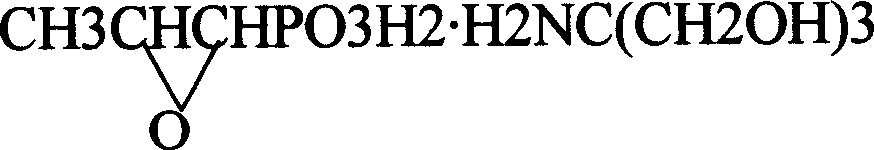
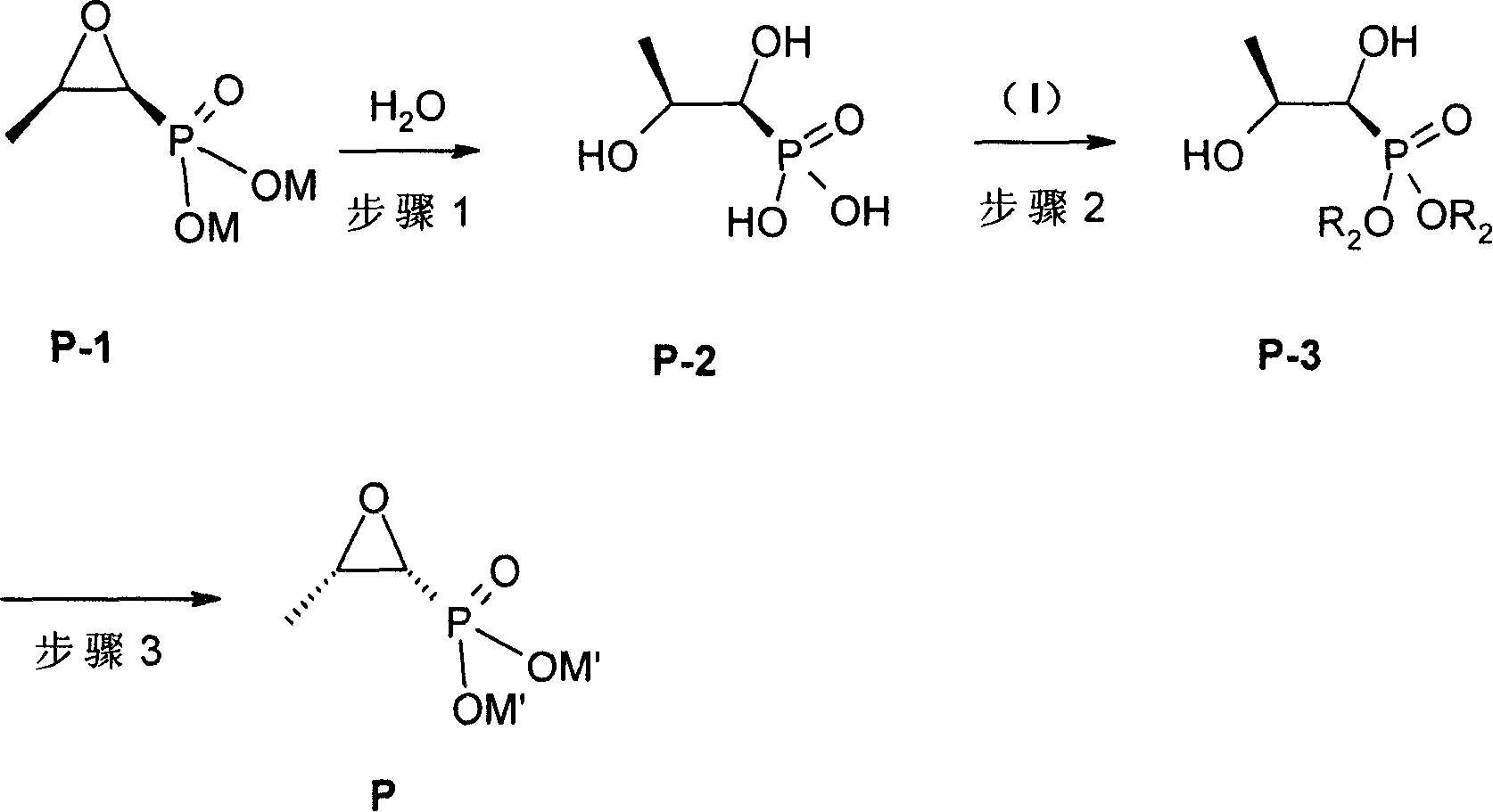
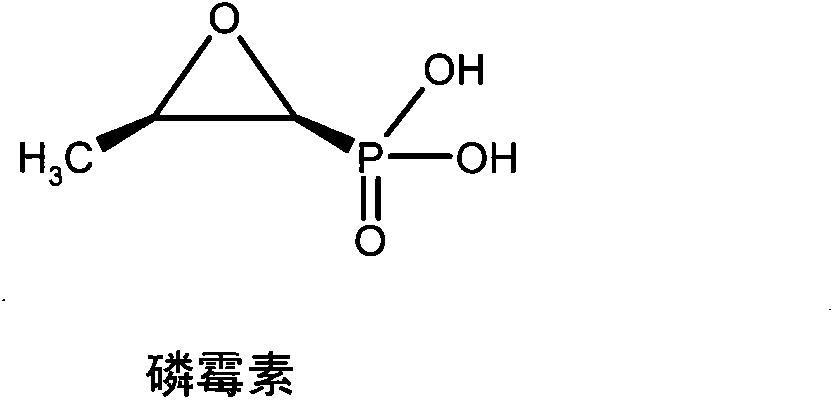
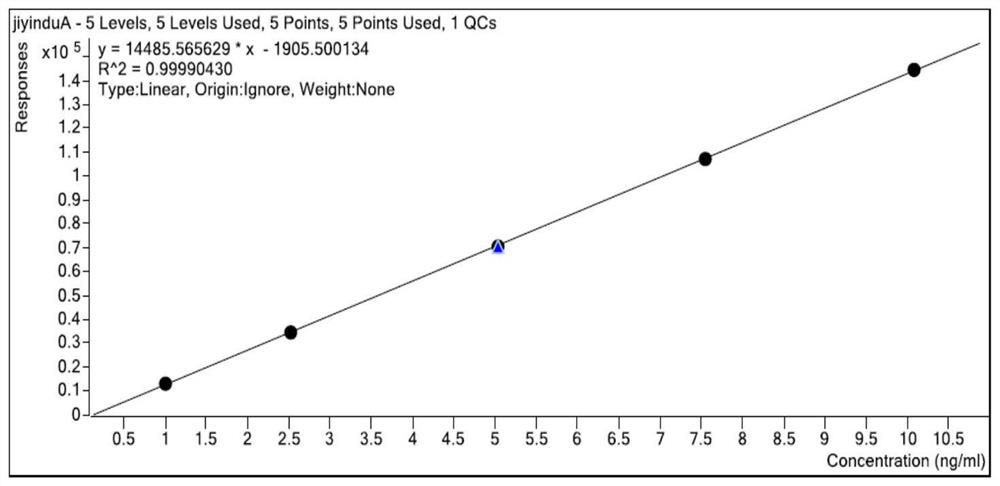
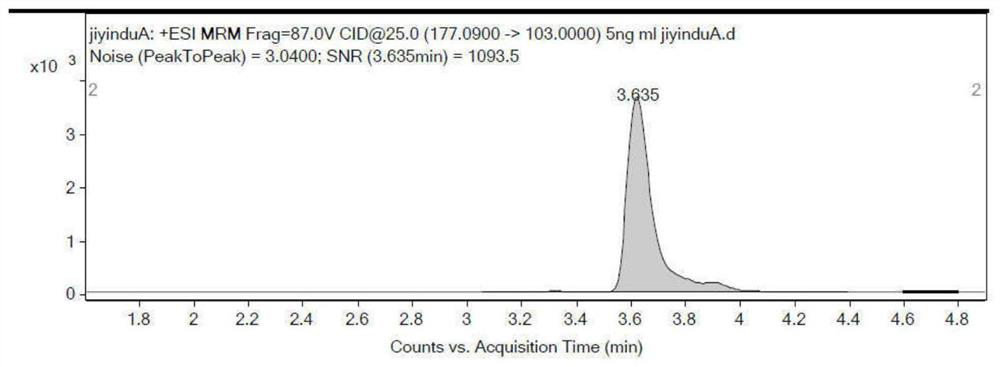
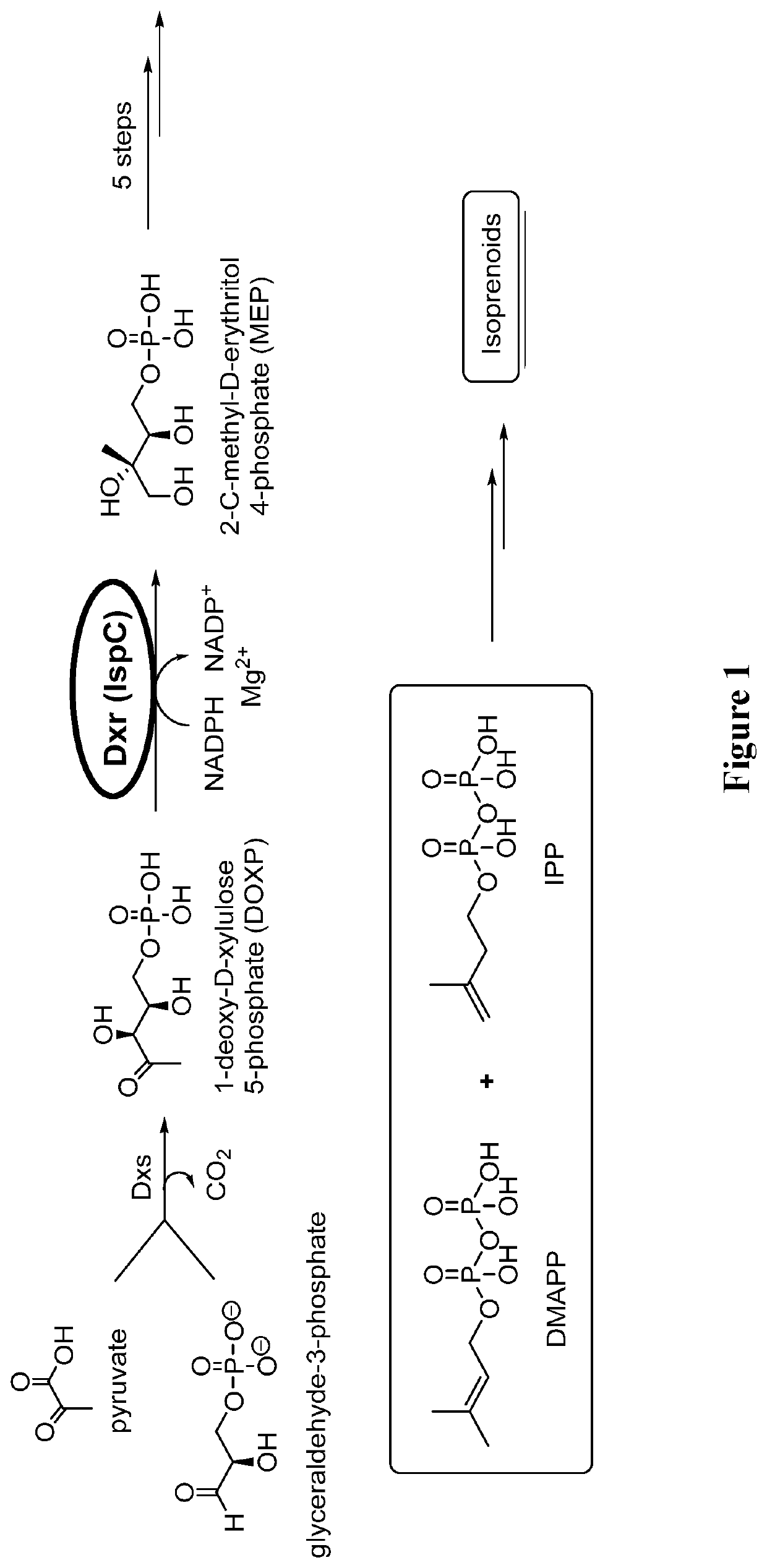
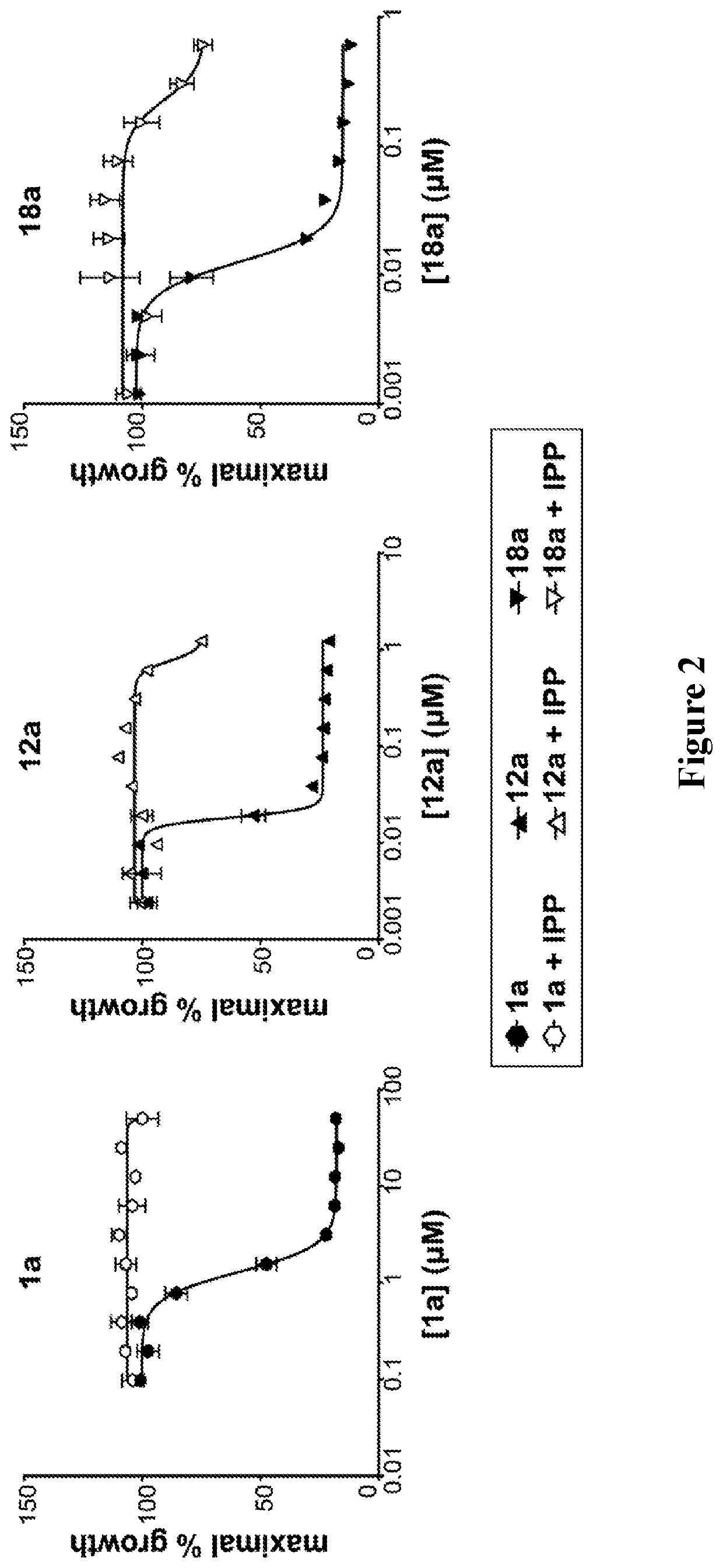
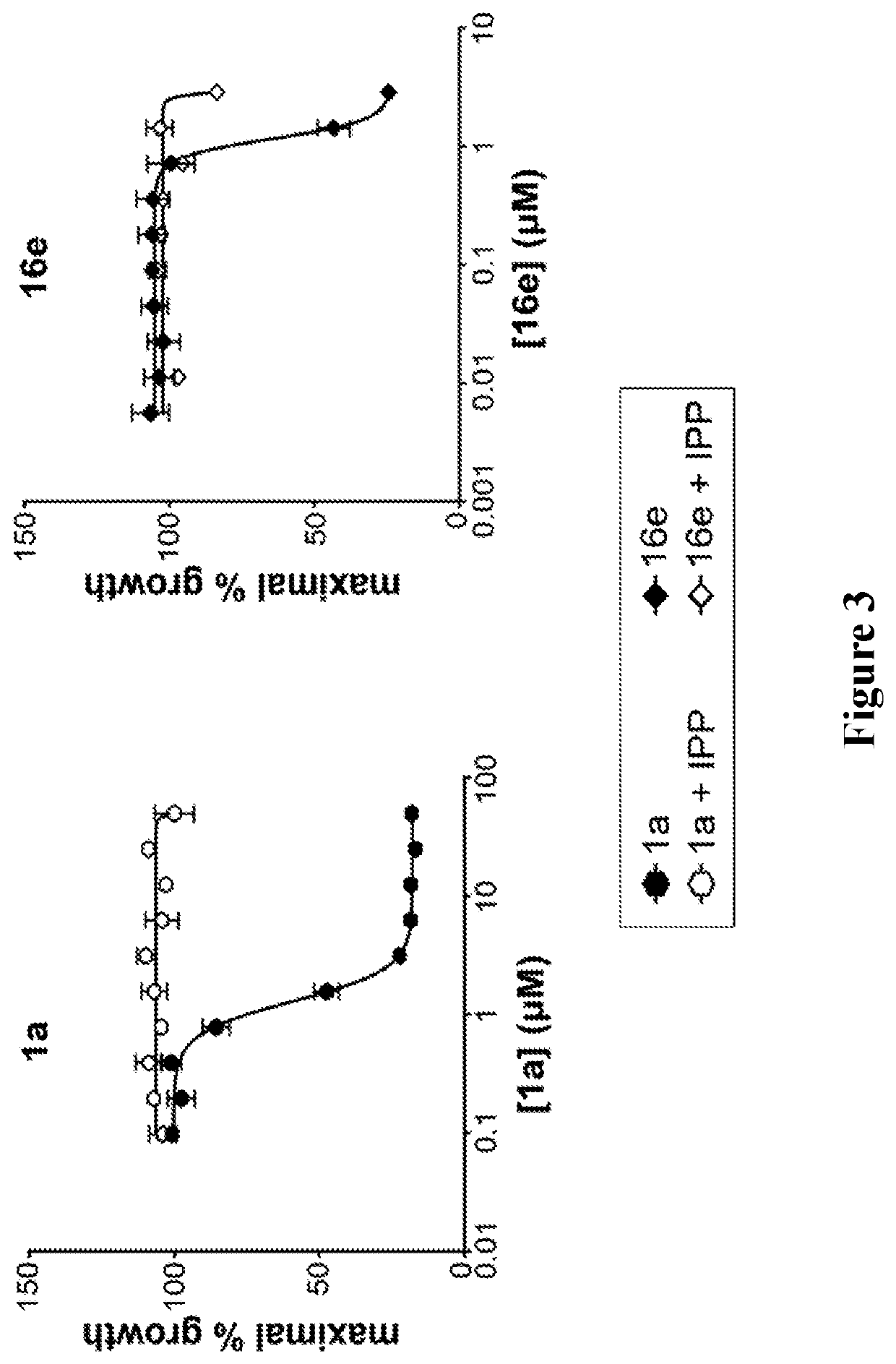
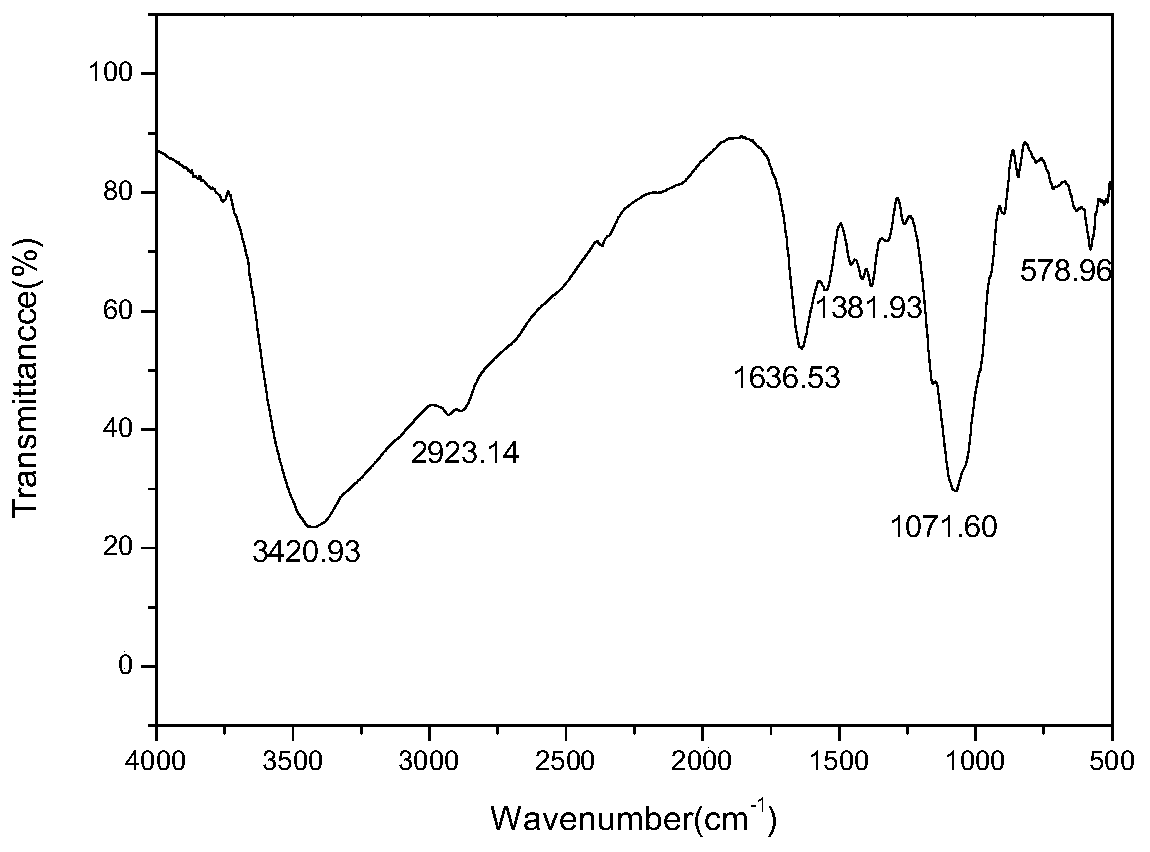
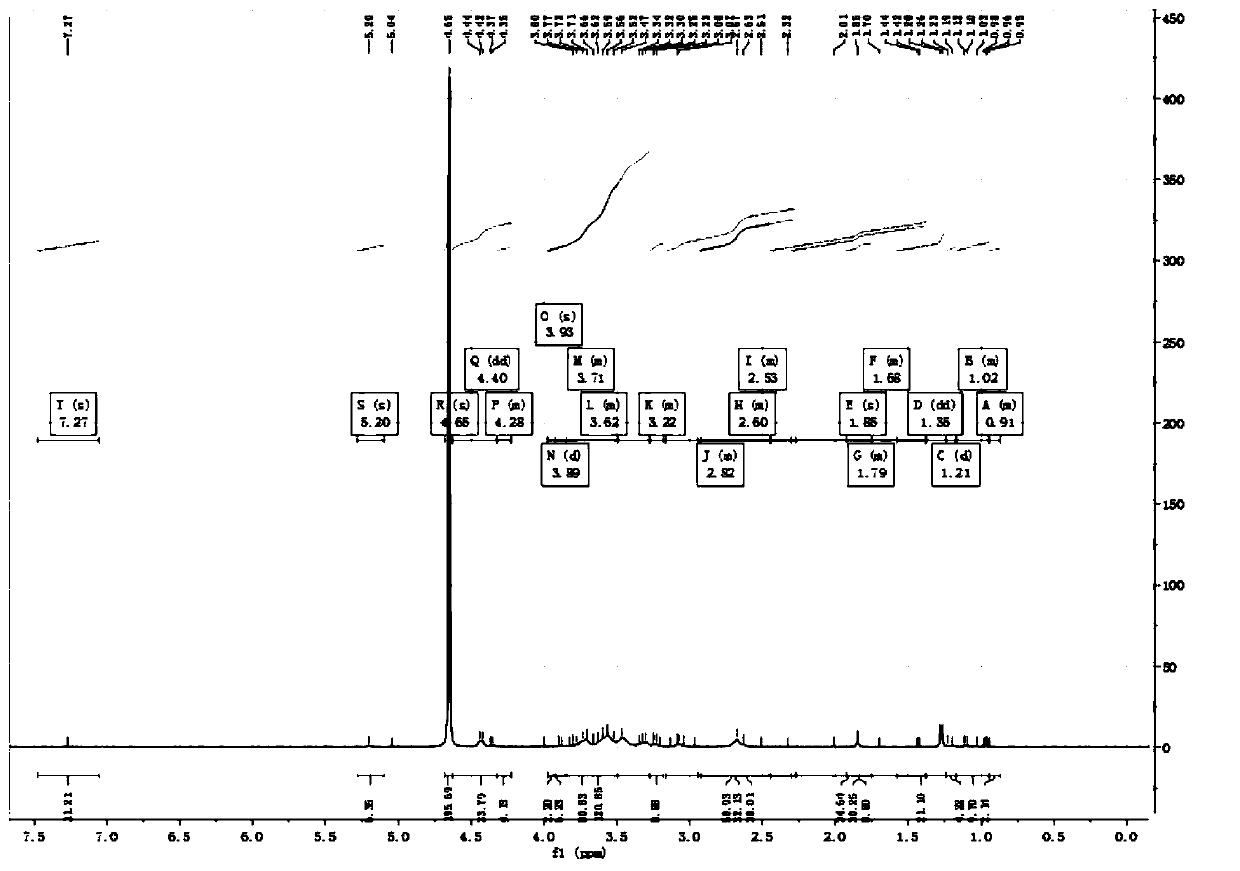
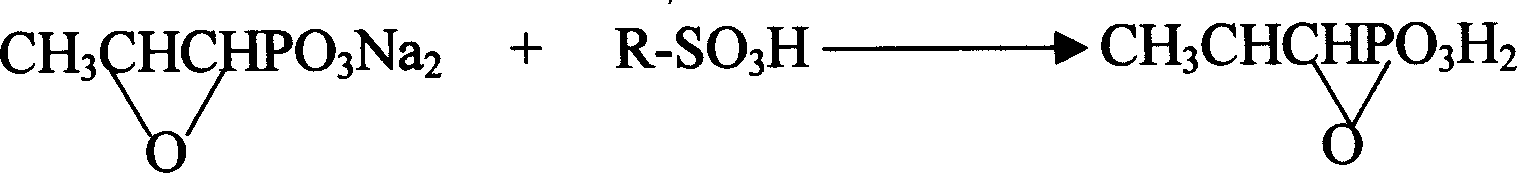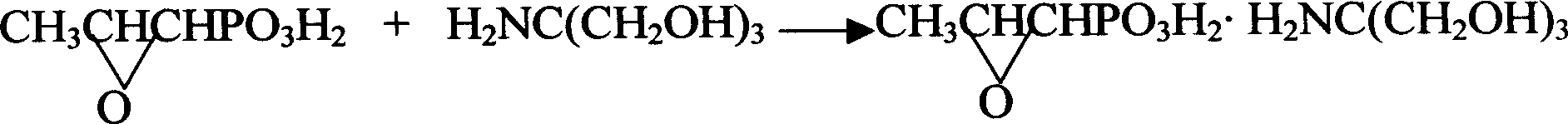Patents
Literature
35 results about "Phosphonomycin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for treating high-concentration phosphonomycin pharmaceutical wastewater and reclaiming phosphorus
InactiveCN101948197ALow toxicityRealize immobilized recyclingMultistage water/sewage treatmentPhosphorus compoundsHigh concentrationPhosphonomycin
The invention relates to a method for treating high-concentration phosphonomycin pharmaceutical wastewater and reclaiming phosphorus. The method is realized by the following two steps: 1) wet oxidation treatment: filling the high-concentration phosphonomycin pharmaceutical wastewater into a high-pressure reactor with a mechanical stirring device, introducing oxygen or air equivalent to 0.5 to 4 times of the wastewater COD into the high-pressure reactor, and maintaining the total pressure in the reactor to be between 3.0 and 15.0MPa, the reacting temperature to be between 200 and 300 DEG C, and the reaction time to between 5 and 120min to ensure that over 99 percent of organic phosphorus in the wastewater is converted into inorganic phosphate; and 2) phosphate reclaiming: adding calcium salt or magnesium salt and ammonium salt into the wastewater treated in the step 1) based on that the molar ratio of Ca:P is 1.7-2.5:1 or the molar ratio of Mg:N:P is 1.0-1.2:1.0-1.2:1, adding acid / alkali solution into the wastewater to maintain the pH value to be between 8.5 and 10.0, reacting for 10 to 60min while stirring, standing for 10 to 30min, and separating solid and liquid so as to obtain a phosphate reclaimed product and supernatant, wherein the supernatant can be discharged to a comprehensive wastewater treatment plant for biological treatment so as to realize standard emission. The method has the advantage of simple operation, and can realize the COD removal rate of the high-concentration phosphonomycin pharmaceutical wastewater to reach 40 to 95 percent, the organic phosphorus removal rate to reach over 99 percent, and the reclaiming rate of the phosphorus in the wastewater to reach over 99 percent.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Novel pulveres fosfomycin trometamol synthetic method
InactiveCN1544440ASolve the problem of rework and reuseIncrease production capacityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsOrganic acidPhosphonomycin
The invention provides a process for synthesizing pulveres fosfomycin trometamol by using phosphonomycin sodium or neutral phosphonomycin sodium containing small amount of organic acid as raw material through the steps of, subjecting 10-16 times of type H cationic ion-exchange resin to exchange reaction in methanol solution at low-temperature, with the methanol solution acting as eluent, thus preparing the methanol solution containing fosfomycin acid, neutralizing the methanol solution with right amount of tromethamine or fosfomycin methanol tromethamine salt so as to obtain the methanol solution of pulveres fosfomycin trometamol, and the end product of the methanol solution of pulveres fosfomycin trometamol is obtained from the methanol solution of pulveres fosfomycin trometamol from decolorizing, filtering, condensing, extracting, filtering and drying.
Owner:NORTHEAST PHARMA GRP
Synthesis for producing levo phosphomycin by dextro phosphomycin
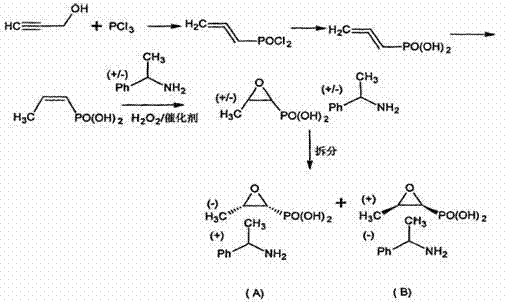
Synthesis of levo-phosphonomycin from dextro-phosphonomycin is carried out by taking dextro-phosphonomycin((+)-(1S,2R)-cis-epoxy propyl phosphoric acid) or dextro-phosphonomycin salt as raw materials and converting into levo-phosphonomycin((-)-(1R, 2S)-cis- epoxy propyl phosphoric acid) or levo-phosphonomycin salt.
Owner:BEIJING COLLAB PHARMA
New method for synthesizing fosfomycin trometamol
InactiveCN102659842ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getLow toxicityOrganic compound preparationGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPhosphonomycinO-Phosphoric Acid
The invention relates to a new method for synthesizing fosfomycin trometamol, which comprises the following steps: directly oxidizing under the catalysis of a chiral ligand through maleic phosphoric acid, obtaining optically-pure free fosfomycin acid and adding an equivalent of tromethamine for neutral reaction to obtain fosfomycin trometamol.
Owner:FARMASINO PHARMA ANHUI +1
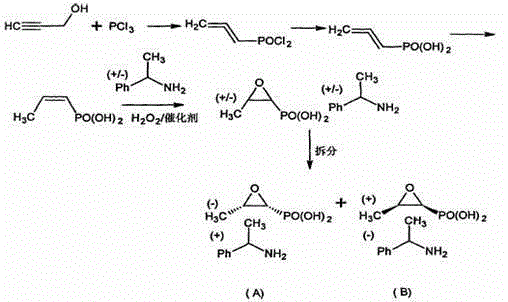
Novel method for preparing fosfomycin phenylethylamine
ActiveCN103113408AAmino preparation from aminesGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPhosphonomycinPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a novel method for preparing fosfomycin phenylethylamine, which comprises the following steps: by using cis-propenylphosphonic acid as a raw material, carrying out oxidation and cyclization under the actions of a catalyst and an oxidizer, carrying out dynamic resolution under specific solvent conditions to precipitate levo-fosfomycin, adding a certain amount of dextro-phenylethylamine, reacting, and refining to obtain the levo-fosfomycin dextro-phenylethylamine. The preparation method has the advantages of low reaction cost, fewer steps, fewer byproducts and low environmental pollution, and is suitable for industrial mass production and prepration.
Owner:JIANGSU SKYRUN PHARMA CO LTD
High performance liquid chromatography method for determining fosfomycin sodium impurities
ActiveCN110887925AImprove retentionGuaranteed bonding densityComponent separationPhosphonomycinO-Phosphoric Acid
The invention relates to a high performance liquid chromatography method for determining fosfomycin sodium impurities. According to the high performance liquid chromatography method, a chromatographiccolumn using octadecylsilane chemically bonded silica as a filler is used, a phosphoric acid aqueous solution-methanol mixed solution is used as a mobile phase, the concentration mass fraction of phosphoric acid in the phosphoric acid aqueous solution is 0.04%-0.06%, and the volume ratio of the phosphoric acid aqueous solution to methanol is 99: 1-99: 5. According to the method, the retention ofstrong polar impurities is enhanced, the complex impurity system of fosfomycin sodium can be effectively separated and the method has good universality and specificity of specific impurities and is high in sensitivity, convenient to operate and moderate in analysis time and thus provides effective guarantee for the quality control of the compound.
Owner:上海峰林生物科技有限公司
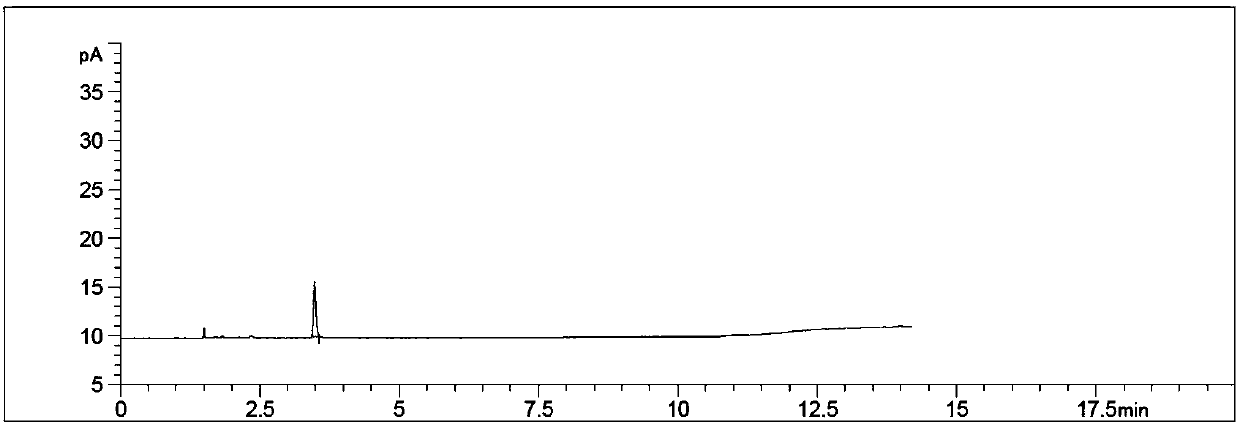
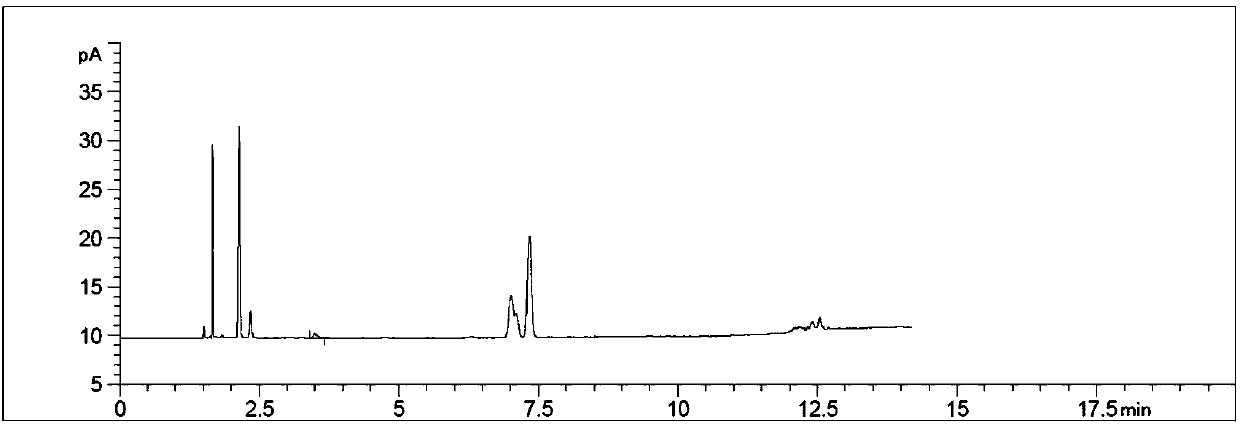
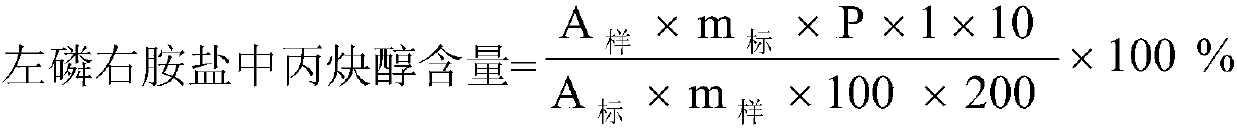
Method for detecting content of propargyl alcohol in phosphonomycin-1-phenethylamine salt by headspace gas chromatography
ActiveCN107607635AEasy to separateGood repeatabilityComponent separationPhosphonomycinRelative standard deviation
Belonging to the field of pharmaceutical analysis, the invention relates to a method for detecting the content of propargyl alcohol in phosphonomycin-1-phenethylamine salt by headspace gas chromatography. The method includes the steps of: (1) preparing the instrument conditions: adopting a capillary packed column using cyanopropyl and methylpolysilicone as the filler as the chromatographic column;(2) preparing a system adaptive solution; (3) preparing a test solution; and (4) performing testing: putting the system adaptive solution into a headspace sample injector, recording the spectrogram,calculating the propargyl alcohol peak area's relative standard deviation RSD that is less than or equal to 10.0%, precisely weighing the test solution and putting it into the headspace sample injector, recording the spectrogram, and calculating the content of propargyl alcohol in phosphonomycin-1-phenethylamine salt. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of good propargyl alcohol separation effect, good method repeatability and durability, good peak reproducibility, good peak shape, simple operation, time saving, high efficiency and the like.
Owner:NORTHEAST PHARMA GRP
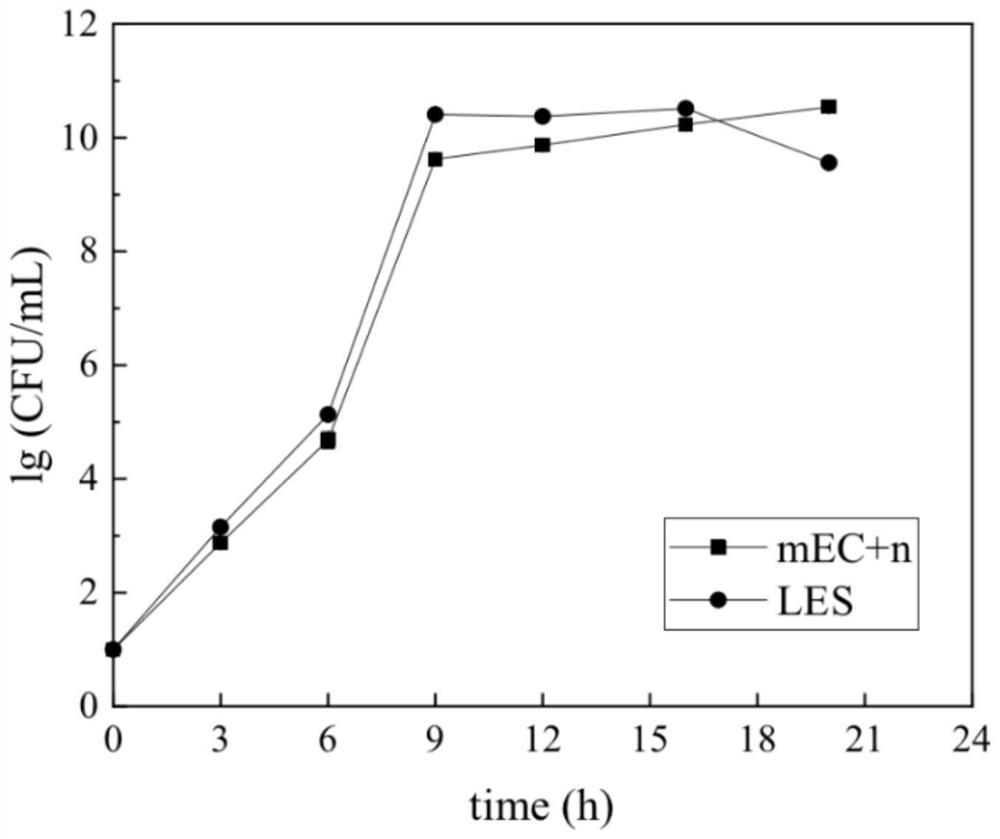
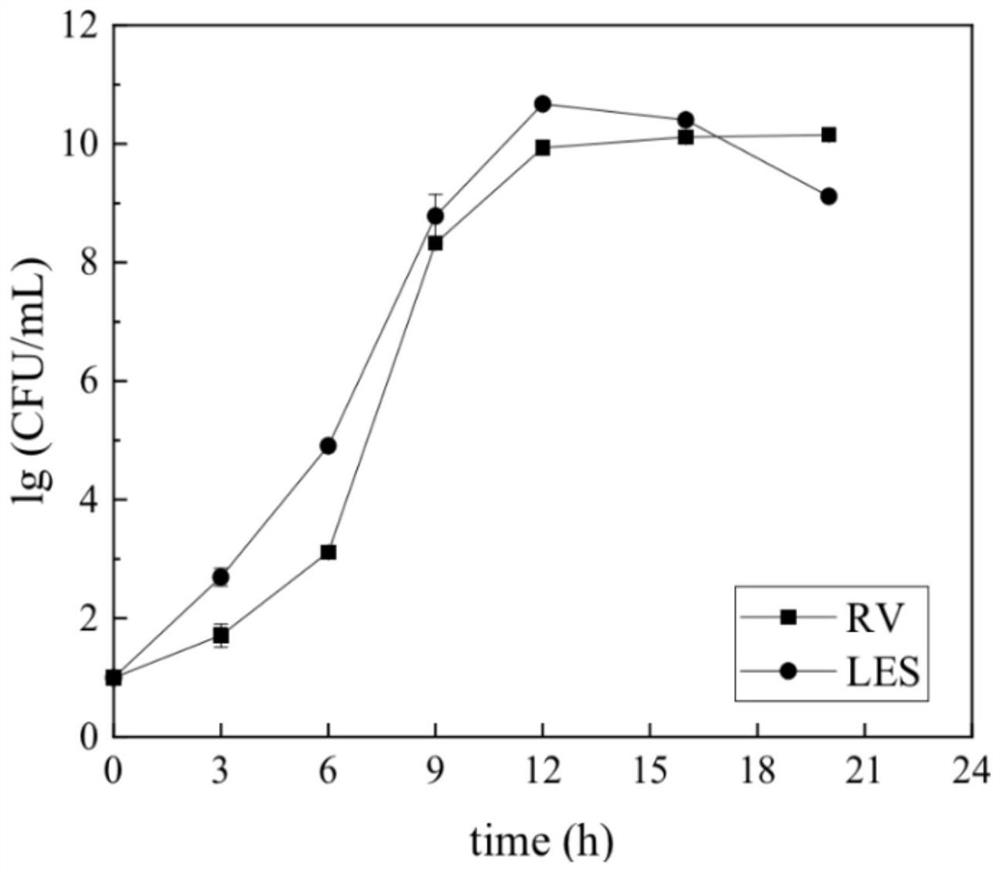
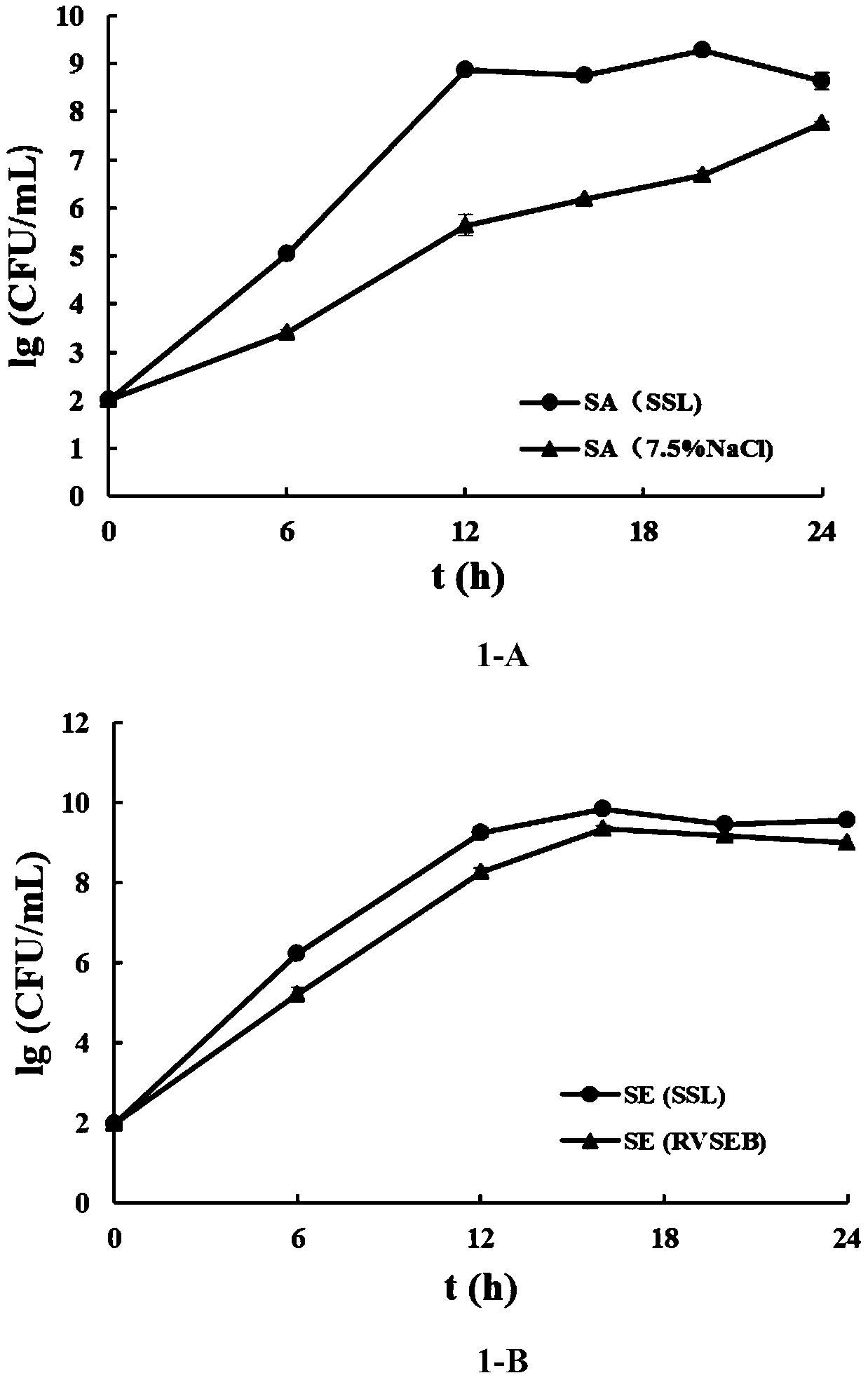
Composite culture medium capable of simultaneously enriching three food-borne pathogenic bacteria and preparation method
InactiveCN112159787AGrowth inhibitionEasy to manufactureBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
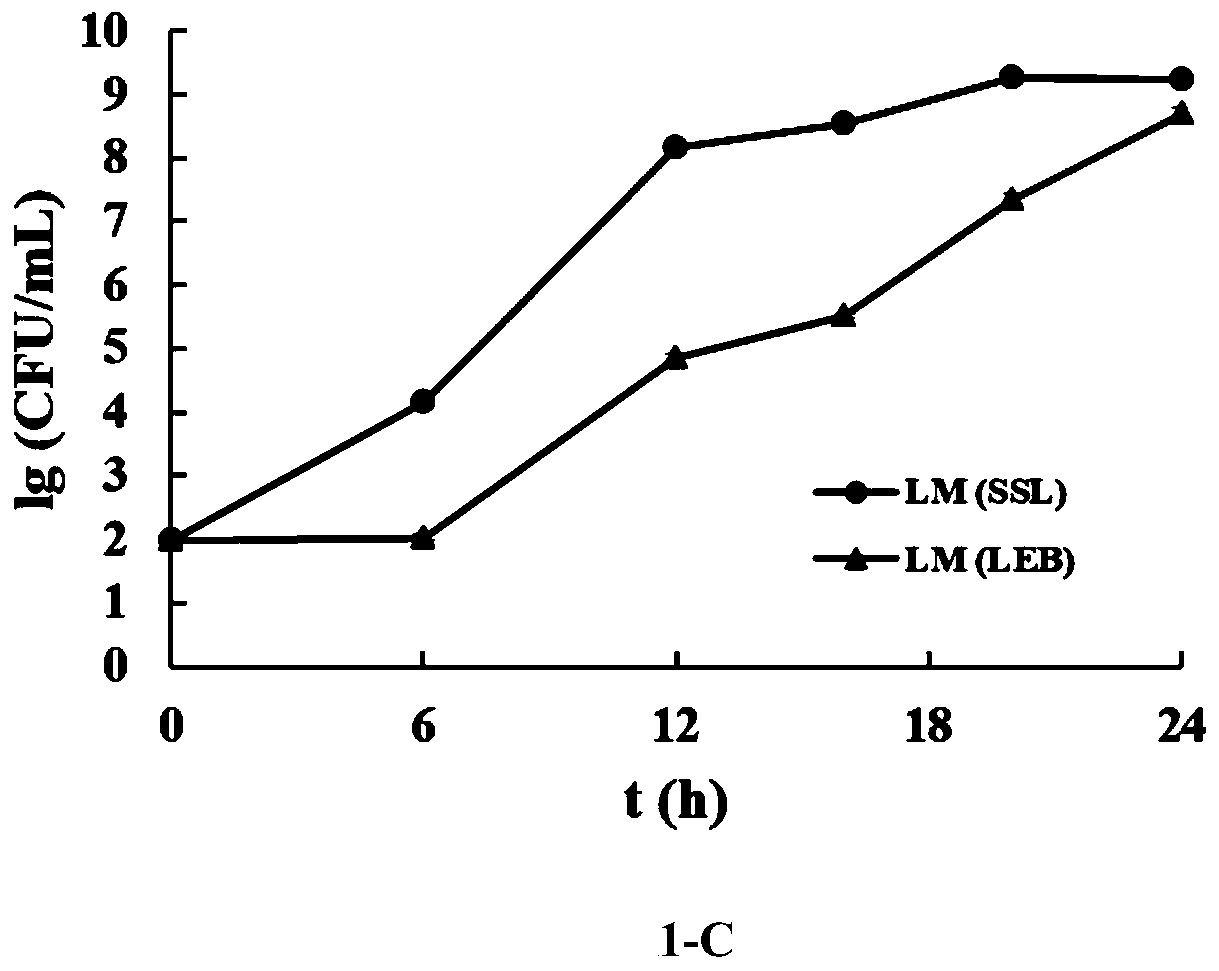
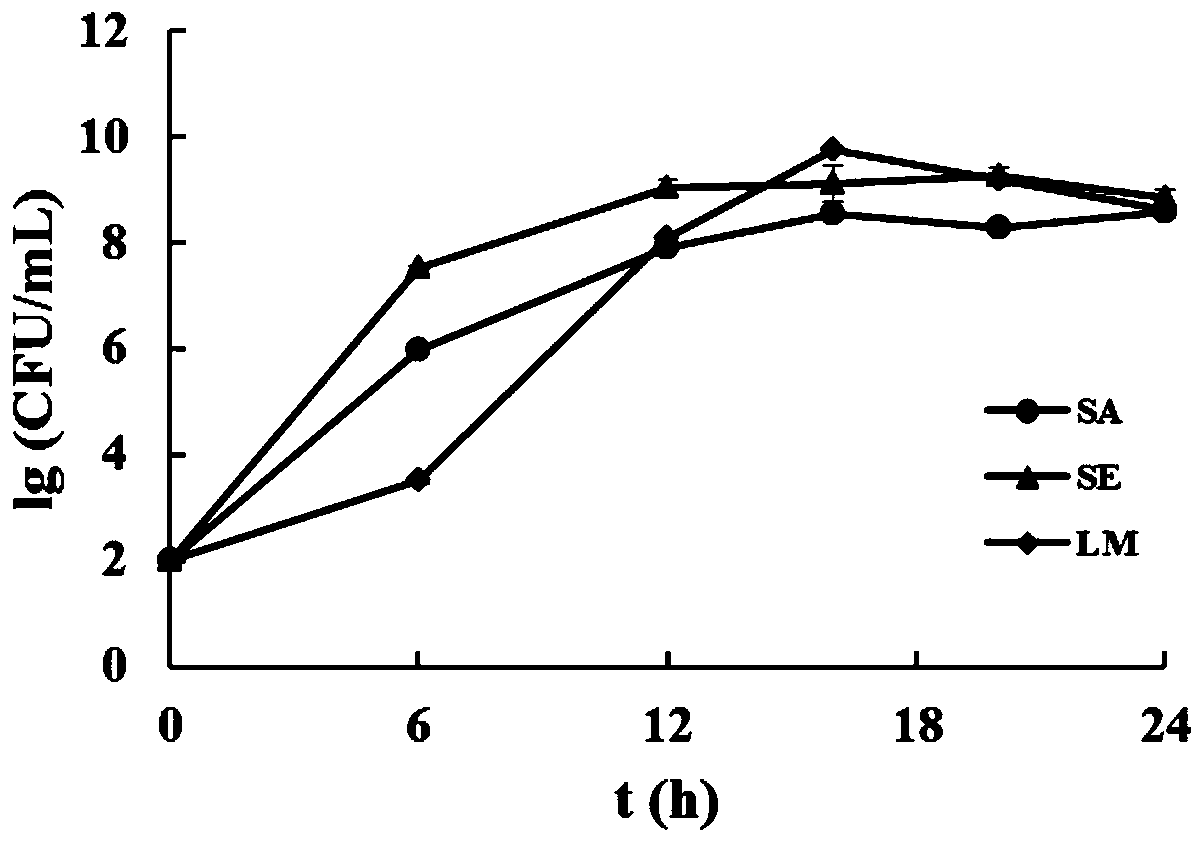
The invention discloses a composite enrichment culture medium capable of simultaneously enriching three food-borne pathogenic bacteria, namely Listeria monocytogenes, Escherichia coli O157:H7 and salmonella, and a preparation method. The formula of the culture medium comprises the following components of, in parts by weight, 15.0-19.0 parts of tryptone, 2.7-3.3 parts of peptone, 5.5-6.5 parts of yeast extract, 4.5-5.5 parts of sodium chloride, 2.25-2.75 parts of dipotassium phosphate, 8.6-10.6 parts of disodium hydrogen phosphate, 1.22-1.48 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 24.0-30.0 parts of peptone, 14.0-18.0 parts of beef powder, 10.0-14.0 parts of soy peptone, 2.0-5.0 parts of glucose, 0.10-0.30 part of actinomycete ketone, 2.5-3.5 parts of mannitol, 4.5-6.5 parts of sodium pyruvate, 0.00125-0.00300 part of acridine yellow, 0.0007813-0.0032500 part of fosfomycin sodium and 1000 parts of distilled water, and the pH value of theculture medium is 6.8-7.4. The single enrichmenteffect of the composite enrichment culture medium is superior to that of respective selective enrichment liquid, growth of non-target bacteria can be well inhibited, under the condition that non-target bacteria exist, the culture medium can further achieve constant-speed and rapid proliferation of the three target bacteria.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
A new method for preparing fosfomycin levofos dexamine salt
ActiveCN103113408BAmino preparation from aminesGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPhosphonomycinChemical synthesis
The invention discloses a novel method for preparing fosfomycin phenylethylamine, which comprises the following steps: by using cis-propenylphosphonic acid as a raw material, carrying out oxidation and cyclization under the actions of a catalyst and an oxidizer, carrying out dynamic resolution under specific solvent conditions to precipitate levo-fosfomycin, adding a certain amount of dextro-phenylethylamine, reacting, and refining to obtain the levo-fosfomycin dextro-phenylethylamine. The preparation method has the advantages of low reaction cost, fewer steps, fewer byproducts and low environmental pollution, and is suitable for industrial mass production and prepration.
Owner:JIANGSU SKYRUN PHARMA CO LTD
Culture medium for composite enrichment of staphylococcus aureus, salmonella and listeria monocytogenes and preparation method
ActiveCN111500509AEasy to prepareThe effect of monoenrichment is excellentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPhosphonomycin
The invention discloses a culture medium for composite enrichment of staphylococcus aureus, salmonella and listeria monocytogenes and a preparation method. The invention belongs to the technical fieldof pre-enrichment culture media of pathogenic bacteria. The culture medium comprises, by mass, 15.0 to 19.0 parts of tryptone, 2.7 to 3.3 parts of peptone, 5.4 to 6.6 parts of yeast extract, 2.25 to2.75 parts of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 8.6 to 10.6 parts of disodium hydrogen phosphate, 1.22 to 1.48 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 13.0 to 17.0 parts of peptone, 18.0 to 21.0 partsof beef powder, 8.0 to 12.0 parts of soy peptone, 0.2 to 0.4 part of actinone, 2.0 to 4.0 parts of mannitol, 4.0 to 5.0 parts of sodium pyruvate, 0.00078 to 0.00156 part of fosfomycin sodium, 0.75 to1.1 parts of lithium chloride and 1000 parts of distilled water, wherein the pH value is 6.8 to 7.4. The single enrichment effect of the composite enrichment culture medium is superior to that of respective selective enrichment liquid, and growth of non-target bacteria can be well inhibited. Under the condition that non-target bacteria exist, the culture medium can also achieve constant-speed andrapid proliferation of the three target bacteria.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for analyzing genotoxic impurities of fosfomycin tromethamine
ActiveCN111257478AEfficient separation and detectionHigh sensitivityComponent separationAgainst vector-borne diseasesPhosphonomycinDiethyl phosphate
The invention provides a method for analyzing genotoxic impurities of fosfomycin tromethamine. The method comprises the following steps: diluting the fosfomycin tromethamine with a diluent, analyzingimpurities by adopting a high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method, taking a formic acid solution as a mobile phase A and an acetonitrile solution as a mobile phase B, and carrying out gradient elution. The concentration of formic acid in the formic acid solution is 0.1-10%. The diluent is an aqueous solution containing 85-95% of methanol. The method for analyzing the genotoxic impurities of the fosfomycin tromethamine, provided by the invention, can be used for more efficiently separating and detecting impurities such as diethyl allyldienophosphate and the like, and hasthe advantages of strong specificity, high sensitivity, simplicity, quickness and low cost.
Owner:上海峰林生物科技有限公司
Pharmaceutical composition having antimicrobial and fast-healing activity for external administration, process for preparing same
InactiveCN102811724AImprove efficacyQuality improvementAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPhosphonomycinPharMed
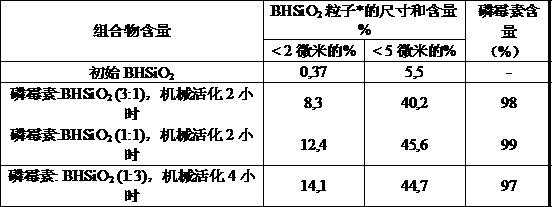
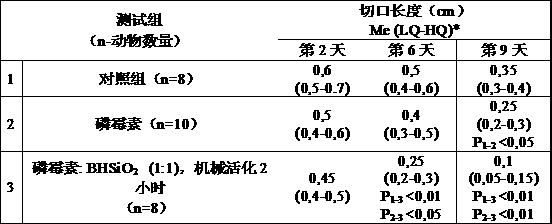
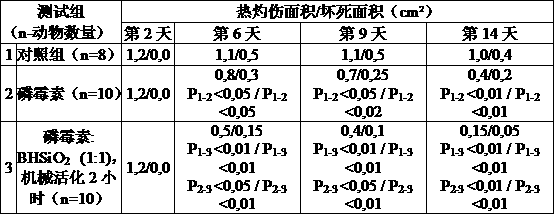
This invention is related to pharmacology, medicine, veterinary science and pharmaceutical industry,in particular to the process for the production of original composite antimicrobial and vulnerary preparations for external administration having an increased therapeutic efficiency in the treatment of skin and soft tissues infections. The claimed pharmaceutical composition contains antibiotic fosfomycin and finely dispersed nanostructured silica dioxide as active agents. The claimed process for the production of the pharmaceutical composition consists in mixing fosfomycin substance with finely dispersed nanostructured silica dioxide, characterized in that the micture of said substances in the weight ratio (25-75% by weight) : (75-25% by weight) respectively is being exposed to mechanical treatment by impact and abrasive actions to increase the weight percentage of the finely dispersed fraction ( 5 micron) to at least 40%.
Owner:维克托历沃维奇·利莫诺夫
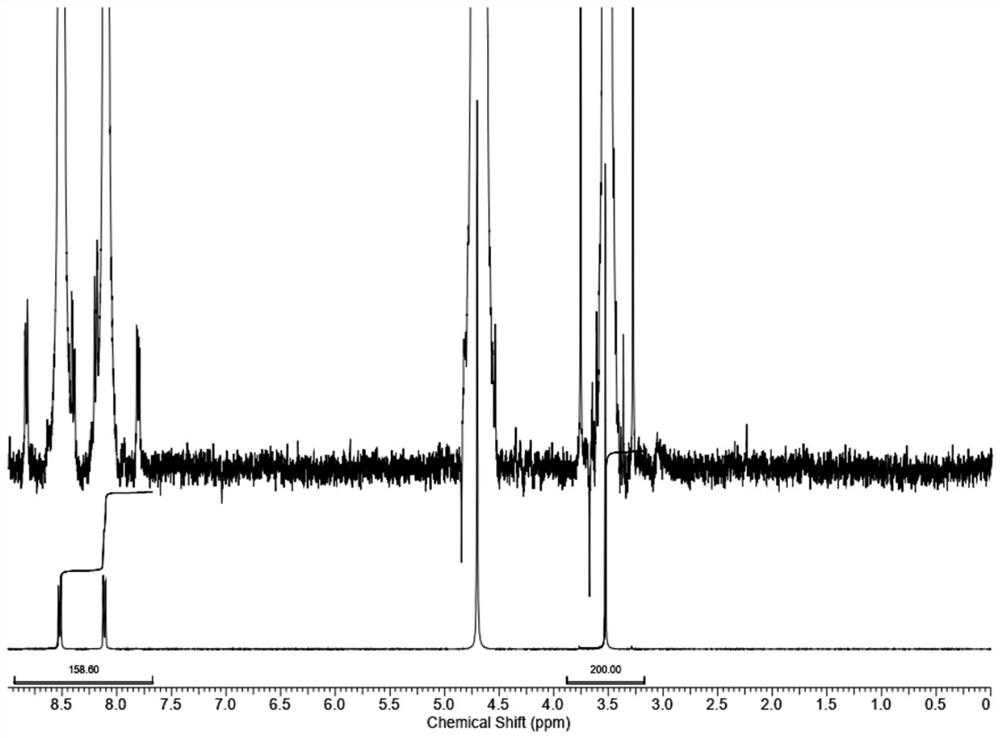
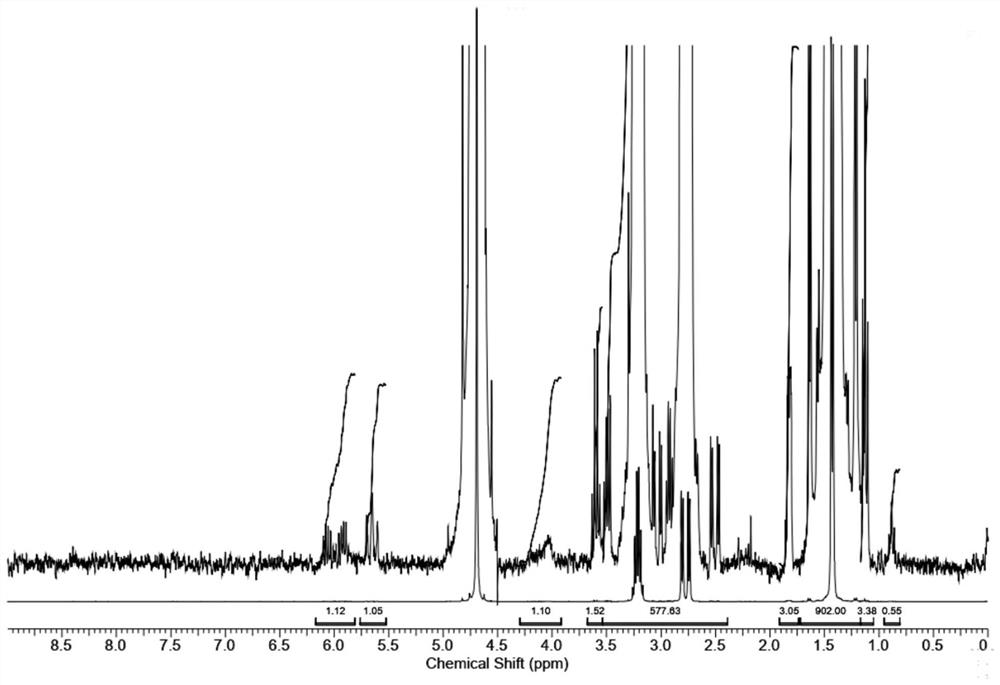
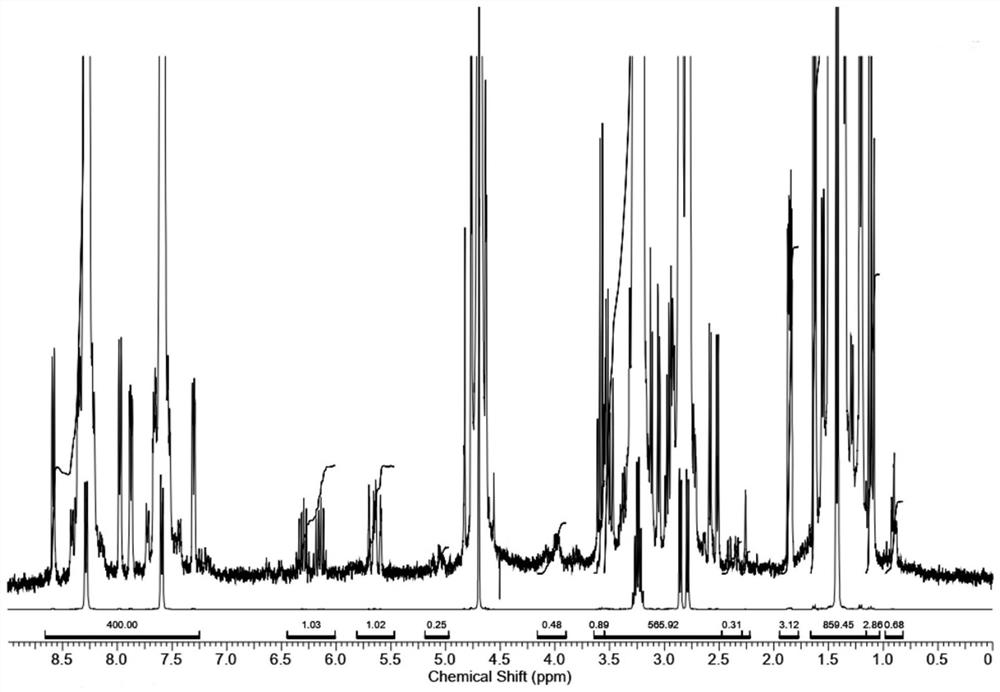
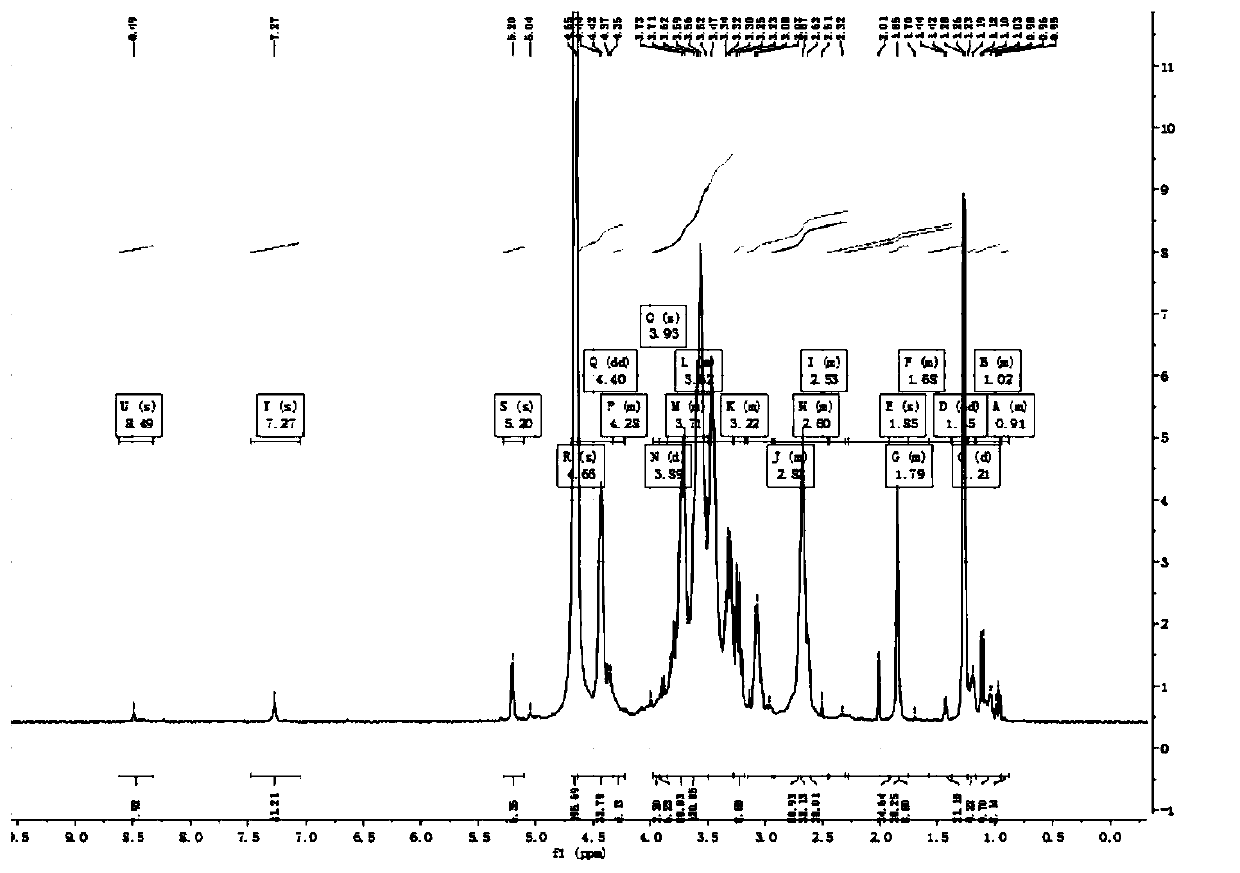
Method for determining related substances in fosfomycin sodium by using nuclear magnetic resonance hydrogen spectrum
PendingCN113916927ASimplified preprocessing timeRapid determinationAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePhosphonomycinSolvent
The invention discloses a method for determining related substances in fosfomycin sodium by using the hydrogen nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The method adopted by the invention is a nuclear magnetic resonance hydrogen spectrum method, preferably, 4-bromopyridine hydrochloride is used as an internal standard substance, more preferably, 4-bromopyridine hydrochloride with the mass fraction of 90% is used as the internal standard substance, and D2O is selected as a deuterated solvent. The method for determining related substances in fosfomycin sodium comprises the following specific steps: (1) precisely weighing a fosfomycin sodium certification batch sample and an internal standard substance, and dissolving thefosfomycin sodium certification batch sample and the internal standard substance in a deuterated solvent to obtain a test solution; (2) precisely measuring the test solution, transferring the test solution into an NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) tube, performing a nuclear magnetic resonance hydrogen spectrum test, and recording a spectrogram, wherein the conditions of the nuclear magnetic resonance hydrogen spectrum test comprise: a Bruker DRX300 nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer equipped with a 5mm multi-core QNP probe; the frequency spectrum width is 3500Hz; the temperature is 296 K; the pulse is 30 degrees; the acquisition time is 4.7 s; and the deuterated solvent is D2O. The determination method disclosed by the invention is simple and easy to implement, high in accuracy and strong in specificity, and can well control impurities in a sample and ensure the quality of the sample.
Owner:广东利玮医药有限公司
Preparation method of intermediate of antibacterial drug
ActiveCN112442084AHigh yieldHigh catalytic activityPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationPhosphonomycinPtru catalyst
The invention provides a preparation method of phosphamycin levophosphorylamine. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving cis-propenylphosphonic acid in an alcohol solvent at room temperature, slowly dropwise adding (+)-alpha-phenylethylamine, regulating the pH value of the formed system to 5.5-6, continuing stirring for 1-3 minutes, adding a silver catalyst, slowly and dropwise adding hydrogen peroxide, continuing stirring for 10-30 minutes, then rapidly heating the system to 50-55 DEG C, conducting filtering while the system is hot, and then cooling, crystallizing andwashing the filtrate successively to obtain the phosphamycin levophosphorylamine. According to the invention, silver carbonate is used as a catalyst, hydrogen peroxide is used as an oxidizing agent,heating is not needed in an oxidative cyclization process, and a reaction can be performed at normal temperature. The silver carbonate has very high catalytic activity in the invention, and compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of small dosage, mild reactions, effective shortening of reaction time, simple post-treatment, and realization of separation of the catalyst from the system only through filtration of the system while the system is hot.
Owner:SINOPHARM ZHIJUN (SHENZHEN) PHARMA CO LTD
Method for screening levo-phosphonomycin bioconversion strain with cis-propene phosphoric acid as substrate
InactiveCN1673344AImprove efficiencyEasy to operateMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphonomycinMicroorganism
The present invention relates to biological conversion / biological catalysis technology and microbe strain screening technology, and is especially the screening police and method of levorotary phosphonomycin bioconverting strain with maleic phosphoric acid as substrate. The screening process includes two steps of initial screening and re-screening. In the initial screening, the selective culture medium has maleic phosphoric acid as only carbon source so as to eliminating most of irrelative microbes. In the re-screening, the strain obtained in the initial screening and the solid culture medium with levorotary phosphonomycin bioconverting strain and maleic phosphoric acid substrate are adopted to sort out the phosphonomycin bioconverting strain. The present invention has greatly raised screening efficiency.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Application of silver catalyst in preparation of antibacterial drug intermediate
InactiveCN112409410AHigh yieldHigh catalytic activityAmino preparation from aminesGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPhosphonomycinPtru catalyst
The invention provides an application of a silver catalyst in preparation of an antibacterial drug intermediate fosfomycin levoforight amine salt. The application is characterized by comprising the following steps: at room temperature, dissolving cis-propenylphosphonic acid in an alcohol solvent, slowly dropwise adding (+) alpha phenylethylamine, regulating the pH value of the system to 5.5-6 after dropwise adding, continuing stirring for 1-3 minutes, and adding the silver catalyst, continuously and slowly dropwise adding hydrogen peroxide, then continuously stirring for 10-30 minutes, quicklyheating the system to 50-55 DEG C, filtering while the system is hot, and cooling, crystallizing and washing the filtrate to obtain the fosfomycin levoforight amine salt. Silver carbonate is used asthe catalyst, hydrogen peroxide is used as an oxidizing agent, heating is not needed in the oxidative cyclization process, and the reaction can be performed at normal temperature. Silver carbonate hasvery high catalytic activity in the invention, and compared with the prior art, the application has the advantages of small dosage, mild reaction, effective shortening of the reaction time, simple post-treatment, and realization of separation of the catalyst from the system only through filtration of the system while the system is hot.
Owner:商河探荣新技术开发中心
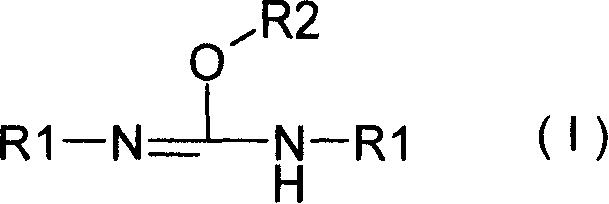
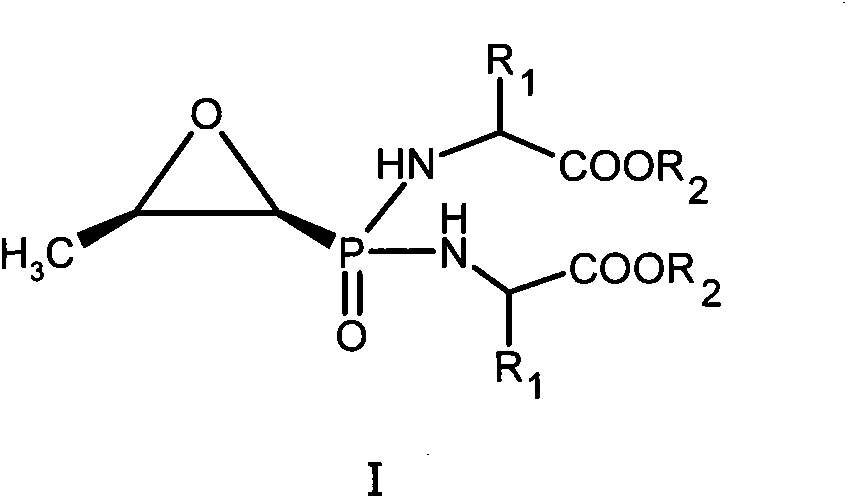
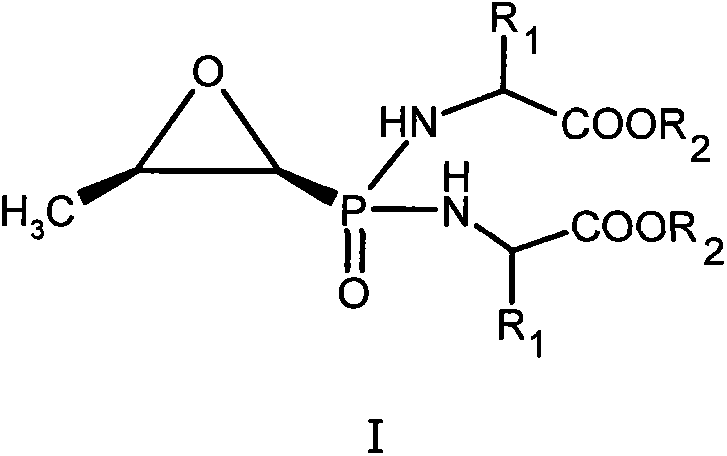
New fosfomycin derivatives and medicinal use thereof
InactiveCN104119384AAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPhosphonomycinPharmaceutical medicine
The invention relates to fosfomycin derivatives represented by formula I, and nontoxic pharmaceutically acceptable salts and hydrates thereof. In the formula I, R1 is H or a C1-6 alkyl group, and R2 is H or a C1-6 alkyl or cycloalkyl group.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
Preparation method of phosphomycin calcium capsules
InactiveCN109010306AImprove solubilitySolve insolubleAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAdditive ingredientAdhesive
The invention discloses a preparation method of phosphomycin calcium capsules. In a preparation process of the phosphomycin calcium capsules, the content of each component raw material is as follows in parts by weight: 30 to 35 parts of phosphomycin calcium, 10 to 20 parts of lactose, 15 to 20 parts of modified starch, 3 to 5 parts of an adhesive, 2 to 4 parts of a lubricant, 30 to 40 parts of purified water and 5 to 20 parts of a medical capsule material. The medical capsule material prepared by the invention has good dissolubility and can be rapidly dissolved into harmless substances absorbed by human bodies after being orally taken; after being disintegrated, a medicine is rapidly absorbed by the human bodies, and the bioavailability of the medicine is easy to improve; starch is used asa medical auxiliary material and is an edible substance so that the starch has no dangers to the human bodies and high safety; compared with common starch, modified starch has a larger specific surface area and the starch with the unit mass can absorb more medical active components; a pore channel of the starch has a porous structure and provides more attachment sites for an attachment object; the dosage of the starch can be saved, and the active components also can be efficiently adsorbed and rapidly dissolved out.
Owner:安徽鼎旺医药有限公司
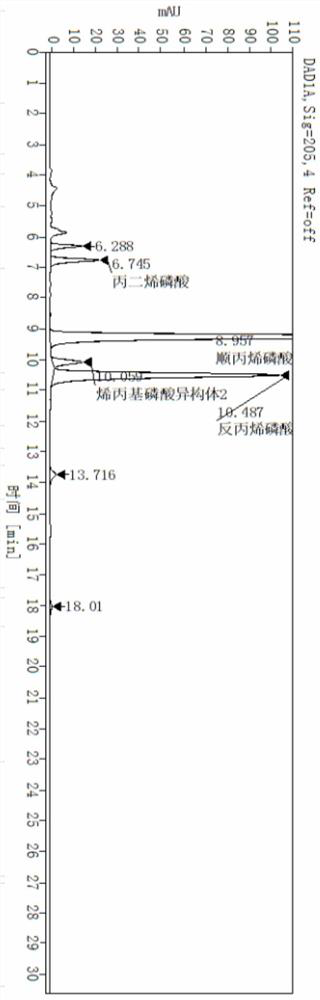
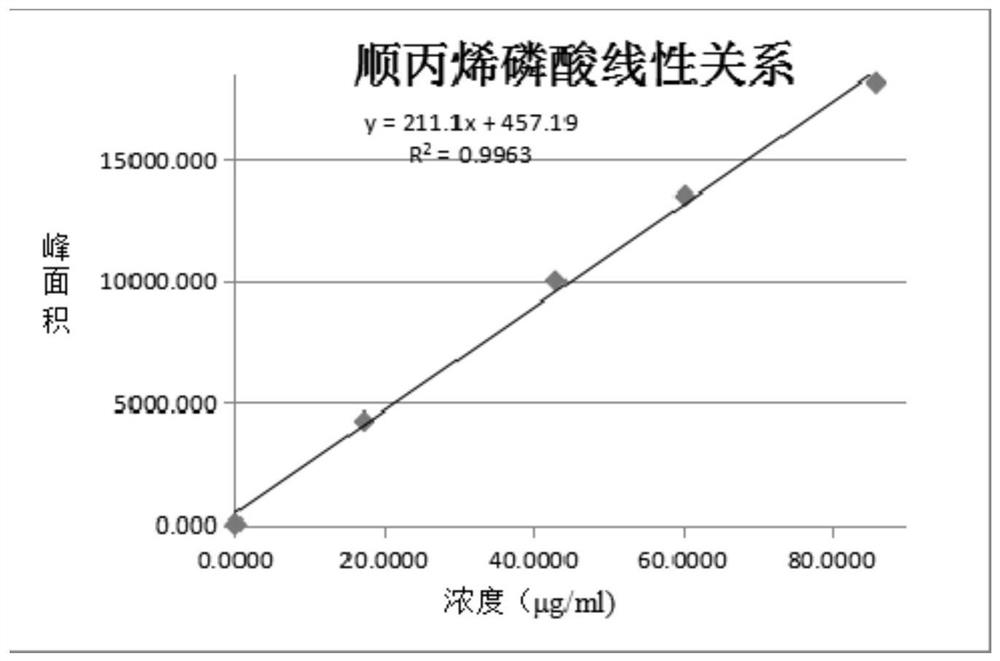
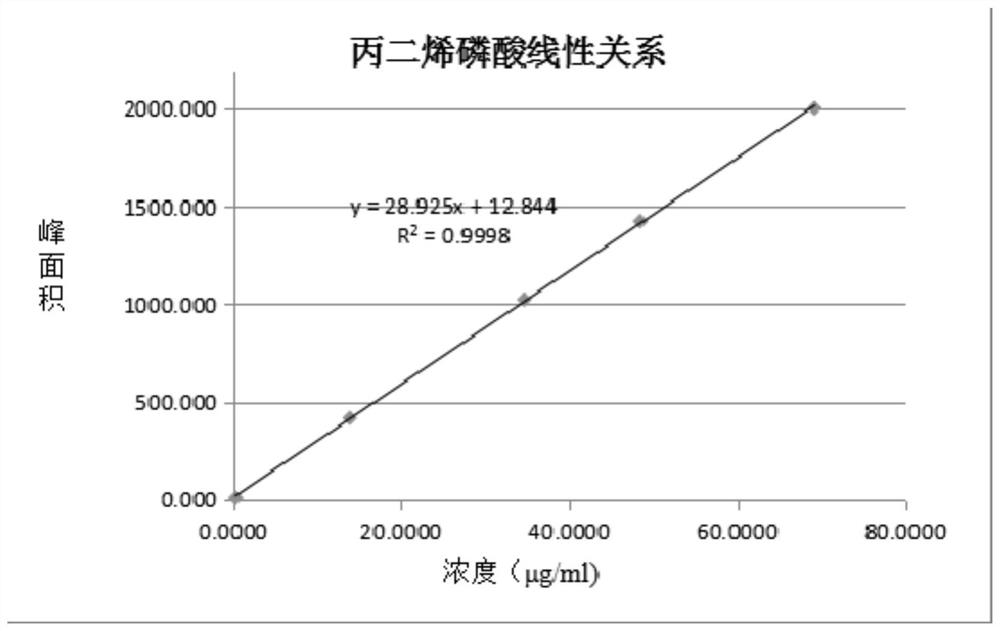
A method for simultaneously detecting fosfomycin and its diols by ion chromatography
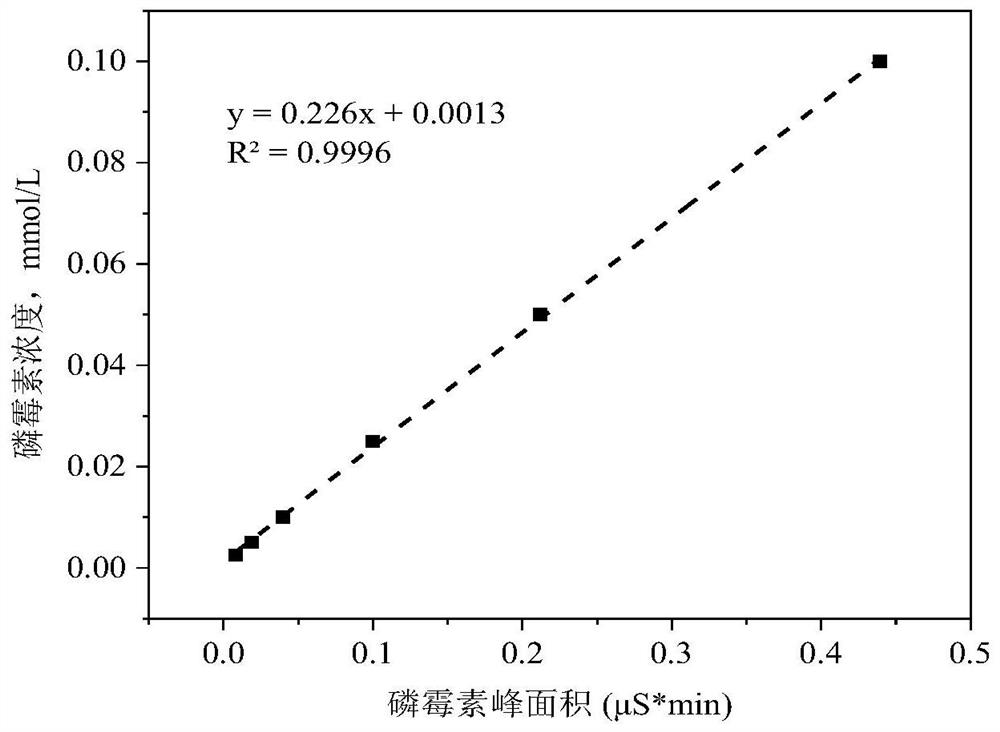
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical substance analysis and detection, and discloses a method for simultaneously detecting fosfomycin and its diols by using ion chromatography. The method that the present invention adopts ion chromatography to detect fosfomycin and its diols simultaneously comprises the following steps: (1) the selection of ion chromatography instrument and chromatographic test conditions: the chromatographic column is a low-capacity hydroxide system cathodic protection column, and the suppressor Adopt electrolytic membrane suppressor, eluent is NaOH or KOH solution; (2) draw fosfomycin standard curve with fosfomycin sodium as standard; (3) take fosfomycin trometamol EP impurity A as standard (4) test and obtain the peak area of fosfomycin and its glycol in the sample, and obtain the corresponding concentration after substituting into the standard curve. The method of the invention has the advantages of good reproducibility, low detection limit, high sensitivity, simple operation, wide use of ion chromatographic equipment, etc., and can simultaneously test fosfomycin and its glycols.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
A kind of analysis method of fosfomycin tromethamine genotoxic impurity
ActiveCN111257478BEfficient separation and detectionHigh sensitivityComponent separationAgainst vector-borne diseasesPhosphonomycinDiethyl phosphate
The invention provides an analysis method for fosfomycin tromethamine genotoxic impurities, the analysis method comprises: diluting fosfomycin tromethamine with a diluent, and then using high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry combined method to carry out the analysis. For the analysis of impurities, the formic acid solution was used as the mobile phase A, and the acetonitrile solution was used as the mobile phase B, and the elution method was gradient elution. In the formic acid solution, the concentration of formic acid is 0.1-10%. The diluent is an aqueous solution containing 85-95% methanol. The method for analyzing fosfomycin tromethamine genotoxic impurities provided by the invention can more efficiently separate and detect impurities such as allene diethyl phosphate, etc., and has the advantages of strong specificity, high sensitivity, simple, rapid and low cost. advantage.
Owner:上海峰林生物科技有限公司
Levo-phosphonomycin biotransformation strain screening method using dextro-phosphonomycin as substrate
ActiveCN1876830BImprove efficiencyEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyPhosphonomycin
The invention relates to biological transformation / biocatalytic technology microbial bacterial strain sieving domain, especially to a sieving policy and method for left-handed fosfomycin biological converting bacterial strain with right-handed fosfomycin as substrate. The said sieving policy and specific method of operation consist of two big steps including bacterial strain culture and conversion product identification in screening process, in which the essential point includes preliminary enrichement of laboratory bacterial and product calibration policy which combines biological calibration with thin-layered chromatography (TLC). Because the bacterial which can be changed from right-handed fosfomycin to left-handed fosfomycin in nature is rare and the lab available bacterial grows up slowly, the preliminary enrichement of laboratory bacterial is very important. Moreover, adopting product calibration policy which combines biological calibration with thin-layered chromatography (TLC), whether there is left-handed fosfomycin in product can be exactly determined.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for detecting impurities in propadiene diethyl phosphate
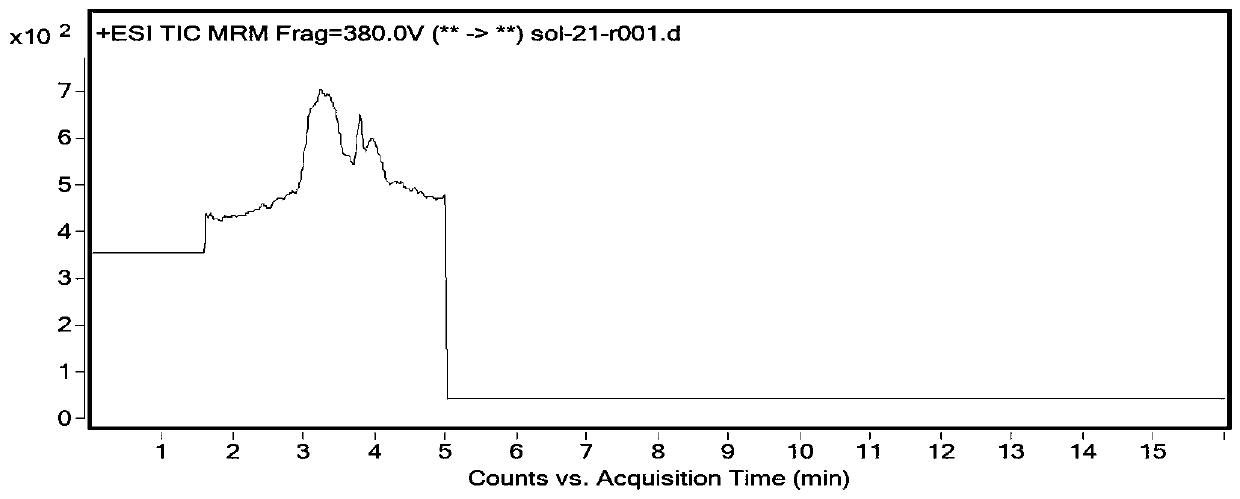
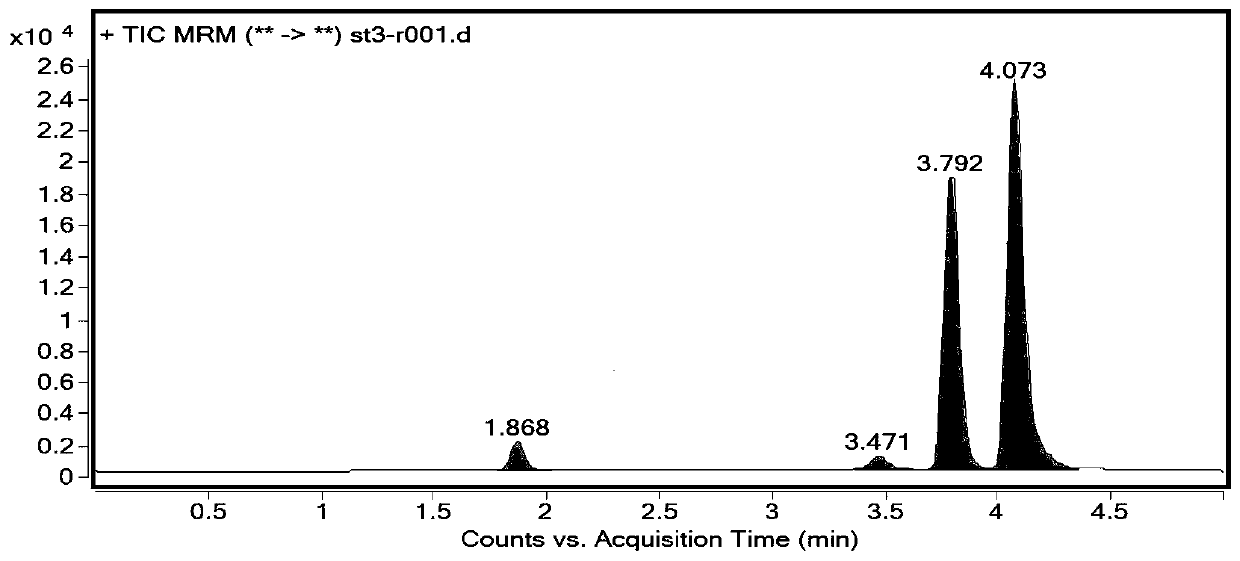
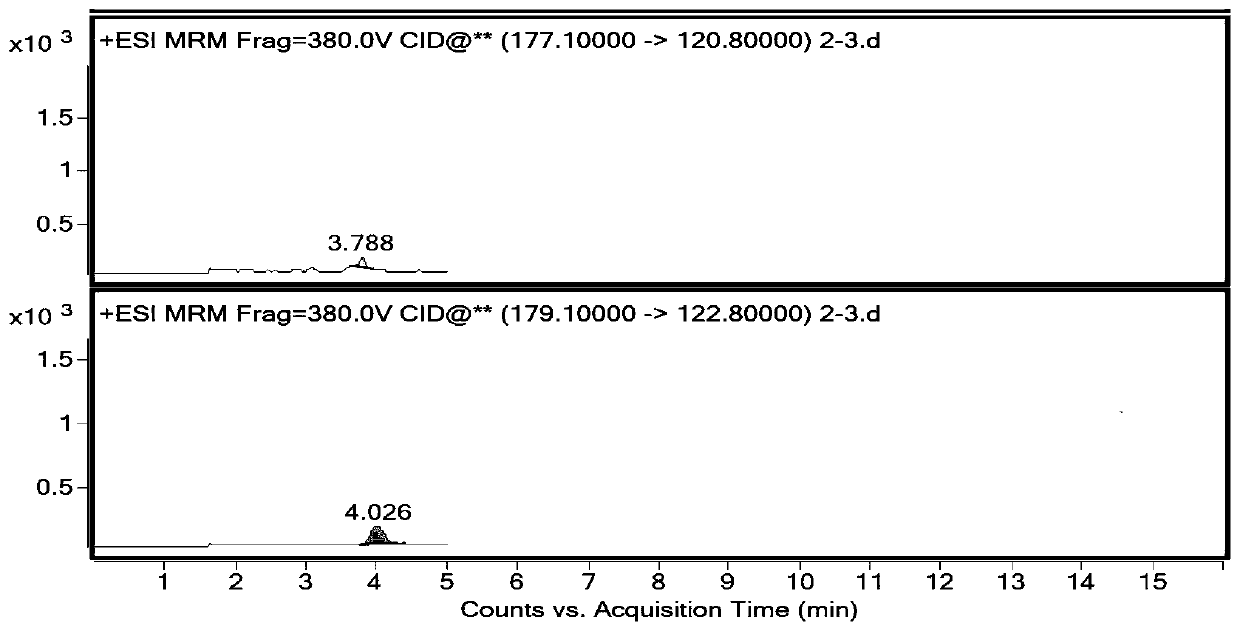
PendingCN114720577AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityComponent separationDiethyl phosphatePhosphonomycin
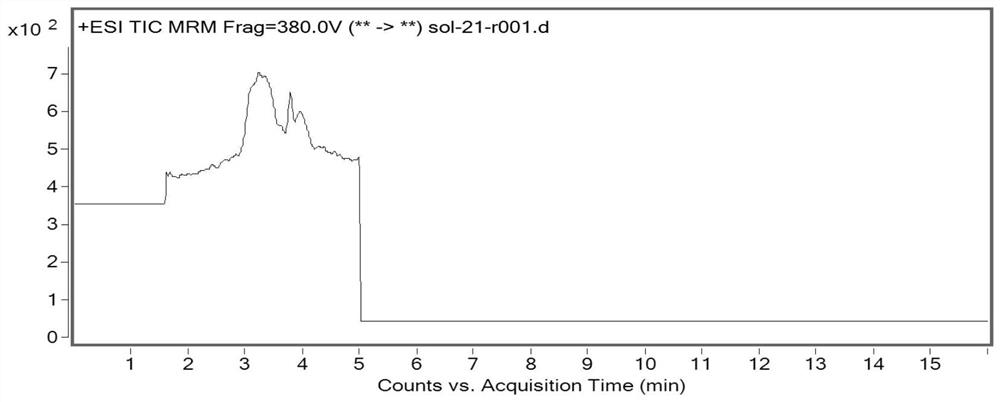
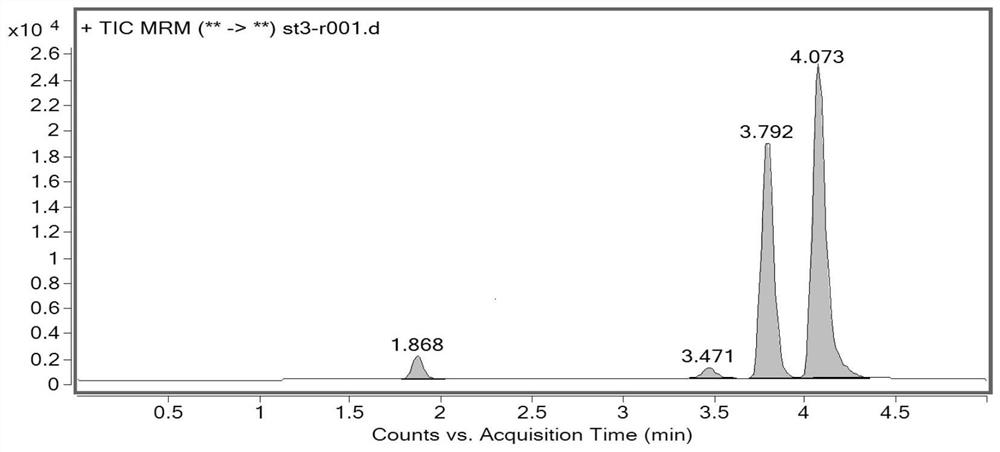
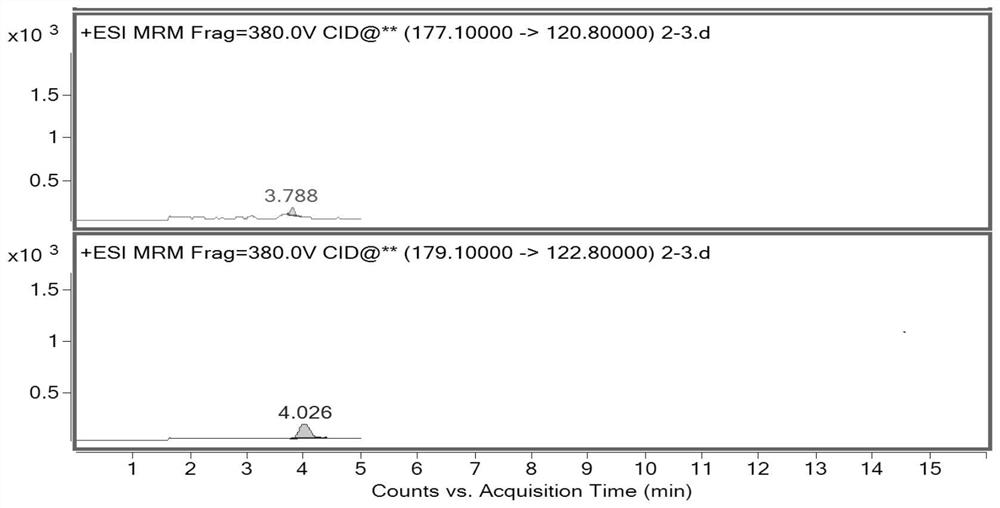
The invention discloses a method for detecting impurities in propadiene diethyl phosphate, which relates to the field of chemical drug analysis, and adopts a triple quadrupole mass spectrometry detector to detect in an ESI positive ion mode and an MRM multi-reaction monitoring mode. According to the present invention, the multi-reaction monitoring mode (MRM) of the high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry is adopted to detect the propadiene diethyl phosphate, such that the sensitivity is high, the specificity is strong, and the propadiene diethyl phosphate in the fosfomycin sodium can be effectively controlled to the toxicological threshold value (TTC), namely 1.5 [mu] g / day.
Owner:上海峰林生物科技有限公司
Alkenyl and beta-substituted phosphonates as antimicrobial agents
ActiveUS11098072B2Antibacterial agentsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPhosphonomycinMalarial parasite
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS +2
Fosfomycin chitosan hybrid salt and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111349117AStable structureImprove biological activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPhosphonomycinPolymer science
The invention provides a fosfomycin chitosan hybrid salt and a preparation method thereof; the fosfomycin chitosan hybrid salt is obtained by salifying two hydroxyl groups of fosfomycin and amino groups on chitosan molecules with the same chain, or salifying two hydroxyl groups of fosfomycin and amino groups on different chitosan chains. The preparation method of the fosfomycin chitosan hybrid salt provided by the invention comprises the steps: by taking phosphonomycin (R)-1-phenethylamine salt as an initial raw material, dissociating fosfomycin sodium by virtue of a sodium hydroxide solution,preparing a fosfomycin acid solution by virtue of cation exchange, carrying out a reaction with chitosan with different molecular weights, and refining, so as to obtain the fosfomycin chitosan hybridsalt. According to the preparation process disclosed by the invention, the fosfomycin chitosan hybrid salts with different molecular weight segment grades can be obtained, the hybrid salts can have different water solubility according to different molecular weights of chitosan, the biological activity is excellent, and the fosfomycin chitosan hybrid salts can be used for antibacterial treatment in different ways.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
A kind of high-performance liquid chromatography method for determining fosfomycin sodium impurity
ActiveCN110887925BImprove retentionImprove compatibilityComponent separationPhosphonomycinO-Phosphoric Acid
The invention relates to a high-performance liquid chromatography method for determining fosfomycin sodium impurities. The high-performance liquid chromatography method uses a chromatographic column utilizing octadecylsilane bonded silica gel as a filler and adopts a phosphoric acid aqueous solution-methanol mixed solution as a mobile phase, wherein the concentration mass fraction of phosphoric acid in the phosphoric acid aqueous solution is 0.04% to 0.04%. 0.06%, the volume ratio of phosphoric acid aqueous solution to methanol is 99:1~99:5. According to the method of the present invention, the retention of highly polar impurities is enhanced, the complex impurity system of fosfomycin sodium can be effectively separated, and it has good versatility and specificity for specific impurities, high sensitivity, convenient operation, and moderate analysis time. It provides an effective guarantee for the quality control of the compound.
Owner:上海峰林生物科技有限公司
Oral care material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111195227ASimple processEasy to operateCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsPhosphonomycinMouth care
The invention discloses an oral care material. The oral care material is prepared from, by weight, 45 to 55 parts of a vinyl pyrrolidone / vinyl phosphocreatine / isopulegol / 1-chloro-2-[2-chloroethoxy(ethenyl)phosphoryl]oxyethane copolymer, 4 to 8 parts of fosfomycin sodium modified hyperbranched polyamino acid, 0.1 to 0.3 part of zinc acrylate, 1 to 2 parts of tea polyphenol, 10 to 20 parts of a Chinese herbal medicine extract, 0.5 to 1.5 parts of a brightening agent, 8 to 15 parts of a filling agent, 2 to 5 parts of a breath freshener, 0.5 to 1.5 parts of a vitamin medicine, 0.5 to 1.5 parts ofa wetting agent and 0.01 to 0.03 part of an initiator. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the oral care material. The oral care material is good in biocompatibility and remarkable inoral care effect, and can effectively reduce and condition the formation of a dental surface membrane, so that bacterial adhesion is remarkably reduced, and meanwhile, the oral care material has theeffects of inhibiting bacteria, repairing cell damage and the like.
Owner:刘海霞
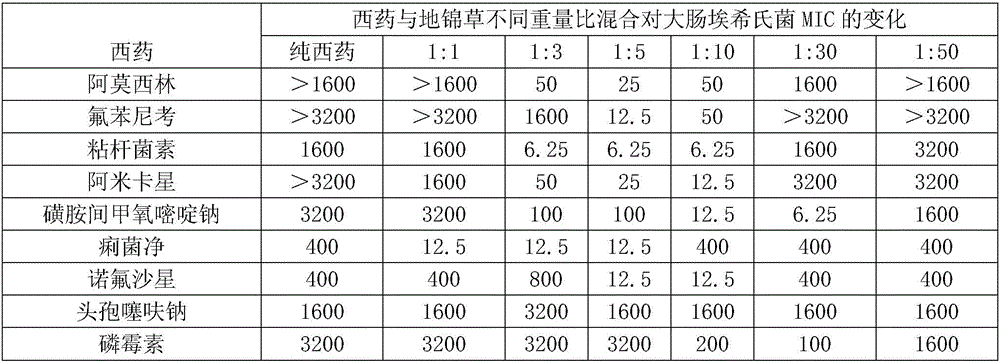
Compound medicine containing humifuse euphorbia herb and phosphonomycin for livestock
InactiveCN106109547AGood synergyGood curative effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPhosphonomycinCurative effect
The invention relates to a compound medicine containing humifuse euphorbia herb and phosphonomycin for livestock. The compound medicine for the livestock is prepared from the phosphonomycin and the humifuse euphorbia herb, wherein the weight ratio of the phosphonomycin to the humifuse euphorbia herb is 1:10 to 1:30. The invention also requires protecting a compound preparation prepared by the compound medicine for the livestock. The compound medicine for the livestock provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that a experimental study proves that since the phosphonomycin and the humifuse euphorbia herb are jointly used according to a specific weight proportion, the compound medicine for the livestock has the advantages of remarkable synergistic effect, fast curative effect, low cost and the like.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Compound pharmaceutical composition capable of improving disease resistance of poultry
InactiveCN106727818AGood treatment effectReverse drug resistanceAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPhosphonomycinDisease
The invention discloses a compound pharmaceutical composition capable of improving the disease resistance of poultry. The compound pharmaceutical composition is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 80-120 parts of rhizoma cibotii, 0.01-0.03 part of sunflower seed oil and 10-20 parts of phosphonomycin. According to the compound pharmaceutical composition capable of improving the disease resistance of the poultry, disclosed by the invention, a compound medicine is composed of the traditional Chinese medicines, namely rhizoma cibotii, sesames and phosphonomycin, wherein phosphonomycin is an antibacterial medicine; rhizoma cibotii and the sunflower seed oil are added into the antibacterial medicine, and the drug resistance of bacteria on the antibacterial medicine can be reversed, so that the treatment effect of the antibacterial medicine is improved; furthermore, the medicine cost and the medicine residue can be greatly reduced by the product disclosed by the invention, and relatively high economic benefits are created for farmers; and meanwhile, the food safety is also ensured.
Owner:防城港市畜牧站
Compositions for eliminating bacterial promotors of colorectal cancer by intraluminal application
PendingUS20210060038A1Improve permeabilityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsPhosphonomycinBiofilm
The present invention provides compositions comprising fosfomycin for reducing or eliminating bacterial promotors of colorectal cancer, whether in the tumor or biofilm, by local administration into the bowel lumen.
Owner:REPONEX PHARMA APS
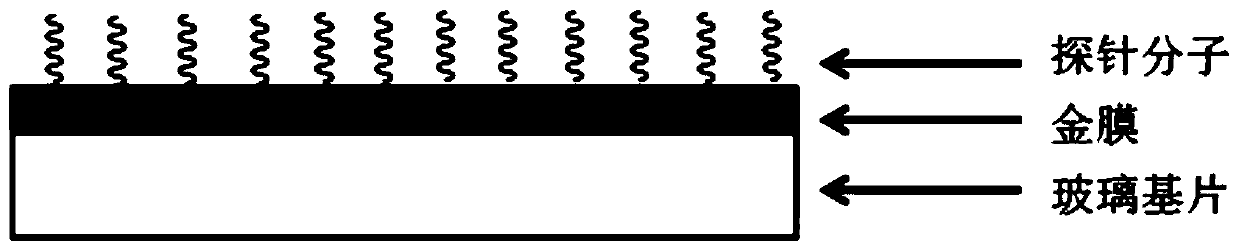
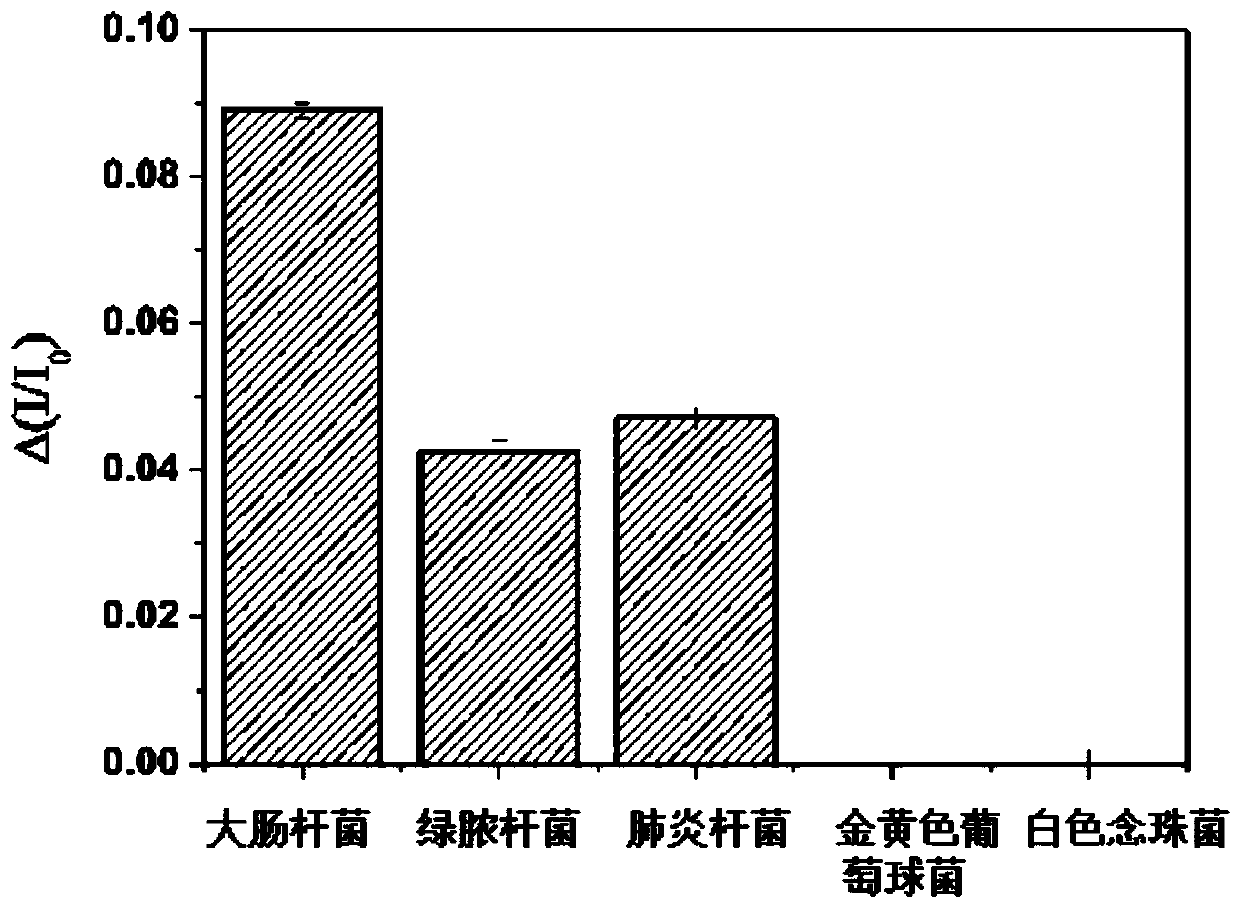
A Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor Chip for Gram-negative Bacteria Detection
ActiveCN108169182BHigh sensitivityGood choiceMaterial analysis by optical meansPhosphonomycinMicronomicin
The invention discloses a surface plasmon resonance sensor chip for detecting gram-negative bacteria and a preparation method and application thereof. The chip comprises a glass substrate layer, a gold film layer and a probe molecular layer. The gold film layer is disposed on the glass substrate layer. The probe molecular layer is disposed on the gold film layer. A probe molecule of the probe molecule layer contains at least one of drug molecules of streptomycin sulfate, kanamycin sulfate, gentamicin sulfate, gentamycin-micronomicin, vistamycin sulfate, neomycin, polymyxin B, rifampicin, chloramphenicol and fosfomycin. The invention also discloses a preparation method and application of the chip. The surface plasmon resonance sensor chip creatively realizes detection of gram-negative bacteria based on surface plasmon resonance, has high sensitivity and good selectivity, has a gram-negative bacterium concentration detection linear range of 10-10<6> CFU / mL and can be used for detecting gram-negative bacteria in solutions such as detection water, drinking water or human body fluids.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com