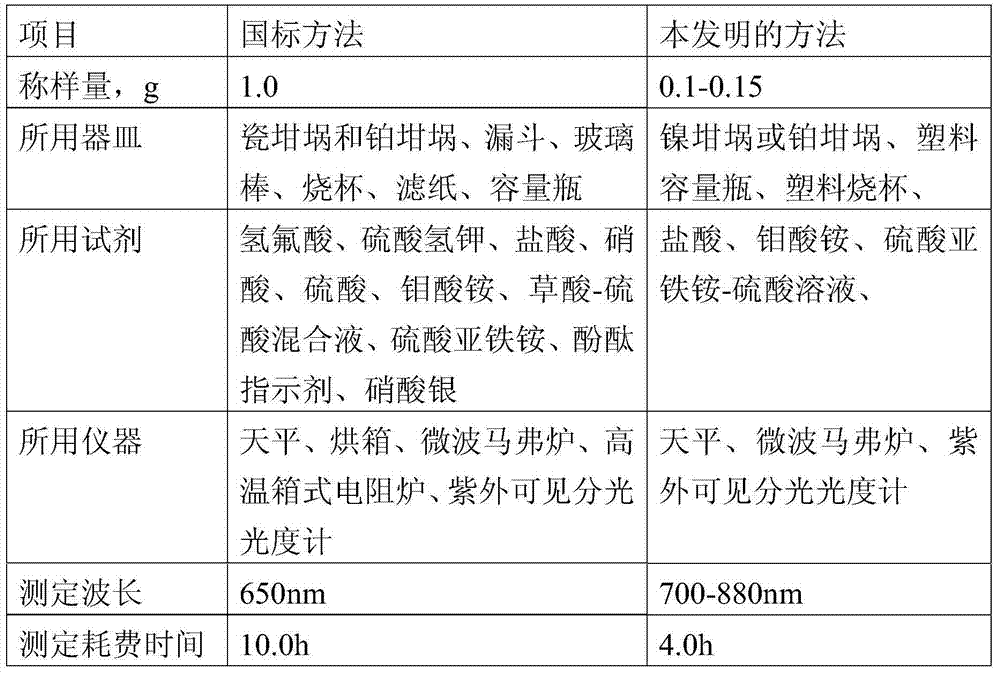
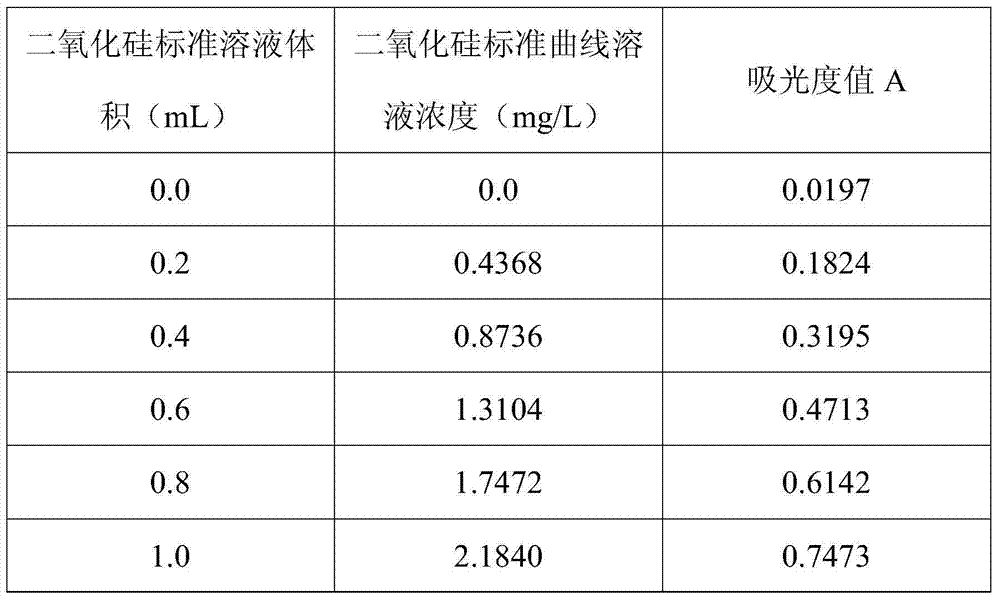
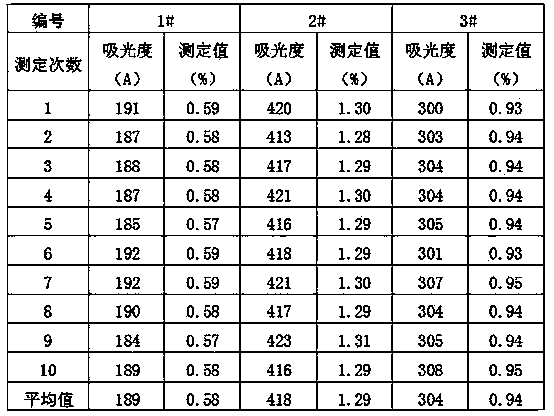
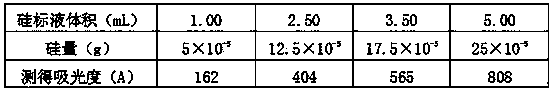
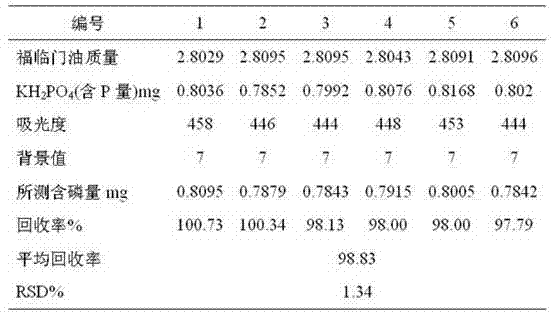
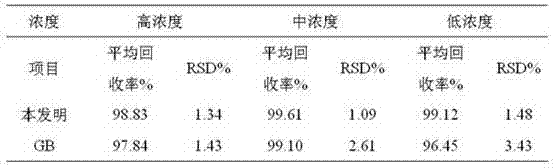
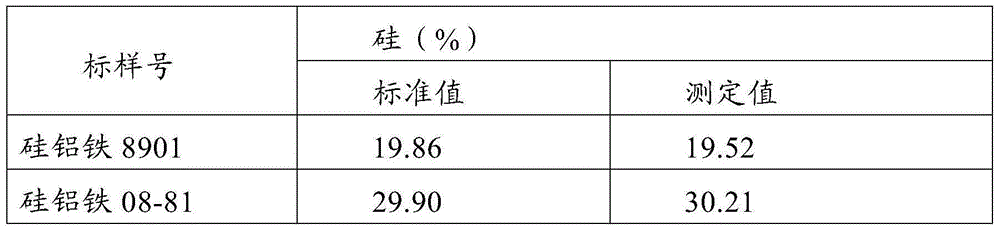
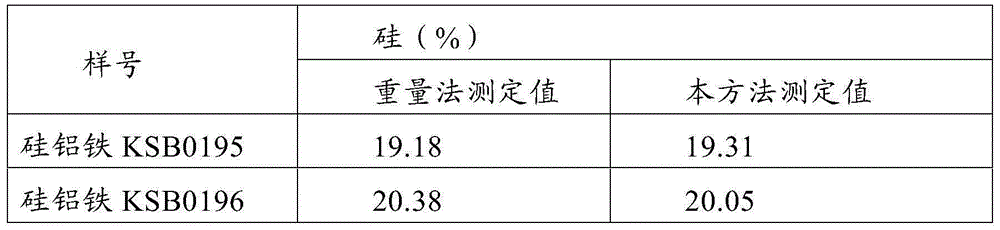
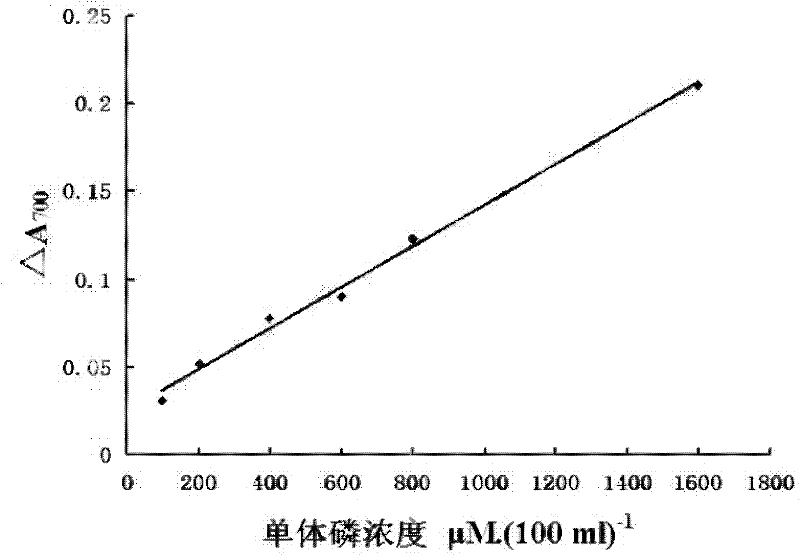
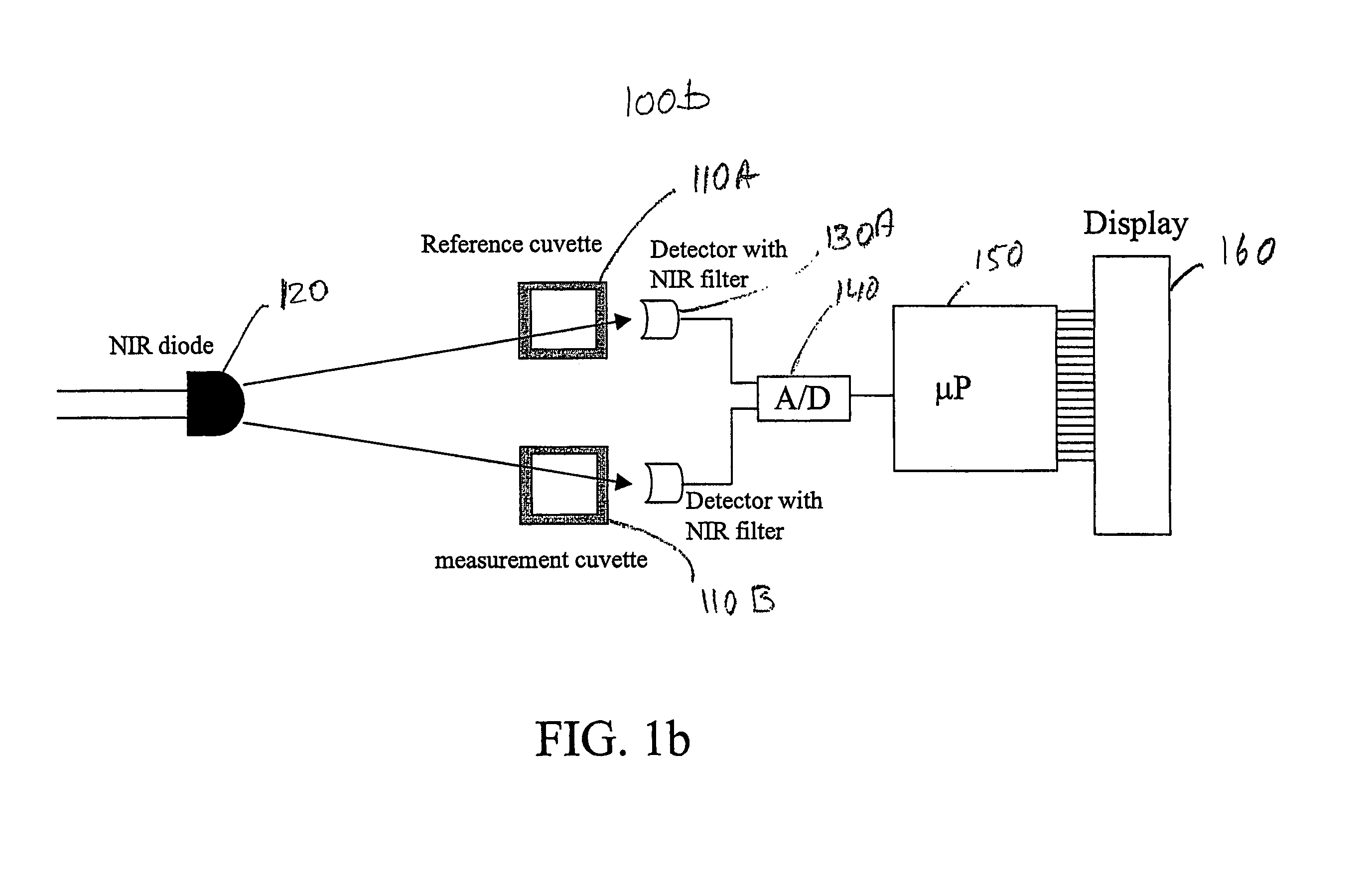
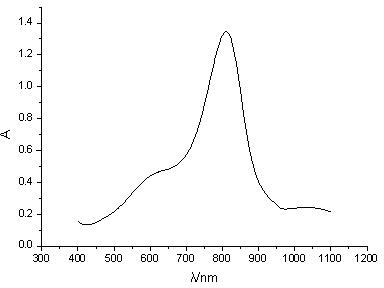
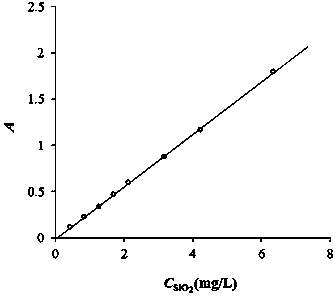
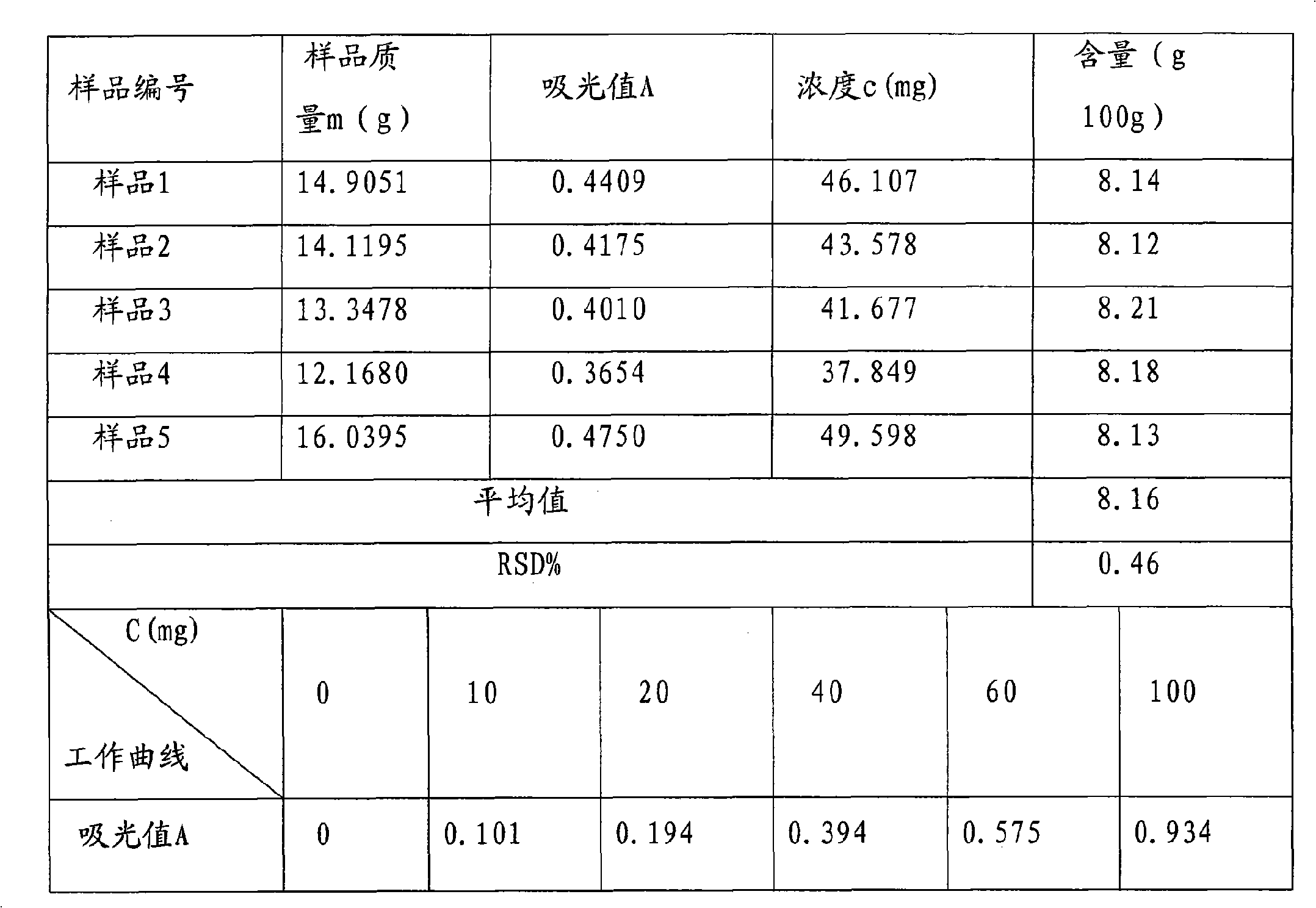
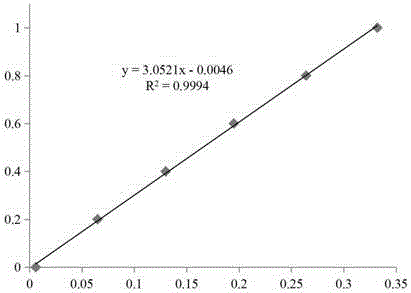
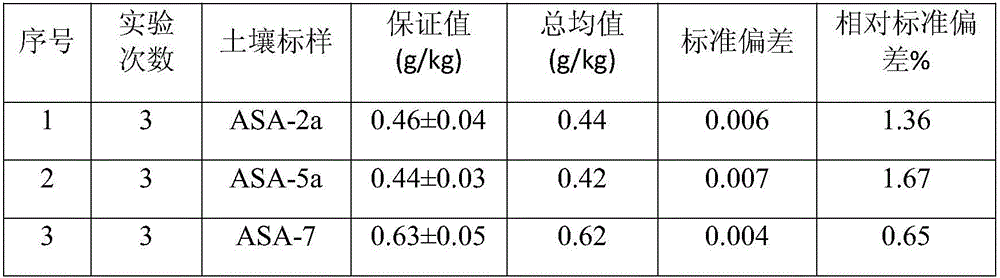
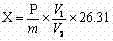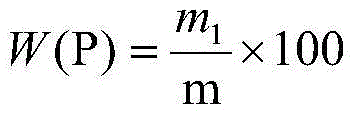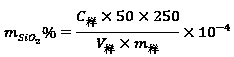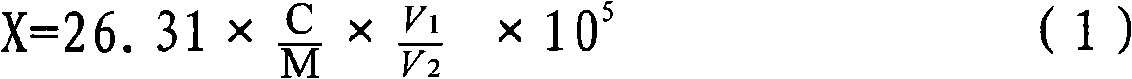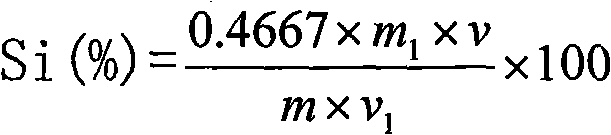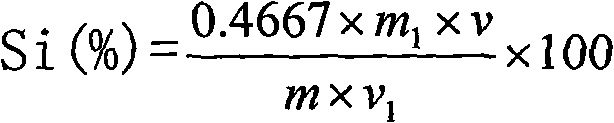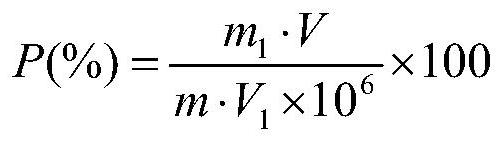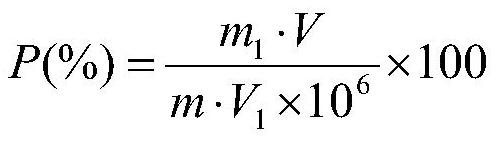Patents
Literature
75 results about "Molybdenum blue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The "heteropoly-molybdenum blues", are used extensively in analytical chemistry and as catalysts. The formation of "isopoly-molybdenum blues" which are intense blue has been used as a sensitive test for reducing reagents. They have recently been shown to contain very large anionic species based on the so-called "big wheel" containing 154 Mo atoms, with a formula [Mo₁₅₄O₄₆₂H₁₄(H₂O)₇₀]¹⁴⁻.
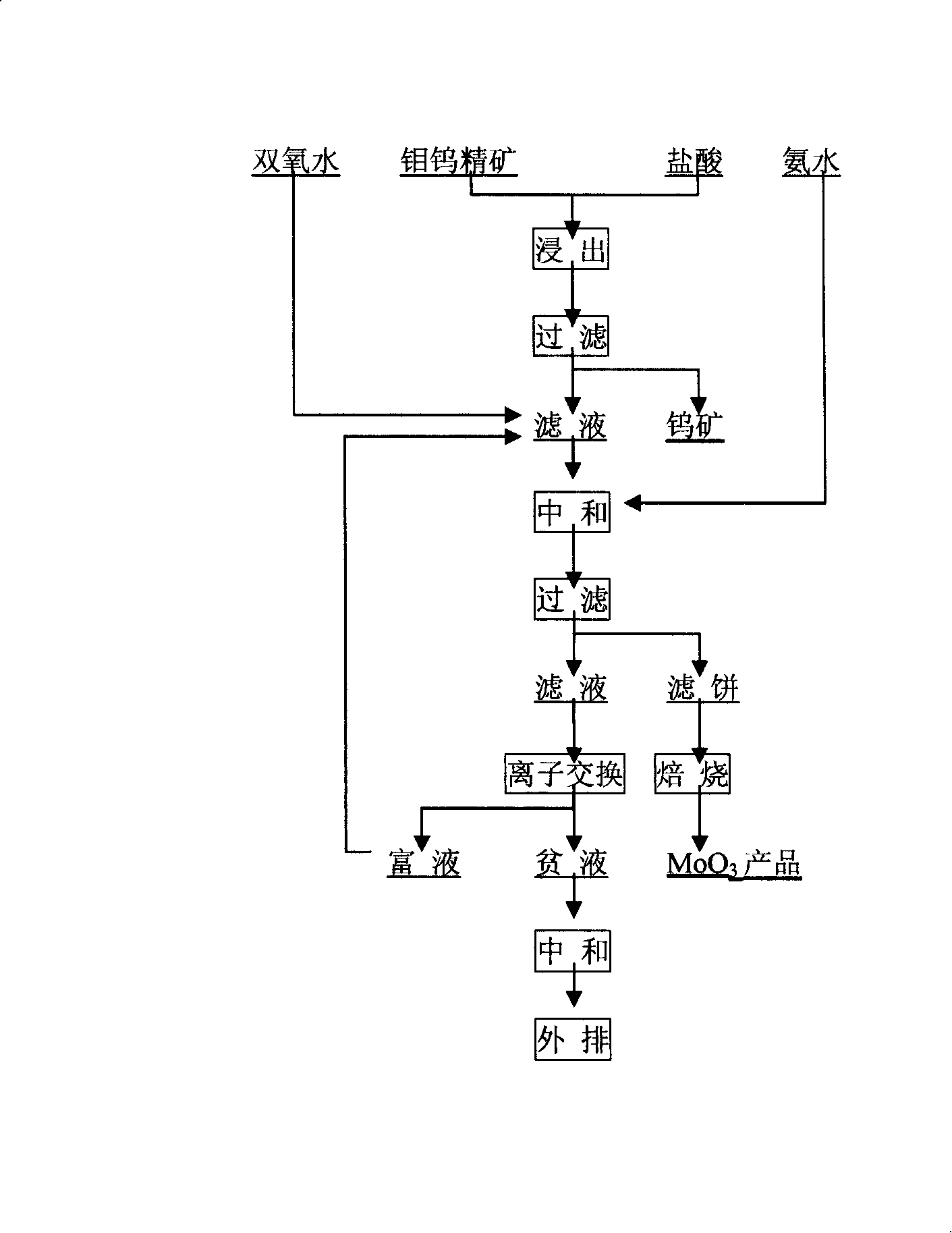
Metallurgical extraction method for molybdenum-tungsten oxide bulk concentrate
InactiveCN101225481AHigh recovery rateSimple processProcess efficiency improvementSolubilityMolybdenum blue
The invention discloses a metallurgic extraction method of molybdenum-tungsten oxide ore and bulk concentrate; wherein, the craft adopts molybdenum-tungsten oxide ore as material; the molybdenum-tungsten oxide is leached by acid and filtered; the filter residue is rough concentrate comprising tungsten; a quantitative oxidant is put into the filtrate; the molybdenum blue is oxidized to high valence molybdenum; the neutralization and sedimentation is processed; the precipitate is filtered, dried, and roasted; the molybdenum oxide which comprises molybdenum above 50% is generated. The metallurgic extraction method of molybdenum-tungsten oxide ore and bulk concentrate has the advantages of (1) high recovery rate, simple working procedure, a small quantity of steps, keeping the total recovery rate of molybdenum between 85% and 95%, (2) preliminarily realizing the separation of molybdenum and tungsten, keeping the molybdenum trioxide product comprise tungsten below 0.75% and keeping the leaching residue comprise molybdenum below 0.7% because of the large solubility difference of molybdenum and tungsten in the acid, and realizing the separation of molybdenum and tungsten well.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU MINERALS COMPOSITIVE UTILIZATION RES INST CHINESE GEOLOGICAL ACAD +1
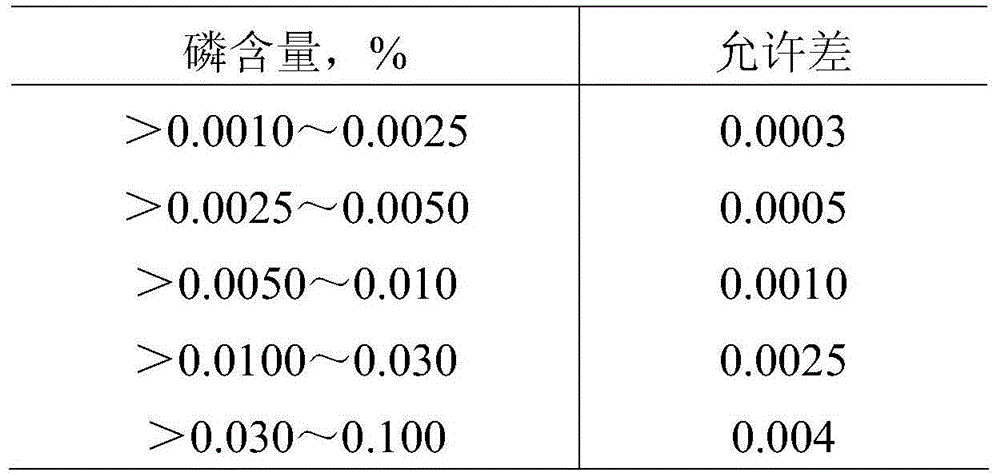
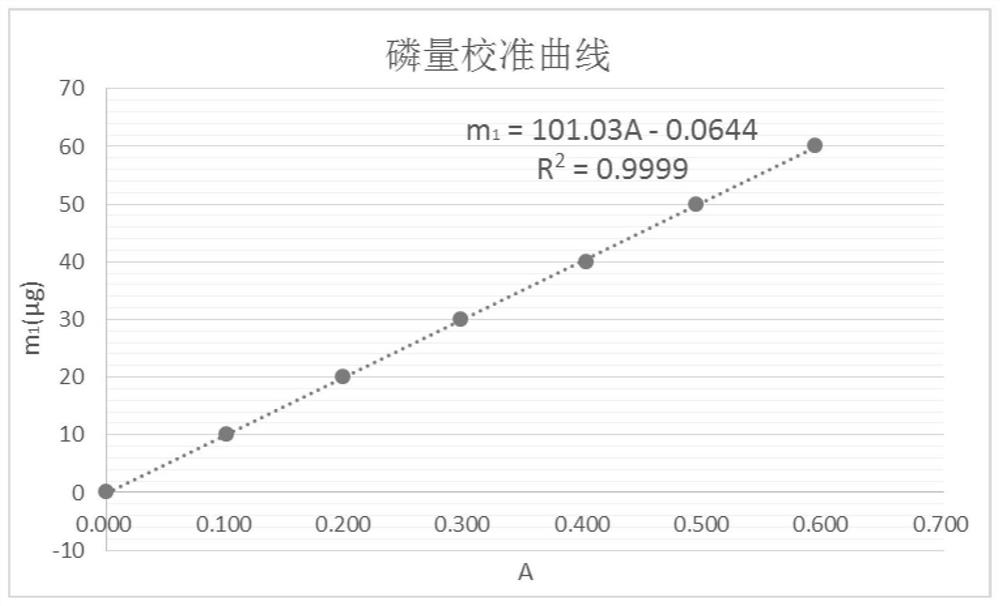
Method for measuring phosphorous content by adopting bismuth phosphomolybdate blue-sulfuric acid photometry
InactiveCN101788494ASolve the problem of drift instabilityAbsorbance unchangedMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationIronstoneAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a measurement method of the phosphorous content in an iron ore, in particular to a method for measuring the phosphorous content by adopting a bismuth phosphomolybdate blue-sulfuric acid photometry. The method comprises the following steps of: weighing 0.25g of sample and putting into a platinum crucible containing about 2g of mixed fusing agent, putting in a muffle furnace with the temperature of 100 DEG C, fusing for 10min and taking out; cleaning the exterior of the platinum crucible, then putting the platinum crucible into a beaker containing about 80ml of hot water, adding 320ml of concentrated HNO on an electric furnace, heating at low temperature and dissolving, leaching the crucible out, taking the beaker out, cooling, then transferring into a 250ml volumetric flask, diluting to a scale and shaking up for later use; sucking 25ml of mother solution of a fusing sample in the platinum crucible, putting into a 50ml volumetric flask, adding 2.5ml of bismuth nitrate solution, 5ml of ammonium molybdate solution, 3ml of 8mol / L sulfuric acid solution and 5ml of ascorbic acid solution (prepared when needed), shaking up, carrying out color comparison at 750nm wavelength, measuring an absorbance value, and carrying out result conversion by using a guide sample with similar ingredients. The invention effectively solves the problem of instable absorbance value in a method for measuring the phosphorous content by adopting a traditional molybdenum blue spectrophotometry and ensures that the absorbance remains unchanged within two hours.
Owner:迁安市津唐球墨铸管有限公司
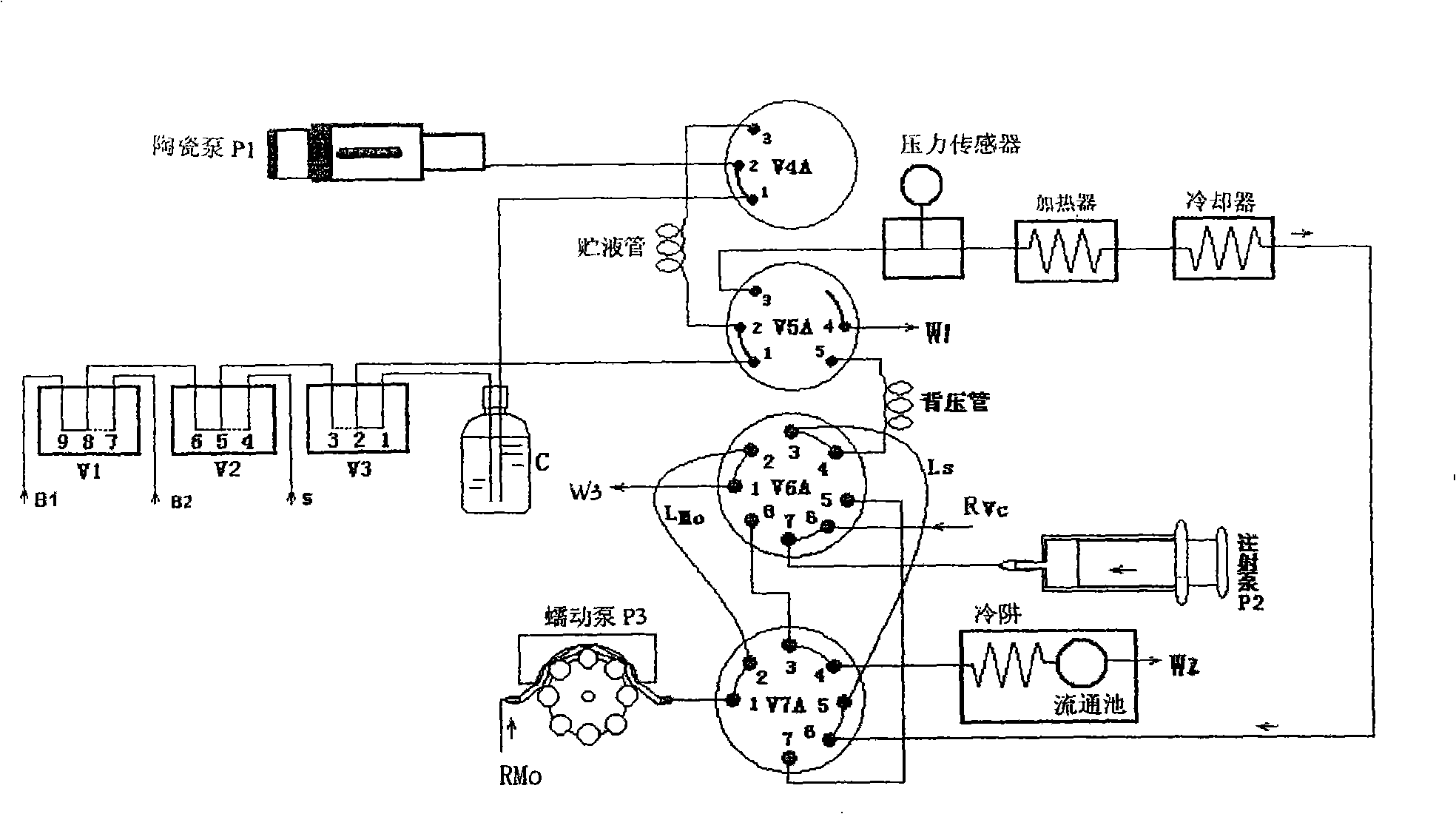
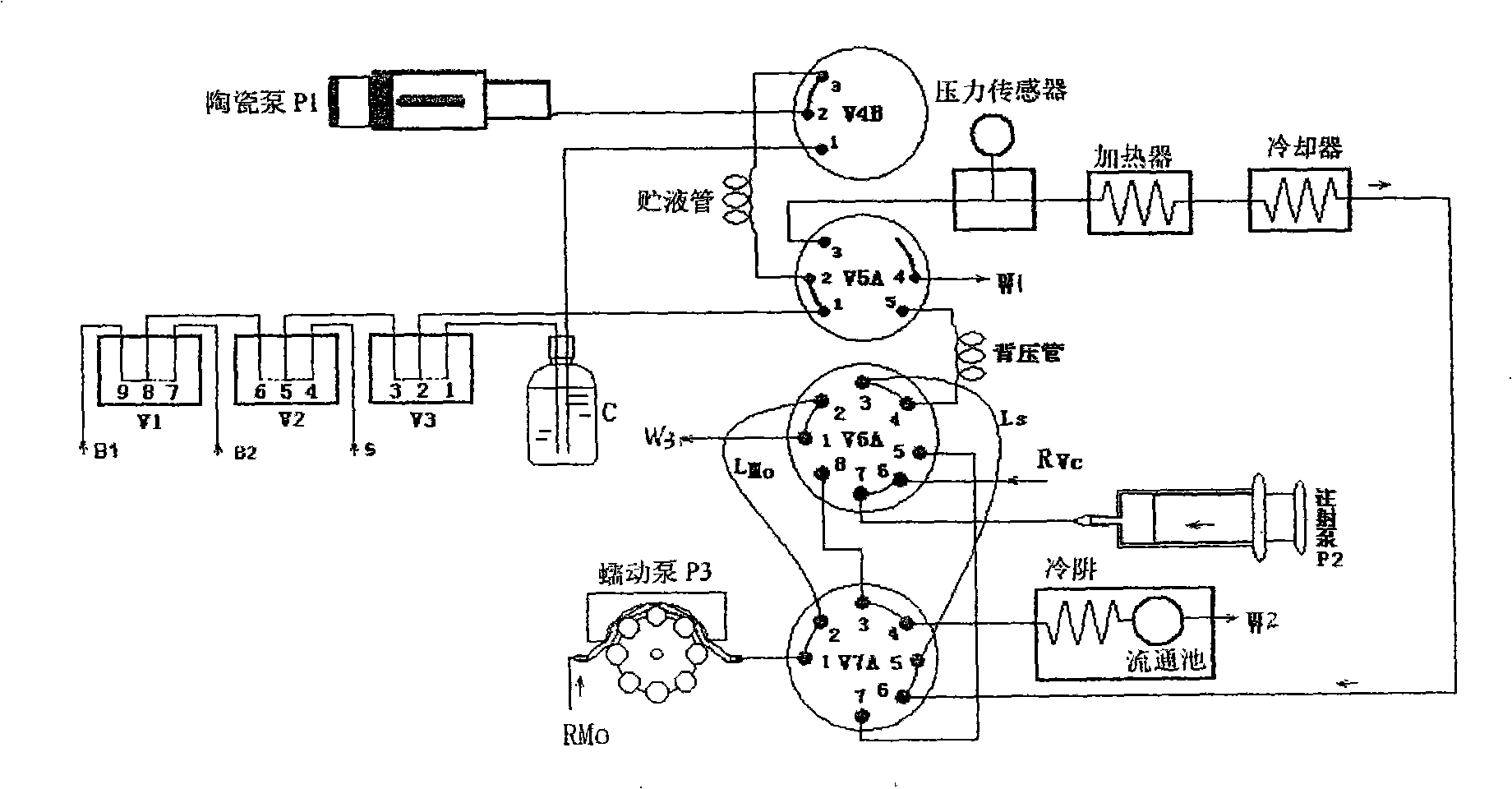
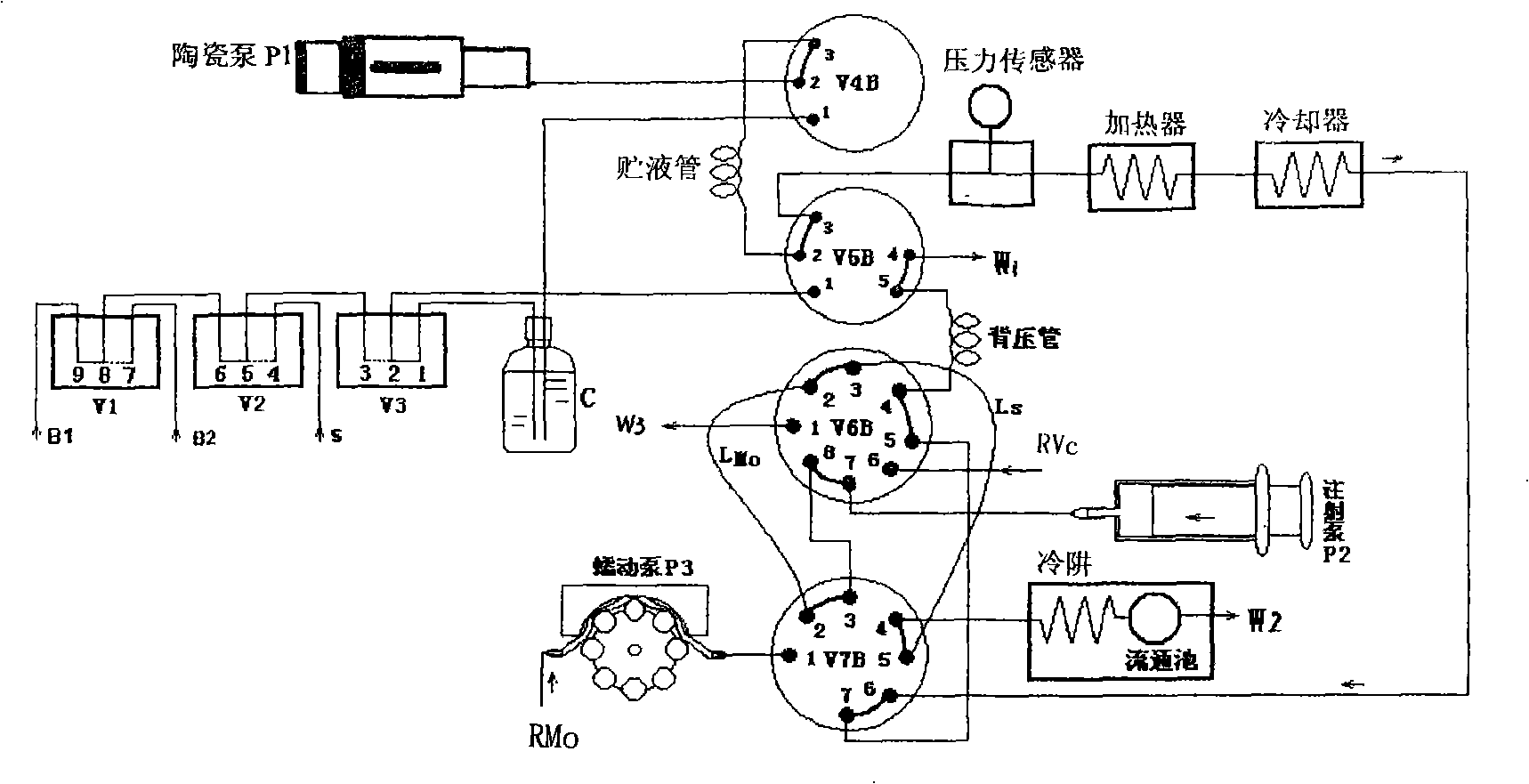
High pressure flow injection water quality total phosphorus analysis system
InactiveCN101320002AHigh boiling pointPrevent gasificationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPeristaltic pumpMolybdenum blue
The invention relates to a high pressure flow injection water quality total phosphorus analyzing system which comprises a heater, a cooler, a photoelectric circulation pool, a digestion agent storing bottle, a sample injection pump, a loading solution injection pump and a chromogenic reagent peristaltic pump which are connected into a system through capillary pipes and a plurality of conversion valves. A solution storing pipe, a quantitative ring and a prolonged back press pipe are connected among the valves. The flowing ways of the system are changed through the conversion of the valves. With the flowing injection way adopted y the system, the steps of molybdenum blue spectrophotometric method for determining phosphorus of water samples and various reagents are automatically and orderly finished in the continuously flowing system. The system has the advantages of simple structure, rapid determination process, convenient operation, accurate quantity, bubble interfere-free performance and high detection precision and is especially applied to the online analyzing total phosphorus in surface water, wastewater and industrial wastewater, thereby realizing the online monitoring on the content of water phosphorus.
Owner:DELIN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Combined determination method for main components in high-carbon ferrochrome slag
InactiveCN104897661AReduce preprocessingTime consumingMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationDecompositionMolybdenum blue
A combined determination method for main components in high-carbon ferrochrome slag. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of: melting a high-carbon ferrochrome sample by a iron crucible; carrying out high-temperature melting decomposition by sodium peroxide; leaching in a 250ml plastic cup filled with water; acidifying and clarifying with sulfuric acid; placing at room temperature to obtain a high-carbon ferrochrome sample mother liquor; conducting constant volume analysis on the high-carbon ferrochrome mother liquor; decomposing the sample at one time; and respectively measuring the chemical composition of SiO2, Al2O3, MgO, CaO and Cr2O3 by 1) determination of Cr2O3 by potassium permanganate oxidation and ammonium ferrous sulfate titration method, 2) determination of SiO2 by a silicon molybdenum blue spectrophotometric method, and 3) determination of Al2O3, MgO and CaO by an EDTA volumetric method. The method greatly reduces the analysis time (determination of SiO2, Al2O3, MgO, CaO and Cr2O3 within four hours), while omits weighing and analysis of Al2O3 by a nickel crucible, and saves a lot of cost analysis.
Owner:HENAN AOXIN ALLOY
Tea-leaf safety quick detection method
ActiveCN101614671AHigh sensitivityGood correlationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationOrganic solventMolybdenum blue
The invention relates to a tea-leaf safety quick detection method, which mainly comprises that: after organophosphorus pesticide and organochlorine pesticide of tea-leaf are extracted by organic solvent, an organic phase is added with an oxidizing and degrading agent and a catalytic auxiliary, and is directly subjected to degradation for a certain period in the ultrasonic condition; inorganic degraded products in the organic phase are extracted; the content of the inorganics is detected by methods such as phospho-molybdenum blue and the like; and the content of organic pesticide components in a sample is calculated according to average proportion; therefore, the method realizes quick extraction and detection, avoids fussy operation such as heating, digestion, solvent volatilization and the like, and does not need expensive equipment such as a chromatograph and the like.
Owner:厦门斯坦道生物科技有限公司
Preparation and application of molybdenum blue micro-tube based on Keggin type silicotungstate
InactiveCN102230220AImprove performancePolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsChemical synthesisMolybdenum blue
The invention belongs to the field of chemical synthetic materials, and specifically relates to preparation and application of molybdenum blue micro-tubes based on Keggin type silicotungstate. In the invention, stable Mo-substituted Keggin type silicotungstate molybdenum blue micro-tubes are prepared from metastable nonsaturated alpha-Keggin heteropolyacid salts by utilizing high redox potential of Mo. According to the invention, the limitation that only saturated tungsten polyoxometallates and molybdenum polyoxometallates are used in the prior art is broken; Keggin type heteropolytungstate micro-tubes comprising different components are assembled through regulation and control of counter cations, and other metal-substituted Keggin type heteropolytungstate micro-tubes with excellent performance are obtained by changing composition of anions of heteropolyoxometallates. Noble metal nanoparticles are immobilized in situ by utilizing stable reducibility of the molybdenum blue micro-tubes.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for determining content of silicon dioxide in rubber through spectrophotometer
InactiveCN103674868AWide measurement rangeSmall amount of sampleColor/spectral properties measurementsAmmonium ferrous sulfateMolybdenum blue
The invention relates to a method for determining the content of silicon dioxide in rubber through a spectrophotometer. The method comprises the steps as follows: subjecting a rubber sample to ashing treatment; adding potassium hydroxide into the ashed sample for treatment so as to convert silicon in the sample into soluble silicate; then reacting a silicon-containing solution with ammonium molybdate in a hydrochloric acid medium; then using ammonium ferrous sulfate for reducing a reaction product in the last step to silicon molybdenum blue, and measuring the absorbance of the silicon molybdenum blue in a position with a set wavelength of 700-880 nm. The method is applied to all rubber except silicon-containing rubber.
Owner:BEIJING RED AVENUE INNOVA
Arsenic meter
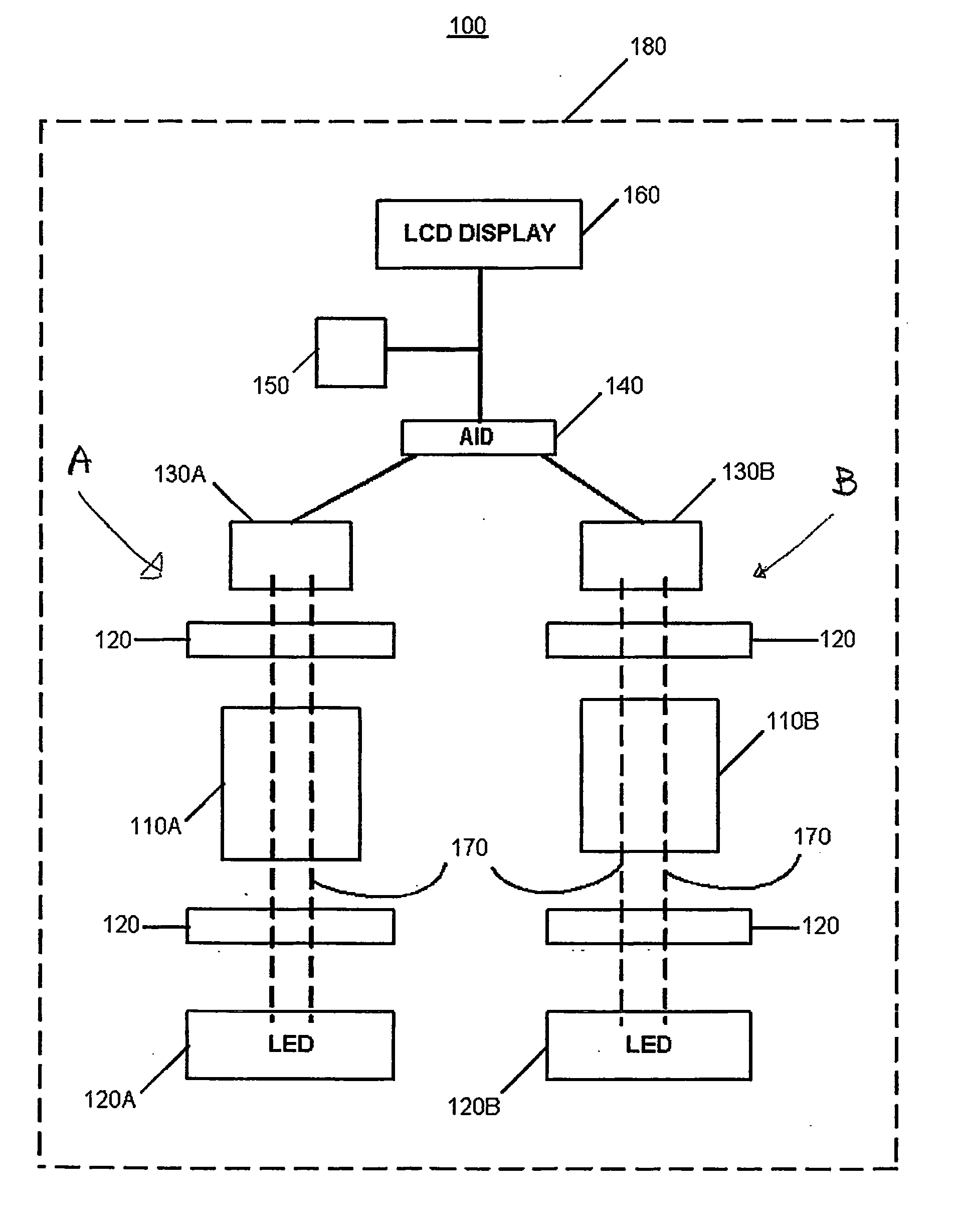
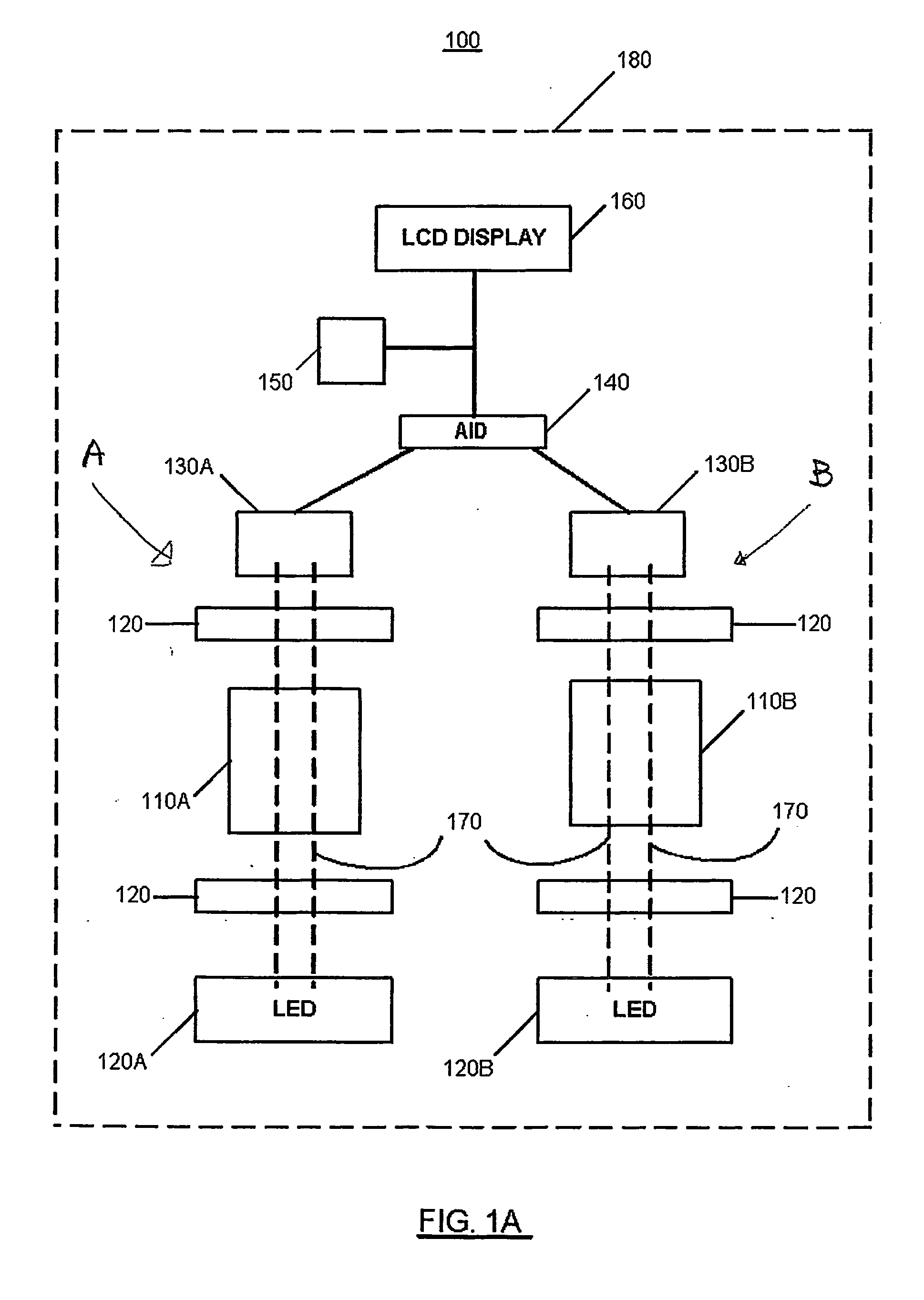
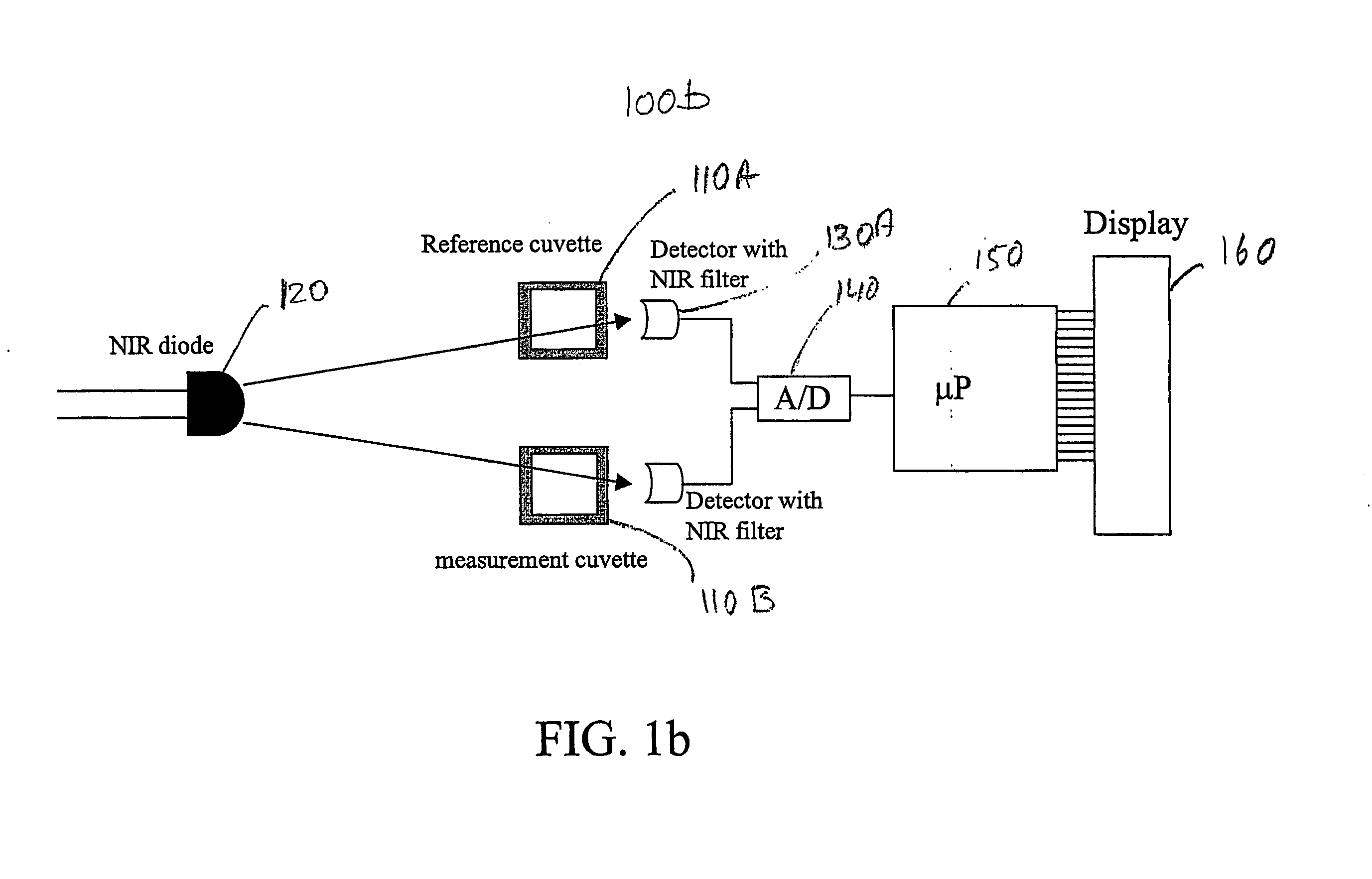
InactiveUS20060007445A1Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMolybdenum blueField tests
A field test-kit for analyzing arsenic concentration in water samples is provided. The kit includes a portable infrared beam photometer for measuring light absorbance in aqueous specimens. An infrared light emitting diode is configured to direct a beam of light through a specimen. A photodetector diode measures the intensity of light passing through the specimen. The photodetector output voltages relate to the light absorbed in the specimen and are displayed on a liquid crystal display screen. The kit is assembled using off-the-shelf electronic and opto-electronic components that have low power requirements. Dry cell batteries or solar cells power the kit. To test for arsenic, molybdenum based chemistries are used to selectively bind and convert arsenates and phosphates in the specimen into molybdenum-blue color complexes. The light absorbance of a specimen with both arsenates and phosphates bound in molybdenum-blue color complexes is compared to that of a reference specimen in which phosphates but not arsenates are bound and converted. The differential light absorbance of the two specimens is used to arrive at a quantitative value for the arsenic concentration in the water sample.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Method for measuring content of silicon in ferromanganese
InactiveCN104237146AImprove accuracyGood precisionPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsWater bathsHeteropoly acid
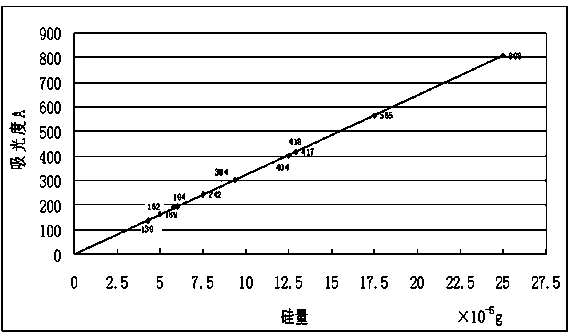
The invention discloses a method for measuring content of silicon in ferromanganese. A standard curve method is adopted, and the measuring method comprises the following steps: heating and dissolving a sample in a water bath by adopting nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid, adding carbamide to decompose and destroy interference of nitrogen oxides, complexing excessive fluorinion by using saturated boric acid, and allowing silicic acid and molybdic acid to yellow silicon molybdenum heteropoly acid under the acidity that c(H<+>) is equal to 0.1-0.6mol / L; adding a sulphosate mixed acid to eliminate interference of phosphorus and arsenic, reducing silicon molybdenum yellow into silicon molybdenum blue by using ascorbic acid, and finally measuring the absorbance. According to the method, after the ferromanganese is dissolved, the interference is eliminated by utilizing various reagents, the silicon is generated into silicon molybdenum blue, the corresponding absorbance is measured, and the content of silicon is obtained. The experiment proves that the method is easy, convenient and rapid to operate, the measured silicon content result is high in accuracy and high in precision, and measurement of silicon in high / medium / low-carbon ferromanganese can be met. The method does not need precious instruments or reagents and has the characteristics of low analysis cost, accuracy and practicality.
Owner:TANGSHAN STAINLESS STEEL
Method for measuring phospholipid in lipid
InactiveCN102175672APrevent splashAvoid burnsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorLipid formationMolybdenum blue
The invention discloses a method for measuring phospholipid in lipid, and the method comprises the following steps: carbonizing, ashing and dissolving of lipid; and molybdenum blue colorimetry measurement of phosphorus, wherein the lipid is carbonized by adding concentrated sulphuric acid, and a hydroxide, a carbonate or a bicarbonate of an alkali metal. In the invention, the concentrated sulphuric acid is used for pre-carbonizing, and alkali is added for reacting, so that the carbonization of different amounts of various lipids can be completed within 15 minutes, splashing and combustion generated in a direct electric furnace heating carbonization procedure are prevented, and the carbonization time is shortened; the hydroxide, carbonate or bicarbonate of the alkali metal is used for displacing ZnO, so that the soluble phosphate with higher thermal decomposition temperature is generated, and the ashing time is shortened; and the ashed product can be dissolved and filtered directly, sothat the following operations are simpler and safer.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Method of determining silicon content in ferro-silico aluminum through silico-molybdenum blue colorimetric method
InactiveCN105223146AReduce operating proceduresReduce manpower expenditureColor/spectral properties measurementsMolybdenum blueVolumetric flask
The invention discloses a method of measuring silicon content in ferro-silico-aluminum through a silico-molybdenum blue colorimetric method and aims at providing the method which is faster, more accurate and more efficient in determining silicon content in ferro-silico aluminum. According to the method, a sodium hydroxide solution is adopted to dissolve most test samples; next, diluted hydrochloric acid-nitric acid is added for dissolving remaining test samples; the test samples are heated, dissolved completely, cooled to room temperature and transferred to a volumetric flask; a certain amount of the solution is taken out and placed into another volumetric flask, ammonium molybdate is added to generate silico-molybdenum yellow, oxalic acid is added to cover interference elements, ammonium ferrous sulfate is added to generate silico-molybdenum blue, and the absorbance of the solution is determined through a spectrophotometer; conversion of the content value of the test samples is conducted through standard samples with similar content of the same variety as the test samples.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA BAOTOU STEEL UNION
A kind of myosin ATP enzyme activity micro-assay method and its application
InactiveCN102288601AOrganic active ingredientsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMyosinAssay
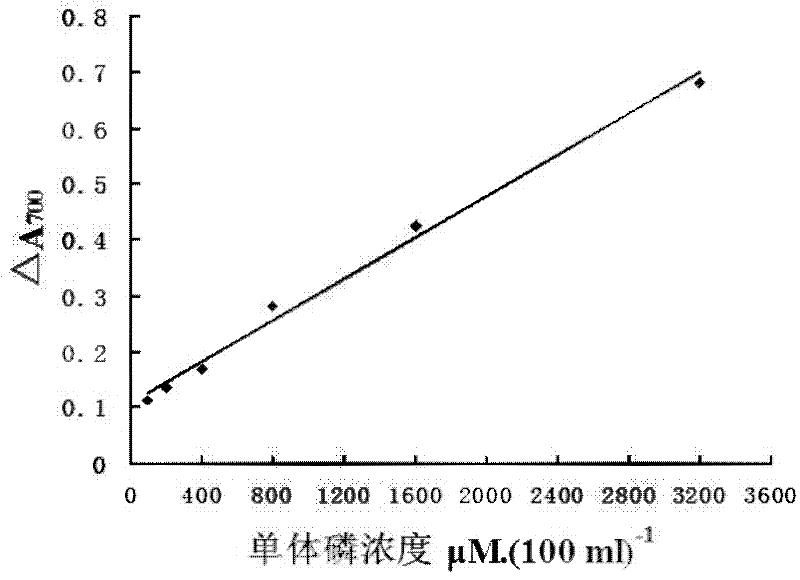
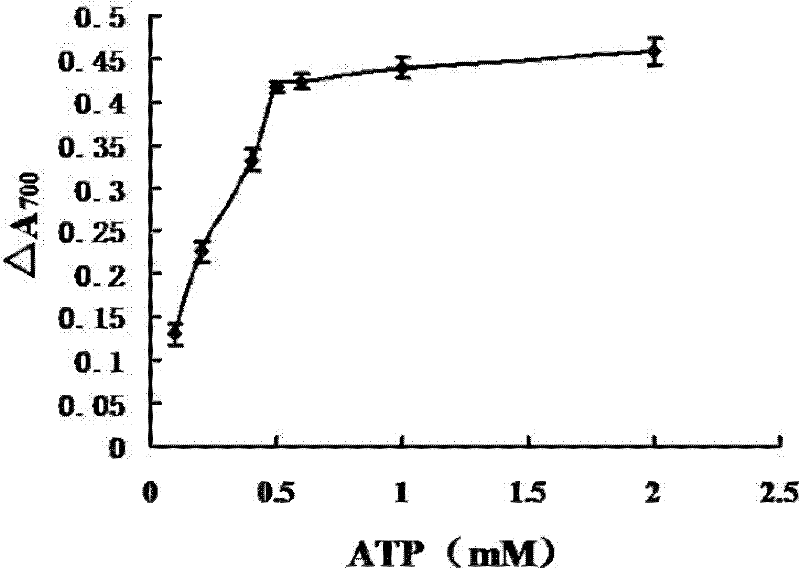
The invention relates to a method for the microdetermination of ATPase activity of myoglobulin, and the method is characterized in that based on the reaction method of a classic molybdenum blue method, the molar ratio of ATP (adenosine-triphosphate) to myoglobulin is controlled at 2000:1 and the molar ratio of ammonium molybdate to stannous chloride is controlled at 5.5:1. The determination method provided by the invention is simple, convenient, fast, high in response value and wide in linear range, and can be applied to the screening of inhibitors. The invention discloses an application of Ruscogenin in inhibiting the ATPase activity of the myoglobulin.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Method for measuring arsenic by iodine solution absorption method
InactiveCN101788495AReduce usageReduce pollutionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsHydrogenHydrazine compound
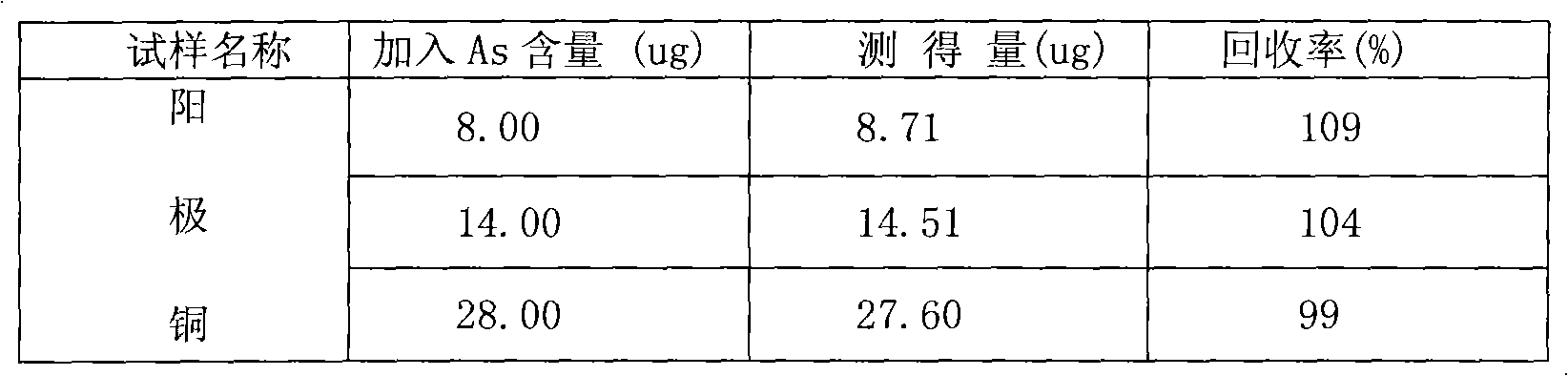
The invention discloses an accurate and reliable method for measuring arsenic by an iodine solution absorption method, which solves the problem that the traditional method produces poisonous waste liquor. In a H2SO4 medium greater than 3.6N, Zn reacts with an acid to produce nascent activated hydrogen; in the presence of KI and acidic SnCl2, As<5+> is reduced into As<3+>, and the trivalent arsenic reacts with the nascent activated hydrogen to produce hydrogen arsenide gas; and the hydrogen arsenide gas is absorbed by an iodine solution and is oxidized into quinquevalent arsenic. In a 0.25 equivalent sulfuric acid medium, the quinquevalent arsenic reacts with ammonium molybdate to produce yellow heteromolybdoarsenic acid. The heteromolybdoarsenic acid is reduced into arsenic molybdenum blue by hydrazine sulfatefor for colorimetric determination. The method for measuring arsenic by iodine solution absorption and the colorimetric determination of the arsenic molybdenum blue is more suitable for the analysis of As in raw materials for copper smelting and semi-finished products of matte anode copper; moreover, the use of poisonous and hazardous reagents is avoided, and environment pollution is reduced.
Owner:BAIYIN NONFERROUS GROUP
Determination method for content of phosphorus in niobium-containing steel
ActiveCN104089958AAccurate determination of phosphorus contentSimple and fast operationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMolybdenum blueSulfite salt
The invention provides a determination method for the content of phosphorus in niobium-containing steel. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out acidolysis on the niobium-containing steel; adding perchloric acid and heating until smoke is formed; adding hydrochloric acid and hydrogen bromide; heating again until the smoke is formed; adding a sodium chromate solution and a sodium sulfite solution in sequence, heating to boiling and then cooling; adding a sodium hydroxide solution and filtering to obtain a mother solution; taking the mother solution and adding perchloric acid until the mother solution is acidic; then adding a bismuth salt solution and an ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate mixed solution to generate a phosphorus-bismuth-molybdenum heteropolyacid complex; adding ascorbic acid to a mixed solution composed of the mother solution, the bismuth salt solution and the ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate mixed solution to reduce the phosphorus-bismuth-molybdenum heteropolyacid complex to bismuth-phosphorus-molybdenum blue to obtain a solution to be detected; and measuring the absorbance of the bismuth-phosphorus-molybdenum blue in the solution to be detected by a spectrophotometric method and calculating to obtain the content of phosphorus in the niobium-containing steel. The determination method has the beneficial effects that no toxic organic reagent is used in the detection process and extraction is not carried out; the operation is simple; and the content of phosphorus in the niobium-containing steel can be accurately determined.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP JIANGYOU CHANGCHENG SPECIAL STEEL
Arsenic meter
InactiveUS7336362B2Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMolybdenum blueField tests
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Method for rapidly measuring content of silicon in catalyst
InactiveCN104142312ALow process temperatureReliable methodMaterial analysis by optical meansMolybdenum blueColor reaction
The invention relates to a method for rapidly measuring the content of silicon in a catalyst. The method comprises the following steps: rapidly dissolving a catalyst sample and a high-purity silicon dioxide standard substance in an alkali solution at high temperature, adding an ethanol-acetone mixed solution serving as a stabilizer under an acidic condition, and then adding ammonium molybdate for color reaction so as to generate yellow silicon molybdenum yellow heteropolyacid; and performing reduction on silicon molybdenum yellow heteropolyacid to obtain silicon molybdenum blue heteropolyacid, making up to the constant volume, measuring the absorbancy at the wavelength of 810nm, and calculating the content of silicon in the sample according to a standard curve of silicon dioxide concentration and absorbancy value. Compared with a conventional silicon dioxide alkali fusion method, the method has the advantages that the sample treatment temperature is low, the treatment speed is high, and silicon in the catalyst is simply measured by a spectrophotometric method.
Owner:RES INST OF SHAANXI YANCHANG PETROLEUM GRP
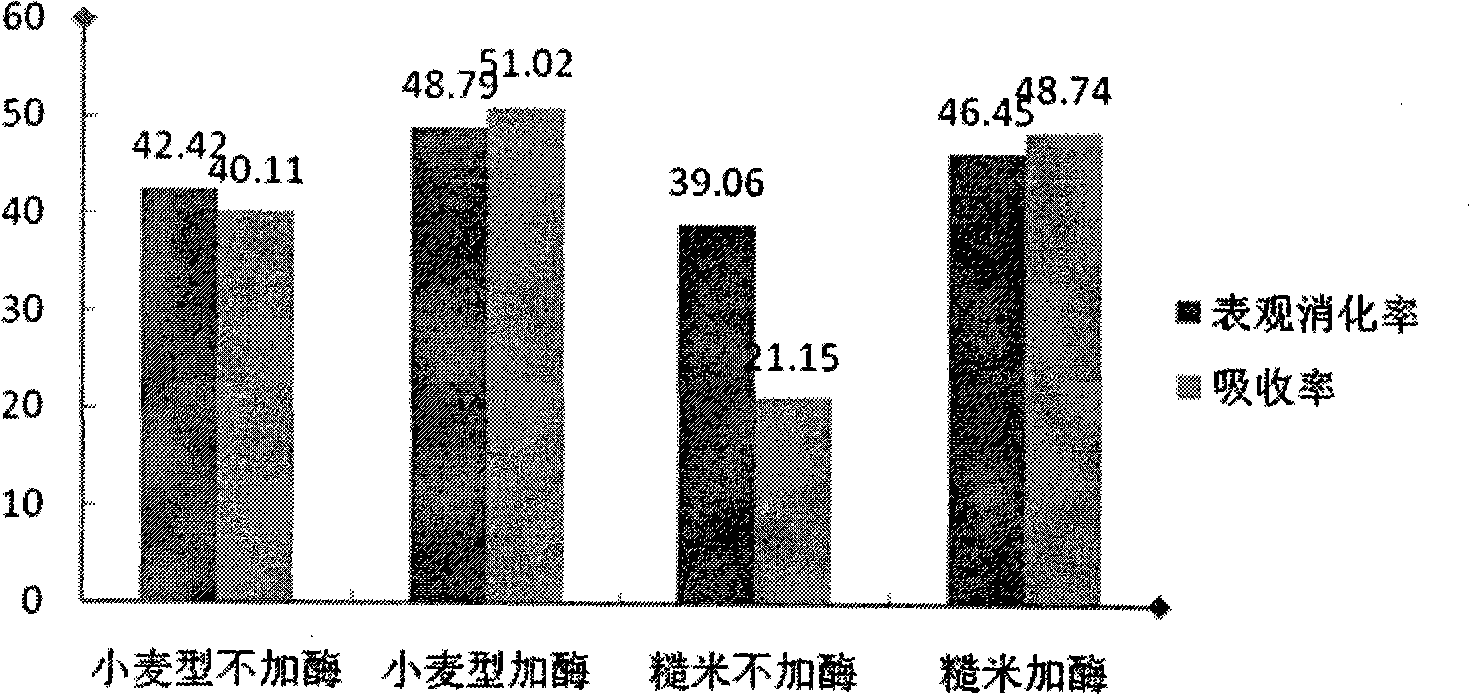
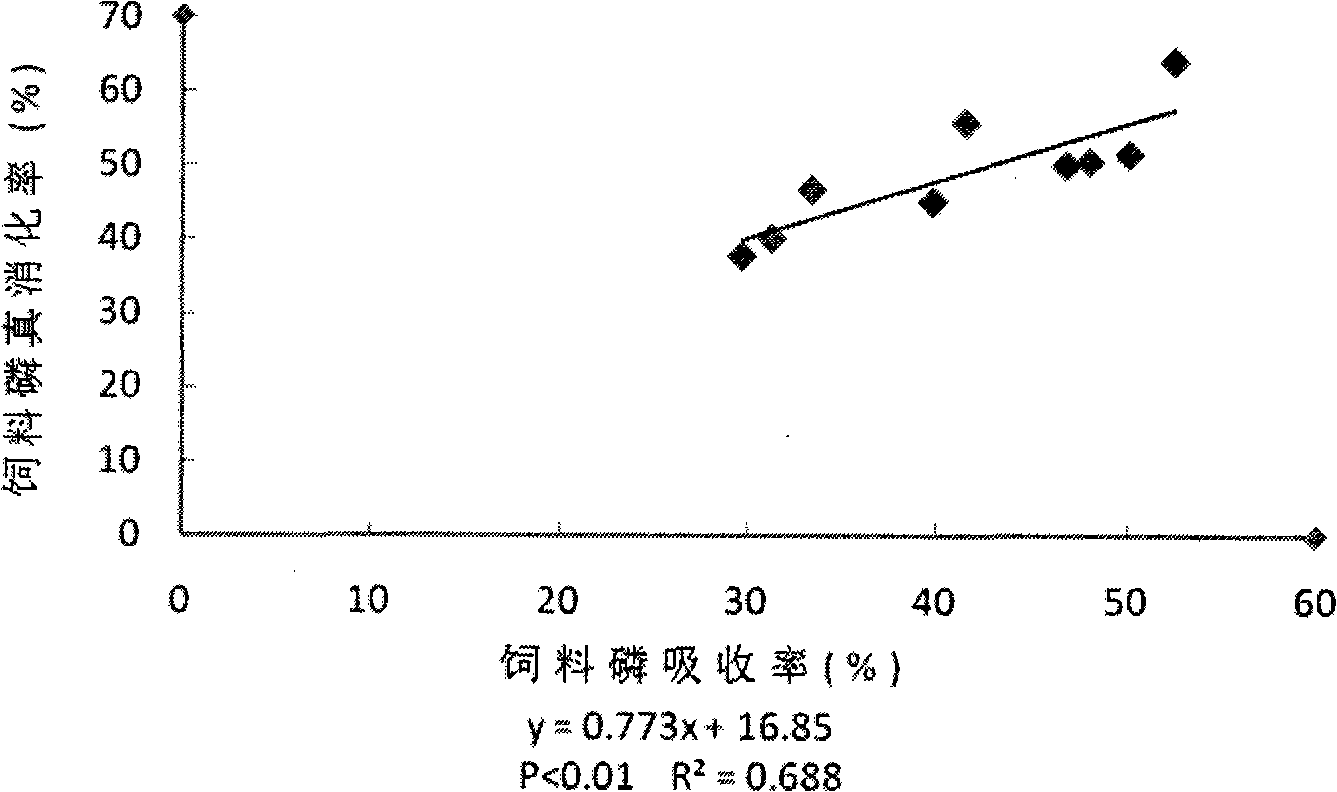
Method for measuring effective phosphorus in feedstuff
InactiveCN101358927AMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationWater bathsMolybdenum blue
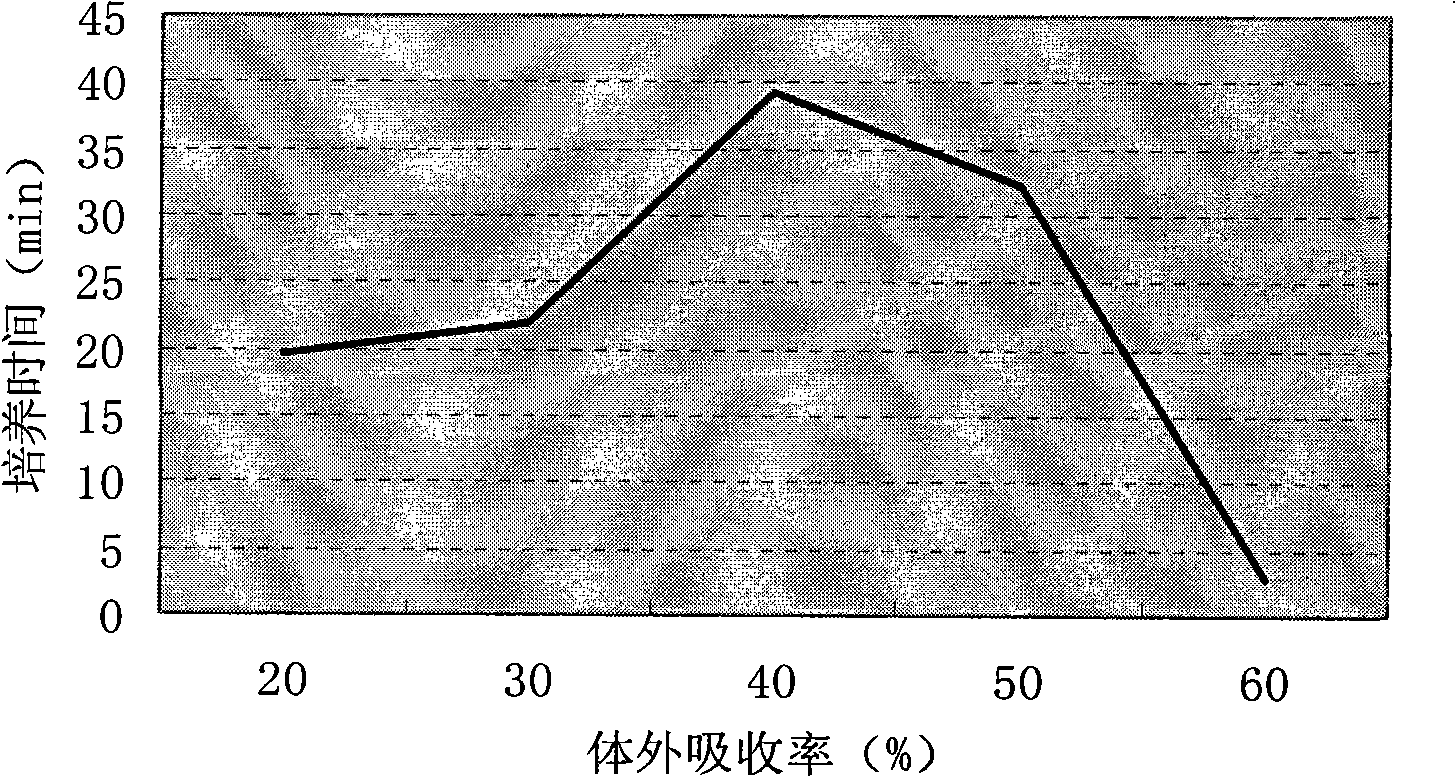
The present invention relates to a novel method of determining available phosphorus in the feed. The method adopts an everted intestinal sac to determine the absorption rate in vitro of feed phosphorus, and comprises the following steps: digesting pepsin, digesting trypsin, absorbing phosphorus of the everted intestinal sac in vitro, and so on. The everted intestinal sac is arranged in a test tube (used for digesting the feed); Tris-Krebs buffer solution of 5mL is added to cover the everted intestinal sac; the mixture is shaken up and cultured for 40 minutes in the constant-temperature water bath of 39 DEG C; the intestinal sac is removed; the surface of the intestinal sac is cleaned by the buffer solution; then the intestinal sac is baked in a clean crucible for 24 hours at the temperature of 105 DEG C; after the intestinal sac is dried, the crucible is burned for 8 hours in a muffle furnace to dissolve the ash; ultimately the molybdenum blue method is used for determining the total content of phosphorus.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Simple egg lecithin content measuring method
InactiveCN101556241AEfficient extractionMeet testing needsPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsMolybdenum bluePhospholipid
The invention relates to a simple spectrophotometry lecithin content measuring method for fresh eggs. The principle of the method comprises the following steps of: separating egg yolk from egg white after the fresh eggs are boiled in boiling water and denatured, then thoroughly extracting grease of the egg yolk with anhydrous ether and transforming the lecithin into inorganic phosphorus compound. Ammonium phosphomolybdate is produced in acid condition and becomes blue molybdenum blue by reduction reaction. Color comparison is conducted under 650nm, phosphorus content is measured, and egg lecithin content is finally computed. As to egg products, the direct adoption of the method can meet the demand of analysis and measuring of daily laboratory. The simple egg lecithin content measuring method has the advantages of easy operation, high selectivity, reliable measuring result and being capable of getting rid of the disturbance of inorganic phosphorus of eggs.
Owner:谱尼测试集团股份有限公司
Determination method for mass fraction of impurity elements contained in steel
InactiveCN103575674AImplement conjoint analysisEasy to operateColor/spectral properties measurementsMolybdenum blueDecomposition
The invention provides a determination method for the mass fraction of impurity elements contained in steel. The determination method comprises the following steps of dissolving a specimen by soluble acid, dropping ammonium persulfate solution, continuously heating and boiling, completing decomposition of ammonium persulfate, dropping hydrogen peroxide, lightly shaking to enable the solution to be clear, heating, boiling and decomposing excessive hydrogen peroxide; dividing the obtained test solution into multiple parts for spare use; adding a part of the test solution to be detected into acid medium, then adding a reducing agent, absorbing escaped arsenic hydride by iodine solution, reducing to generate arsenic molybdenum blue with ammonium molybdate, and calculating and determining the mass fraction of the arsenic on the basis of light absorbance of the arsenic molybdenum blue. The determination method further comprises the step of determining the mass fractions of silicon, manganese and phosphorus elements in other parts of test solution. The determination method provided by the invention has the advantages that the test material decomposition and the test solution preparation are not needed additionally and independently, conjoint analysis can be realized, and a reagent is saved; process operations of distillation and separation and the like are not needed; compared with the method for treating the test solution by discharging perchloric acid smoke and sulfuric acid smoke, the determination method provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that the emission of toxic and harmful gas is reduced and the risk is lowered.
Owner:GUANGXI YUCHAI MASCH CO LTD
Method for testing amino silicon oil content in chitosan fiber
ActiveCN101435777ANo risk of contaminationSimple methodChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceFiberMeasurement cost
The invention provides a method for testing the content of amino-silicone oil in chitosan fiber, which relates to a chitosan fiber production process. The method comprises the following steps: the chitosan fiber is subjected to ashing treatment; silicon in the amino-silicone oil is oxidized so as to obtain silicon dioxide; the silicon dioxide is subjected to nitrolysis through nitric acid, so as to prepare silicic acid; the silicic acid reacts with ammonium molybdate to form molybdenum yellow; the molybdenum yellow is reduced into molybdenum blue through ferrous sulphate; and finally the absorbance of a solution after color development at the wavelength of 595 nanometers is determined by use of a spectrophotometer, so as to figure out the silicon oil content of the fiber. As the method for testing the content of amino-silicone oil in chitosan fiber adopts the spectrophotometer to measure the oil quantity of the amino-silicone oil in the chitosan fiber, the method is simple, reliable and easy to operate, not only saves measurement cost, but also causes no pollution to environment, and has the advantages of short reaction time, high accuracy, low cost and high efficiency.
Owner:QINGDAO JIFA GROUP
Improved determination method of available silicon in soil
InactiveCN106769933AHigh detection sensitivityHigh detection accuracyPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsRelative standard deviationMolybdenum blue
The invention discloses an improved determination method of available silicon in soil, and belongs to the field of environmental protection. In the method, based on the silicon-molybdenum blue spectrophotometry, silicon and ammonium molybdate generate a silicon-molybdenum yellow complex under a certain acidity, then the acidity is increased, the silicon-molybdenum yellow complex is reduced to silicon-molybdenum blue with ascorbic acid, and colorimetry is carried out. The detection limit of the method on available silicon in soil is 1.2 mg / kg, and the relative standard deviation is smaller than 3.0%. According to the method, hydrochloric acid is used for replacing sulfuric acid to regulate pH, 2 g / L ascorbic acid is used for replacing 15 g / L ascorbic acid to reduce silicomolybdic acid, the colorimetric wavelength is adjusted to be 680 nm from original 700 nm, and the detection sensitivity and accuracy are improved more greatly.
Owner:江苏中宜金大分析检测有限公司 +1
Bacillus stratosphericus strain and application thereof
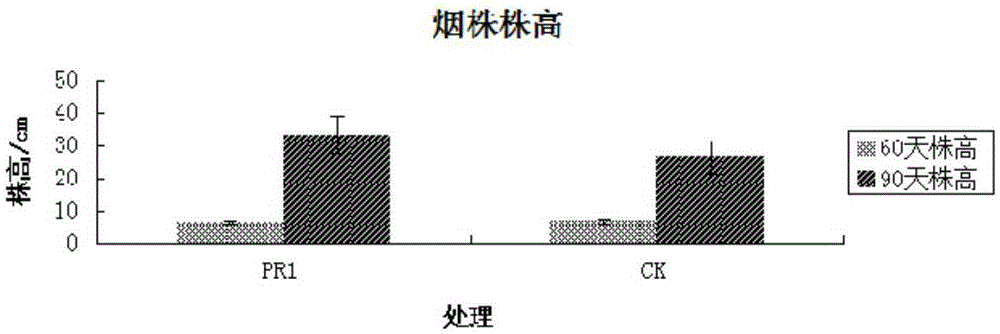
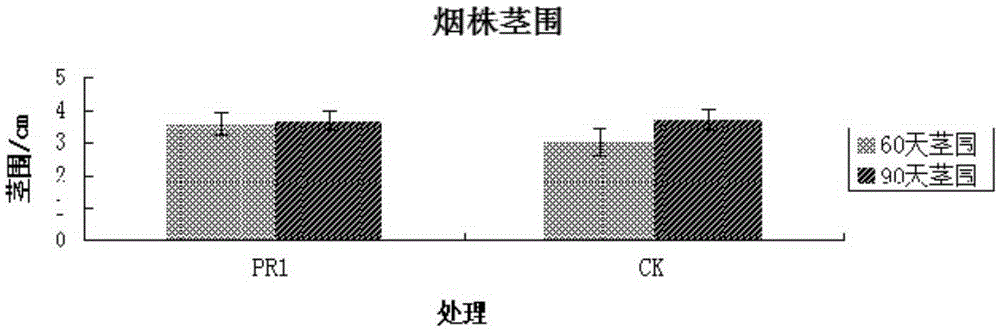
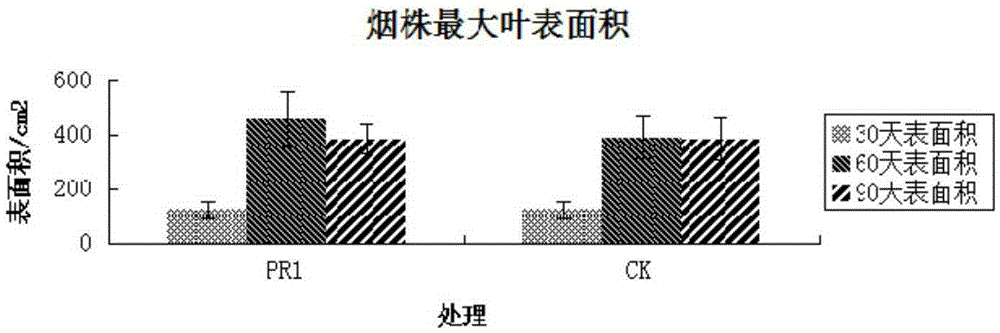
The invention discloses a Bacillus stratosphericus strain and application thereof. The strain is classified and named as Bacillus stratosphericus PR1, collected at the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, in Number 3 of Number 1 yard on the Beichen west road in the Chaoyang District of Beijing, on 28th, August, 2014 and numbered as CGMCC No.9612. The strain has good degrading effect on protein, and enzyme activity, of protease generated by the strain is 7.493 IU, measured by a Folin-phenol method; the strain has good phosphorus dissolving effect measured by using a phosphate dissolving ring method and a molybdenum blue spectrophotometry method; the strain has good green-keeping effect by using a green-keeping method, and cytokinin can be generated. It shows that the PR1 strain has potential application value in promoting tobacco growth.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO HUNAN INDAL CORP
Method for determining and analyzing Si content in carbon material
InactiveCN102564961AReduce biasSimple and fast operationColor/spectral properties measurementsMolybdenum blueHeteropoly acid
The invention provides a method for determining and analyzing Si content in a carbon material. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: with anhydrous sodium carbonate or / and boric acid as a solvent, melting the ash obtained by firing the carbon material; leaching out a test solution by use of a diluted hydrochloric acid solution; adjusting the PH value of the test solution, and then adding ammonium molybdate so that the silicon forms silicon-molybdenum heteropoly acid; reducing the silicon-molybdenum heteropoly acid into silicon-molybdenum blue by a reducing agent in a high-acidity sulfuric acid medium; and analyzing and determining the Si content by a colorimetric method. The method for determining and analyzing Si content in a carbon material, provided by the invention, is simple to operate and has high accuracy.
Owner:SNTO TECH GRP
Molybdenum blue assay for measurement of chemical species
InactiveCN110168377AAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemical speciesMolybdenum blue
A process for measuring a concentration of a chemical species in an aqueous sample employing polyvinylpyrrolidone. The process comprises : providing an aqueous sample containing the chemical species;mixing the aqueous sample with a first reagent that comprises a solution of a molybdenum VI salt to provide a first solution; mixing the first solution with a second reagent that comprises a reducingagent to form a second solution; and measuring a property of the second solution to determine the concentration of the chemical species. Polyvinylpyrrolidone is added to the aqueous sample, the firstreagent, the first solution or the second solution. The intensity of light absorbed or transmitted by the second solution may be used to determine the concentration of the chemical species.
Owner:国家海洋学中心
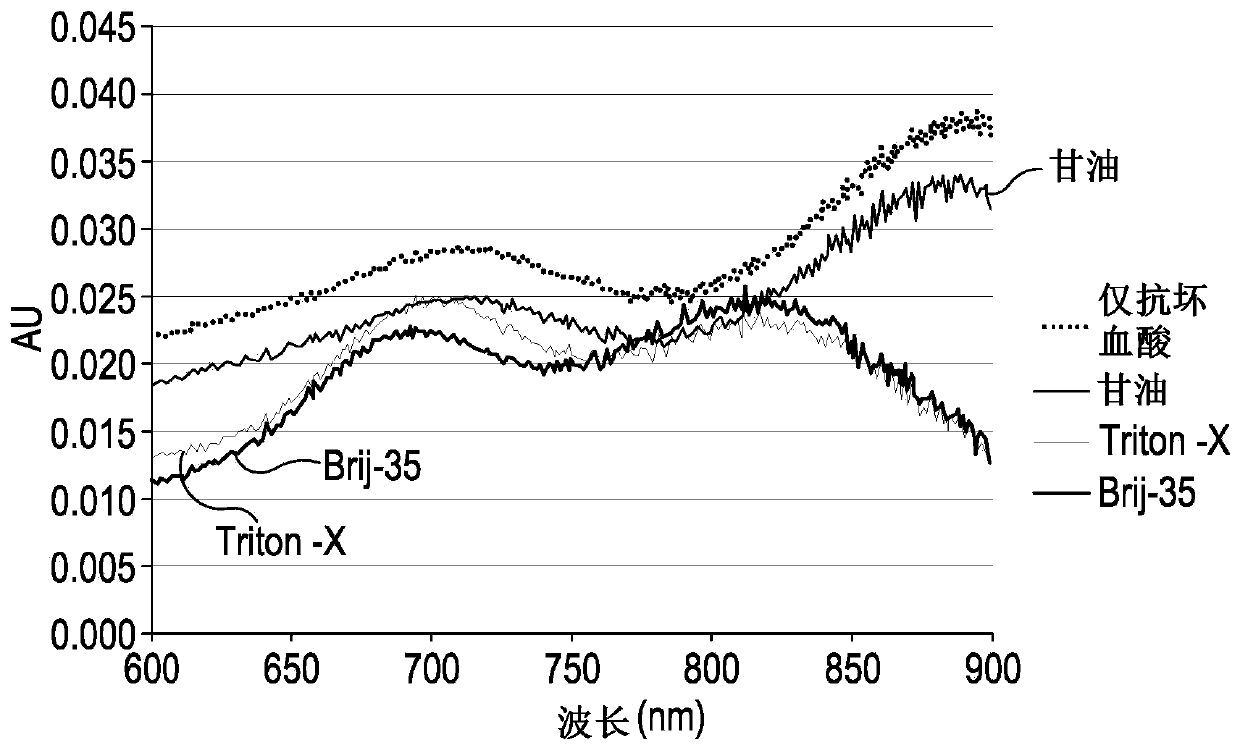
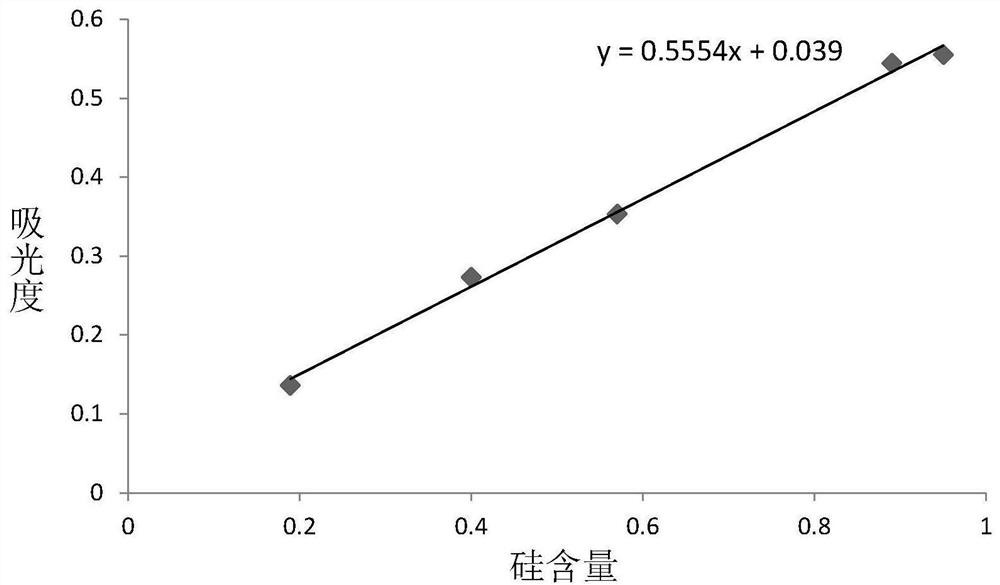
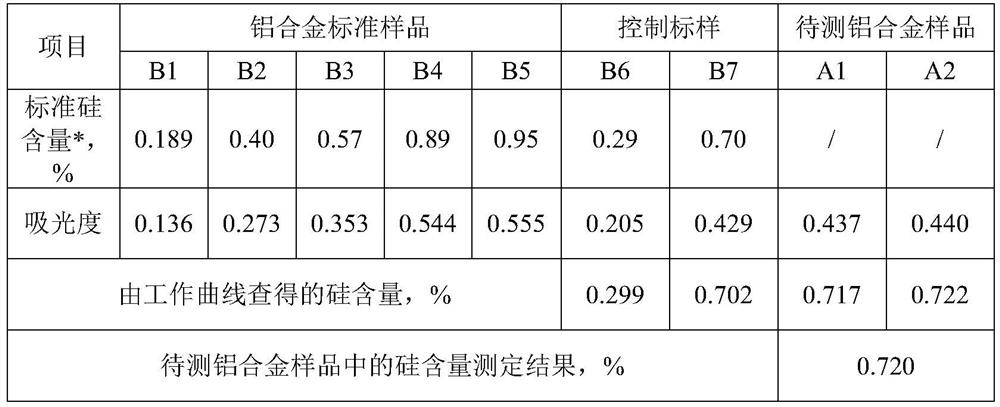
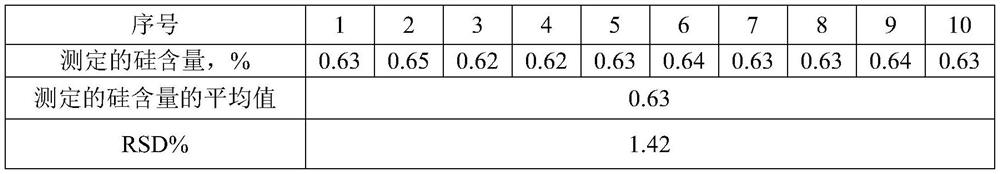
Method for detecting silicon content in aluminum alloy
InactiveCN112051227AAccurate determination of silicon contentExpand the measurement rangeColor/spectral properties measurementsAmmonium ferrous sulfateMolybdenum blue
The invention provides a method for detecting the content of silicon in an aluminum alloy, which comprises the following steps: (1) sequentially carrying out alkali dissolution and acidification treatment on an aluminum alloy sample to obtain a sample solution; treating the sample solution with ammonium molybdate to enable a silicon component in the sample solution to form a silicon molybdenum yellow complex, and adding ammonium ferrous sulfate into the silicon molybdenum yellow complex to reduce the silicon molybdenum yellow complex into a silicon molybdenum blue complex to obtain a to-be-detected solution; measuring the absorbance of the to-be-measured liquid at the wavelength of 650 + / -10nm; and (2) establishing a silicon content absorbance working curve by adopting the standard sample,and determining the silicon content in the aluminum alloy sample to be measured according to the working curve and the absorbance measurement result of the aluminum alloy sample to be measured. The detection method provided by the invention can accurately determine the silicon content of the aluminum alloy, and has a wide silicon content determination range.
Owner:CRRC QIQIHAR ROLLING CO LTD
Method for treating molybdenum blue-containing solution by ion exchange process
InactiveCN102154551ALarge adsorption capacityAvoid pollutionProcess efficiency improvementMolybdenum blueDesorption
The invention discloses a method for treating a molybdenum blue-containing solution by an ion exchange process. In the method, macroporous anion exchange resin is contacted with the molybdenum blue-containing solution to adsorb molybdenum blue in a stirred tank reactor; and a desorbing agent is added into the resin after adsorption for desorption. The method is easy to operate and is low in cost, and the reacted resin can be reused.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for determining phosphorus content in iron ore by bismuth-phosphorus-molybdenum blue
InactiveCN111650194AEasy to measureGuaranteed detection accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationHydroxylamineMolybdenum blue
The invention relates to a method for determining phosphorus content in iron ore by bismuth-phosphorus-molybdenum blue, and the method comprises the following steps: weighing 0.1-0.25 g of sample, putting into a beaker, adding hydrochloric acid, heating to dissolve for 3-5 minutes, adding nitric acid and sulfuric acid, evaporating to a wet salt state, taking down, slightly cooling, and adding water to a scale of 20mL to obtain a solution; then filtering; after the filtering, adding a sodium hydroxide solution, sulfuric acid and a potassium sodium tartrate solution for acidity adjustment; thenadding a bismuth nitrate solution, an ammonium molybdate solution and an ascorbic acid-hydroxylamine hydrochloride mixed solution for color development, and diluting to a constant volume of 100 mL ofa mother solution; and finally, measuring and calculating the phosphorus content in the sample according to a bismuth-phosphorus-molybdenum blue light intensity method in the prior art. The method hasthe advantages that the concentrated hydrochloric acid, the concentrated nitric acid and the concentrated sulfuric acid are uniquely adopted to dissolve the sample in the beaker, the detection cost is remarkably reduced and the detection efficiency is improved while the detection accuracy and precision are ensured, and the reproducibility is good; the device is suitable for laboratories of various levels.
Owner:MCC NORTH (DALIAN) ENG TECH CO LTD
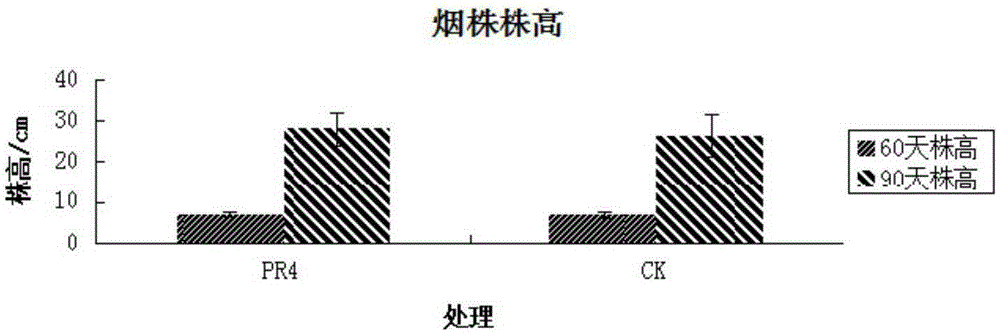
Serratia nematodiphila strain and application thereof
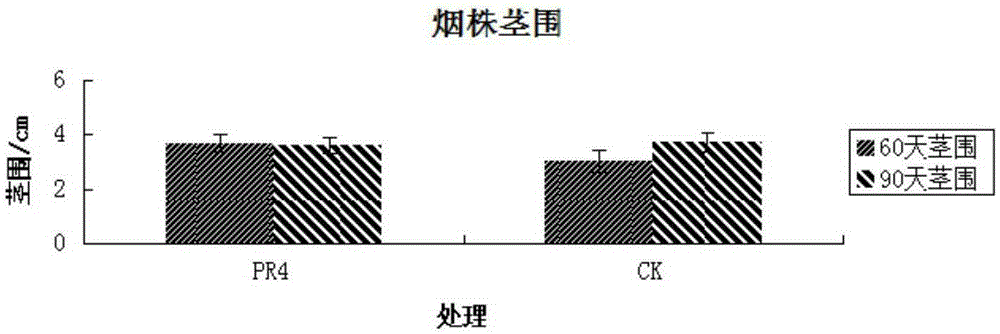
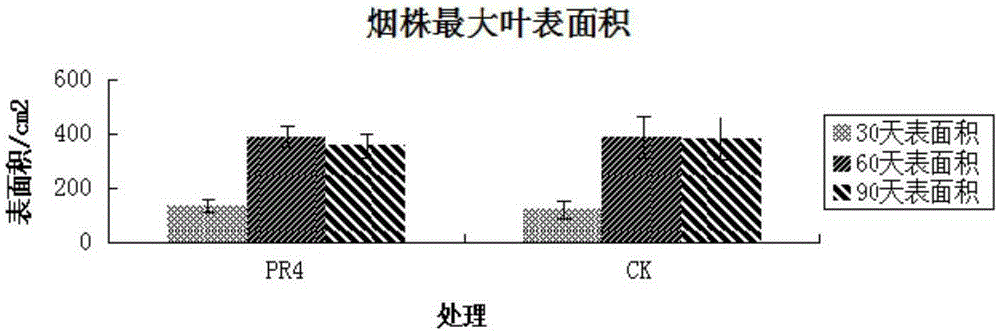
The invention discloses a Serratia nematodiphila strain and application thereof. The strain is classified and named as Serratia nematodiphila PR4, collected at the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, in Number 3 of Number 1 Yard on the Beichen west road in the Chaoyang District of Beijing, on 28th, August, 2014 and numbered as CGMCC No.9614. The strain has good degrading effect on protein. Enzyme activity, of protease generated by the strain, measured by a Folin-phenol method is 3.03 IU. The strain has good phosphorus dissolving effect measured by using a molybdenum blue spectrophotometry method. It shows that the PR4 strain has potential application value in promoting tobacco growth.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO HUNAN INDAL CORP
Measuring method of content of arsenic in water body
InactiveCN107941726AAvoid it happening againThe test method is simpleColor/spectral properties measurementsArsineMolybdate
The invention relates to the technical field of water body detection, in particular to a measuring method of the content of arsenic in a water body. The method comprises the following steps: dispersing manganese dioxide with oxidizability into a water body, heating and stirring the water body, and oxidizing all 3<+> arsenic ions in the water body into 5<+> arsenic ions, so as to reduce the toxicity of arsenic in the water body during detection and improve the detection safety; and ensuring that pentavalent arsenic and molybdenic acid are interacted to produce an arsenic molybdate molybdenic acid mixture, and ensuring that the mixture is reduced into molybdenum blue to perform color development in boiling water to perform the detection of the content of arsenic. The method has the advantages that low-valent arsenic ions are oxidized with an oxidizing agent, the producing of toxic gaseous arsenide hydrogen is avoided, the testing mode is simple, the flow is simplified, and the method issafe and reliable.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH QINGDAO NEW ENERGY MATERIALS TECH RES INST CO LTD
Method for measuring concentration of silicate in high-concentration hydrogen sulfide hydrothermal solution
ActiveCN105954216AImprove accuracyEasy to operateColor/spectral properties measurementsHigh concentrationMolybdenum blue
The present invention relates to a method for measuring the concentration of silicate in a high-concentration hydrogen sulfide hydrothermal solution. The concentration of sulfur ions in a water sample is measured by a sulfide ionic selective electrode, and sulfur ions are removed based on the precipitation method. Firstly, silicate-sulfur ion standard solutions of different concentrations are prepared, and the pH values of the solutions are adjusted to be 5.00-6.00. After that, a zinc sulfate solution is added to precipitate sulfur ions into zinc sulfide precipitates. The solutions are aged for several hours and then are filtered, so that the precipitates in the solutions are removed. Filtrates are obtained for later use. Based on the silico-molybdenum blue spectrophotometry, the absorbance of each filtrate at the wavelength of 810 nm is measured, and then a silicate-sulfur ion standard curve is drawn. In the same condition, the absorbance of the high-concentration hydrogen sulfide hydrothermal solution water sample is measured. Based on the standard curve, the concentration of silicate in the high-concentration hydrogen sulfide hydrothermal solution water sample is figured out. The above method is simple in operation and avoids the measurement trouble caused by easily oxidized sulfur ions. Therefore, the measurement result is more accurate. The reliability of measuring the silicate content in the hydrothermal solution is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com