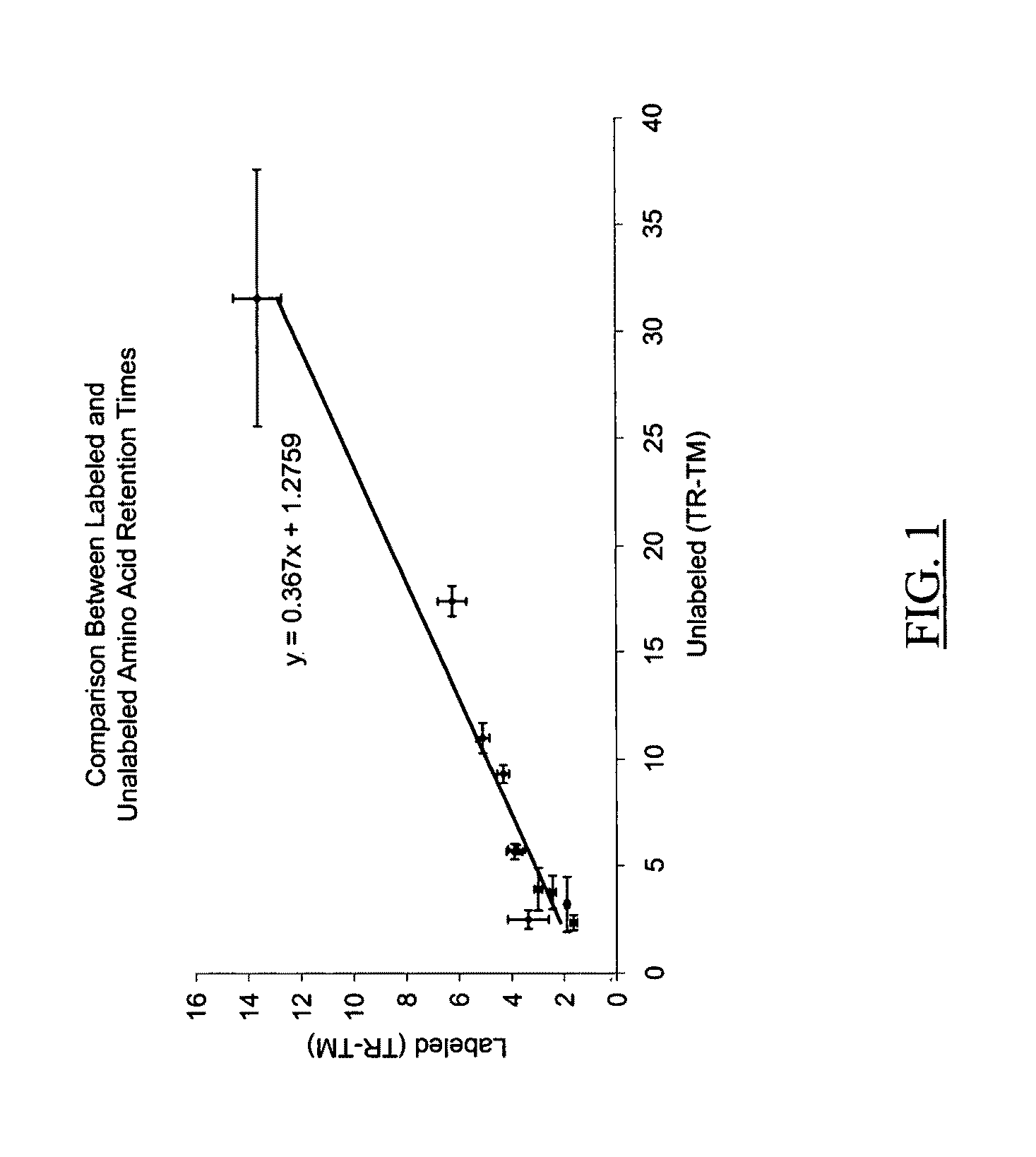
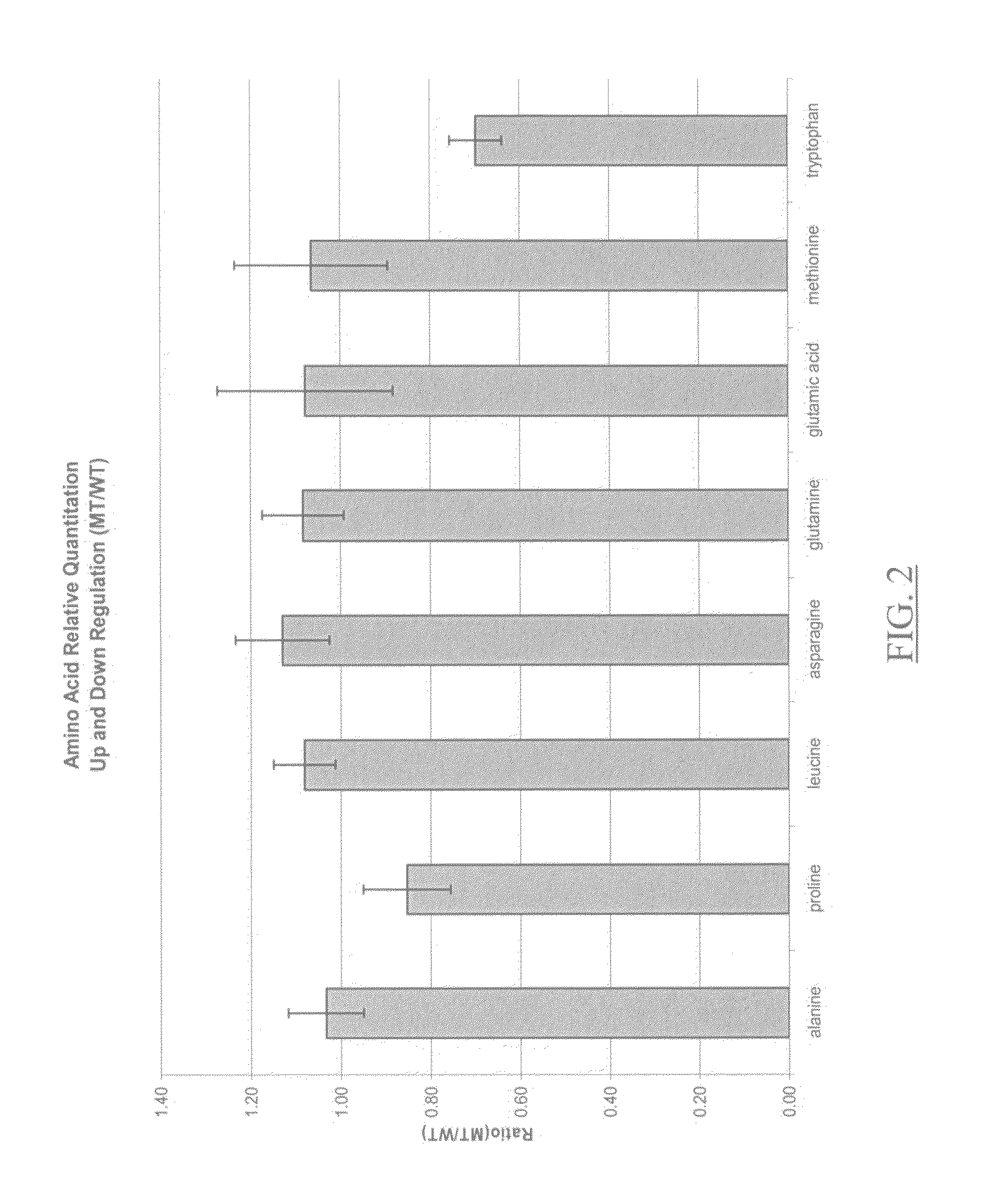
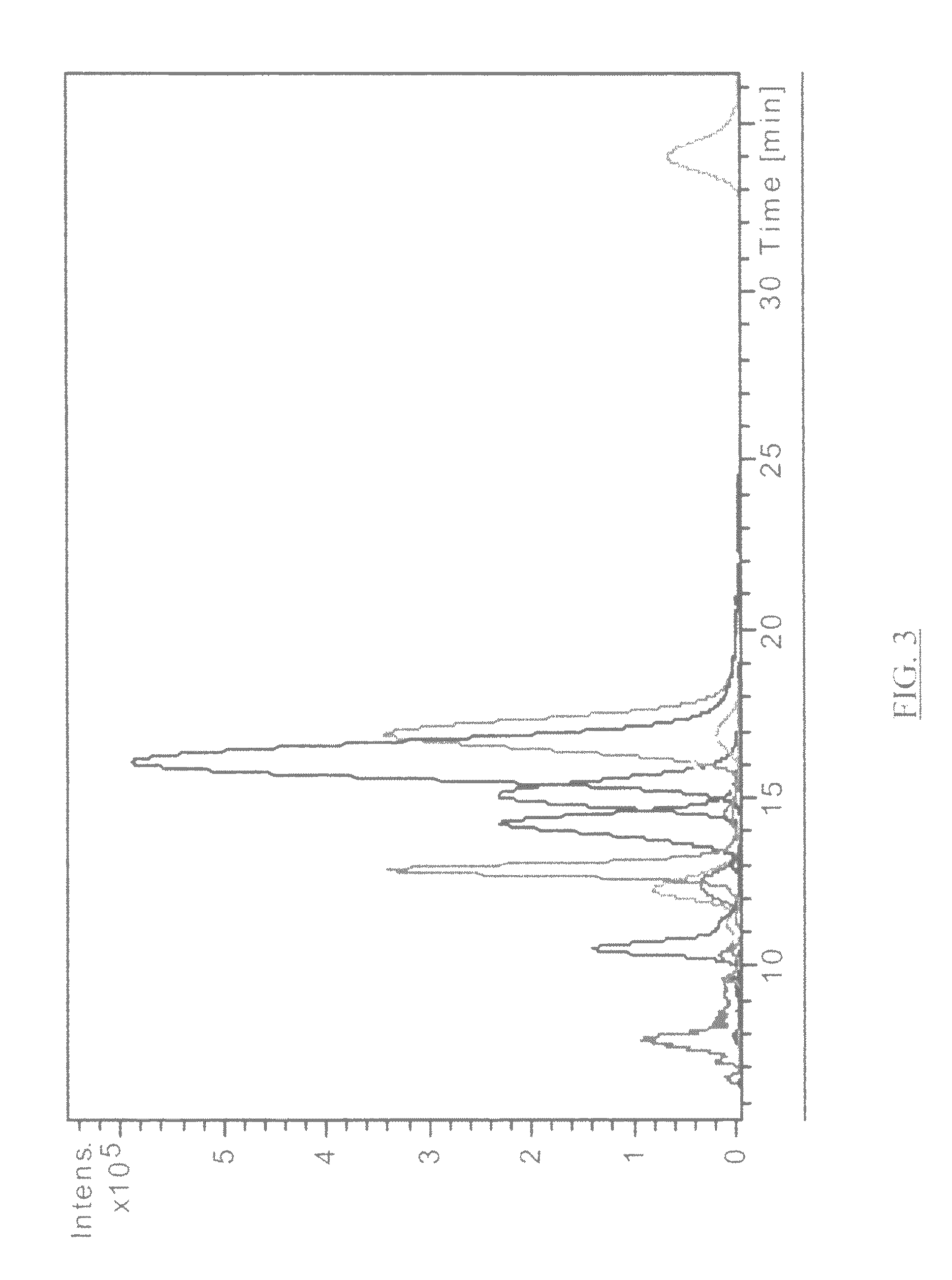
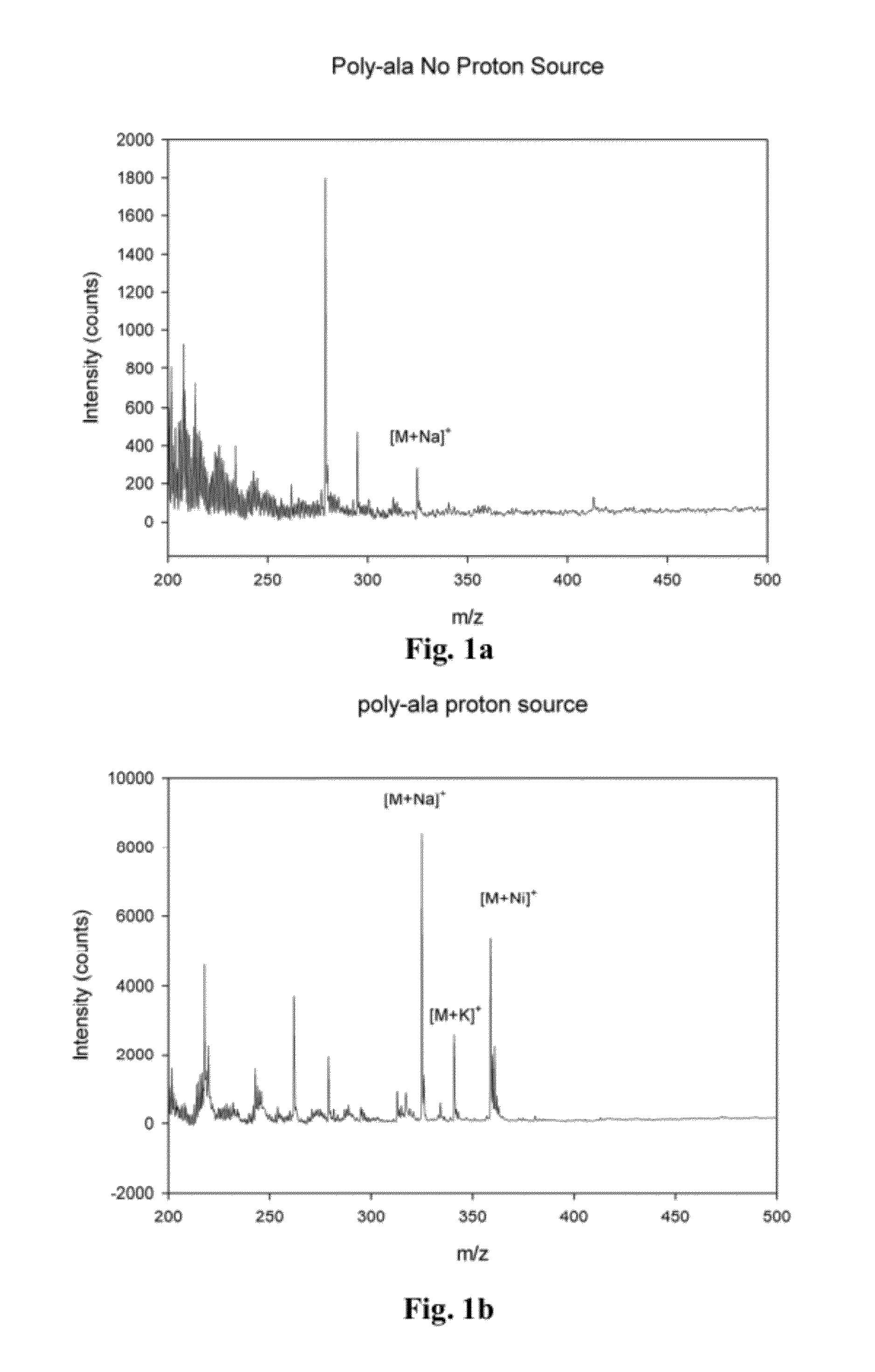
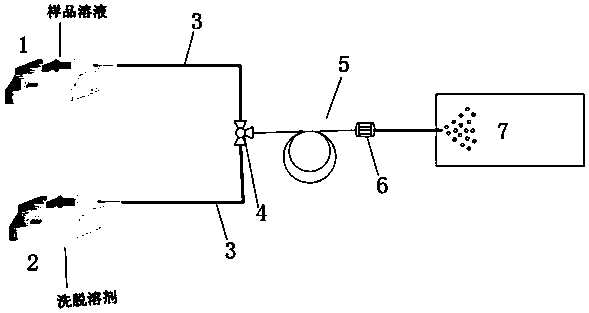
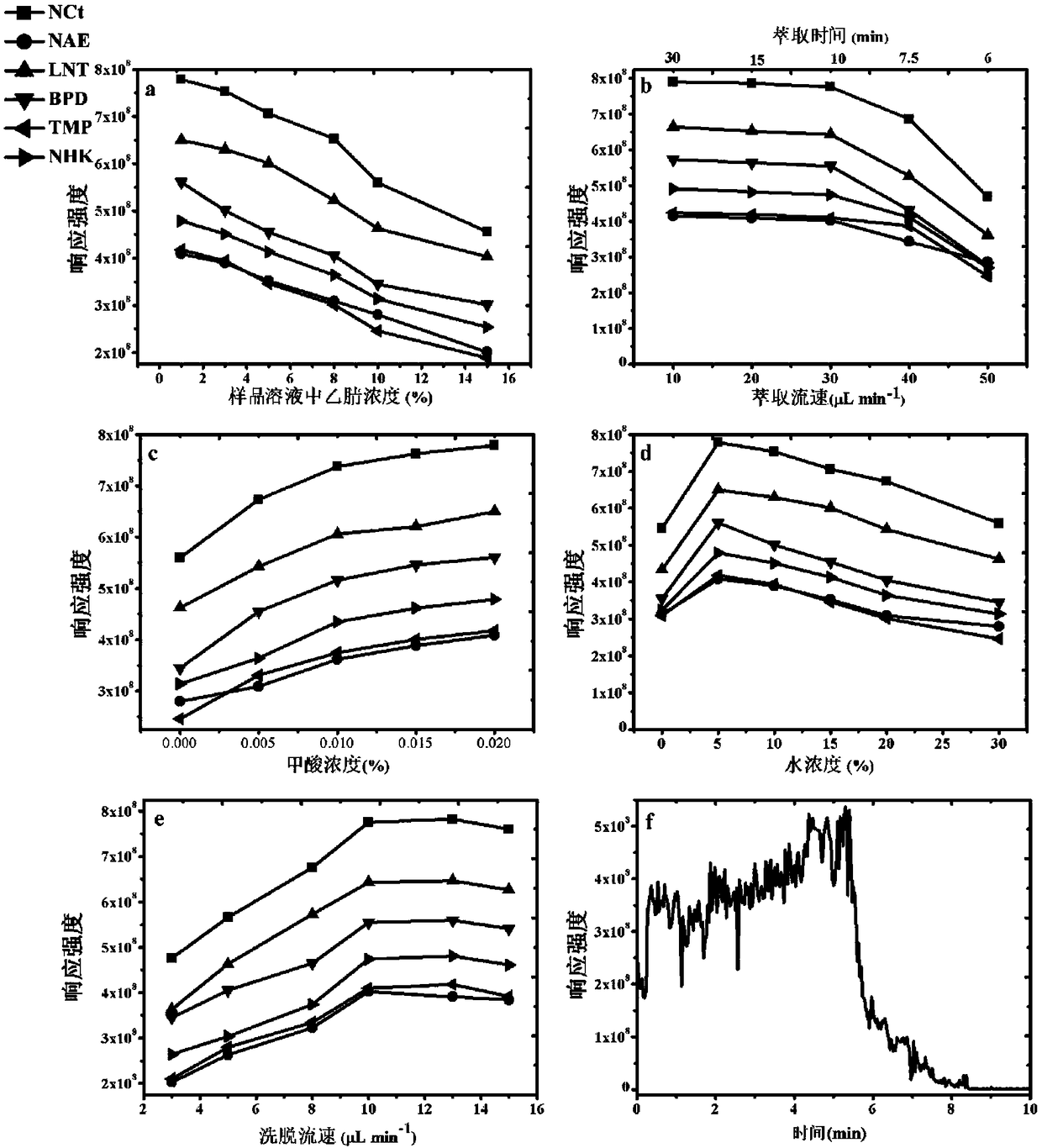
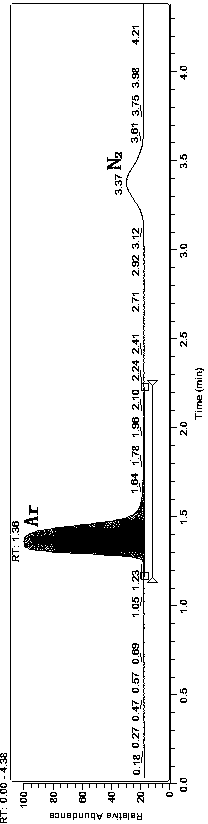
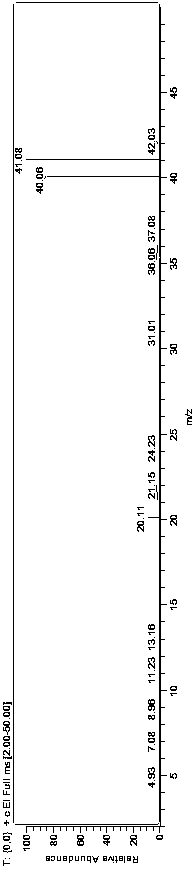
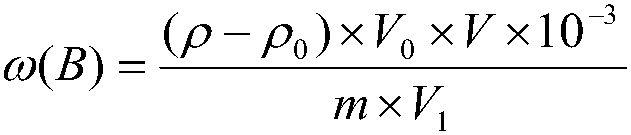Patents
Literature
77 results about "Aerosol mass spectrometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aerosol mass spectrometry is the application of mass spectrometry to aerosol particles. Aerosol particles are defined as solid and liquid particles suspended in a gas (air), with size range of 3 nm to 100 μm in diameter. Aerosol particles are produced from natural and anthropogenic sources, through a variety of different processes that include; wind-blown suspension, and combustion of fossil fuels and biomass. Analysis of aerosol particles is important because of their major impacts on the global climate change, visibility, regional air pollution and human health. Aerosol particles are very complex in structure and can contain thousands of different chemical compounds within a single particle. Due to this complexity the instrumentation used to analysis these particles must have the ability to separate based on size and in real-time provide information on their chemical composition. To meet these requirements for analysis, mass spectrometry instrumentation is used and they provide high sensitivity and the ability to detect a wide molecular mass range. Aerosol mass spectrometry can be divided into two categorizes; off-line and on-line. Off-line mass spectrometry is performed on collected particles. On-line mass spectrometry is performed on particles introduced in real time.
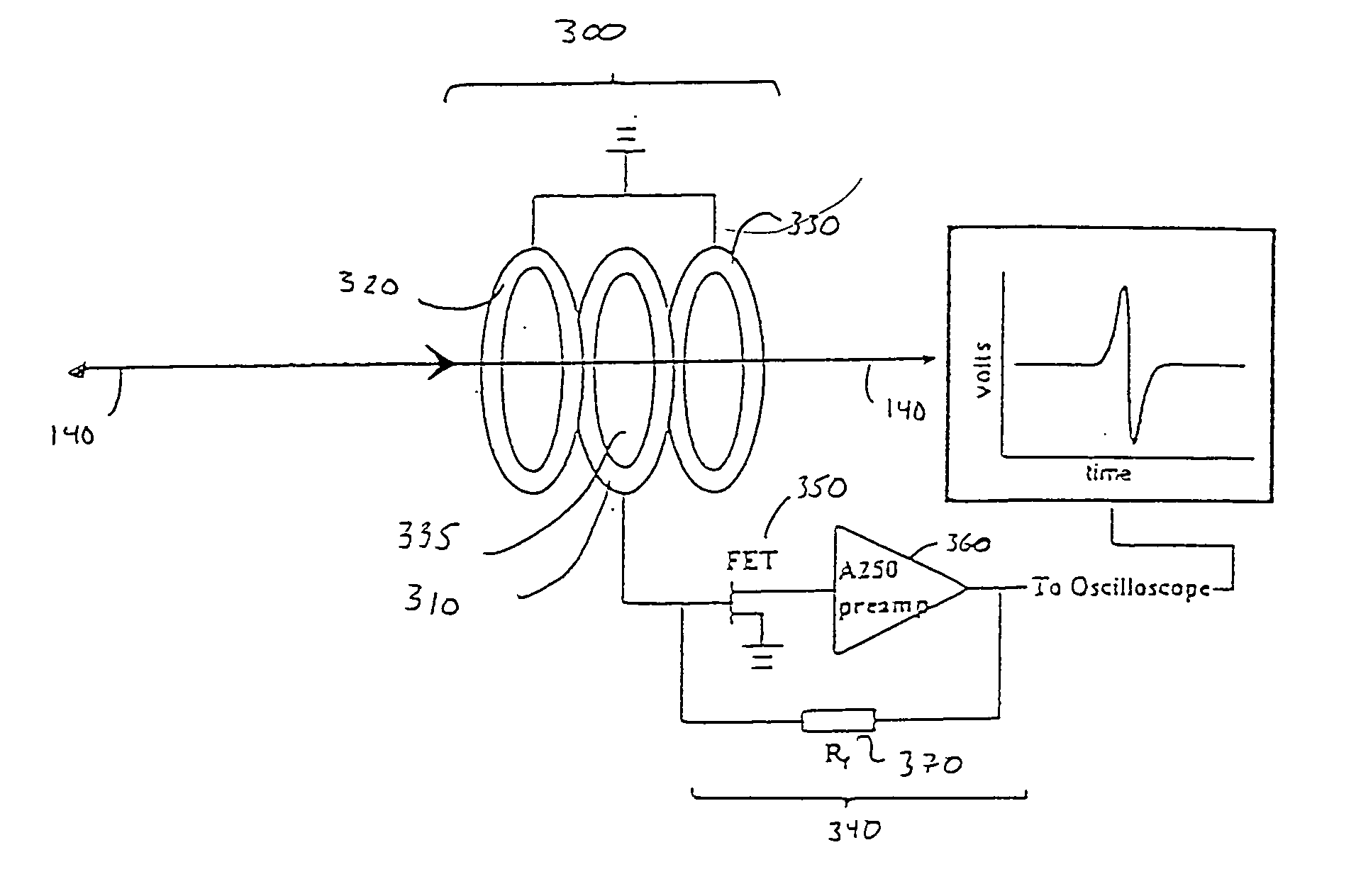
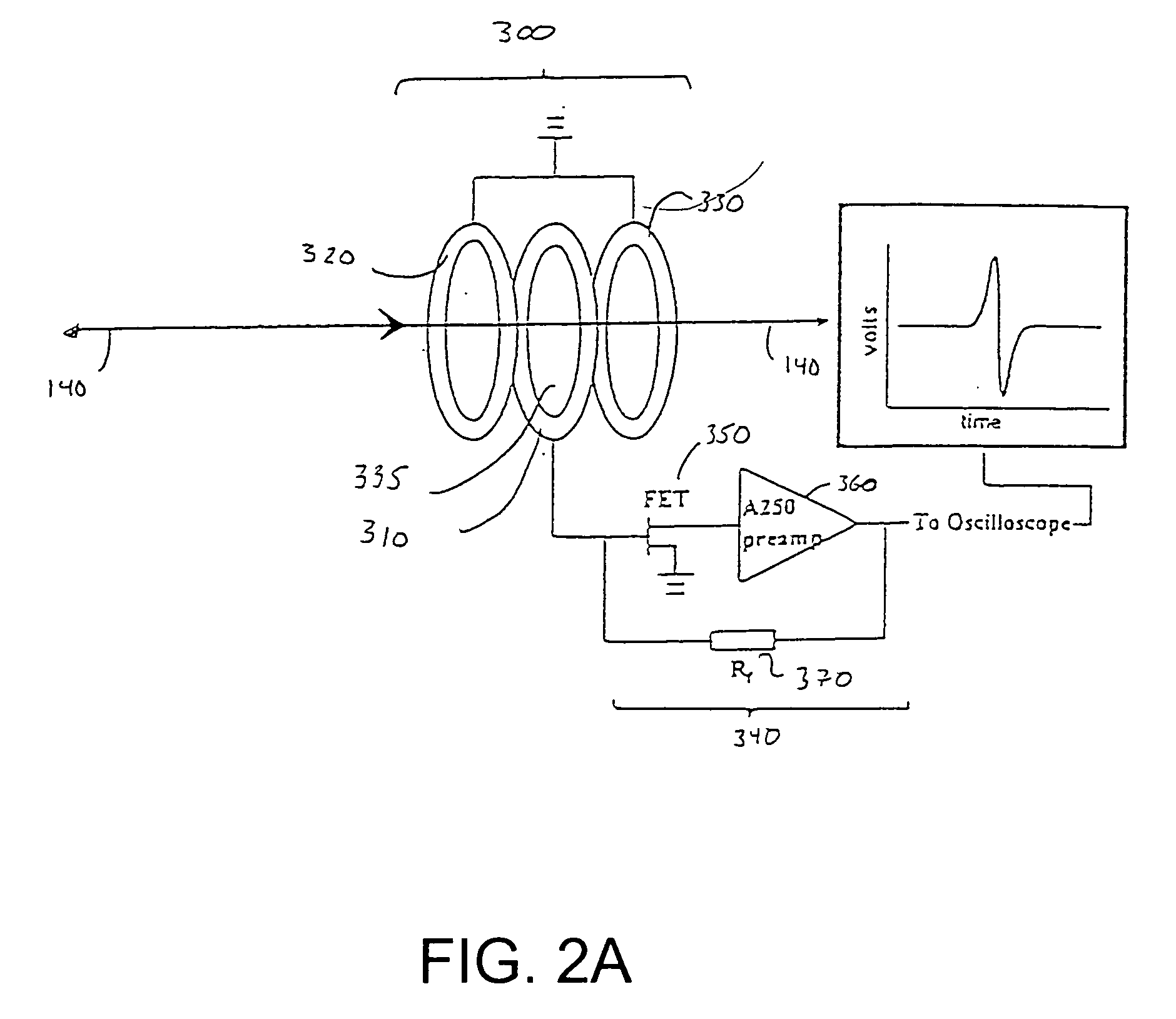
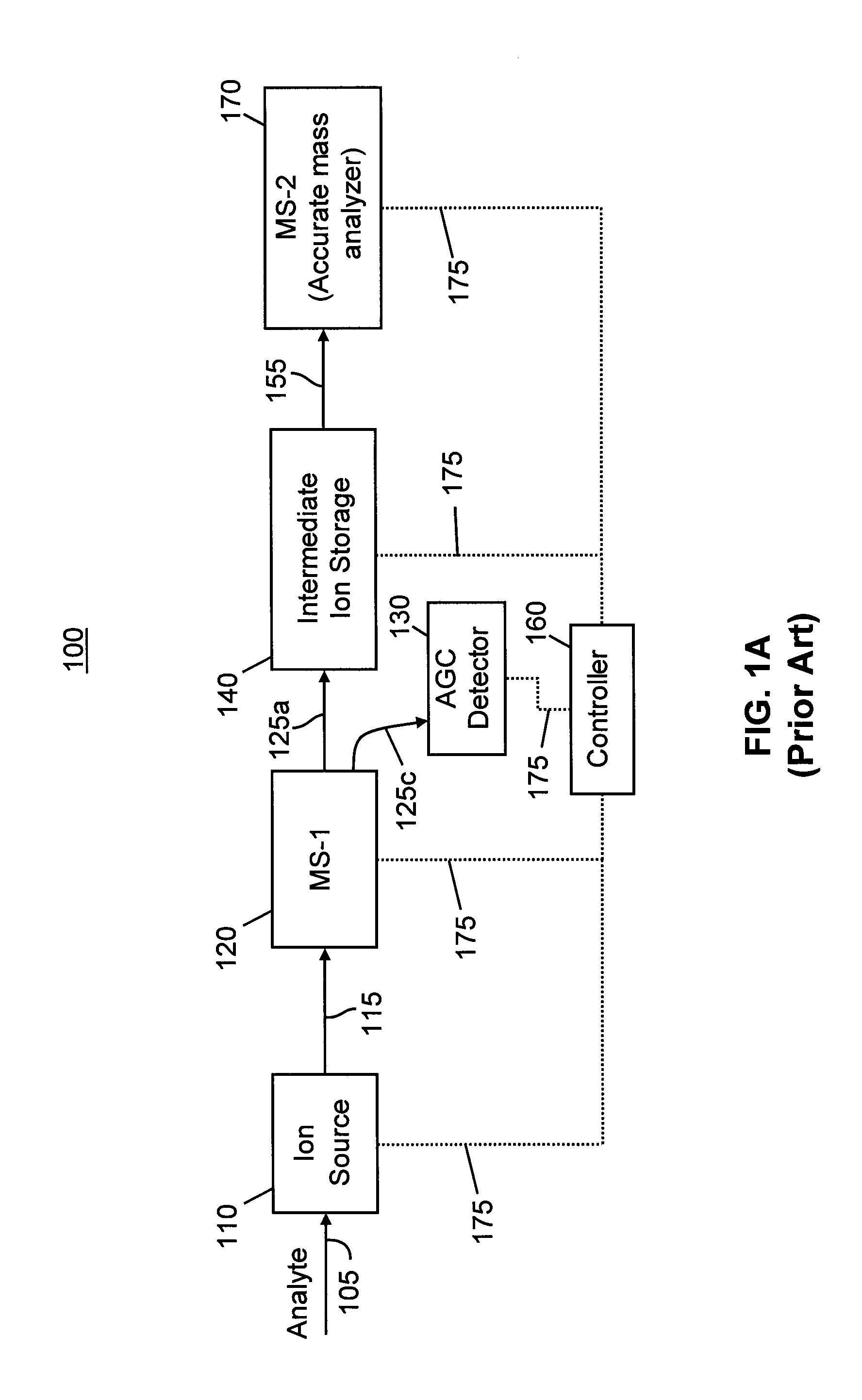
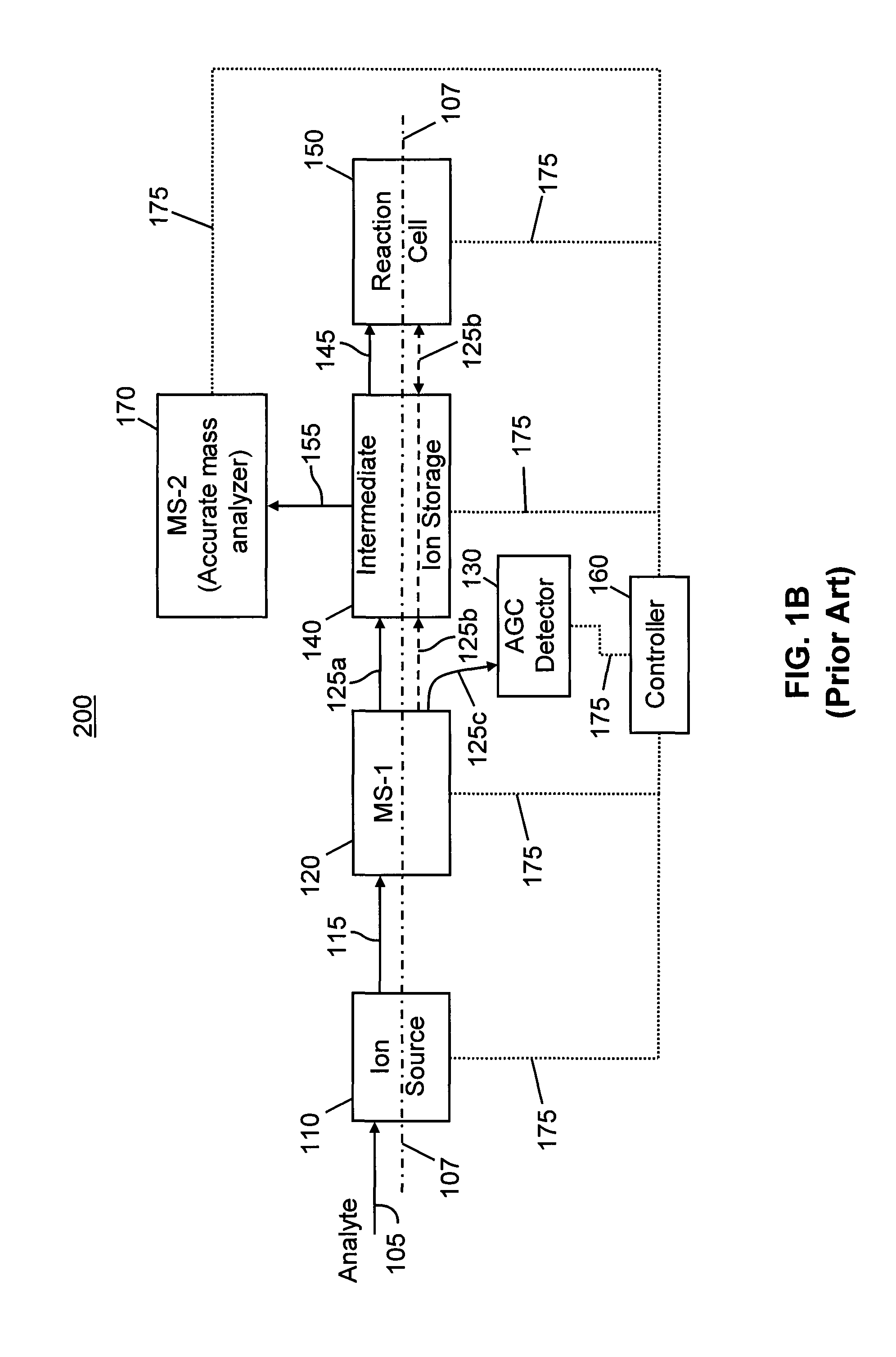
Inductive detection for mass spectrometry
ActiveUS20040169137A1Improve accuracyHigh resolutionTime-of-flight spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsGas phaseBiopolymer
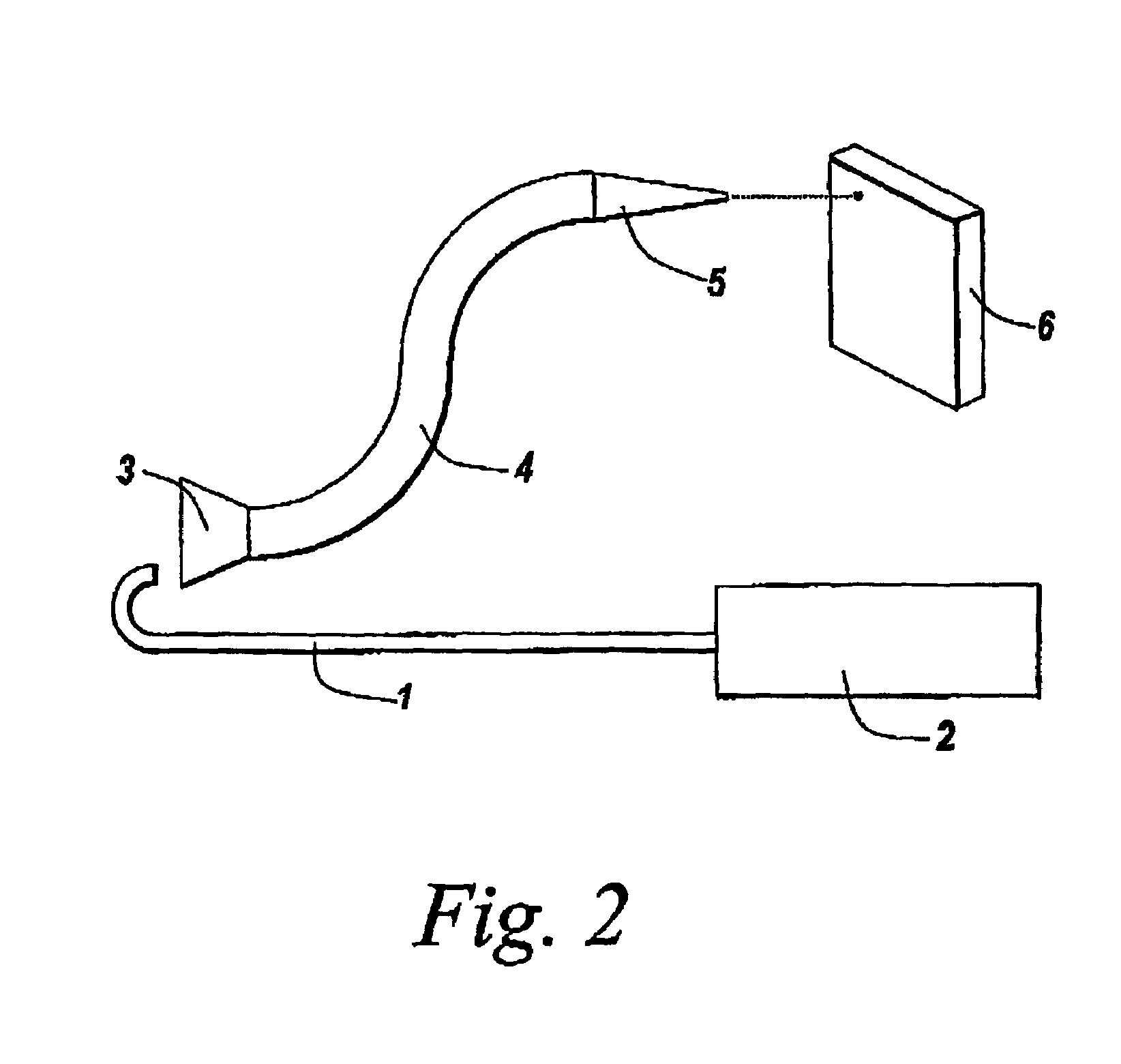
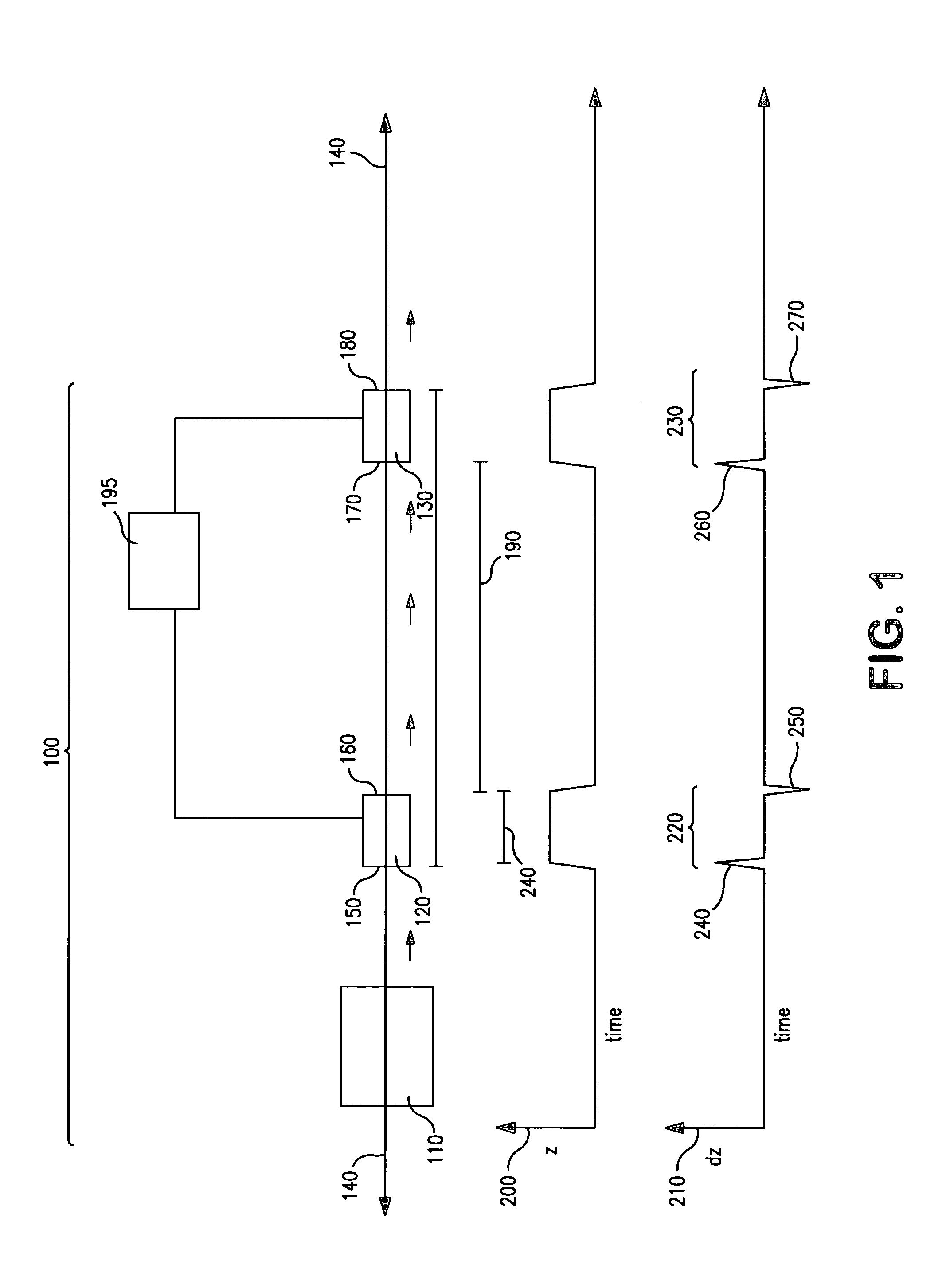
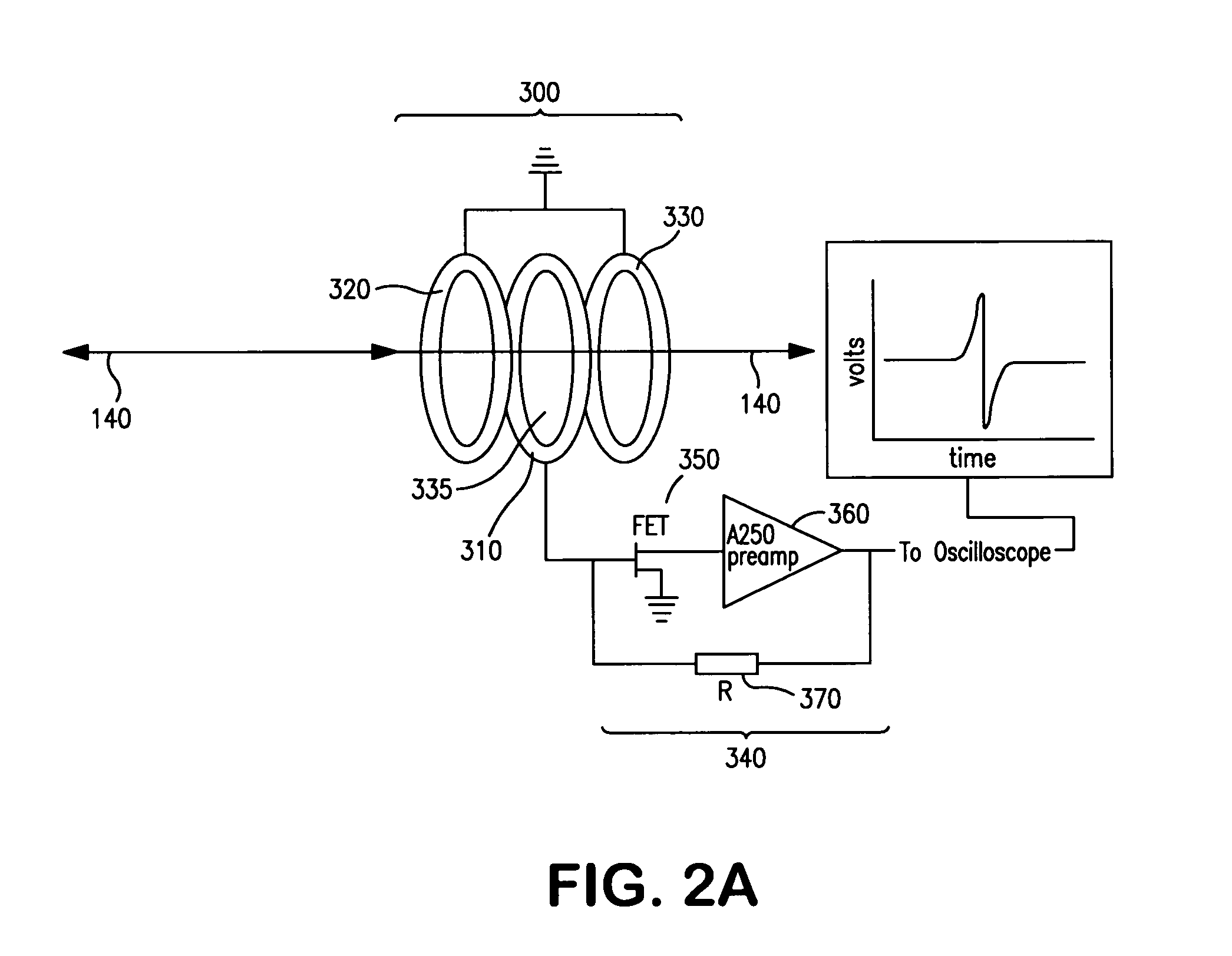
The invention provides devices, device configurations and methods for improved sensitivity, resolution and efficiency in mass spectrometry, particularly as applied to biological molecules, including biological polymers, such as proteins and nucleic acids. More particularly, the invention provides methods and devices for analyzing and detecting electrically charged particles, especially suitable for gas phase ions generated from high molecular weight compounds. In one aspect, the invention provides devices and methods for determining the velocity, charged state or both of electrically charged particles and packets of electrically charged particles. In another aspect, the invention provides methods and devices for the time-of-flight analysis of electrically charged particles comprising spatially collimated sources. In another aspect, the invention relates to multiple detection using inductive detectors, improved methods of signal averaging and charged particle detection in coincidence.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Thermoelectrically cooled water trap
InactiveUS7000490B1Low detection sensitivityEasy to removeWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationThermoelectric coolingWater vapor
A water trap system based on a thermoelectric cooling device is employed to remove a major fraction of the water from air samples, prior to analysis of these samples for chemical composition, by a variety of analytical techniques where water vapor interferes with the measurement process. These analytical techniques include infrared spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, ion mobility spectrometry and gas chromatography. The thermoelectric system for trapping water present in air samples can substantially improve detection sensitivity in these analytical techniques when it is necessary to measure trace analytes with concentrations in the ppm (parts per million) or ppb (parts per billion) partial pressure range. The thermoelectric trap design is compact and amenable to use in a portable gas monitoring instrumentation.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
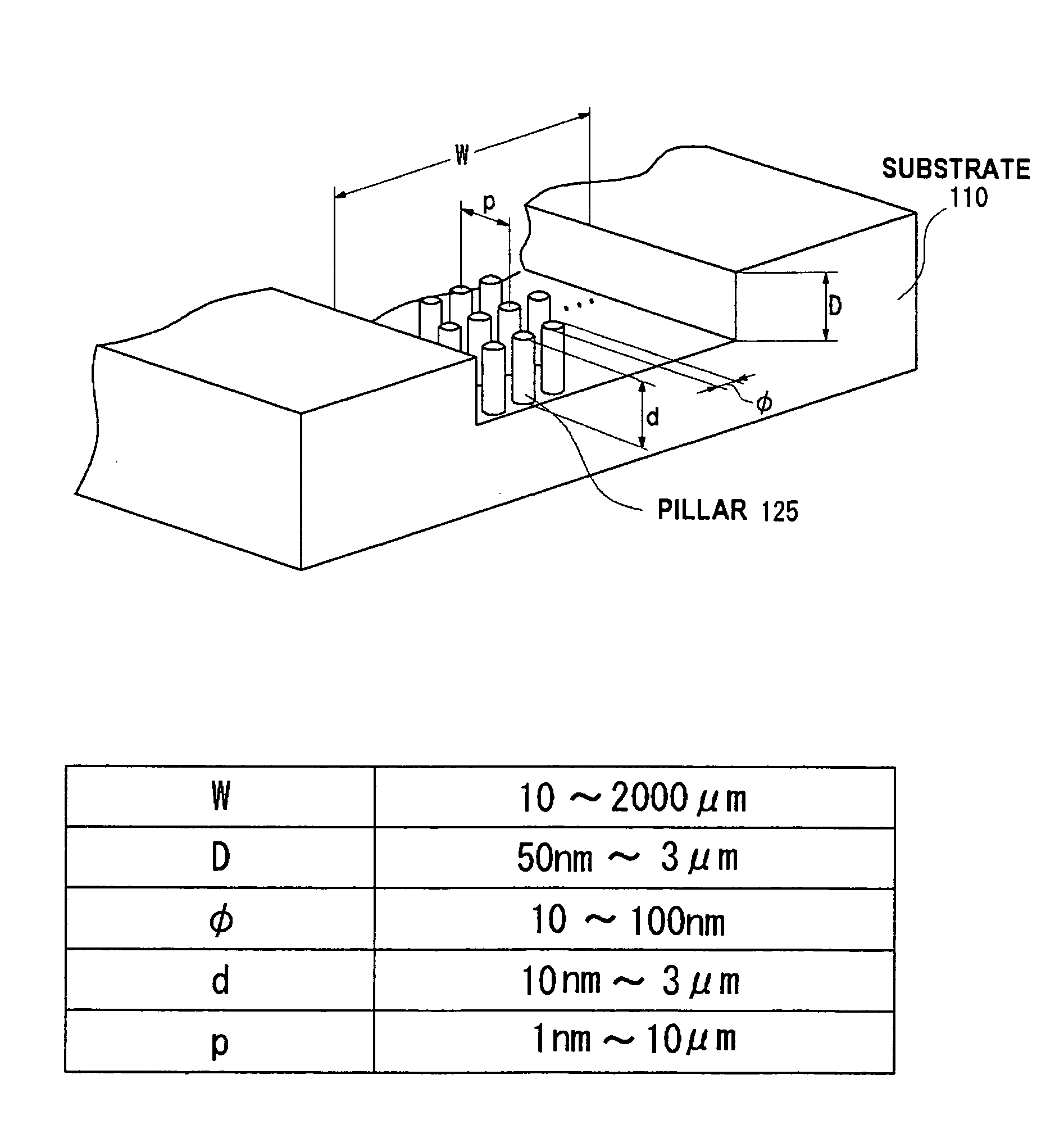
Adsorption, detection and identification of components of ambient air with desorption/ionization on silicon mass spectrometry (DIOS-MS)
InactiveUS7564027B2Prevent thermal degradationOptical radiation measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPhysicsMass spectrum analysis
The present invention provides a device, system, and associated methods to actively or passively sample air by directing it onto the surface of a porous light-absorbing semiconductor, for example, a desorption / ionization on porous silicon (“DIOS”) chip. Upon adsorption of an analyte, the surface may be analyzed directly by laser desorption / ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Because the process of laser desorption / ionization and subsequent mass detection does not require elevated temperatures, thermal degradation of analytes is avoided.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Inductive detection for mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7078679B2Improve accuracyHigh resolutionTime-of-flight spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsGas phaseBiopolymer
The invention provides devices, device configurations and methods for improved sensitivity, resolution and efficiency in mass spectrometry, particularly as applied to biological molecules, including biological polymers, such as proteins and nucleic acids. More particularly, the invention provides methods and devices for analyzing and detecting electrically charged particles, especially suitable for gas phase ions generated from high molecular weight compounds. In one aspect, the invention provides devices and methods for determining the velocity, charged state or both of electrically charged particles and packets of electrically charged particles. In another aspect, the invention provides methods and devices for the time-of-flight analysis of electrically charged particles comprising spatially collimated sources. In another aspect, the invention relates to multiple detection using inductive detectors, improved methods of signal averaging and charged particle detection in coincidence.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
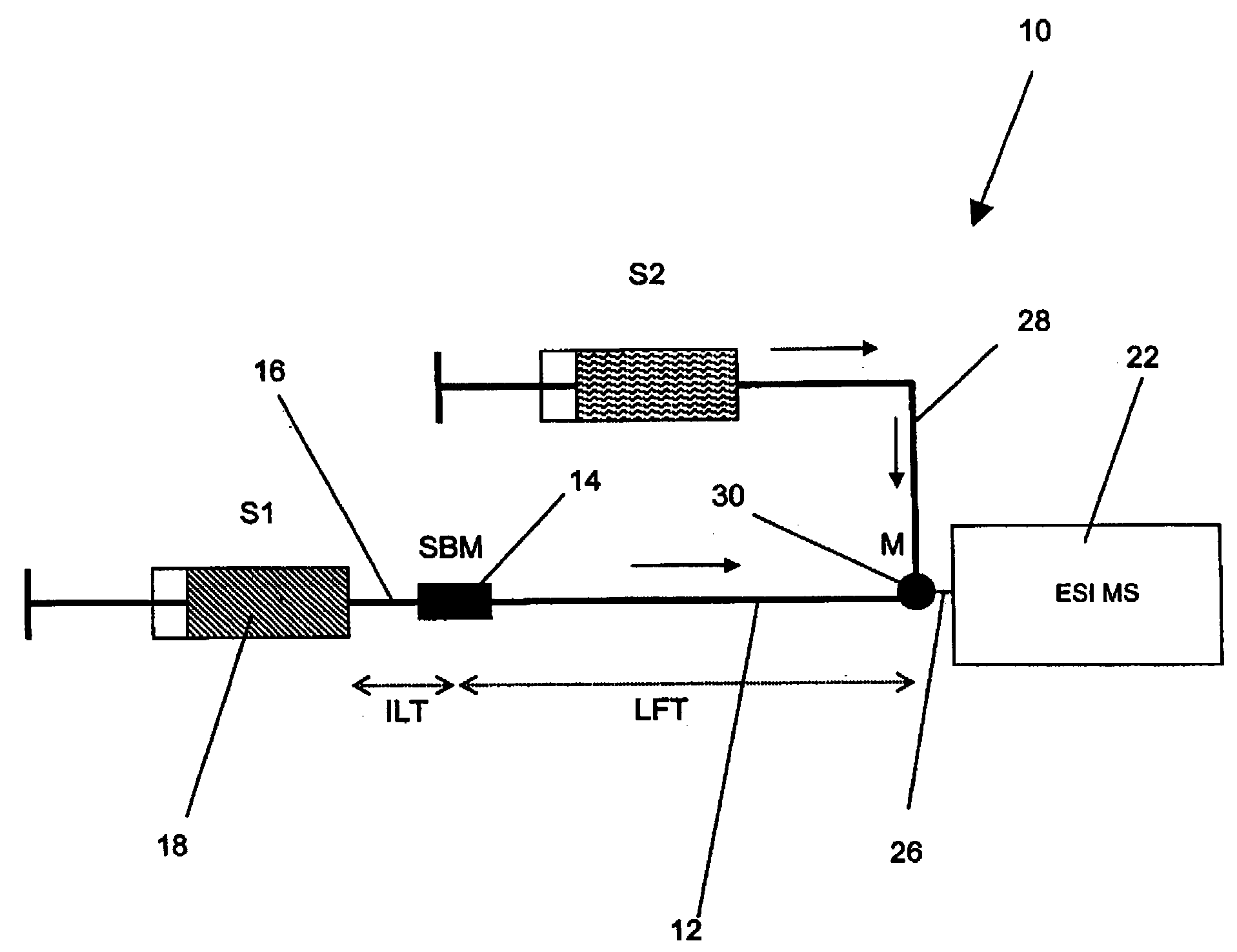
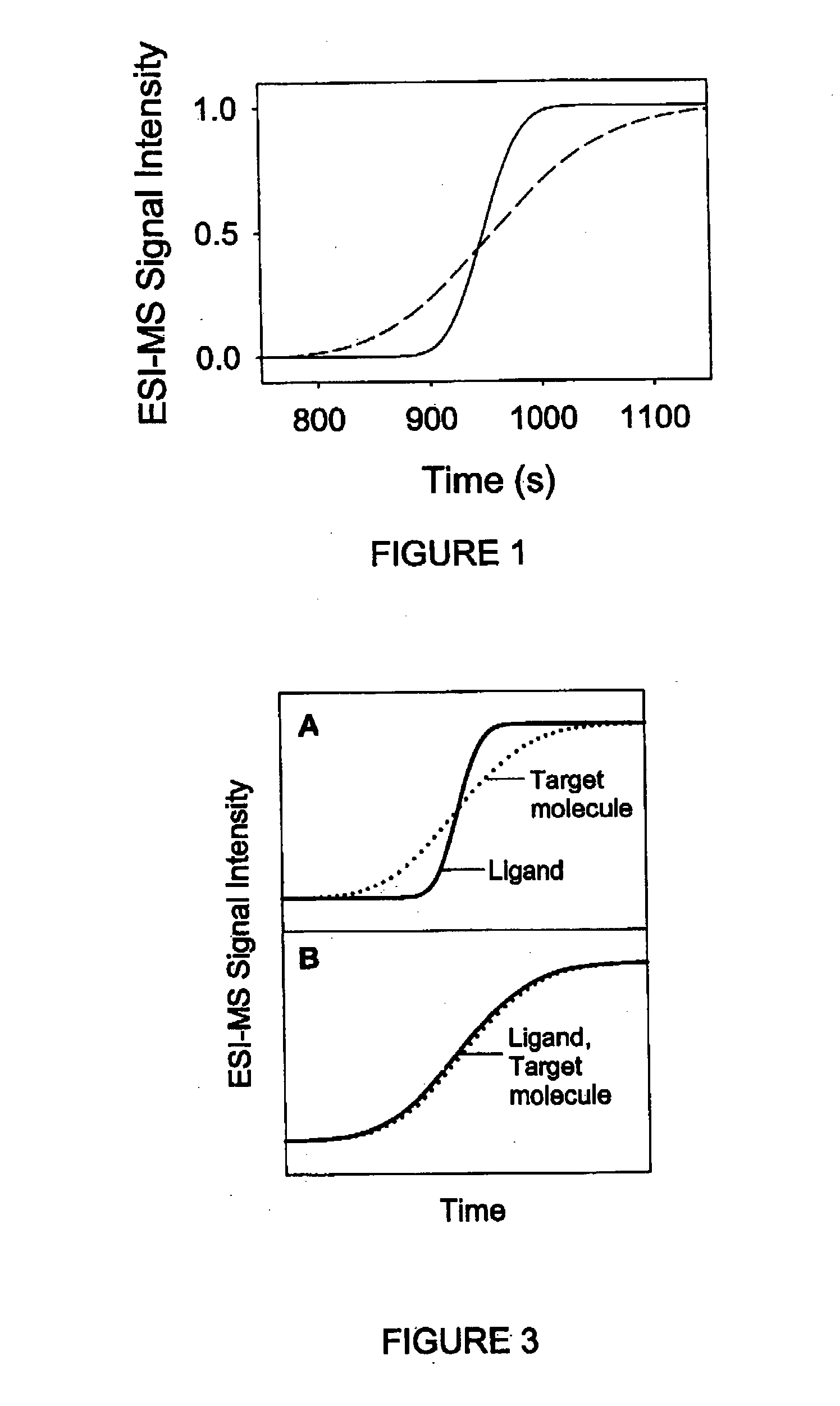
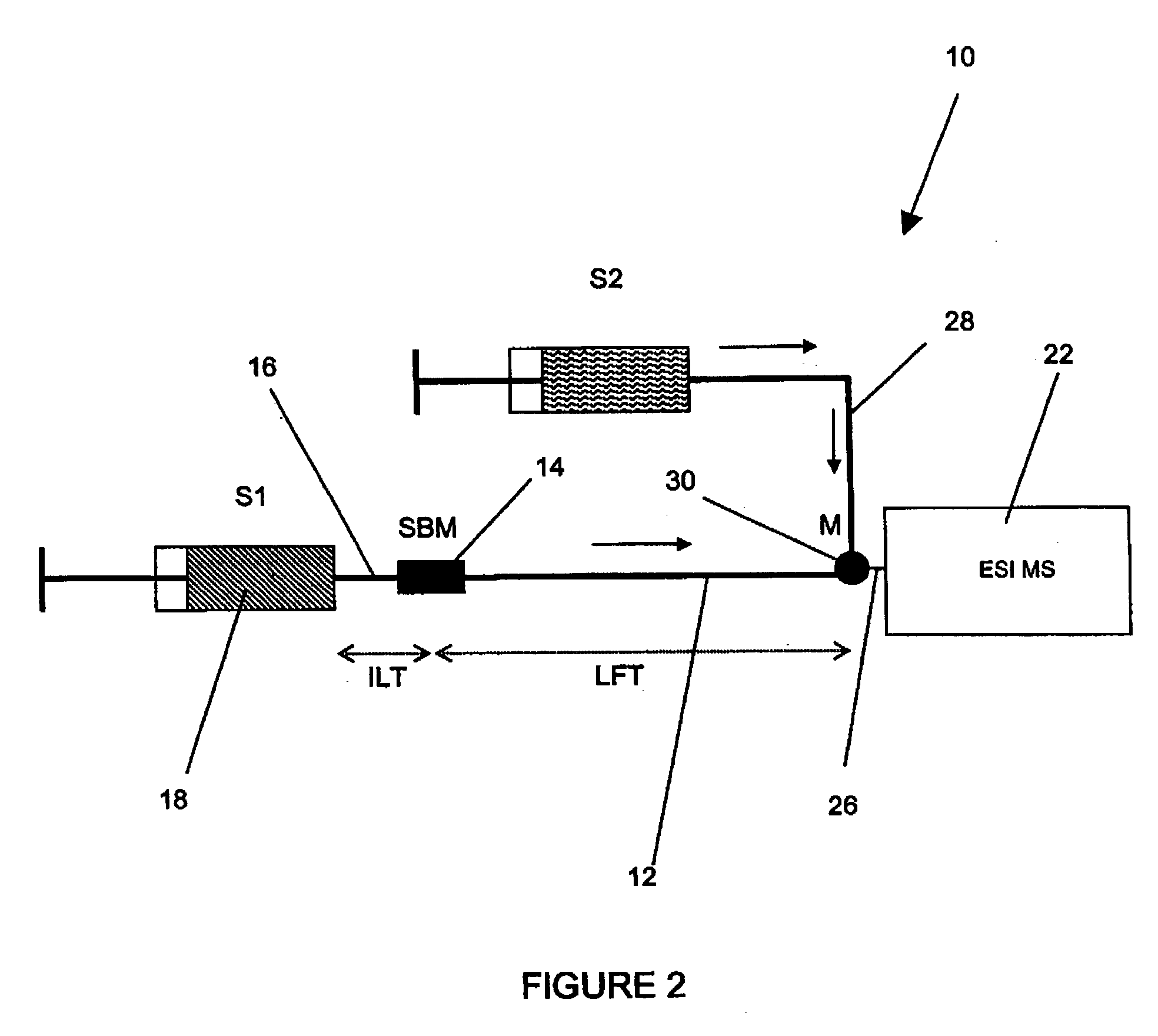
Method and apparatus for the detection of noncovalent interactions by mass spectrometry-based diffusion measurements
InactiveUS20030234356A1Accurate measurementShorten the timeSamples introduction/extractionSurface/boundary effectHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsGas phase
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for detecting the noncovalent binding of a potential ligand (such as a drug candidate) to a target, e.g. a biochemical macromolecule such as a protein. The method is based on the Taylor dispersion of an initially sharp boundary between a carrier solution, and an analyte solution that contains the potential ligand(s) and the target. Dispersion profiles of one or more potential ligands are monitored by mass spectrometry at the exit of the laminar flow tube. Potential ligands will usually be relatively small molecules that have large diffusion coefficients. In the absence of any noncovalent interactions in solution, very steep dispersion profiles are expected for these potential ligands. However, a ligand that binds to a large target in solution, will show an apparent diffusion coefficient that is significantly reduced, thus resulting in a more extended dispersion profile. Noncovalent binding can therefore be detected by monitoring dispersion profiles of potential ligands in the presence and in the absence of the target. In contrast to other mass spectrometry-based methods for detecting noncovalent interactions, this method does not rely on the preservation of specific noncovalent interactions in the gas phase. This method has an excellent sensitivity and selectivity, therefore it can be used for testing multiple potential ligands simultaneously. The method is therefore useful for the high throughput screening of compound libraries.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
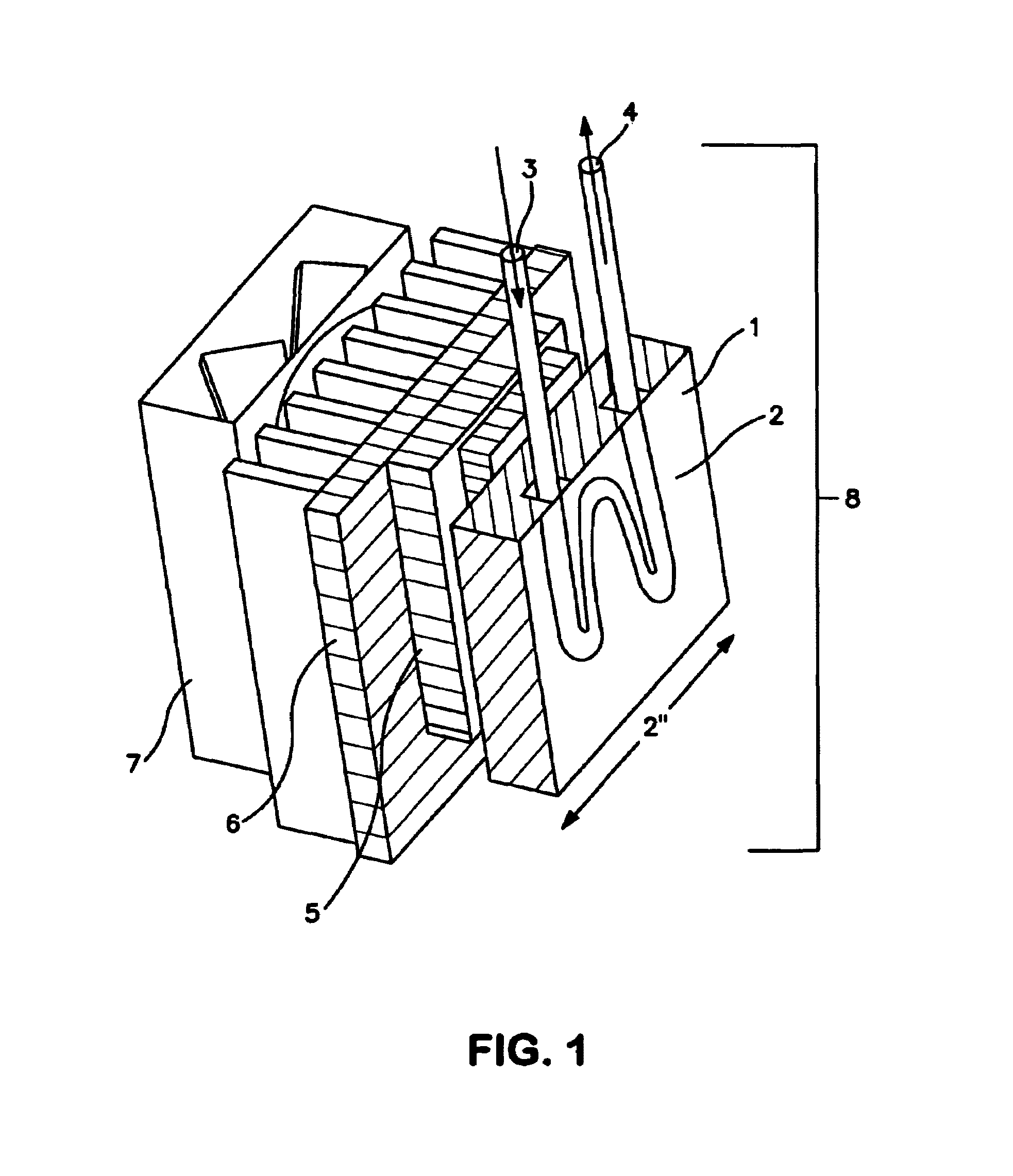
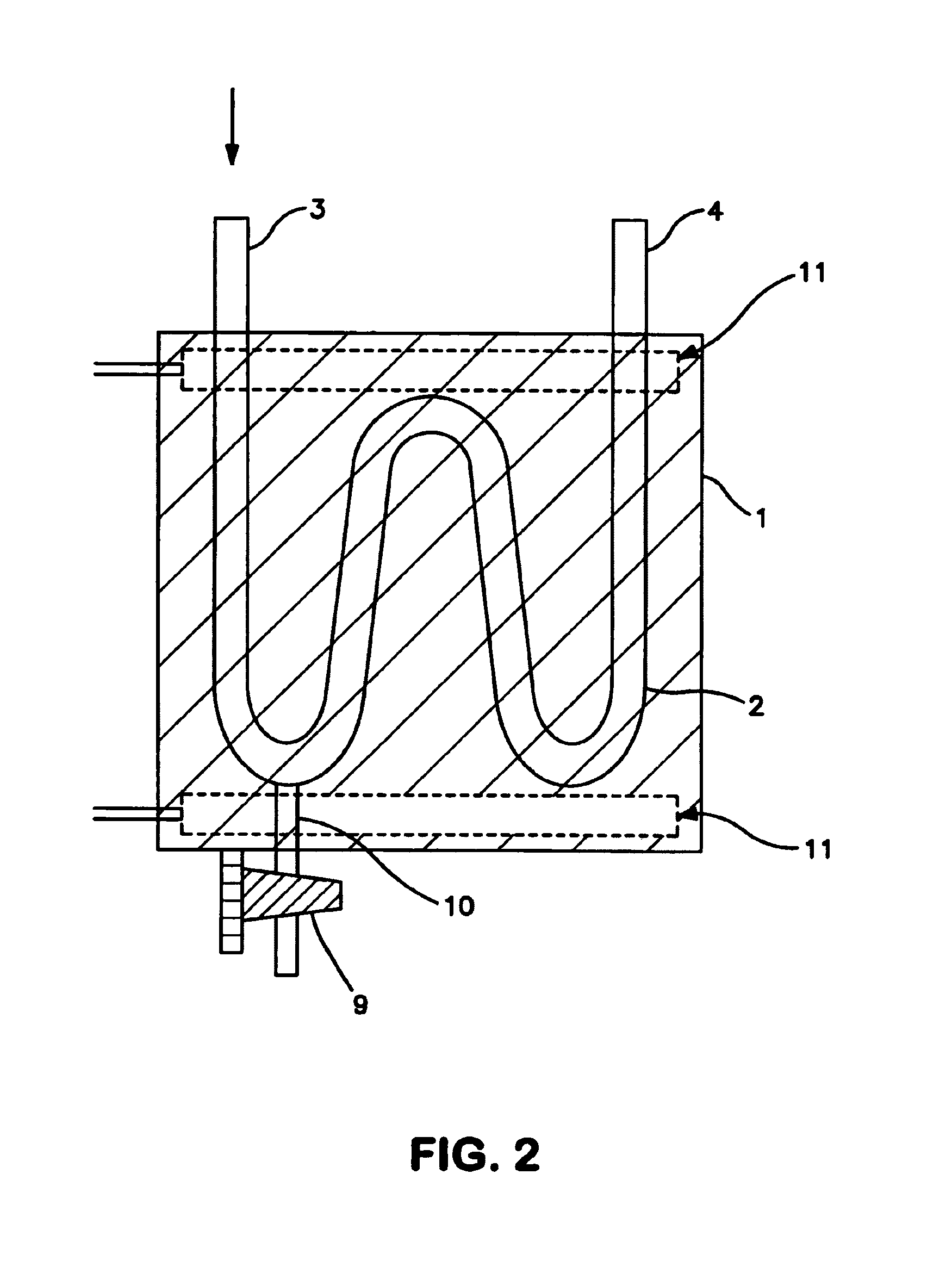
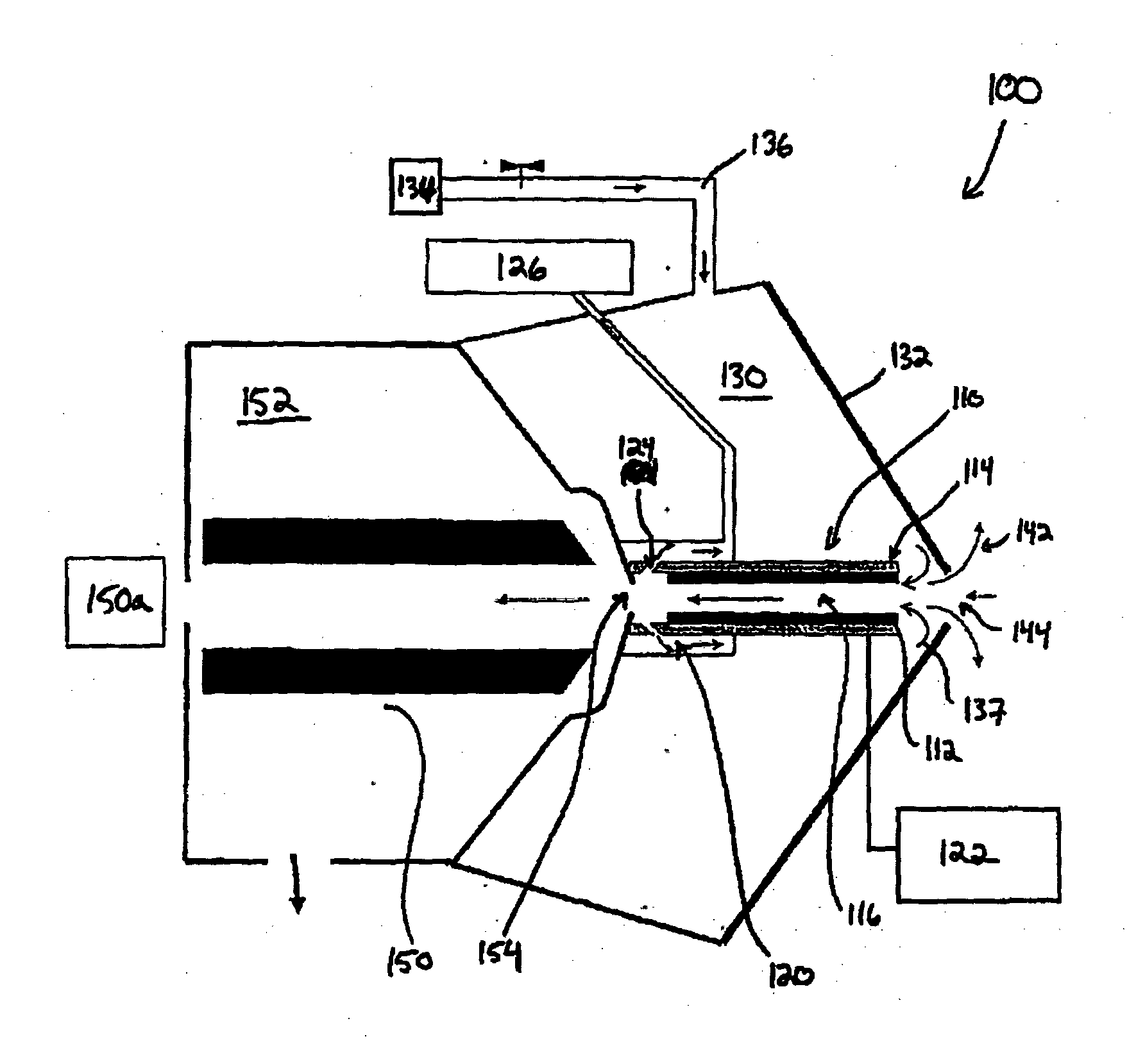
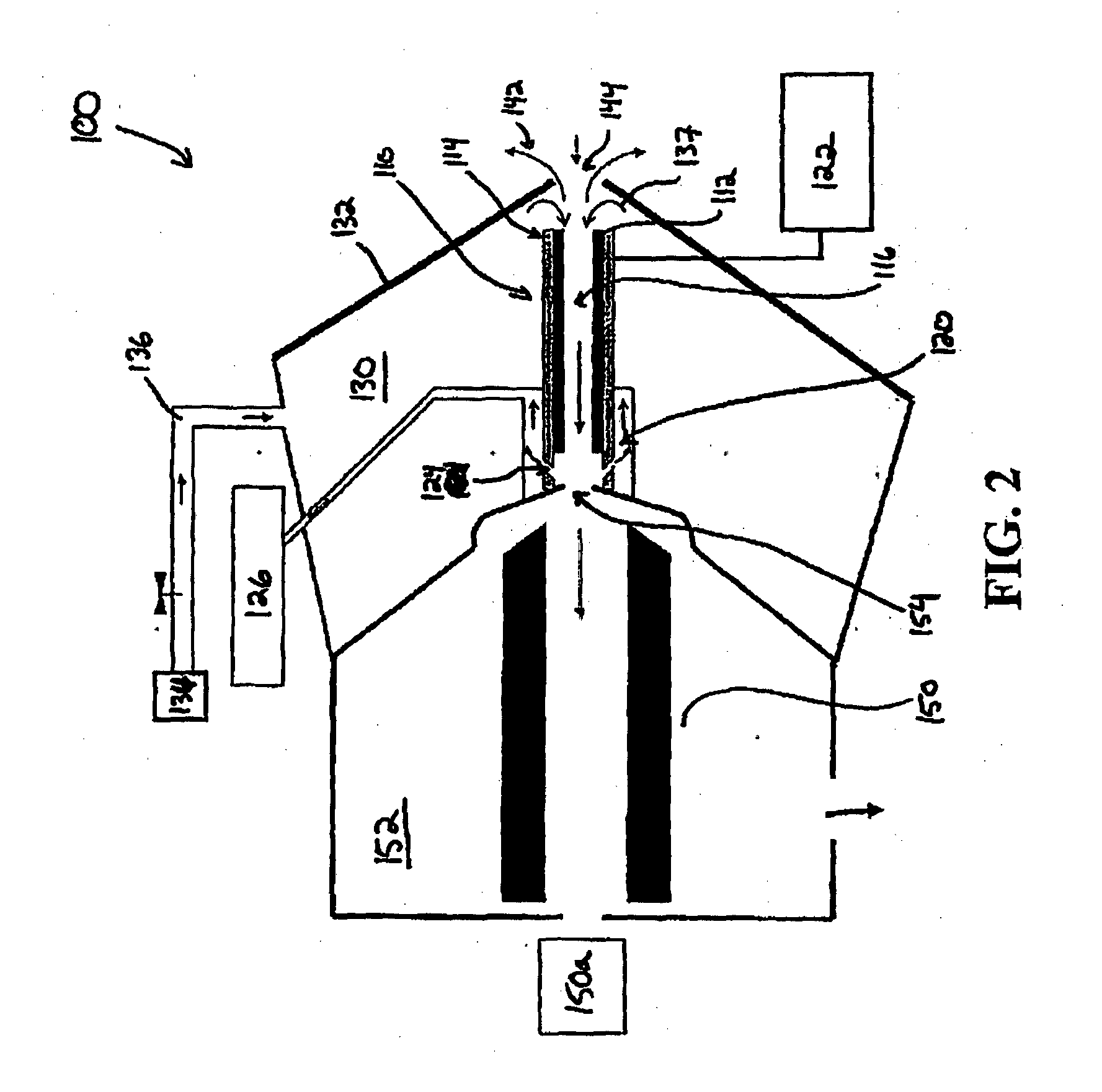
Aerosol mass spectrometer with particle size selection
InactiveCN103426712AReduce storageReduce the difficulty of analysisDynamic spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionSynchronous motorParticle beam
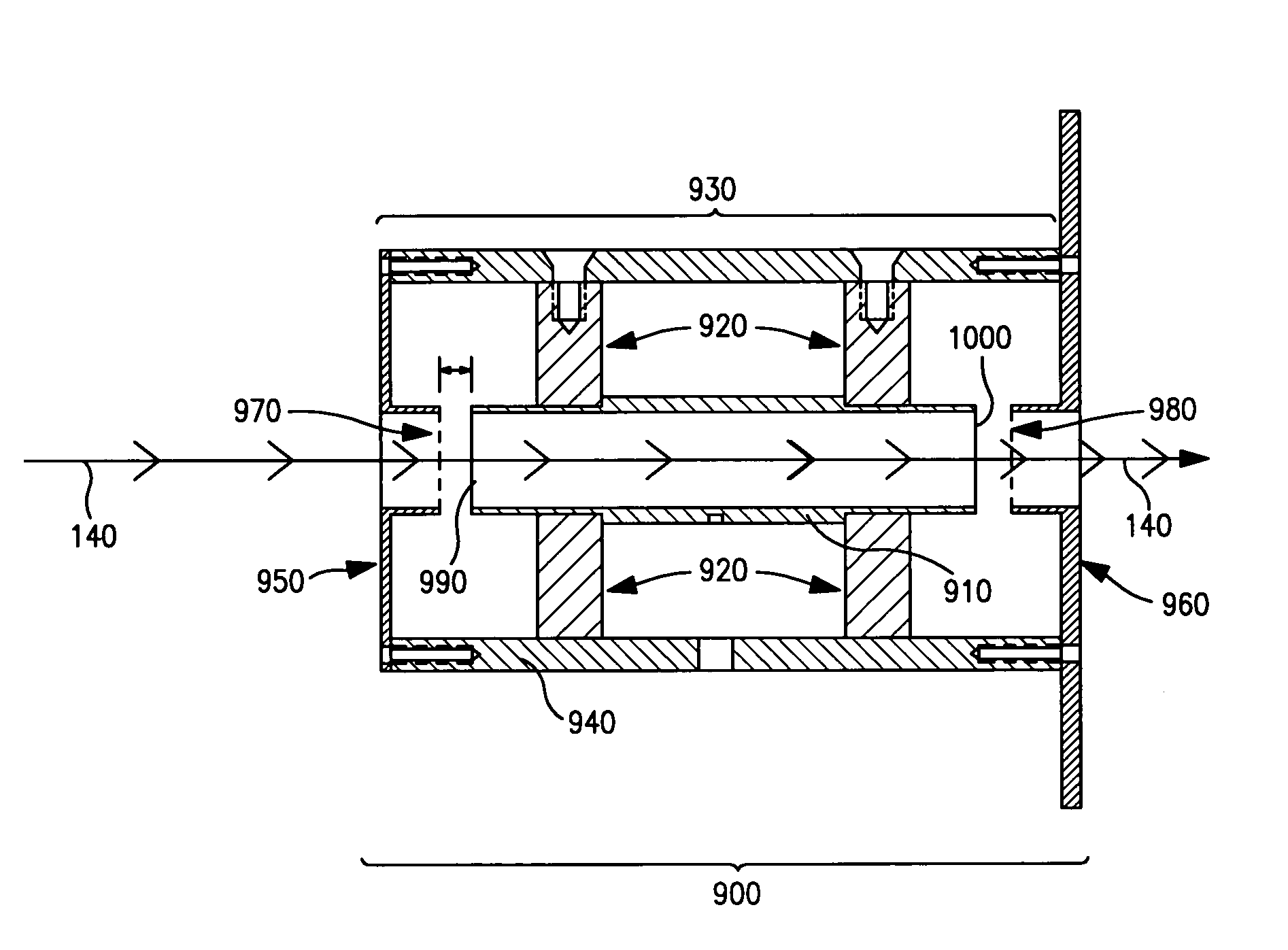
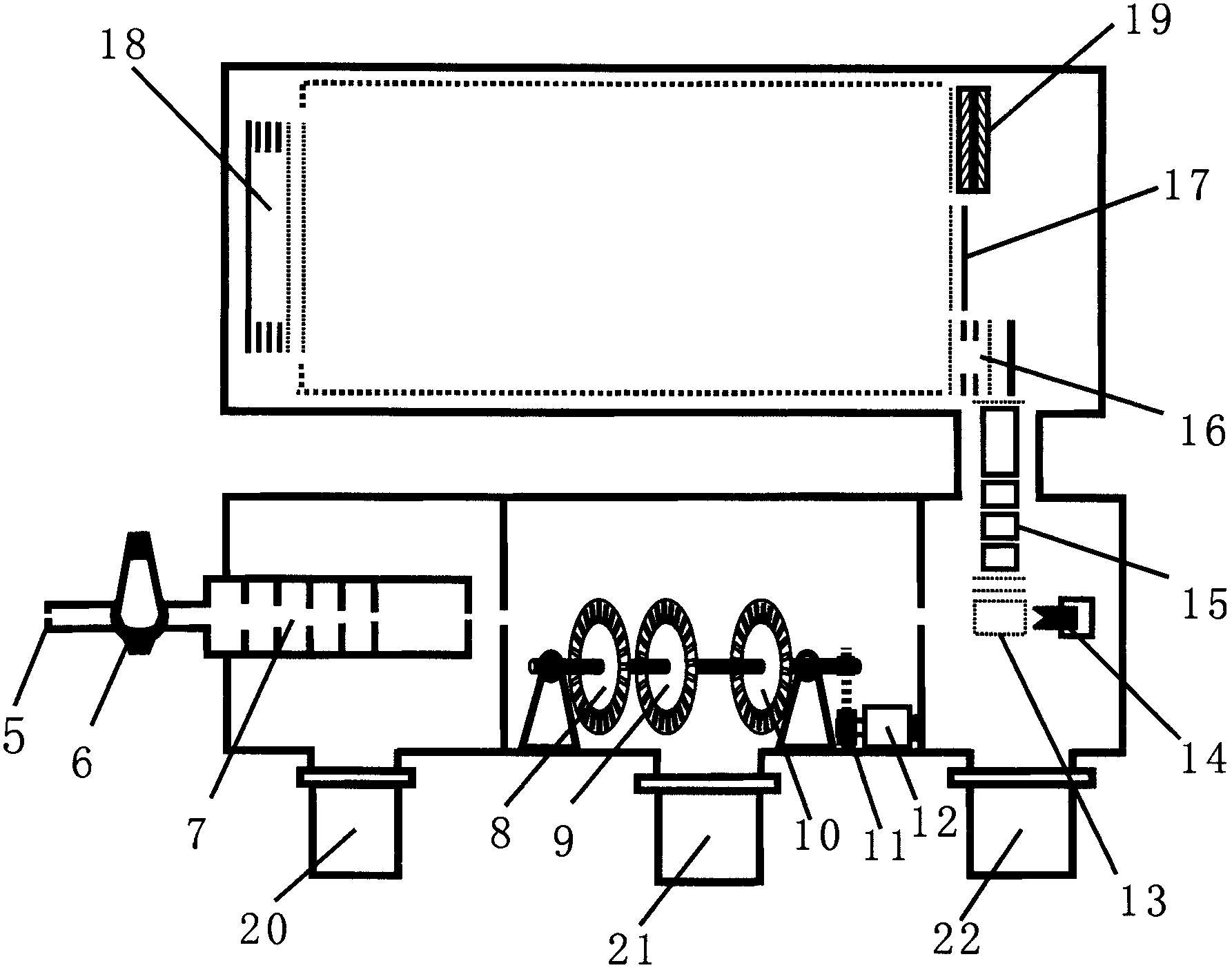
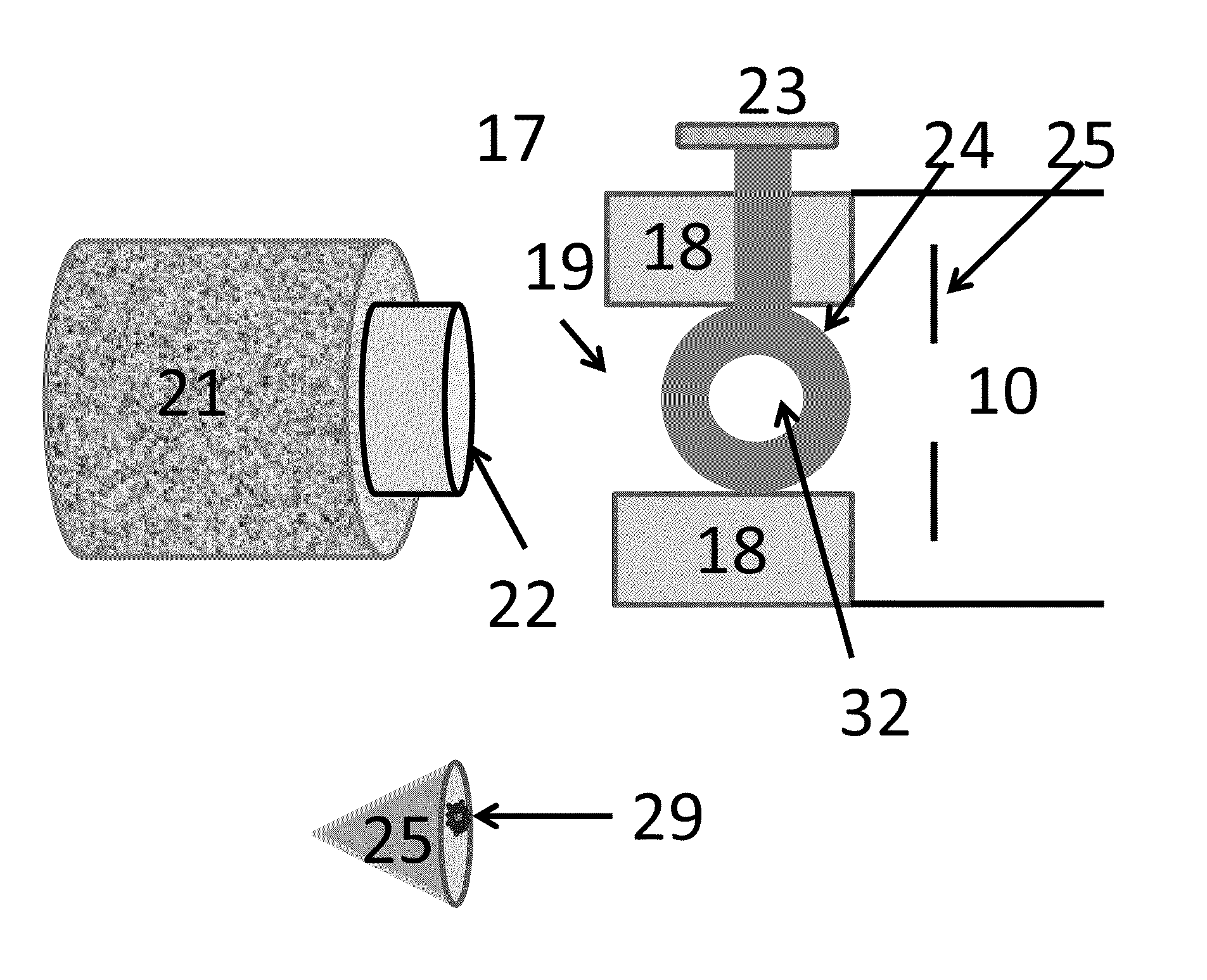
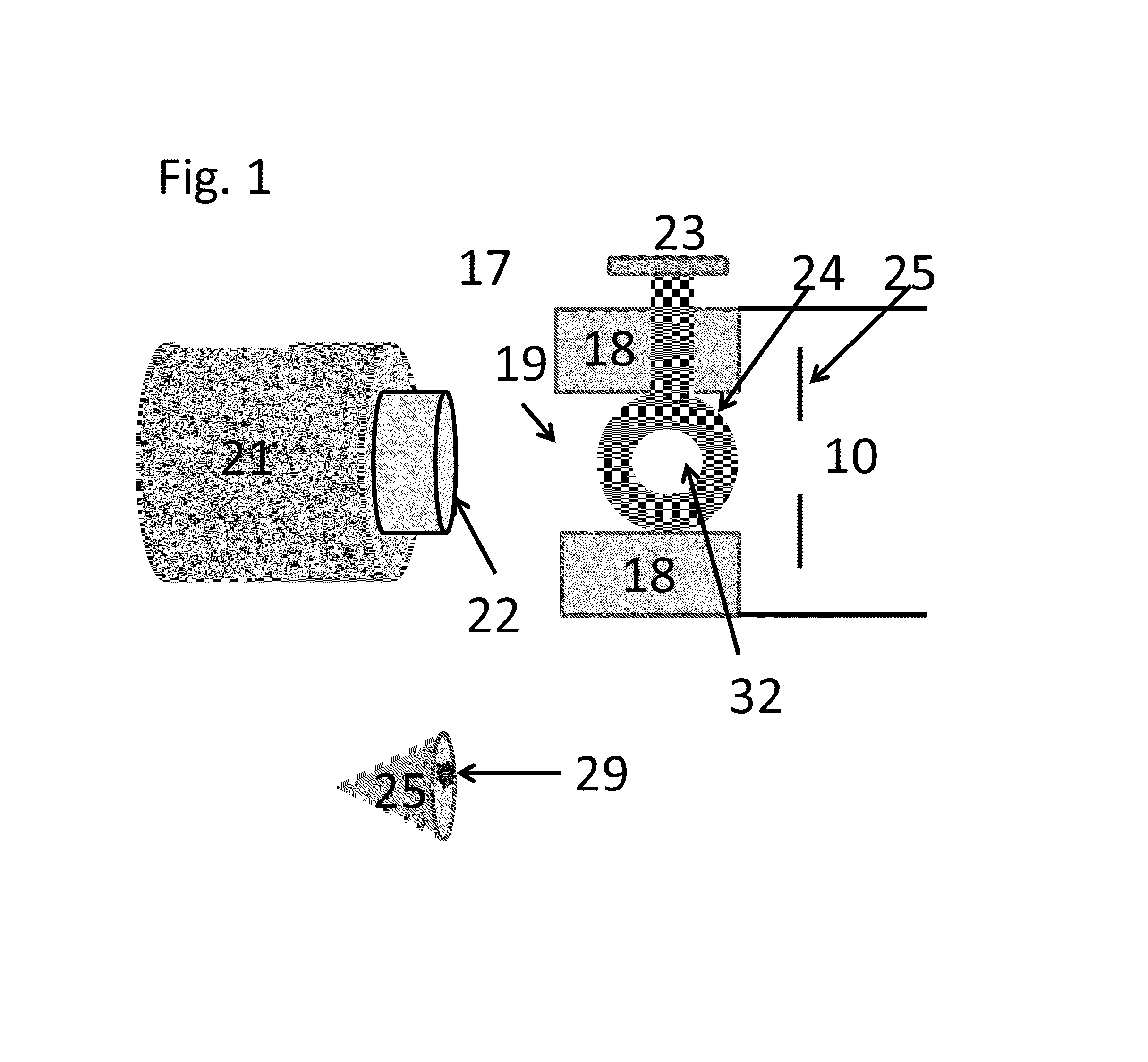
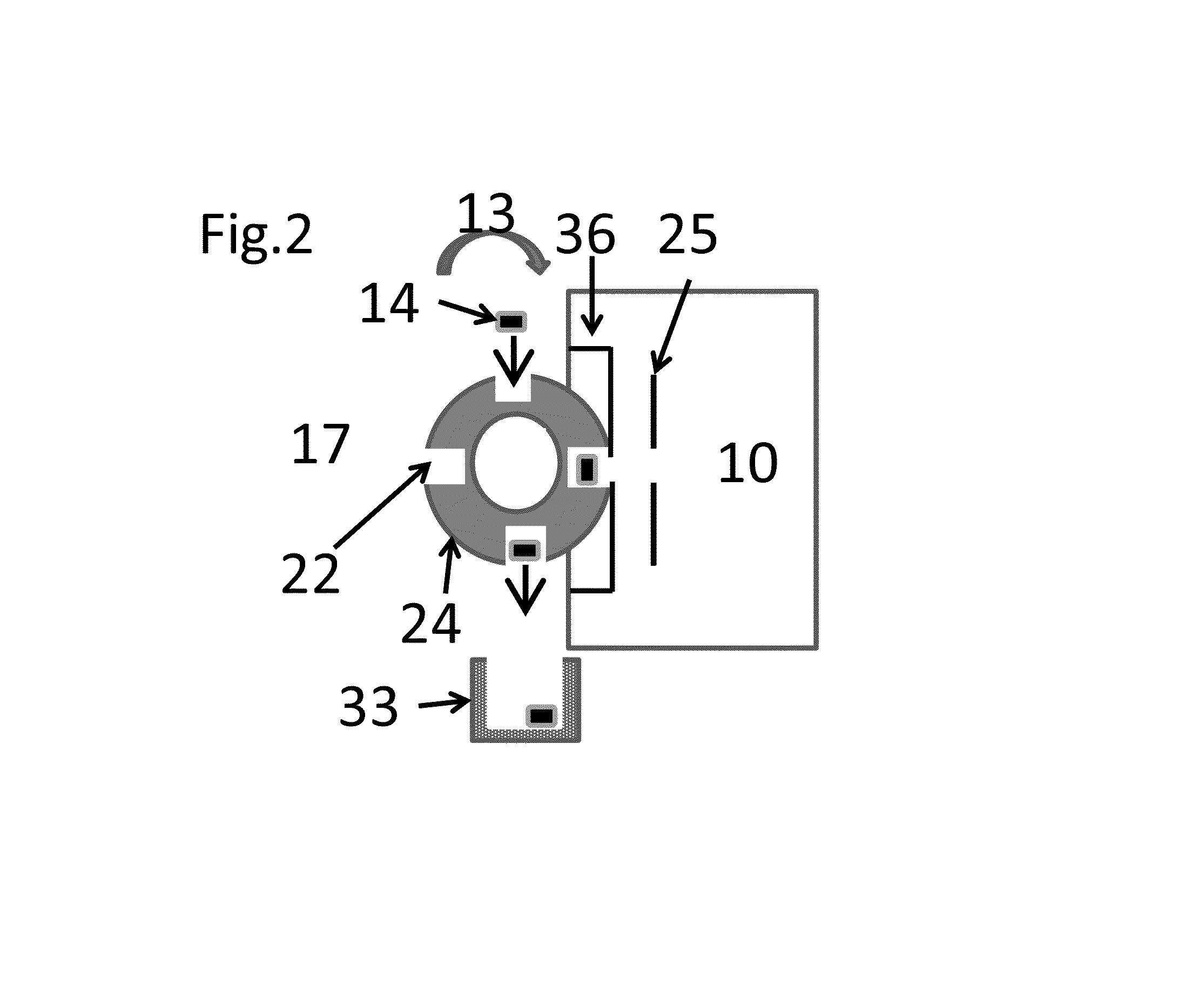
The invention applies for an aerosol mass spectrometer with particle size selection, wherein the aerosol mass spectrometer can simultaneously select the particle size, the concentration and the chemical component of the atmospheric aerosol. The aerosol mass spectrometer uses a sampling hole with the diameter of 100 micrometers to carry out direct sampling on an aerosol in a natural environment; aerosol particles are focused into a particle beam flow with the 0.5-milimeter diameter by a pneumatic focusing lens; the aerosol particles are selected by a particle size selector that is formed by three coaxial rotating plates with slits, wherein the rotating plates of the particle size selector are driven by a synchronous motor and the frequency of the synchronous motor power supply can be adjusted continuously; an aerosol particle that is selected by the particle size selector is gasified by a gasifier with the high temperature from 600 to 700 degrees; gas after gasification is ionized by an electron collision ionizer; a generated ion is detected by a W type reflection type mass spectrum apparatus so as to obtain the mass spectrum of the aerosol. Therefore, information including the particle size, the concentration and the chemical composition of the organic aerosol can be obtained by analyzing the sampling rate, the frequency of the synchronous motor power supply and the obtained mass spectrum.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and methods for ionizing compounds using matrix-assistance for mass spectrometry and ion mobility spectrometry
ActiveUS9105458B2Speed up evaporationIncreased desolvationSamples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGas phaseMass analyzer
An ionization method for use with mass spectrometry or ion mobility spectrometry is a small molecule compound(s) as a matrix into which is incorporated analyte. The matrix has attributes of sublimation or evaporation when placed in vacuum at or near room temperature and produces both positive and negative charges. Placing the sample into a region of sub-atmospheric pressure, the region being in fluid communication with the vacuum of the mass spectrometer or ion mobility spectrometer, produces gas-phase ions of the analyte for mass-to-charge or drift-time analysis without use of a laser, high voltage, particle bombardment, or a heated ion transfer region. This matrix and vacuum assisted ionization process can operate from atmosphere or vacuum and produces ions from large (e.g. proteins) and small molecules (e.g. drugs) with charge states similar to those observed in electrospray ionization.
Owner:MSTM LLC
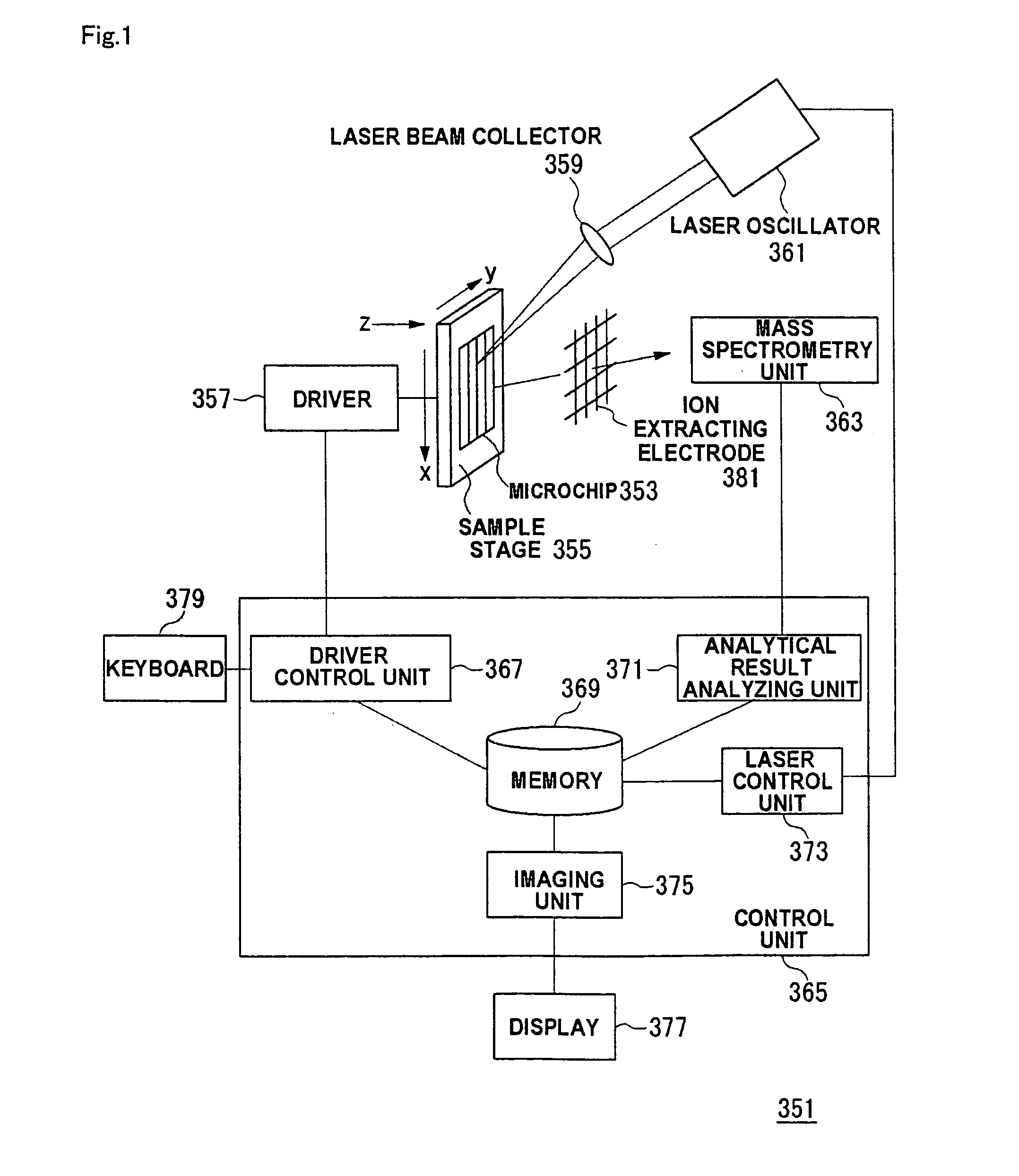
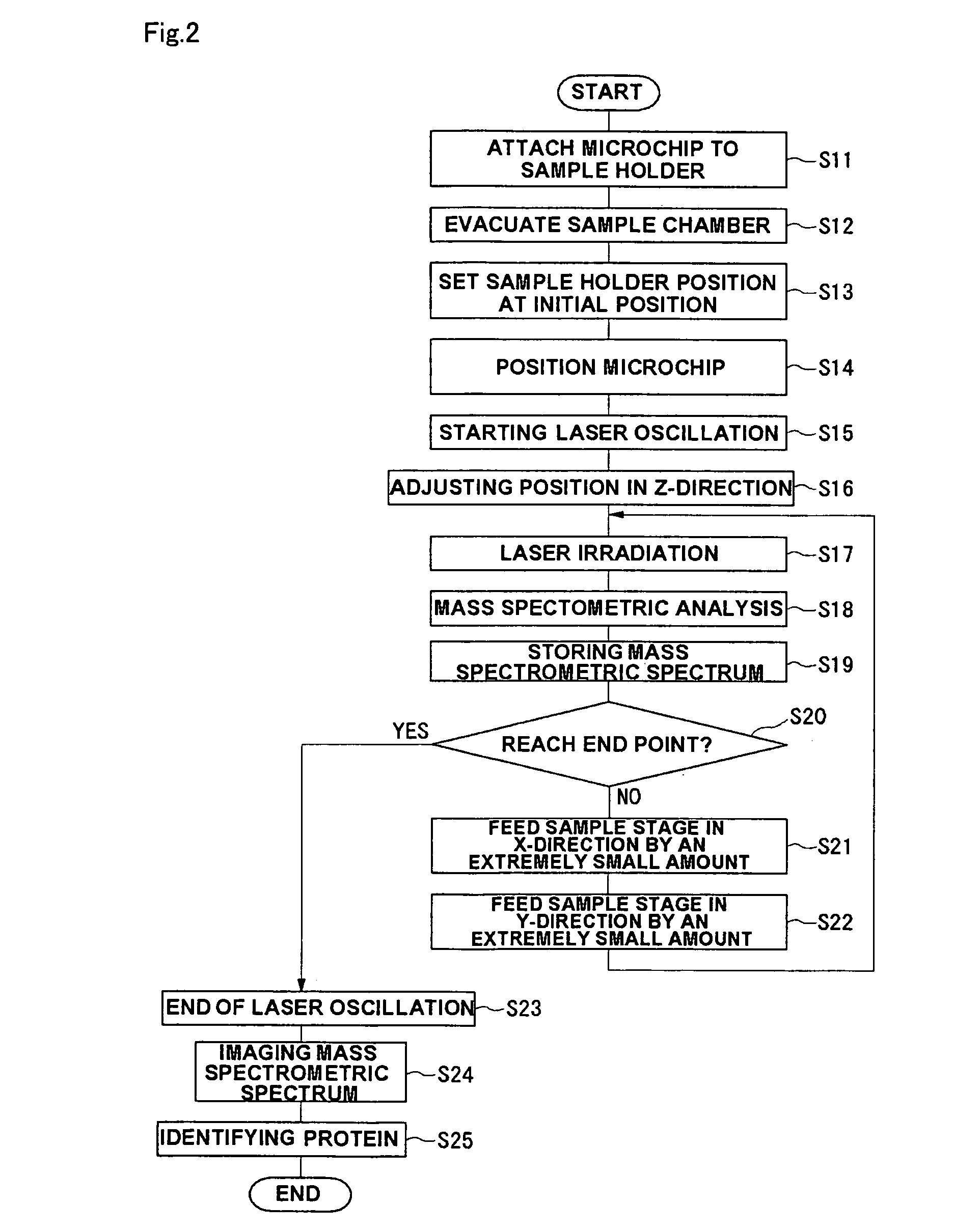
Mass spectrometric system and mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7586091B2Efficiently sample separationImprove accuracyElectrolysis componentsComponent separationDisplay deviceMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
After a sample is previously separated into plural components in a channel formed in a microchip (353), the channel is irradiated along a separation direction with a laser beam from a laser oscillator (361) to sequentially ionize each fraction separated in the channel. The ionized fraction is detected by a mass spectrometry unit (363) and analyzed by an analytical result analyzing unit (371). The analytical result is stored in a memory (369) while associated with position information in a driver control unit (367) and information on laser beam irradiation condition in a laser control unit (373), and the analytical result is imaged by an imaging unit (375). The imaged analytical result is displayed on a display (377).
Owner:NEC CORP
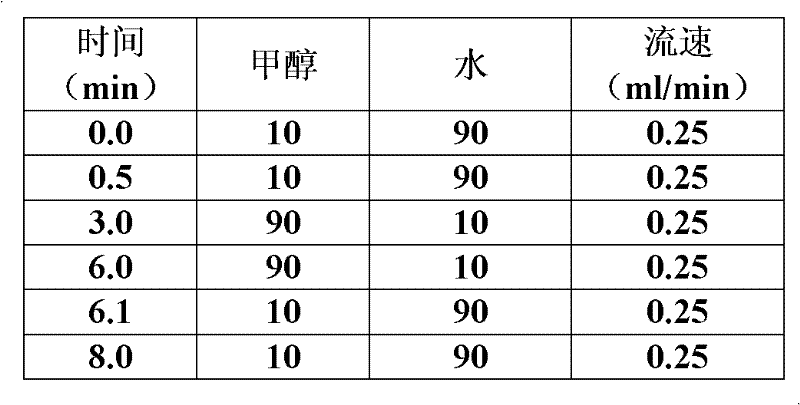
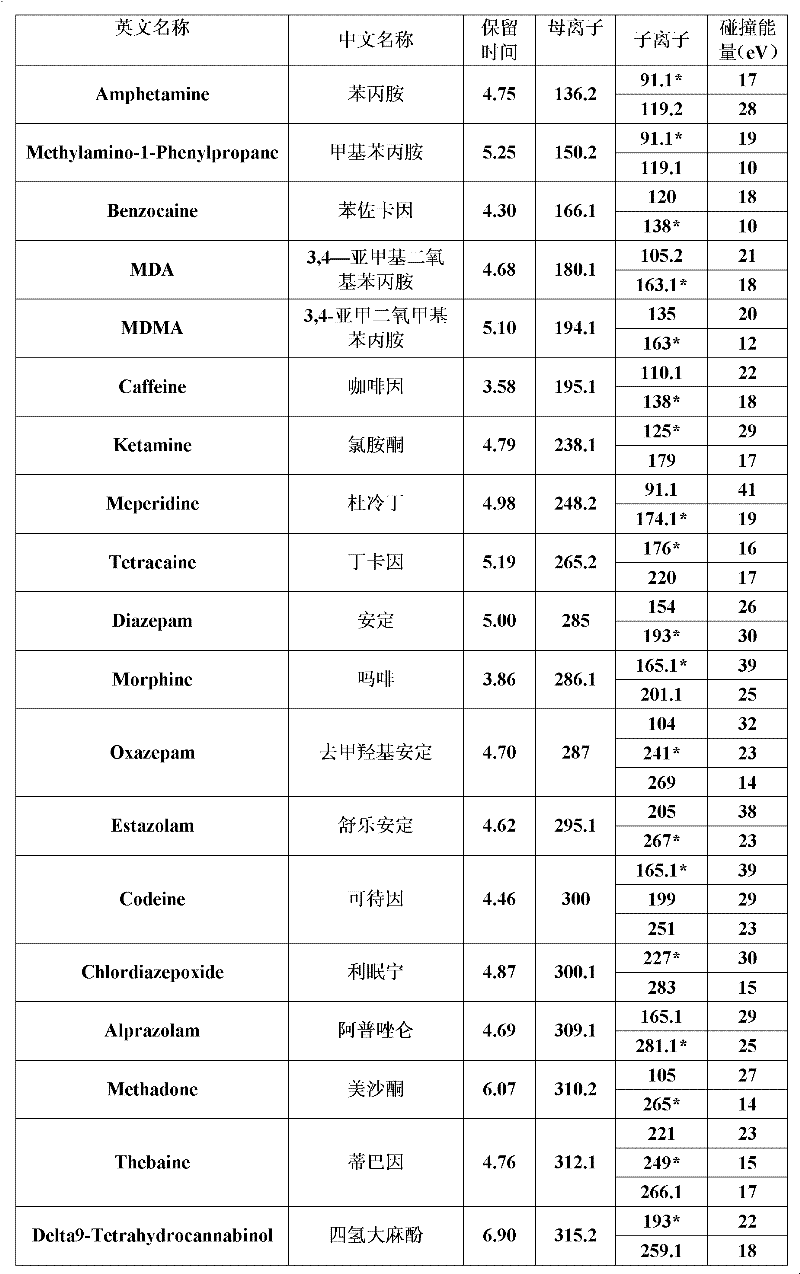
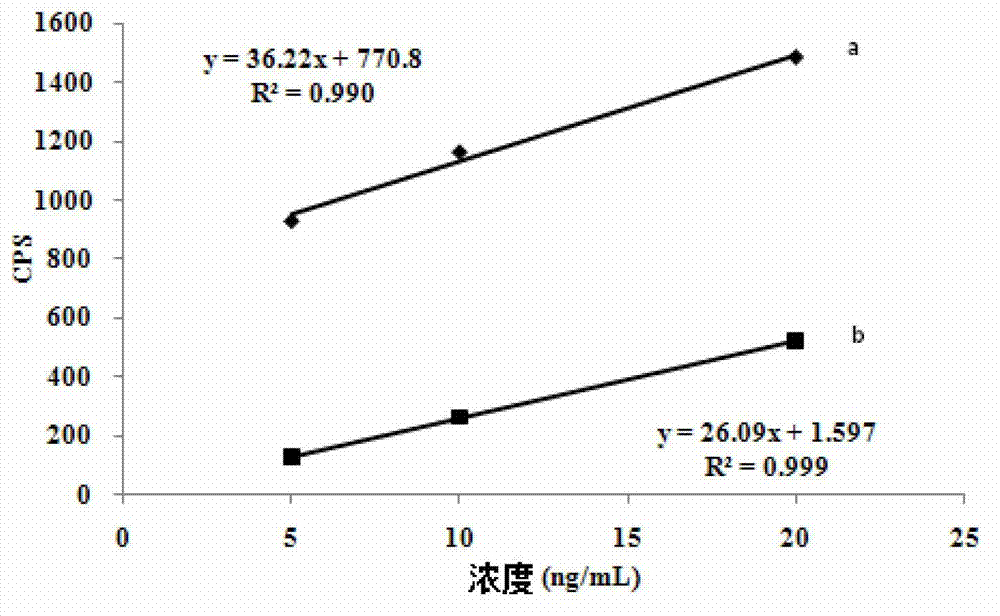
Method for detecting 33 kinds of narcotic drugs in urine by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
InactiveCN102200530AThe pre-processing process is simpleEasy to operateComponent separationRetention timeNarcotic drugs
The invention discloses a method for detecting 33 kinds of narcotic drugs in urine by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: carrying out extraction and purification on samples by using a liquid-liquid extraction method, adding a sodium hydroxide solution into the obtained object so as to realize albuminous degeneration and pH-value adjustment of the obtained object, and adding ethyl acetate into the obtained mixture so as to carry out extraction on the obtained mixture through liquid-liquid extraction, then obtaining to-be-tested samples; carrying out determination on the to-be-tested samples by using a liquid chromatography-tandem quadrupole mass spectrometer, wherein, except for that barbiturates in the to-be-tested samples are analyzed in a negative ion mode, the other compounds in the to-be-tested samples are analyzed in a positive ion mode; and through taking the relative retention time of each narcotic drug and the abundance ratio of a monitoring ion pair of each narcotic drug as the qualitative basis, calculating the residual quantity of each narcotic drug in the samples according to the peak area or peak height of each narcotic drug. By using the method disclosed by the invention, 33 kinds of narcotic drugs can be analyzed at one time, and the test cost is reduced, meanwhile, the method is strong in pertinence, simple in operation, fast in detection speed, wide in detection surface, and easy to popularize and apply. The method can be used in the quick detection and positive result confirmation of entry-exit inspection and quarantine bureaus, disease control centers and public security departments.
Owner:LIANYUN PORT IMMIGRATION INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA
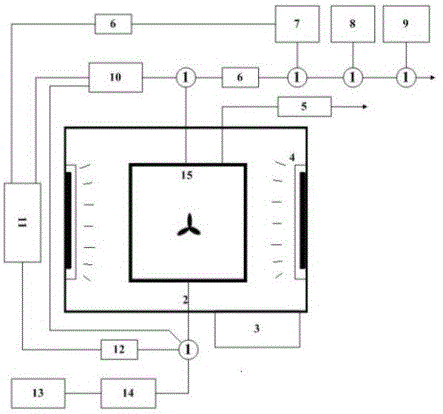
Method and device for studying mechanism that secondary organic aerosol is produced by photo-oxidation transformation of fuel coal
ActiveCN105606758AAccurate captureSimple and fast operationChemical analysis using combustionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansProton-transfer-reaction mass spectrometrySpectrometer
The invention discloses a method for studying a mechanism that secondary organic aerosol is produced by photo-oxidation transformation of fuel coal. The method comprises the steps: subjecting raw coal to chemical component and particle size analysis via a single particle aerosol mass spectrometer according to the principle of laser ablation; detecting chemical component and particle size distributions of volatile organic matters and particulate matters in fuel coal by using proton transfer reaction mass spectrometry and single particle aerosol mass spectrometry; by using a smog box system, inspecting parameters such as chemical components and particle size of gas and particulate matters in the fuel coal in a photochemical reaction within different combustion times, and their variation trends, analyzing intermediate state data, and comparing data of a static coal erosion experiment and a static coal combustion experiment to obtain the mechanism that secondary organic aerosol is produced by photo-oxidation transformation of fuel coal. The invention also discloses a device. It is possible to simulate transformation processes of the fuel coal in different atmospheric environments, accurately capture intermediate state products of the fuel coal and quantify the effects of coal combustion and post-combustion photo-oxidation.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Application of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry in drug testing of hemin
The invention relates to an application of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry in drug testing of hemin. A method for measuring concentration of stable isotope iron in animal plasma is carried out by an ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry) method and comprises the following steps of: providing an inductively coupled plasma source mass spectrometer; determining operating conditions of the ICP-MS; providing stable isotope iron powder, marked hemin, internal standard elements and the like; preparing standard solution and internal standard solution; preparing ICP-MS diluent; establishing a standard curve; measuring the stable isotope iron concentration in the plasma; and adding the ICP-MS diluent into a sample tube containing animal plasma sample containing iron, mixing uniformly and putting the sample tube into a refrigerator to be refrigerated, and determining the concentration of the iron in the plasma by the obtained standard curve. The application of the inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry in the drug testing of the hemin has well performances, e.g., the method has well quantification lower limit, accuracy, absolute recovery test, sample stability, medium effect and quality control requirement, and can be taken as a content measurement method for analyzing the content of the stable isotope iron in a biological sample such as the plasma.
Owner:新疆科丽生物技术有限公司
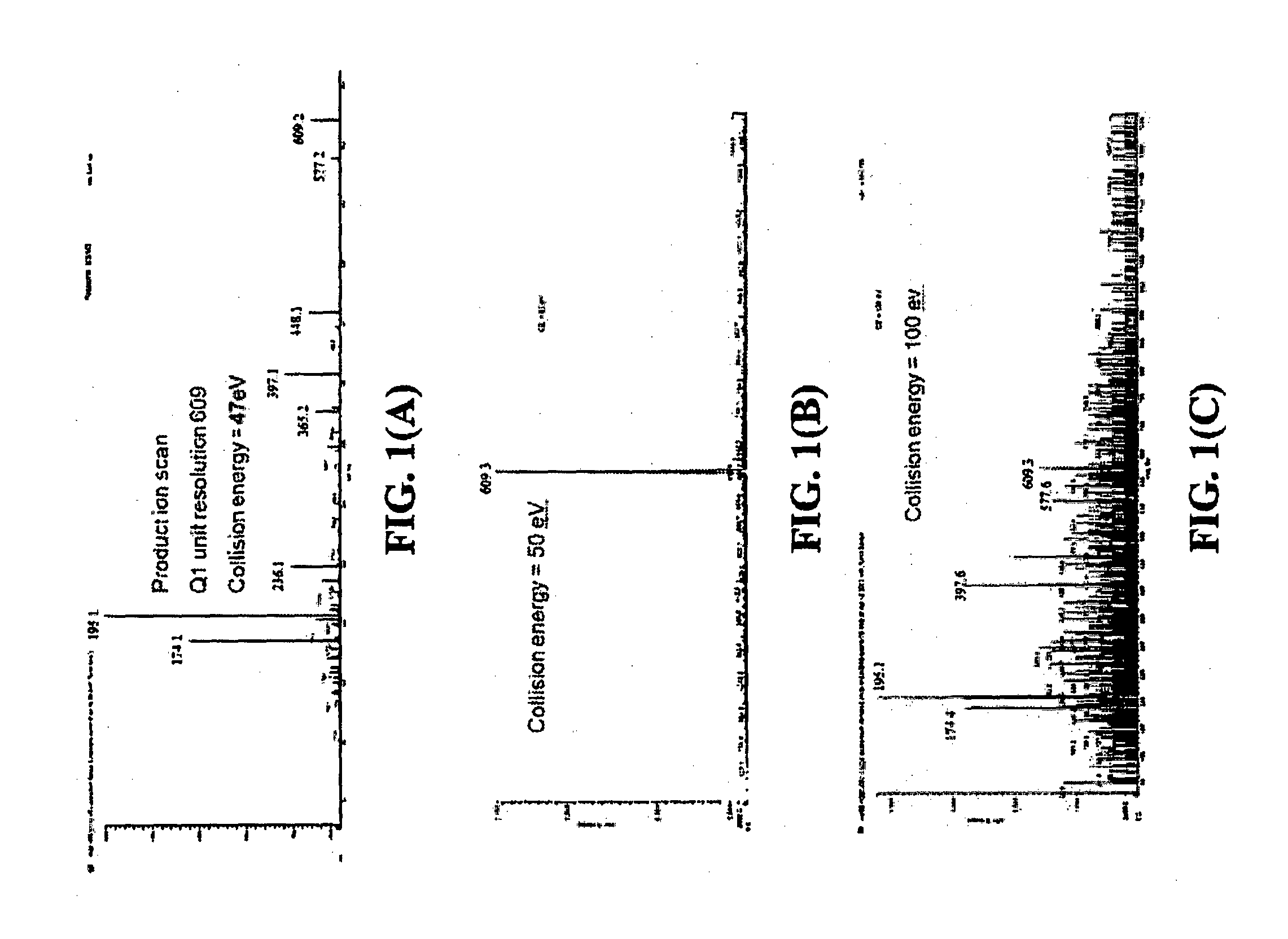
Methods and systems for matching product ions to precursor in tandem mass spectrometry
InactiveUS8395113B2Improve accuracyIncrease powerMolecular entity identificationIsotope separationElemental compositionMass analyzer
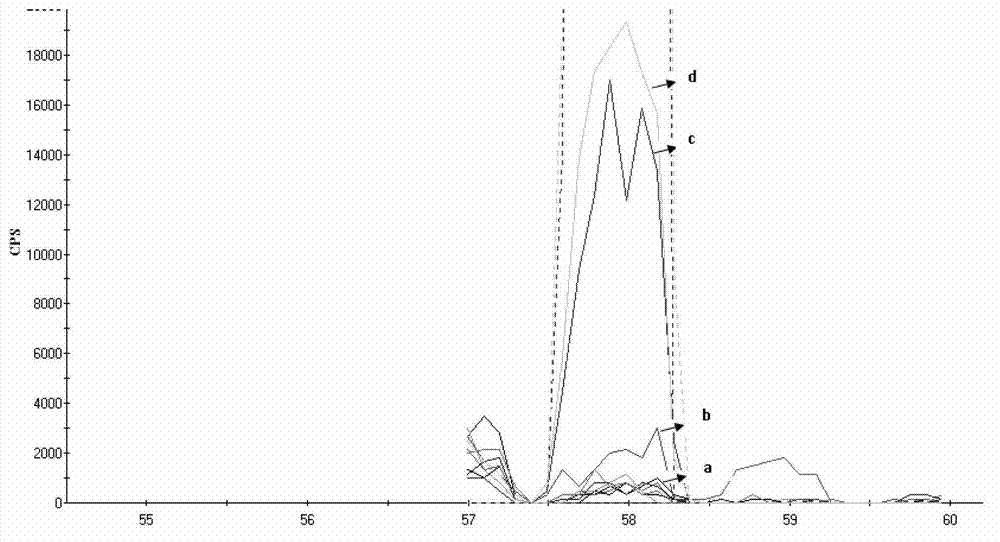
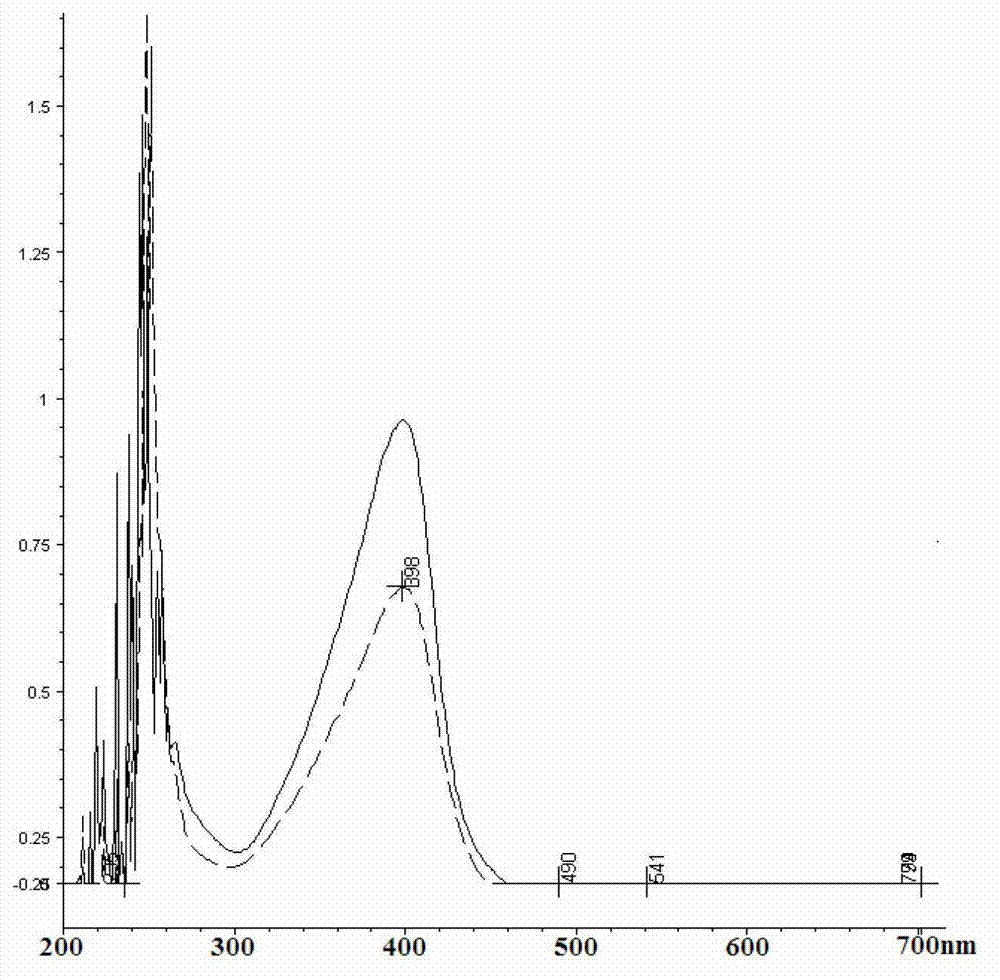
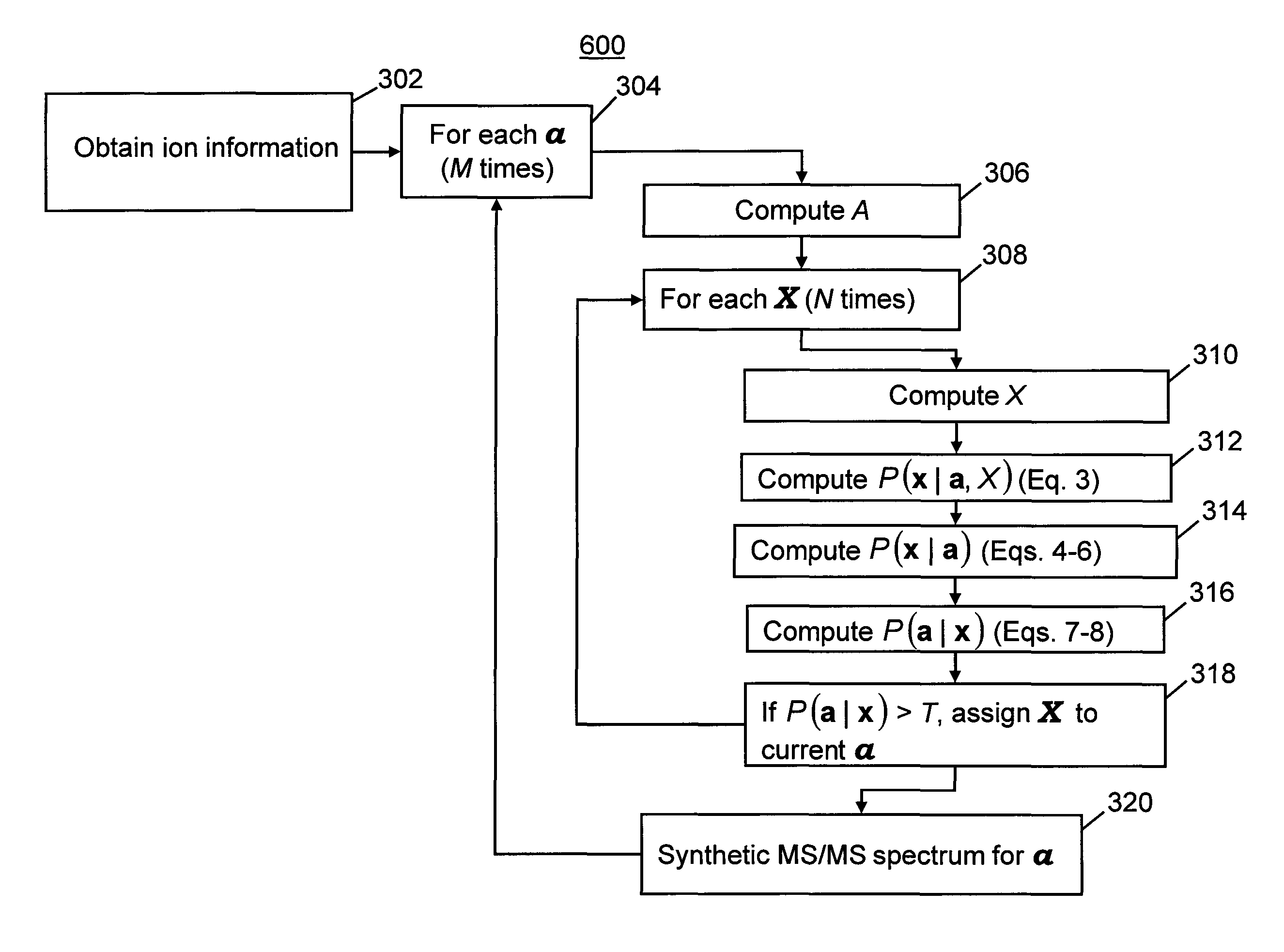
Methods of tandem mass spectrometry (MS / MS) for use in a mass spectrometer are disclosed, the methods characterized by the steps of: (a) providing a sample of precursor ions comprising a plurality of ion types, each ion type comprising a respective range of masses; (b) generating a mass spectrum of the precursor ions using the mass spectrometer so as to determine a respective mass value or mass value range for each of the precursor ion types; (c) estimating an elemental composition for each of the precursor ion types based on the mass value or mass value range determined for each respective ion type; (d) generating a sample of fragment ions comprising plurality of fragment ion types by fragmenting the plurality of precursor ion types within the mass spectrometer; (d) generating a mass spectrum of the fragment ion types so as to determine a respective mass value or mass value range for each respective fragment ion type; (e) estimating an elemental composition for each of the fragment ion types based on the mass value or mass value range determined for each respective fragment ion type; and (f) calculating a set of probability values for each precursor ion type, each probability value representing a probability that a respective fragment ion type or a respective pair of fragment ion types was derived from the precursor ion type. Some embodiments may include a step (g) of generating a synthetic MS / MS spectrum for each respective precursor ion type based on the calculated probability values.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
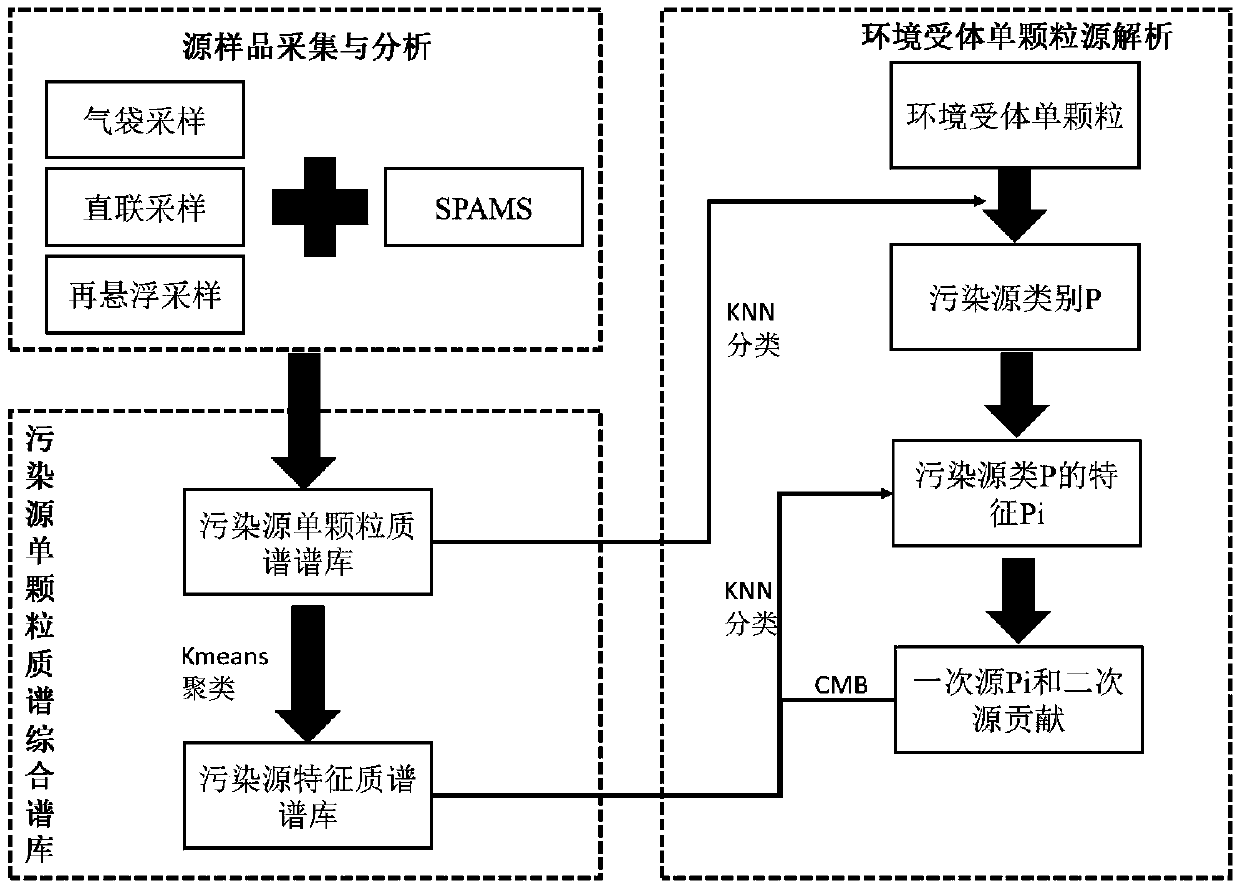
Method for performing particle source analysis by using single-particle aerosol mass spectrometer
InactiveCN108680473AImprove time resolutionHigh particle size resolutionCharacter and pattern recognitionParticle size analysisSecondary emissionNear neighbor
The invention provides a method for performing particle source analysis by using a single-particle aerosol mass spectrometer and relates to the field of atmospheric particle source analysis. Accordingto the method, a KNN (K Nearest Neighbor) classifier and a CMB (Cosmic Microwave Background) source analysis model are combined, single-particle mass spectrometry information of the pollution sourceas well as environmental receptor single-particle mass spectrometry characteristic and particle size information are fully utilized, the contribution of the primary emission source and secondary emission source of the particles on single environmental receptor particle can be rapidly solved, and refined source analysis results with high time resolution and high particle size resolution can be obtained. The method has excellent popularization and application prospects.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Ionizable isotopic labeling reagents for relative quantification by mass spectrometry
ActiveUS7982070B2Improve ETD analysisConvenient charging statusComponent separationOrganic compound preparationMetaboliteIsotopic labeling
Relative quantification of metabolites by Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry (ESI-MS) requiring a mechanism for simultaneous analysis of multiple analytes in two or more samples. Labeling reagents that are reactive to particular compound classes and differ only in their isotopic kit facilitating relative quantification and providing tangible evidence for the existence of specific functional groups. Heavy and light isotopic forms of methylacetimidate were synthesized and used as labeling reagents for quantification of amine-containing molecules, such as biological samples. Heavy and light isotopic forms of formaldehyde and cholamine were also synthesized and used independently as labeling reagents for quantification of amine-containing and carboxylic acid-containing molecules, such as found in biological samples. Advantageously, the labeled end-products are positively charged under normal acidic conditions involving conventional Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (LC / MS) applications. Labeled primary and secondary amine and carboxylic acid end-products also generated higher signals concerning mass-spectra than pre-cursor molecules and improved sensitivity. Improved accuracy concerning relative quantification was achieved by mixing heavy and light labeled Arabidopsis extracts in different ratios. Labeling strategy was further employed to ascertain differences in the amounts of amine-containing metabolites for two strains of Arabidopsis seeds.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
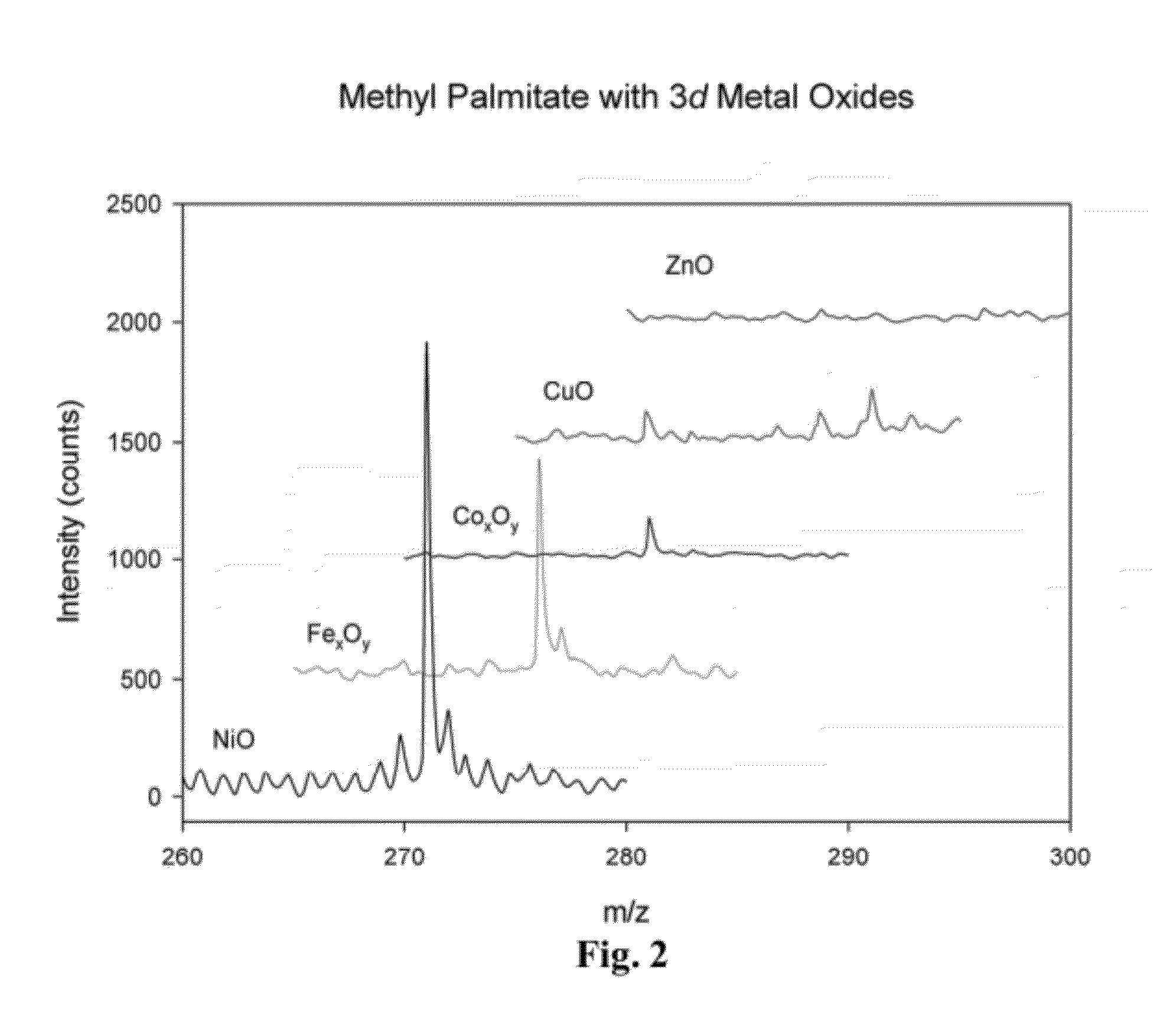
Metal oxide laser ionization-mass spectrometry
ActiveUS20120261567A1Material analysis by optical meansIsotope separationChemical compoundPhysical chemistry
Disclosed herein are metal oxides, metal oxide surfaces, and methods of using metal oxides and metal oxide surfaces for matrix-free analysis, identification, and characterization of small molecular mass compounds. The disclosed compounds and methods may be used with laser desorption / ionization-mass spectrometry. The disclosed surfaces may aid in producing mass / charge spectra having low or no interference found with traditional matrices. In some aspects, the method may be used to produce molecular ions. The disclosed compounds, surfaces, and methods may be used to analyze complex mixtures including fuels, vegetable shortening, lipid extracts from a variety of organic sources such as animals, plants, bacteria, algae, viruses, etc
Owner:VOORHEES KENT J +2
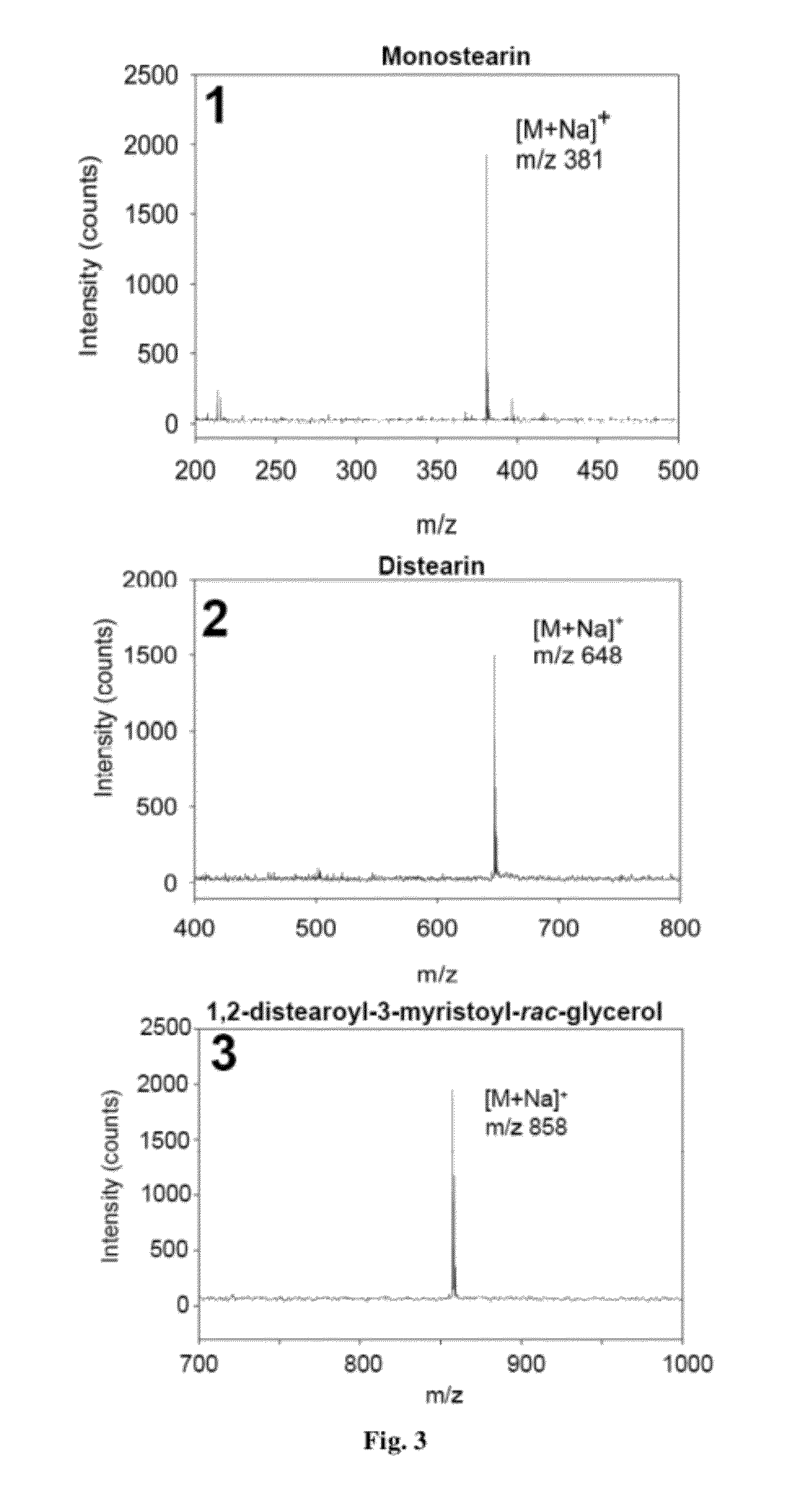
Methods and systems for mass spectrometry
InactiveUS8415619B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationIsotope separationGas phaseSolvent
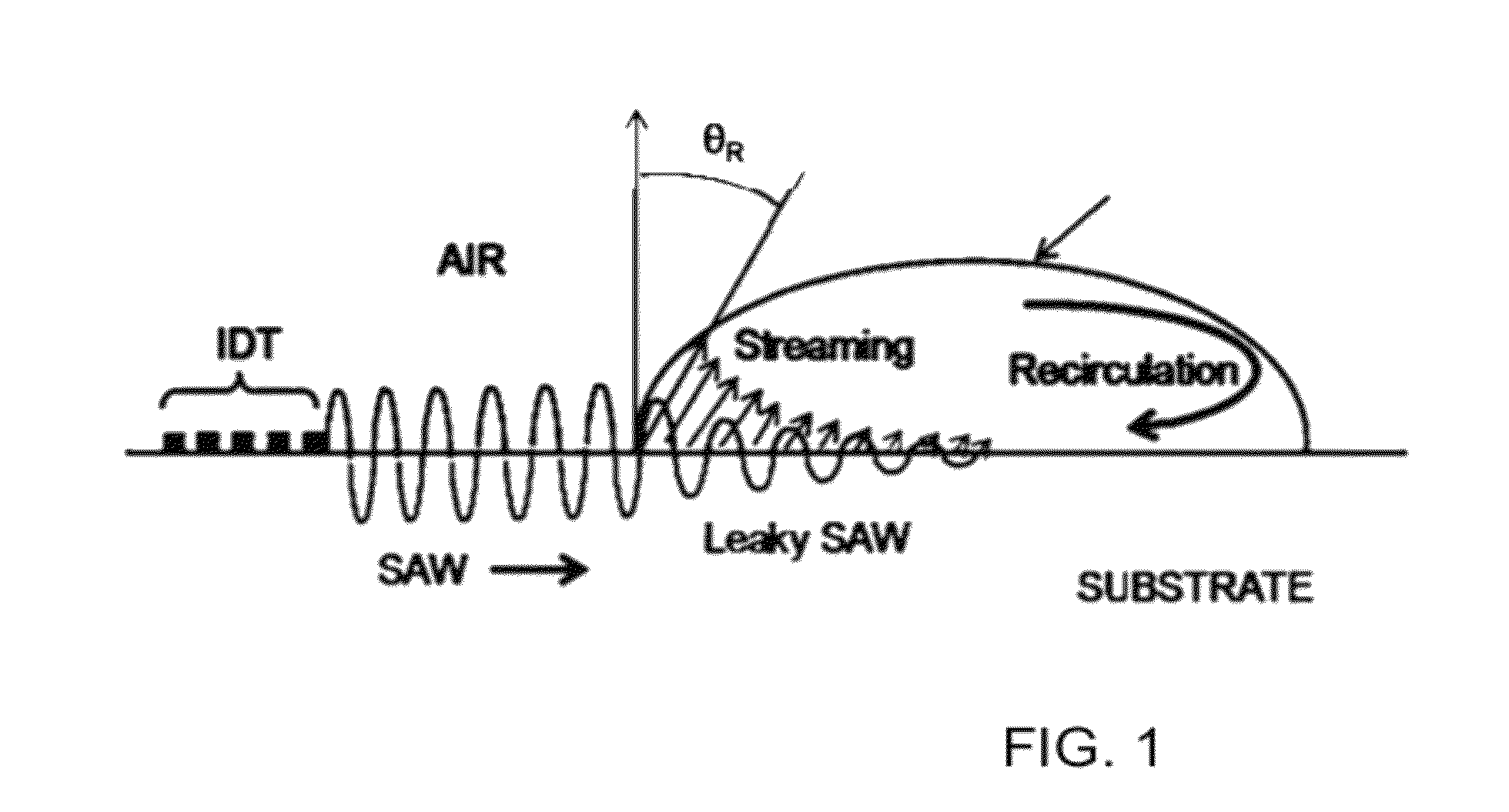
The present invention relates generally to mass spectrometry. The present invention relates more particularly to methods and systems for use in mass spectrometric identification of a variety of analytes, including high molecular weight species such as proteins. One embodiment of the invention is a method for analyzing an analyte. The method includes nebulizing a suspension of the analyte in a solvent with a surface acoustic wave transducer; and performing mass spectrometry on the nebulized suspension. The surface acoustic wave transducer can be used, for example, to transfer non-volatile peptides and proteins (as well as other analyztes, such as oligonucleotides and polymers) to the gas phase at atmospheric pressure. Nebulization using surface acoustic waves can be conducted in a discontinuous or pulsed mode, similar to that used in MALDI, or in a continuous mode, as in ESI.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GLASGOW +1
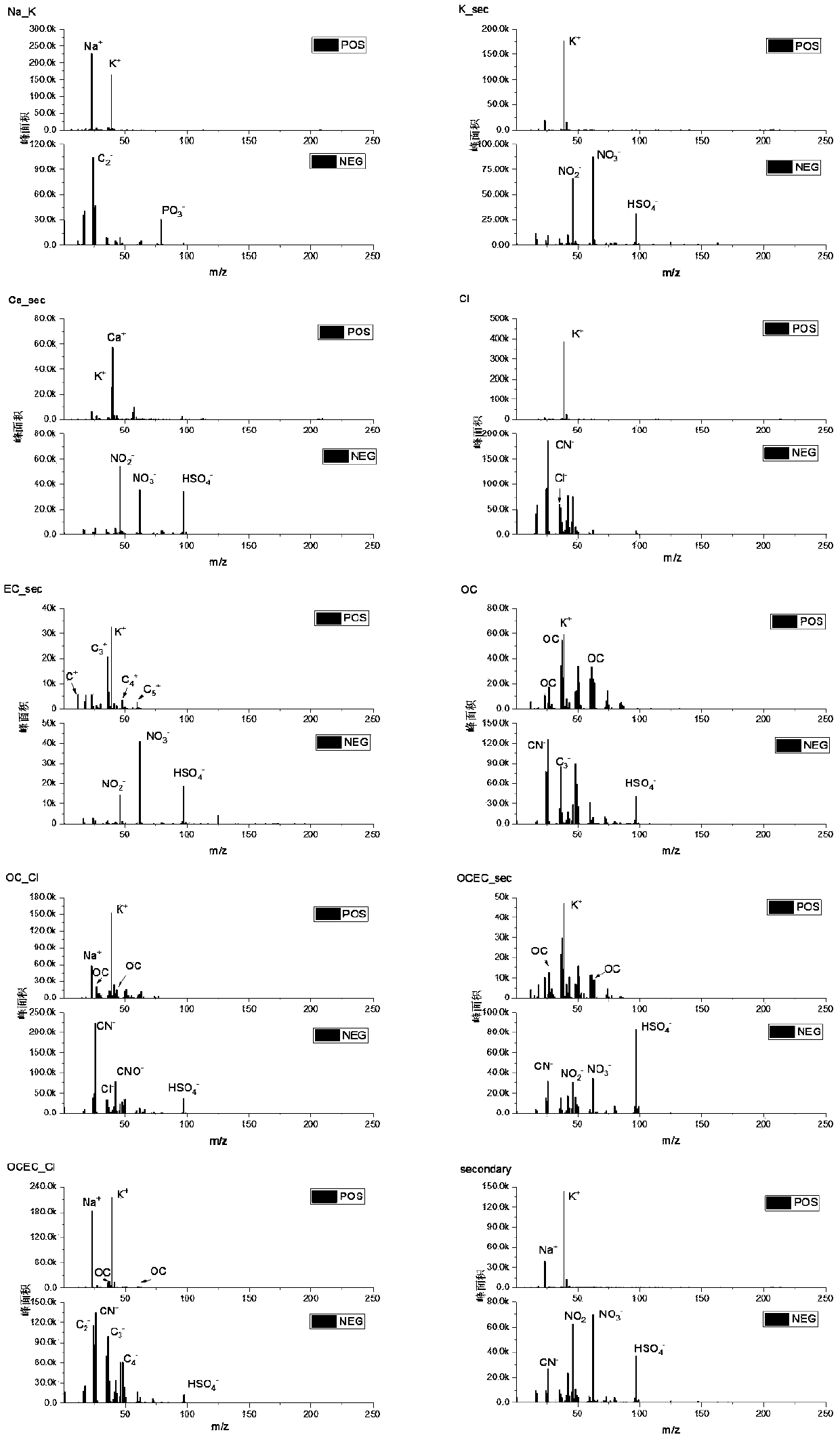
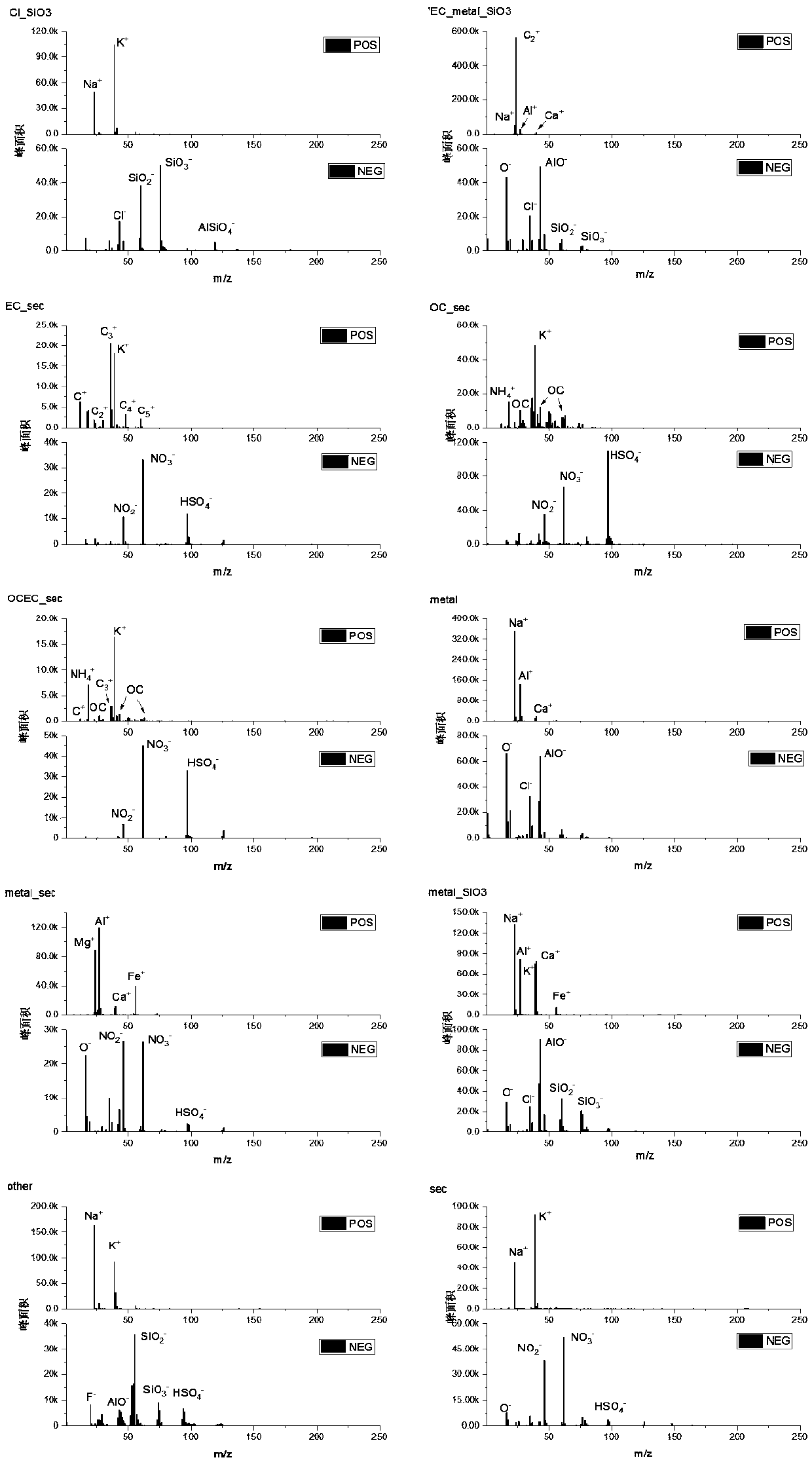
Atmospheric organic aerosol detection and source analysis method
ActiveCN109187288AImprove spatial resolutionRealize long-term observationMaterial analysisWater insolubleImage resolution
The invention discloses an atmospheric organic aerosol detection and source analysis method. By virtue of offline collection of atmospheric aerosol samples, the spatial resolution of the atmospheric aerosol samples and the size range of particles measured by an aerosol mass spectrometer (AMS) can be widened, and long-term observation of the aerosol can be realized. By virtue of water-soluble and water-insoluble extracted samples, the total components of the organic aerosol can be maximally reduced. The method comprises the following steps: respectively measuring water-soluble organic samples and water-insoluble organic samples by using the AMS, and measuring to obtain an initial water-soluble organic mass spectrum matrix and an initial water-insoluble organic mass spectrum matrix; analyzing the water-soluble organic samples by using a TOC (Total Organic Carbon) analyzer, analyzing the water-insoluble organic samples by using an OC / EC (Organic Carbon / Elemental Carbon) analyzer, and correcting the data acquired by the AMS; performing PMF analysis to obtain factors, and performing correlation comparison with molecular markers measured by the GC-MS (Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometer) and LC-MS (Liquid Chromatograph-Mass Spectrometer), thereby improving the source analysis result accuracy. In addition, the filter membrane collection and sample analysis method is simple in operation, and the manpower and equipment maintenance cost is greatly saved.
Owner:南京天博环境检测技术有限公司
Ion pair antiphase chromatography and mass spectrometry combined detection method for low-molecule heparin part degradation products
ActiveCN103454372AFine characterizationImprove detection levelComponent separationChromatographic separationUltraviolet absorption
The invention relates to an ion pair antiphase chromatography and mass spectrometry combined detection method for low-molecule heparin part degradation products. All components of the low-molecule heparin part degradation products are detected in a manner of combining ion pair antiphase chromatography and high-resolution mass spectrometer; all the components in a sample are separated through the ion pair antiphase chromatography, and a precise molecule weight is obtained through the high-resolution mass spectrometer, so that sugar chain sequence information, including structures of two ends, lengths of sugar chains and substitution numbers of acetyl and sulfuric acid, of all the components is calculated, so that the structures of the low-molecule heparin part degradation products can be finely represented. The ion pair antiphase chromatography and mass spectrometry combined detection method can detect the structures of the two ends, the lengths of the sugar chains and the substitution numbers of the acetyl and the sulfuric acid of the low-molecule heparin part degradation products; the problem in the prior art that only an ultraviolet absorption atlas for degradation of low-molecule heparin parts can be obtained is solved; the ion pair antiphase chromatography and mass spectrometry combined detection method has a high practicability value in improvement of the detection level of heparin and guarantee of drug safety.
Owner:HEBEI CHANGSHAN BIOCHEM PHARMA
Contamination Filter for Mass Spectrometer
ActiveUS20160118234A1Increased signal noiseReduce the amount requiredMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIsotope separationMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMass analyzer
Methods and systems for performing mass spectrometry are provided herein. In accordance with various aspects of the applicants' teachings, the methods and systems can utilize an ion mobility spectrometer operating at atmospheric or low-vacuum pressure to remove the major contributors to the contamination and degradation of critical downstream components of a mass spectrometer located within a high-vacuum system (e.g., ion optics, mass filters, detectors), with limited signal loss.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
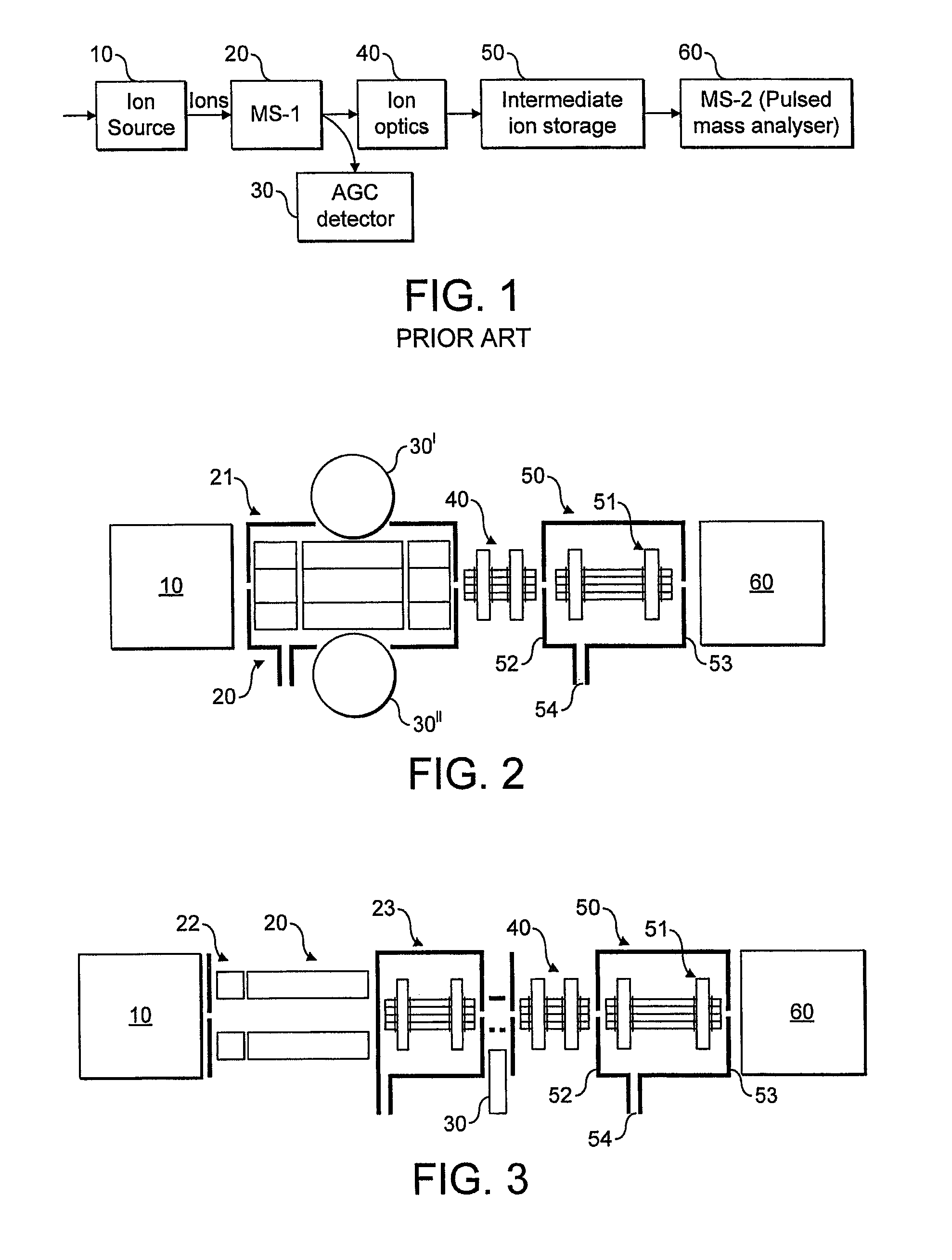
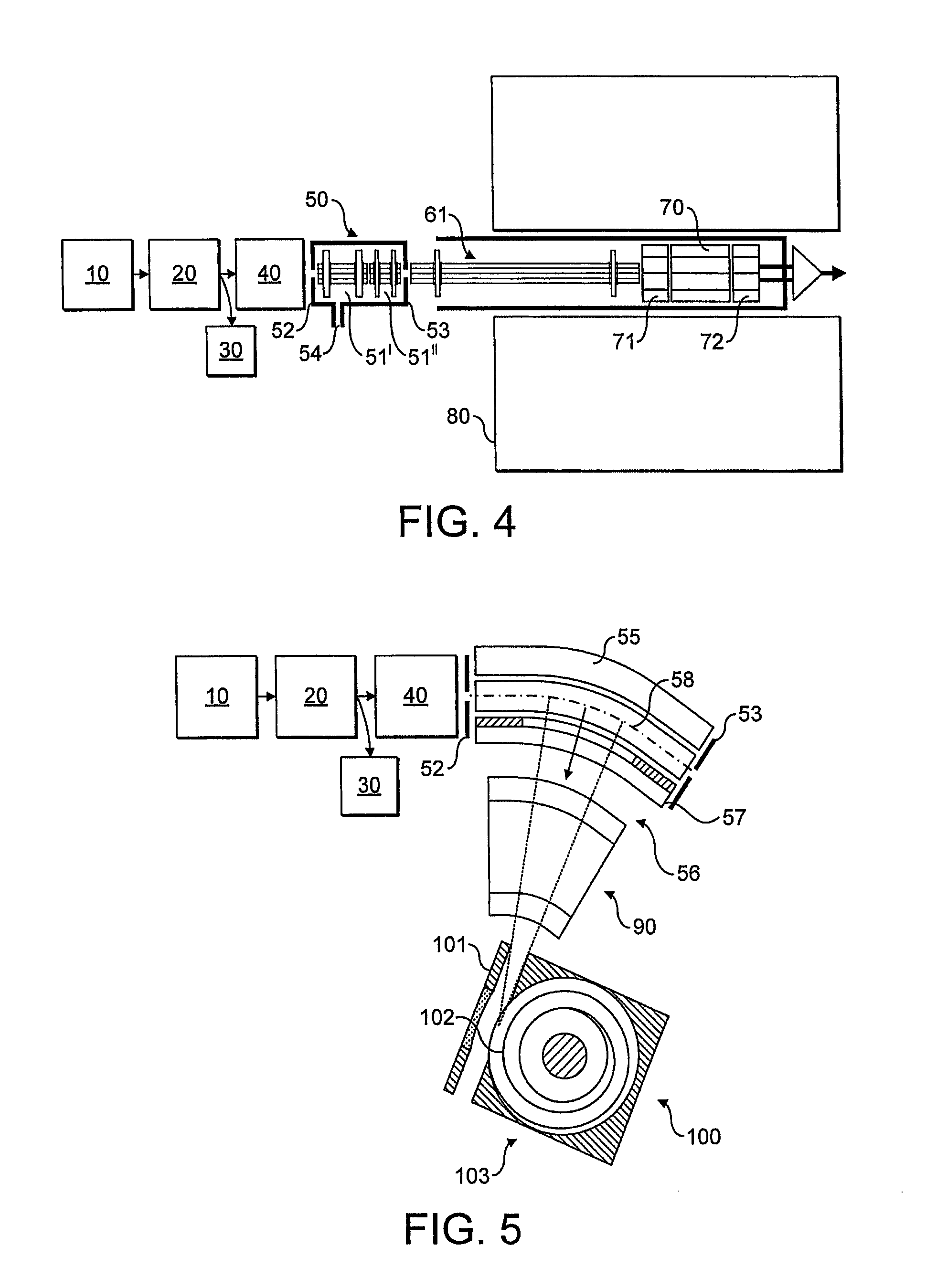
Multiple ion injection in mass spectrometry
ActiveUS8410424B2Adequate movementLarge dynamic rangeStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryPhysical chemistry
This invention relates to mass spectrometry that includes ion trapping in at least one of the stages of mass analysis. In particular, although not exclusively, this invention relates to tandem mass spectrometry where precursor ions and fragment ions are analysed. A method of mass spectrometry is provided comprising the sequential steps of: accumulating in an ion store a sample of one type of ions to be analysed; accumulating in the ion store a sample of another type of ions to be analysed; and mass analysing the combined samples of the ions; wherein the method comprises accumulating the sample of the one type of ions and / or the sample of another type of ions to achieve a target number of ions based on the results of a previous measurement of the respective type of ions.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
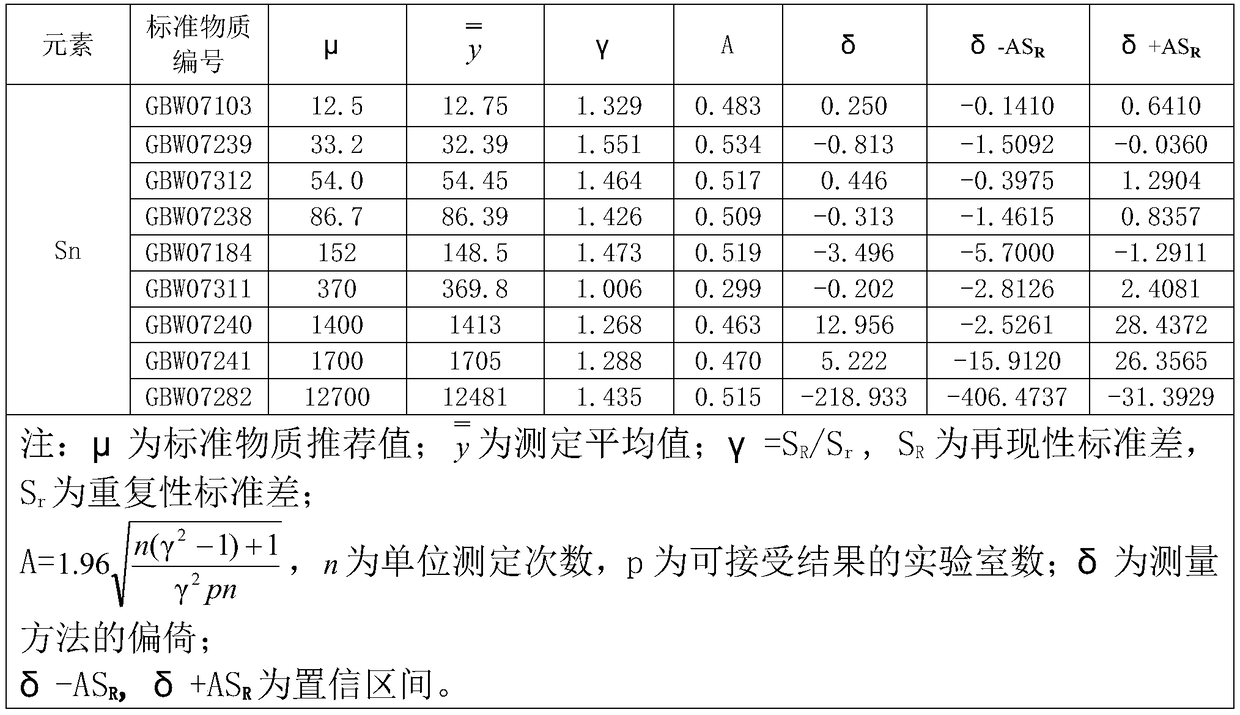
Method for determining content of tin in tin ore by alkali melting-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
InactiveCN108828052AReduce labor intensityNo harmMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEvaporationVolumetric flask
The invention discloses a method for determining the content of tin in a tin ore by alkali melting-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. The method comprises the steps: melting and decomposinga sample by sodium oxide, leaching by hot water, acidifying by hydrochloric acid, transferring the solution into a volumetric flask, and separately taking a clarifying liquid; diluting by nitric acid, allowing the sample to enter radio frequency plasma through a sample injection system, and carrying out evaporation, dissociation, atomization and ionization in a high temperature rectangular tube;separating ions by a double-cone interface, an ion mirror and a quadrupole mass analyzer according to the mass / charge size; and finally, detecting by an ion detector, quantitatively analyzing the content of tin by a calibration curve method, and thus quickly, accurately and effectively determining the content of tin in the tin ore. At the same time, the method improves the work efficiency, reducesthe labor intensity of operators, does not cause harm to bodies of the operators, and also has significant social benefits.
Owner:青海省核工业地质局核地质研究所 +1
Applications of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry in boron detection of water-based gel
ActiveCN103399079AReduce dosageLow detection limitPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansWater basedInductively coupled plasma
The invention discloses a detecting method of boron in water-based gel. Characteristics are that, interfering substances and solvents with relatively low boiling point in the water-based gel are removed by pre-digestion, so as to eliminate hidden dangers that may be caused by digestion process; pre-digested samples are subjected to digestion, and is added into an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer; and at the same time a internal standard is added for quantitative analysis. According to the detecting method, the vertical coordinate represents the ratio of mass-to-charge ratio strength of boron that is to be measured to mass-to-charge ratio strength of a corresponding internal standard element, the horizontal coordinate represents the content of boron that is to be measured to the content of the corresponding internal standard element, and a standard work curve is built. The content of boron is calculated according to the standard work curve. Advantages of the detecting method are that, sample dosage is low, operation is simple, detecting time is short, detection limit is low, and the like.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO GUANGXI IND
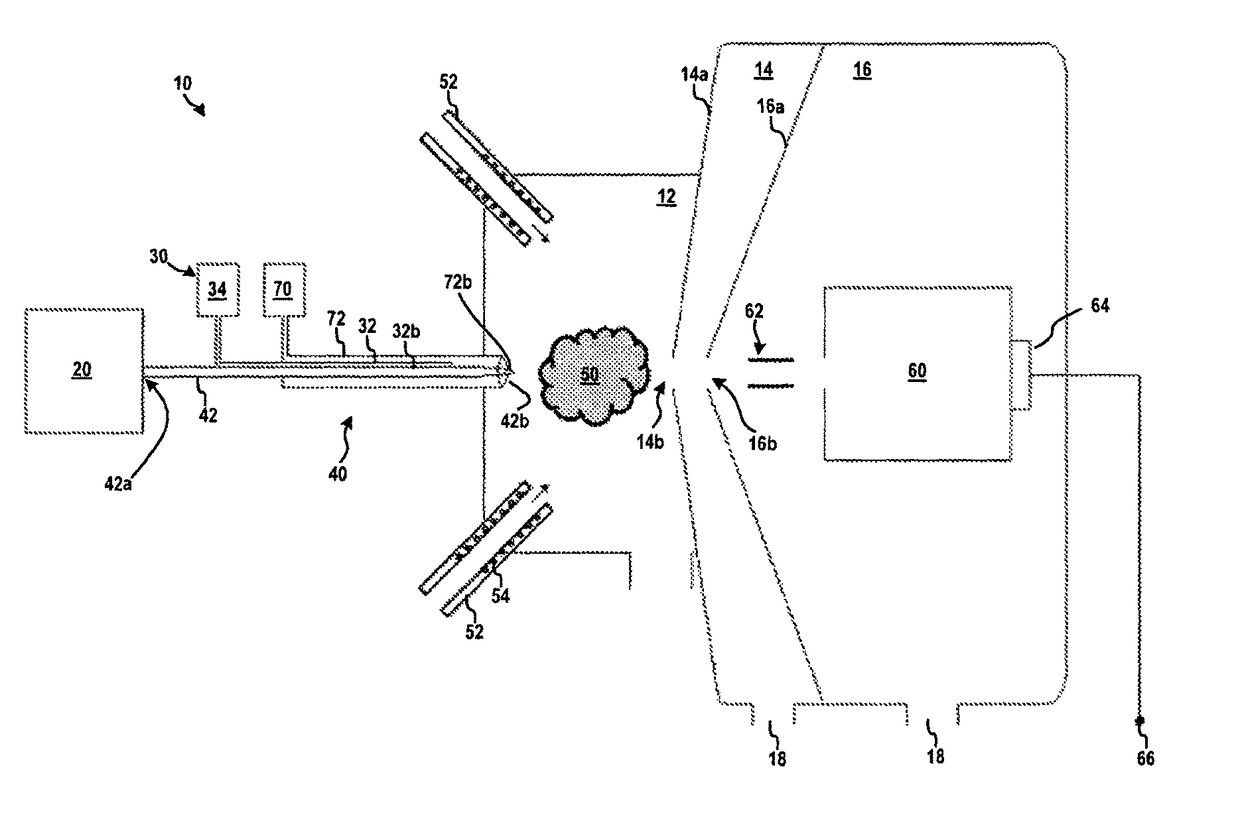
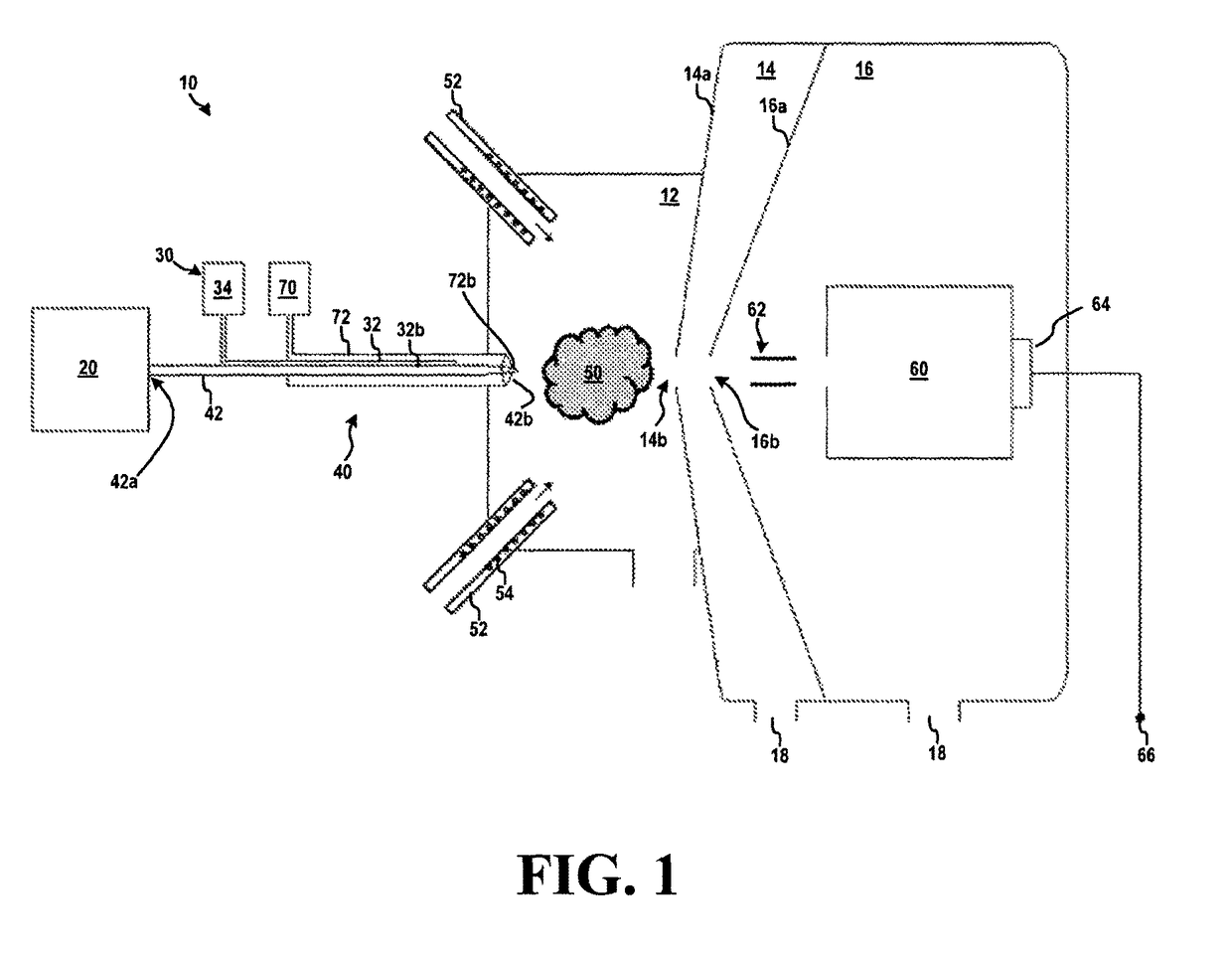
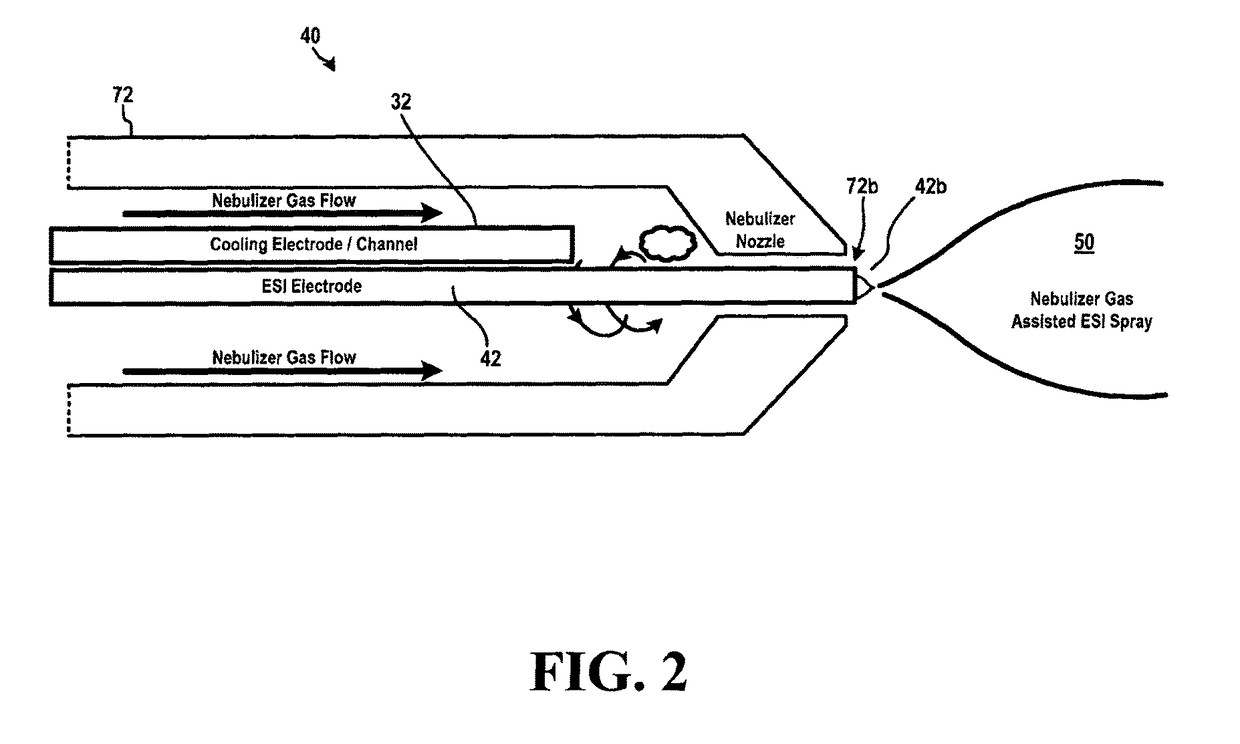
Ion source for mass spectrometry
ActiveUS9870904B2Increased desolvationIncrease flow rateComponent separationSamples introduction/extractionMass analyzerMass spectrometry imaging
Systems and methods for delivering a sample to a mass spectrometer are provided. In one aspect, the systems and methods can provide efficient cooling of an ion source probe to prevent overheating and the resulting degradation in ion sampling. In some aspects, such cooling can result in improved consistency and / or efficiency of ion formation. Moreover, ion source cooling in accordance with various aspects of the present teachings can allow for the use of higher temperatures in the ionization chamber (thereby improving desolvation) and / or can enable the use of lower flow rate sample sources than with conventional techniques.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
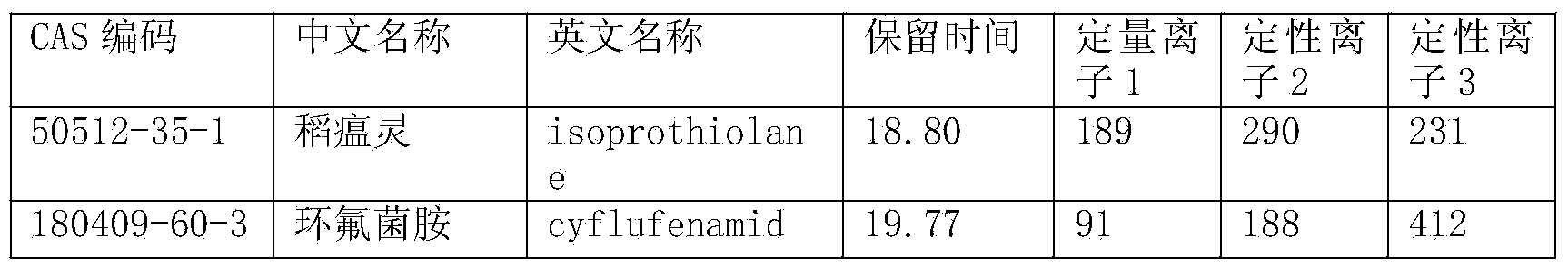
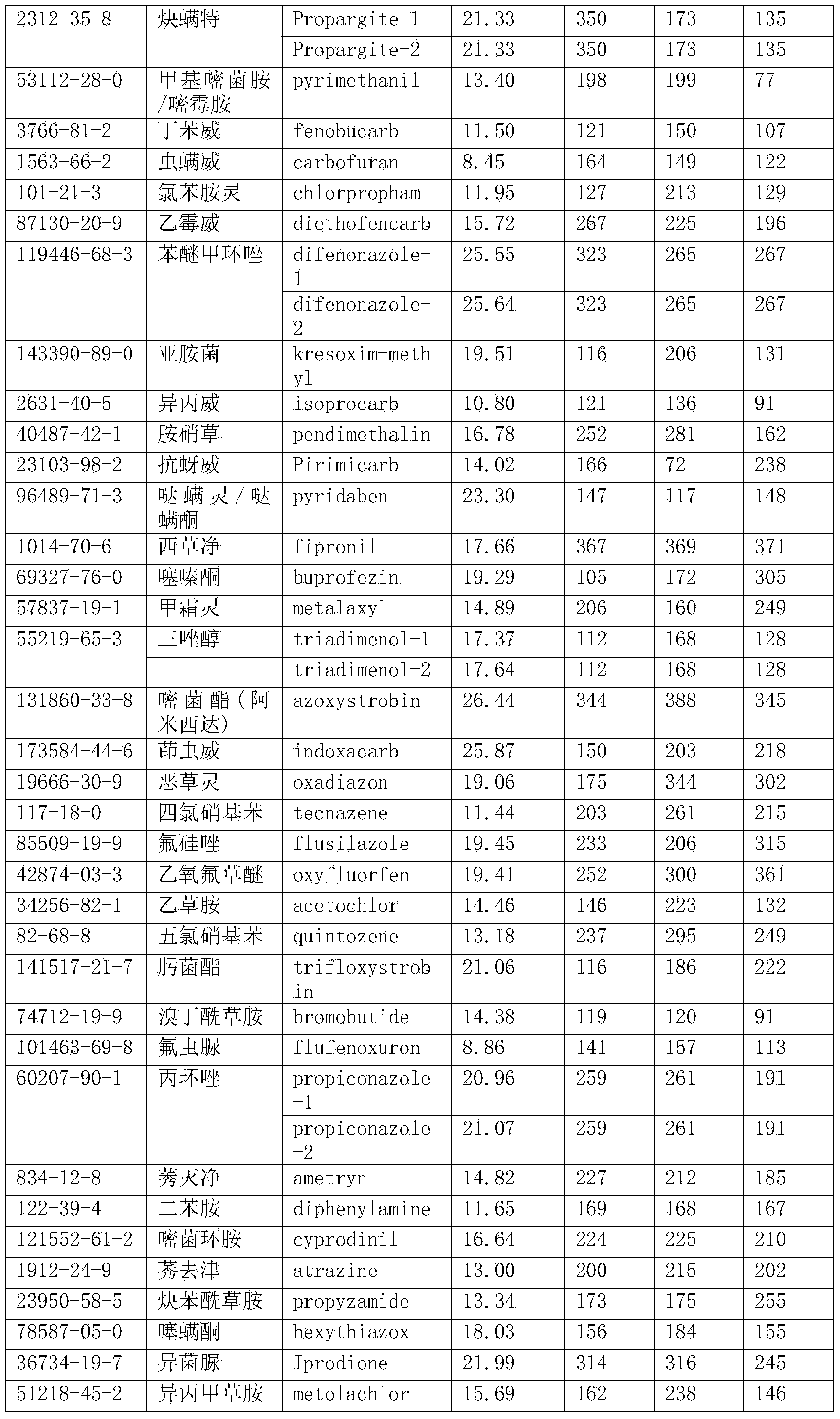
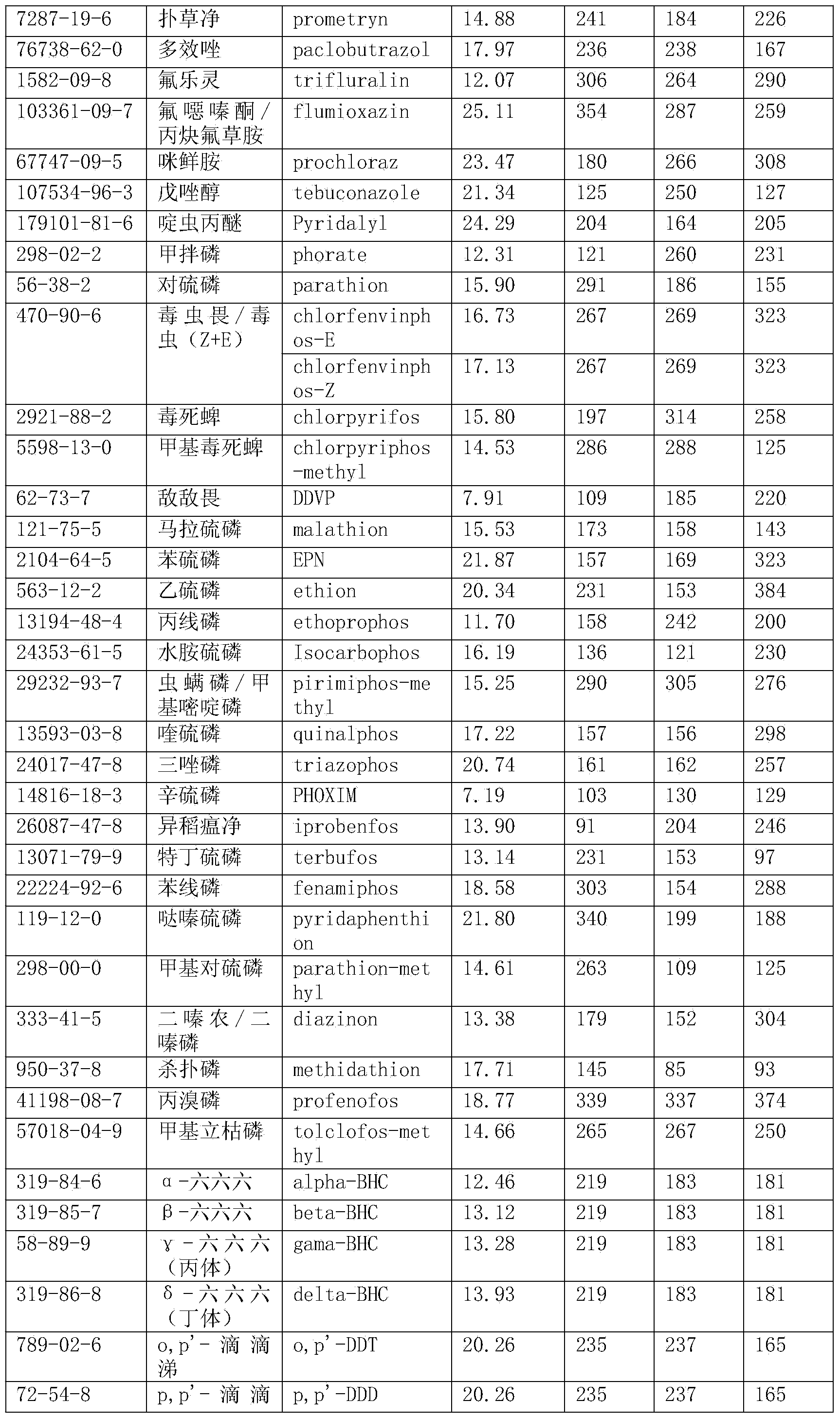
Method for detecting pesticide residues in tea by using gas chromatograph-mass spectrometry
InactiveCN103884788AImprove purification effectAccurate purification effectComponent separationAutosamplerGas phase
The invention discloses a method for detecting pesticide residues in tea by using gas chromatograph-mass spectrometry. The method comprises the following steps: preparing 109 types of pesticide samples into a mixed standard working solution; setting parameters of an automatic gas chromatograph-mass spectrometer fitted sampler; generating standard curve models of 109 types of pesticides in the gas chromatograph-mass spectrometer; putting crushed tea matrixes to be detected in a centrifugal tube to prepare a solution containing tea pesticide residues to be detected; analyzing the solution containing the tea pesticide residues obtained in the step 6 according to the parameters of the gas chromatograph-mass spectrometer set in the step 2 and the standard curve models of 109 types of pesticides generated in the gas chromatograph-mass spectrometer in the step 3 to obtain detection results. The method is capable of detecting up to 109 types of tea pesticide residues. Compared with the prior art, the method is excellent and accurate in purification effect.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Species Detection Using Mass Spectrometry
ActiveUS20160086782A1Reduce generationIsotope separationTesting foodMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMass spectrometry imaging
Systems and methods are provided for species detection using mass spectrometry. In various embodiments, a multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) experiment is performed on a sample targeting one or more peptide transitions that are unique to one or more species using a tandem mass spectrometer. One or more measured product ion spectra are received from the tandem mass spectrometer using the processor. The one or more measured product ion spectra are compared to product ions of the one or more peptide transitions that are unique to one or more species using the processor. One or more species of the sample are detected by reporting product ions of the one or more peptide transitions that are unique to one or more species that match the one or more measured product ion spectra using the processor.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
Method for analyzing four benzene and toluene metabolites in urine through liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
ActiveCN103175921ASimplified processing stepsShort analysis timeComponent separationUltra high pressureMetabolite
The invention discloses a method for analyzing four benzene and toluene metabolites in urine through liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. The method comprises the following steps: preparing mixed master standard operating fluid with series concentration, performing instrument analysis, and forming a standard curve according to the linear relation between the response value and the operating master standard concentration; taking a urine sample to be tested, and adding a mixed operating standard solution containing four characteristic metabolite isotope internal standard substances; adsorbing a target compound by using solid-phase extraction small column, and then performing instrument analysis; obtaining the response value of the four characteristic metabolites; and solving the concentration of the four characteristic metabolites in the urine sample according to the known coefficient f. The ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method is adopted in the instrument analysis, and the chromatographic column is an inverse phase C18 chromatographic column with the particle size of less than 2mu m. According to the method, the sample pretreatment steps are simplified, the sample instrument analysis time is shortened, and the quantitative accuracy is high; and meanwhile, the instrument detection limit and the method detection limit in the method are extremely low, and the detection rate of the low-concentration non-professional exposure population is improved.
Owner:南京品生医学检验实验室有限公司
Method for SPME (solid phase micro-extraction)-MS (mass spectrometry) combined online enrichment detection of nicotine compounds in tobaccos
ActiveCN108828114AImprove enrichment effectGood choiceComponent separationSolid-phase microextractionMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The invention discloses a method for SPME (solid phase micro-extraction)-MS (mass spectrometry) combined online enrichment detection of nicotine compounds in tobaccos. By means of online combination of a Poly(DVB-co-NIPPAm-co-MBAA) polymerized monolithic micro-extraction column and API-MS (atmospheric pressure ionization mass spectrometry), online enrichment detection of the nicotine compounds inthe tobaccos is realized. By means of online combination of the monolithic micro-extraction column and the API-MS and with application of noncovalent-bond interaction such as hydrogen bond, pi-pi bondand hydrophobicity of the surface of the monolithic micro-extraction column with the nicotine compounds, the method is applied to enrichment of harmful nicotine substances, and online analysis of thenicotine compounds can be realized. The method is simple, cheap and easy to operate, the multiple harmful nicotine components in tobaccos are rapidly extracted and enriched, detection sensitivity ofthe method is improved, matrix interference is reduced, and the high-efficient detection requirement for the nicotine compounds in tobaccos is met.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for analyzing argon mass number abundance value and specific value in argon by GC-MS (gas chromatography-mass spectrometry) method
InactiveCN103823012AReduce mistakesSimple methodComponent separationMass numberGas chromatography–mass spectrometry
The invention relates to a method for analyzing the argon mass number abundance value and the specific value in argon by a GC-MS (gas chromatography-mass spectrometry) method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) enabling carrier gas with the purity greater than 99.99% to pass through a purifier so as to enable the purity of the purified carrier gas to be greater than 99.999%; (2) introducing the purified carrier gas into a chromatographic column in which a to-be-detected argon sample is arranged in a gas chromatograph, deoxidizing the to-be-detected argon sample in a nickel contact agent tube after adsorption and desorption effects, and finally measuring in a mass detector so as to obtain an ion flow chromatogram and a mass spectrogram respectively; and (3) acquiring the mass number abundance values of 20Ar, 36Ar, 37Ar, 38Ar, 40Ar, 41Ar and 42Ar in argon respectively by a selected ion method according to the ion flow chromatogram and the mass spectrogram, and determining the specific value according to the relative standard deviation RSD being less than or equal to 5%. The method provided by the invention can be applied to noninvasive detection of human health, human body medical science and animal and plant research.
Owner:LANZHOU CENT FOR OIL & GAS RESOURCES INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CAS
Method for measuring isotopic abundance ratio of uranium in particles through accelerator mass spectrometry
InactiveCN104535598AImprove accuracyEliminate distractionsPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionMass spectrometry measurementMicroparticle
The invention relates to a control device for the irradiation dose of an irradiation device, and provides a method for measuring the isotopic abundance ratio of uranium in particles through accelerator mass spectrometry. The method aims to solve the problems that an analysis method for the isotopic abundance ratio of uranium in existing environment sample particles is not high in analysis result accuracy, and interference is serious in the analysis process. The method comprises the following steps that 1, the sample particles are separated from a carrier and transferred to a graphite flake through ultrasonic oscillation; 2, the sample particles are transferred into a scanning electron microscope; 3, the uranium-bearing particles are found; 4, the uranium-bearing particles are dissolved; 5, a target is manufactured; 6, ruling is carried out; 7, accelerator parameters needed by each uranium isotope are determined; 8, the counting rate of each uranium isotope is measured; 9, the isotopic abundance ratio of the uranium is calculated. The problem that isotopic abundance ratio analysis of the uranium in the particles has polyatomic ion interference is solved, abundance sensitivity is obviously improved, the obtained analysis result is accurate, and the defect in an existing analysis method is overcome.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Method for analyzing CO stable isotope mass number abundance ratio through chromatography-mass spectrometry
The invention relates to a method for analyzing the CO stable isotope mass number abundance ratio through chromatography-mass spectrometry. The method comprises the following steps: (1) building a CO stable isotope ratio mathematical model; (2) filling a carrier gas with the purity of 99.999% into a purifier, and obtaining the purified carrier gas with the purity of over 99.9999% or over 99.99999%; (3) filling the purified carrier gas into a chromatographic column which contains a sample to be measured and is arranged in a gas chromatograph, after the adsorption and desorption, measuring CO in the sample to be measured through a mass detector, and obtaining the mass numbers of 28, 29, 30 and 31 of CO in the gas to be measured are obtained; and (4) putting the mass numbers of 28, 29, 30 and 31 of CO in the gas to be measured, and obtaining 6 CO isotope mass number abundance ratios. The method realizes the purpose of finely expressing the CO source through building the mathematical model, and can be applied to non-traumatic detection of human health, human body medicine and animal and botanical researches.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCES CAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com