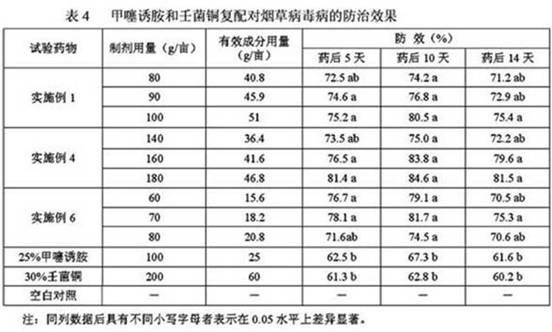
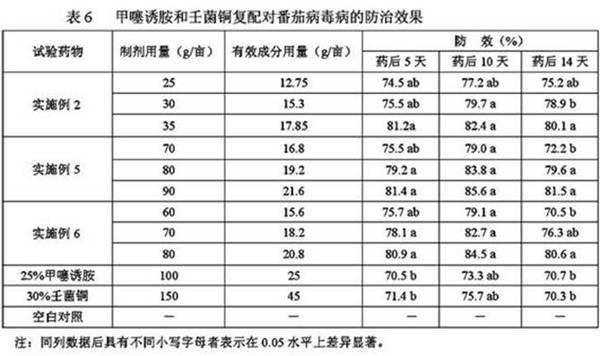
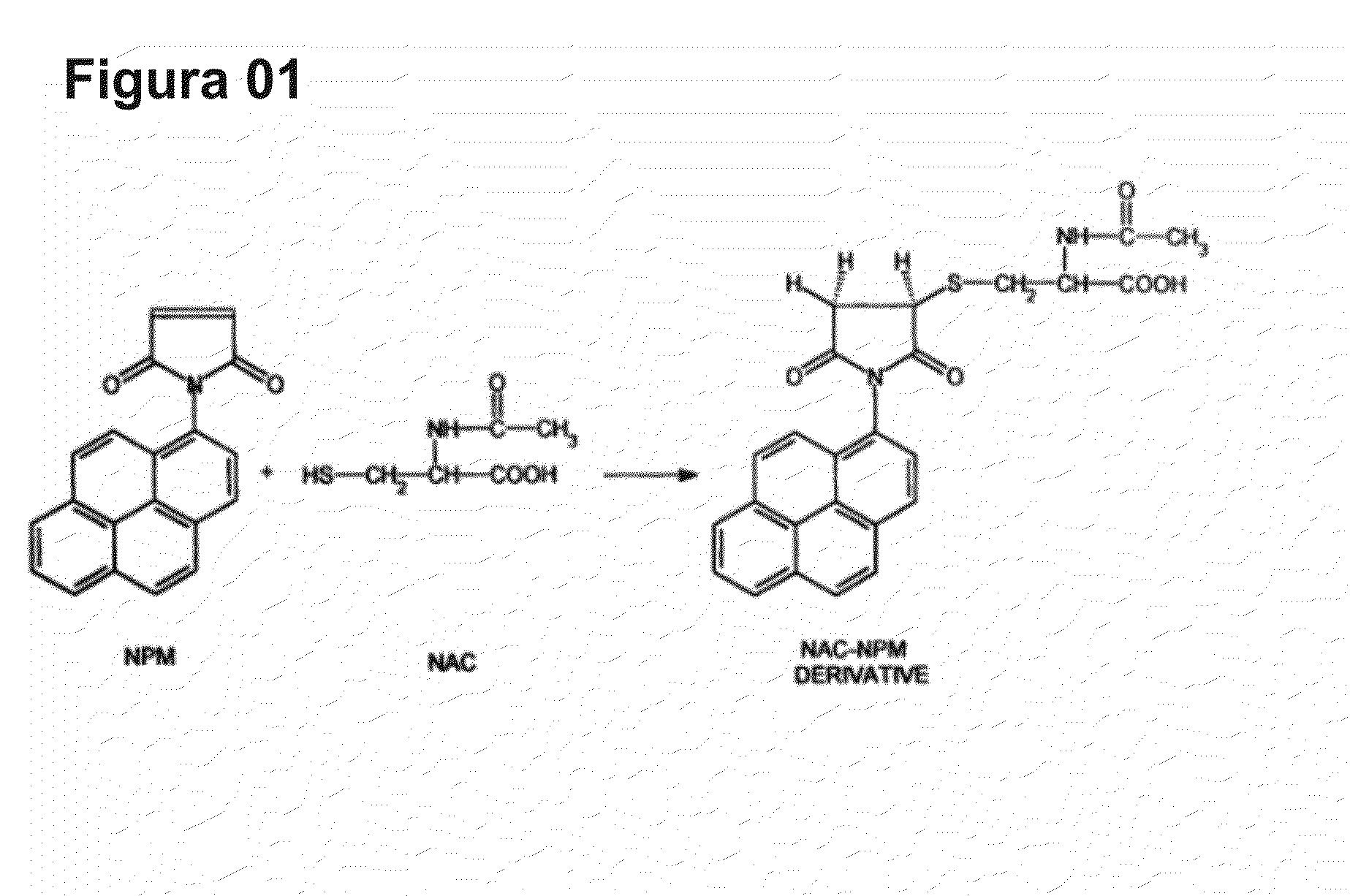
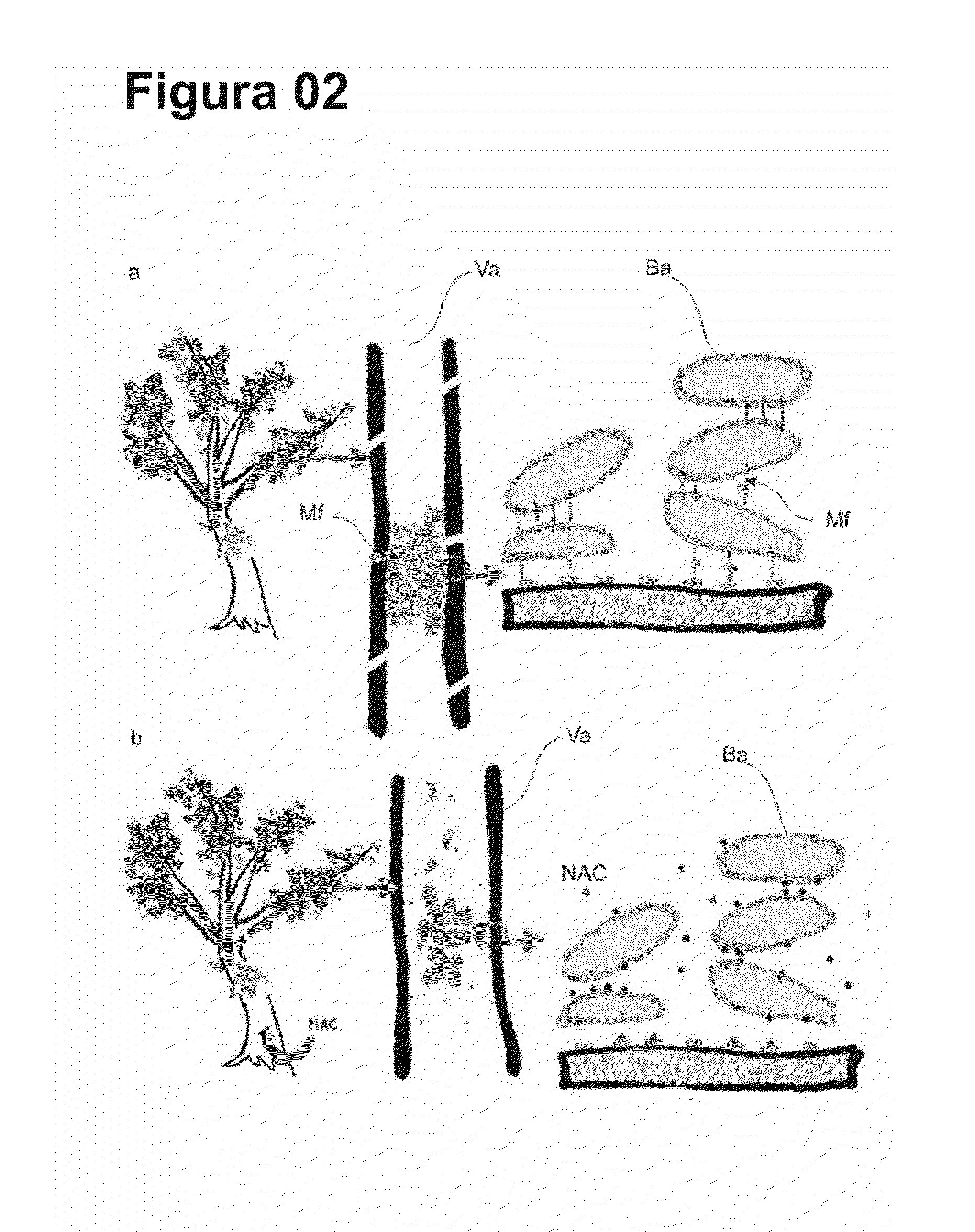
Patents
Literature
285 results about "Canker disease" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Canker, plant disease, caused by numerous species of fungi and bacteria, that occurs primarily on woody species. Symptoms include round-to-irregular sunken, swollen, flattened, cracked, discoloured, or dead areas on the stems (canes), twigs, limbs, or trunk.
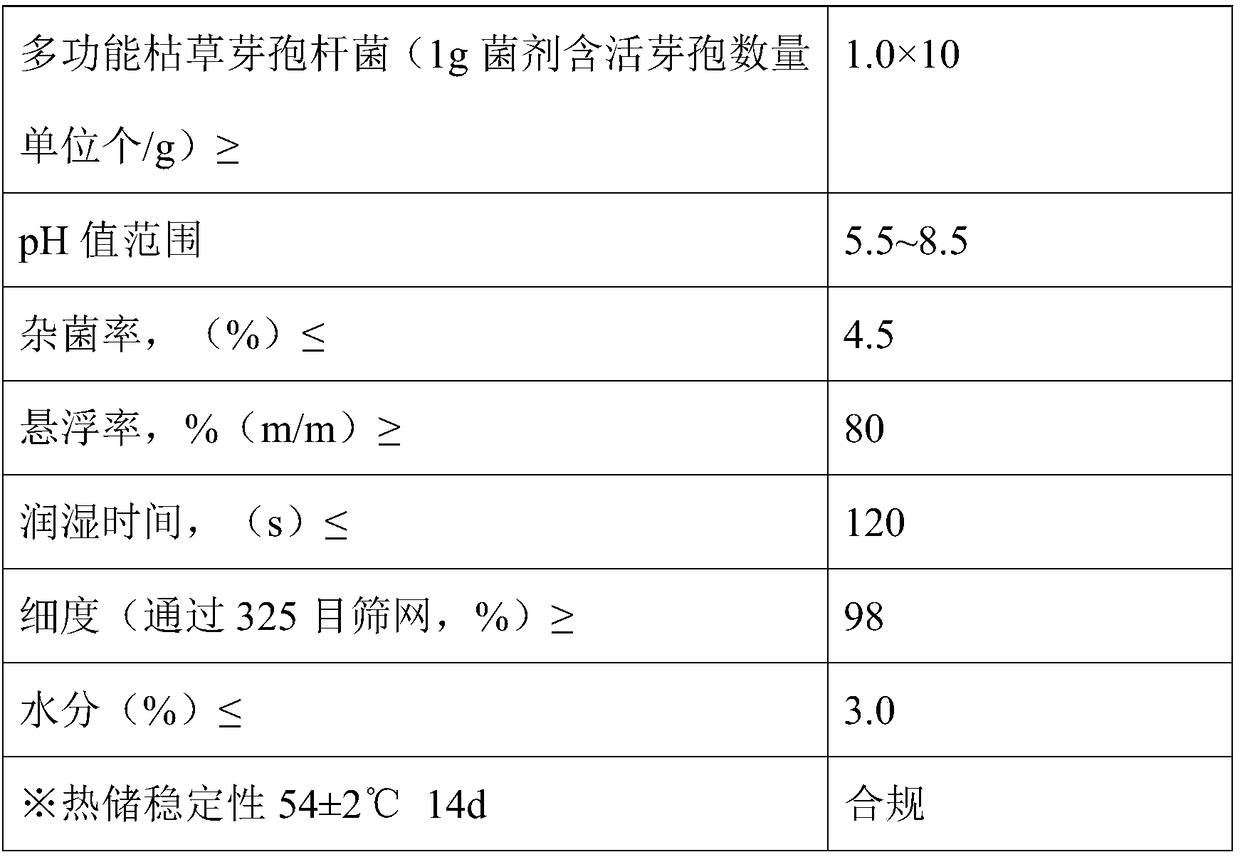
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens K-8 and bactericide thereof
ActiveCN103131655AExtended shelf lifeSimple manufacturing methodBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyBacillus amyloliquefaciens
The invention provides bacillus amyloliquefaciens K-8 and bactericide thereof. The preservation number of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens K-8 strain is CGMCCNO.6486. The bactericide takes the bacillus amyloliquefaciens K-8 strain as an active ingredient. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens K-8 strain is cultured to obtain a liquid bactericide, and a solid bactericide can be obtained by adding a carrier or mixture of the carrier and auxiliaries into the liquid bactericide. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens K-8 strain and the bactericide thereof provided by the invention can be used for effectively preventing and treating diseases such as bacterial wilt, wilt, angular spot, banded sclerotial blight, rice false smut, soft rot, rot, canker and root rot. The bactericide is simple to prepare and easy to use, is applicable to industrialized production and has wide application prospect.
Owner:内蒙古永太化学有限公司
Thiazole zincium suspension agent and method for producing the same
ActiveCN101194611ANo pollution in the processHealth hazardBiocideOrganic chemistryBiotechnologyBacterial disease
The invention discloses a thiazole zinc suspending agent and process for preparation, wherein, the suspending agent contains thiazole zinc 5-60%, wetting agent 3-8%, dispersing agent 1-5%, thickening agent 0-3%, anti-freeze agent 0-5%, antiseptic 0-1% and defoaming agent 0-0.5% and water allowance. The medicament is evenly dispersed and manufactured by adopting arts of combination of sandblast or high-shear homogeneity and sandblast, or combination of high-shear homogeneity and high pressure homogeneity. The medicament has high efficiency, which can effectively prevent and cure bacterial diseases such as rice bacterial blight, striped disease and citrus ulcer and the like, and uses water as dispersed medium, and has little environmental pollution and low toxicity. The preparation has excellent performance, which can be stored for two years without deposition and phenomenon of lamination. The invention has long life span of a goods shelf, and is not easily burnt and is safe to store and transport.
Owner:ZHEJIANG XINNONG CHEM CO LTD +1
Burkholderia pyrrocinia and application thereof in control of dothiorella gregaria
ActiveCN101555458ARapid identificationAccurate identificationBiocidePlant growth regulatorsFungal endophyteMicrobiology
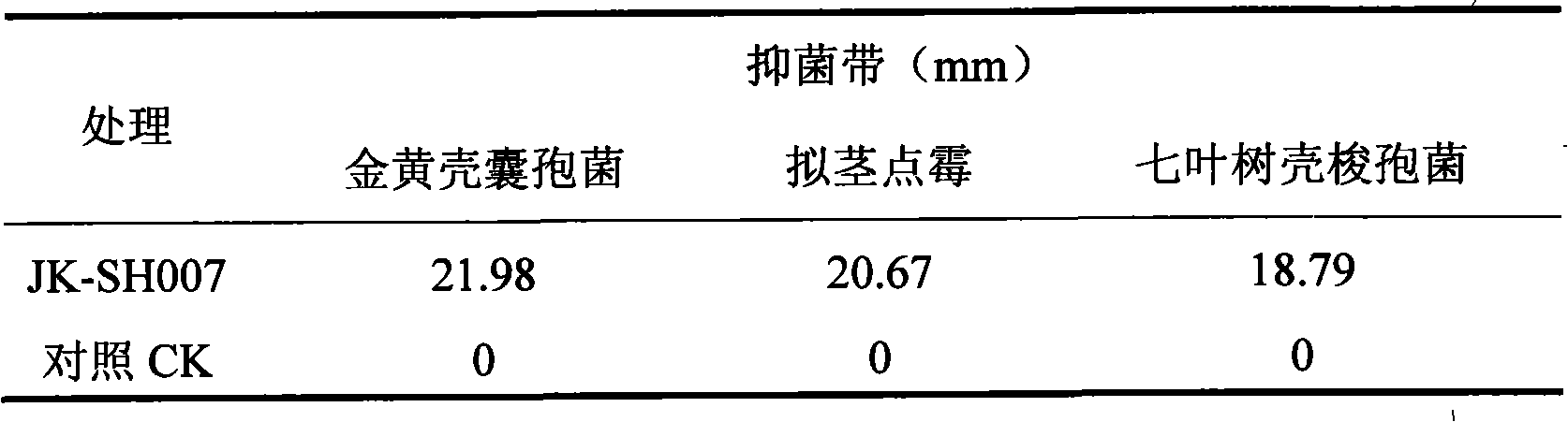
The invention discloses a burkholderia pyrrocinia JK-SH007 which is classified and named as burkholderia pyrrocinia and preserved in China center for type culture collection (CCTCC) with the preservation number of M 209028 and the preservation date of February 18th, 2009. The invention also discloses the application of the burkholderia pyrrocinia in controlling dothiorella gregaria and promoting poplar to grow. The invention further provides a bactericide for controlling dothiorella gregaria, which is obtained by inoculating the JK-SH007 in a culture medium to be fermented and cultured. The JK-SH007 is plant endophyte which has strong inhibiting effect for botryosphaeria dothidea of the poplar and antagonism for various pathogenic fungis, and has the advantages of simple culture condition, easy storage and commercial process as well as good developing and applying prospect.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Endogenetic streptomycete for preventing kiwi berry bacterial canker and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101486982AInhibit synthesisGood water solubilityBiocideBacteriaStreptomyces glaucusKiwi fruit
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological pesticides and discloses a method for identifying a Streptomyces glaucus sp.nov yangling TIASA5 strain and a method for preparing an active substance of the strain and applications of the method. The strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Center of Microbial Culture Collection Management Committee in Microbiology Institute, Chinese Academy of Science on August 16th, 2007 with the preservation number of CGMCC No.2132. The strain has better preventive and therapeutic effects on bacterial canker of kiwi fruits. The strain is separated from plant tissues, generates active metabolite that does not have toxic action to the plant tissues, and has stability, convenient spraying and convenient popularization and application.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Murcott cultivation and management method
InactiveCN104969818AIncrease productionQuality improvementCultivating equipmentsPlant LousesYoung tree
The present invention provides a murcott cultivation and management method. The method comprises the steps of plantation and treelet management comprising plantation and tree crown cultivation; resulting tree management comprising nutrient and water management, training and pruning, and blossom and fruit preservation; and control of major diseases and pests comprising anthracnose, cankers, melanosis, plant louses and red spiders. With adoption of the murcott cultivation and management method provided by the present invention, the yield and quality of the murcott can be effectively raised.
Owner:吴伦忠
Streptomyces samsunensis and application thereof
ActiveCN108102961AGood inhibitory effectEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideBacteriaColletotrichum fragariaeMicrobiology
The invention provides actinomycetes which is streptomyces samsunensis XJC-2-6, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M 2017620. The streptomyces samsunensis XJC-2-6 provided by the invention has anantagonism on fusarium oxysporum f.sp cubense No. 4, curvularia fallax, curvularia lunata, btoryosphaeria dothidea, colletotrichum acutatum, colletotrichum gloeosporioides, colletotrichum fragariae,botrytis cinerea, fusarium oxysporum (schl.) f.sp cucumerinum owen, colletotrichum acutatum, pyricularia oryae cav, fusahum graminearum sehw, botryosphaeria dothidea and the like, has wide developmentspace on prevention and treatment of Panama disease of banana, microscler streak disease of banana, large grey speck disease of banana, tree canker of banana, anthracnose of pepper, anthracnose caused by colletotrichum gloeosporioides, anthracnose of strawberry, disease caused by botrytis cinerea, fusarium wilt of cucumber, anthracnose of mango, rice blast, wheat scab, ring rot of apple and the like, and has very good development and application prospects.
Owner:HAIKOU EXPERIMENTAL STATION CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI +1
Streptomycete for producing volatile antibacterial substances and application thereof
ActiveCN108977382AGrowth inhibitionReduce severityBiocideBacteriaLaboratory culturePratylenchus zeae
The invention provides streptomycete for producing volatile antibacterial substances and application thereof. The streptomycete is named as Streptomycesmicionensis TF78; the streptomycete was collected to Guangdong Microbiological Culture Collection Center on October 25th, 2017, and the collection number is GDMCC NO:60254. The streptomycete has the inhibiting functions on the pathogenic bacteria of cucumber blight, tomato gray mold, teak canker, banana fungal stem rot, rice blast fungi, mango phomopsis leaf spot, mango pestalotiopsis leaf spot, mango botryosphaeria branch blight, mango anthracnose and the like.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Kiwifruit tree canker preventing and controlling agent and using method thereof
InactiveCN102057938AHigh cure rateThe preparation process is simple and reliableBiocidePlant growth regulatorsVitamin CPyrrolidinones
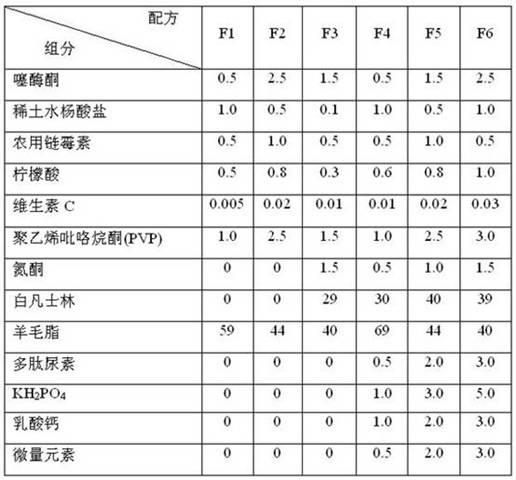
The invention discloses a kiwifruit tree canker preventing and controlling agent and a using method thereof. The preventing and controlling agent comprises the following components in part by weight: 0.1 to 3 parts of benziothiazolinone, 0.05 to 1 part of rare earth salicylate, 0.05 to 1 part of agricultural streptomycin, 0.05 to 1 part of citric acid, 0.001 to 0.03 part of vitamin C, 0.5 to 5 parts of polyvinylpyrrolidone and 40 to 80 parts of lanolin. Iron oxide red water does not flow out of a wound after the kiwifruit tree canker preventing and controlling agent is used for 1 to 3 days, and the wound can be cured in 5 to 7 days, so the preventing and controlling agent has the characteristics of short time, quick response, high cure rate, simple and convenient preparation process, no three wastes (waste water, waste gas and industrial residues) during production and use and environmental friendliness, and is safe and efficient.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Preventive method for kiwifruit canker
InactiveCN102511351AAvoid cankerImprove the growing environmentCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyLime sulfur
A preventive method for kiwifruit canker includes system approaches of breaking down invasion ways of germs, avoiding proper temperature for the germs, managing water, fertilizer and soil, managing plants, managing sterilization, managing freeze protection and the like. The preventive method has the advantages that lime sulfur basic solution can be applied to wounds of the kiwifruit plants to break down the invasion ways of the germs; as the germs only attack at the temperature range of from 5 DEG C to 29 DEG C, avoiding the proper temperature for the germs to manage pruning can avoid canker;managing water, fertilizer and soil can improve growth environment for the plants and improve germ resistance of the plants; managing the plants can also improve disease resistance of the plants; managing sterilization can kill the germs; managing freeze protection can also avoid germ invasion due to plant injury; and using the series of system approaches can effectively avoid kiwifruit canker.
Owner:CHONGQING HONGYI AGRI
Kiwifruit canker control method and comprehensive control agent
ActiveCN102293137AChanging the perception that ulcer disease is incurableChanging the Incurable PerspectiveBiocideFertilising methodsAgricultural scienceAgricultural engineering
The invention provides a control method and integrated control agent for actinidia cankers. The control method and integrated control agent provided by the invention not only are good in bactericide and fertilizer effects, but also are easy to use and cost-saving, and can facilitate the improvement of toughness and disease resistance of an actinidiaceae tree, increase the yield of the actinidiaceae tree, and improve the fruit quality of the actinidiaceae tree. In the invention, through adopting the combination of an effective nutrient fertilizer and a bactericide, good bactericide and bio-fertilizer effects are achieved, therefore, the control method provided by the invention is a new high-tech integrated control method and a new resource combination, and can thoroughly control the harm of actinidia cankers to actinidiaceae trees.
Owner:吴新忠
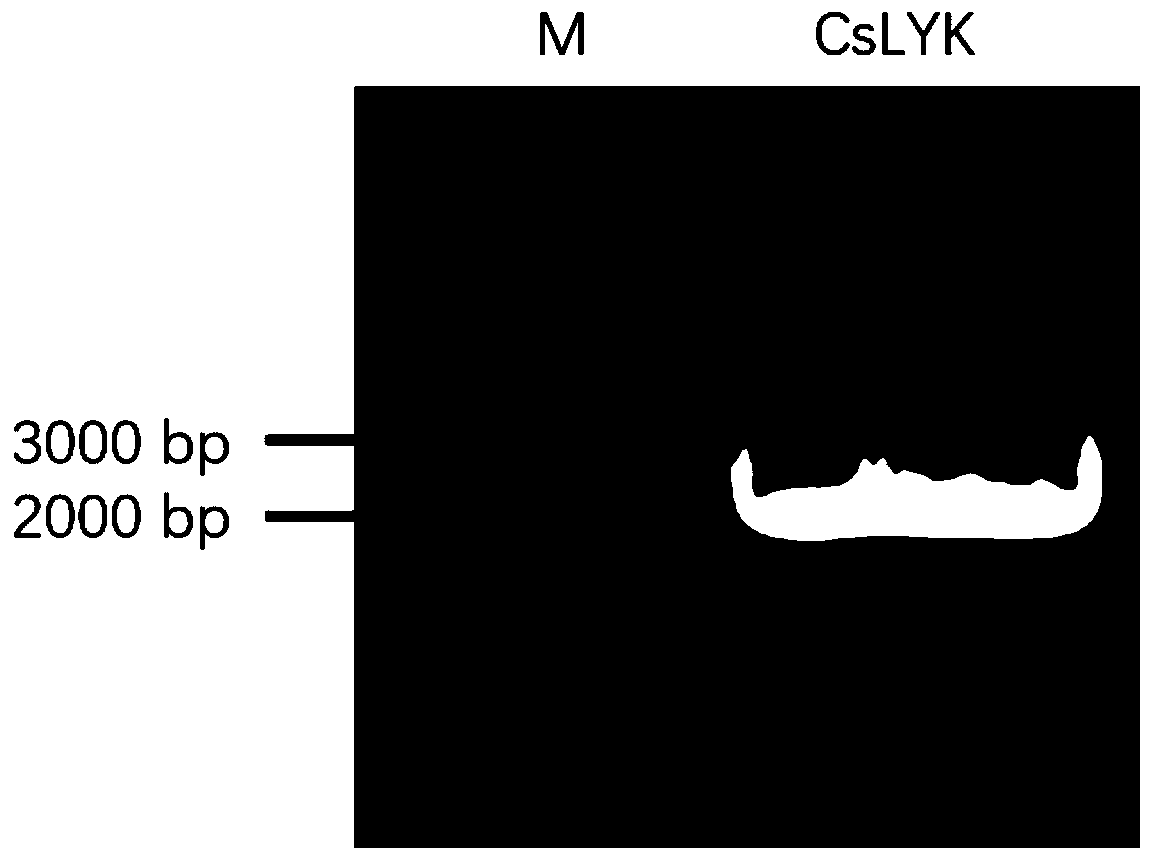
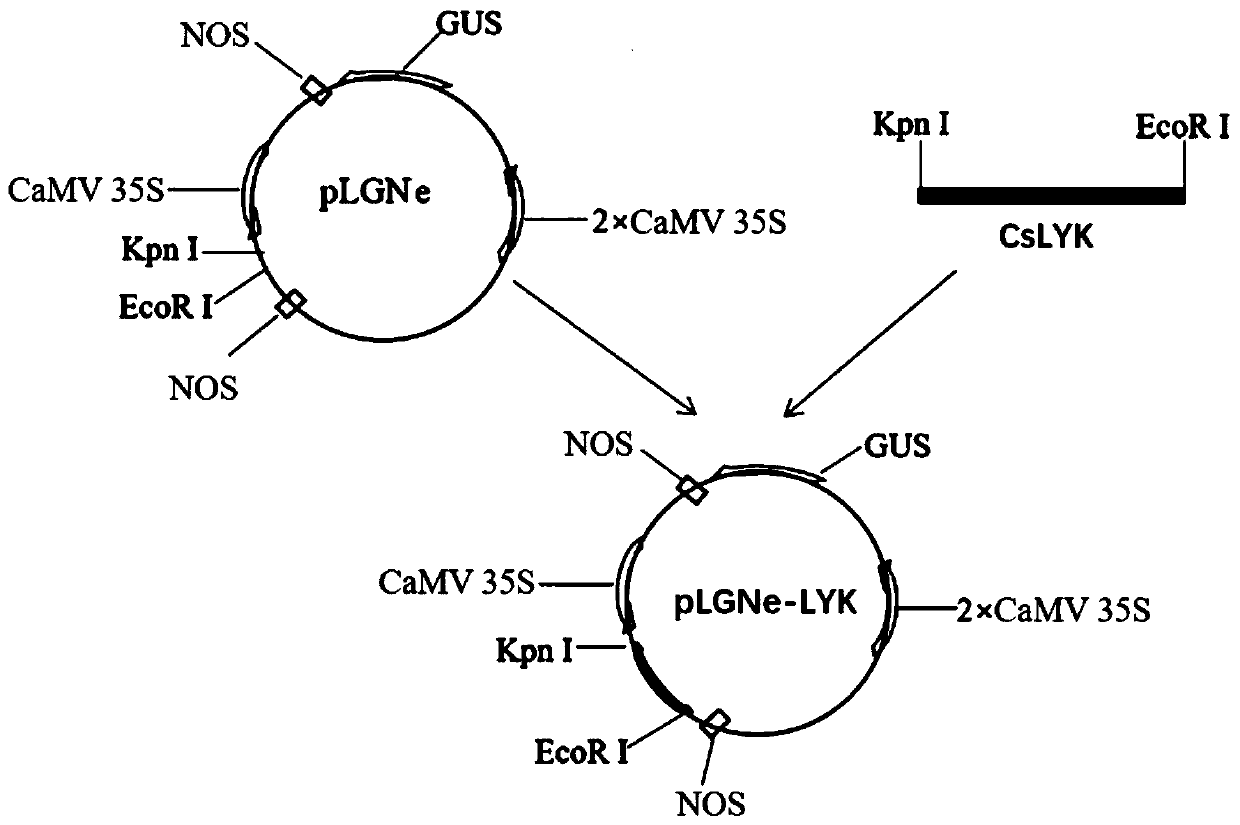
Application of CsLYK gene and encoded protein thereof in improving resistance to citrus canker
ActiveCN110819607AIncrease resistanceReduced incidence of ulcer diseaseMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesBiotechnologyCitrus volkameriana
The invention discloses application of CsLYK gene and an encoded protein thereof in improving resistance to citrus canker. The encoded protein of the CsLYK gene is a citrus LysM-like receptor proteinphosphokinase, and is named CsLYK protein. The nucleotide sequence of the CsLYK gene is a nucleotide sequence shown in SED ID No. 1; the protein sequence of the CsLYK gene is an amino acid sequence shown in SED ID No. 2. The invention also protects a breeding method of citrus resisting bacterial canker, and the method comprises following steps of integrating a citrus LysM-like receptor protein phosphokinase-encoding gene into a citrus through an overexpression vector to effectively improve citrus resistance to bacterial canker. The invention has great application value for breeding of citrus resisting bacterial canker; thereby laying the foundation of genetic breeding of citrus resisting canker, and vigorously promoting the development and application of citrus resisting canker genetic engineering.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Bacillus subtilis for controlling citrus canker
InactiveCN103173394AGood prevention and control effectEnhanced inhibitory effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyThielaviopsis basicola
The invention relates to a bacillus subtilis CCCQ080 with stronger activity prevention for citrus canker, belonging to the field of agriculture disease biological control. The bacillus subtilis is obtained by being separated from natural environment host leaves and is identified according to the morphological characteristics and molecular biology. The bacillus subtilis has very strong inhibition effect on the citrus canker, and also has good control effect on the citrus canker. Furthermore, the bacillus subtilis also has broad-spectrum antagonistic activity, has stronger inhibition effect on pathogenic bacteria such as citrus canker pathogen and tobacco angular leaf spot pathogen, and also has good inhibition effect on pathogenic fungus such as tobacco botrytis cinerea, apple canker pathogenic bacteria and thielaviopsis basicola. The secondary metabolite of the bacillus subtilis contains cellulase, protease, siderophore and the like. The biological film of the canker pathogenic bacteria can be destroyed by the fermentation filtrate of the bacillus subtilis, and the environment-friendly biopesticide can be produced by bacterial fermentation or secondary metabolite extraction technology, so that the bacillus subtilis has important business development and application value.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
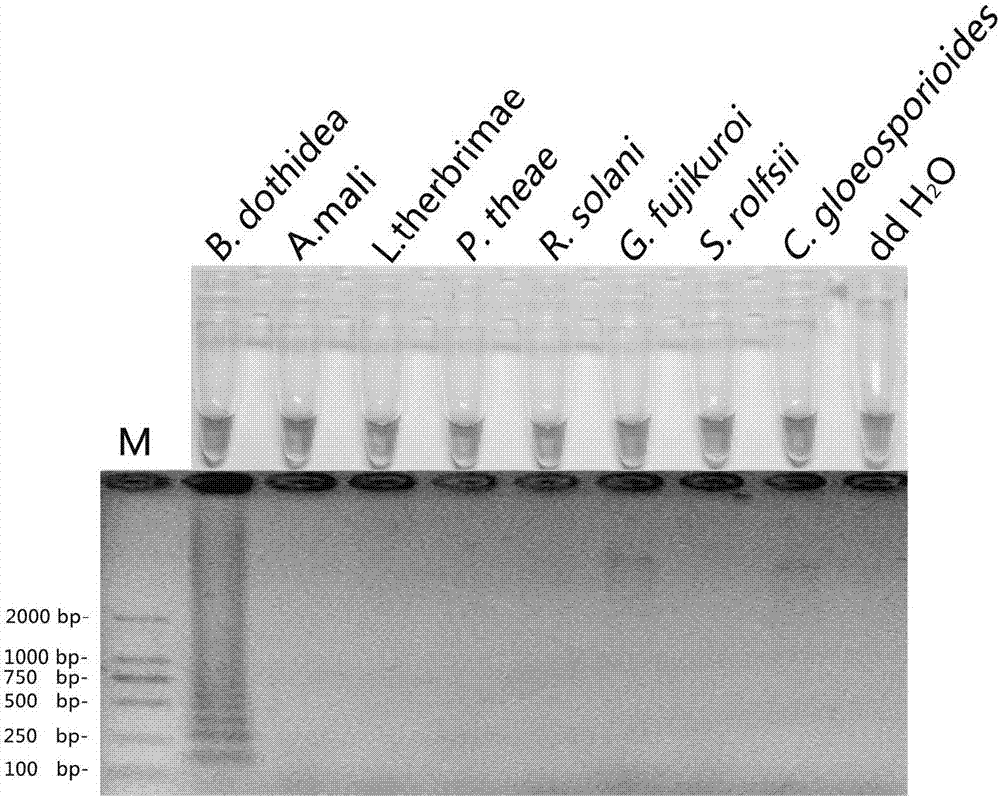
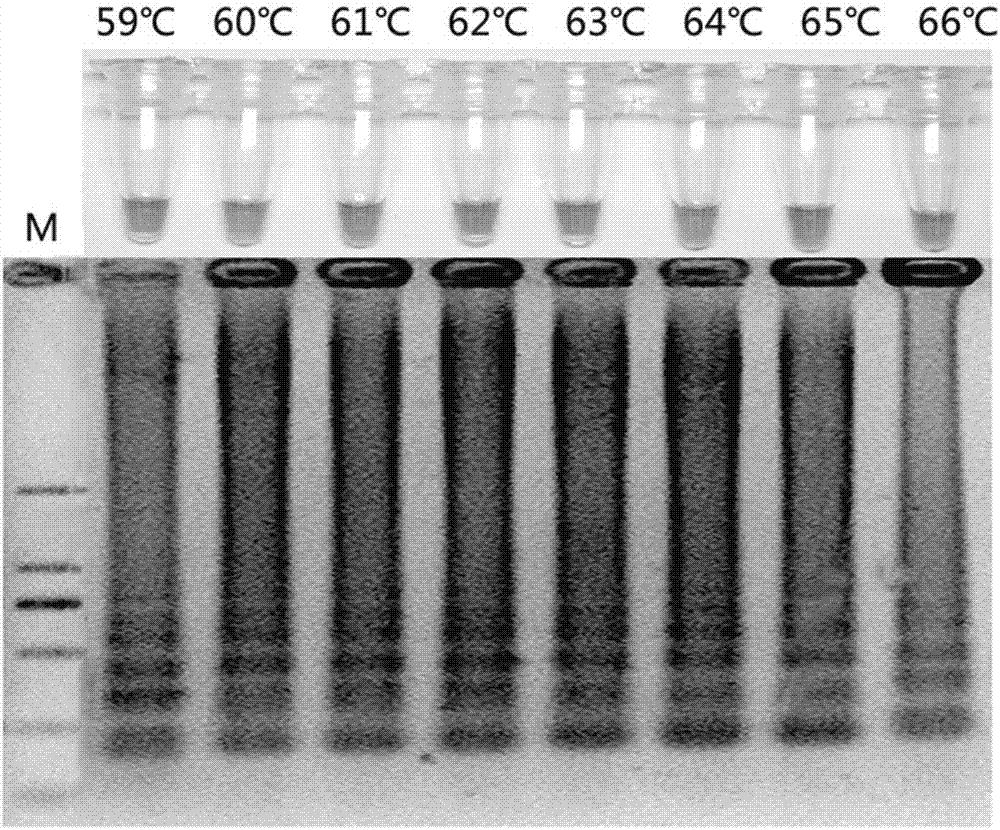
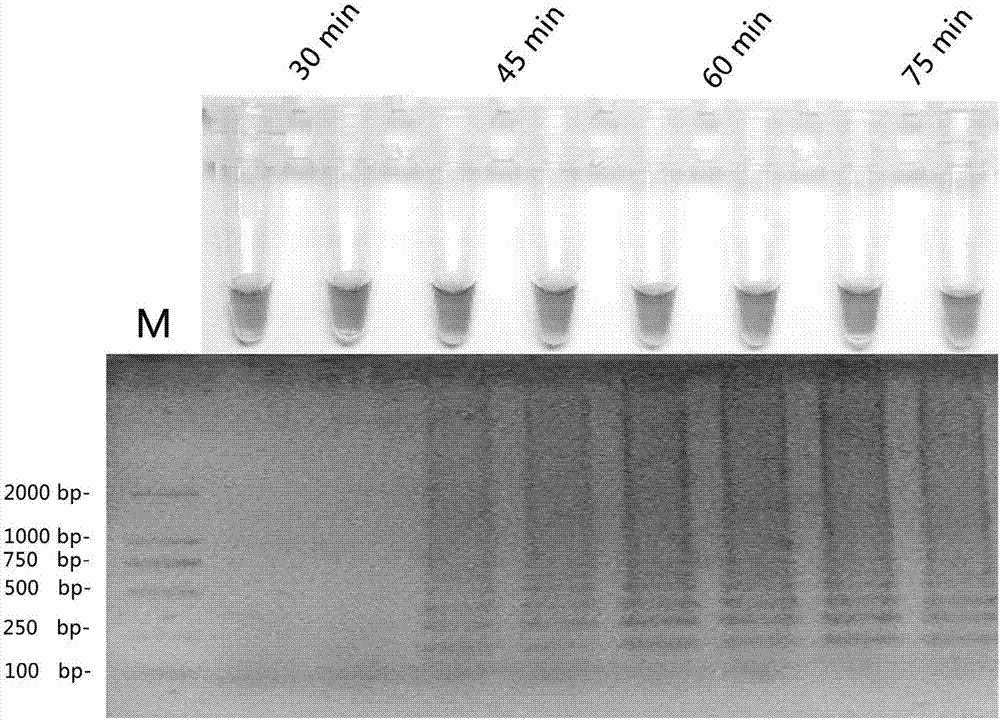
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) method for detecting pathogenic bacteria of canker disease of carya cathayensis
ActiveCN106868142AQuick checkImprove practicalityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesCarya cathayensisGlycine
The invention discloses a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) method for detecting pathogenic bacteria of canker disease of carya cathayensis. An LAMP primer composition is composed of four primers. The invention further discloses an LAMP kit used for detecting pathogenic bacteria of canker disease of carya cathayensis. The kit comprises the previous LAMP primer composition and further comprises 10*ThermoPol Buffer, dNTPs, MgCl2, glycine betaine, hydroxynaphthol blue, 8 U / muL Bst DNA polymerase and ddH2O. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the LAMP primers are designed according to a conserved region fragment sequence of beta-tubulin genes, the fast molecular detection technology system and reaction conditions are optimized, the pathogenic bacteria of the canker disease of carya cathayensis can be subjected to LAMP detection, the method is simple and convenient in reaction process, short in detection period, high in specificity and high in sensitivity, and the detection results can be observed by naked eyes.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Bactericide composition aiming at plant bacteria and fungus diseases and application thereof
ActiveCN103004879ASynergistic effect is obviousHigh field control efficiencyBiocideFungicidesAlternariaCitrus volkameriana
The invention relates to the technical field of pesticides, and particularly relates to a bactericide composition which takes zhongshengrnycin and copper oxychloride as effective ingredients, has an obvious and enlarged bacteriocidal spectrum and no phytotoxicity, and is used for treating plant bacterial diseases as well as fungal diseases. The weight proportion of the zhongshengrnycin to the copper oxychloride is 1:5-60. The bactericide composition has obvious synergistic effect, high field prevention effect and a wide bacteriocidal spectrum, is used for preventing and treating cucumber bacterial angular leaf spot, cucumber downy mildew, tomato bacterial macula disease, tomato leaf mold, pumpkin soft rot, watermelon bacterial angular leaf spot, watermelon sponge, apple alternaria leaf spot, apple brown blotch, pear scabs, grape downy mildew, grape powdery mildew, anthracnose of grape, jujube rust diseases, jujube anthracnose, citrus canker, citrus scab, citrus anthracnose, peanut leaf spot diseases and peronophythora litchii, and has the advantages of good effect and reduction of prevention and treatment cost.
Owner:福建凯立生物制品有限公司
Bacillus subtilis strain and application thereof
InactiveCN108118019AFast growth and reproductionShort fermentation cycleBiocideBacteriaDiseaseMicroorganism
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganism application, in particular to a bacillus subtilis strain and an application thereof. The bacillus subtilis strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on Jan 22rd, 2018 with the preservation number of CGMCC NO.15250. The strain provided by the invention can prevent and treat multiple fungal andbacterial diseases and are applied to Chinese cabbage soft rot, citrus canker, tobacco wildfire, tobacco bacterial wilt and rice bacterial leaf blight at present.
Owner:北京新正和农业科技有限公司
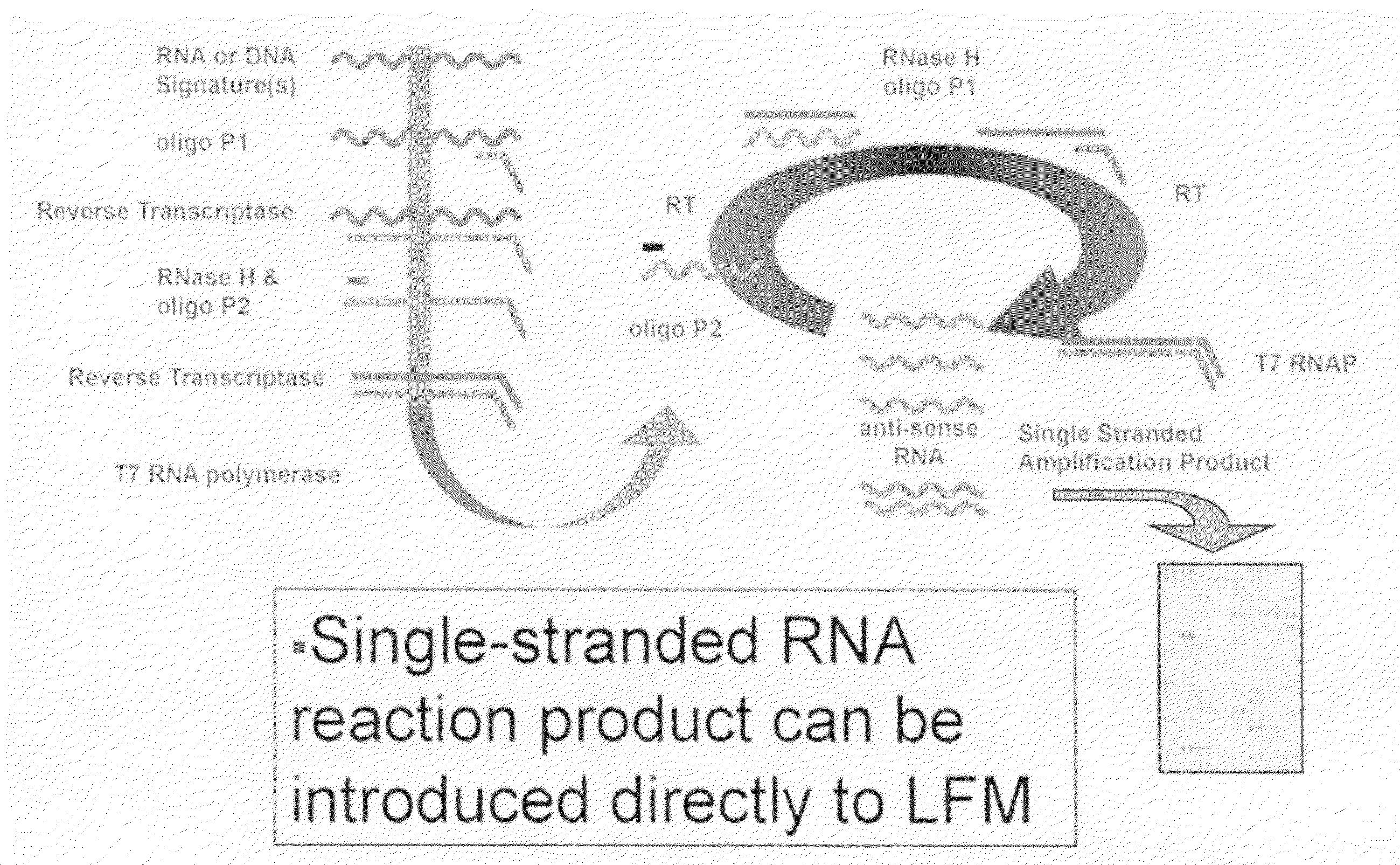
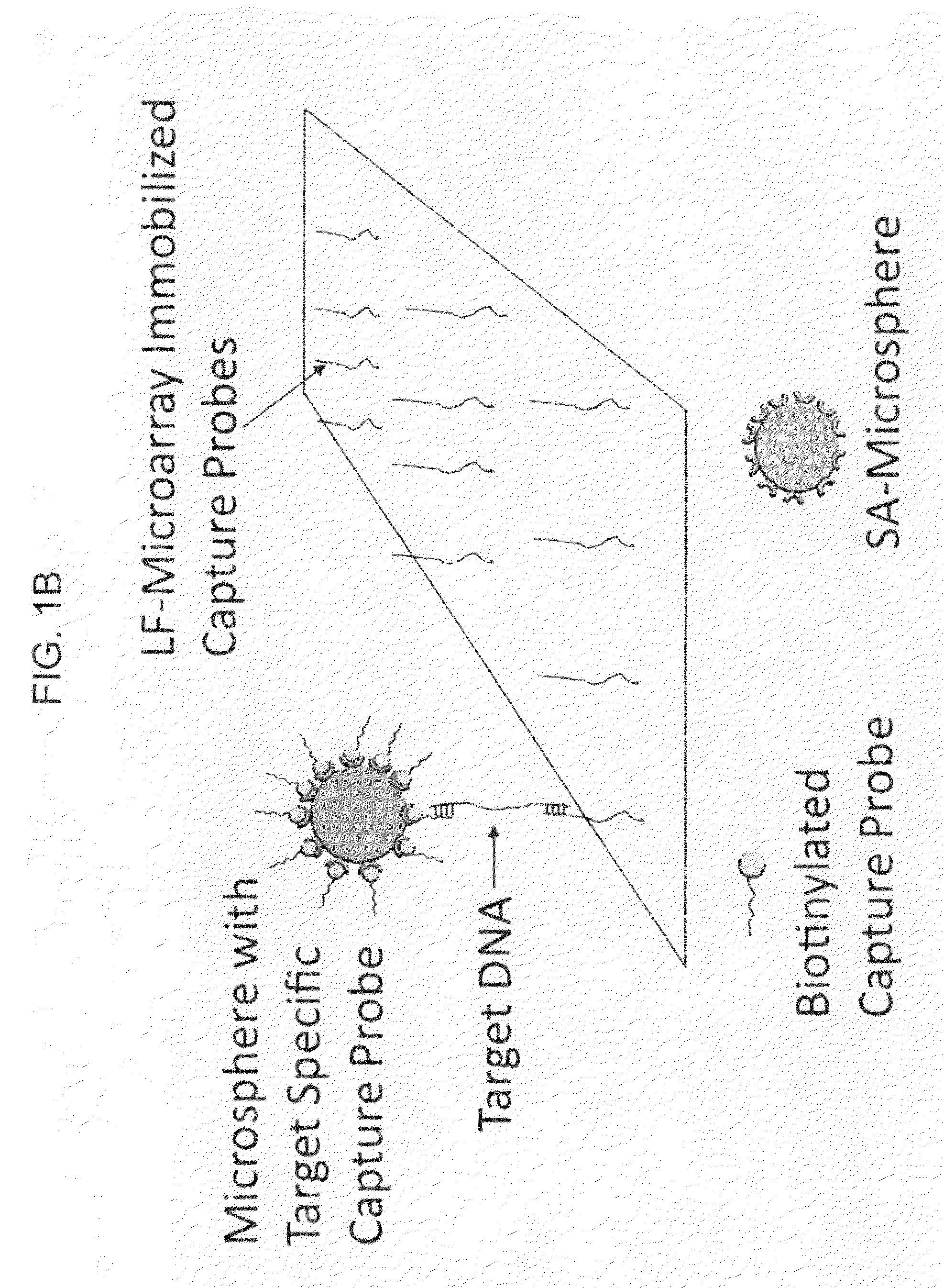
Multiplexed lateral flow microarray assay for detection of citrus pathogens Xylella fastidiosa and Xanthomonas axonopodis PV citri
InactiveUS20100029496A1Highly efficient isothermal amplification techniqueExcellent linear dynamic rangeMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningFluorescenceGene targeting
The invention provides highly sensitive and specific assays for the major citrus pathogens Xylella fastidiosa and Xanthomonas axonopodis, including a field deployable multiplexed assay capable of rapidly assaying for both pathogens simultaneously. The assays are directed at particular gene targets derived from pathogenic strains that specifically cause the major citrus diseases of citrus variegated chlorosis (Xylella fastidiosa 9a5c) and citrus canker (Xanthomonas axonopodis pv citri). The citrus pathogen assays of the invention couple a highly efficient isothermal amplification technique with lateral flow nucleic acid hybridization detection, thereby providing an inexpensive and facile means of rapidly detecting pathogen nucleic acid targets while circumventing hardware requirements for fluorescence detection and PCR thermocycling. The citrus pathogen assays of the invention offer femtomole sensitivity, excellent linear dynamic range, and rapid and specific detection.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Organic fertilizer controlling hickory canker disease, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105541474AVisible canker effectReduce biological activityBioloigcal waste fertilisersOrganic fertiliser preparationHazardous substancePlant growth
The invention discloses an organic fertilizer used for controlling hickory canker disease. The organic fertilizer is prepared from the raw materials of, by weight, 40-60 parts of traditional Chinese medicine dreg, 50-70 parts of crop straws, 0.5-1.5 parts of a fertilizer synergist, 3-7 parts of urea, 0.5-2 parts of a straw fermentation inoculant, 1-2 parts of cellulase, and 1-2 parts of brown sugar. The invention also provides a preparation method of the organic fertilizer used for controlling hickory canker disease. With the organic fertilizer, botryosphaeria dothidea activity can be substantially reduced, and hickory tree canker resistance can be enhanced. The organic fertilizer also contains organic matters, nitrogen, phosphorous, potassium and various medium and trace elements necessary for plant growth. The nutrition is comprehensive and balanced. With the organic fertilizer, soil physiochemical properties can be substantially improved, plant root system growth can be promoted, soil microbial activity can be enhanced, and soil harmful substance pollution can be reduced.
Owner:ANHUI SIERTE FERTILIZER IND
High throughput test method for tomato bacterial disease by locking-type probe
InactiveCN103215357AShorten detection timeImprove intercept detection rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyDisease
The invention relates to a high throughput test method for a tomato bacterial disease, and more particularly relates to a high throughput test method which can utilize a locking probe to carry out reverse dot blot hybridization on tomato bacterial wilt original bacteria, tomato ulcer pathogenic bacteria and a tomato spot disease, and belongs to the crop preventing and curing disease and exit and entry plant quarantine range. The high throughput test method provided by the invention is based on a rolling circle amplification technology of the locking probe, a pair of universal primers are utilized for amplifying multiple pathogens, then, the high throughput test method and a reverse dot blot are combined together, a result is judged through a chromogenic reaction, the testing time of the traditional tomato bacterial disease is shortened, the specificity and the sensitivity of the detection are guaranteed, and the high throughput test is realized. According to the method, the testing cycle of the traditional pathogenic bacteria can be shortened, the cargo clearance can be increased, the intercept and capture relevance ratio of epidemic situations of imported bulk farm-product is improved, the pest invasion capacity is improved, the cargo clearance of cargoes imported and exported at ports in China is accelerated, and the enterprise cost is reduced and the high throughput test method has the important meanings.
Owner:FUQING ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU OF P R C
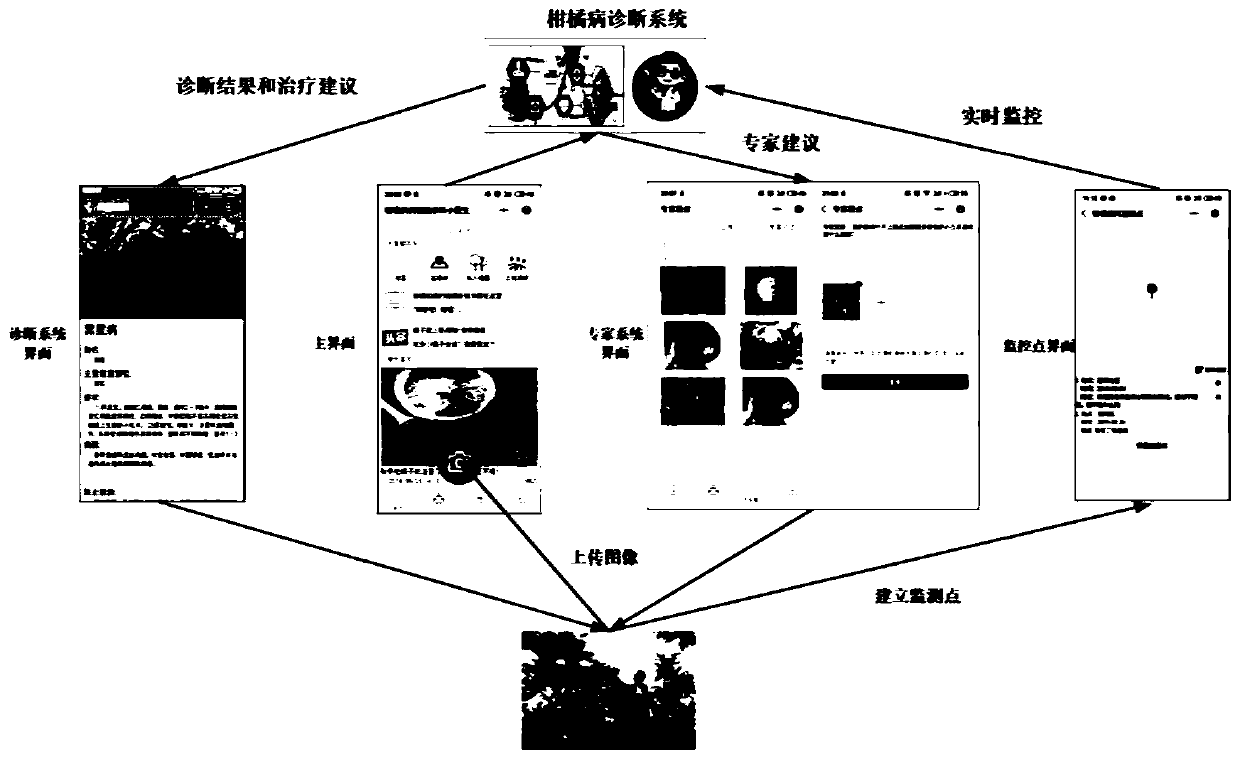
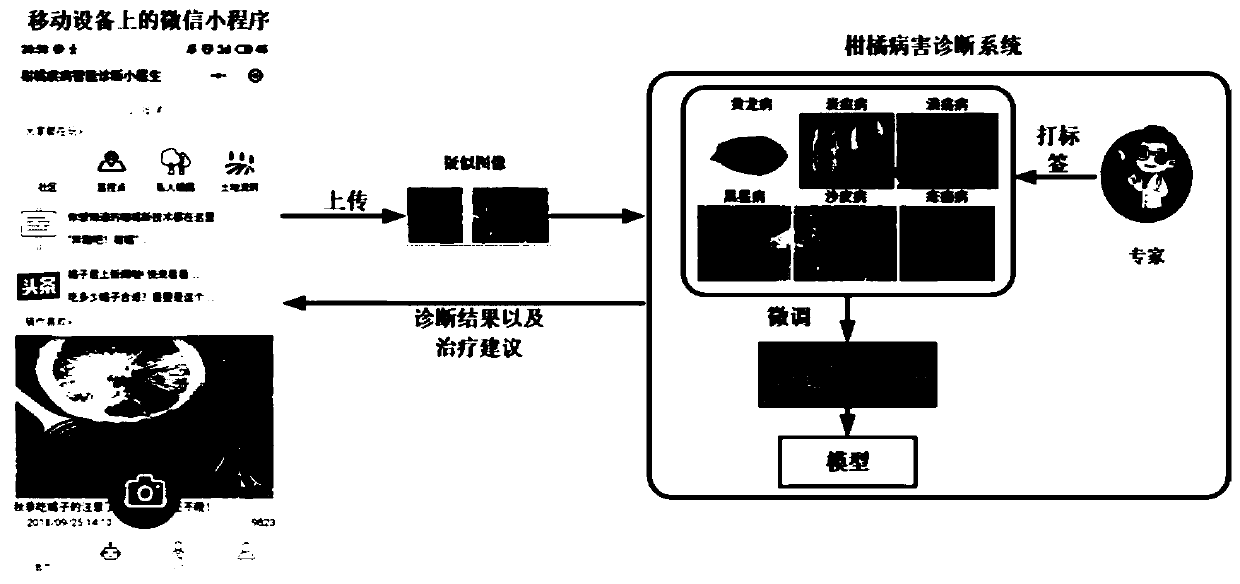
Intelligent citrus disease and pest diagnosis method and system based on deep learning
ActiveCN110245720AImprove learning abilityEfficient feature expression abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData setNetwork model
The invention discloses an intelligent citrus disease and pest diagnosis method and system based on deep learning. The intelligent citrus disease and pest diagnosis method comprises the steps: 1, establishing an image data set of six citrus diseases including Huanglongbing, anthracnose, canker, black spot, sand paper rust and scabis based on expert experience; 2, expanding the training set and the test set by using five data enhancement methods; using the enhanced training set and verification set to train the simplified DenseNet network, and storing the model in the system; evaluating the performance of the model by using the test set; and 3, establishing a citrus disease diagnosis system on the basis of the WeChat applet, photographing / uploading images by a user through a mobile phone by using the applet, performing diagnosis through the uploaded trained convolutional network model, and returning an intelligent diagnosis result and pest control suggestions to the user to realize intelligent diagnosis of citrus diseases and pests.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Chinese gooseberry canker control medicament and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to the field of Chinese gooseberry canker control, in particular to a Chinese gooseberry canker control medicament. The Chinese gooseberry canker control medicament is prepared from the following steps: in accordance with weight ratio, 10 parts of edible vegetable oil is adopted; 2 parts of branches including willow branches, peach branches, siberian elm branches, cassia nomame branches, pagoda tree branches, melia azedarach branches, pentangular maple branches in equal proportion are sliced into pieces; the edible vegetable oil and the branches are put into a vessel and stewed into paste on fire; when the paste is cooled at the temperature of 70 DEG C, 0.1 part of a lime sulphur is added, stirred and cooled and the paste is coated in a felt cloth piece. After 3-4 years on the spot use in the Chinese gooseberry specialized cooperatives in Yaozhuang village, Jiawang District in Xuzhou City, the effective rate of the Chinese gooseberry canker control plaster can reach 95 %, the plaster is a traditional Chinese medicine agent and free from western medicine contamination and drug residues and the Chinese gooseberry has no medical harm to human bodies.
Owner:刘新成
Bactericidal composition, pesticide and application thereof
The invention discloses a bactericidal composition, a pesticide and application thereof. The bactericidal composition comprises the following components of N-(5-methyl-1,3-thiazole-2-yl)-4-methyl-1,2,3-thiadiazole-5-formamide and cuppric nonyl phenolsulfonate in a weight ratio of (1:50)-(50:1). The bactericidal composition is used as an active component and combined with agromedically acceptable auxiliary components together so as to form a pesticide with a sterilization effect; the pesticide can effectively prevent crop diseases, such as rice bacterial leaf blight, citrus canker, pseudomonas solanacearum, tobaccomosaivirus, pepper virus disease, tomato virus disease and the like; the effect of the pesticide is obviously higher than that of a double-component single agent; and a remarkable synergetic effect is achieved, the application dosage of each single agent can be effectively reduced, the better effects of enlarging sterilization scope and delaying plant pesticide-resistance are achieved, the duration is prolonged, and a remarkable promotional value is obtained.
Owner:LIER CHEM CO LTD
Glycyrrhizic acid removal glycyrrhiza flavonoid and medicament composition thereof
InactiveCN101747307AImprove processing stabilityGood repeatabilityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryLicorice acidWastewater
The invention provides glycyrrhizic acid removal glycyrrhiza flavonoid for treating a canker disease and a medicament composition thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking wastewater generated by producing glycyrrhizic acid and waste dregs as raw materials and then carrying out a series of steps like alkalization reaction, separate deacidification, acid-base conversion, macro porous resin absorption and purification and the like. In a prepared sample, the content of the glycyrrhiza flavonoid is high and can maximally reach 98 percent, and the content of the glycyrrhizic acid is very low and is only 0.1-1 percent; and the glycyrrhiza flavonoid is further prepared into various preparations suitable for clinical application. The glycyrrhizic acid removal glycyrrhiza flavonoid and the preparation method thereof adopts the acid-base reaction, conversion and traditional Chinese medicine modern separation and purification technology and has the advantages of novel process, suitable industrialized production and strong practicability.
Owner:JIANGSU TIANSHENG PHARMA
One strain of streptomyceslavendulae X33 and applications thereof
The invention discloses a strain of streptomyceslavendulae X33, and the preservation number is CCTCC No. M2013163. The bacterial strain and the fermentation liquid thereof can be used to prevent and treat vegetable penicillium digitatum, penicilliosis, sour rot disease, and canker disease and shoot blight of trees caused by botryosphaeriaspp. The streptomyceslavendulae X33 has the advantages of no toxic or side effect, simple preparation technology, low cost, and user-friendliness, is capable of preventing and treating various plant diseases at the same time, and has a prominent preventing and treating effect.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Cysteine amino-acid compound (or its analogues) used in the disruption of microbial biofilms when treating or preventing diseases caused by phytopathogenic bacteria known to attack plants of agricultural interest
Cysteine amino-acid compound (or its analogues) used in the disruption of microbial biofilms by treatment of prevention of diseases generated by phytopathogenic bacteria attacking plants of agricultural interest represented by an innovative solution within the agriculture sector, where said compound can be used in the pharmacological form, as a drug associated with fertilizer for the combat of bacterial diseases which form microbial biofilms, such as citrus variegated chlorosis (CVC), citric canker’, huanlongbing (HLB) disease or ‘greening’, amongst other, which inventive concept, as such, never before completed, resides in the benefit deriving from the cysteine amino-acid, and all of its analogues, in the inhibitory action and progressive disruption of the microbial biofilm thus liberating the nutritive flux and hydration of the root to the upper part of the plant and the subsequent regression of the disease symptoms, with the added advantage that the cysteine amino-acid compound is non-toxic, guaranteeing healthy production of foods by plants of agricultural interest that are totally healthy, without toxic residues in their composition, as well as when said compound is applied there is risk to the environment due to the rapid absorption, notably within the area in which it is applied, where such predicates of disease combat, with the exception of toxic collateral effects still guarantee that the final crop and harvest will have a higher productivity per hectare.
Owner:INST AGRONOMICO DE CAMPINAS
Separation for endophytic actinomycetes of kiwifruit roots and application thereof
ActiveCN106635884APromoting effect is goodIncrease the number of rootsPlant growth regulatorsBiocideActinidiaGrowth promoting
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Formula, preparation method and application of tree plaster medicine fertilizer ointment having strengthening and diseases preventing functions to forest trees
InactiveCN104671929AIncrease nutrient tree vigorEnhance tree vigorFertilizer mixturesMedicineTree trunk
The invention discloses a formula and a preparation method of a tree plaster medicine fertilizer ointment having strengthening and diseases preventing functions to forest trees. The tree plaster medicine fertilizer ointment is matched with a tree plaster adhesive tape to control forest tree trunk diseases and preferably poplar canker and bark rot, and strengthen the vigor of the forest trees. The ointment has the advantages of high medicine fertilizer utilization efficiency and no pollution to environment, and solves the technical problem of difficult artificial medicine spraying of high trees or inconvenient soil fertilization.
Owner:텐진인스티튜트오브플랜트프로텍션
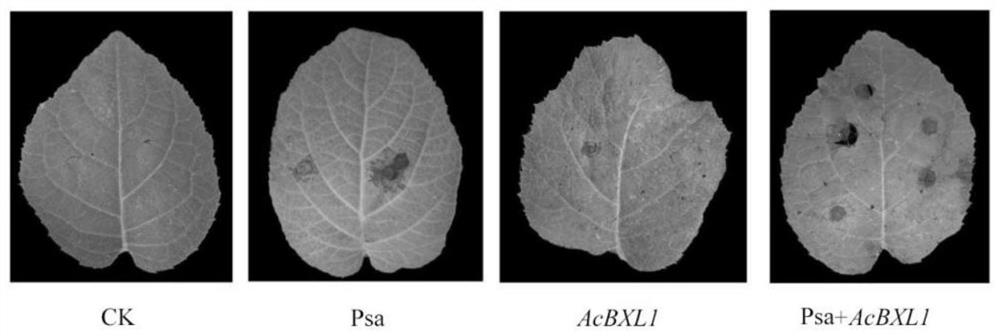
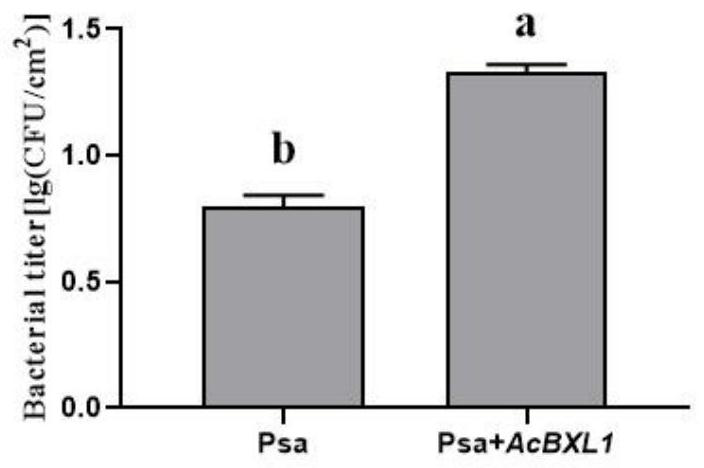
Kiwi fruit canker susceptible gene AcBXL1 and application thereof
ActiveCN113604490ASusceptibleThe promotion effect is obviousFermentationPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologyTransforming Genes
The invention discloses a kiwi fruit canker susceptible gene AcBXL1 and application thereof. The gene AcBXL1 and the sequence of the encoding protein thereof are respectively shown as SEQ ID NO: 1 and 2. According to the invention, through analysis of kiwi fruit genome and transcriptome, the gene sequence of kiwi fruit AcBXL1 is successfully obtained, and through transient expression and stable transformation genetic transformation experiments, the gene AcBXL1 is proved to have the function of promoting the susceptibility of kiwi fruit to canker, thus laying the foundation for creating new disease-resistant varieties for follow-up gene editing and controlling canker.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Pesticidal composition for treating and preventing poplar canker
PendingCN107258816APlay a role in disease preventionPlay a healing roleBiocidePlant growth regulatorsIodophorBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention provides a pesticidal composition for treating and preventing poplar canker. The pesticidal composition comprises a pesticidal active ingredient and auxiliaries, wherein the pesticidal active ingredient is an inorganic fungicide and accounts for 0.5% to 5% the total weight of the pesticidal composition, and the inorganic fungicide comprises one or a mixture of two or more of copper salts, iodine tincture, iodophor and sulfur. The pesticidal composition provided by the invention can be used for effectively preventing and treating common diseases of poplars such as canker and rot; the effect duration of pesticidal compositions in the market at present is about 10 days, and the effect duration of the pesticidal composition provided by the invention is long and is generally 12 to 24 months, so that the effect duration is effectively prolonged, and the investment of funds is reduced; and furthermore, by using the pesticidal composition, the consumption of pesticides can be obviously lowered, the environment is protected, and the environmental pollution is reduced.
Owner:天津市瀚葳园林植物保护技术有限公司
Pruning method for blueberries
InactiveCN109042024AEffective pruningIncrease productionCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsFreeze injuryPruning
The invention discloses a pruning method for blueberries. The method involves the pruning time and principle, pruning of saplings, pruning of mature trees, regeneration and invigoration, pruning in autumn and winter, bud removing and pruning in summer. The pruning method for the blueberries is characterized by comprising the following pruning step that the pruning time and principle are set, wherein the idea tree form to the blueberries should achieve the purposes that tree bodies are straight, and the tops of the tree bodies are opened; during pruning, firstly, branches with freeze injuries,mechanical injuries or diseases and insect pests are pruned; secondly, intertwined branches are pruned to avoid infection of the canker due to mutual friction; thirdly, branches hindering row operation are pruned, and fourthly, short overgrowing branches which are under crown closure are pruned. The method is implemented in the dormancy period of the branches, pruning should be selected at the early spring in cold northern regions, and at this moment, the branches suffering from freeze injuries can be identified and removed; for warm southern regions, pruning can be conducted after harvestingin summer and the dormancy period in winter. By effectively pruning plants, larger yield can be achieved, the number of base growing branches can be reduced, and the size of the tree bodies can also be reduced.
Owner:贵州高原蓝生态农业科技开发有限公司
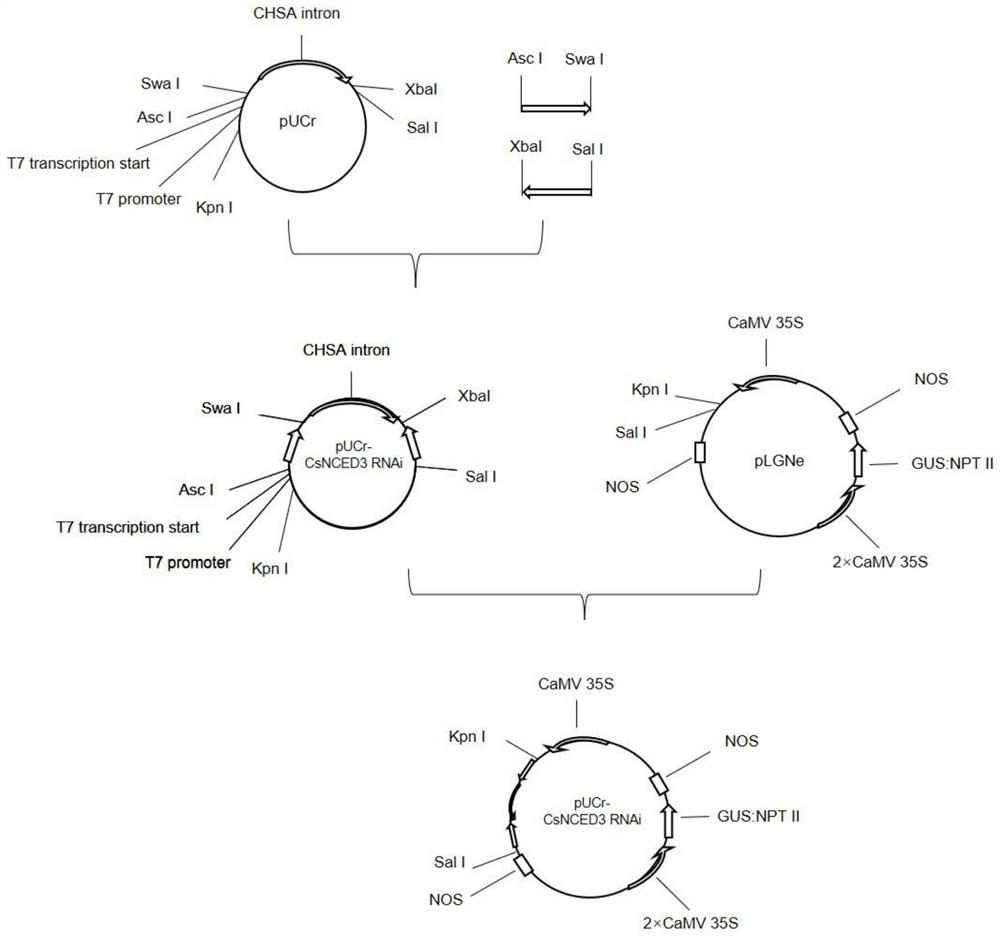
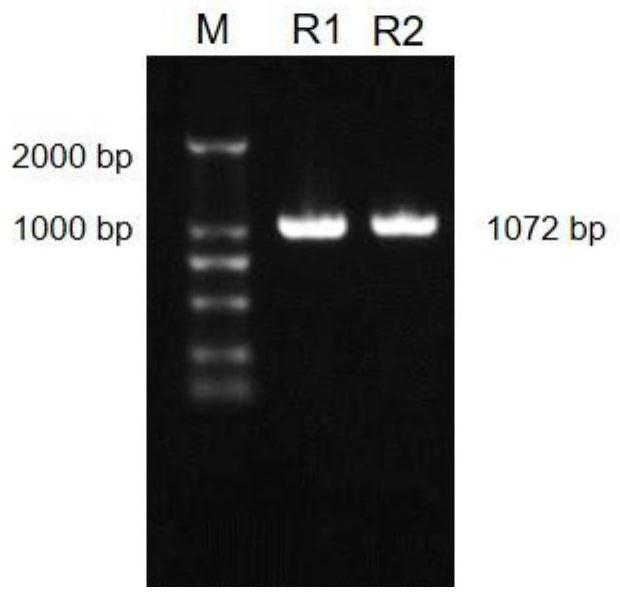
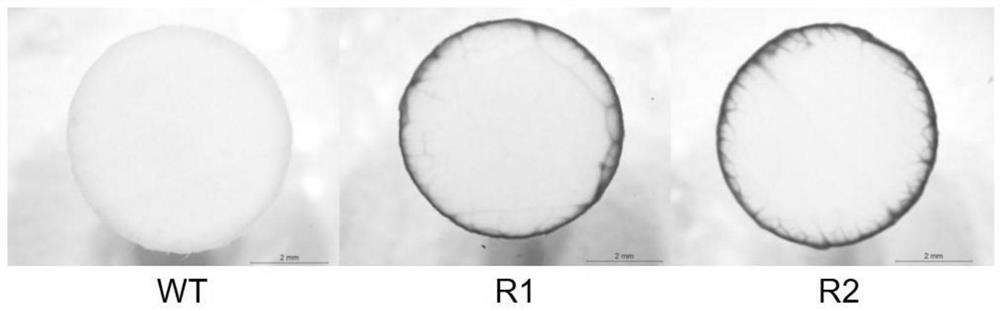
Method for improving canker resistance of citrus by utilizing CsNCED3 gene silencing
PendingCN114395570AIncrease resistanceReduce the severity of the diseaseOxidoreductasesFermentationBiotechnologyCitrus volkameriana
The invention discloses a method for improving canker resistance of citrus by utilizing CsNCED3 gene silencing. The method comprises the following steps: (1) cloning a citrus CsNCED3 gene segment; (2) constructing an interference expression vector of the CsNCED3 gene segment; and (3) transforming the citrus by the interference expression vector to obtain a transgenic plant. According to the method, CsNCED3 gene silencing is utilized, citrus CsNCED3 gene segments are cloned, an interference expression vector is constructed, and then citrus is transformed, so that the expression quantity of the obtained transgenic plant CsNCED3 is remarkably reduced to 29% of that of the existing citrus, and the canker attack degree can be reduced to 47% of that of the existing citrus, and therefore, the method can improve the canker resistance of the plant to a certain extent.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com