Patents
Literature
188 results about "Float zone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
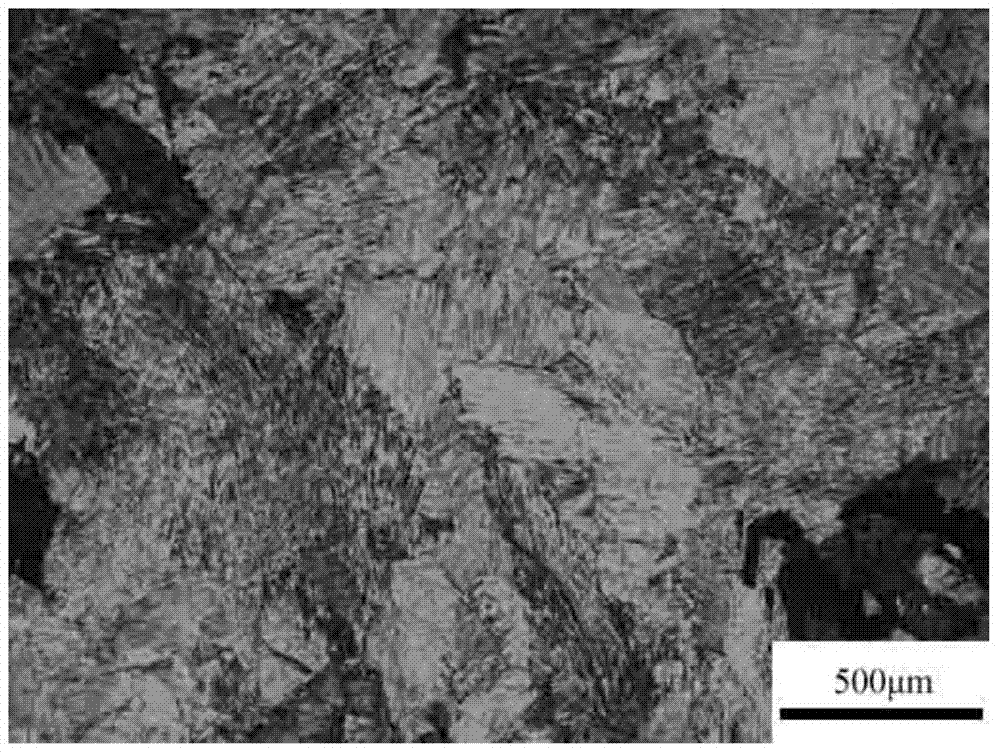
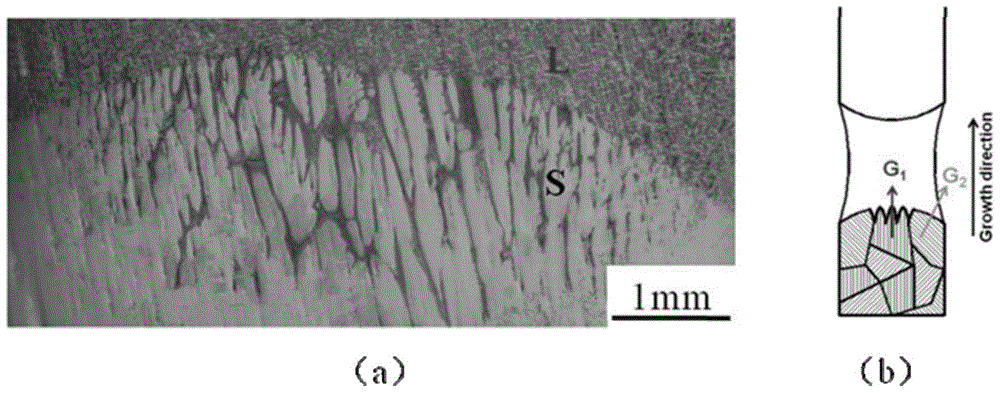
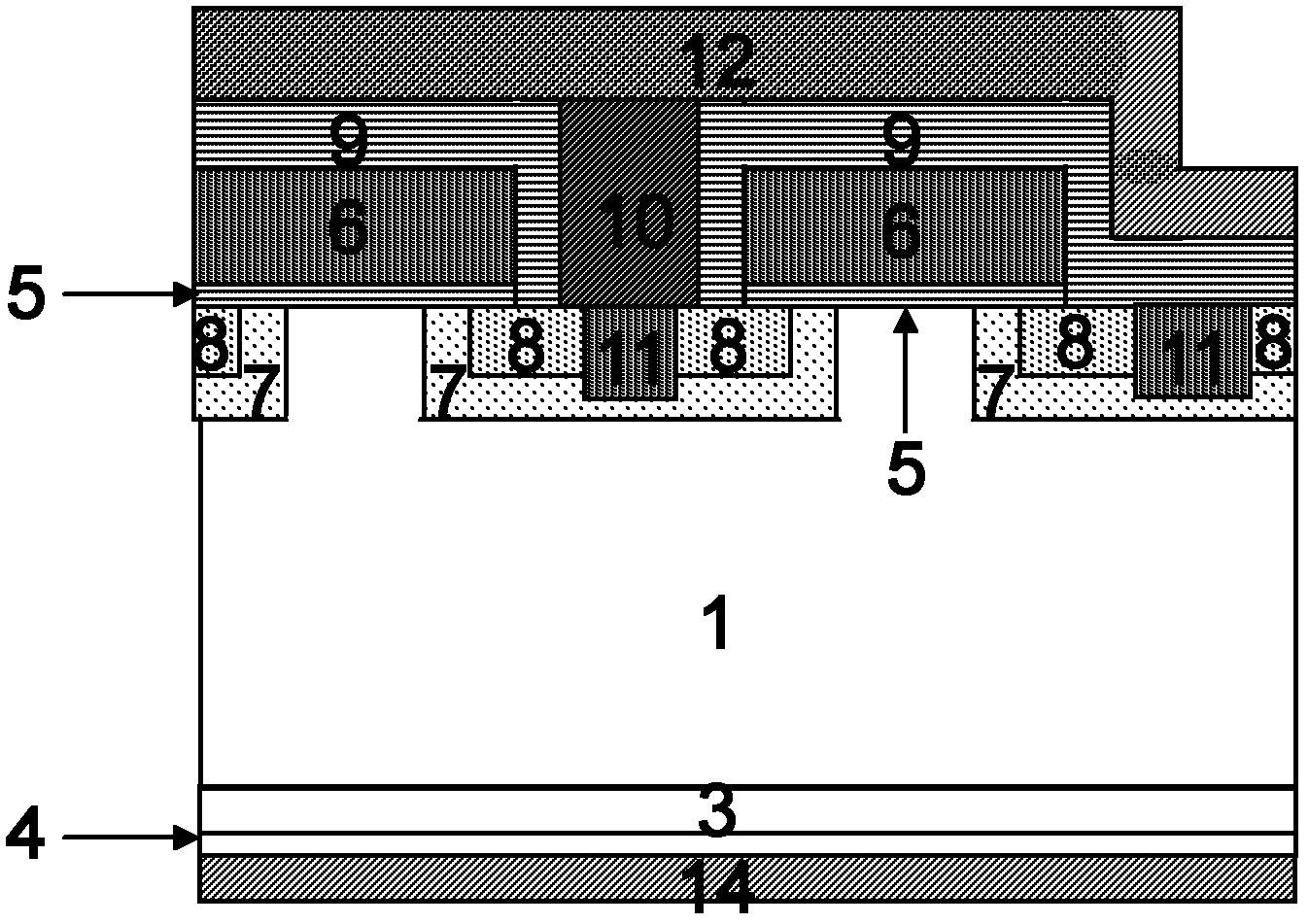
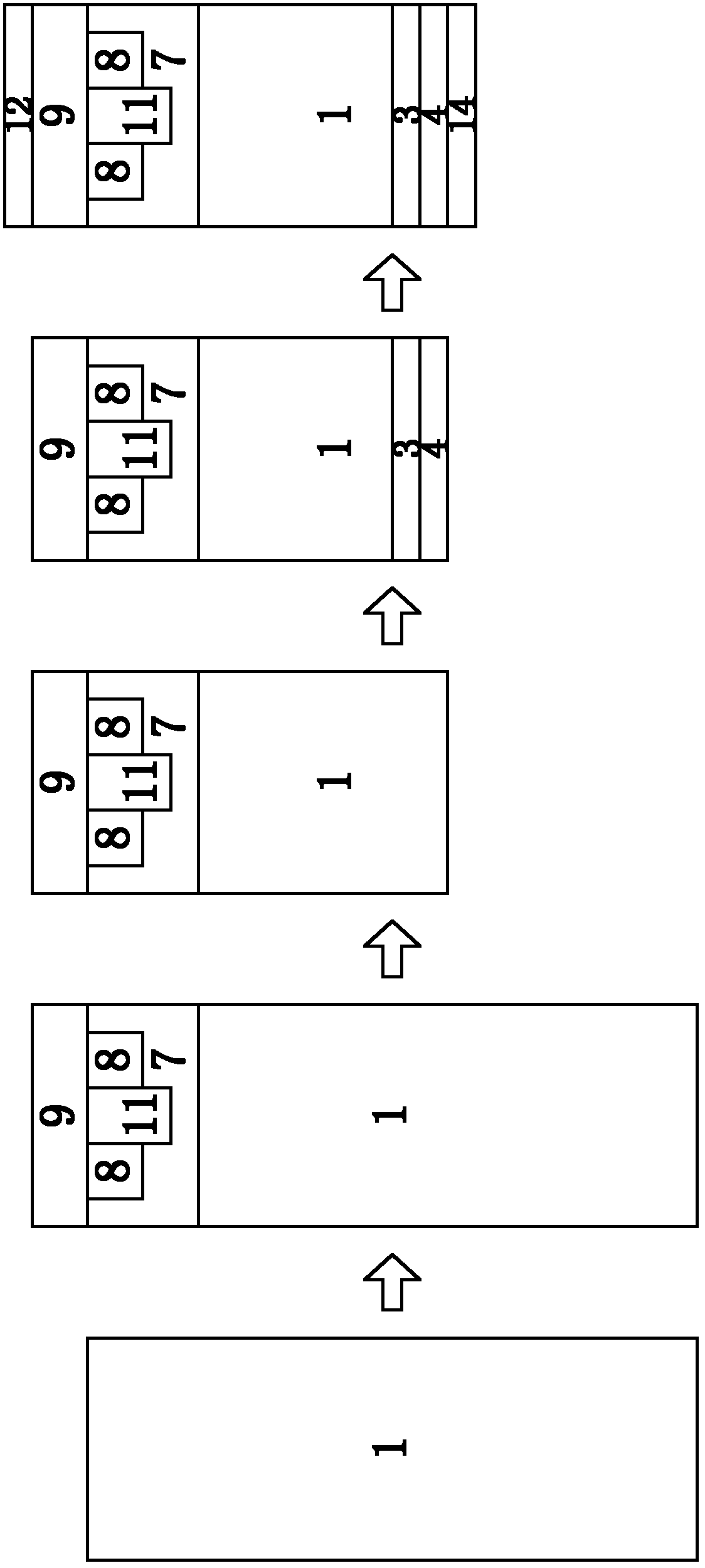
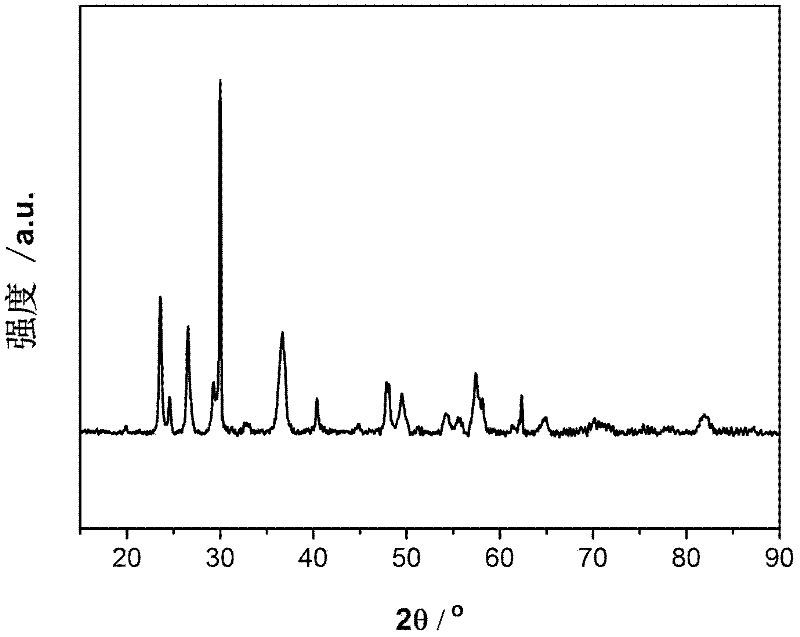
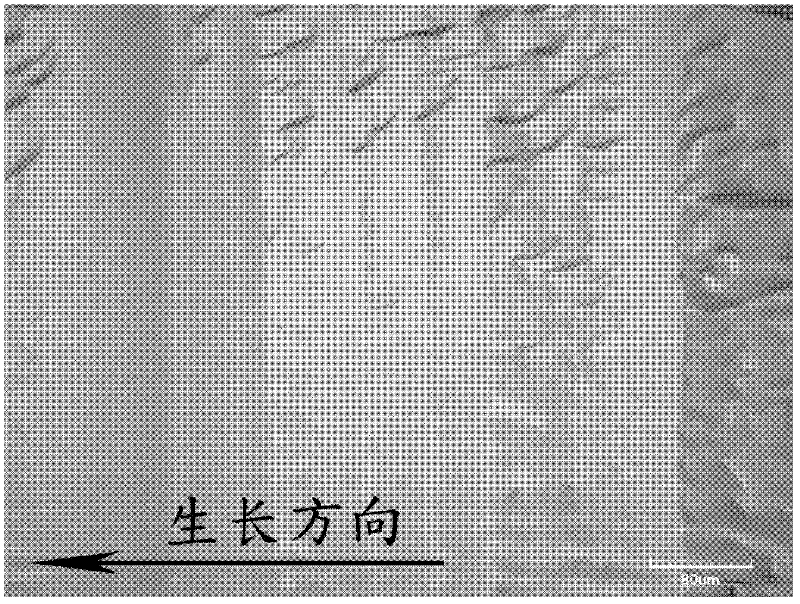
Directional TiAl-based alloy and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103789598AImprove high temperature mechanical propertiesKeep low densityDirectional solidificationMaterials science
The invention discloses directional TiAl-based alloy and a preparation method thereof. According to the atomic percentage, TiAl alloy components are expressed as Ti-(40-50)Al-aNb-bCr-cMo-dV-eMn, wherein in the formula, a, b, c, d, e are atomic percentages, a+b+c+d+e is less than or equal to 10, and the balance is Ti. The method for preparing the columnar crystal TiAl-based alloy includes the following steps that mother alloy is smelted through vacuum induction suspension, and a mother alloy cast rod is prepared through vacuum suction casting; an optical floating zone crystal growth system is adopted, argon is used as protection gas, the flow speed is 3-3.6L / min, the width of a regional heating zone is 6-6.7mm, heat treatment is performed on the TiAl-based alloy cast rod, the heating temperature is controlled to be 1250-1350 DEG C, the drawing speed is in the range of 3-13 micrometers per second, and the columnar crystal TiAl-based alloy is prepared. Compared with a directional solidification technology, in the preparation method, peritectic reaction is omitted, and therefore peritectic segregation is avoided; the problem that refractory metal and alloy, such as tungsten and molybdenum, with direction tissue cannot be prepared through the direction solidification technology can also be solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
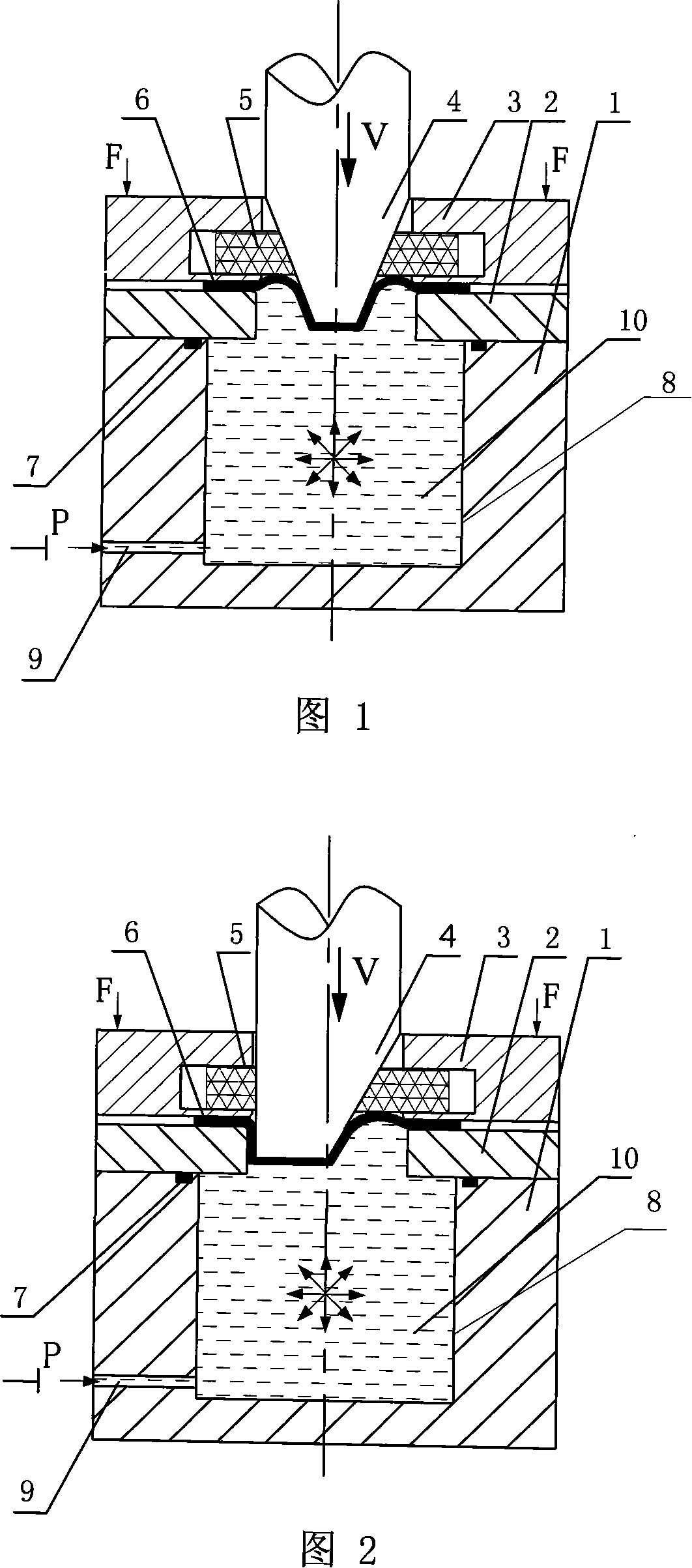
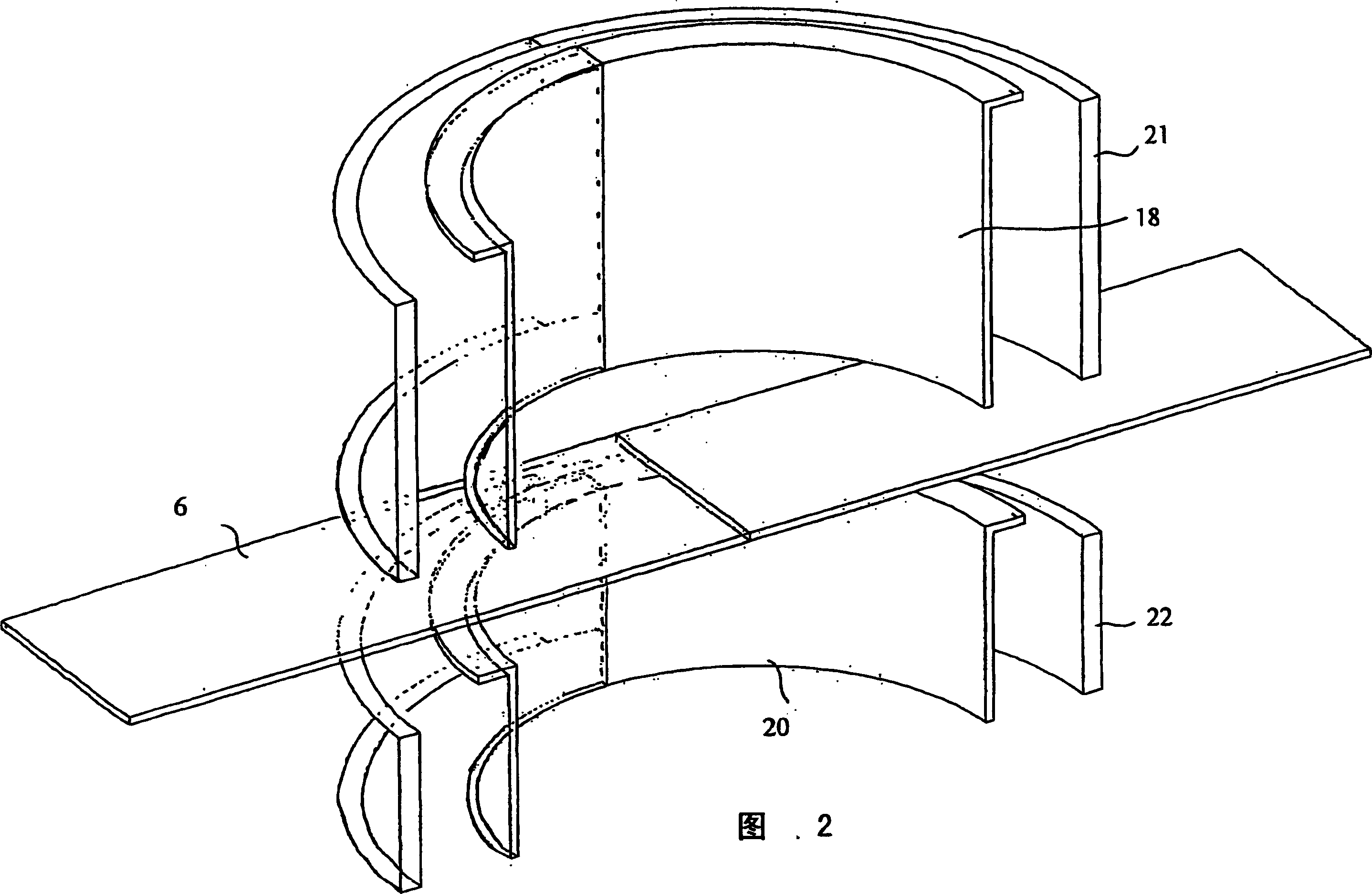
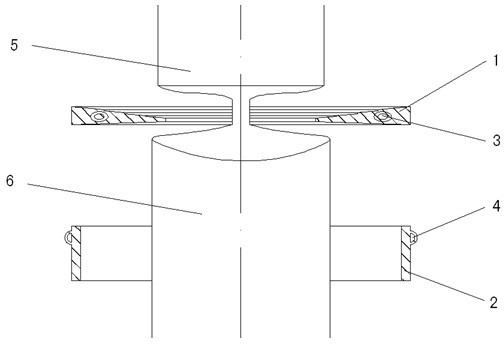
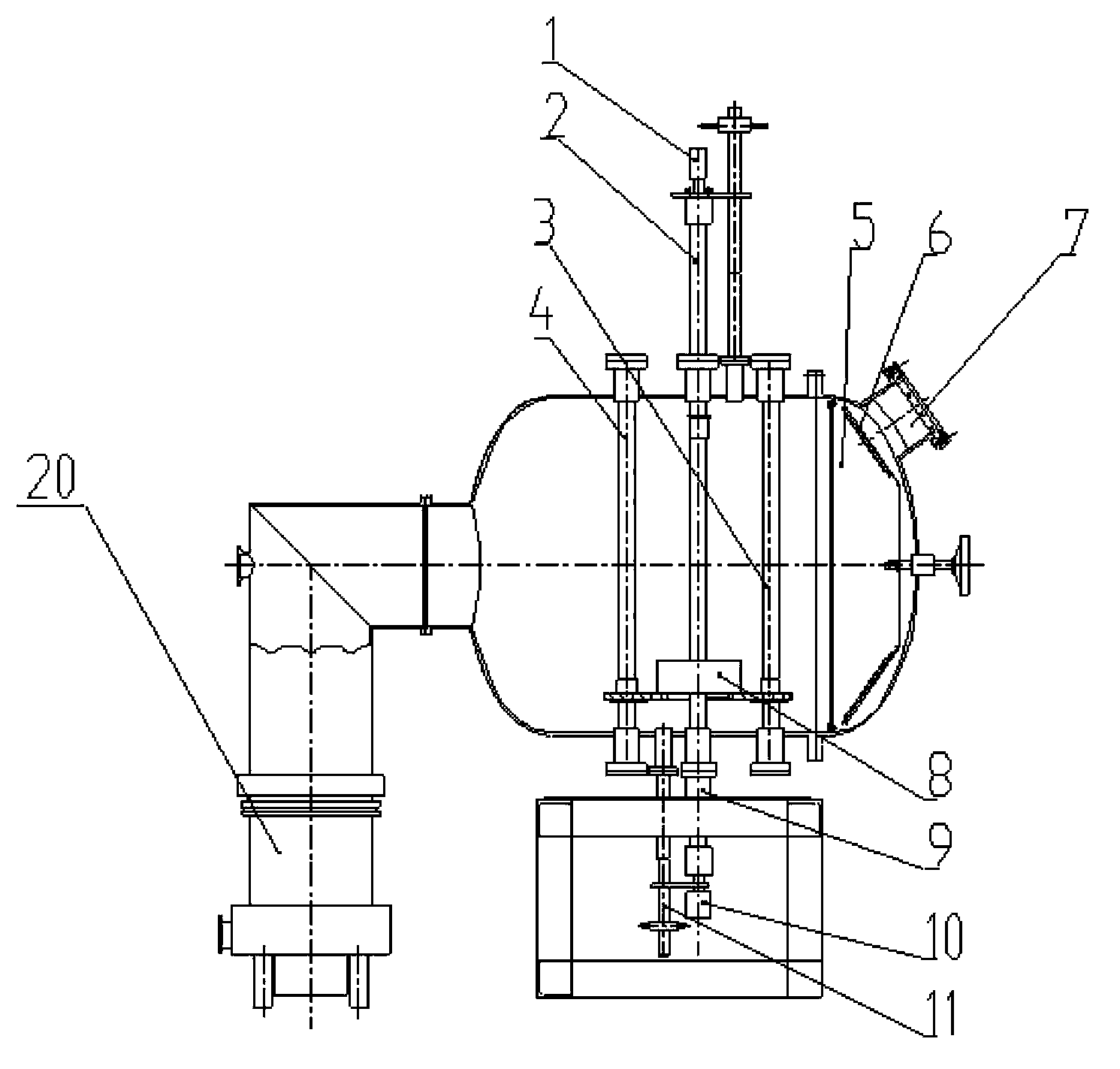
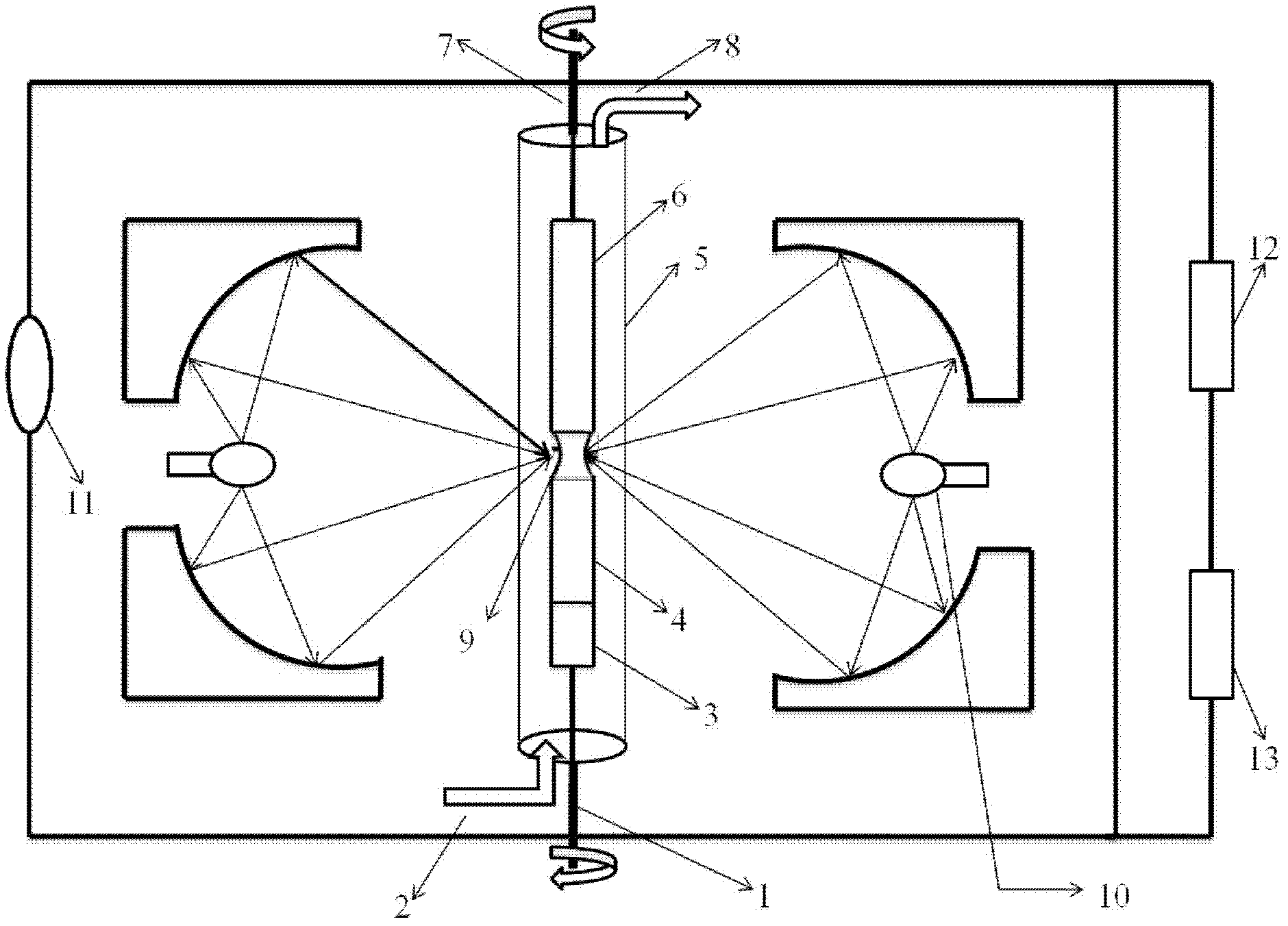
Device for preventing suspension area from breaking while taper piece filling liquid and drawing deep forming and forming method
InactiveCN101147940AReduce frictionReduce friction, so that the surface of the billet is fully protectedShaping toolsEngineeringMechanical engineering
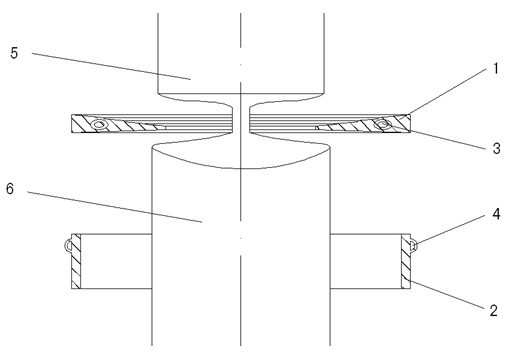
The present invention relates to a conical component forming device capable of preventing floating zone from being broken when the conical component is formed by adopting liquid-charging and drawing process and its forming method. Said conical component forming device is characterized by that its rigid edge-pressing ring is set over a concave die, in said rigid edge-pressing ring interior a recessed groove is cut, a flexible supporting ring is placed in the recessed groove interior, said concave die is placed on the fluid medium cavity, and its liquid-injecting hole is connected with its hydraulic system. Its forming method includes the following steps; (1), making the liquid-injecting hole on the cavity body be communicated with the hydraulic system; (2), placing a plate blank on the concave die; (3), making the rigid edge-pressing ring be moved downwards and apply edge-pressing force; and (4), making convex die be downwards moved until the plate blank is drawn into the concave die interior with the convex die so as to obtain a formed conical component.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Silicon and silicon/germanium light-emitting device, methods and systems
A light-emitting device and optical communication system based on the light-emitting device is disclosed. The light-emitting device is formed in a float-zone substrate. The light-emitting device includes on the substrate lower surface a reflective layer and on the upper surface spaced apart doped regions. The portion of the upper surface between the doped regions is textured and optionally covered with an antireflection coating to enhance light emission. The light-emitting device can operate as a laser or as a light-emitting diode, depending on the reflectivities of the antireflection coating and the reflective layer.
Owner:INTEL CORP
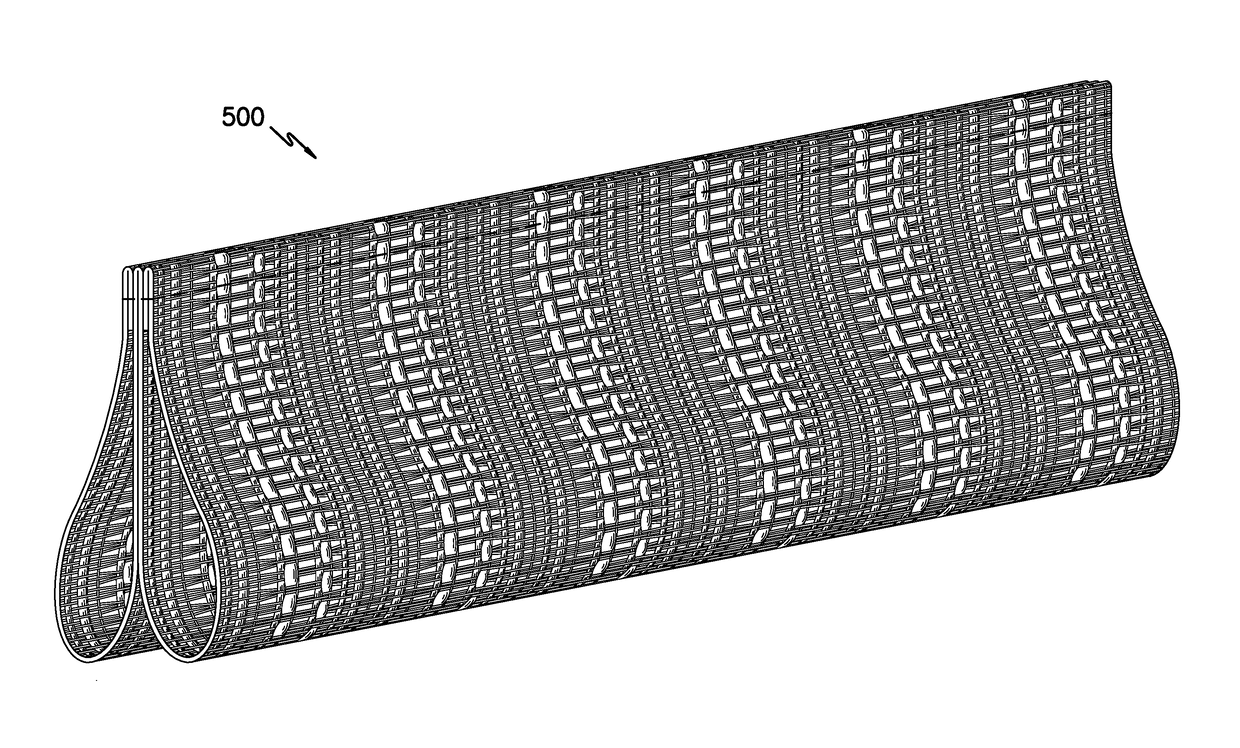
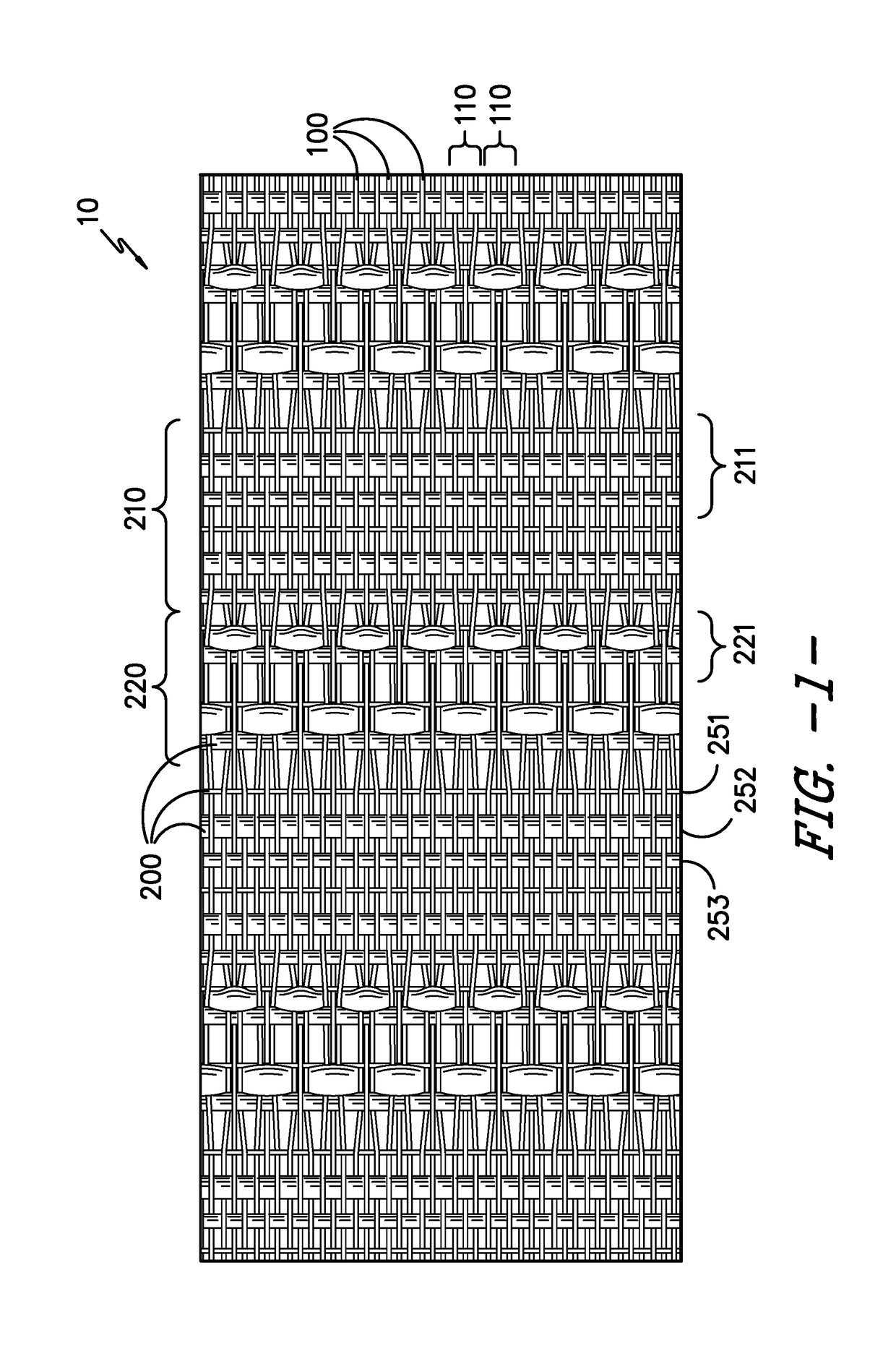
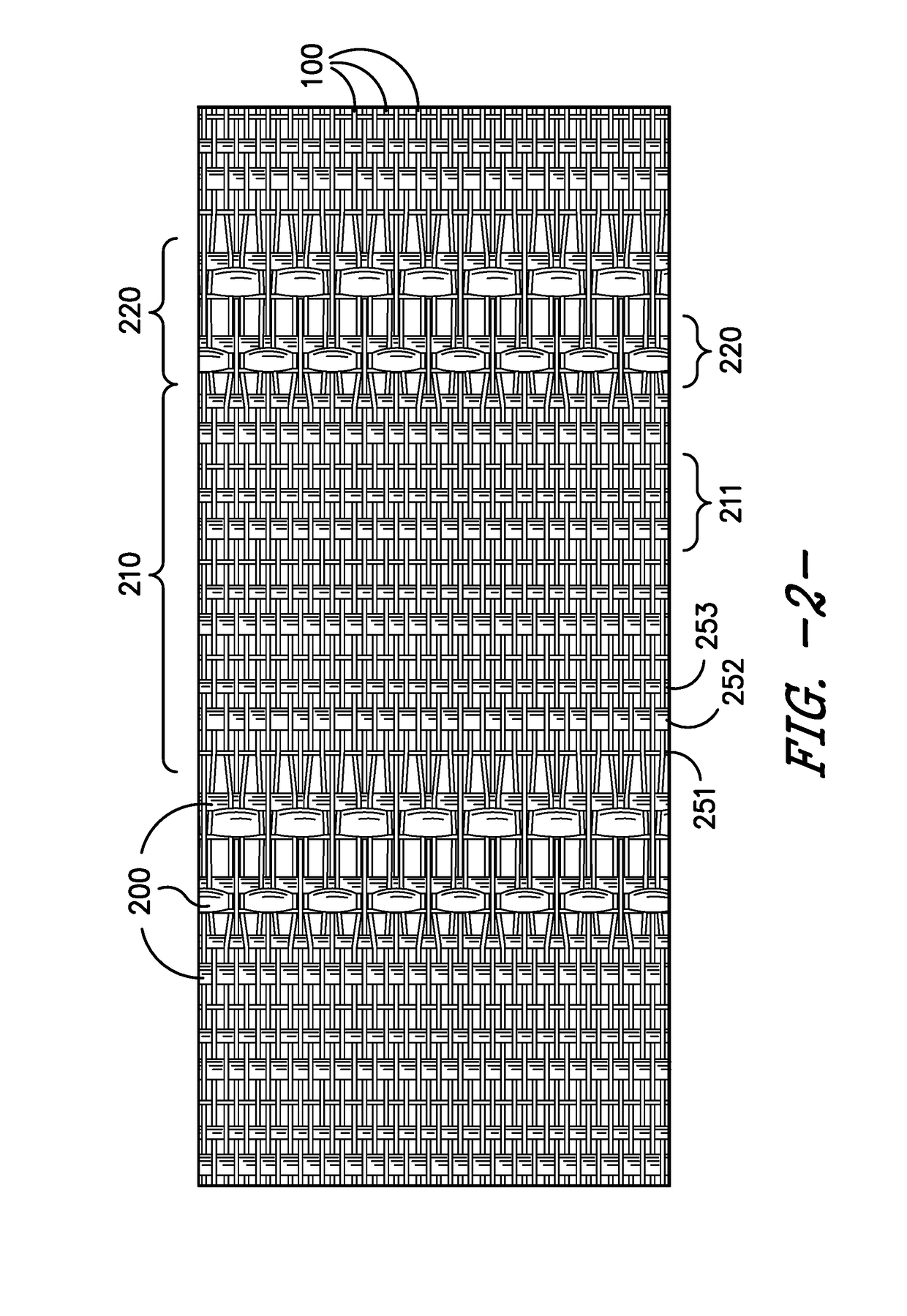
Partial float weave fabric
ActiveUS20170145603A1Optical fibre/cable installationCable installations in underground tubesEngineeringWeft yarn
A woven fabric containing an alternating pattern containing first weave zones and partial float weave zones. The woven fabric contains a plurality warp yarns arranged into groupings of warp yarns. In each first weave zone, the picks of weft yarns contain a repeating first weft pattern. In each partial float zone, the picks of weft yarns within the partial float weave zone contain a repeating second weft pattern of at least one monofilament yarn and at least one multiple-inserted multifilament yarn. Within the partial float zone, only a portion of the warp yarns within at least a portion of the warp groupings float over 3 weft yarns including floating over at least one multiple-inserted multifilament weft yarn in at least a portion of weft pattern repeats. An innerduct structure containing the woven fabric is also described.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Method and apparatus for preparing major diameter single crystal
InactiveCN1847468AMake up for heat lossHigh Inductive Heat InputPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsSingle crystalEngineering
Owner:SCHOTT AG
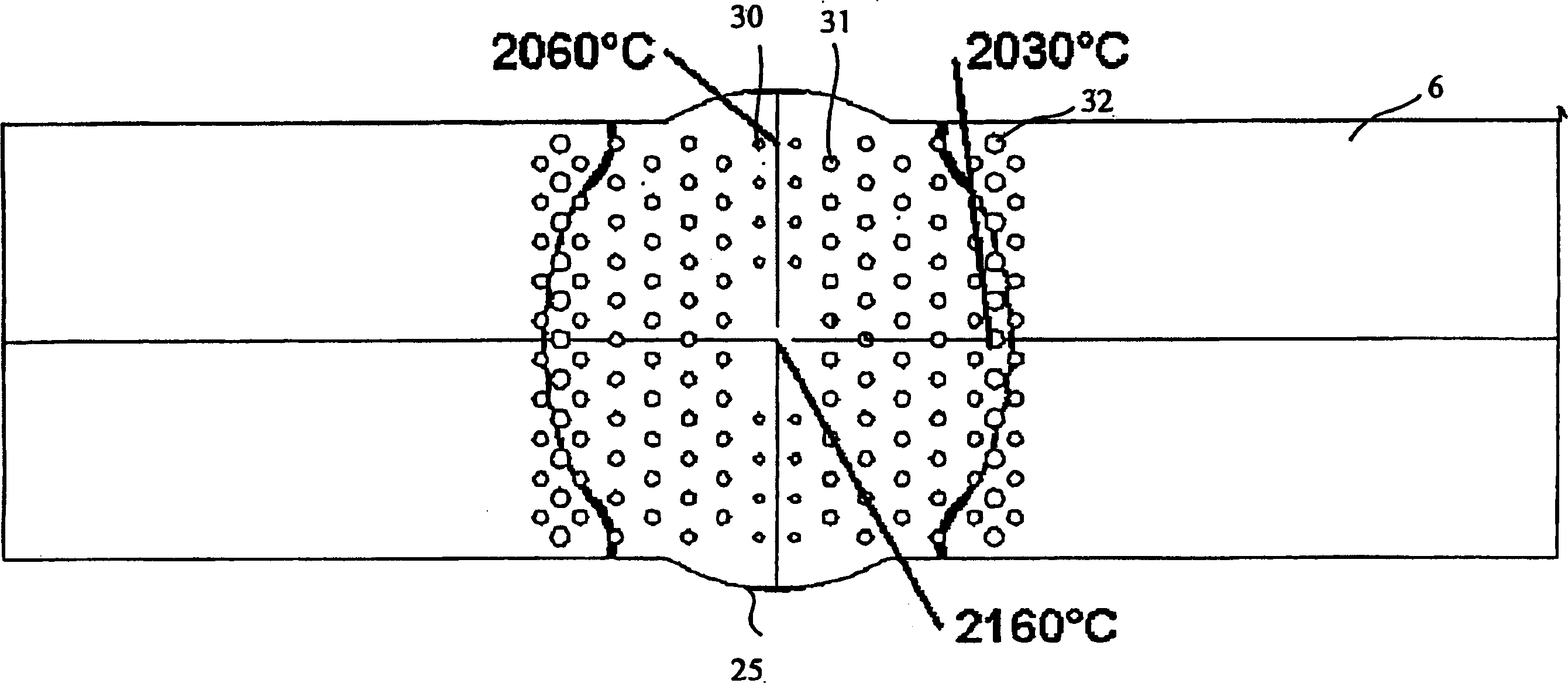
10<5> K/cm temperature gradient directional solidification device and directional solidification method
ActiveCN102051668AUniform tissueGood orientationPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsIndiumZone melting
The invention relates to a 10<5> K / cm temperature gradient directional solidification device and a directional solidification method. The 100000 K / cm temperature gradient directional solidification device is characterized in that laser light generated by a laser horizontally passes through a plate lens to enter a vacuum chamber, intersects vertically the axis of a drawing system, and is used for heating a preform; and liquid gallium-indium-tin alloy serves as cooling medium. The distance between the lower surface of a melting zone and the liquid level of the liquid gallium-indium-tin alloy is 1mm to 5 mm. When directional solidification is performed to the preform, the power of the laser is increased to 200 w to 1400 w. After the preform is zone-melted, a drawing mechanism is started to enable the preform to move at the speed of 1 to 300 microns per second and to be cooled, so that directional solidification of the preform is accomplished. In the invention, laser floating zone melting is combined with liquid metal cooling, so that the obtained oxide eutectic in-situ composite is uniform in structure, fine and compact, has good directing property, and is remarkably improved in mechanical property and other functions, the sizes and the shapes of produced function materials can satisfy the application of various photoelectric components.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
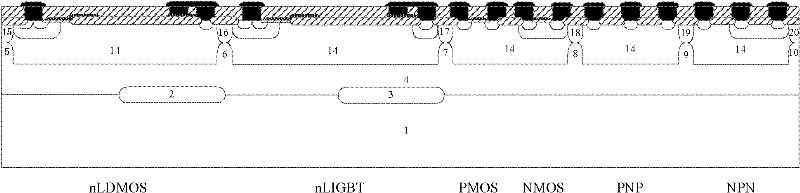
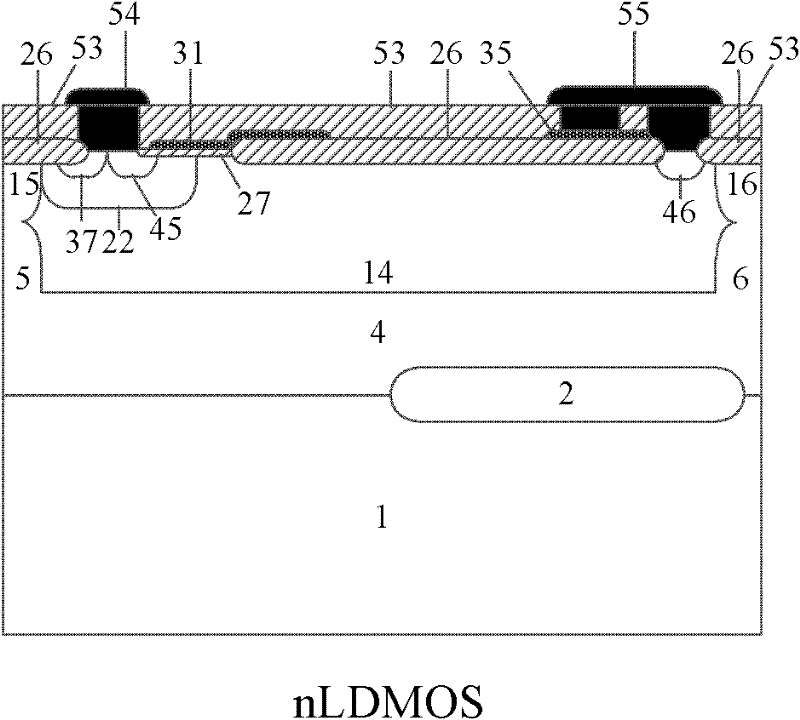
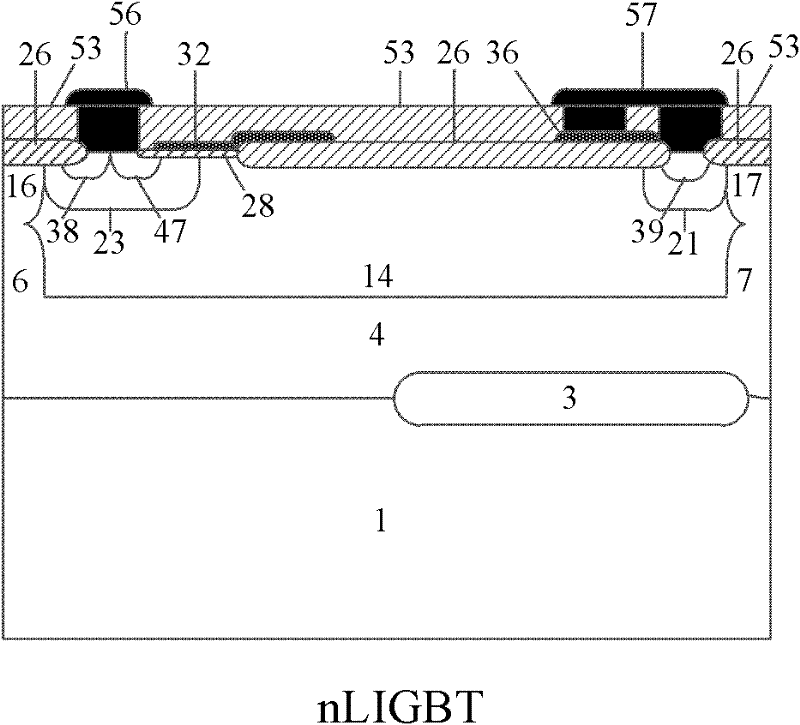
P-type epitaxial layer-based binary coded decimal (BCD) integrated device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102194818AIncrease manufacturing costReduce manufacturing costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLow voltageHigh pressure
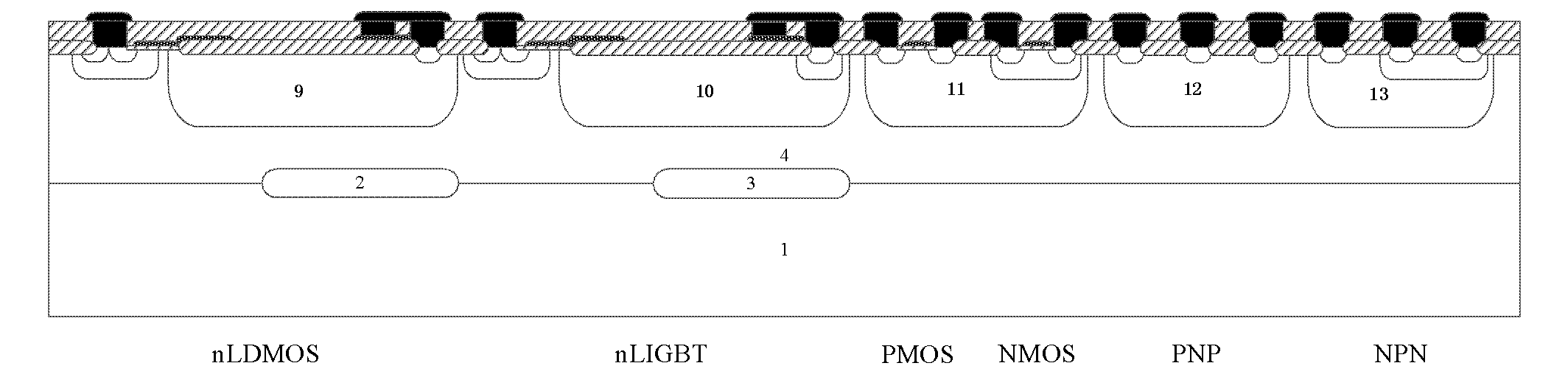
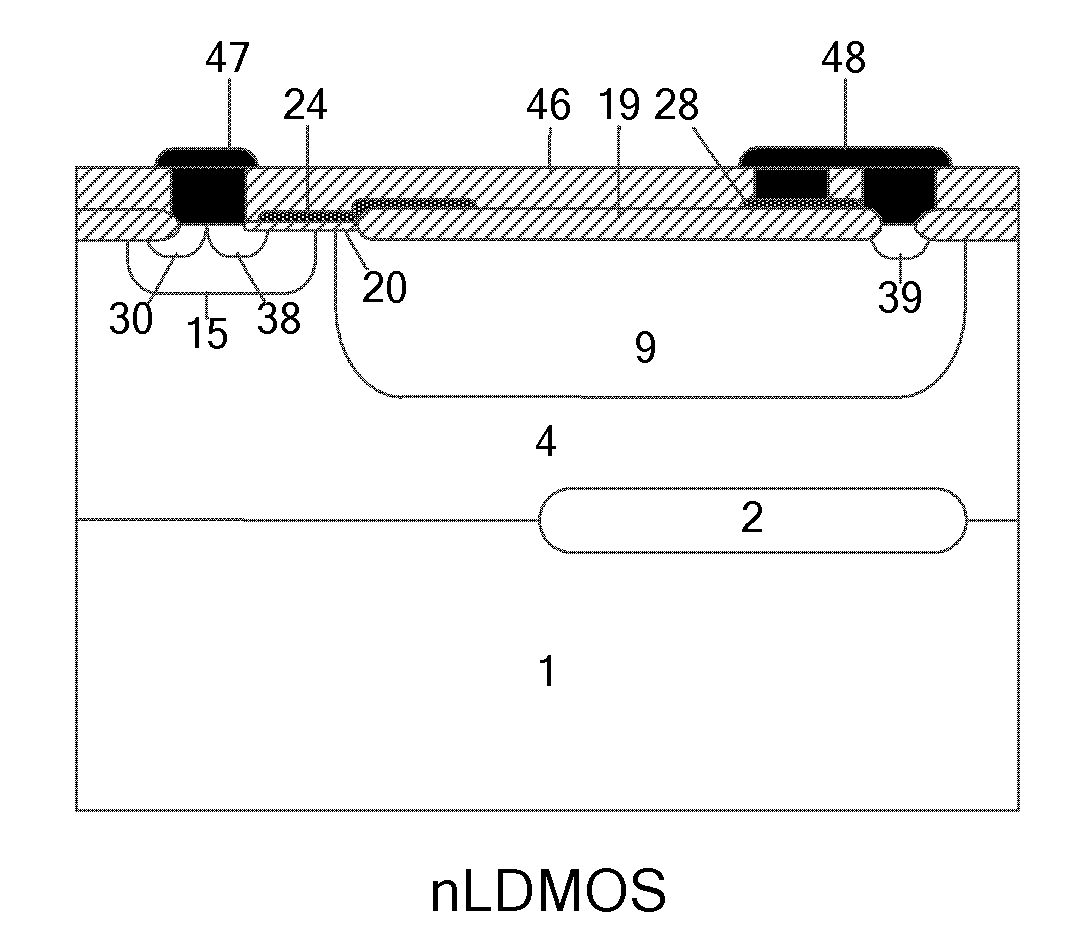
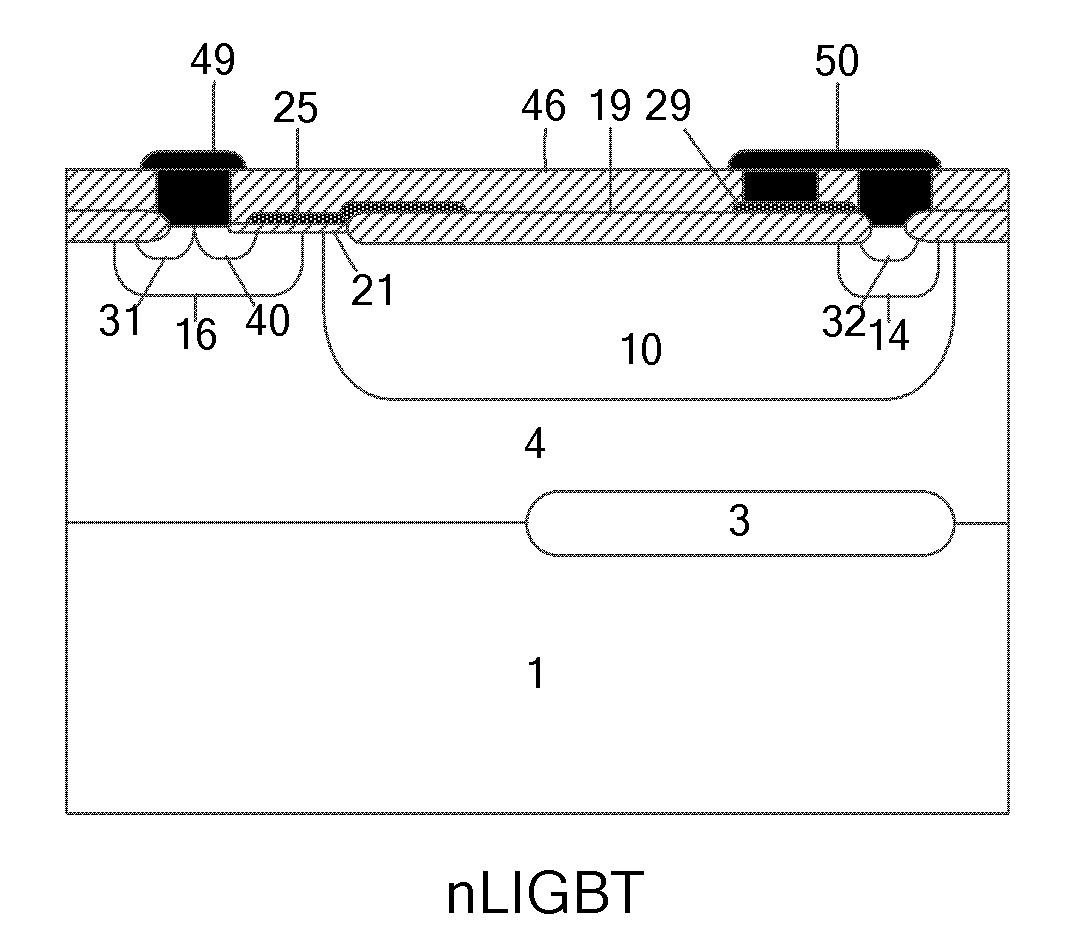
The invention discloses a P-type epitaxial layer-based binary coded decimal (BCD) integrated device and a manufacturing method thereof and belongs to the technical field of semiconductor power devices. A high-voltage n laterally diffused metal oxide semiconductor (LDMOS) device, a high-voltage n lateral insulated gate bipolar transistor (LIGBT) device, a low-voltage P-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) device, a low-voltage N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) device, a low-voltage plug-and-play (PNP) device and a low-voltage negative-positive-negative (NPN) device are integrated on the same substrate; various devices are manufactured in a P-type epitaxial layer on the surface of a P-type substrate and are self-isolated through the P-type epitaxial layer; an N-type buried layer is formed between the P-type substrate below a high-voltage device and the P-type epitaxial layer; and the N-type buried layer can (or cannot) be formed on the P-type epitaxial layer on two sides below a low-voltage device. Due to the introduction of the N-type buried layer, a lower-resistivity silicon chip can be used as a substrate under the same breakdown voltage, and increase of chip manufacturing cost brought by a manufactured monocrystalline silicon chip by a floating zone (FZ) method is avoided; therefore, the manufacturing cost of the chip is reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Metal porous body manufacturing method
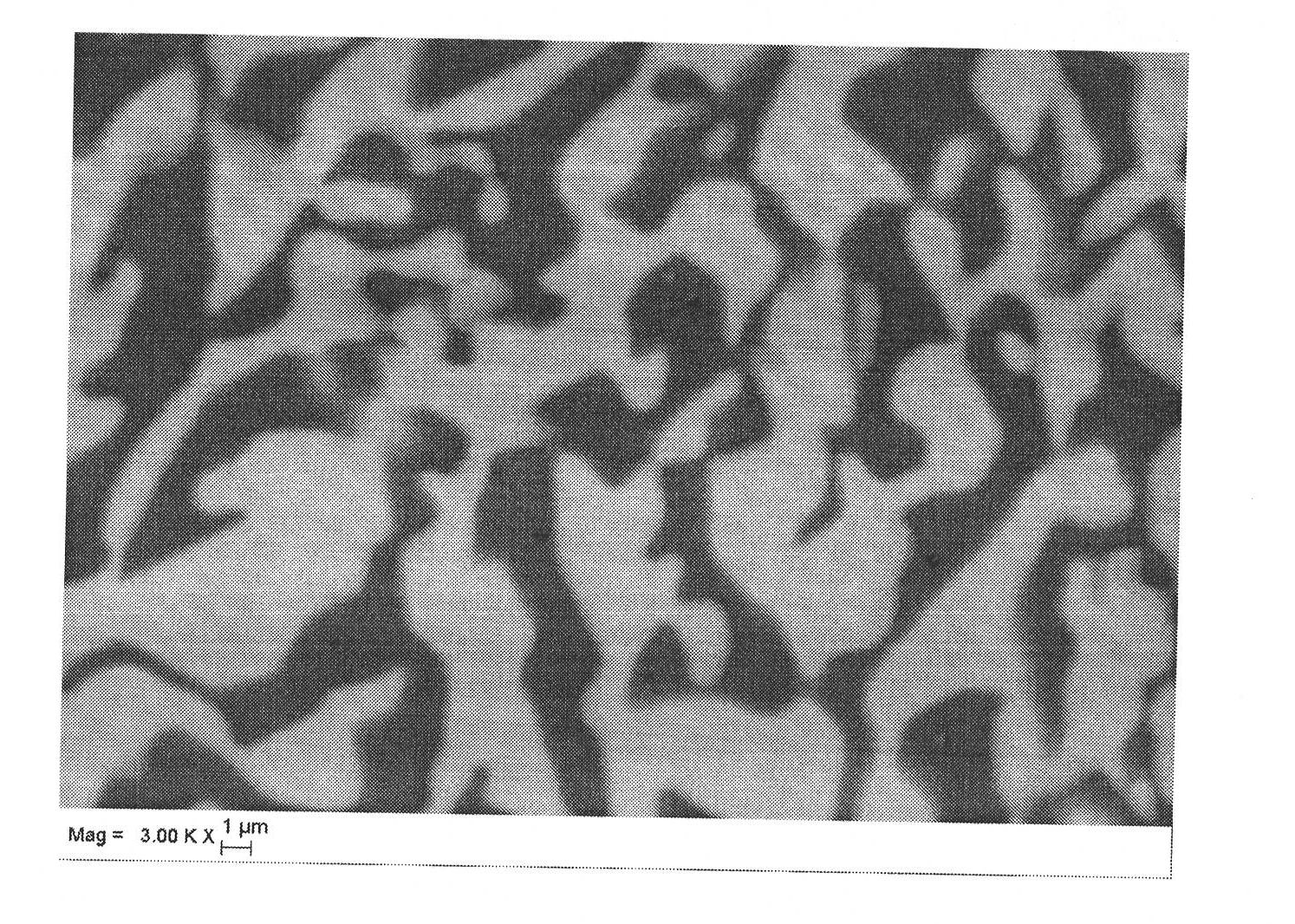
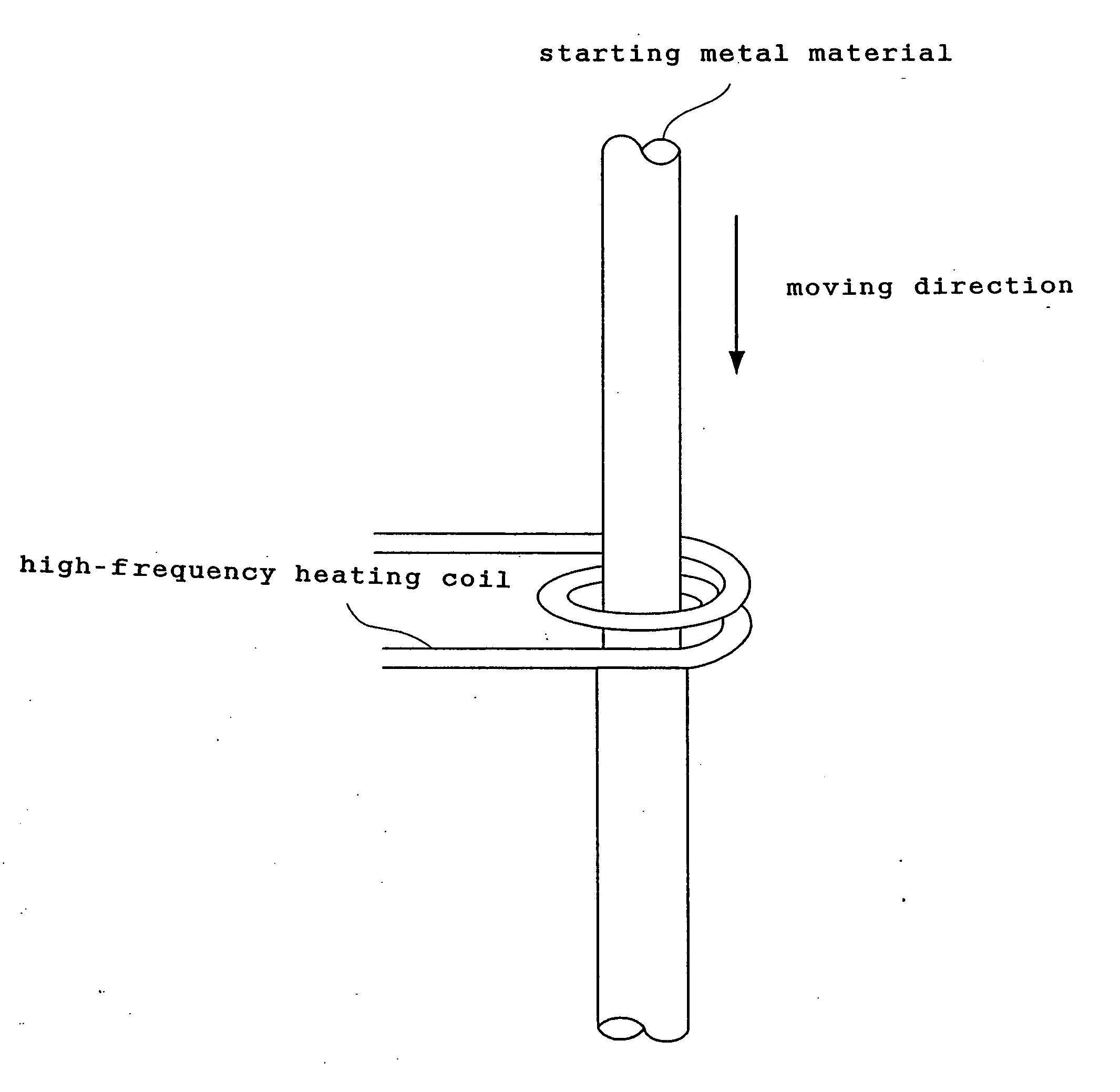
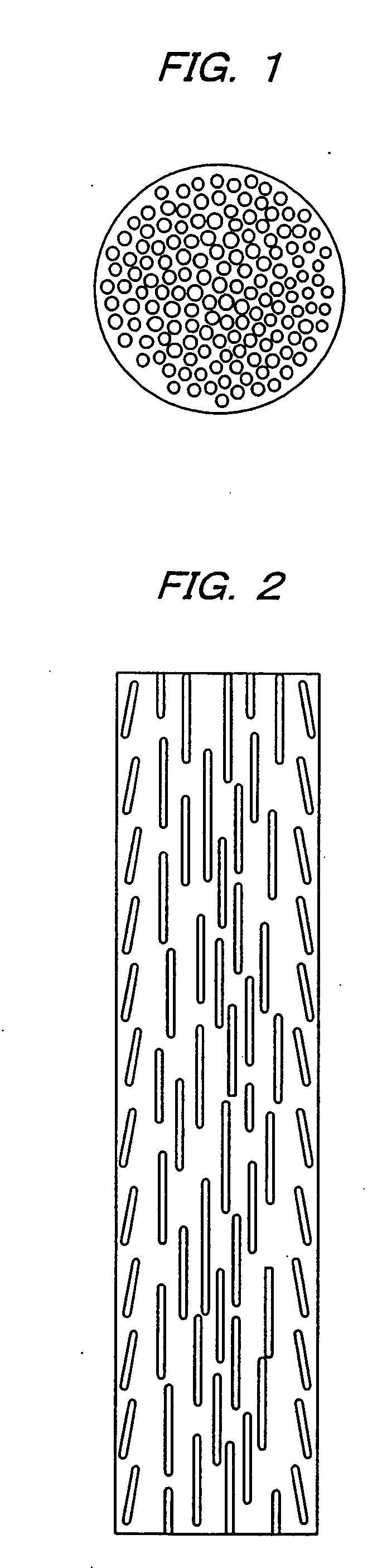
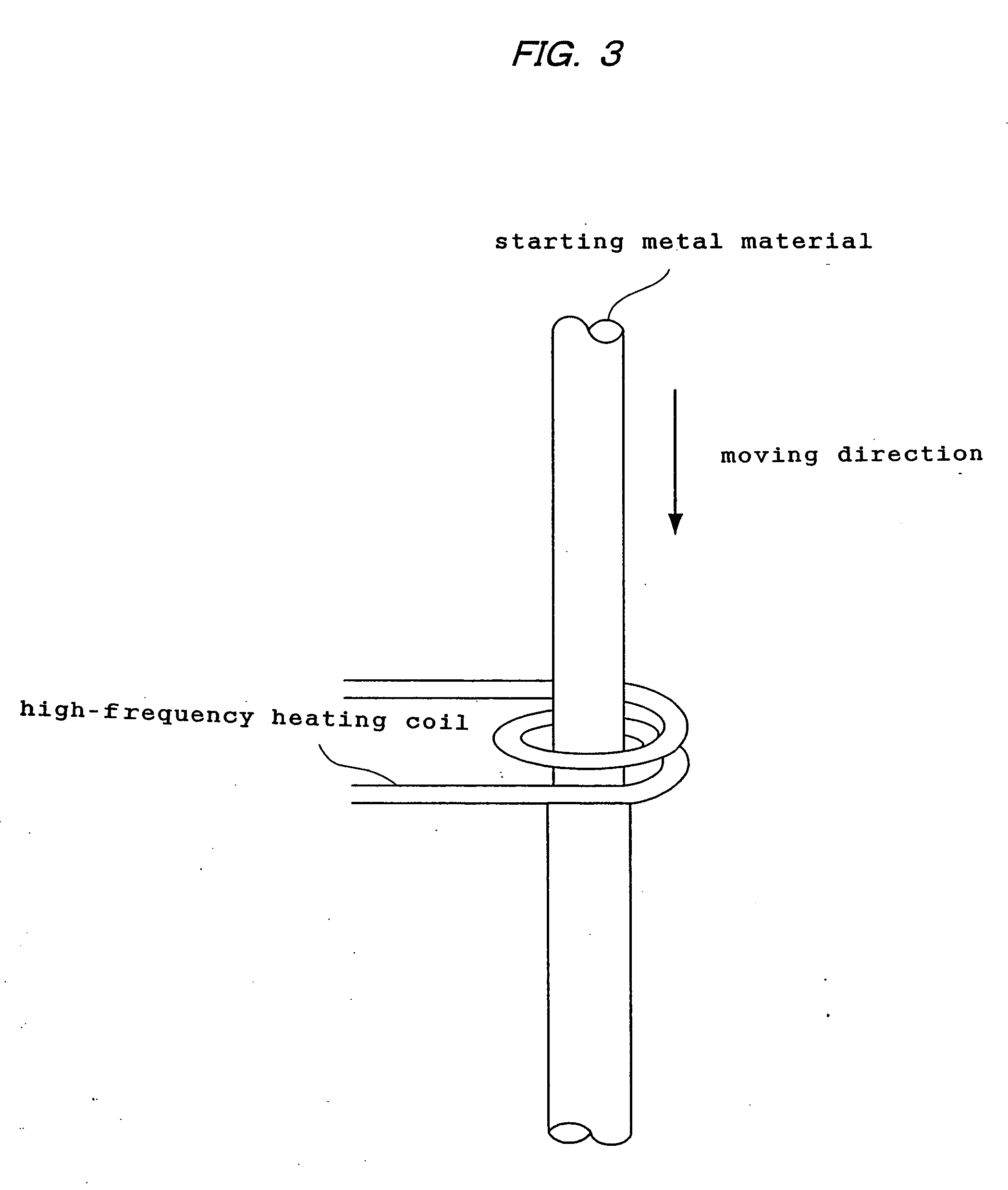
The present invention provides a process for producing a porous metal body, the process comprising: melting part of a starting metal material in succession while moving the material by a floating zone melting method under a gas atmosphere to dissolve a gas into a resultant molten metal; and solidifying the molten metal zone in succession by cooling. According to the process of the present invention, even when the starting metal material is of low thermal conductivity, a porous metal body with uniform and micro pores grown only in the longitudinal direction is produced.
Owner:NAKAJIMA HIDEO
Thermal system and technology for producing float zone doped single crystal silicon having size phi of 6 inches
ActiveCN102358951ASolve the problem of prone to dislocation and broken bractsSolve the \"stab\" problemPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsAngular degreesSingle crystal
The invention relates to a thermal system and a technology for producing a float zone doped single crystal silicon having a size phi of 6 inches. The thermal system comprises a coil and a heat preservation cylinder. An upper surface of the coil has an inclined multi-stepped coil structure. An external diameter phi of the coil is in a range of 350+50 / -50 millimeters. An internal diameter phi of the coil is in a range of 50+2 / -2 millimeters. The thickness of the coil is in a range of 30+2 / -2 millimeters. A diameter phi of the heat preservation cylinder is in a range of 350+50 / -50 millimeters. The height of the heat preservation cylinder is in a range of 100+20 / -20 millimeters. A distance between the coil and the heat preservation cylinder is in a range of 100+50 / -50 millimeters. The technology is characterized in that impurity gas is fed into a furnace chamber in shoulder extension, wherein a lower shaft rotating speed is in a range of 7 to 10 revolutions per minute and a shoulder extension angle is in a range of 40+2 / -2 degrees; and in equal-diameter growth, a lower shaft has a falling speed of 3 to 4 millimeters per minute and a rotating speed of 3 to 5 revolutions per minute and coil pulser power is 60 to 70% of rated power. Through the thermal system which is a novel thermal system and adjustment on technological parameters, the float zone doped single crystal silicon having a size phi of 6 inches can be successfully prepared by drawing, and dislocation and burr generation problems produced easily in production of a float zone doped single crystal silicon with a large size are solved, and thus market demands on single crystal silicon with a large size are satisfied.
Owner:ZHONGHUAN ADVANCED SEMICON MATERIALS CO LTD +1
High-temperature rare earth oxide laser crystal and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101871125AQuality improvementHigh speedPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsSpace groupRare earth
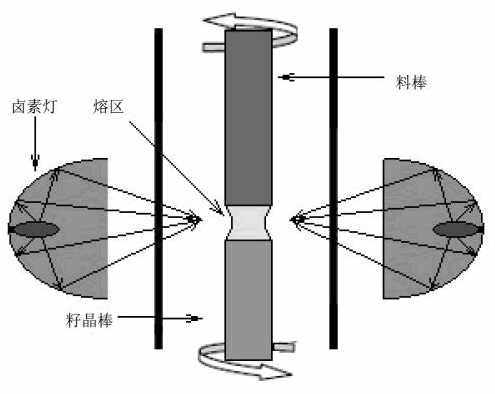
The invention relates to a rare earth oxide crystal and a preparation method thereof. The structural general formula of the crystal is (LnxRe1-x)2O3, the crystal belongs to a cubic crystal system, the space group is Ia3, and the crystal is in a bixbyite structure. The preparation method of the rare earth oxide laser crystal comprises the following steps of: firstly, manufacturing polycrystalline materials by taking Re2O3 and Ln2O3 as raw materials; then, manufacturing material bars; and filling the material bars into an optical floating zone growing furnace for growing according to a floating zone method. The method of the invention has high speed and short cycle, a crucible is not needed in crystal growth, the pollution on the crystal is reduced, and the growing crystal has high transparency and less cracks and is suitable for laser devices.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Bipolar CMOS DMOS (BCD) integrated device based on N type extension layer and manufacture method thereof
InactiveCN102201406AIncrease manufacturing costReduce manufacturing costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSLow voltage
A bipolar CMOS DMOS (BCD) integrated device based on a N type extension layer and a manufacture method thereof, which belongs to the semiconductor power device technology field, are disclosed. In the invention, a high voltage nLDMOS device, a high voltage nLIGB device, a low voltage PMOS device, a low voltage NMOS device, a low voltage PNP device and a low voltage NPN device are integrated on a same substrate. All devices are made in an N type extension layer arranged on a surface of a P type extension layer which is on a surface of a P type substrate. And junction isolations of the devices are realized through P<+> isolation regions. N type buried layers are arranged between the P type substrate and the P type extension layer, wherein the P type substrate and the P type extension layer are under the high voltage devices. N type buried layers are / are not arranged between the P type extension layer and the N type extension layer, wherein the P type extension layer and the N type extension layer are under the low voltage devices. The N type buried layers are introduced in the invention to realize that silicon chips with lower resistivity can be used as the substrate at a same breakdown voltage. In the prior art, float-zone technique is adopted to manufacture monocrystalline silicon pieces, which can increase the chip manufacturing costs. In the invention, the float-zone technique is not used so that the chip manufacturing costs can be reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
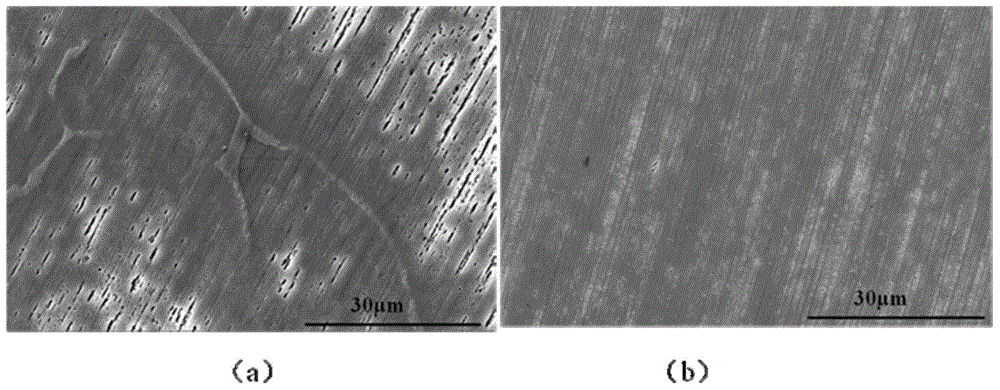
Method for preparing (110) float zone silicon crystal
ActiveCN101974779AMeet the requirements for preparing silicon materials for high-efficiency solar cellsMeeting Silicon Material Requirements for High Efficiency Solar CellsPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsSingle crystalEngineering
The invention discloses a method for preparing a (110) float zone silicon crystal. The key point of the technical scheme is that: 1, in the seeding technology, by controlling and adjusting the descending speed of a lower shaft and adjusting the power, the seeding neck diameter is controlled in a range from 2 to 6 mm, wherein the seeding neck diameter is more than or equal to 1.5 times the diameter of a single crystal; 2, in the shouldering technology, by controlling and adjusting the descending speed and rotating speed of the lower shaft and the descending speed and rotating speed of an upper shaft and adjusting the power, the shouldering angle is 50+ / -5 degrees; and 3, in the ending technology, the ending length is more than 1.2 times the diameter of the single crystal, and the minimum tail diameter is less than or equal to 5mm. The method overcomes the defects that the (110) silicon single crystal prepared by the conventional direct pulling method has high impurity content and cannot meet the requirement on the silicon single crystal of a high-efficiency solar cell, and successfully prepares a low-impurity content and long-service life (110) dislocation-free float zone silicon crystal by a floating zone method, wherein the (110) float zone silicon crystal has the dislocation density of less than or equal to 500 units / cm<2> and the minority carrier lifetime of more than or equal to 300us, and meets the requirement of a silicon material for preparing the high-efficiency solar cell.
Owner:ZHONGHUAN ADVANCED SEMICON MATERIALS CO LTD +1
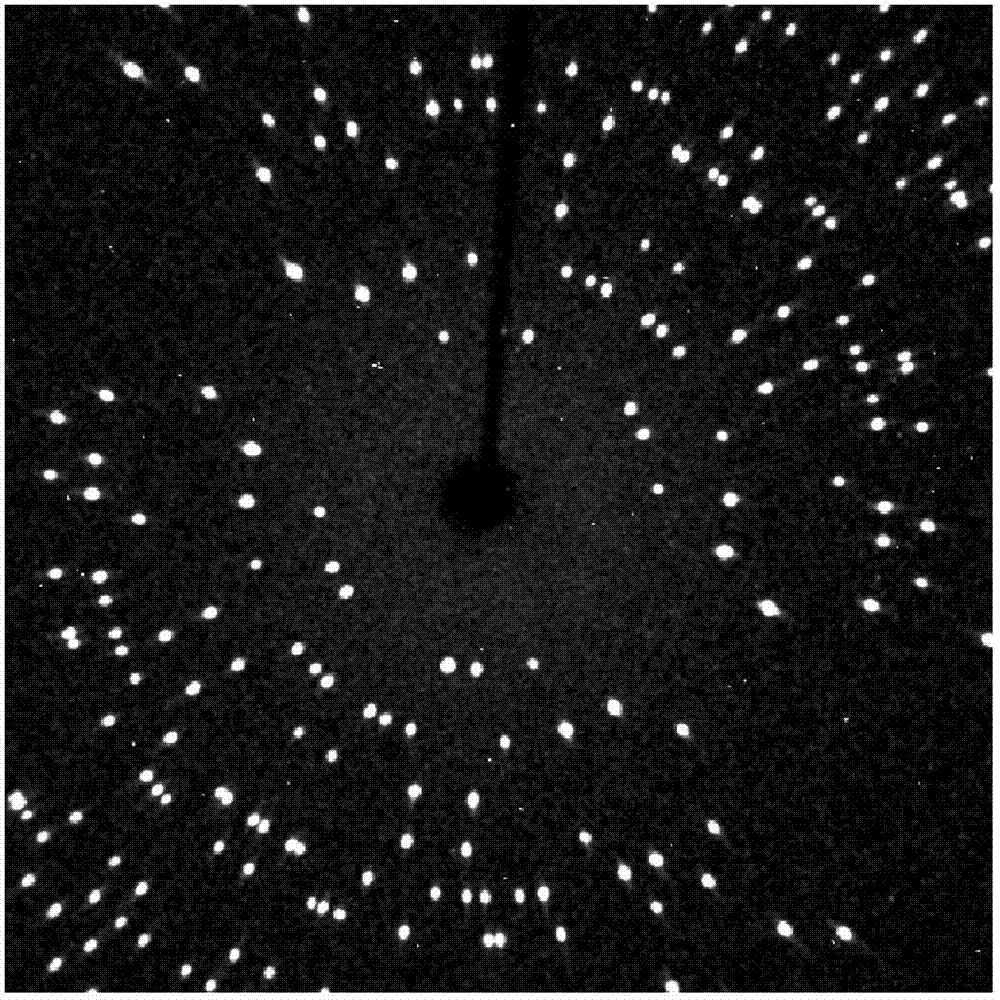
High-temperature high-strength TiAl-Nb monocrystal and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104878452AImprove high temperature mechanical propertiesSolve pollutionPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsDifferential pressureSingle crystal
The invention discloses a high-temperature high-strength TiAl-Nb monocrystal and a preparation method thereof. Based on the atomic percent, the high-temperature high-strength TiAl-Nb monocrystal comprises the alloy components: Ti-(43-47) Al-(6-10)Nb-(0.1-1)(C, Si), and the balance of Ti. The preparation method comprises the following steps: smelting TiAl-Nb button-shaped master alloy ingot casting by using an electro-magnetic induction suspension method; preparing a cylindrical rod-shaped sample by means of differential pressure suction casting or gravity casting; directionally condensing the cylindrical bar by using an optical float-zone crystal growth system to guarantee that the heating power is between 65% and 70%, the growth velocity is 5-30mm / h, the relative rotation speed is 20-40r / min and the argon flow protection is carried out for 3-5L / min; finally obtaining a TiAl-Nb monocrystal test bar; and performing desegregation heat treatment on the TiAl-Nb monocrystal bar to finally obtain the monocrystal test sample. By adopting the TiAl-Nb monocrystal alloy material prepared by using preparation method disclosed by the invention, the alloy pollution caused by a traditional Bridgman directional condensation method can be effectively avoided, a solid-liquid interface shape during condensation is controlled by regulating the heating power so as to quickly obtain the TiAl-Nb monocrystal, and after the desegregation of the TiAl-Nb monocrystal, the high-strength TiAl-Nb monocrystal alloy of which the yield strength is 637MPa at a temperature of 900 DEG C, the elongation percentage is 8.1% and the ductile-brittle transition temperature is not lower than 900 DEG C can be obtained.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Silicon single crystal produced by crucible-free float zone pulling
InactiveUS20030024469A1Stable flowIncreased riskPolycrystalline material growthSiliconCrucibleNitrogen
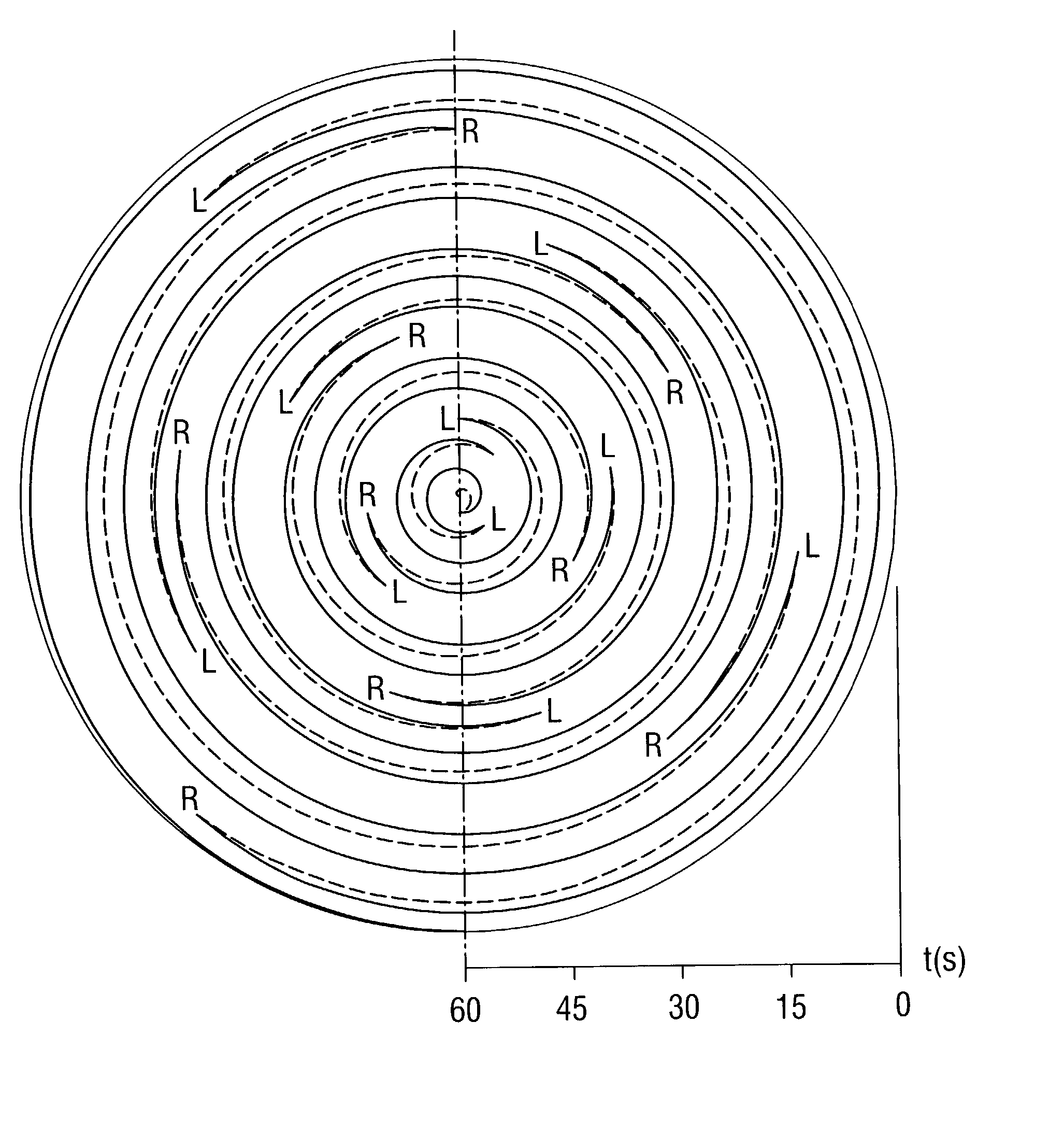
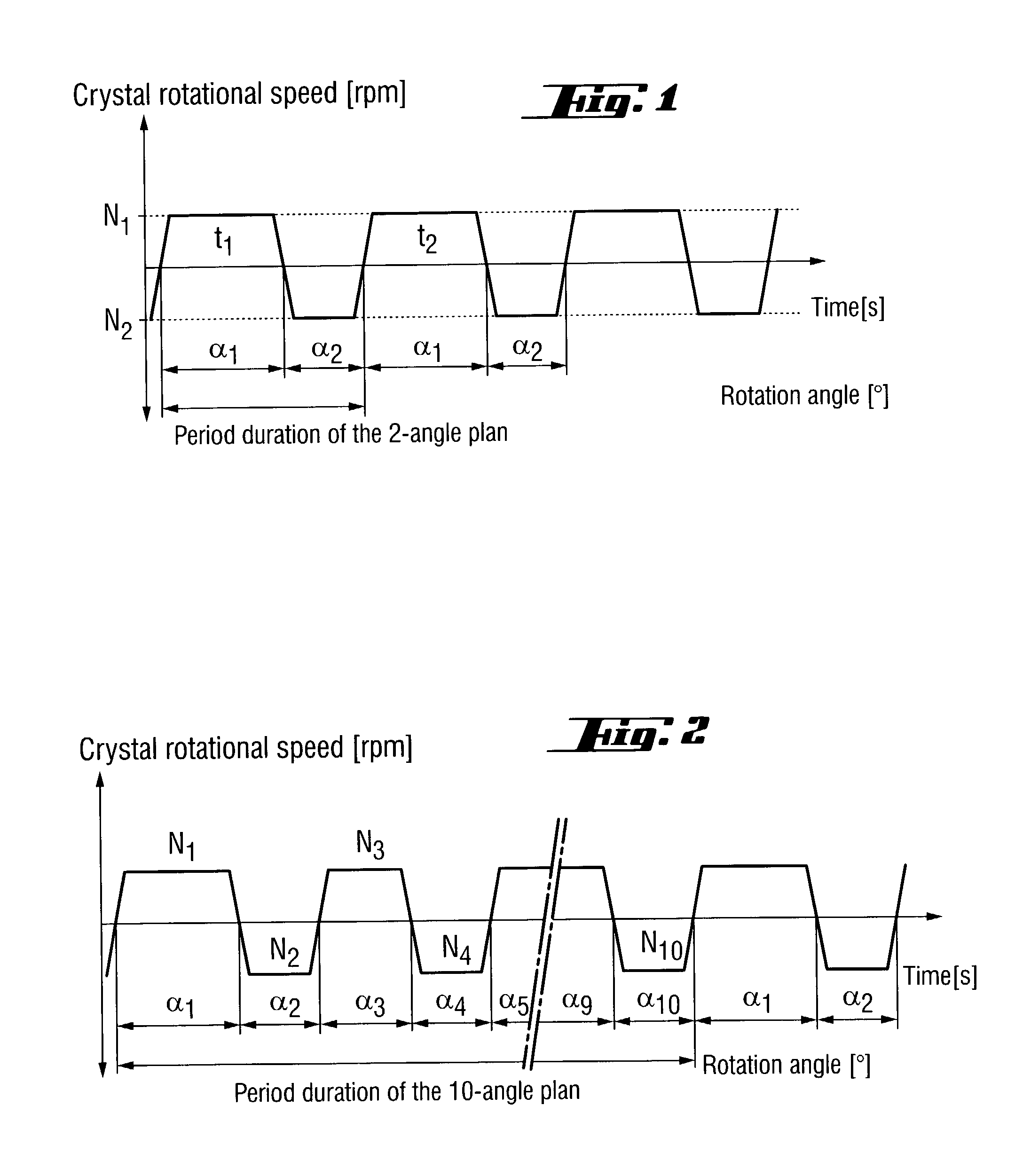
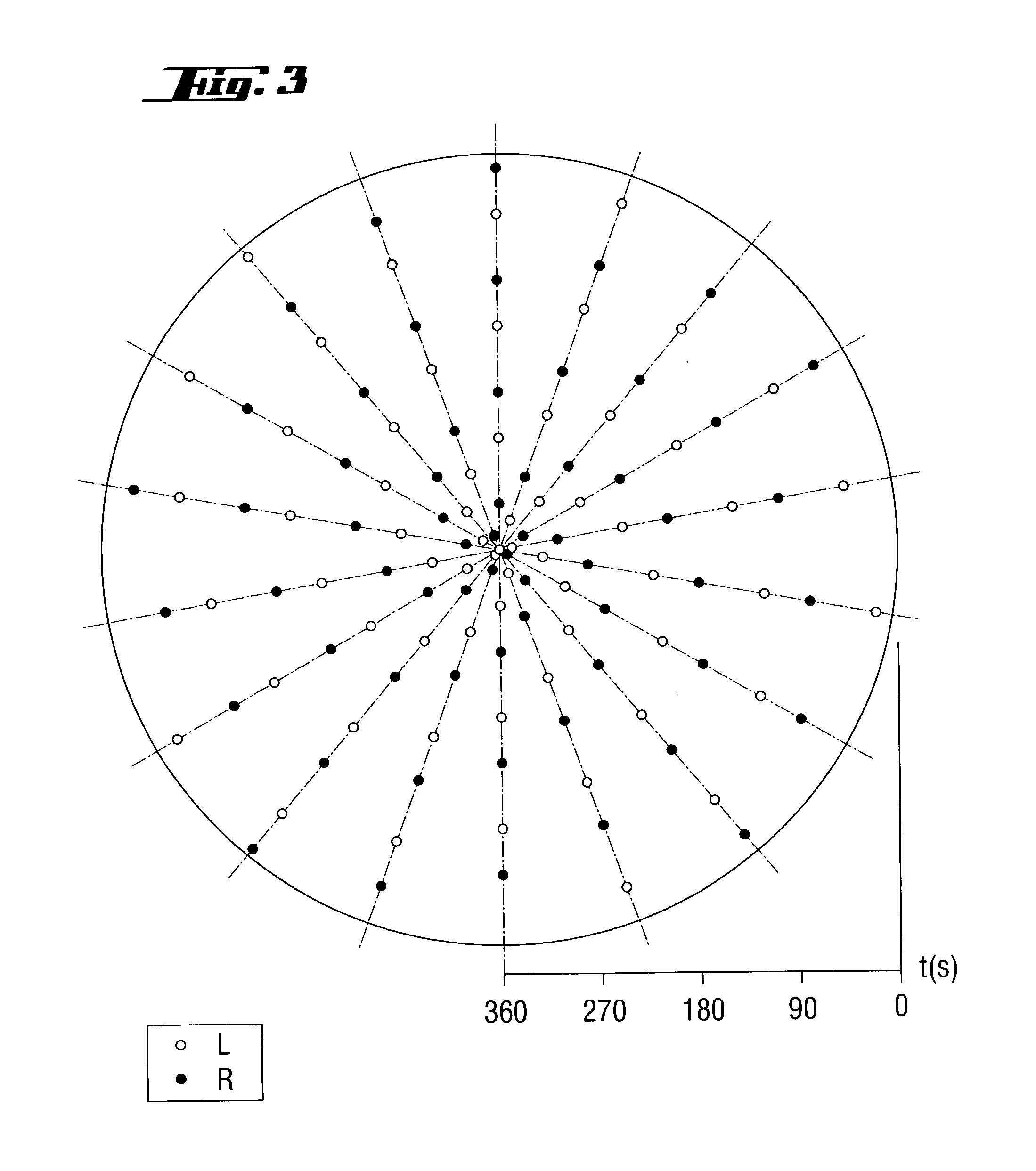
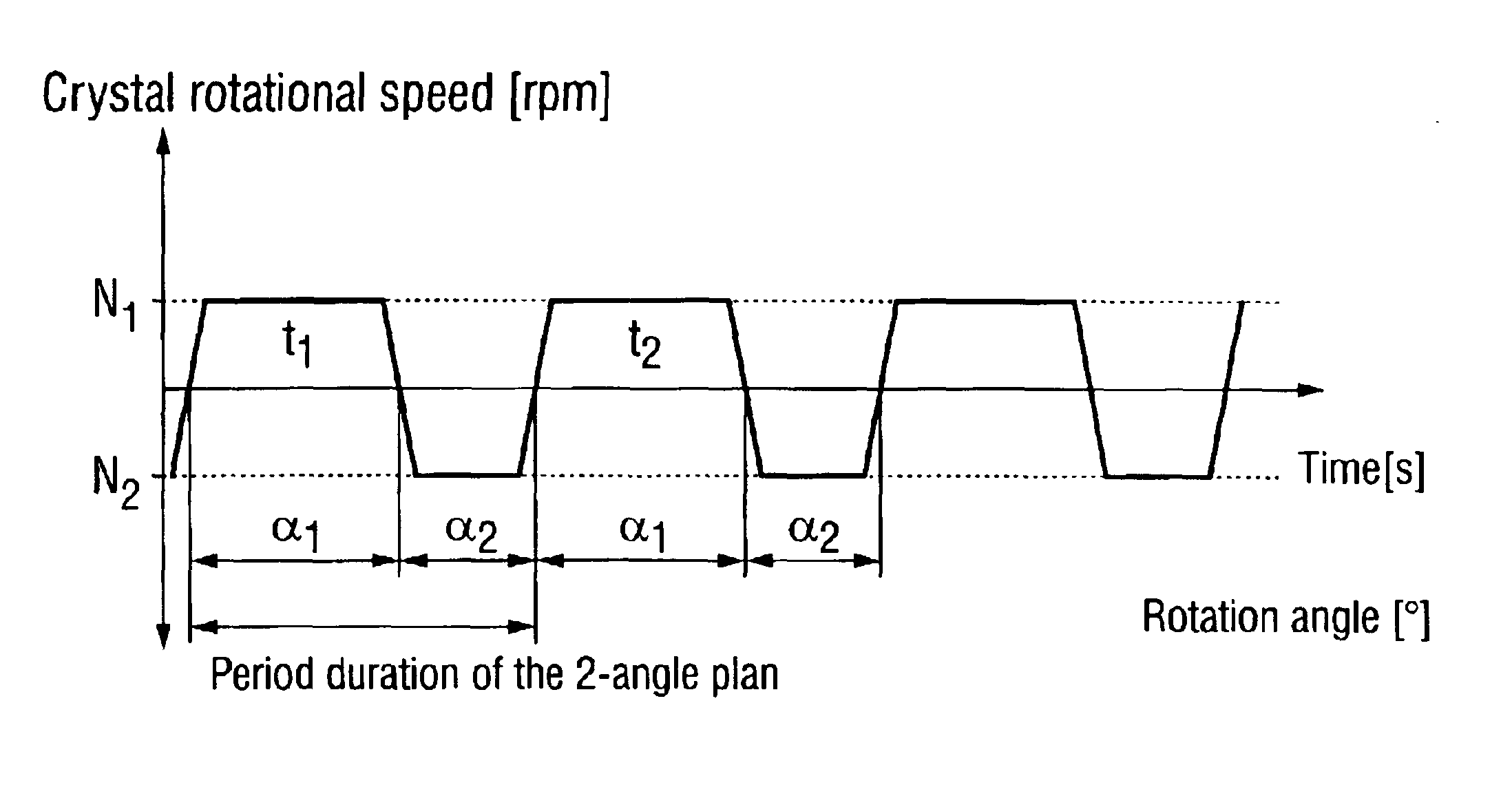
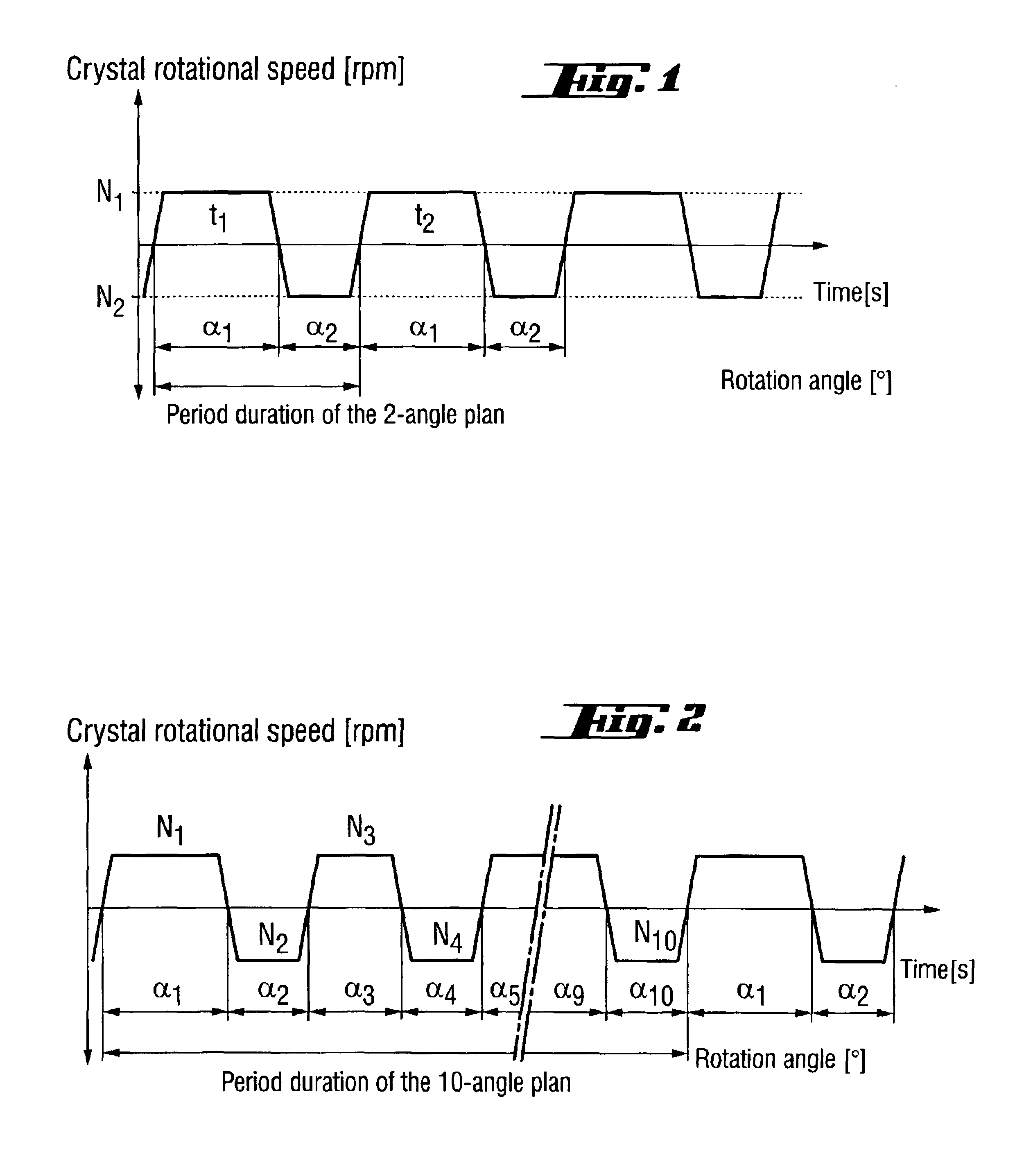
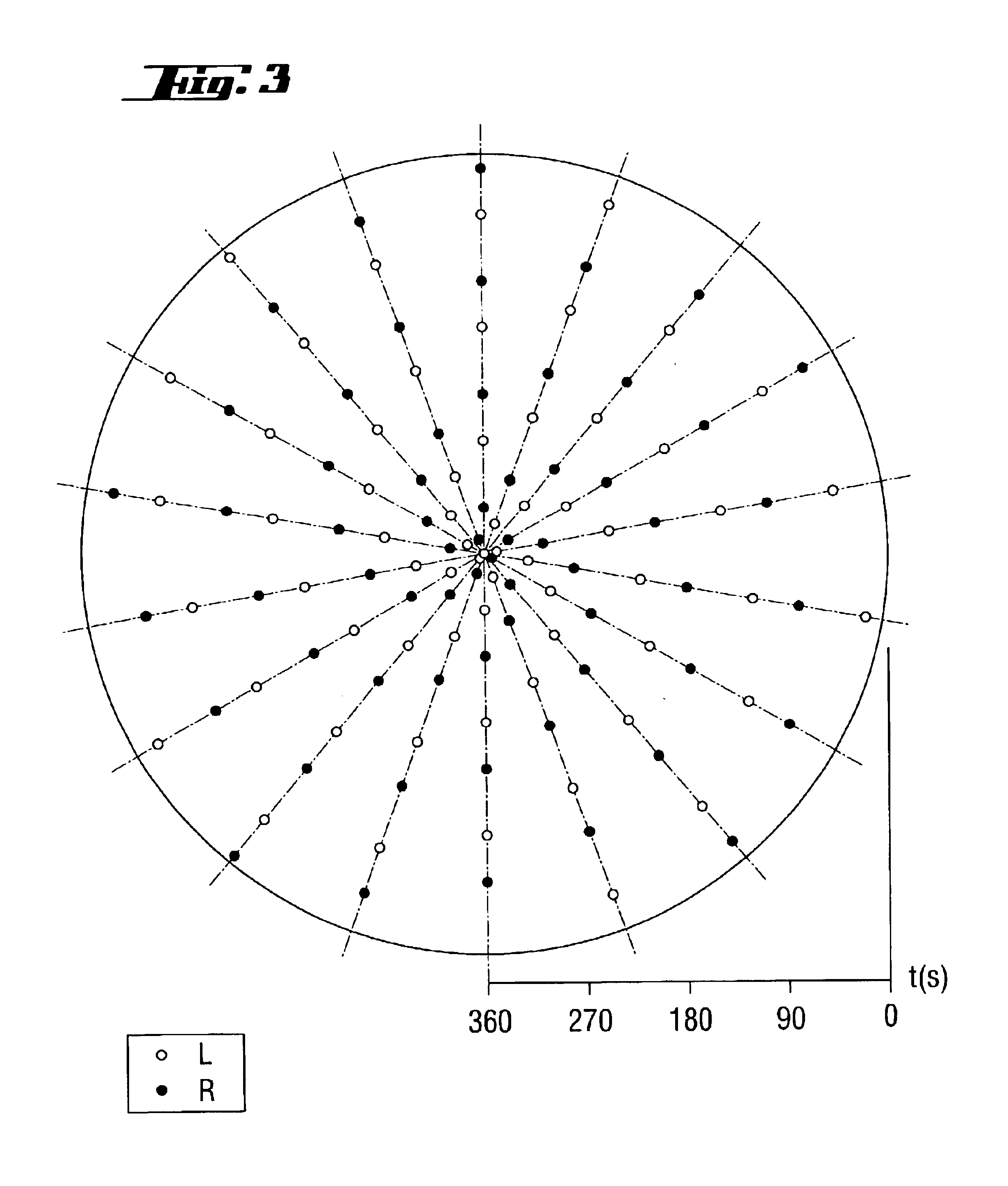
A silicon single crystal is produced by crucible-free float zone pulling, has a diameter of at least 200 mm over a length of at least 200 mm and is free of dislocations in the region of this length. A silicon wafer is separated from the silicon single crystal by a process for producing the silicon single crystal. The silicon single crystal is produced by crucible-free float zone pulling in a receptacle, in which an atmosphere of inert gas and nitrogen exerts a pressure of 1.5-2.2 bar, the atmosphere being continuously exchanged, with the volume of the receptacle being exchanged at least twice per hour. A flat coil with an external diameter of at least 220 mm is inserted in order to melt a stock ingot. The single crystal is pulled at a rate in a range from 1.4-2.2 mm / min and is periodically rotated through a sequence of rotation angles. The direction of rotation is changed, after each rotation, by a rotation angle belonging to the sequence, a change in the direction of rotating defining a turning point on the circumference of the single crystal, and at least one recurring pattern of turning points is formed, in which the turning points are distributed on straight lines which are oriented parallel to the z-axis and are uniformly spaced apart from one another.
Owner:SILTRONIC AG
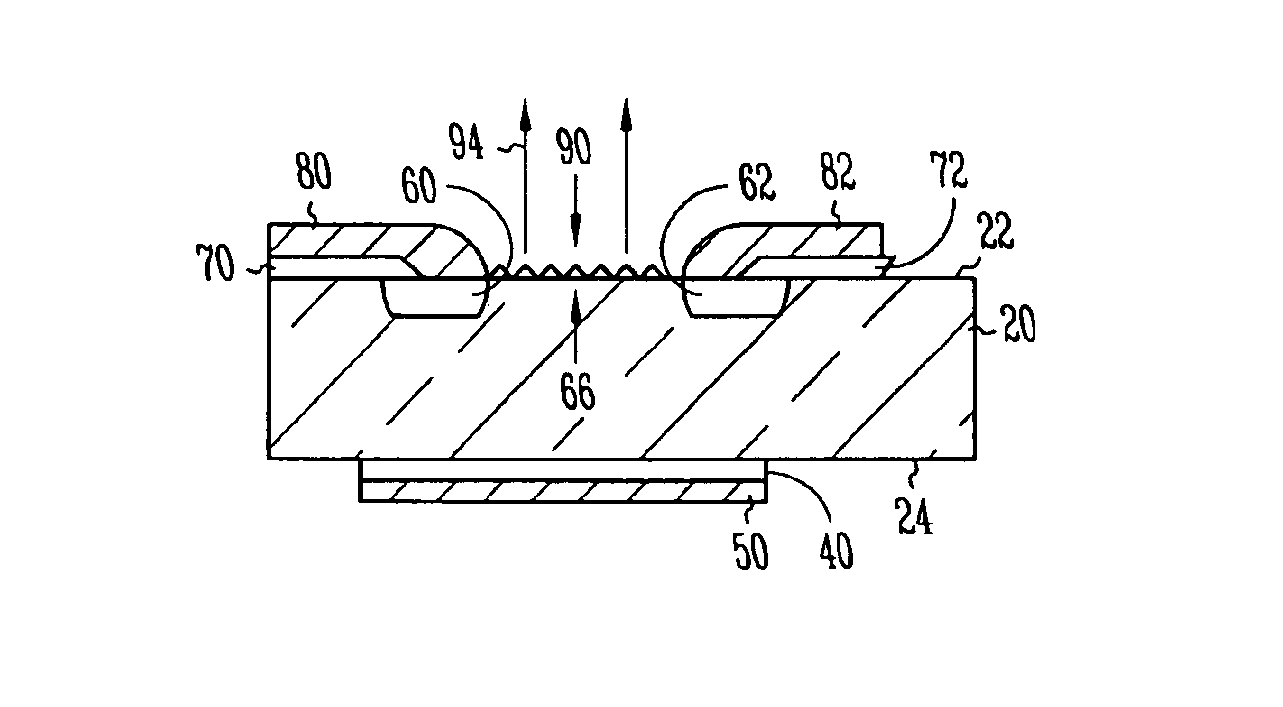
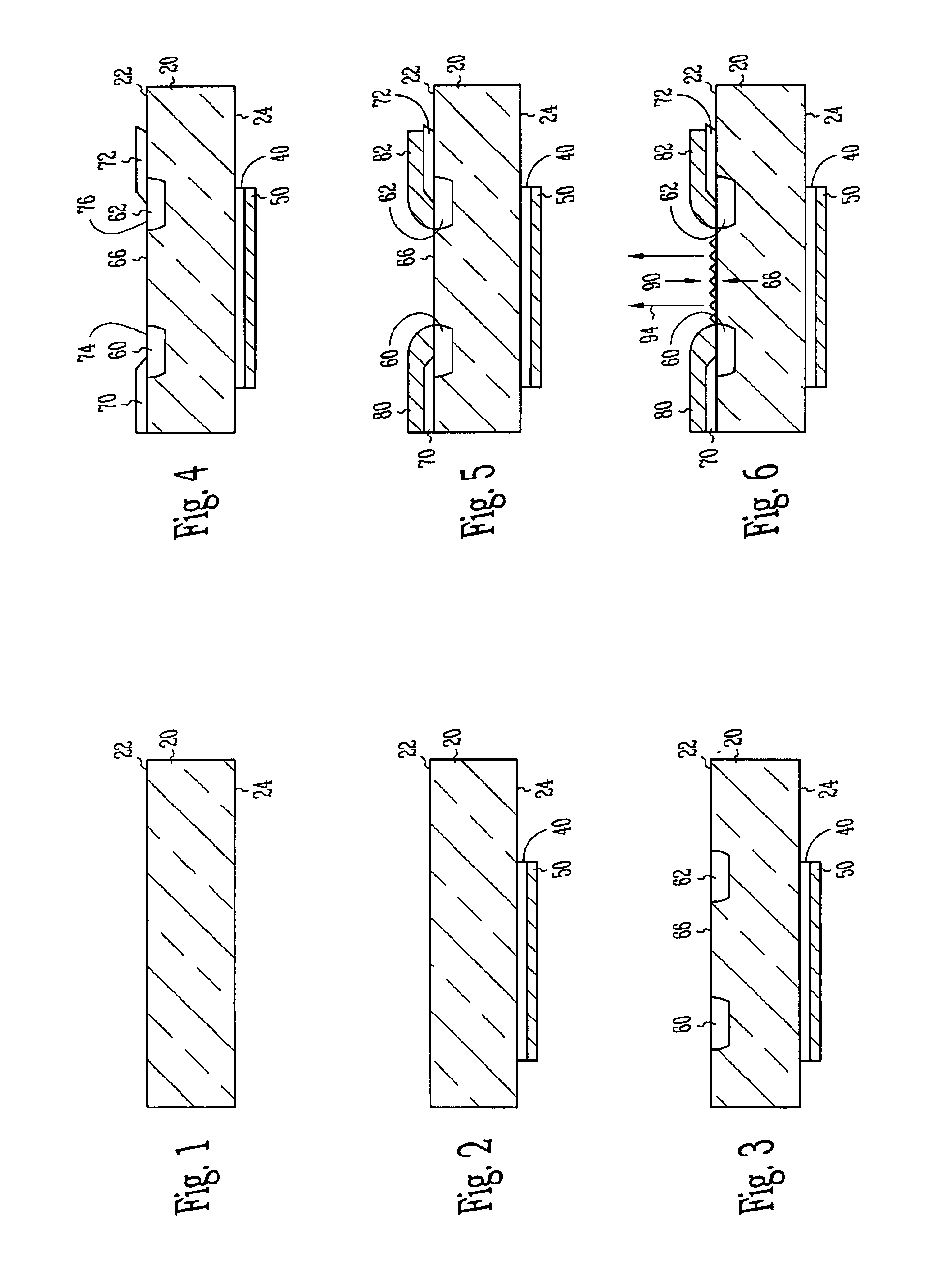
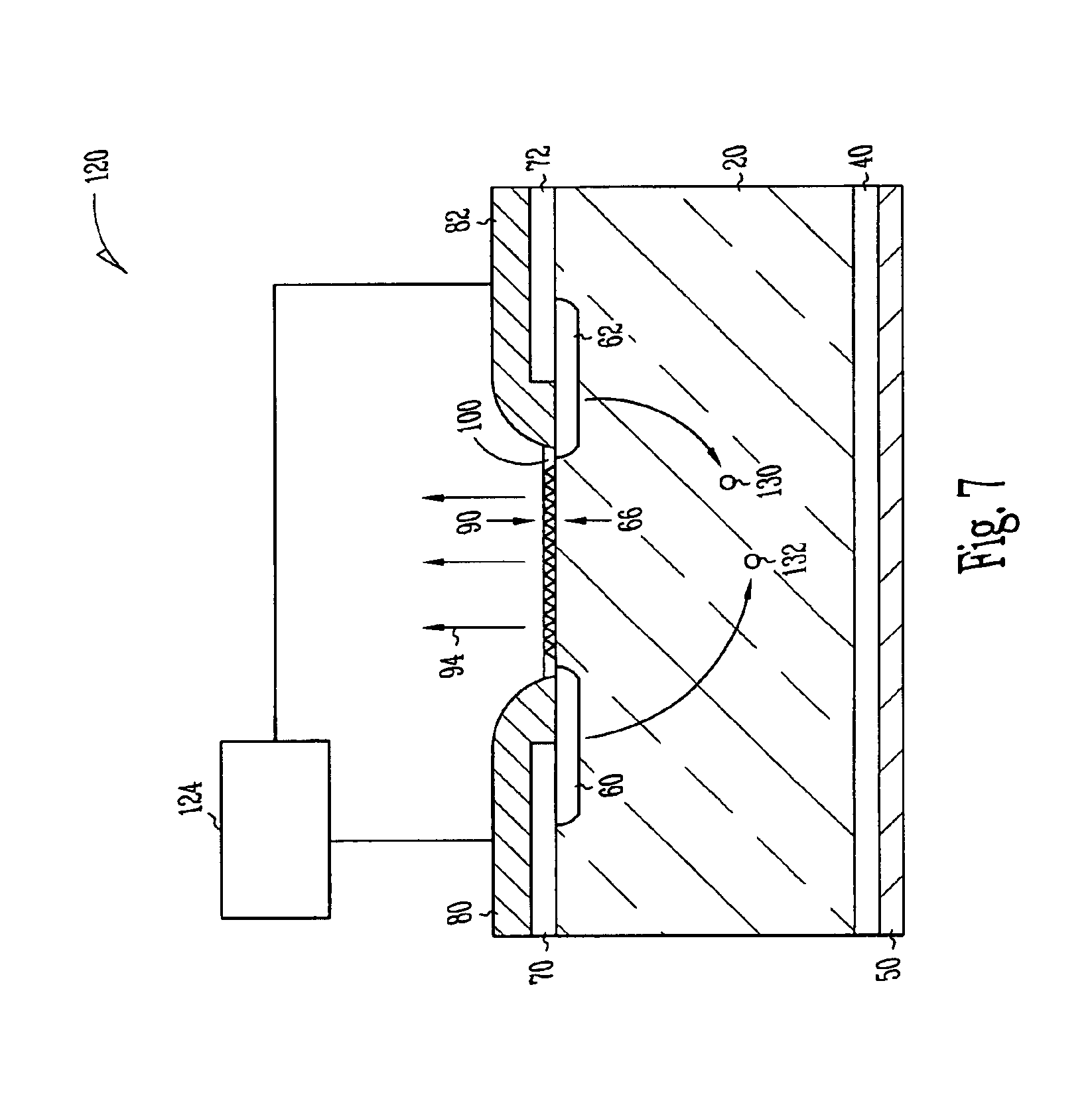
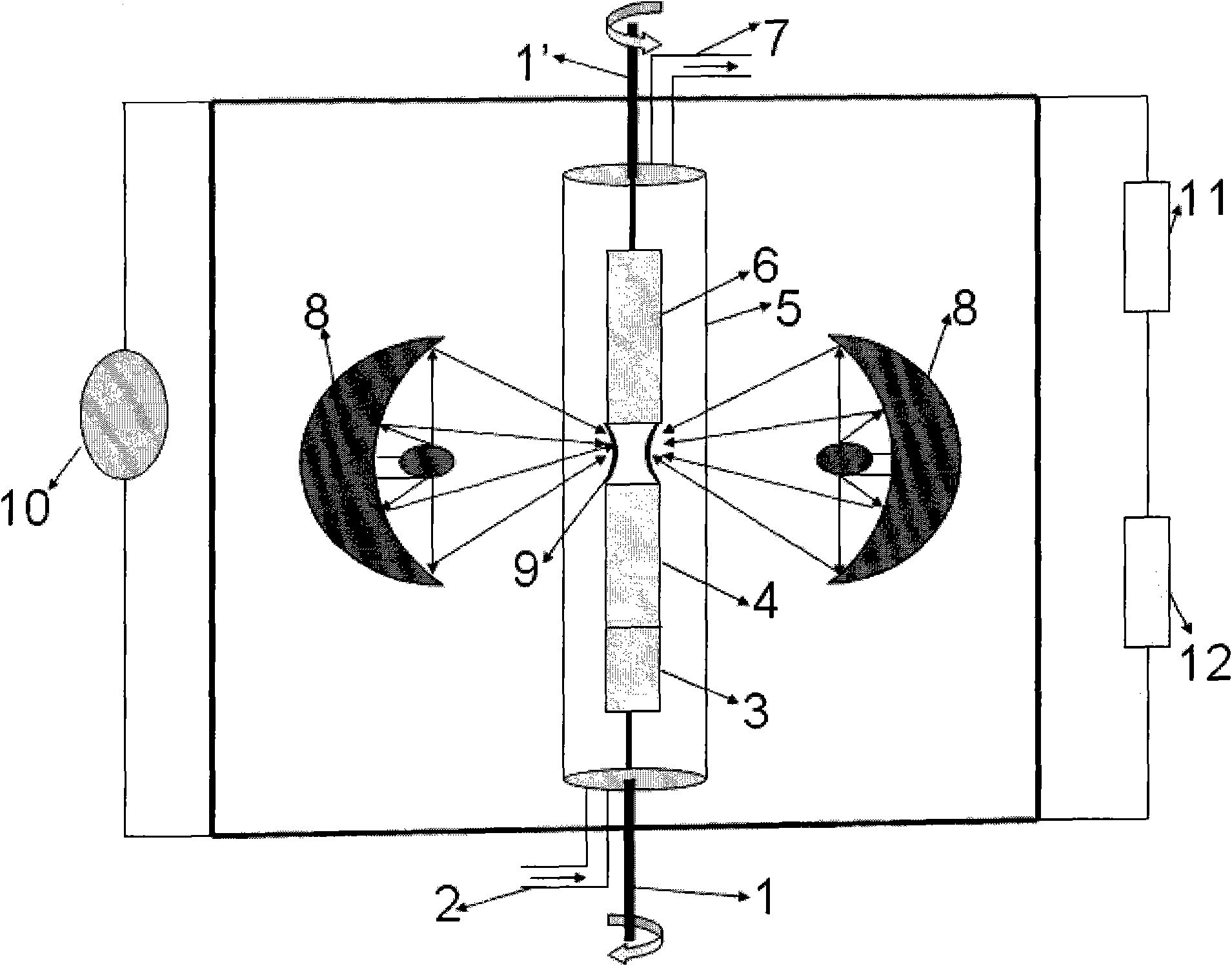
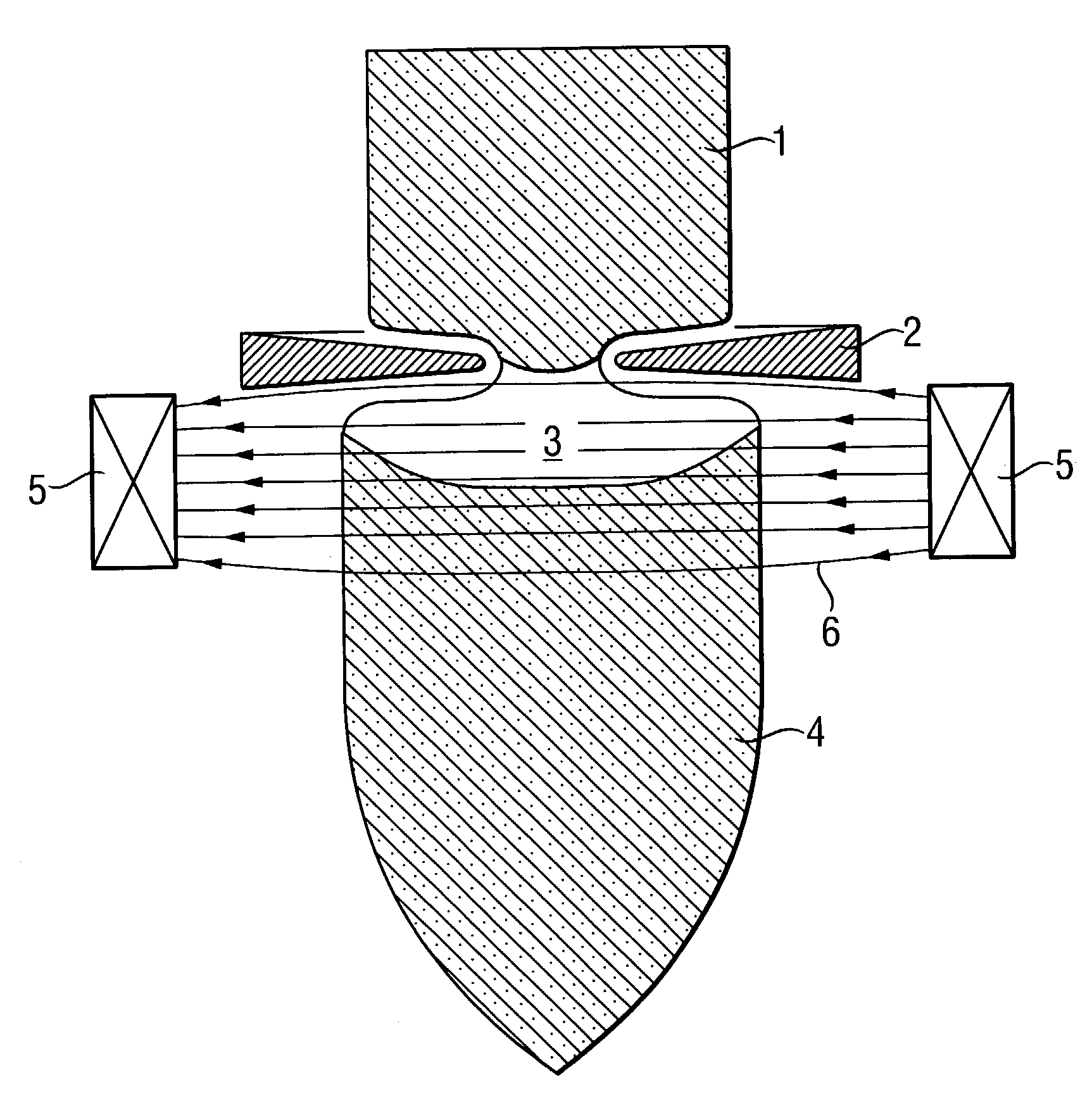
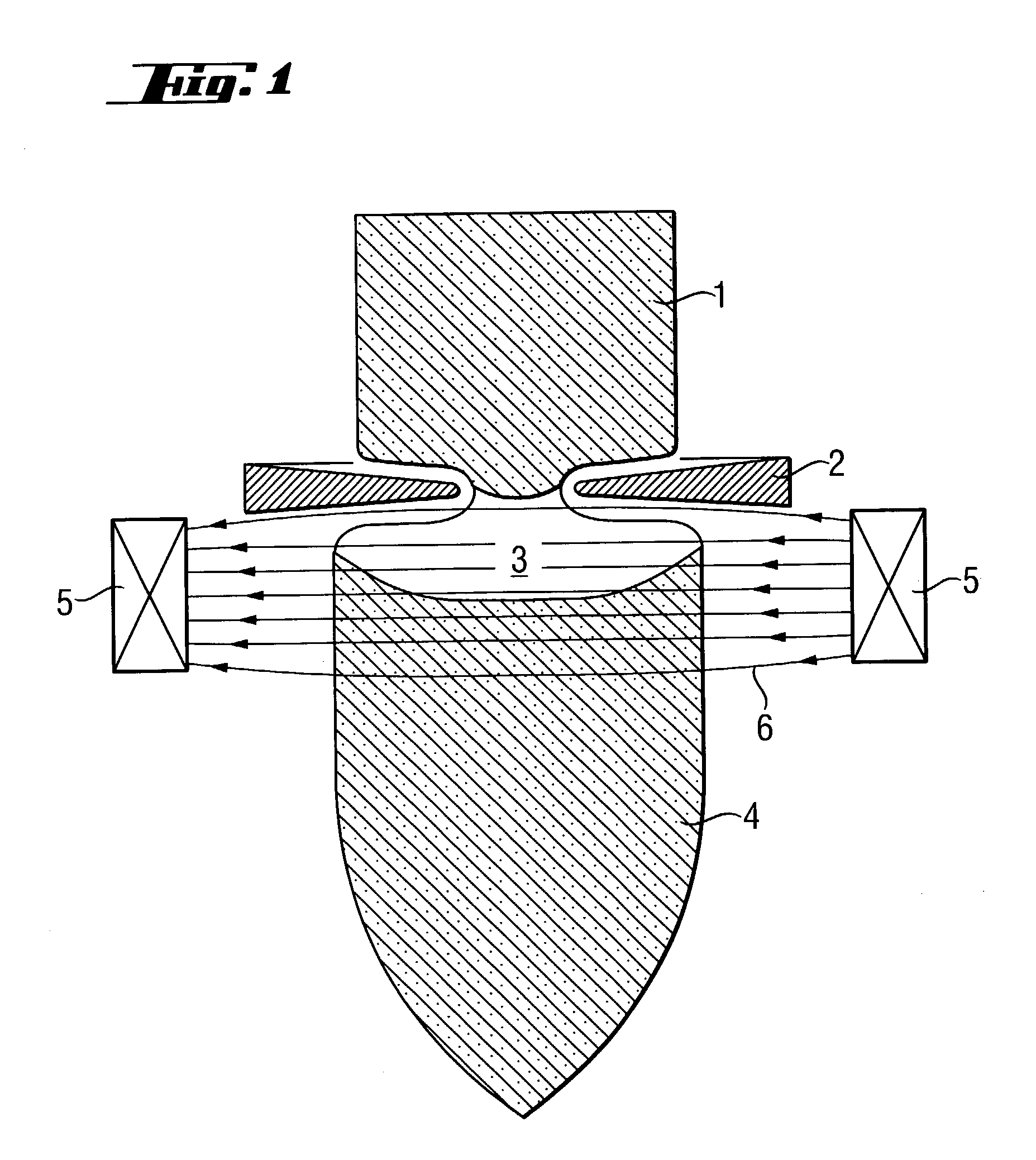
Floating zone melting apparatus
InactiveUS20100307406A1Reduce loadBy zone-melting liquidsFrom frozen solutionsZone meltingInfra-red color
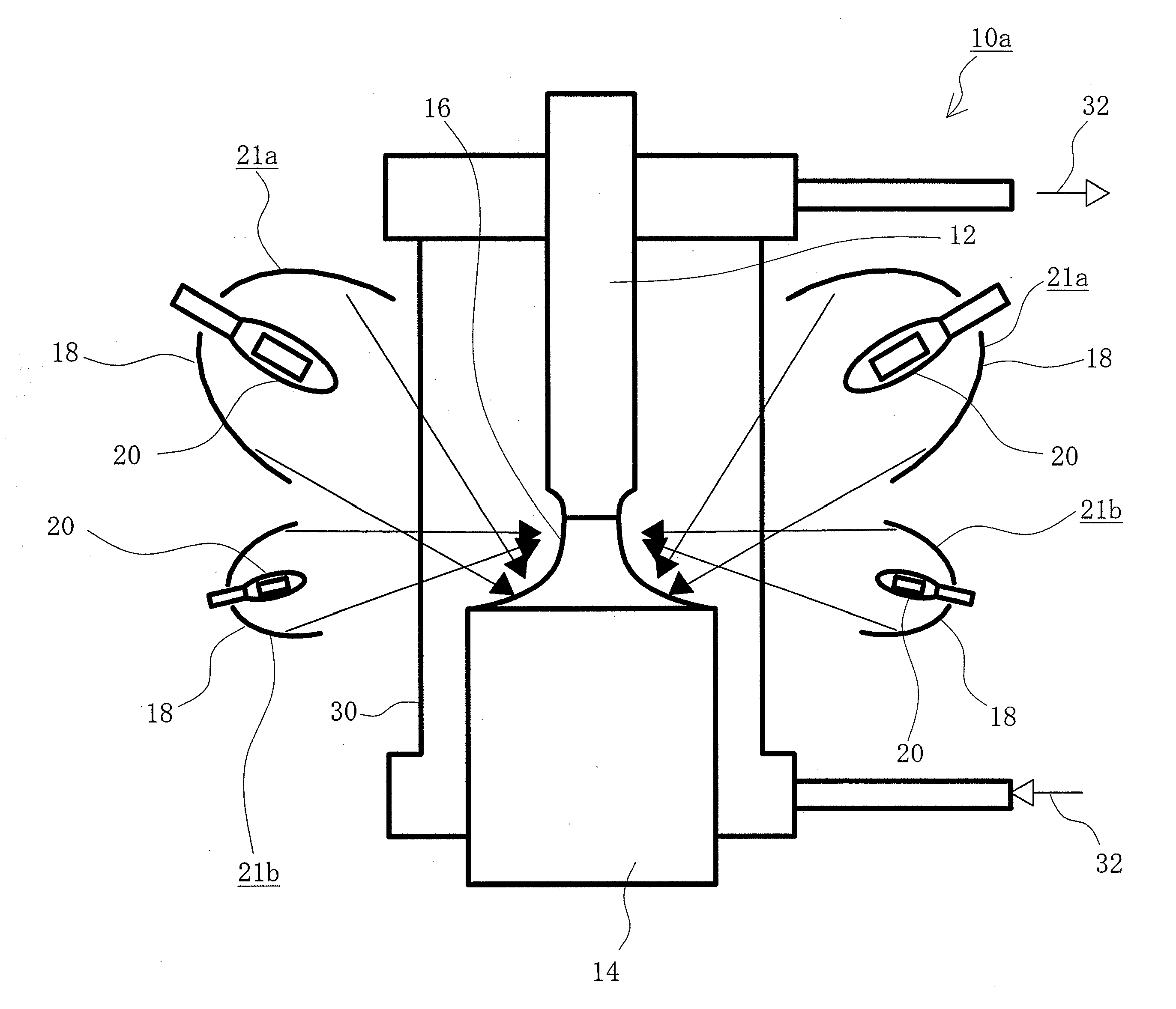
This invention provides a floating zone melting apparatus in which a sample rod especially having a large diameter can be stably melted with a certainty and the crystal being grown can retain a flat shape at the interface of the solid phase and the liquid phase, whereby a single crystal having a large diameter can be grown.[Problem] It is an object to provide a floating zone melting apparatus of the infrared concentration heating type in which a sample is set in a sample chamber made of a transparent quartz tube, an atmospheric gas is introduced into the sample chamber, infrared rays emitted from a plurality of infrared ray irradiation means are converged to the sample to heat and melt the sample in this state, thereby obtaining a melt, and the melt is solidified on a seed crystal to grow a single crystal. The plurality of infrared ray irradiation means comprise a plurality of infrared ray irradiation means of the downward irradiation type that emit an infrared ray downward from an oblique upper direction and a plurality of infrared ray irradiation means of the upward irradiation type that emit an infrared ray upward from an oblique lower direction.
Owner:CRYSTAL SYST
Doped semiconductor wafer of float zone pulled semiconductor material, and process for producing the semiconductor wafer
InactiveUS20030192470A1Polycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsElectrical resistance and conductanceDopant
A doped semiconductor wafer of float zone-pulled semiconductor material contains a dopant added to a molten material and has a radial macroscopic resistance distribution of less than 12% and striations of -10% to +10%. There is also a process for producing a doped semiconductor wafer by float zone pulling of a single crystal and dividing up the single crystal, in which process, during the float zone pulling, a molten material which is produced using an induction coil is doped with a dopant. It is exposed to at least one rotating magnetic field and is solidified. The single crystal which is formed during the solidification of the molten material is rotated. The single crystal and the magnetic field are rotated with opposite directions of rotation and the magnetic field has a frequency of 400 to 700 Hz.
Owner:SILTRONIC AG
Method for growing RFeO3 photomagnetic function crystal by secondary melting method
InactiveCN102011188AQuality improvementImprove the finishPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsCzochralski methodPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to the field of research on growth of RFeO3 photomagnetic function crystal, an optical floating zone secondary melting method is a brand new and efficient growth method for the materials at present. In the method, high-purity ferric oxide and rare earth oxide are used as raw materials to prepare a material bar through processes of milling, sintering, isostatic pressing and the like according to chemical proportion, and then, the material bar is placed in an optical floating zone furnace to grow in air atmosphere. A surface of a single crystal prepared by the method has ideal surface finish, density and uniformity, a characteristic peak of the single crystal is obviously increased, and FWHM is obviously reduced, so that crystallization quality of the crystal is greatly improved, a pure-phase integral RFeO3 crystal can be obtained more easily; simultaneously, the method has high efficiency and can appropriately adjust growth speed in a rang of 1-9mm / h according to different application goals, that is unachievable to traditional methods, such as a pulling method, a hydrothermal method, a descending method and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
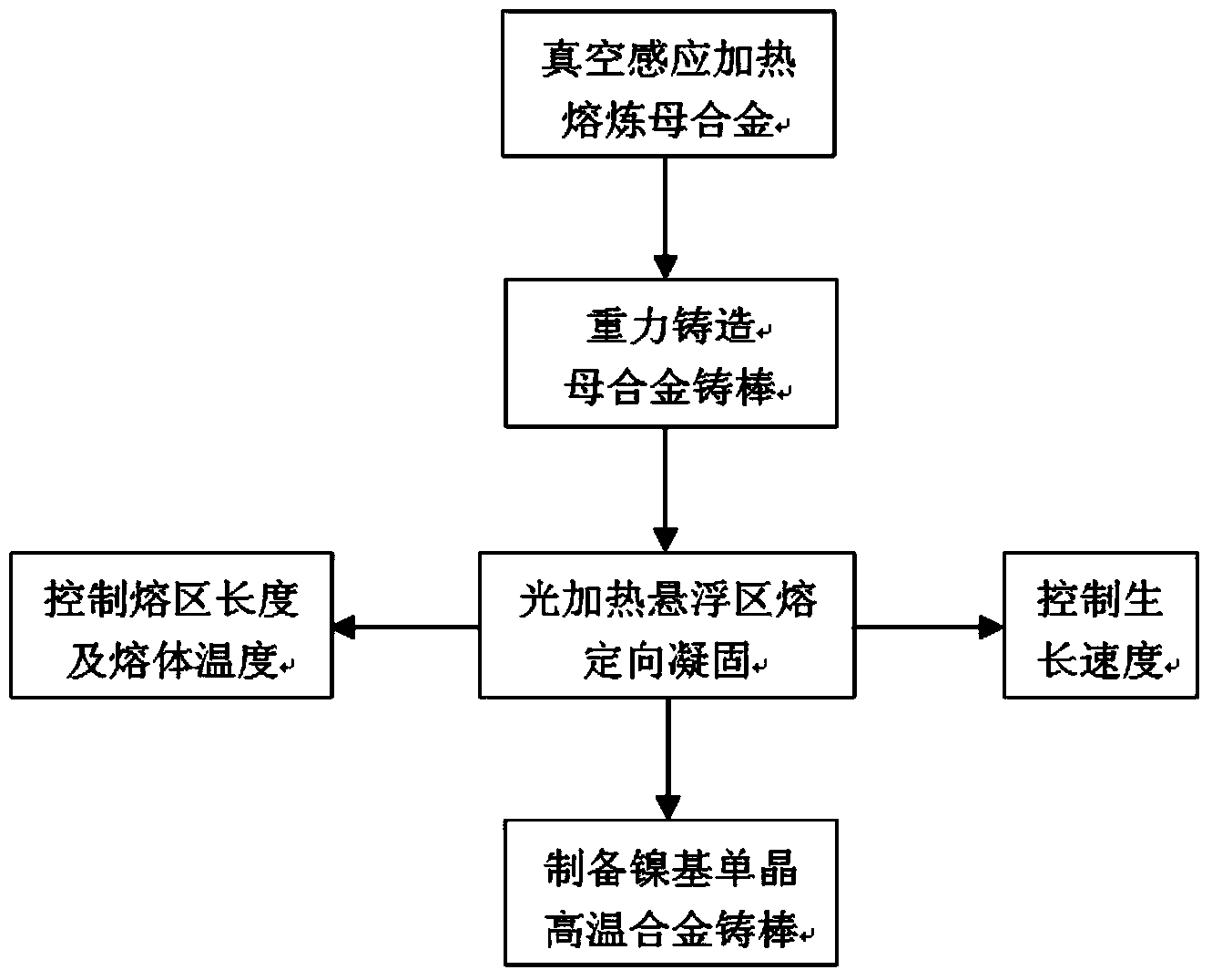
Preparation of nickel-base single-crystal high-temperature alloy through light floating zone melting directional solidification method
InactiveCN103757704AUniform tissueNo pollution in the processPolycrystalline material growthEutectic material solidificationLight guideZone melting
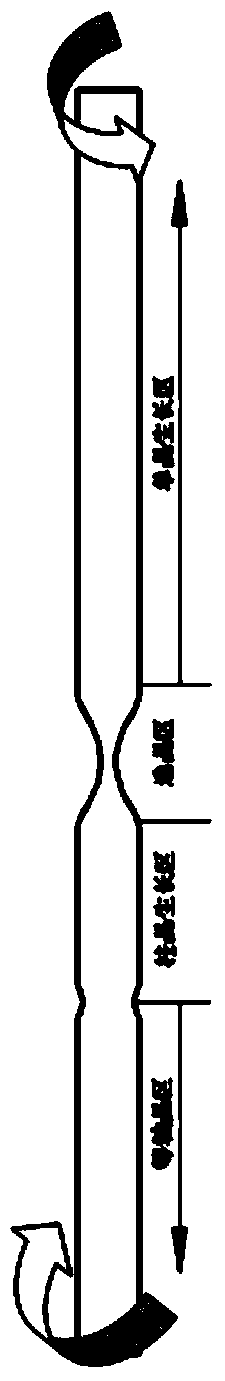
The invention discloses a method for preparing a nickel-base single-crystal high-temperature alloy through a light floating zone melting directional solidification method. The light floating zone melting directional solidification method is used to prepare the nickel-base single-crystal high-temperature alloy, and an infrared light guide temperature measuring device is used for measuring the temperature. The operation process is as follows: a 60-100mm test bar and a 30-50mm test bar are respectively fixed at the upper end and the lower end of light heating floating zone melting equipment, and the light heating floating zone melting equipment is vacuumized to 3*10<-3>Pa, argon is enabled to flow at the rate of 5mL / min, the upper and lower test bars rotate in the opposite directions at the rate of 20-30r / min, a heating power supply is turned on to raise the temperature to 1450-1500 DEG C at the heating rate of 10-15 DEG C per minute, the temperature is preserved for 3-5min, then the upper and lower ends of the test bars are jointed and drawn at the speed of 1-5mm / h to prepare a single crystal.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +3
Intrinsic luminescent scintillation crystal magnesium tantalum oxide, and preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN108221055AStable structureImprove flicker performancePolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsHexagonal crystal systemScintillation crystals
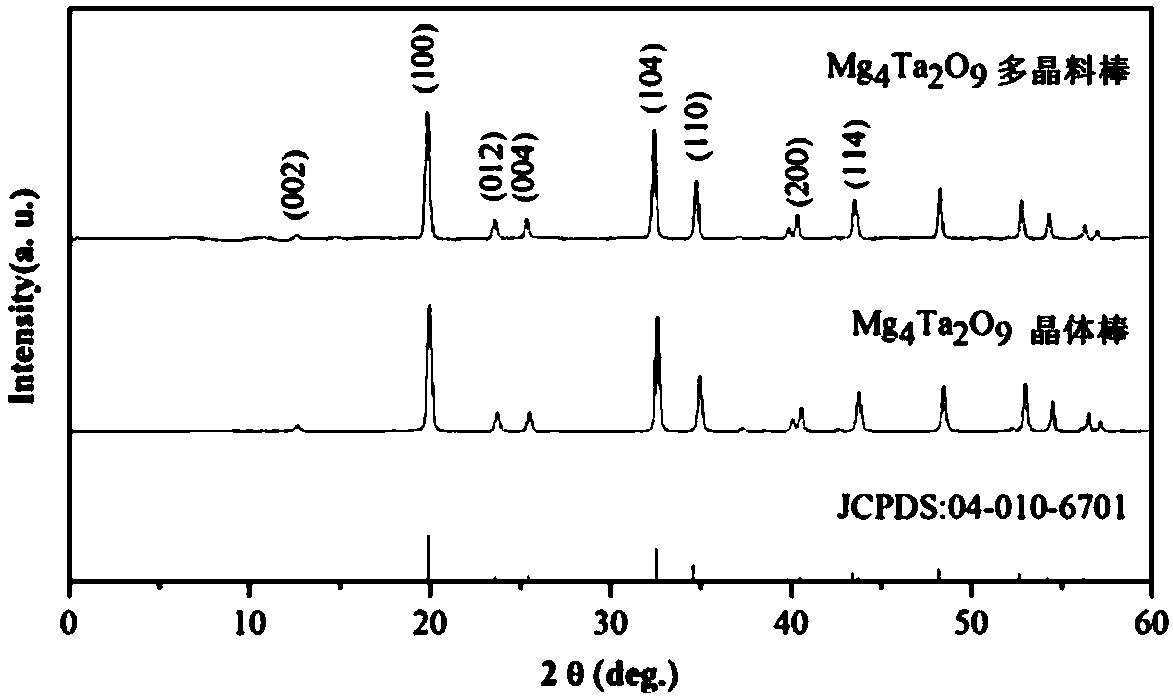
The invention provides a scintillation crystal magnesium tantalum oxide. The chemical formula of the crystal is Mg4Ta2O9, the crystal belongs to a hexagonal crystal system and has an ilmenite structure, the scintillation light yield is 16000 photons / M eV, the decay time is 5 [mu]s, and the energy resolution is 6.2%. The invention also provides a use of the Mg4Ta2O9 as a scintillation crystal material, and a preparation method of the Mg4Ta2O9. The preparation method comprises the following steps: MgO and Ta2O5 which are used as initial powders are uniformly mixed according to a molar ratio of 4.04:1, and are processed to form a raw material rod, the raw material rod is pre-sintered to obtain a pure-phase, dense and uniform polycrystalline rod, and the colorless and transparent rod-shaped crystal having a size of phi 4 mm * L 62 mm grows by adopting an optical floating zone technology. The method has the advantages of stable melting zone, simplicity in operation, effectiveness in inhibition of the volatilization of MgO, and maintenance of uniform composition and stable crystal quality.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
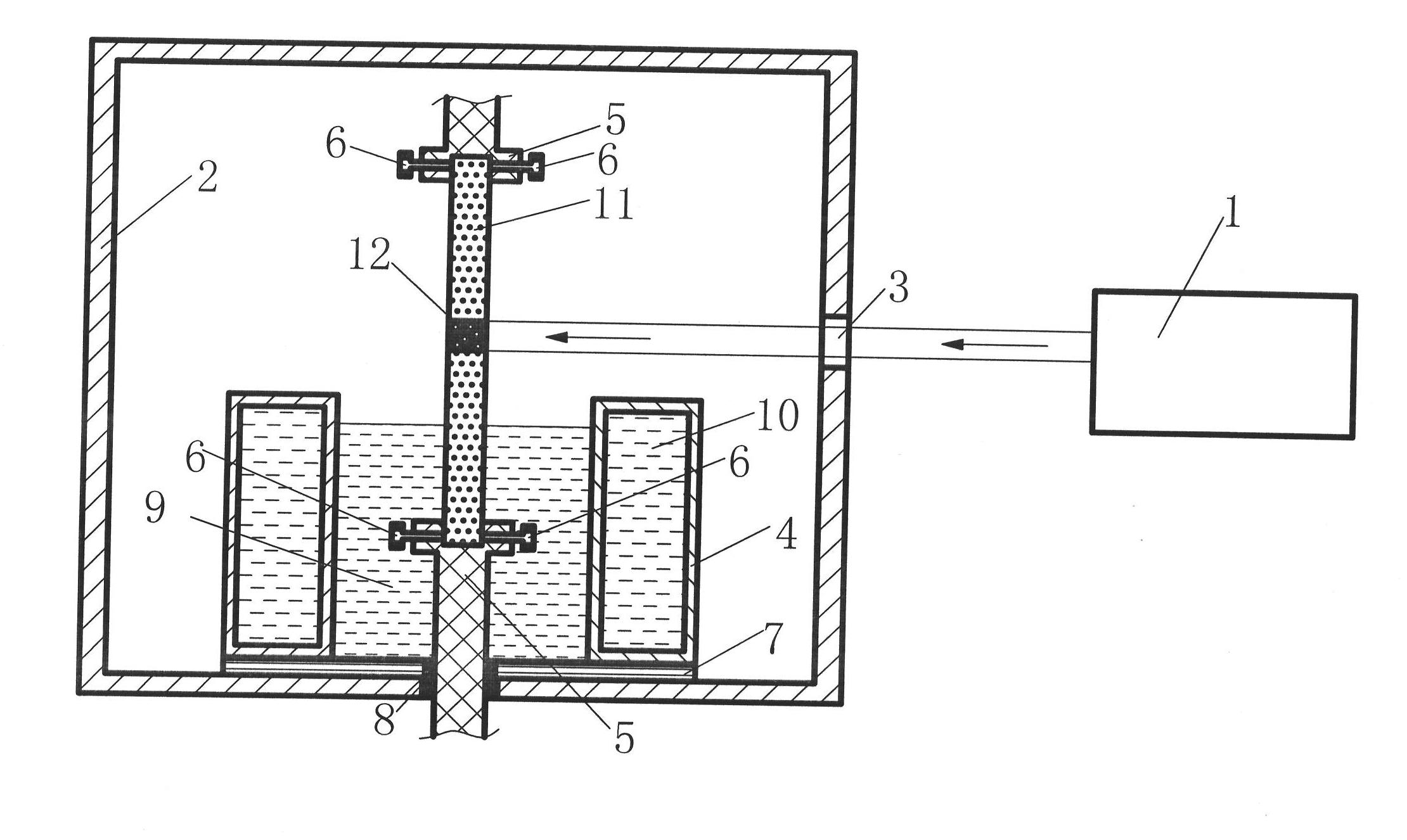
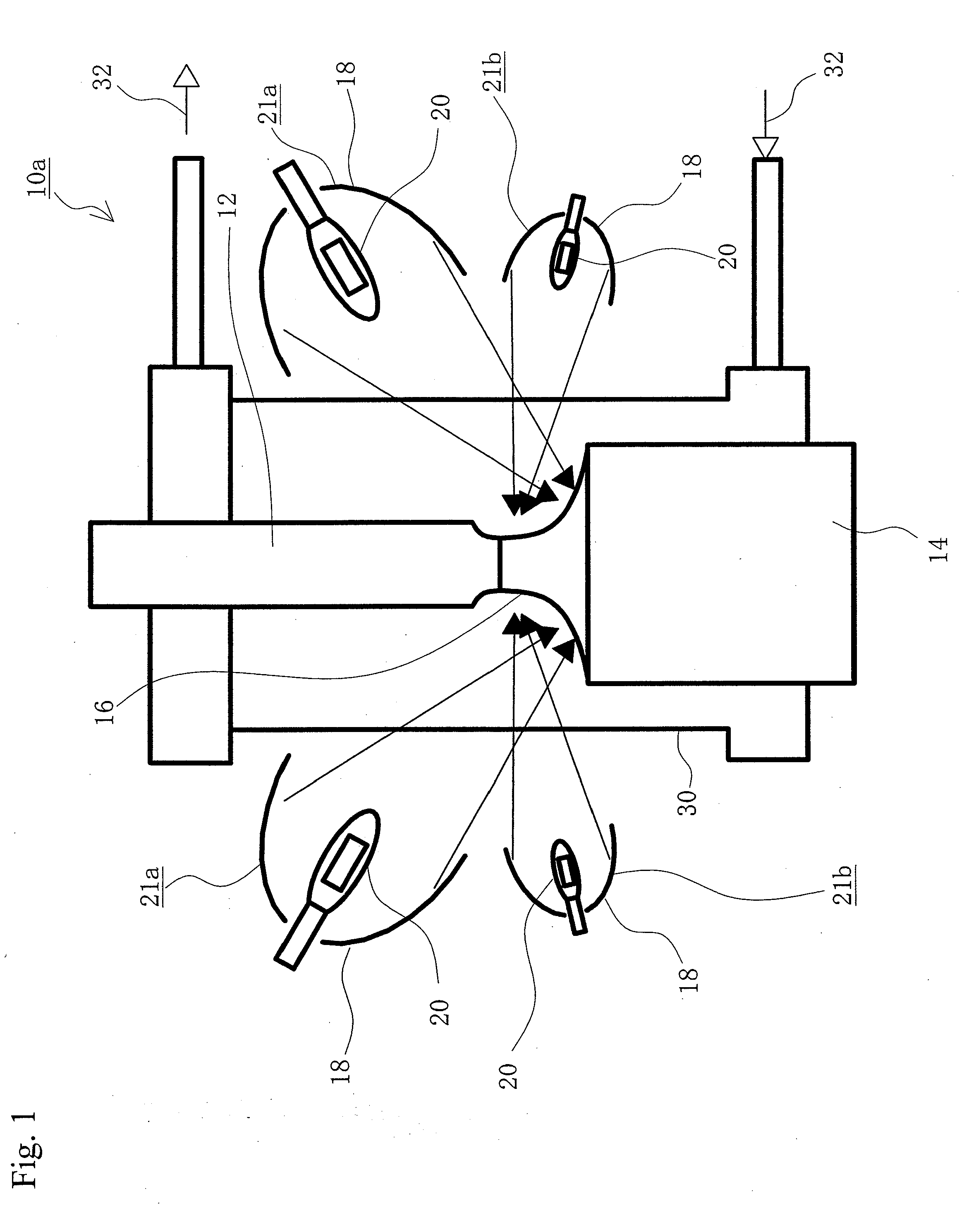
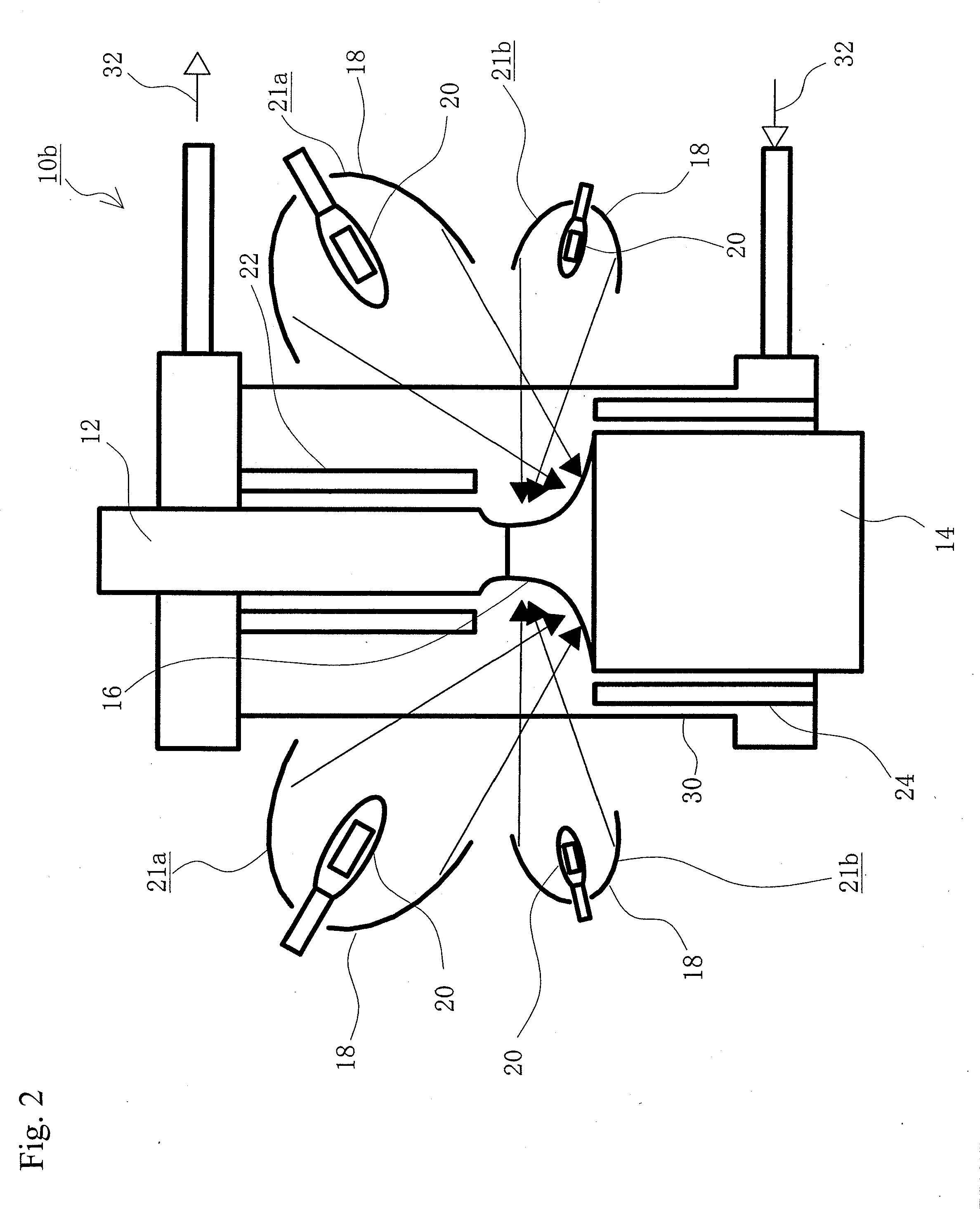
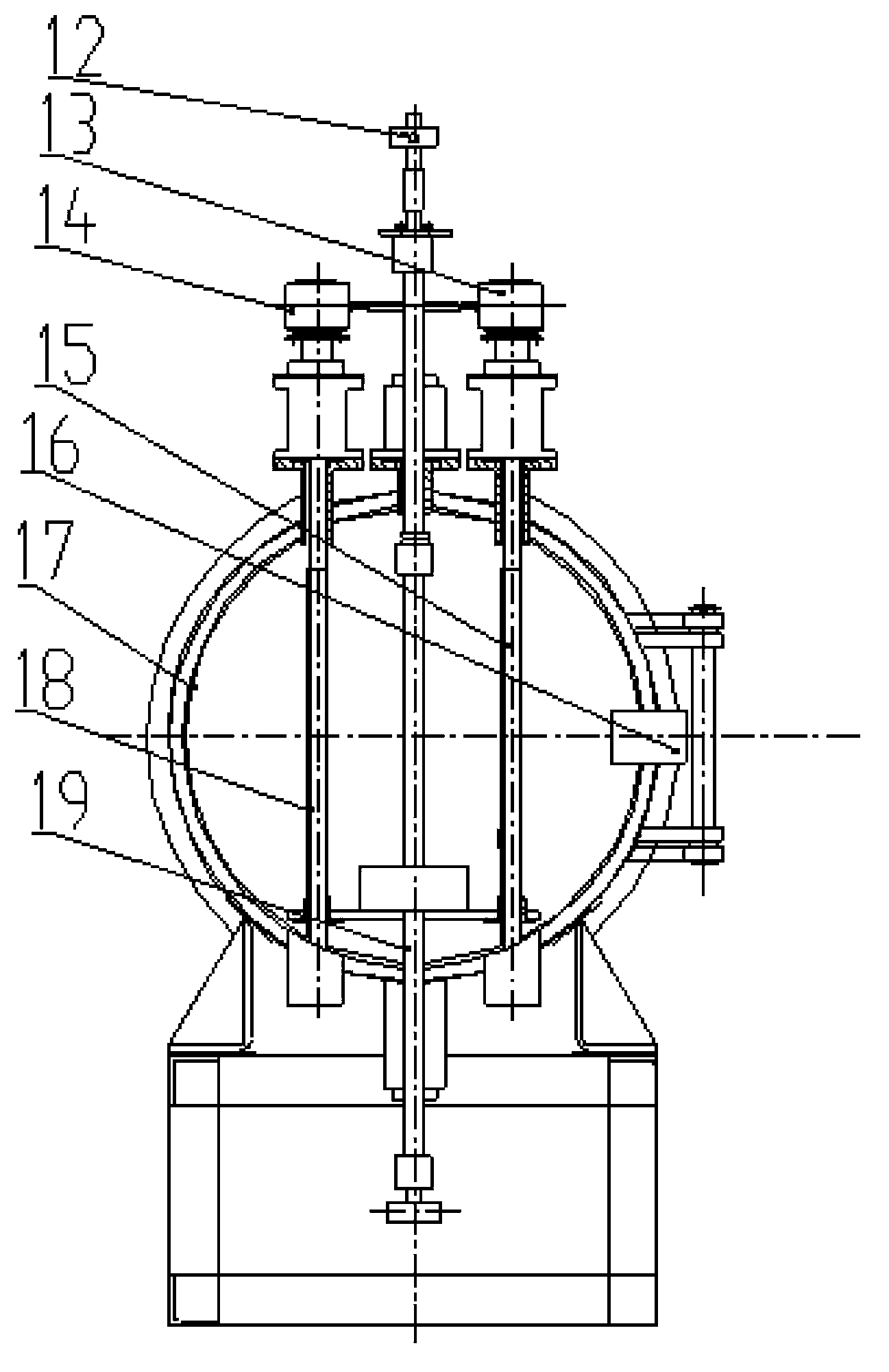
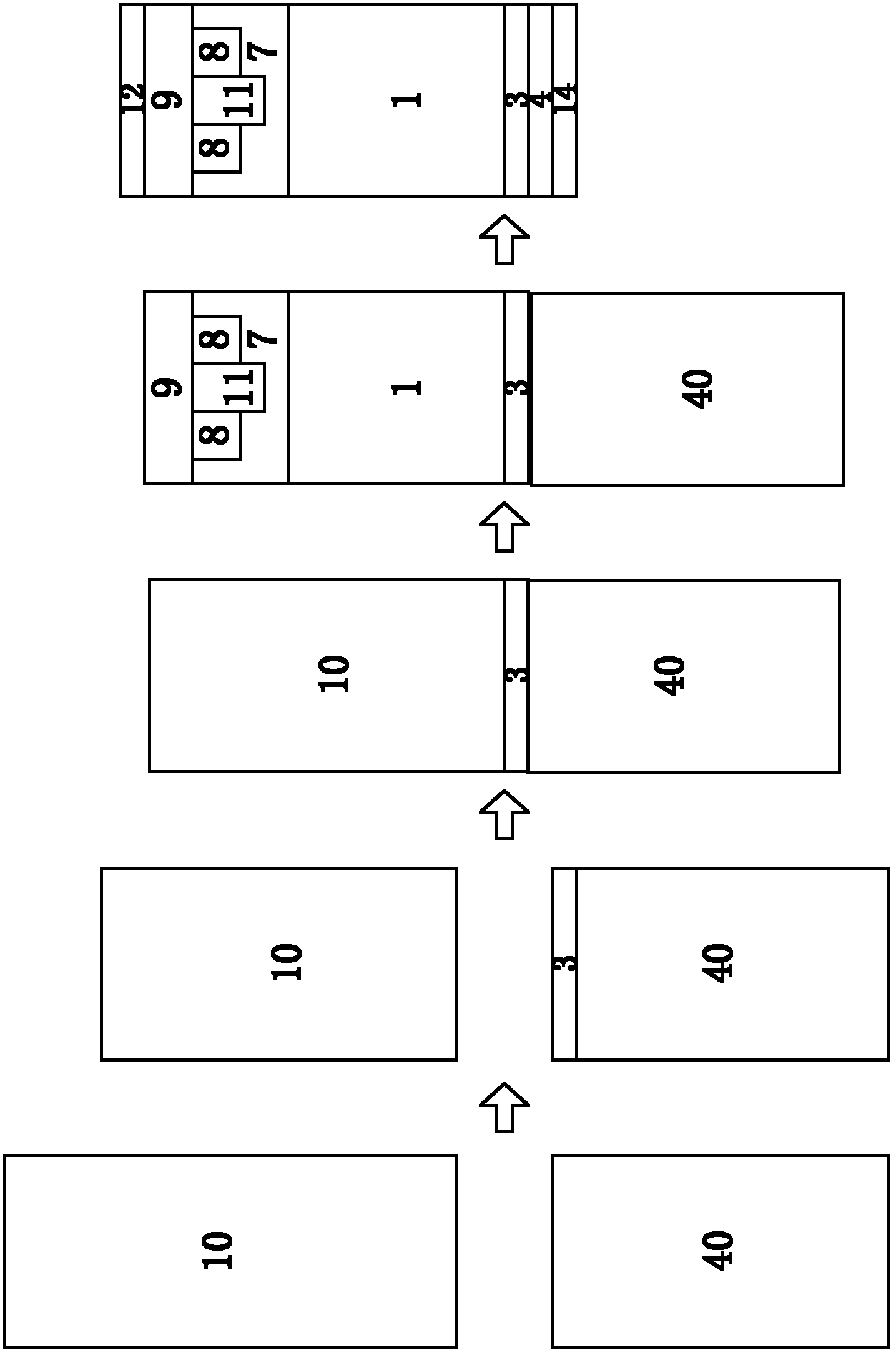
Single crystal manufacturing method and device
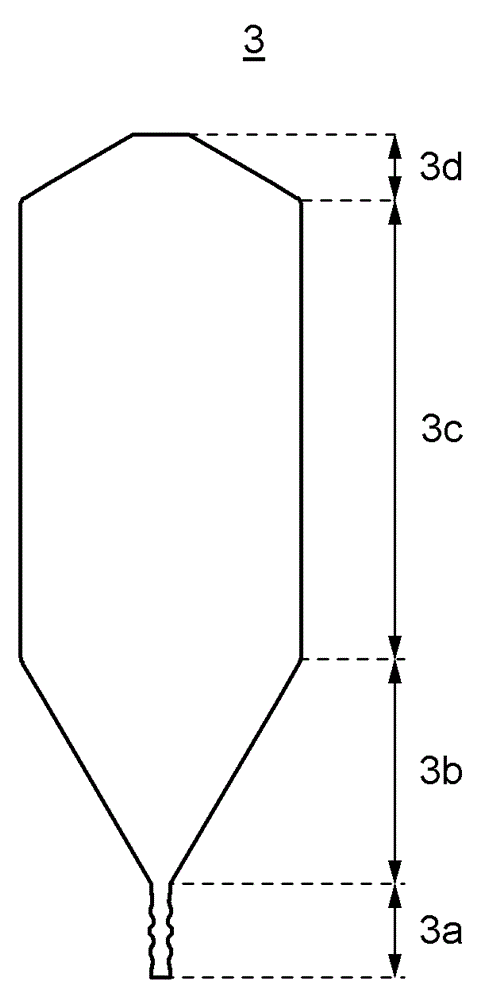
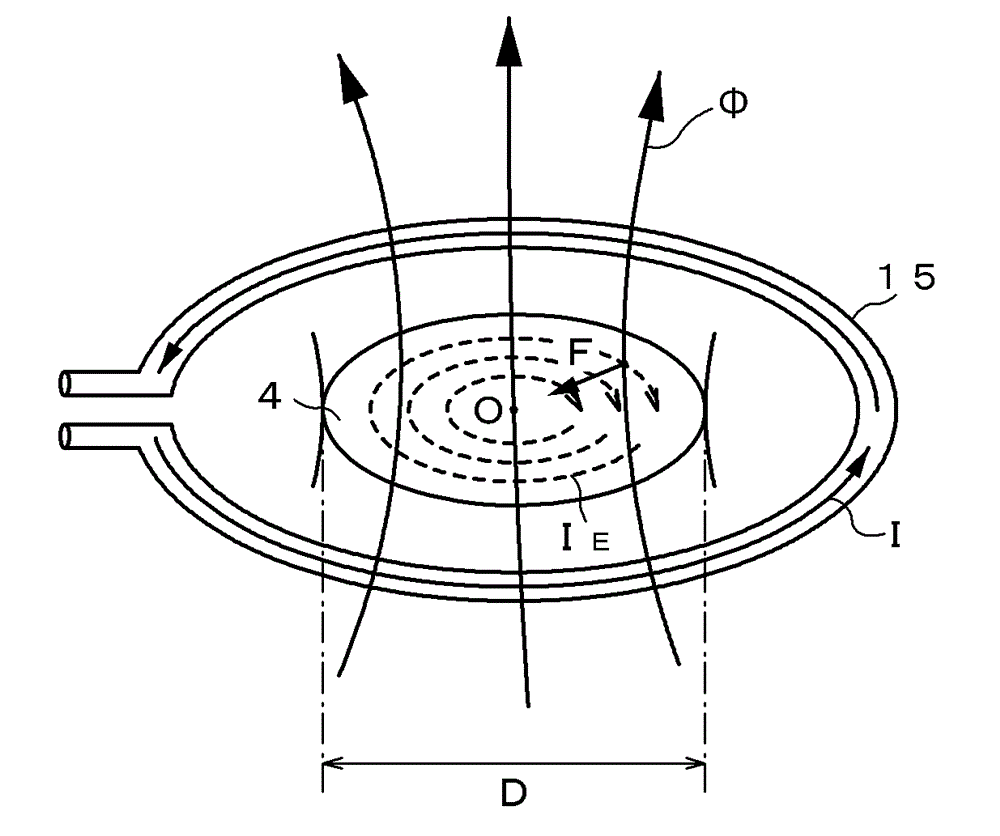
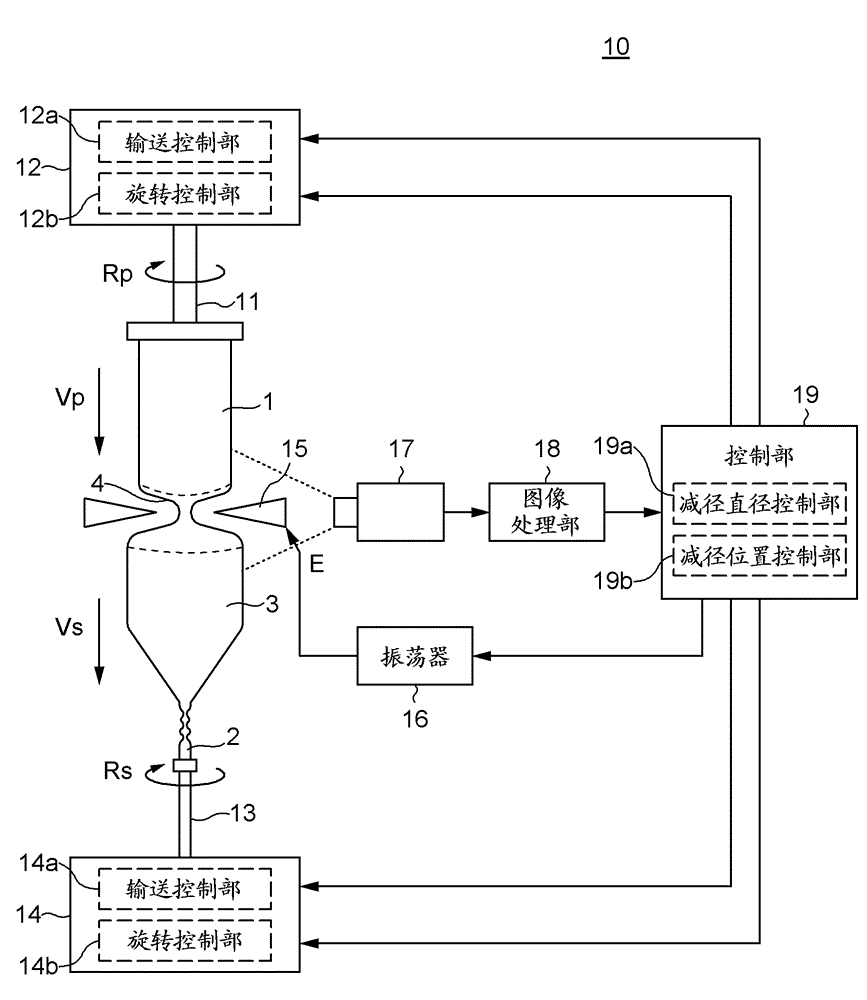
ActiveCN105297131AReliable no misalignmentReduce the frequency of misalignmentPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsPower flowEngineering
The invention provides a single crystal manufacturing method and device. The single crystal manufacturing method using the floating zone method comprises a welding process: heating the front end part of a raw material rod and melting the front end part of a raw material rod, and welding the front end part of a raw material rod to a seed crystal of a crystal conveying mechanism; a reducing process, reducing the diameter of the single crystal in the mode for realizing non-mal-position; a cone part forming process: expanding the diameter and enabling the single crystal to grow; and a straight body part forming process: enabling the single crystal to grow with maintained diameter. The reducing process includes: a diameter reducing control process: operating the current supplied to an induction heating coil and performing PID control for the reduced diameter of the single crystal; and a reducing position control process: operating the descent rate of the single crystal so as to perform PID control for the reducing position of the single crystal. Therefore, the reducing process automation can be realized and the mal-location generation frequency of the single crystal can be reduced after transferring to the cone part forming process.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
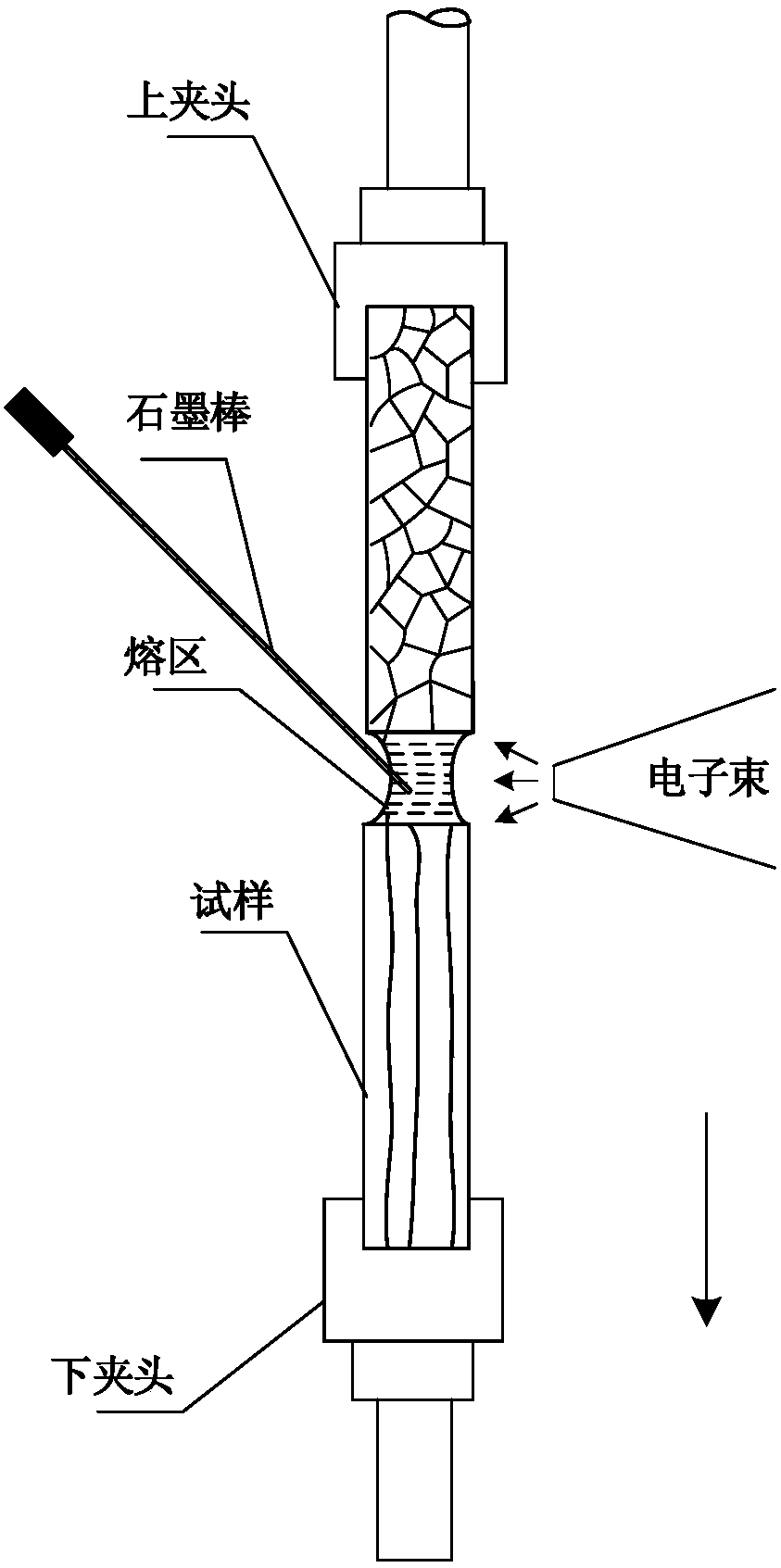
Electron beam zone melting furnace and method for carrying out float zone purification on material
ActiveCN103882509AQuick changeSatisfy purificationPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsElectrical resistance and conductanceZone melting
The invention relates to an electron beam zone melting furnace and a method for carrying out float zone purification on a material. The electron beam zone melting furnace comprises a furnace body arranged on a work table, an annular electron gun arranged in the furnace body, and a material fixation device arranged in the furnace body, wherein the annular electron gun sleeves on the outer cycle of a material during melting, a refrigeration system, a vacuum unit and a rocker arm mechanism of a control panel are arranged, the material fixation device comprises a pair of rotatable rod material clamping heads fixed on the upper end and the lower end of the furnace body and capable of being adjusted up and down, an electron gun lifting system capable of driving the electron gun to move up and down during melting is further provided and at least comprises a set of screws respectively driven by a servomotor and a supporting and placing plate for the electron gun, the pair of the double screws are respectively arranged on both sides of the material during melting, and the supporting and placing plate for the electron gun is horizontally fixed on the pair of the double screws. According to the present invention, the melting furnace adopts the electron beam to carry out float zone purification on the material difficultly melting at a high temperature, such that the difficult problems that purification of the material difficultly melting at the high temperature, crystal production and the like can not be achieved only with the current resistance zone melting furnace and the sensing zone melting furnace are solved.
Owner:GRIMAT ENG INST CO LTD
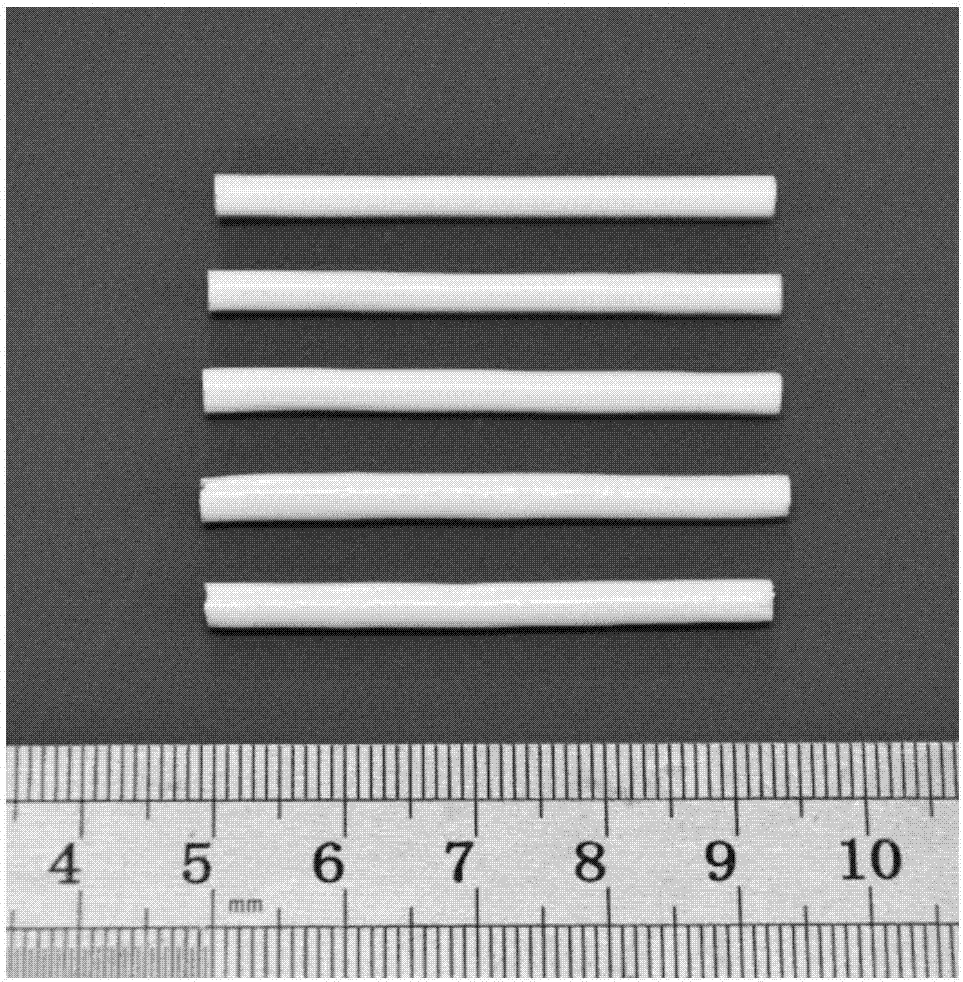
Preparation method of large-dimension multi-element rare earth boride (Ce0.9Pr0.1)B6 single crystal
InactiveCN102808215ALarge growth sizeQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsBorideDiffractometer
The invention discloses a preparation method of a multi-element rare earth boride (Ce0.9Pr0.1)B6 single crystal, and belongs to the technical field of rare earth boride hot cathode materials. At present, the research about the multi-element rare earth boride single crystal is little; further, the prepared single crystal is small in dimension and low in purity; and the requirement of actual application cannot be met. By using the preparation method, the high-quality and large-dimension multi-element rare earth boride (Ce0.9Pr0.1)B6 single crystal is prepared by adopting a method for combining discharge plasma sintering with floating zone melting. The (Ce0.9Pr0.1)B6 single crystal prepared by using CeB6 and PrB6 powder as raw materials is a phi4.5 mm*40 mm cylinder, and the test result of a single-crystal diffractometer shows that the single crystal is favorable in quality and a twin crystal phenomenon does not occur.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
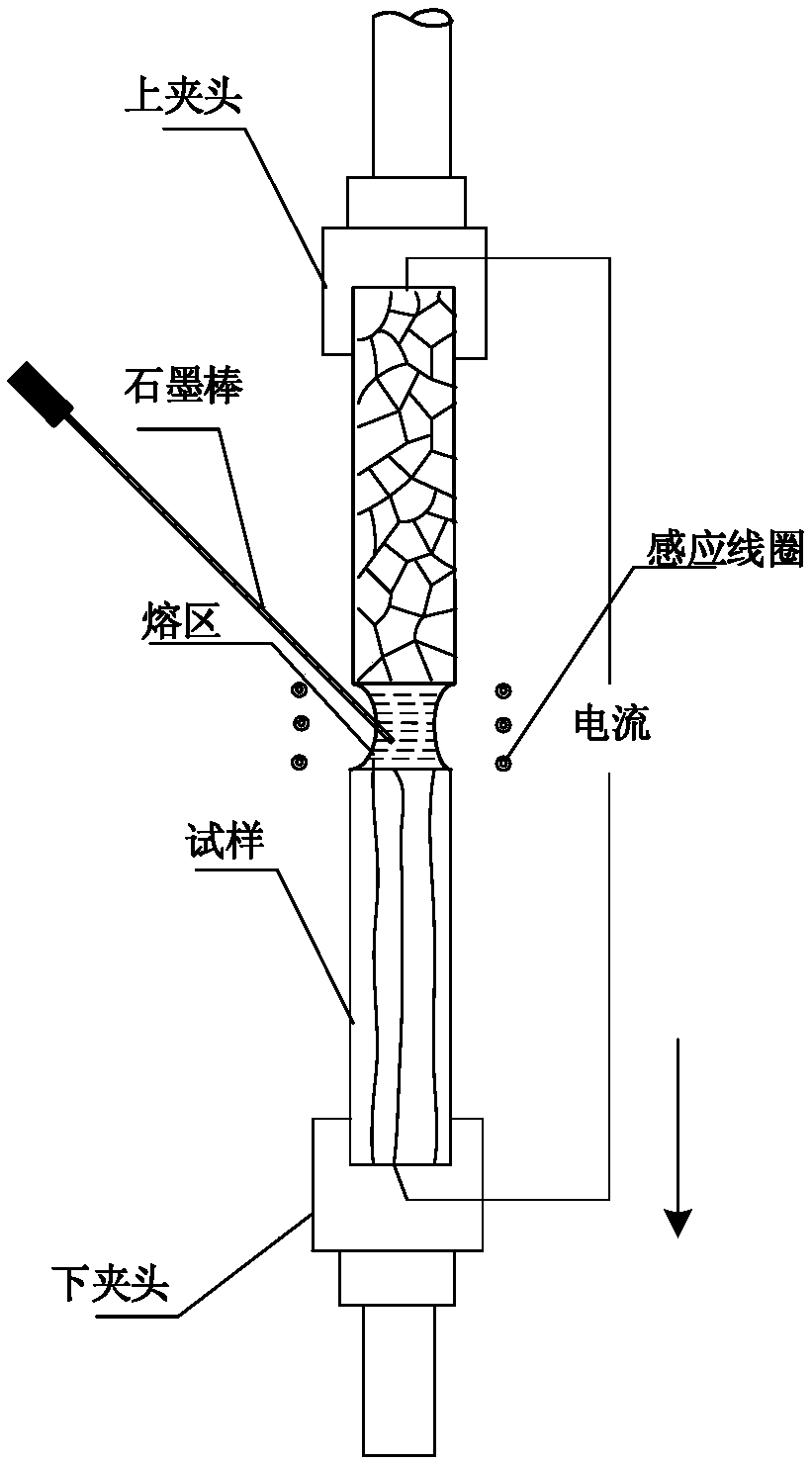
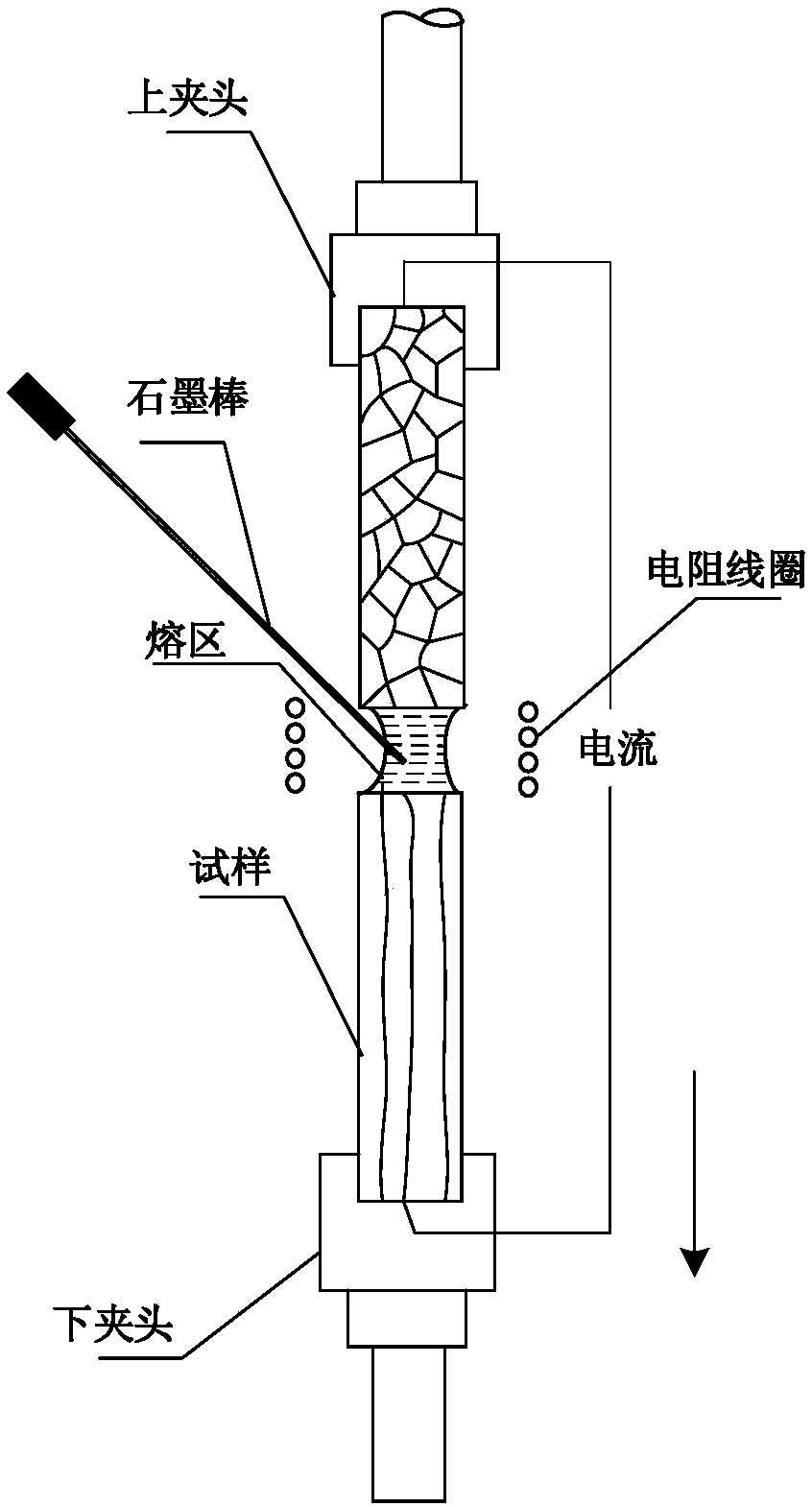
Graphene/metal composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a graphene / metal composite material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) weighing a metal rod and a high-purity carbon rod in percentage by mass, wherein the high-purity carbon rod accounts for 1%-30%; (2) clamping the cleaned metal rod on an upper chuck and a lower chuck of a withdrawing system of a directional solidification furnace adopting a floating zone method, clamping the high-purity carbon rod on a clamp beside the withdrawing system, and enabling the bottom end of the high-purity carbon rod to be in contact with amelting zone of the metal rod; and (3) performing vacuum-pumping on the directional solidification furnace adopting the floating zone method, performing directional solidification on the metal rod, controlling length of a melting zone to be 1-50 mm, moving the metal rod from top to bottom at a rate of 1-5000 [mu]m / s, and rotating along the axis of the withdrawing system; and enabling the bottom end of the high-purity carbon rod to be within the melting zone of the metal rod all the time. According to the graphene / metal composite material obtained by the method disclosed by the invention, carbon exists in a metal lattice in the form of graphene, and the two-phase interface is good in combination, so that conductivity of the material is favorably improved.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Carbon-silicon-tungsten-yttrium lamellar structure high-niobium titanium-aluminum alloy and preparation method thereof
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Silicon single crystal produced by crucible-free float zone pulling
A silicon single crystal is produced by crucible-free float zone pulling, has a diameter of at least 200 mm over a length of at least 200 mm and is free of dislocations in the region of this length. A silicon wafer is separated from the silicon single crystal by a process for producing the silicon single crystal. The silicon single crystal is produced by crucible-free float zone pulling in a receptacle, in which an atmosphere of inert gas and nitrogen exerts a pressure of 1.5-2.2 bar, the atmosphere being continuously exchanged, with the volume of the receptacle being exchanged at least twice per hour. A flat coil with an external diameter of at least 220 mm is inserted in order to melt a stock ingot. The single crystal is pulled at a rate in a range from 1.4-2.2 mm / min and is periodically rotated through a sequence of rotation angles. The direction of rotation is changed, after each rotation, by a rotation angle belonging to the sequence, a change in the direction of rotating defining a turning point on the circumference of the single crystal, and at least one recurring pattern of turning points is formed, in which the turning points are distributed on straight lines which are oriented parallel to the z-axis and are uniformly spaced apart from one another.
Owner:SILTRONIC AG
Method of manufacturing field termination type insulated gate bipolar translator (IGBT) component in patching mode
InactiveCN103137474AReduce the chance of fragmentationHuge cost savingsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIon implantationMetal
The invention discloses a method of manufacturing a field termination type insulated gate bipolar translator (IGBT) component in a patching mode. The method comprises the steps of selecting a first silicon base and a second silicon base of floating zone single crystal silicon, thinning the thickness of the first silicon base, and forming an n-shaped heavy doping field blocking-up zone on the front surface of the second silicon base through ion injection and annealing technology; integrating the back face of the first silicon base and the front face of the second silicon base through bonding technology; manufacturing a front face structure of the IGBT component on the front face of the first silicon base until depositing front face metal as an emission electrode; and thinning the second silicon base from the back face, and depositing the back face metal as a collector. The method of manufacturing the IGBT component in the patching mode does not need production technology for extremely thin slices with thickness less than 70 nanometers, thereby effectively reducing the slice breaking rate of slice technology, and saving enormous cost of purchasing new machines and equipment.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Method for growing large size Ta2O5 single crystal by using floating zone method
ActiveCN102312293AProcess advantagesNo macro defectsPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsRoom temperatureCrystal growth rate
The invention relates to a method for growing a large size Ta2O5 single crystal by using a floating zone method, and belongs to the field of crystal growth. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out ball milling and drying for a Ta2O5 powder material; placing the treated Ta2O5 powder material in a rubber tube, and carrying out isostatic pressing for the material to prepare a biscuit rod; carrying out sintering for the biscuit rod to obtain a polycrystalline rod; adopting the biscuit rod or the polycrystalline rod as the material rod, and adopting the polycrystalline or the Ta2O5 single crystal as the seed crystal, wherein the seed crystal and the material rod form a straight line in a vertical direction, and the contact point and a halogen lamp are at the same horizontal line; heating the material rod and the seed crystal until the material rod and the seed crystal are molten, wherein the heating rate is 30-60 DEG C per minute; adjusting the rotation speeds and the rotation directions of the material rod and the seed crystal, then carrying out inoculation; adopting the movement of a focusing lens or the up and down movement of the rod to enable the molten zone to be far away from the focusing point, enable the temperature of the molten zone to be decreased to realize the crystallization, wherein the crystal growth rate is 10-60 mm / h; cooling the grown crystal to the room temperature. With the method provided by the present invention, the growth period is short; the preparation efficiency is high; the Ta2O5 single crystal can be rapidly grown, wherein the grownTa2O5 single crystal has characteristics of size in centimeter magnitude, no macroscopic defect and high quality.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for producing gas phase heavy phosphorus-doped float zone silicon single crystal
ActiveCN101979719AAvoid problems that damage coilsSolve the ignition problemPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsChemical reactionGas phase
The invention relates to a method for producing a gas phase heavy phosphorus-doped float zone silicon single crystal. The method comprises float zone gas phase heavily doping and crystal pulling processes. In the process, a water-cooled electromagnetic copper coil with double waterways is adopted so that the temperature of the coil can be controlled between 10 and 20 DEG C; therefore, the coil is prevented from being damaged by a chemical reaction of phosphorus and the copper coil at a high temperature; and simultaneously the problem of a coil spark caused by thermal ionization of phosphorus impurities near the coil is solved. The gas phase heavy phosphorus-doped float zone silicon single crystal produced by the method has the characteristics of: oxygen content below 1ppm, axial resistivity uniformity of within + / -10 percent and resistivity of 0.002 Ohm.cm, well meets the strict requirement of a transient voltage suppressor (TVS) on a silicon substrate material, and meets the requirement of a TVS device on the silicon substrate material.
Owner:ZHONGHUAN ADVANCED SEMICON MATERIALS CO LTD +1
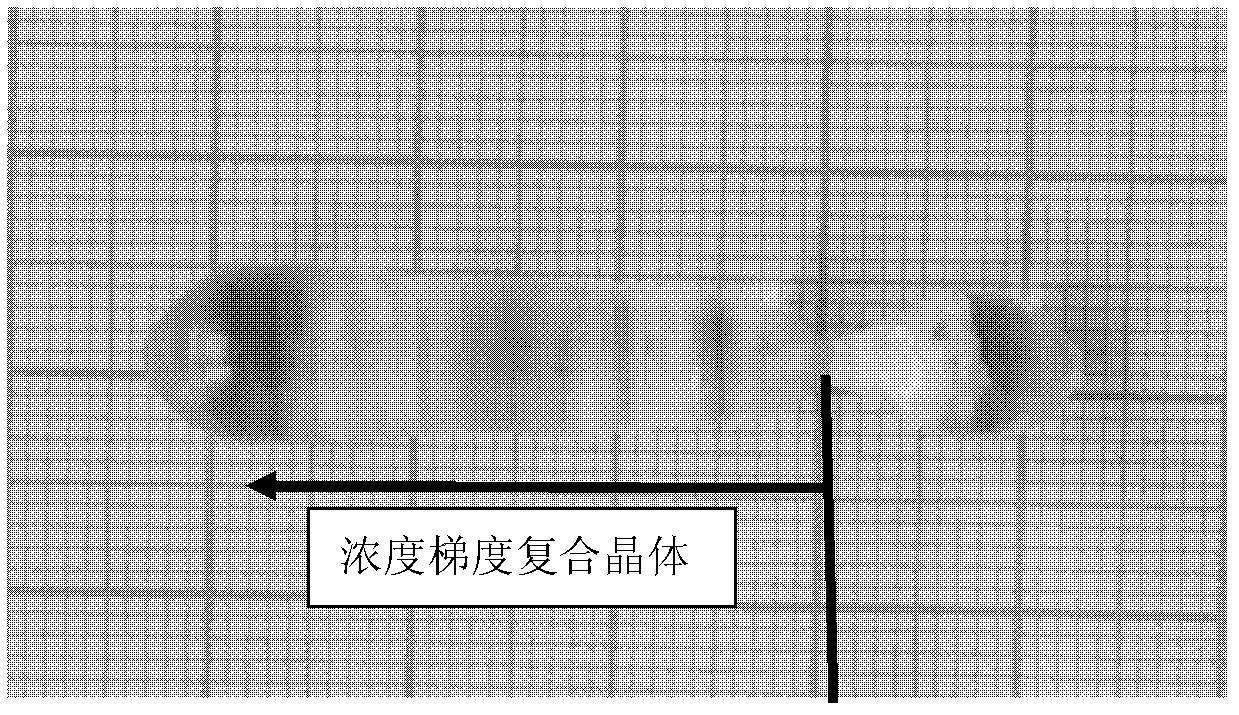
Garnet composite crystal with multi-segment doping concentration gradient and growing method thereof
ActiveCN102534790AHigh transparencyReduce crackingPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsCrystallographyConcentration gradient
The invention relates to a garnet composite crystal with a multi-segment doping concentration gradient and a growing method thereof. The garnet composite crystal has the following structural general formula: (Lnx1Re1-x1) 3B2C3O12 / (Lnx2Re1-x2) 3B2C3O12 / (Lnx3Re1-x3) 3B2C3O12 / ... / (LnxnRe1-xn) 3B2C3O12, wherein Ln is equal to Nd or Yb or Tm or Ho, x1 is more than 0 and less than 1, x2 is more than 0 and less than 1, x3 is more than 0 and less than 1, xn is more than 0 and less than 1, and n is more than 3; Re is equal to Lu, Y or Gd; B is equal to Sc, Al or Ga; and C is equal to Al or Ga; and the garnet composite crystal has a garnet structure. The growing method comprises the following steps of: making the composite crystal grow by an optical float-zone method; proportioning the raw materials according to chemometry in the general formula; preparing polycrystal charge bars according to the predesigned segments and length; and loading the polycrystal charge bars into an optical float-zone furnace for growing. The method has the advantages of high speed, short cycle, no crucible in the process crystal growth, less pollution on crystals, obvious gradient concentration segments and relatively simple process. The growing crystals have high transparency and few cracks and are suitable for growing of the garnet composite crystals with the concentration gradients.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
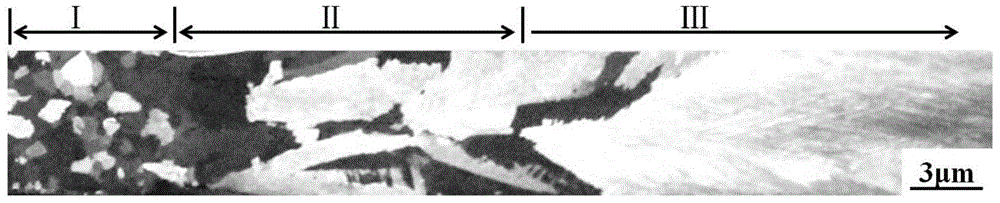
Preparation method of oxidecocrystal structureceramic powder
The invention discloses a preparation method of oxideeutecticstructureceramic powder. The method comprises the following steps: preparing an eutecticmaterial with fine and uniform tissue through a laser floating zone melting technology, then preserving a microcosmiceutectic structure with strong interface bonding into eutectic powder through crushing and screening, and further preparing eutectic powder with certain particle size distribution, thereby effectively reserving an eutecticstructure in an initial eutectic sample into a sinteredeutectic crystalthrough reasonable collocation of lamellar spaces and eutectic powder particle size of the initial eutectic sample. Theoxideeutecticstructureceramic powder is in a typicaleutectic morphology; eutecticmaterials with different lamellar spaces are obtained by changing the withdrawal rate during a laser floating zone melting process; eutectic powder with differentparticle size distribution is obtained through the combination of the withdrawal rate and ball milling time.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com