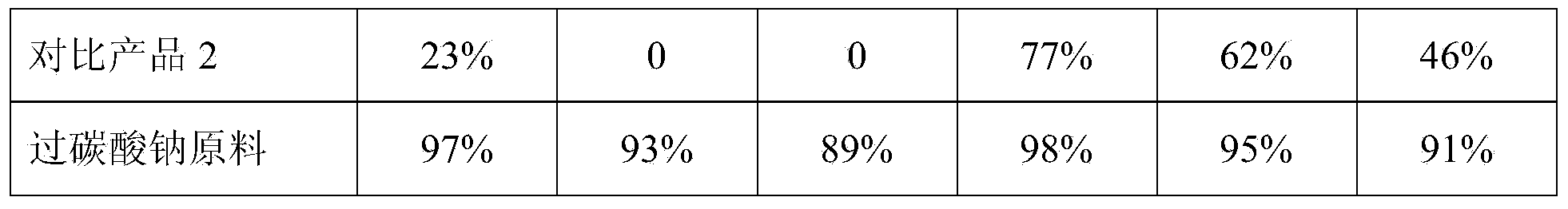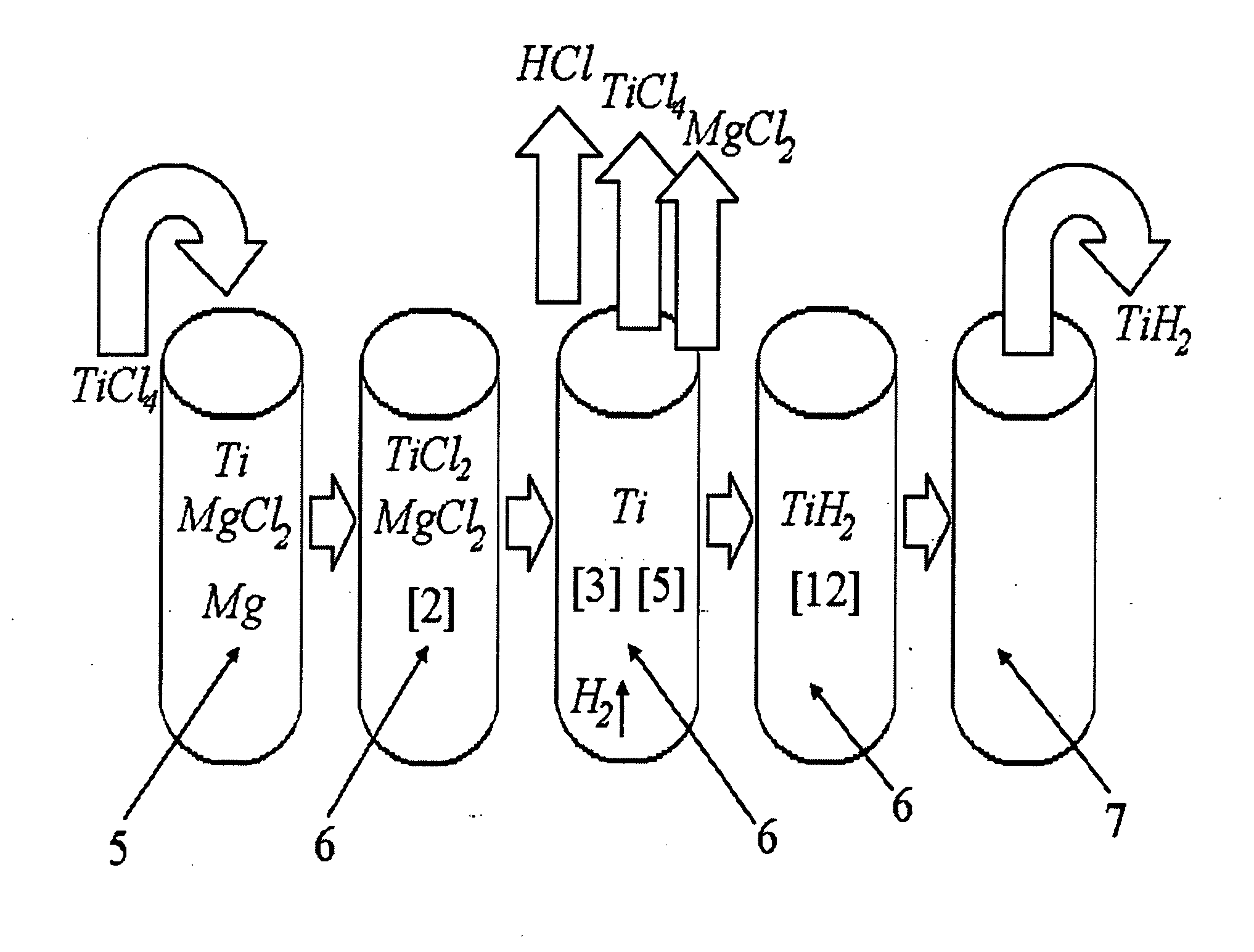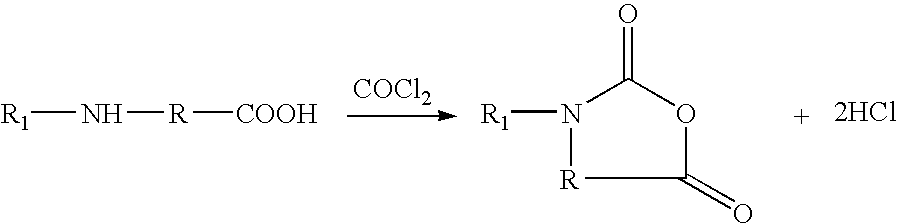Patents
Literature
124 results about "Low chloride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hypochloremia is an electrolyte imbalance and is indicated by a low level of chloride in the blood. The normal adult value for chloride is 97-107 mEq/L.
Alkylated cyclodextrin compositions and processes for preparing and using the same
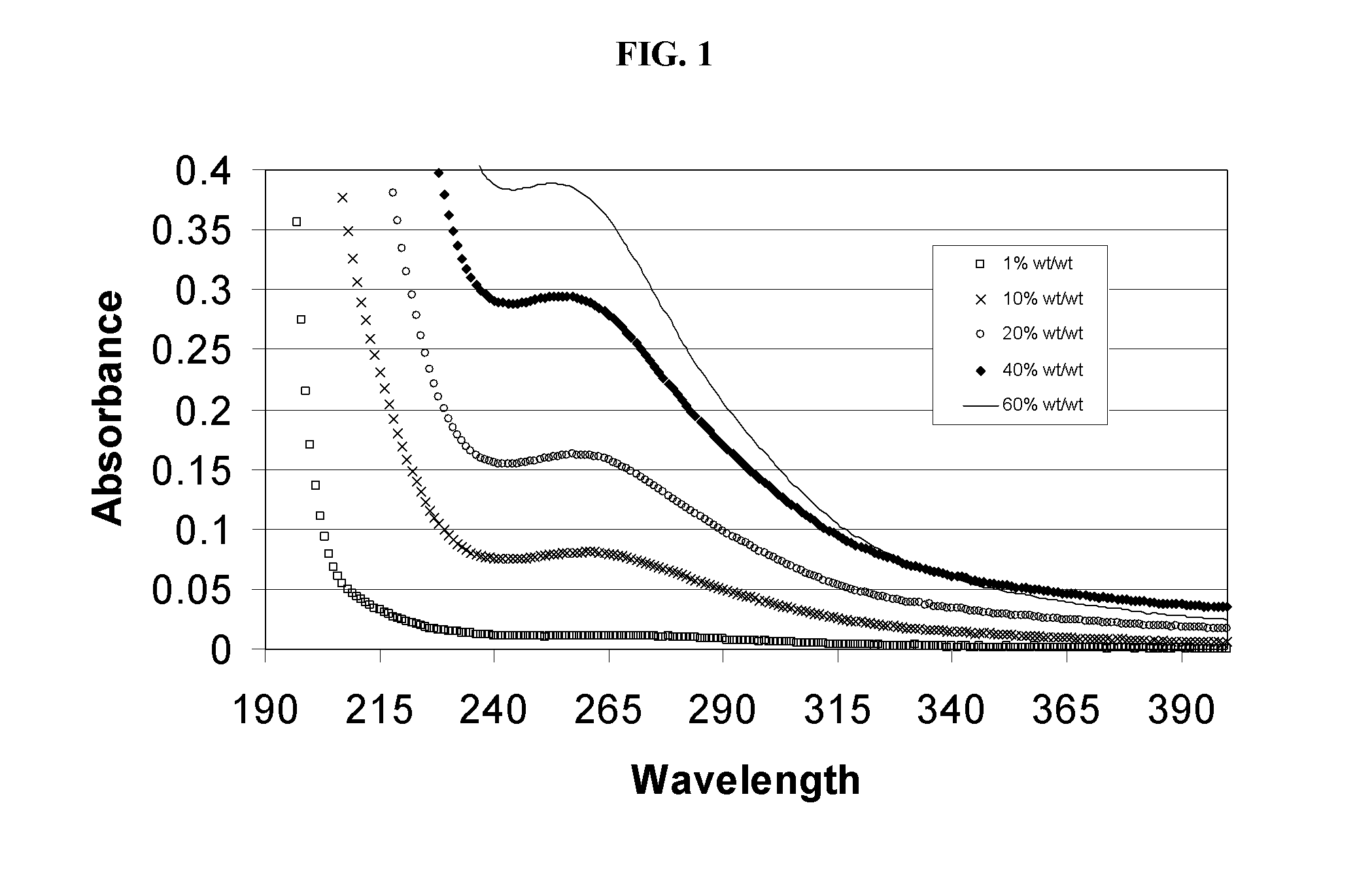
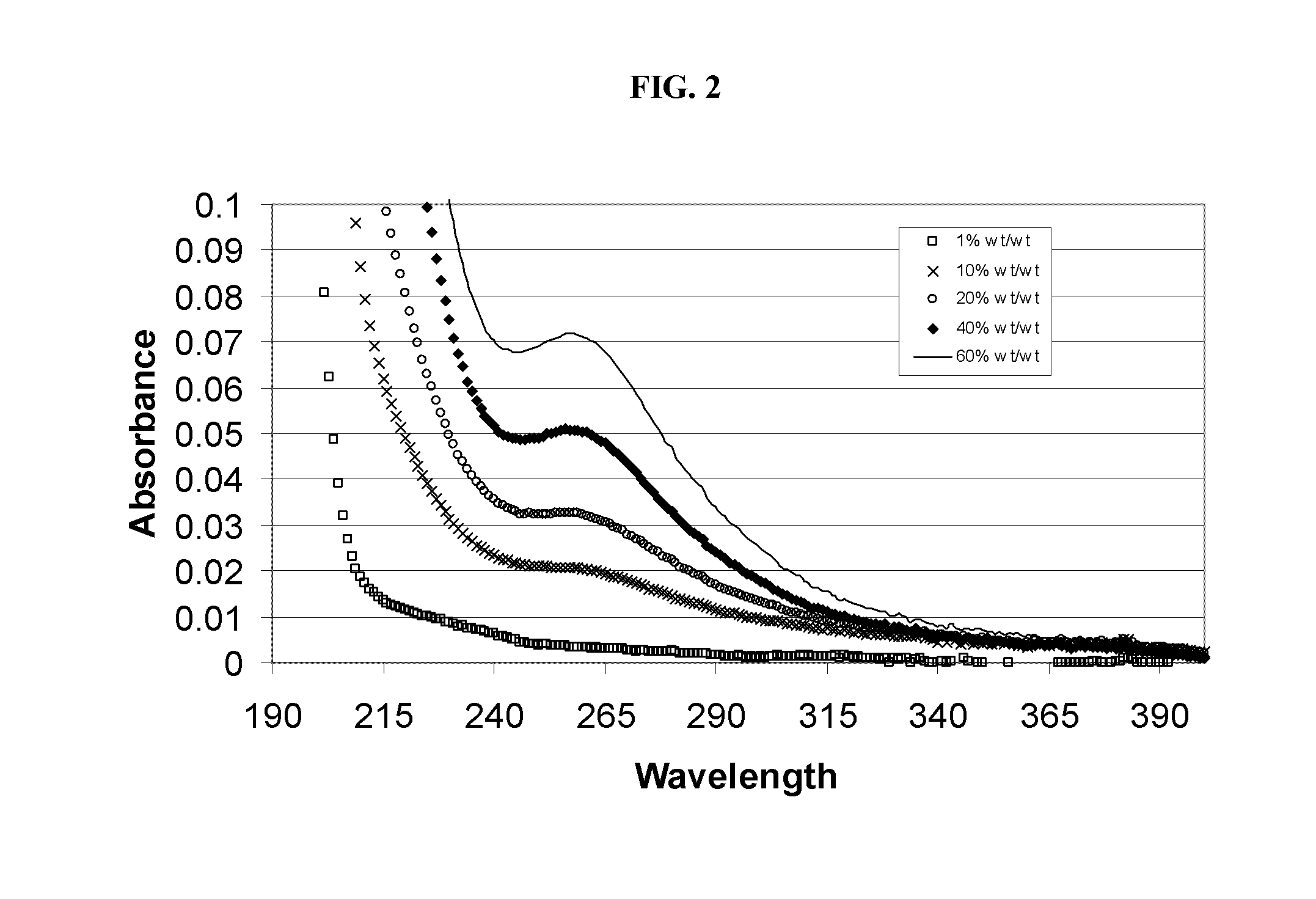
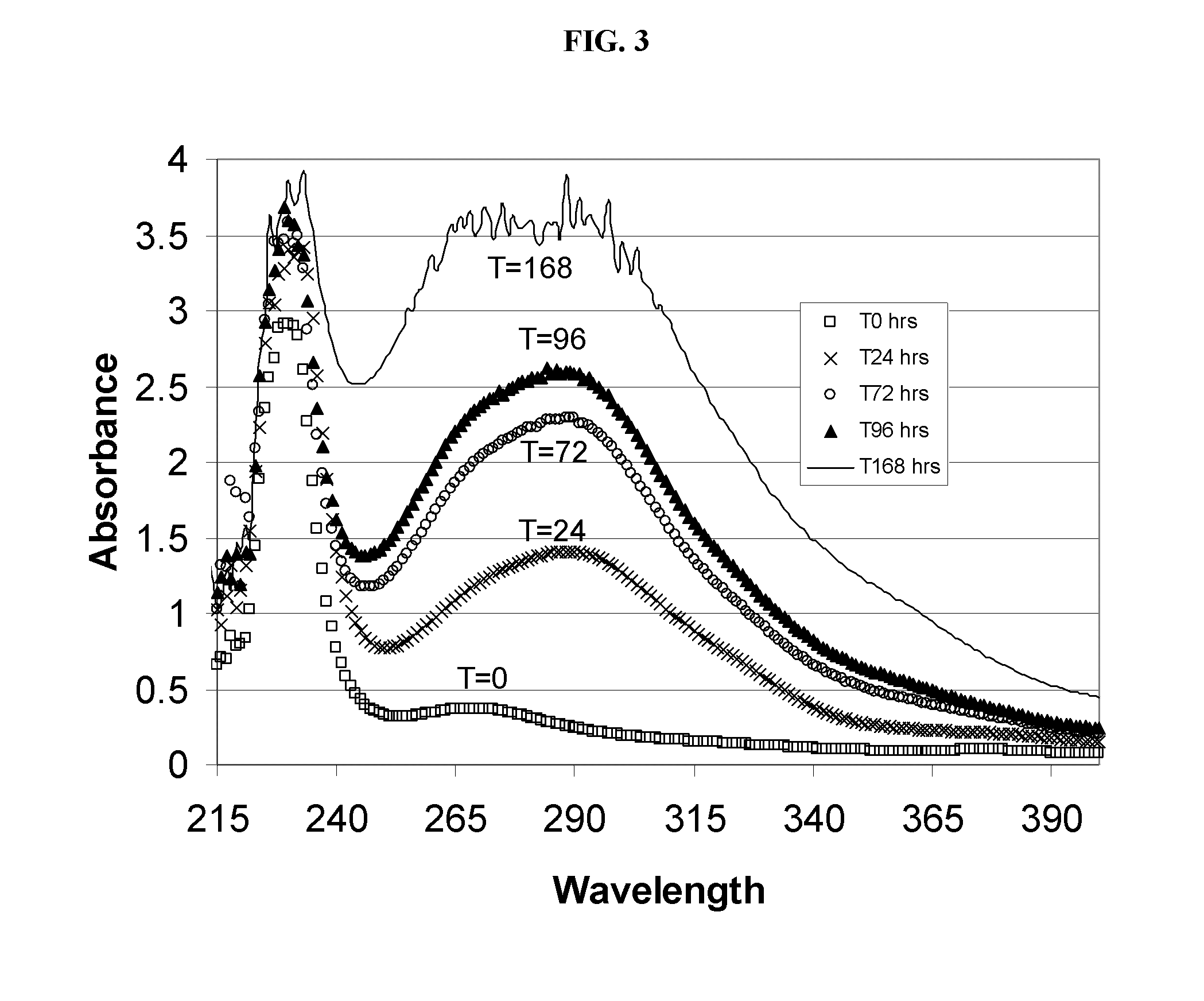
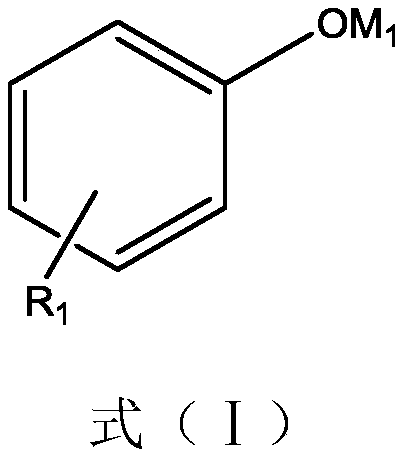
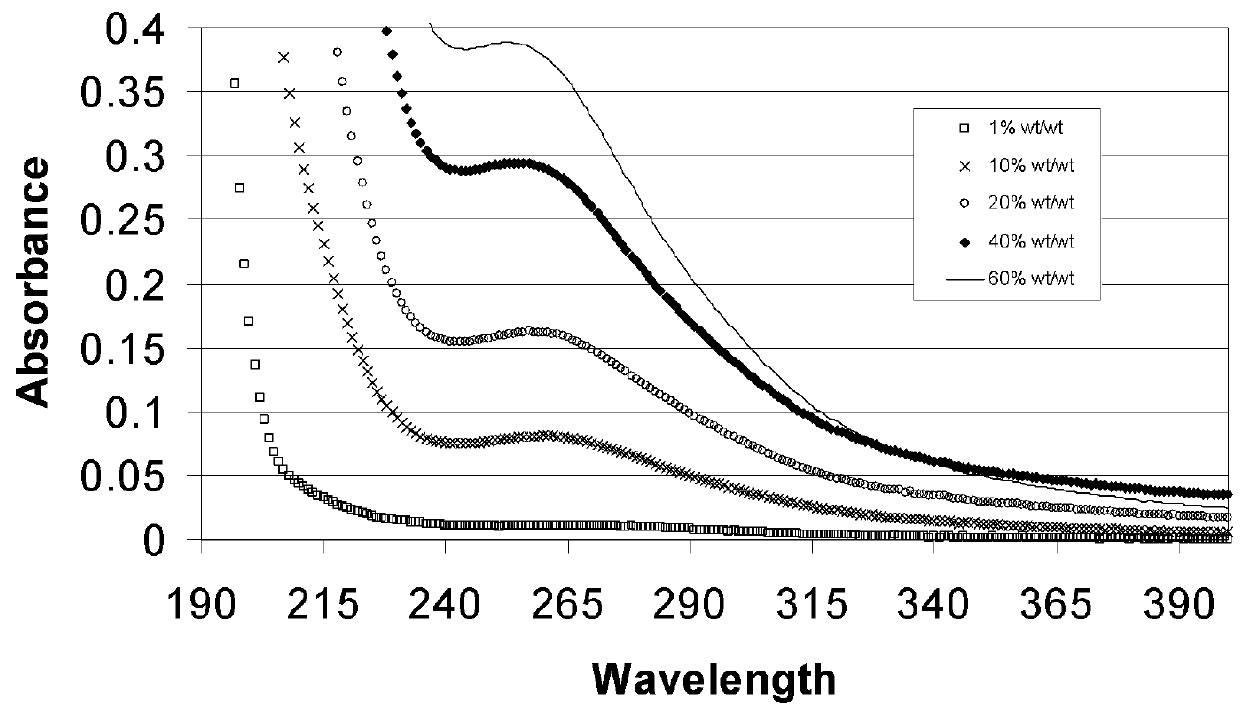
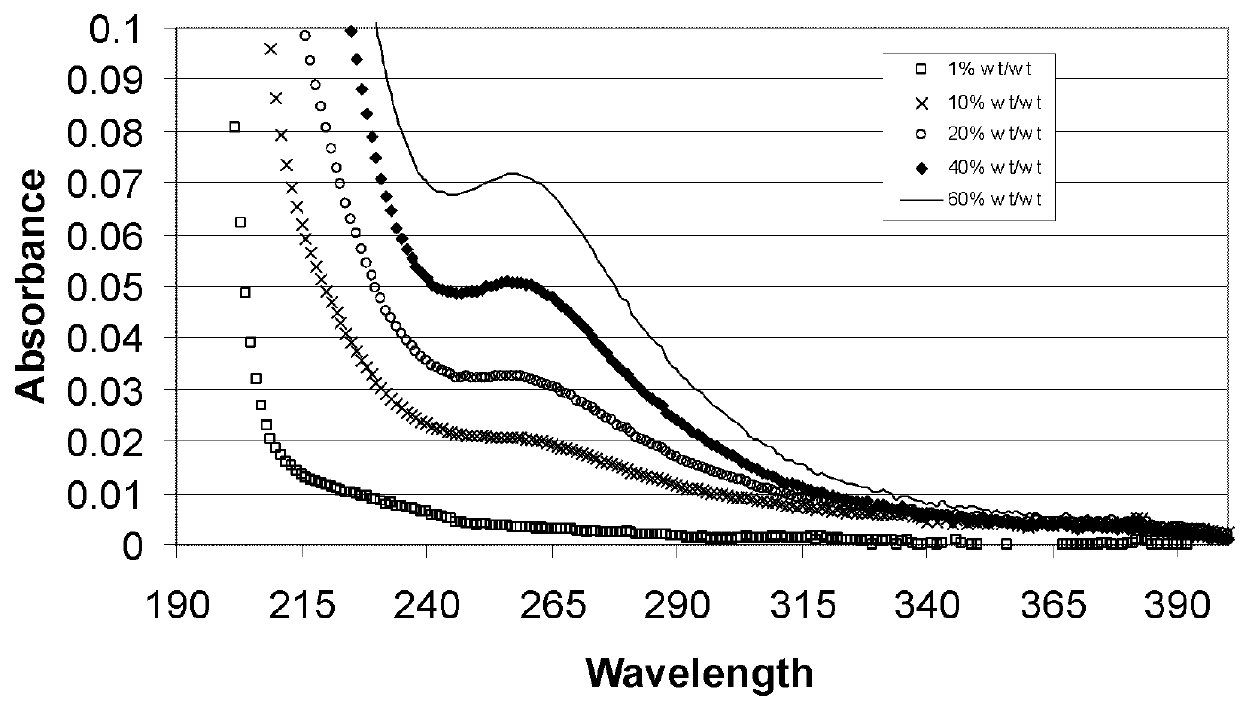
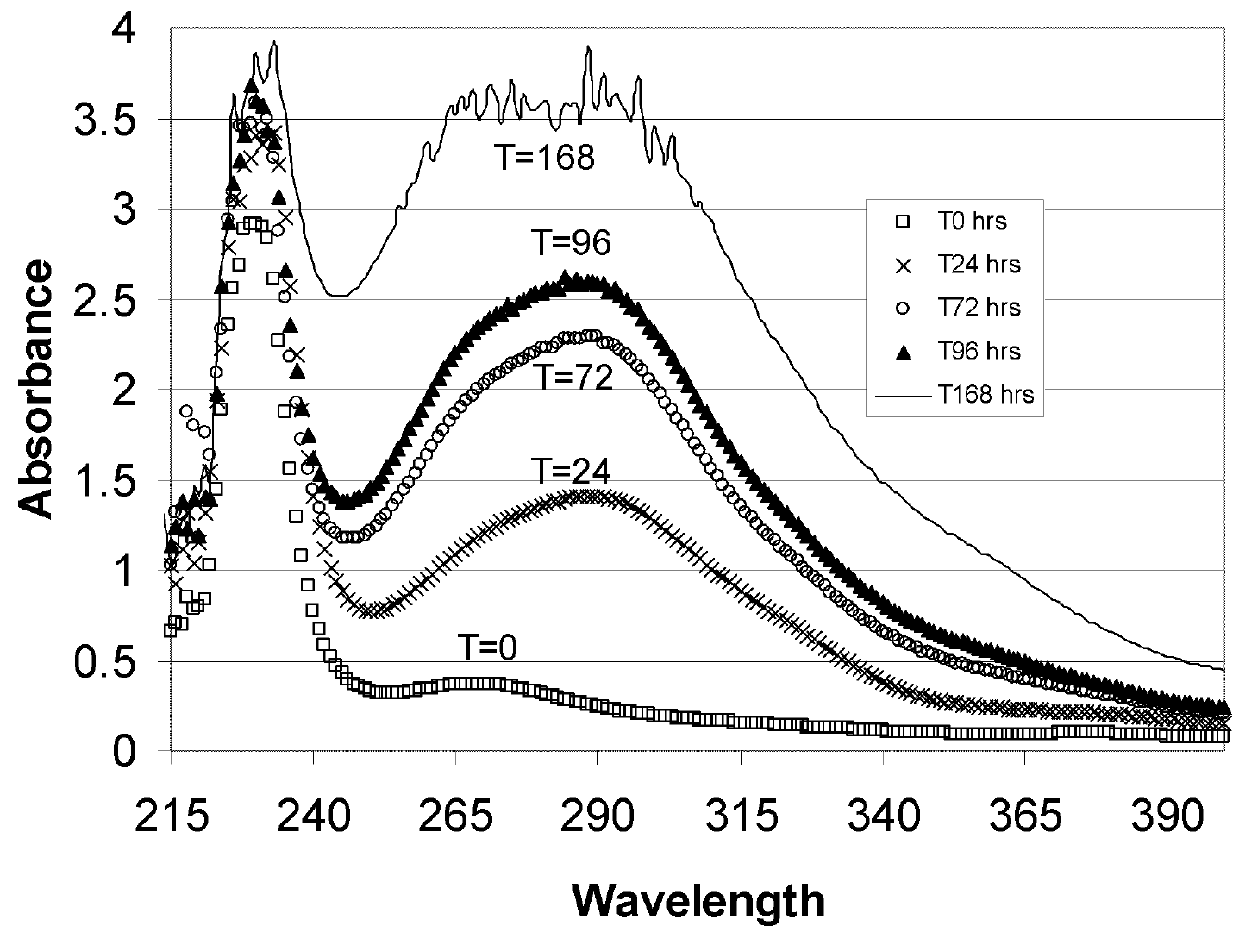
The present invention related to low-chloride alkylated cyclodextrin compositions, along with processes for preparing and using the same. The processes of the present invention provide alkylated cyclodextrins with low levels of drug-degrading agents and chloride.
Owner:CYDEX PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Early-strong-fast-hard end capping anchorage mortar material for fragment-free railway plate
ActiveCN101508547APrevent shrinkage crackingVolume stabilitySolid waste managementBallastwaySlagRebar
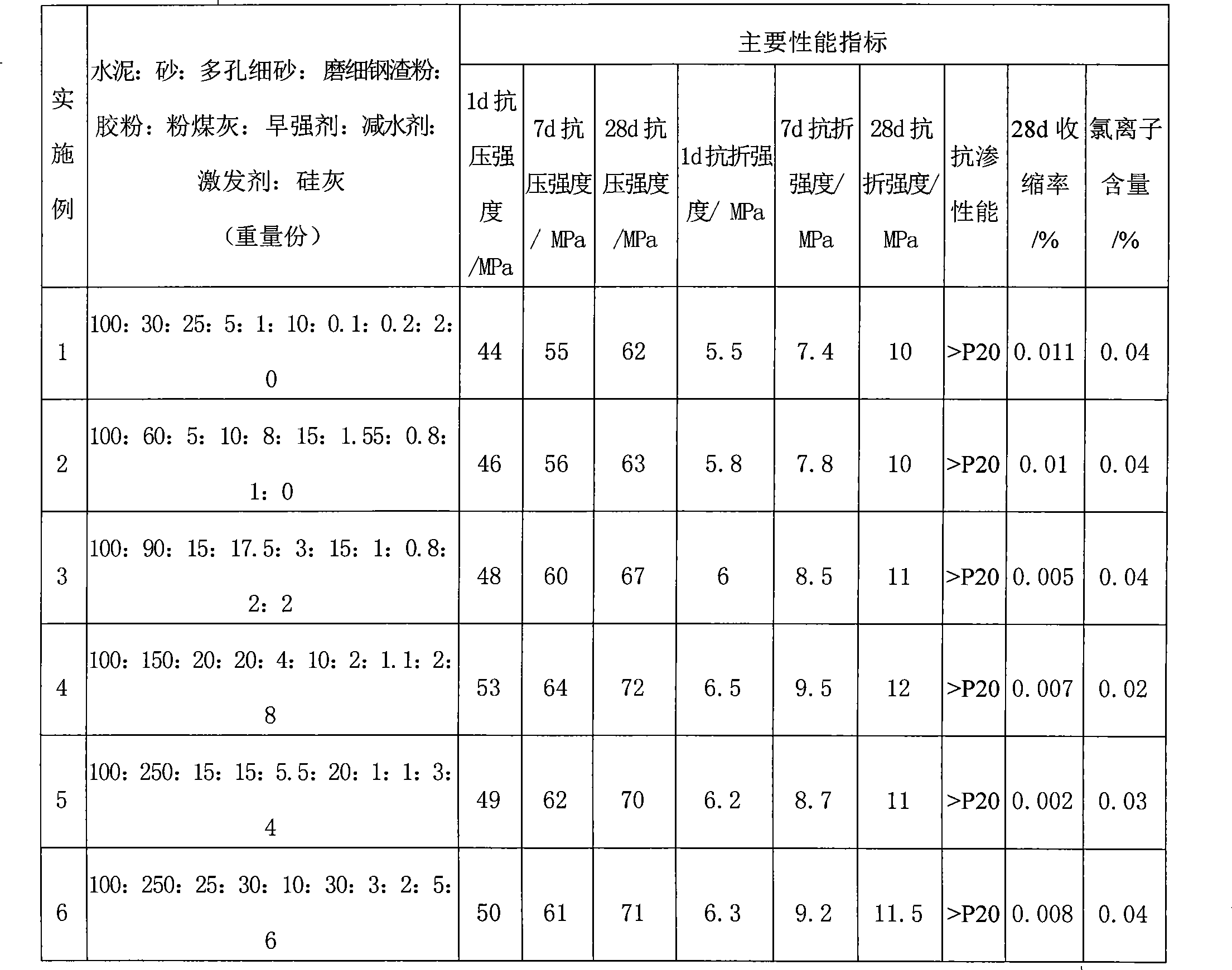
The invention relates to an early strength fast hardening terminated anchor mortar material, which is characterized in that the material is formed by mixing and stirring cement, sand, porous fine sand, finely ground steel slag powder, fly ash, an early strength agent, rubber powder, silicon ash, a water reducing agent and an excitant. The parts by weight of the components are as follows: 100 parts of cement, 30-250 parts of sand, 5-25 parts of porous fine sand, 5-30 parts of finely ground steel slag powder, 10-30 parts of fly ash, 0.1-3 parts of early strength agent, 1-10 parts of rubber powder, 0-8 parts of silicon ash, 0.2-2 parts of water reducing agent and 1-5 parts of excitant. Finely ground converter slag which is naturally stored for 3-6 months is adopted for the finely ground steel slag powder and the specific surface area is 400-800m / kg; the content of magnesium oxide is 8-15%; the porous fine sand is shale ceramic sand or fly ash ceramic sand or the mixture of the shale ceramic sand and the fly ash ceramic sand based on random mixture ratio, with grain size of 0.10-2.6mm. The material provided by the invention has good mechanical property and adhesive property, low chloride ion content and shrinkage property, and high impermeability and anti-cracking performance, thereby preventing the prestressed reinforcement of track slabs from rusting.
Owner:RAILWAY ENG RES INST CHINA ACADEMY OF RAILWAY SCI +1
Low-shrink anchorage sealing material for CRTS I type ballastless track slabs of high speed railway
InactiveCN102001844AImproved microstructural featuresAchieve early high compressive strength requirementsCohesive strengthMetakaolin
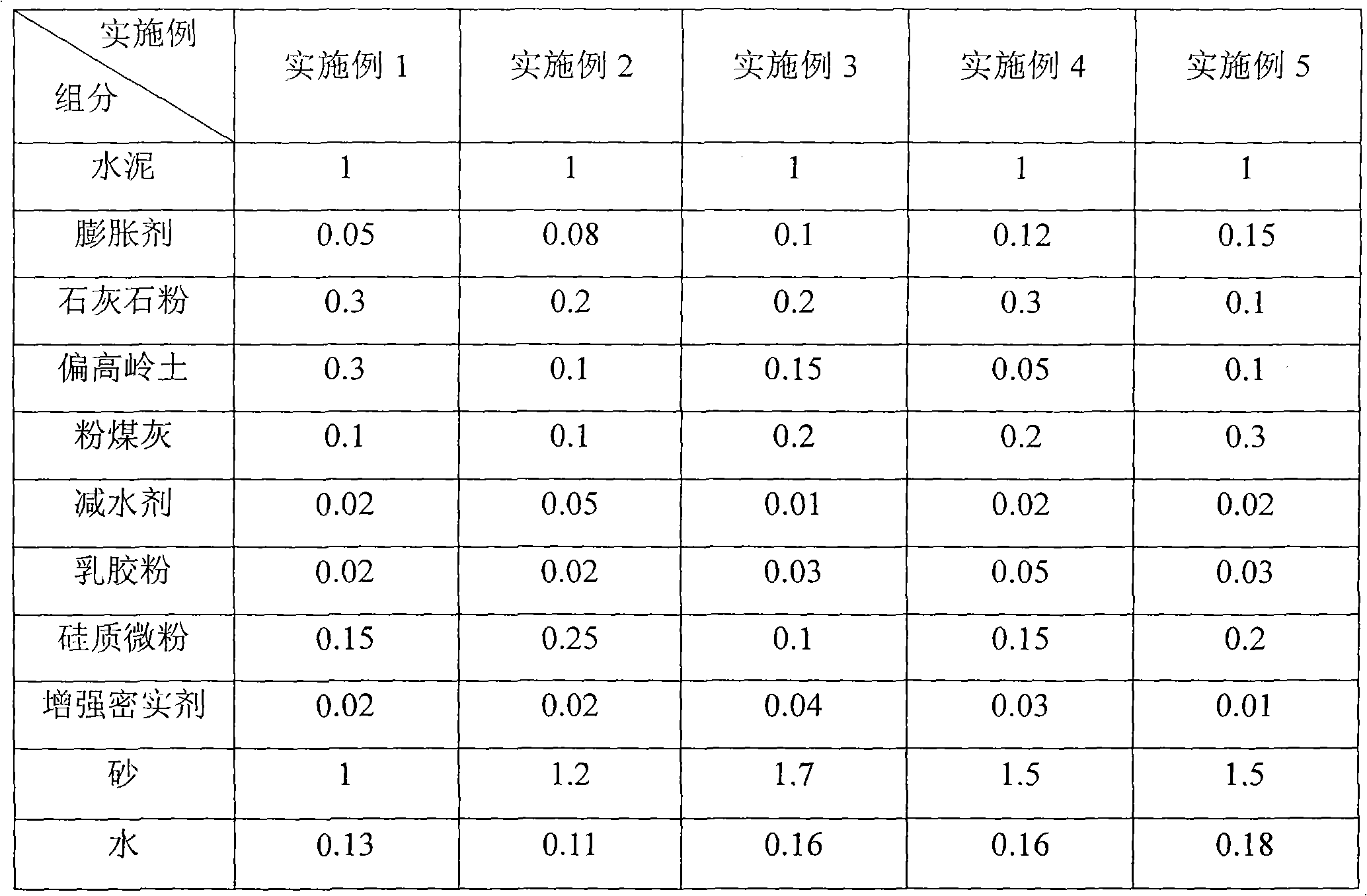
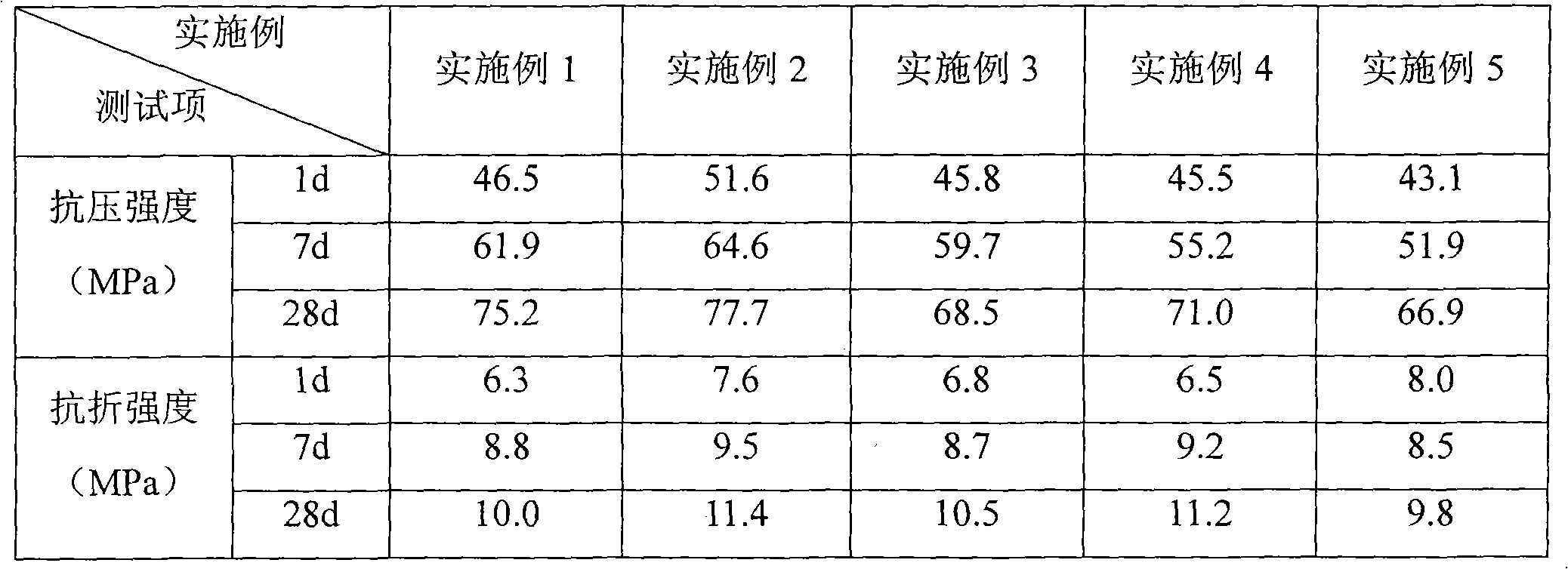
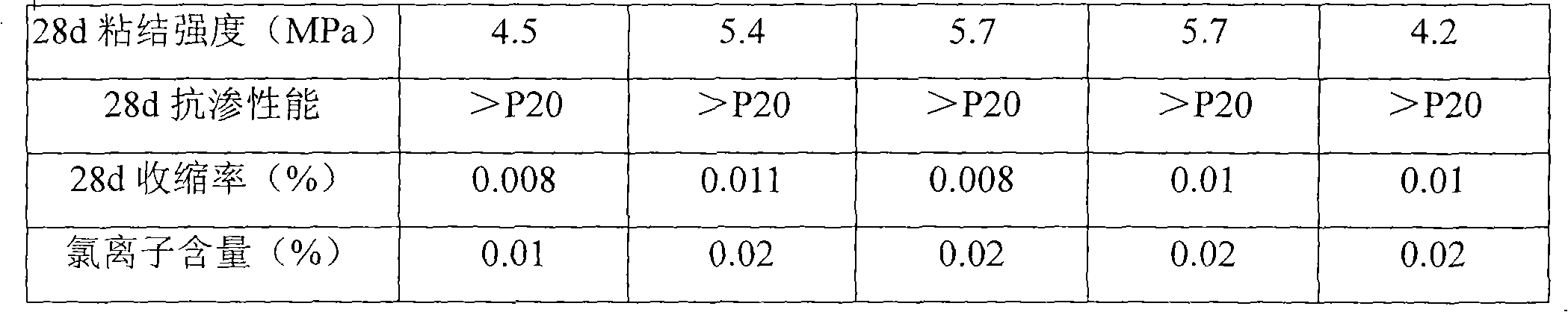
The invention relates to a low-shrink anchorage sealing material for CRTS I type ballastless track slabs of a high speed railway, which is characterized by comprising the following components in proportion: 1 cement, 0.05-0.15 swelling agent, 0.1-0.3 limestone powder, 0.05-0.3 metakaolin, 0.1-0.3 coal ash, 0.01-0.05 water reducer, 0.02-0.05 emulsoid powder, 0.1-0.25 siliceous micropowder, 0.01-0.04 enhanced compacting agent, 1.0-2.0 sand, and 0.1-0.2 water. The material of the invention has the characteristics of low shrinkage rate, high compressive strength and cohesive strength, high osmosis resistance and low chloride ion content, and can be used for anchorage sealing of prestress tension holes of the CRTS I type ballastless track slabs of the high speed railway.
Owner:RAILWAY ENG RES INST CHINA ACADEMY OF RAILWAY SCI
Pipeline dredging agent with stable oxygenation effect and preparation method of pipeline dredging agent
ActiveCN103937624AGood insulation performanceShort contact distanceSurface-active non-soap compounds and soap mixture detergentsOrganic non-surface-active detergent compositionsDissolutionOxygen
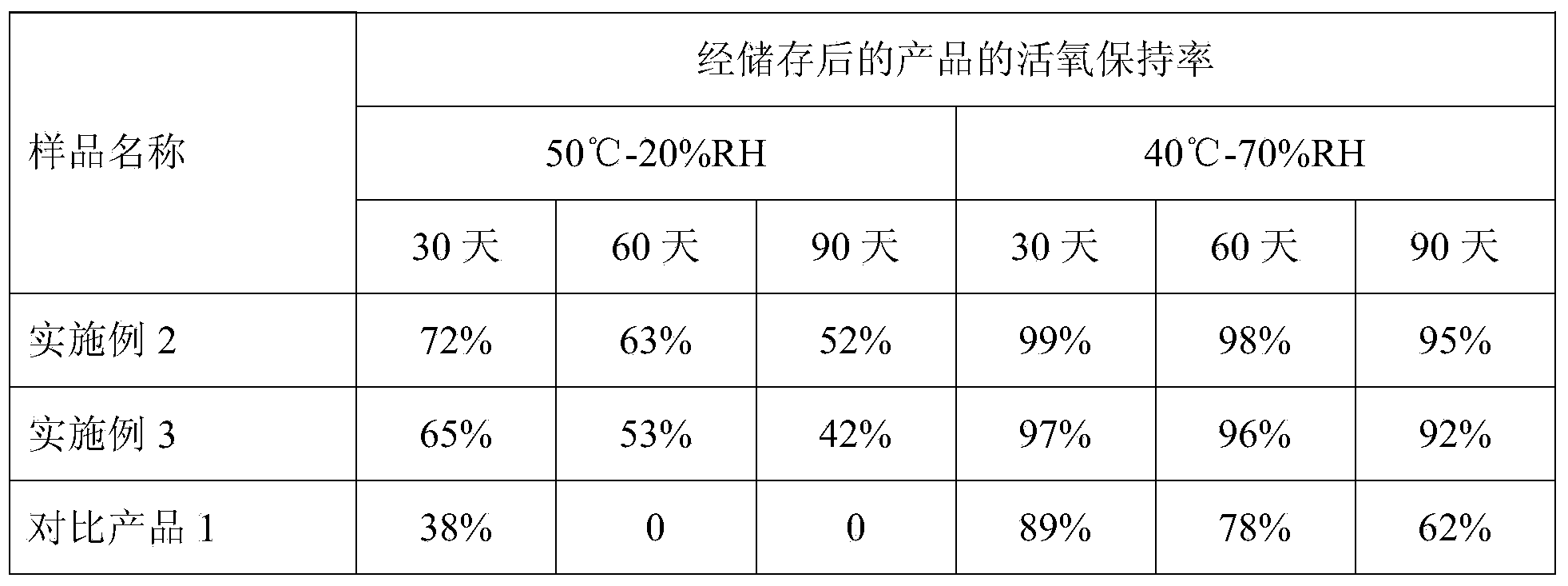
The invention discloses a pipeline dredging agent with a stable oxygenation effect and a preparation method of the pipeline dredging agent. The pipeline dredging agent comprises strong base, a non-volatile liquid, special powder, an oxygen bleaching agent and a chlorine bleach, and can further comprises an additive, and is prepared through a special feeding process. The combination of the non-volatile liquid and the special powder is innovatively introduced, so that the oxygenation stability and the anti-caking property of a product in a storage process are greatly improved, and the dust amount and the nose chocking feeling are reduced and alleviated. The product disclosed by the invention also has the advantages of rapid dissolution, stable heat radiation, low chloride smell, low metal corrosion, easy production and machining and the like, is applicable to dredging or cleaning and maintaining drainage pipelines, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:广州超威生物科技有限公司
Preparation method of low-chloride high-purity germanium dioxide
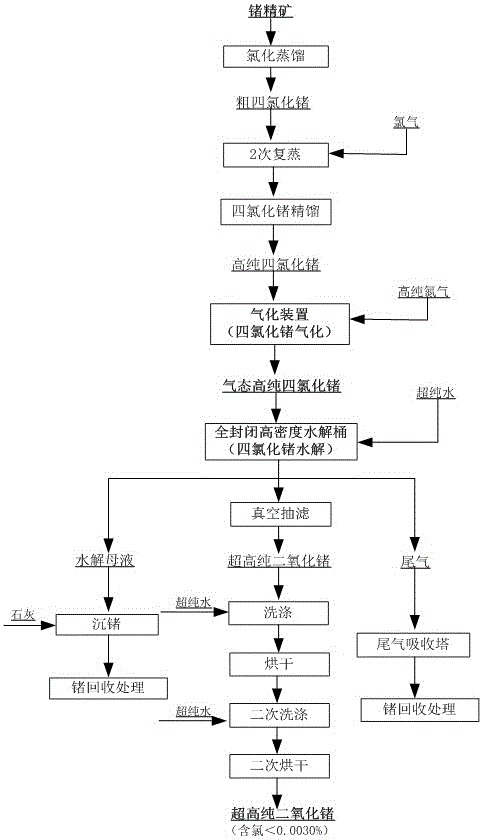
InactiveCN106564933ALow chlorine contentAvoid insufficient hydrolysisGermanium dioxideFiltrationNitrogen
Owner:YUNNAN LINCANG XINYUAN GERMANIUM IND +1
Activated sludge culture method suitable for high-salt sewage
InactiveCN102502955ASolve difficult biochemical processing problemsAchieve removalSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentActivated sludgeWater quality
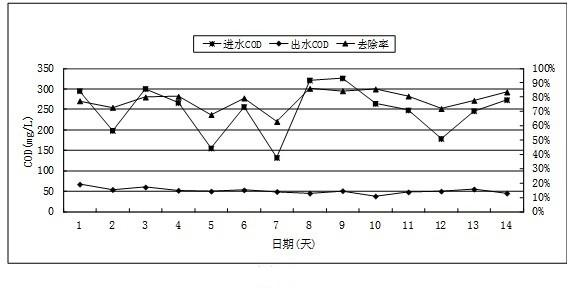
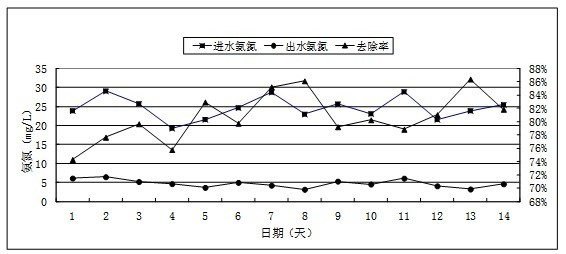
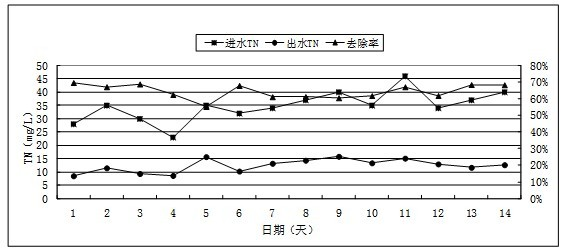
The invention discloses an activated sludge culture method suitable for high-salt sewage, and the culture method comprises the following steps of: (1) aeration; (2) intermittent water charging to improve chloride ion loading; (3) continuous water charging. Sewage with a low chloride ion concentration is cultured firstly; after activated sludge suitable for the low chloride ion concentration is successfully cultured, the chloride ion concentration is increased gradually (intermittent water charging); after activated sludge suitable for a high chloride ion concentration is generated, the hydraulic loading is increased (continuous water charging), and thus activated sludge which can treat high-salt sewage is obtained. The method can culture activated sludge which can treat sewage with a chloride ion concentration of below 7000 mg / L; the sludge concentration reaches 2500-4000 mg / L; certain removing effect on COD, TN, ammonia nitrogen, and the like is realized; and the effluent quality meets the national discharge grade one B standard. The invention effectively solves the problem of difficult biochemical treatment of high-salt municipal sewage in coastal regions, and has the characteristics of simple culture and low cost.
Owner:TANGSHAN PORT DEV ZONE SEWAGE TREATMENT
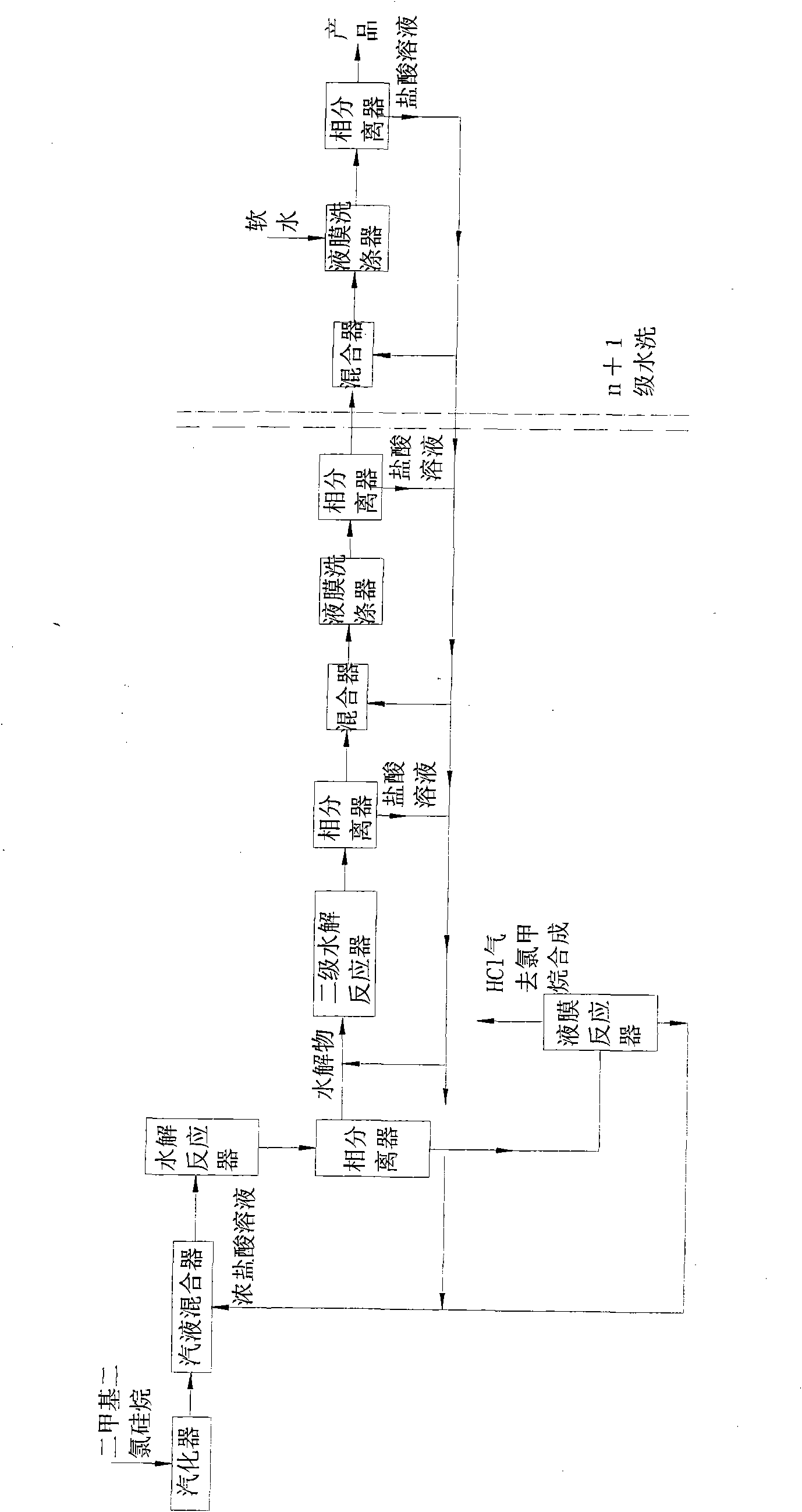
Method for hydrolyzing dimethyldichlorosilane in saturated acid
The invention relates to a hydrolysis technology of methyl chlorosilane, in particular to a technology for hydrolyzing dimethyldichlorosilane in saturated acid and preparing high cyclosiloxane and hydrolysate with low chloride ions. The technology is characterized by comprising the following steps: mixing vaporized dimethyldichlorosilane with concentrated hydrochloric acid to perform hydrolysis reaction, sending the reaction solution to a phase separator for separation, using the separated crude hydrolysate and concentrated hydrochloric acid to perform hydrolysis reaction again, sending the reaction solution to the phase separator to separate hydrolysate and acid solution, washing the hydrolysate with water, sending the hydrolysate to the phase separator to separate polydimethylsiloxane and acid solution, sending the concentrated hydrochloric acid separated through the first hydrolysis separation to a liquid membrane reactor to separate hydrogen chloride gas, and sending concentrated hydrochloric acid back to the hydrolysis reactor for circular reaction, wherein the acid solutions separated through the other steps are also used for circular reaction. By adopting the method of the invention, the operation process is simplified, the energy consumption is reduced and the production cost is lowered.
Owner:ZHENJIANG JIANGNAN CHEM
Independent production of electrolyzed acidic water and electrolyzed basic water
An apparatus for the selective production of electrolyzed water is provided, wherein the apparatus allows for the production and discharge of either electrolyzed acidic water or electrolyzed basic water to be independently without the corresponding production and discharge of the other. In certain embodiments, the present invention can provide a low chloride electrolyzed acidic water or a low chloride electrolyzed basic water.
Owner:EAU TECH
Device and method for oxidizing and removing elemental mercury by using wet flue gas desulfurization wastewater
InactiveCN104084028APromote catalysisAvoid dependenceDispersed particle separationAir preheaterAir compressor
The invention relates to a device and a method for oxidizing and removing elemental mercury by using wet flue gas desulfurization wastewater. The device comprises a boiler, wherein the boiler is connected with a SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) denitration device through a coal economizer; the SCR denitration device is connected with a limestone-gypsum wet desulphurization tower through an air pre-heater and a dust remover; a chimney is arranged on the limestone-gypsum wet desulphurization tower; atomizing nozzles are distributed in a flue between the coal economizer and the SCR denitration device; the atomizing nozzles are connected with a desulfurization wastewater tank through a slurry pump; an air compressor is connected with the atomizing nozzles and used for supplying compressed air for the atomizing nozzles in the atomizing process. By virtue of the device and the method, the problem that combustion low-chloride coal elemental mercury is difficultly discharged is solved, and the problem of treatment of the desulfurization wastewater is solved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
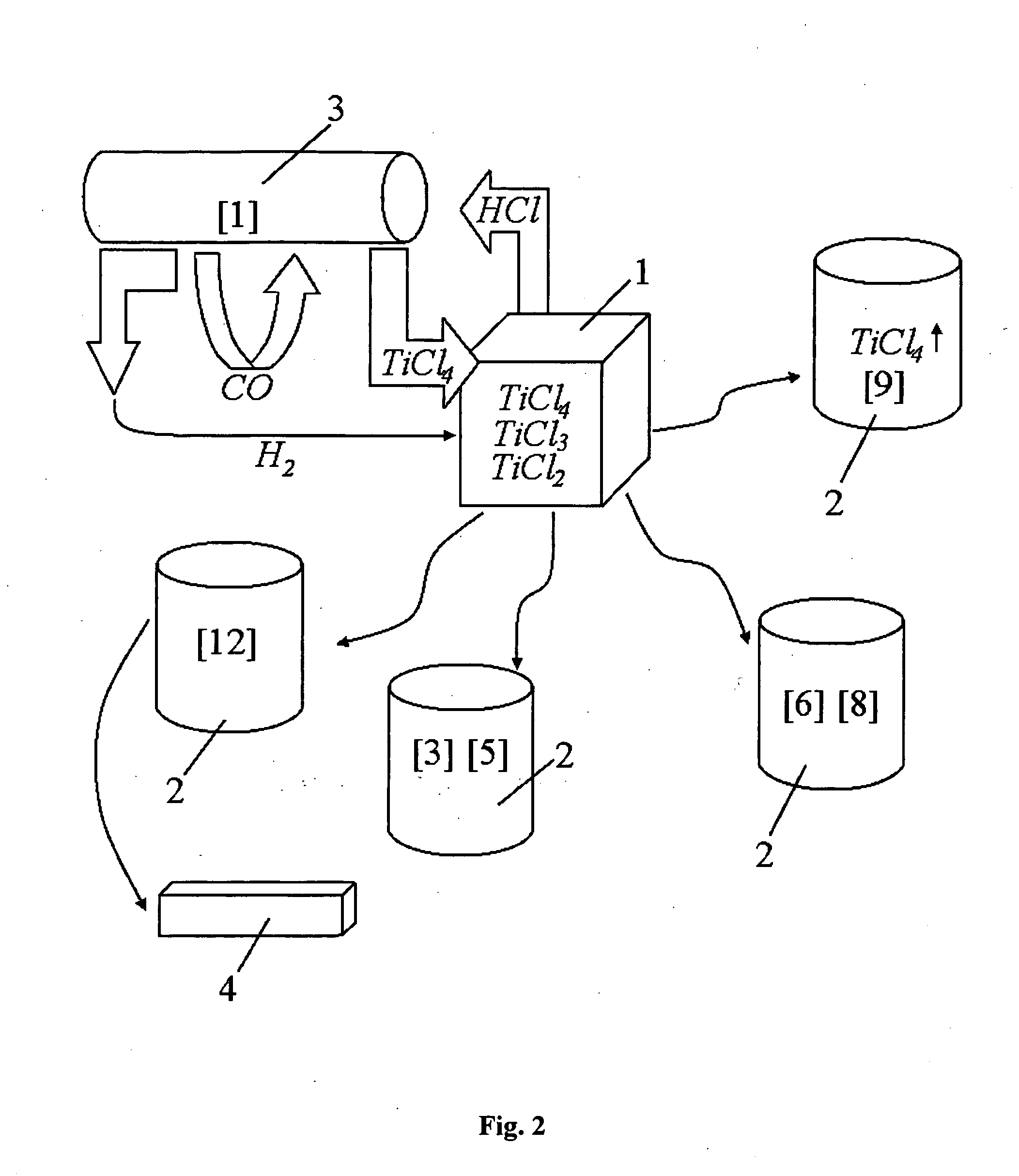
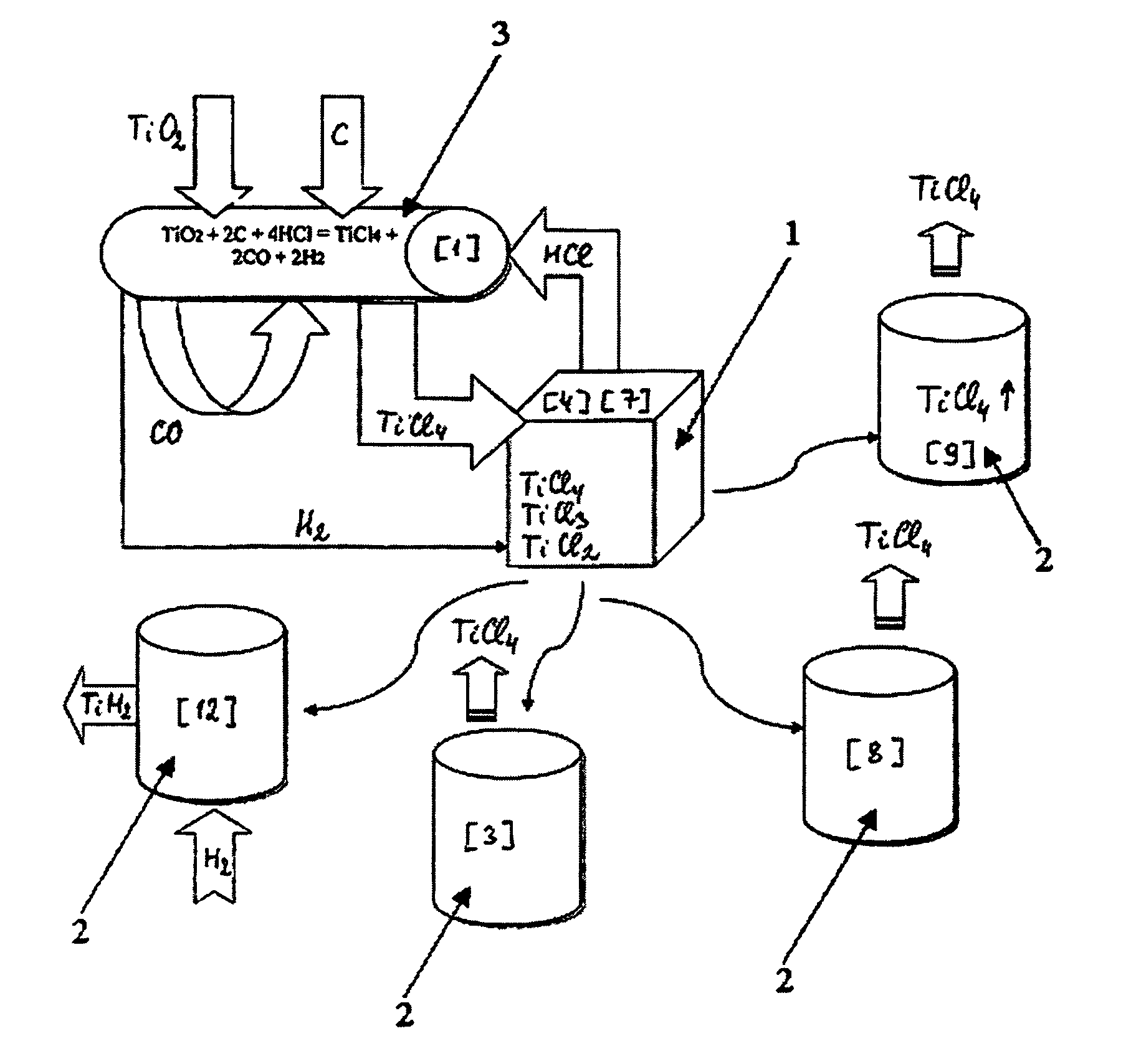
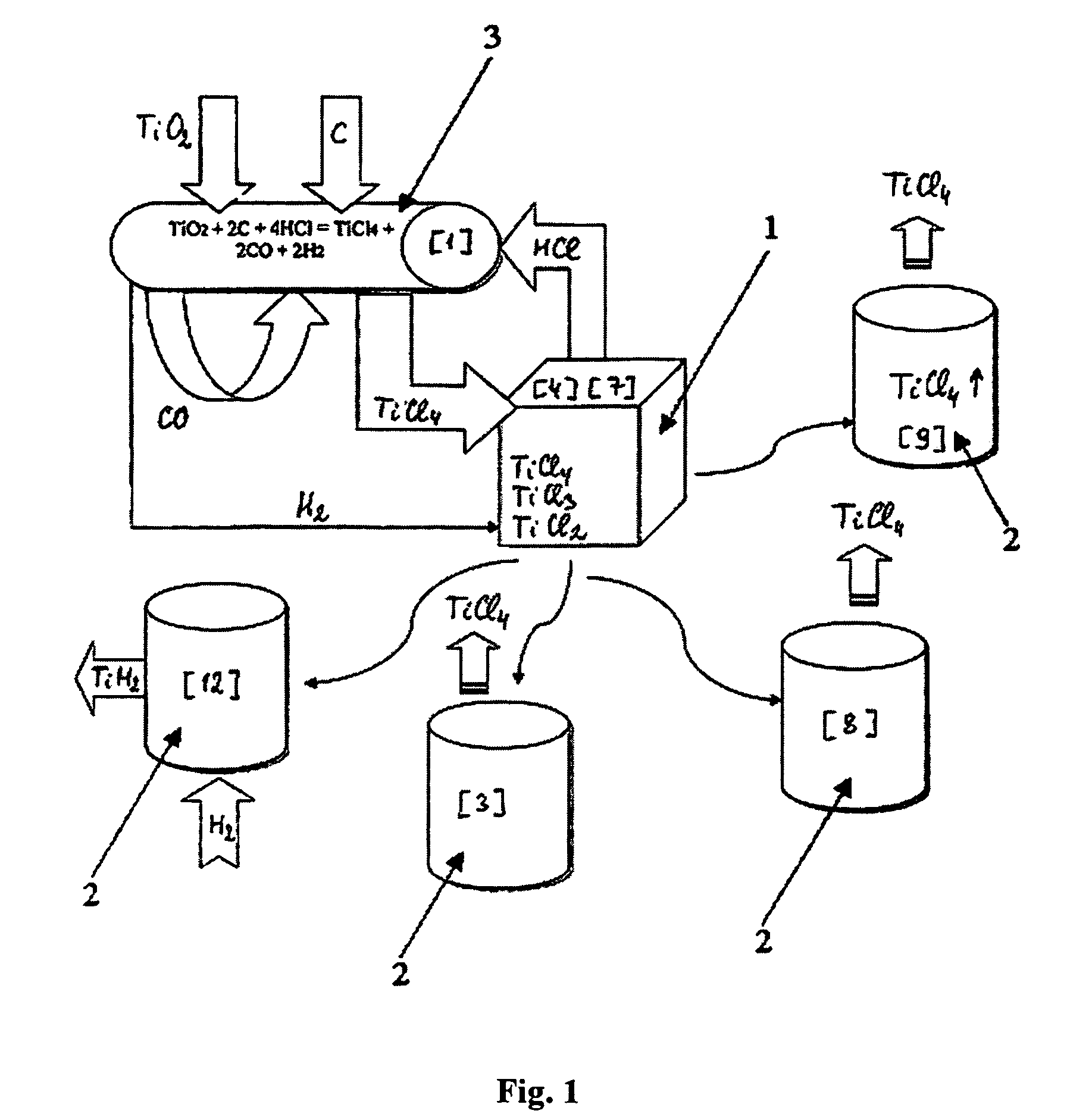
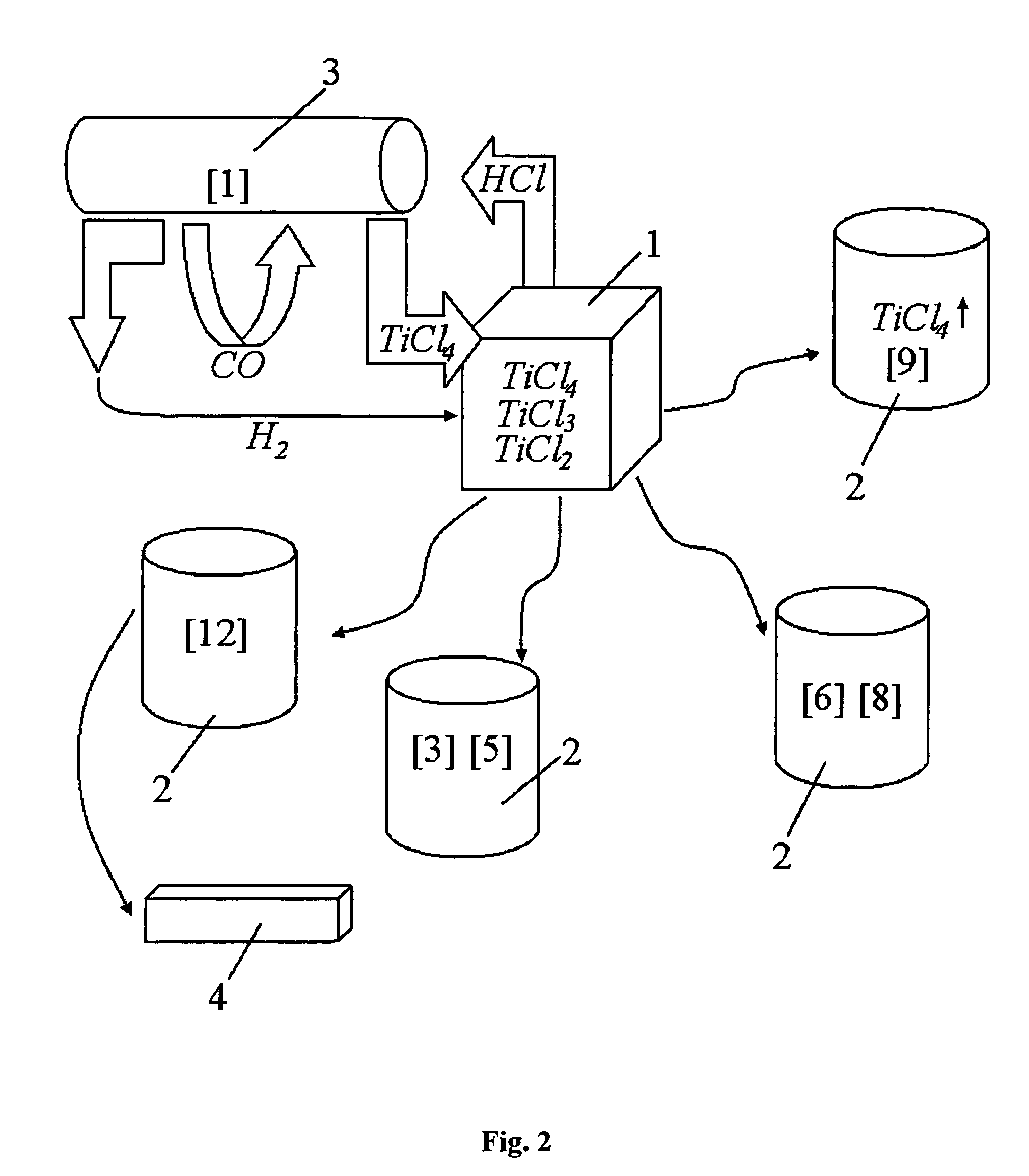
Continuous and semi-continuous process of manufacturing titanium hydride using titanium chlorides of different valency
InactiveUS20110171116A1Reduce manufacturing costCost-effective and highly-productive manufactureTransition element hydridesTitanium chlorideOxygen
The invention relates to the manufacture of titanium hydride powder using continuous or semi-continuous process, and using titanium slag or synthetic rutile as raw materials, while hydrogen, titanium tetrachloride, titanium trichloride, titanium dichloride, and hydrogen chloride are participate as intermediate reaction products. The continuous comprises: (a) reduction of TiCl4 to low titanium chlorides followed by cooling a mixture, (b) separating of residual TiCl4 from solid low chlorides by heating the mixture in argon or vacuum up to 150° C. followed by removing the titanium tetrachloride from the mixture, (c) dissociation of TiCl3 to TiCl2 at 450° C. in vacuum followed by removal of gaseous titanium tetrachloride from the reaction zone, condensation to the liquid, and returning back into the reaction retort, (d) dissociation of TiCl2 in vacuum at 750-850° C. to manufacture fine powder of metallic titanium and titanium tetrachloride, whereby hydrogen heated up to 1000° C. is used to accelerate this reaction, and (e) saturation of the fine titanium powder by hydrogen at 400-640° C. to manufacture final product of titanium hydride powder which is free of oxygen or nitrogen. The semi-continuous process includes the Kroll's process as the very first step.
Owner:ADMA PRODS
Alkylated cyclodextrin compositions and processes for preparing and using the same
The present invention related to low-chloride alkylated cyclodextrin compositions, along with processes for preparing and using the same. The processes of the present invention provide alkylated cyclodextrins with low levels of drug-degrading agents and chloride.
Owner:CYDEX PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Low-chloride phosphorus potassium fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101525256AHigh in nutrientsReduce chlorine contentEnergy inputPotassium fertilisersWater vaporHearth
The invention relates to a low-chloride phosphorus potassium fertilizer and a preparation method thereof, in particular to a method for preparing the low-chloride phosphorus potassium fertilizer by melting and sintering potassium chloride, phosphorite powder and quartz sand, and the invention belongs to the production field of phosphorus potassium compound fertilizer. In the method, the potassium chloride, the phosphorite powder, the quartz sand or diatomite, insoluble potassic ore and boric anhydride are used as raw materials; coal, heavy oil or natural gas are used as fuel; or an electric cooker is used as a high-temperature heat source; and the phosphorus potassium fertilizer is produced by melting and sintering in steam atmosphere. The reaction is carried out in a blast furnace, an open hearth or the electric cooker, and the melting temperature is 800-1600 DEG C. The method produces the phosphorus potassium fertilizer by the potassium chloride and the phosphorite powder directly and has simplified process; the prepared phosphorus potassium fertilizer has high total nutrient and the low content of chloride and can be used for chlorophobic crops; the phosphorus potassium fertilizer contains two elements of phosphor and potassium required by the crops in large amount at the same time; the percentage content of K2O is 10%-18%; the percentage content of P2O5 is 15%-30%; the content of chlorine ion is less than 3%; and the total nutrient is 30%-45%.
Owner:中国-阿拉伯化肥有限公司
Process for manufacturing lower chlorides of titanium
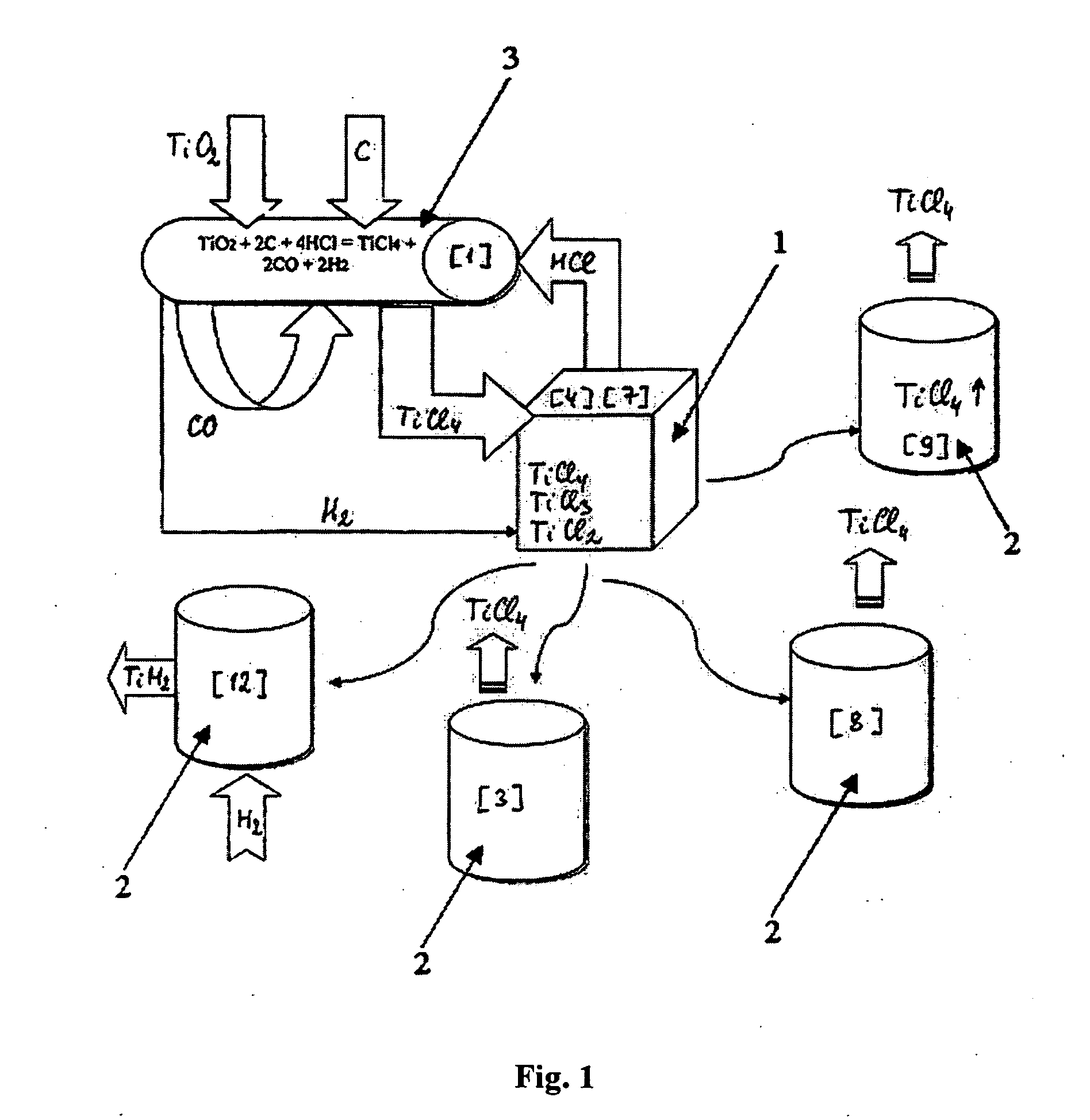
A process for preparation of lower chlorides of titanium is provided, in which titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) is reduced using a reducing agent in at least one molten alkali metal salt at a temperature of about 300 to about 1400 DEG C to obtain a reduced mass containing lower chlorides of titanium. A process for preparation of titanium metal from the lower chlorides of titanium is also provided.
Owner:凯基·霍尔穆斯吉·格哈达
Processed mineral additive for reducing concrete permeability and increasing strength
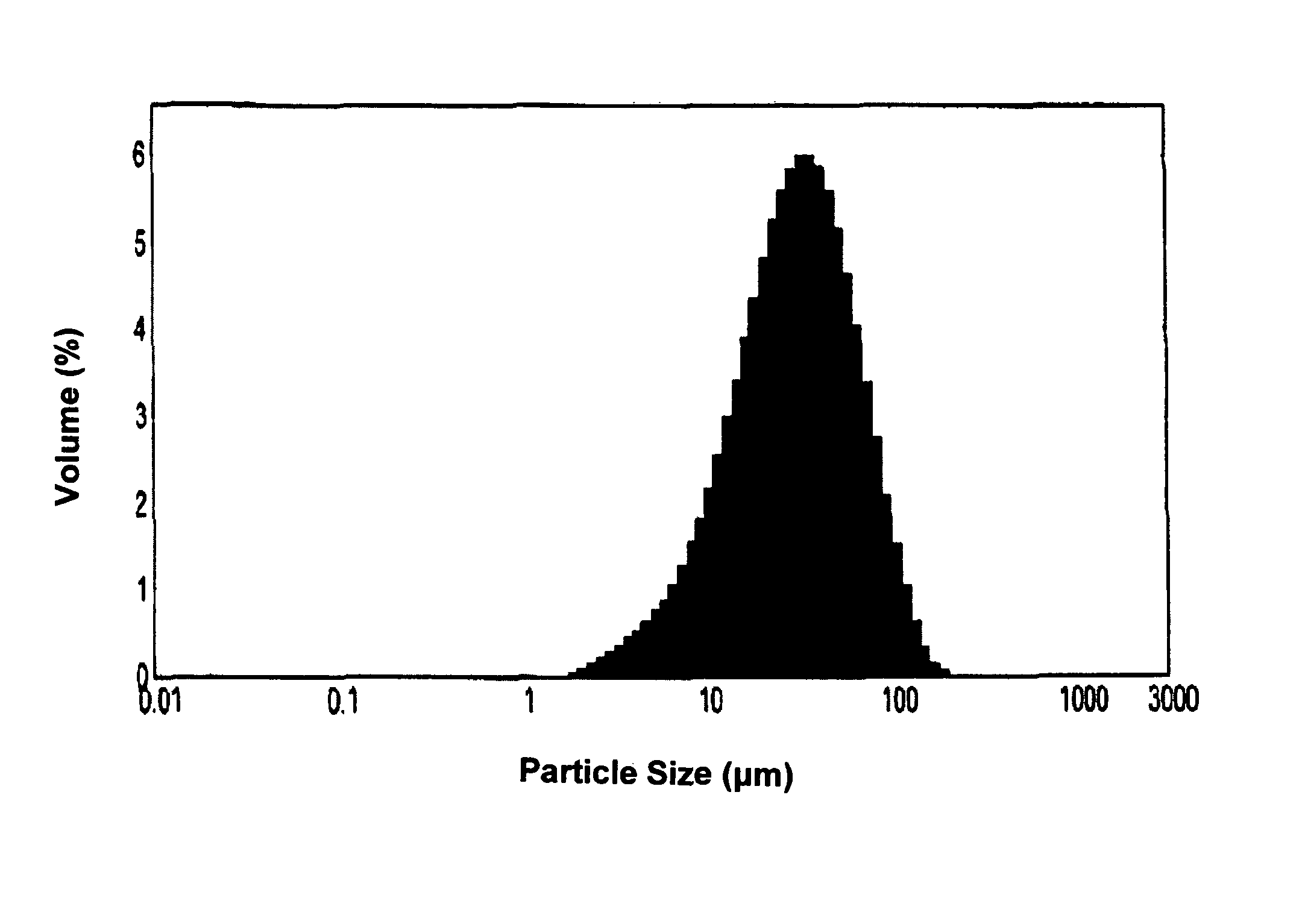
A concrete additive includes expanded perlite with a volume weighted mean particle size of approximately 10-100 μm. The perlite further includes at least one additional component to improve workability and compensate for the natural tendency of expanded perlite to absorb water from the concrete mix. The additional component can include: water; a superplasticizer such as polycarboxylates, naphthalene sulfonate, and melamine sulfonate; or a hydrophobic compound such as salts of fatty acids, fatty acids, silanes, and siloxanes. The additive can be made in the form of a flowable powder or a flowable slurry. Concrete containing this additive displays superior properties to conventional concrete, including extremely high thermal resistance and high strength, low chloride ion permeability, and good early strength. The expanded perlite is a readily available raw material and the finished concrete is extremely cost effective for applications where a high strength structural concrete must withstand high temperatures.
Owner:CENTSTAR
Snowmelt agent
InactiveCN101671539AImprove snow removal effectGood snow removal effectOther chemical processesRoad surfaceSnowmelt
The invention relates to a snowmelt agent, which is a composite snowmelt agent and comprises the following components and contents (weight) in percentage by weight: 80 to 95 percent of acetate and 5 to 20 percent of chloride. Compared with the prior art, the snowmelt agent has good snow removing effect and low chloride content, can reduce the corrosivity of the snowmelt agent obviously, effectively protects pavement and bridges, prolongs the service life of public facilities and reduces the cost while achieving excellent snow removing effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI CITY CHANGNING DISTRICT JUNIOR SCI &TECH GUIDANCE STATION +2
Continuous and semi-continuous process of manufacturing titanium hydride using titanium chlorides of different valency
InactiveUS8388727B2Cost-effective and highly-productive manufactureImprove machining productivityTransition element hydridesTitanium chlorideTitanium(II) chloride
Owner:ADMA PRODS
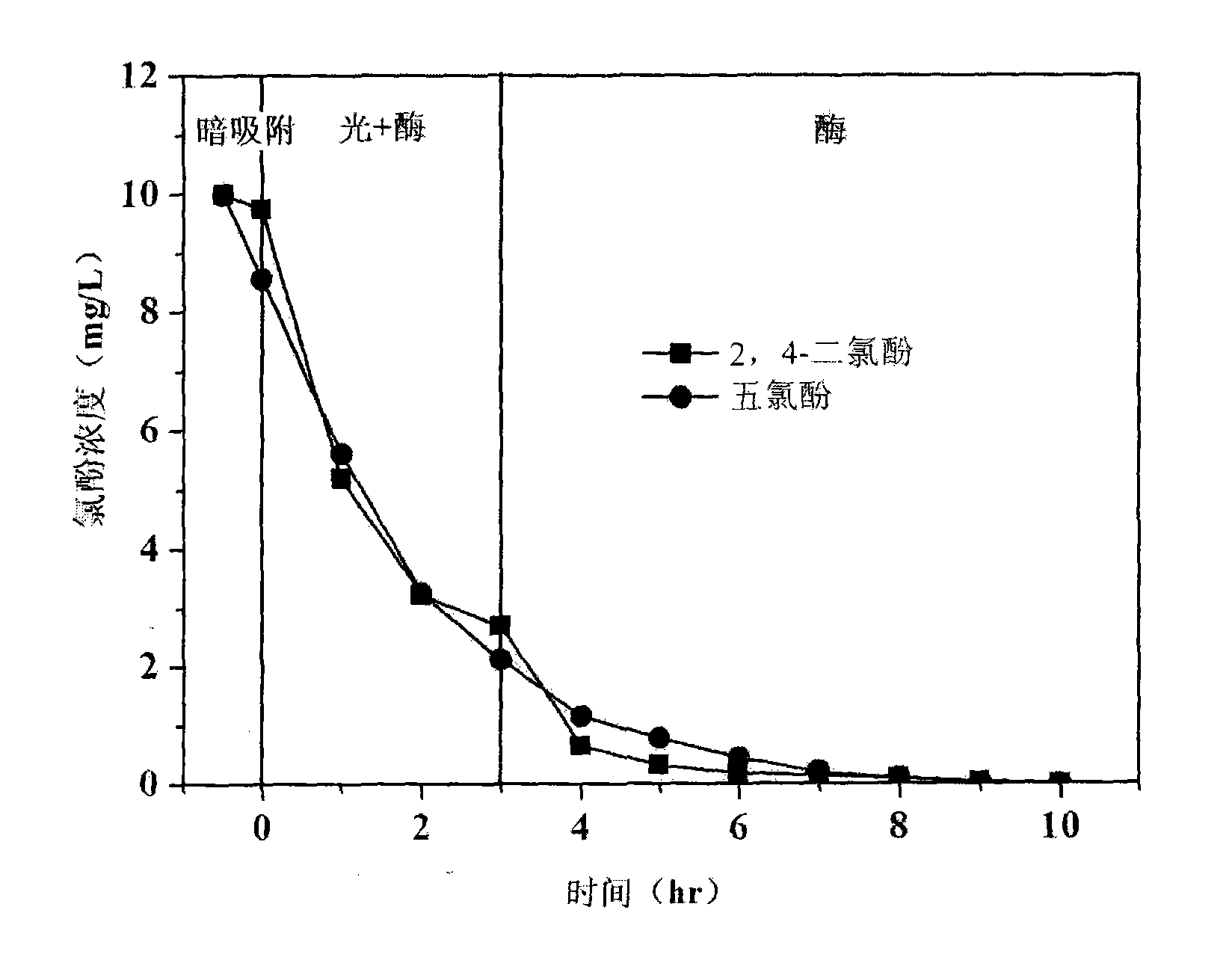
Method for treating waste water polluted by composite chlorophenol with coordination of visible light-laccase
InactiveCN101638253AEfficient and thorough pollutionSimple processWater/sewage treatment by irradiationEnergy based wastewater treatmentSewageChlorophenol
The invention discloses a method for treating waste water polluted by composite chlorophenol with coordination of visible light-laccase, comprising the following steps: regulating the pH value of waste water polluted by the composite chlorophenol; mixing the laccase and the waste water to be treated, and carrying out the following processes such as photocatalysis treatment, light-tight treatment,photocatalyst extraction, filter, separation and recovery and the like. The laccase is utilized to catalyze low chloride chlorophenols in the waste water to enable the low chloride chlorophenols to fast aggregate to form sedimentation; and high chloride chlorophenols in the waste water are treated by photocatalysis and oxidation through visible lights to achieve the purpose of completely purifyingcomposite chlorophenol waste water with high efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
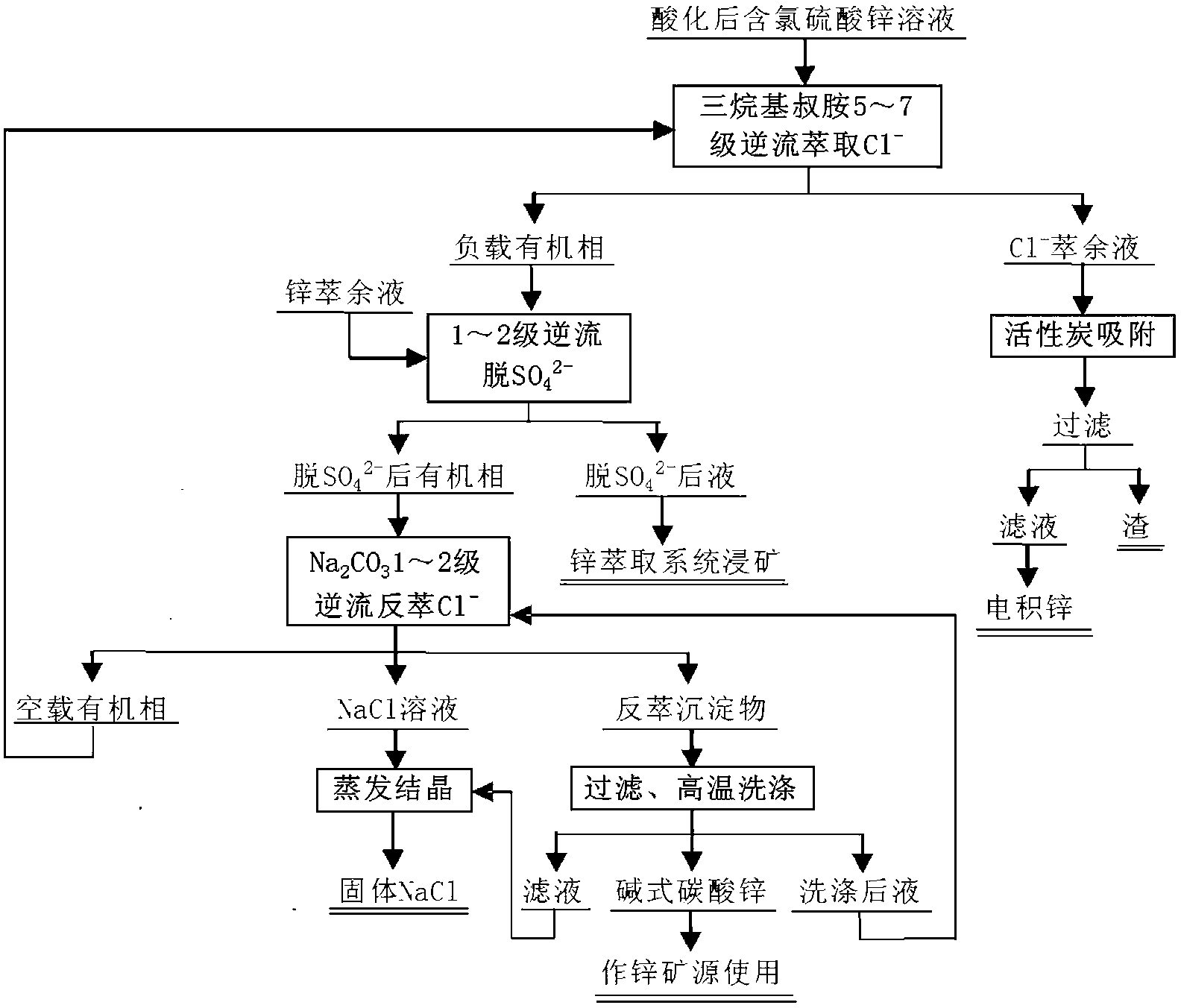
Method for removing chlorine from chlorine-containing zinc sulfate solution
ActiveCN103060561AEasy to evaporate and crystallizePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementKeroseneRaffinate
The invention belongs to the technical field of wet metallurgy, in particular relates to a method for purifying and separating chloride ions from a chlorine-containing zinc sulfate solution generated in a zinc electrolyzing process. The method comprises the following steps: (1) forming an organic extraction phase by using trialkyl tertiary amine, octyl alcohol and sulfonated kerosene 260 #, and stirring and mixing the organic extraction phase into an acid solution containing chloride zinc sulfate, thereby separating out a chloride-loaded organic phase and a low-chloride-content extraction raffinate; (2) deoiling and adsorbing the low-chloride-content extraction raffinate and then sending to an electric zinc accumulating process; (3) mixing the chloride-loaded organic phase into an extraction raffinate in a zinc extracting process, and sending an obtained subsequent fluid in which SO42 is removed into an zinc extracting system to perform a mineral leaching while stirring and mixing an obtained organic phase into a sodium carbonate solution to perform a reverse extraction; (4) returning a no-load organic phase obtained by the reverse extraction process to the step (1) to be recycled; utilizing two-hydrated alkali type zinc carbonate (a reverse extraction sediment) as a zinc mineral resource; separating out a two-hydrated alkali type zinc carbonate sediment from a reverse extraction subsequent fluid; carrying out a recycling reverse extraction by adding sodium carbonate to a clear solution; and after enabling the chloride (Cl) to reach a setting concentration, evaporating and crystallizing the chloride to obtain an industry body NaCl (sodium chloride). The method provided by the invention is low in cost, high in efficiency and easy to control and free of the discharge of 'three wastes'.
Owner:YUNNAN XIANGYUNFEILONG RESOURCES RECYCLING TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing high-purity low-chloride electroplated copper oxide
InactiveCN103011250AAvoid bringing inGuaranteed purityCopper oxides/halidesDistillationCarbonization
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-purity low-chloride electroplated copper oxide. The method comprises the following steps: taking copper, liquid ammonia and high-purity carbon dioxide as raw materials; preparing stronger ammonia water at first; then pumping high-purity carbon dioxide into the stronger ammonia water; preparing and obtaining carbonated ammonia water through controlling the carbonization degree; achieving reaction between the carbonated ammonia water and copper under a certain air pressure to obtain a copper and ammonia complexing solution; preparing heavy high-purity cupric subcarbonate through heating, ammonia distillation, separation, washing, drying and screening; and heating, calcining and decomposing the heavy cupric subcarbonate to obtain high-purity low-chloride electroplated copper oxide. According to the invention, as carbon dioxide serves as the raw material, the problem that the raw material for producing cupric subcarbonate by adopting a traditional method carries heavy metal ions, chloride ion and other impurities is solved, the reaction speed is increased, the production period is shortened, the production efficiency is greatly improved, the impurity content is low, high purity and activity are realized, and the product can be applied more widely. The method has the advantages of high yield, low energy consumption, little pollution and low cost.
Owner:TAIXING SMELTING PLANT
Fast setting low permeability cement and concrete
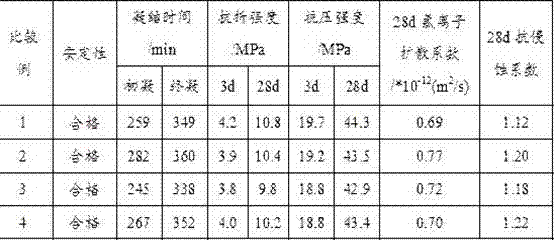
A calcium sulfoaluminate-based concrete with a permeability of less than 1000 Coulombs. Rapid-setting low chloride-ion permeability calcium sulfoaluminate (CSA) cements and concretes include CSA and a suitable polymer such as a sol-gel derived, organic-inorganic, silica based hybrid coating solutions of polystyrene-butylacrylate polymers containing active silanol groups protected by hydroxyl groups containing polyalcohol, or other polymers. Such polymers may be added as powders or as liquid in the finish mill. Other rapid-setting low chloride-ion permeability (CSA) cements and concretes include CSA with selected particle size distributions, and do not require use of any polymer. These CSA cements and concretes have low chloride-ion permeability, high early strength, fast setting times, low-shrinkage, and high freeze-thaw resistance.
Owner:CSA RES LLC
Alkylated cyclodextrin compositions and processes for preparing and using the same
The present invention related to low-chloride alkylated cyclodextrin compositions, along with processes for preparing and using the same. The processes of the present invention provide alkylated cyclodextrins with low levels of drug-degrading agents and chloride.
Owner:CYDEX PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Method for preparing isocyanate with low chloride content
ActiveCN110396057AIsocyanic acid derivatives purification/separationCompound organicChloral derivative
The invention discloses a method for preparing isocyanate with low chloride content. A reaction is performed between a compound organic salt and crude isocyanate under acidic conditions, a precipitateis removed in a simple filtration mode, the acid content is further reduced in an inert gas stripping mode, and a residual solvent is removed in a vacuum distillation mode. Through the method, the content of a chlorinated derivative impurity is reduced to 0.1% or below, the acid content is reduced to less than 10 ppm, meanwhile, side reactions are avoided, and the yield can reach 90% or above; and the chlorine content of the isocyanate obtained by using the method can be reduced, so that preparation of down-stream products is improved obviously.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD +1
Low-chloride AFFF ( aqueous film-forming foam) extinguishing agent
The invention relates to a low-chloride AFFF (aqueous film-forming foam) extinguishing agent. The low-chloride AFFF extinguishing agent comprises components in percentage by mass as follows: 12%-30% of a composite carbon-hydrogen surfactant, 2%-5% of a fluorocarbon surfactant, 0.1%-1% of a foam stabilizer, 1%-10% of an anti-freezing agent, 3%-5% of a solubilizer and the balance of water, wherein the composite carbon-hydrogen surfactant is composition of an anionic surfactant and a nonionic surfactant. The low-chloride AFFF extinguishing agent is an environment-friendly AFFF extinguishing agent with low chlorine content, and is mainly used for preventing and fighting hydrocarbon fires. The chlorine ion content of a product is very low, so that the corrosion rate of the product is very low, and corrosion to various storage containers is effectively reduced, so that the product is applicable to various storage containers and is particularly applicable to storage containers made of metal such as stainless steel and the like.
Owner:兴化市成顺消防科技研究院有限公司
Preparation method of low-chloride high-purity cobalt carbonate
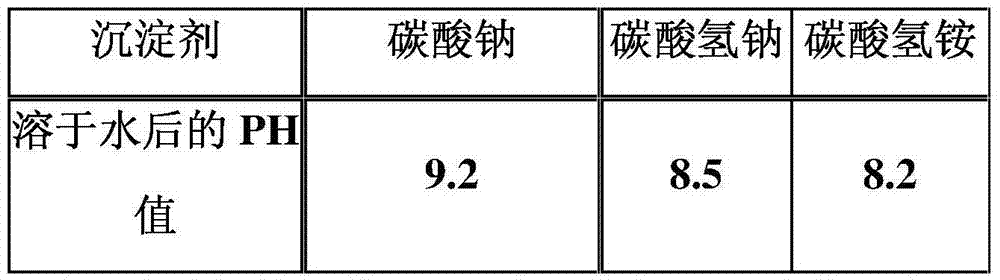
The invention relates to a preparation method of low-chloride high-purity cobalt carbonate. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps: using ammonium bicarbonate as a precipitator, adding ammonium bicarbonate which accounts for 4-6 times of molar ratio of cobalt chloride into a cobalt chloride solution containing a foam inhibitor at one time under the conditions of normal temperature and continuous agitation, standing for at least 12 hours, washing a product obtained, filtering and drying to obtain a high-purity cobalt carbonate product. Content of chlorine in the prepared high-purity cobalt carbonate product is less than 500ppm, but the content of chlorine in the prior art is high than 1000ppm. Meanwhile, the preparation method has a simple technology; by the use of ammonium bicarbonate, there is no introduction of new impurity elements; and with the addition of the foam inhibitor, speed of carbon dioxide overflowing from the solution is reduced so as to achieve the effect of full reaction. Thus, purity of the product is raised; overswelling is avoided; and capacity is greatly increased.
Owner:NINGXIA ORIENT TANTALUM IND
Synthesis of amino acid, N-carboxyanhydrides
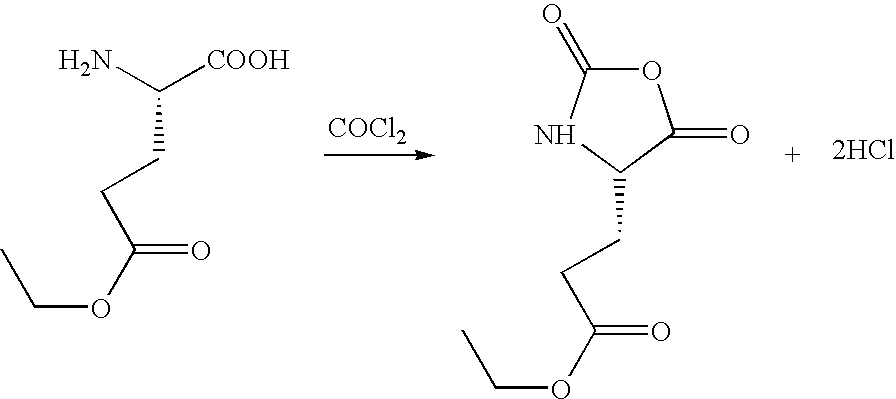
ActiveUS20060106229A1Easy to handleFaster rateOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationN carboxyanhydrideCarbonylation
A process for producing N-carboxyanhydrides is disclosed. The process produces N-carboxyanhydrides as a product and HCl as a by-product. The HCl by-product is purged from the reaction mixture by passing a purge gas through the reaction mixture as a carbonylation reagent is reacting with an amino acid or a salt thereof. The N-carboxyanhydrides produced by this process have a relatively lower chloride impurity content, relatively higher yields can be achieved, and the N-carboxyanhydrides can be produced on a larger scale.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Preparation method of low iron and low chloride hydroxyethylidene-1,1-diphosphonic acid (HEDP)
InactiveCN103435645AAvoid mixingGuaranteed clean productionGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsCrystallizationElectronics
The invention provides a preparation method of low iron and low chloride hydroxyethylidene-1,1-diphosphonic acid (HEDP) to meet the requirements of the special industries such as electronics and the like on iron ions, chloride ions and the like in HEDP products. The preparation method is specially characterized by recrystallizing common HEDP solution to obtain the special low iron and low chloride HEDP product. The preparation method has the prominent benefits that by repeatedly recrystallizing common HEDP to remove the iron and chloride ions, the special requirements of the industries such as electronics and the like are met and the application field of HEDP is expanded.
Owner:SHANDONG TAIHE WATER TREATMENT TECH CO LTD
Special compound admixture for marine concrete
The invention relates to a special compound admixture for marine concrete and a preparation method of the admixture and belongs to the technical application field of inorganic nonmetallic materials. The admixture is prepared from raw materials in percentage by weight as follows: 11%-28% of metakaolin, 16%-32% of refined quartz sand, 12%-31% of waste silica powder, 8%-22% of a chloride ion adsorbent, 4%-6% of sodium nitrite, 3%-6% of sodium sulfate, 5%-9% of calcium sulphoaluminate and 2%-4% of a polycarboxylate superplasticizer. The materials used by the special compound admixture for marine concrete are common and available components, and the marine concrete prepared from the admixture has higher early strength and later strength, higher anti-penetrability performance and sulfate corrosion resistance and low chloride ion diffusion coefficient.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
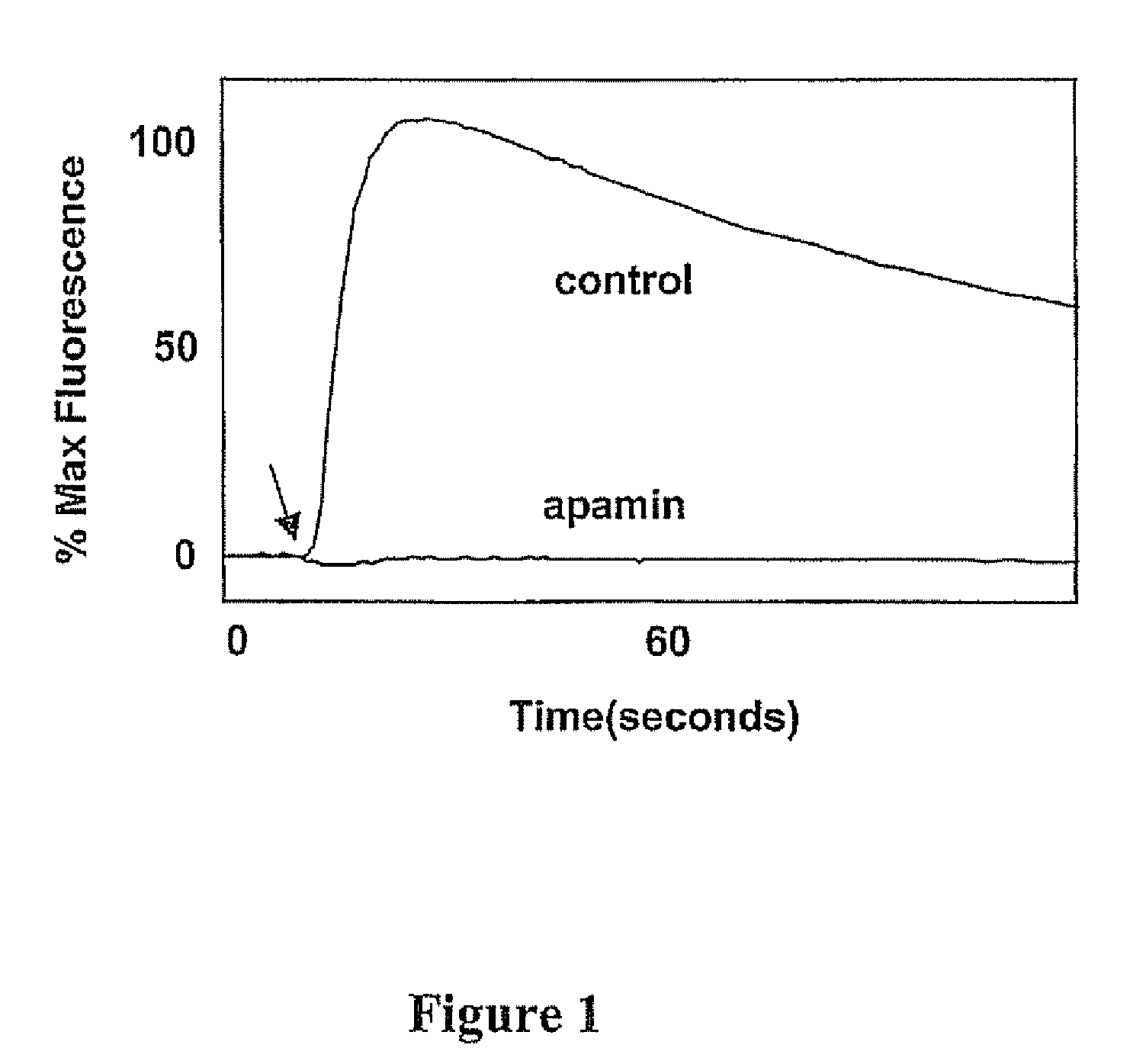
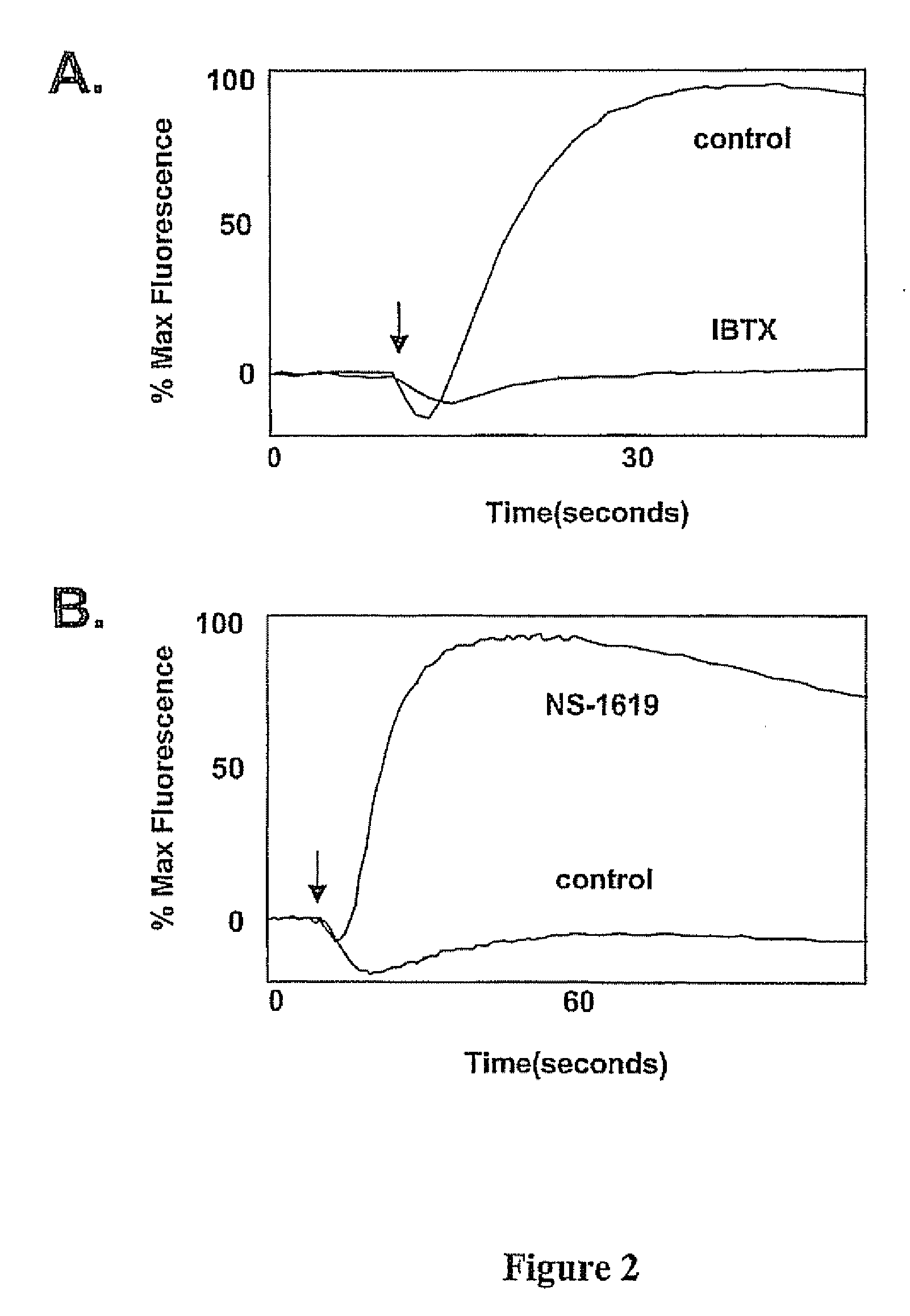
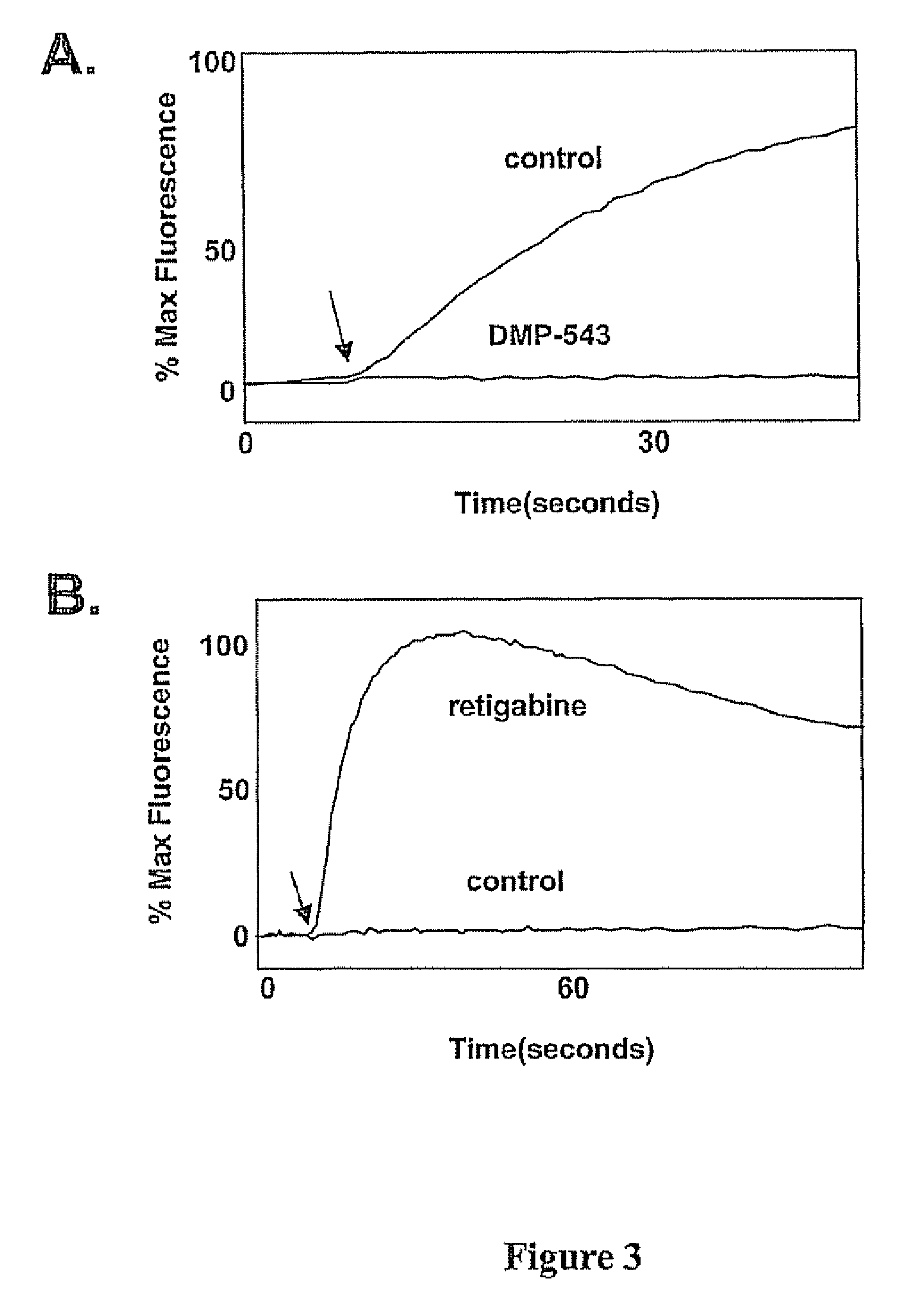
Method for detecting modulators of ion channels using thallium (i) sensitive assays
InactiveUS20070172815A1Robust and consistent resultMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingCation PumpPhysical chemistry
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Processed mineral additive for reducing concrete permeability and increasing strength
A durable concrete composition includes a cementitious material comprising cement and ground expanded perlite, coarse aggregate, fine aggregate, and sufficient water for adequate workability. The resulting concrete displays a number of superior properties to conventional concrete, including extremely high thermal resistance coupled with high strength, low chloride ion permeability, and good early strength. The ground expanded perlite is a readily available material and the finished concrete is extremely cost effective for applications where a high strength structural concrete must withstand high temperatures. The mixture can be handled and placed by conventional methods and is compatible with existing conventional concrete additives.
Owner:ANDERSON TERRY L +2
Alkylated cyclodextrin compositions and processes for preparing and using the same
ActiveUS10040872B2Tetrapeptide ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsCyclodextrinAlkylation
The present invention related to low-chloride alkylated cyclodextrin compositions, along with processes for preparing and using the same. The processes of the present invention provide alkylated cyclodextrins with low levels of drug-degrading agents and chloride.
Owner:CYDEX PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com