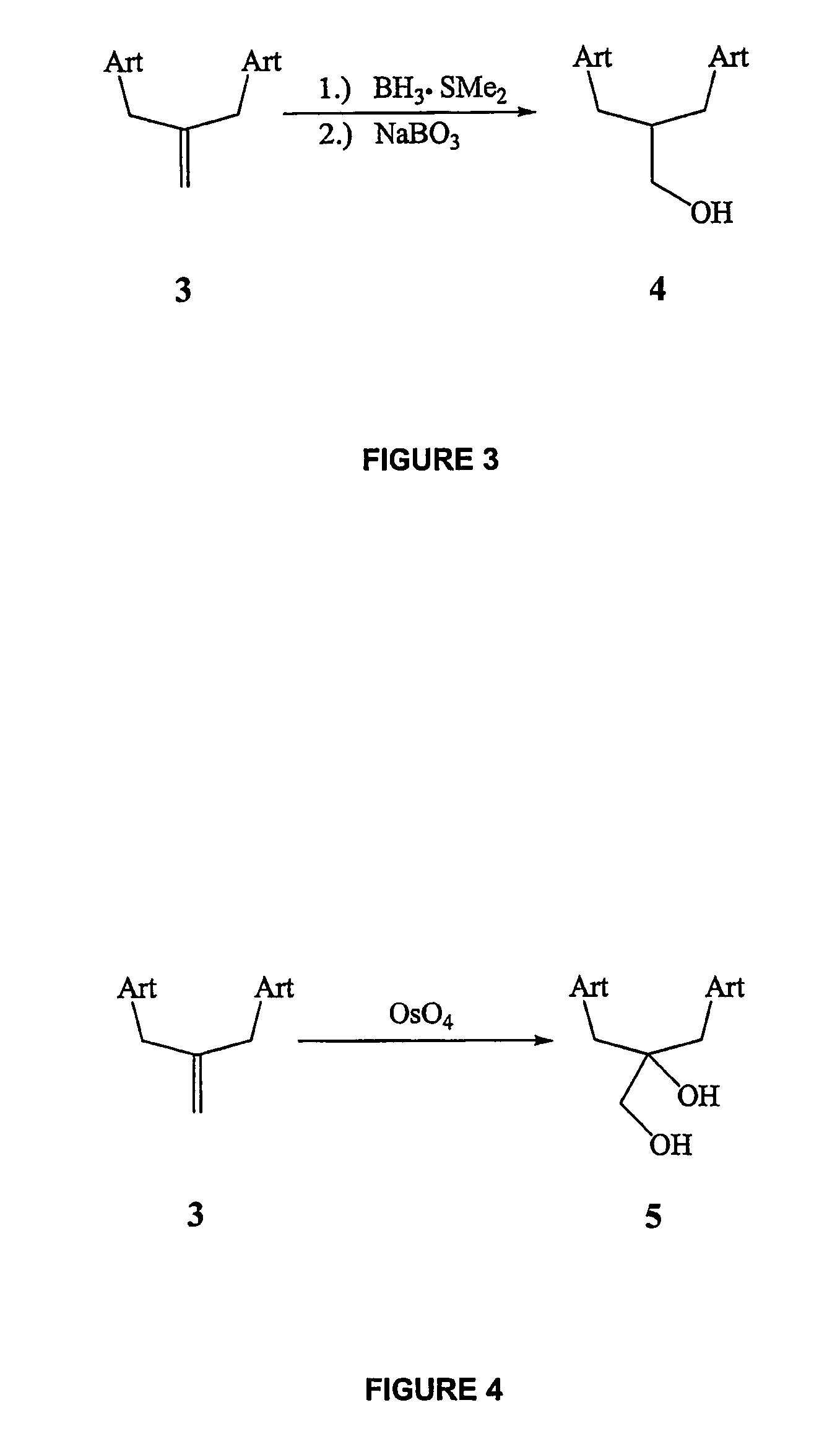
Orally active, antimalarial, anticancer, artemisinin-derived trioxane dimers with high selectively, stability and efficacy and methods of making the same
ActiveUS20060142377A1Easy to transformPotent and selective anticancer activityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideO-Phosphoric AcidCancer cell
In only two steps and in 65% overall yield, natural trioxane artemisinin (I) was converted on gram scale into C-10-carba trioxane dimer (3). This new, very stable dimer was then transformed easily in one additional step into four different dimers (4-7). Alcohol and diol dimers (4 and 5) and ketone dimer (7) are 10 times more antimalarially potent in vitro than artemisinin (1), and alcohol and diol dimers (4 and 5) are strongly inhibitory but not cytotoxic toward several human cancer cell lines. Water-soluble carboxylic acid derivatives (8a-10c and 12) were easily prepared from dimers (4-6); they are thermally stable even at 60° C. for 24 hours, are more orally efficacious as antimalarials than either artelinic acid or sodium artesunate, and have potent and selective anticancer activities. Further derivitization of the alcohol dimers (4 and 17), diol dimer (5) and ketone (7) has produced a number of analogs also antimalarially active in vitro at sub-nanomolar concentrations (most notably: pyridine N-oxides (13, 15, 18, 23, 24 and 25), phosphoric acid triesters (26 and 27), sulfonamide (40) and cyclic carbonate (41)). In addition, dimers (13 and 19) are more efficacious (when administered both orally and i.v.) and less toxic (when administered intraperitoneally to mice as a single dose) than clinically-used sodium artesunate, thereby giving them a better antimalarial therapeutic index than sodium artesunate.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method for preparing high-nitrogen-content porous carbon material by utilizing biomass, product and application thereof
InactiveCN108163853AWell-developed pore structurePromote formationCarbon compoundsPorous carbonSorbent
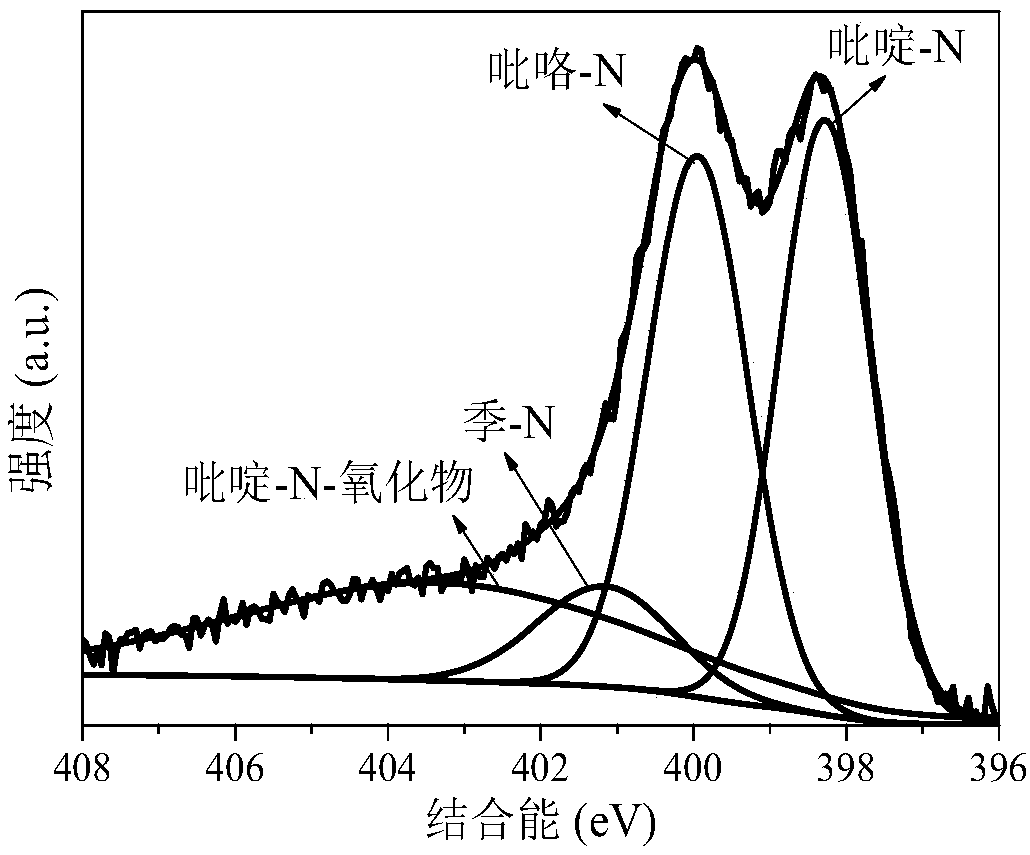
The invention discloses a method for preparing a high-nitrogen-content porous carbon material by utilizing biomass, a product and application thereof. The preparation process is as follows: pulverizing and drying the biomass, mixing the biomass and an activating agent uniformly, performing rapid pyrolysis on the mixture under the atmosphere of ammonia gas, and carrying out reaction between the activating agent and the biomass waste to etch a carbon skeleton to form a developed pore structure; meanwhile, a large amount of holes are formed, nitrogen atoms in the ammonia gas occupy the holes rapidly to form rich active nitrogen-containing functional groups (pyridine-N, pyrrole-N, quaternary-N and pyridine-N-oxide), so that a large amount of nitrogen elements are enriched in pyrolytic carbon;furthermore, the own action of the ammonia gas and the synergistic effect of the activating agent and the ammonia gas can promote formation of coke pores and nitrogen-containing functional groups, anda functional high-nitrogen-content porous carbon material with rich activated nitrogen-containing functional groups is finally formed and has wide application prospect in the fields of catalysts, adsorbents, electrode materials and the like, so that high-additional-value utilization of the biomass is realized.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of N-pyridine oxide
ActiveCN102060760AEasy to makeAtom utilization is highOrganic chemistryPhysical/chemical process catalystsPhosphoric acidPyridine-N-oxide
The invention discloses a preparation method of N-pyridine oxide. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of preparing a phosphorus-tungsten-silicon composite catalyst by taking sodium tungstate, phosphoric acid and silicon dioxide as raw materials, and oxidizing pyridine under the action of the catalyst by taking hydrogen peroxide solution as an oxidizer to obtain the target product. The invention solves the problems of long reaction time, large energy consumption, complex post-treatment and the like in the traditional preparation method of the N-pyridine oxide, and optimizes the technological line of the reaction. The preparation method has the advantages of simple process, mild reaction condition and fast reaction speed, is convenient to operate, and is suitable for industrial production; in addition, the transformation ratio of the pyridine is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI TIANYANG HOT MELT ADHESIVE CO LTD +1
Novel 1 2 4-triazole compound
A novel 1,2,4-triazole compound which is useful as a therapeutic agent for hyperuricemia and gout due to hyperuricemia is provided. A compound is represented by the following general formula (1): wherein R2 represents an unsubstituted or substituted pyridyl group, R1 represents a similar pyridyl group, a pyridine-N-oxide group corresponding to these pyridyl groups, or a phenyl group, and R3 represents hydrogen or a lower alkyl group substituted with pivaloyloxy group and R3 bonds to a nitrogen atom in the ring. A process for production of a compound by reacting a nitrile and a hydrazide, and a therapeutic agent, particularly a xanthine oxidase inhibitor are also provided.
Owner:FUJI YAKUHIN CO LTD
Synthetic method for preparing pyridine N-oxide
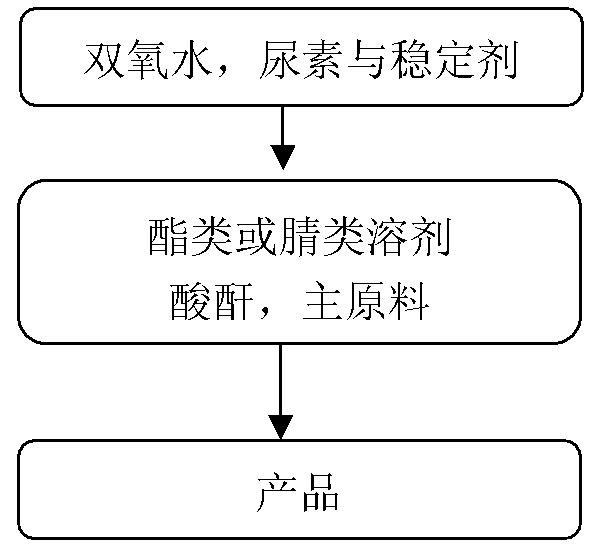
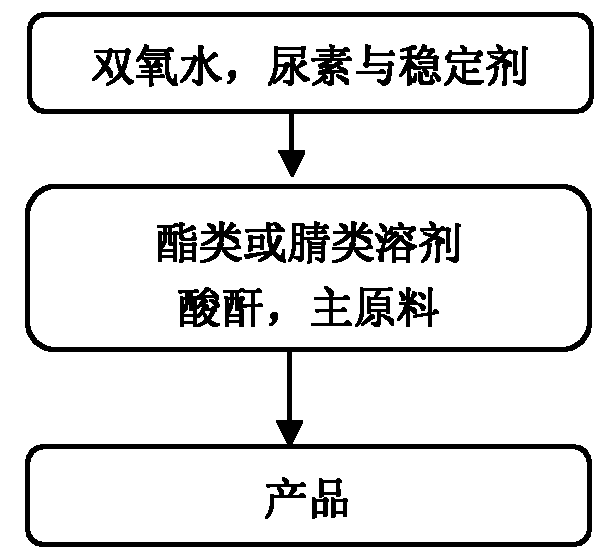
Provided is a synthetic method for preparing pyridine N-oxide. According to the method, raw materials which are commercialized on the market are selected, or pyridine, monosubstituted pyridine or polysubstituted pyridine derivatives which are easy to prepare are used as starting materials, and the materials are oxidized by urea-hydrogen peroxide compound so to prepare the final product. The advantages of the invention are as follows: 1, the raw materials used in the invention are easily available and cheap and are commercialized or easily preparable raw materials, meeting requirements for large scale production; 2, a safer oxidation method is employed in the invention, thereby avoiding condensation of acetate containing hydrogen peroxide and greatly improving safety factors of production; 3, chemical reaction conditions required in the invention are mild, the operation is simple, little pollution to environment is produced, and the method is technically mature for large scale production.
Owner:ASYMCHEM LAB TIANJIN
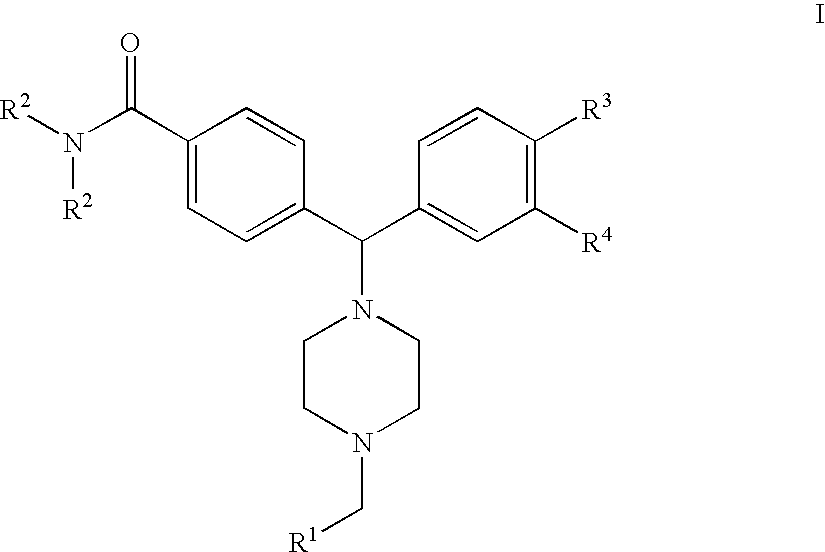
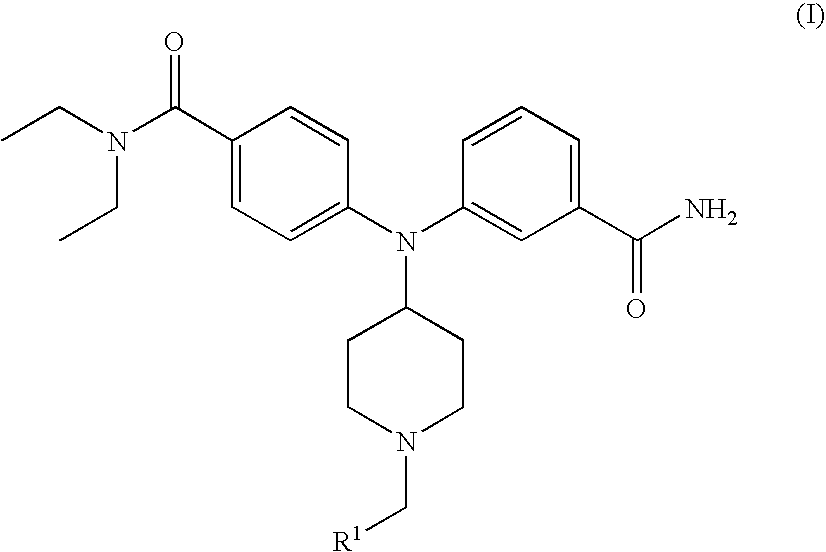
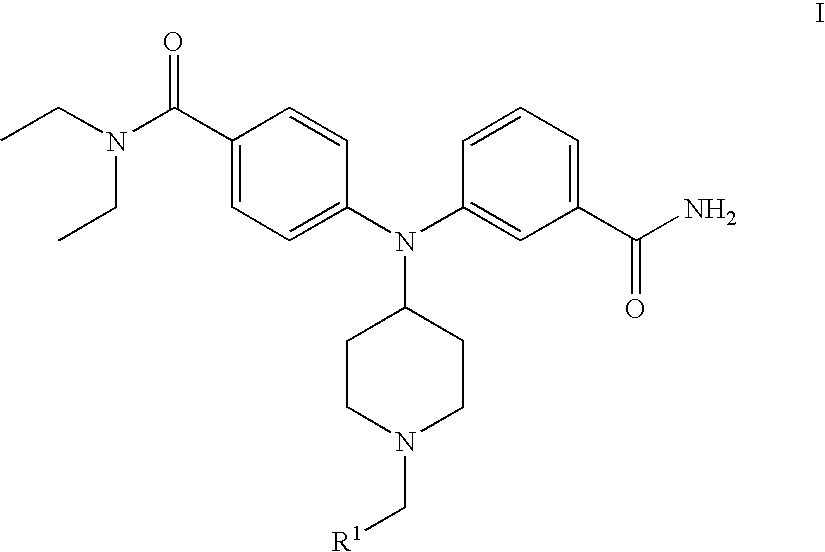
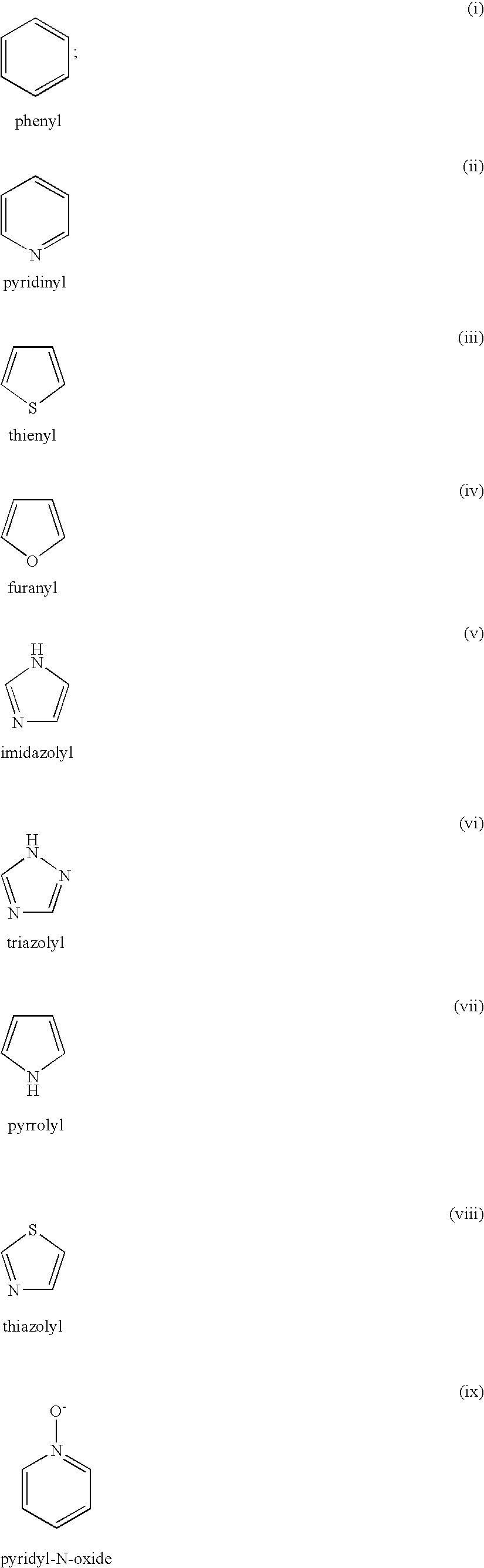
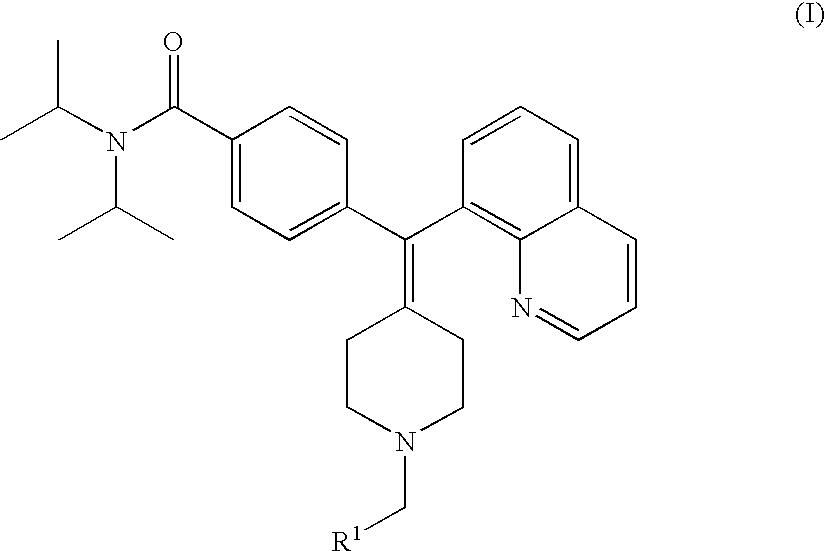
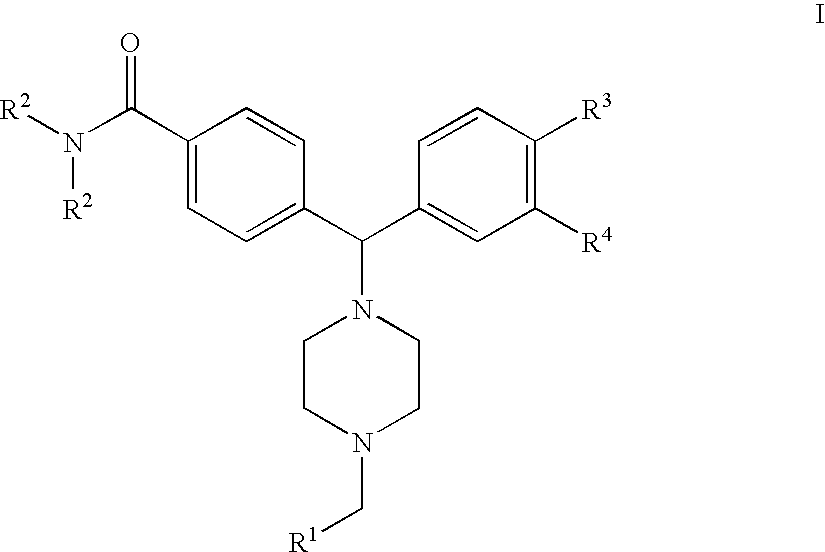
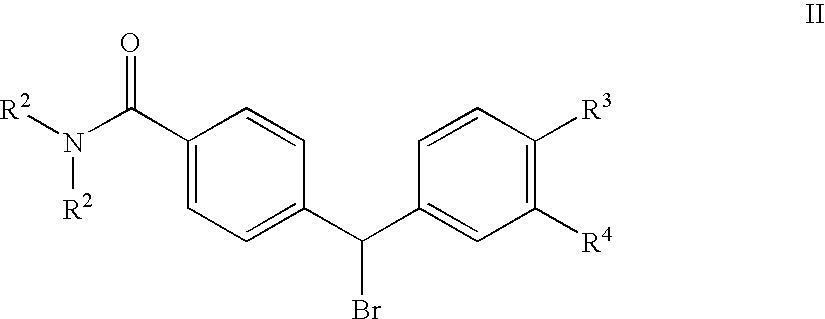
4(phenyl-piperazinyl-methyl) benzamide derivatives and their use for the treatment of pain anxiety or gastrointestinal disorders
Compounds of general formula I R1 is selected from any one of phenyl, pyridinyl, thienyl, furanyl, imidazolyl, pyrrolyl, triazolyl, thiazolyl, and pyridine N-oxide; R2 is independently selected from ethyl and isopropyl; R3 is independently selected from hydrogen and fluoro; R4 is independently selected from —OH, —NH2 and —NHSO2R5; and R5 is independently selected from hydrogen, —CF3 and C1–C6 alkyl, or salts thereof or separate enantiomers and salts thereof; where each R1 heteroaromatic ring may optionally and independently be further substituted by 1, 2 or 3 substituents selected from straight and branched C1–C6 alkyl, NO2, CF3, C1–C6 alkoxy, chloro, fluoro, bromo, and iodo. The substitutions on the heteroaromatic ring may take place in any position on said ring systems; are disclosed and claimed in the present application, as well as separate enantiomers of the compounds and salts and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the novel compounds and their use in therapy, in particular in the management of pain, anxiety and functional gastrointestinal disorders.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Derivatives of 1-phenyl-2-pyridinyl alkyl alcohols as phosphodiesterase inhibitors
ActiveUS20130102576A1Novel methodBiocideLiquid surface applicatorsDiseasePhosphodiesterase inhibitor
Compounds, pyridine N-oxides, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts of formula (I) are useful as inhibitors of the phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) enzyme and for preventing and / or treating diseases of the respiratory tract characterized by airway obstruction, such as asthma or COPD.
Owner:CHIESI FARM SPA
4-(phenyl-(piperidin-4-yl)-amino)-benzamide derivatives and their use for the treatment of pain, anxiety or gastrointestinal disorders
Compounds of general formula IR1 is selected from any one of phenyl, pyridinyl, pyrrolyl, thienyl, furanyl, imidazolyl, triazolyl, and pyridine N-oxide; where each R1 phenyl ring and R1 heteroaromatic ring may optionally and independently be further substituted by 1, 2 or 3 substituents selected from straight and branched C1–C6alkyl, NO2, CF3, C1–C6alkoxy, chloro, fluoro, bromo, and iodo. The substitutions on the phenyl ring and on the heteroaromatic ring may take place in any position on said ring systems; are disclosed and claimed in the present application, as well as their pharmaceutically acceptable salts and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the novel compounds and their use in therapy, in particular in the management of pain, anxiety and functional gastrointestinal disorders.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Orally active, antimalarial, anticancer, artemisinin-derived trioxane dimers
InactiveUS7417156B2Easy to transformPotent anticancer activityBiocideAnimal repellantsCancer cellPhosphoric acid
In only two steps and in 65% overall yield, natural trioxane artemisinin (I) was converted on gram scale into C-10-carba trioxane dimer (3). This new, very stable dimer was then transformed easily in one additional step into four different dimers (4-7). Alcohol and diol dimers (4 and 5) and ketone dimer (7) are 10 times more antimalarially potent in vitro than artemisinin (I), and alcohol and diol dimers (4 and 5) are strongly inhibitory but not cytotoxic toward several human cancer cell lines. Water-soluble carboxylic acid derivatives (8a-10c and 12) were easily prepared from dimers (4-6); they are thermally stable even at 60° C. for 24 hours, are more orally efficacious as antimalarials than either artelinic acid or sodium artesunate, and have potent and selective anticancer activities. Further derivitization of the alcohol dimers (4 and 17), diol dimer (5) and ketone (7) has produced a number of analogs also antimalarially active in vitro at sub-nanomolar concentrations (most notably: pyridine N-oxides (13, 15, 18, 23, 24 and 25), phosphoric acid triesters (26 and 27), sulfonamide (40) and cyclic carbonate (41)). In addition, dimers (13 and 19) are more efficacious (when administered both orally and i.v.) and less toxic (when administered intraperitoneally to mice as a single dose) than clinically-used sodium artesunate, thereby giving them a better antimalarial therapeutic index than sodium artesunate.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
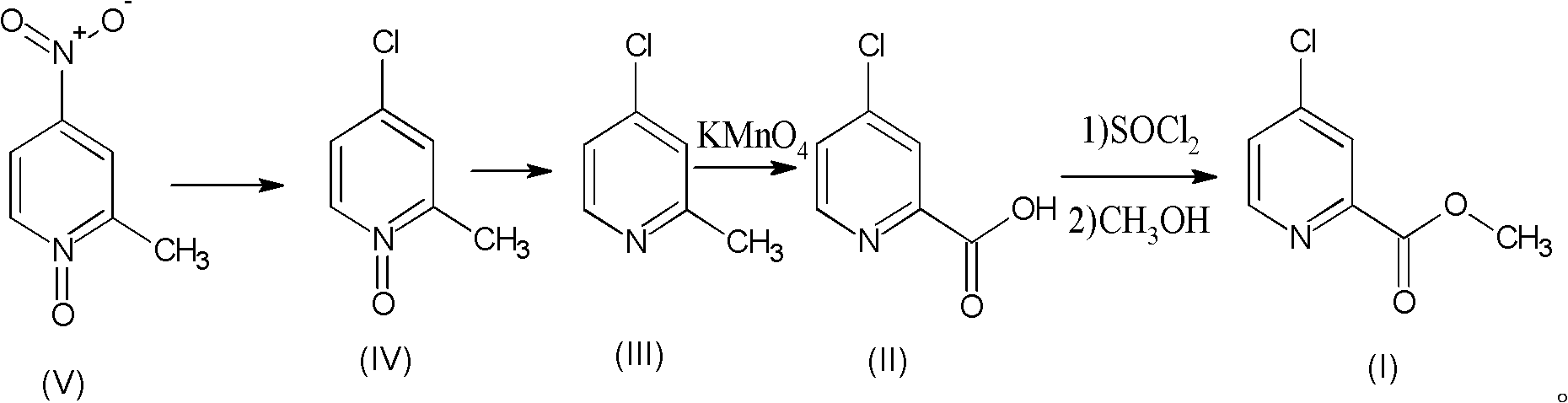
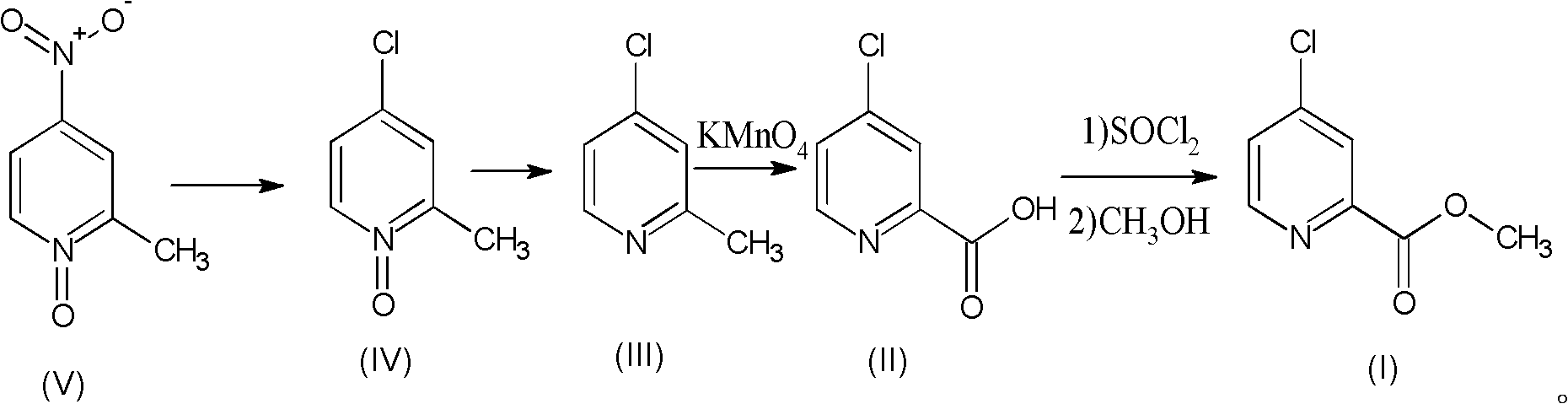
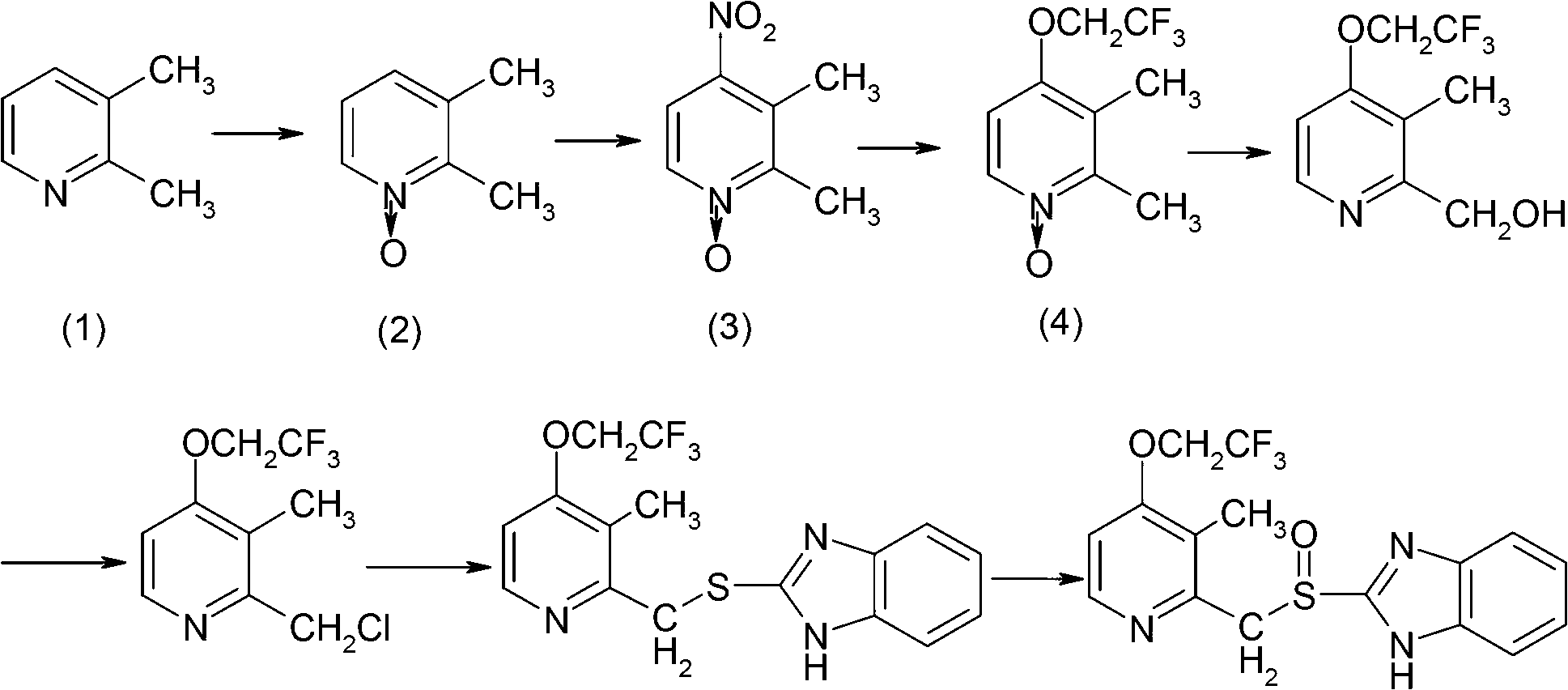
Preparation process of high-purity 4-chloro-2-pyridinecarboxylate hydrochloride
The invention relates to a preparation process of high-purity 4-chloro-2-pyridinecarboxylate hydrochloride, which comprises the following steps of reacting 2-methyl-4-nitropyridine-N-oxide taken as a starting raw material with hydrochloric acid to obtain 4-chloro-2-methyl-pyridine-N-oxide; then dripping phosphorus trichloride into an organic solvent, carrying out reaction for generating 4-chloro-2-methylpyridine, further adding potassium permanganate into water for carrying out oxidation reaction, thus obtaining 4-chloro-2-picolinate; and mixing the 4-chloro-2-picolinate with the catalytic amount of DMF (dimethyfumarate), dripping thionyl chloride, and finally carrying out esterification reaction with methanol so as to obtain the 4-chloro-2-pyridinecarboxylate hydrochloride. The total yield can be up to 36.8%, and the purity can be 99.8% according to the HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography) detection. The process has the advantages of being rich in raw material resources, small in whole process pollution, conductive to controlling three wastes and easy for realizing industrial production.
Owner:SHANDONG JINCHENG PHARMACEUTICAL GROUP CO LTD
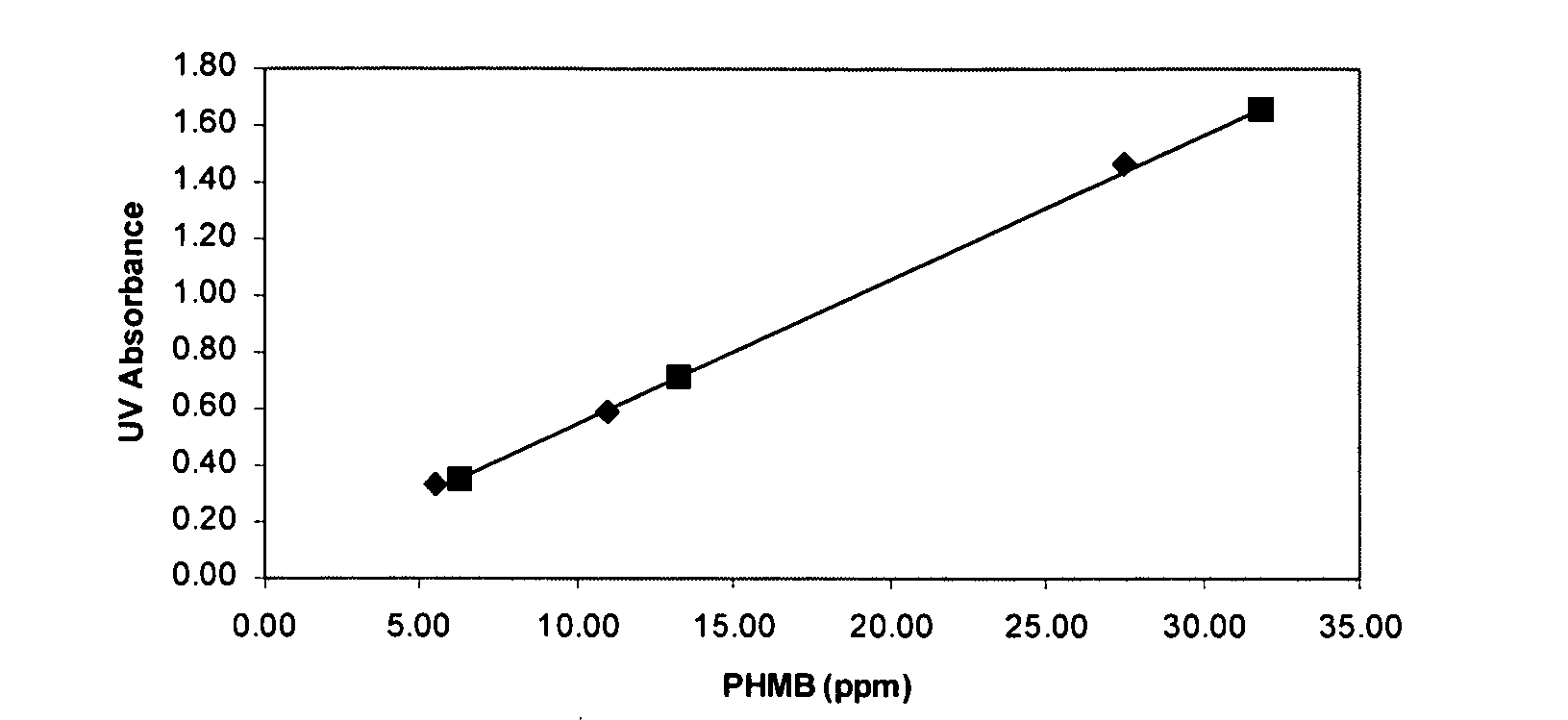
Synthesis method for high-quality and low-cost bispyrithione
The invention discloses a synthesis method for synthesizing high-quality and low-cost bispyrithione and relates to a synthesis method for the bispyrithione. The synthesis method comprises the following steps of: 1, performing mild oxidation reaction on halogenated pyridine and hydrogen peroxide in the presence of a catalyst to synthesize halogenated pyridine-N-oxide; 2, extracting and purifying the halogenated pyridine-N-oxide by using a solvent; 3, reacting the purified halogenated pyridine-N-oxide and a sulfhydrylation reagent under the alkaline condition to obtain 2-mercaptopyridine-N-oxide sodium; reacting 4,2-mercaptopyridine-N-oxide sodium under the acid condition to obtain 2-mercaptopyridine-N-oxide; and reacting 5,2-mercaptopyridine-N-oxide and oxidant to obtain a targeted product bispyrithione. By the method, the quality stability of a product can reach more than 99.5 percent; reaction conditions are mild; and cost is low.
Owner:BINHAI COUNTY MINGHONG FINE CHEM
Industrial production method of chloromethyl pyridine derivative
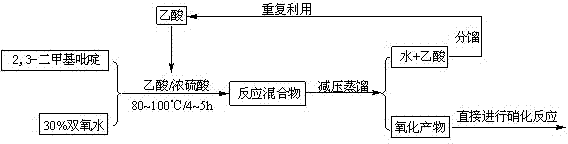
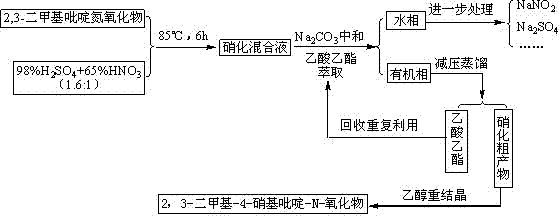
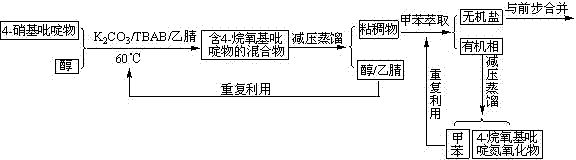
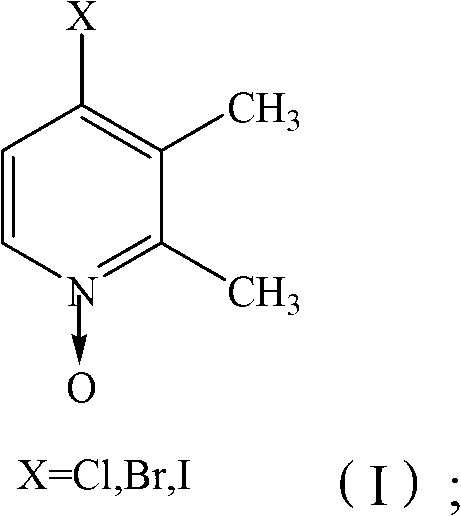
InactiveCN103539729AReduce manufacturing costLow priceOrganic chemistryNitrogen oxidesPyridine-N-oxide
The invention discloses an industrial production method of a chloromethyl pyridine derivative. The industrial production method comprises an oxidation reaction process, a nitration reaction process, a replacement reaction process, a rearrangement hydrolysis reaction process and a chloromethylation reaction process. 2,3-dimethyl pyridine as a raw material undergoes an oxidation reaction to produce a pyridine N-oxide, the pyridine N-oxide undergoes a nitration reaction to produce 2,3-dimethyl-4-nitropyridine-N-oxide, the 2,3-dimethyl-4-nitropyridine-N-oxide undergoes a replacement reaction to produce 4-alkoxypyridine-N-oxide, the 4-alkoxypyridine-N-oxide undergoes a rearrangement hydrolysis reaction to produce a 2-hydroxy-4-alkoxypyridine compound, and the 2-hydroxy-4-alkoxypyridine compound undergoes a chloromethylation reaction to produce the refined chloromethyl pyridine compound. The industrial production method realizes recycle of waste produced in production, realizes environmental protection and waste comprehensive utilization, changes waste into values and injurants into benefits, greatly reduces a production cost and improves product competitiveness.
Owner:ANHUI COSTAR BIOCHEM CO LTD
4-(phenyl-piperdin-4-ylidene methyl)-benzamide derivatives and their use for the treatment of pain, anxiety or gastrointestinal disorders
InactiveUS6838468B2Good analgesic effectImprove side effectsBiocideNervous disorderDiseasePyridine-N-oxide
Compounds of general formula I[Chemical formula should be inserted here. Please see paper copy] R1 is selected from any one of phenyl, pyridinyl, pyrrolyl, thienyl, furanyl, imidazolyl, triazolyl, and pyridine N-oxide; where each R1 phenyl ring and R1 heteroaromatic ring may optionally and independently be further substituted by 1,2 or 3 substituents selected from straight and branched C1-C6 alkyl, NO2, CF3, C1-C6 alkoxy, chloro, fluoro, bromo, and iodo. The substitutions on the phenyl ring and on the heteroaromatic ring may take place in any position on said ring systems; are disclosed and claimed in the present application, as well as their pharmaceutically acceptable salts and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the novel compounds and their use in therapy, in particular in the management of pain, anxiety and functional gastrointestinal disorders.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Metal organic frame based on pyridine oxide ligand, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106632027AImprove stabilityEasy to recycleCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationSuzuki reactionPyridine-N-oxide
The invention discloses a metal organic frame based on a pyridine oxide ligand, and a preparation method and application thereof. The structural formula of the metal organic frame Zn-MOF is (ZnLBr2)n, wherein L refers to the pyridine oxide ligand L with the structural formula shown as below, and n refers to a non-zero natural number. A preparation method of the pyridine oxide ligand L includes (1), preparing 3, 5-dihalogenated pyridine into 3, 5-dihalogenated pyridine-N-oxide; (2), subjecting the 3, 5-dihalogenated pyridine-N-oxide to Suzuki reaction to obtain the pyridine oxide ligand L. According to the preparation method of the metal organic frame based on the pyridine oxide ligand, ZnBr2 liquor is laid on pyridine oxide ligand L liquor, and standing is performed to obtain a colorless monocrystal, namely the metal organic frame Zn-MOF. When the metal organic frame serves as a catalyst, reaction temperature is mild, reaction time is short, activity is high, catalyst consumption is low, the catalyst is easy to recycle, catalyst utilization rate is increased, and cost is reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
4(Phenyl-piperazinyl-methyl) benzamide derivatives and their use for the treatment of pain anxiety or gastrointestinal disorders
Compounds of general formula I R<1 >is selected from any one of phenyl, pyridinyl, thienyl, furanyl, imidazolyl, pyrrolyl, triazolyl, thiazolyl, and pyridine N-oxide; R<2 >is independently selected from ethyl and isopropyl; R<3 >is independently selected from hydrogen and fluoro; R<4 >is independently selected from -OH, -NH2 and -NHSO2R<5>; and R<5 >is independently selected from hydrogen, -CF3 and C1-C6 alkyl, or salts thereof or separate enantiomers and salts thereof; where each R<1 >heteroaromatic ring may optionally and independently be further substituted by 1, 2 or 3 substituents selected from straight and branched C1-C6 alkyl, NO2, CF3, C1-C6 alkoxy, chloro, fluoro, bromo, and iodo. The substitutions on the heteroaromatic ring may take place in any position on said ring systems; are disclosed and claimed in the present application, as well as separate enantiomers of the compounds and salts and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the novel compounds and their use in therapy, in particular in the management of pain, anxiety and functional gastrointestinal disorders.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Use of polymers in dishwashing compositions for the removal of grease and oil from plastic dishware, and dishwashing compositions
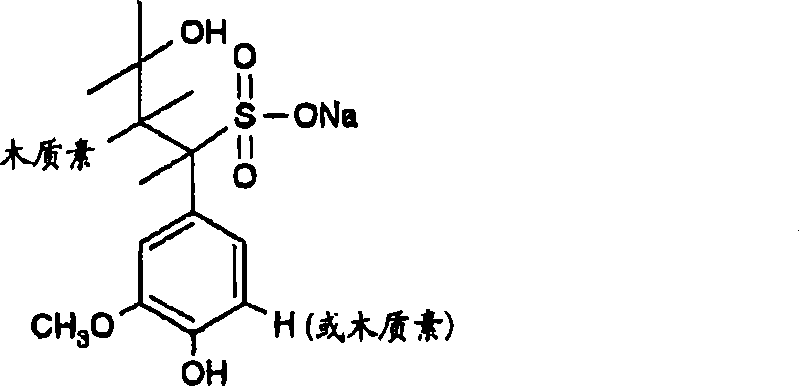
InactiveCN101023157AEasy to cleanOrganic detergent compounding agentsAnionic surface-active compoundsPyridine-N-oxideCopolymer
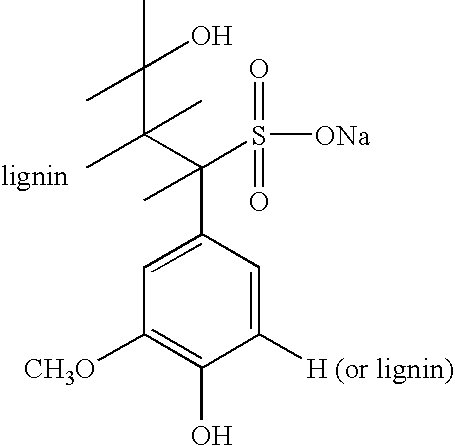
The present invention relates to the use of a copolymer comprising at least one first monomer and at least one second monomer, said first monomer being selected from the group of acrylate, substituted acrylate, maleate, or substituted maleate, and said second monomer being selected from styrene or substituted styrene, wherein the weight ratio of said first monomer to said second monomer is from 80:20 to 20:80; polyvinyl pyrrolidone; polyvinyl pyridine N-oxide; lignin-sulphonate; polyethylene-imine alkoxylates; and mixtures thereof; in dishwashing cleaning compositions for the removal of grease and oil from plastic dishware. The present invention also relates to a dishwashing cleaning composition, comprising from 0.0001% to 5% by weight of the composition of a copolymer comprising at least one first monomer and at least one second monomer, said first monomer being selected from the group of acrylate, substituted acrylate, maleate, or substituted maleate, and said second monomer being selected from styrene or substituted styrene, wherein the weight ratio of said first monomer to said second monomer is from 80:20 to 20:80, and from 10% to 60% by weight of the composition of a surfactant system, the surfactant system comprising at least 0.5% by weight of the composition of an amine oxide. The present invention also relates to a kit comprising a container and the dishwashing composition, and to a process of cleaning dishware using the dishwashing cleaning composition.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Preparation method of lansoprazole intermediate
InactiveCN102838537AEasy to recycleAvoid reaction explosion hazardOrganic chemistryLansoprazolePyridine-N-oxide
The invention provides a preparation method of a lansoprazole intermediate. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: mixing trifluoroethanol with 2, 3-dimethyl-4-chloropyridine-N-oxide and inorganic alkali compounds, and conducting reflux reaction to obtain 2, 3-dimethy-4-trifluoroethyoxyl-pyridine-N-oxide. Since the 2, 3-dimethyl-4-chloropyridine-N-oxide is used as raw materials, the trifluoroethanol not only is used as a reaction raw material, but also is used as a reaction solvent and other solvents are not needed to be introduced, the complex post-treatment of recovering the trifluoroethanol through fractionation is avoided and the step of post-reaction treatment is simplified; and since cheap and easy-to-obtain industrial alkali compounds such as potassium carbonate and potassium hydroxide are used, not only can the reaction be conducted smoothly and is the yield high, but also catalysts for catalysis are not needed, the step of complex catalyst recovery is not needed, the post-reaction treatment becomes simple, the degree of safety is high, the cost is lower and the yield is high.
Owner:SHOUGUANG FUKANG PHARMA
Method for preparing pyridine N-oxide
ActiveCN101570509AImprove conversion rateLong stable operation timeOrganic chemistryMolecular sieve catalystsConvex structurePyridine-N-oxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing pyridine N-oxide, which is characterized in that the pyridine N-oxide is prepared by mixing pyridine, oxygen, hydrogen, diluent gas, solvent and catalyst for contact reaction at 0-180 DEG C and 0.1-3.0 MPa, wherein the mol ratio of the pyridine to the oxygen to the hydrogen to the diluent gas is 1:0.1-10:0.1-10:0-100, the mass ratio of the pyridine to the catalyst is 0.5-50:1, and the mass ratio of the solvent to the catalyst is 20-1000:1, and in addition, the catalyst is microporous titanium silicon material or compound containing the microporous titanium silicon material, an oxide formed by the microporous titanium silicon material has the formula of xTio2.100SiO2.yEmOn.zE, wherein x is equal to 0.001-50.0, y+z is equal to 0.005-20.0, y / z is less than 5, E can be one or more of such noble metals as Ru, Rh, Pd, Re, Os, Ir, Ag, Pt and Au, and both m and n are the numbers meeting the need of the oxidation of the E. The grains of the epoxy propanol can be in hollow structures or concavo-convex structures, and the method ensures the high conversion rate, the good selectivity and the long operation period of the pyridine.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Preparation method of 4-trifluoroethoxyl pyridine-N-oxide derivative
The invention provides a preparation method of a 4-trifluoroethoxyl pyridine-N-oxide derivative. In the method, 4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxyl)pyridine oxide, 2,3-dimethyl-2-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxyl)pyridine oxide and 2-methyl-3-chlorin-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxyl)pyridine oxide are prepared by taking a readily-available 4-nitro-N-pyridine oxide derivative and 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol as raw materials under the action of a strong alkali. The reaction conditions are mild, and operation is simple.
Owner:SHANGHAI SINOFLUORO SCI
Method for synthetizing medical intermediate heterocyclic group pyridine N-oxide
The invention relates to a method for synthetizing medical intermediate heterocyclic group pyridine N-oxide of the following chemical formula (II). The method comprises the steps that in an inert gas atmosphere, compound of the formula (I) and tetrahydrofuran are added to a reaction still, then catalyst, alkali, oxidizing agents and addition agents are sequentially added into the reaction still, stirring is carried out to warming up to 80-100 DEG C to carry out reaction for 8-10 hours, the chemicals are cooled down to room temperature after reaction, a saturated salt solution is added to the chemicals, extraction is carried out for three times through diethyl ether, organic phases are combined, anhydrous magnesium sulfate is adopted for drying, vacuum concentration is carried out, and column purification is carried out to obtain the compound of the chemical formula (II) (please see the specification), wherein R is selected from H, halogen, C1-C6 alkyl groups and phenyl groups with or without substituent groups. According to the method, target products can be obtained in high yield through appropriate selection and combination of the catalyst, the alkali, the addition agents and the oxidizing agents, and the method has wide application prospects and industrialized potential productivity in the technical field of medical intermediate synthetic technology and the field of organic chemical synthesis.
Owner:福建未来药业有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com