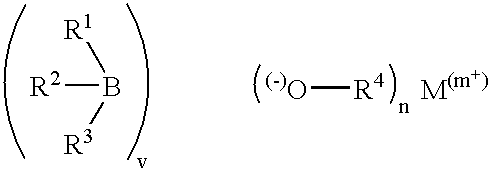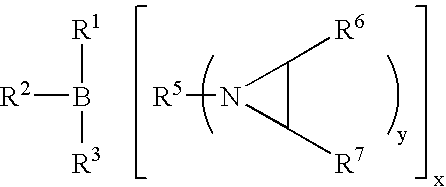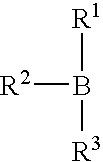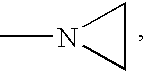Patents
Literature
103results about How to "Maintain bond strength" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
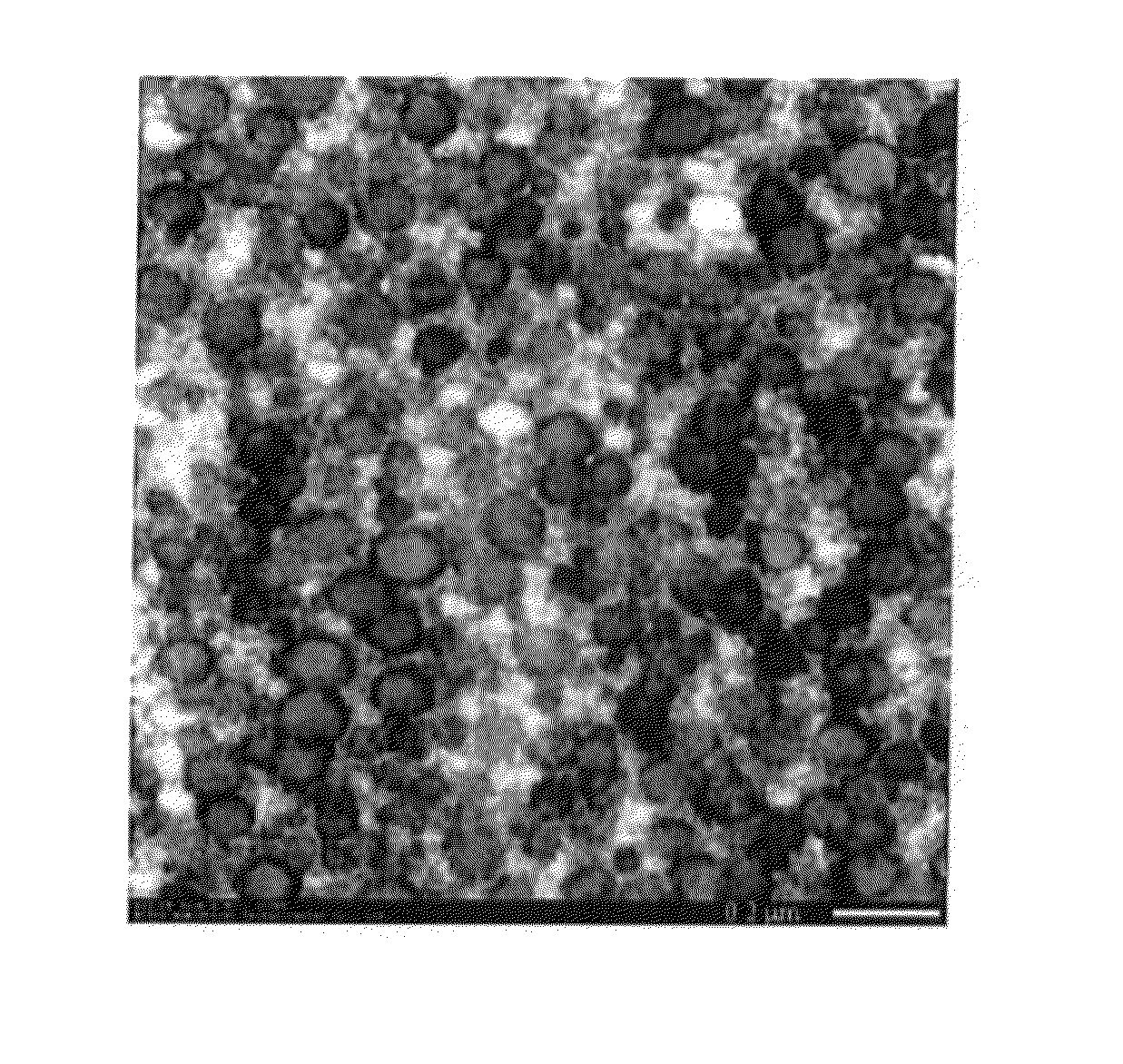
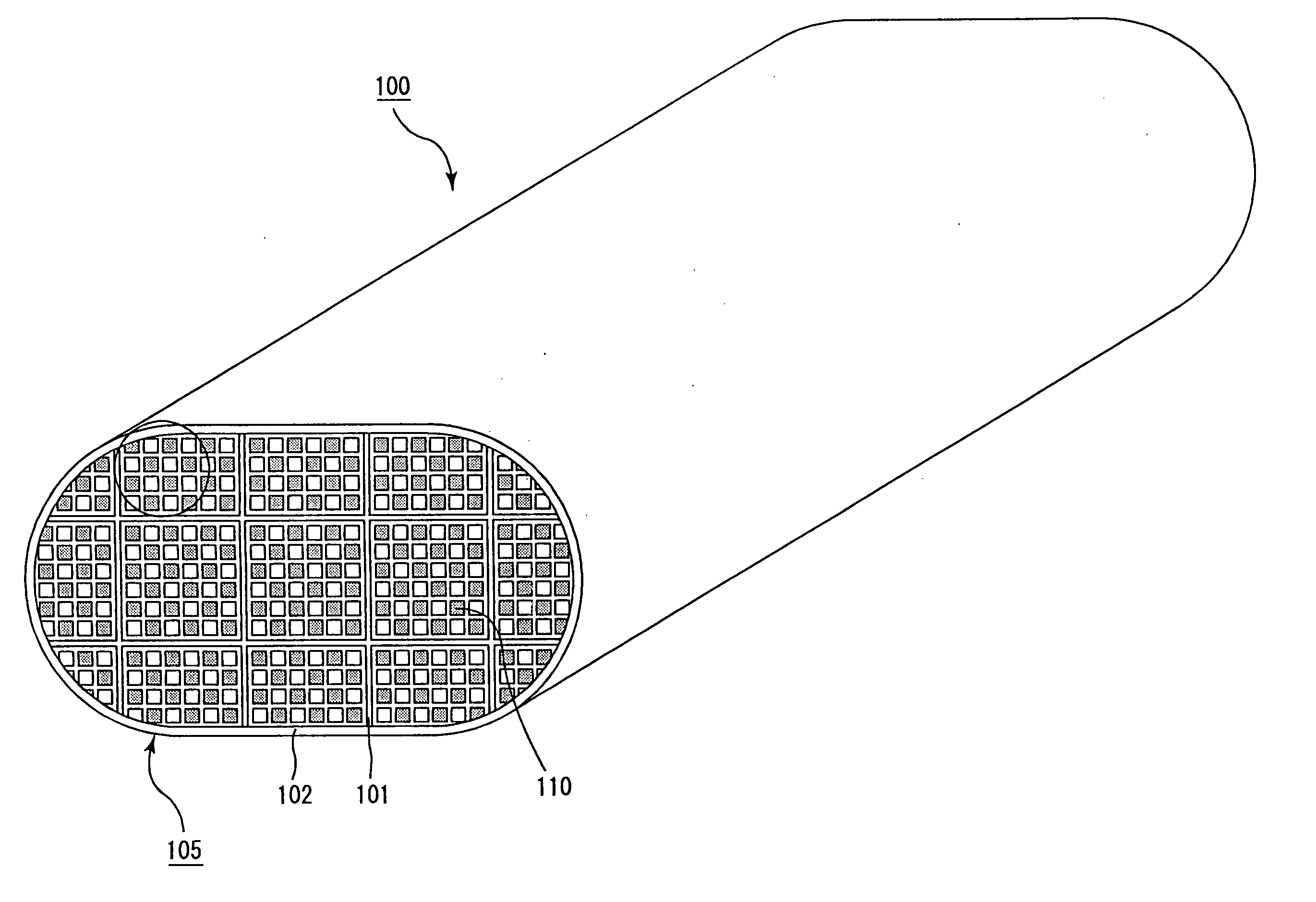
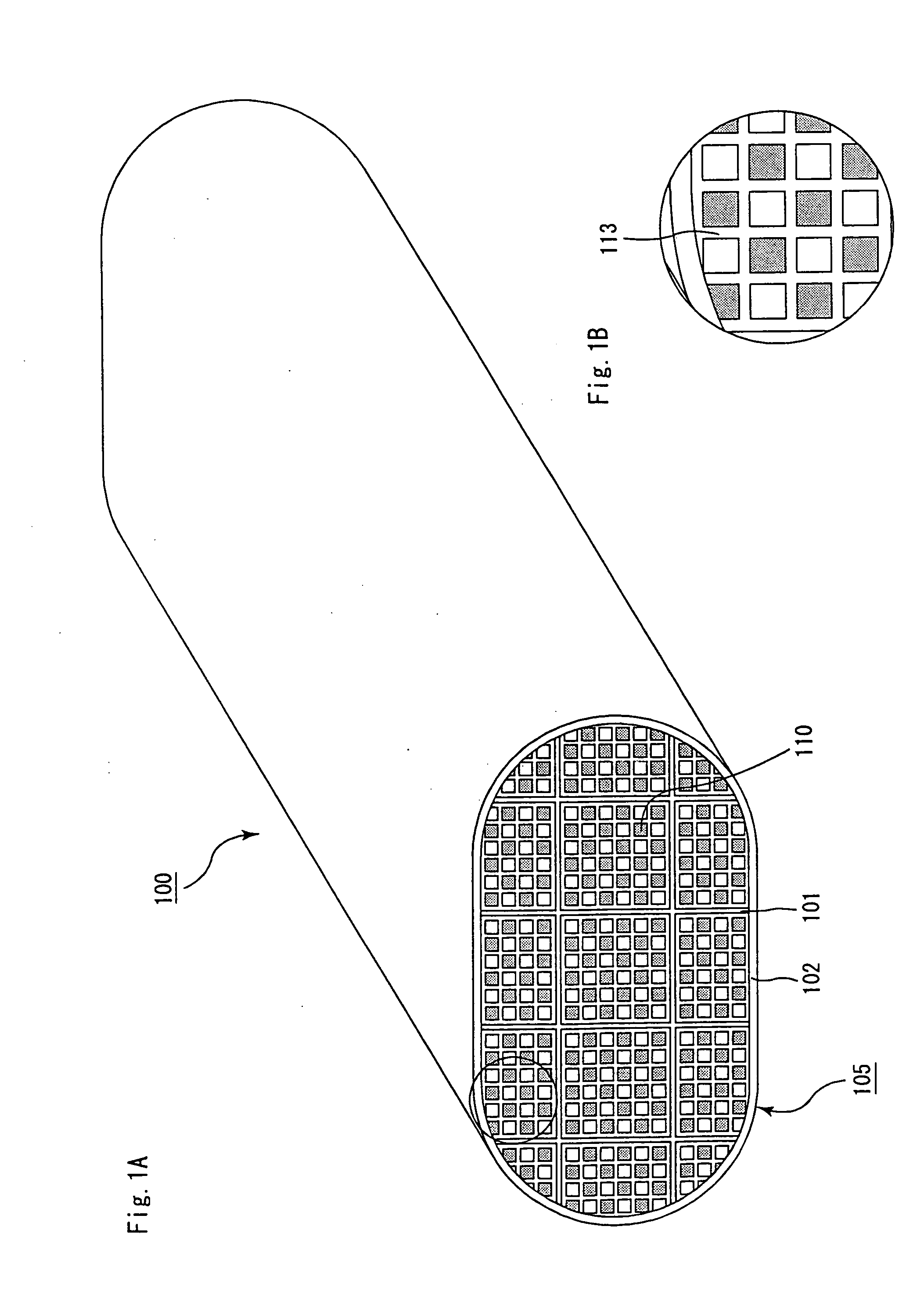
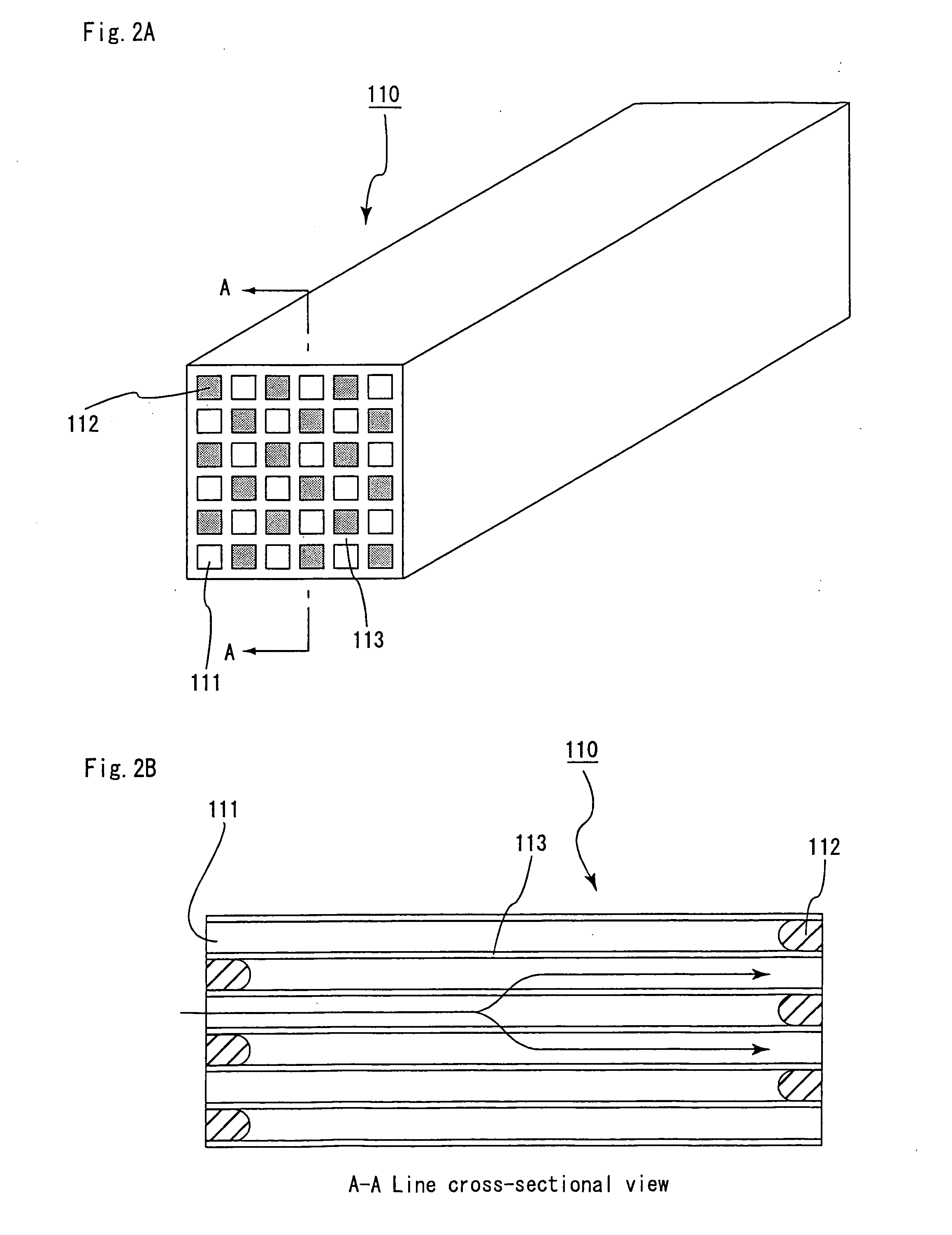
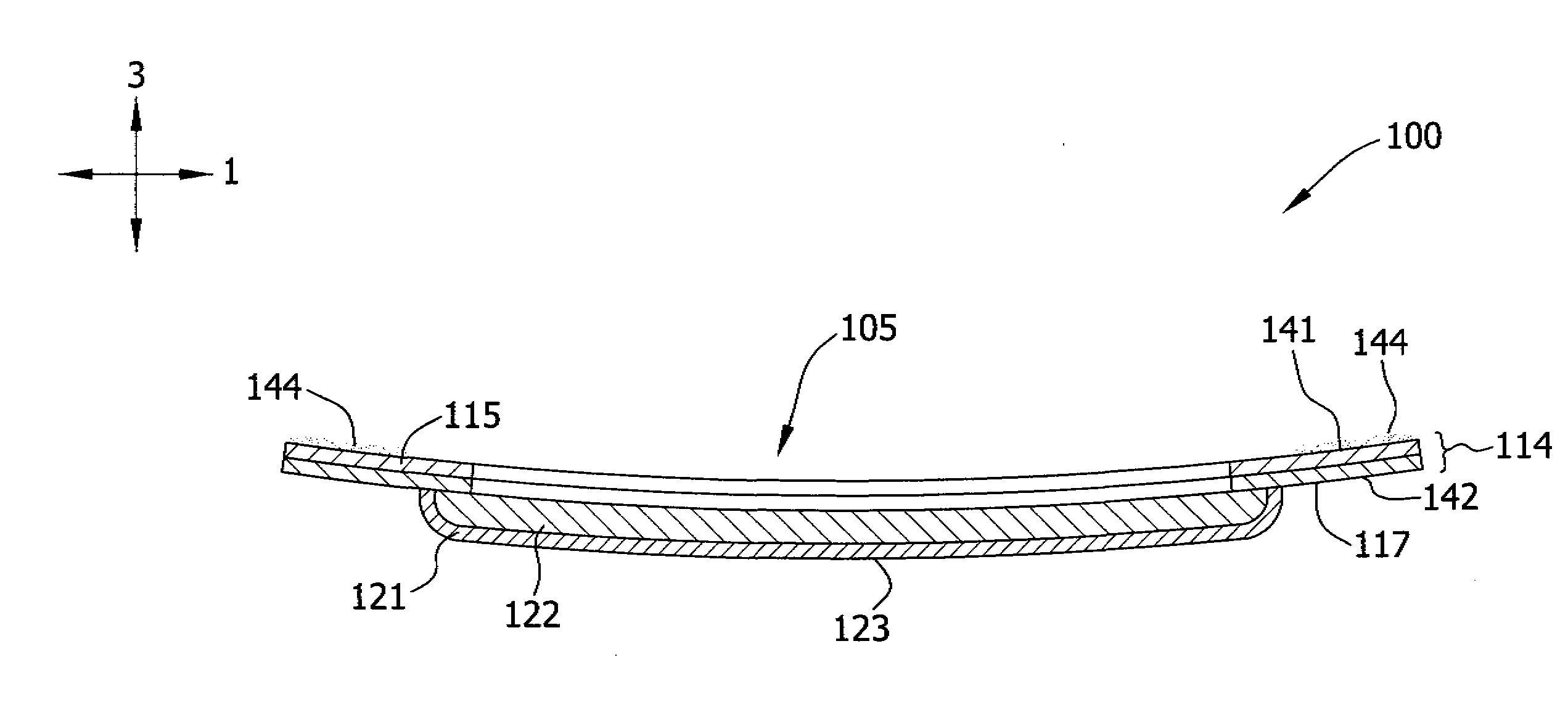
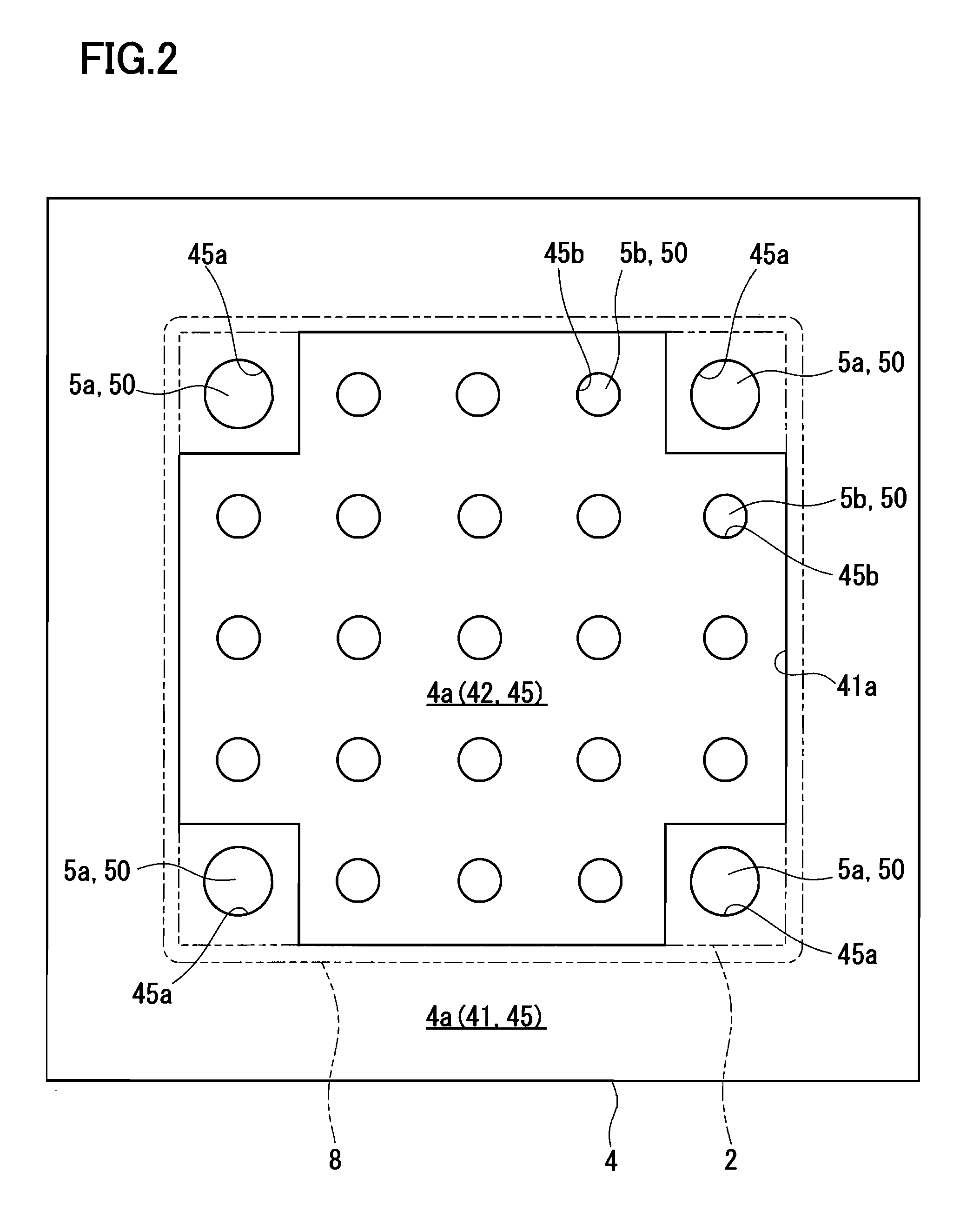
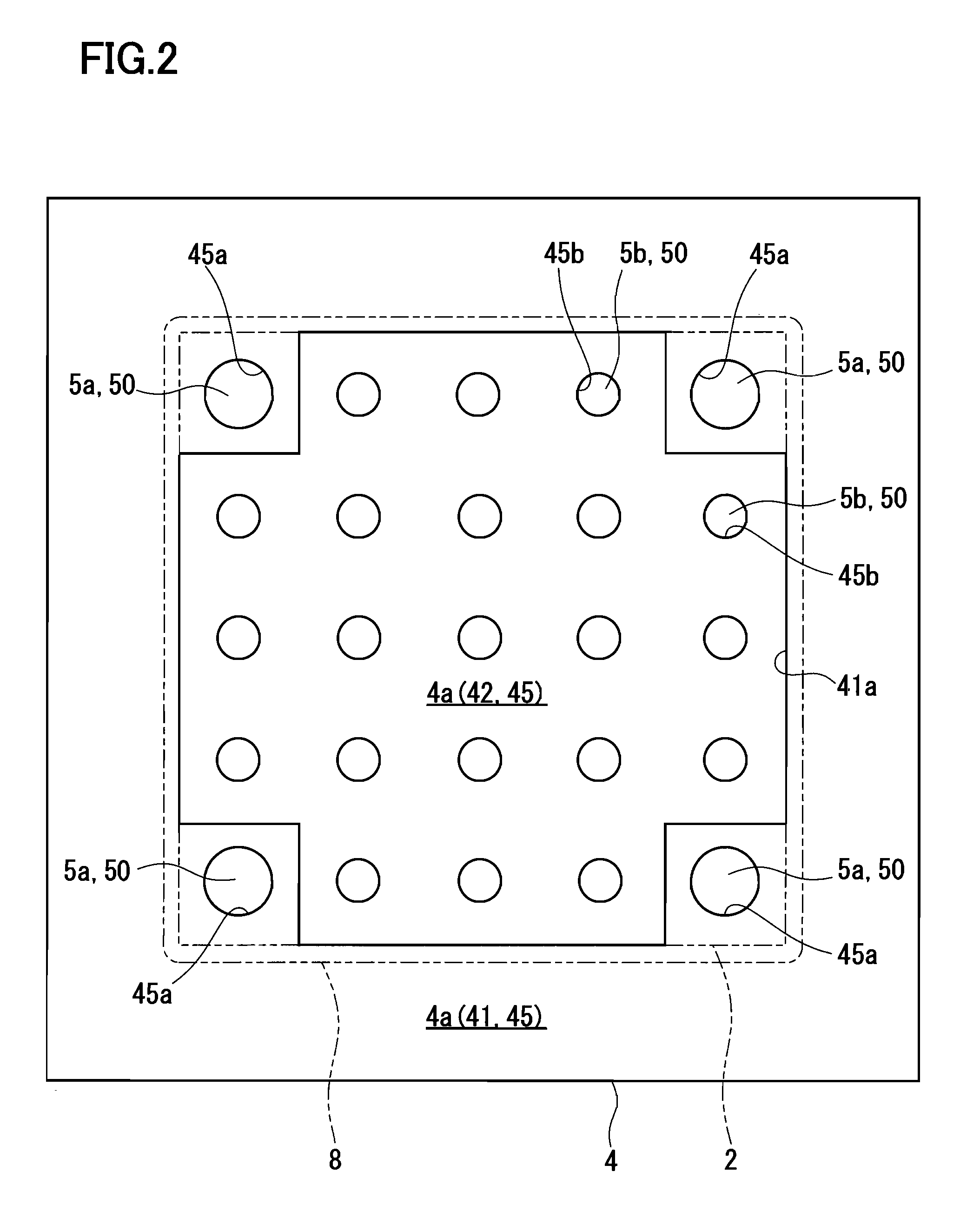
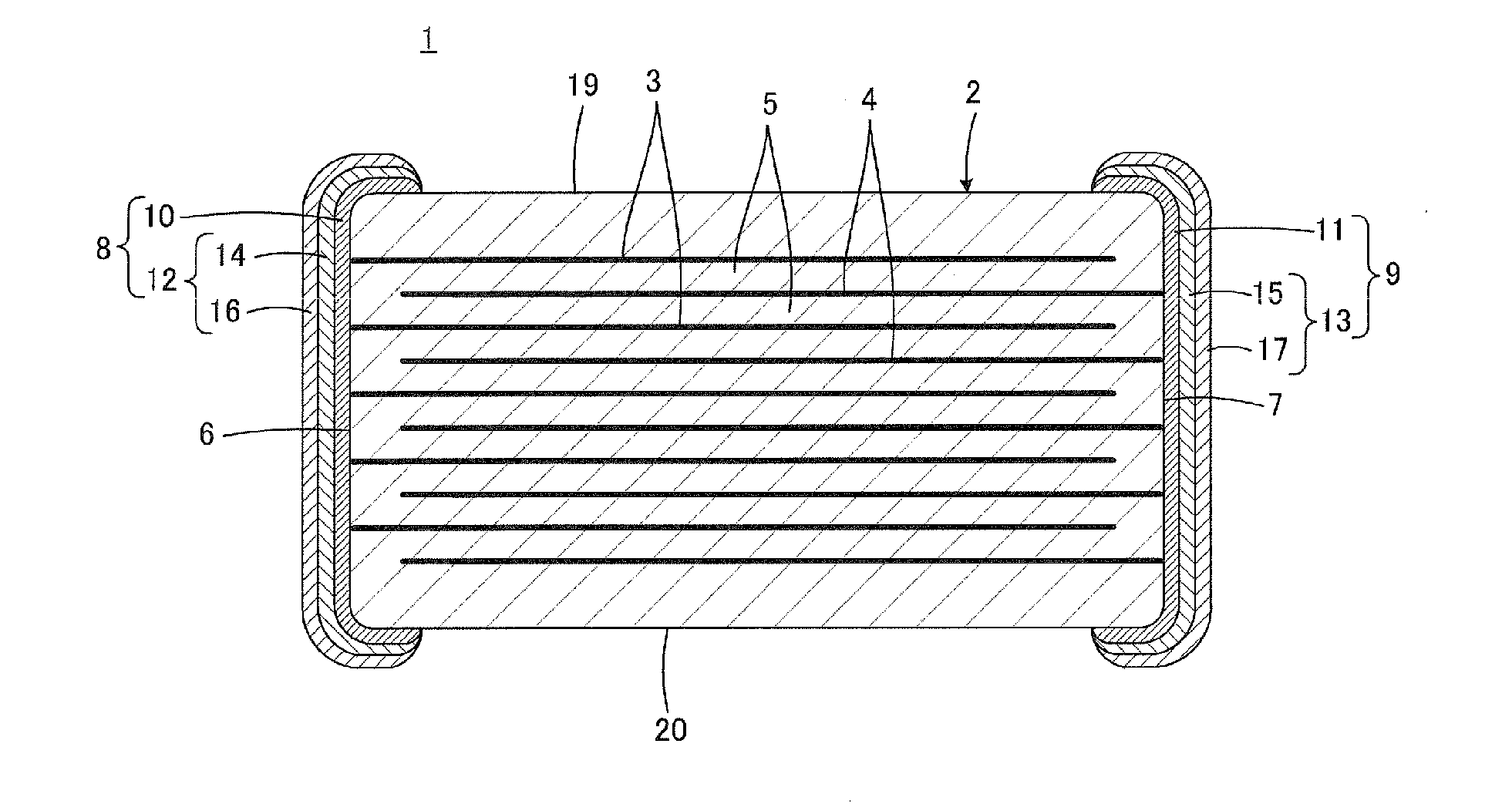
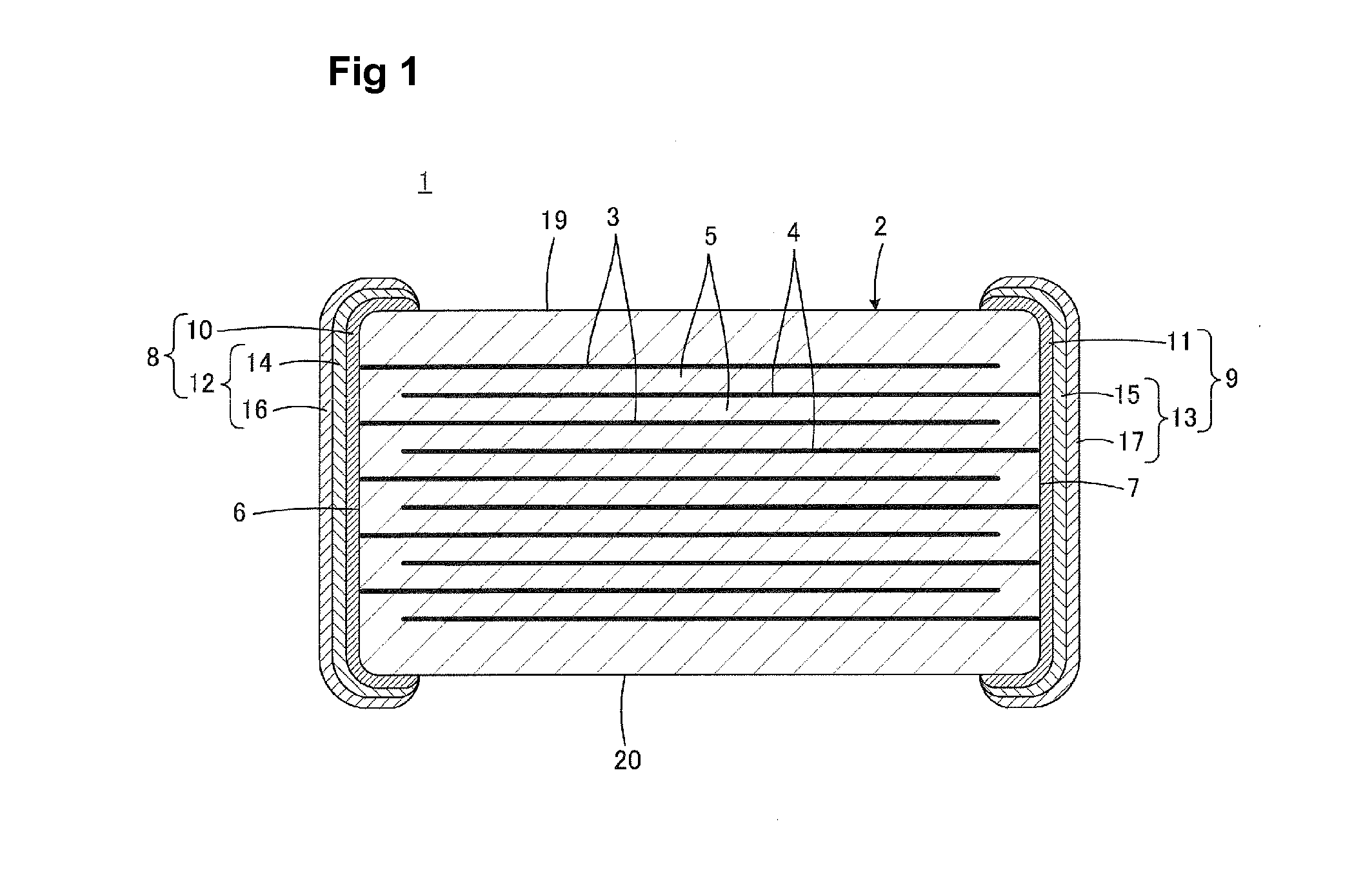
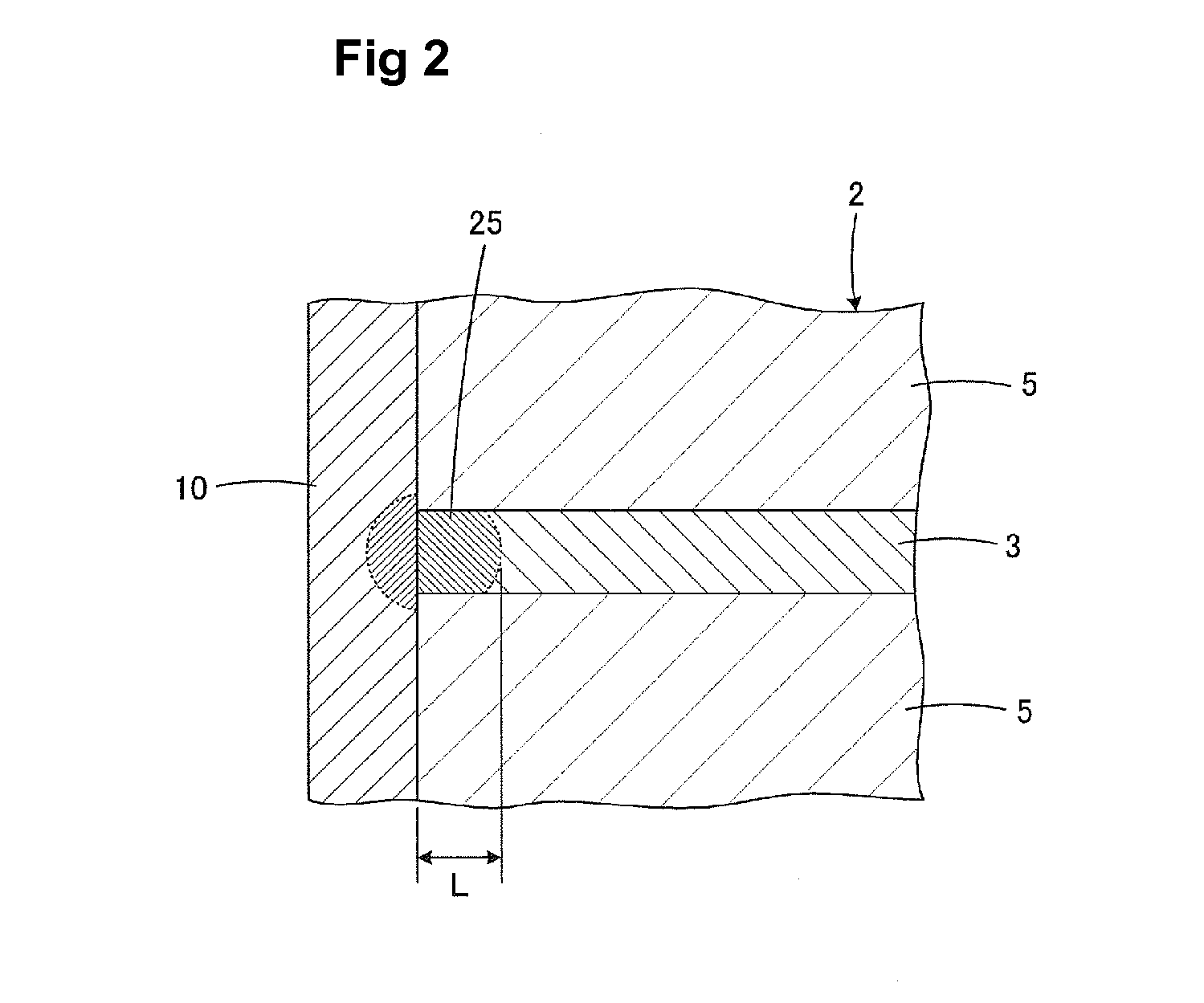
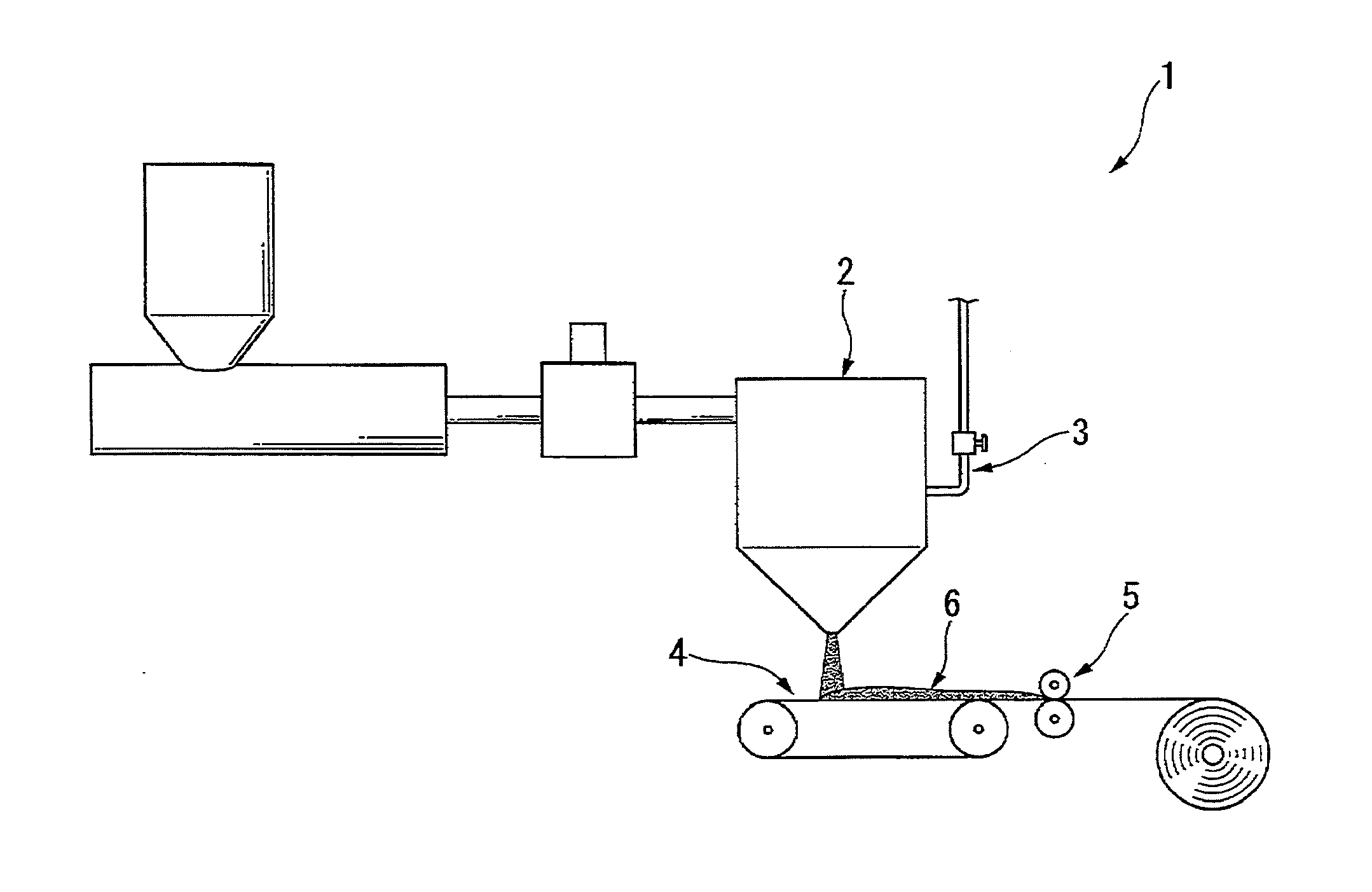
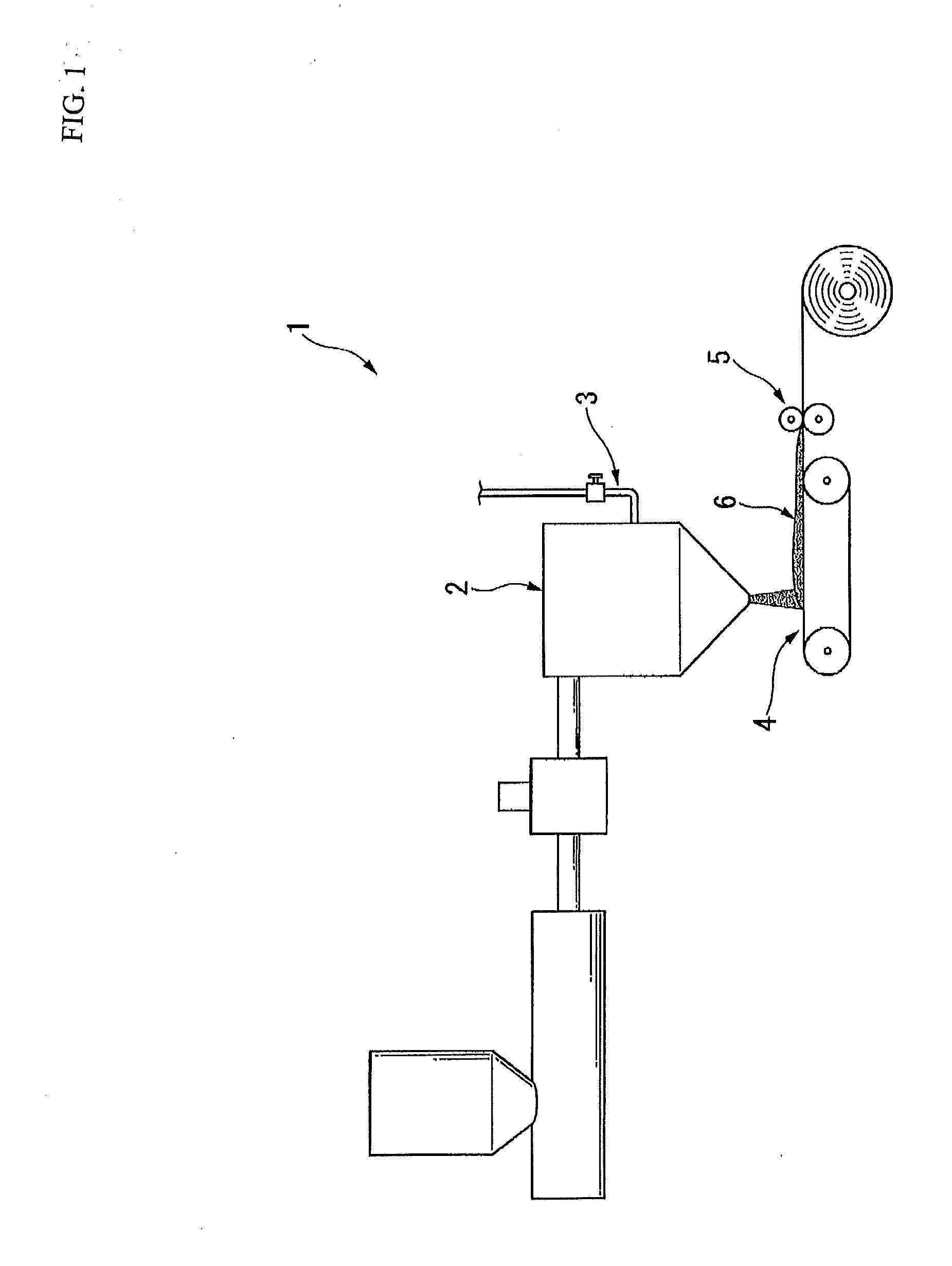
Honeycomb structural body and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20050247038A1Great resistance to physical impactIncreased durabilityCatalyst carriersGas treatmentDiagonalHoneycomb structure
A honeycomb structural body comprising: a ceramic block having a flat shape in which a plurality of honeycomb units are bonded to each other through a sealing material layer, said honeycomb unit mainly comprises porous ceramic and includes a large number of through holes placed in parallel with one another in a longitudinal direction with a partition wall interposed therebetween; and a sealing material layer formed on a peripheral portion thereof, wherein the sealing material layer among the honeycomb units on a cross section perpendicular to the longitudinal direction has a pattern that is formed in a diagonal direction with respect to a major axis of a shape forming a contour of the cross section.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Multifunctional Acrylate Skin-Adhesive Composition
ActiveUS20100121304A1Improve bindingMaintain bond strengthPowder deliveryCosmetic preparationsMedicineAcrylate
Improved skin-adhesive compositions for bonding a substrate, such as an absorbent article, to skin are disclosed. More particularly, the skin-adhesive composition has an improved, yet gentle, adhesion to the skin of a user, while maintaining strong, effective bonding to various inanimate, non-skin substrates. In one embodiment, the skin-adhesive composition can provide one or more skin benefit agents to the user. The skin-adhesive composition may applied to an absorbent article, such as a panty-liner, sanitary napkin, or an incontinence article, for directly adhering the article to the skin of a user.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
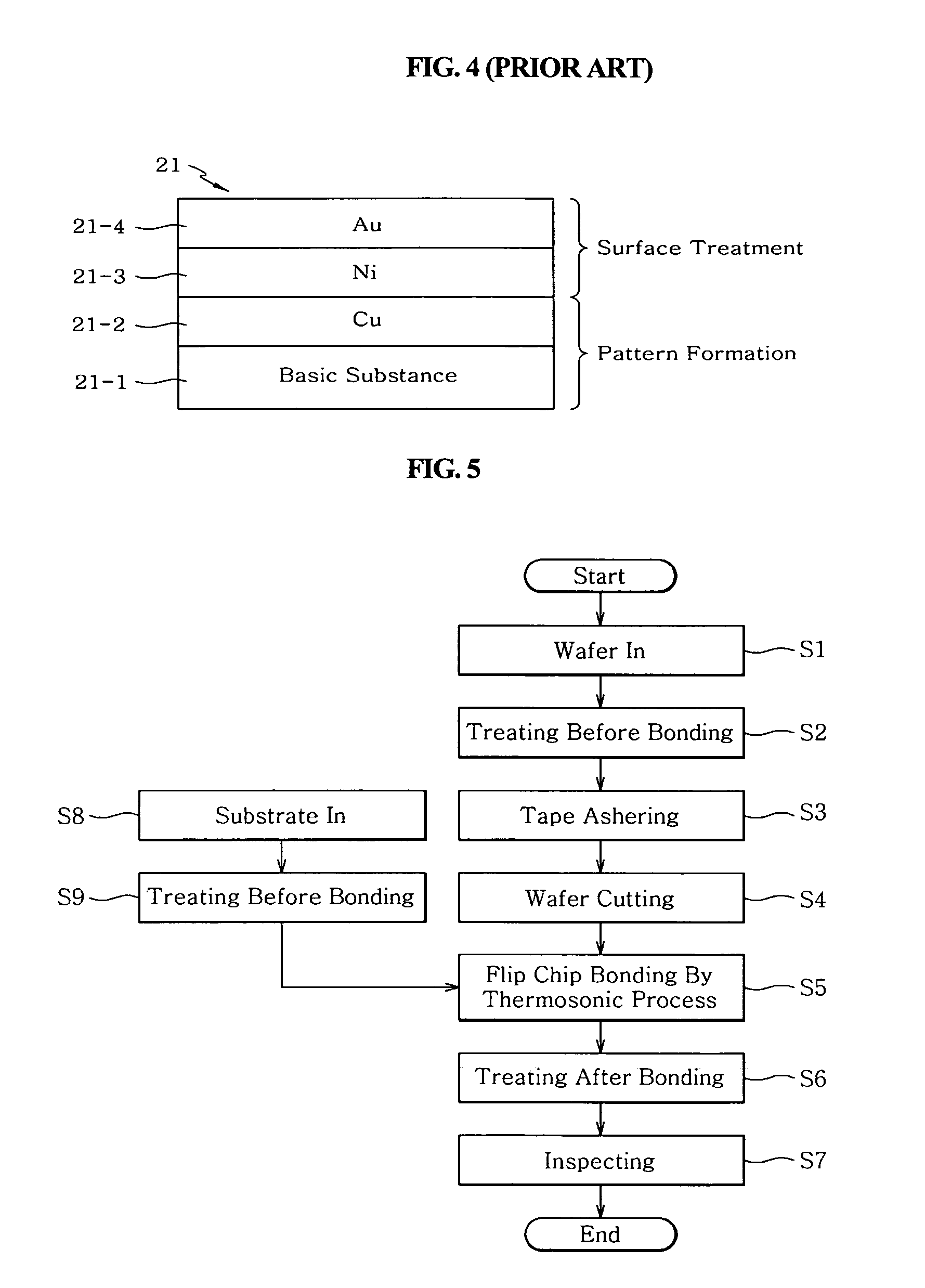
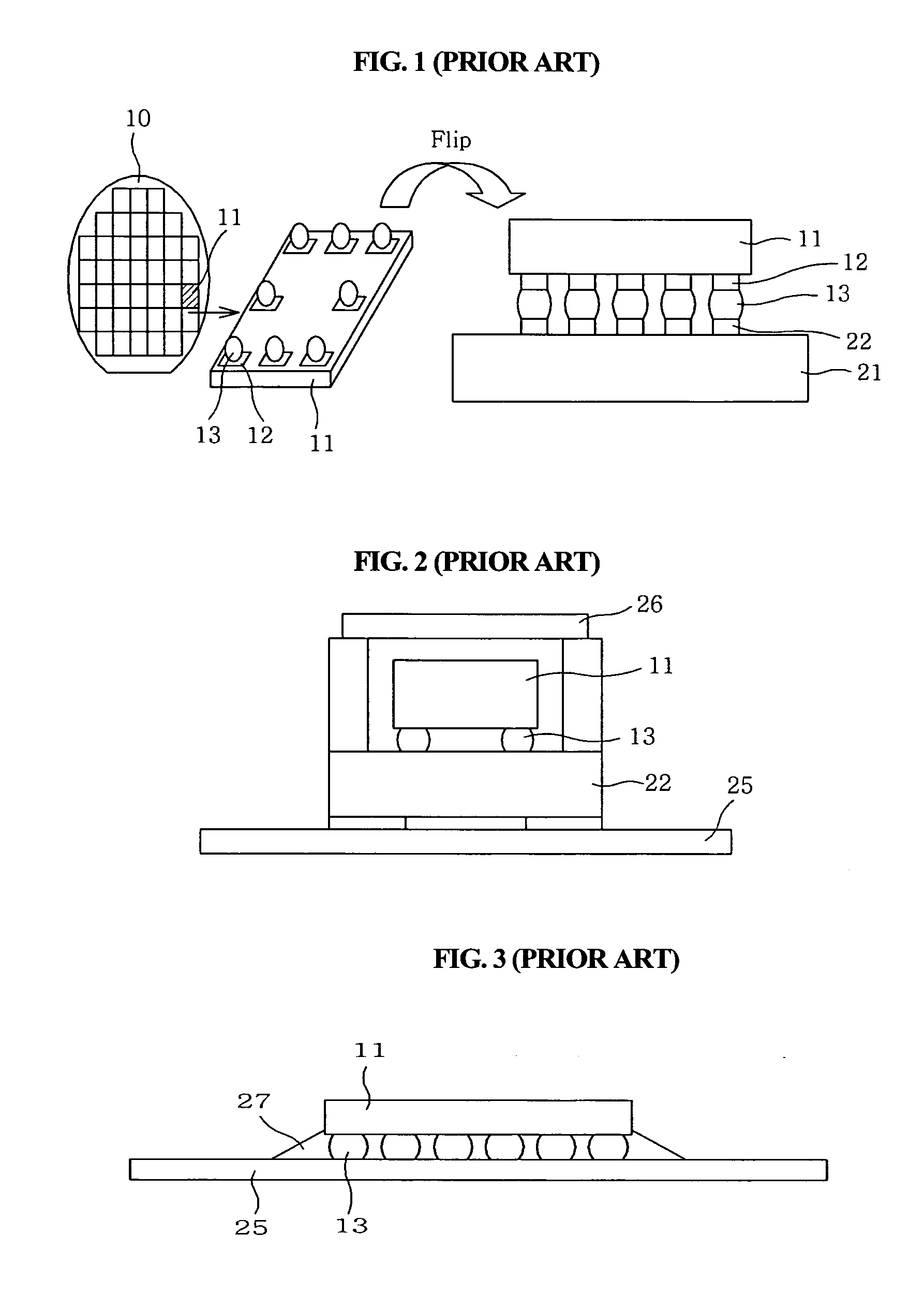
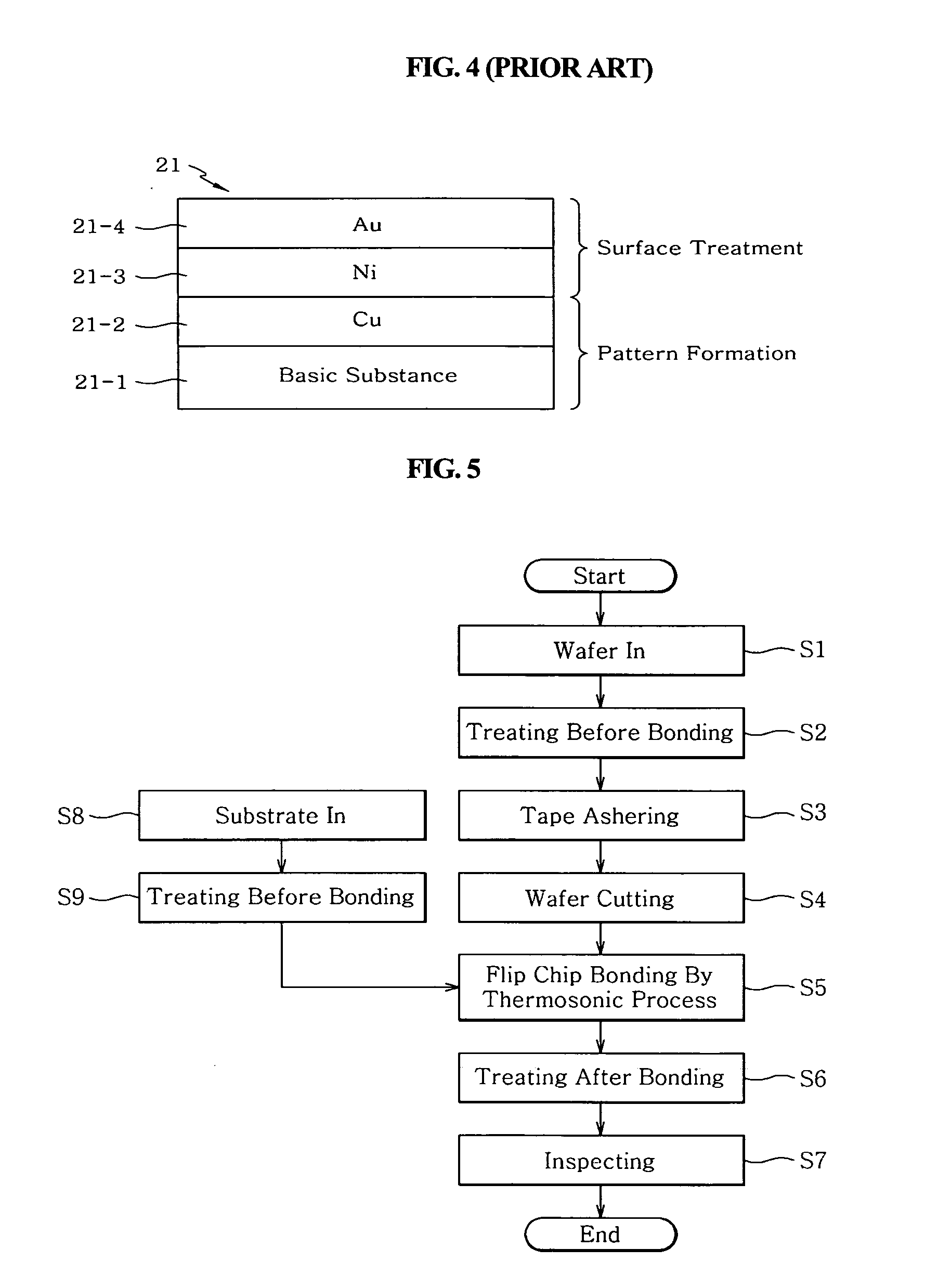
Flip chip bonding method for enhancing adhesion force in flip chip packaging process and metal layer-built structure of substrate for the same
InactiveUS7115446B2Increase productivityImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAdhesion forceWafering
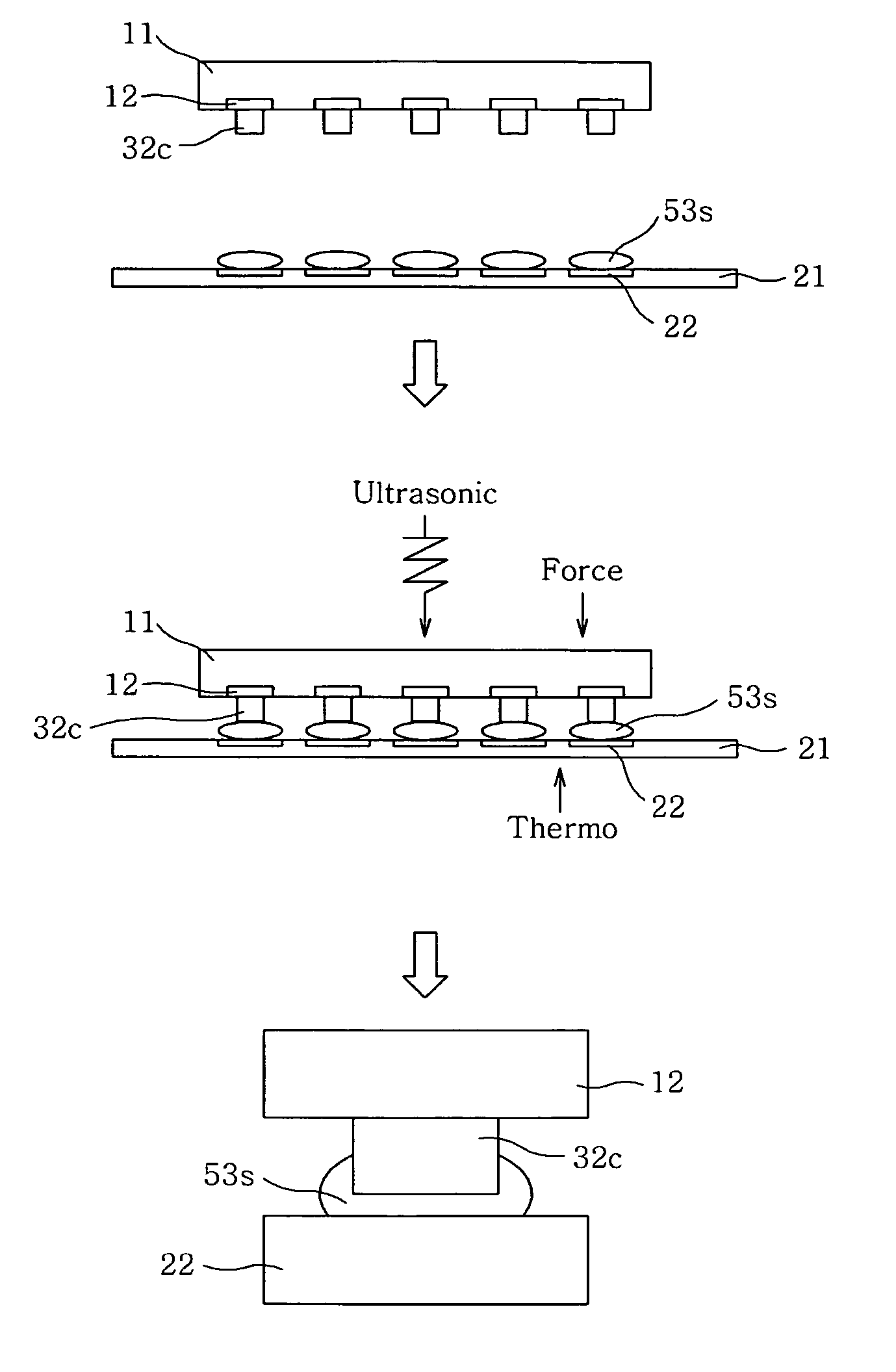
A flip chip bonding method and substrate architecture are disclosed for enhancing bonding performance between a chip and a substrate by forming a bump on the chip or the substrate. The flip chip bonding method includes performing pretreatment of a wafer having chips, dicing, and obtaining the pretreated individual chip; performing pretreatment of a substrate; aligning the pads of the pretreated chip with the pads of the pretreated substrate, and bonding the chip and the substrate together by applying an ultrasonic wave and heat using a collet and simultaneously applying pressure. Post treatment is performed by filling or molding resin after bonding. The chip or the substrate is formed with a plated bump, a stud bump or a wedge bump. The stud bump or the wedge bump can be additionally formed on the plated bump.
Owner:KOO JA UK +1
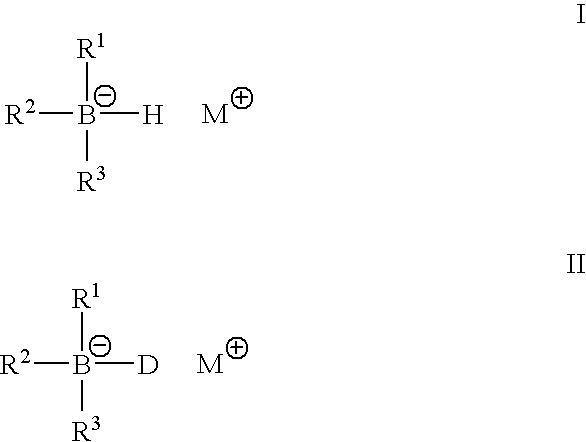
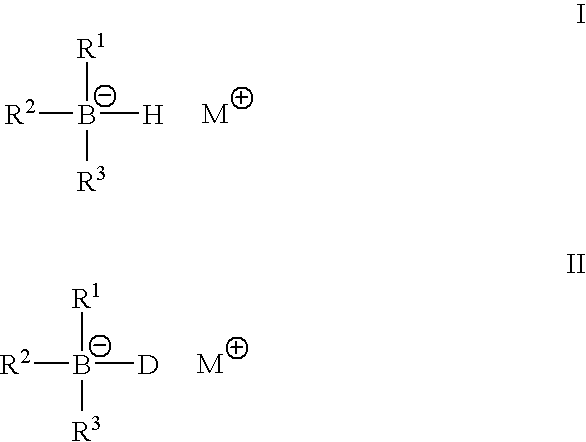
Metal alkyl borphydride polymerisation initiators, polymerisable compositions, and uses thereof
InactiveUS6844080B2Wide rangeImprove impact resistanceSynthetic resin layered productsOrganic non-macromolecular adhesiveLithiumPolyolefin
Metal alkyl borohydrides are used as initiators of polymerisation, particularly in adhesive compositions for bonding a wide range of substrates including low surface energy substrates such as polyolefins. As described, the metal alkyl borohydrides are of the formula I or II. whereinR1 is C1-C10 alkyl,R2 and R3, which may be the same or different, are H, D, C1-C10 alkyl or C3-C10 cycloalkyl, phenyl, or phenyl-substituted C1-C10 alkyl or C3-C10 cycloalkyl, provided that any two of R1-R3 may optionally be part of a carbocyclic ring, andM+ is a metal ion.In particular, alkali metal trialkyl borohydrides are used, the alkali metal salt being selected from: Lithium triethylborohydride, Sodium triethylborohydride, Potassium triethylborohydride, Lithium tri-sec-butylborohydride, Sodium tri-sec-butylborohydride, Potassium tri-sec-butylborohydride, and Lithium triethylborodeuteride. Other exemplified compounds which are less effective on low surface energy substrates include Lithium 9-borabicyclo [3.3.1]-nonane (9BBN) hydride, Lithium thexylborohydride, Lithium trisiamylborohydride and Potassium trisiamylborohydride.
Owner:HENKEL IP & HOLDING GMBH
Sound-permeable film, electronic component with sound-permeable film, and method of producing circuit board having electronic component mounted thereon
ActiveUS8141678B2Improve heat resistanceHigh levelPrinted circuit assemblingLamination ancillary operationsForeign matterPorous membrane
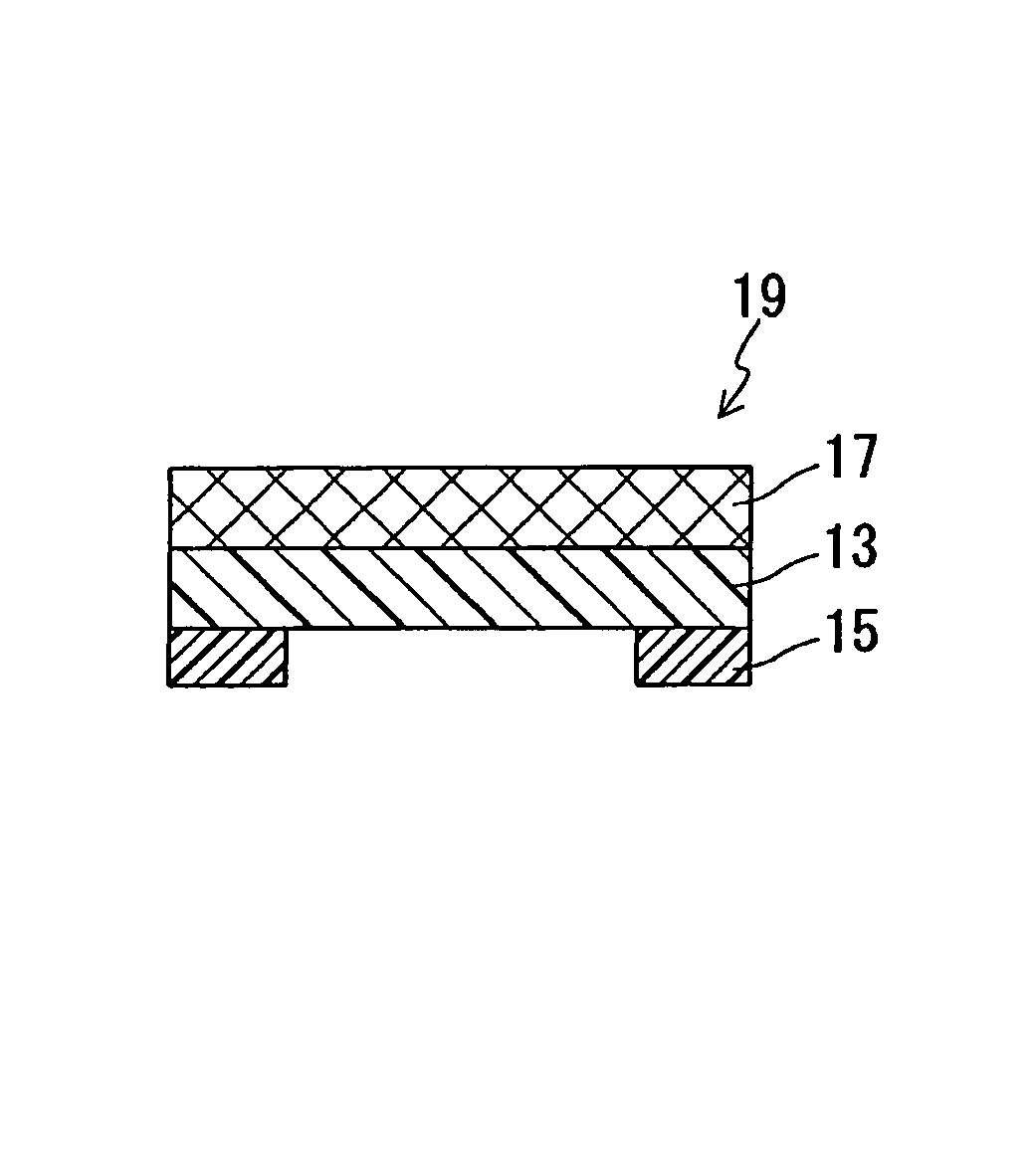
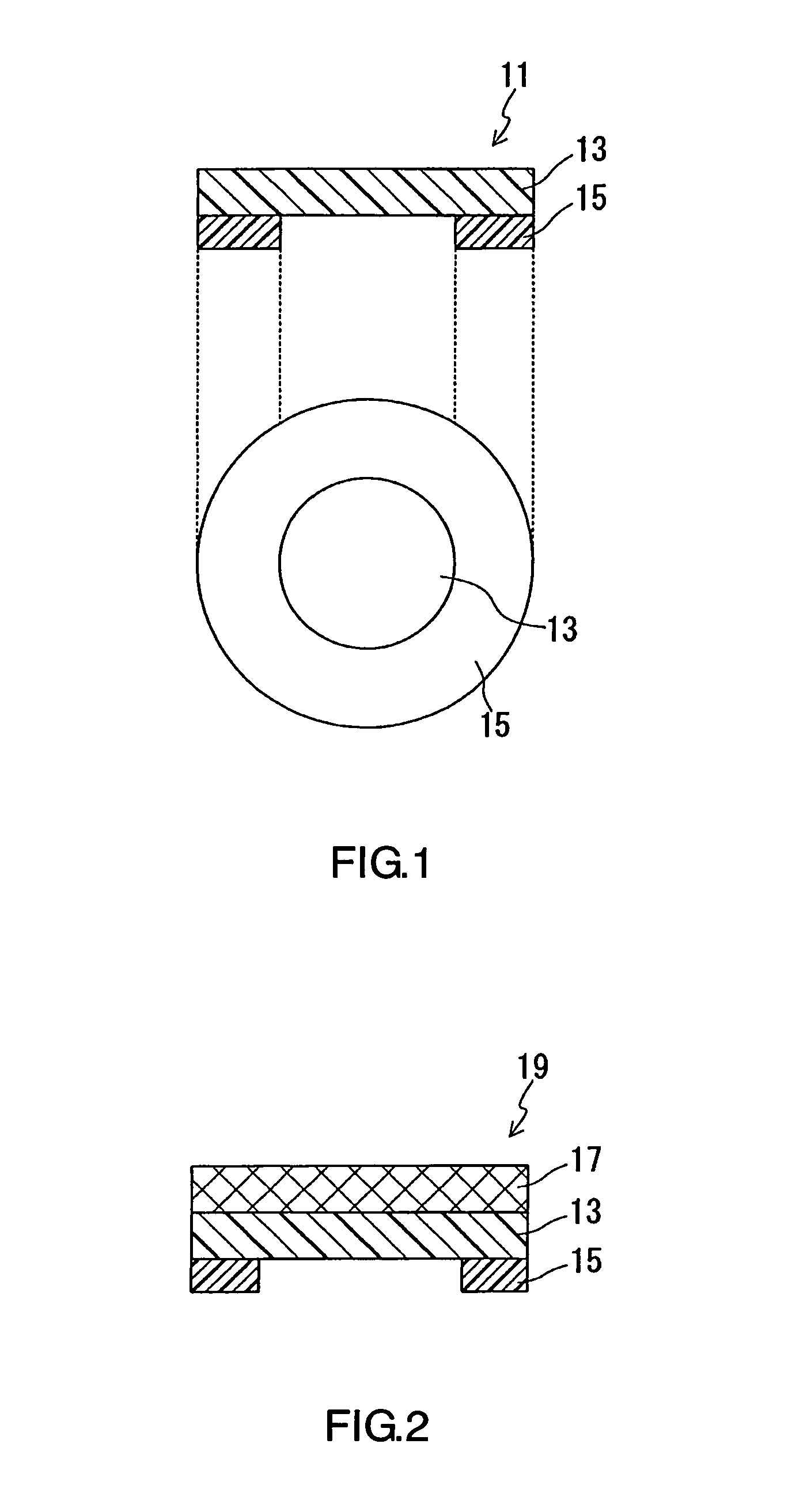
A sound-permeable film (11) includes: a porous membrane (13) that contains polytetrafluoroethylene as its main component, allows sound to pass therethrough, and prevents an foreign object such as a water drop from passing therethrough; and a heat-resistant double-sided adhesive sheet (15) that is disposed on a part of at least one of main surfaces of the porous membrane (13).
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Light-emitting diode structure, transfer assembly, and transfer method using the same
ActiveUS20180204973A1Easy transferMaintain bond strengthSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesSpiteEngineering
The present invention is intended to provide a light-emitting diode (LED) structure which can be easily transferred onto another substrate, a transfer assembly whose adhesive strength with LED structures can be maintained in spite of repetitive transfer processes, LED structures and a transfer assembly for selectively transferring the LED structures, and a transfer method using the same.
Owner:KOREA PHOTONICS TECH INST
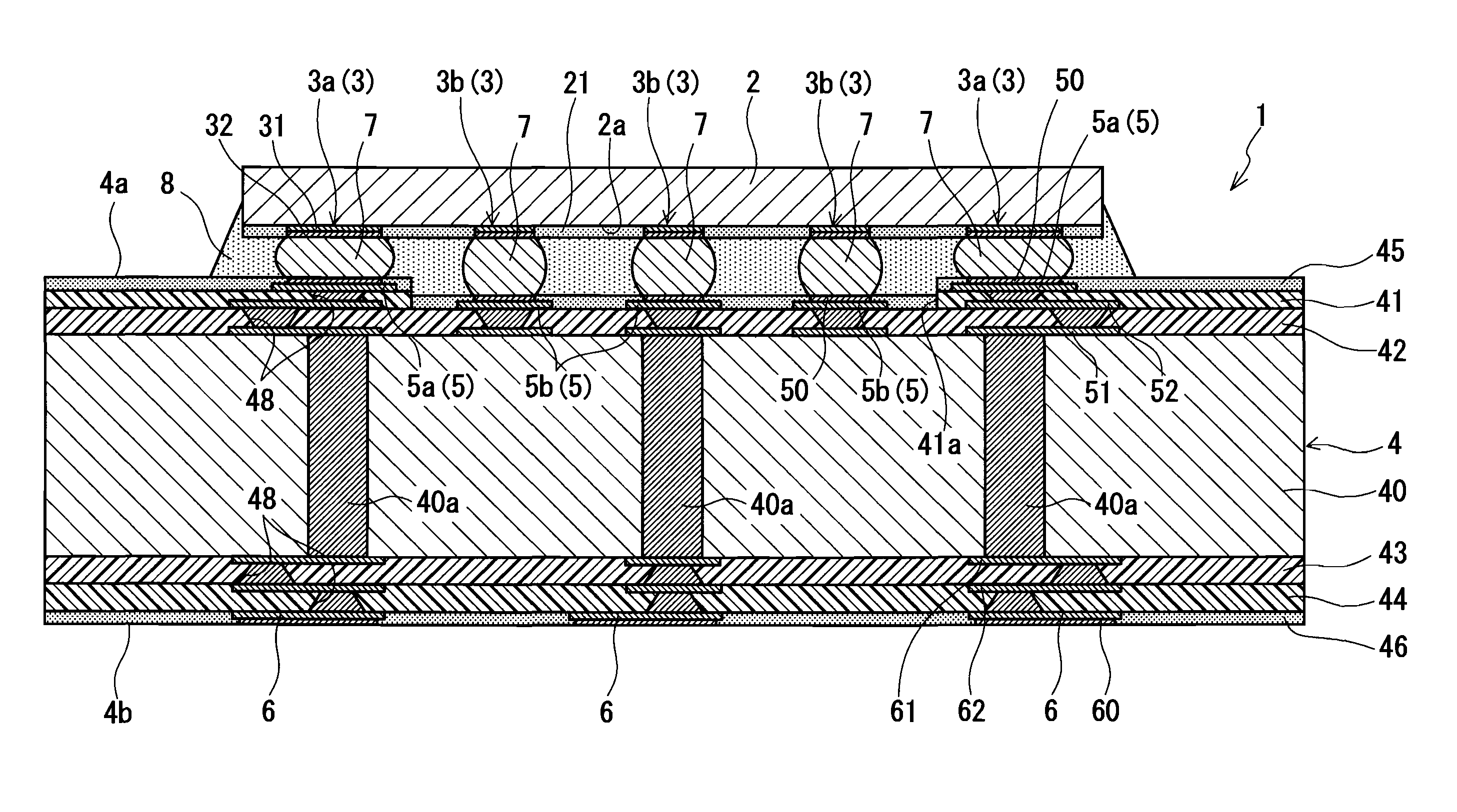
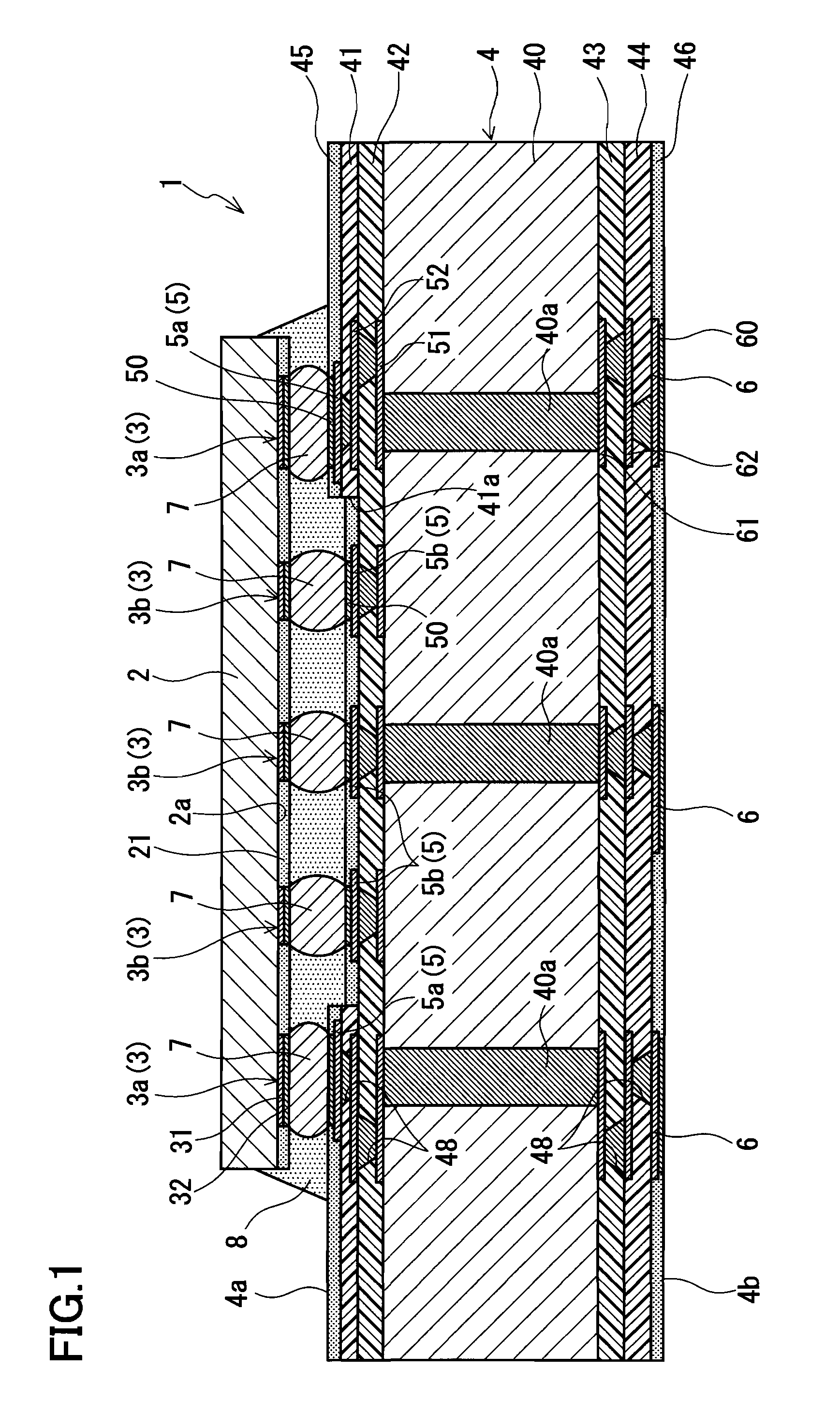
Semiconductor device, and method of manufacturing multilayer wiring board and semiconductor device
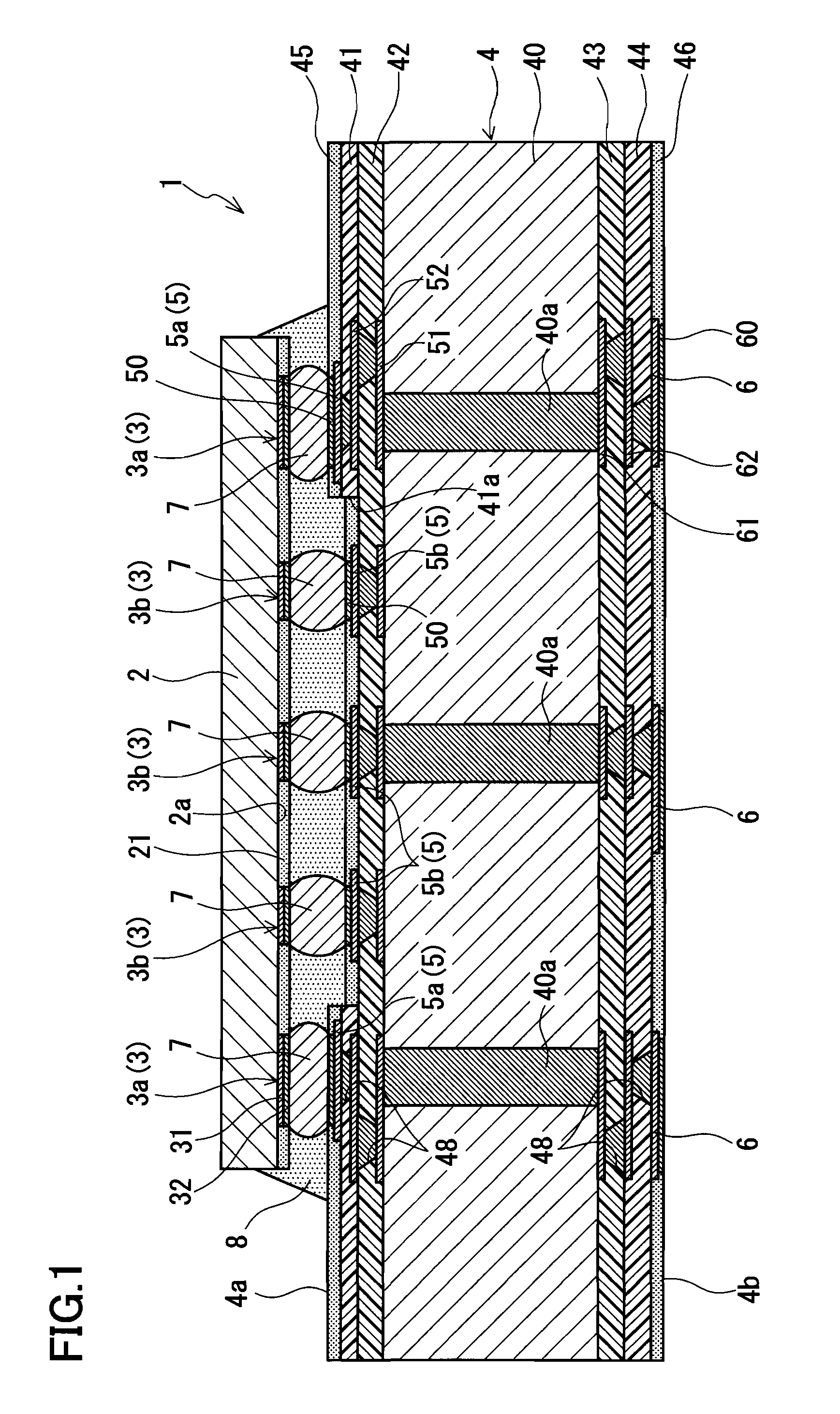
ActiveUS20100140800A1Avoid crackingReducing stress appliedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuits stress/warp reductionSemiconductor chipEngineering
A semiconductor device includes a multilayer wiring board and a semiconductor chip mounted on the multilayer wiring board. Electrode pads of the semiconductor chip include: first electrode pads including electrode pads respectively disposed in the vicinity of corners of the back surface of the semiconductor chip; and second electrode pads other than the first electrode pads. Connection pads of the multilayer wiring board include: first connection pads connected to the first electrode pads via bumps; and second connection pads connected to the second electrode pads via bumps. The first connection pads are supported by a first insulating region made of a thermoplastic resin, and the second connection pads are supported by a second insulating region made of a thermosetting resin.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
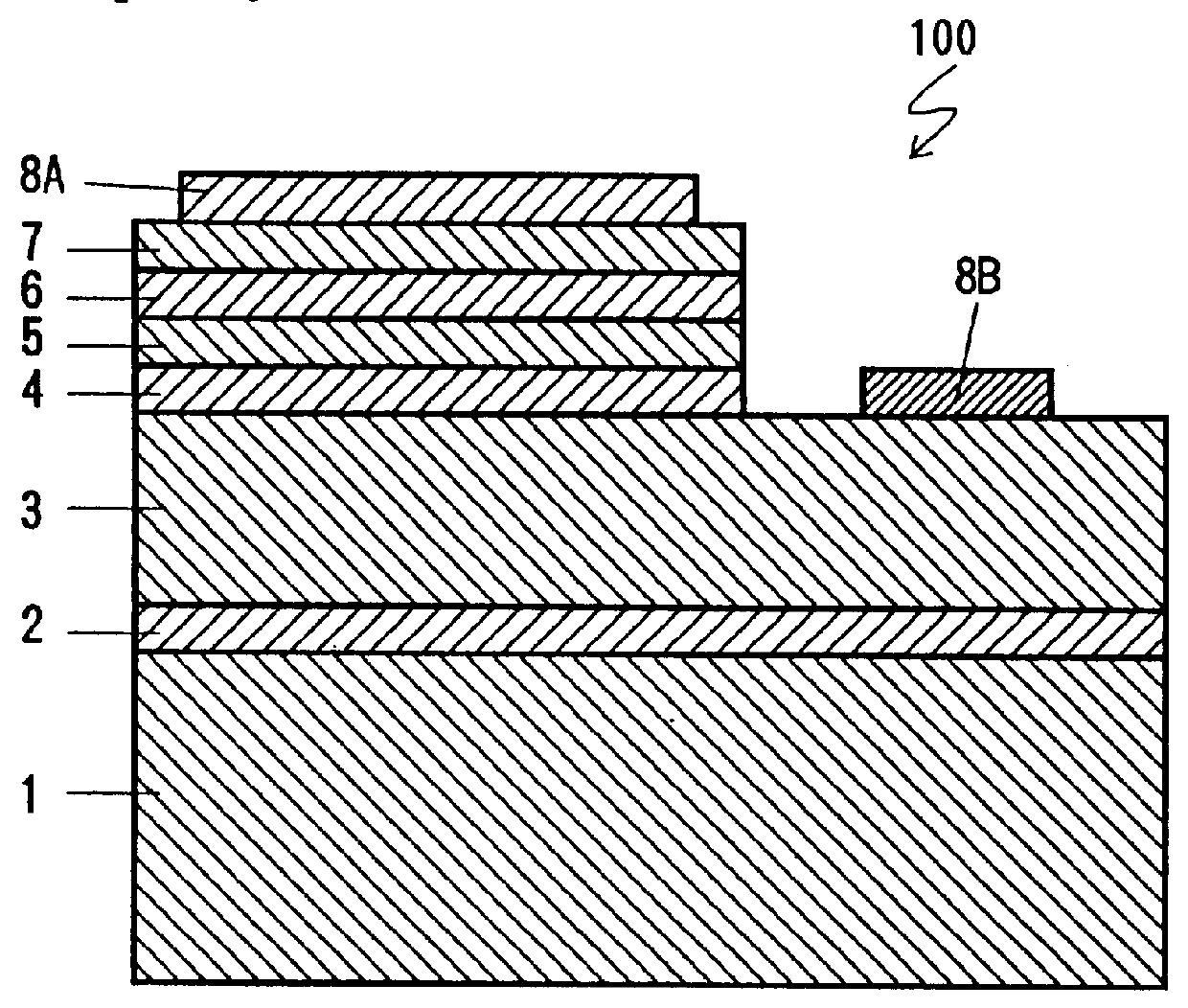
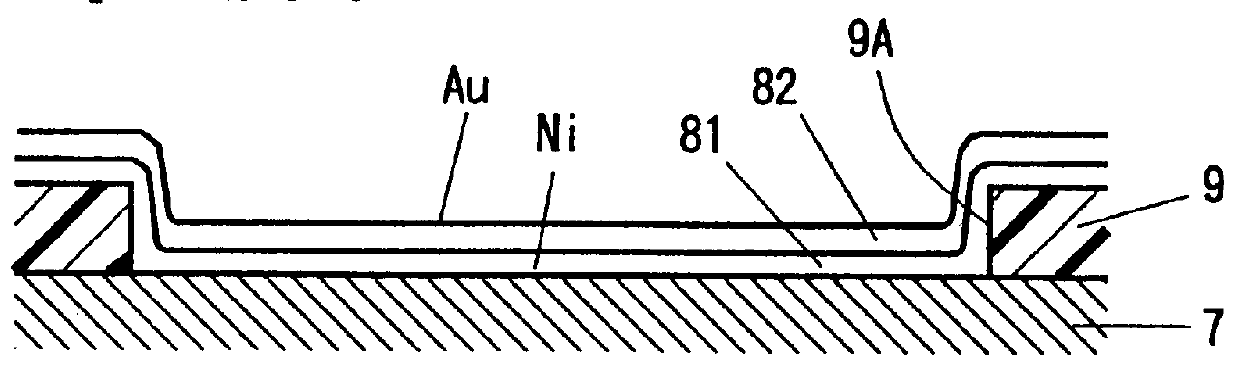
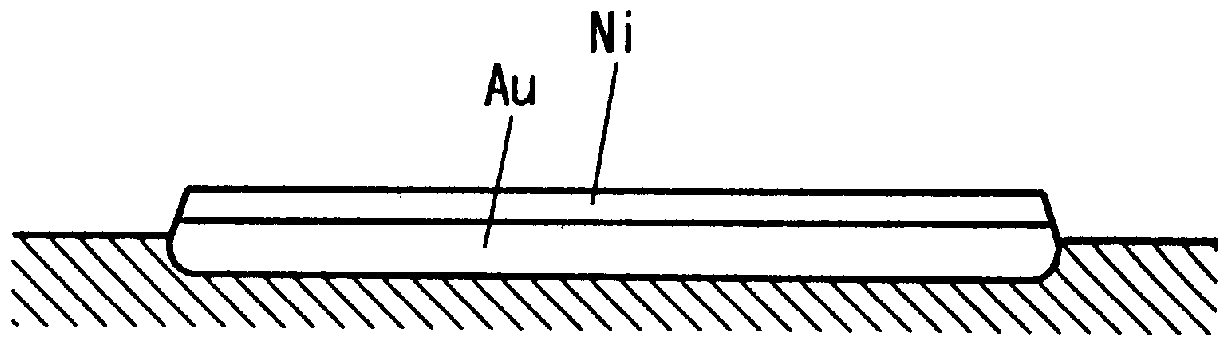
Methods and devices related to electrodes for p-type group III nitride compound semiconductors
InactiveUS6121127AHigh bonding strengthHigh ionization potentialSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCompound (substance)Metal electrodes
An electrode for a Group III nitride compound semiconductor having p-type conduction that has a double layer structure. The first metal electrode layer comprising, for example, nickel (Ni) and the second metal electrode layer comprising, for example, gold (Au). The Ni layer is formed on the Group III nitride compound semiconductor having p-type conduction, and the Au layer is formed on the Ni layer. Heat treatment changes or reverses the distribution of the elements Ni and Au. Namely, Au is distributed deeper into the Group III nitride compound semiconductor than is Ni. As a result, the resistivity of the electrode is lowered and its ohmic characteristics are improved as well as its adhesive strength.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Sound-Permeable Film, Electronic Component with Sound-Permeable Film, and Method of Producing Circuit Board Having Electronic Component Mounted Thereon
ActiveUS20090268928A1Improve heat resistanceReduce in quantityPrinted circuit assemblingLoudspeaker screensForeign matterPorous membrane
A sound-permeable film (11) includes: a porous membrane (13) that contains polytetrafluoroethylene as its main component, allows sound to pass therethrough, and prevents an foreign object such as a water drop from passing therethrough; and a heat-resistant double-sided adhesive sheet (16) that is disposed on a part of at least one of main surfaces of the porous membrane (13).
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Flip chip bonding method for enhancing adhesion force in flip chip packaging process and metal layer-built structure of substrate for the same
InactiveUS20050110163A1Improve reliabilityIncrease productivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectroplatingCollet
A flip chip bonding method and substrate architecture are disclosed for enhancing bonding performance between a chip and a substrate by forming a bump on the chip or the substrate. The flip chip bonding method includes performing pretreatment of a wafer having chips, dicing, and obtaining the pretreated individual chip; performing pretreatment of a substrate; aligning the pads of the pretreated chip with the pads of the pretreated substrate, and bonding the chip and the substrate together by applying an ultrasonic wave and heat using a collet and simultaneously applying pressure. Post treatment is performed by filling or molding resin after bonding. The chip or the substrate is formed with a plated bump, a stud bump or a wedge bump. The stud bump or the wedge bump can be additionally formed on the plated bump.
Owner:KOO JA UK +1
Semiconductor device, and method of manufacturing multilayer wiring board and semiconductor device
ActiveUS8324740B2Maintain bond strengthAvoid crackingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipEngineering
A semiconductor device includes a multilayer wiring board and a semiconductor chip mounted on the multilayer wiring board. Electrode pads of the semiconductor chip include: first electrode pads including electrode pads respectively disposed in the vicinity of corners of the back surface of the semiconductor chip; and second electrode pads other than the first electrode pads. Connection pads of the multilayer wiring board include: first connection pads connected to the first electrode pads via bumps; and second connection pads connected to the second electrode pads via bumps. The first connection pads are supported by a first insulating region made of a thermoplastic resin, and the second connection pads are supported by a second insulating region made of a thermosetting resin.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for improving bonding of circuit substrates to metal and articles formed thereby
InactiveUS20050208278A1Improve adhesionHigh bonding strengthInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementAdhesive processes with surface pretreatmentElastomerCopper foil
A method of forming a circuit material comprises disposing an adhesion promoting elastomer composition between a conductive copper foil and a thermosetting composition; and laminating the copper foil, adhesion promoting composition, and thermosetting composition to form the circuit material. The adhesion promoting layer may be uncured or partially cured before contacting with the curable thermosetting composition. Preferably the adhesion promoting layer has electrical characteristics such as dissipation factor, dielectric breakdown strength, water absorption, and dielectric constant that are similar to and / or compatible with the electrical characteristics of the thermosetting composition.
Owner:WORLD PROPERTIES
Thermoplastic polymer composition and molded article
ActiveUS20130157069A1Excellent in flexibility , mechanical property and moldabilityMaintain adhesive strengthFilm/foil adhesivesSynthetic resin layered productsPolypropyleneCeramic
A thermoplastic polymer composition which is excellent in flexibility, mechanical properties, moldability, and particularly in heat resistance and is capable of adhering to ceramics, metals, and synthetic resins even at low temperature (for example, 190° C. or lower) without the treatment with a primer, and a molded product produced by using the thermoplastic polymer composition are described. The thermoplastic polymer composition includes 100 parts by mass of a thermoplastic elastomer (A), 1 to 100 parts by mass of a polyvinyl acetal resin (B), and 5 to 100 parts by mass of a polar group-containing polypropylene resin (C). The thermoplastic elastomer (A) is a block copolymer which is constituted by a polymer block including aromatic vinyl compound units and a polymer block including isoprene units, butadiene units, or isoprene / butadiene units wherein the total of a content of 1,2-bonding and a content of 3,4-bonding is 40 mol % or more, or the thermoplastic elastomer (A) is a hydrogenated product of the block copolymer.
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
Optical device, method of manufacturing the same, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20110169118A1Reduce yieldCharacteristic is impairedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMiniaturizationEngineering
The present invention is has an object of providing an optical device miniaturized while maintaining bonding strength between a semiconductor substrate and a light-transmissive plate, reducing possibility of warpage, and maintaining yields and design flexibility, a method of manufacturing the optical device, and an electronic apparatus. The optical device according to the present invention includes a semiconductor substrate having one surface in which a light-receiving element is formed; and a light-transmissive plate provided above the semiconductor substrate so as to cover the light-receiving element. The semiconductor substrate and the light-transmissive plate are partially bonded above a light-receiving unit of the semiconductor substrate. The light-receiving element is formed in the light-receiving unit.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Initiator systems, polymerisable compositions, and uses thereof for bonding low surface energy substrates
InactiveUS6939932B2Reduction and elimination of yellowingEasy to prepareFireproof paintsAntifouling/underwater paintsSurface energyChemistry
Use of an initiator system comprising:a combination of an organoborane and a polyaziridine, in a ratio ofaziridine groups to boron atoms of greater than 1.3:1,as an initiator of polymerisation in an adhesive composition for bonding a low surface energy substrate;provided that the initiator system does not contain more than a trace amount of a complex of organoborane with a complexing agent selected from:an amine other than a polyaziridine;a complexing agent comprising at least one hydroxide;a complexing agent comprising at least one alkoxide; oramidine complexing agent.An initiator system as described is of the formula VI: wherein R1 is C1-C10 alkyl,R2 and R3, which may be the same or different, are, C1-C10 alkyl or C3-C10 cycloalkyl, phenyl, or phenyl-substituted C1-C10 alkyl or C3-C10 cycloalkyl, provided that any two of R1-R3 may optionally be part of a carbocyclic ring;R5 is a polyvalent radical,R6 and R7 which may be the same or different are H or C1-C10 alkyl, particularly C1-4 alkyl, especially methyl, andy is a number of at least 2, particularly 2-4, especially 3, and the value of x multiplied by y is greater than 1.3.Particular examples of initiator compounds include, trimethylol propane tris(3-(2-methyl aziridino))propionate and trimethylol propane tris-3-N-aziridinyl propionate.
Owner:LOCTITE (R&D) LIMITED
Electroconductive Paste and Substrate Using the Same for Mounting Electronic Parts
InactiveUS20080261049A1Improve conductivityIncrease resistanceSynthetic resin layered productsConductive materialEpoxyConductive paste
The conductive paste of the invention comprises a conductive powder and a binder component, wherein the conductive powder is composed of metal powder which is copper powder or copper alloy powder partially covered on the surface with silver, and is either a mixture of roughly spherical metal powder and flat metal powder, or roughly spherical or flat metal powder alone, and wherein the binder component contains a mixture of an epoxy resin and an imidazole compound with a hydroxyl group or a mixture of an epoxy resin and an imidazole compound with a carboxyl group.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
Thin film transistor substrate, method of manufacturing the same, and liquid crystal display panel having the same
ActiveUS20080074572A1Maintain bond strengthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid-crystal displayPellicle membrane
This invention relates to a thin film transistor substrate, a method of manufacturing the same, and a liquid crystal display panel including the same. The thin film transistor substrate includes a substrate, gate lines disposed on the substrate and extending in one direction, common voltage lines disposed on the substrate and spaced apart from the gate lines, and a gate insulating film disposed on the gate lines and the common voltage lines, the gate insulating film having first contact holes exposing a part of each common voltage line. Common electrodes are disposed on the gate insulating film and are connected to the common voltage lines through the first contact holes. Data lines are disposed on the gate insulating film and extend in a direction crossing the gate lines and thin film transistors are disposed at crossings of the gate lines and the data lines. The thin film transistors are connected to the gate lines and the data lines and include source electrodes and drain electrodes. Pixel electrodes are connected to the thin film transistors.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Liquid crystal panel seal barrier and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7724341B2Maintain bond strengthImprove display qualityNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
Owner:SHARP KK
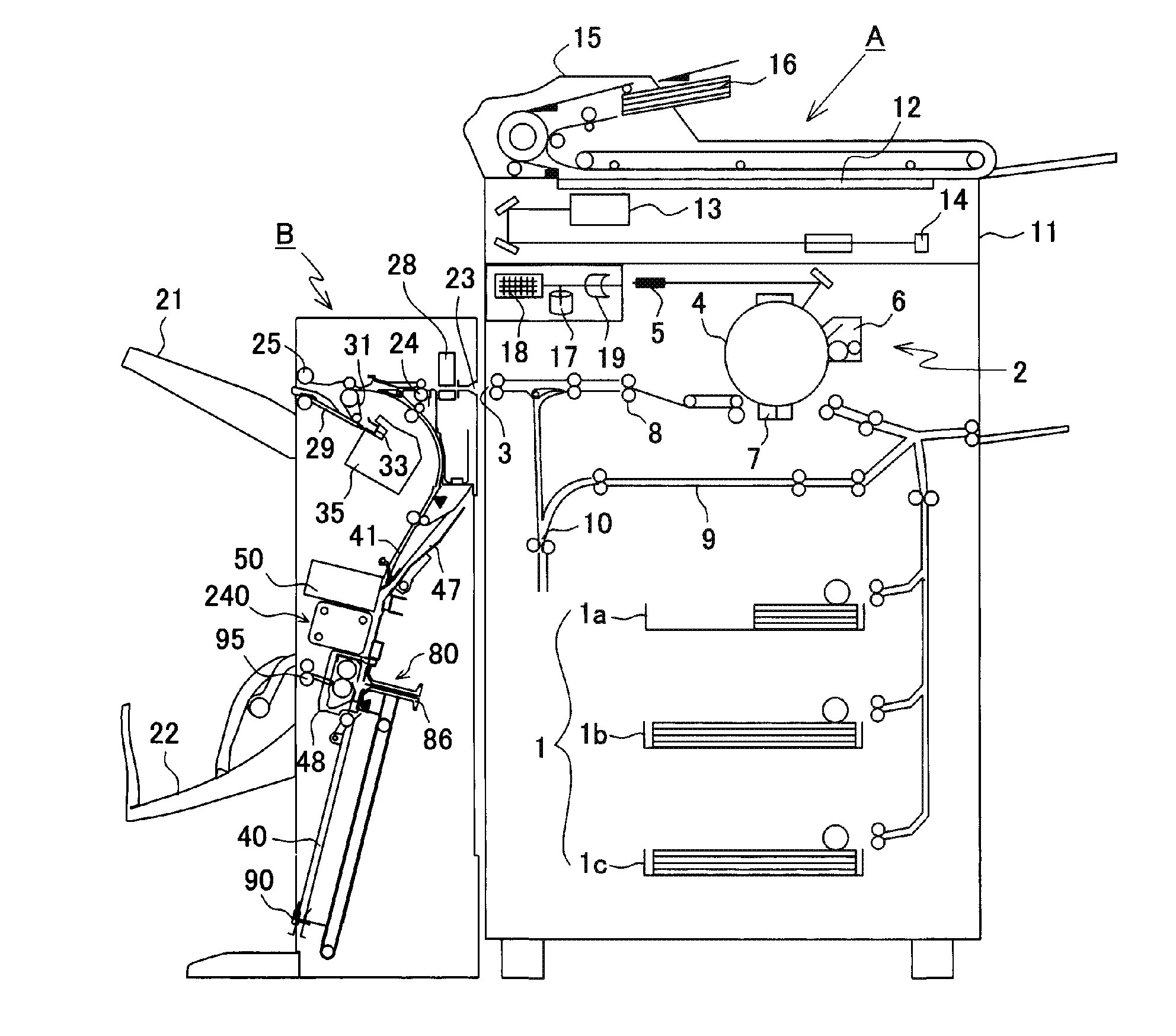
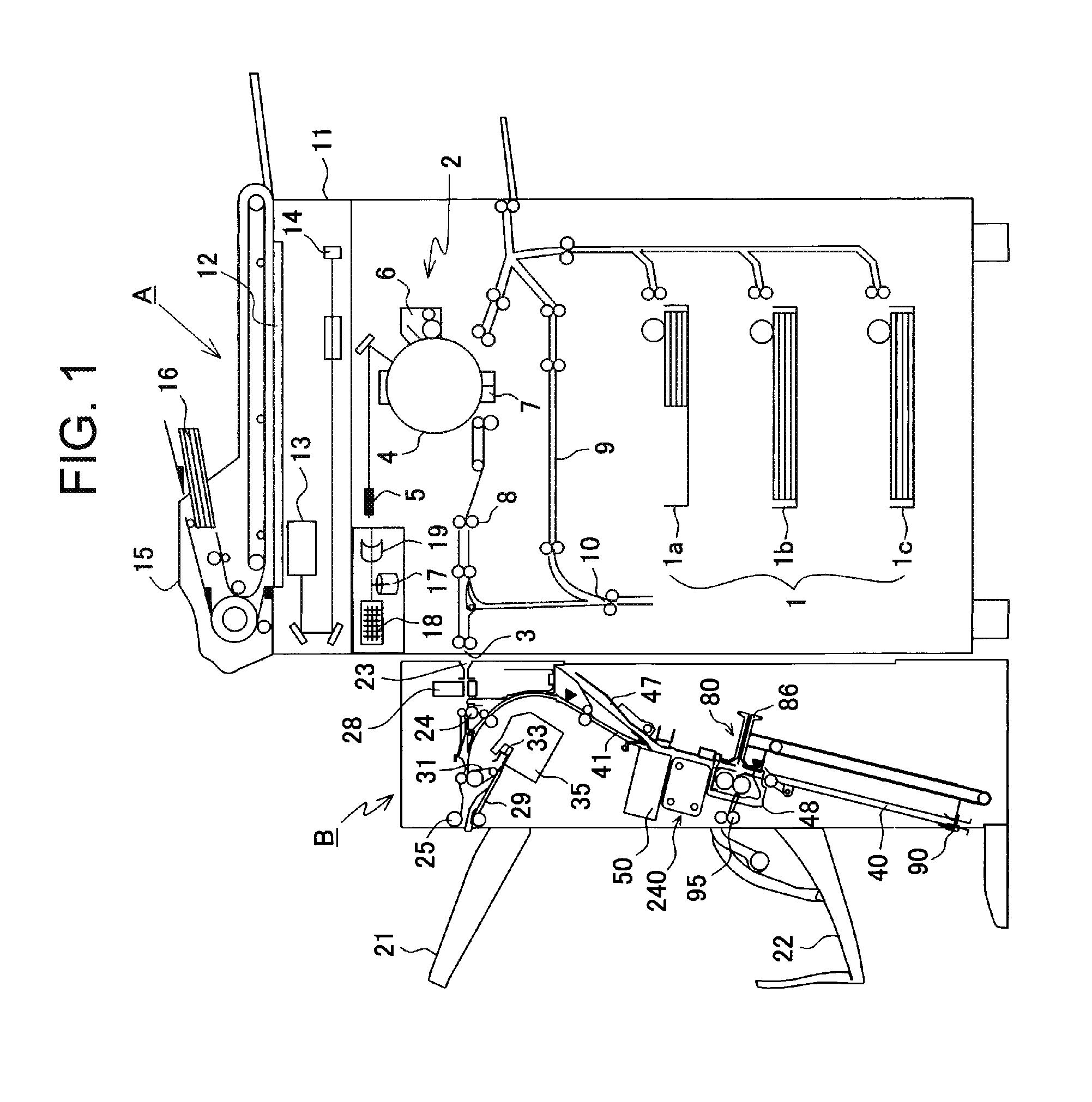
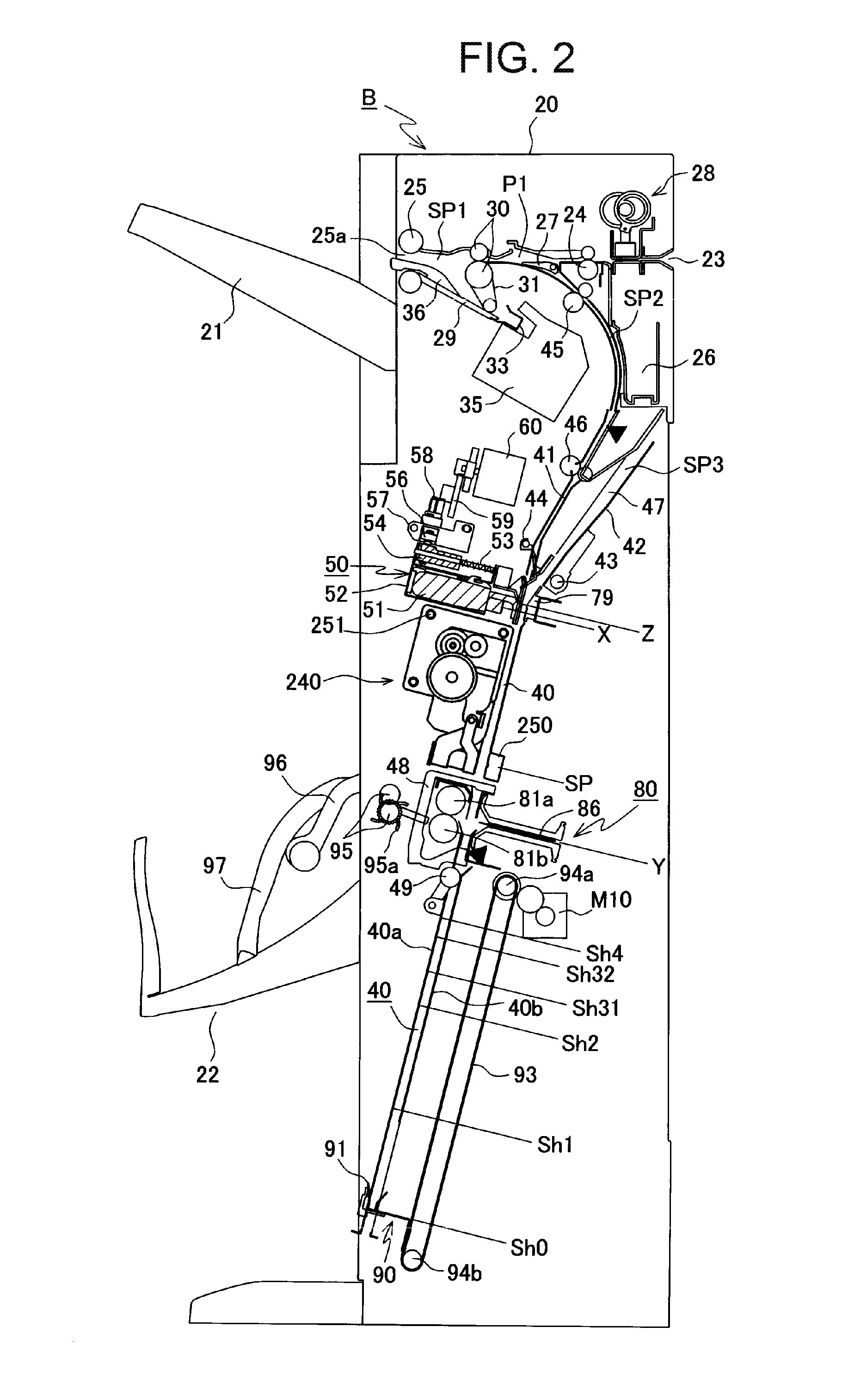
Sheet processing device and image forming device provided with the same
ActiveUS20160313687A1Reduce speedImprove productivityBookletsFunction indicatorsStackerAdhesive bonding
A sheet processing device includes: an adhesive-binding unit that applies an adhesive onto sheets stored in a stacker section one by one and adhesive-binds the sheets; a staple-binding unit that staple-binds sheets accumulated in the stacker section by means of staples; and a folding mechanism section having a folding roller that folds the adhesive-bound or staple-bound sheet bundle in two at a binding position of the adhesive-binding unit or staple-binding unit and a folding blade that pushes the bound sheet bundle into the folding roller. A folding speed of the folding mechanism section for the sheet bundle bound by the adhesive-binding unit is lower than a folding speed for the sheet bundle bound by the staple-binding unit; thereby, productivity of the folding processing is improved and occurrence of the peeling-off or break during the folding processing is reduced.
Owner:COPYER
Heat-sensitive pressure-sensitive adhesive and heat-sensitive adhesive material
InactiveUS7993732B2High bonding strengthLess reduction in adhesive strengthFilm/foil adhesivesSynthetic resin layered productsVitrificationPropionate
A heat-sensitive pressure-sensitive adhesive which contains at least a thermoplastic resin and a thermofusible material, wherein the thermoplastic resin has a glass transition temperature of −70° C. to −30° C., and the thermofusible material comprises triphenylphosphine, and at least any one of tris(2,4-di-t-butylphenyl)phosphite and tetrakis[3-(3,5-di-t-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate]methane, or a heat-sensitive pressure-sensitive adhesive which contains at least a thermoplastic resin, a thermofusible material and a non-thermofusible material, wherein the thermofusible material contains triphenylphosphine.
Owner:RICOH KK
Plasticizer-resistant pressure-sensitive adhesive composition and adhesive article
InactiveUS7744998B2High initial bond strengthMaintain bond strengthLayered productsAmide/imide polymer adhesivesMeth-Plasticizer
There is provided a pressure-sensitive adhesive composition which has a high initial adhesive strength to an adherend containing a plasticizer and can maintain the adhesive strength even after long-term use. A plasticizer-resistant pressure-sensitive adhesive composition comprising a copolymer obtained by polymerizing a monomer mixture comprising (a) an aromatic-containing (meth)acrylate monomer, (b) a nitrogen-containing vinyl monomer, and (c) an alkyl(meth)acrylate monomer, an alkyl group of which has 4 to 14 carbon atoms.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Laminated ceramic electronic component and manufacturing method therefor
ActiveUS20110234045A1Prevented from being meltedMaintain bond strengthPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCeramic layered productsCopper platingMoisture resistance
In a method of forming a plating layer for an external terminal electrode by applying, for example, copper plating to an end surface of a component main body with respective ends of internal electrodes exposed, and then applying a heat treatment at a temperature of about 1000° C. or more in order to improve the adhesion strength and moisture resistance of the external terminal electrode, the plating layer may be partially melted to decrease the bonding strength of the plating layer. In the step of applying a heat treatment at a temperature of about 1000° C. or more to a component main body with plating layers formed thereon, the average rate of temperature increase from room temperature to the temperature of about 1000° C. or more is set to about 100° C. / minute or more. This average rate of temperature increase maintains a moderate eutectic state in the plating layer and ensures a sufficient bonding strength of the plating layer.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Motor
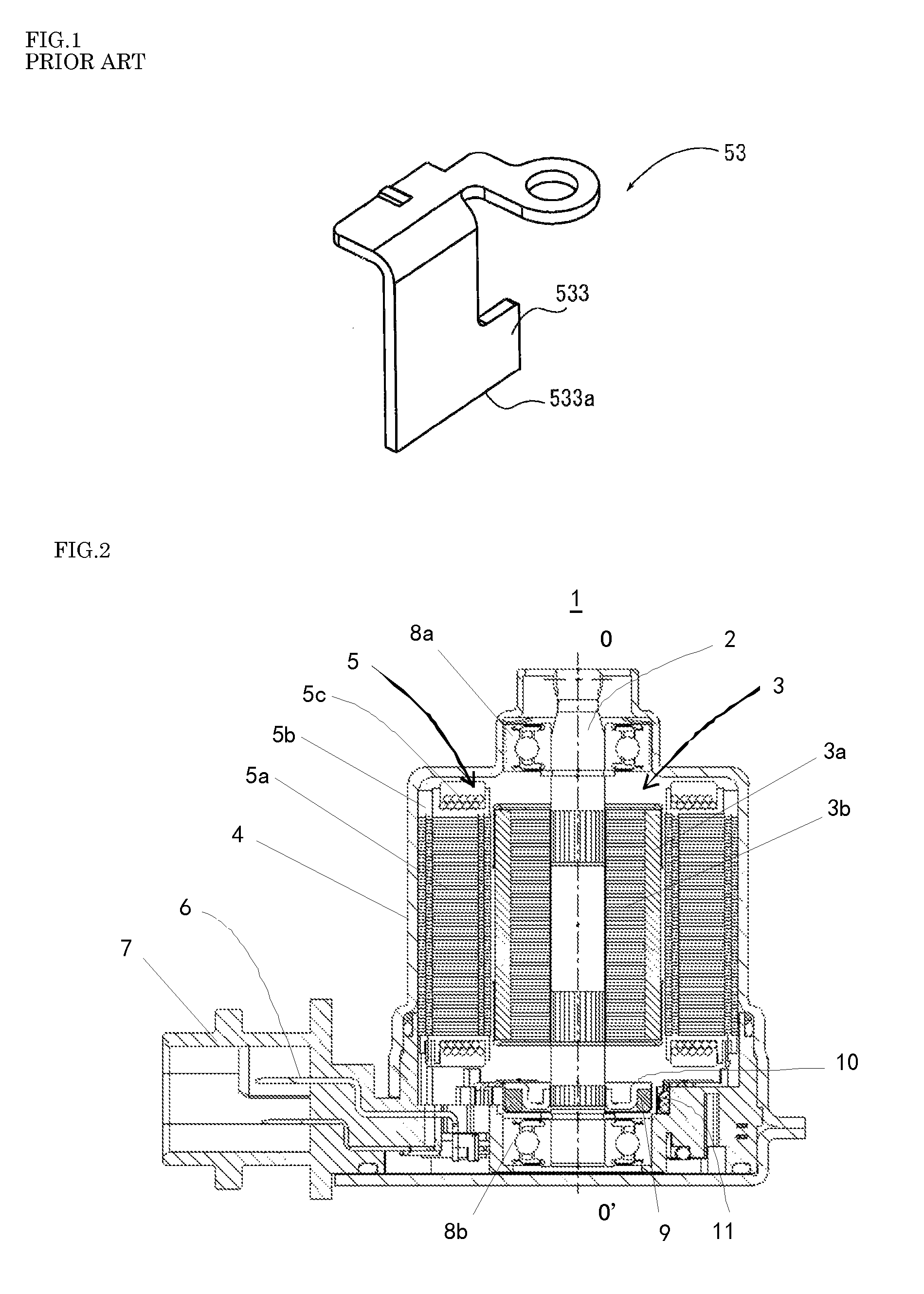
ActiveUS9509196B2Easy to transformAvoid disconnectionAssociation with control/drive circuitsWindingsEngineeringElectronic component
A motor includes a stator around which an armature coil is wound, a bus bar unit including a coil-connection bus bar electrically connected to the armature coil and an electronic-component-connection bus bar to which a plurality of electronic components is welded, and a bus bar holding member arranged to hold the bus bar unit. The electronic-component-connection bus bar includes an electronic component welding portion including a plurality of welding points at which the electronic components are welded to a leading end of the electronic component welding portion, a base portion held by the bus bar holding member, and a connection portion configured to interconnect the electronic component welding portion and the base portion. A distance between the welding points adjoining each other is larger than a width of a thinnest section of the connection portion.
Owner:NIDEC CORP
Solar cell module
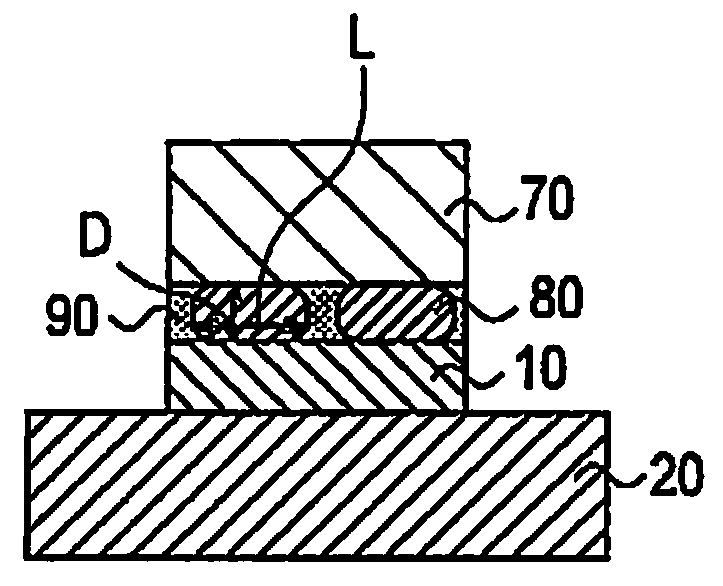
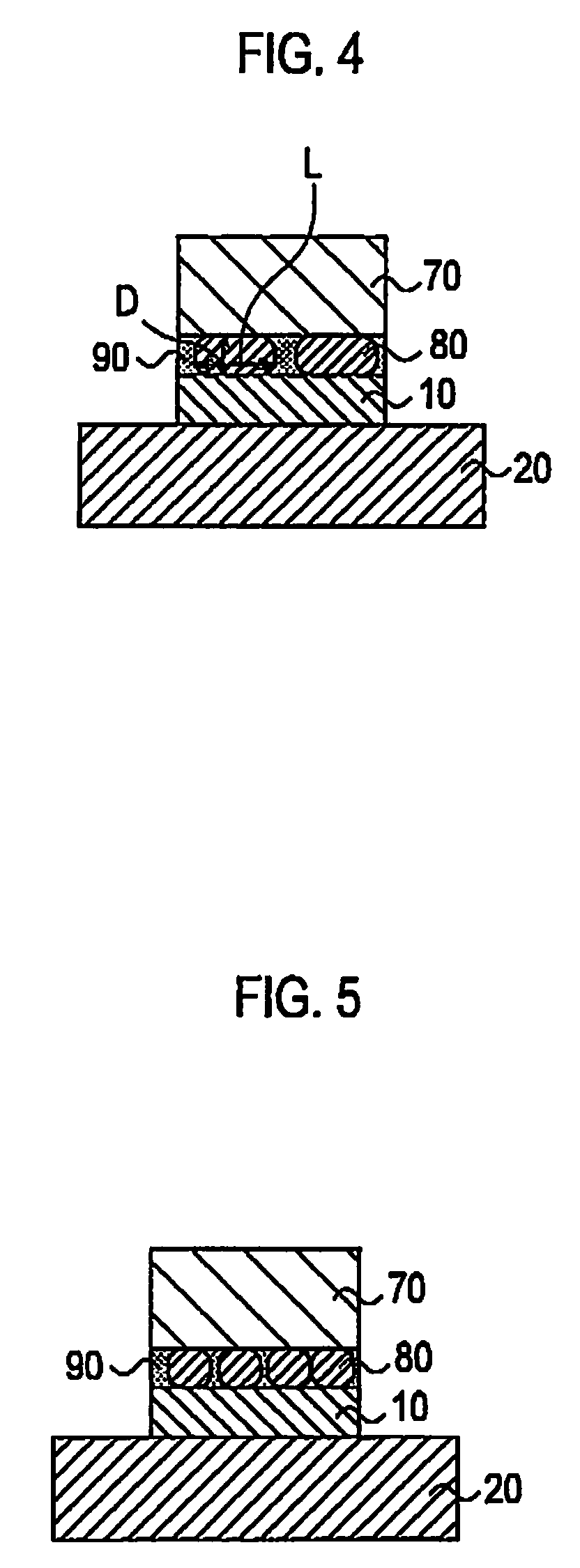
InactiveUS20090277492A1Suppresses reduction in module outputImprove reliabilityPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationSolar cellPlane parallel
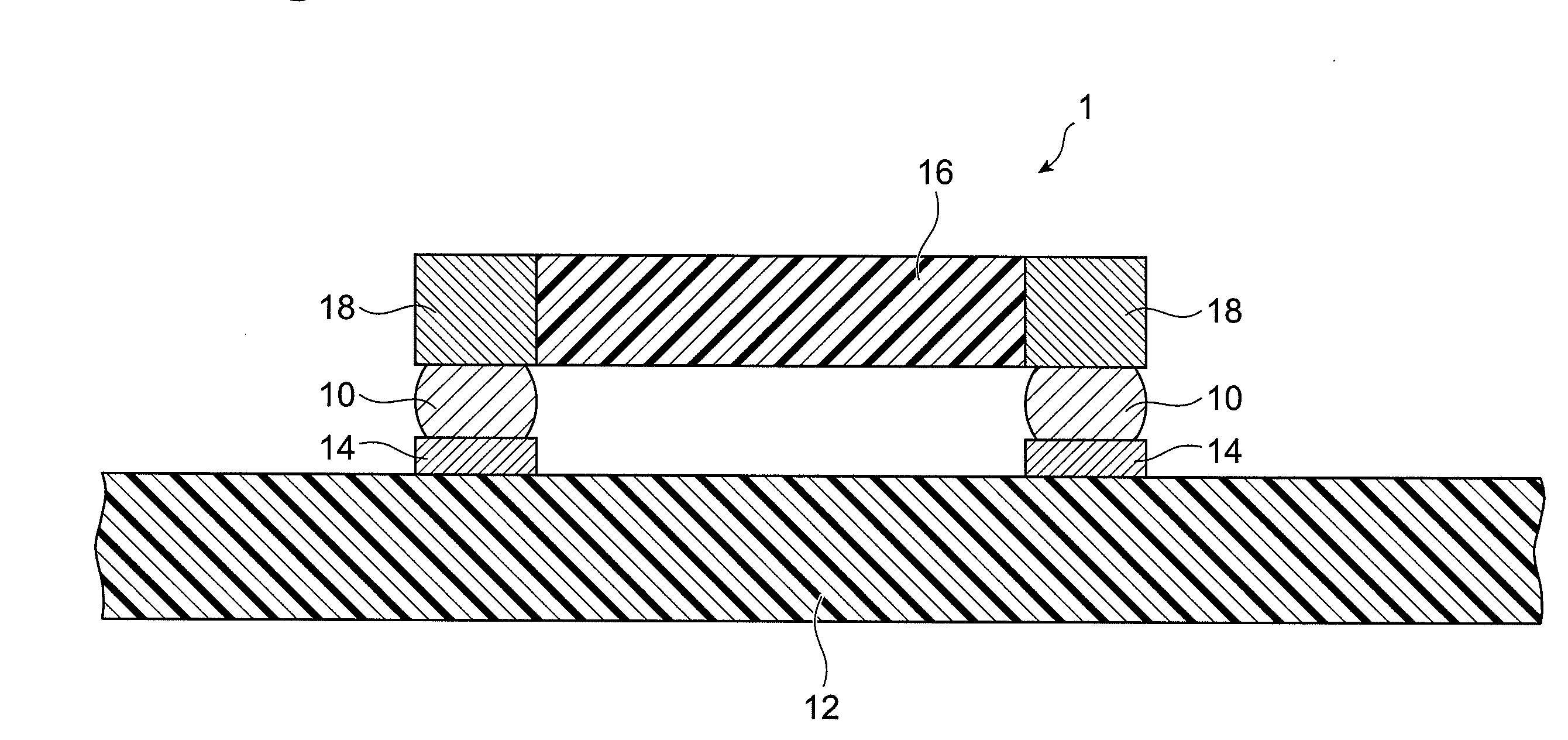
In a solar cell module, a plurality of solar cells are arranged between a front-surface protection member and a back-surface protection member, and electrodes of the plurality of solar cells is electrically connected to each other by a wring member. The solar cell module includes an adhesive layer including a resin 90 and a plurality of conductive particles 80, between the electrodes 10 and the wiring member 70. Each conductive particle 80 has a flattened shape that a maximum thickness D in a plane perpendicular to a solar cell 20 is smaller than a maximum length L in a plane parallel to the solar cell 20. Both ends of each conductive particle 80 in a thickness direction are respectively in contact with one of the electrodes 10 and the wiring member 70.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Primer resin for semiconductor device and semiconductor device
InactiveUS20100207282A1Improve heat resistanceLess shrinkage stressSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsAdhesive processes with surface pretreatmentEpoxyDevice material
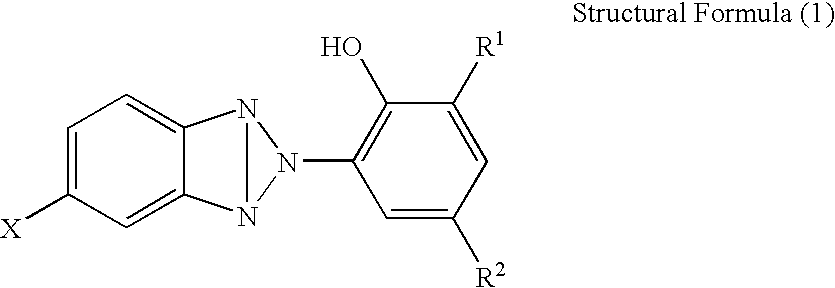
The present invention relates to a primer resin for semiconductor devices which comprises a polyamide resin represented by the following formula (1):(wherein, R1 represents a tetravalent aromatic tetracarboxylic acid residue selected from the group consisting of pyromellitic acid, 3,4,3′,4′-diphenyl ether tetracarboxylic acid, 2,3,6,7-naphthalenetetracarboxylic acid and 3,4,3′,4′-benzophenone tetracarboxylic acid, R2 represents at least one kind of divalent diamine residue selected from the group consisting of diamino-4,4′-hydroxydiphenylsulfone, 4,4′-diamino-3,3′5,5′-tetraethyldiphenylmethane and 1,3-bis-(aminophenoxy)benzene, and n is a repeating number and represents a positive number of 10 to 1000) and has a lead frame comprising copper or 42 alloy, a semiconductor device having said primer resin layer between a lead frame comprising copper or 42 alloy and a cured product of a sealing resin, and a semiconductor sealing epoxy resin composition containing said primer resin; and said semiconductor device has an extremely improved adhesiveness between said lead frame and a cured product of a sealing resin composition and also is excellent in heat resistance and low moisture absorption.
Owner:NIPPON KAYAKU CO LTD
Method for waterproofing substrate
InactiveUS20140050525A1Increased durabilityLow temperature flexibilityPaving reinforcementsIn situ pavingsRoad surfaceSynthetic resin
A method for waterproofing a substrate, the method including adhering an adhesive member obtained by using an active hydrogen-containing synthetic resin, to a urethane-based waterproof layer to laminate a pavement adhesive layer; applying or spraying an isocyanate group-containing compound onto the pavement adhesive layer; and paving an asphalt mixture on the surface of the pavement adhesive layer.
Owner:DYFLEX CORP
Conductive paste and method for producing a semiconductor device using the same
ActiveUS20160326044A1Improve heat resistanceMaintain bond strengthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIndiumTe element
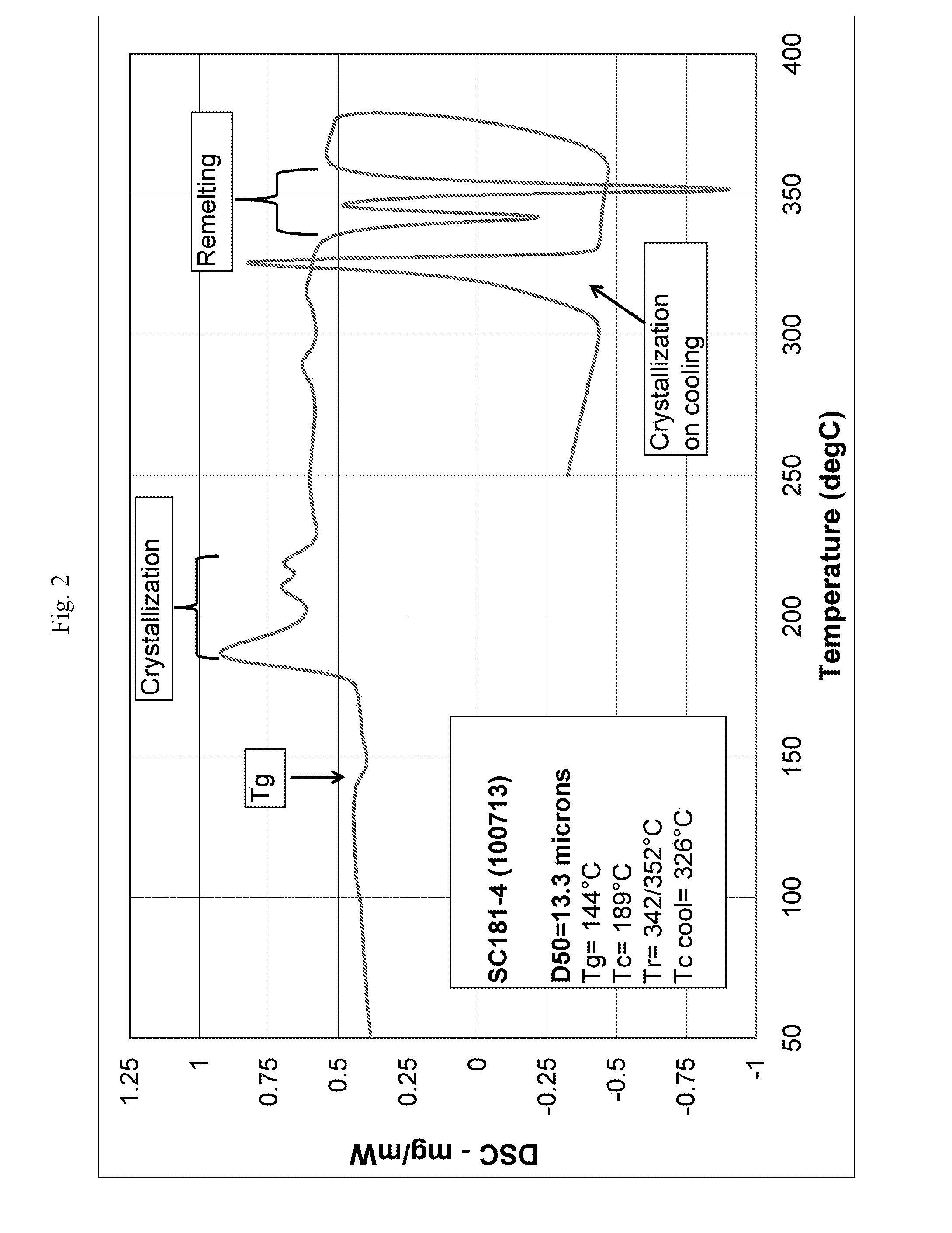
A conductive paste including (A) conductive particles, (B) a glass frit containing substantially no lead, arsenic, tellurium, and antimony, and (C) a solvent. The glass frit (B) has a remelting temperature of 320 to 360° C., wherein the remelting temperature is indicated by a peak top of at least one endothermic peak having an endotherm of 20 J / g or more in a DSC curve as measured by a differential scanning calorimeter. The conductive paste can also include at least one metal oxide (D) selected from the group consisting of tin oxide, zinc oxide, indium oxide, and copper oxide. The glass frit (B) can further include (B-1) Ag2O, (B-2) V2O5, and (B-3) MoO3. The conductive paste can achieve binding at a relatively low temperature (such as 370° C. or lower) and maintains a bond strength at a relatively high temperature (such as 300 to 360° C.).
Owner:NAMICS CORPORATION
Method for manufacturing image display device
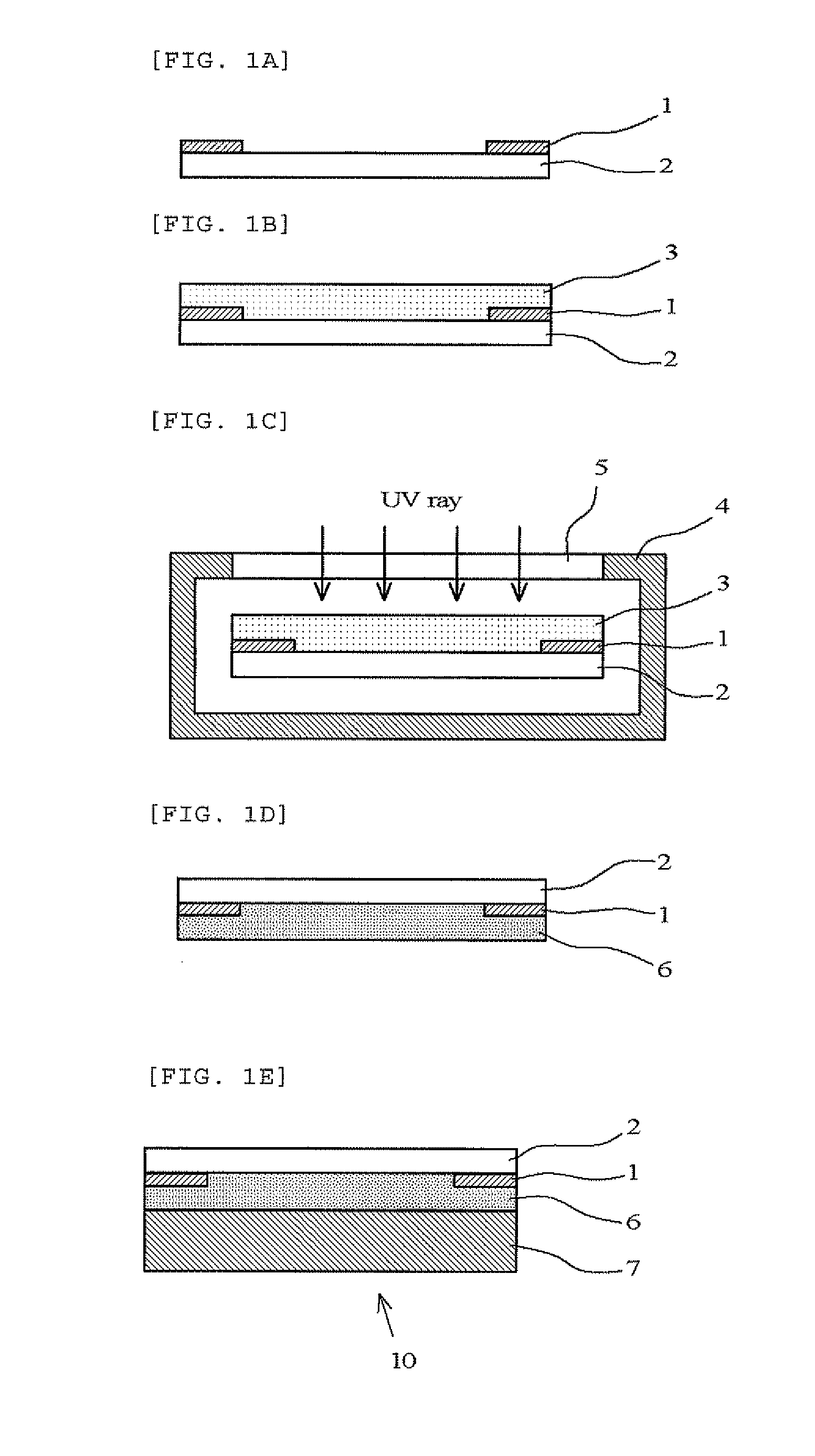
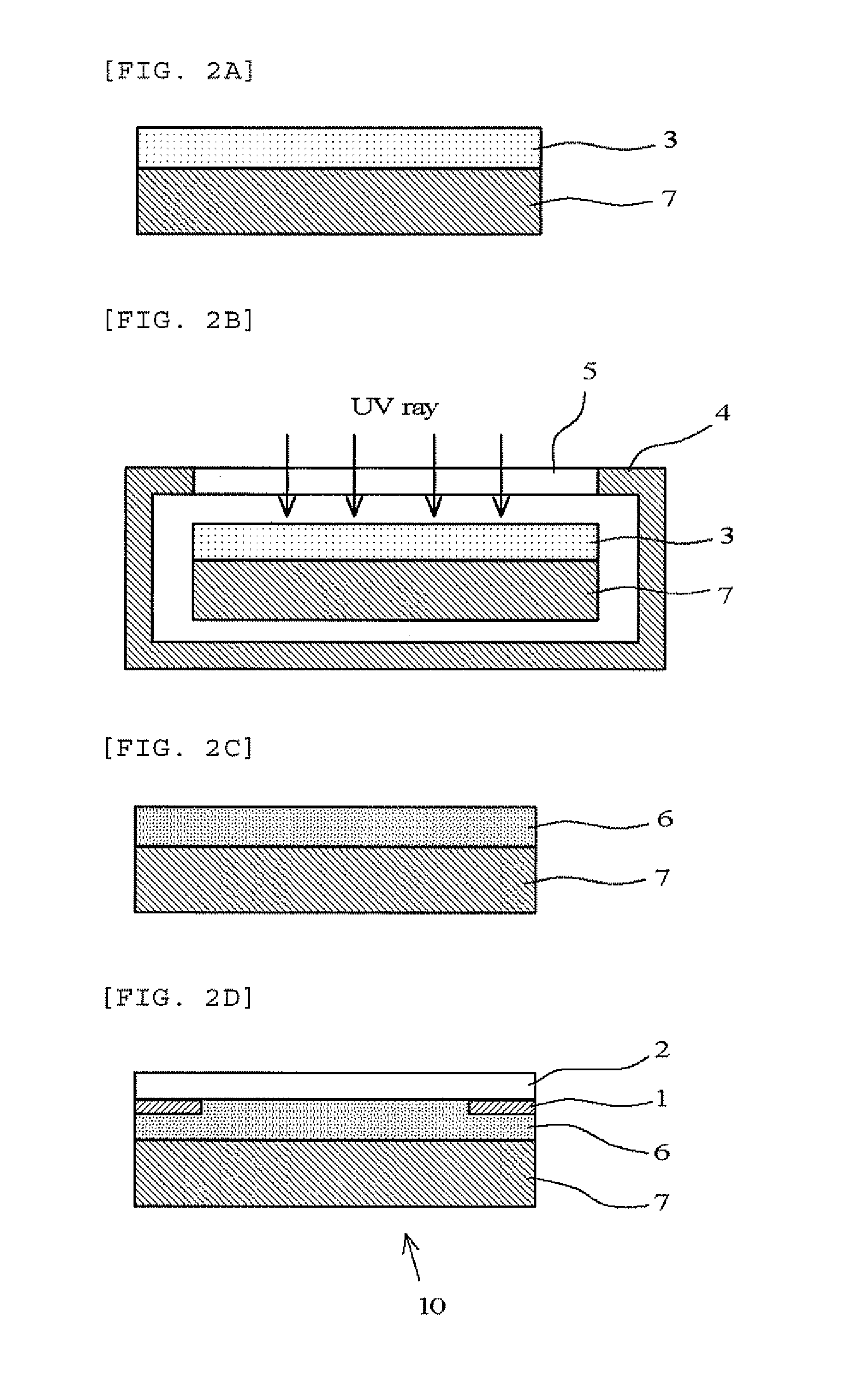
InactiveUS20140065744A1Maintain bond strengthExclude influenceElectroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUltravioletEngineering
A liquid photocurable resin composition not containing a thermal polymerization initiator is applied to a surface of a light-transmitting cover member having a light-shielding layer or a surface of an image display member, irradiated with ultraviolet rays under an atmosphere where the oxygen concentration is significantly decreased and cured, to form a light-transmitting cured resin layer. Subsequently, the image display member and the light-transmitting cover member are stacked through the light-transmitting cured resin layer to manufacture an image display device of the present invention.
Owner:DEXERIALS CORP
Adhesive used for low surface energy surface bonding, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110157361AGood high and low temperature resistanceIncrease intermolecular forcesNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesEster polymer adhesivesFunctional monomerSurface energy
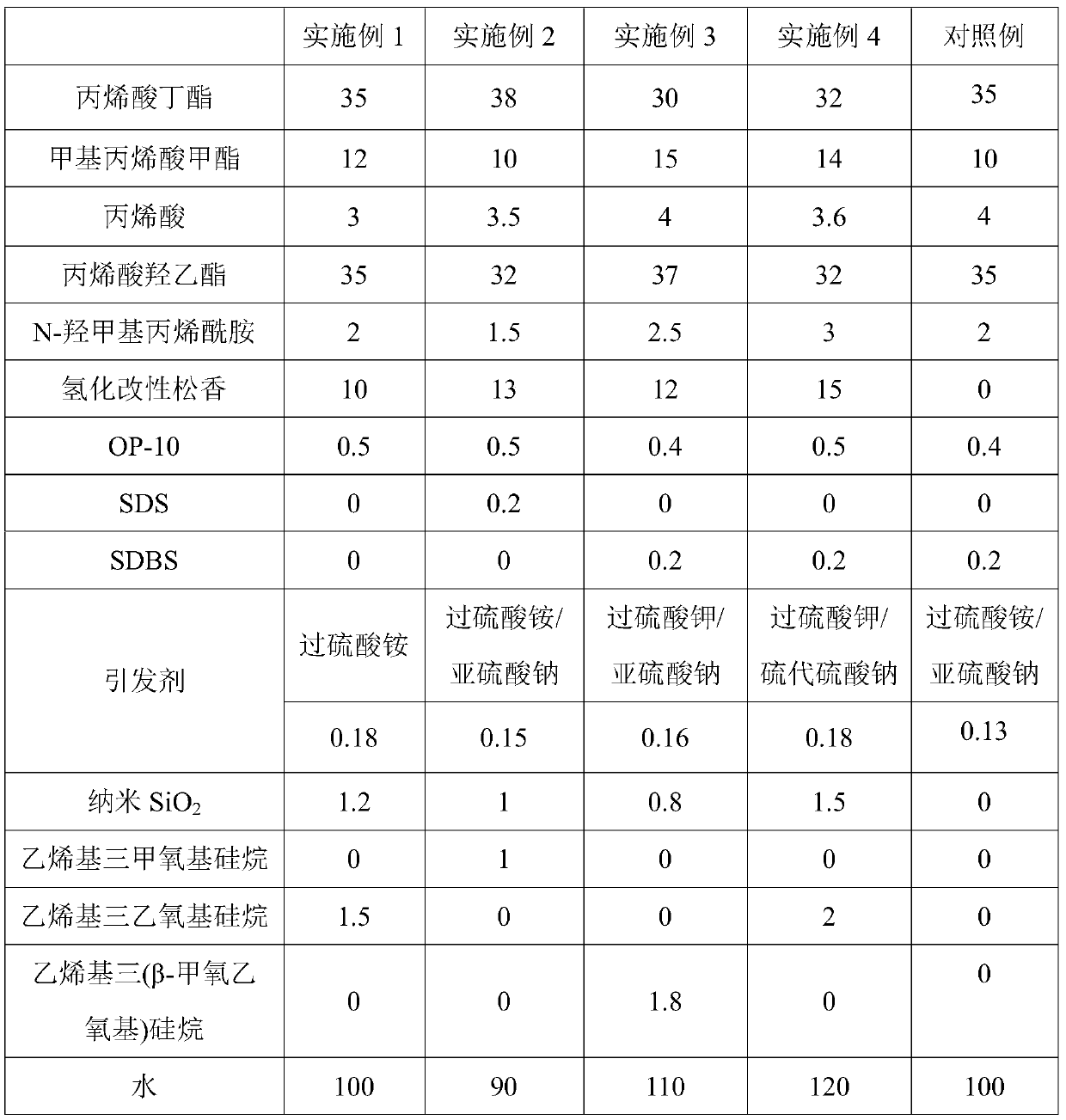
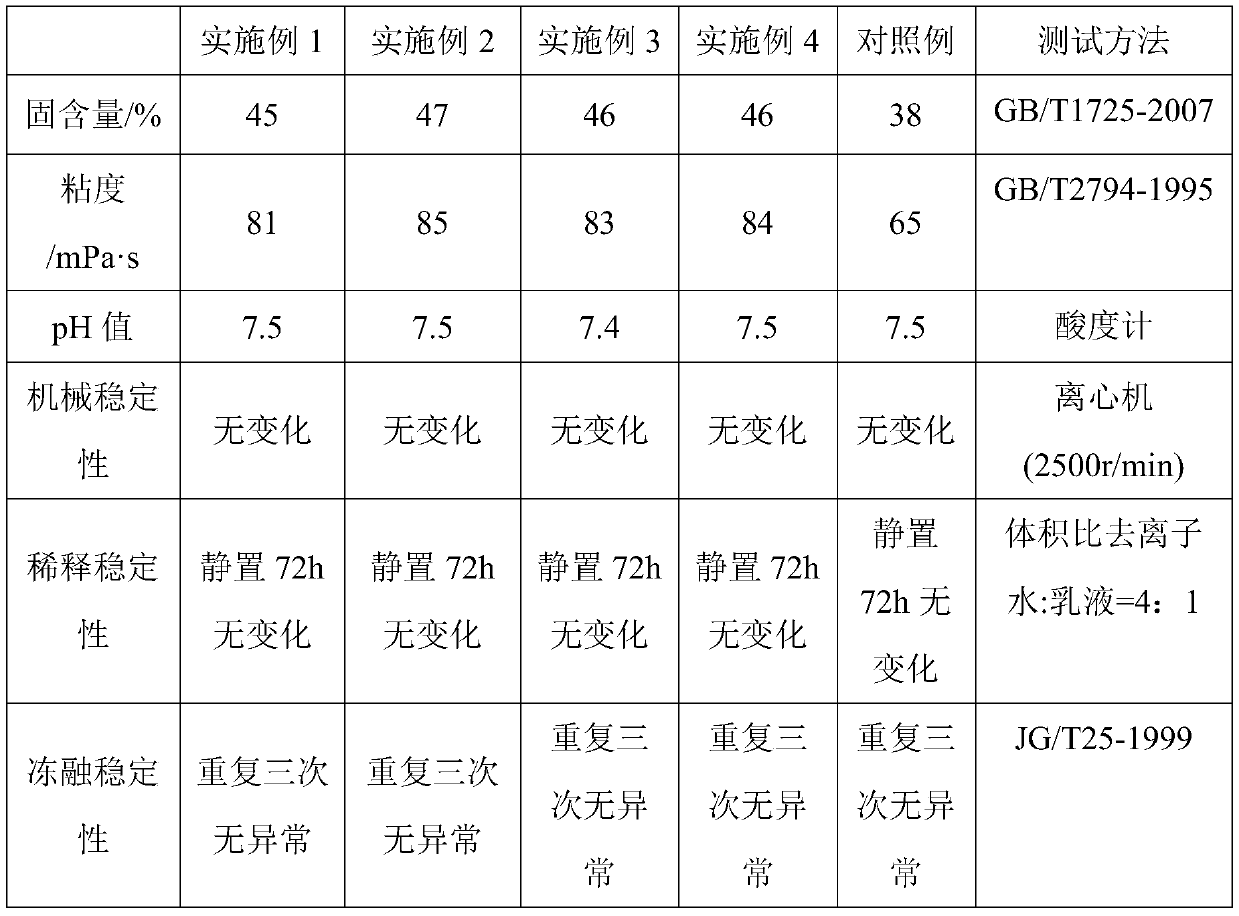
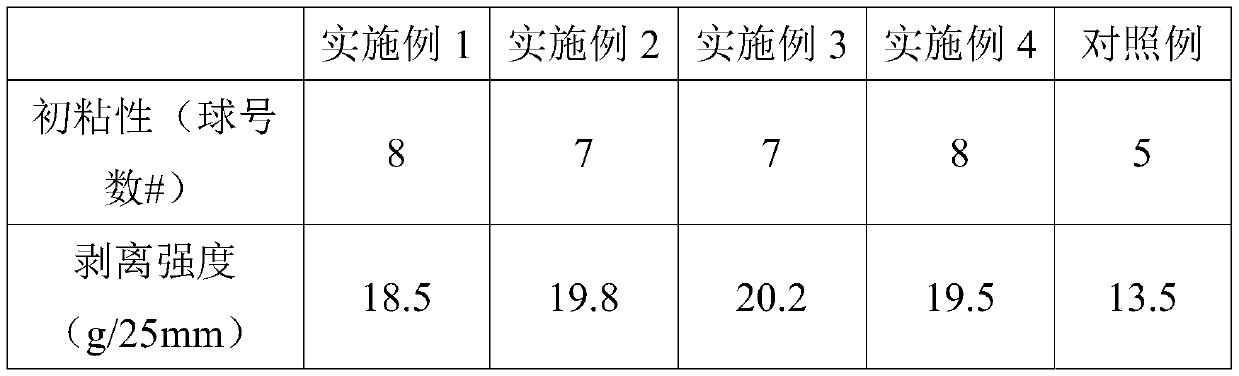
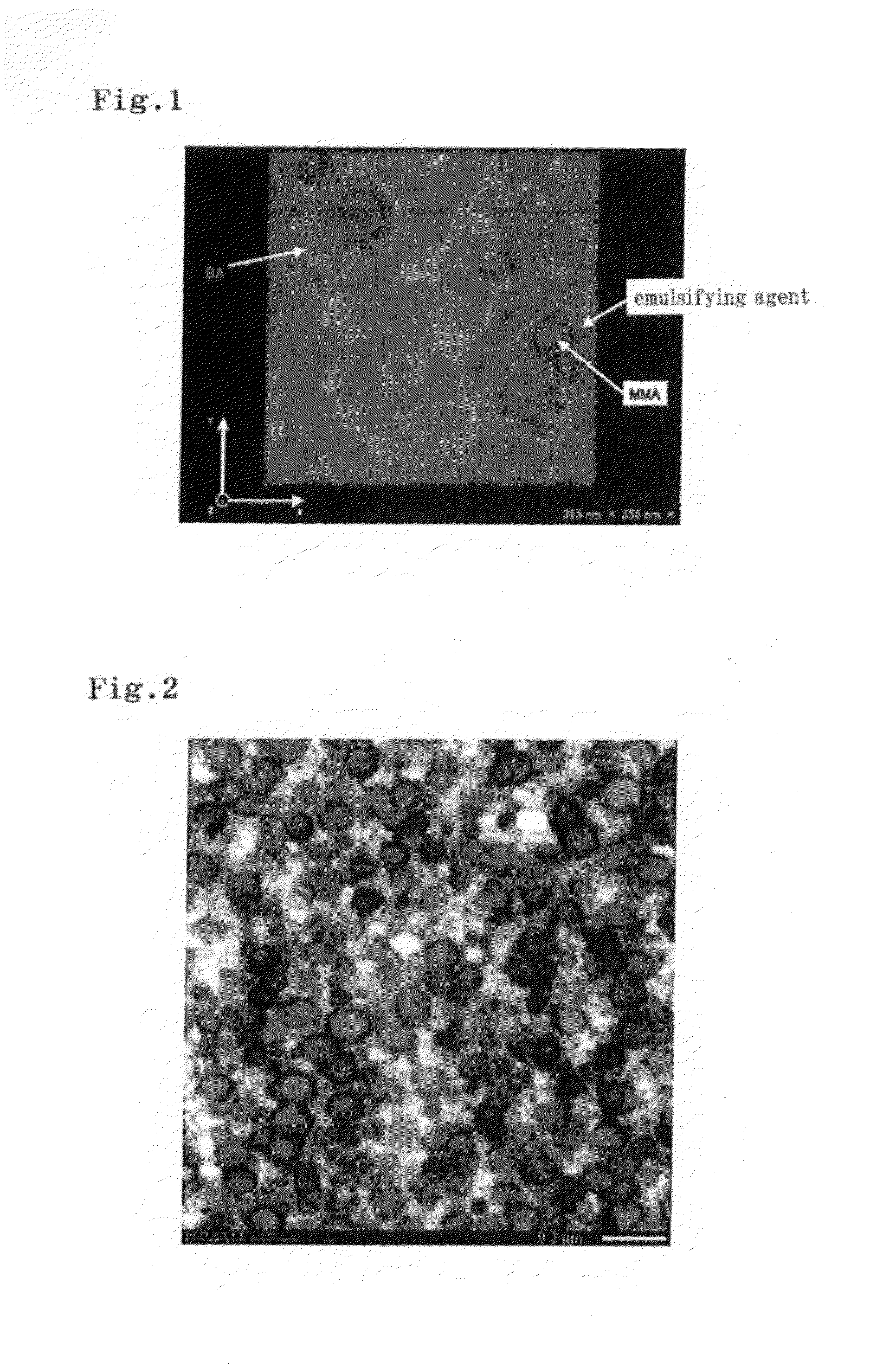
The invention discloses an adhesive used for low surface energy surface bonding. The adhesive used for low surface energy surface bonding is composed of, by weight, 30 to 40 parts of butyl acrylate, 10 to 15 parts of methyl methacrylate, 3 to 4 parts of acrylic acid, 30 to 40 parts of hydroxyethyl acrylate, 1 to 3 parts of N-hydroxymethyl acrylamide, 10 to 15 parts of hydrogenation modified rosin,0.5 to 1 part of an emulsifier, 0.1 to 0.2 parts of an initiator, 0.5 to 1.5 parts of nano-SiO2, 1 to 2 parts of an unsaturated silane coupling agent, and 80 to 120 parts of water. According to a preparation method, a nonsaturated silane coupling agent is adopted for surface treatment of nanometer particles, and then organic-inorganic nanometer composite pressure-sensitive adhesive emulsion synthesis is carried out so as to obtain a finished product. acrylic ester is taken as a main component, cooperation of soft and hard monomers and functional monomers is adopted, hydrogenation modified rosin is adopted for modification of the viscosity, and the siloxane coupling agent is adopted for modification of nano-SiO2, so that the adhesive possesses excellent wettability and bonding performanceon low surface energy materials.
Owner:SHENZHEN NIKTO TAPE NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Adhesive layer for optical film, optical film having adhesive layer, image display device, and detachment method for optical film
ActiveUS20130248118A1Reduce adhesive strengthHigh cohesive strengthNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesLamination ancillary operationsPressure sensitiveWater dispersible
A pressure-sensitive adhesive layer for an optical film made from an aqueous dispersion-type pressure-sensitive adhesive composition, wherein the aqueous dispersion-type pressure-sensitive adhesive composition is an aqueous dispersion comprising a water-dispersible (meth)acryl-based copolymer (A) having a glass transition temperature from −55° C. to less than 0° C.; and a water-soluble or water-dispersible component (B) having a glass transition temperature of 0° C. or more, a mixture ratio (A) / (B) is in the range of 50-97 / 3-50, the component (B) forms domains with maximum lengths between 1 nm and 200 nm in a resin component made of the (meth)acryl-based copolymer (A), and the pressure-sensitive adhesive layer has a haze value (H20) of 1% or less when having a thickness of 20 μm. The pressure-sensitive adhesive layer for an optical film, which is made from an aqueous dispersion-type pressure-sensitive adhesive composition has good reworkability or recyclability, and has a sufficient level of durability.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com