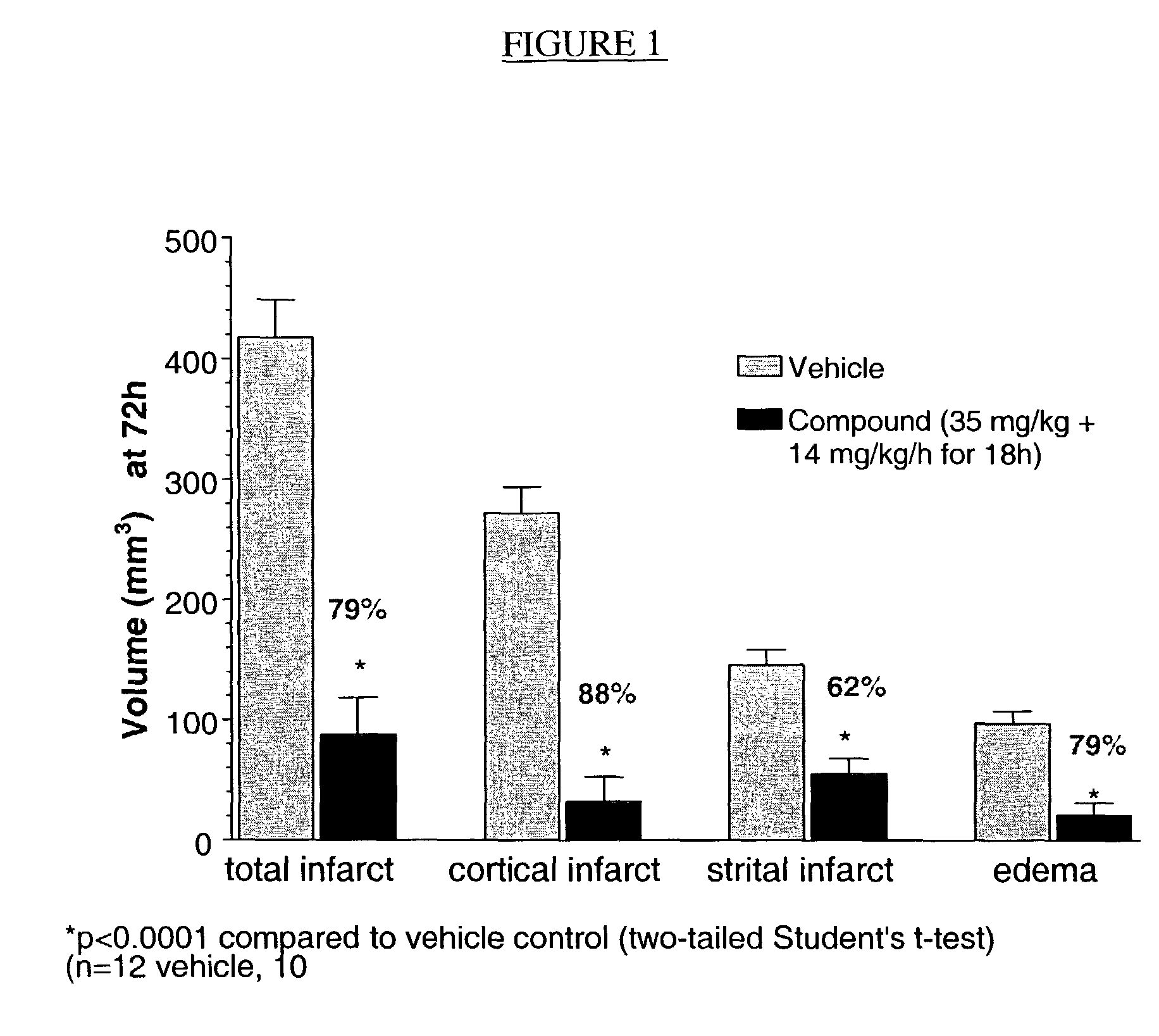
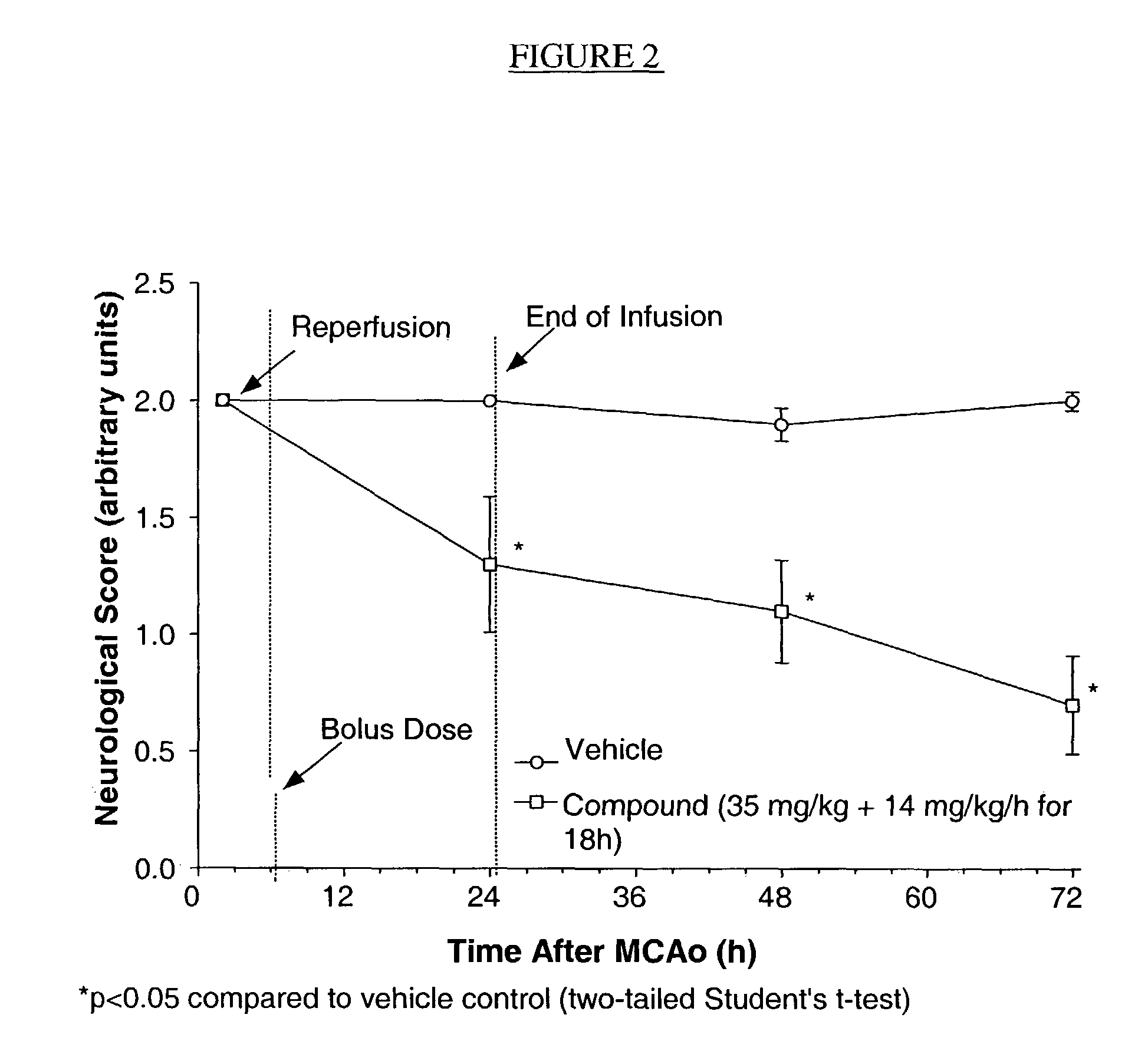
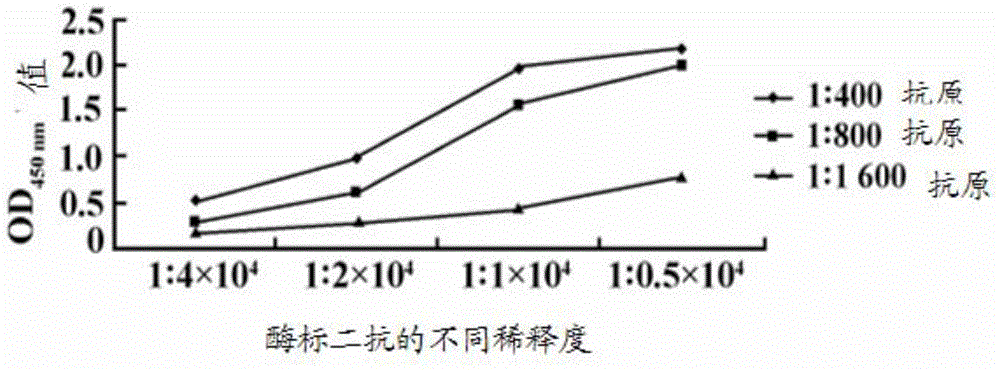
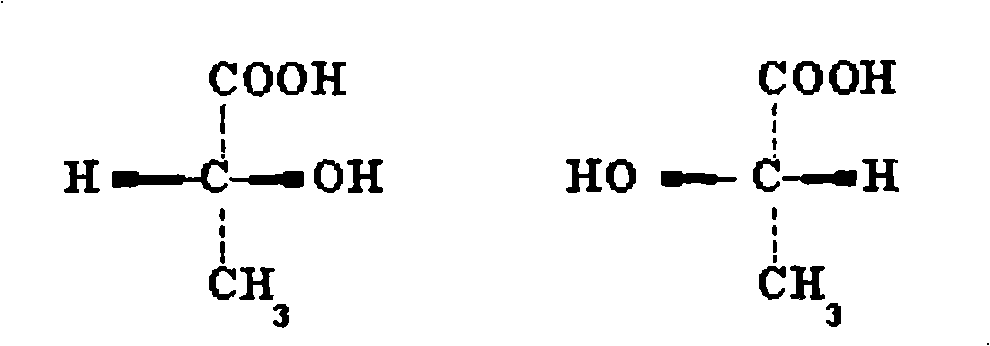Patents
Literature
129results about How to "Reduce the severity of the disease" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bio-organic compound fertilizer
InactiveCN101781149AImprove fat retention capacityImprove buffering effectFertilizer mixturesPotassiumOrganic compound
The invention relates to a bio-organic compound fertilizer, which comprises the following components in part by weight: 10 to 30 parts of organic matter, 2 to 10 parts of compound microbial inoculants, 5 to 20 parts of humic acid, 5 to 20 parts of amino acid, 4 to 10 parts of chitin, 1 to 5 parts of polypeptide, 530 parts of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, 5 to 10 parts of secondary and trace elements, 5 to 15 parts of algae fertilizer, 5 to 10 parts of zeolite powder and 1 to 5 parts of synergistic agent. Through the scientific and rational formula, the bio-organic compound fertilizer achieves nutritive equilibrium and can satisfy the need of crop growth in nutrient. The microbial inoculants are added to quickly degrade natural macromolecular organic compounds into the organic fertilizer and decompose organic pollutants, which effectively improves the capacity of crops in the absorption of nutrient components, reduces the waste of the fertilizer and reduces the damage of the chemical fertilizer to soil to further achieve the nutritive equilibrium, satisfy the need of the crop growth in the nutrient, achieve the aims of low investment and high output value, improve the quality of the crops and improve the economic benefit brought by the crops.
Owner:张钧
Compositions comprising stat3 sirna and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20100298409A1Reduce severityReduce the severity of the diseaseOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticCell biologySTAT3
The present invention provides nucleic acid molecules that inhibit STAT3 expression. Methods of using the nucleic acid molecules are also provided.
Owner:INTRADIGM CORP
Compositions useful as inhibitors of GSK-3
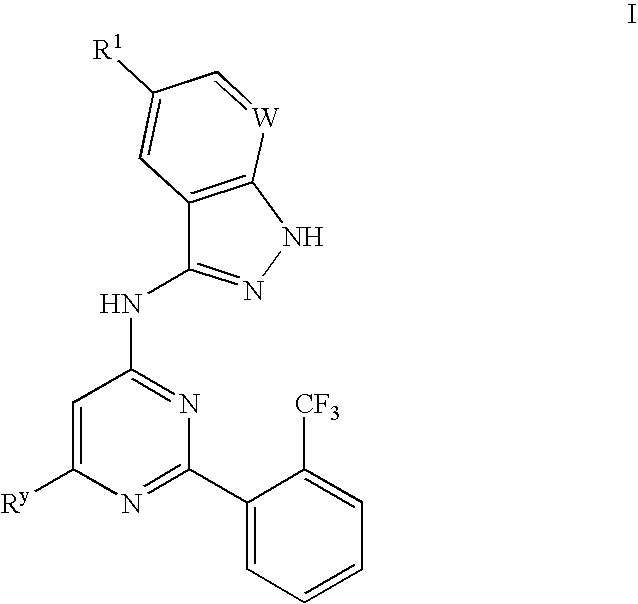
InactiveUS7491730B2Inhibiting GSK- activityAlleviate the conditionBiocideSenses disorderBiochemistryOrganic chemistry
The present invention provides a compound of formula I:or a pharmaceutically acceptable derivative thereof. These compounds are inhibitors of protein kinases, particularly inhibitors of GSK3 mammalian protein kinase. The invention also provides pharmaceutically acceptable compositions comprising the compounds of the invention and methods of utilizing those compounds and compositions in the treatment of various protein kinase mediated disorders.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
Hybridoma cell strain and secretion monoclonal antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN104694480AGood neutralizing activityHigh bonding strengthImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsMaternal antibodyEpidemic diarrhea
The invention discloses a hybridoma cell strain and an anti-porcine-epidemic-diarrhea-virus monoclonal antibody produced by the hybridoma cell strain. The anti-porcine-epidemic-diarrhea-virus monoclonal antibody has the preventing and / or treating function for porcine epidemic diarrhea viruses, solves the problem of piglet epidemic diarrhea virus infection caused when existing vaccines and maternal antibodies are insufficient, overcomes the defect that an existing vaccine is single in prevention function and can also be used for developing diagnostic reagent products for the porcine epidemic diarrhea viruses.
Owner:LUOYANG PULIKE WANTAI BIOTECH
Lawsonia intracellularis immunological proteins
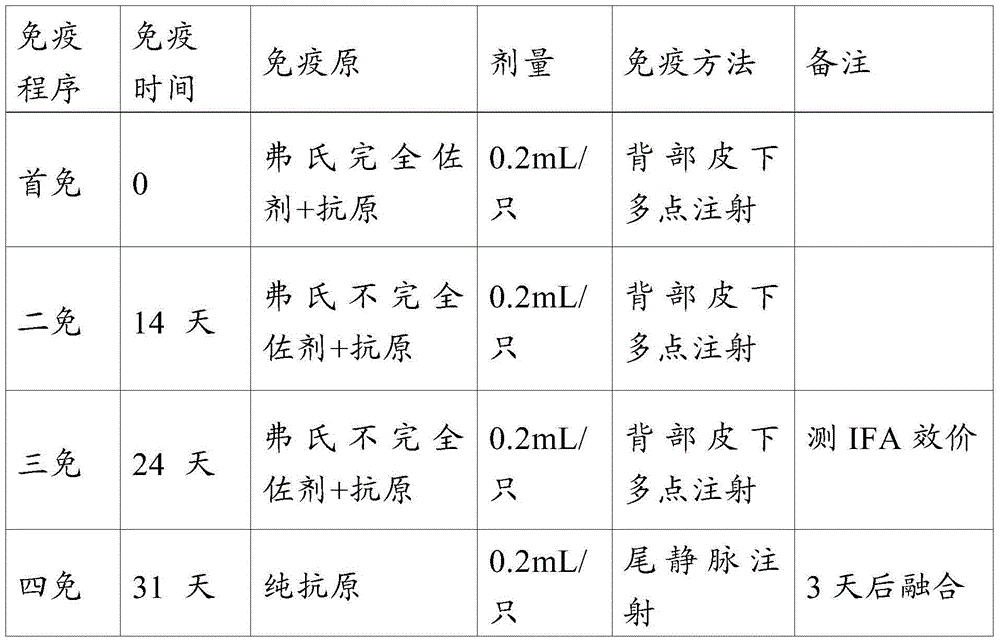
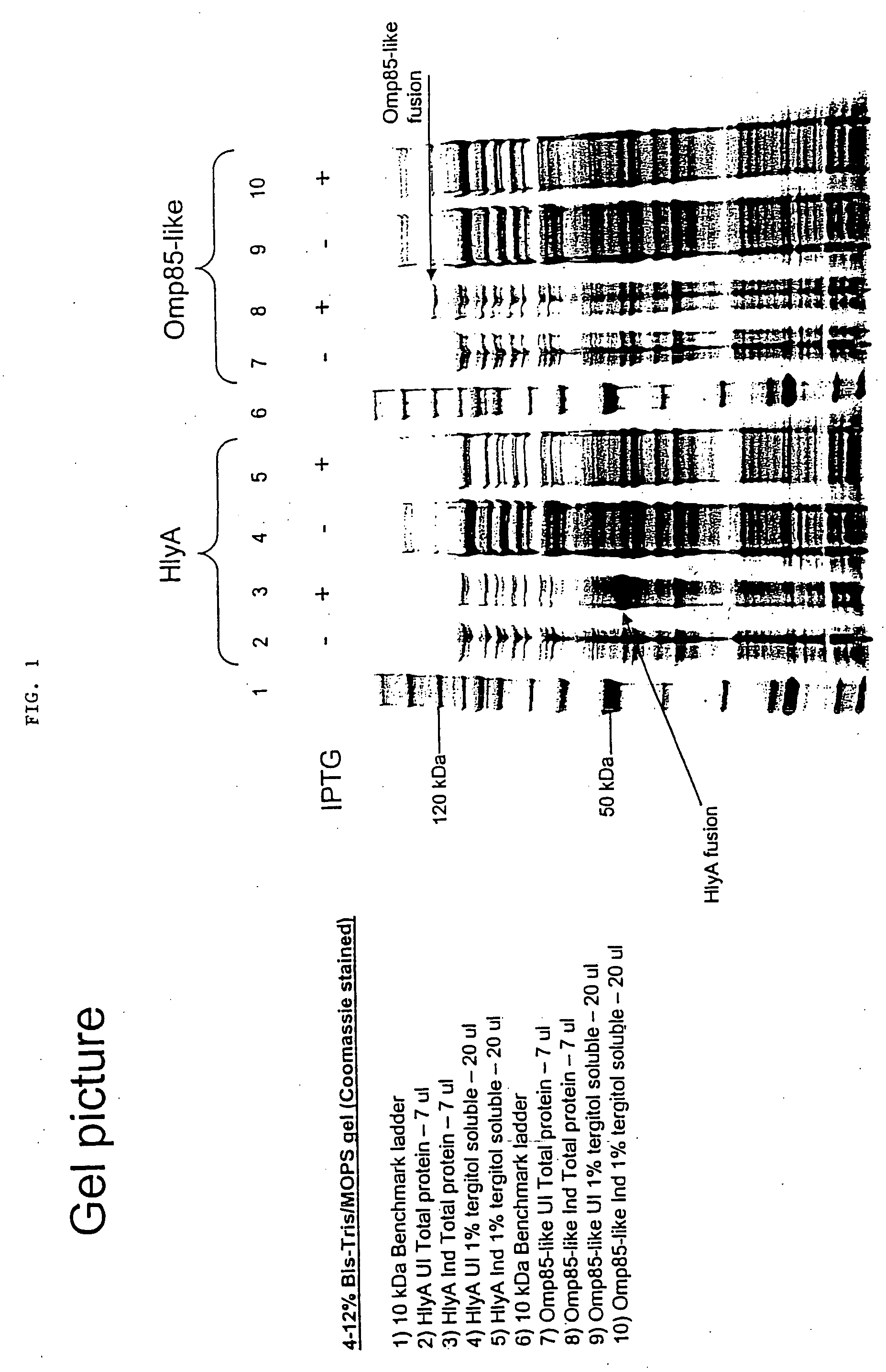
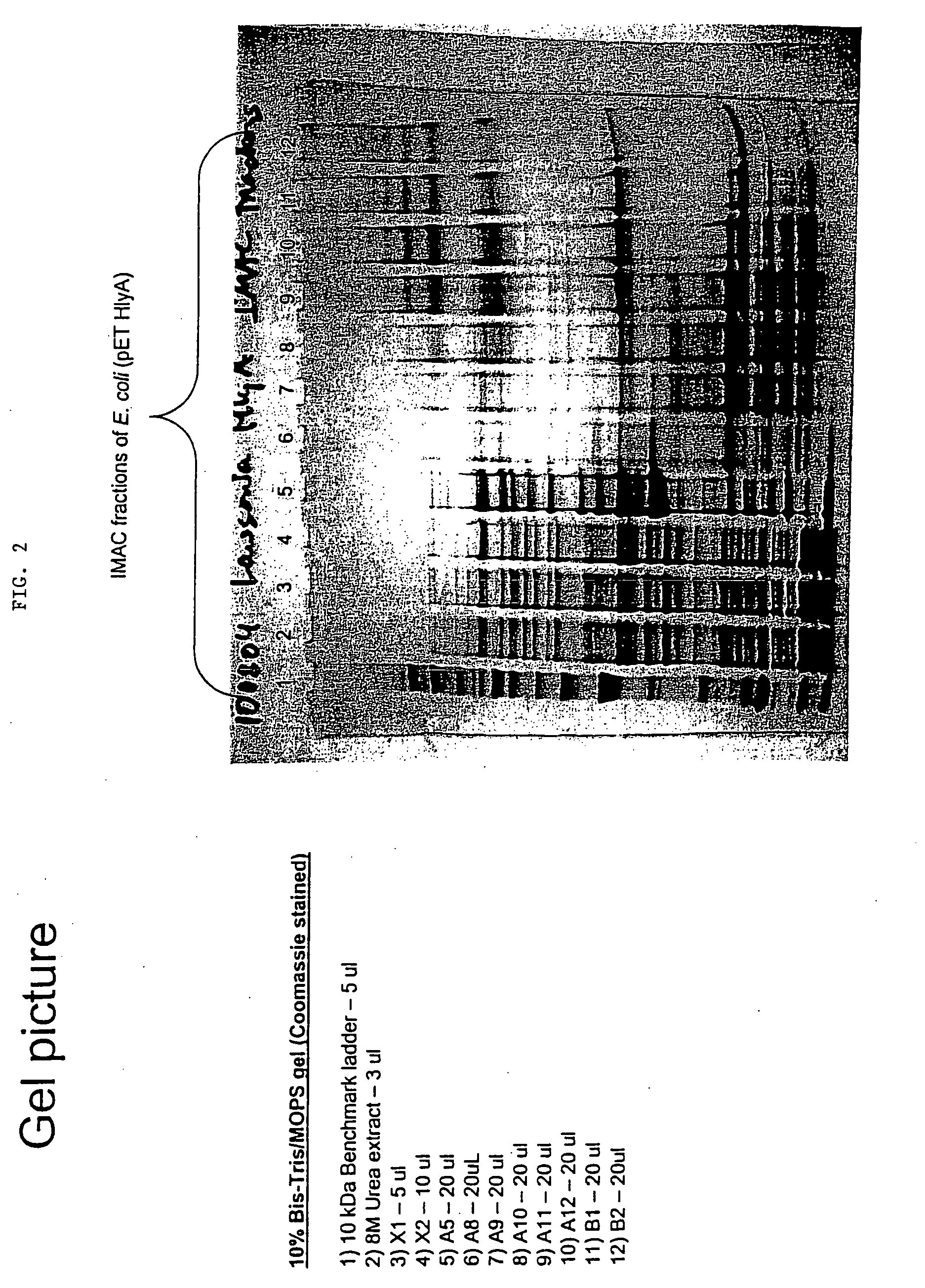
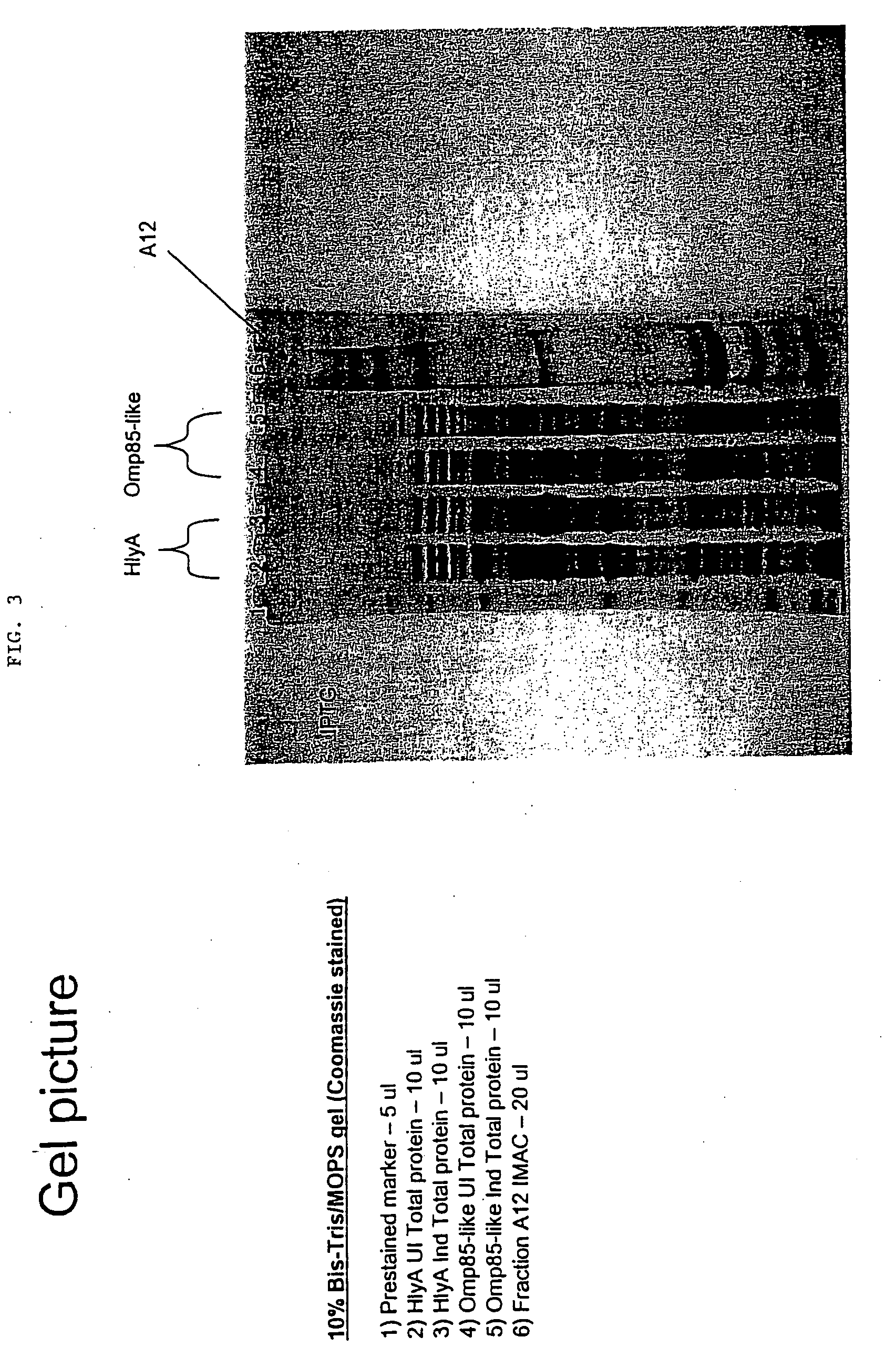
InactiveUS20080279893A1Improve the immunityReduce the severity of the diseaseAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsA-DNAImmunogenicity
The present invention provides nucleic acid and amino acid sequences useful as the immunogenic portion of vaccines or immunogenic compositions effective for lessening the severity of the clinical symptoms associated with Lawsonia intracellularis infection or conferring protective immunity to an animal susceptible to such infection. Preferred amino acid sequences are selected from the group consisting of 1) a polypeptide comprising a sequence selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID Nos.: 1-455, SEQ ID No 466, or the polypeptide encoded by SEQ ID No: 456, SEQ ID No: 457 or SEQ ID No: 466; 2) any polypeptide that has at least 85% sequence homology, more preferably at least about 90% sequence homology, still more preferably at least about 95% sequence homology, even more preferably at least about 97% sequence homology, still even more preferably at least about 98% sequence homology, and even more preferably at least about 99% sequence homology to the polypeptide of 1); 3) any immunogenic portion of the polypeptides of 1) and / or 2) 4) the immunogenic portion of 3), comprising at least 300, 290, 280, 270, 260, 250, 240, 230, 220, 210, 200, 190, 180, 170, 160, 150, 140, 130, 120, 110, 100, 90, 80, 70, 60, 50, 45, 40, 35, 30, 25, 20, 18, 15, 13, 10, or most preferably 9 contiguous amino acids included in the sequences of SEQ ID No: 1-455, SEQ ID No: 456, or the amino acid sequence encoded by SEQ ID No: 457 or SEQ ID No: 466; and / or 5) a polypeptide that is encoded by a DNA that codes for a peptide comprising the sequence of SEQ ID No: 1-455 or SEQ ID No: 466. Thus, the nucleic acid sequences encoding such proteins, or the proteins themselves are included in vaccine compositions, together with veterinary-acceptable carrier and administered to an animal in need thereof.
Owner:BOEHRINGER LNGELHEIM VETMEDICA GMBH
Tuberculosis subunit vaccine containing unite adjuvant
ActiveCN103386128AEnhance cellular immunityEnhance humoral immune responseAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsTuberculomaAdjuvant
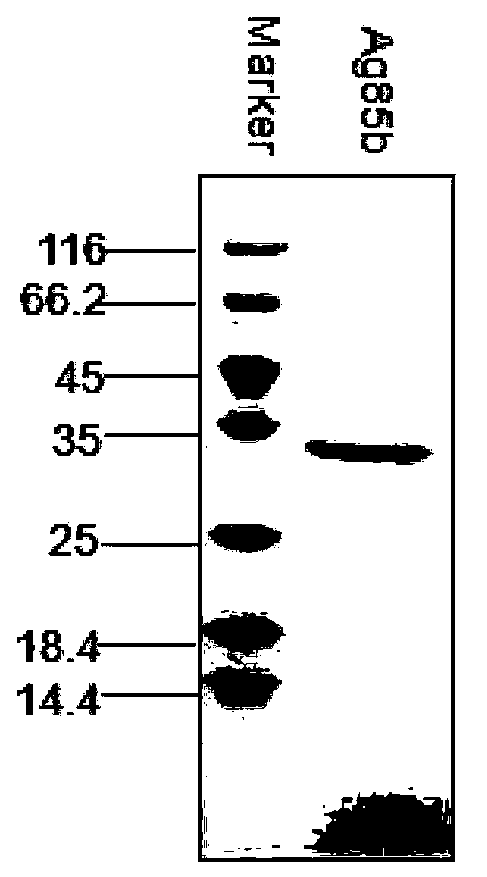
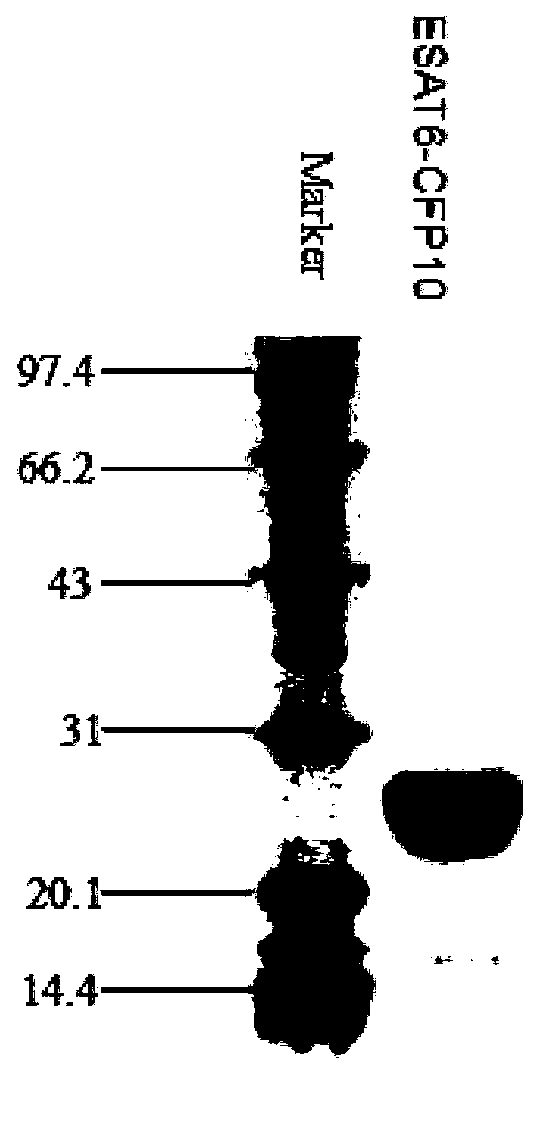
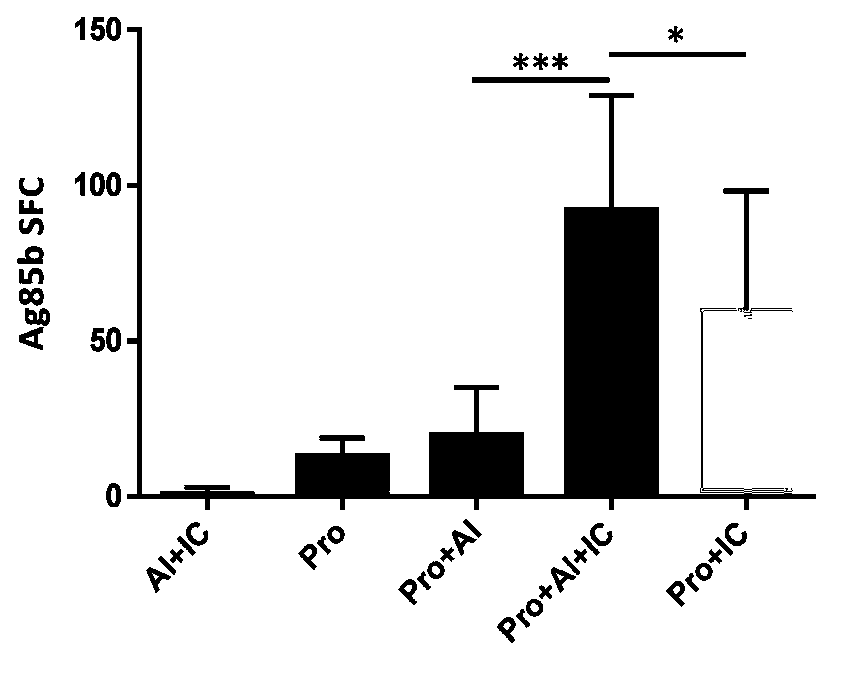
The invention provides a novel tuberculosis mycobacterium subunit vaccine containing unite adjuvant, which takes Ag85b protein, ESAT 6-CFP10 fusion protein as antigen component, and aluminum and PolyIC as a composite adjuvant. The adjuvant provided by the invention can effectively improve cellular immunity response of body to the tuberculosis subunit vaccine; at the same time, the adjuvant combines with the tuberculosis mycobacterium antigen Ag85b protein, ESAT6-CFP10 fusion protein, therefore the immunization effect is better than the compatibility effect of using other single adjuvant component and Ag85b protein and ESAT6-CFP10 fusion protein.
Owner:NAT INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
Wound or tissue dressing comprising lactic acid bacteria
InactiveCN101641121ARelieve symptomsReduce the severity of the diseaseAbsorbent padsBandagesVagococcusBacteroides
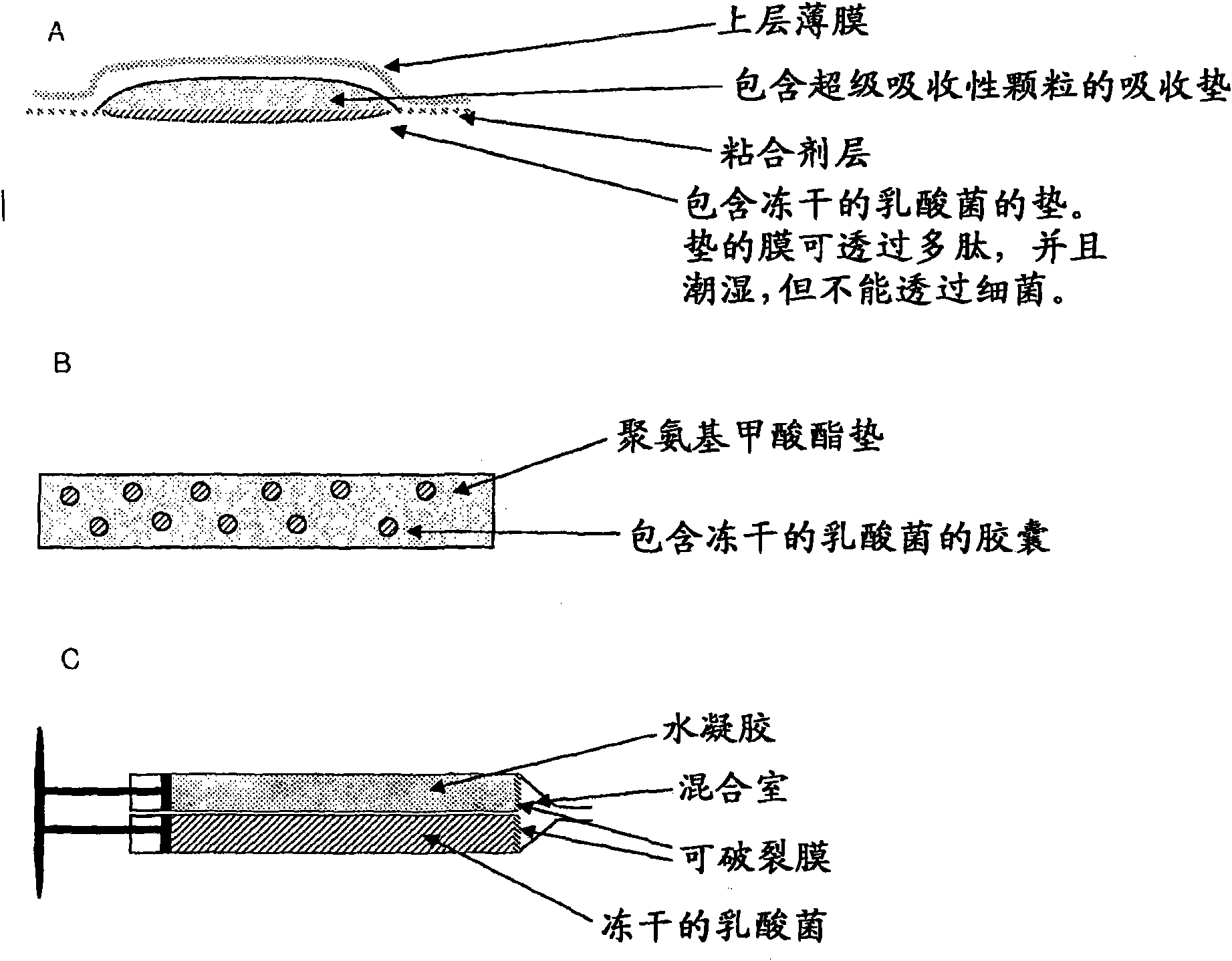
The present invention is directed to a wound or tissue dressing comprising a bacteria having the property of producing lactic acid from sugars by fermentation of the sugars. The bacteria preferably belongs to the family of lactic acid bacteria. The family of lactic acid bacteria refers to any bacteria belonging to a genus selected from the group consisting of Carnobacterium, Enterococcus, Lactobacillus, Lactococcus, Leuconostoc, Oenococcus, Pediococcus, Streptococcus, Tetragenococcus, Vagococcus and Weissella. There is also provided a wound or tissue dressing comprising an absorbent compound for absorbing wound exudate, wherein said wound or tissue dressing is attached to or comprises a lactic acid bacterium. The utility of the present invention is demonstrated by use of the wound or tissue dressings in methods for treating a wound or damaged tissue in an individual, said method comprising the steps of contacting said wound or damaged tissue with the wound or tissue dressing accordingto the invention, thereby treating the wound or damaged tissue. The treatment results in healing of the wound or in accelerated healing of the wound. There is also provided the use of a lactic acid bacteria in the manufacture of a wound or tissue dressing for treating or accelerating the healing of a wound in an individual.
Owner:FERROSAN MEDICAL DEVICES
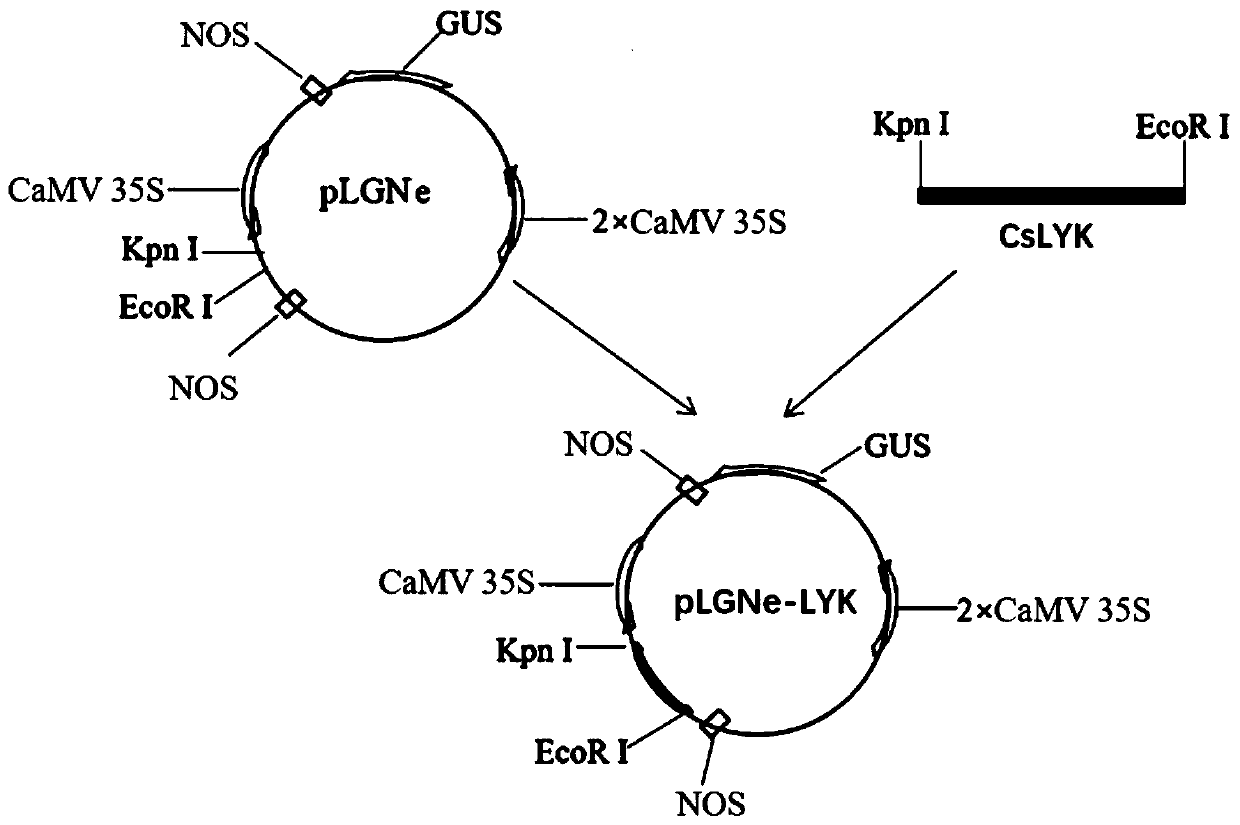
Application of CsLYK gene and encoded protein thereof in improving resistance to citrus canker
ActiveCN110819607AIncrease resistanceReduced incidence of ulcer diseaseMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesBiotechnologyCitrus volkameriana
The invention discloses application of CsLYK gene and an encoded protein thereof in improving resistance to citrus canker. The encoded protein of the CsLYK gene is a citrus LysM-like receptor proteinphosphokinase, and is named CsLYK protein. The nucleotide sequence of the CsLYK gene is a nucleotide sequence shown in SED ID No. 1; the protein sequence of the CsLYK gene is an amino acid sequence shown in SED ID No. 2. The invention also protects a breeding method of citrus resisting bacterial canker, and the method comprises following steps of integrating a citrus LysM-like receptor protein phosphokinase-encoding gene into a citrus through an overexpression vector to effectively improve citrus resistance to bacterial canker. The invention has great application value for breeding of citrus resisting bacterial canker; thereby laying the foundation of genetic breeding of citrus resisting canker, and vigorously promoting the development and application of citrus resisting canker genetic engineering.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Proteins expressed by mycobacterium tuberculosis and not by bcg and their use as diagnostic reagents and vaccines
InactiveUS20070224123A1Avoid the build processReduce the severity of the diseaseCompounds screening/testingAntibacterial agentsTuberculosis mycobacteriumOpen reading frame
The invention provides polypeptides encoded by open reading frames present in the genome of Mycobacterium tuberculosis but absent from the genome of BCG and diagnostic and prophylactic methodologies using these polypeptides.
Owner:NEW JERSEY UNIVESITY OF MEDICINE & DENTISTRY OF
Seed coating agent for preventing ginger wilt
The invention relates to a seed coating agent, in particular to a seed ginger seed coating agent for preventing ginger wilt. The seed ginger seed coating agent provided by the invention adopts active ingredients of low-toxicity reagents, which are safe to non-target organisms and environment, do not have adverse harm to human bodies and are suitable for the seed ginger treatment. Particularly, a compound recipe used by the seed coating agent can effectively utilize the efficient sterilizing effect of bromothalonil, meanwhile, a good protection effect of pyrimidine nucleoside antibiotics is utilized, and the medicine effect is enhanced, so the seed ginger seed coating agent has good effects of preventing and treating the ginger wilt. Meanwhile, the sterilization mechanisms of bromothalonil, pyrimidine nucleoside antibiotics and the zhongshengmycin are diverse from each other, and the generation of medicine resistance of ginger wilt germs can be effectively relieved.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Medicine for increasing immunocompetence of children and its preparing process
ActiveCN1544040AEnhance phagocytosisIncrease contentPill deliveryImmunological disordersImmunocompetenceRecurrent respiratory tract infections
The invention discloses a medicament for enhancing children's immunocompetence which comprises the following constituents with parts by weight, astragalus root 75-85, dried orange peel 5.5-7, white atractylodes rhizome 50-60, Chinese yam 75-85, ledebouriella root 22-32, oyster 75-85. The traditional Chinese composition according to the invention has the function of improving body immunocompetence. The invention also discloses the process for preparing the medicament.
Owner:广州康和药业有限公司
Disease resistant plants
ActiveUS20100017913A1Improve the immunityReduce the severity of the diseaseBiocideTissue cultureDiseaseDisease resistant
The invention provides transgenic plants with resistance to infection by a root-infecting fungal plant pathogen such as Phymatotrichopsis omnivora. Also provided are methods of making such plants. Further provided are nucleic acid vectors for producing such a plant. Additionally, methods are provided for growing a dicotyledonous plant that is resistant to root rot disease in soil that comprises Phymatotrichopsis omnivora, or another pathogen.
Owner:NOBLE RES INST LLC
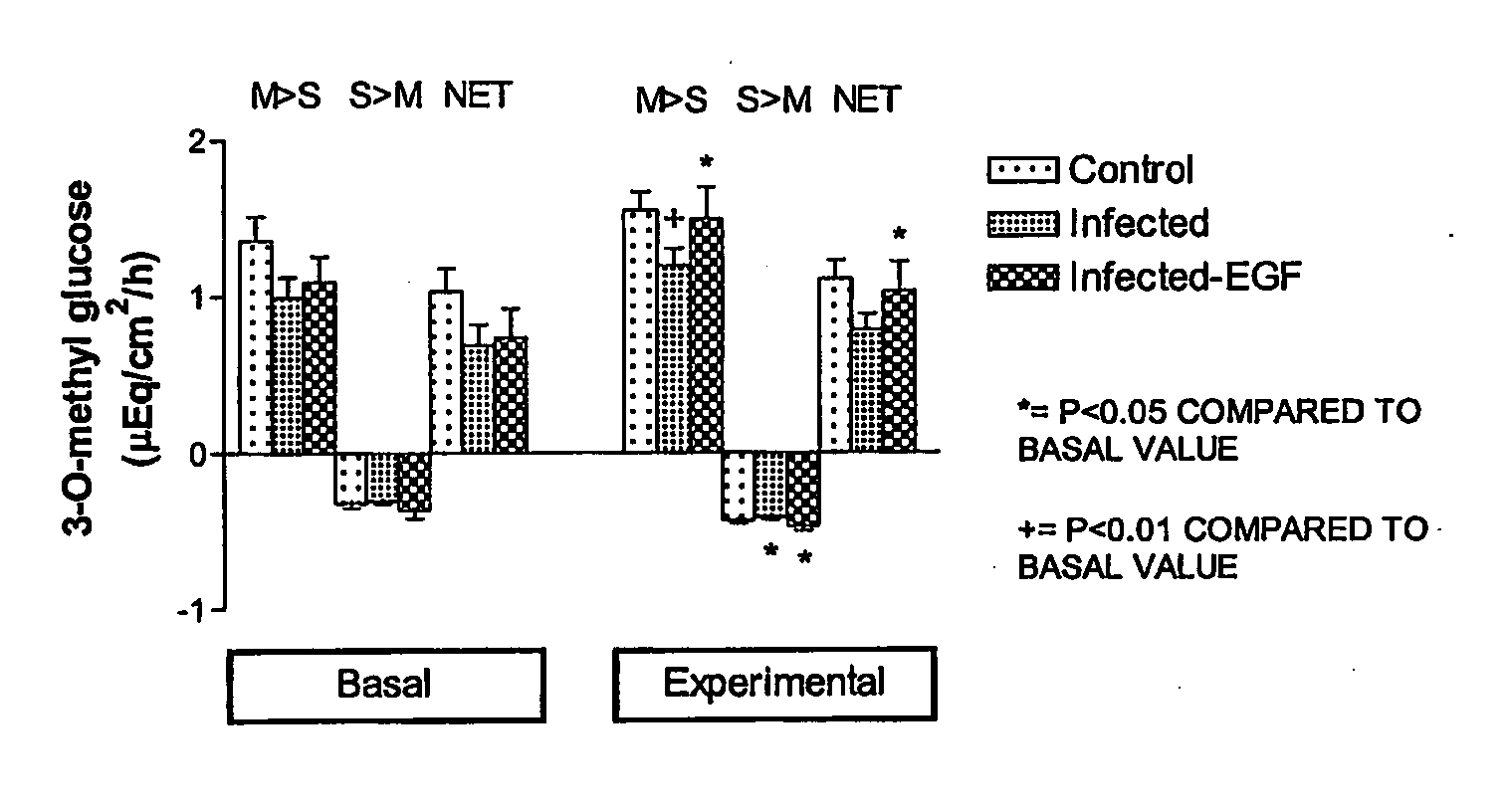
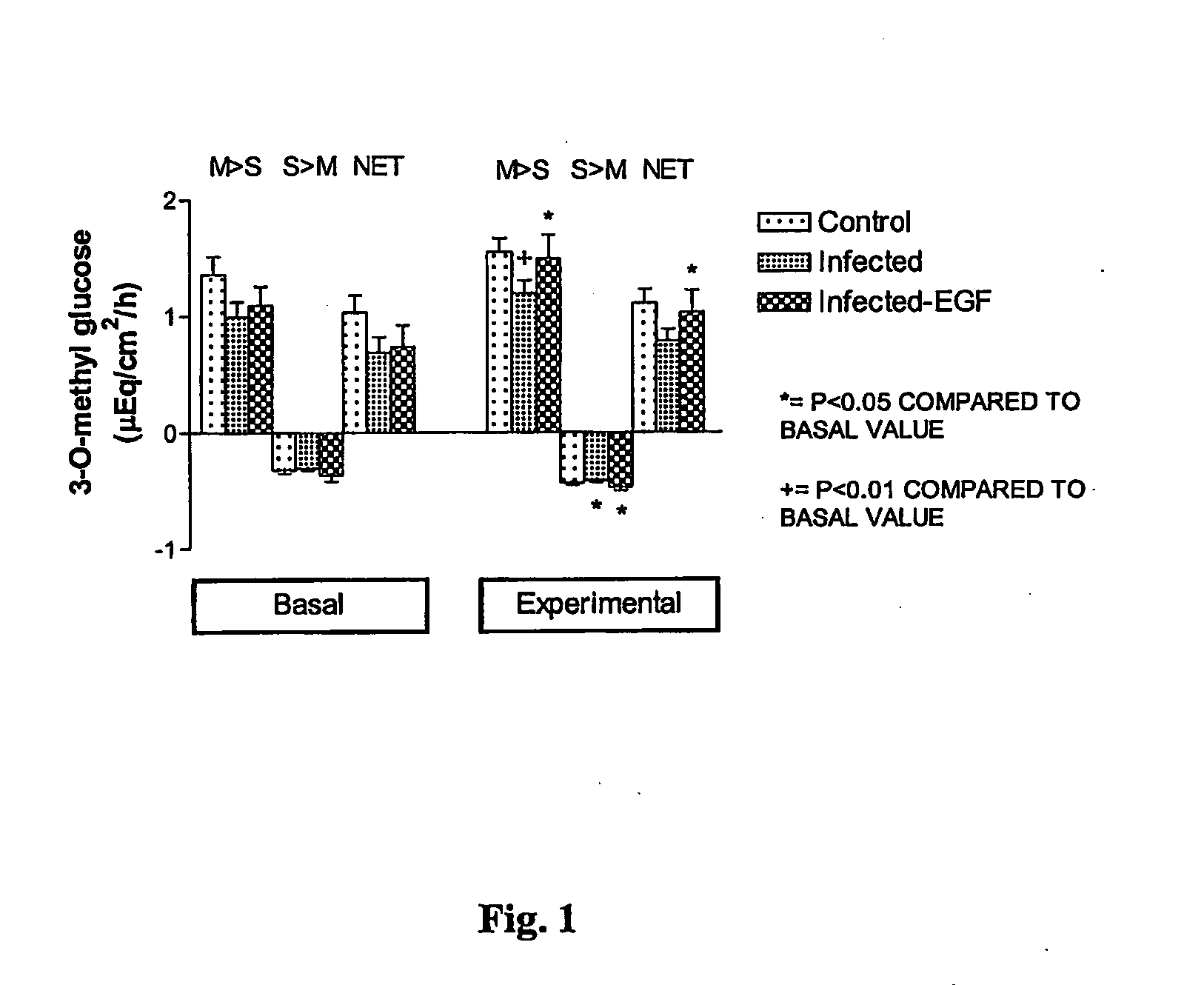
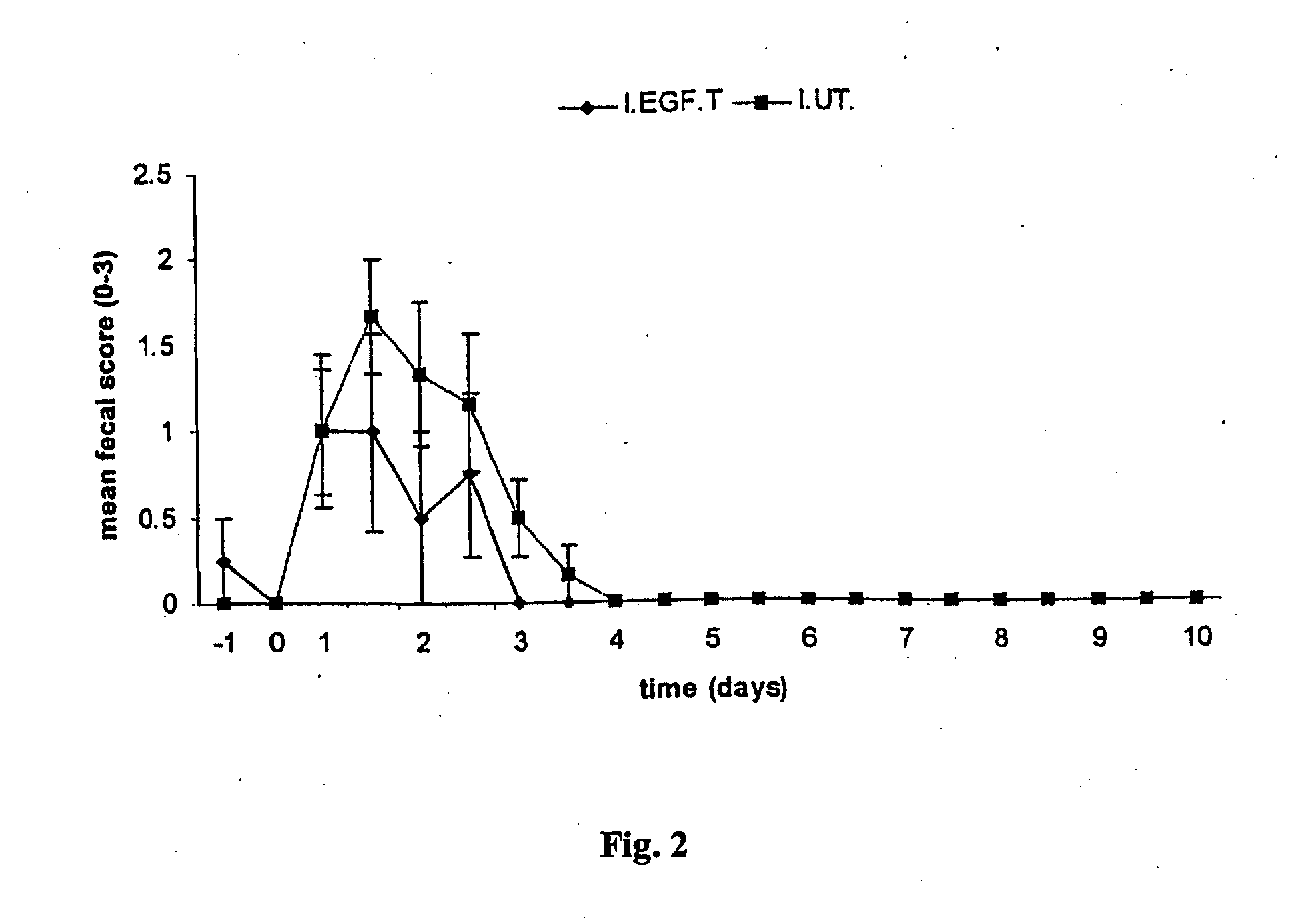
Rehydration compositions comprising epidermal growth factor (EGF)
InactiveUS20110245171A1Promote wound repairEasy to transportPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemHuman epidermal growth factor receptorAgonist
The invention comprises 1) an oral composition, including an oral rehydration composition or solution, comprising an effective amount of a compound selected from epidermal growth factor (EGF) and agonists to the epidermal growth factor receptor, 2) a kit comprising an oral rehydration composition containing an effective amount of a compound selected from epidermal growth factor and agonists to the epidermal growth factor receptor, and 3) methods for the treatment and prevention of dehydration and diarrhea, and enhancing intestinal healing, reducing bacterial colonization, reducing the incidence of weight loss, increasing food uptake, enhancing rehydration, and enhancing mucosal healing in an animal having diarrhea.
Owner:AB BIOPHARMA
Acinetobacter lactucae and application thereof to degradation of quorum-sensing signal molecule DSF
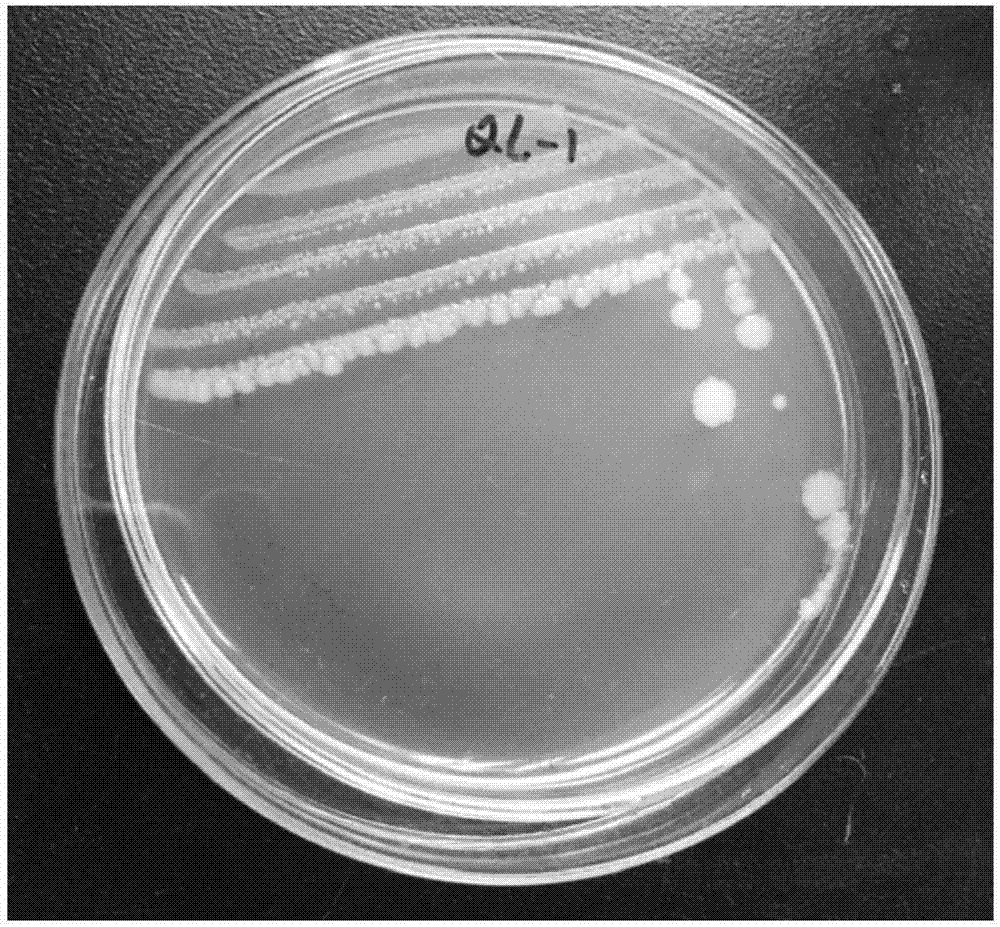
ActiveCN107964516AHigh degradation activityReduce the severity of the diseaseBiocideBacteriaXanthomonas campestrisSignalling molecules
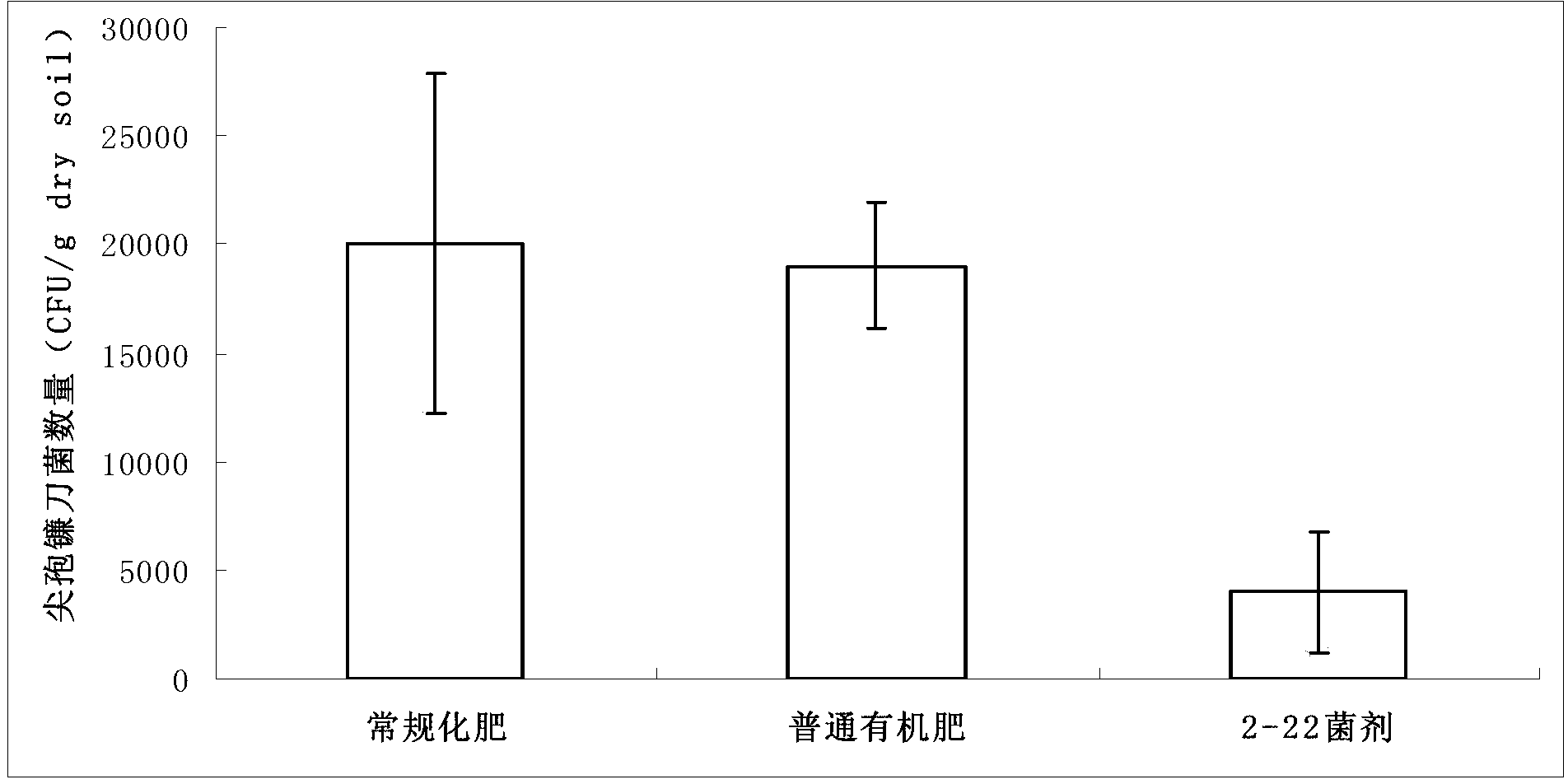
The invention discloses Acinetobacter lactucae and an application thereof to degradation of a quorum-sensing signal molecule DSF (diffusible signal factor). The invention provides a bacterial strain of Acinetobacter lactucae QL-1, the bacterial strain is preserved in a China Center for Type Culture Collection on September 11th, 2017, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2017487. The bacterialstrain can employ the quorum-sensing signal molecule DSF as a sole carbon source for growth, and 2mM of DSF signal molecules can be completely degraded in 15 hours with high degradation activity andstable degradation performance. The bacterial strain QL-1 has substantial biocontrol effects for black rot caused by Xanthomonas campestris XC1, and the bacterial strain also has characteristics of fast growth speed, simple cultivation method, good adaptation capability without easy variation, and great application potential for promotion of control of pathogens which are pathogenic depending on DSF; and at the same time, the product can reduce the problem of abuse of pesticides, and provides a new thinking for biological control of plant diseases.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Fertilizer for preventing bacterial wilt and promoting growth special for tomatoes
InactiveCN106242843AReduce the severity of the diseaseImprove disease resistanceSuperphosphatesMagnesium fertilisersPhosphorous acidMetasilicate
The invention discloses a fertilizer for preventing bacterial wilt and promoting growth special for tomatoes. The fertilizer is prepared from pig manure, chicken manure, earthworm manure, bagasse, crucifer, urea, superphosphate, potassium sulphate, manganese sulfate, magnesium sulfate, ferrous sulfate, ammonium molybdate, borax, prohexadione-calcium, calcium metasilicate, calcium carbonate, phosphorous acid, heteroauxin, humic acid, attapulgite, bentonite, microbial flora, alkyl glycoside, oligosaccharins and polyaspartic acid. The fertilizer for preventing bacterial wilt and promoting growth special for the tomatoes is reasonable in formula, comprehensive in nutrition and capable of promoting growth of the tomatoes, the disease resistance of tomato plants is improved, and bacterial wilt can be effectively prevented and controlled.
Owner:ANHUI SIERTE FERTILIZER IND
Fungal agent for prevention and control of watermelon fusarium wilt and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103255064AImprove the effect of disease preventionDecreased blight incidenceBiocideFungiBiotechnologyDisease
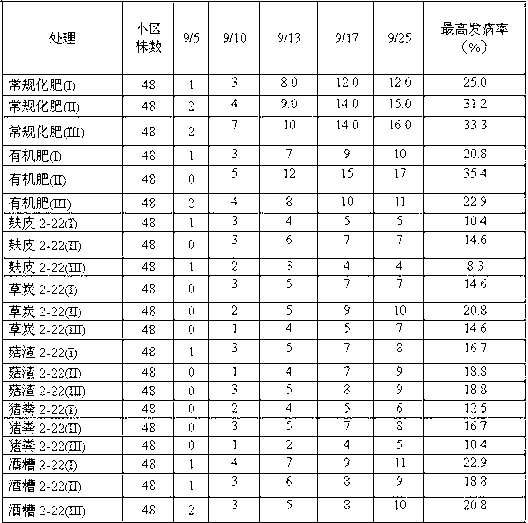
Belonging to the technical field of biological prevention and control of soil borne diseases of melons, the invention discloses a fungal agent for prevention and control of watermelon fusarium wilt and a preparation method thereof. The method includes: preparation of mediums of different levels and preparation of an adsorption carrier; slant strain culture; shake flask strain propagation; production fermentation tank culture; solid agent preparation and other steps. In the invention, a Hypocrea atroviridis strain 2-22CGMCCNo.7128 is taken as the strain, which is prepared into a liquid and / or solid agent by fermentation, so that the attack time of watermelon fusarium wilt can be delayed, and the incidence can be reduced by over 40%. After watermelons undergo a continuous second crop, a good disease prevention effect can still be maintained. The agent provided in the invention has the advantages of rich raw materials, simple process, low cost, and a shelf life of more than half a year, and can be popularized and applied in watermelon planting areas.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Preparation method of sophora flavescens freeze dried powder injection
InactiveCN1830443AAvoid degradationEnsure complete removalOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryMANNITOL/SORBITOLUltrafiltration
A freeze-dried powder injection of kurarinol for treating chronic hepatitis B, anaphylaxis and inflammation is prepared from kurarinol through depositing in water, cold storage, ultrafiltration, adding mannitol and disodium versenate in dark condition and N2 atmosphere, pouring in containers, freeze drying and sealing.
Owner:巴里莫尔制药(通化)有限公司
Fermented traditional Chinese medicine formula for treating diabetes
InactiveCN108853350AInhibit releaseLower blood sugar levels that induce diabetesMetabolism disorderFungi medical ingredientsFlavorPesticide
The invention discloses a fermented traditional Chinese medicine formula for treating diabetes. According to a weight ratio, the fermented traditional Chinese medicine formula comprises 15 to 25 partsof herba dendrobii officinale, 15 to 25 parts of radix salviae miltiorrhizae, 15 to 25 parts of bitter gourd, 25 to 35 parts of common yam rhizome, 25 to 35 parts of inonotus obliquus, 45 to 55 partsof lucid ganoderma and 15 to 25 parts of poria cocos; all the ingredients are fermented for 5 to 7 days under the condition of 40 to 70 DEG C to obtain a fermented material, and the fermented material is dried and ground into fine power to obtain fermented traditional Chinese medicine. By means of the comprehensive action among the inonotus obliquus, the herba dendrobii officinale, the poria cocos and the lucid ganoderma, the fermented traditional Chinese medicine formula can inhibit release of fatty acid, can reduce a streptozotocin induced glycosuria blood glucose level, can promote utilization and a conversion rate of tissues to saccharide and can reduce a mobidity degree of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus; by means of fermentation, on one hand, flavor is improved, effective ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine can be absorbed by the human body more easily, and a pharmacological function is enhanced; on the other hand, residual pesticide and heavy metal in the raw traditional Chinese medicine materials can be removed.
Owner:大连金石斛生物技术有限公司
Method for improving canker resistance of citrus by utilizing CsNCED3 gene silencing
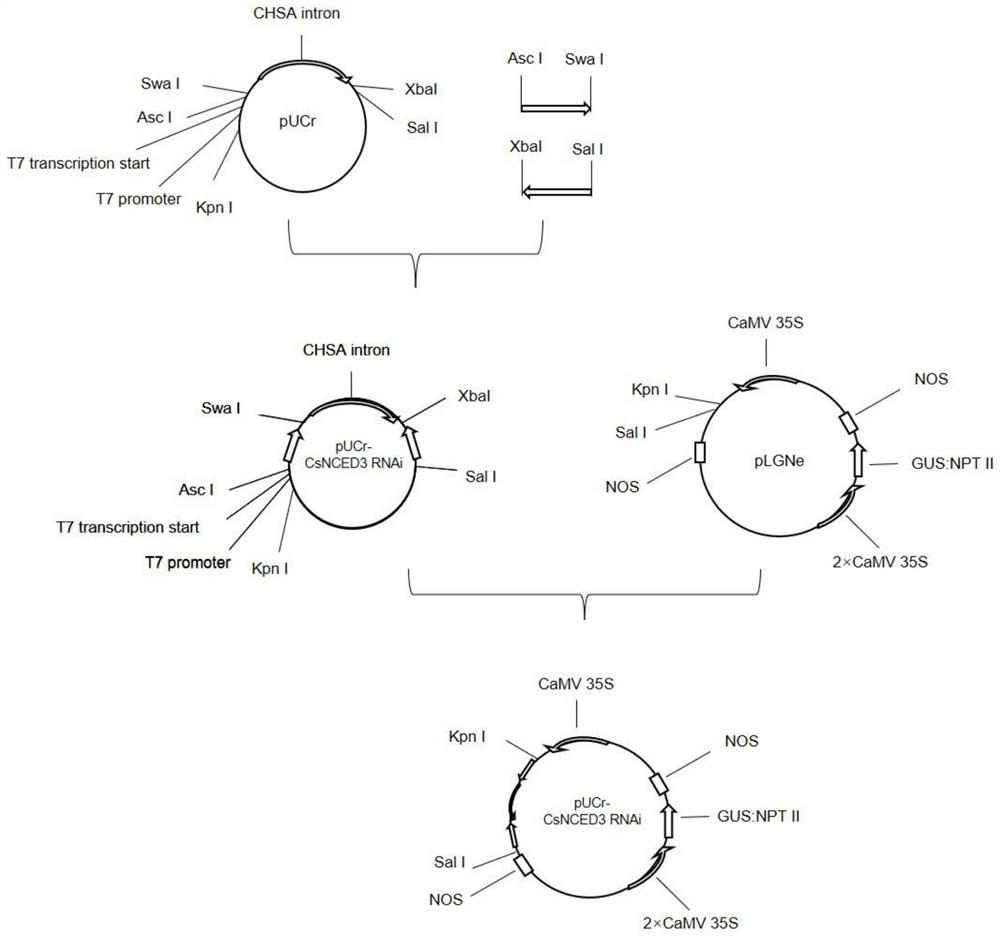
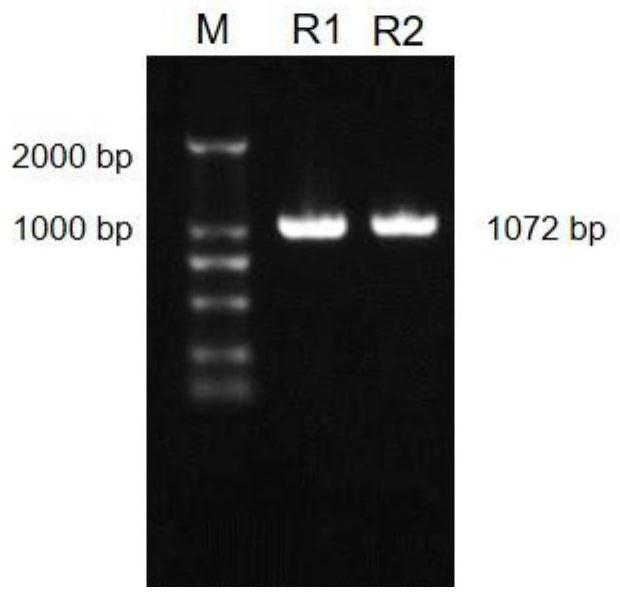
PendingCN114395570AIncrease resistanceReduce the severity of the diseaseOxidoreductasesFermentationBiotechnologyCitrus volkameriana
The invention discloses a method for improving canker resistance of citrus by utilizing CsNCED3 gene silencing. The method comprises the following steps: (1) cloning a citrus CsNCED3 gene segment; (2) constructing an interference expression vector of the CsNCED3 gene segment; and (3) transforming the citrus by the interference expression vector to obtain a transgenic plant. According to the method, CsNCED3 gene silencing is utilized, citrus CsNCED3 gene segments are cloned, an interference expression vector is constructed, and then citrus is transformed, so that the expression quantity of the obtained transgenic plant CsNCED3 is remarkably reduced to 29% of that of the existing citrus, and the canker attack degree can be reduced to 47% of that of the existing citrus, and therefore, the method can improve the canker resistance of the plant to a certain extent.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
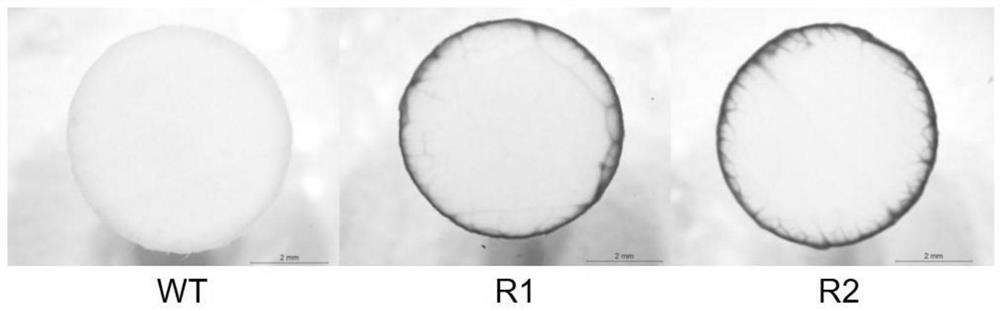
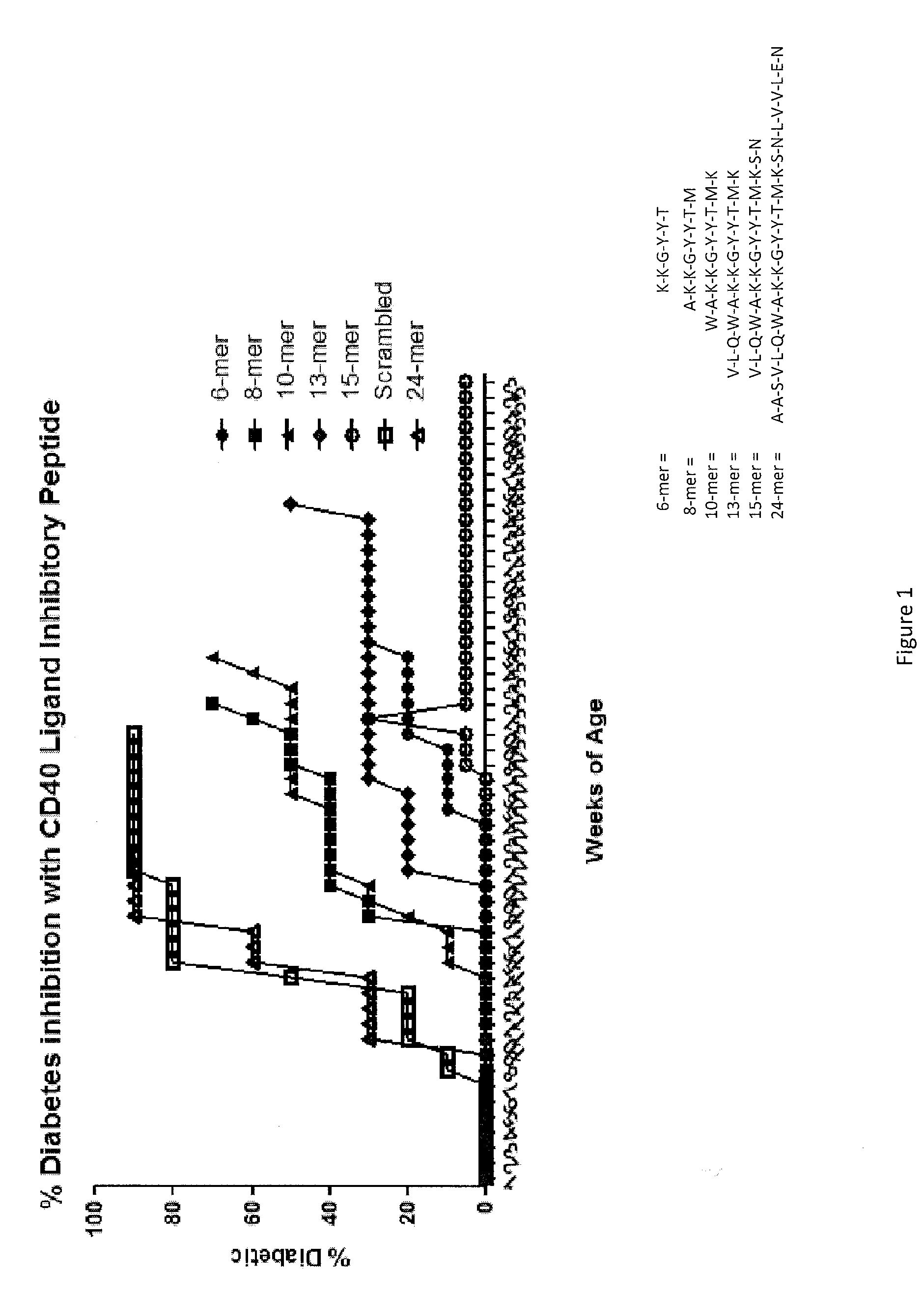
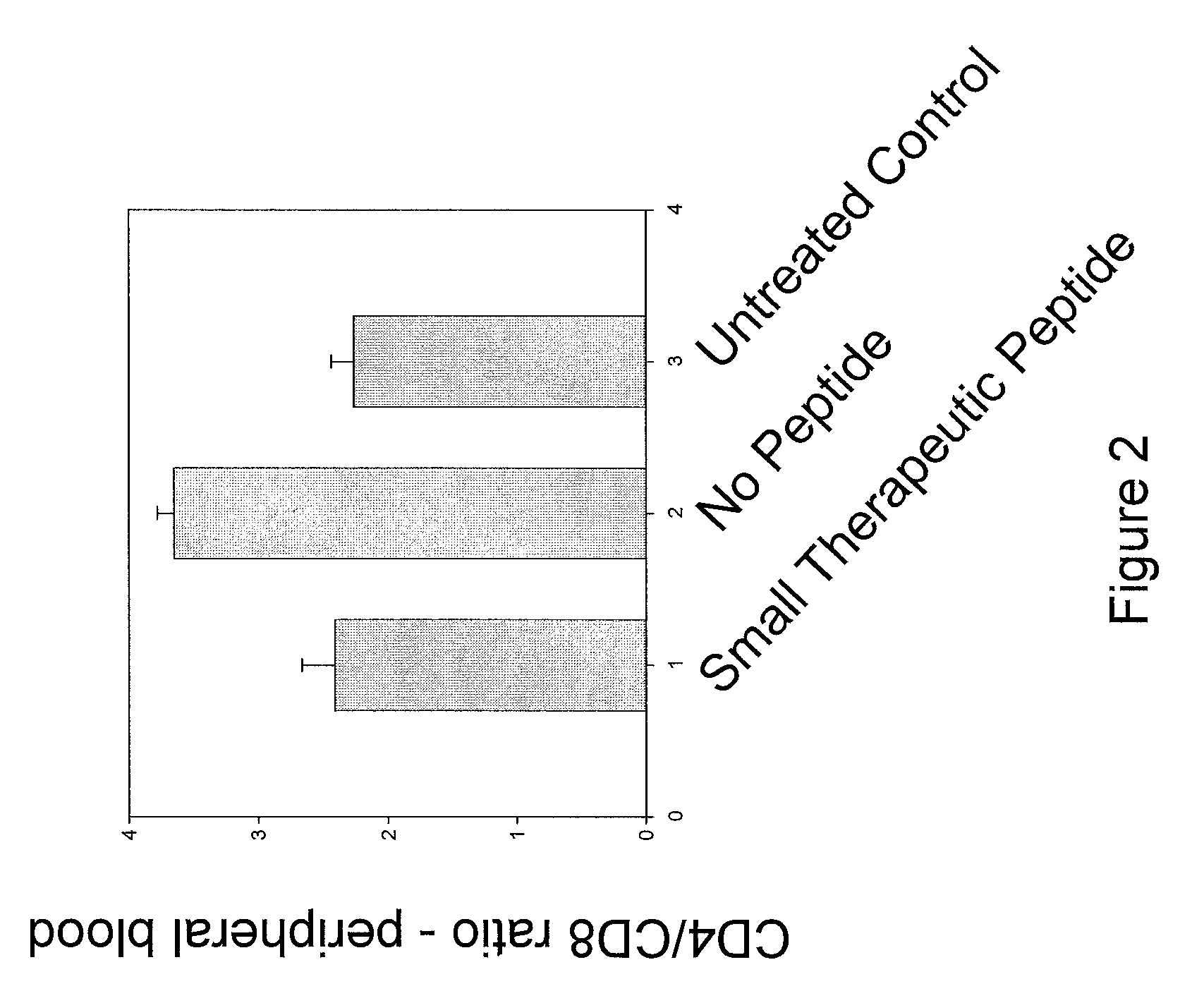
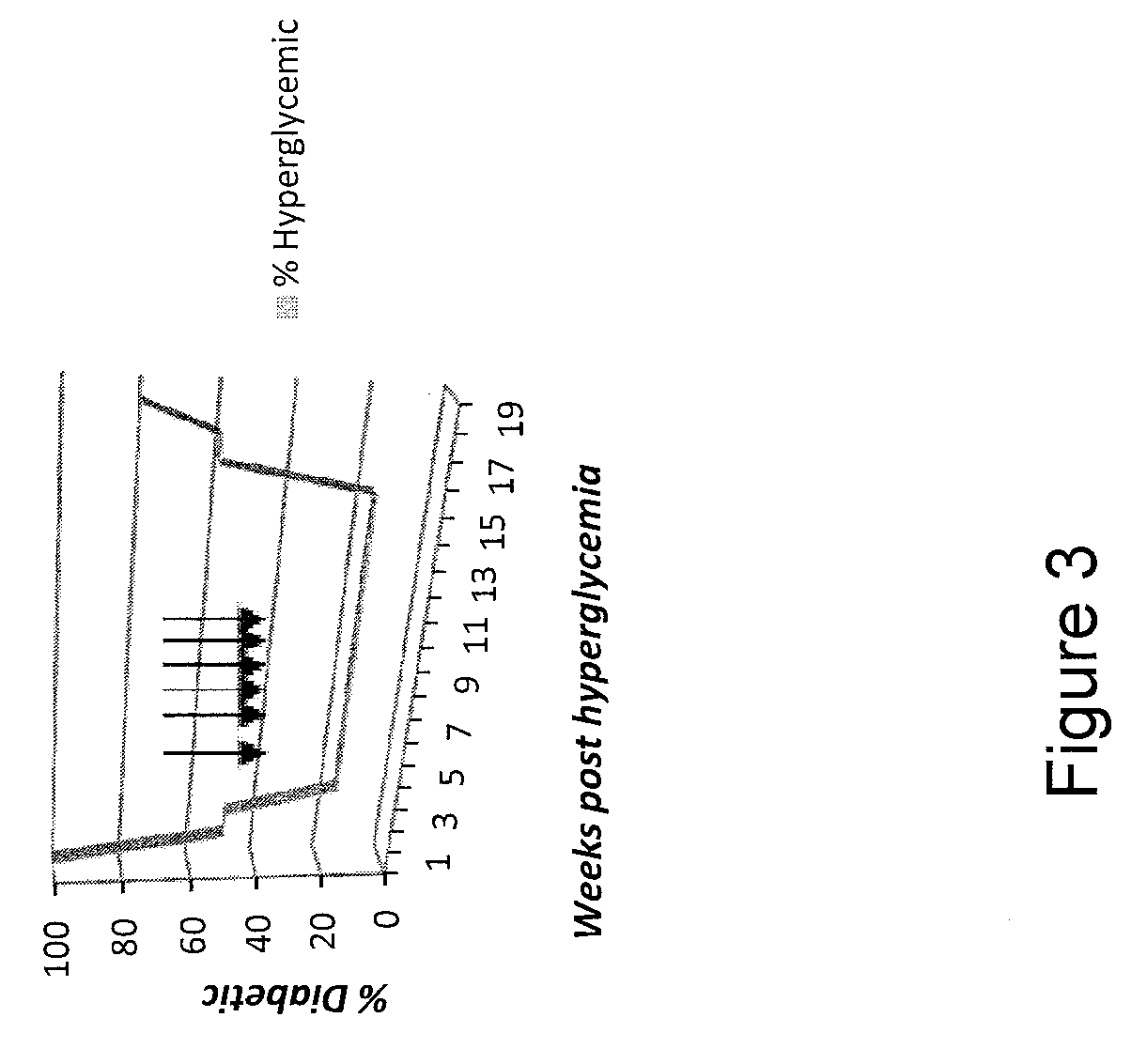
Peptides for modulating t-cell activity and uses therof
ActiveUS20130236495A1Lower Level RequirementsReduce the severity of the diseasePeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesDiseaseDiabetes mellitus
The present invention provides methods and materials for treating and preventing autoimmune diseases. In particular, the present invention relates to the discovery that small peptides are capable of interacting with CD40, thereby interfering with the ability of CD40 to interact with CD 154, which is important in inflammation. The present invention also relate to the use of such peptides in reducing the inflammatory response, and in particular, the autoimmune inflammatory response. The present invention also relates to the use of such short peptides to prevent or reverse autoimmune disease, and particular, diabetes, in individuals suffering from such disease. It also relates to methods and materials for detecting T-cells that express CD40 (Th40 cells). Also provided are kits for reducing inflammation, treating autoimmune diseases, or detecting Th40 cells.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
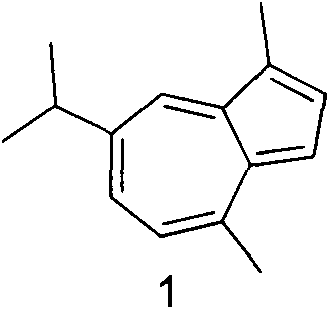
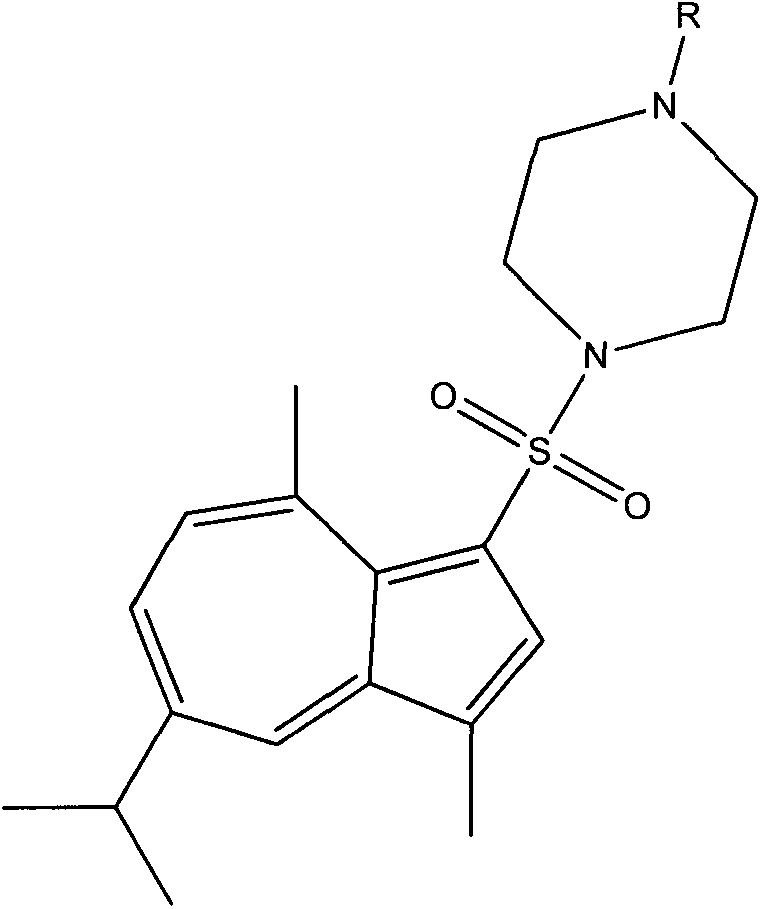
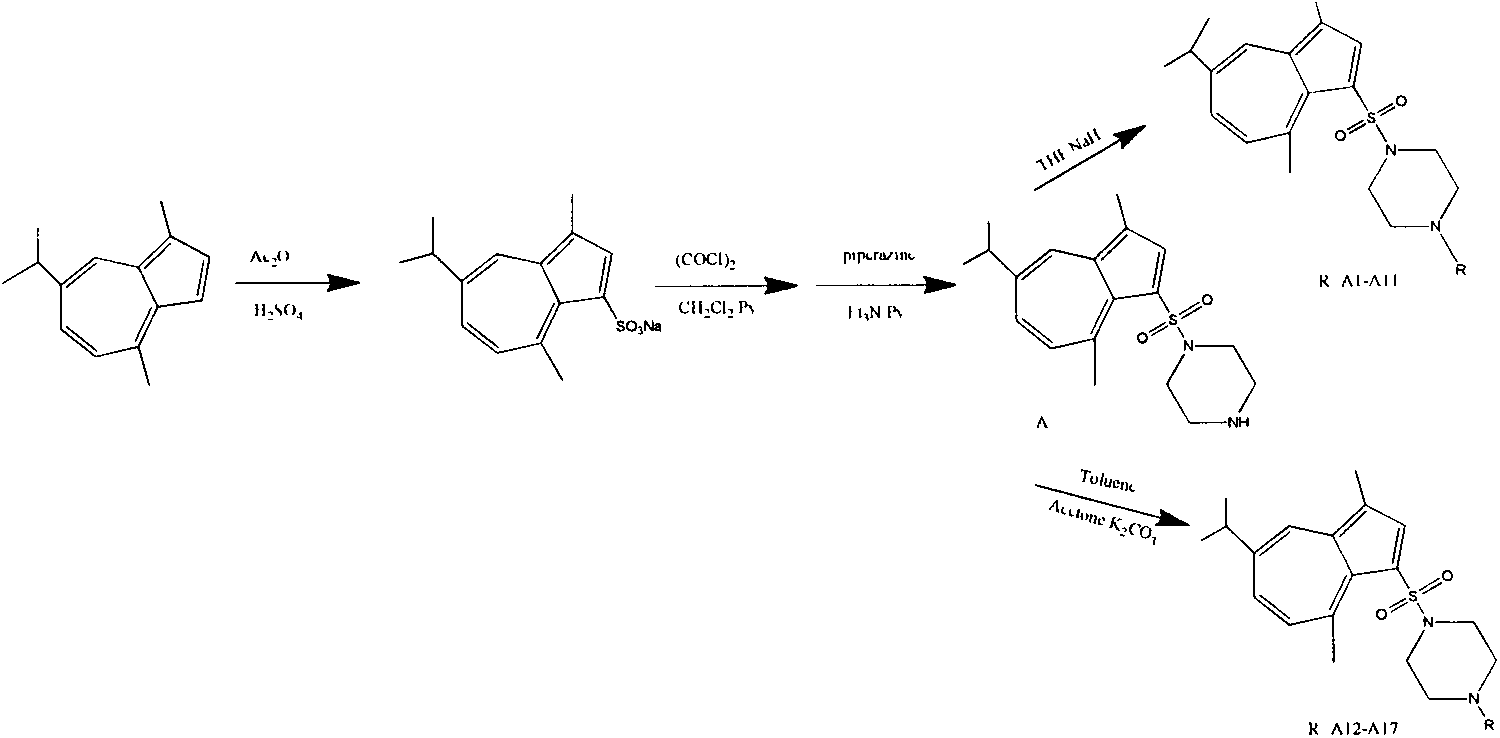
Synthesis of 1-substituent-5-isopropyl-3, 8-dimethyl azulenyl sulfonyl piperazine and anti-gastric ulcer activity research
ActiveCN103159702AGood curative effectReduce the severity of the diseaseOrganic chemistryDigestive systemAlcoholStructural formula
The invention discloses a guaiazulene derivative 1-substituent-5-isopropyl-3, 8-dimethyl azulene sulfonyl piperazine, wherein the structural formula is as follows: in which R is C6H5O2S, 4-CH3C6H4, COCH3, SO2CH3, COCH2C1, COC6H5, 1-SO2-4-BrC6H4, CH2C6H5, CH2CO2C2H5, CH3, COCF3, iso-C3H7, C4H9, 1-CH2-4-CH3C6H4, 1-CH2-2-C1C6H4, n-C3H7, C2H5, and other substances are respectively represented by A, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10, A11, A12, A13, A14, A15, A16 and A17. Part of compounds can remarkably alleviate the pathological degree of gastric ulcer of mice by absolute ethyl alcohol, and the gastric ulcer fraction is remarkably different from that of a model. The preparation method comprises preparation of 1-substituent-5-isopropyl-3, 8-dimethyl azulene sulfonyl piperazine.
Owner:SICHUAN GUOKANG PHARMA
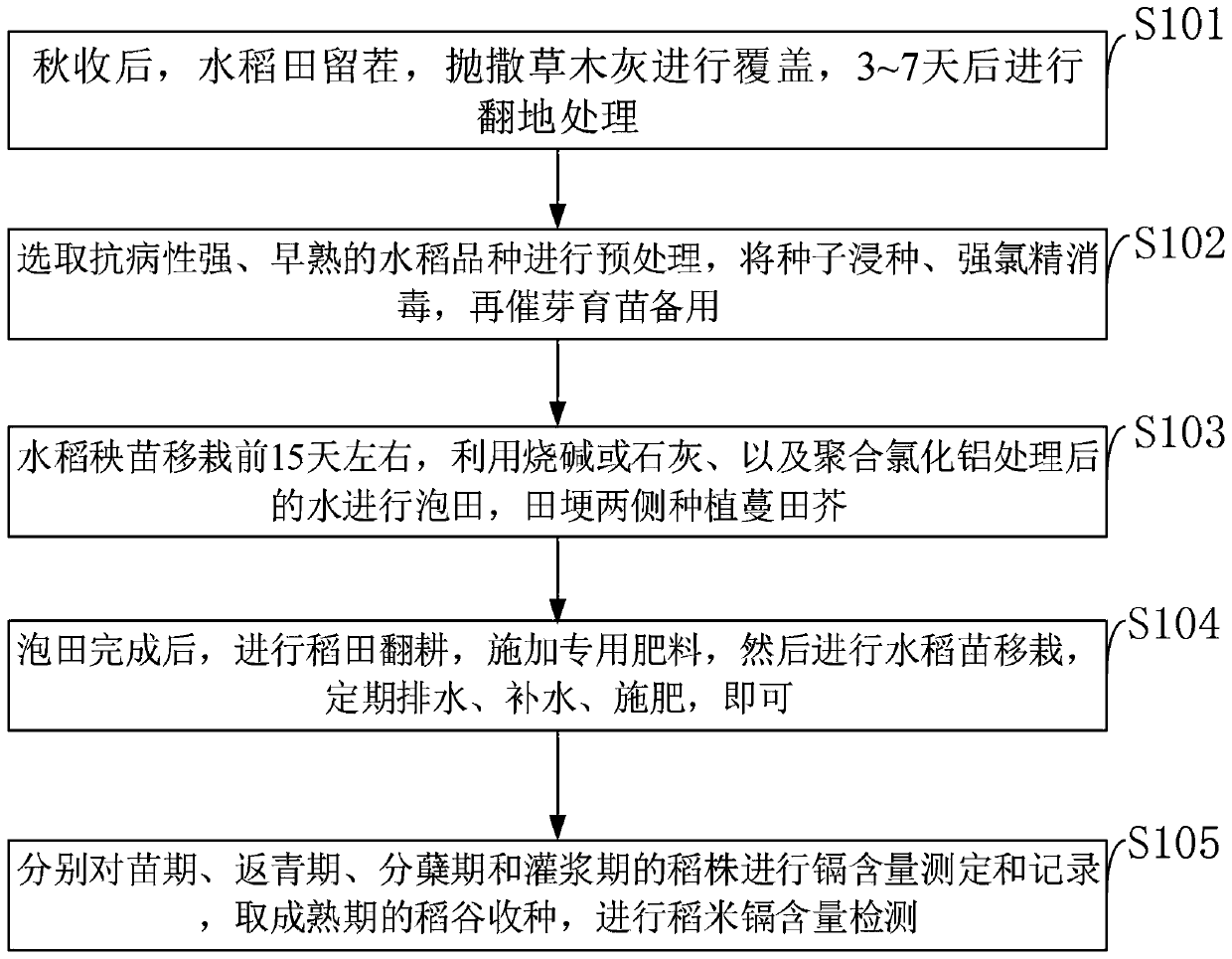
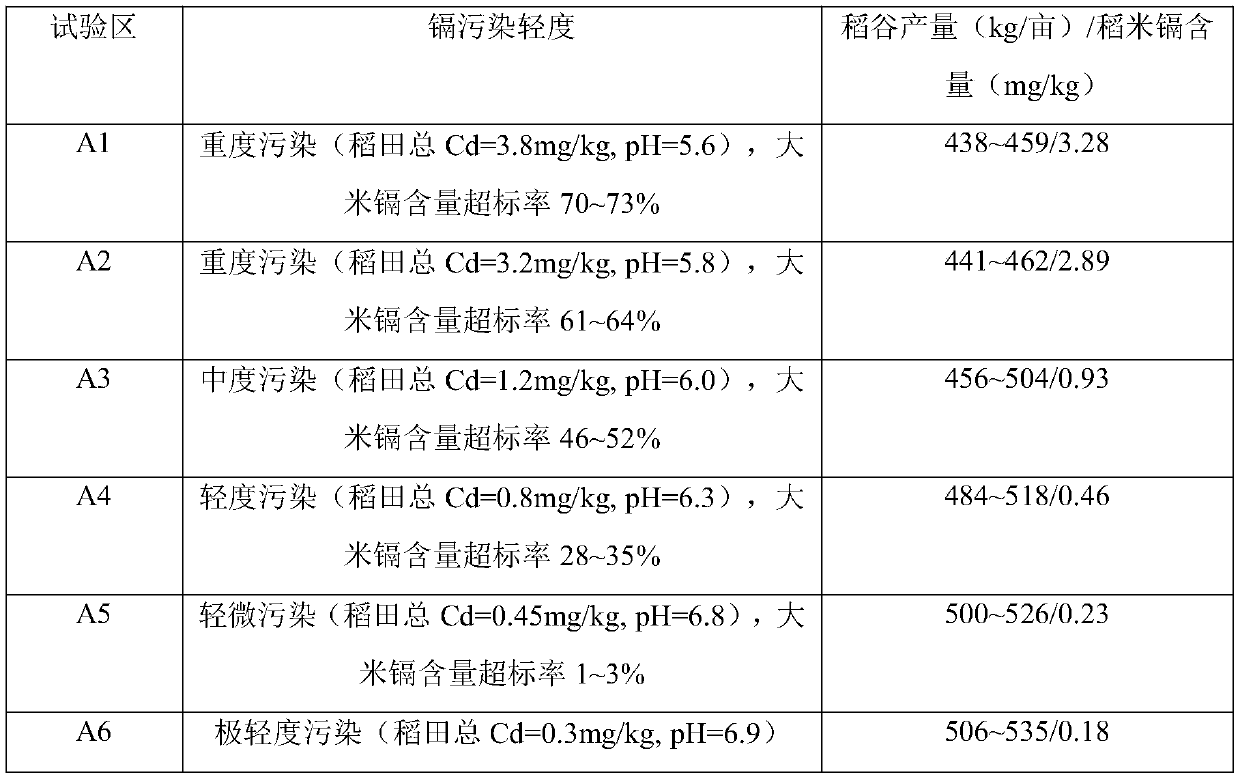
Rice production method for lowering heavy metal cadmium pollution
InactiveCN109744102AReduce acidityReduce pollutionOther chemical processesOrganic fertilisersDiseaseSteeping
The invention belongs to the technical field of rice production, and discloses a rice production method for lowering heavy metal cadmium pollution. The rice production method for lowering heavy metalcadmium pollution comprises the steps: after autumn harvest, stubble is left in a paddy field, plant ash is scattered for covering, plowing treatment is conducted after 3-7 days, and heavy metal polluted water is prevented from entering the paddy field; early-mature rice varieties with high disease resistance are selected to be pretreated, and seeds are soaked, disinfected through trichloroisocyanuric acid, and then subjected to pregermination and seedling culture for standby application; about 15 days before transplanting of rice seedlings, water treated through caustic soda or lime and polyaluminum chloride conducts field steeping, and arabis gemmifera is planted on the two sides of ridges; and after field steeping is completed, the paddy field is ploughed, special fertilizer is applied,then the rice seedlings are transplanted, and regular drainage, water replenishing and fertilization are conducted. The adopted method is simple and good in effect, the cadmium treatment cost is lowered, the economic benefits of farmers are increased, the rice yield is increased, and food safety is ensured.
Owner:HUNAN HYBRID RICE RES CENT
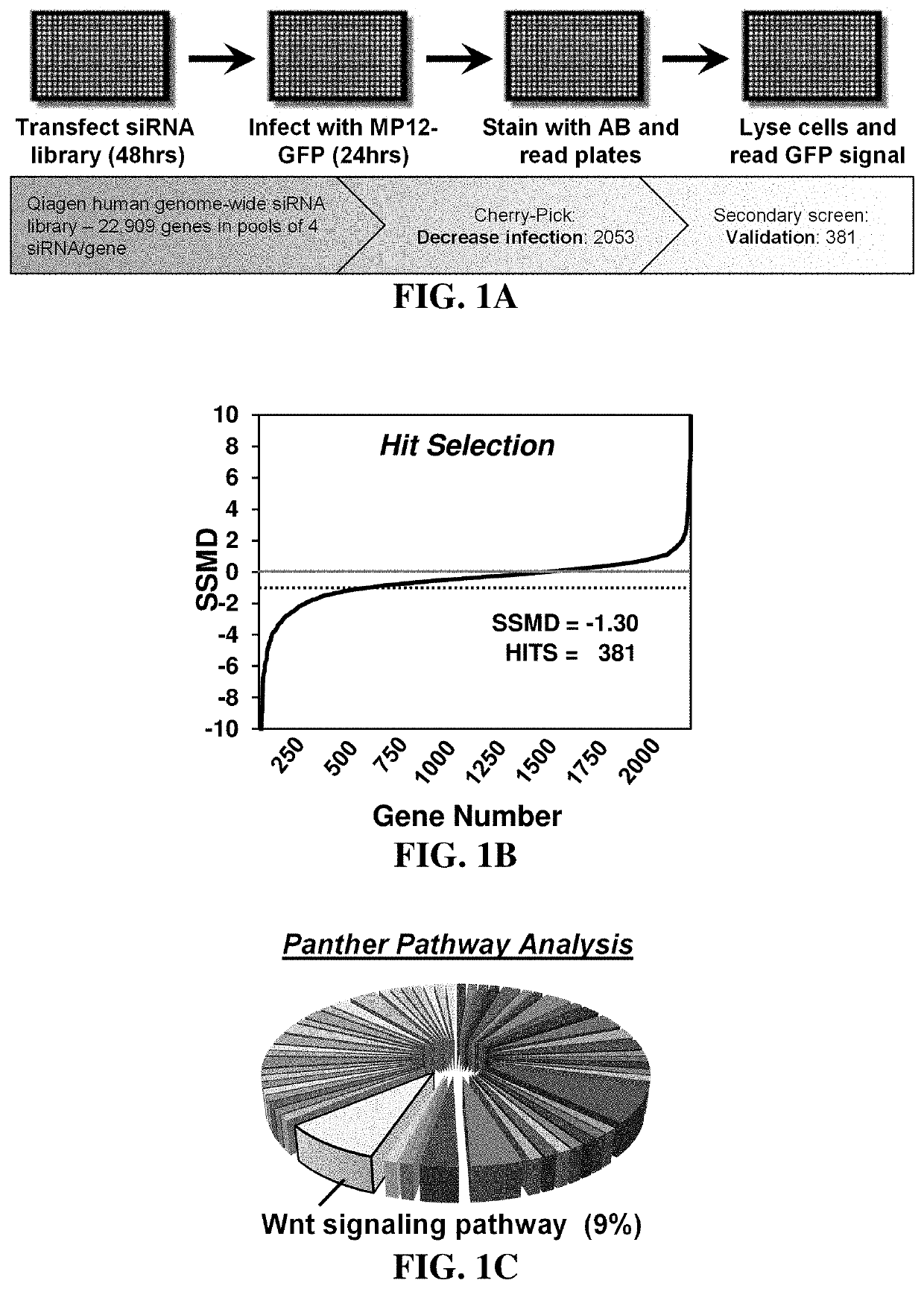
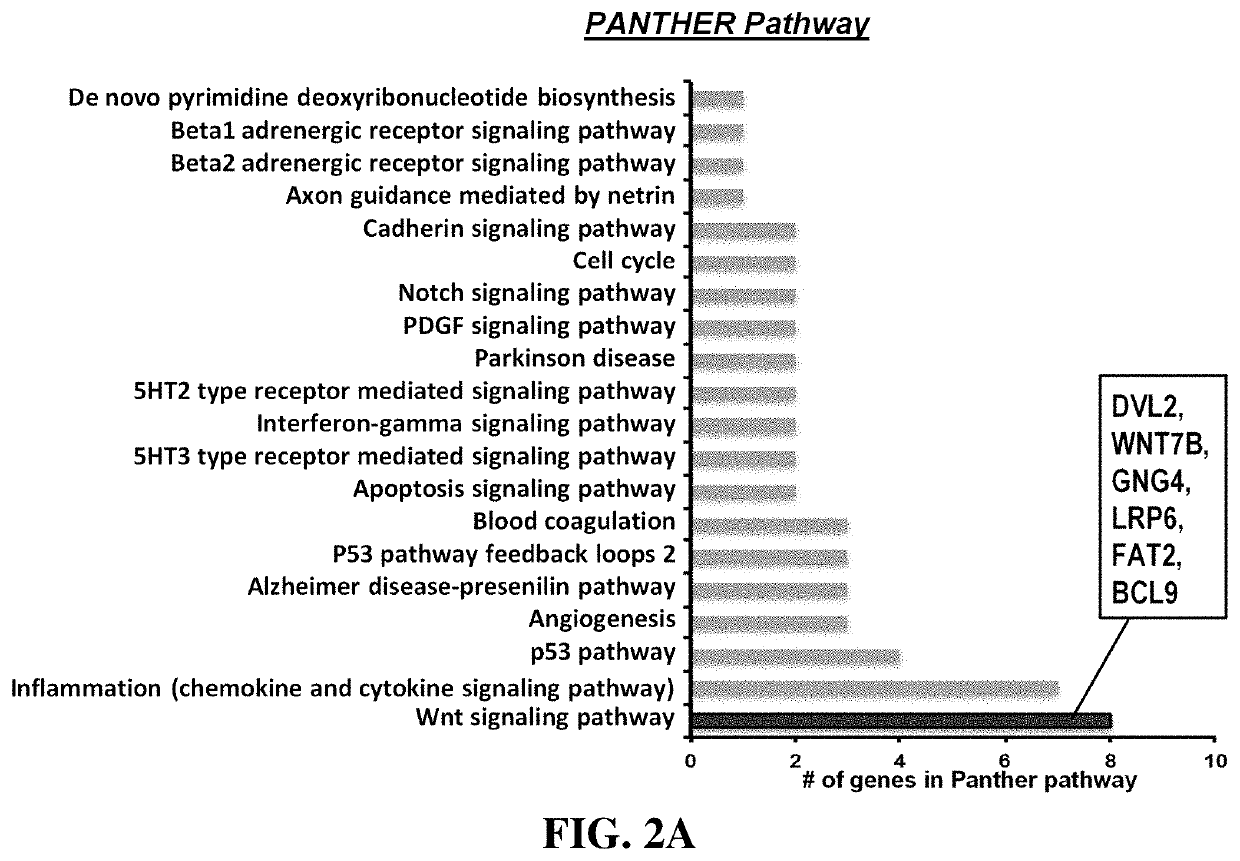
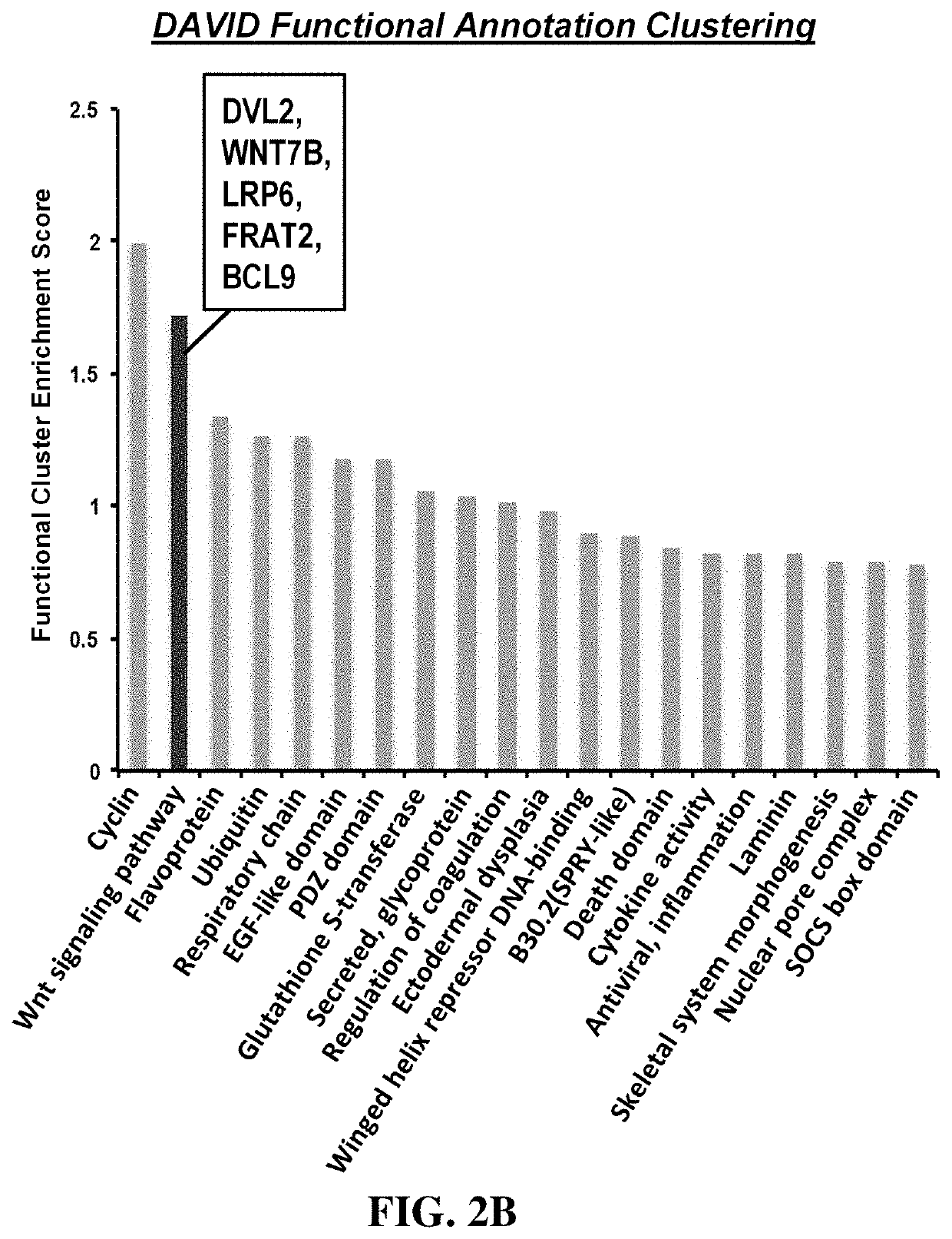
Methods for treating diseases related to the wnt pathway
ActiveUS10624949B1Relieve symptomsDiminishment of extentPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomeDisease status
The present invention relates to methods for treating a disease, in which the disease arises from dysregulation of the Wnt signaling pathway. In some instances, the disease can be treated by administering a Wnt pathway inhibitory compound. In other instances, the method optionally includes conducting a genome-wide screening to determine one or more genes resulting in a reduced disease state and then identifying the gene(s) as being involved in the Wnt signaling pathway.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
A bactericidal composition containing metalaxyl and difenoconazole
InactiveCN102258031AThe effect of disease controlThe effect of the disease is goodBiocideFungicidesFungal diseasePreservative
The invention provides a fungicidal composition containing metalaxyl-ethyl and difenoconazole. The present invention is characterized in that the content of each component of the suspending agent of metalaxyl-fine and difenoconazole is (mass fraction): 0.1-70% of metalaxyl-fine, 0.1-70% of difenoconazole, dispersed 1-15% agent, 1-15% wetting agent, 1-5% antifreeze, 0.1-5% preservative, 0.1-5% defoamer, 0.1-5% thickener, water balance. The invention can be used for disinfection treatment of crop seeds, and can effectively prevent and control various fungal diseases caused by higher fungi and lower fungi.
Owner:北京绿色农华作物科技有限公司
Application of benserazide hydrochloride in preparing medicine for treating acute inflammation
ActiveCN106727470AGood treatment effectGood effectOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticInflammatory factorsTreatment effect
The invention relates to application of benserazide hydrochloride in preparing medicine for treating acute inflammation and belongs to the technical field of biological medicine. According to the application of benserazide hydrochloride in preparing medicine for treating acute inflammation, a treating effect of the benserazide hydrochloride on acute inflammation is researched through animal experiments, and experiment results show that the benserazide hydrochloride has an inhibiting effect on inflammatory factors generated by mouse acute inflammation caused by lipopolysaccharide. Specifically, a C57BL / 6 mouse acute inflammation model is induced to be constructed through the lipopolysaccharide, different concentrations of benserazide hydrochloride is utilized to treat the mouse, results show that the benserazide hydrochloride can reduce inflammatory factor level generated by C57BL / 6 mouse acute inflammation and pathological change degree of hepatic tissues, and the low dosage benserazide hydrochloride has the optimal effect. The benserazide hydrochloride is prepared into varieties of preparation required by clinic by adding carriers accepted by pharmacy, and the application of benserazide hydrochloride in preparing medicine for treating acute inflammation has the beneficial effect of providing a novel path for preparing acute inflammation medicine.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Secreted proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and their use as vaccines and diagnostic reagents
InactiveUS7595383B1Avoid the build processReduce the severity of the diseaseBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsSecretory proteinMycobacterium moriokaense
The invention provides mycobacterium tuberculosis polypeptides and genes encoding them for use in diagnostic and prophylactic methodologies.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Pgk1 protein, recombinant plasmid for expressing Pgk1 protein, recombinant probiotic for expressing Pgk1 protein and application
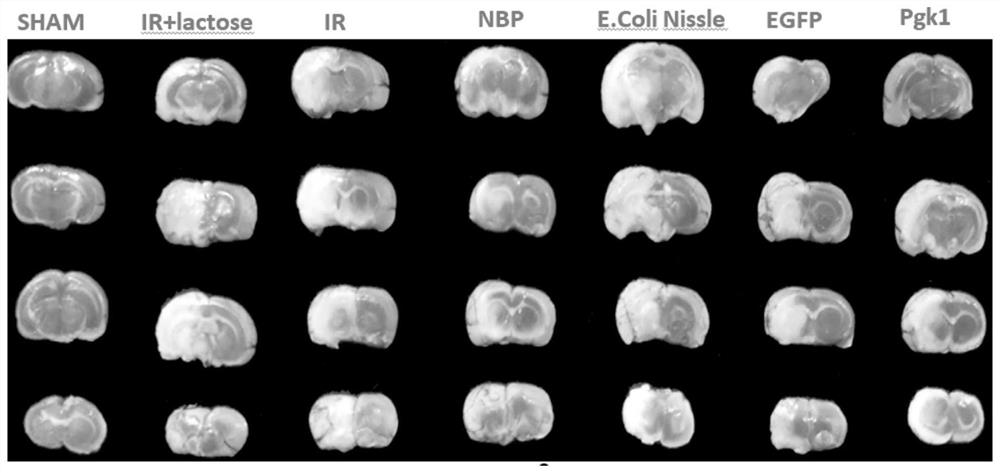
PendingCN113604494AReduced infarct volumeImprove neurobehavioralNervous disorderBacteriaExpression proteinMolecular biology
The invention belongs to the field of biological medicine, and particularly relates to a Pgk1 protein, a recombinant plasmid for expressing the Pgk1 protein, a recombinant probiotic for expressing the Pgk1 protein and application. According to the invention, firstly, inserting a Pgk1 gene into an expression vector pET-28a to obtain a recombinant plasmid for expressing Pgk1; and secondly, introducing the recombinant plasmid into an Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 tolerant bacterium, so that a functional recombinant probiotic is obtained. The recombinant probiotics can effectively inhibit cell death, improve the cerebral infarction volume and reduce blood sugar while efficiently expressing the Pgk1 protein, has a remarkable curative effect on cerebrovascular diseases and diabetes mellitus, has higher curative effect than that of clinical drugs, and has a good clinical application prospect.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
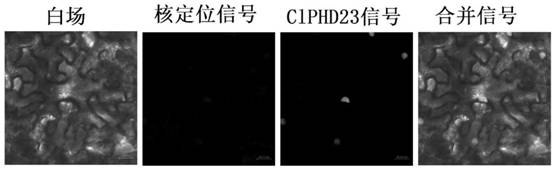
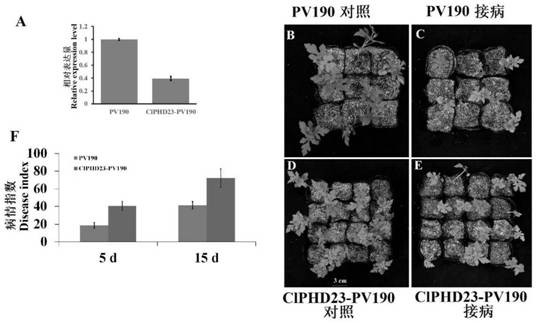
Wilt-resistant PHD transcription factor ClPHD23 as well as gene, expression vector, transformant and application thereof
ActiveCN112694524AEffective regulation of resistanceDelayed onsetBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPlant genetic engineering
The invention discloses a wilt-resistant PHD transcription factor ClPHD23 as well as a gene, an expression vector, a transformant and application thereof, and belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering. The amino acid sequence of the wilt-resistant PHD transcription factor ClPHD23 is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The wilt-resistant PHD transcription factor ClPHD23 provided by the invention can effectively regulate and control the resistance of plants to wilt, so that the onset time is delayed, and the onset degree is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Recombination human interferon alpha-2b oral adhesive plaster and its making method
InactiveCN1513548AFacilitate diffusion and absorptionImprove immunityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsCarboxymethyl celluloseMedicine
An oral picking for preventing and treating SARS is prepared from recombinant human interferon alpha-2b, hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose or carboxymethyl cellulose, and Kabopu through proportionally mixing and pressing. Its preparing process is also disclosed.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Clerodendranthus spicatus anti-urinary-stone extract and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN100546596CHas anti-kidney stone effectIncrease urine outputUrinary disorderPlant ingredientsAglyconeEthyl acetate
The invention discloses a kidney tea anti-urinary calculus extract and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of extracts and applications of Chinese herbal medicines. The method comprises: (1) soaking, extracting, and concentrating kidney tea and methanol at a weight: volume ratio of 1:4 to 10 to obtain an extract mixture; 1 proportion mixing and dissolving; (3) Extract the solution with petroleum ether first, then extract with ethyl acetate and concentrate to obtain the extract; (4) Chromatography, elute, collect and concentrate the extract to obtain the kidney tea extract Material A component. It is a fat-soluble flavonoid aglycone compound, which can significantly improve the symptoms of urinary stones, reduce the amount of stones, increase urine output, help stone discharge and anti-inflammatory effects. It can be directly, compounded or further separated and extracted, and can be used for anti-calculus, stone expulsion, diuretic and anti-inflammatory drugs in the urinary system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUB TROPICS CROP INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com